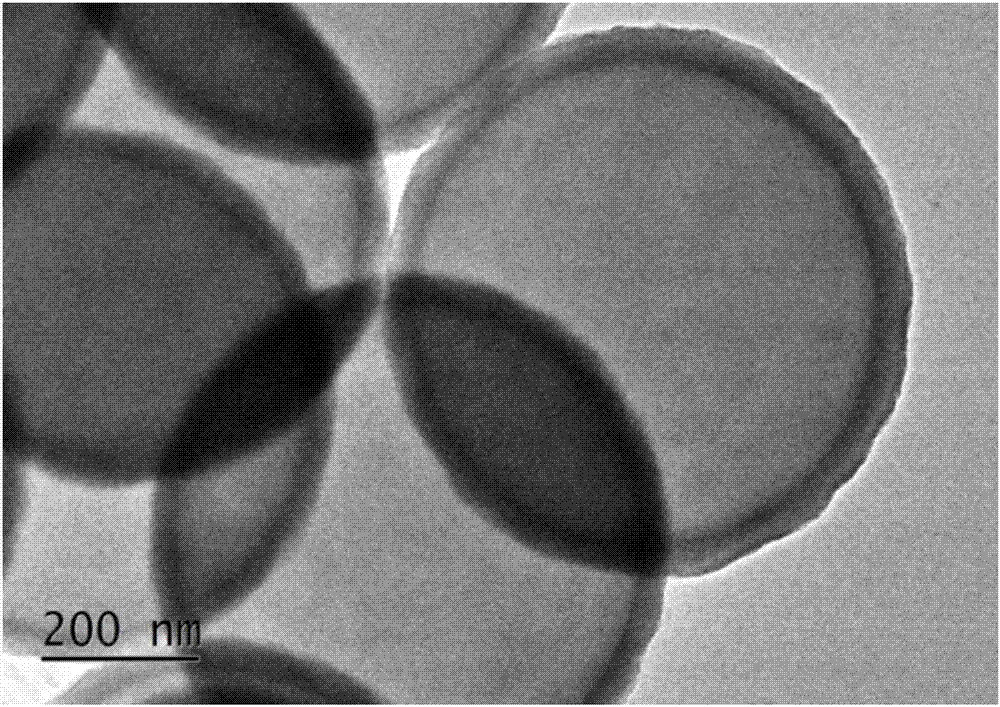
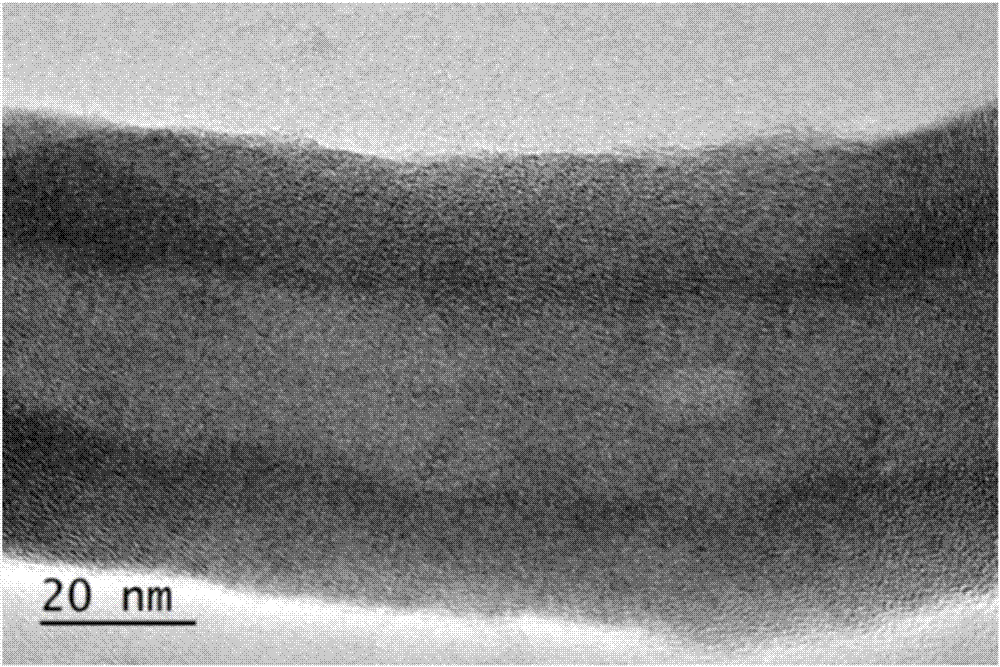
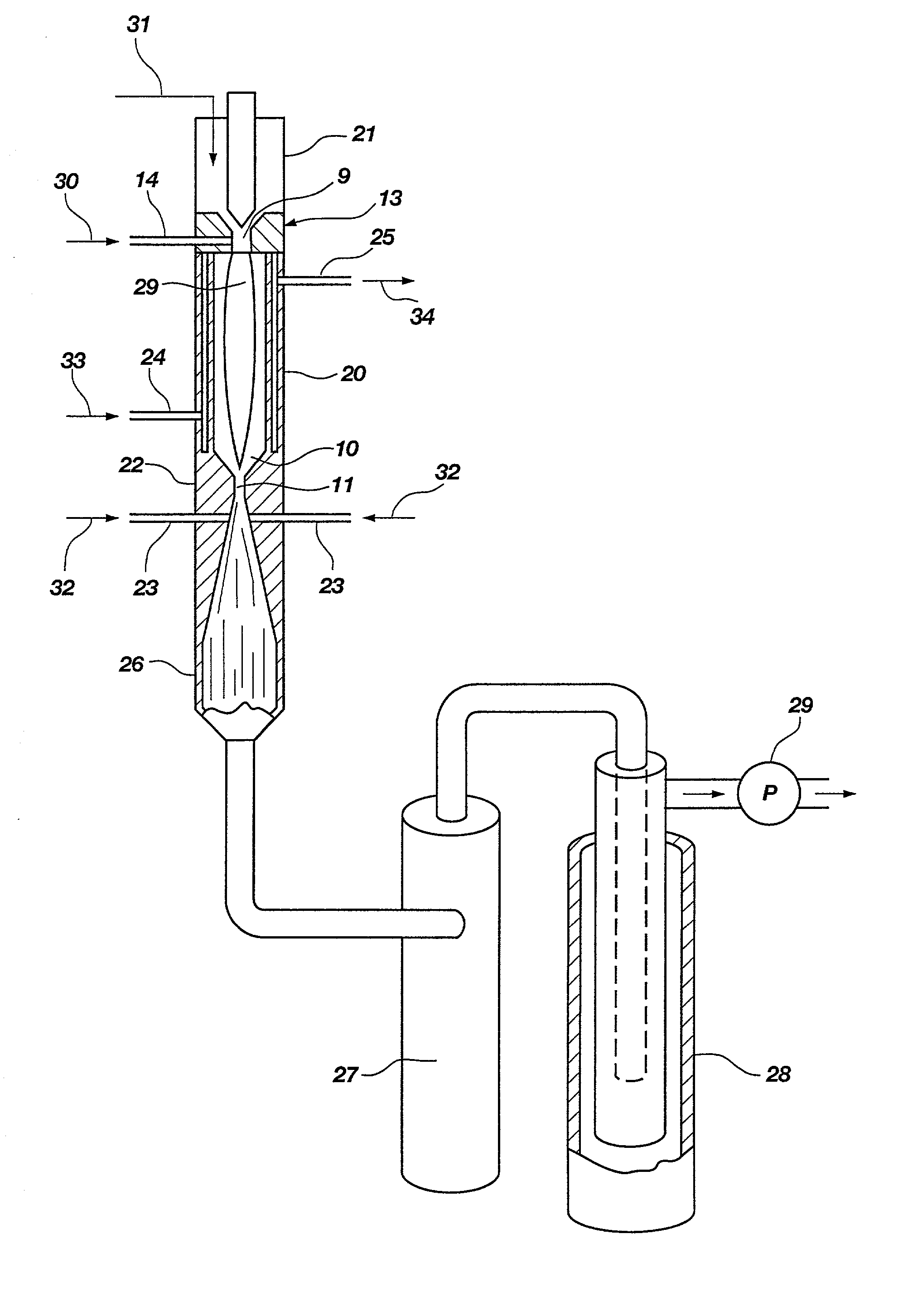
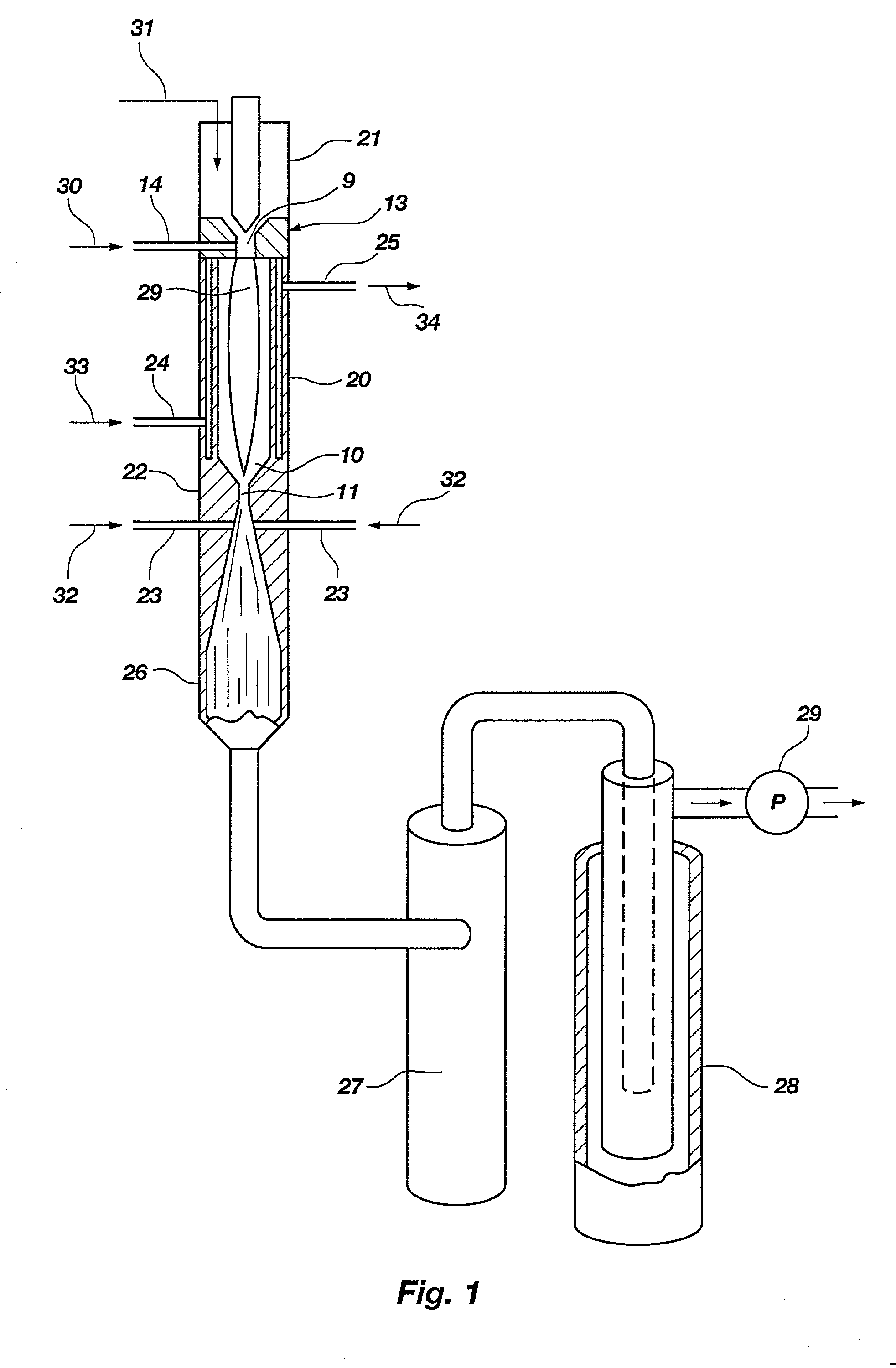
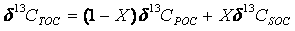Patents
Literature
253 results about "Elemental carbon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Elemental carbon refers to the inorganic forms of carbon which can be found in crystalline and amorphous forms. Crystalline forms have elemental carbon atoms arranged in a regular pattern while the carbon atoms in amorphous forms do not have regular patterns.
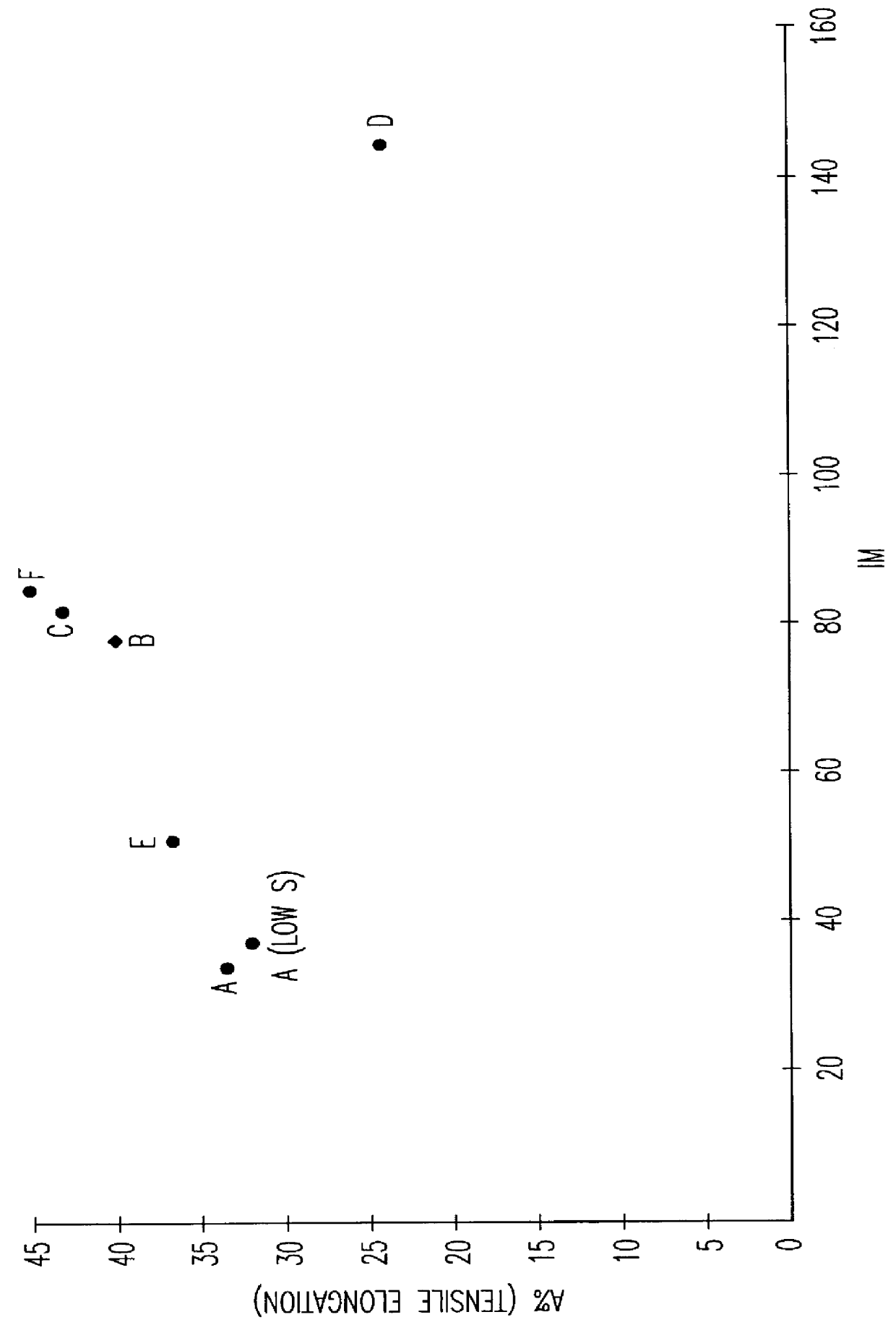
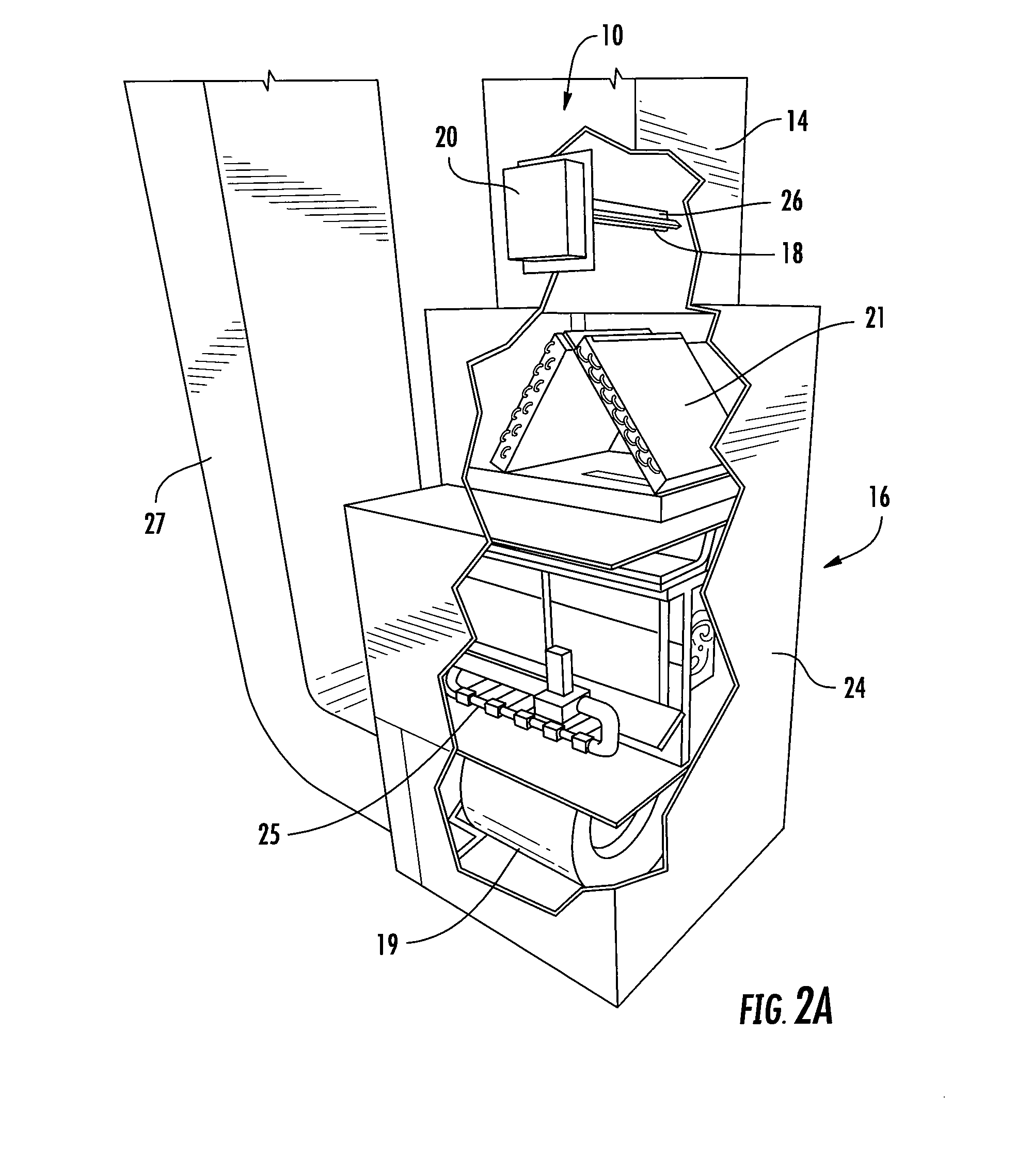
Austenoferritic stainless steel having a very low nickel content and a high tensile elongation
InactiveUS6096441ALow nickel contentImproved general propertyHeat treatment process controlElectric furnaceSulfurManganese
An austenoferritic stainless steel with high tensile elongation includes iron and the following elements in the indicated weight amounts based on total weight: carbon<0.04% 0.4%<silicon<1.2% 2%<manganese<4% 0.1%<nickel<1% 18%<chromium<22% 0.05%<copper<4% sulfur<0.03% phosphorus<0.1% 0.1%<nitrogen<0.3% molybdenum<3% the steel having a two-phase structure of austenite and ferrite and comprising between 30% and 70% of austenite, wherein Creq=Cr %+Mo %+1.5 Si % Nieq=Ni %+0.33 Cu %+0.5 Mn %+30 C %+30 N % and Creq / Nieq is from 2.3 to 2.75, and wherein IM=551-805(C+N)%-8.52 Si %-8.57 Mn %-12.51 Cr %-36 Ni %-34.5 Cu %-14 Mo %, IM being from 40 to 115.
Owner:UGITECH
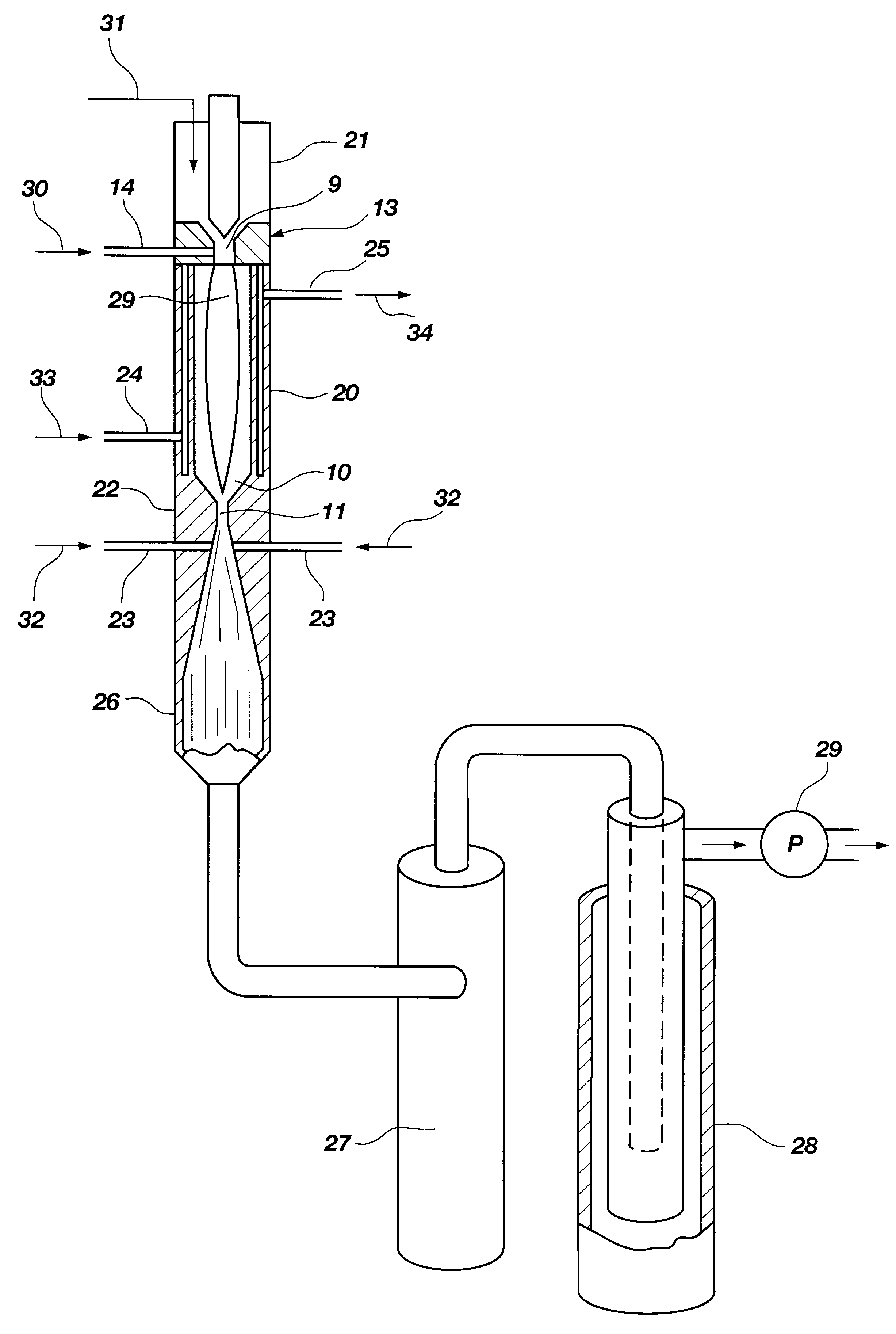
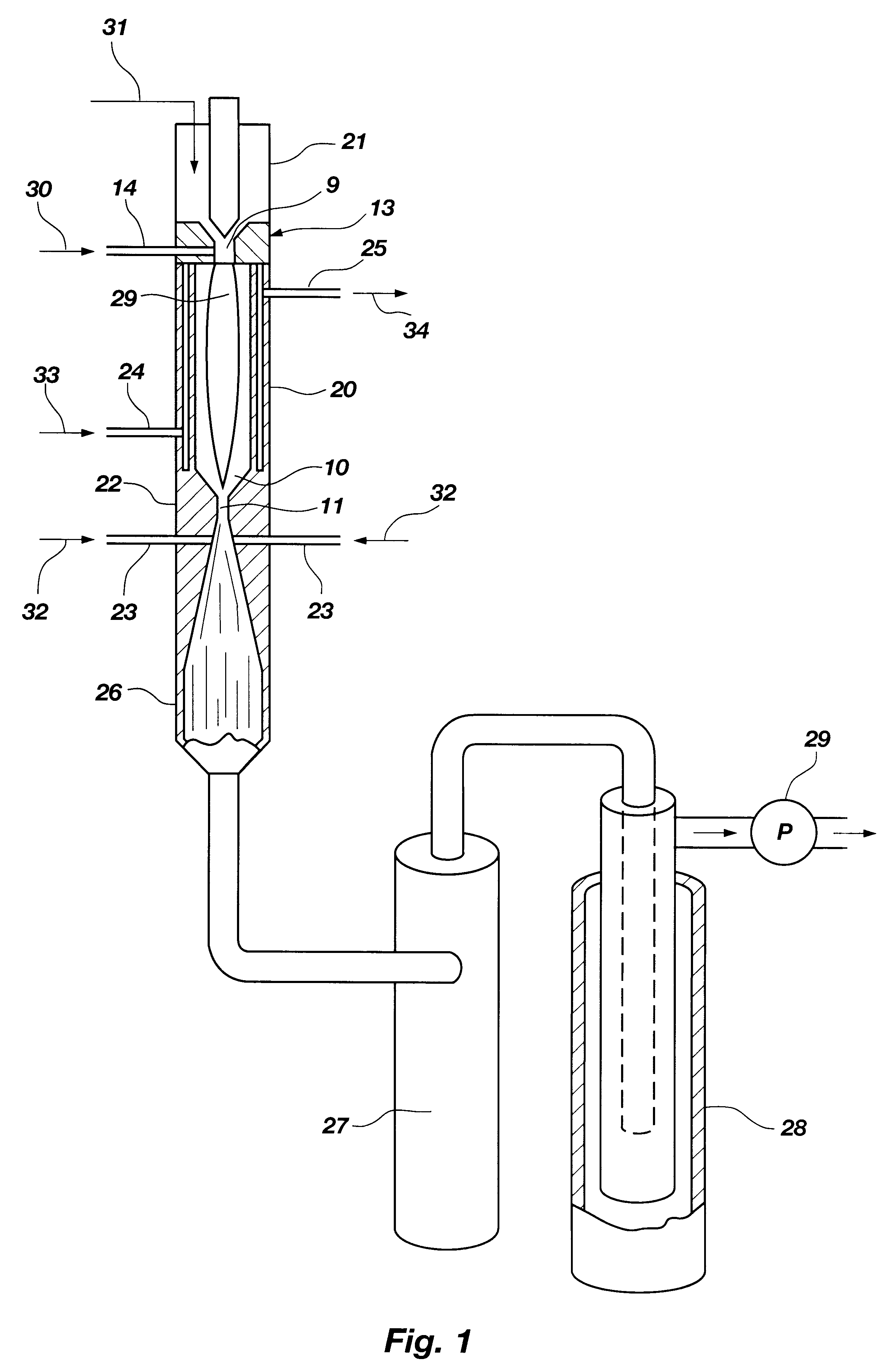
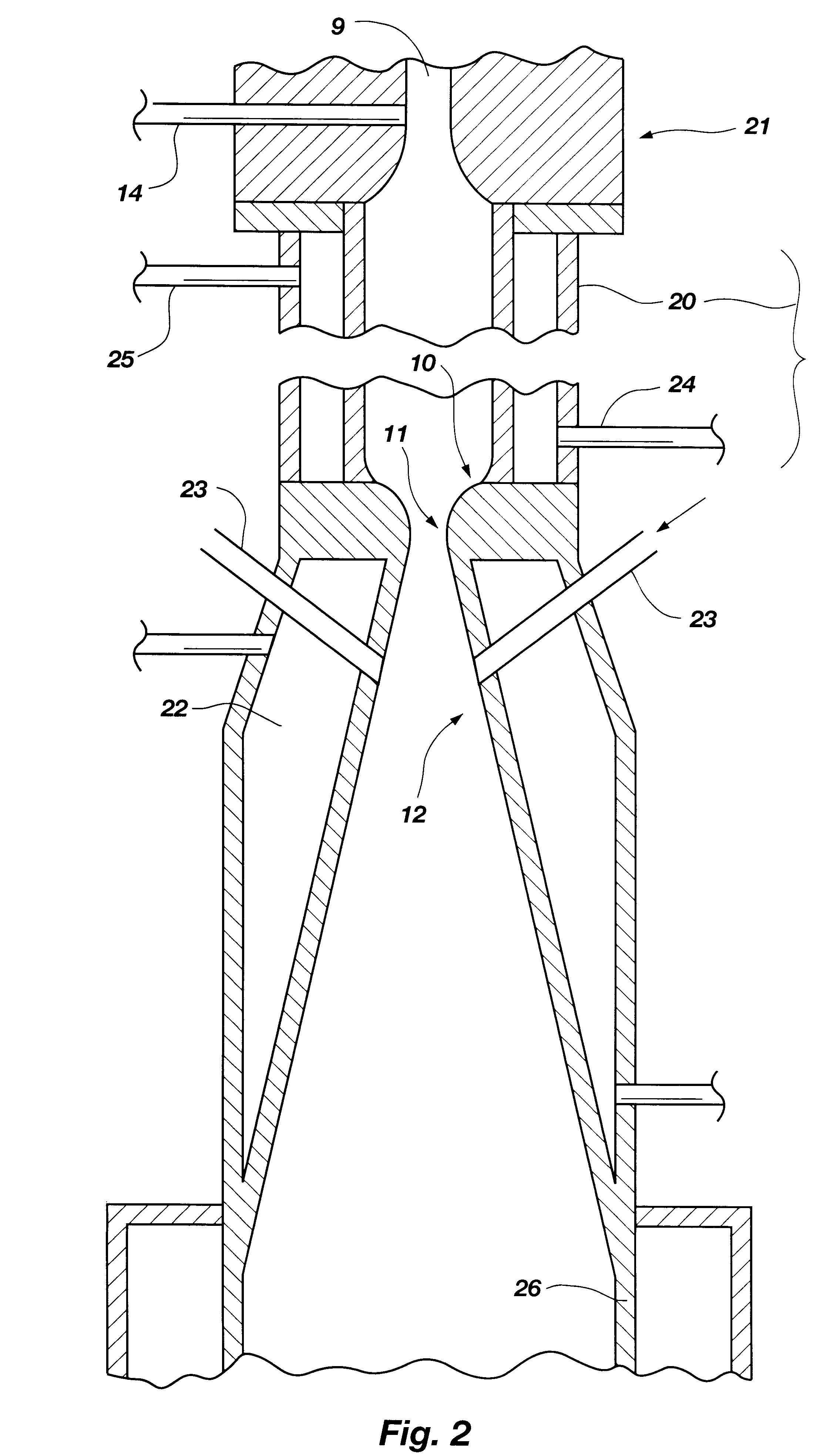
Hydrogen and elemental carbon production from natural gas and other hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6395197B1High quench rateAddressing slow performanceHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesEnergy inputUnsaturated hydrocarbonHydrogen fuel
Diatomic hydrogen and unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced as reactor gases in a fast quench reactor. During the fast quench, the unsaturated hydrocarbons are further decomposed by reheating the reactor gases. More diatomic hydrogen is produced, along with elemental carbon. Other gas may be added at different stages in the process to form a desired end product and prevent back reactions. The product is a substantially clean-burning hydrogen fuel that leaves no greenhouse gas emissions, and elemental carbon that may be used in powder form as a commodity for several processes.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Sulfide coated particle as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107983272AUniform thicknessThickness is easy to controlCobalt sulfidesZinc sulfidesMetallic sulfideLithium-ion battery
The invention discloses a sulfide coated particle as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The sulfide coated particle comprises a core and a shell coating the core, wherein the core is prepared from at least one of metal, oxide, metal hydroxide, metal inorganic salt, elemental carbon or oxysome thereof, carbide, nitride, semiconductor and organic matter; the shell is prepared from metal sulfide. The to-be-coated core is mixed with the metal salt, a reducing agent and a sulfur source with a liquid phase method, metal sulfide is precipitated to the particle surface through in-situ reduction, and uniform, continuous and controllable coating of the core surface with metal sulfide is realized. The coating method is simple, reaction conditions are mild, universality is high,a coating layer is controllable in thickness, complete and uniform, and the sulfide coated particle has quite broad practical application prospect in the fields of electrocatalysis, lithium ion batteries, biomedicine and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Hydrogen and elemental carbon production from natural gas and other hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20020151604A1Addressing slow performanceReduce momentumHydrogenOrganic compound preparationUnsaturated hydrocarbonHydrogen fuel
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Nanotube-containing composite bodies, and methods for making same
InactiveUS20060062985A1Improve propertiesImprove fracture toughnessMaterial nanotechnologyNon-woven fabricsChemical reactionBonding process
A composite material featuring comminuted or otherwise well dispersed and separated nanotubes reinforcing a matrix featuring metal, ceramic and / or polymer. In a preferred embodiment, the nanotubes feature elemental carbon, and the composites can be produced using a molten silicon metal infiltration technique, which may be pressurized or not, for example, a siliconizing or a reaction-bonding process. In this preferred embodiment, carbon nanotubes may be prevented from chemically reacting with the silicon infiltrant by an interfacial coating disposed between the carbon nanotubes and the infiltrant. A reaction-bonded composite body containing even a small percentage of carbon nanotubes possessed a significant increase in electrical conductivity as compared to a reaction-bonded composite not containing such nanotubes, reflecting the high electrical conductivity of the nanotubes. When the nanotubes are well dispersed throughout the preform, mechanical property enhancements start to become noticeable, such as fracture toughness enhancement.
Owner:KARANDIKAR PRASHANT G
Microstructured high-temperature hybrid material, its composite material and method of making
This invention provides a hybrid material that exhibits strength, stiffness and ability to resist high temperatures. This hybrid material essentially consists of component A and component B. Component A is selected from the group consisting of inorganic compounds, oxides, carbides, nitrides, borides, and combinations thereof. Component B is selected from the group comprising elemental carbon, inorganic compounds, oxides, carbides, nitrides, borides, and combinations thereof. Component B comprises a plurality of units, each of the units substantially exhibiting a shape, such that this shape substantially exhibits a long dimension and a short dimension, with the short dimension being in a direction that is essentially perpendicular to the direction of the long dimension and the short dimension being in the range from 0.1 nm to 0.5 μm. Each of the units of component B is substantially in contact with and substantially bonded to at least one of the units of component A.
Owner:CHUNG DEBORAH D L
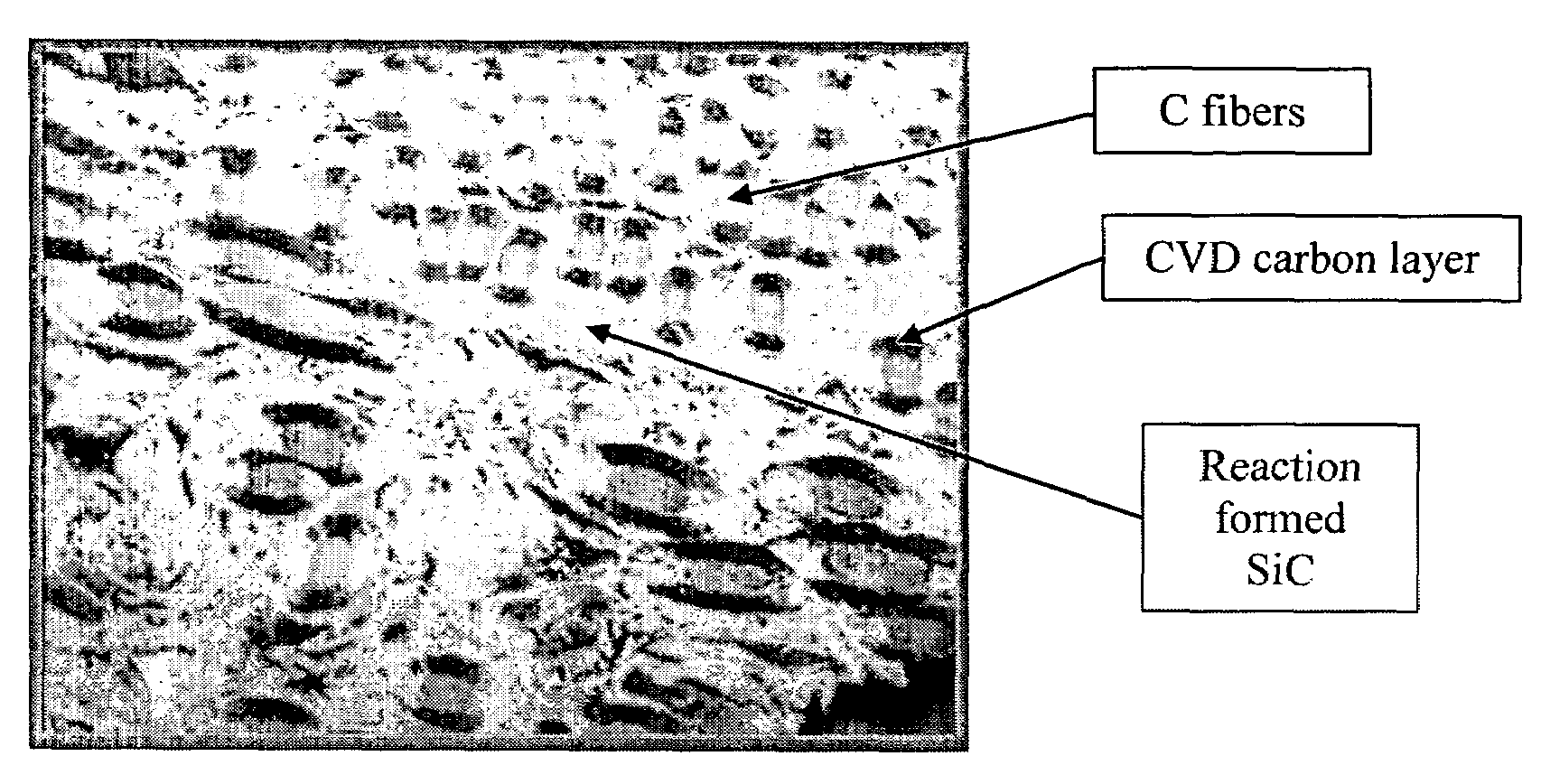
Boron carbide based ceramic matrix composites
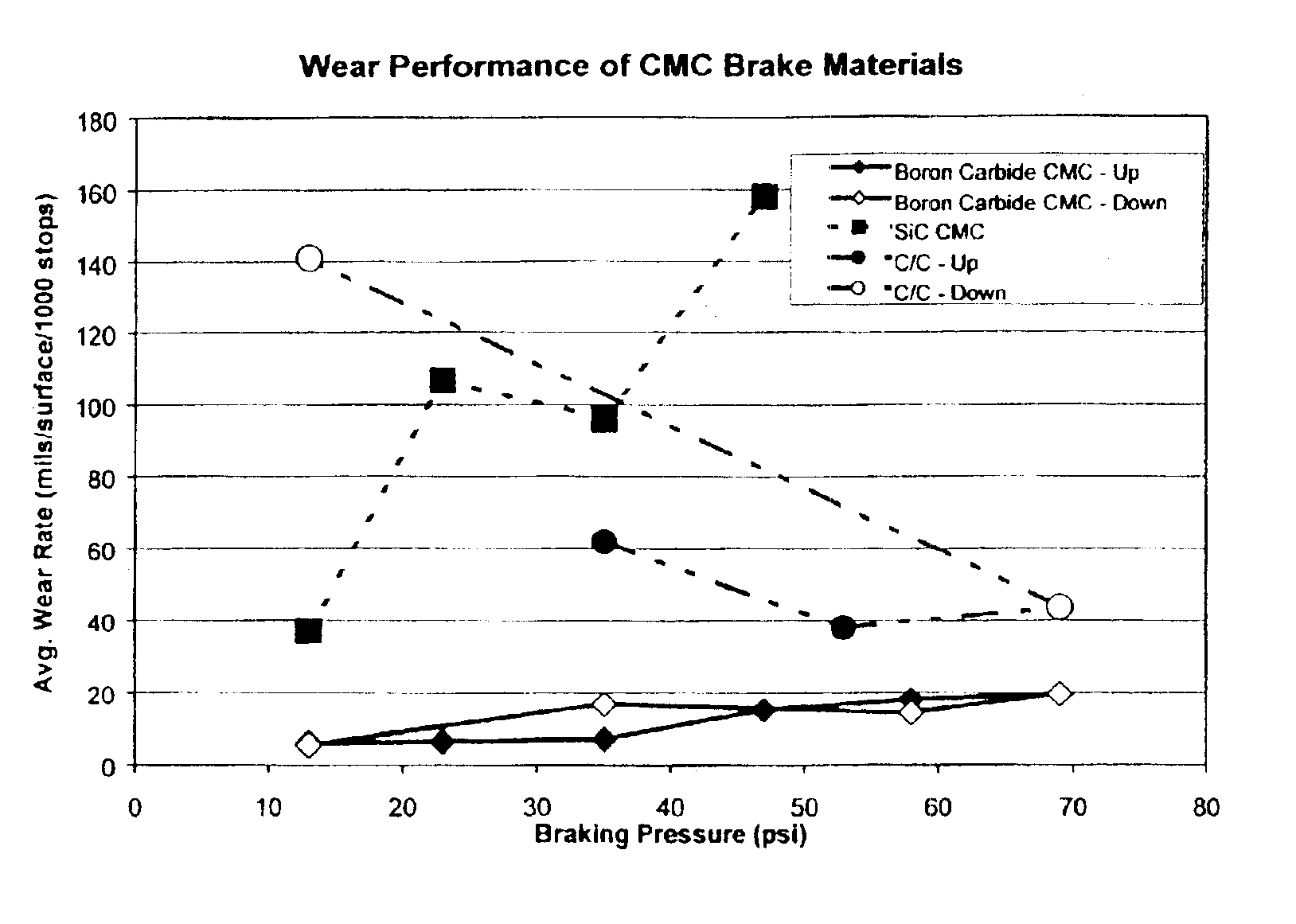
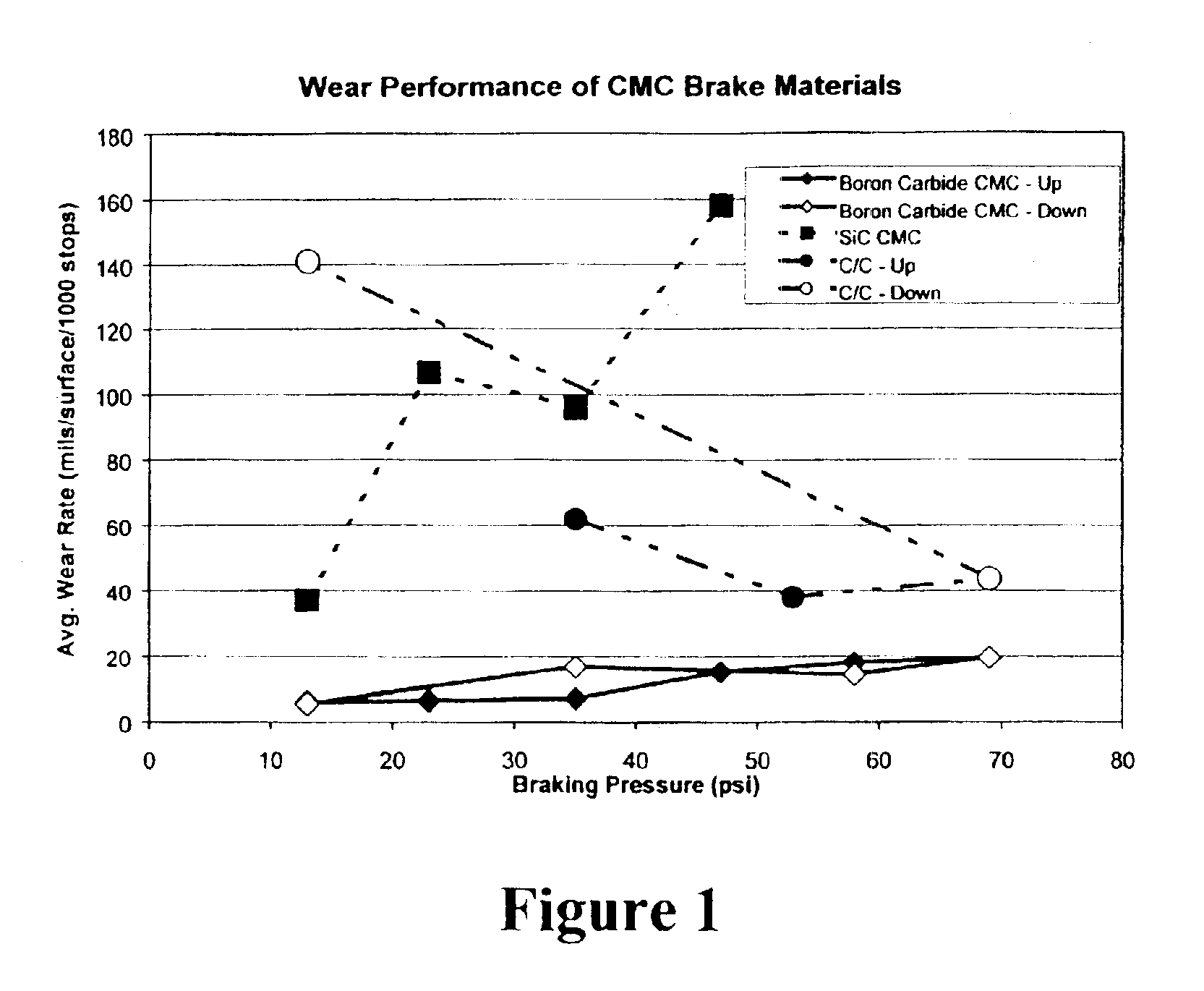
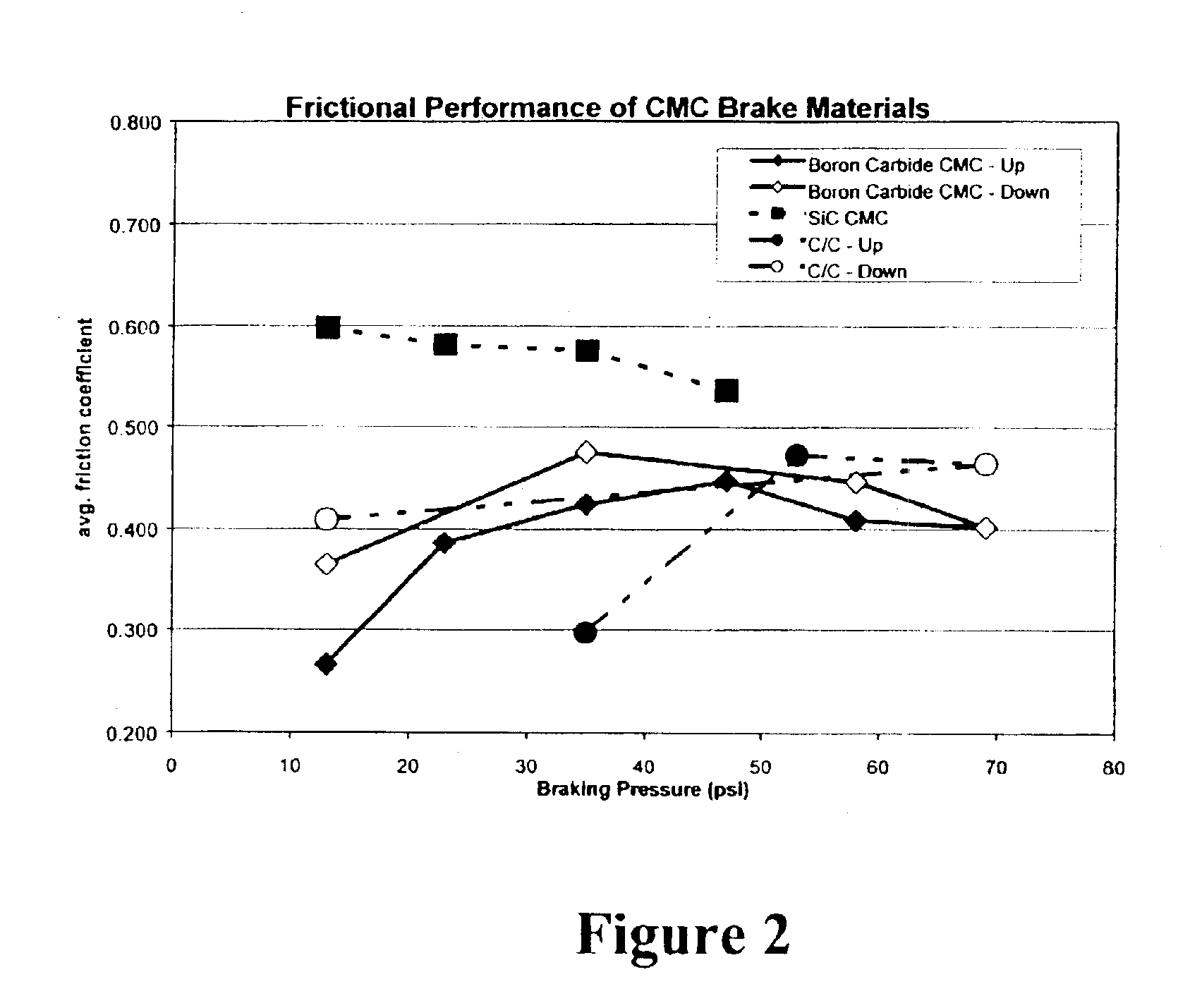
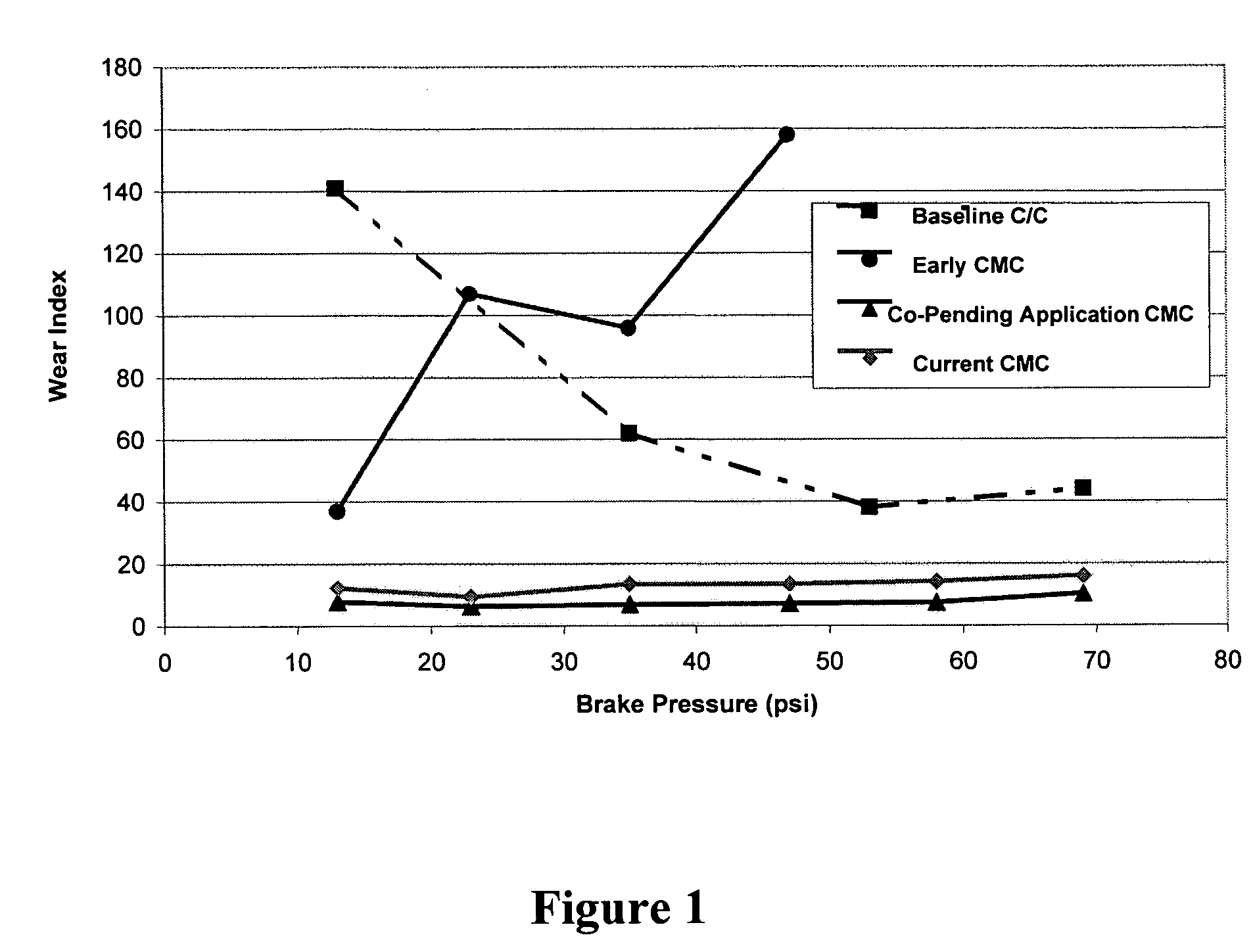
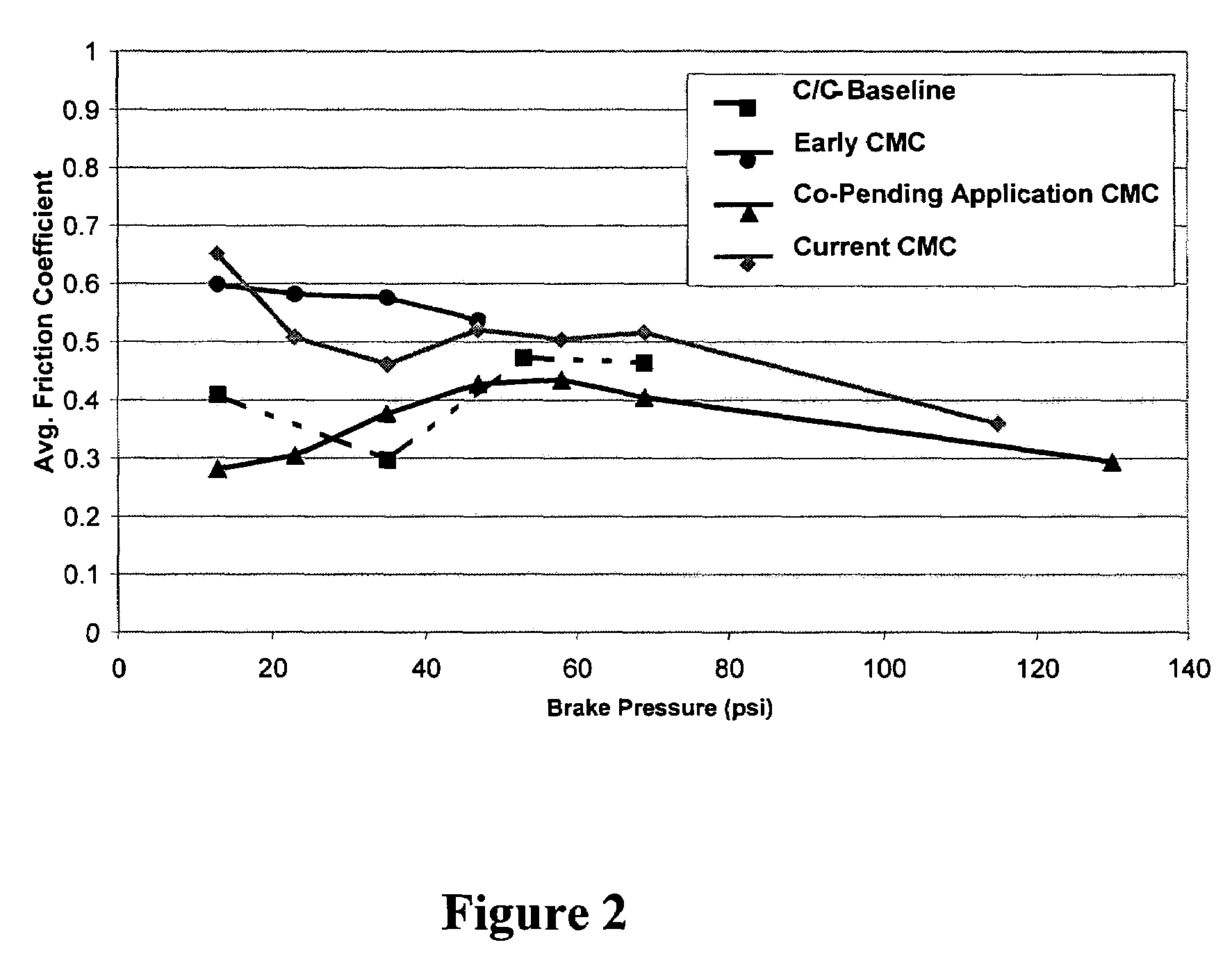
InactiveUS6855428B2Big advantageReduce wear rateBraking discsPretreated surfacesSilicon matrixBoron carbide
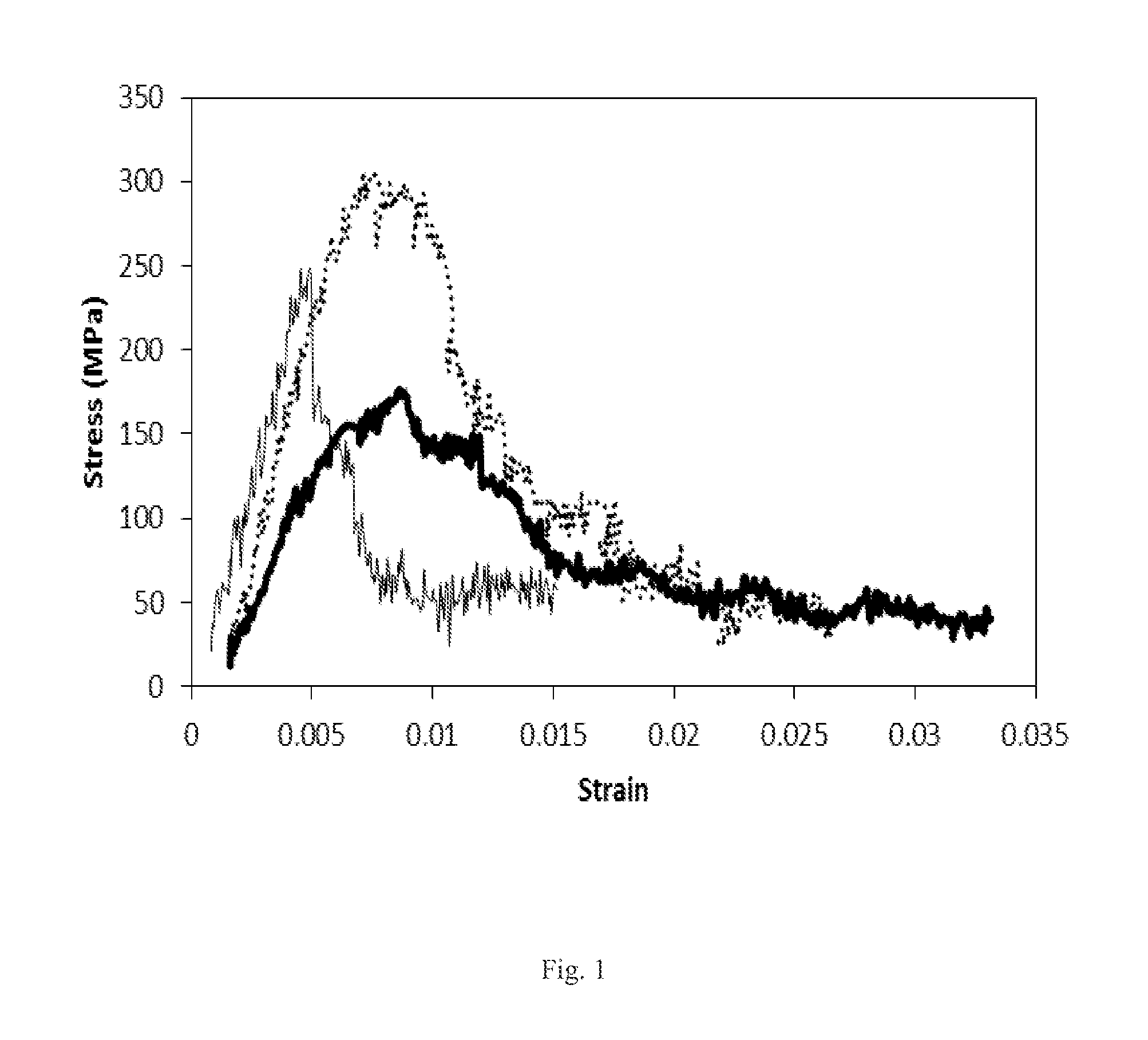
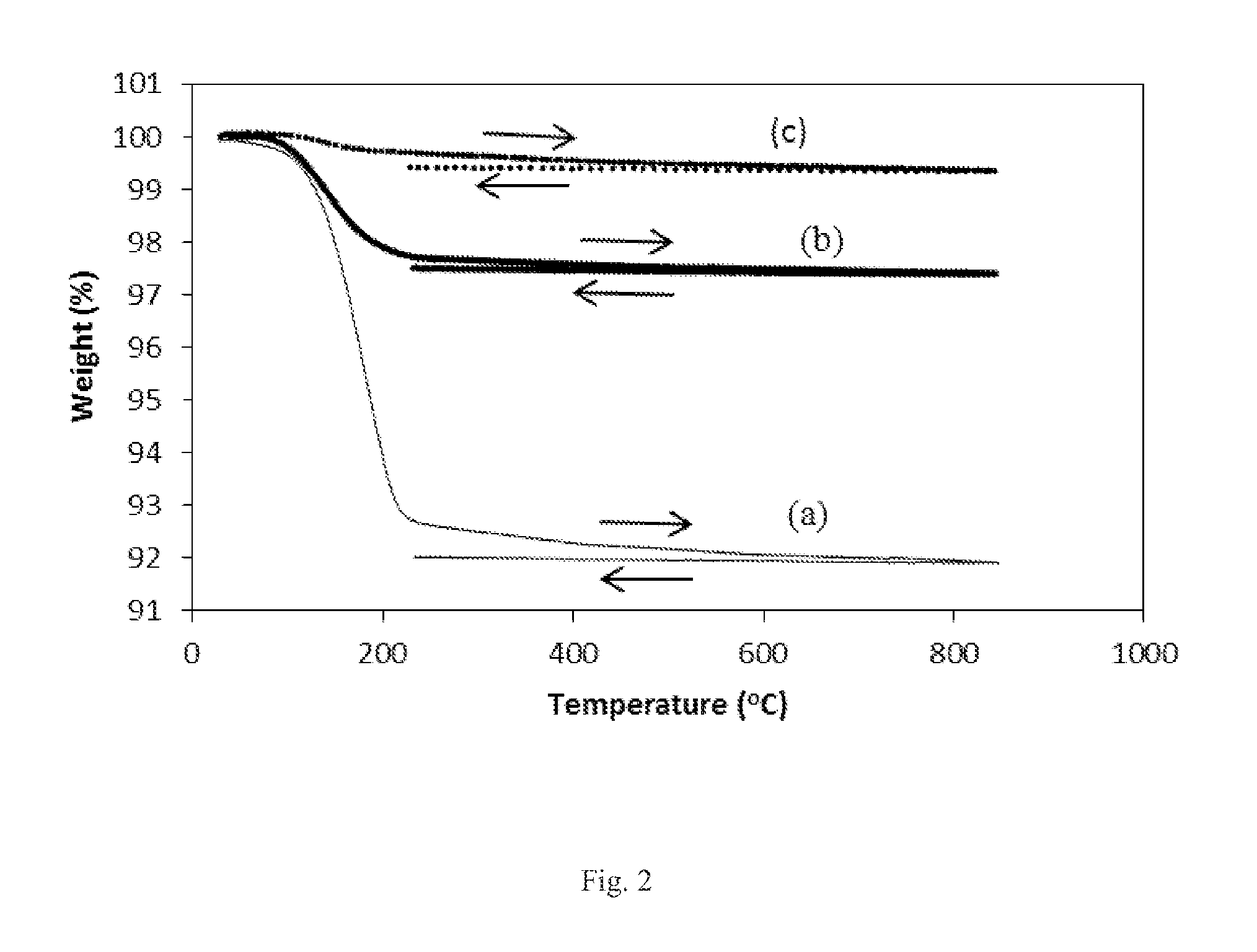
The present invention is a composite material and process to produce same. That material comprises a fibrous structure which is initially predominantly coated with elemental carbon; that fibrous structure is then subsequently predominantly coated with at least one ceramic material, e.g., boron carbide, which is non-reactive with silicon. The composite material also comprises a silicon matrix which is continuous and predominantly surrounds the fibrous structure, which has been initially predominantly coated with elemental carbon and subsequently predominantly coated with at least one ceramic material. The matrix which has a fine grain crystalline structure of predominantly 20 microns or less in size. The at least one ceramic material is discontinuous within that matrix. The fibrous material pulls out of the elemental carbon, which initially predominantly coats that fibrous structure, when the composite is subjected to fracture.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Synthesis of Metal Compounds Under Carbothermal Conditions
InactiveUS20050255026A1Economical and convenient processLower capability requirementsPhosphatesLithium compoundsOxidation stateGraphite
Active materials of the invention contain at least one alkali metal and at least one other metal capable of being oxidized to a higher oxidation state. Preferred other metals are accordingly selected from the group consisting of transition metals (defined as Groups 4-11 of the periodic table), as well as certain other non-transition metals such as tin, bismuth, and lead. The active materials may be synthesized in single step reactions or in multi-step reactions. In at least one of the steps of the synthesis reaction, reducing carbon is used as a starting material. In one aspect, the reducing carbon is provided by elemental carbon, preferably in particulate form such as graphites, amorphous carbon, carbon blacks and the like. In another aspect, reducing carbon may also be provided by an organic precursor material, or by a mixture of elemental carbon and organic precursor material.
Owner:LITHIUM WERKS TECH BV +1
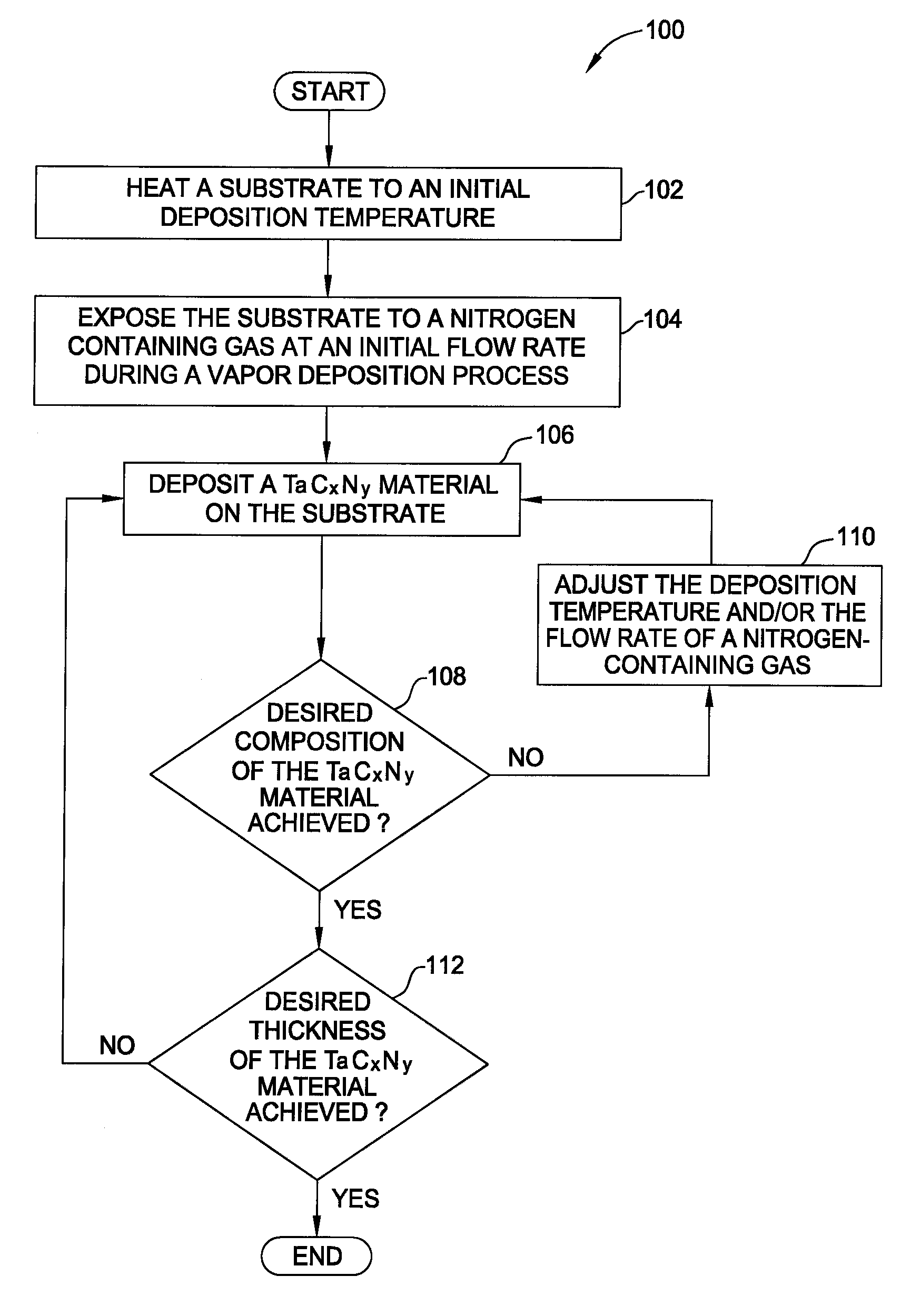
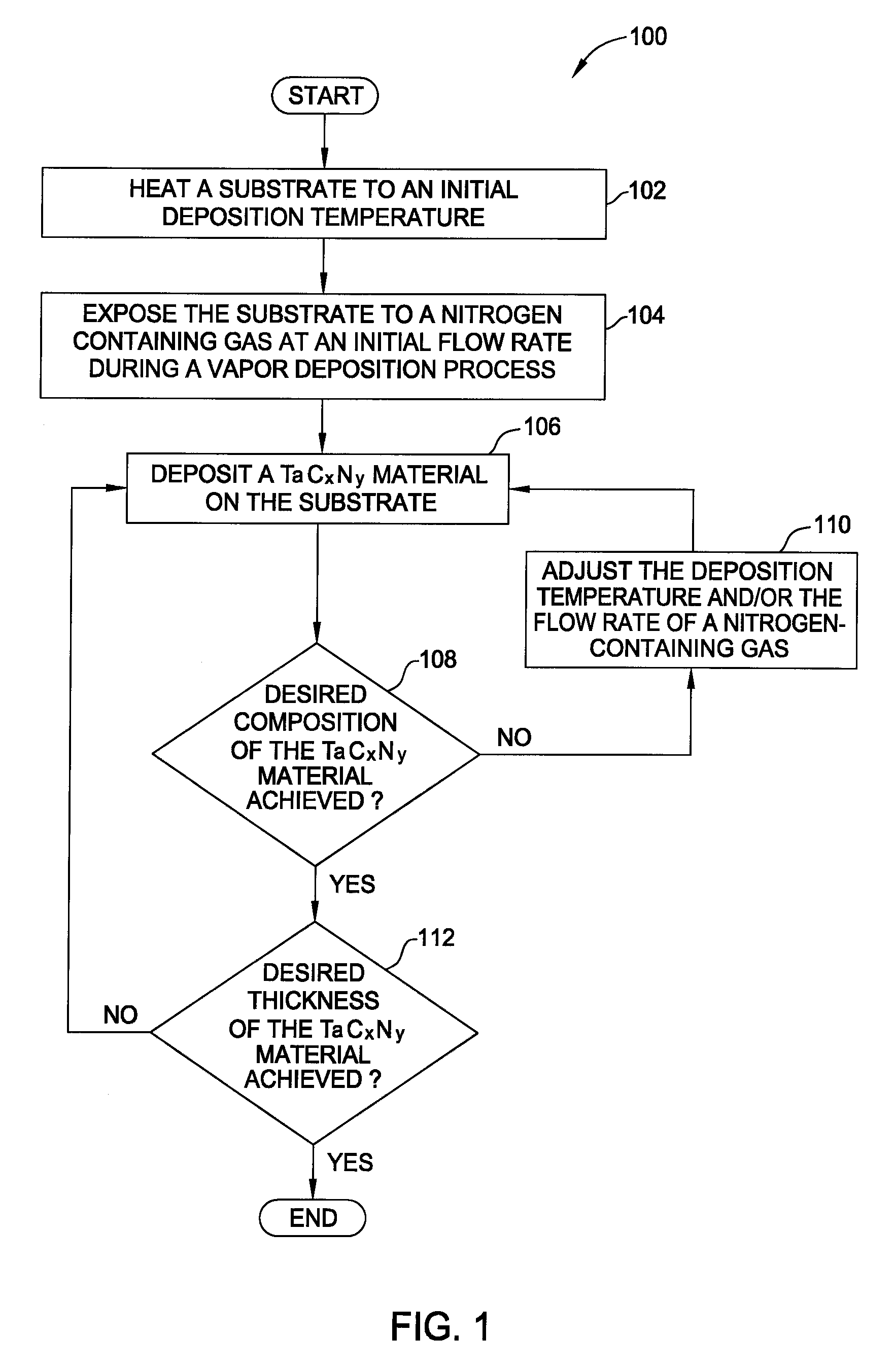
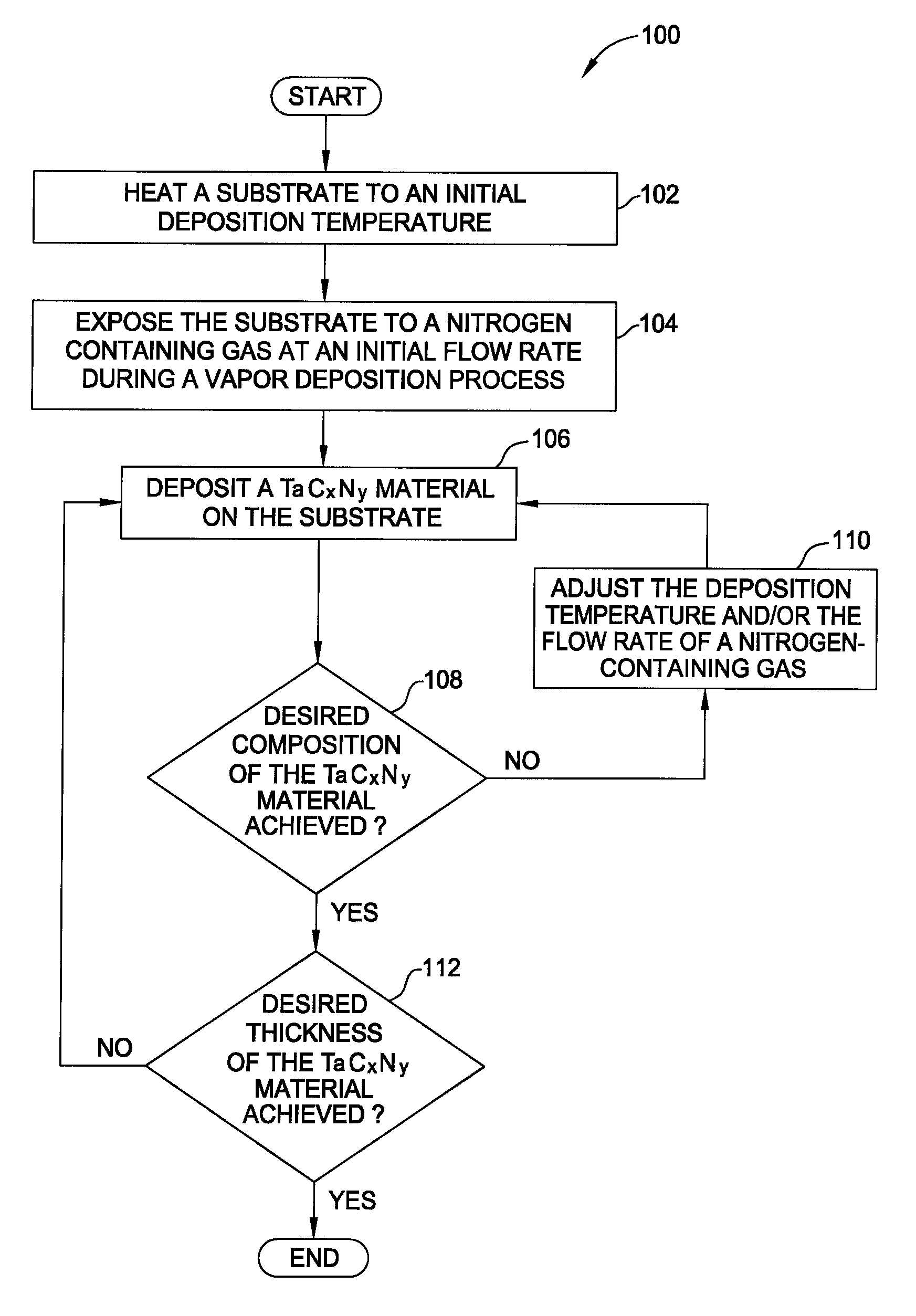
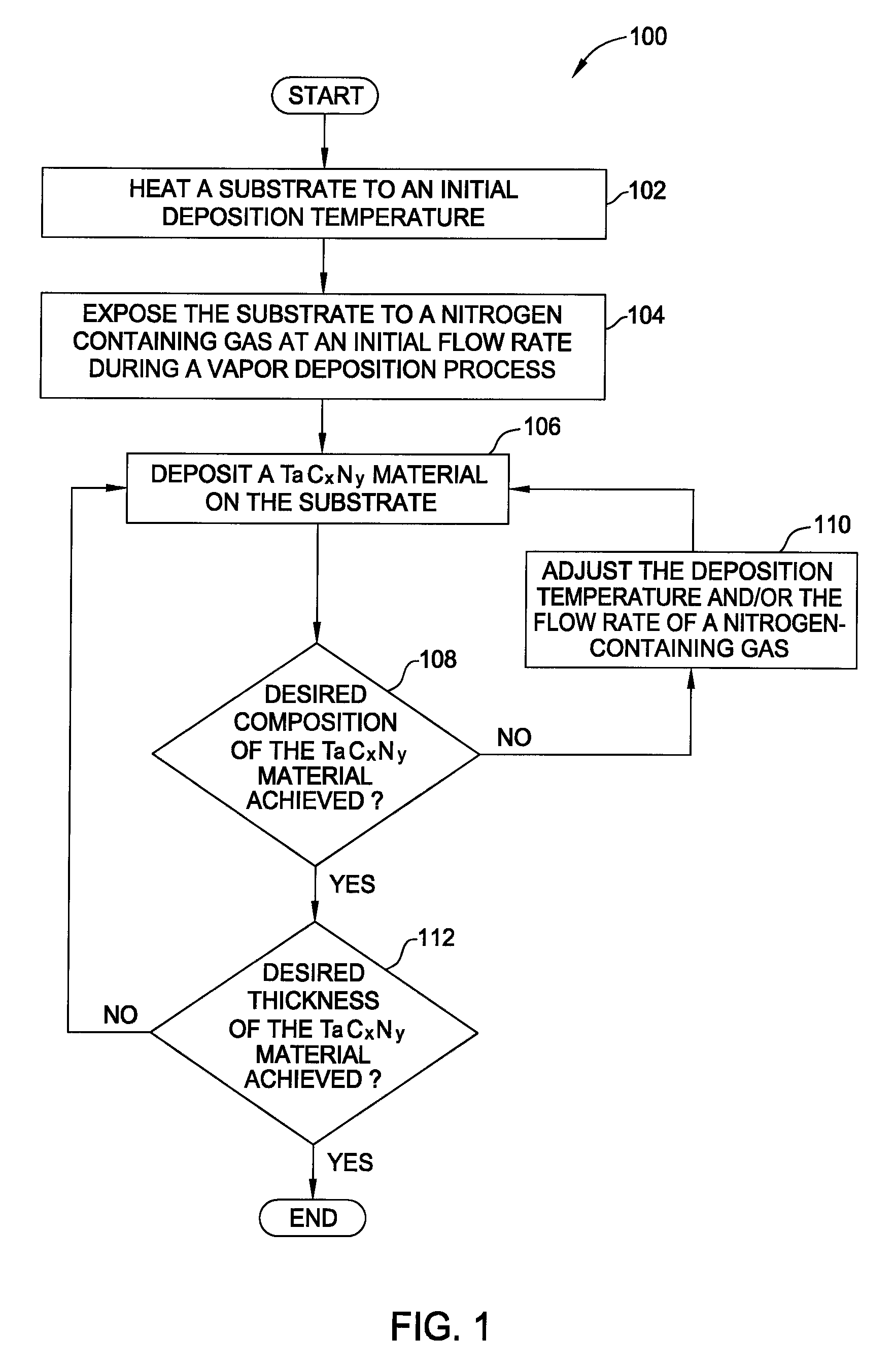
Vapor deposition processes for tantalum carbide nitride materials
ActiveUS20090081868A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseElemental carbon
Embodiments of the invention generally provide methods for depositing and compositions of tantalum carbide nitride materials. The methods include deposition processes that form predetermined compositions of the tantalum carbide nitride material by controlling the deposition temperature and the flow rate of a nitrogen-containing gas during a vapor deposition process, including thermal decomposition, CVD, pulsed-CVD, or ALD. In one embodiment, a method for forming a tantalum-containing material on a substrate is provided which includes heating the substrate to a temperature within a process chamber, and exposing the substrate to a nitrogen-containing gas and a process gas containing a tantalum precursor gas while depositing a tantalum carbide nitride material on the substrate. The method further provides that the tantalum carbide nitride material is crystalline and contains interstitial carbon and elemental carbon having an interstitial / elemental carbon atomic ratio of greater than 1, such as about 2, 3, 4, or greater.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Combined gasification and vitrification system
ActiveUS20070261303A1Lower cost of capitalMinimizes energyMuffle furnacesTransportation and packagingVitrificationCombustion
An optimized gasification / vitrification processing system having a gasification unit which converts organic materials to a hydrogen rich gas and ash in communication with a joule heated vitrification unit which converts the ash formed in the gasification unit into glass, and a plasma which converts elemental carbon and products of incomplete combustion formed in the gasification unit into a hydrogen rich gas.
Owner:INENTEC
Synthesis of metal compounds under carbothermal conditions
InactiveUS7060206B2Economical and convenient processLower capability requirementsCell electrodesSulfur compoundsOxidation stateGraphite
Active materials of the invention contain at least one alkali metal and at least one other metal capable of being oxidized to a higher oxidation state. Preferred other metals are accordingly selected from the group consisting of transition metals (defined as Groups 4–11 of the periodic table), as well as certain other non-transition metals such as tin, bismuth, and lead. The active materials may be synthesized in single step reactions or in multi-step reactions. In at least one of the steps of the synthesis reaction, reducing carbon is used as a starting material. In one aspect, the reducing carbon is provided by elemental carbon, preferably in particulate form such as graphites, amorphous carbon, carbon blacks and the like. In another aspect, reducing carbon may also be provided by an organic precursor material, or by a mixture of elemental carbon and organic precursor material.
Owner:LITHIUM WERKS TECH BV
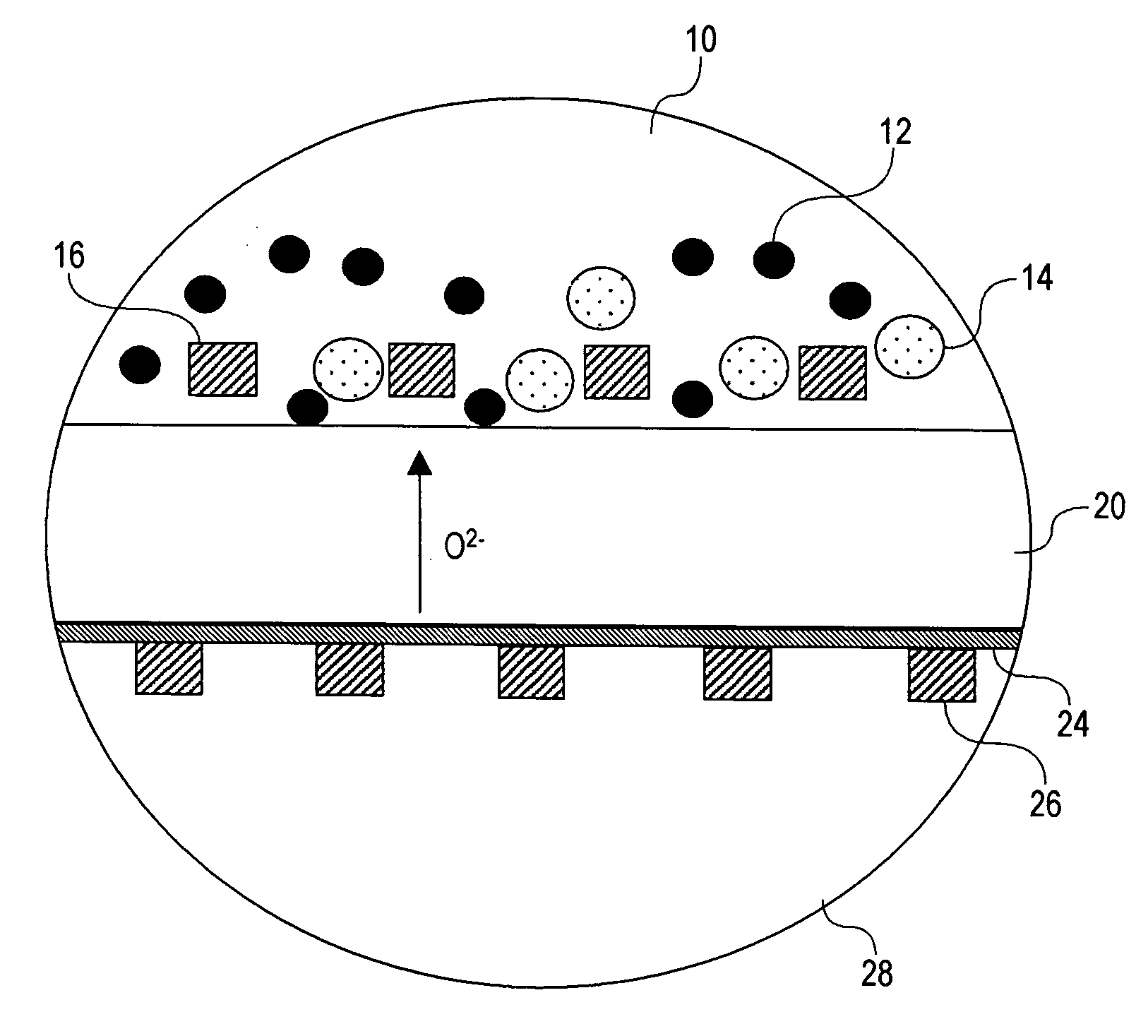
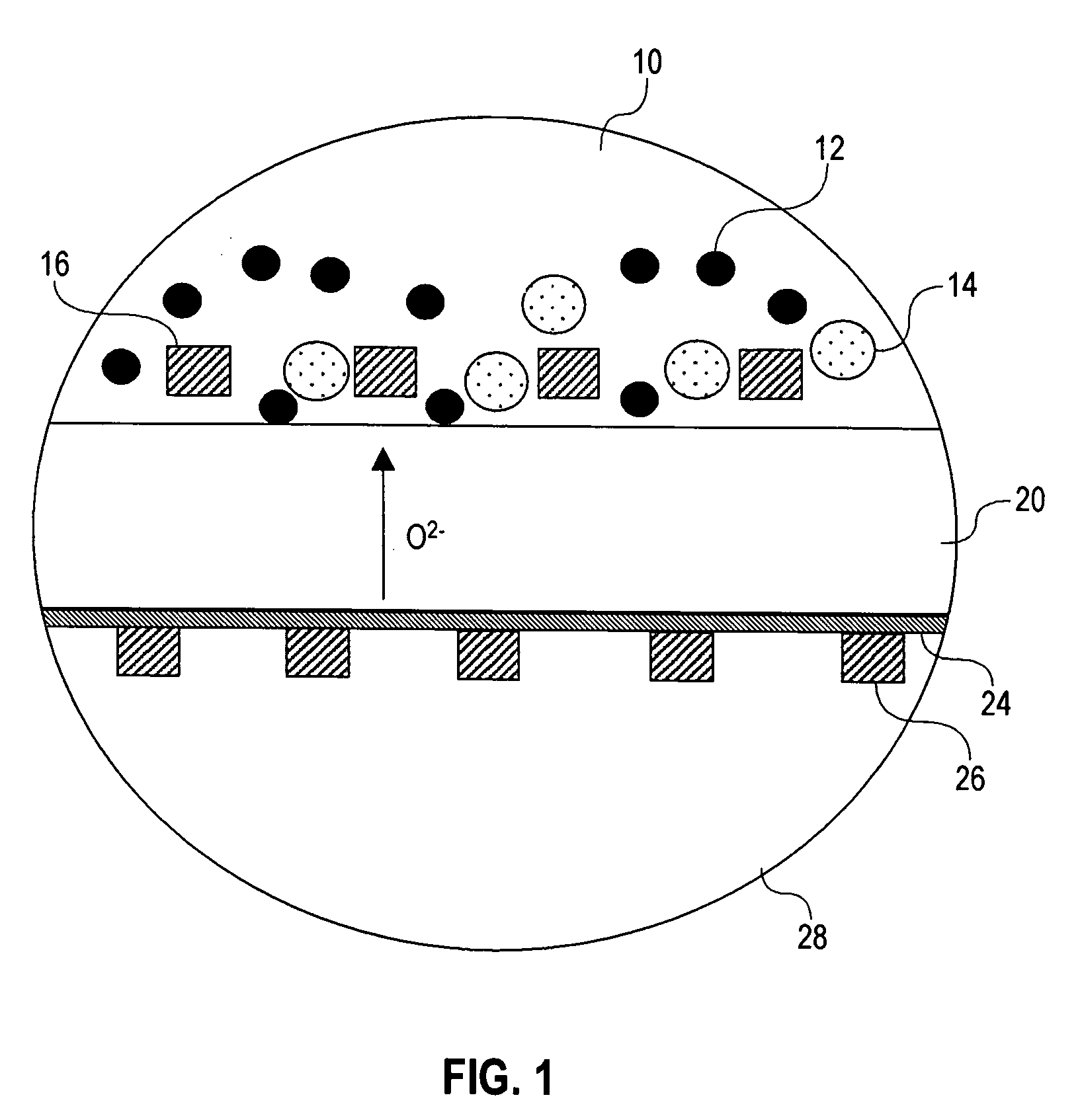
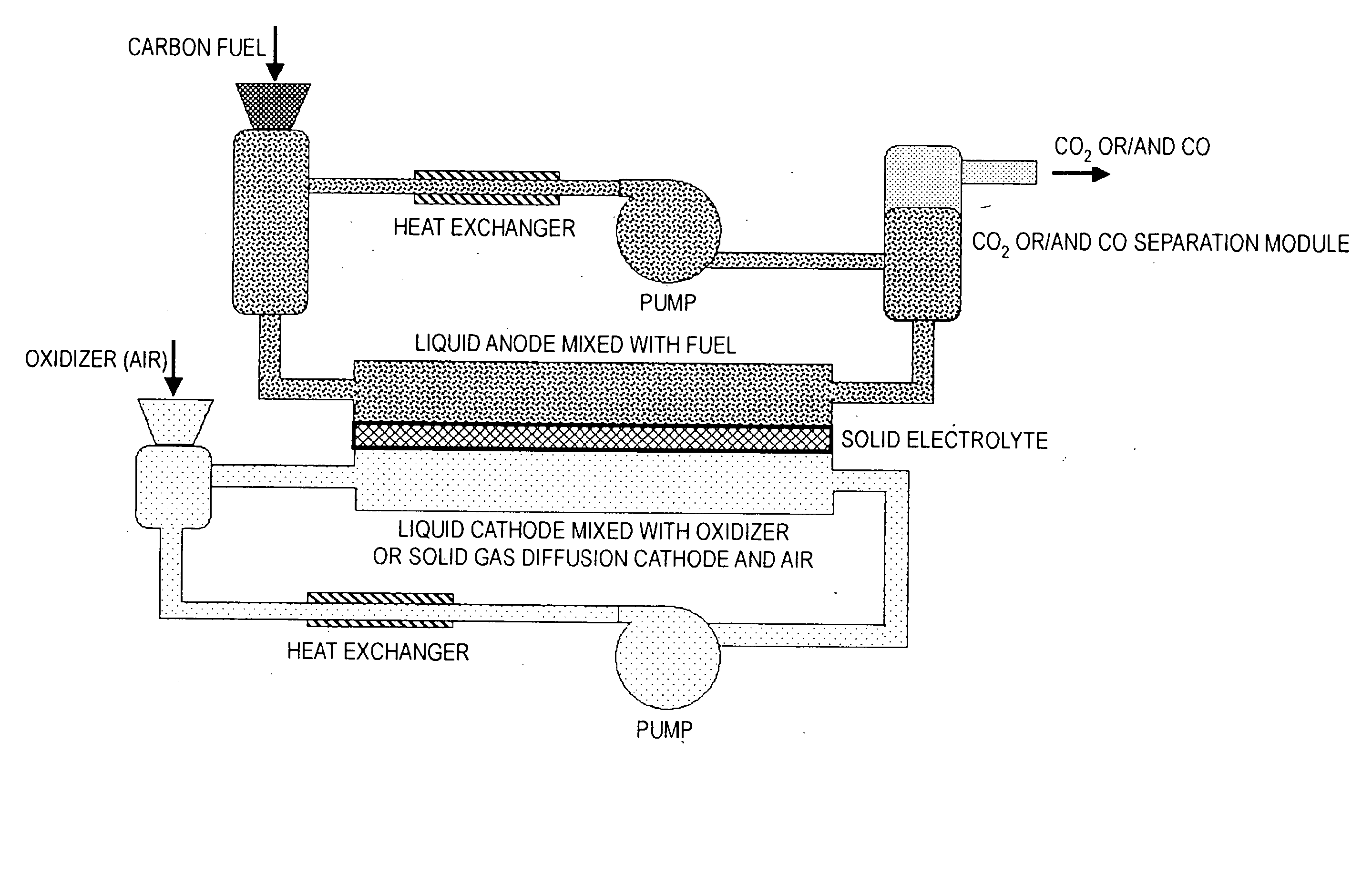
Liquid anode electrochemical cell
InactiveUS20060019132A1High voltageIncrease powerFuel cells groupingCell electrodesFuel cellsLiquid cathode
An electrochemical cell is provided which has a liquid anode. Preferably the liquid anode comprises molten salt and a fuel, which preferably has a significant elemental carbon content. The supply of fuel is preferably continuously replenished in the anode. Where the fuel contains or pyrolizes to elemental carbon, the reaction C+2O2−→CO2+4e− may occur at the anode. The electrochemical cell preferably has a solid electrolyte, which may be yttrium stabilized zirconia (YSZ). The electrolyte is connected to a solid or liquid cathode, which is given a supply of an oxidizer such as air. An ion such as O2− passes through the electrolyte. If O2− passes through the electrolyte from the anode to the cathode, a possible reaction at the cathode may be O2+4e−→2O2−. The electrochemical cell of the invention is preferably operated as a fuel cell, consuming fuel and producing electrical current.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
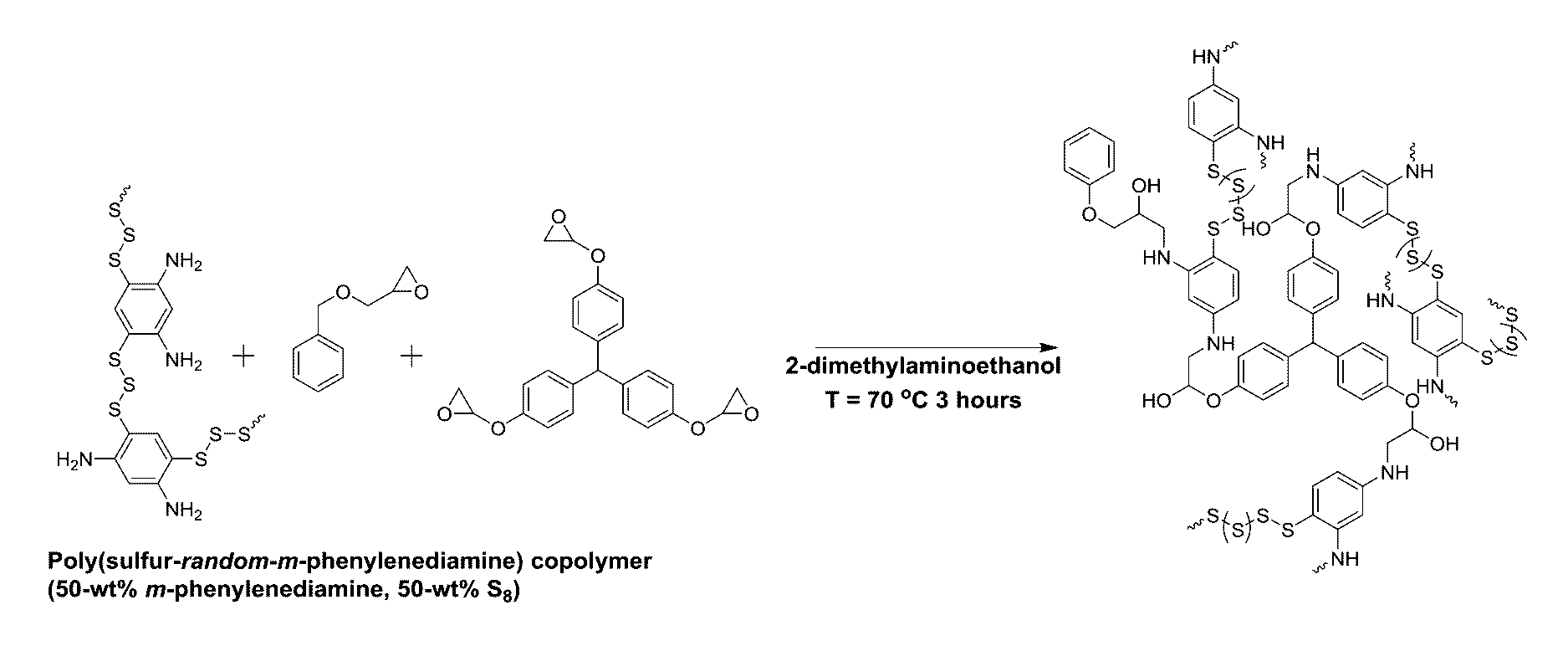
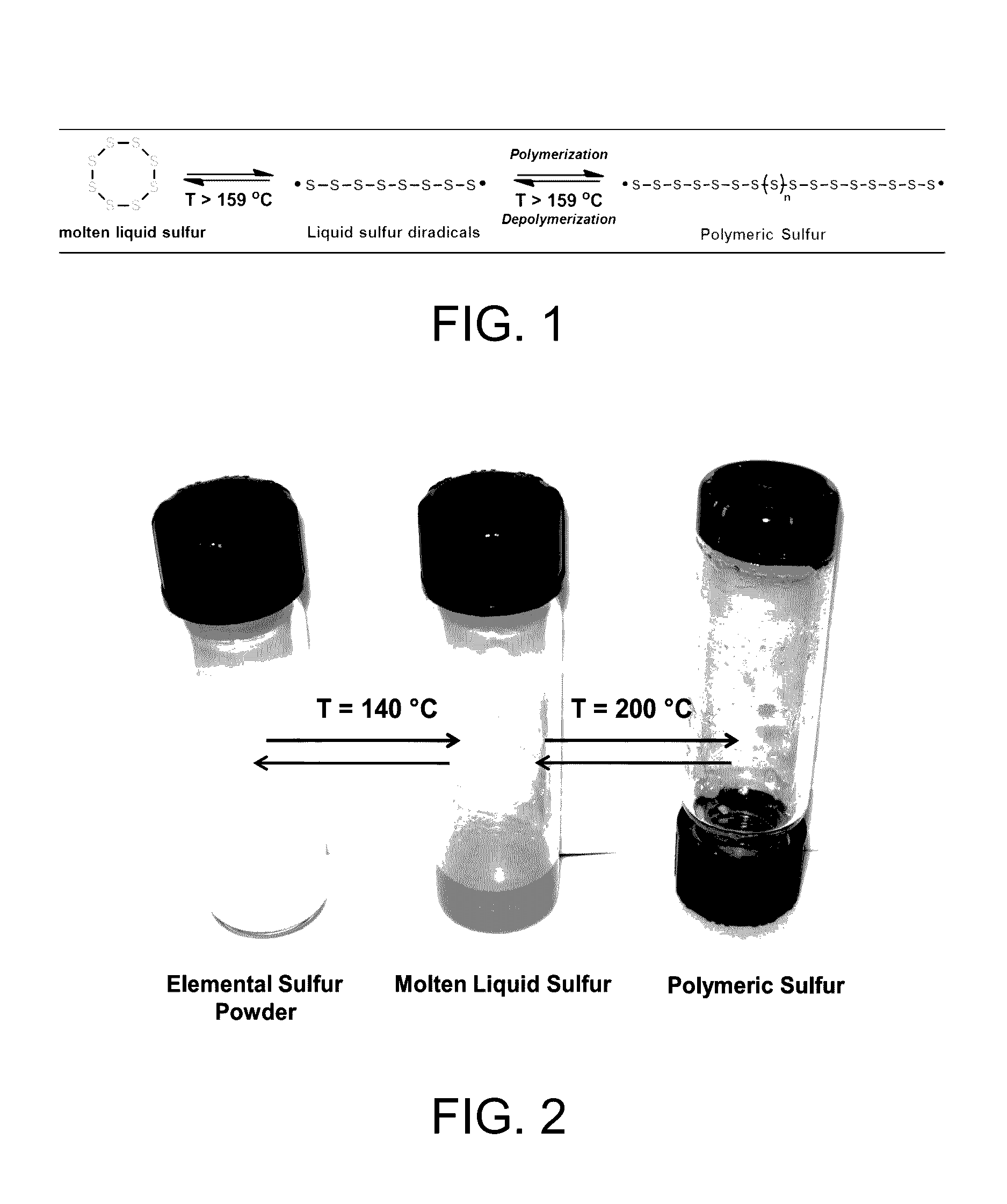
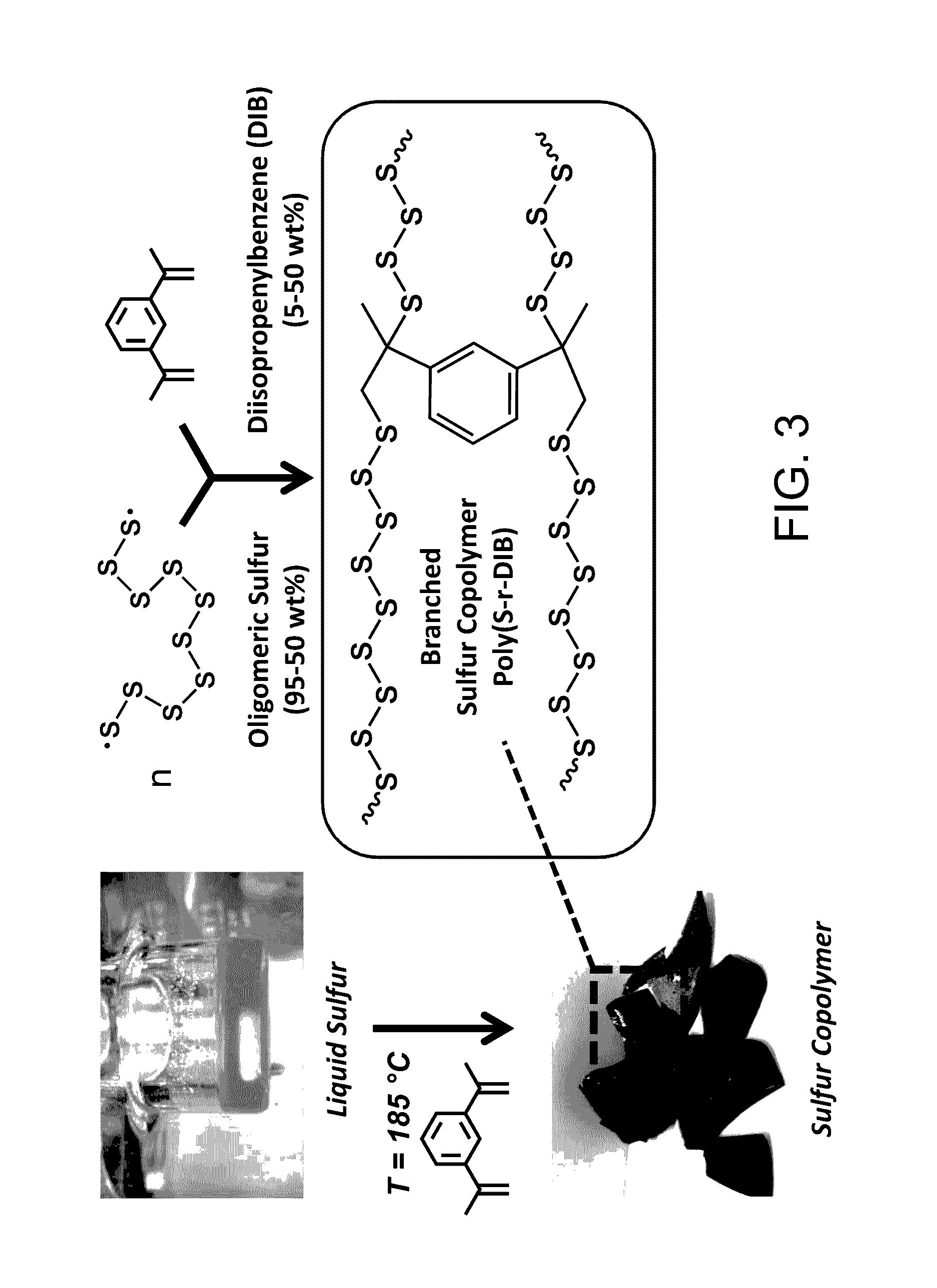
Sulfur composites and polymeric materials from elemental sulfur
ActiveUS9567439B1Increase heightSimple materialBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCeramic compositeSulfide
Sulfur composites and polymeric materials having a high sulfur content and prepared from elemental sulfur as the primary chemical feedstock. The sulfur copolymers are prepared by the polymerization of elemental sulfur with one or more monomers of amines, thiols, sulfides, alkynylly unsaturated monomers, nitrones, aldehydes, ketones, thiiranes, ethylenically unsaturated monomers, or epoxides. The sulfur copolymers may be further dispersed with metal or ceramic composites or copolymerized with elemental carbon, photoactive organic chromophores, or reactive and solubilizing / biocompatible moieties. The sulfur composites and polymeric materials feature the ability self-healing through thermal reformation. Applications utilizing the sulfur composites and polymeric materials may include electrochemical cells, optics, H2S donors and antimicrobial materials.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
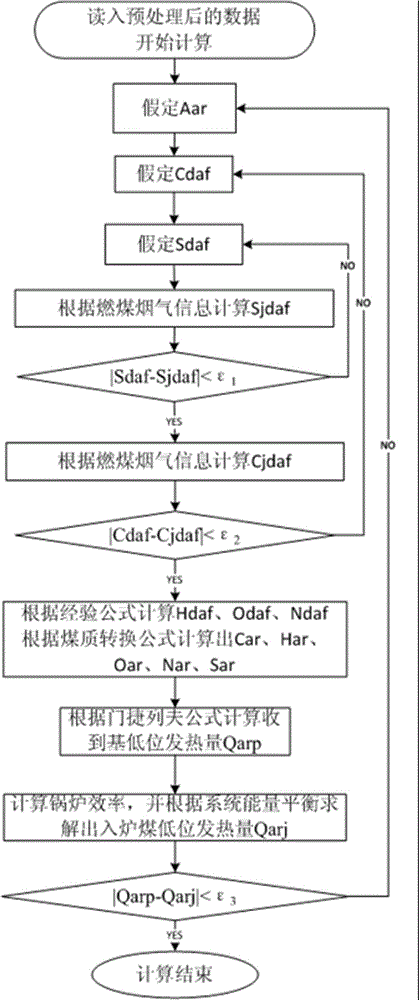
Coal-fired boiler coal quality on-line soft measurement method and system
ActiveCN104698149ARealize online measurementLow implementation costFuel testingSpecial data processing applicationsProcess engineeringEngineering
The invention discloses a coal-fired boiler coal quality on-line soft measurement method and system. The coal-fired boiler coal quality on-line soft measurement method includes the steps of (S100) the contents of the as received basis ash content Aar, the dry ash-free basis elemental carbon Cdaf and the dry ash-free basis elemental sulphur Sdaf are assumed; (S200) the uncompleted burned carbon consumption correction amount TCucr, the oxygen volume VO2-daf, the nitrogenn volume VN2-daf and CO2 volume gamma CO2, CO2 and SO2 gross capacity VRO2-daf are calculated according to the contents; (S300) iteration solving is carried out on the dry ash-free basis sulphur calculation value Sdafj, the dry ash-free basis carbon calculation value Cdafj and the fuel low-level heating amount calculation value Qarj according to the calculation values in the step (S200), and the values are output. Coal quality on-line soft measurement is achieved through the adoption of fire coal moisture on-line measurement information, boiler smoke data and unit running state data.
Owner:CHANGZHOU IND TECH RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of making clear glass composition
A technique of manufacturing glass having fairly clear color and / or high visible transmission is provided. In certain example embodiments of this invention, it has surprisingly been found that by using carbon-containing compound(s) including CxHyOz.mH2O, excellent melting and refining can be achieved in the manufacture of glass, and not as much ferrous iron is formed compared to the use of elemental carbon as a refining agent. Such compound(s) are especially advantageous when highly transparent clear glass is desired, in that less ferrous iron is formed and thus transmittance and coloration can be improved.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Vapor deposition processes for tantalum carbide nitride materials
ActiveUS7585762B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDeposition temperatureGas phase
Embodiments of the invention generally provide methods for depositing and compositions of tantalum carbide nitride materials. The methods include deposition processes that form predetermined compositions of the tantalum carbide nitride material by controlling the deposition temperature and the flow rate of a nitrogen-containing gas during a vapor deposition process, including thermal decomposition, CVD, pulsed-CVD, or ALD. In one embodiment, a method for forming a tantalum-containing material on a substrate is provided which includes heating the substrate to a temperature within a process chamber, and exposing the substrate to a nitrogen-containing gas and a process gas containing a tantalum precursor gas while depositing a tantalum carbide nitride material on the substrate. The method further provides that the tantalum carbide nitride material is crystalline and contains interstitial carbon and elemental carbon having an interstitial / elemental carbon atomic ratio of greater than 1, such as about 2, 3, 4, or greater.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Boron carbide based ceramic matrix composites
The present invention is a composite material, a process and a product formed by the process. The composite is formed by a process that includes forming a fibrous structure comprising fibers into a preform, coating the fibers of the fibrous structure preform with elemental carbon to impregnate that preform, infiltrating the preform with boron carbide to form an impregnated green body. The impregnated green body is infiltrated with liquid naphthalene or other carbon precursor, which is thereafter pyrolyzed to form a carbon char. Then, the char infiltrated green body is infiltrated with molten silicon to form a continuous matrix throughout the composite. The silicon in the continuous matrix is reacted with the carbon char to form silicon carbide.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Radial counterflow shear electrolysis
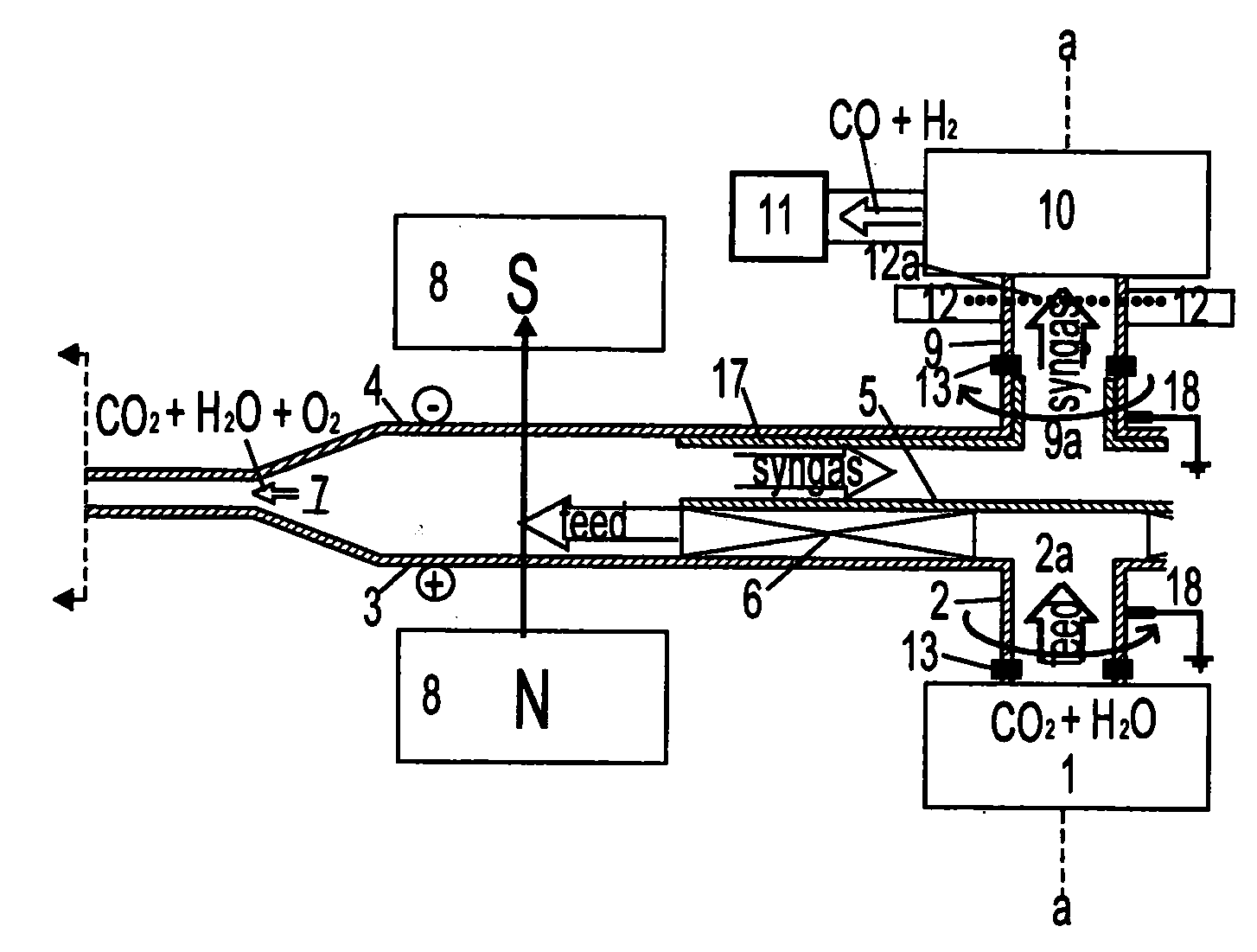
InactiveUS20090200176A1Clutter productionImprove the immunityCellsSurface reaction electrolytic coatingElectrolysisCarbon nanotube
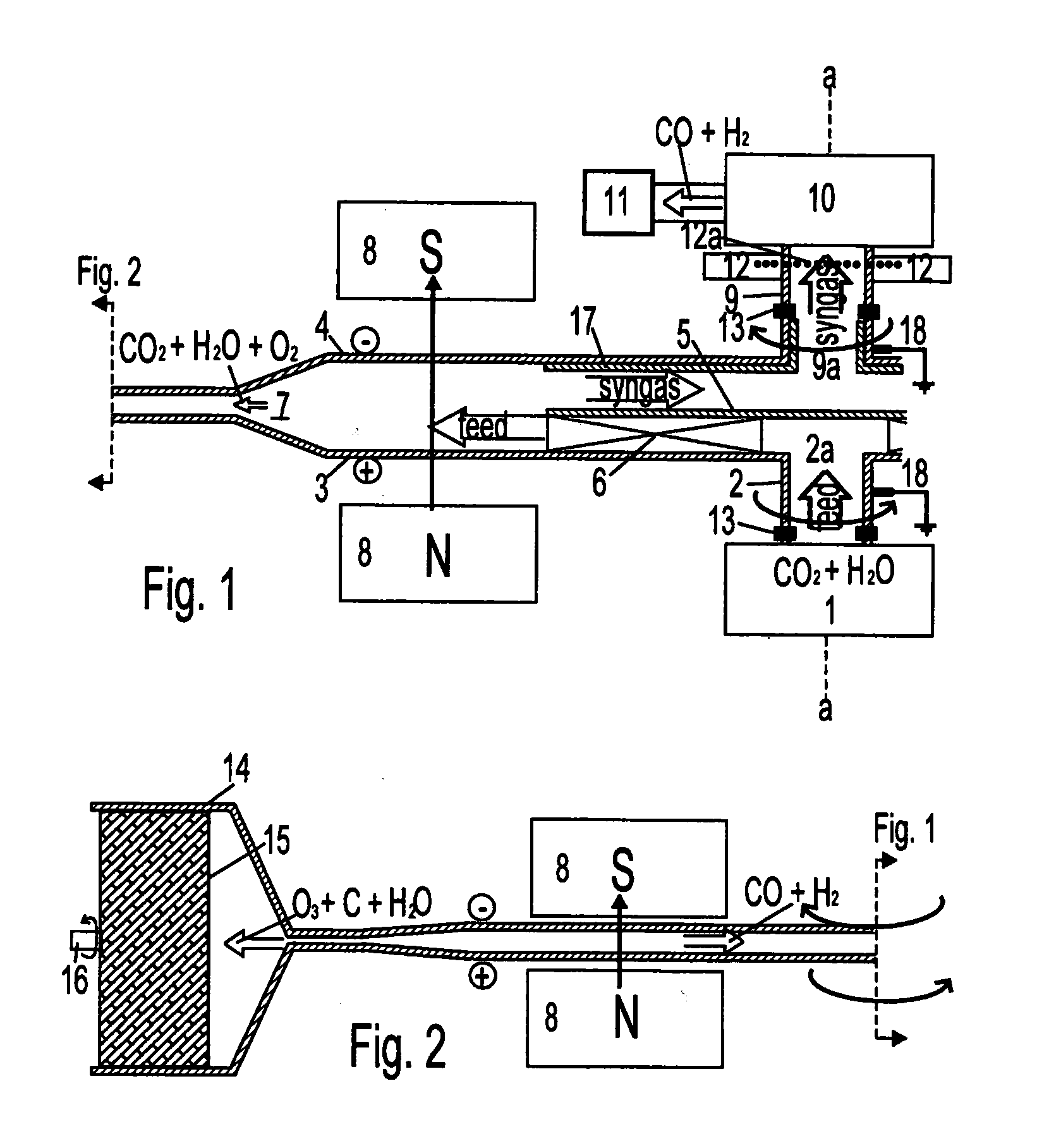
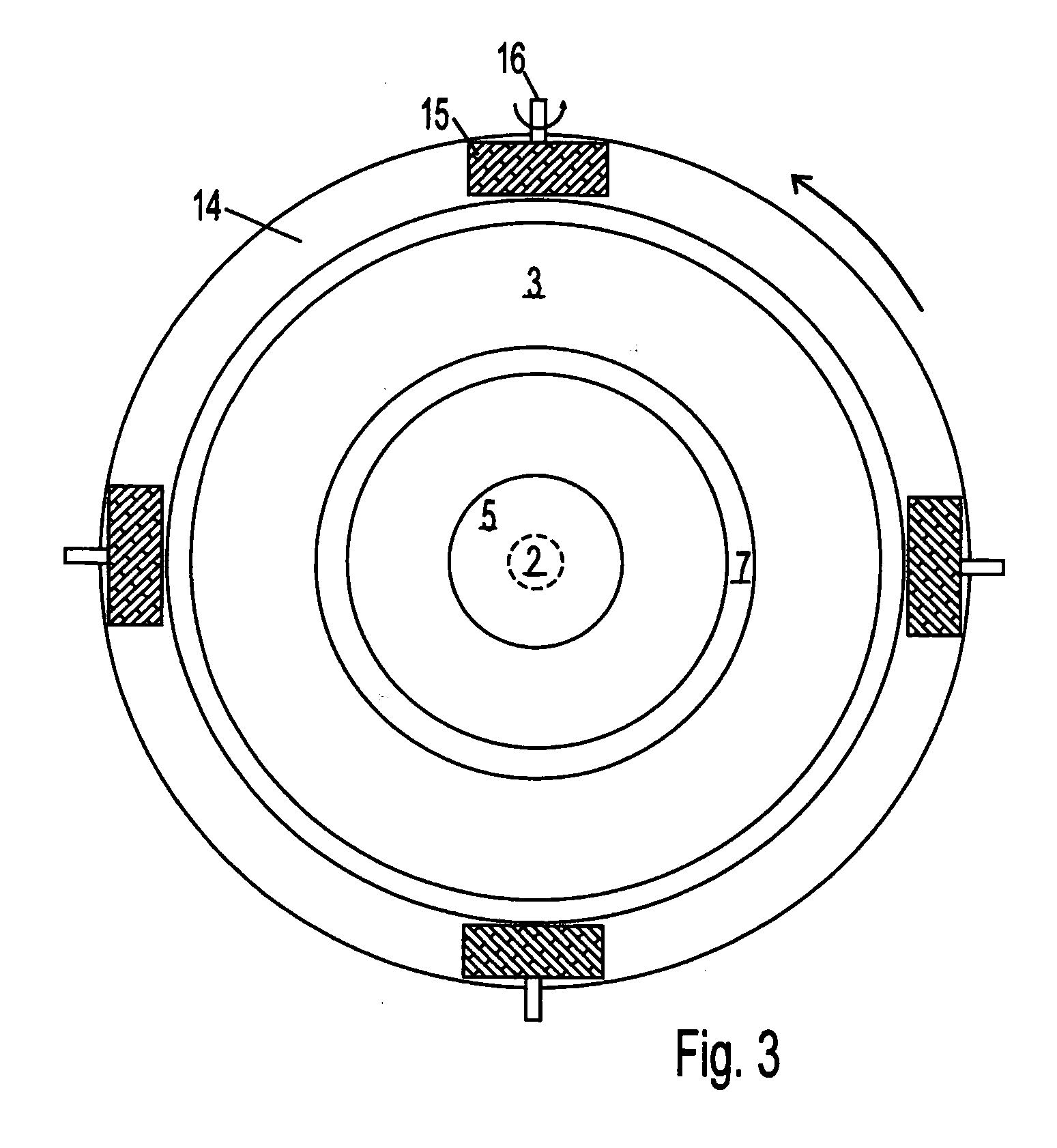
Coaxial disk armatures, counter-rotating through an axial magnetic field, act as electrolysis electrodes and high shear centrifugal impellers for an axial feed. The feed can be carbon dioxide, water, methane, or other substances requiring electrolysis. Carbon dioxide and water can be processed into syngas and ozone continuously, enabling carbon and oxygen recycling at power plants. Within the space between the counter-rotating disk electrodes, a shear layer comprising a fractal tree network of radial vortices provides sink flow conduits for light fractions, such as syngas, radially inward while the heavy fractions, such as ozone and elemental carbon flow radially outward in boundary layers against the disks and beyond the disk periphery, where they are recovered as valuable products, such as carbon nanotubes.
Owner:VORSANA INC
Adsorptive photo-catalytic oxidation air purification device
An air purification system formed from an adsorptive photocatalytic oxidation device and a method of regenerating the oxidation device is disclosed. The air purification system may be configured to be installed within an air duct of a central air handling system. The air purification system may also include an ultraviolet light emitted by the ultraviolet light source to break down captured volatile organic compounds into elemental carbon dioxide and water vapor, and to irradiate air moving past the ultraviolet light and surfaces to reduce contaminants. The ultraviolet light source may be positioned to expose the adsorptive photocatalytic oxidation device to ultraviolet light emitted by the ultraviolet light source to break down captured volatile organic compounds into elemental carbon dioxide and water vapor, and to irradiate air moving past the ultraviolet light to reduce contaminants.
Owner:TRIATOMIC ENVIRONMENTAL
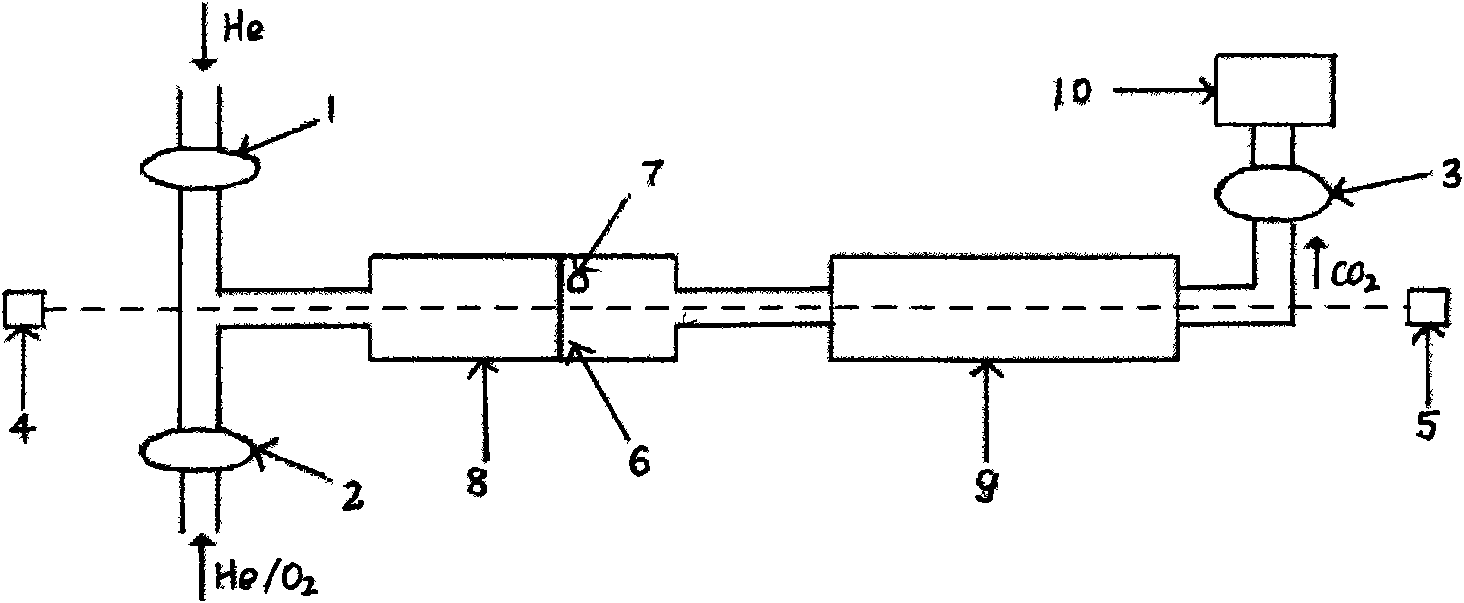
Equipment and method for automatically detecting mass concentration of organic carbon/elemental carbon in atmospheric aerosol
ActiveCN101592607ASolve the problem of inability to measure organic carbonSimple structurePreparing sample for investigationTransmissivity measurementsCombustionDecomposition
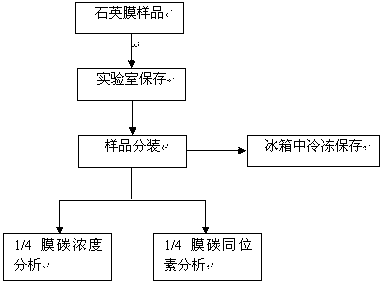
The invention discloses equipment and a method for automatically detecting mass concentration of organic carbon / elemental carbon in atmospheric aerosol. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, collecting particles to be detected on a quartz filter film; and heating the quartz filter film loaded with the particles in the environment of He gas, taking the carbon volatilized during the temperature rise as the organic carbon, heating the quartz filter film in the environment of He / O2 carrier gas, during which the elemental carbon is oxidized, decomposed and escapes. Through the whole process, a laser beam is irradiated on the quartz film, the transmission light of the laser beam is weakened in the carbonization of the organic carbon and strengthened in the oxidizing decomposition of the elemental carbon. The dividing point of the organic carbon and the elemental carbon is decided at the time when the transmission light of the laser beam recovers the original optical intensity, namely the carbon detected before the time is taken as the organic carbon, and the carbon detected after the time is taken as the elemental carbon. The equipment consists of the quartz filter film, a combustion furnace, an oxidation furnace, a CO2 detector, and a laser detection unit. The method realizes detecting the mass concentration of the organic carbon / elemental carbon in the atmospheric aerosol more scientifically and accurately.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of producing a melt-infiltrated ceramic matrix composite article
A process for producing silicon-containing CMC articles. The process entails producing a matrix slurry composition that contains at least one resin binder and a SiC powder. The SiC powder is a precursor for a SiC matrix of the CMC article and the resin binder is a precursor for a carbon char of the matrix. A fiber reinforcement material is impregnated with the slurry composition to yield a preform, which is then heated to form a porous preform that contains the SiC matrix and porosity and to convert the resin binder to the carbon char that is present within the porosity. Melt infiltration of the porosity is then performed with molten silicon or a molten silicon-containing alloy to react the carbon char and form silicon carbide that at least partially fills the porosity within the porous preform. The carbon char constitutes essentially all of the elemental carbon in the porous preform.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Liquid anode electrochemical cell
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
System and method for surface hardening of refractory metals
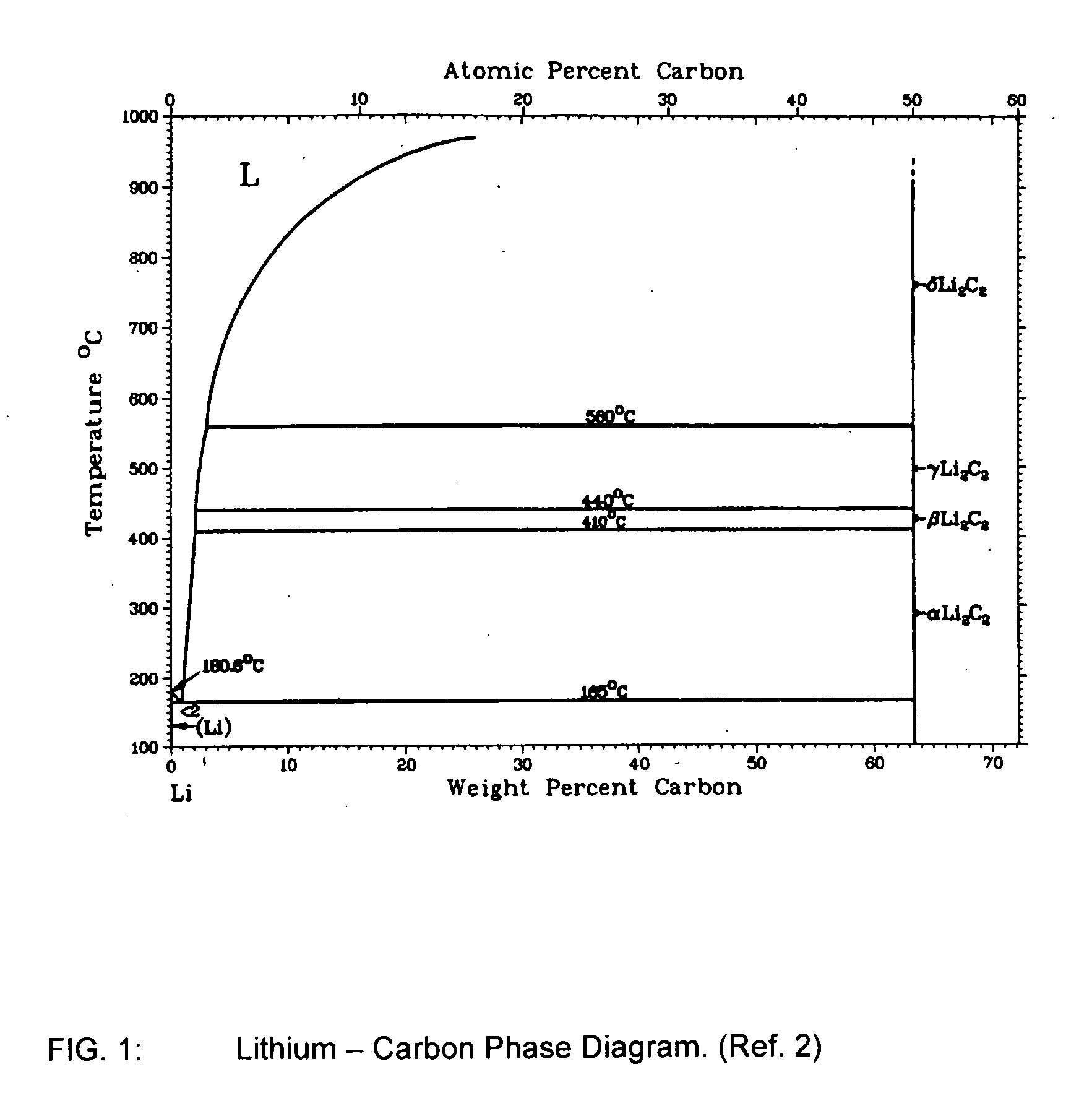
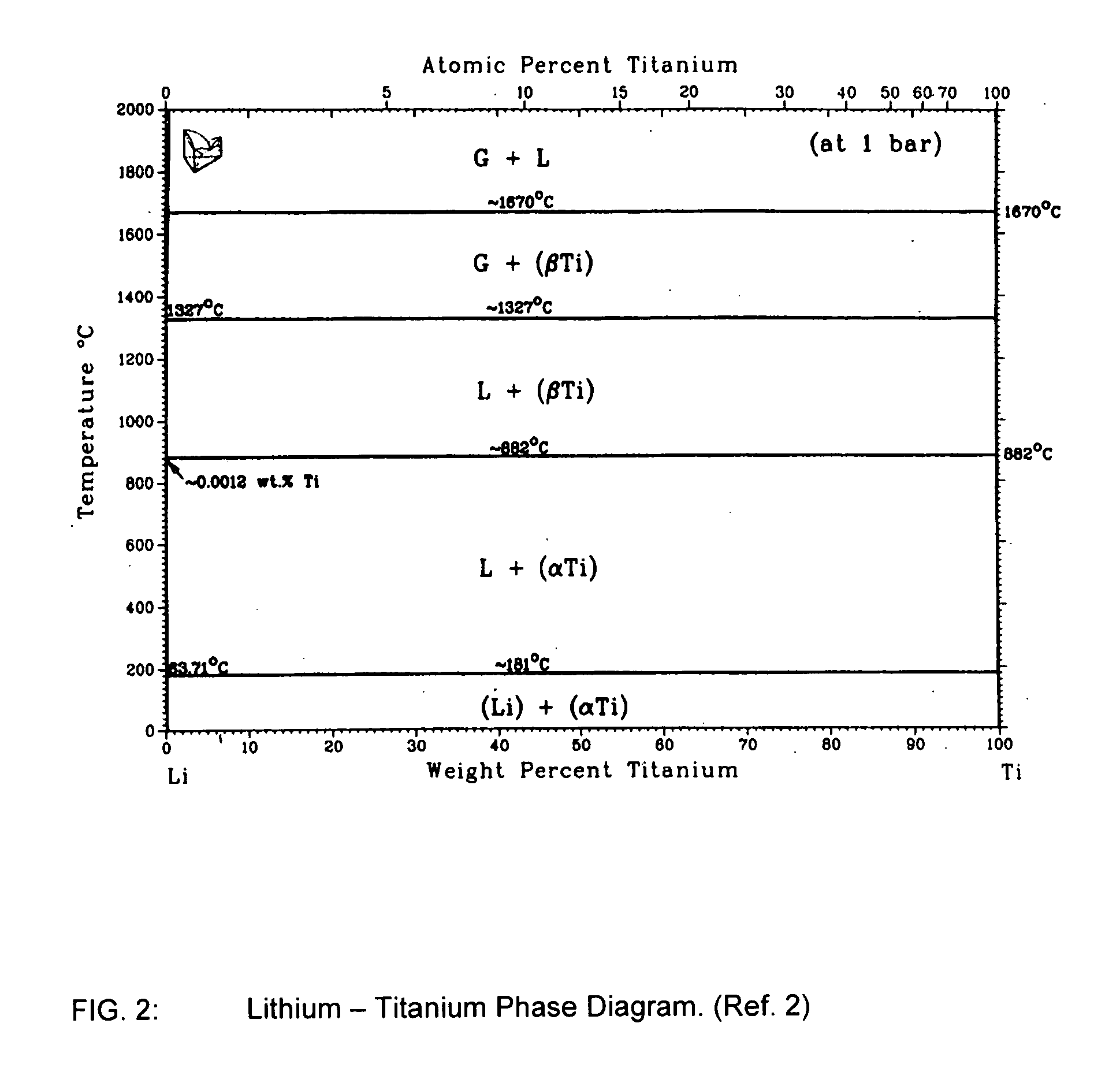
A process of converting an outer layer of an object made of a refractory metal, such as titanium, into a carbide of the refractory metal. A molten metal, such as molten lithium, is placed adjacent the outer surface of the object. The lithium does not react with the titanium, nor is it soluble within the titanium to any significant extent at the temperatures involved. The molten lithium contains elemental carbon, that is, free carbon atoms. At high temperature, the carbon diffuses into the titanium, and reacts with titanium atoms to form titanium carbide in an outer layer. Significantly, no other atoms are present, such as hydrogen or oxygen, which can cause problems, because they are blocked by the molten lithium.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS LAND & ARMAMENTS LP
Method for analyzing source of secondary organic carbon in ambient air fine particles
InactiveCN103226128AAvoid errorsThe analysis results are accurate and reliableMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSoil scienceFine particulate
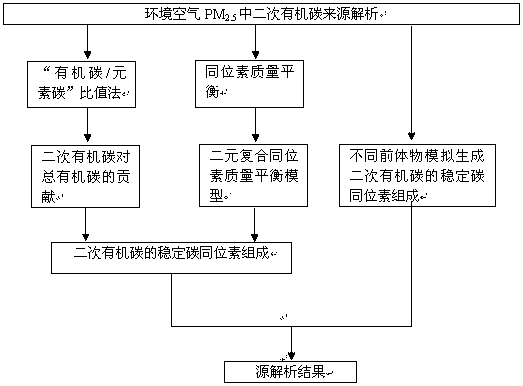
The invention relates to a method for analyzing a source of secondary organic carbon in ambient air fine particles. The method comprises: determining concentrations and stable carbon isotope compositions of organic carbon and elemental carbon in ambient air fine particle PM2.5; calculating to obtain stable carbon isotope composition of secondary organic carbon in the ambient air fine particle PM2.5; and finally adopting a stable carbon isotope technology to analyze a source of the secondary organic carbon in the ambient air fine particle PM2.5. According to the present invention, a binary composite isotope mass balance model is adopted to calculate the carbon isotope composition of the secondary organic carbon, such that problems that the secondary organic carbon is difficultly separated from the organic carbon and determination of the carbon isotope composition of the secondary organic carbon is difficult are solved, a new method for analyzing the source of the secondary organic carbon is provided, and problems that tracers are limited and identification is difficult of the existing organic molecule tracer method are avoided.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
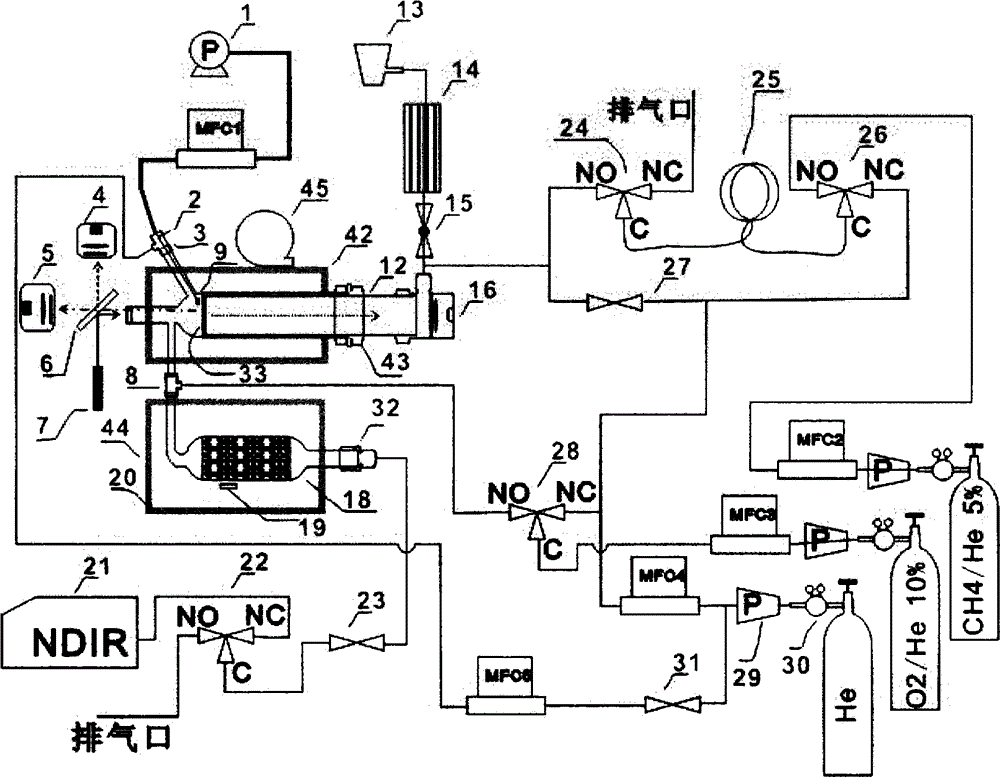
Orthogonal light path-based equipment for online monitoring concentration of organic carbon/elemental carbon in PM (Particulate Matter) 2.5
ActiveCN104132893AReal-time acquisitionAutomate analysisColor/spectral properties measurementsMicrocontrollerOptoelectronics
The invention discloses orthogonal light path-based equipment for online monitoring the concentration of organic carbon / elemental carbon in PM (Particulate Matter) 2.5. The orthogonal light path-based equipment comprises an on-line sampling unit, a sample processing and detecting unit and an orthogonal light path system, and is characterized in that the sampling unit comprises a vacuum pump, a mass flow controller, a quartz filtering membrane, a ball valve, a volatilizable organic matter denuder, and a PM2.5 cutting head; the sample processing and detecting unit comprises a digestion furnace, an oxidation furnace, a gas path control network, a carrier gas source and a non-deviation infrared detector; the orthogonal light path system comprises a laser, a light beam splitter, a reference light path photoelectric detection unit, a quartz filtering membrane transmission light path photoelectric detection unit and a reflection light path photoelectric detection unit; and three gases of high-purity He, 5 percent O2 / He and 5 percent CH4 / He are required to be controlled by a gas path valve network by a singlechip. The orthogonal light path-based equipment is capable of simultaneously detecting light intensity values of incident laser, sampled reflected light and transmitted light of the quartz filtering membrane, and relatively accurately achieving the segmentation of the organic carbon and the elemental carbon.
Owner:CECEP TIANRONG TECH CO LTD
Method for on board decarbonization of hydrocarbon fuels in a vehicle
ActiveUS20100175639A1Significant positive effectRaise the ratioHydrogenInternal combustion piston enginesHydrogenInternal combustion engine
A method and apparatus for the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions by the on-hoard treatment of a portion or all of the hydrocarbon fuel used to power an internal combustion engine mounted in a conventional transportation vehicle, utilize known decarbonization technology to break the fuel's hydrogen-carbon bond. The compounds are then cooled and separated into (1) elemental carbon powder that is stored on-board for later recovery and industrial use, and (2) hydrogen, or a hydrogen-rich gas stream, that is burned as a fuel in the ICE and / or diverted to other on-board energy related applications.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
SiC ceramic structural part and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108947537AReduce porosityHigh densityAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusPorositySelective laser sintering
The invention discloses a SiC ceramic structural part and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: mixing SiC powder, C powder and adhesive powder, and preparing a ceramic body by SLS (Selective Laser Sintering). Firstly, appropriate grain composition uniform mixed powder is selected for printing forming, and the ceramic body is treated by an isostatic cool pressingtechnology, so that powder particles in the ceramic body are tightly arranged, and the density of the ceramic body is improved; and then, by virtue of siliconizing reaction sintering, SiC is formed byelemental silicon and elemental carbon particles in the sintering process, presence of the elemental silicon in the test piece is reduced, the density of the test piece is further improved by the SiCproduced in the reaction, the porosity of the test piece is reduced, and the mechanical property of the test piece is improved; and when the SiC ceramic is subjected to 3D printing in the method, thepowder C serves as one of the raw materials, the grain composition of the powder C and powder SiC is adjusted, and preparation is made for subsequent isostatic cool pressing and reactive sintering. The structural part prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has the density of 3.01-3.11g / cm<3> and the bending strength of 290-330 MPa.
Owner:NAT INST CORP OF ADDITIVE MFG XIAN
Synthesis of metal compounds useful as cathode active materials
The active material of the present invention includes at least one alkali metal and at least one other metal capable of being oxidized to a higher oxidation state. Preferred other metals are accordingly selected from transition metals (as defined in groups 4-11 of the periodic table), and certain other non-transition metals such as tin, bismuth and lead. The active material can be synthesized through a single-step reaction or a multi-step reaction. In at least one step of the synthesis reaction, reducing carbon is used as a starting material. In one aspect, the reducing carbon is supplied by elemental carbon, preferably in particulate form such as graphite, amorphous carbon, carbon black, and the like. On the other hand, the reducing carbon can also be supplied from an organic precursor material, or a mixture of elemental carbon and an organic precursor material.
Owner:VALENCE TECH INC
Method of producing silicon carbide
InactiveUS6554897B2Avoid depositionPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesGraphitePhysical separation
A method of producing silicon carbide (SiC), by introducing into the interior of a furnace a quantity of relatively pure elemental silicon and a quantity of elemental carbon; subjecting the interior of the furnace to a vacuum; and heating the silicon and carbon to a temperature of 1500° C.-2200° C. to vaporize the silicon and to react it with the carbon to produce silicon carbide. Several embodiments are described for producing a heating or lighting element and a high temperature sensor, respectively, in which the carbon is in the form of a shaped body made of a mixture of finely-divided particles of carbon in a binder, and the silicon is in the form of finely-divided particles applied to the outer surface of the shaped body. A further embodiment is described for producing silicon carbide powder, in which the carbon and silicon are each in the form of finely-divided particles, and are physically separated from each other by a graphite sheet permeable to silicon vapor.
Owner:SILBID
Method And System For Removing Pollutants And Greenhouse Gases From A Flue Gas
InactiveUS20120121489A1Increase productivityCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsCounter flowCarbon particle
The invention relates to a method for removing pollutants and greenhouse gases SO2, NOx, and CO2 from a flue gas stream, comprising the steps of: a) contacting natural seawater with a flue gas in a counter flow, co-current flow or cross flow direction for a given period of time to remove SO2 from the flue gas; b) contacting treated alkaline water to the flue gas in a counter flow, co-current flow or cross flow direction to remove CO2 and NOx from the flue gas and generate oxygen and carbon particles; and c) collecting or emitting the flue gas after step b). The invention also relates to a system for removing pollutants and greenhouse gases SO2, NOx, and CO2 from a flue gas stream. The method and the system of the invention are significantly more economical and convenient and do not cause harm to the environments. The invention also exhibits a novel and unique feature that elemental carbon and oxygen are generated as final products and can be recovered as an energy source.
Owner:ECOSPEC GLOBAL TECH PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com