Patents
Literature
1221 results about "Oxidation state" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The oxidation state, sometimes referred to as oxidation number, describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state, which may be positive, negative or zero, is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic, with no covalent component. This is never exactly true for real bonds.
Coupled electrochromic compounds with photostable dication oxidation states
InactiveUS6249369B1High photochemical stabilityTenebresent compositionsNon-linear opticsAction spectrumElectronic communication
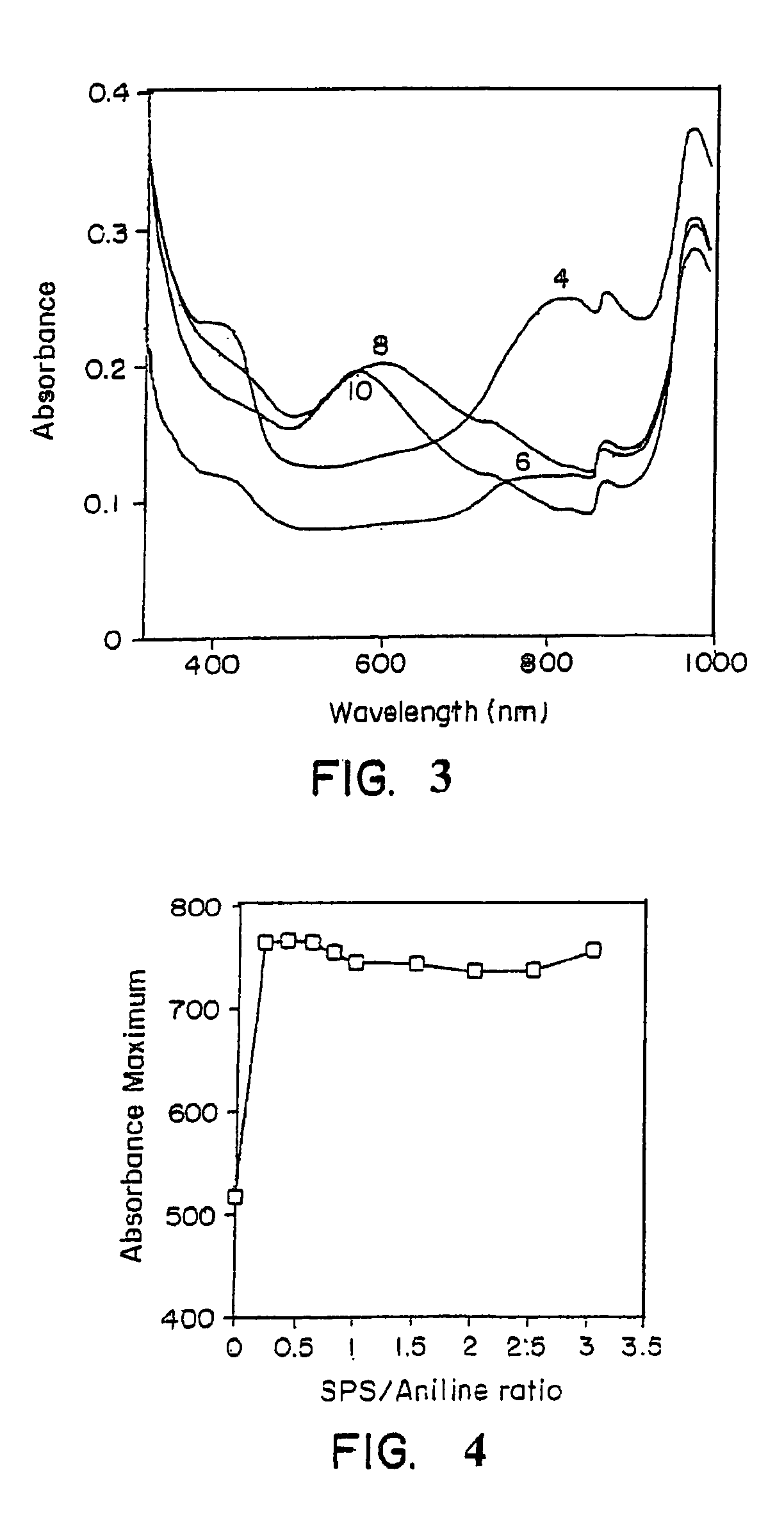
Coupling of anodic electrochromic compounds by a covalent bond or a bridge link which provides for electronic communication between the coupled electrochromic compounds results in coupled electrochromic compounds which exhibit greater stability as well as electrochromic activity that differs from the monomeric electrochromic compounds. Extension of the absorption spectrum into the near-infrared region of the spectrum is frequently observed. The coupled electrochromic compounds are highly suitable for use in electrochromic media used to produce electrochromic devices.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
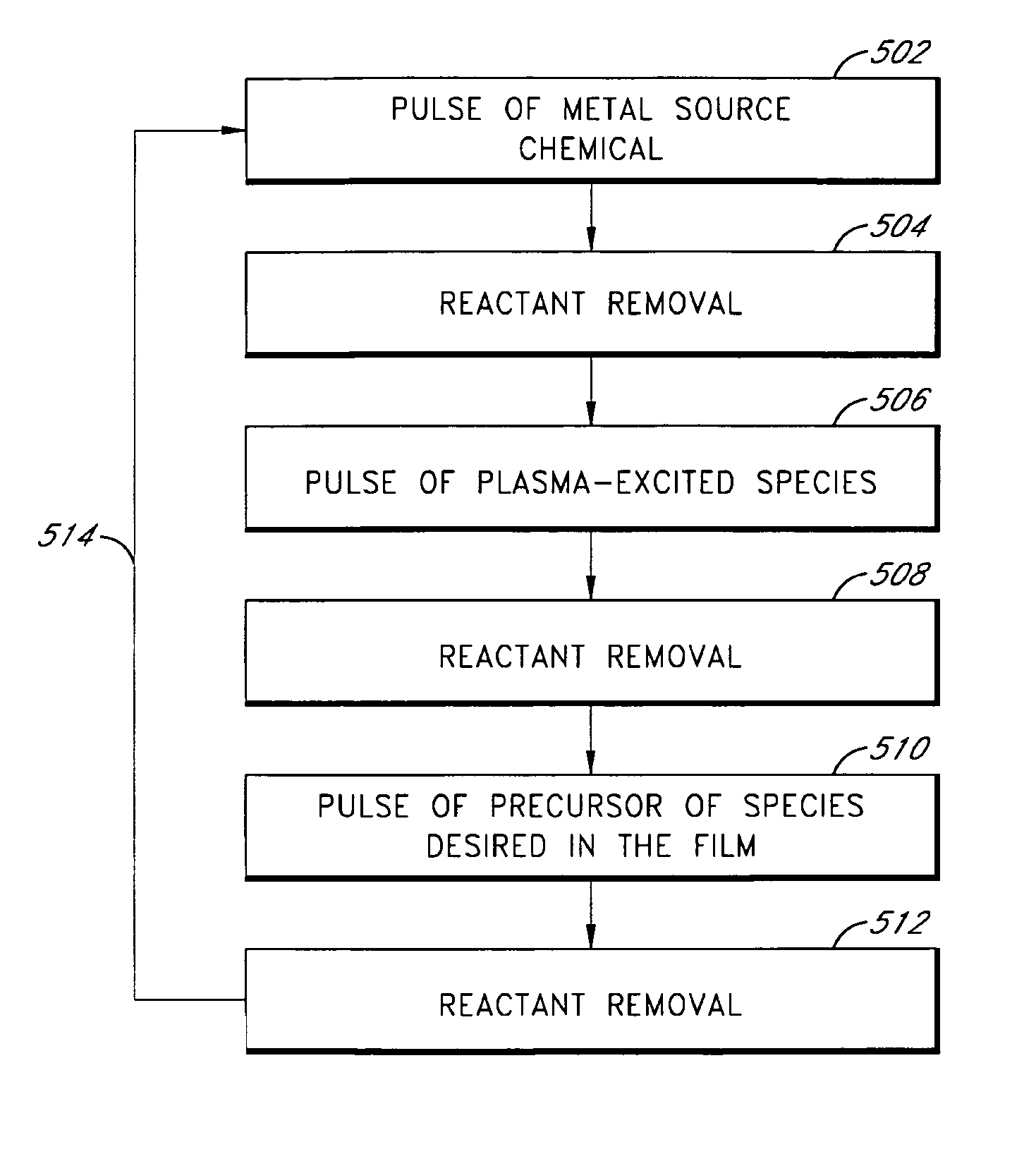
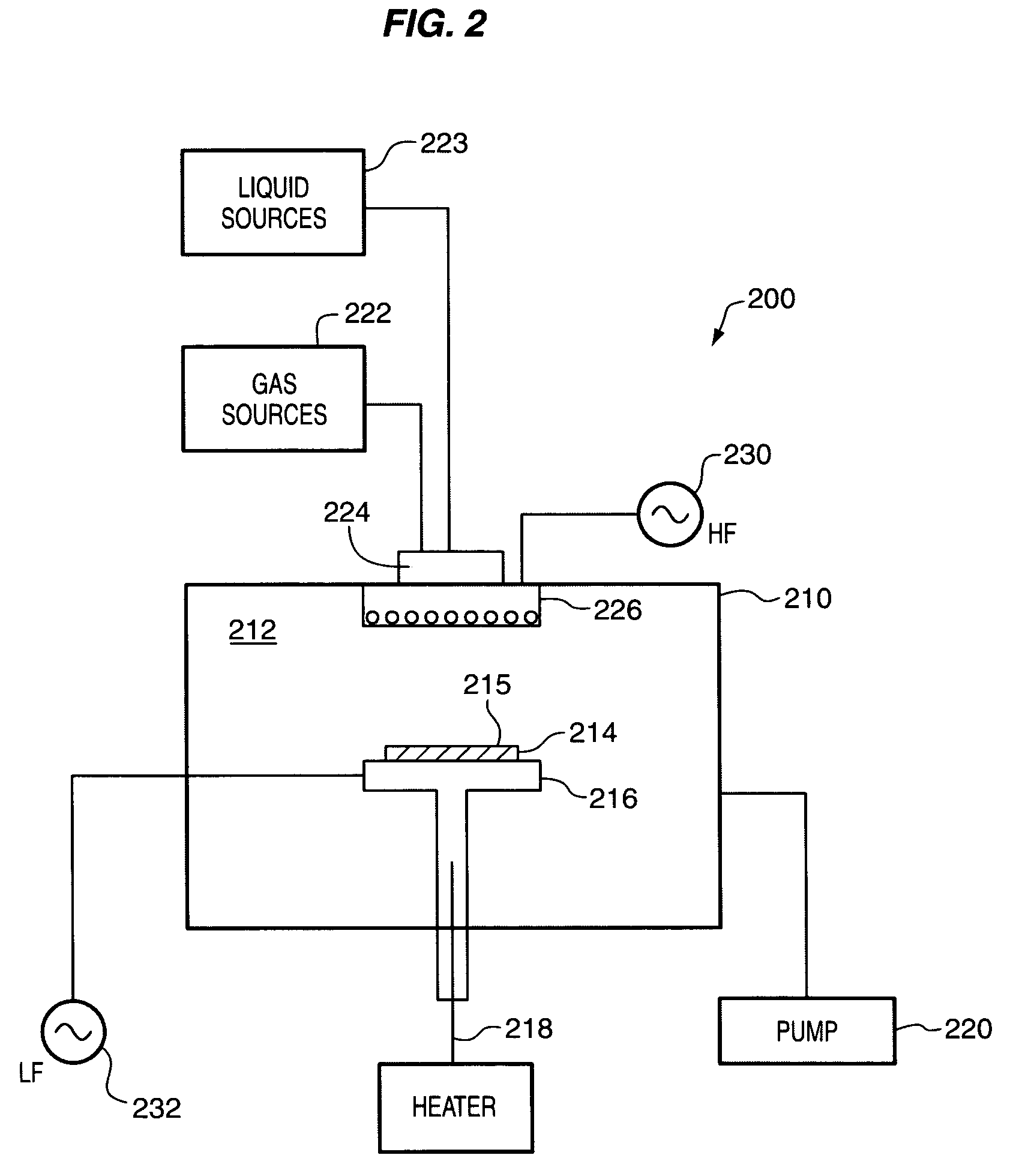
Controlled composition using plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition
ActiveUS7727864B2Easily and accurately adjusted to a desired valueSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingOxidation stateWork function
Metallic-compound films are formed by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD). According to preferred methods, film or thin film composition is controlled by selecting plasma parameters to tune the oxidation state of a metal (or plurality of metals) in the film. In some embodiments, plasma parameters are selected to achieve metal-rich metallic-compound films. The metallic-compound films can be components of gate stacks, such as gate electrodes. Plasma parameters can be selected to achieve a gate stack with a predetermined work function.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
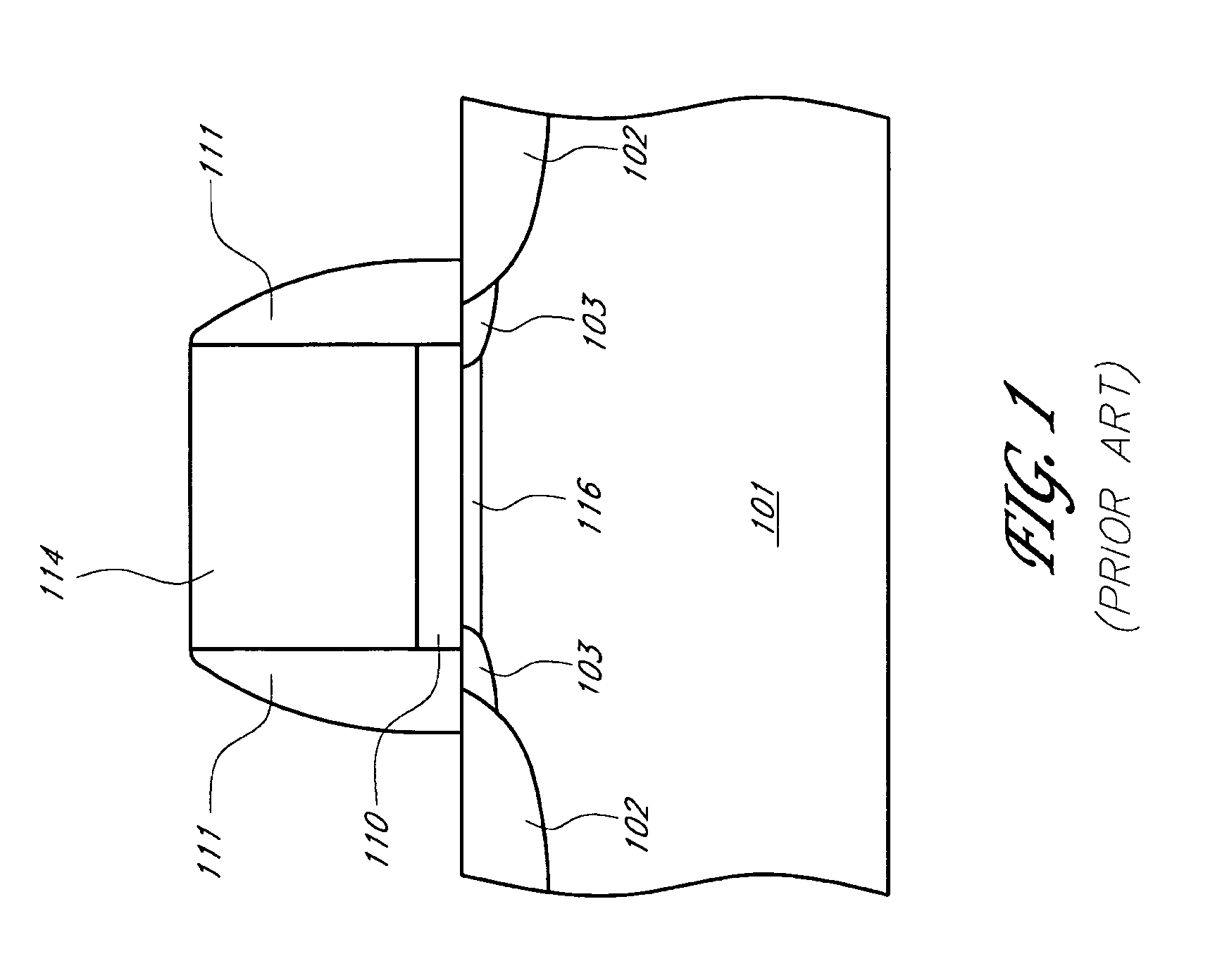
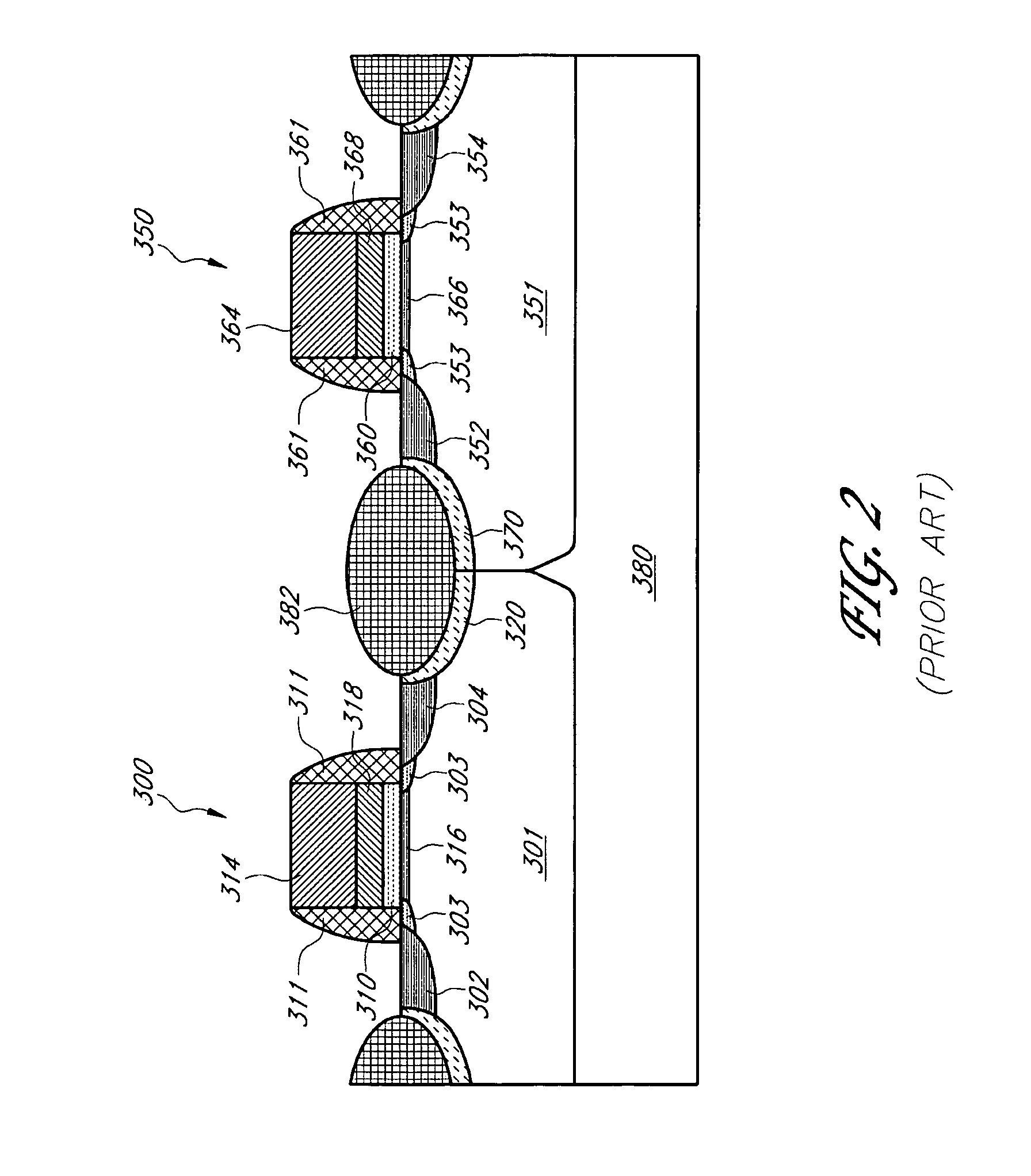
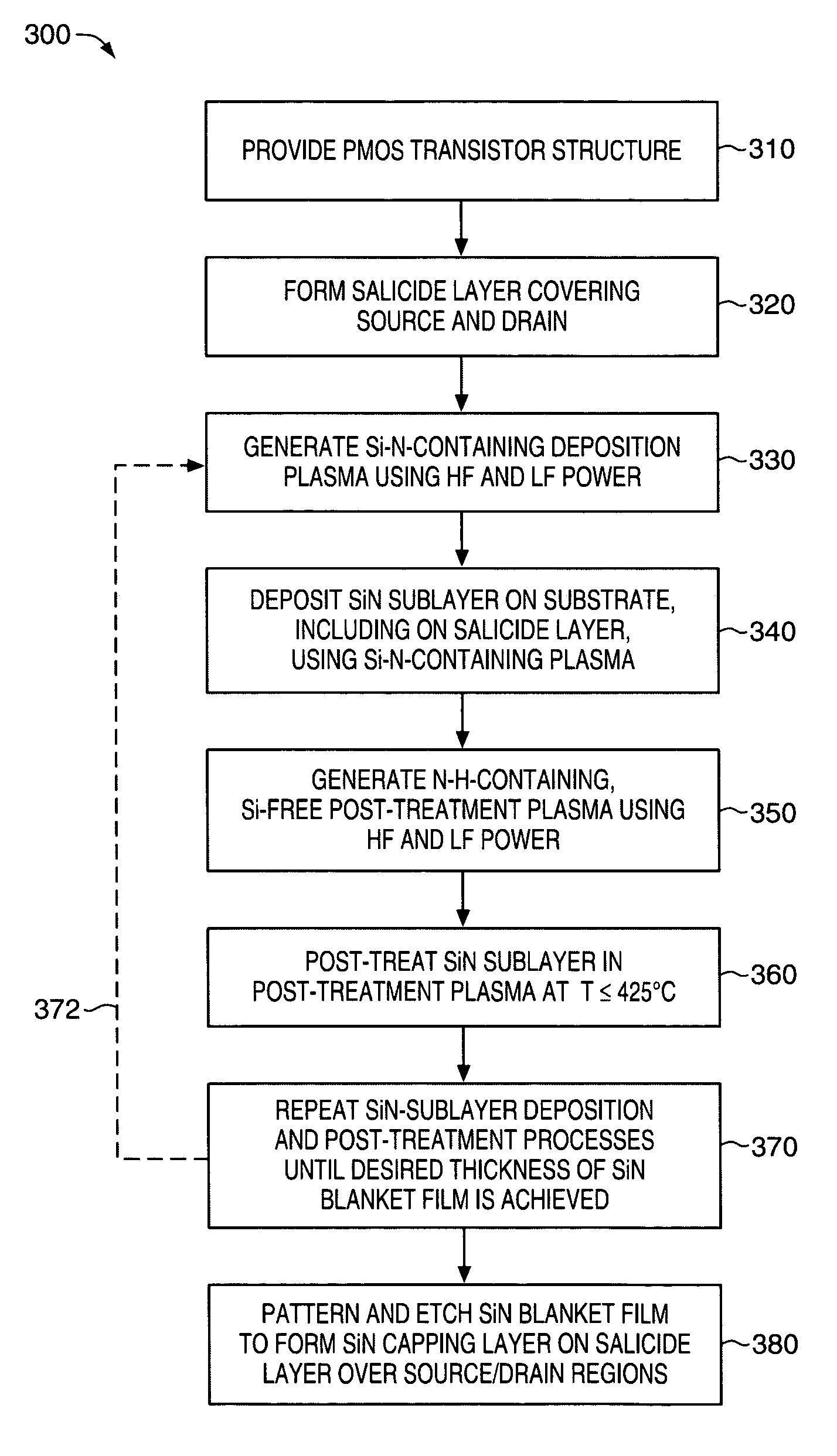
PMOS transistor with compressive dielectric capping layer
ActiveUS7214630B1Preserving material qualityImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSalicideOxidation state
A salicide layer is deposited on the source / drain regions of a PMOS transistor. A dielectric capping layer having residual compressive stress is formed on the salicide layer by depositing a plurality of PECVD dielectric sublayers and plasma-treating each sublayer. Compressive stress from the dielectric capping layer is uniaxially transferred to the PMOS channel through the source-drain regions to create compressive strain in the PMOS channel. To form a compressive dielectric layer, a deposition reactant mixture containing A1 atoms and A2 atoms is provided in a vacuum chamber. Element A2 is more electronegative than element A1, and A1 atoms have a positive oxidation state and A2 atoms have a negative oxidation state when A1 atoms are bonded with A2 atoms. A deposition plasma is generated by applying HF and LF radio-frequency power to the deposition reactant mixture, and a sublayer of compressive dielectric material is deposited. A post-treatment plasma is generated by applying HF and LF radio-frequency power to a post-treatment gas that does not contain at least one of A1 atoms and A2 atoms. Compressive stress in the dielectric sublayer is increased by treating the sublayer in the post-treatment plasma. Processes of depositing a dielectric sublayer and post-treating the sublayer in plasma are repeated until a desired thickness is achieved. The resulting dielectric layer has residual compressive stress.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
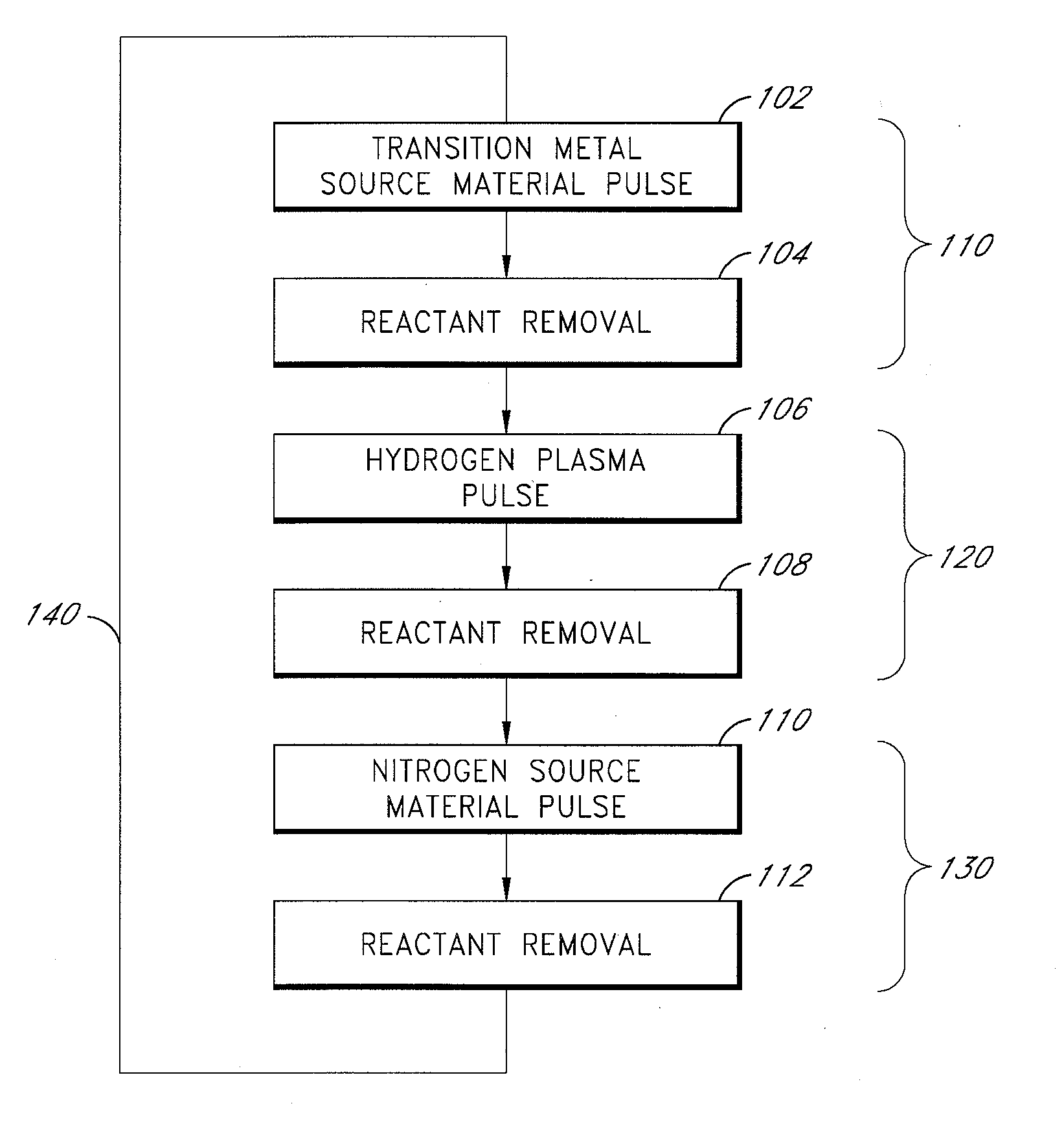
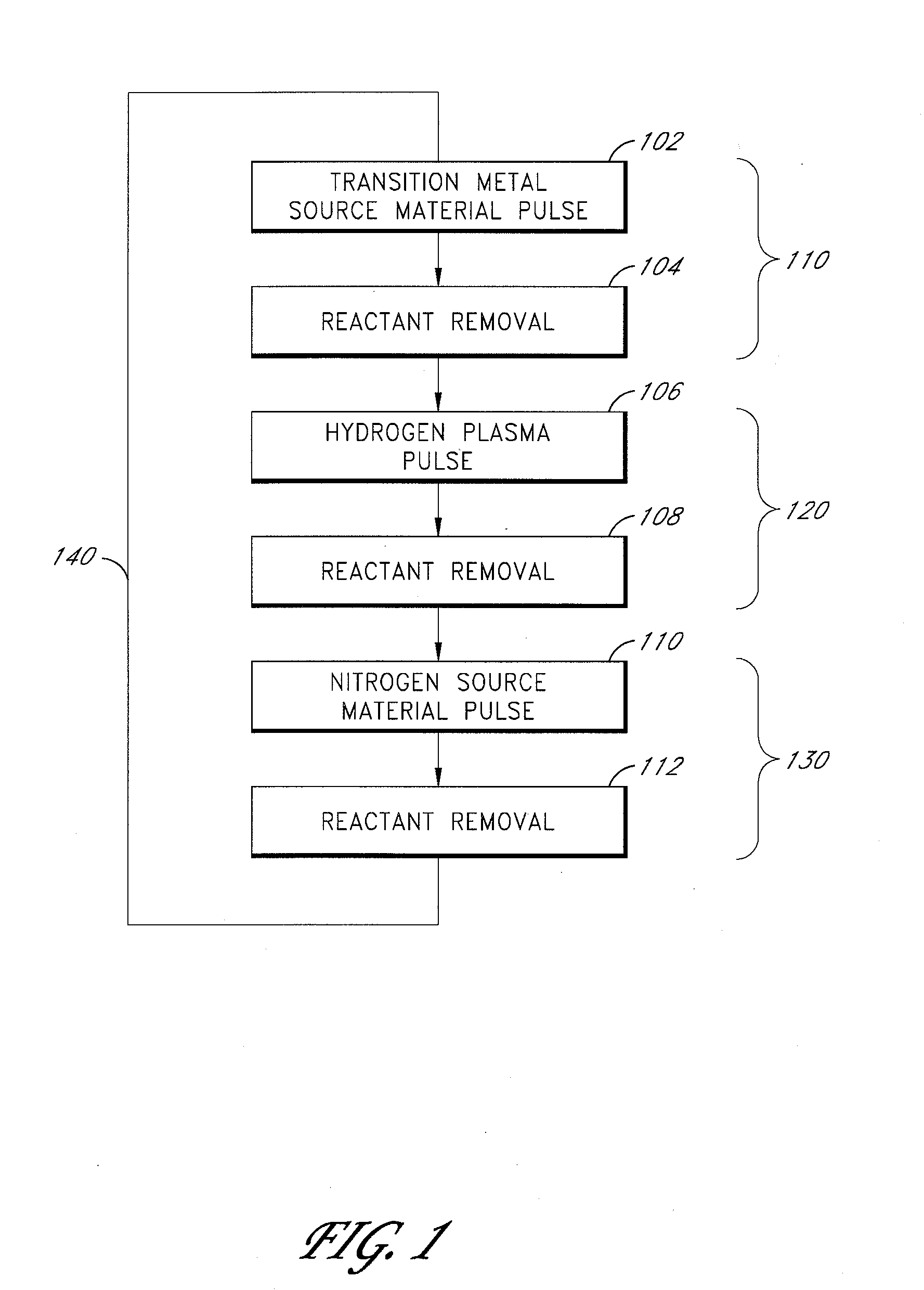
Plasma-enhanced ald of tantalum nitride films
ActiveUS20080182411A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenSource material
Methods of controllably producing conductive tantalum nitride films are provided. The methods comprise contacting a substrate in a reaction space with alternating and sequential pulses of a tantalum source material, plasma-excited species of hydrogen and nitrogen source material. The plasma-excited species of hydrogen reduce the oxidation state of tantalum, thereby forming a substantially conductive tantalum nitride film over the substrate. In some embodiments, the plasma-excited species of hydrogen react with and removes halide residues in a deposited metallic film.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Catalyst composition, method of polymerization, and polymer therefrom
Owner:UNIVATION TECH LLC
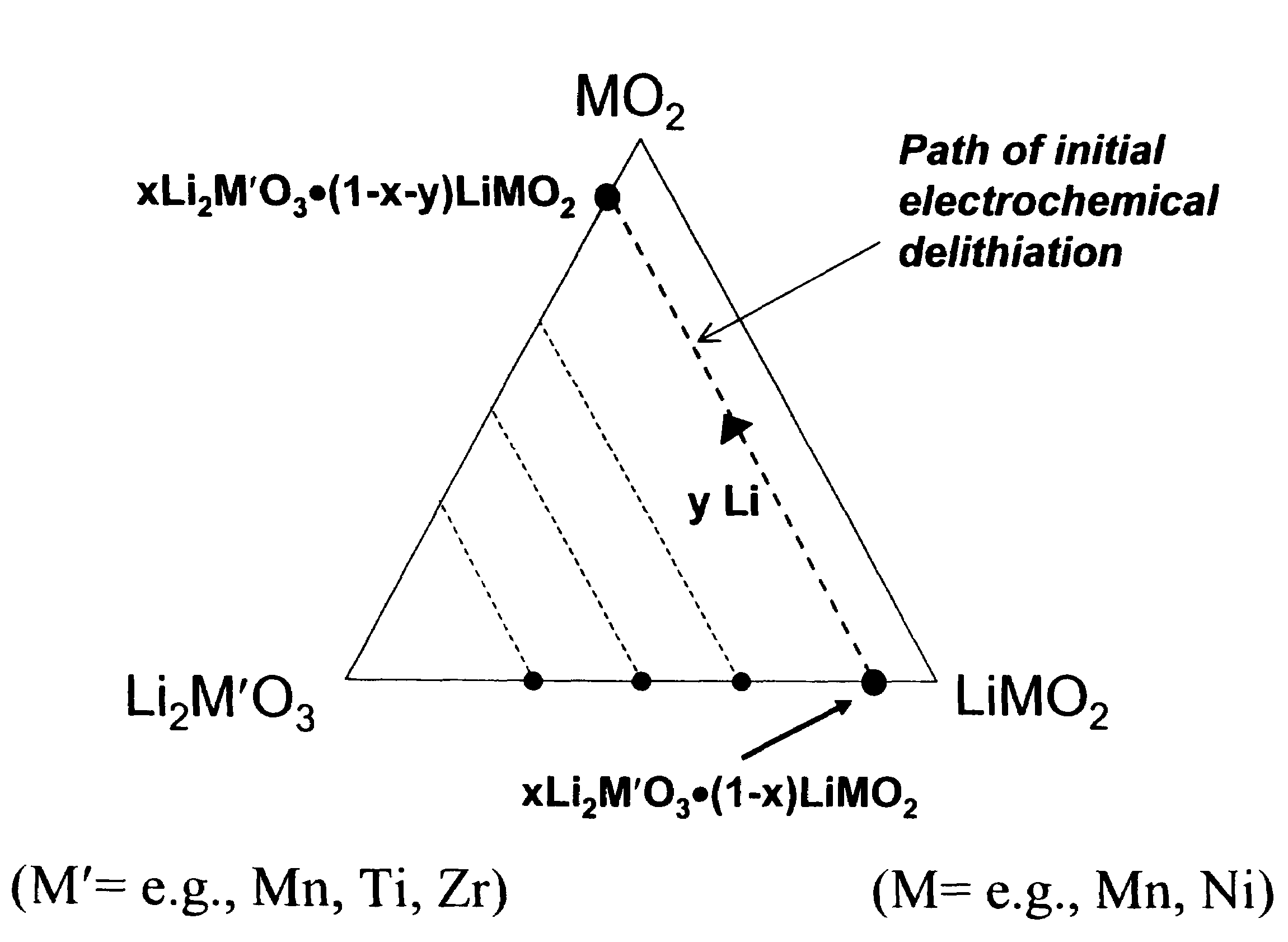
Lithium metal oxide electrodes for lithium cells and batteries
InactiveUS7135252B2Improve structural stabilityImprove stabilityZirconium compoundsSecondary cellsLithium metalOxidation state
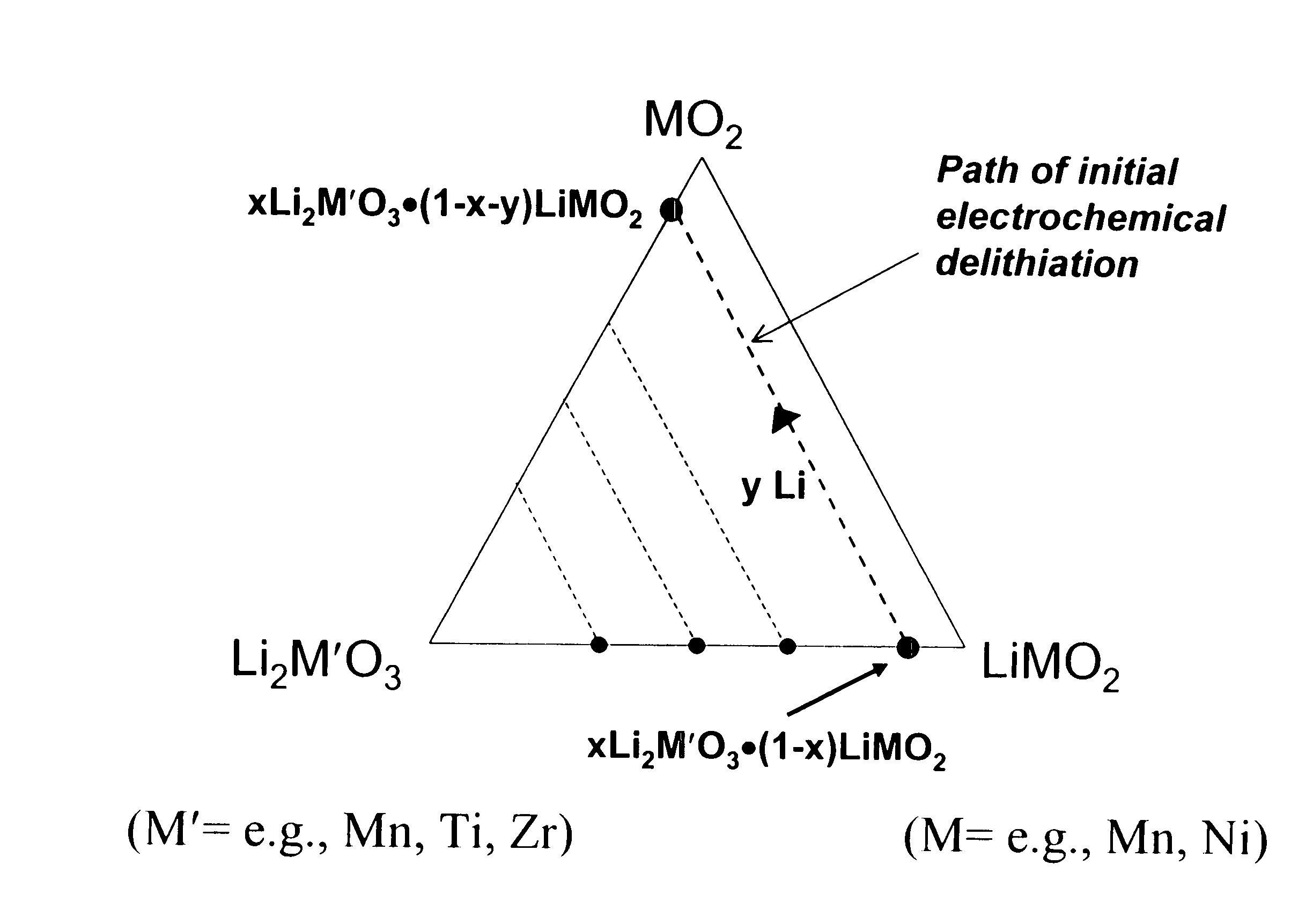
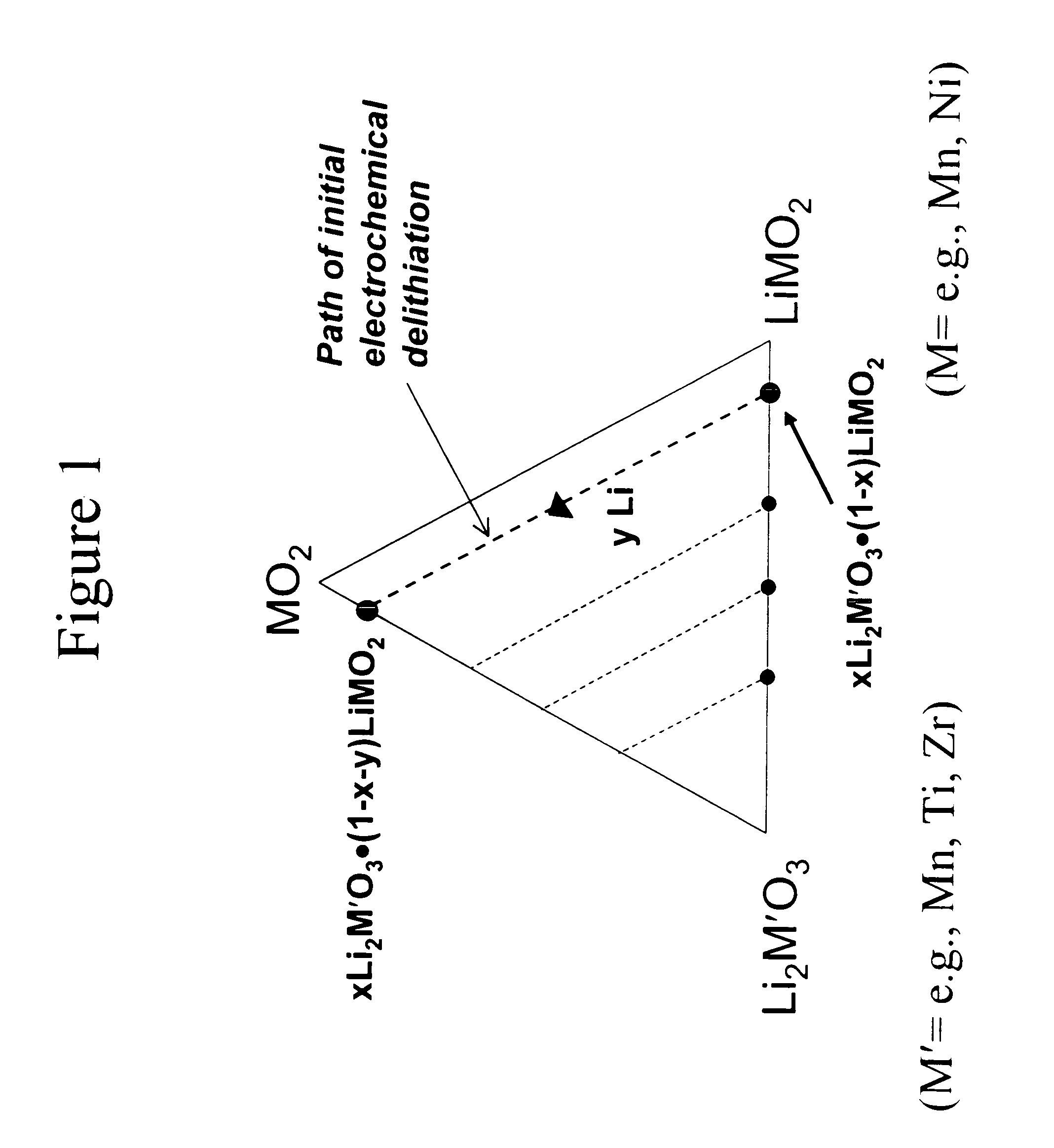
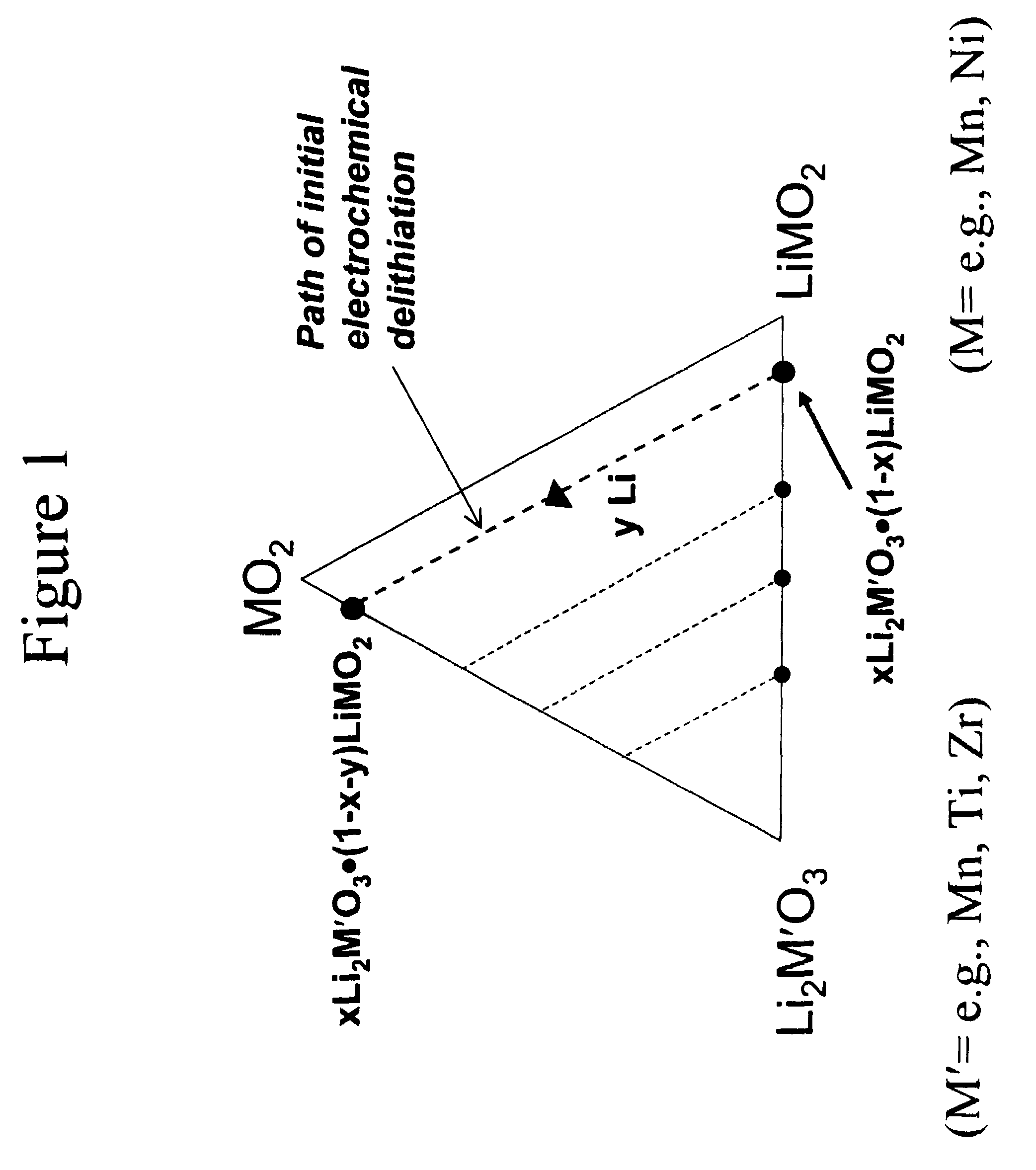
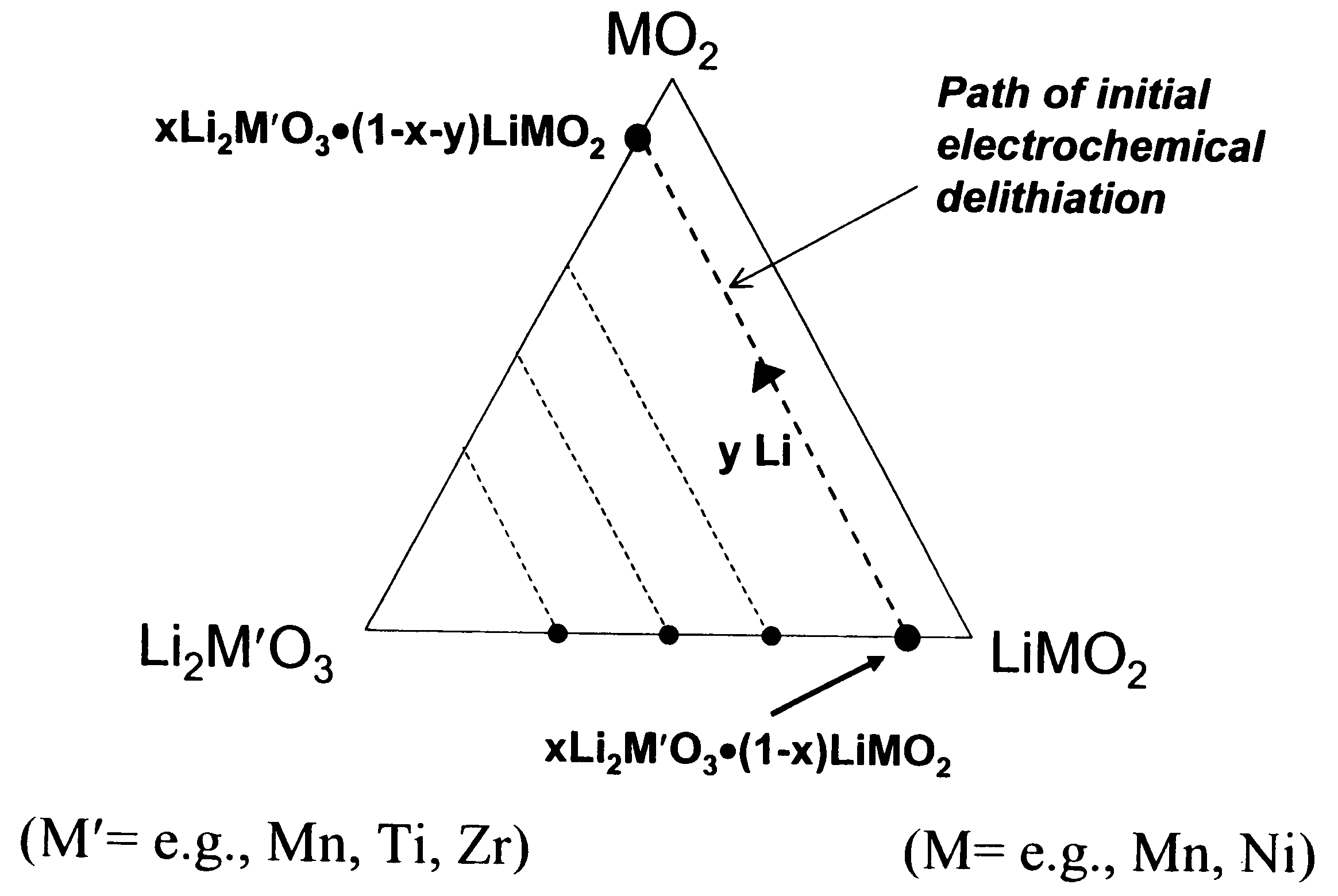
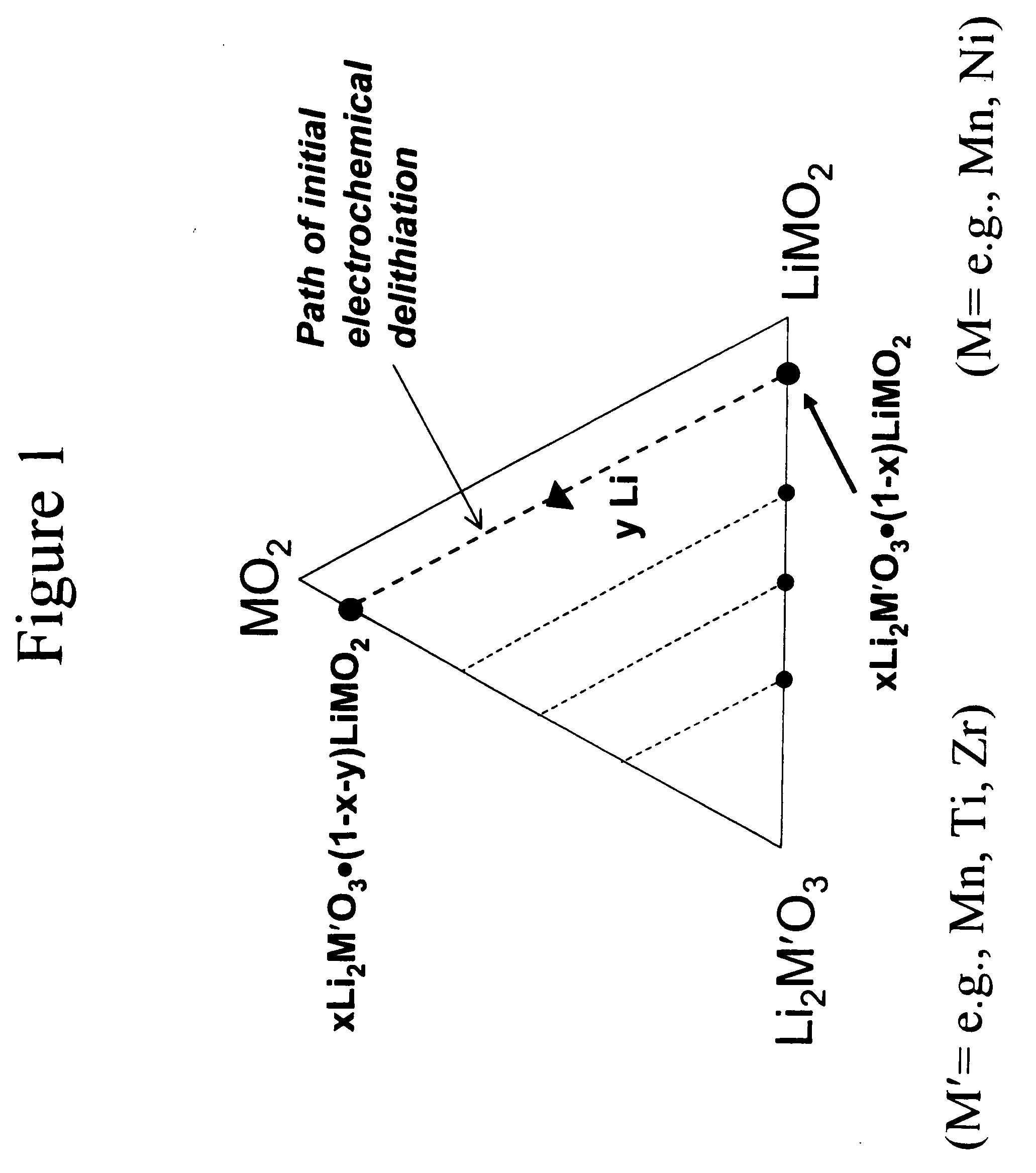
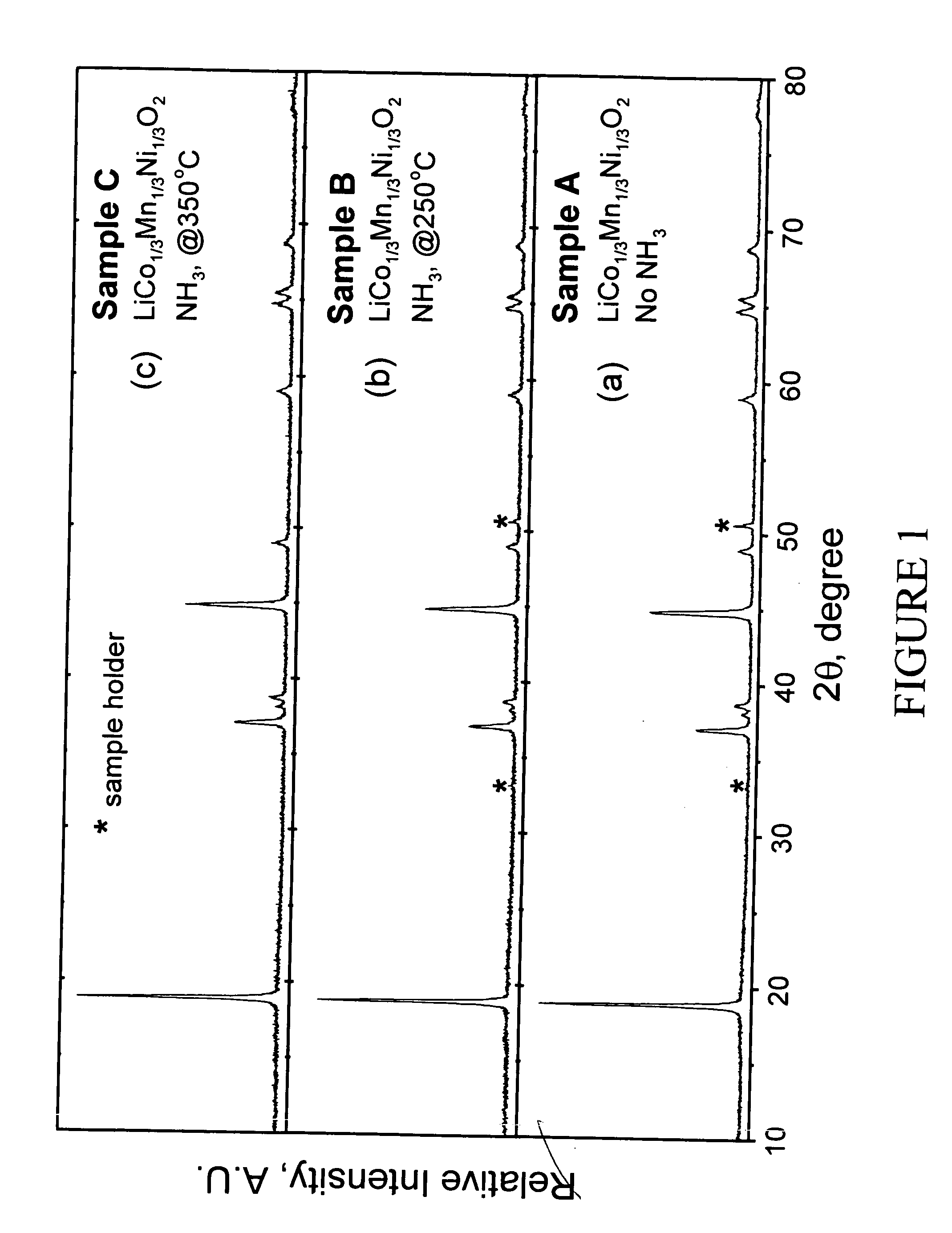
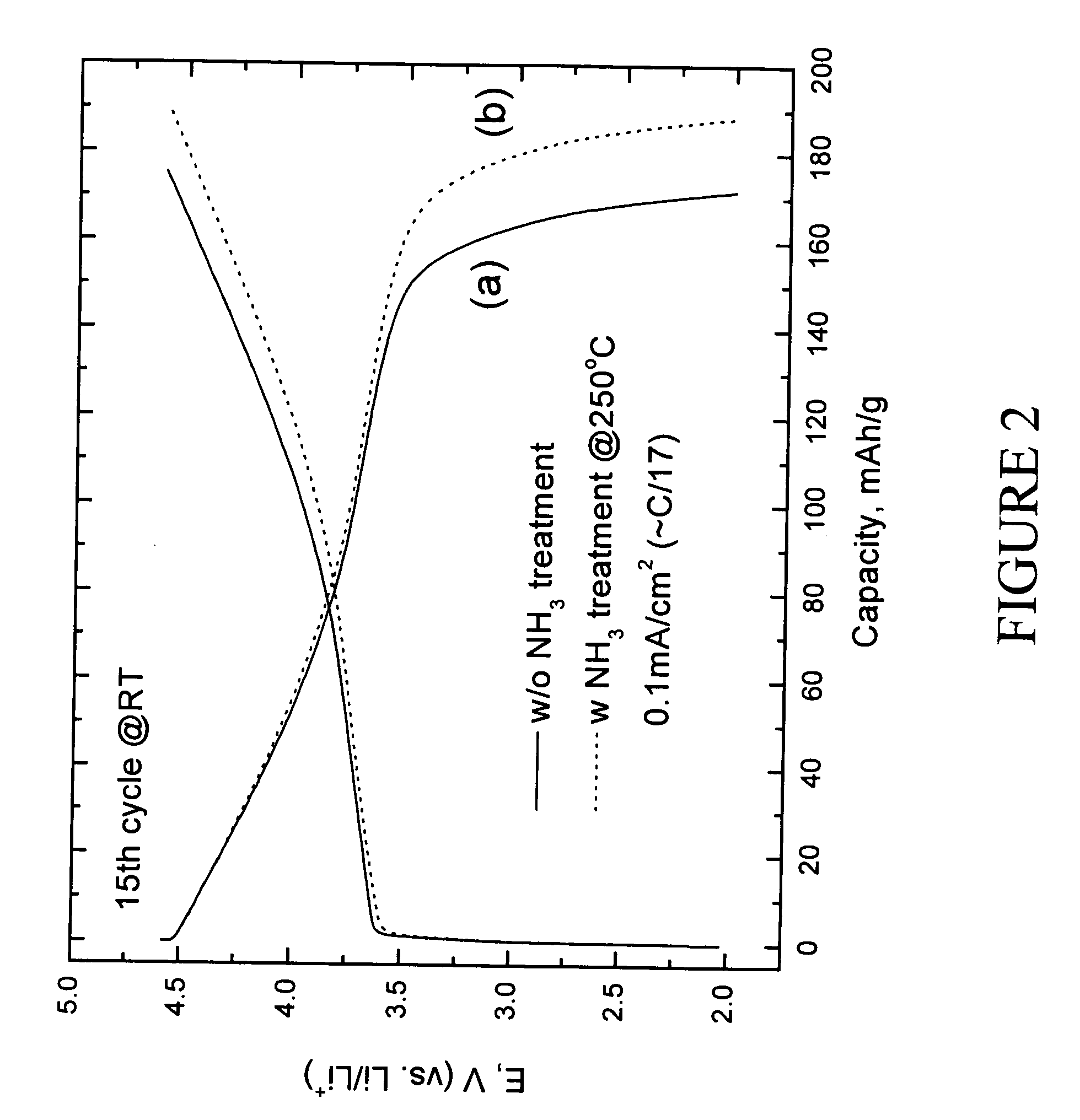
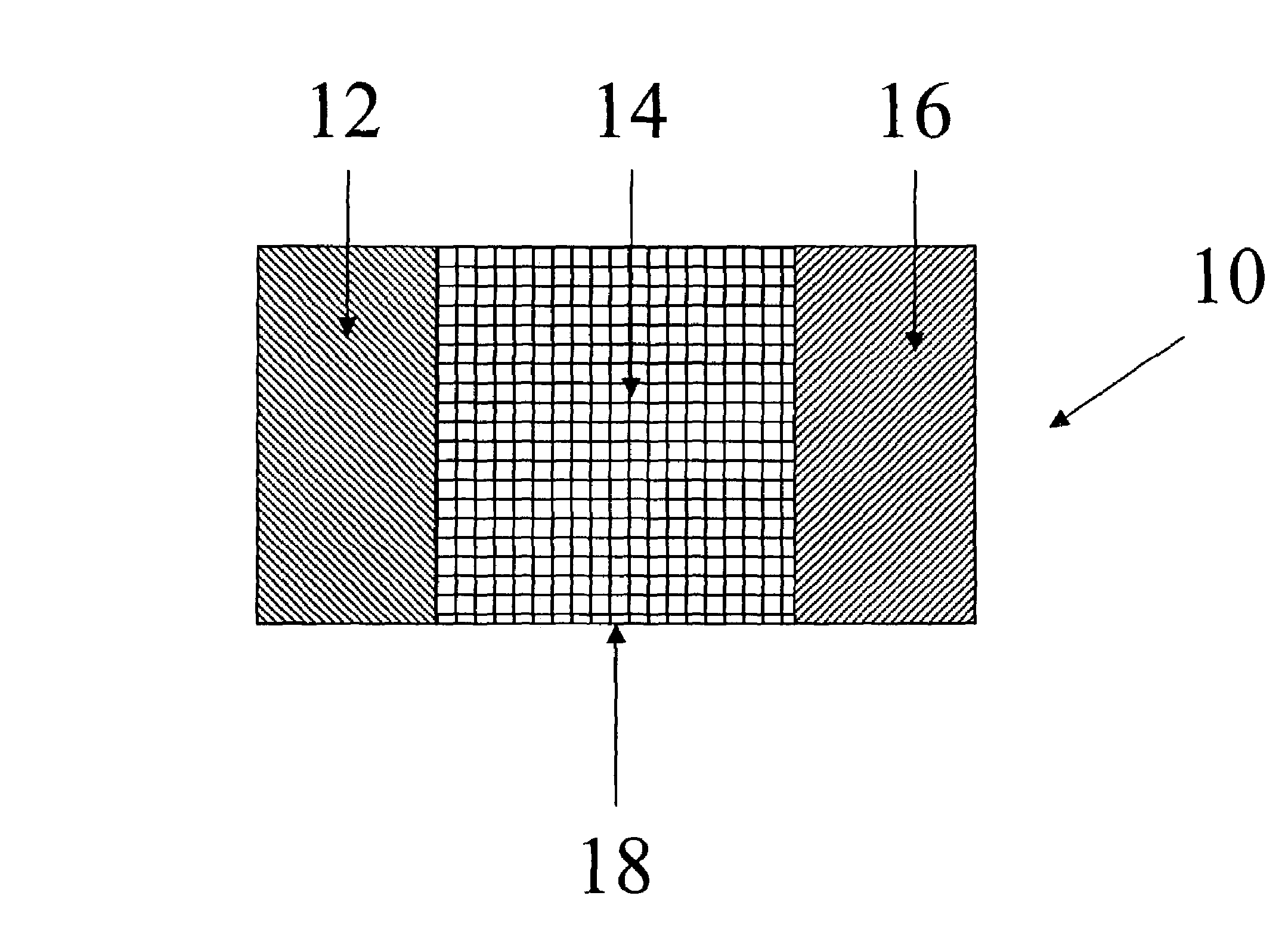
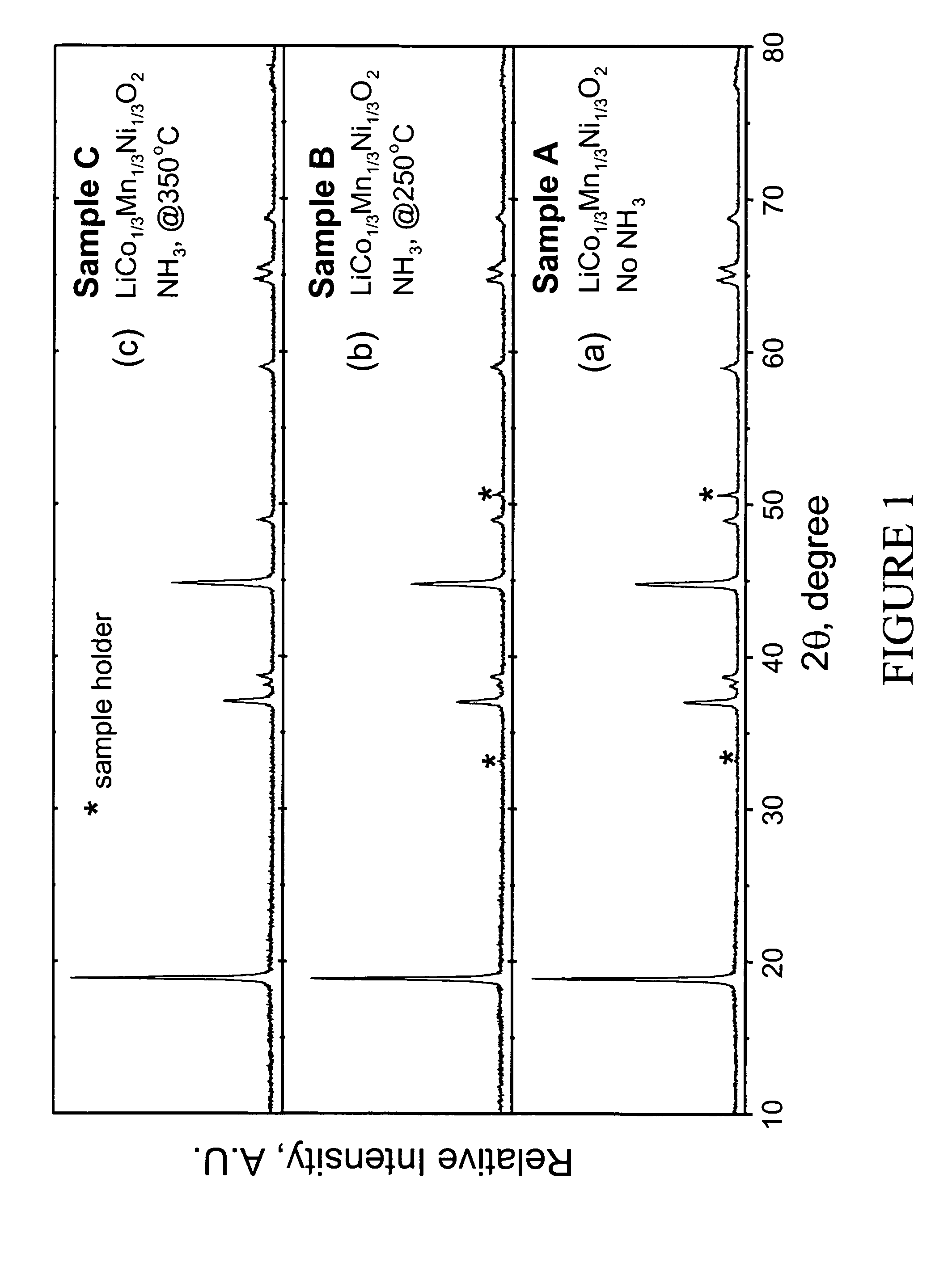
A lithium metal oxide positive electrode for a non-aqueous lithium cell is disclosed. The cell is prepared in its initial discharged state and has a general formula xLiMO2.(1-x)Li2M′O3 in which 0<x<1, and where M is more than one ion with an average trivalent oxidation state and with at least one ion being Ni, and where M′ is one or more ions with an average tetravalent oxidation state. Complete cells or batteries are disclosed with anode, cathode and electrolyte as are batteries of several cells connected in parallel or series or both.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF THE +1
Combustion looping using composite oxygen carriers
ActiveUS20050175533A1Increase surface areaImprove energy conversion efficiencyHydrogen productionIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationHydrogenCombustion
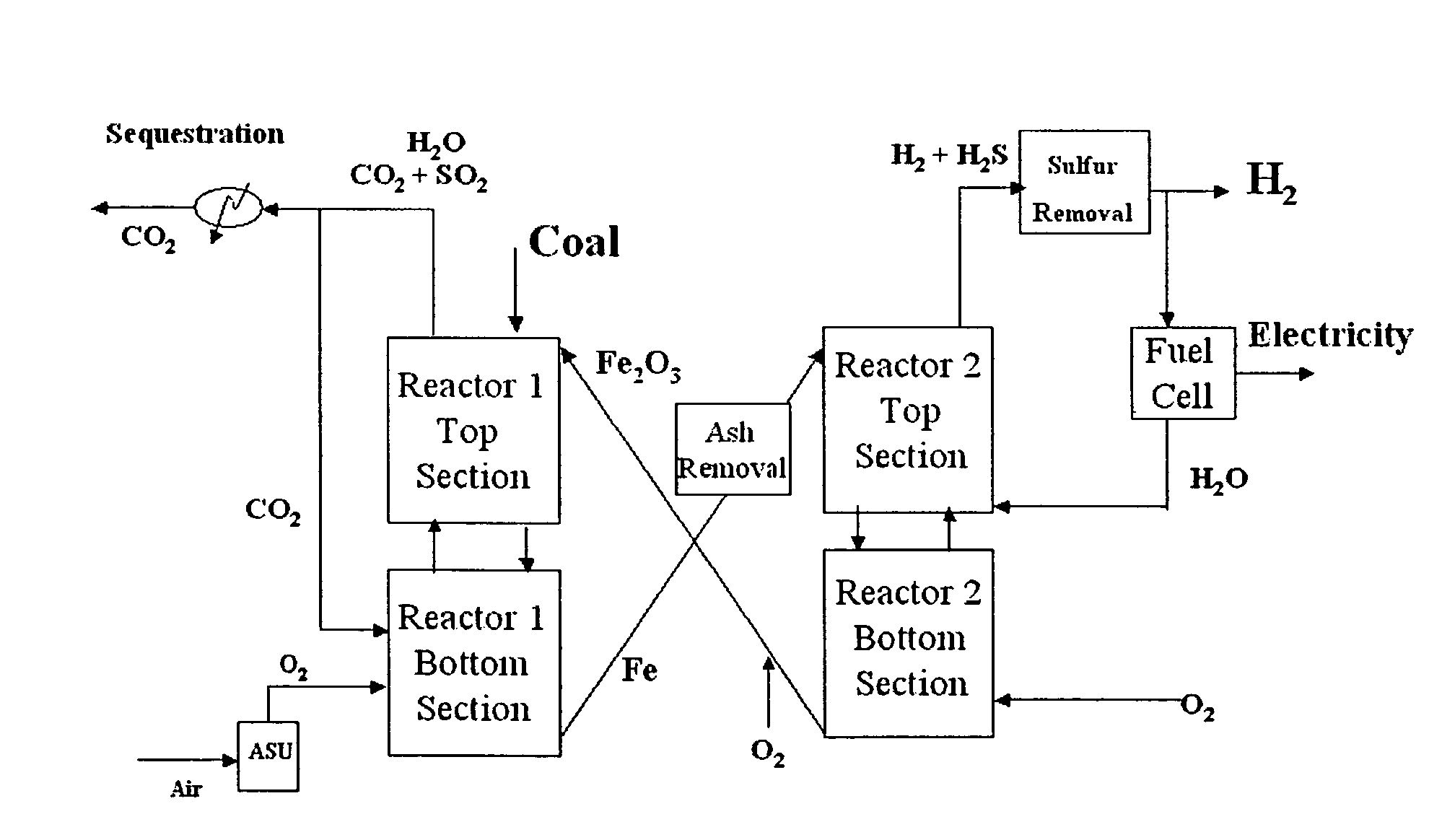
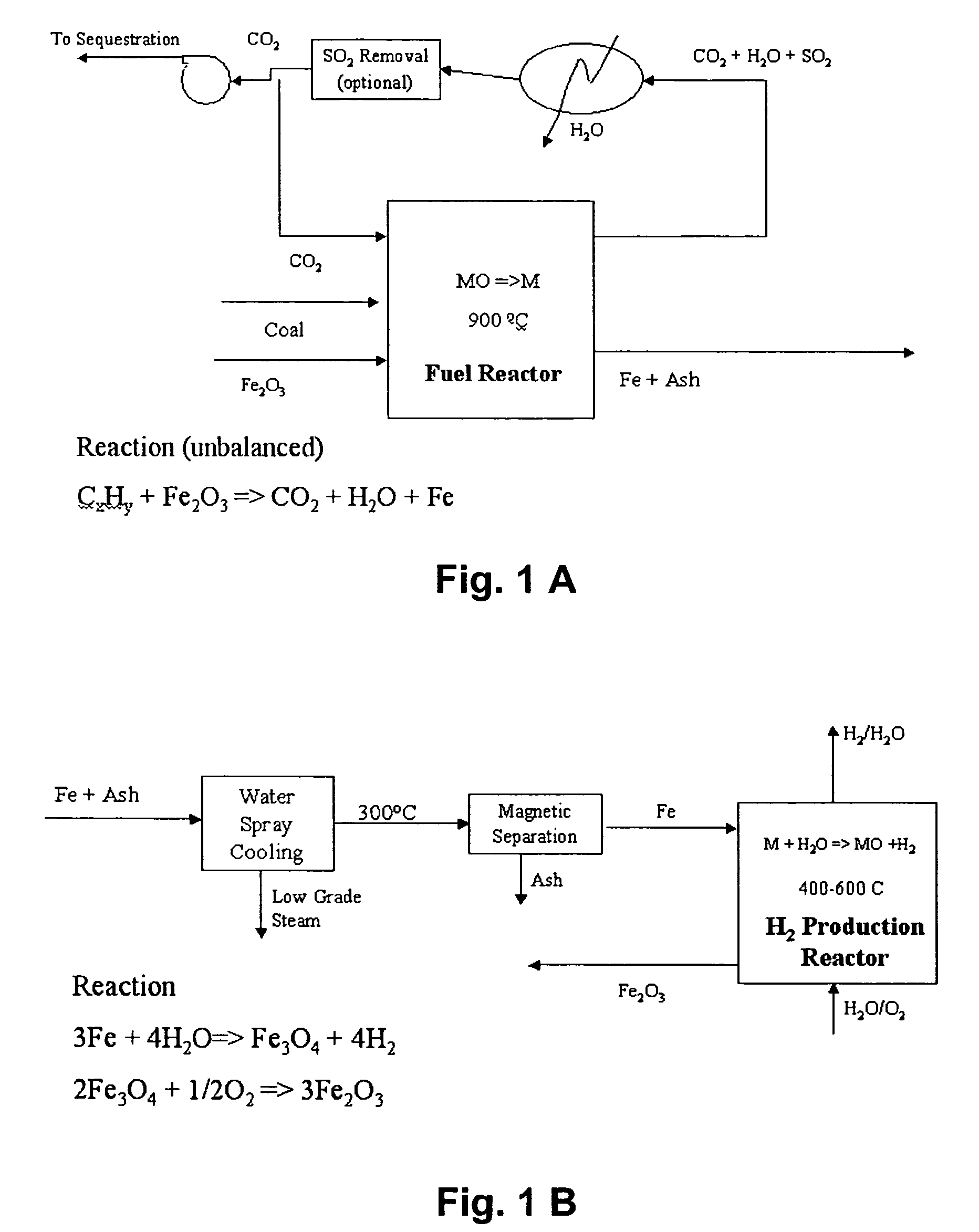
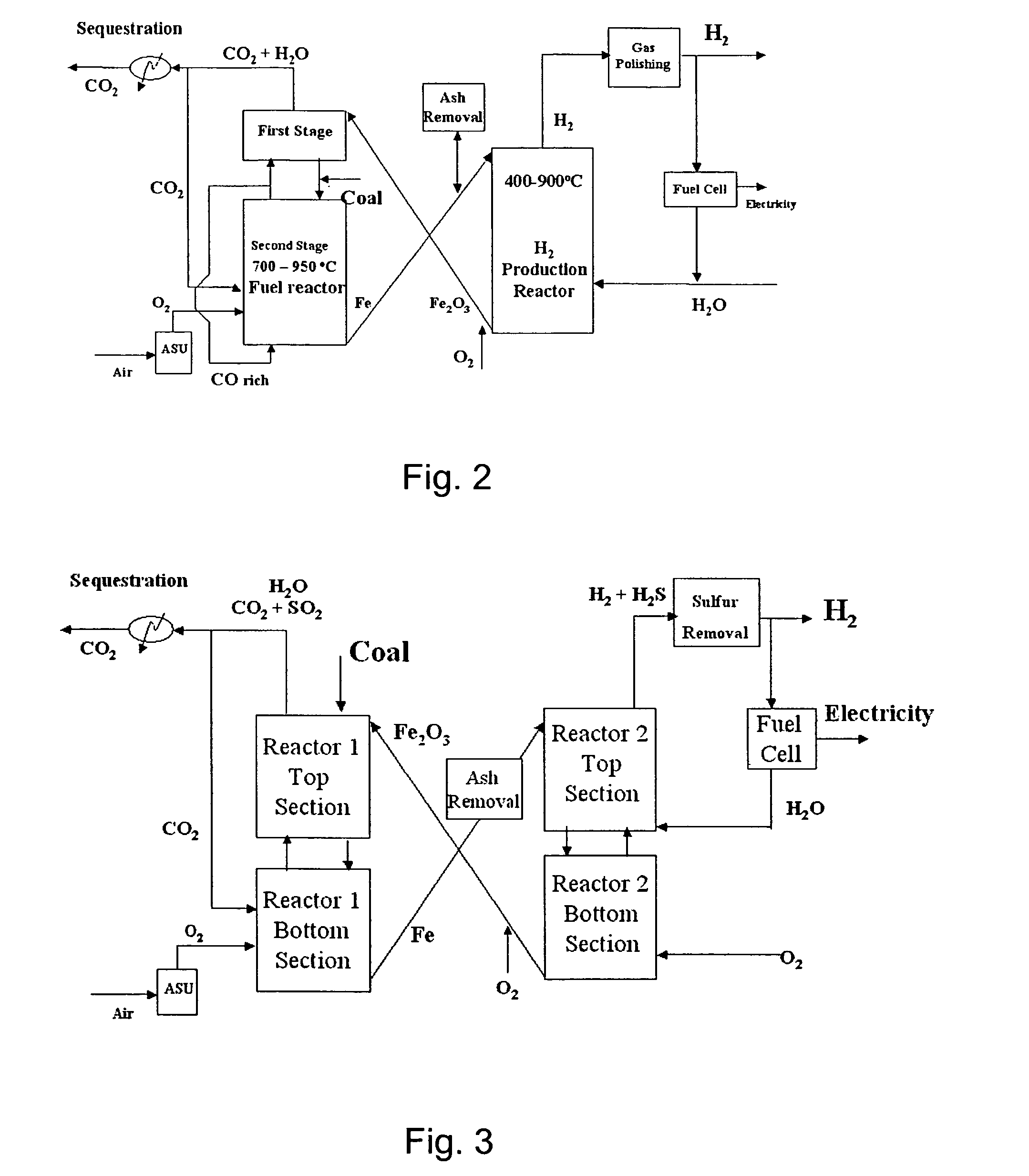
A method for producing hydrogen gas is provided and comprises reducing a metal oxide in a reduction reaction between a carbon-based fuel and a metal oxide to provide a reduced metal or metal oxide having a lower oxidation state, and oxidizing the reduced metal or metal oxide to produce hydrogen and a metal oxide having a higher oxidation state. The metal or metal oxide is provided in the form of a porous composite of a ceramic material containing the metal or metal oxide. The porous composite may comprise either a monolith, pellets, or particles.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
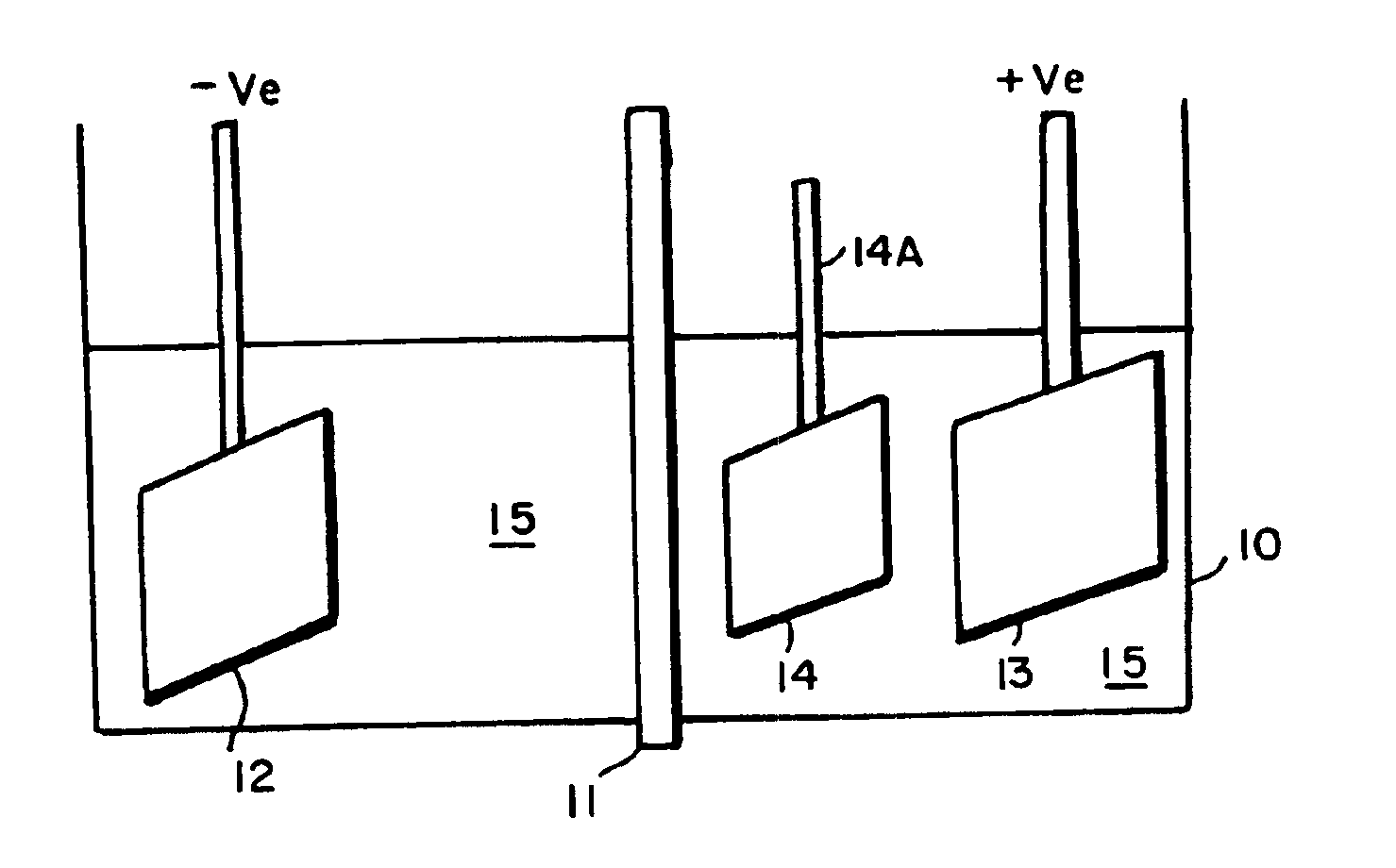
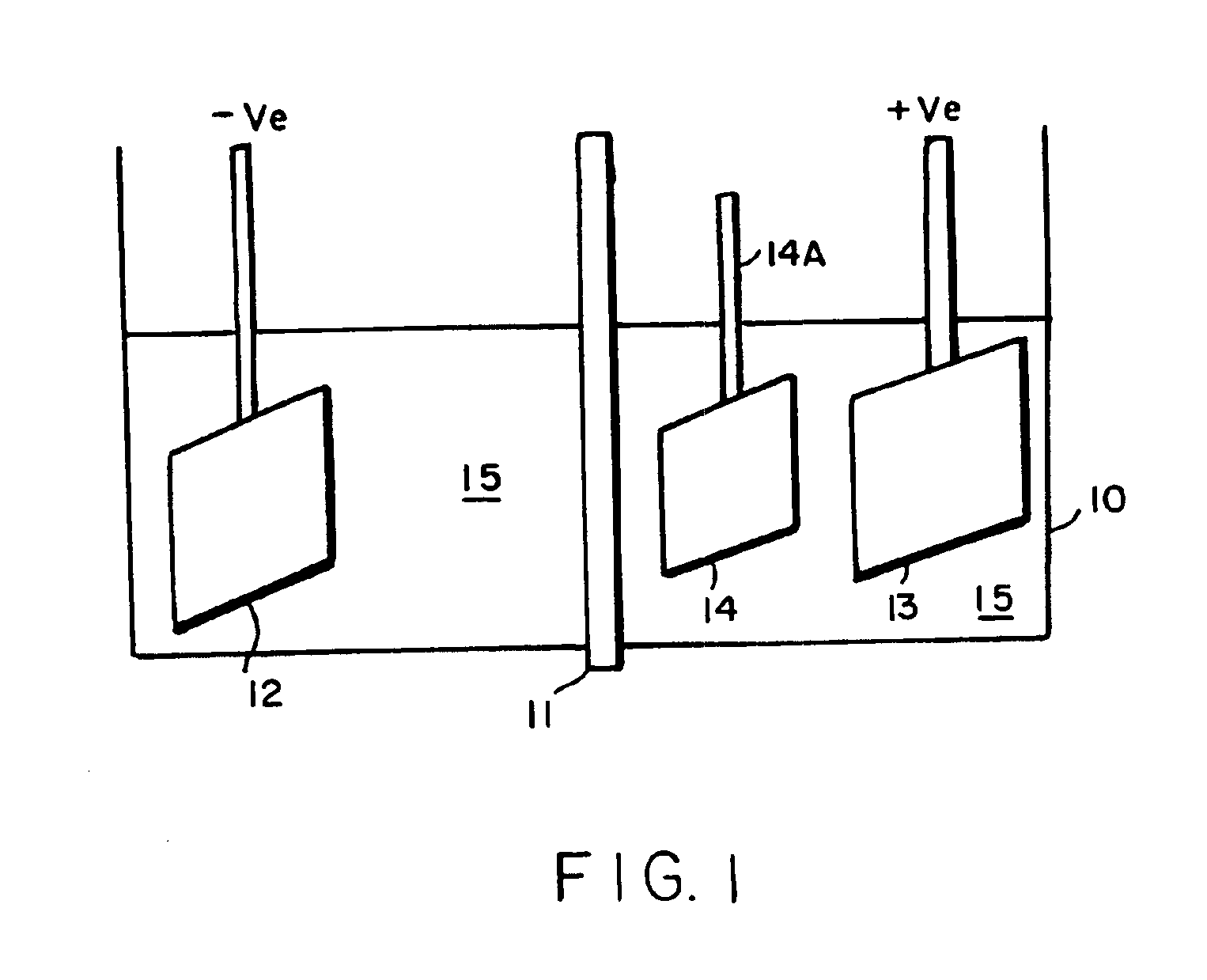
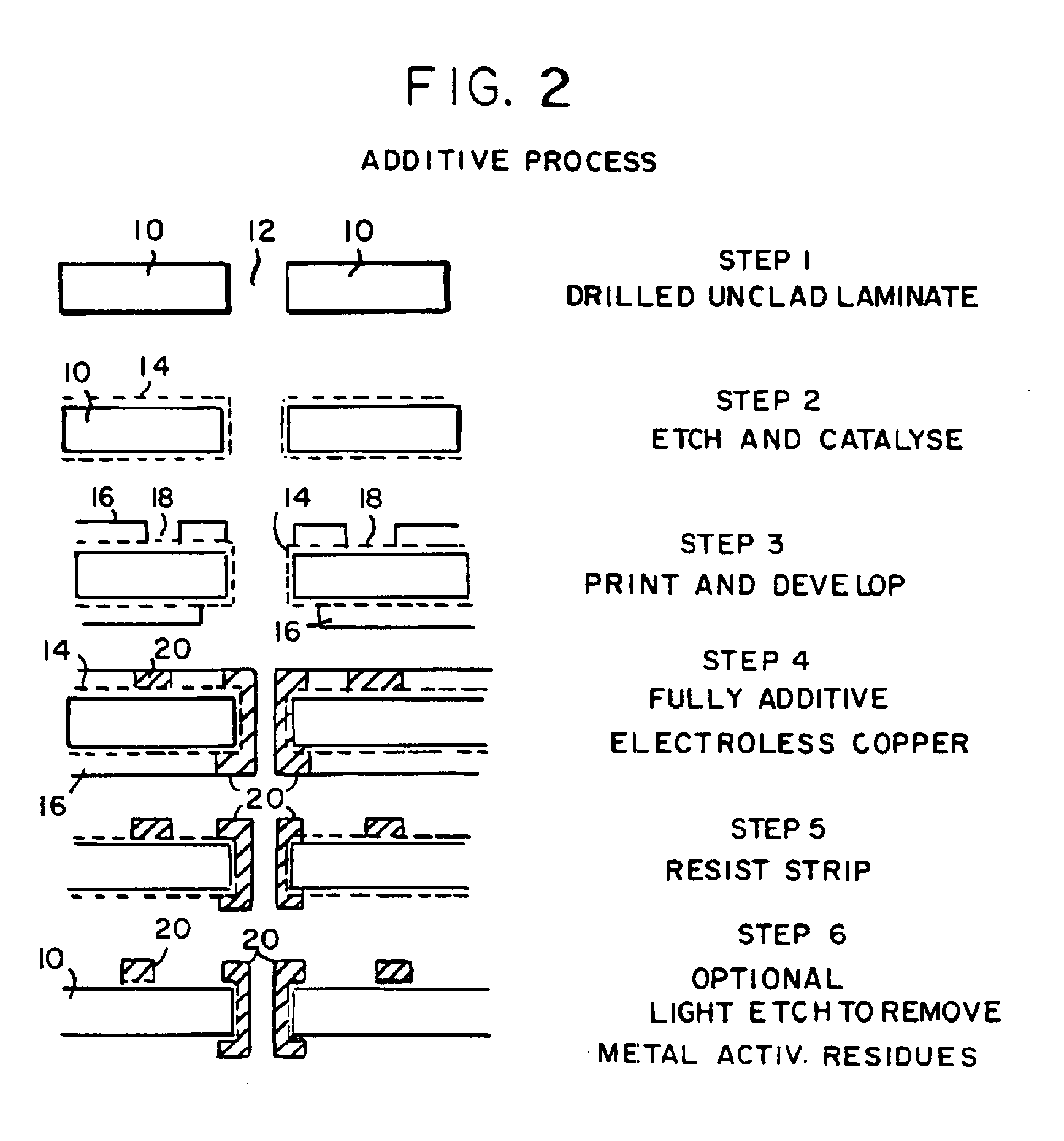
Electroless plating processes
InactiveUS6861097B1Reducing problem encounteredSimple methodPaper/cardboard articlesDecorative surface effectsPolymeric surfaceOxidation state
The invention includes processes for combined polymer surface treatment and metal deposition. Processes of the invention include forming an aqueous solution containing a metal activator, such as an oxidized species of silver, cobalt, ruthenium, cerium, iron, manganese, nickel, rhodium, or vanadium. The activator can be suitably oxidized to a higher oxidation state electrochemically. Exposing a part to be plated (such as an organic resin, e.g. a printed circuit board substrate) to the solution enables reactive hydroxyl species (e.g. hydroxyl radicals) to be generated and to texture the polymer surface. Such texturing facilitates good plated metal adhesion. As part of this contacting process sufficient time is allowed for both surface texturing to take place and for the oxidized metal activator to adsorb onto said part. The part is then contacted with a reducing agent capable of reducing the metal activator to a lower ionic form, or a lower oxidation state. That reduction can result in the formation of metallic catalytic material over the surface of the part. The reduced metal activator can then function to catalyze the electroless deposition of metal such as copper from solution by contacting the part with the plating solution.
Owner:SHIPLEY CO LLC
Lithium metal oxide electrodes for lithium cells and batteries
InactiveUS7468223B2Improve electronic conductivityLess costlyLi-accumulatorsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLithium metalOxidation state
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
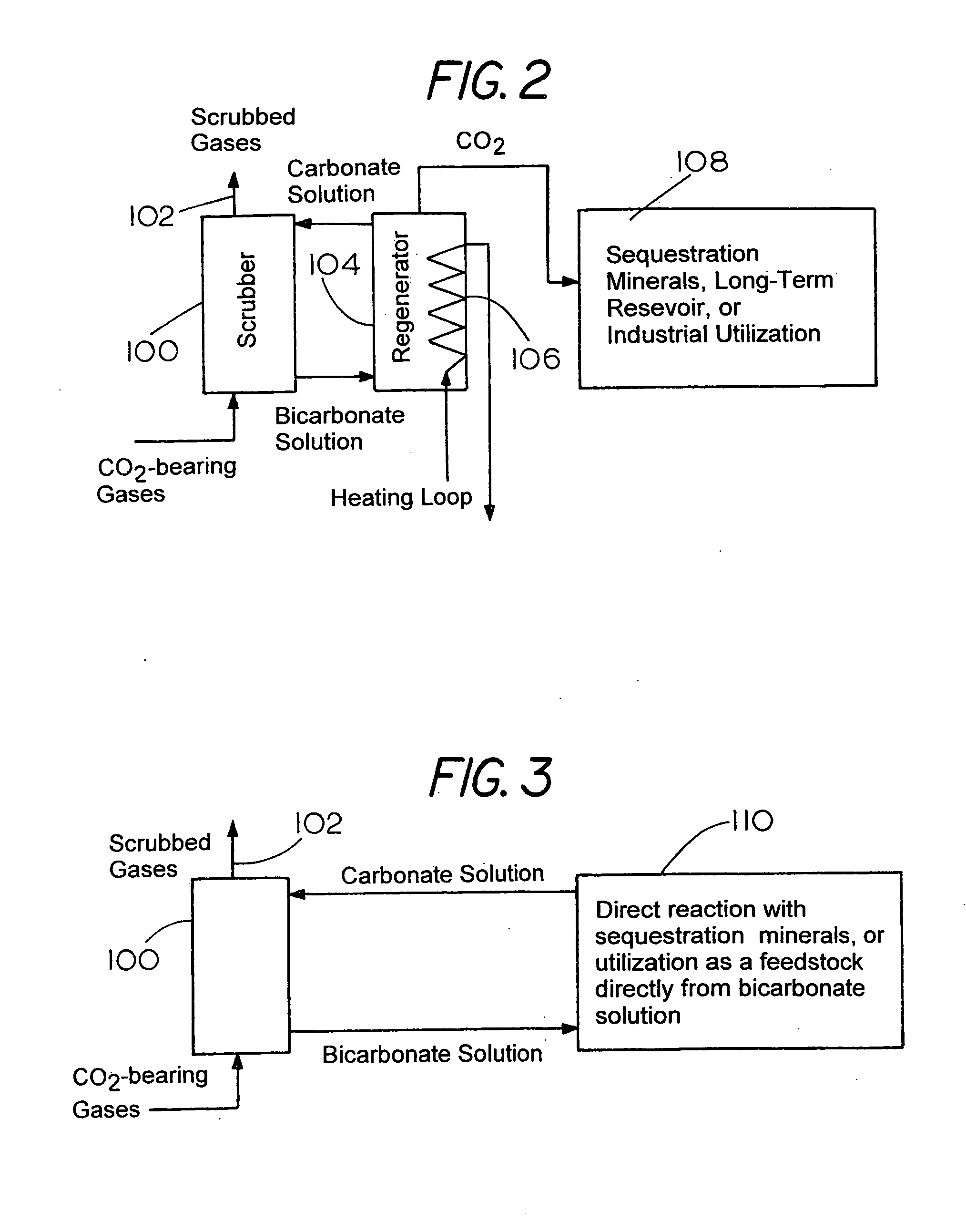
Capture and Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide in Flue Gases
ActiveUS20090202410A1Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPigmenting treatmentAlkaline earth metalOxidation state
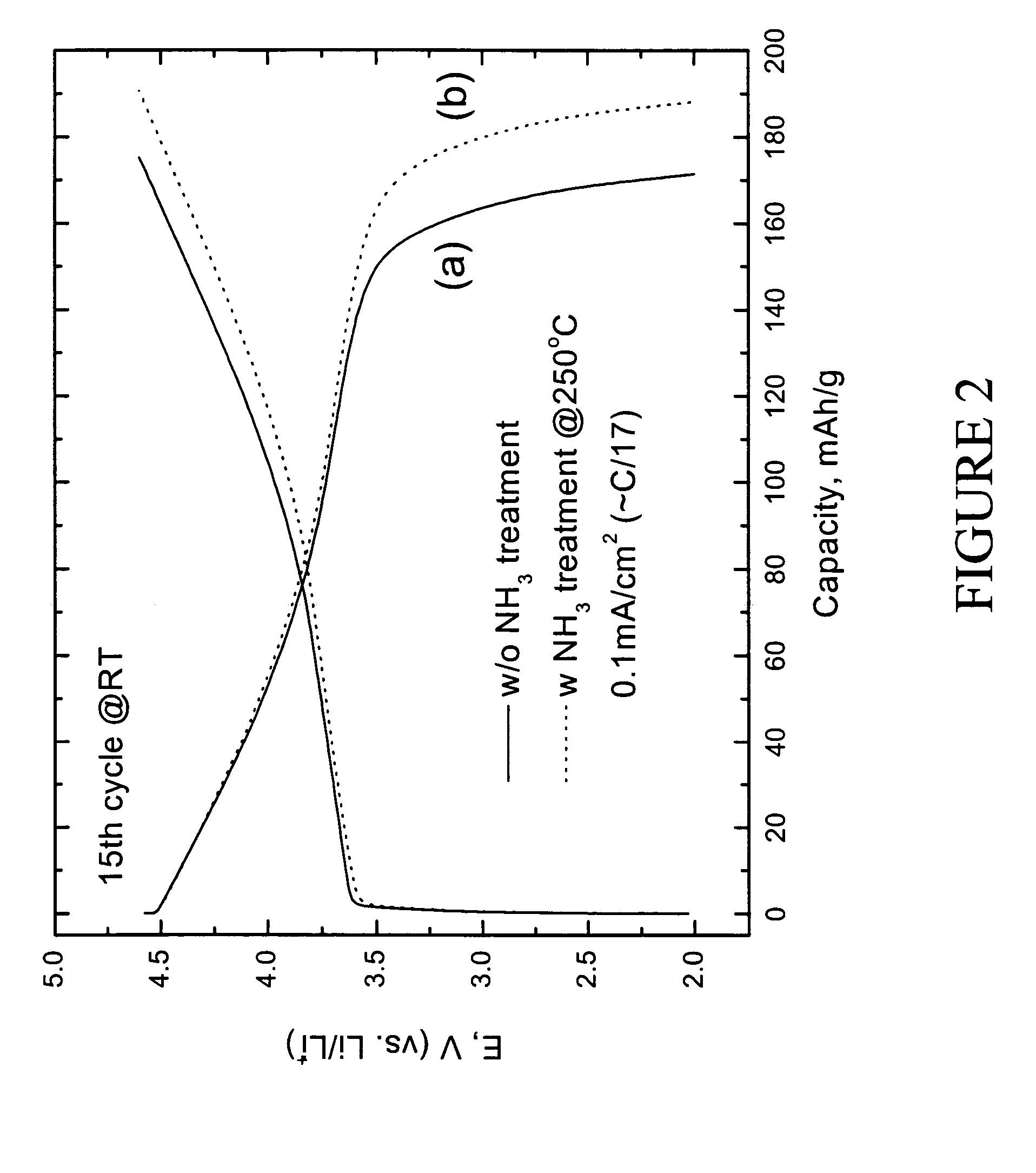
There is provided a process for the capture and sequestration of carbon dioxide that would otherwise enter the atmosphere and contribute to global warming and other problems. CO2 capture is accomplished by reacting carbon dioxide in flue gas with an alkali metal carbonate, or a metal oxide, particularly containing an alkaline earth metal or iron, to form a carbonate salt. A preferred carbonate for CO2 capture is a dilute aqueous solution of additive-free (Na2CO3). Other carbonates include (K2CO3) or other metal ion that can produce both a carbonate and a bicarbonate salt. Examples of suitable metal oxides include several alkaline earths including CaO and MgO. The captured CO2 is preferably sequestered using any available mineral or industrial waste that contains calcium magnesium or iron in non-carbonate forms, or iron in the Fe+2 oxidation state.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
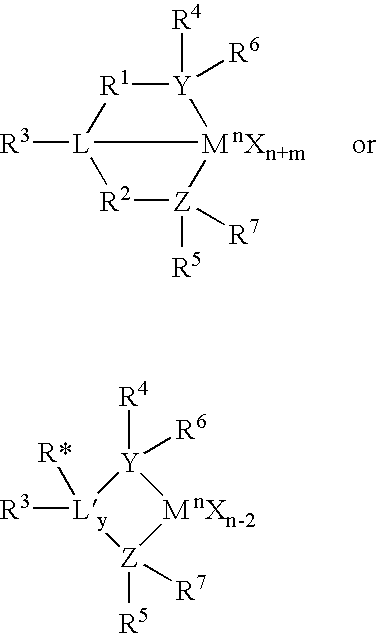
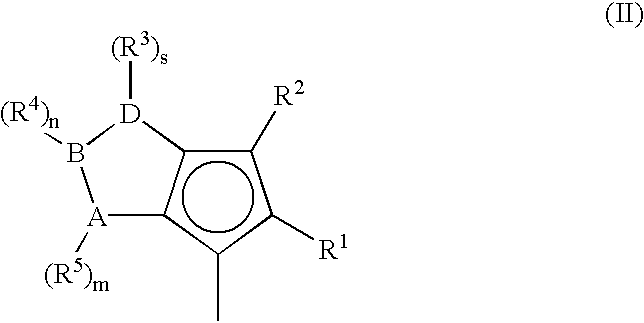
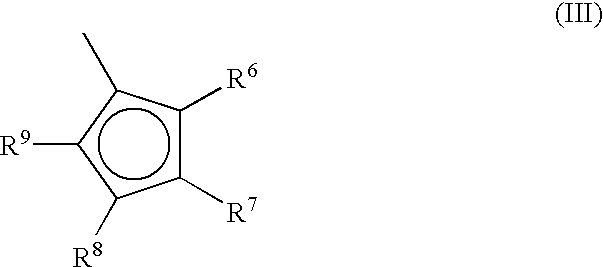
Metallocene compounds, process for their preparation and their use in catalytic systems for the polymerization of olefins
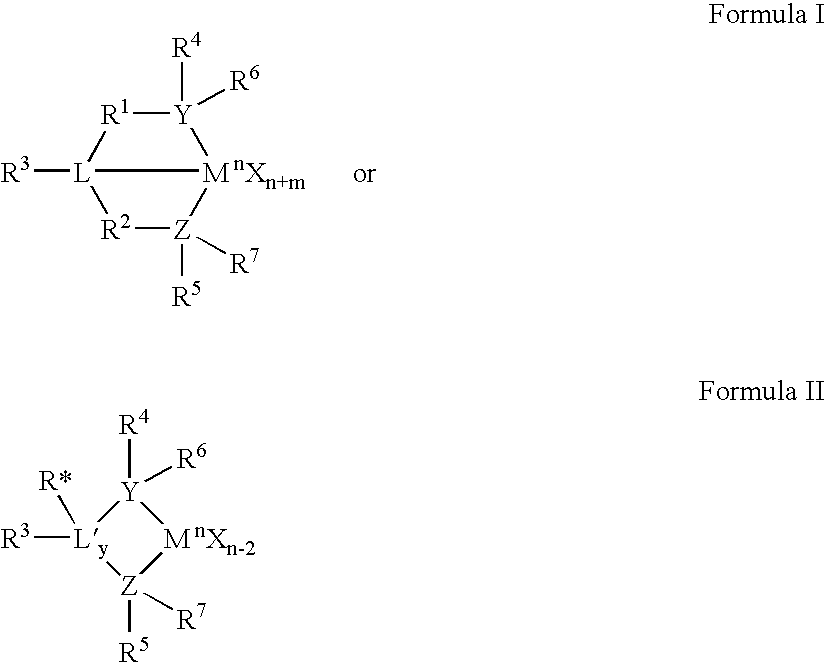
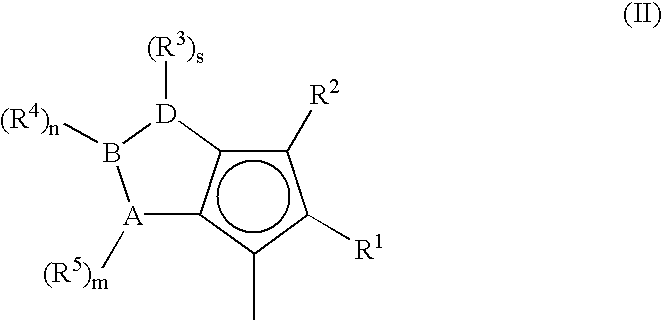
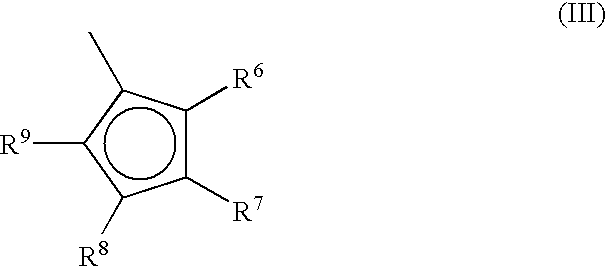
A class of metallocene compounds is disclosed having the general formula (I):wherein Y is a moiety of formula (II)wherein A, B and D, same or different from each other, are selected from an element of the groups 14 to 16 of the Periodic Table of the Elements (new IUPAC version), with the exclusion of nitrogen and oxygen; R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are hydrogen or hydrocarbon groups, Z is selected from a moiety of formula (II) as described above and from a moiety of formula (III):wherein R6, R7, R8 and R9, are hydrogen or hydrocarbon groups; L is a divalent bridging group; M is an atom of a transition metal selected from those belonging to group 3, 4, 5, 6 or to the lanthanide or actinide groups in the Periodic Table of the Elements (new IUPAC version), X, same or different, is hydrogen, a halogen, a R10, OR10, OSO2CF3, OCOR10, SR10, NR102 or PR102 group, wherein the substituents R10 are hydrogen or alkyl groups; p is an integer of from 0 to 3, being equal to the oxidation state of the metal M minus 2.The above metallocenes are particular useful in the polymerization of propylene.
Owner:BASELL POLYOLEFINE GMBH
Lithium metal oxide electrodes for lithium cells and batteries
InactiveUS20060099508A1Improve structural stabilityImprove stabilityLi-accumulatorsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLithium metalOxidation state
A lithium metal oxide positive electrode for a non-aqueous lithium cell is disclosed. The cell is prepared in its initial discharged state and has a general formula xLiMO2.(1−x)Li2M′O3 in which 0<x<1, and where M is one or more ion with an average trivalent oxidation state and with at least one ion being Mn or Ni, and where M′ is one or more ion with an average tetravalent oxidation state. Complete cells or batteries are disclosed with anode, cathode and electrolyte as are batteries of several cells connected in parallel or series or both.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
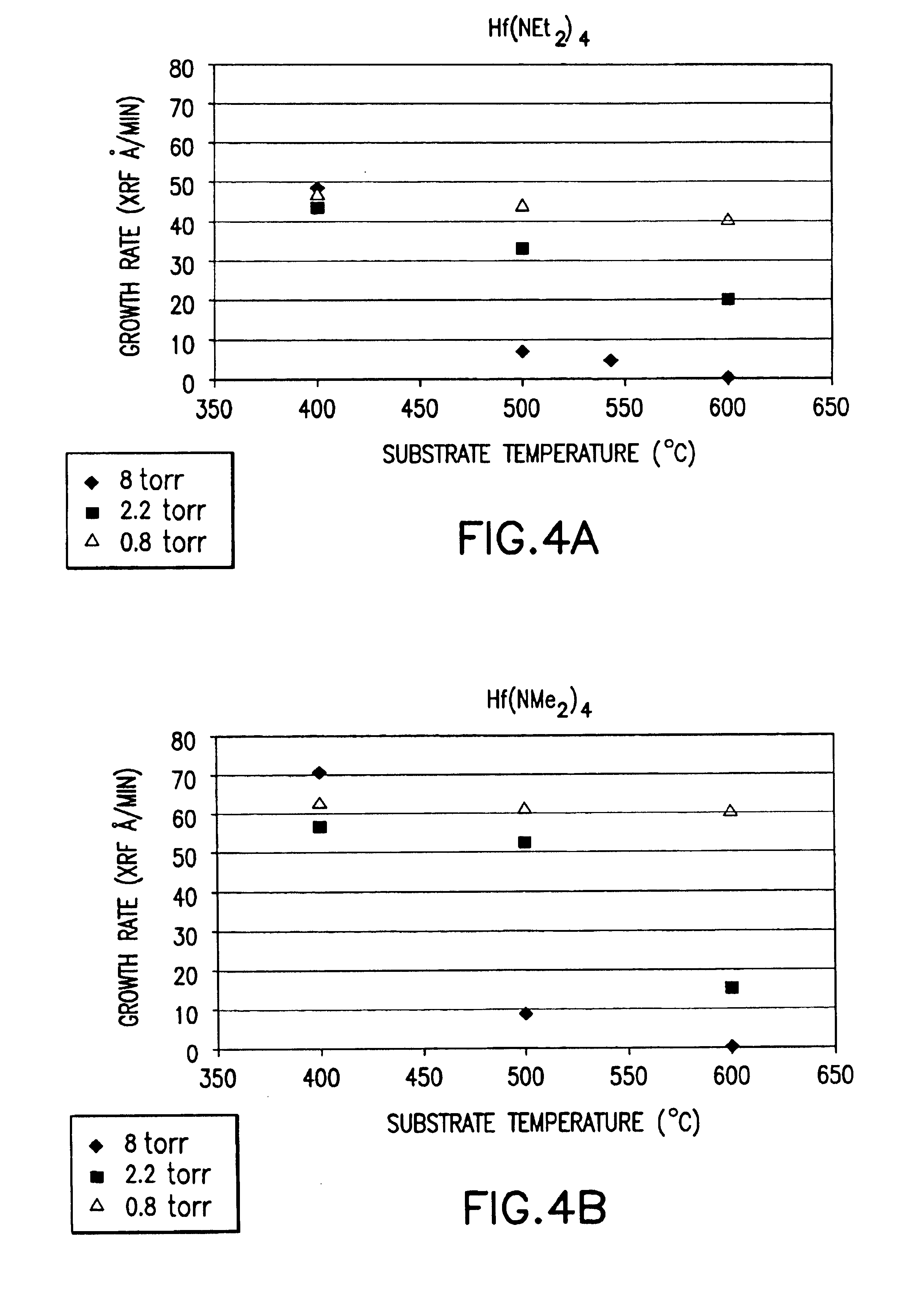
Source reagent compositions for CVD formation of gate dielectric thin films using amide precursors and method of using same
InactiveUS6869638B2Group 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGate dielectricHydrogen
A CVD Method of forming gate dielectric thin films on a substrate using metalloamide compounds of the formula M(NR1R2)x, or wherein M is Zr, Hf, Y, La, Lanthanide series elements, Ta, Ti, or Al; N is nitrogen; each of R1 and R2 is same or different and is independently selected from H, aryl, perfluoroaryl, C1-C8 alkyl, C1-C8 perfluoroalkyl, alkylsilyl; and x is the oxidation state on metal M; and an aminosilane compound of the formula HxSiAy(NR1R2)4-x-y or wherein H is hydrogen; x is from 0 to 3; Si is silicon; A is a halogen; Y is from 0 to 3; N is nitrogen; each of R1 and R2 is same or different and is independently selected from the group consisting of H, aryl, perfluoroaryl, C1-C8 alkyl, and C1-C8 perfluoroalkyl; and n is from 1-6. By comparison with the standard SiO2 gate dielectric materials, these gate dielectric materials provide low levels of carbon and halide impurity.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Metallocene compounds, process for their preparation and their use in catalytic systems for the polymerization of olefins
A class of metallocene compounds is disclosed having general formula (I) wherein Y is a moiety of formula (II) wherein A, B, and D, same or different from each other, are selected from an element of the groups 14 to 16 of the Periodic Table of the Elements (new IUPAC version), with the exclusion of nitrogen and oxygen; R<1>, R<2>, R<3>, R<4 >and R<5 >are hydrogen or hydrocarbon groups, Z is selected from a moiety of formula (II) as described above and from a moiety of formula (III) wherein R<6>, R<7>, R<8 >and R<9>, are hydrogen or hydrocarbon groups; L is a divalent bridging group; M is an atom of a transition metal selected from those belonging to group 3, 4, 5, 6 or to the lanthanide or actinide groups in the Periodic Table of the Elements (new IUPAC version), X, same or different, is hydrogen, a halogen, a R<10>, OR<10>, OSO2CF3, OCOR<10>, SR<10>, NR<10>2 or PR<10>2 group, wherein the substituents R<10 >are hydrogen or alkyl groups; p is an integer of from 1 to 3, being equal to the oxidation state of the metal M minus 2. The above metallocenes are particularly useful in the polymerization of propylene.
Owner:BASELL POLYOLEFINE GMBH
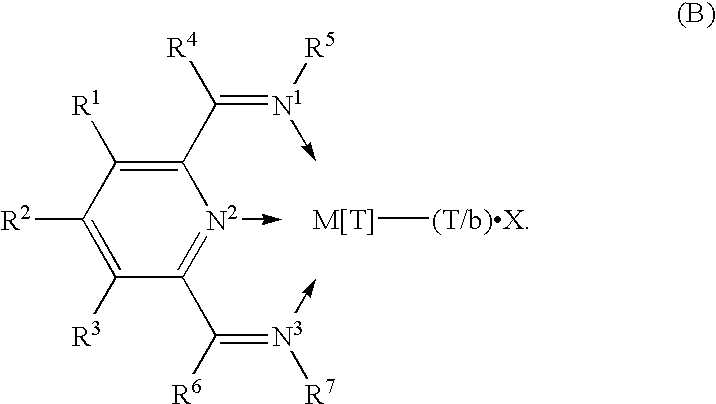
Polymerization catalysts
InactiveUS7148304B2Improve performanceImproved processing propertyRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogenHalogen
A catalyst for the polymerization of 1-olefins is disclosed, which comprises (1) a compound of Formula B wherein M is Fe[II], Fe[III], Co[I], Co[II], Co[III], Mn[I], Mn[II], Mn[III], Mn[IV], Ru[II], Ru[III] or Ru[IV]; X represents an atom or group covalently or ionically bonded to the transition metal M; T is the oxidation state of the transition metal M and b is the valency of the atom or group X; R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 and R7 are independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, hydrocarbyl, substituted hydrocarbyl, heterohydrocarbyl or substituted heterohydrocarbyl; and when any two or more of R1–R7 are hydrocarbyl, substituted hydrocarbyl, heterohydrocarbyl or substituted heterohydrocarbyl, said two or more can be linked to form one or more cyclic substituents; and (2) a further catalyst. Copolymers made using the catalyst having specific physical properties are also disclosed
Owner:INEOS SALES (UK) LTD
Metal oxide processing methods and systems
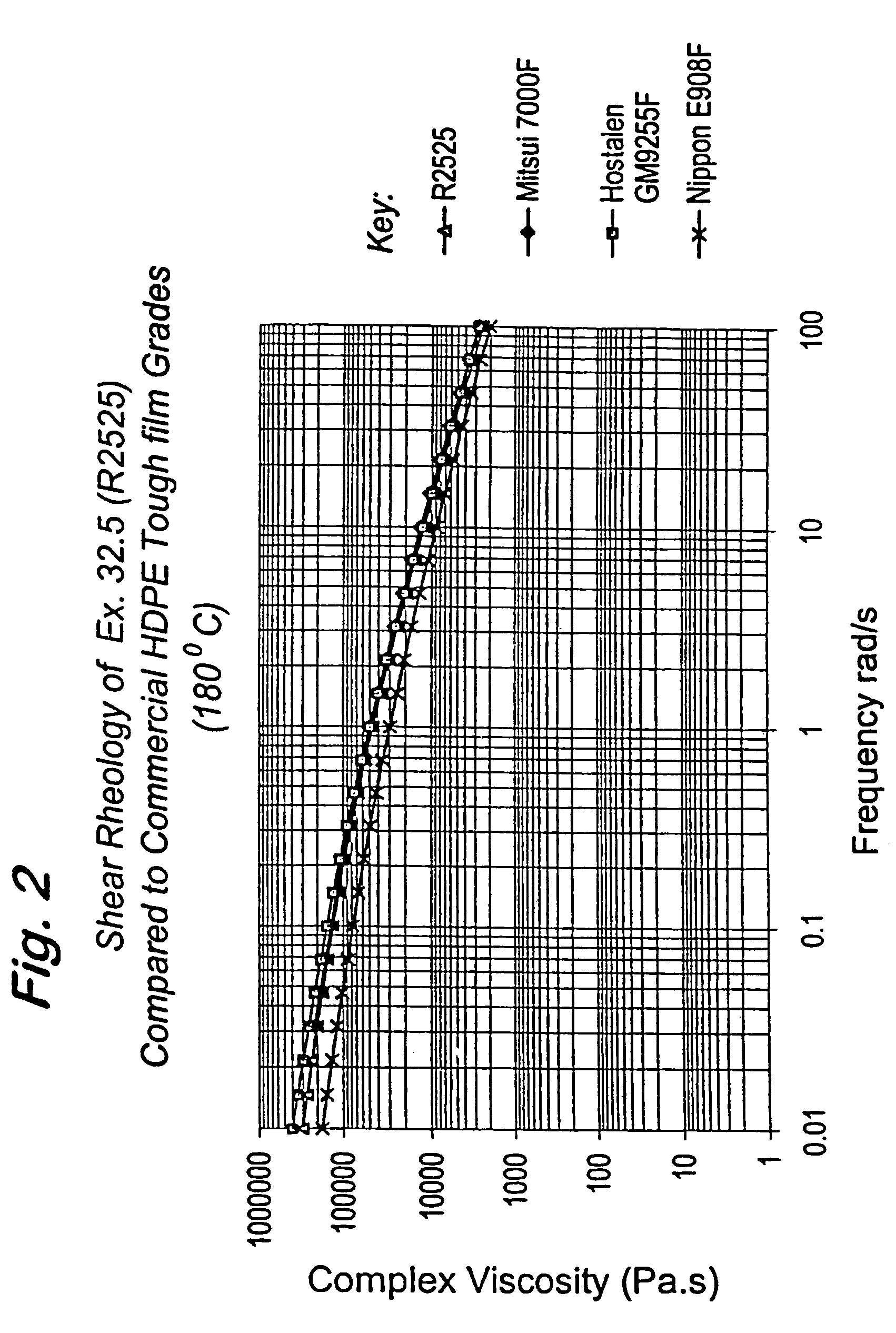
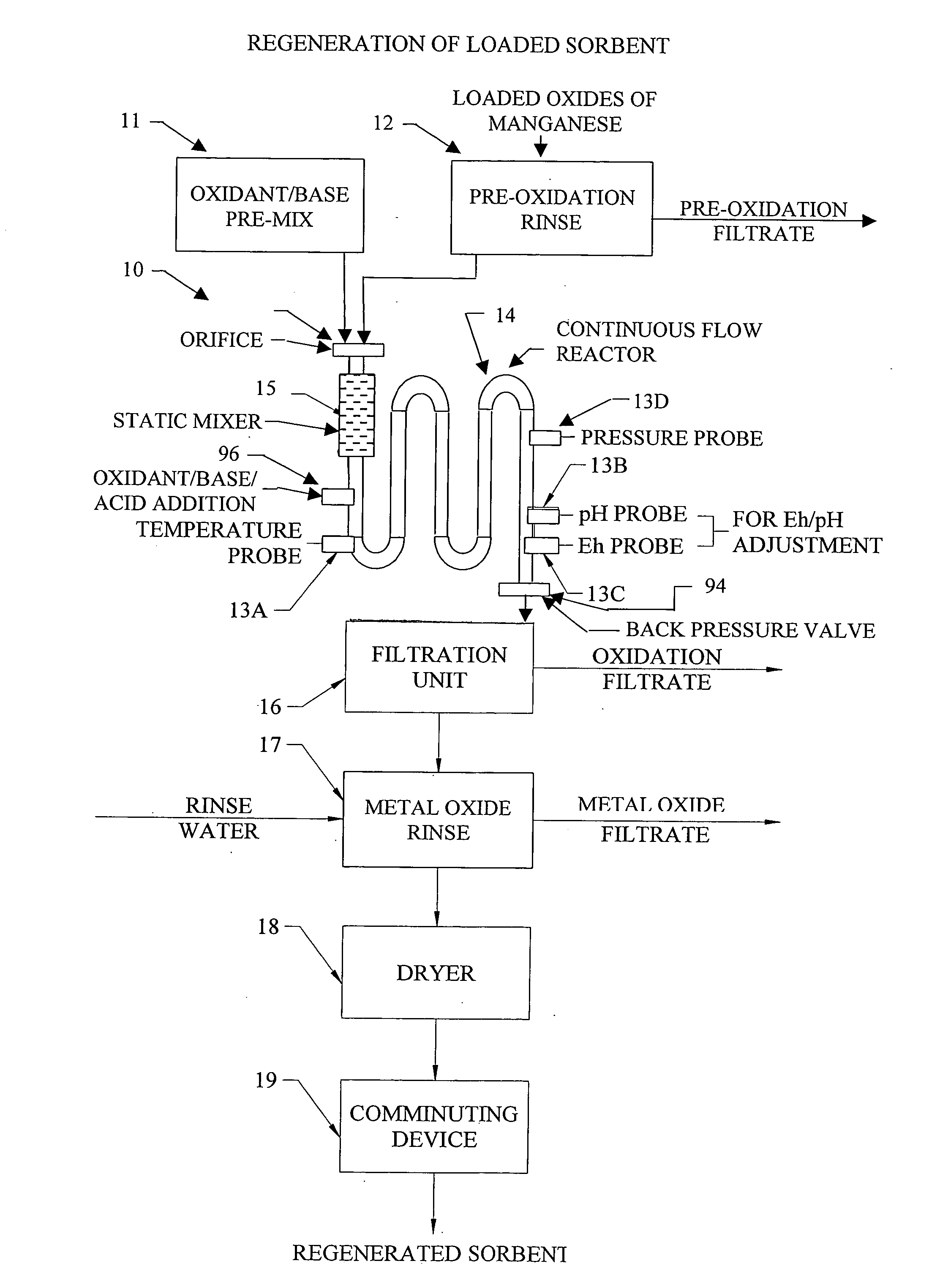
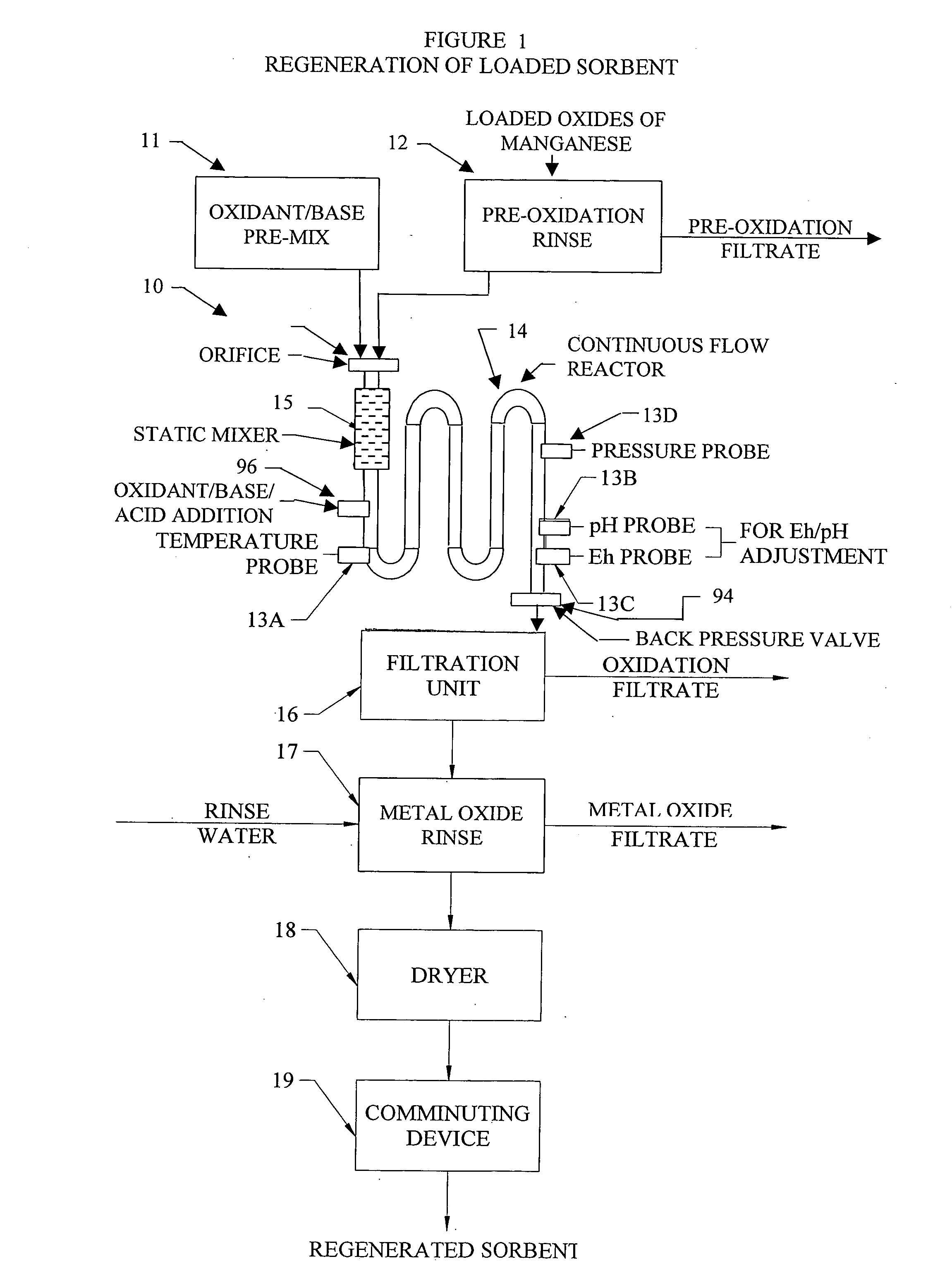
InactiveUS20050074380A1Move quicklyIncrease load capacityCombination devicesTemperatue controlIndustrial gasBatch processing
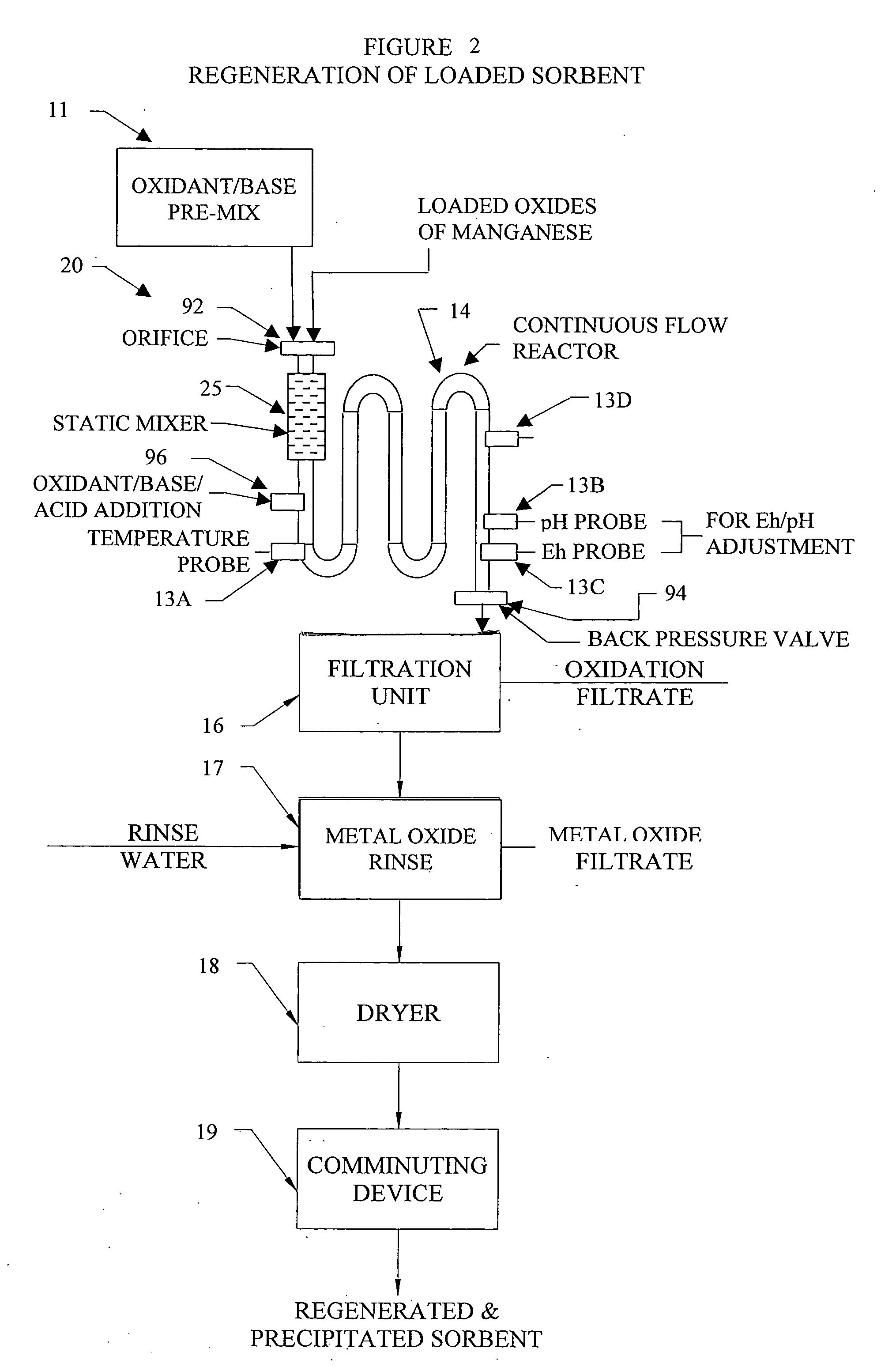
Methods and systems for processing metal oxides from metal containing solutions. Metal containing solutions are mixed with heated aqueous oxidizing solutions and processed in a continuous process reactor or batch processing system. Combinations of temperature, pressure, molarity, Eh value, and pH value of the mixed solution are monitored and adjusted so as to maintain solution conditions within a desired stability area during processing. This results in metal oxides having high or increased pollutant loading capacities and / or oxidation states. These metal oxides may be processed according to the invention to produce co-precipitated oxides of two or more metals, metal oxides incorporating foreign cations, metal oxides precipitated on active and inactive substrates, or combinations of any or all of these forms. Metal oxides thus produced are, amongst other uses; suitable for use as a sorbent for capturing or removing target pollutants from industrial gas streams or drinking water or aqueous streams or for personal protective respirators.
Owner:ENVIROSCRUB TECH CORP
Lithium metal oxide electrodes for lithium batteries
ActiveUS20050026040A1Increase capacityImprove cycle stabilityCellsElectrode thermal treatmentLithium metalOxidation state
An uncycled electrode for a non-aqueous lithium electrochemical cell including a lithium metal oxide having the formula Li(2+2x) / (2+x)M′2x / (2+x)M(2-2x) / (2+x)O2-δ, in which 0≦x<1 and δ is less than 0.2, and in which M is a non-lithium metal ion with an average trivalent oxidation state selected from two or more of the first row transition metals or lighter metal elements in the periodic table, and M′ is one or more ions with an average tetravalent oxidation state selected from the first and second row transition metal elements and Sn. Methods of preconditioning the electrodes are disclosed as are electrochemical cells and batteries containing the electrodes.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
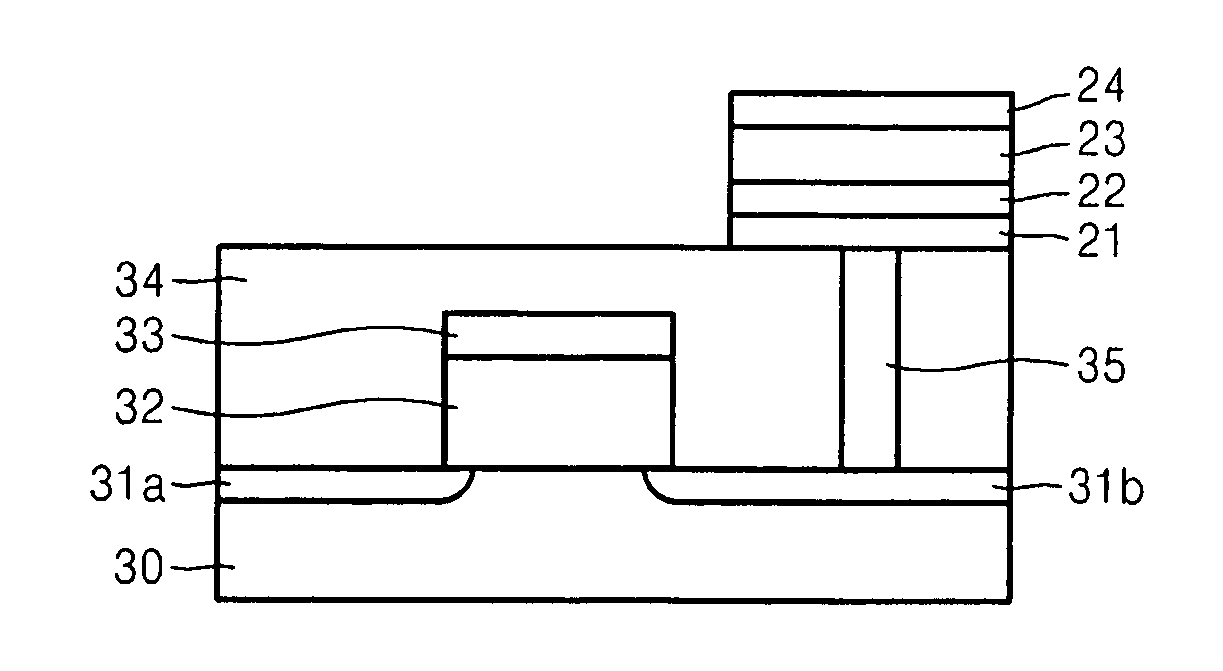
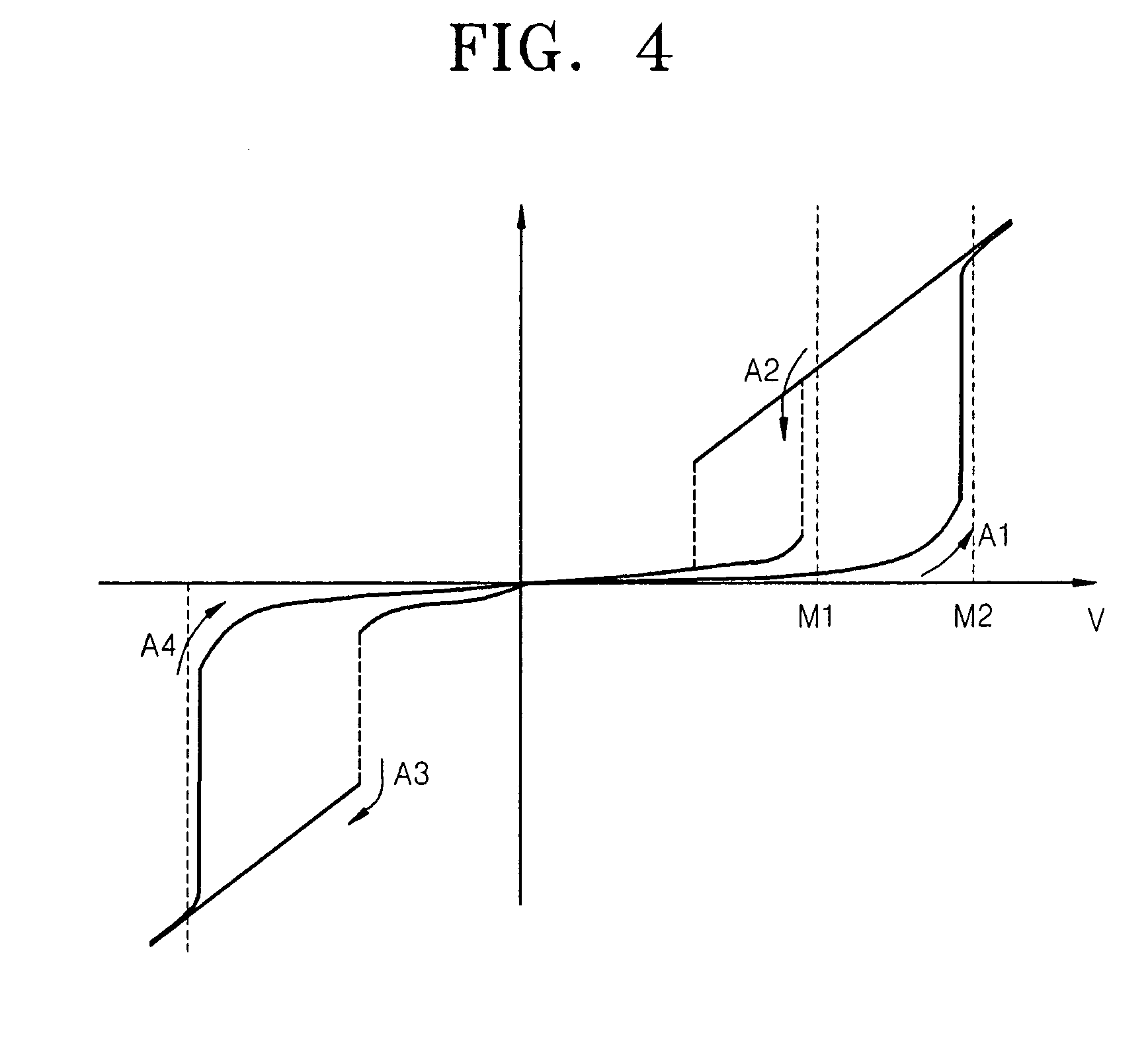
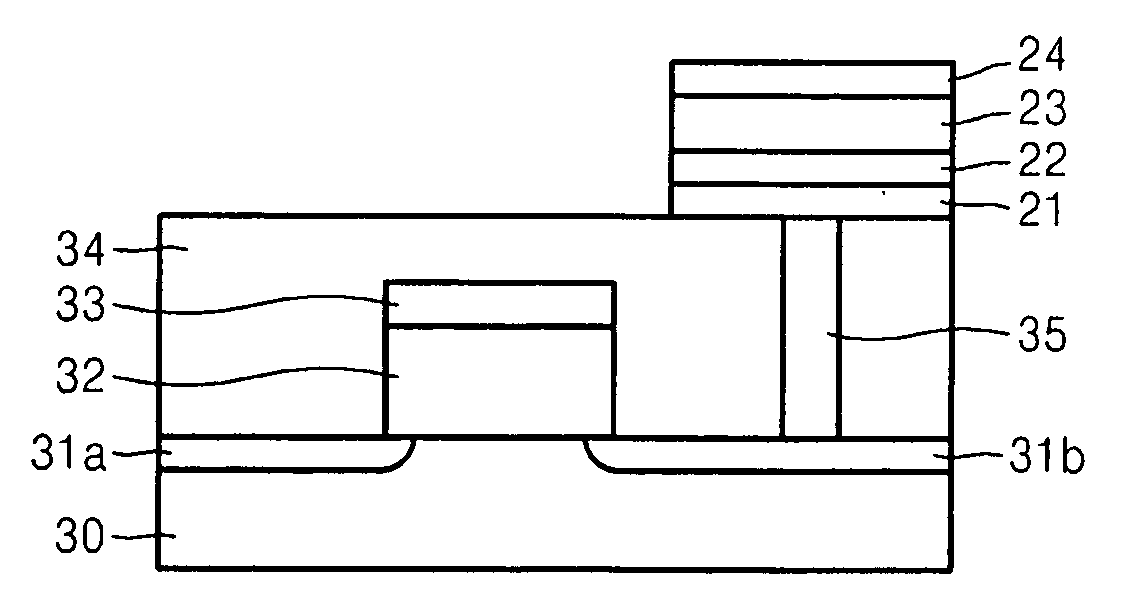
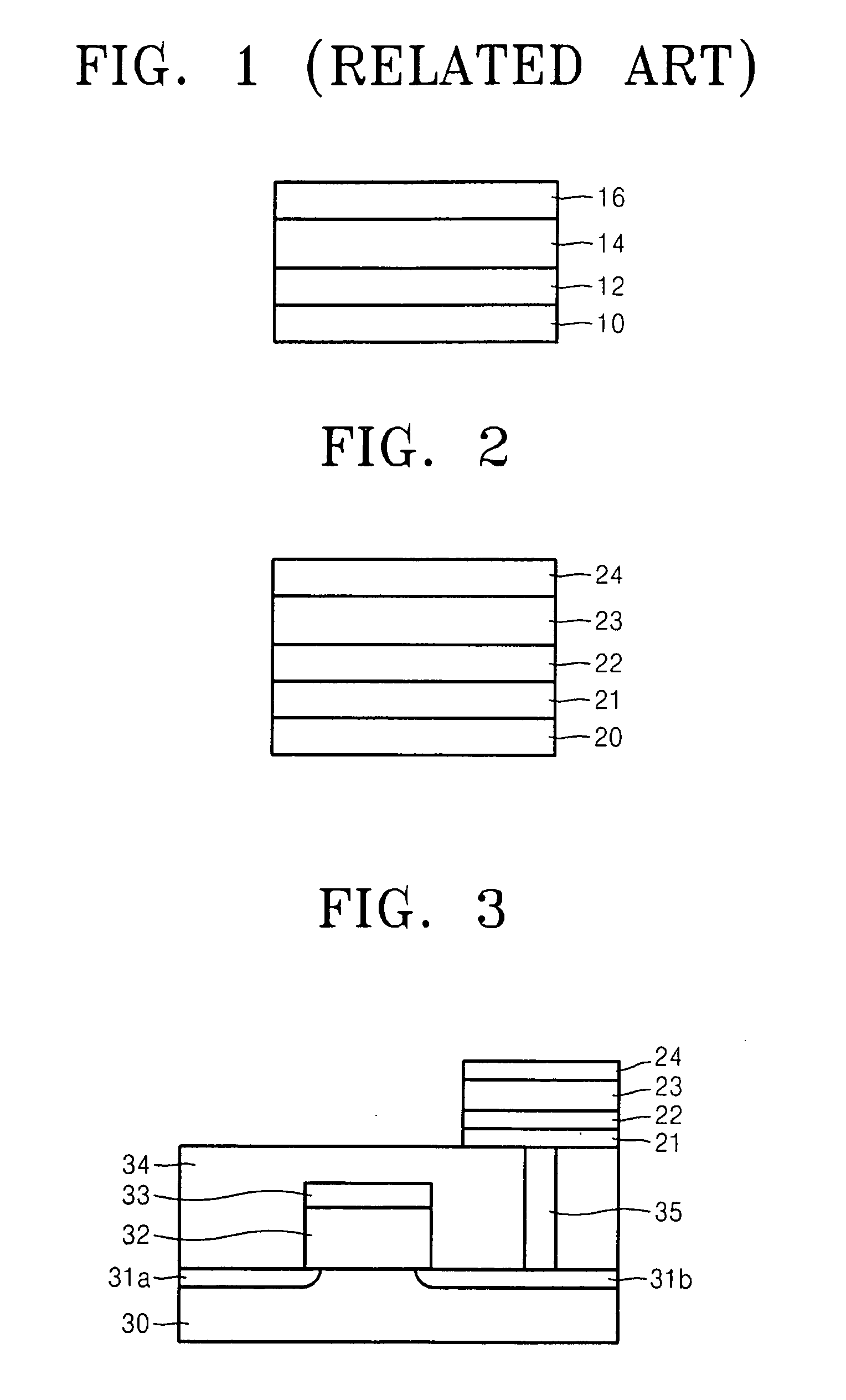
Electrode structure having at least two oxide layers and non-volatile memory device having the same
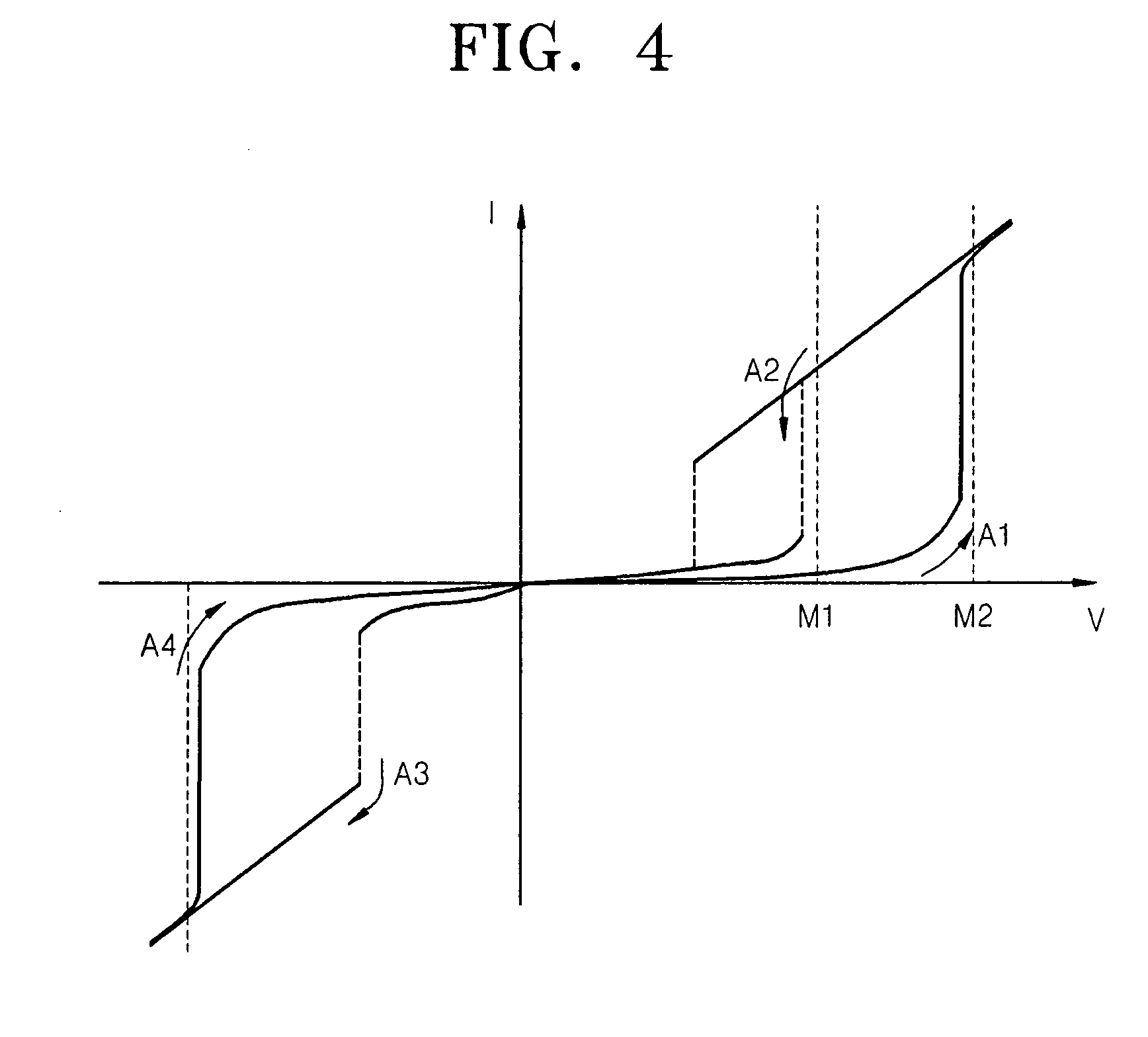
ActiveUS7417271B2Less complex constructionImprove switching characteristicsVehicle seatsAcoustic signal devicesOxidation stateEngineering
An electrode structure having at least two oxide layers that more reliably switch and operate without the use of additional devices and a non-volatile memory device having the same are provided. The electrode structure may include a lower electrode, a first oxide layer formed on the lower electrode, a second oxide layer formed on the first oxide layer and an upper electrode formed on the second oxide layer wherein at least one of the first and second oxide layers may be formed of a resistance-varying material. The first oxide layer may be formed of an oxide having a variable oxidation state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hydrodewaxing catalyst for diesel oil distillate and its preparing method
ActiveCN1952074AHigh yieldExcellent isomerization performancePetroleum wax recoveryWaxMolecular sieve
The invention disclosed a catalyst to lower the freezing point of the diesel oil. The catalyst includes carrier that contains reshaped molecular sieve and hydrogenated metal. The molecular sieve is reshaped by VIB group metal, the content of which in the molecular sieve is 1wt%-40wt% (by oxidation state). The content of the molecular sieve and the metal are 10wt%-90wt% (by oxidation state) and 0.1wt%-40wt% (by oxidation state) respectively. The reshaping agent can modify the acid substance and the bore size on the surface of the molecular sieve so as to match the catalyst's isomerizing function and structure-selective splitting function well; it can make the splitting reaction proceeds according to the lock-and-key mechnanism and ensure the reaction proceeds properly without over splitting; it can improve the quality of the diesel oil and increase its yield. The invention can be used in the deparaffinage of the material that contains wax, especially in the process to lower the freezing point of the diesel oil distillate. It can not only lower the freezing point, but also increase the diesel oil yield substantially.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Lithium metal oxide electrodes for lithium batteries
InactiveUS20060188781A1Increase capacityImprove cycle stabilityActive material electrodesAlkali metal oxidesLithium metalOxidation state
An uncycled preconditioned electrode for a non-aqueous lithium electrochemical cell including a lithium metal oxide having the formula Li(2+2x) / (2+x)M′2x / (2+x)M(2−2x) / (2+x)O2−δ, in which 0≦x<1 and δ is less than 0.2, and in which M is a non-lithium metal ion with an average trivalent oxidation state selected from two or more of the first row transition metals or lighter metal elements in the periodic table, and M′ is one or more ions with an average tetravalent oxidation state selected from the first and second row transition metal elements and Sn, and an uncycled electrode of the formula xLi2M′O3.(1−x)LiMO2, in which 0≦x<1, and in which M is a non-lithium metal ion with an average trivalent oxidation state selected from two or more first-row transition metals or lighter metal elements in the periodic table, and M′ is one or more ions with an average tetravalent oxidation state selected from the first- and second-row transition metal elements and Sn, the electrode being preconditioned in a proton-containing medium with a pH<7.0. Methods of preconditioning the electrodes are disclosed as are electrochemical cells and batteries containing the electrodes.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
Lithium metal oxide electrodes for lithium batteries
InactiveUS7314682B2Electrode thermal treatmentActive material electrodesLithium metalOxidation state
An uncycled electrode for a non-aqueous lithium electrochemical cell including a lithium metal oxide having the formula Li(2+2x) / (2+x)M′2x / (2+x)M(2−2x) / (2+x)O2−δ, in which 0≦x<1 and δ is less than 0.2, and in which M is a non-lithium metal ion with an average trivalent oxidation state selected from two or more of the first row transition metals or lighter metal elements in the periodic table, and M′ is one or more ions with an average tetravalent oxidation state selected from the first and second row transition metal elements and Sn. Methods of preconditioning the electrodes are disclosed as are electrochemical cells and batteries containing the electrodes.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Combustion looping using composite oxygen carriers
ActiveUS7767191B2Increase surface areaImprove energy conversion efficiencyHydrogen productionIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationHydrogenCombustion
A method for producing hydrogen gas is provided and comprises reducing a metal oxide in a reduction reaction between a carbon-based fuel and a metal oxide to provide a reduced metal or metal oxide having a lower oxidation state, and oxidizing the reduced metal or metal oxide to produce hydrogen and a metal oxide having a higher oxidation state. The metal or metal oxide is provided in the form of a porous composite of a ceramic material containing the metal or metal oxide. The porous composite may comprise either a monolith, pellets, or particles.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
Process for the manufacture of 1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene
ActiveUS7829748B1Physical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offAlkaline earth metalOxidation state
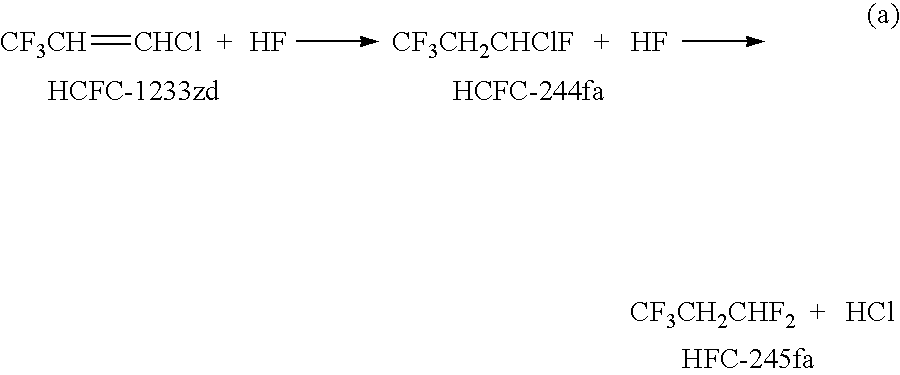
The invention provides an economic process for the manufacture of 1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene (HFO-1234ze) by a two stage process. A vapor phase hydrofluorination of 1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene (HCFC-1233zd) into 1-chloro-1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropane (HCFC-244fa) and / or 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane (HFC-245fa) is conducted, followed by the thermal dehydrochlorination of HCFC-244fa and dehydro fluorination of HFC-245fa into HFO-1234ze in the presence of a catalyst which comprises one or more of alkali metal halides, alkaline earth metal halides, halogenated metal oxides, zero oxidation state metals, zinc halides, palladium halides, and activated carbon.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Oxygen scavenging compositions and packaging comprising said compositions
InactiveUS20060180790A1Removing hazeRecord information storageOrganic/inorganic per-compounds compounding agentsOxidation stateCompound (substance)
The instant invention concerns a composition comprising a base polymer, at least one compound of the formula E-(L-E)x wherein: E is and L is a linking group; and at least one transition metal in a positive oxidation state. The invention also concerns packages containing walls comprising such compositions, methods of forming such packages, and methods of packaging an oxygen-sensitive item within such a package
Owner:PLASTIPAK PACKAGING
Copper-manganese mixed oxide cathode material for use in alkaline cells having high capacity
ActiveUS20080090138A1Cell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesStructural waterMixed oxide
The present invention relates to a copper-manganese mixed oxide cathode material, which is suitable for use in a cathode of an electrochemical cell, and which has the formula MnxCuyOz,.nH2O, wherein the oxidation state of Cu is between about +1 and about +3, the oxidation state of Mn is between about +2 and about +7, x is equal to about 3−y, y is less than about 3, z is calculated or experimentally determined, using means known in the art, based on the values of x and y, as well as the oxidation states of Mn and Cu, and nH2O represents the surface and structural water present in the mixed oxide material. The present invention further relates to an electrochemical cell comprising an anode, a cathode, and a separator disposed between the anode and cathode, and an electrolyte in fluid communication with the anode, the cathode and the separator, wherein the cathode comprises the noted cathode material. The present invention still further relates to such an active cathode material, or an alternative cathode material, wherein the copper-manganese mixed oxide comprises a defect spinel-type structure, which is also suitable for use as a cathode component of an alkaline electrochemical cell.
Owner:ENERGIZER BRANDS
Enzymatic template polymerization
InactiveUS20050079533A1Limiting parasitic branchingImprove electricityNanotechMicrobiological testing/measurementRedox enzymesConductive polymer
A conductive polymer is formed enzymatically in the presence of a polynucleotide template. The method includes combining at least one redox monomer with a polynucleotide template and a redox enzyme, such as horseradish peroxidase, to form a reaction mixture. The monomer aligns along the template before or during the polymerization. Therefore, the polynucleotide template thereby affects the molecular weight and conformation of the conductive polymer. When the conductive polymer is complexed to a polynucleotide duplex, the conformation of the polynucleotide duplex can be modulated by changing the oxidation state of the conductive polymer.
Owner:SAMUELSON LYNNE A +6
Gasoline sulfur reduction in fluid catalytic cracking
InactiveUS6852214B1Reduce sulfur contentLow sulfurCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsOxidation stateGasoline
The sulfur content of liquid cracking products, especially the cracked gasoline, of the catalytic cracking process is reduced by the use of a sulfur reduction additive comprising a porous molecular sieve which contains a metal in an oxidation state above zero within the interior of the pore structure of the sieve. The molecular sieve is normally a large pore size zeolite such as USY or zeolite beta or an intermediate pore size zeolite such as ZSM-5. The metal is normally a metal of Period 4 of the Periodic Table, preferably zinc or vanadium. The sulfur reduction catalyst may be used in the form of a separate particle additive or as a component of an integrated cracking / sulfur reduction catalyst.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP +1
Electrode structure having at least two oxide layers and non-volatile memory device having the same
ActiveUS20070200158A1Less complex constructionImprove switching characteristicsTransistorVehicle seatsOxidation stateEngineering
An electrode structure having at least two oxide layers that more reliably switch and operate without the use of additional devices and a non-volatile memory device having the same are provided. The electrode structure may include a lower electrode, a first oxide layer formed on the lower electrode, a second oxide layer formed on the first oxide layer and an upper electrode formed on the second oxide layer wherein at least one of the first and second oxide layers may be formed of a resistance-varying material. The first oxide layer may be formed of an oxide having a variable oxidation state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Source reagent compositions for CVD formation of gate dielectric thin films using amide precursors and method of using same
InactiveUS7005392B2Group 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesVacuum evaporation coatingArylGate dielectric
A CVD Method of forming gate dielectric thin films on a substrate using metalloamide compounds of the formula M(NR1R2)x, wherein M is selected from the group consisting of: Zr, Hf, Y, La, Lanthanide series elements, Ta, Ti, Al; N is nitrogen; each of R1 and R2 is same or different and is independently selected from the group consisting of H, aryl, perfluoroaryl, C1–C8 alkyl, C1–C8 perfluoroalkyl, alkylsilyl and x is the oxidation state on metal M; and an aminosilane compound of the formula HxSi(NR1R2)4-x, wherein H is hydrogen; x is from 0 to 3; Si is silicon; N is nitrogen; each of R1 and R2 is same or different and is independently selected from the group consisting of H, aryl, perfluoroaryl, C1–C8 alkyl, and C1–C8 perfluoroalkyl. By comparison with the standard SiO2 gate dielectric materials, these gate dielectric materials provide low levels of carbon and halide impurity.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
High density non-volatile memory device
InactiveUS20050041494A1Suitable mechanical propertyPrevent charge leakageNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesChemical synthesisFault tolerance
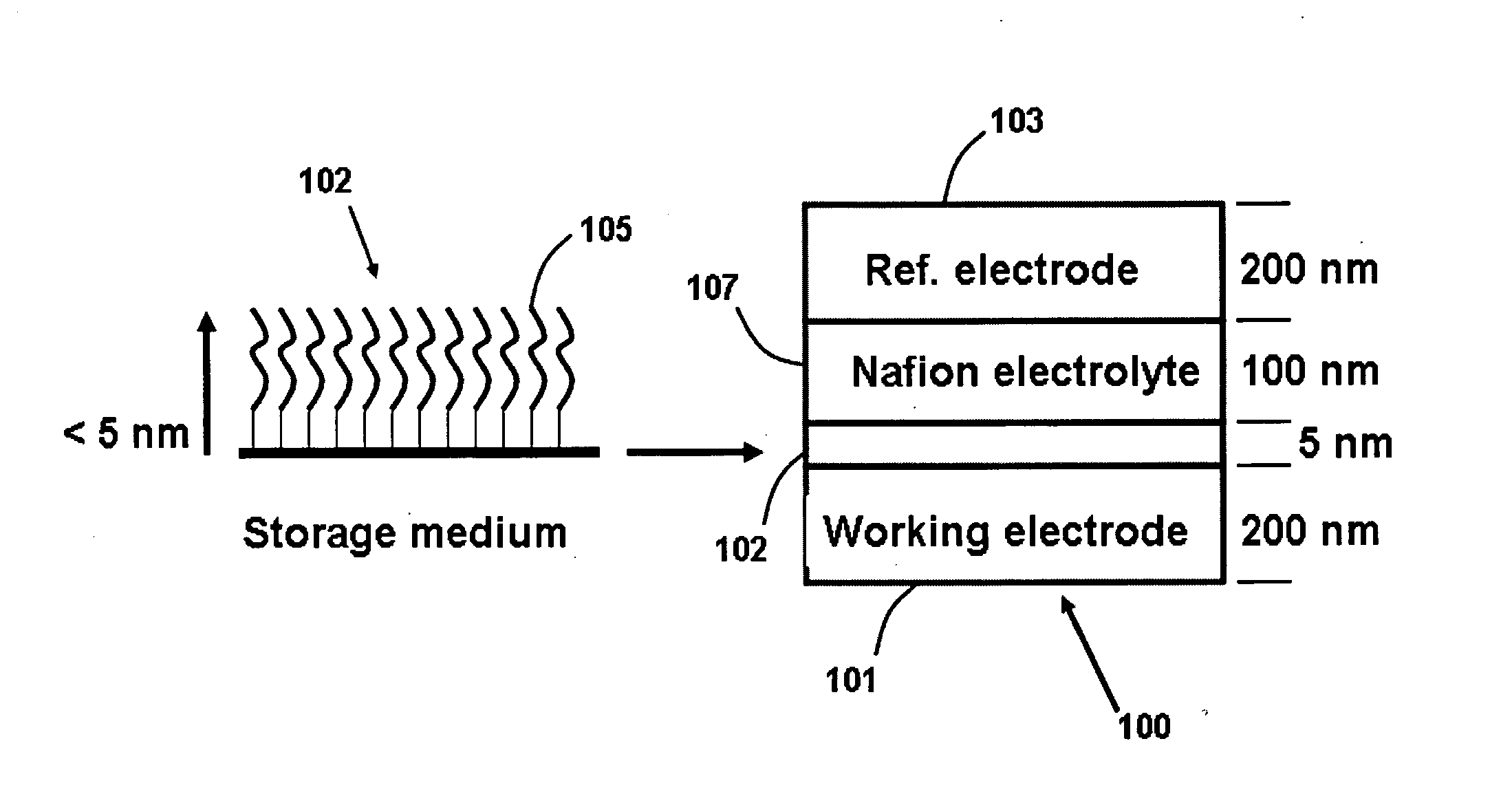
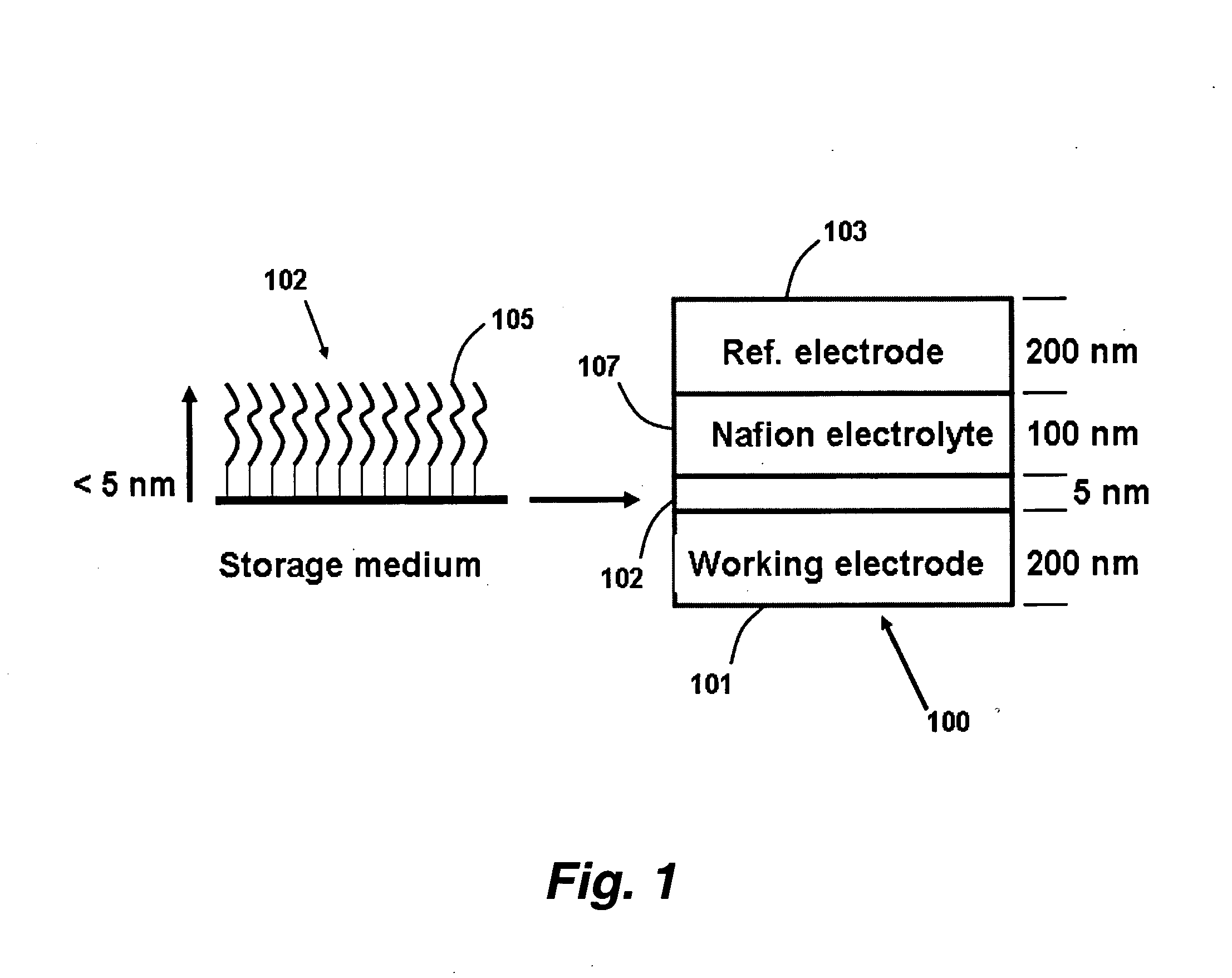
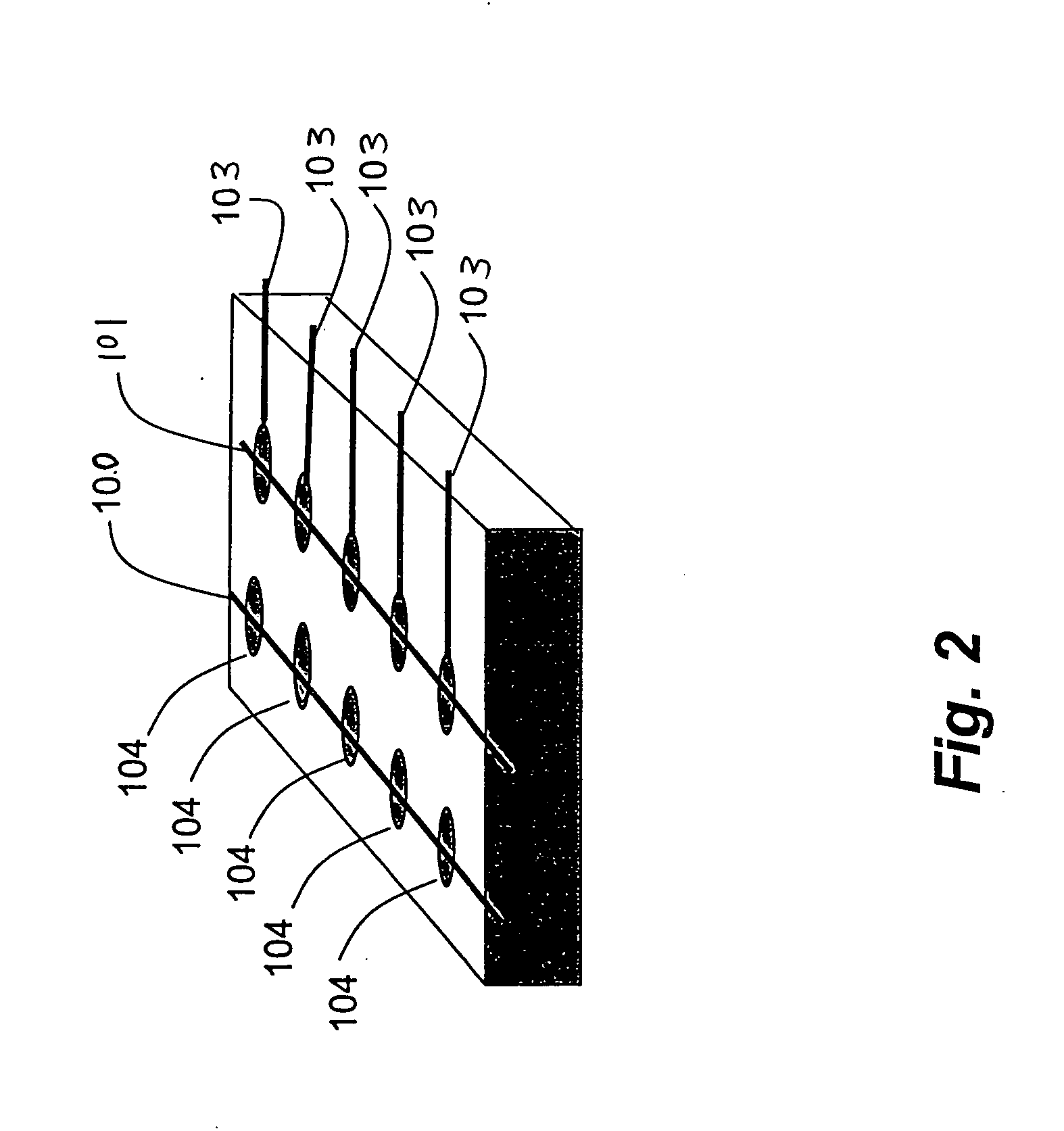
This invention provides novel high density memory devices that are electrically addressable permitting effective reading and writing, that provide a high memory density (e.g., 1015 bits / cm3), that provide a high degree of fault tolerance, and that are amenable to efficient chemical synthesis and chip fabrication. The devices are intrinsically latchable, defect tolerant, and support destructive or non-destructive read cycles. In a preferred embodiment, the device comprises a fixed electrode electrically coupled to a storage medium having a multiplicity of different and distinguishable oxidation states wherein data is stored in said oxidation states by the addition or withdrawal of one or more electrons from said storage medium via the electrically coupled electrode.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com