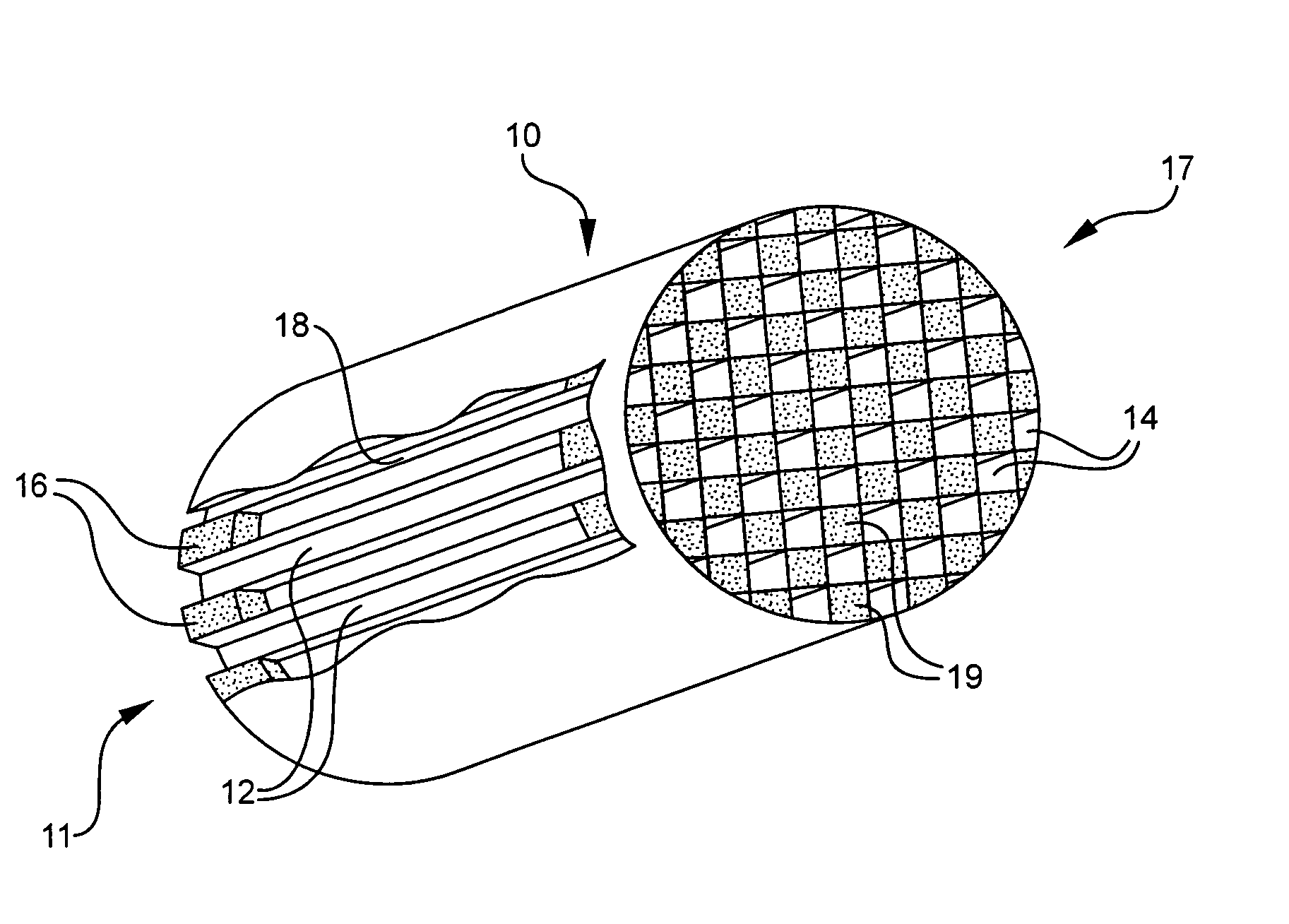
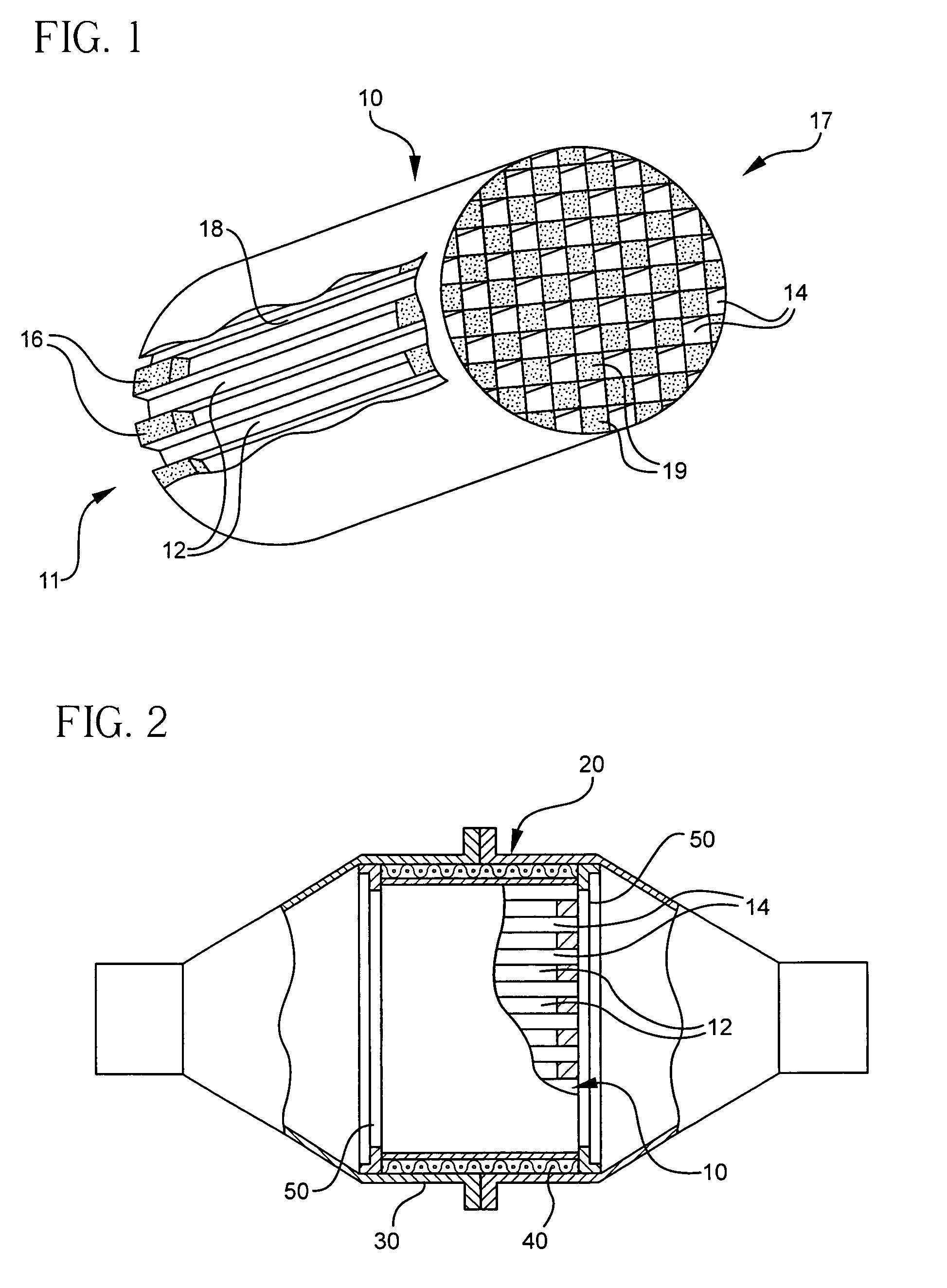
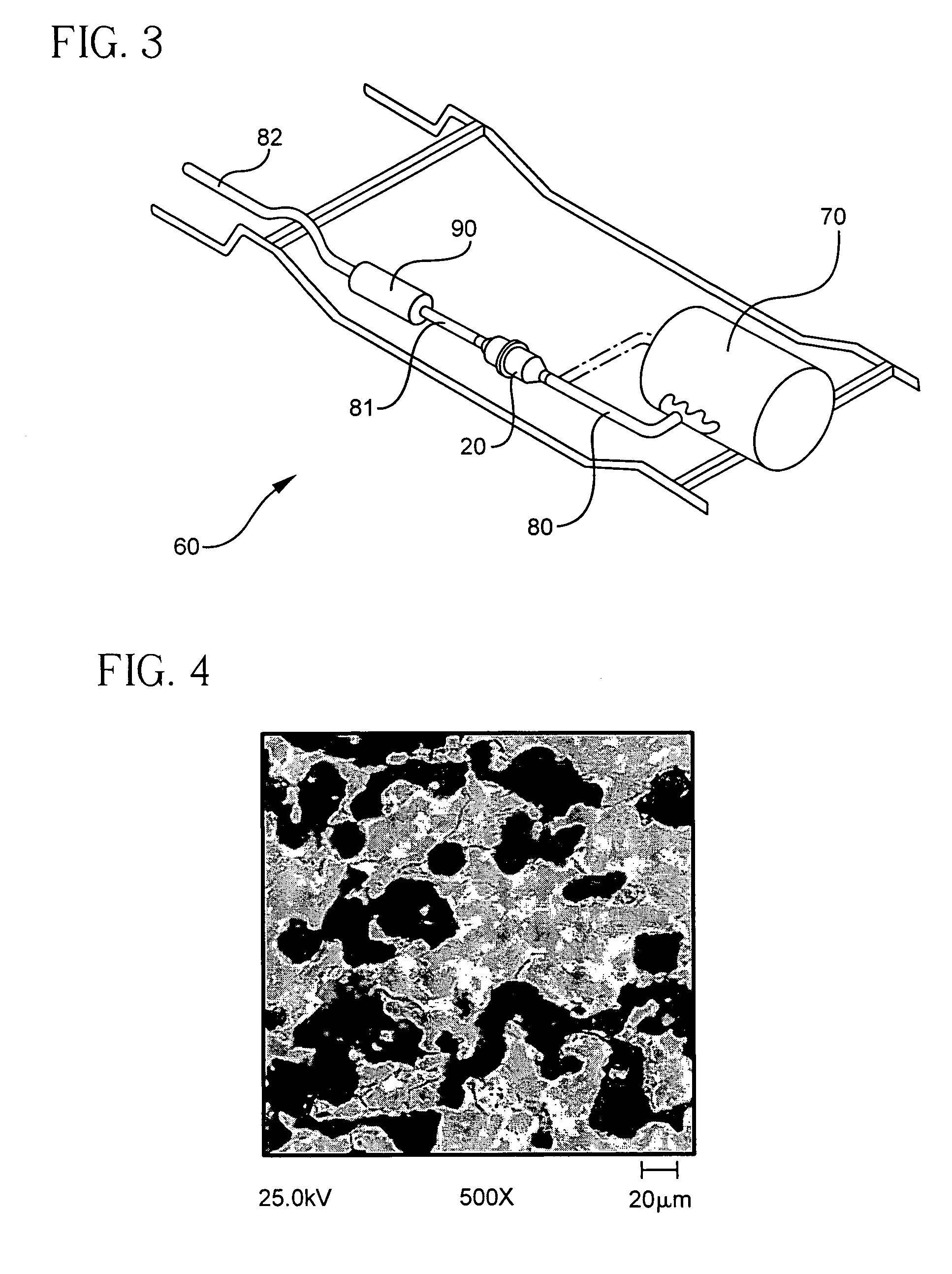
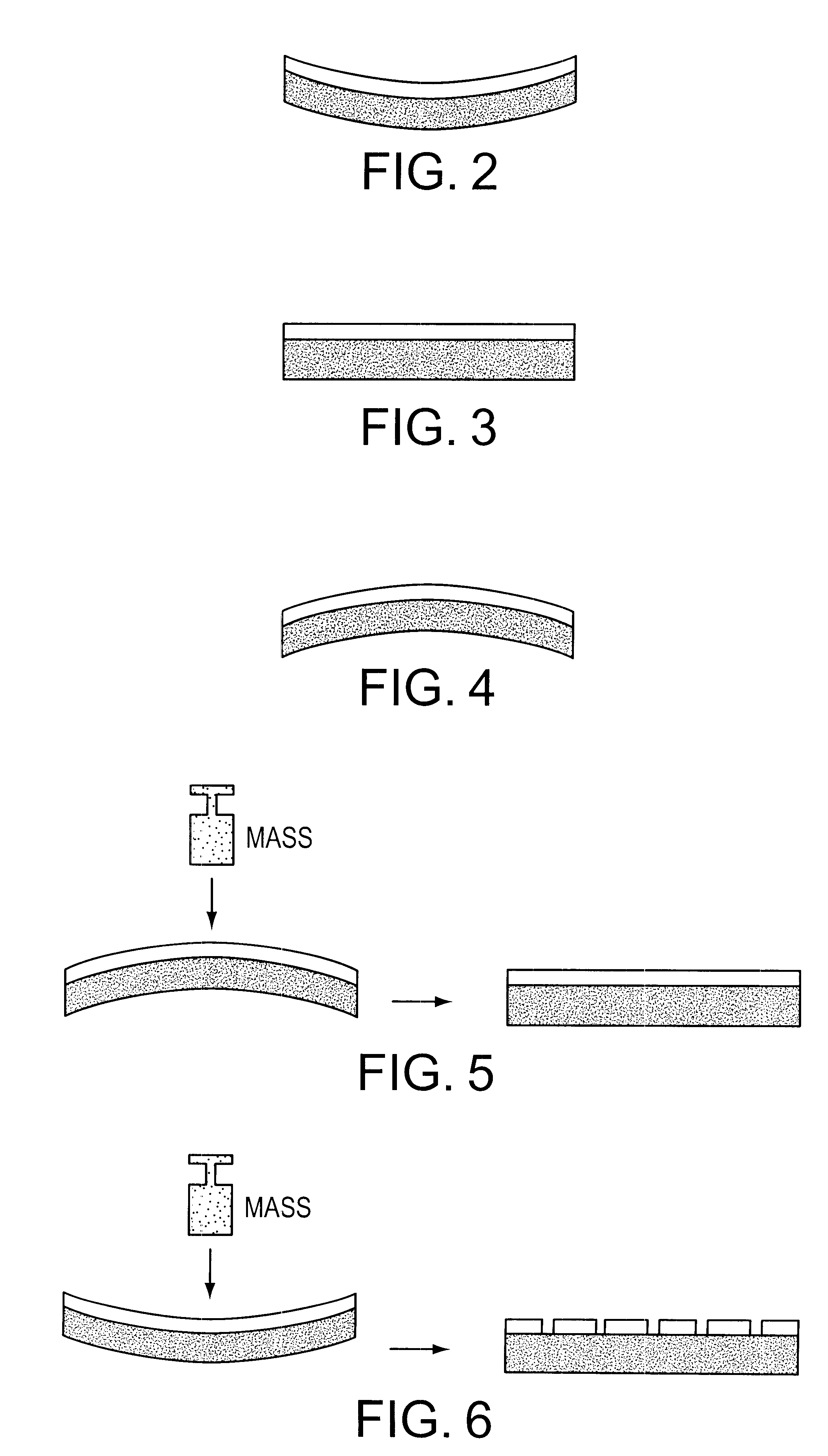
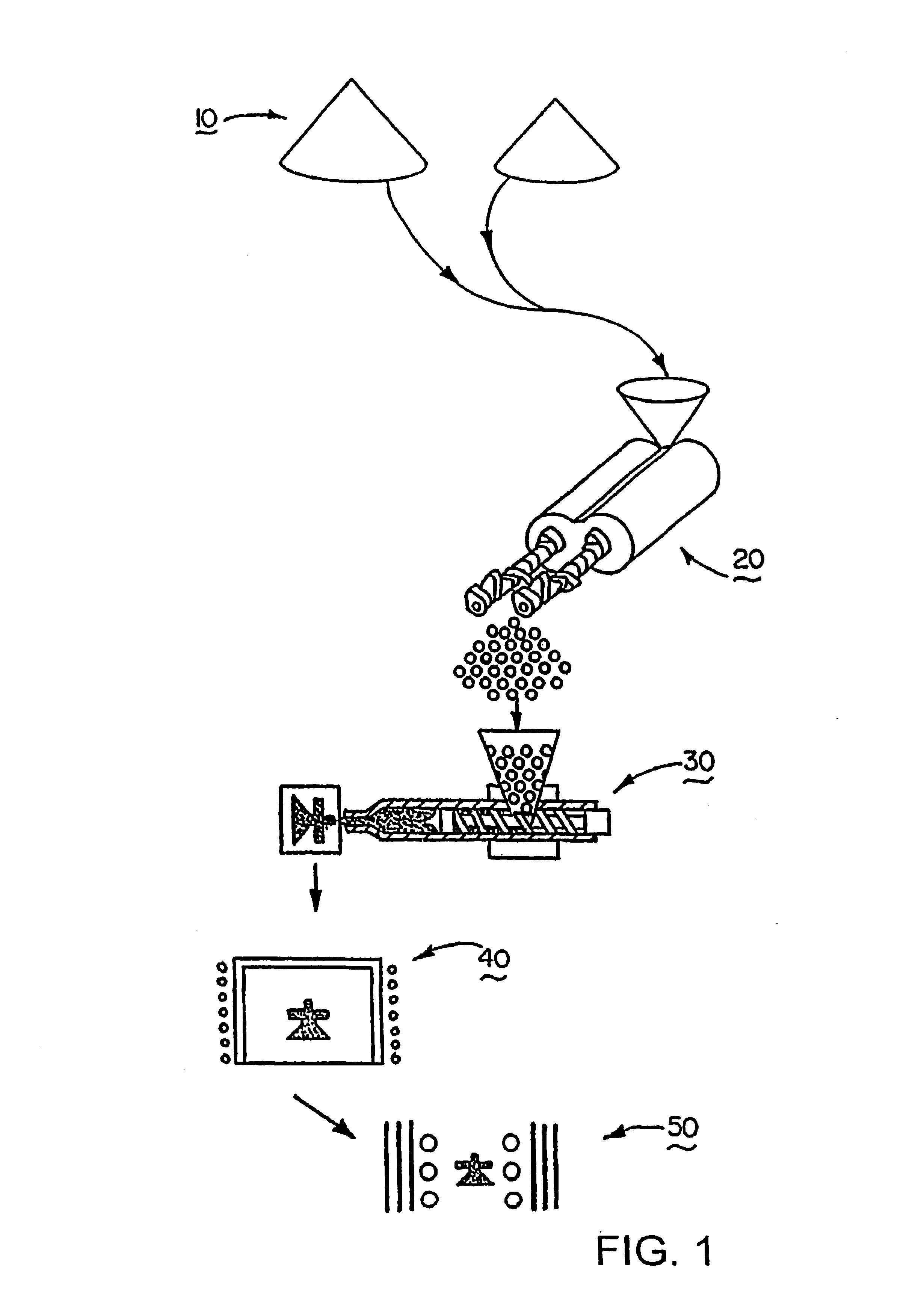
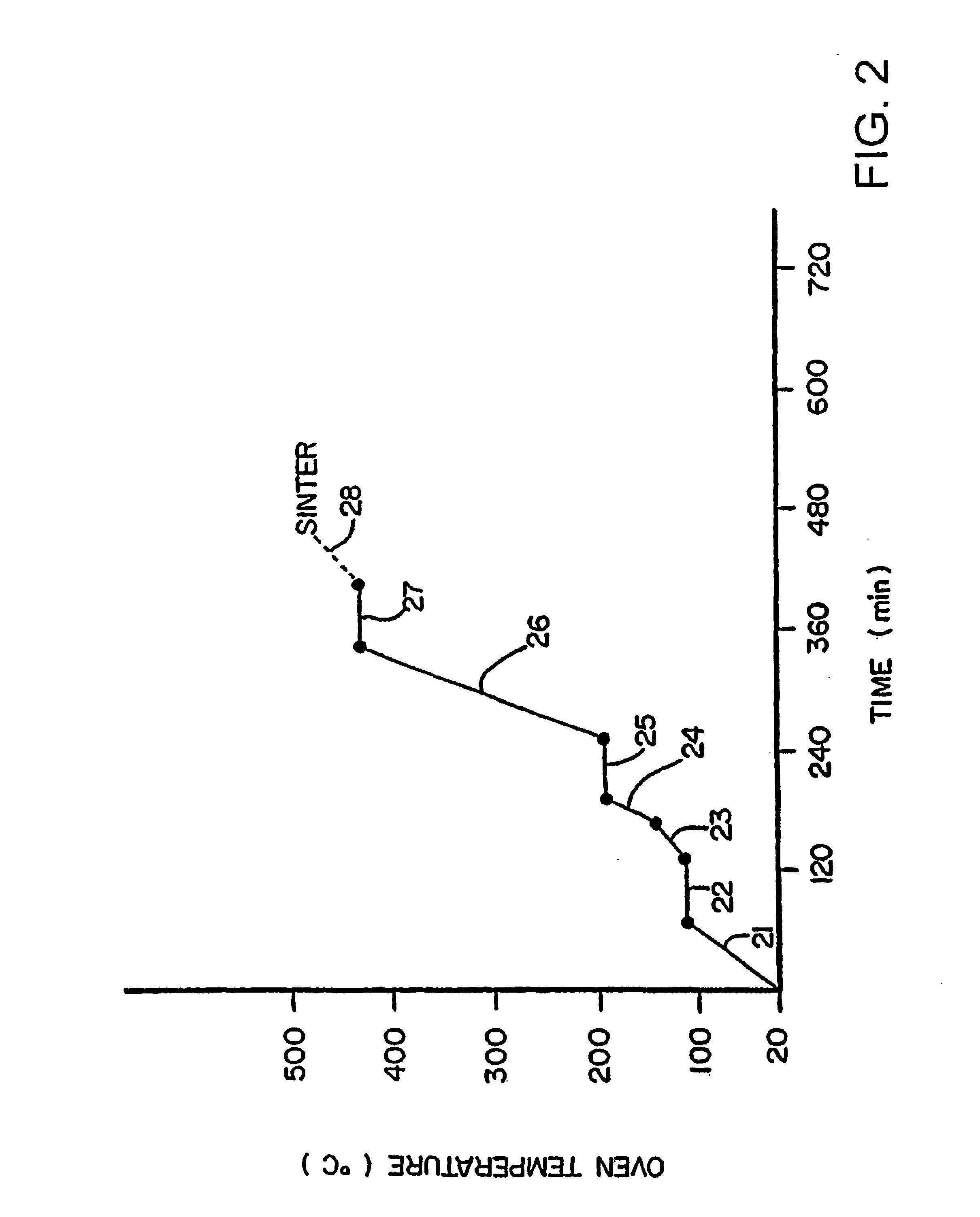
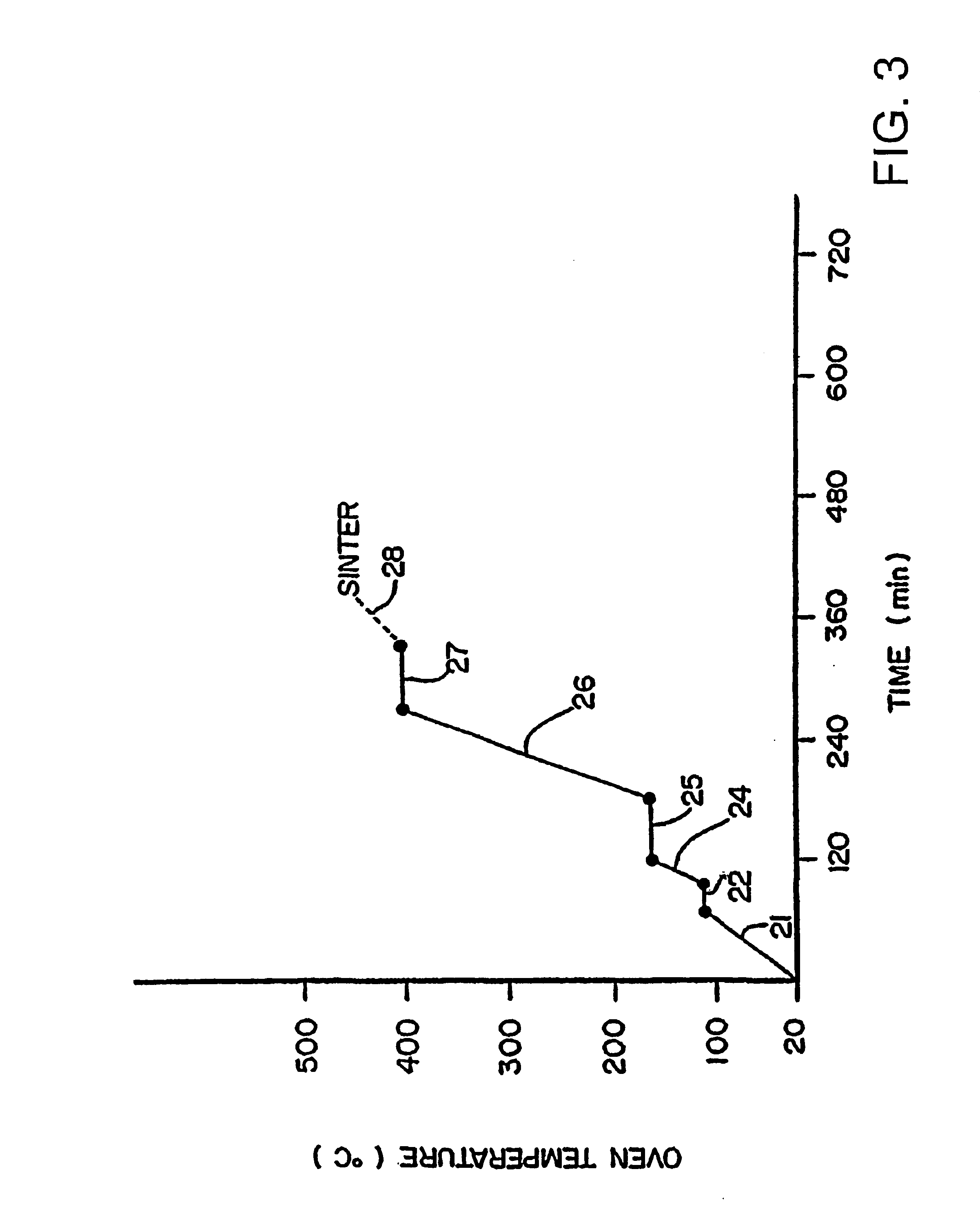
Patents
Literature
9831 results about "Green body" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A green body is an object whose main constituent is weakly bound clay material, usually in the form of bonded powder or plates before it has been sintered or fired. In ceramic engineering, the most common method for producing ceramic components is to form a green body comprising a mixture of the ceramic material and various organic or inorganic additives, and then to fire it in a kiln to produce a strong, vitrified object. Additives can serve as solvents, dispersants (deflocculants), binders, plasticizers, lubricants, or wetting agents.
Ceramic slurry preparation and 3D (three dimensional) printing light curing molding method
ActiveCN106810215ALow viscosityHigh solid contentAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusFlexural strengthVolumetric Mass Density
The invention provides a ceramic slurry preparation and 3D (three dimensional) printing light curing molding method. 25-85vol% of ceramic powder and 15-75vol% of an optical resin premix solution are mainly involved, and the method includes: A), preparation of the optical resin premix : namely stirring a low polymer, a reactive diluent, a photoinitiator, a dispersing agent, a photosensitizer and a sensitizer according to a certain proportion under intermediate speed for 0.5-3 hours to enable the components to be mixed evenly; B), placing the premix solution and the ceramic powder in a ball mill according to certain volume for ball-milling for 5-15 hours to prepare the ceramic slurry high in solid content and low in viscosity; subjecting the ceramic slurry to curing molding layer by layer gradually on a 3D light curing molding machine to obtain a ceramic green body prior to aftertreatment of drying, degreasing, sintering and the like to obtain ceramic part. The method is high in preparation molding precision and free of molds to prepare complex structure parts, the ceramic product can reach more than 92% in density, 320-1750MPa in flexural strength and 1800-4500MPa in compression strength.
Owner:重庆摩方科技有限公司
Method for rapid forming of a ceramic work piece
InactiveUS6217816B1Rapid productionPrevent dislocationAdditive manufacturing apparatusFeeding arrangmentsHeat fusionLaser beams
An inorganic binder and a dissolving agent are put into ceramic powder. They are mixed to form a plastic green mixture. Then the said mixture is formed into a thin green layer. Preferably, this thin green layer will be preheated and dried such that the thin green layer will be hardened due to the bonding effect of the inorganic binder. A portion of the thin green layer exposed under a directed high-energy beam is sintered, preferably by a laser beam, to cause ceramic molecules to bond together locally due to heat fusion. By controlling the scanning path of the high-energy beam, a two-dimensional thin cross section of the ceramic part in arbitrary form can be produced. A second thin ceramic layer can be built onto the first thin ceramic layer and bonded to it by the same method. After multiple repetitions of this procedure a three dimensional ceramic part can be fabricated layer upon layer. The green portion, which is not scanned by the high-energy beam, will be removed with suitable method. A ceramic part can be rapidly produced in this way.
Owner:NAT SCI COUNCIL
Multi-layer ceramic substrate and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6153290AFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh densityInductor
The present invention provides a method for producing a high-density multi-layer ceramic substrate with stable characteristics, the substrate incorporating therein a passive component such as a high-precision capacitor or inductor. The method comprises the steps of providing compact blocks containing a green ceramic functional material to form the passive components; providing a composite green laminate having a plurality of ceramic green sheets comprising a ceramic insulating material and in which the compact blocks are built in pre-disposed spaces and a paste containing a metal inducing, during firing, oxidation reaction accompanied by expansion is provided in space between inside walls of the spaces and the compact blocks; firing the composite green laminate in a state in which the laminate is sandwiched by the sheet-like supports formed of green ceramics that cannot be sintered at the sintering temperature, so as to prevent shrinkage of the laminate; and removing the unsintered sheet-like supports.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Three-dimensional through-hole or part-hole interconnecting porous metal foam and its preparing method
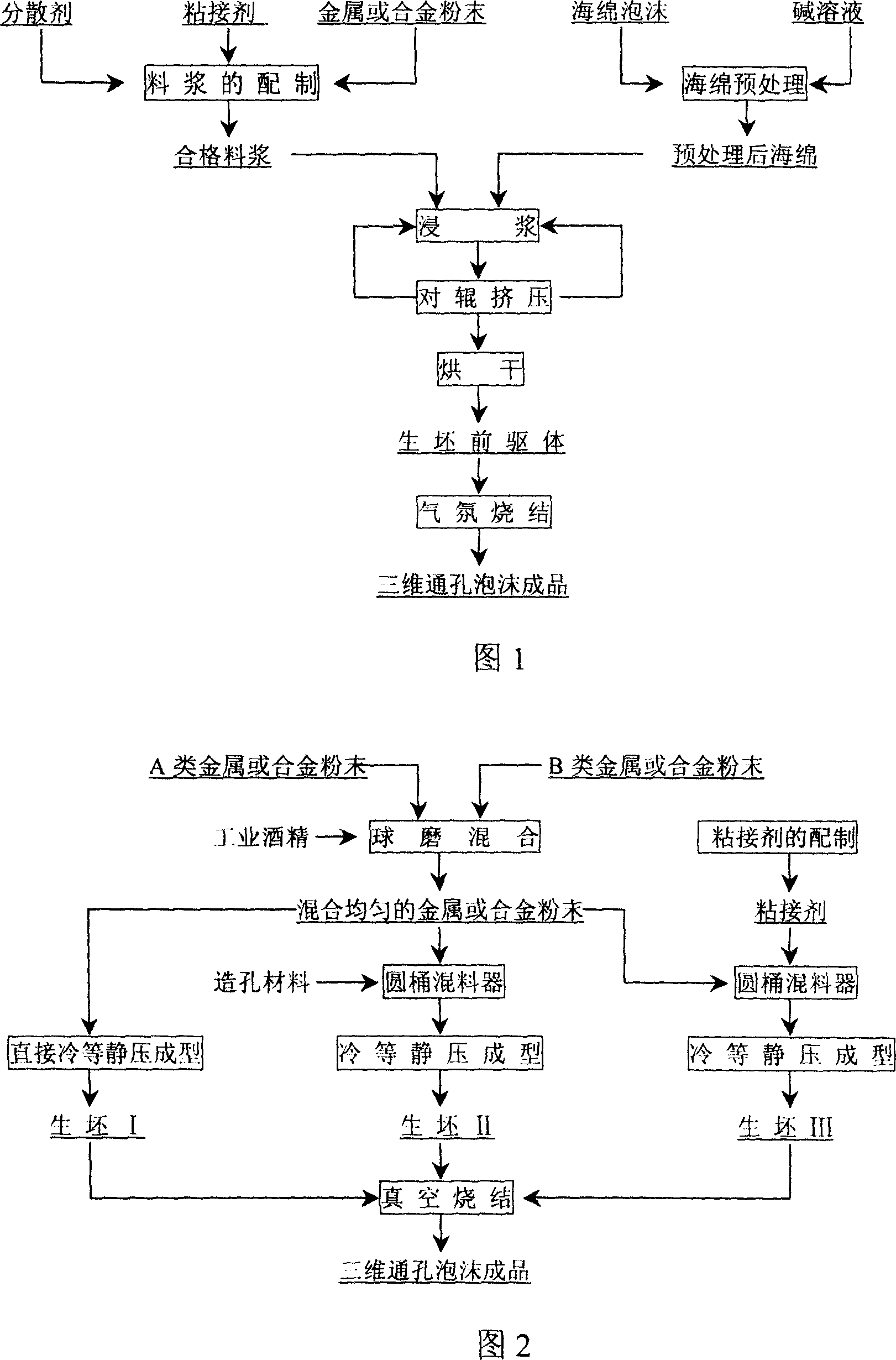
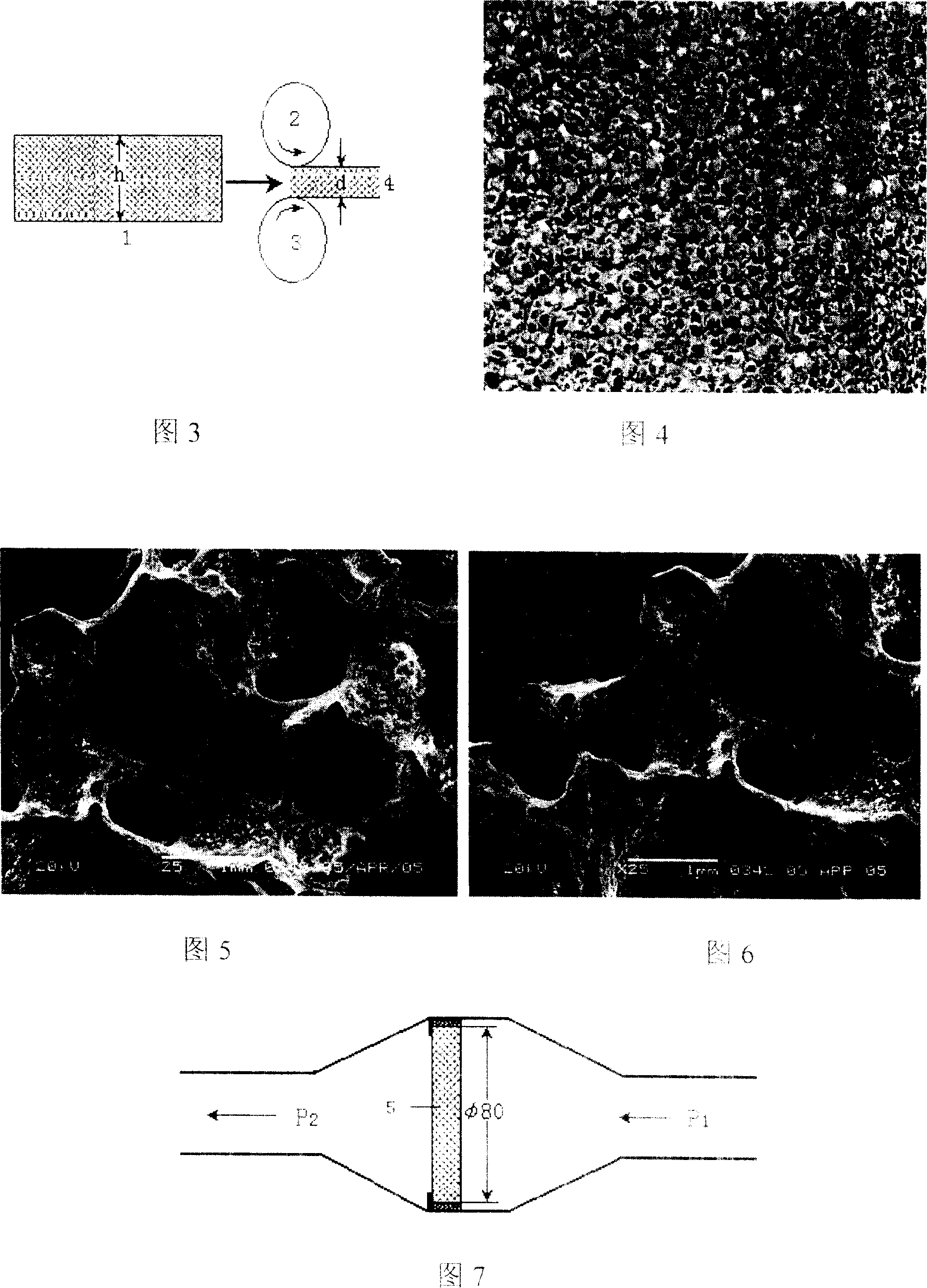
The invention relates to a multi-hole foamed metal material and the manufacturing method. It includes the following steps: equally dispersing metal or alloy powder that has the particle diameter at 1-100um into solution contains adhesive agent to make slime, pouring the slime into through-hole polyurethane sponge foam, after taking drying and sintering, the material would be gained. It also could be make by the method of directly isostatic cool pressing one or more metal or alloy powder, isostatic cool pressing after mixing with pore forming material or isostatic cool pressing after mixing with adhesive agent solution to gain green pressing that would be sintered in vacuum furnace to make the material. The invention could be used to process vehicle tail gas and could also be used to filter the smoke form thermal power station or metallurgical furnace.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Porous SiC-bodies with micro-channels and process for their fabrication
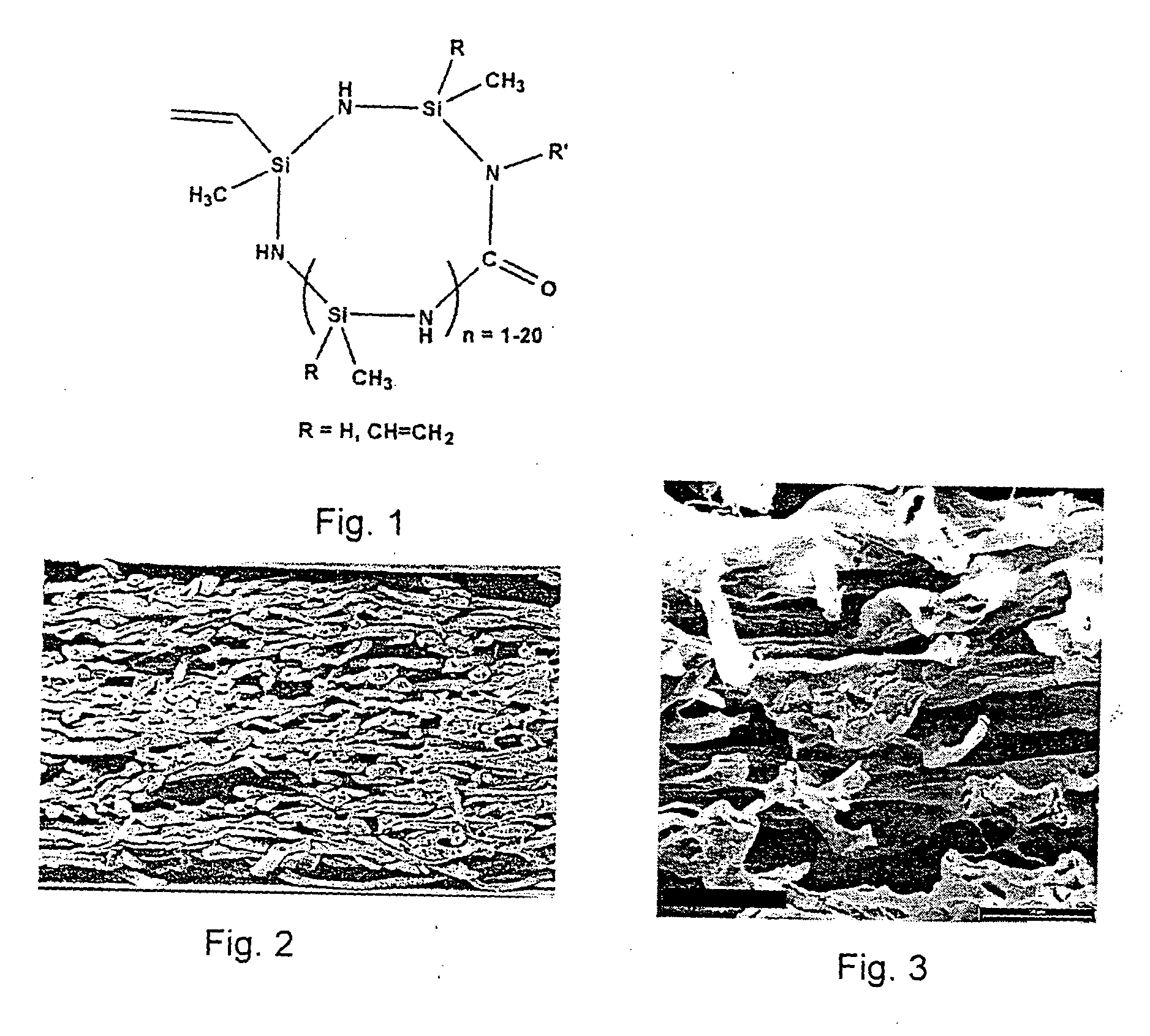
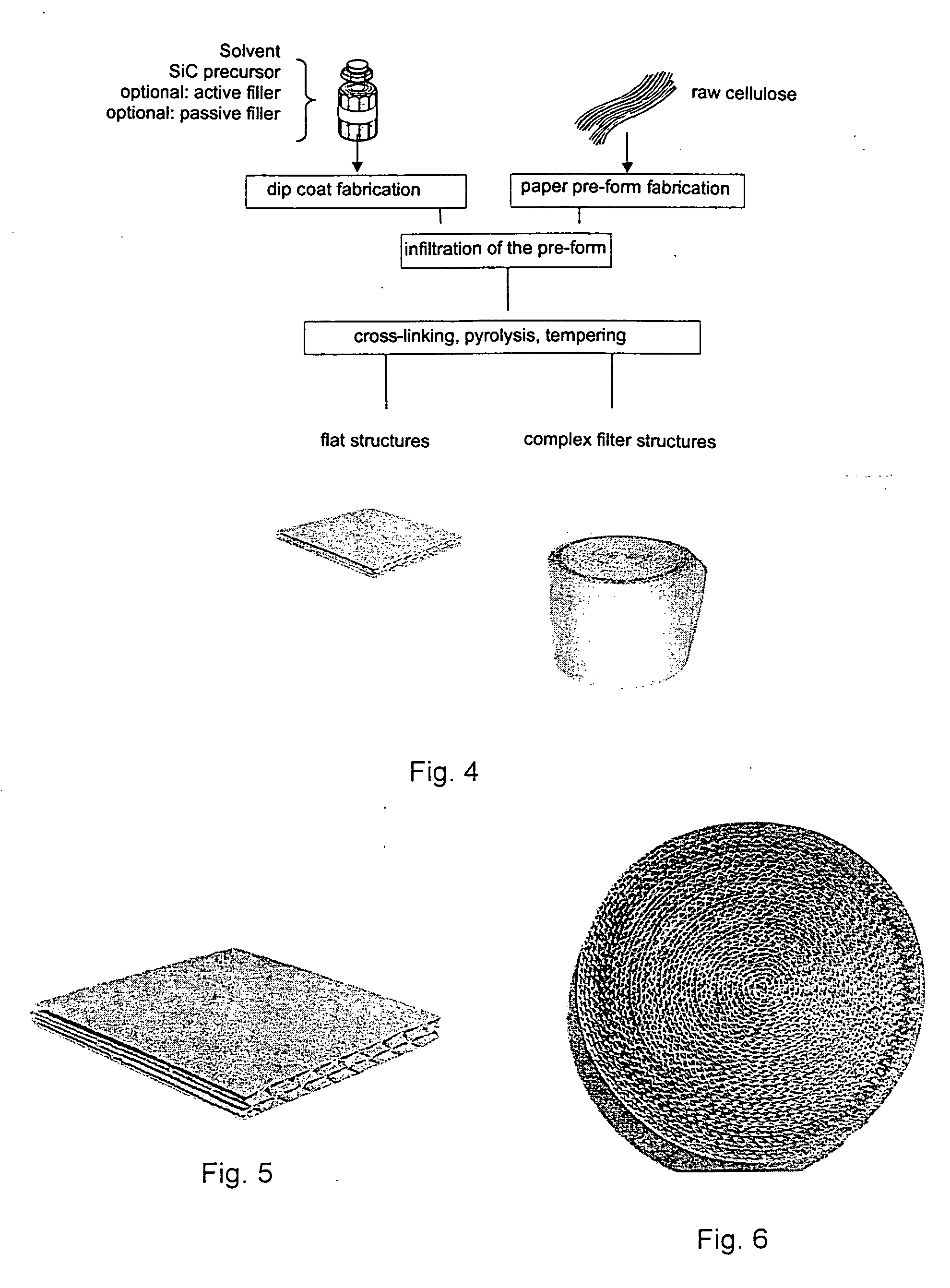
InactiveUS20060121266A1Large effective internal surface areaImprove filtering effectInternal combustion piston enginesLayered productsParticulatesCellulose
Process for the fabrication of porous bodies mainly constituted by SiC containing ceramic with a microstructure which is interfused with micro-channels which consists of the process steps a) Provision of a pre-body made from cellulose or pulp b) Fabrication of an infiltration solution or a slurry consisting of (A) solvent, polysilazane, polysilane and / or polycarbosilane or (B) solvent, polysilazane and / or polysilane as well as active metallic fillers and / or passive ceramic fillers. c) Infiltrating the body with infiltration solution or slurry d) Cross-linking of the polysilazane, polycarbosilane and / or polysilane while generating a solid green body e) Ceramization through pyrolysis of the green body in an inert-gas atmosphere. f) Removal of residual carbon with an oxidizing thermal process, thereof producible catalyst carriers or carbon particulate filters as well as Porous ceramic which is made from at least 80% SiC in which the porous ceramic features a microstructure with micro-channels consisting mainly of SiC coated micro-channels featuring an average diameter between 1 and 25 μm and webs of SiC located between the micro-channels as well as additional ceramic materials with a content below 20 wt %.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
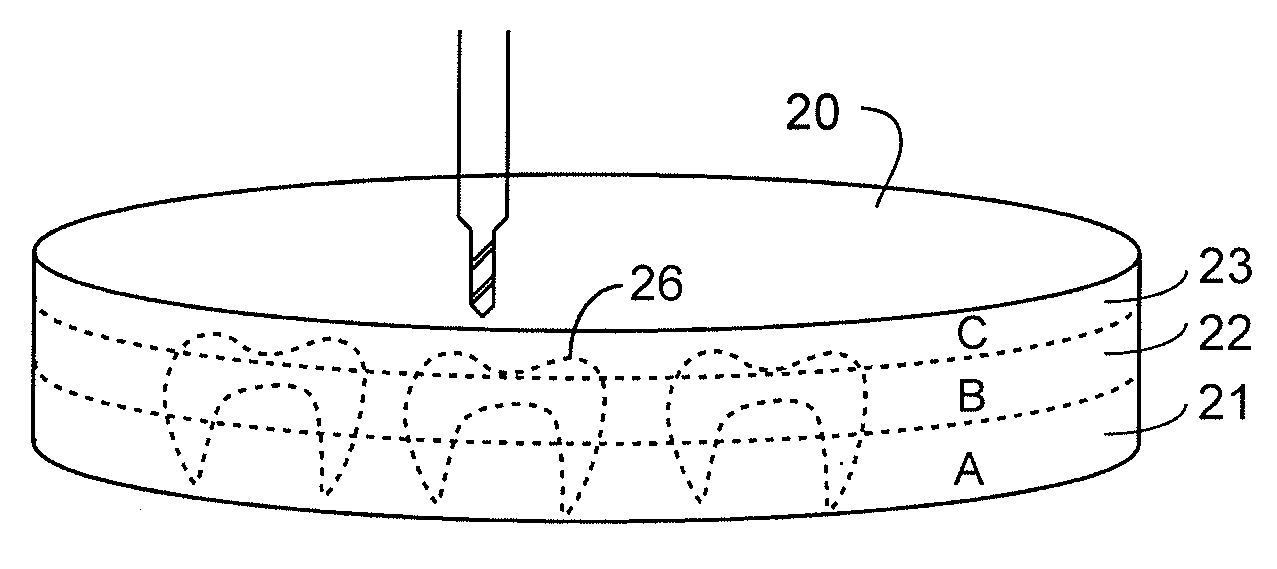
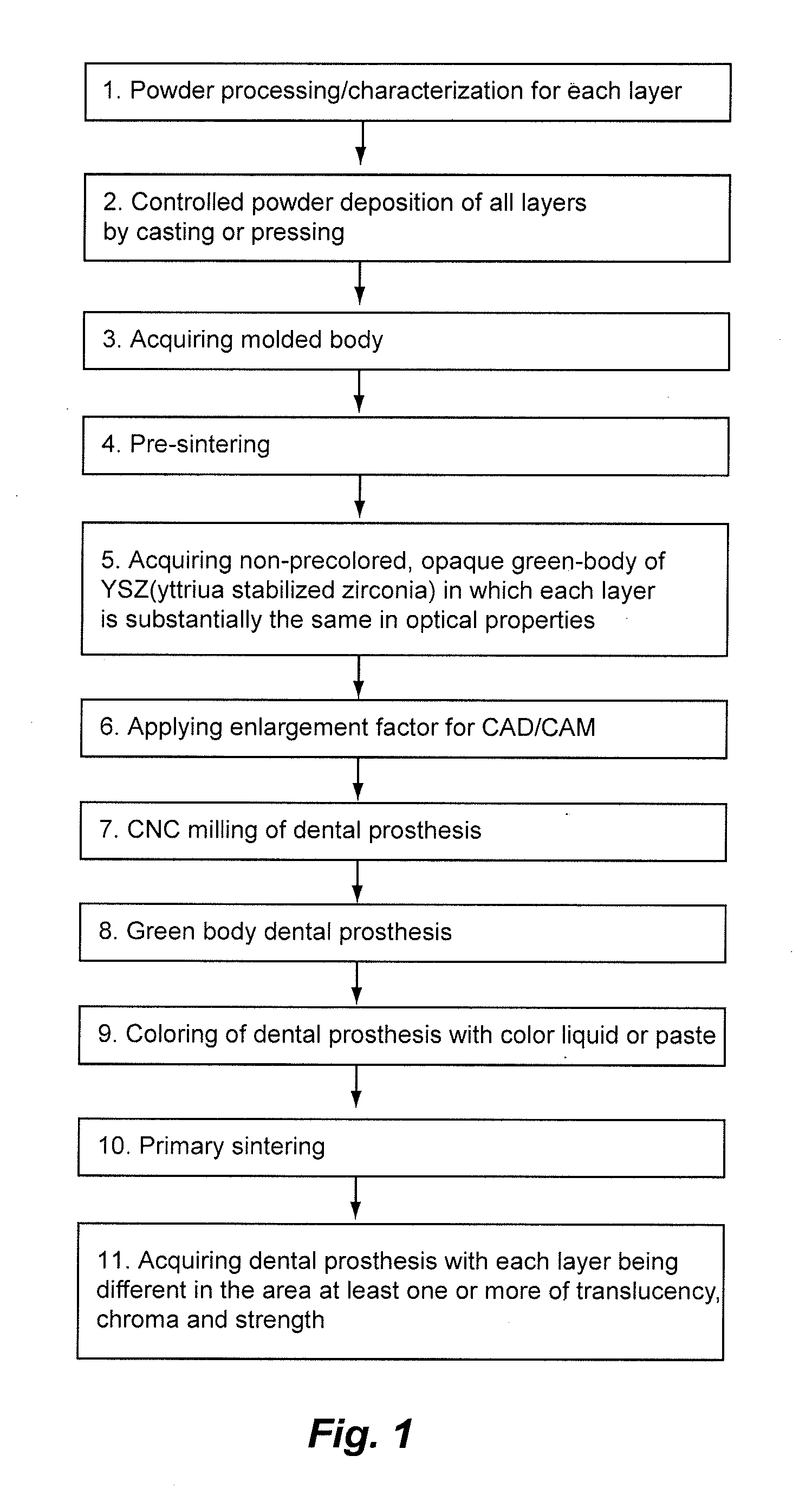
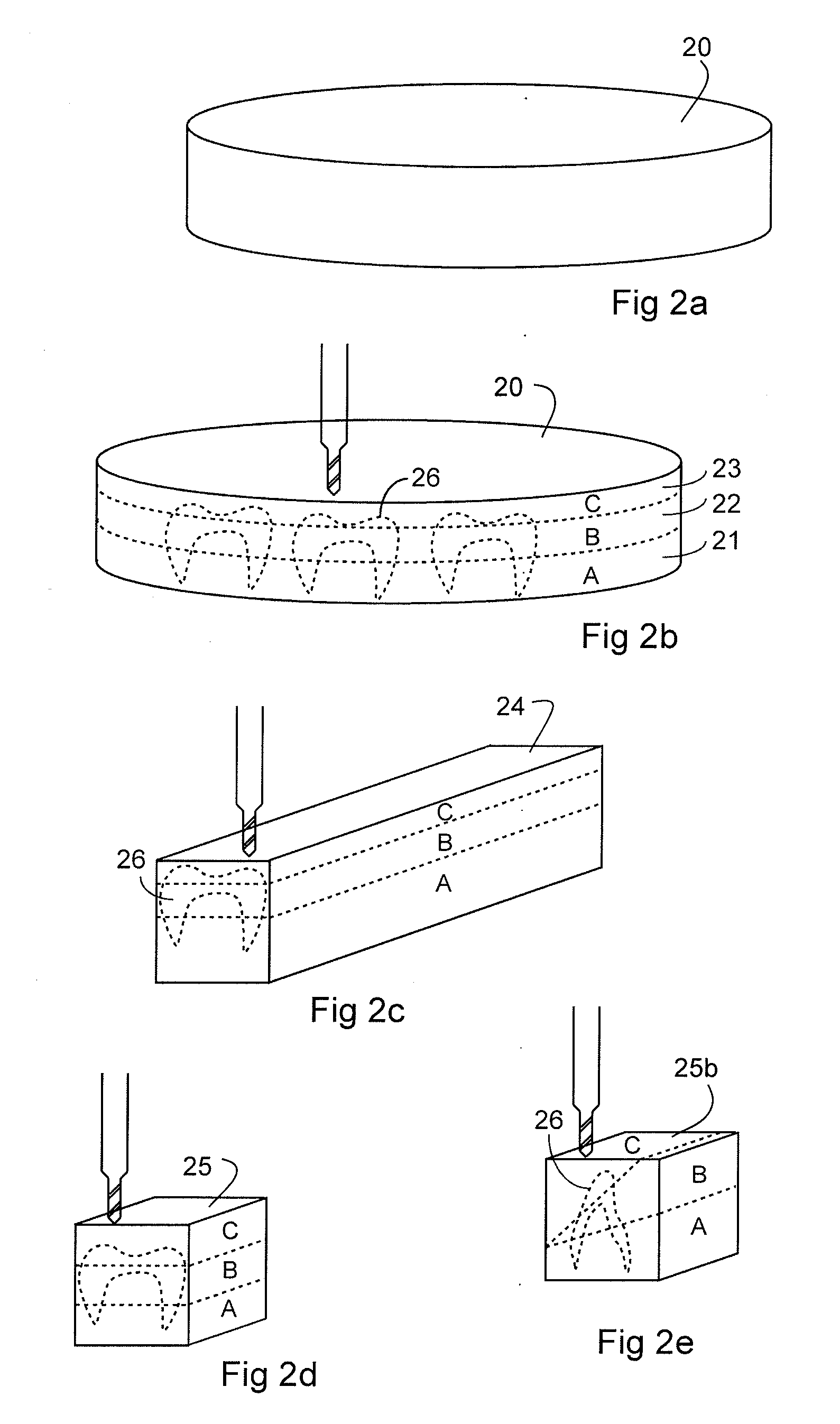
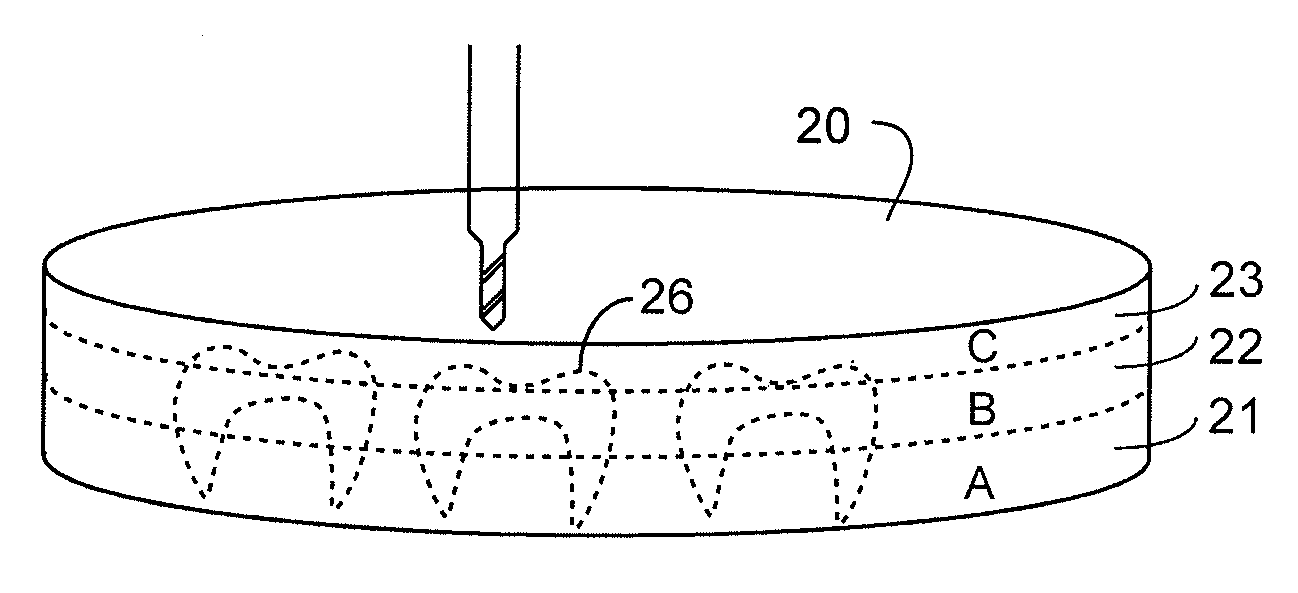
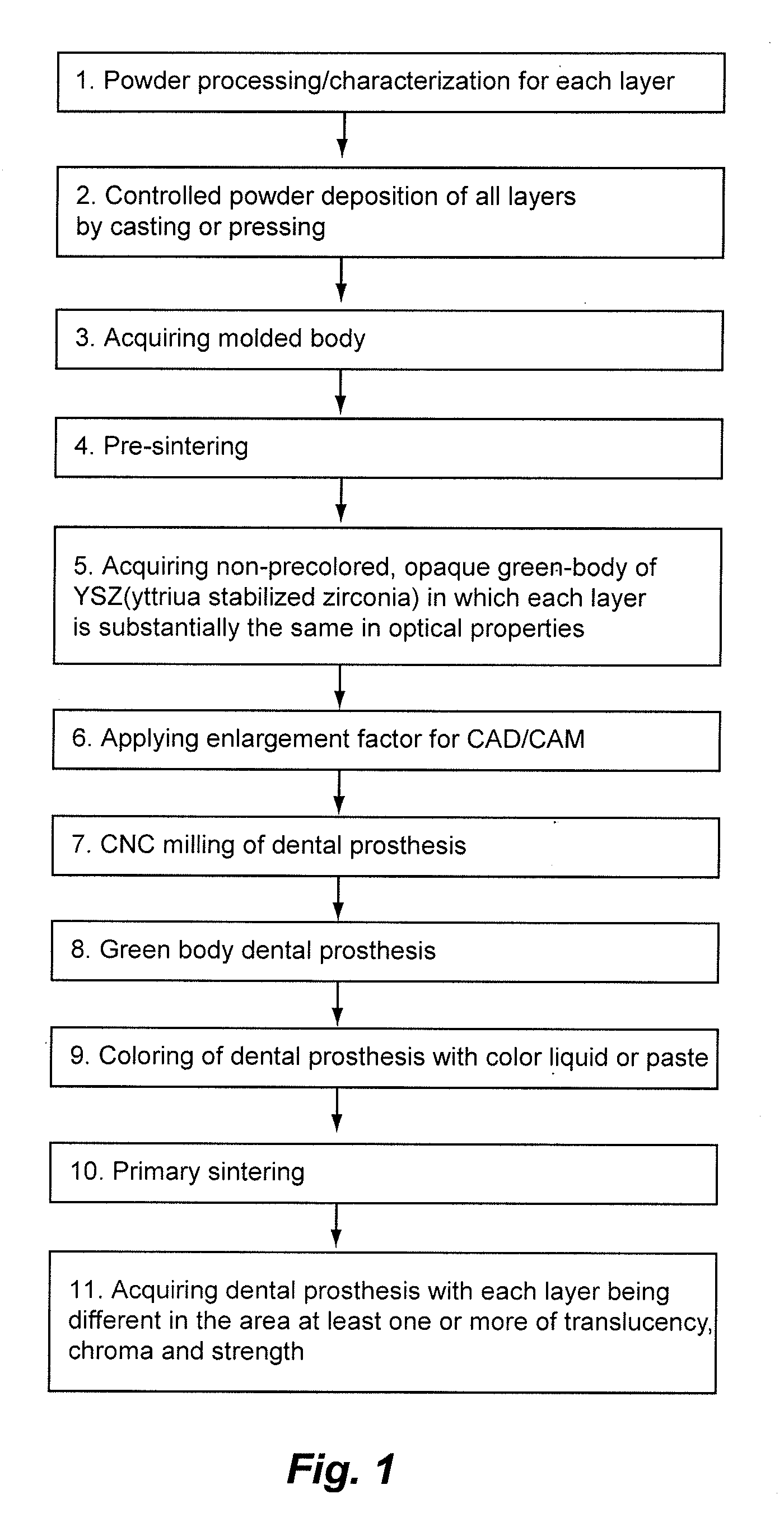
Non-Pre-Colored Multi-Layer Zirconia Dental Blank that has a Gradual Change in Translucency through a Thickness After Sintering
ActiveUS20130221554A1Small productImproved and more natural optical characteristicArtificial teethCeramic layered productsIncreased translucencyChemical composition
Owner:B & D DENTAL
Dental restorations formed by solid free-form fabrication methods
InactiveUS6994549B2Manufacture of restorationAdditive manufacturing apparatusImpression capsFree formThin layer
Solid free form fabrication techniques such as fused deposition modeling and three-dimensional printing are used to create a dental restoration. Three-dimensional printing comprises inkjet printing a binder into selected areas of sequentially deposited layers of powder. Each layer is created by spreading a thin layer of powder over the surface of a powder bed. Instructions for each layer may be derived directly from a CAD representation of the restoration. The area to be printed is obtained by computing the area of intersection between the desired plane and the CAD representation of the object. All the layers required for an aesthetically sound restoration can be deposited concurrently slice after slice and sintered / cured simultaneously. The amount of green body oversize is equivalent to the amount of shrinkage which occurs during sintering or curing. While the layers become hardened or at least partially hardened as each of the layers is laid down, once the desired final shaped configuration is achieved and the layering process is complete, in some applications it may be desirable that the form and its contents be heated or cured at a suitably selected temperature to further promote binding of the powder particles.
Owner:JENERICPENTRON
3-D Printing of near net shape products
InactiveUS20100279007A1Easy to handleHigh porosityAdditive manufacturingCeramic shaping apparatusPorosityCeramic metal
The disclosed method relates to manufacture of a near net-shaped products such as ceramic containing products such as ceramic-metal composites. The method entails forming a mixture of a build material and a binder and depositing that mixture onto a surface to produce a layer of the mixture. An activator fluid then is applied to at least one selected region of the layer to bond the binder to the build material to yield a shaped pattern. These steps may be repeated to produce a porous whitebody that is heat treated to yield a porous greenbody preform having a porosity of about 30% to about 70%. The greenbody then is impregnated with a molten material such as molten metal. Where the build material is SiC, the molten metal employed is Si to generate a SiC—Si composite.
Owner:STORM DEV LLC +1
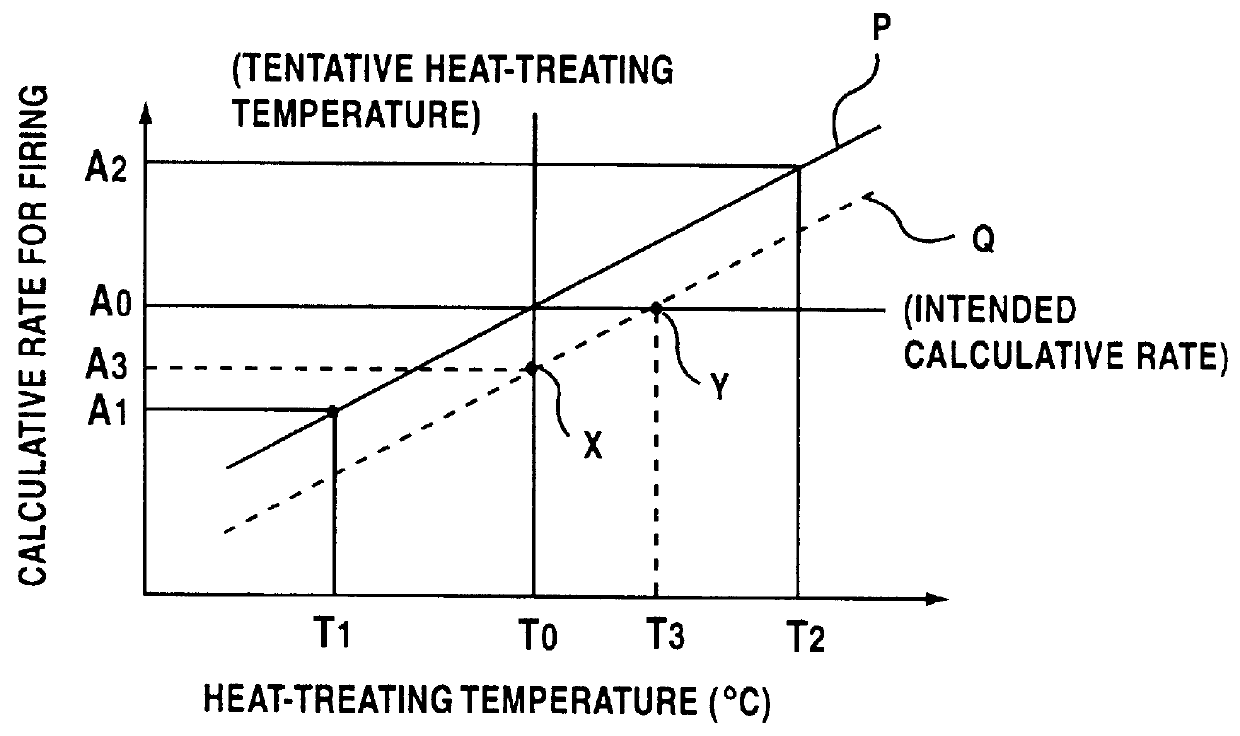
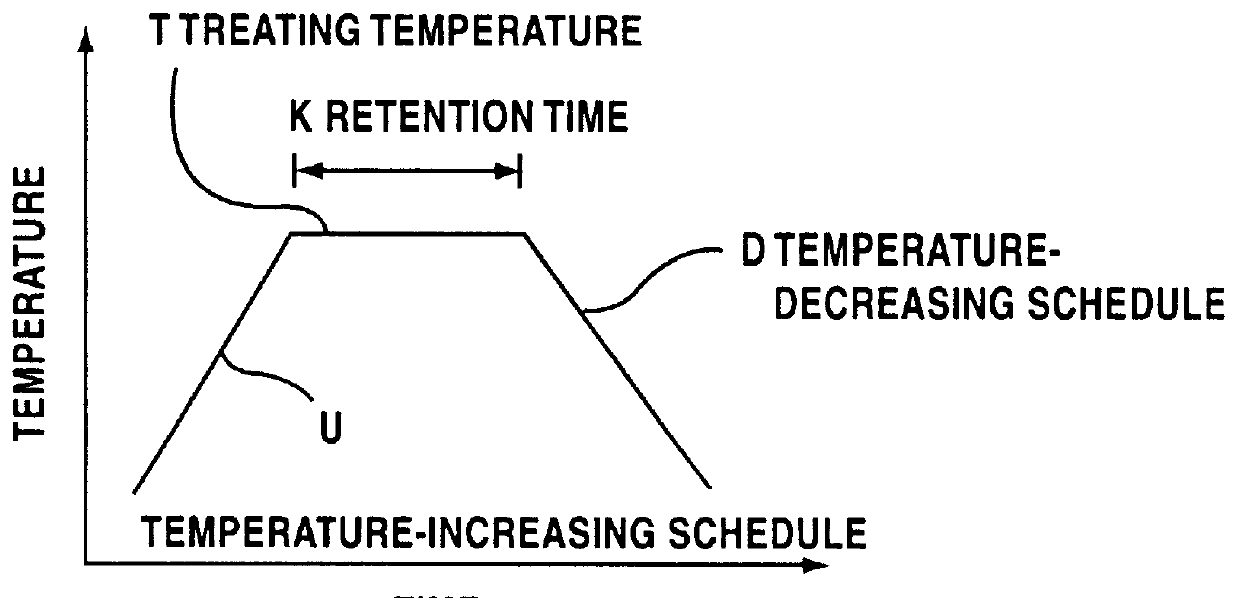
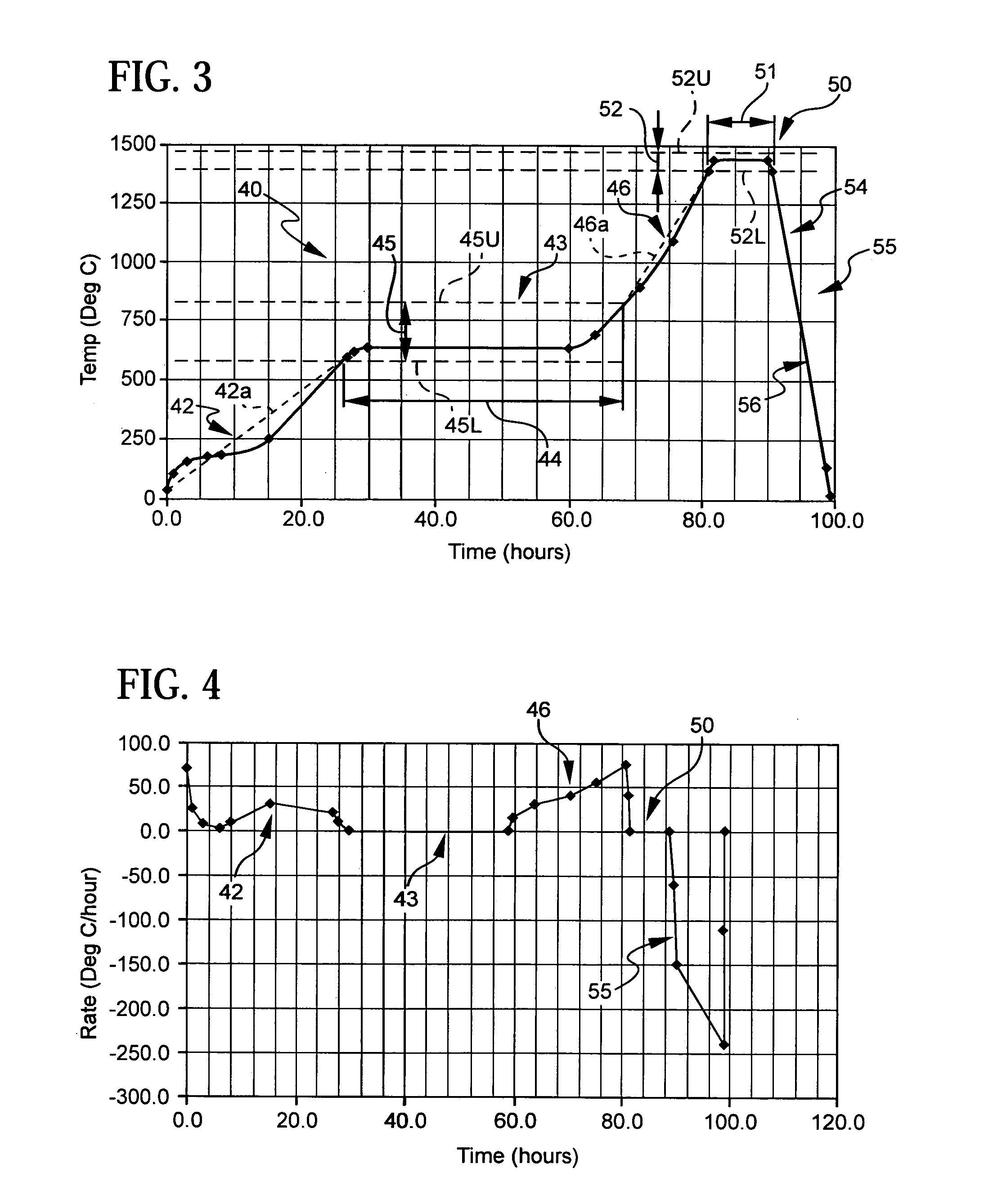
Method for controlling firing shrinkage of ceramic green body
A method of controlling the amount of firing shrinkage of a ceramic green body prepared by molding a ceramic powder (A) to a desired value A1 by heat treating the powder at a temperature T1 that provides the firing shrinkage A1 at a predetermined firing temperature. The temperature T1 is determined based on an established correlation between an amount of firing shrinkage at the predetermined firing temperature and a heat-treatment temperature of a powder (B) having a composition similar to that of the powder (A) in such an extent that a total amount of a greatest common content of an individual component common between the powders (A) and (B) in terms of percent is 90% by weight or more, and satisfying such a relation that the spherical diameter of powder (A) is within a range of + / - 30% relative to the spherical diameter (Rs) of the powder (B) and that its average degree of aggregation (+E,uns x+EE ) is within the range from +E,fra 1 / 2+EE fold to 2 fold relative to the average degree of aggregation (+E,uns x+EE ) of the powder (B).
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Aluminum titanate ceramic forming batch mixtures and green bodies including pore former combinations and methods of manufacturing and firing same
InactiveUS20070006561A1Low exothermic reaction and exothermic reactionReduction tendencyDispersed particle filtrationTransportation and packagingCeramic moldingSolvent
A ceramic forming batch mixture including inorganic batch materials, such as sources of alumina, titania, and silica, a pore former combination including first and second pore formers with different compositions; an organic binder; and a solvent. Also disclosed is a method for producing a ceramic article involving mixing the inorganic batch materials with the pore former combination having first and second pore formers of different composition, adding an organic binder and a solvent, forming a green body; and firing the green body. A green body having a combination of first and second pore formers with different compositions is disclosed, as are several methods for firing to produce ceramic articles such as aluminum titanate.
Owner:CORNING INC
Cementitious composites having wood-like properties and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20080099122A1Harder to saw, nail or screwLow densityPlastic recyclingLaminationPorosityBuilding product
A method of manufacturing a cementitious composite includes: (1) forming mixing an extrudable cementitious composition by first forming a fibrous mixture comprising fibers, water and a rheology modifying agent and then adding hydraulic cement; (2) extruding the extrudable cementitious composition into a green extrudate, wherein the green extrudate is characterized by being form-stable and retaining substantially a predefined cross-sectional shape; (3) removing a portion of the water by evaporation to reduce density and increase porosity; and (4) causing or allowing the hydraulic cement to hydrate to form the cementitious composite. Such a process yields a cementitious composite that is suitable for use as a wood substitute. The wood-like building products can be sawed, nailed and screwed like ordinary wood.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Controlled pore size distribution porous ceramic honeycomb filter, honeycomb green body, batch mixture and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20070119135A1Lower wash-coated pressure dropQuantity minimizationCombination devicesExhaust apparatusSago palmSource material
A porous ceramic honeycomb filter manufactured from an oxide-based ceramic material having a pore size distribution with d1≧7.0 microns. Preferably, the oxide-based material is cordierite or aluminum titanate. Alternatively, the filter contains a cordierite-containing ceramic body with a narrow pore size distribution with db≦1.00, wherein db=(d90−d10) / d50. Also disclosed is a batch mixture, method and honeycomb green body made from mixture of inorganic source materials selected from the group of magnesia sources, alumina sources, and silica sources, and a pore former having a narrow particle size distribution with dps≦0.90, wherein dps={(dp90−dp10) / dp50}. The pore former is preferably selected from a group consisting of canna starch, sago palm starch, green mung bean starch, and single-mode potato starch.
Owner:CORNING INC
Proppant Particles Formed From Slurry Droplets and Method of Use
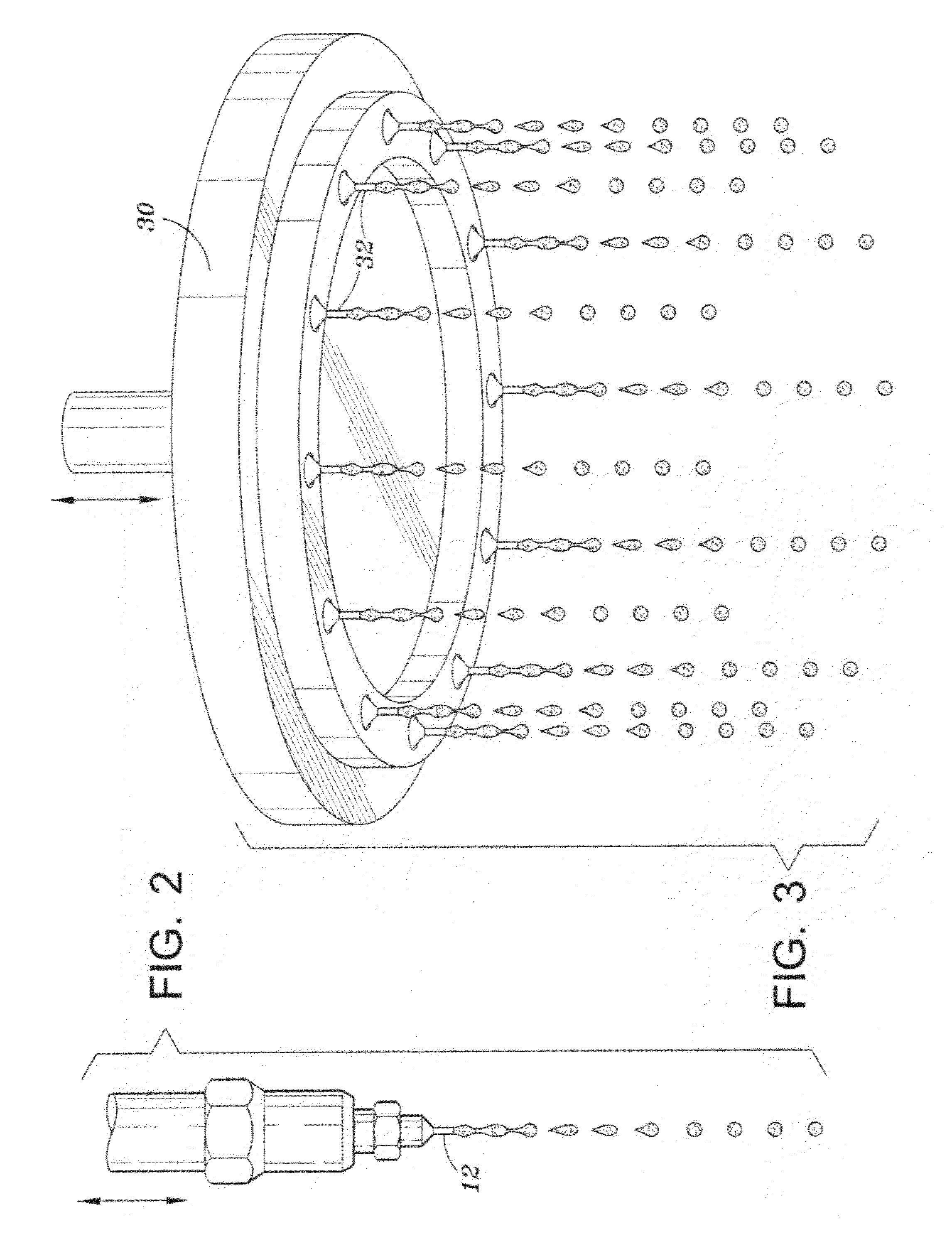
Proppant material for hydraulic fracturing is provided. The particles of the proppant are formed by drip casting. A slurry of finely divided ceramic particles is flowed through nozzles and formed into droplets under the influence of vibration. Uniform sized, smooth surface, spherical green particles are formed. The green particles are dried and sintered to form the proppant. The proppant is used in the process of hydraulic fracturing of wells.
Owner:CARBO CERAMICS
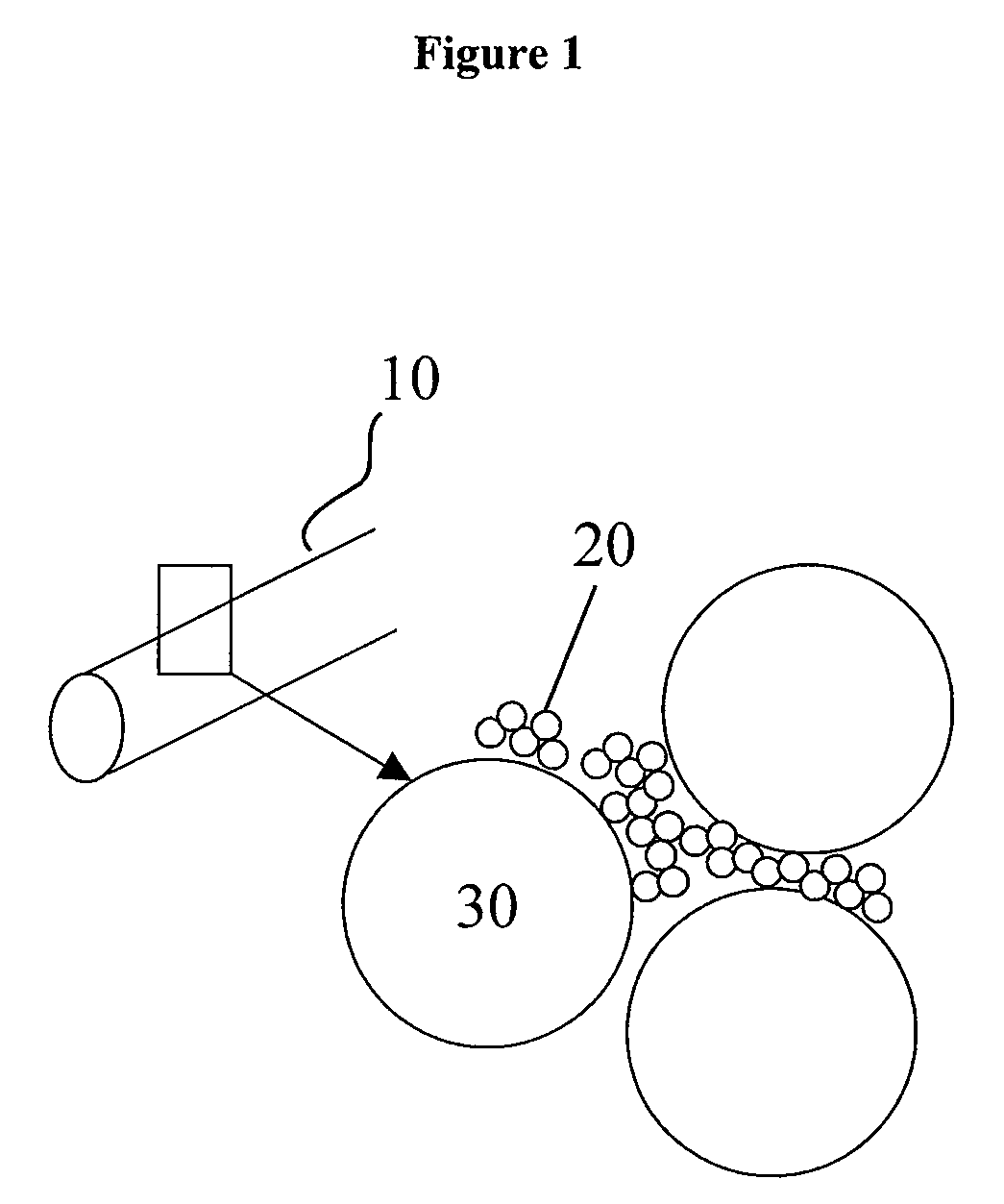
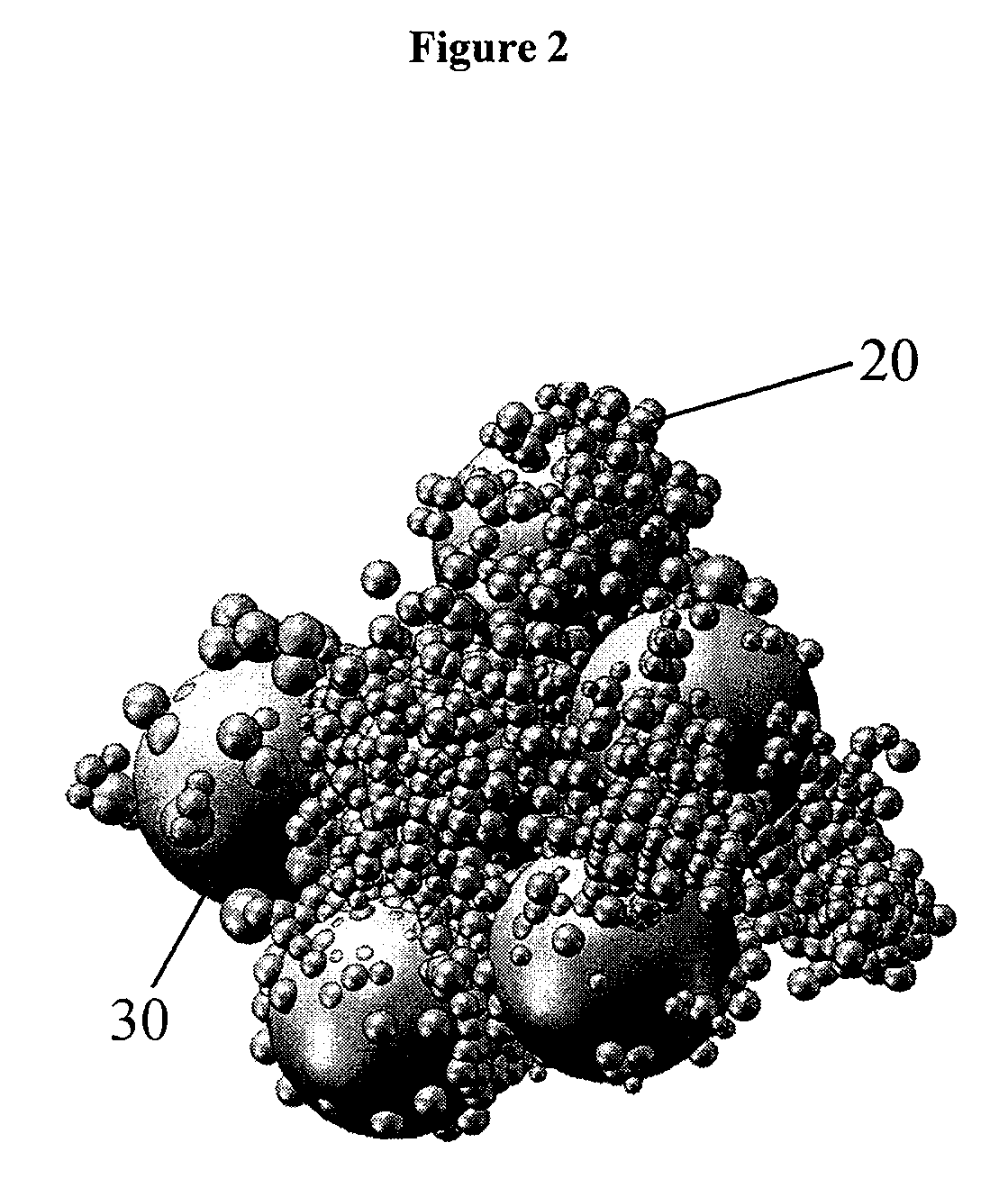
Method of electrophoretic deposition of ceramic bodies for use in manufacturing dental appliances
InactiveUS6059949AHigh strengthImprove toughnessElectrolysis componentsTeeth fillingMetallurgyElectrophoresis
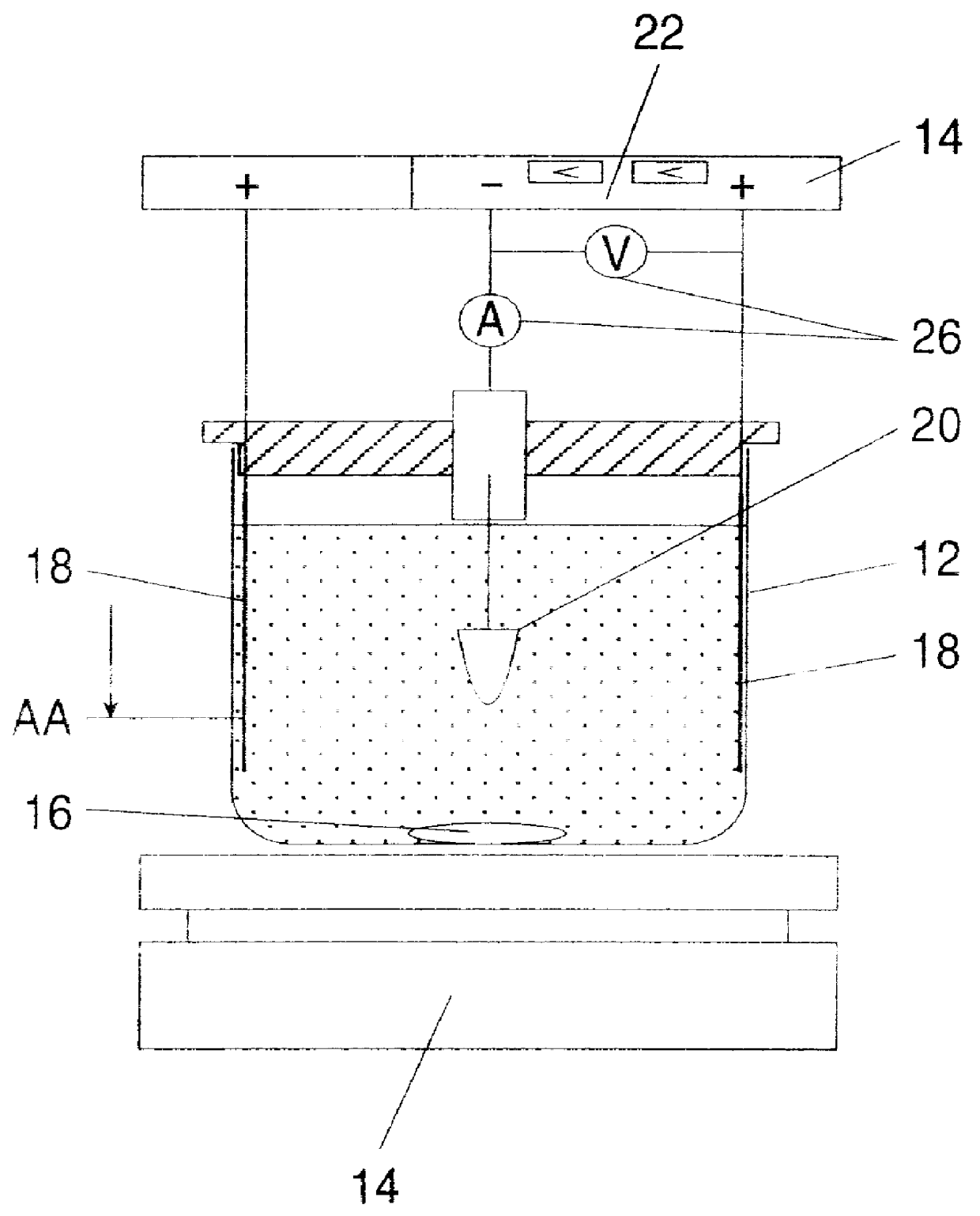
A method for electrophoretic deposition of ceramic particles as a green body shaped as a dental appliance, the method comprising the steps of (a) forming a suspension of the ceramic particles in a first polar solvent, the ceramic particles constituting at least about 5% of the first suspension by weight; (b) passing a direct electrical current through the first suspension, using a deposition electrode shaped as the dental appliance to form a green body; (c) coating the green body with glass particles; and (d) sintering the resultant coated body for obtaining a glass coated all-ceramic dental appliance.
Owner:CEREL CERAMIC TECH
Solar heat-reflective roofing granules, solar heat-reflective shingles, and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20110086201A1Improve solar heat reflectivityRoof covering using tiles/slatesRoof improvementMetallurgyDegree Celsius
A process for preparing roofing granules includes forming kaolin clay into green granules and sintering the green granules at a temperature of at least 900 degrees Celsius to cure the green granules until the crystalline content of the sintered granules is at least ten percent as determined by x-ray diffraction.
Owner:CERTAINTEED CORP
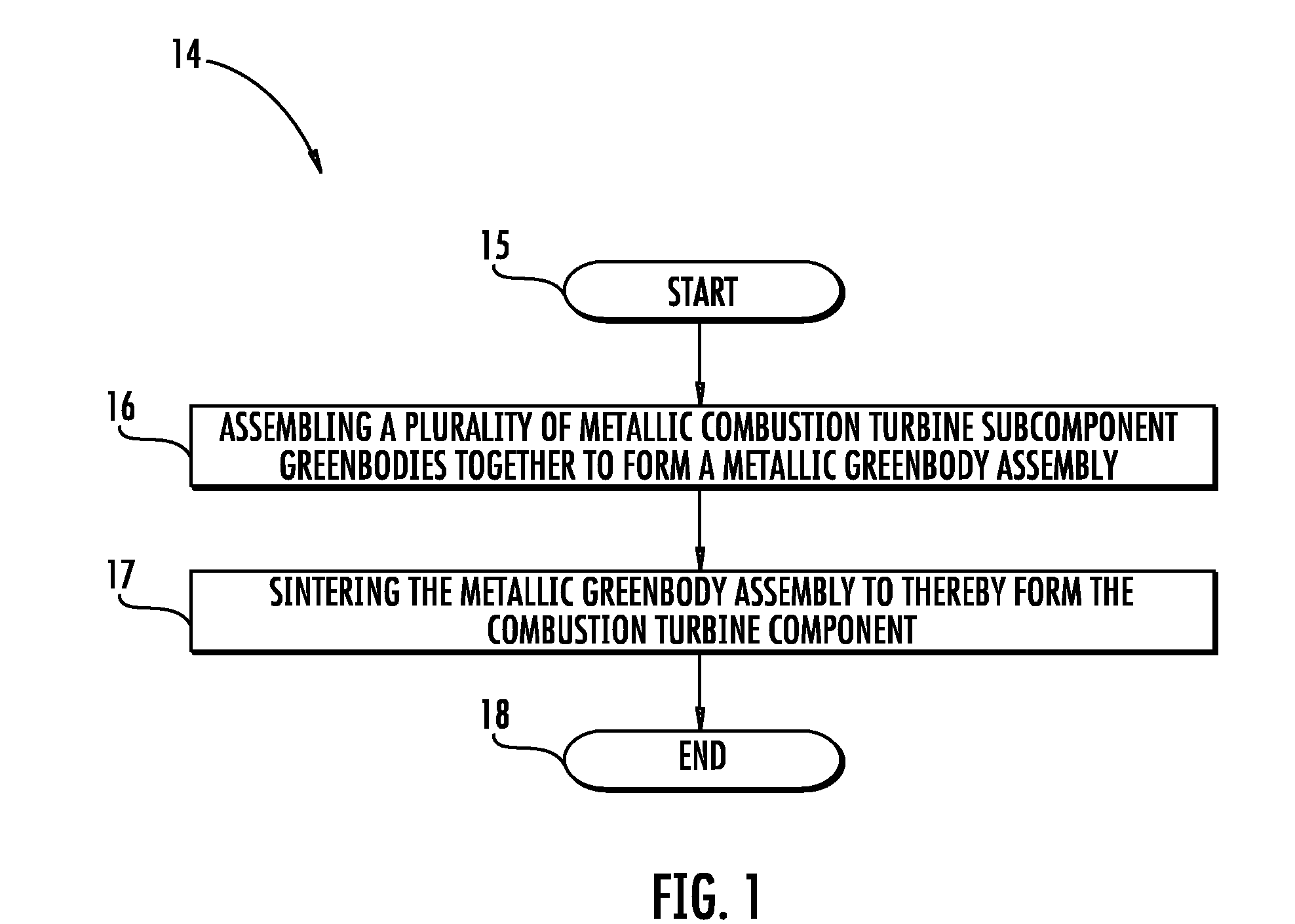
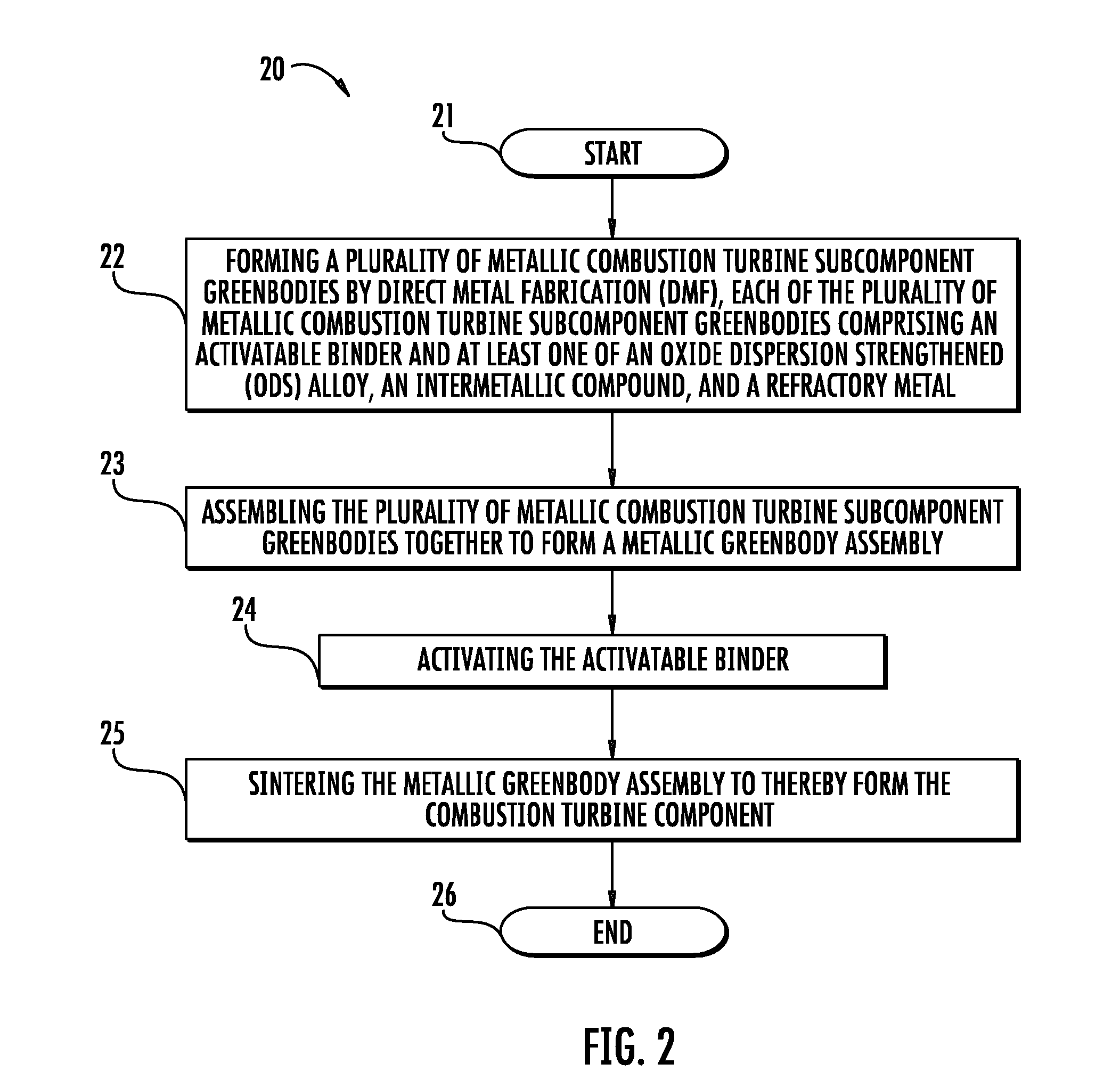
Method of Making a Combustion Turbine Component from Metallic Combustion Turbine Subcomponent Greenbodies
InactiveUS20090183850A1Improve cooling effectHigh temperature resistanceTurbinesAdditive manufacturingCombustionMetal fabrication
A method of making a combustion turbine component includes assembling a plurality of metallic combustion turbine subcomponent greenbodies together to form a metallic greenbody assembly and sintering the metallic greenbody assembly to thereby form the combustion turbine component. Each of the plurality of metallic combustion turbine subcomponent greenbodies may be formed by direct metal fabrication (DMF). In addition, each of plurality of metallic combustion turbine subcomponent greenbodies may include an activatable binder and the activatable binder may be activated prior to sintering.
Owner:MIKRO SYSYTEMS INC +1
Extruded fiber reinforced cementitious products having wood-like properties and ultrahigh strength and methods for making the same
InactiveUS20100136269A1High yield stressImmediate form stabilityLayered productsPlastic recyclingPorosityFlexural strength
A method of manufacturing a cementitious composite including: (1) mixing an extrudable cementitious composition by first forming a fibrous mixture comprising fibers, water and a rheology modifying agent and then adding hydraulic cement; (2) extruding the extrudable cementitious composition into a green extrudate, wherein the green extrudate is characterized by being form-stable and retaining substantially a predefined cross-sectional shape; (3) removing a portion of the water by evaporation to reduce density and increase porosity; and (4) heating the green extrudate at a temperature from greater than 65° C. to less than 99° C. is disclosed. Such a process yields a cementitious composite that is suitable for use as a wood substitute. Particularly, by using higher curing temperatures for preparing the cementitious building products, the building products have a lower bulk density and a higher flexural strength as compared to conventional products. The wood-like building products can be sawed, nailed and screwed like ordinary wood.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Porous, non-degradable implant made by powder molding
InactiveUS20080213611A1Sufficient pore volumeSufficient volumeLayered productsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDecompositionShell molding
Owner:CINVENTION AG
Non-Pre-Colored Multi-Layer Zirconia Dental Blank that has a Gradual Change in Chroma through a Thickness After Sintering
InactiveUS20130224454A1Small productImproved and more natural optical characteristicArtificial teethCeramic layered productsChemical compositionDentistry
Owner:B & D DENTAL
Methods of forming a metallic or ceramic article having a novel composition of functionally graded material and articles containing the same
ActiveUS20140087210A1Improve fracture toughnessLow costAdditive manufacturing apparatusLayered productsCarbideFunctionally graded material
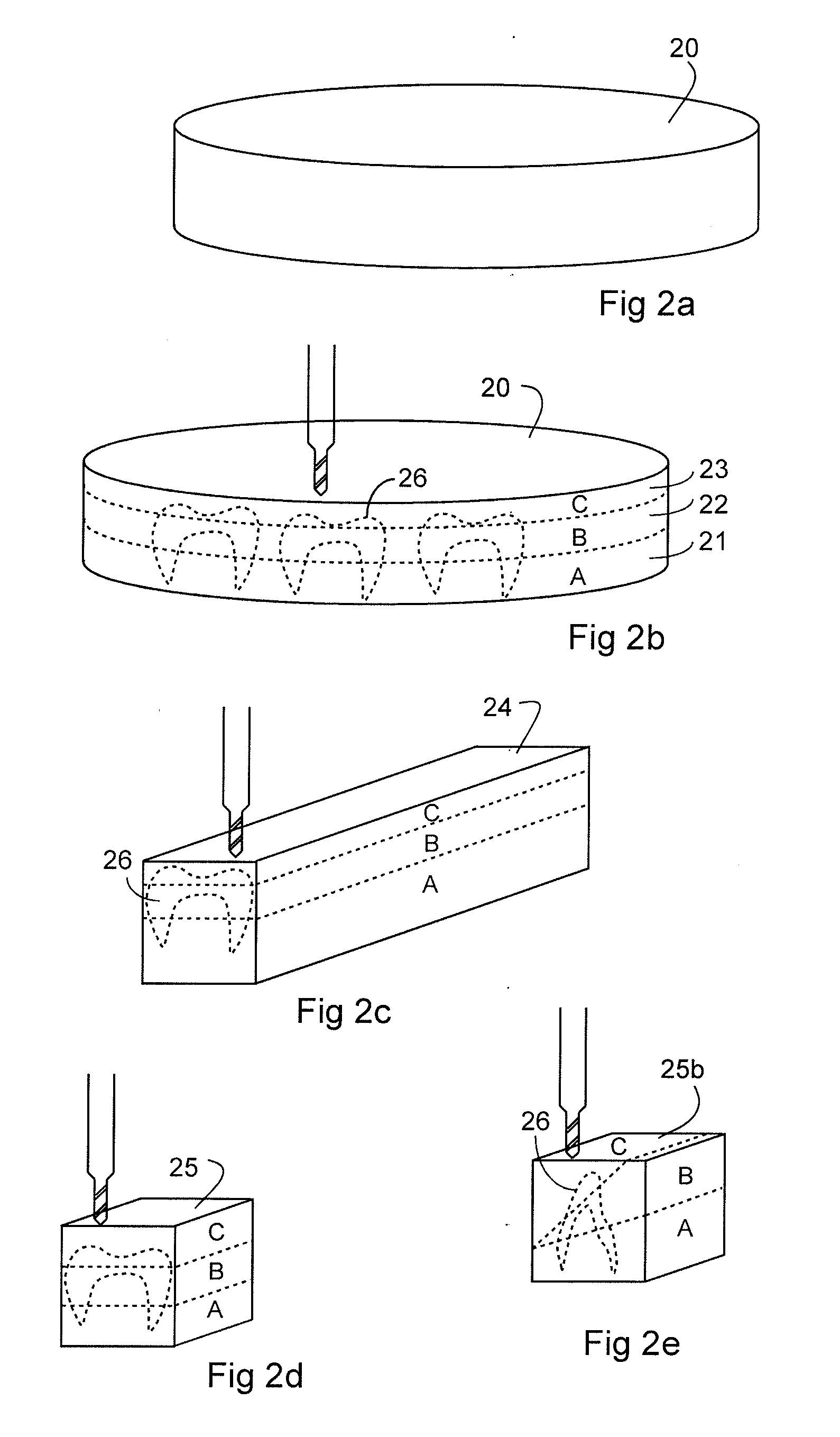
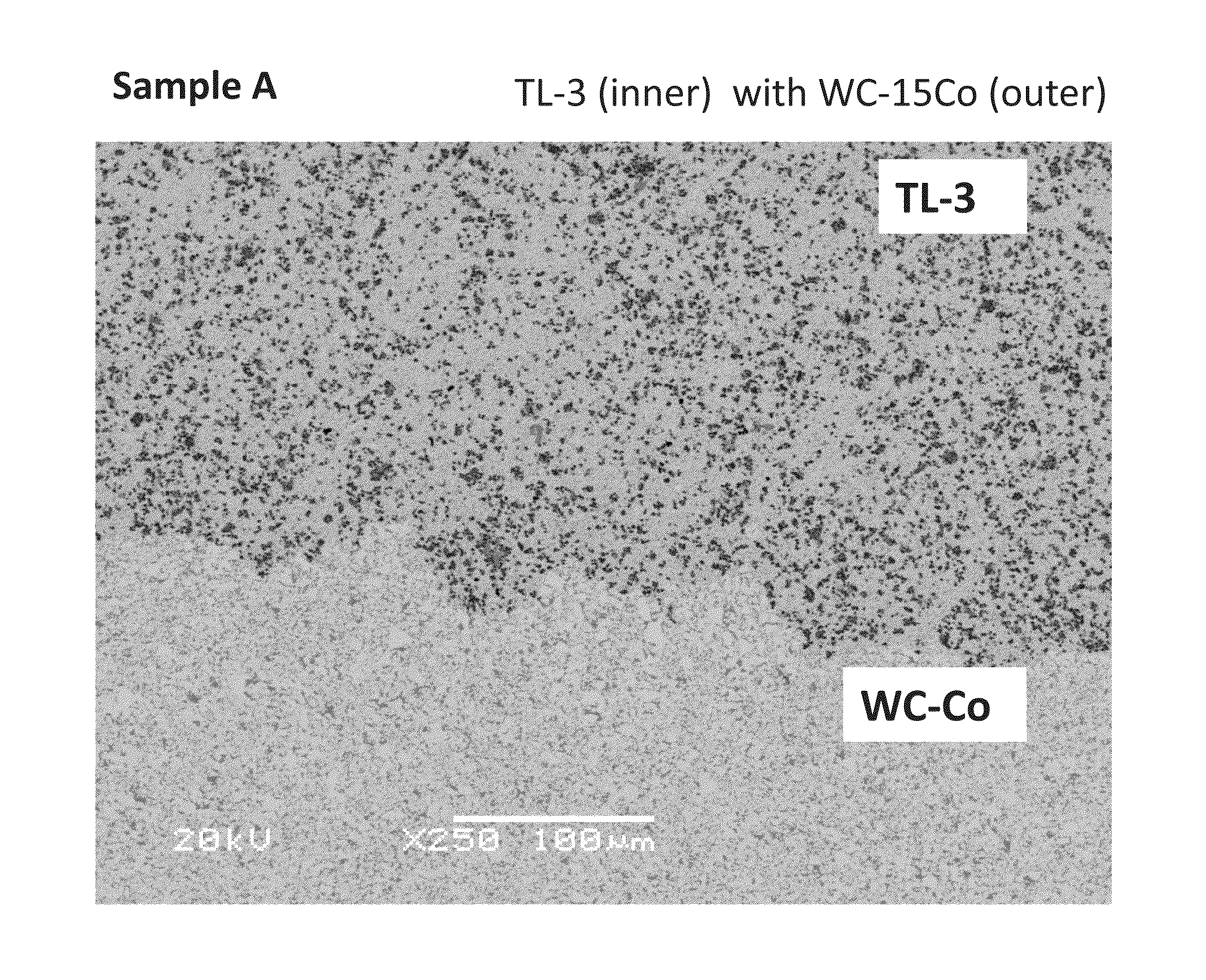
There is disclosed a method of making a metallic or ceramic component, such as a cutting or forming tool, from at least two distinct powder precursors. In one embodiment, the method comprising forming a first mixture comprised of a plurality of coated particles, such as Tough-Coated Hard Powder (TCHP) composite particles created by encapsulating extremely hard core particles with very tough binder and structural materials, and at least one support powder, such as a carbide, typically WC—Co. The mixture is formed into a green body and sintered to form a functionally graded or multicomponent article. Non-limiting examples of the articles made from the disclosed methods are also disclosed and include drills, mills, cutting tools, forming tools, wires dies and mechanical components.
Owner:ETERNALOY HLDG GMBH
Aluminum titanate ceramic articles and methods of making same
ActiveUS7259120B2Reduced strengthLower firing temperatureInternal combustion piston enginesSilencing apparatusAlkaline earth metalRare earth
An aluminum titanate ceramic article having a predominant crystal phase of aluminum titanate and a material composition including aluminum, titanium, silica, an alkaline earth metal (e.g., at least one selected from the group of strontium, calcium, barium, or combinations), and a rare earth metal (e.g., at least one selected from the group consisting of yttrium, lanthanum, and combinations) and methods of making such aluminum titanate bodies are described. An oxide of yttrium metal or lanthanide metals is preferably used as a sintering aid in combination with the other compositional components to enable firing of the resulting green body at a lower heating temperature of less than 1500° C., and more preferably between 1400°-1450° C., with a preferable hold time of less than 8 hours, more preferably of 6 to 8 hours.
Owner:CORNING INC
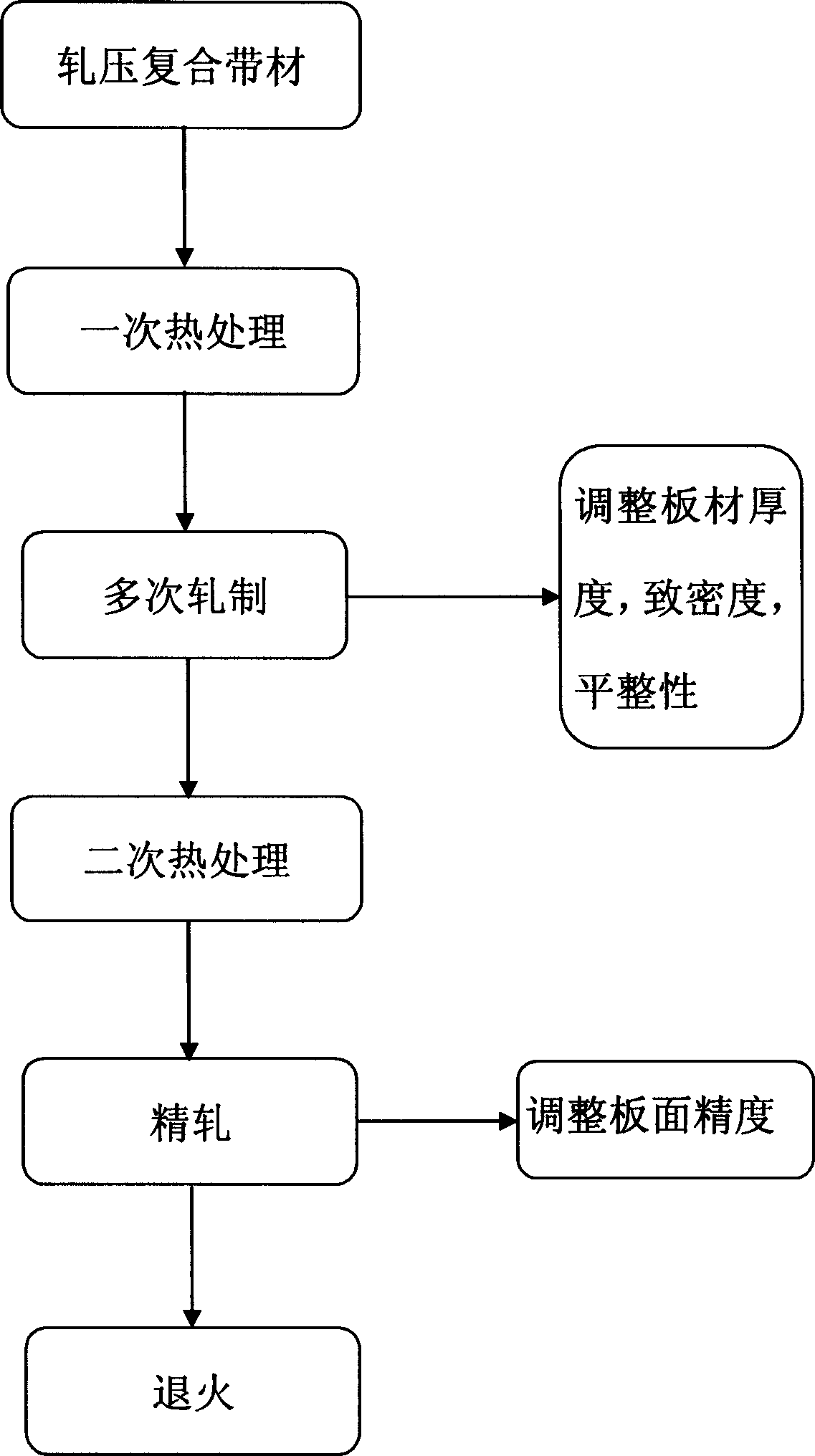
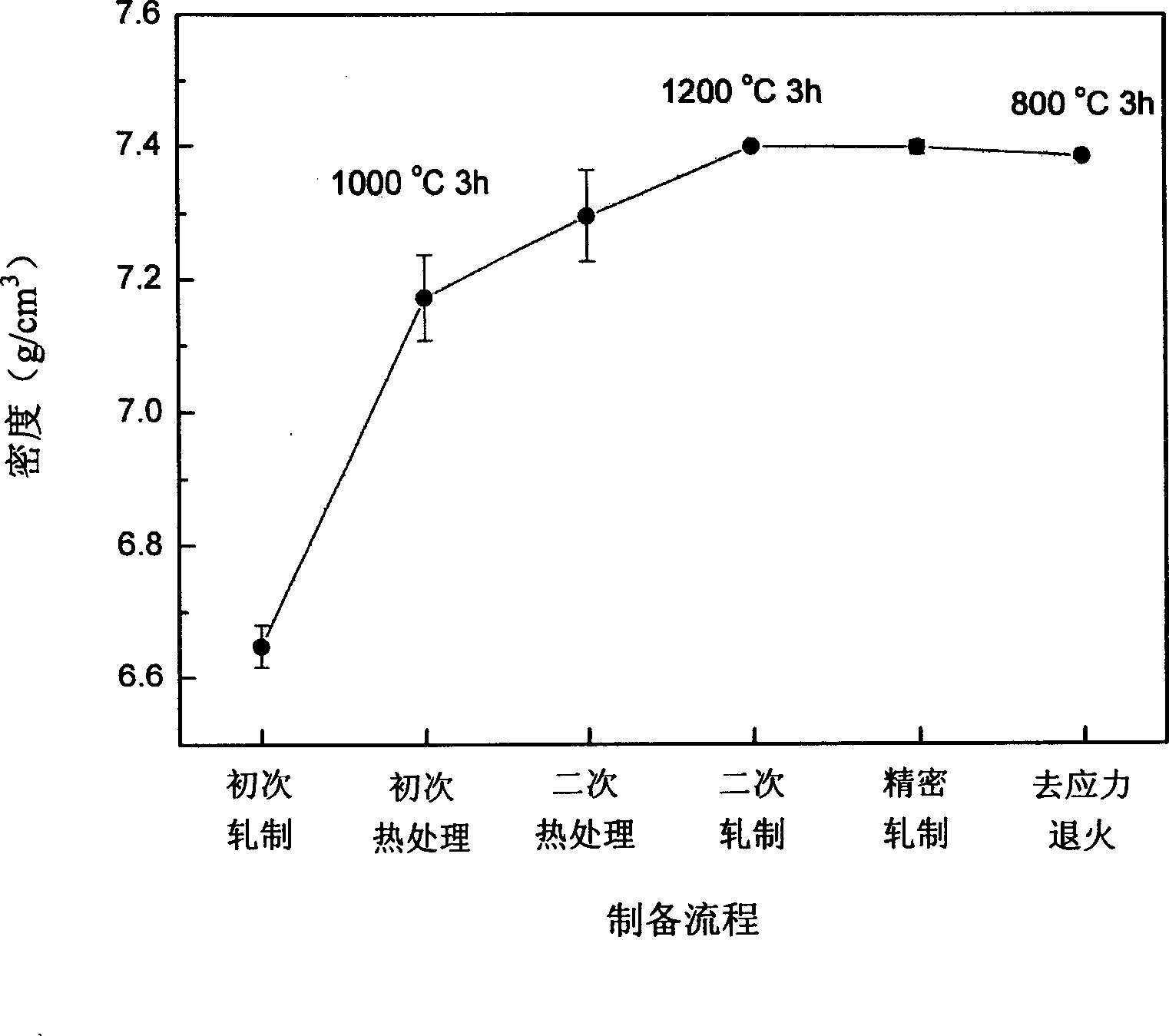
High-silica silicon-steel sheet heat treatment and multiple cold-rolling method
InactiveCN1528921AOvercoming limitations that cannot be processed by calenderingEasy to operateHigh silicaSilicon
The invention provides a method for producing high brittleness silicon steel board by using two times of heat process and multiple tracks cold-roll adjustment compound technology in different temperature range to control the extending performance of belt material rolling. It carries on baking process to high silicon steel shin board green compact produced by powder pressing method in low temperature range, controls the content of silicon in irn particles in shin boards, the board material can maintain the malleability. It carries on multiple rolling cold process when the silicon steel board is brittled, thus controls the thickness smooth property, and compactability of board. Then carries on secondary baking processing in high temperature, thus there obtains th even silicon steel board. Finally, carries on stress adjustment and relief annealing process, thus the product can be obtained.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Manufacture method and device of three-dimensional workpiece
InactiveCN101422963AReduce the staircase effectHigh resolutionLiquid surface applicatorsIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser sinteringAdhesive
The invention provides a method and equipment using organic adhesive mixed solvent and powder to manufacture three-dimensional workpieces. The work principle is as follows: the raw materials are stirred into slurry, which is laid as a green compact thin layer that can disintegrate in disintegrant; the green compact thin layer can form a workpiece thin layer that does not disintegrate in the disintegrant after scanned by an energy beam; in such a cycle, the steps of laying the thin layer and energy beam scanning are repeated, and then the three-dimensional workpiece can be formed; and the disintegant is used for separating the green compact not scanned by the energy beam from the workpiece, thus remaining the needed three-dimensional workpiece. The invention is widely applicable to manufacturing plastic, metallic, ceramic and compound workpieces, can avoid the defects of a selective laser sintering method, can use fine and very thin powder and therefore, can manufacture a finished product which is better than that made in the traditional selective laser sintering method in surface roughness and texture fineness, in addition, through subsequent densified sintering, the metallic and ceramic workpieces can have the strength superior to that in the traditional selective laser sintering method.
Owner:OUKESI INT
Osseointegrative surgical implant
InactiveUS20160015483A1Improve primary stabilityPromote healingSuture equipmentsDental implantsCeramic compositeSurgical implant
Embodiments of the present invention provide an osseointegrative implant and related tools, components and fabrication techniques for surgical bone fixation and dental restoration purposes. In one embodiment an all-ceramic single-stage threaded or press-fit implant is provided having finely detailed surface features formed by ceramic injection molding and / or spark plasma sintering of a powder compact or green body comprising finely powdered zirconia. In another embodiment a two-stage threaded implant is provided having an exterior shell or body formed substantially entirely of ceramic and / or CNT-reinforced ceramic composite material. The implant may include one or more frictionally anisotropic bone-engaging surfaces. In another embodiment a densely sintered ceramic implant is provided wherein, prior to sintering, the porous debound green body is exposed to ions and / or particles of silver, gold, titanium, zirconia, YSZ, α-tricalcium phosphate, hydroxyapatite, carbon, carbon nanotubes, and / or other particles which remain lodged in the implant surface after sintering. Optionally, at least the supragingival portions of an all-ceramic implant are configured to have high translucence in the visible light range. Optionally, at least the bone-engaging portions of an all-ceramic implant are coated with a fused layer of titanium oxide.
Owner:OSSEODYNE SURGICAL SOLUTIONS LLC
Mixtures For Forming Porous Constructs
Provided are methods comprising at least one metal powder with an extractable material and a composition comprising a polyol, a hydrophilic polymer, or both in order to form a mixture in which the metal powder and the extractable material assume respective positions. The composition functions as a homogenizing agent that allows the mixture to remain well-mixed for extended periods of time under ambient conditions. Also provided are green bodies and porous constructs, including implants, that are made in accordance with the disclosed methods. The green bodies and porous constructs have a substantially uniform porosity that is at least partially attributable to the ability of the composition to maintain the metal powder and the extractable material in their respective positions prior to sintering.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
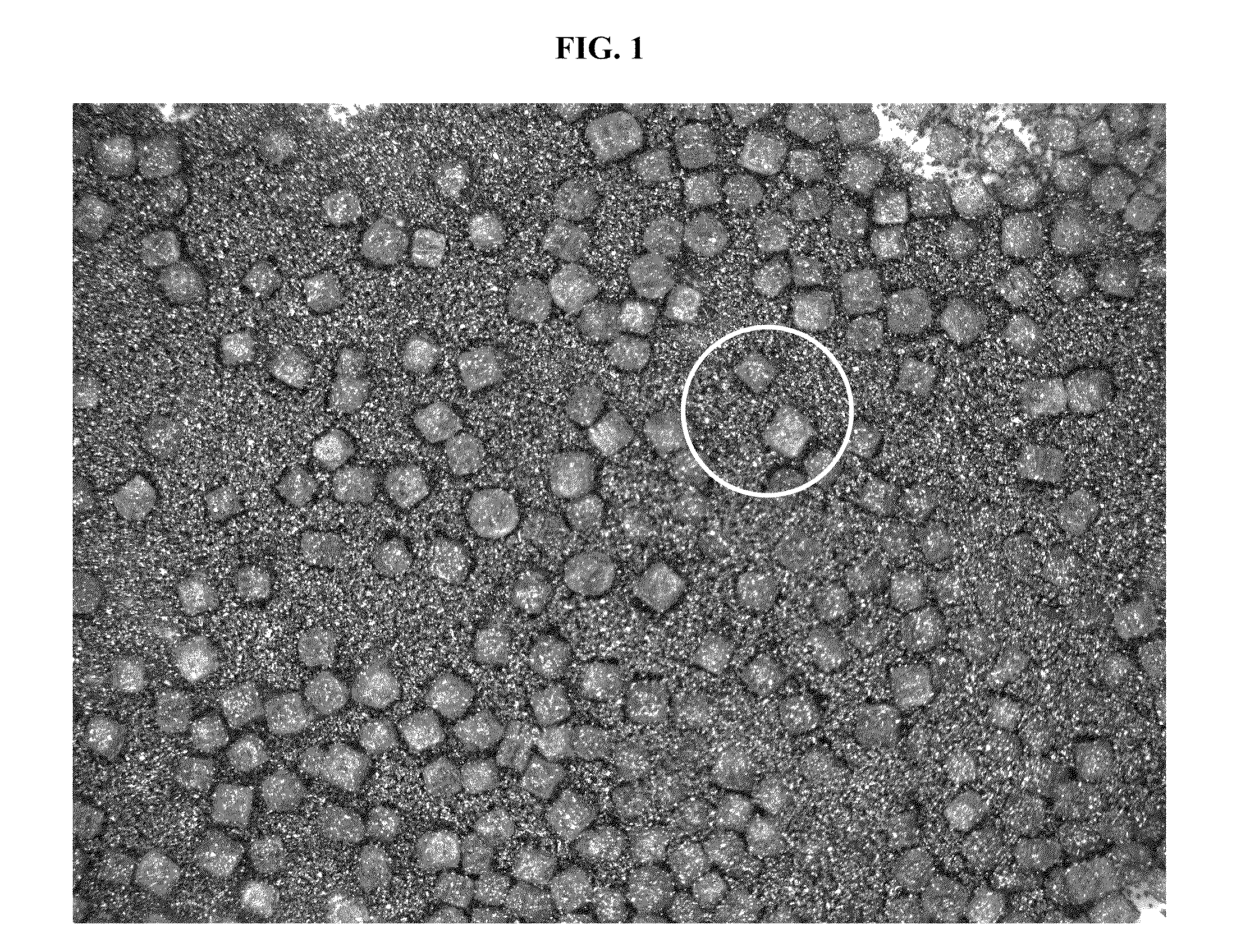
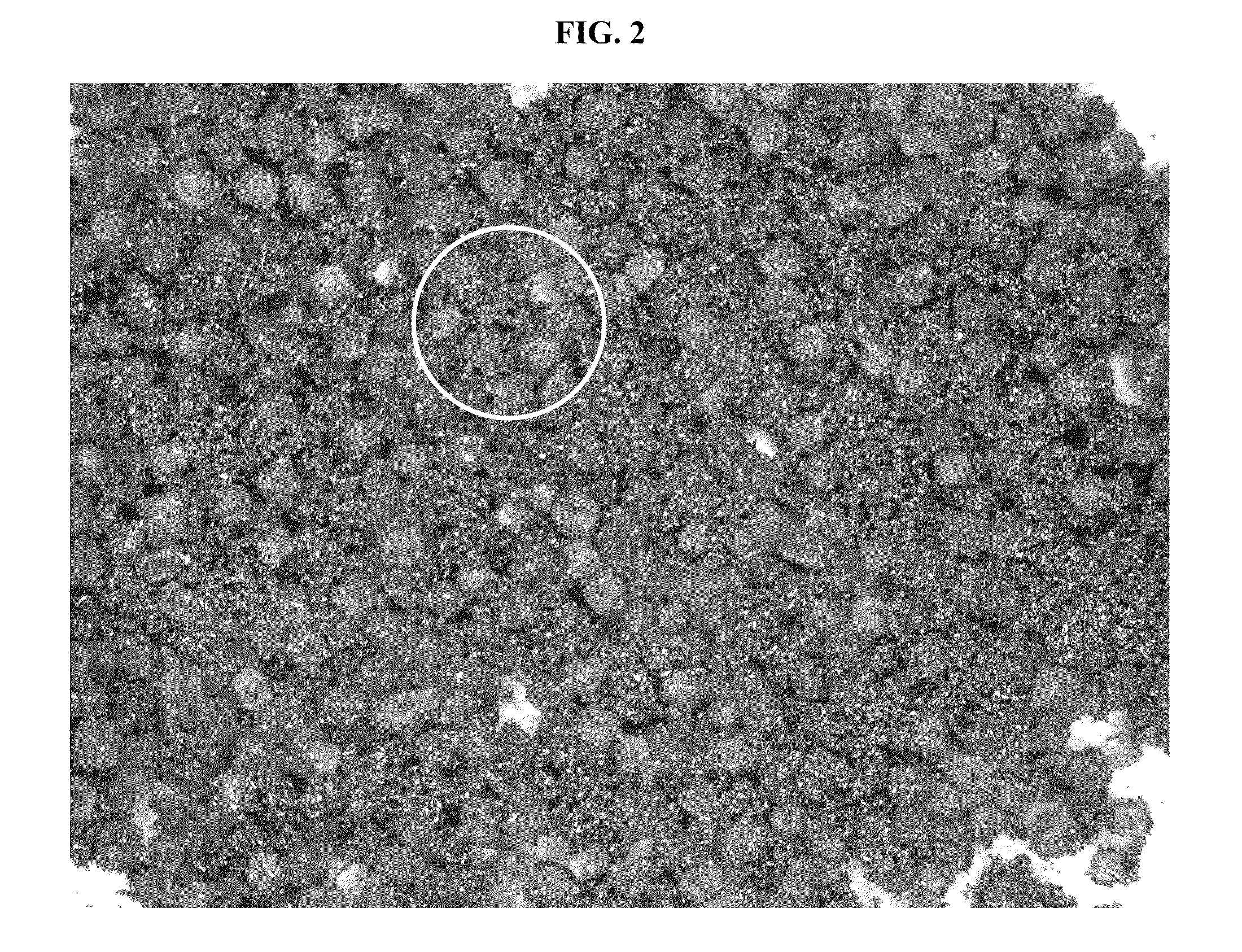
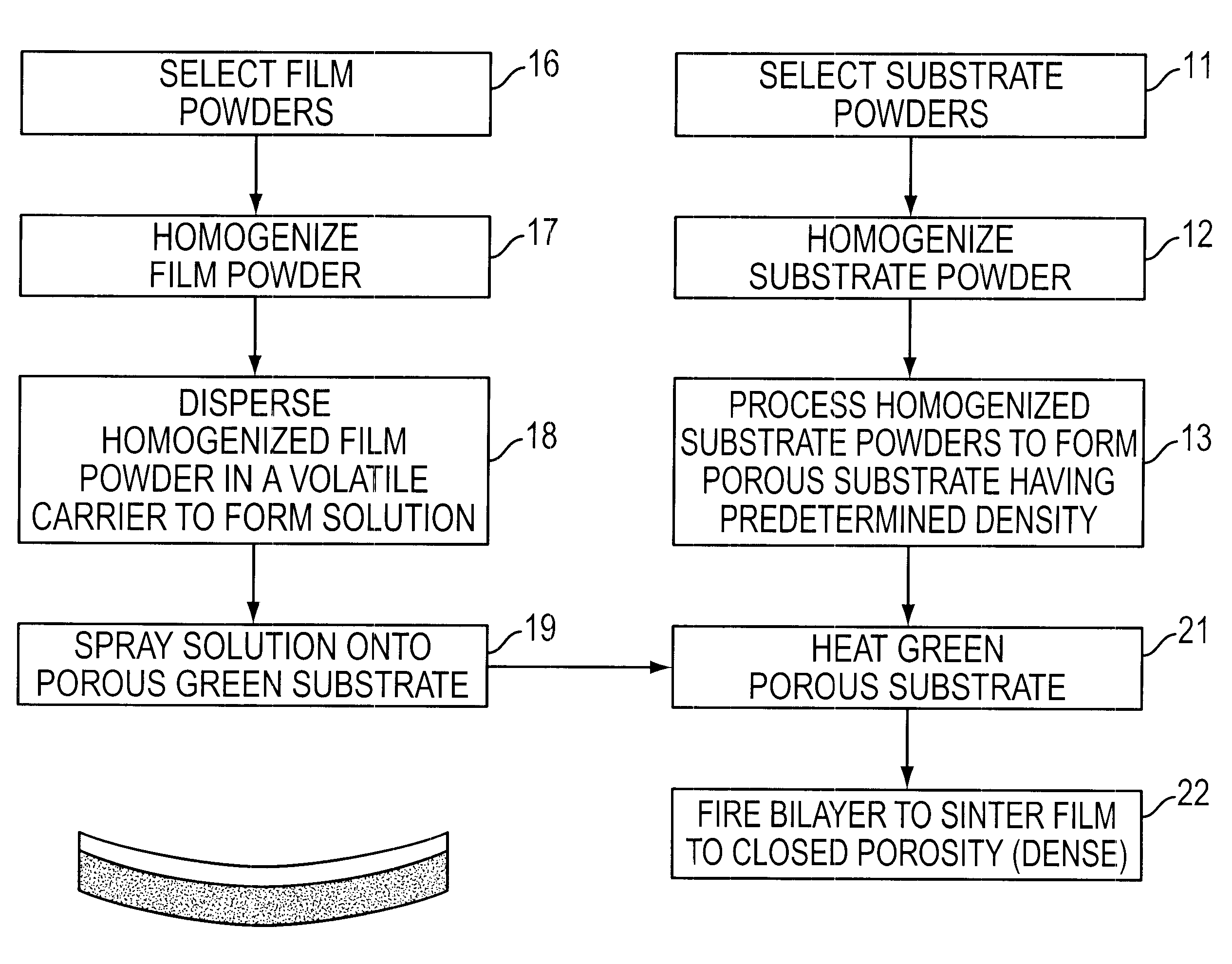
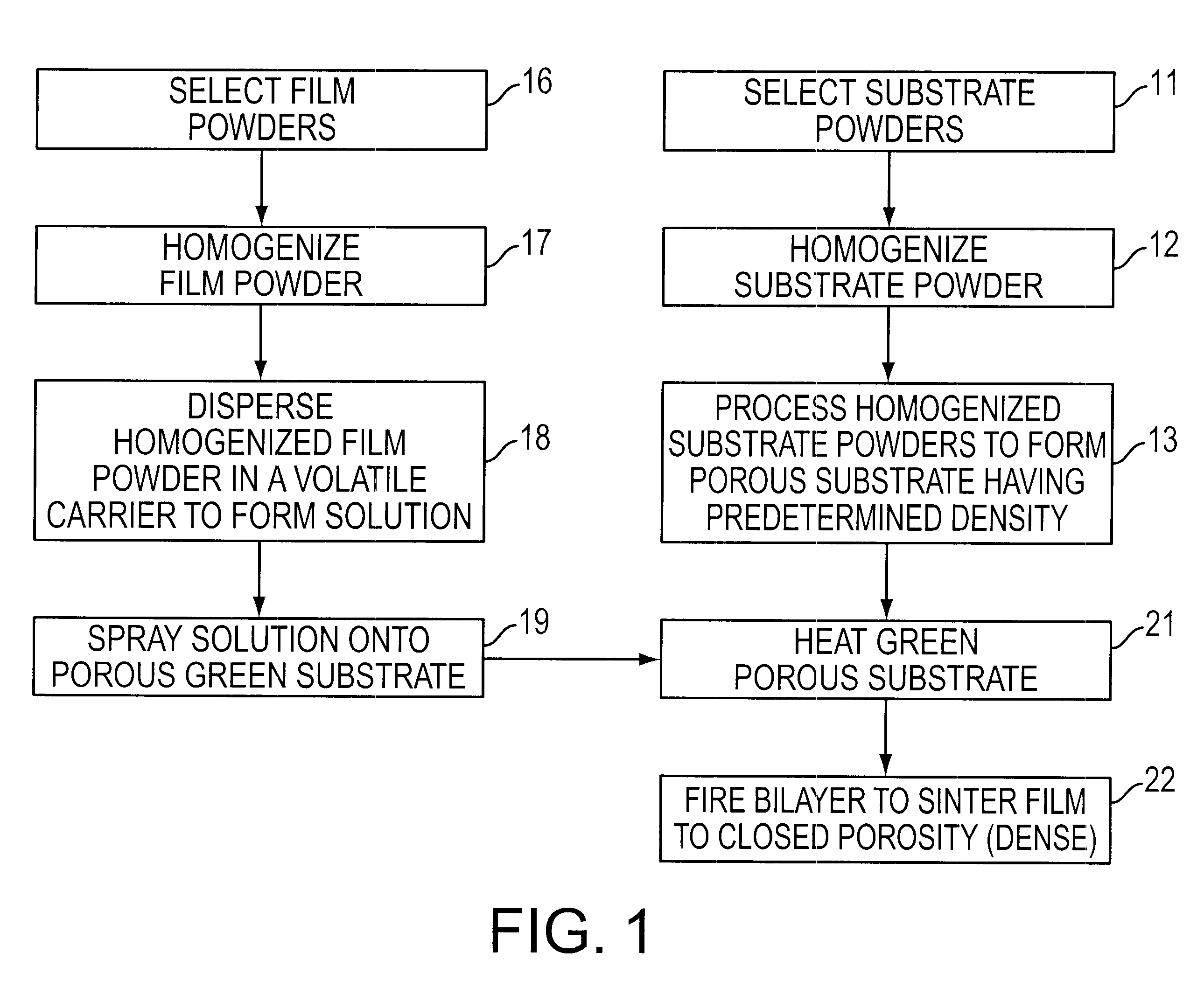
Method for making thin, flat, dense membranes on porous substrates
InactiveUS6458170B1Quality improvementImprove flatnessFuel cell auxillariesElectrode carriers/collectorsPorous substrateMaterials science
A method of fabricating a thin, flat dense membrane on a porous substrate in which the green substrate is selected to have a predetermined shrinkage on firing which matches or is greater than the shrinkage of a thin uniformly applied film on firing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
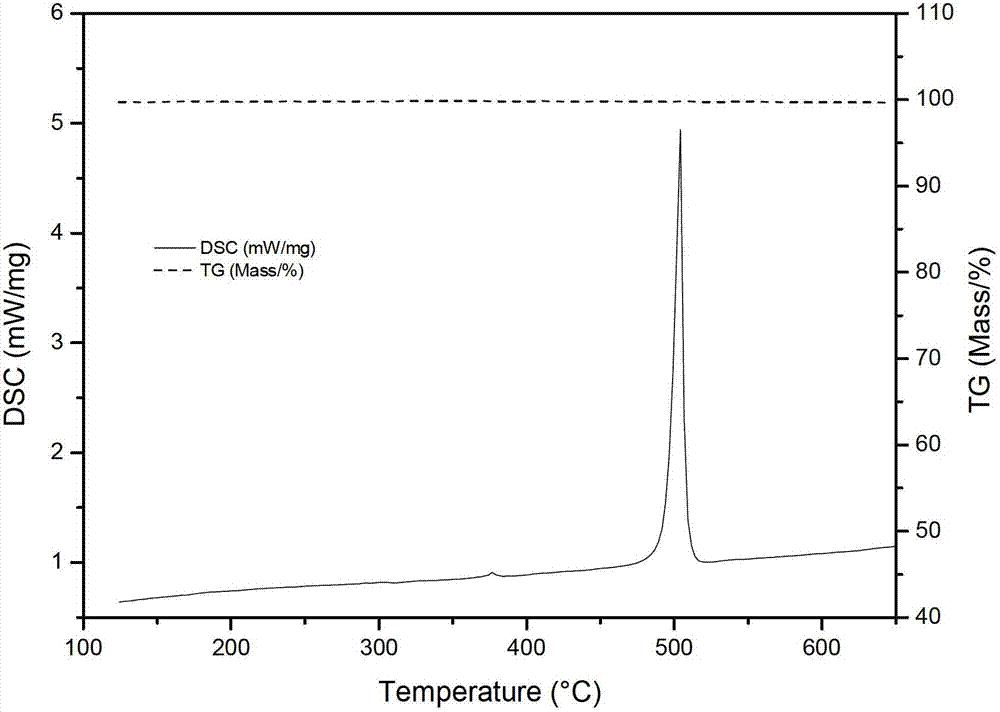
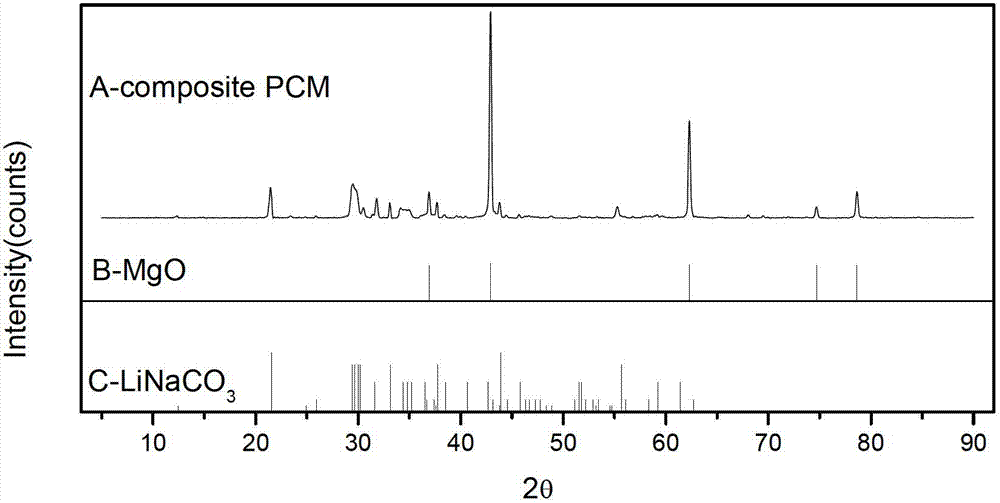
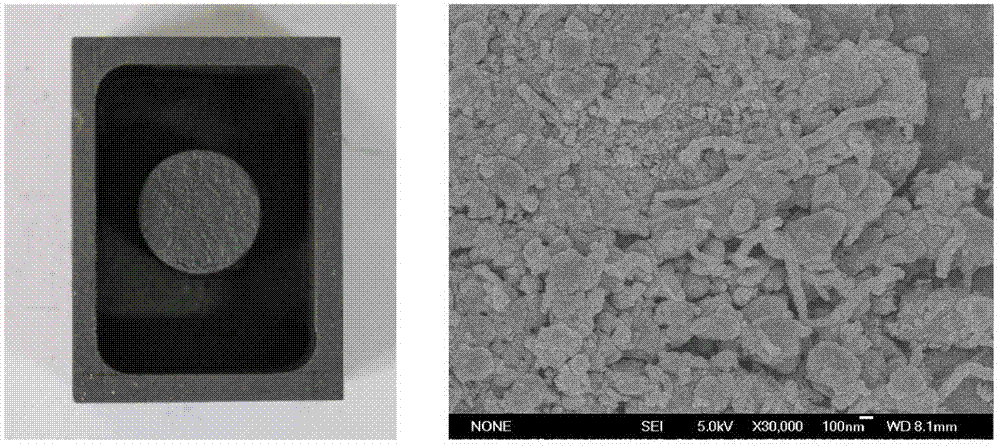
Medium-high temperature composite structural heat storage material, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102888209AHigh phase change enthalpyGood chemical compatibilityHeat-exchange elementsMicro nanoMass ratio
The invention relates to a medium-high temperature (120-1000 DEG C or higher) composite structural heat storage material. The medium-high temperature composite structural heat storage material comprises an inorganic salt phase change latent heat material, a sensitive heat storage material and a heat conduction reinforcing material, wherein the mass ratio of the inorganic salt phase change latent heat material to the sensitive heat storage material is of 1: (0.1-10); and the heat conduction reinforcing material is of 0.0001-1kg / (kg heat storage material) based on mass ratio. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: uniformly mixing the inorganic salt phase change latent heat material with the sensitive heat storage material and the heat conduction reinforcing material; pressurizing to form green blank; and then heating and sintering, so as to obtain the medium-high temperature composite structural heat storage material. The medium-high temperature composite structural heat storage material provided by the invention is capable of obviously reducing the corrosion resistance of the sensitive heat storage material; meanwhile, the thermal conductivity of the composite heat storage material is markedly improved by virtue of the micro-nano doping of the heat conduction reinforcing material; and moreover, high heat storage density is achieved, and wide application prospect is provided.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for 3D ceramic printing forming
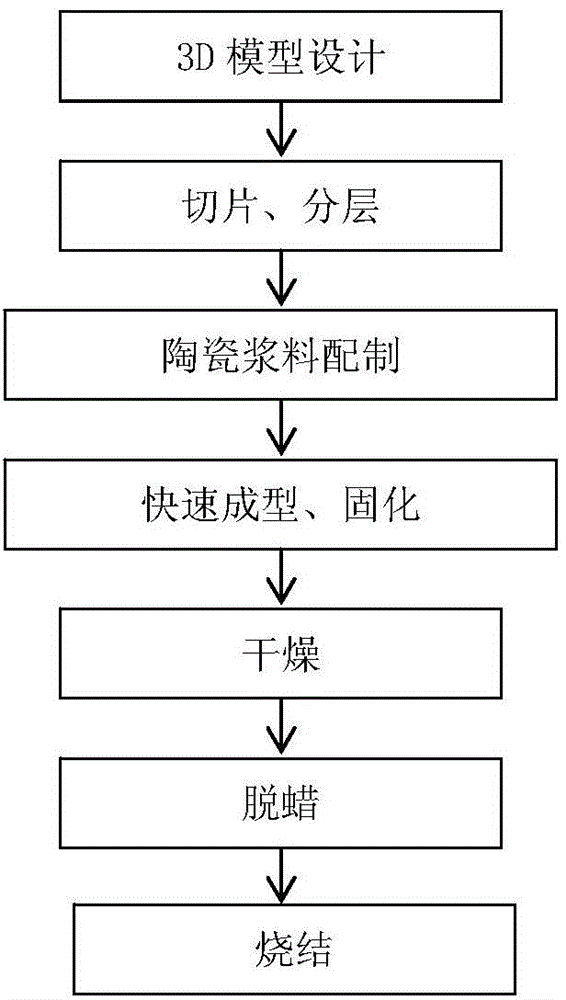
ActiveCN104526838ARapid Dieless ManufacturingShorten the development cycleCeramic shaping apparatusSlurry3d printer
The invention discloses a method for 3D ceramic printing forming. The method comprises the following steps that (1) a 3D model of a target part is established; (2) layering processing is performed, and layered data are imported into a manufacturing program; (3) ceramic slurry is prepared; (4) the prepared ceramic slurry is added into a 3D printer to be made into a ceramic green body quickly formed; (5) the green body is cured at curing temperature for 10 min-60 min and then is placed in a drying oven for drying; (6) the dried green body is dewaxed and sintered to be made into the target part. The method is simple in technology and low in equipment cost; the distance between powder particles in the ceramic slurry can be reduced in the extrusion process, and therefore density is high; besides, the method is not limited by the type of ceramic particles and the shape of the part and is suitable for manufacturing ceramic products made of various ceramic materials and in various complex shapes.
Owner:NINGBO VULCAN TECH CO LTD
Production method for sintered metal-ceramic layered compact and production method for thermal stress relief pad
InactiveUS20050002818A1Reduce in quantityEfficient executionThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentTransportation and packagingMicrowaveStress relief
The present invention provides a production method for a sintered metal-ceramic layered compact, comprising steps of: filling and layering a metal powder and a ceramic powder, or filling and layering a metal powder, a mixed powder of a metal powder and a ceramic powder, and a ceramic powder; forming a green compact of the layered powders by compacting the layered powders; and sintering a layer including the metal of the green compact at a temperature of lower than a melting point of the metal by heating by irradiation of microwaves in a non-oxidizing atmosphere.
Owner:HITACHI POWDERED METALS COMPANY
Binder system and method for particulate material cross-reference to related application
InactiveUS6846862B2Avoiding downtime for coolingDistribute quicklyTransportation and packagingFibre treatmentWaxPolyester
The present invention relates to a binder composition comprising an aliphatic polyester polymer: an ethylenebisamide wax; and a guanidine wetting agent. The composition may also contain an additive which accelerates or extends debinding of the binder composition, and to a method for forming a sintered part by powder injection molding, including the steps of forming a green composition comprising a binder and an inorganic powder, wherein the binder is a composition comprising an aliphatic polyester polymer, an ethylenebisamide wax, and a guanidine wetting agent, and may further include an additive which accelerates or delays completion of debinding of the binder; melting the composition; injecting the composition into a mold for a part; heating the part to a temperature at which the binder decomposes; heating the part to a temperature at which the inorganic powder is sintered.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com