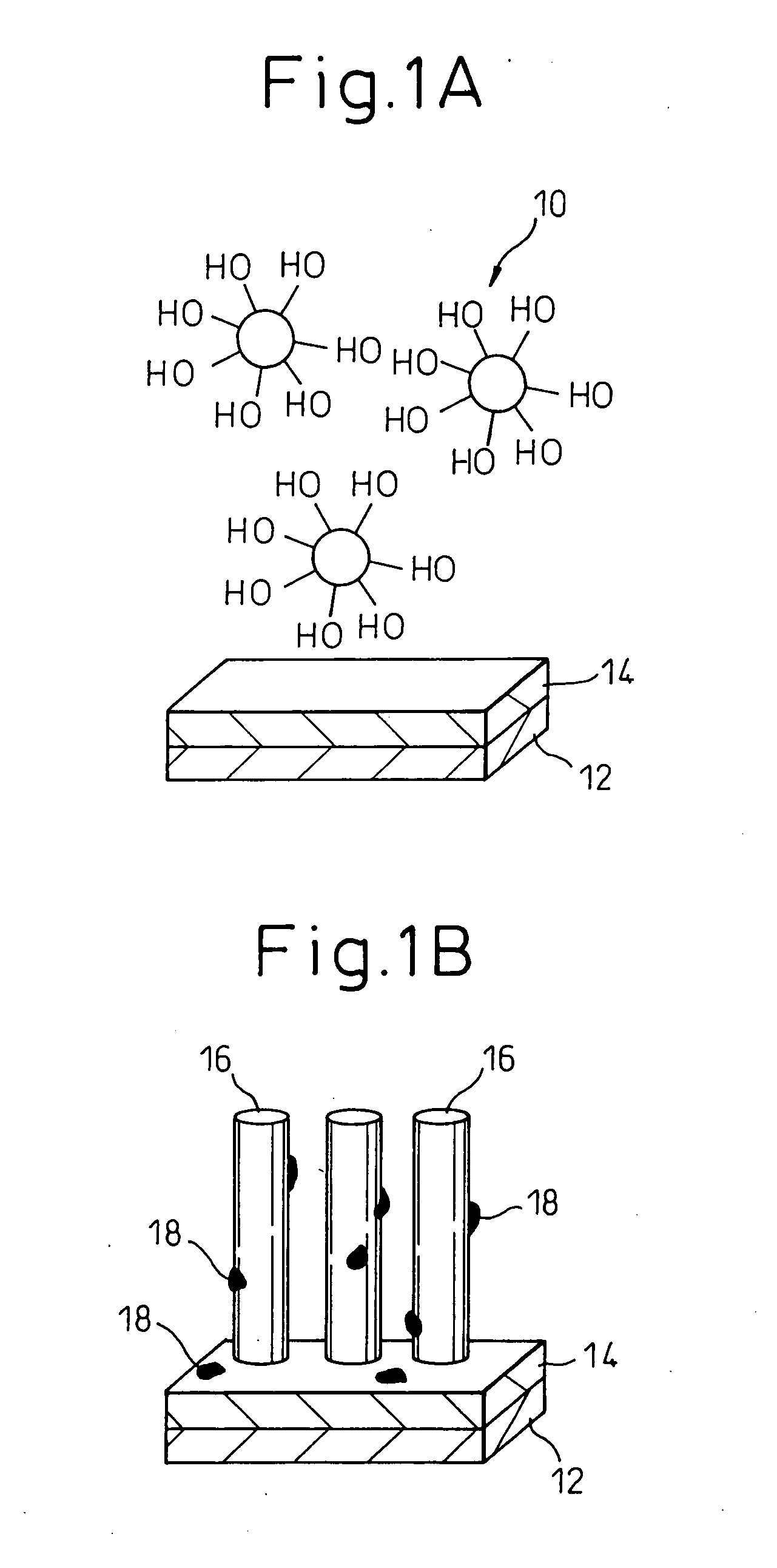
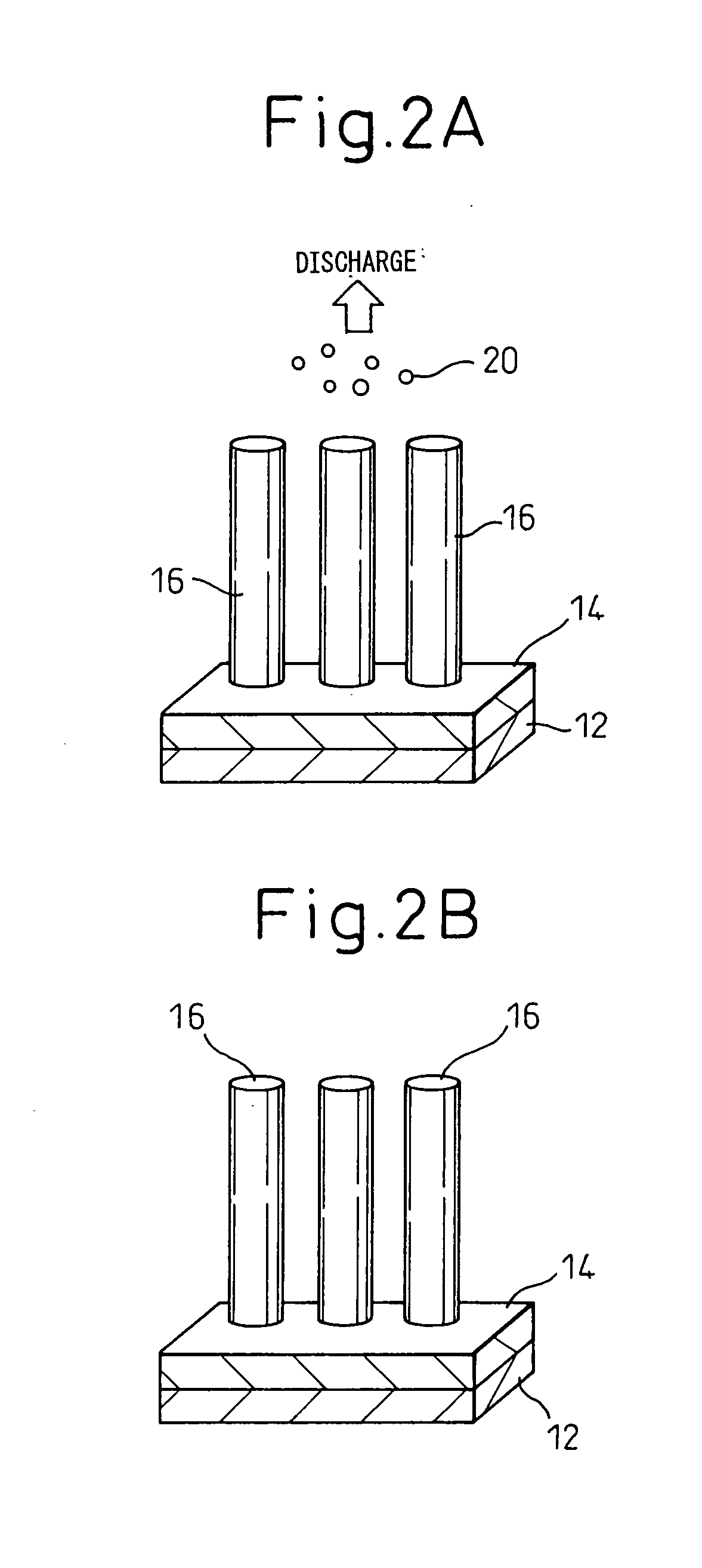
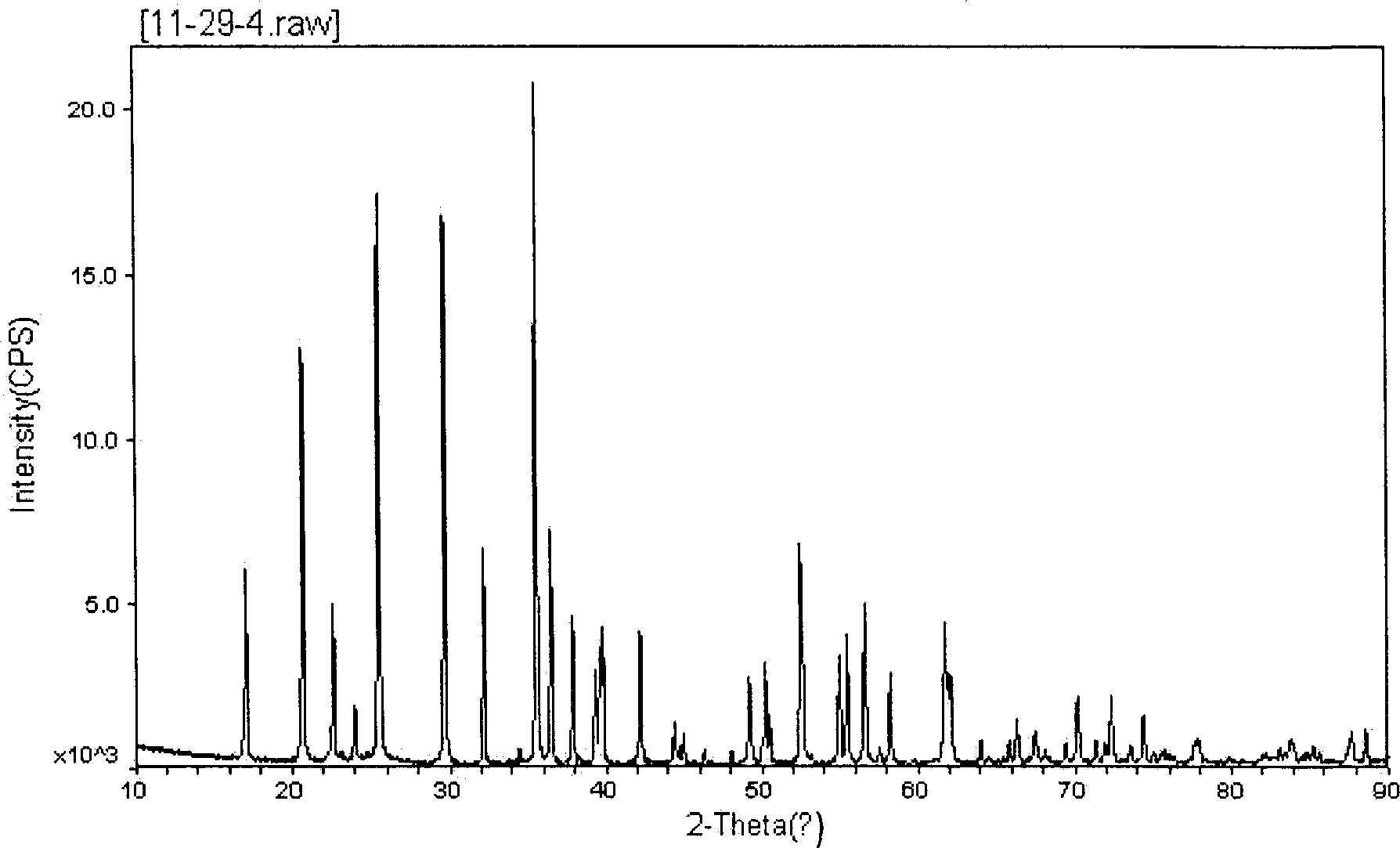
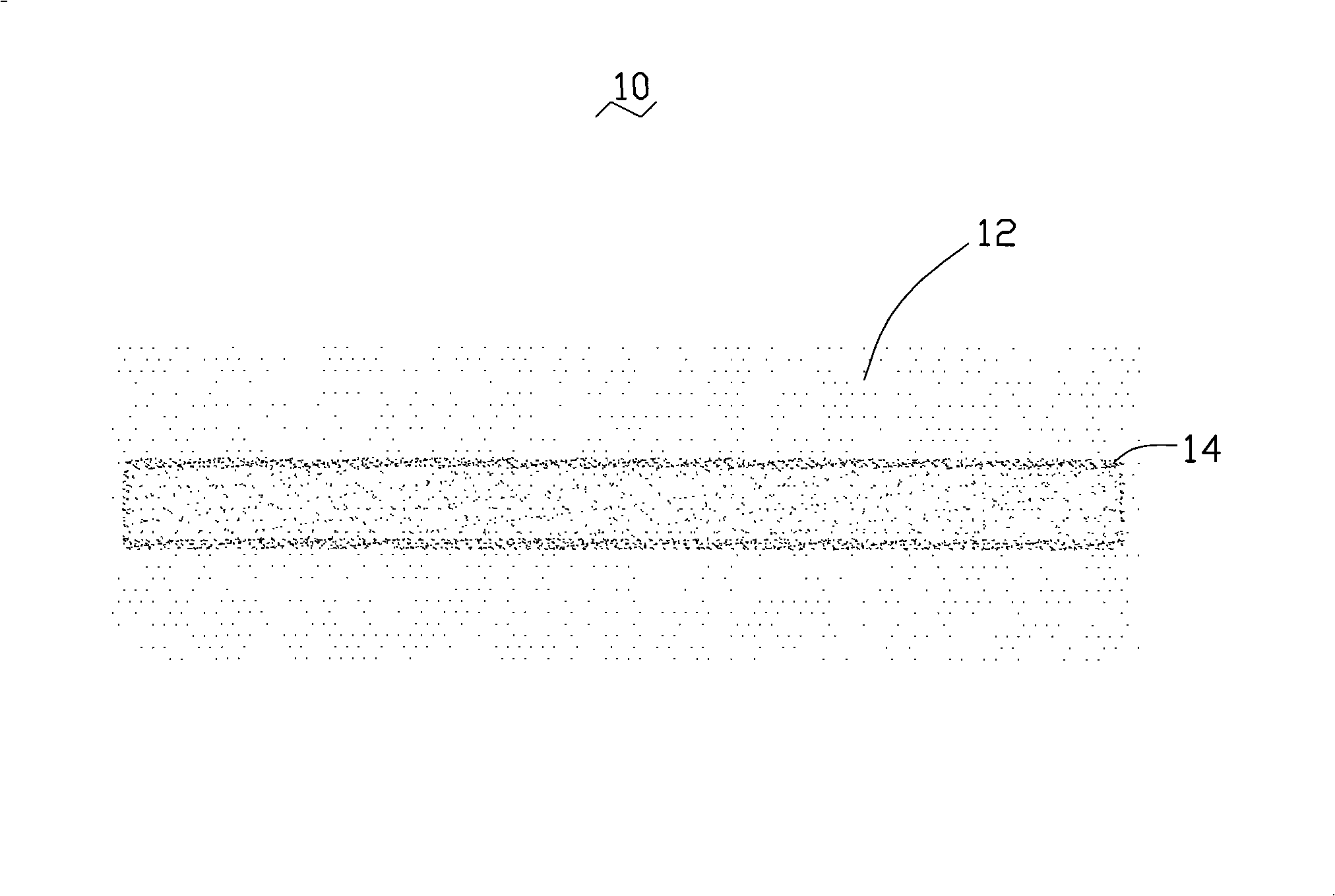
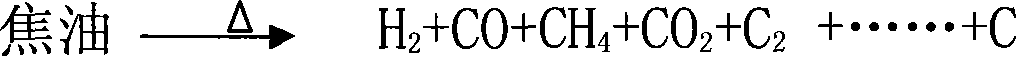Patents
Literature
880 results about "Residual carbon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
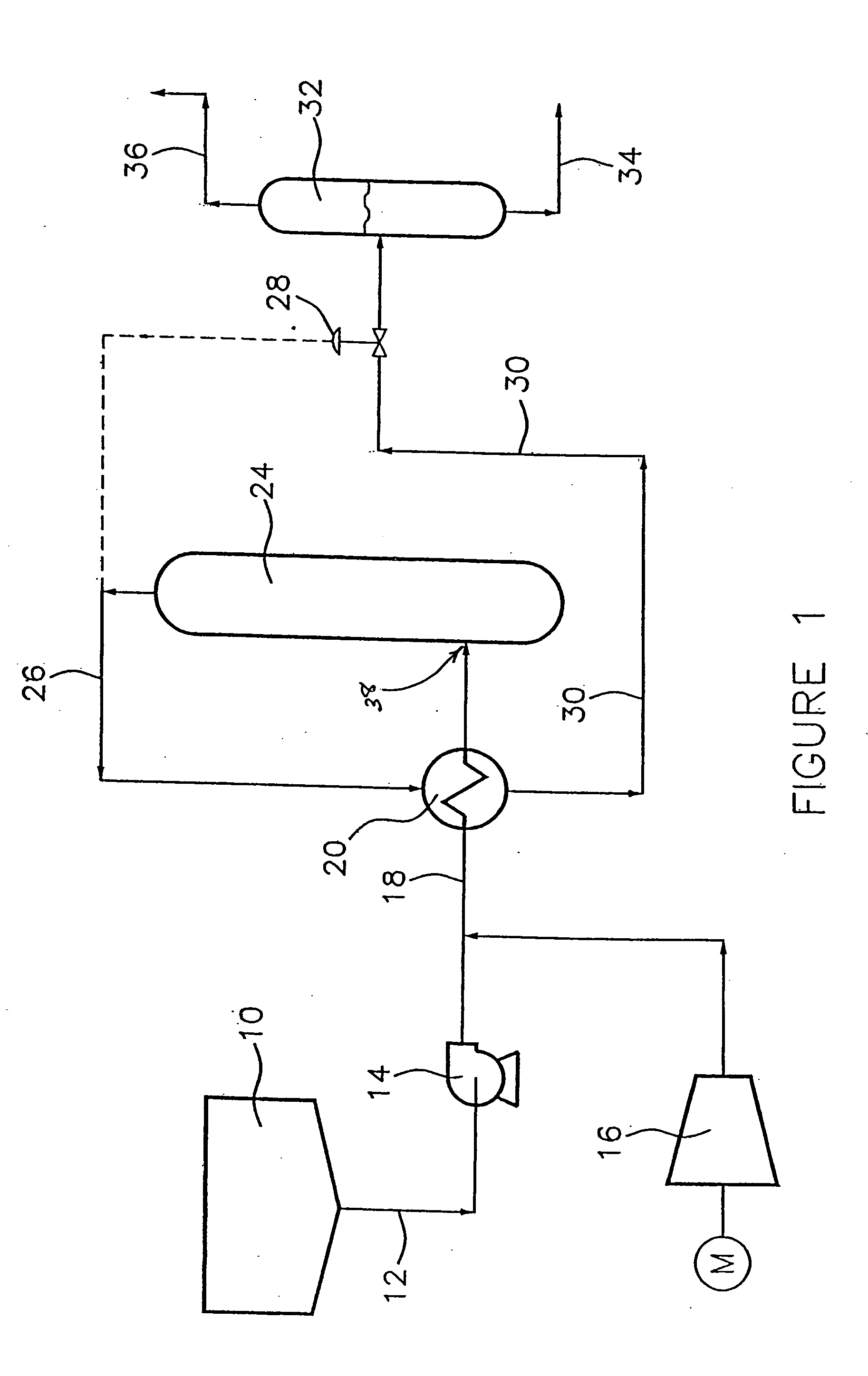
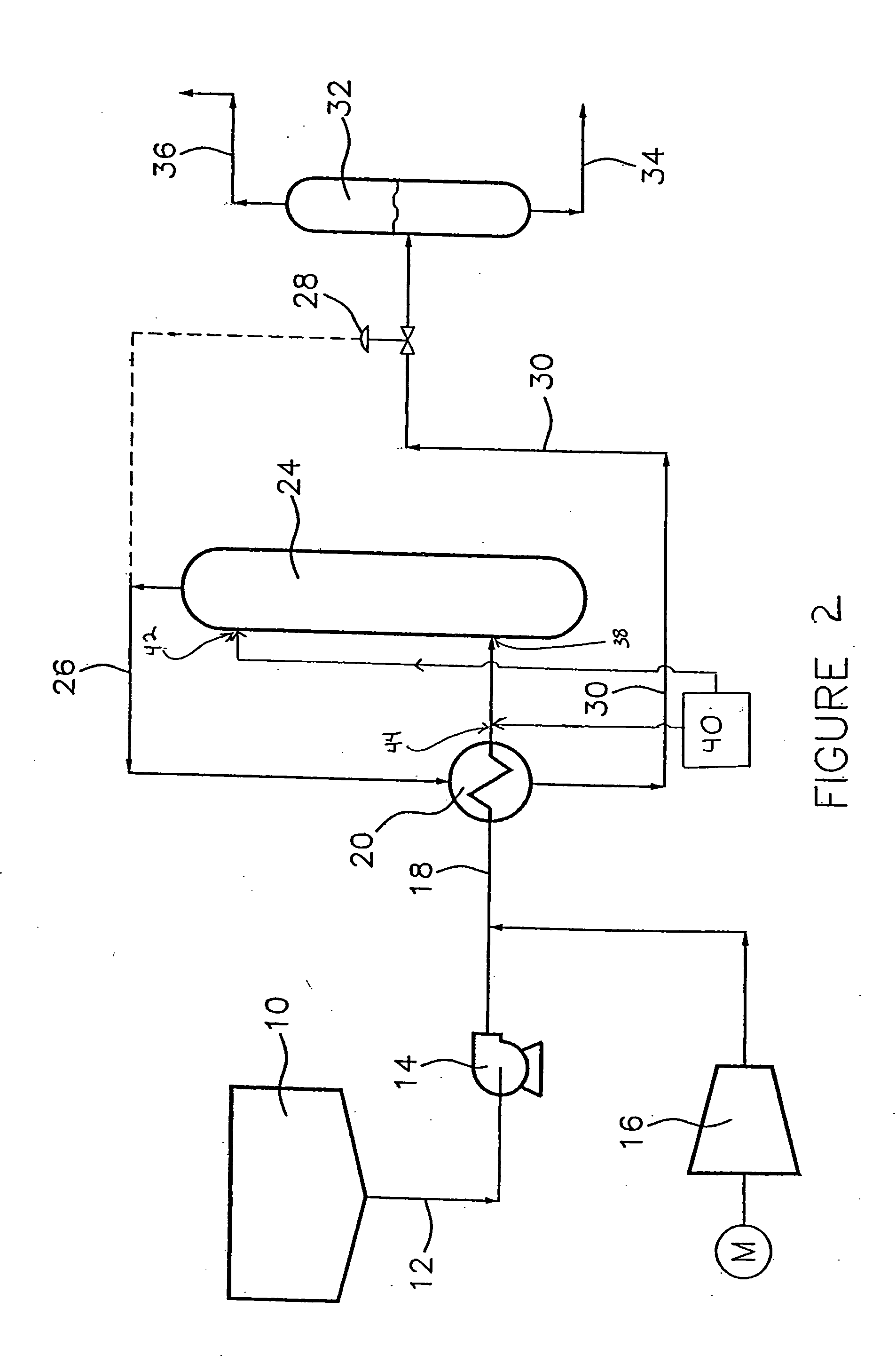
The residual carbon content of a coked carbon-containing brick or shape is an indication of how much carbon may be available, in service, to resist slag attack on, or oxidation loss of, that body. Apparent carbon yield gives an estimate of the relative efficiency of the total carbonaceous matter to be retained as residual carbon.
Formation of a liquid-like silica layer by reaction of an organosilicon compound and a hydroxyl forming compound
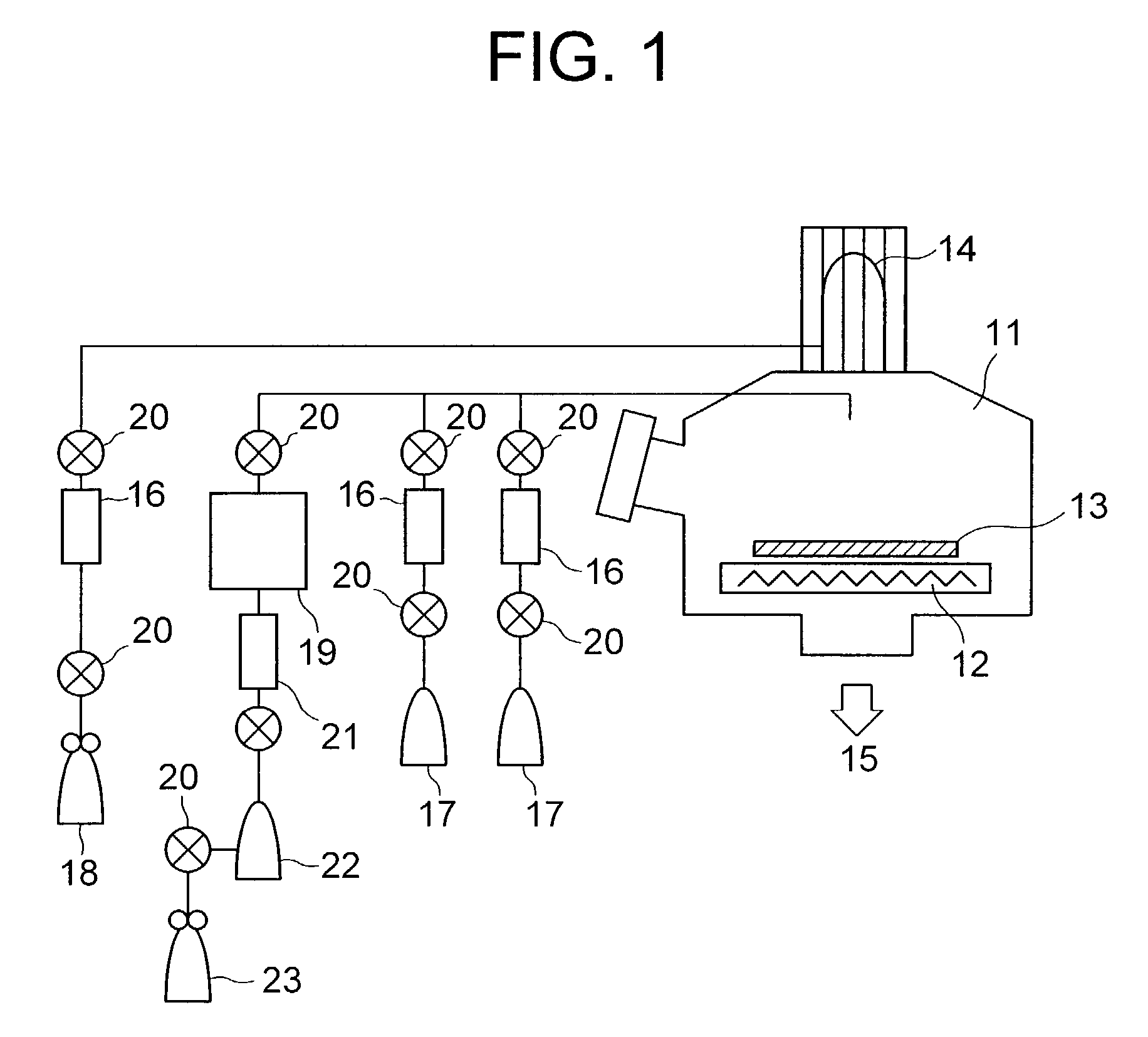
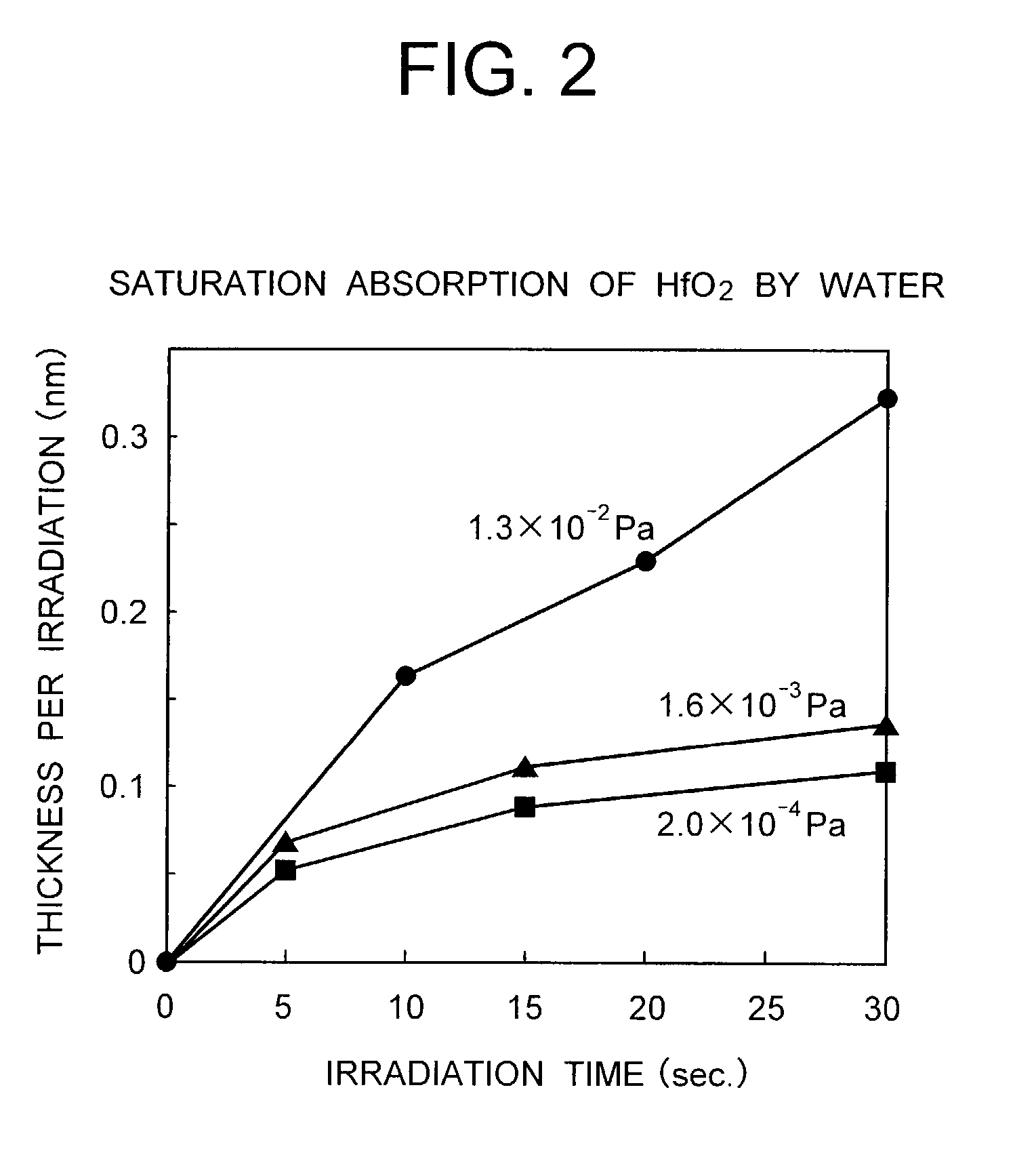
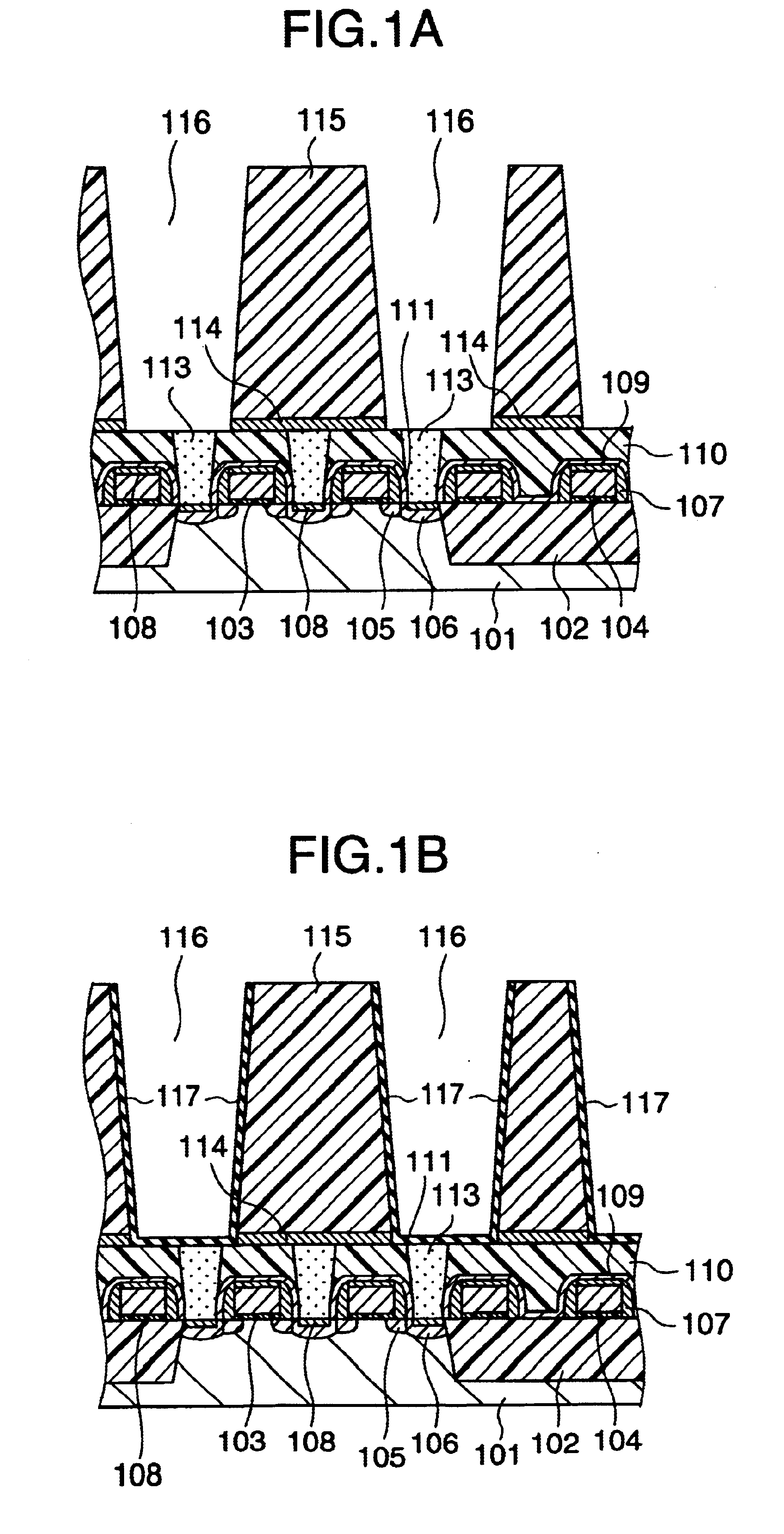
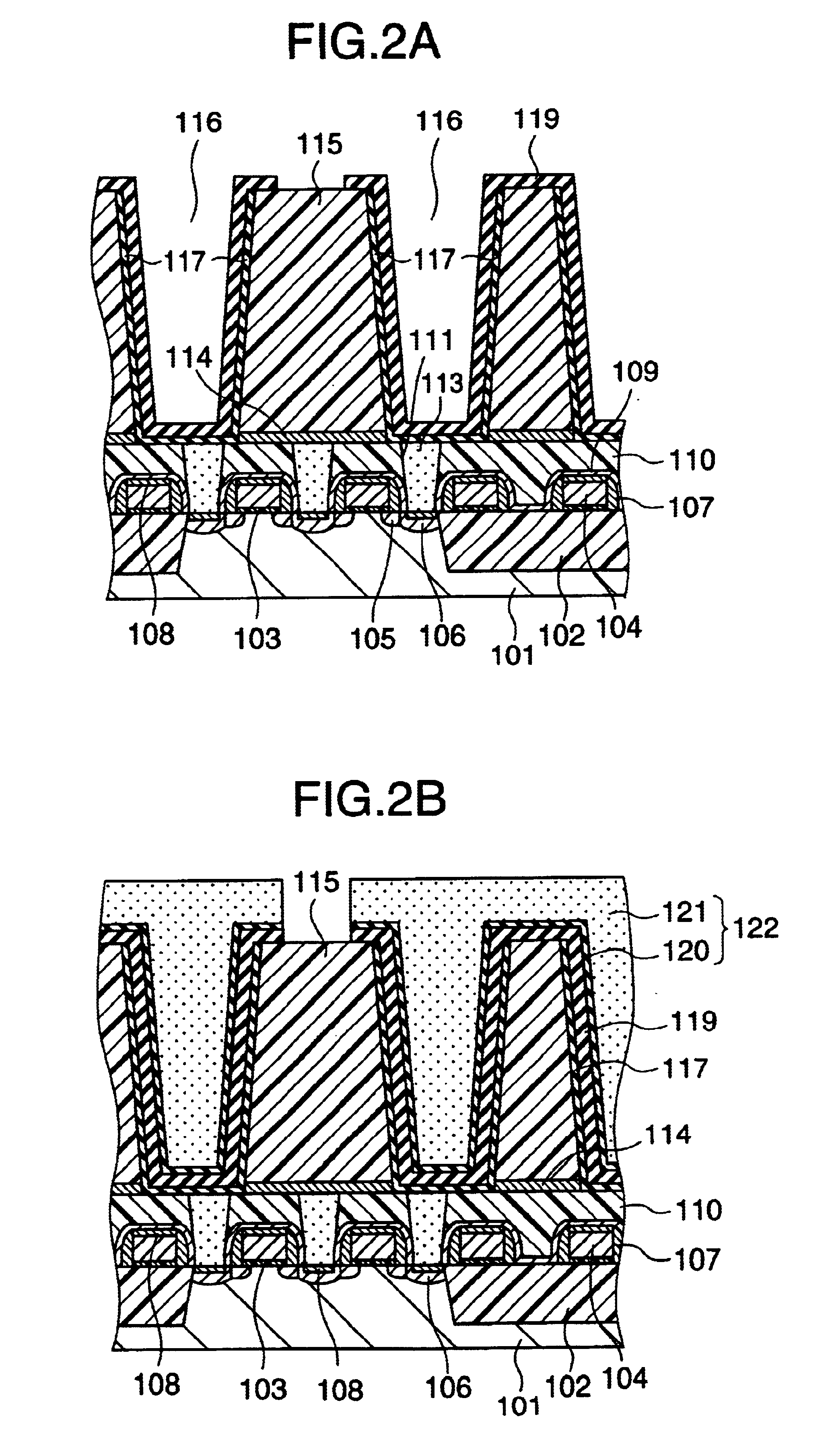
InactiveUS6413583B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilicon oxideSilicon dioxide
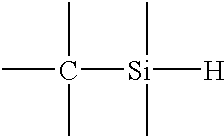
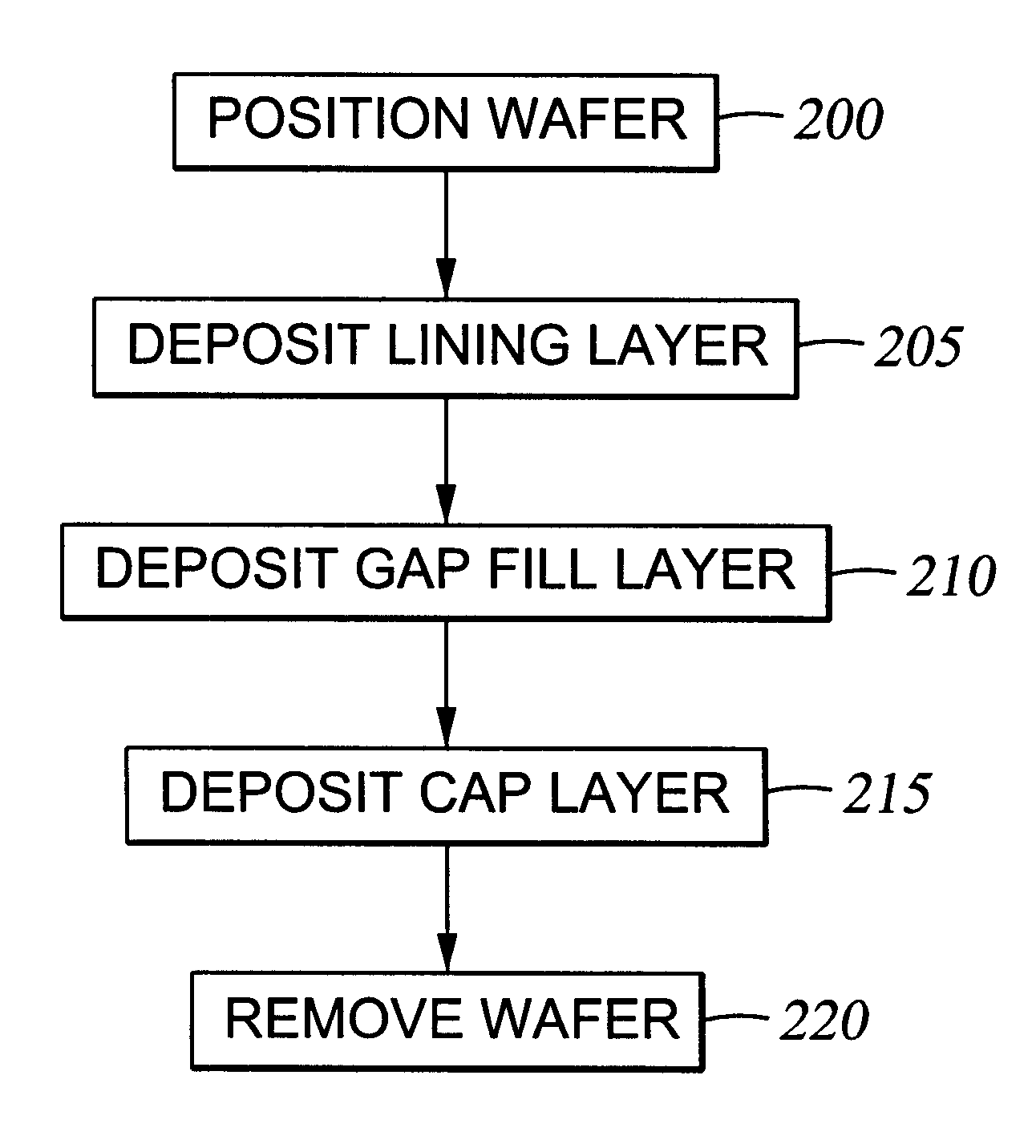
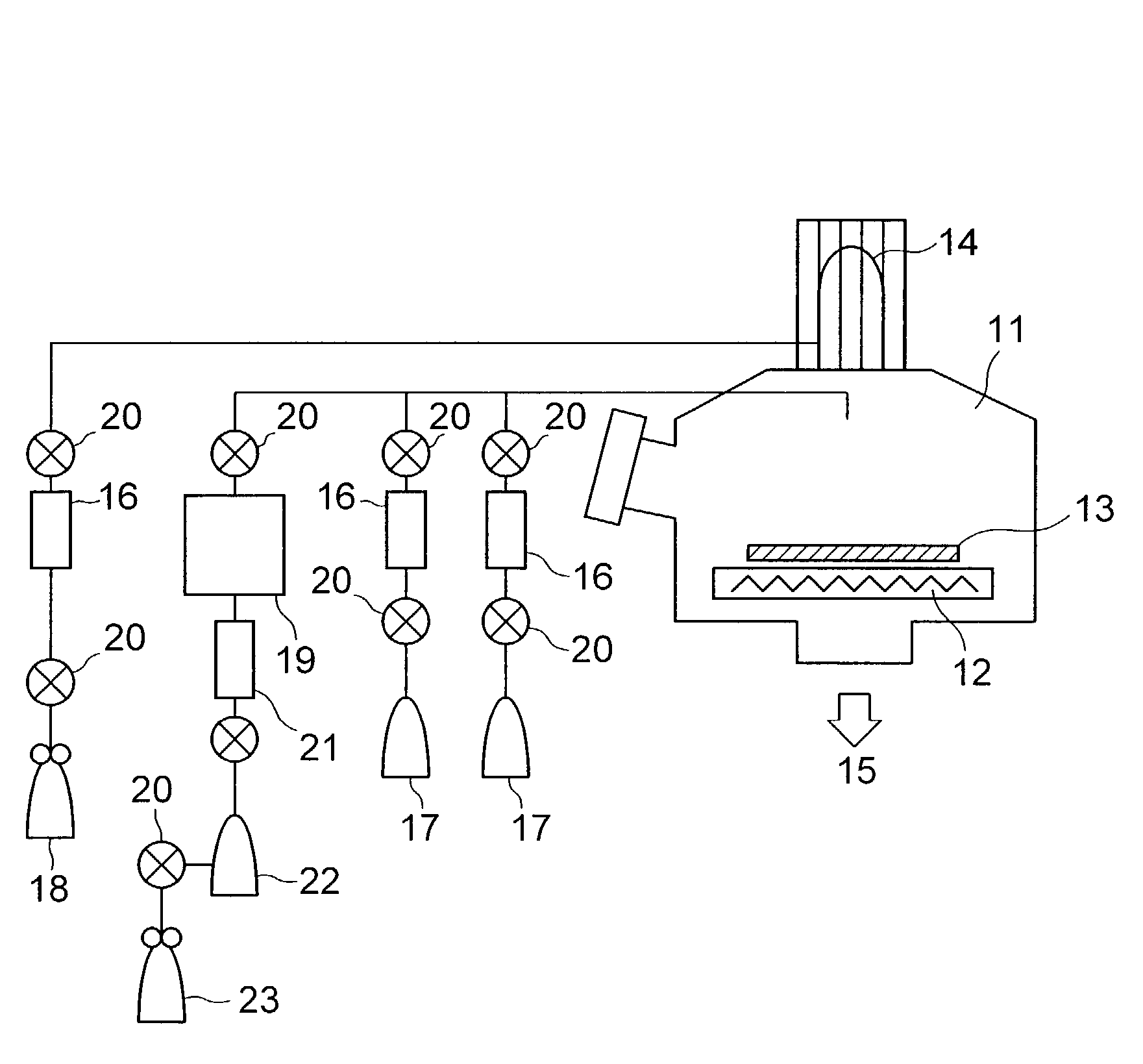
A method for depositing silicon oxide layers having a low dielectric constant by reaction of an organosilicon compound and a hydroxyl forming compound at a substrate temperature less than about 400° C. The low dielectric constant films contain residual carbon and are useful for gap fill layers, pre-metal dielectric layers, inter-metal dielectric layers, and shallow trench isolation dielectric layers in sub-micron devices. The hydroxyl compound can be prepared prior to deposition from water or an organic compound. The silicon oxide layers are preferably deposited at a substrate temperature less than about 40° C. onto a liner layer produced from the organosilicon compound to provide gap fill layers having a dielectric constant less than about 3.0.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for vapor deposition of a metal compound film
InactiveUS20020172768A1Improve film propertiesEfficiently stackedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLanthanideNitrogen
A method for forming a metal compound film includes alternate irradiation of an organometal compound and oxygen or nitrogen radicals to deposit monoatomic layers of the metal compound. The organometal compound includes zirconium, hafnium, lanthanide compounds. The resultant film includes little residual carbon and has excellent film characteristic with respect to leakage current.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Device isolation technology on semiconductor substrate
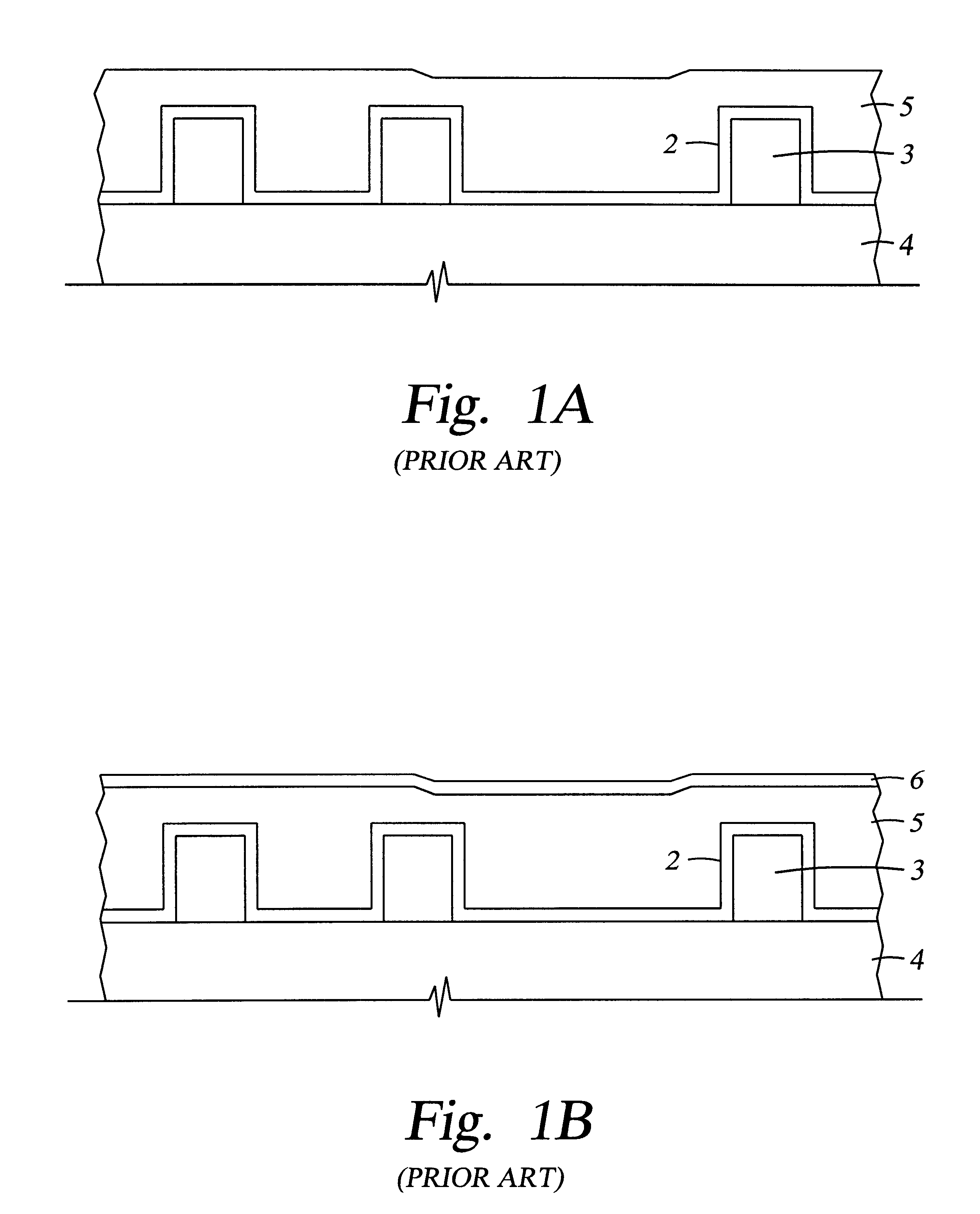
A method of forming device isolation regions on a trench-formed silicon substrate and removing residual carbon therefrom includes providing a flowable, insulative material constituted by silicon, carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen or any combination of two or more thereof; forming a thin insulative layer, by using the flowable, insulative material, in a trench located on a semiconductor substrate wherein the flowable, insulative material forms a conformal coating in a silicon and nitrogen rich condition whereas in a carbon rich condition, the flowable, insulative material vertically grows from the bottom of the trenches; and removing the residual carbon deposits from the flowable, insulative material by multi-step curing, such as O2 thermal annealing, ozone UV curing followed by N2 thermal annealing.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Porous SiC-bodies with micro-channels and process for their fabrication
InactiveUS20060121266A1Large effective internal surface areaImprove filtering effectInternal combustion piston enginesLayered productsParticulatesCellulose
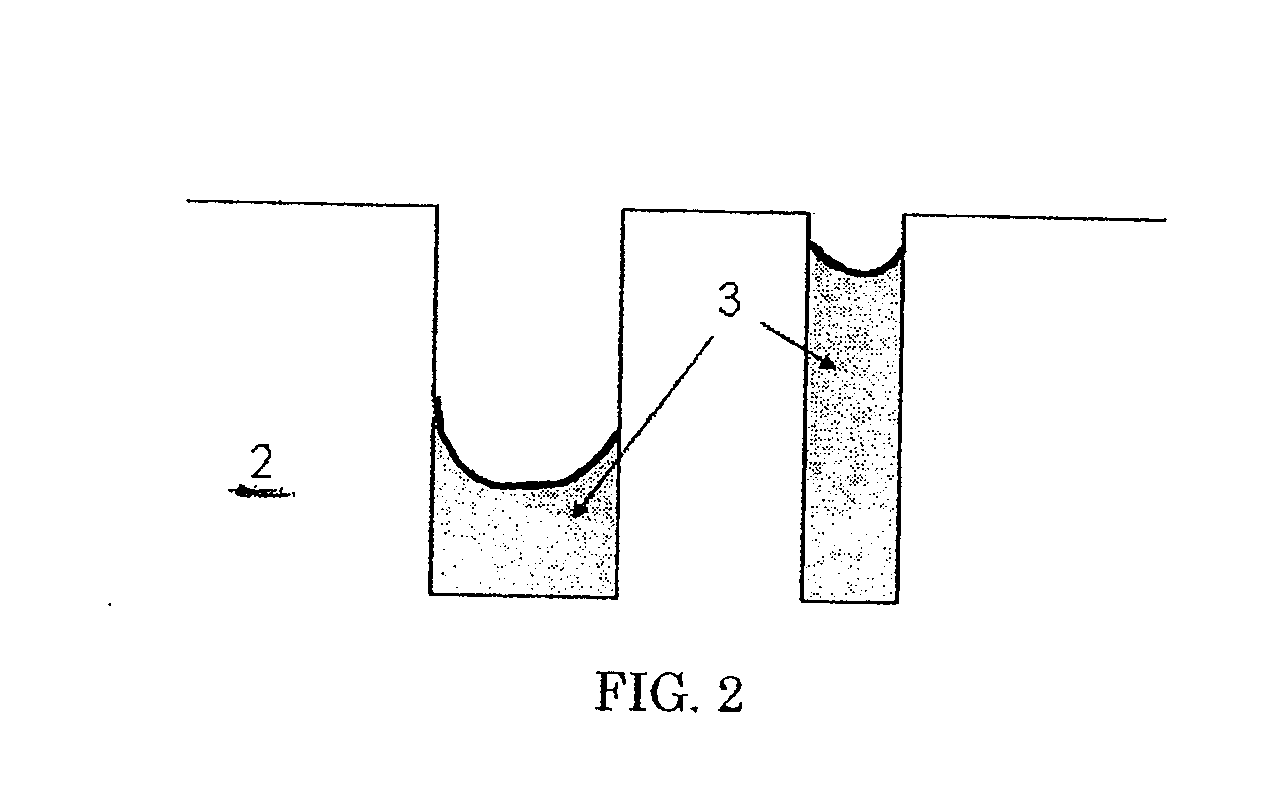
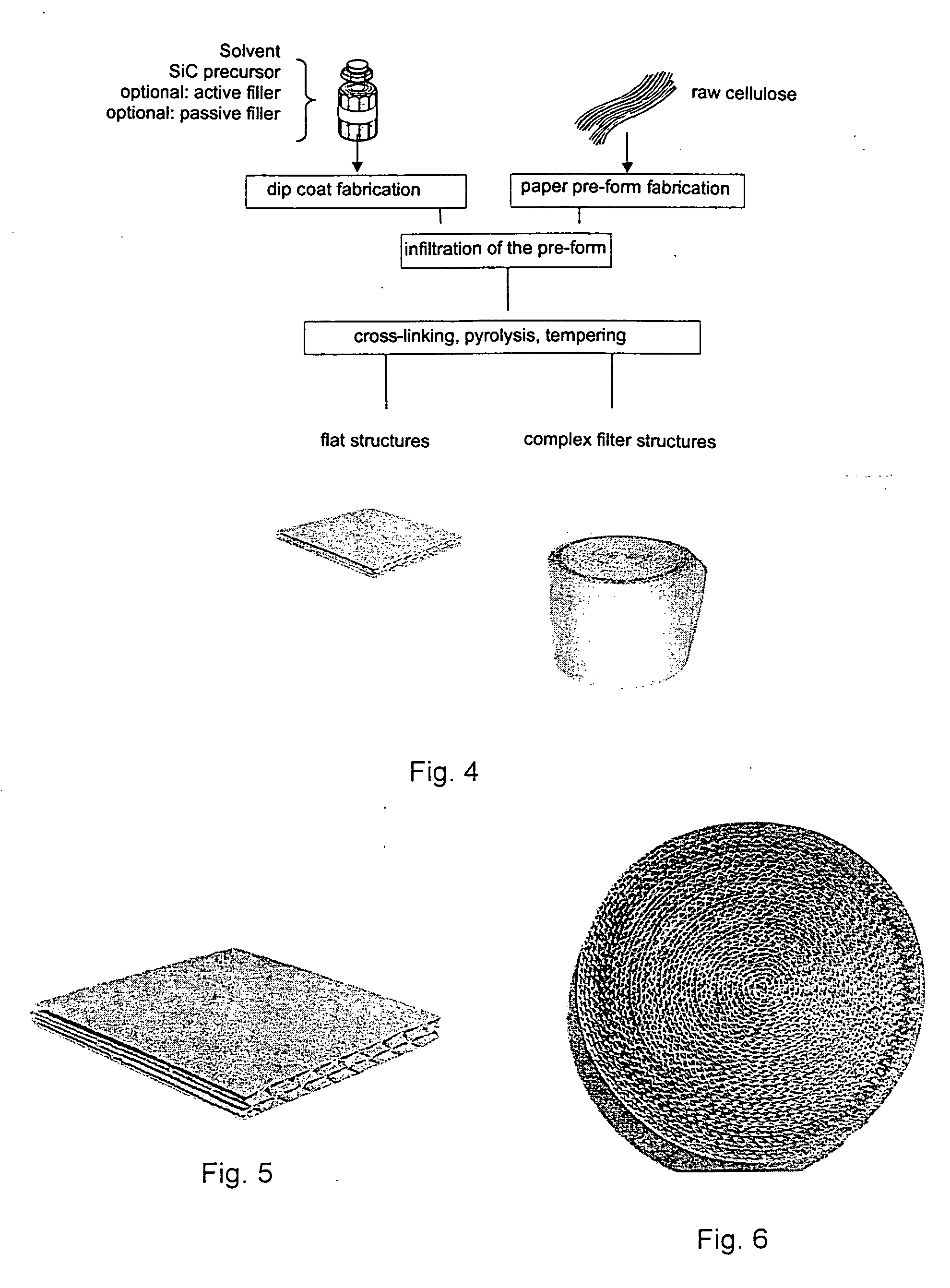
Process for the fabrication of porous bodies mainly constituted by SiC containing ceramic with a microstructure which is interfused with micro-channels which consists of the process steps a) Provision of a pre-body made from cellulose or pulp b) Fabrication of an infiltration solution or a slurry consisting of (A) solvent, polysilazane, polysilane and / or polycarbosilane or (B) solvent, polysilazane and / or polysilane as well as active metallic fillers and / or passive ceramic fillers. c) Infiltrating the body with infiltration solution or slurry d) Cross-linking of the polysilazane, polycarbosilane and / or polysilane while generating a solid green body e) Ceramization through pyrolysis of the green body in an inert-gas atmosphere. f) Removal of residual carbon with an oxidizing thermal process, thereof producible catalyst carriers or carbon particulate filters as well as Porous ceramic which is made from at least 80% SiC in which the porous ceramic features a microstructure with micro-channels consisting mainly of SiC coated micro-channels featuring an average diameter between 1 and 25 μm and webs of SiC located between the micro-channels as well as additional ceramic materials with a content below 20 wt %.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
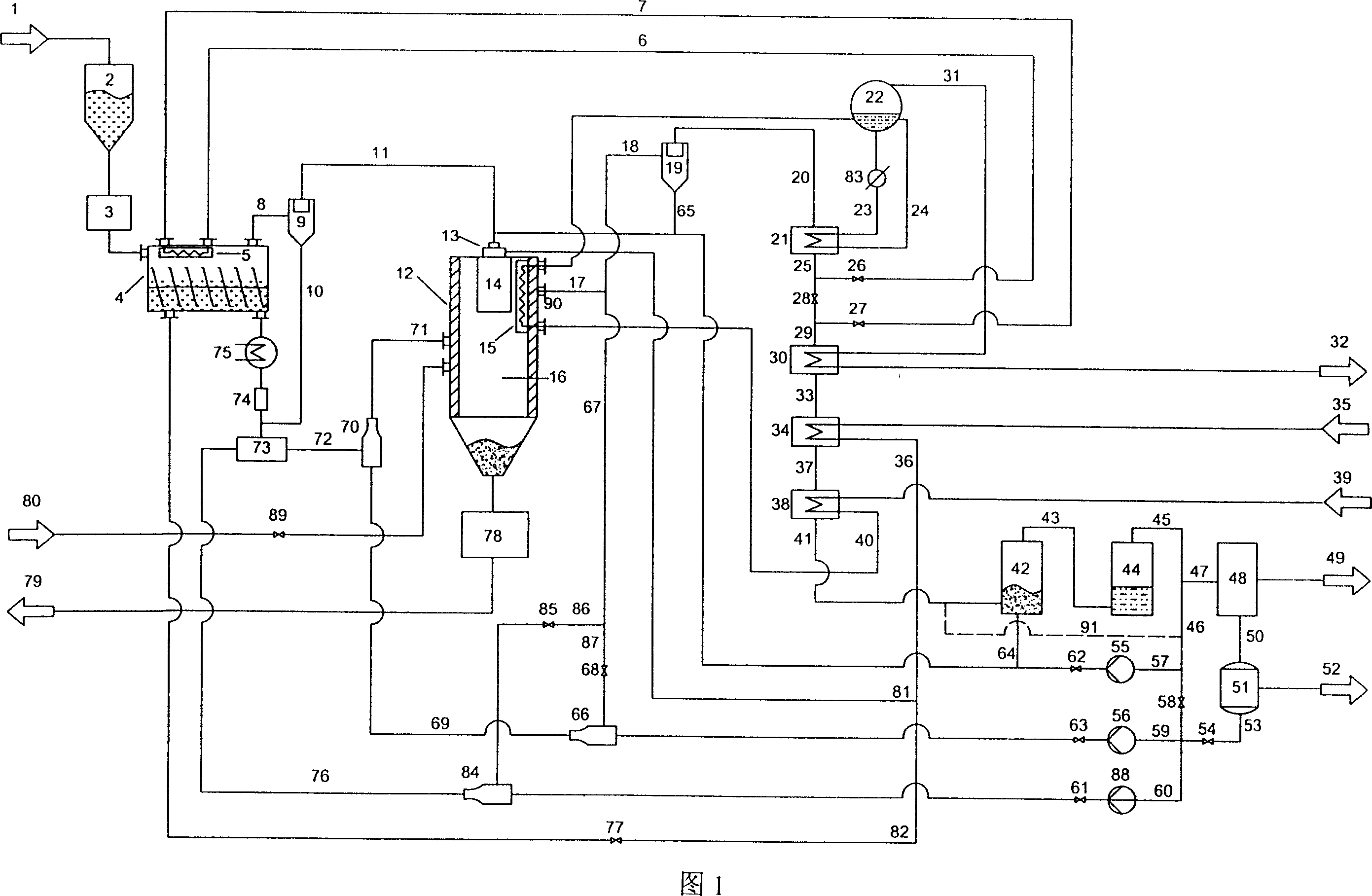
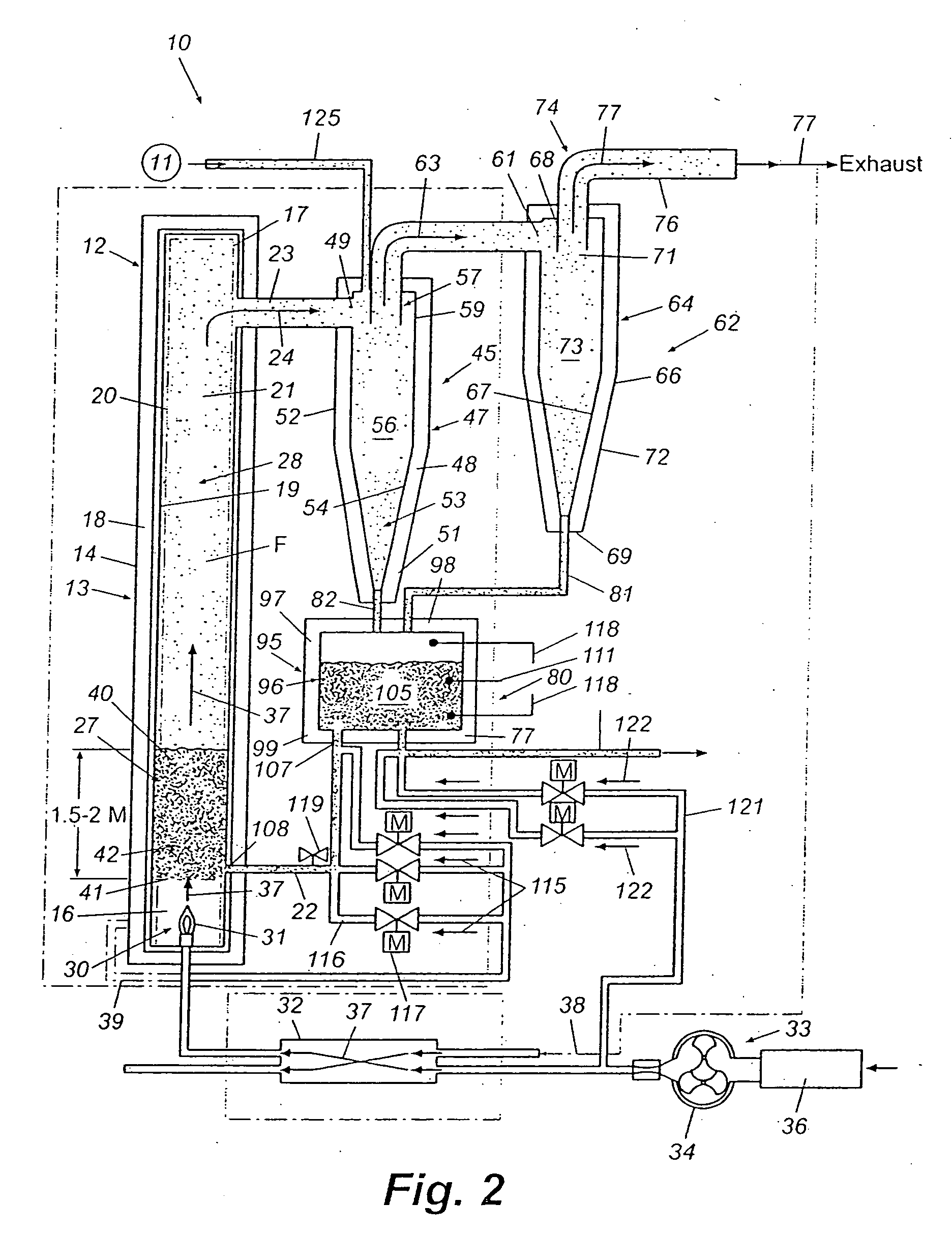
Iron production method of operation in a rotary hearth furnace and improved furnace apparatus
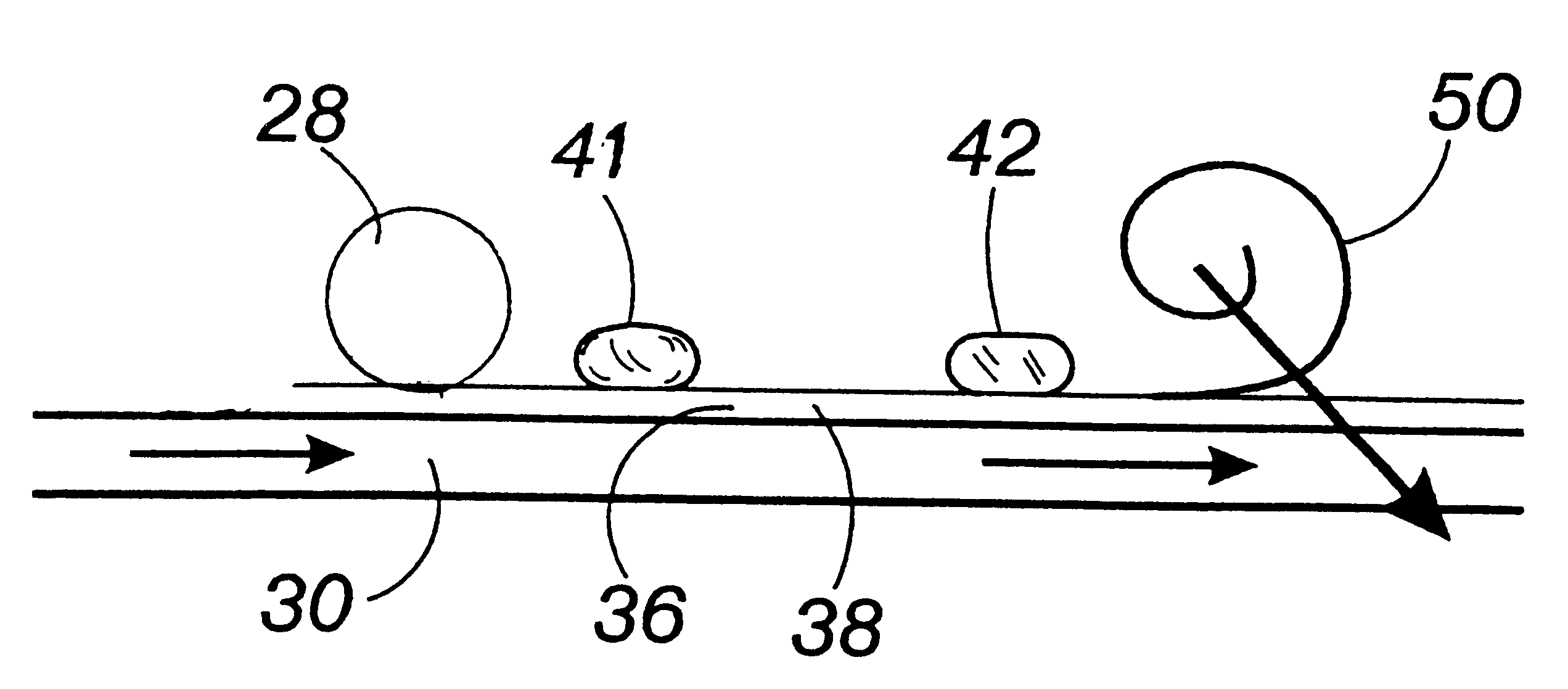
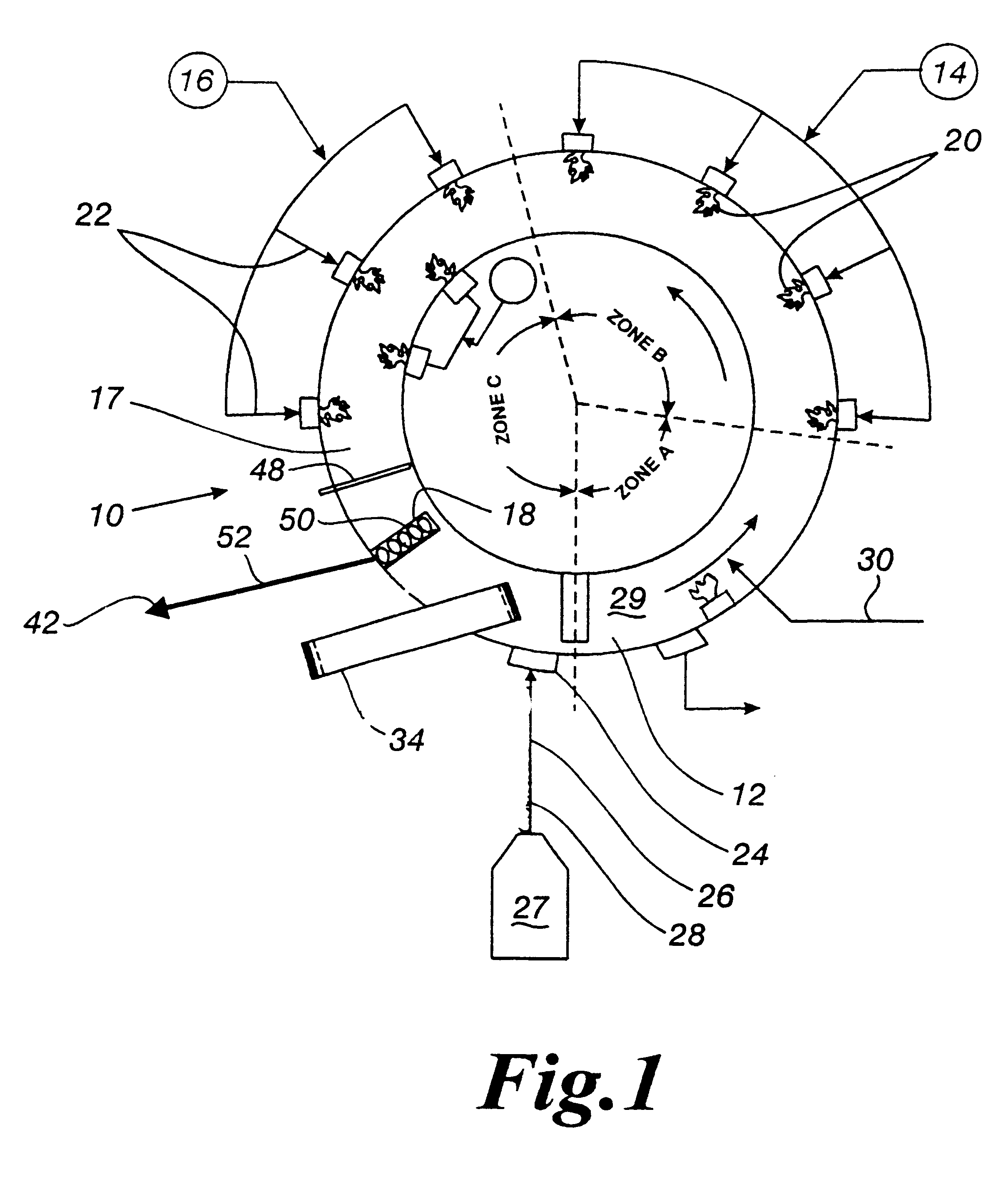
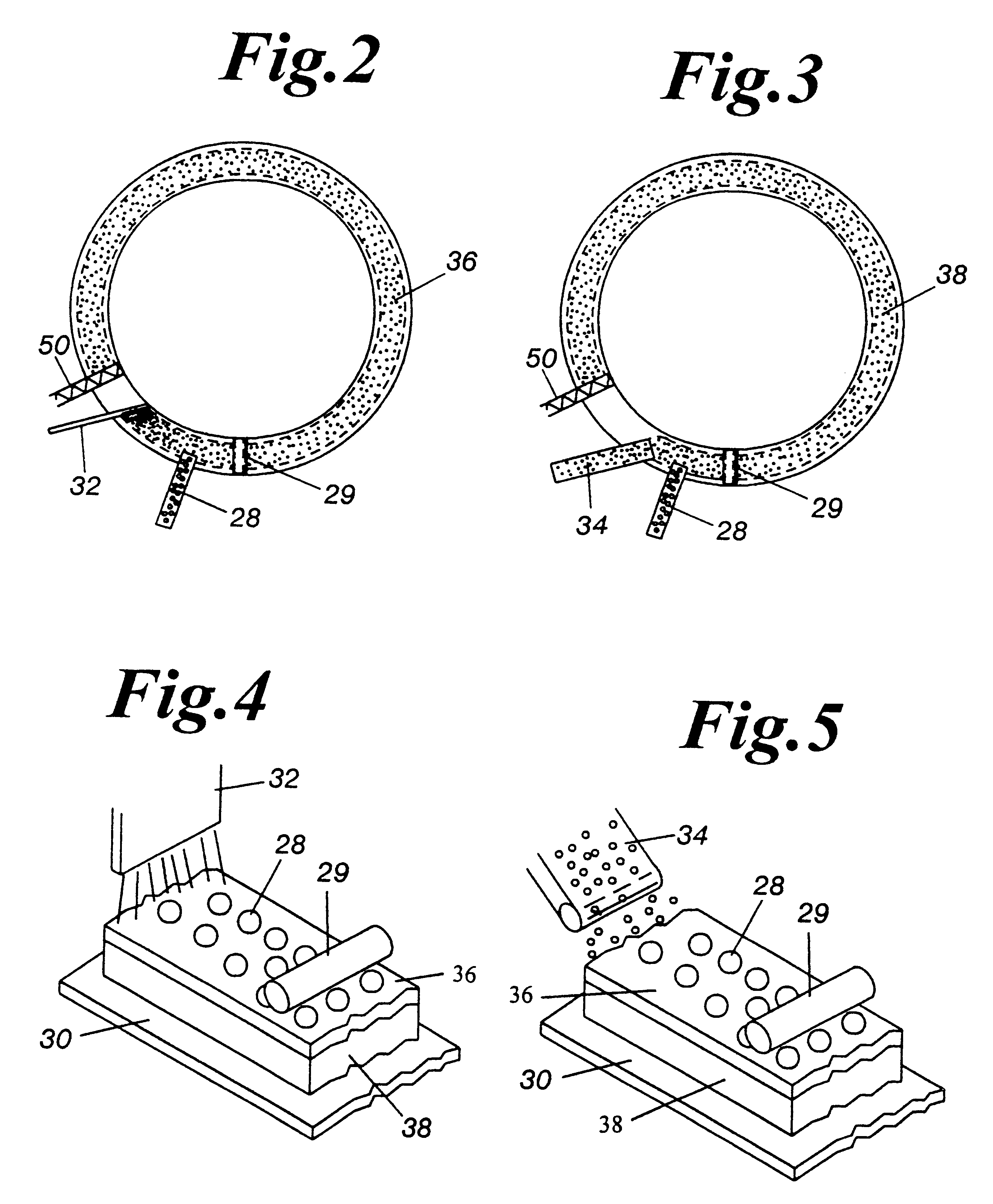
The present invention is an apparatus and method for the direct reduction of iron oxide utilizing a rotary hearth furnace to form a high purity carbon-containing iron metal button. The hearth layer may be a refractory or a vitreous hearth layer of iron oxide, carbon, and silica compounds. Additionally, coating materials may be introduced onto the refractory or vitreous hearth layer before iron oxide ore and carbon materials are added, with the coating materials preventing attack of the molten iron on the hearth layer. The coating materials may include compounds of carbon, iron oxide, silicon oxide, magnesium oxide, and / or aluminum oxide. The coating materials may be placed as a solid or a slurry on the hearth layer and heated, which provides a protective layer onto which the iron oxide ores and carbon materials are placed. The iron oxide is reduced and forms molten globules of high purity iron and residual carbon, which remain separate from the hearth layer. An improved apparatus includes a cooling plate that is placed in close proximity with the refractory or vitreous hearth layer, cooling the molten globules to form iron metal buttons that are removed from the hearth layer. The improvements due to the present apparatus and method of operation provide high purity iron and carbon solid buttons, which are separate from slag particulates, and discharged without significant loss of iron product to the interior surfaces of the furnace.
Owner:MIDREX INT B V ROTTERDAM
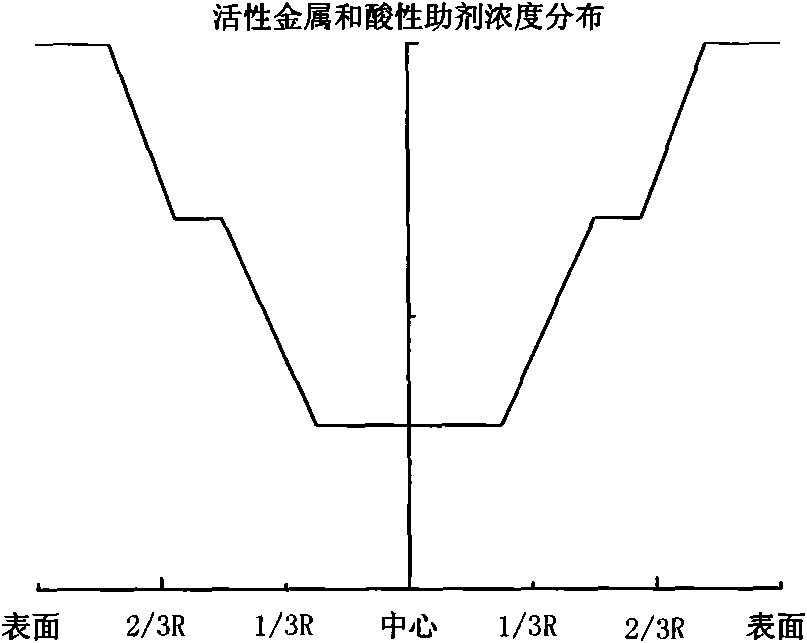
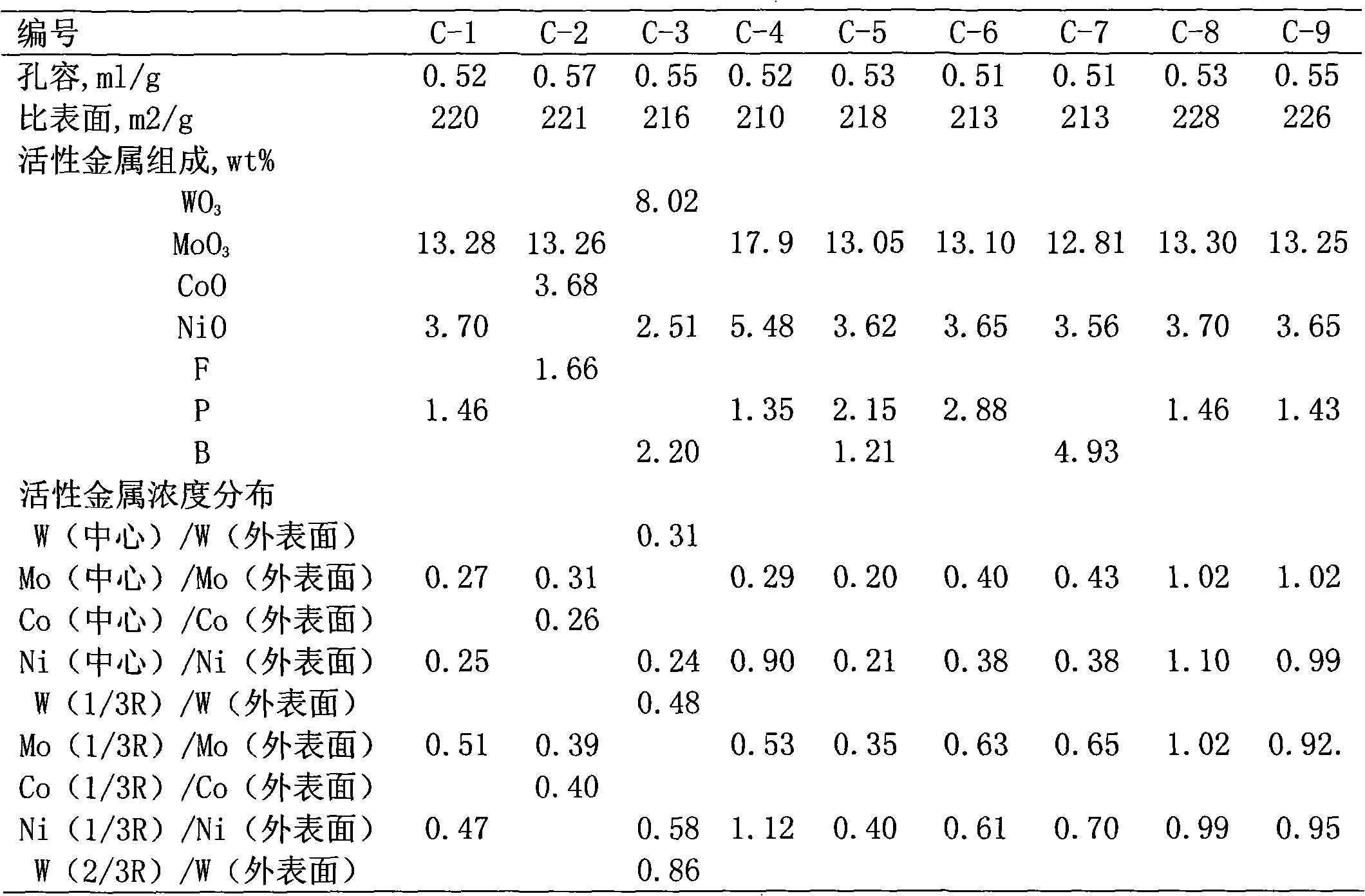
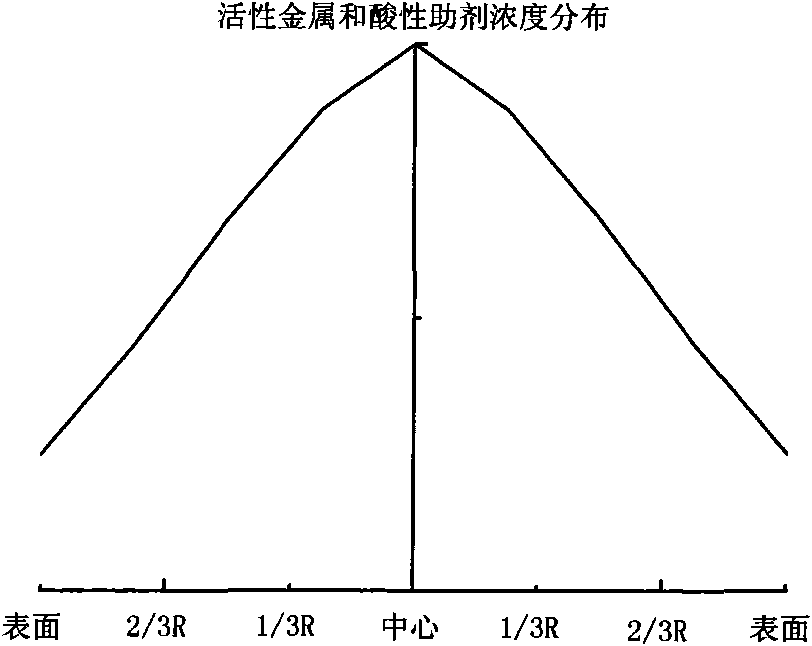
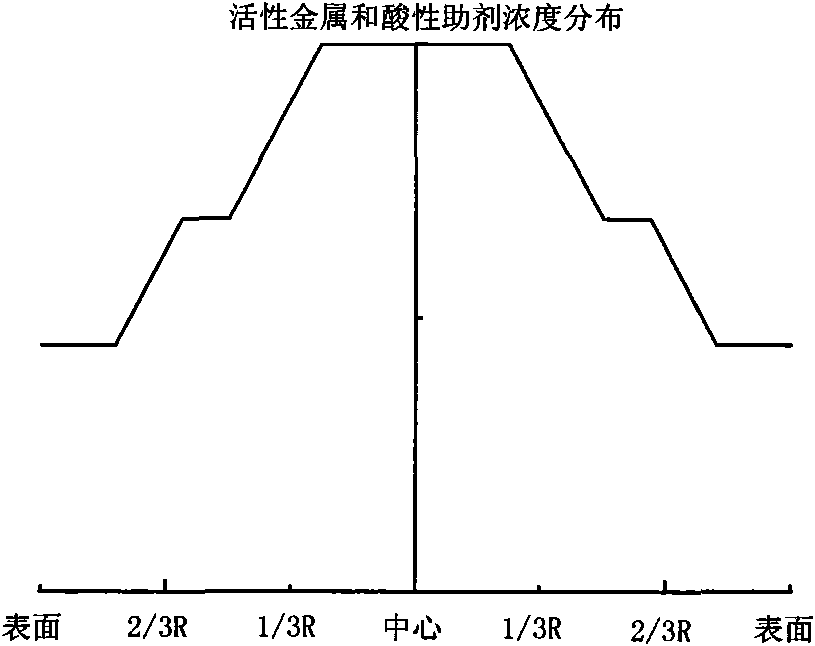
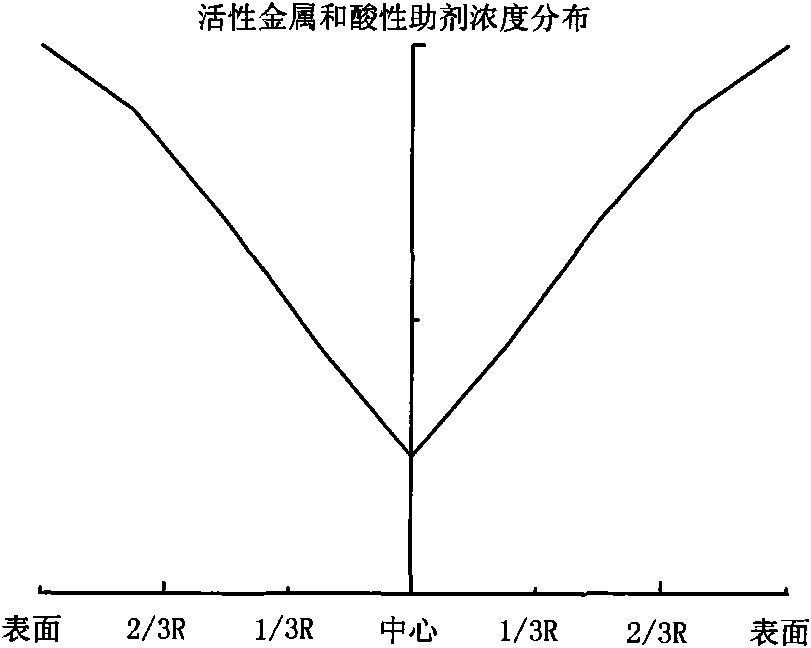
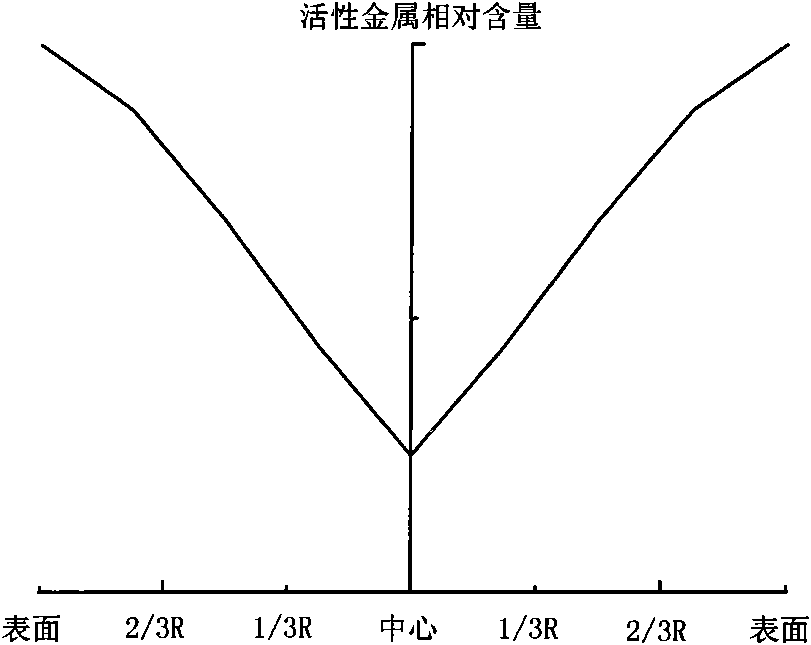
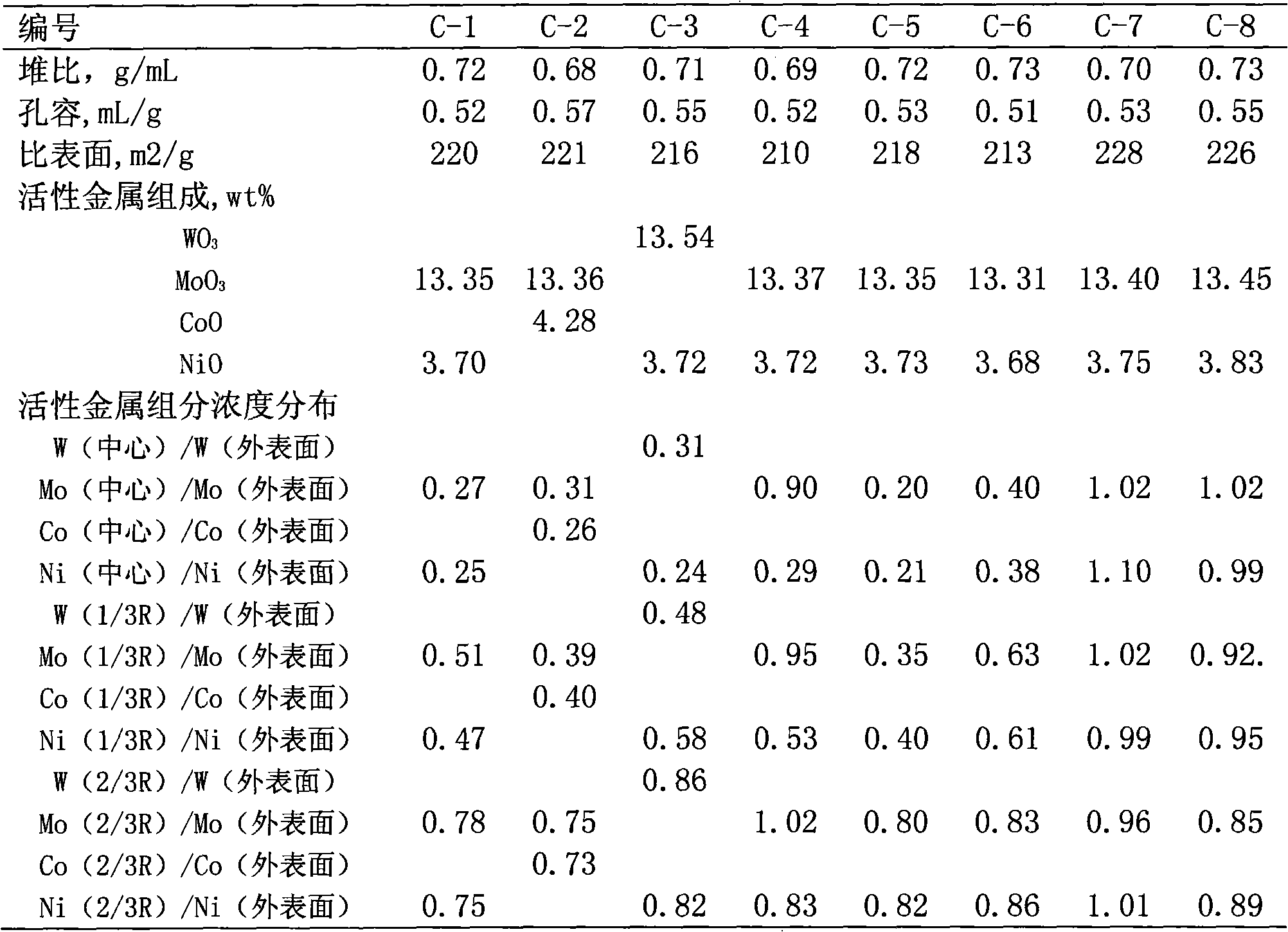
Hydrogenation catalyst showing gradient increase and distribution of concentration of active metal and acid additive and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101927176AImprove desulfurizationPromote denitrificationCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHigh concentrationResidual carbon
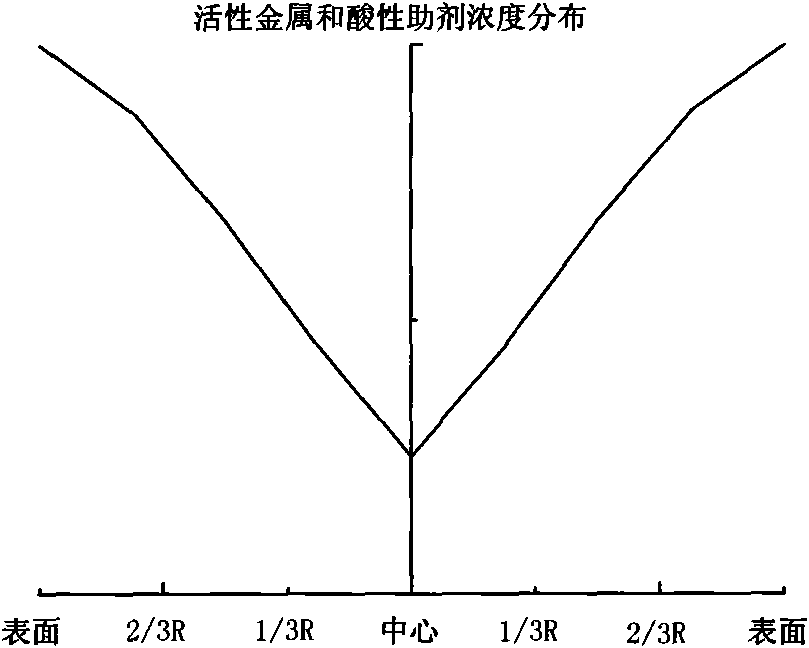
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hydrogenation catalyst showing gradient increase and distribution of concentration of an active metal and an acid additive. The method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing a relatively dilute active metallic solution and an acid additive solution and deionized water, and then gradually adding a relatively concentrated active metallic solution and an acid additive solution to dip a carrier under a saturate condition during the dipping process; or preparing an active metallic solution and an acid additive solution with different concentrations, and then dipping the active metallic impregnation liquid and the acid additive solution on the carrier in a low-to-high order based on the concentrations; or dipping the carrier with the low-concentration acid additive solution and the deionized water, and gradually adding the high-concentration acid additive solution to the impregnation liquid during the dipping process; drying and roasting; dipping the carrier with the low-concentration active metallic solution and the deionized water, and gradually adding the high-concentration active metallic solution to the impregnation liquid during the dipping process; or dipping the carrier with the active metallic solution followed by the acid additive solution. The method of the invention has higher desulfuration activity, higher denitrification activity and higher residual carbon removal activity, higher stability and simple preparation process.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
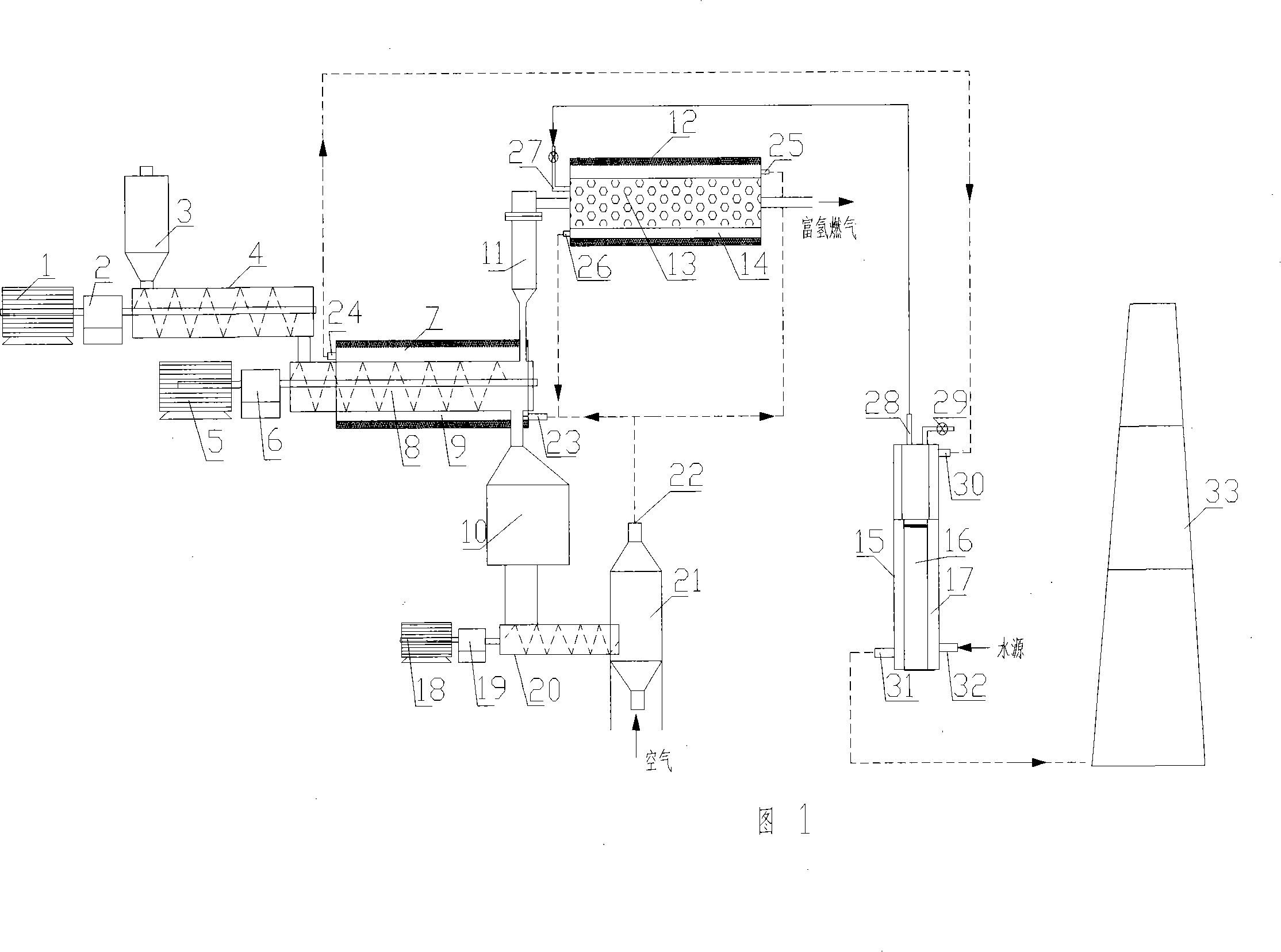
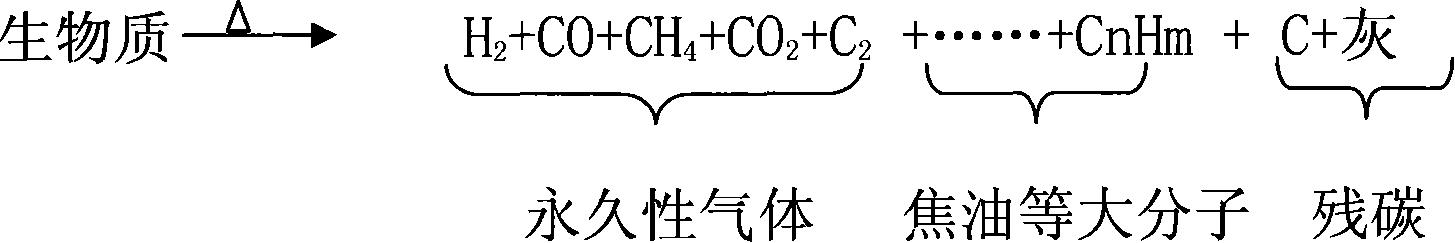
Method and device for preparing biomass hydrogen-rich combustion gas
InactiveCN101100621AReduce material requirementsReduce control requirementsHydrogenGaseous fuelsWater vaporGas phase
Production of biomass hydrogen-enriching fuel gas is carried out by thermal cracking for biomass raw materials at 550-650 deg. C under isolated air, converting it into gas-phase product and residual carbon, separating residual carbon from gas-phase product, transferring out of reacting system, burning to obtain heat energy, cracking at 800-950 deg. C and reforming into hydrogen, methane and other light hydrocarbons. It combines bitter spar catalyst and steam; it can eliminate tar, decrease methane content and increase hydrogen content. Hydrogen content reaches to 30%-55 wt%.
Owner:ENERGY RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing photocuring-formed high-density ceramic
The invention relates to the technical field of ceramic preparation, in particular to a method for preparing photocuring-formed high-density ceramic. According to the method, by optimizing the components and matching of slurry, the slurry is suitable for 3D printing preparation of a high-density ceramic special-shaped piece green body which is complex in structure, and no corresponding mold needs to be especially manufactured. Moreover, when the solid content of the slurry is lower than 40 vol%, the slurry can still be used for manufacturing the high-density ceramic green body, and the relative density of high-density ceramic which is manufactured ultimately can reach up to 99%. The green body is dried in a liquid state drying mode, and thus the method is suitable for manufacturing the high-density ceramic green body which is complex and precise in structure. The two-step degreasing method of vacuum / atmosphere protection latex flow and air latex flow is adopted in the method for conducting latex flow, and therefore the defects of deformation, cracking, blistering and the like of the green body can be reduced. The relative density of the high-density ceramic which is prepared through the method is above 90%, the Vickers hardness is above 12 GPa, and the content of residual carbon is smaller than 0.5 wt%.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Compositely circulating high temperature gasifying process for making synthetic gas with biomass
ActiveCN1931959AImprove grindabilityAvoid burnsBiofuelsSpecial form destructive distillationSyngasTar
The compositely circulating high temperature gasifying process for making synthetic gas with biomass includes the steps of low temperature charring, powdering, high temperature gasifying, separating carbon containing clinker, purifying synthetic gas, and circulating utilization of synthetic gas. Biomass material is first pyrolyzed into pyrolyzed gas and charcoal and the pyrolyzed gas is burnt incompletely in the high temperature gasifying furnace to produce gasifying agent and heat; the charcoal is powdered and fed to the reducing area in the high temperature gasifying furnace to produce reduction reaction with the gasifying agent; and the fly ash and residual carbon produced in the purification are returned to the burning area in the high temperature gasifying furnace. The present invention can produce synthetic gas with CO and H2 content up to 72 %, and has gasifying efficiency of 80-84 % and carbon converting rate over 99 %.
Owner:WUHAN KAIDI ENG TECH RES INST CO LTD
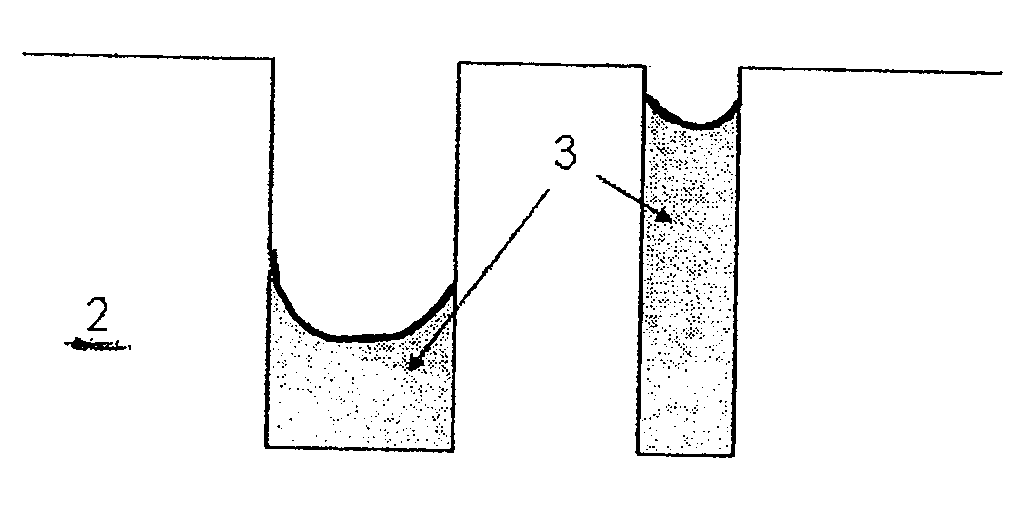
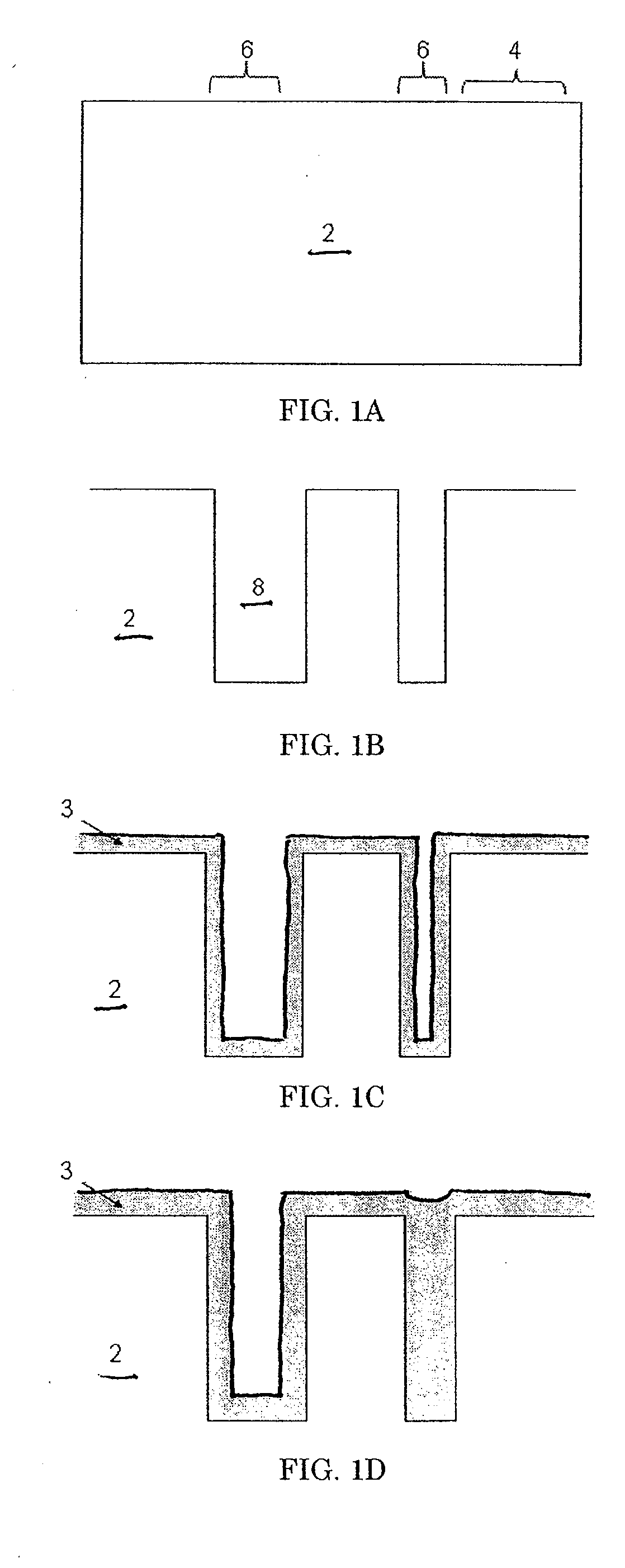
Method of eliminating residual carbon from flowable oxide fill
InactiveUS7205248B2Readily eliminating carbonReducing carbon levelSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingResidual carbonAspect ratio
Methods of forming an oxide layer such as high aspect ratio trench isolations, and treating the oxide substrate to remove carbon, structures formed by the method, and devices and systems incorporating the oxide material are provided.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
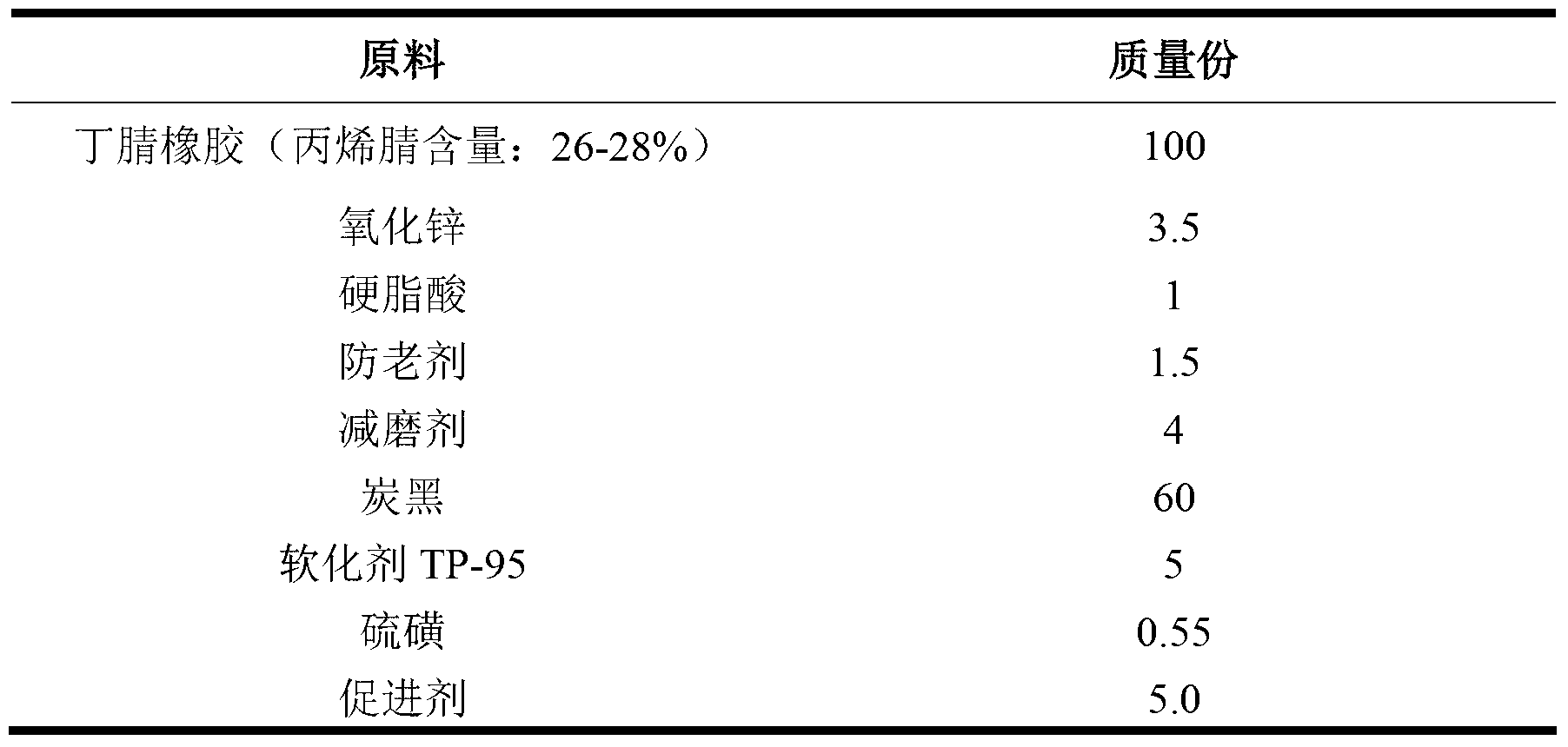
Cold-resistant wear-resistant nitrile rubber sealing material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103289150ACompatibility is reasonableImprove wear resistanceOther chemical processesPolymer scienceNitrile rubber
The invention discloses a cold-resistant wear-resistant nitrile rubber sealing material which comprises the following raw materials of: by weight, 100 parts of nitrile rubber, 3.5-8 parts of zinc oxide, 1 part of stearic acid, 1.5-3.5 parts of an antioxidant, 0.5-4.0 parts of an antifriction agent, 60-115 parts of carbon black, 2-10 parts of TP-95, 0.3-1.0 parts of a vulcanizing agent and 3.0-5.5 parts of an accelerant. A preparation method of the nitrile rubber sealing material comprises the steps of plasticating the nitrile rubber, adding the zinc oxide, the stearic acid, the antioxidant and the antifriction agent to carry out mixing, adding 1 / 2 of the carbon black to continue mixing after last mixing, then adding the residual carbon black and TP-95 to continue mixing, discharging glue stock and refining the glue stock with turning, obtaining a segment of rubber compound and placing the segment of the rubber compound, adding the rubber compound to a rubber covered roll of an open mill, adding the accelerant to carry out mixing, milling and packaging in a triangular bag, adjusting thickness and discharging material sheets. The nitrile rubber sealing material provided by the invention has better cold resistance and wear resistance.
Owner:GUANGZHOU JST SEALS TECH
Method and apparatus for combustion of residual carbon in fly ash
InactiveUS20060180060A1Lower Level RequirementsDecrease in levelSolid fuel combustionIncinerator apparatusParticulatesCombustion
Owner:CONSOL ENG
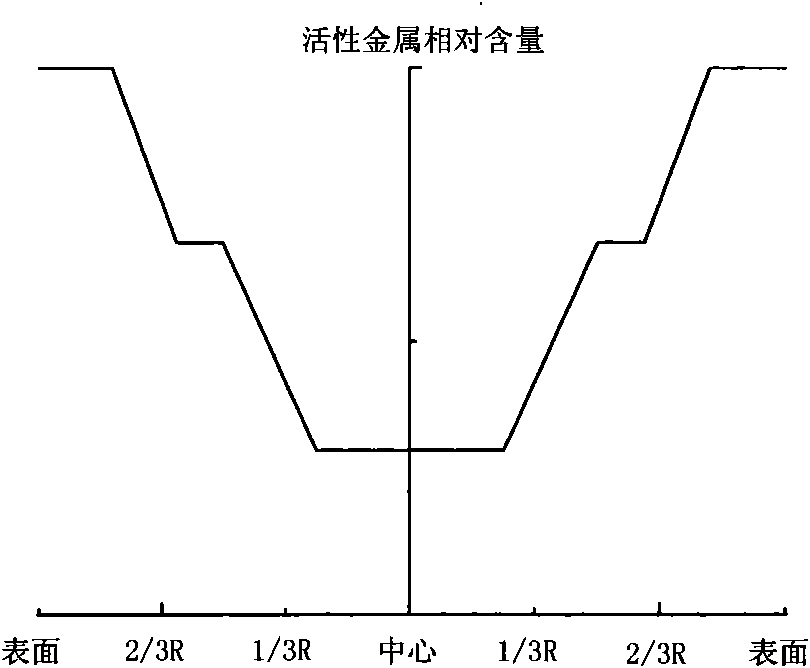
Grading composition of hydrogenation catalyst
ActiveCN101928592AGood demetallizationGood charcoal removalRefining to eliminate hetero atomsPorosityMetal catalyst
The invention relates to a grading composition of a hydrogenation catalyst. From top to bottom, a reactor is filled with hydrodemetallization and a hydrodesulfurization catalyst; raw materials flow from top to bottom, and along with the flowing direction of raw materials, the activity of the catalyst gradually increases, the pore size gradually decreases, the grain size gradually decreases and the porosity gradually decreases; the hydrodemetallization catalyst and the hydrodesulfurization catalyst are both formed by one or more demetallization catalysts; concentrations of active metal components and acid auxiliary agents are in nonuniform distribution, and from the surface to the center of catalyst grains, the concentrations of the active metal components and acid auxiliary agents of the hydrodemetallization catalyst are of gradient increase, and the concentrations of the active metal components and acid auxiliary agents of the hydrodesulfurization catalyst are of gradient decrease; and based on weight content, the demetallization catalyst accounts for 15 to 80 percent, and the desulfurization catalyst accounts for 20 to 85 percent. The grading composition of the invention is applied to hydrogenation catalysis of oil and residual oil of heavy ends and has the advantages of possessing better activity and stability of demetallization, residual carbon removal and desulfurization, controlling temperature rise of a catalyst bed and degreasing the deactivation speed of the catalyst.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
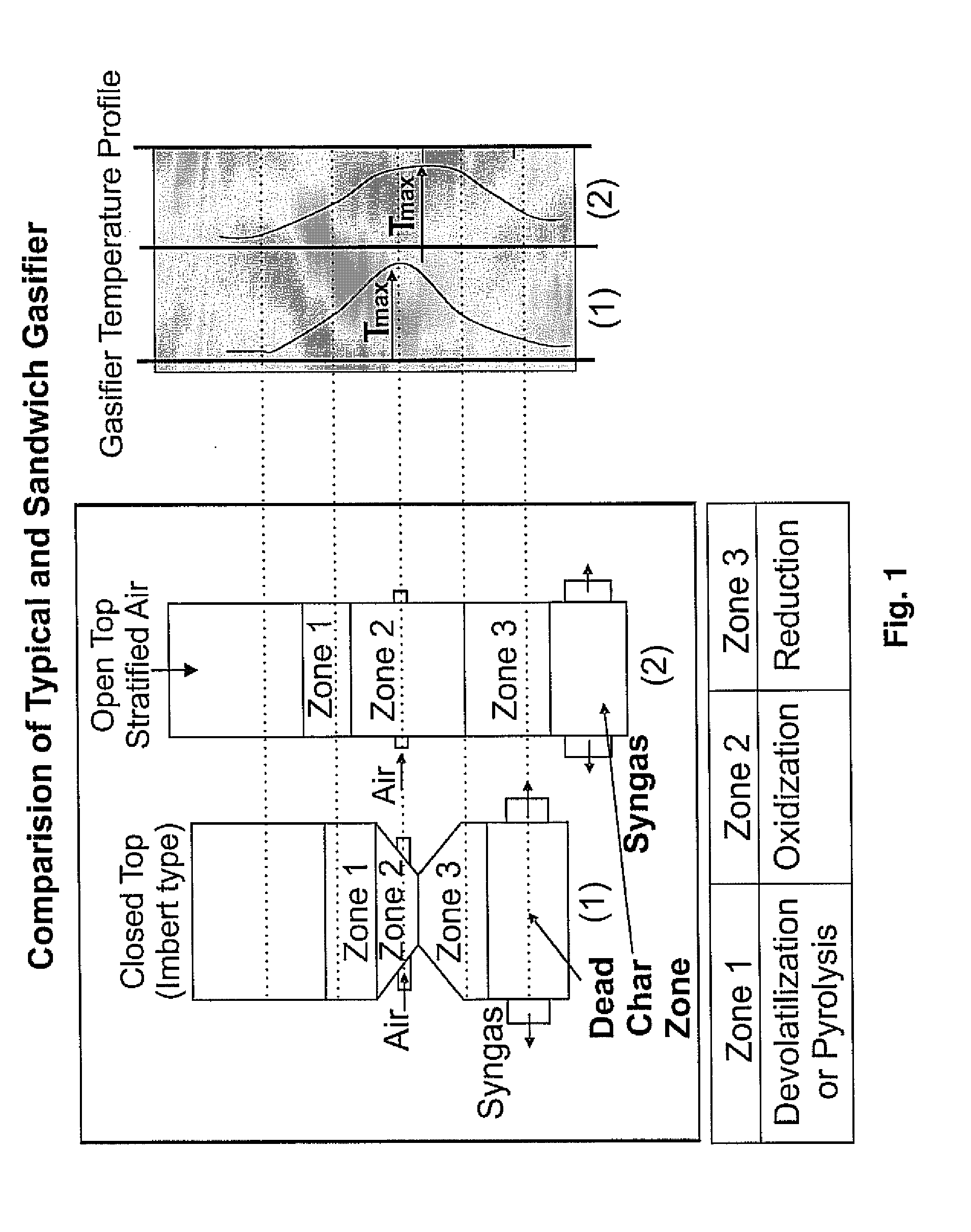
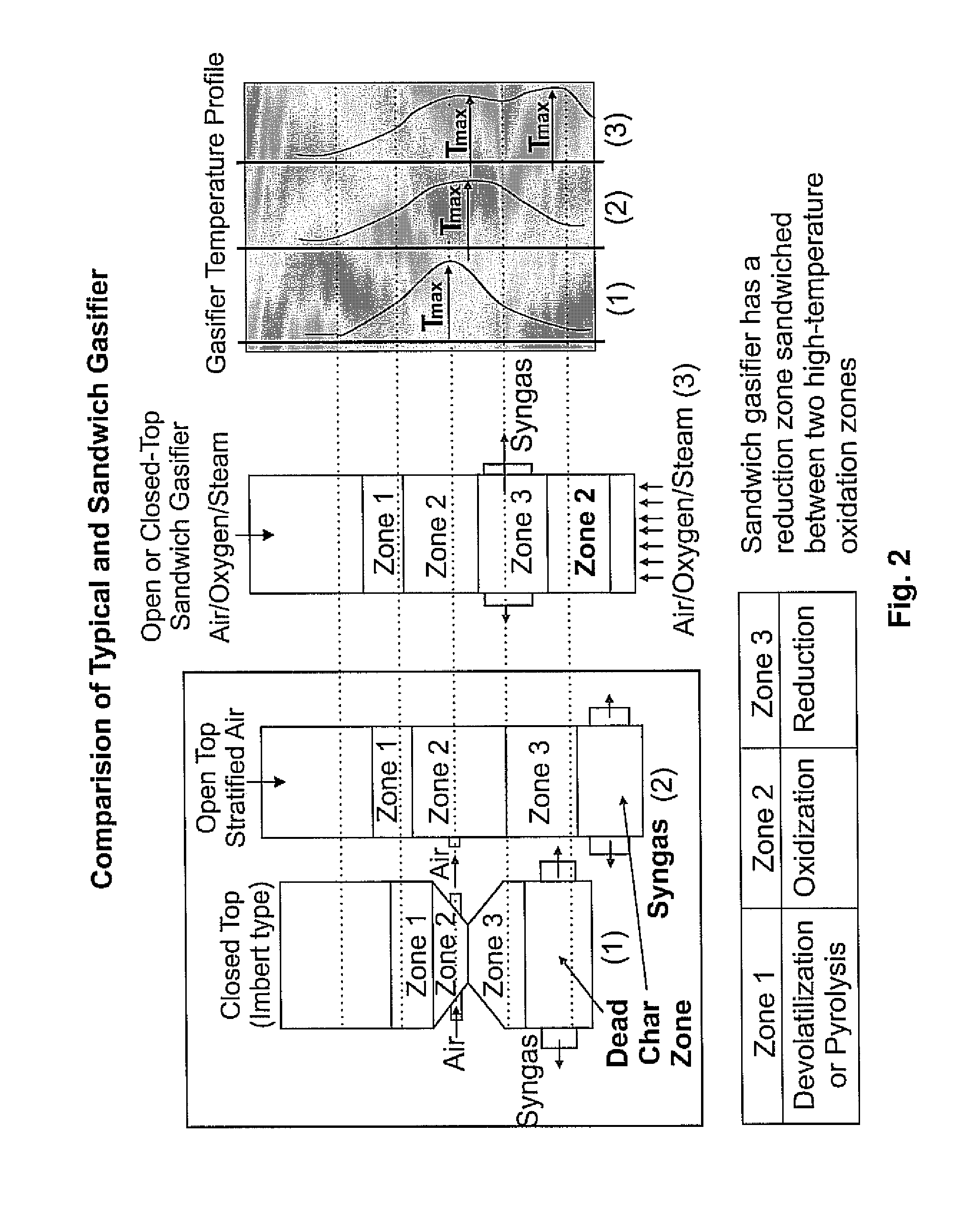
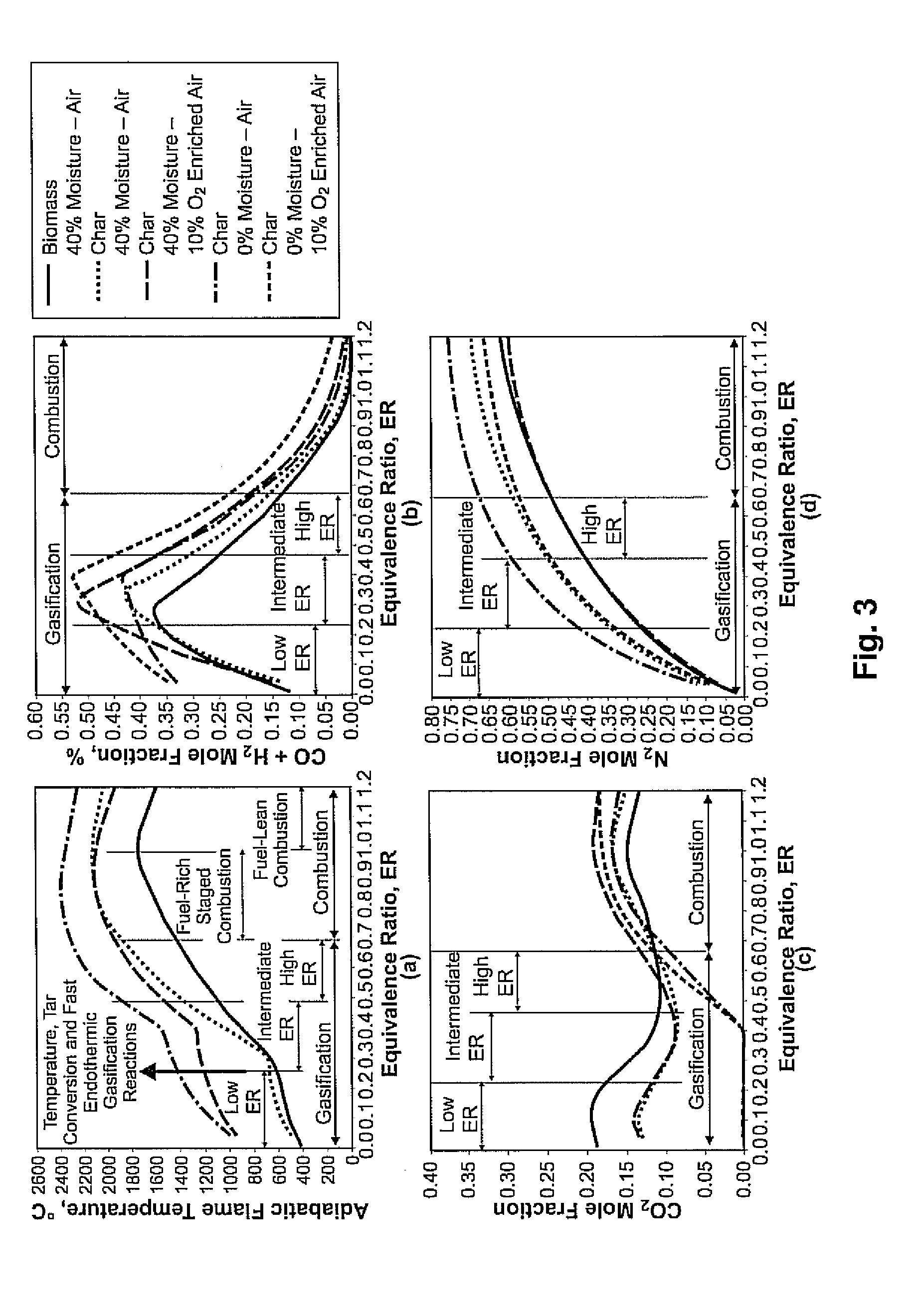
Sandwich gasification process for high-efficiency conversion of carbonaceous fuels to clean syngas with zero residual carbon discharge
ActiveUS20120036777A1Easy to controlHydrogenGasification processes detailsSyngasChemical composition
The present invention discloses a gasifier and / or a gasification process that provides a long, uniform temperature zone in the gasifier, regardless of the particle size, chemical composition, and moisture content of the fuel by sandwiching a reduction zones between two oxidation zones. The gasifier and / or gasification process has a char that is more energy-dense and almost devoid of moisture that affords for an additional (or char) oxidation zone with a temperature that is higher than a first oxidation zone which is closer to a evaporation and devolatilization zone. As such, the additional (or char) oxidation zone contributes to augmenting the reduction zone temperature, thereby providing a favorable dual impact in improving syngas composition and near-complete conversion of the tar.
Owner:SINGULARITY ENERGY TECH LLC
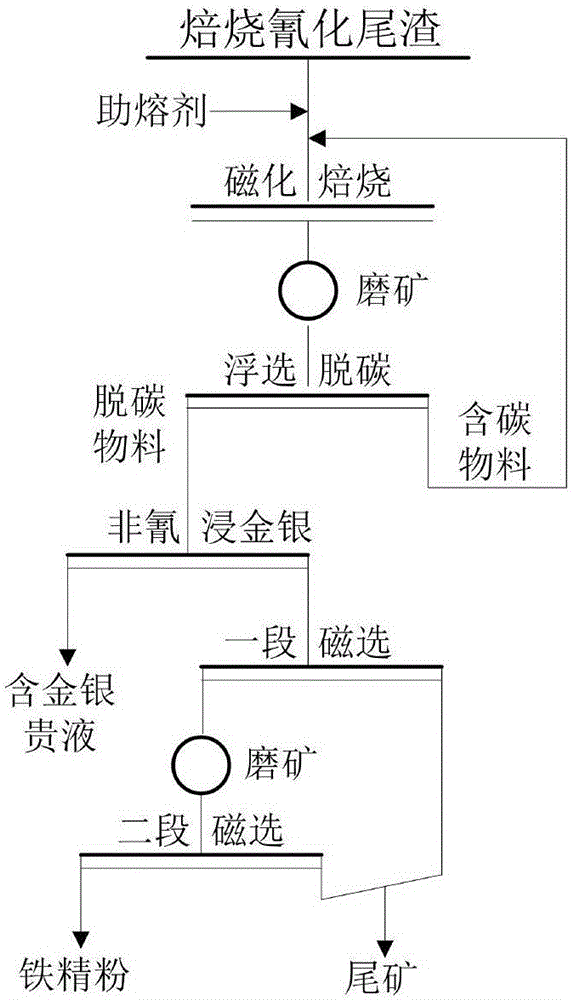
Method for recycling and synchronous harmless treatment of gold, silver and iron in roasting-cyanidation tailings
ActiveCN106498177ARealize harmless treatmentLow toxicityProcess efficiency improvementSilicate mineralsGold leaching
The invention provides a method for recycling and synchronous harmless treatment of gold, silver and iron in roasting-cyanidation tailings, and belongs to the technical field of metallurgical waste residue utilization. The method comprises the following steps: mixing dried roasting-cyanidation tailings with a fluxing agent and a reducing agent; carrying out roasting at 750 to 900 DEG C for 3 to 5 hours; conducting water quenching on hot roasted sand for cooling; carrying out ore grinding and flotation to remove residual carbon; leaching gold and silver with an environment-friendly gold leaching agent; and conducting magnetic separation on the leaching residue to obtain fine iron powder. Containing no highly toxic cyanide, the rejects belong to general industry solid waste. As the fluxing agent is added for magnetic roasting, not only can gold and silver coated with an iron mineral be exposed, but also the fluxing agent can perform a solid-phase reaction with a silicate mineral to generate a dissoluble silicate, and gold and silver coated with the dissoluble silicate can also be exposed after ore grinding. According to the method, gold, silver and iron in the roasting-cyanidation tailings are recycled, harmless treatment is realized synchronously, and the purpose of clean production is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method of manufacturing carbon nanotubes
A method of manufacturing carbon nanotubes that is capable of growing carbon nanotubes on a substrate by a CVD method without giving rise to residual carbon impurities is provided. The method of manufacturing carbon nanotubes according to the present invention is a method in which carbon nanotubes are grown on a substrate by a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process using a reaction gas containing a compound for the carbon source, wherein a compound having a carbon skeleton and a functional group which is effective for removing carbon impurities that deposit during the growth of carbon nanotubes is used as the compound for the carbon source.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for preparing olivine structure lithium iron phosphate
InactiveCN1800003ASolve easy oxidationSolve the problem of difficult to mix evenlyPhosphorus compoundsLithium iron phosphateMaterial synthesis
The invention discloses a making method of chrysolite-structured ferric lithium phosphate, which is characterized by the following: mixing the bivalent Fe source compound, P source compound and oxidant at LiFePO4 chemical gauge; controlling the pH value equal to 1-8; filtering; cleaning; drying; generating about 100 nm FePO4 pioneer body; putting the mixture of FePO4 pioneer body and Li source compound and reducer in the furnace; calcining the mixture in the non-oxidized atmosphere to make LiFePO4. The invention prevents the ferrous ion from oxygenizing and difficult blending of raw material, which improves the material synthesis and property to cover the residual carbon on the LiFePO4 particle.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Composite electromagnetic shielding material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101409999AUnrestricted contentWide range of choicesLamination ancillary operationsMagnetic/electric field screeningResidual carbonCarbon nanotube
The invention provides a composite electromagnetic shielding material, comprising a polymer and a plurality of carbon nano-tubes; wherein, a plurality of carbon nano-tubes are arranged in the polymer in the form of carbon nano-tube film. A preparation method used for preparing the composite electromagnetic shielding material comprises the steps as follows: a carbon nano-tube array is provided; atleast a carbon nano-tube film is gained by the pulling in the carbon nano-tube array by a tensile tool; a substrate is provided; at least a carbon nano-tube film is attached to the substrate, thus forming the carbon carbon-tube film structure and removing the residual carbon nano-tube film structure out of the substrate; the carbon nano-tube film structure is composed with the polymer, thus gaining the composite electromagnetic shielding material.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Hydrogenation catalyst with active metal component concentration in gradient increase and distribution and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101927169AImprove desulfurizationPromote denitrificationCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSal ammoniacHigh concentration
The invention relates to a hydrogenation catalyst with active metal component concentration in gradient increase and distribution and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing compounds of metal in VIB and / or VIII family with deionized water or ammonia to prepare a metal impregnating solution by using Al2O3 or Al2O3 containing SiO2, TiO2 and ZrO2 as a vector; preparing the hydrogenation catalyst by using a saturated impregnation method; gradually adding denser metal solution for saturated impregnation of the vector by preparing more dilute solutions of metal in VIB and / or VIII family or deionized water; or impregnating the vector first with the metal impregnating solution with low concentration and then with the metal impregnating solution with high concentration by preparing metal solutions of different concentrations; drying for 1 to 8 hours at 80 DEG C to 150 DEG C; and baking for 2 to 6 hours in an air of 300 DEG C to 650 DEG C. The catalyst has the advantages of high desulfurization, denitrification, residual carbon removing activity and stability, simple preparation and lower preparation cost and is suitable for the field of heavy oil hydrogenation.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Wet oxidation process and system
InactiveUS20050171390A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationWater treatment parameter controlAdvanced oxidation processResidual carbon
A process and system for the destruction of compounds having a carbon-hetero atom bond. The process includes wet oxidation at elevated temperature and pressure of an aqueous mixture of at least one compound having a carbon-hetero atom bond to substantially destroy the carbon-hetero atom bond of the at least one compound. The resulting oxidized material may be further treated in an advanced oxidation process to destroy any residual carbon-hetero atom bonds remaining.
Owner:SIEMENS WATER TECH HLDG CORP
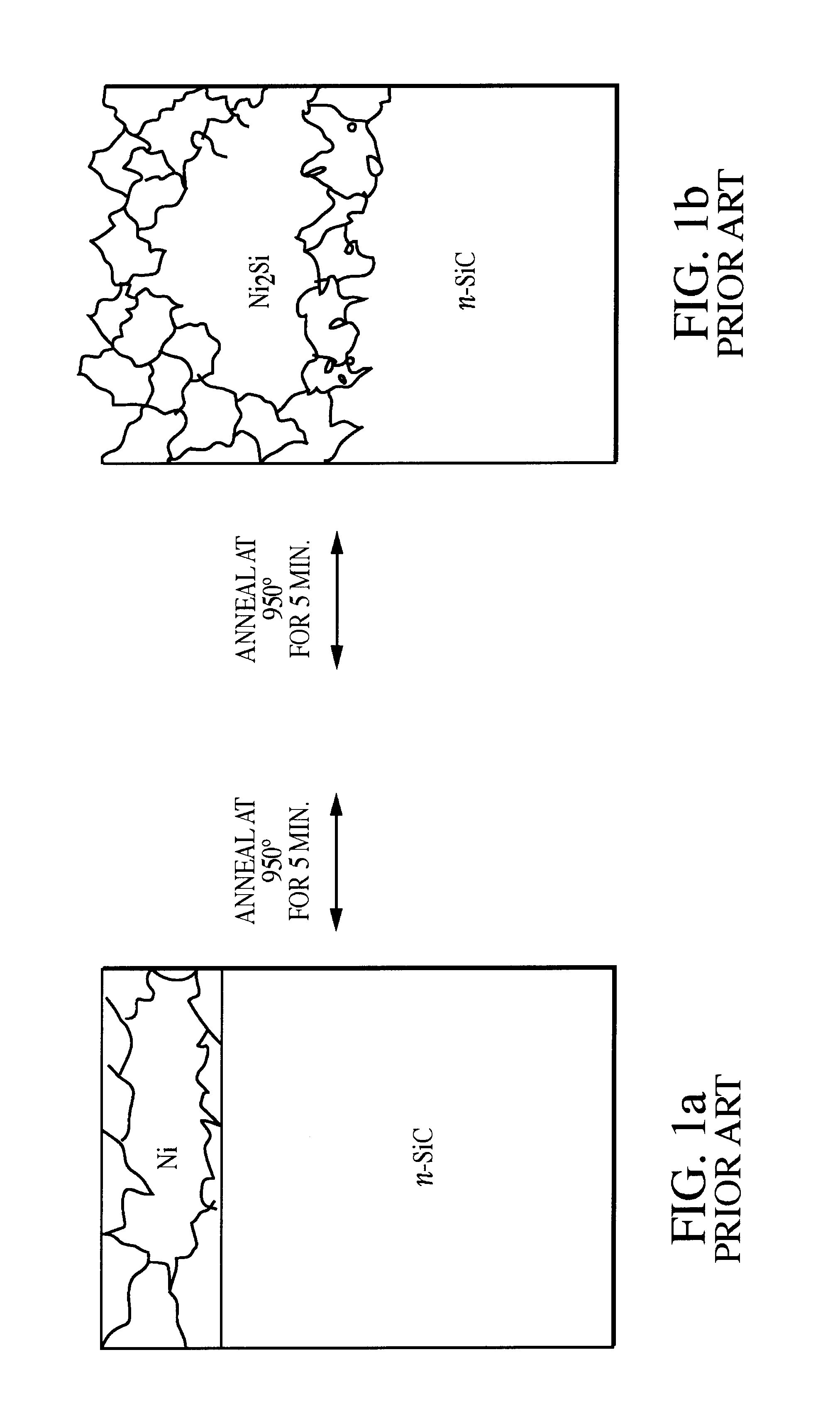
Formulation and fabrication of an improved Ni based composite Ohmic contact to n-SiC for high temperature and high power device applications
InactiveUS6759683B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetallurgyElectrical instability
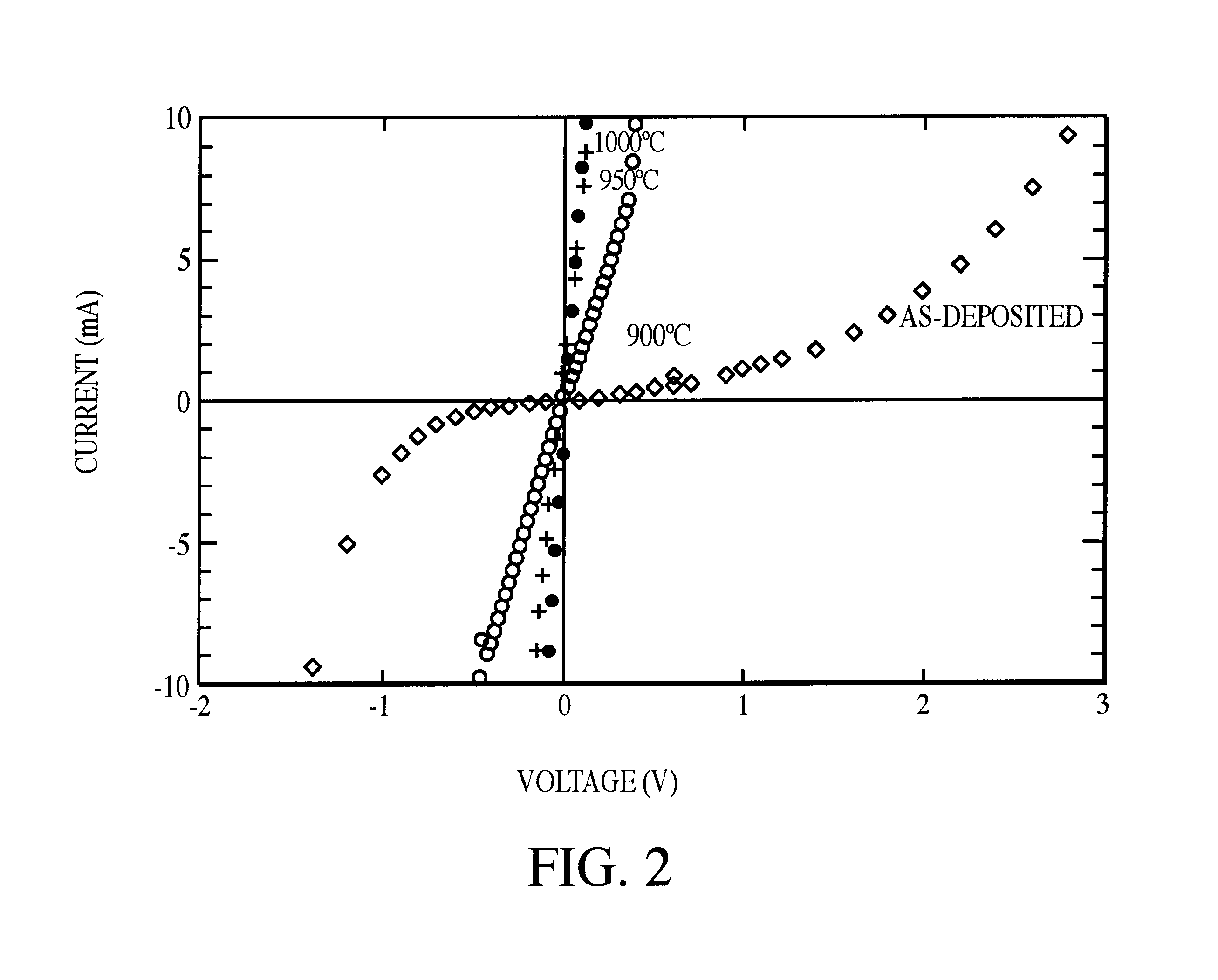
A composite Pt / Ti / WSi / Ni Ohmic contact has been fabricated by a physical deposition process which uses electron beam evaporation and dc-sputter deposition. The Ni based composite Ohmic contact on n-SiC is rapid thermally annealed (RTA) at 950° C. to 1000° C. for 30s to provide excellent current-voltage characteristics, an abrupt, void free contact-SiC interface, retention of the as-deposited contact layer width, smooth surface morphology and an absence of residual carbon within the contact layer and / or at the Ohmic contact-SiC interface. The annealed produced Ni2Si interfacial phase is responsible for the superior electrical integrity of the Ohmic contact to n-SiC. The effects of contact delamination due to stress associated with interfacial voiding has been eliminated. Wire bonding failure, non-uniform current flow and SiC polytype alteration due to extreme surface roughness have also been abolished. The Ohmic contact also avoids electrical instability associated with carbon inclusions within the contact metallization and / or at the contact-SiC interface, that occur under prolonged high temperature and power device operations. Overall, this contact is reliable for high temperature and high power operations and the stresses inclusive of use under those conditions.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Production of acetic acid with high conversion rate
InactiveUS20120078012A1Physical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidMetal catalyst
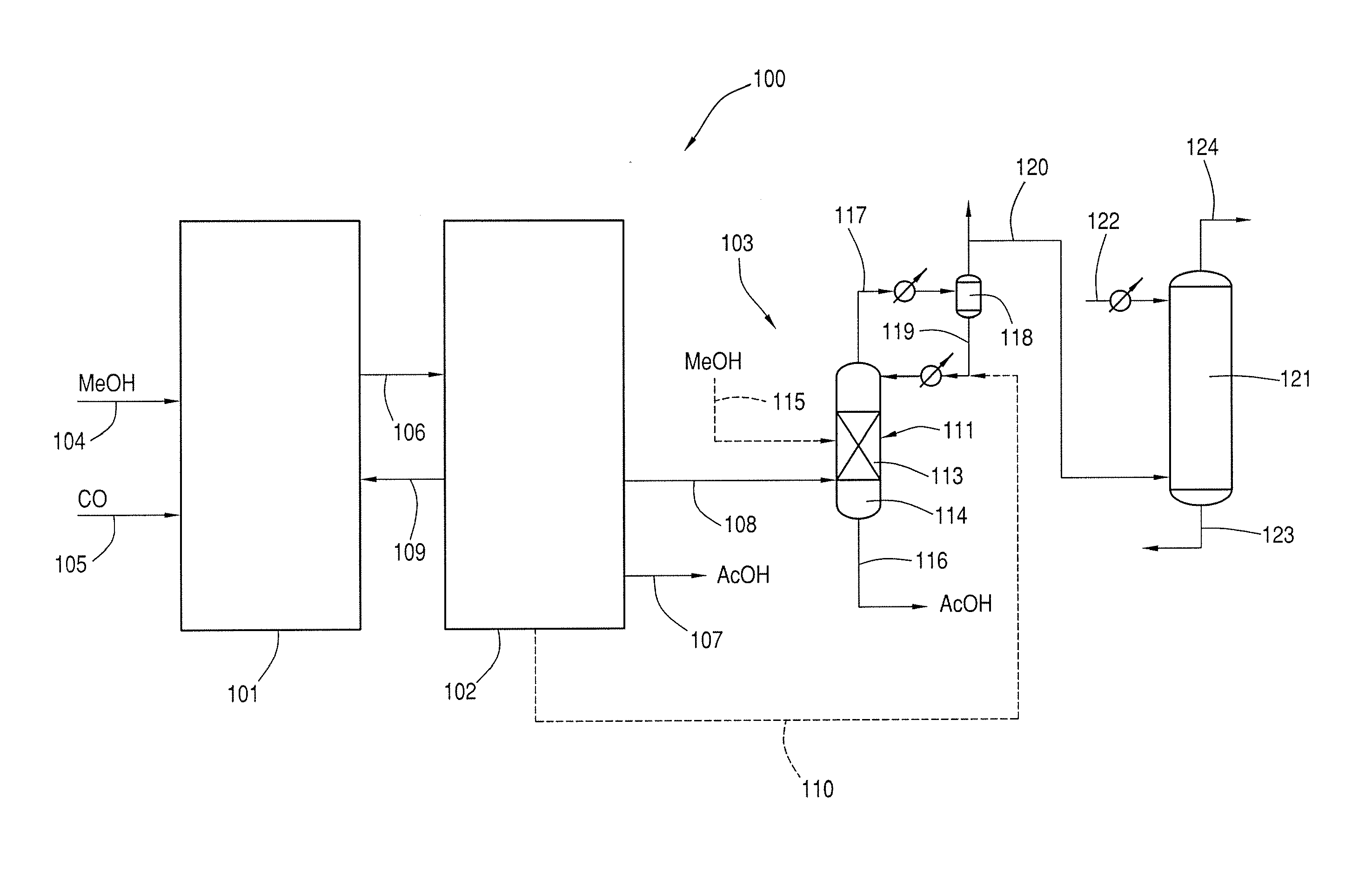
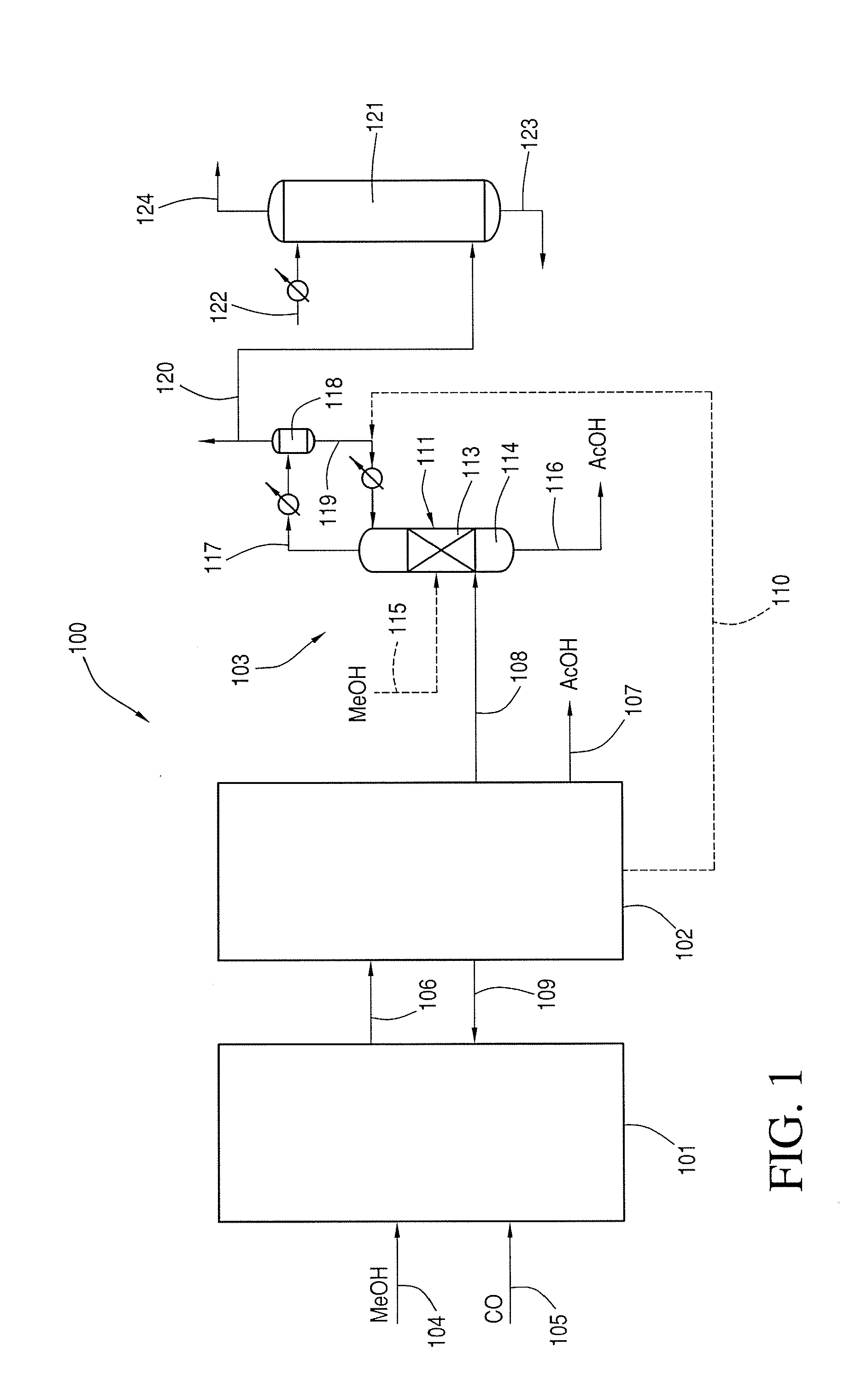
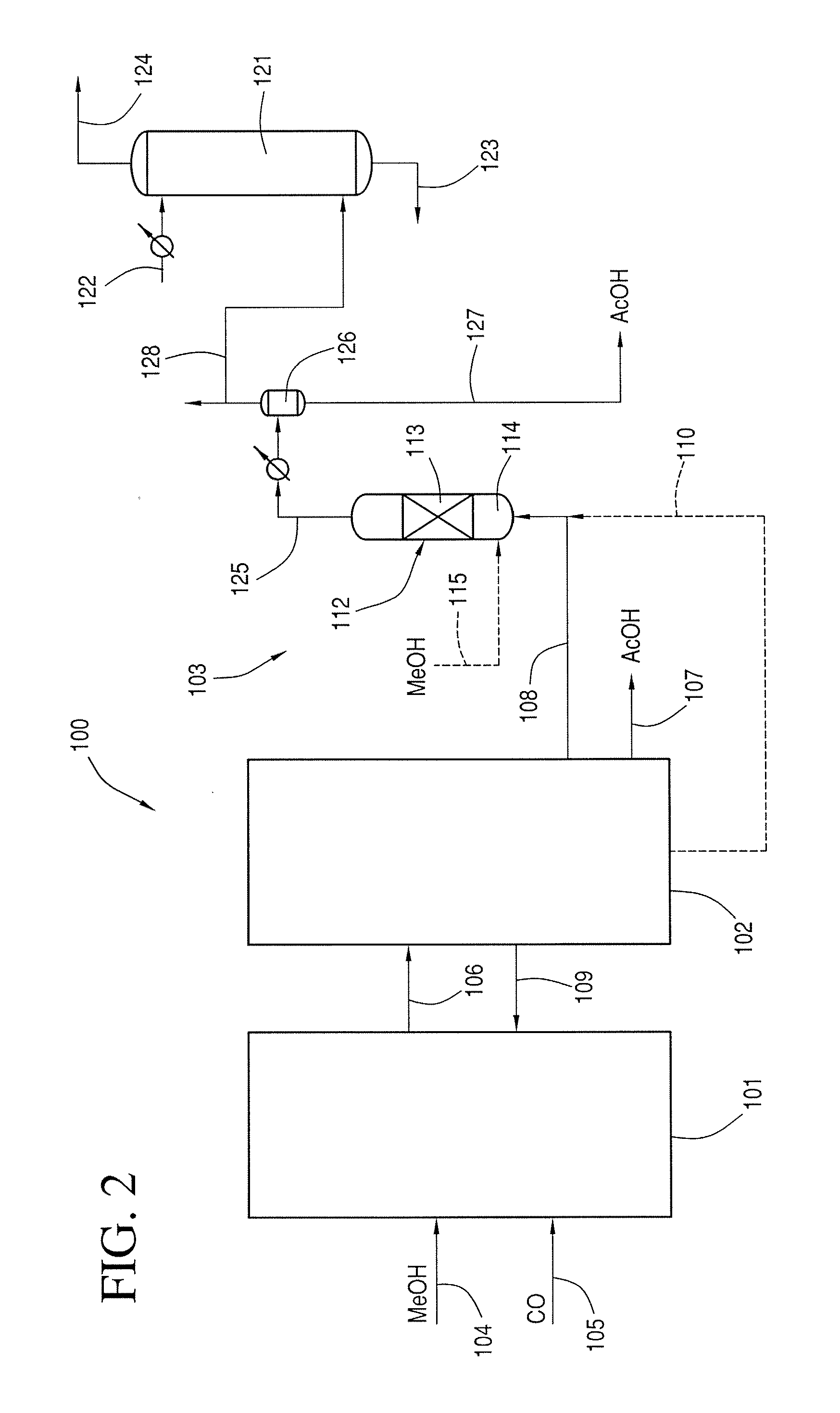
A process for producing acetic acid comprising the steps of reacting carbon monoxide and at least one of methanol and a methanol derivative in a first reactor under conditions effective to produce a crude acetic acid product; separating the crude acetic acid product into at least one derivative stream, at least one of the at least one derivative stream comprising residual carbon monoxide; and reacting at least a portion of the residual carbon monoxide with at least one of methanol and a methanol derivative over a metal catalyst in a second reactor to produce additional acetic acid.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
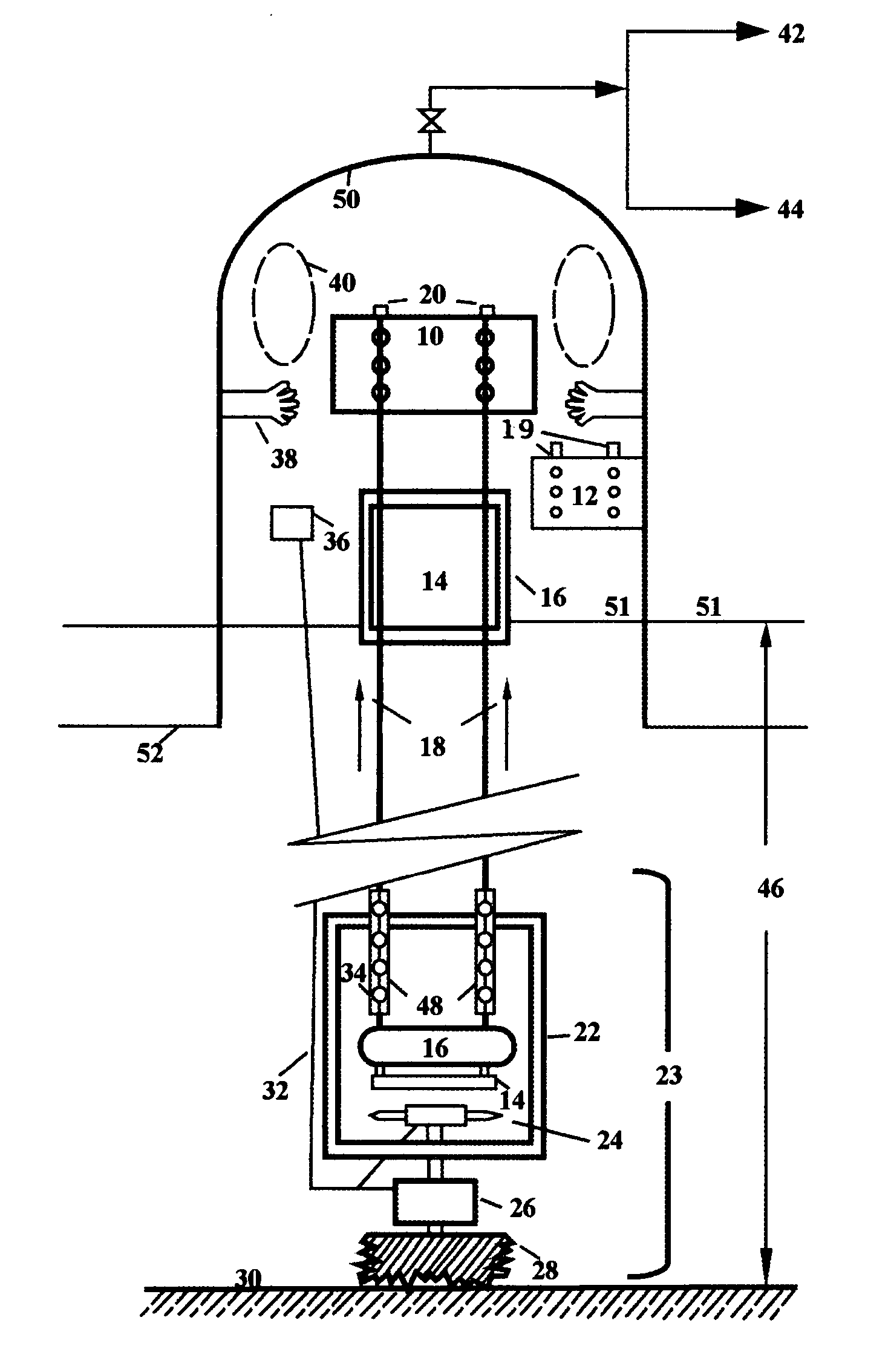
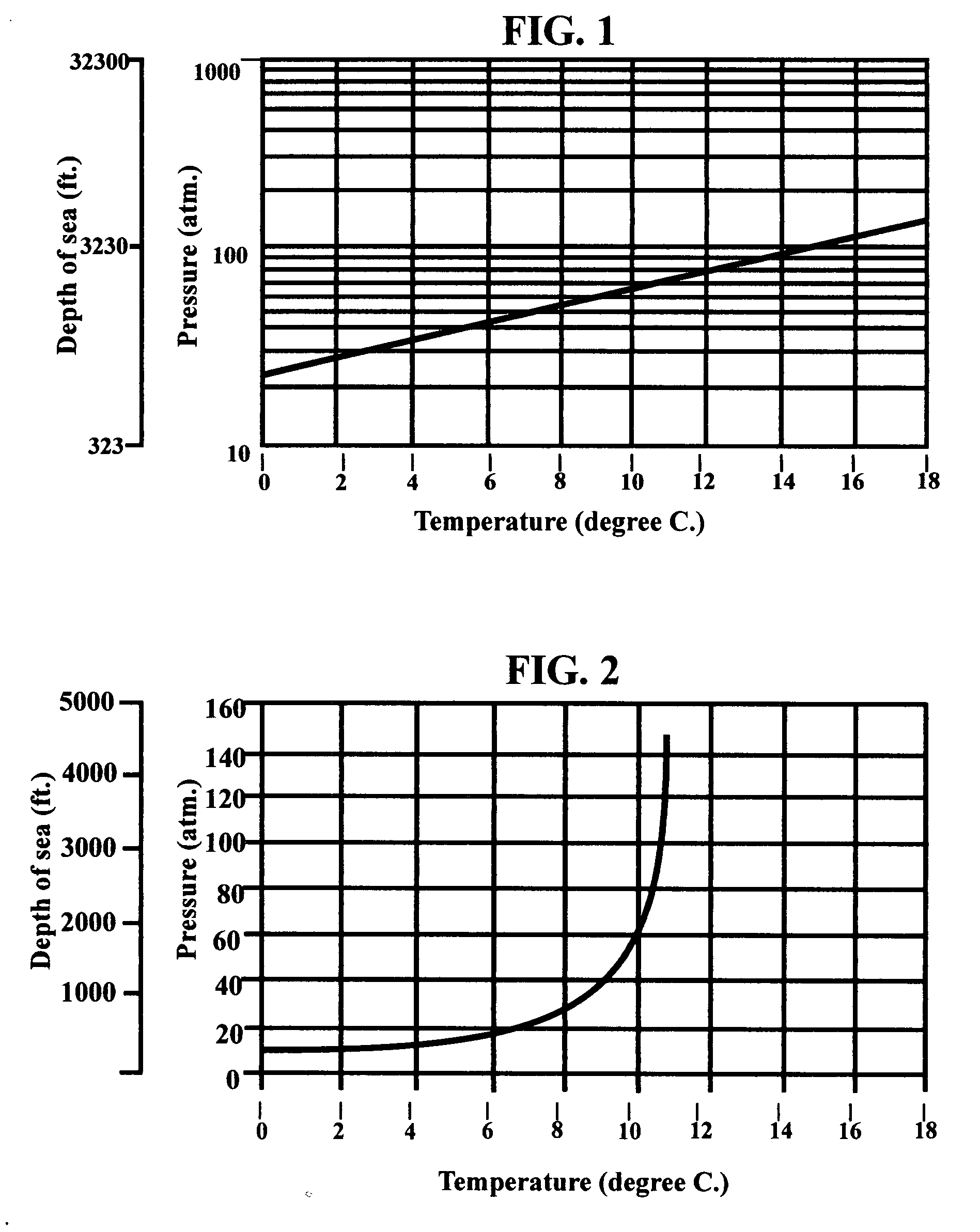
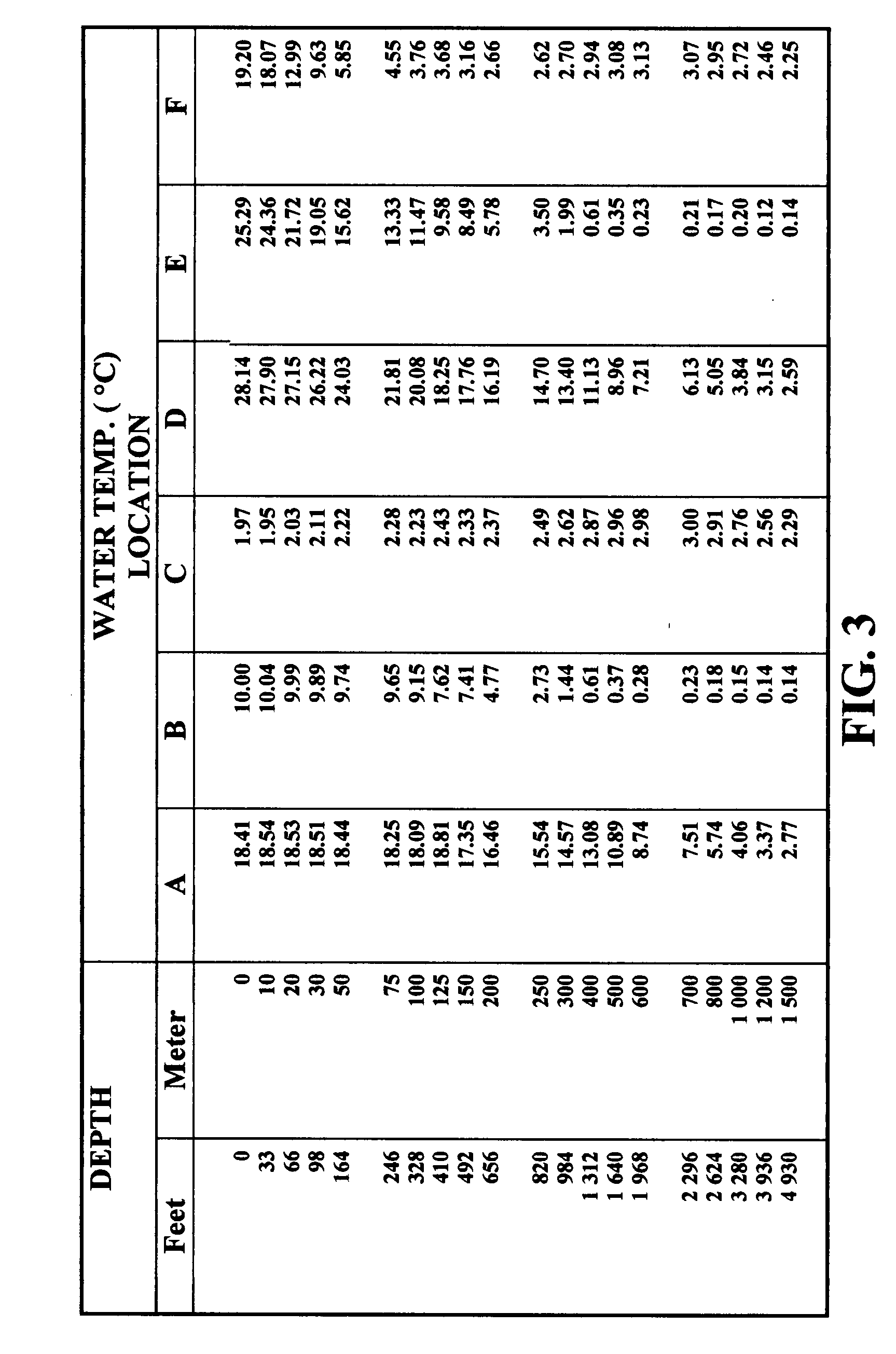
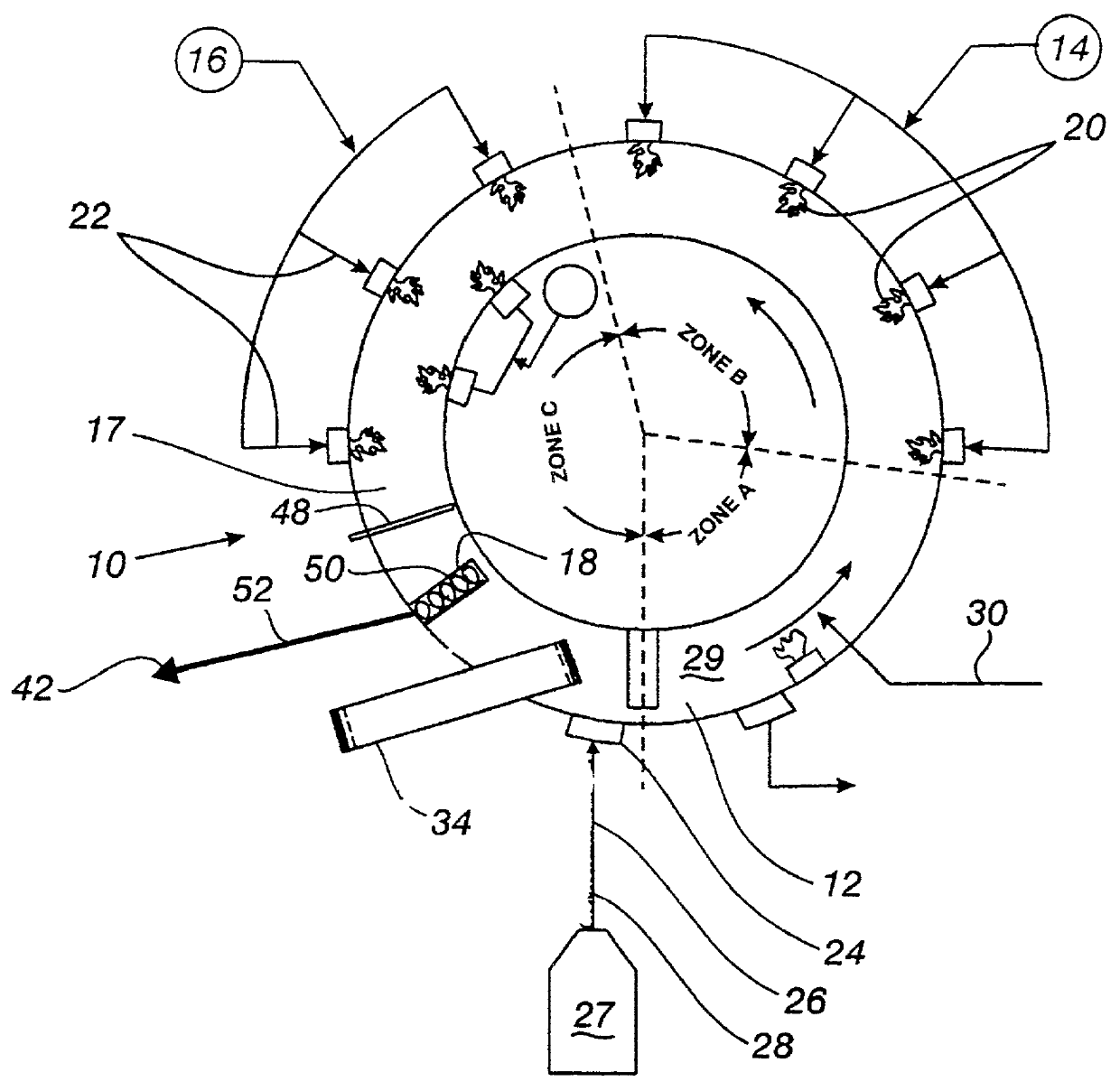
Mining methane, sequestering carbon dioxide and farming in oceans
The present invention is a multiple purposed system of producing methane from its hydrates and sequestering carbon dioxide into its hydrates. Methane hydrates mixed with mud, prepared with methane mining assembly 23 are brought to sea surface by a series of buckets 16 attaching to rotating chains 18. The decomposed methane is collected into the methane dome 50 and is processed into liquefied natural gas or synthetic liquid fuels. Liquid carbon dioxide is brought down through a tube 70 and a sequestering device 86 into the sea where the pressure and the temperature are adequate for carbon dioxide hydrates to form and settle down to the sea bottom. The unconverted gaseous carbon dioxide is collected into carbon dioxide dome 49 and is liquefied again for recycling. A specially designed marine plantation, comprising of plurality of planting units 352 and a fleet of seeding and harvesting boats, is employed to remove the residual carbon dioxide from the sequestering, to alleviate the global warming, to serves as an abundant source of renewable energy, and as a huge sink for carbon. In addition, it could provide a profusion of less-polluted seafood. The operations of mining methane, sequestering carbon dioxide and marine plantation are fully integrated and optimized
Owner:CHENG SHANG I
Iron production method of operation in a rotary hearth furnace and improved furnace apparatus
The present invention is an apparatus and method for the direct reduction of iron oxide utilizing a rotary hearth furnace to form a high purity carbon-containing iron metal button. The hearth layer may be a refractory or a vitreous hearth layer of iron oxide, carbon, and silica compounds. Additionally, coating materials may be introduced onto the refractory or vitreous hearth layer before iron oxide ore and carbon materials are added, with the coating materials preventing attack of the molten iron on the hearth layer. The coating materials may include compounds of carbon, iron oxide, silicon oxide, magnesium oxide, and / or aluminum oxide. The coating materials may be placed as a solid or a slurry on the hearth layer and heated, which provides a protective layer onto which the iron oxide ores and carbon materials are placed. The iron oxide is reduced and forms molten globules of high purity iron and residual carbon, which remain separate from the hearth layer. An improved apparatus includes a cooling plate that is placed in close proximity with the refractory or vitreous hearth layer, cooling the molten globules to form iron metal buttons that are removed from the hearth layer. The improvements due to the present apparatus and method of operation provide high purity iron and carbon solid buttons, which are separate from slag particulates, and discharged without significant loss of iron product to the interior surfaces of the furnace.
Owner:MIDREX INT B V ROTTERDAM
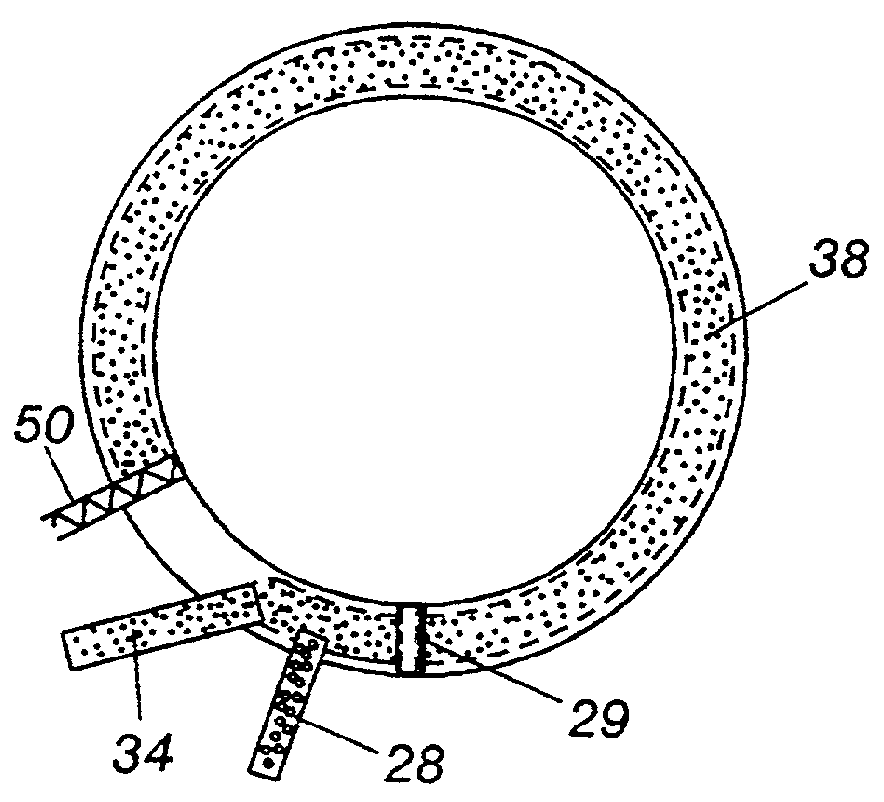
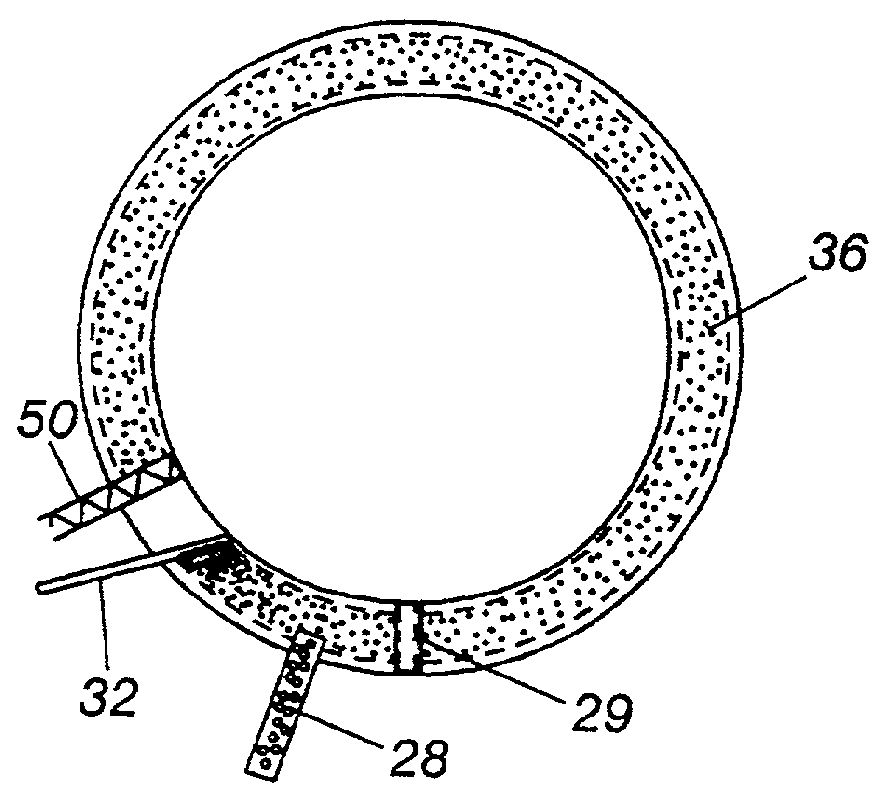
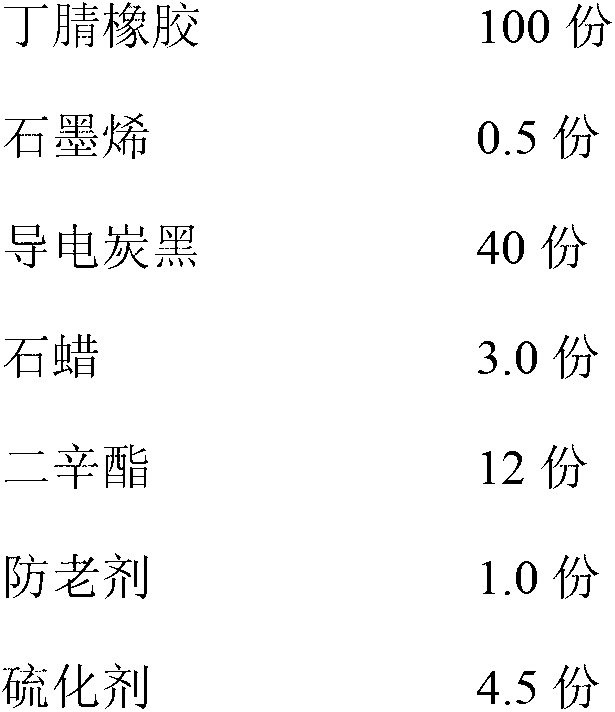
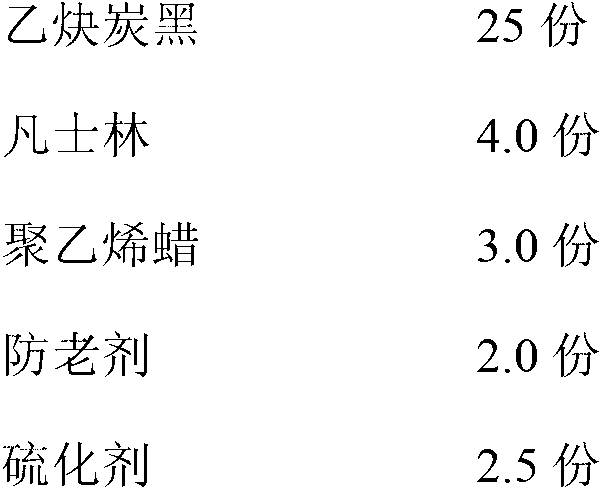
Strippable semiconductive shielding rubber for rubber insulation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103122085AHighly cleanAvoid performance biasPower cables with screens/conductive layersPlasticizerResidual carbon
The invention relates to a strippable semiconductive shielding rubber for rubber insulation and a preparation method thereof. The strippable semiconductive shielding rubber comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of nitrile-butadiene rubber, 0.5-8 parts of graphene, 10-40 parts of conductive carbon black, 7-15 parts of plasticizer, 1-2 parts of anti-aging agent and 2.5-4.5 parts of vulcanizing agent, wherein the nitrile-butadiene rubber is a solar one; the minimum surface-diameter ratio of the graphene is 1000; the plasticizer is one or a mixture of paraffin, dioctyl ester, stearic acid and the like; and the vulcanizing agent is a peroxide vulcanizing system. The preparation method comprises the following steps: plasticating the nitrile-butadiene rubber twice (10 minutes for each time), and standing at normal temperature for 12 hours; adding the graphene into the plasticated nitrile-butadiene rubber, evenly mixing, and adding 1 / 2 of the conductive carbon black or acetylene carbon black; 3 minutes later, adding the residual carbon black and the plasticizer, and compounding for 2 minutes; sequentially adding various assistants, finally adding the vulcanizing agent, compounding for 1 minute, and then discharging, wherein the compounding temperature is not higher than 120 DEG C; and after discharging, tabletting semiconductive shielding gum on a tabletting machine to prepare the semiconductive shielding rubber. The semiconductive shielding rubber provided by the invention is easy to process and strip and high in conductivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI LEVSON ENTERPRISE GRP
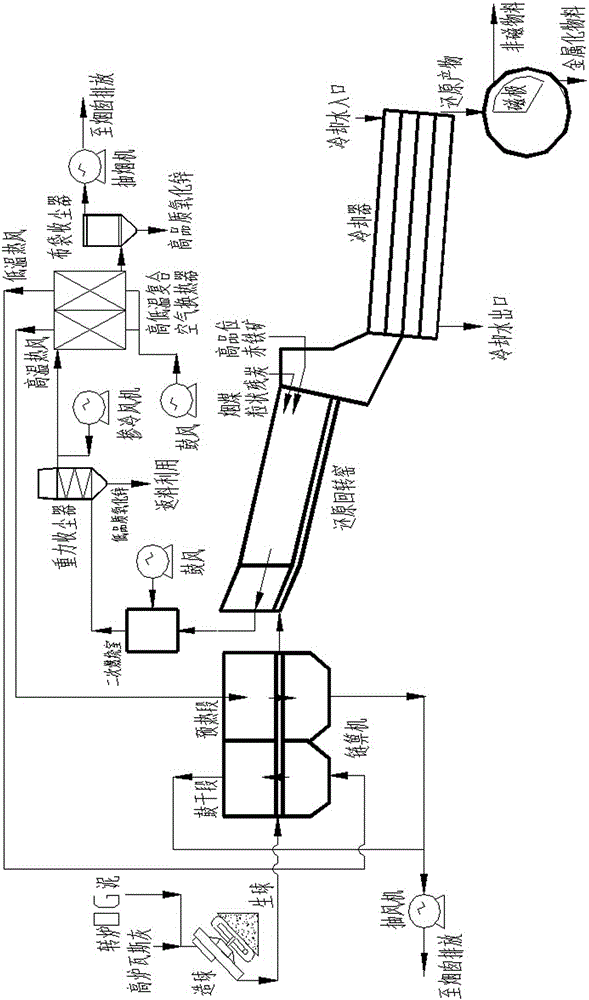
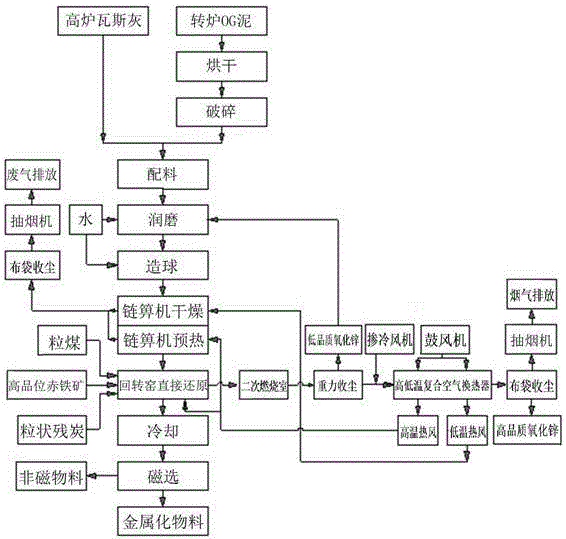
Method for treating high-zinc iron-containing slime through utilizing rotary kiln
ActiveCN106367600AEfficient use ofReduce loadRotary drum furnacesProcess efficiency improvementLarge particleMagnetic separation
The invention relates to a method for treating high-zinc iron-containing slime through utilizing a rotary kiln. The method comprises the steps that blast furnace gas ash and converter OG mud are mixed and pelletized; wet pellets are dried and preheated, and a drying and preheating heat source is hot air generated by high-temperature flue gas of the rotary kiln after passing through a high-low temperature composite air heat exchanger; a pea coal spray gun, a carbon residue spray gun and an ore grain spray gun are arranged at a kiln head of the rotary kiln, and high-volatile matter coal, residual carbon and high-grade iron ore are sprayed into the kiln; the dried pellets are fed into the rotary kiln, and high-temperature metallized pellets are obtained after the dried pellets are subjected to direct reduction and high-temperature solidification in the rotary kiln; after being cooled to the normal temperature, materials like the metallized pellets and excess carbon residue are subjected to magnetic separation, and metallized pellets are obtained; and large-particle dust is removed from the high-temperature flue gas of the rotary kiln, the high-temperature flue gas enters the high-low temperature composite air heat exchanger to be cooled, the cooled flue gas enters a bag-type dust collector, and zinc oxide powder is recycled. According to the method, the high-zinc iron-containing slime generated by iron and steel enterprises is efficiently utilized, and environmental pollution caused by stacking of the high-zinc iron-containing slime is solved.
Owner:GANSU JIU STEEL GRP HONGXING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
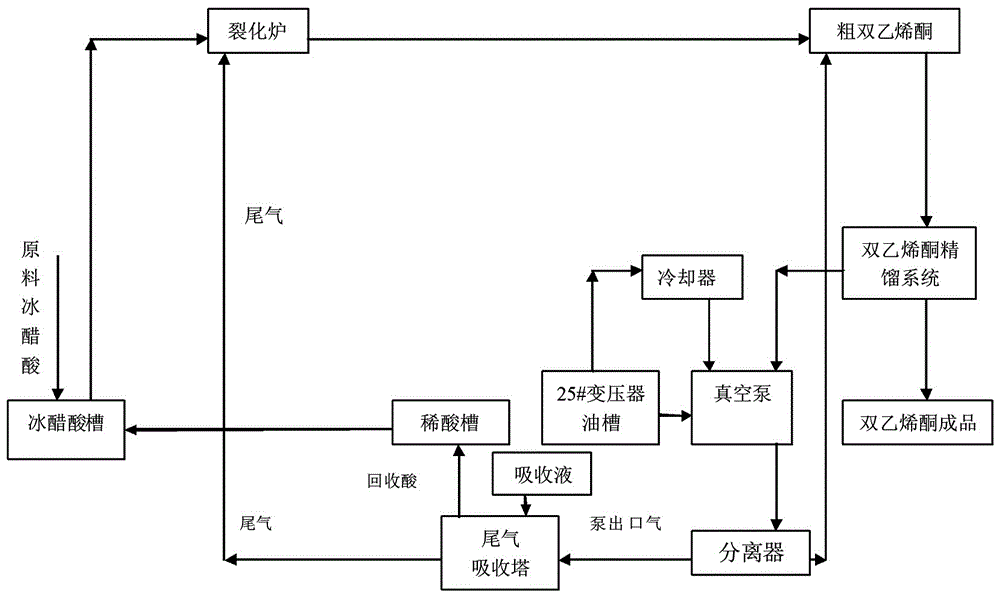
Cooling method for rectification vacuum pump in ketene dimer production
InactiveCN106349191AReduce pollutionEmission reductionOrganic chemistryPositive displacement pump componentsNitrogen gasVacuum pump
The invention relates to a cooling method for rectification vacuum pump in ketene dimer production, wherein the method comprises the steps of: placing 25#transformer oil in an oil groove with cooling pipe, when the rectification vacuum pump is operating, pumping the 25#transformer from the oil cooler to the pump for cooling and sealing, combining the ketene dimer taken back from the bottom connected by the rectification vacuum pump to coarse ketene dimer section. The outlet gas of the rectification vacuum pump is pumped in tail gas absorber to spray and absorb ketene dimer. When acid content of circulating recycling liquid reaches 35-50%, the liquid is sent to glacial acetic acid for recycling, and residual carbon dioxide and nitrogen are pumped in the cracking still as fuel. The cooling method of rectification vacuum pump in ketene dimer production utilizes oil to replace water as cooling and sealing of vacuum pump, and uses soft water to absorb gases such as ketene dimer in the vacuum pump, which not only saves a great deal of water reduces emission, but also takes back ketene dimer to save resources and reduce environmental pollution.
Owner:ANHUI JINGHE IND
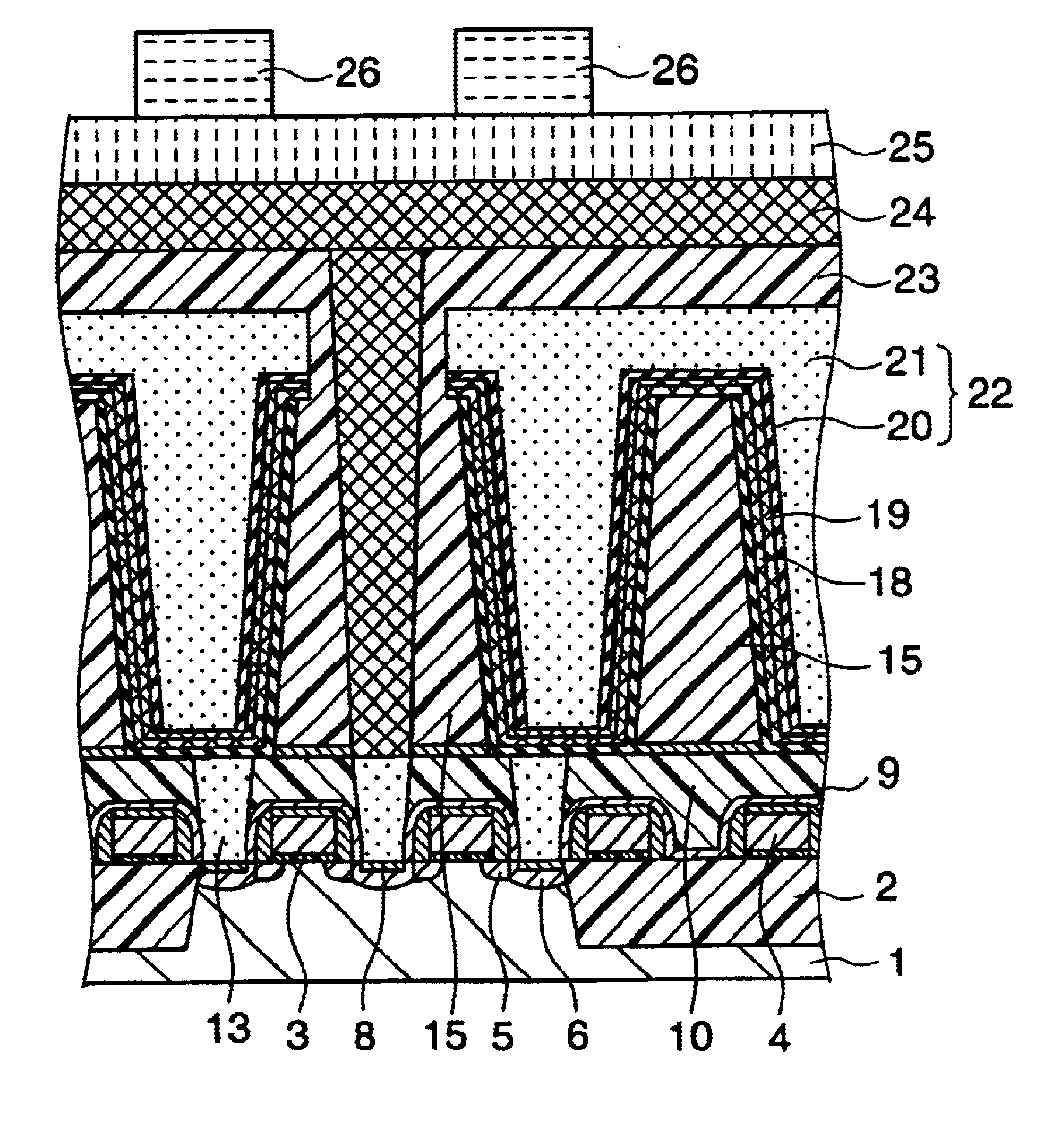
Method for forming capacitor
InactiveUS6875667B2Capacitance value can be largeEnsuring stability of manufactureTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricSilicon oxide
A capacitor is provided that is optimal for use in DRAM and has high dielectric constant, and allows leakage current flowing therethrough to be maintained at a low level, and further, permits dependence of the leakage current on temperatures to be small. That is, capacitor openings are formed in an inter layer silicon oxide layer and a TiN film is patterned so that TiN films are left only within the openings to form lower electrodes within the openings. Subsequently, a Zr- and / or Hf-containing oxide film (represented by the formula, multicomponent Zr.sub.x.Hf.sub.1-x.O.sub.2 film (0≦x≦1)) formed from a metal-containing organic compound as a reactant and a Ti-containing oxide film are laminated to form capacitor dielectrics. After deposition of the Zr- and / or Hf-containing oxide film, the Zr- and / or Hf-containing oxide film is subjected to heat treatment to be performed in an oxidizing ambient to remove residual carbon being retained in the Zr- and / or Hf-containing oxide film, leading to formation of a capacitor that is optimal for use in DRAM and has high dielectric constant, and allows leakage current flowing therethrough to be maintained at a low level.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
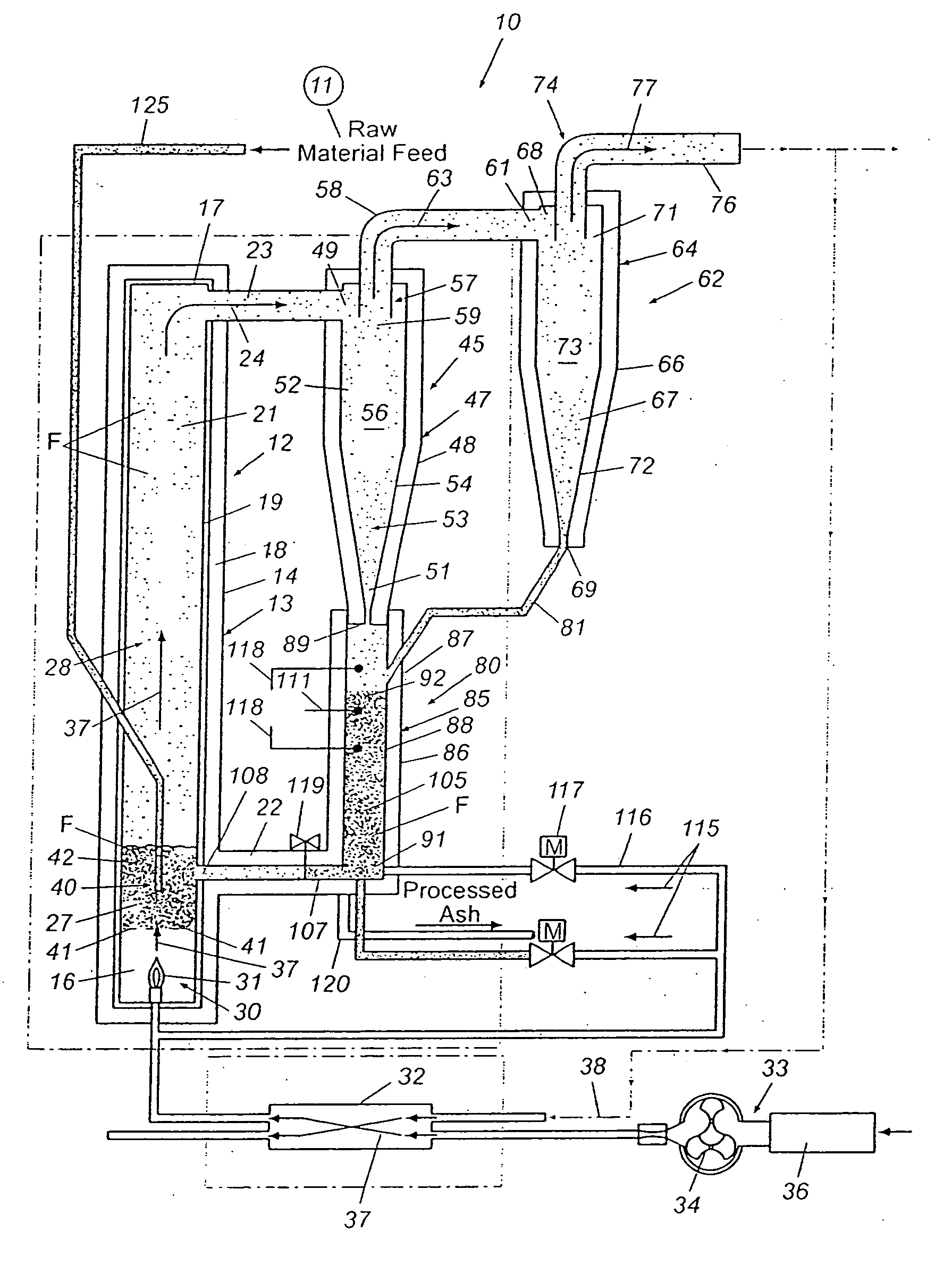
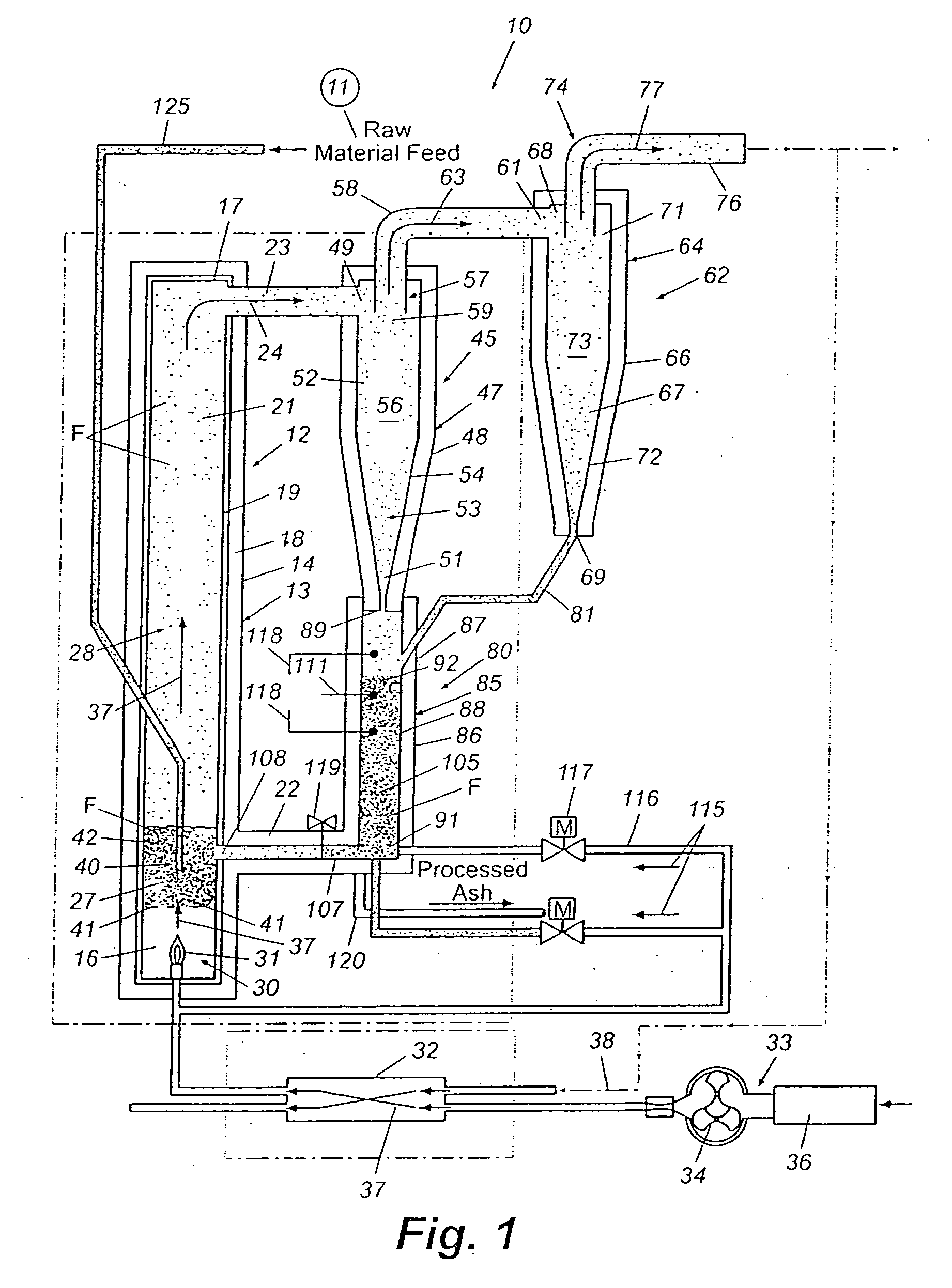
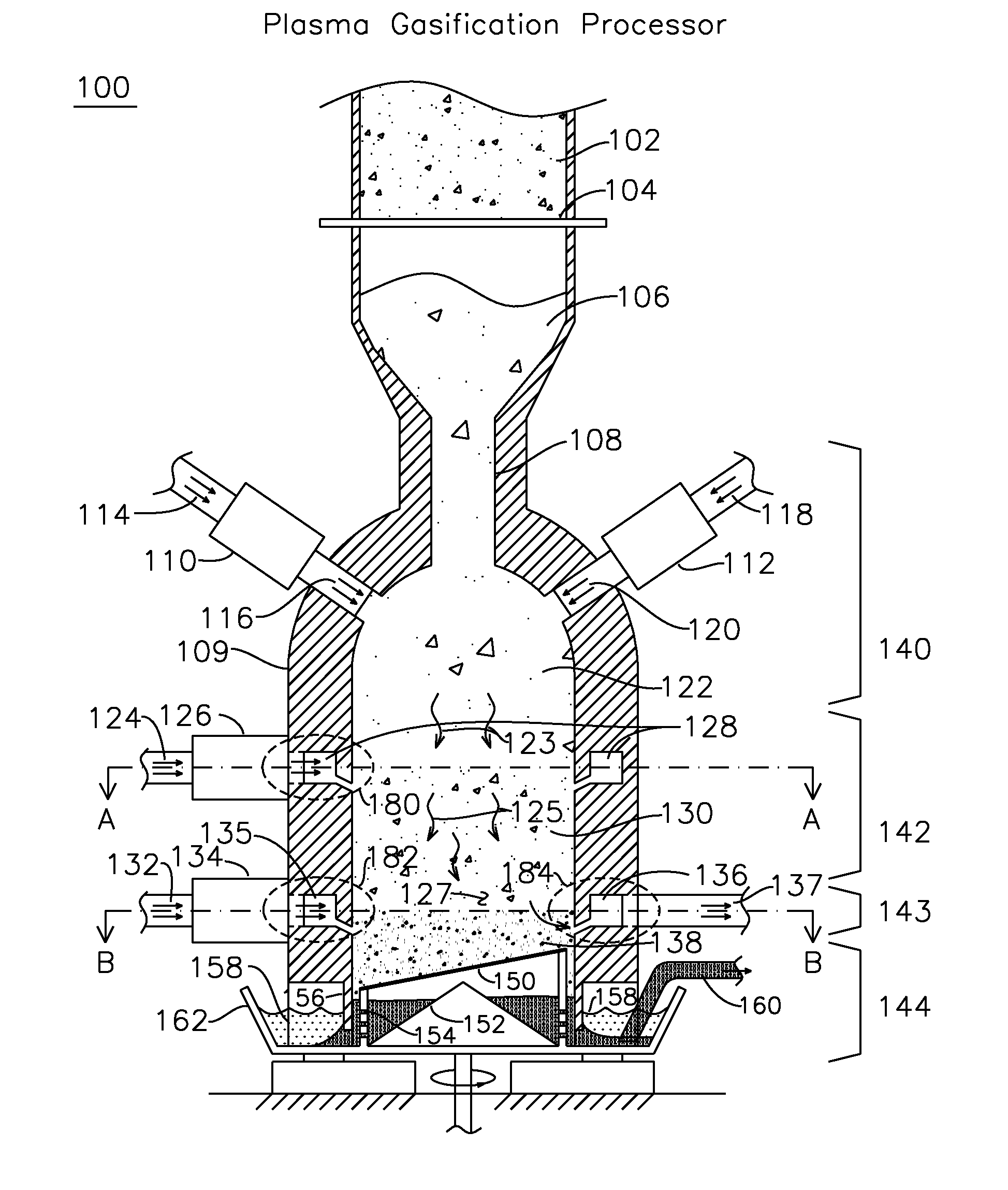
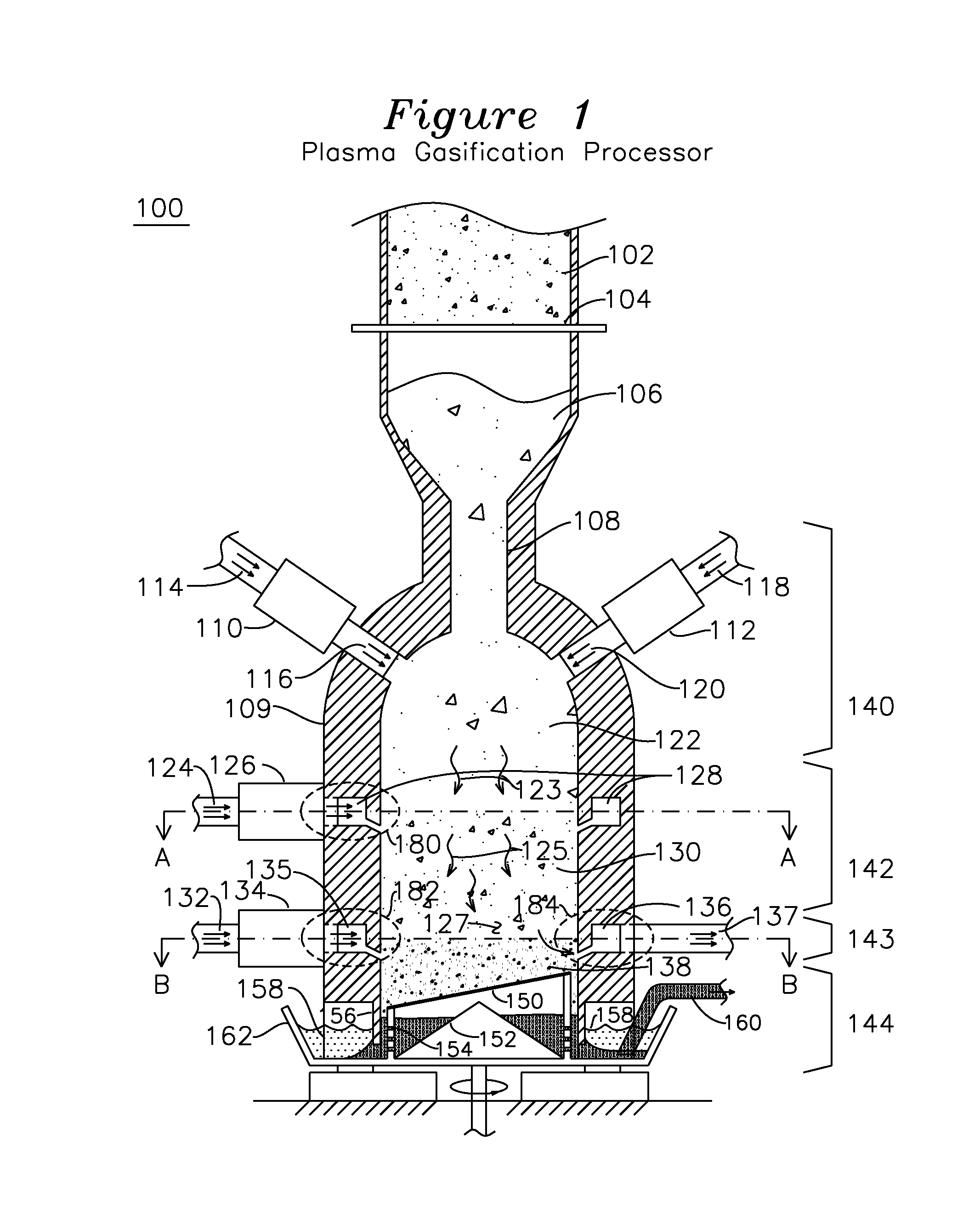
Multi-ring Plasma Pyrolysis Chamber
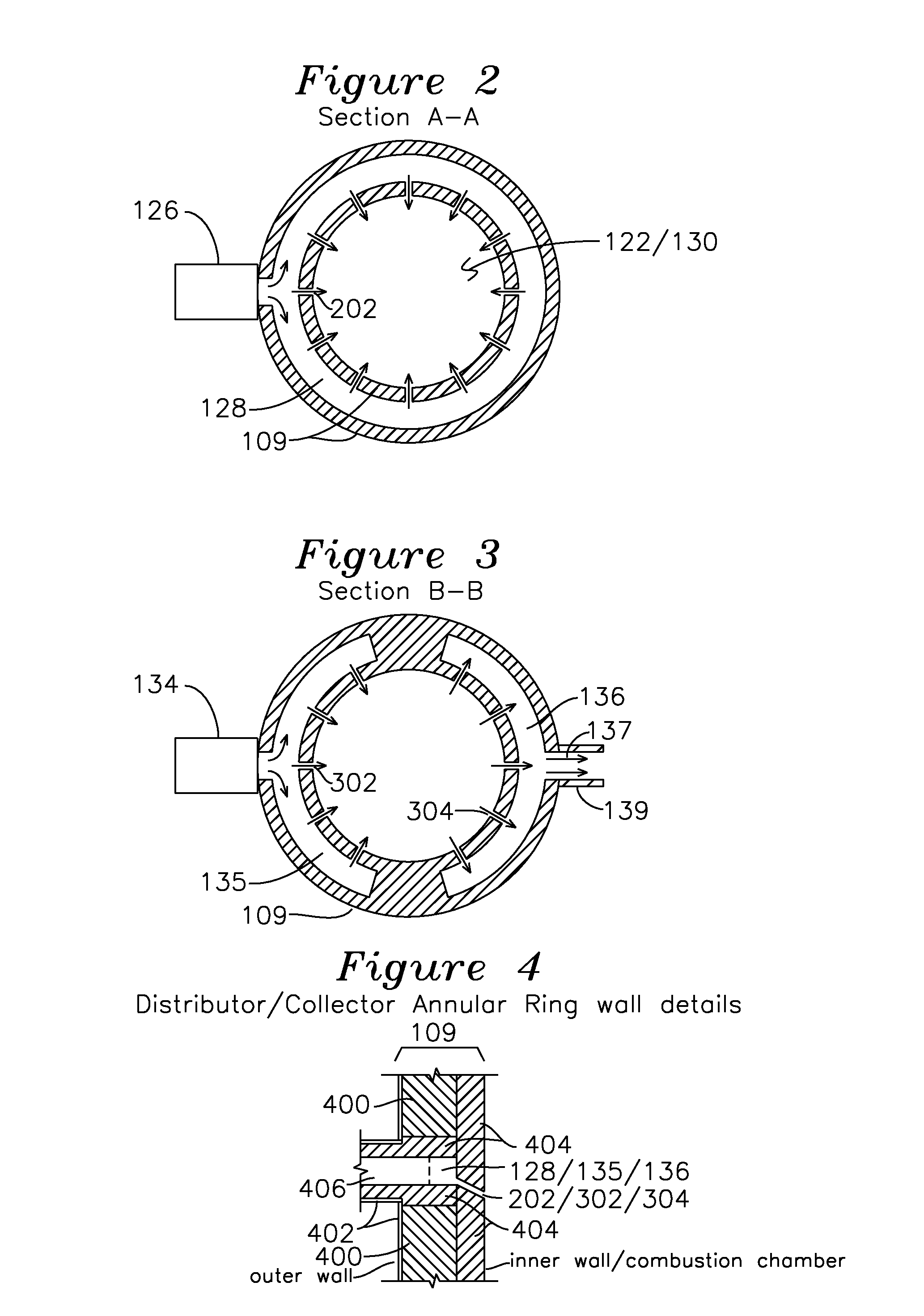
A pyrolysis chamber for the extraction of combustible gasses from biomass waste such as wood chips has a gravity fed chamber, where fuel passes, in succession, through a pre-heating zone, an oxidation and reduction zone, a gas outlet zone and a solids offloading zone. The pre-heating zone has plasma torches which direct an air plasma into the chamber, thereby pre-heating the fuel to a temperature of 1200-1500° C., after which the fuel enters the oxidation and reduction zone, where it is exposed to a steam plasma of 1500° C. which travels through plasma torches to an annular ring distributor surrounding the chamber and having apertures directing the steam plasma into the chamber, thereby providing enhanced generation of combustible gasses of CO and H2. The combustible gasses are removed in the gas outlet zone, which has a half annular ring collector removing combustible gasses out of the chamber and half annular ring distributor injecting an air plasma into the chamber for gasification of the ash residual carbon. A solids offloading part has a rotating grate for the removal of ash and slag for delivery to a water trough.
Owner:OAKS PLASMA
Diesel particulate filter (DPF) carbon accumulation estimation method
InactiveCN104832258AImprove calculation accuracyEasy to judgeInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust treatment electric controlEstimation methodsResidual carbon
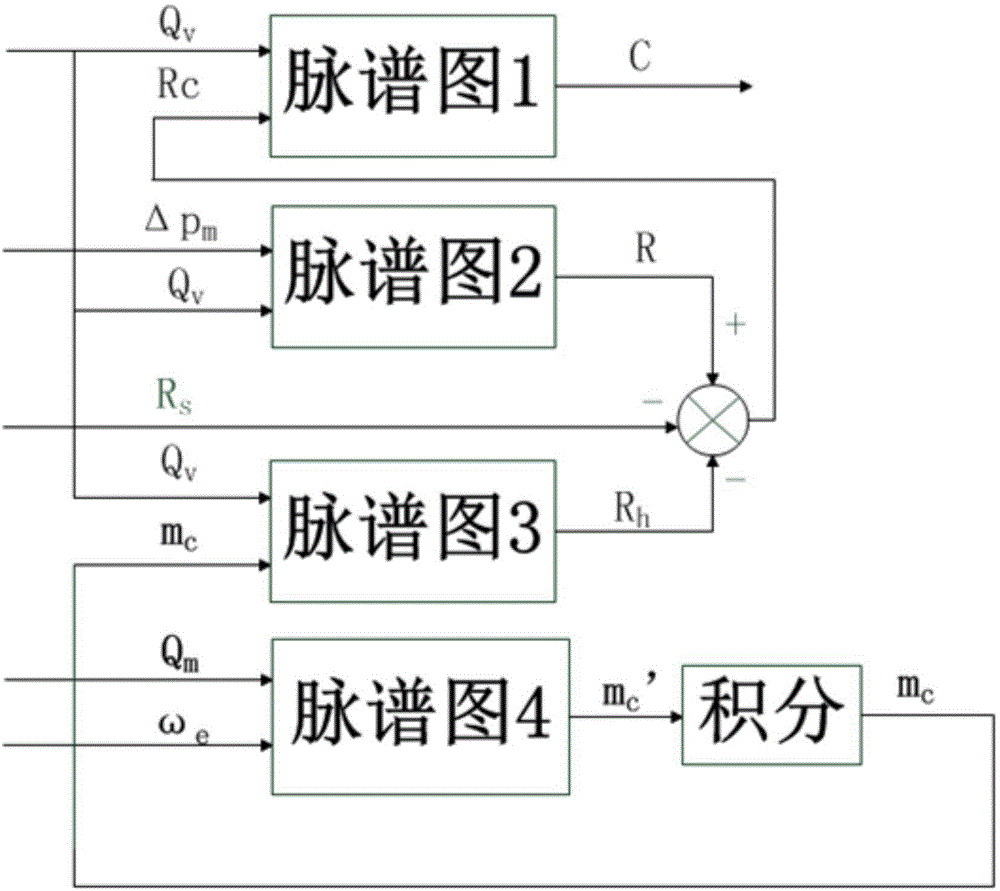
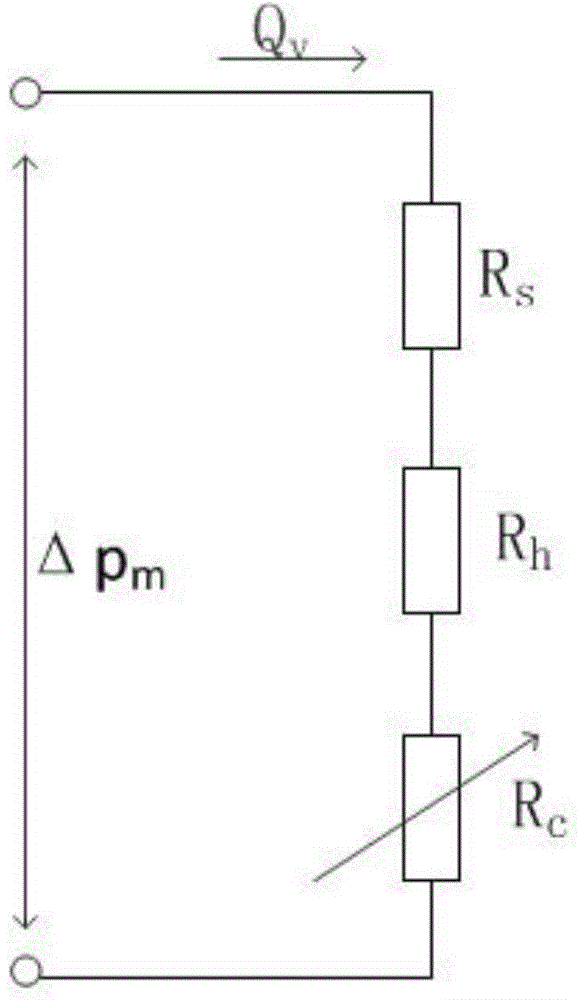
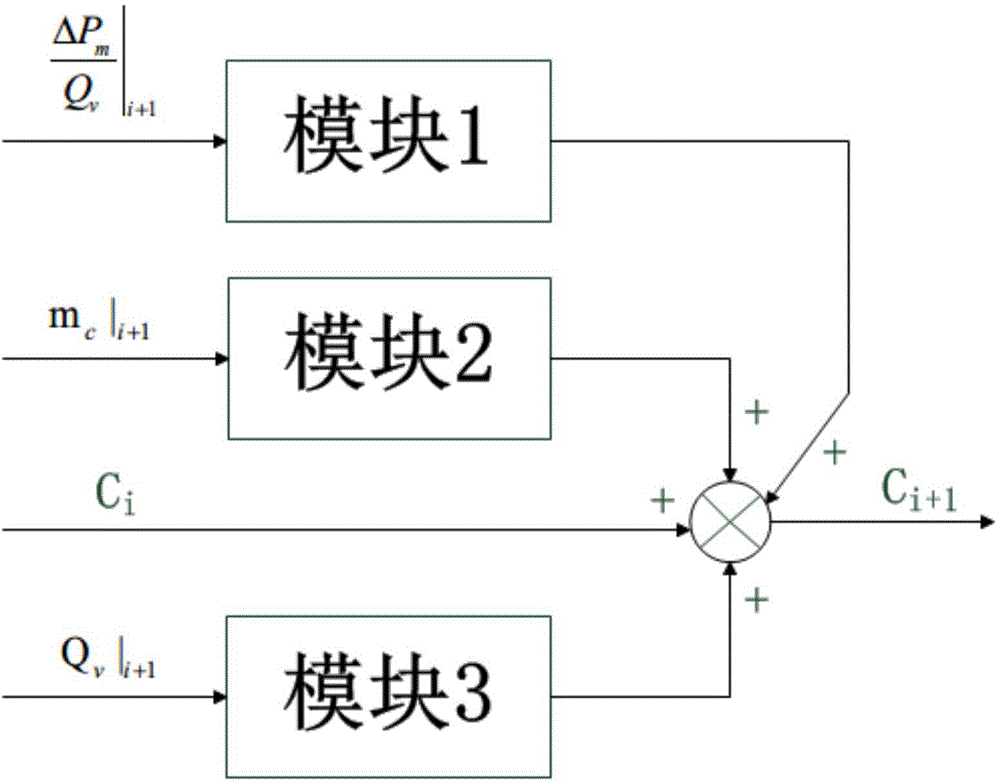
The invention discloses a diesel particulate filter (DPF) carbon accumulation estimation method. The difference between total pressure before a DPF and total pressure after the DPF is detected by a pressure difference sensor, the total flow resistance of the DPF is obtained according to the difference between the total pressure before the DPF and the total pressure after the DPF and exhaust gas volume flow, the flow resistance generated by the residual carbon of the DPF is obtained according to ash content mass and the exhaust gas volume flow, white carrier flow resistance and the flow resistance generated by the residual carbon subtracted from the total flow resistance gives flow resistance generated by accumulated carbon, and according to the flow resistance generated by the accumulated carbon and the exhaust gas volume flow, carbon accumulation can be obtained; the ash content mass is obtained by integrating exhaust gas mass flow and the rotational speed of an engine. The carbon accumulation increment estimation method put forward by the invention can work out the increment of carbon accumulation on the basis of current total flow resistance, current ash content mass and current exhaust gas volume flow, and then obtains current carbon accumulation. The precision of the DPF carbon accumulation estimation obtained by the method disclosed by the invention is higher, moreover, parameters, the physical meaning of which is unclear, in conventional estimation methods are prevented from being used, the estimation process is quicker and more accurate, and thereby the accuracy of DPF regeneration opportunity judgment is greatly increased.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com