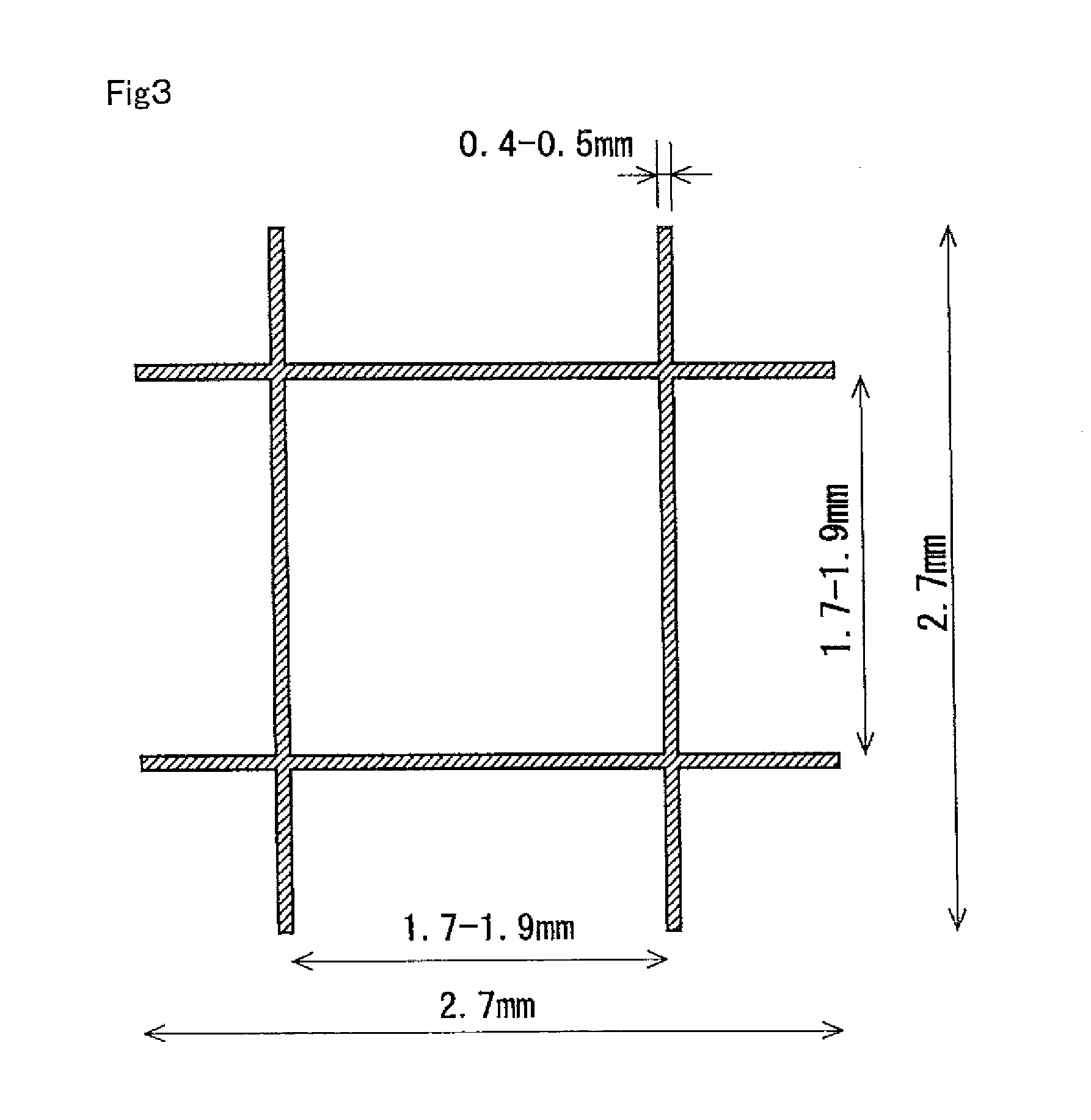
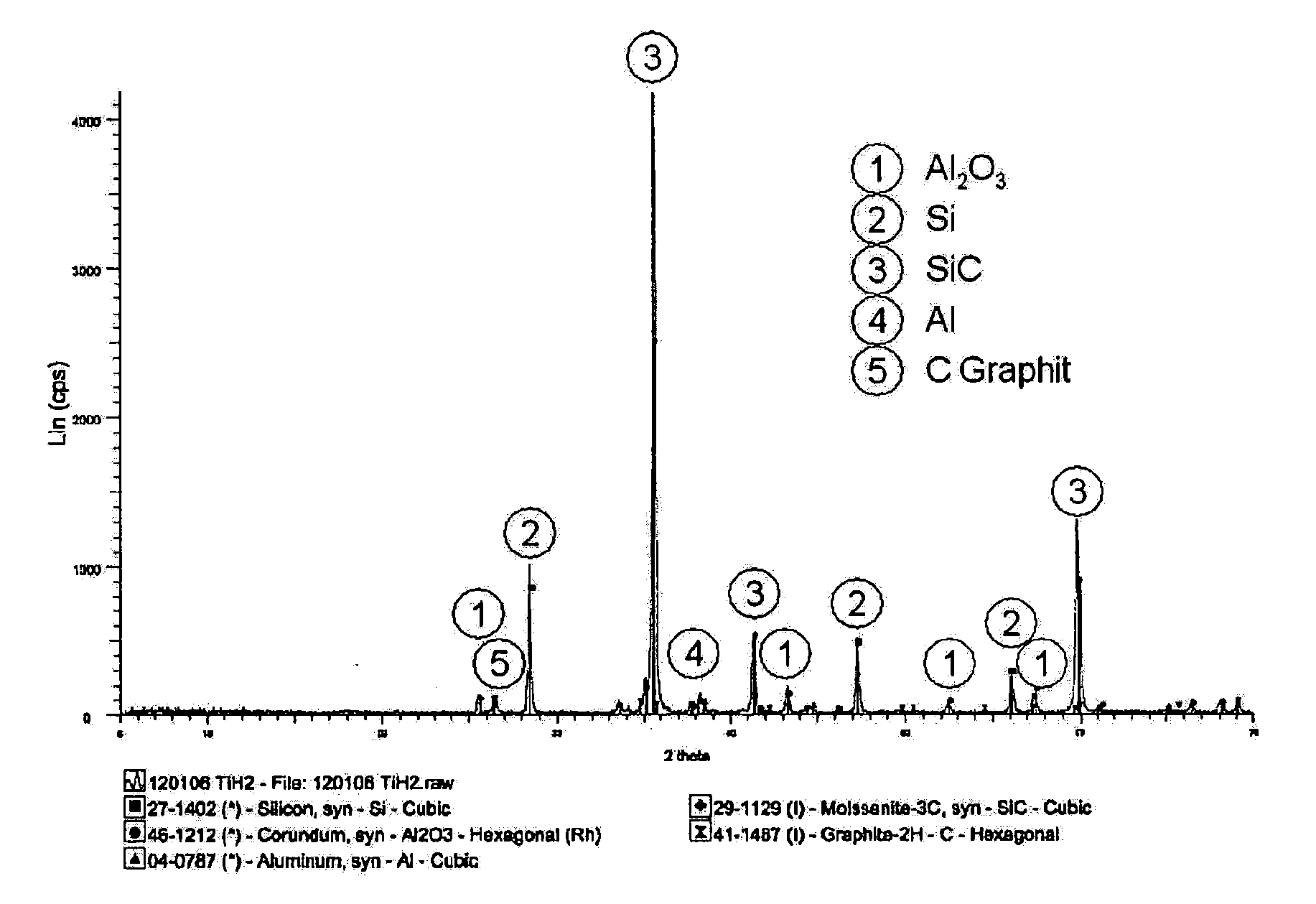
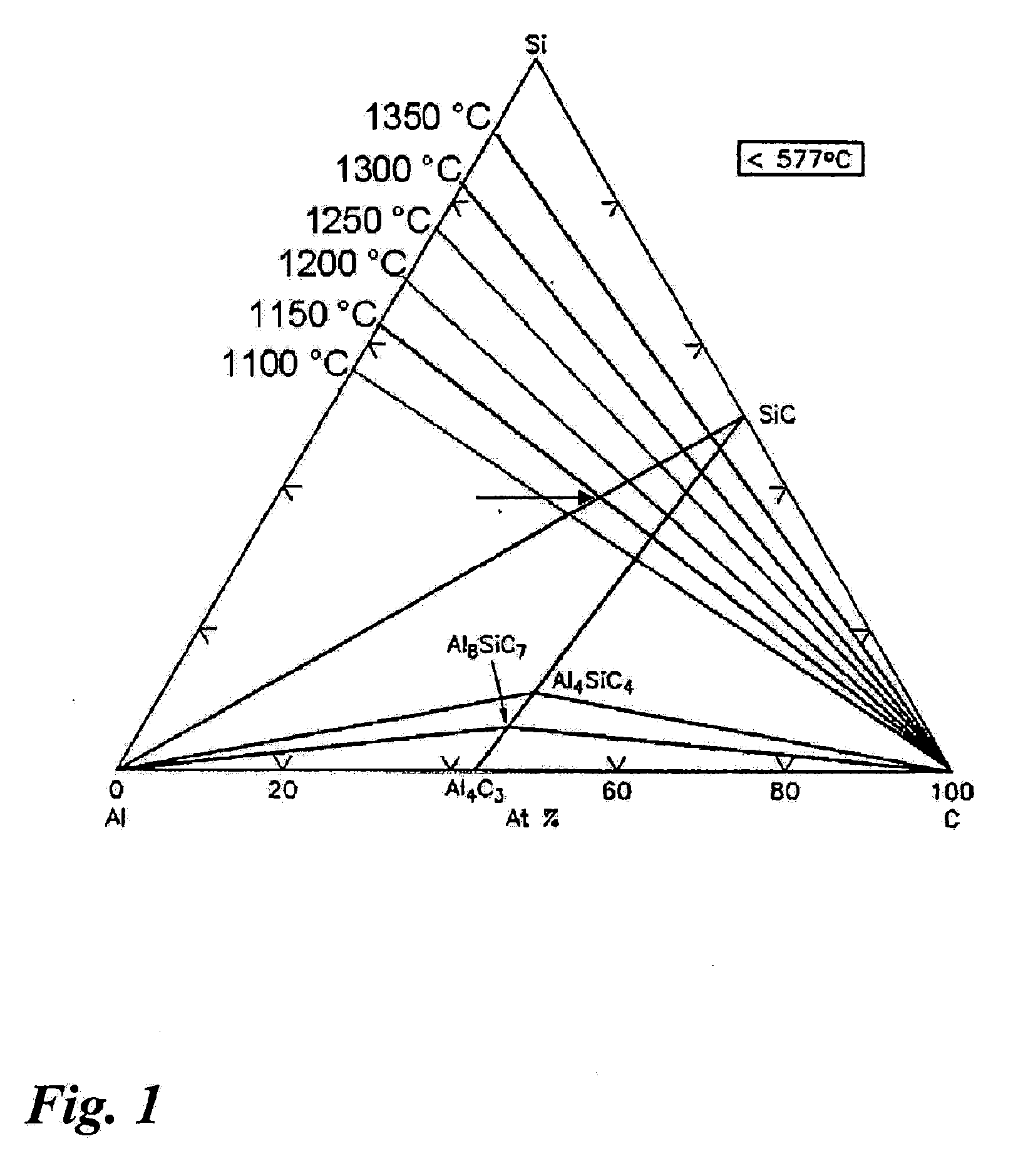
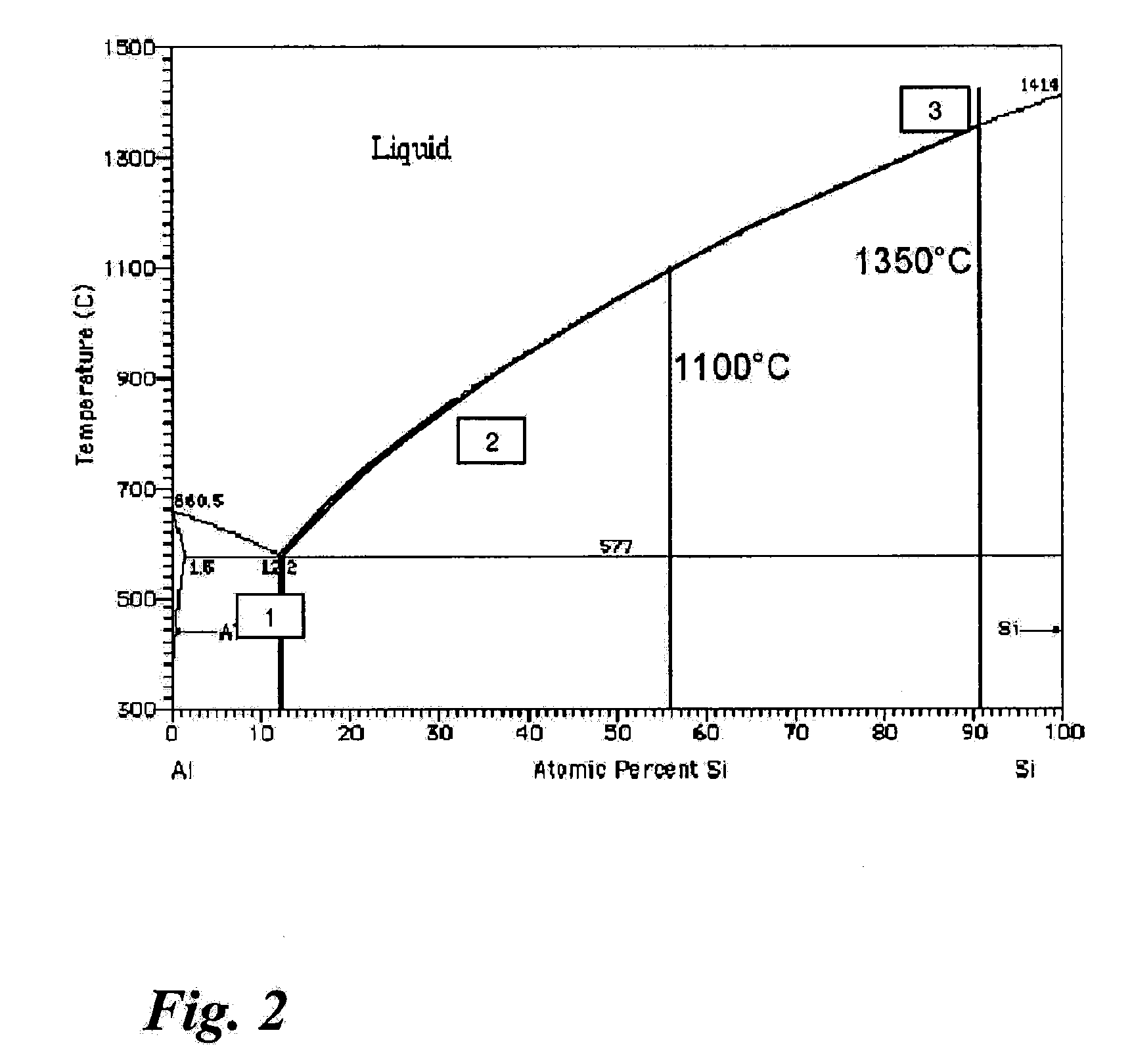
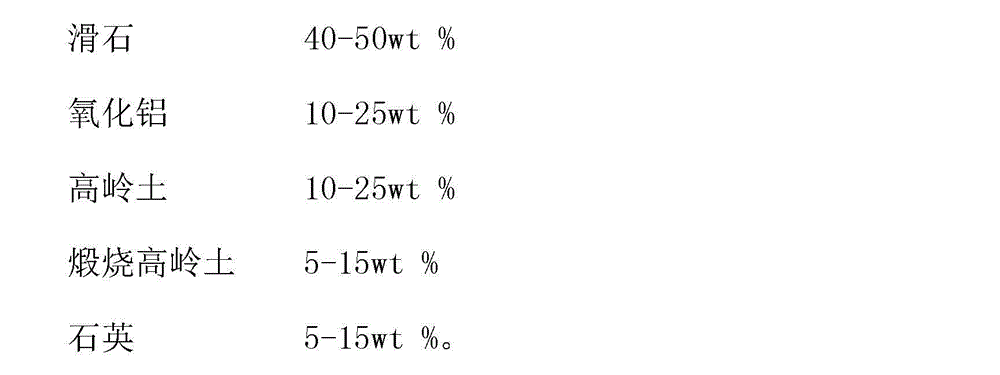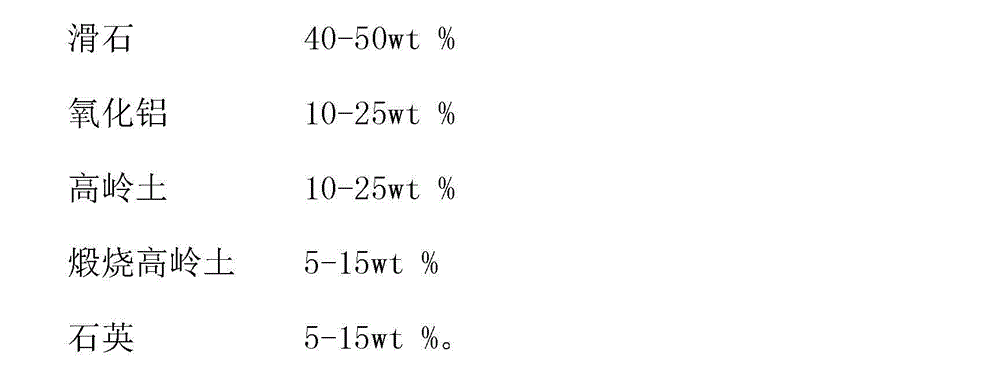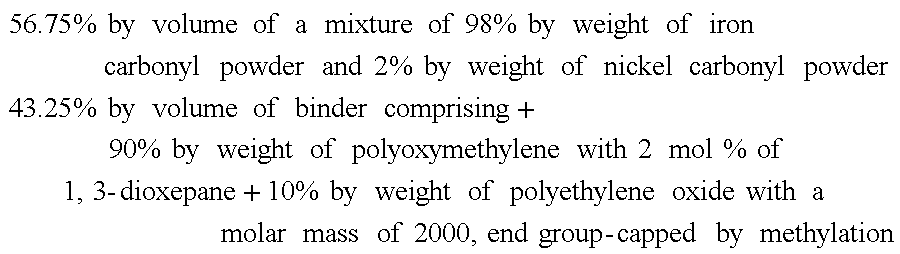Patents
Literature
302 results about "Ceramic molding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The ceramic molding process is an easy production method which guarantees the precision required, and also gives a good surface finish, using a high temperature method to better structure and shape parts. This process also gives a low grade of toleration and is not very expensive.
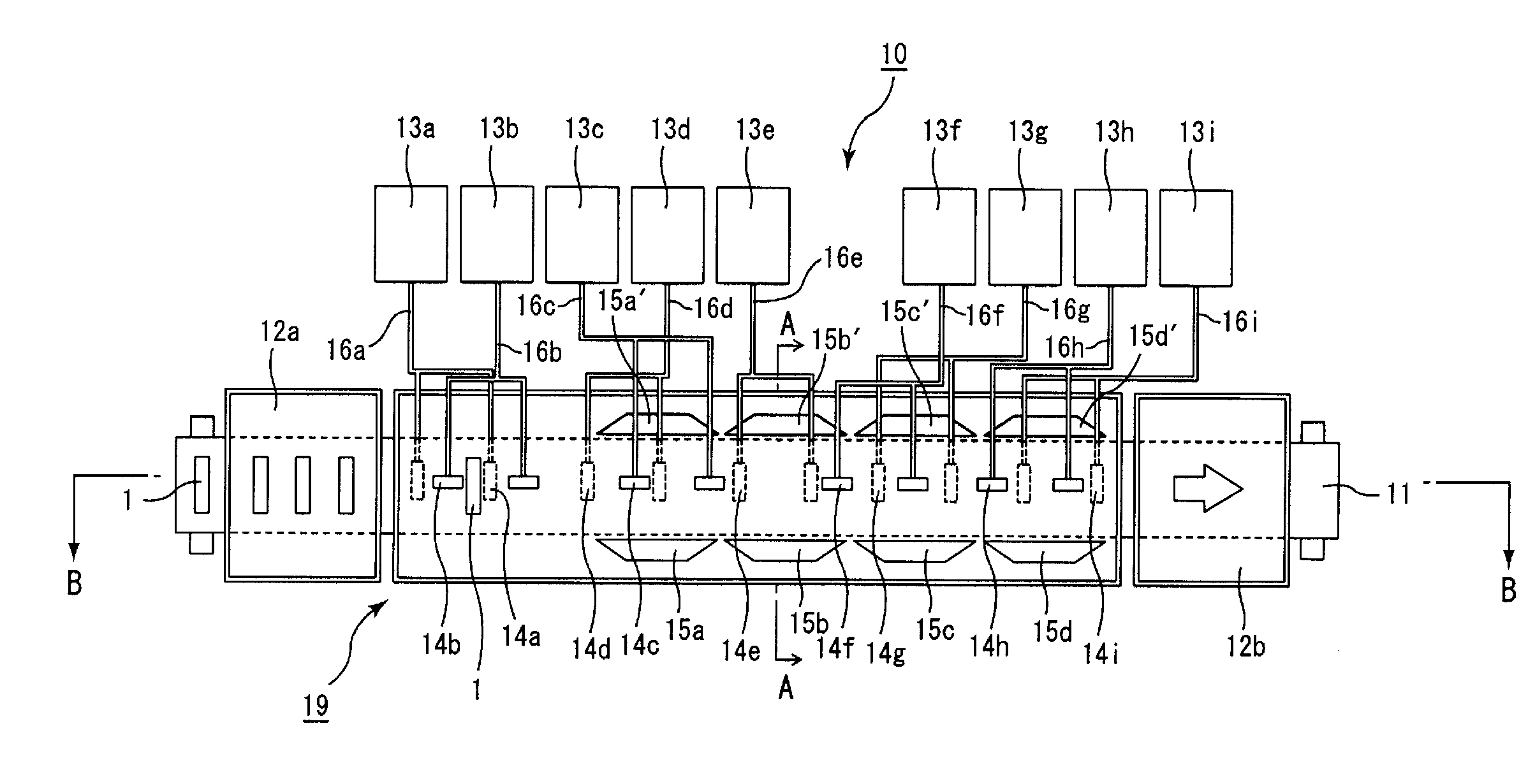
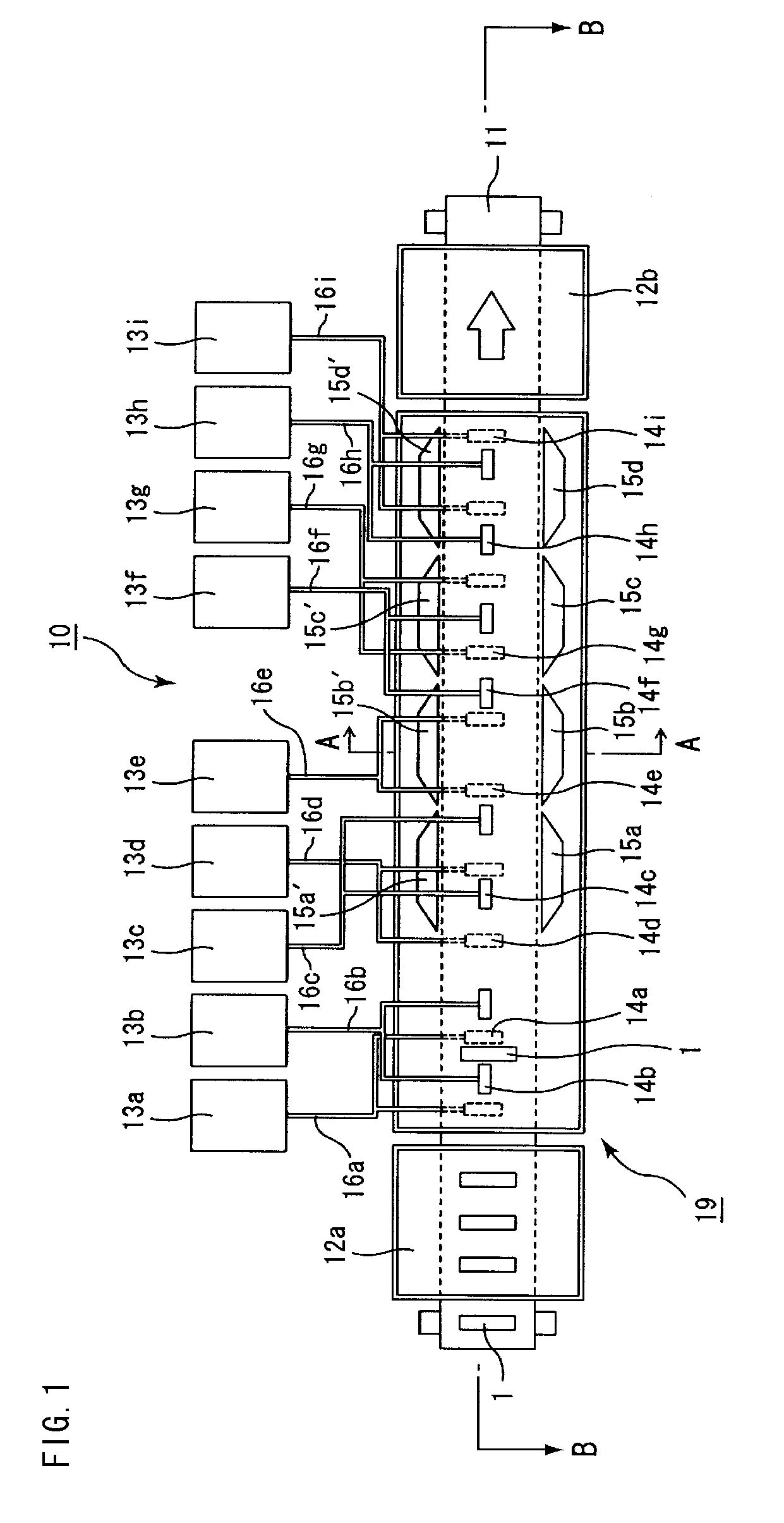
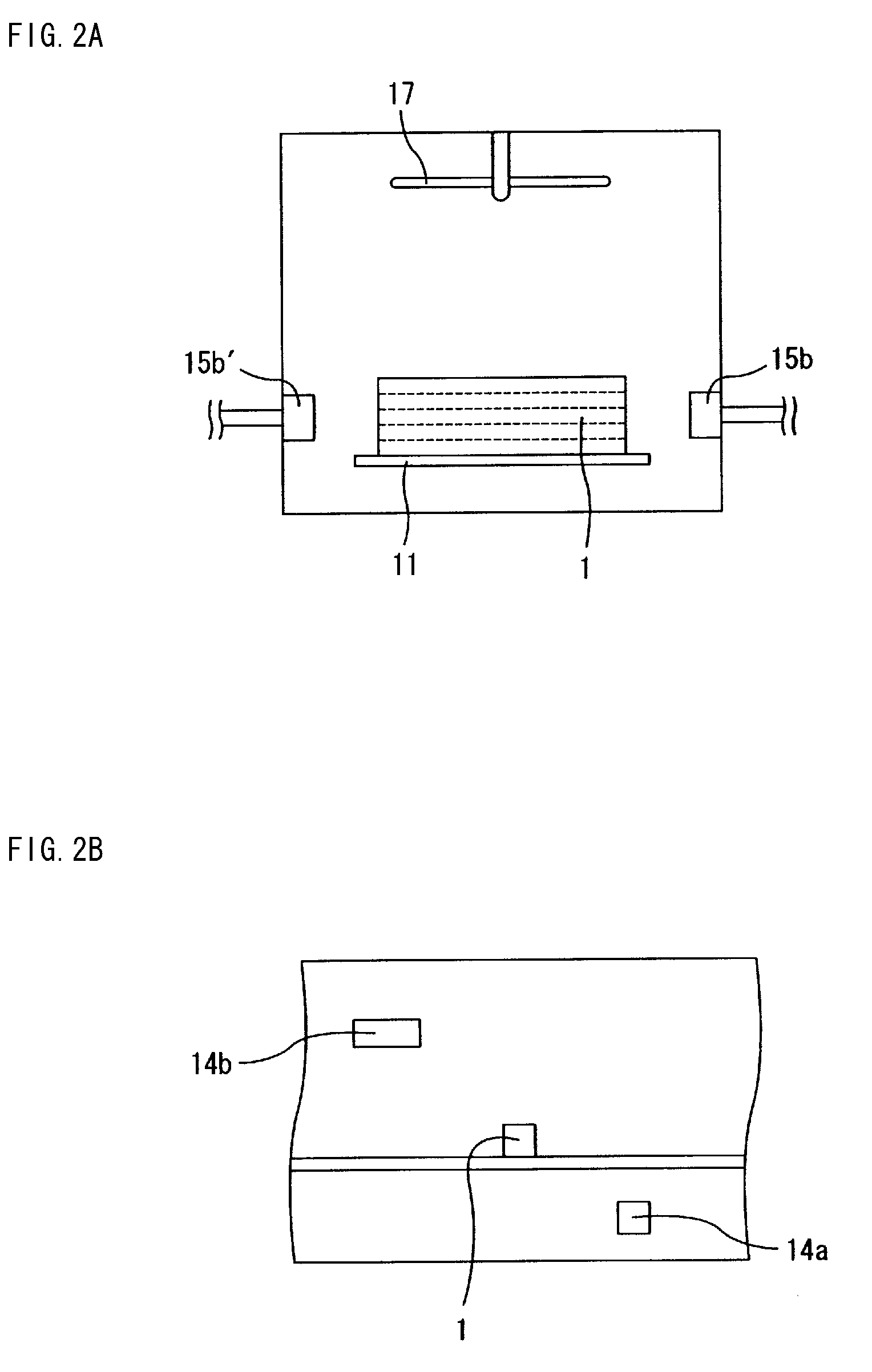
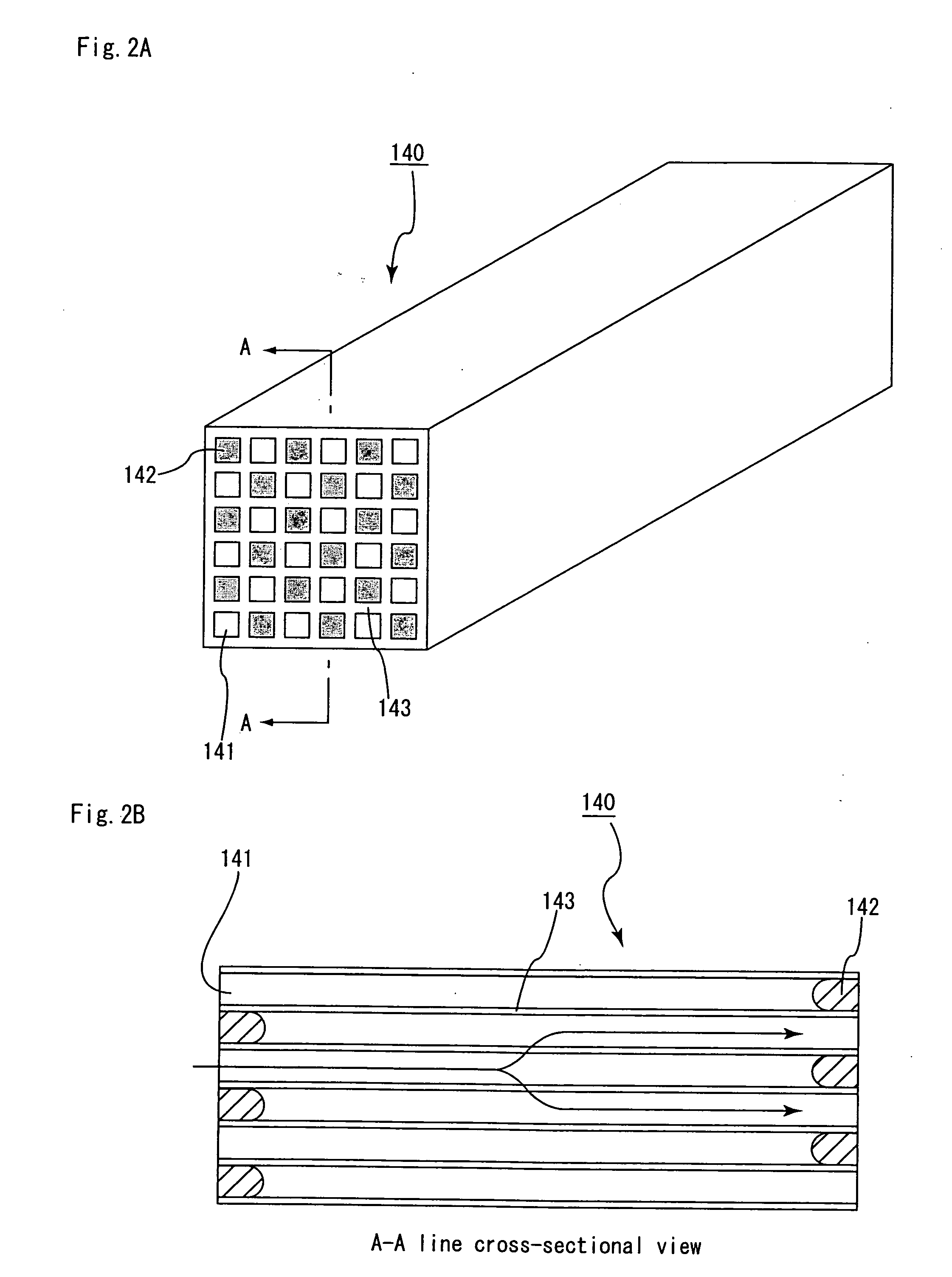
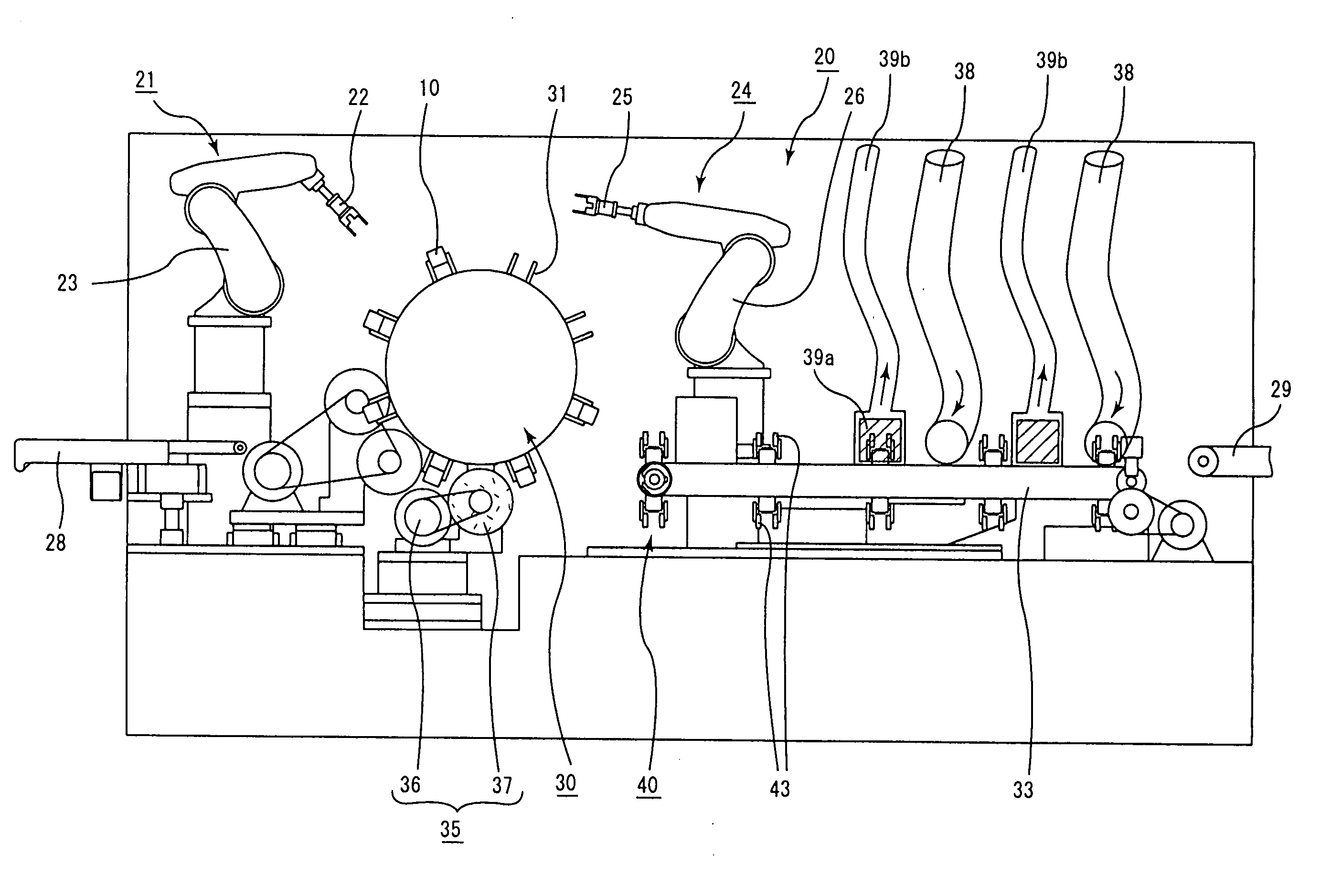
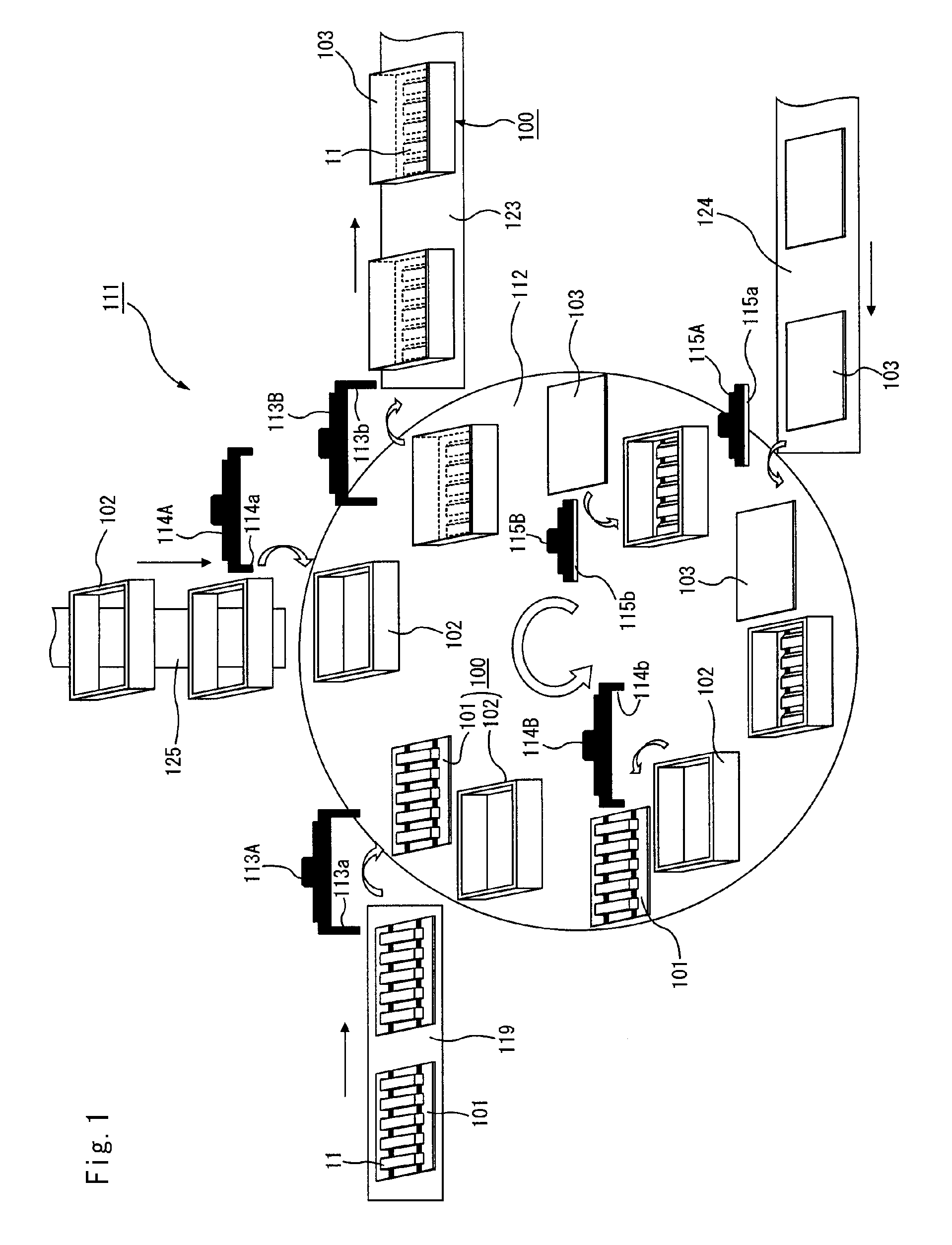
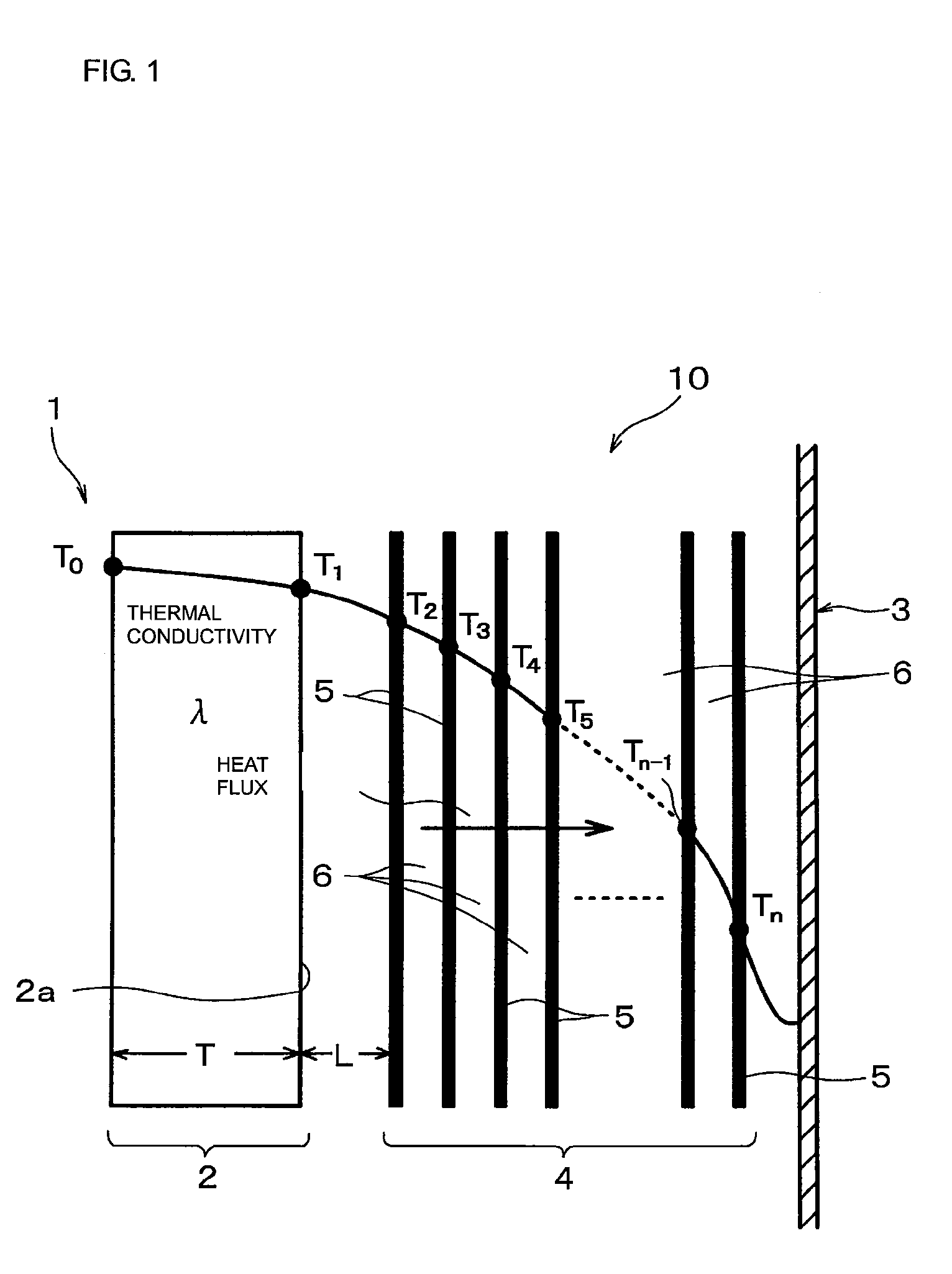
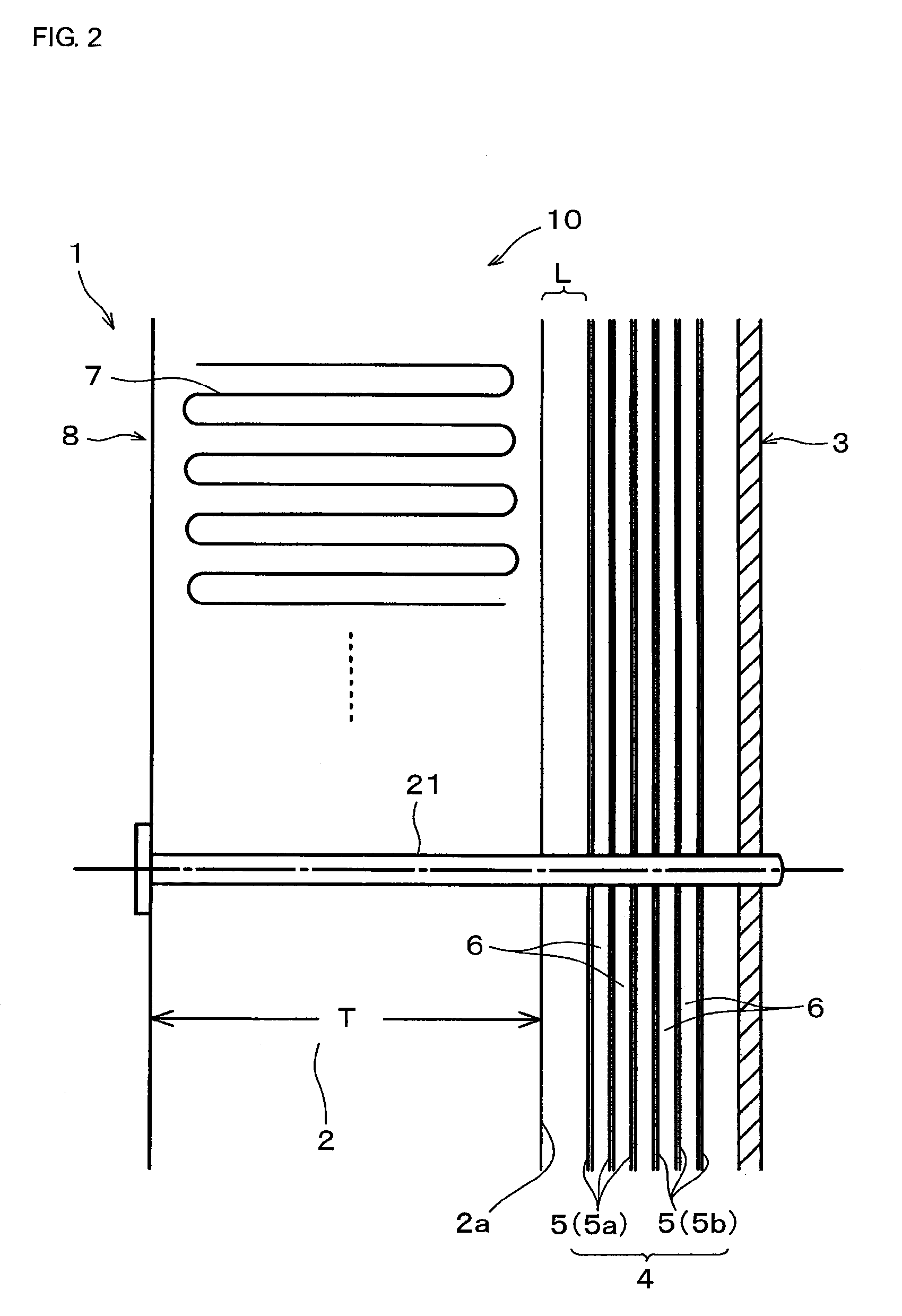
Drying apparatus, method for drying ceramic molded body, and method for manufacturing honeycomb structure
InactiveUS20080136062A1Remove moistureDrying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsCeramic moldingIrradiation
A drying apparatus including a conveying member configured to convey an item to be dried, a plurality of microwave irradiation portions disposed alternately at an upper side and a lower side of the conveying member, and a plurality of hot air blowing portions. The microwave irradiation portions are configured to irradiate the item to be dried with microwaves in an alternating manner from the upper side and the lower side. The hot air blowing portions are configured to apply hot air to the item to be dried in parallel with irradiation of the microwaves by the microwave irradiation portions.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Aluminum titanate ceramic forming batch mixtures and green bodies including pore former combinations and methods of manufacturing and firing same
InactiveUS20070006561A1Low exothermic reaction and exothermic reactionReduction tendencyDispersed particle filtrationTransportation and packagingCeramic moldingSolvent
A ceramic forming batch mixture including inorganic batch materials, such as sources of alumina, titania, and silica, a pore former combination including first and second pore formers with different compositions; an organic binder; and a solvent. Also disclosed is a method for producing a ceramic article involving mixing the inorganic batch materials with the pore former combination having first and second pore formers of different composition, adding an organic binder and a solvent, forming a green body; and firing the green body. A green body having a combination of first and second pore formers with different compositions is disclosed, as are several methods for firing to produce ceramic articles such as aluminum titanate.
Owner:CORNING INC
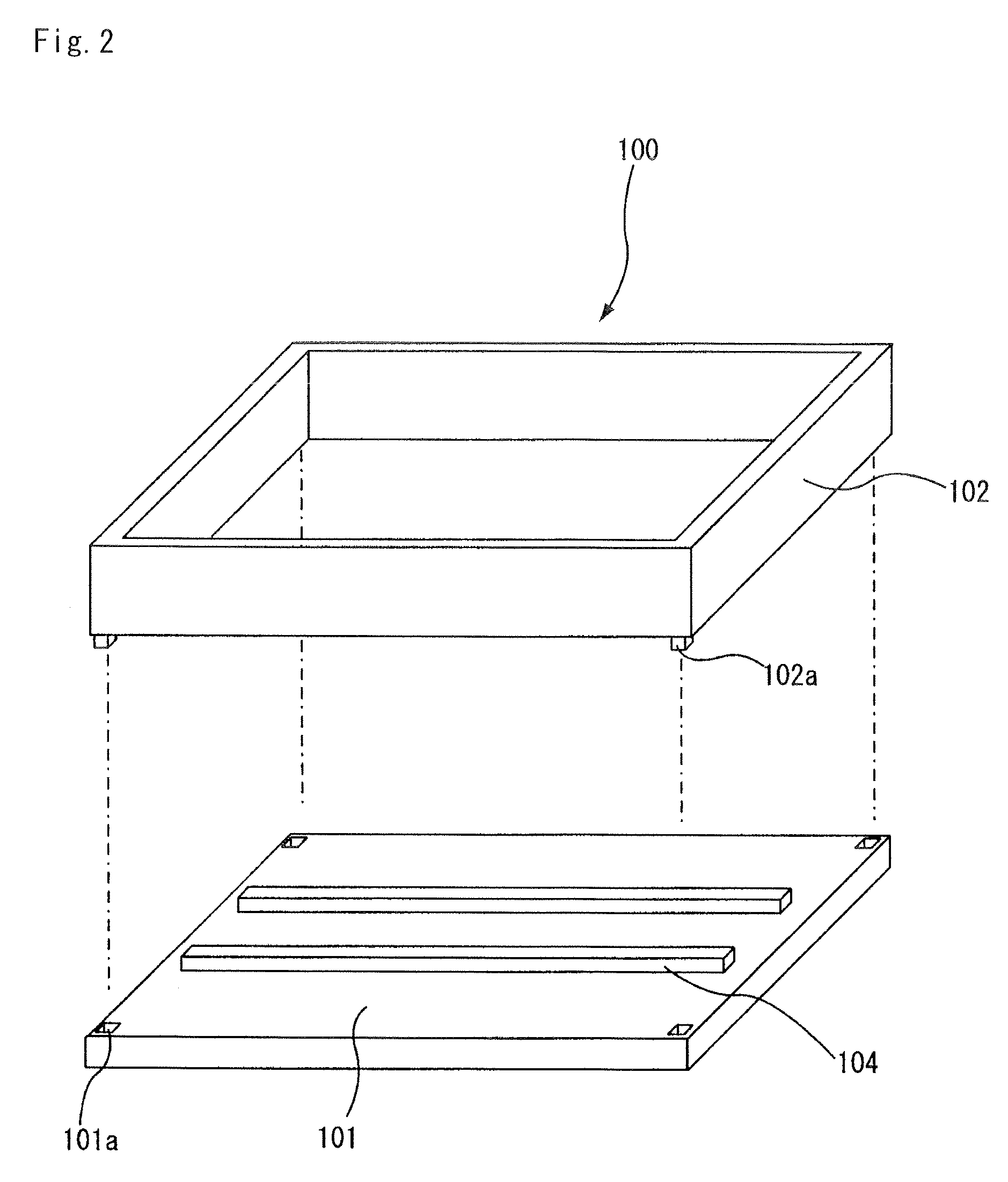
Degreasing jig, method for degreasing ceramic molded body, and method for manufacturing honeycomb structured body
A degreasing jig according to the present invention is a degreasing jig for degreasing of a ceramic molded body containing a ceramic powder, a binder, and a dispersion medium, comprising a bottom plate for placing the ceramic molded body thereon, and an air-permeable cover member provided in a manner to cover the ceramic molded body.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
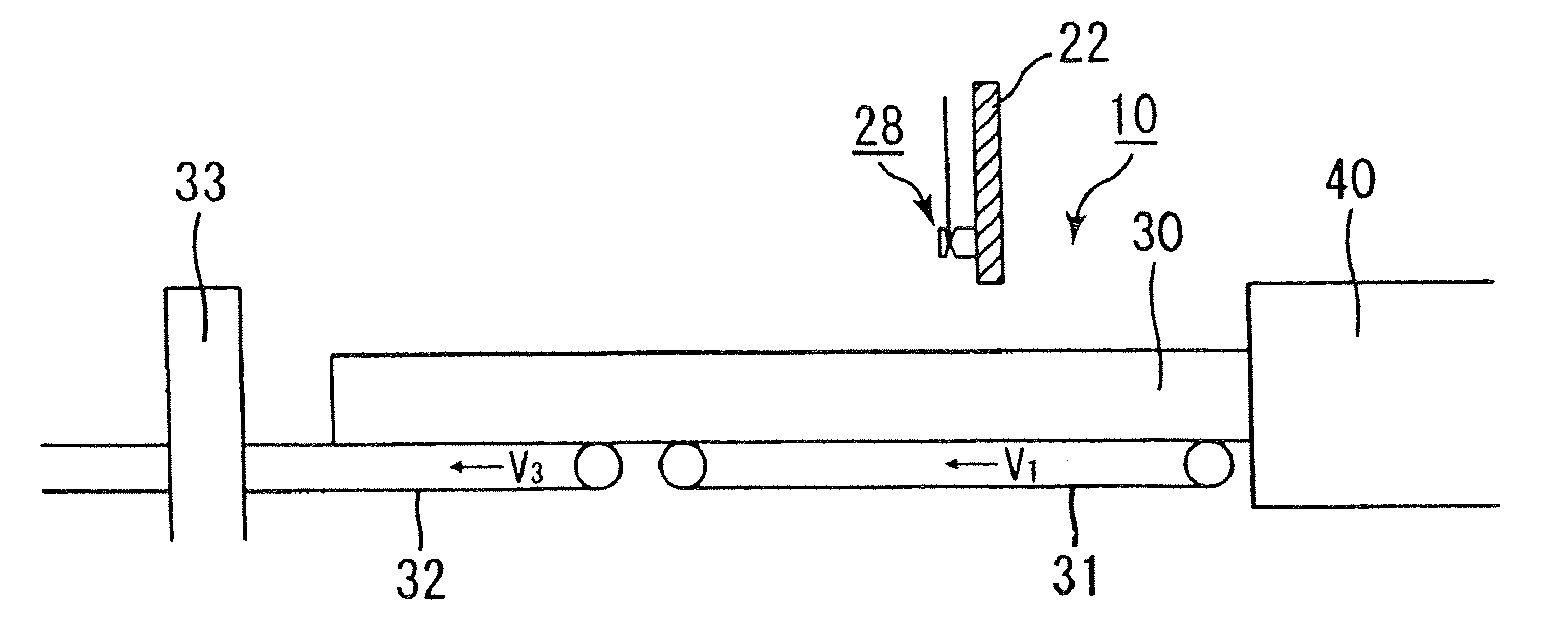
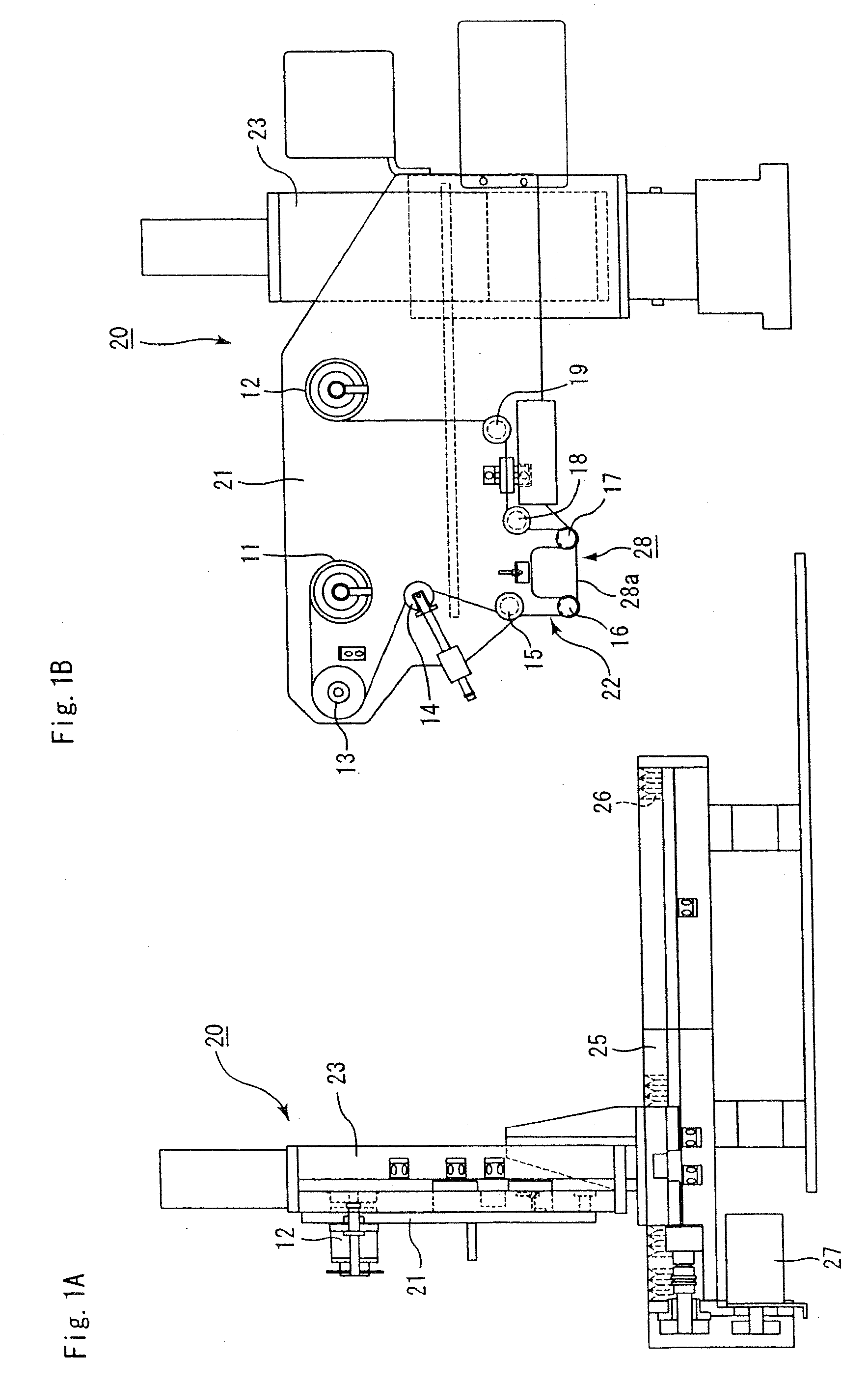
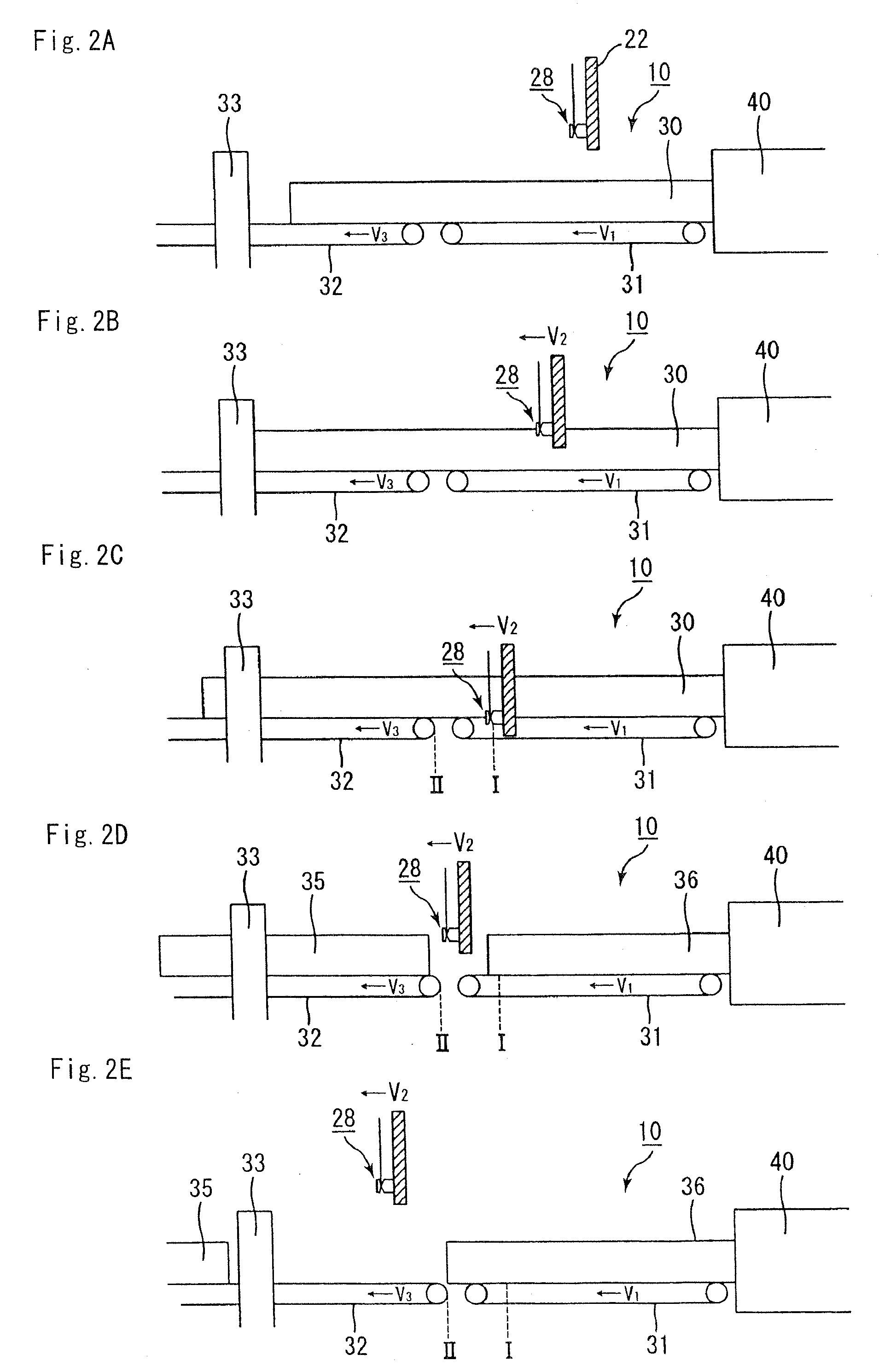
Molded body cutting apparatus, method for cutting ceramic molded body and method manufacturing honeycomb structured body
A molded body cutting apparatus according to the present invention comprising a first conveyer member that conveys an extrusion-molded pillar-shaped ceramic molded body a cutting member that moves in a direction parallel to a movement direction of the above mentioned first conveyer member while moving also in a vertical direction, and cuts the above mentioned ceramic molded body to a predetermined length by passing through the interior of the above mentioned ceramic molded body and a second conveyer member that conveys a cut ceramic molded body cut to a predetermined length by the above mentioned cutting member, wherein a conveyance speed of the above mentioned first conveyer member and a movement speed of the above mentioned cutting member in the above mentioned parallel direction are almost the same, before the above mentioned ceramic molded body is cut, and each of the conveyance speed of the above mentioned first conveyer member, the movement speed of the above mentioned cutting member in the above mentioned parallel direction, and a conveyance speed of the above mentioned second conveyer member becomes faster toward the latter, after the above mentioned ceramic molded body is cut.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
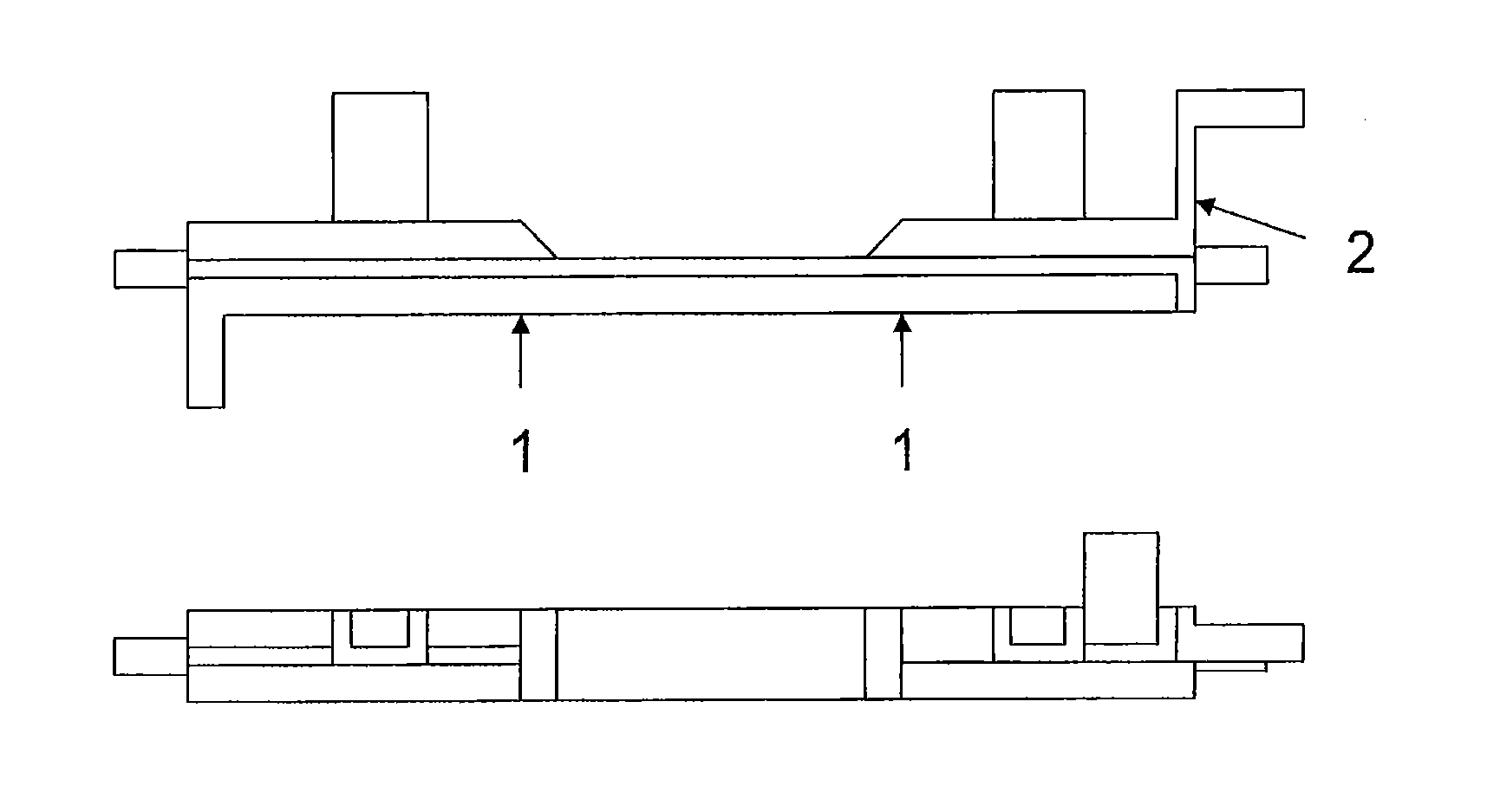
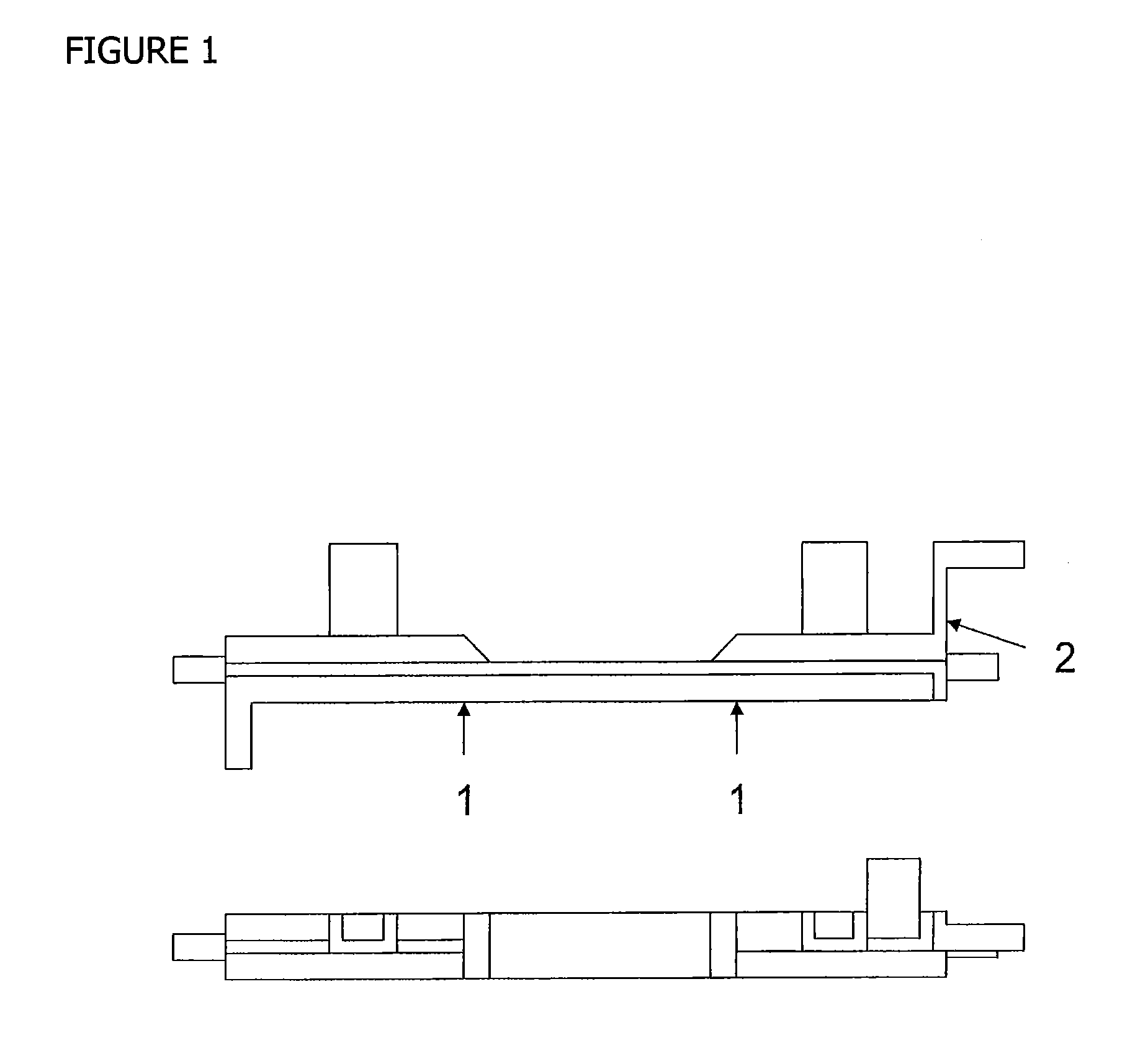
End face processing apparatus, end face processing system, end face processing method for honeycomb molded body, and manufacturing method for honeycomb structure
The end face processing apparatus of the present invention is an end face processing apparatus for processing the cut face of a cut ceramic molded body, which comprises an air blowing outlet and an extraneous material removal member, and is configured to remove burrs remaining on the cut face from the time of cutting as well as powder adhering to the cut face and on the periphery thereof using the extraneous material removal member and air from the air blowing outlet.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Firing jig assembling apparatus, firing jig disassembling apparatus, circulating apparatus, method for firing ceramic molded body, and method for manufacturing honeycomb structure
A circulating apparatus includes a firing jig assembling apparatus, a firing furnace, a firing jig disassembling apparatus, and a transporting conveyor. The firing jig assembling apparatus includes a lid member attaching mechanism that attaches the lid member to a predetermined position of the firing jig placed on the table or the conveyor; and a jig delivering mechanism that delivers the firing jig which has the ceramic molded body being mounted thereon and the lid member being attached thereto, to the firing furnace. The firing jig disassembling apparatus further includes a jig receiving mechanism that receives the firing jig which has the fired ceramic molded body being mounted thereon and the lid member being attached thereto, from the firing furnace; and a lid member detaching mechanism that detaches the lid member from the firing jig placed on the table or the conveyor with the lid member being attached thereto.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
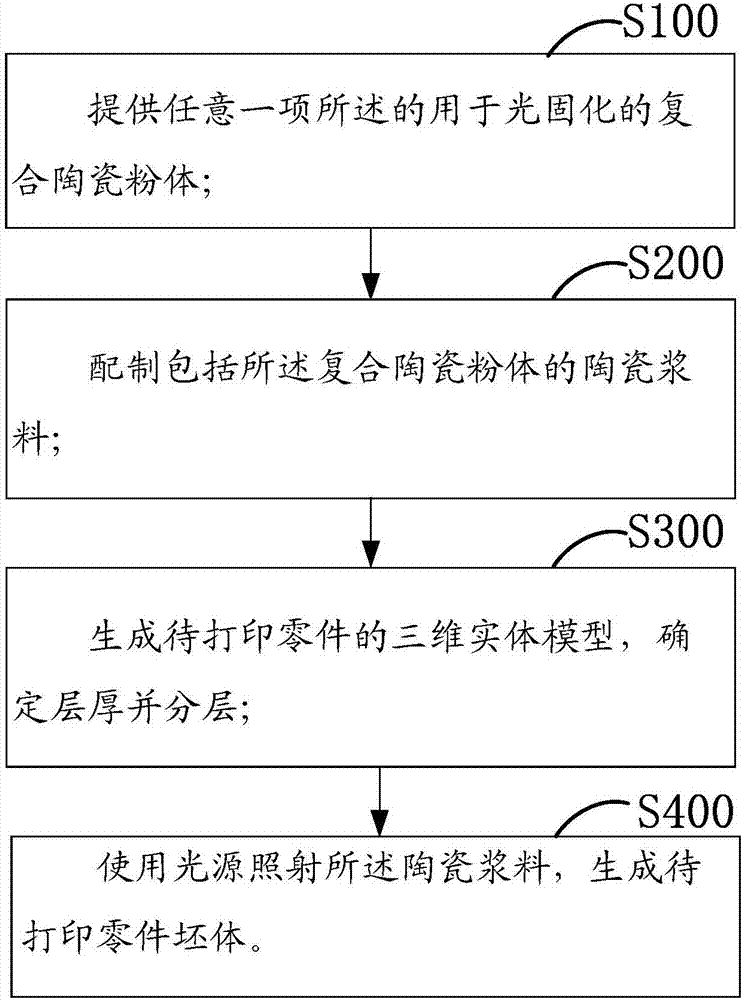
Method for preparing zirconium oxide ceramic by 3D (Three Dimensional) printing based on photo-curing molding
InactiveCN106673646AHigh surface finishHigh precisionAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurface finishPolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of 3D (Three Dimensional) printing and particularly relates to a method for preparing zirconium oxide ceramic by 3D printing based on photo-curing molding. The invention provides a composition which is prepared from the following raw materials: ceramic powder, a pre-mixed solution, a photoinitiator and a dispersant. The invention further provides a preparation method for preparing the zirconium oxide ceramic by utilizing the composition; and the preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing slurry, molding, curing, drying, degreasing and sintering. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the molding efficiency is high, and ceramic particles are uniformly dispersed; a prepared blank body is not cracked or deformed, is dense and uniform and has good surface gloss finish, high precision and excellent blank body performances; and meanwhile, the method also has the advantage of high preparation efficiency. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the technical defects of a zirconium oxide ceramic molding method in the prior art that the dependence on a mold is too great and a complicated and precise structure cannot be prepared are overcome.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Honeycombed porous ceramic having high thermal conductivity and ultralow expansion coefficient
ActiveCN103145439AGood coating effectImprove mechanical propertiesCeramicwareCeramic moldingCrystal orientation
A honeycombed porous ceramic having a high thermal conductivity and an ultralow expansion coefficient relates to the technical field of the silicate industry. The ceramic having a low even negative thermal expansion coefficient and a high thermal conductivity is obtained through treating a rare earth mixture, potassium phosphotungstate, zirconium oxide and amorphous quartz particles as a sintering aid, and expansion coefficient and thermal conductivity adjustment agents, and the ceramic has a high-orientation sheet iolite structure and has a good catalyst coating performance and good mechanical strengths; and ethylene oxide having different molecular weights are adopted as a ceramic molding binder, rapeseed oil or peanut oil is treated as a primary molding lubrication agent, a paste goes through a high-pressure extruder orientation extruding channel, a crystal orientation carding die and a honeycombed porous die to obtain a green body having high-orientation arranged crystals, and a special sintering curve is adopted to obtain the ceramic. The above whole ceramic preparation process flow and the above formula are economic, stable and environmentally-friendly.
Owner:安徽中鼎美达环保科技有限公司
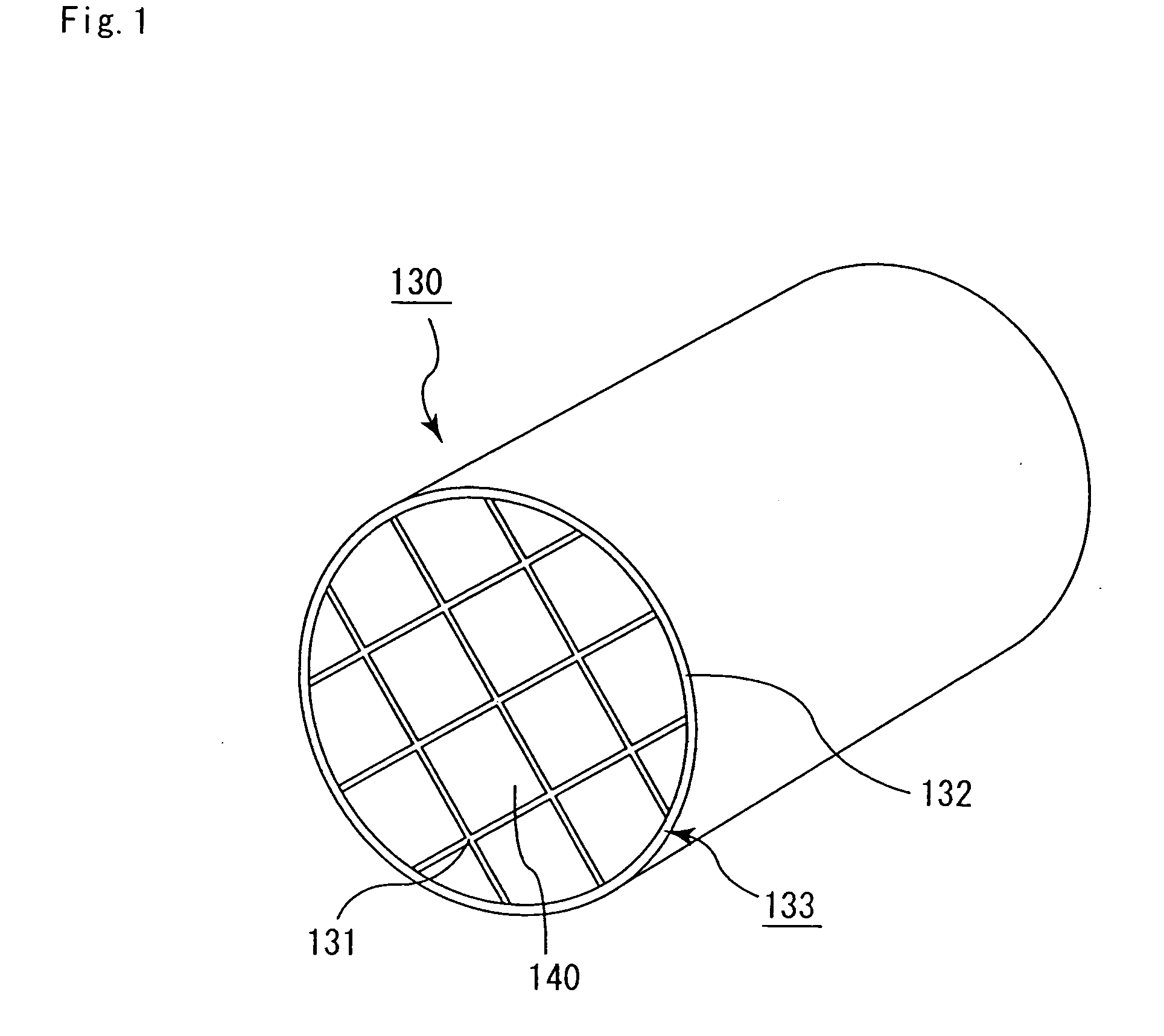
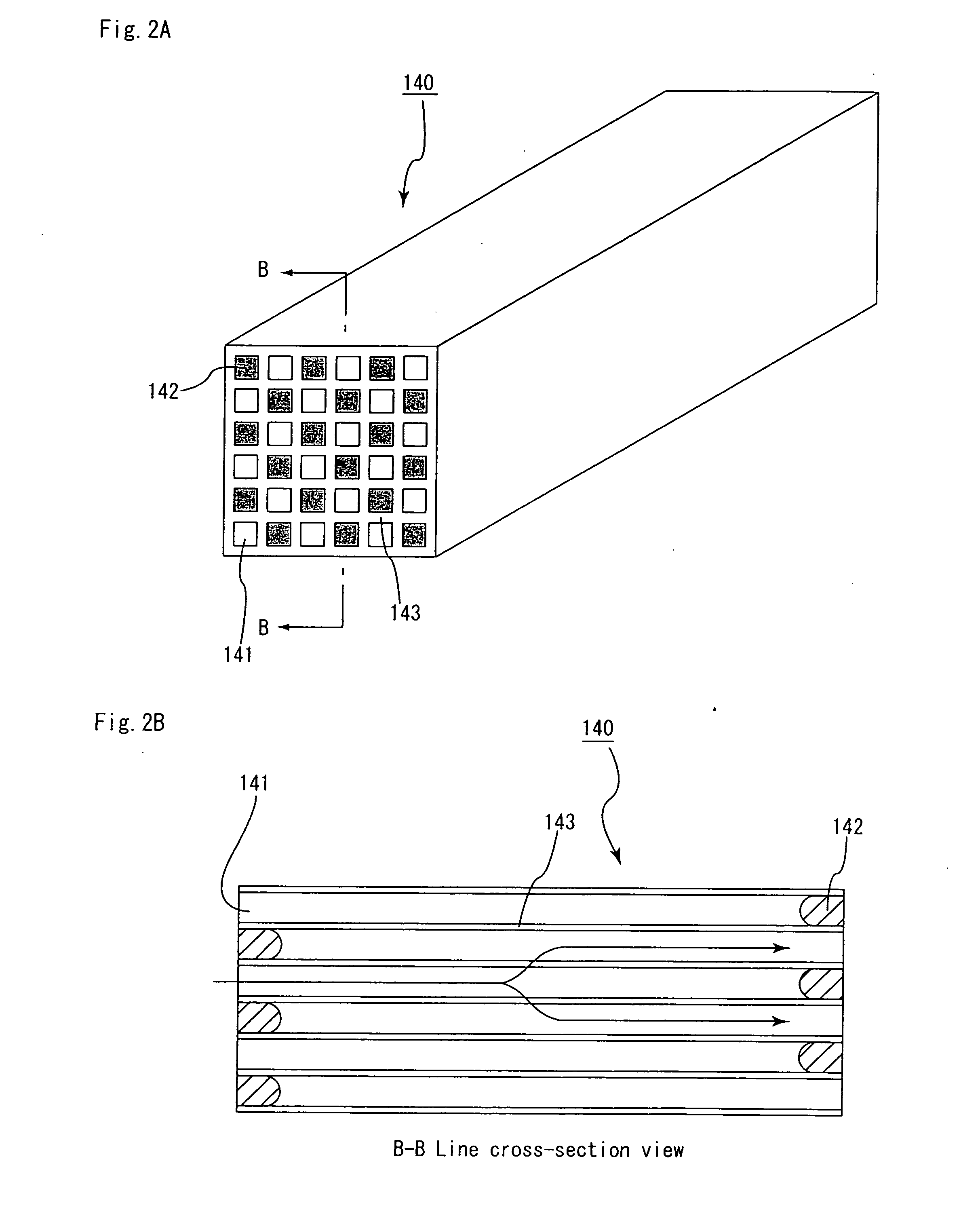
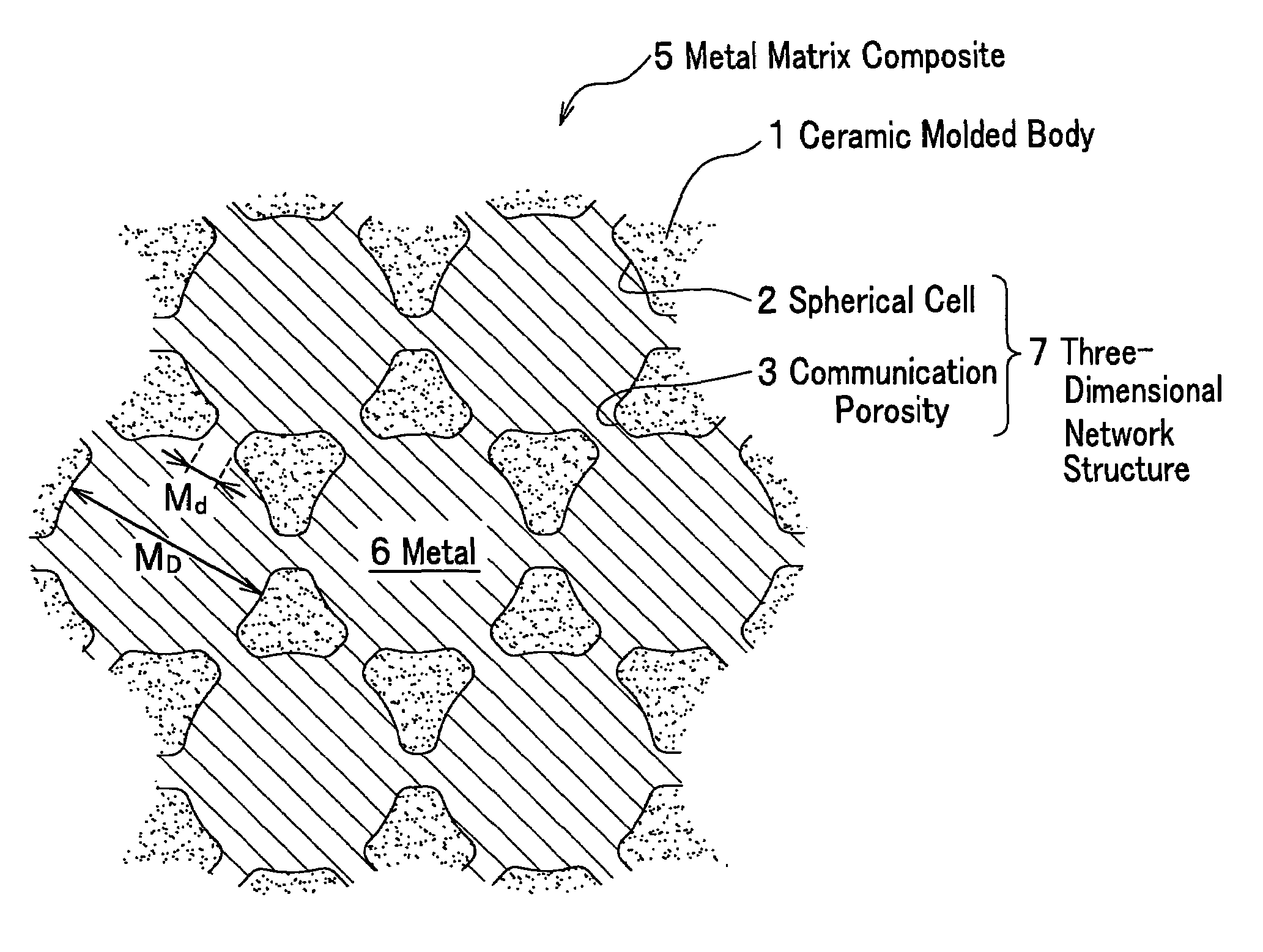
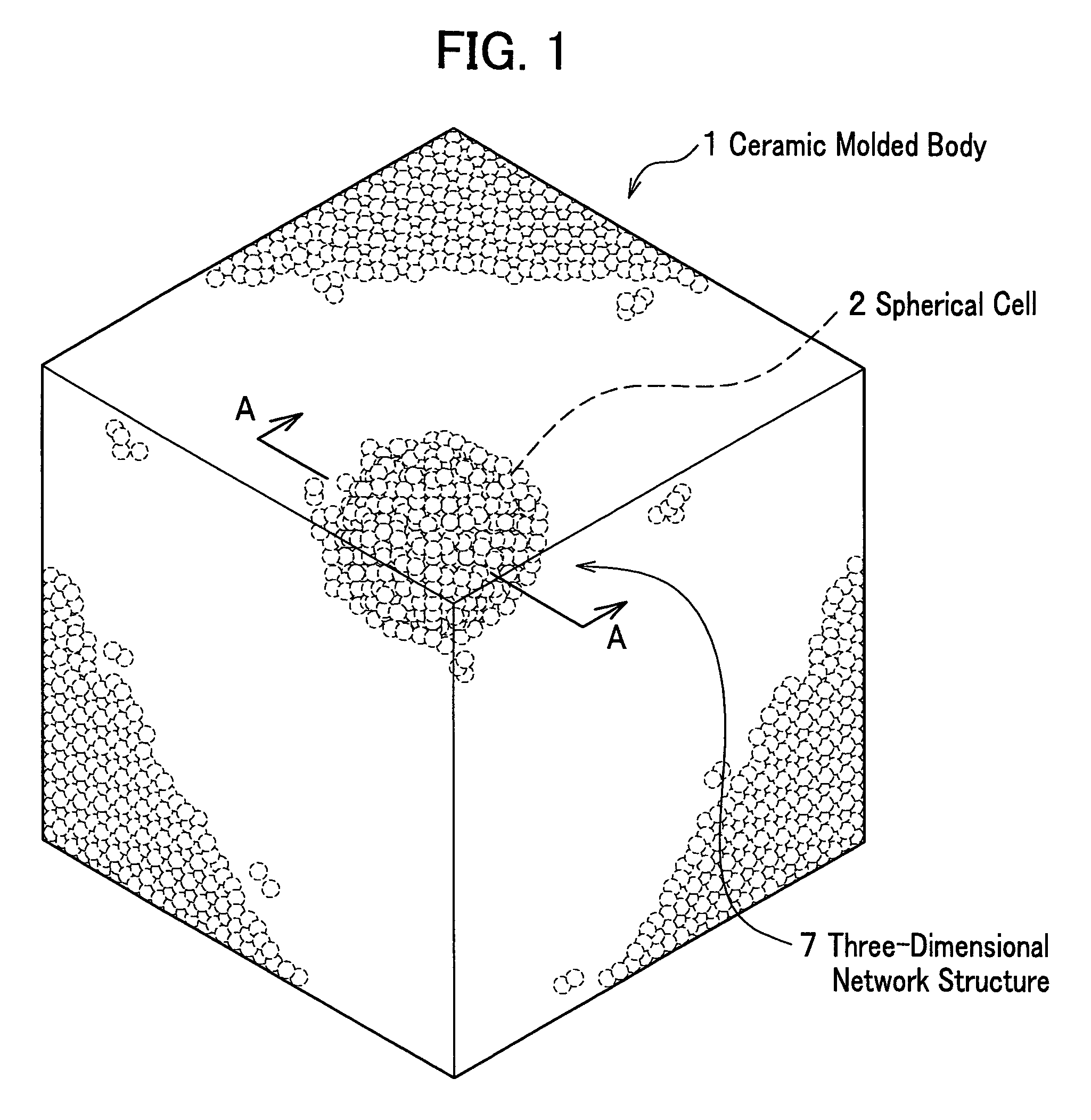
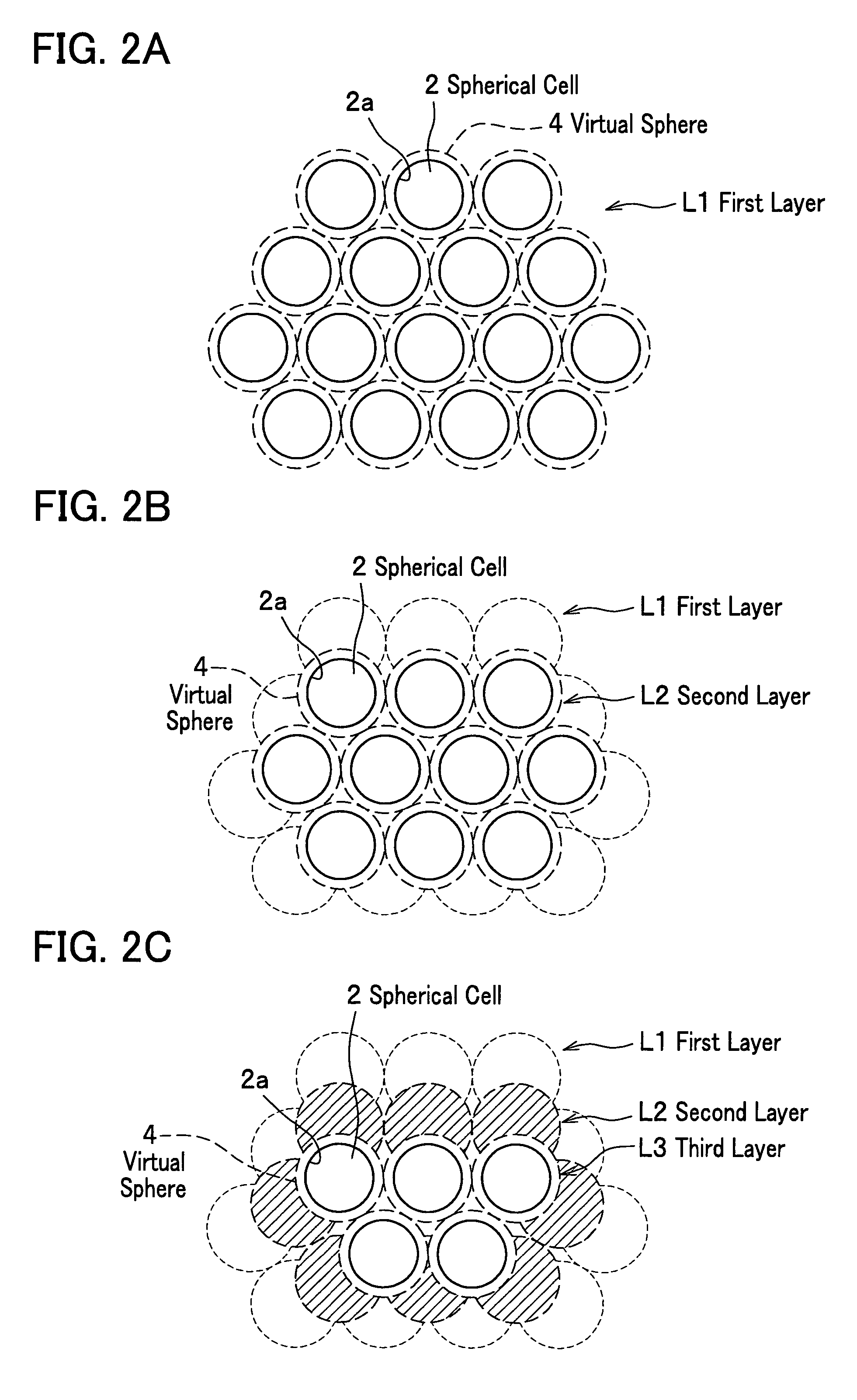
Ceramic molded body and metal matrix composite
InactiveUS20060057356A1Improve reducibilityReduce volume ratioLayered productsCeramic shaping apparatusPorosityCeramic molding
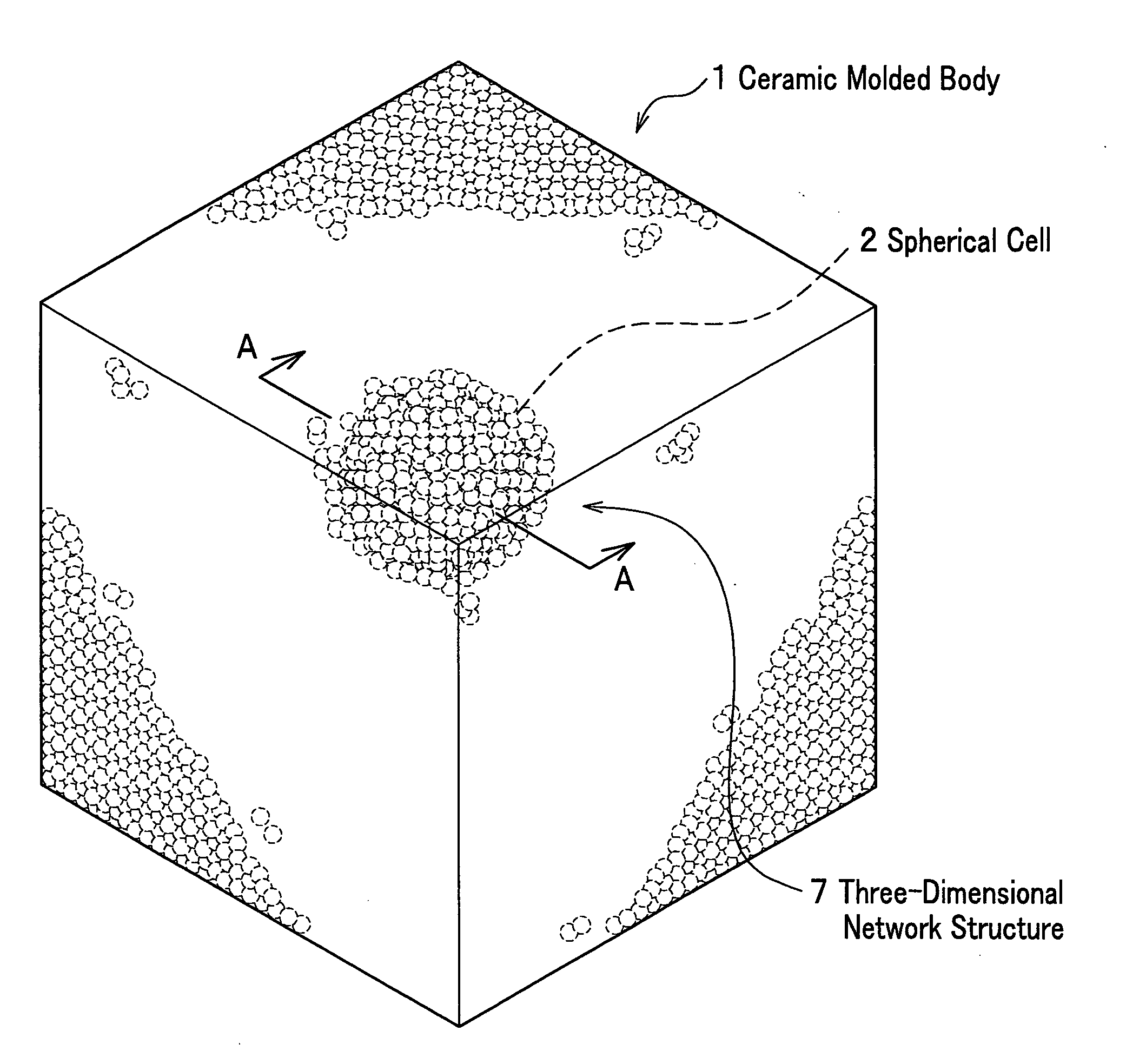
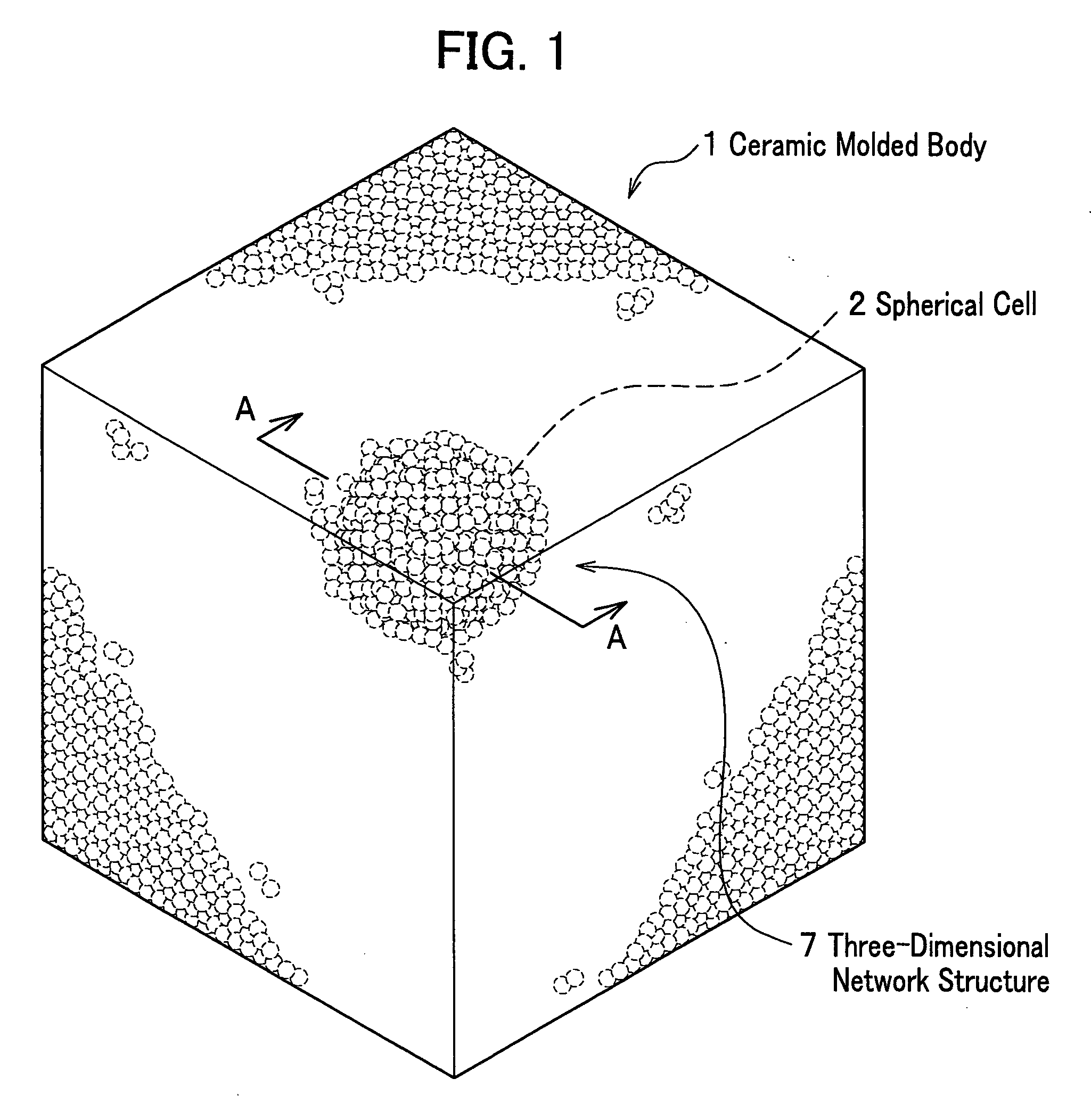
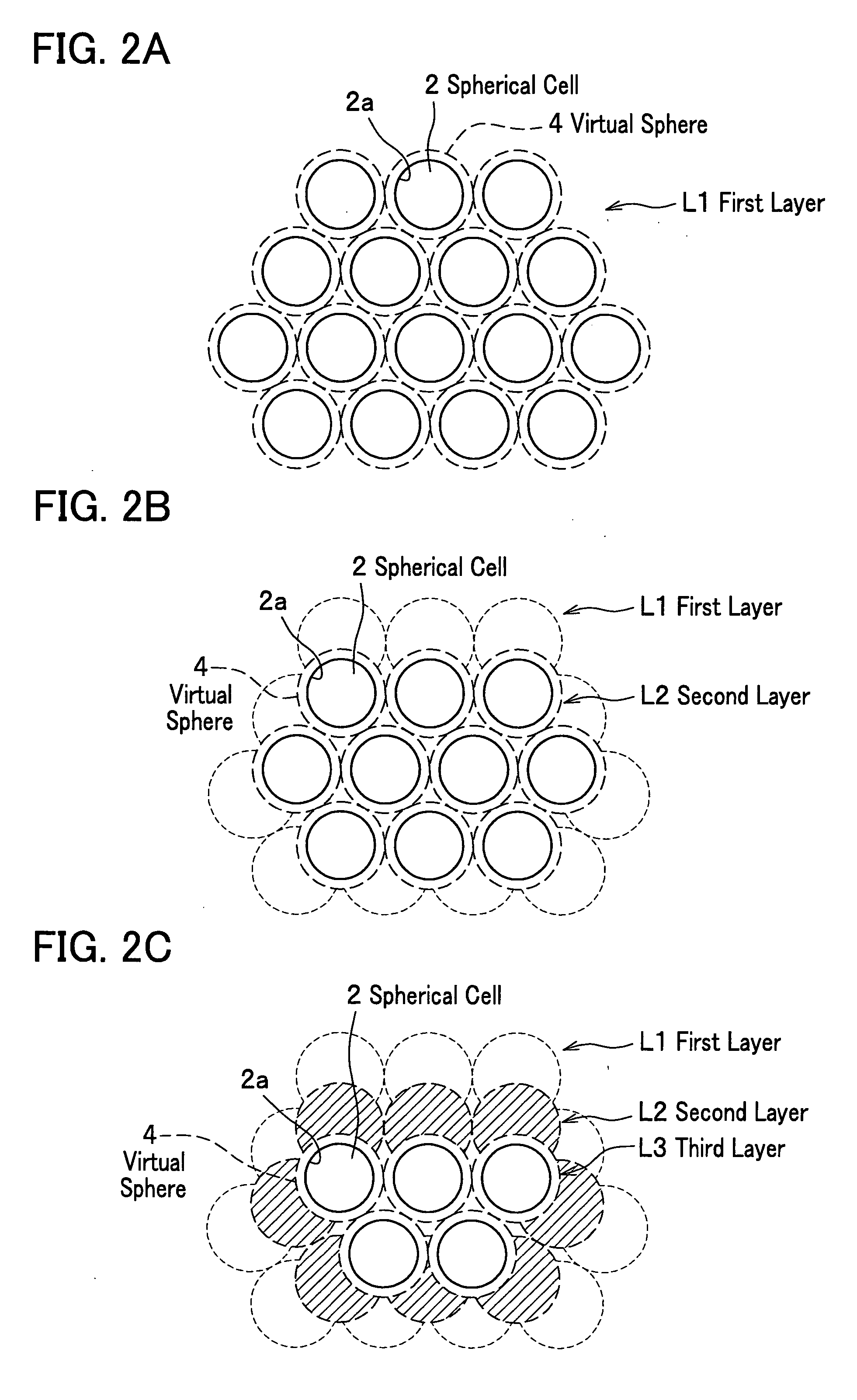
The ceramic molded body of the present invention includes spherical cells of a spherical bubble plurally formed therein: in the ceramic molded body the spherical cells neighboring each other are communicated through communication porosities and form a three-dimensional network structure, and a ratio (Md / MD) of a median (Md) of inner diameters of the communication porosities to a median (MD) of inner diameters of the spherical cells is less than 0.5. In the ceramic molded body used for manufacturing a metal matrix composite, a metal is filled within the spherical cells and the communication porosities.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
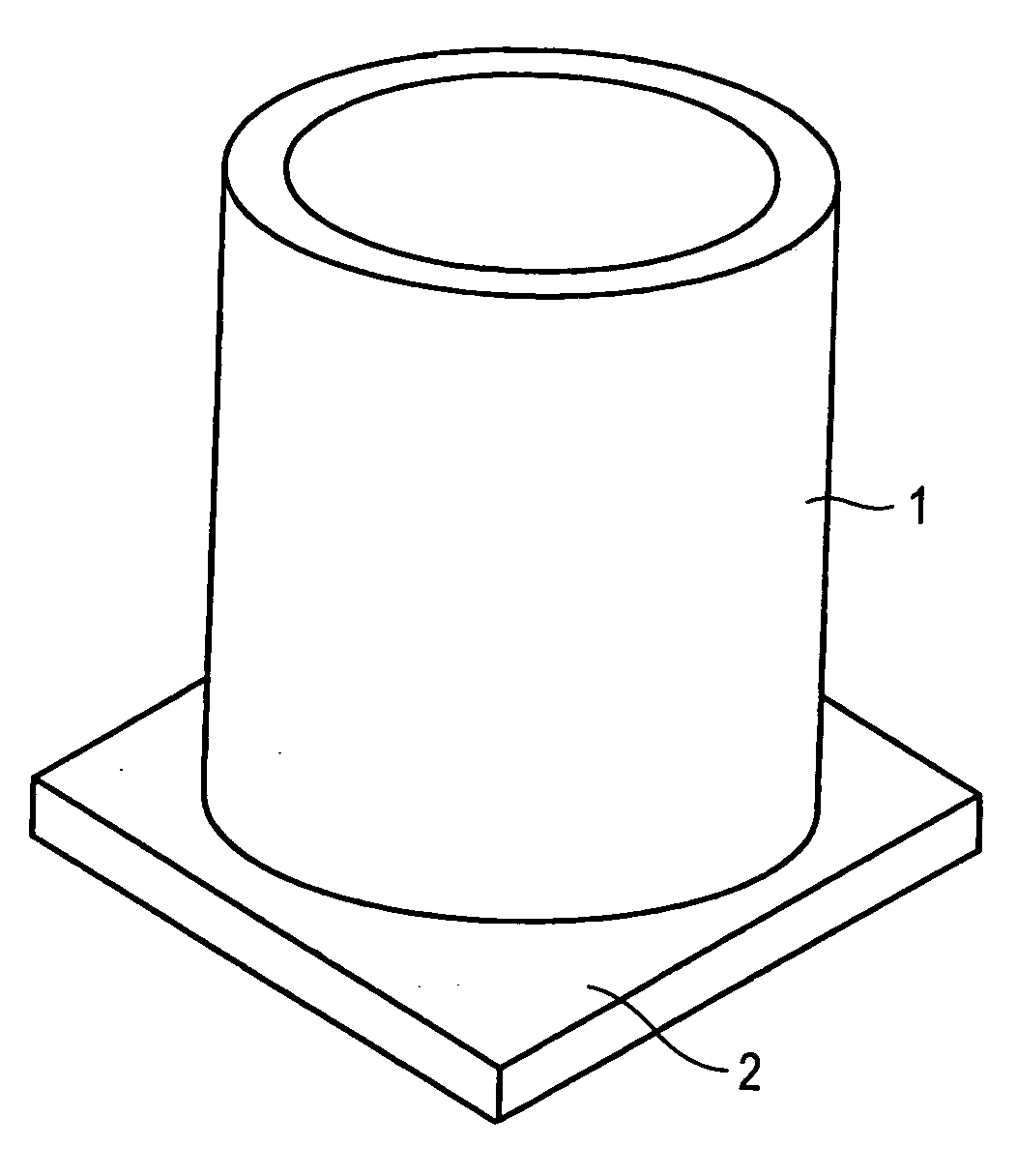
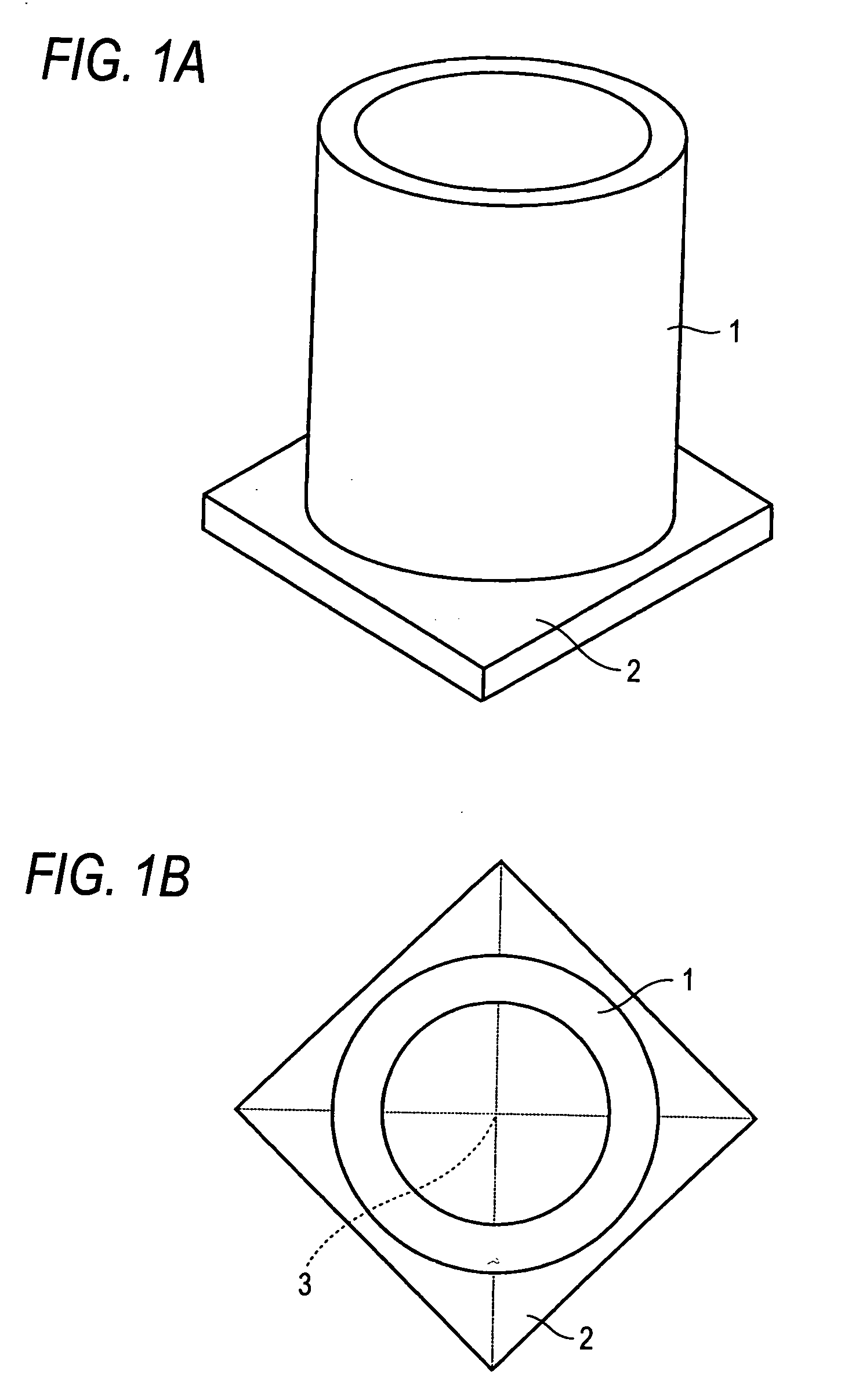
Cylindrical sputtering target, ceramic sintered body, and process for producing sintered body
ActiveUS20060151321A1High densityQuality improvementCellsVacuum evaporation coatingCeramic sinteringHigh density
A hollow cylindrical ceramic sintered body having high density, a process for producing the sintered boy, and a cylindrical ceramic sputtering target having high quality without cracks or breakage, are disclosed. The hollow cylindrical ceramic sintered body is obtained by placing a cylindrical ceramic molding to be sintered on a plate-like ceramic molding having a coefficient of sintering shrinkage similar to that of the cylindrical ceramic molding, and then sintering the resulting assembly, thereby obtaining a hollow cylindrical ceramic sintered body having a relative density of 95% or higher. The cylindrical ceramic sputtering target is prepared using the hollow cylindrical ceramic sintered body.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Normal temperature methane high-efficiency adsorption material
ActiveCN105312026AHigh separation factorLow separation factorProductsOther chemical processesCeramic compositeCeramic molding
The invention relates to a normal temperature methane high-efficiency adsorption material and a preparation method thereof. The material is characterized in that a metal organic skeleton composite material containing transition metals Fe III, Zn II, Cu II, Ni II and Co III grows on an active carbon ceramic mainly prepared from active carbon and molecular sieve in an in situ manner. The preparation method of the normal temperature methane high-efficiency adsorption material comprises the following steps: carrying out dry mixing and ball milling on one or more of chlorides and sulfates of Fe<3+>, Zn<2+>, Cu<2+>, Ni<2+> and Co<3+>, high-specific surface area coconut shell active carbon, Y molecular sieve, attapulgite, kaolin and methyl cellulose in proportion, adding a certain amount of water, carrying out wet mixing, kneading, carrying out vacuum pugging, ageing, carrying out extrusion molding, drying in the shade, carrying out microwave irradiation sizing to obtain an active carbon ceramic molding material containing transition metals, immersing the molding material in a mixed solution containing an organic solvent, an deprotonated alkali and an organic carboxylic acid ligand according to a certain ratio, reacting at 120-180DEG C for 6-24h, carrying out solid-liquid separation, washing, and carrying out microwave vacuum drying to obtain a metal organic skeleton-active carbon ceramic composite material. The material has the characteristics of large specific surface area, developed aperture, high compressive strength, large methane adsorption capacity and high CH4 / N2 and CH4 / CO2 separation coefficients, and can be widely used in the fields of methane pressure swing adsorption separation and low-concentration methane recovery.
Owner:江苏瑞丰科技实业有限公司
Insulative ceramic compact
InactiveUS20020027018A1Satisfactory high-frequency characteristicLow dielectric constantFixed capacitor dielectricCeramicsCeramic moldingSilicon oxide
An insulative ceramic compact is composed of a fired mixture of (A) a MgAl2O4, Mg3B2O6 and / or Mg2B205 ceramic powder, and (3) a glass powder including from about 13 to 50% by weight of silicon oxide in terms of SiO2, from 8 to 60% by weight of boron oxide in terms of B2O3, about 20% by weight or less of aluminum oxide in terms of A12O3, and from about 10 to 55% by weight of magnesium oxide in terms of MgO. The insulative ceramic compact can be obtained by firing at low temperatures of about 1000° C. or less, can be obtained by sintering with Ag or Cu, has a low dielectric constant and a high Q value, and is suitable for use in the high-frequency range.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method for the production of an oxide ceramic shaped part and a part produced by such method
InactiveUS20050164045A1Low production costImprove aestheticsImpression capsWood working apparatusOxide ceramicPowder mixture
A method for producing an oxide ceramic shaped part includes pressing a powder provided with a binding material or a powder mixture of an oxide ceramic into a shaped part, pre-sintering the shaped part at substantially atmospheric pressure and a temperature of 600 to 1,300° C., and evacuating a closed container in which the pre-sintered shaped part is disposed with the shaped part having a maximum density of 10 to 90%. The container is at an absolute pressure of less than 40 mbar. Subsequently, an infiltration material is applied onto the shaped part via infiltration with the infiltration material operating to seal off the shaped part relative to the surrounding atmosphere. The length of time of the infiltration is preferably 1 to 10 minutes.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Process for producing metallic or ceramic shaped bodies
ActiveUS20120235330A1Speed up the processCeramic shaping apparatusClaywaresPolyoxymethylenePolymer dissolution
A process for producing a metallic or ceramic shaped body from a thermoplastic material comprisingA) 40 to 65% inorganic sinterable powder AB) 35 to 60% binderB1) 50 to 95% polyoxymethylene homo- or copolymers;B2) 5 to 50% of a polymer dissolved or dispersed in B1) with a particle size of less than 1 μm,andC) 0 to 5% by volume of a dispersing aid,by injection molding or extrusion to give a green body, removing the binder and sintering, which comprises removing the binder bya) treating the molding with a solvent which extracts the binder component B2) from the molding and in which the binder component B1) is insoluble,b) removing the solvent from the molding by drying, andc) treating the molding in an acid-containing atmosphereis described.
Owner:BASF AG
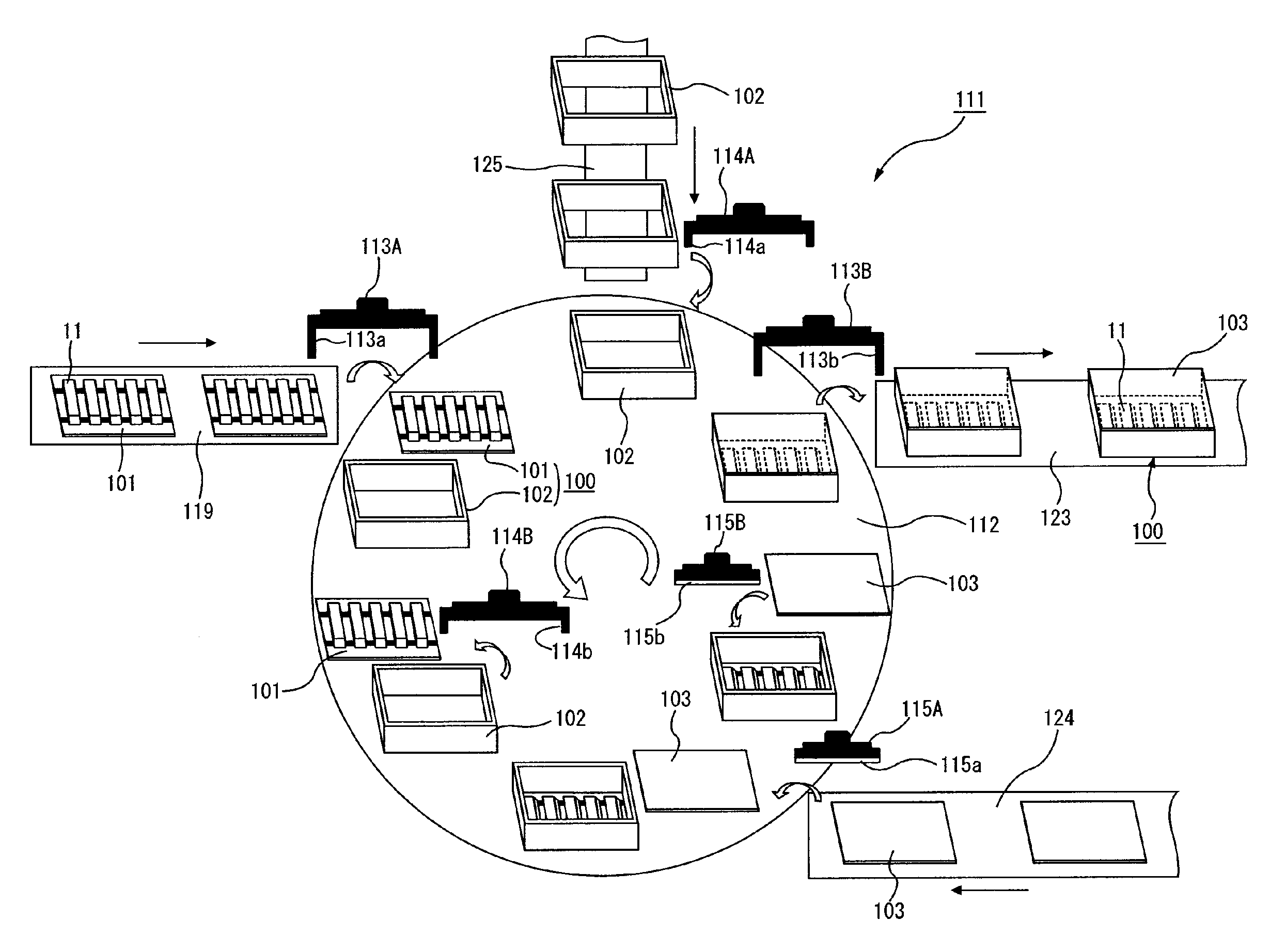
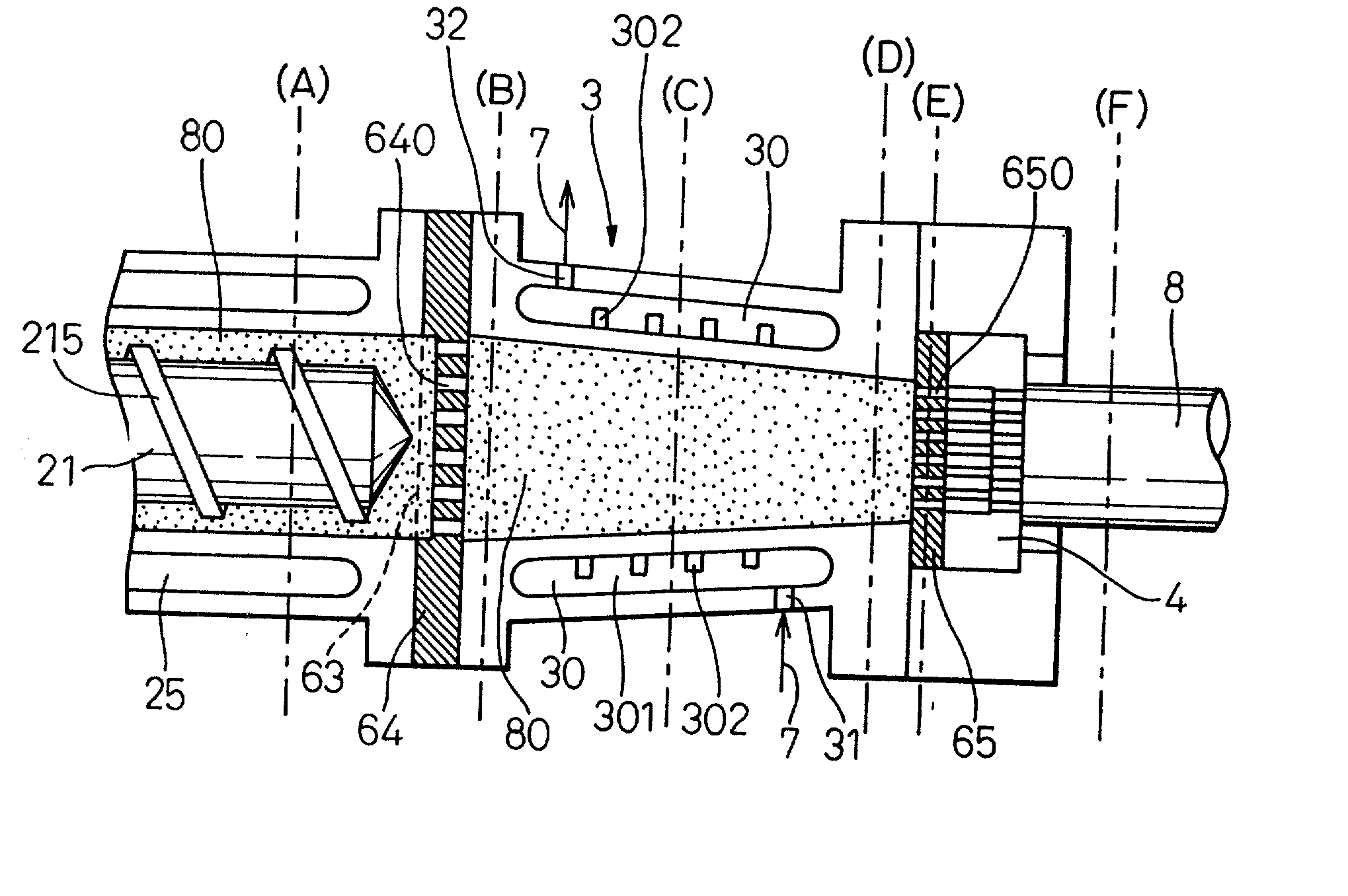
Production method of ceramic moldings and apparatus therefor
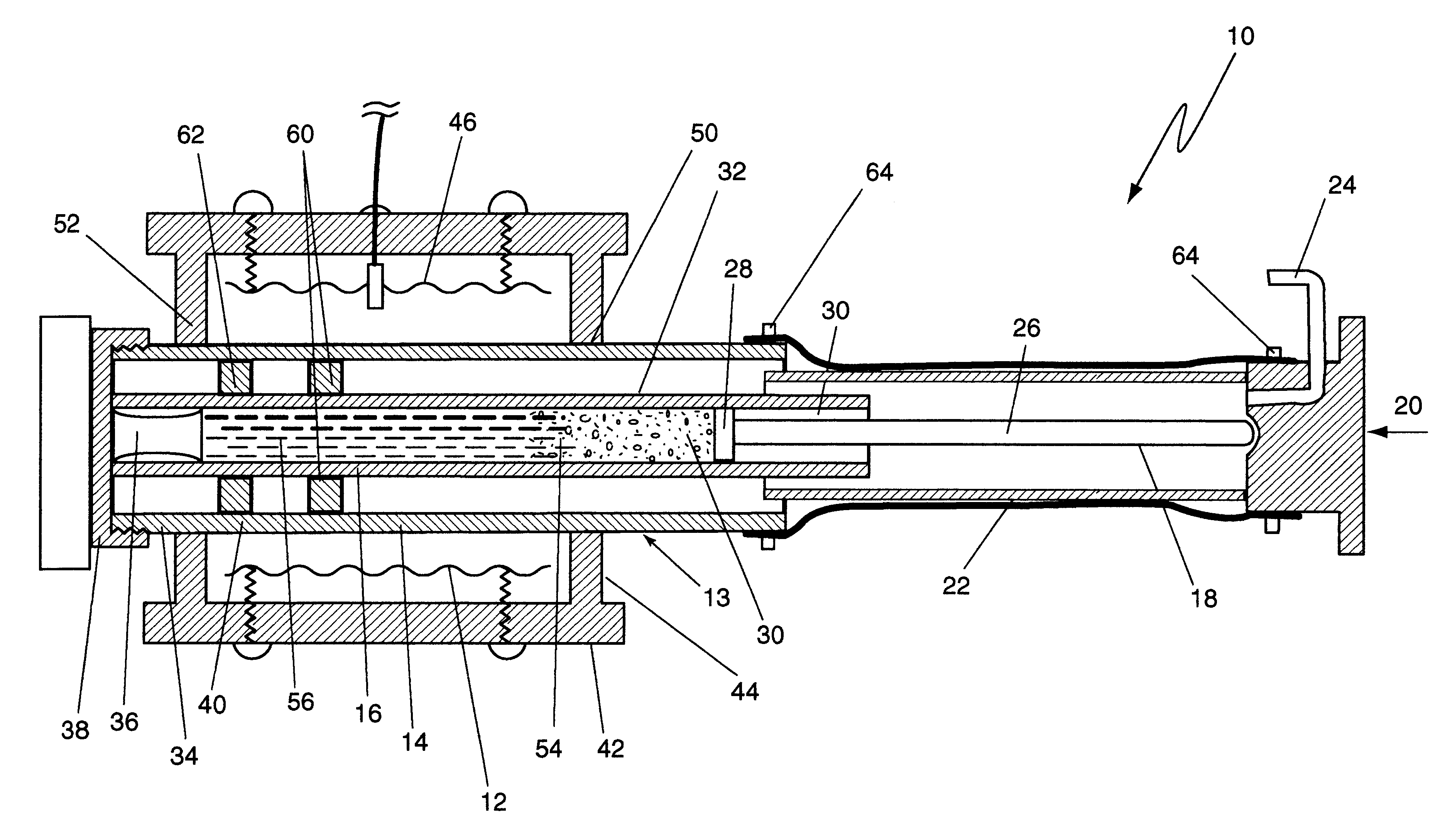
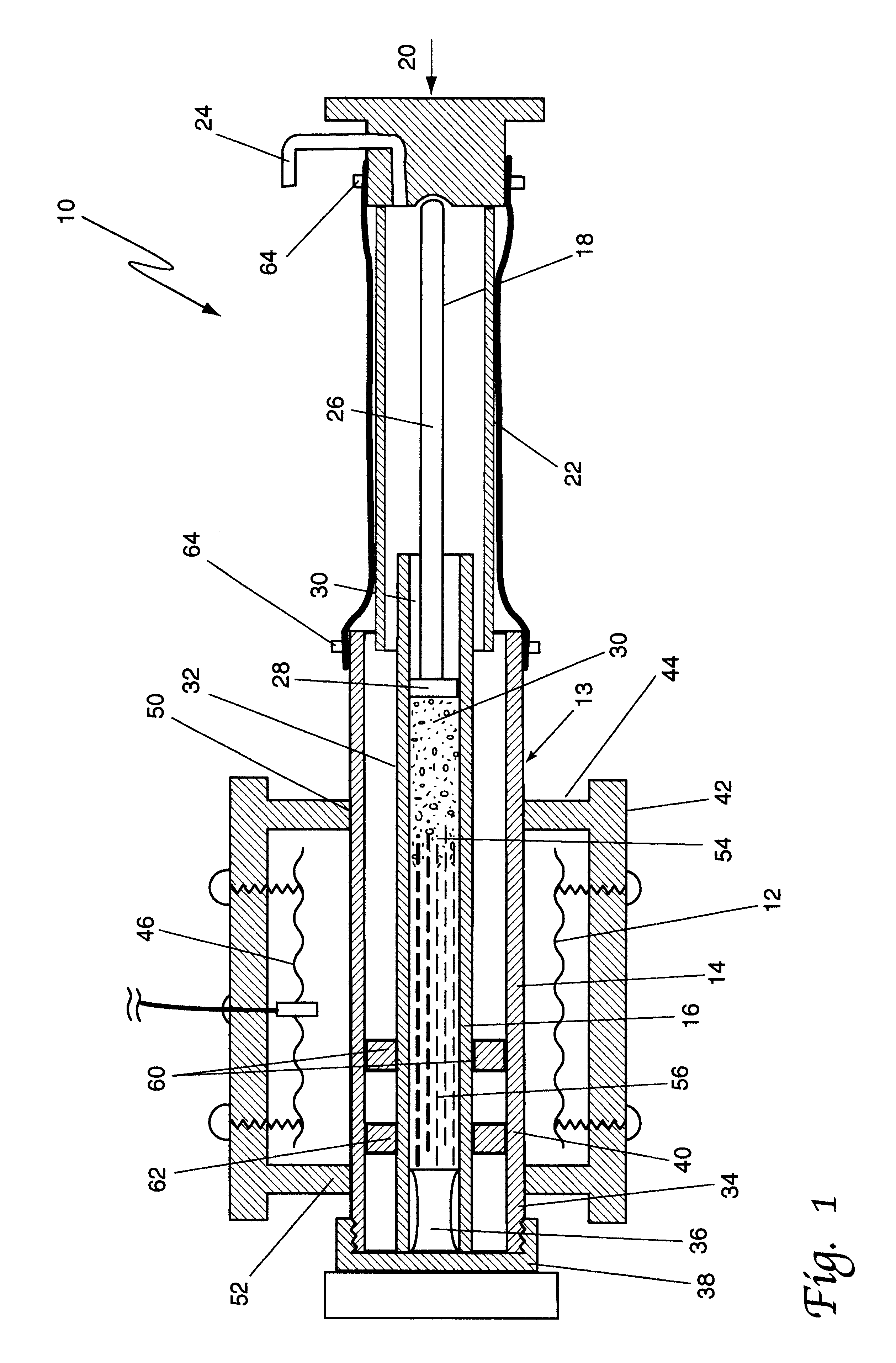
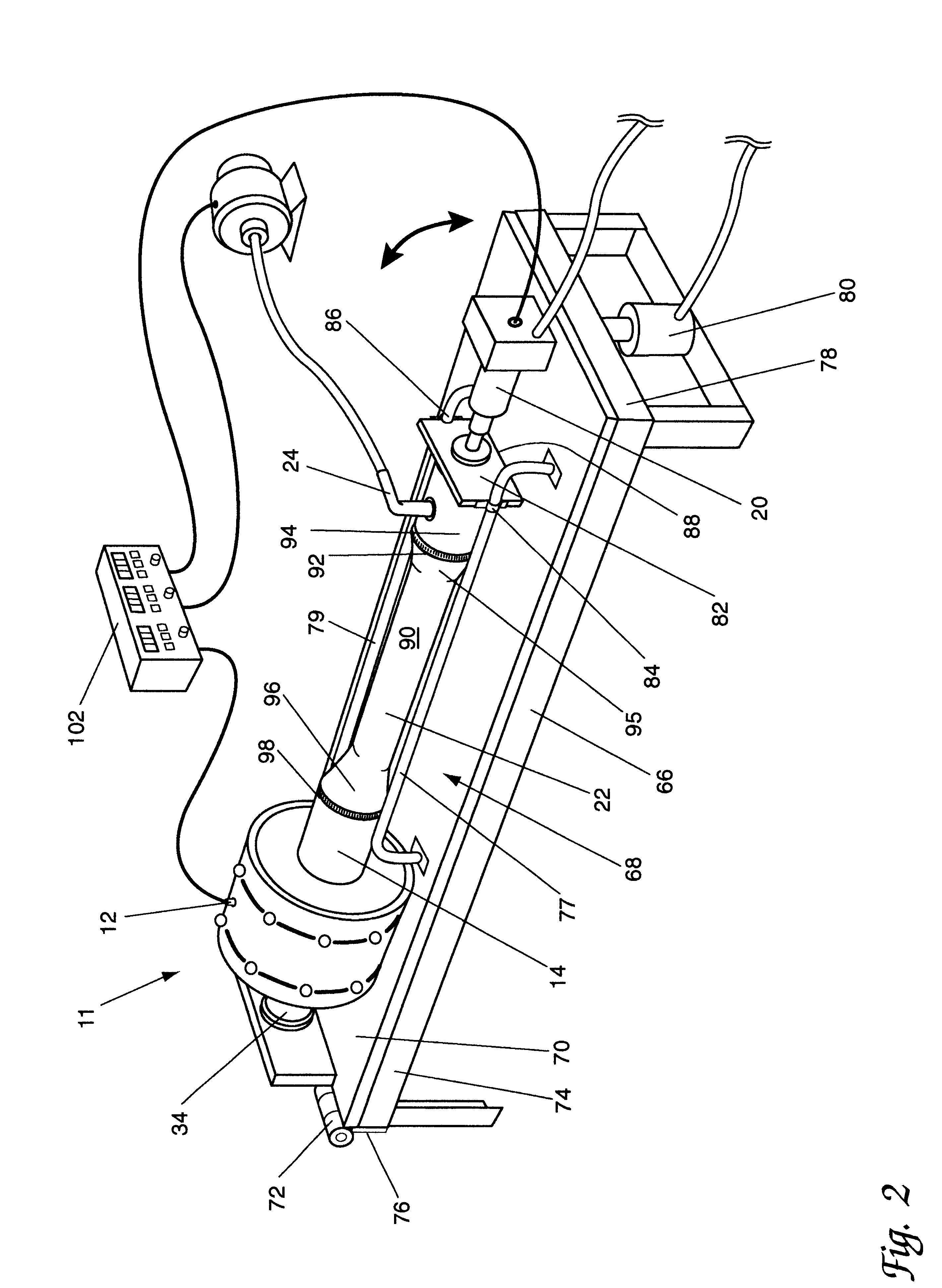
InactiveUS20020167102A1Easy to shapeEasy to controlFrozen sweetsConfectioneryMetallurgyCeramic molding
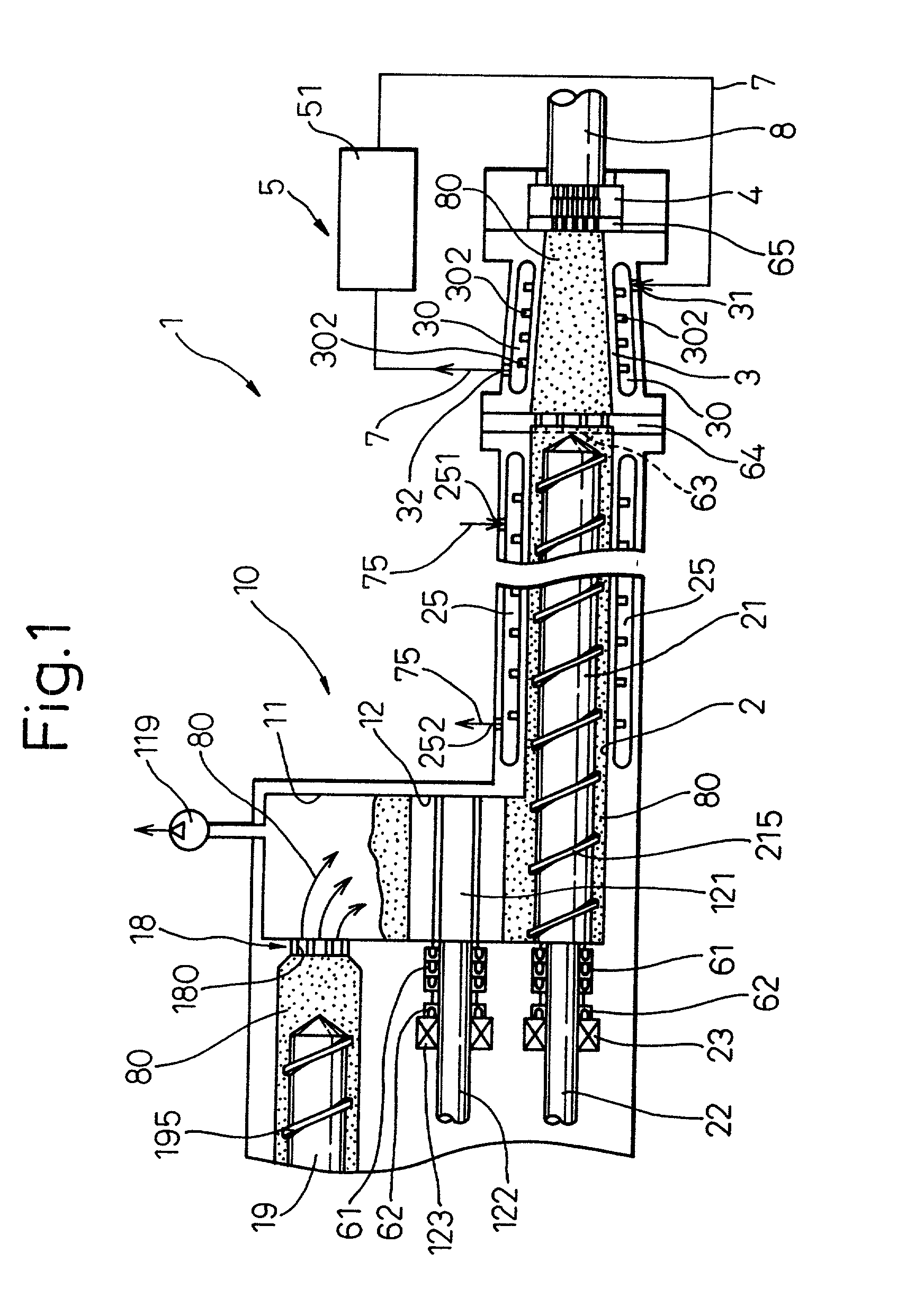
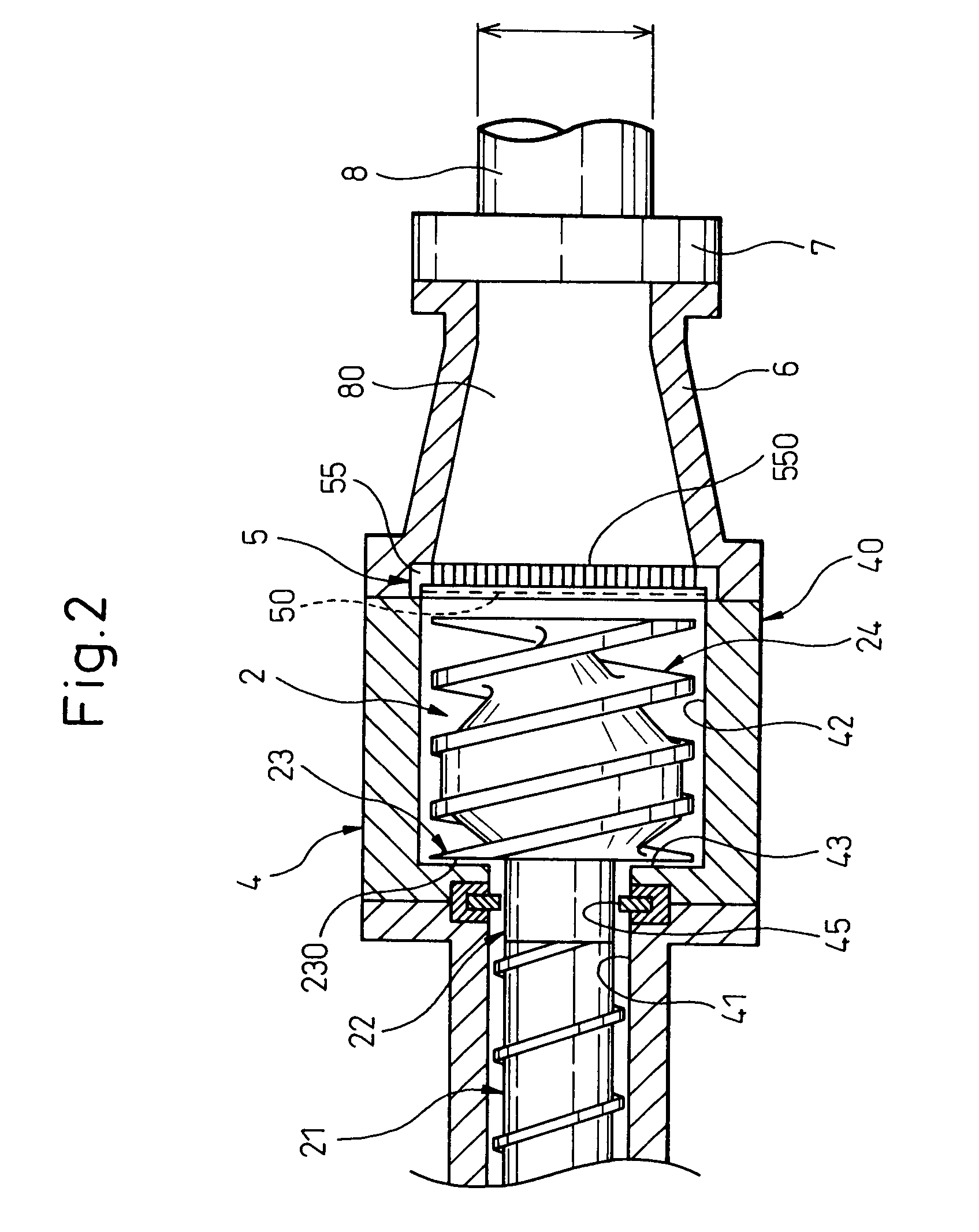
In a method of producing a ceramic molding 8 having a desired shape by extruding a ceramic material 80 pressure-fed into a resistance pipe 3 from a mold 4 by using a production apparatus including a screw type extruder 10 and the mold 4 connected to the distal end of the extruder 10 through the resistance pipe 3, the ceramic material 80 pressure-fed from the extruder 10 into the resistance pipe 3 is heated or cooled from round the periphery of the resistance pipe 3 so as to control the shape of the ceramic molding 8 extruded from the mold 4.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Process for producing hollow microspheres and process for producing porous molded ceramic
InactiveCN102256695AFirmly attachedQuantity can be controlled arbitrarilyOther chemical processesMicroballoon preparationFoaming agentMicrosphere
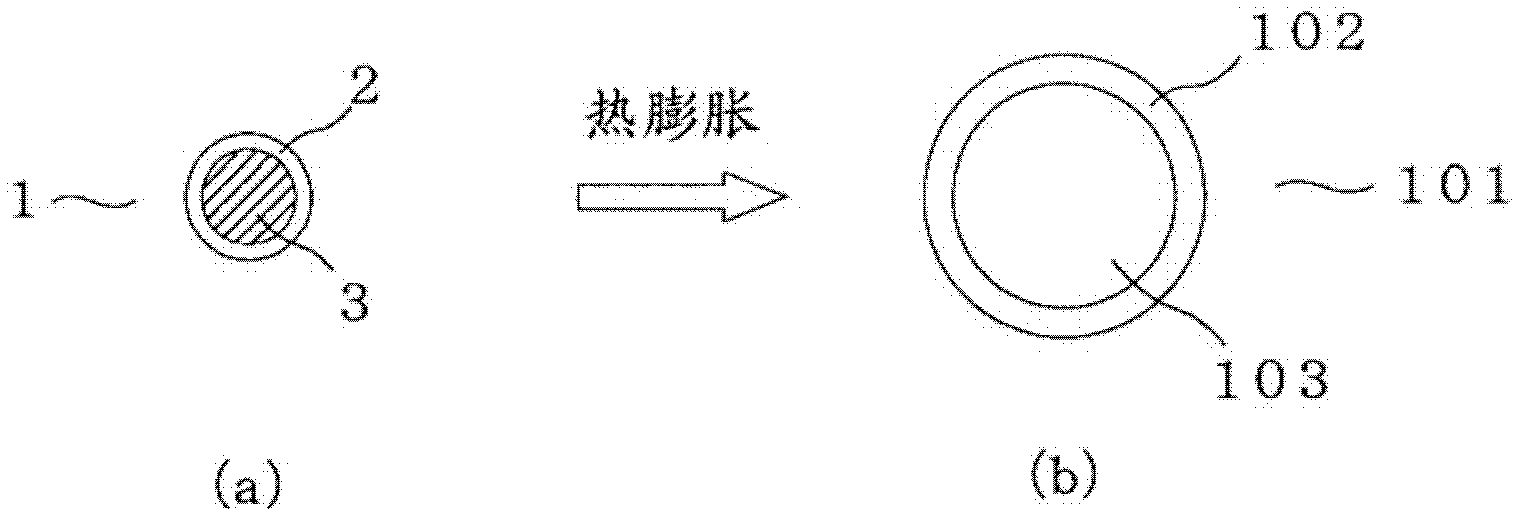
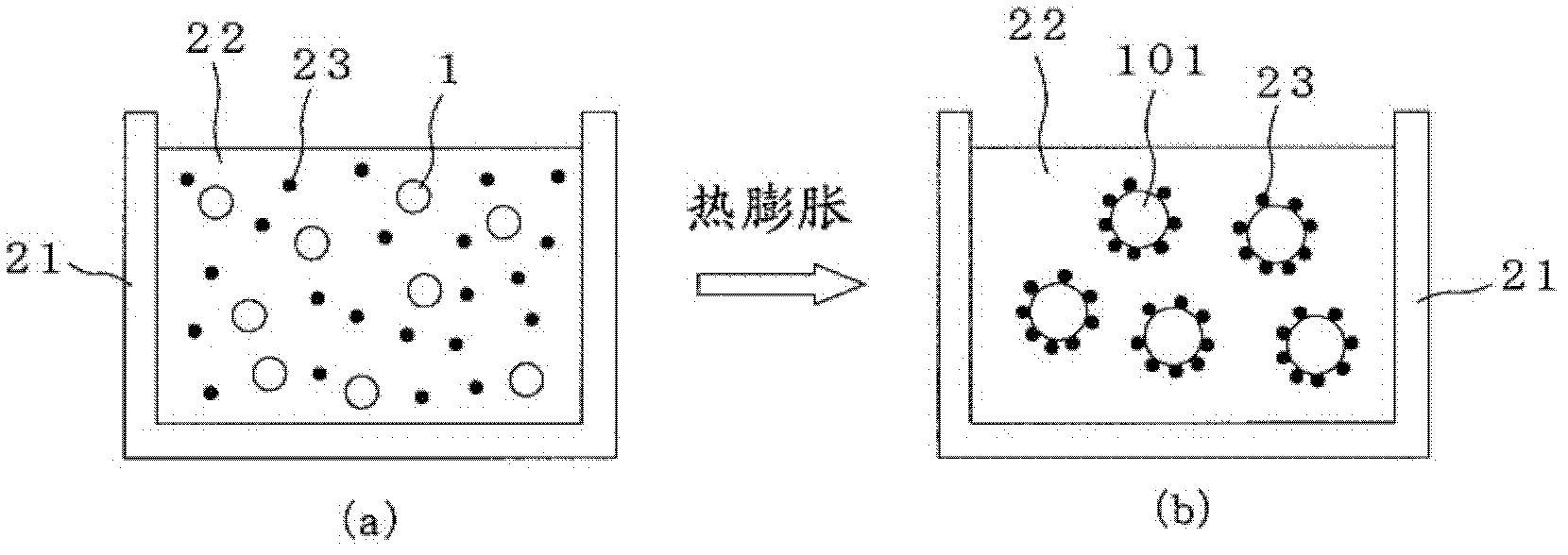
The invention provides a process for producing hollow microspheres which comprises: a step (1) in which heat-expandable microspheres having a microcapsular structure comprising a shell formed from a thermoplastic resin and, encapsulated therein, a blowing agent capable of gasifying or generating a gas and a solid material having an average particle diameter or average major-axis length smaller than the average particle diameter of the heat-expandable microspheres are dispersed in a liquid dispersion medium to prepare a slurry; and a step (2) in which the heat-expandable microspheres are heated in the slurry to soften and thermally expand the shells thereof, thereby forming hollow microspheres having the solid material adherent to the surface of the softened shells.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Conductive pattern formation ink, conductive pattern and wiring substrate
InactiveUS20090145638A1Improve reliabilityStably ejectedNanotechConductive layers on insulating-supportsWater basedGas analysis
A conductive pattern formation ink which can be stably ejected in the form of liquid droplets and form a conductive pattern having high reliability, a conductive pattern having high reliability, and a wiring substrate provided with the conductive pattern and having high reliability are provided. The conductive pattern formation ink is used for forming a conductive pattern by ejecting the ink in the form of liquid droplets on a surface of a ceramic molded body using a liquid droplet ejecting method, the ceramic molded body being made of a material containing ceramic particles and a binder. The ink contains a water-based dispersion medium, and metal particles dispersed in the water-based dispersion medium, wherein the water-based dispersion medium contains oxygen molecules and nitrogen molecules, and wherein when the water-based dispersion medium is analyzed using a gas chromatography method, a total amount of the oxygen and nitrogen molecules contained in the water-based dispersion medium is 12 ppm or less.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Composition for ceramic bonding and ceramic bonded article
The present invention provides a composition for ceramic bonding, which comprises 3-55% by volume of ceramic particles, 1-25% by volume of inorganic binder, and a liquid medium, wherein the composition further contains hollow particles. The invention also provides a ceramic bonded article comprising a ceramic bonding layer formed by applying the composition to a bonding surface of a ceramic molded body and then heating the composition applied.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD +1
Apparatus for extruding ceramic molding
InactiveUS7101166B2Quality improvementUniform supplyShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersRotary stirring mixersCeramic moldingShell molding
The extruding apparatus has the molding die to form the ceramic molding, the screw extruder containing the extrusion screw to knead and guide the ceramic material toward the molding die. The extrusion screw is comprised of the pressure screw part and the diffusion screw part. The diffusion screw part provided at the front end of the extrusion screw has a diameter greater than the screw diameter of the pressure screw part.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Conductive pattern formation ink, method of forming conductive pattern, conductive pattern and wiring substrate
InactiveUS20090145640A1Improve reliabilityConductive layers on insulating-supportsOrganic chemistryWater basedCeramic molding
A conductive pattern formation ink capable of forming a conductive pattern having high reliability, a conductive pattern having high reliability, a method of forming a conductive pattern having high reliability, and a wiring substrate provided with the conductive pattern and having high reliability are provided. The conductive pattern formation ink is used for forming a conductive pattern by ejecting the ink from a liquid droplet ejection head on a surface of a ceramic molded body made of a material containing ceramic particles and a binder, the liquid droplet ejection head having ejection portions for ejecting the ink in the form of liquid droplets and an ejection surface on which the ejection portions open. The ink contains a water-based dispersion medium, metal particles dispersed in the water-based dispersion medium, and a surface tension adjuster that is contained in the water-based dispersion medium and adjusts surface tension of the ink, wherein in the ink whose surface tension is adjusted by the surface tension adjuster, a contact angle of the ink with respect to the ejection surface of the liquid droplet ejection head at 25° C. is in the range of 50 to 90°, and a contact angle of the ink with respect to the surface of the ceramic molded body at 25° C. is in the range of 45 to 85°.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
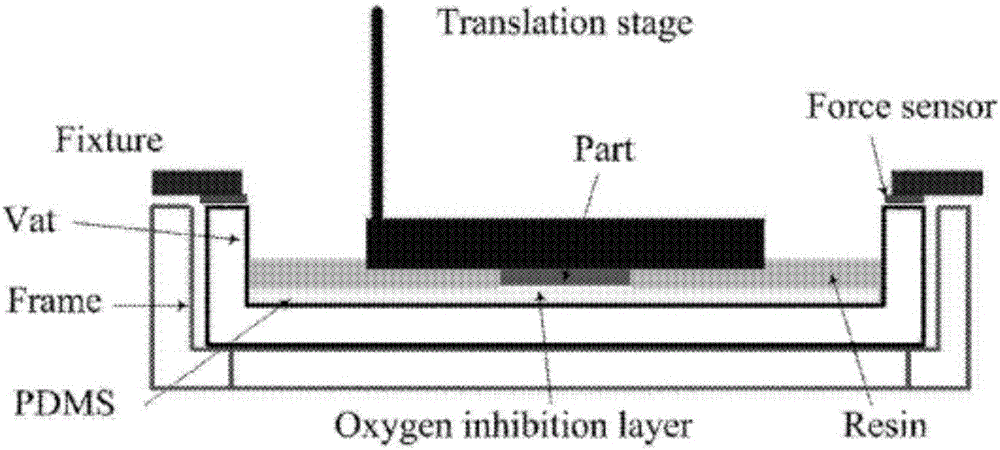
Apparatus for hot vacuum extrusion of ceramics
This specification discloses a method and apparatus for forming and extruding ceramic materials. The apparatus utilizes a vacuum chamber mounted within a heating chamber or element; and the ceramic forming chamber is mounted within the vacuum chamber. A press is slidably mounted within vacuum and forming chambers in order to apply pressure to the ceramic materials during the heating step and subsequently during the ceramics extrusion step. The heating chamber applies heat to the vacuum chamber and forming chamber during the sintering and extrusion step. The forming chamber preferably remains in position within the vacuum chamber during the entire ceramic article manufacturing process.
Owner:CERAMEXT LLC
Composite ceramic powder and ceramic forming method
ActiveCN107540379AReduce absorptionIncrease reflectionAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic moldingComposite ceramic
The invention provides composite ceramic powder which is used for photo curing. The composite ceramic powder comprises a ceramic powder body and a wrapping lawyer wrapping the ceramic powder body, andthe color of the wrapping layer is lighter than that of the ceramic powder body. The invention further provides a ceramic forming method. The method comprises the steps that the composite ceramic powder which is used for photo curing is provided; ceramic slurry with the composite ceramic powder is prepared; a three-dimensional solid model of parts to be printed is established, the thickness of aprinting layer is determined, and the three-dimensional solid model is layered according to the layer thickness; the ceramic slurry is subjected to photo curing three-dimensional printing, and part bodies are prepared.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Epoxy mould material for ceramic forming and its preparation method
InactiveCN1962757AStable thixotropyEasy to processCeramic shaping apparatusFiltration separationEpoxyCeramic molding
The invention discloses a preparing method of porous mould through heating W / O typed aqueous dispersion, which comprises the following parts: 100 parts of liquid epoxide resin, 40-70 parts of hardener, 5-10 parts of surface activator with non-ionic typed surface activator with multiple HLB values, 200-350 parts of filler with silica and glass microball, 3-5 parts of white carbon black and 80-140 parts of water.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Porous ceramics shaped body, and process for producing same
InactiveUS20120003464A1Improve filtering effectControlled pore characteristicsLayered productsFiltration separationCeramic moldingTitanium
The process for producing a porous ceramics shaped body comprises a step of firing a shaped body of a starting material mixture which contains an aluminum source powder and a titanium source powder, andthe aluminum source powder satisfies the below formula (1a):(Da90 / Da10)1 / 2<2 (1a)wherein Da90 is a particle diameter corresponding to a cumulative percentage of 90% on a volume basis and Da10 is a particle diameter corresponding to a cumulative percentage of 10% on a volume basis, and these are determined from a particle size distribution of the aluminum source powder measured by a laser diffractometry.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Porous beta-sic-containing ceramic molded article comprising an aluminum oxide coating, and method for the production thereof
ActiveUS20090173050A1High passage densitySmall wall thicknessCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesCeramic moldingPore diameter
The invention concerns a process for the production of a porous β-SiC-bearing ceramic molded body that includes an aluminum oxide layer at the surface of the pores and passages of the porous β-SiC-bearing ceramic molded body. The invention further concerns a porous β-SiC-bearing ceramic molded body which has pores of a mean pore size in the range of between 0.1 urn and 50 μm and an aluminum oxide layer at the surface of the open pores and passages.
Owner:HELSA AUTOMOTIVE GMBH & CO KG
Ceramic molded body and metal matrix composite
InactiveUS7357976B2Improve reducibilityReduce volume ratioLayered productsCeramic shaping apparatusPorosityCeramic molding
The ceramic molded body of the present invention includes spherical cells of a spherical bubble plurally formed therein: in the ceramic molded body the spherical cells neighboring each other are communicated through communication porosities and form a three-dimensional network structure, and a ratio (Md / MD) of a median (Md) of inner diameters of the communication porosities to a median (MD) of inner diameters of the spherical cells is less than 0.5. In the ceramic molded body used for manufacturing a metal matrix composite, a metal is filled within the spherical cells and the communication porosities.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
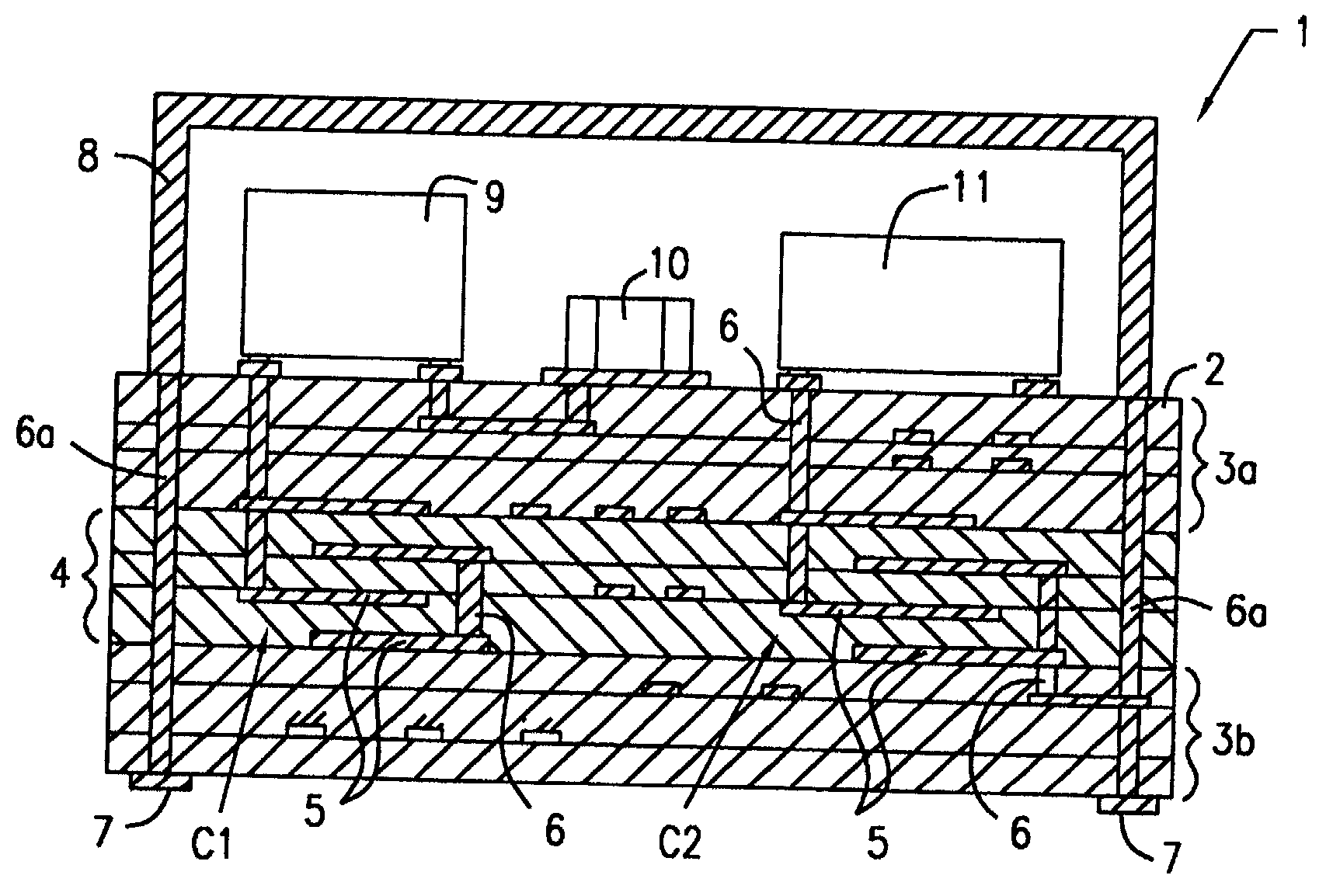
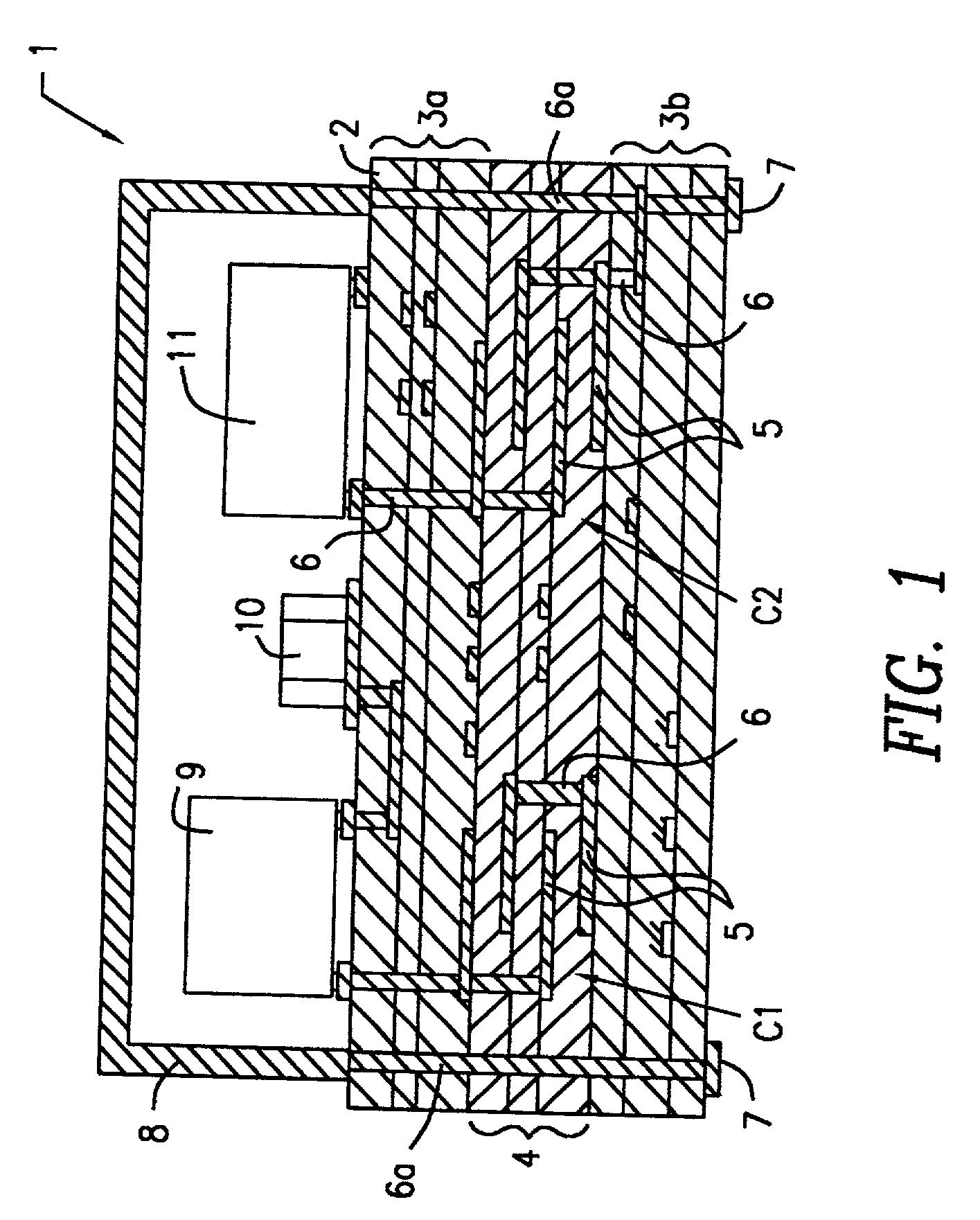
Heat-treating furnace
ActiveUS20090029307A1Avoid breakingEfficient preparationFurnace typesCeramic layered productsCeramic moldingComputer module
A heat treating furnace capable of continuously performing binder removal and subsequent firing without requiring a complicated configuration and increasing the equipment size and cost, for example, for degreasing a ceramic molding which is to be fired in a process for manufacturing a ceramic electronic component. A heat insulator is disposed to surround a heat treatment region in a case, and a reflector is disposed between the inner wall of the case and the insulator in order to reflect heat transferred from the heat treatment region through the heat insulator. A module heater including a heater embedded in the insulator is used. As the reflector, there is used a reflector having a structure in which a plurality of thin plates is arranged so that the main surfaces are arranged in parallel to each other with a predetermined space between the adjacent main surfaces.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
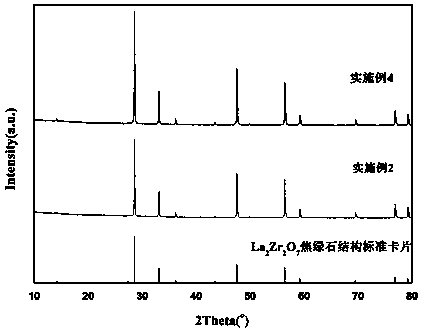
Large-size block La2Zr2O7 ceramic material and hot pressed sintering preparation process thereof
ActiveCN103803972ARealize large-scale industrial productionGood molding effectHigh intensityLarge size
The invention discloses a large-size block La2Zr2O7 ceramic material and a hot pressed sintering preparation process thereof. The process comprises the following steps: sintering and molding a mixed powder raw material of La2O3 and ZrO2 or a La2Zr2O7 powder raw material prepared by a co-precipitation method under the common effects of heat and force to prepare the large-size block La2Zr2O7 ceramic. The essentials of the process are as follows: the cooperative control of a temperature program and a pressure program in a hot pressed sintering process can be used for solving the problem of block ceramic cracking caused by great heat stress generated by low heat conductivity of the La2Zr2O7; temperature adjusting and controlling parameters comprise a heating speed, heat-preservation temperature and time, a cooling rate, and annealing temperature and time; pressure adjusting and controlling parameters comprise a starting pressurizing pressure, a pressurizing and pressure-releasing speed, and pressure maintaining pressure and time. The molding performance of the La2Zr2O7 ceramic prepared by the process is good, the density is high and the appearance specification size is great; the large-size block La2Zr2O7 ceramic material has a high-strength low heat conduction property and can be produced in a large scale.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Sizing material for improving ceramic shaped body prepared by gel pouring shaping method
InactiveCN1948223AImprove stabilityStability is not affectedMixing operation control apparatusClay processing apparatusCross-linkCeramic molding
The present invention relates to a slurry material for preparing ceramic forming body. The described slurry material is made up by using water, ceramic powder, N-substituted acrylamide or methyl acrylamide monomer, cross-linking agent and water-soluble azo initiator, and can be used for improving gel injection forming process. Its preparation method includes the following steps: (1), using water, ceramic powder, N-substituted acrylamide or methyl acrylamide monomer, cross-linking agent and water-soluble azo initiator to make them into pre-mixing liquor, then adding ceramic powder boy under the condition of stirring so as to obtain the slurry. The mass percentage of added pre-mixing liquor is 10-100% of ceramic powder body; (2), in the pre-mixing liquor the mass percentage concentration of added monomer is 2-50% of pre-mixing liquor; the mass percentage concentration of added initiator is 0.1-10% of pre-mixing liquor; and the mass percentage concentration of added cross-linking agent is 0-10% of pre-mixing liquor.
Owner:SHANGHAI GAOCHENG CREATIVE TECH GRP
Metal-supported solid oxide fuel cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103872366ALow costAvoid difficultiesFinal product manufactureCell electrodesCeramic moldingElectrical battery
A provided metal-supported solid oxide fuel cell comprises an electrolyte layer and porous electrode precursor layers at two sides of the electrolyte layer, an anode active material is deposed on the hole inner wall of the porous electrode precursor layer at one side for forming the cell anode, a cathode active material is deposed on the hole inner wall of the porous electrode precursor layer at the other side for forming the cell cathode, and the porous electrode precursor layers at two sides both comprise a porous alloy layer. According to the technical scheme, a rare earth ceramic material in a cell support of a total ceramic structural solid oxide fuel cell is replaced by alloy, so that cost is substantially reduced. The cell support is prepared by utilizing conventional ceramic molding technology, so that the technology is simplified, the cost is low, the operability is high, and batch production is facilitated. The anode material and the cathode material are deposed at the hole inner walls of the porous alloy electrode precursor layers at two side of the electrolyte by employing a chemical liquid-phase deposition process, so that the preparation difficulty of the electrodes of the metal-supported solid oxide fuel cell is solved, and the metal-supported solid oxide fuel cell has good electrochemical properties.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com