Patents
Literature
5026 results about "Layer thickness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Layer thickness is a measure of the height of each successive addition of material in the additive manufacturing or 3D printing process in which layers are stacked. It is one of the essential technical characteristics of every 3D printer; the layer thickness is essentially the resolution of the z-axis, which is the vertical axis.
Barrier material and process for Cu interconnect
InactiveUS20060113675A1Improved electromigration performanceImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorDiffusion barrier
A semiconductor diffusion barrier layer and its method of manufacture is described. The barrier layer includes of at least one layer of TaN, TiN, WN, TbN, VN, ZrN, CrN, WC, WN, WCN, NbN, AlN, and combinations thereof. The barrier layer may further include a metal rich surface. Embodiments preferably include a glue layer about 10 to 500 Angstroms thick, the glue layer consisting of Ru, Ta, Ti, W, Co, Ni, Al, Nb, AlCu, and a metal-rich nitride, and combinations thereof. The ratio of the glue layer thickness to the barrier layer thickness is preferably about 1 to 50. Other alternative preferred embodiments further include a conductor annealing step. The various layers may be deposited using PVD, CVD, PECVD, PEALD and / or ALD methods including nitridation and silicidation methods.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
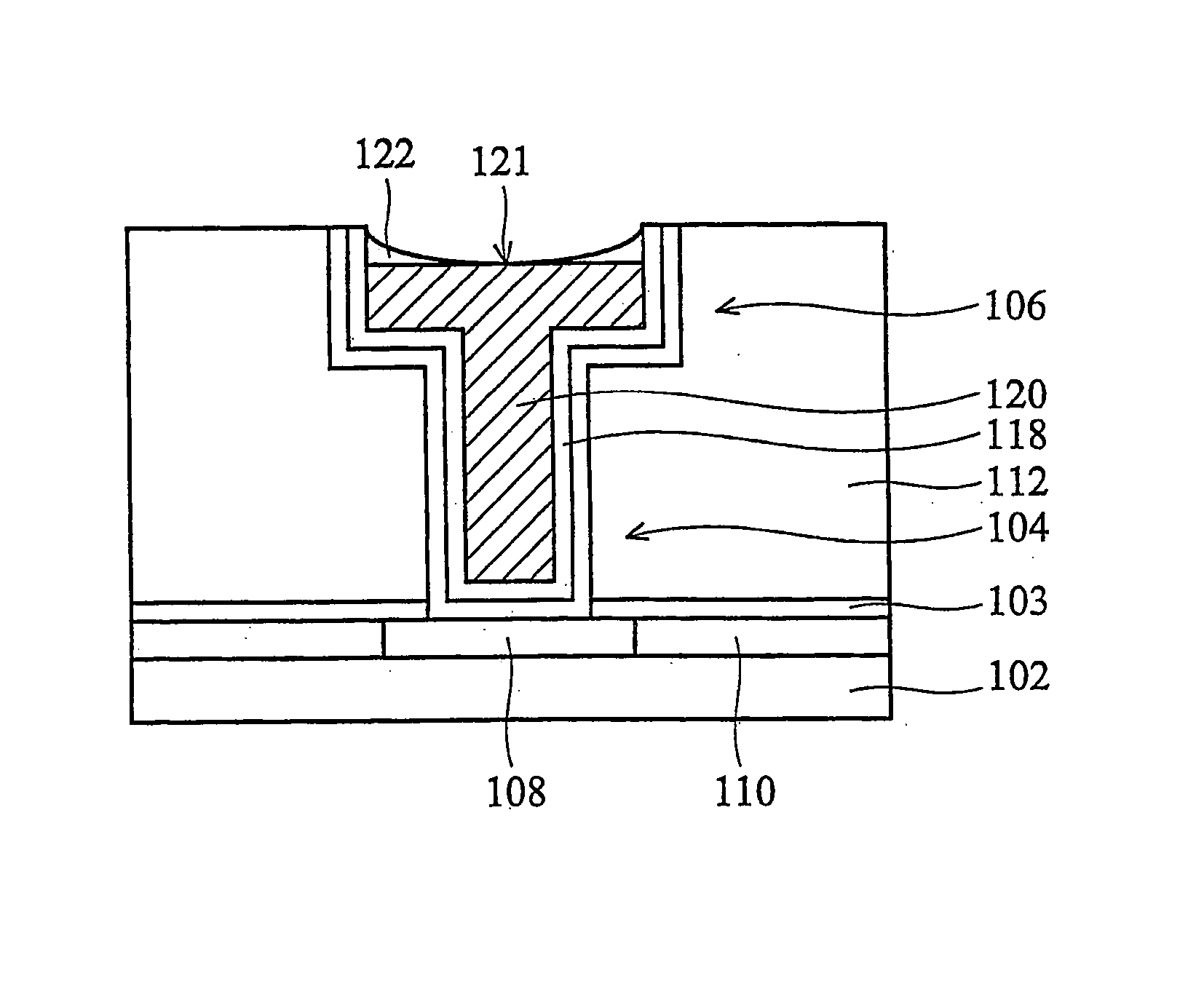
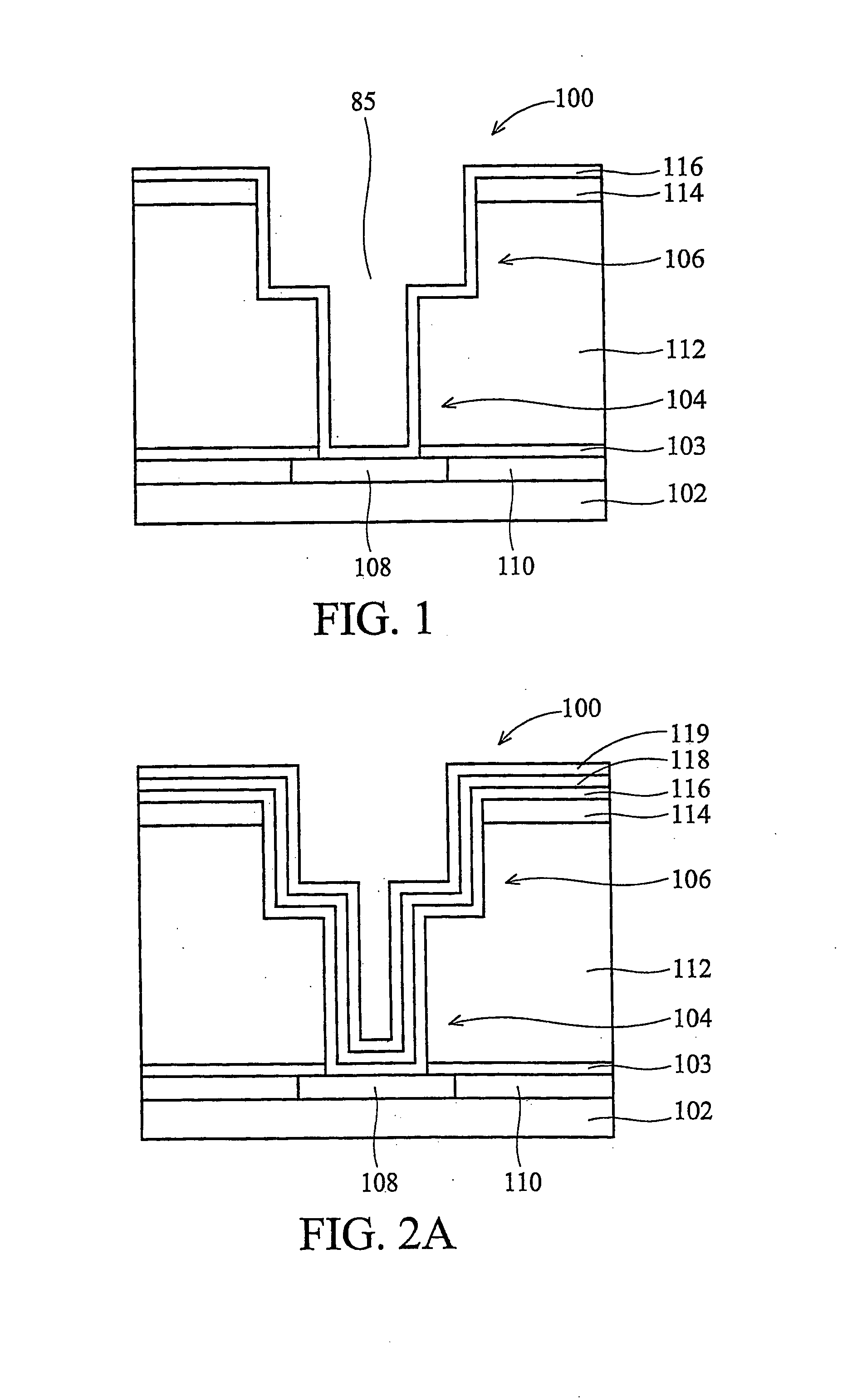
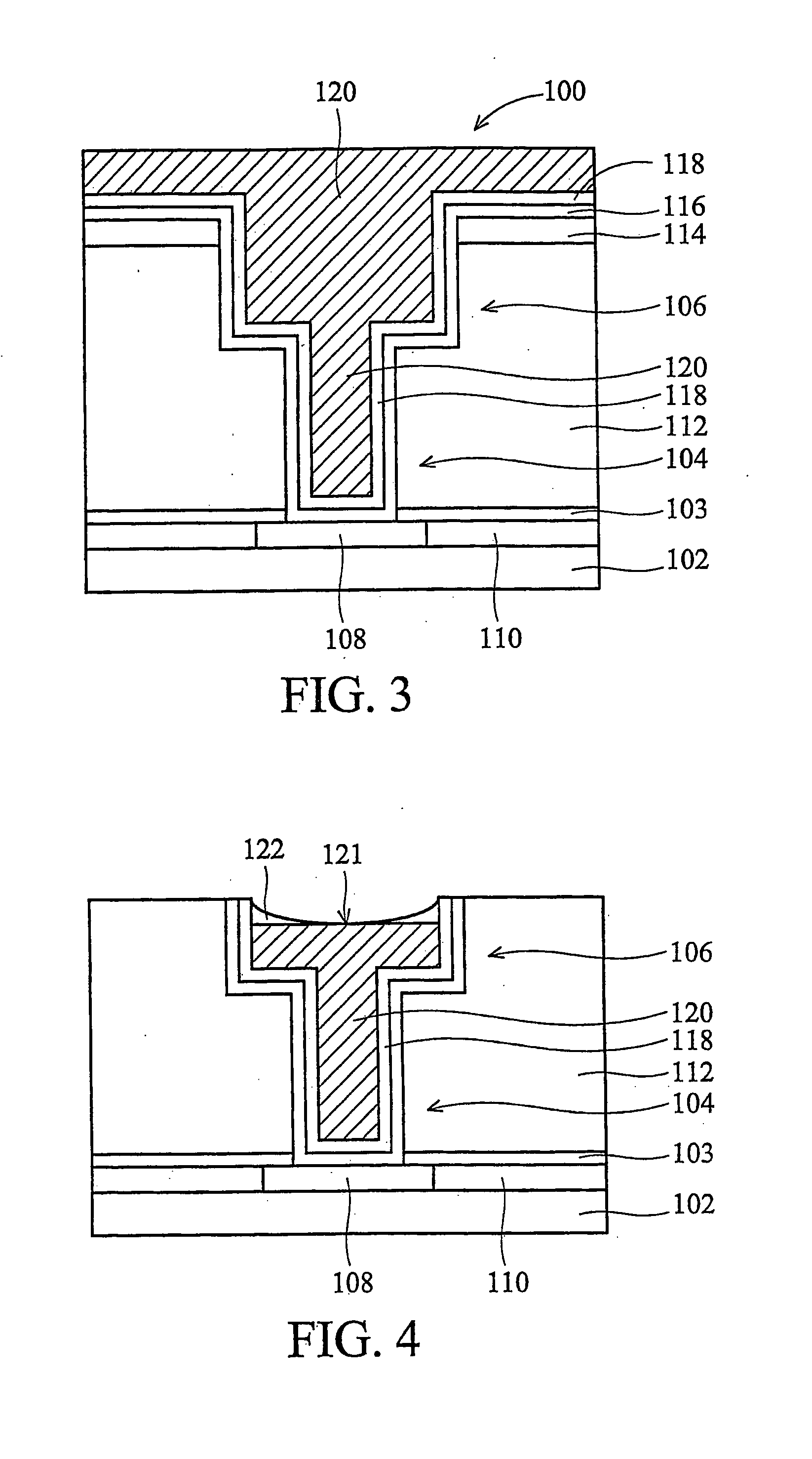
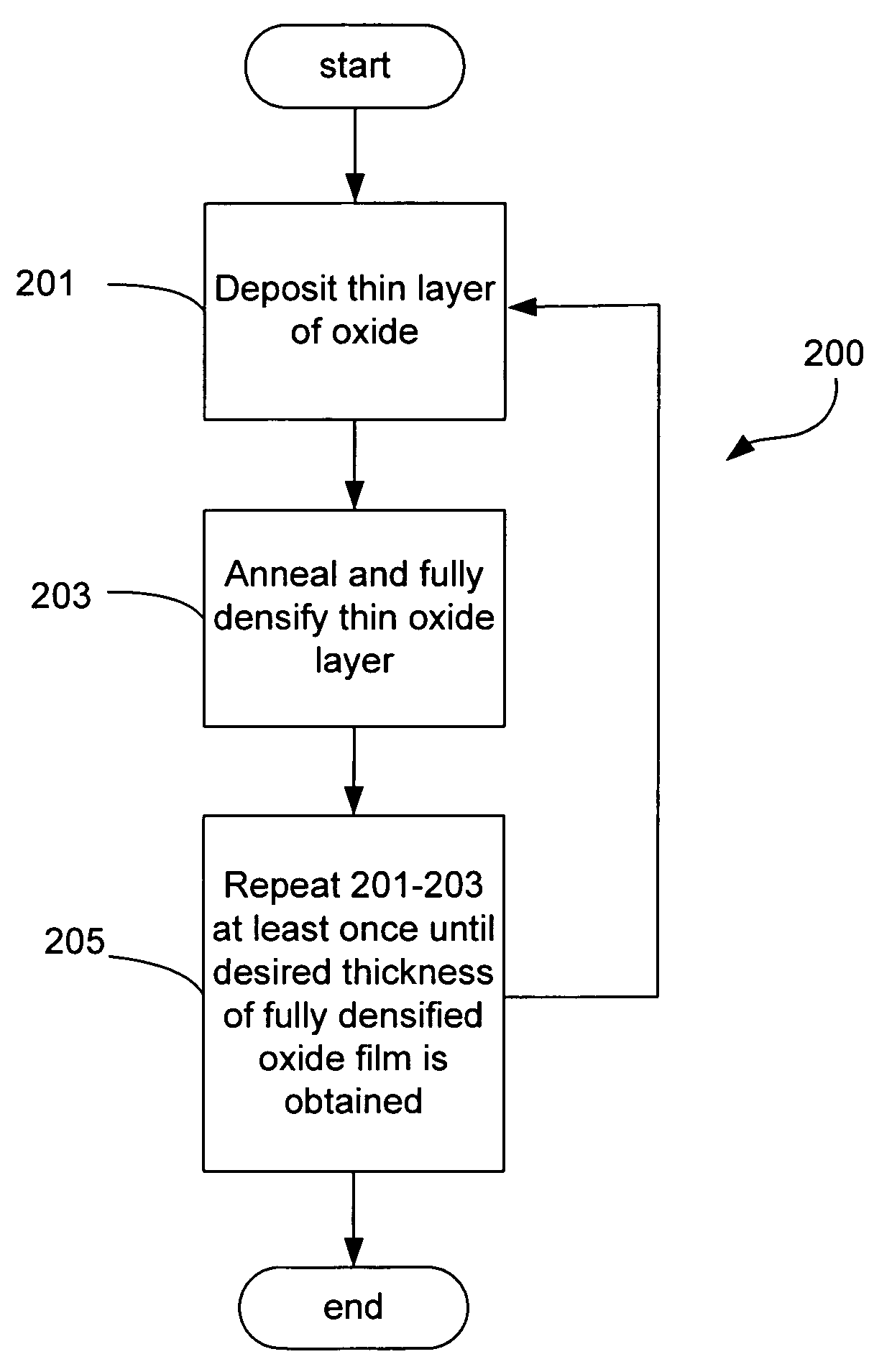
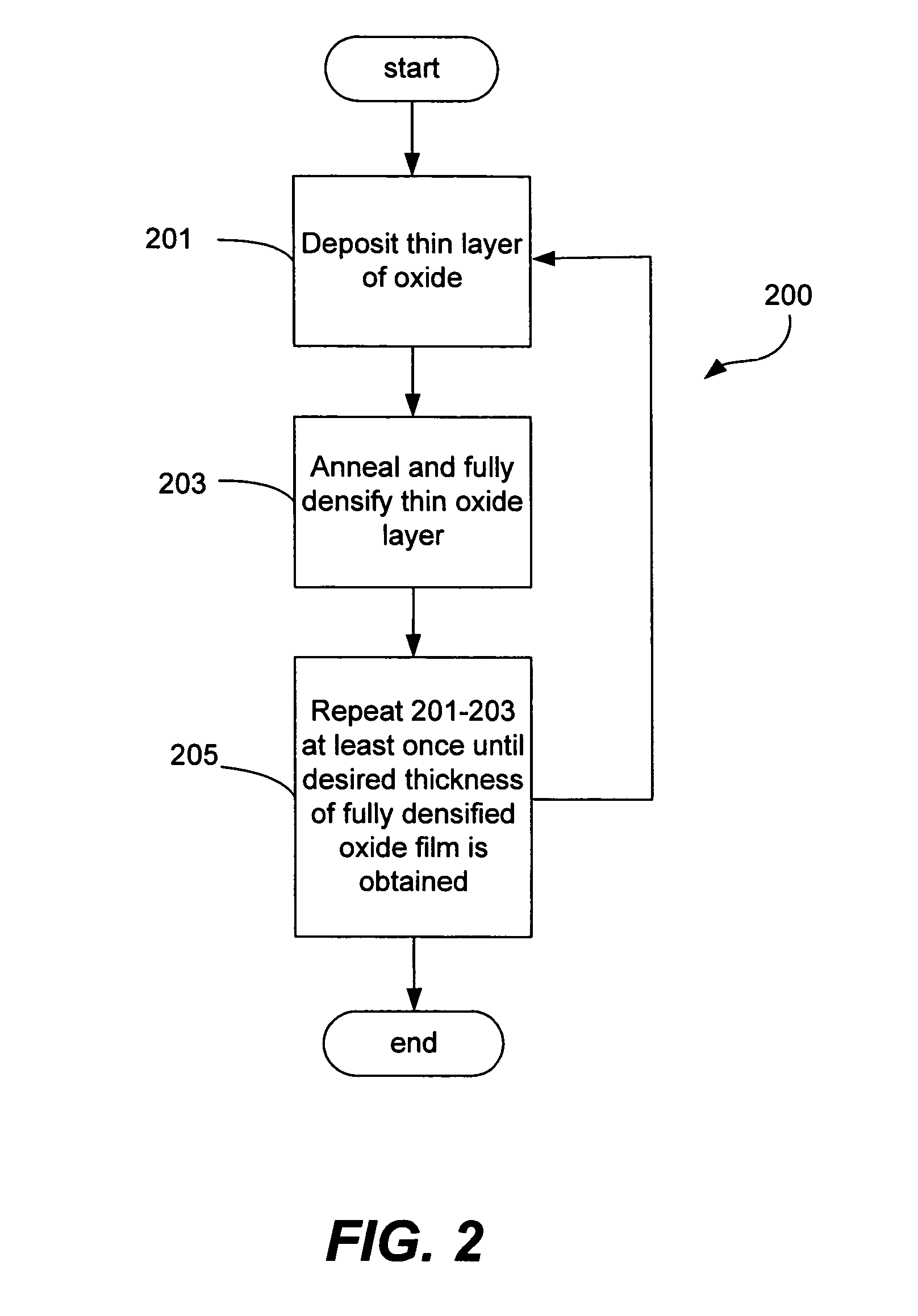
Sequential deposition/anneal film densification method
ActiveUS7790633B1Maintaining film propertyMaintain propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcedure AgentsOptoelectronics
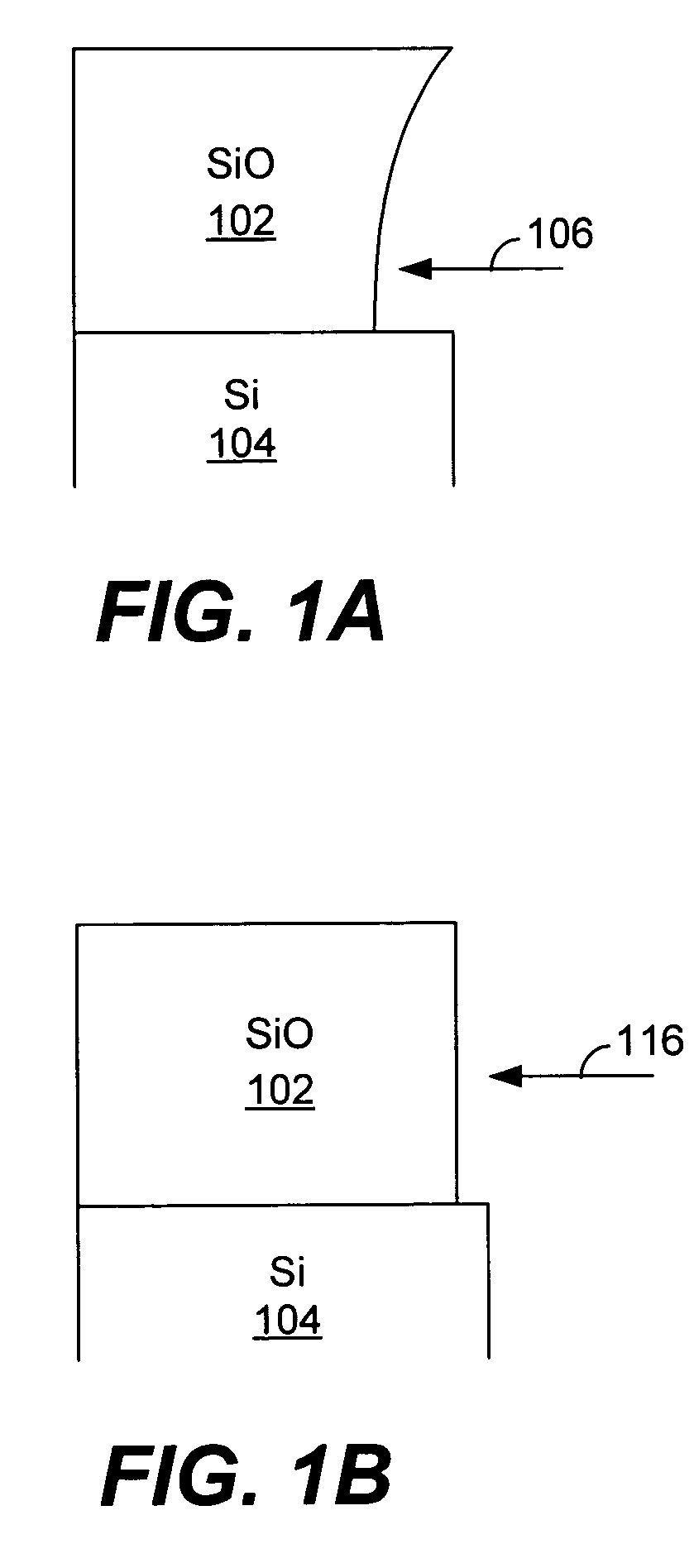
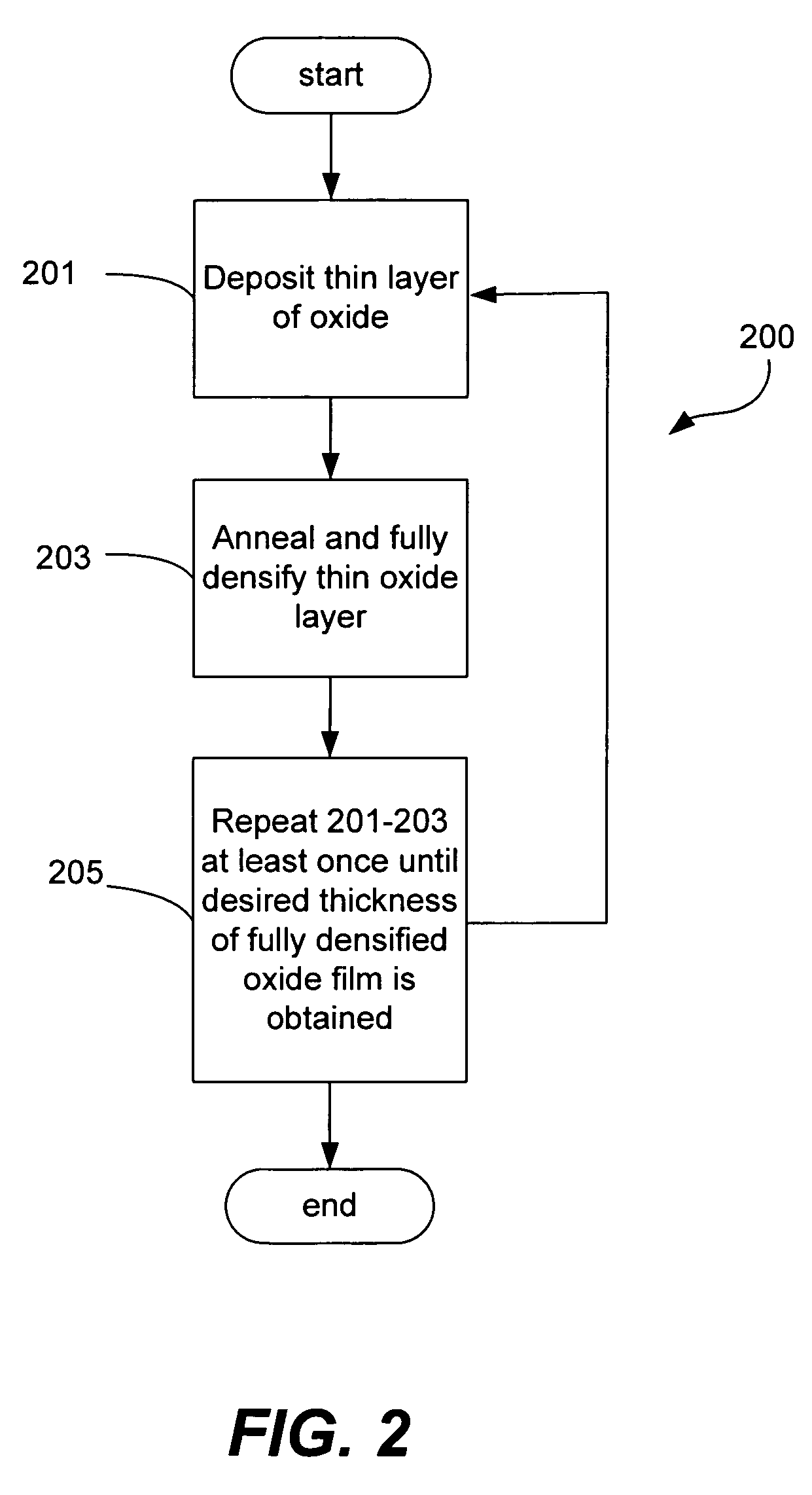
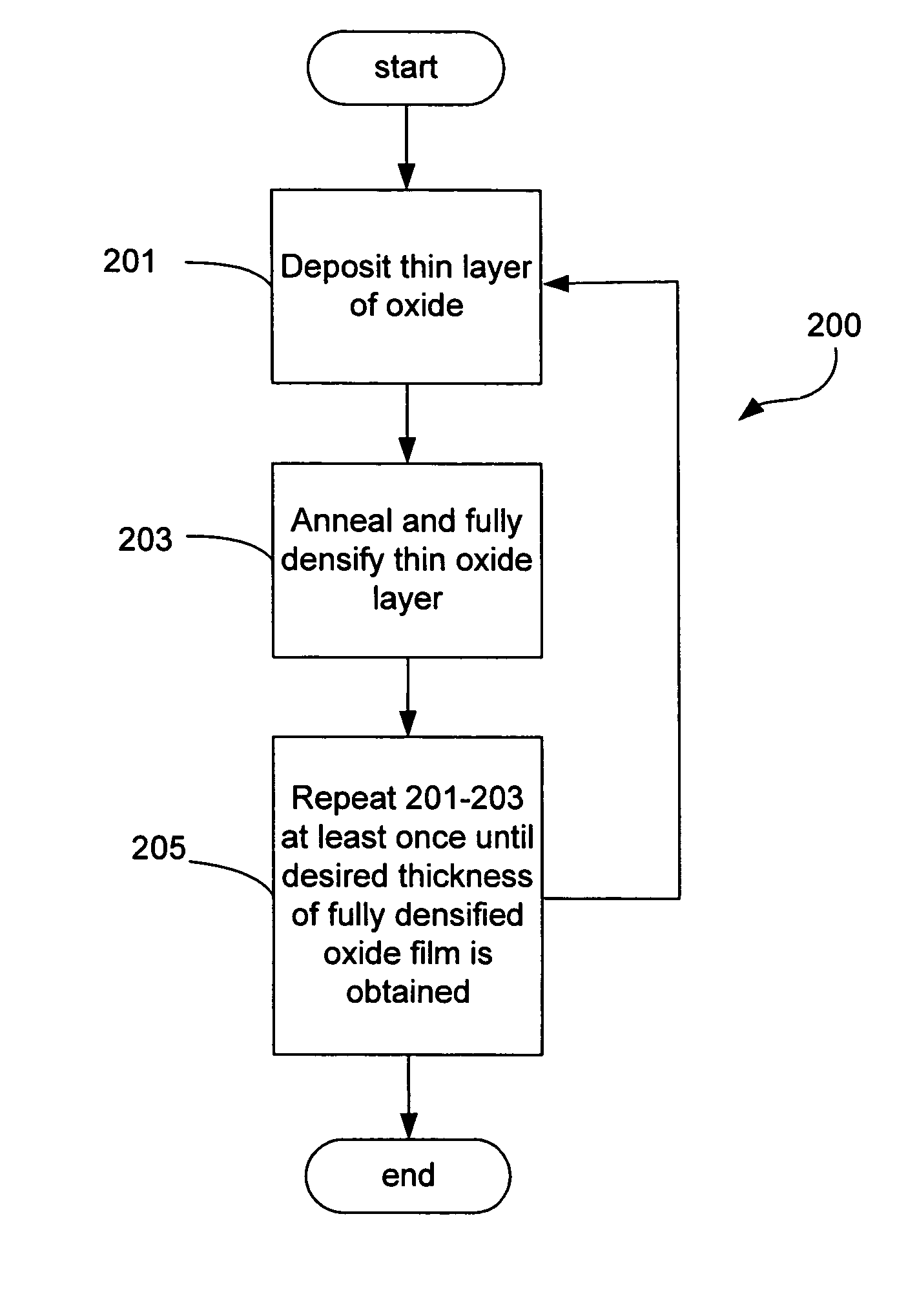
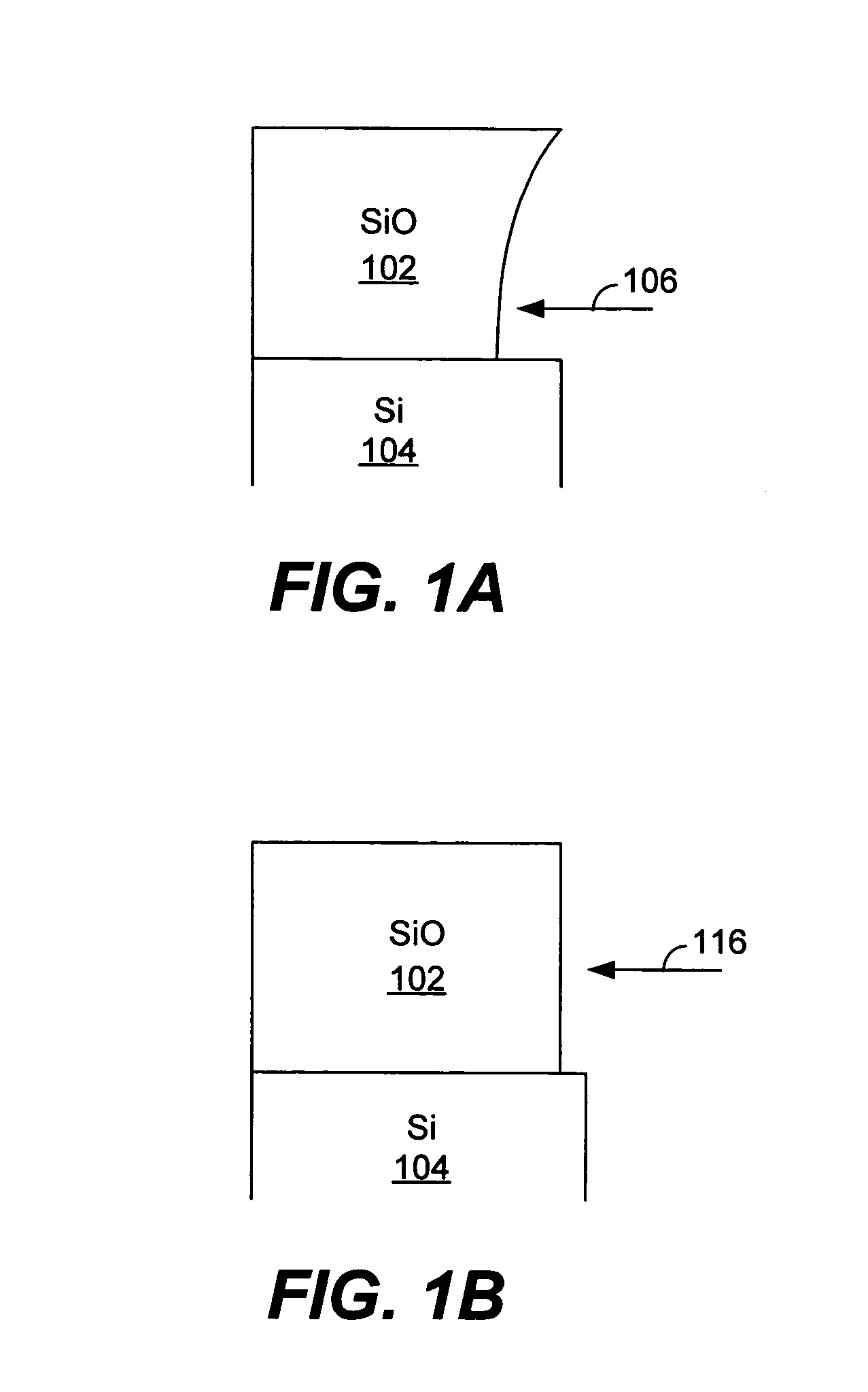
A silicon dioxide-based dielectric layer is formed on a substrate surface by a sequential deposition / anneal technique. The deposited layer thickness is insufficient to prevent substantially complete penetration of annealing process agents into the layer and migration of water out of the layer. The dielectric layer is then annealed, ideally at a moderate temperature, to remove water and thereby fully densify the film. The deposition and anneal processes are then repeated until a desired dielectric film thickness is achieved.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Sequential deposition/anneal film densification method
ActiveUS7148155B1Maintaining film propertyMaintain propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectric membraneThin membrane
A silicon dioxide-based dielectric layer is formed on a substrate surface by a sequential deposition / anneal technique. The deposited layer thickness is insufficient to prevent substantially complete penetration of annealing process agents into the layer and migration of water out of the layer. The dielectric layer is then annealed, ideally at a moderate temperature, to remove water and thereby fully densify the film. The deposition and anneal processes are then repeated until a desired dielectric film thickness is achieved.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
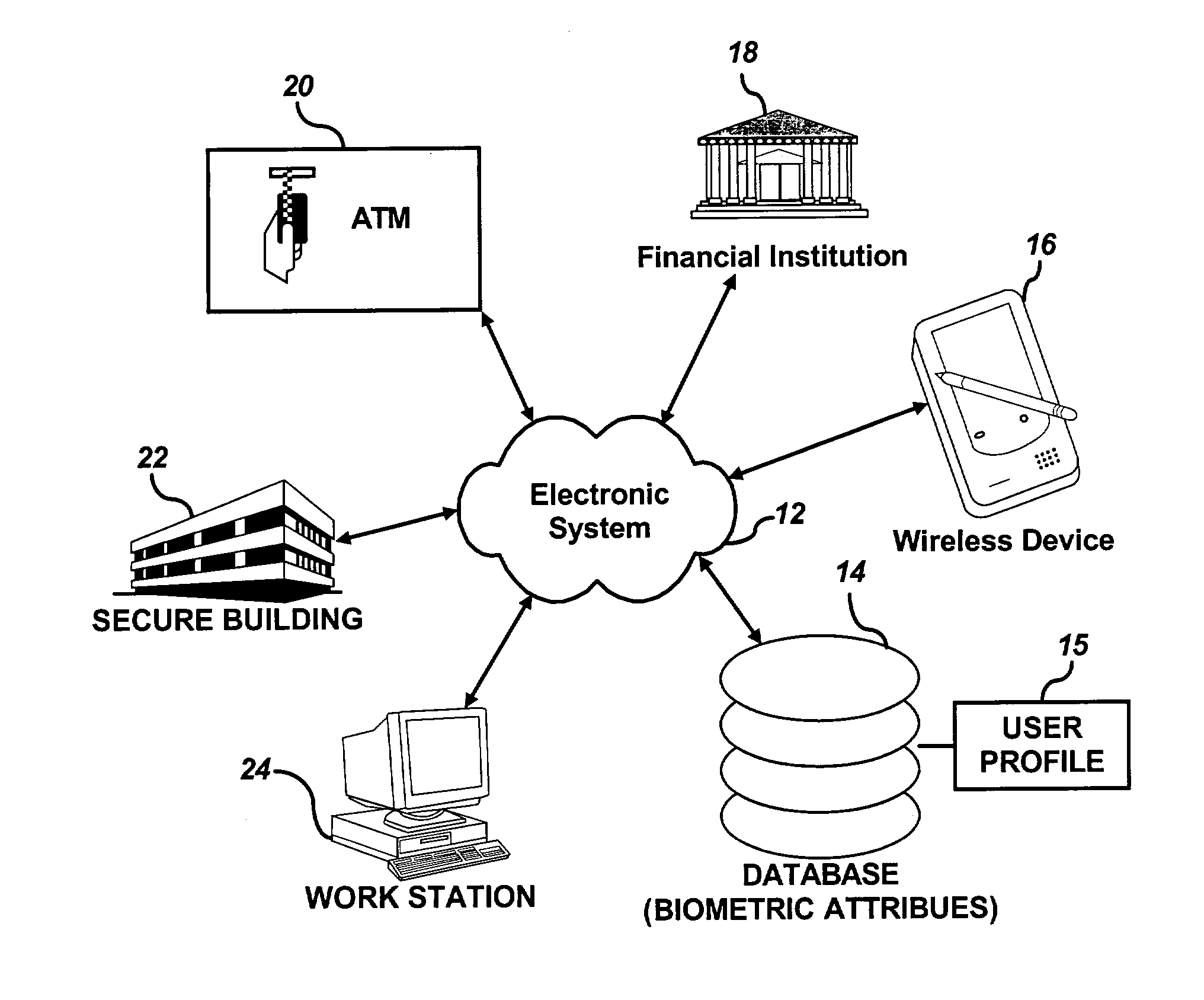
Random biometric authentication utilizing unique biometric signatures
InactiveUS20030163710A1Accurate authenticationSecure user accessDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUser inputLayer thickness
A user can be challenged to provide at least one randomly selected biometric attribute. The randomly selected biometric attribute input by the user is automatically compared to a plurality of biometric attributes of the user contained in a user profile. The user can then be authenticated if the randomly selected biometric attribute input by the user matches at least one of the plurality of biometric attributes of the user contained in the user profile. Biometric attributes analyzed according to the methods and systems of the present invention, include, but are not limited to, for example, fingerprints, iris, retina, and / or tissue characteristics, such as skin morphology, skin layer thickness, collage density and orientation, tissue hydration, optical patent length differences, etc.
Owner:IP VENUE LLC
Coated nanoparticles and quantum dots for solution-based fabrication of photovoltaic cells
CIGS absorber layers fabricated using coated semiconducting nanoparticles and / or quantum dots are disclosed. Core nanoparticles and / or quantum dots containing one or more elements from group IB and / or IIIA and / or VIA may be coated with one or more layers containing elements group IB, IIIA or VIA. Using nanoparticles with a defined surface area, a layer thickness could be tuned to give the proper stoichiometric ratio, and / or crystal phase, and / or size, and / or shape. The coated nanoparticles could then be placed in a dispersant for use as an ink, paste, or paint. By appropriate coating of the core nanoparticles, the resulting coated nanoparticles can have the desired elements intermixed within the size scale of the nanoparticle, while the phase can be controlled by tuning the stochiometry, and the stoichiometry of the coated nanoparticle may be tuned by controlling the thickness of the coating(s).
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Controlled patterning and growth of single wall and multi-wall carbon nanotubes
Method and system for producing a selected pattern or array of at least one of a single wall nanotube and / or a multi-wall nanotube containing primarily carbon. A substrate is coated with a first layer (optional) of a first selected metal (e.g., Al and / or Ir) and with a second layer of a catalyst (e.g., Fe, Co, Ni and / or Mo), having selected first and second layer thicknesses provided by ion sputtering, arc discharge, laser ablation, evaporation or CVD. The first layer and / or the second layer may be formed in a desired non-uniform pattern, using a mask with suitable aperture(s), to promote growth of carbon nanotubes in a corresponding pattern. A selected heated feed gas (primarily CH4 or C2Hn with n=2 and / or 4) is passed over the coated substrate and forms primarily single wall nanotubes or multiple wall nanotubes, depending upon the selected feed gas and its temperature. Nanofibers, as well as single wall and multi-wall nanotubes, are produced using plasma-aided growth from the second (catalyst) layer. An overcoating of a selected metal or alloy can be deposited, over the second layer, to provide a coating for the carbon nanotubes grown in this manner.
Owner:NASA +1
Full-carbon coaxial line and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103943925AStable structureFast heat conductionCarbon-silicon compound conductorsWaveguidesElectrical conductorCoaxial line
The invention discloses a full-carbon coaxial line and a manufacturing method of the full-carbon coaxial line, and belongs to the technical field of integrated circuits. Graphene serves as a monatomic layer thickness, is coiled into a cylinder and form an inner conductor of the coaxial line with a small radius (can be as small as the nm level), and the inner conductor of the coaxial line transfers currents. Meanwhile, a signal layer or multiple layers of graphene serve(s) as an outer conductor of the coaxial line to form a boundary of electromagnetic waves in a space, and graphite oxide serves as medium materials between the inner conductor and the outer conductor to limit and guide oriented transmission of electromagnetic wave energy. The coaxial line is quite small in size and applicable to radio-frequency and microwave integrated circuits.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
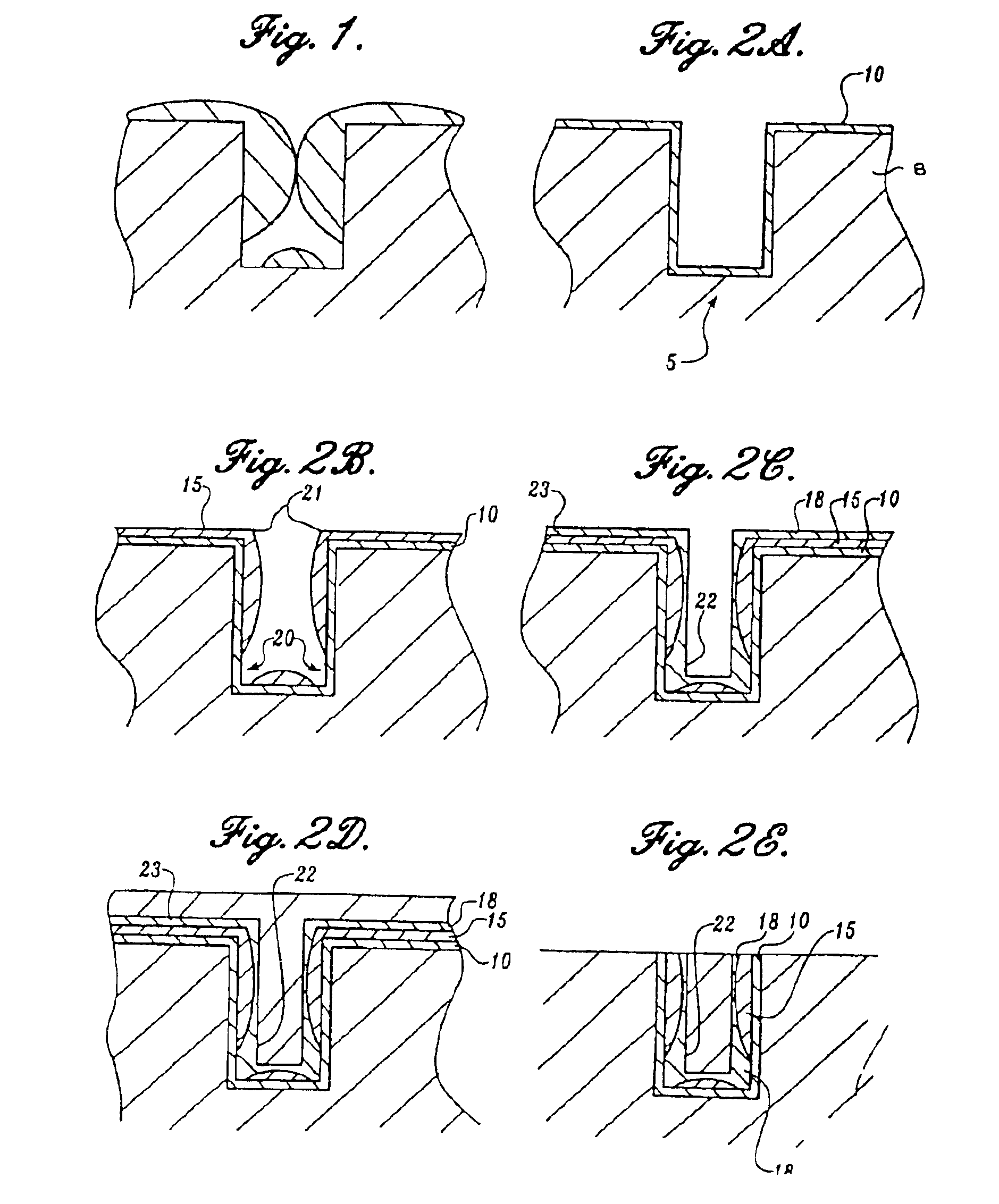
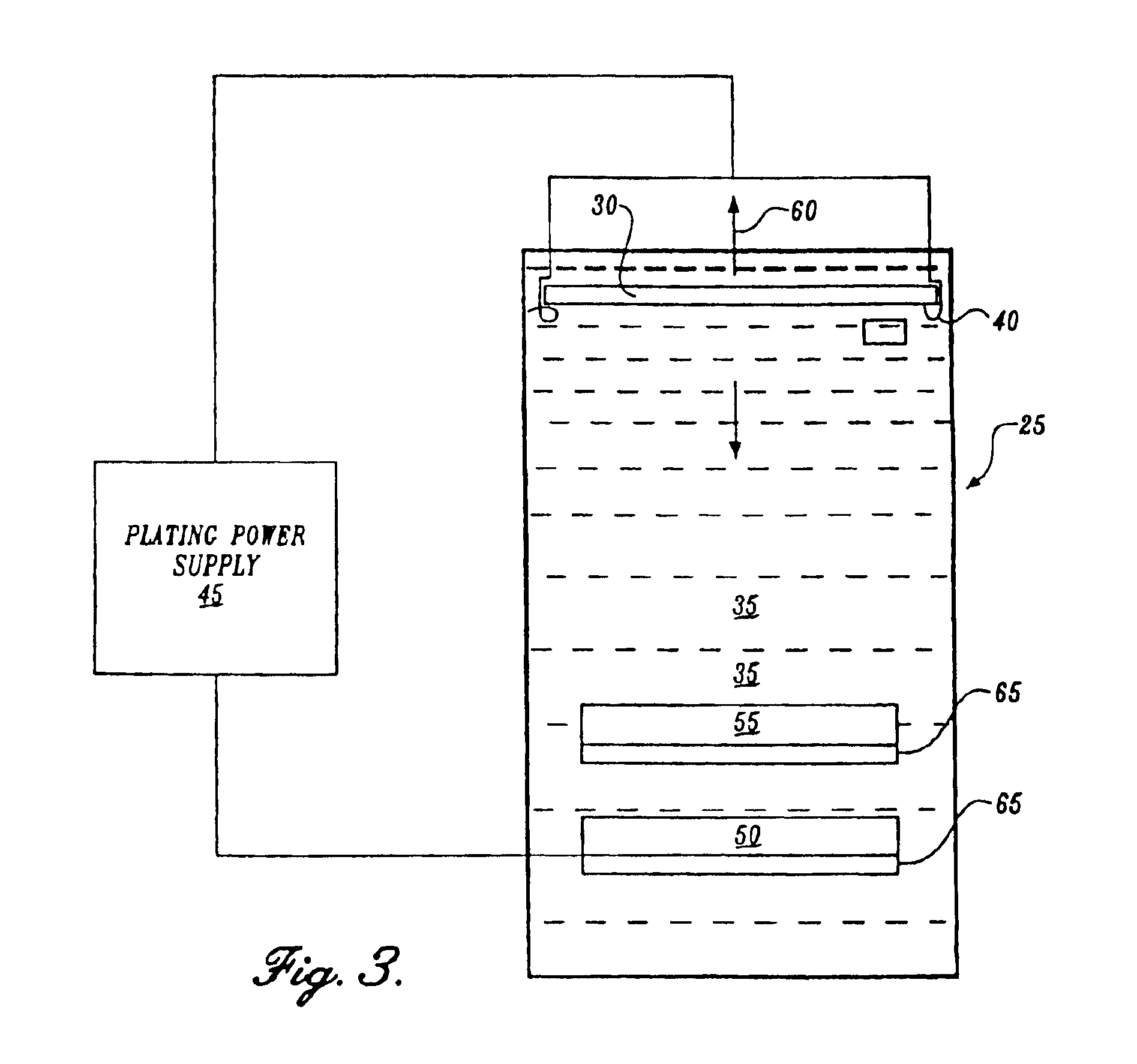
Apparatus and method for electrolytically depositing copper on a semiconductor workpiece
A process for applying a metallization interconnect as to a semiconductor workpiece having a barrier layer deposited on a surface thereof is set forth. The process includes the forming of an ultra-thin metal seed layer on the barrier layer. The ultra-thin seed layer having a thickness of less than or equal to about 500 Angstroms. The ultra-thin seed layer is then enhanced by depositing additional metal thereon to provide an enhanced sed layer. The enhanced seed layer has a thickness at all points on sidewalls of substantially all recessed features distributed within the workpiece that is equal to or greater than about 10% of the nominal seed layer thickness over an exteriorly disposed surface of the workpiece.
Owner:SEMITOOL INC
SiGe (silicon germanium) source and drain area manufacturing method
ActiveCN104201108AReduce thicknessAvoid stress relaxationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationEngineering
The invention discloses a SiGe (silicon germanium) source and drain area manufacturing method. A multi-layer structure which comprises alternately stacked buffer layers and main body layers is formed by a method that the SiGe epitaxial growth of the buffer layer and the main body layers is alternated repeatedly and accordingly the thickness of every high Ge concentration of SiGe main body layer is effectively reduced and shared into every layer of main body layer and accordingly the stress relaxation due to the fact that thickness of every main body layer exceeds the critical thickness is avoided; the Ge content of every layer of SiGe main body layer is further improved to enable the stress of the SiGe source leakage on a channel to be increased; an SiGe process window is enlarged due to the repeated epitaxy and accordingly the process stability is enhanced and accordingly the device performance is improved; the stress can be effectively improved without increase of the process difficulty and accordingly the process is stable and controllable and the cost is low.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
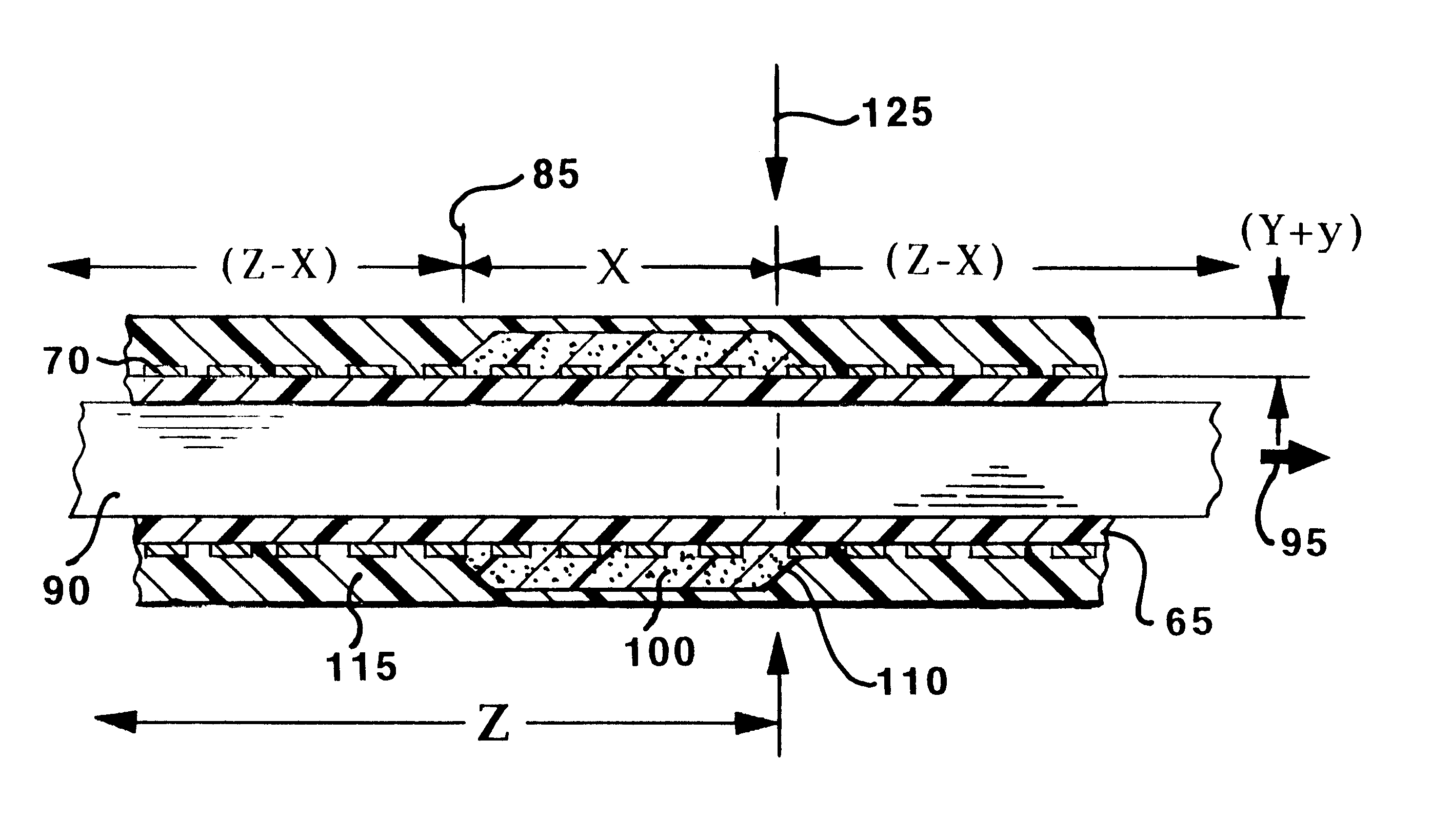
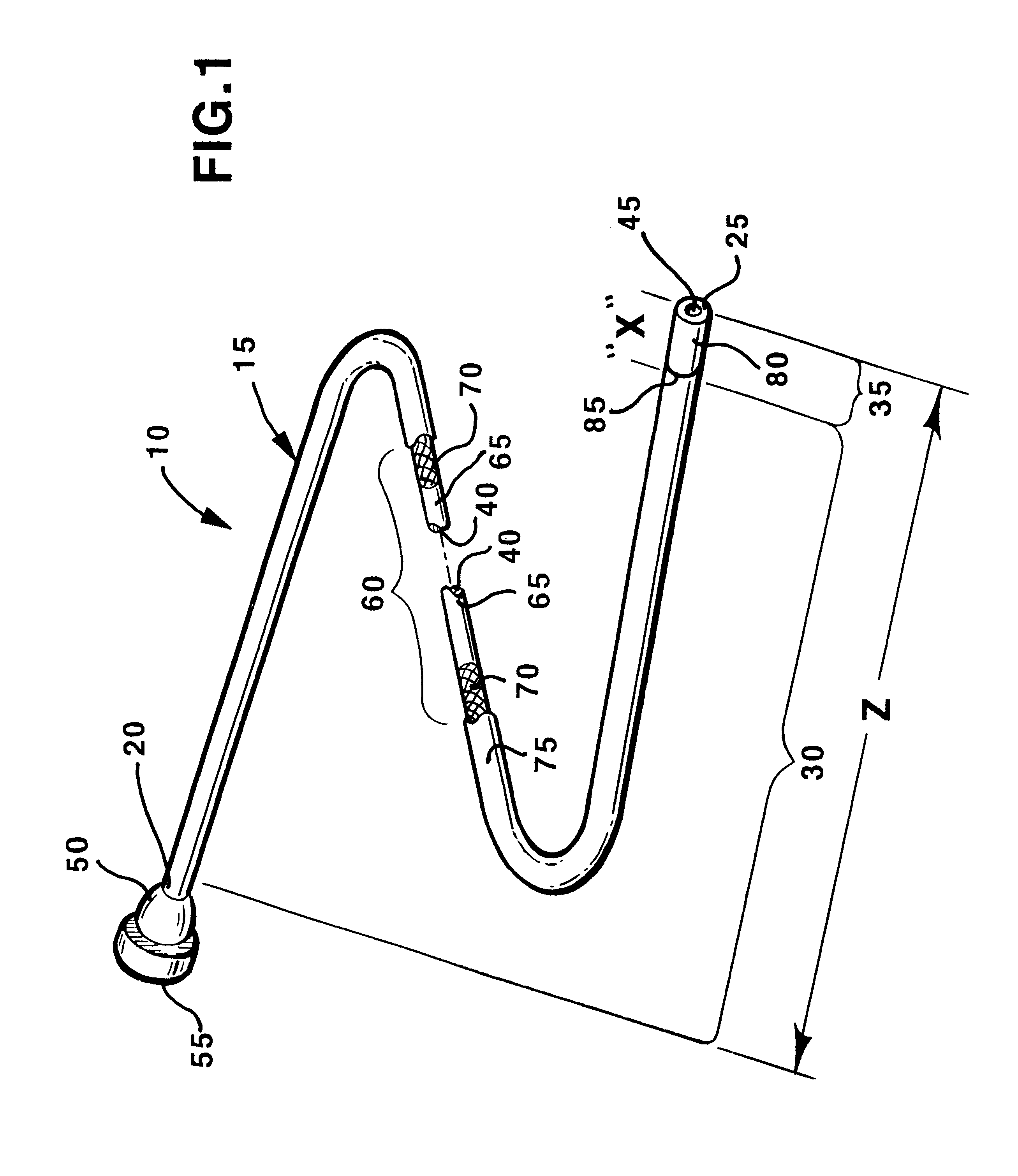
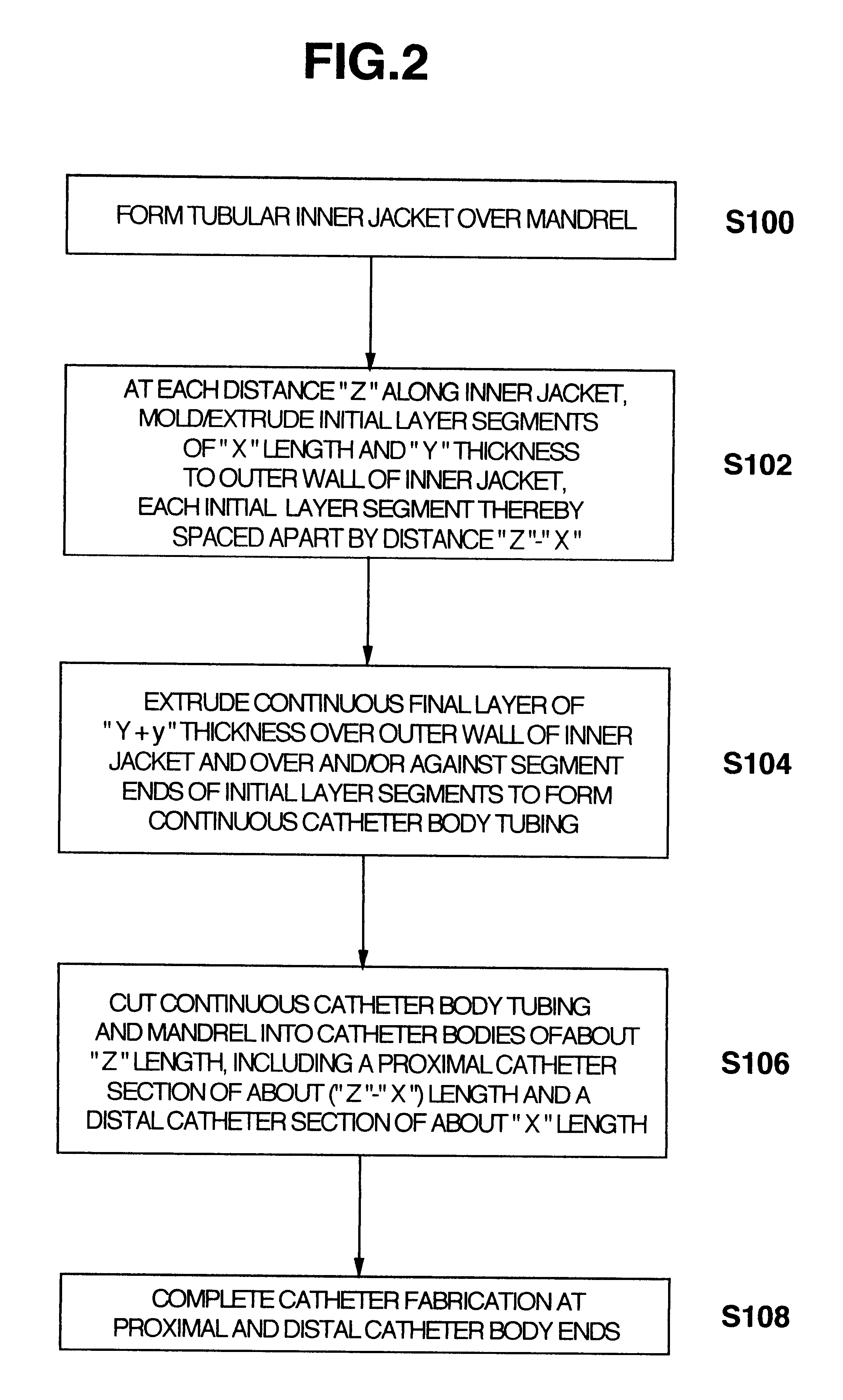
Multiple segment catheter and method of fabrication
Methods of fabricating medical vascular catheters adapted to be inserted into a blood vessel from an incision through the skin of a patient for introducing other devices or fluids for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes and particularly methods for fabricating such catheters with catheter bodies having catheter sections of differing flexibility are disclosed. Such catheter bodies having a proximal catheter body end and a distal catheter body end and formed of a proximal section and at least one distal section that have differing flexibilities are formed in a process comprising the steps of: (1) forming a continuous tubular inner jacket preferably of an inner liner and a reinforcement layer; (2) forming initial layer segments having an initial layer thickness along the length of the inner jacket from a material of first durometer hardness, whereby each initial layer segment is separated by a separation distance: (3) forming a final layer of a material of second durometer hardness with a second layer thickness over the tubular inner jacket along the separation distances and over and / or against the proximal and distal initial layer ends of the initial layer segments to form a continuous catheter body tubing; (4) severing the continuous catheter body tubing into catheter body lengths including a proximal catheter section formed of the material of second hardness and a distal catheter section of the material of first hardness; and (5) completing the catheter fabrication at the proximal catheter body end and the distal catheter body end. Centerless grinding of the catheter body or body tubing, formation of Intermediate catheter body sections, distal soft tips, and discontinuities in the reinforcement layer formed prior to step (2) are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Fiber containing filter media
InactiveUS20040038014A1Efficient removalLow efficiencySynthetic resin layered productsUltrafiltrationPolymer scienceFilter media
Improved filtration media or filter bodies can be made from fine fiber and can be formed into a filtration structure having no internal defects. The filter media or filter body comprises a collection of spot in fiber with defined fiber diameter, layer thickness and media solidity. The fine fiber is formed into a media body and obtains substantial flux and filtration efficiency. The filtration media or body can comprise single or multiple layers of fine fiber combined into the improved filter body.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Method and device for producing a component
InactiveUS20130055568A1High build rateSpeed up preparationTurbinesAdditive manufacturing apparatusMetallurgyLayer thickness
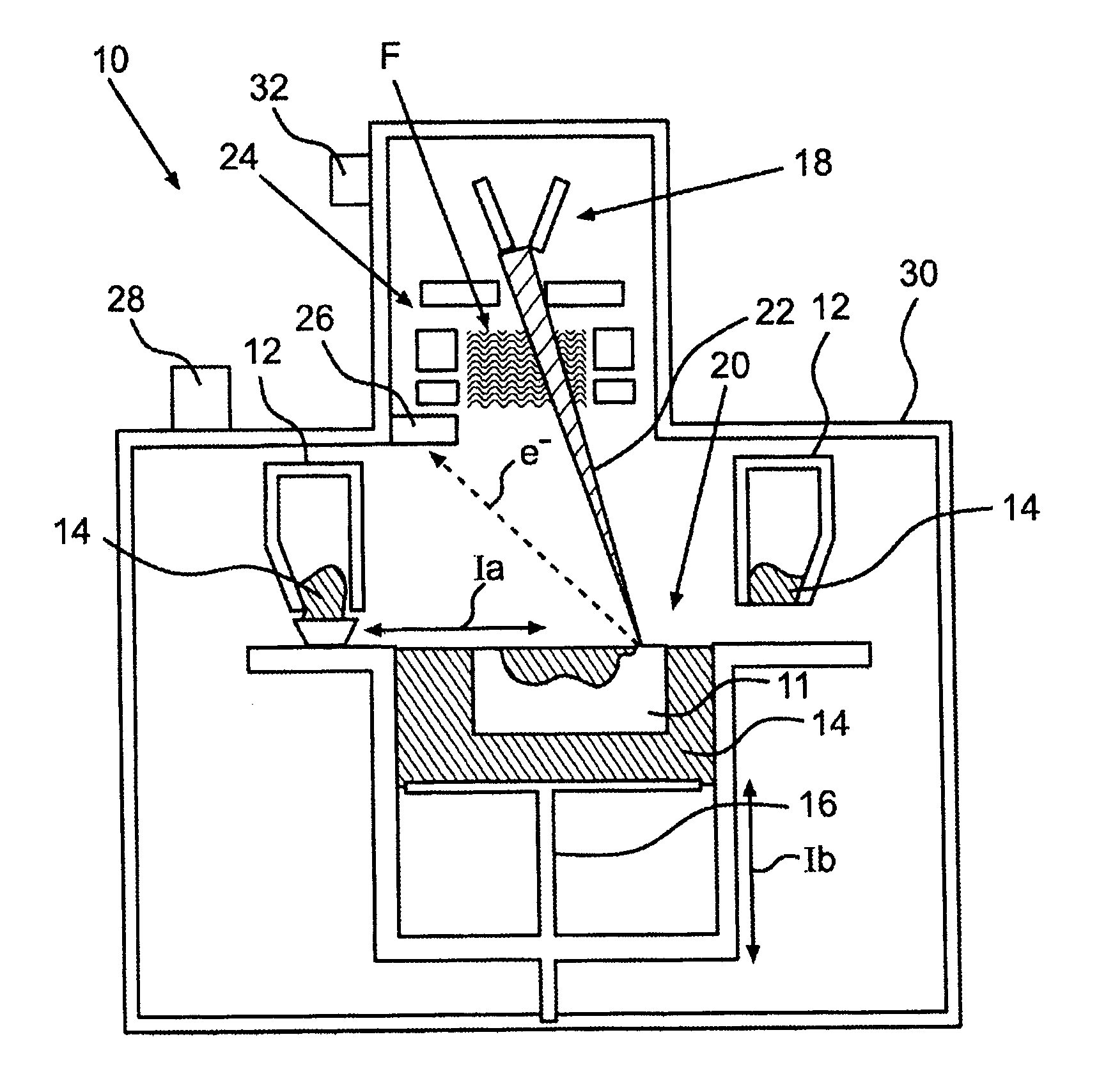
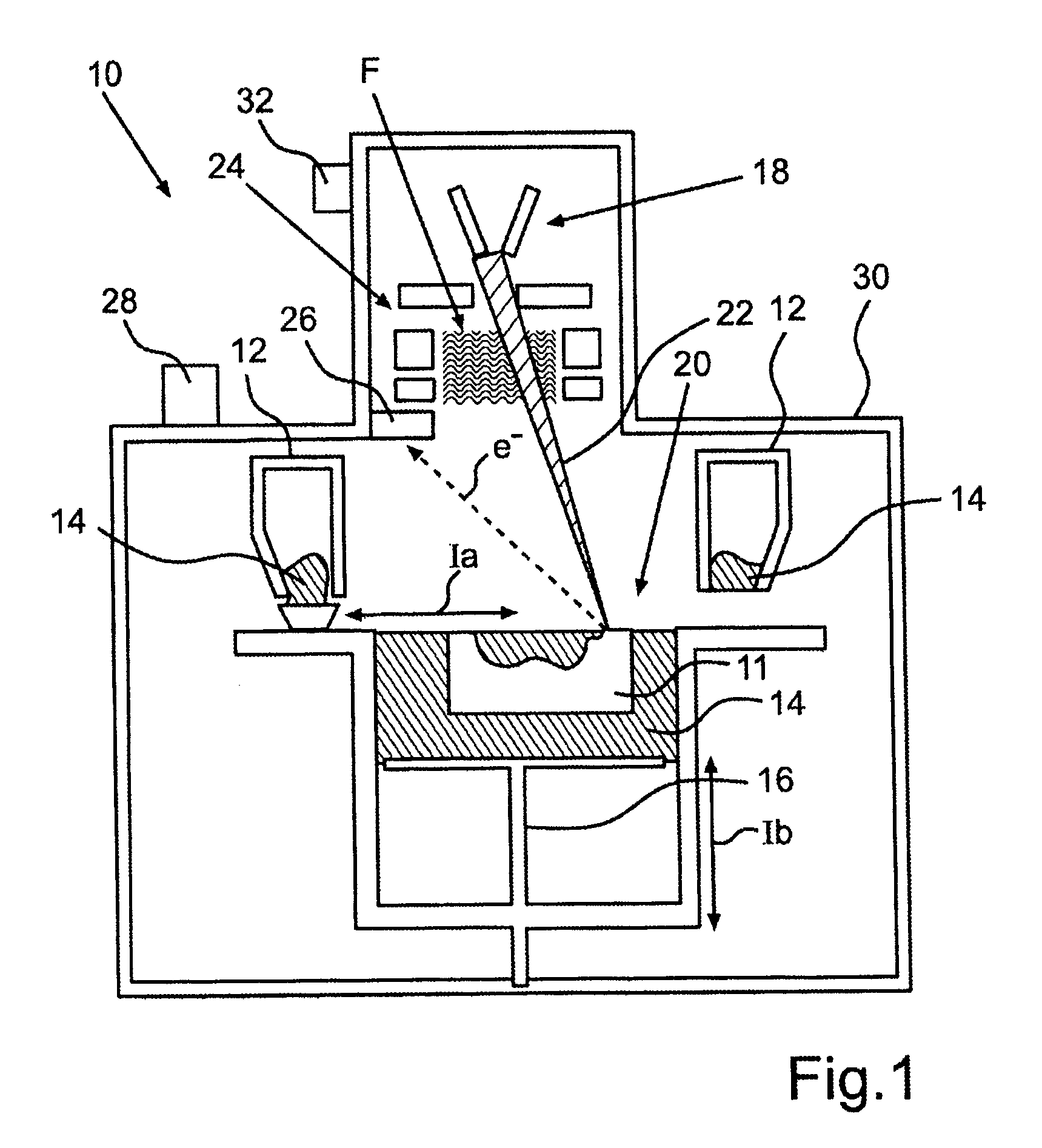
A method for manufacturing a component, in particular a component of a turbine or a compressor, in which at least these steps are carried out: application in layers of at least one powdered component material to a component platform in the area of a buildup and joining zone; melting and / or sintering locally in layers of the component material by supplying energy with the aid of at least one electron beam in the area of the buildup and joining zone; lowering of the component platform in layers by a predefined layer thickness; and repeating steps a) through c) until completion of the component. During the manufacturing, electrons emitted due to the interaction of the electron beam with the component material are detected, after which material information, characterizing the topography of the melted and / or sintered component material, is ascertained on the basis of the emitted electrons. Alternatively or additionally, the component material is melted and / or sintered by at least two, preferably at least four electron beams.
Owner:GLOBAL BEAM TECH +1
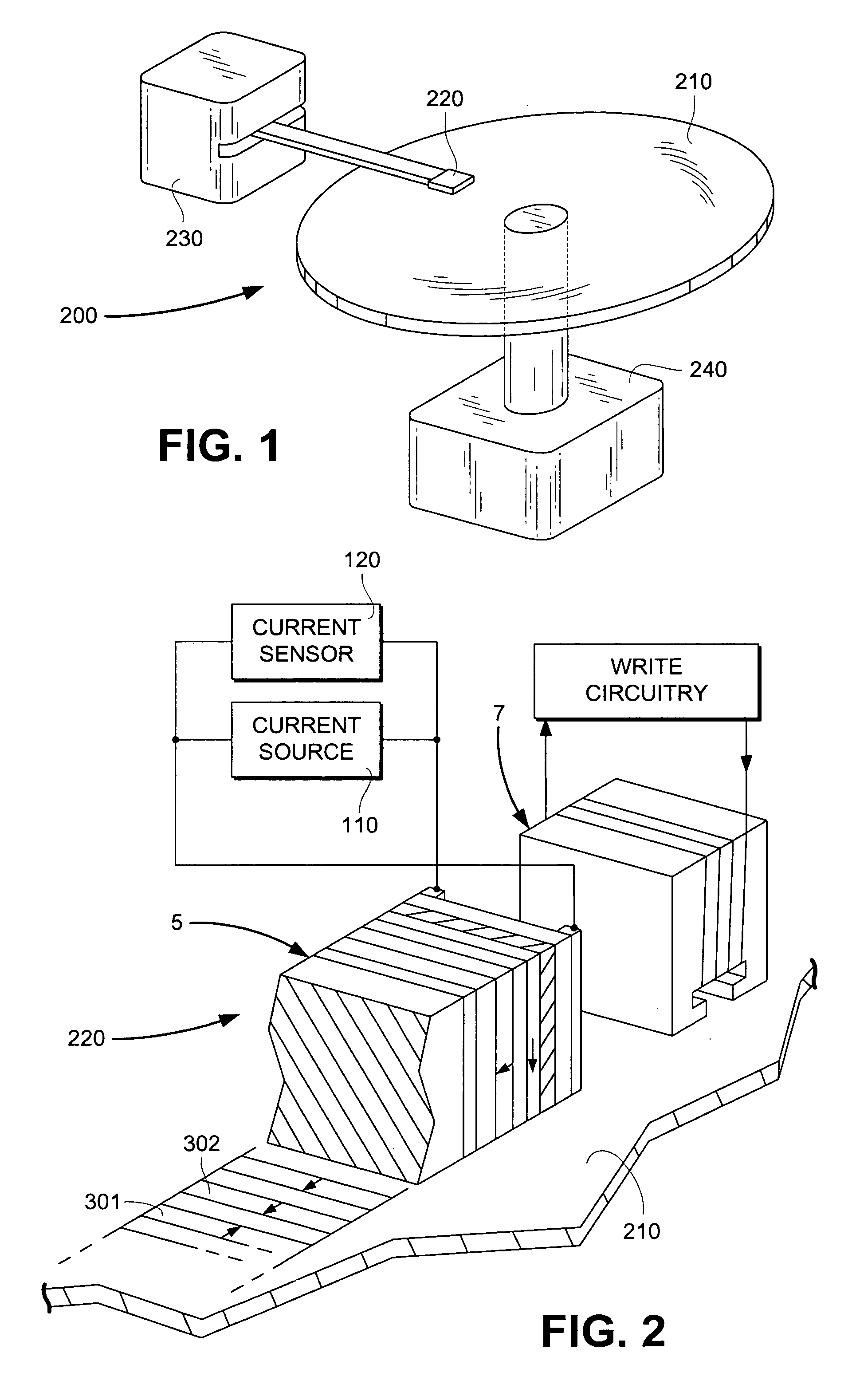
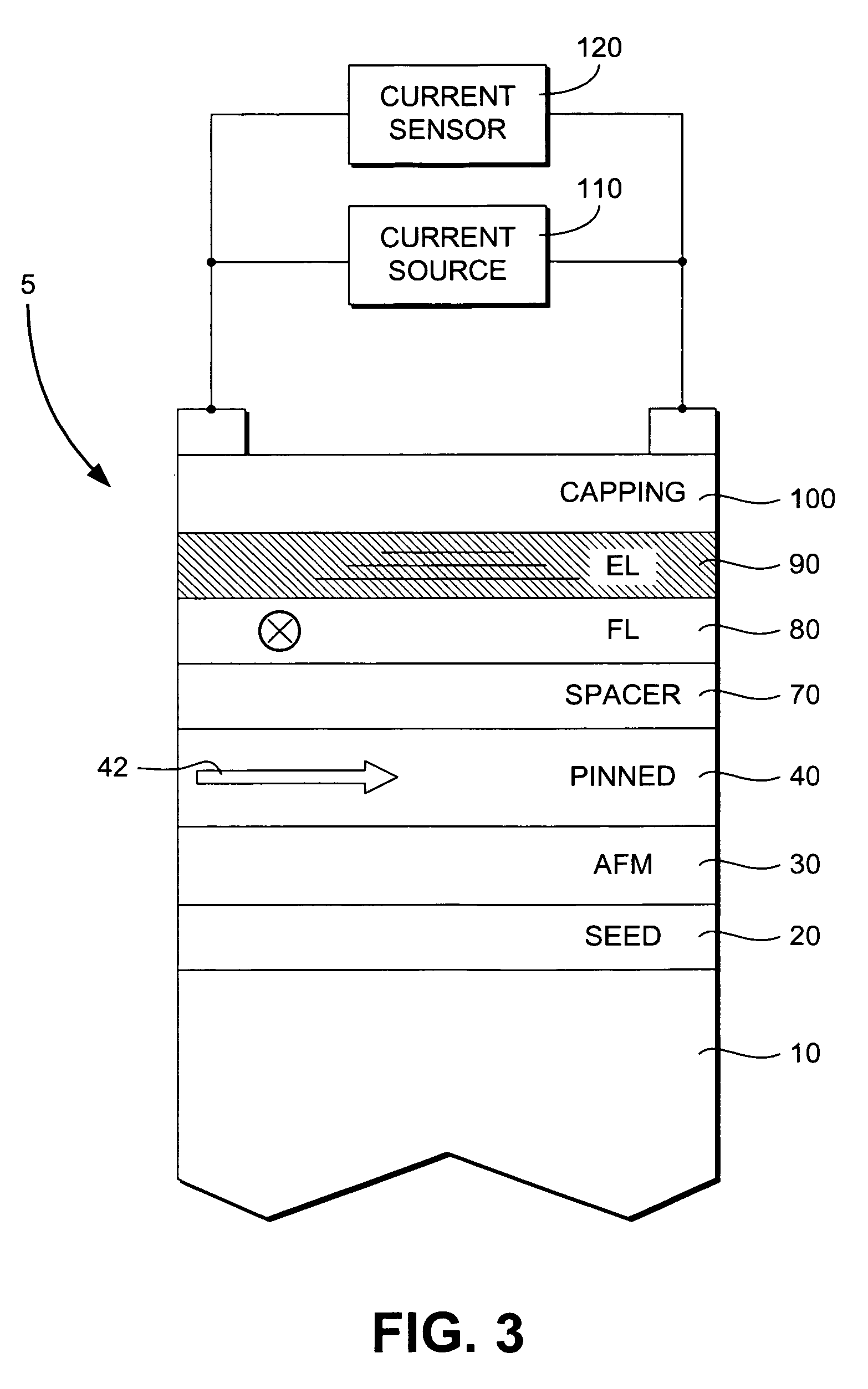
Spin valve sensor having a nonmagnetic enhancement layer adjacent an ultra thin free layer
InactiveUS7196880B1Effective bias point controlReduce thicknessNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMean free pathElectronic properties
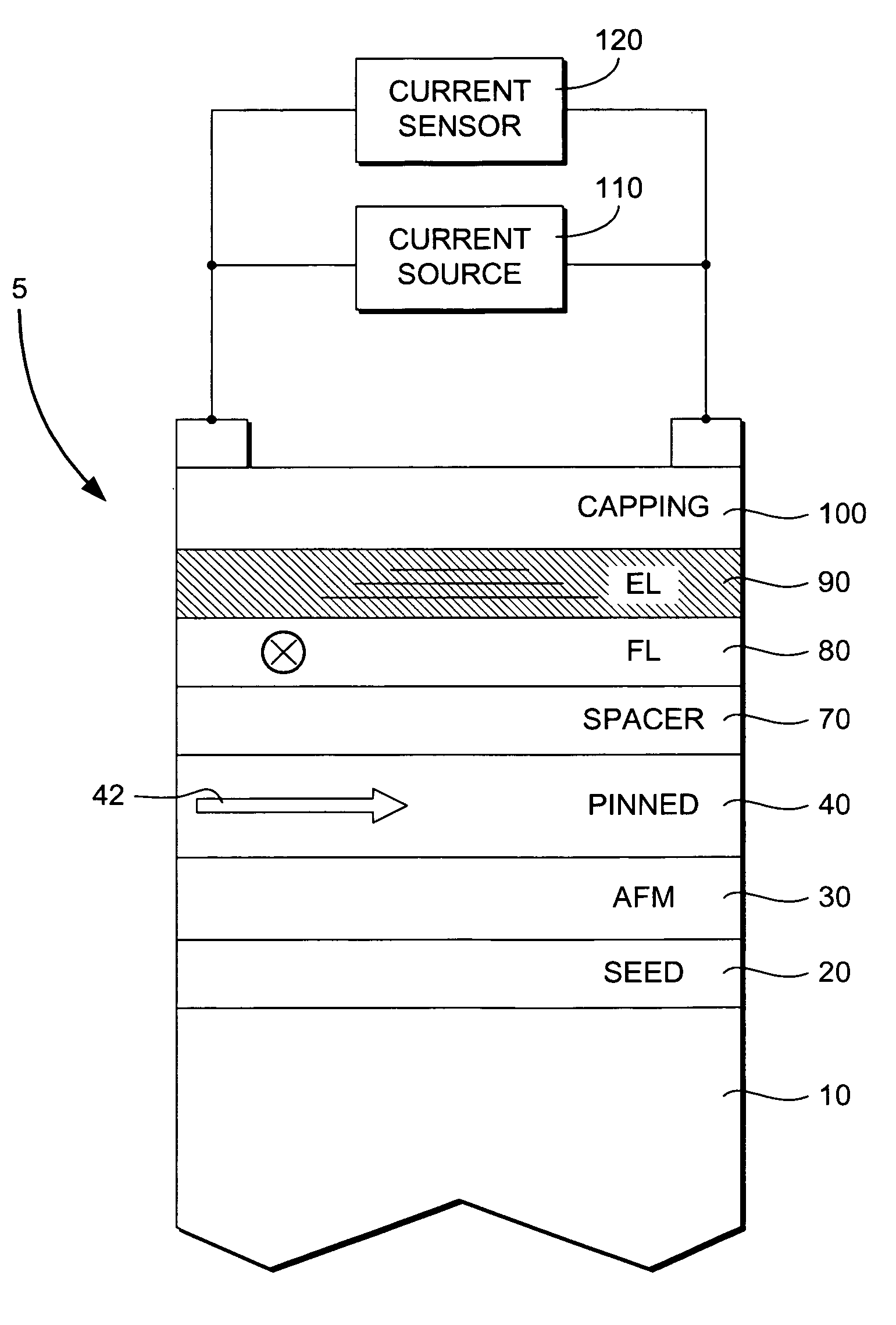
A spin valve device includes a non-magnetic enhancement layer adjacent an ultra thin free layer. The thickness of the free layer may be less than the mean free path of a conduction electron through the free layer. The GMR ratio is significantly improved for free layer thicknesses below 50 Å. The enhancement layer allows electrons to travel longer in their spin state before encountering scattering sites. The electronic properties of the enhancement layer material can be matched with the adjacent free layer without creating a low resistance shunt path. Because the free layer may be made ultra thin and the enhancement layer is formed of a nonmagnetic material, less magnetic field is required to align the free layer, allowing for improved data density. Also, the enhancement layer allows for effective bias point control by shifting sensor current density distribution.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Glass with high frictive damage resistance
ActiveUS20120282449A1Improve initial strengthImprove the immunityDecorative surface effectsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceLayer thickness
A glass article exhibiting improved resistance to fictive surface damage and a method for making it, the method comprising removing a layer of glass from at least a portion of a surface of the article that is of a layer thickness at least effective to reduce the number and / or depth of flaws on the surface of the article, and then applying a friction-reducing coating to the portion of the article from which the layer of surface glass has been removed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Developing apparatus, process cartridge, and electrophotographic image forming apparatus including an elastic member preventing a gap between a developing agent carrier and a layer thickness limiter from changing, and an electrophotographic image forming apparatus detachably mounting such process cartridge
The present invention relates to a developing apparatus for developing an electrostatic latent image formed on an electrophotographic photosensitive drum using a developing agent, including a developing agent carrier for supplying the developing agent to the photosensitive drum to develop the electrostatic latent image formed on the photosensitive drum, a layer thickness limiting member for limiting the layer thickness of the developing agent carried on a surface of the developing agent carrier, the layer thickness limiting member being disposed with a gap to the developing agent carrier, a sealing member for restricting the developing agent from leaking out of an end in a longitudinal direction of the developing agent carrier, and an elastic member arranged in contact with the developing agent carrier to prevent the gap between the developing agent carrier and the layer thickness limiting member from changing upon bending of the developing agent carrier. The elastic member is in contact with the developing agent carrier at an outer position with respect to a position at which the sealing member is disposed.
Owner:CANON KK
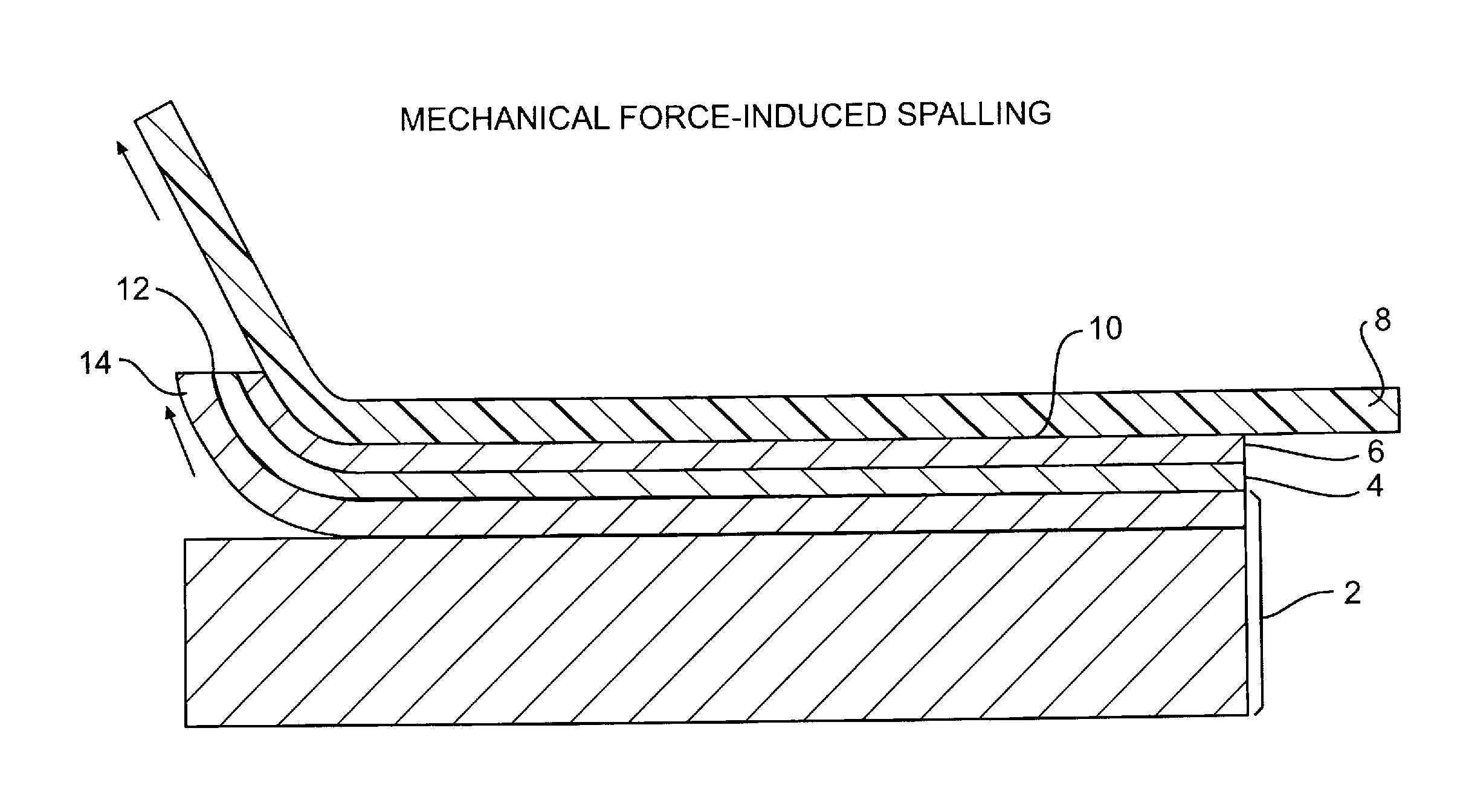
Thin substrate fabrication using stress-induced substrate spalling
ActiveUS20100311250A1Increase cost per Watt valueImprove efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStress inducedActive solar
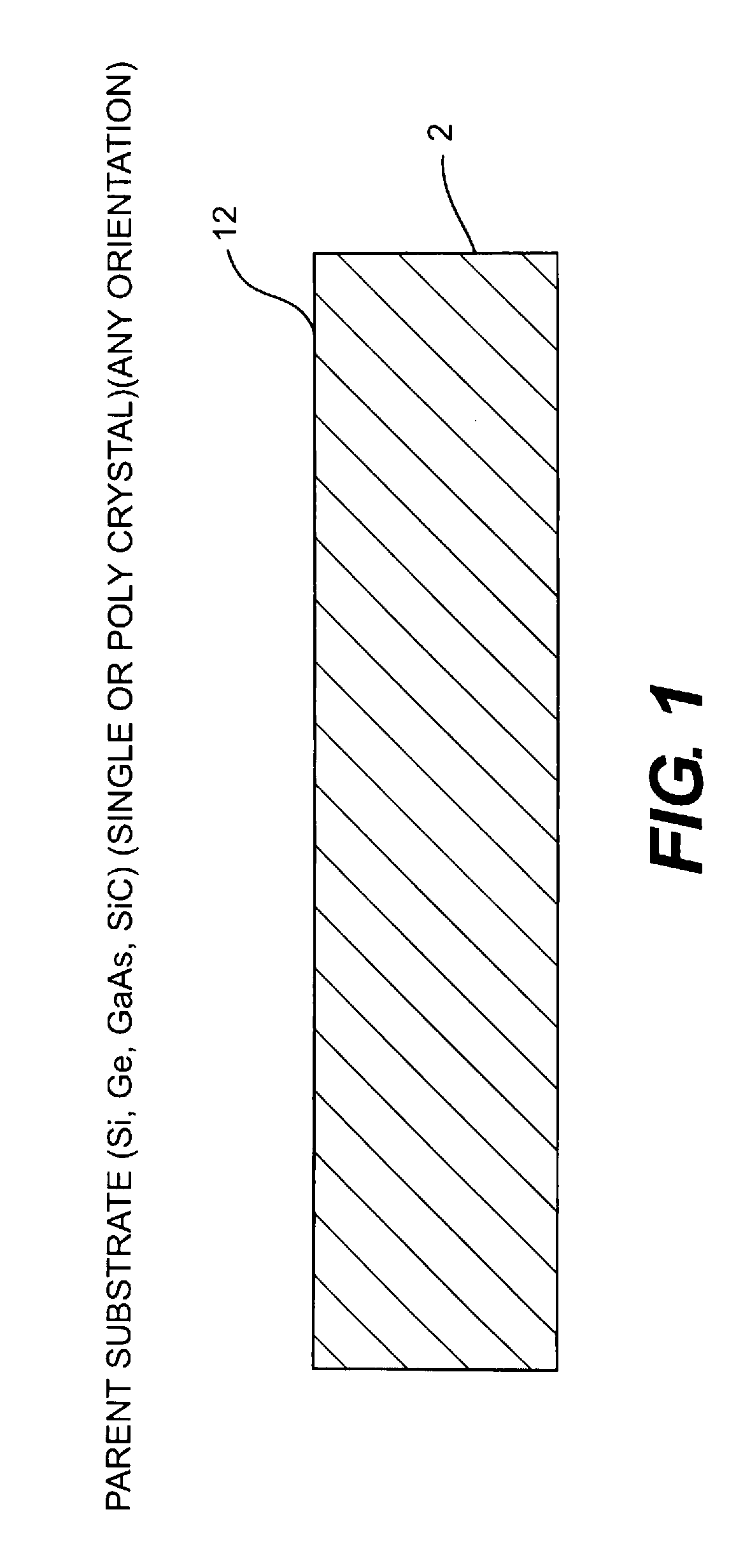
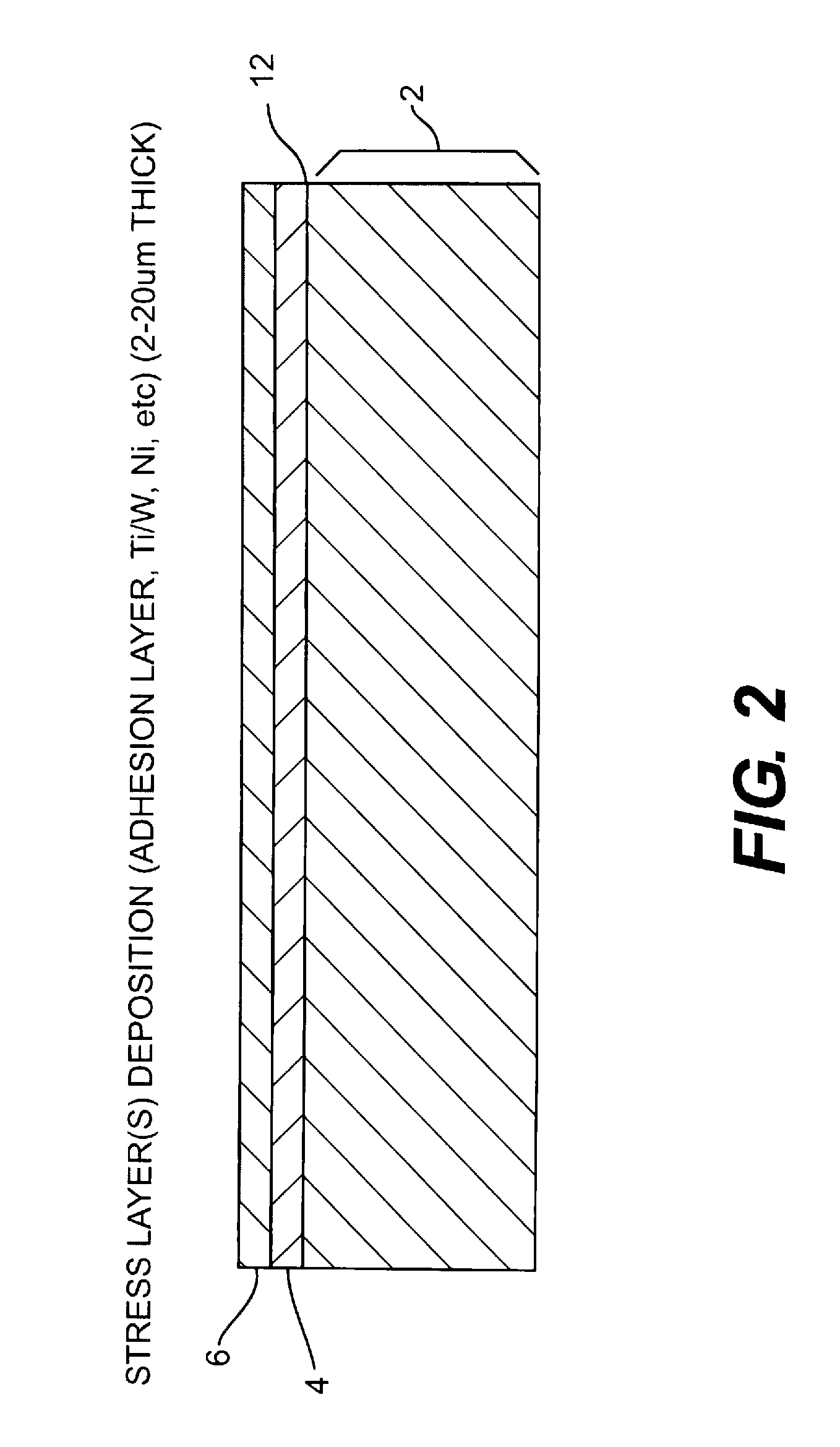
A method for manufacturing a thin film direct bandgap semiconductor active solar cell device comprises providing a source substrate having a surface and disposing on the surface a stress layer having a stress layer surface area in contact with and bonded to the surface of the source substrate. Operatively associating a handle foil with the stress layer and applying force to the handle foil separates the stress layer from the source substrate, and leaves a portion of the source substrate on the stress layer surface substantially corresponding to the area in contact with the surface of the source substrate. The portion is less thick than the source layer. The stress layer thickness is below that which results in spontaneous spalling of the source substrate. The source substrate may comprise an inorganic single crystal or polycrystalline material such as Si, Ge, GaAs, SiC, sapphire, or GaN. In one embodiment the stress layer comprises a flexible material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Selective deposition modeling with curable phase change materials
InactiveUS20030083771A1Improve mechanical propertiesEasy to disassembleAdditive manufacturing apparatusConfectionerySelective depositionPhase change
A selective deposition modeling method and apparatus for dispensing a curable phase change material. The dispensing temperature of the material is set at or less than a thermally stable temperature value for the material in which the reactive component of the material remains substantially uncured when held at the temperature for a desired time period. The dispensed material is provided with an environment that enables the material to solidify to form layers of the object. The solidified material is normalized to a desired layer thickness and is then cured by exposure to actinic radiation. In a preferred embodiment a UV curable phase change material is dispensed at about 80° C. and has a viscosity of about 13 to about 14 centipoise at this temperature. The cured material provides substantially increased physical properties over thermoplastic phase change materials previously used in selective deposition modeling.
Owner:3D SYST INC
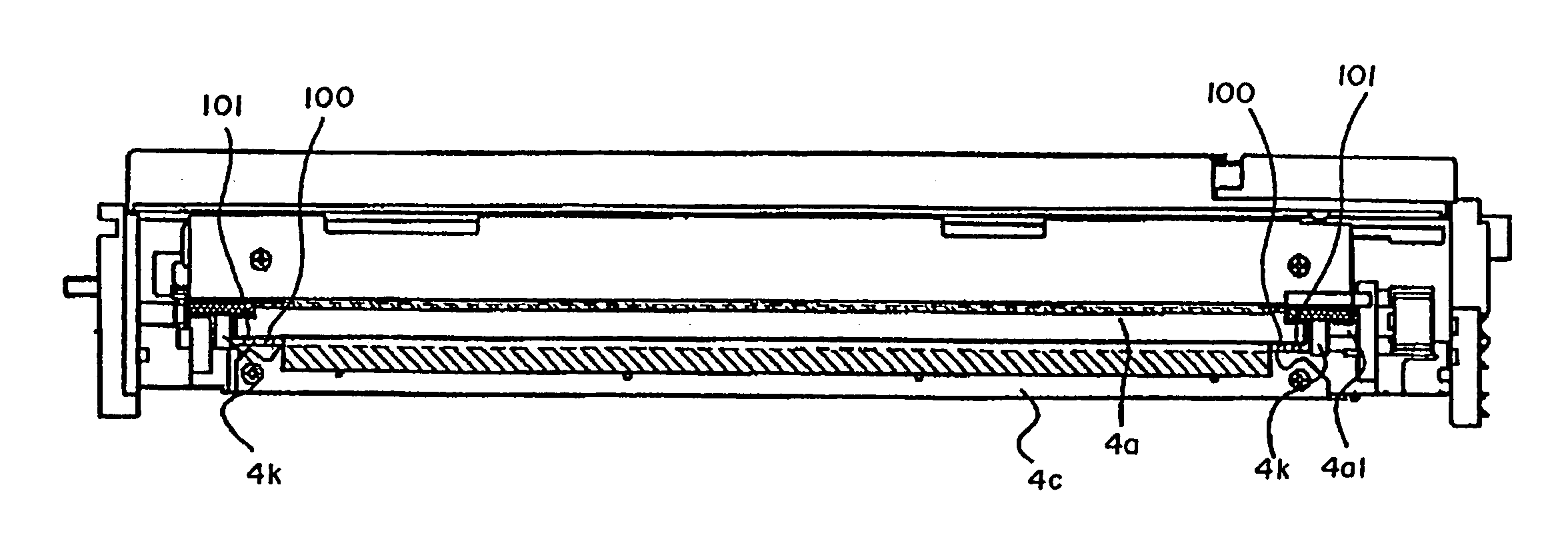
Image developing device with sealing members for preventing toner leakage
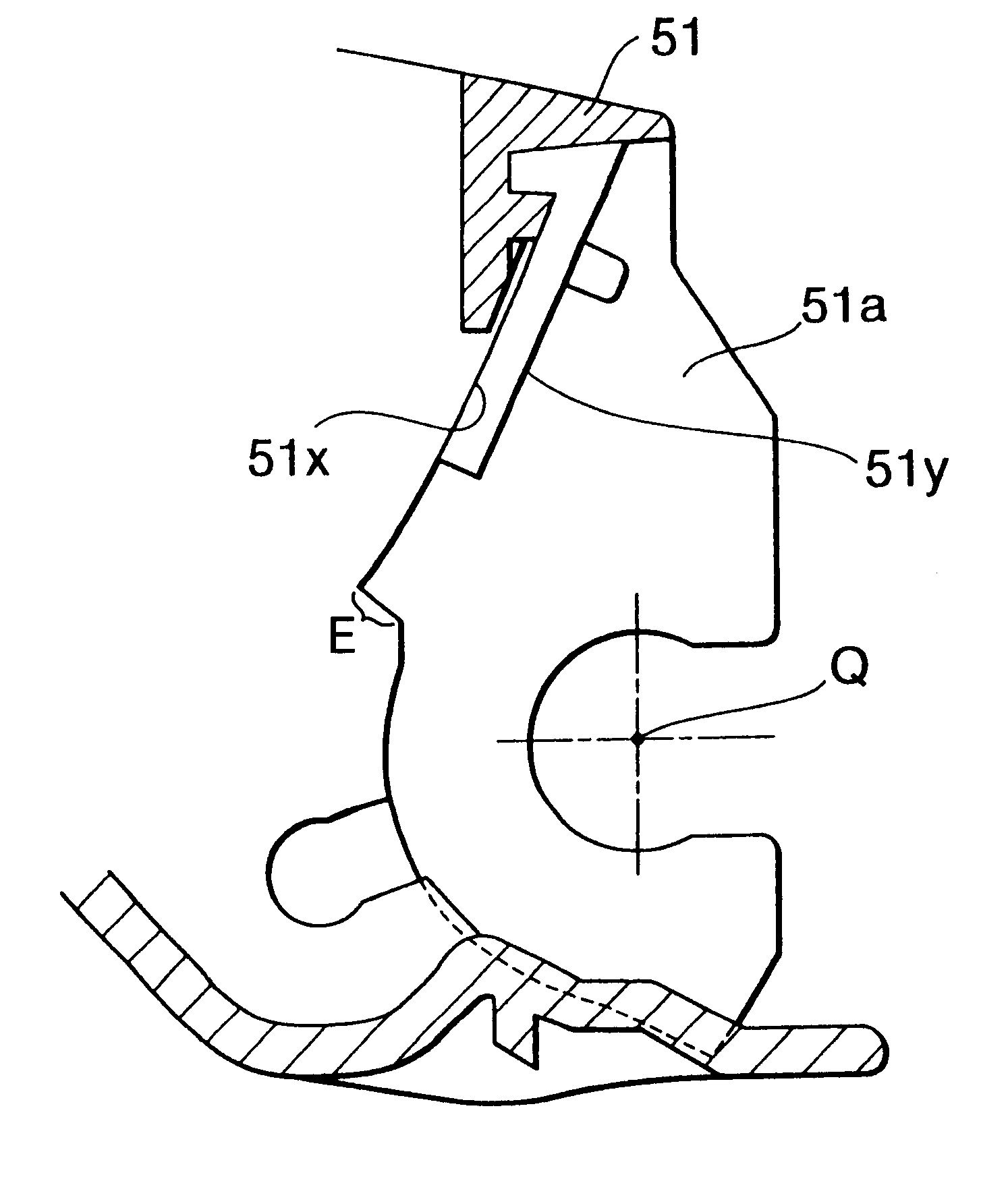
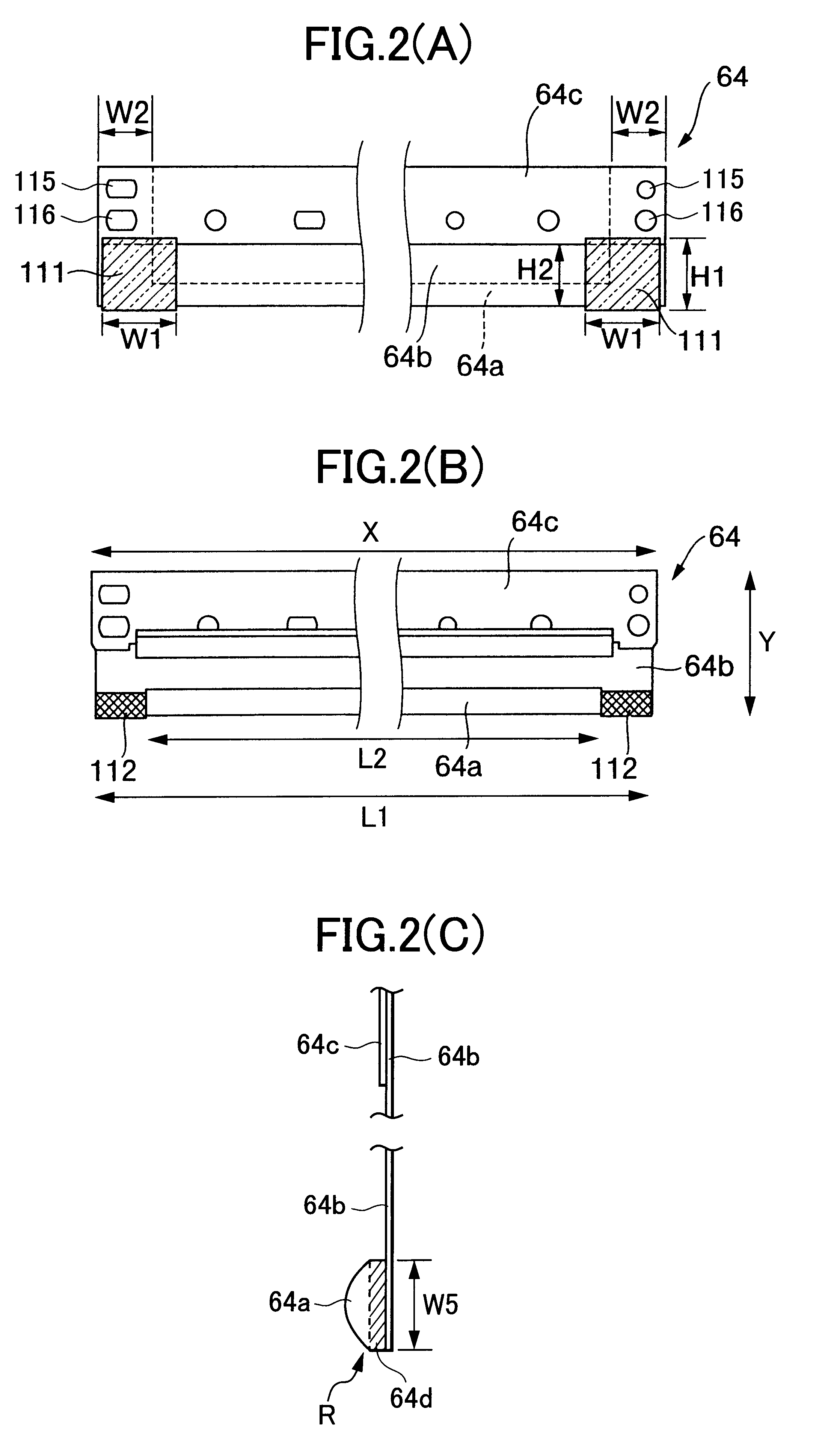
A layer thickness regulating blade 64 has a plate spring 64b and a pressing number 64a fixed thereto. The plate spring 64b is formed longer than the pressing member 64a so that both ends of the plate spring 64b are exposed. A front surface resilient foam seal 112 made from sponge is attached to the exposed portions, in contact with sides of the pressing member 64a. Further, a Teflon(TM) film 113 is attached on the plate spring 64b so as to cover the front surface resilient foam seal 112. A sponge side seal 111 is adhered to the rear surface of the plate spring 64b. A sponge side seal 107 is adhered to the developing case 51 at a position that confronts the blade side seal 111. An end seal 106 is adhered across a step portion E of the developing case 51 and the upper end of the base seal 104, and can compressing deform with the blade side seal 111 and the upper side seal 107.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Nitride semiconductor component and process for its production
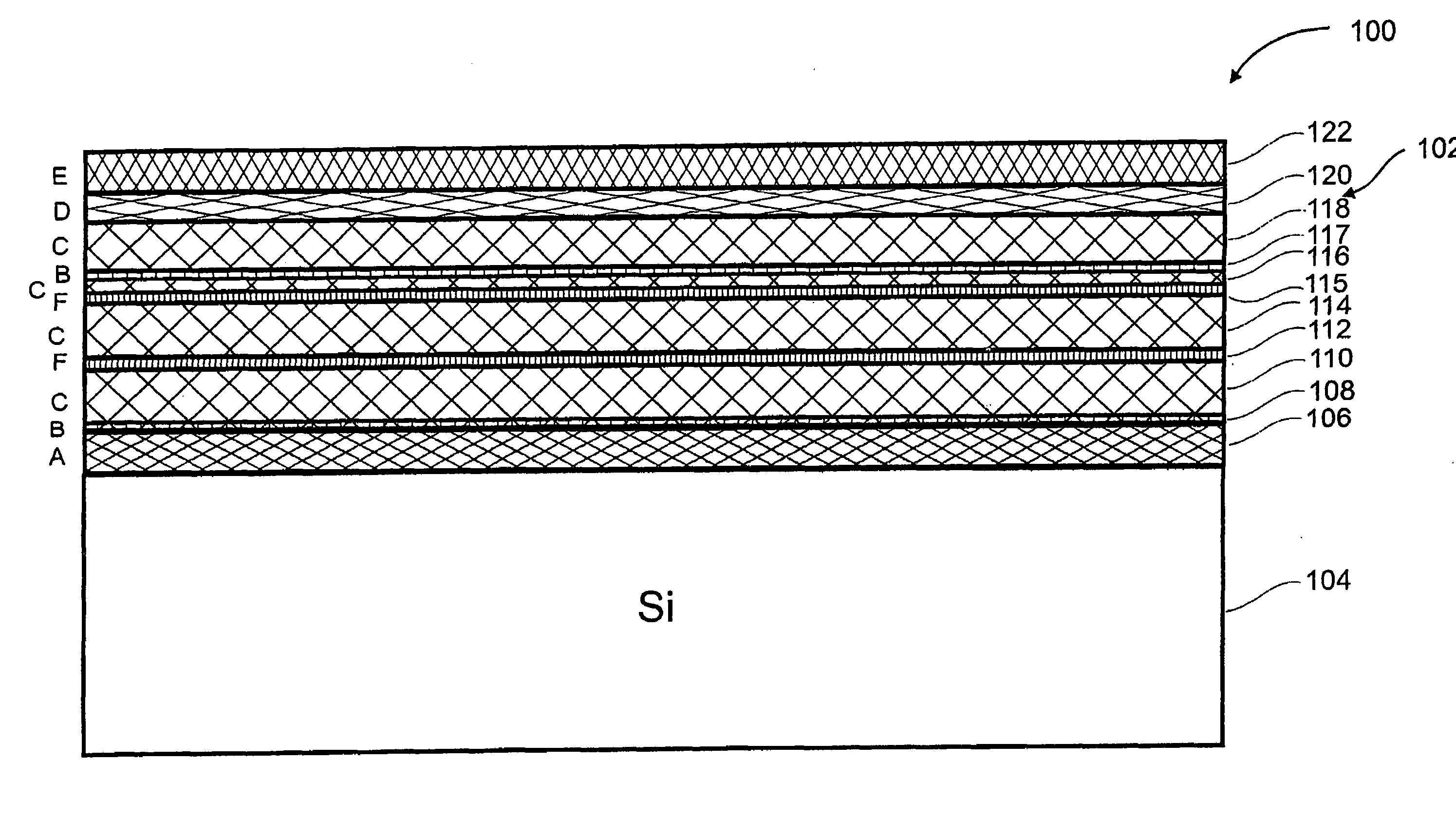
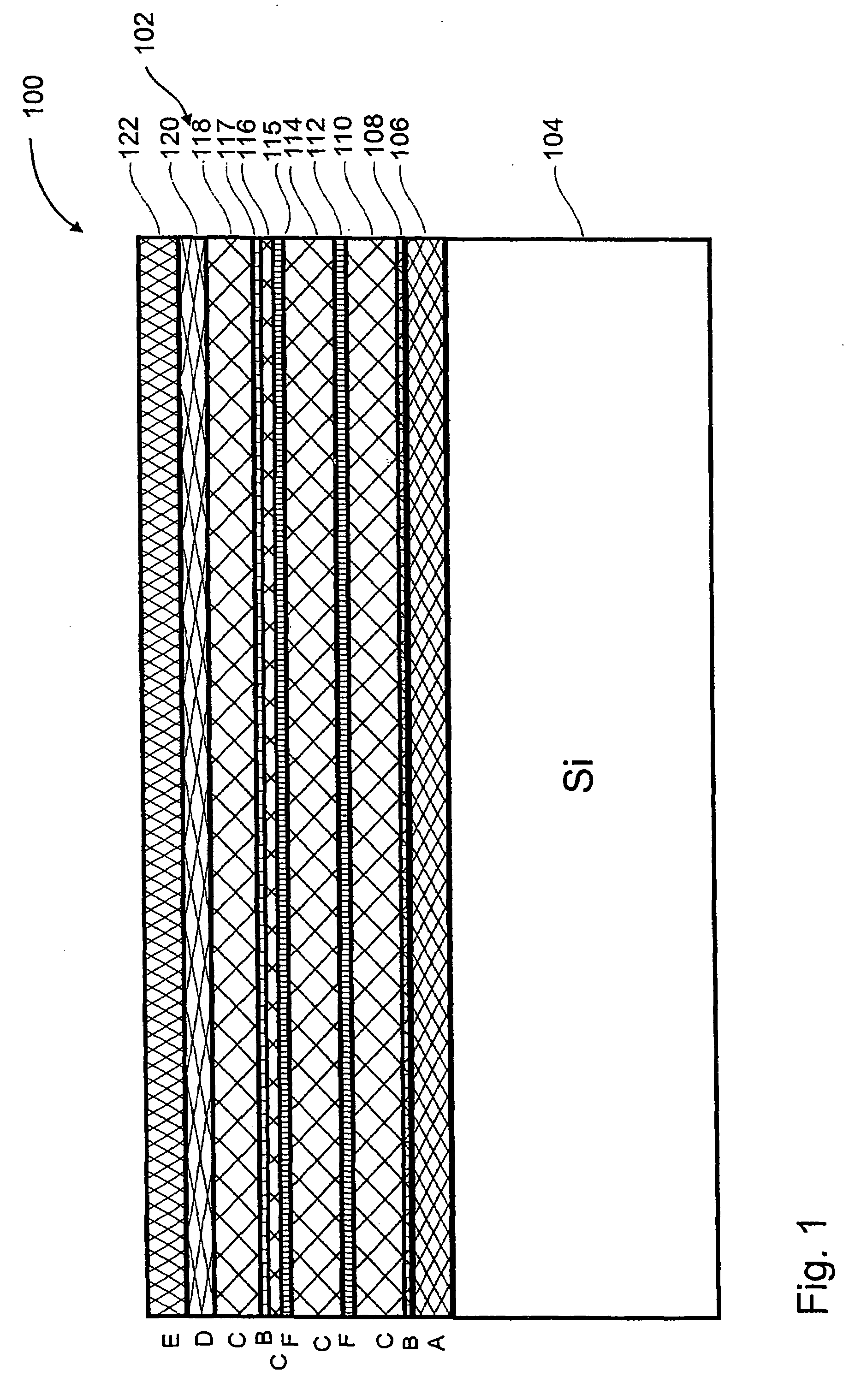
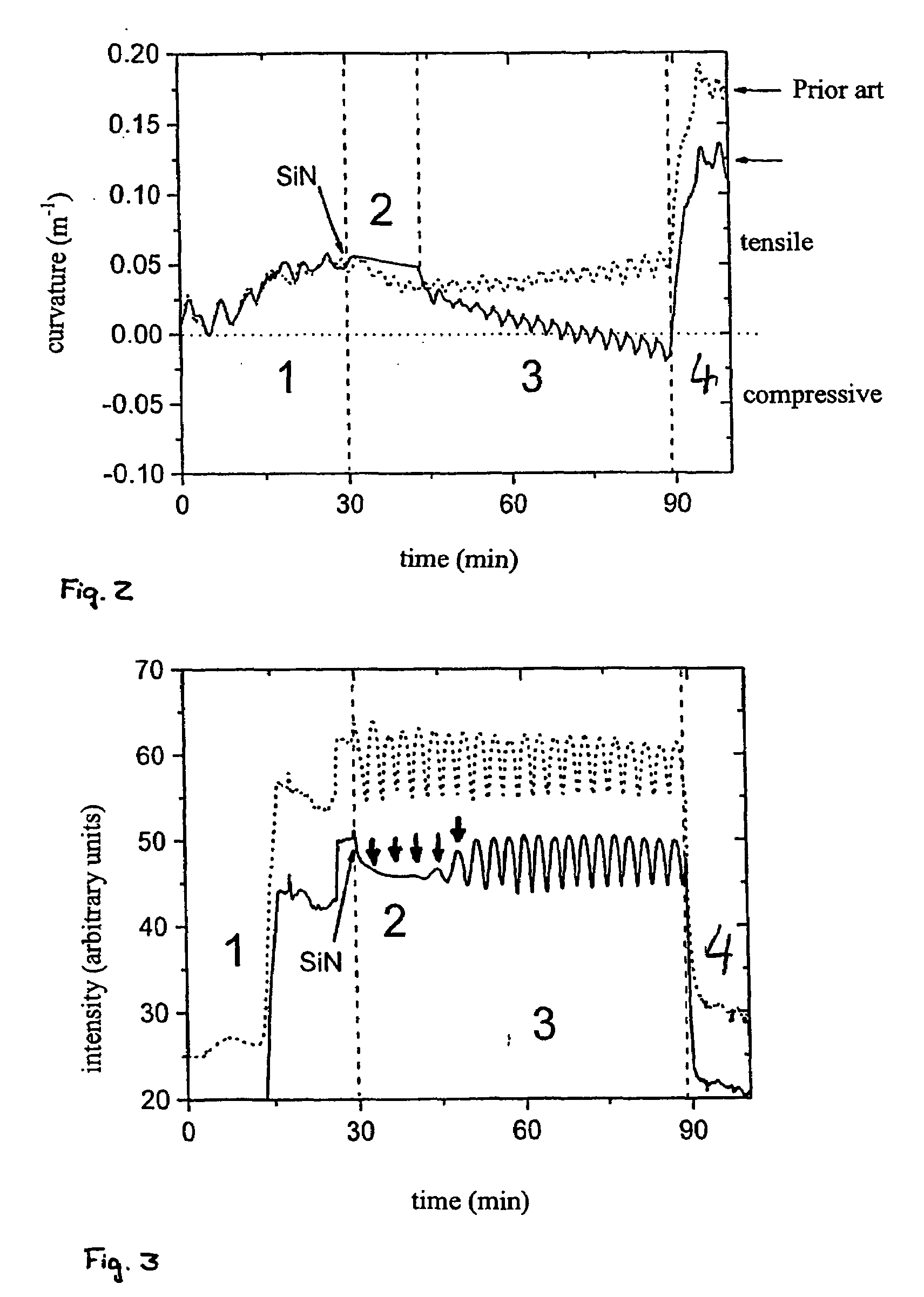
ActiveUS20070197004A1Cheap productionIncrease compressive stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLayer thicknessNucleation
The invention relates to a process for the production of a layer structure of a nitride semiconductor component on a silicon surface, comprising the steps:provision of a substrate that has a silicon surface;deposition of an aluminium-containing nitride nucleation layer on the silicon surface of the substrate;optional: deposition of an aluminium-containing nitride buffer layer on the nitride nucleation layer;deposition of a masking layer on the nitride nucleation layer or, if present, on the first nitride buffer layer;deposition of a gallium-containing first nitride semiconductor layer on the masking layer,wherein the masking layer is deposited in such a way that, in the deposition step of the first nitride semiconductor layer, initially separate crystallites grow that coalesce above a coalescence layer thickness and occupy an average surface area of at least 0.16 μm2 in a layer plane of the coalesced nitride semiconductor layer that is perpendicular to the growth direction.
Owner:AZUR SPACE SOLAR POWER +1
Liquid applicator and method of use
An applicator for dispensing uniform thickness layers of liquid to surfaces and especially surgical sealants to surgical sites to create, in situ, a surgical incise drape is disclosed. The applicator employs a supported thin layer of foam which achieves layer thickness which are substantially independent of the pressure applied to the applicator during use. Methods of using the applicator are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED MEDICAL SOLUTIONS PLYMOUTH
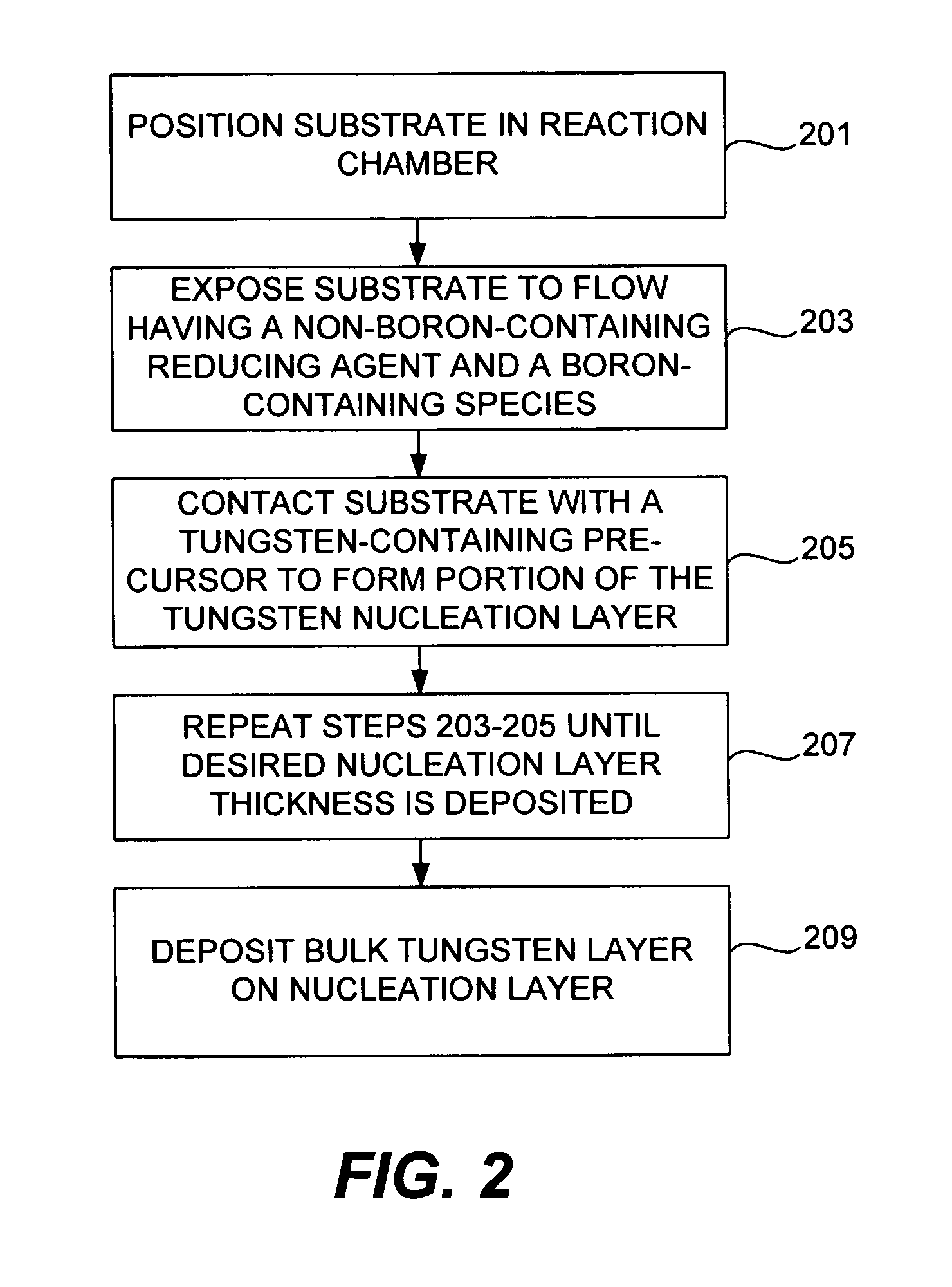
Methods for growing low-resistivity tungsten film
InactiveUS7589017B2Low resistivityGood step coverageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingBoron containingLayer thickness
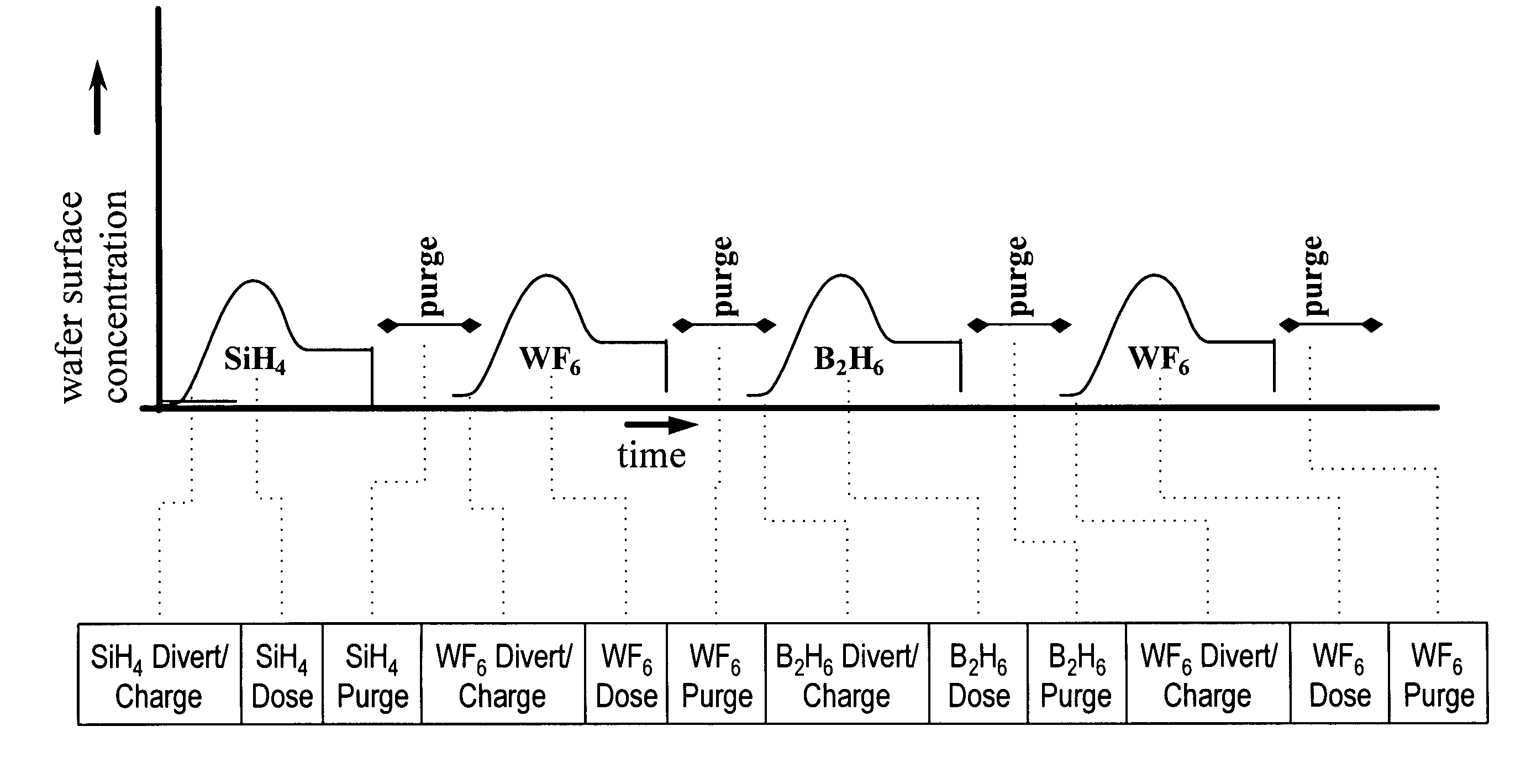
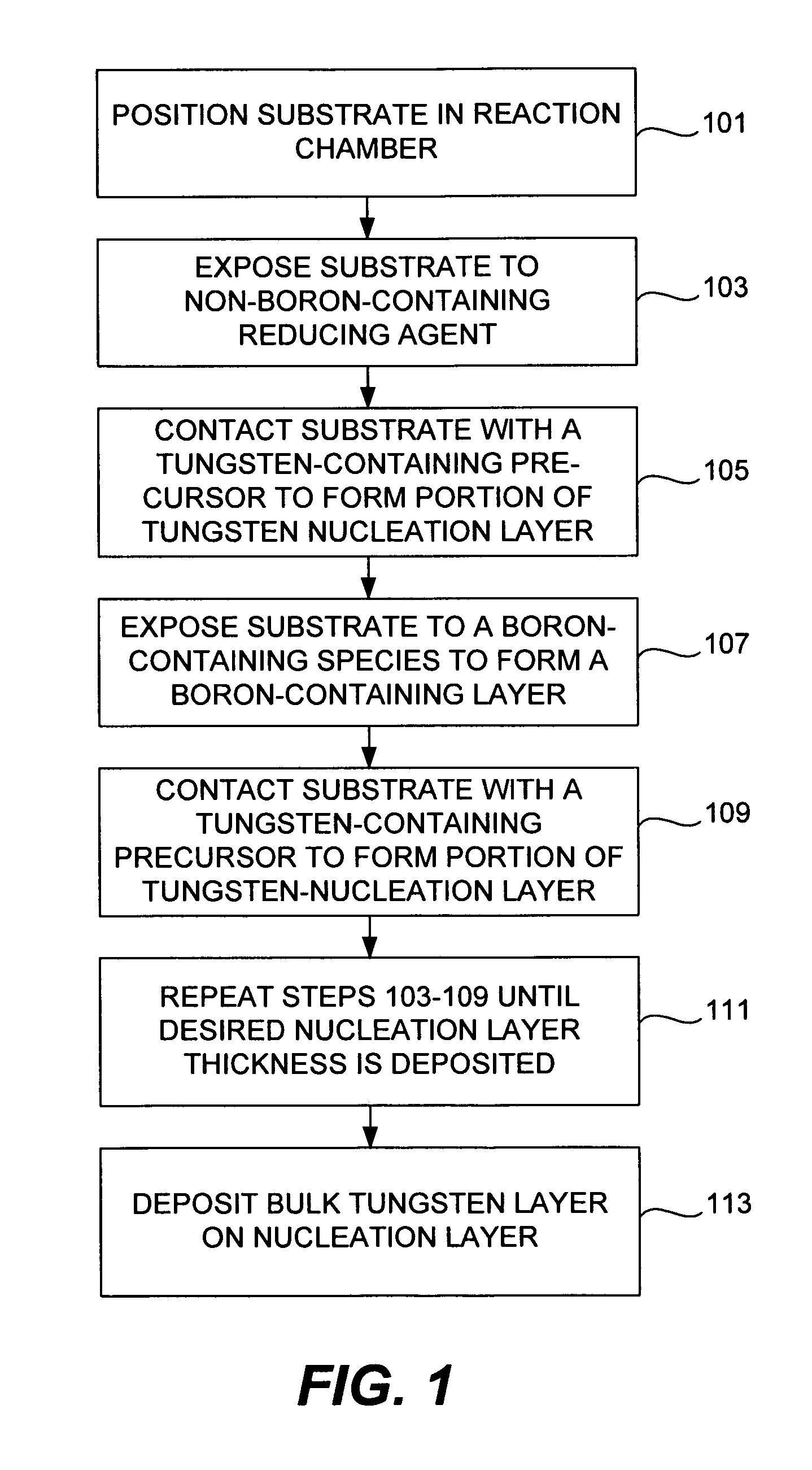
Improved methods for depositing low resistivity tungsten films are provided. The methods involve depositing a tungsten nucleation layer on a substrate and then depositing a tungsten bulk layer over the tungsten nucleation layer to form the tungsten film. The methods provide precise control of the nucleation layer thickness and improved step coverage. According to various embodiments, the methods involve controlling thickness and / or improving step coverage by exposing the substrate to pulse nucleation layer (PNL) cycles at low temperature. Also in some embodiments, the methods may improve resistivity by using a high temperature PNL cycle of a boron-containing species and a tungsten-containing precursor to finish forming the tungsten nucleation layer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method for the construction of a laminated compound
ActiveUS20080001331A1Additive manufacturing apparatusElectric discharge heatingCompound aEngineering
A method or procedure for the construction of a laminated compound or mould made up of a number of layers of particle material on top of each other, which are hardened and joined to each other in predetermined onsite areas, which can differ from each other depending on position and expansion, so that from the predetermined hardened areas of the laminated compound at least one mould is formed. The layers are deposited individually one after another in predetermined layer thickness by the dispensing of particle material from a dispensing device during its movement above a working field and according to computer data in predetermined areas.
Owner:VOXELJET AG
Selective deposition modeling with curable phase change materials
InactiveUS6841116B2Improve mechanical propertiesEasy to disassembleConfectionerySweetmeatsSelective depositionPhase change
A selective deposition modeling method and apparatus for dispensing a curable phase change material. The dispensing temperature of the material is set at or less than a thermally stable temperature value for the material in which the reactive component of the material remains substantially uncured when held at the temperature for a desired time period. The dispensed material is provided with an environment that enables the material to solidify to form layers of the object. The solidified material is normalized to a desired layer thickness and is then cured by exposure to actinic radiation. In a preferred embodiment a UV curable phase change material is dispensed at about 80° C. and has a viscosity of about 13 to about 14 centipoise at this temperature. The cured material provides substantially increased physical properties over thermoplastic phase change materials previously used in selective deposition modeling.
Owner:3D SYST INC
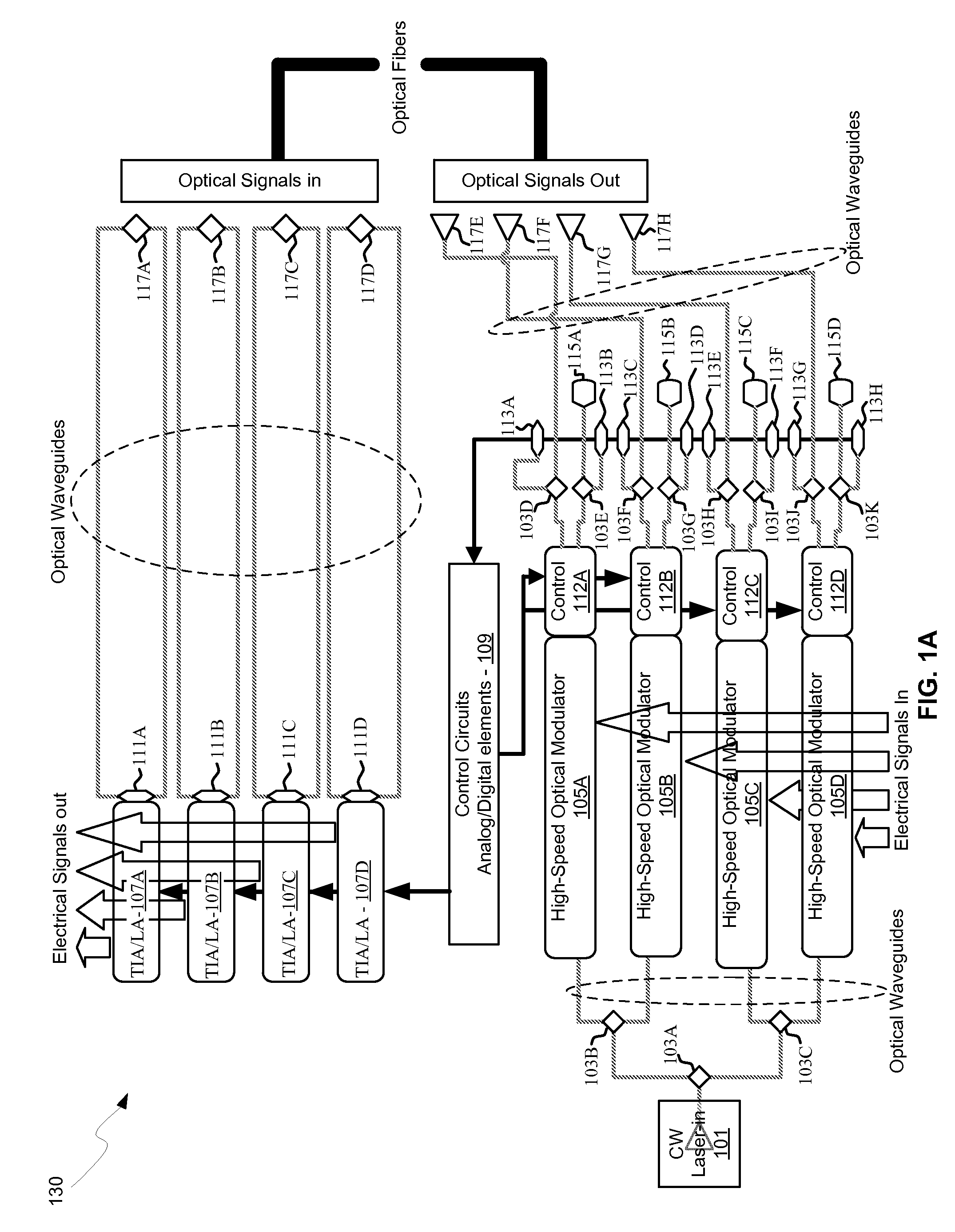
Method and system for monolithic integration of photonics and electronics in CMOS processes
ActiveUS20100059822A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoi cmosEtching
Methods and systems for monolithic integration of photonics and electronics in CMOS processes are disclosed and may include fabricating photonic and electronic devices on a single CMOS wafer with different silicon layer thicknesses. The devices may be fabricated on a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) wafer utilizing a bulk CMOS process and / or on a SOI wafer utilizing a SOI CMOS process. The different thicknesses may be fabricated utilizing a double SOI process and / or a selective area growth process. Cladding layers may be fabricated utilizing one or more oxygen implants and / or utilizing CMOS trench oxide on the CMOS wafer. Silicon may be deposited on the CMOS trench oxide utilizing epitaxial lateral overgrowth. Cladding layers may be fabricated utilizing selective backside etching. Reflective surfaces may be fabricated by depositing metal on the selectively etched regions. Silicon dioxide or silicon germanium integrated in the CMOS wafer may be utilized as an etch stop layer.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Developing device frame unit, developing device, process cartridge, and manufacturing method of the developing device frame unit
ActiveUS7933534B2Improve sealingReduce component countElectrographic process apparatusElastomerEngineering
A developing device frame unit supporting a regulating member regulating the layer thickness of developer on a developer carrier. The unit includes a frame having a seal forming portion, first and second, first and second end seals contactable to the carrier surface to prevent carrier-axial-direction leaking of the developer, and a blade sealer sealing between the regulating member and the frame to prevent developer leaking when the regulating member is mounted. The blade sealer is an elastomer resin material which is injection-molded with a metal mold and in the seal forming portion where the end seals are provided. The blade sealer connects the end seals with each other, and a protrusion provided by a squeezed-out portion of the resin material is provided by injecting, into a space defined by the metal mold, the seal forming portion, and the end seal seals, a resin material volume larger than a volume of the space.
Owner:CANON KK
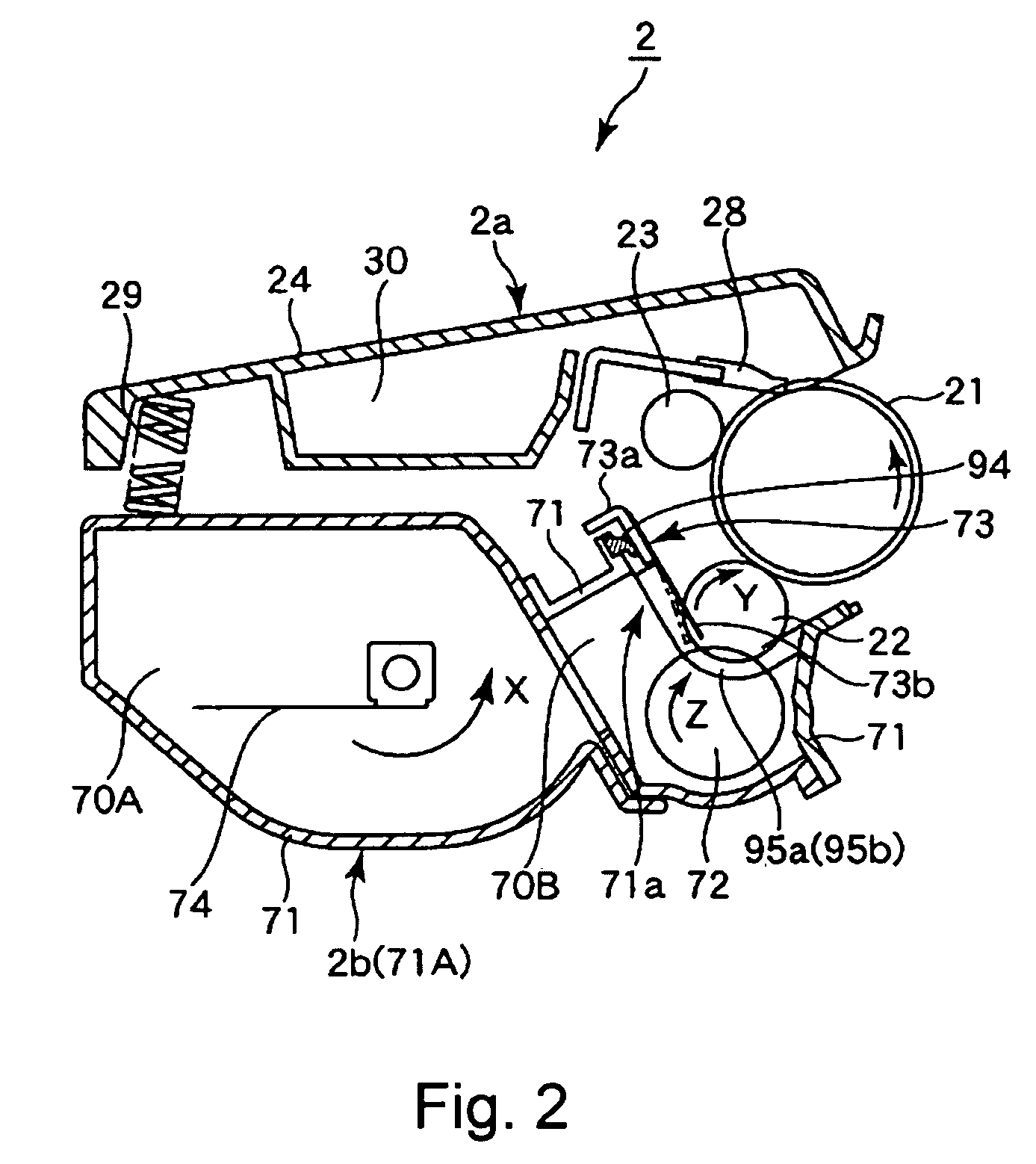
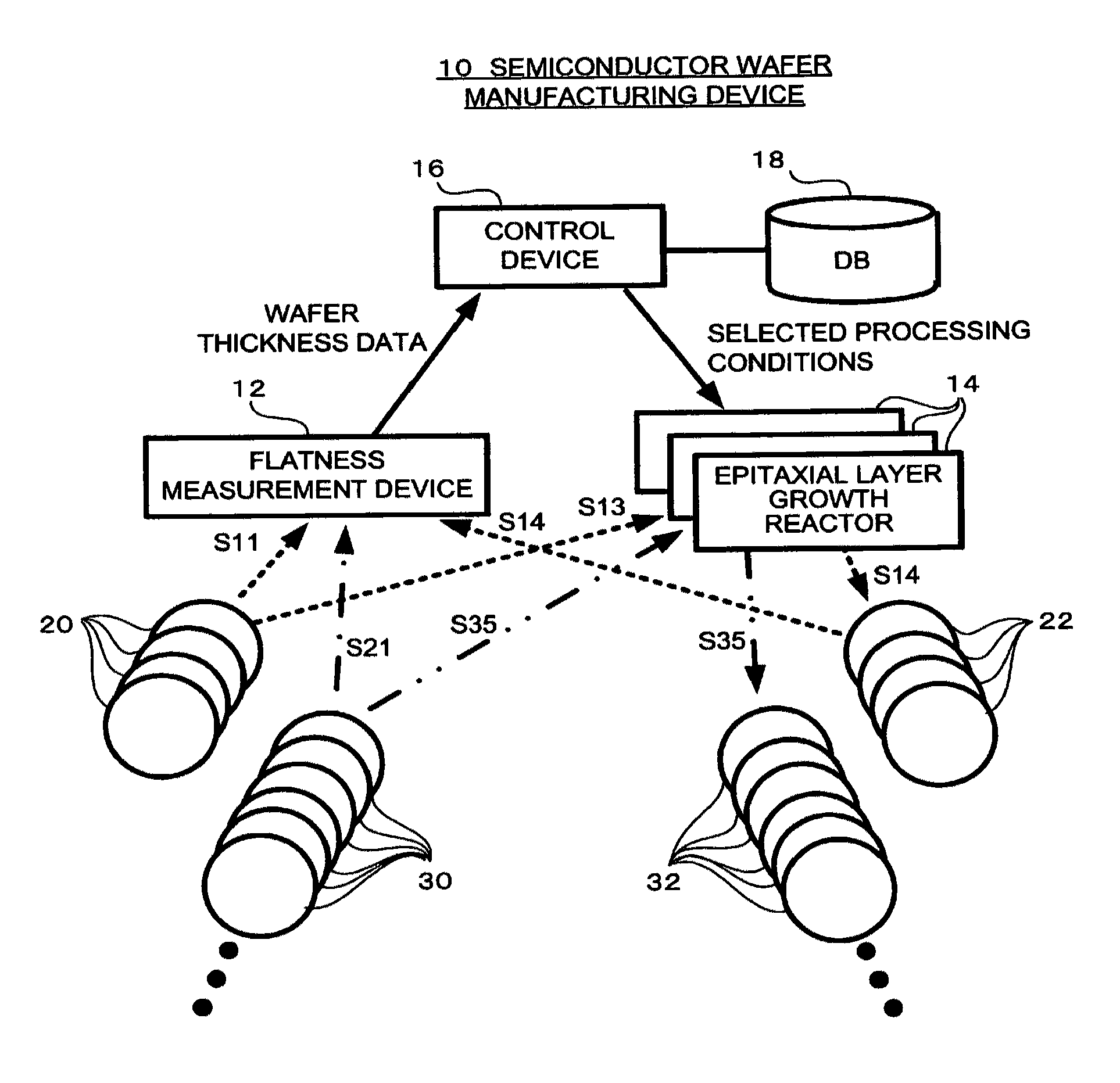
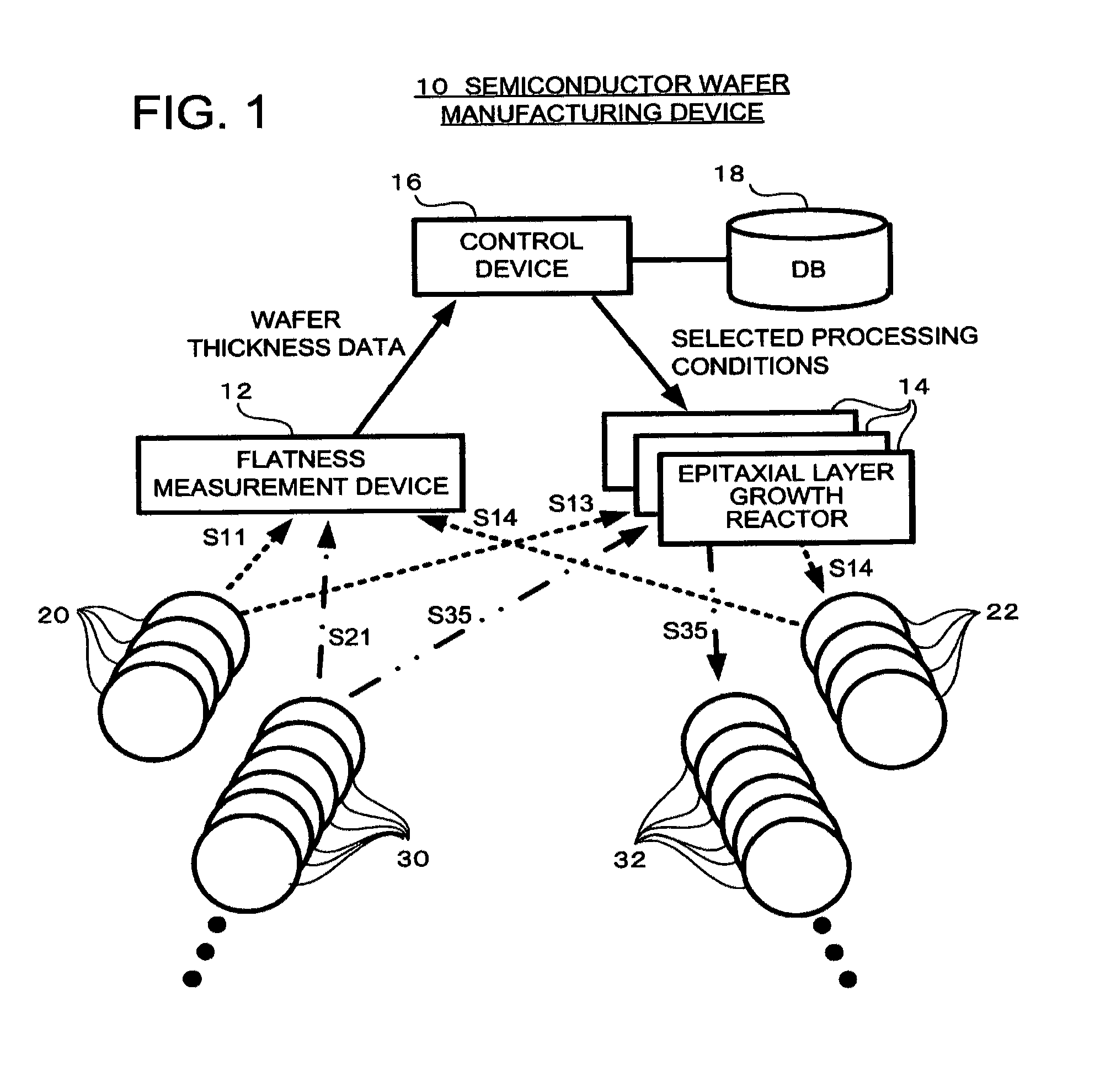
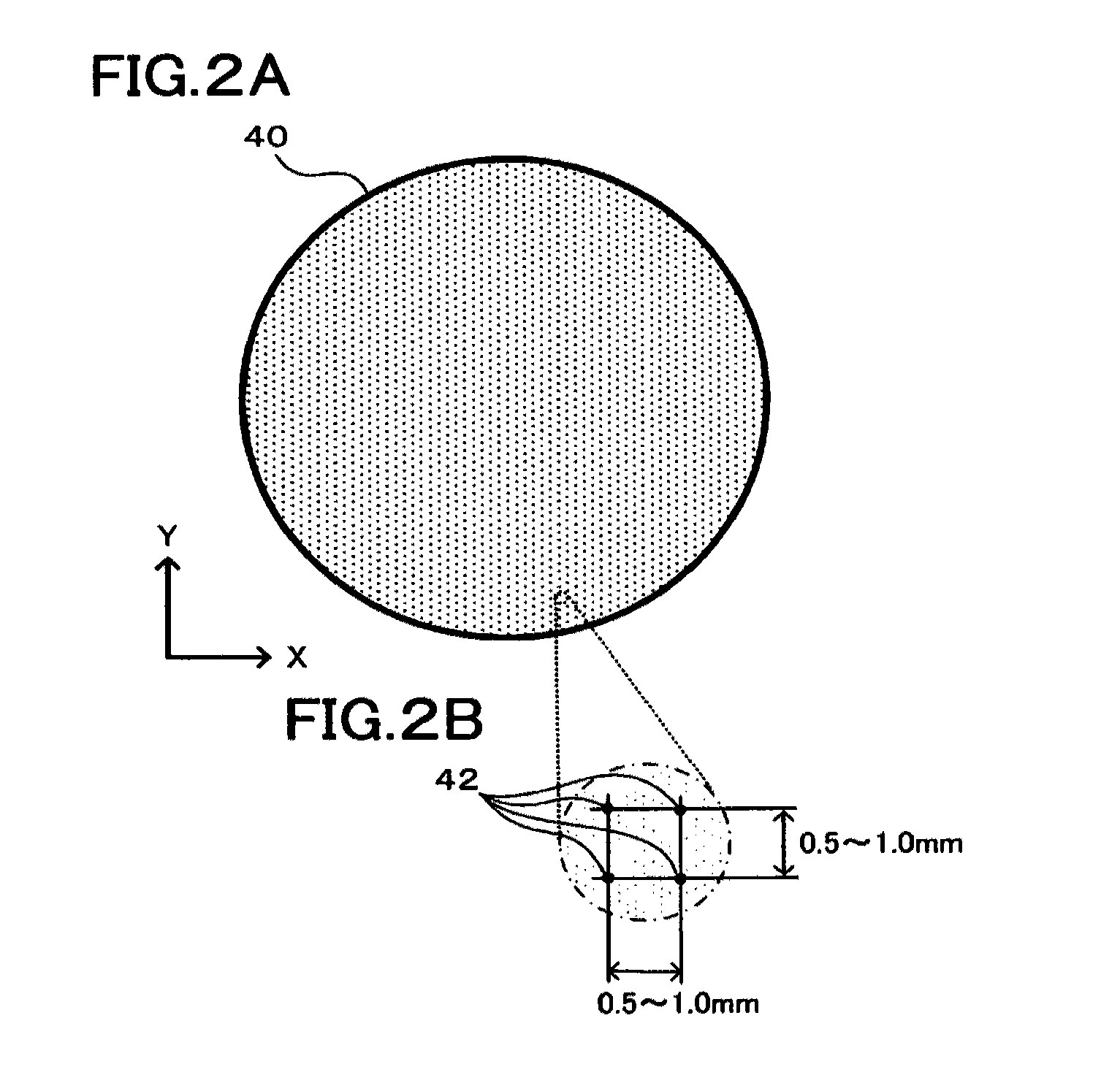
Device and method for manufacturing a semiconductor wafer
ActiveUS8196545B2Reliable manufacturingEnhance the imageProgramme controlLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringLayer thickness
Owner:SUMCO TECHXIV
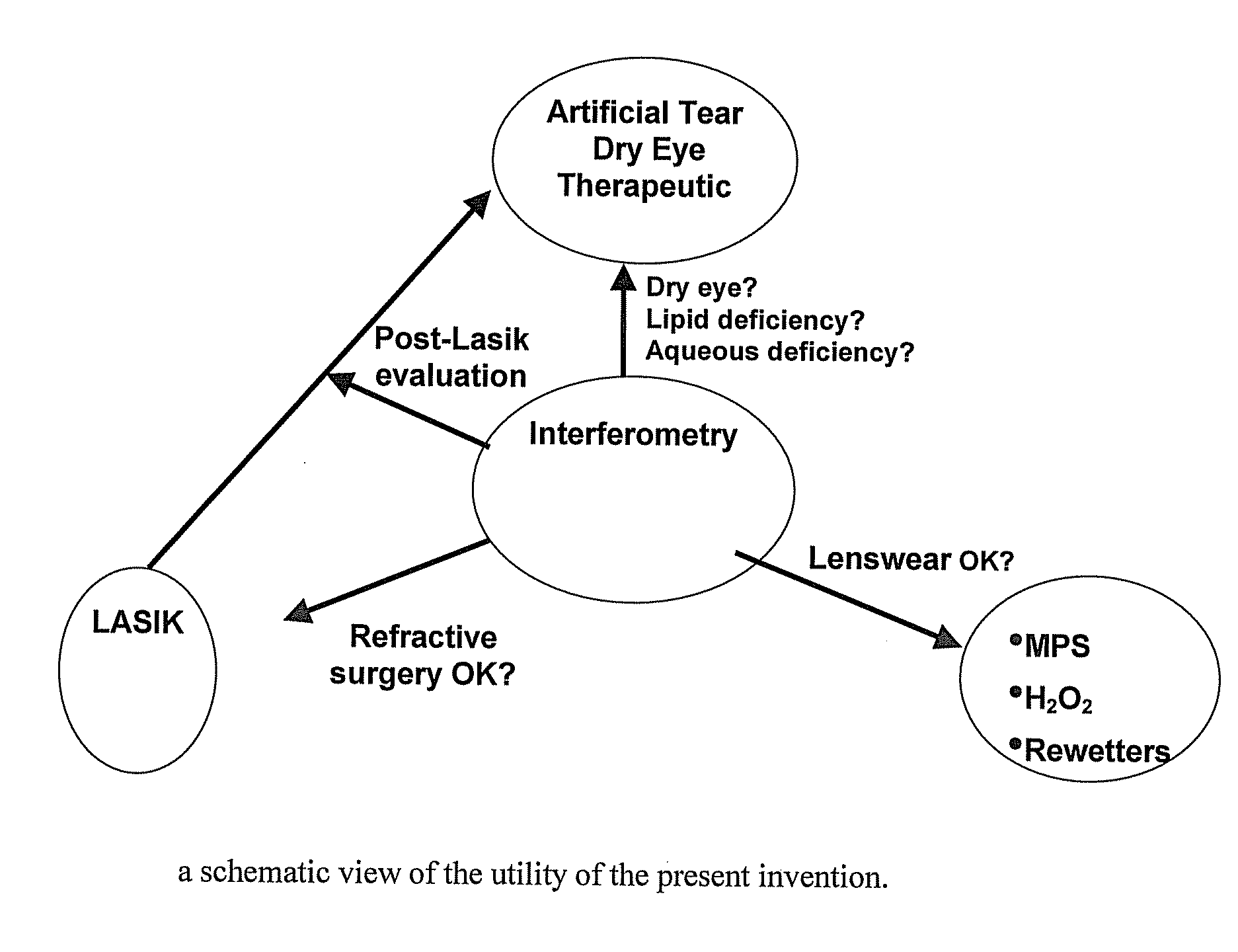
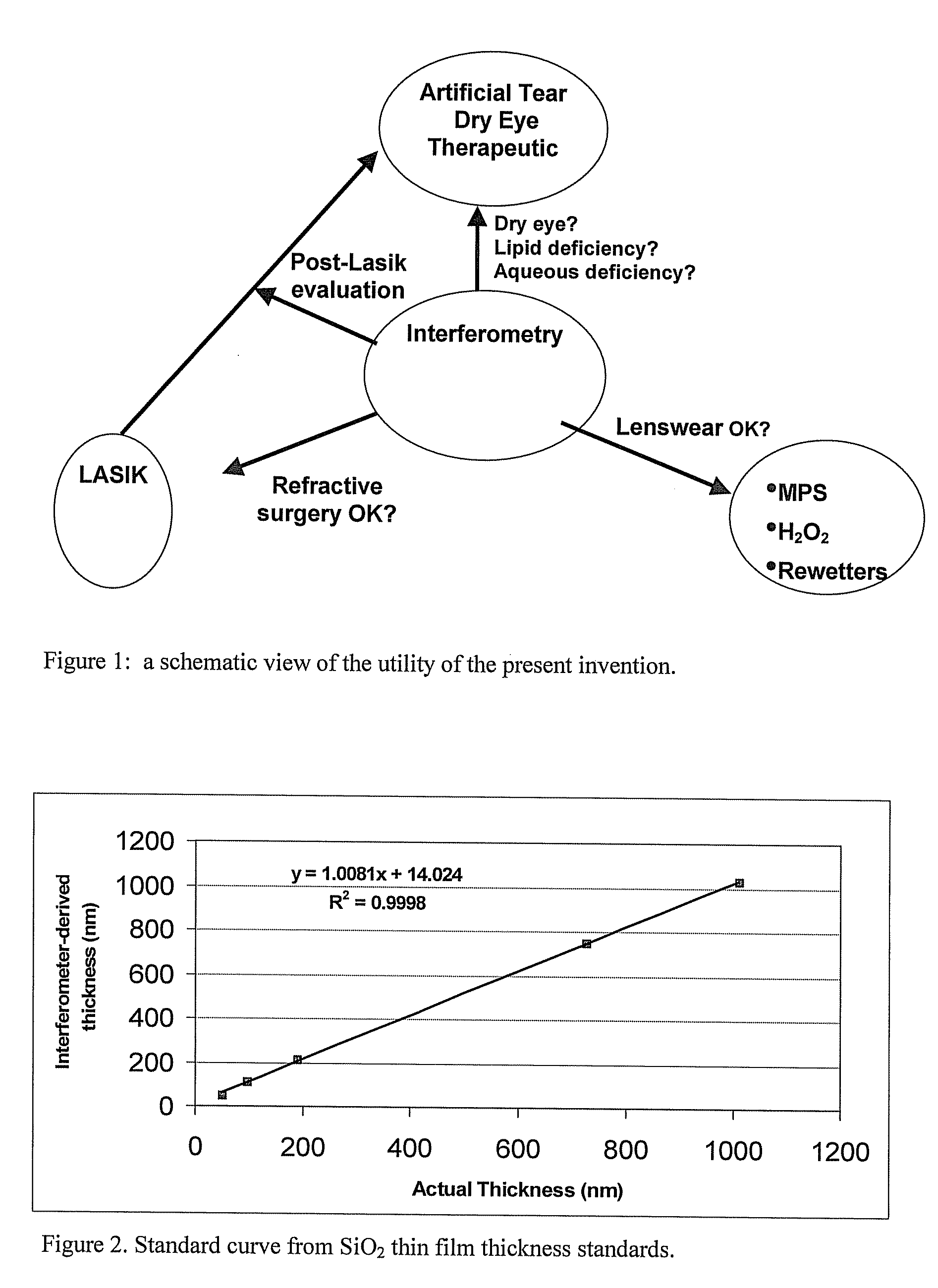
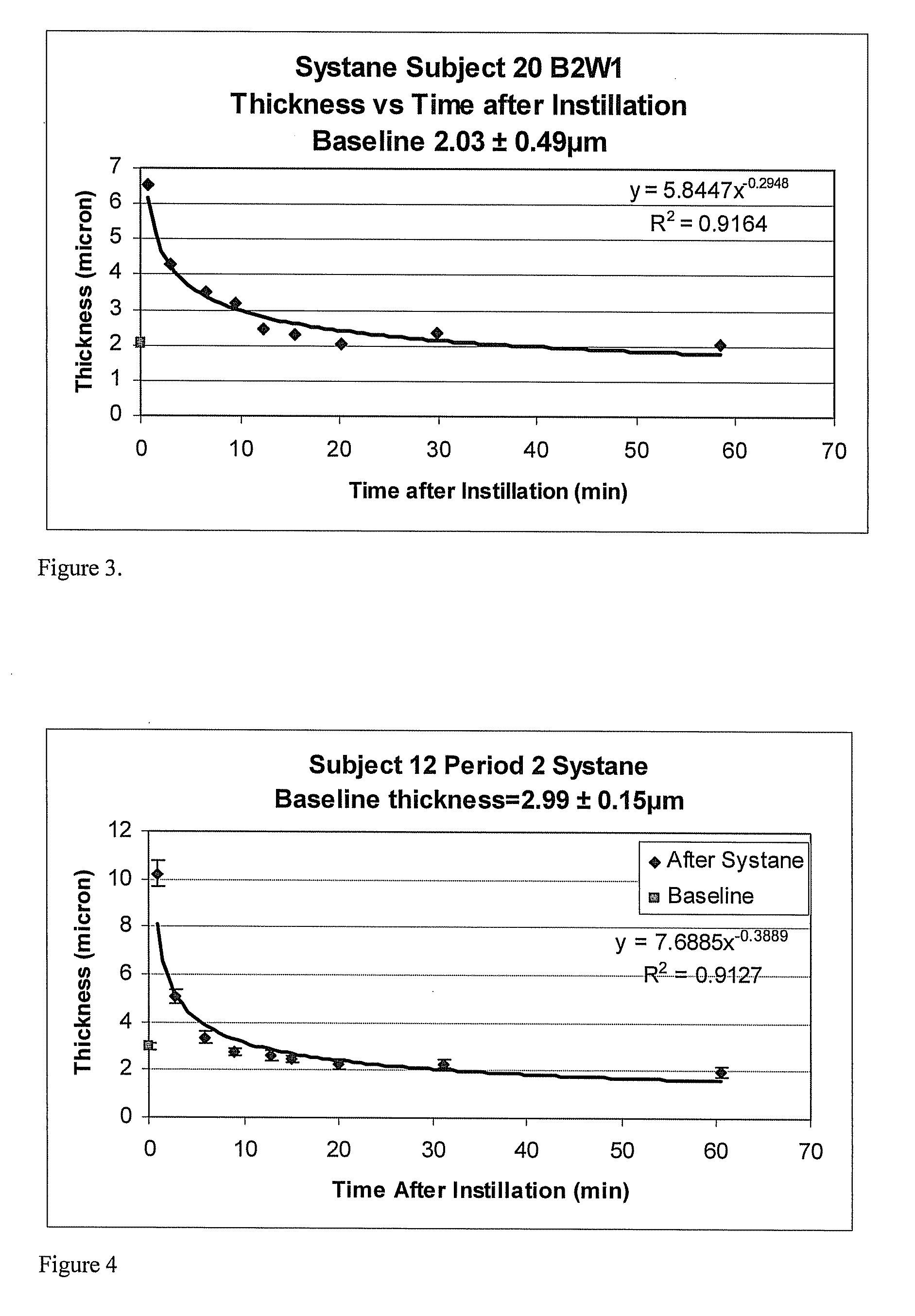
Methods and devices for measuring tear film and diagnosing tear disorders
Methods and devices measure eye blinks and tear film lipid and aqueous layer thickness before and following ophthalmic formula application onto the ocular surface, especially wherein the ophthalmic formula is an artificial tear. The methods and devices are suitable for dry eye diagnosis. The methods and devices are suitable for use to evaluate ophthalmic formula effects on the tear film and to use such information to diagnose ophthalmic formula treatment of ocular disease conditions such as dry eye in the absence of contact lens wear or post-surgical eye drop treatment and diagnosis. The methods and devices are also suitable for use in the optimization of ophthalmic drug dosage forms and sustained drug release.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Method and system for shaped glasses and viewing 3d images
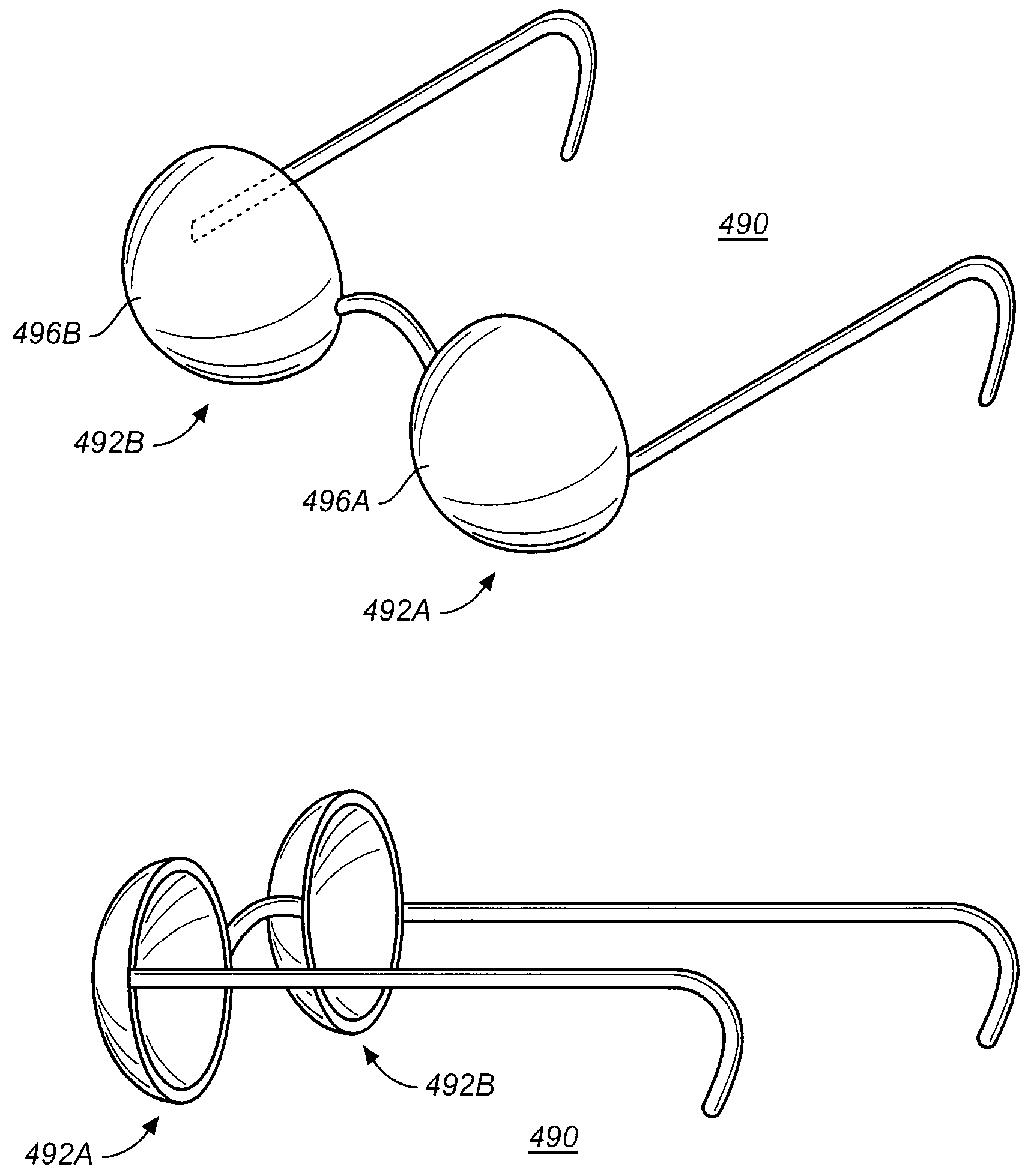
ActiveUS20080278807A1Reduce the wavelength shiftStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systems3d imageComplementary filter
Shaped glasses have curved surface lenses and spectrally complementary filters disposed on the curved surface lenses configured to compensate for wavelength shifts occurring due to viewing angles and other sources. The spectrally complementary filters include guard bands to prevent crosstalk between spectrally complementary portions of a 3D image viewed through the shaped glasses. In one embodiment, the spectrally complementary filters are disposed on the curved lenses with increasing layer thickness towards edges of the lenses. The projected complementary images may also be pre-shifted to compensate for subsequent wavelength shifts occurring while viewing the images.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method for creating and preserving alignment marks for aligning mask layers in integrated circuit manufacture
InactiveUS6261918B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringIntegrated circuit
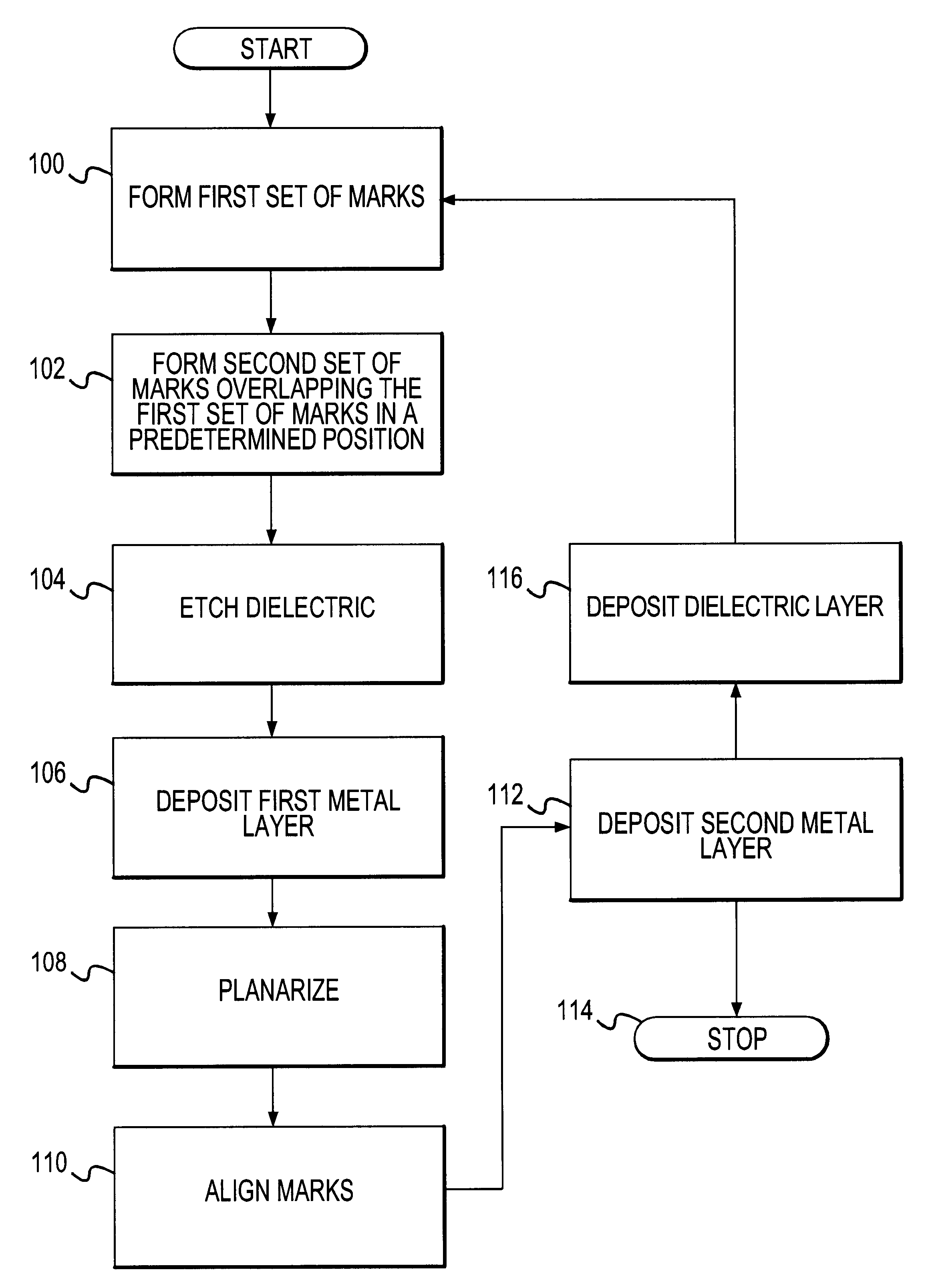
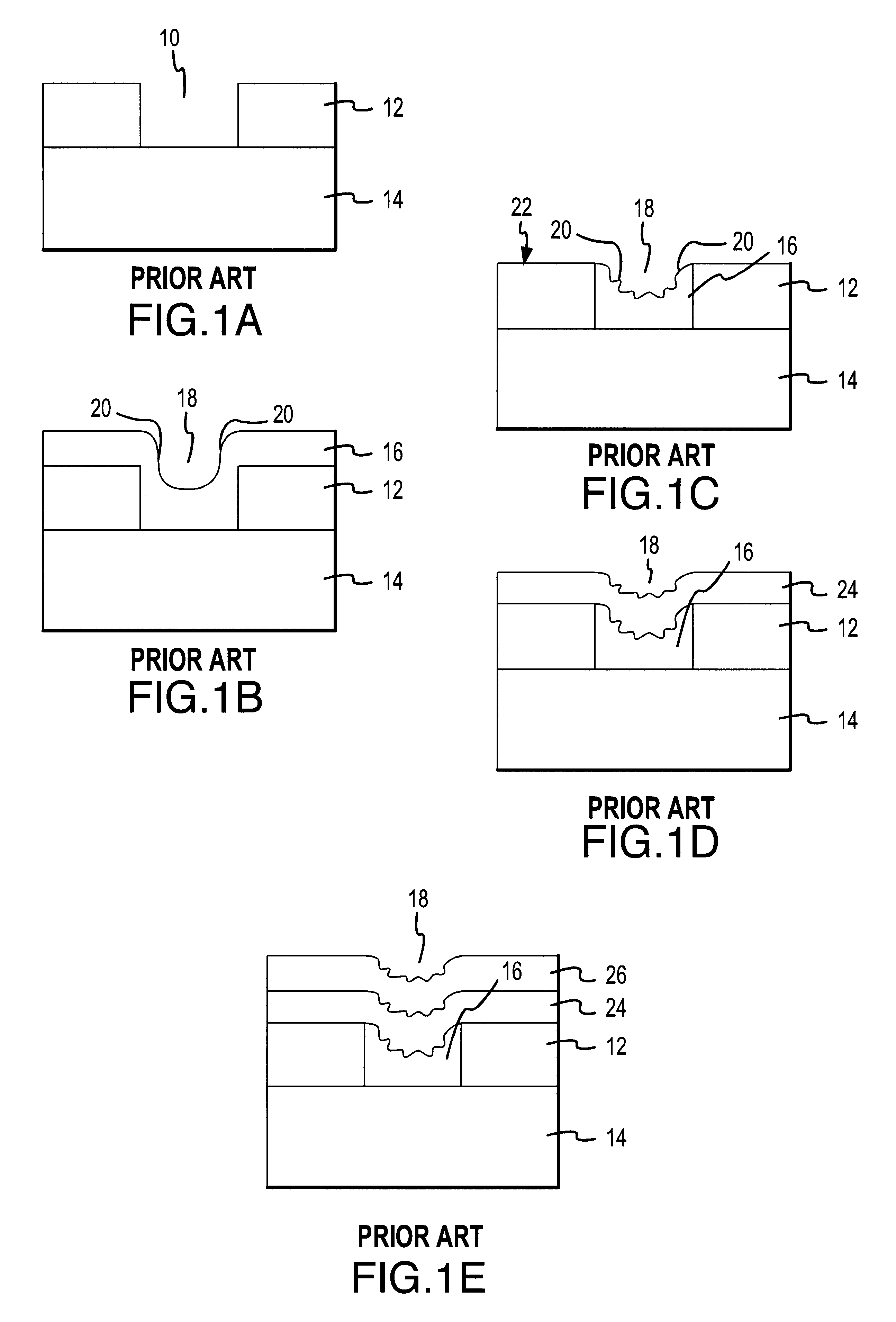
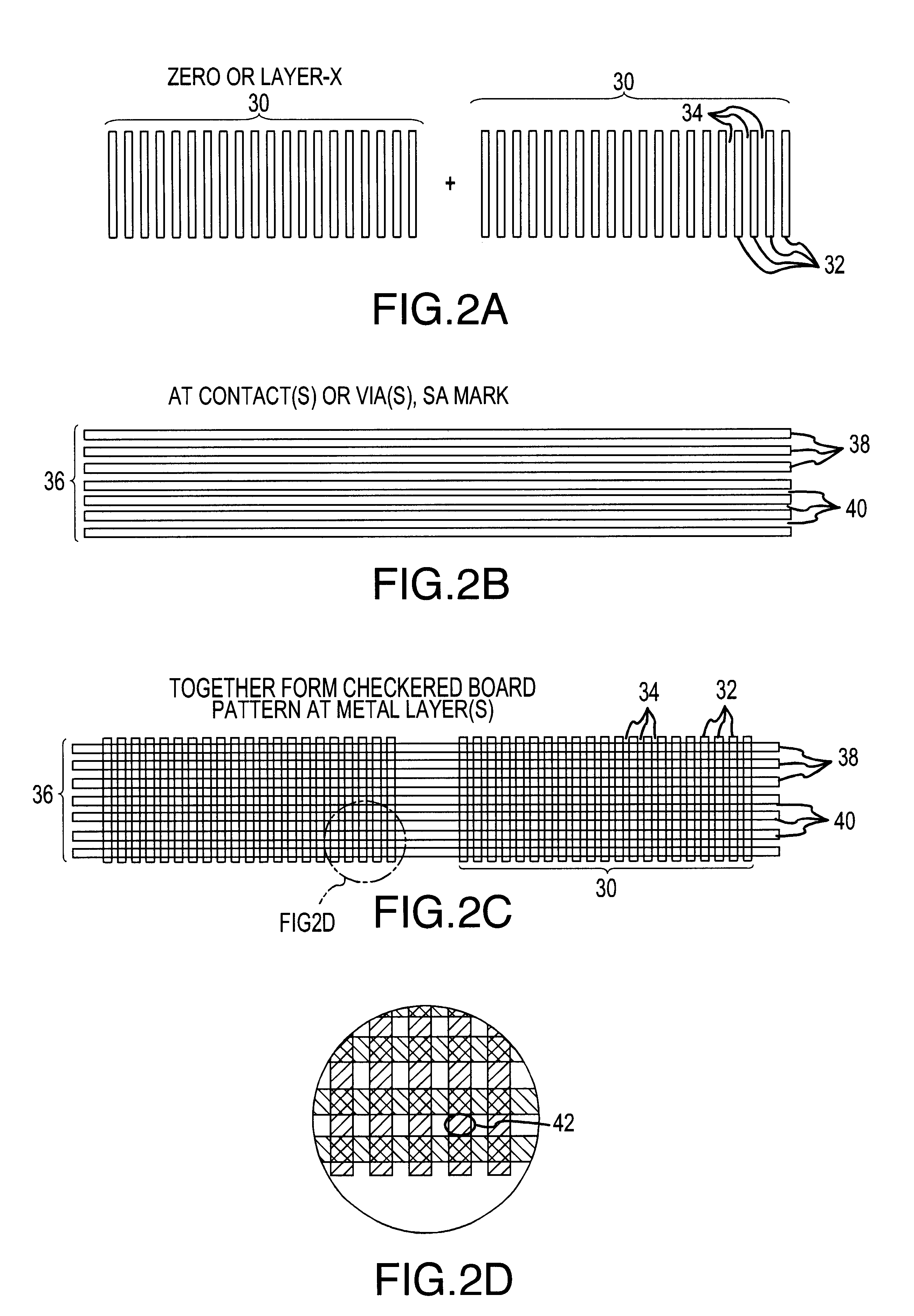
A method for creating and preserving alignment marks used for aligning mask layers in integrated circuit formation including the steps of creating a first set of marks within a reference layer to form a basic alignment mark, creating a second set of marks overlapping the first set of marks and positioned perpendicular to the first set of marks in the same reference layer to form a preservation pattern, and etching the reference layer to form a substantially checkerboard-type pattern where portions of the first set of marks are recessed within a thickness of the reference layer. After creating the checkerboard-type pattern formed from the first and second marks, a first metal a layer may be deposited to fill in any recesses contained within the pattern. CMP follows without damaging the segmented portions of the first set of marks which lie recessed within a thickness of the reference layer. Finally, the preserved portions of the first set of marks are aligned with pattern marks for a second metal layer.
Owner:NEWPORT FAB
Liquid crystal device and electronic apparatus
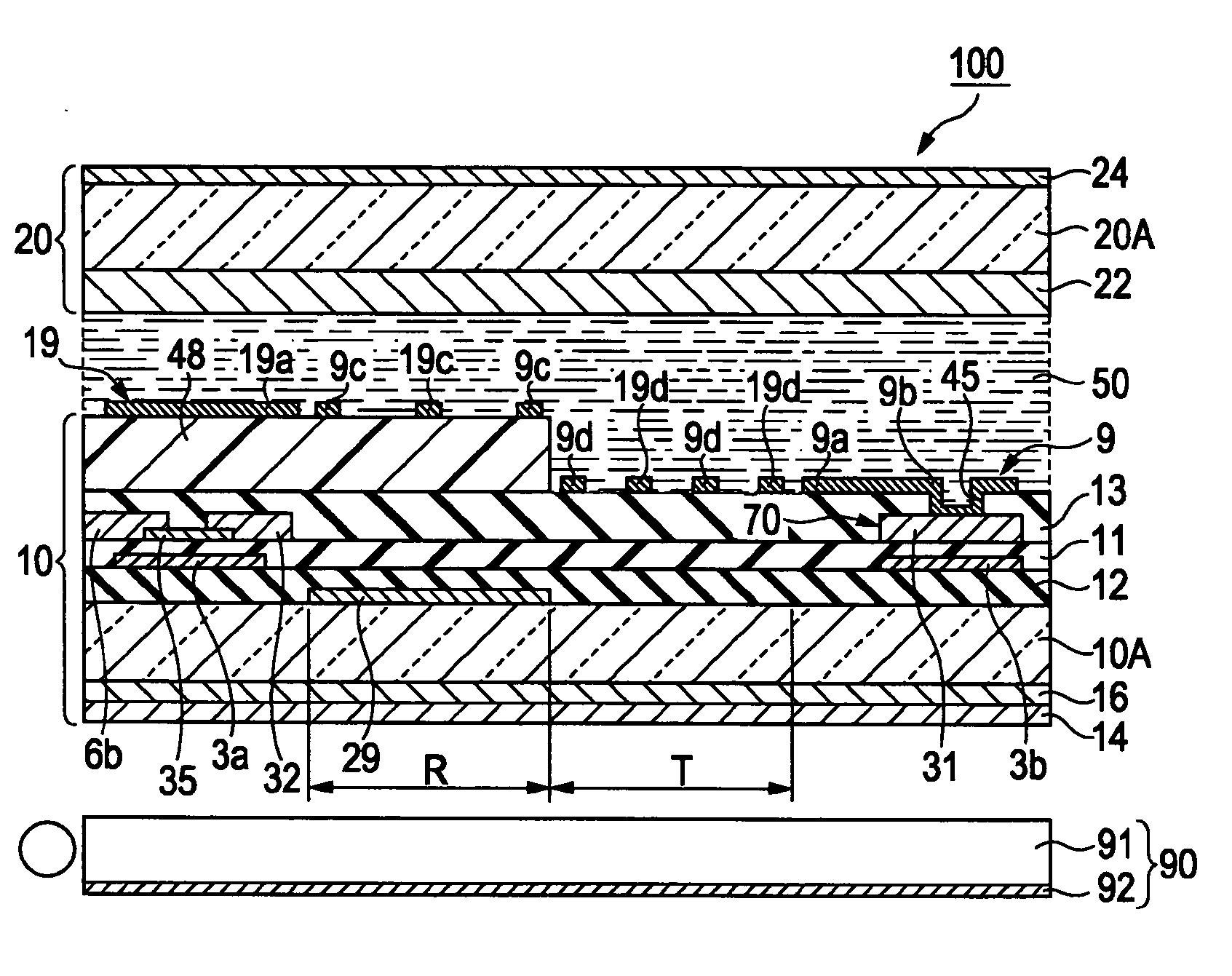
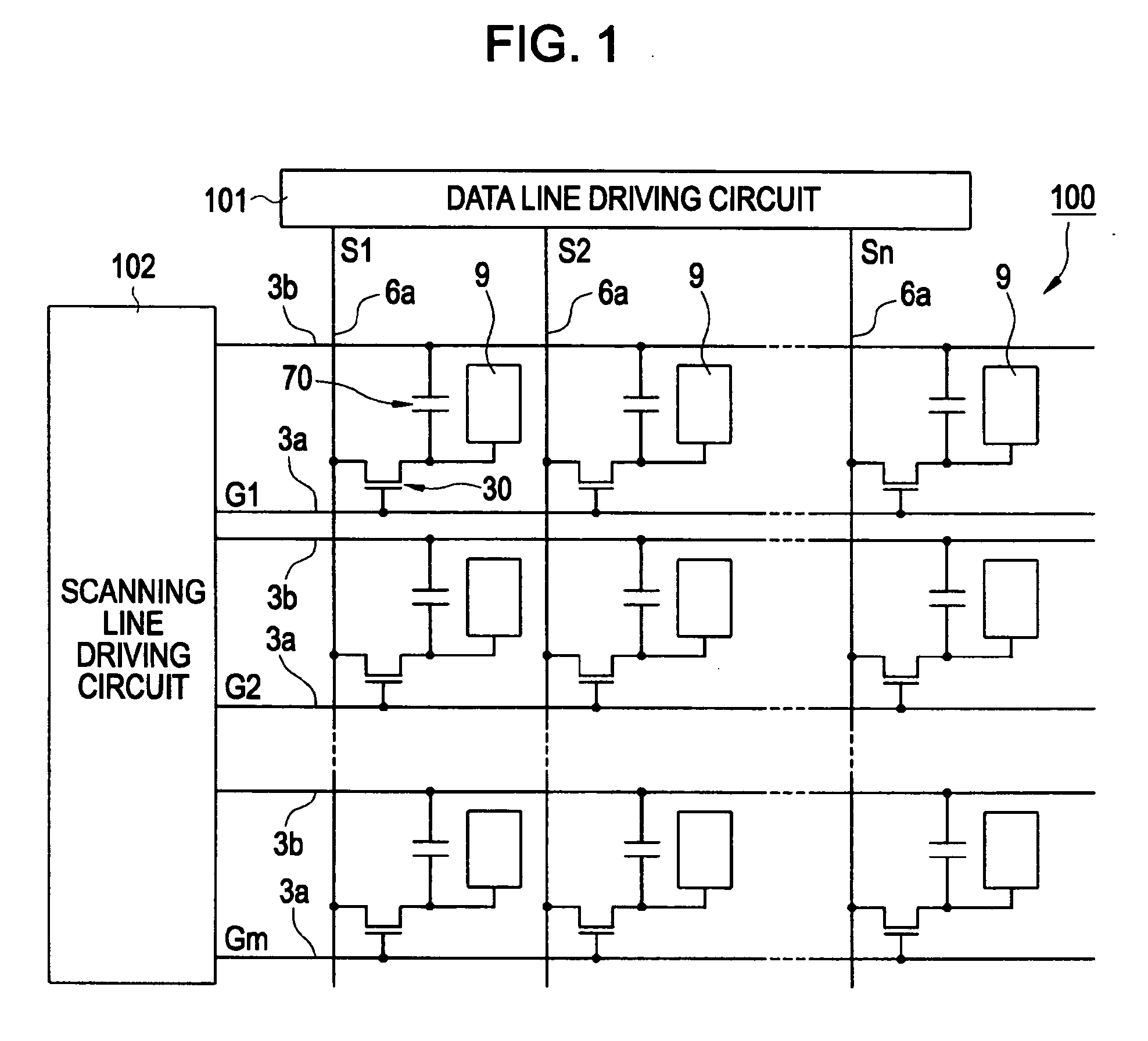
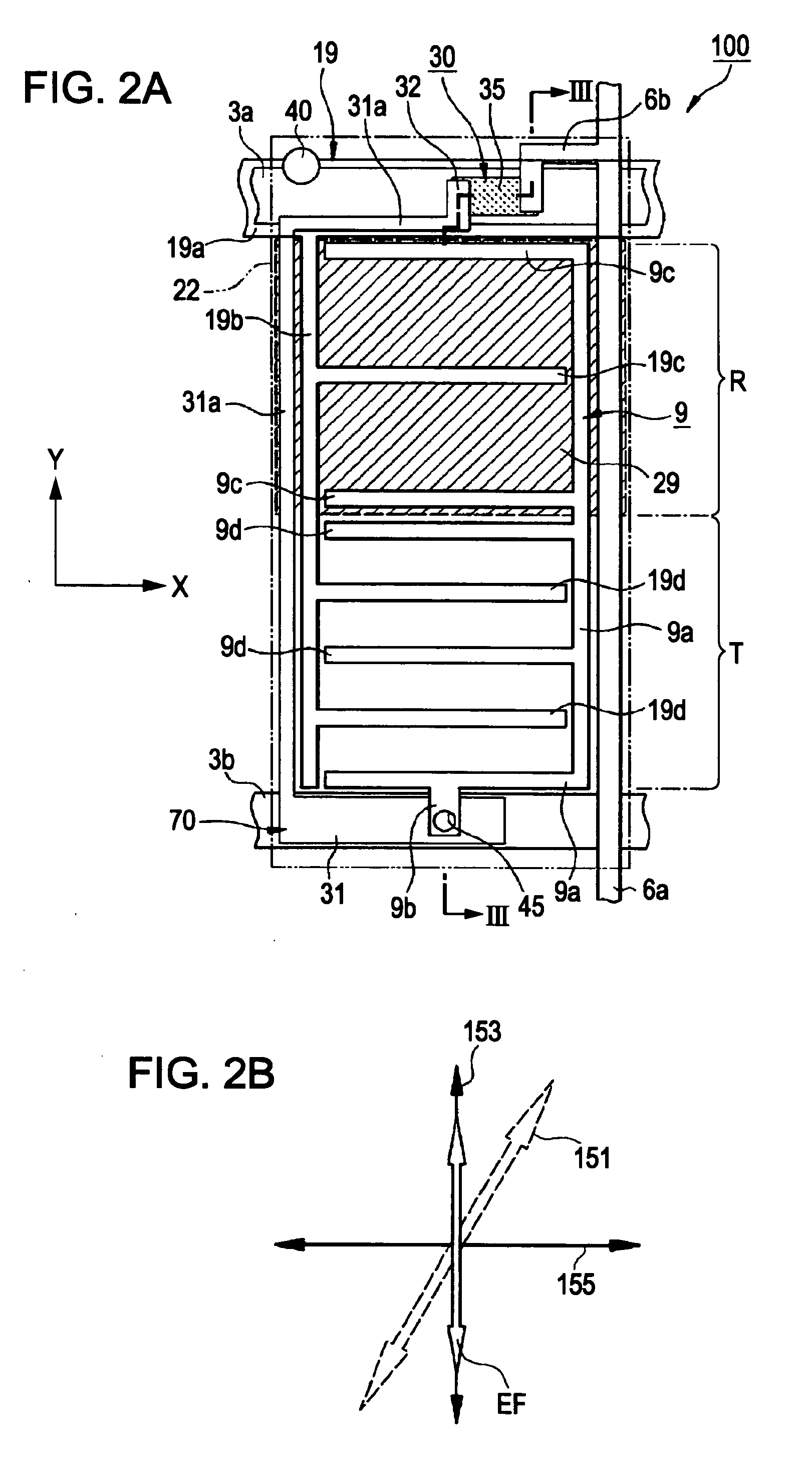
InactiveUS20060267891A1Easy to displayLarge widthStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLayer thicknessElectric field
A liquid crystal device includes first and second substrates which are arranged so as to face each other with a liquid crystal layer interposed therebetween, and first and second electrodes which are provided on the first substrate facing the liquid crystal layer. The liquid crystal layer is driven by electric fields generated between the first and second electrodes. A reflective display region for reflective display and a transmissive display region for transmissive display are provided in each of a plurality of subpixel regions. A liquid-crystal-layer-thickness-adjusting layer is provided in at least the reflective display region so as to vary the thickness of the liquid crystal layer in the subpixel region. A gap between the first and second electrodes in a main direction of an electric field in the transmissive display region is narrower than a gap between the first and second electrodes in a main direction of an electric field in the reflective display region.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com