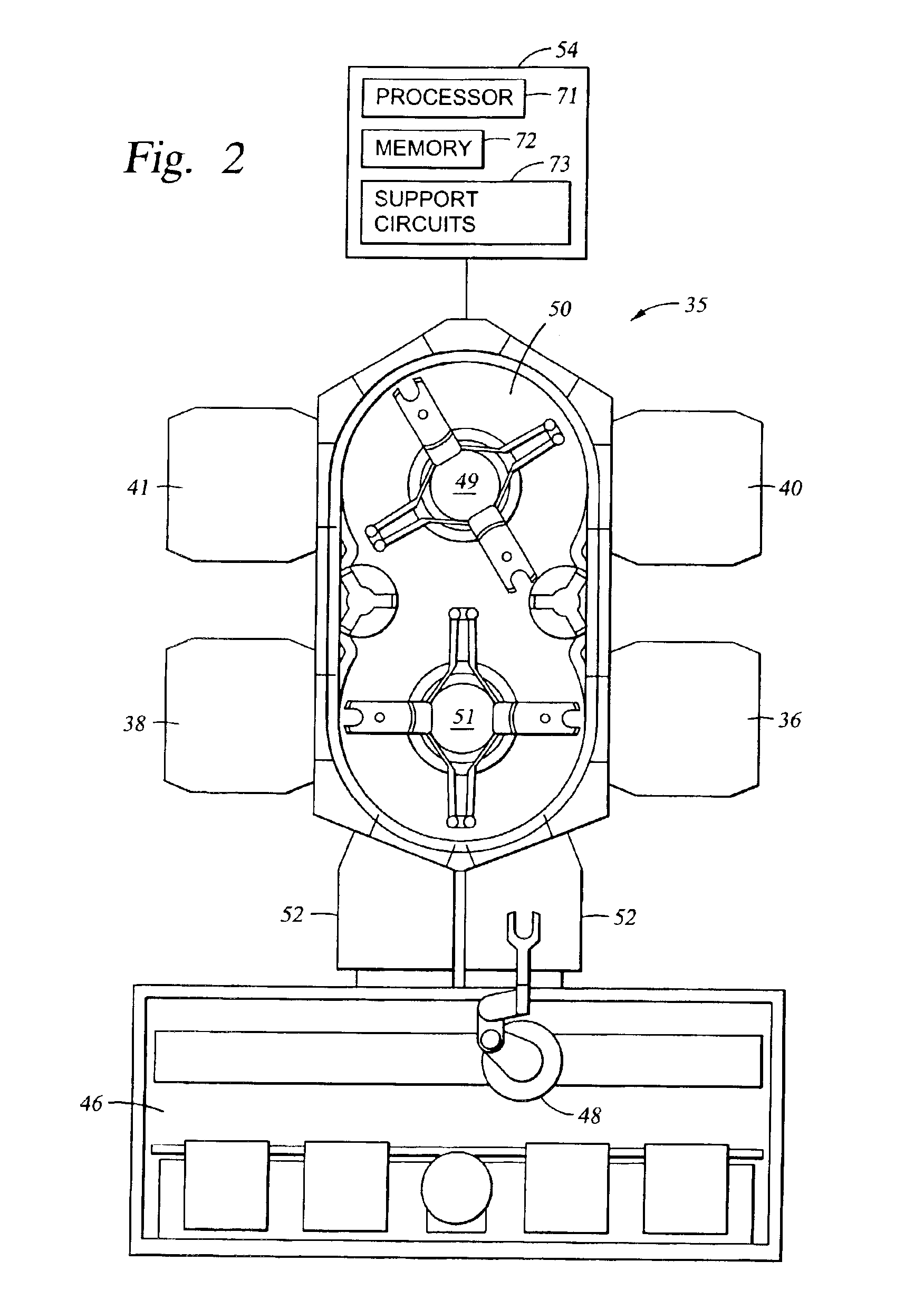
Patents
Literature
267 results about "Tungsten film" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tungsten film is photographic film designed to accurately represent colors as perceived by humans under tungsten light; the more usual color films are "daylight films", balanced to produce accurate colours under direct light from the sun or electronic flash. Tungsten film was developed for photographers who use tungsten lights, also known as photofloods, which have a much lower color temperature than daylight, at 3200 kelvins. It also renders colors more accurately than daylight film under ordinary household incandescent lighting.
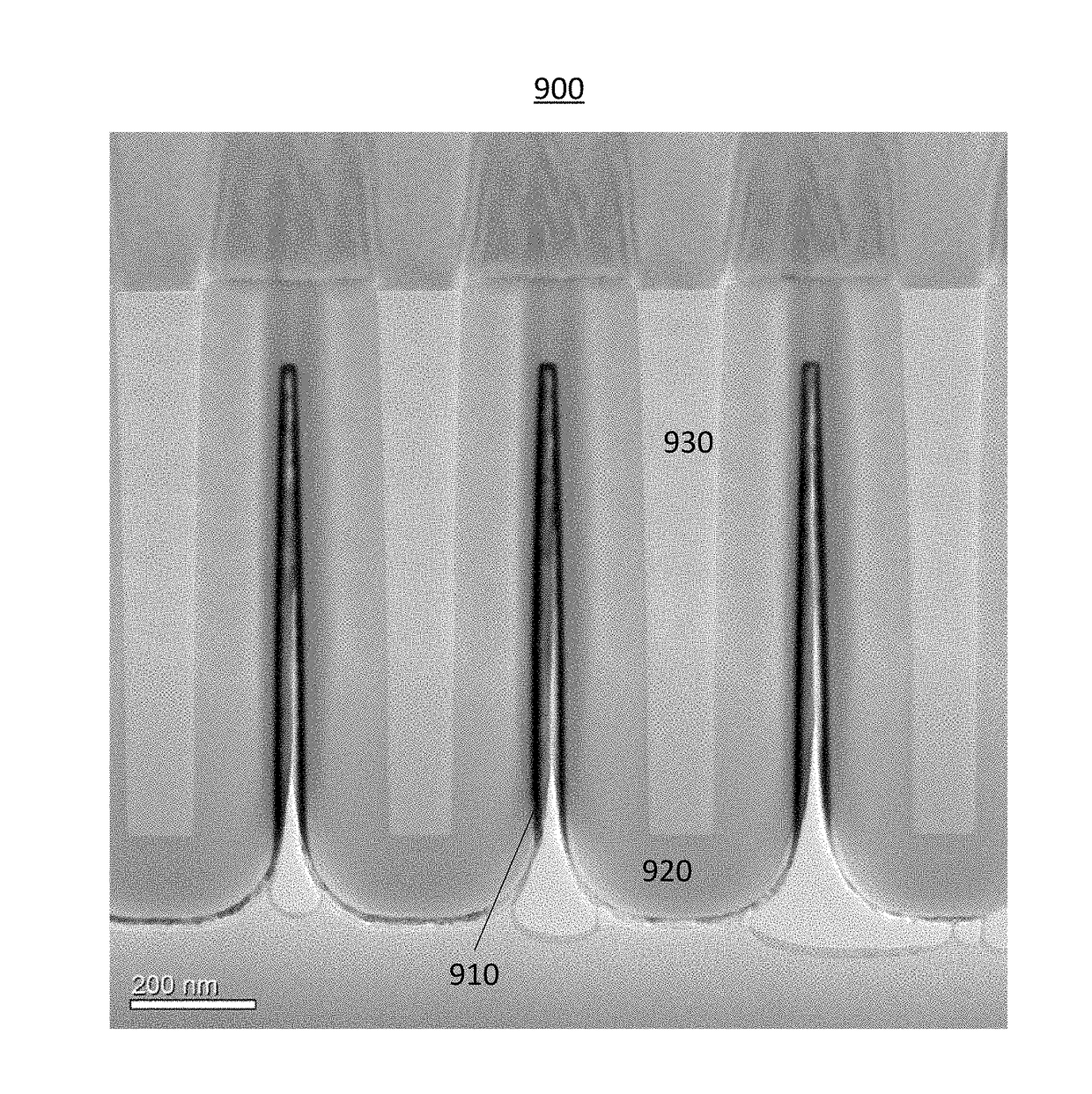
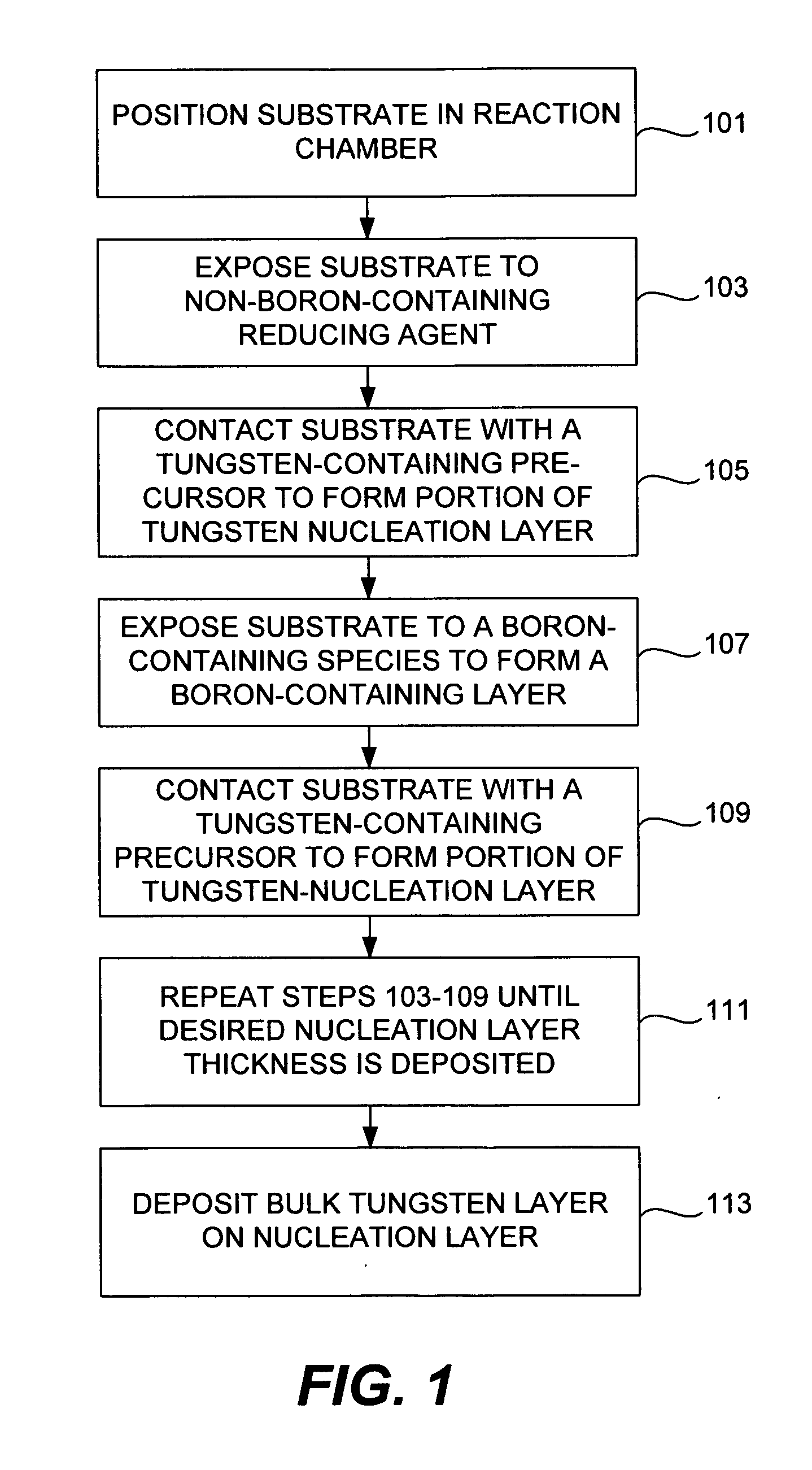
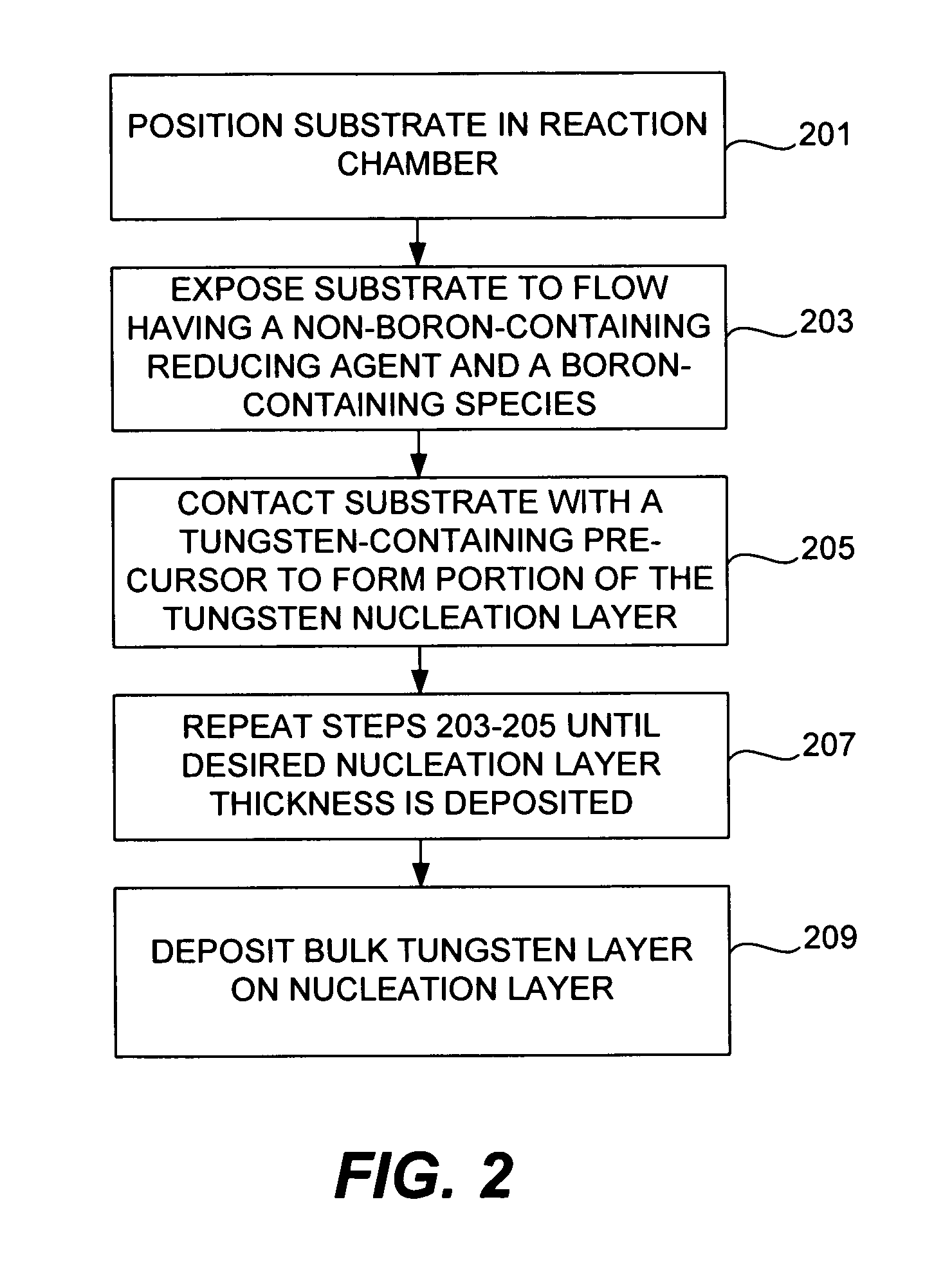
Selective deposition of tungsten
ActiveUS20180025939A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHydrogenSelective deposition
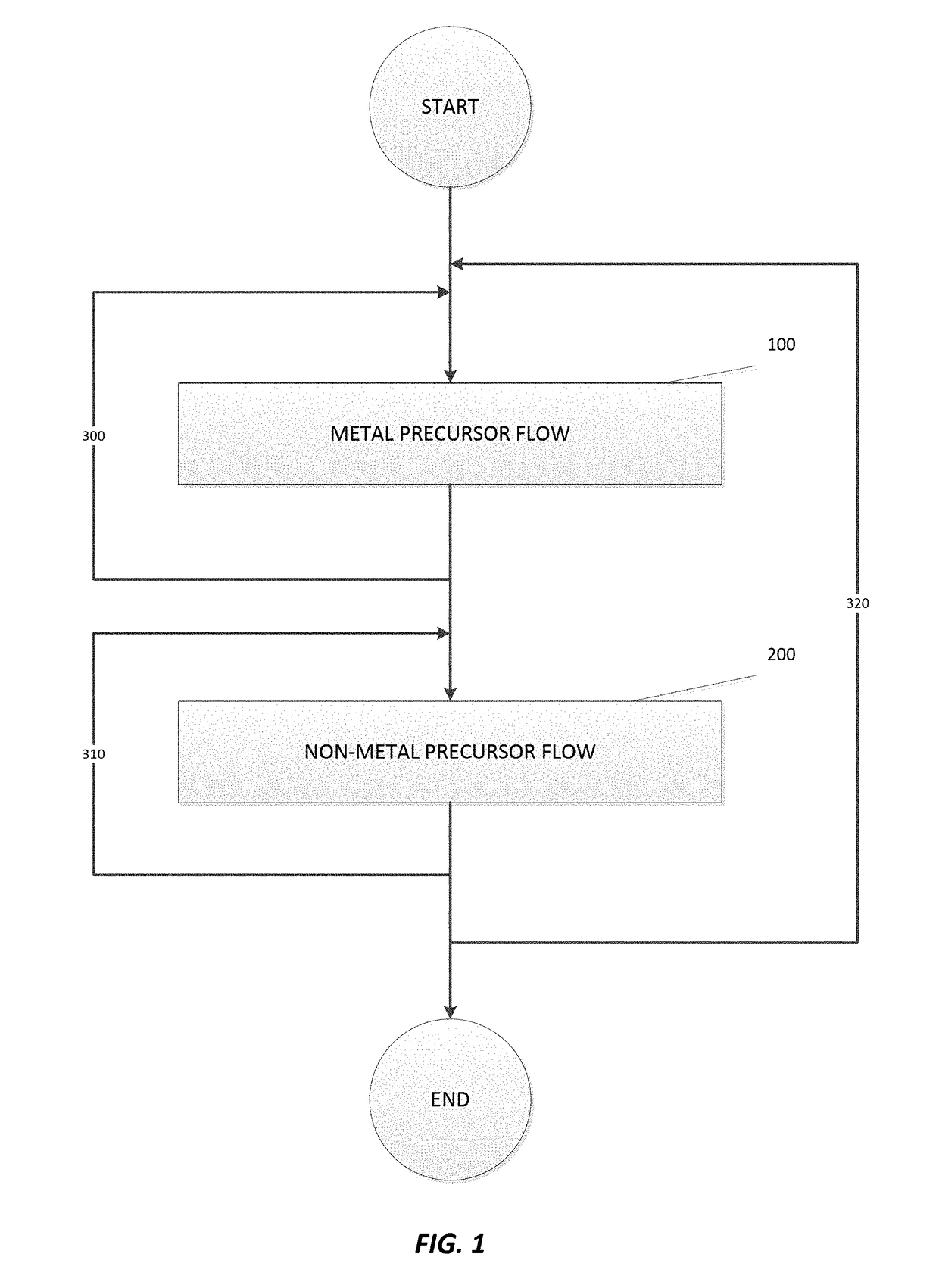
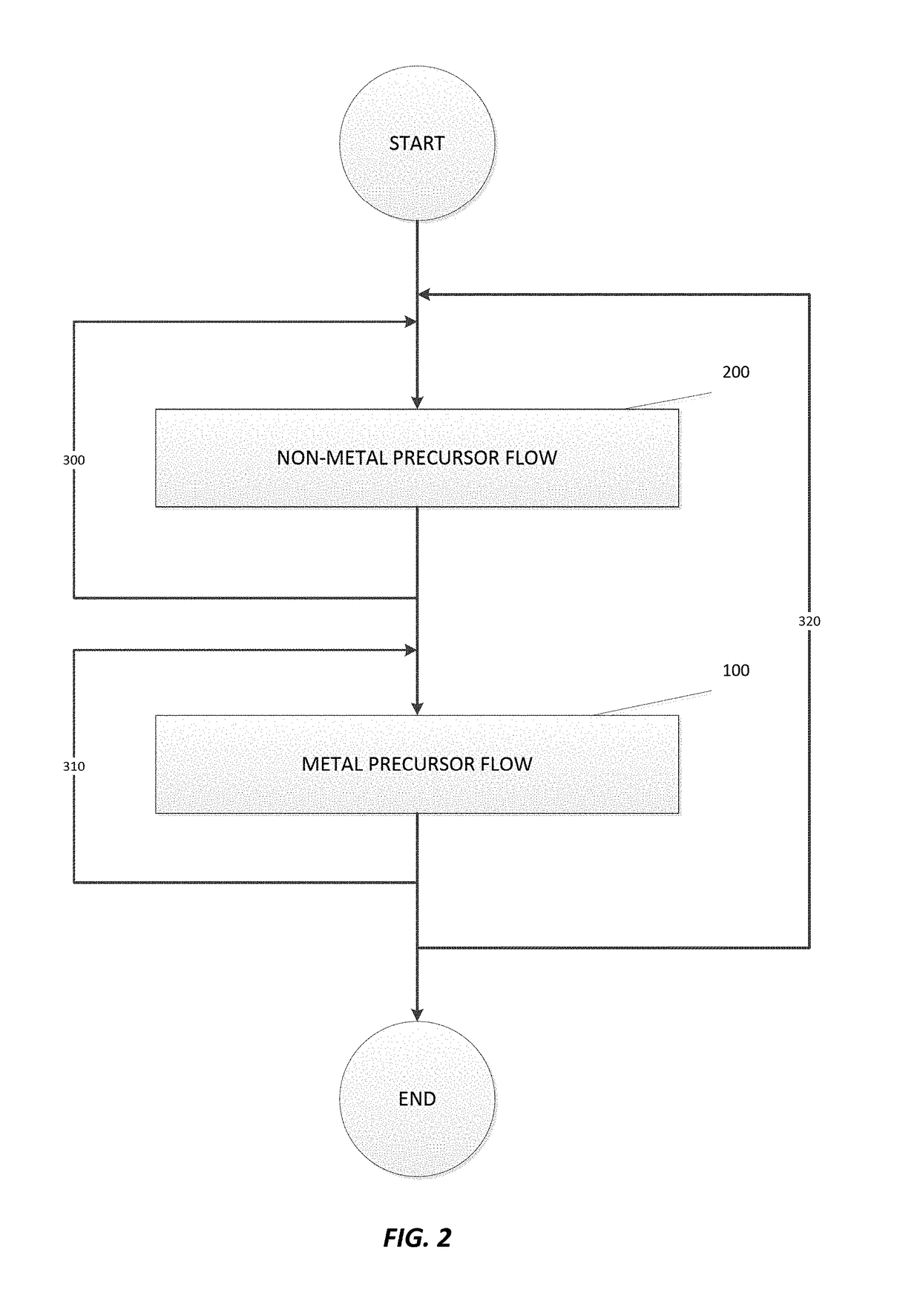
A method for selectively depositing a metal film onto a substrate is disclosed. In particular, the method comprising flowing a metal precursor onto the substrate and flowing a non-metal precursor onto the substrate, while contacting the non-metal precursor with a hot wire. Specifically, a reaction between a tungsten precursor and a hydrogen precursor selectively forms a tungsten film, where the hydrogen precursor is excited by a tungsten hot wire.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Methods for growing low-resistivity tungsten for high aspect ratio and small features
InactiveUS20080254623A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenGas phase
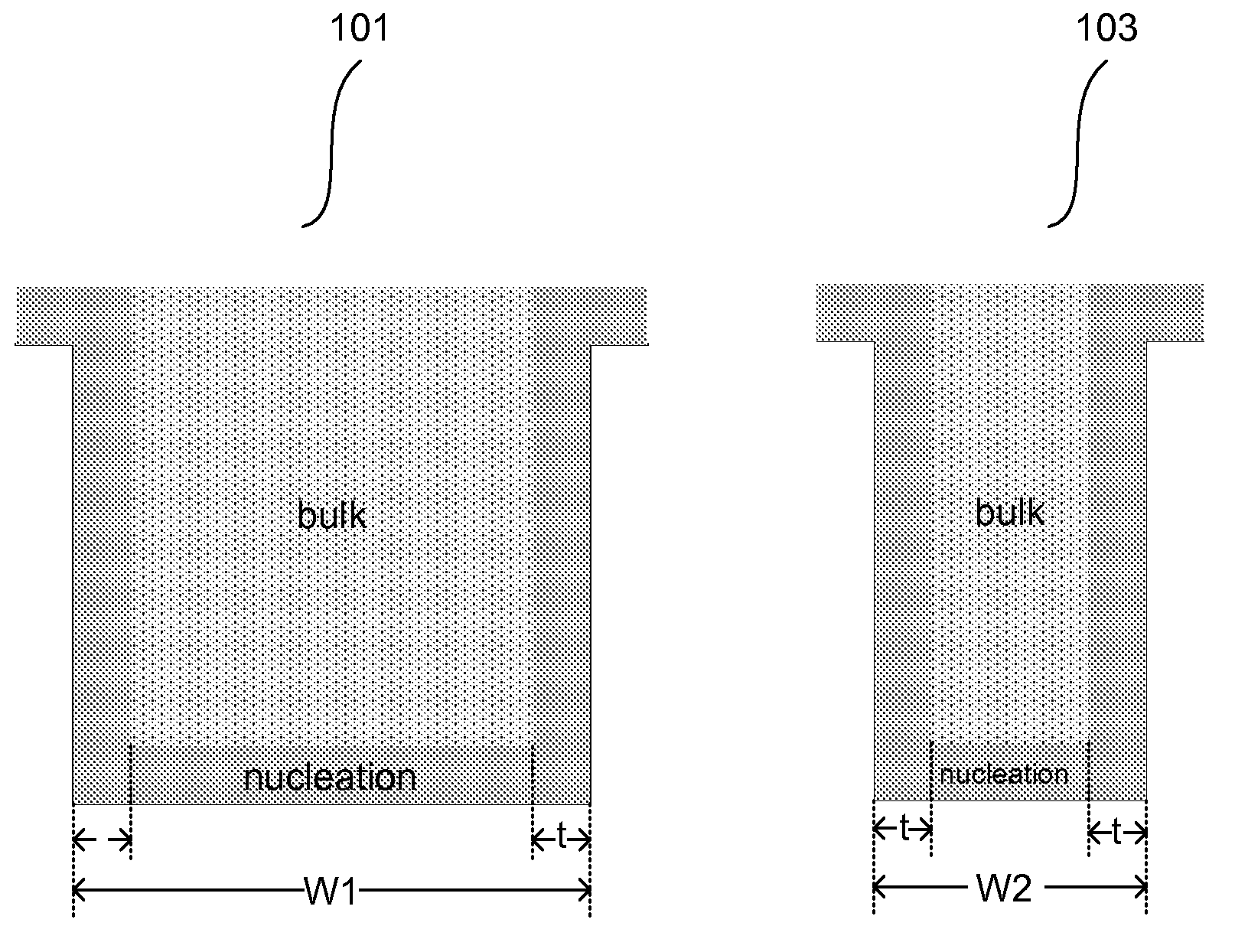
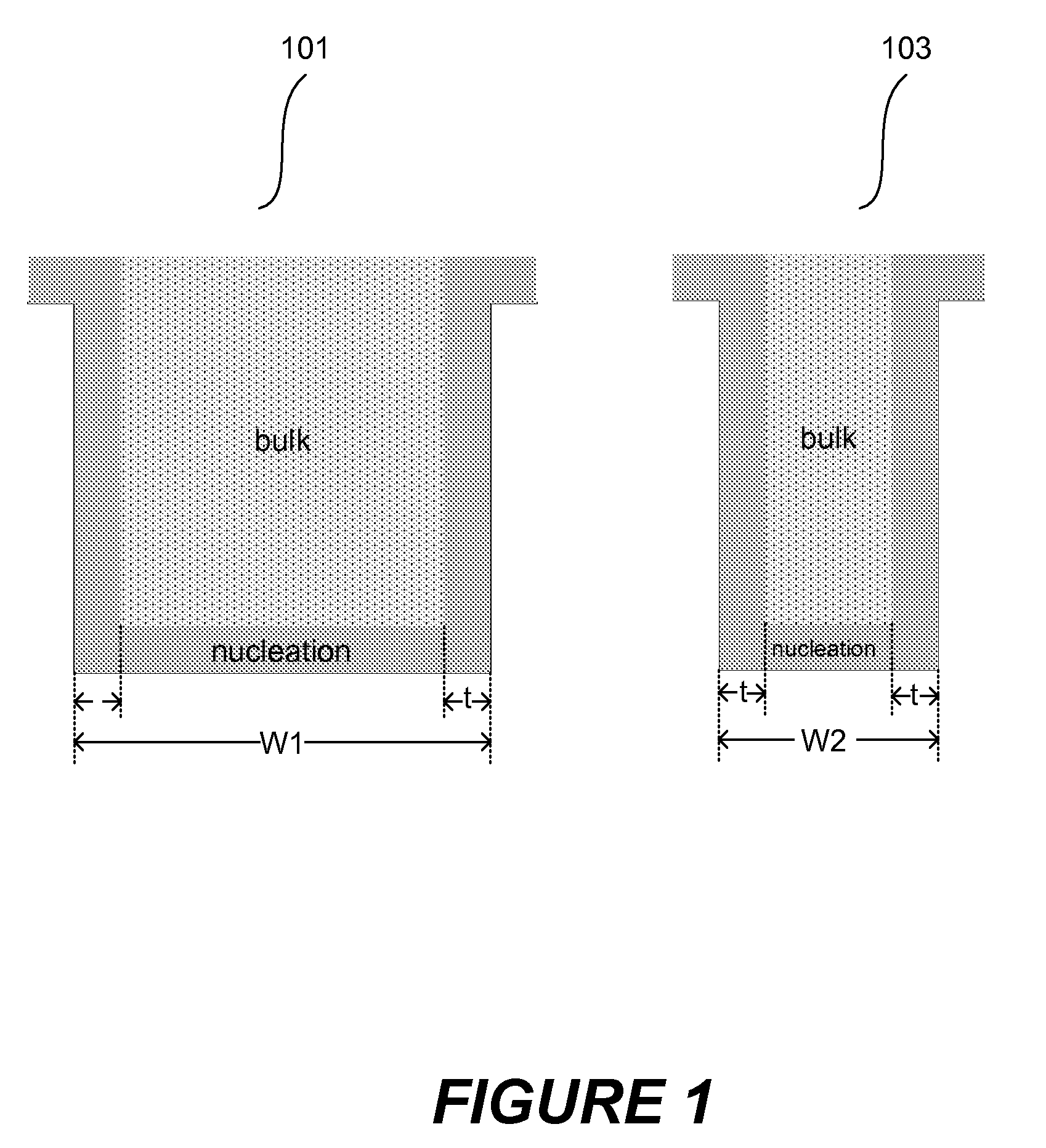
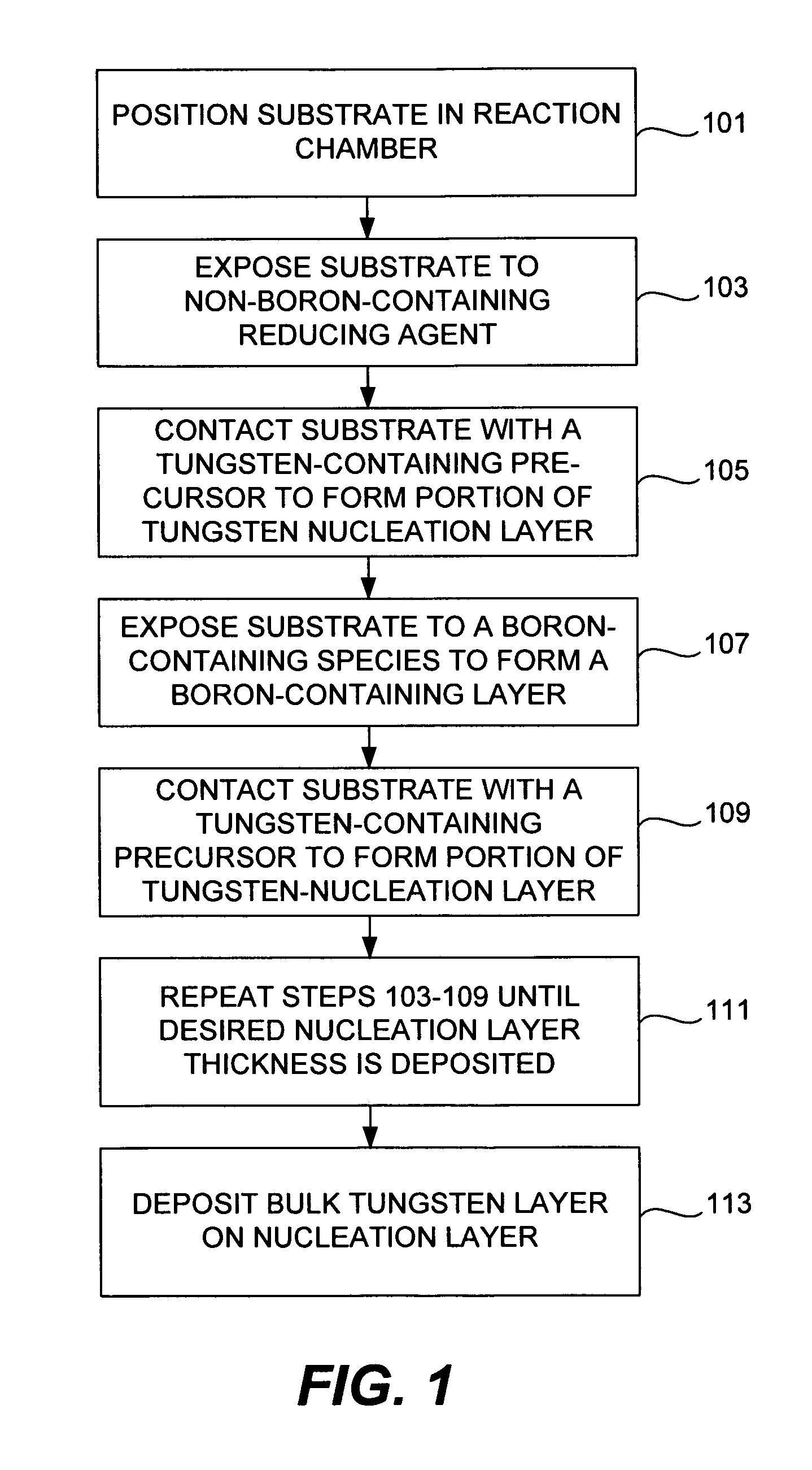
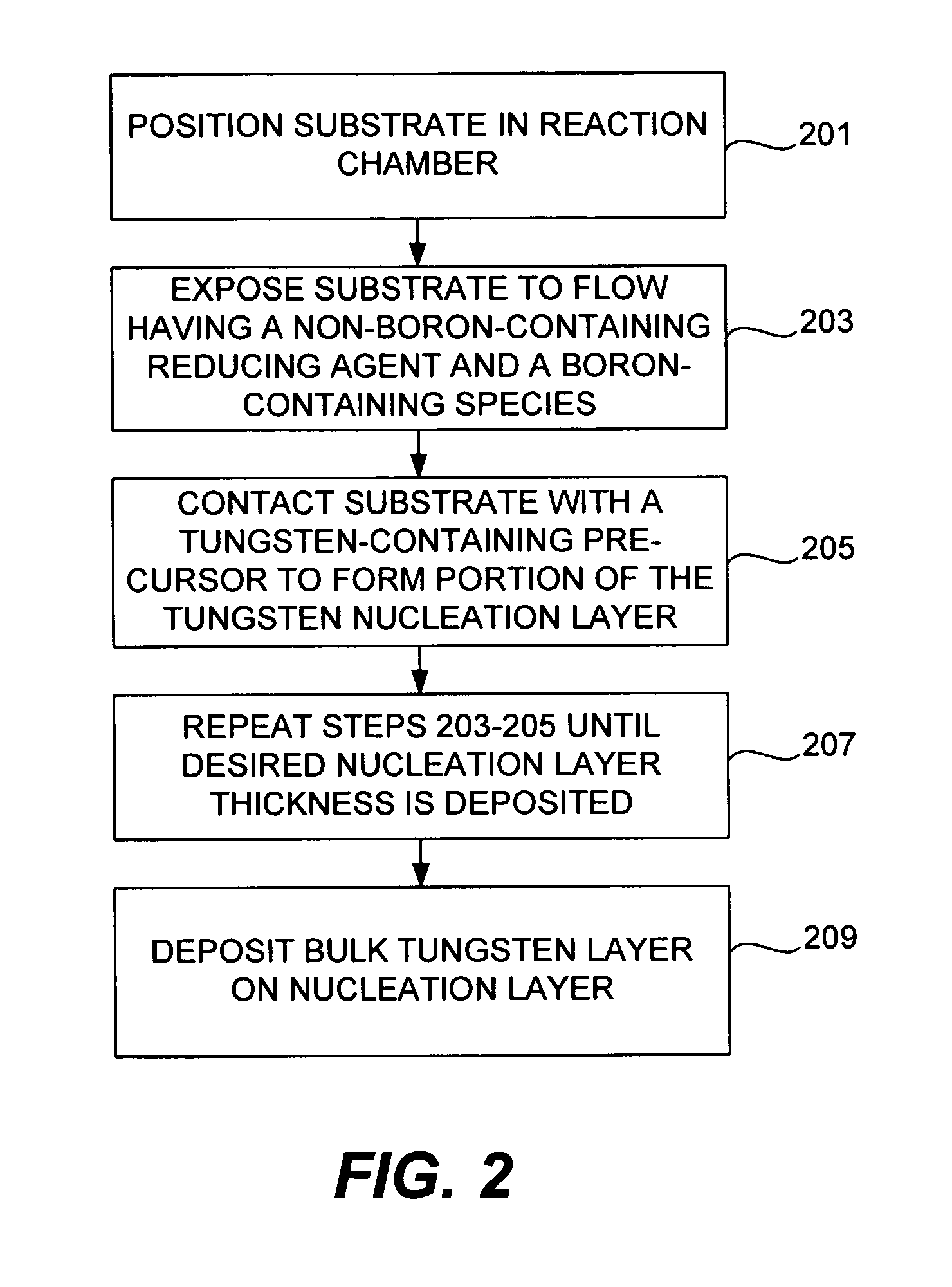
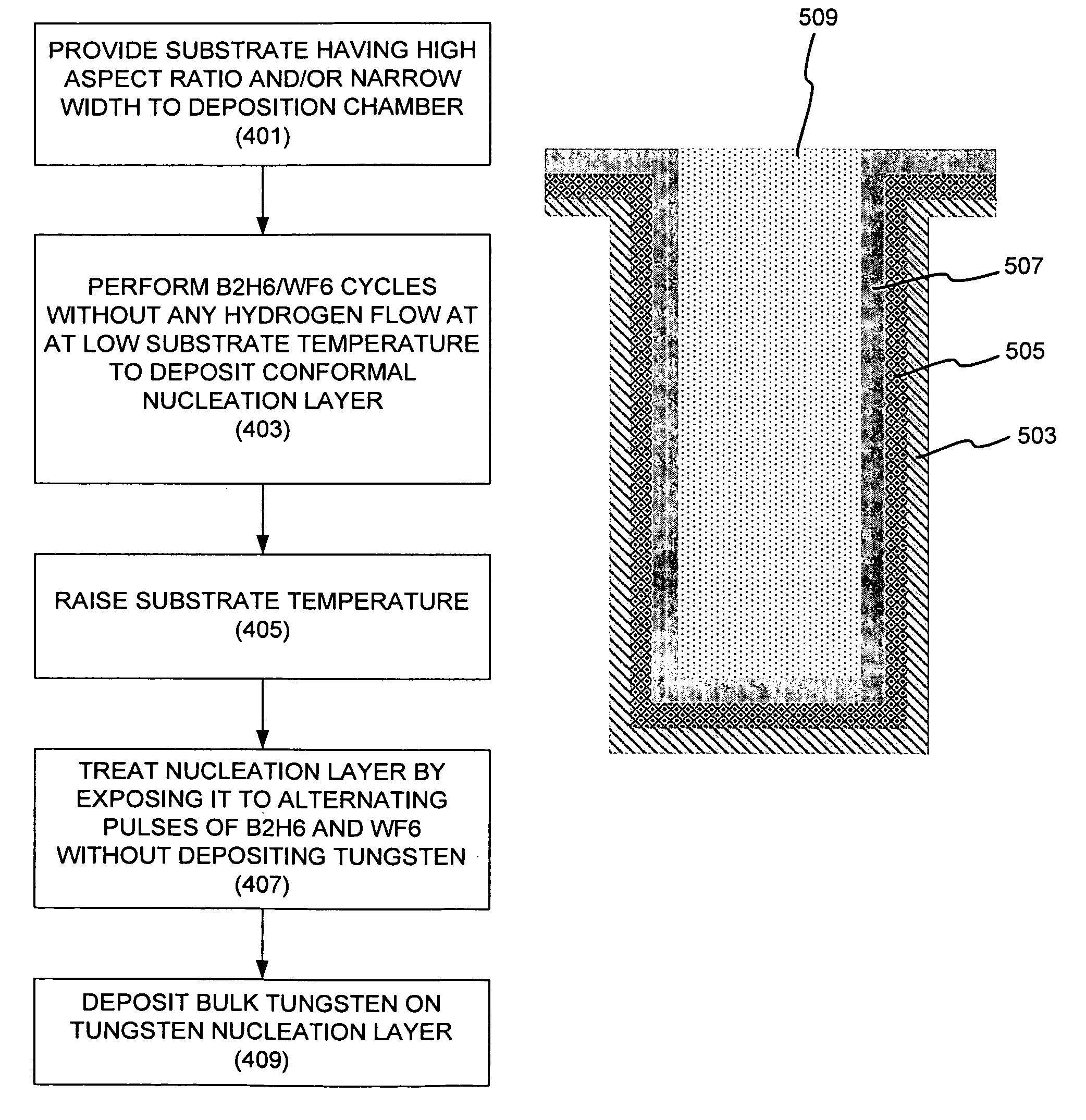
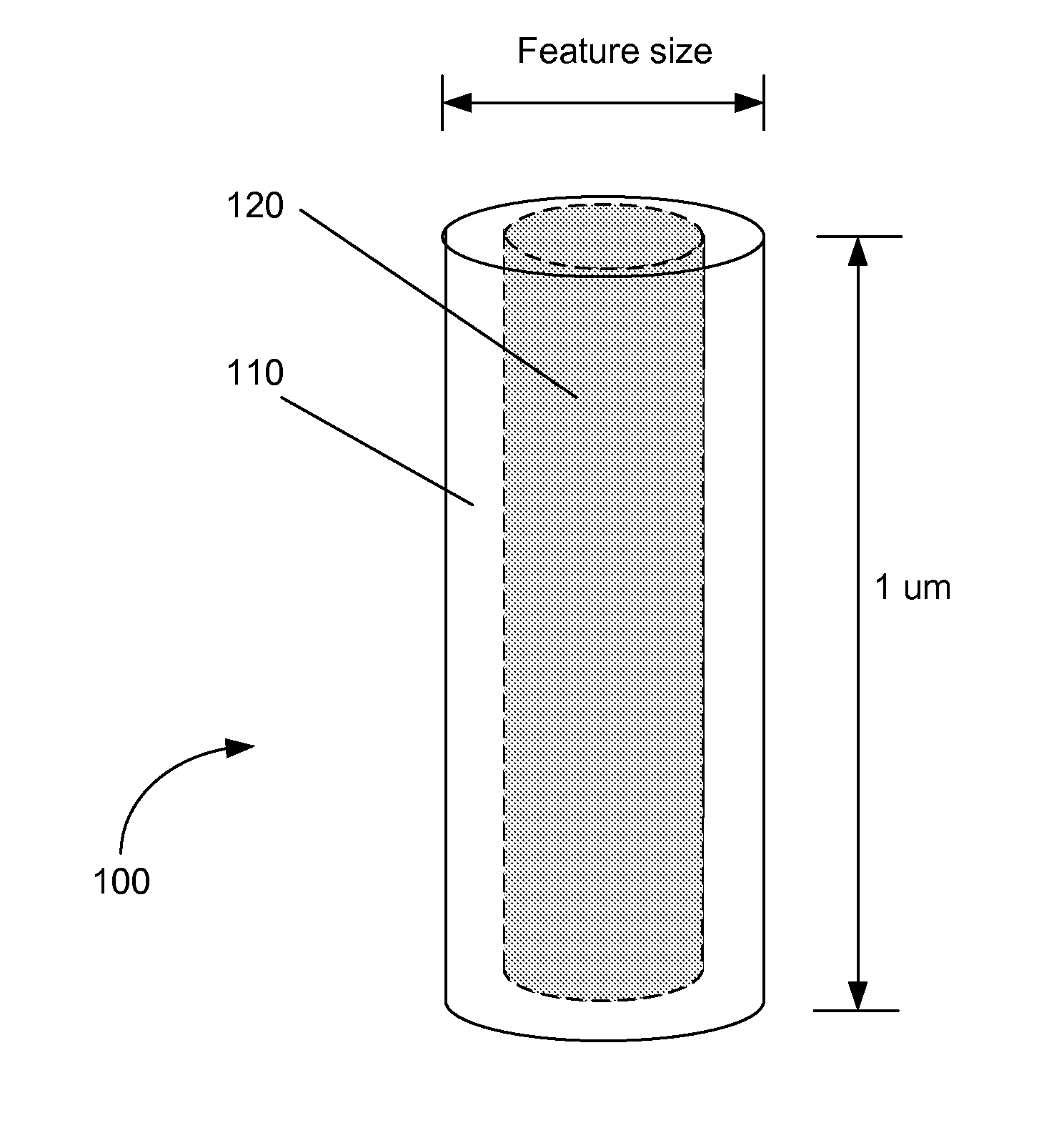
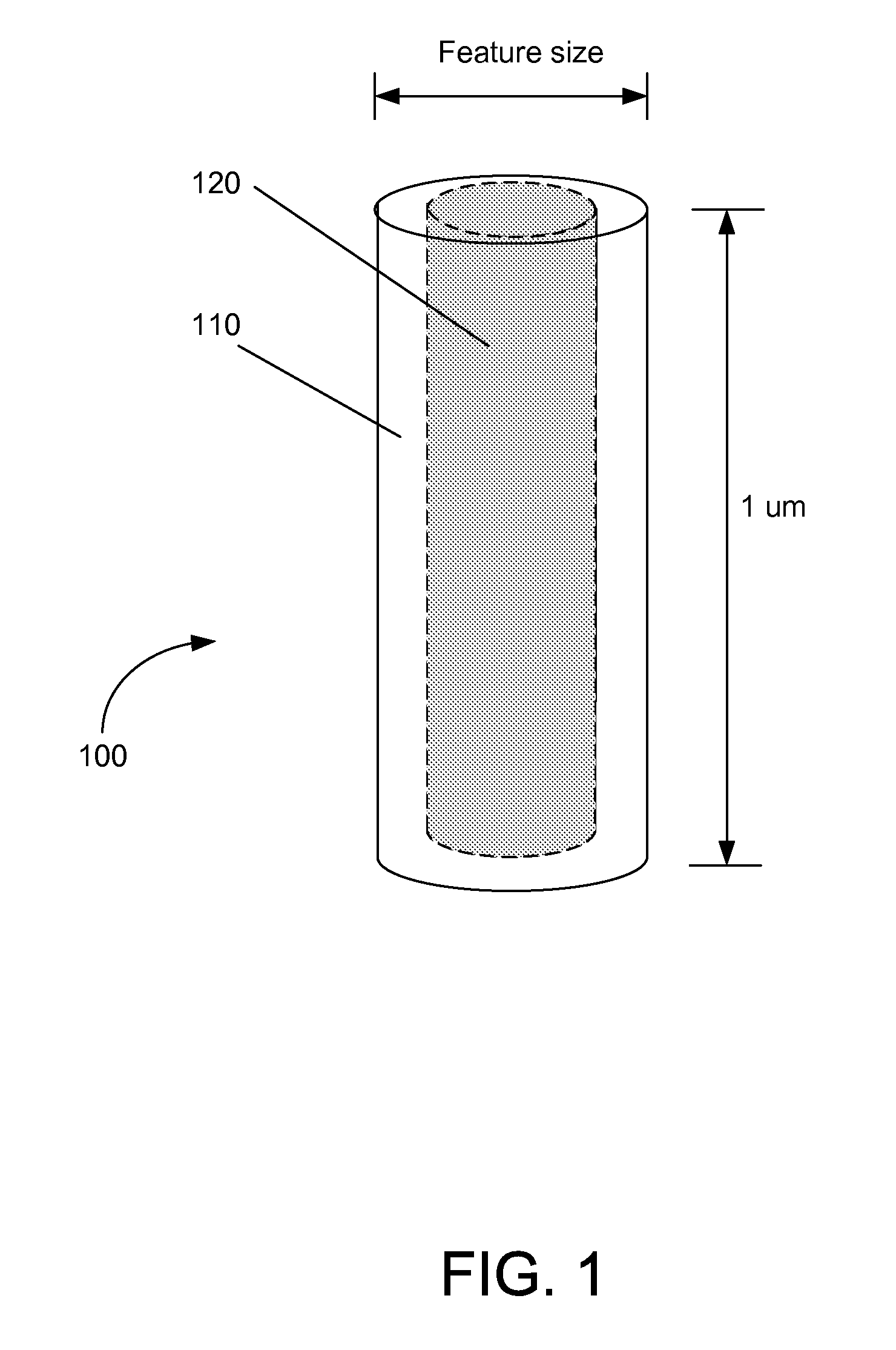
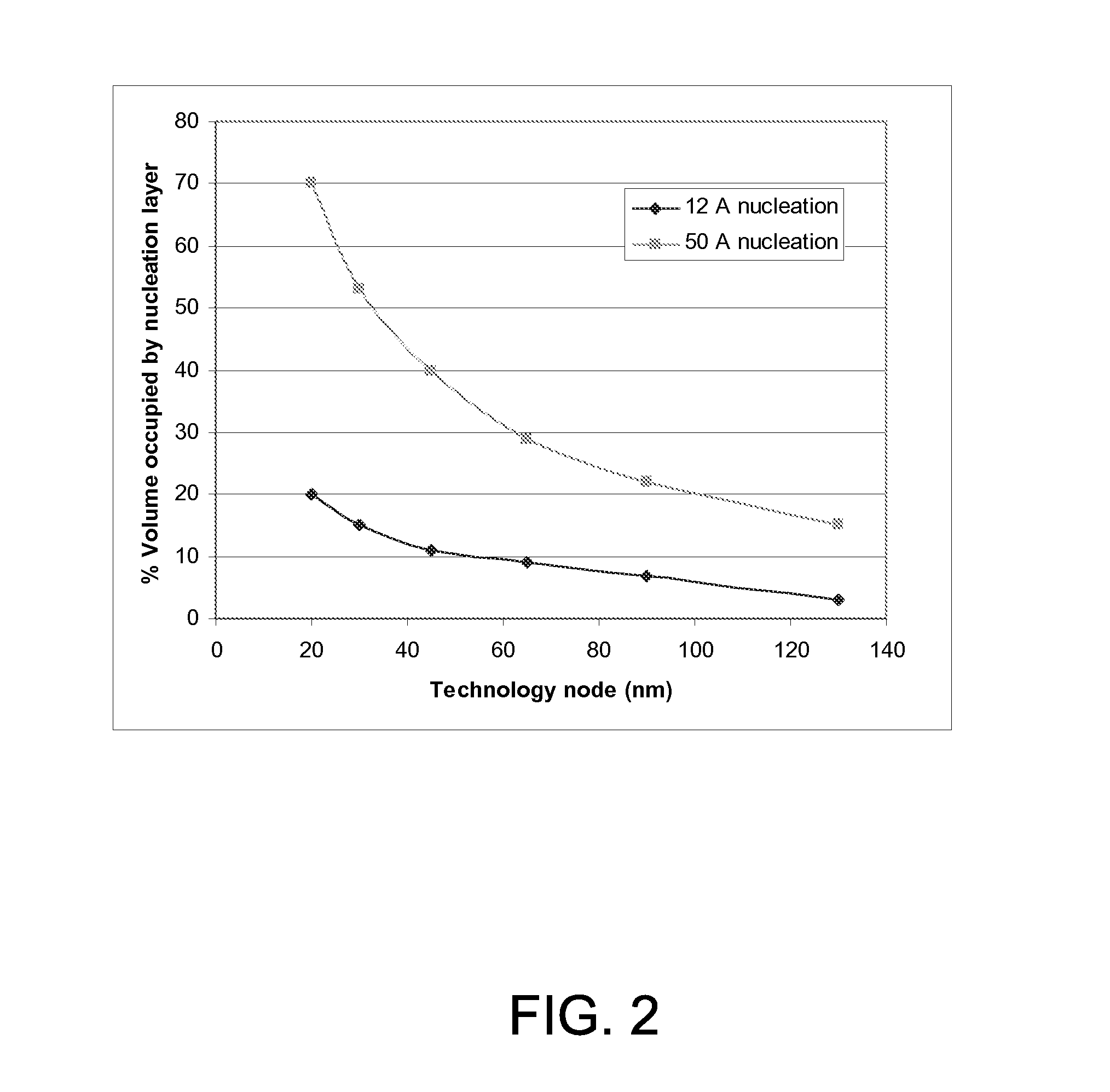
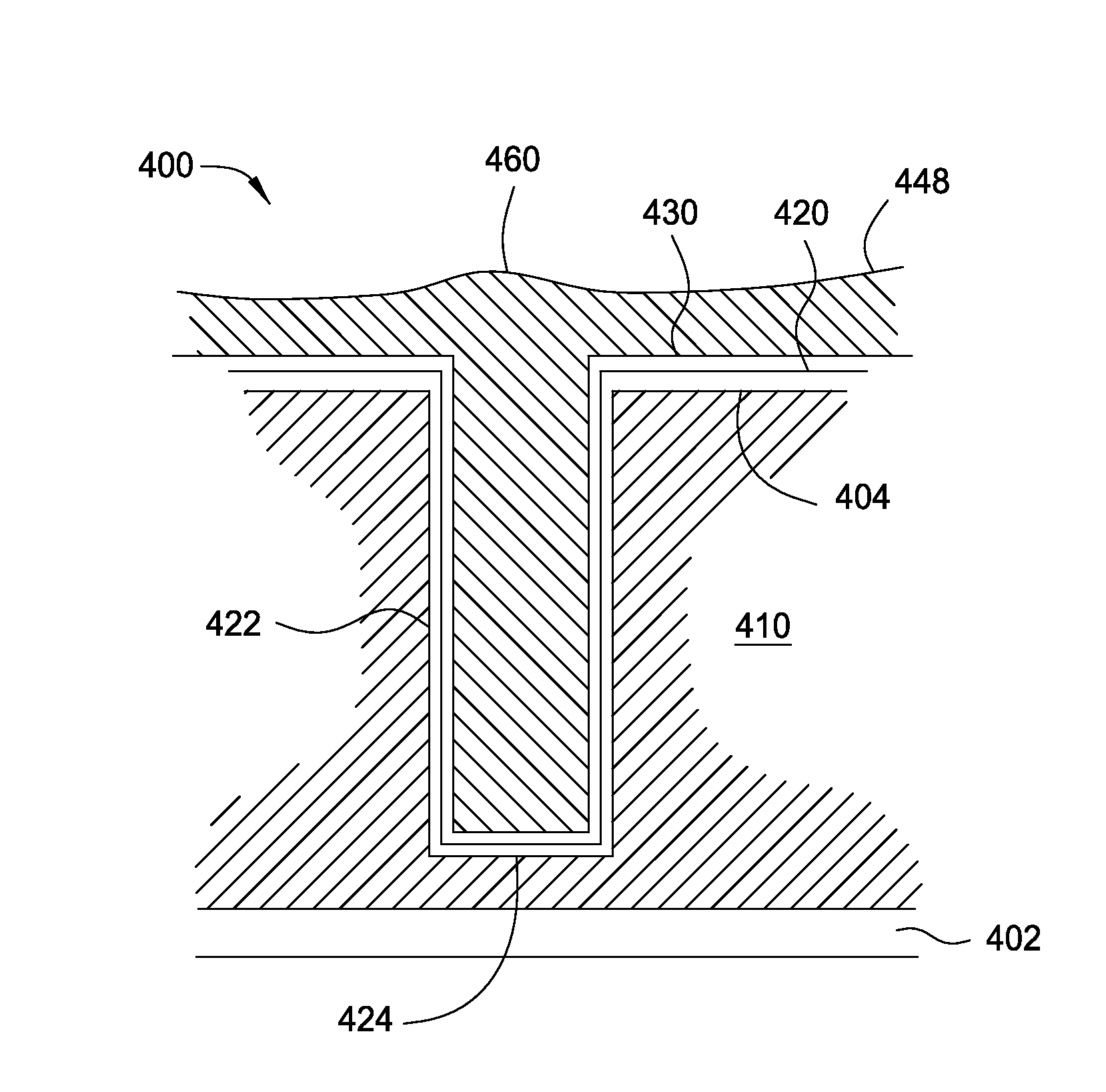
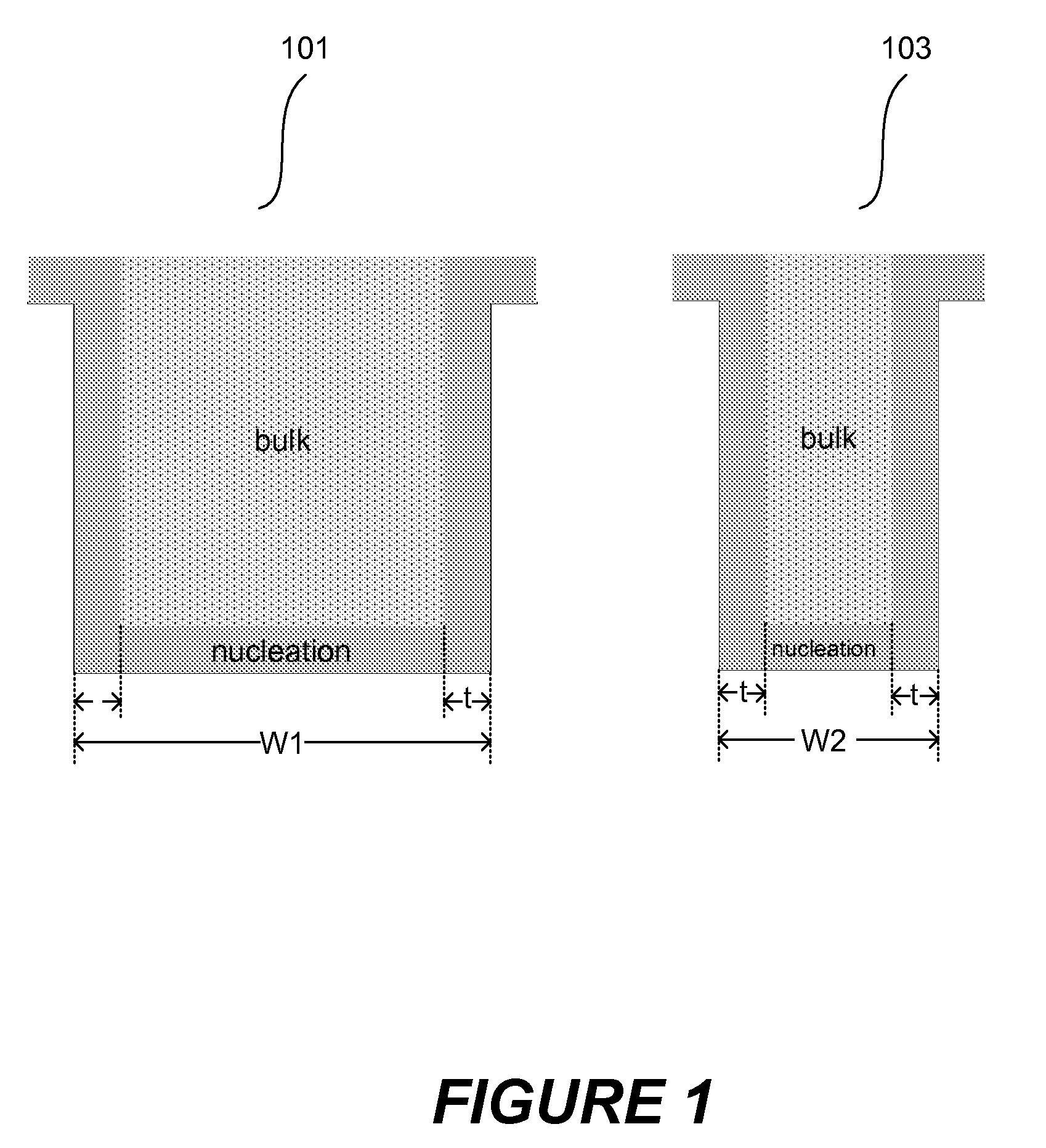
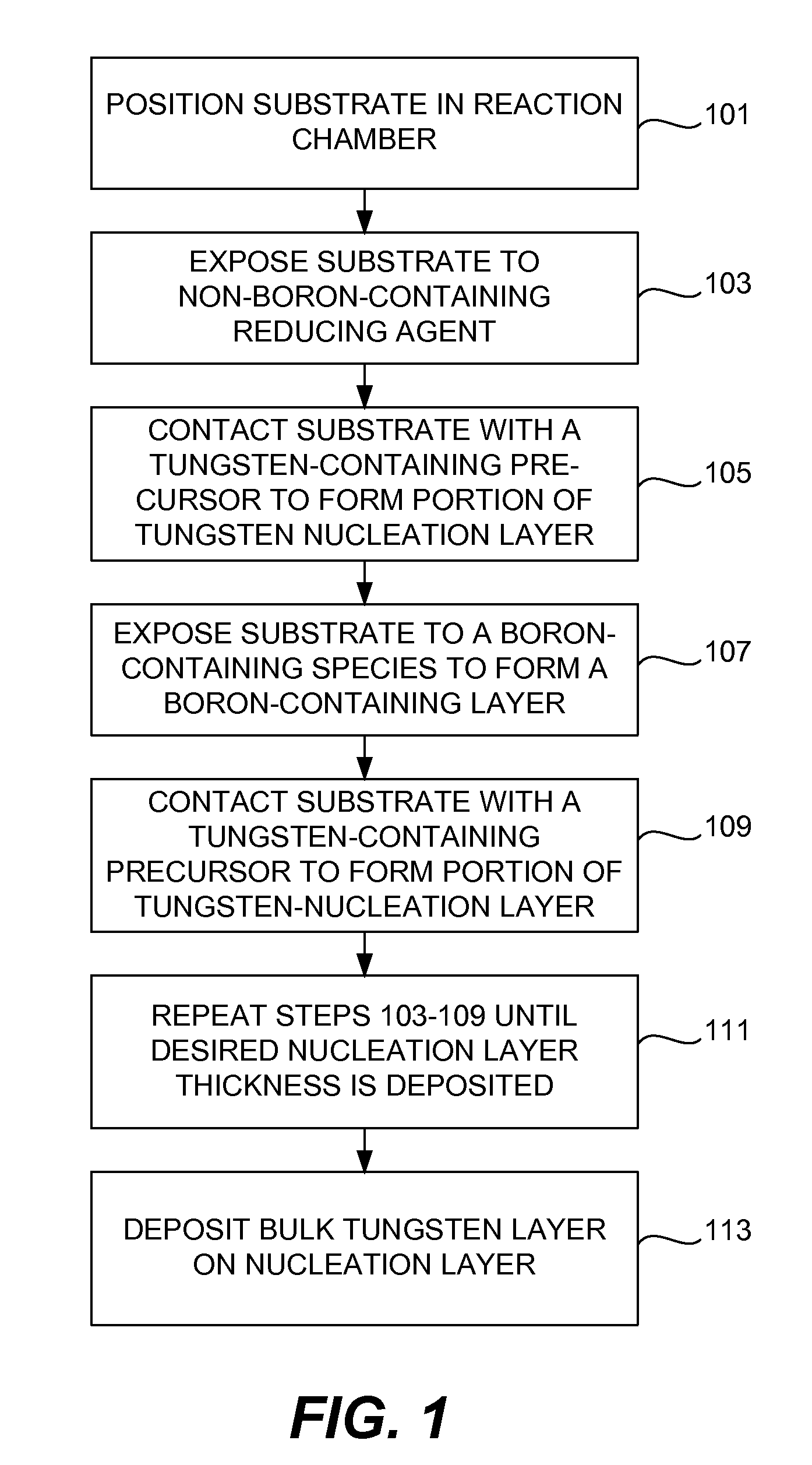
The present invention addresses this need by providing methods for depositing low resistivity tungsten films in small features and features having high aspect ratios. The methods involve depositing very thin tungsten nucleation layers by pulsed nucleation layer (PNL) processes and then using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to deposit a tungsten layer to fill the feature. Depositing the tungsten nucleation layer involves exposing the substrate to alternating pulses of a boron-containing reducing agent and a tungsten-containing precursor without using any hydrogen gas, e.g., as a carrier or background gas. Using this process, a conformal tungsten nucleation layer can be deposited to a thickness as small as about 10 Angstroms. The feature may then be wholly or partially filled with tungsten by a hydrogen reduction chemical vapor deposition process. Resistivities of about 14 μΩ-cm for a 500 Angstrom film may be obtained.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Ruthenium as an underlayer for tungsten film deposition
InactiveUS20060128150A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesRutheniumTitanium
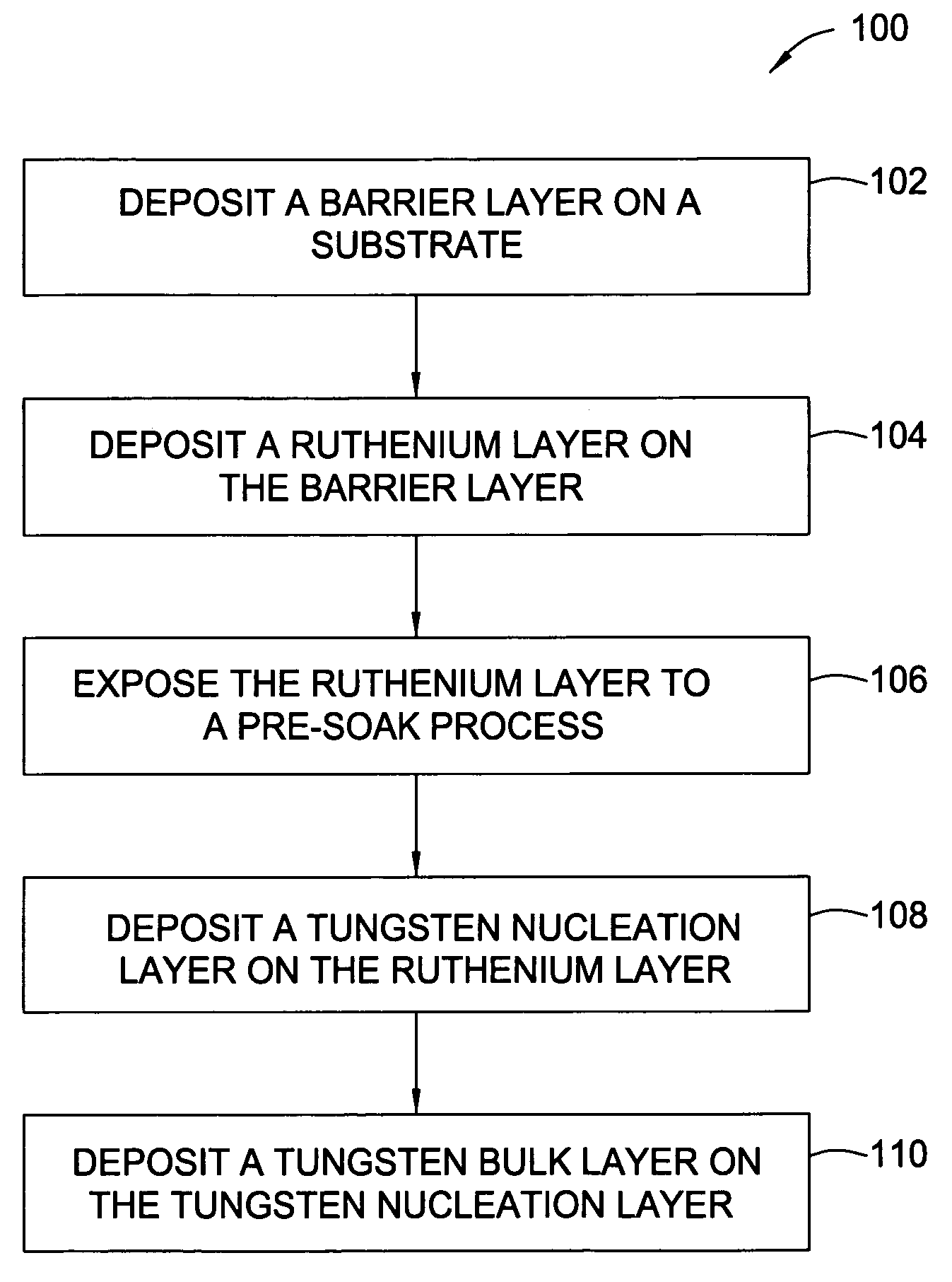
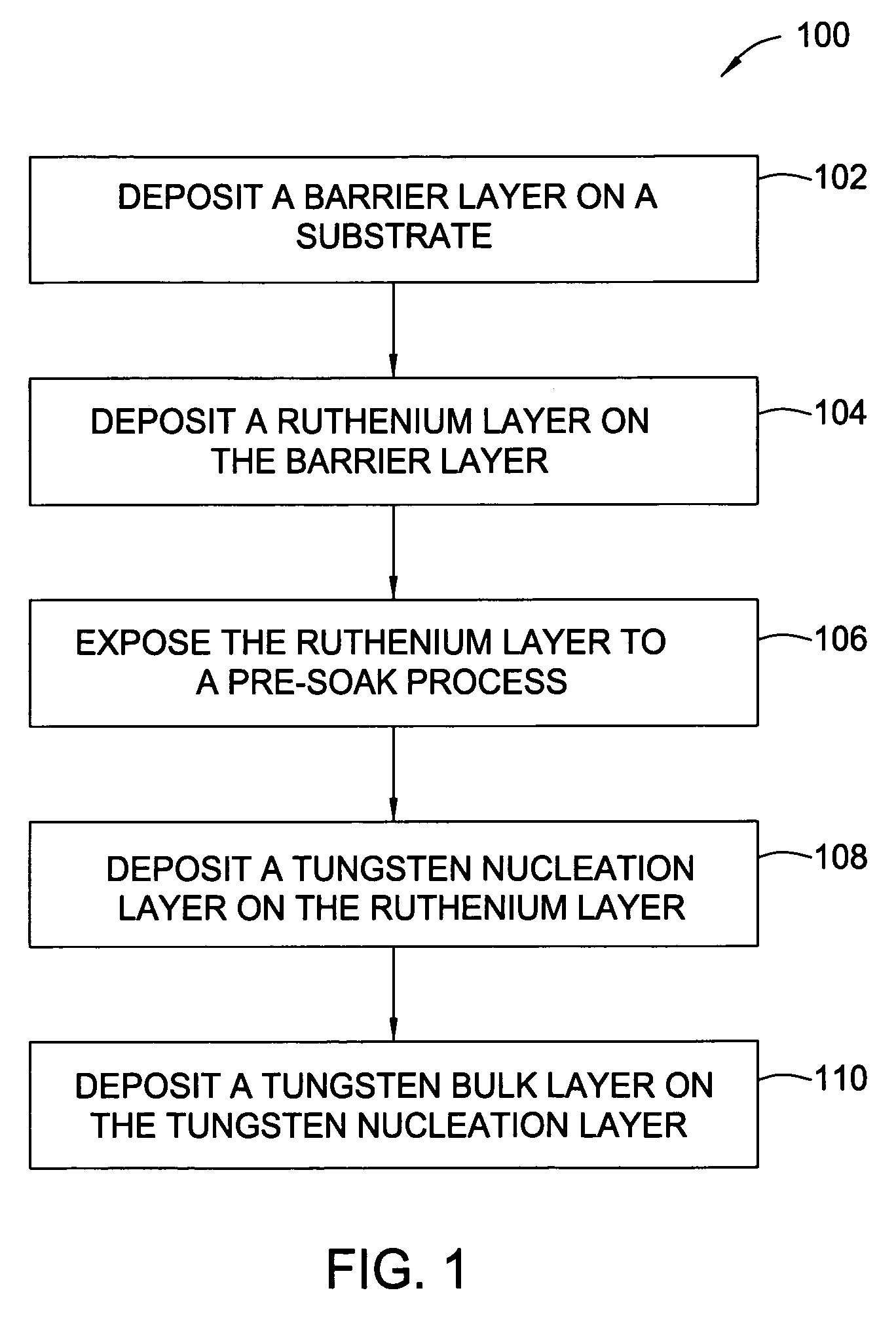
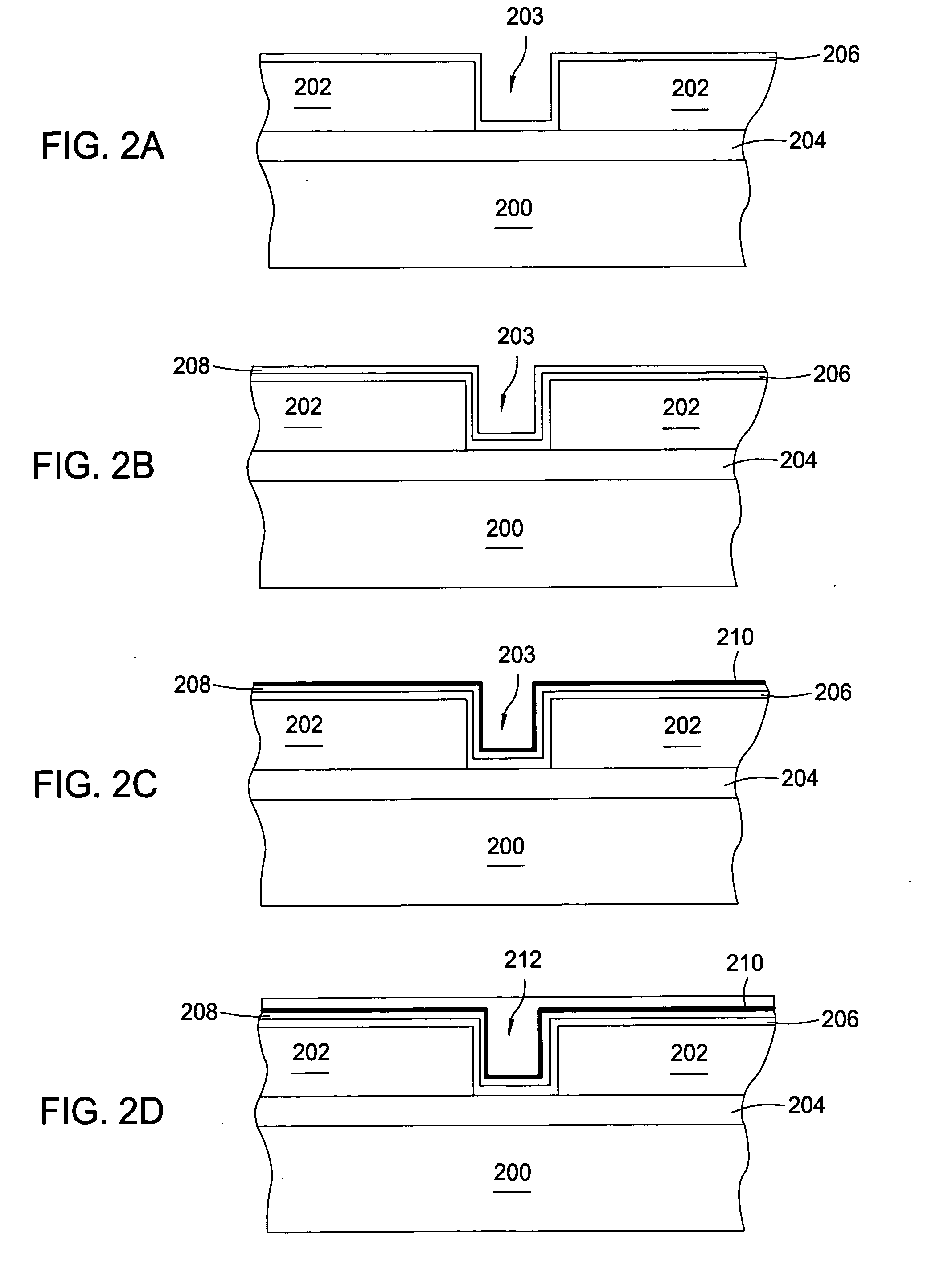
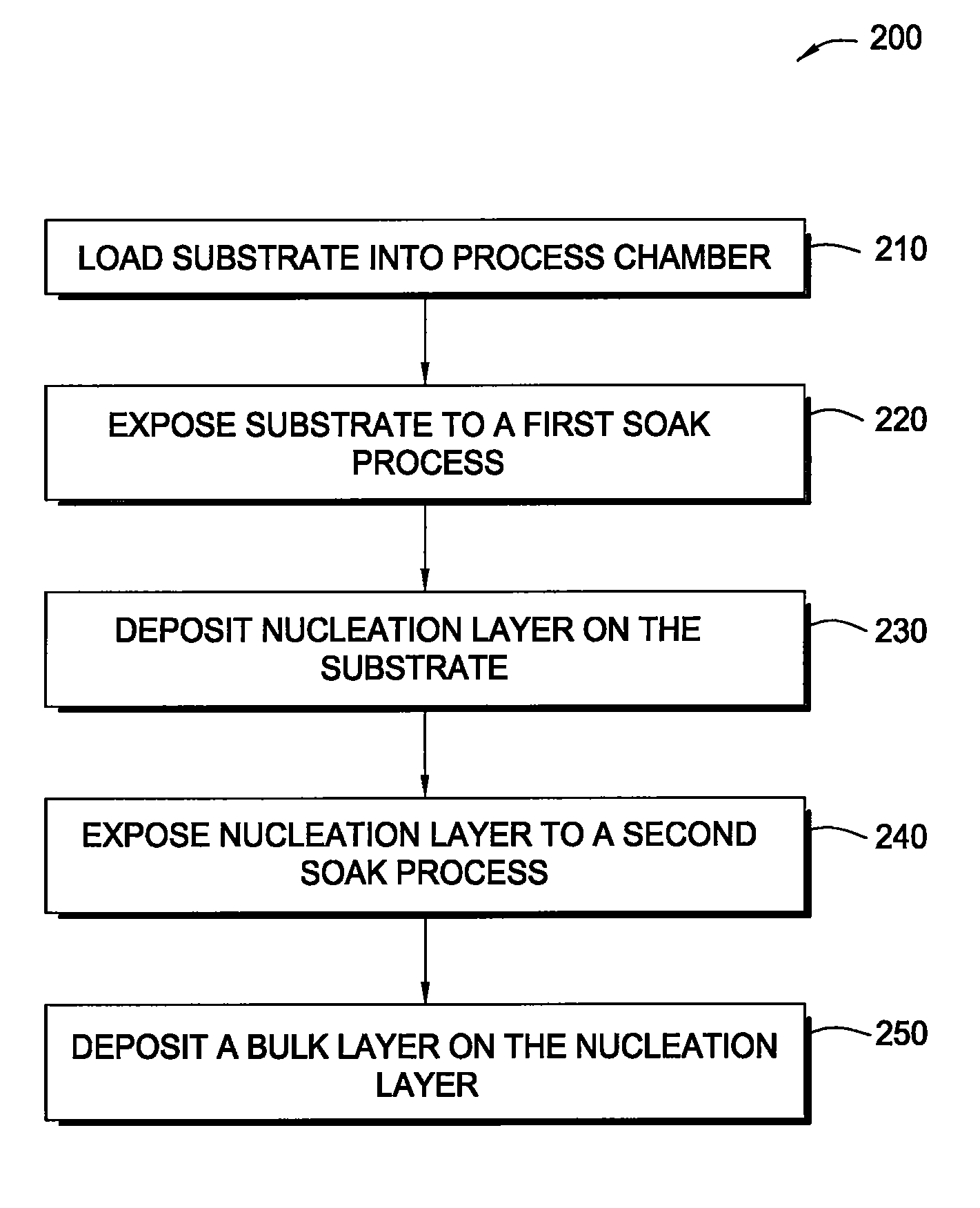
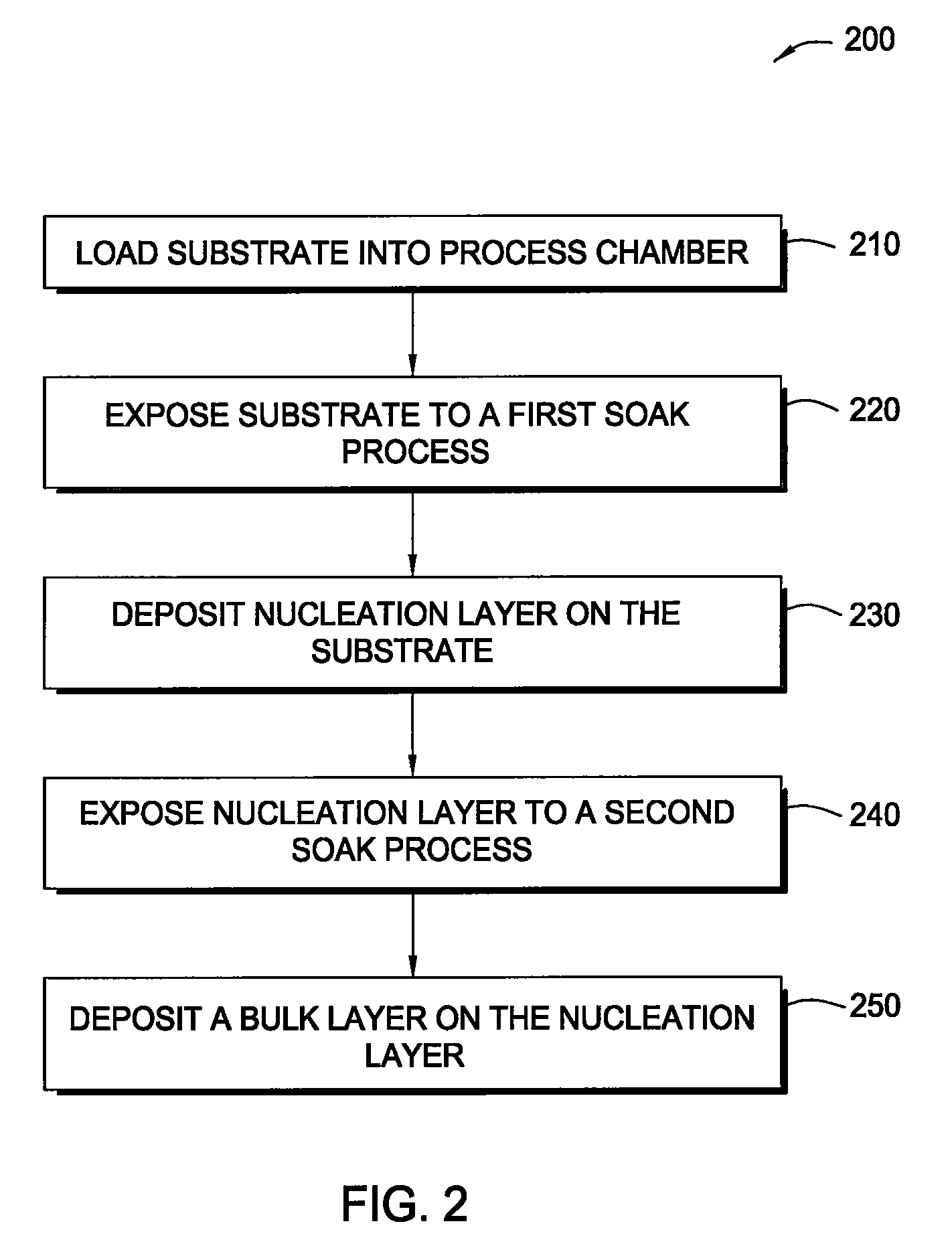
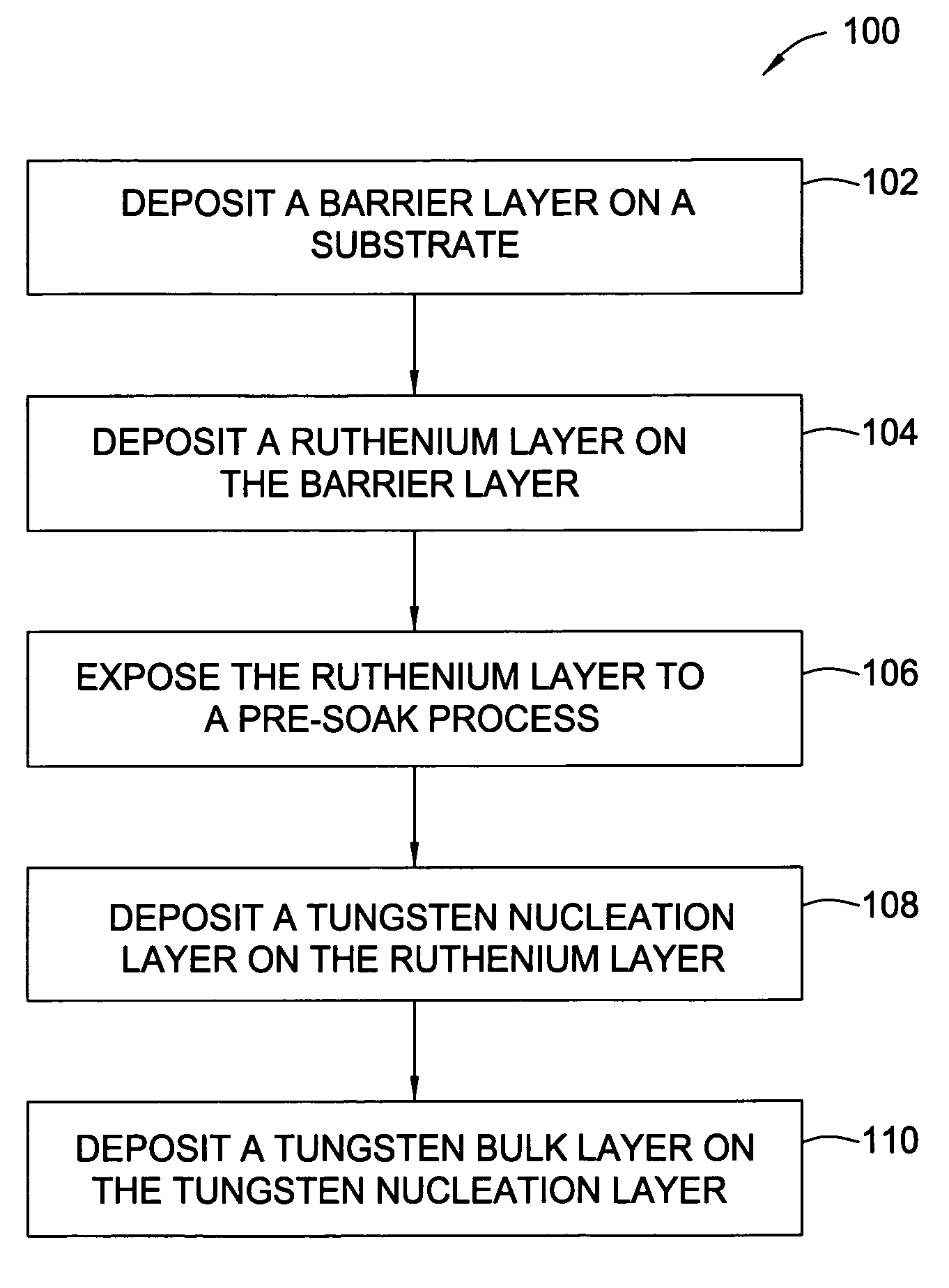
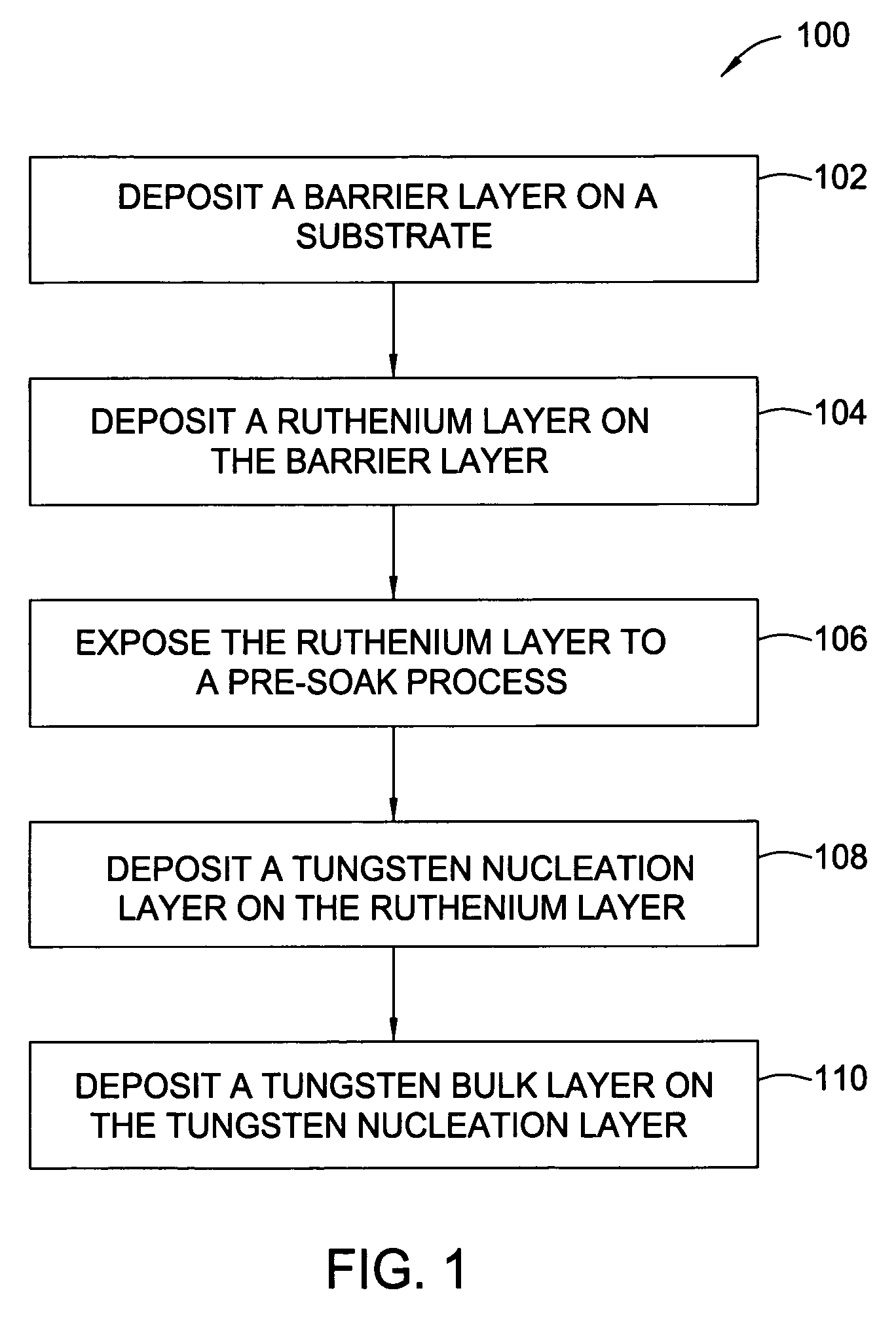
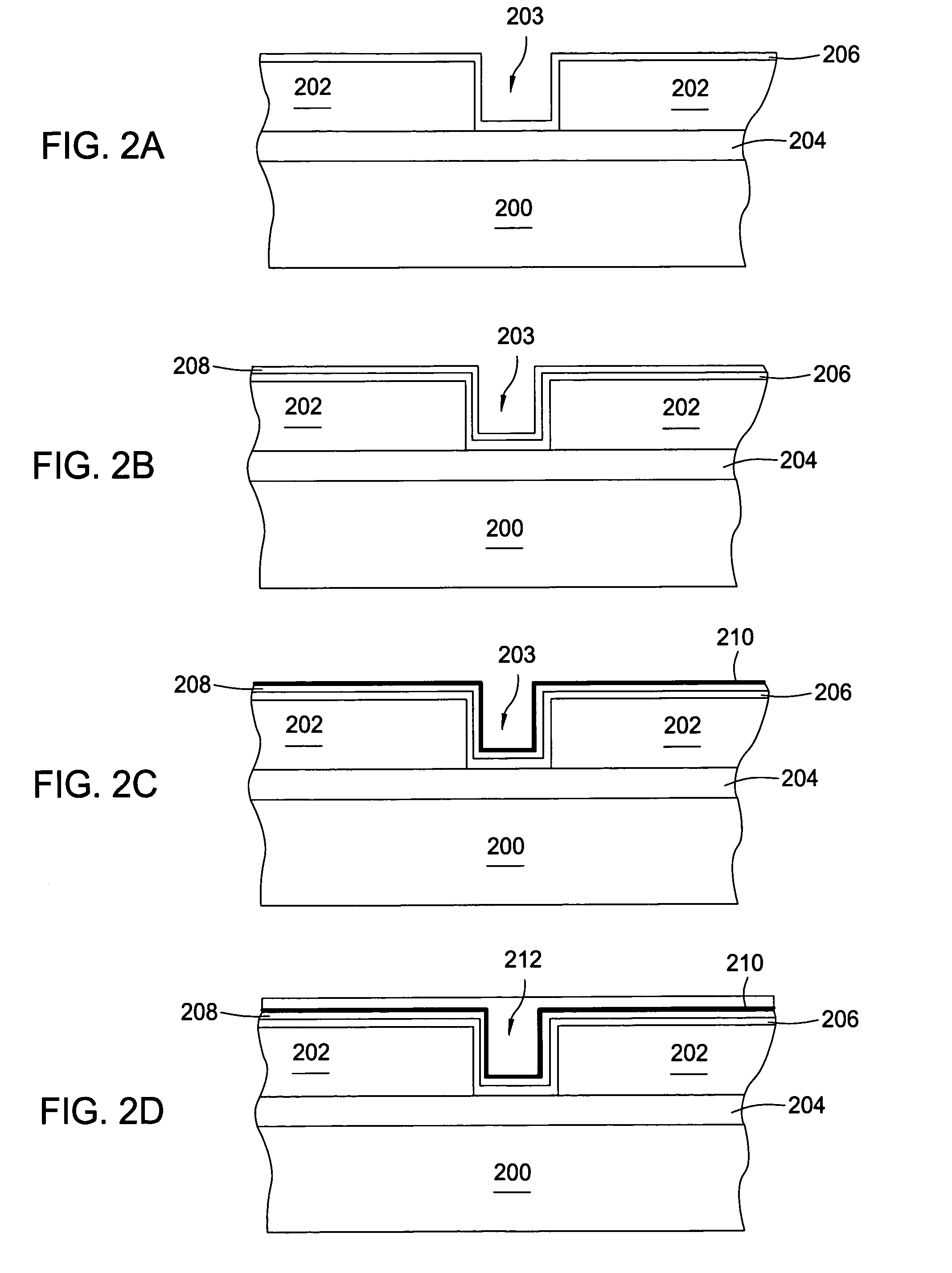
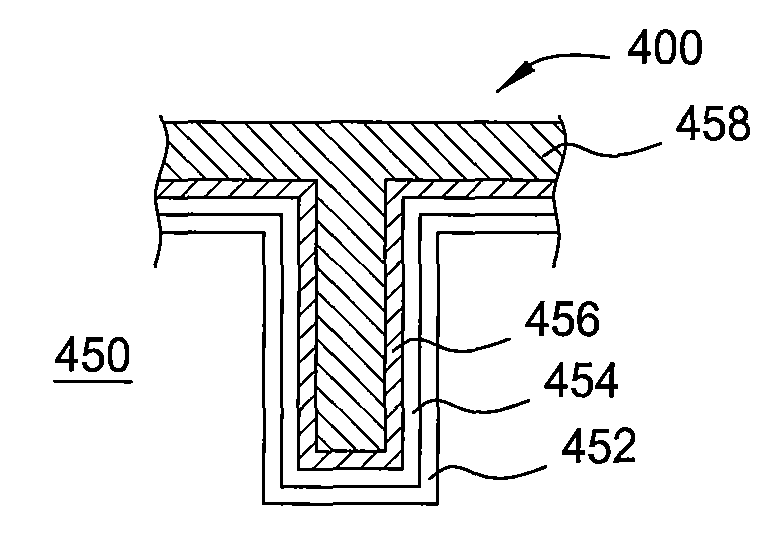
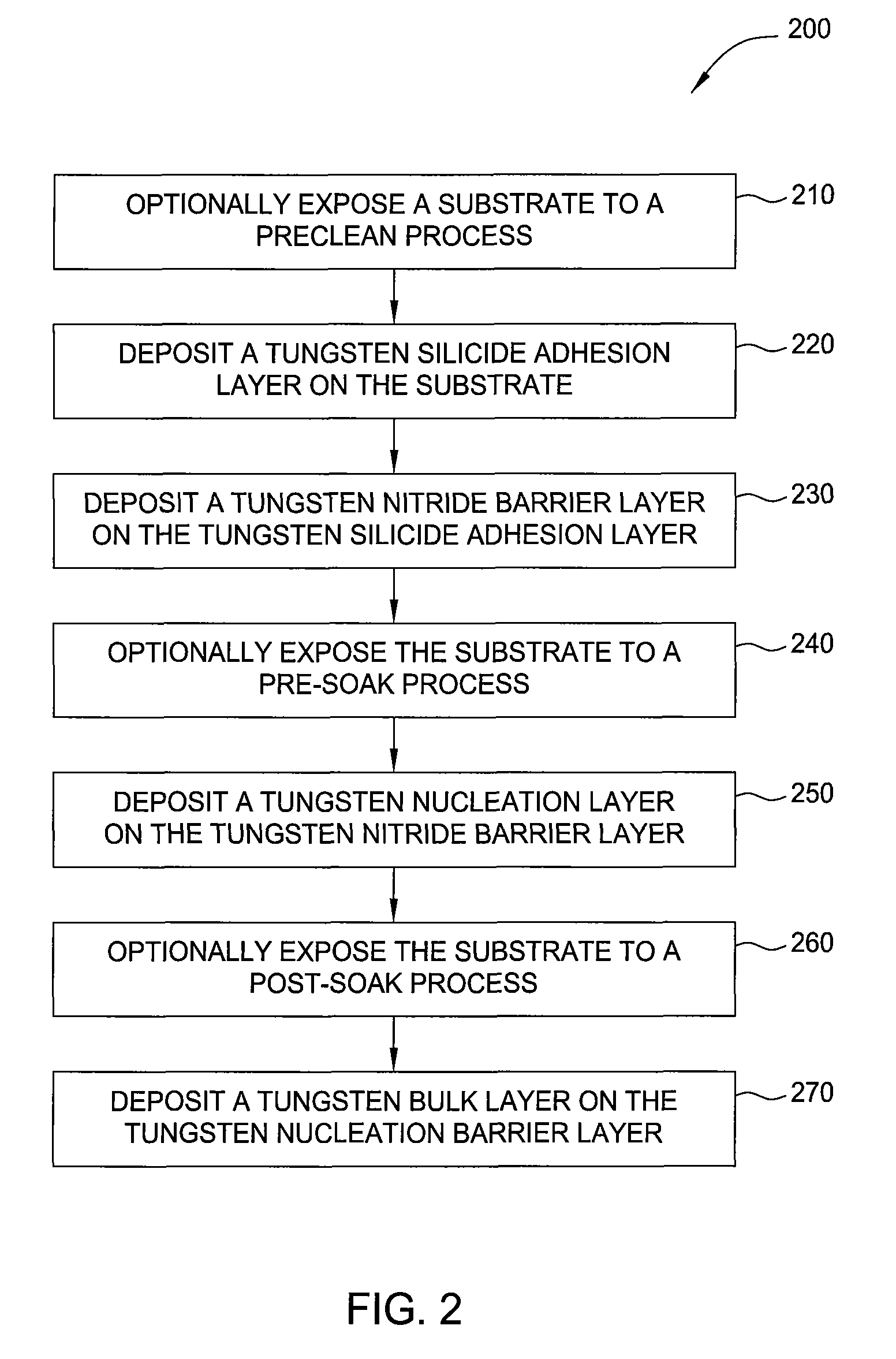
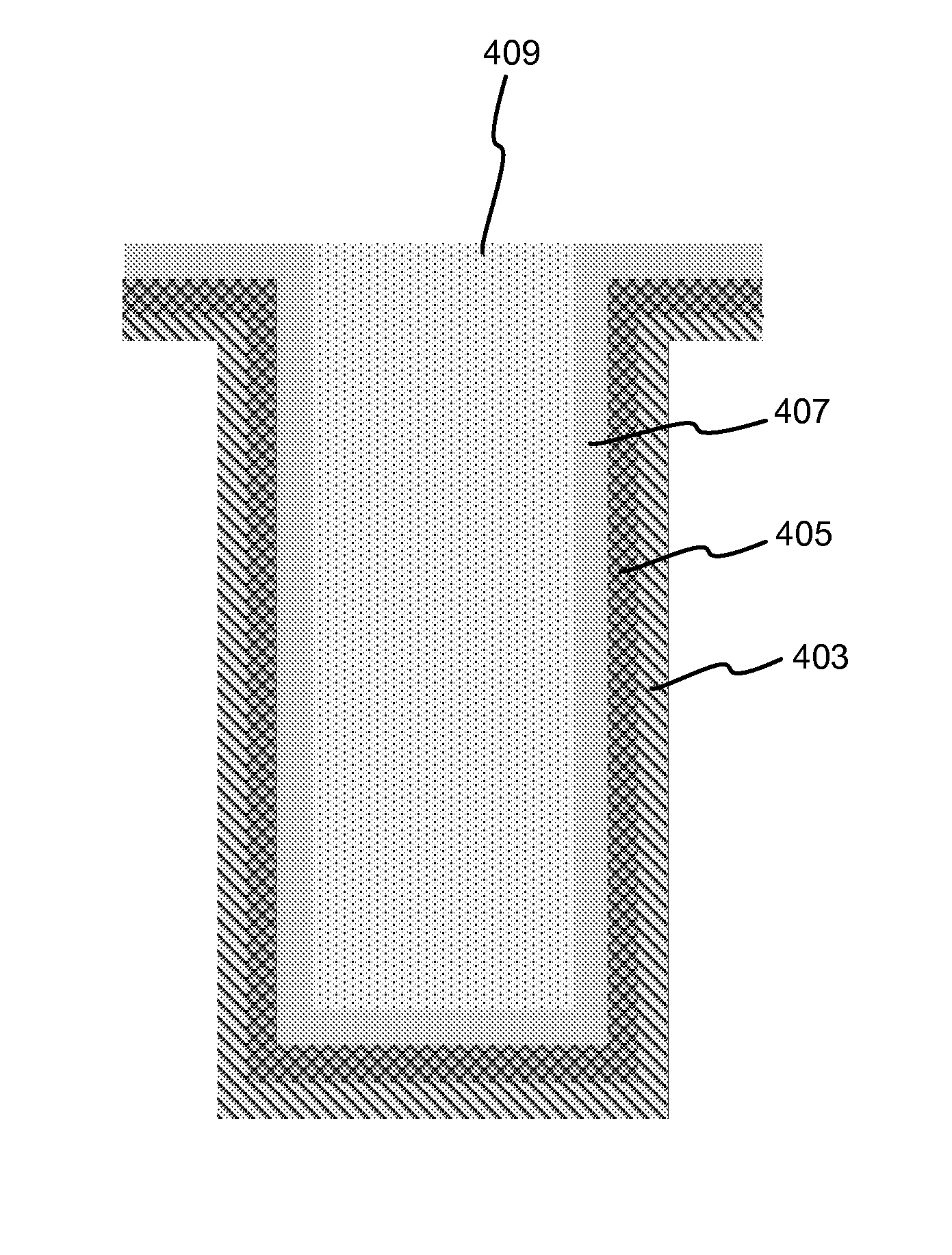
In one embodiment, a method for depositing a tungsten-containing film on a substrate is provided which includes depositing a barrier layer on the substrate, such as a titanium or tantalum containing barrier layer and depositing a ruthenium layer on the barrier layer. The method further includes depositing a tungsten nucleation layer on the ruthenium layer and depositing a tungsten bulk layer on the tungsten nucleation layer. The barrier layer, the ruthenium layer, the tungsten nucleation layer and the tungsten bulk layer are independently deposited by an ALD process, a CVD process or a PVD process, preferably by an ALD process. In some examples, the substrate is exposed to a soak process prior to depositing a subsequent layer, such as between the deposition of the barrier layer and the ruthenium layer, the ruthenium layer and the tungsten nucleation layer or the tungsten nucleation layer and the tungsten bulk layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for reducing tungsten film roughness and improving step coverage
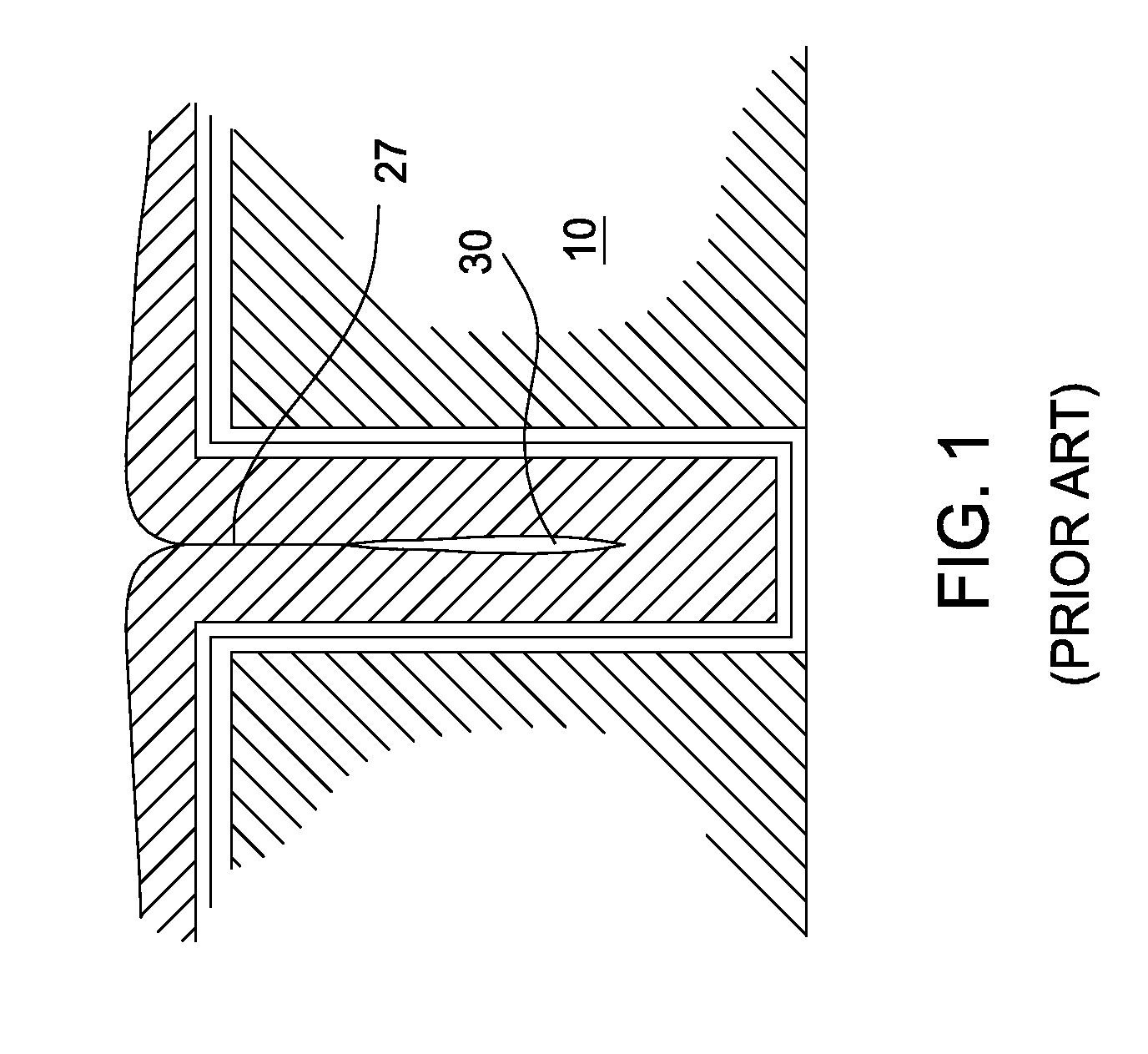
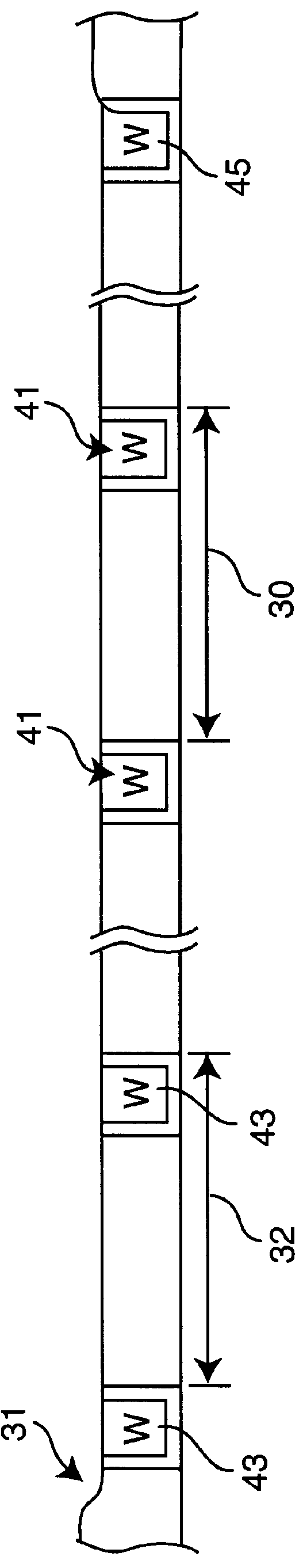
InactiveUS20050031786A1Increase probabilityLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefuse receptaclesNucleationSemiconductor
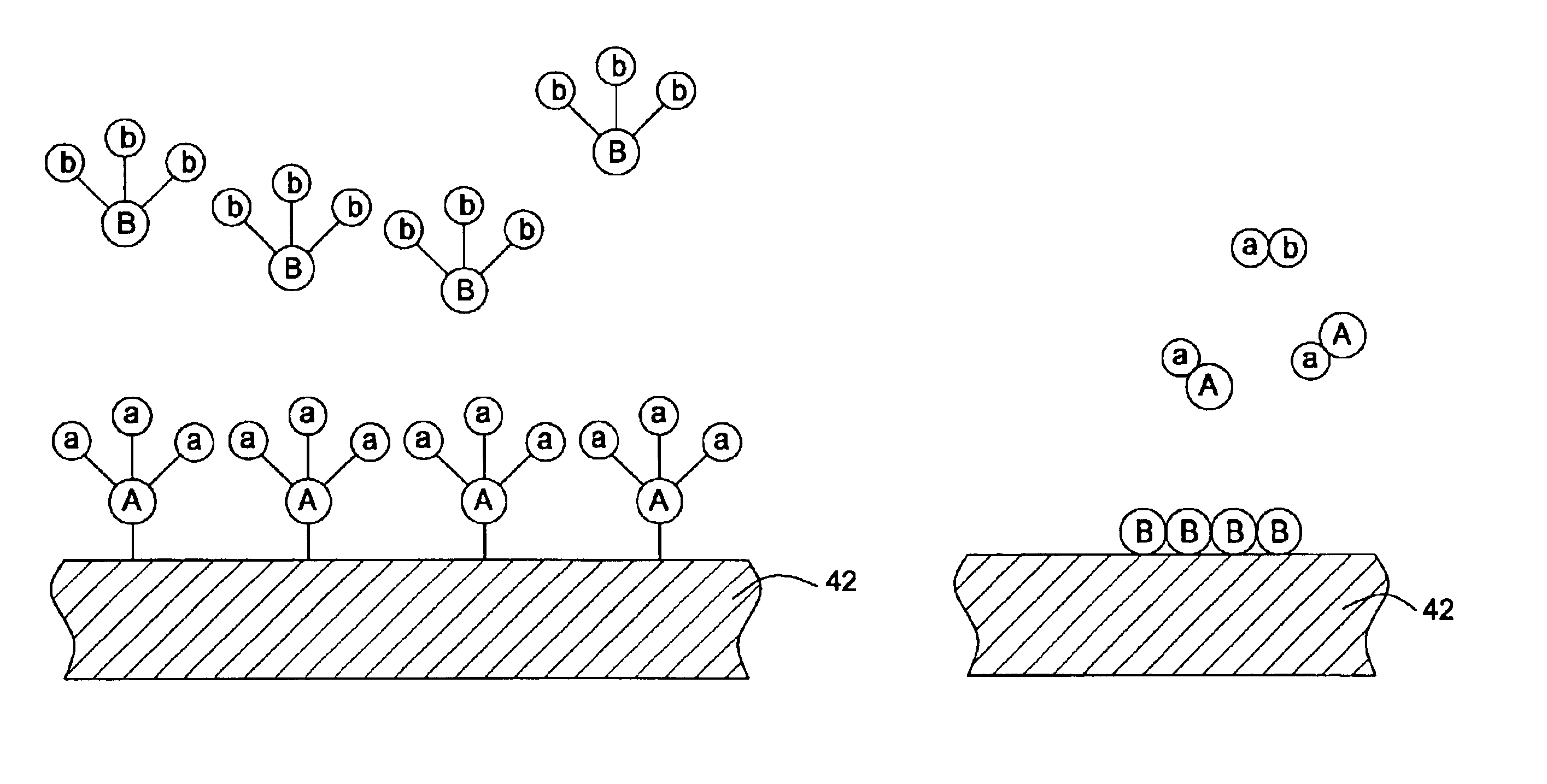
A tungsten nucleation film is formed on a surface of a semiconductor substrate by alternatively providing to that surface, reducing gases and tungsten-containing gases. Each cycle of the method provides for one or more monolayers of the tungsten film. The film is conformal and has improved step coverage, even for a high aspect ratio contact hole.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method for reducing tungsten film roughness and improving step coverage
InactiveUS7141494B2Increase probabilityLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefuse receptaclesNucleationTungsten film
A tungsten nucleation film is formed on a surface of a semiconductor substrate by alternatively providing to that surface, reducing gases and tungsten-containing gases. Each cycle of the method provides for one or more monolayers of the tungsten film. The film is conformal and has improved step coverage, even for a high aspect ratio contact hole.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Atomic layer deposition of tungsten materials
ActiveUS7964505B2Improve conductivityImprove throughputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenSilanes
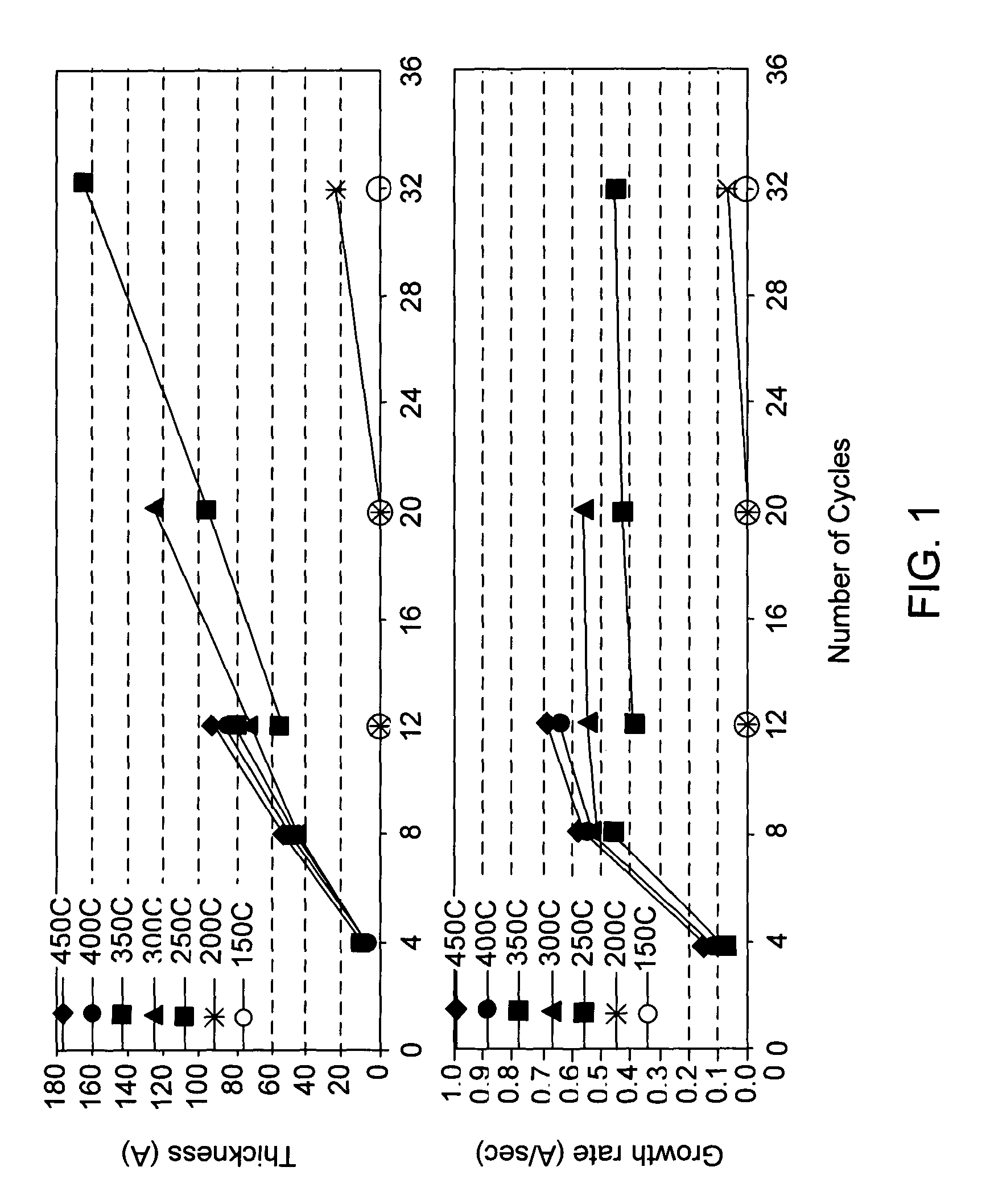
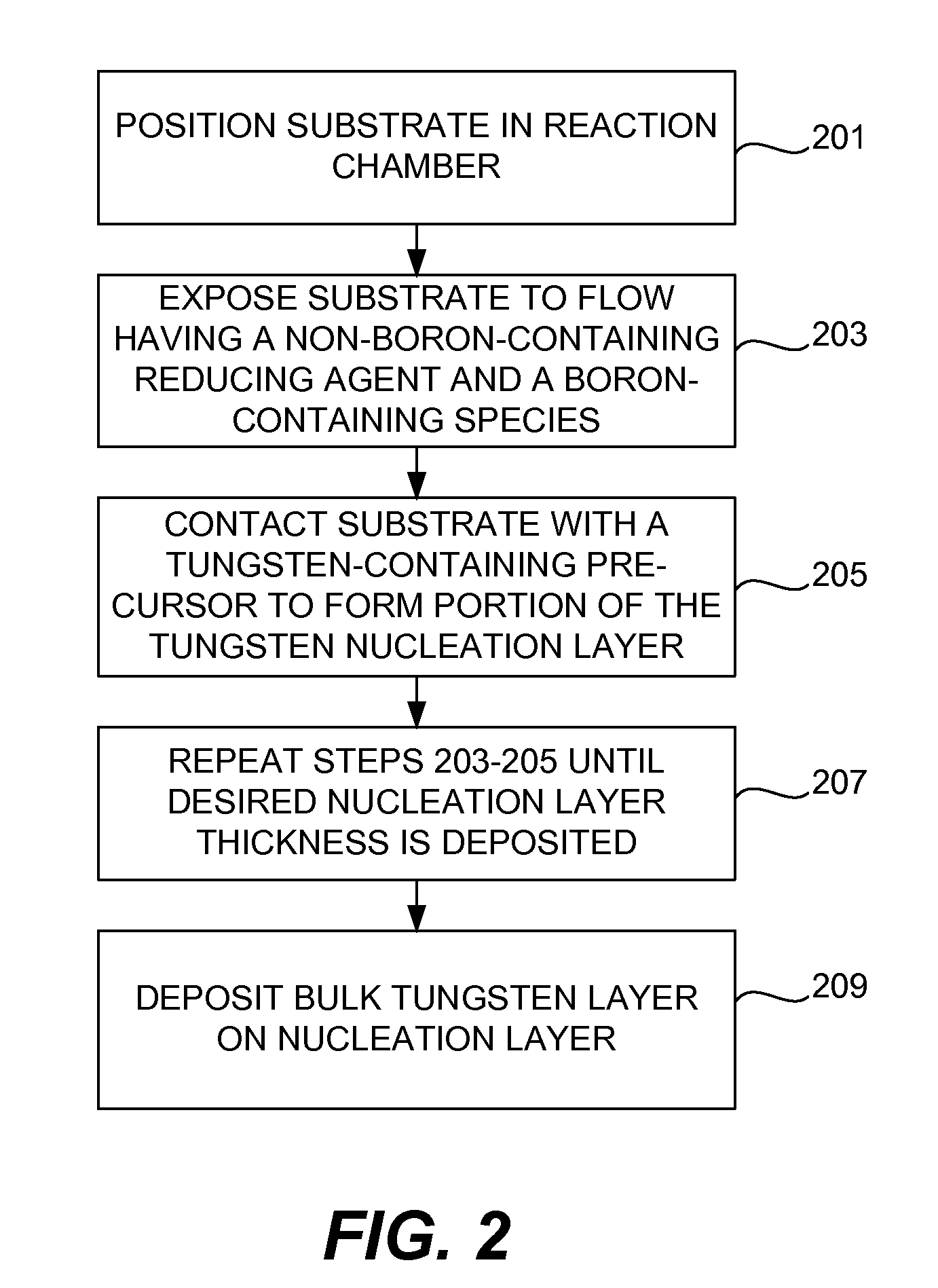
Embodiments of the invention provide an improved process for depositing tungsten-containing materials. The process utilizes soak processes and vapor deposition processes, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD) to provide tungsten films having significantly improved surface uniformity and production level throughput. In one embodiment, a method for forming a tungsten-containing material on a substrate is provided which includes positioning a substrate within a process chamber, wherein the substrate contains an underlayer disposed thereon, exposing the substrate sequentially to a tungsten precursor and a reducing gas to deposit a tungsten nucleation layer on the underlayer during an ALD process, wherein the reducing gas contains a hydrogen / hydride flow rate ratio of about 40:1, 100:1, 500:1, 800:1, 1,000:1, or greater, and depositing a tungsten bulk layer on the tungsten nucleation layer. The reducing gas contains a hydride compound, such as diborane, silane, or disilane.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus for depositing tungsten after surface treatment to improve film characteristics
InactiveUS6936538B2Reduce fluorine contentHigh resistivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical speciesNucleation
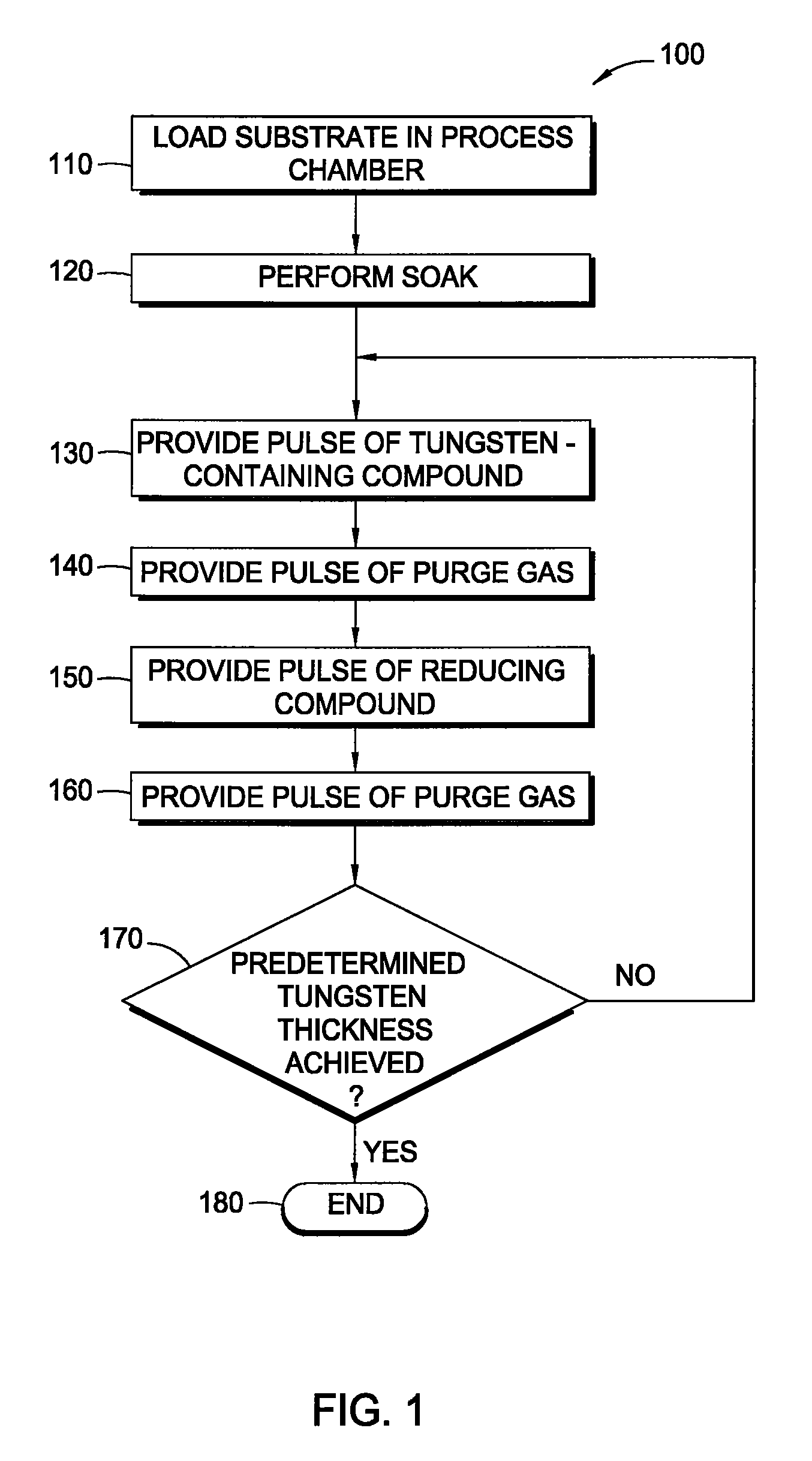
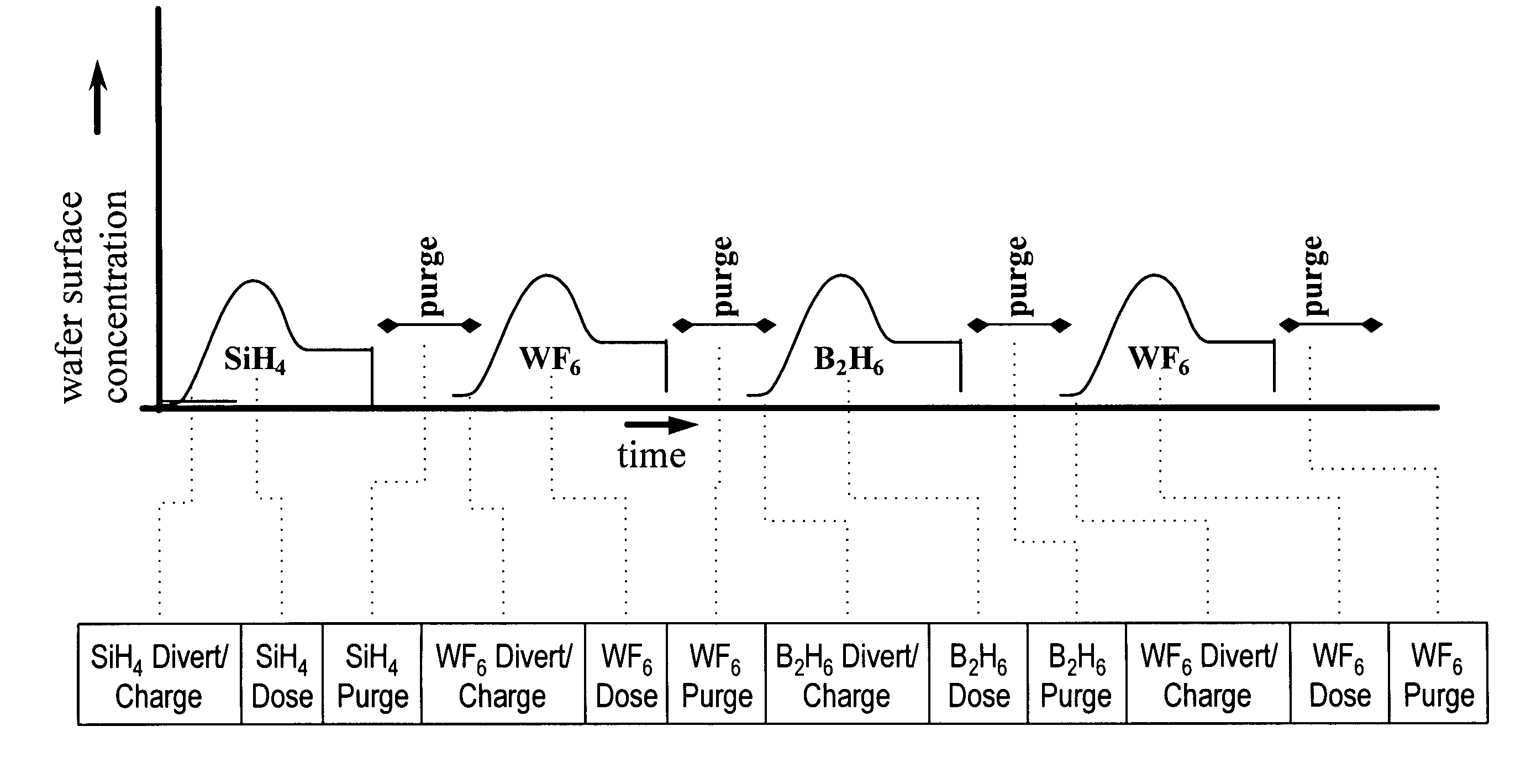
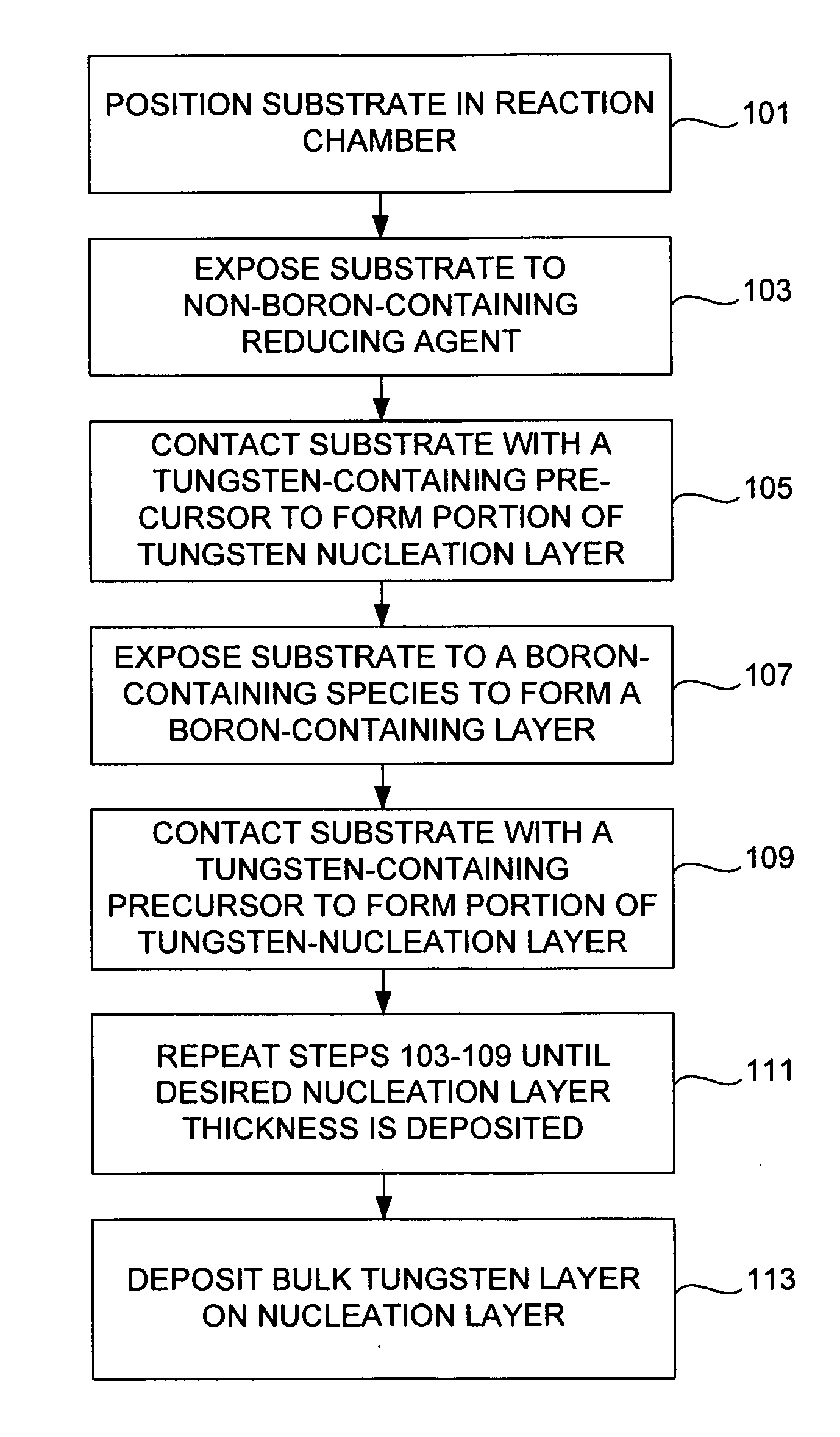
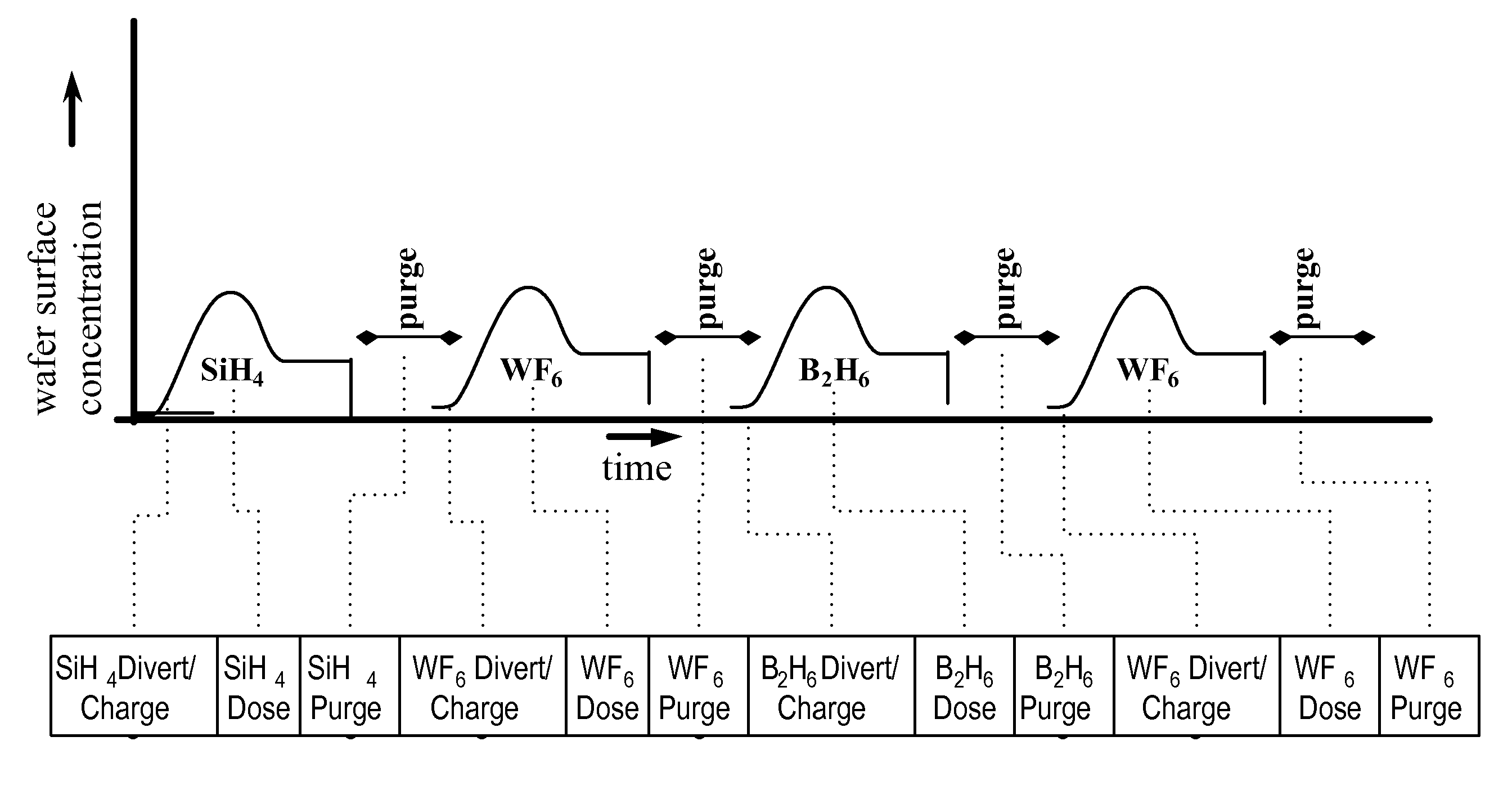
A method and system to form a refractory metal layer over a substrate includes introduction of a reductant, such as PH3 or B2H6, followed by introduction of a tungsten containing compound, such as WF6, to form a tungsten layer. It is believed that the reductant reduces the fluorine content of the tungsten layer while improving the step coverage and resistivity of the tungsten layer. It is believed that the improved characteristics of the tungsten film are attributable to the chemical affinity between the reductants and the tungsten containing compound. The chemical affinity provides better surface mobility of the adsorbed chemical species and better reduction of WF6 at the nucleation stage of the tungsten layer. The method can further include sequentially introducing a reductant, such as PH3 or B2H6, and a tungsten containing compound to deposit a tungsten layer. The formed tungsten layer can be used as a nucleation layer followed by bulk deposition of a tungsten layer utilizing standard CVD techniques. Alternatively, the formed tungsten layer can be used to fill an aperture.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods for growing low-resistivity tungsten film
InactiveUS7589017B2Low resistivityGood step coverageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingBoron containingLayer thickness
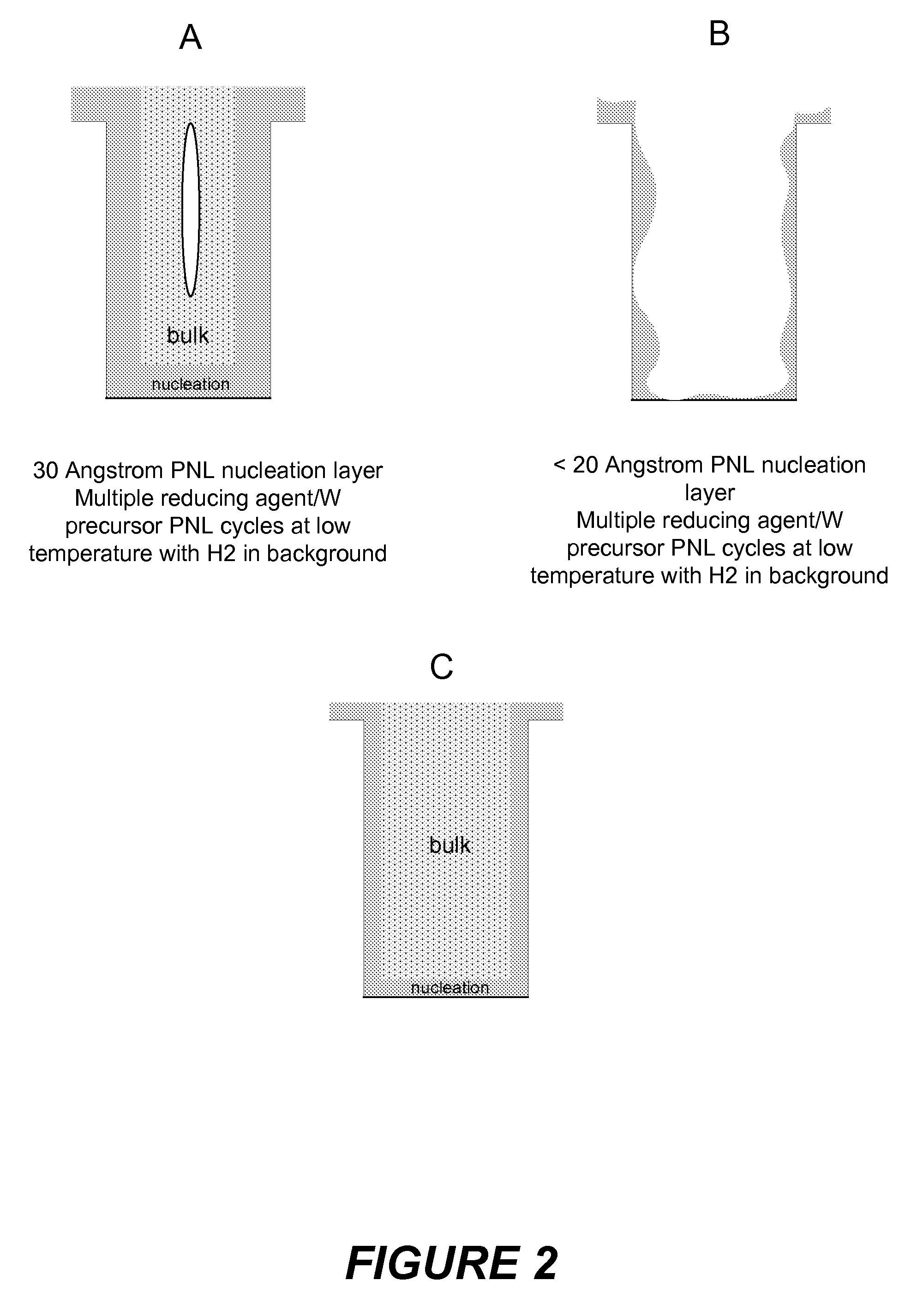
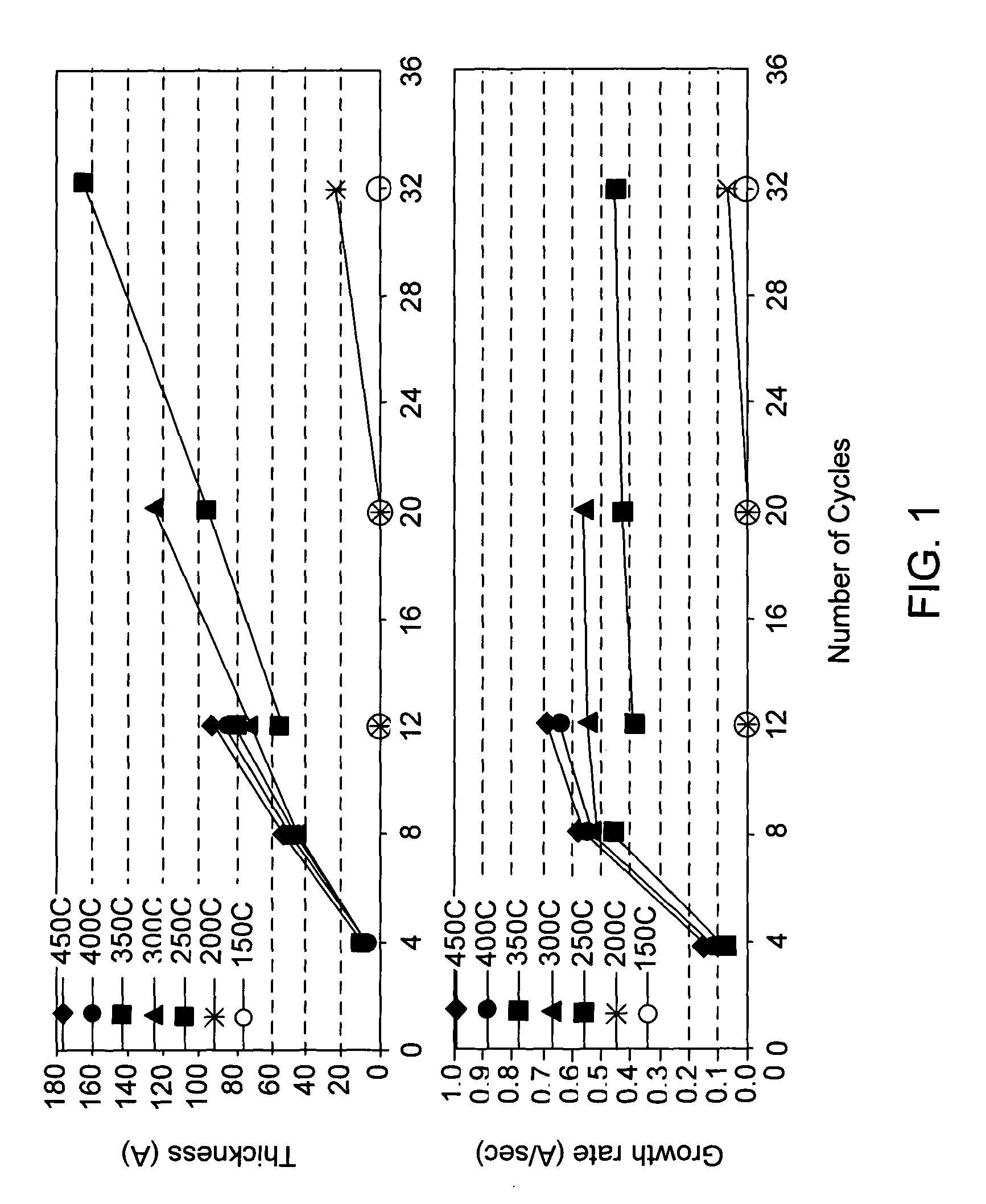
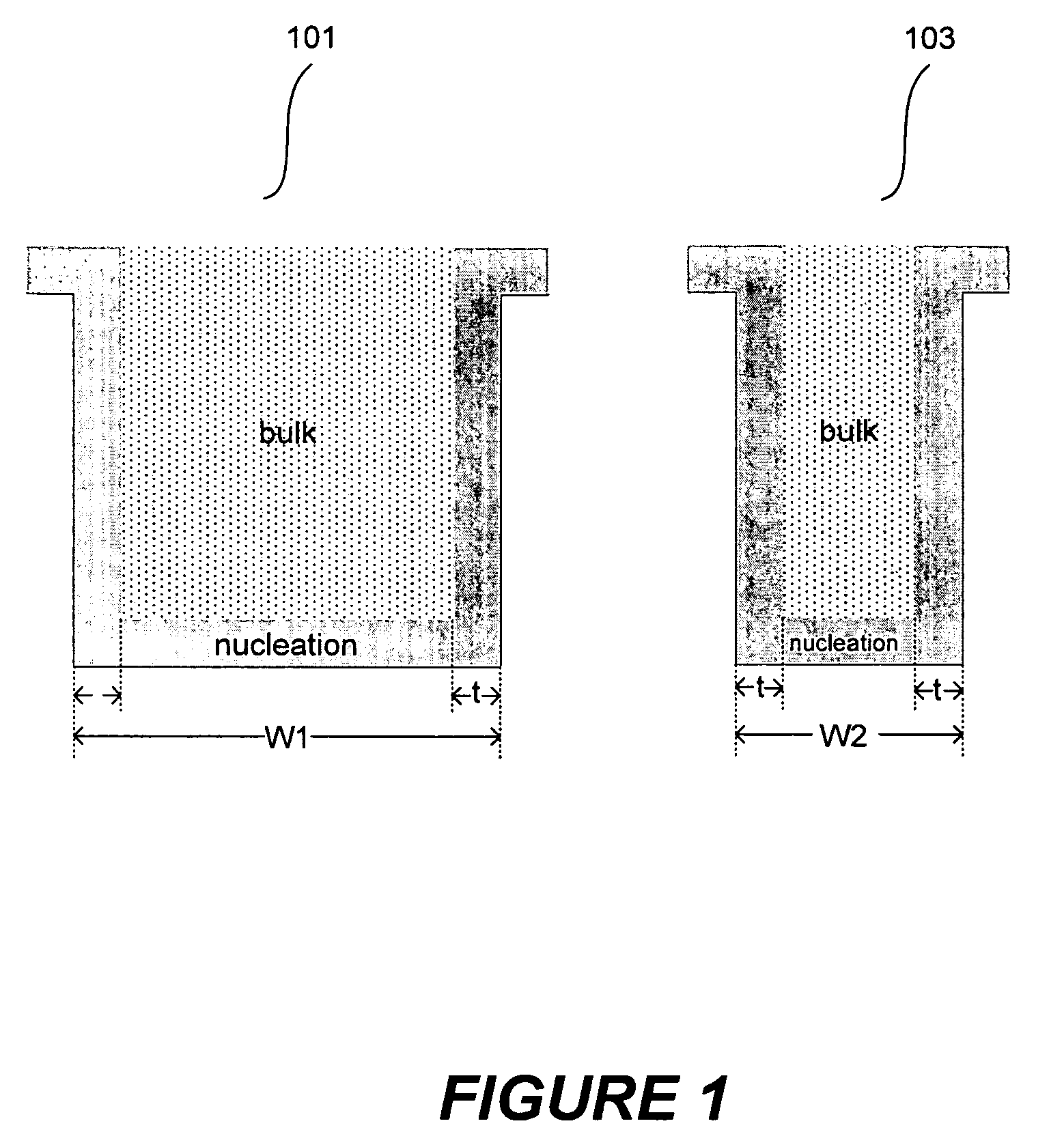
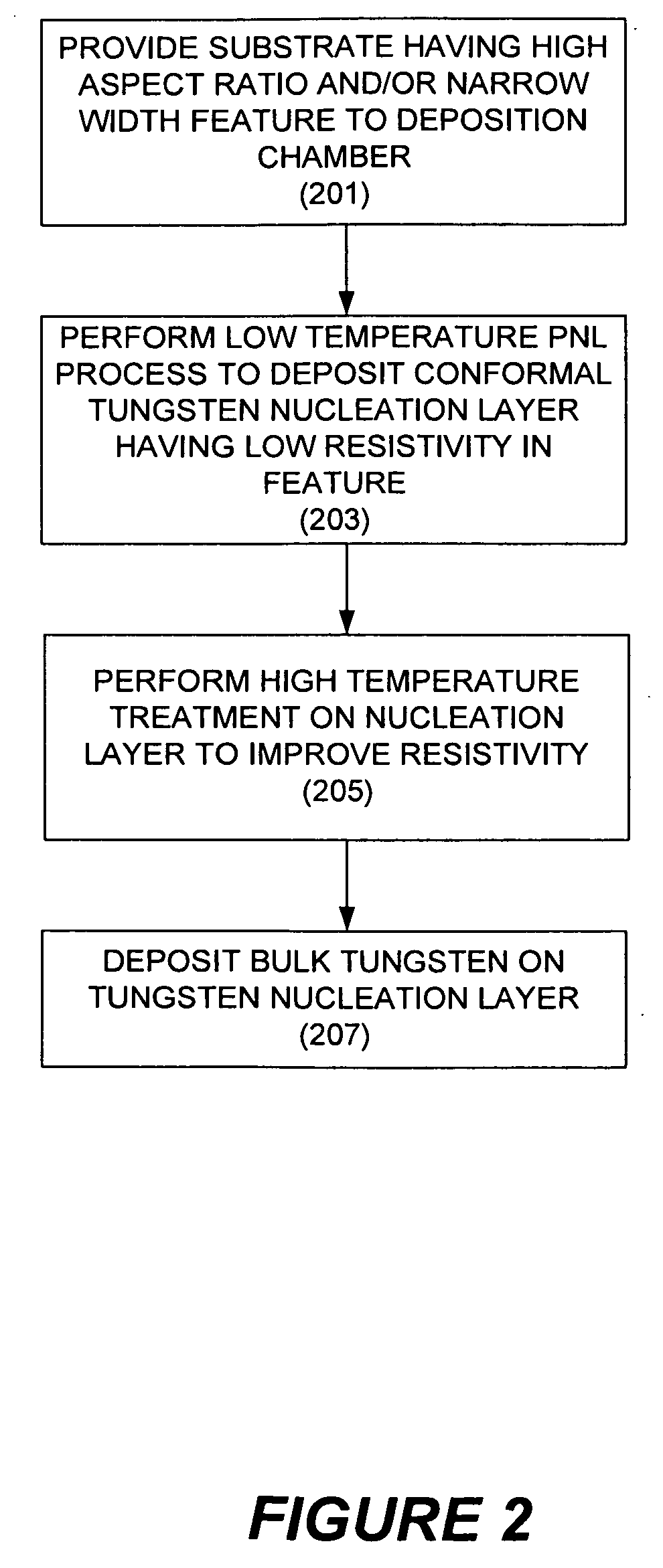
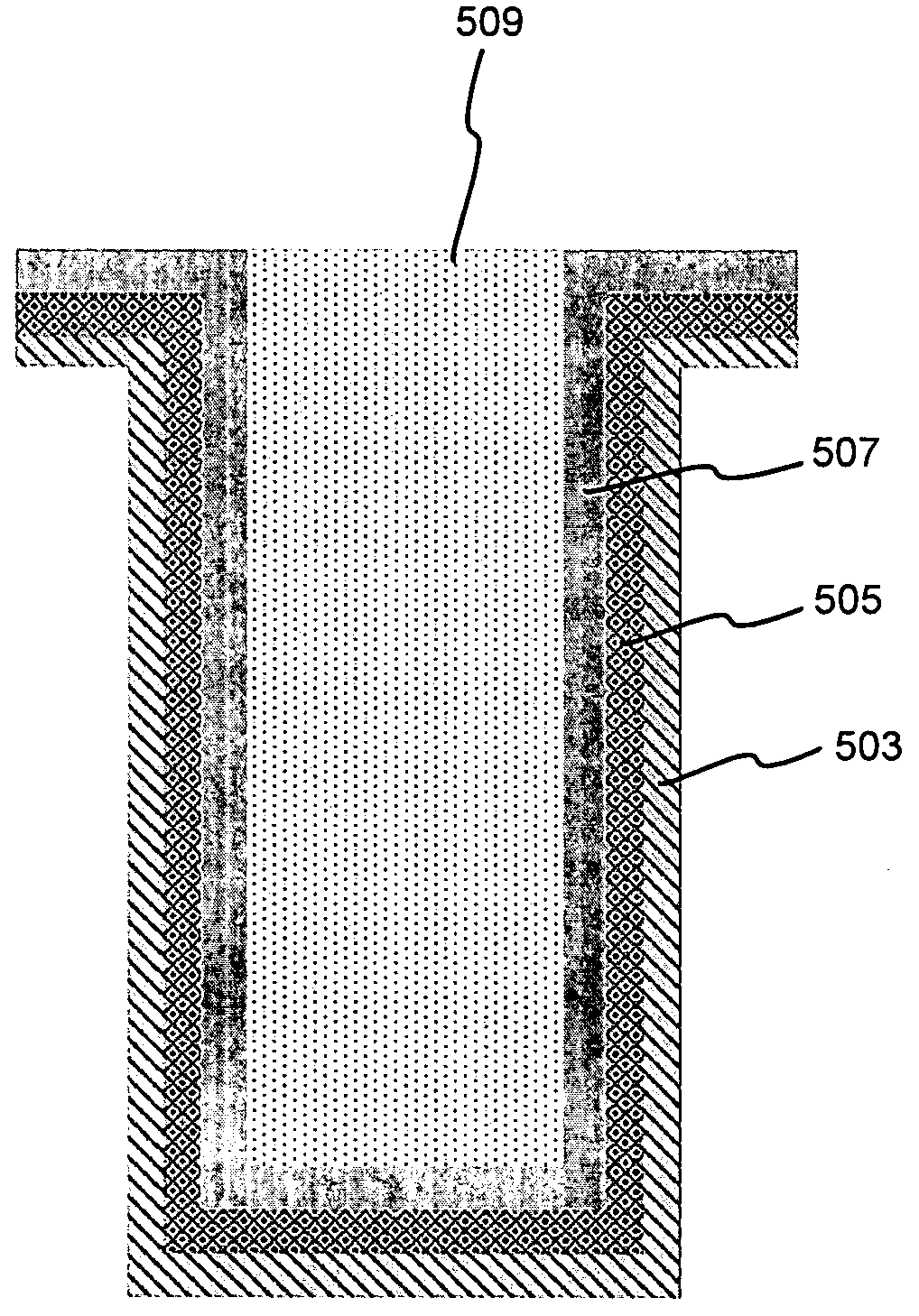
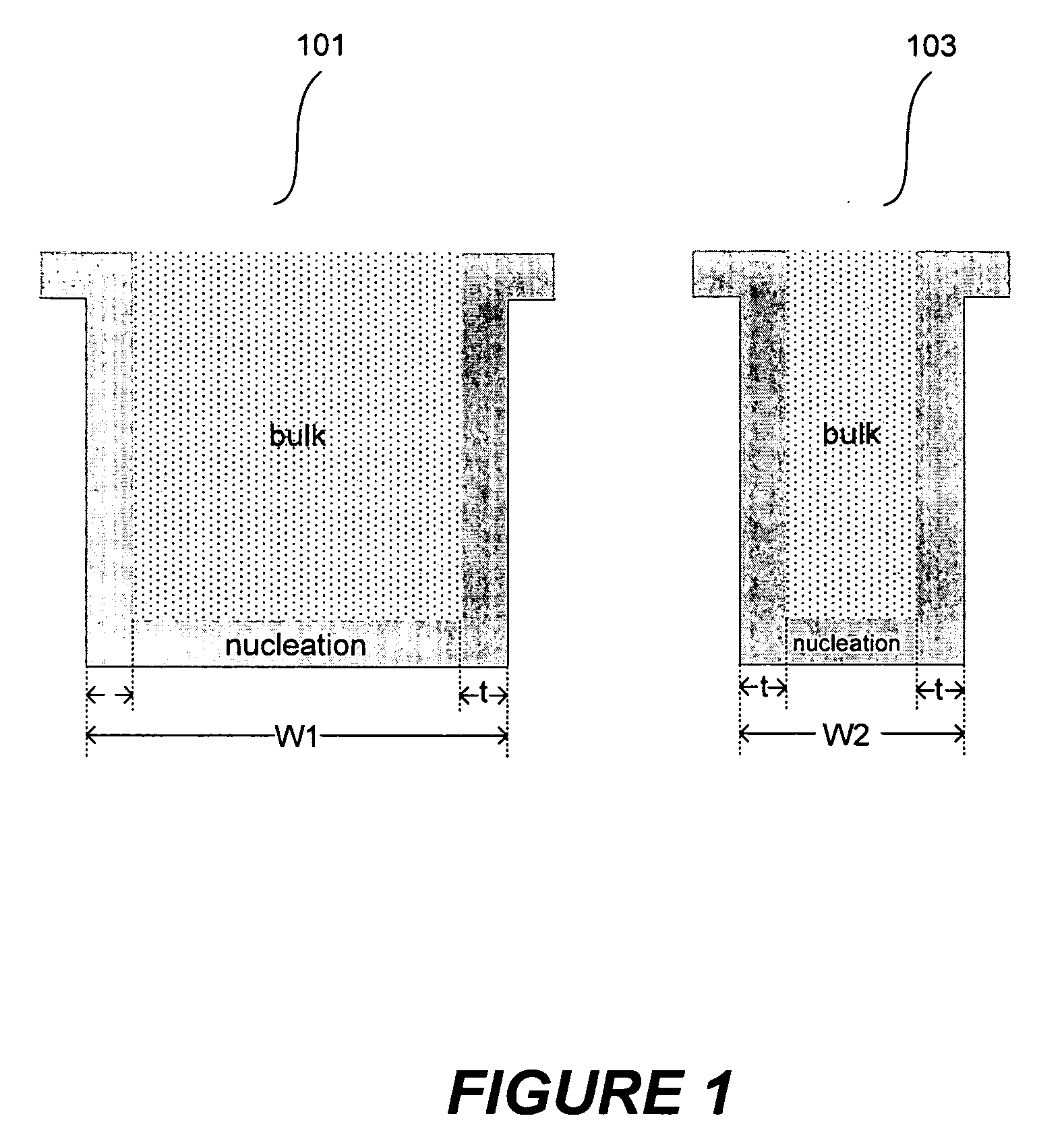
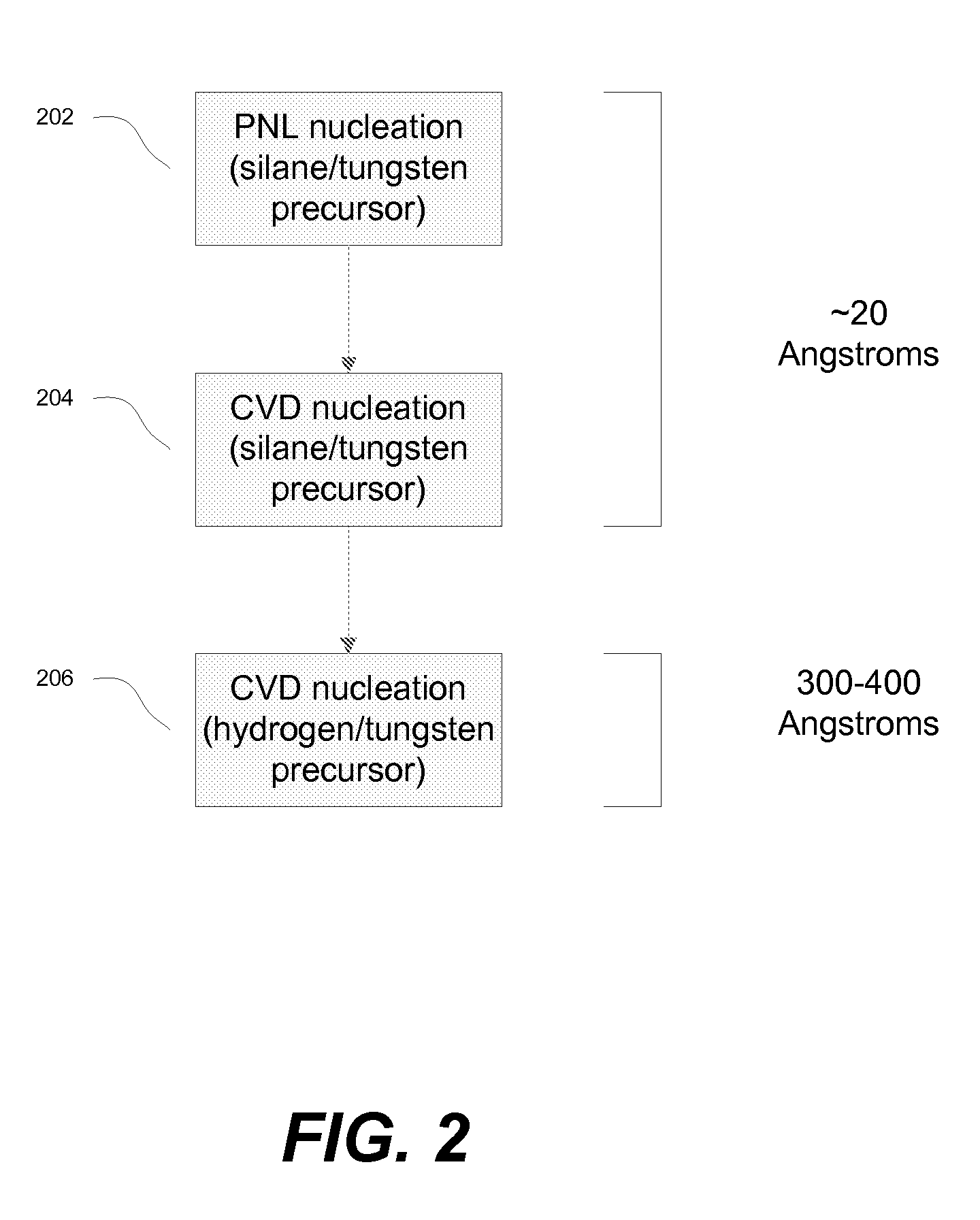
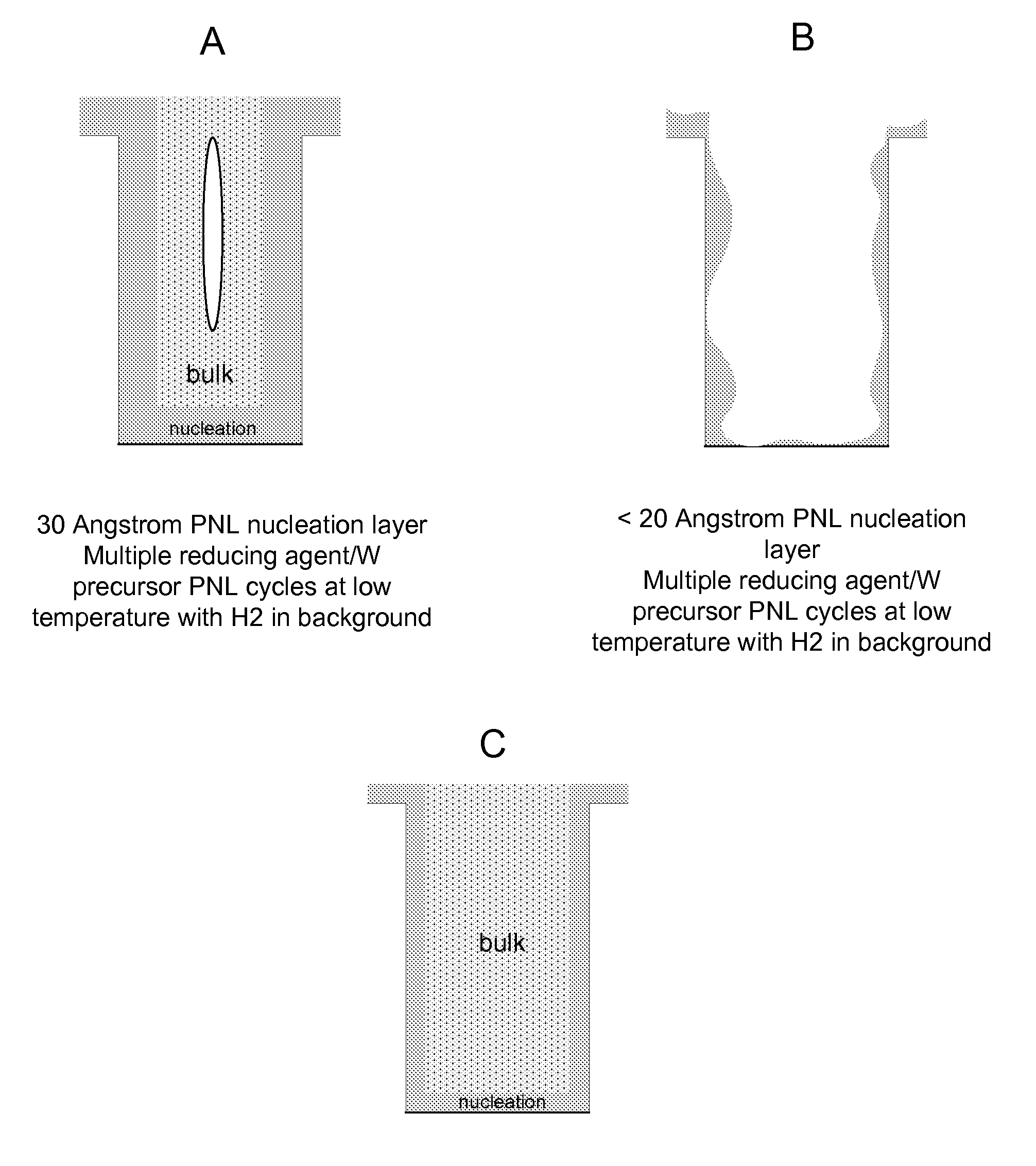
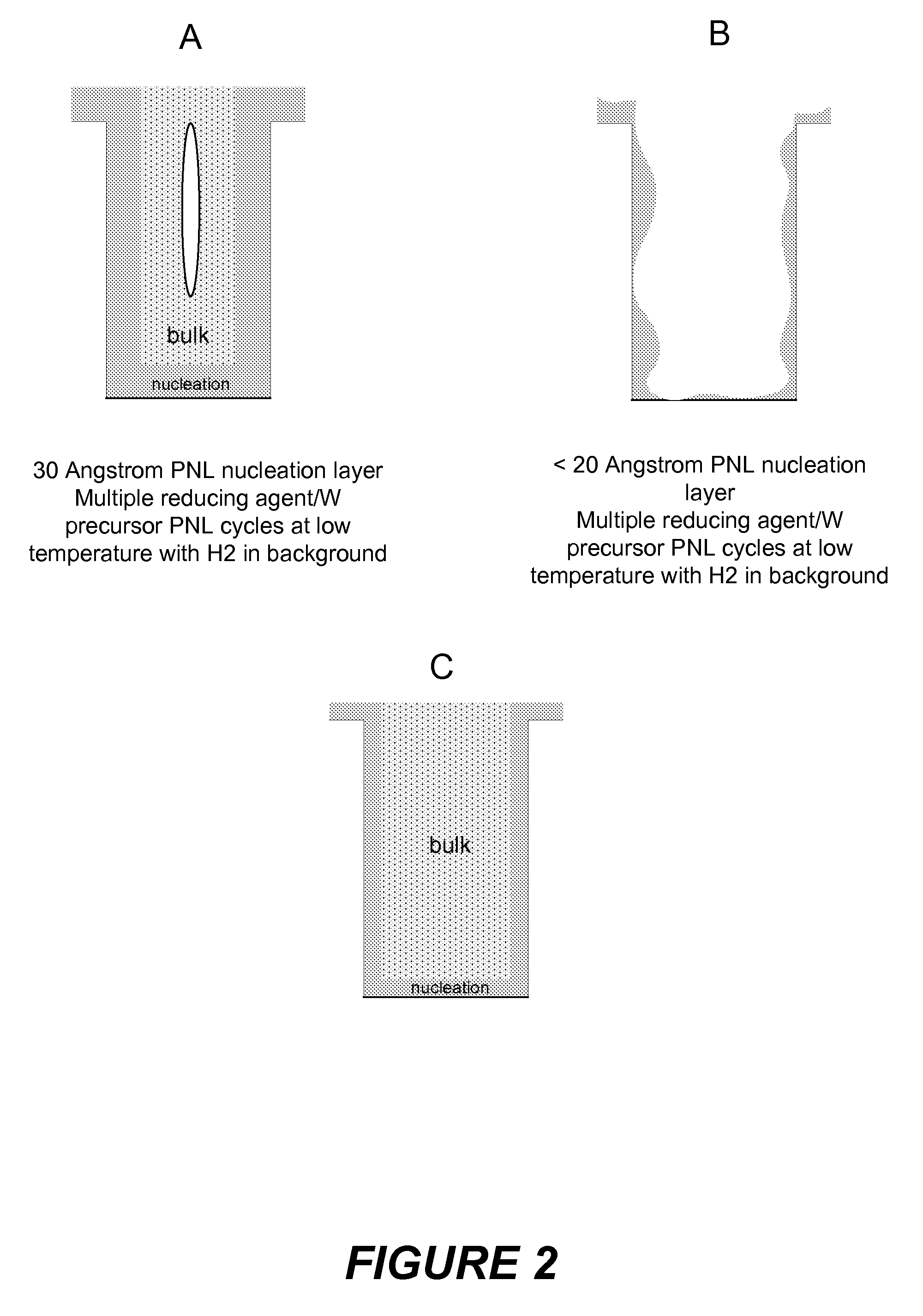
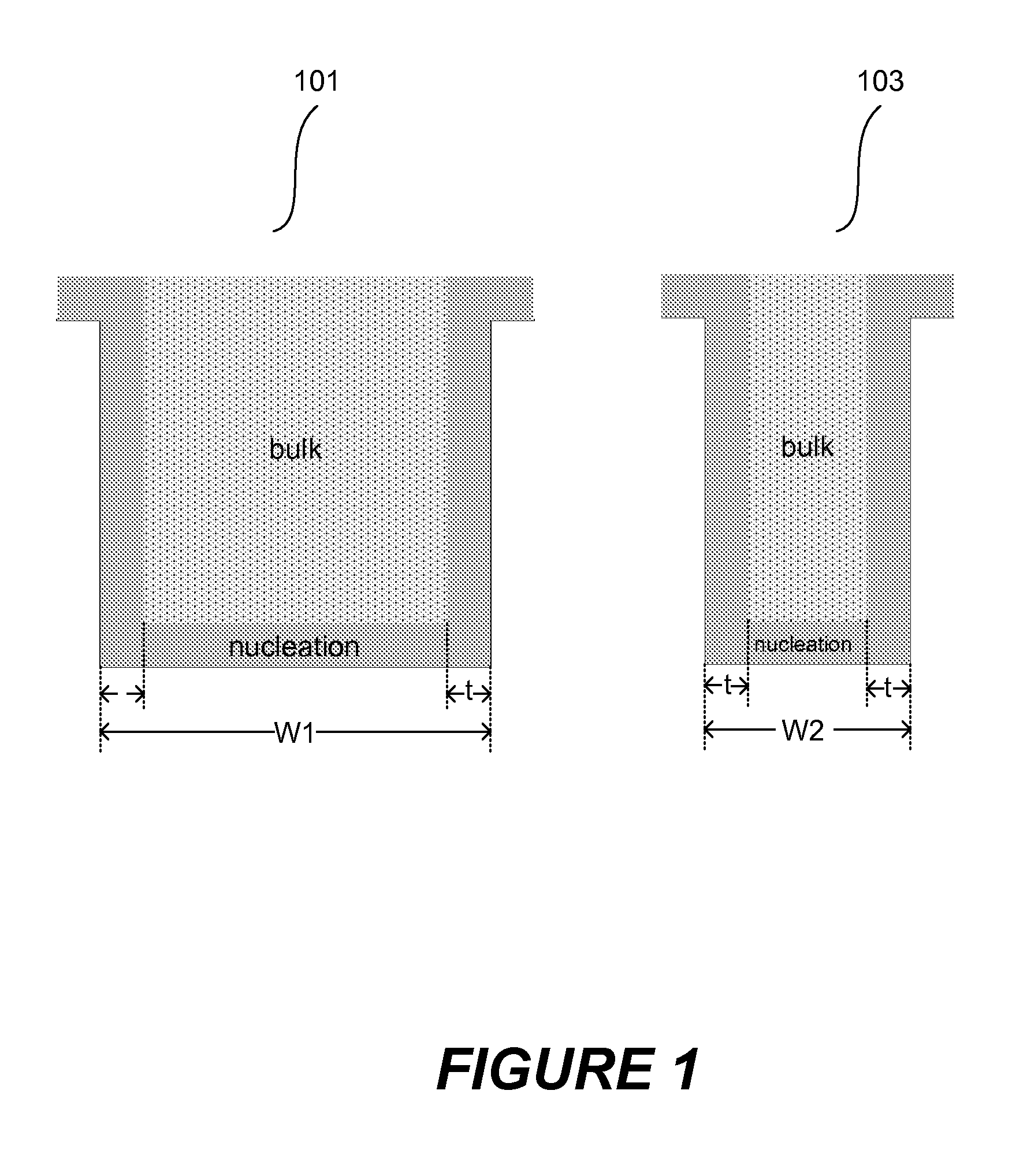
Improved methods for depositing low resistivity tungsten films are provided. The methods involve depositing a tungsten nucleation layer on a substrate and then depositing a tungsten bulk layer over the tungsten nucleation layer to form the tungsten film. The methods provide precise control of the nucleation layer thickness and improved step coverage. According to various embodiments, the methods involve controlling thickness and / or improving step coverage by exposing the substrate to pulse nucleation layer (PNL) cycles at low temperature. Also in some embodiments, the methods may improve resistivity by using a high temperature PNL cycle of a boron-containing species and a tungsten-containing precursor to finish forming the tungsten nucleation layer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods for forming all tungsten contacts and lines
InactiveUS20090163025A1Improve adhesionGood baseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBit lineNucleation
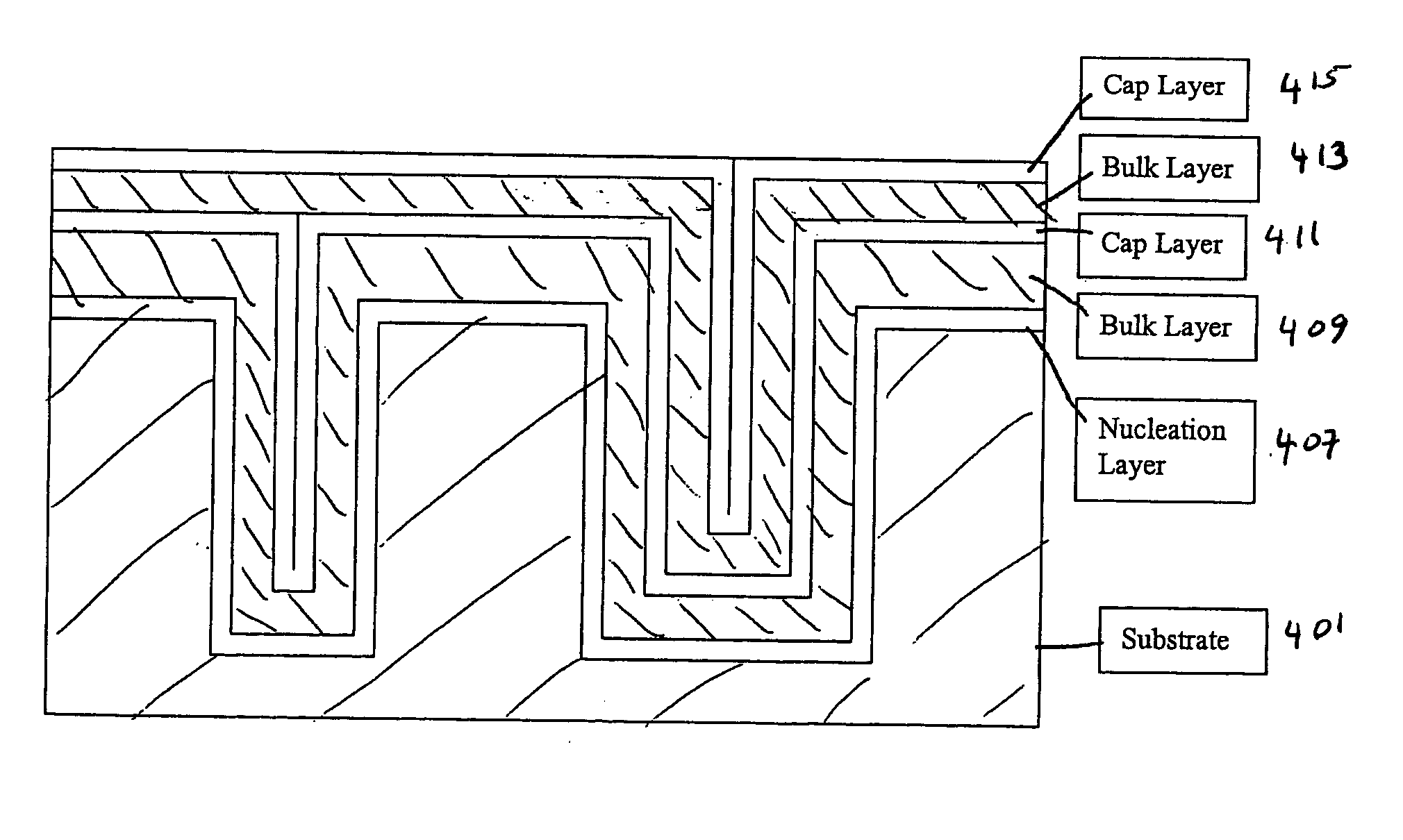
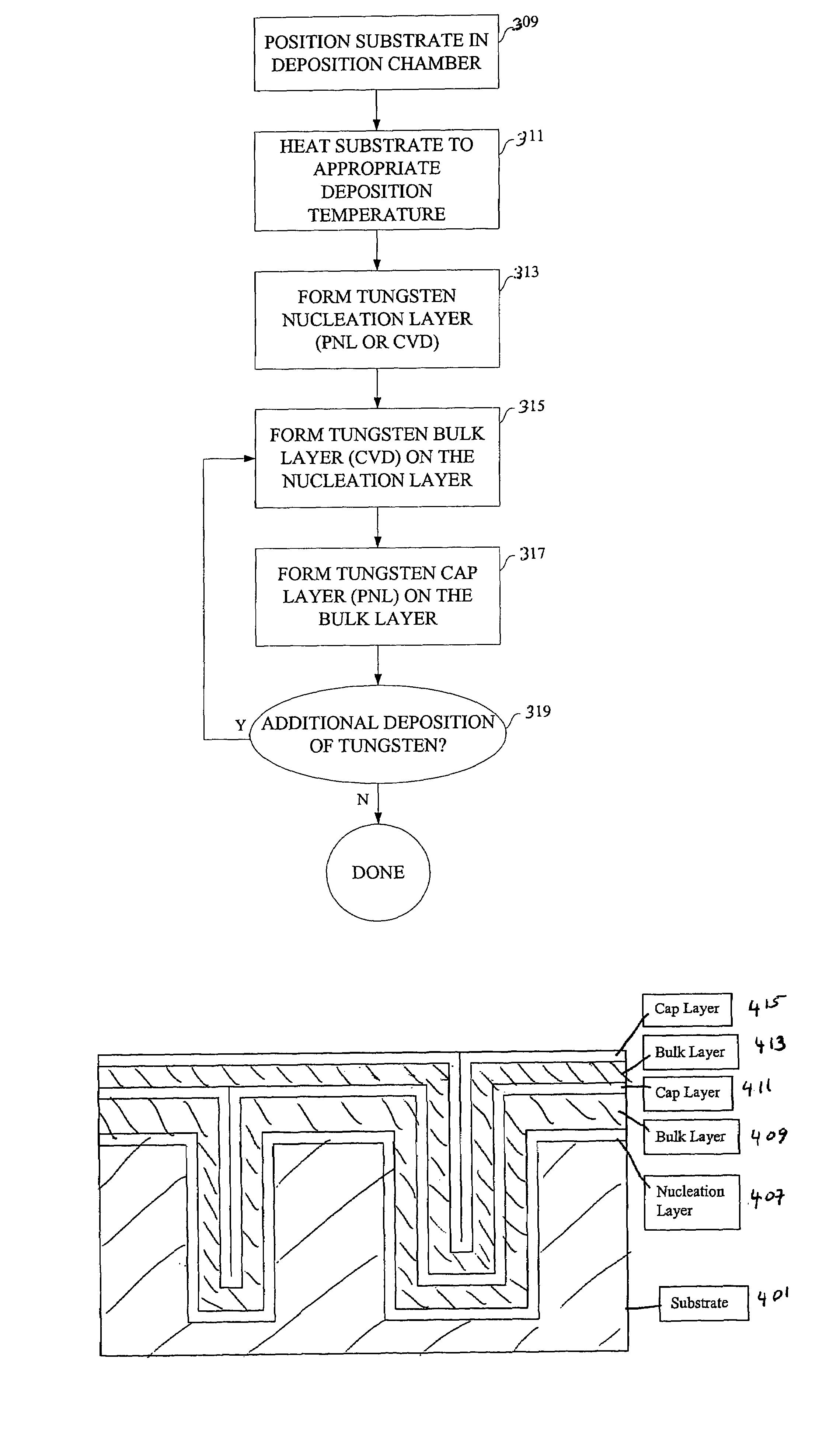
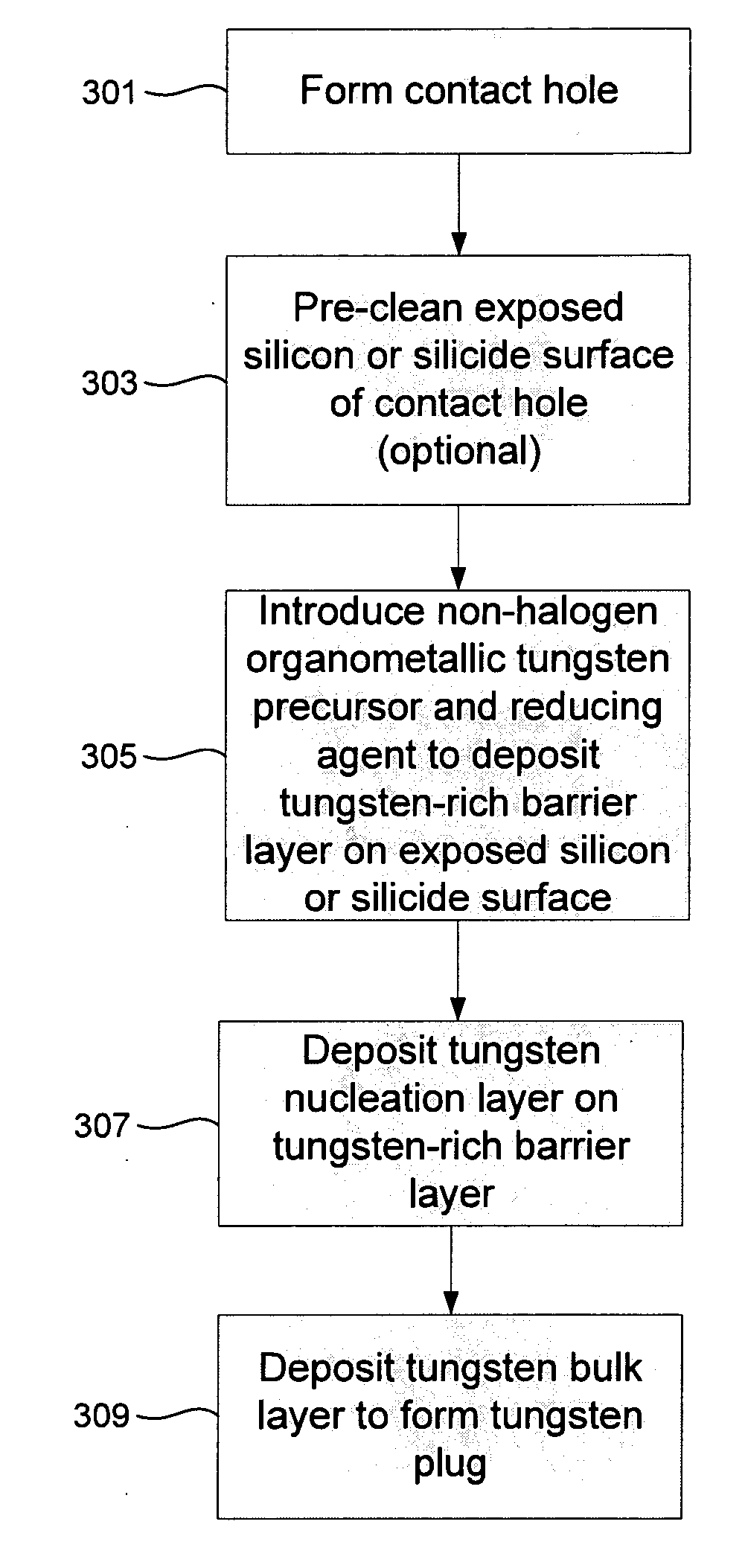
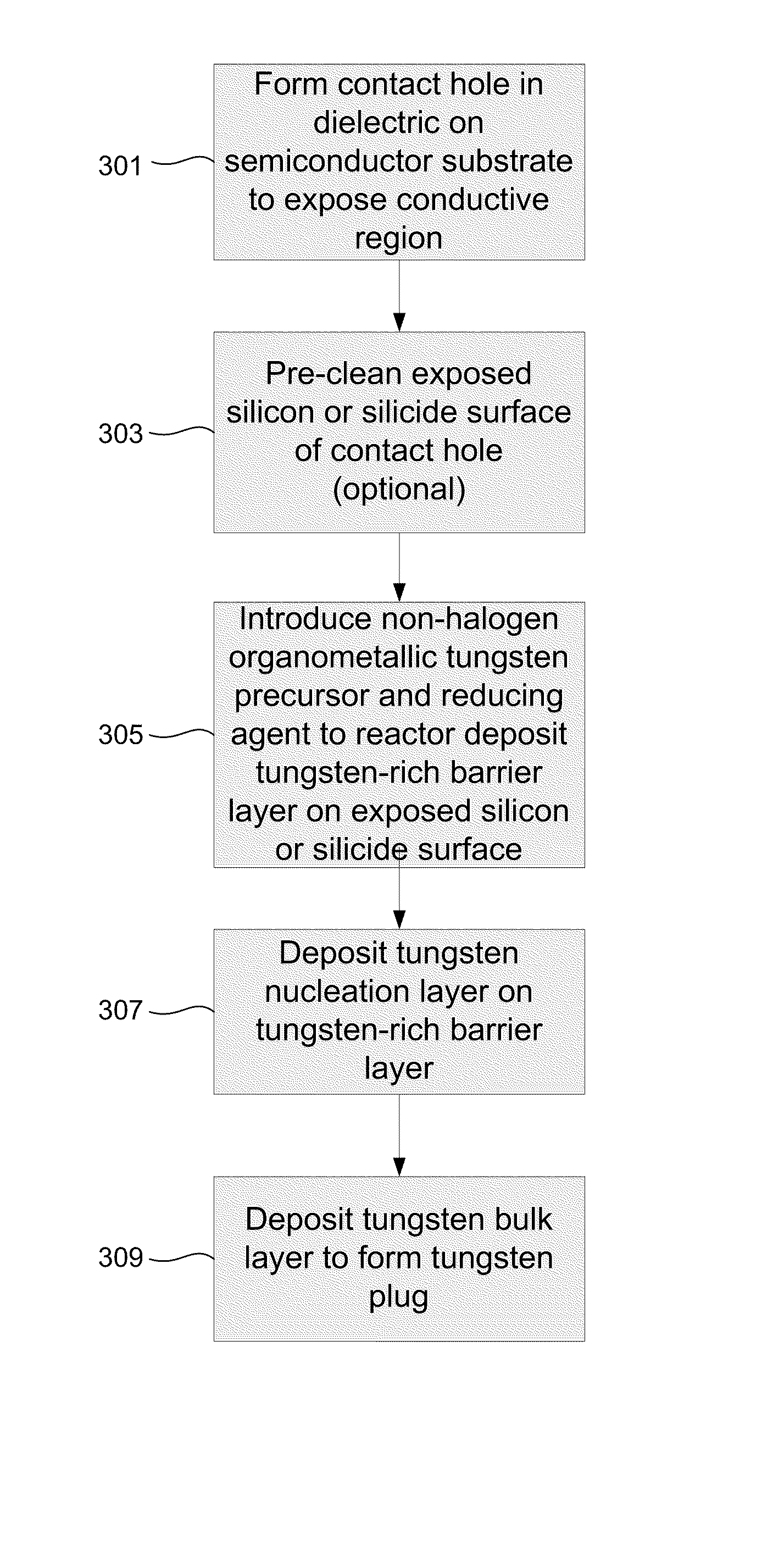
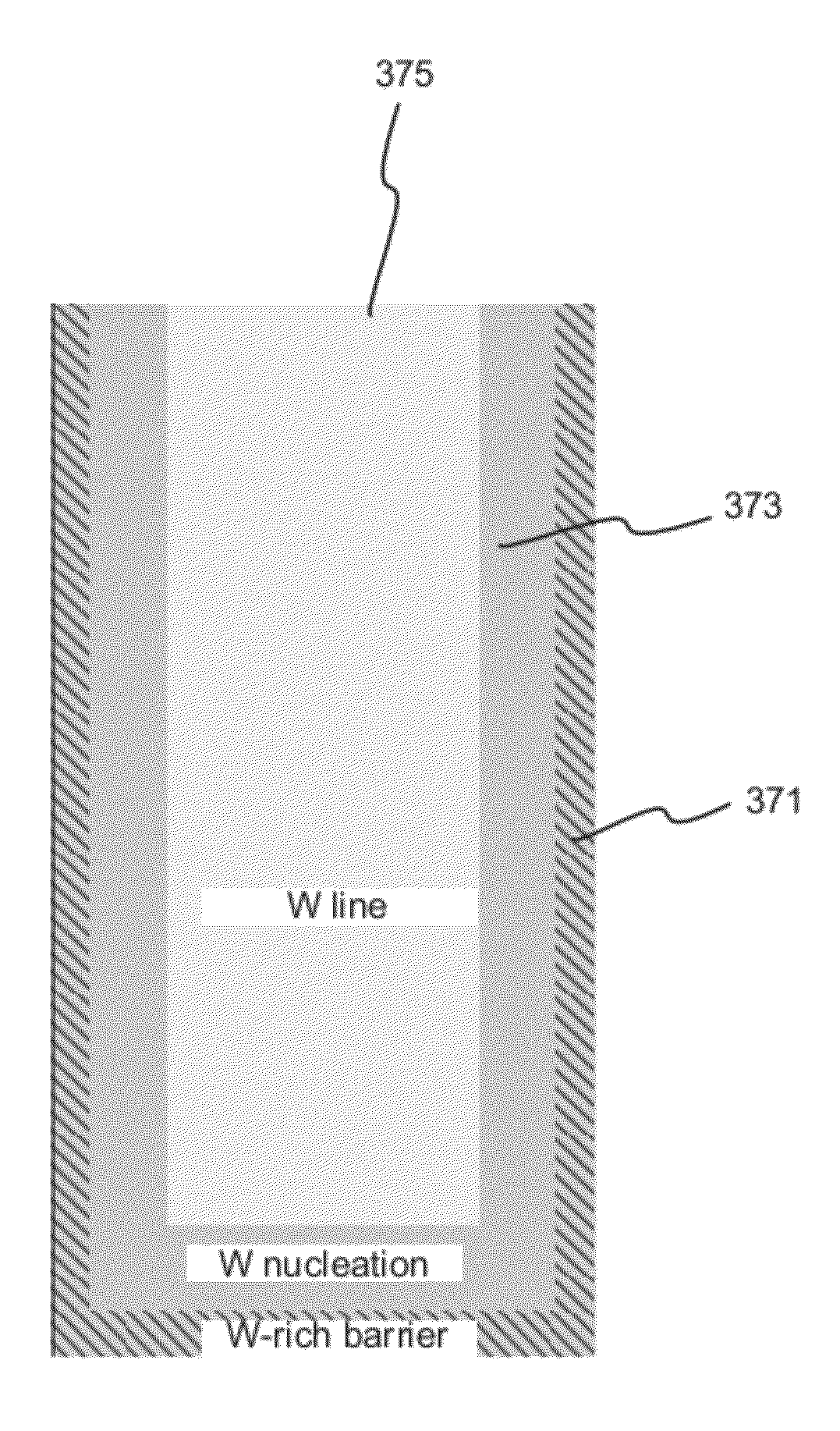
Novel low-resistivity tungsten film stack schemes and methods for depositing them are provided. The film stacks include a mixed tungsten / tungsten-containing compound (e.g., WC) layer as a base for deposition of tungsten nucleation and / or bulk layers. According to various embodiments, these tungsten rich layers may be used as barrier and / or adhesion layers in tungsten contact metallization and bitlines. Deposition of the tungsten-rich layers involves exposing the substrate to a halogen-free organometallic tungsten precursor. The mixed tungsten / tungsten carbide layer is a thin, low resistivity film with excellent adhesion and a good base for subsequent tungsten plug or line formation.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Formation of composite tungsten films
InactiveUS6939804B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNucleationTungsten film
Methods for the deposition of tungsten films are provided. The methods include depositing a nucleation layer by alternatively adsorbing a tungsten precursor and a reducing gas on a substrate, and depositing a bulk layer of tungsten over the nucleation layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for improving uniformity and adhesion of low resistivity tungsten film
ActiveUS7772114B2Improve uniformityLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingOptoelectronicsNucleation
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method for depositing thin tungsten film with low resistivity and robust micro-adhesion characteristics
InactiveUS8058170B2Improve uniformityLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenNucleation
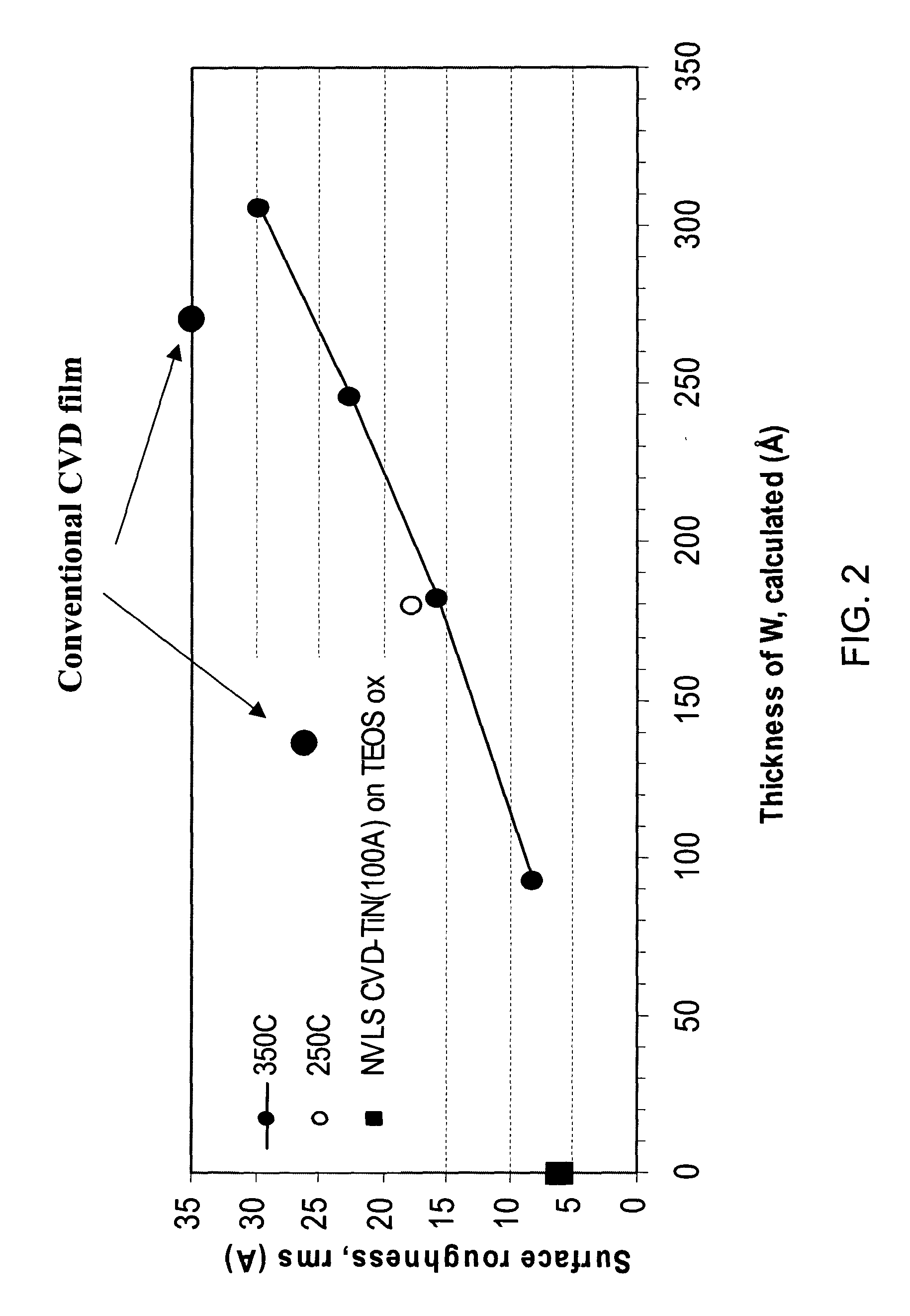
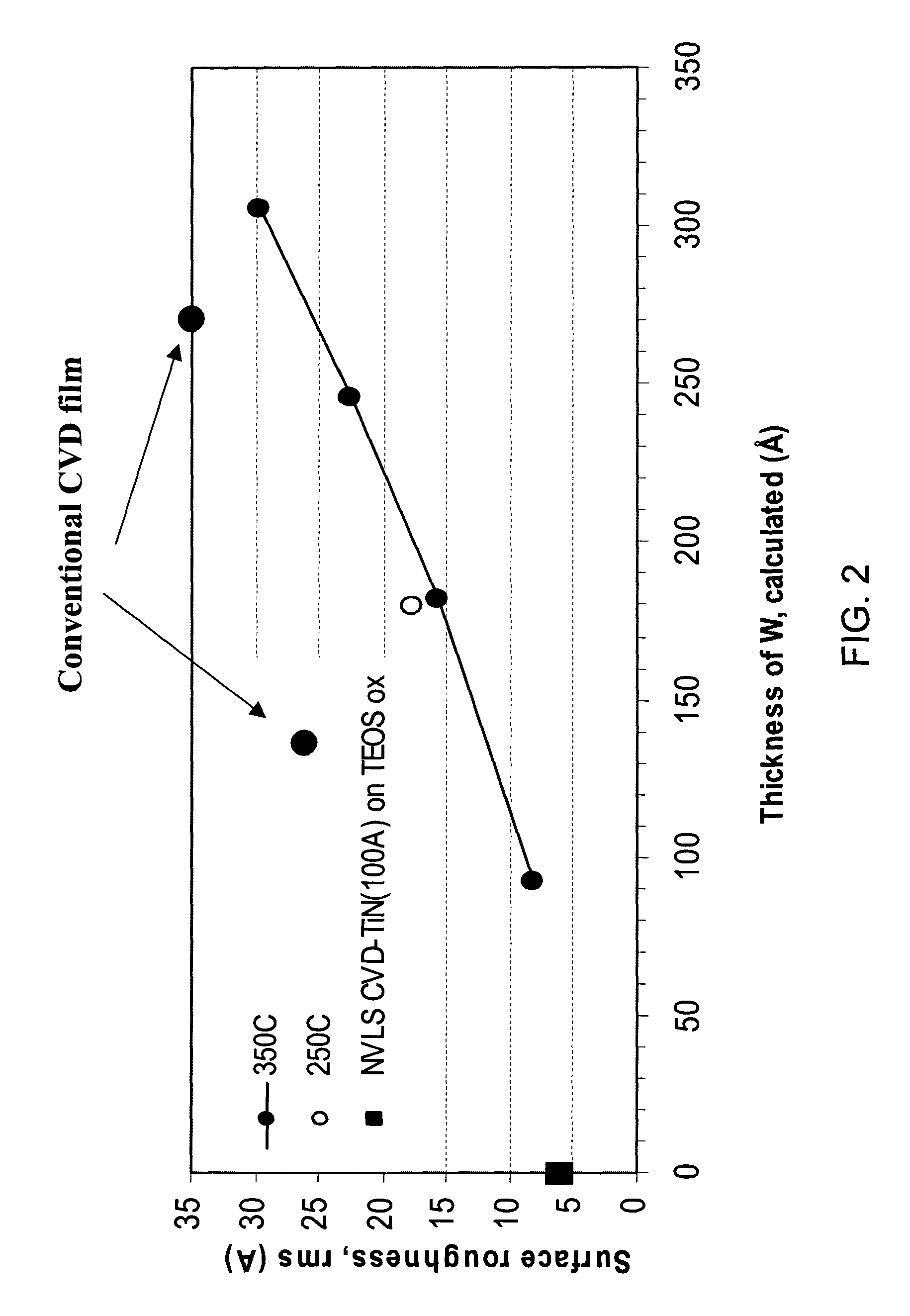
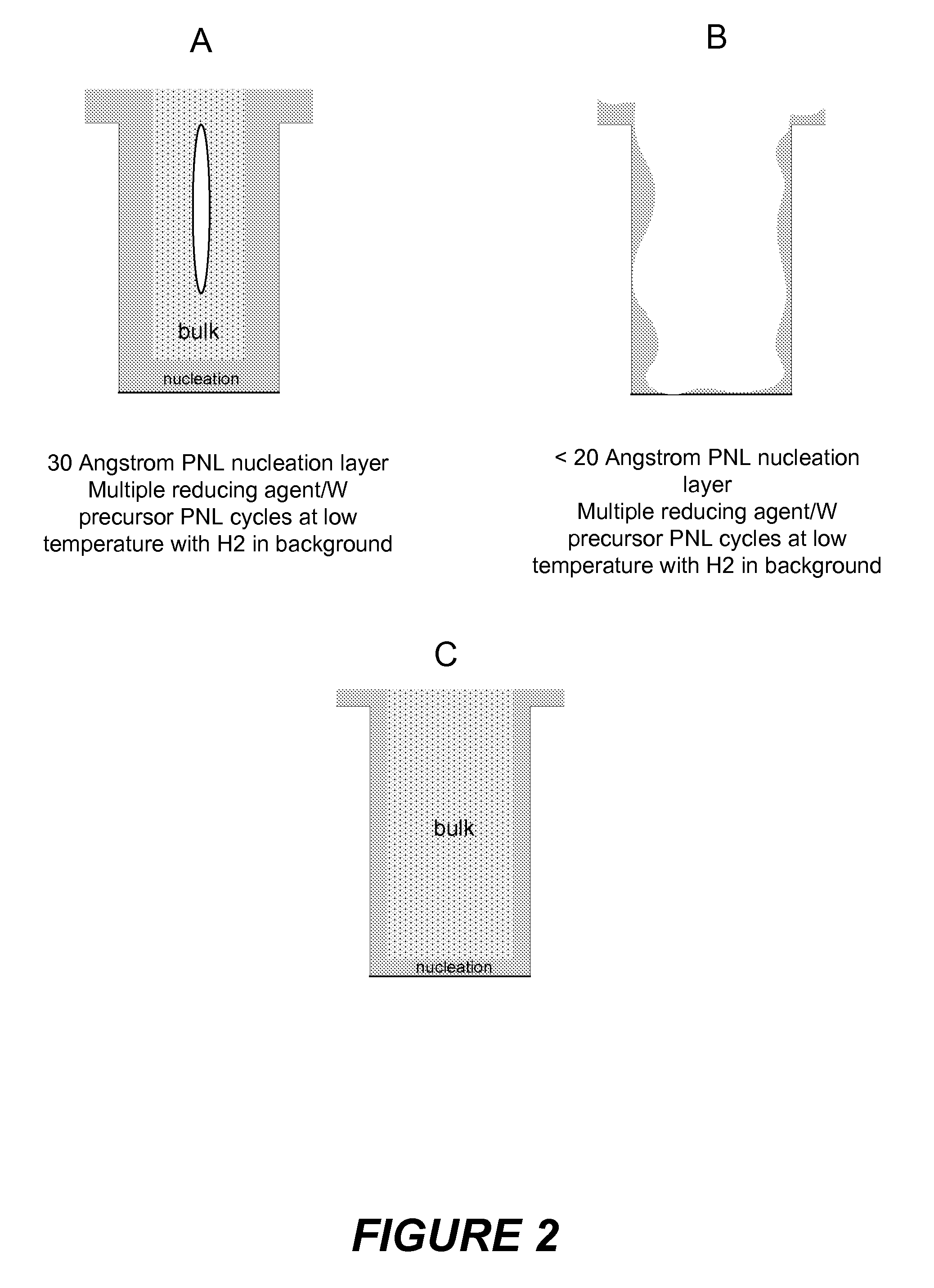
Methods of forming low resistivity tungsten films with good uniformity and good adhesion to the underlying layer are provided. The methods involve forming a tungsten nucleation layer using a pulsed nucleation layer process at low temperature and then treating the deposited nucleation layer prior to depositing the bulk tungsten fill. The treatment operation lowers resistivity of the deposited tungsten film. In certain embodiments, the depositing the nucleation layer involves a boron-based chemistry in the absence of hydrogen. Also in certain embodiments, the treatment operations involve exposing the nucleation layer to alternating cycles of a reducing agent and a tungsten-containing precursor. The methods are useful for depositing films in high aspect ratio and / or narrow features. The films exhibit low resistivity at narrow line widths and excellent step coverage.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Ruthenium as an underlayer for tungsten film deposition
In one embodiment, a method for depositing a tungsten-containing film on a substrate is provided which includes depositing a barrier layer on the substrate, such as a titanium or tantalum containing barrier layer and depositing a ruthenium layer on the barrier layer. The method further includes depositing a tungsten nucleation layer on the ruthenium layer and depositing a tungsten bulk layer on the tungsten nucleation layer. The barrier layer, the ruthenium layer, the tungsten nucleation layer and the tungsten bulk layer are independently deposited by an ALD process, a CVD process or a PVD process, preferably by an ALD process. In some examples, the substrate is exposed to a soak process prior to depositing a subsequent layer, such as between the deposition of the barrier layer and the ruthenium layer, the ruthenium layer and the tungsten nucleation layer or the tungsten nucleation layer and the tungsten bulk layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Plug or via formation using novel slurries for chemical mechanical polishing
InactiveUS6046099AOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntegrated circuit manufacturingPotassium ferricyanide
Novel slurries for the chemical mechanical polishing of thin films used in integrated circuit manufacturing. A tungsten slurry of the present invention comprises an oxidizing agent, such as potassium ferricyanide, an abrasive such as silica, and has a pH between two and four. The tungsten slurry of the present invention can be used in a chemical mechanical planarization process to polish back a blanket deposited tungsten film to form plugs or vias. The tungsten slurry can also be used to polish copper, tungsten silicide, and titanium nitride. A second slurry, which is a 9:1 dilution of the tungsten slurry is ideal for chemical mechanical polishing of titanium nitride films. A third slurry of the present invention comprises a fluoride salt, an abrasive such as silica and has a pH< / =8. The third slurry can be used to polish titanium films.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods for depositing ultra thin low resistivity tungsten film for small critical dimension contacts and interconnects
ActiveUS20100267235A1High aspect ratio featurePromote migrationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGas phaseNucleation
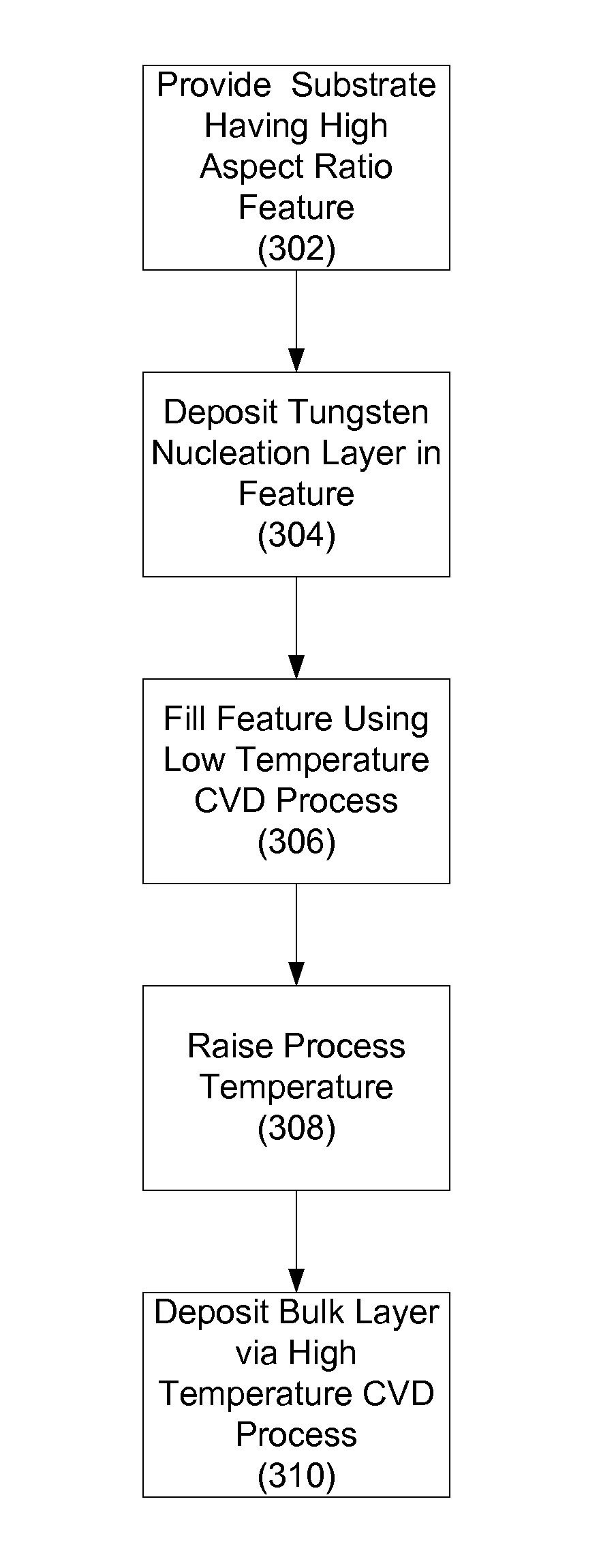
Provided are methods of void-free tungsten fill of high aspect ratio features. According to various embodiments, the methods involve a reduced temperature chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process to fill the features with tungsten. In certain embodiments, the process temperature is maintained at less than about 350° C. during the chemical vapor deposition to fill the feature. The reduced-temperature CVD tungsten fill provides improved tungsten fill in high aspect ratio features, provides improved barriers to fluorine migration into underlying layers, while achieving similar thin film resistivity as standard CVD fill. Also provided are methods of depositing thin tungsten films having low-resistivity. According to various embodiments, the methods involve performing a reduced temperature low resistivity treatment on a deposited nucleation layer prior to depositing a tungsten bulk layer and / or depositing a bulk layer via a reduced temperature CVD process followed by a high temperature CVD process.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method for improving uniformity and adhesion of low resistivity tungsten film
ActiveUS20090149022A1Improve uniformityLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNucleationTungsten film
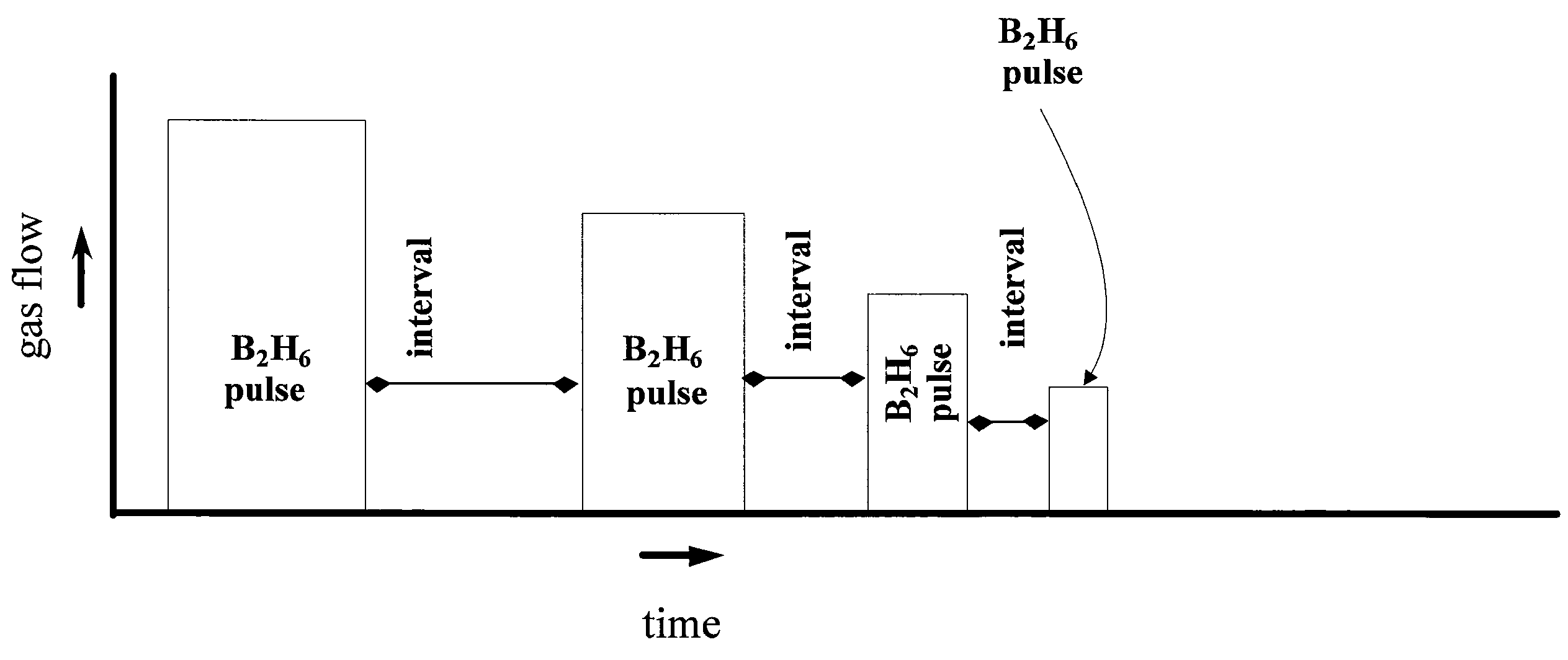
Methods of improving the uniformity and adhesion of low resistivity tungsten films are provided. Low resistivity tungsten films are formed by exposing the tungsten nucleation layer to a reducing agent in a series of pulses before depositing the tungsten bulk layer. According to various embodiments, the methods involve reducing agent pulses with different flow rates, different pulse times and different interval times.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Tungsten deposition with tungsten hexafluoride (WF6) etchback
ActiveUS20150050807A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseContinuous flow
Implementations described herein generally relate to methods for forming tungsten materials on substrates using vapor deposition processes. The method comprises positioning a substrate having a feature formed therein in a substrate processing chamber, depositing a first film of a bulk tungsten layer by introducing a continuous flow of a hydrogen containing gas and a tungsten halide compound to the processing chamber to deposit the first tungsten film over the feature, etching the first film of the bulk tungsten layer using a plasma treatment to remove a portion of the first film by exposing the first film to a continuous flow of the tungsten halide compound and an activated treatment gas and depositing a second film of the bulk tungsten layer by introducing a continuous flow of the hydrogen containing gas and the tungsten halide compound to the processing chamber to deposit the second tungsten film over the first tungsten film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for depositing thin tungsten film with low resistivity and robust micro-adhesion characteristics
InactiveUS20100159694A1Improve uniformityLow resistivityLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenNucleation
Methods of forming low resistivity tungsten films with good uniformity and good adhesion to the underlying layer are provided. The methods involve forming a tungsten nucleation layer using a pulsed nucleation layer process at low temperature and then treating the deposited nucleation layer prior to depositing the bulk tungsten fill. The treatment operation lowers resistivity of the deposited tungsten film. In certain embodiments, the depositing the nucleation layer involves a boron-based chemistry in the absence of hydrogen. Also in certain embodiments, the treatment operations involve exposing the nucleation layer to alternating cycles of a reducing agent and a tungsten-containing precursor. The methods are useful for depositing films in high aspect ratio and / or narrow features. The films exhibit low resistivity at narrow line widths and excellent step coverage.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods for improving uniformity and resistivity of thin tungsten films
ActiveUS7655567B1Low resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGas phaseNucleation
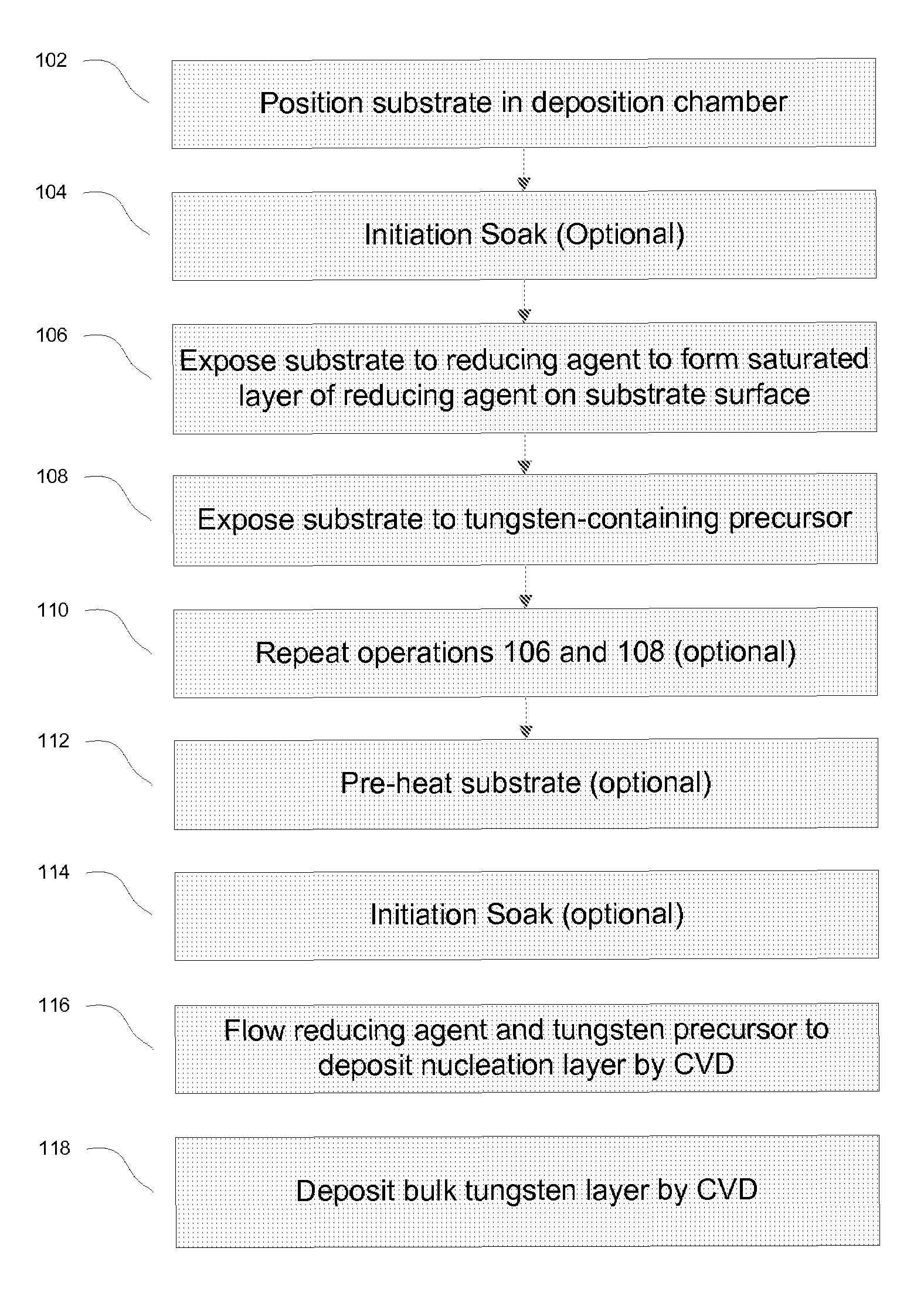
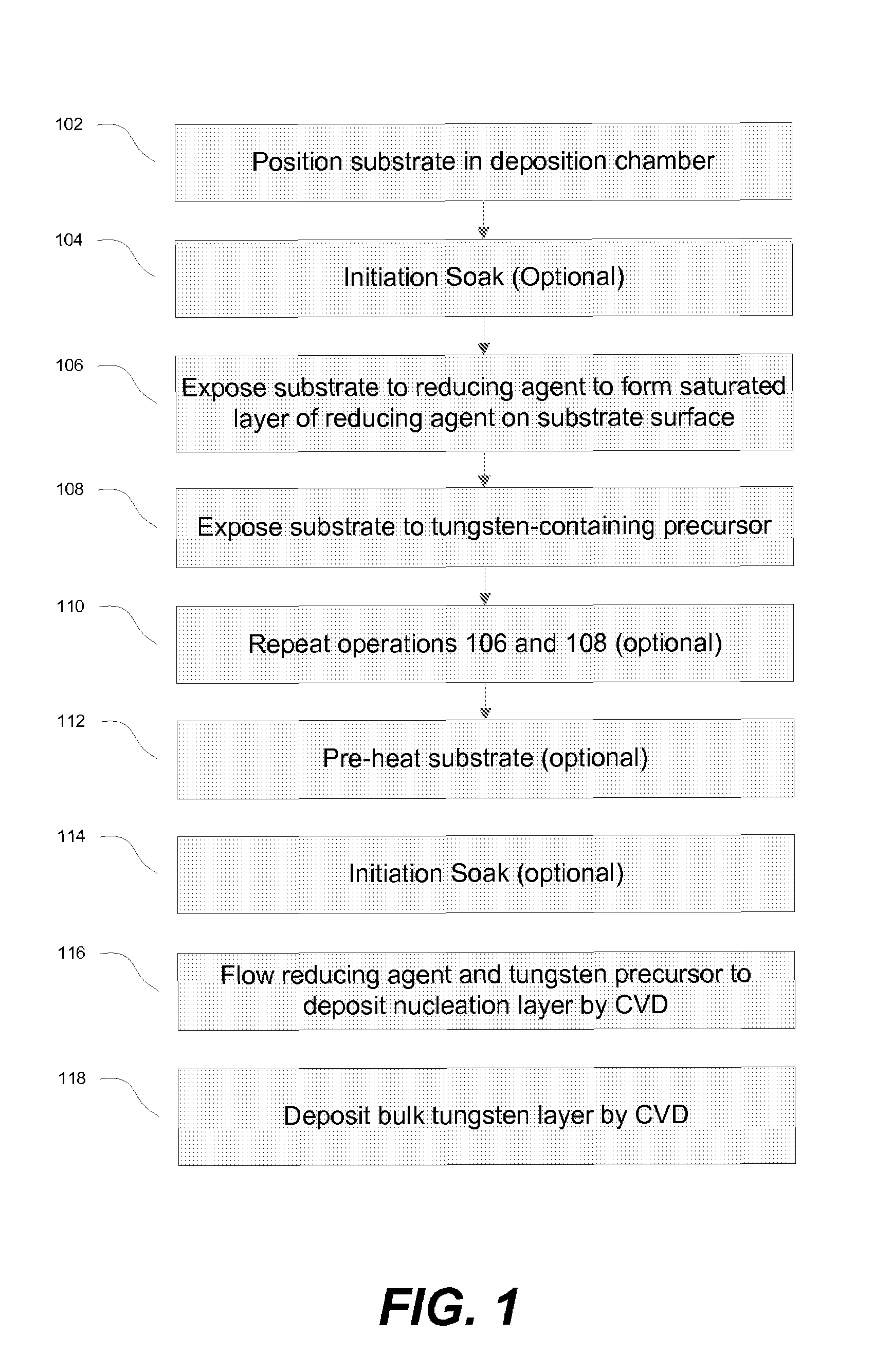
The methods described herein relate to deposition of low resistivity, highly conformal tungsten nucleation layers. These layers serve as a seed layers for the deposition of a tungsten bulk layer. The methods are particularly useful for tungsten plug fill in which tungsten is deposited in high aspect ratio features. The methods involve depositing a nucleation layer by a combined PNL and CVD process. The substrate is first exposed to one or more cycles of sequential pulses of a reducing agent and a tungsten precursor in a PNL process. The nucleation layer is then completed by simultaneous exposure of the substrate to a reducing agent and tungsten precursor in a chemical vapor deposition process. In certain embodiments, the process is performed without the use of a borane as a reducing agent.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method for forming tungsten contacts and interconnects with small critical dimensions
InactiveUS20100267230A1High aspect ratio featurePromote migrationLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceGas phase
Provided are methods of void-free tungsten fill of high aspect ratio features. According to various embodiments, the methods involve a reduced temperature chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process to fill the features with tungsten. In certain embodiments, the process temperature is maintained at less than about 350° C. during the chemical vapor deposition to fill the feature. The reduced-temperature CVD tungsten fill provides improved tungsten fill in high aspect ratio features, provides improved barriers to fluorine migration into underlying layers, while achieving similar thin film resistivity as standard CVD fill. Also provided are methods of depositing thin tungsten films having low-resistivity. According to various embodiments, the methods involve performing a reduced temperature low resistivity treatment on a deposited nucleation layer prior to depositing a tungsten bulk layer and / or depositing a bulk layer via a reduced temperature CVD process followed by a high temperature CVD process.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods for growing low-resistivity tungsten film
InactiveUS20080124926A1Control thicknessGood step coverageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingBoron containingImproved method
Improved methods for depositing low resistivity tungsten films are provided. The methods involve depositing a tungsten nucleation layer on a substrate and then depositing a tungsten bulk layer over the tungsten nucleation layer to form the tungsten film. The methods provide precise control of the nucleation layer thickness and improved step coverage. According to various embodiments, the methods involve controlling thickness and / or improving step coverage by exposing the substrate to pulse nucleation layer (PNL) cycles at low temperature. Also in some embodiments, the methods may improve resistivity by using a high temperature PNL cycle of a boron-containing species and a tungsten-containing precursor to finish forming the tungsten nucleation layer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Sacrificial erosion control features for chemical-mechanical polishing process
InactiveUS6087733ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTungsten filmCompound (substance)
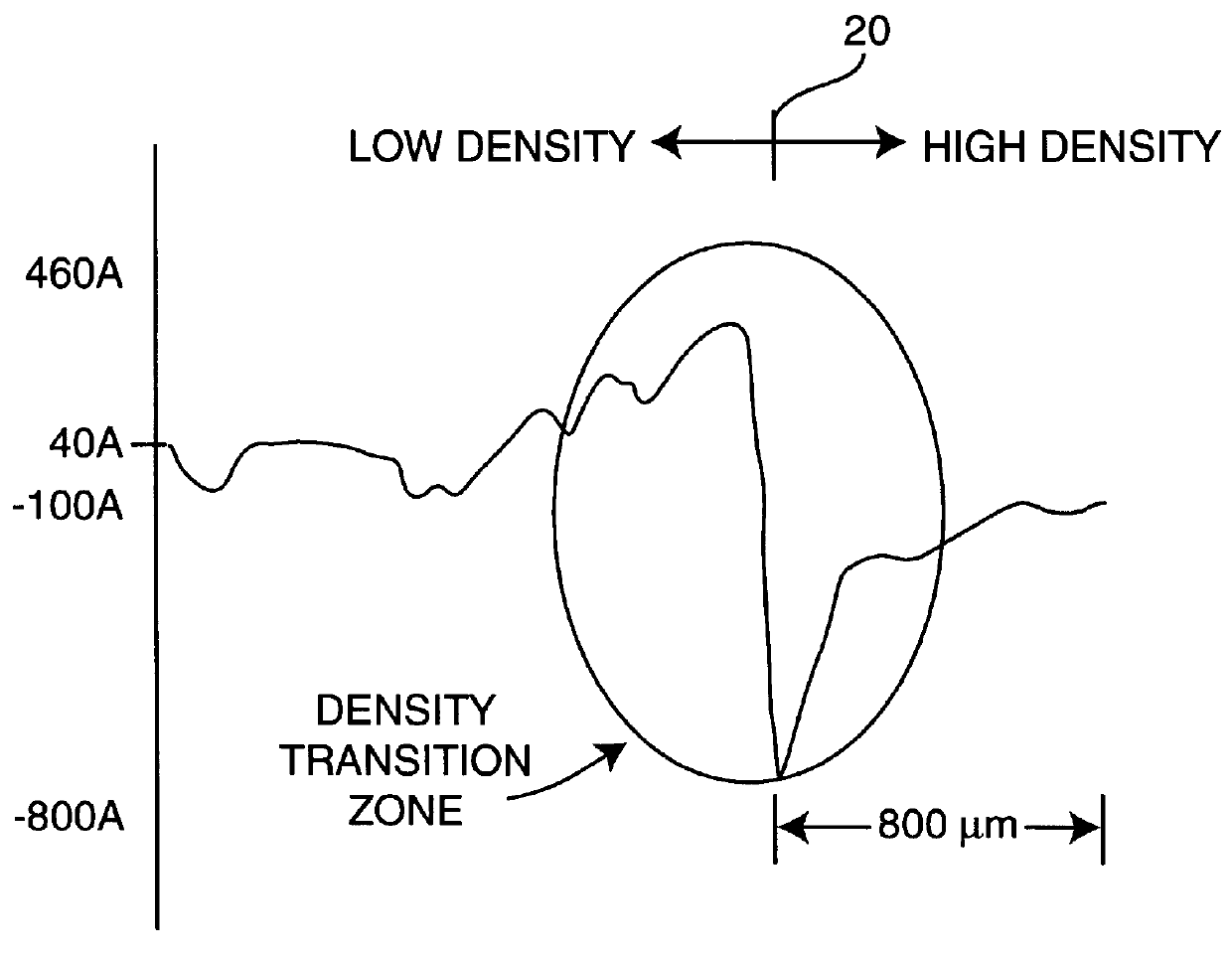
A method and apparatus for compensating for the effects of nonuniform planarization in chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP) such as the erosion occurring from the removal of titanium nitride / tungsten films is disclosed. In the context of alignment marks, dummy marks are disposed on both sides of the actual alignment marks providing a similar feature density as the alignment marks. During the CMP, the dummy marks reside in the area of nonuniform erosion, leaving the actual marks in an area of uniform erosion. The present invention may also be used to control underlayer erosion variations in the high feature density device areas adjacent to the low feature density open areas by providing dummy features in the low feature density areas.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods for growing low-resistivity tungsten for high aspect ratio and small features
InactiveUS7955972B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenGas phase
The present invention addresses this need by providing methods for depositing low resistivity tungsten films in small features and features having high aspect ratios. The methods involve depositing very thin tungsten nucleation layers by pulsed nucleation layer (PNL) processes and then using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to deposit a tungsten layer to fill the feature. Depositing the tungsten nucleation layer involves exposing the substrate to alternating pulses of a boron-containing reducing agent and a tungsten-containing precursor without using any hydrogen gas, e.g., as a carrier or background gas. Using this process, a conformal tungsten nucleation layer can be deposited to a thickness as small as about 10 Angstroms. The feature may then be wholly or partially filled with tungsten by a hydrogen reduction chemical vapor deposition process. Resistivities of about 14 μΩ-cm for a 500 Angstrom film may be obtained.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Vapor deposition of tungsten materials
InactiveUS7732327B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseTungsten nitride
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
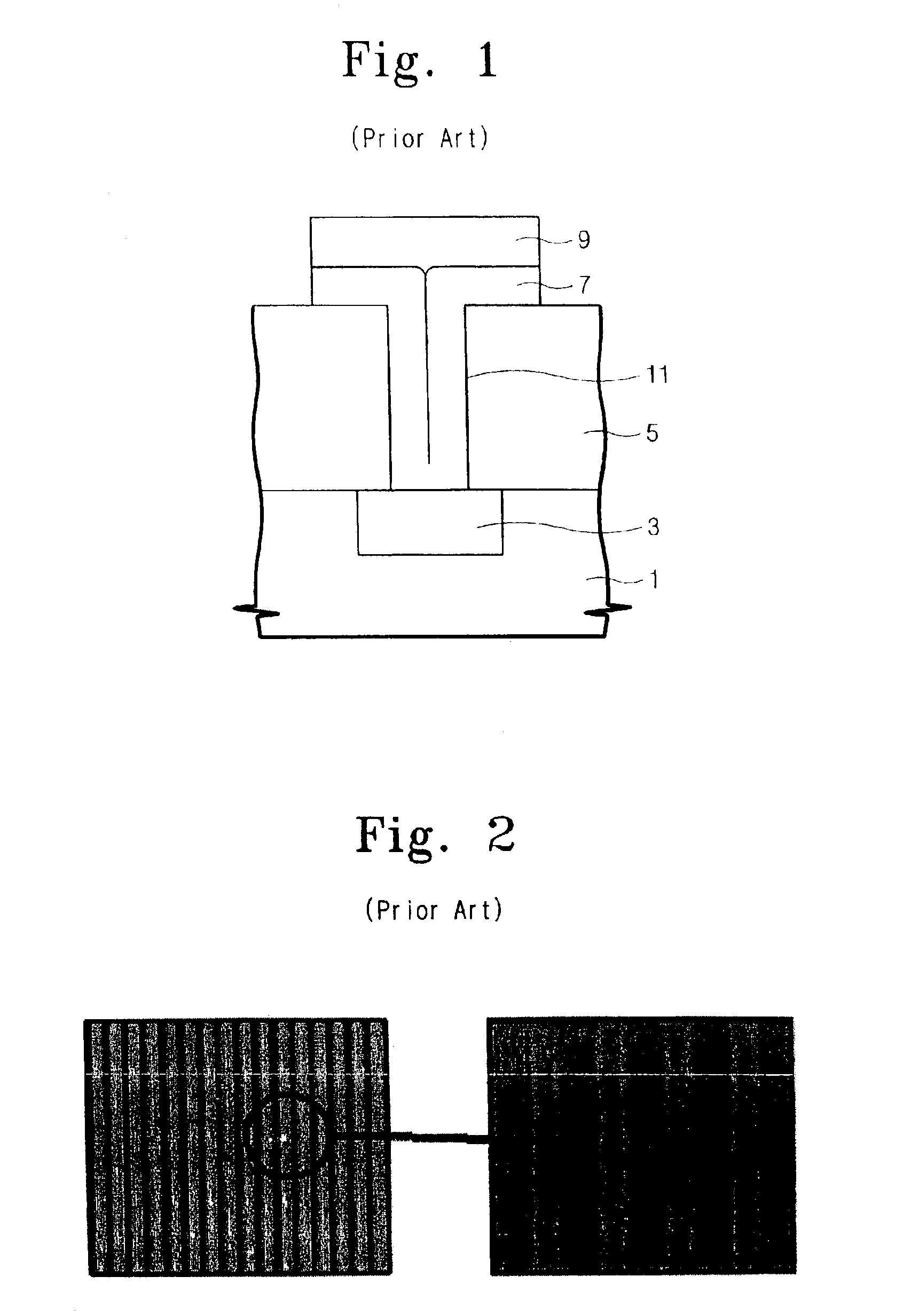
Method for forming an electrical interconnection providing improved surface morphology of tungsten
InactiveUS6908848B2Mitigating and eliminating and undesirableGood step coverageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRough surfaceInterconnection
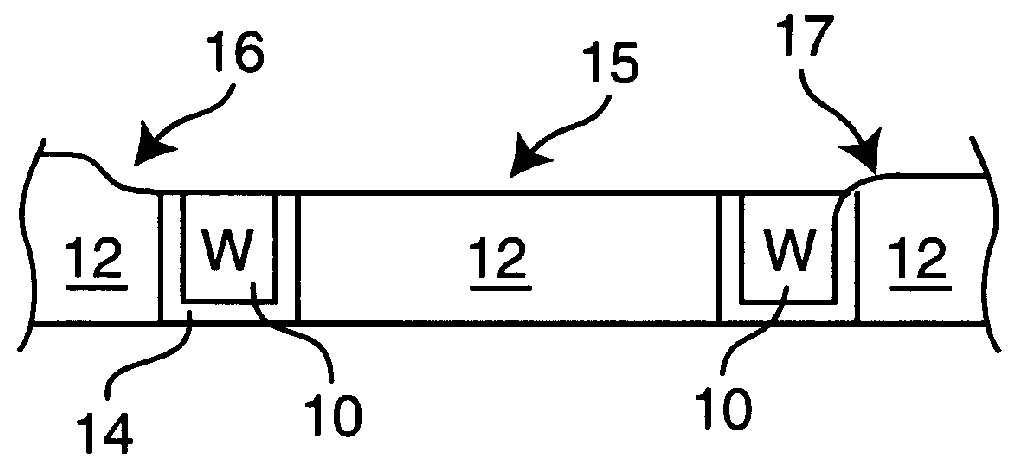
In a fabrication method for forming an electrical interconnection of CVD tungsten film, a contact hole is formed in a dielectric layer. A lower conductive layer is formed in the contact hole and over the dielectric layer. A portion of the lower conductive layer is removed. As a result, the dielectric layer is exposed. An upper conductive layer is formed over the lower conductive layer and over the dielectric layer. The lower conductive layer has a rough surface and the upper conductive layer has a smooth surface. In this manner, following patterning of conductive stripes over the conductive layer, residue is mitigated, and thus, inadvertent interconnection of neighboring stripes is eliminated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
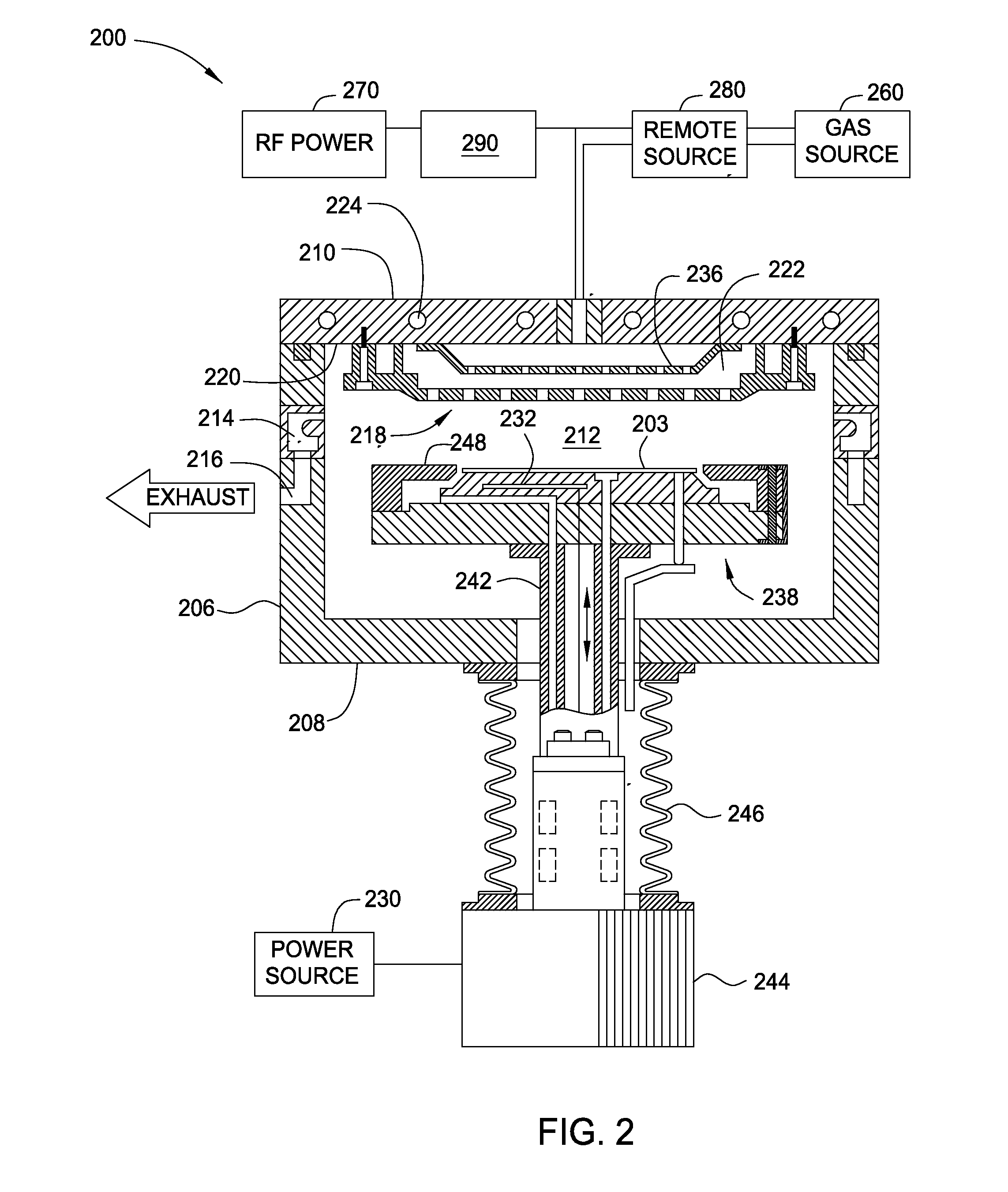
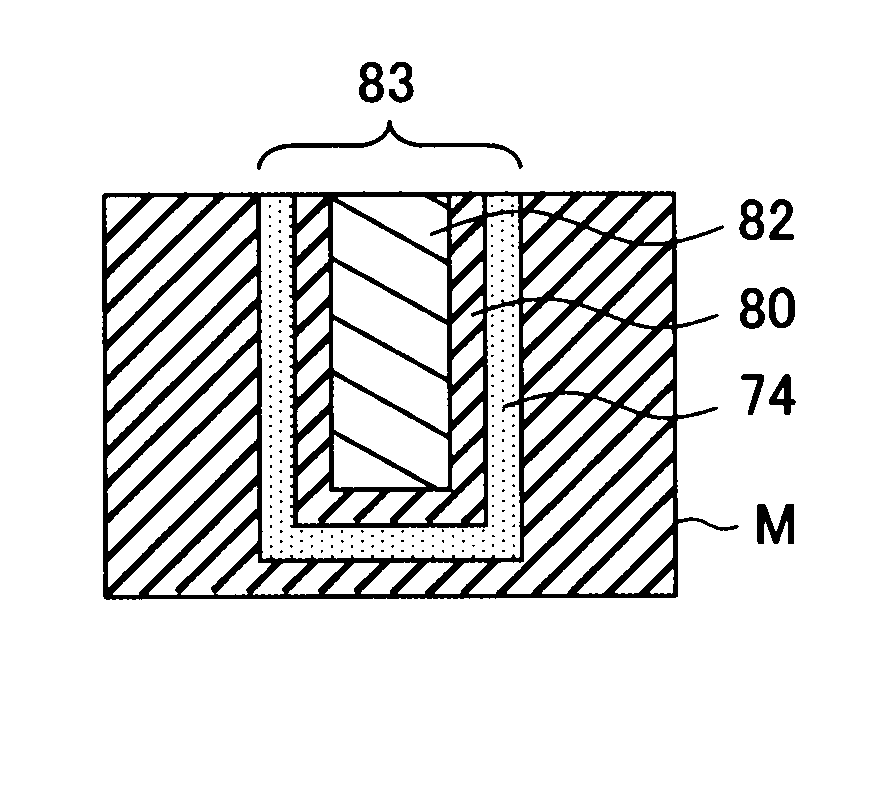
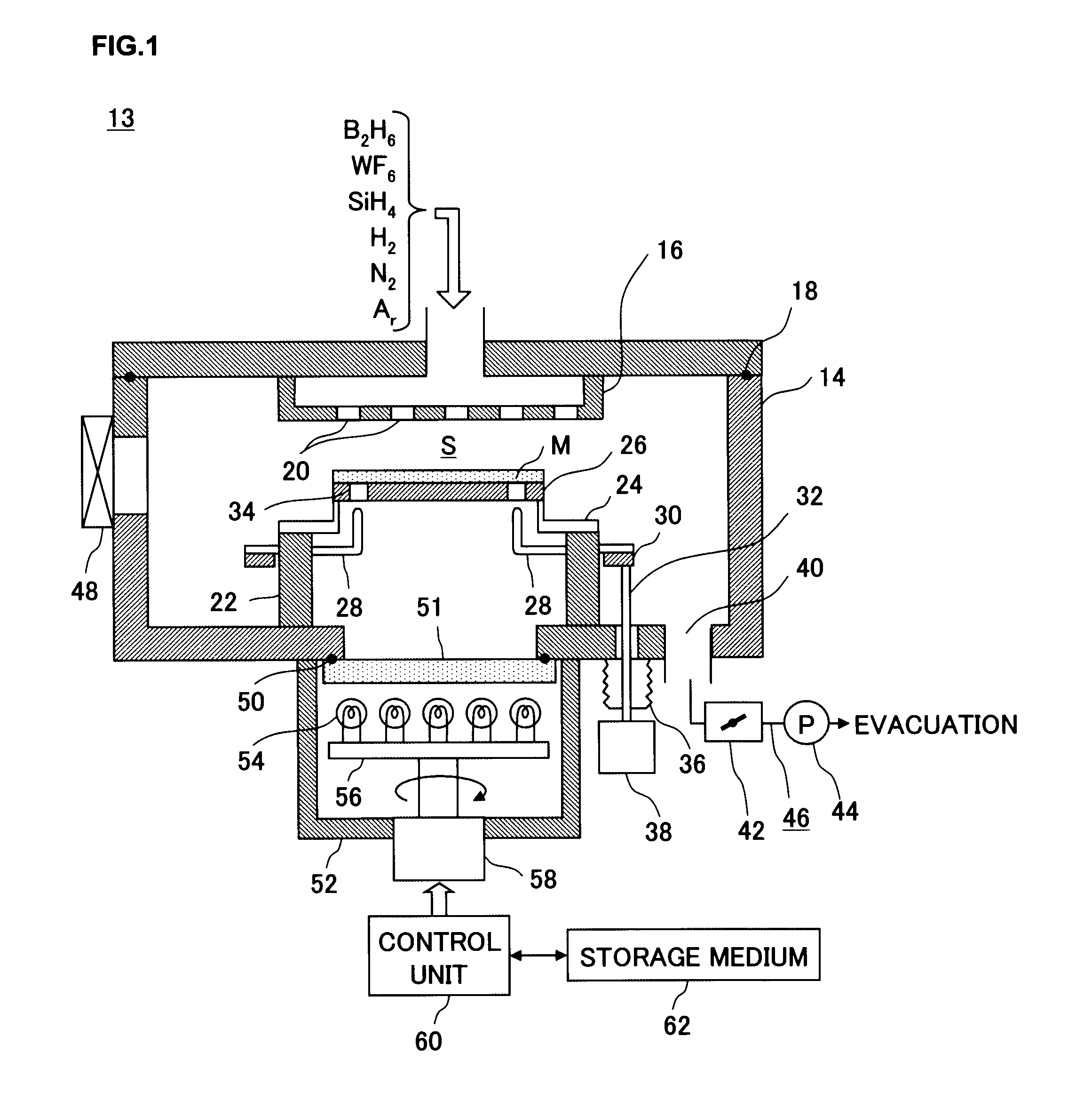
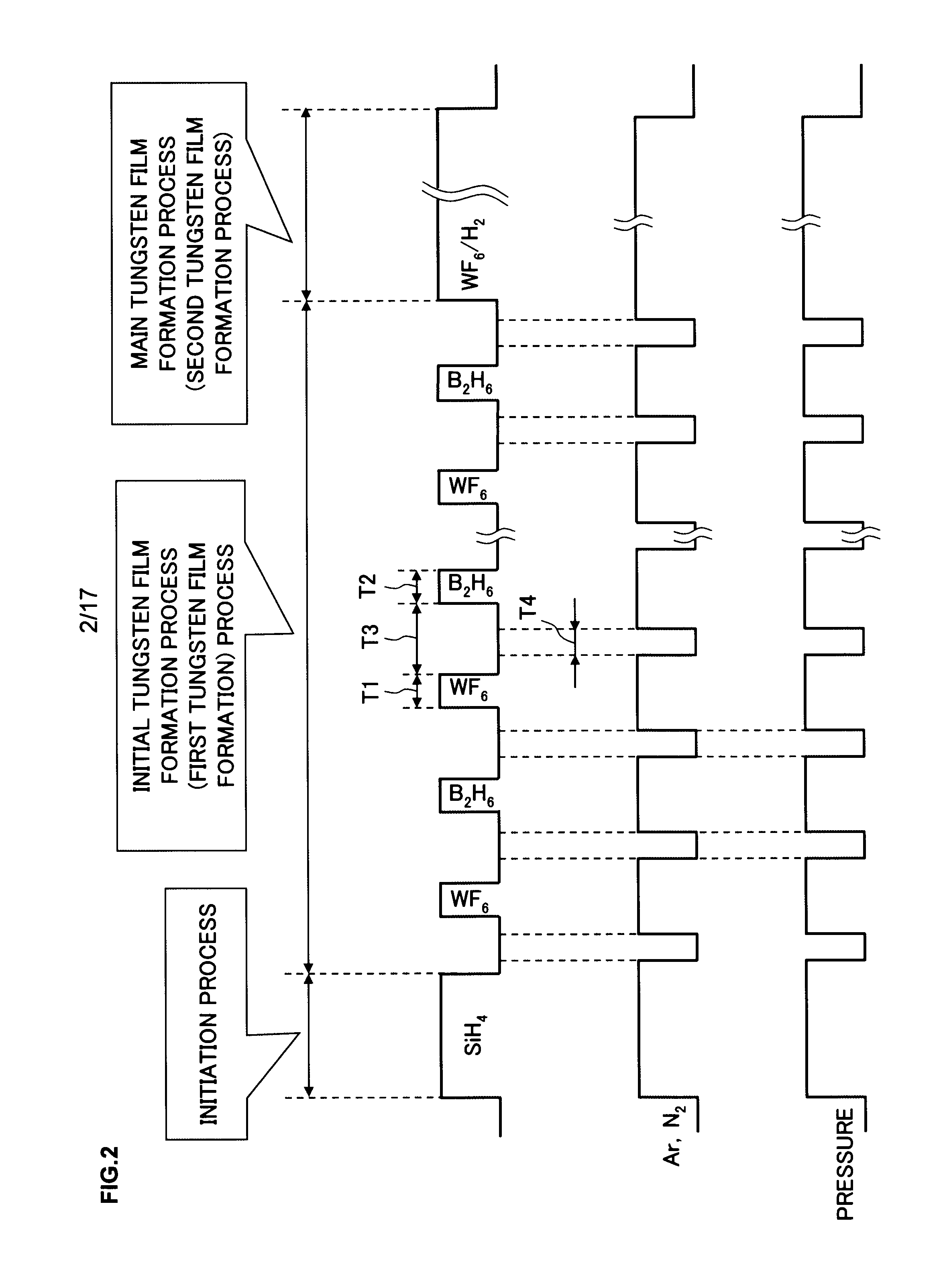
Method for forming tungsten film, film-forming apparatus, storage medium and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20090045517A1Specific resistance of the tungsten filmInhibition formationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesProduct gasGas supply
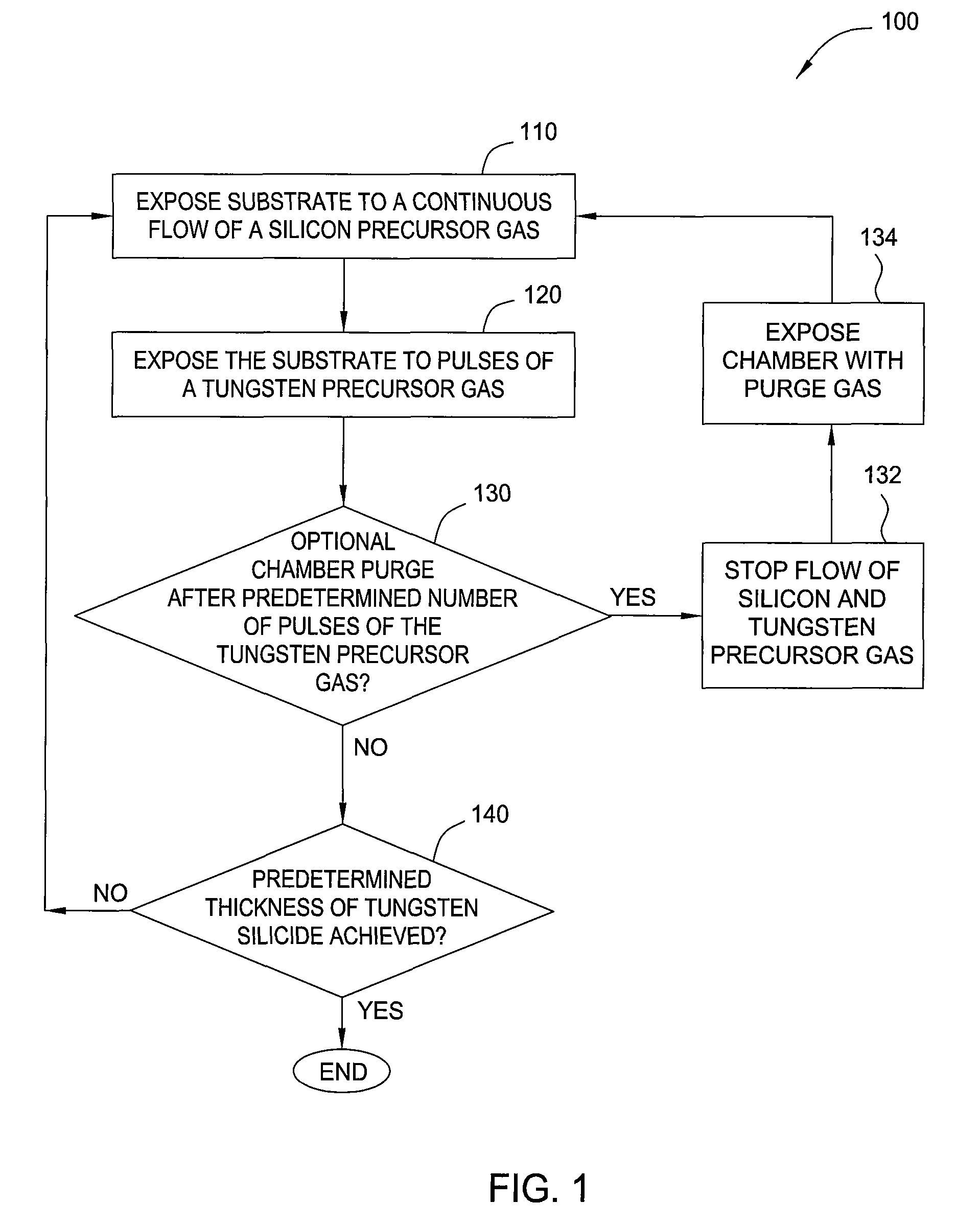
A tungsten film with a lower specific resistance and a lower fluorine concentration over its boundary with the base barrier layer, which adheres to the barrier layer with a high level of reliability, compared to tungsten films formed through methods in the related art, is formed.The tungsten film is formed through a process in which a silicon-containing gas is delivered to a wafer M placed within a processing container 14 and a process executed after the silicon-containing gas supply process, in which a first tungsten film 70 is formed by alternately executing multiple times, a tungsten-containing gas supply step for supplying a tungsten-containing gas and a hydrogen compound gas supply step for supplying a hydrogen compound gas with no silicon content with a purge step in which an inert gas is supplied into the processing container and / or an evacuation step for evacuating the processing container executed between the tungsten-containing gas supply step and the hydrogen compound gas supply step.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Methods for forming all tungsten contacts and lines
InactiveUS8053365B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNucleationTungsten film
Novel low-resistivity tungsten film stack schemes and methods for depositing them are provided. The film stacks include a mixed tungsten / tungsten-containing compound (e.g., WC) layer as a base for deposition of tungsten nucleation and / or bulk layers. According to various embodiments, these tungsten rich layers may be used as barrier and / or adhesion layers in tungsten contact metallization and bitlines. Deposition of the tungsten-rich layers involves exposing the substrate to a halogen-free organometallic tungsten precursor. The mixed tungsten / tungsten carbide layer is a thin, low resistivity film with excellent adhesion and a good base for subsequent tungsten plug or line formation.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods for growing low-resistivity tungsten film
InactiveUS20100035427A1Low resistivityGood step coverageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingBoron containingLayer thickness
Improved methods for depositing low resistivity tungsten films are provided. The methods involve depositing a tungsten nucleation layer on a substrate and then depositing a tungsten bulk layer over the tungsten nucleation layer to form the tungsten film. The methods provide precise control of the nucleation layer thickness and improved step coverage. According to various embodiments, the methods involve controlling thickness and / or improving step coverage by exposing the substrate to pulse nucleation layer (PNL) cycles at low temperature. Also in some embodiments, the methods may improve resistivity by using a high temperature PNL cycle of a boron-containing species and a tungsten-containing precursor to finish forming the tungsten nucleation layer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods for growing low-resistivity tungsten for high aspect ratio and small features
InactiveUS20110223763A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenGas phase
The present invention addresses this need by providing methods for depositing low resistivity tungsten films in small features and features having high aspect ratios. The methods involve depositing very thin tungsten nucleation layers by pulsed nucleation layer (PNL) processes and then using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to deposit a tungsten layer to fill the feature. Depositing the tungsten nucleation layer involves exposing the substrate to alternating pulses of a boron-containing reducing agent and a tungsten-containing precursor without using any hydrogen gas, e.g., as a carrier or background gas. Using this process, a conformal tungsten nucleation layer can be deposited to a thickness as small as about 10 Angstroms. The feature may then be wholly or partially filled with tungsten by a hydrogen reduction chemical vapor deposition process. Resistivities of about 14 μΩ-cm for a 500 Angstrom film may be obtained.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods for forming all tungsten contacts and lines
ActiveUS20120040530A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNucleationTungsten film
Novel low-resistivity tungsten film stack schemes and methods for depositing them are provided. The film stacks include a mixed tungsten / tungsten-containing compound (e.g., WC) layer as a base for deposition of tungsten nucleation and / or bulk layers. According to various embodiments, these tungsten rich layers may be used as barrier and / or adhesion layers in tungsten contact metallization and bitlines. Deposition of the tungsten-rich layers involves exposing the substrate to a halogen-free organometallic tungsten precursor. The mixed tungsten / tungsten carbide layer is a thin, low resistivity film with excellent adhesion and a good base for subsequent tungsten plug or line formation.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com