Method for forming tungsten contacts and interconnects with small critical dimensions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Introduction
[0025]In the following description, numerous specific details are set forth in order to provide a thorough understanding of the present invention, which pertains to forming thin tungsten films. Modifications, adaptations or variations of specific methods and structures shown and discussed herein will be apparent to those skilled in the art and are within the scope of this invention.
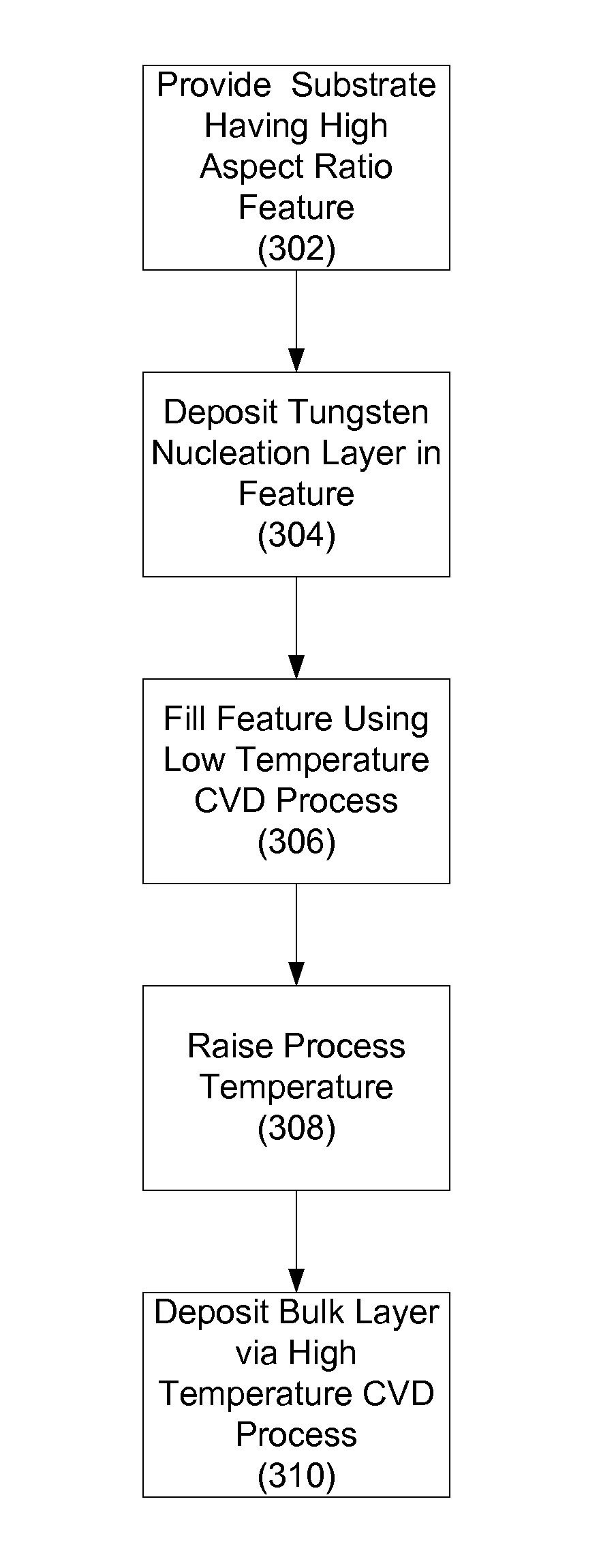
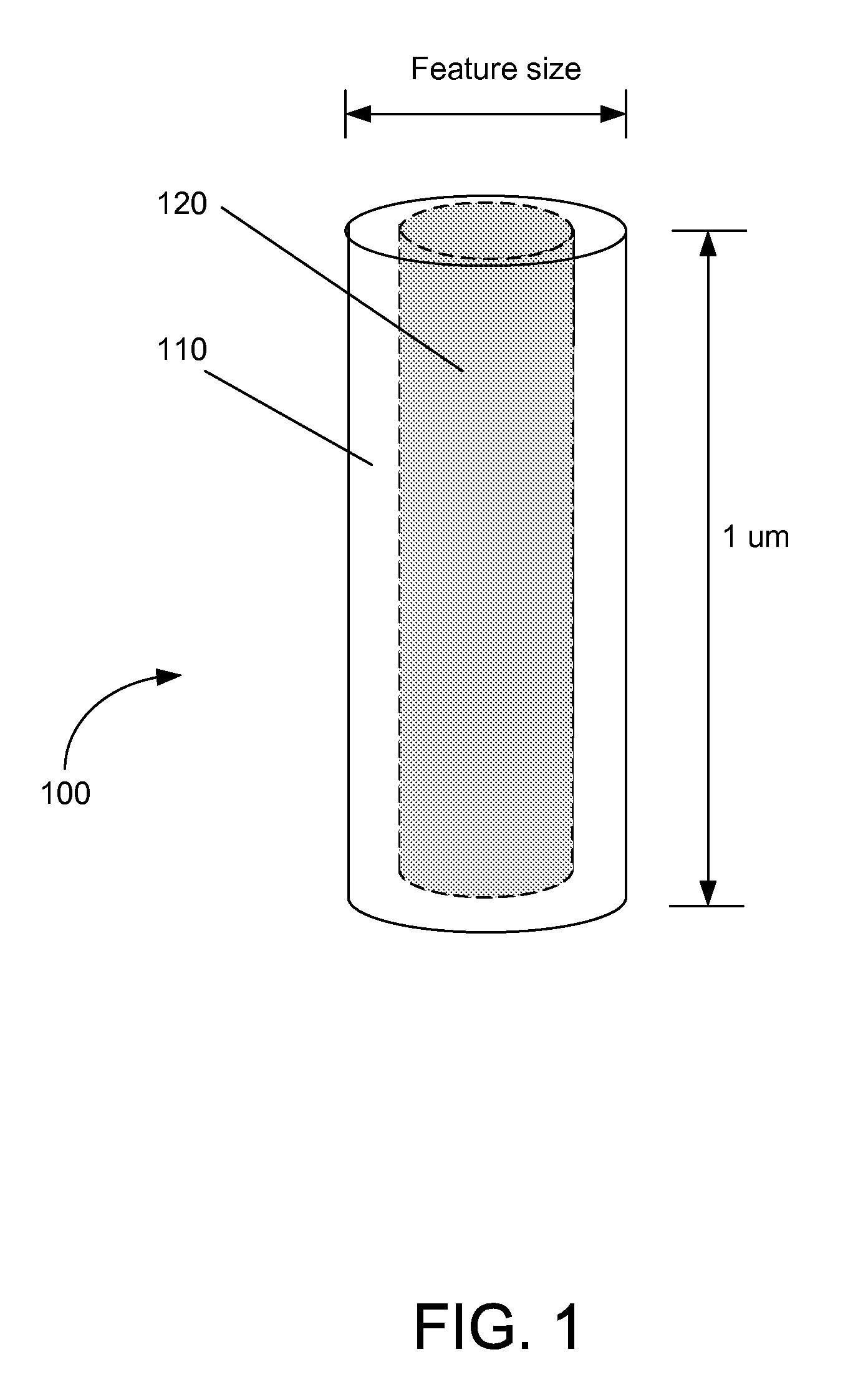
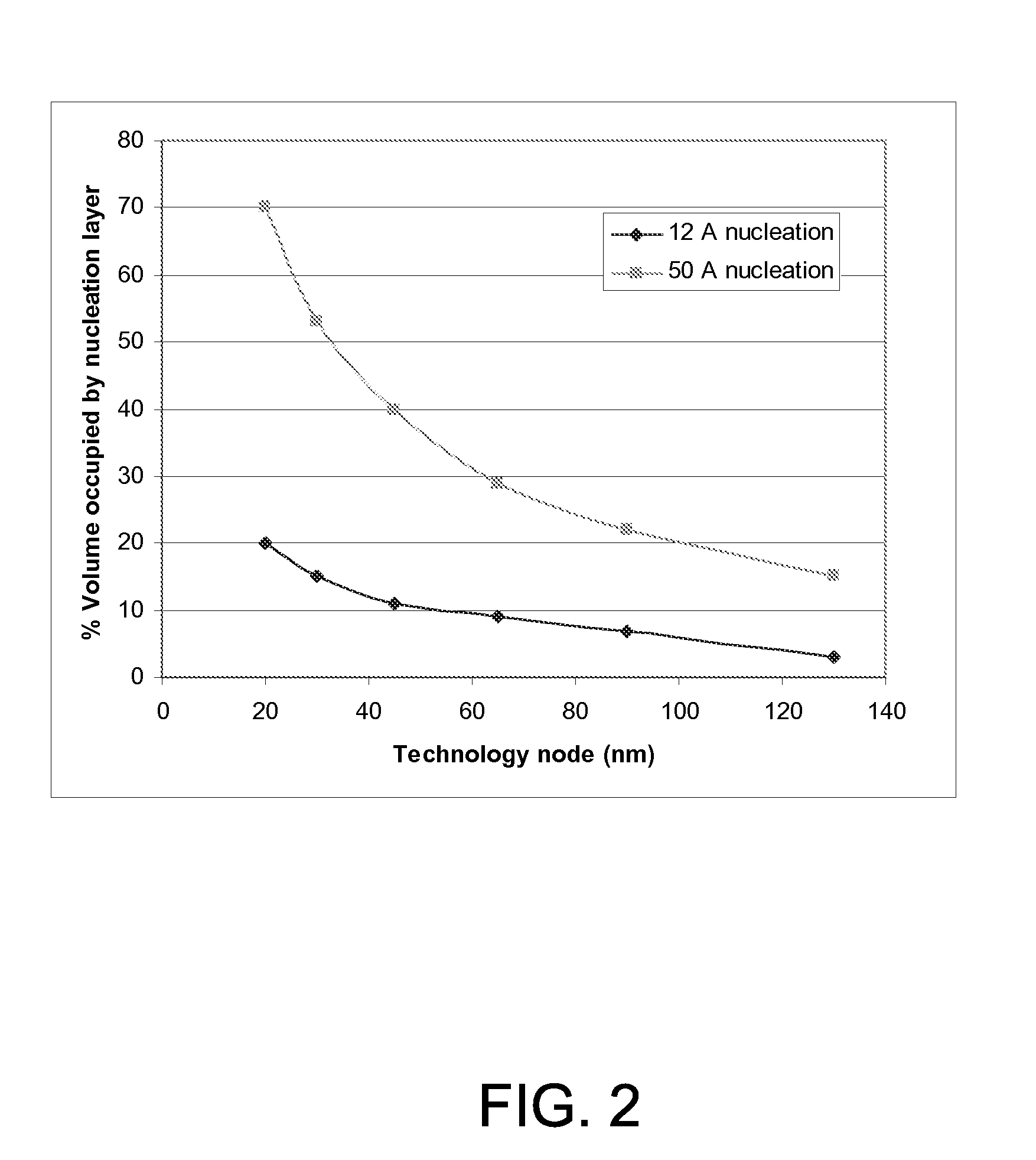
[0026]Extending tungsten to sub-32 nm technologies is critical to maintaining via / contact performance and reliability in both memory and logic devices. There are various challenges in tungsten fill as devices scale to smaller technology nodes. One challenge is preventing an increase in resistance due to the thinner films in contacts and vias. As features become smaller, the tungsten (W) contact or line resistance increases due to scattering effects in the thinner W film. While efficient tungsten deposition processes require tungsten nucleation layers, these layers typically have higher electri...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com