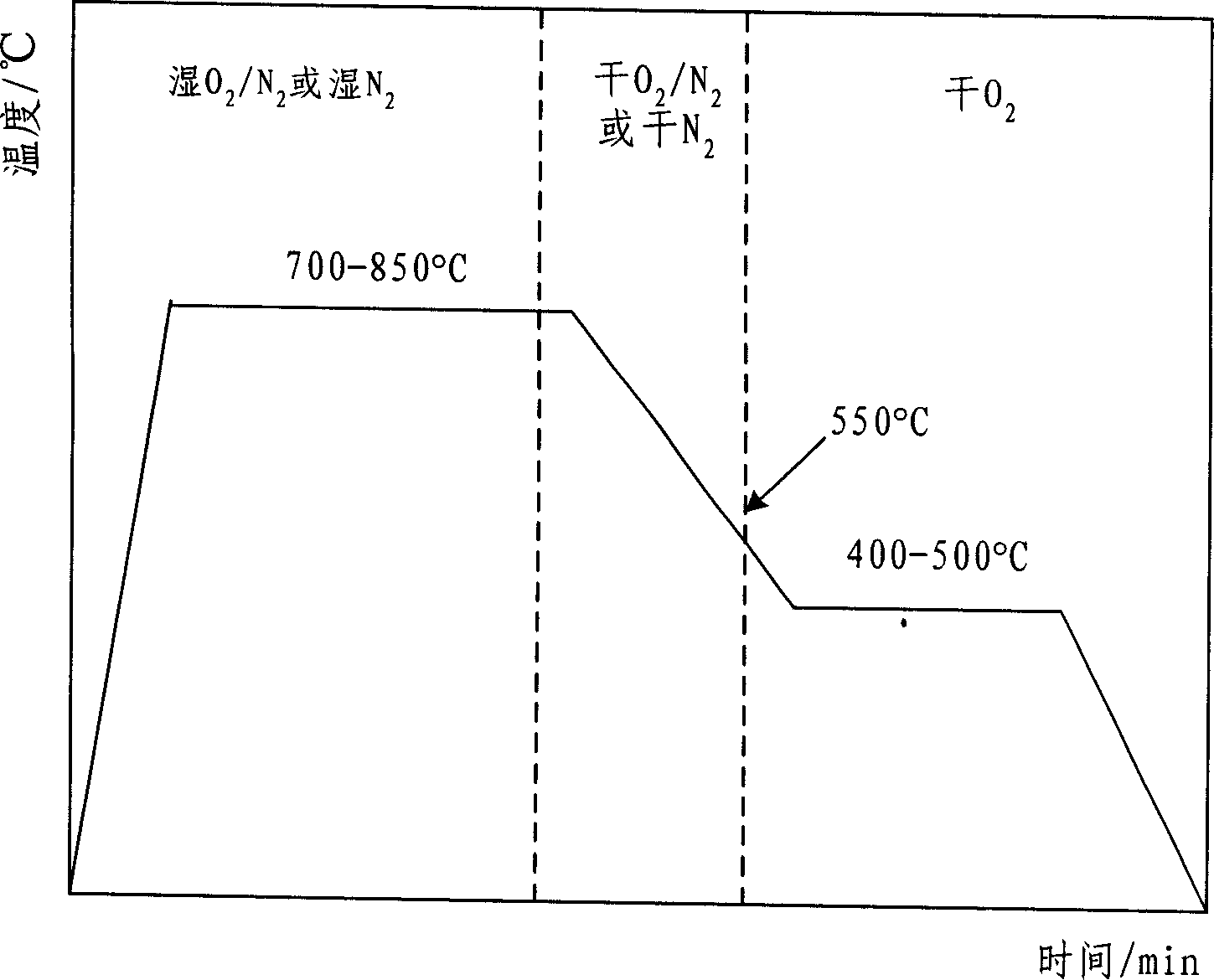
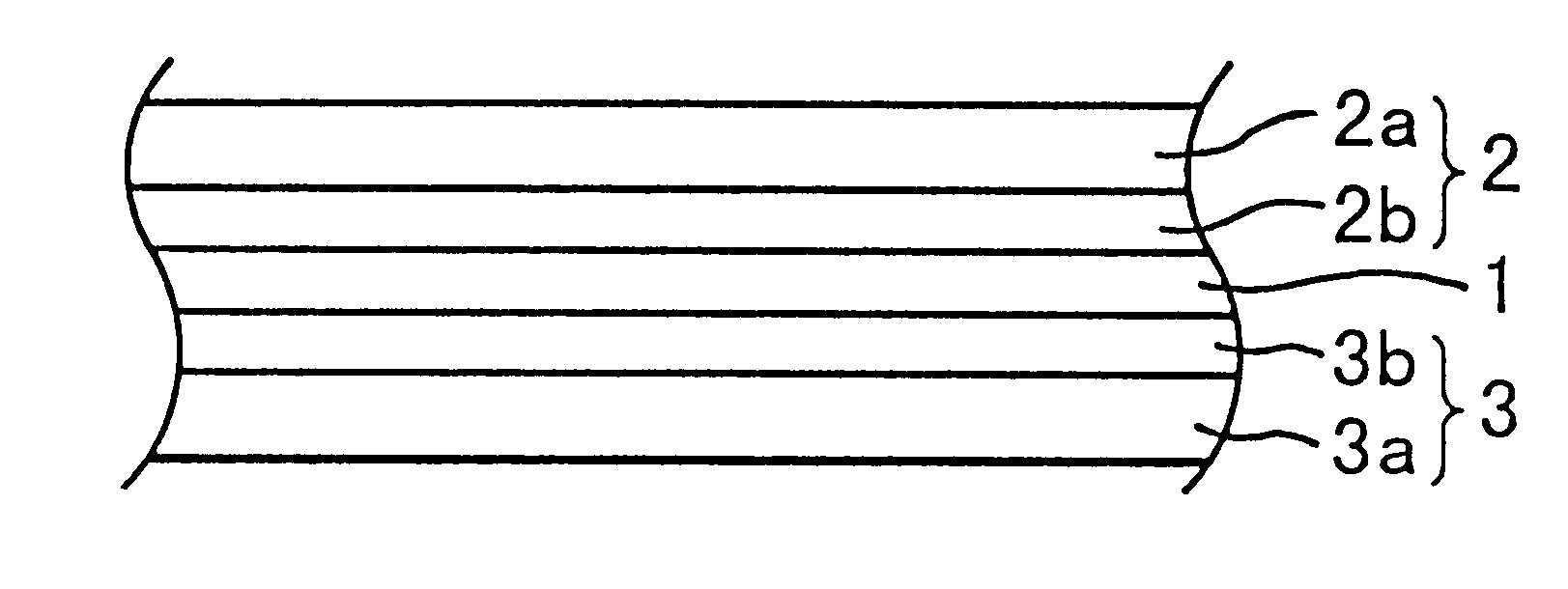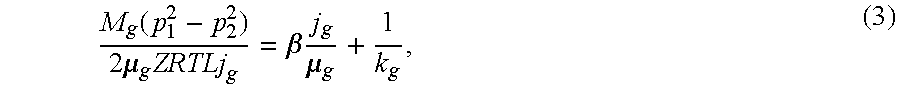Patents
Literature
191results about How to "Reduce fluorine content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
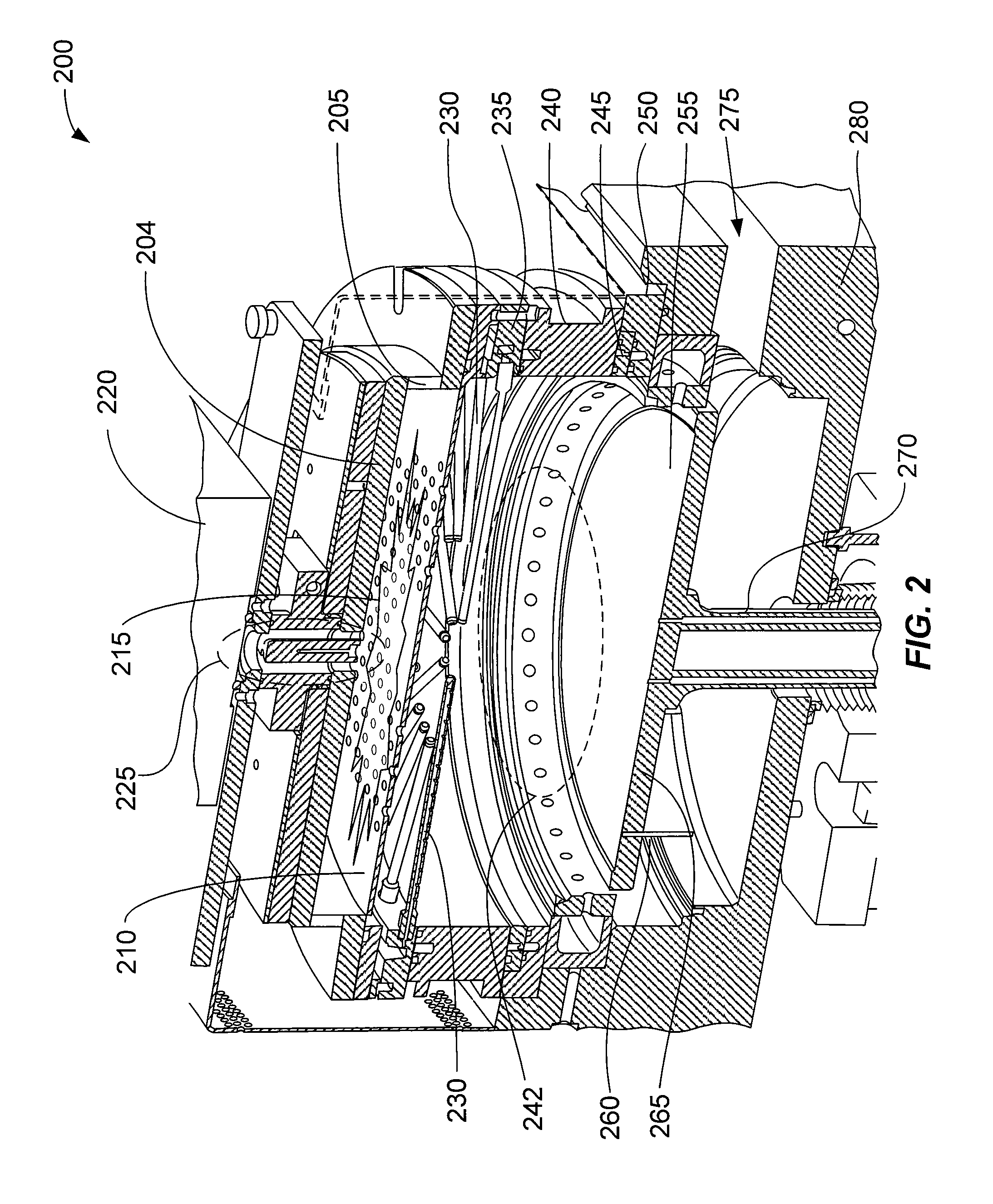
Flowable dielectric equipment and processes
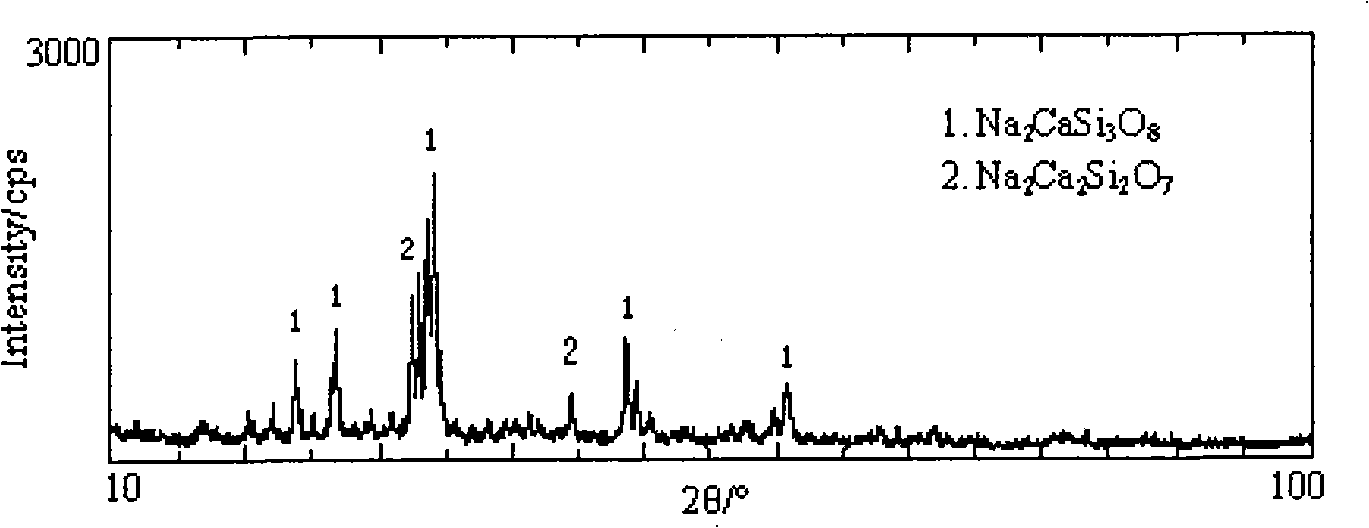
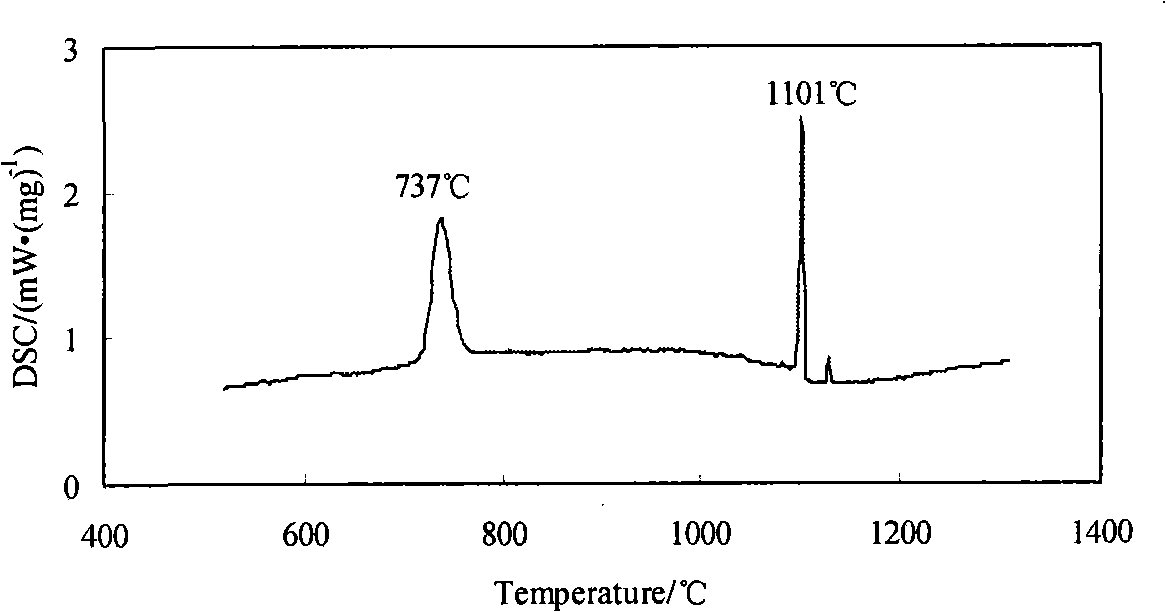
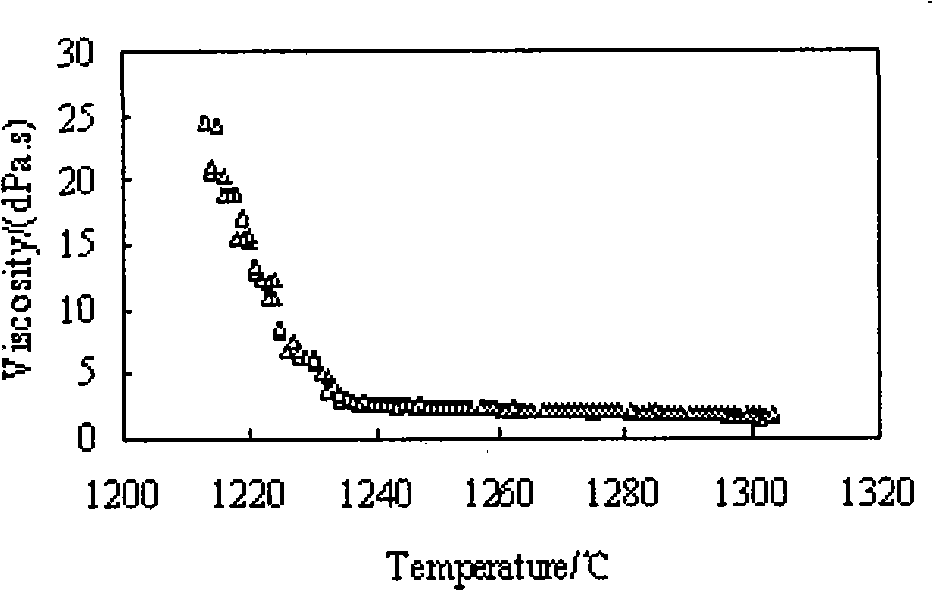
ActiveUS20090280650A1Reduce carbon contentReduce fluorine contentElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsDielectric layerMaterials science
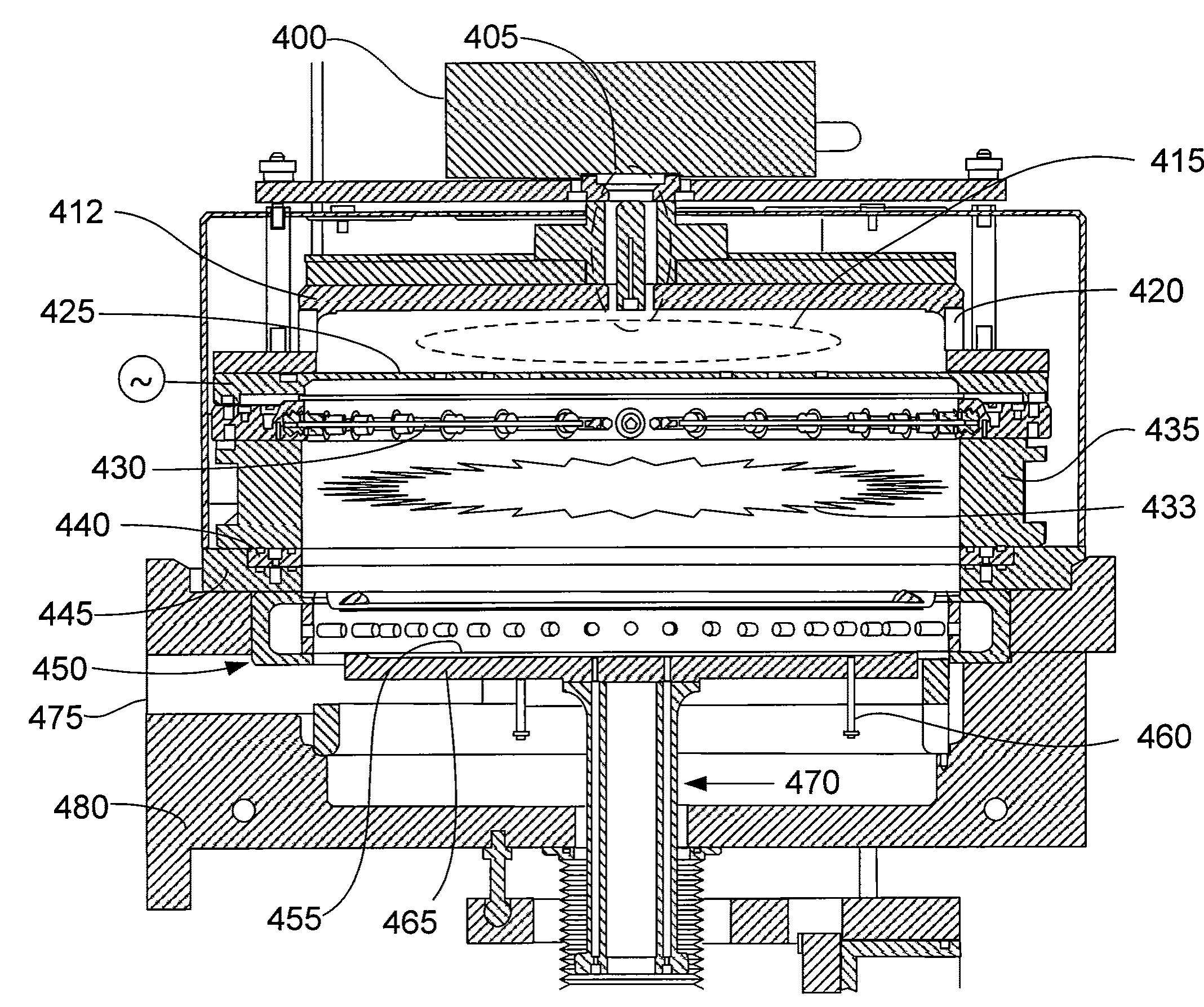
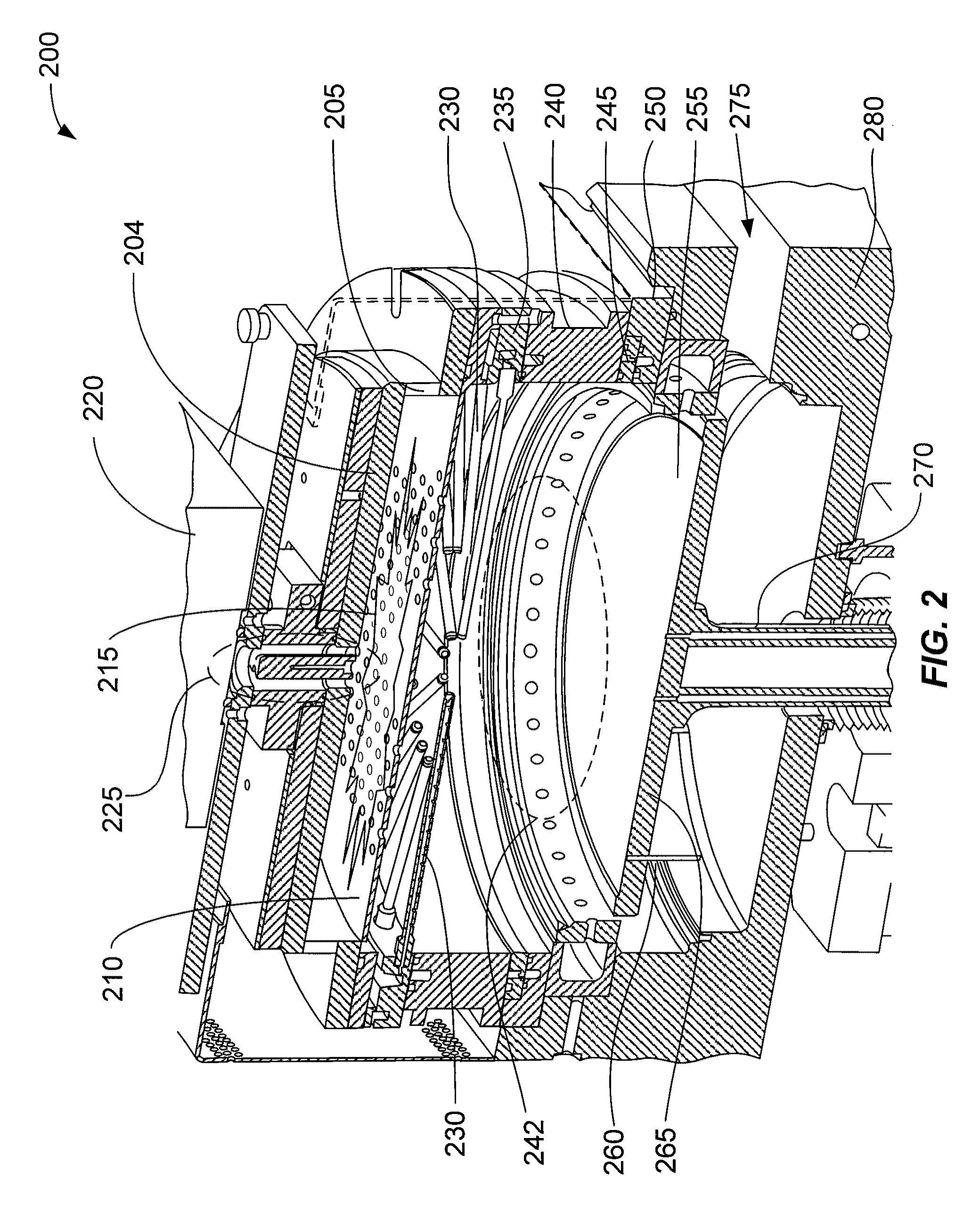
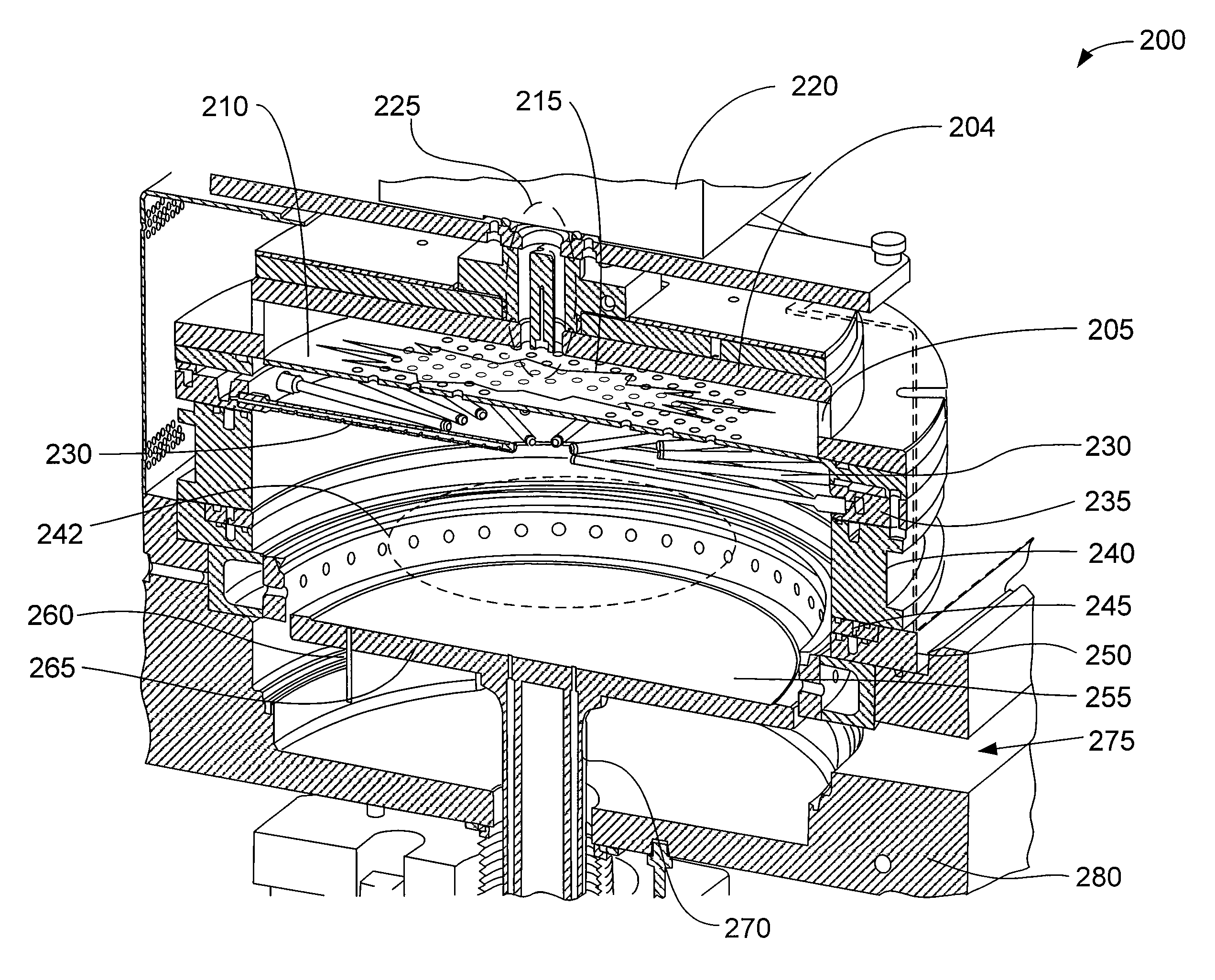
Methods of depositing and curing a dielectric material on a substrate are described. The methods may include the steps of providing a processing chamber partitioned into a first plasma region and a second plasma region, and delivering the substrate to the processing chamber, where the substrate occupies a portion of the second plasma region. The methods may further include forming a first plasma in the first plasma region, where the first plasma does not directly contact with the substrate, and depositing the dielectric material on the substrate to form a dielectric layer. One or more reactants excited by the first plasma are used in the deposition of the dielectric material. The methods may additional include curing the dielectric layer by forming a second plasma in the second plasma region, where one or more carbon-containing species is removed from the dielectric layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Flowable dielectric equipment and processes
InactiveUS20090277587A1Reduce carbon contentReduce fluorine contentElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaProcess engineering
Substrate processing systems are described that may include a processing chamber having an interior capable of holding an internal chamber pressure different from an external chamber pressure. The systems may also include a remote plasma system operable to generate a plasma outside the interior of the processing chamber. In addition, the systems may include a first process gas channel operable to transport a first process gas from the remote plasma system to the interior of the processing chamber, and a second process gas channel operable to transport a second process gas that is not treated by the remote plasma system. The second process gas channel has a distal end that opens into the interior of the processing chamber, and that is at least partially surrounded by the first process gas channel.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
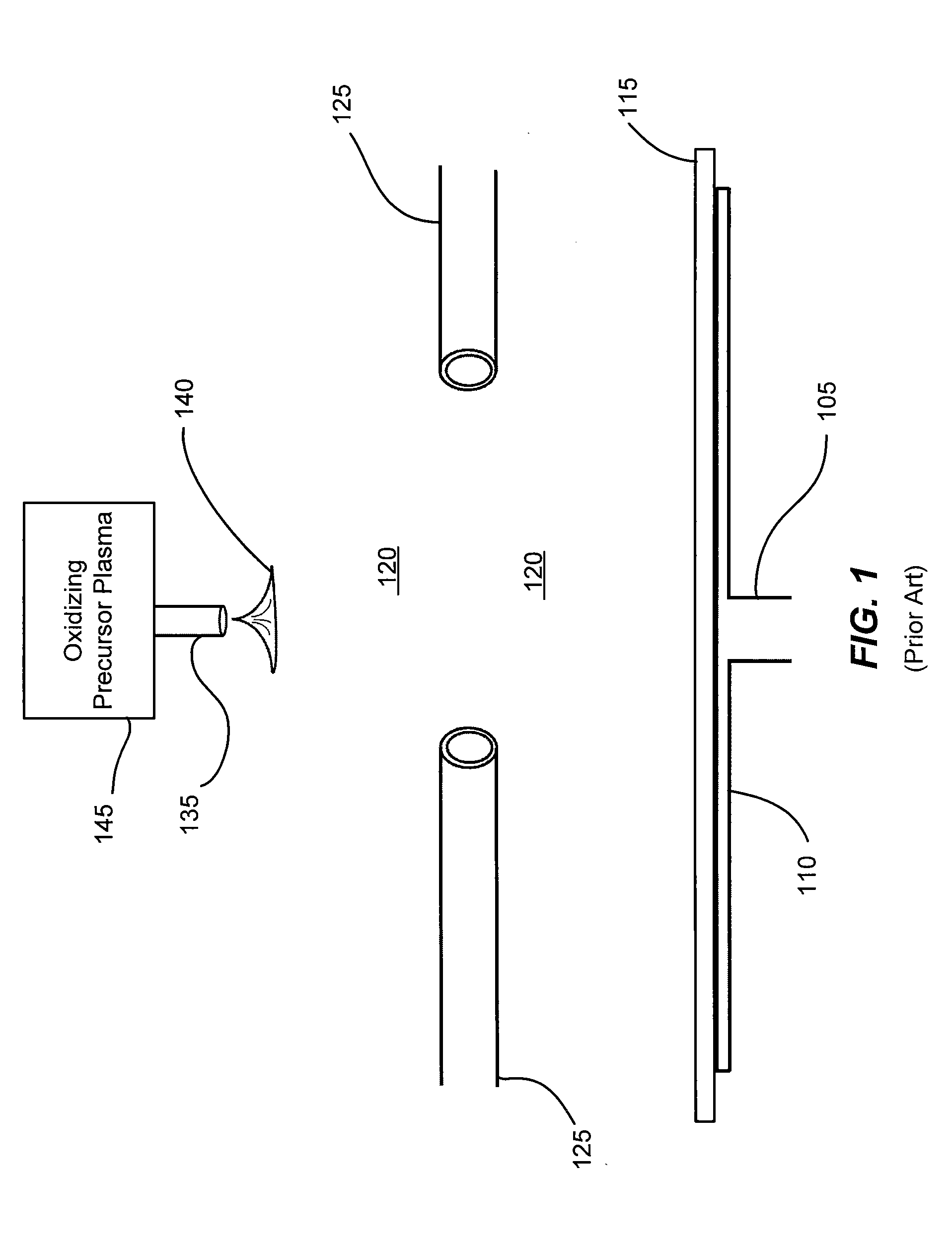
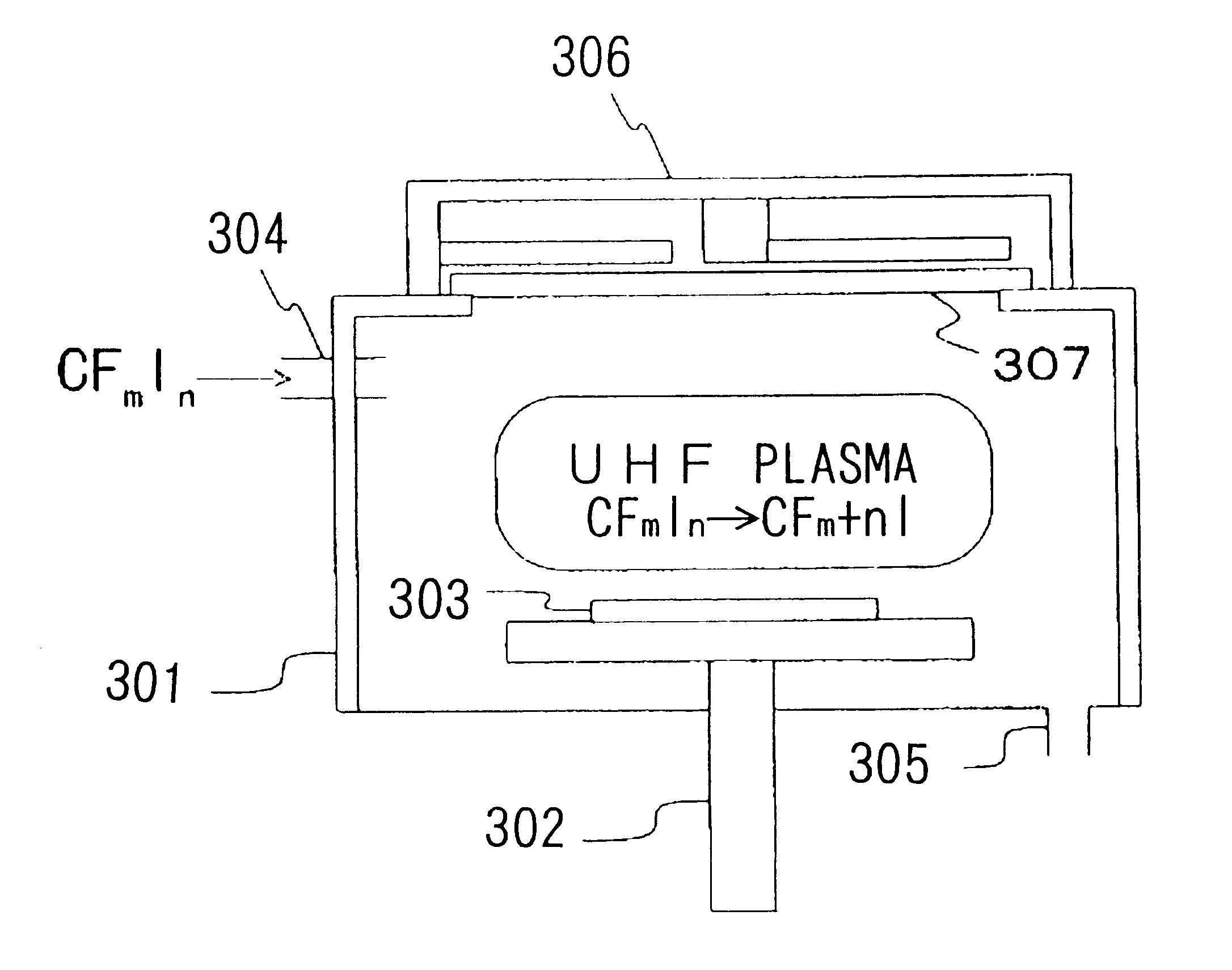
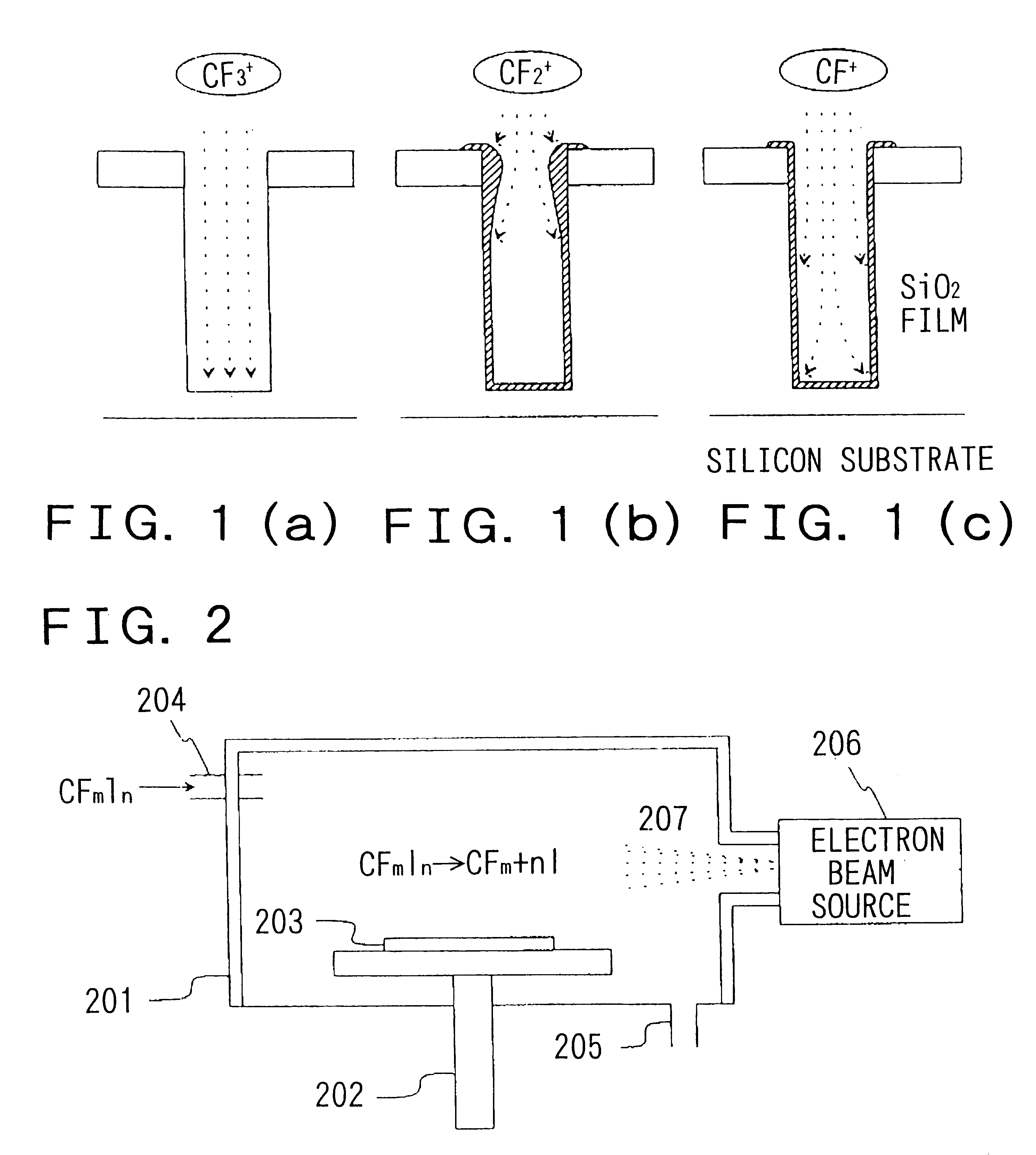
Process and apparatus for treating a substrate
InactiveUS6177147B1Increase freedomHigh accuracyElectric discharge heatingDecorative surface effectsHalogenIon
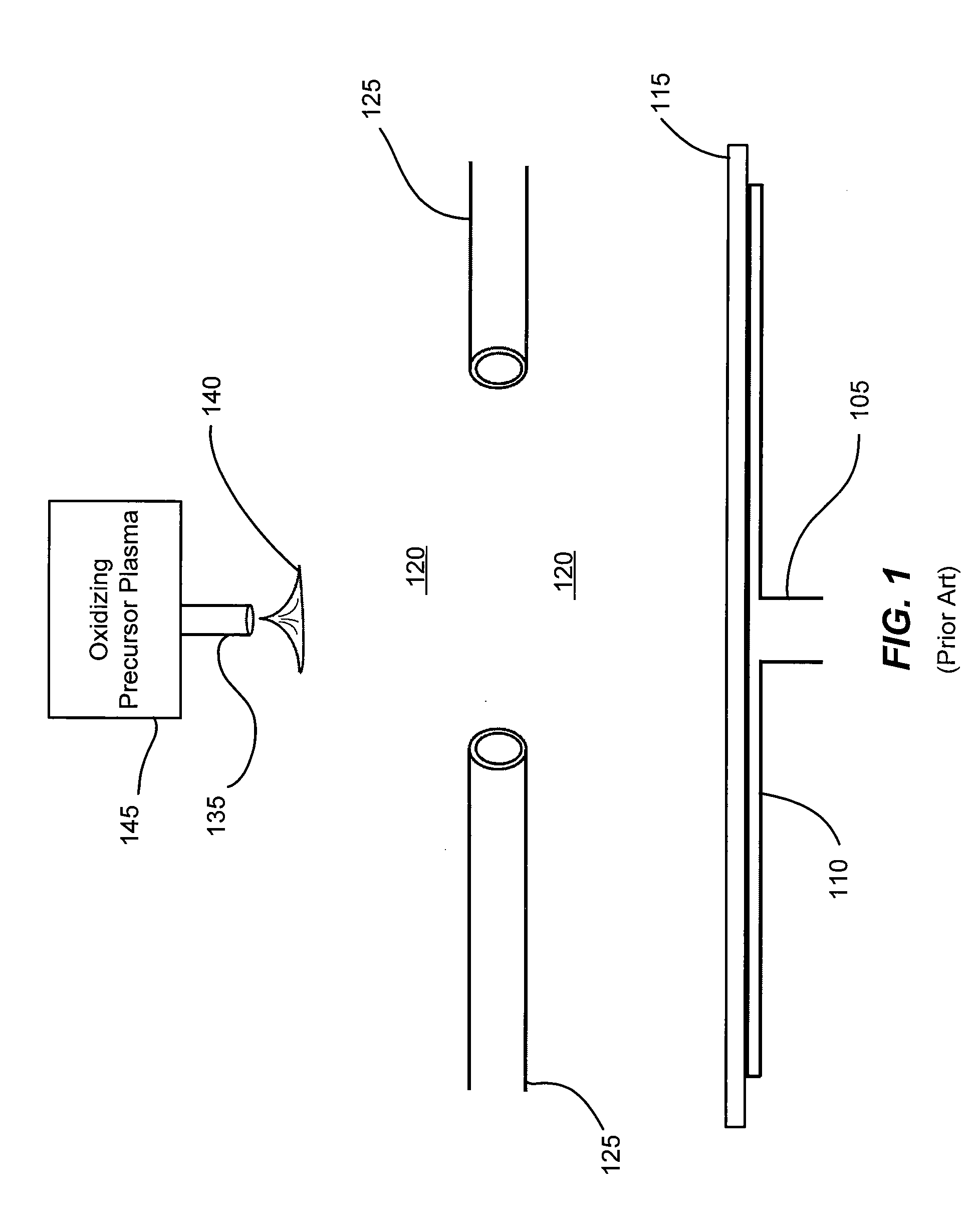
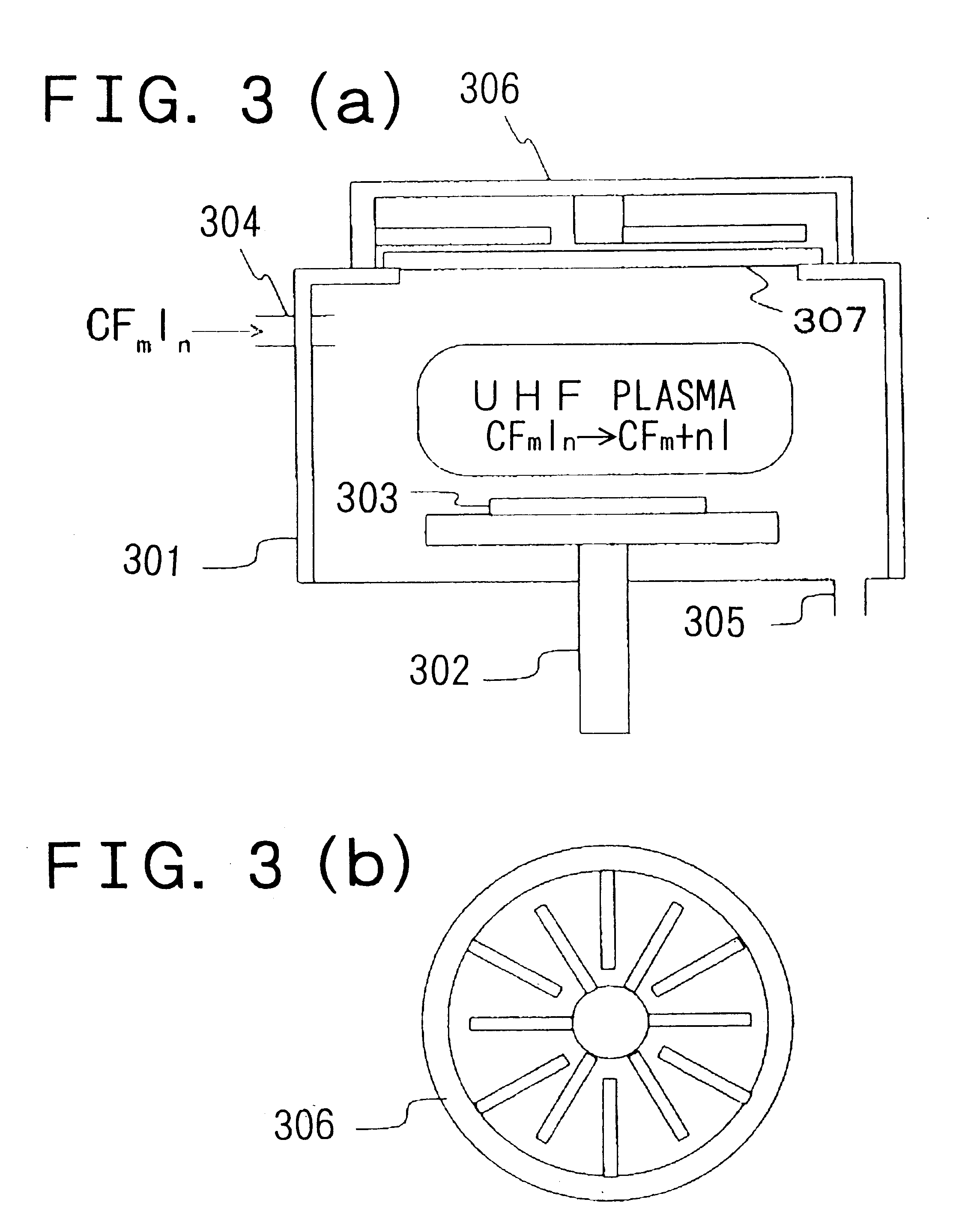
To produce a desirable amount of desirable radical and / or ion in treating a substrate such as etching the substrate, depositing a thin film on the substrate and the like by using plasma and the like. As a treating gas, a gas such as CFmIn and the like containing both a strongly bonded halogen element (F etc.) and weakly bonded halogen element (I etc.) is used. A substrate is treated by active species produced by exciting the treating gas by an excitation means capable of providing an energy which cannot dissociate the strong bond but can dissociate the weak bond. Preferable excitation means is capable of emitting a monochromatic irradiation, having a single value of excitation energy, such as electron beam, light etc., or otherwise capable of providing plasma, having a peak energy value of electrons and sharp electron energy distribution, such as UHF plasma etc.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus for depositing tungsten after surface treatment to improve film characteristics
InactiveUS20050208763A1Reduce fluorine contentExpand coverageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical speciesNucleation
A method and system to form a refractory metal layer over a substrate includes introduction of a reductant, such as PH3 or B2H6, followed by introduction of a tungsten containing compound, such as WF6, to form a tungsten layer. It is believed that the reductant reduces the fluorine content of the tungsten layer while improving the step coverage and resistivity of the tungsten layer. It is believed that the improved characteristics of the tungsten film are attributable to the chemical affinity between the reductants and the tungsten containing compound. The chemical affinity provides better surface mobility of the adsorbed chemical species and better reduction of WF6 at the nucleation stage of the tungsten layer. The method can further include sequentially introducing a reductant, such as PH3 or B2H6, and a tungsten containing compound to deposit a tungsten layer. The formed tungsten layer can be used as a nucleation layer followed by bulk deposition of a tungsten layer utilizing standard CVD techniques. Alternatively, the formed tungsten layer can be used to fill an aperture.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High-sodium low-fluorine continuous casting mould fluxes and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to high-sodium low-fluorine covering slag, which is prepared from raw materials of wollastonite, limestone, quartz sand, fluorite, bauxite, manganese carbonate, magnesia, hydrous borax, industrial soda, lithium carbonate, and carbonaceous materials, and the chemical components of the covering slag meets the following weight percentage: more than 30 and less than 34 percent of CaO, more than 30 and less than 38 percent of SiO2, more than 12 and less than 25 percent of Na2O, less than 4 percent of MgO, less than 8 percent of MnO, less than 4 percent of B2O3, less than 1.5 percent of Li2O, less than 4 percent of Al2O3, less than 2 percent of F, more than 4 percent and less than 10 percent of C, and the balance being impurities. In the covering slag, the ratio of sigma CaO to the SiO2 is controlled to between 0.8 and 1.15 to ensure that the fused mass of the covering slag does not separate out crystals at high temperature and liquid slag in a slag film can lubricate a casting blank. Aiming at that the content of fluorine has adverse influence on environment and equipment, the invention adopts high-sodium low-fluorine continuous casting covering slag which not only can meet the requirement of coordinated control of heat transfer and lubrification of a continuous casting covering slag for crack sensitive steel to cast casting blank with good surface quality, but also can reduce the fluorine content in air and secondary cooling water, thus the air pollution is reduced and the corrosion of fluorine-contained water to equipment is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Soil repellency aqueous dispersions, soil repellant soft articles, and methods of making the same
ActiveUS20110311757A1Improve efficiencySoftMaterial nanotechnologyStain/soil resistant fibresFiberYarn
A soil repellency aqueous dispersion for treating various fibers, yarns, and textiles is disclosed. The dispersion provides superior soil resistance when compared to known fluorochemical and silicone fiber treatments. The dispersion comprises clay nanoparticle components and fluorochemicals that can be applied to the fibers, yarns, and textiles using known methods.
Owner:INV PERFORMANCE SURFACES LLC
Thermoplastic fluorinated polyurethane elastomer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103242505AExcellent surface and mechanicsThe preparation process is convenient and quickIsocyanatePerfluoropolyether
The invention discloses a thermoplastic fluorinated polyurethane elastomer and a preparation method thereof. The thermoplastic fluorinated polyurethane elastomer is composed of non-fluorinated macromolecular polyols, perfluor polyether glycol, a micromolecular chain extender and polyisocyanates; and the preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding perfluor polyether glycol and non-fluorinated macromolecular polyols into a container; after the obtained fluorinated composite resin is stirred for 10-20 minutes at a speed of 2000-3000 r / min, carrying out vacuum dehydration on the obtained fluorinated composite resin; sequentially adding polyisocyanates and the micromolecular chain extender into the obtained product; continuing to stir the obtained mixture for 3-5 minutes, and pouring the obtained mixture in a preheated die; and after the obtained mixture is subjected to curing forming for 2-4 hours at a controlled temperature of 15-30 DEG C, respectively carrying out vacuum curing on the obtained product for 1-2 hours at a temperature of 50-80 DEG C, carrying out vacuum curing on the obtained product for 1-2 hours at a temperature of 90-110 DEG C, and carrying out vacuum curing on the obtained product for 15-24 hours at a temperature of 120-140 DEG C, thereby obtaining the thermoplastic fluorinated polyurethane elastomer with a low fluoride content and excellent surface and mechanical properties.
Owner:SHANGHAI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Vinylidene fluoride copolymer for gel-form solid electrolyte formation, solid electrolyte, and battery
InactiveUS6372388B1Appropriate level of ionic conductivityImprove adhesionLead-acid accumulatorsConductive materialPolymer electrolytesHeat resistance
A solid polymer electrolyte having improved ionic conductivity and adhesion with an electroconductive substrate and also remarkably enhanced heat resistance is formed with a vinylidene fluoride copolymer which contains 50-97 mol. % of vinylidene fluoride monomer and 0.1-5 mol. % of an unsaturated dibasic acid monoester or an epoxy group-containing vinyl monomer and further has been crosslinked, thereby improving the performances of a non-aqueous battery, such as a lithium ion battery.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Method for treating high-concentration acidic wastewater containing phosphorus and fluorine
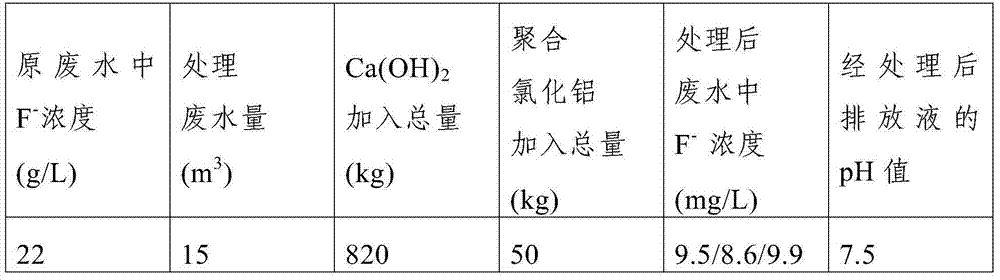
InactiveCN102070267AReduce fluorine contentReduce phosphorus contentWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentAluminium saltsChemistry
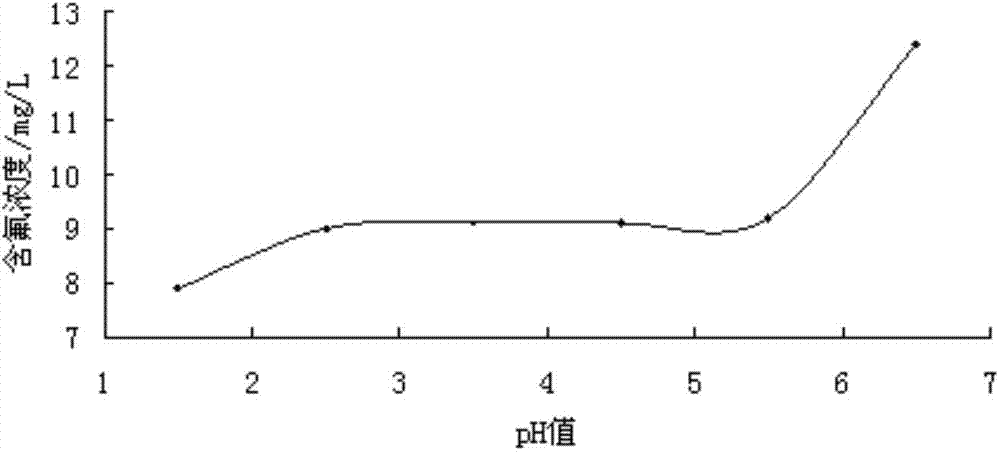
The invention discloses a method for treating acidic wastewater containing phosphorus and fluorine, which comprises the following steps: (1) firstly, adding calcium hydroxide into the acidic wastewater containing phosphorus and fluorine, and controlling the pH value of the system at 12-14 to obtain a precipitate-containing reaction system which is marked as a reaction system 1; (2) removing the precipitate in the reaction system 1, adding sulfuric acid into the residual liquid to regulate the pH value to 9-11, and then, adding aluminum sulfate to regulate the pH value to 6-7, thereby obtaining a precipitate-containing reaction system 2; and (3) settling down the precipitate in the reaction system 2, and removing the precipitate to obtain the treated wastewater. In the wastewater treated by the method disclosed by the invention, the content of fluorine is lower than 10 mg / L, the content of phosphorus is lower than 0.5 mg / L, and the pH value is 6-7, thus the treated wastewater achieves the Discharge Standard of Water Pollutants for Phosphate Fertilizer Industry (GB 15580-95). In the whole technological process, water overflows under the action of the gravity without an external energy supply, thereby saving the energy.
Owner:湖北大峪口化工有限责任公司
Collosol of yttrium barium cupper oxygen superconducting film and process for preparing high temp. superconducting film thereof
InactiveCN1792806AShorten heat treatment timeEasy to makeSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesPolymer scienceOxygen
A sol of the Y-Ba-Cu-O (YBCO) superconductor film is proportionally prepared from yttrium acetate, barium acetate, copper acetate, trifluoroacetic acid, water, alpha-methylacrylic acid, divinyltriamine and methanol. A process for preparing the high-temp superconductor film from said sol is also disclosed.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Advanced treatment method of fluoride-containing wastewater
ActiveCN105060579AStable chemical propertiesHigh densityMultistage water/sewage treatmentCalcium hydroxideFlocculation
The invention discloses an advanced treatment method of fluoride-containing wastewater. The method comprises steps as follows: S1, precipitation: the fluoride-containing wastewater is collected and sent into an adjusting tank, calcium hydroxide slurry is added to the adjusting tank, the pH value of the adjusting tank is controlled to range from 4 to 6 after even mixing, and the mixture is left to stand for precipitation; S2, flocculation: the wastewater subjected to precipitation treatment is introduced into a reaction tank, a PAC and PAM combined flocculating agent is added, and the mixture is stirred and left to stand; S3, electrocoagulation: the wastewater subjected to flocculation treatment is introduced into an electrolytic bath, an electrolyte is added, electrocoagulation treatment is performed after energization, the mixture is left to stand, drained water enters a water outlet tank, a base is added, the pH is adjusted to range from 9 to 11, activated carbon powder is added, and the mixture is evenly stirred; S4, adsorption: the wastewater subjected to microfiltration treatment is introduced into an adsorption tank, the pH of the wastewater is adjusted to range from 4 to 6, a modification adsorbent is added, and the mixture is left to stand after being evenly mixed. With the adoption of the treatment technology, the content of fluoride in the wastewater is reduced to be lower than 1.0 mg / L, and the whole treatment technology is simple, mature, practical, economical and reasonable.
Owner:ANHUI JINYANG FLUORINE CHEM
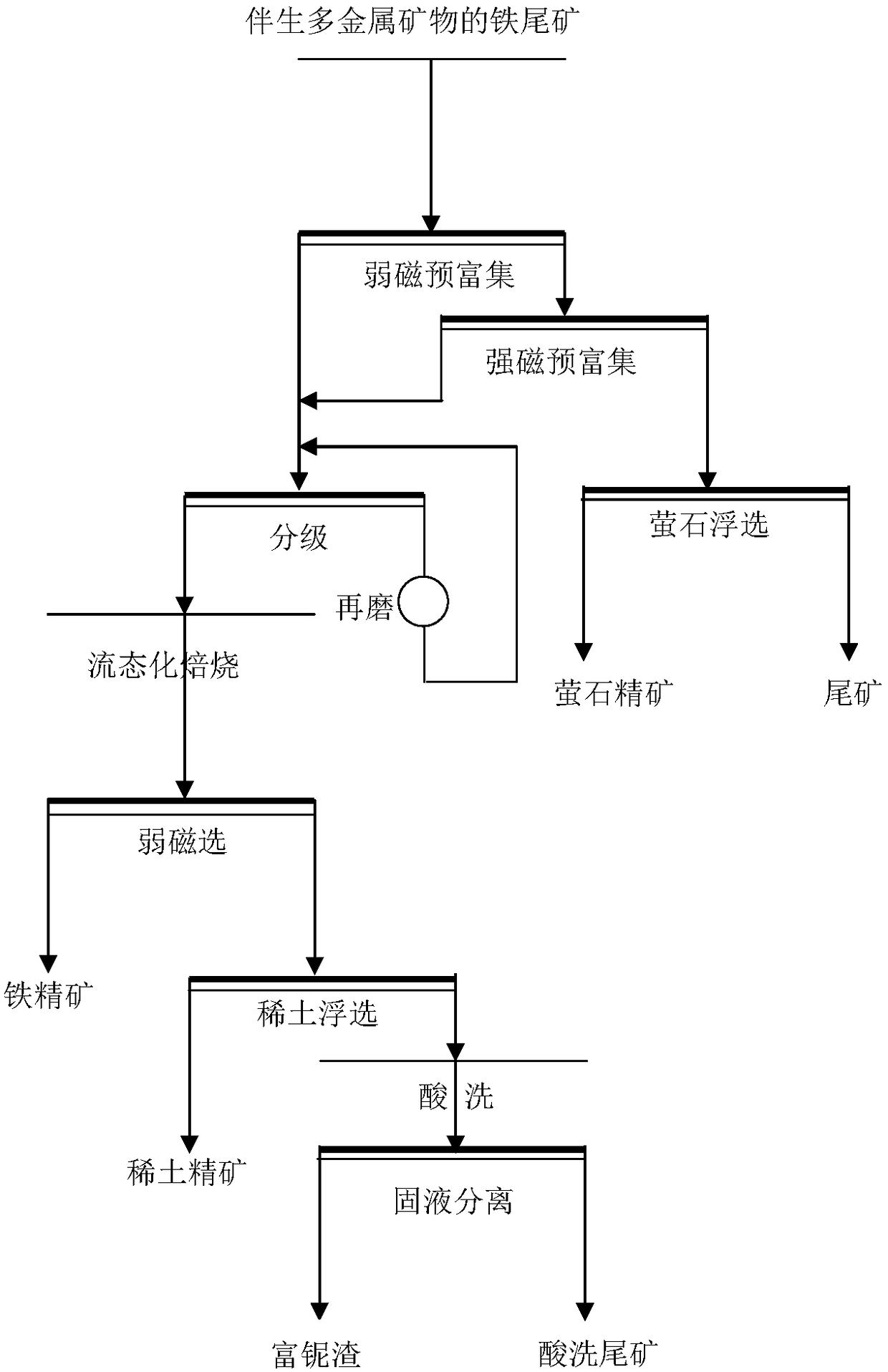
Mineral separation method for recycling iron, rare earth, fluorite and niobium from iron tailings of associated multi-metal minerals
ActiveCN108480037ALess amount of reducing agentReduce the amount of fluorite flotationWet separationLower intensityHigh intensity
The invention relates to a mineral separation method for recycling iron, rare earth, fluorite and niobium from iron tailings of associated multi-metal minerals, and belongs to the fields of mineral process engineering and comprehensive recycling of resources. The mineral separation method for recycling iron, rare earth, fluorite and niobium from iron tailings of associated multi-metal minerals comprises the following steps: carrying out low intensity magnetic separation and high intensity magnetic separation pre-concentration by taking bayan obo tailings as raw materials, then carrying out fluid bed roasting on obtained pre-concentrated concentrates, and carrying out low intensity magnetic separation operation on roasted minerals obtained by roasting so as to obtain weak-magnetism concentrates and rare-earth-containing weak-magnetism tailings; and carrying out rare earth flotation operation on the weak-magnetism tailings to obtain rare earth flotation concentrates and rare earth flotation tailings finally, then carrying out acid leaching process on the rare earth flotation tailings to obtain niobium-enriched slag and acid pickling tailings, and meanwhile, carrying out fluorite flotation operation on pre-concentrated strong-magnetism tailings to obtain fluorite flotation concentrates and fluorite flotation tailings. By the method, fluorite concentrates, iron core concentrates, rare earth concentrates and the niobium-enriched slag are obtained finally, and thus, the bayan obo tailings are utilized comprehensively.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
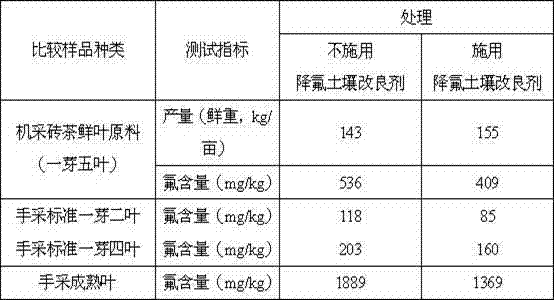
Soil amendment and method for reducing fluorine content of fresh brick tea leaves
ActiveCN102352253AReduce fluorine contentGuarantee quality and safetyAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersBrickPotassium
The invention provides a soil amendment for reducing fluorine content of fresh brick tea leaves, and belongs to the technical field of fluorine reduction of fresh leaf raw materials in tea gardens. The soil amendment comprises: by weight, 158 to 476 parts of dolomite powder, 15 to 55 parts of quicklime, 50 to 150 parts of turf and 4 to 12 parts of potassium chloride. The invention also provides amethod which aims mainly at reducing fluorine content of fresh brick tea leaves, and utilizes reasonably dolomite powder, quicklime, turf and potassium chloride. Dolomite powder and quicklime in the soil amendment can improve obviously a pH value of acid soil, and change an existence form of fluorine in soil. Turf (meadow peat) in the soil amendment is an organic matter ore body formed by yearly accumulation of half-rotten plants, is rich in humic substances, and has strong adsorbability and permeability. Potassium chloride in the soil amendment contains chloride ions and monovalent anions ofan element which is congeneric with fluorine, and can influence the effectiveness of fluorine in soil and the absorption of fluoride ions by tea trees.
Owner:TEA RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Plasma display panel and process for producing the same and thin film
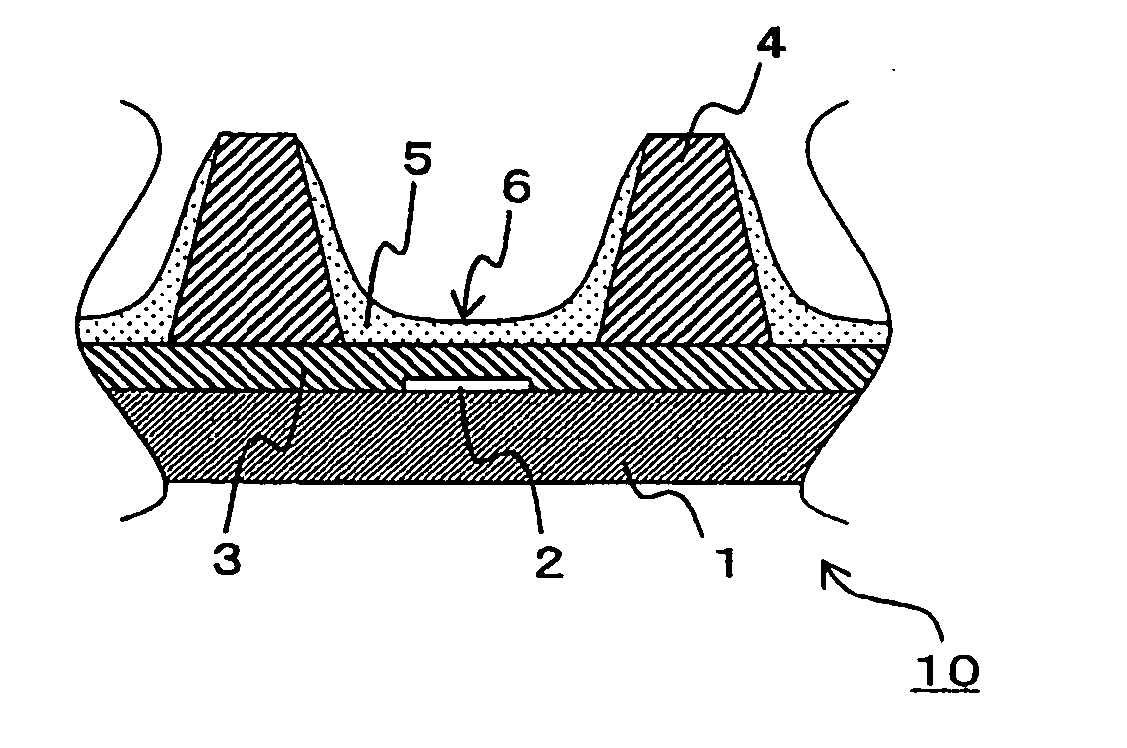
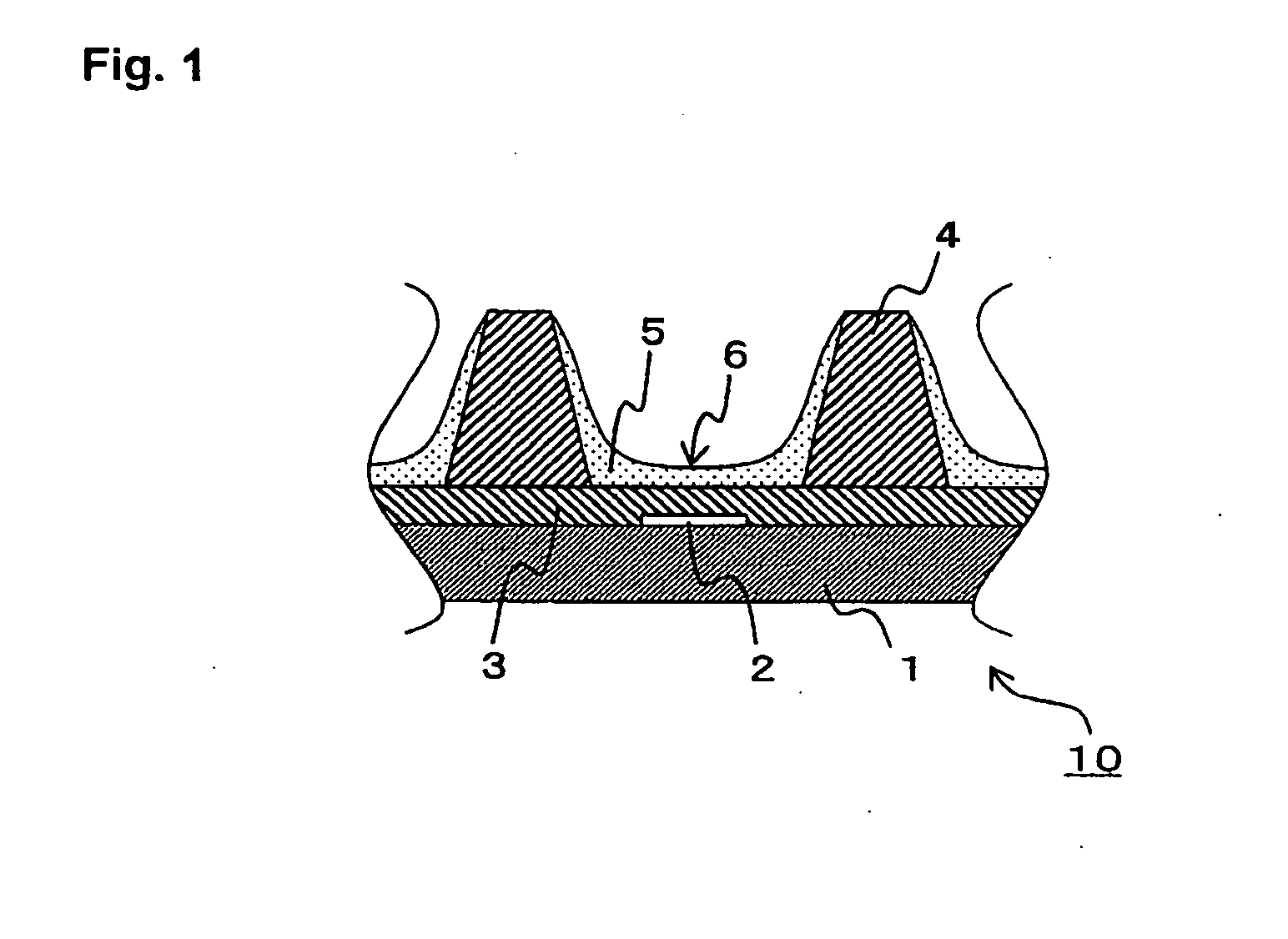
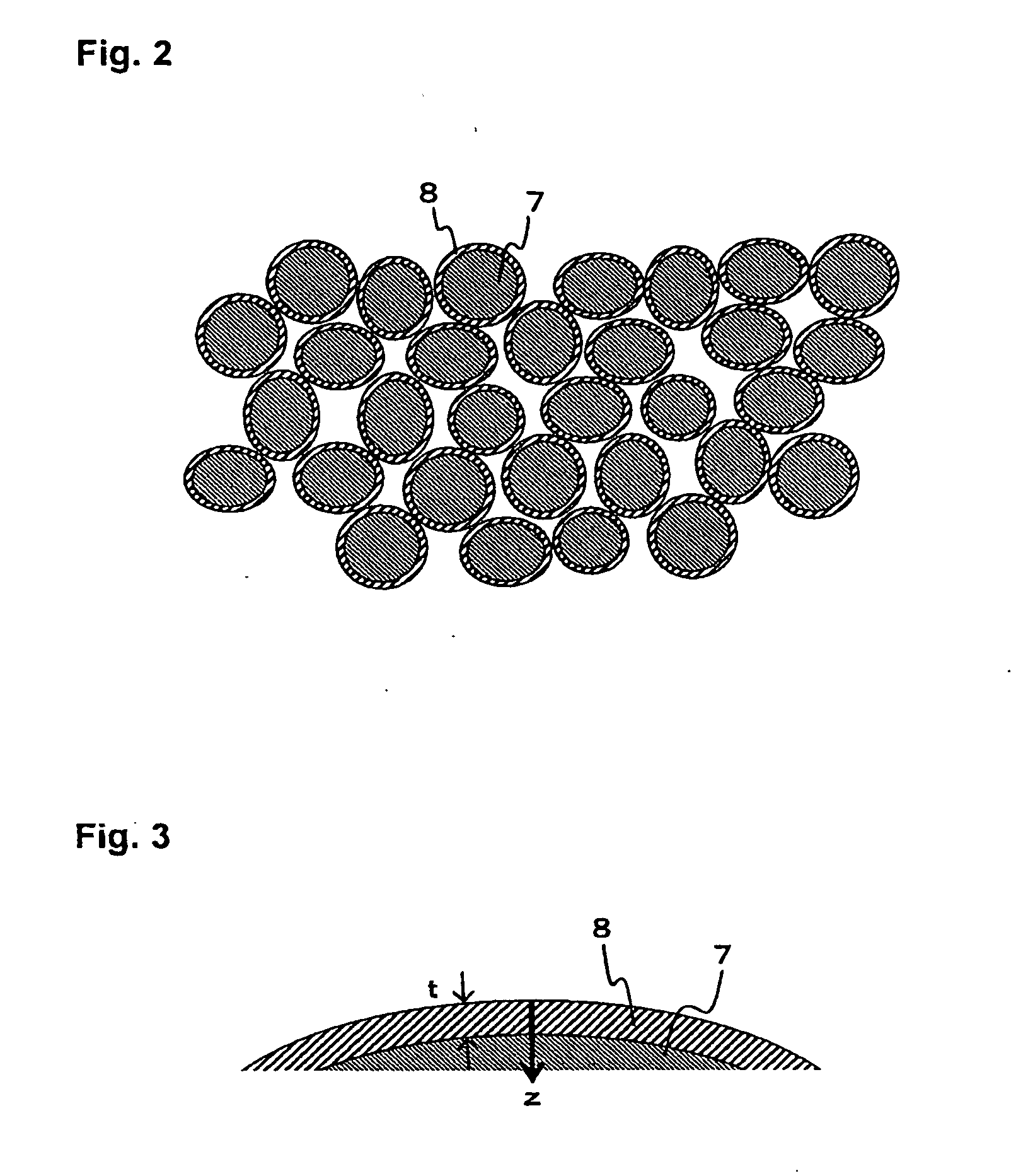
InactiveUS20050040765A1Increase brightnessSuppress DiffuseTube/lamp screens manufactureAddress electrodesPhosphorGas phase
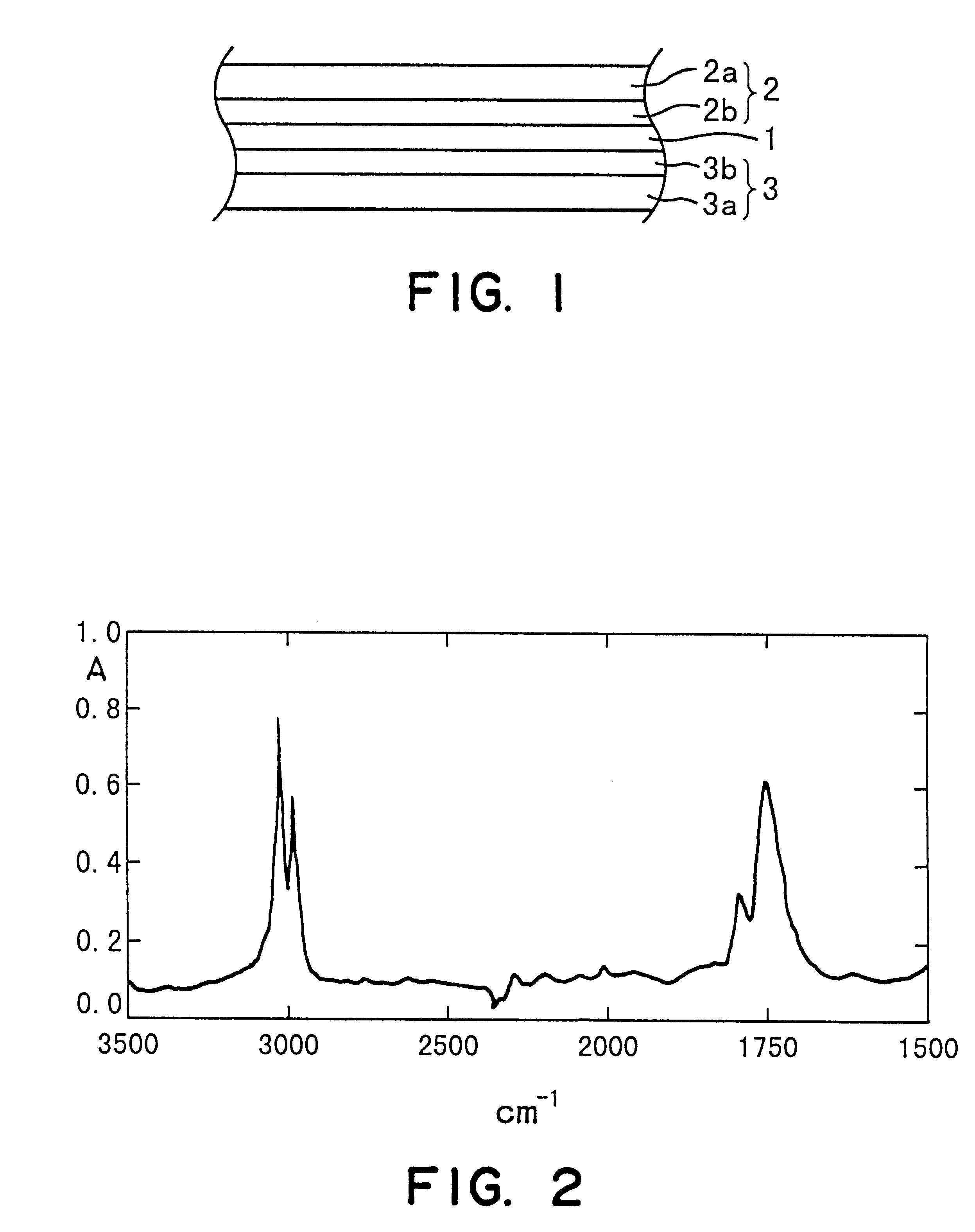
A fluorine-containing precoating (not shown) is formed to cover a phosphor particle (7) by, for example, a physical vapor deposition of a fluoride. Then, a fluorine-containing coating (8) covering the phosphor particle (7) is formed by supplying fluorine into the precoating. Thus obtained phosphor particle (7) with the coating (8) is applied in the form of a paste to a substrate (1) on each electrode (2) is between adjacent two ribs (4) to form a phosphor layer (6) including the phosphor particles (7) between the ribs (4) on the substrate (1). The substrate (1) is positioned with respect to another substrate (not shown) having electrodes thereon to form discharge spaces between the substrates. The discharge spade is filled with a discharge gas to produce a plasma display panel (PDP).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Fluorinated polyoxyalkylene glycol diester surfactants
InactiveUS20100099837A1Improve performanceReduce concentrationOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesAmmoniumPhotochemistry
A fluorinated polyoxyalkylene glycol diester surfactant of formula 1B—X—COCH2O—[—CpH2pO—]n—CH2CO—X—Ra (1)whereinB is M or Ra,M is an ionizable hydrogen, ammonium, alkali metal, or alkaline earth metal,p is from about 2 to about 4,n is from about 5 to about 43,X is O, S, or SCH2CH2O,Ra is Rf(CH2CF2)d—(CgH2g)—; Rf[OCF2CF2]r(CgH2g)—;Rf(CH2)h[(CF2CF2)i(CH2CH2)j]k—; or RfOY—;Y is CFHCF2O(CH2CH2O)v—(CgH2g)—; CFHCF2O(CwH2w)—; orCF(CF3)CONH—(CgH2g)—;each Rf is independently CcF(2c+1) wherein c is 1 to about 6;d is 1 to about 3; g is 1 to about 4; s is 0 or 1; r is 1 to about 4; h is 1 to about 6; i, j, and k are each independently 1, 2, or 3, or a mixture thereof;provided that the total number of carbon atoms in Rf(CH2)h[(CF2CF2)i(CH2CH2)j]k—is from about 8 to about 22; v is 1 to about 4;and w is from about 2 to about 12.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for preparing yttrium-barium-copper-oxygen super conductive-film sol-gel
InactiveCN1850723AShorten heat treatment timeEasy to makeSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesPorosityOxygen
This invention discloses sol-gel preparation method of yttrium barium copper oxygen superconducting film. The materials are acetic yttrium, acetic barium, acetic copper, their mol ratio is that acetic yttrium 1 part, acetic barium 2 parts, acetic copper 3-4 parts, trifluoroacetic acid 4-10 parts, water 20-160 parts, acrylic acid 6-40, diethylene triamine 1-5, methanol 60-240, benzoyl acetone 1-10. Fluorine content of the sol is low, components are easy to adjust, chemical stability is good, and preparation process is simple. High temperature superconductive film made by this sol is easy to get superconductive thickness film, its technique repeatability is high, this method can be used to make large area yttrium barium copper oxygen film, the film porosity is low, surface purify is good, and good superconducting characteristic.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Prevention and remediation of water and condensate blocks in wells
InactiveUS20120071372A1Reduce fluorine contentLow costFlushingDrilling compositionOrganic chemistryCopolymer
The present invention relates to a method of removing and preventing water and condensate blocks in wells by contacting a subterranean formation with a composition comprising a low molecular weight fluorinated copolymer having perfluoro alkyl moieties which are no longer than C6. A fluorinated copolymer of low molecular weight of about 50,000 g / mol and a method of preparing the same are also disclosed.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Wax-containing water-and-oil repellent agent and preparation method, textile
The invention provides a wax-containing water-and-oil repellent agent, preparation technology and application, wherein the wax-containing water-and-oil repellent agent comprises the following components in percentage by mass: fluoropolymer 20%-30%, (modified) polyethylene wax emulsion 3%-40%, surfactant 1-5%, hydrophilic solvent 4-20%, PH adjustment auxiliary agent 0.001-3% and water. The water-and-oil repellent agent provided by the invention has an excellent water-and-oil repelling effect, and an environmental protection property. In-situ polymerization technology is adopted in the invention; compared with prior art, the fluorine-containing material can play a better role of water-and-oil repelling, and the content of elemental fluorine in the decrease the water-and-oil repellent agent can be reduced.
Owner:福建省晋江新德美化工有限公司
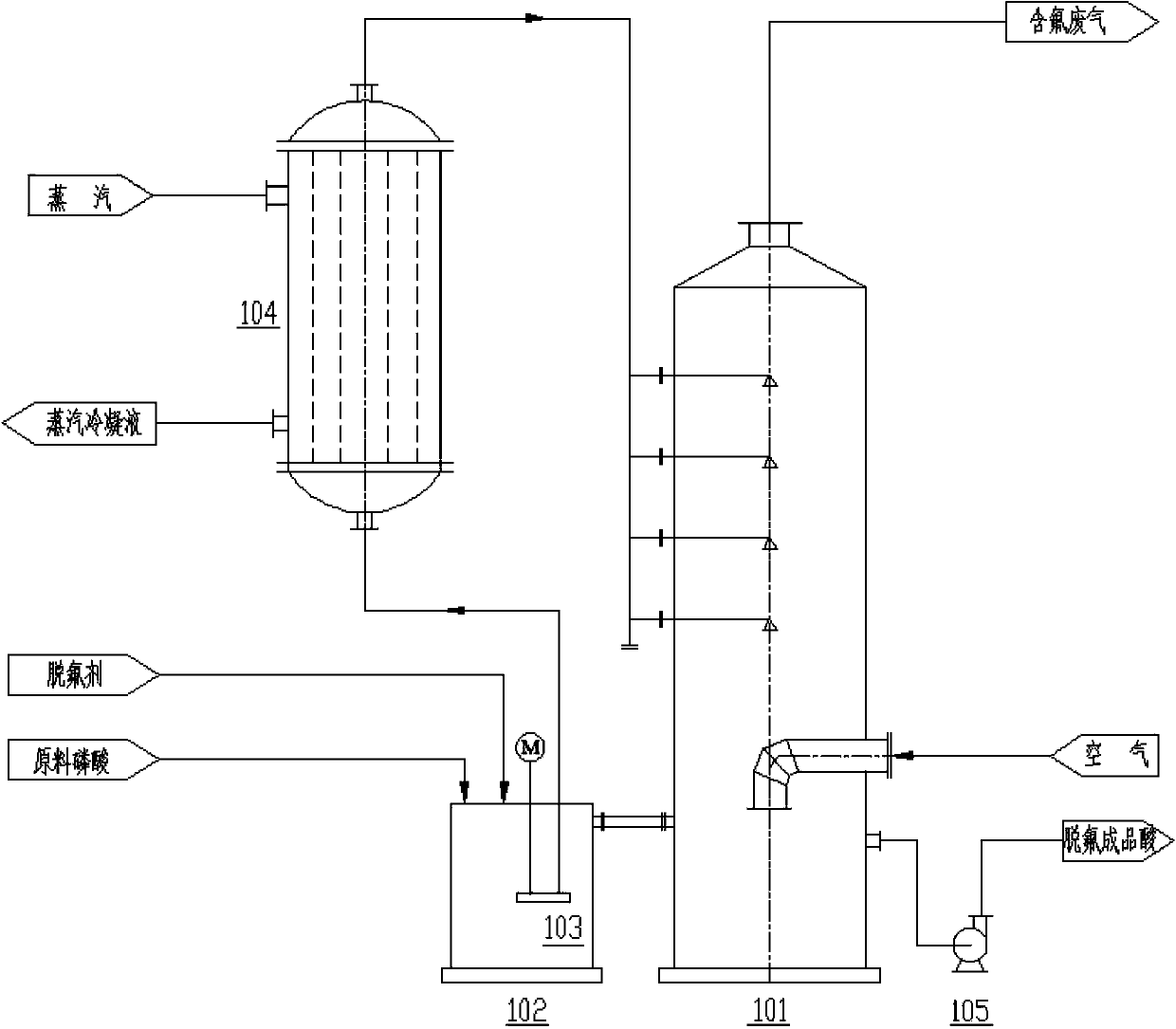
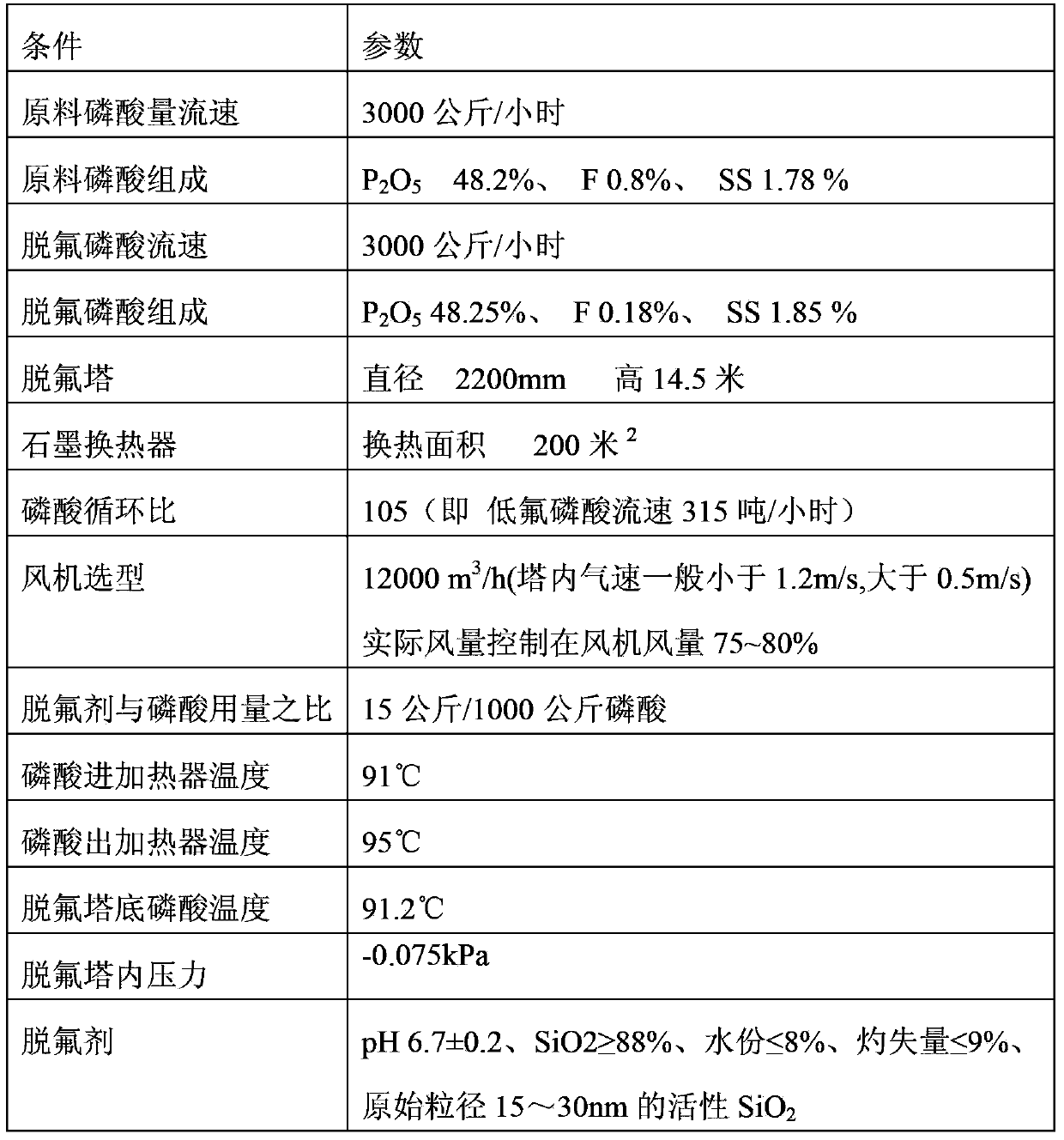
Tower type air stripping defluorination method for phosphoric acid
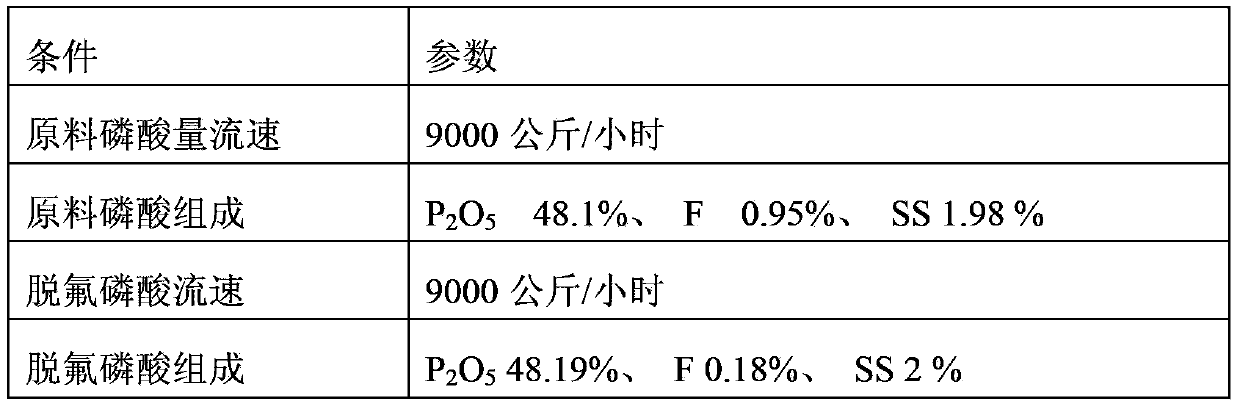
ActiveCN104176719AReduce fluorine contentThe fluorine content is lower thanPhosphorus compoundsO-Phosphoric AcidPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a tower type air stripping defluorination method for phosphoric acid. The method includes: firstly mixing the raw material fluorine-containing phosphoric acid, a defluorination agent and defluorinated phosphoric acid flowing out of the bottom of a defluorination tower to obtain low fluorine phosphoric acid, then heating the low fluorine phosphoric acid to 90-105DEG C, and leading it into the defluorination tower; spraying the low fluorine phosphoric acid in the tower through at least one layer of nozzles at the upper part inside the defluorination tower, introducing air from the lower part of the defluorination tower to make the low fluorine phosphoric acid and air fully contact to complete defluorination; discharging the fluorine-containing exhaust gas generated during defluorination from the top of the defluorination tower, mixing part or all of the defluorinated phosphoric acid generated at the bottom of a defluorination tower with the fluorine-containing phosphoric acid and the defluorination agent to obtain the low fluorine phosphoric acid to carry out defluorination circulation, and leading the other part of the defluorinated phosphoric acid out of the defluorination tower to obtain a finished phosphoric acid product. The process provided by the invention can reduce the fluorine content of phosphoric acid to a phosphorus-fluorine ratio (P2O5 / F) of greater than or equal to 260, and compared with the prior art, the fluorine content of the phosphoric acid is significantly reduced.
Owner:SINOPEC NANJING ENG & CONSTR +1
Settling agent in wet-method phosphoric acid concentration processing process
An excellent settling agent used for processing the concentration of wet-method phosphoric acid is prepared by sending 40-93 parts by mass of an anionic flocculating agent, 1-30 parts by mass of a non-ionic flocculating agent, 1-40 parts by mass of an adsorbent and 0-20 parts by mass of a fluorine removal agent to a stirring tank, controlling the temperature of the stirring tank in a range of 60-80DEG C through heating and heat insulation via a jacket, and allowing the solution obtained after stirring ending to stand for 10-40min. The excellent settling agent has the advantages of low prices and easy purchasing of the above used raw materials, simple preparation, less consumption, obvious shortening of the settling time of the concentration of wet-method phosphoric acid, effective reduction of the fluorine content, reduction of the contents of cations comprising Al<3+>, Fe<3+>, Ca<2+>, Mg<2+>, Si<4+> and the like, and realization of the clear texture and low impurity content of the produced concentrated wet-method phosphoric acid, and provides a high-quality raw material for subsequent production.
Owner:HUBEI XINGFA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Fluoroalkyl ether sulfonate surfactants
InactiveUS20100120980A1Good dispersionIncrease polymerization rateCosmetic preparationsOrganic chemistryChemistryEther
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Fluorine-containing acidic wastewater treatment method
ActiveCN104773877AReduce fluorine contentMeet emission standardsWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentCombined methodSlurry
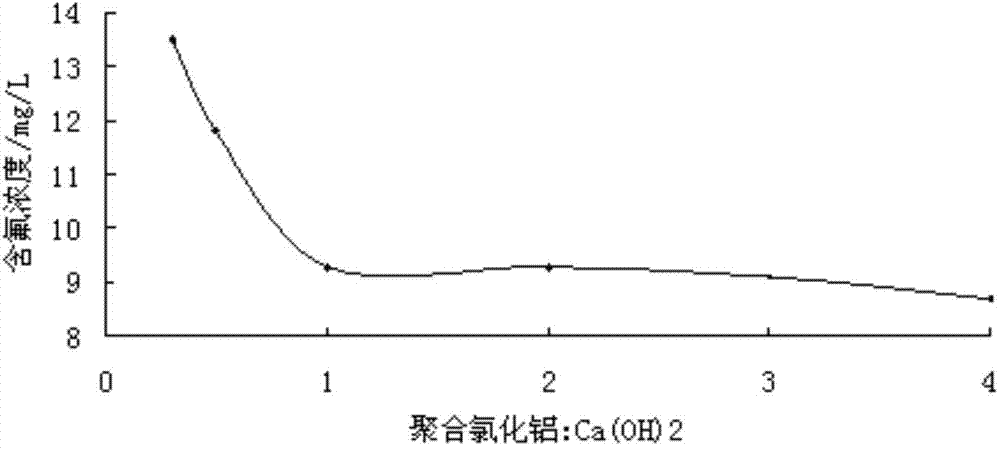
The invention provides a fluorine-containing acidic wastewater treatment method comprising the following steps: 1, the fluorine-containing acidic wastewater is placed in a recovery tank and is subjected to natural sedimentation; 2, filtering is carried out, such that a filtrate is obtained; 3, a calcium hydroxide slurry is added into the filtrate, such that primary sedimentation treatment is carried out, until the pH value of the filtrate is 5-6; 4, a mixed solution of calcium hydroxide and polyaluminum chloride is added into the filtrate, such that secondary sedimentation treatment is carried out, until the pH value of the filtrate is 7-8; and 5, filtering is carried out with a microporous filter. According to the invention, a traditional process is improved. Production wastewater is first subjected to a filtering pretreatment, such that residual insoluble molybdenum disulfide and other impurities left in the wastewater are recovered; and the filtrate is treated with a calcium salt precipitation and aluminum salt fluorine-removing combined method, such that a purpose of fluorine-containing wastewater treatment is achieved. With the method, the fluorine content in wastewater is reduced to below 10mg / L, such that a discharge standard is reached.
Owner:JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO LTD
Actinic-ray- or radiation-sensitive resin composition, actinic-ray- or radiation-sensitive film and method of forming pattern
ActiveUS20150338736A1Good influenceReduce fluorine contentSteroidsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPolymer scienceMethyl group
Provided is an actinic-ray- or radiation-sensitive resin composition including a resin (A) and any of compounds (B) of general formula (I) below. (In general formula (I), Rf represents a fluorine atom or a monovalent organic group containing at least one fluorine atom; R1 represents a hydrogen atom or a monovalent substituent containing no fluorine atom; X1 represents a monovalent organic group having at least two carbon atoms, or a methyl group in which a substituent other than a fluorine atom is optionally introduced, provided that X1 may be bonded to R1 to thereby form a ring; and Z represents a moiety that when exposed to actinic rays or radiation, is converted to a sulfonic acid group, an imidic acid group or a methide acid group.)
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Technology for treatment of fluorine-boron-containing wastewater during Ceftezole acid preparation
InactiveCN102963999AReduce fluorine contentIncrease valueMultistage water/sewage treatmentNature of treatment waterAlkali freePotassium
The invention discloses a technology for treatment of fluorine-boron-containing wastewater during Ceftezole acid preparation. According to the technology, boric acid and fluoboric acid are remove from wastewater respectively by a two-stage neutralization reaction, so that the fluorine content of the industrial wastewater is decreased to 5mg / l, the boron content is reduced to 5mg / l, and the pH of the wastewater is 6-7, thus meeting the national wastewater discharge standards. The technology has the advantages of simple operation, small investment, and large by-product value. Calcium borate can be used for alkali-free glass fiber production, and potassium fluoborate can be used as a catalyst for polypropylene synthesis.
Owner:江苏德峰药业有限公司
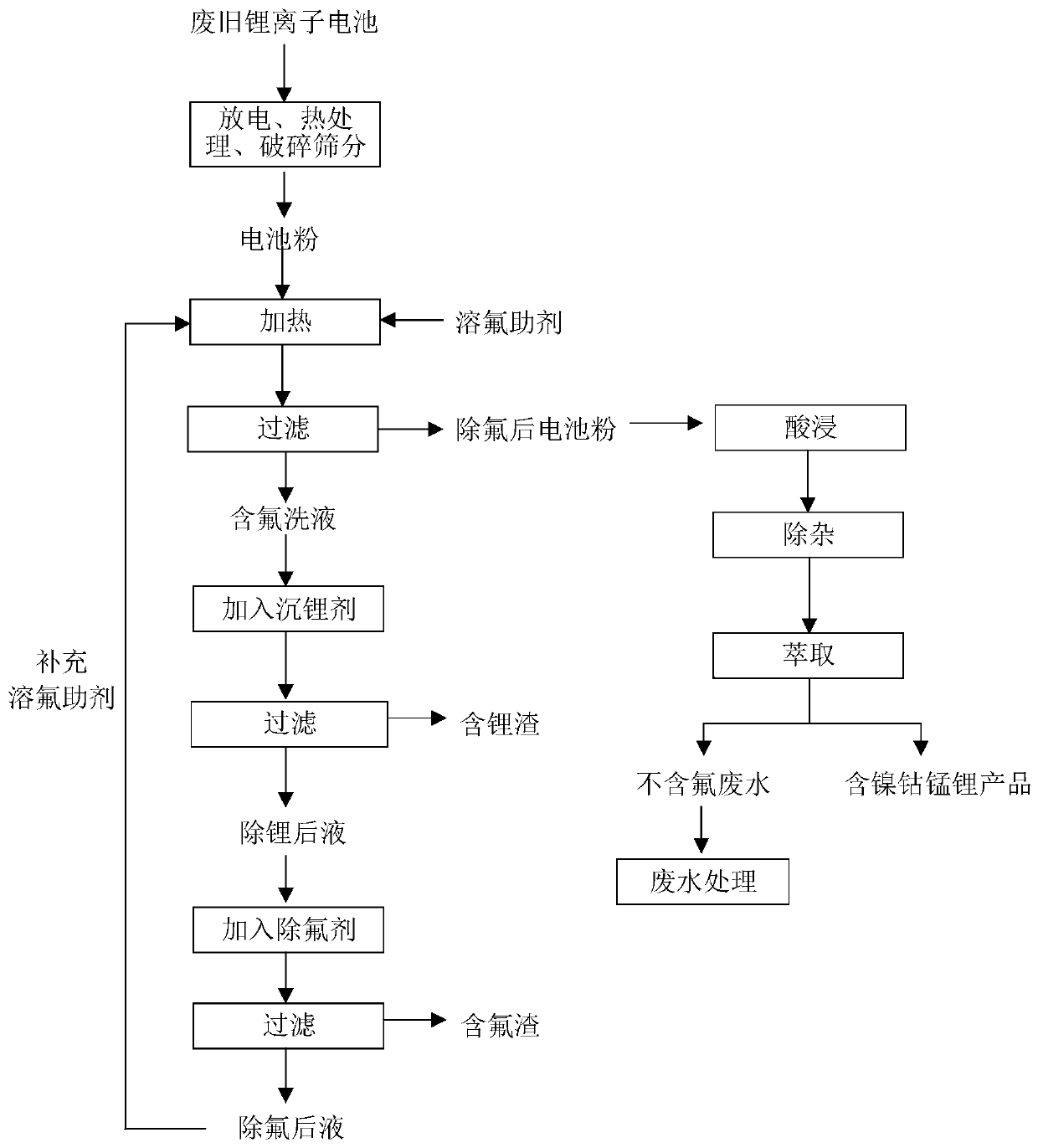
Recovery method for front-section defluorination of waste lithium ion battery
PendingCN110994062ASolve a series of problems caused by fluorineReduce fluorine contentWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingPhysical chemistryLithium-ion battery
The invention relates to a recovery method for front-section defluorination of a waste lithium ion battery and a defluorination treatment method for the recovery front-section of the waste lithium ionbattery. The defluorination treatment method comprises the following steps of mixing the fluorine-containing battery powder with a fluorine dissolving aid solution, heating, stirring and filtering toobtain the defluorinated battery powder and the fluorine-containing washing liquor; adding a lithium precipitation agent into the fluorine-containing washing liquid, heating, stirring and filtering to obtain the lithium-containing slag and the lithium-removed liquid; adding a fluorine removal agent into the lithium-removed solution, stirring and filtering to obtain the fluorine-containing slag and the fluorine-removed solution; and preparing the defluorinated solution into a fluorine-dissolving auxiliary solution, and repeating the steps. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, thefluorine content of the waste lithium ion battery can be reduced to be less than 0.11% before the waste lithium ion battery enters a recovery process, the fluorine removal rate is up to 90%, a seriesof problems caused by fluorine in a battery recovery process can be favorably solved. The method has high cyclic utilization rate of a washing liquid, great reduces the use amount of water, saves thecost, and has the great application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +2
Process of preparing filter material for reducing fluoride content and improving water quality
InactiveCN101088604AGood effectSimple processing technologyOther chemical processesAluminium silicatesInorganic saltsFilter material
The present invention is process of preparing filter material for reducing fluoride content and improving water quality, and the filter material has the advantages of simple preparation process, simple use, low cost, high fluoride content reducing effect and other advantages. The process includes the following steps: sorting natural zeolite material and crushing to 5-8 mesh; high temperature roasting at 900-1000 deg.c for 3-4 hr; cooling and treating in 30 % concentration hydrochloric acid for 18-24 hr; washing and soaking in inorganic salt solution for 12-24 hr; flushing and soaking in sodium health solution for 10-30 hr; flushing and soaking in 1-5 % concentration alum solution for 10-16 hr to activate; acid-alkali balancing; drying and water maintaining treatment to obtain the product.
Owner:山东乾天工贸有限公司 +1
Fluorinated polyoxyalkylene glycol diester surfactants
InactiveUS8022107B2Improve performanceReduce concentrationOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesAlkaline earth metalPhotochemistry
A fluorinated polyoxyalkylene glycol diester surfactant of formula 1B—X—COCH2O—[—CpH2pO—]n—CH2CO—X—Ra (1)whereinB is M or Ra,M is an ionizable hydrogen, ammonium, alkali metal, or alkaline earth metal,p is from about 2 to about 4,n is from about 5 to about 43,X is O, S, or SCH2CH2O,Ra is Rf(CH2CF2)d—(CgH2g)—; Rf[OCF2CF2]r(CgH2g)—; Rf(CH2)h[(CF2CF2)i(CH2CH2)j]k-; or RfOY—;Y is CFHCF2O(CH2CH2O)v-(CgH2g)—; CFHCF2O(CwH2w)—; or CF(CF3)CONH—(CgH2g)—;each Rf is independently CcF(2c+1) wherein c is 1 to about 6;d is 1 to about 3; g is 1 to about 4; or 1; r is 1 to about 4; h is 1 to about 6; i, j, and k are each independently 1, 2, or 3, or a mixture thereof; provided that the total number of carbon atoms in Rf(CH2)h[(CF2CF2)i(CH2CH2)j]k— is from about 8 to about 22; v is 1 to about 4; and w is from about 2 to about 12.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
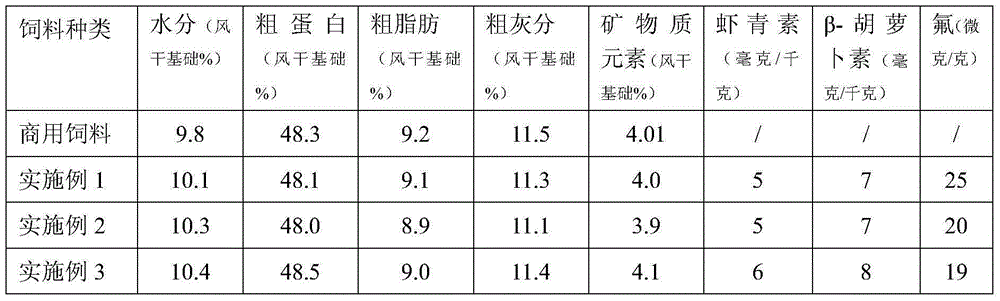
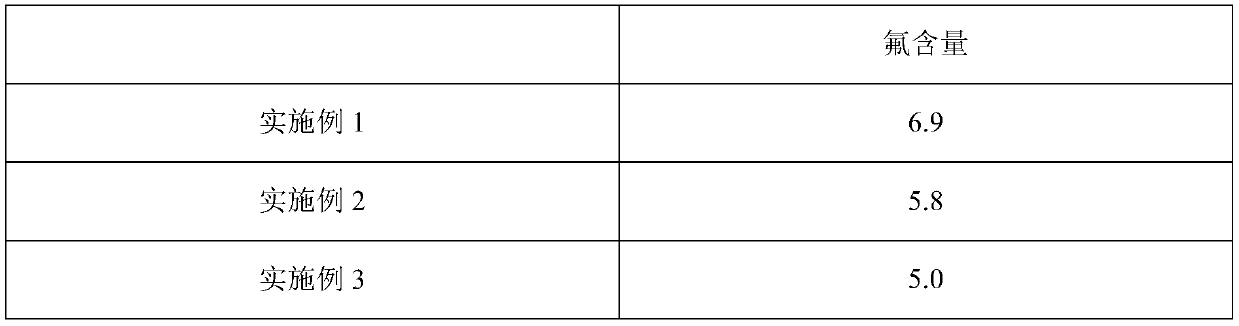
Fish feed using euphausia superba as the main raw material and a preparation method thereof
The present invention relates to fish feed using euphausia superba as the main raw material and a preparation method thereof. The feed consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-40 parts of euphausia superba head powder with a fluorine content less than 80 mu / g, 10-15 parts of soy protein concentrate powder, 8-15 parts of corn protein powder, 1-3 parts of squid paste, 0.5-1 part of kelp powder, 0.1-0.3 part of dried eucommia folium powder and 0.1-0.3 part of L-Ascorbate-2-Monophosphate. The fish feed uses combined characteristics of euphausia superba head powder chemical compositions and fish growth to design other raw materials so that the fish feed is reasonable and safe in formulation structure, can meet comprehensive demands of fish for nutrient substances, significantly improve the fish survival rate and growth rate, and reduce the feed coefficient.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
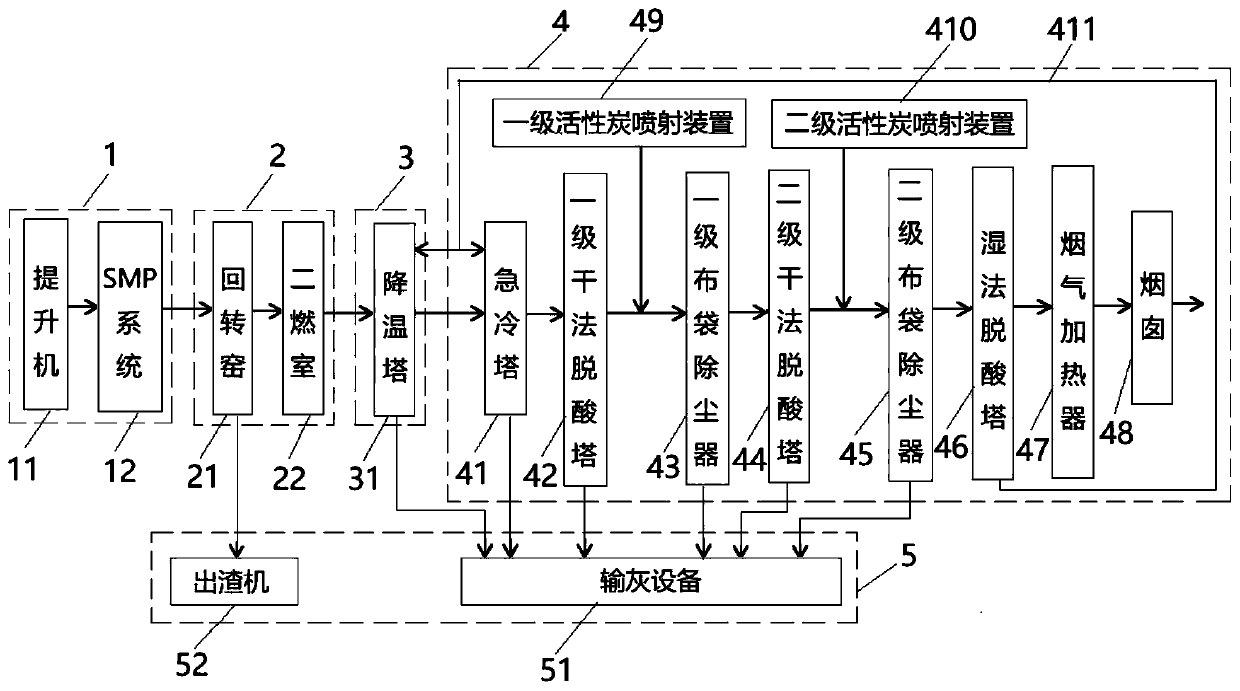
Systems and method for hazardous waste incineration
InactiveCN111006221AConforms to emptying standardsAvoid pollutionIncinerator apparatusCooling towerCombustion chamber
The invention provides a system and a method for hazardous waste incineration. The system comprises a feeding system, an incineration system, a cooling system and a flue gas treatment system which aresequentially arranged; the feeding system comprises an elevator and an SMP system which are arranged in sequence; the incineration system comprises a rotary kiln and a secondary combustion chamber which are sequentially communicated, and is used for sequentially pyrolyzing fed materials twice until the fed materials are completely pyrolyzed to obtain double-pyrolyzed flue gas; the cooling systemcomprises a cooling tower and is used for cooling the double-pyrolyzed flue gas to obtain cooled flue gas; the flue gas treatment system comprises a quench tower, a first-stage dry deacidification tower, a first-stage bag-type dust collector, a second-stage dry deacidification tower, a second-stage bag-type dust collector, a wet deacidification tower, a flue gas heater, a chimney and a first-stageactivated carbon spraying device which are connected in sequence, and further comprises a first-stage activated carbon spray device used for carrying out a series of treatments on the cooled flue gasand completely discharging the treated flue gas. The method uses the system to incinerate hazardous wastes. The system and the method can be used for incinerating hazardous wastes with high sulfur, chlorine and fluorine contents.
Owner:CECEP CLEAN TECH DEV CO LTD
Lithium ion battery electrolytic solution treatment method
InactiveCN110845040AImprove hydrolysis efficiencyImprove the completeness of hydrolysisGas treatmentWater contaminantsElectrolytic agentFlocculation
The invention provides a lithium ion battery electrolytic solution treatment method, which comprises: (1) preparing a calcium hydroxide solution; (2) adding an acid solution into a lithium ion batteryelectrolytic solution, and carrying out hydrolysis treatment to obtain a hydrolysis solution; (3) adding a calcium hydroxide solution into the hydrolysis solution in a dropwise manner, and stirring to generate waste gas and a solid-liquid mixture; and (4) carrying out absorption treatment and separation treatment on the waste gas, and carrying out flocculation precipitation treatment and separation treatment on the solid-liquid mixture. According to the invention, with the method, the acid solution is added to carry out hydrolysis treatment, the calcium hydroxide solution is added into the hydrolysis solution in a dropwise manner to carry out flocculation precipitation treatment and the like, so that the fluorine content in the liquid phase is reduced; and the fluorine content in the separated liquid phase is smaller than 10 ppm through close fit interaction of the steps (2), (3) and (4).
Owner:广东风华新能源股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com