Soil amendment and method for reducing fluorine content of fresh brick tea leaves
A technology of soil improver and fluorine content, applied in soil conditioning materials, chemical instruments and methods, organic fertilizers, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
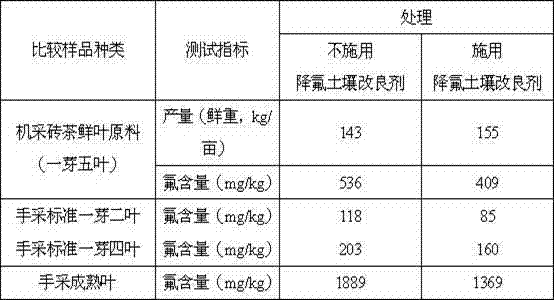
[0018] In 2010, a test was carried out on the production tea garden, using no soil improver to reduce the fluorine content in fresh brick tea leaves as a control, and one month before brick tea picking, the soil improver was applied once at a rate of 460kg / mu, and applied in the tea garden On the soil surface, lightly plow the soil after spreading. The soil conditioner contains 317kg of dolomite powder passed through a 200 mesh sieve, 35kg of quicklime passed through a 100 mesh sieve, 100kg of peat (dry weight) and 8kg of potassium chloride. Pick fresh brick tea after 30 days. Leaf raw materials were used to count the output, and fresh brick tea leaf raw materials were collected at the same time, dried and pulverized to determine the fluorine content. The results showed that after the application of defluoridation soil amendment, the yield of fresh brick tea leaf raw materials increased, and the fluorine content of fresh brick tea leaf raw materials decreased from 536mg / kg when...
Embodiment 2
[0022] The test was carried out on the production tea garden, with no application of the soil improver for reducing the fluorine content in the fresh brick tea leaves as a control, and one month before the brick tea was picked, the soil improver was applied once at a rate of 227kg / mu on the soil surface of the tea garden. After spreading the soil, the soil is lightly plowed. The soil improver contains 158kg of dolomite powder passed through a 200 mesh sieve, 15kg of quicklime passed through a 100 mesh sieve, 50kg of peat (dry weight) and 4kg of potassium chloride. After 30 days, fresh brick tea leaves are picked. The output is counted, and the fresh leaf raw materials of brick tea are collected at the same time, and the fluorine content is determined after drying and pulverizing. It can also achieve the technical effect similar to that of Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0024] The test was carried out on the production tea garden, taking no application of the soil improver for reducing the fluorine content in the fresh brick tea leaves as a control, and one month before the brick tea was picked, the soil improver was applied once at a rate of 693kg / mu on the soil surface of the tea garden. After spreading the soil, carry out shallow plowing of the soil. The soil improver contains 476kg of dolomite powder passed through a 200 mesh sieve, 55kg of quicklime passed through a 100 mesh sieve, 150kg of peat (dry weight) and 12kg of potassium chloride. After 30 days, fresh brick tea leaves are picked. The output is counted, and the fresh leaf raw materials of brick tea are collected at the same time, and the fluorine content is determined after drying and pulverizing. It can also achieve the technical effect similar to that of Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com