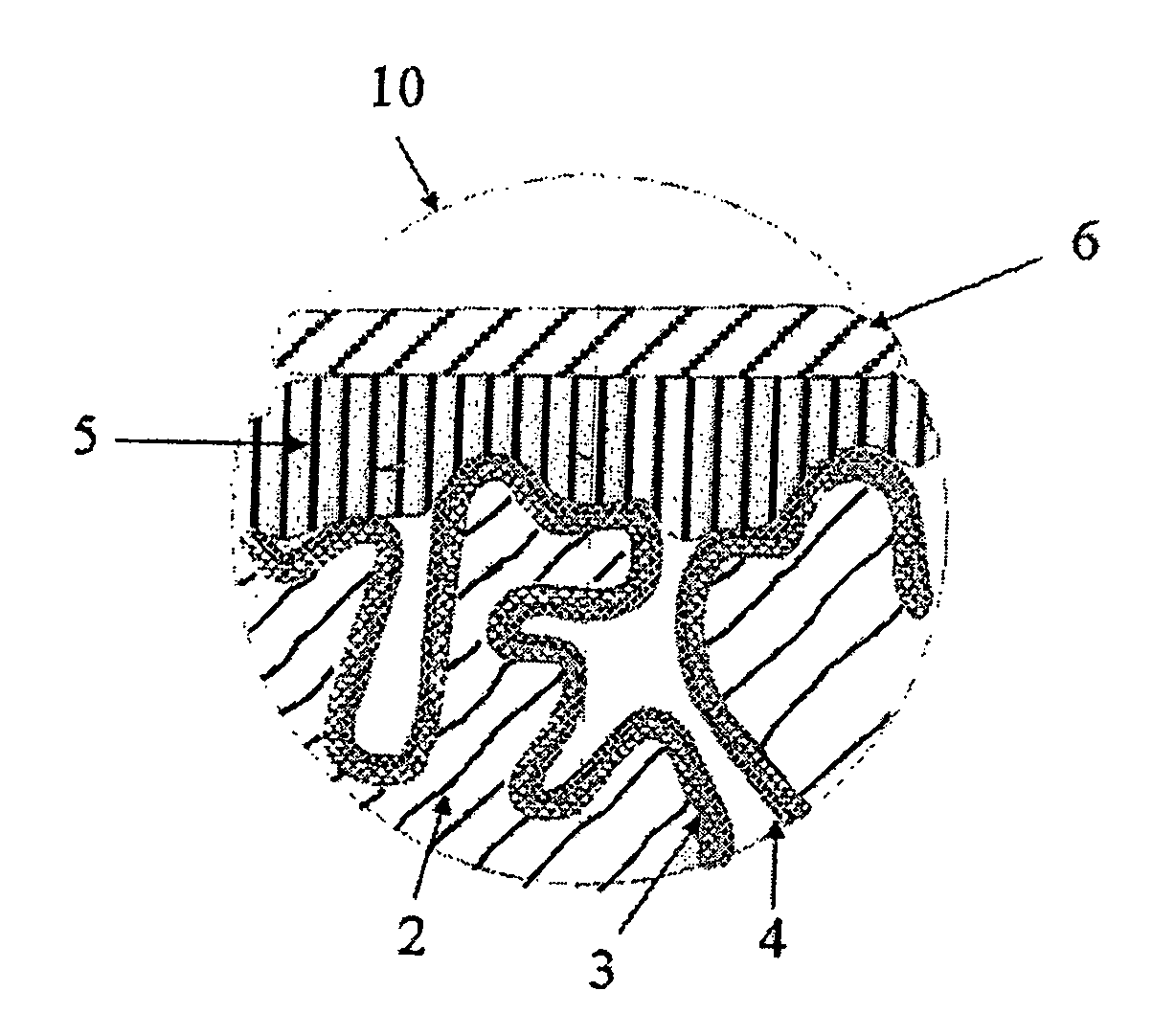
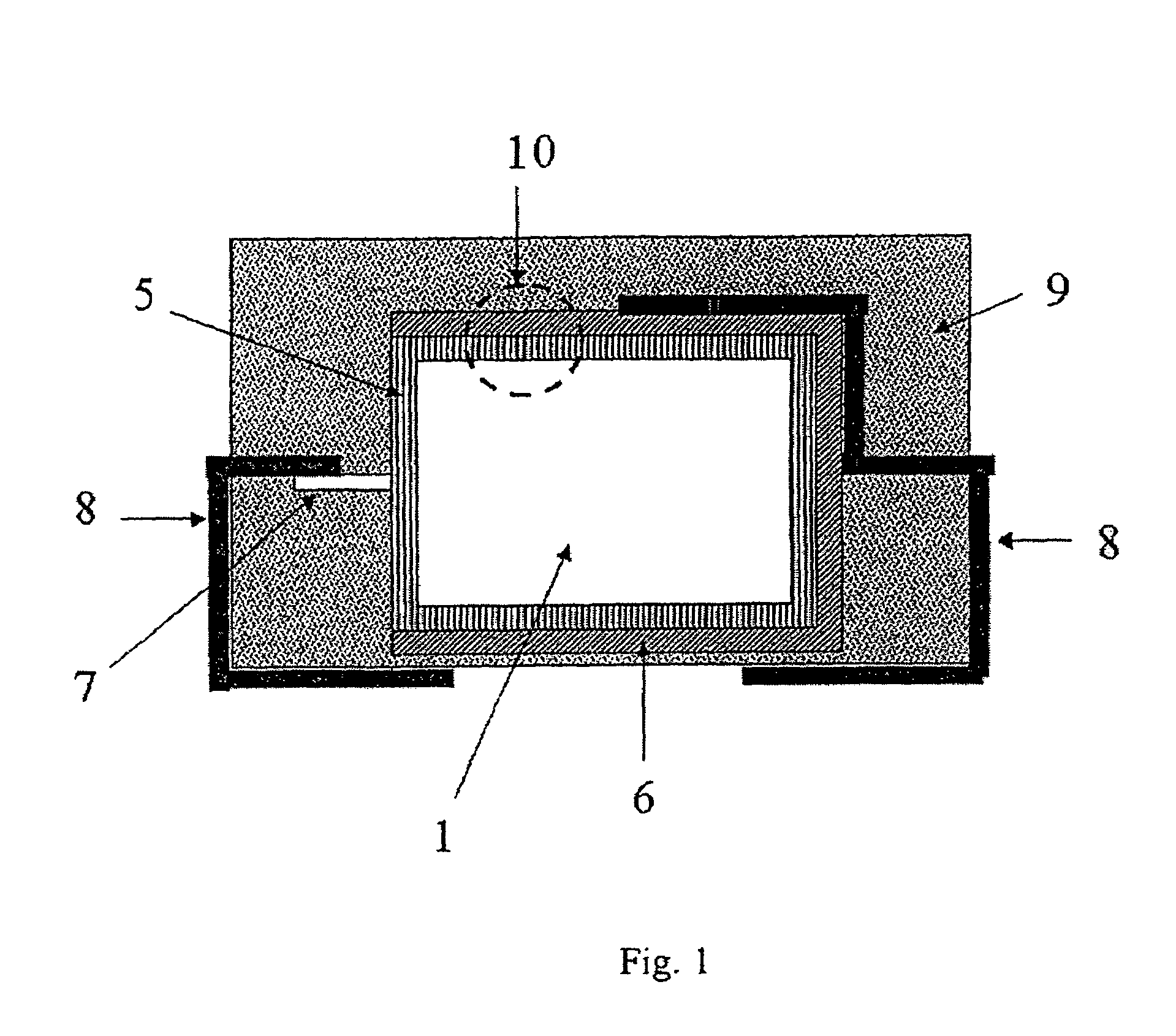
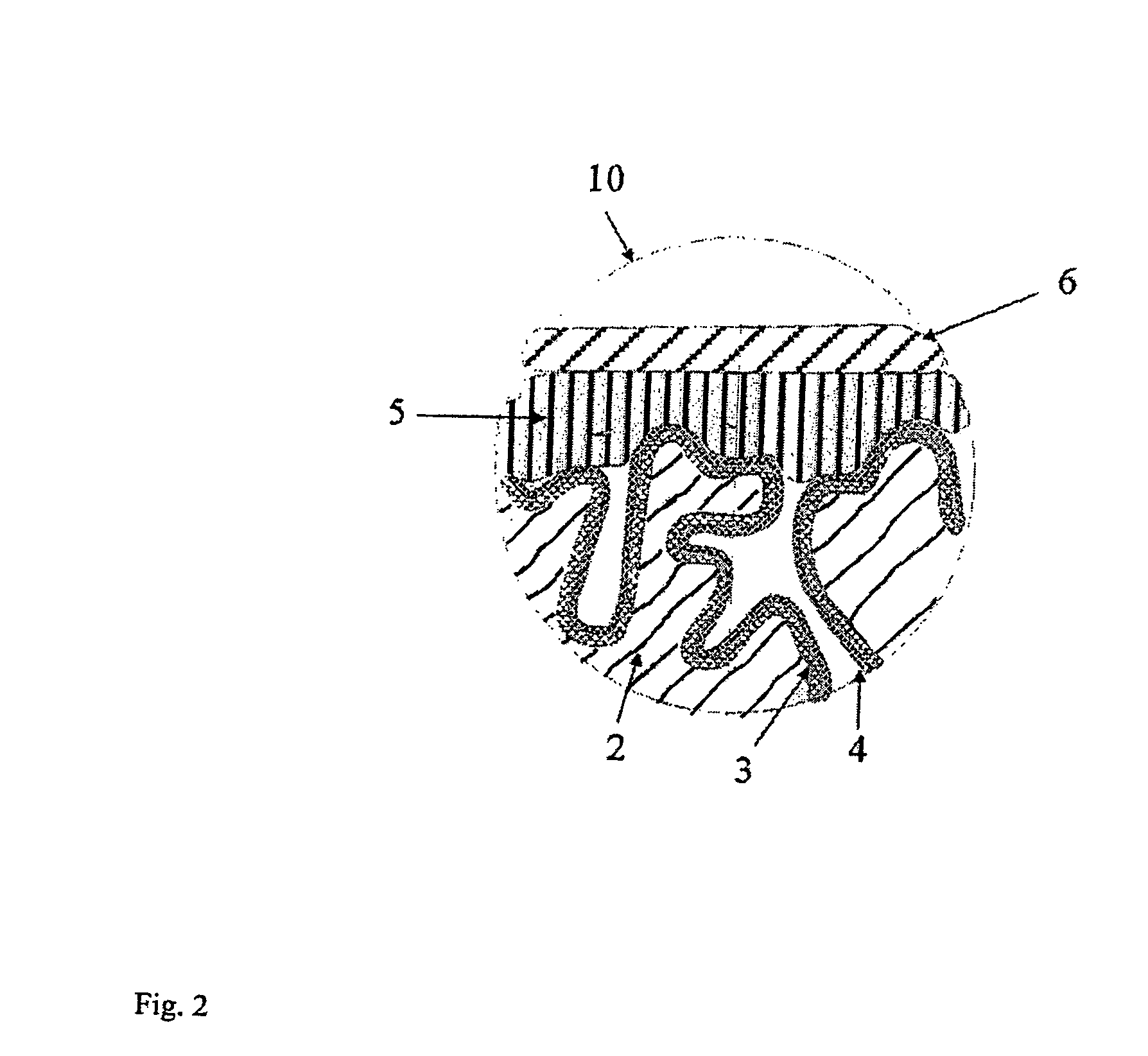
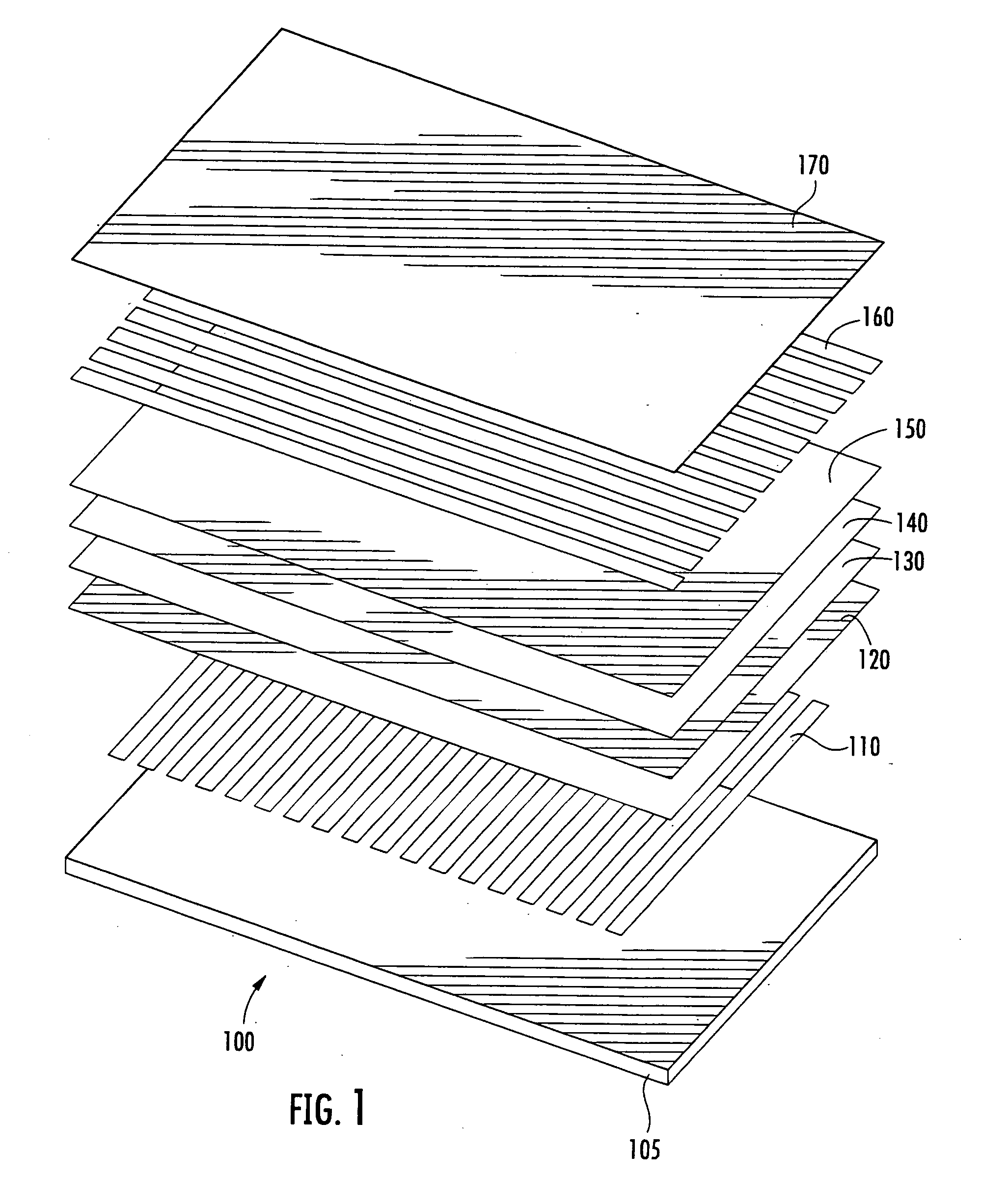
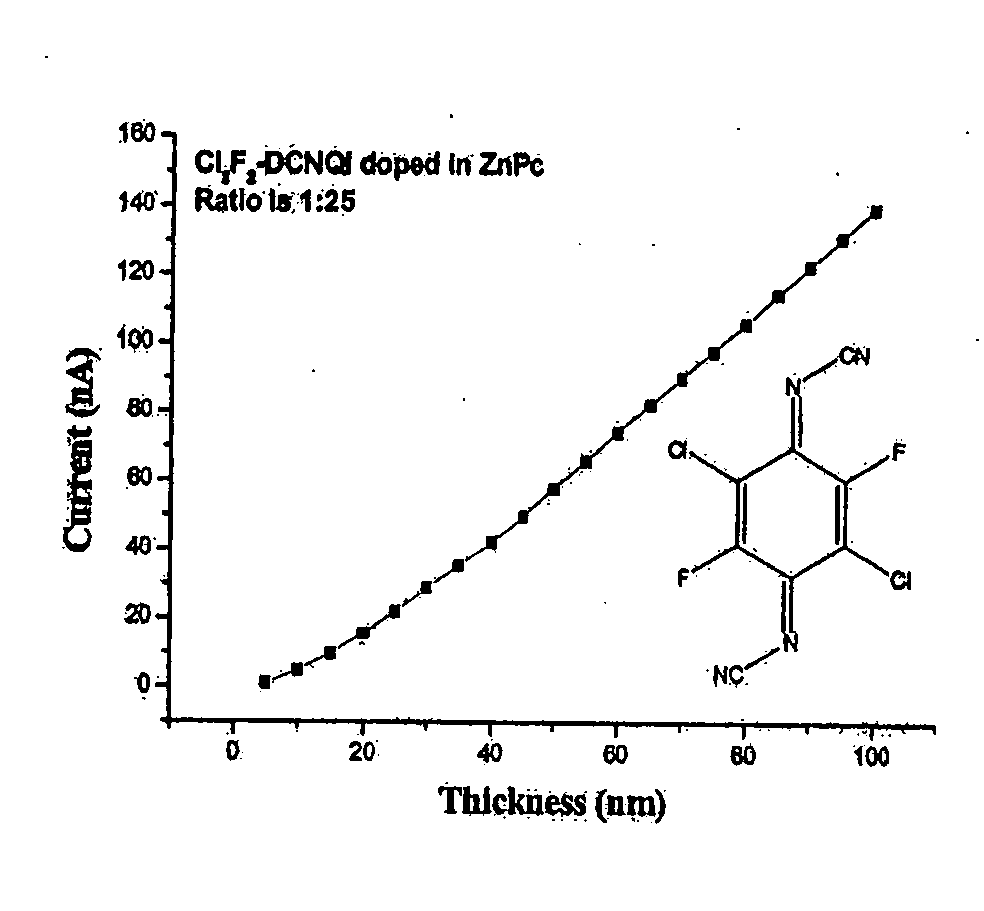
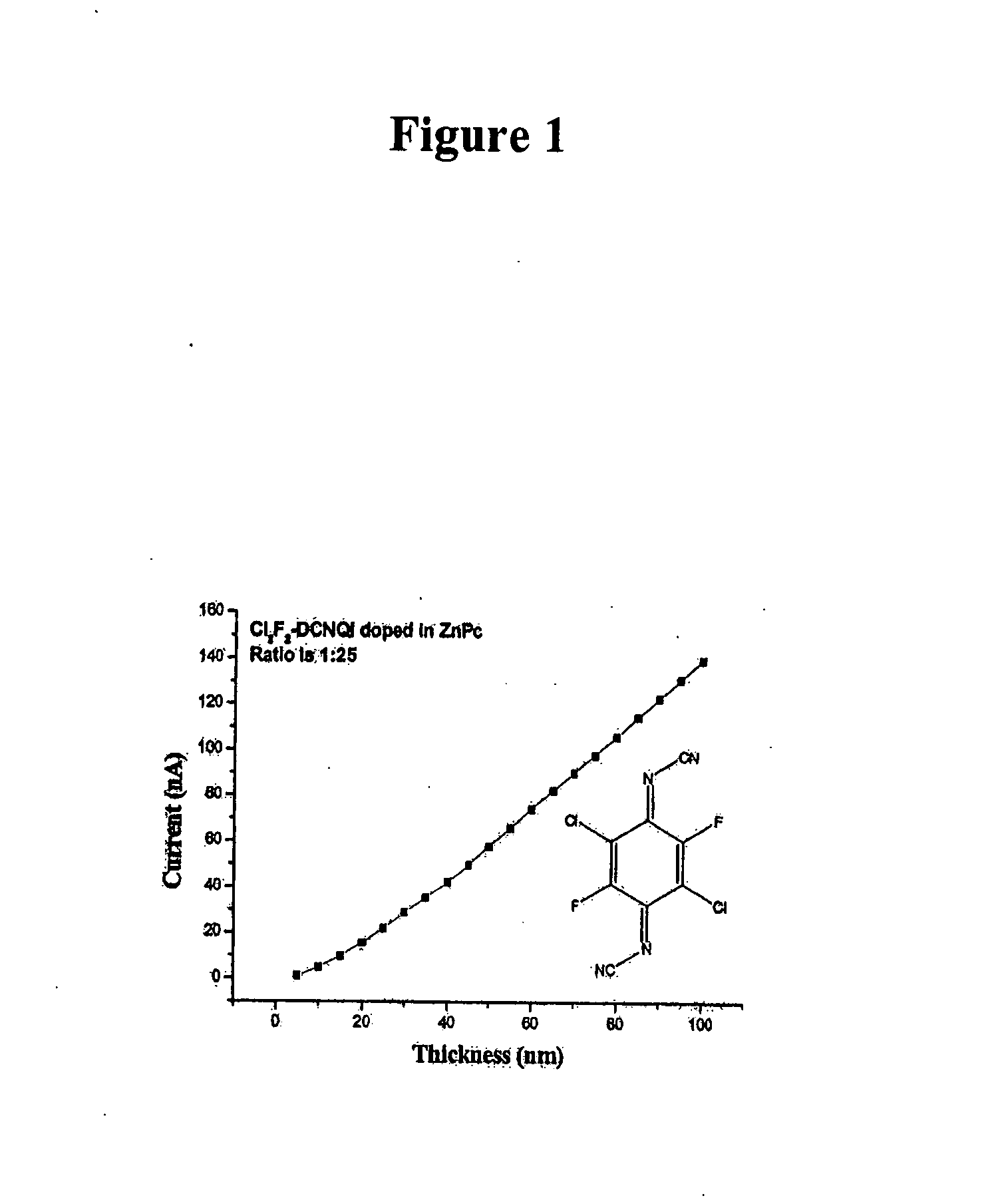
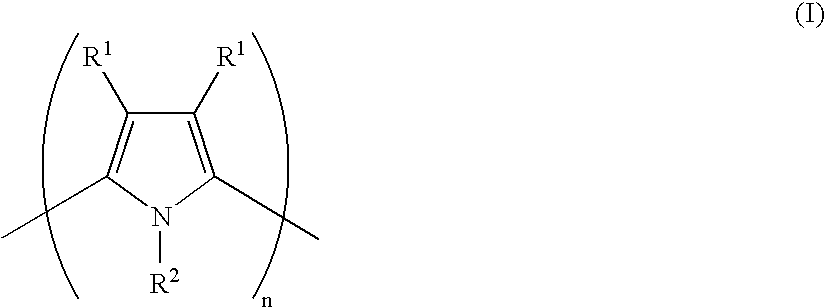Patents
Literature
13773results about "Conductive material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
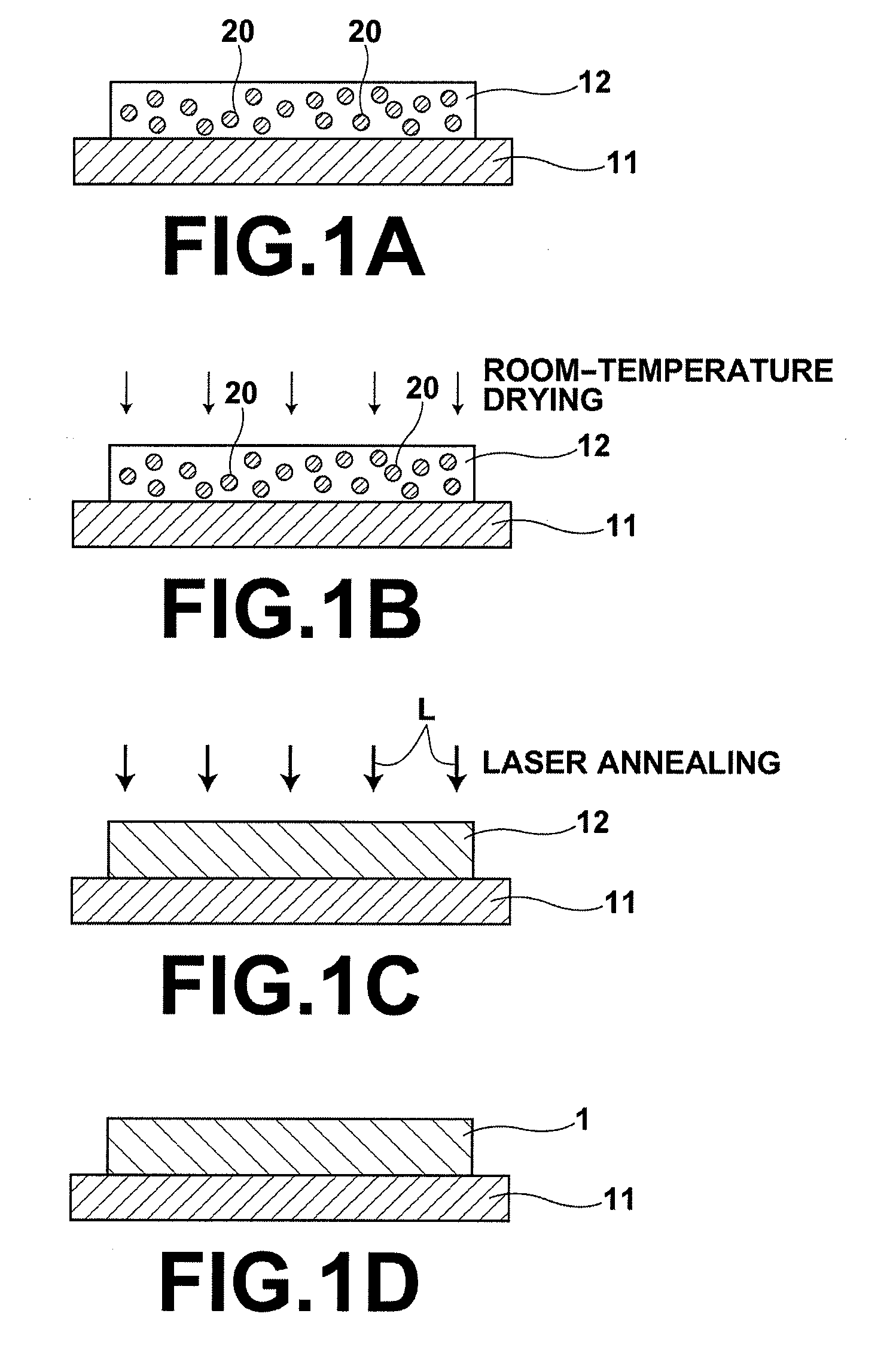
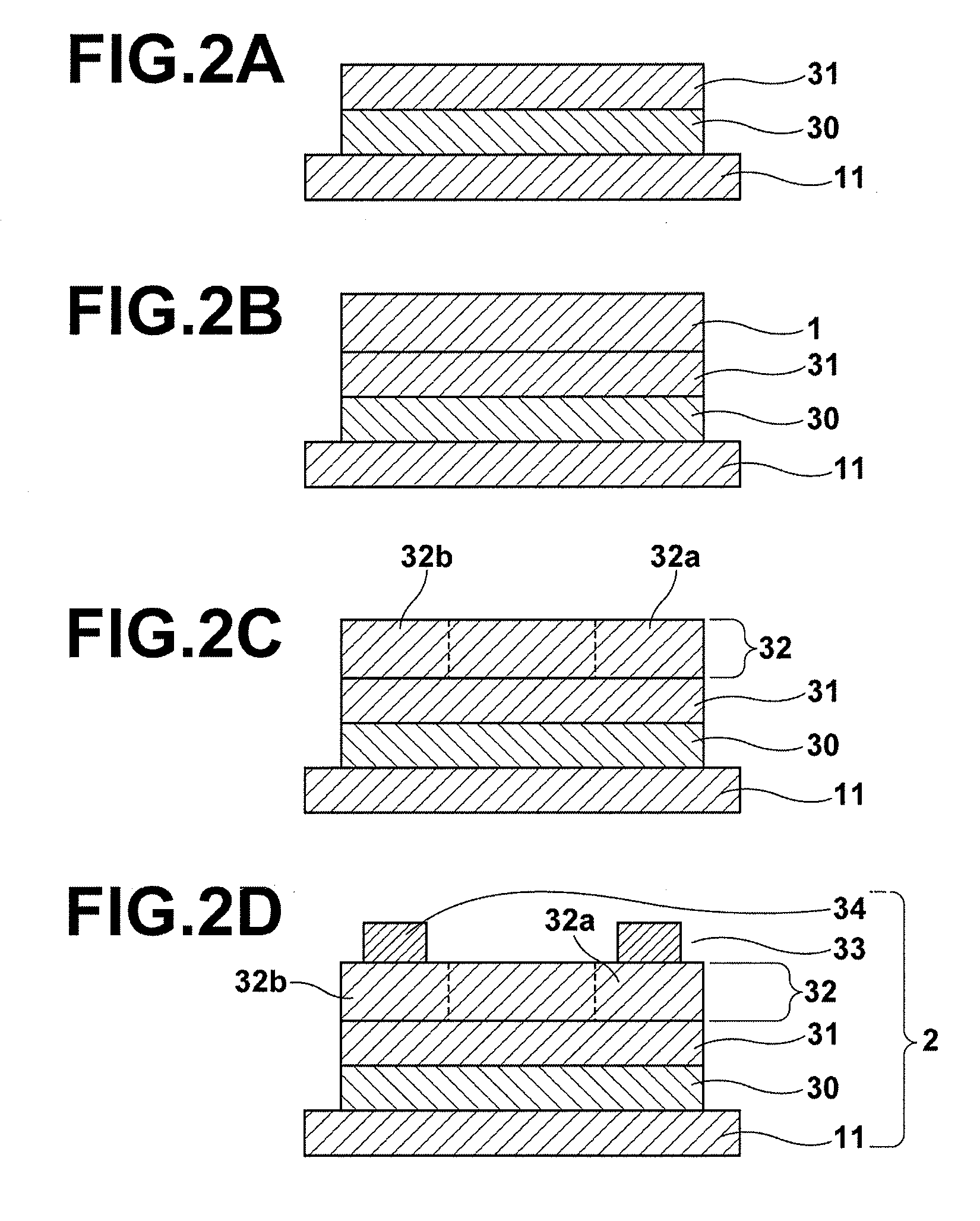
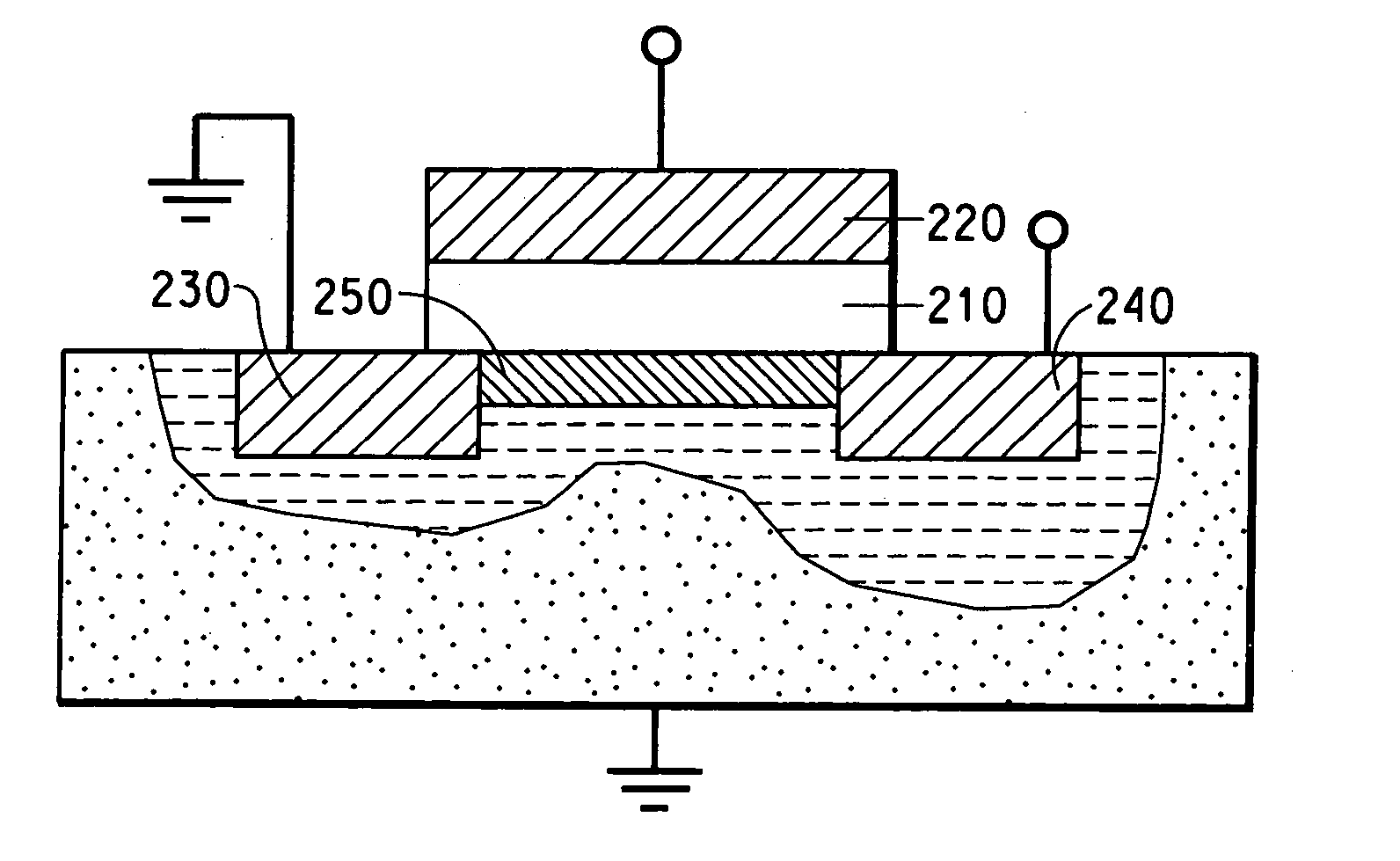
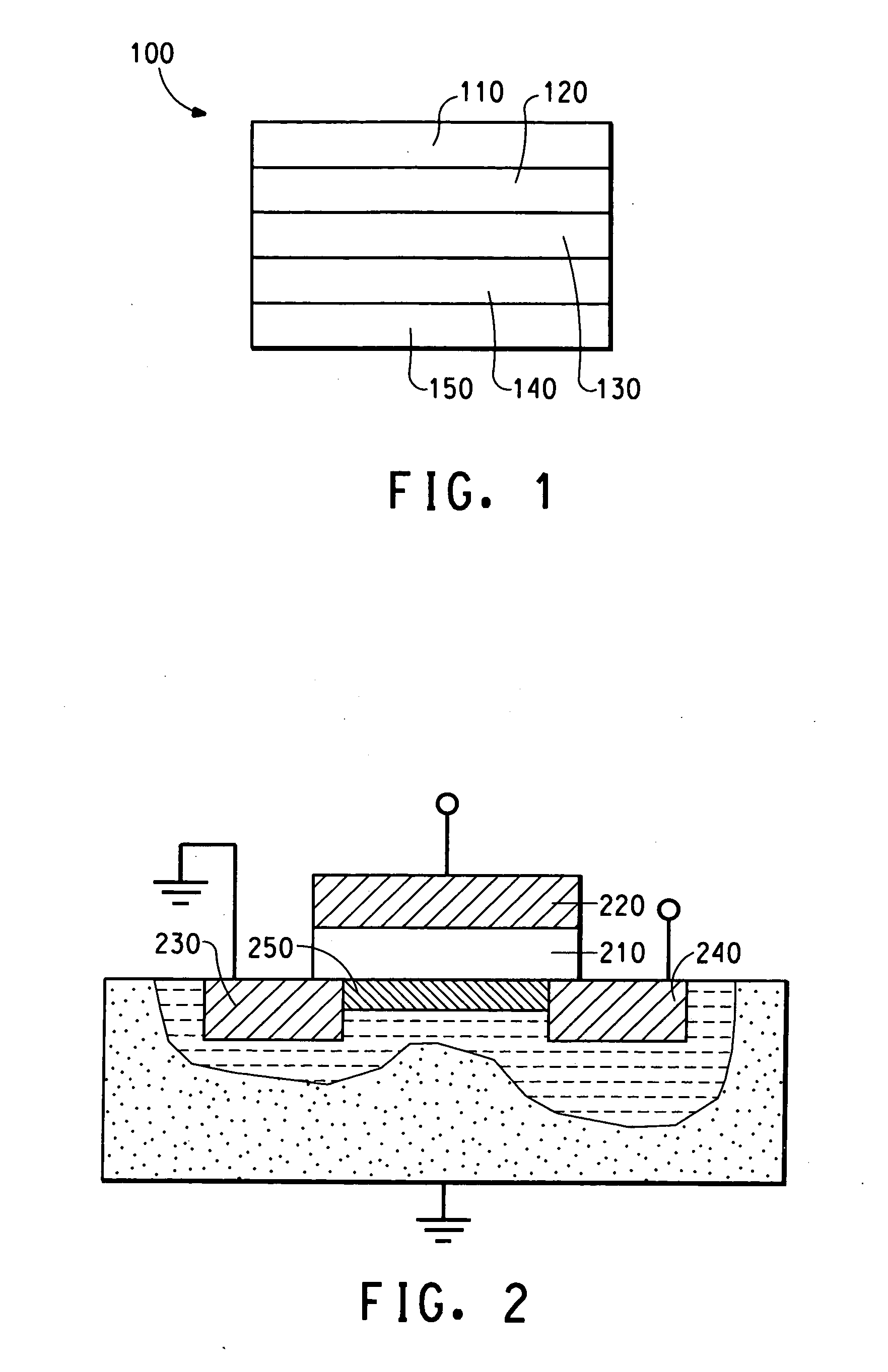
Process for producing oriented inorganic crystalline film, and semiconductor device using the oriented inorganic crystalline film
ActiveUS20090152506A1Orientation can be controlledLow costFrom gel stateFrom solid stateOrganic solventDevice material
In a process for producing an oriented inorganic crystalline film, a non-monocrystalline film containing inorganic crystalline particles is formed on a substrate by a liquid phase technique using a raw-material solution which contains a raw material and an organic solvent, where the inorganic crystalline particles have a layered crystal structure and are contained in the raw material. Then, the non-monocrystalline film is crystallized by heating the non-monocrystalline film to a temperature equal to or higher than the crystallization temperature of the non-monocrystalline film so that part of the inorganic crystalline particles act as crystal nuclei.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
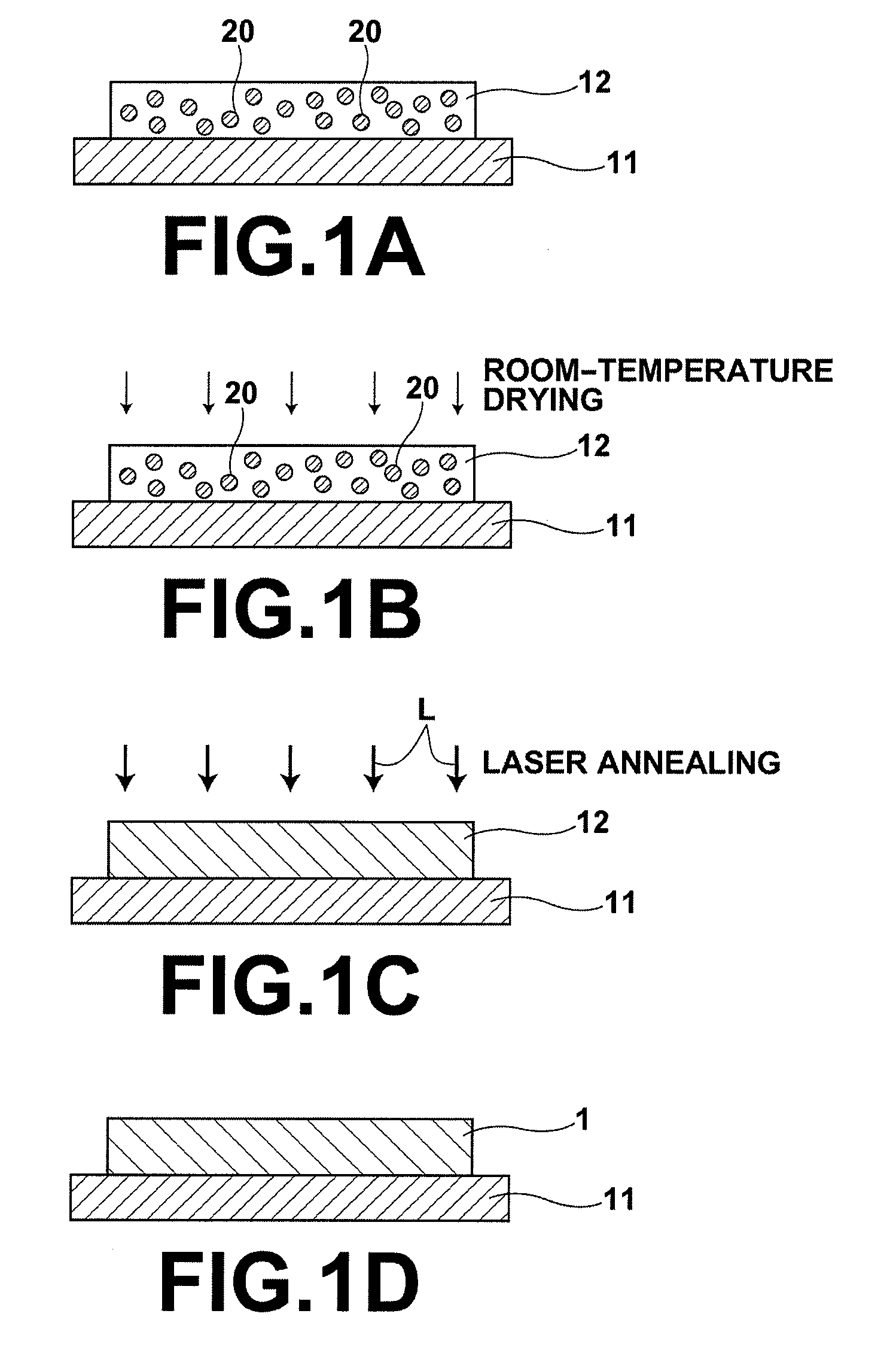
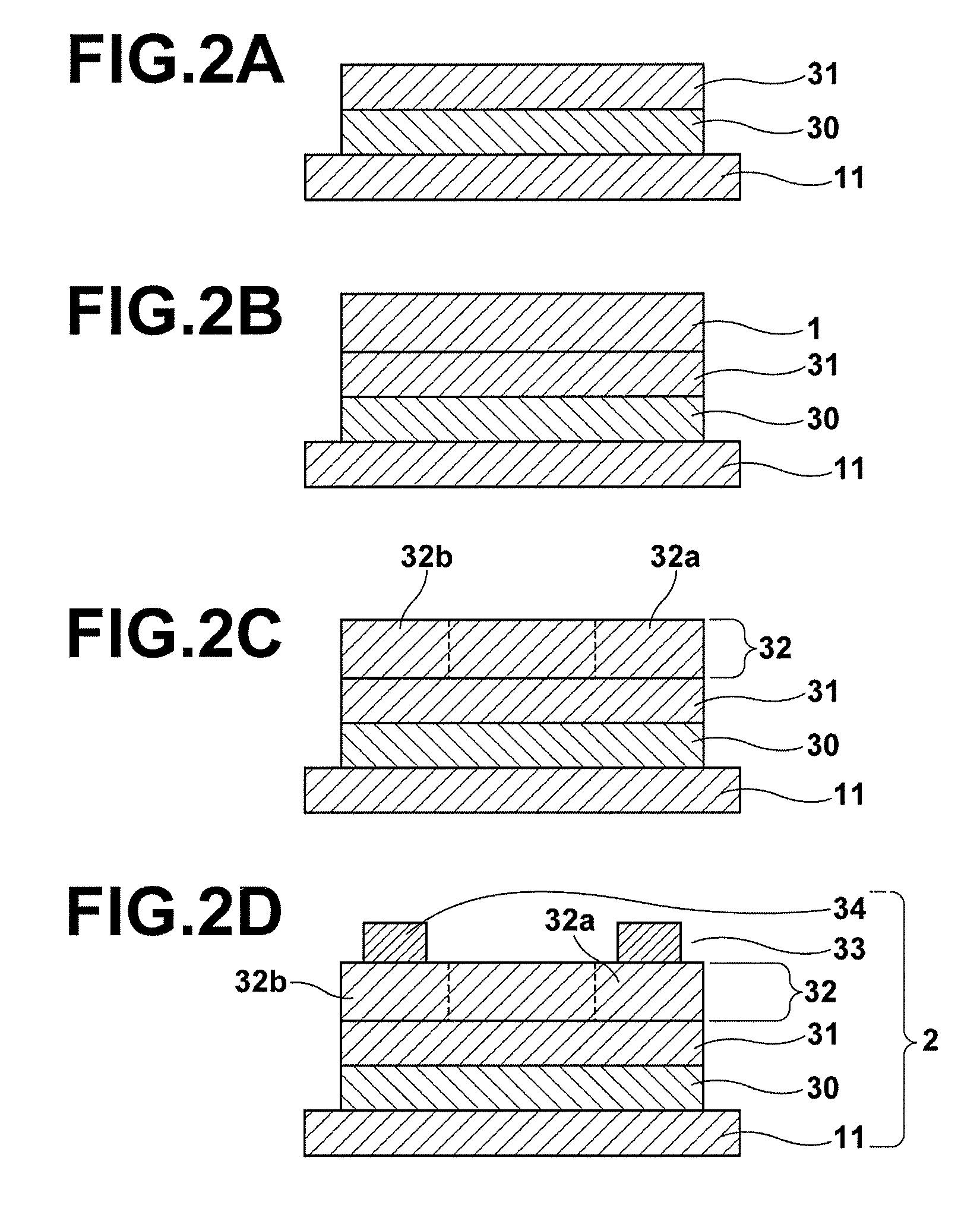
Process for producing oriented inorganic crystalline film, and semiconductor device using the oriented inorganic crystalline film
ActiveUS8202365B2Orientation can be controlledLow costFrom gel stateFrom solid stateOrganic solventCrystal structure
In a process for producing an oriented inorganic crystalline film, a non-monocrystalline film containing inorganic crystalline particles is formed on a substrate by a liquid phase technique using a raw-material solution which contains a raw material and an organic solvent, where the inorganic crystalline particles have a layered crystal structure and are contained in the raw material. Then, the non-monocrystalline film is crystallized by heating the non-monocrystalline film to a temperature equal to or higher than the crystallization temperature of the non-monocrystalline film so that part of the inorganic crystalline particles act as crystal nuclei.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Electrolytic capacitors with a polymeric outer layer
ActiveUS6987663B2Reduce leakage currentLow ESRHybrid capacitor electrolytesSolid electrolytic capacitorsPolymer scienceElectrolysis
Electrolytic capacitors having low equivalent series resistance and low leakage current are described. The electrolytic capacitors include a solid electrolyte layer of a conductive material in particular a conductive polymer, and an outer layer that includes binders, polymeric anions and conductive polymers (e.g., polythiophenes). Also described is a method of preparing electrolytic capacitors that involves forming the conductive polymer of the solid electrolyte layer in situ by means of chemical oxidative polymerization or electrochemical polymerization. Electronic circuits that include the electrolytic capacitors are also described.
Owner:HERAEUS PRECIOUS METALS GMBH & CO KG
Charge transport layers and organic electron devices comprising same
InactiveUS20070181874A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsTransport layerHole transport layer
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
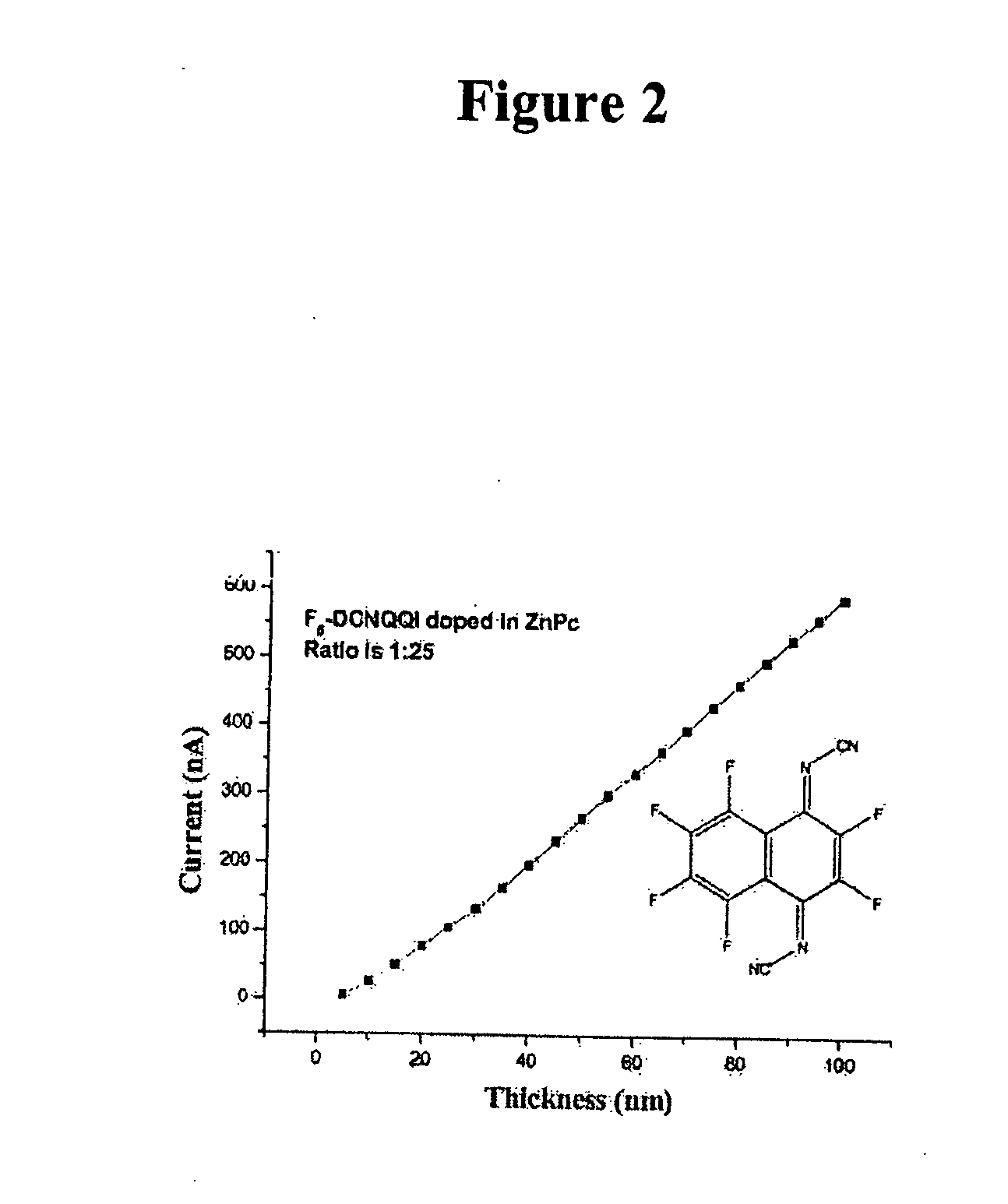
Method of doping organic semiconductors with quinone derivatives and 1, 3, 2 - dioxaborine derivatives
The invention relates to the use of an organic mesomeric compound as organic dopant for doping an organic semiconducting matrix material for varying the electrical properties thereof. In order to be able to handle organic semiconductors more easily in the production process and to be able to produce electronic components with doped organic semiconductors more reproducibly, a quinone or quinone derivative or a 1,3,2-dioxaborine or a 1,3,2-dioxaborine derivative may be used as a mesomeric compound, which under like evaporation conditions has a lower volatility than tetrafluorotetracyanoquinonedimethane (F4TCNQ).
Owner:KUEHL OLAF +4
Water dispersible polypyrroles made with polymeric acid colloids for electronics applications
InactiveUS20050205860A1Material nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrolytesWater dispersiblePolypyrrole
Compositions are provided comprising aqueous dispersions of at least one polypyrrole and at least one colloid-forming polymeric acids at methods of making such compositions. The new compositions are useful in electronic devices including organic electronic devices such as organic light emitting diode displays, memory storage, electromagnetic shielding, electrochromic displays,and thin film transistors, field effect resistance devices.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Low noise cable providing communication between electronic sensor components and patient monitor
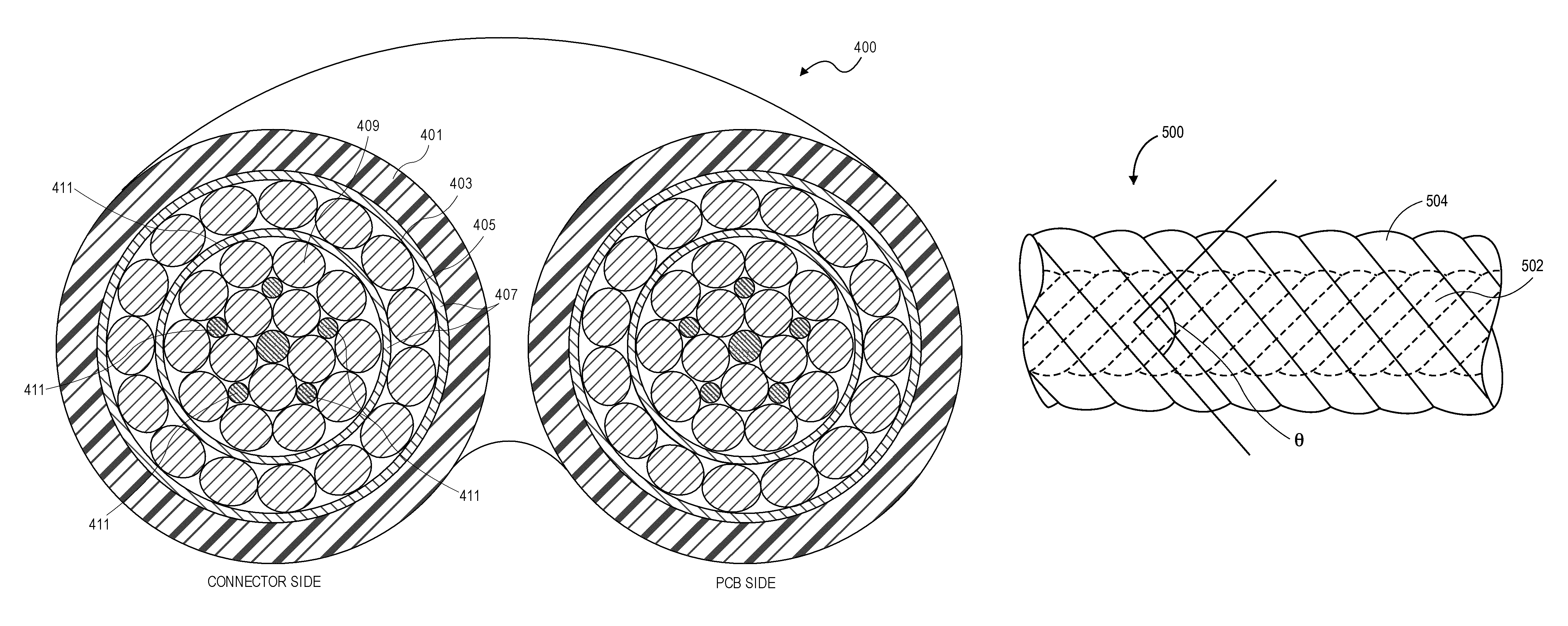
ActiveUS9245668B1Reduce crosstalkNot hindering sensor placementDiagnostics using lightConductive materialLow noiseEngineering
A physiological measurement system can include a low noise patient cable that connects a monitor and a noninvasive optical sensor. The cable has a plurality of emitter wires configured to communicate a drive signal between the monitor and at least one emitter. The cable also has a plurality of detector wires configured to communicate a physiological signal between at least one detector responsive to the emitter and the monitor. The emitter and detector wires are orthogonally disposed so that crosstalk between the two functionally different wires is mitigated.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Conductive adhesive agent and process for manufacturing article using the conductive adhesive agent
ActiveUS20060038304A1Fully curedUniform thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive materialPolymer scienceFluid viscosity
The present invention provides a conductive adhesive agent capable of being diluted with a solvent to give good coating workability and allowing formation of a conductive joint excellent in both thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity by inhibiting a gas generated when a binder resin is heat-cured after attachment of a part. The conductive adhesive agent according to the present invention is a conductive adhesive agent wherein, based on 100 parts by weight of silver powder having an average particle diameter of micrometers, which is used for a conductive medium, e.g. as a main component, 1 to 10 parts by weight of silver fine particles having an average particle diameter of nanometers is used in combination therewith and 5 to 15 parts by weight of thermosetting resin as a binder resin component and 10 parts or less by weight of solvent for adjustment of a fluid viscosity are blended therein as essential components, and by selection of such a blending ratio, generation of a gas component during heating and curing of the thermosetting resin to prevent formation of voids, and at the same time, fabrication of a conductive joint excellent in thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity is achieved.
Owner:HARIMA CHEM INC +1
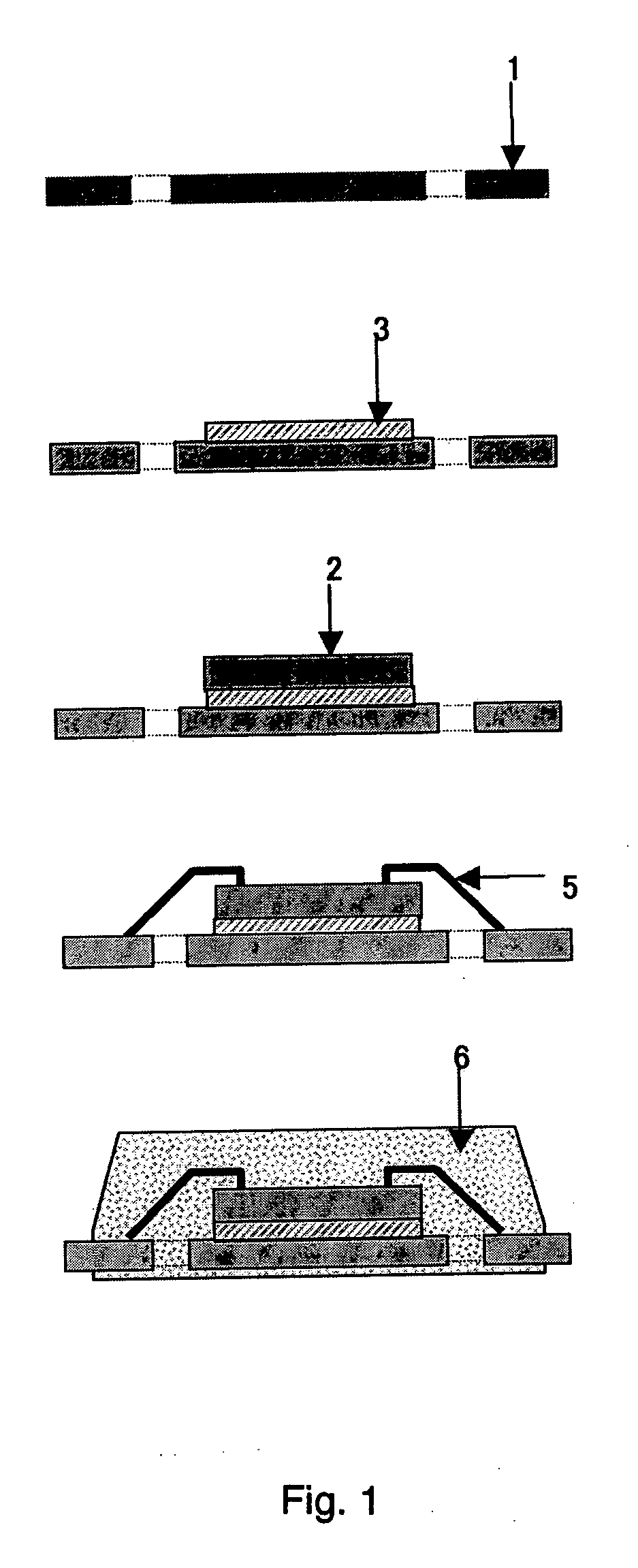
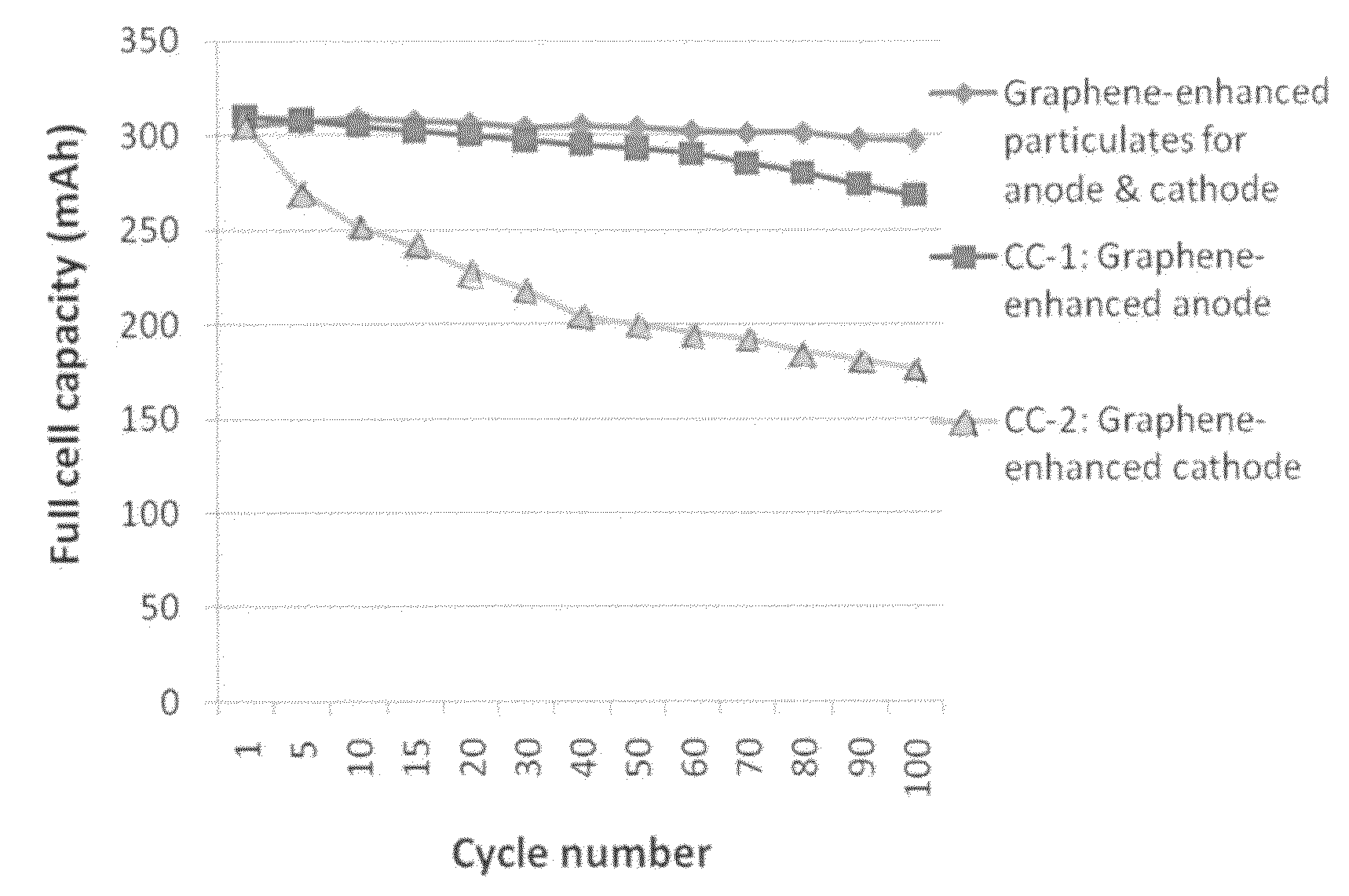
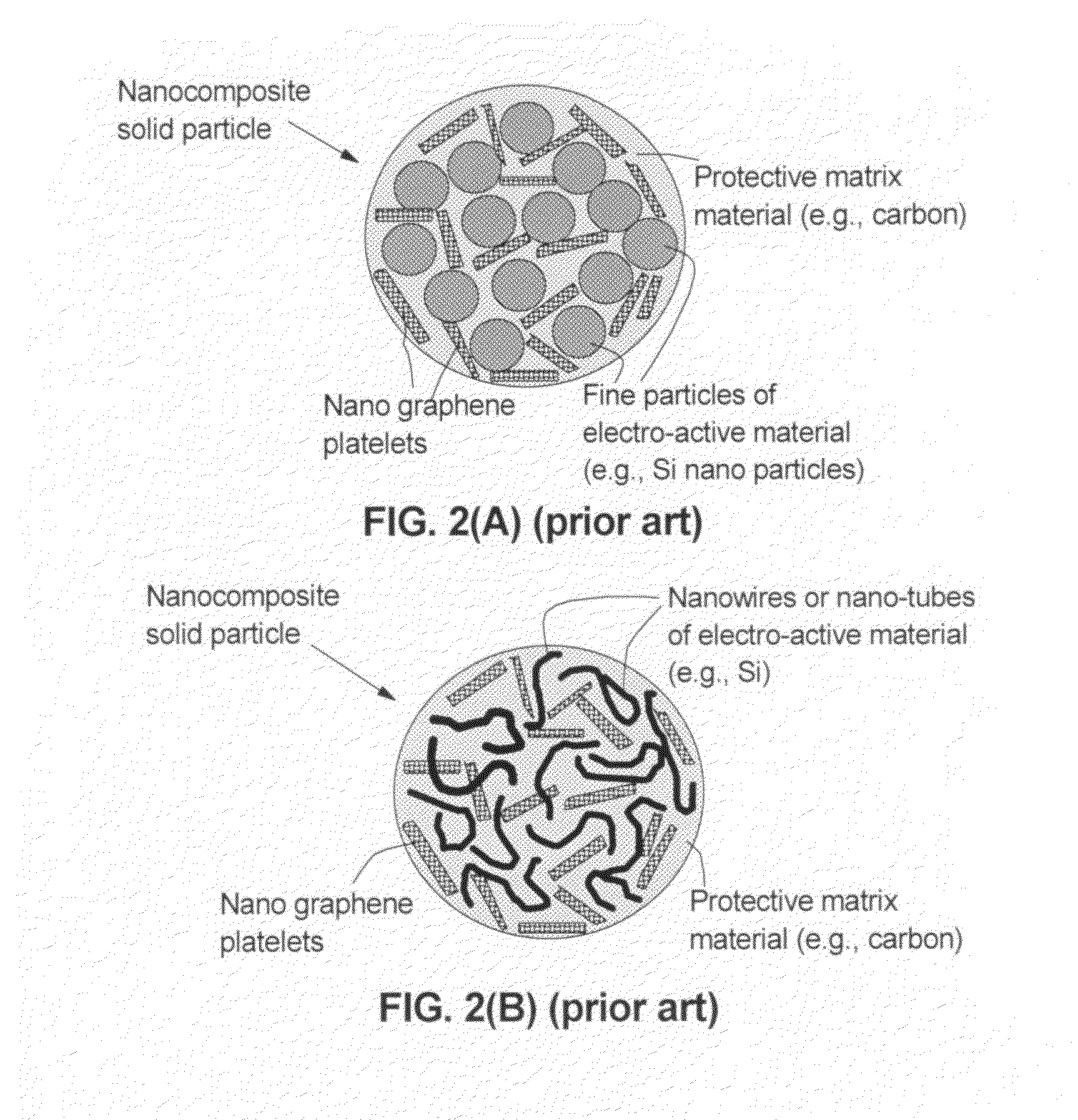
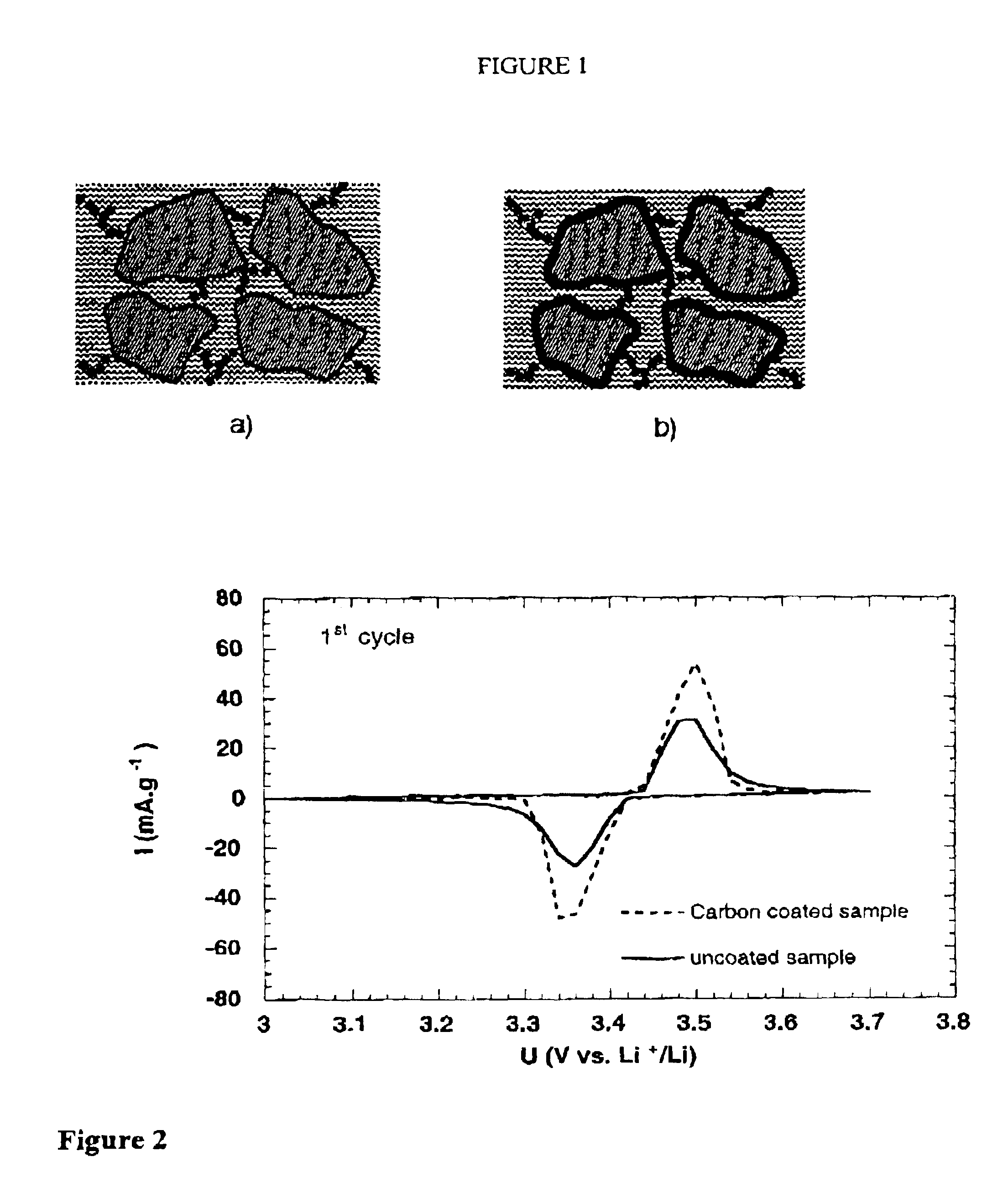
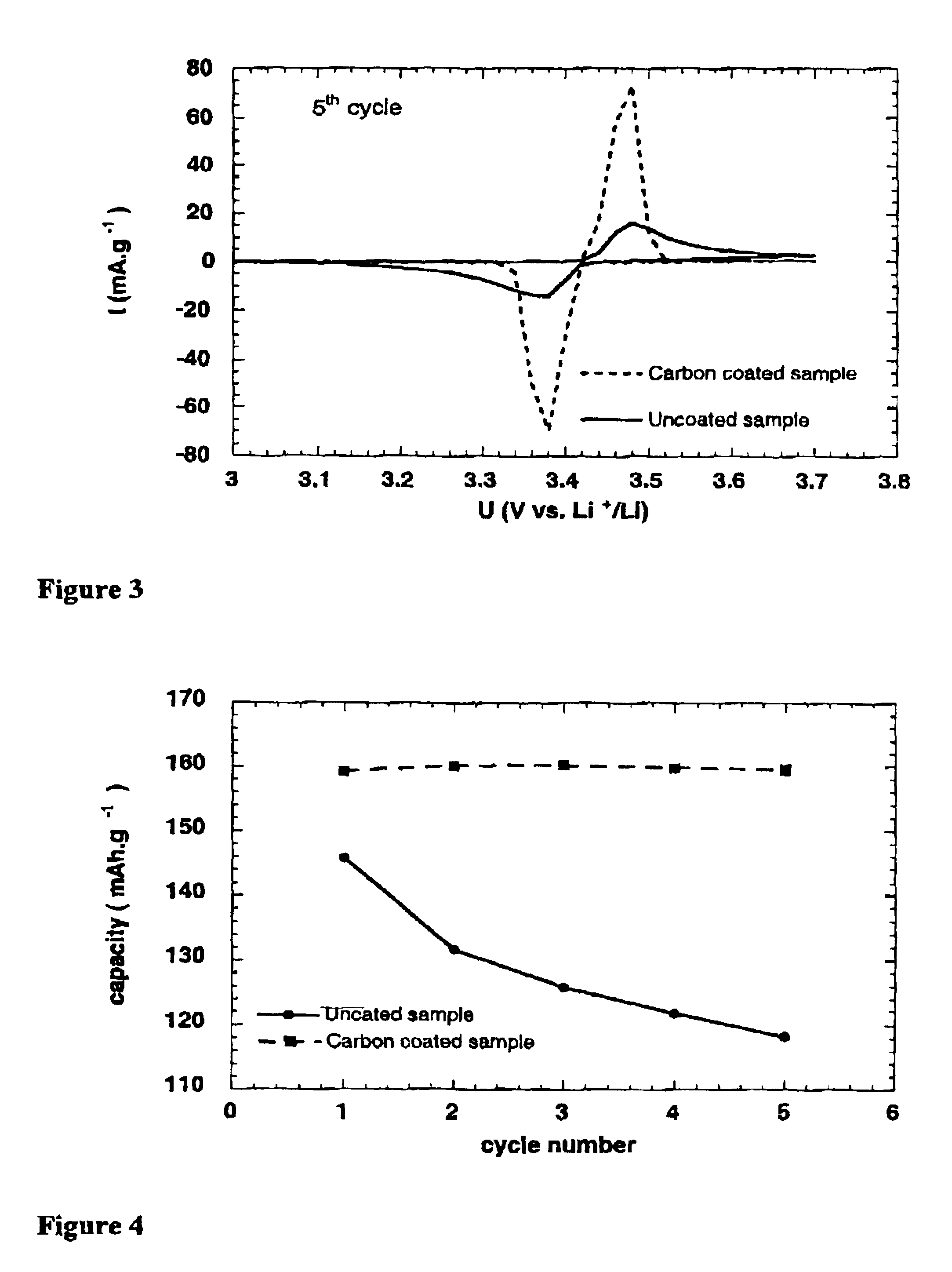
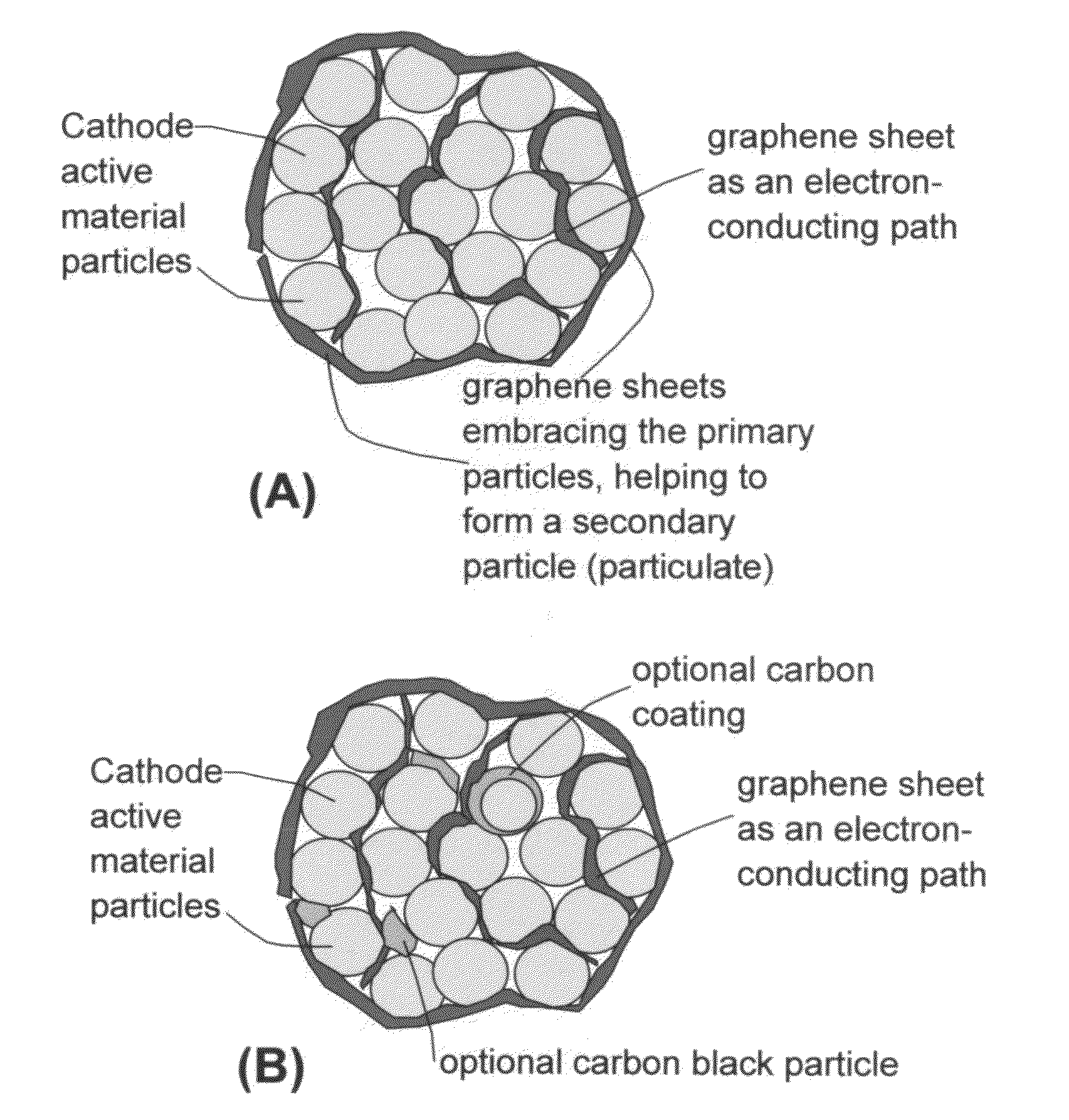
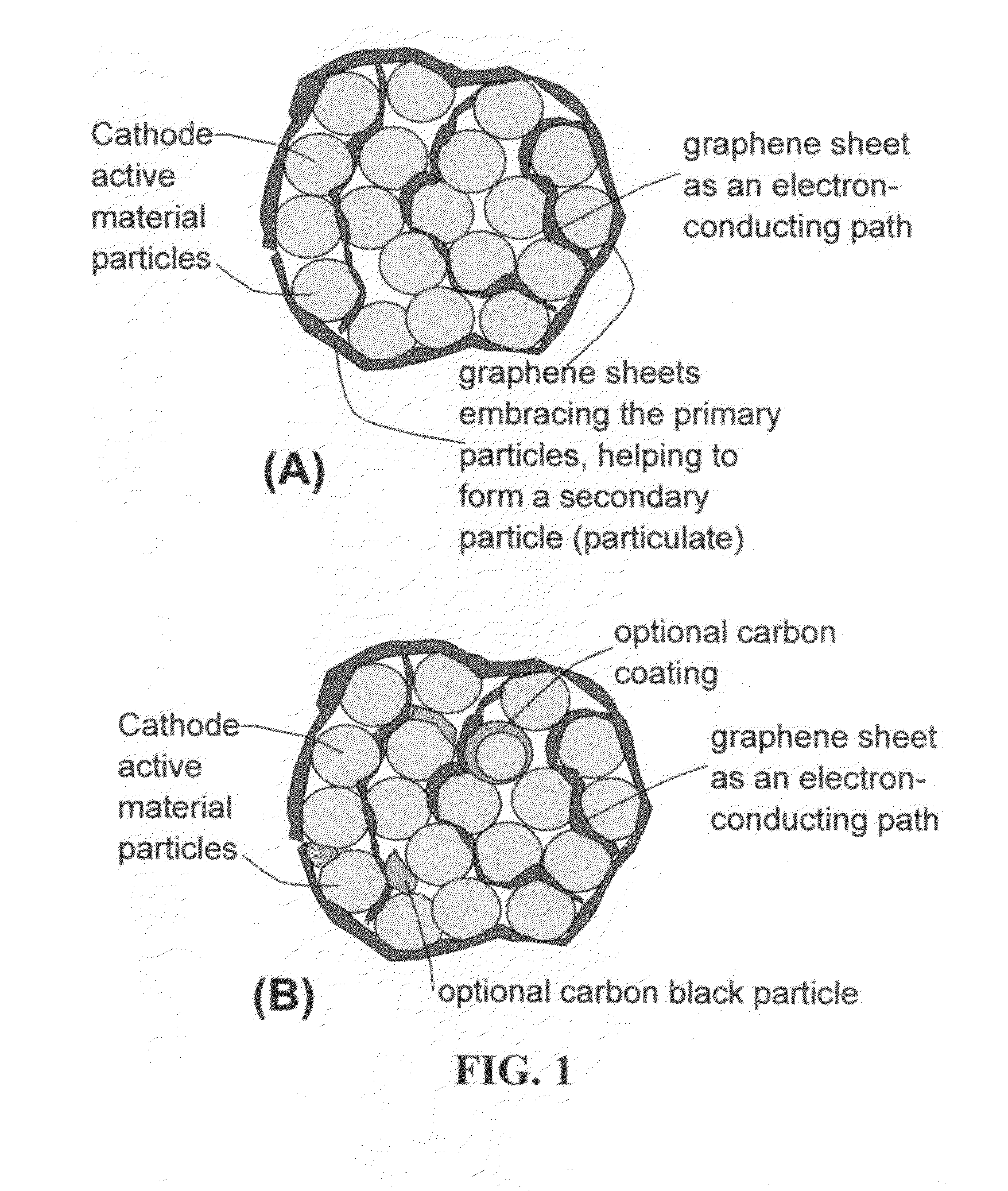
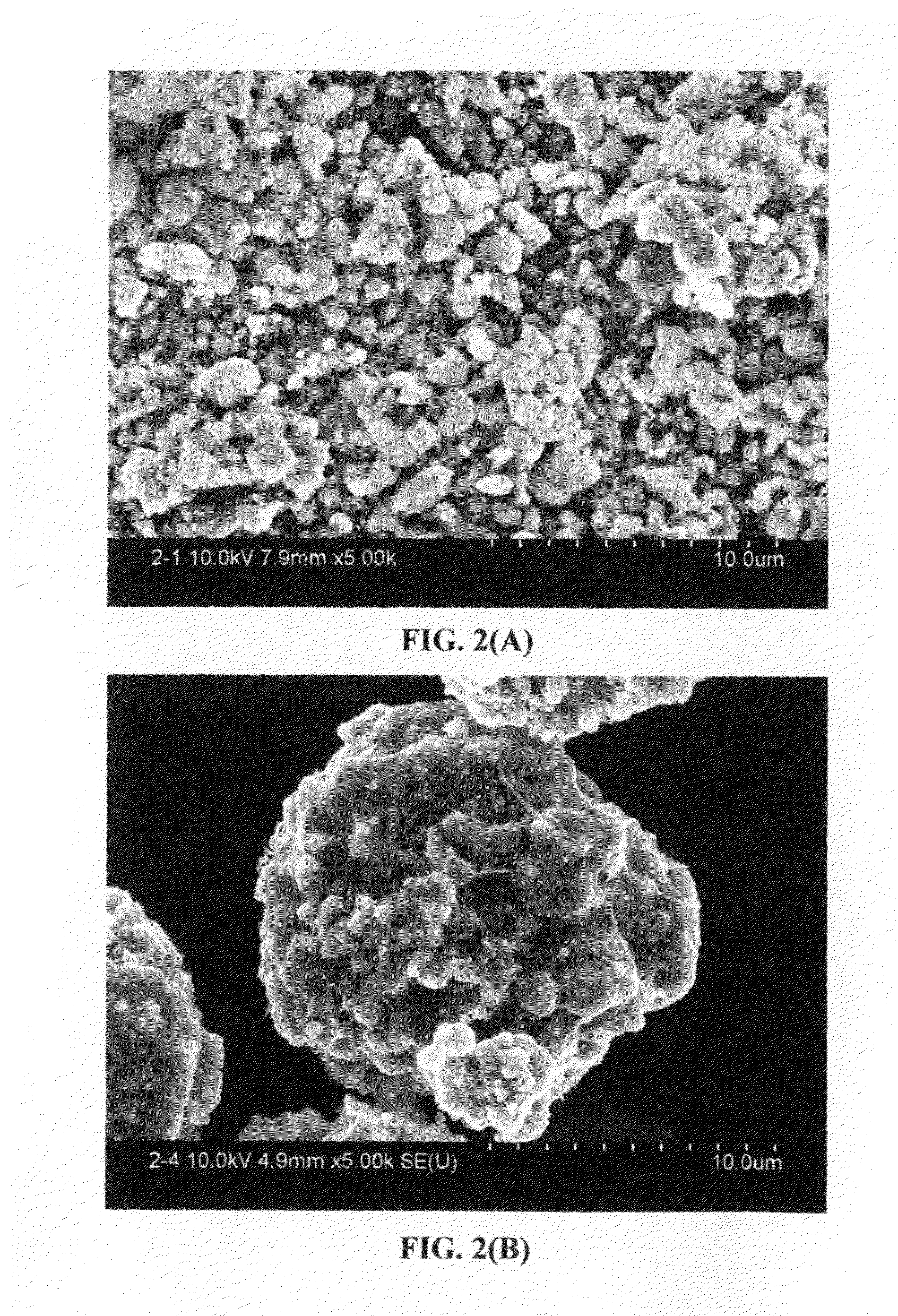
Graphene-enhanced anode particulates for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS20120064409A1Enhanced Li-ion insertionIncrease capacityNon-metal conductorsMaterial nanotechnologyParticulatesMicroparticle
A nano graphene-enhanced particulate for use as a lithium-ion battery anode active material, wherein the particulate is formed of a single sheet of graphene or a plurality of graphene sheets and a plurality of fine anode active material particles with a size smaller than 10 μm. The graphene sheets and the particles are mutually bonded or agglomerated into the particulate with at least a graphene sheet embracing the anode active material particles. The amount of graphene is at least 0.01% by weight and the amount of the anode active material is at least 0.1% by weight, all based on the total weight of the particulate. A lithium-ion battery having an anode containing these graphene-enhanced particulates exhibits a stable charge and discharge cycling response, a high specific capacity per unit mass, a high first-cycle efficiency, a high capacity per electrode volume, and a long cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
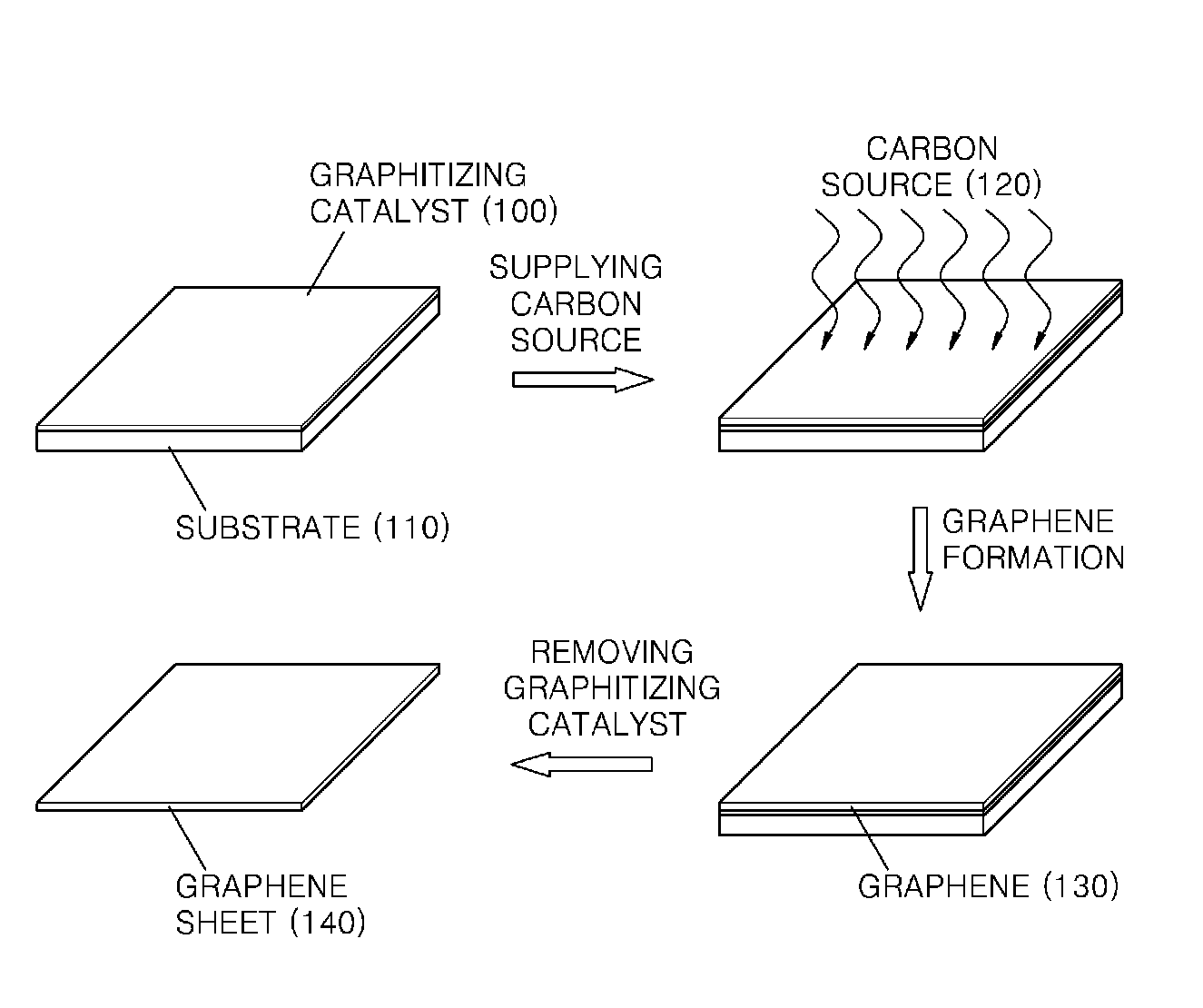
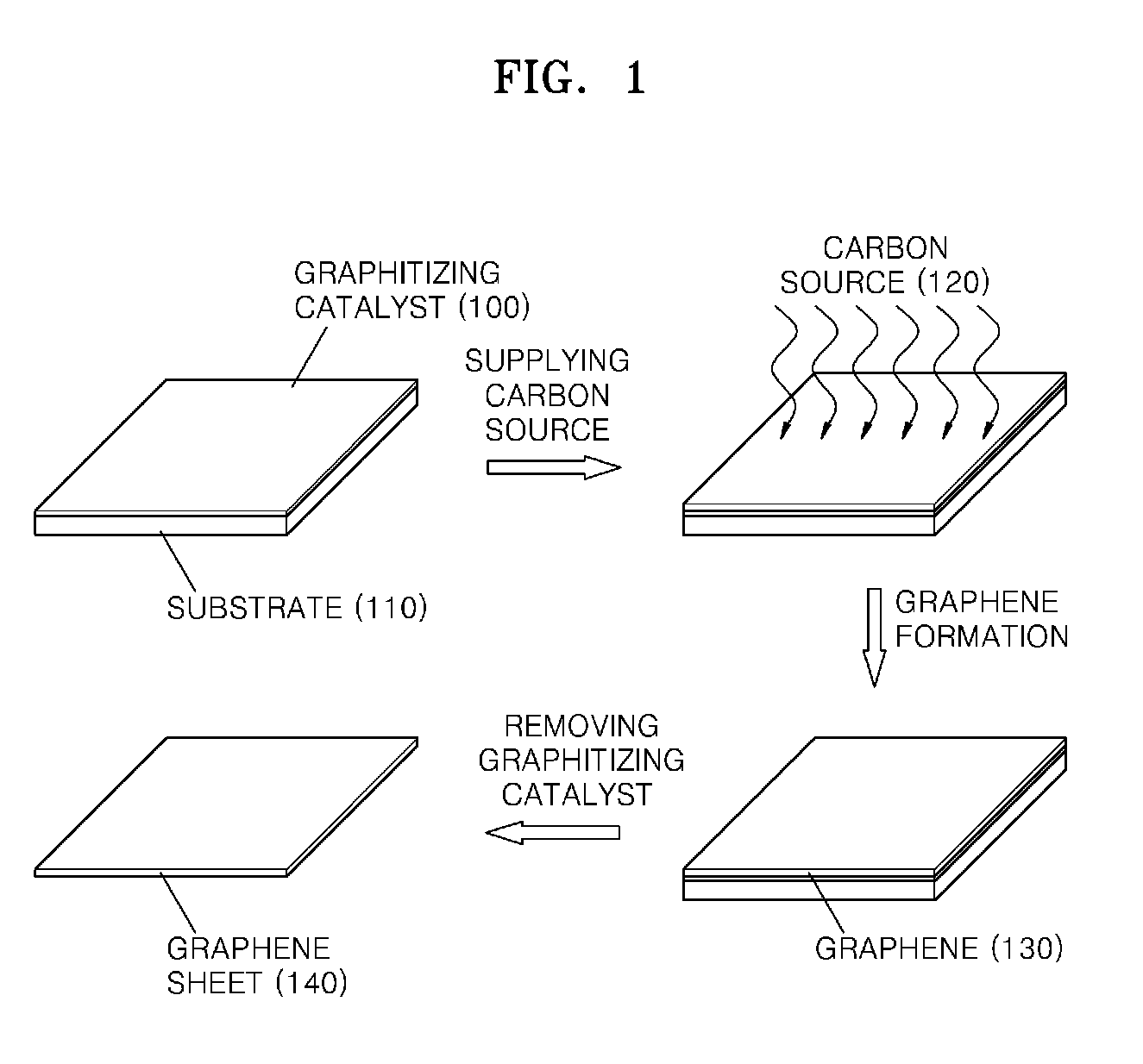
Graphene sheet and method of preparing the same
An economical method of preparing a large-sized graphene sheet having a desired thickness includes forming a film, the film comprising a graphitizing catalyst; heat-treating a gaseous carbon source in the presence of the graphitizing catalyst to form graphene; and cooling the graphene to form a graphene sheet. A graphene sheet prepared according to the disclosed method is also described.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Graphene film as transparent and electrically conducting material
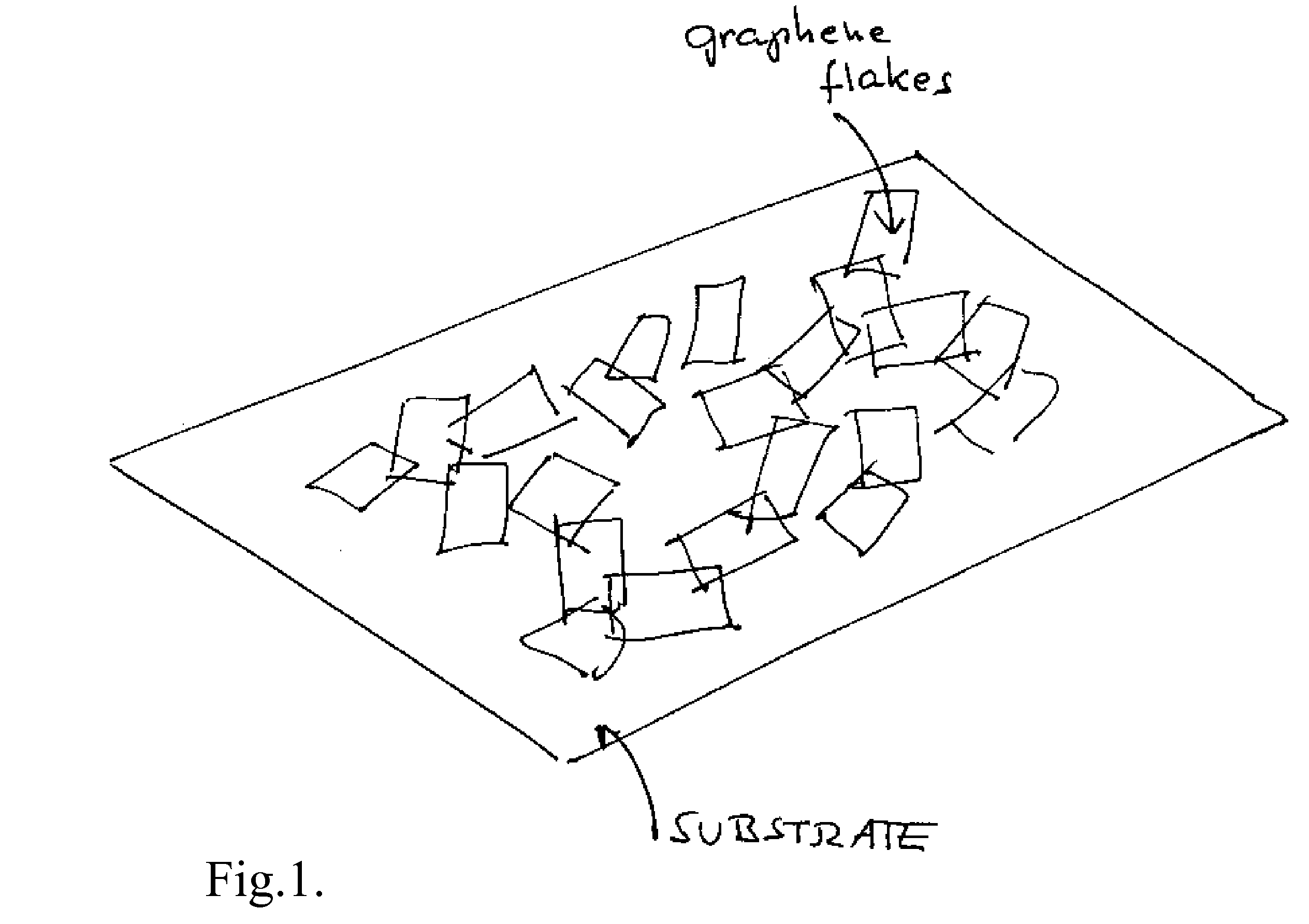
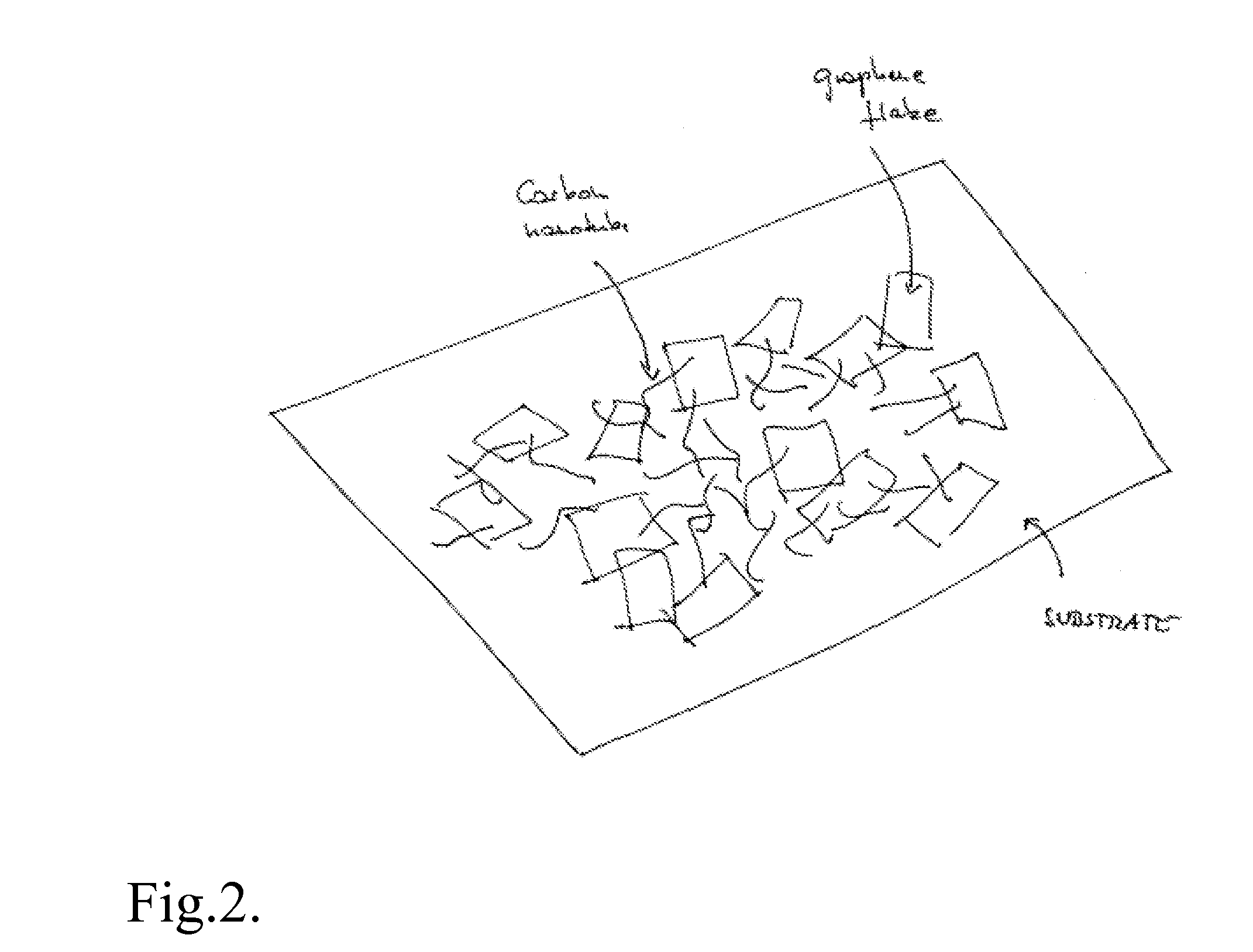
ActiveUS20070284557A1Material nanotechnologyConductive materialGraphene flakeTransparent conducting film
A transparent and conductive film comprising at least one network of graphene flakes is described herein. This film may further comprise an interpenetrating network of other nanostructures, a polymer and / or a functionalization agent(s). A method of fabricating the above device is also described, and may comprise depositing graphene flakes in solution and evaporating solvent therefrom.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Coatings comprising carbon nanotubes and methods for forming same
InactiveUS7060241B2Reduce manufacturing costImprove efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyConductive layers on insulating-supportsSingle-Walled NanotubeCoating
Owner:NANO C INC
Electrical conductors formed from mixtures of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition compounds
The present invention relates to a thick film formed of a mixture of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition (MOD) compounds in an organic liquid vehicle and a process for advantageously applying them to a substrate by silk screening or other printing technology. The mixtures preferably contain metal flake with a ratio of the maximum dimension to the minimum dimension of between 5 and 50. The vehicle may include a colloidal metal powder with a diameter of about 10 to about 40 nanometers. The concentration of the colloidal metal in the suspension can range from about 10 to about 50% by weight. The MOD compound begins to decompose at a temperature of approximately about 200 DEG C. to promote consolidation of the metal constituents and bonding to the substrate which is complete at temperatures less than 450 DEG C. in a time less than six minutes. The mixtures can be applied by silk screening, stencilling, gravure or lithography to a polymer-based circuit board substrate for producing rigid and flexible printed wiring boards in a single operation with negligible generation of hazardous wastes. The same mixtures can be used in place of solder to assemble circuits by bonding electrical components to conductors as well as to make the conductors themselves.
Owner:PARELEC
Electrically conductive polymer composition
InactiveUS6184280B1Sufficient electrical conductivityImprove polymer propertiesOther chemical processesConductive materialPolymer scienceCarbon fibers
An electrically conductive polymer composition comprises a moldable organic polymer having hollow carbon microfibers and an electrically conductive white powder uniformly dispersed therein, the carbon fibers being present in an amount of 0.01 wt. % to less than 2 wt. % and the electrically conductive white powder being present in an amount of 2.5-40 wt. %, each percent range based on the total weight of the composition, the amounts of carbon microfibers and white powder being sufficient to simultaneously impart the desired electrical conductivity to the composition and white pigmentation to the composition.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP +1
Multi-layer conductor with carbon nanotubes
The present invention is directed to an electronically conductive article comprising at least one conductive carbon nanotube layer in contact with at least one conductive layer comprising electronically conductive polymer.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
PVC nanocomposite manufacturing technology and applications
InactiveUS20080194736A1Material nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentPolymer scienceManufacturing technology
The present invention relates to a process and a product of forming polymer (especially PVC) nanocomposites with a variety of nanofillers. The present invention provides a method for forming a polymer nanocomposite, comprising powder mixing a composition comprising polymer resin, a nanofiller, and a coupling agent for a residence time of about 4 to about 8 minutes to form a dry blend and extruding the dry blend in an extrusion process. Additionally, the present invention relates to a polymer nanocomposite formed by a process, comprising powder mixing a polymer resin, a nanofiller, and a coupling agent for a residence time of about 4 to about 8 minutes to form a dry blend and extruding the dry blend in an extrusion process to achieve homogeneous dispersion of nanofillers in the polymer matrix.
Owner:FORMOSA PLASTICCS CORP
Electroactive high storage capacity polyacetylene-co-polysulfur materials and electrolytic cells containing same
InactiveUS6117590AHigh storage capacity per unit weightFacilitates electron transportElectrode manufacturing processesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsElectrochemical cellElectrode material
The present invention relates to novel electroactive energy storing polyacetylene-co-polysulfur (PAS) materials of general formula (C2Sx)n wherein x is greater than 1 to about 100, and n is equal to or greater than 2. This invention also relates to novel rechargeable electrochemical cells containing positive electrode materials comprised of said polyacetylene-co-polysulfur materials with improved storage capacity and cycle life at ambient and sub-ambient temperatures.
Owner:THE BANK OF NEW YORK +1
Highly catalytic screen-printing ink
ActiveUS7018568B2Easy to produceConductive layers on insulating-supportsConductive materialConductive polymerPrinting ink
The invention is directed to conductive polymer compositions, catalytic ink compositions (e.g., for use in screen-printing), electrodes produced by deposition of an ink composition, methods of making, and methods of using thereof. An exemplary ink material comprises platinum black and / or platinum-on-carbon as the catalyst, graphite as a conducting material, a polymer binding material, and an organic solvent. The polymer binding material is typically a copolymer of hydrophilic and hydrophobic monomers. The conductive polymer compositions of the present invention can be used, for example, to make electrochemical sensors. Such sensors can be used in a variety of analyte monitoring devices to monitor analyte amount or concentrations in subjects, for example, glucose monitoring devices to monitor glucose levels in subjects with diabetes.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Composite transparent conductors and methods of forming the same
ActiveUS20080259262A1Improve drawing legibilityMaterial nanotechnologyNon-insulated conductorsMaterials scienceMetal nanowire
Composite transparent conductors are described, which comprise a primary conductive medium based on metal nanowires and a secondary conductive medium based on a continuous conductive film.
Owner:CHAMP GREAT INTL
High quality large area bulk non-polar or semipolar gallium based substrates and methods
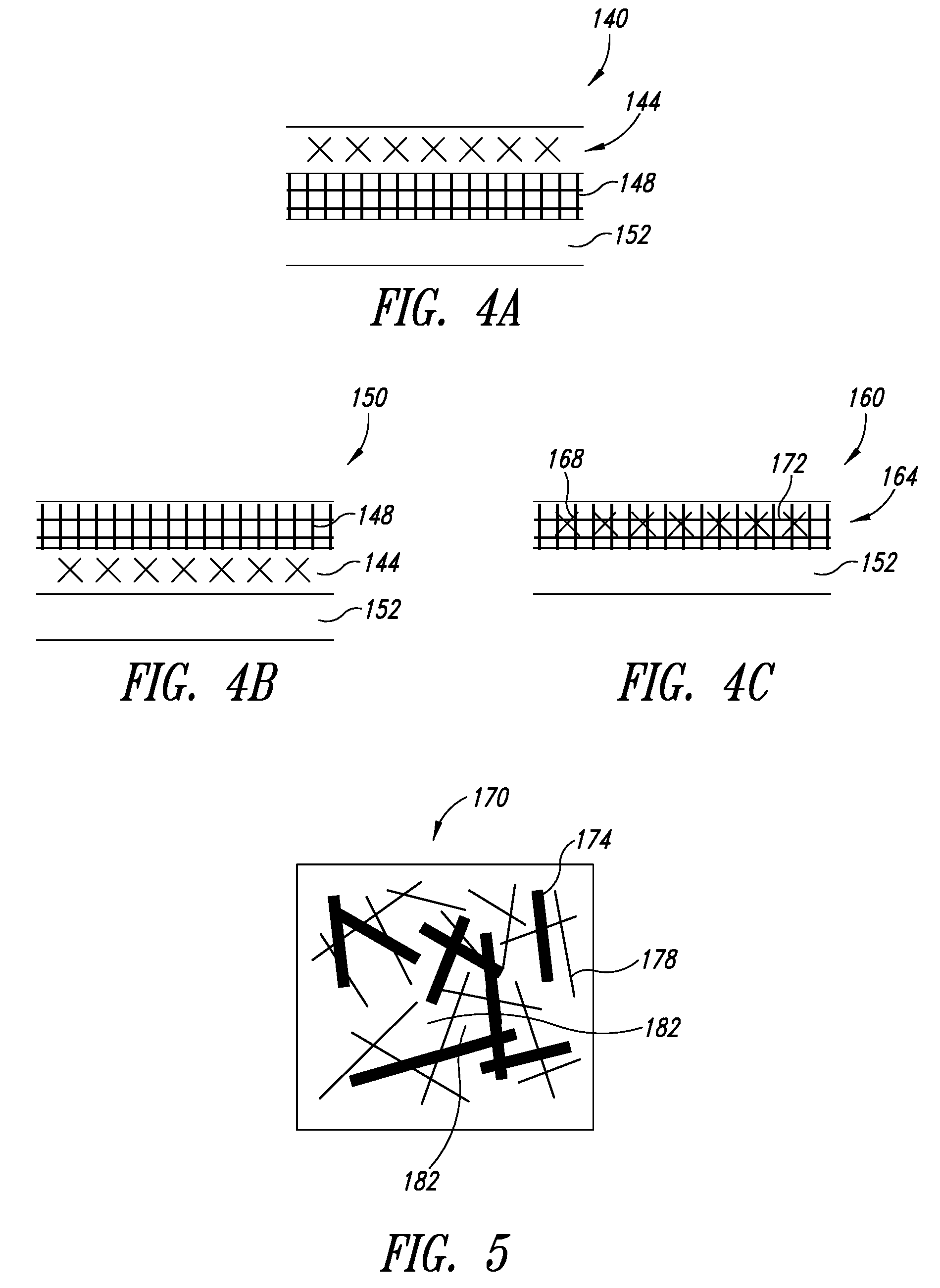
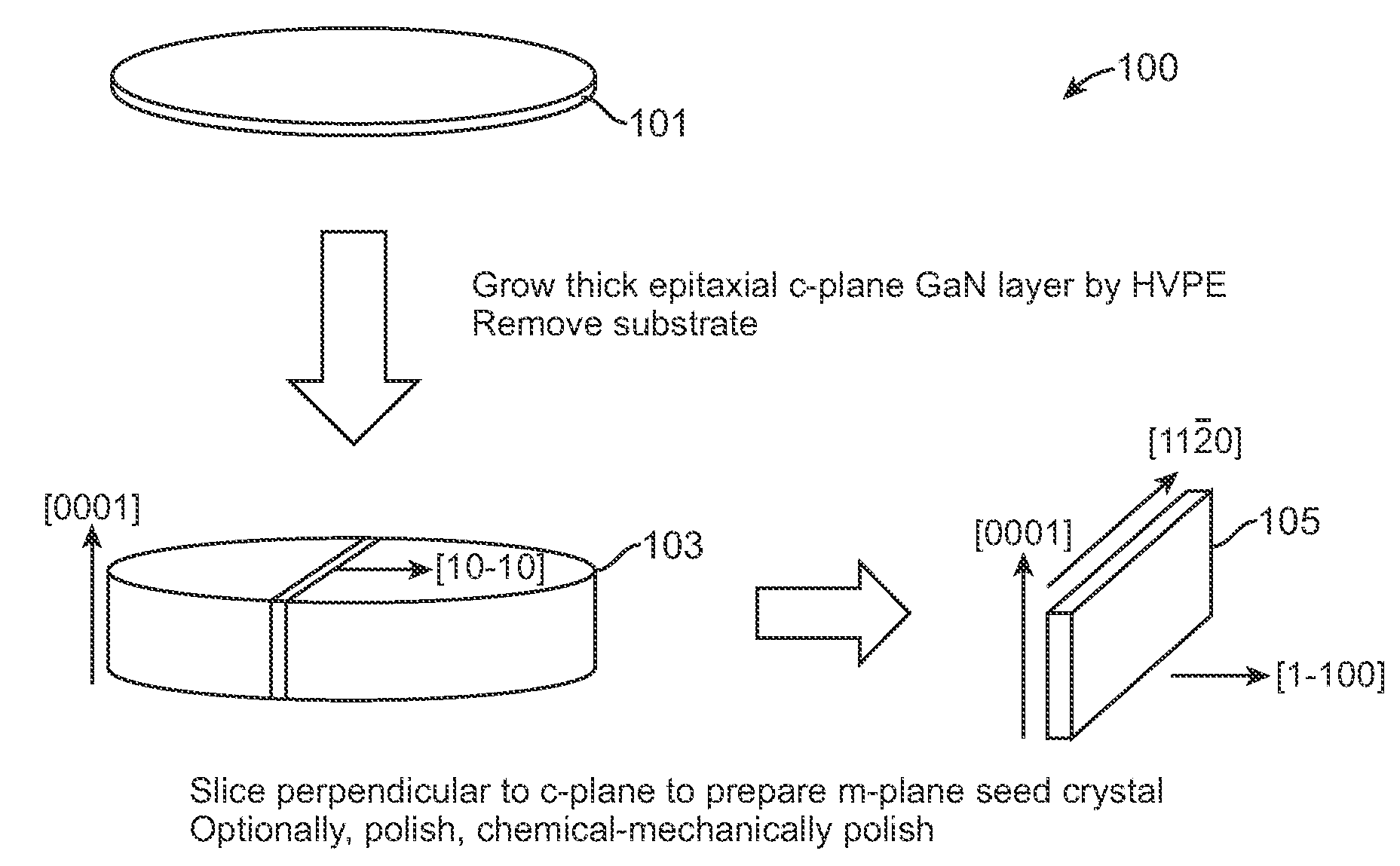
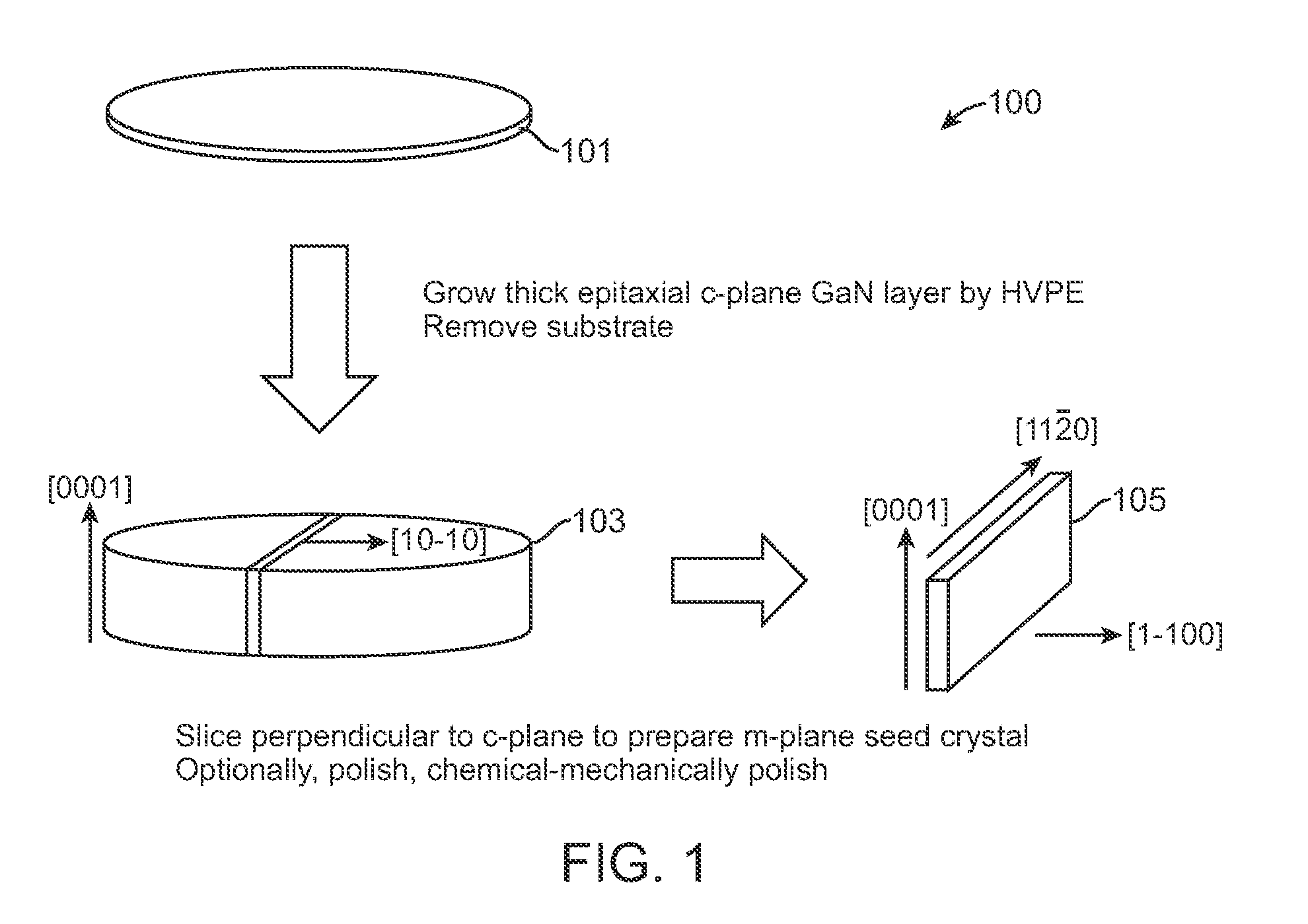
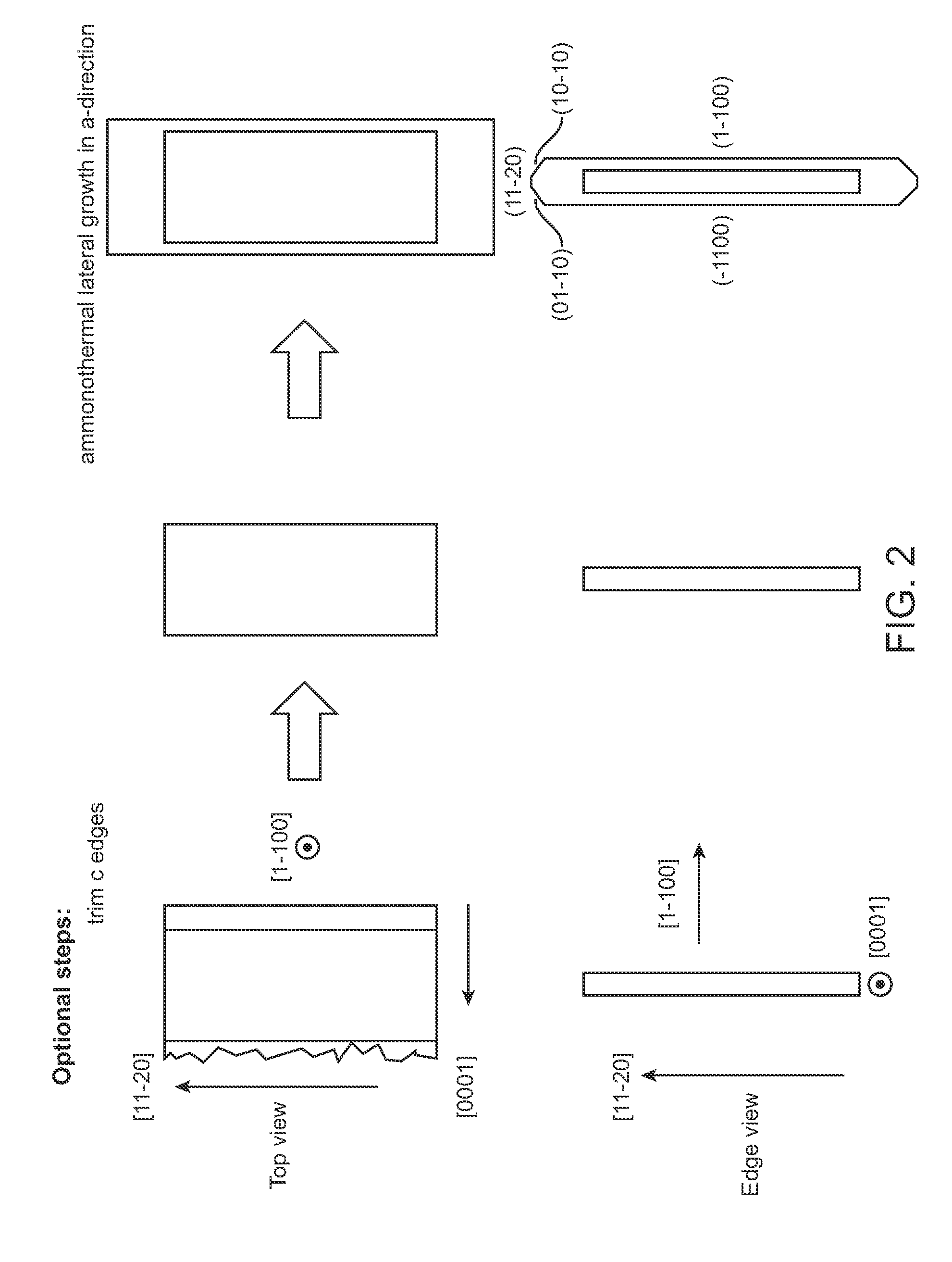
InactiveUS20100003492A1Great area of substrateCost-effective manufacturingPolycrystalline material growthConductive materialPhotodetectorSolar cell
A large area nitride crystal, comprising gallium and nitrogen, with a non-polar or semi-polar large-area face, is disclosed, along with a method for making. The crystal is useful as a substrate for a light emitting diode, a laser diode, a transistor, a photodetector, a solar cell, or for photoelectrochemical water splitting for hydrogen generation.
Owner:SORAA
Electrode materials with high surface conductivity
InactiveUS6855273B2Electrode manufacturing processesDouble layer capacitorsSurface conductivityIon exchange
The present invention concerns electrode materials capable of redox reactions by electrons and alkaline ions exchange with an electrolyte. The applications are in the field of primary (batteries) or secondary electrochemical generators, super capacitors and light modulating system of the super capacitor type.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
Polycrystalline group iii metal nitride with getter and method of making
ActiveUS20100151194A1Simple and cost-effective to manufactureCost-effectiveConductive materialRecord information storageNitrogenNitride
A gettered polycrystalline group III metal nitride is formed by heating a group III metal with an added getter in a nitrogen-containing gas. Most of the residual oxygen in the gettered polycrystalline nitride is chemically bound by the getter. The gettered polycrystalline group III metal nitride is useful as a raw material for ammonothermal growth of bulk group III nitride crystals.
Owner:SLT TECH
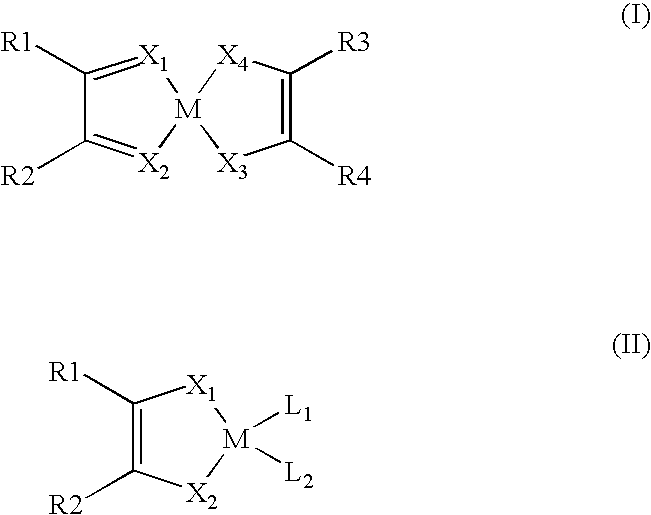
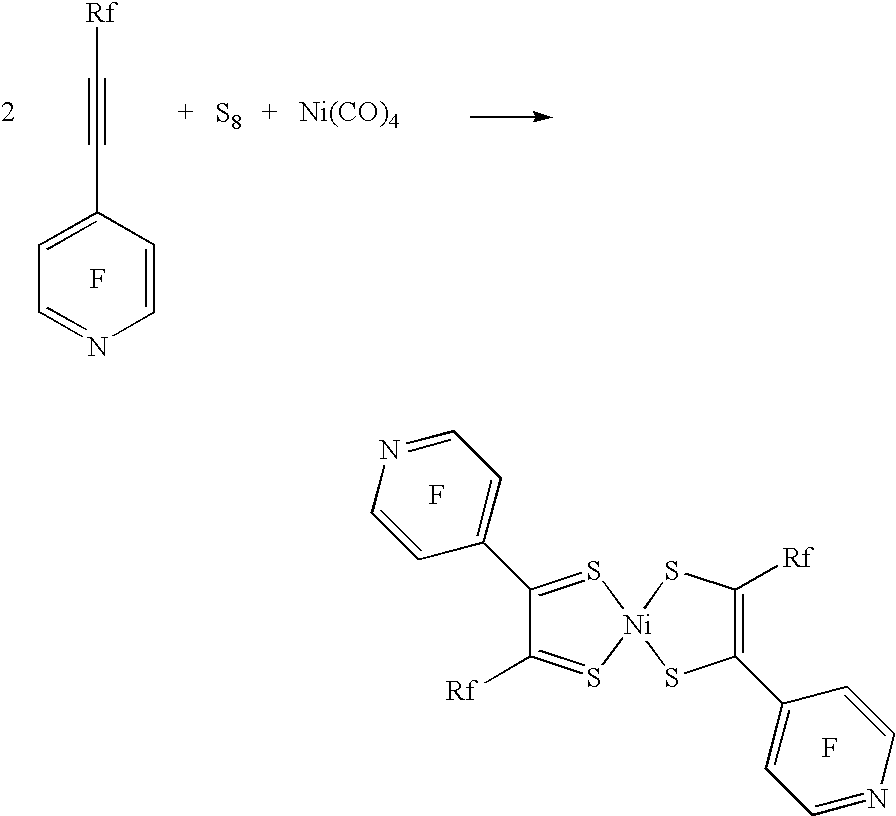
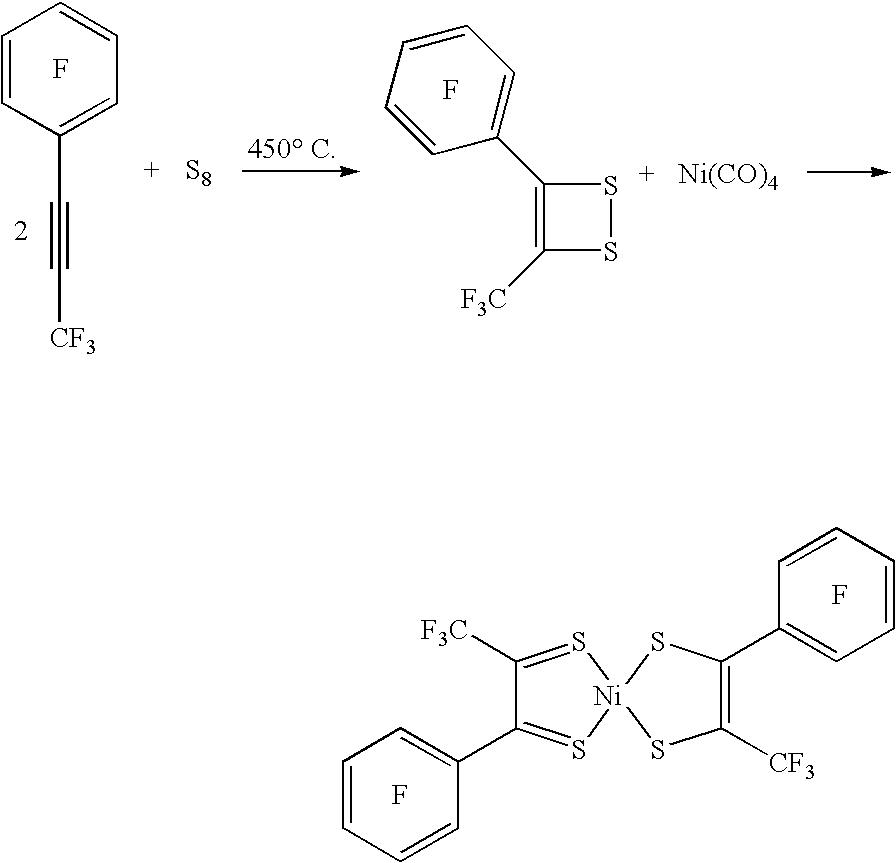
Square Planar Transition Metal Complexes and Organic Semiconductive Materials Using Them as Well as Electronic or Optoelectric Components
The present invention relates to square planar transition metal complexes and their use in organic semiconductive materials as well as in electronic or optoelectronic components.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
Graphene-Enhanced cathode materials for lithium batteries
ActiveUS20120058397A1Short timeEasy dischargeNon-metal conductorsMaterial nanotechnologyParticulatesCvd graphene
A nano graphene-enhanced particulate for use as a lithium battery cathode active material, wherein the particulate is formed of a single or a plurality of graphene sheets and a plurality of fine cathode active material particles with a size smaller than 10 μm (preferably sub-micron or nano-scaled), and the graphene sheets and the particles are mutually bonded or agglomerated into an individual discrete particulate with at least a graphene sheet embracing the cathode active material particles, and wherein the particulate has an electrical conductivity no less than 10−4 S / cm and the graphene is in an amount of from 0.01% to 30% by weight based on the total weight of graphene and the cathode active material combined.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Composition containing carbon nanotubes having coating thereof and process for producing them
ActiveUS20060052509A1Not impair characteristicImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsColloidal silicaConductive polymer
The object of the present invention is to provide a carbon nanotube composition that does not impair the characteristics of the carbon nanotubes itself, allows the carbon nanotubes to be dispersed or solubilized in a solvent, does not cause separation or aggregation of the carbon nanotubes even during long-term storage, has superior electrical conductivity, film formability and moldability, can be easily coated or covered onto a base material, and the resulting coated film has superior moisture resistance, weather resistance and hardness; a composite having a coated film composed thereof; and, their production methods. In order to achieve this object, the present invention provides a carbon nanotube composition that contains a conducting polymer (a) or heterocyclic compound trimer (i), a solvent (b) and carbon nanotubes (c), and may additionally contain a high molecular weight compound (d), a basic compound (e), a surfactant (f), a silane coupling agent (g) and colloidal silica (h) as necessary; a composite having a coated film composed of the composition; and, their production methods.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Electrode material comprising graphene composite materials in a graphite network formed from reconstituted graphene sheets
ActiveUS20110111303A1Weight increaseIncrease storage capacityConductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialGraphiteCvd graphene
A durable electrode material suitable for use in Li ion batteries is provided. The material is comprised of a continuous network of graphite regions integrated with, and in good electrical contact with a composite comprising graphene sheets and an electrically active material, such as silicon, wherein the electrically active material is dispersed between, and supported by, the graphene sheets.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
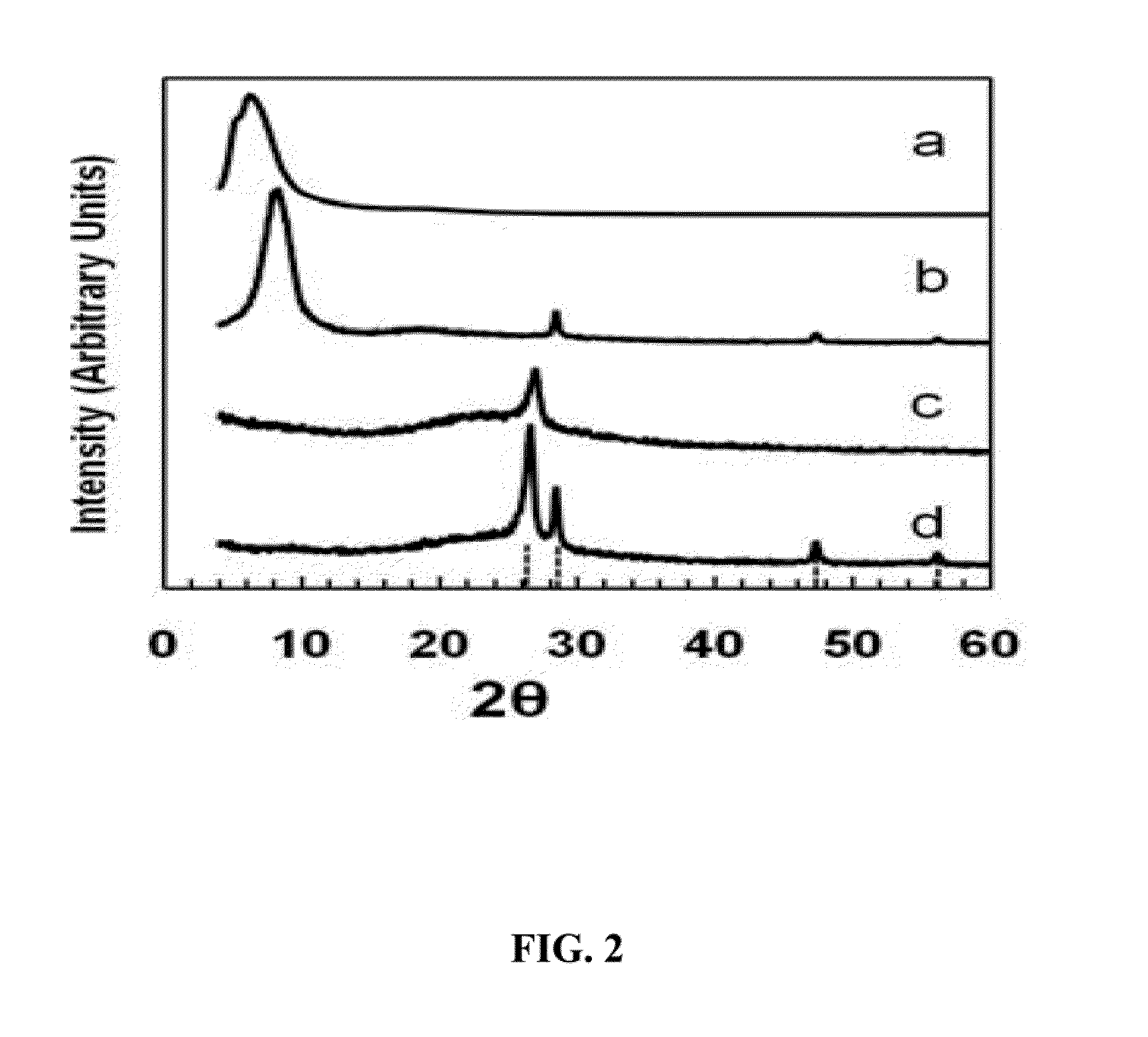
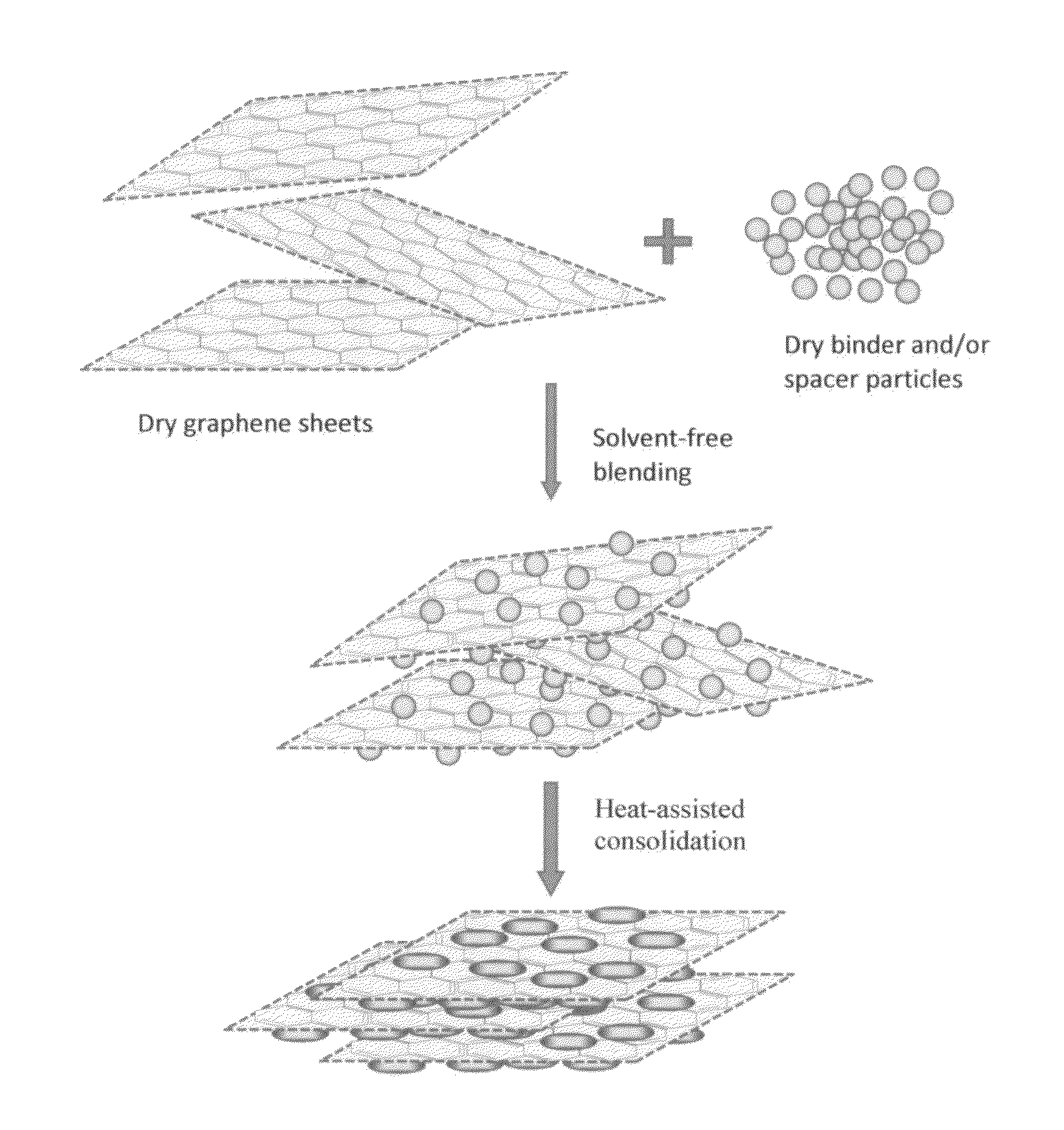
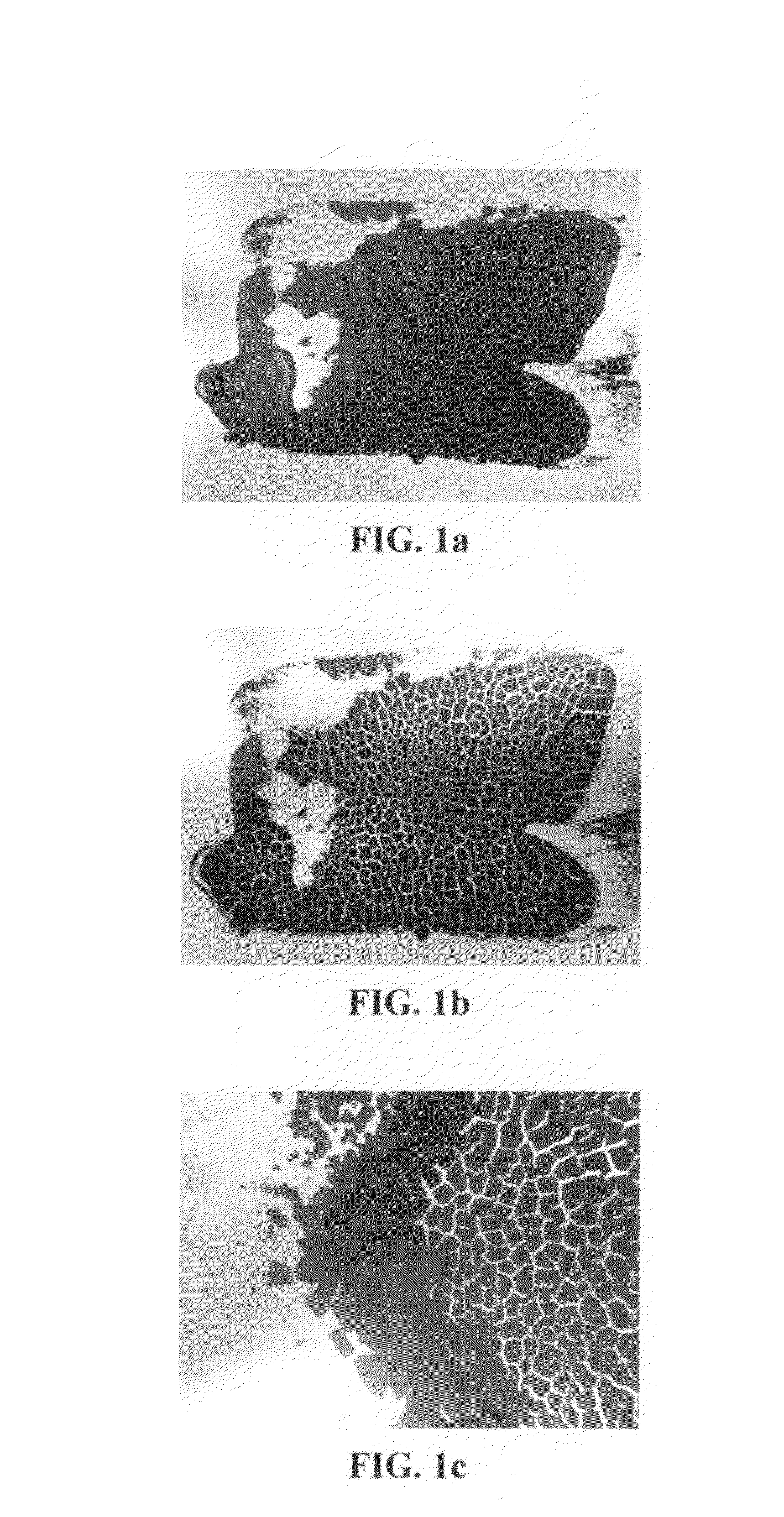
Solvent-free process based graphene electrode for energy storage devices
PendingUS20140030590A1Inexpensive and durable and highly reliableHigh capacitanceMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesGraphene flakeSolvent free
Disclosed is an electrode for an electrochemical energy storage device, the electrode comprising a self-supporting layer of a mixture of graphene sheets and spacer particles and / or binder particles, wherein the electrode is prepared without using water, solvent, or liquid chemical. The graphene electrode prepared by the solvent-free process exhibits many desirable features and advantages as compared to the corresponding electrode prepared by a known wet process. These advantages include a higher electrode specific surface area, higher energy storage capacity, improved or higher packing density or tap density, lower amount of binder required, lower internal electrode resistance, more consistent and uniform dispersion of graphene sheets and binder, reduction or elimination of undesirable effect of electrolyte oxidation or decomposition due to the presence of water, solvent, or chemical, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
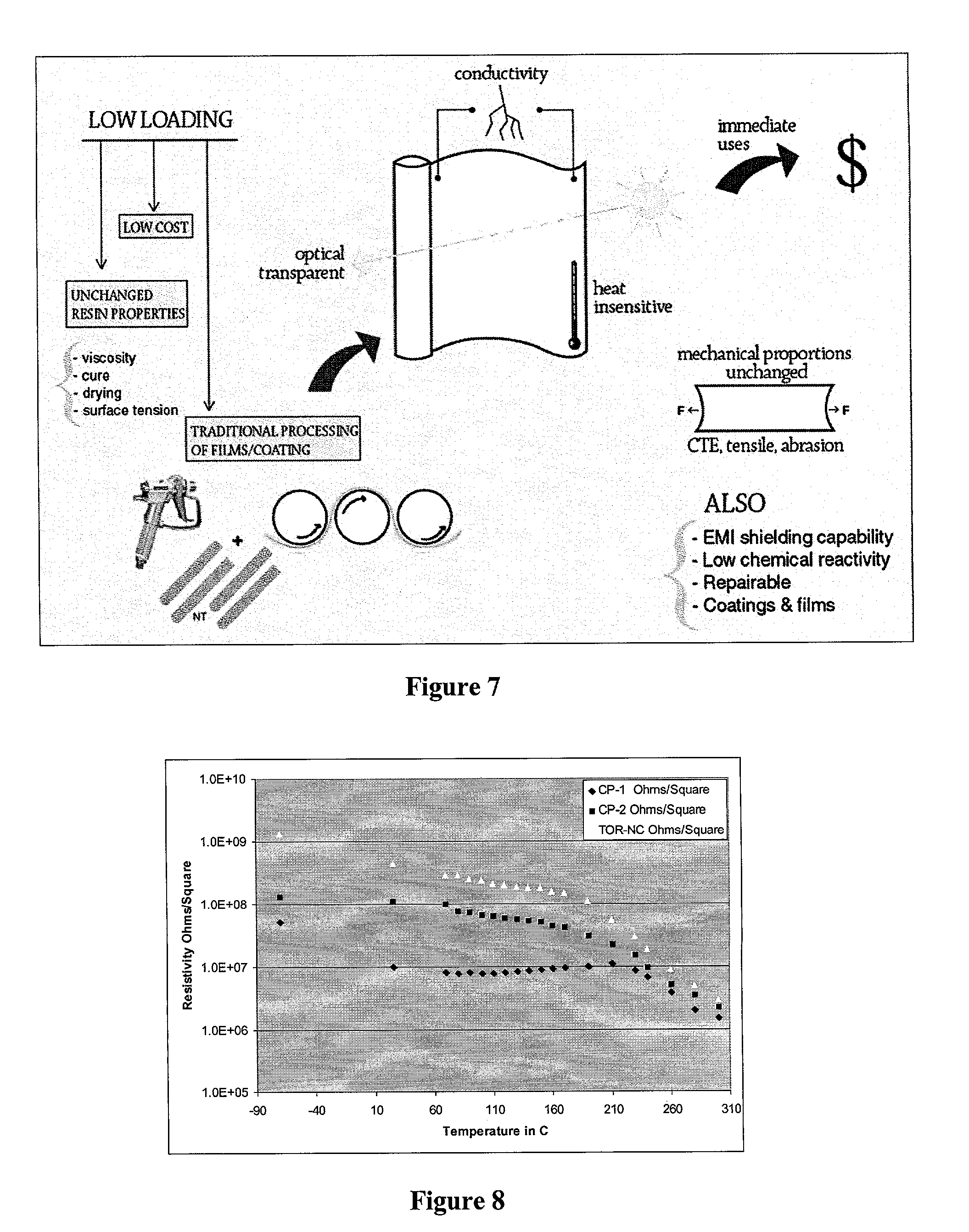
Fluoropolymer binders for carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coatings
InactiveUS20060113510A1Reduce conductivityFunction increaseNanoinformaticsConductive materialThermoplasticOptical transparency
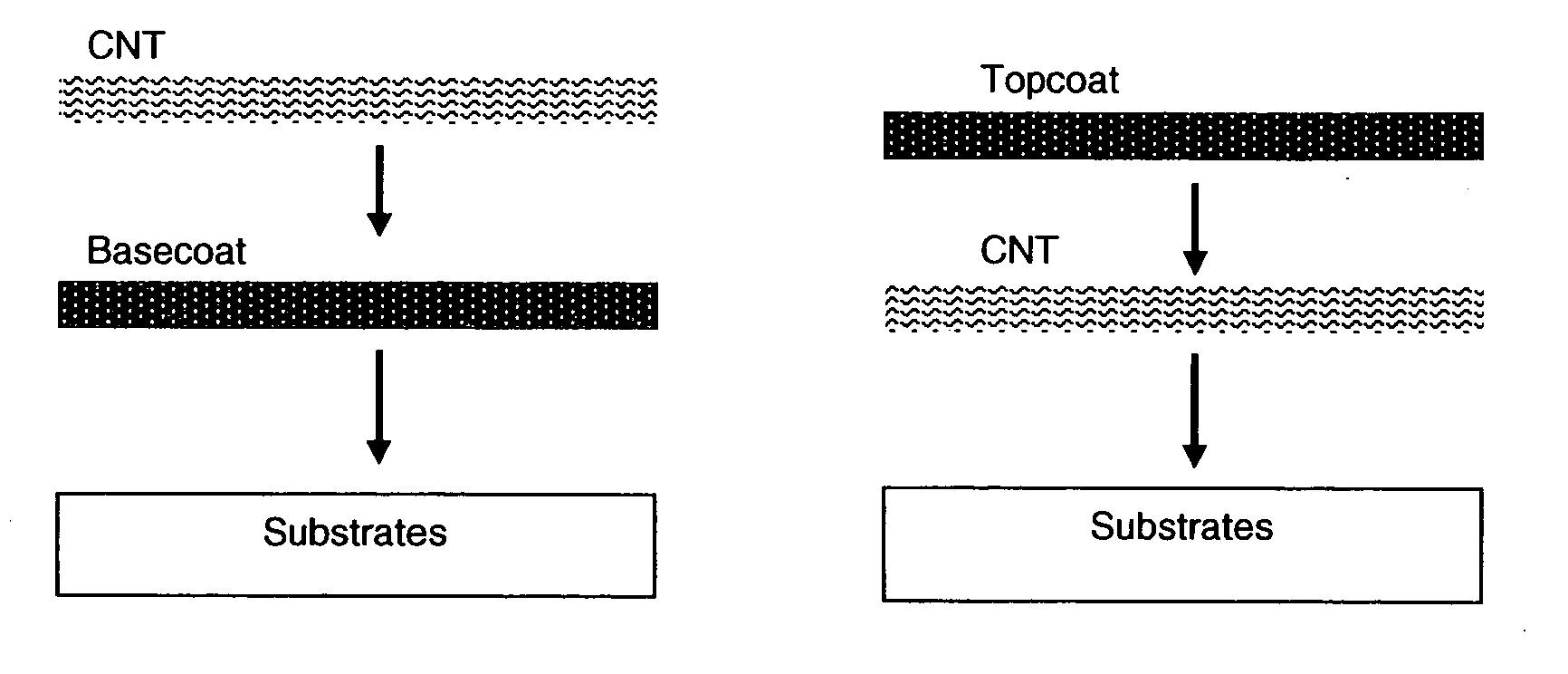
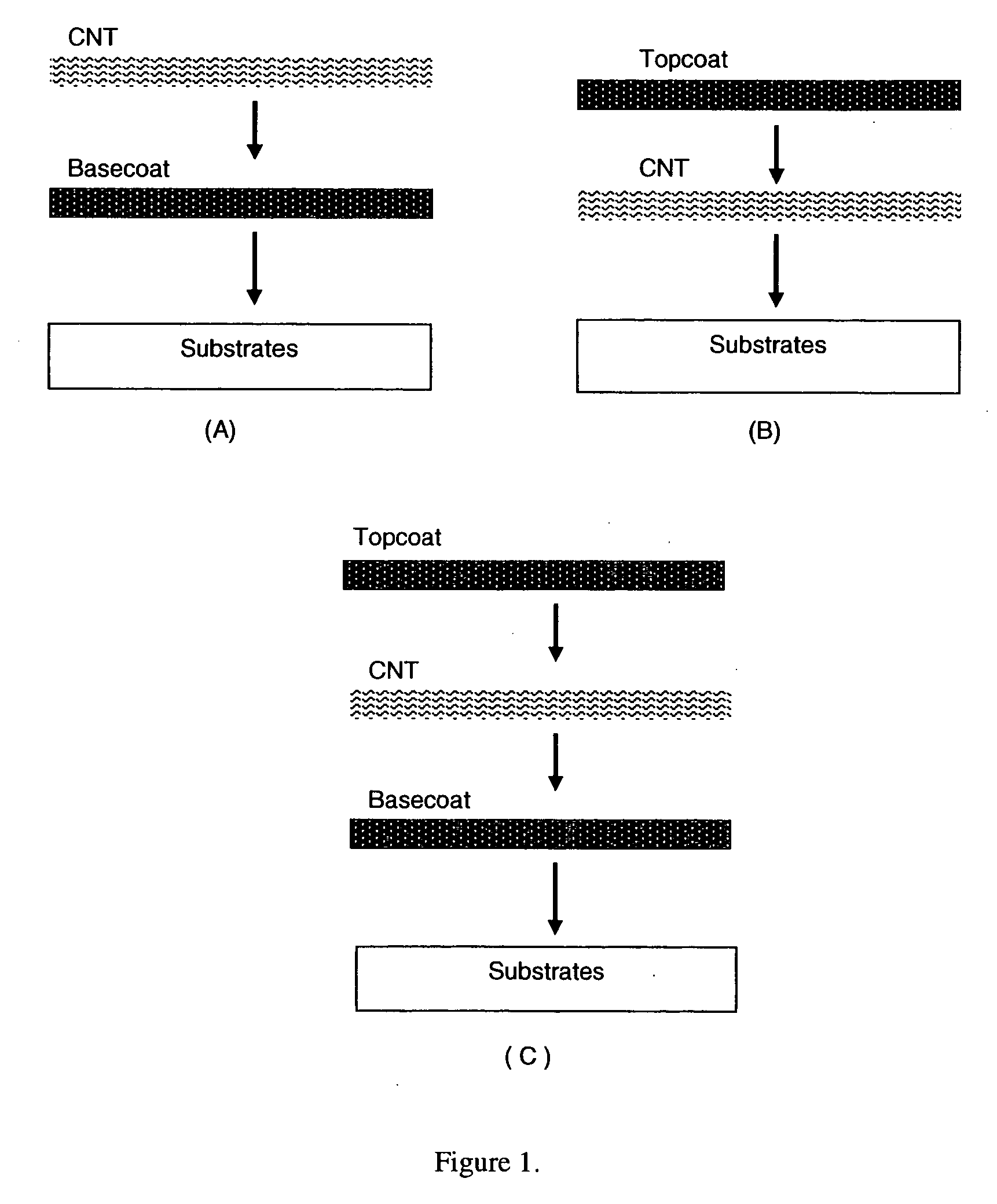
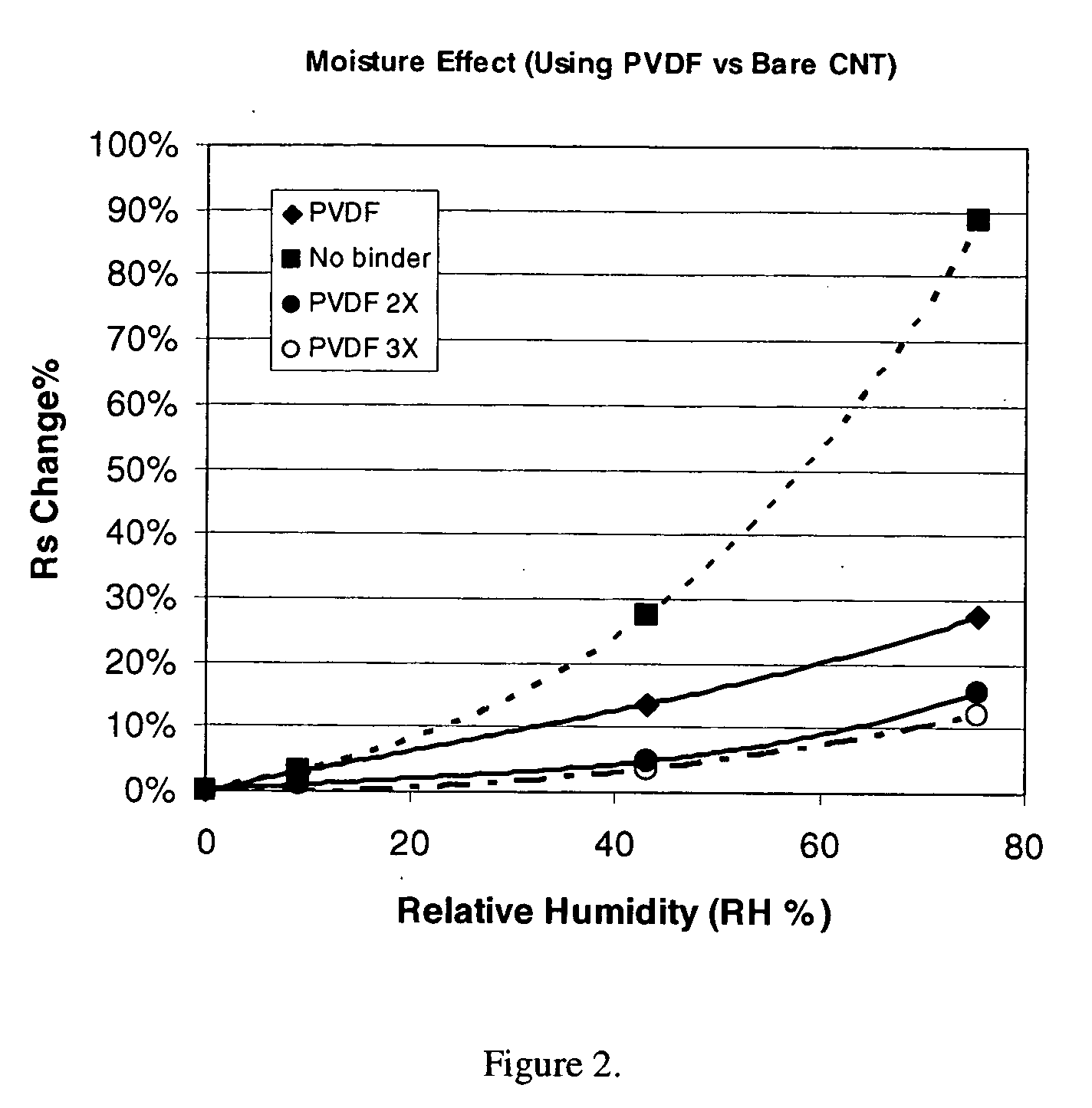
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using carbon nanotubes (CNT) and, in particular, single wall carbon nanotubes, with polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from carbon nanotubes applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration. This provides for enhancement of properties such as moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics or thermosets, or a combination thereof. Polymers may also be insulative or inherently electrical conductive, or any combination of both. Polymers may comprise single or multiple layers as a basecoat underneath a CNT coating, or a topcoat above a CNT coating, or combination of the basecoat and the topcoat forming a sandwich structure. A fluoropolymer containing binder, which is a solution of one fluoropolymer or a blend of fluoropolymers, which may be formulated with additives, is applied onto a carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coating at nanometer level of thickness on a clear substrate such as PET and glass. The fluoropolymers or blend can be either semi-crystalline (with low level of crystallinity) or amorphous, preferably to be amorphous with low refraction index. Binder coating thickness can be adjusted by changing binder concentration, coating speed and / or other process conditions. This binder coating significantly improves optical transparency, and also maintain or increases conductivity of the CNT-based coating. With other benefits such as abrasion, thermal and moisture resistance, this binder coating and the resulting products is used for display and electronic applications.
Owner:EIKOS
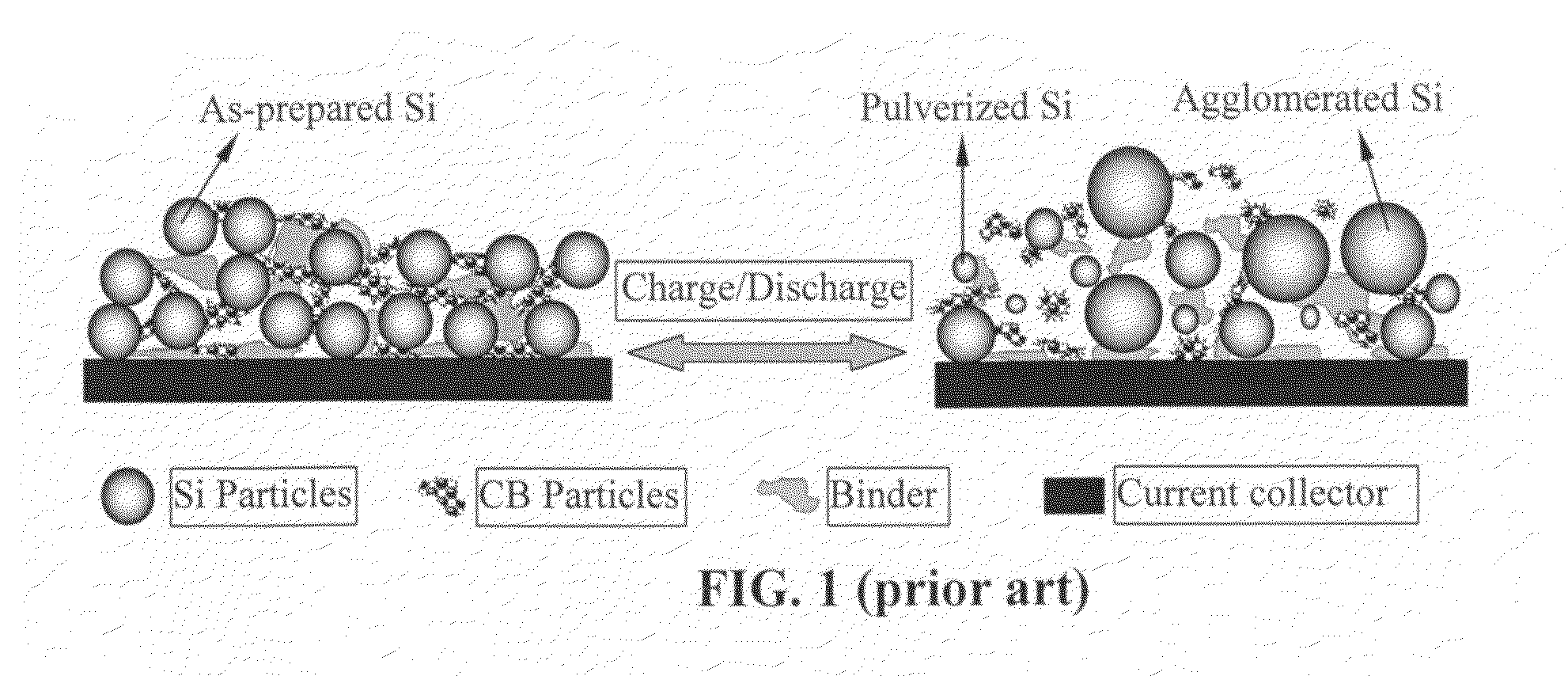
Hybrid anode compositions for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS20090117466A1Superior multiple-cycle behaviorSmall capacity fadeAlkaline accumulatorsConductive materialHybrid materialSodium-ion battery
The present invention provides an exfoliated graphite-based hybrid material composition for use as an electrode, particularly as an anode of a lithium ion battery. The composition comprises: (a) micron- or nanometer-scaled particles or coating which are capable of absorbing and desorbing alkali or alkaline metal ions (particularly, lithium ions); and (b) exfoliated graphite flakes that are substantially interconnected to form a porous, conductive graphite network comprising pores, wherein at least one of the particles or coating resides in a pore of the network or attached to a flake of the network and the exfoliated graphite amount is in the range of 5% to 90% by weight and the amount of particles or coating is in the range of 95% to 10% by weight. Also provided is a lithium secondary battery comprising such a negative electrode (anode). The battery exhibits an exceptional specific capacity, excellent reversible capacity, and long cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Si/c composite, anode active materials, and lithium battery including the same
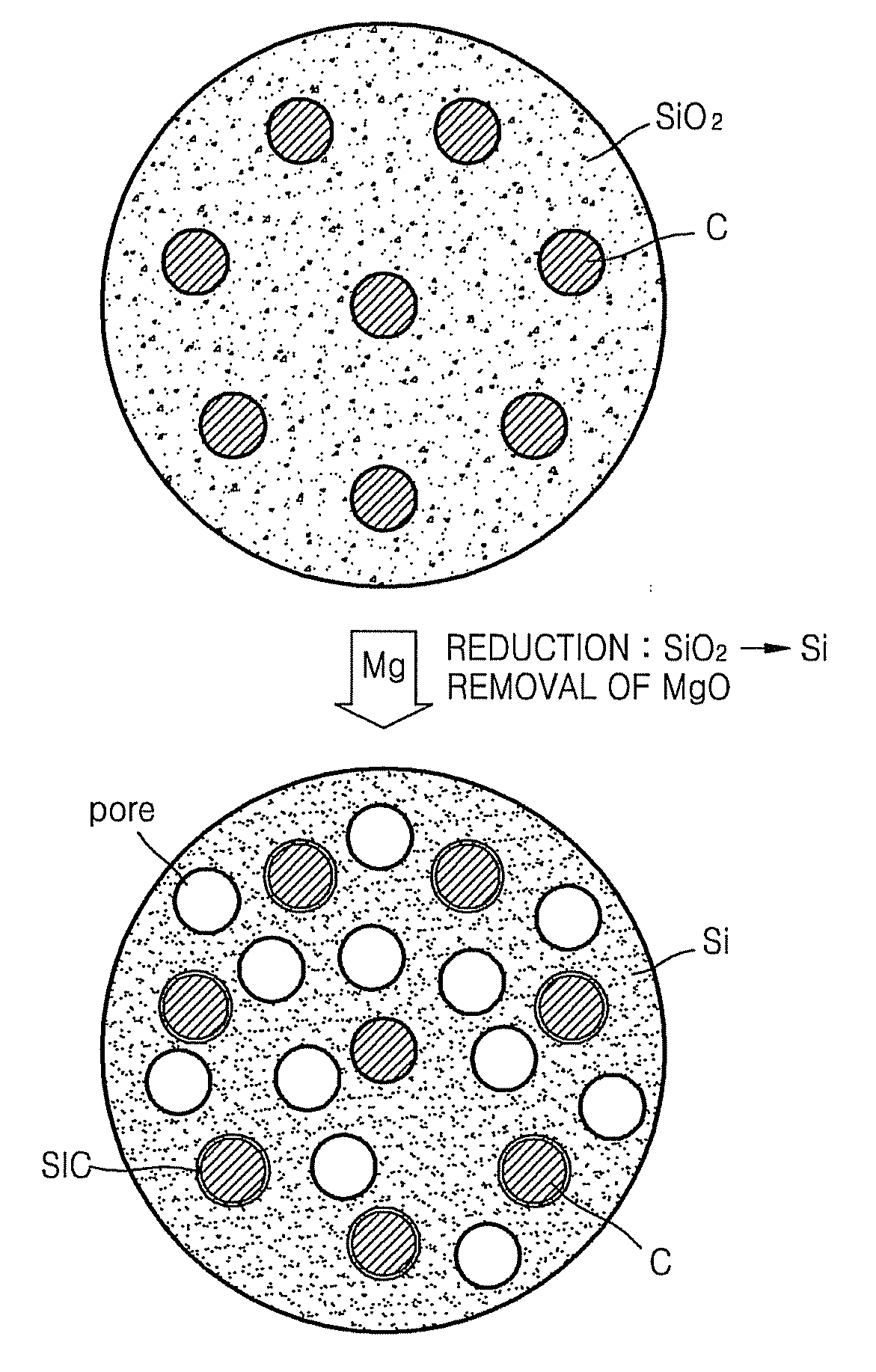
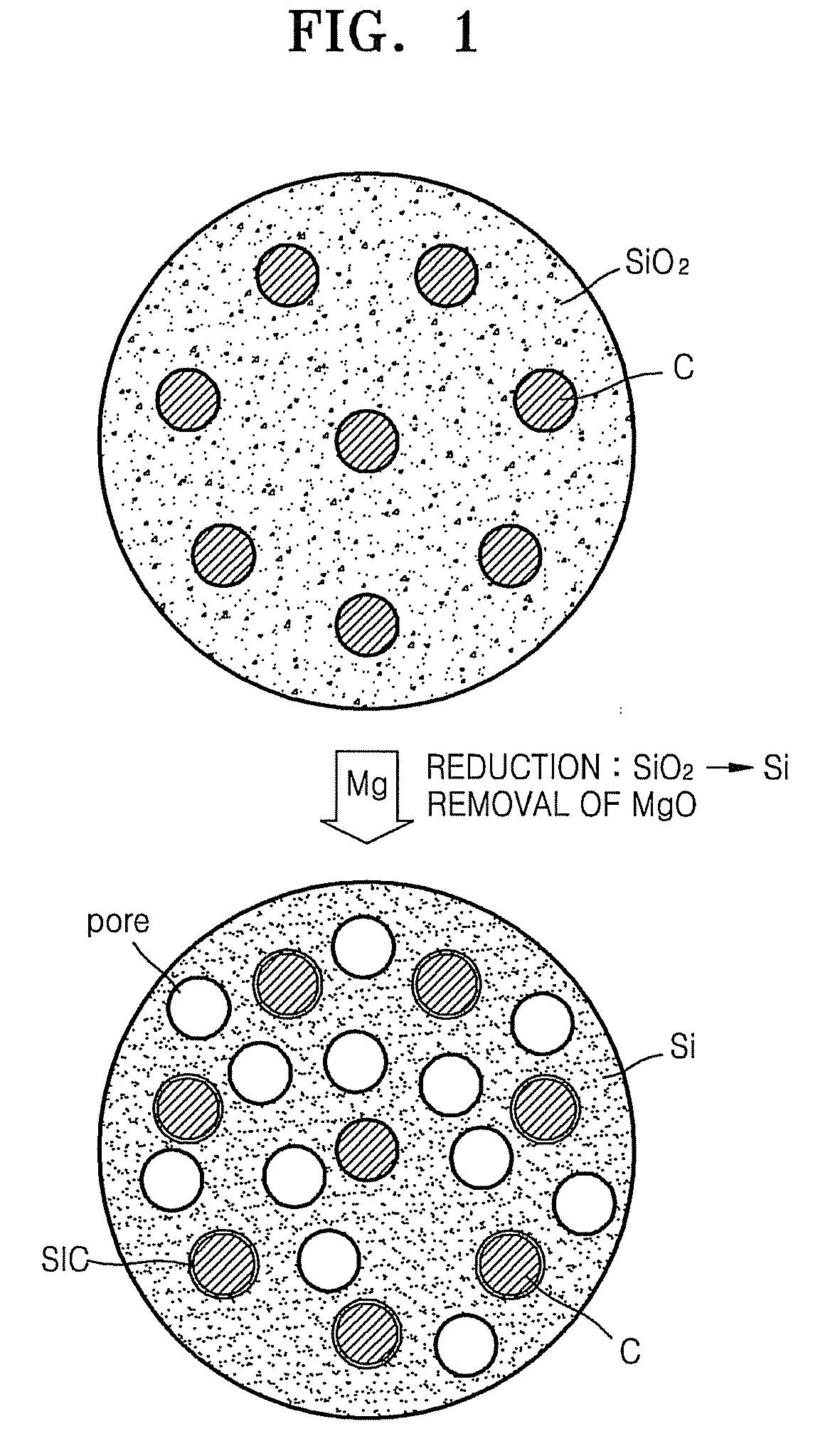
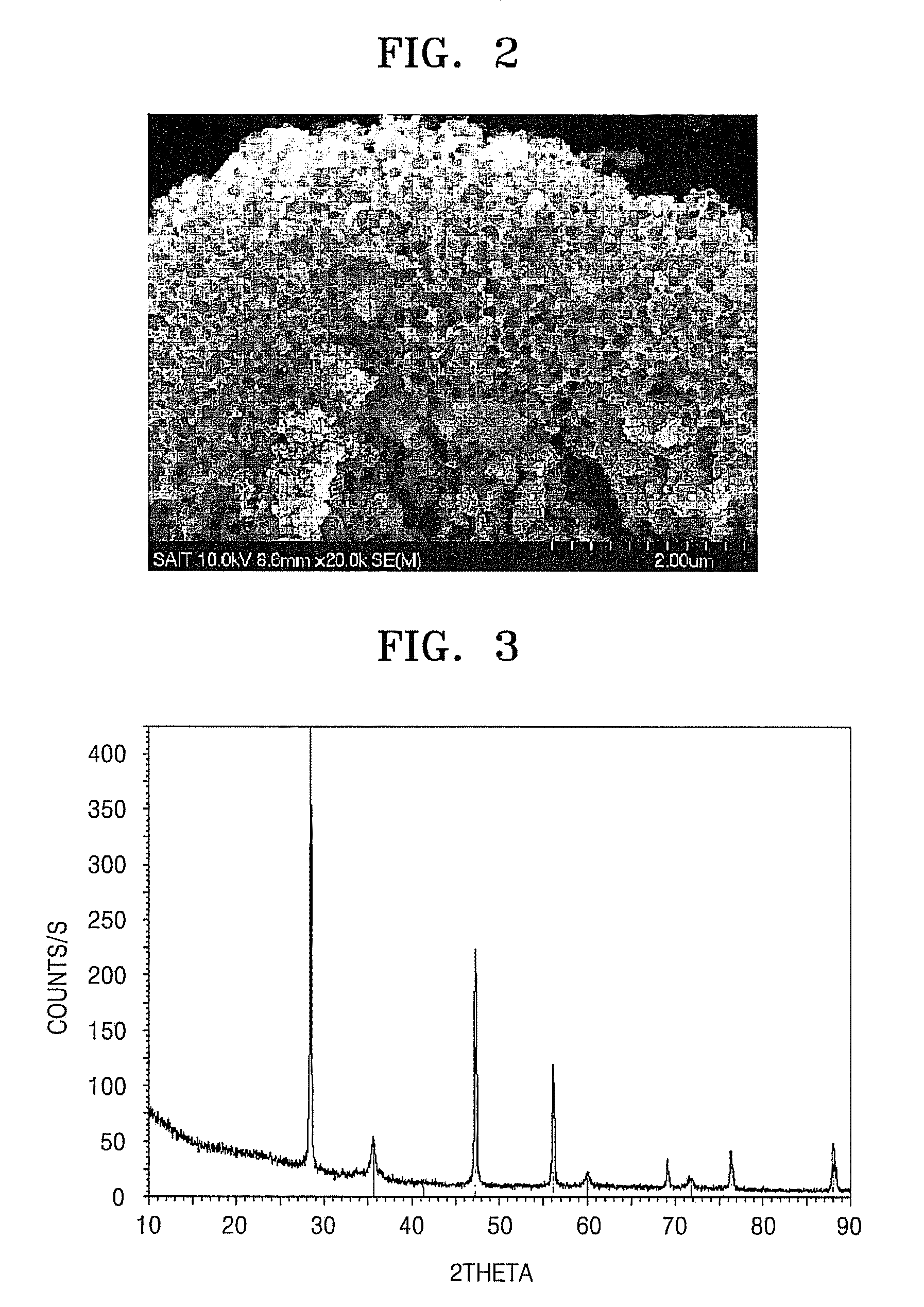
ActiveUS20090029256A1Improve initial Coulombic efficiencyGood capacity retentionLiquid surface applicatorsElectrode manufacturing processesLithium-ion batteryPorous silicon
An Si / C composite includes carbon (C) dispersed in porous silicon (Si) particles. The Si / C composite may be used to form an anode active material to provide a lithium battery having a high capacity and excellent capacity retention.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com