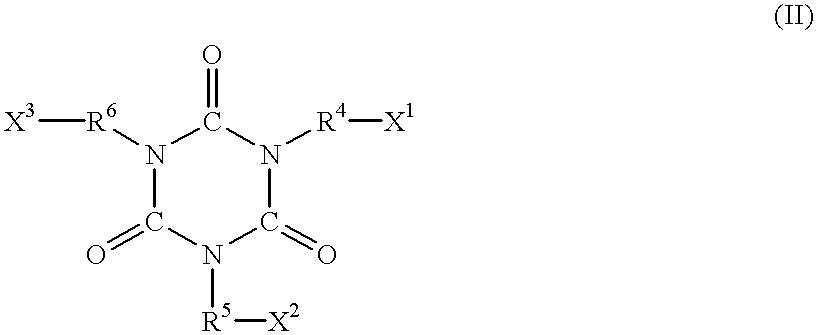
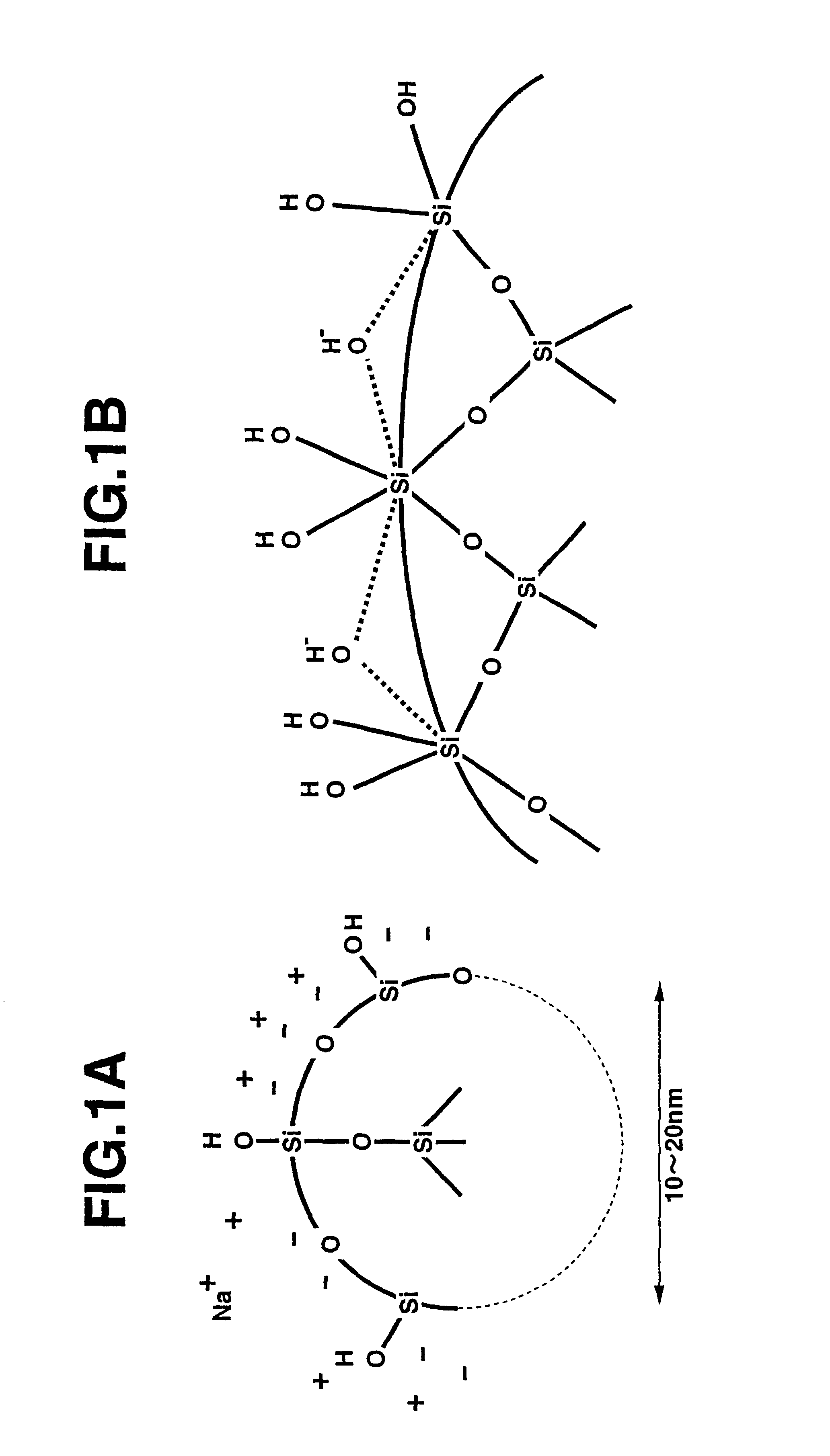
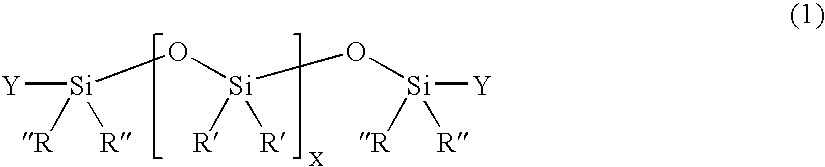
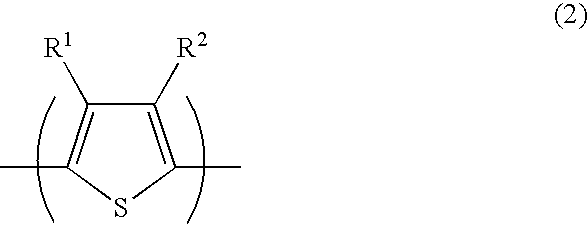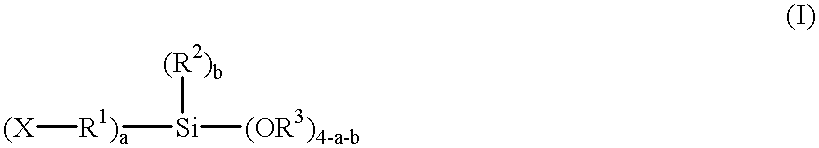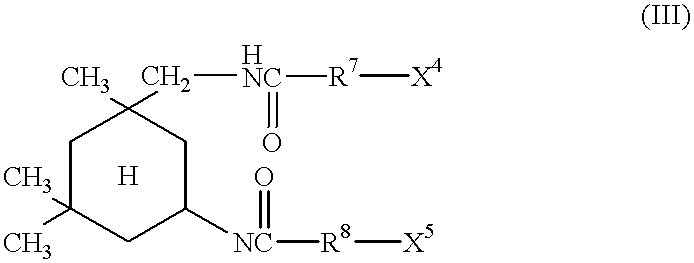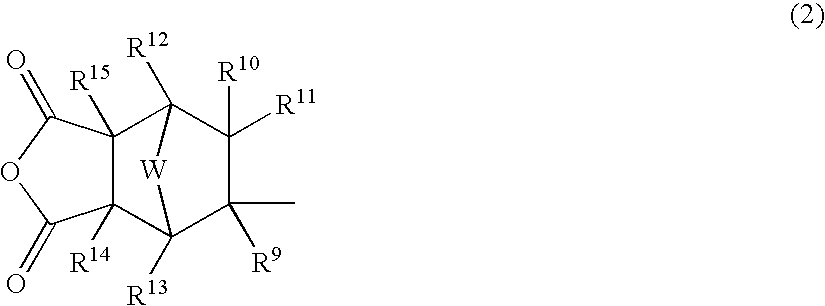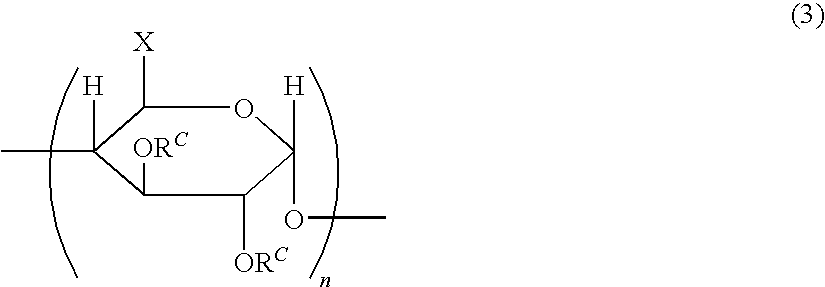Patents
Literature
1778 results about "Colloidal silica" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Colloidal silicas are suspensions of fine amorphous, nonporous, and typically spherical silica particles in a liquid phase.
Composition containing carbon nanotubes having coating thereof and process for producing them
ActiveUS20060052509A1Not impair characteristicImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsColloidal silicaConductive polymer
The object of the present invention is to provide a carbon nanotube composition that does not impair the characteristics of the carbon nanotubes itself, allows the carbon nanotubes to be dispersed or solubilized in a solvent, does not cause separation or aggregation of the carbon nanotubes even during long-term storage, has superior electrical conductivity, film formability and moldability, can be easily coated or covered onto a base material, and the resulting coated film has superior moisture resistance, weather resistance and hardness; a composite having a coated film composed thereof; and, their production methods. In order to achieve this object, the present invention provides a carbon nanotube composition that contains a conducting polymer (a) or heterocyclic compound trimer (i), a solvent (b) and carbon nanotubes (c), and may additionally contain a high molecular weight compound (d), a basic compound (e), a surfactant (f), a silane coupling agent (g) and colloidal silica (h) as necessary; a composite having a coated film composed of the composition; and, their production methods.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
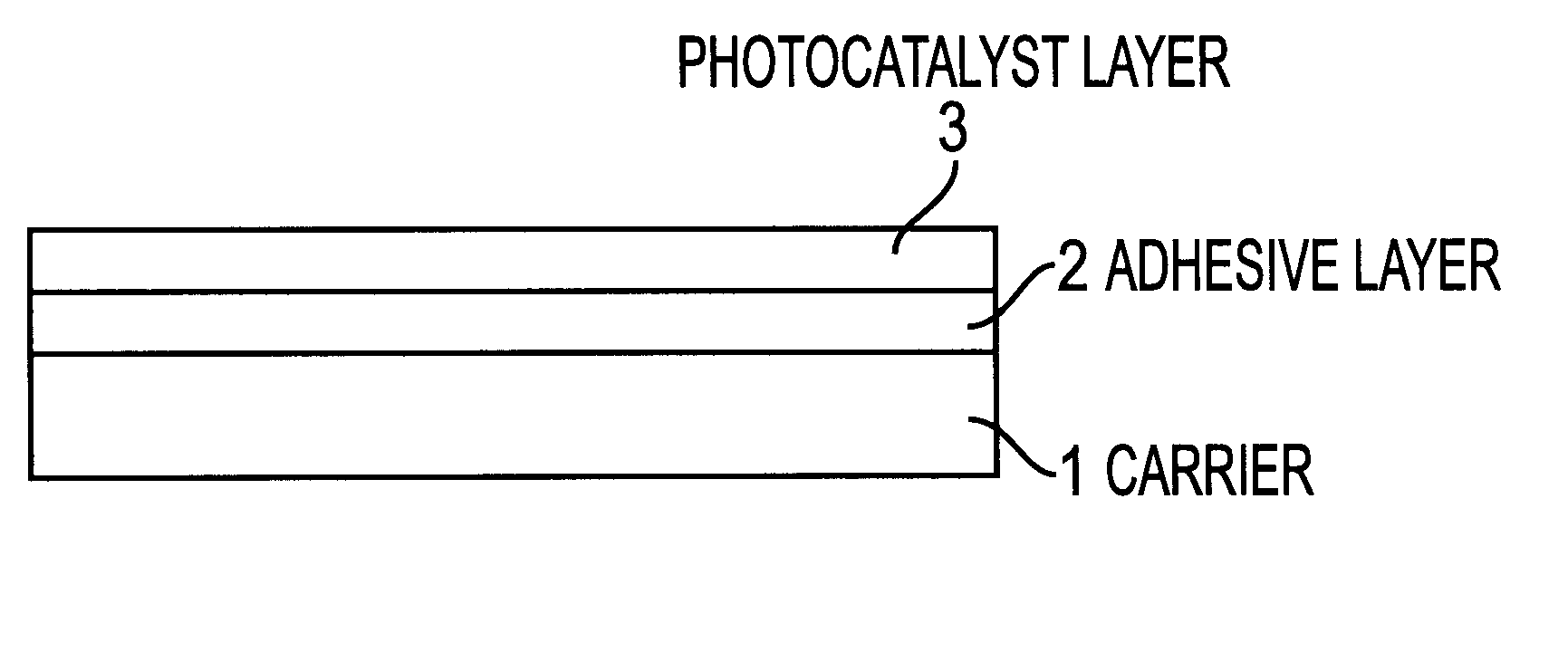
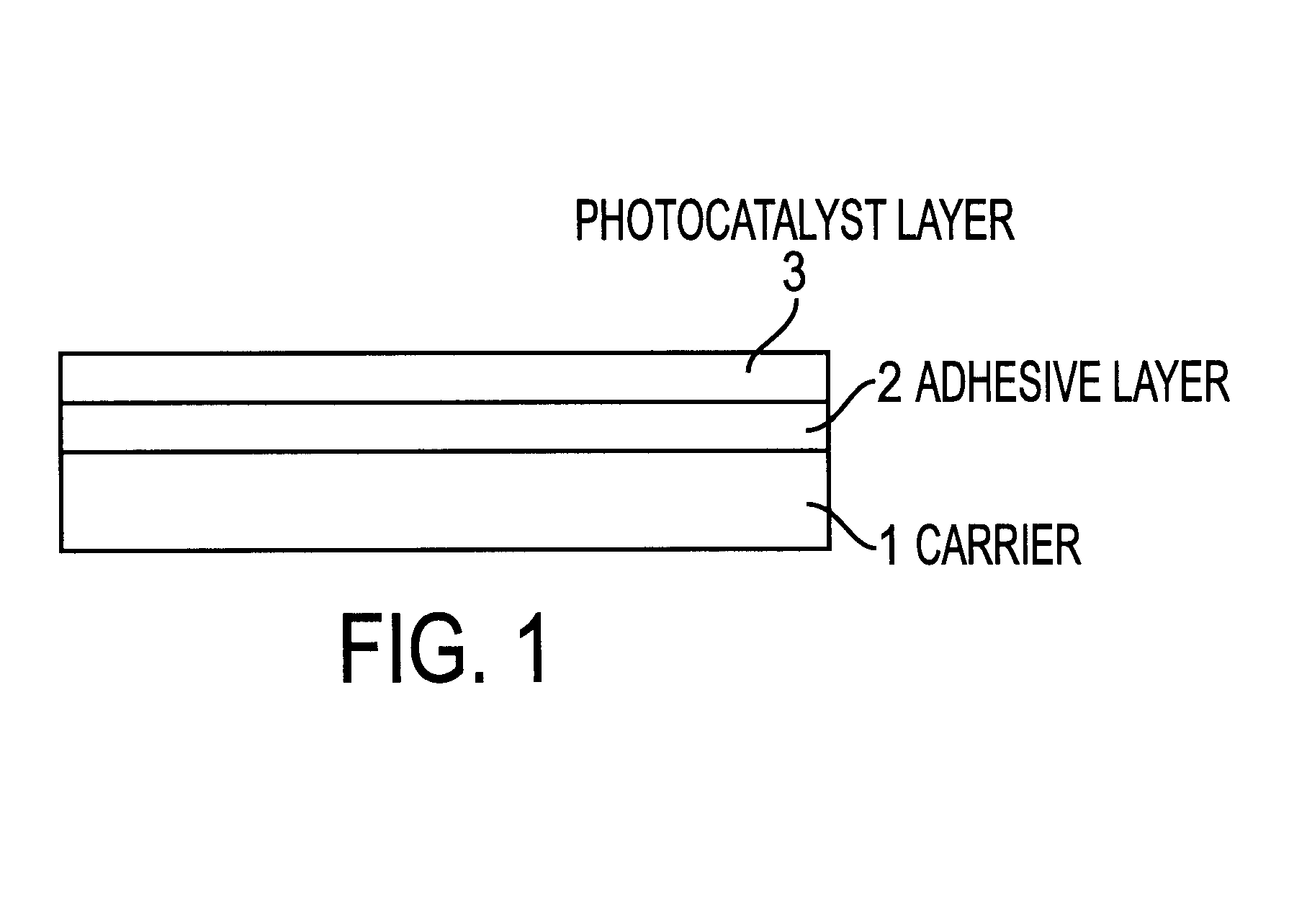
Photocatalyst-carrying structure and photocatalyst coating material
InactiveUS6228480B1Promote decompositionImprove adhesionGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsColloidal silicaColloid
The present invention provides a photocatalyst-carrying structure which has a structure, wherein an adhesive layer is provided in between a photocatalyst layer and a substrate, the adhesive layer is composed of silicon-modified resin, polysiloxane-containing resin or colloidal silica-containing resin, and for forming the photocatalyst layer a composition comprising a metal oxide gel or a metal hydroxide gel and a photocatalyst is used. Further, the present invention also provides a photocatalyst coating agent for producing a photocatalyst-carrying structure which contains silicon compound, at least one metal oxide sol or metal hydroxide sol, and at least one photocatalyst powder or sol.
Owner:NIPPON SODA CO LTD
Methods for prevention of surface adsorption of biological materials to capillary walls in microchannels
InactiveUS7252928B1Inhibit bindingPrevent and reduce adsorptionNanotechElectrolysis componentsSilica particleLipid formation
Methods for reducing surface adsorption of biological materials to the walls of microfluidic conduits in microscale devices are provided. In an example of the methods, one or more colloidal-size particles, such as colloidal silica particles, are flowed in a fluid within the microfluidic conduit in the presence of one or more adherent biological materials (such as one or more proteins, cells, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids and the like) to adsorb to the materials and prevent them from binding to the capillary walls of the microfluidic conduit. Other adsorption inhibition agents such as detergents and nonaqueous solvents can be used alone or in combination with colloidal particles to reduce surface adsorption in microfluidic conduits.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Method for making hydrophobic non-aggregated colloidal silica
A method for making hydrophobic non-aggregated colloidal silica comprising reacting an aqueous suspension of a hydrophilic non-aggregated colloidal silica having an average particle diameter greater than about 4 nm with a silicon compound at a pH less than about pH 4 in the presence of a sufficient quantity of a water-miscible organic solvent to facilitate contact of the hydrophilic non-aggregated colloidal silica with the silicon compound. The method is conducted at a temperature within a range of about 20 DEG C. to 250 DEG C. for a period of time sufficient to form a hydrophobic non-aggregated colloidal silica. The hydrophobic non-aggregated colloidal silicas prepared by the present method are particularly useful as fillers in silicone compositions such as adhesives, rubbers, and sealants.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
Increased thermal conductivity monolithic zeolite structures
A monolith comprises a zeolite, a thermally conductive carbon, and a binder. The zeolite is included in the form of beads, pellets, powders and mixtures thereof. The thermally conductive carbon can be carbon nano-fibers, diamond or graphite which provide thermal conductivities in excess of about 100 W / m·K to more than 1,000 W / m·K. A method of preparing a zeolite monolith includes the steps of mixing a zeolite dispersion in an aqueous colloidal silica binder with a dispersion of carbon nano-fibers in water followed by dehydration and curing of the binder is given.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Photodiffusion sheet and backlight unit using this
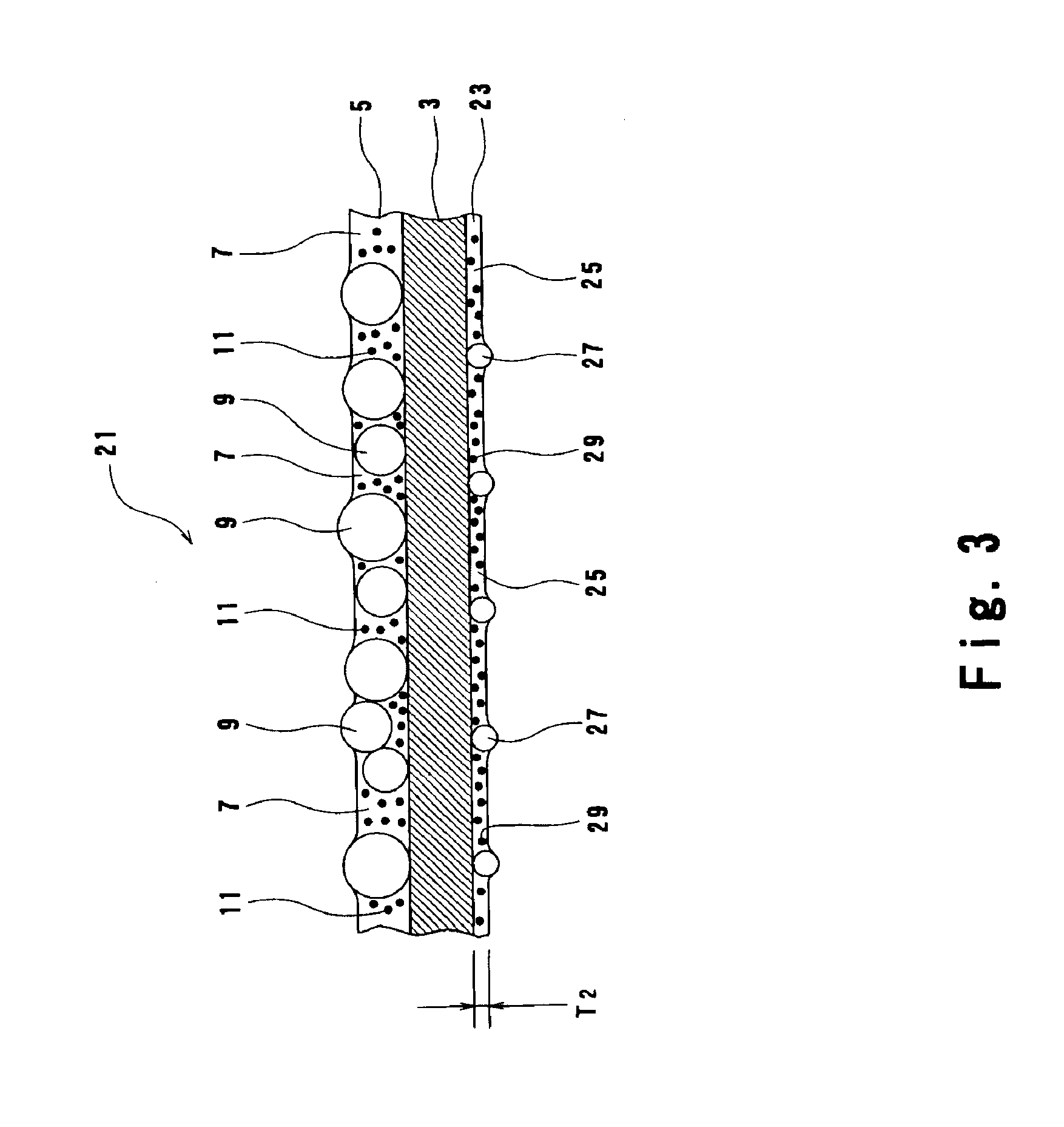
InactiveUS6852396B1Preferable sticking-proof abilityHeat resistantMechanical apparatusMirrorsColloidal silicaMicrometer
It is an object of the present invention to provide a light diffusing sheet that has a less tendency to be deflected due to heat generated by a lamp and a back light unit using this. The light diffusing sheet of the present invention comprises a base sheet and a light diffusing layer provided on a surface of the base sheet. The light diffusing layer is formed by dispersing resinous beads and a fine inorganic filler into a binder. It is preferable that the fine inorganic filler has an averaged particle diameter of not smaller than 5 nanometers and smaller than 1 micrometer. It is preferable that the amount of the fine inorganic filler to be mixed is 10 parts to 500 parts by weight for 100 parts by weight of a polymer component in the binder. As the fine inorganic filler, colloidal silica is used.
Owner:KEIWA INCORPORATED
Barrier polishing liquid and chemical mechanical polishing method
InactiveUS20070181534A1Sufficient rateSufficient polishing ratePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesOrganic acidColloidal silica
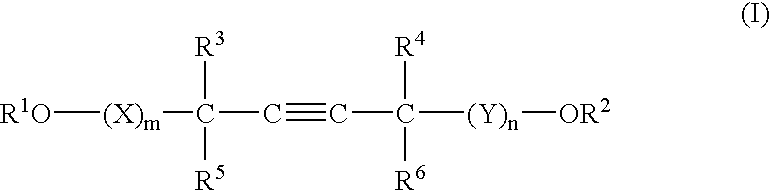
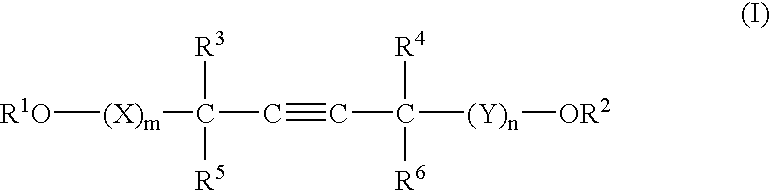
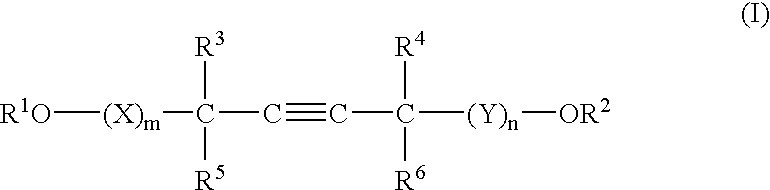
A barrier polishing liquid is provided that includes (a) a nonionic surfactant represented by Formula (I) below, (b) at least one type of organic acid selected from the group consisting of an aromatic sulfonic acid, an aromatic carboxylic acid, and a derivative thereof, (c) colloidal silica, and (d) benzotriazole or a derivative thereof.(In Formula (I), R1 to R6 independently denote a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbons, X and Y independently denote an ethyleneoxy group or a propyleneoxy group, and m and n independently denote an integer of 0 to 20.) There is also provided a chemical mechanical polishing method that includes supplying the barrier polishing liquid to a polishing pad on a polishing platen at a flow rate per unit area of a semiconductor substrate per unit time of 0.035 to 0.25 mL / (min·cm2), and polishing by making the polishing pad and a surface to be polished move relative to each other while they are in a contacted state.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Aqueous dispersion for chemical mechanical polishing
InactiveUS6527818B2Pigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesColloidal silicaOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATE
There is provided an aqueous dispersion for CMP with an excellent balance between chemical etching and mechanical polishing performance. The aqueous dispersion for CMP of the invention is characterized by comprising an abrasive, water and a heteropolyacid. Another aqueous dispersion for CMP according to the invention is characterized by comprising an abrasive, water, a heteropolyacid and an organic acid. Yet another aqueous dispersion for CMP according to the invention is characterized by comprising colloidal silica with a primary particle size of 5-100 nm, water and a heteropolyacid. Preferred for the heteropolyacid is at least one type selected from among silicomolybdic acid, phosphorotungstic acid, silicotungstic acid, phosphoromolybdic acid and silicotungstomolybdic acid. Preferred for the organic acid is at least one selected from among oxalic acid, malonic acid, succinic acid, glutaric acid, adipic acid, maleic acid, fumaric acid, phthalic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid and citric acid.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
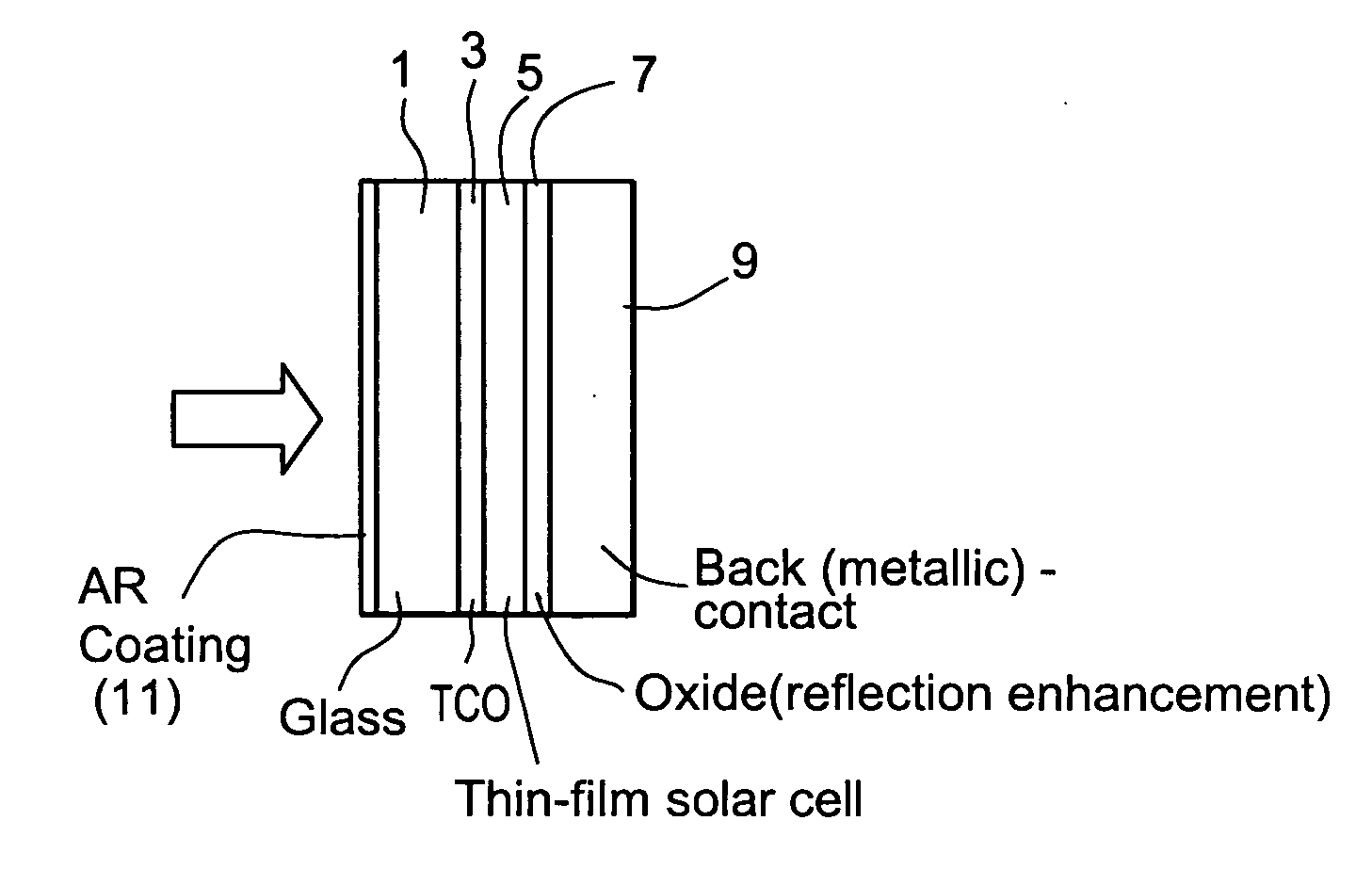
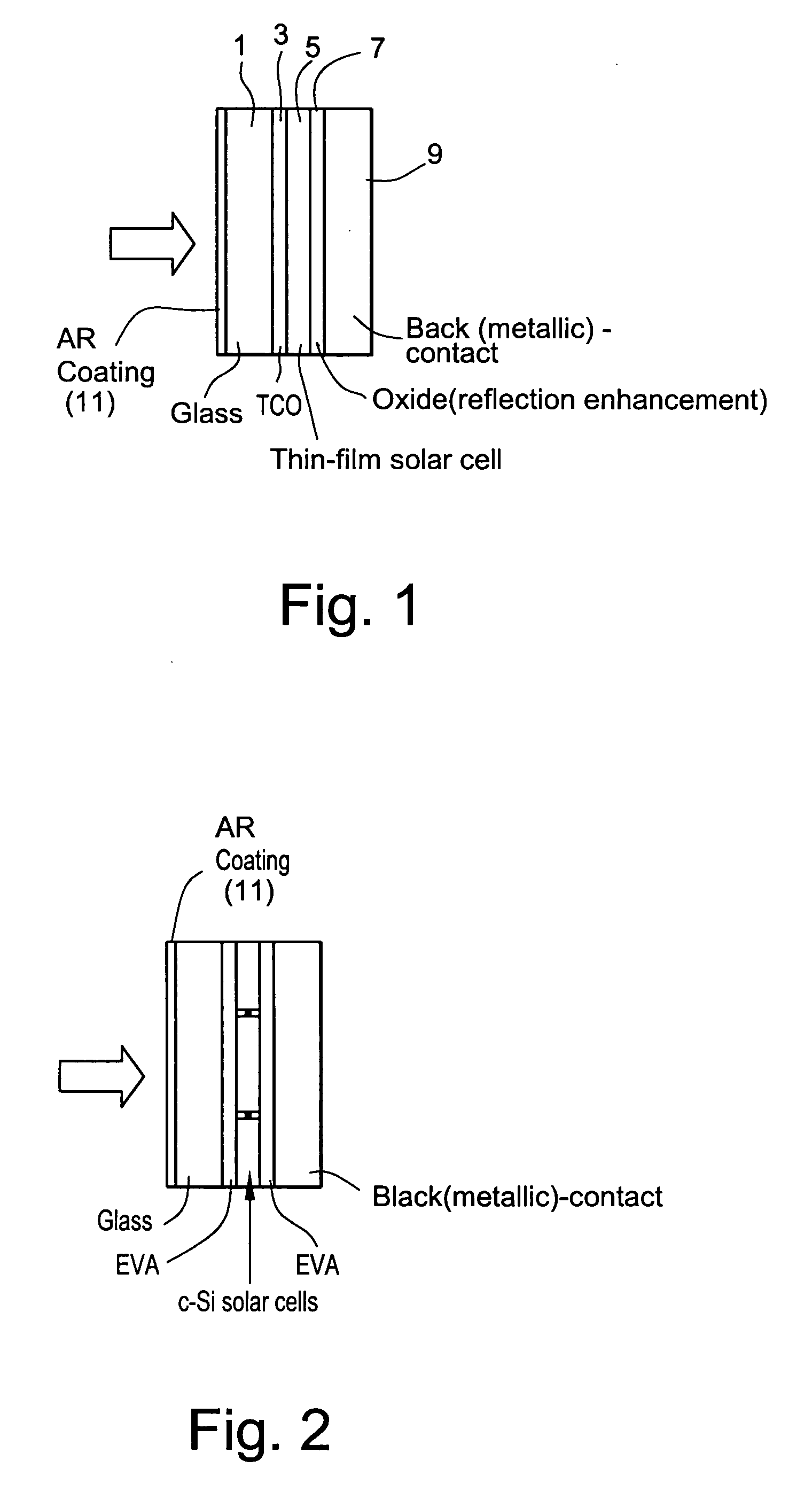
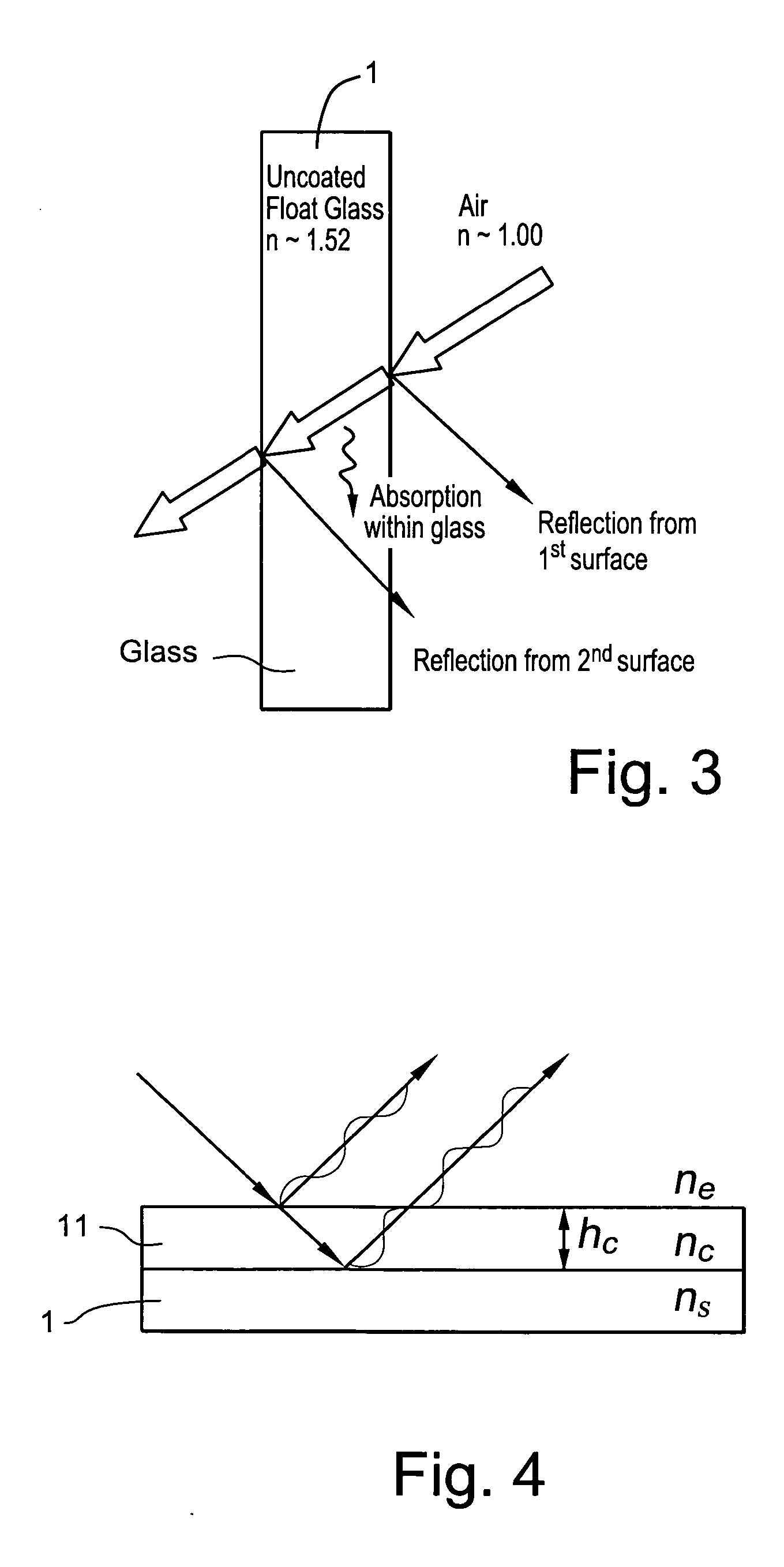
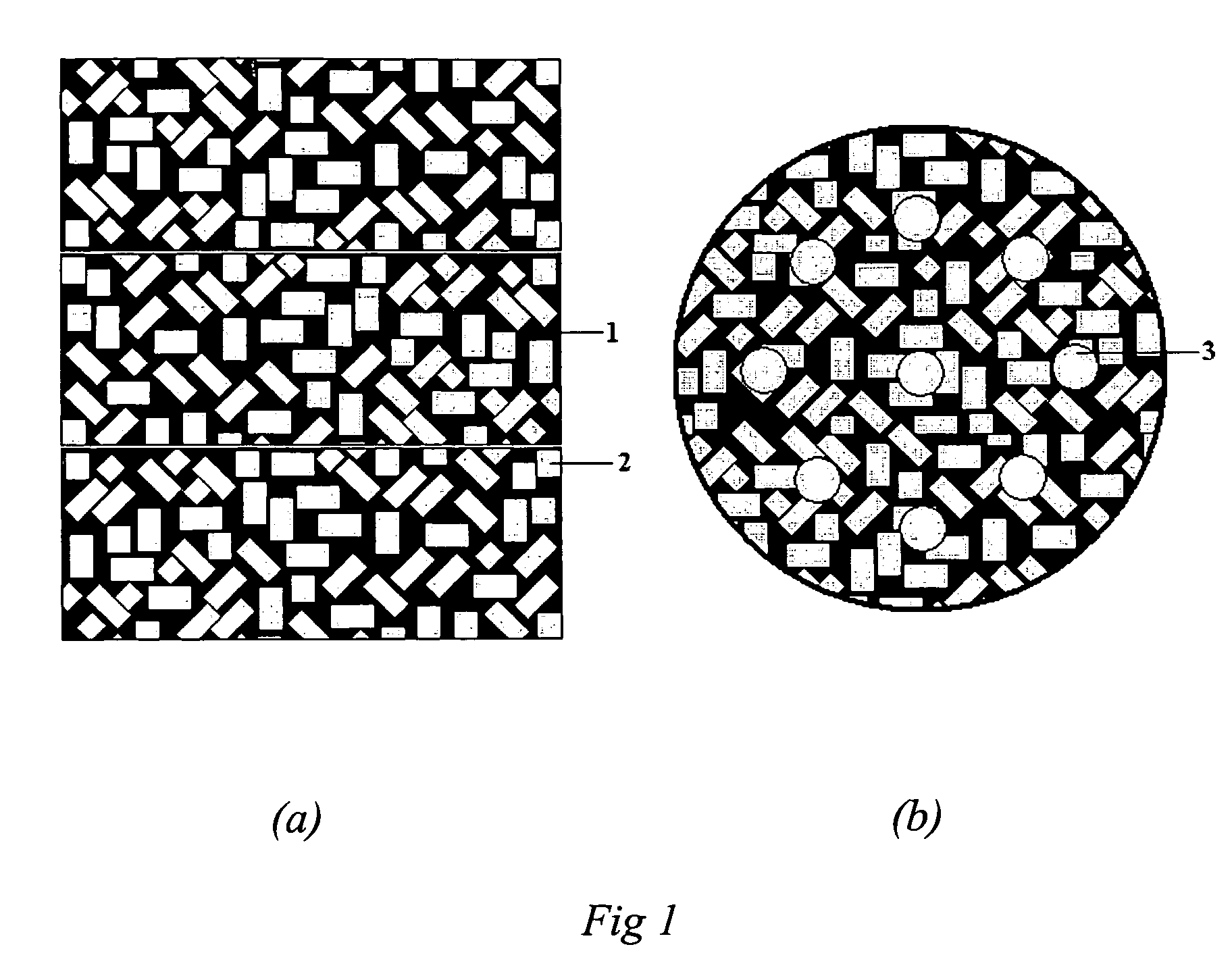
Method of making solar cell/module with porous silica antireflective coating
InactiveUS20070074757A1Improved anti-reflection (AR) coatingReduce reflectionCoatingsPhotovoltaic energy generationColloidal silicaAnti-reflective coating
A solar cell includes an improved anti-reflection (AR) coating provided on an incident glass substrate. In certain example embodiments, the AR coating includes a layer comprising porous silica. The porous nature of the silica inclusive layer permits the refractive index (n) of the silica inclusive layer to be reduced, thereby decreasing reflection and permitting more radiation to make its way to the active layer(s) of the solar cell. In certain example embodiments, a coating solution may be formed by mixing a colloidal silica solution and a polymeric silica solution, then applying the coating solution to a substrate and curing the same in order to form an AR coating.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Colloidal silica composition
ActiveUS20040077768A1Reduce dispersionImprove suppression propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentSilane compoundsColloidal silica
The invention relates to a method of producing a stable substantially aqueous silanized colloidal silica dispersion having a silica content of at least about 20 wt %, comprising mixing at least one silane compound and colloidal silica particles, wherein the weight ratio of silane to silica is from about 0.003 to about 0.2. The invention also relates to a dispersion obtainable by the method, and to a stable substantially aqueous silanized colloidal silica dispersion having a silica content of at least about 20 wt %, wherein the weight ratio of silane to silica is from about 0.003 to about 0.2. The invention further concerns the use of the dispersion for coatings applications and as an additive.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL CHEM INT BV
Cleaner for hard surfaces
InactiveUS20050239674A1Avoid Excessive CondensationEasy to cleanInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsColloidal silicaColloid
Cleaner for hard surfaces, especially glass. Application of the cleaner containing a colloidal silica sol results in a modification of the streaming potential of the surface by −5 to −50 mV. The cleaner can be used to hydrophilize and clean hard surfaces by contact.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Methods of using colloidal silica based gels
Methods of controlling flow through a subterranean formation may include providing a cement slurry, a colloidal silica, and an activator. The methods may include introducing the cement slurry, the colloidal silica, and the activator into a portion of a well bore that penetrates a subterranean formation The methods may include allowing the cement slurry, colloidal silica, and activator to remain static.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Thermal protective coating for ceramic surfaces
ActiveUS6921431B2Extended shelf lifeConvenience to workFireproof paintsOther chemical processesColloidal silicaSodium Bentonite
A coating admixture, method of coating and substrates coated thereby, wherein the coating contains colloidal silica, colloidal alumina, or combinations thereof; a filler such as silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide, titanium dioxide, magnesium oxide, calcium oxide and boron oxide; and one or more emissivity agents such as silicon hexaboride, carbon tetraboride, silicon tetraboride, silicon carbide, molybdenum disilicide, tungsten disilicide, zirconium diboride, cupric chromite, or metallic oxides such as iron oxides, magnesium oxides, manganese oxides, chromium oxides, copper chromium oxides, cerium oxides, terbium oxides, and derivatives thereof. In a coating solution, an admixture of the coating contains water. A stabilizer such as bentonite, kaolin, magnesium alumina silicon clay, tabular alumina and stabilized zirconium oxide is also added.
Owner:WESSEX
Colloidal silica containing silica secondary particles having bent structure and/or branched structure, and method for producing same
ActiveUS8529787B2Improve polishing rateLarge aspect ratioSilicaOther chemical processesColloidal silicaColloid
This invention provides a dense, high-purity colloidal silica containing silica secondary particles having a branched and / or bent structure, and a production method thereof. Specifically, this invention provides a method for producing a colloidal silica, comprising the steps of 1) preparing a mother liquid containing an alkali catalyst and water, and having a pH of 9 to 12; and 2) adding a hydrolysis liquid obtained by hydrolysis of an alkyl silicate to the mother liquid, wherein the step of adding the hydrolysis liquid to the mother liquid sequentially comprises A) step 1 of adding the hydrolysis liquid until the pH of the resulting liquid mixture becomes less than 7; B) step 2 of adding an aqueous alkali solution until the pH of the liquid mixture becomes 7 or more; and C) step 3 of adding the hydrolysis liquid while maintaining the pH of the liquid mixture at 7 or more, and a colloidal silica containing silica secondary particles having a branched and / or bent structure, obtained by this method.
Owner:FUSO CHEM
Coating composition forming wear-resistant coat and article covered with the coat
A coating composition forming a abrasion resistant coating comprising (A) an ultraviolet-curable silicone prepared by chemically modifying particulate colloidal silica with a specific silane compound, (B) a monomer mixture comprising a (meth)acrylate having a specific isocyanate skeleton and a urethane poly(meth)acrylate having an alicyclic skeleton, and (C) a photo-polymerization initiator. By using a urethane poly(meth)acrylate having an alicyclic skeleton as part of the component (B) and the component (A) having an enhanced reactivity of chemical modification, the compatibility of the component (A) with the component (B) is improved to give a cured coating with excellent wear resistance, weather resistance and durability.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Aqueous dispersion
ActiveUS20040097600A1Effective and stableShorten drying timeMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentSilica particleSilane compounds
The invention relates to a method of producing an aqueous dispersion comprising mixing at least one silane compound and colloidal silica particles to form silanized colloidal silica particles, mixing said silanized colloidal silica particles with an organic binder to form the dispersion. The invention also relates to a dispersion obtainable by the method, and the use thereof.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL CHEM INT BV
Exhaust gas purifying catalyst and method of producing same
InactiveUS6589901B2Improve heat resistanceReduce stickingInternal combustion piston enginesMolecular sieve catalystsColloidal silicaColloid
An exhaust gas purifying catalyst for exhaust gas discharged from an automotive internal combustion engine. The catalyst comprises a substrate over which a hydrocarbons adsorbing material layer is formed as a lower layer to absorb hydrocarbons contained in exhaust gas. The hydrocarbons adsorbing material layer contains zeolite and colloidal silica which has undergone firing. The colloidal silica is in a chain-like form and / or a spherical form before and after the firing. Additionally, a catalyst component layer is formed as an upper layer over the hydrocarbons adsorbing material layer. The catalyst component layer contains a catalyst metal.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Dental composite materials
A polymerizable dental composition, comprising a polymerizable resin composition; and a filler composition comprising a bound, nanostructured colloidal silica
Owner:PENTRON CLINICAL TECH
Controllable Synthesis of Porous Carbon Spheres, and Electrochemical Applications Thereof
InactiveUS20110082024A1Good dispersionExcellent ORR activityMaterial nanotechnologyReactant parameters controlColloidal silicaSmall droplet
The invention disclosed relates to porous carbon of spherical morphology having tuned porosity and to a method of making same, comprising: (a) providing a precursor solution, by combining in an aqueous solution a colloidal silica template material and a water-soluble pyrolyzable carbon source, wherein the particle size of the colloidal silica template and the colloidal silica / carbon source weight ratio are controlled, (b) atomizing the precursor solution into small droplets by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis (c) directing the droplets into a high temperature furnace operating at a temperature of 700-1200° C., under an inert gas atmosphere, where the droplets are transformed into solid spherical composite carbon / silica particles, (d) collecting the resulting composite carbon / silica particles exiting from the furnace, and (e) removing the silica from the particles, to provide substantially pure porous carbon of spherical morphology having tuned porosity defined by surface area and pore size. The porous carbon according to the invention is used as catalyst supports in PEM fuel cells, as electrodes in supercapacitors and lithium in batteries, for hydrogen storage and as earners for drug delivering.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
CMP slurry for metallic film, polishing method and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
A CMP slurry for metallic film is provided, which includes water, 0.01 to 0.3 wt %, based on a total quantity of the slurry, of polyvinylpyrrolidone having a weight average molecular weight of not less than 20,000, an oxidizing agent, a protective film-forming agent containing a first complexing agent for forming a water-insoluble complex and a second complexing agent for forming a water-soluble complex, and colloidal silica having a primary particle diameter ranging from 5 to 50 nm.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Low-cost, user-friendly hardcoating solution, process and coating
InactiveUS6265029B1Excellent abrasion resistanceArticle accumulatePretreated surfacesCoatingsColloidal silicaSilanes
An improved, user-friendly silane / silica sol copolymer hardcoating composition for protecting optical plastic and other substrates (including wood, metals, glass, plastics and most coated articles) from scratching is able to be manufactured at lower costs and to provide much-improved ease of use in transportation, storage, dipbath (or other coating tank) stability, and blush resistance in ordinary cleanroom atmospheres. The silane / silica sol copolymer is formed as a direct reaction product of an acidic silica sol and monomethyltrialkoxysilane, preferably substantially monomethyltriethoxysilane, in ratios of 30:70 to 70:30, most preferably about 40:60. A tail solvent aids blush resistance, reduces internal stress and permits adhesion to unprimed polycarbonate. Optionally, colloidal silica sol dissolved in water-miscible solvent may be reacted in a second stage with acidic aqueous colloidal silica sol earlier silanized with monomethyltrialkoxysilane.
Owner:LEWIS WILLIAM
Thermal protective coating for ceramic surfaces
ActiveUS20050051057A1Extend working lifeReduce surface temperatureFireproof paintsOther chemical processesColloidal silicaSodium Bentonite
A coating admixture, method of coating and substrates coated thereby, wherein the coating contains colloidal silica, colloidal alumina, or combinations thereof; a filler such as silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide, titanium dioxide, magnesium oxide, calcium oxide and boron oxide; and one or more emissivity agents such as silicon hexaboride, carbon tetraboride, silicon tetraboride, silicon carbide, molybdenum disilicide, tungsten disilicide, zirconium diboride, cupric chromite, or metallic oxides such as iron oxides, magnesium oxides, manganese oxides, chromium oxides, copper chromium oxides, cerium oxides, terbium oxides, and derivatives thereof. In a coating solution, an admixture of the coating contains water. A stabilizer such as bentonite, kaolin, magnesium alumina silicon clay, tabular alumina and stabilized zirconium oxide is also added.
Owner:WESSEX
Composition and method for polishing a sapphire surface
InactiveUS20060196849A1Simple compositionImprove methodOther chemical processesDecorative surface effectsColloidal silicaSlurry
An improved composition and method for polishing a sapphire surface is disclosed. The method comprises abrading a sapphire surface, such as a C-plane or R-plane surface of a sapphire wafer, with a polishing slurry comprising an abrasive amount of an inorganic abrasive material such as colloidal silica suspended in an aqueous medium having a salt compound dissolved therein. The aqueous medium has a basic pH and includes the salt compound in an amount sufficient to enhance the sapphire removal rate relative to the rate achievable under the same polishing conditions using a the same inorganic abrasive in the absence of the salt compound.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Combinations of resin compositions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050131106A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsColloidal silicaFilling materials
A composition for use as underfill material is provided. The underfill material includes a first curable transparent resin composition and a second curable fluxing resin composition. The first curable resin composition includes at least one aromatic epoxy resin in combination with a solvent, a functionalized colloidal silica dispersion, and at least one other component selected from the group consisting of cycloaliphatic epoxy monomers, aliphatic epoxy monomers, hydroxy aromatic compounds and combinations and mixtures thereof, thereby forming a solvent-modified resin. The second curable fluxing composition includes at least one epoxy resin. The combination of the two resin compositions is useful in producing underfill materials and is suitable for use as an encapsulant for electronic chips.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Polishing liquid
ActiveUS20100167547A1InhibitionHigh rateOther chemical processesDecorative surface effectsColloidal silicaDevice material
A polishing liquid for a chemical mechanical polishing of a semiconductor device includes (a) a carboxylic acid compound having one or more carboxy groups, (b) colloidal silica particles having a ζ potential of −10 mV to −35 mV when used in the polishing liquid, (c) a benzotriazole derivative, (d) an anionic surfactant, and (e) an oxidizing agent, and the polishing liquid has a pH of from 5.0 to 8.0.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Glass fibers and mats having improved surface structures in gypsum boards
ActiveUS20050202258A1Easy to separateSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsColloidal silicaSilanes
A gypsum board having roughened surface glass fiber reinforcement. The roughened surface of glass fiber is created by incorporating nano or micro particles of colloidal silica or clay or other inorganic particles in a silane based sizing composition. The sizing coating is partially or completely cured and incorporated in gypsum wet mix either as additions of chopped fibers or as placement of roughened surface glass fiber mats at selected locations within a cast gypsum sheet. The roughened surface of glass fiber with nano or micro particles compliantly bonded with silane polymer transfers load from gypsum to glass fibers providing improved strength and flexure resistance of gypsum boards.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE INT INC
Coating film for building material
A building material and a method for coating a substrate for the building material with a coating film having a variety of functions relating to an environment such as mildew resistance, deodorization, antibacterial activity and air purification in addition to the anti-staining effect by having an excellent hydrophilicity. The method for coating the substrate for a building material comprises the steps of; coating a coating material comprising a hydrophilic polymer and a photocatalyst on the substrate, and drying the coating material to form a coating film containing the photocatalyst, wherein the hydrophilic polymer is at least one selected from the group consisting of methyl silicate, liquid glass, colloidal silica, poly(meth)acrylate, and polytetrafluoroethylene graft-polymerized with sulfonic acid, and the photocatalyst is at least one selected from the group consisting of titanium oxide coated with zeolite, titanium oxide coated silica and titanium oxide coated with apatite.
Owner:NICHIHA CORP
Increased thermal conductivity monolithic zeolite structures
A monolith comprises a zeolite, a thermally conductive carbon, and a binder. The zeolite is included in the form of beads, pellets, powders and mixtures thereof. The thermally conductive carbon can be carbon nano-fibers, diamond or graphite which provide thermal conductivities in excess of about 100 W / m·K to more than 1,000 W / m·K. A method of preparing a zeolite monolith includes the steps of mixing a zeolite dispersion in an aqueous colloidal silica binder with a dispersion of carbon nano-fibers in water followed by dehydration and curing of the binder is given.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Polishing composition and polishing method
InactiveUS20050205837A1Suitable for useOther chemical processesDecorative surface effectsColloidal silicaTetramethylammonium hydroxide
A polishing composition includes silicon dioxide, an alkaline compound, an anionic surfactant, and water. The silicon dioxide is, for example, colloidal silica, fumed silica, or precipitated silica. The alkaline compound is, for example, potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, ammonia, tetramethylammonium hydroxide, piperazine anhydride, or piperazine hexahydrate. The anionic surfactant is at least one selected from a sulfonic acid surfactant, a carboxylic acid surfactant, and a sulfuric acid ester surfactant. The polishing composition can be suitably used in applications for polishing a silicon wafer.
Owner:FUJIMI INCORPORATED
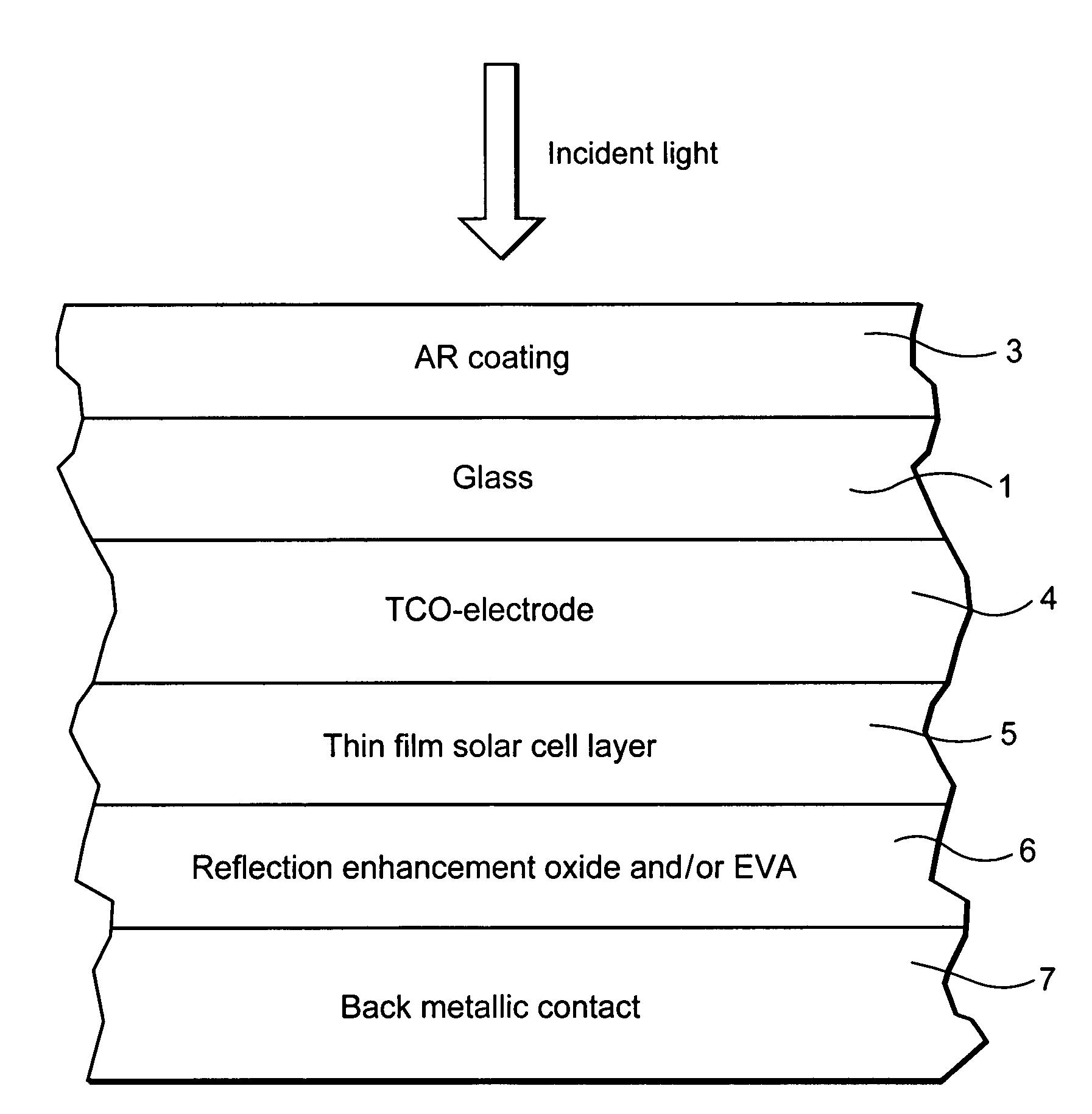
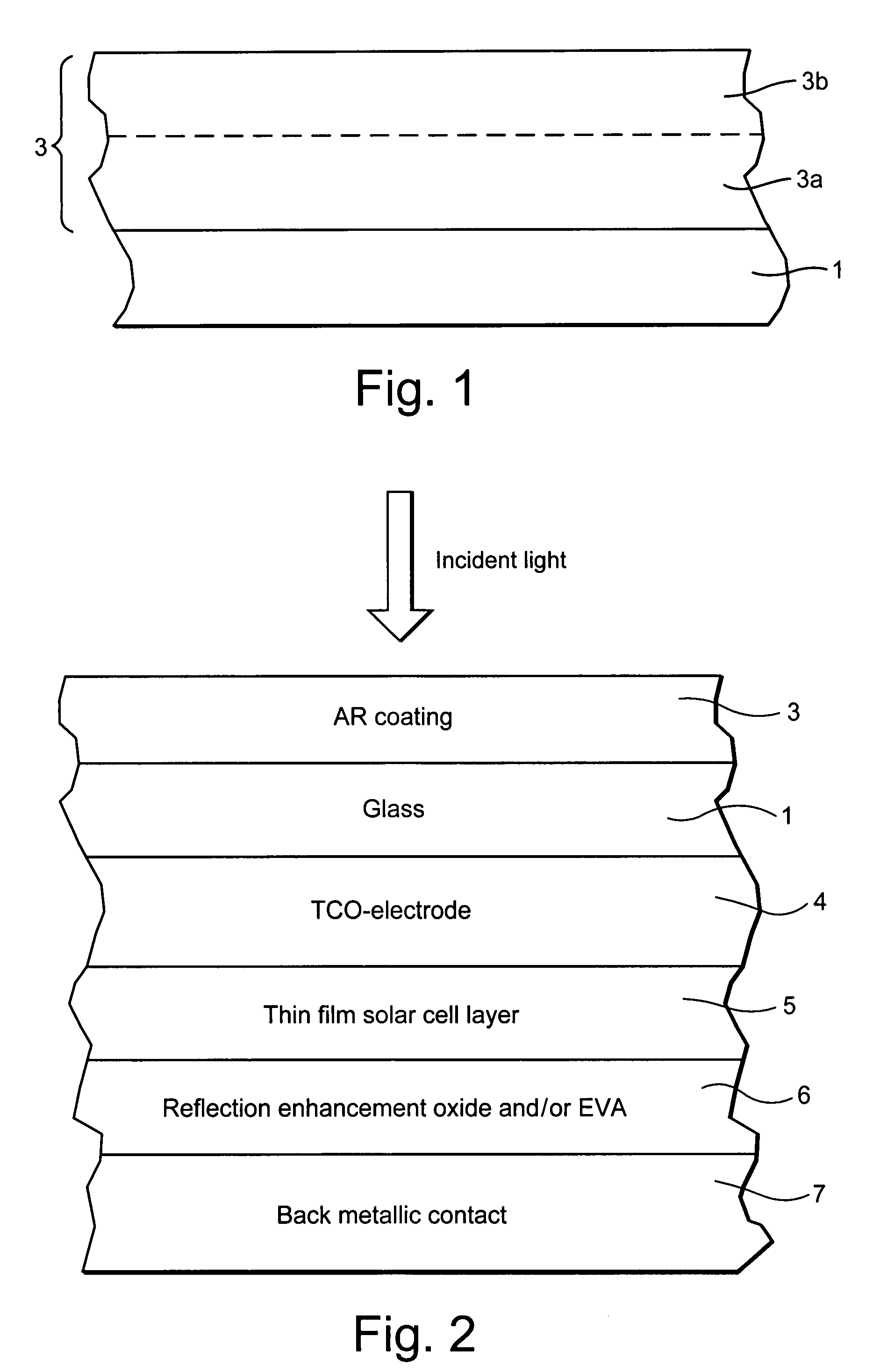
Method of making a photovoltaic device with antireflective coating
InactiveUS7767253B2High light transmittanceIncrease power and efficiencySpecial surfacesCoatingsColloidal silicaSilanes
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com