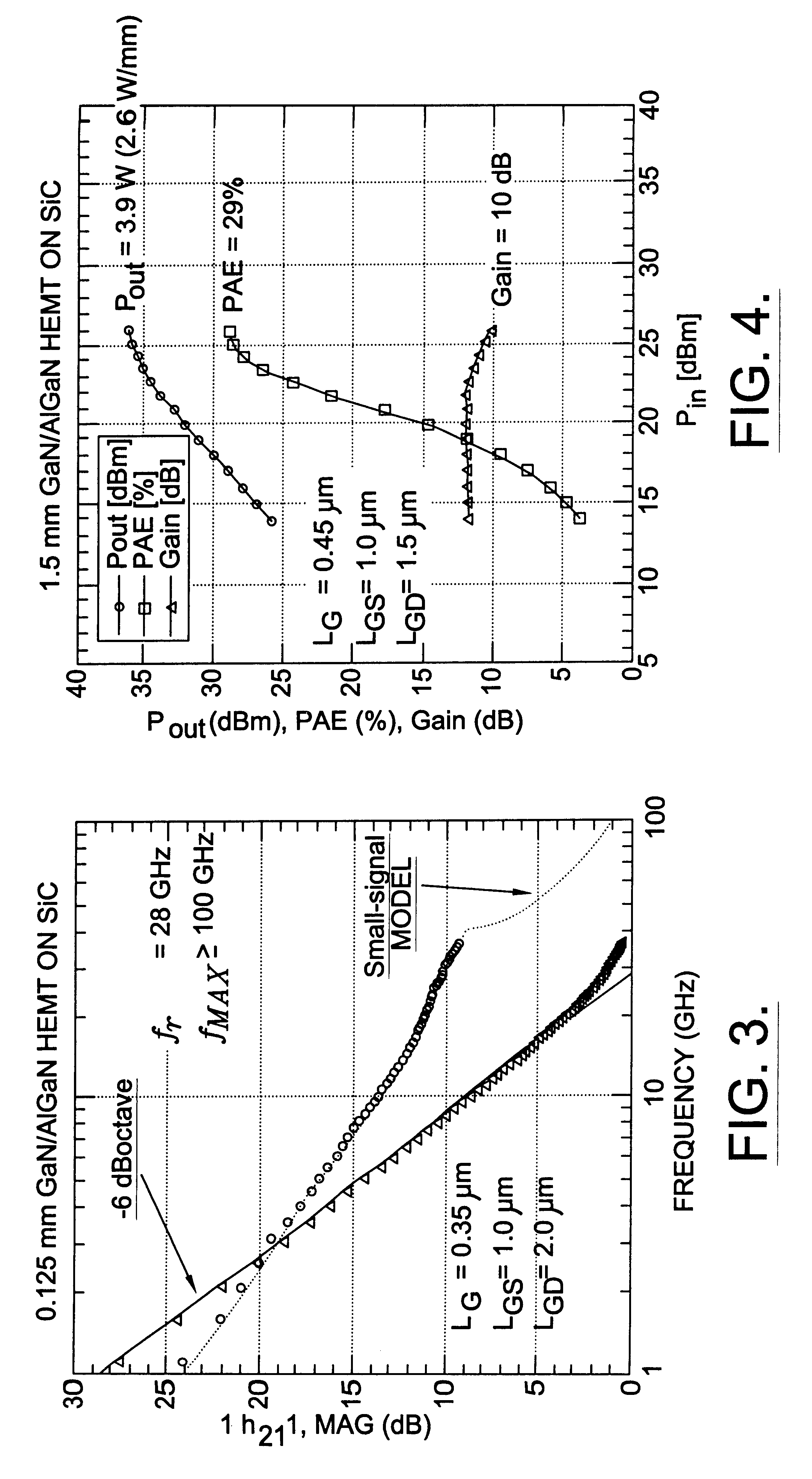
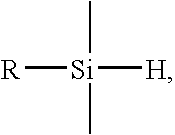Patents
Literature
19294 results about "Silicon carbide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum /kɑːrbəˈrʌndəm/, is a semiconductor containing silicon and carbon. It occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite. Synthetic SiC powder has been mass-produced since 1893 for use as an abrasive. Grains of silicon carbide can be bonded together by sintering to form very hard ceramics that are widely used in applications requiring high endurance, such as car brakes, car clutches and ceramic plates in bulletproof vests. Electronic applications of silicon carbide such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and detectors in early radios were first demonstrated around 1907. SiC is used in semiconductor electronics devices that operate at high temperatures or high voltages, or both. Large single crystals of silicon carbide can be grown by the Lely method and they can be cut into gems known as synthetic moissanite.
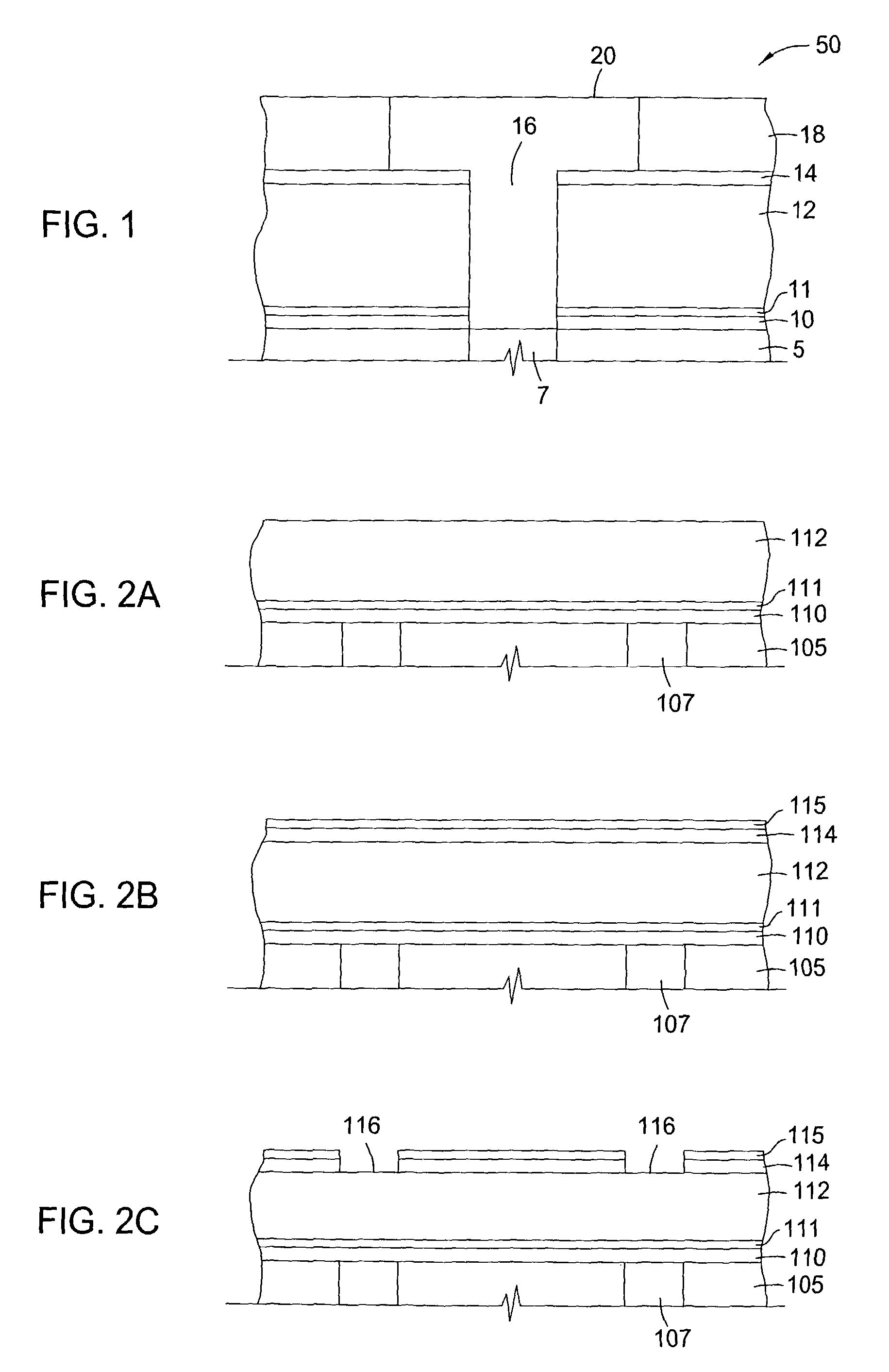
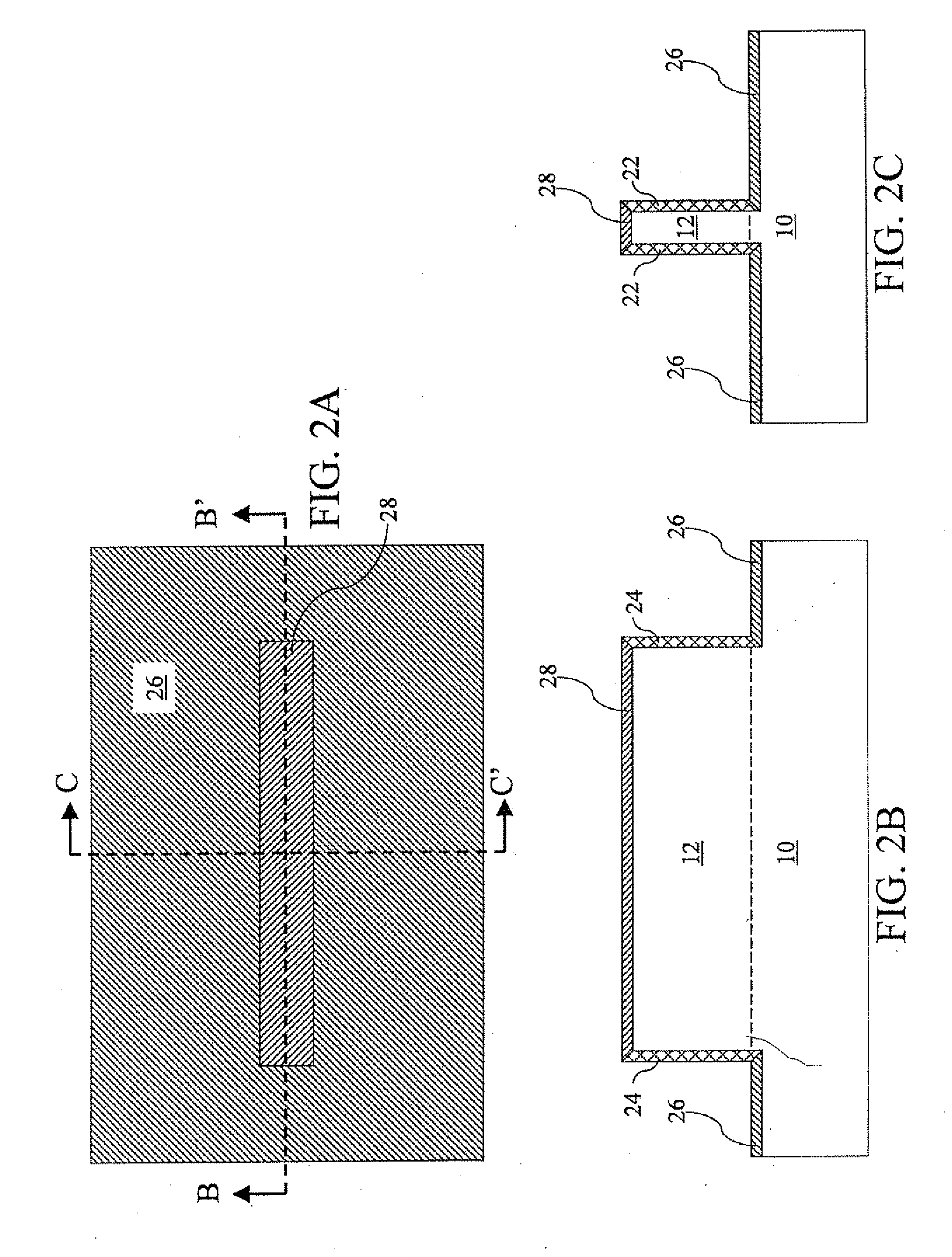
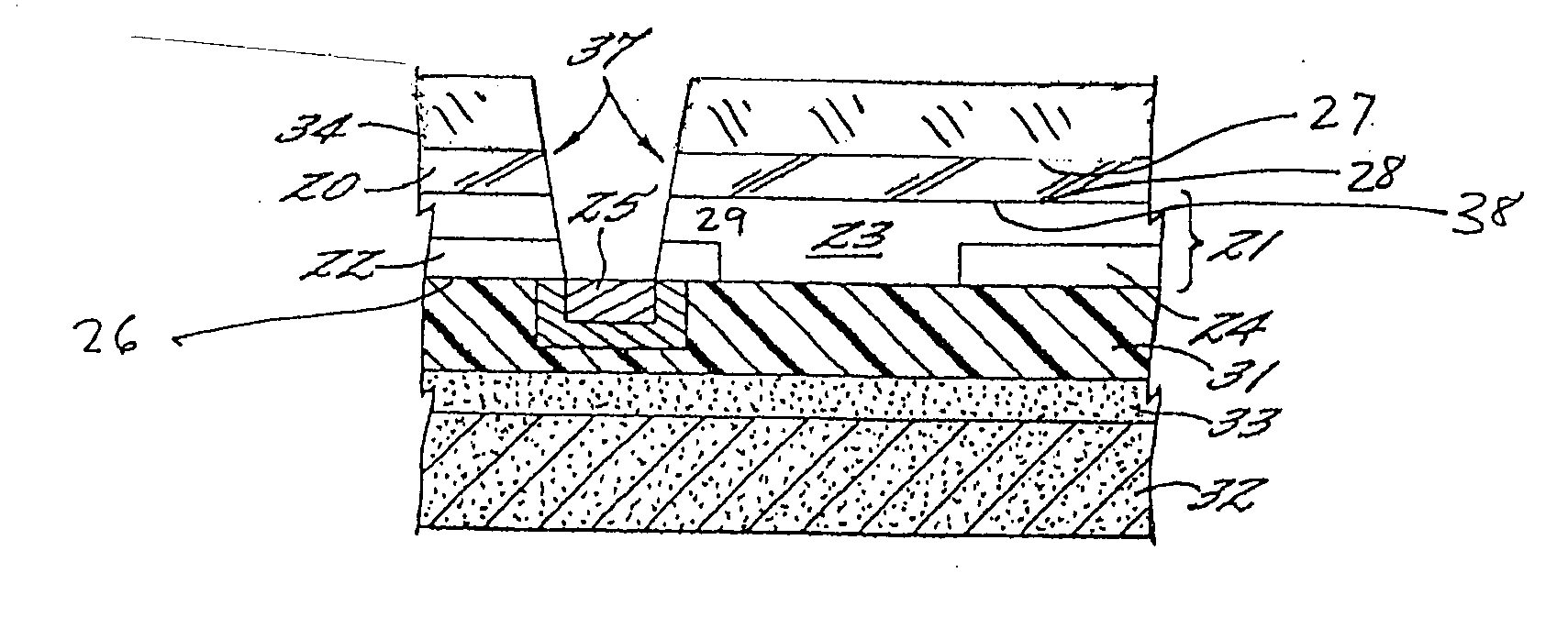
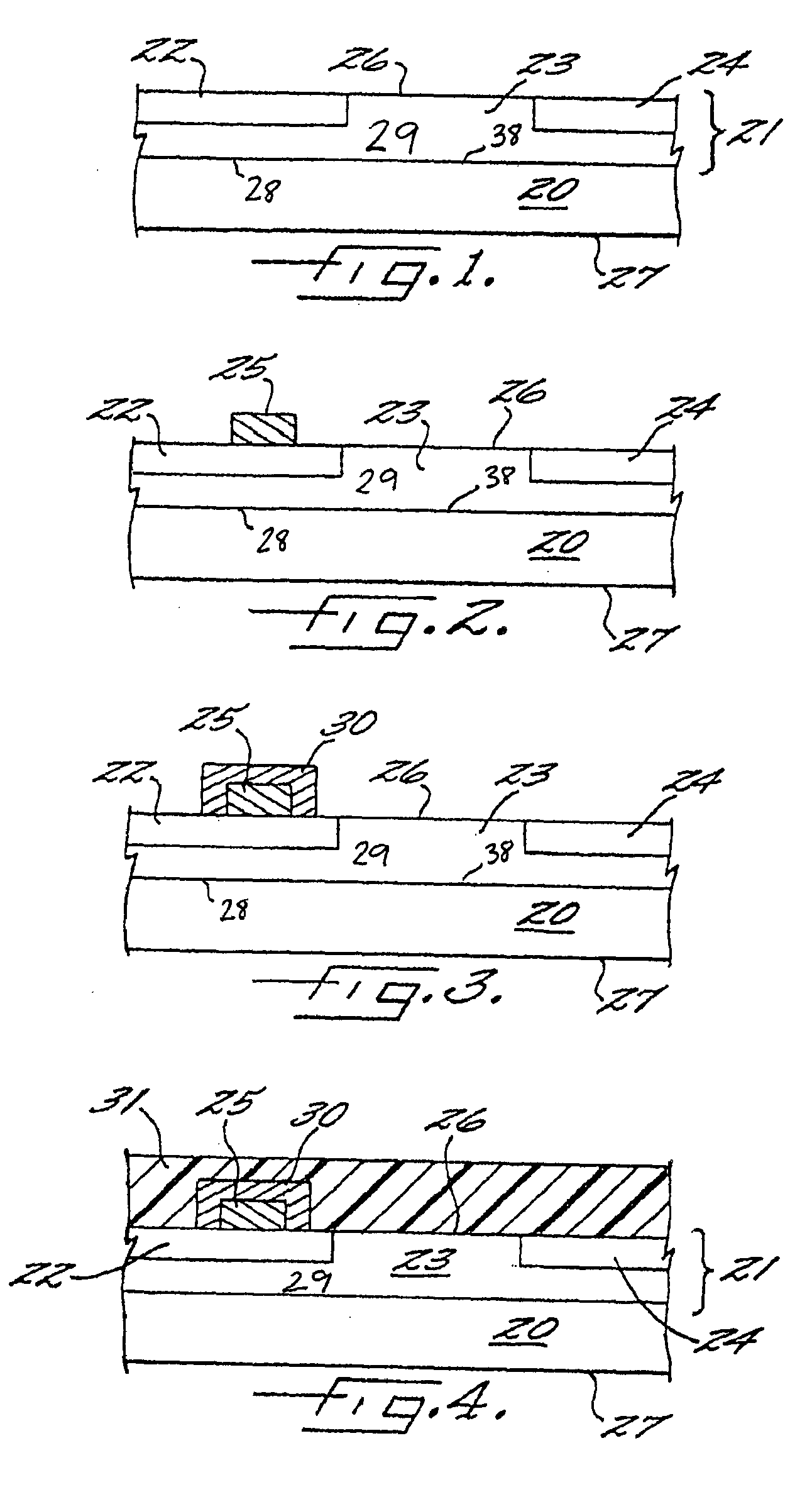
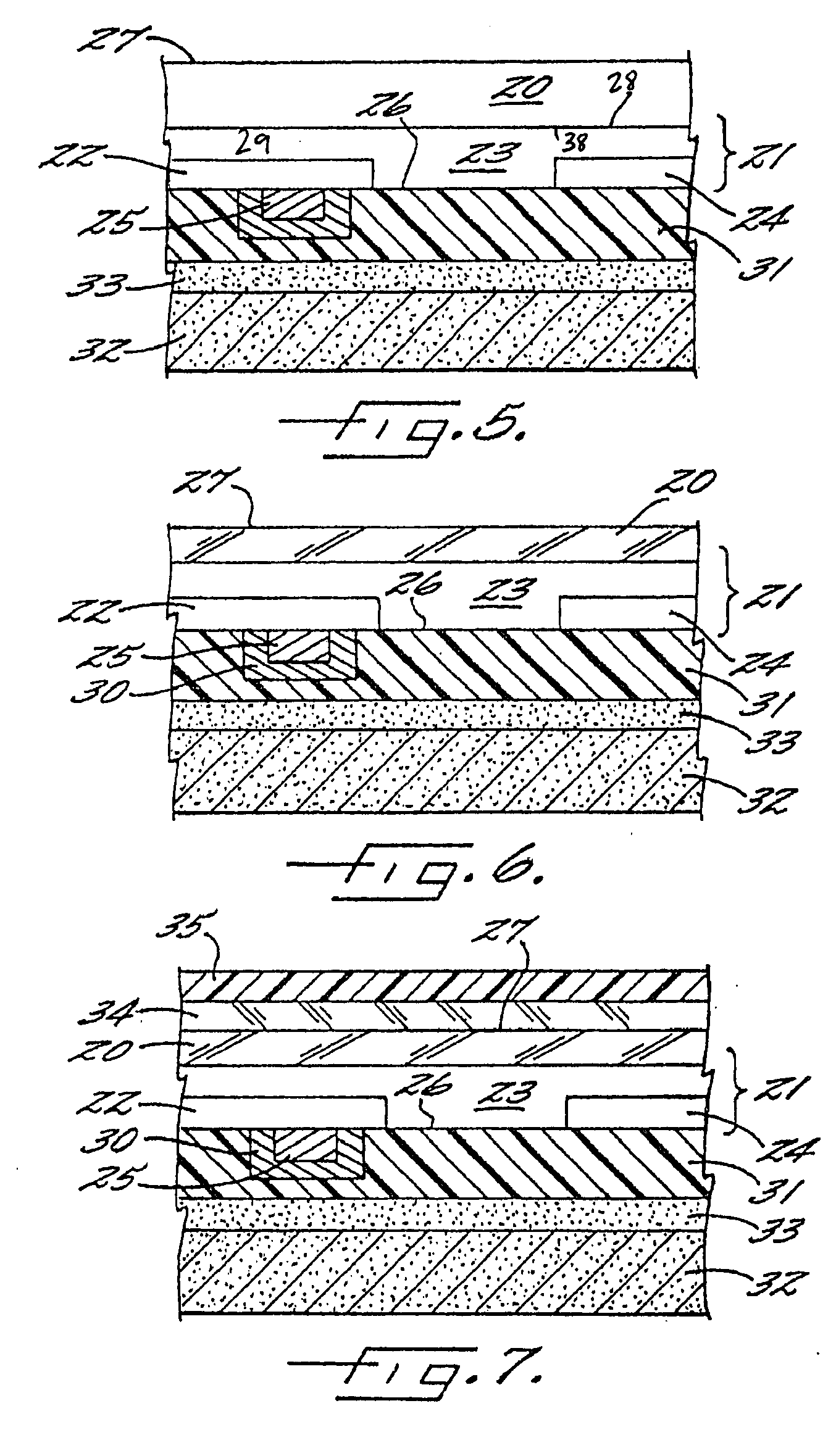
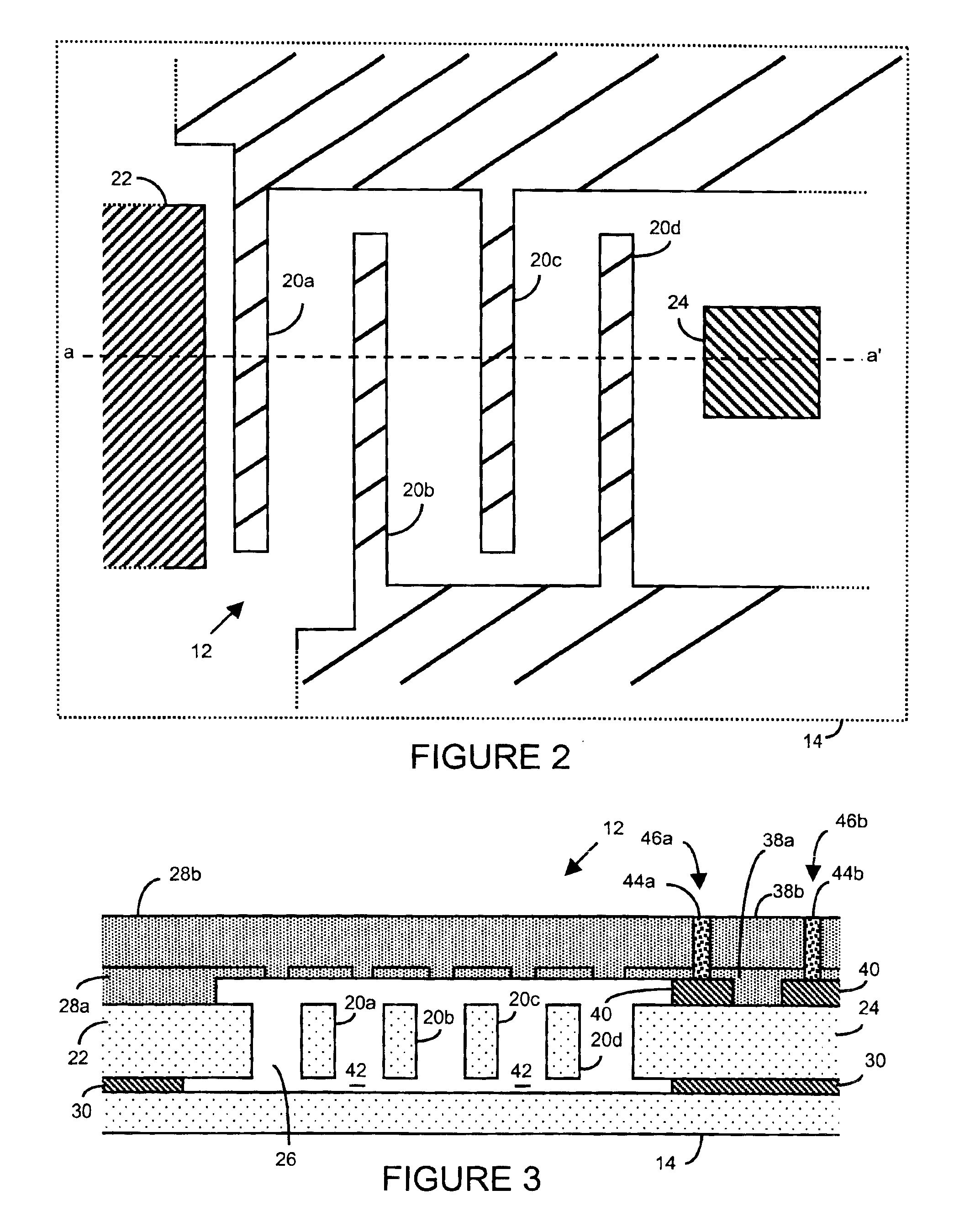
Group III nitride photonic devices on silicon carbide substrates with conductive buffer interlay structure
InactiveUS6201262B1Avoid crackingEasy to manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStress inducedStress relieving
An optoelectronic device with a Group III Nitride active layer is disclosed that comprises a silicon carbide substrate; an optoelectronic diode with a Group III nitride active layer; a buffer structure selected from the group consisting of gallium nitride and indium gallium nitride between the silicon carbide substrate and the optoelectronic diode; and a stress-absorbing structure comprising a plurality of predetermined stress-relieving areas within the crystal structure of the buffer structure, so that stress-induced cracking that occurs in the buffer structure occurs at predetermined areas rather than elsewhere in the buffer structure.
Owner:CREE INC
Nitride based transistors on semi-insulating silicon carbide substrates
InactiveUS6316793B1Quality improvementImprove thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGallium nitrideMaterials science
A high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) is disclosed that includes a semi-insulating silicon carbide substrate, an aluminum nitride buffer layer on the substrate, an insulating gallium nitride layer on the buffer layer, an active structure of aluminum gallium nitride on the gallium nitride layer, a passivation layer on the aluminum gallium nitride active structure, and respective source, drain and gate contacts to the aluminum gallium nitride active structure.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Group III nitride photonic devices on silicon carbide substrates with conductive buffer interlayer structure
InactiveUS6187606B1Avoid crackingMinimize and eliminate heterobarrierSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStress inducedStress relieving
An optoelectronic device with a Group III Nitride active layer is disclosed that comprises a silicon carbide substrate; an optoelectronic diode with a Group III nitride active layer; a buffer structure selected from the group consisting of gallium nitride and indium gallium nitride between the silicon carbide substrate and the optoelectronic diode; and a stress-absorbing structure comprising a plurality of predetermined stress-relieving areas within the crystal structure of the buffer structure, so that stress-induced cracking that occurs in the buffer structure occurs at predetermined areas rather than elsewhere in the buffer structure.
Owner:CREE INC
Semi-insulating silicon carbide without vanadium domination
InactiveUS6218680B1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease the number ofPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDevice formTrapping
Owner:CREE INC
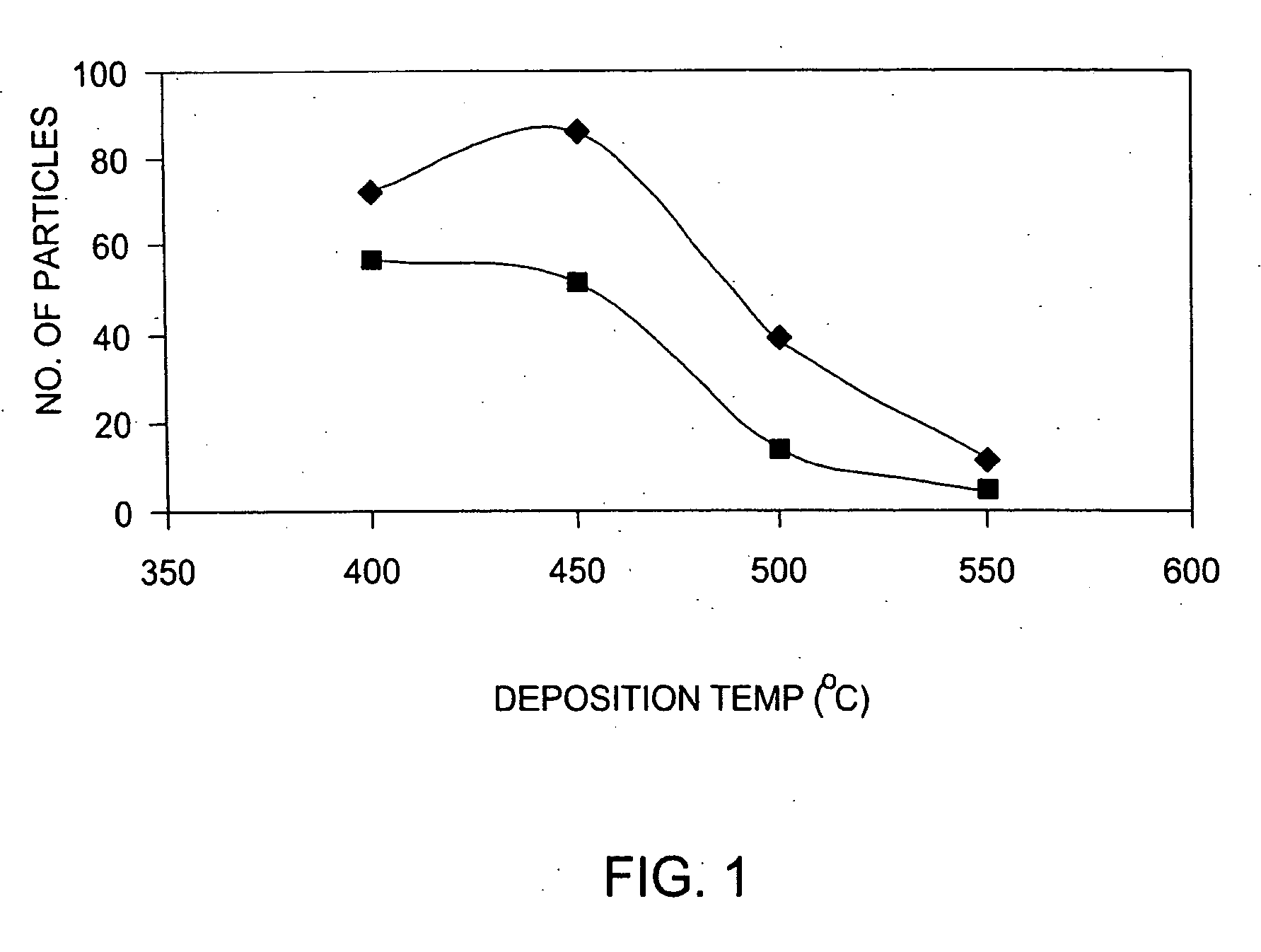
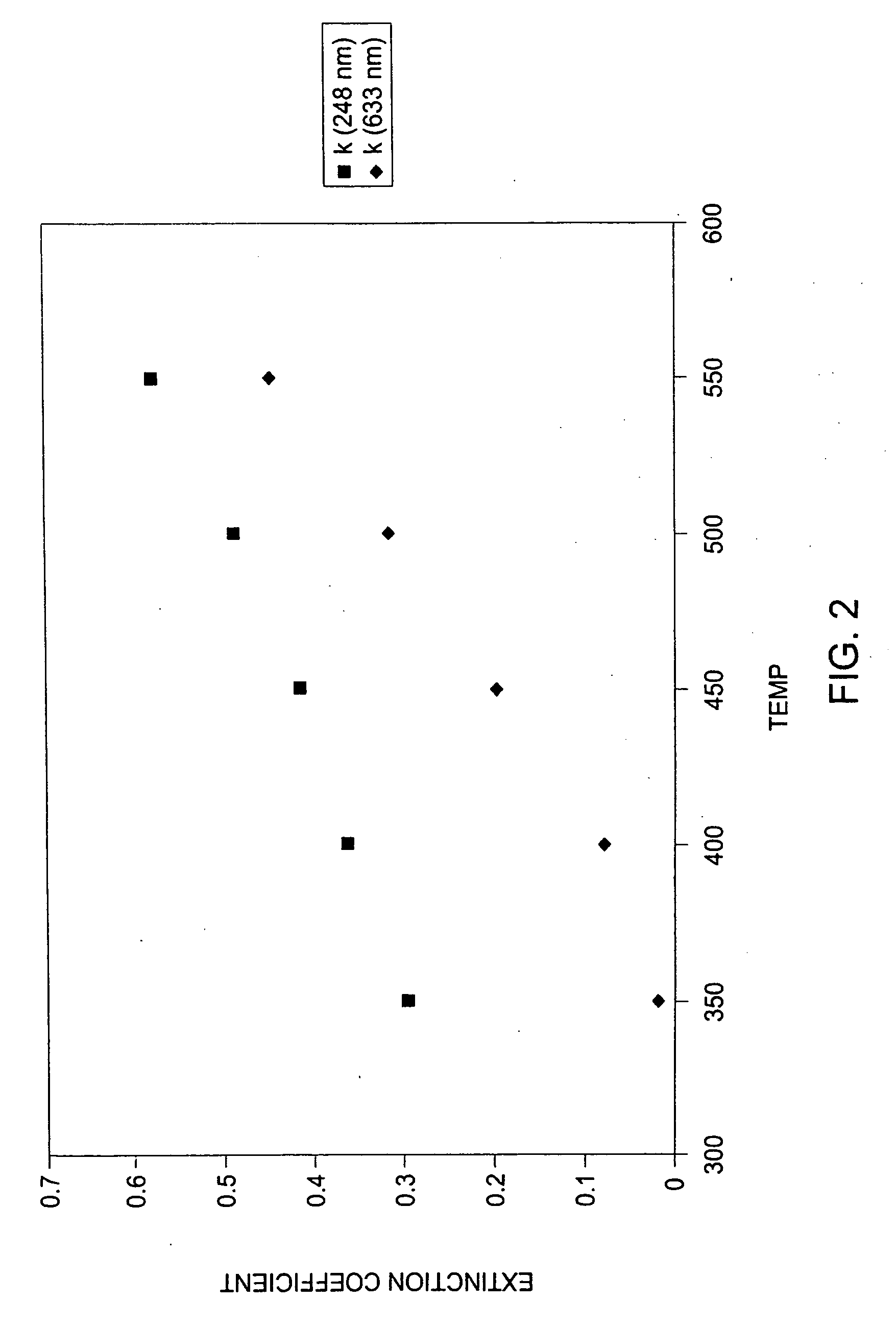
Methods for the reduction and elimination of particulate contamination with CVD of amorphous carbon
InactiveUS20060014397A1Minimal defect formationReduce particle pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesVariable thicknessMicroparticle
A method is provided for forming an amorphous carbon layer, deposited on a dielectric material such as oxide, nitride, silicon carbide, carbon doped oxide, etc., or a metal layer such as tungsten, aluminum or poly-silicon. The method includes the use of chamber seasoning, variable thickness of seasoning film, wider spacing, variable process gas flows, post-deposition purge with inert gas, and post-deposition plasma purge, among others, to make the deposition of an amorphous carbon film at low deposition temperatures possible without any defects or particle contamination.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
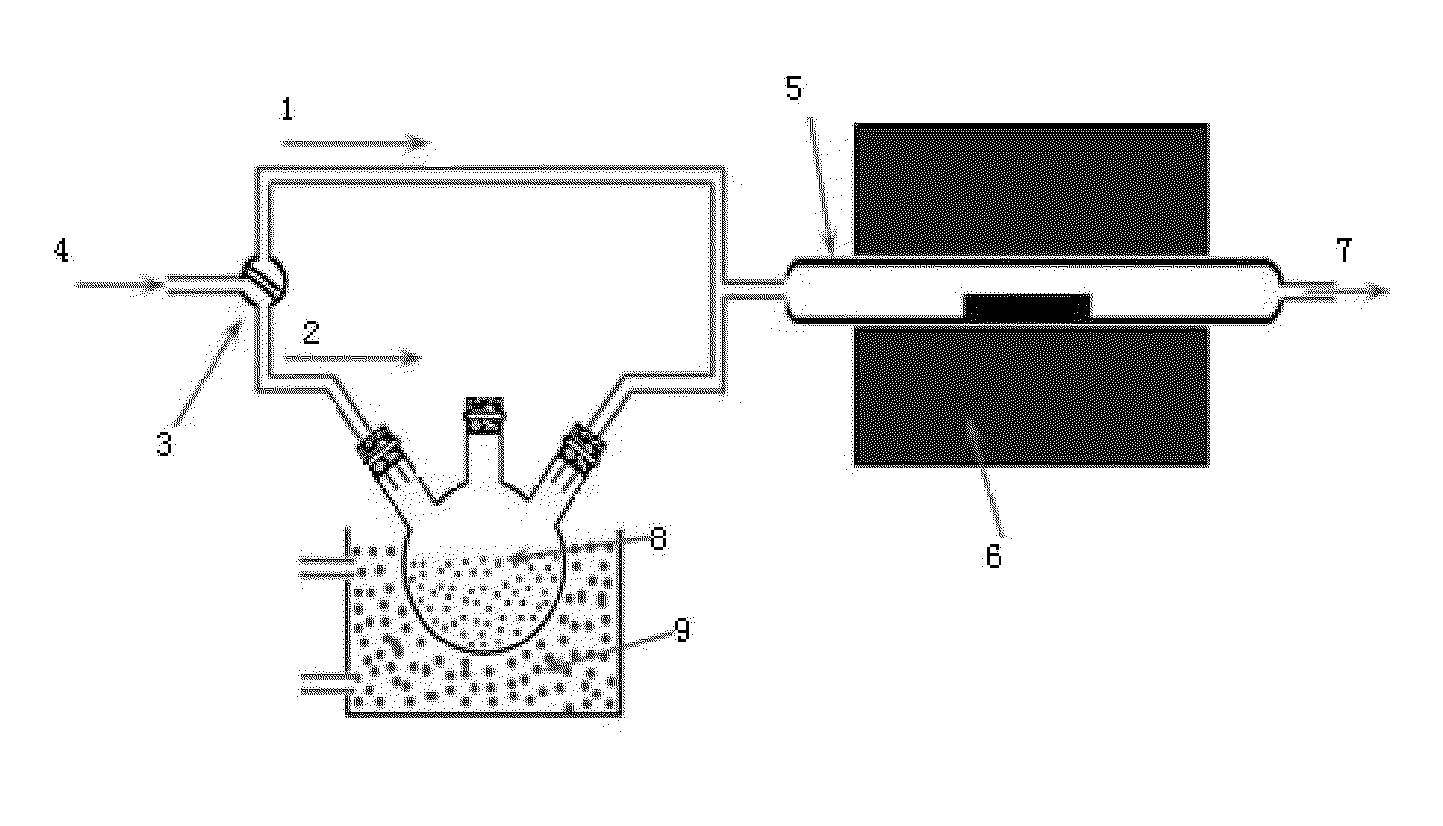
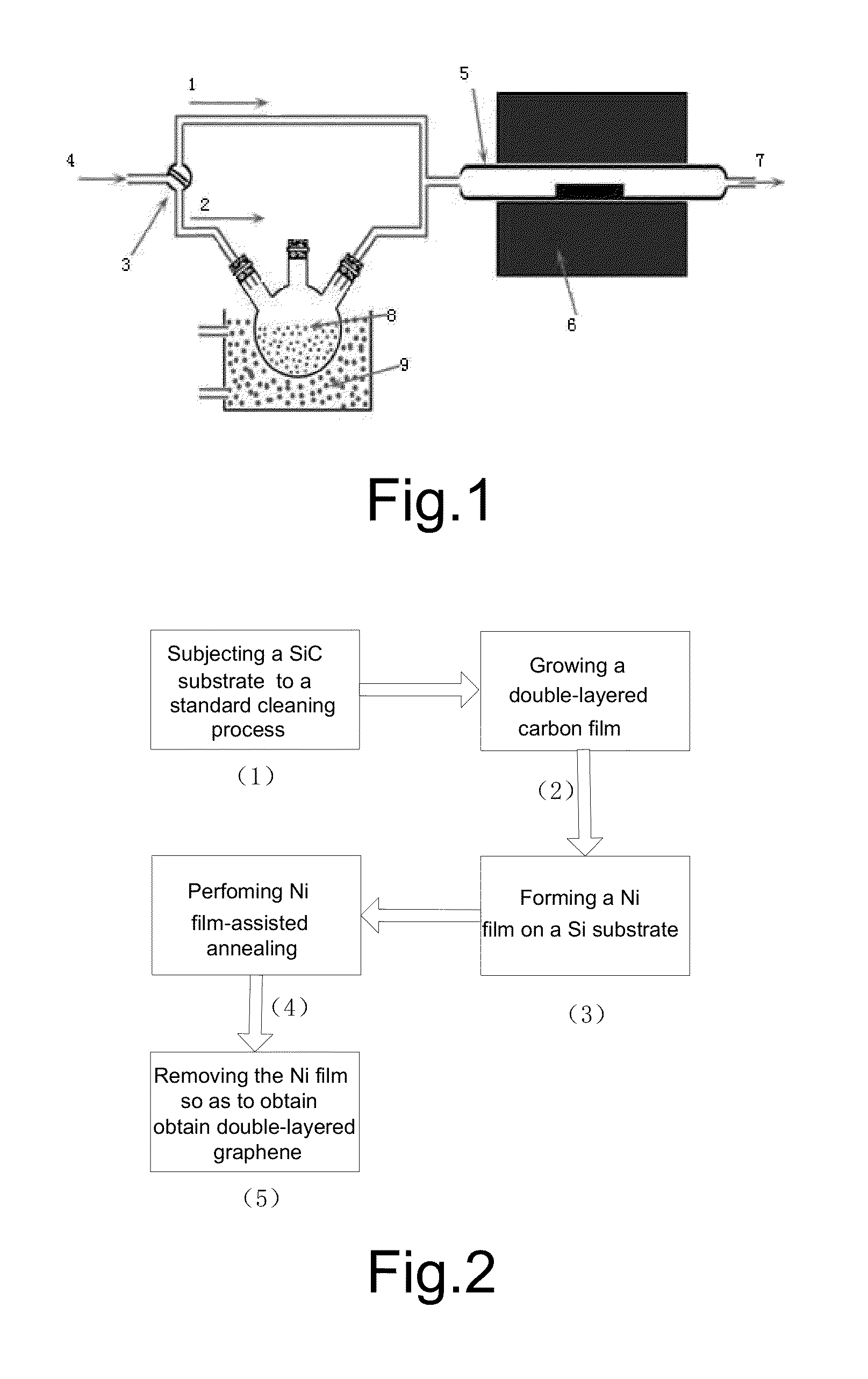
Process for Preparing Graphene on a SiC Substrate Based on Metal Film-Assisted Annealing
ActiveUS20140367642A1Simply and energy-efficientFlat surfaceMaterial nanotechnologyVacuum evaporation coatingCarbon filmElectron beam deposition
Provided is a process for preparing graphene on a SiC substrate, based on metal film-assisted annealing, comprising the following steps: subjecting a SiC substrate to a standard cleaning process; placing the cleaned SiC substrate into a quartz tube and heating the quartz tube up to a temperature of 750 to 1150° C.; introducing CCl4vapor into the quartz tube to react with SiC for a period of 20 to 100 minutes so as to generate a double-layered carbon film, wherein the CCl4 vapor is carried by Ar gas; forming a metal film with a thickness of 350 to 600 nm on a Si substrate by electron beam deposition; placing the obtained double-layered carbon film sample onto the metal film; subsequently annealing them in an Ar atmosphere at a temperature of 900 to 1100° C. for 10-30 minutes so as to reconstitute the double-layered carbon film into double-layered graphene; and removing the metal film from the double-layered graphene, thereby obtaining double-layered graphene. Also provided is double-layered graphene prepared by said process.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Ceramic sheath type thermocouple
InactiveUS6102565AThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsHeat resistanceWhiskers
This ceramic sheath type thermocouple has a long service life, an improved temperature measuring responsibility and an improved temperature measuring precision, and enables repetitive use. The ceramic sheath type thermocouple has its protective tube 1 formed of a heat resisting ceramics selected from silicon nitride, sialon and silicon carbide. In the protective tube 1 are installed a pair of W-Re wires that are connected to form a joint portion constituting a temperature measuring point 5. A filler made of Si3N4 reaction-sintered ceramics is loaded into the front end portion of the protective tube to enclose the W-Re wires. Another filler made of SiC whisker with a heat conductivity smaller than that of the filler of the front end portion is loaded into the rear portion of the protective tube. An inert gas is sealed in the protective tube. Alternatively, the temperature measuring portion may be formed by exposing from the front end portion of the protective tube the joint portion where the ends of the W-Re wires are connected. The temperature measuring portion is coated with a cover film that is made of silicon carbide, silicon nitride or a composite of these, all having excellent heat resisting and corrosion resisting properties.
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
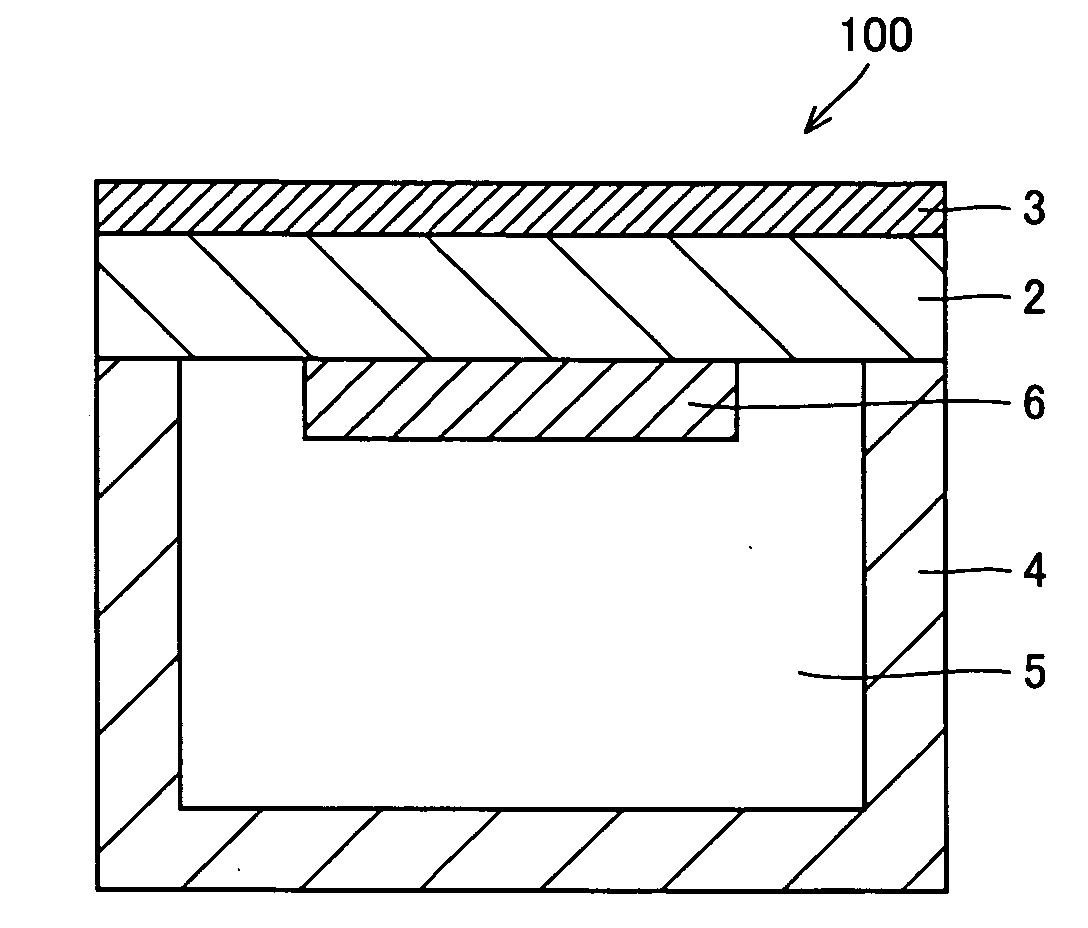
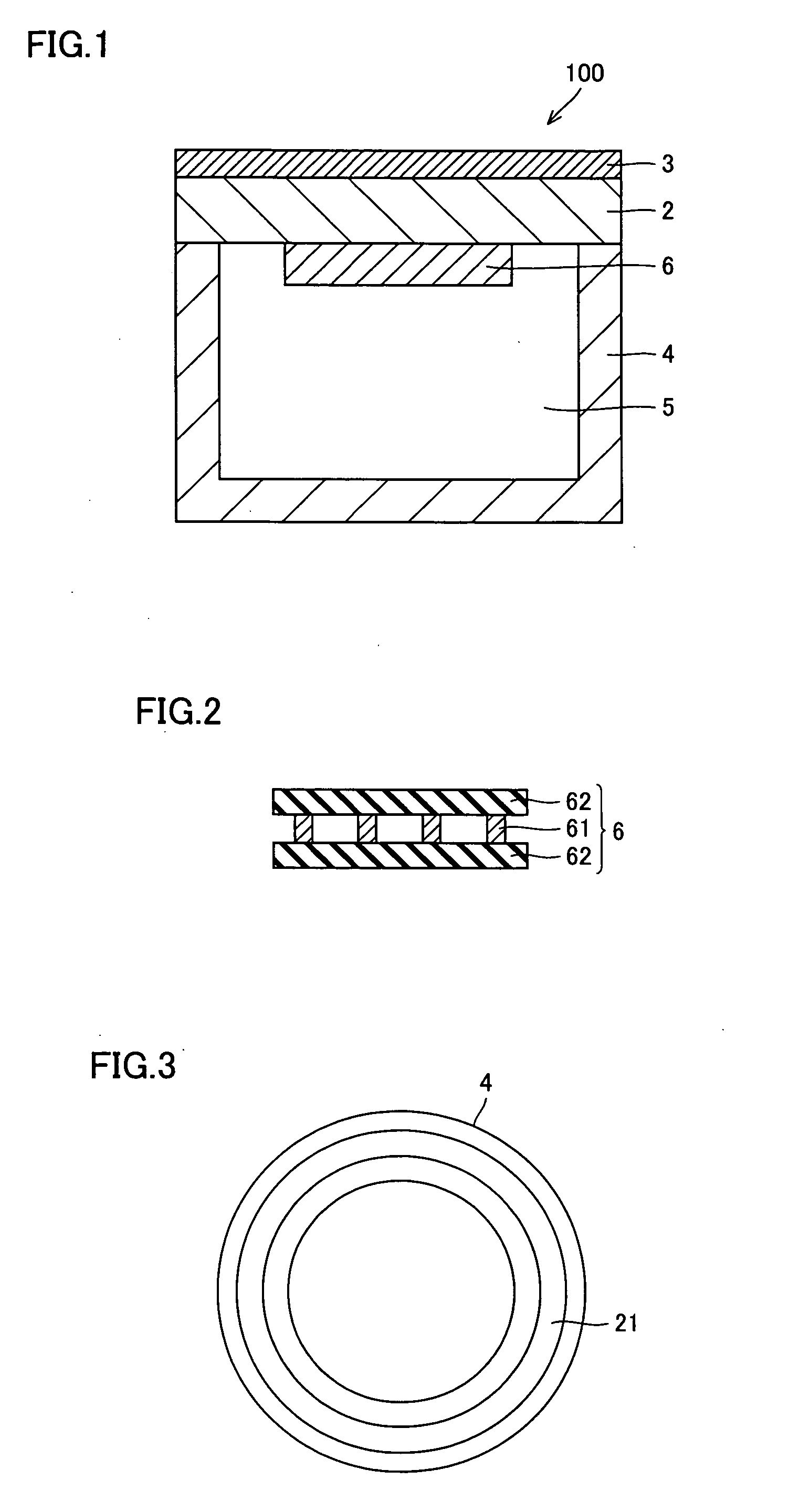
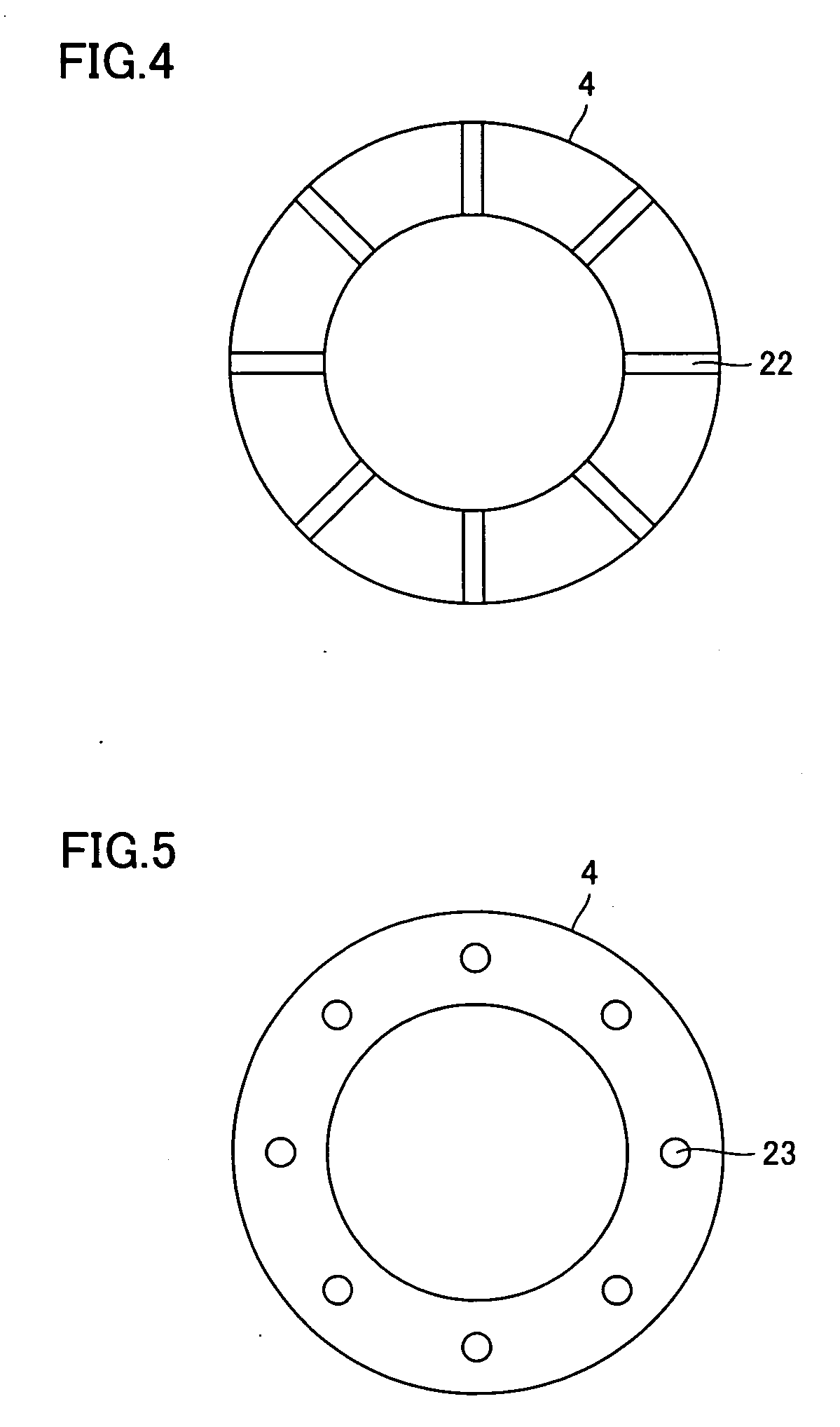
Wafer holder, heater unit used for wafer prober having the wafer holder, and wafer prober having the heater unit
InactiveUS20090050621A1Improve thermal uniformityAvoid measuringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHot plates heating arrangementsEngineeringSilicon
A wafer holder that prevents positional deviation of the wafer mounted on the wafer-mounting surface of a chuck top and enables better thermal uniformity of the wafer, as well as a heater unit including the wafer holder and a wafer prober mounting these are provided. The wafer holder has a chuck top mounting and fixing the wafer and a supporter supporting the chuck top, and the chuck top has water absorption of at least 0.01% and preferably at least 0.1%. Preferable material of the chuck top is a composite of metal and ceramics, and particularly, a composite of aluminum and silicon carbide, or a composite of silicon and silicon carbide.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
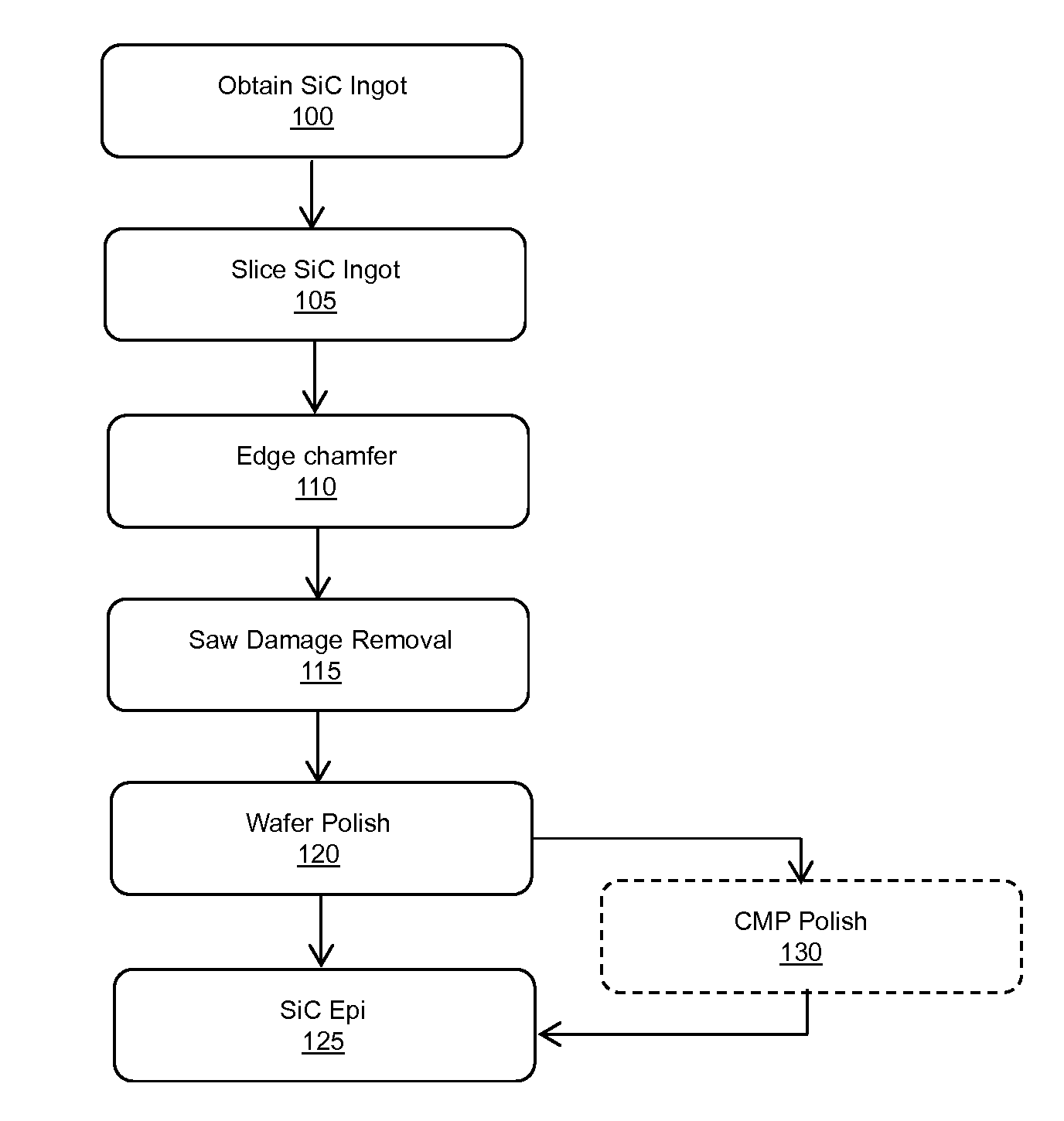
Flat sic semiconductor substrate
ActiveUS20140117380A1Efficient polishingImprove performanceEdge grinding machinesPolycrystalline material growthCrystallographyWafering
Methods for manufacturing silicon carbide wafers having superior specifications for bow, warp, total thickness variation (TTV), local thickness variation (LTV), and site front side least squares focal plane range (SFQR). The resulting SiC wafer has a mirror-like surface that is fit for epitaxial deposition of SiC. The specifications for bow, warp, total thickness variation (TTV), local thickness variation (LTV), and site front side least squares focal plane range (SFQR) of the wafer are preserved following the addition of the epitaxy layer.
Owner:SK SILTRON CSS LLC
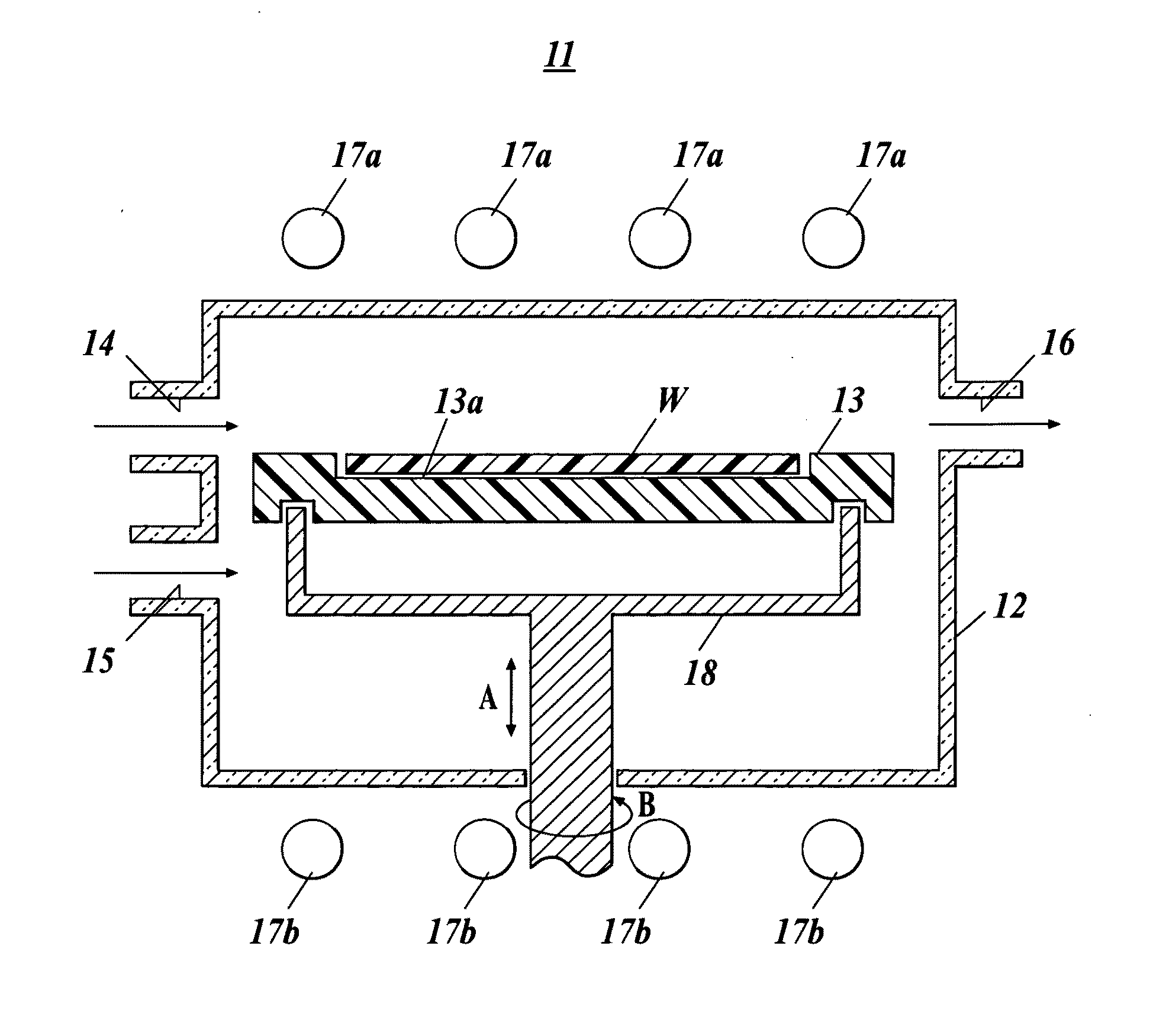
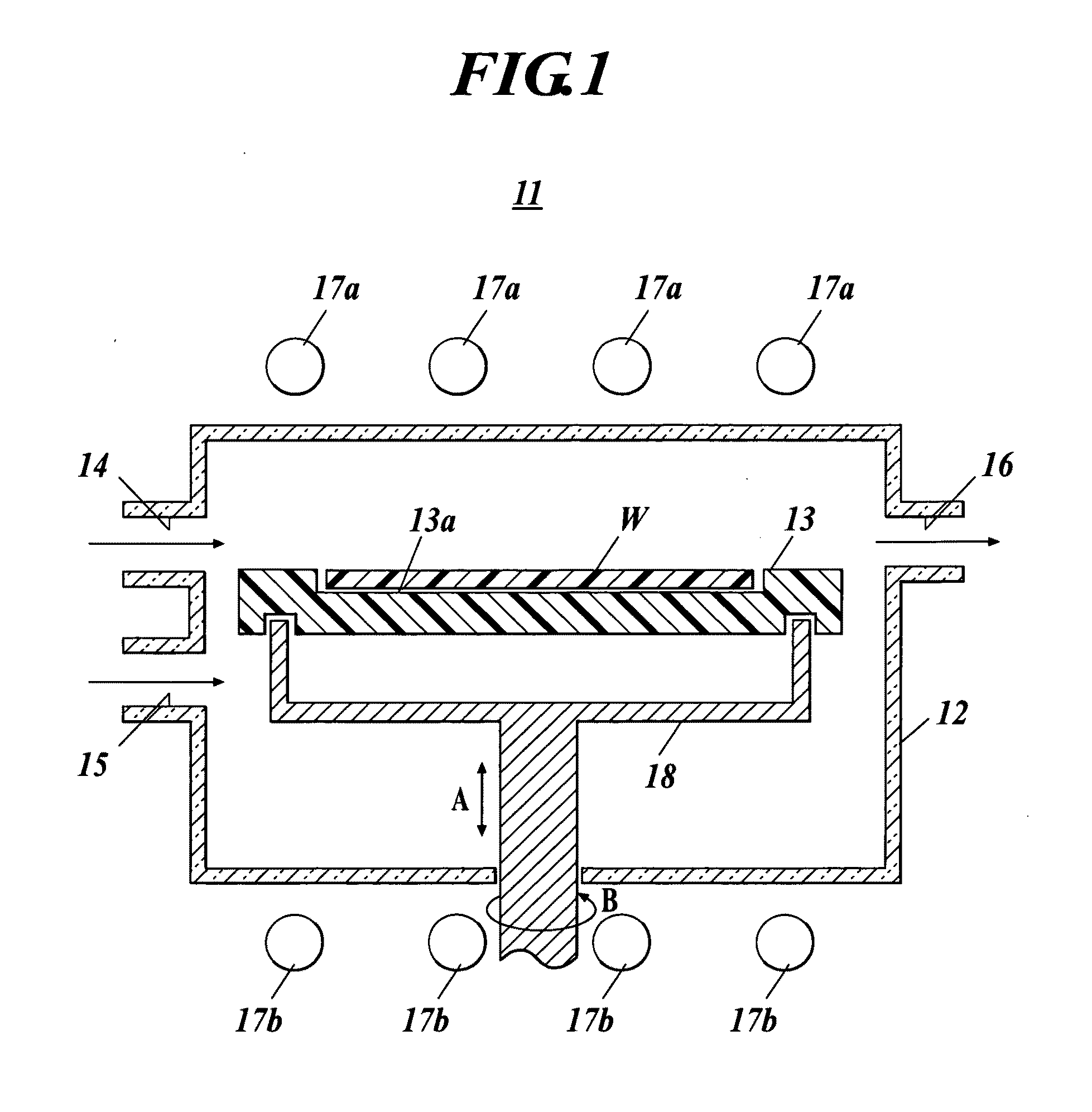
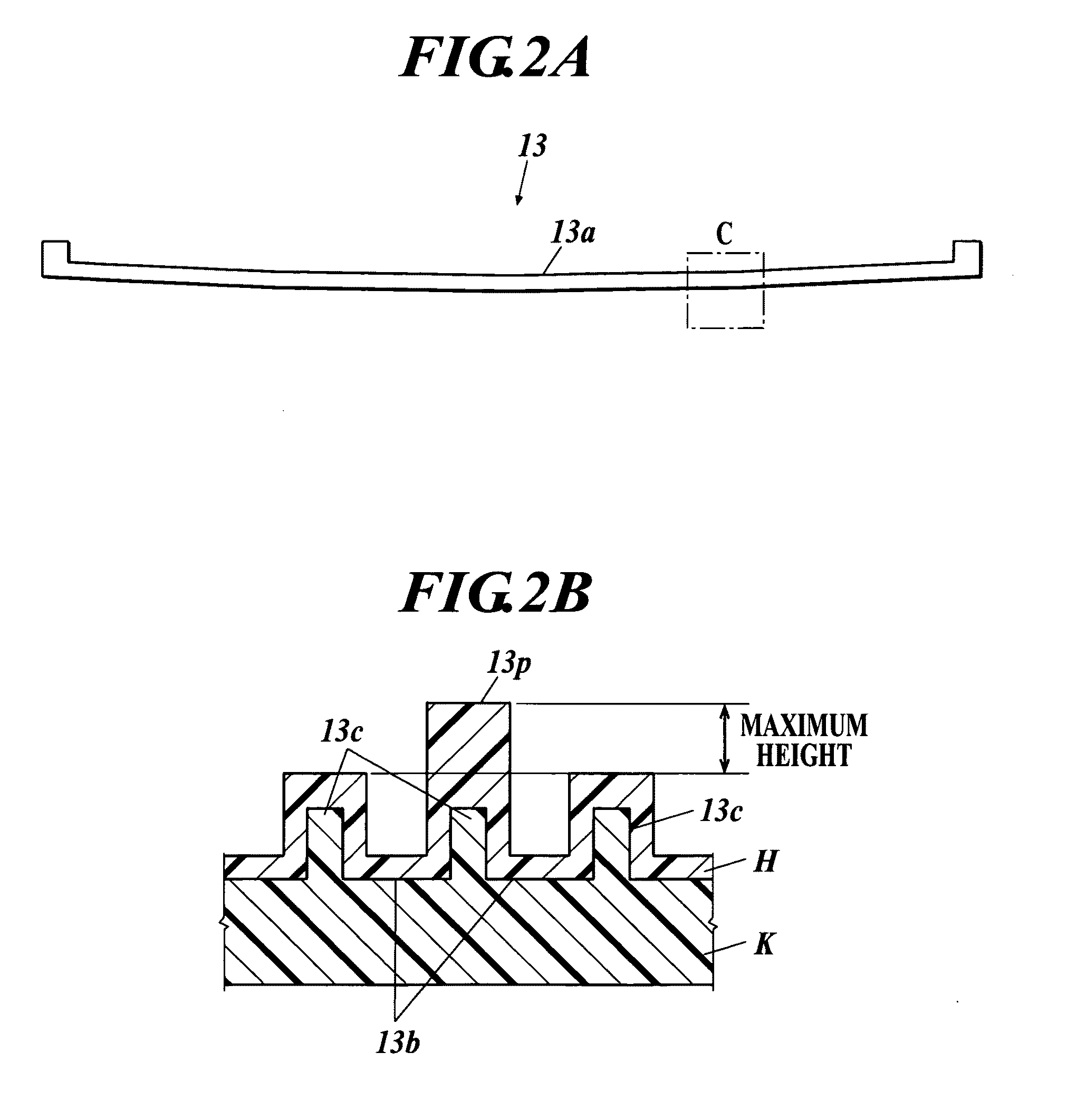
Susceptor and method for manufacturing silicon epitaxial wafer
ActiveUS20100129990A1Avoid stickingPolycrystalline material growthLiquid surface applicatorsSusceptorWafering
Provided is a susceptor 13 for manufacturing an epitaxial wafer, comprising a mesh-like groove 13b on a mount face on which a silicon substrate W is to be mounted, wherein a coating H of silicon carbide is formed on the mount face, and the coating has a surface roughness of 1 μm or more in centerline average roughness Ra and a maximum height of a protrusion 13p generated in forming the coating H of 5 μm or less. Thus, defects such as warping and slip as well as adhesion of the silicon substrate to the susceptor are prevented.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Baffled liner cover
ActiveUS7736437B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringTower
Owner:HANGZHOU DUNYUANJUXIN SEMICON TECH CO LTD
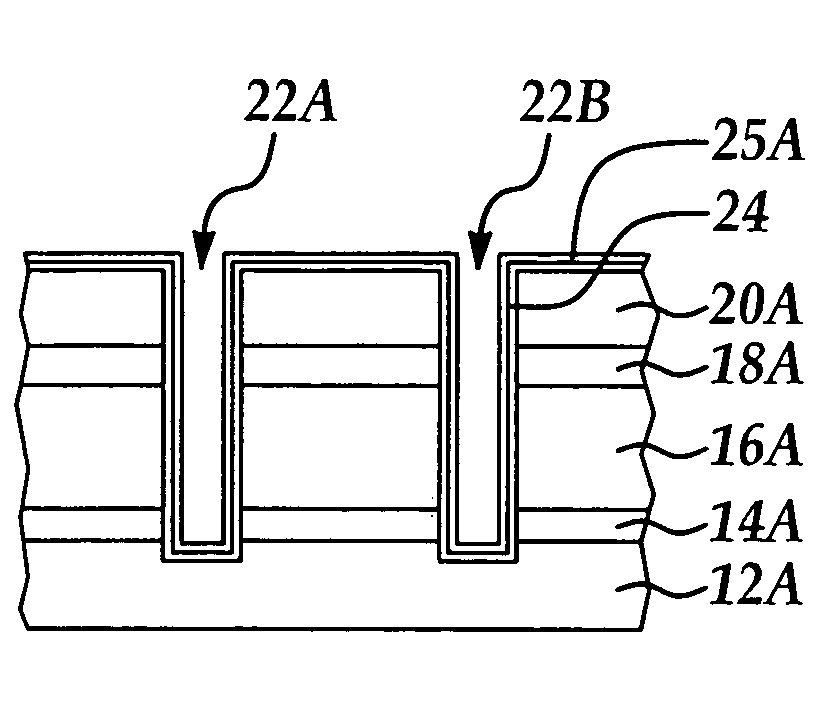
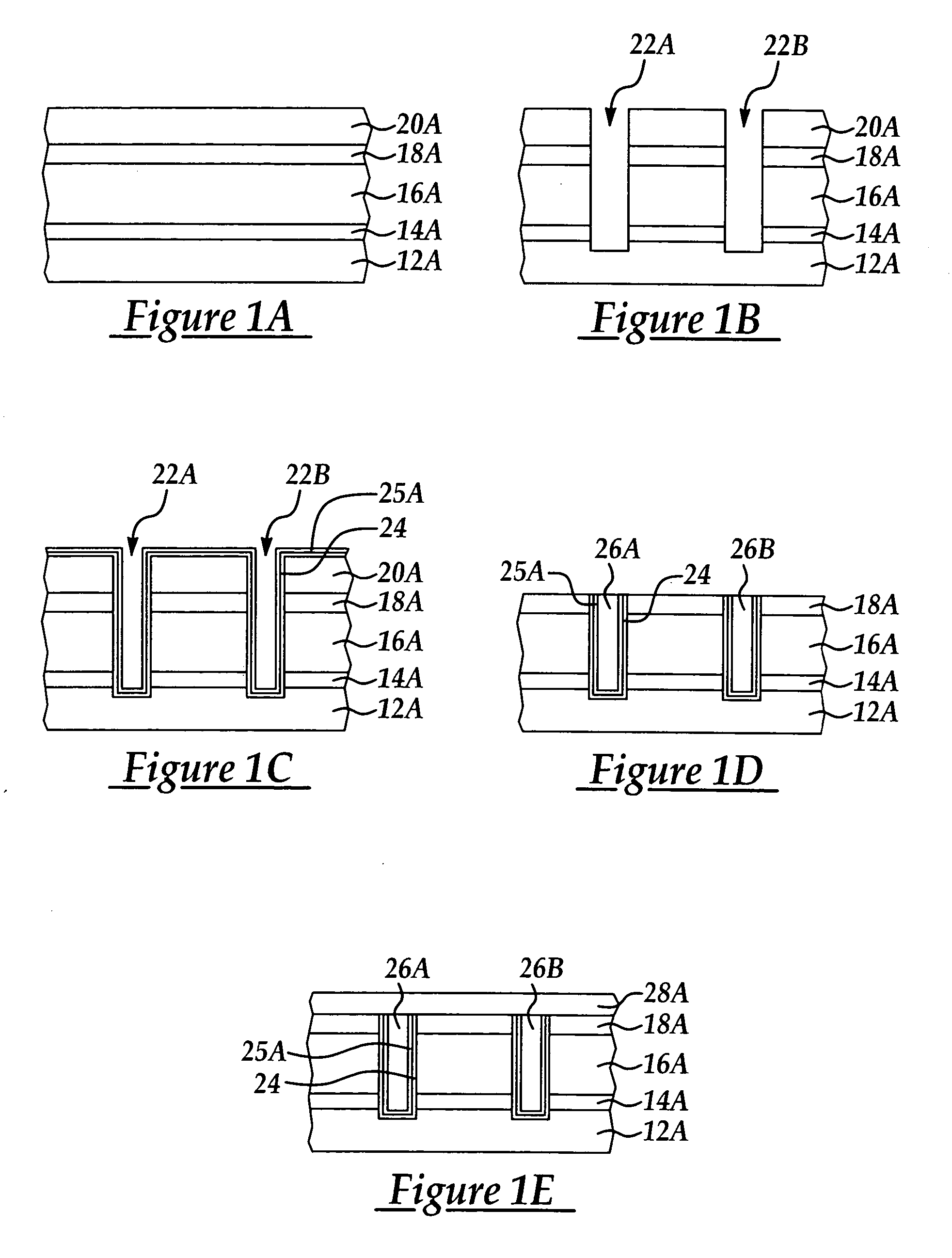
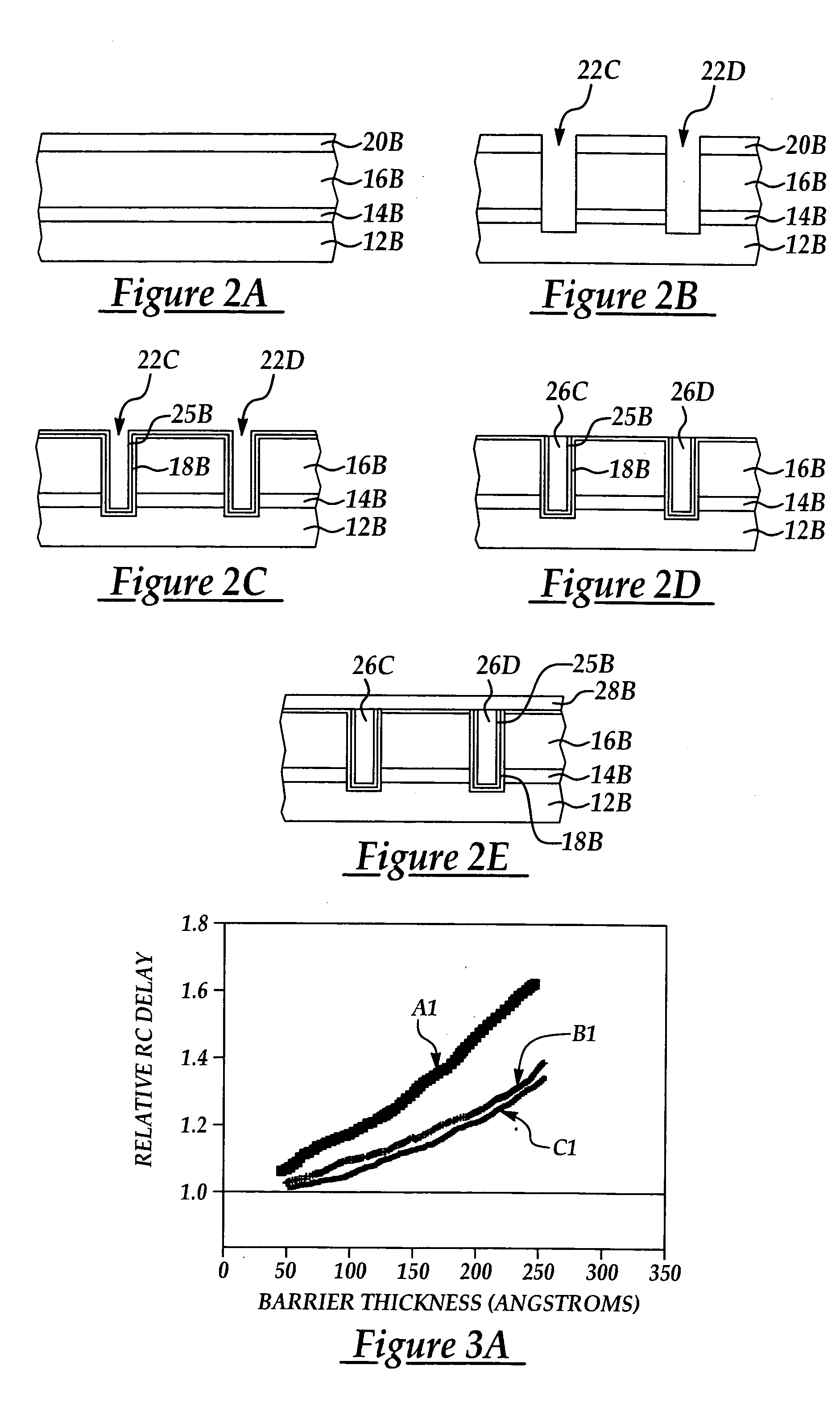
Two-layer film for next generation damascene barrier application with good oxidation resistance
InactiveUS7749563B2Low dielectric constantLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenPhenyl group
A method is provided for processing a substrate including providing a processing gas comprising an organosilicon compound comprising a phenyl group to the processing chamber, and reacting the processing gas to deposit a low k silicon carbide barrier layer useful as a barrier layer in damascene or dual damascene applications with low k dielectric materials. A method is provided for depositing a silicon carbide cap layer that has substantially no phenyl groups attached to silicon atoms from a processing gas comprising an oxygen-free organosilicon compound on a low k silicon carbide barrier layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Graphene-based transistor
ActiveUS20090020764A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantGate dielectric
A graphene layer is formed on a surface of a silicon carbide substrate. A dummy gate structure is formed over the fin, in the trench, or on a portion of the planar graphene layer to implant dopants into source and drain regions. The dummy gate structure is thereafter removed to provide an opening over the channel of the transistor. Threshold voltage adjustment implantation may be performed to form a threshold voltage implant region directly beneath the channel, which comprises the graphene layer. A gate dielectric is deposited over a channel portion of the graphene layer. After an optional spacer formation, a gate conductor is formed by deposition and planarization. The resulting graphene-based field effect transistor has a high carrier mobility due to the graphene layer in the channel, low contact resistance to the source and drain region, and optimized threshold voltage and leakage due to the threshold voltage implant region.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
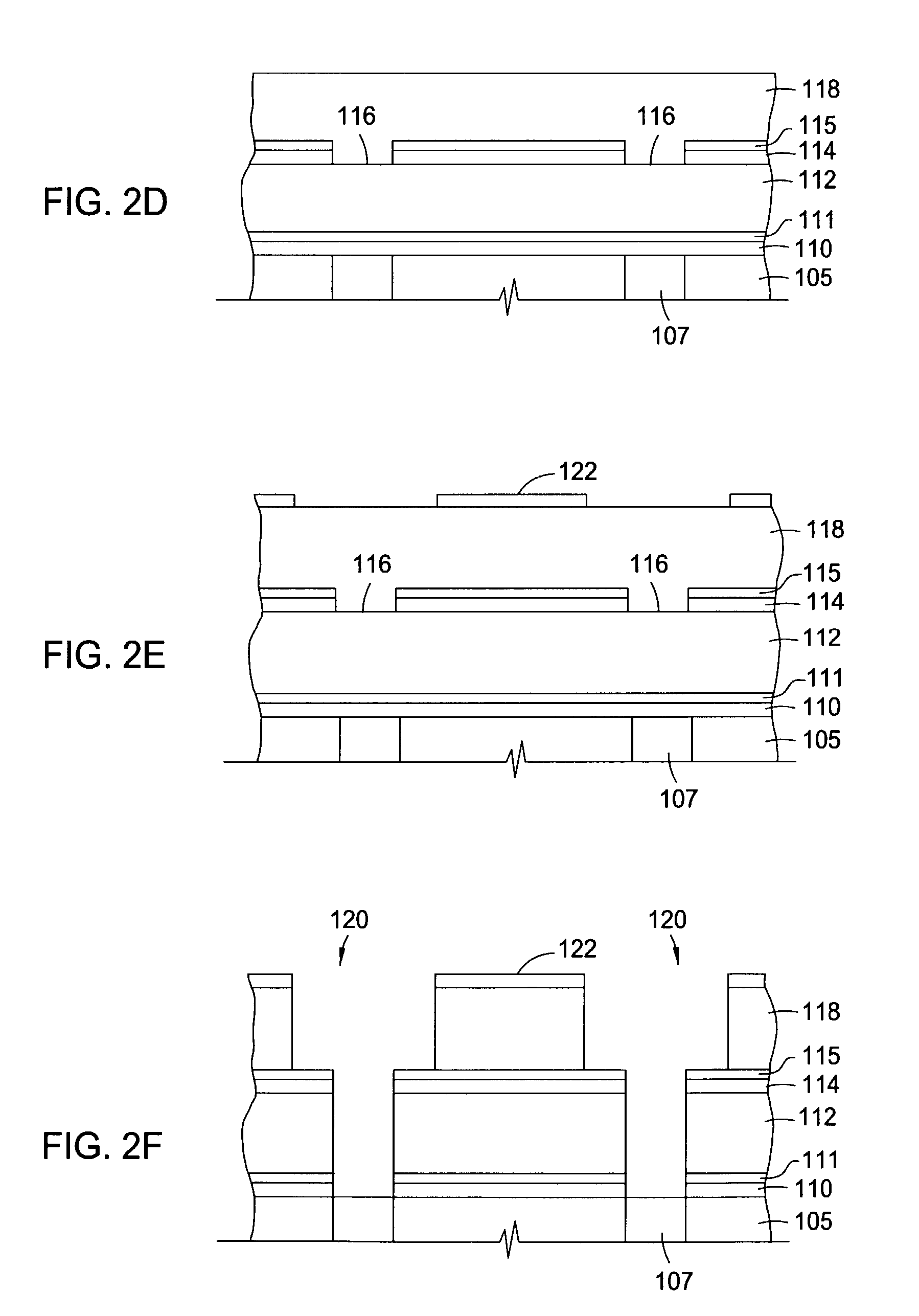
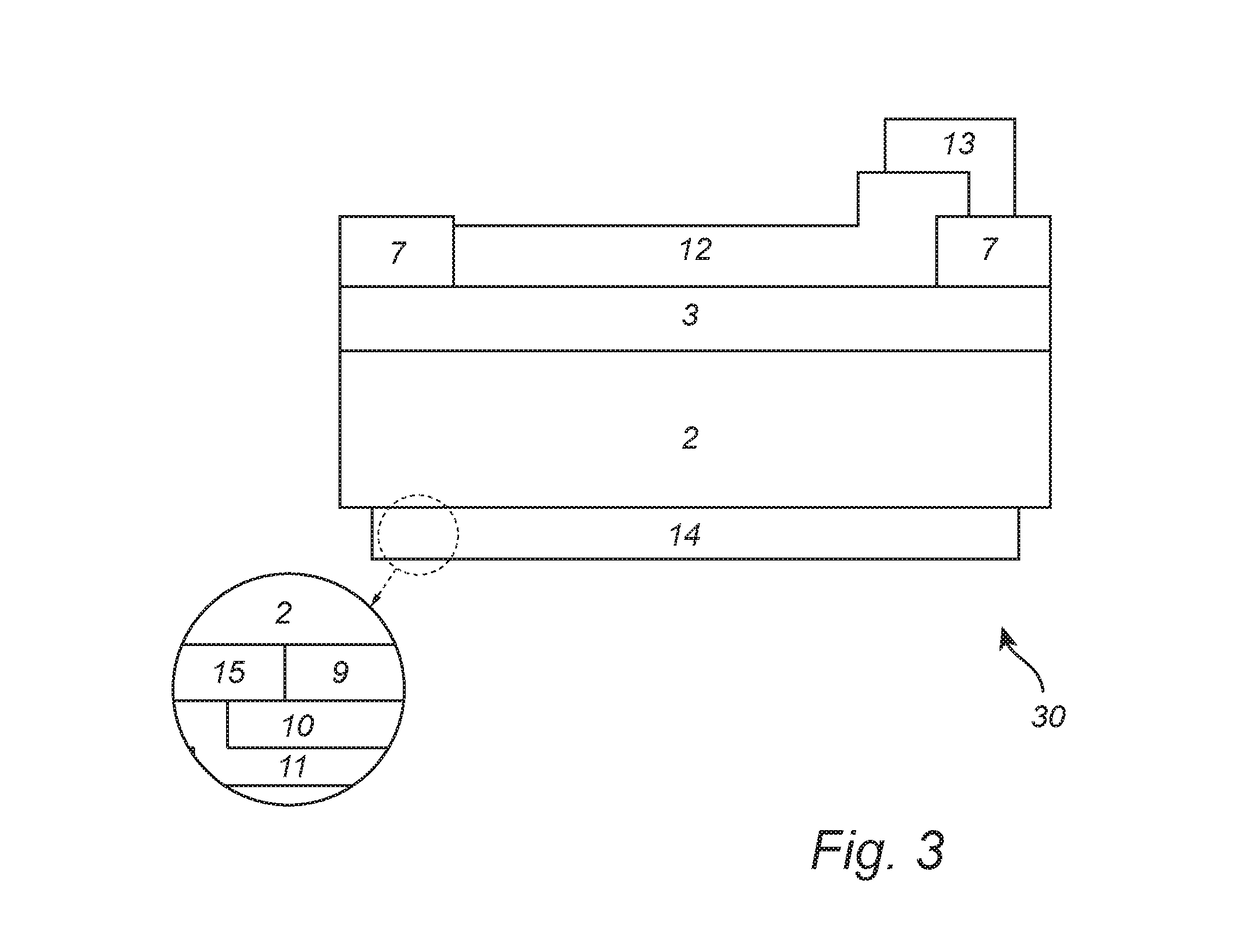
Method of Forming Vias in Silicon Carbide and Resulting Devices and Circuits
InactiveUS20090104738A1Eliminate needSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesInductanceSemiconductor
A method of fabricating an integrated circuit on a silicon carbide substrate is disclosed that eliminates wire bonding that can otherwise cause undesired inductance. The method includes fabricating a semiconductor device in epitaxial layers on a surface of a silicon carbide substrate and with at least one metal contact for the device on the uppermost surface of the epitaxial layer. The opposite surface of the substrate is then ground and polished until it is substantially transparent. The method then includes masking the polished surface of the silicon carbide substrate to define a predetermined location for at least one via that is opposite the device metal contact on the uppermost surface of the epitaxial layer and etching the desired via in steps. The first etching step etches through the silicon carbide substrate at the desired masked location until the etch reaches the epitaxial layer. The second etching step etches through the epitaxial layer to the device contacts. Finally, metallizing the via provides an electrical path from the first surface of the substrate to the metal contact and to the device on the second surface of the substrate.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Stacked non-volatile memory with silicon carbide-based amorphous silicon thin film transistors
ActiveUS20070215954A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous siliconTransistor
A stacked non-volatile memory device uses amorphous silicon based thin film transistors stacked vertically. Each layer of transistors or cells is formed from a deposited a-Si channel region layer having a predetermined concentration of carbon to form a carbon rich silicon film or silicon carbide film, depending on the carbon content. The dielectric stack is formed over the channel region layer. In one embodiment, the dielectric stack is an ONO structure. The control gate is formed over the dielectric stack. This structure is repeated vertically to form the stacked structure. In one embodiment, the carbon content of the channel region layer is reduced for each subsequently formed layer.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
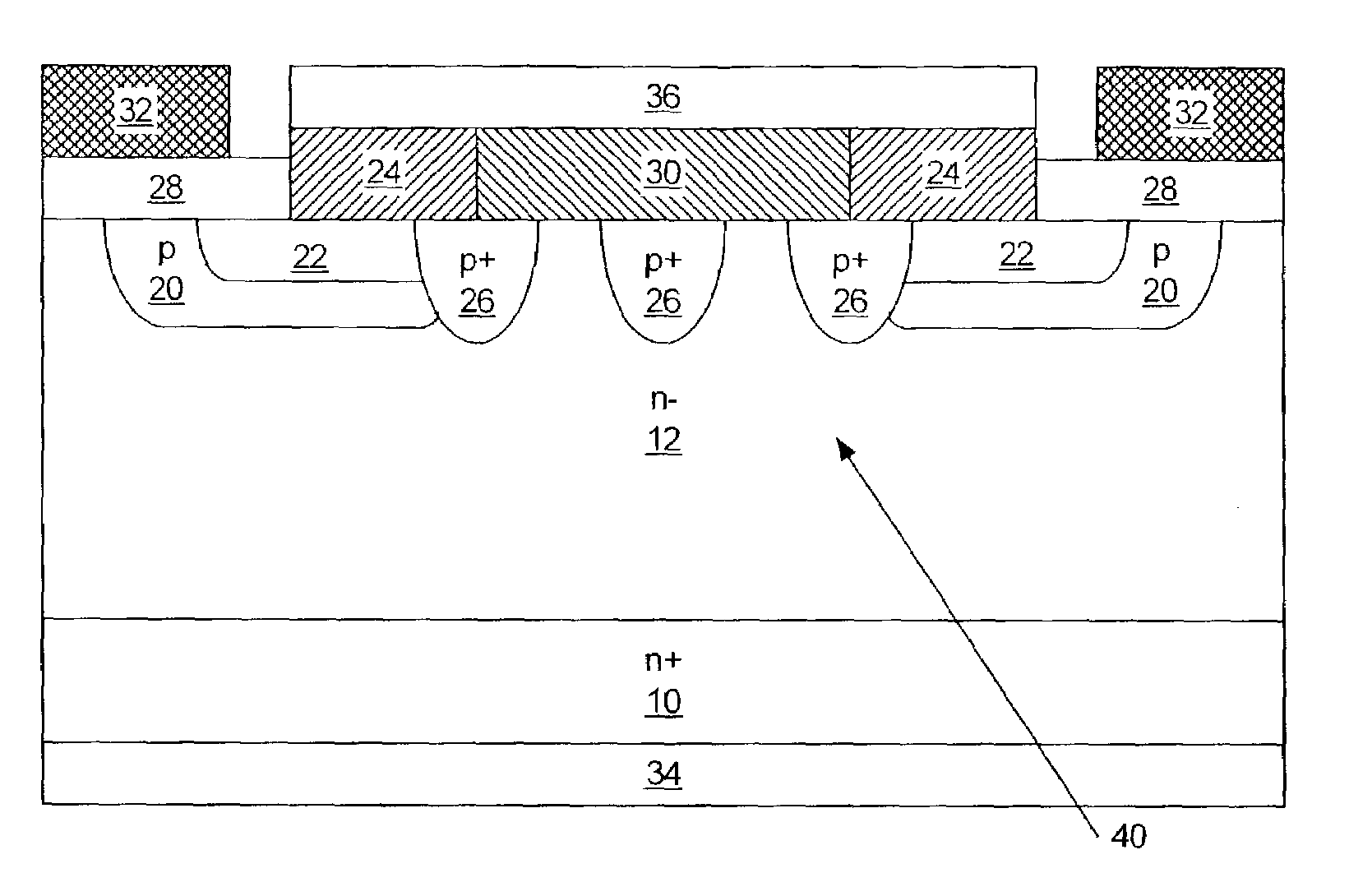
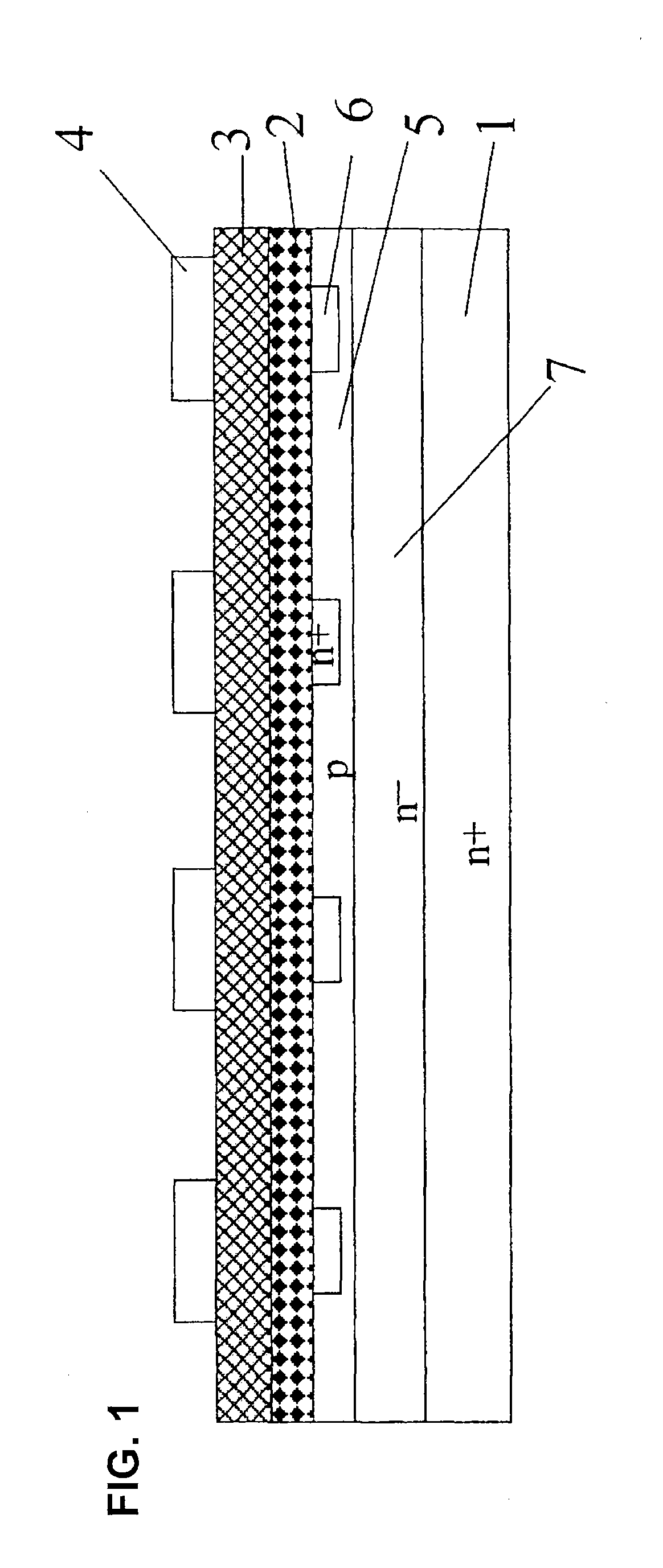
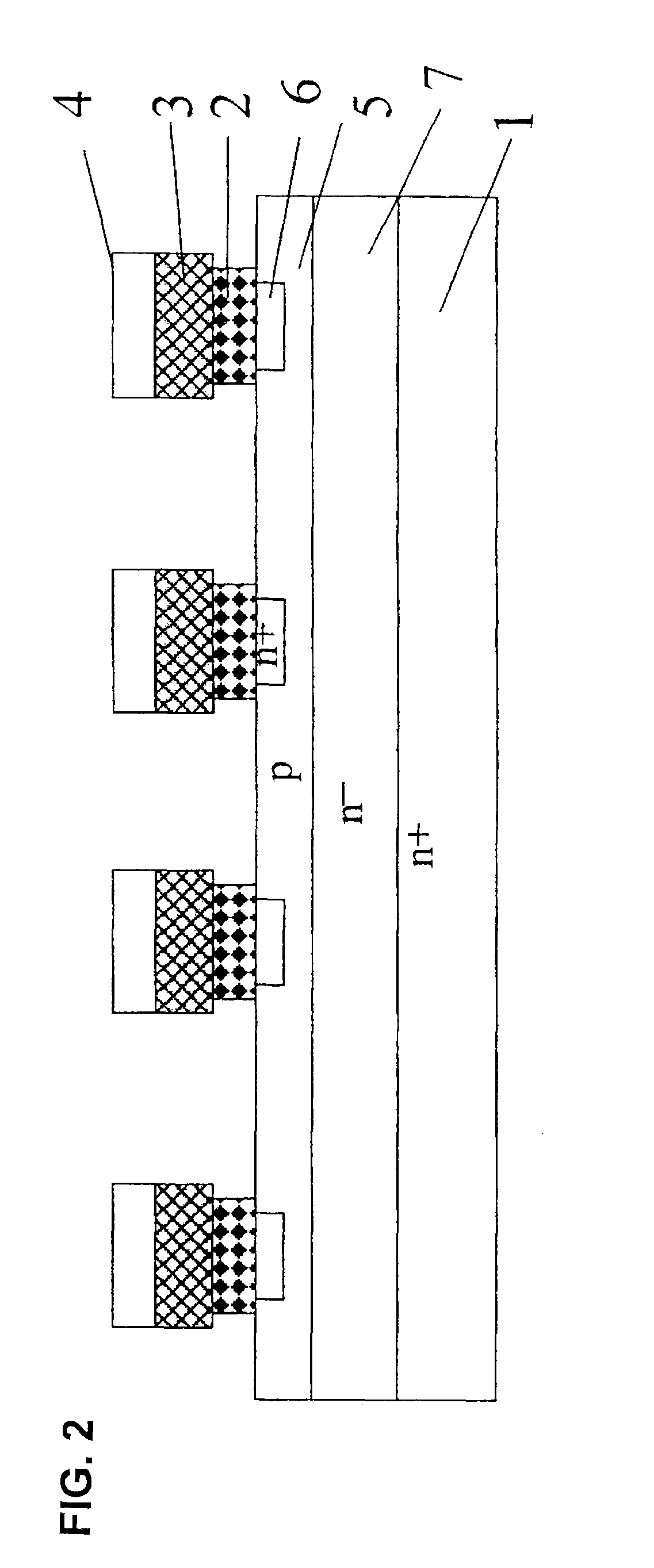
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and silicon carbide semiconductor device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20160336392A1Lower on-resistanceImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
A silicon carbide semiconductor device capable of achieving a decrease in ON resistance and an increase in breakdown voltage and a method for manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor device. A silicon carbide semiconductor device includes a silicon carbide substrate and a drift layer. The drift layer includes a breakdown voltage holding layer extending from a point where a doping concentration has a predetermined value to a surface of the drift layer. The doping concentration in the breakdown voltage holding layer continuously decreases from the point where the doping concentration has the predetermined value to a modulation point located further toward the surface of the drift layer than a midpoint in a film thickness direction of the breakdown voltage holding layer. The doping concentration in the breakdown voltage holding layer continuously increases from the modulation point to the surface of the drift layer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for producing gate stack sidewall spacers
A method for forming sidewall spacers on a gate stack by depositing one or more layers of silicon containing materials using PECVD process(es) on a gate structure to produce a spacer having an overall k value of about 3.0 to about 5.0. The silicon containing materials may be silicon carbide, oxygen doped silicon carbide, nitrogen doped silicon carbide, carbon doped silicon nitride, nitrogen doped silicon oxycarbide, or combinations thereof. The deposition is performed in a plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition chamber and the deposition temperature is less than 450° C. The sidewall spacers so produced provide good capacity resistance, as well as excellent structural stability and hermeticity.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
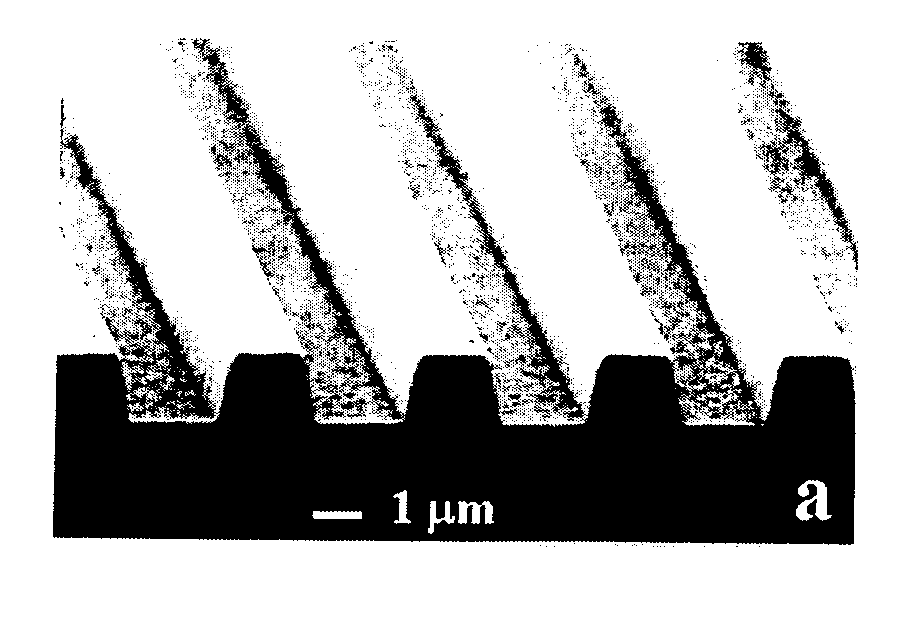
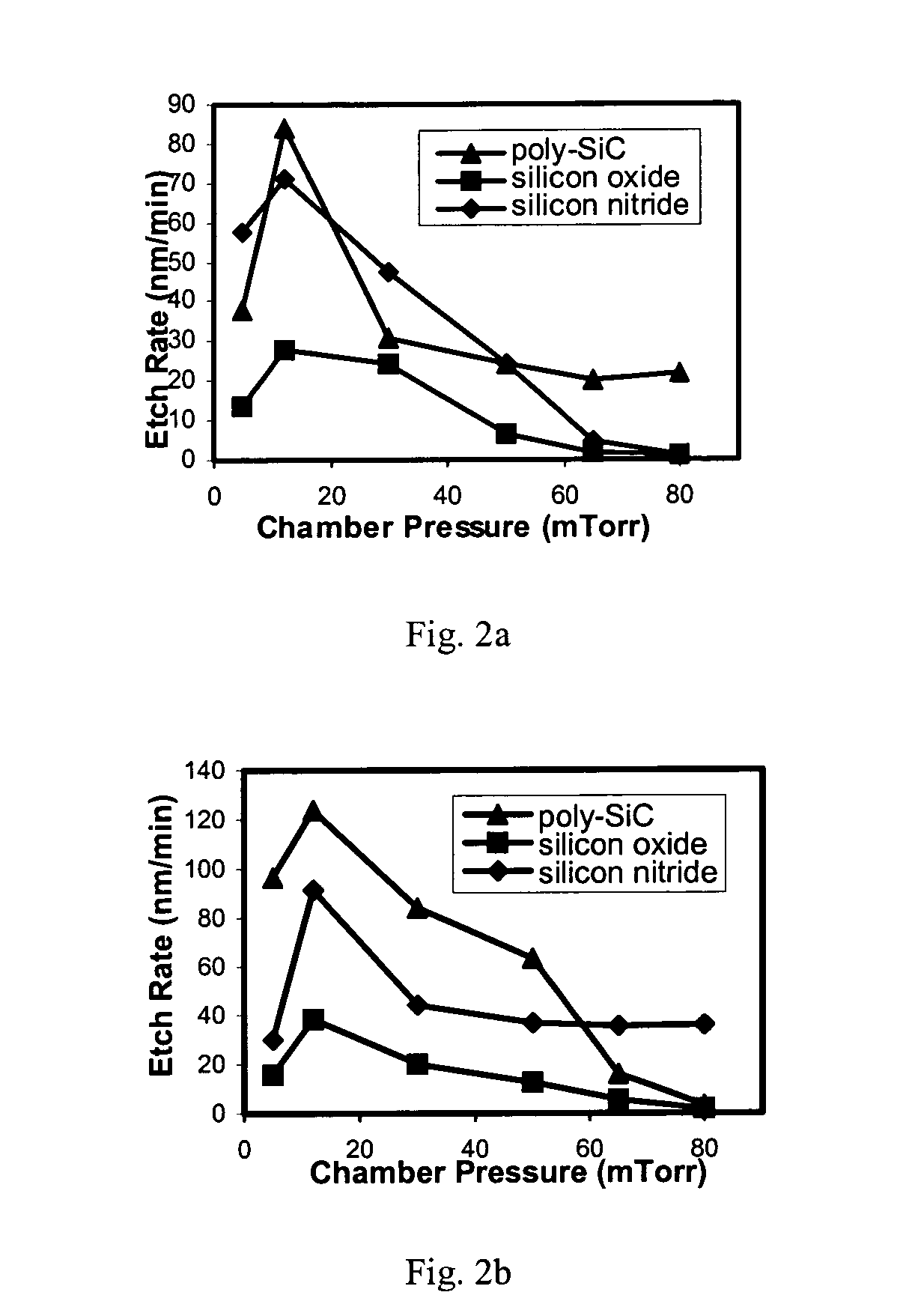
Selective etching of silicon carbide films
ActiveUS20050001276A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesDecorative surface effectsMask layerSilicon carbide
A method of etching silicon carbide using a nonmetallic mask layer. The method includes providing a silicon carbide substrate; forming a non-metallic mask layer by applying a layer of material on the substrate; patterning the mask layer to expose underlying areas of the substrate; and etching the underlying areas of the substrate with a plasma at a first rate, while etching the mask layer at a rate lower than the first rate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
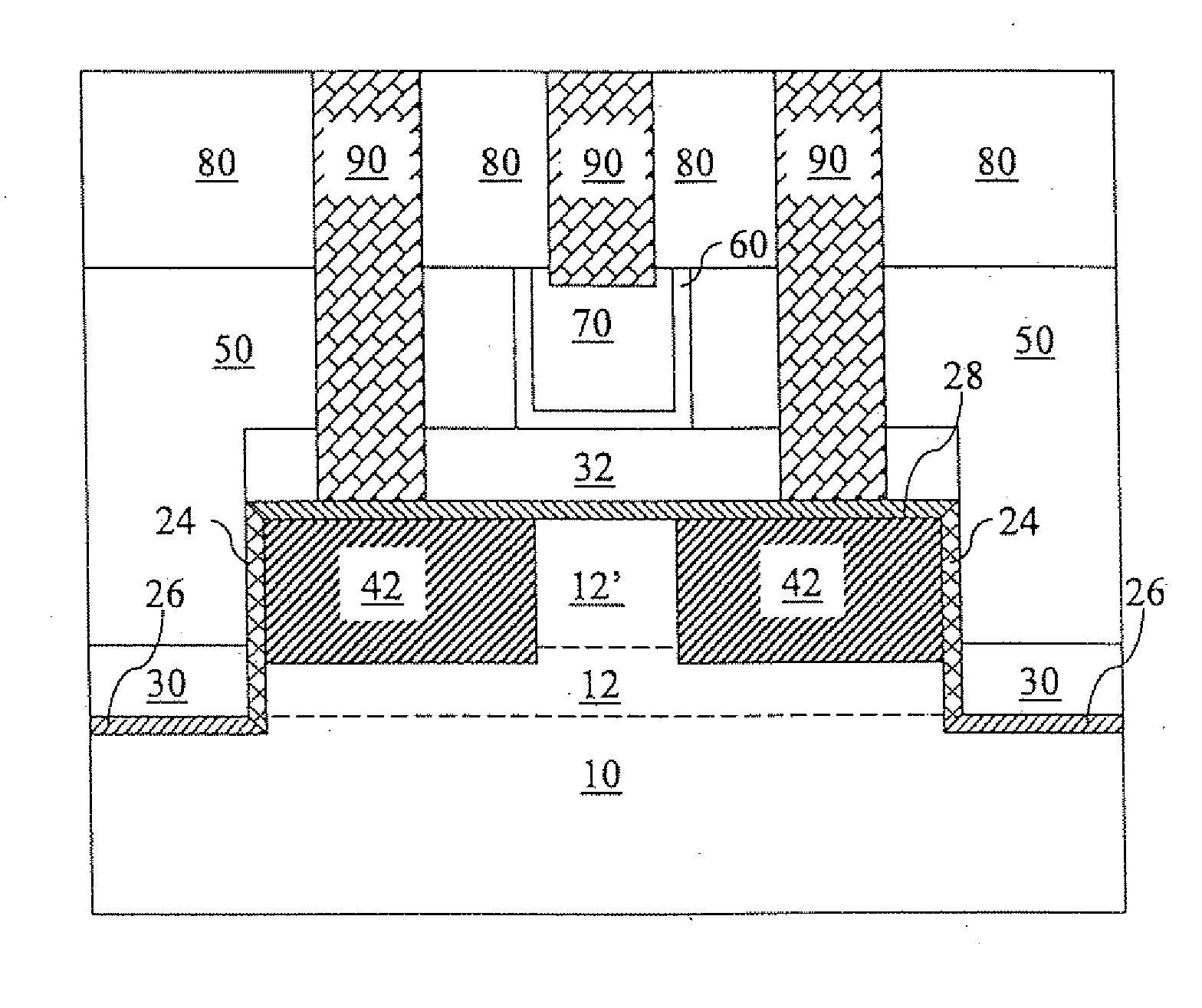
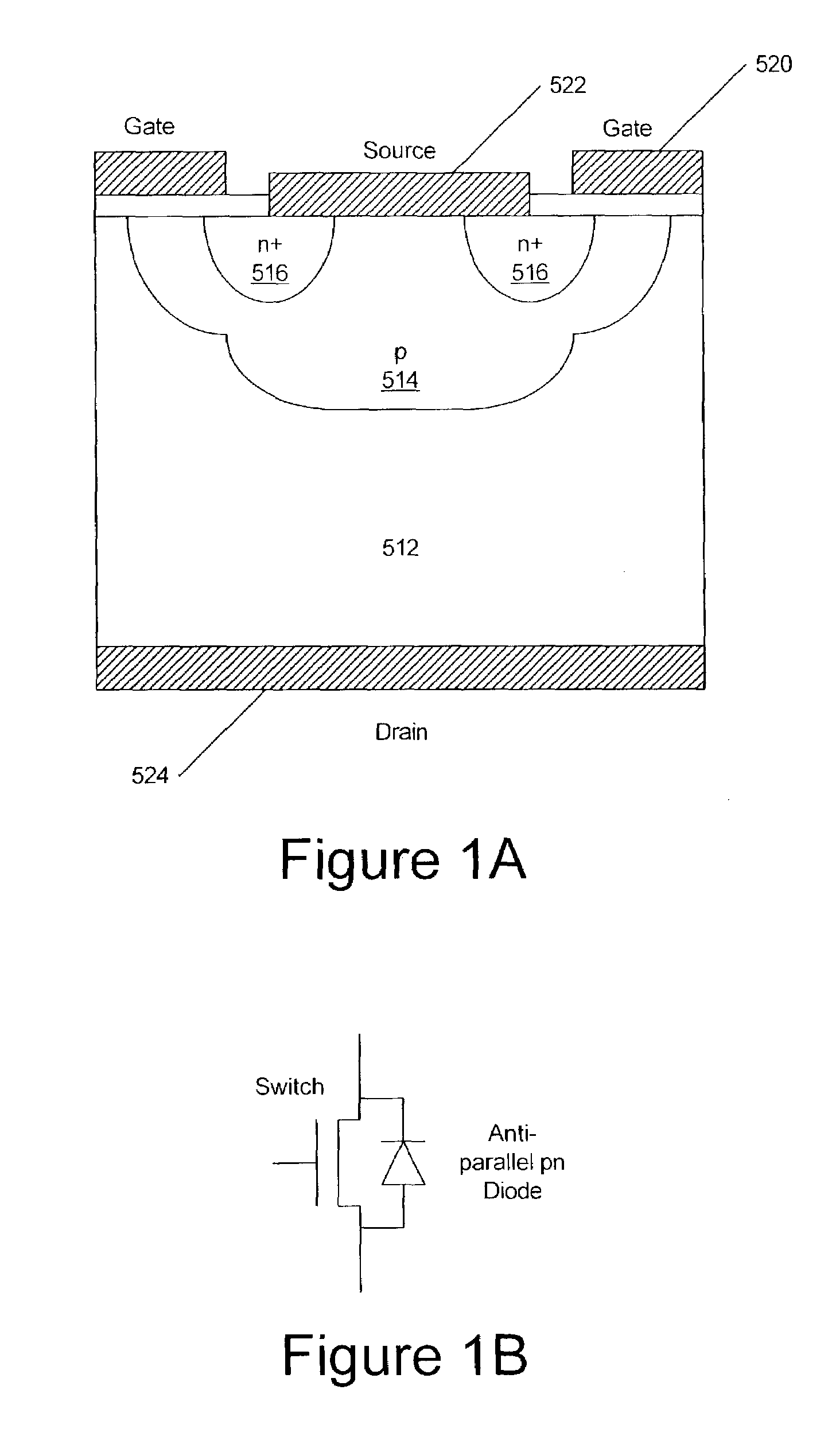
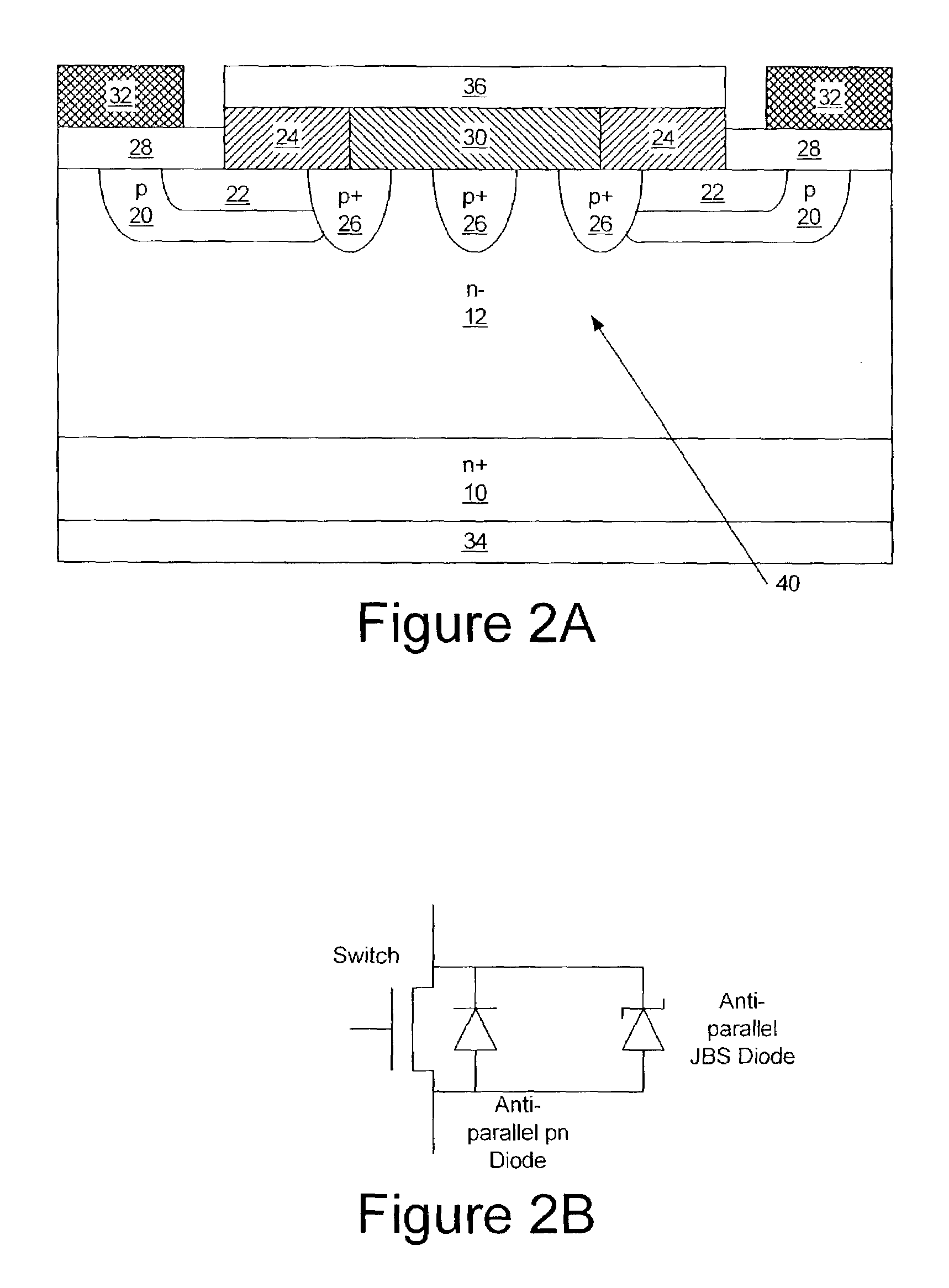
Silicon carbide MOSFETs with integrated antiparallel junction barrier Schottky free wheeling diodes and methods of fabricating the same
Silicon carbide semiconductor devices and methods of fabricating silicon carbide semiconductor devices have a silicon carbide DMOSFET and an integral silicon carbide Schottky diode configured to at least partially bypass a built in diode of the DMOSFET. The Schottky diode may be a junction barrier Schottky diode and may have a turn-on voltage lower than a turn-on voltage of a built-in body diode of the DMOSFET. The Schottky diode may have an active area less than an active area of the DMOSFET.
Owner:CREE INC
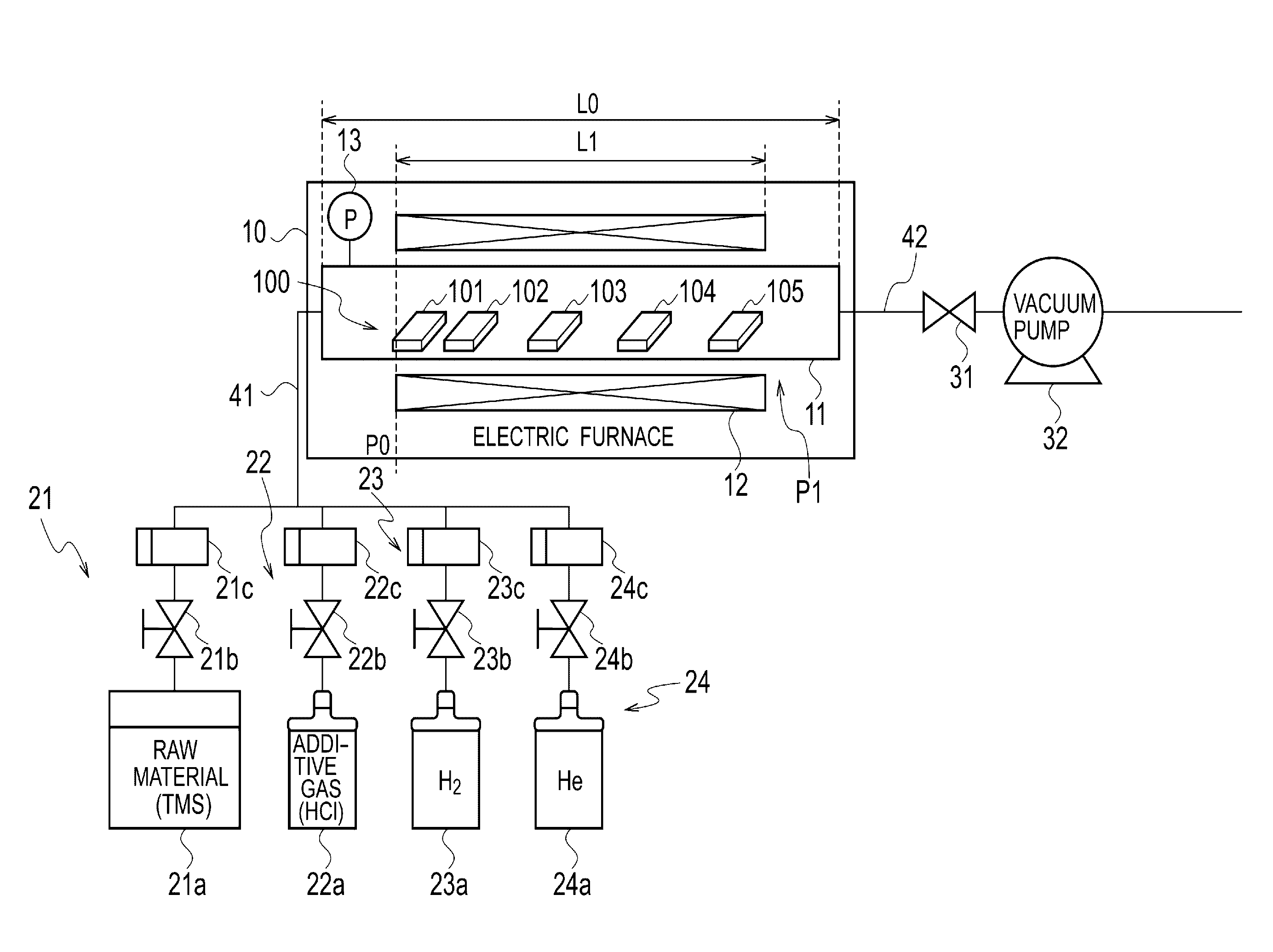
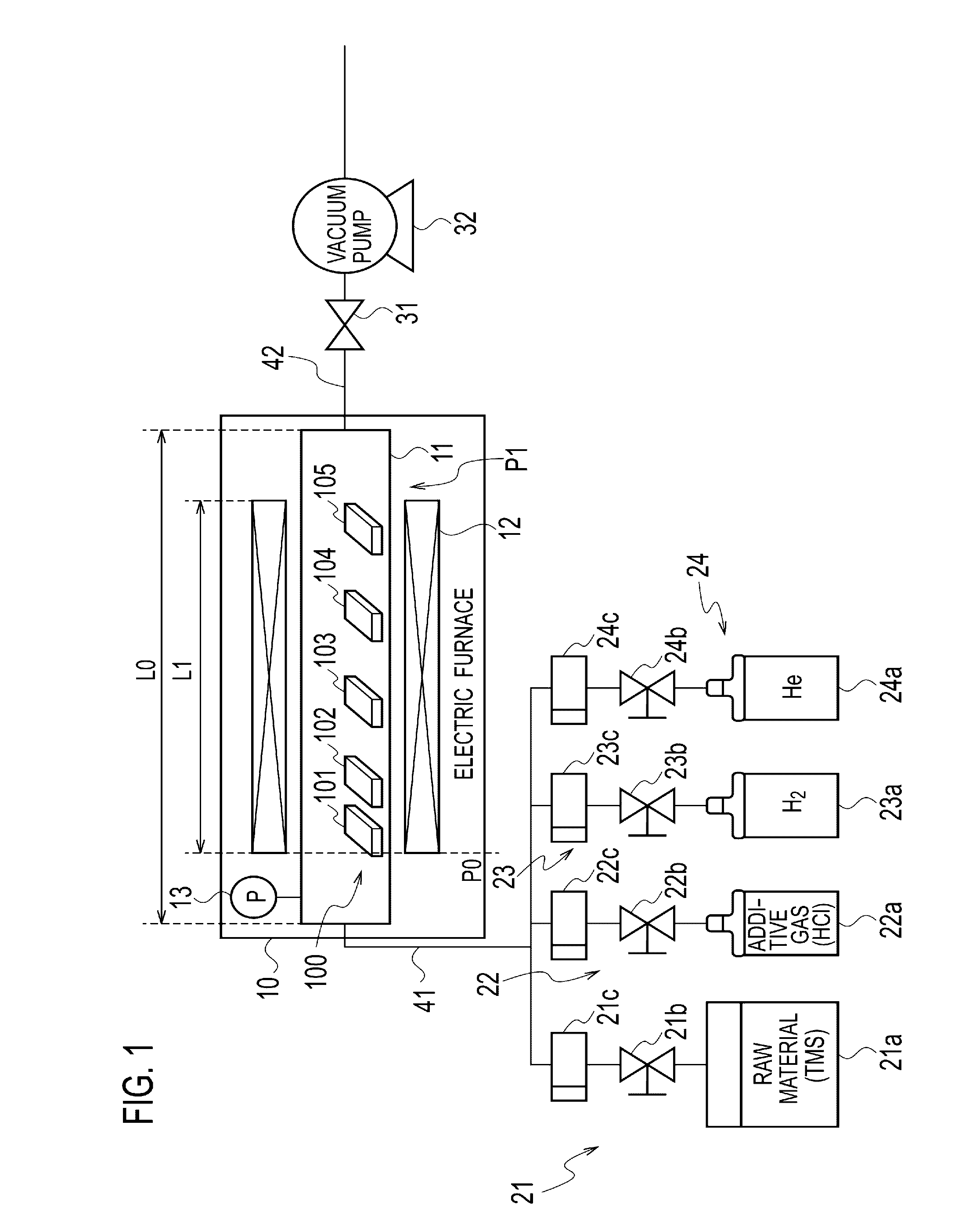
Heat-resistant composite material production method and production device
ActiveUS20160305015A1Reduce generationImprove mass productionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingChlorideChemical vapor deposition
In the present embodiment, in the production of a heat-resistant composite material resulting from impregnating a ceramic fiber preform with silicon carbide, a mixed gas containing starting material gas, an additive gas, and a carrier gas is supplied to a substrate having a minute structure such as a preform stored in an electric furnace, silicon carbide is deposited to form a film by means of a chemical vapor deposition method or a chemical vapor infiltration method, and the film formation growth speed and embedding uniformity are controlled by means of the amount of additive gas added to the starting material gas, the starting material gas contains tetramethylsilane, and the additive gas contains a molecule containing chlorine such as methyl chloride or hydrogen chloride. The film formation growth speed and embedding uniformity of the silicon carbide are both achieved.
Owner:IHI CORP +1
Method for producing group iii - group v vertical light-emitting diodes
ActiveUS20080099780A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesInterface layerLight-emitting diode
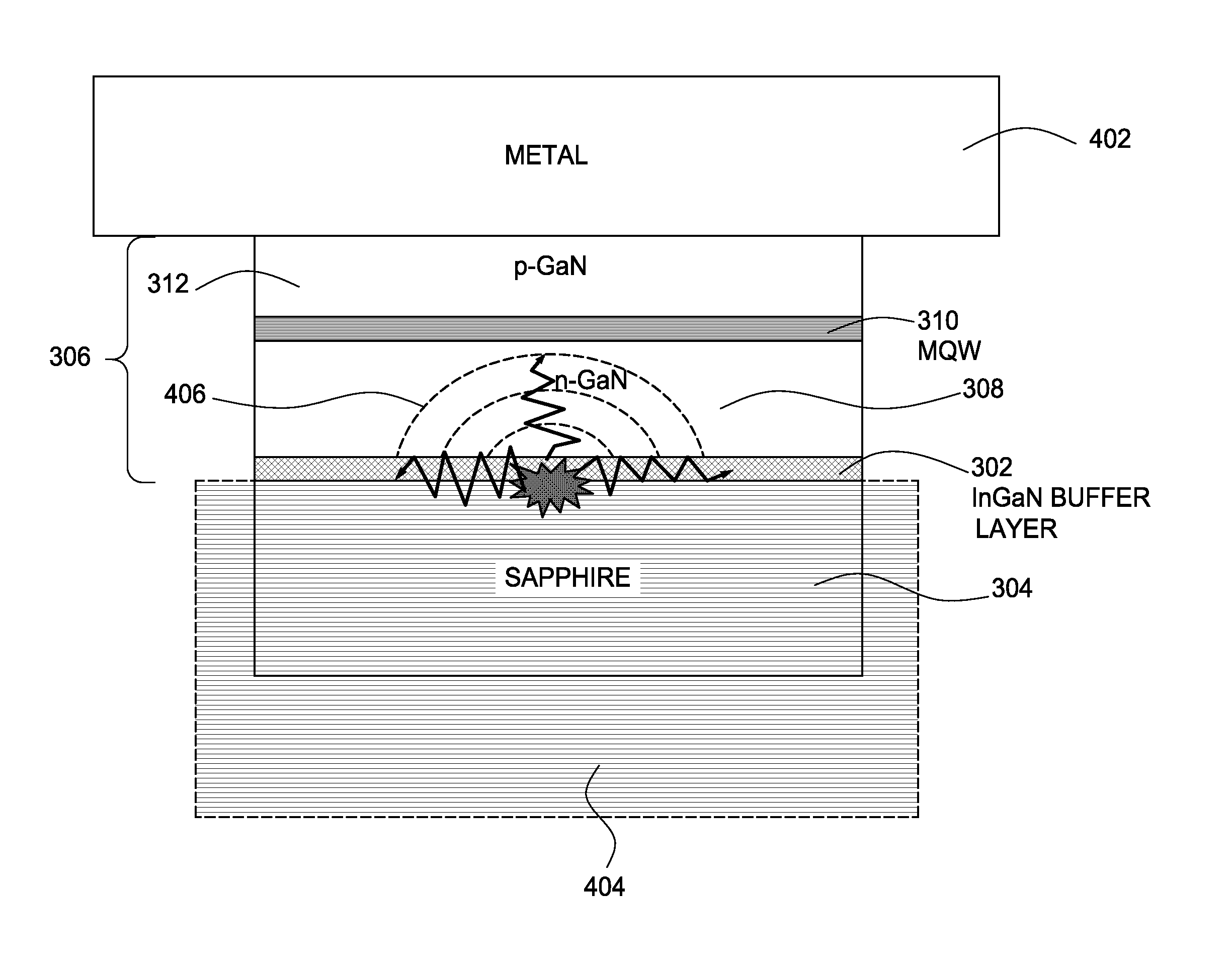
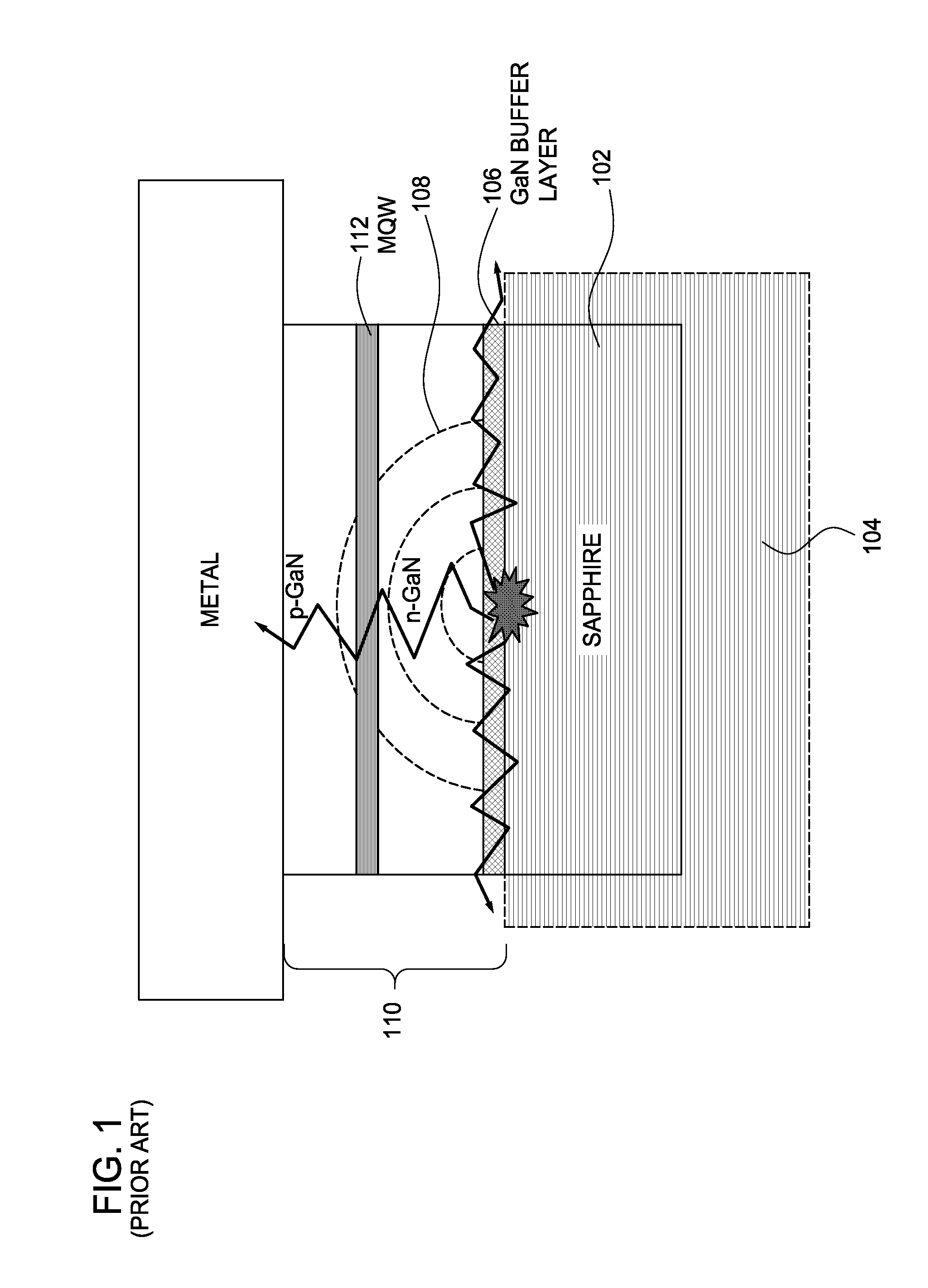
A method of producing one or more vertical light-emitting diode (VLED) dies having a light-emitting diode (LED) stack comprising Group III-Group V combinations of elements (e.g., GaN, AlN, InN, AlGaN, InGaN, and InAlGaN) and a metal substrate is provided. The techniques include forming an InGaN or InAlGaN interface layer above a suitable growth-supporting substrate, such as sapphire or silicon carbide (SiC), and forming the LED stack above the interface layer. Such an interface layer may absorb a majority of the energy from a laser pulse used during laser lift-off of the growth-supporting substrate in an effort to prevent damage to the light emitting layers of the LED stack, which may result in improved brightness performance over VLED dies produced with conventional buffer layers.
Owner:SEMILEDS OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
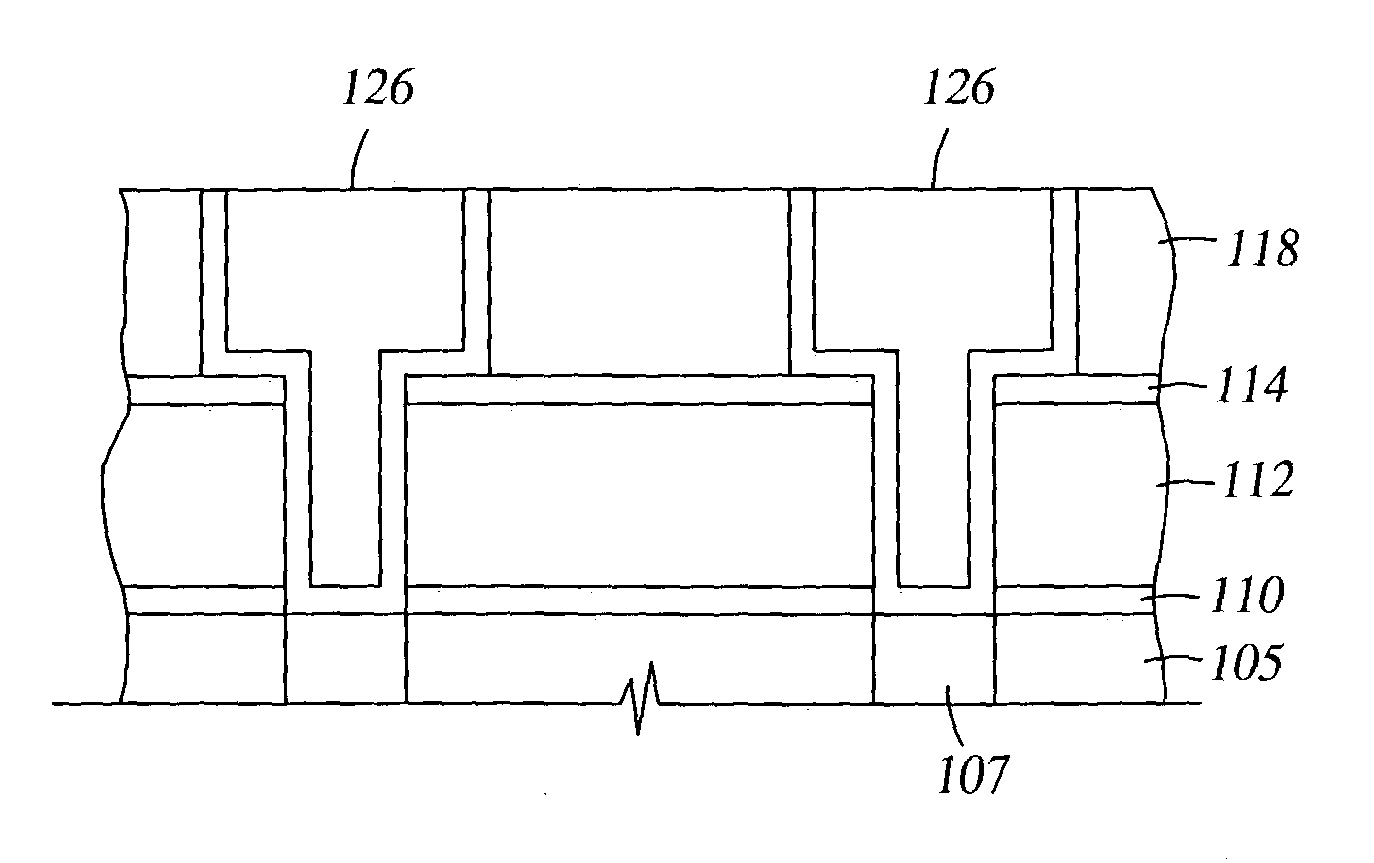
Fabrication Method of Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Device
The following defects are suppressed: when an interlayer insulating film including a silicon carbide film and an organic insulating film is dry-etched to form interconnection grooves over underlying Cu interconnections, an insulating reactant adheres to the surface of the underlying Cu interconnections exposed to the bottom of the interconnection grooves, or the silicon carbide film or the organic insulating film exposed to the side walls of the interconnection grooves are side-etched. When a lamination film made of a silicon oxide film, an organic insulating film, a silicon oxide film, an organic insulating film and a silicon carbide film is dry-etched to form interconnection grooves over Cu interconnections, a mixed gas of SF6 and NH3 is used as an etching gas for the silicon carbide film to work side walls of the interconnection grooves perpendicularly and further suppress defects that a deposit or a reactant adheres to the surface of the Cu interconnections exposed to the bottom of the interconnection grooves.
Owner:ENOMOTO HIROYUKI +2
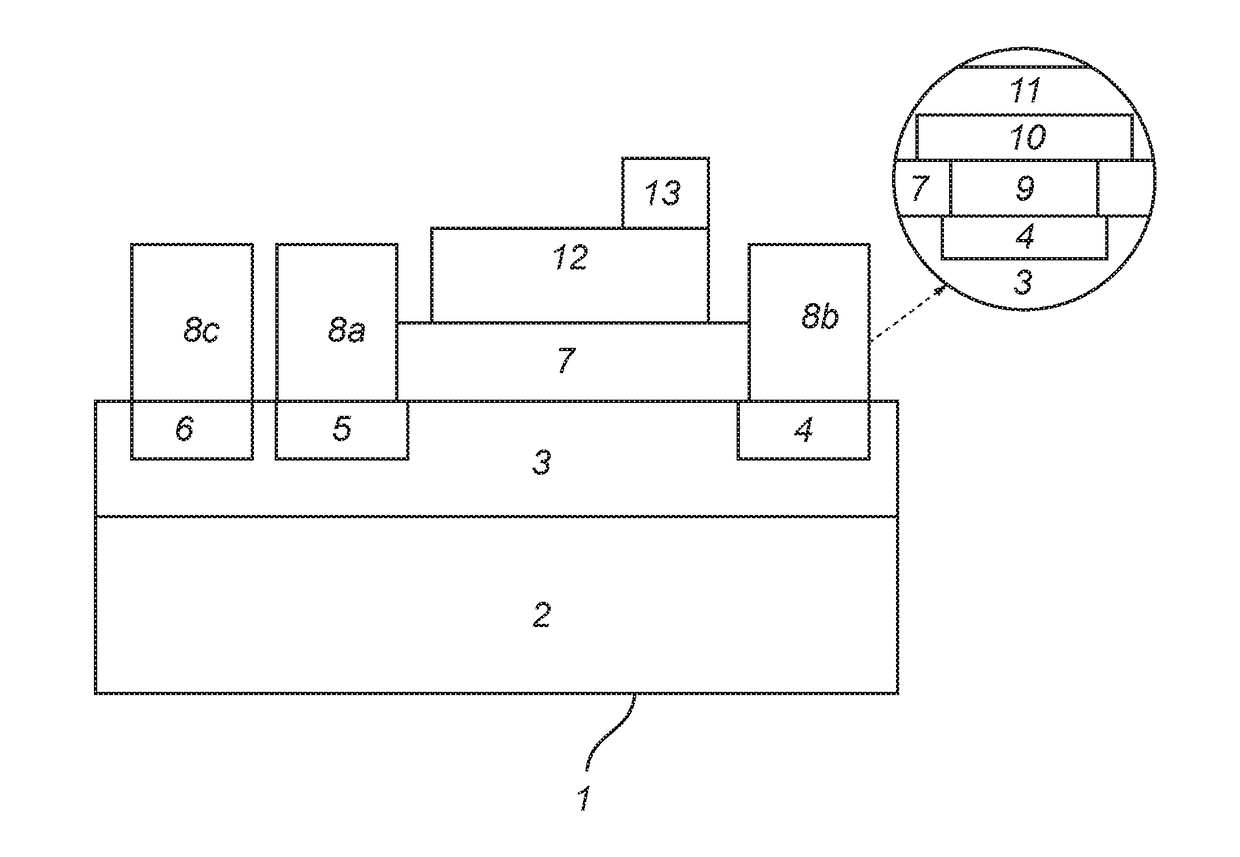
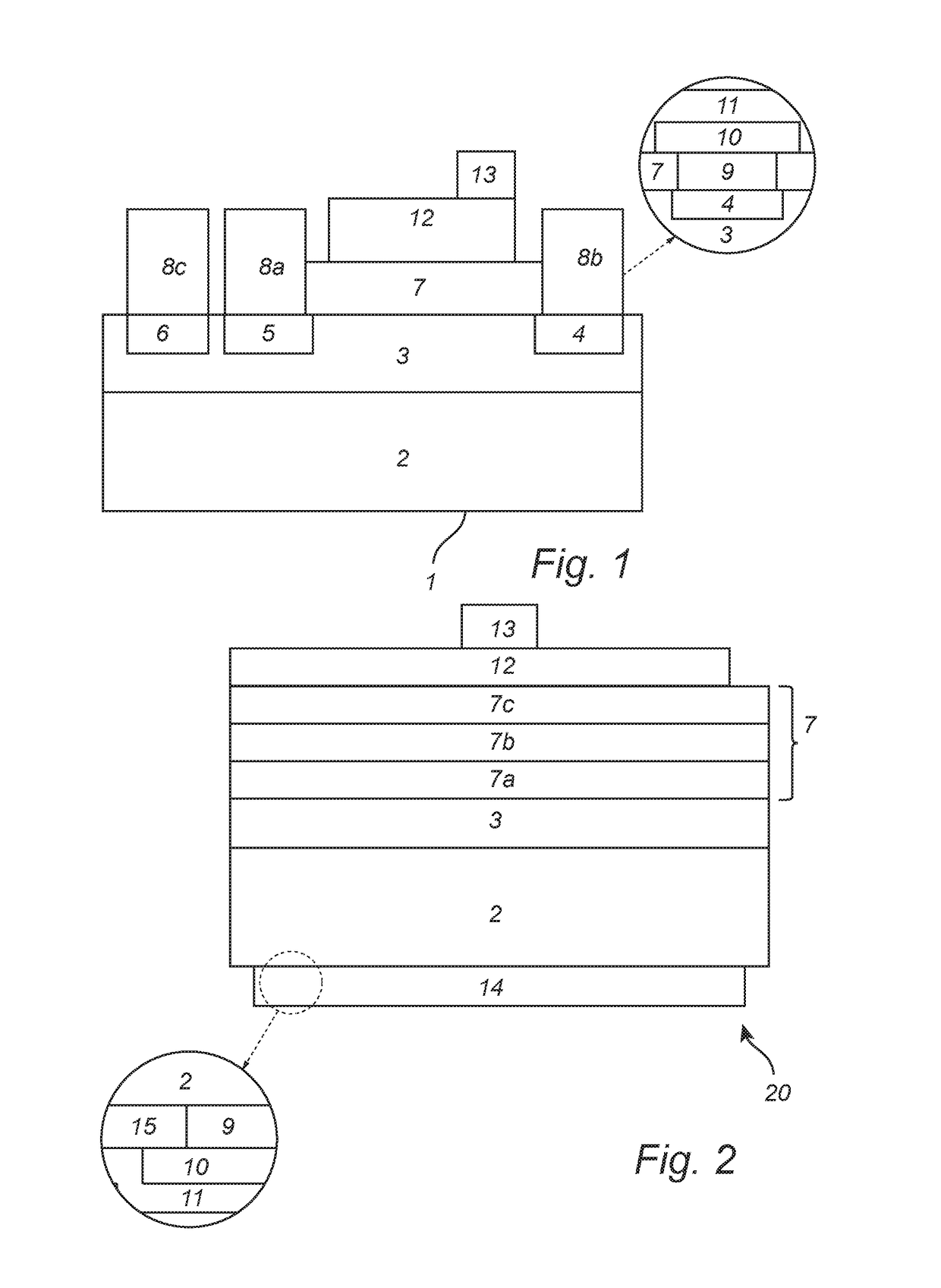
Manufacturing method of a silicon carbide semiconductor device
InactiveUS8071482B2Smooth curveImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductorDry etching
A manufacturing method for a silicon carbide semiconductor device is disclosed. It includes an etching method in which an Al film and Ni film are laid on an SiC wafer in this order and wet-etched, whereby a two-layer etching mask is formed in which Ni film portions overhang Al film portions. Mesa grooves are formed by dry etching by using this etching mask.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Silicon carbide based field effect gas sensor for high temperature applications
InactiveUS20180011052A1Change electrical propertiesLong-term reliable operationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactSemiconductor structure
A field effect gas sensor, for detecting a presence of a gaseous substance in a gas mixture, the field effect gas sensor comprising: a SiC semiconductor structure; an electron insulating layer covering a first portion of the SiC semiconductor structure; a first contact structure at least partly separated from the SiC semiconductor structure by the electron insulating layer; and a second contact structure conductively connected to a second portion of the SiC semiconductor structure, wherein at least one of the electron insulating layer and the first contact structure is configured to interact with the gaseous substance to change an electrical property of the SiC semiconductor structure; and wherein the second contact structure comprises: an ohmic contact layer in direct contact with the second portion of the SiC semiconductor structure; and a barrier layer formed by an electrically conducting mid-transition-metal oxide covering the ohmic contact layer.
Owner:VOLVO CAR CORP
Copper damascene barrier and capping layer
InactiveUS20060024954A1Improve electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnti-reflective coatingEngineering
A method for forming a damascene with improved electrical properties and resulting structure thereof including providing at least one dielectric insulating layer overlying a first etch stop layer; forming an anti-reflectance coating (ARC) layer prior to a photolithographic patterning process; forming at least one opening extending through a thickness portion of the at least one dielectric insulating layer and first etch stop layer according to said photolithographic patterning and an etching process; blanket depositing a barrier layer including material selected from the group consisting of silicon carbide and silicon oxycarbide to line the at least one opening; blanket depositing a refractory metal liner over the barrier layer; blanket depositing at least one metal layer to fill the at least one opening; and, removing at least the at least one metal layer overlying the at least one opening level according to a chemical mechanical polish (CMP) process.
Owner:WU ZHEN CHENG +3
Baffled liner cover
ActiveUS20070181066A1High trafficPrevent fallingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringTower
A baffled liner cover supported at the top of a liner surrounding a wafer support tower for semiconductor thermal processing. The cover may present a continuous horizontal surface for preventing particles from falling within the liner but present horizontal extending gas passageways in a baffle assembly to allow the flow of processing gas through the cover. In one embodiment, the baffle assembly includes a cup-shaped member disposed in a central aperture of a top plate having an open top, a continuous bottom, horizontal holes through the sides, and a flange around sides defining a convolute annular passage. Alternatively, the planar top plate may included slanted holes therethrough or vertical holes occupying a small fraction of the surface area. The liner and cover may be composed of quartz, silicon carbide, or preferably silicon.
Owner:HANGZHOU DUNYUANJUXIN SEMICON TECH CO LTD
Methods for transferring a useful layer of silicon carbide to a receiving substrate
InactiveUS20050266659A1Easy to recycleSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessOptoelectronics
Owner:SOITEC SA
Method of fabricating microelectromechanical systems and devices having trench isolated contacts
InactiveUS6936491B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSolid-state devicesEngineeringMicroelectromechanical systems
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a MEMS device, and technique of fabricating or manufacturing a MEMS device, having mechanical structures encapsulated in a chamber prior to final packaging and a contact area disposed at least partially outside the chamber. The contact area is electrically isolated from nearby electrically conducting regions by way of dielectric isolation trench that is disposed around the contact area. The material that encapsulates the mechanical structures, when deposited, includes one or more of the following attributes: low tensile stress, good step coverage, maintains its integrity when subjected to subsequent processing, does not significantly and / or adversely impact the performance characteristics of the mechanical structures in the chamber (if coated with the material during deposition), and / or facilitates integration with high-performance integrated circuits. In one embodiment, the material that encapsulates the mechanical structures is, for example, silicon (polycrystalline, amorphous or porous, whether doped or undoped), silicon carbide, silicon-germanium, germanium, or gallium-arsenide.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method of improving stability in low k barrier layers
InactiveUS20040137756A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHydrogenPhenyl group
A method is provided for processing a substrate including providing a processing gas comprising hydrogen gas and an organosilicon compound comprising a phenyl group to the processing chamber, and reacting the processing gas to deposit a low k silicon carbide barrier layer useful as a barrier layer in damascene or dual damascene applications with low k dielectric materials.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
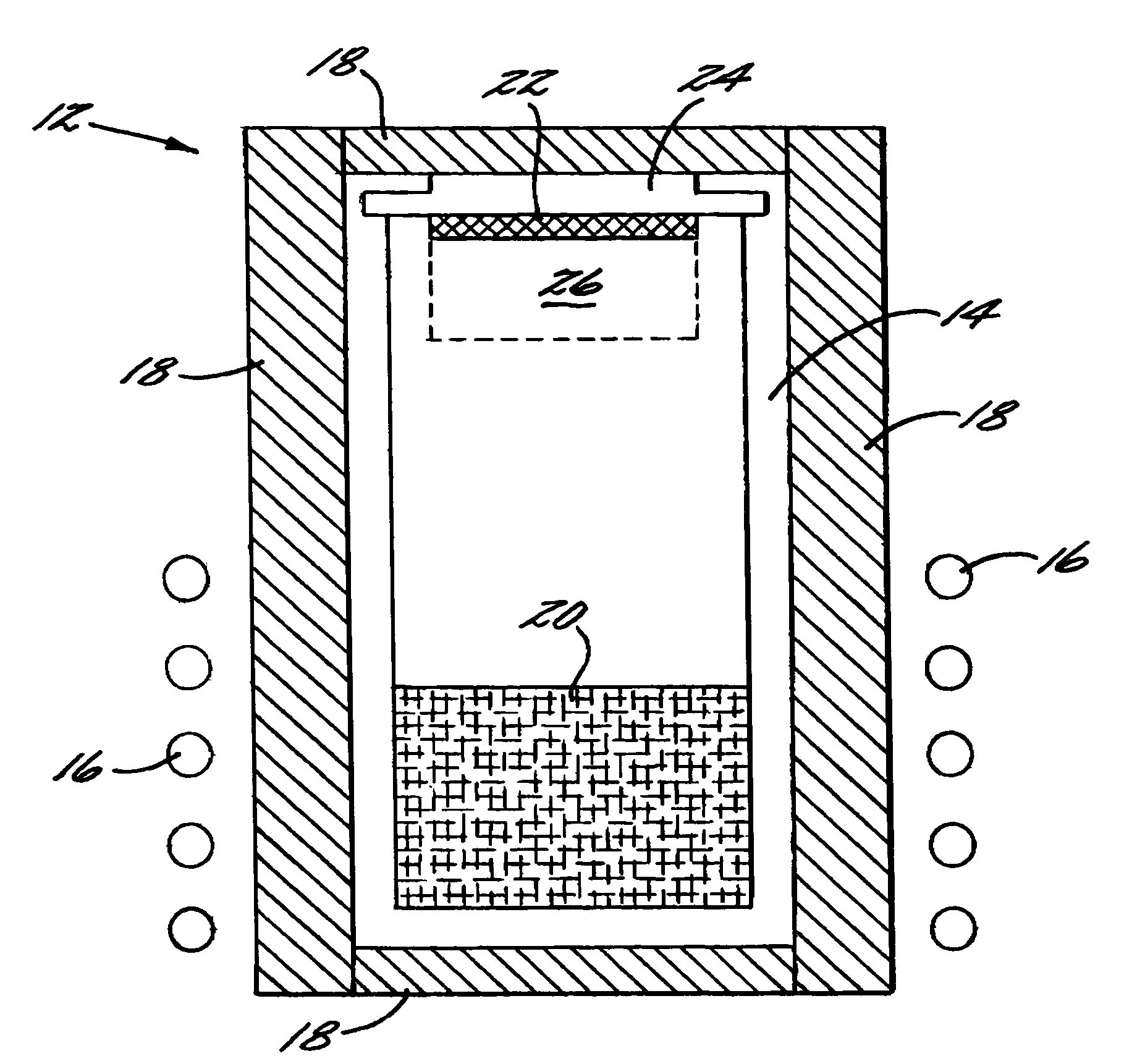
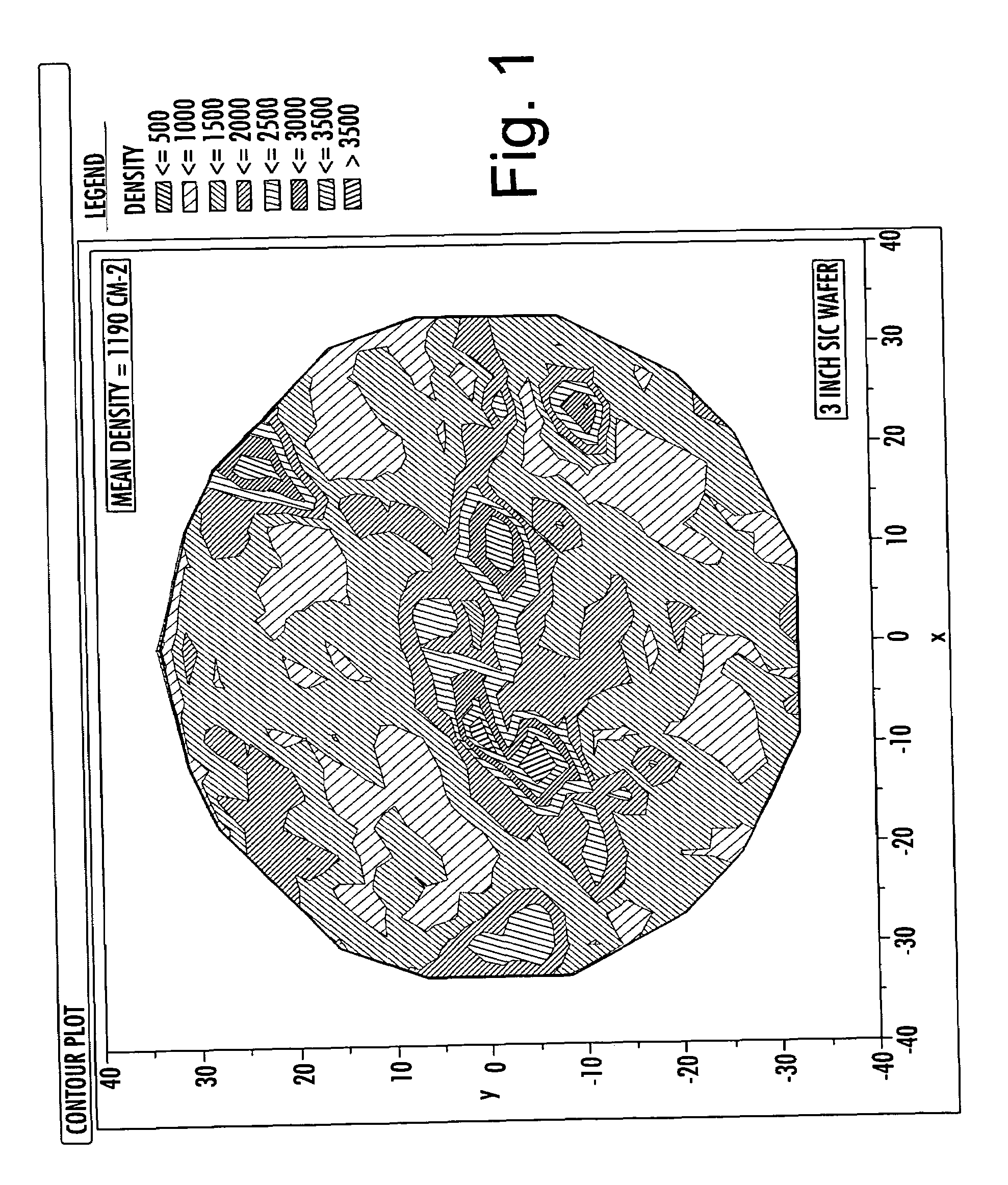
Low 1c screw dislocation 3 inch silicon carbide wafer
ActiveUS7314520B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystalDislocation
A high quality single crystal wafer of SiC is disclosed having a diameter of at least about 3 inches and a 1 c screw dislocation density of less than about 2000 cm−2.
Owner:CREE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com