Patents
Literature
6355 results about "Device form" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
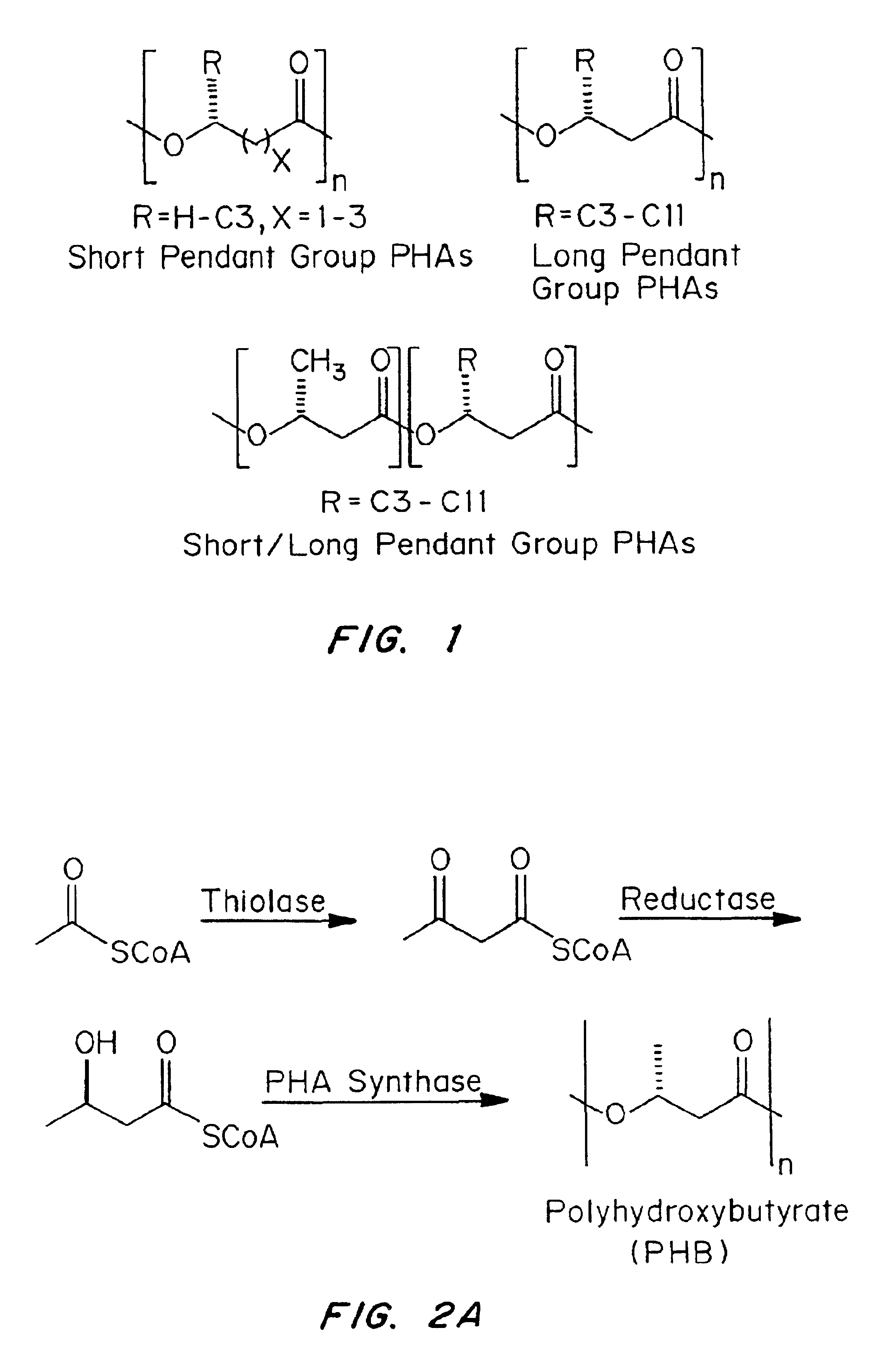
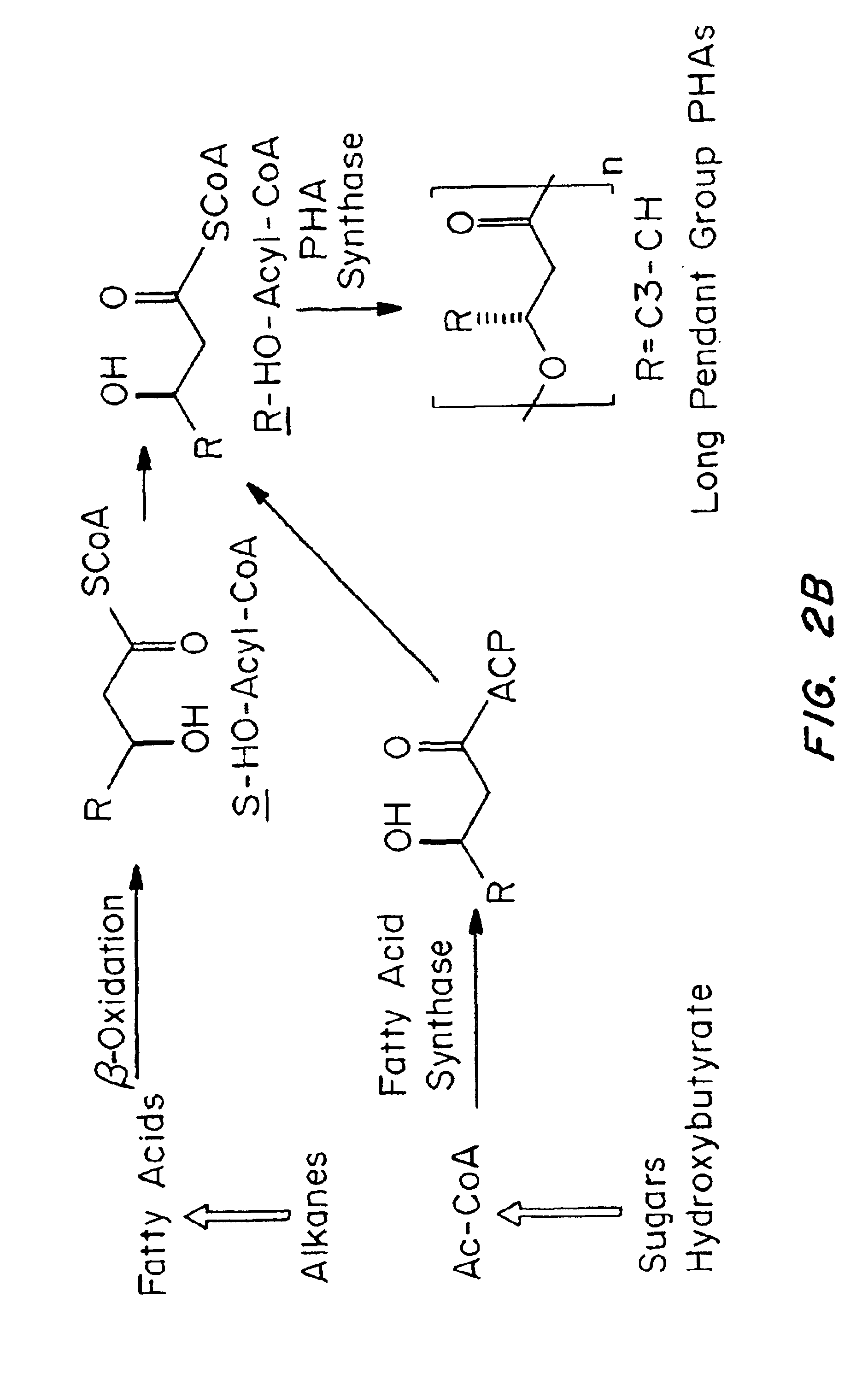
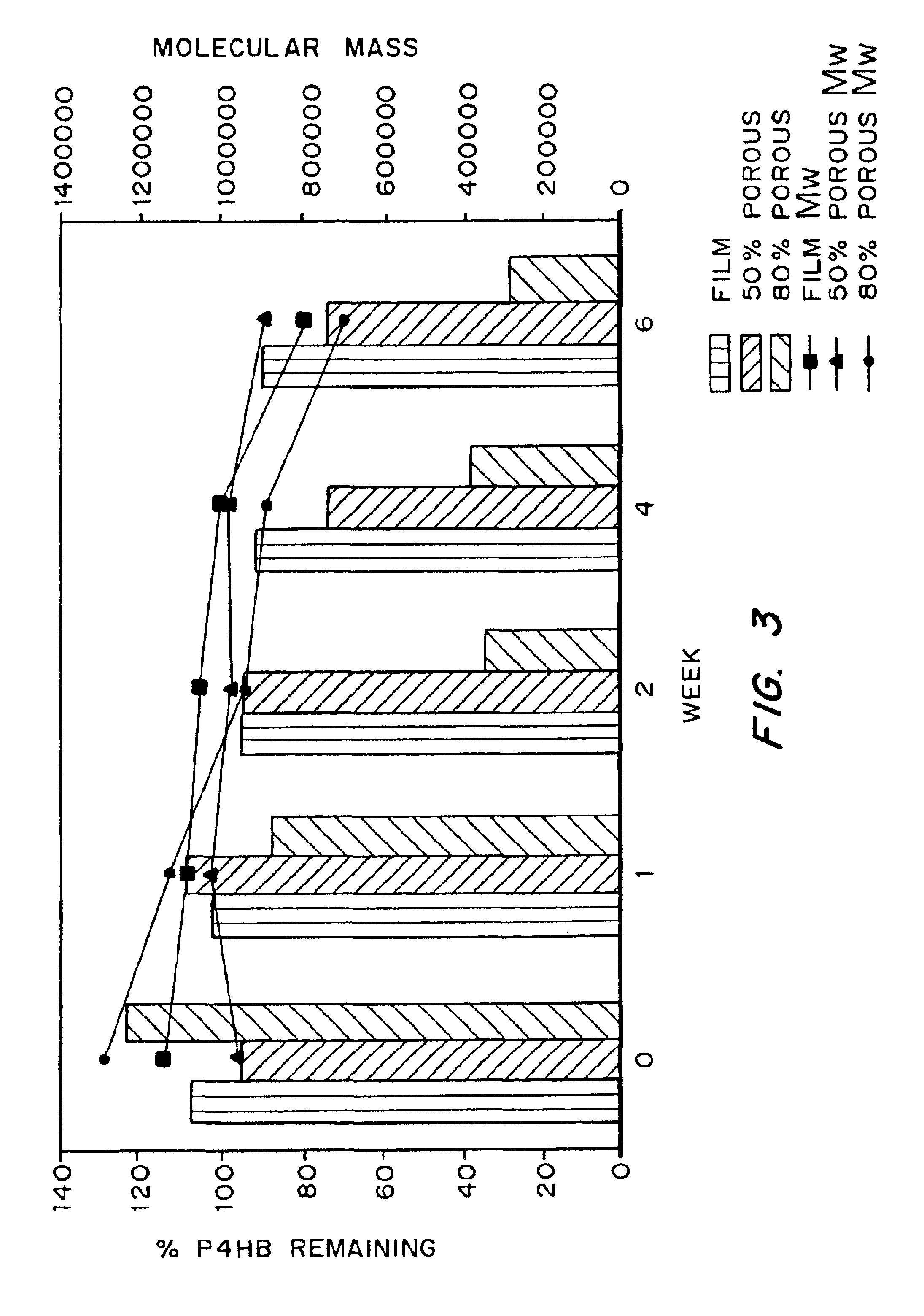
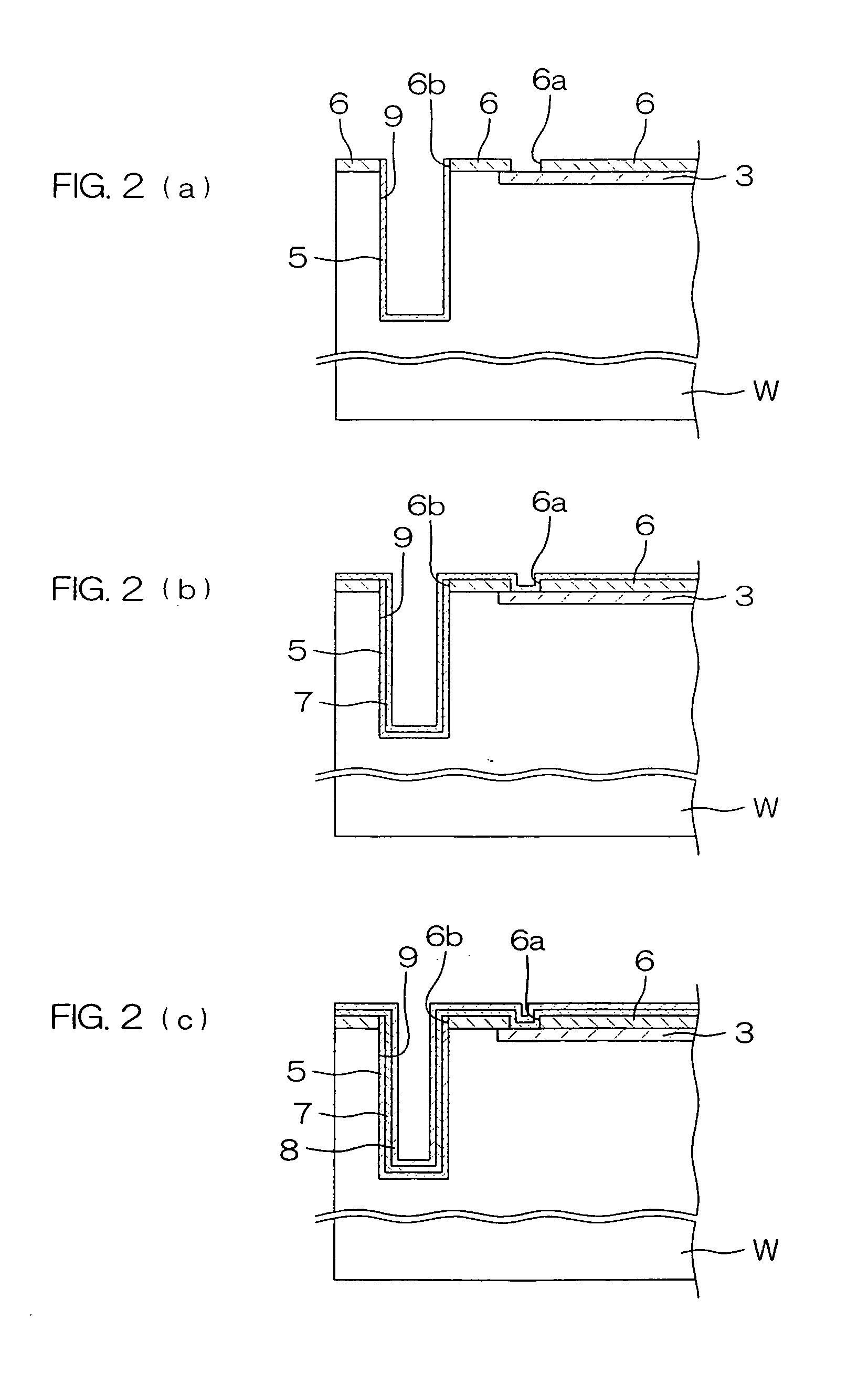
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
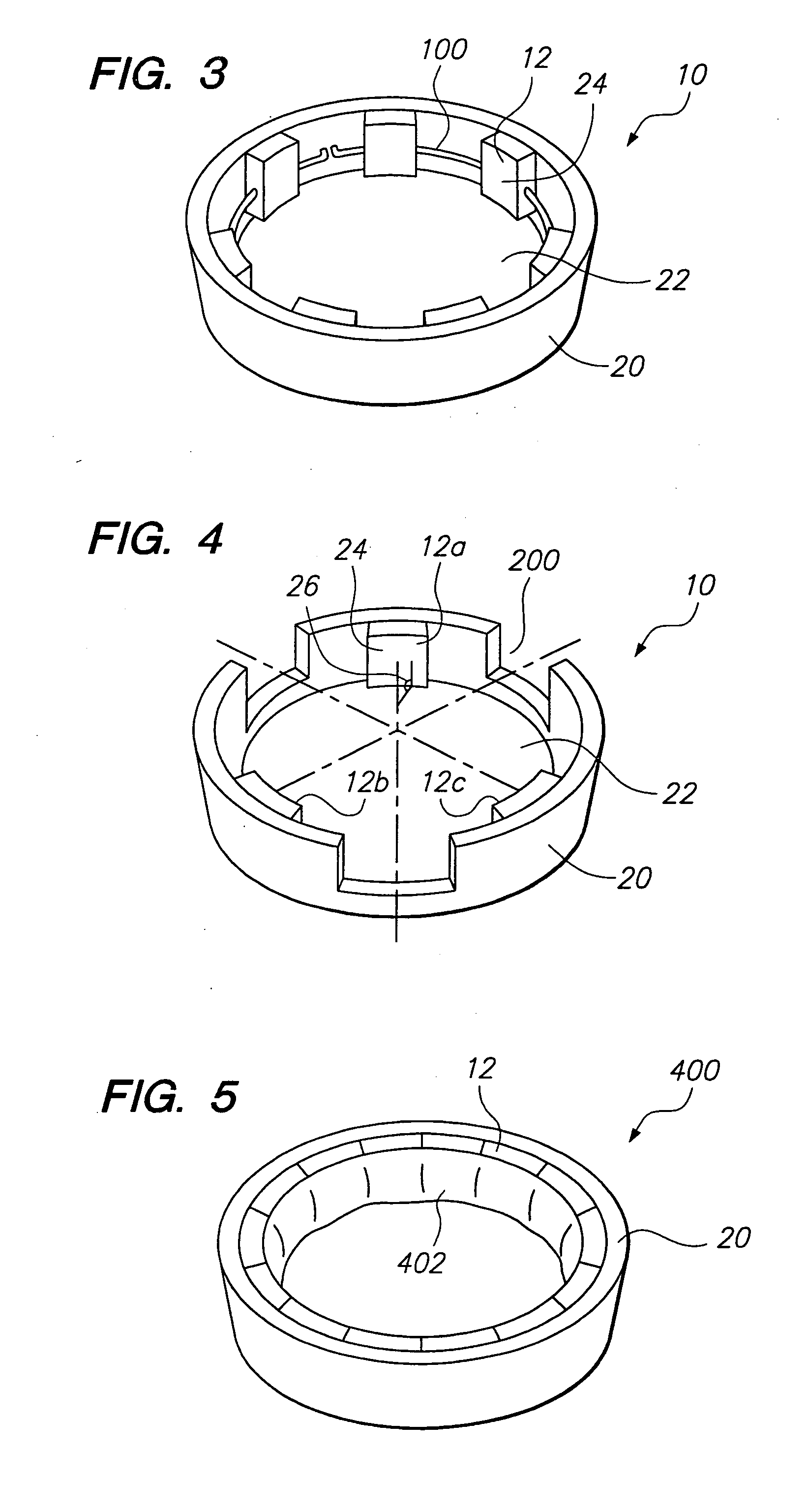
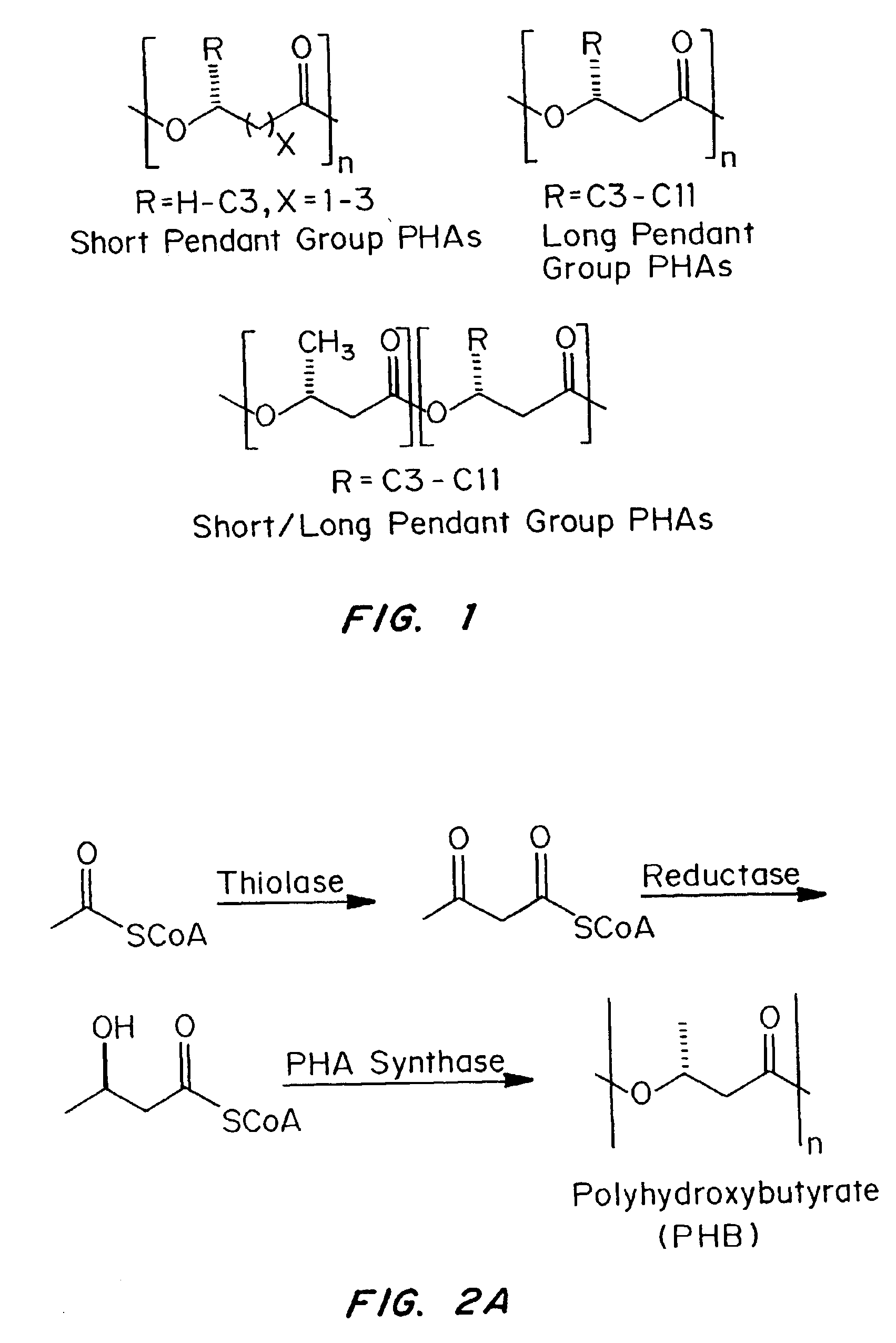
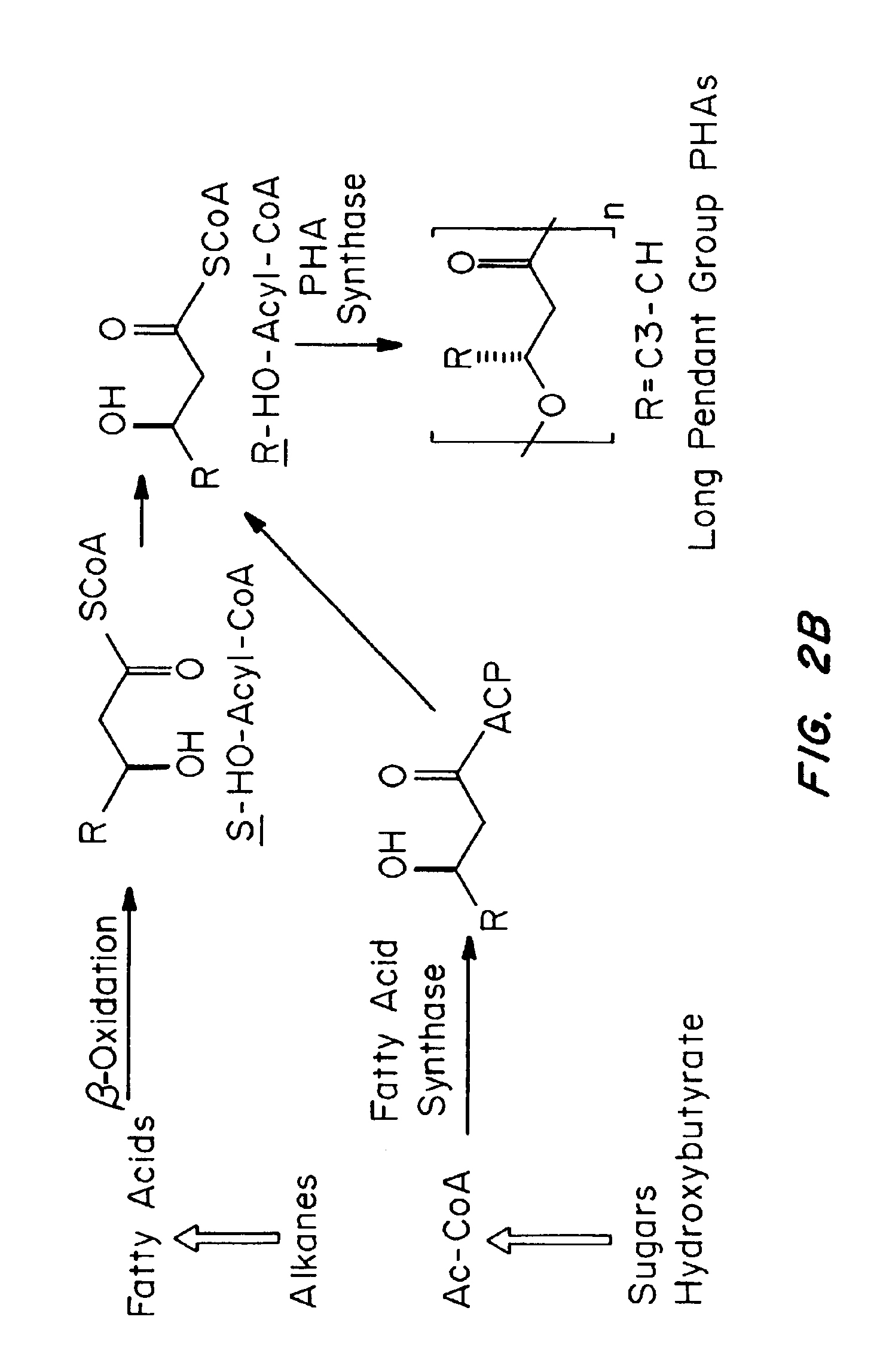
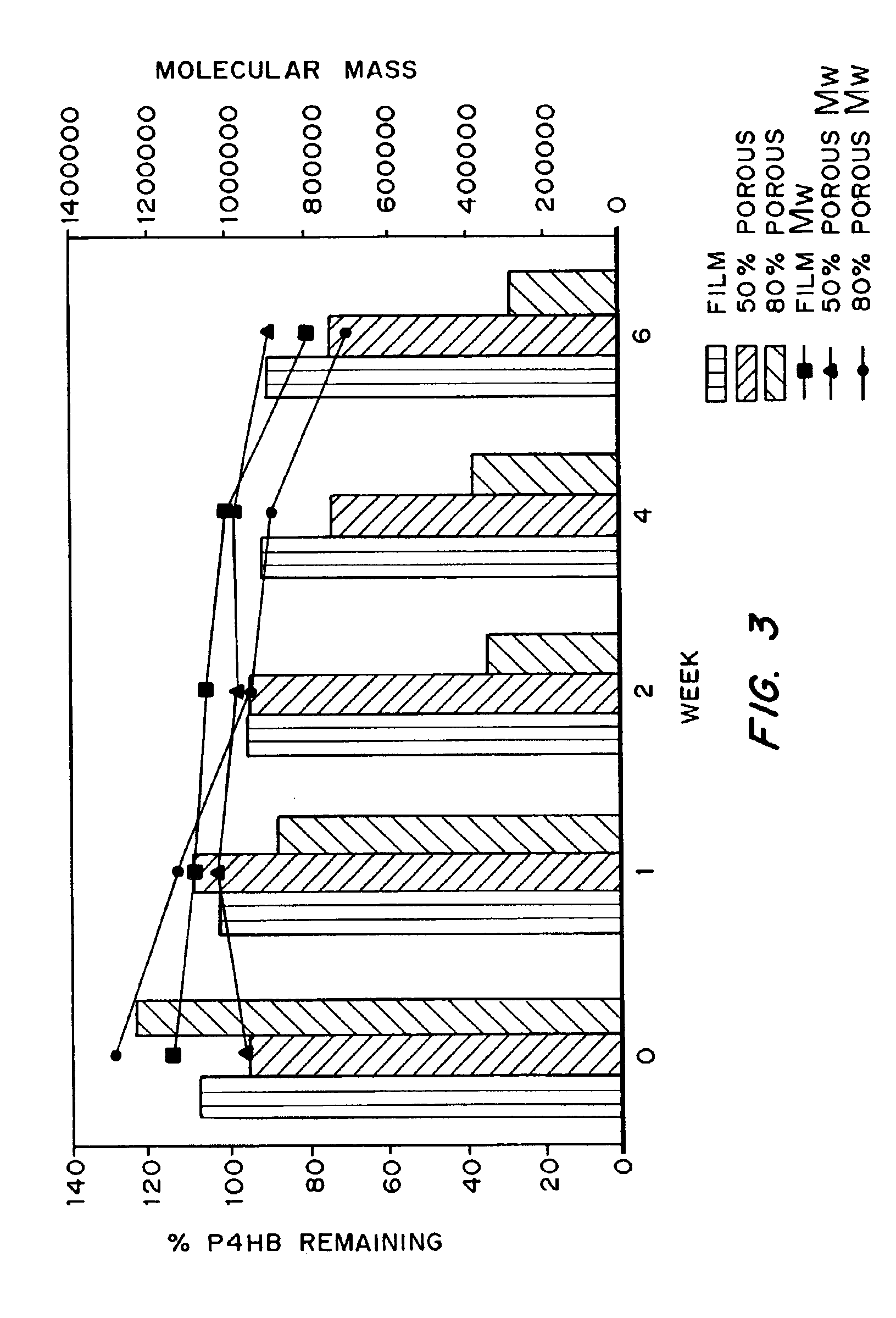
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
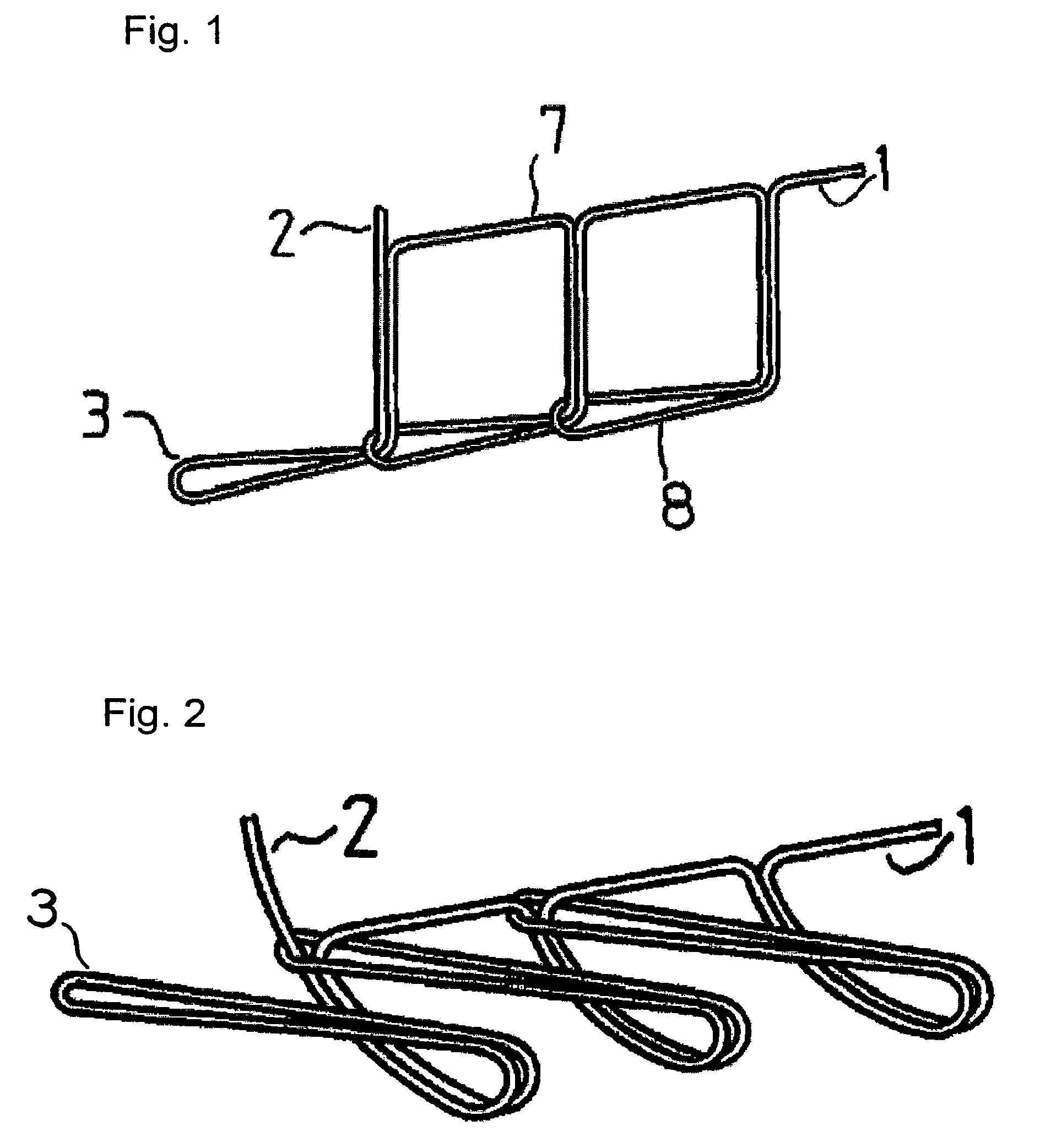
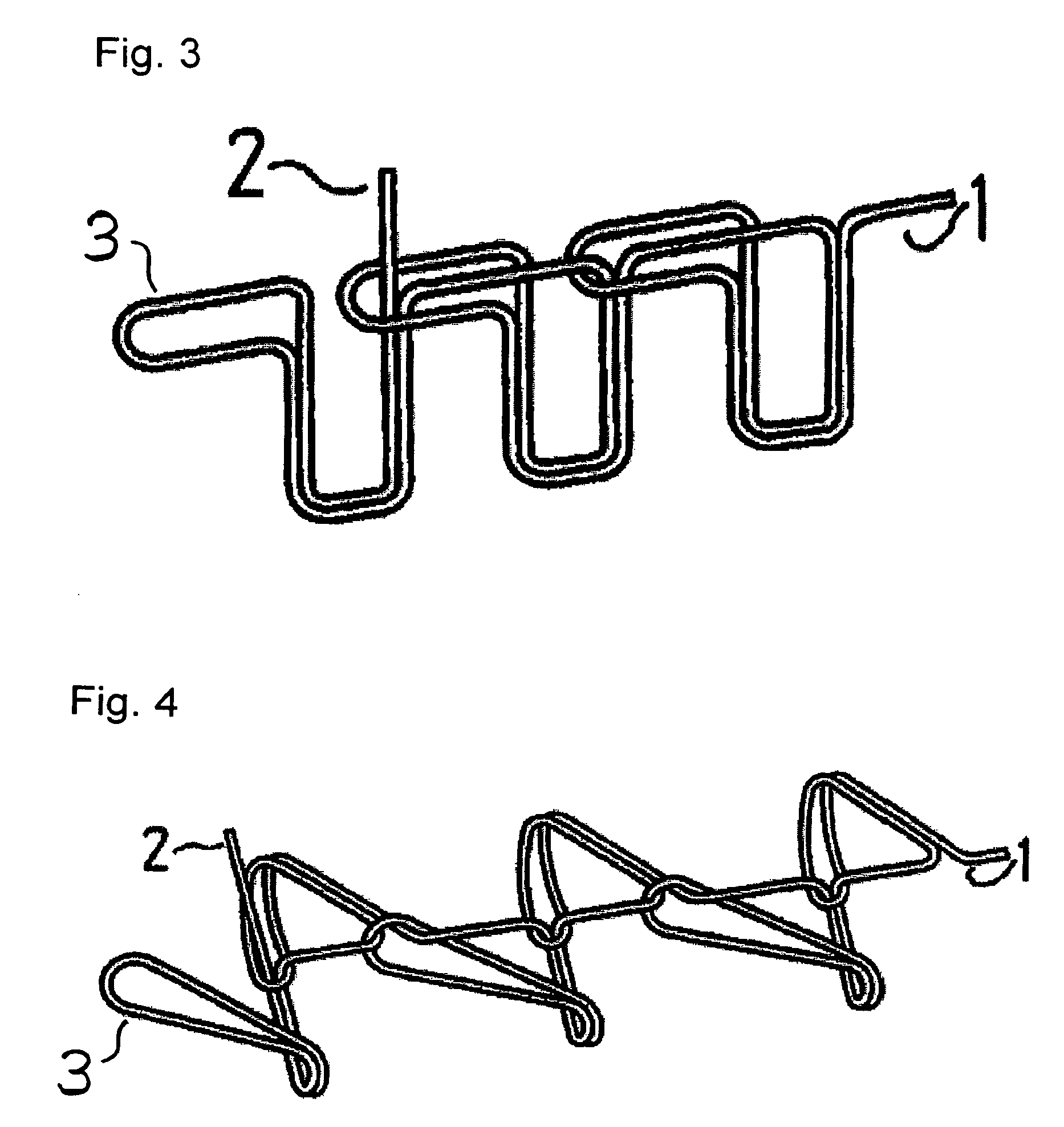
Suture reinforcement material for automatic suturing device
Owner:GUNZE LTD
Methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis
InactiveUS20060106381A1Effective treatmentPermit flexionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnDevice form
Surgical implants are configured for placement posteriorly to a spinal canal between vertebral bodies to distract the spine and enlarge the spinal canal. In the preferred embodiments the device permits spinal flexion while limiting spinal extension, thereby providing an effective treatment for treating spinal stenosis without the need for laminectomy. The invention may be used in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine. Numerous embodiments are disclosed, including elongated, length-adjustable components coupled to adjacent vertebral bodies using pedicle screws. The preferred embodiments, however, teach a device configured for placement between adjacent vertebral bodies and adapted to fuse to the lamina, facet, spinous process or other posterior elements of a single vertebra. Various mechanisms, including shape, porosity, tethers, and bone-growth promoting substances may be used to enhance fusion. The tether may be a wire, cable, suture, or other single or multi-filament member. Preferably, the device forms a pseudo-joint in conjunction with the non-fused vertebra. Alternatively, the device could be fused to the caudal vertebra or both the cranial and caudal vertebrae.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Semi-insulating silicon carbide without vanadium domination
InactiveUS6218680B1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease the number ofPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDevice formTrapping
Owner:CREE INC
Atomizer for an aerosol delivery device formed from a continuously extending wire and related input, cartridge, and method
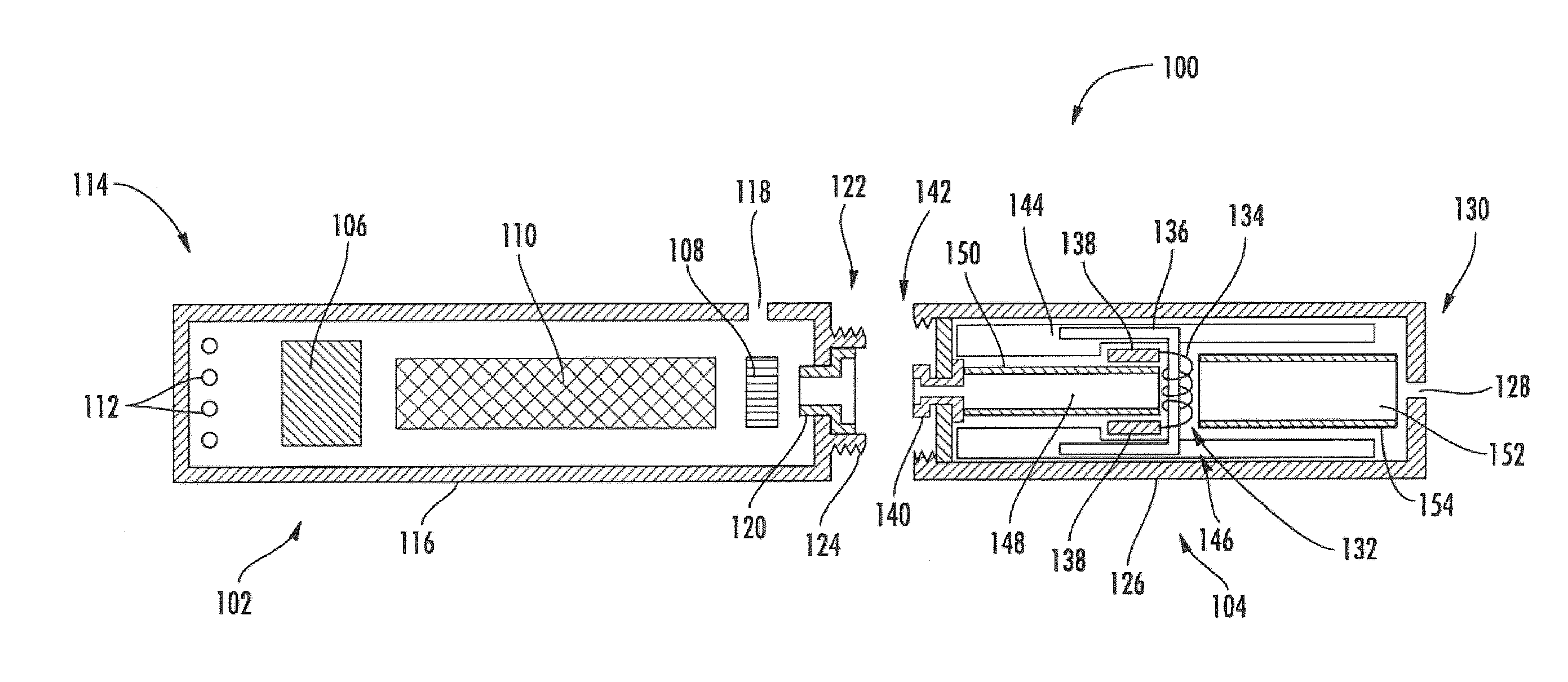
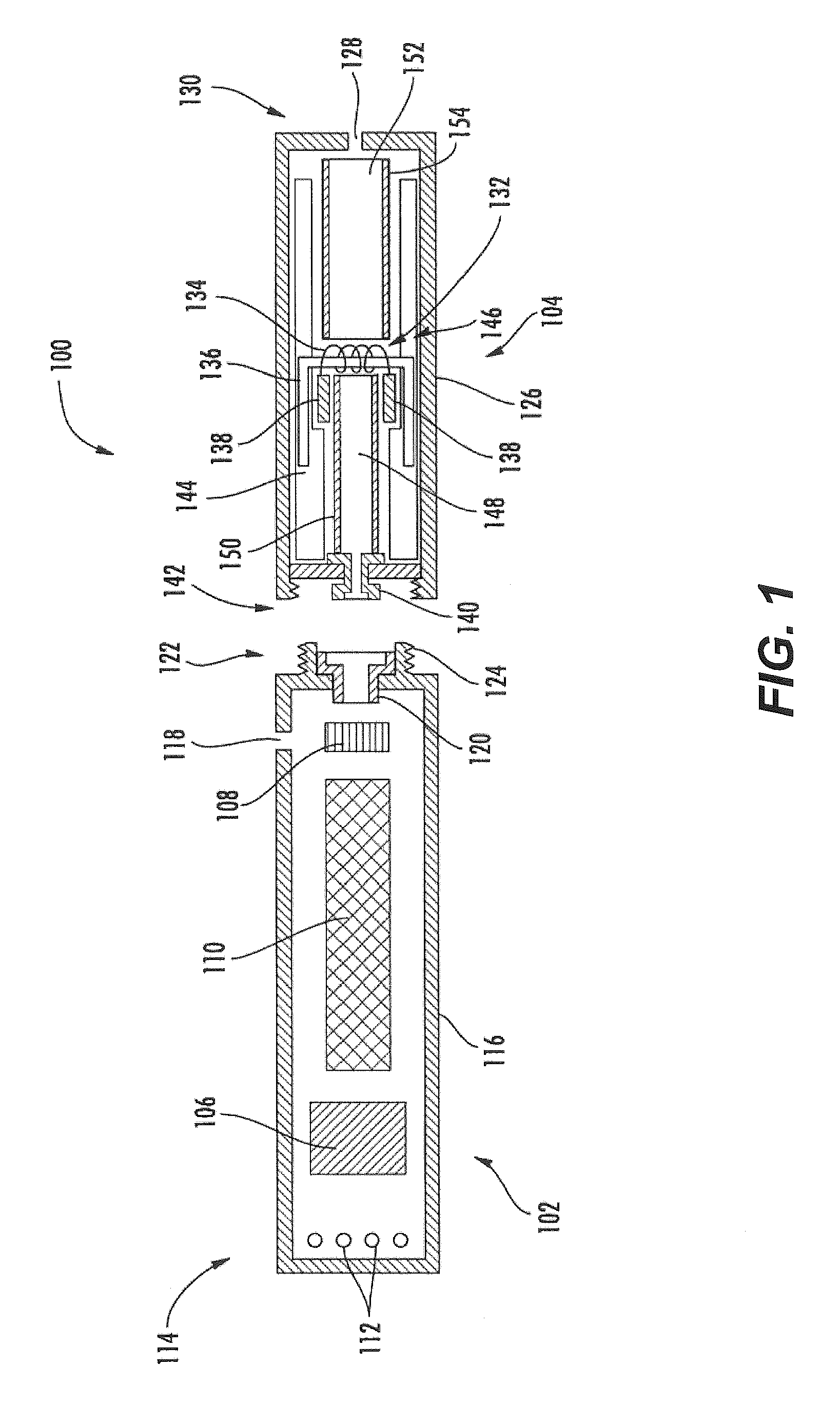
ActiveUS20140270730A1Steam generation heating methodsOhmic-resistance electrodesDevice formAerosol delivery
The present disclosure relates to atomizers for an aerosol delivery device such as a smoking article. The atomizer may include a liquid transport element and a wire continuously extending along a longitudinal length thereof. The wire may define end portions, contact portions, and a heating portion. The wire may be continuously wound about the liquid transport element such that each of the portions of the wire defines coils. A related input, cartridge, and method of forming atomizers also provided.
Owner:RAI STRATEGIC HLDG INC
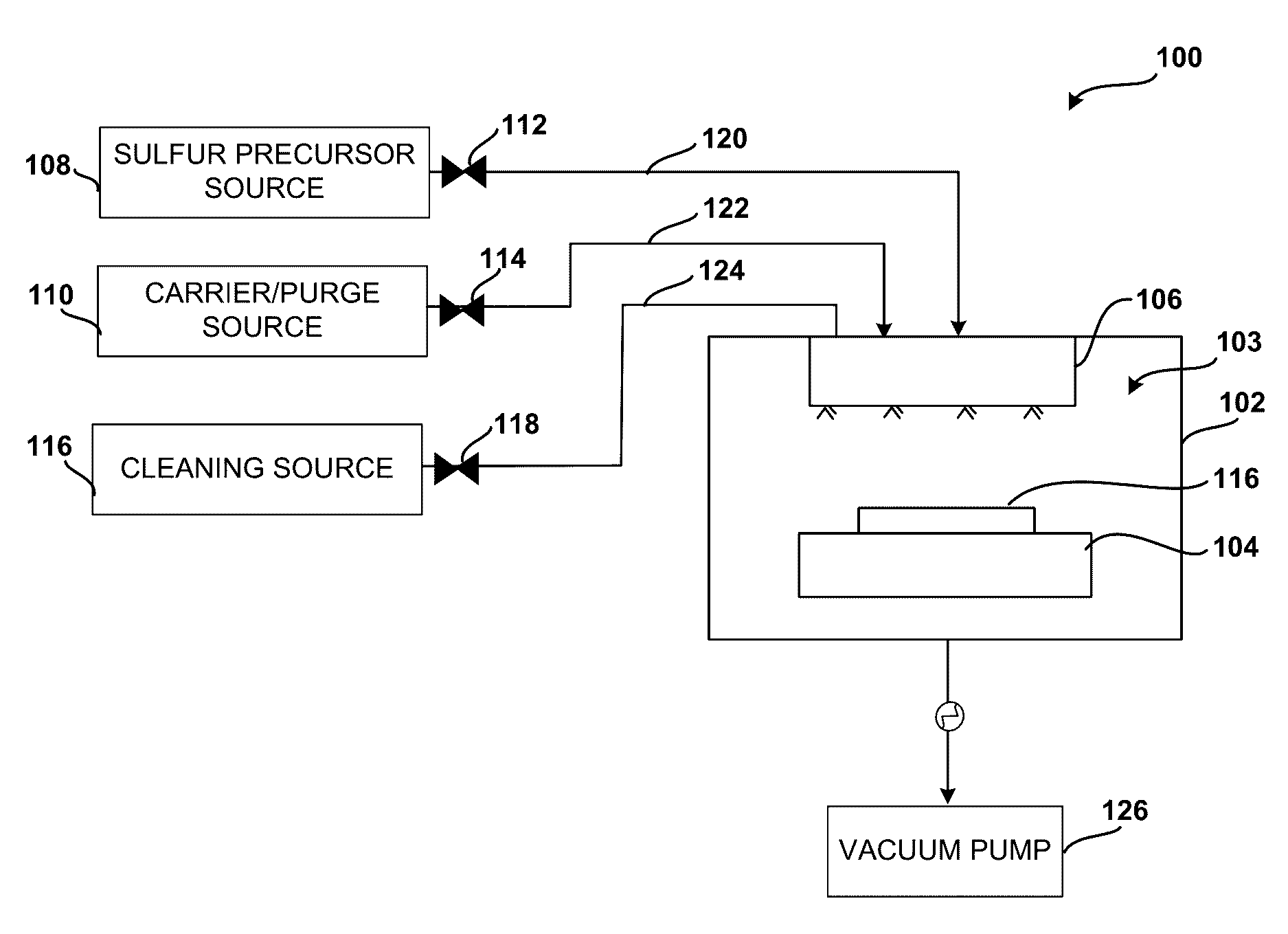
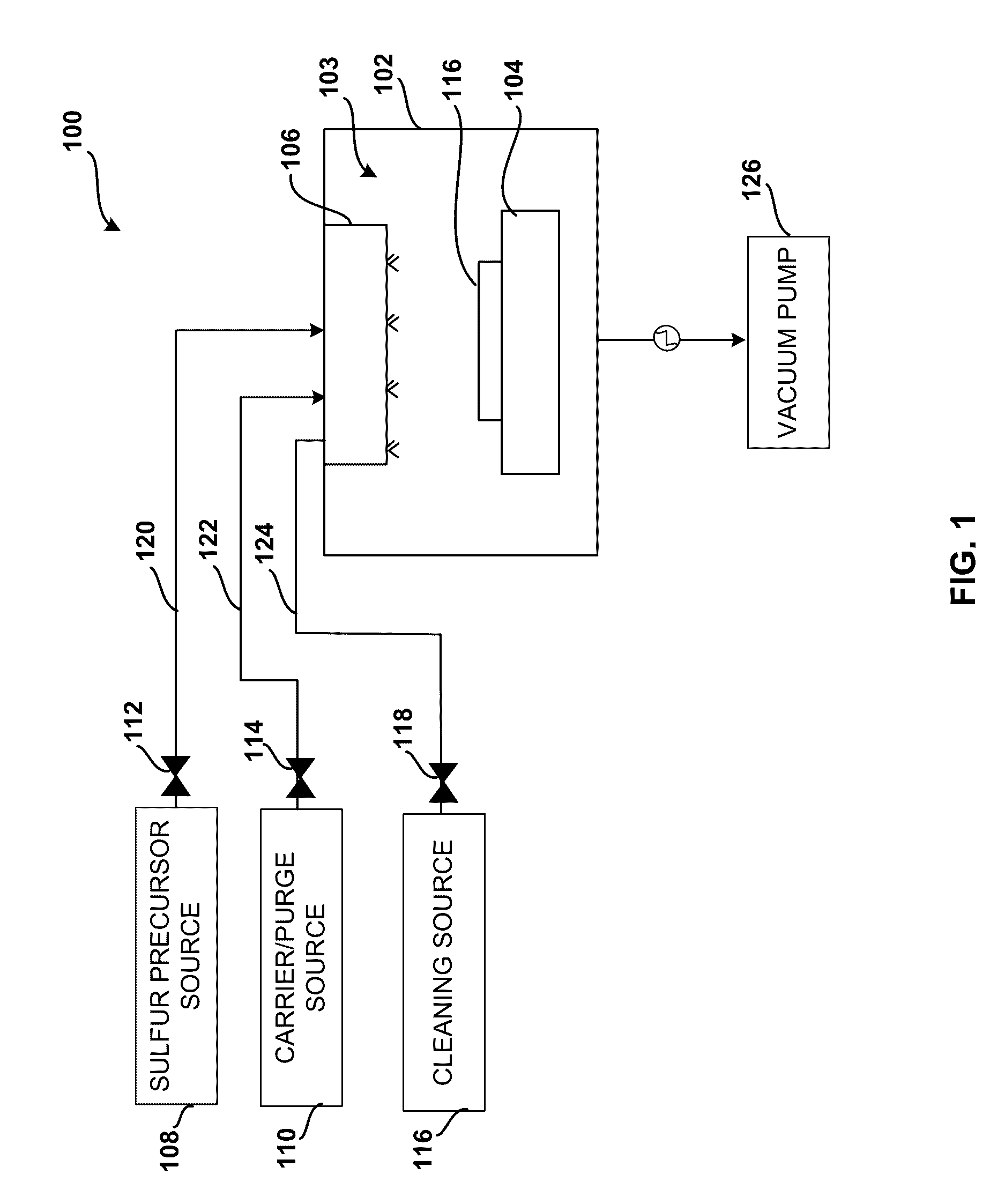
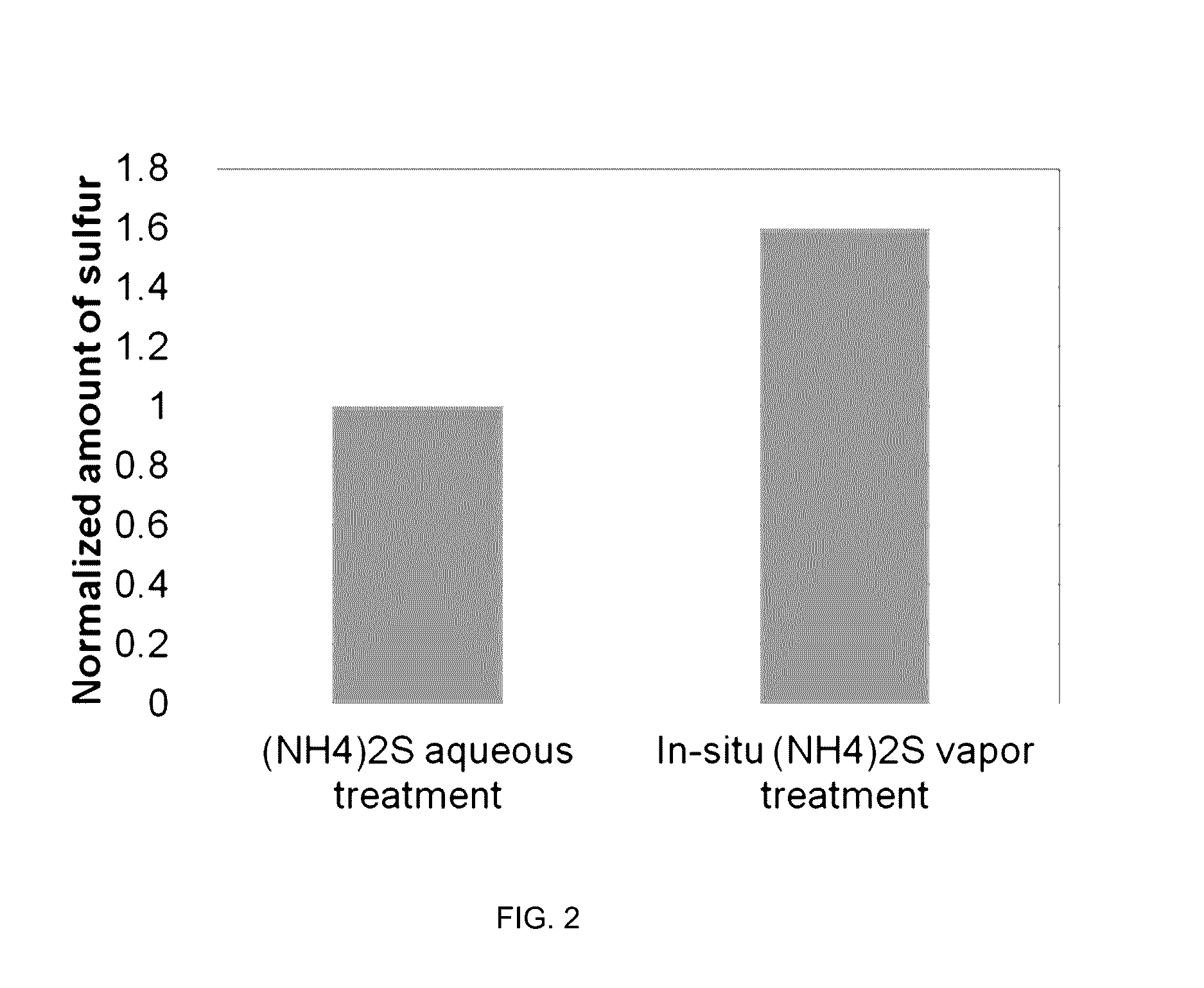
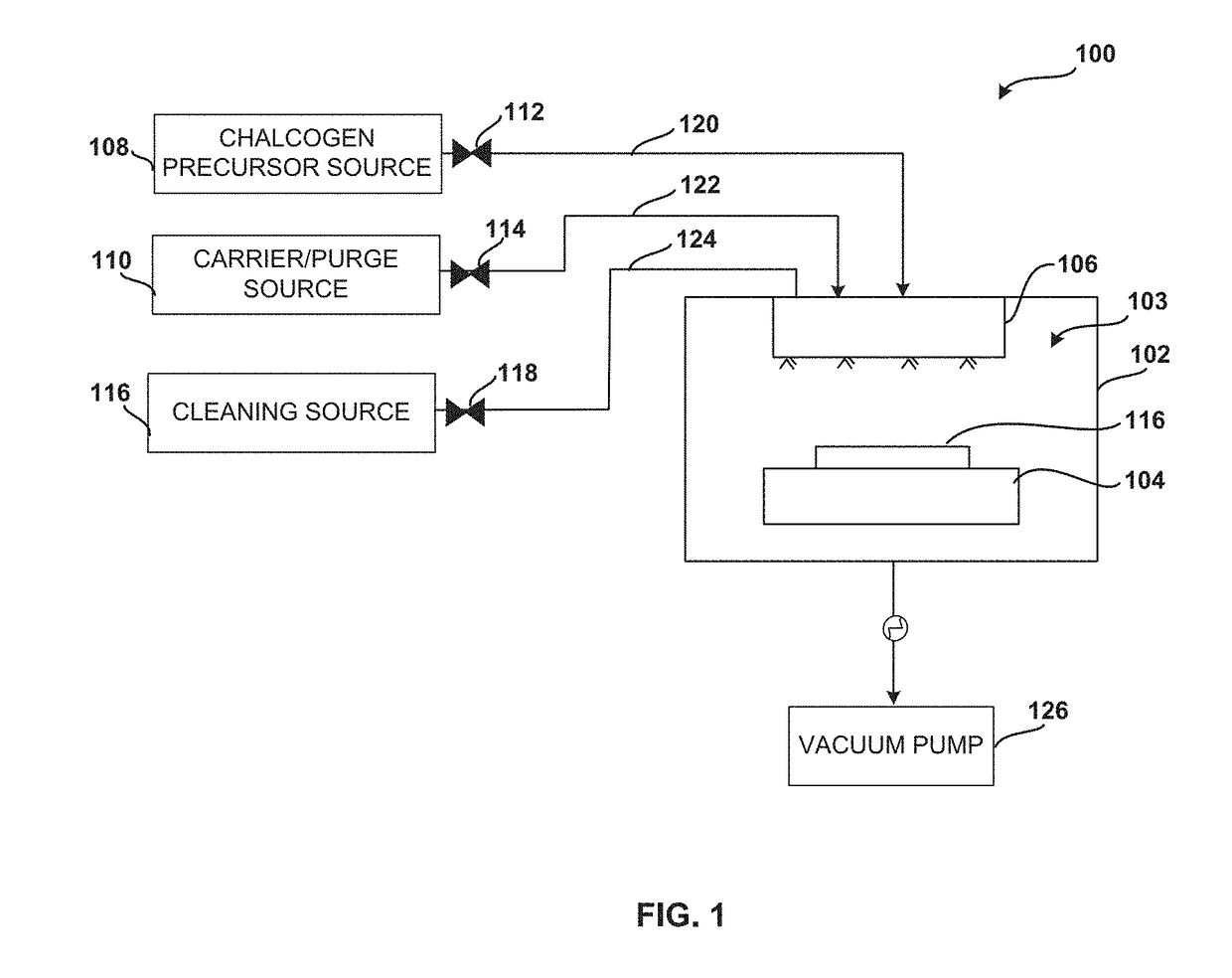
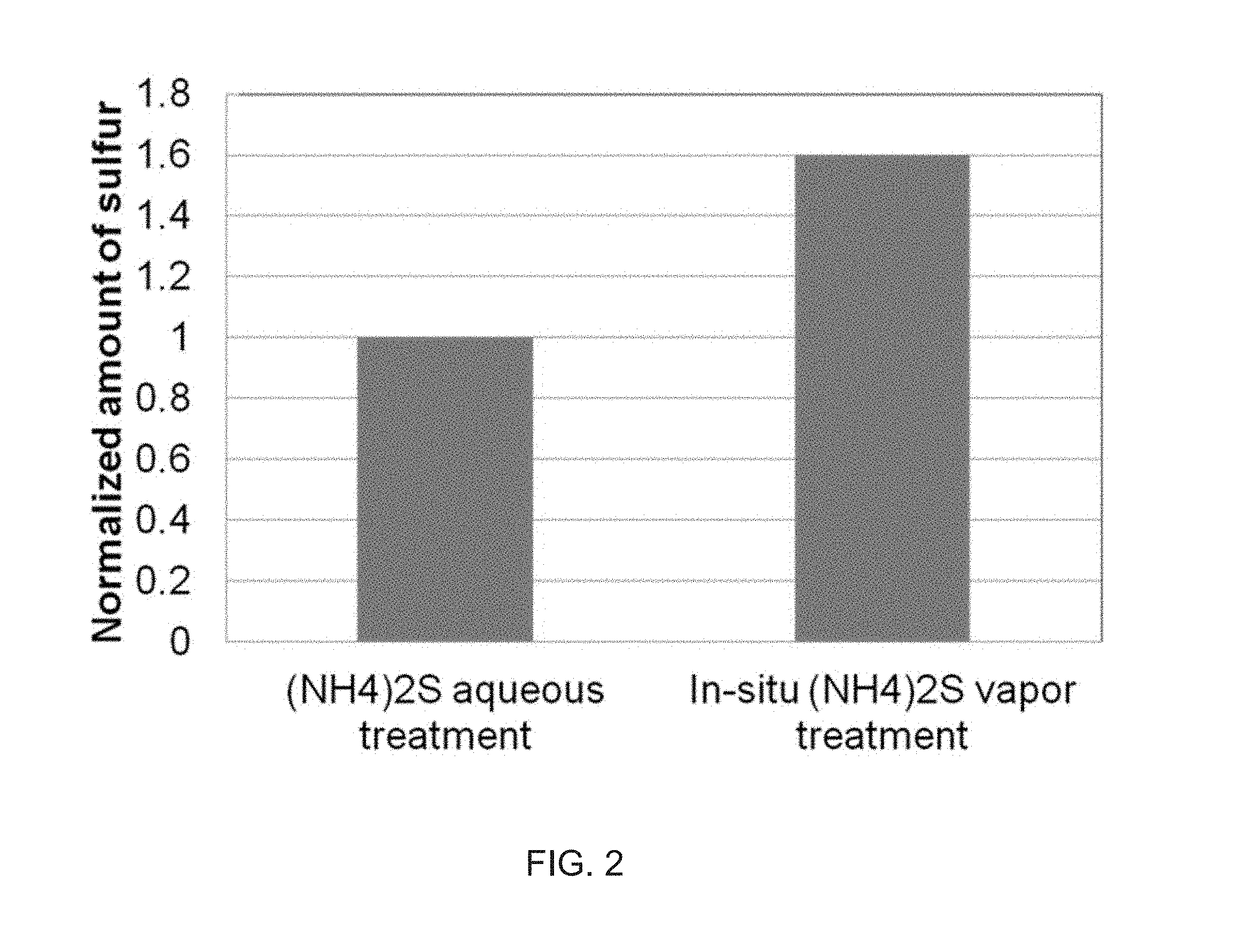
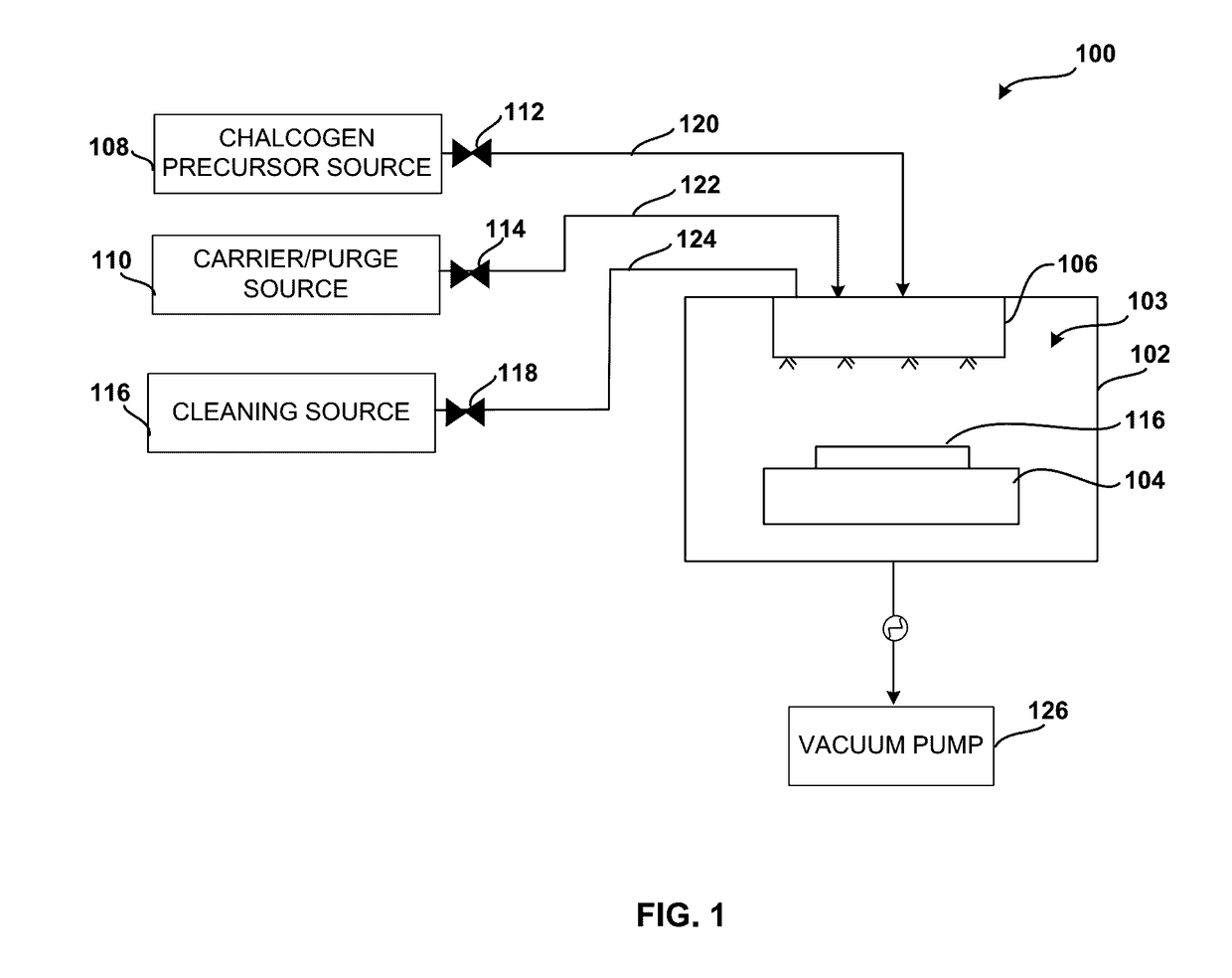
System and method for gas-phase sulfur passivation of a semiconductor surface
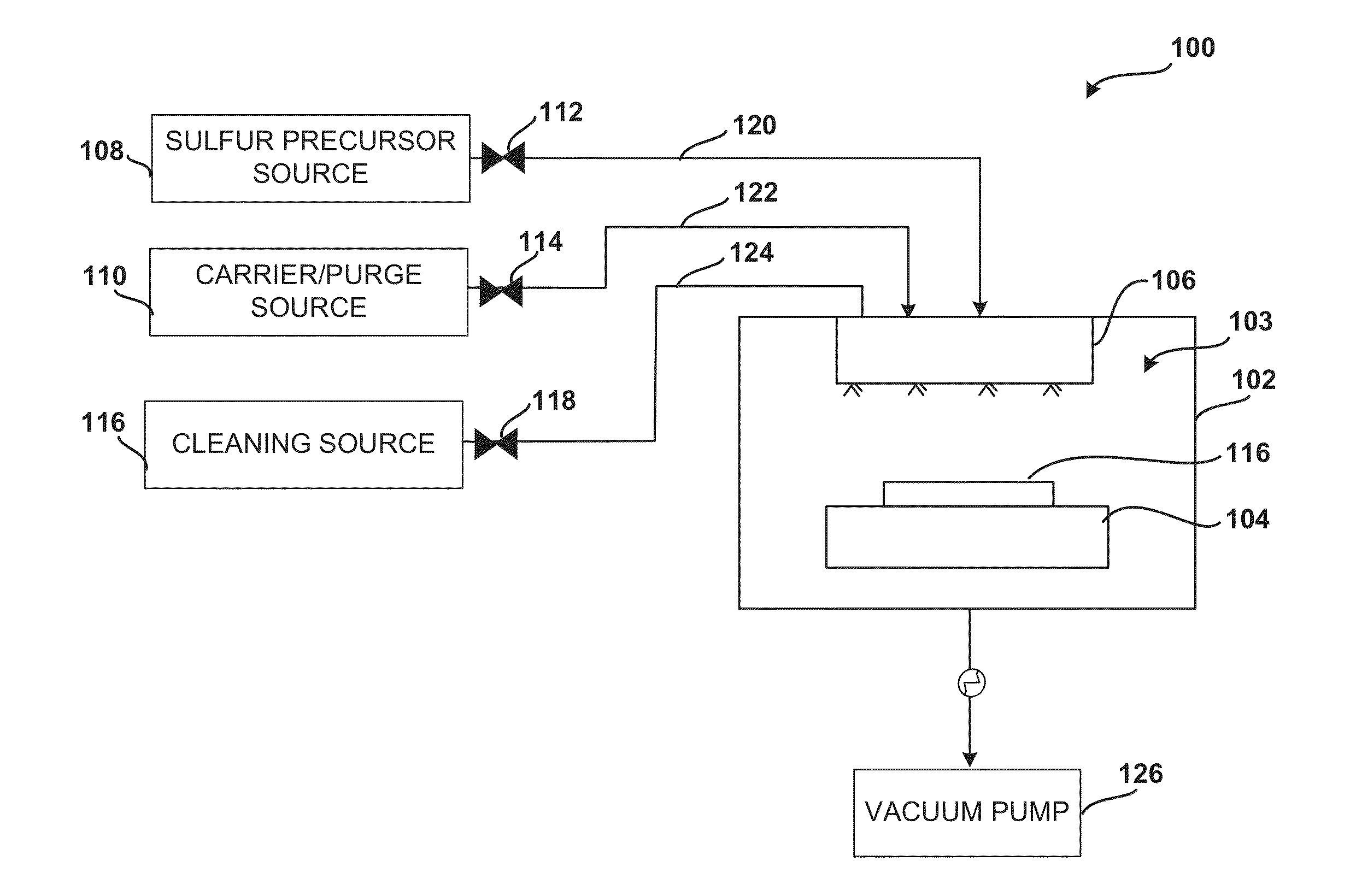
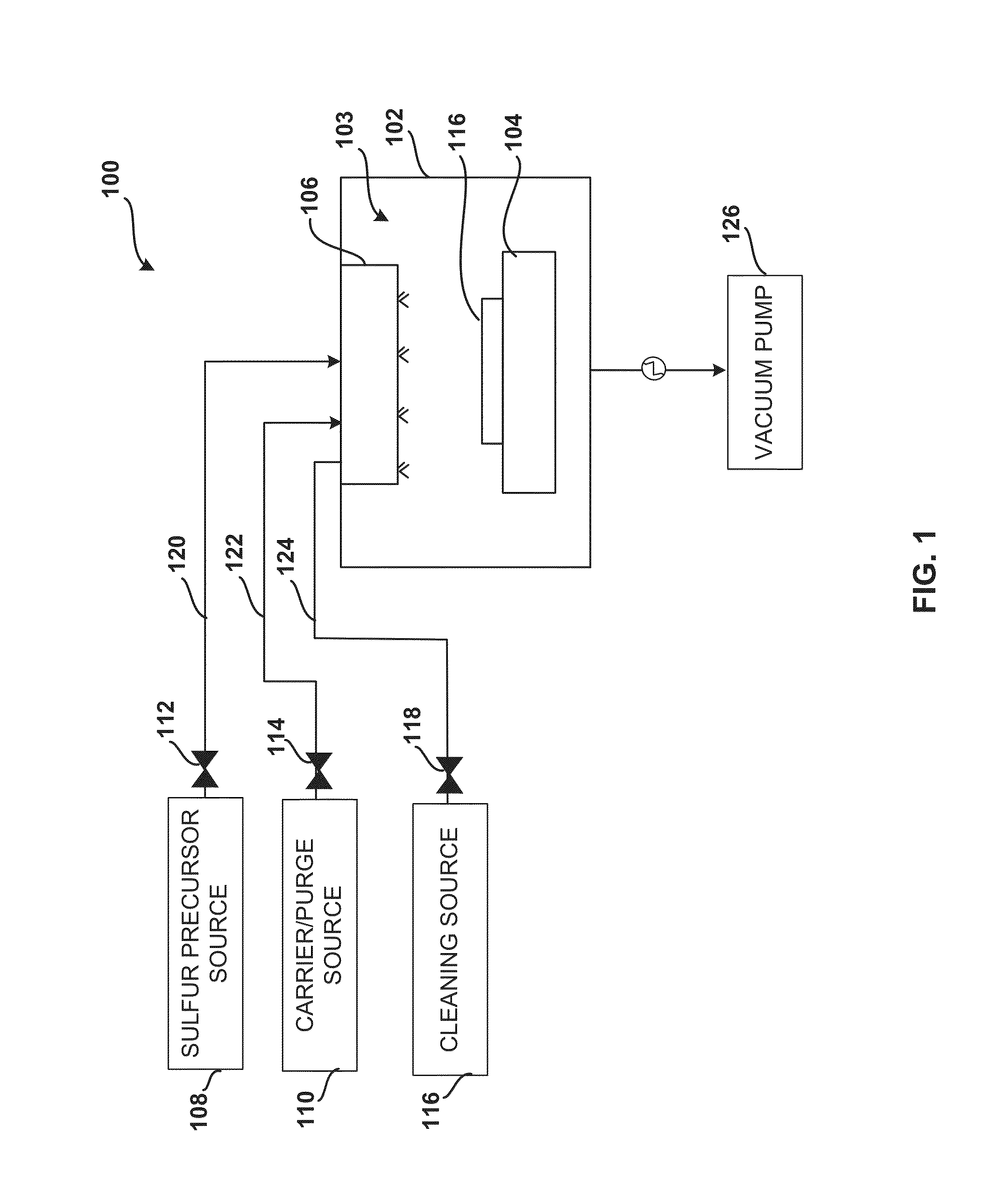
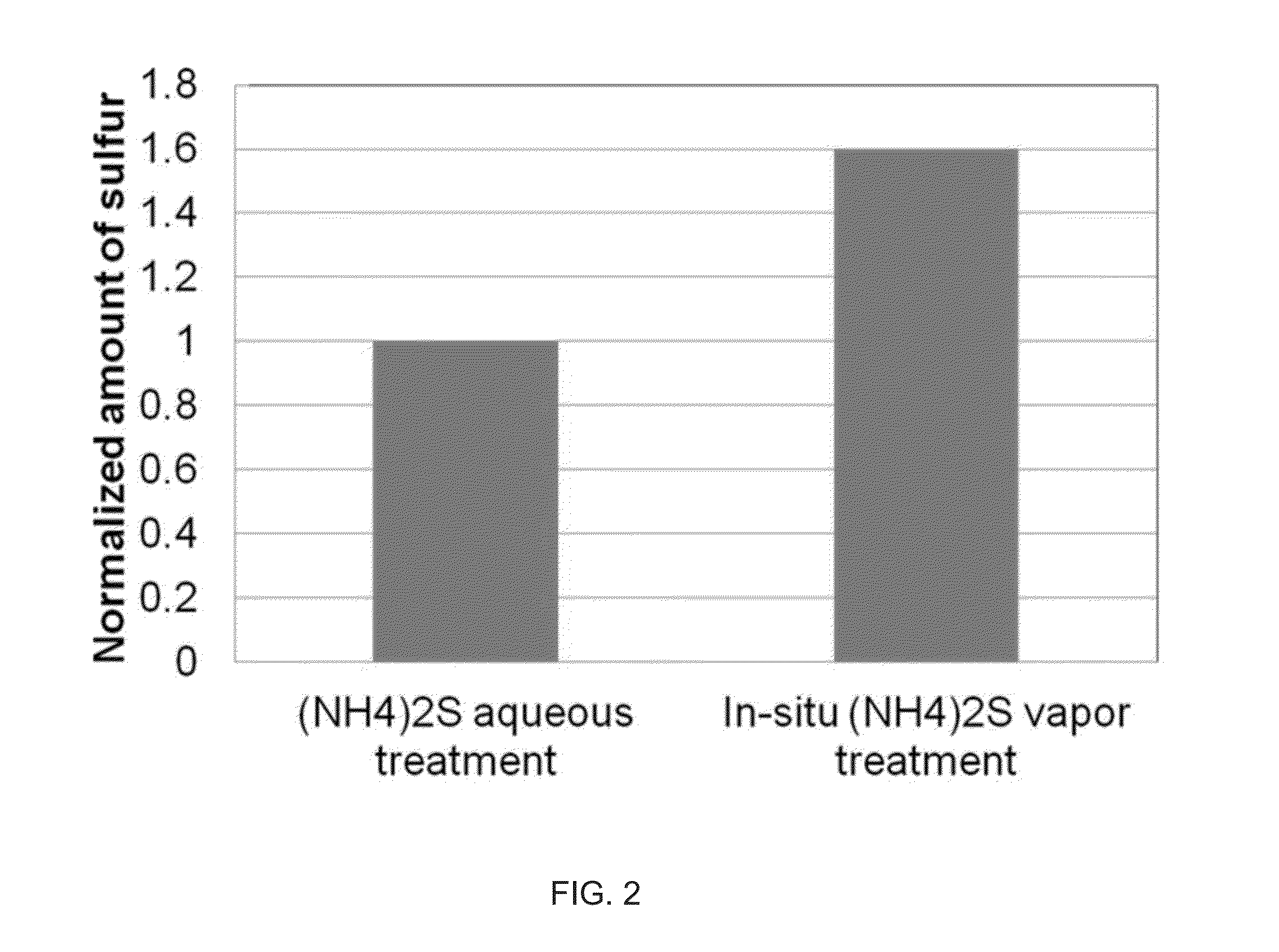
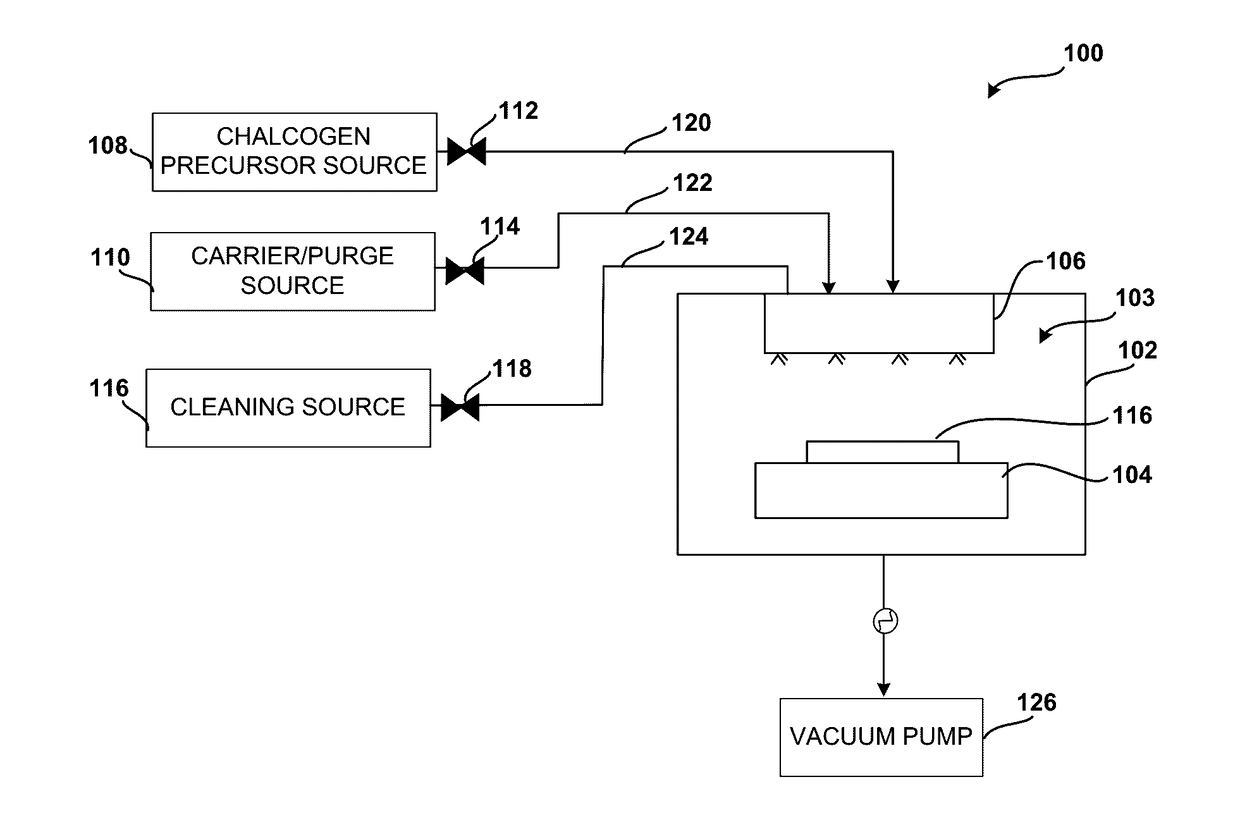
ActiveUS20140027884A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGas phaseDevice form
Improved methods and systems for passivating a surface of a high-mobility semiconductor and structures and devices formed using the methods are disclosed. The method includes providing a high-mobility semiconductor surface to a chamber of a reactor and exposing the high-mobility semiconductor surface to a gas-phase sulfur precursor to passivate the high-mobility semiconductor surface.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
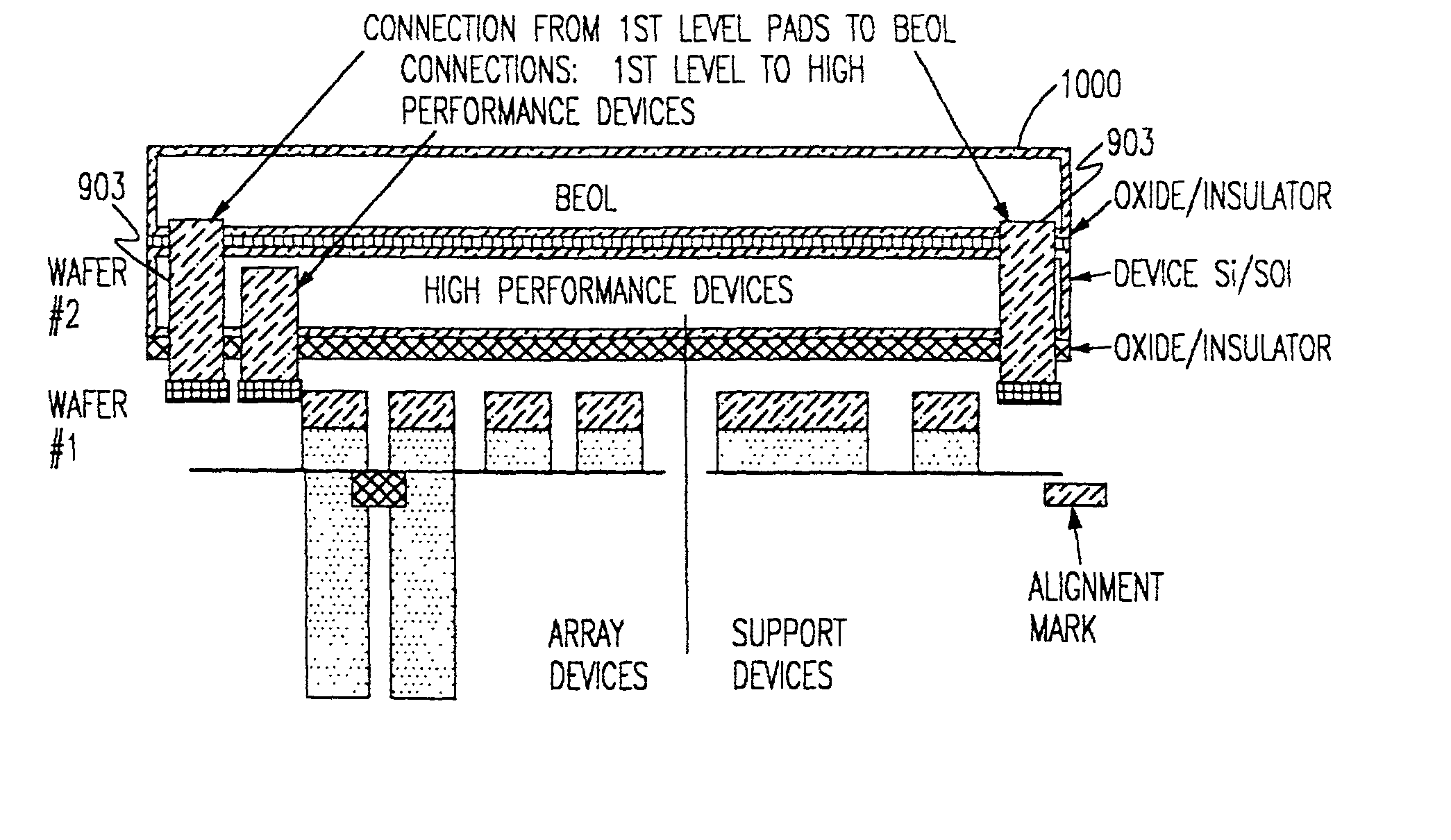
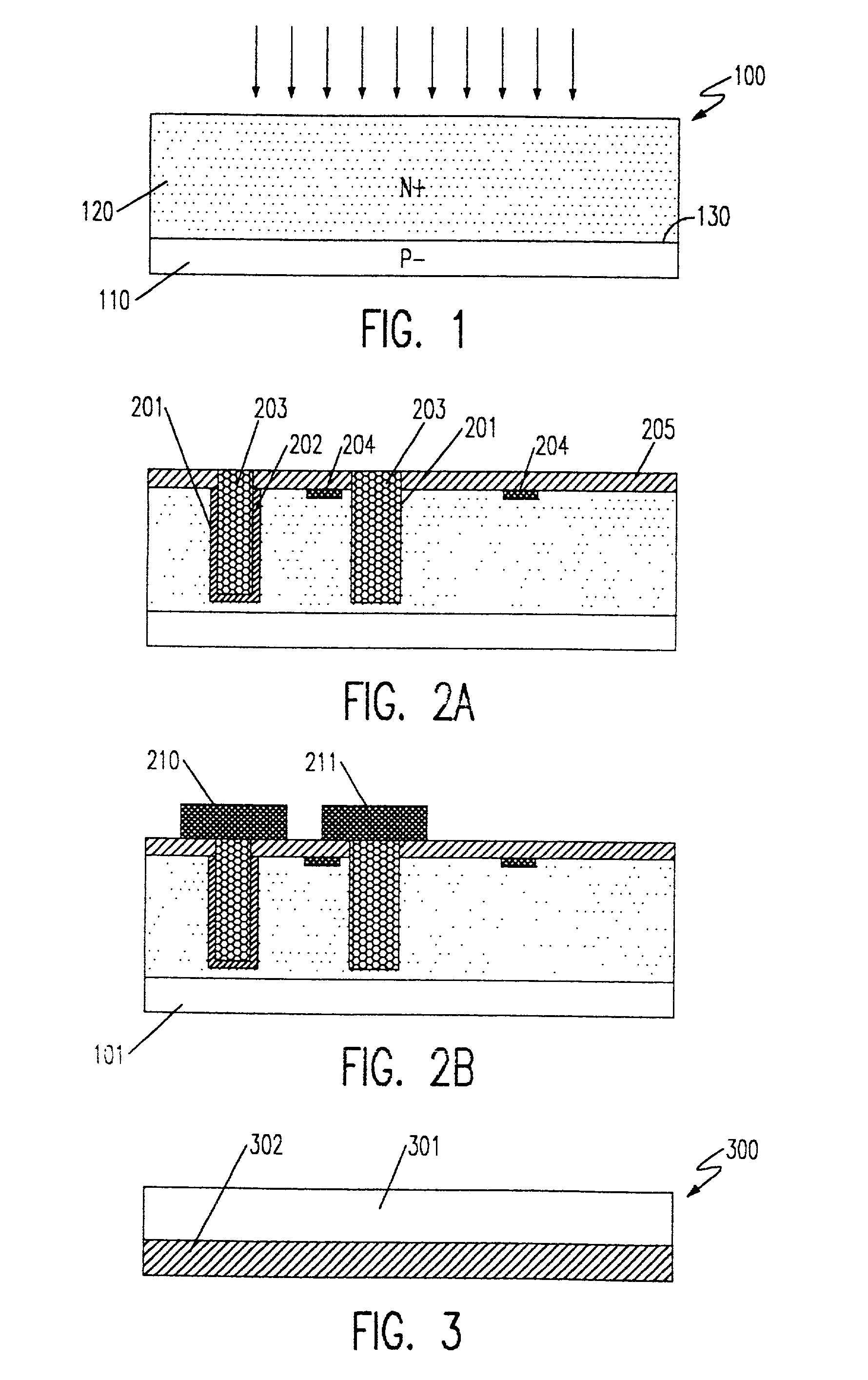
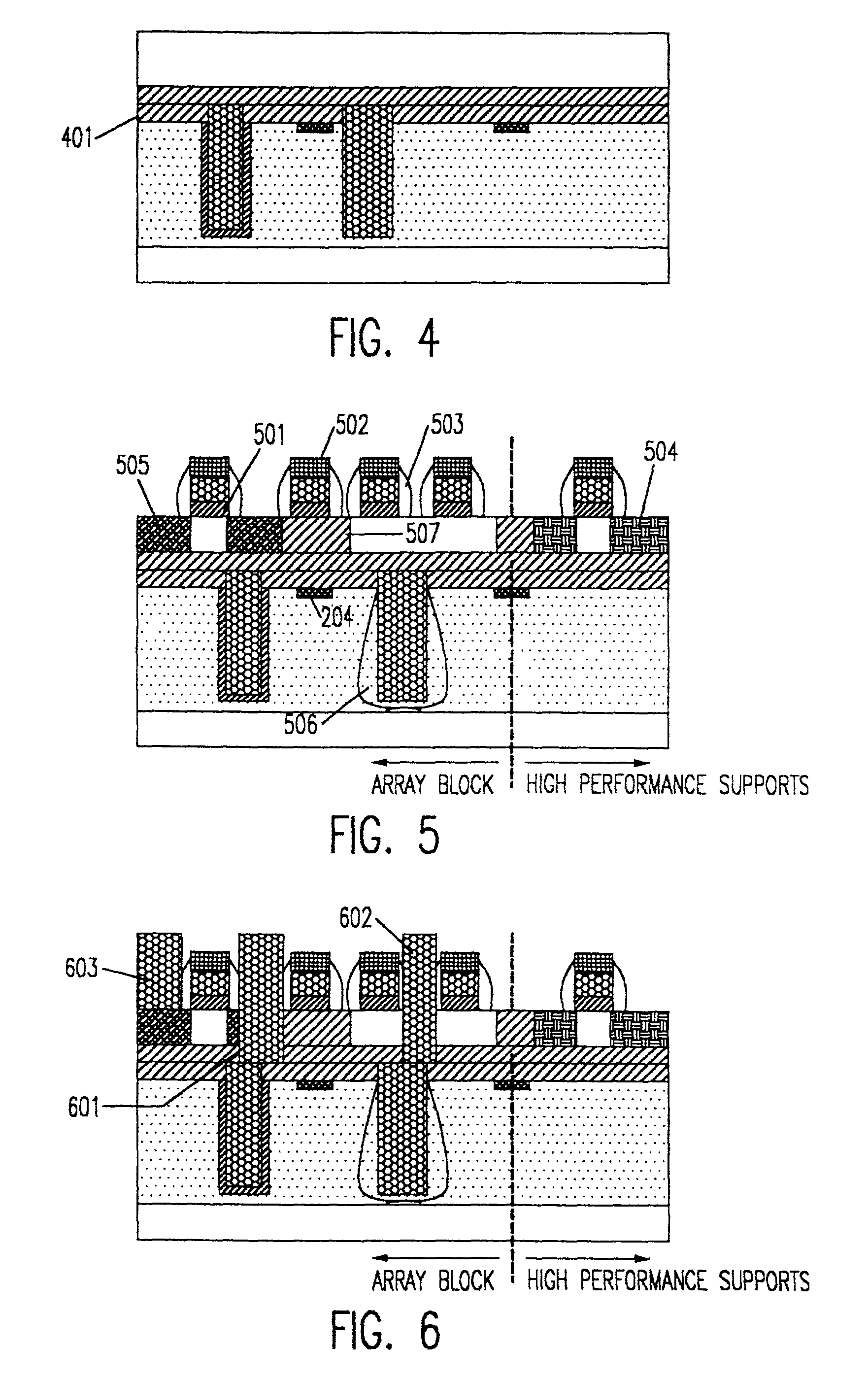
SOI stacked DRAM logic
A composite, layered, integrated circuit formed by bonding of insulator layers on wafers provides for combination of otherwise incompatible technologies such as trench capacitor DRAM arrays and high performance, low power, low voltage silicon on insulator (SOI) switching transistors and short signal propagation paths between devices formed on respective wafer layers of a chip. In preferred embodiments, an SOI wafer is formed by hydrophilic bonding of a wafer over an integrated circuit device and then cleaving a layer of the second wafer away using implanted hydrogen and low temperature heat treatment. Further wafers of various structures and compositions may be bonded thereover and connections between circuit elements and connection pads in respective wafers made using short vias that provide fast signal propagation as well as providing more numerous connections than can be provided on chip edges.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Substrate heat treatment apparatus
A substrate heat treatment apparatus includes a heat-treating plate having a flat upper surface, support devices formed of a heat-resistant resin for contacting and supporting a substrate, a seal device disposed annularly for rendering gastight a space formed between the substrate and heat-treating plate, and exhaust bores for exhausting gas from the space. The support devices are formed of resin, and the upper surface of the heat-treating plate is made flat, whereby a reduced difference in the rate of heat transfer occurs between contact parts and non-contact parts on the surface of the substrate. Consequently, the substrate is heat-treated effectively while suppressing variations in heat history over the surface of the substrate.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
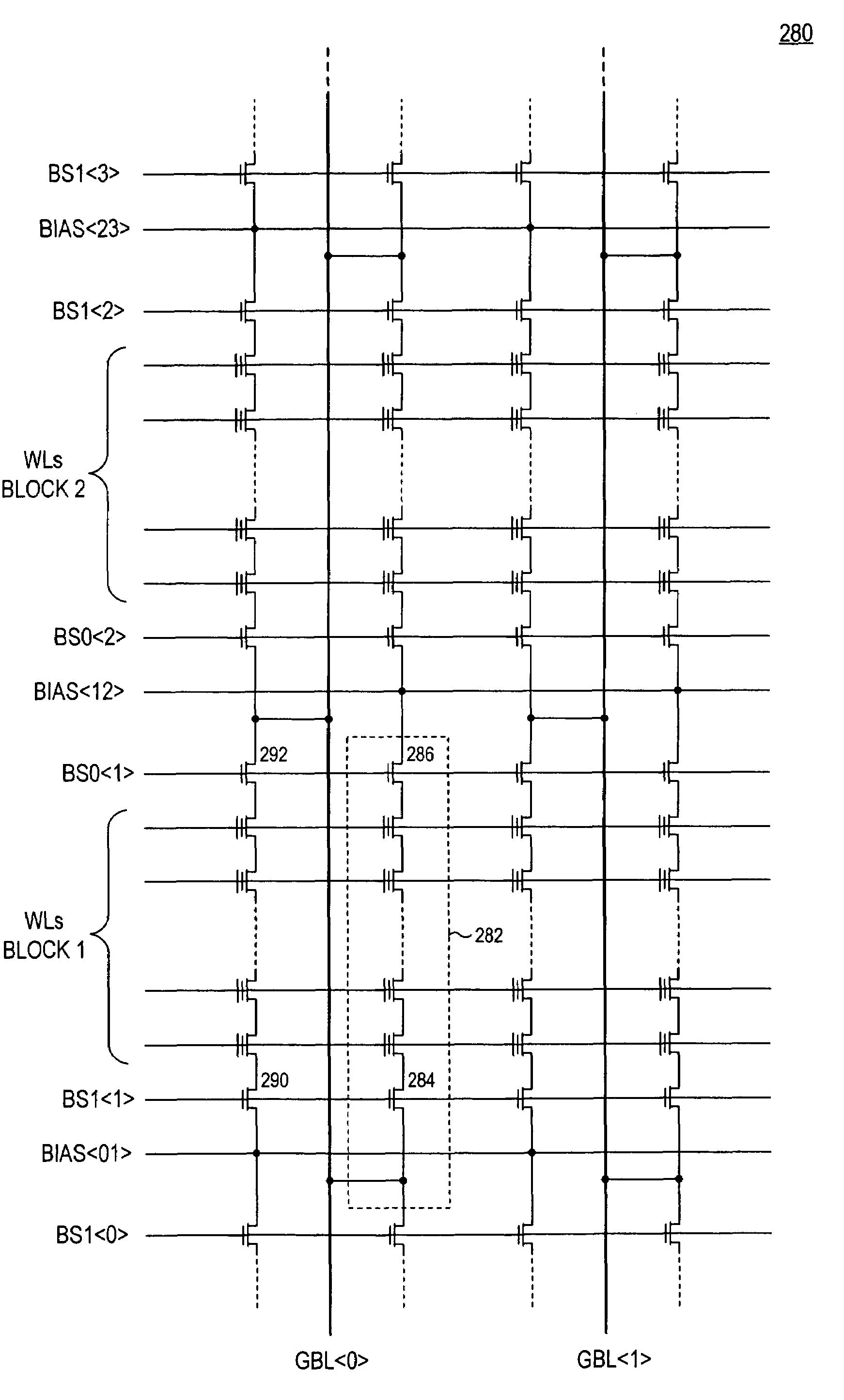
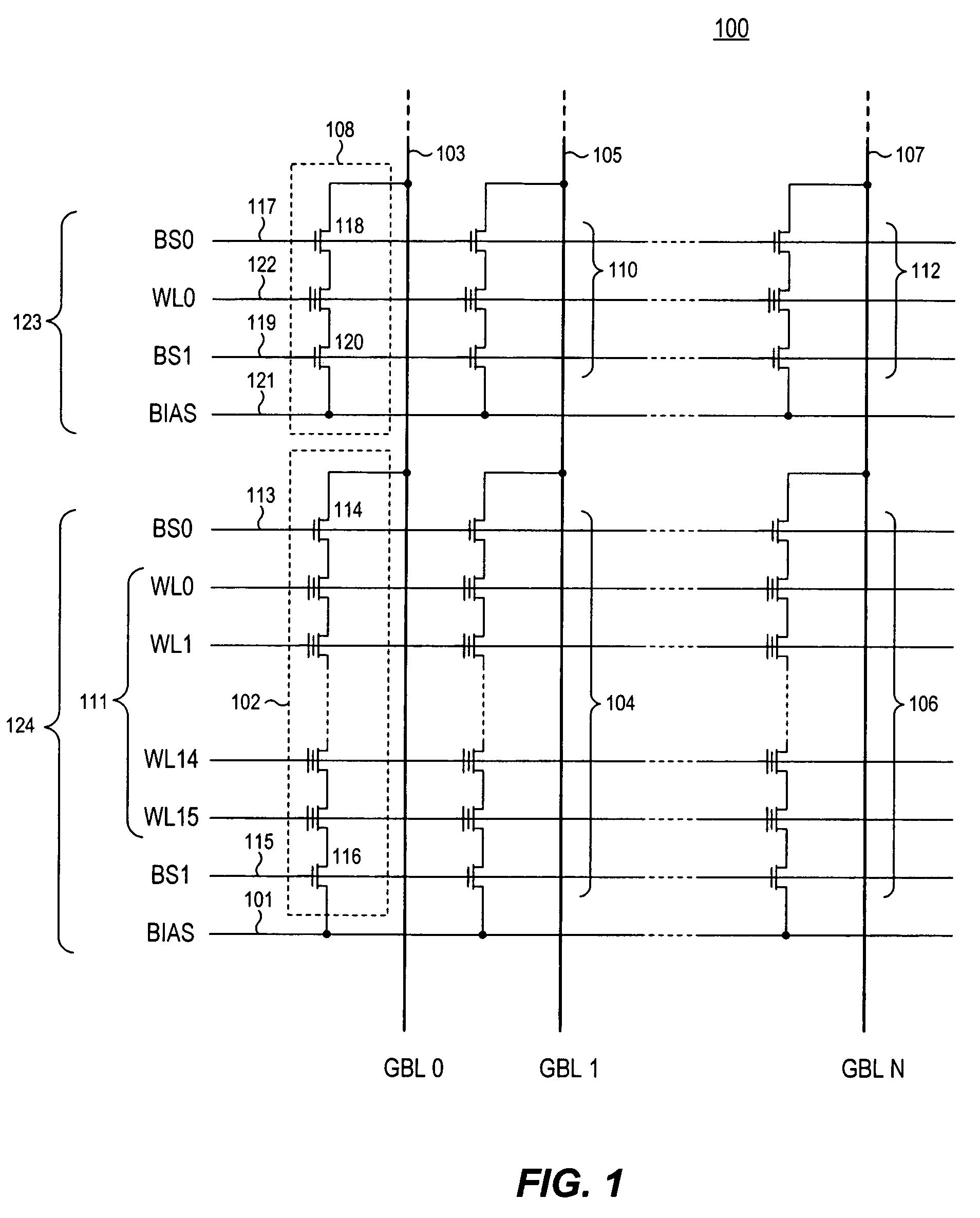
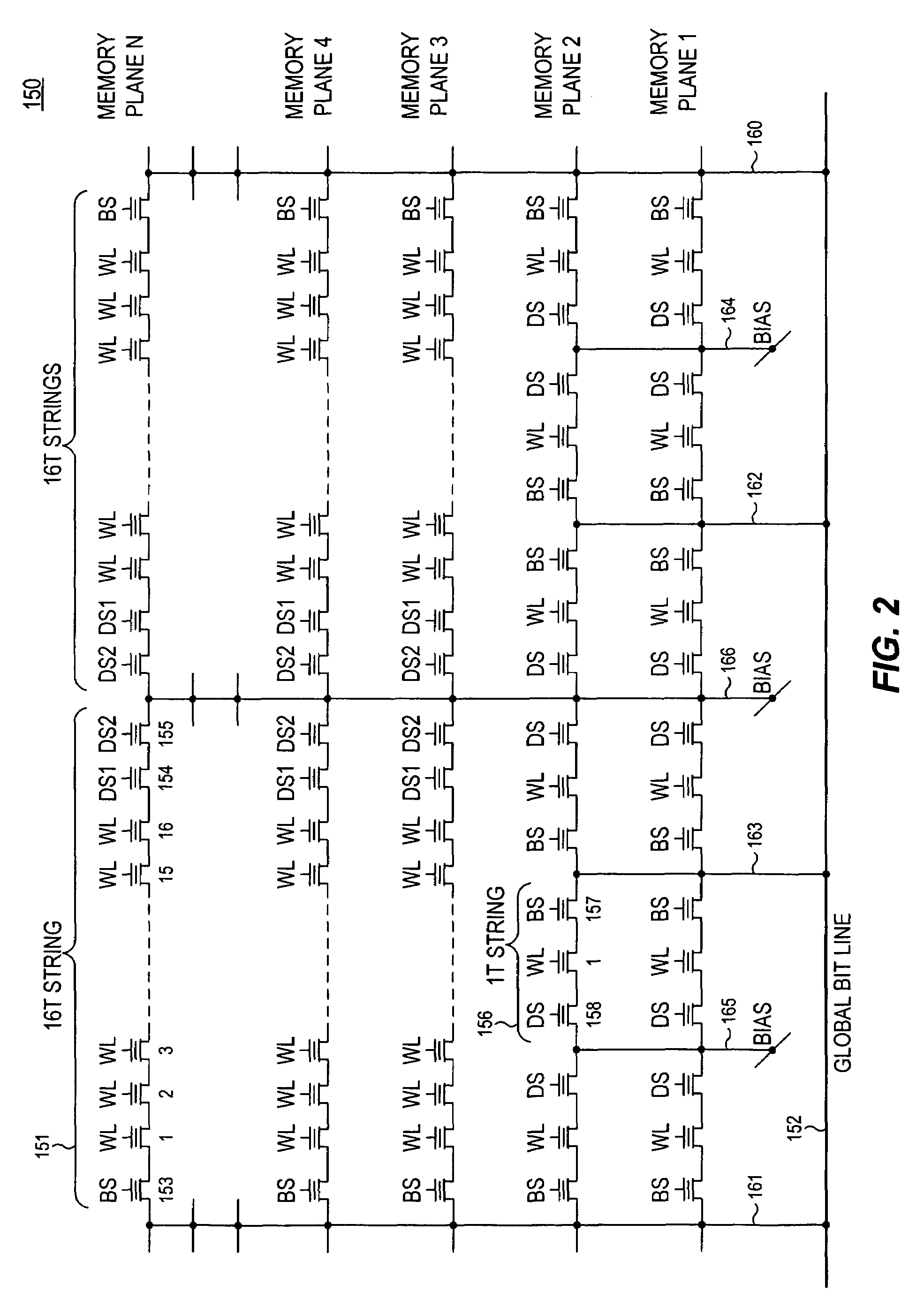
Integrated circuit including memory array incorporating multiple types of NAND string structures
ActiveUS7177191B2High densityGood flexibilitySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDevice formParallel computing
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
CMOS devices with a single work function gate electrode and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20070090416A1Lower threshold voltageEasy to manufactureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSDevice form
Described herein are a device utilizing a gate electrode material with a single work function for both the pMOS and nMOS transistors where the magnitude of the transistor threshold voltages is modified by semiconductor band engineering and article made thereby. Further described herein are methods of fabricating a device formed of complementary (pMOS and nMOS) transistors having semiconductor channel regions which have been band gap engineered to achieve a low threshold voltage.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
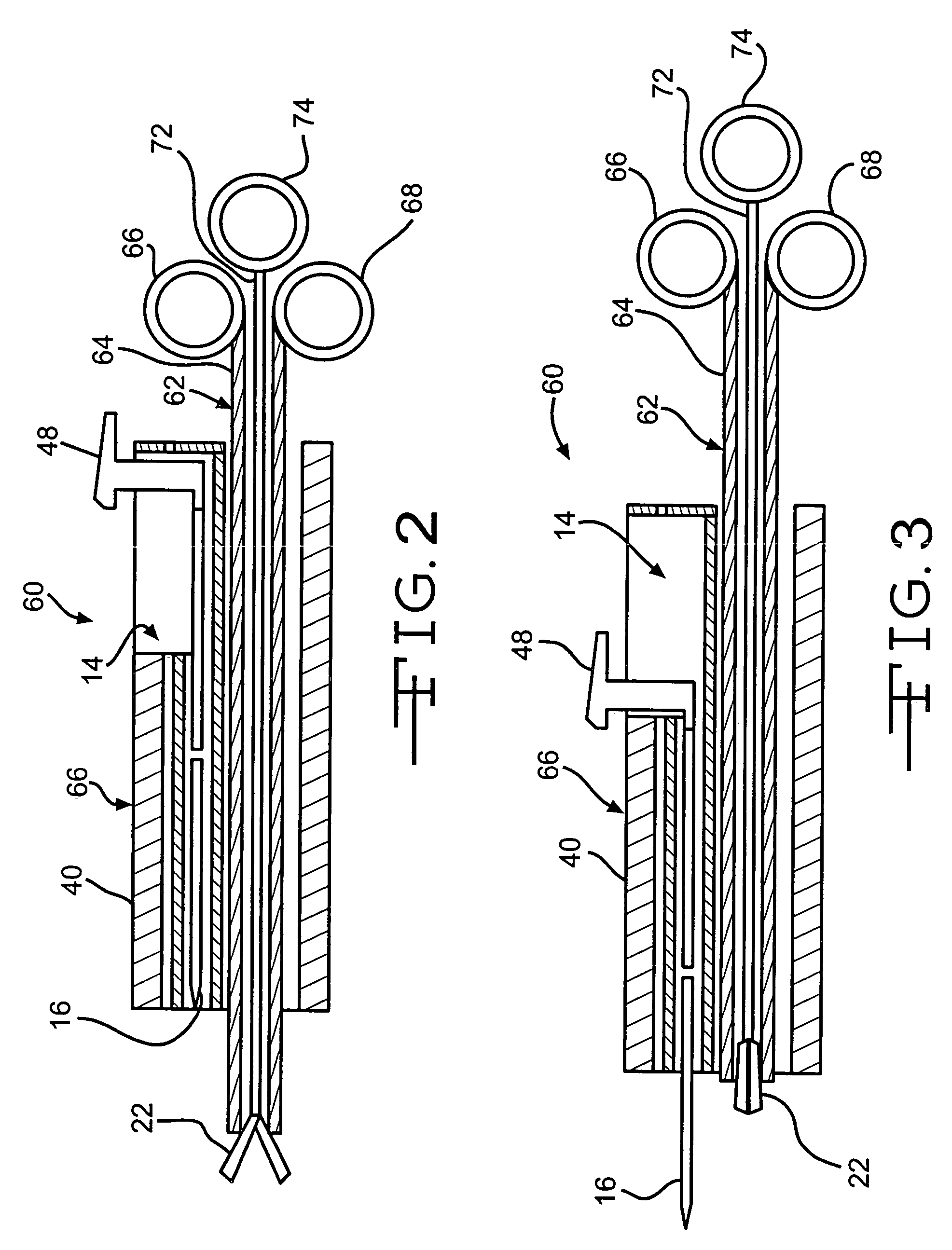
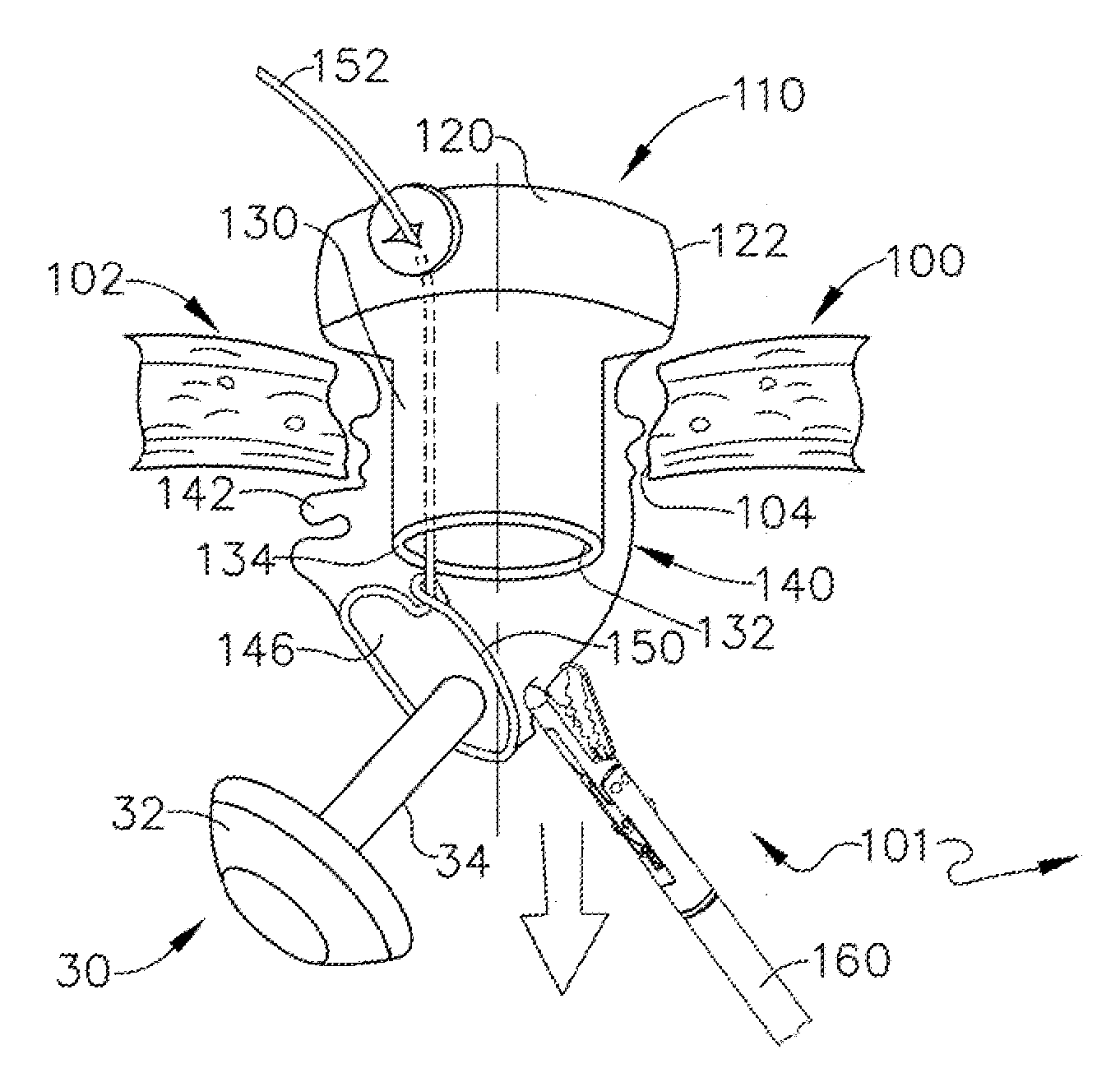
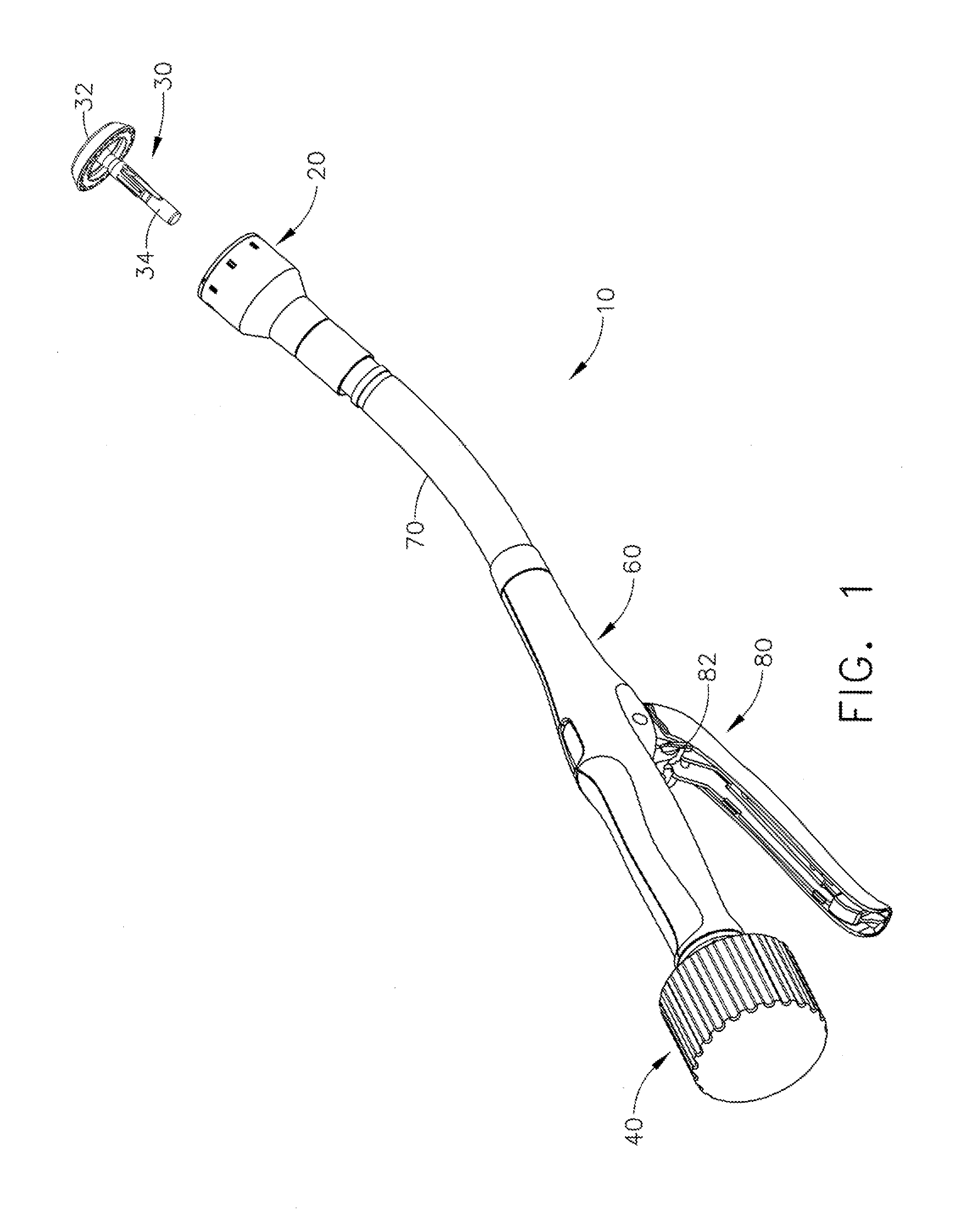
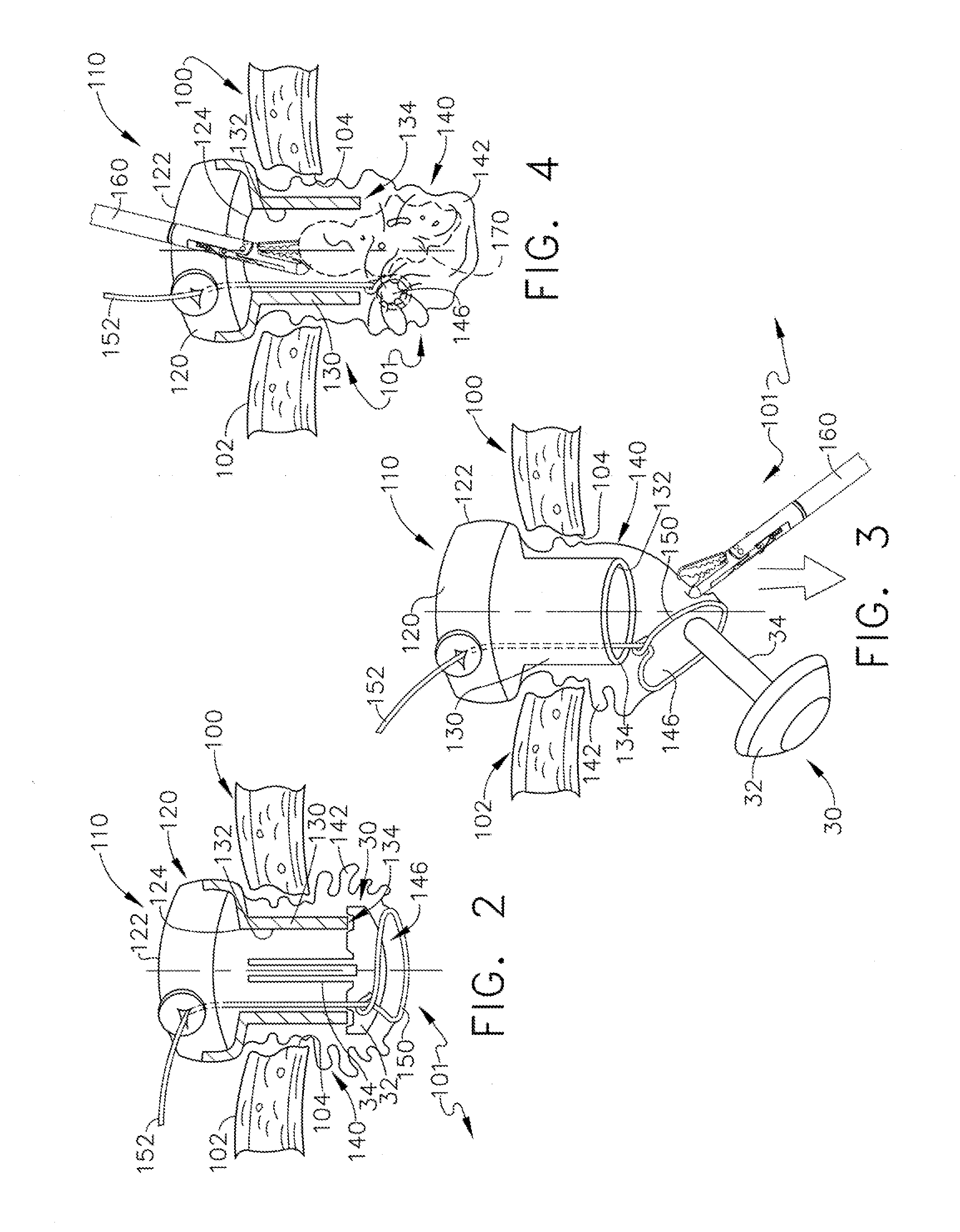
Device and method for intralumenal anastomosis
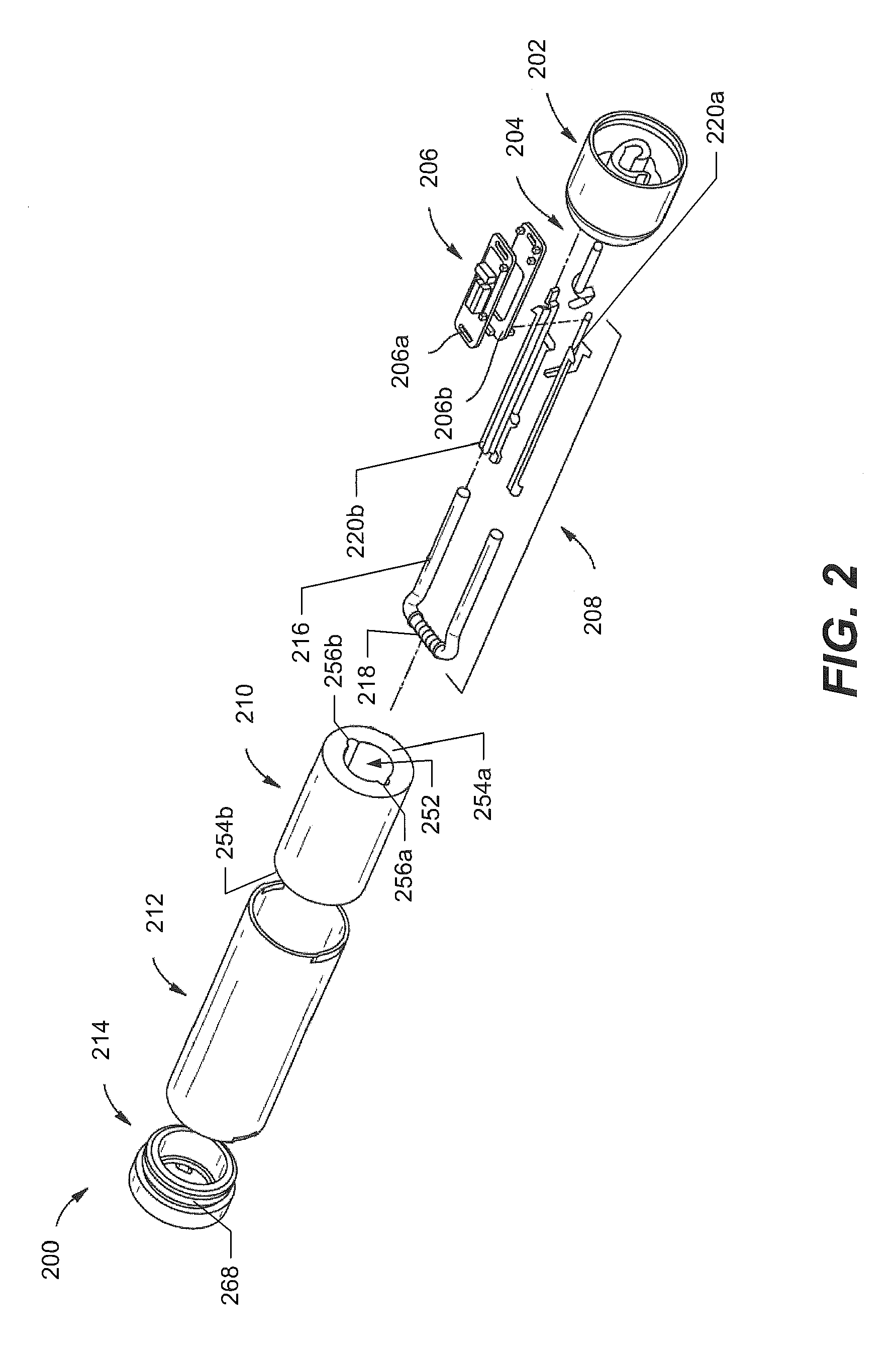
An anastomosis device formed from a Shape Memory Alloy (SME) wire that is annealed into a tight coil (e.g., flat coil, helical coil, cylindrical coil) that is subsequently substantially straightened (e.g., straight, longitudinally stretched spring-like shape) for being constrained within an elongate member of an anastomosis introducer instrument. After positioning and holding two tissue walls of adjacent lumens into apposition with a distally presented grasper of the instrument, a piercing tip of the anastomosis device is dispensed and inserted through the tissue walls before being allowed to relax to its tight coil shape, thereby forming the anastomosis attachment. The anastomosis device is released from the anastomosis introducer instrument, such as by fully dispensing its proximal end. Thereby, efficient single lumen anastomosis of gastrointestinal, bilatory, or other vessels may be achieved with a minimum of laparoscopic punctures, or perhaps performed fully as an endoscopic procedure.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
System and method for gas-phase sulfur passivation of a semiconductor surface
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
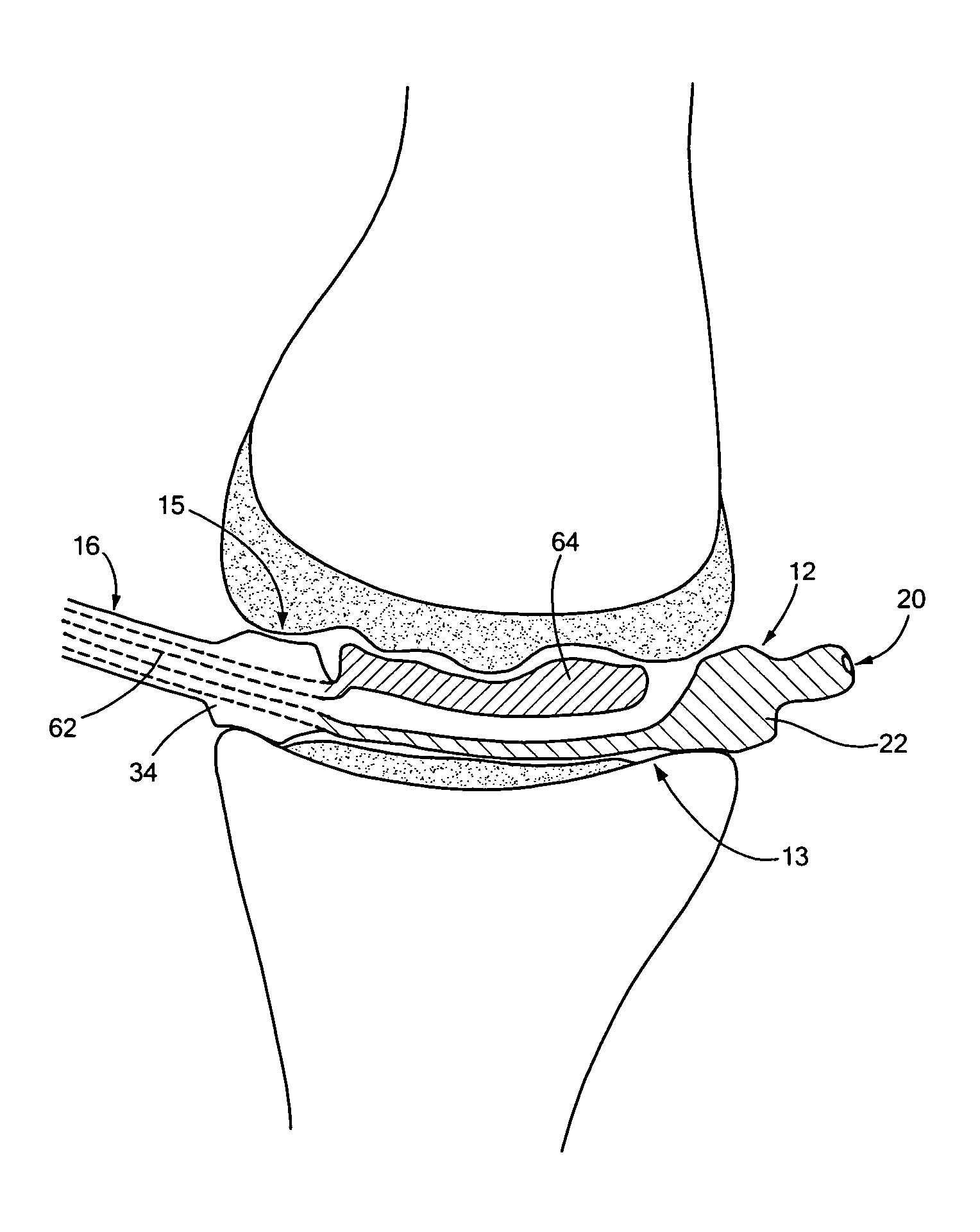
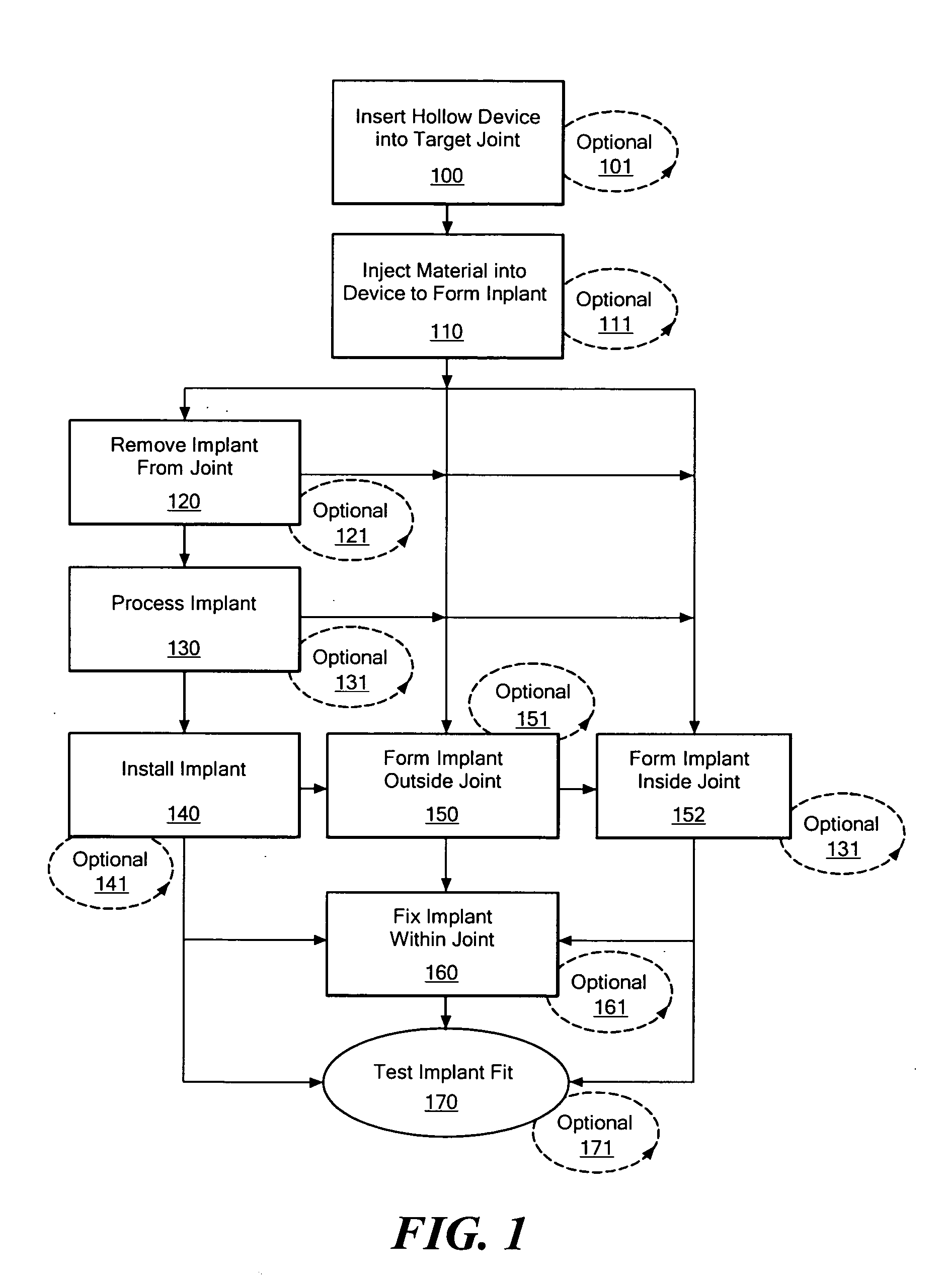
Joint arthroplasty devices formed in situ
InactiveUS20070250169A1Improve accuracyImage analysisWrist jointsArticular surfacesJoint arthroplasty
Disclosed herein are methods and devices for repairing articular surfaces. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function.
Owner:CONFORMIS
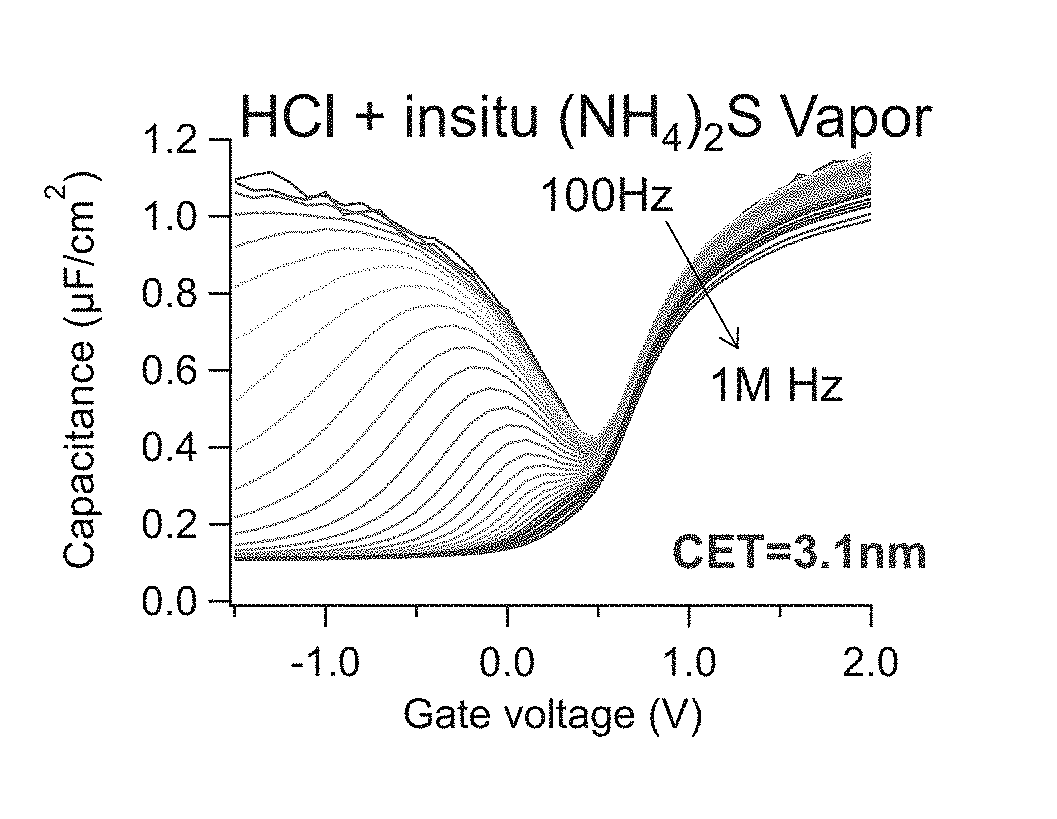
System and method for gas-phase passivation of a semiconductor surface
Improved methods and systems for passivating a surface of a high-mobility semiconductor and structures and devices formed using the methods are disclosed. The method includes providing a high-mobility semiconductor surface to a chamber of a reactor and exposing the high-mobility semiconductor surface to a gas-phase chalcogen precursor to passivate the high-mobility semiconductor surface.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
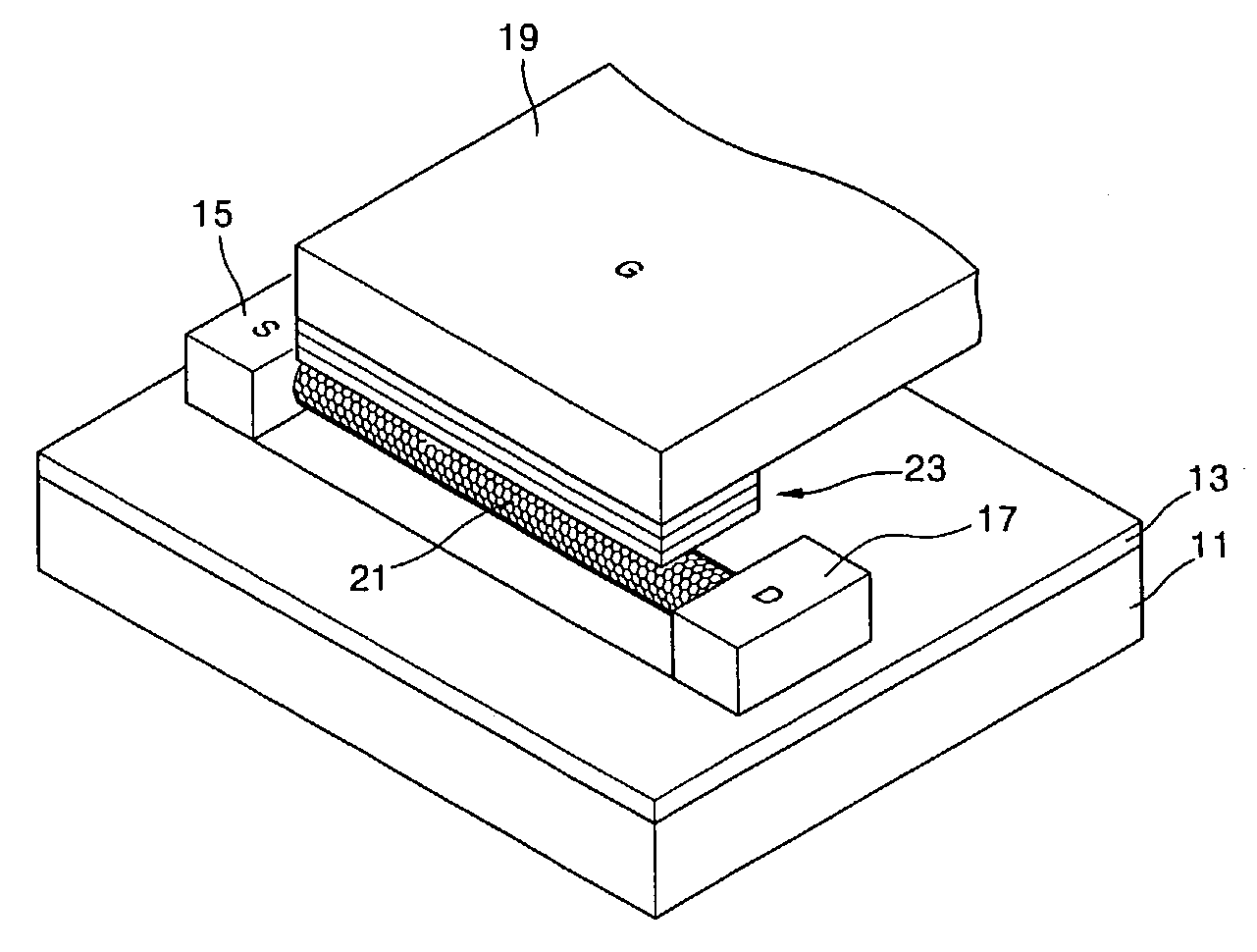
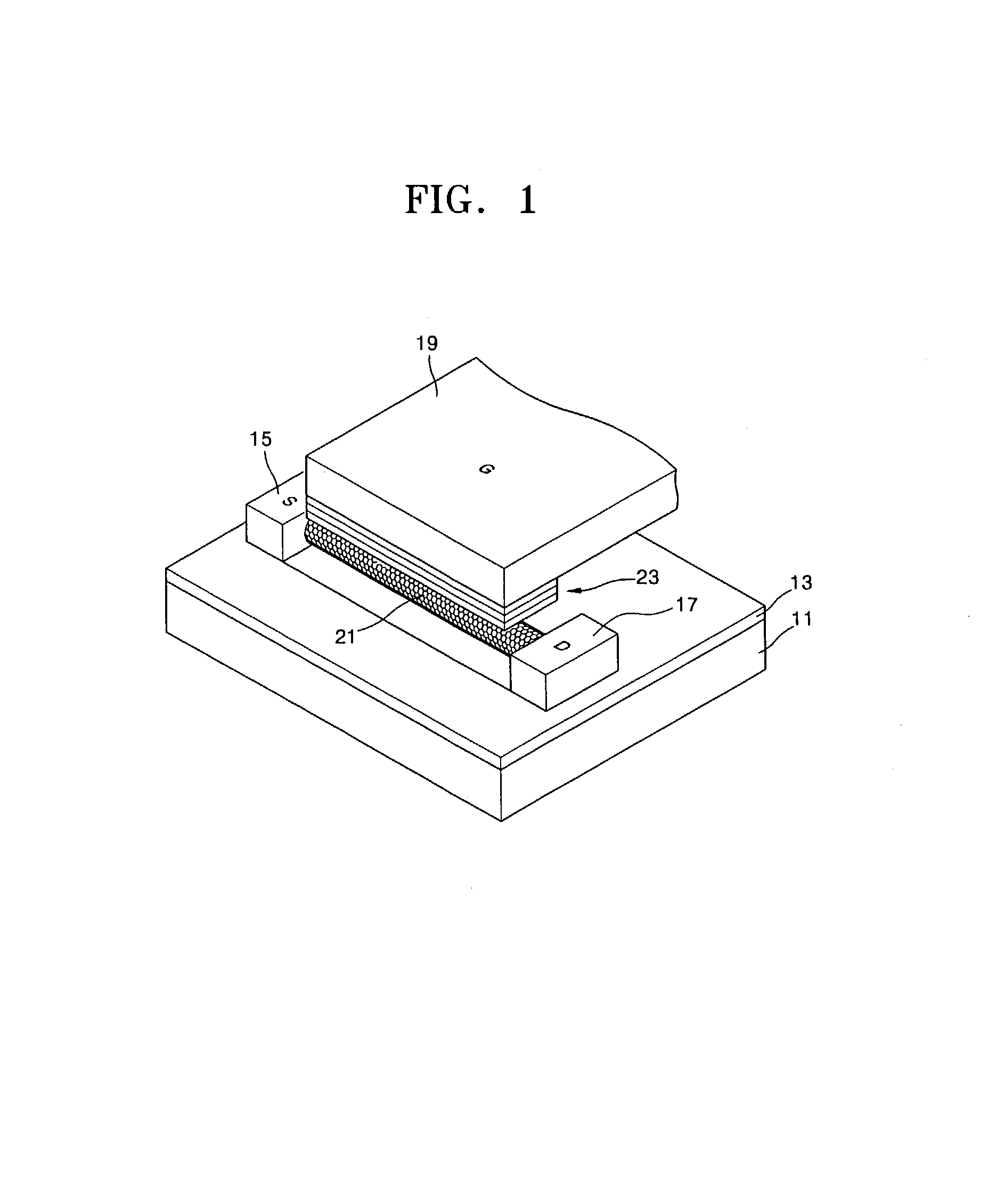
Focused ultrasound system for surrounding a body tissue mass
ActiveUS20060058678A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorDevice form
A focused ultrasound system includes an ultrasound transducer device forming an opening, and having a plurality of transducer elements positioned at least partially around the opening. A focused ultrasound system includes a structure having a first end for allowing an object to be inserted and a second end for allowing the object to exit, and a plurality of transducer elements coupled to the structure, the transducer elements located relative to each other in a formation that at least partially define an opening, wherein the transducer elements are configured to emit acoustic energy that converges at a focal zone.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6867247B2Reduce probabilityHigh porositySuture equipmentsStentsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
System and method for gas-phase passivation of a semiconductor surface
ActiveUS20170117202A1Low Dit valueSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGas phaseDevice form
Improved methods and systems for passivating a surface of a high-mobility semiconductor and structures and devices formed using the methods are disclosed. The method includes providing a high-mobility semiconductor surface to a chamber of a reactor and exposing the high-mobility semiconductor surface to a gas-phase chalcogen precursor to passivate the high-mobility semiconductor surface.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
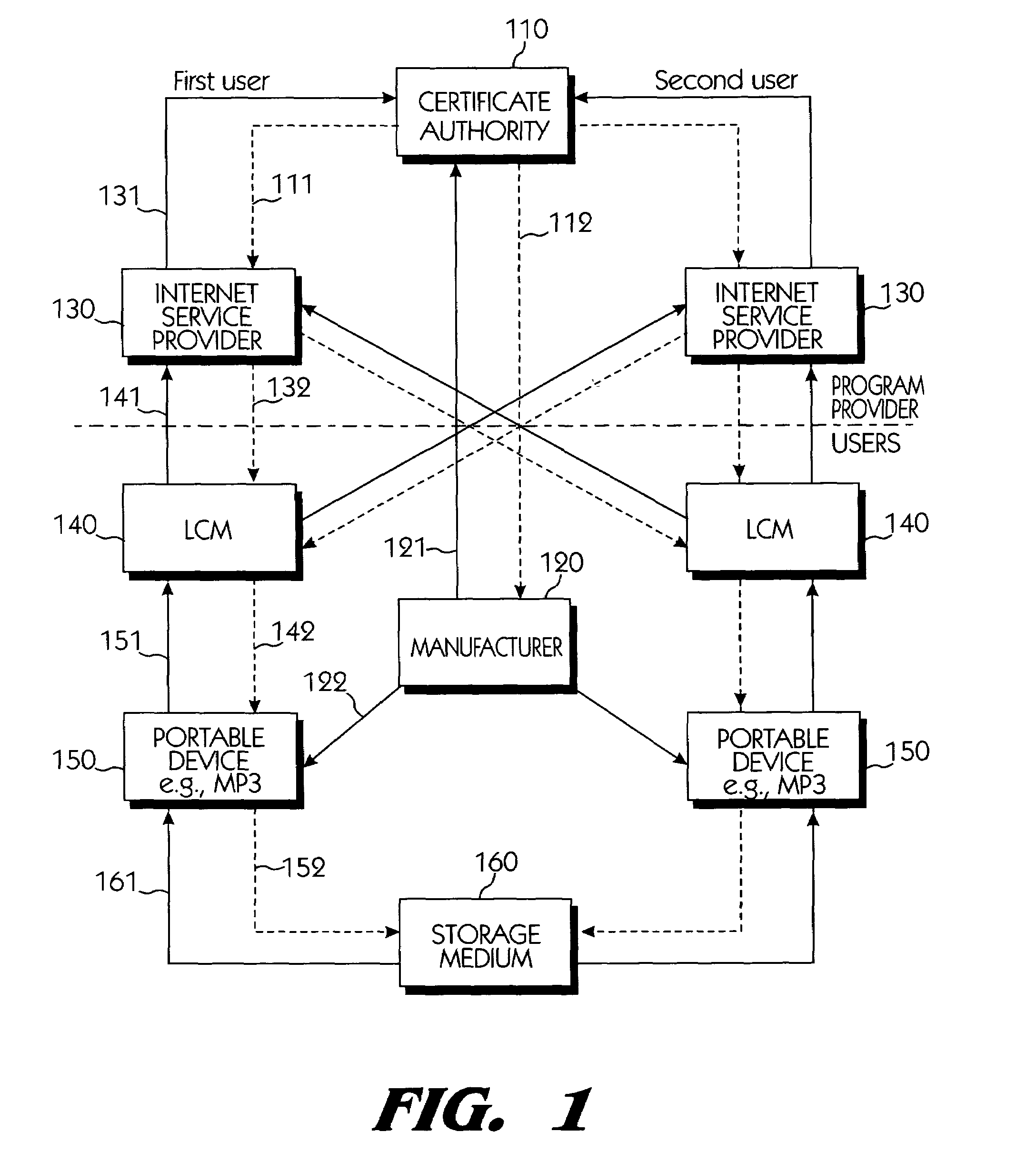
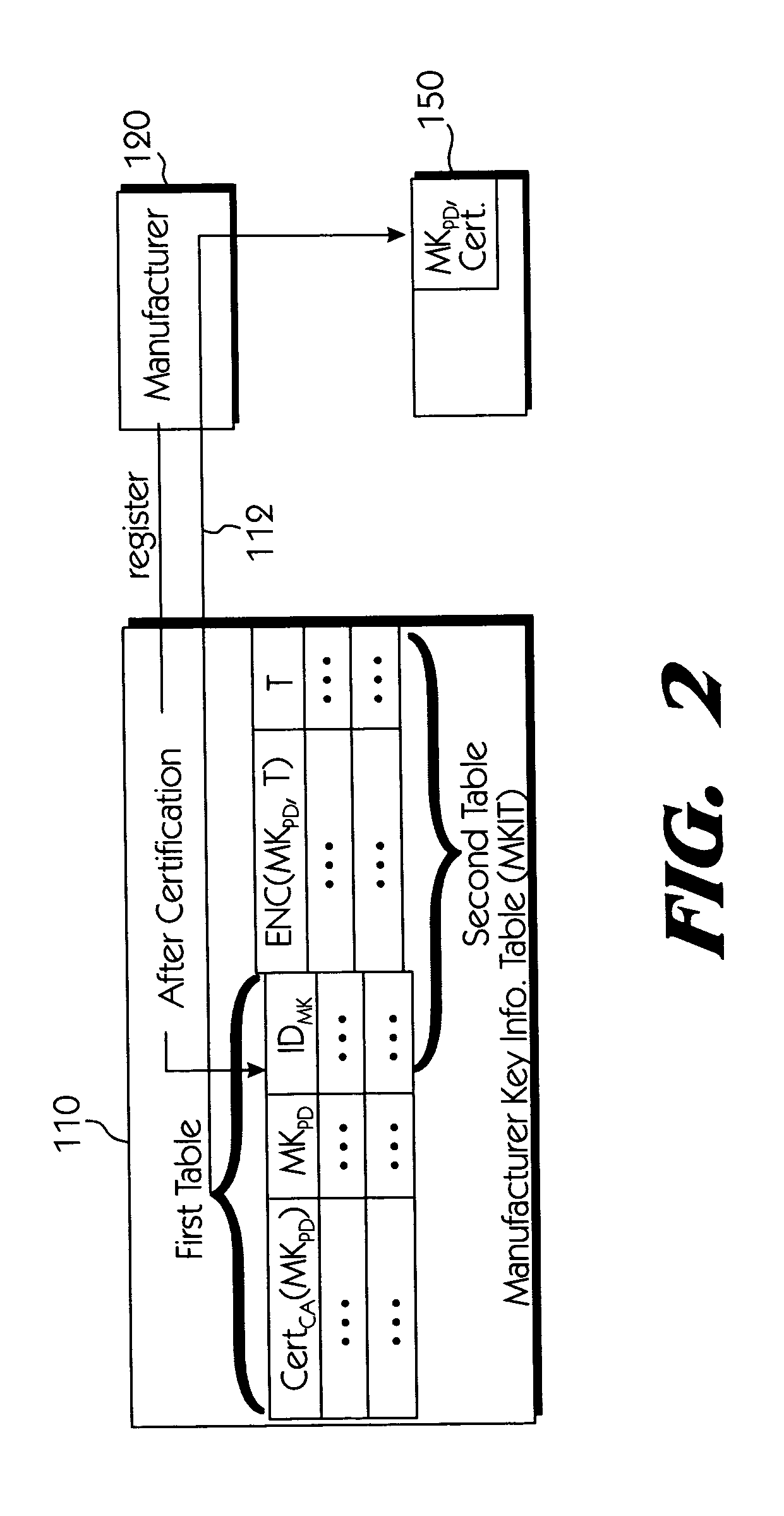
Copy protection system for portable storage media
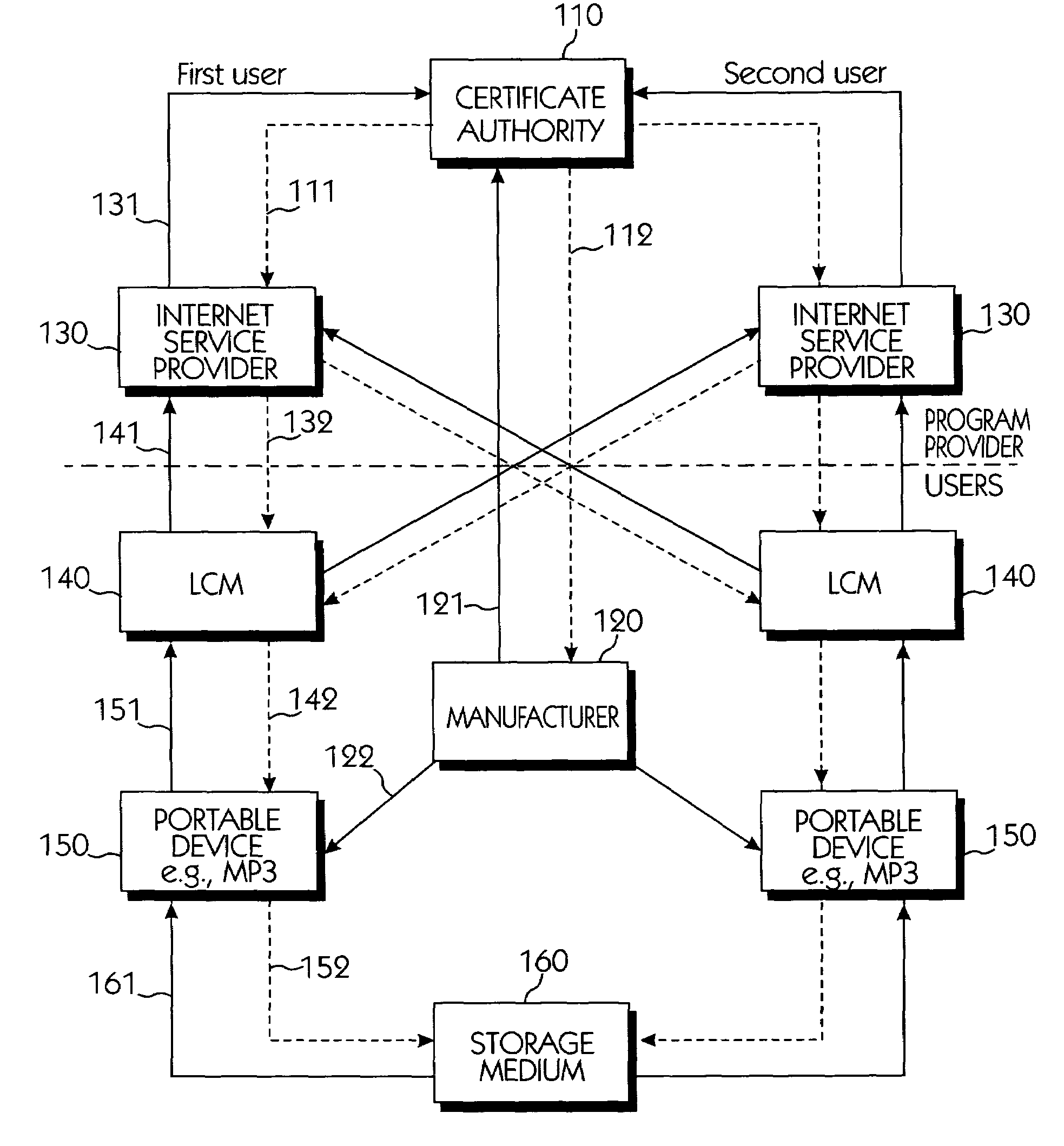
InactiveUS6950941B1Limited abilityKey distribution for secure communicationData processing applicationsDevice formDigital content
Systems connected to users generate a plurality of keys which are mutually shared, and download and upload digital contents by using secret channels formed between the systems. An information provider receives an authorization from a certificate authority. A licensed SDMI compliant module (LCM) is authenticated through the information provider, and the information provider and the LCM form a channel. A portable device is authenticated from the information provider through the LCM, and the LCM and the portable device form a channel. The digital content between the LCM and the portable device is downloaded and uploaded according to respective control state data of the LCM and the portable device. The system can use a physical address of a bad sector formed in the portable medium during the manufacturing process for preventing an illegal copy of the downloaded digital contents through the portable device after the digital contents have been downloaded.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
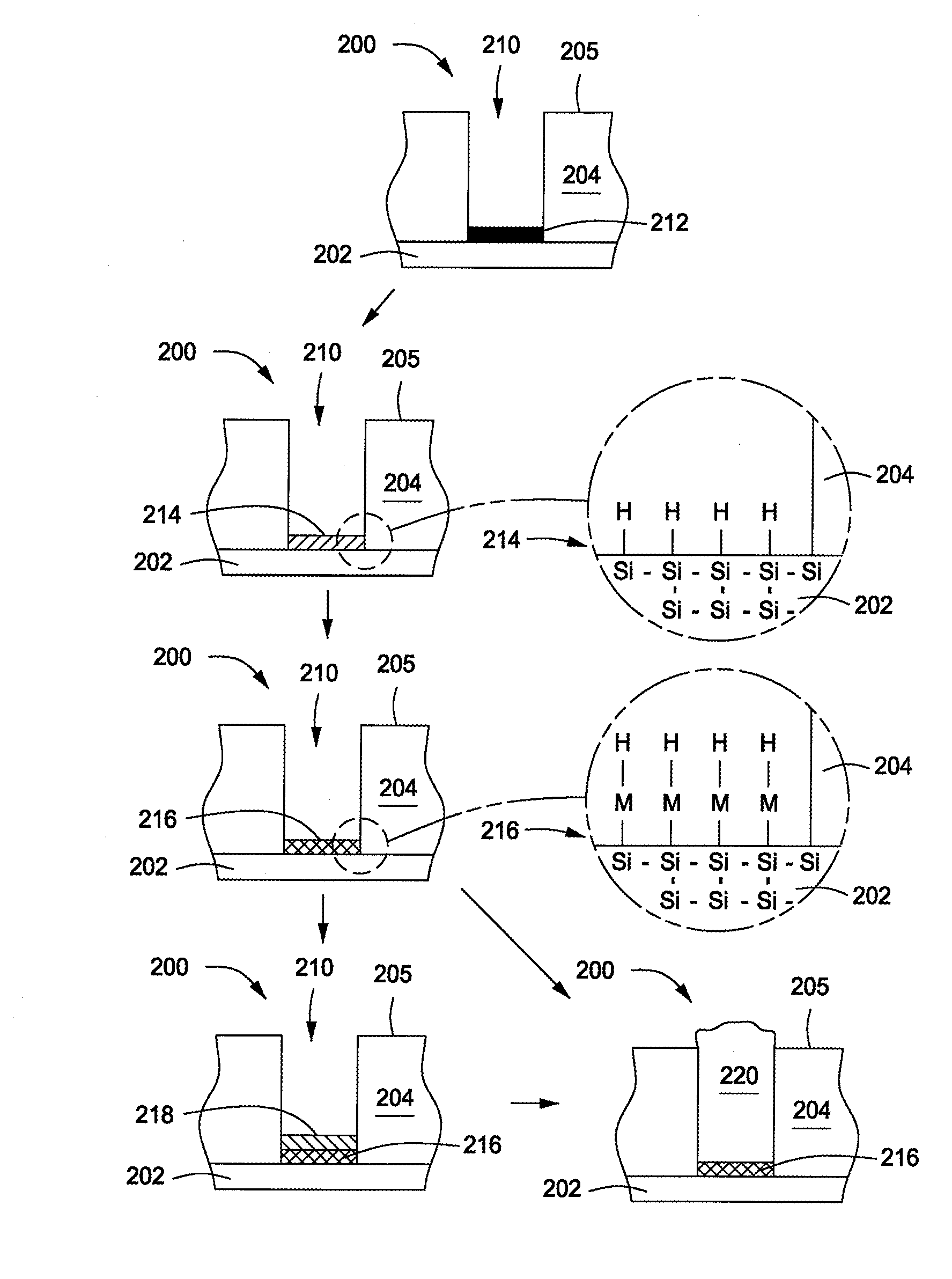
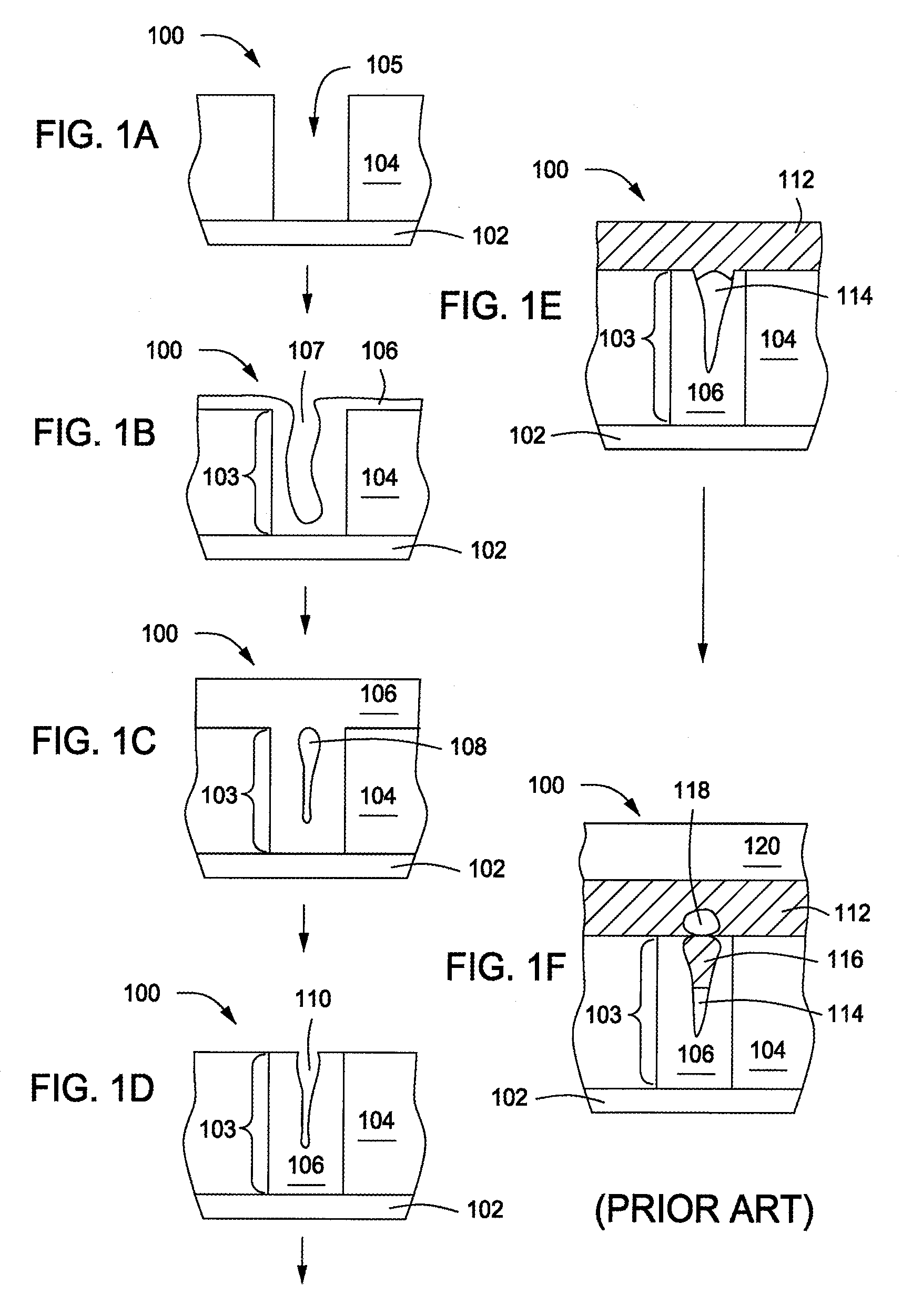
Method of selectively depositing a thin film material at a semiconductor interface
InactiveUS20070108404A1Detergent mixture composition preparationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice formMetal silicide
Embodiments of the invention provide processes to form a high quality contact level connection to devices formed on a substrate. In one embodiment, a method for depositing a material on a substrate is provided which includes exposing the substrate to a buffered oxide etch solution to form a silicon hydride layer during a pretreatment process, depositing a metal silicide layer on the substrate, and depositing a first metal layer (e.g., tungsten) on the metal silicide layer. The buffered oxide etch solution may contain hydrogen fluoride and an alkanolamine compound, such as ethanolamine diethanolamine, or triethanolamine. The metal silicide layer may contain cobalt, nickel, or tungsten and may be deposited by an electroless deposition process. In one example, the substrate is exposed to an electroless deposition solution containing a solvent and a complexed metal compound.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Forming radio frequency integrated circuits
Method of forming a radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) is provided. The RFIC comprises one or more electronic devices formed in a semiconductor substrate and one or more passive devices on a dielectric substrate, arranged in a stacking manner. Electrical shield structure is formed in between to shield electronic devices in the semiconductor substrate from the passive devices in the dielectric substrate. Vertical through-silicon-vias (TSVs) are formed to provide electrical connections between the passive devices in the dielectric substrate and the electronic devices in the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
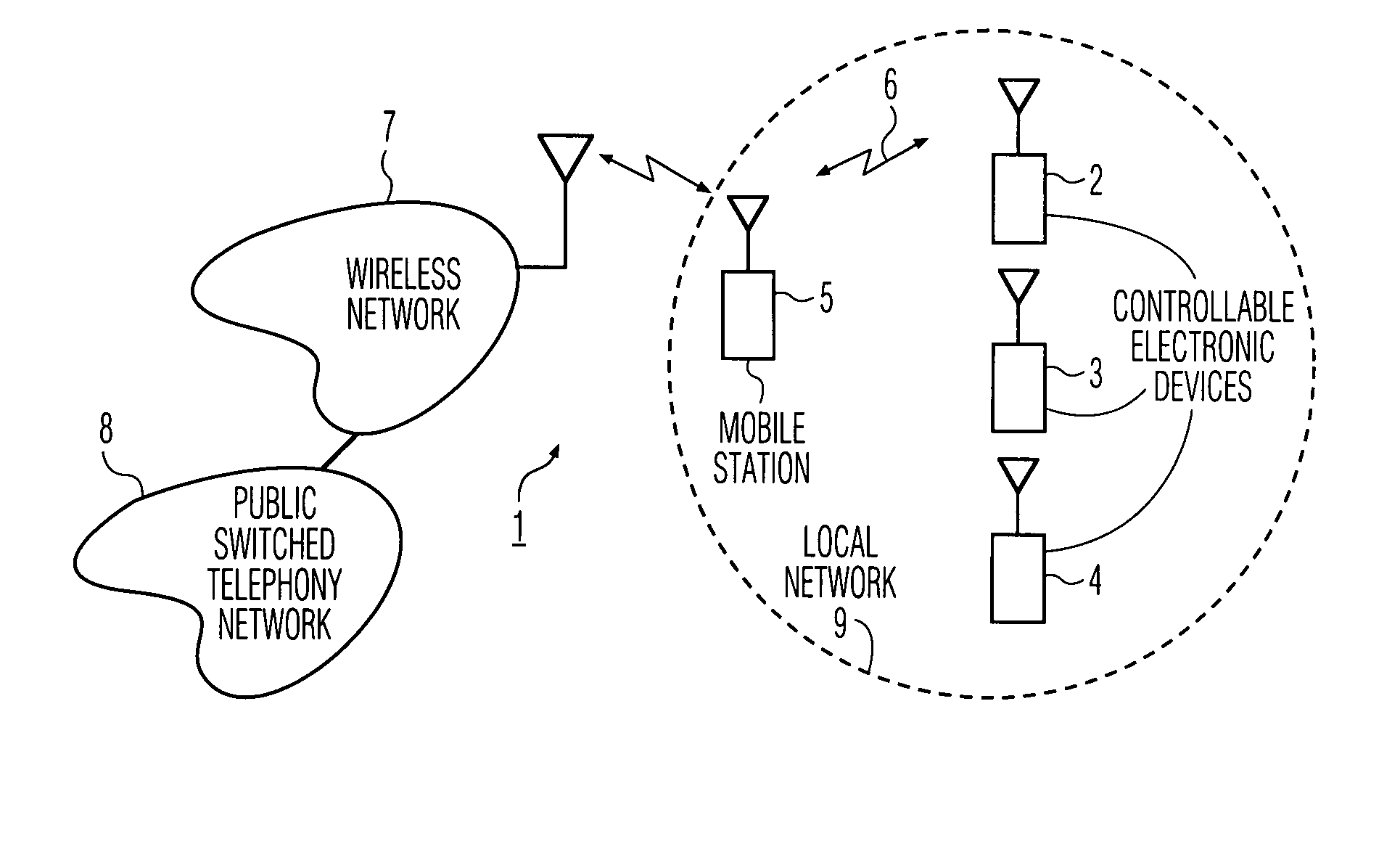
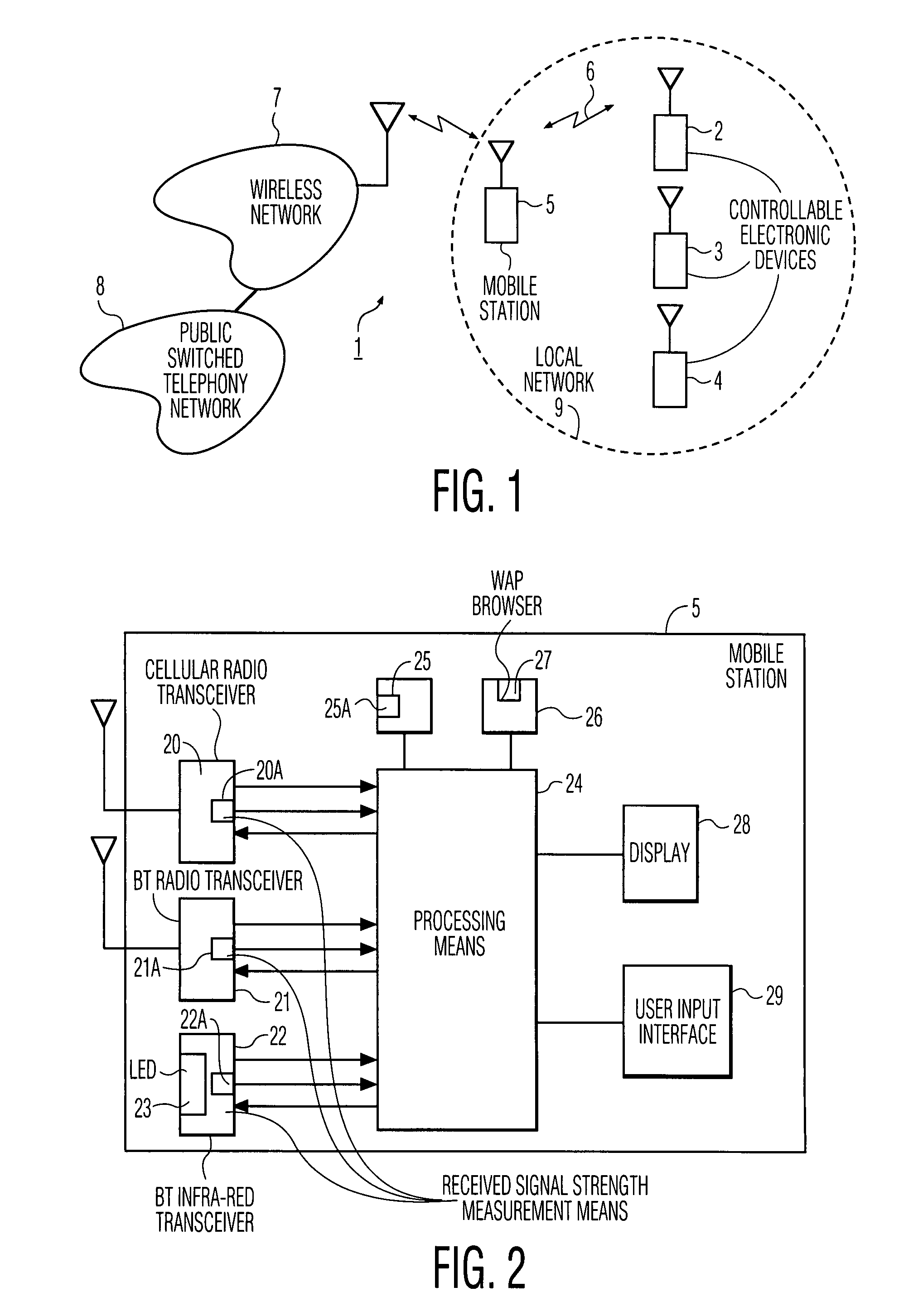
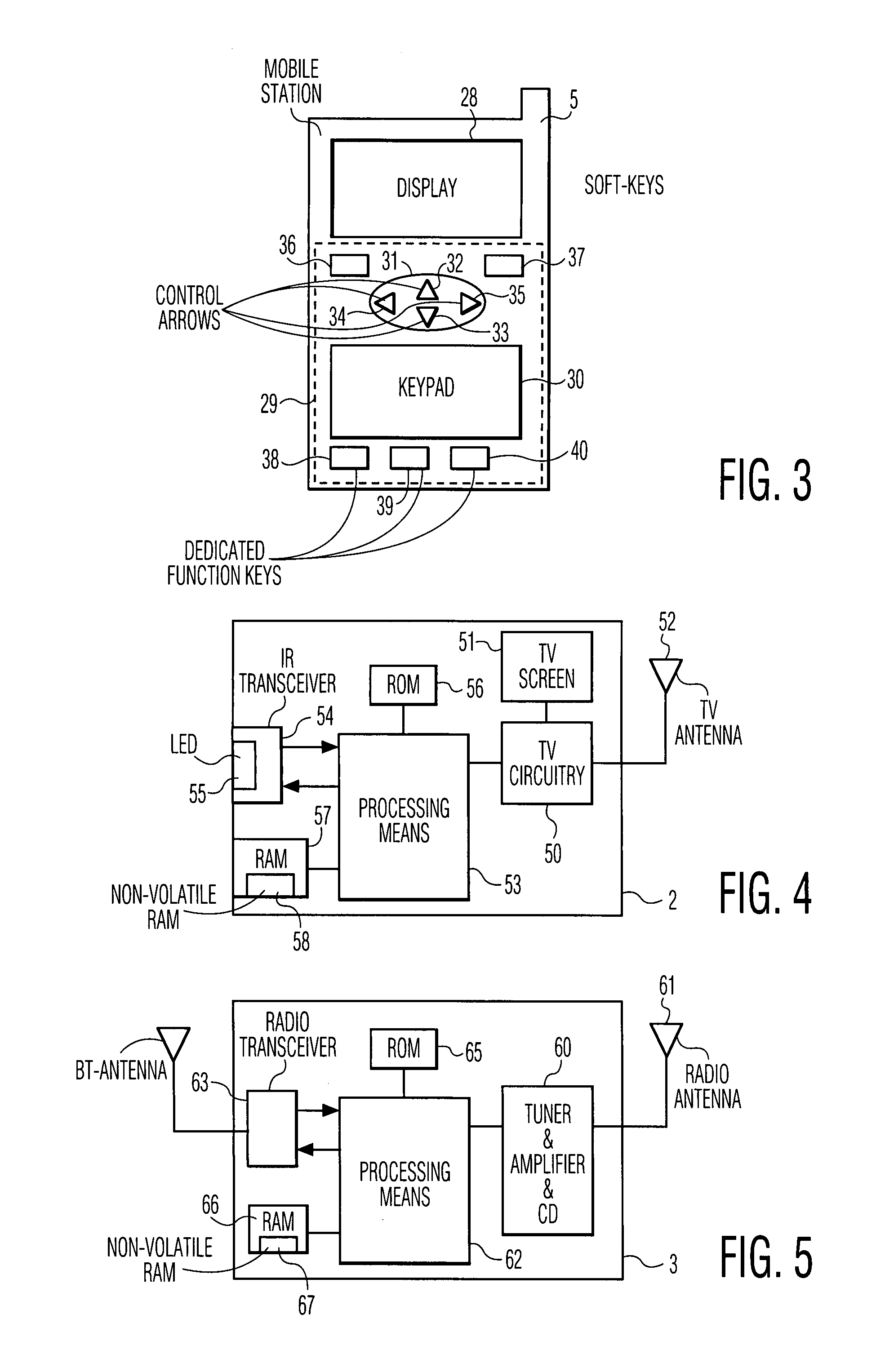
Remote control of an electronic device through downloading of a control interface of the electronic device in a mobile station
InactiveUS7894474B1Easy to operateReduce storage capacityElectric signal transmission systemsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsTelecommunications linkCommunications system
A wireless communication system includes a number of controllable electronic devices and a mobile station for communication with one of the controllable electronic devices through a short-range wireless communication link, when in-range with the one controllable electronic device. The mobile station includes a display screen and a browser. The mobile station and the one controllable electronic device form a client-server pair. Through the short-range wireless communication link, the client requests the server to download a control interface stored at the server. Upon downloading, a browser is used to navigate through control menu pages included in the control interface, and to post control parameter settings to the server. In the server, a program runs to interpret received control parameter settings, to invoke a control action in accordance with the received control parameter settings, and to instruct the client what to do next.
Owner:HOME CONTROL SINGAPORE
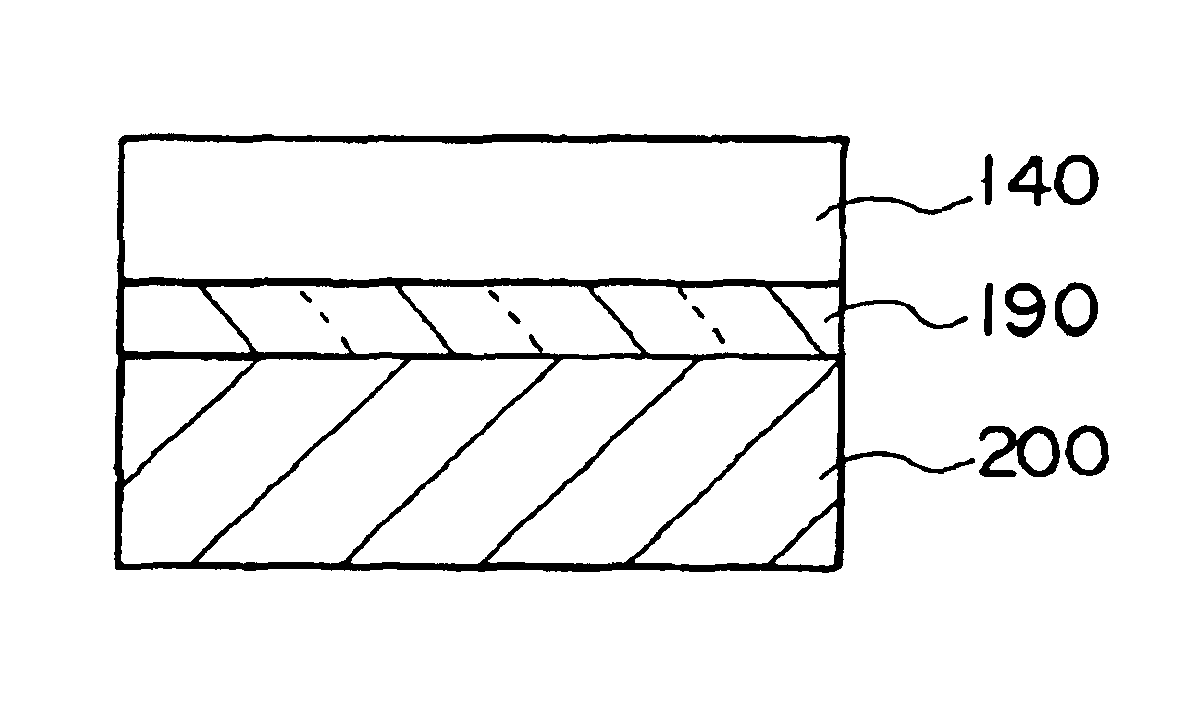
Thin film device transfer method, thin film device, thin film integrated circuit device, active matrix board, liquid crystal display, and electronic apparatus
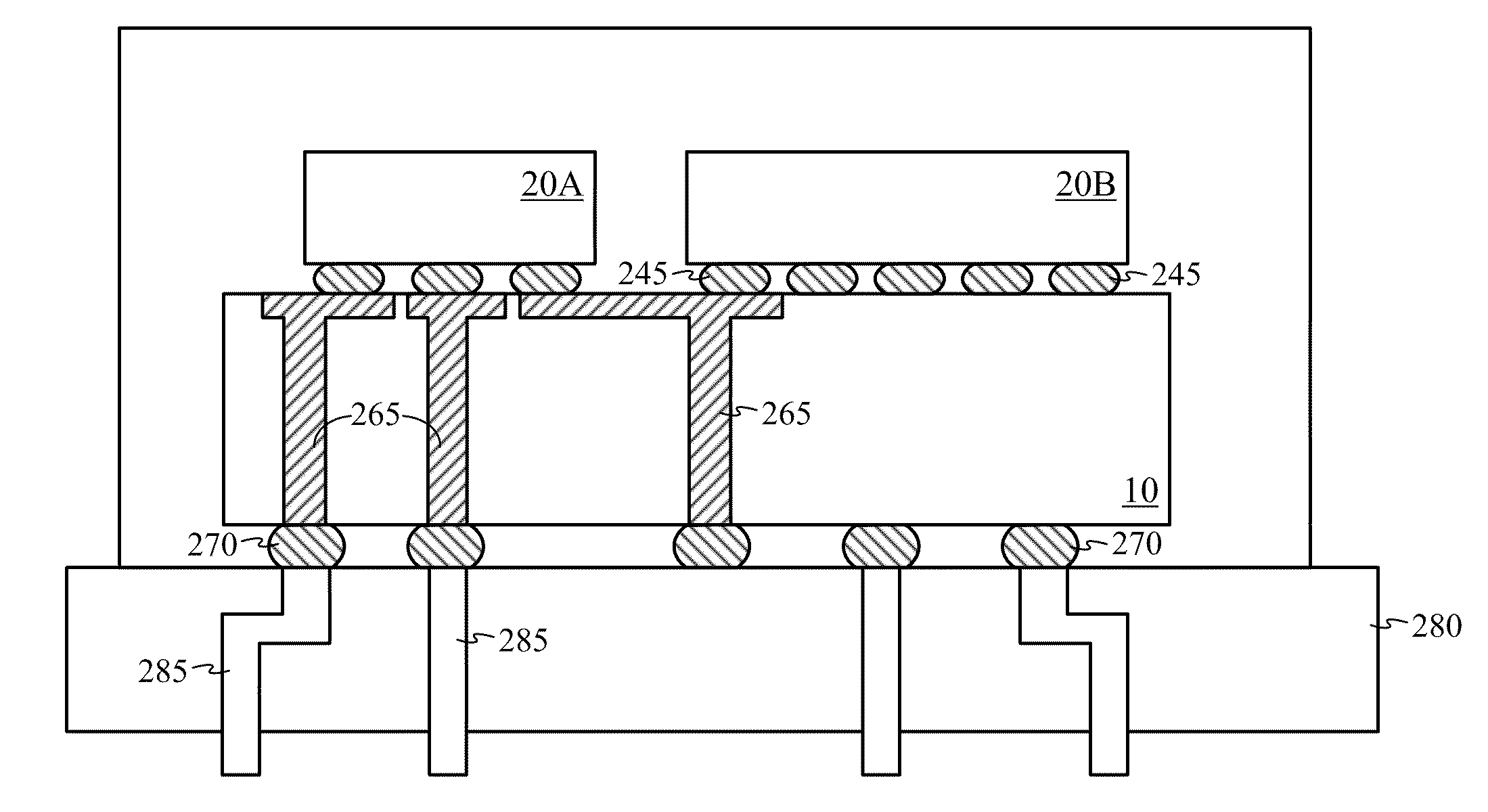
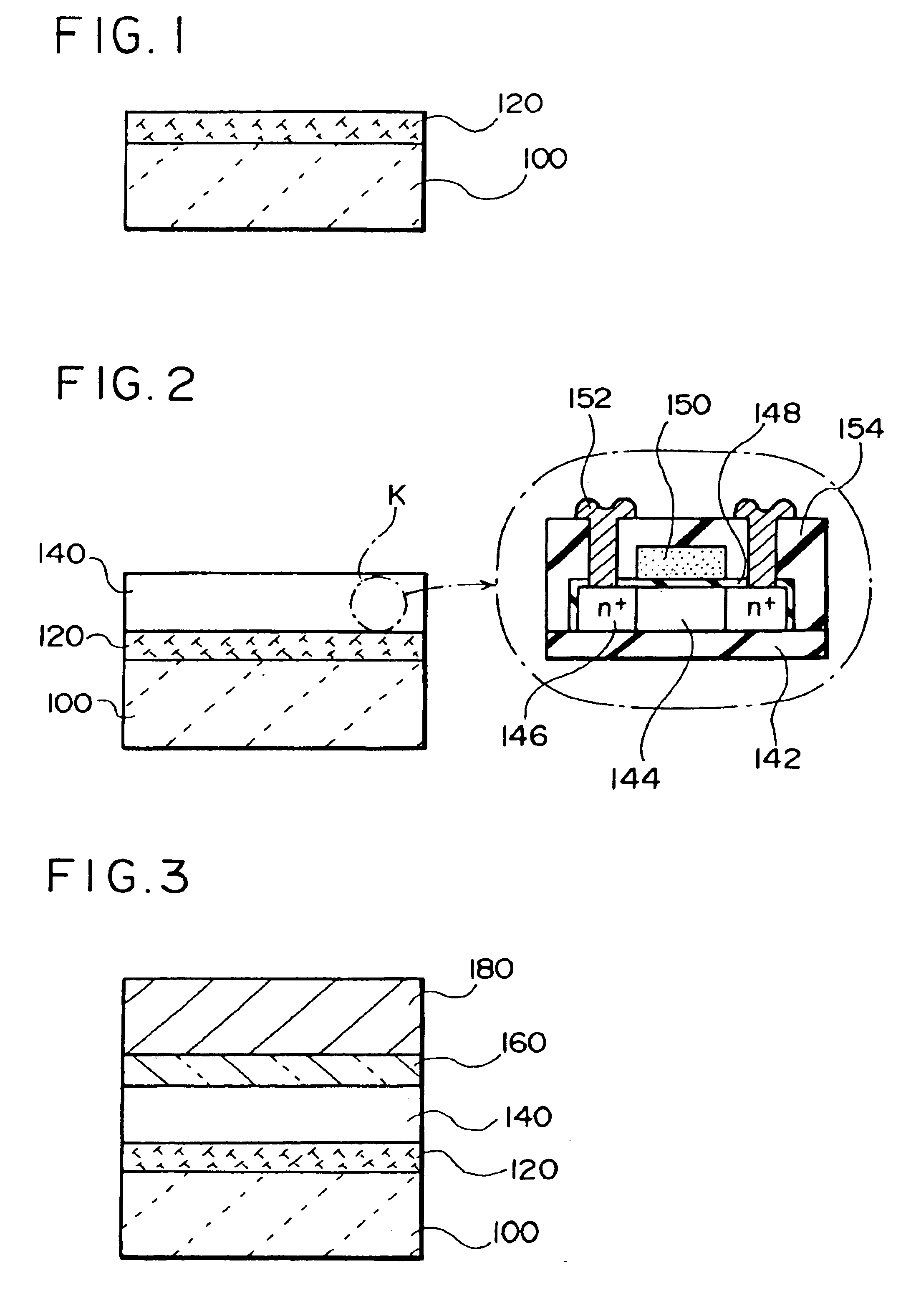
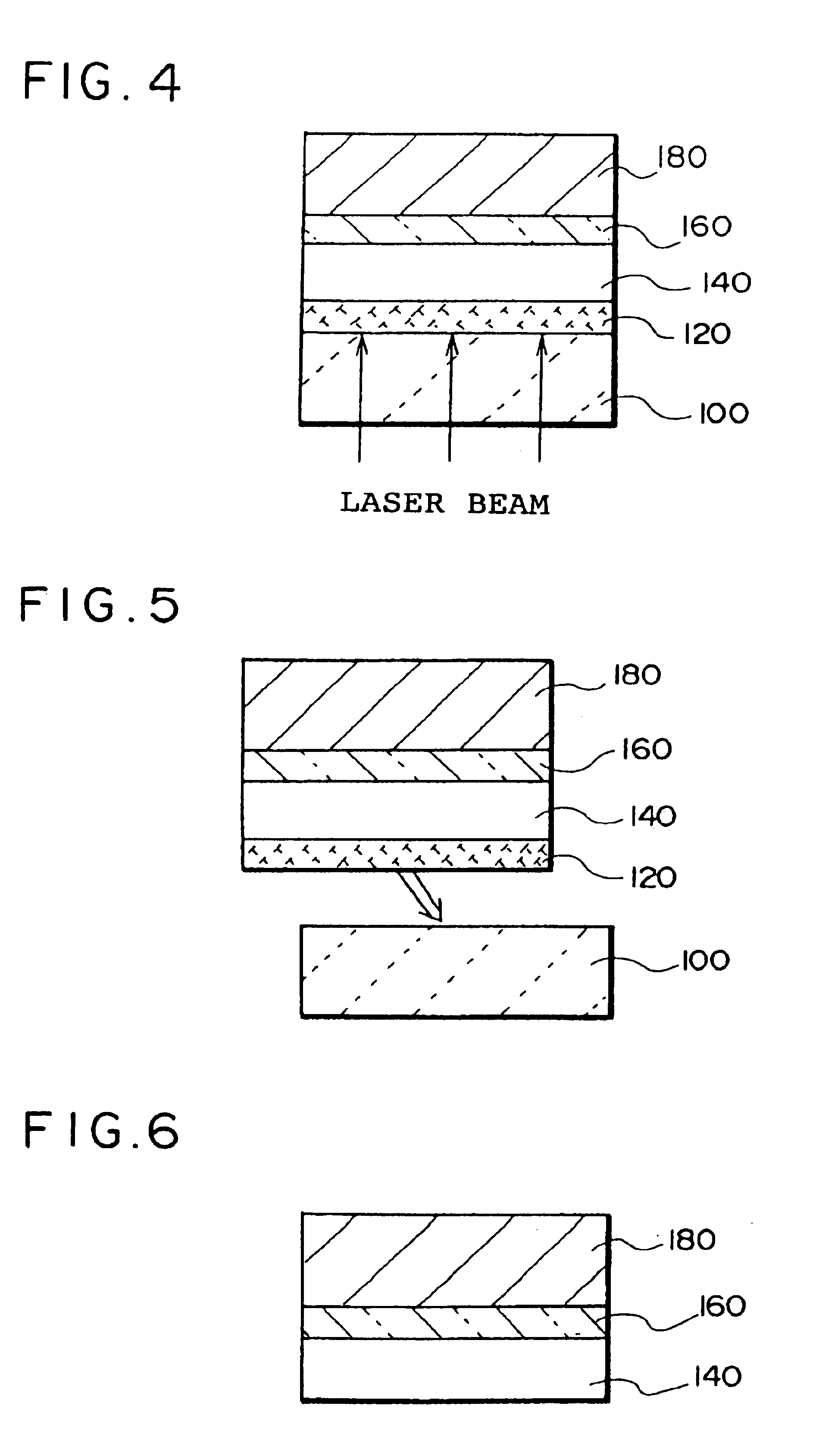
A thin film device fabrication method in which a thin film device formed on a substrate are transferred to a primary destination-of-transfer part and then the thin film device is transferred to a secondary destination-of-transfer part. A first separation layer (120) made of such a material as amorphous silicon is provided on a substrate (100) which allows passage of laser. A thin film device (140) such as TFTs are formed on the substrate (100). Further, a second separation layer (160) such as a hot-melt adhesive layer is formed on the thin film devices (140), and a primary destination-of-transfer part (180) is mounted thereon. The bonding strength of the first separation layer is weakened by irradiation with light, and the substrate (100) is removed. Thus, the thin film device (140) is transferred to the primary destination-of-transfer part. Then, a secondary destination-of-transfer part (200) is attached onto the bottom of an exposed part of the thin film device (140) via an adhesive layer (190). Thereafter, the bonding strength of the second separation layer is weakened by such means as thermal fusion, and the primary destination-of-transfer part is removed. In this manner, the thin film device (140) can be transferred to the secondary destination-of-transfer part (200) while maintaining layering relationship with respect to the substrate (100).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
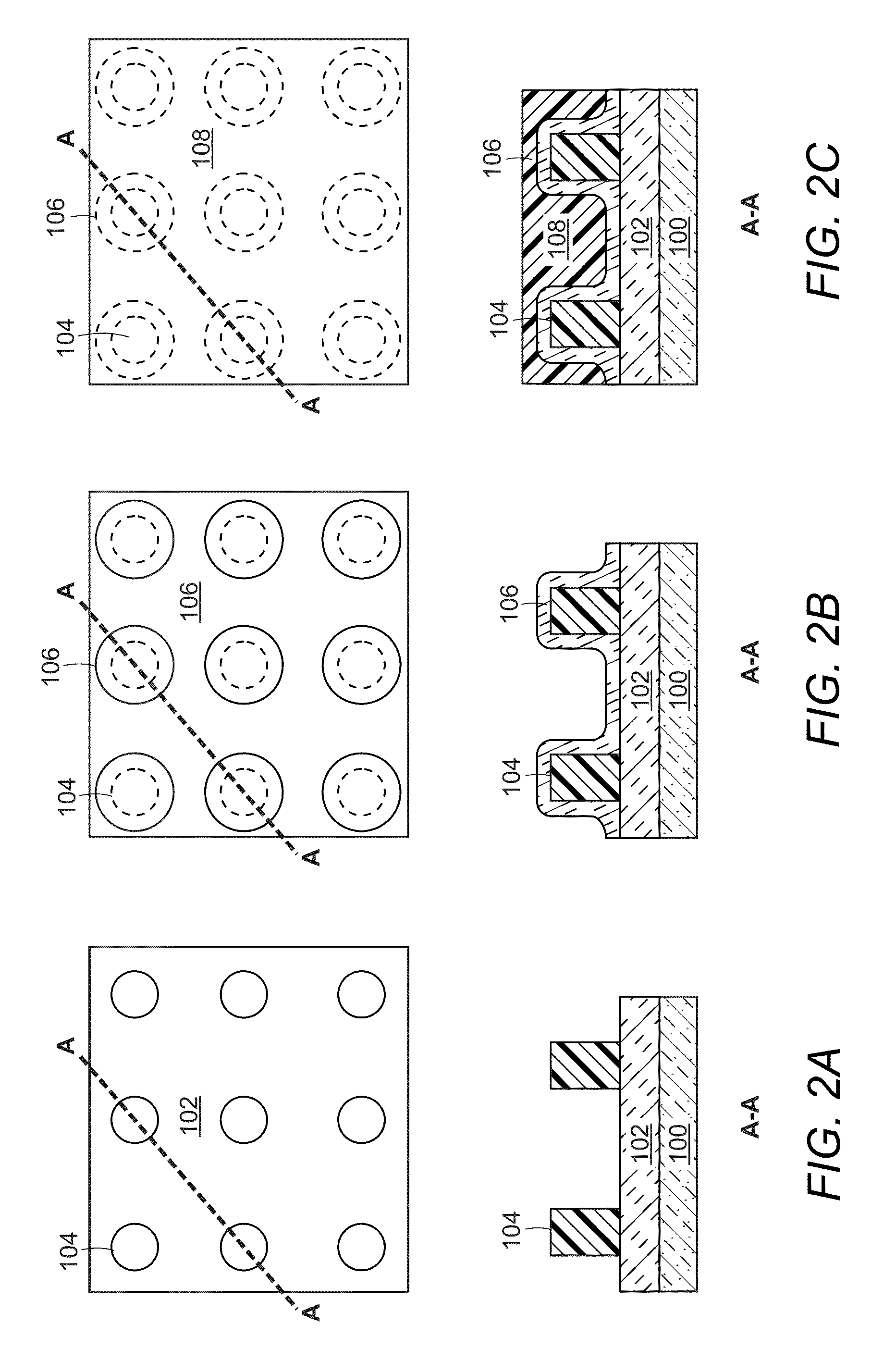
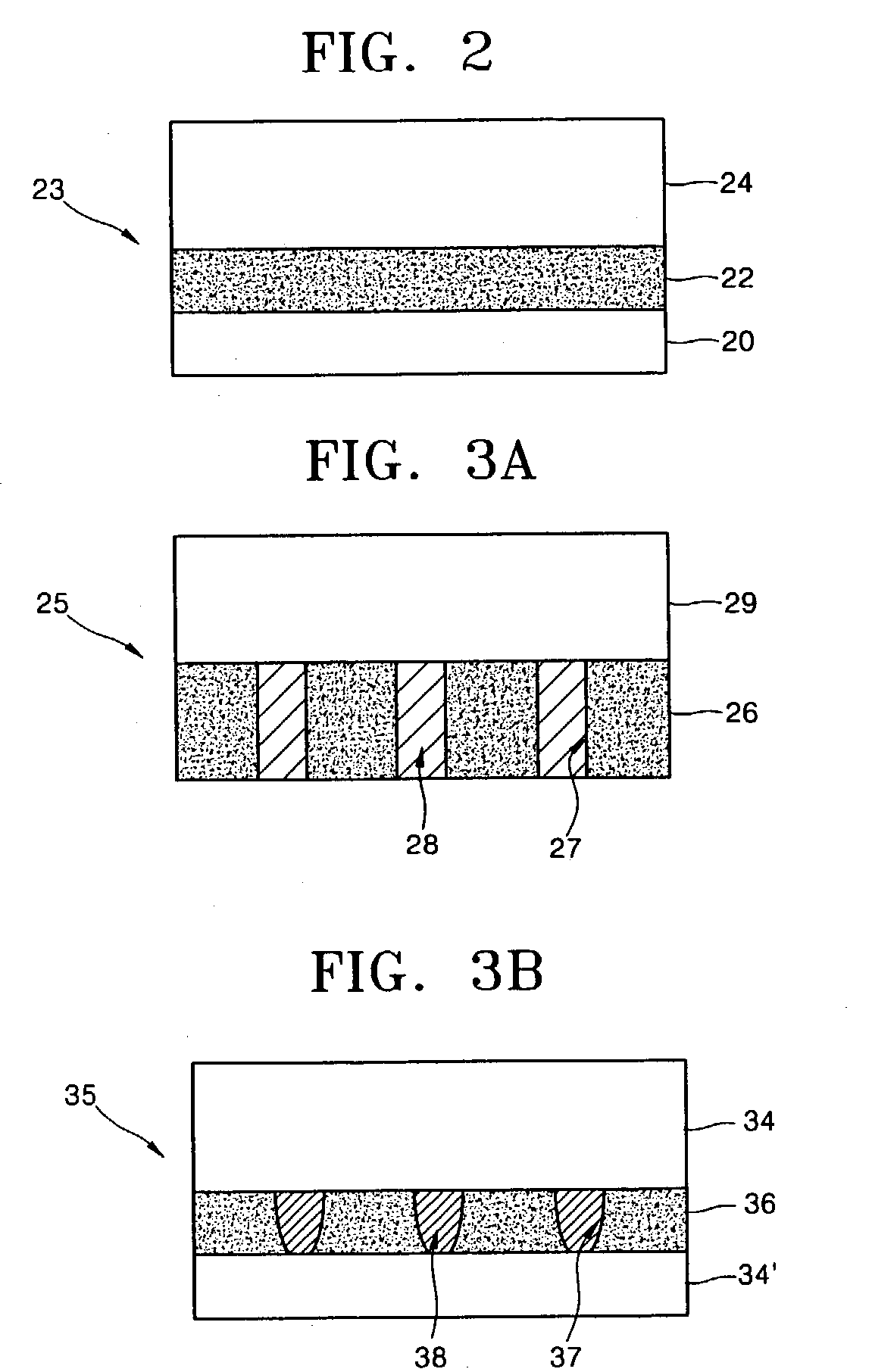
Contact hole formation methods
Methods of forming contact holes comprising: (a) providing a substrate comprising a plurality of post patterns over a layer to be patterned; (b) forming a hardmask layer over the post patterns and the layer to be patterned; (c) coating a pattern treatment composition over the hardmask layer, wherein the pattern treatment composition comprises a polymer comprising a reactive surface attachment group and a solvent; and optionally baking the substrate; wherein the polymer becomes bonded to the hardmask layer to form a polymer layer over the hardmask layer; and (d) treating the substrate with a rinsing agent comprising a solvent to remove residual, unbound said polymer, thereby forming a first hole disposed between a plurality of surrounding post patterns. The method is free of exposing the polymer to activating radiation from coating the pattern treatment composition to treating the substrate with the solvent. Also provided are pattern treatment compositions and electronic devices formed by the methods. The inventions find particular applicability in the manufacture of semiconductor devices for providing high resolution contact hole patterns.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
Surgical access devices with anvil introduction and specimen retrieval structures
Surgical access devices are disclosed. In various forms, the access devices form at least one passageway through which various surgical instruments and tools may be admitted into the body cavity. Various embodiments may be configured to support an anvil for a circular stapling device therein. Various forms employ a flexible bag for retrieval of specimen from the body cavity.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
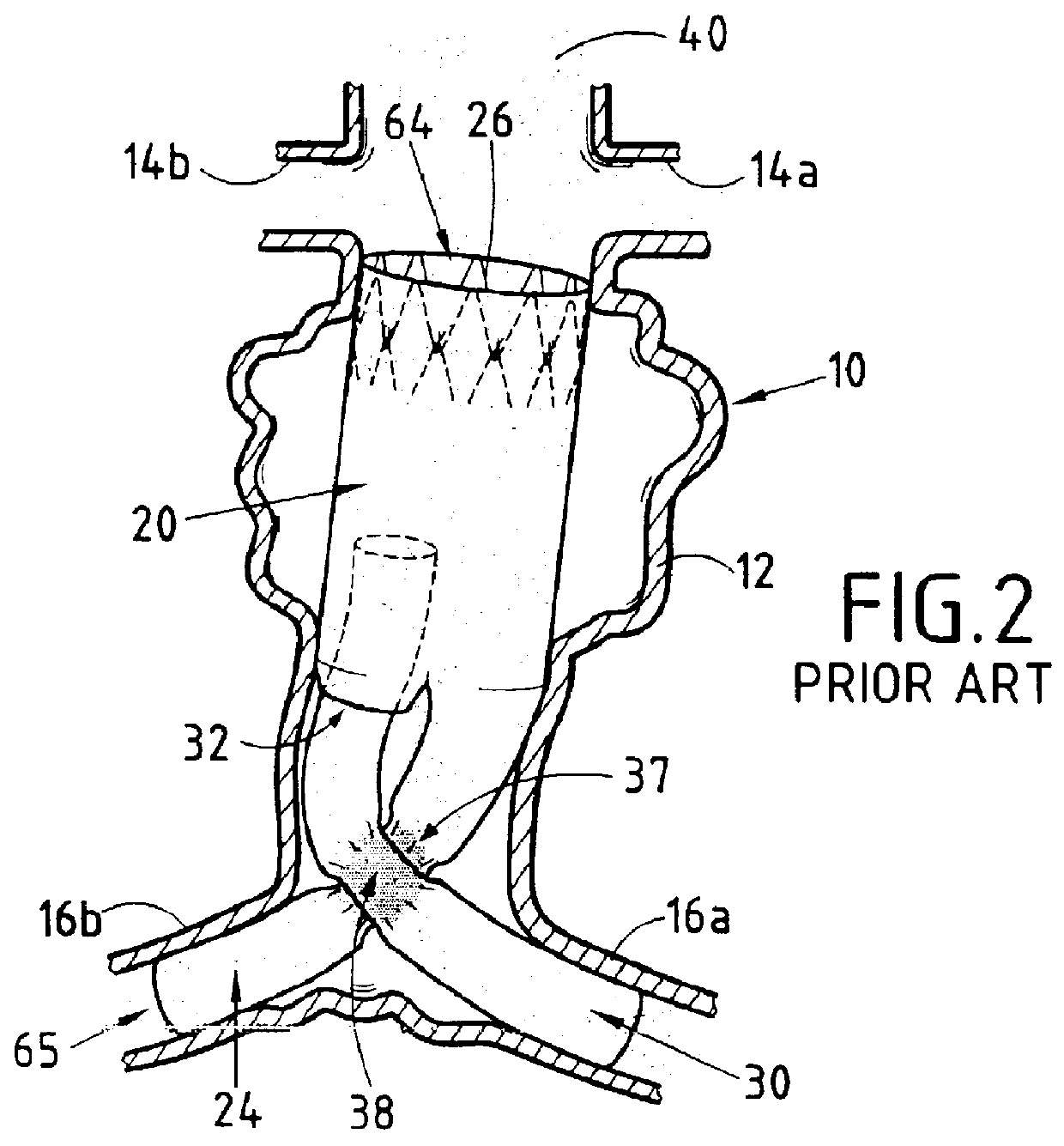
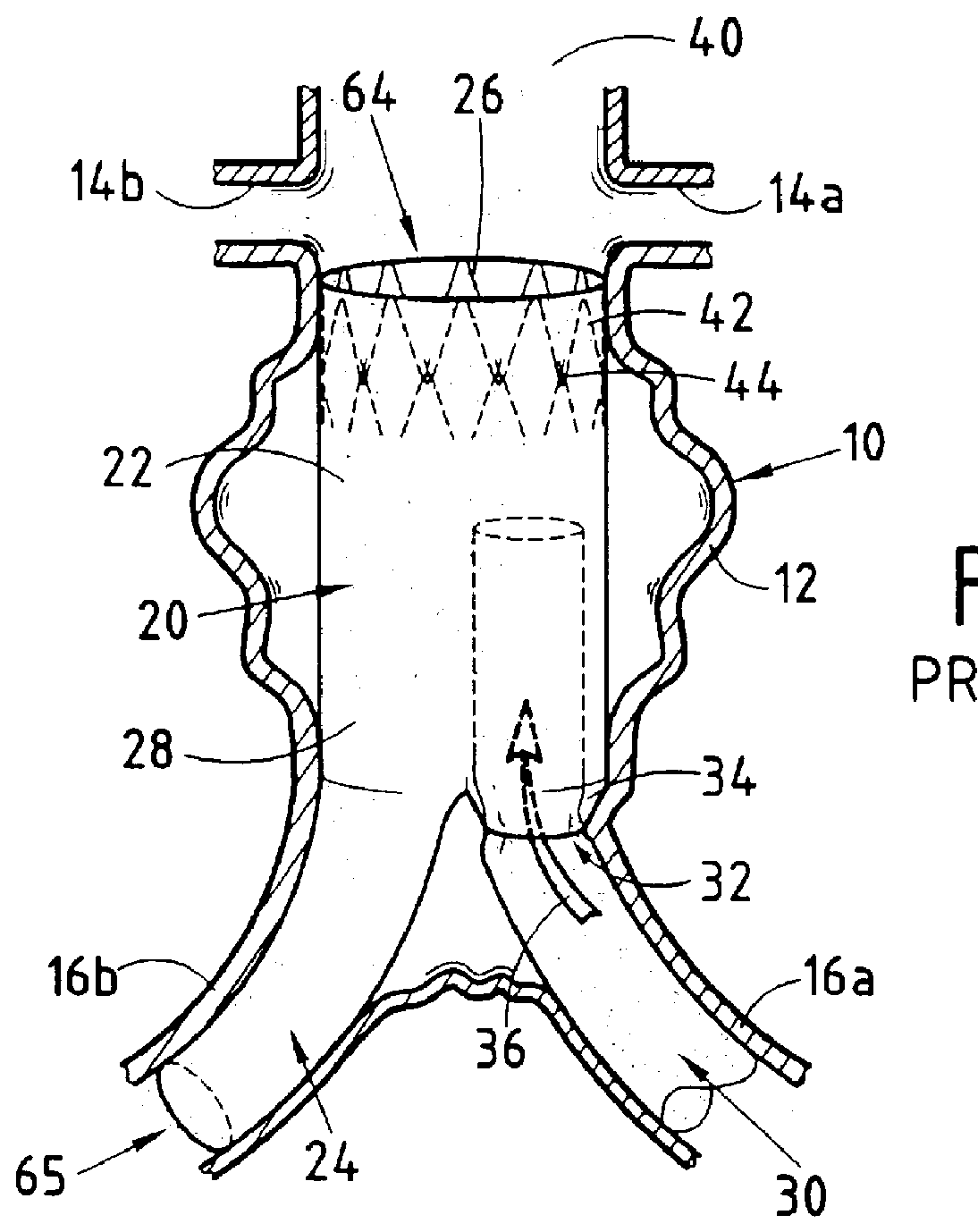
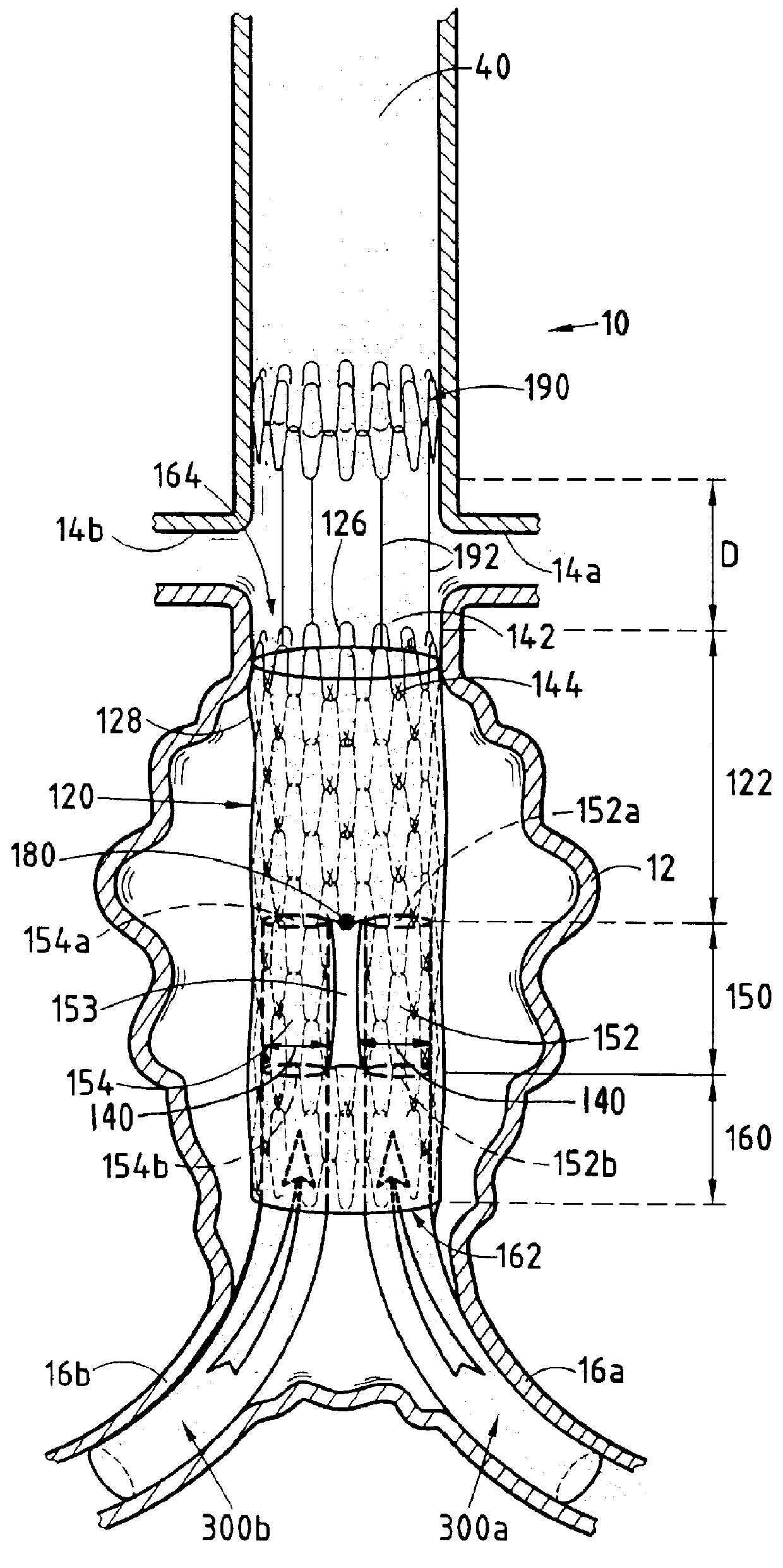
Device forming an endoluminal intracorporeal endoprosthesis, in particular for the abdominal aorta
The invention relates to a device forming an endoluminal endoprosthesis. The device comprises at least a first segment, and upstream from said segment, at a predetermined distance therefrom, it comprises a "fixing" upstream segment made of a biocompatible material so as to be deployable from a closed or non-deployed position for insertion purposes to a deployed working position, the deployed working position being designed to be located in a healthy zone of blood vessel and being separated from the first segment by a predetermined distance defined by links of predetermined length. The invention makes it easy to recatheterize a blood vessel such as the abdominal aorta suffering from an aneurysm.
Owner:LEGONA ANSTALT
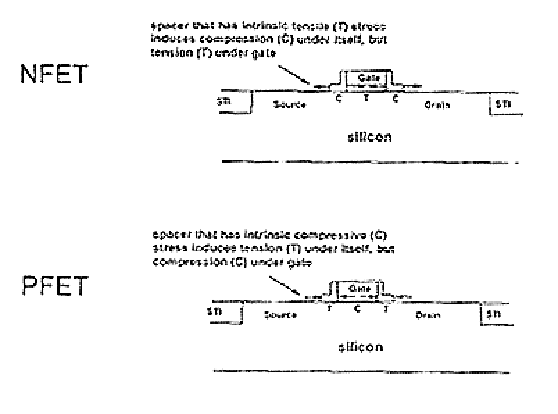
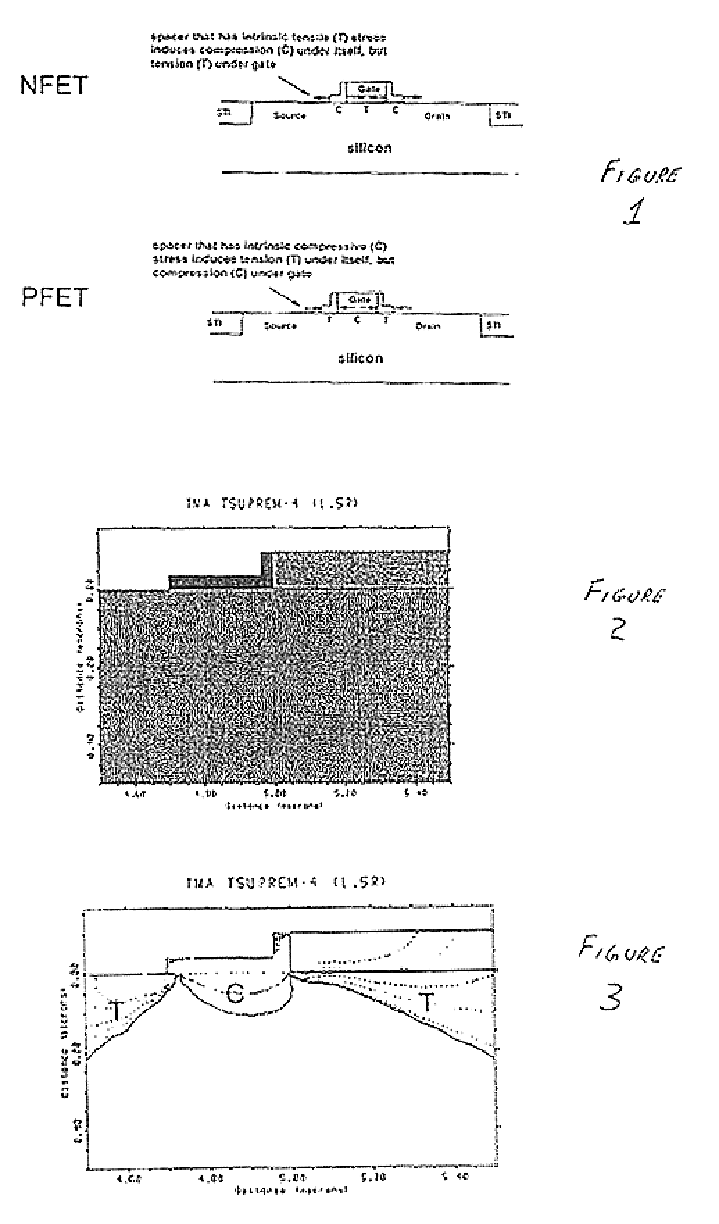
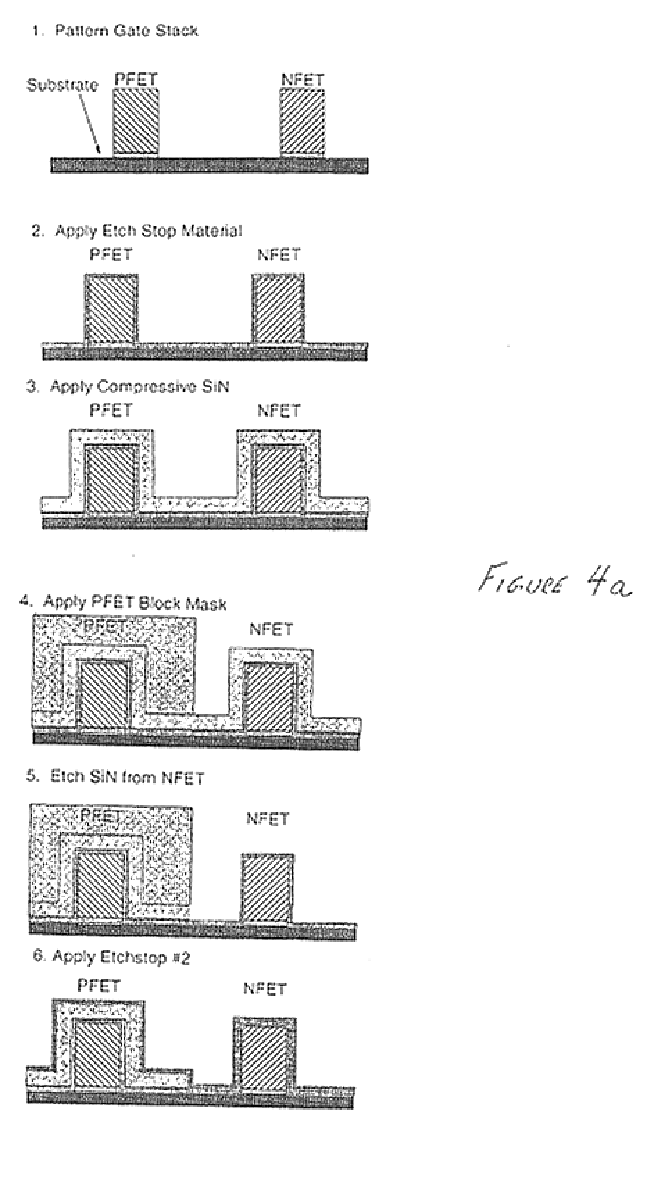
Stress inducing spacers
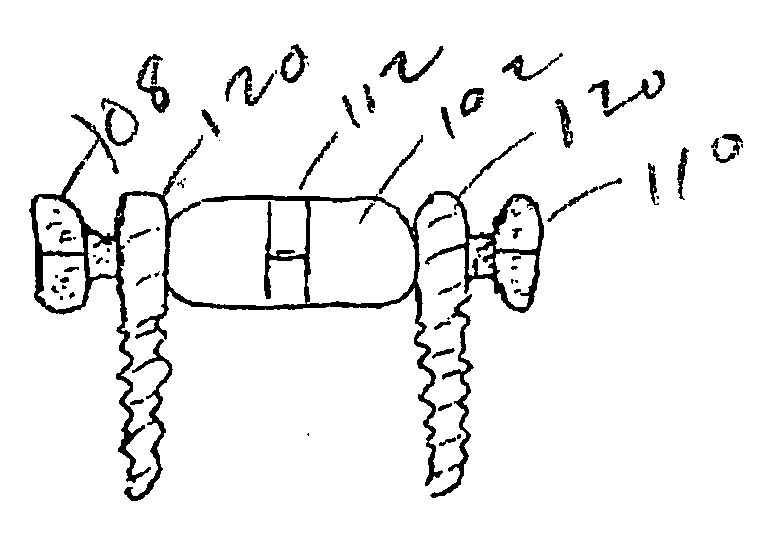
InactiveUS6825529B2Different stressImprove performanceTransducer detailsSolid-state devicesStress inducedDevice form
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
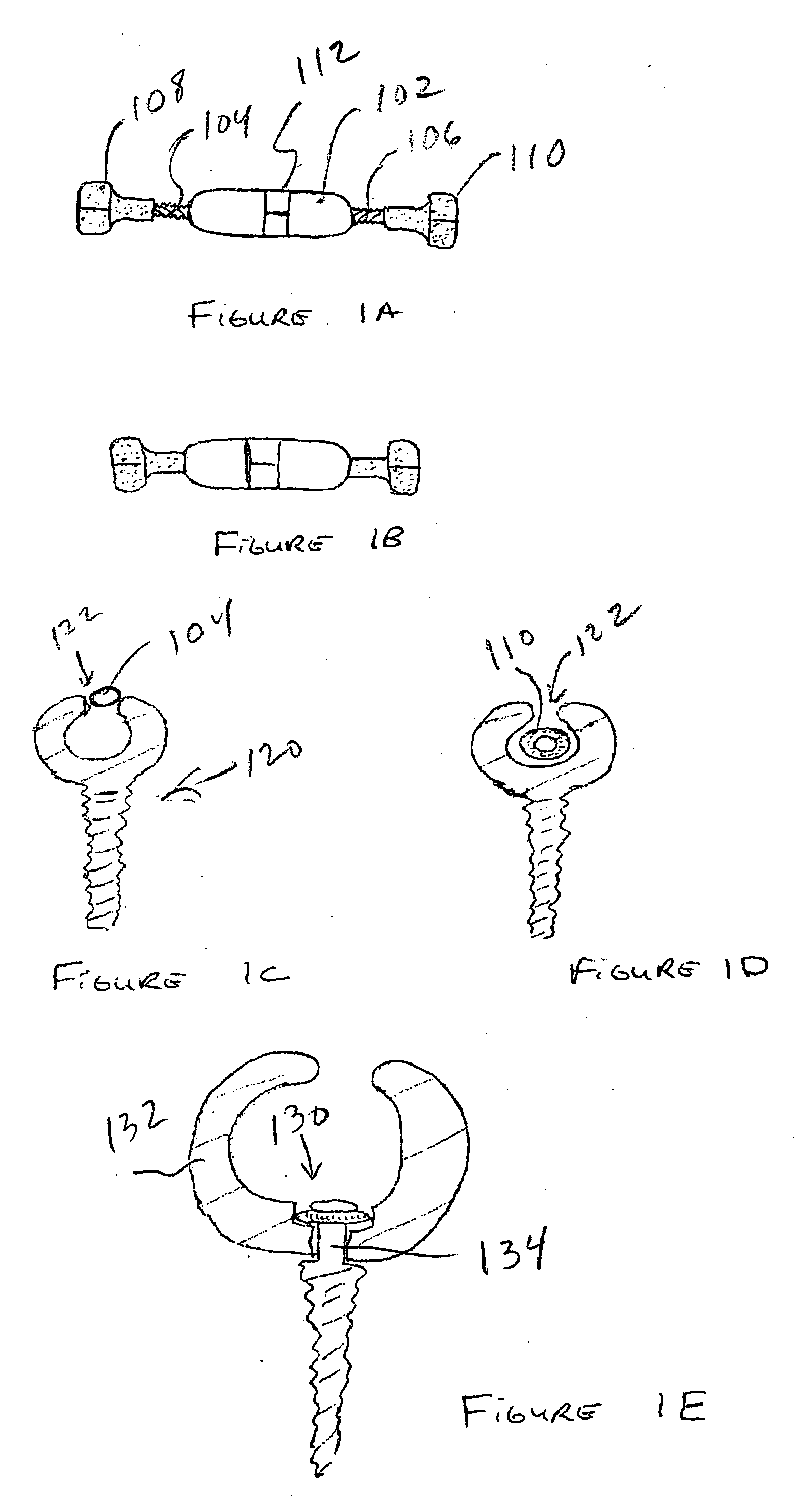
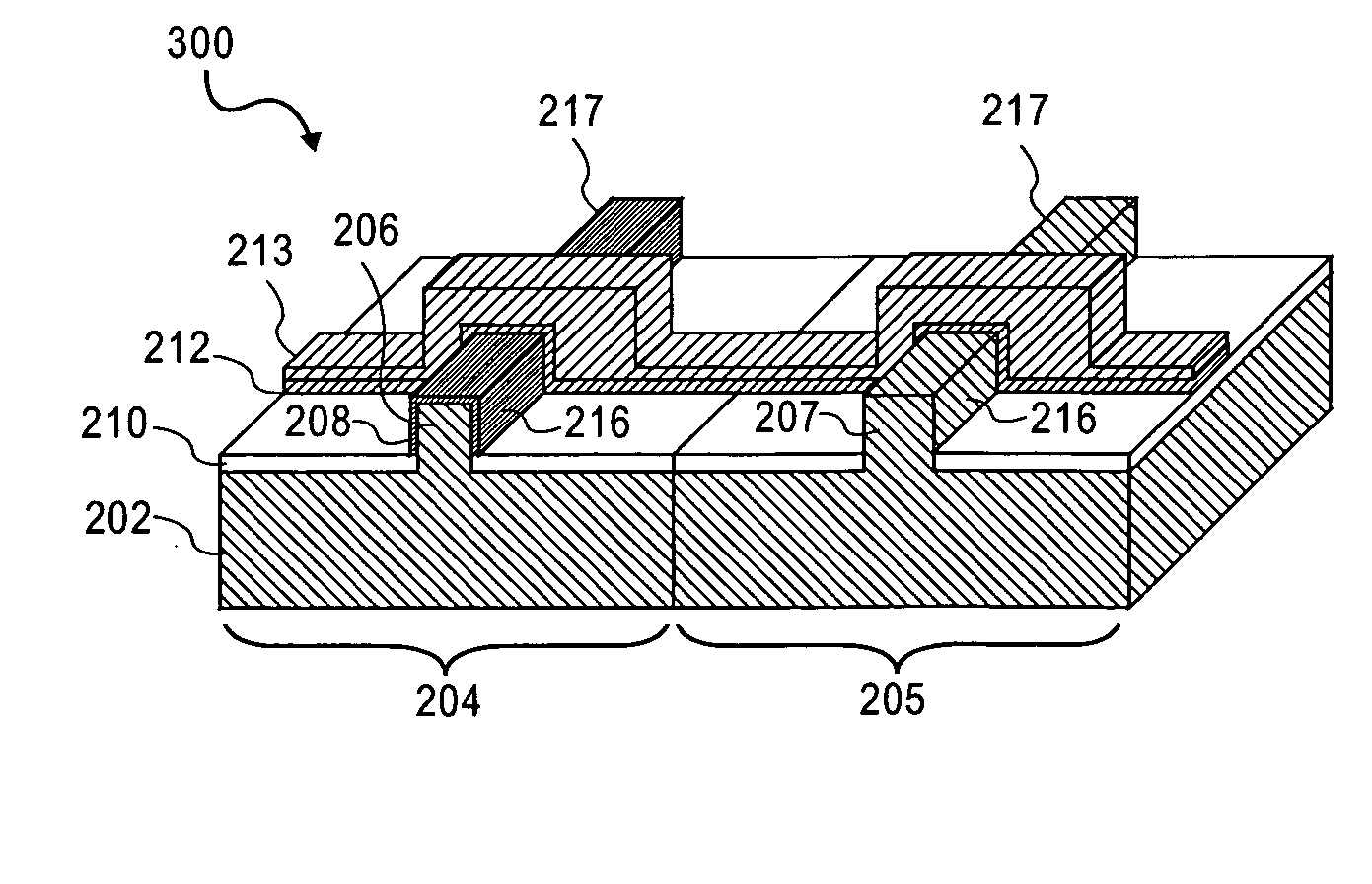
Semiconductor chip and manufacturing method for the same, and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050151228A1Improve reliabilityThe connection is tight and firmSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice formSemiconductor chip
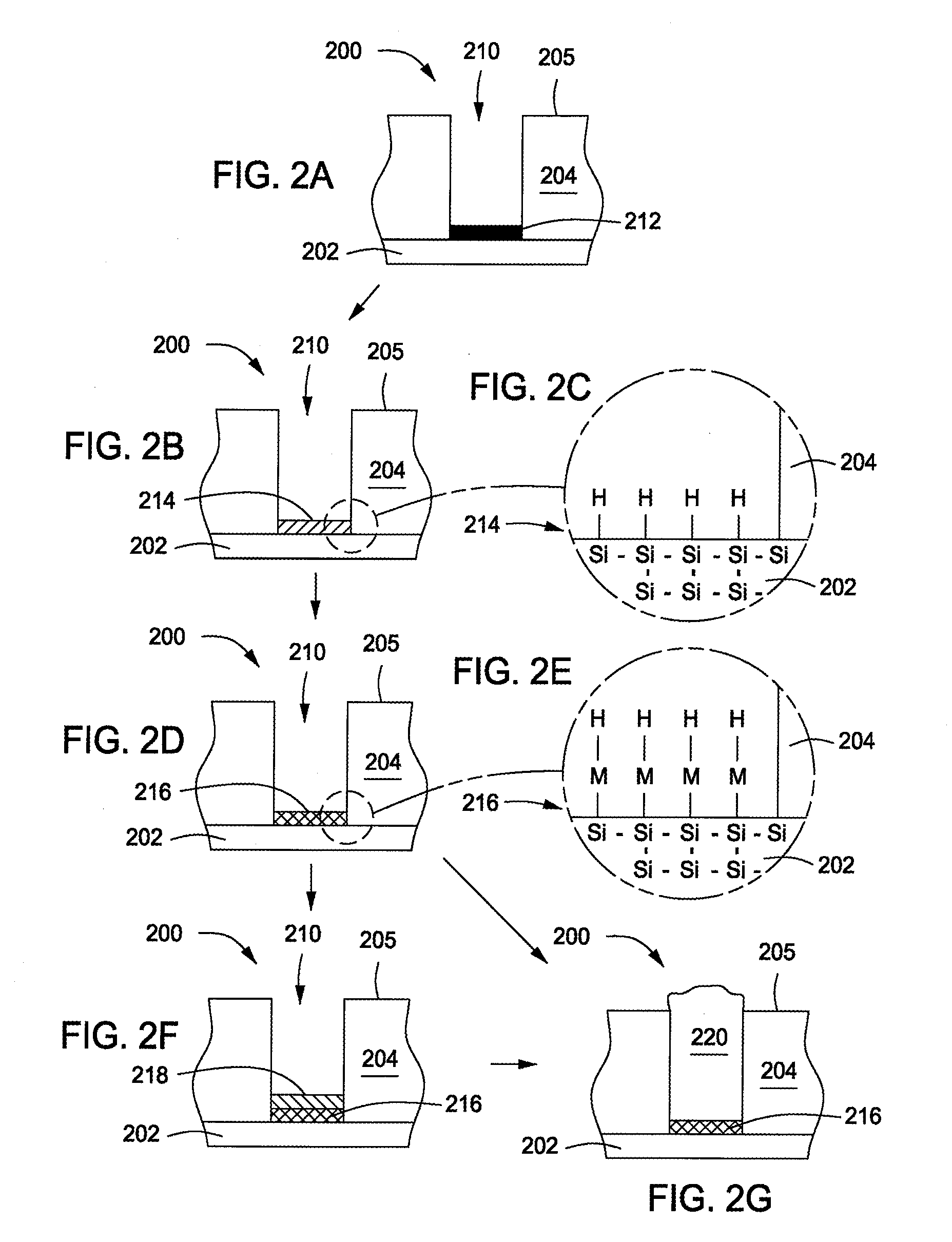
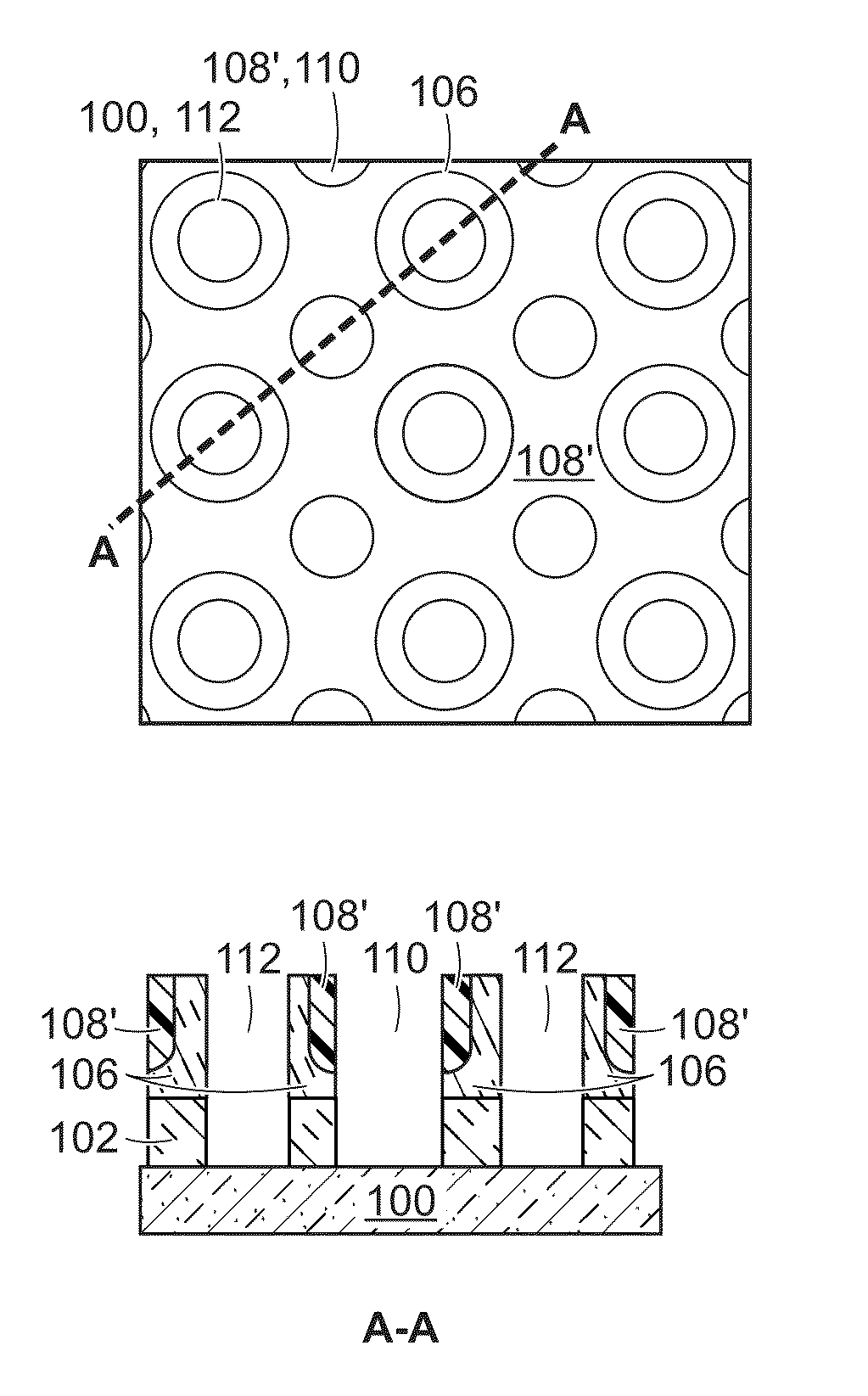
The invention provides a semiconductor chip manufacturing method including the steps of: forming a concave portion extended in the thickness direction of a semiconductor substrate which has a front surface and a rear surface and has a function device formed on the front surface, from the front surface; forming an oxidation preventive film made of an inert first metal material by supplying the first metal material onto the inner wall surface of the concave portion; supplying a second metal material containing a metal which is oxidized more easily than the first metal material to the inside of the concave portion after the step of forming the oxidation preventive film; electrically connecting the second metal material supplied to the inside of the concave portion and the function device; and thinning the semiconductor substrate so that the thickness thereof becomes thinner than the depth of the concave portion by removing the semiconductor substrate from the rear surface while leaving the oxidation preventive film.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP +3
Memory device utilizing carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS7015500B2Increase in malfunctionIncrease resistanceTransistorIndividual molecule manipulationDevice formCarbon nanotube
A fast, reliable, highly integrated memory device formed of a carbon nanotube memory device and a method for forming the same, in which the carbon nanotube memory device includes a substrate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a carbon nanotube having high electrical and thermal conductivity, a memory cell having excellent charge storage capability, and a gate electrode. The source electrode and drain electrode are arranged with a predetermined interval between them on the substrate and are subjected to a voltage. The carbon nanotube connects the source electrode to the drain electrode and serves as a channel for charge movement. The memory cell is located over the carbon nanotube and stores charges from the carbon nanotube. The gate electrode is formed in contact with the upper surface of the memory cell and controls the amount of charge flowing from the carbon nanotube into the memory cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
SOI stacked dram logic
A composite, layered, integrated circuit formed by bonding of insulator layers on wafers provides for combination of otherwise incompatible technologies such as trench capacitor DRAM arrays and high performance, low power, low voltage silicon on insulator (SOI) switching transistors and short signal propagation paths between devices formed on respective wafer layers of a chip. In preferred embodiments, an SOI wafer is formed by hydrophilic bonding of a wafer over an integrated circuit device and then cleaving a layer of the second wafer away using implanted hydrogen and low temperature heat treatment. Further wafers of various structures and compositions may be bonded thereover and connections between circuit elements and connection pads in respective wafers made using short vias that provide fast signal propagation as well as providing more numerous connections than can be provided on chip edges.
Owner:IBM CORP
Backside contact for touchchip
InactiveUS6326689B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact formationContact pad
A contact is formed within an active region of a substrate at the edge of a die, preferably within the first metallization level in the active region of the substrate. An opening having sloped sidewalls is then etched into the back side of the substrate, exposing a portion of the active region contact. An interconnect is formed on the opening sidewall to connect the active region contact with a die contact pad on the backside surface of the substrate. The active region contact preferably spans a boundary between two die, with the opening preferably etched across the boundary to permit inter-connects on opposing sidewalls of the opening to each contact the active region contact within different die, connecting the active region contact to die contact pads on different dice. The dice are then separated along the boundary, through the active region contact which becomes two separate active region contacts. By forming a shared contact opening spanning two dice, the backside contact is formed around the die edge and the backside surface area necessary for the contact opening is minimized. The backside contact allows direct placement of the integrated circuit die on contacts within the packaging, such as a ball grid array, eliminating the need for wire bonds. The need for a pad etch through passivation material overlying active devices on the front side of the die is also eliminated, and no mask levels are added for the devices formed on the front side.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com