Patents
Literature
782 results about "Contact formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
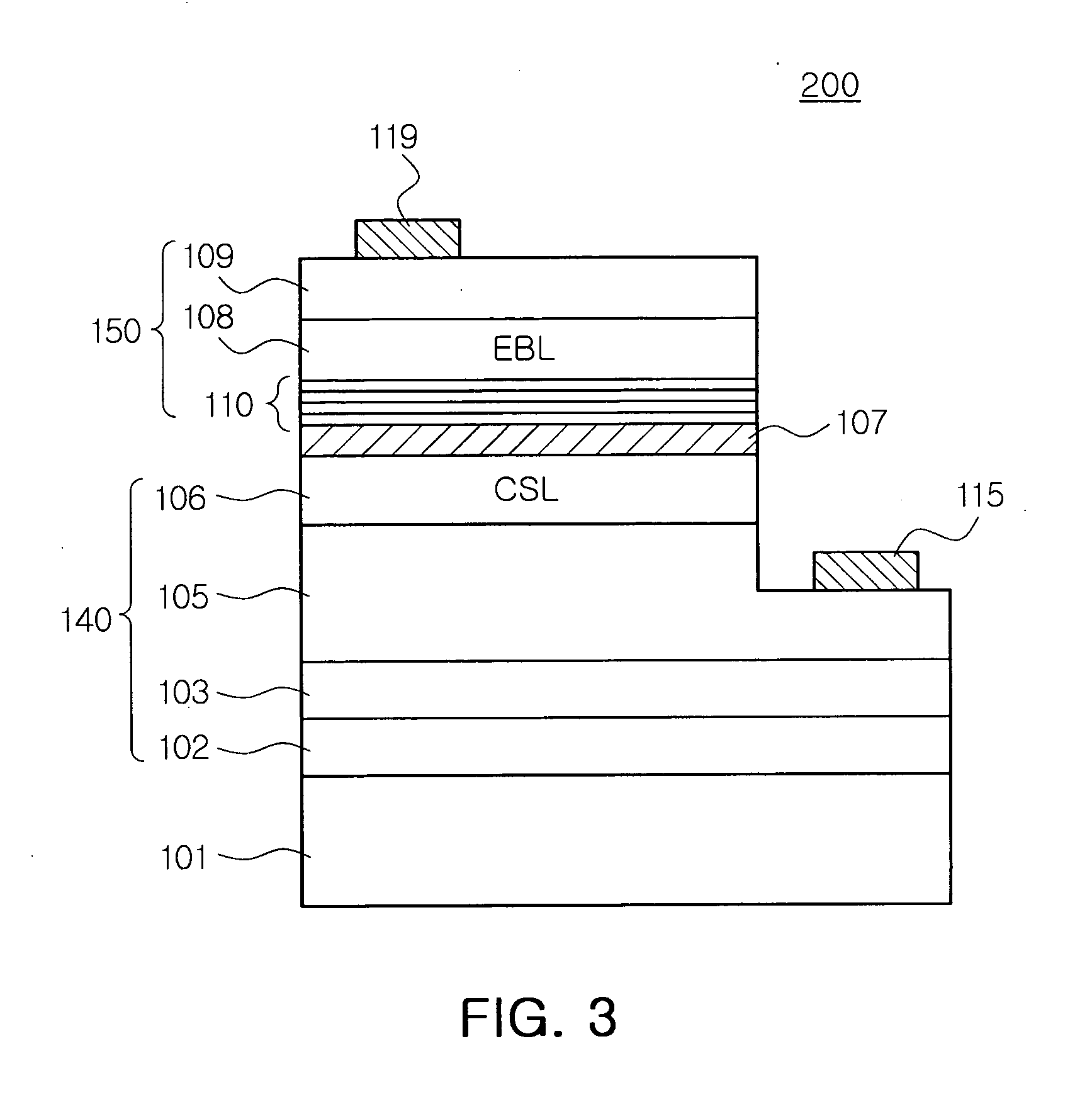
Organic devices, organic electroluminescent devices and organic solar cells
ActiveUS20060008740A1Reduce harmLower barrier heightElectric discharge tubesElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic solar cellSimple Organic Compounds
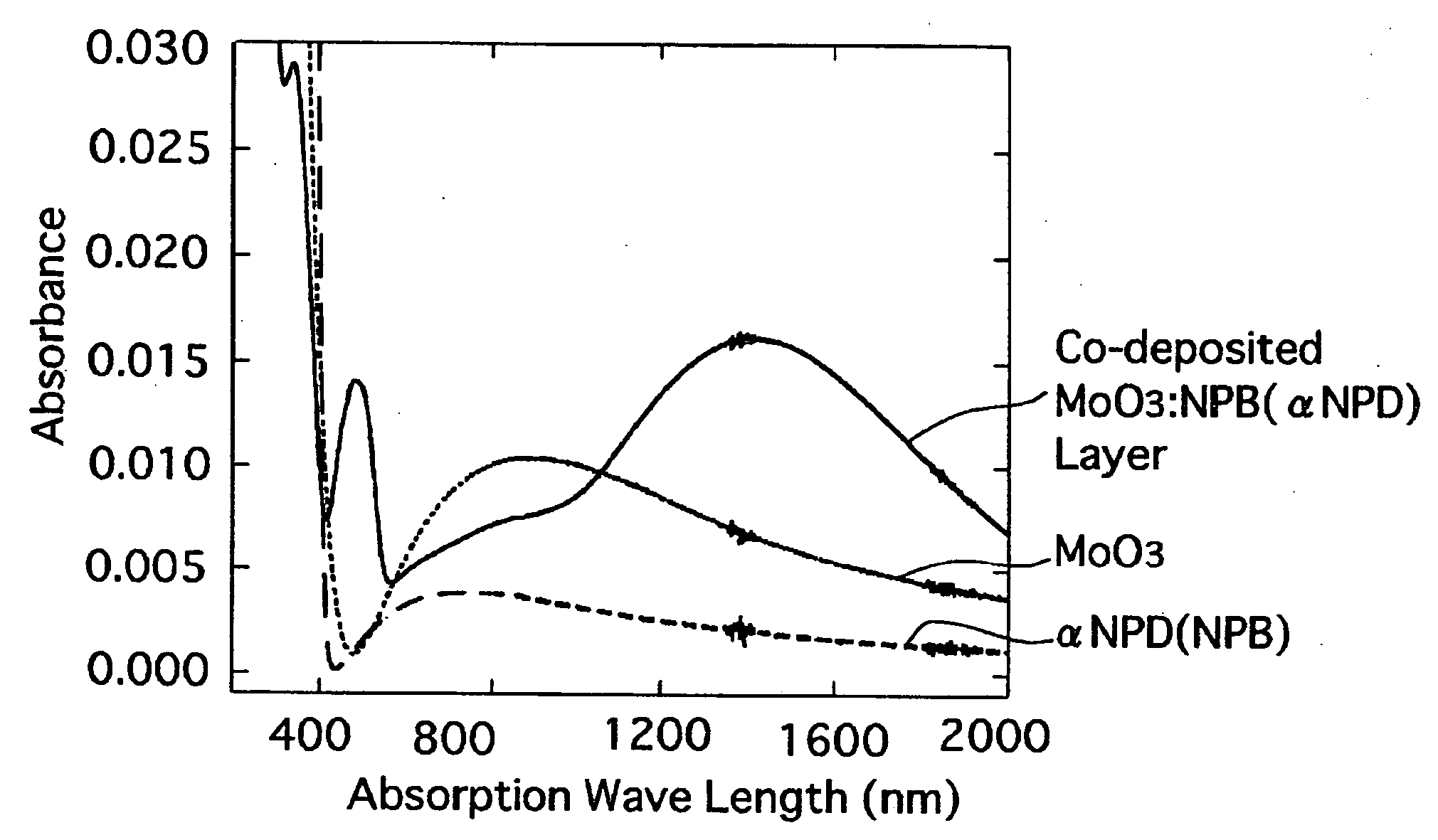
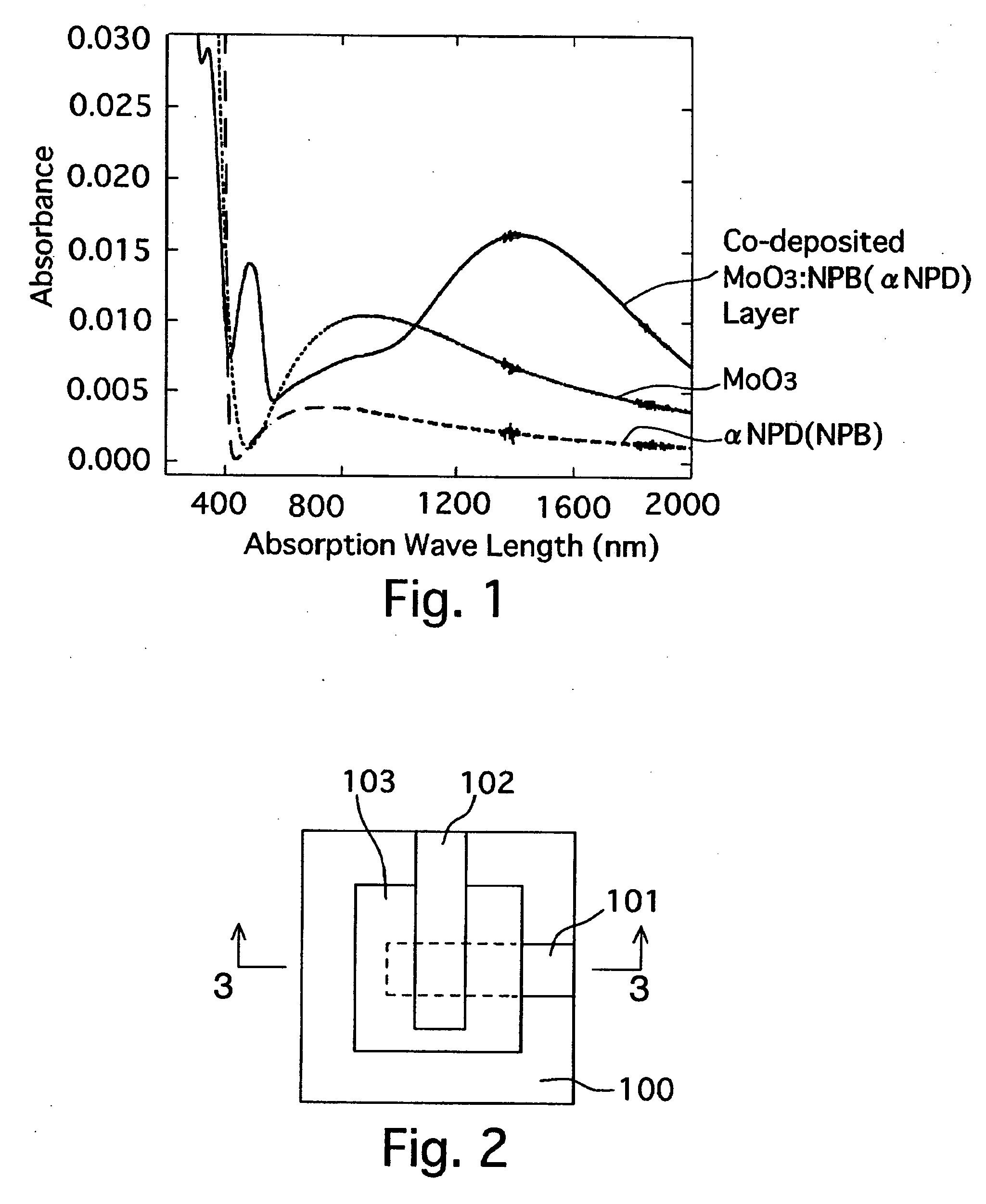
An organic device, including an organic compound having charge-transporting ability (i.e., transporting holes and / or electrons) and / or including organic light emissive molecules capable of emitting at least one of fluorescent light or phosphorescent light, has a charge transfer complex-contained layer including a charge transfer complex formed upon contact of an organic hole-transporting compound and molybdenum trioxide via a manner of lamination or mixing thereof, so that the organic hole-transporting compound is in a state of radical cation (i.e., positively charged species) in the charge transfer complex-contained layer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +1
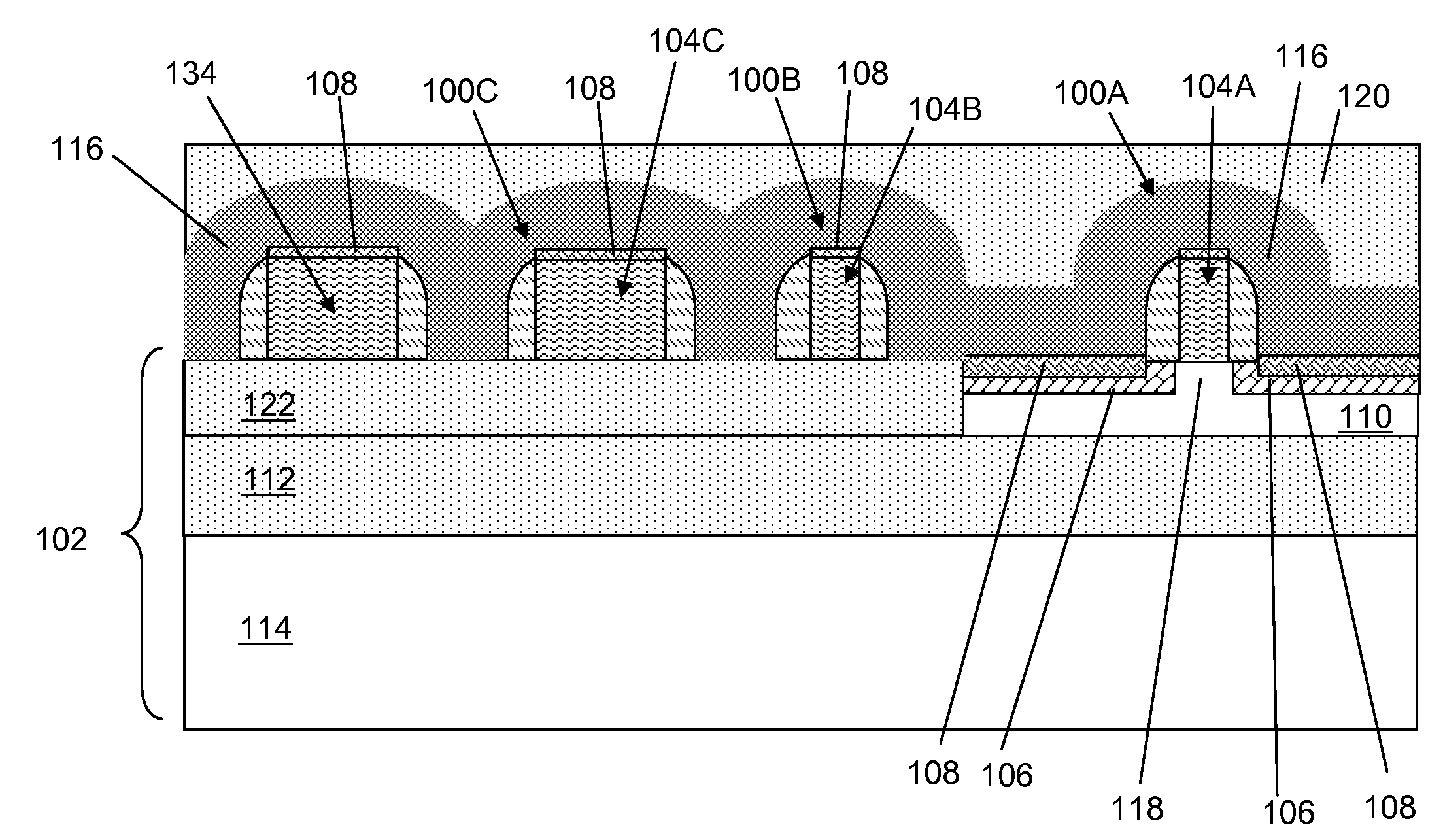
Methods of forming wiring to transistor and related transistor
InactiveUS7666723B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSoi substrate
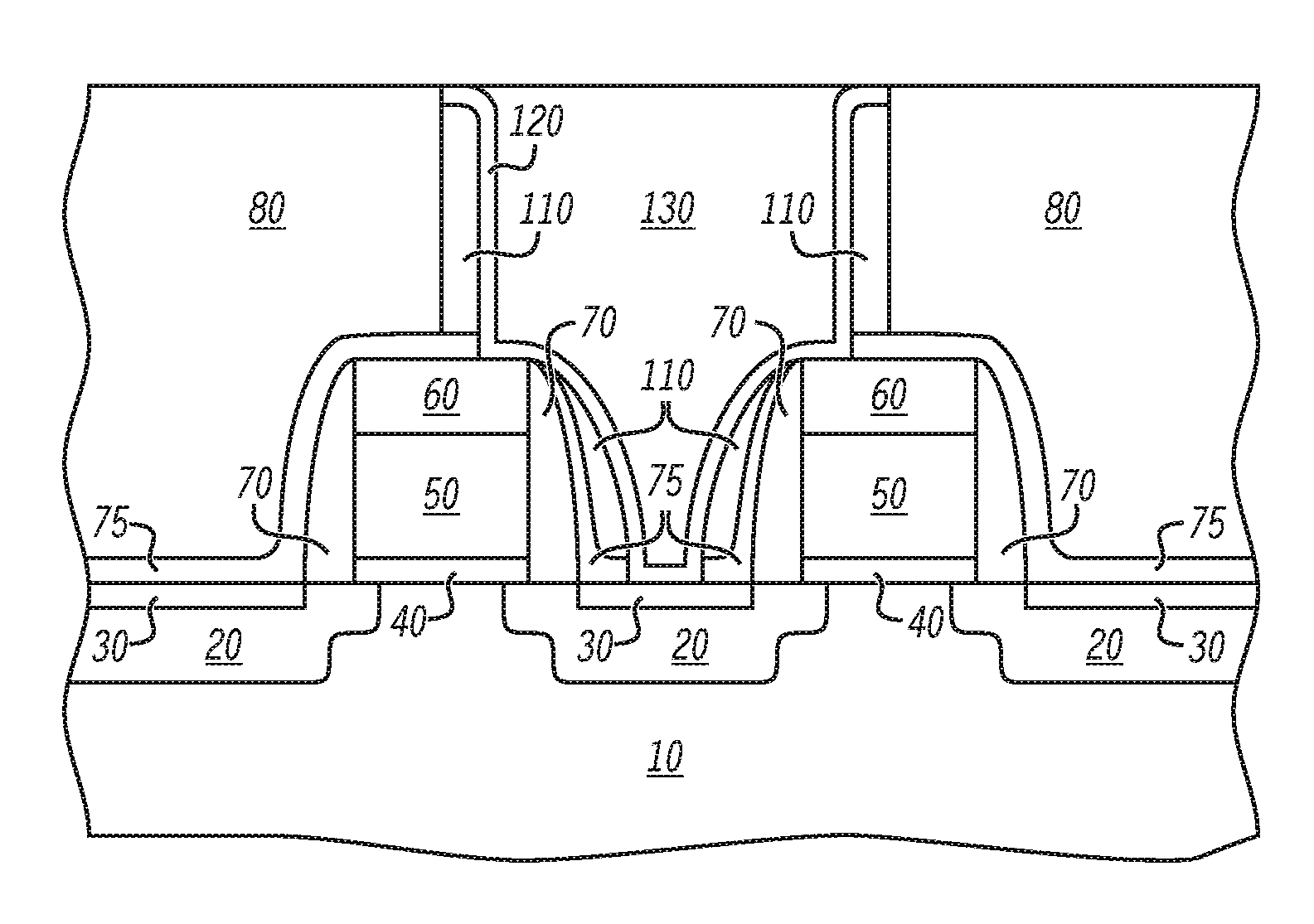
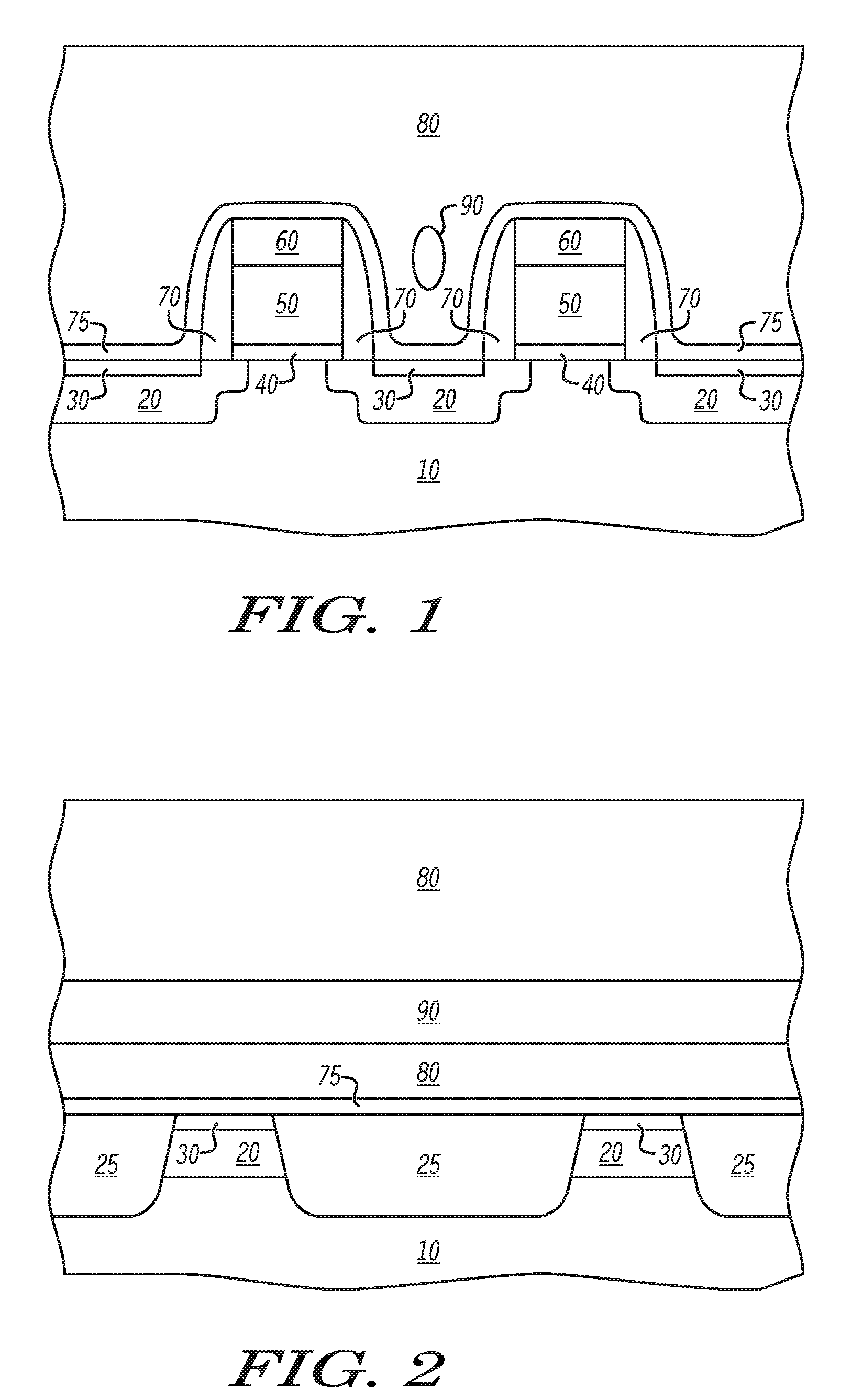
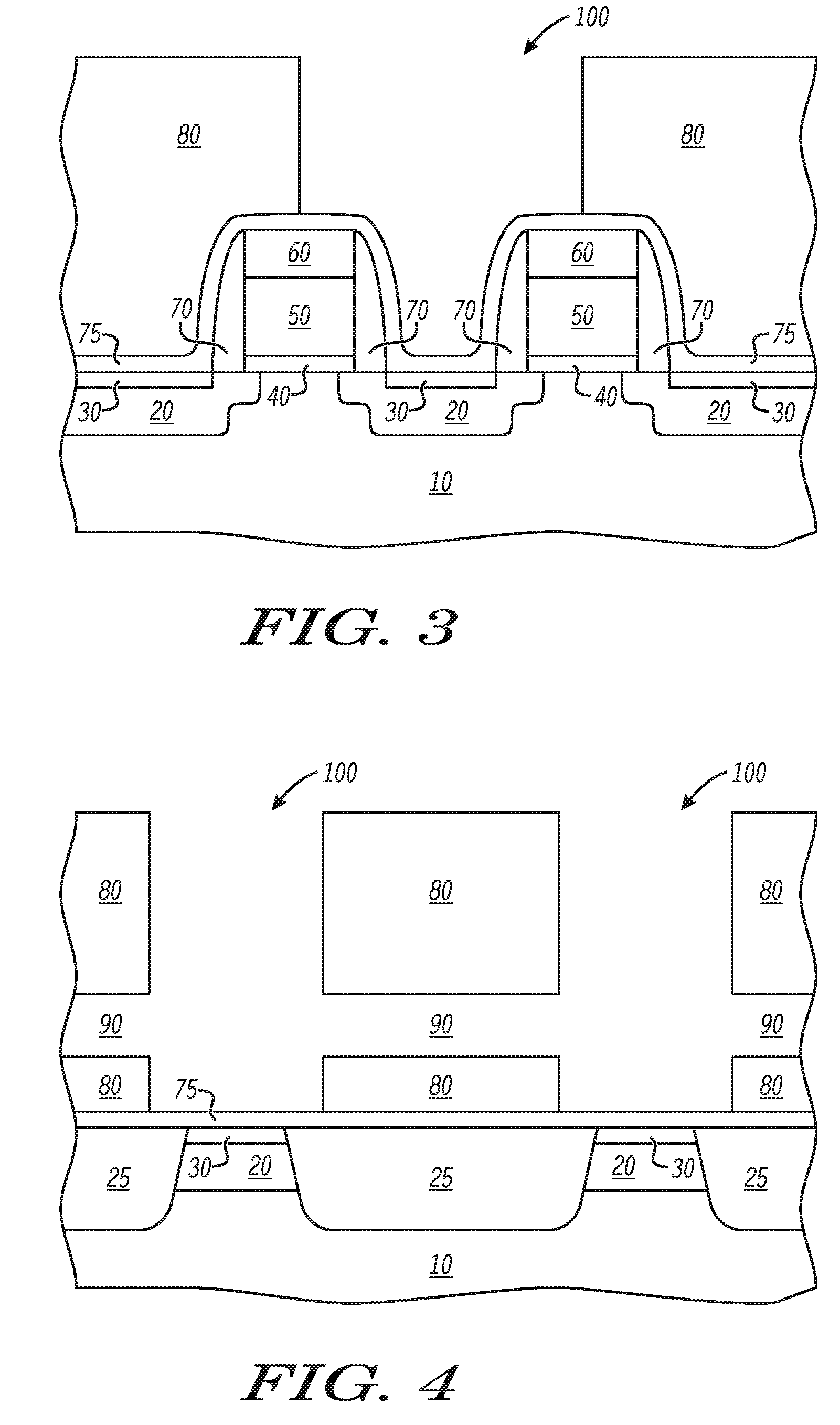
Methods of wiring to a transistor and a related transistor are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method includes a method of forming wiring to a transistor, the method comprising: forming a transistor on a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) substrate using masks that are mirror images of an intended layout, the forming including forming a gate and a source / drain region for each and a channel, the SOI substrate including a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) layer, a buried insulator layer and a silicon substrate; forming a dielectric layer over the transistor; bonding the dielectric layer to another substrate; removing the silicon substrate from the SOI substrate to the buried insulator layer; forming a contact to each of the source / drain region and the gate from a channel side of the gate; and forming at least one wiring to the contacts on the channel side of the gate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Backside contact for touchchip
InactiveUS6326689B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact formationContact pad
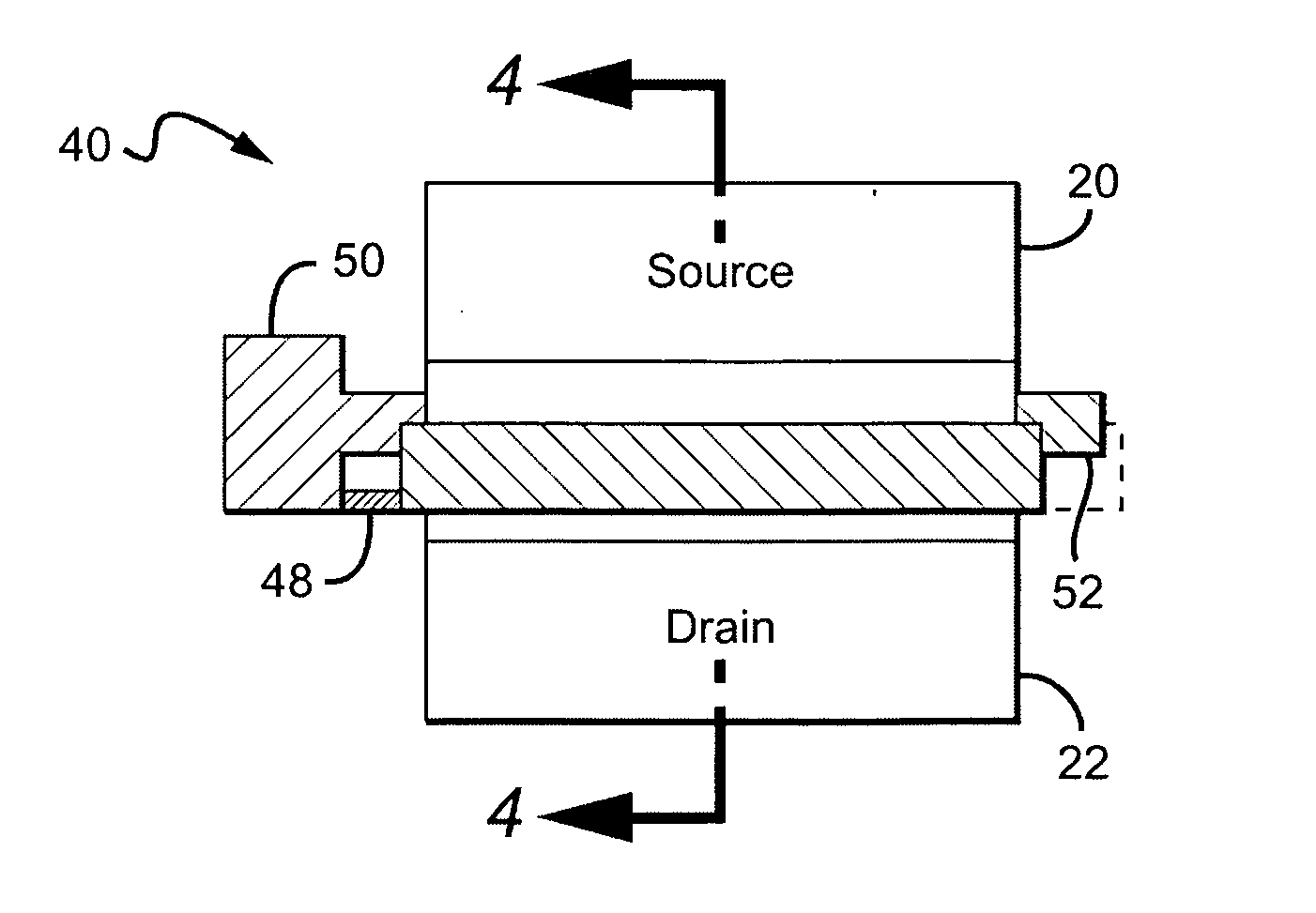
A contact is formed within an active region of a substrate at the edge of a die, preferably within the first metallization level in the active region of the substrate. An opening having sloped sidewalls is then etched into the back side of the substrate, exposing a portion of the active region contact. An interconnect is formed on the opening sidewall to connect the active region contact with a die contact pad on the backside surface of the substrate. The active region contact preferably spans a boundary between two die, with the opening preferably etched across the boundary to permit inter-connects on opposing sidewalls of the opening to each contact the active region contact within different die, connecting the active region contact to die contact pads on different dice. The dice are then separated along the boundary, through the active region contact which becomes two separate active region contacts. By forming a shared contact opening spanning two dice, the backside contact is formed around the die edge and the backside surface area necessary for the contact opening is minimized. The backside contact allows direct placement of the integrated circuit die on contacts within the packaging, such as a ball grid array, eliminating the need for wire bonds. The need for a pad etch through passivation material overlying active devices on the front side of the die is also eliminated, and no mask levels are added for the devices formed on the front side.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
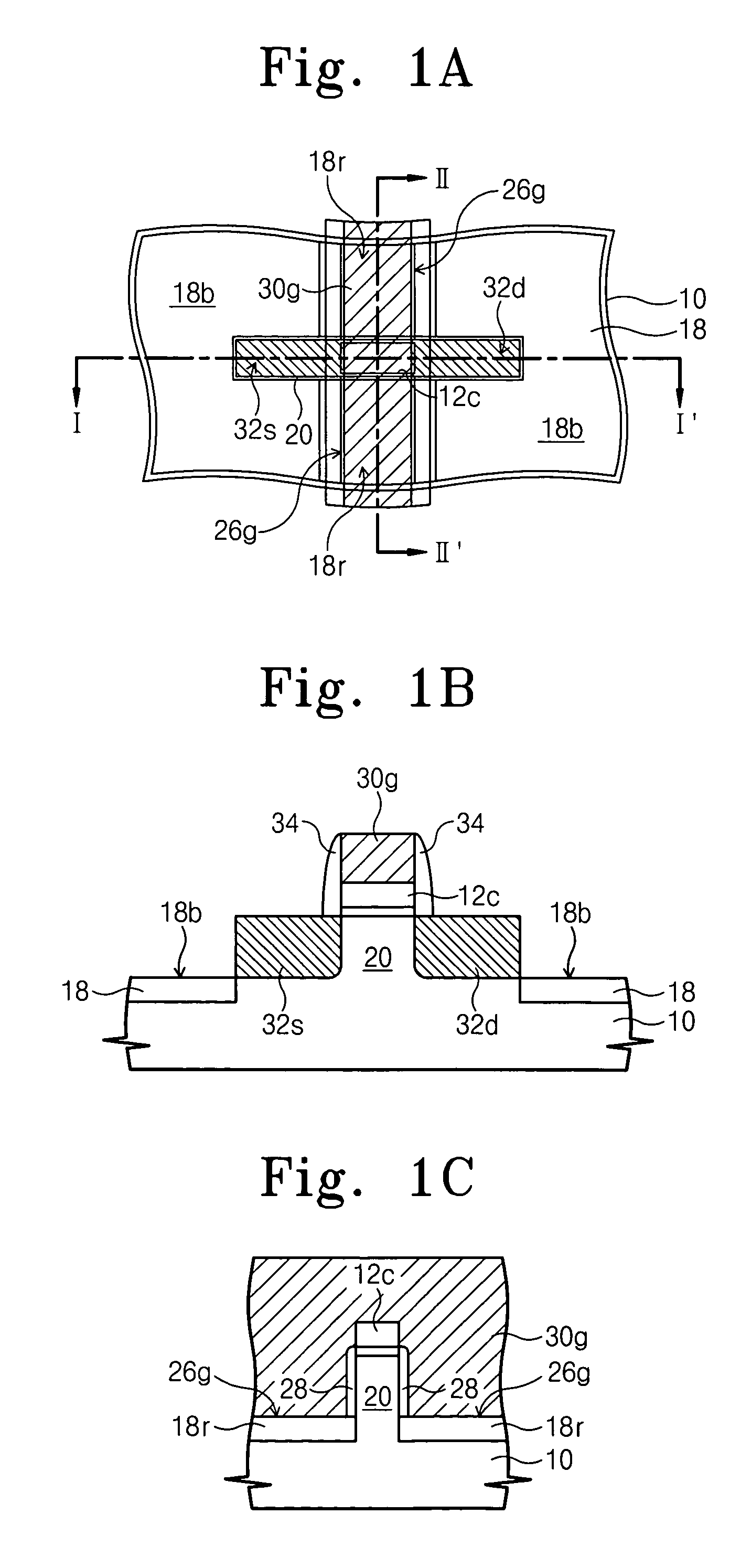
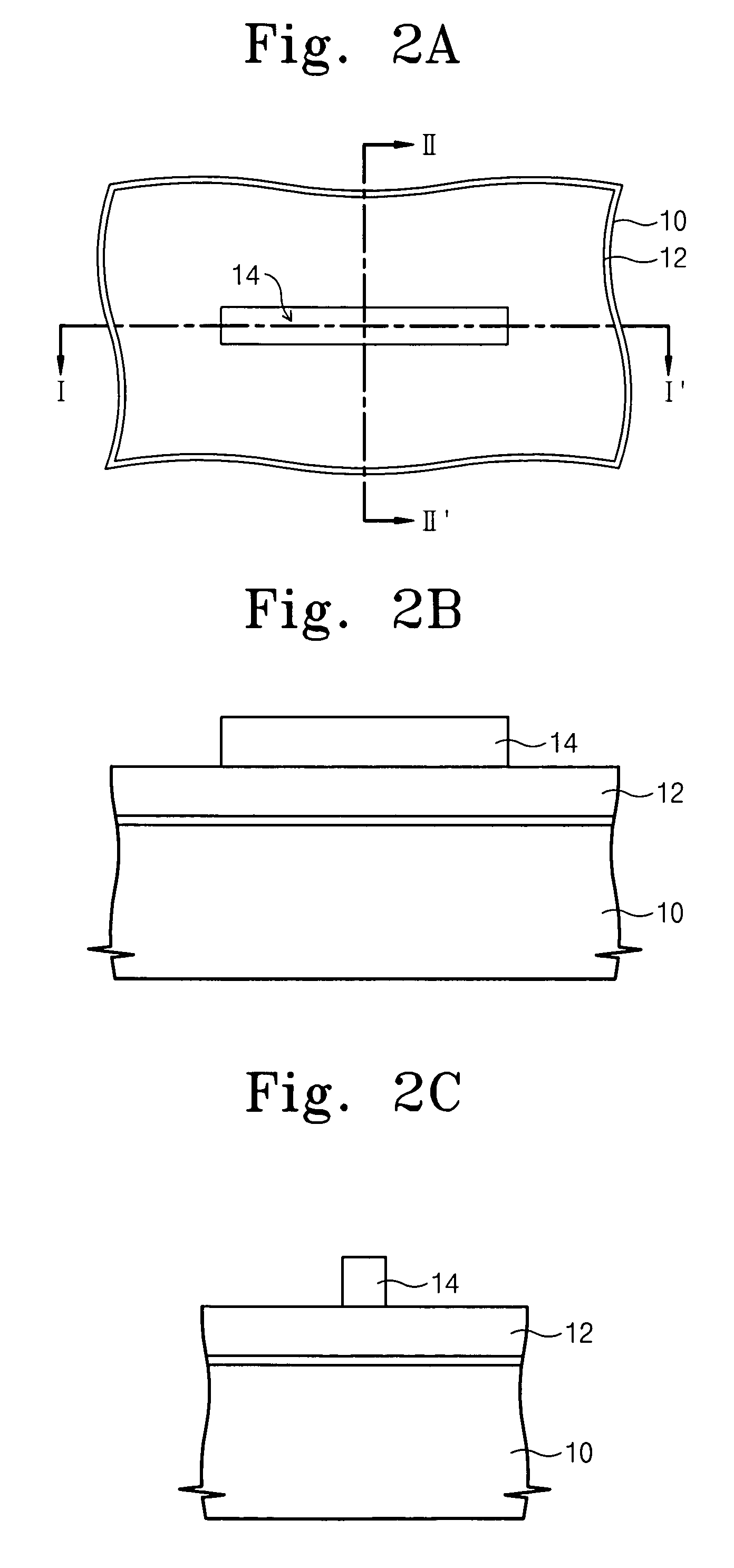
Semiconductor device with tapered gate and insulating film
InactiveUS6646287B1Reduce in quantityReduce manufacturing costTransistorSolid-state devicesContact formationActive matrix
In a semiconductor device, typically an active matrix display device, the structure of TFTs arranged in the respective circuits are made suitable in accordance with the function of the circuit, and along with improving the operating characteristics and the reliability of the semiconductor device, the manufacturing cost is reduced and the yield is increased by reducing the number of process steps. A semiconductor device has a semiconductor layer, an insulating film formed contacting the semiconductor layer, and a gate electrode having a tapered portion on the insulating film, in the semiconductor device, the semiconductor layer has a channel forming region, a first impurity region for forming a source region or a drain region and containing a single conductivity type impurity element, and a second impurity region for forming an LDD region contacting the channel forming region, a portion of the second impurity region is formed overlapping a gate electrode, and the concentration of the single conductivity type impurity element contained in the second impurity region becomes larger with distance from the channel forming region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method of blocking a void during contact formation process and device having the same
InactiveUS20080272492A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact formationEngineering
An electronic device can include conductive regions. A void can extend between different portions of an insulating layer. Different openings can intersect the void. A liner layer can substantially block the void, substantially preventing subsequently forming an electrical leakage path along the void. In one aspect, a stressor layer can be deposited over the conductive regions prior to forming the insulating layer. The liner layer can be formed over the stressor layer within the different openings through the insulating layer. In another aspect, an etch-stop layer can be formed over a silicide layer prior to forming the insulating layer. After removing a portion of the liner layer, a portion of the etch-stop layer can be removed to expose the silicide layer within the different openings. In yet another aspect, a nitride layer can lie between a substrate and the insulating layer and include a section of the openings.
Owner:NXP USA INC
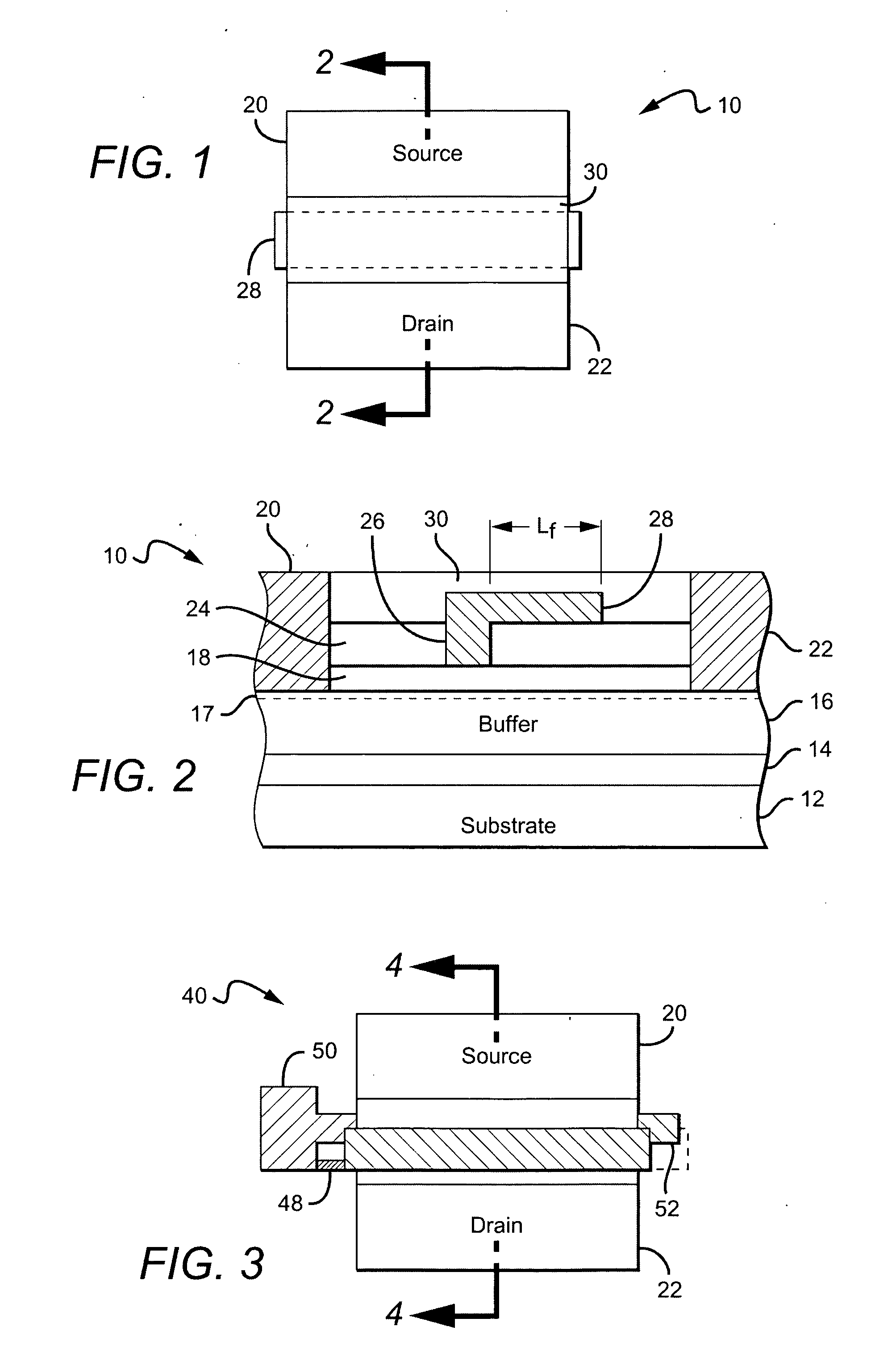
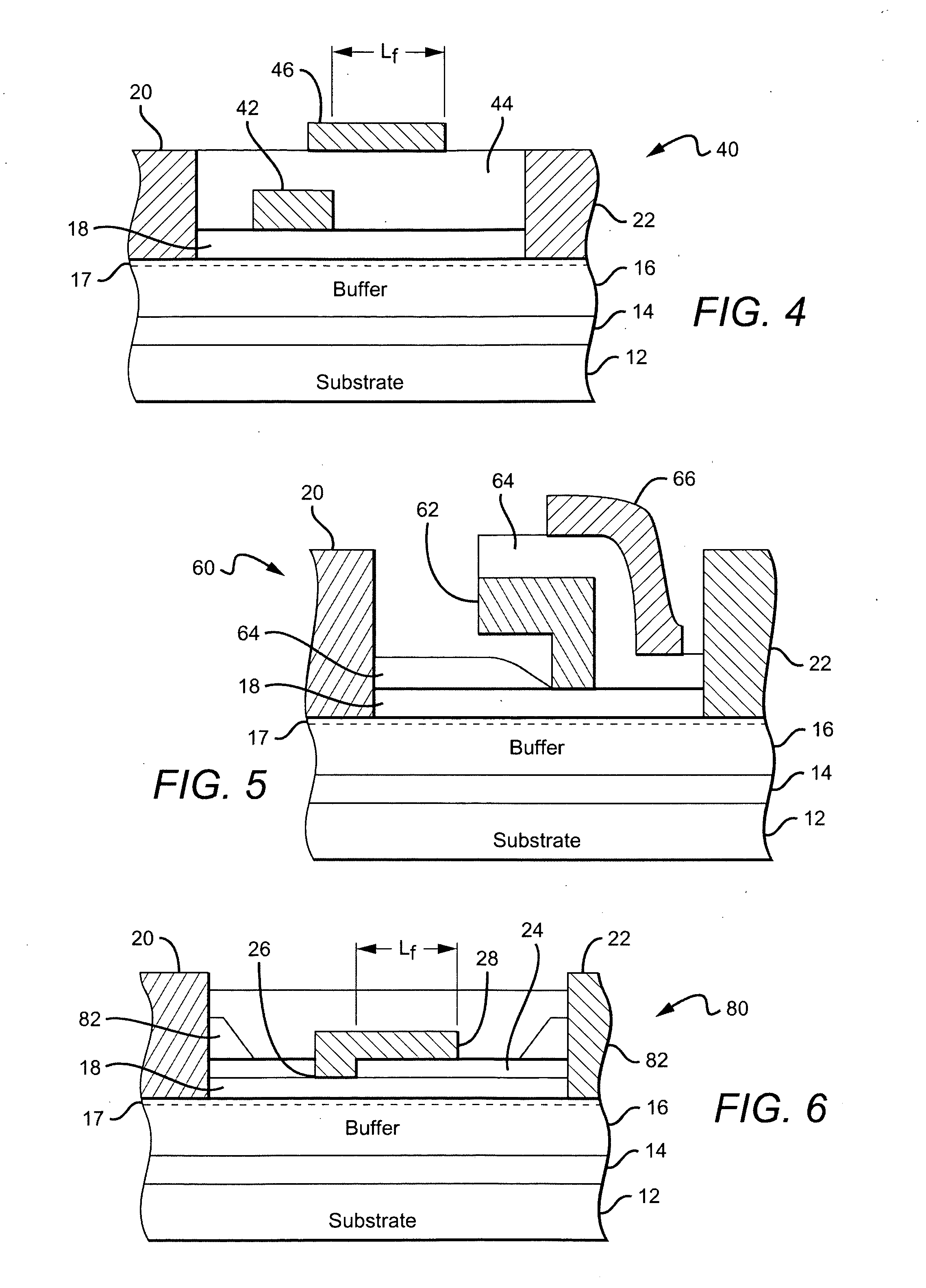
Wide bandgap transistor devices with field plates
Owner:CREE INC
Display device, manufacturing method thereof, and television set
InactiveUS20060027804A1Improve mobilityLow resistivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContact formationDisplay device
A manufacturing method of a display device having TFTs capable of high-speed operation with few variations of threshold voltage is provided, in which materials are used with high efficiency and a small number of photomasks is required. The display device of the invention comprises a gate electrode layer and a pixel electrode layer formed over an insulating surface, a gate insulating layer formed over the gate electrode layer, a crystalline semiconductor layer formed over the gate insulating layer, a semiconductor layer having one conductivity type formed in contact with the crystalline semiconductor layer, a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer formed in contact with the semiconductor layer having one conductivity type, an insulating later formed over the source electrode layer, the drain electrode layer, and the pixel electrode layer, a first opening formed in the insulating layer to reach the source electrode layer or the drain electrode layer, a second opening formed in the gate insulating layer and the insulating layer to reach the pixel electrode layer, and a wiring layer formed in the first opening and the second opening to electrically connect the source electrode layer or the drain electrode layer to the pixel electrode layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light emitting apparatus and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20030089991A1Improve barrier propertiesInhibit deteriorationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSimple Organic CompoundsContact formation
The purpose of the invention is to improve reliability of a light emitting apparatus comprising TFTs and organic light emitting elements. The light emitting apparatus according to the invention having thin film transistors and light emitting elements, comprises; a second inorganic insulation layer on a gate electrode, a first organic insulation layer on the second inorganic insulation layer, a third inorganic insulation layer on the first organic insulation layer, an anode layer formed on the third inorganic insulation layer, a second organic insulation layer overlapping with the end of the anode layer and having an inclination angle of 35 to 45 degrees, a fourth inorganic insulation layer formed on the upper surface and side surface of the second organic insulation layer and having an opening over the anode layer, an organic compound layer formed in contact with the anode layer and the fourth inorganic insulation layer and containing light emitting material, and a cathode layer formed in contact with the organic compound layer containing the light emitting material, wherein the third inorganic insulation layer and the fourth inorganic insulation layer are formed with silicon nitride or aluminum nitride.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
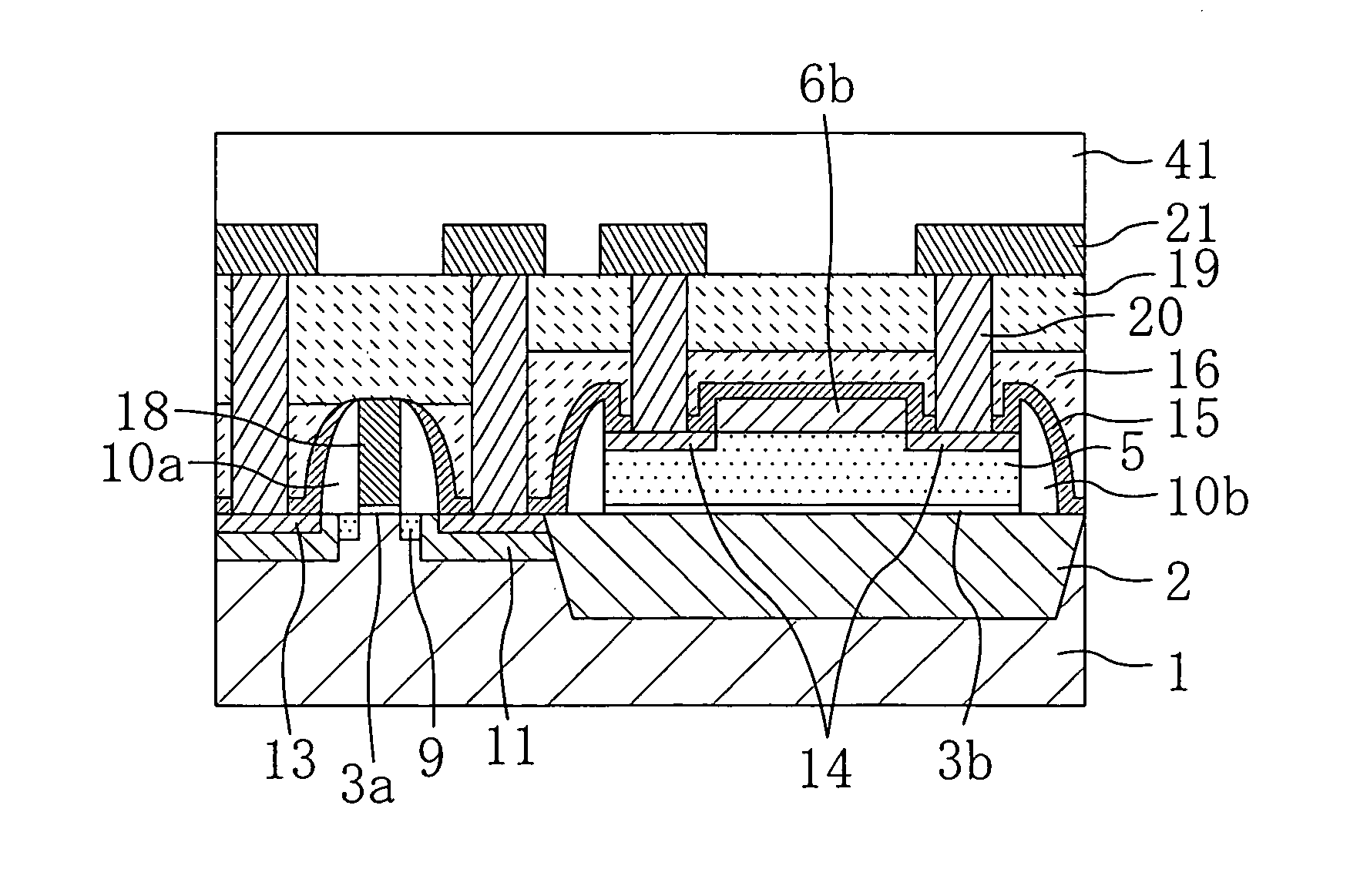
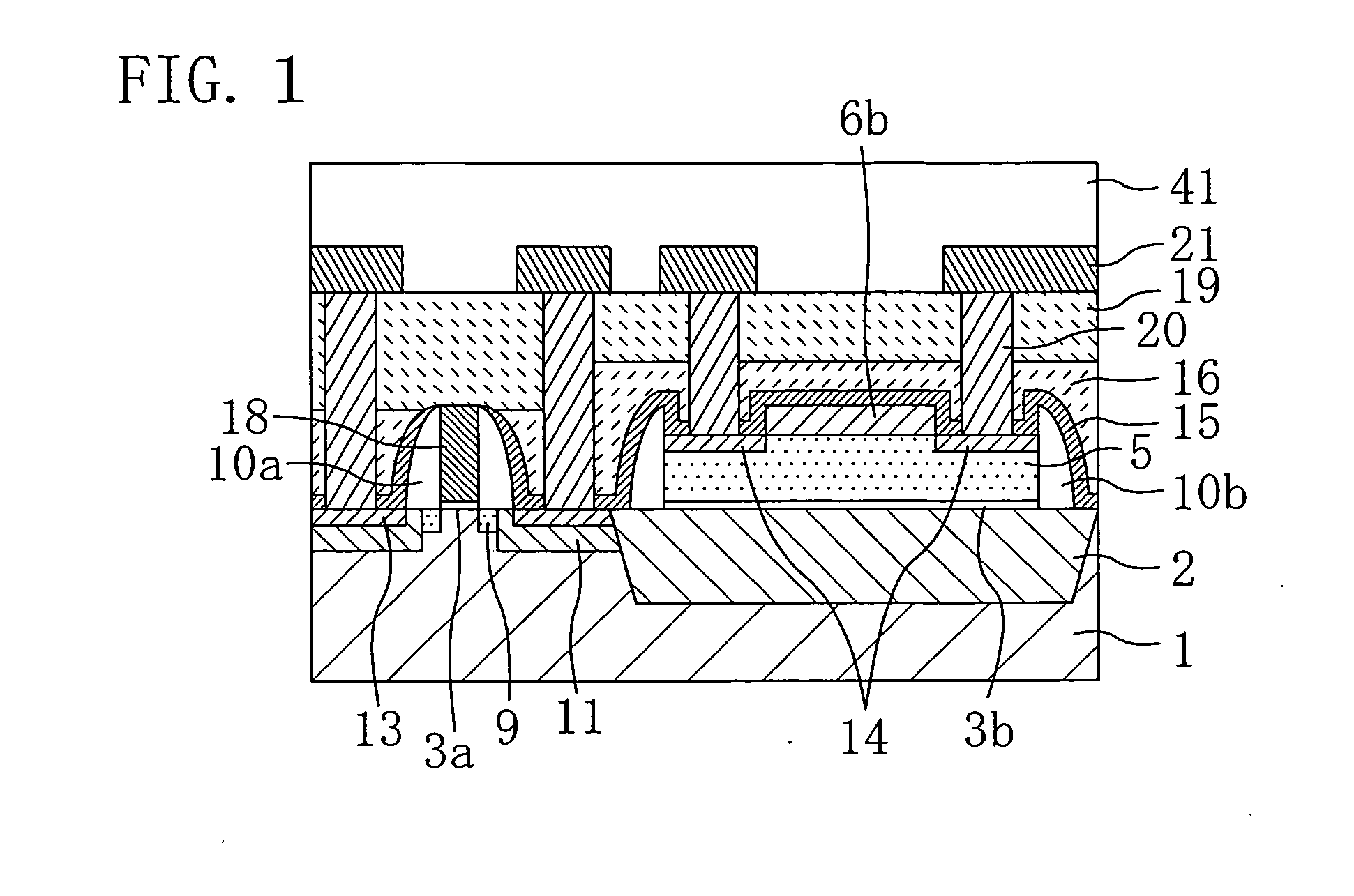
Probing device and manufacturing method thereof, as well as testing apparatus and manufacturing method of semiconductor with use thereof
InactiveUS6900646B2High densityImprove accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingContact formationElectricity
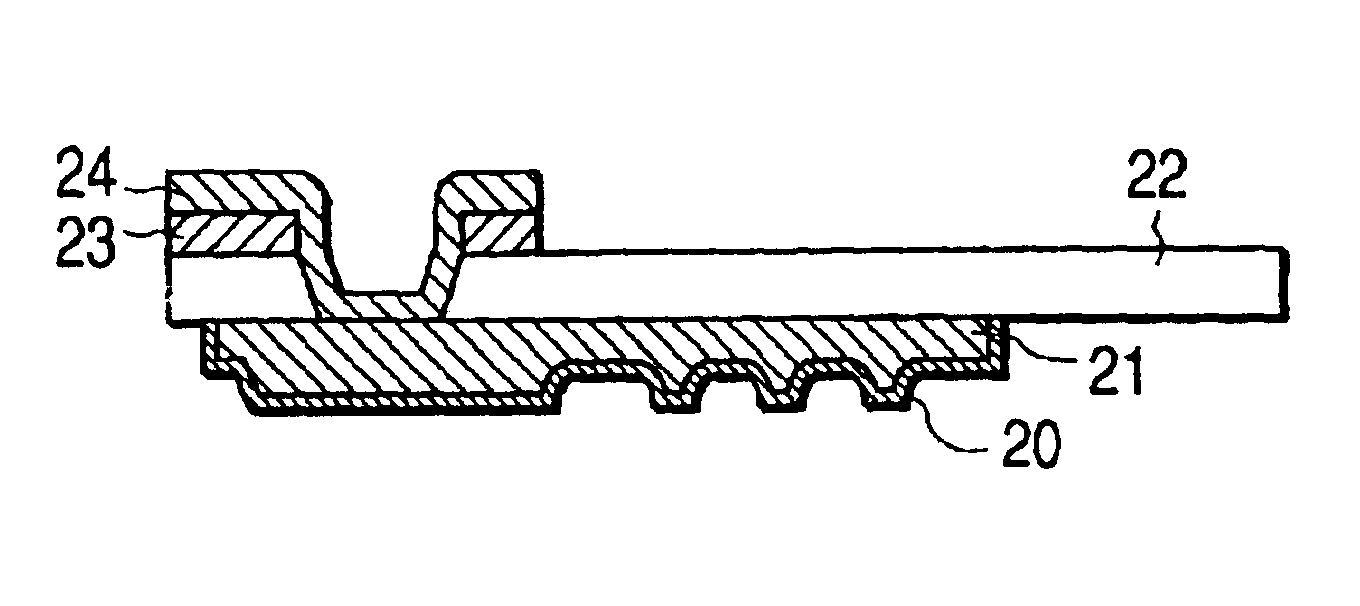
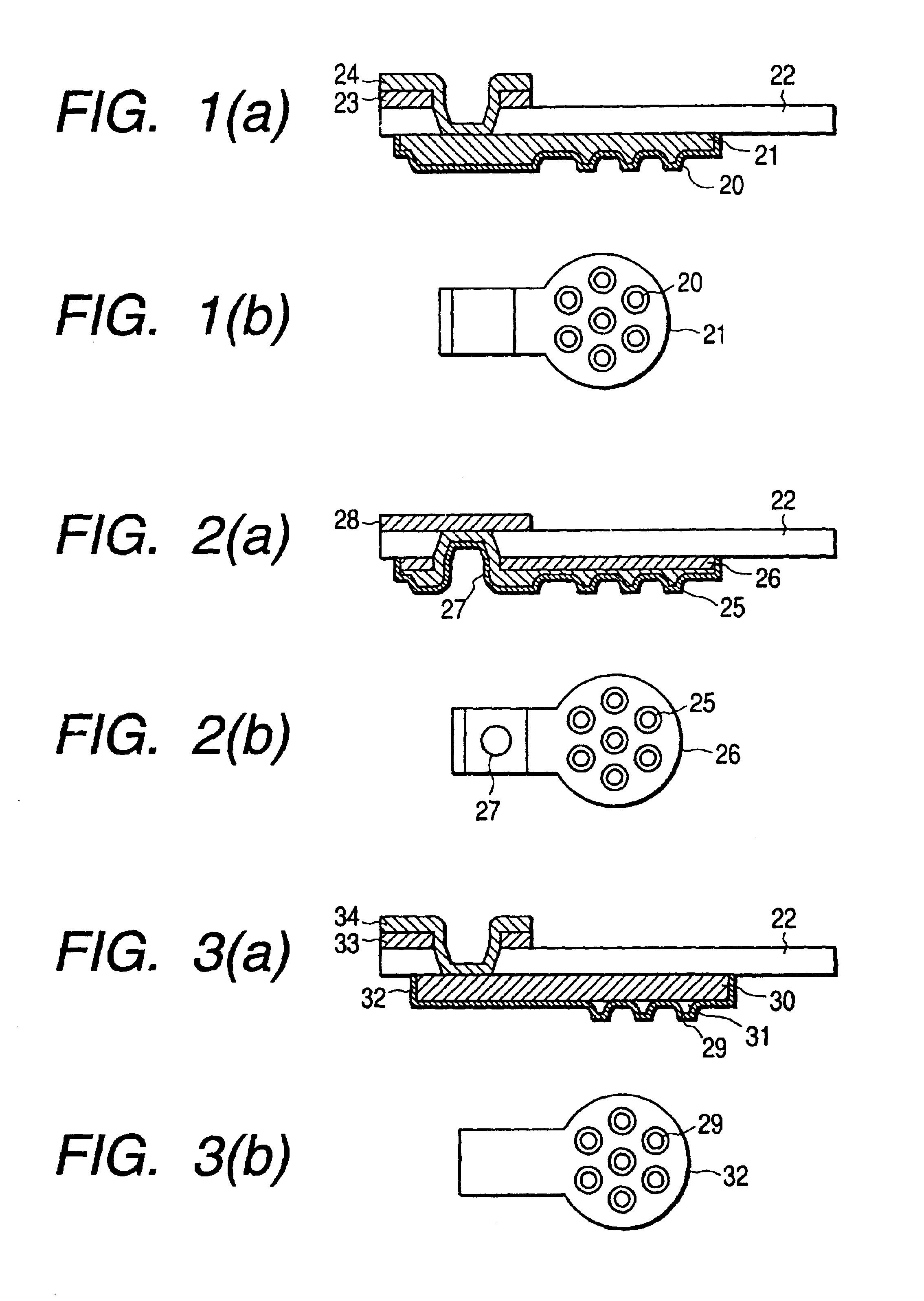
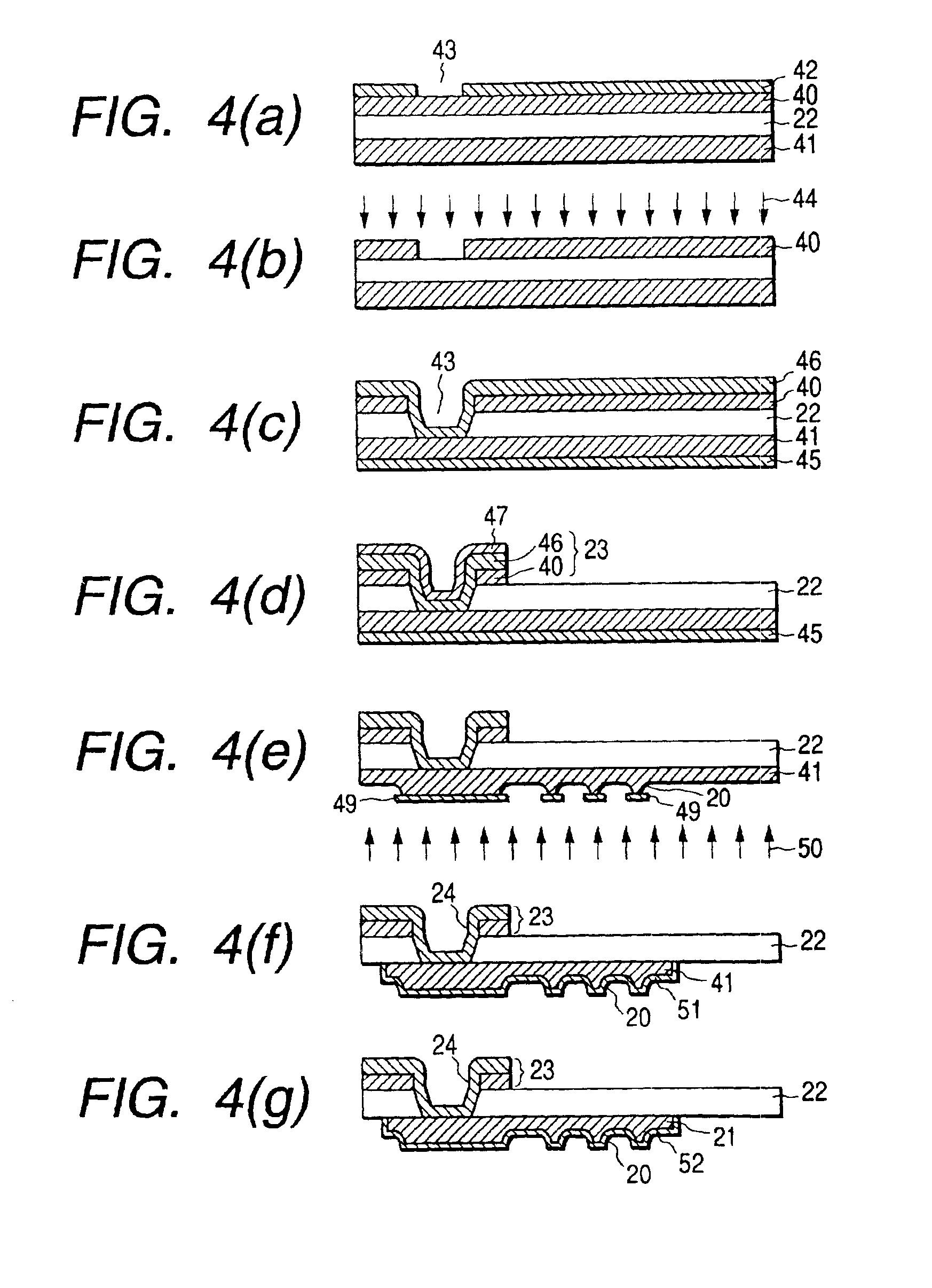
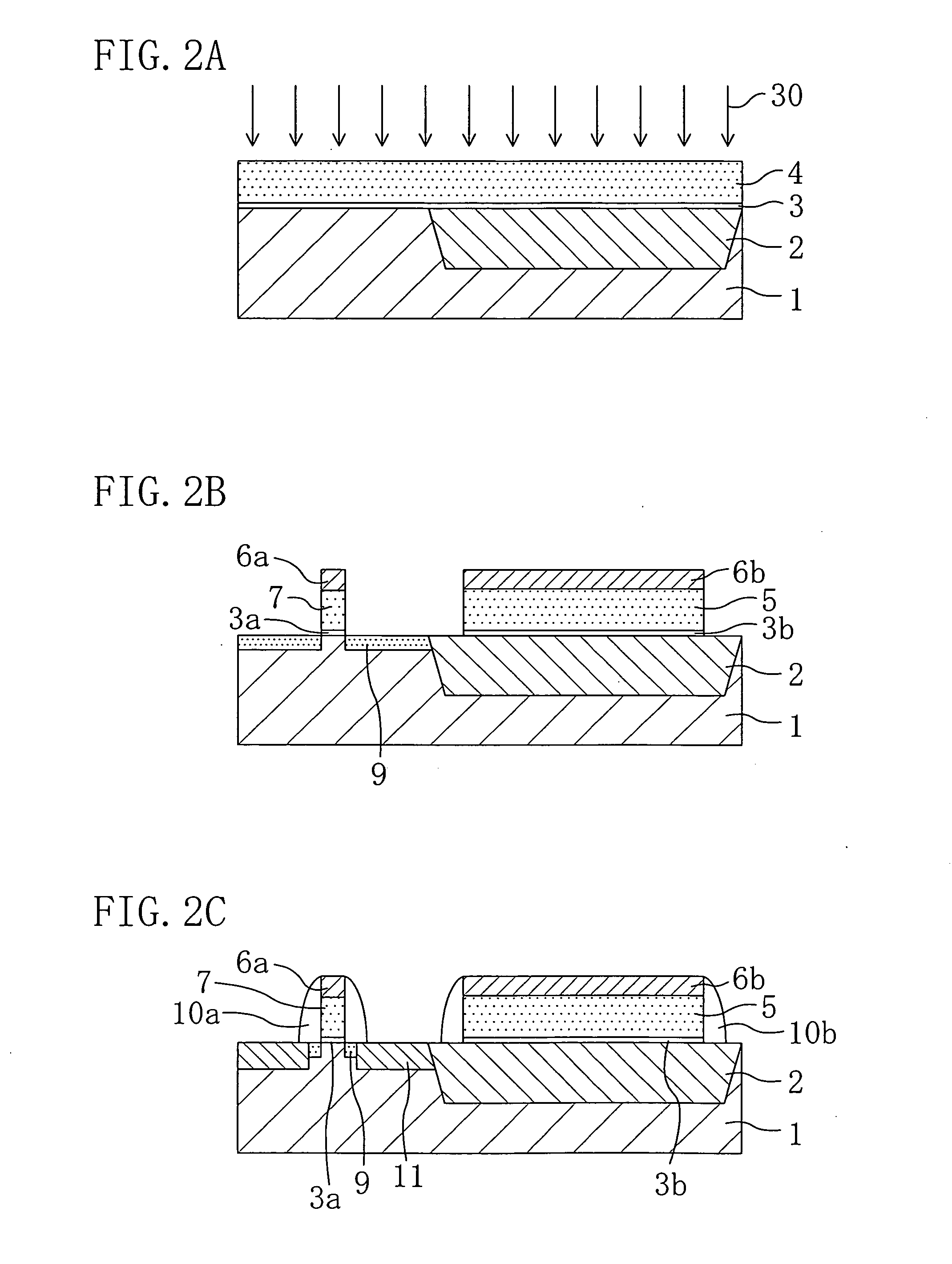
A probing device for electrically contacting with a plurality of electrodes 3, 6 aligned on an object 1 to be tested so as to transfer electrical signal therewith, comprising: a wiring sheet being formed by aligning a plurality of contact electrodes 21, 110b, corresponding to each of said electrodes, each being planted with projecting probes 20, 110a covered with hard metal films on basis of a conductor thin film 41 formed on one surface of an insulator sheet 22 of a polyimide film by etching thereof, while extension wiring 23, 110c for electrically connecting to said each of said contact electrodes being formed on basis of a conductor thin film formed on either said one surface or the other surface opposing thereto of said insulator sheet of the polyimide film; and means for giving contacting pressure for obtaining electrical conduction between said extension wiring and said object to be tested by contacting tips of said projecting contact probe formed onto said each contact electrode through giving pressuring force between said wiring sheet and said object to be tested.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for bottomless deposition of barrier layers in integrated circuit metallization schemes
InactiveUS6852635B2Avoid depositionPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsContact formationEngineering
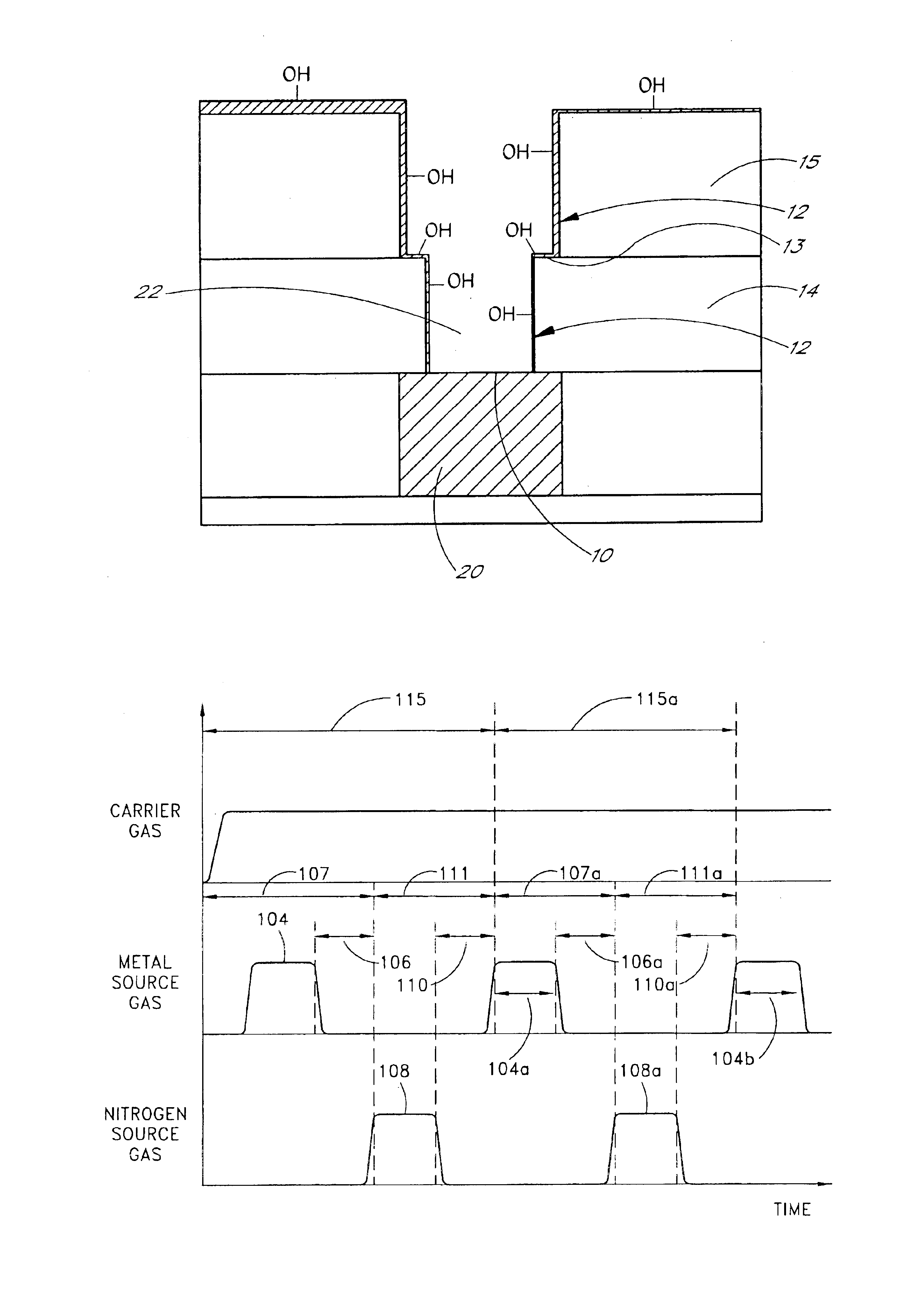
Methods are disclosed for selective deposition on desired materials. In particular, barrier materials are selectively formed on insulating surfaces, as compared to conductive surfaces. In the context of contact formation and trench fill, particularly damascene and dual damascene metallization, the method advantageously lines insulating surfaces with a barrier material. The selective formation allows the deposition to be “bottomless,” thus leaving the conductive material at a via bottom exposed for direct metal-to-metal contact when further conductive material is deposited into the opening after barrier formation on the insulating surfaces. Desirably, the selective deposition is accomplished by atomic layer deposition (ALD), resulting in highly conformal coverage of the insulating sidewalls in the opening.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICROELECTRONICA CENT VZW (IMEC) +2
Nitride semiconductor light emitting device
ActiveUS20080251781A1Reduce crystal defect densityIncrease brightnessSemiconductor devicesContact formationInter layer
There is provided a nitride semiconductor light emitting device including: an n-type semiconductor region; an active layer formed on the n-type semiconductor region; a p-type semiconductor region formed on the active layer; an n-electrode disposed in contact with the n-type semiconductor region; a p-electrode formed on the p-type semiconductor region; and at least one intermediate layer formed in at least one of the n-type semiconductor region and the p-type semiconductor region, the intermediate layer disposed above the n-electrode, wherein the intermediate layer is formed of a multi-layer structure where at least three layers with different band gaps from one another are deposited, wherein the multi-layer structure includes one of an AlGaN layer / GaN layer / InGaN layer stack and an InGaN layer / GaN layer / AlGaN layer stack.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
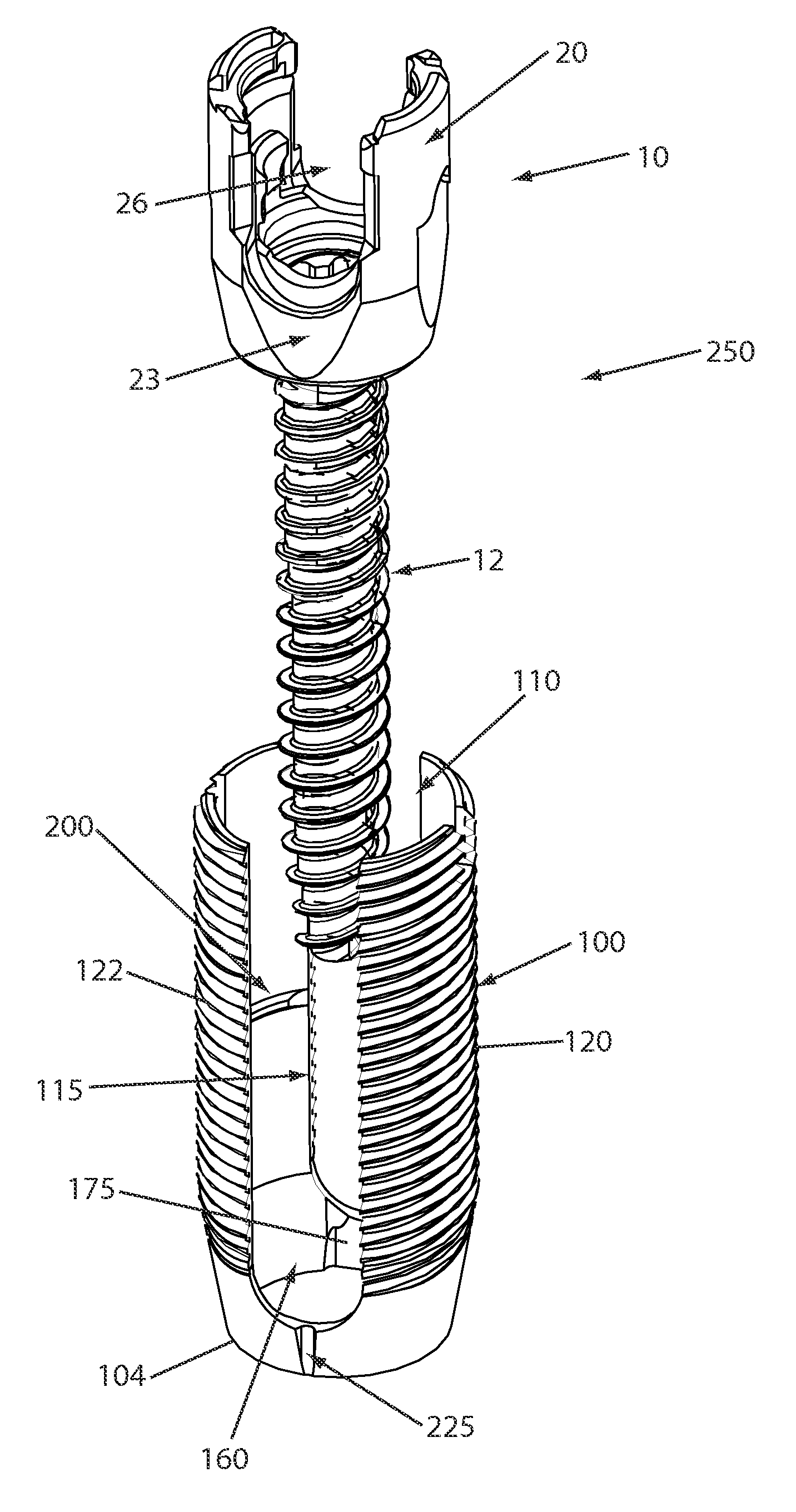
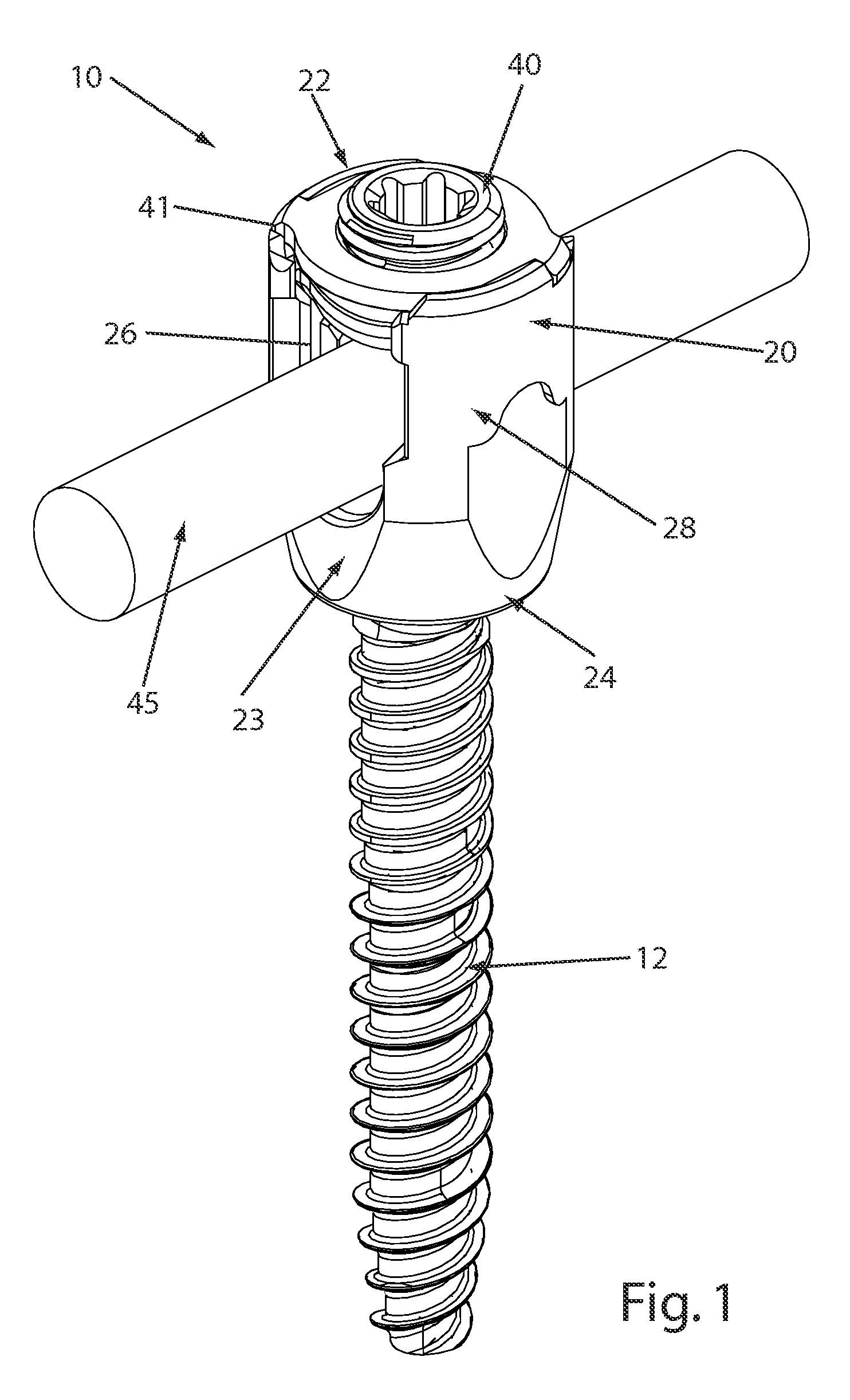
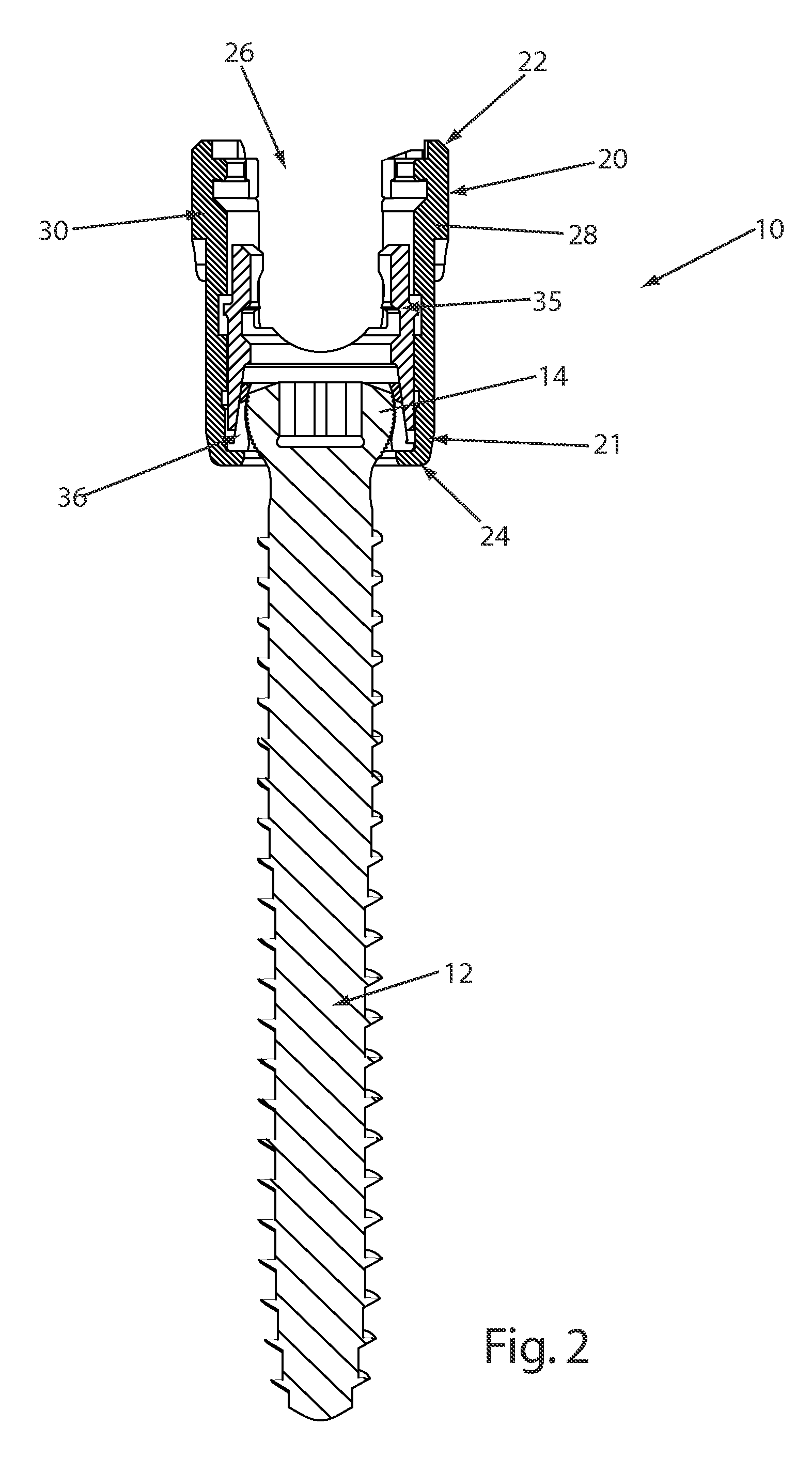
Reduction sleeve
A reduction sleeve for facilitating insertion of a spinal rod into a rod-receiving channel formed in a bone fixation element. The reduction sleeve may include a through-bore sized and configured to receive the bone fixation element and a substantially transverse channel sized and configured to receive the spinal rod. The channel being substantially aligned with the rod-receiving channel formed in the bone fixation element so that, once the bone fixation element has been inserted into the reduction sleeve, the spinal rod can pass through the aligned channels. The reduction sleeve may also include at least one break-off point or region for facilitating breaking and removal of the reduction sleeve once the spinal rod has been clamped into the rod-receiving channel of the bone fixation element. The reduction sleeve may also include a plurality of threads formed thereon for engaging a reduction instrument, an alignment mechanism so that the bone fixation element can only be inserted into the reduction sleeve when the rod-receiving channels are aligned, and an inwardly projecting protrusion formed on the inner surface of the reduction sleeve so that, once inserted, the projection contacts a top surface formed on the bone fixation element.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Magnetoresistive element and magnetoresistive random access memory including the same
ActiveUS20090080238A1Lower average currentMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesContact formationMagnetic reluctance
The present invention provides a low-resistance magnetoresistive element of a spin-injection write type. A crystallization promoting layer that promotes crystallization is formed in contact with an interfacial magnetic layer having an amorphous structure, so that crystallization is promoted from the side of a tunnel barrier layer, and the interface between the tunnel barrier layer and the interfacial magnetic layer is adjusted. With this arrangement, it is possible to form a magnetoresistive element that has a low resistance so as to obtain a desired current value, and has a high TMR ratio.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
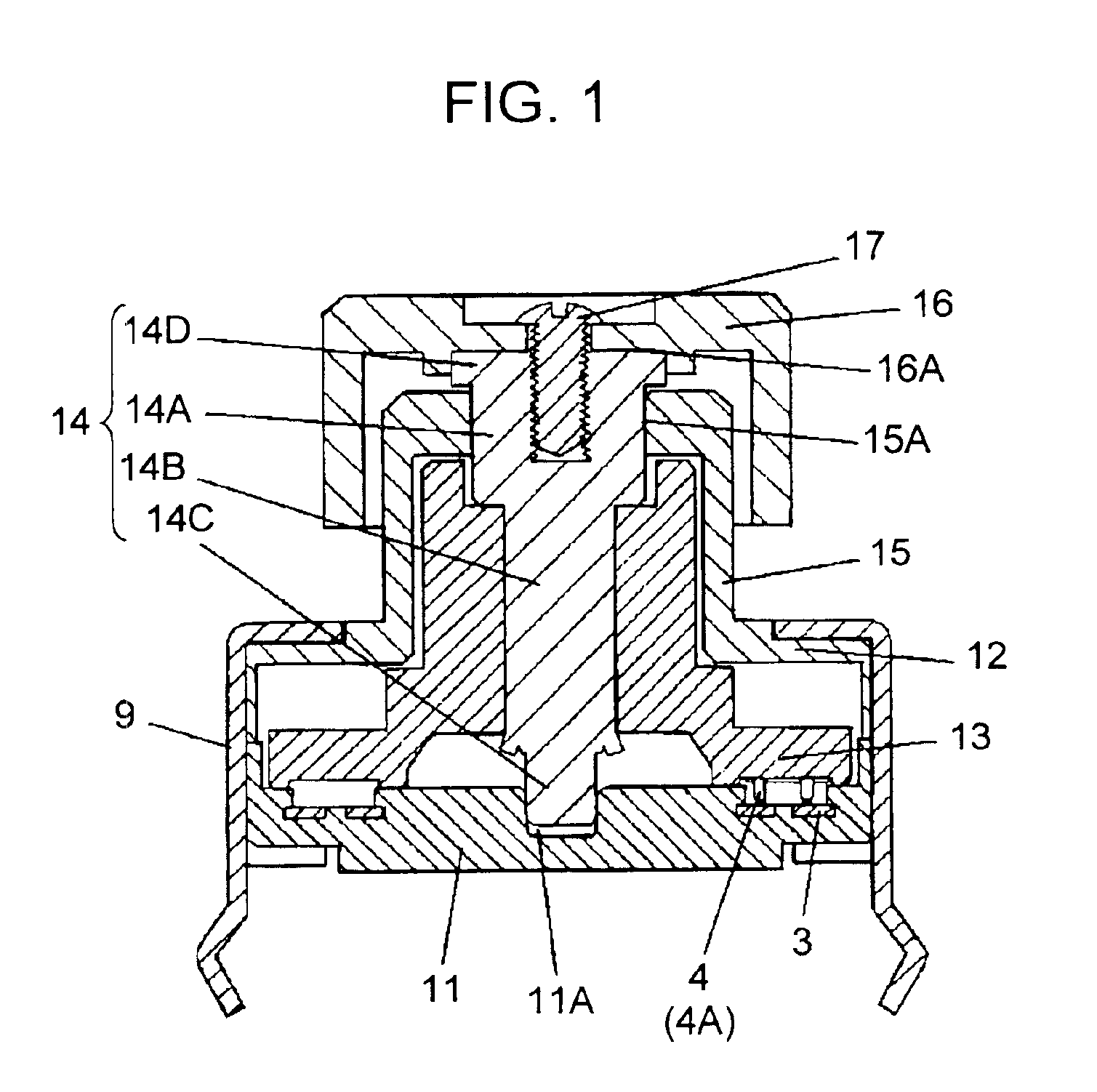
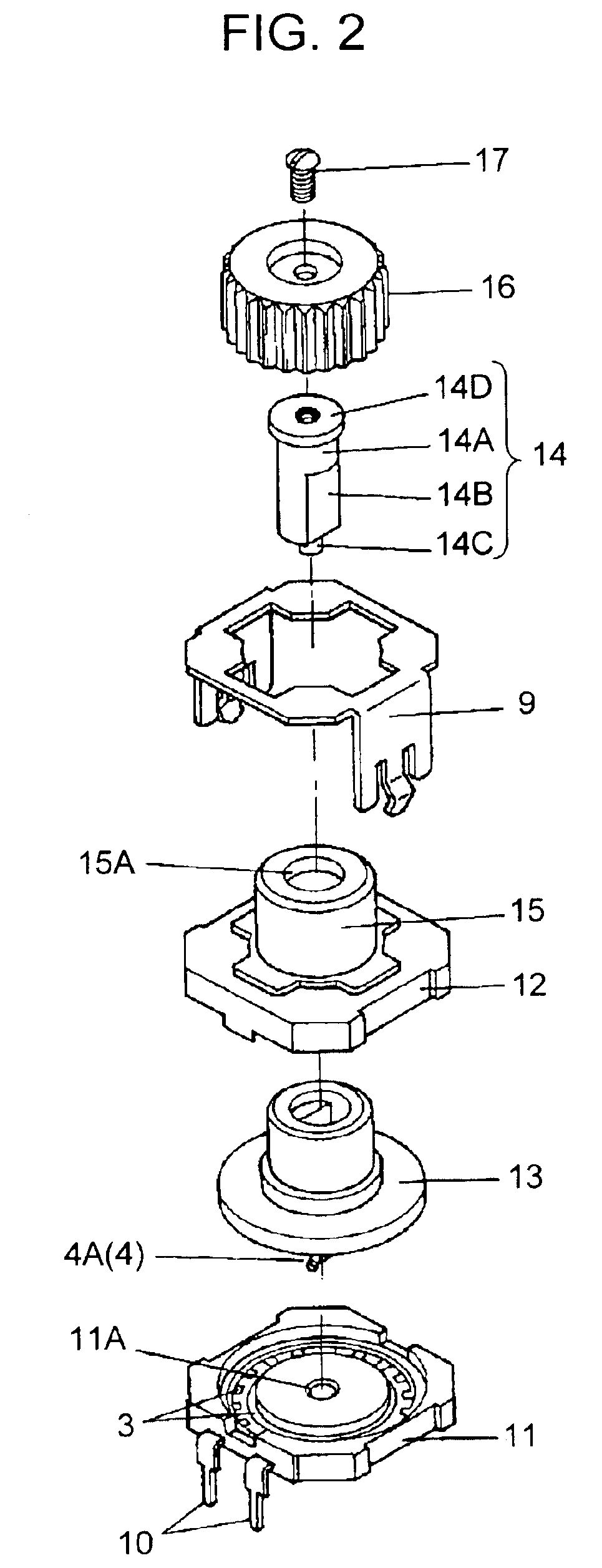
Rotary manipulation type electronic component
InactiveUS6998553B2Contact operating partsResisitors with sliding contactContact formationEngineering
A rotary manipulation type electronic component includes a space formed by a case. A base houses a rotating body holding a resilient contact as a movable element. A comb-like contact is formed as a fixed element. A first bushing in the case and a second bushing in the base rotatably support a rotating shaft that rotates together with the rotating body. An inner bottom face of a cap-shaped knob is secured onto an end of the rotating shaft so that the knob receives a barrel portion, which supports the rotating shaft as a portion of the case.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
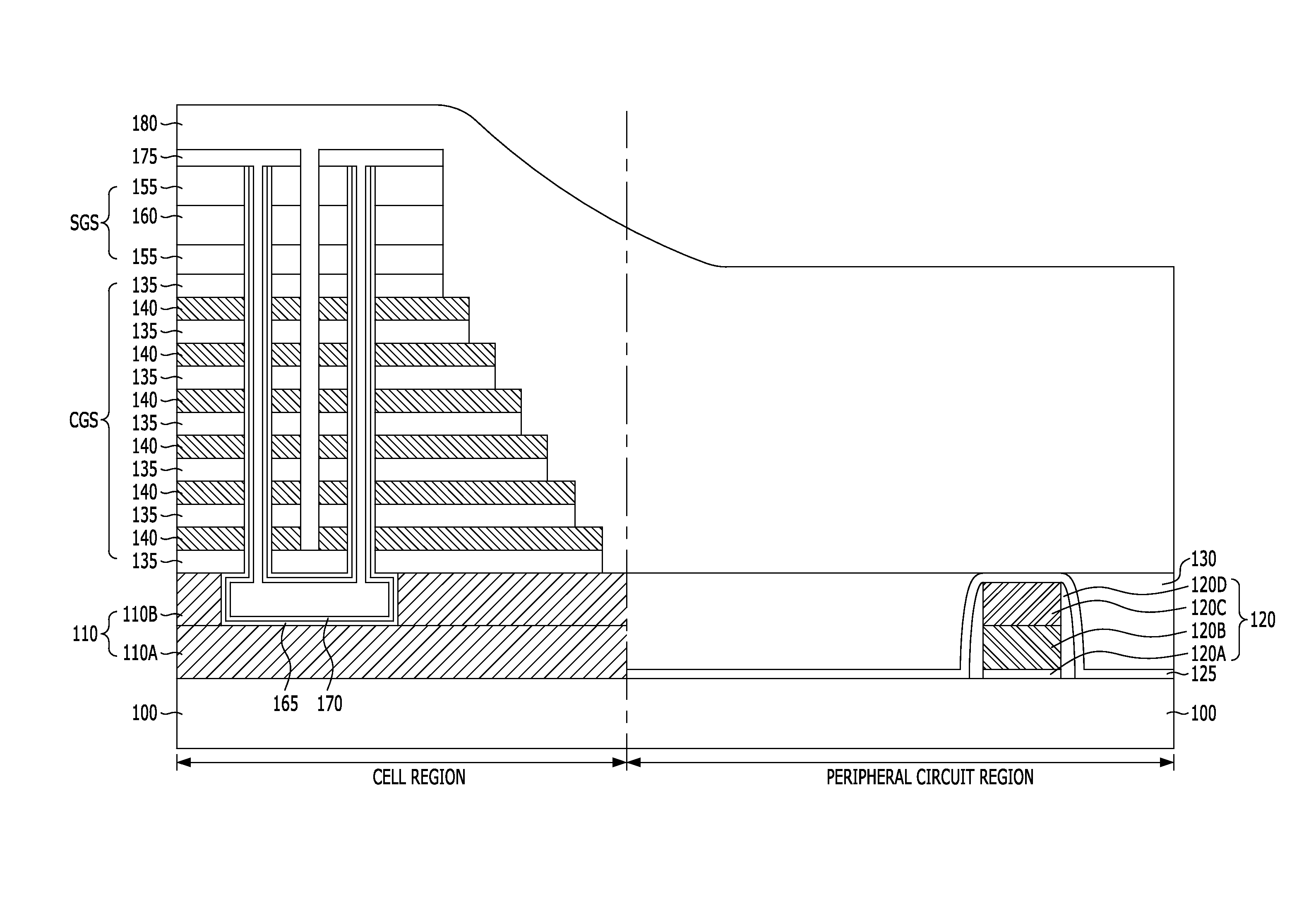
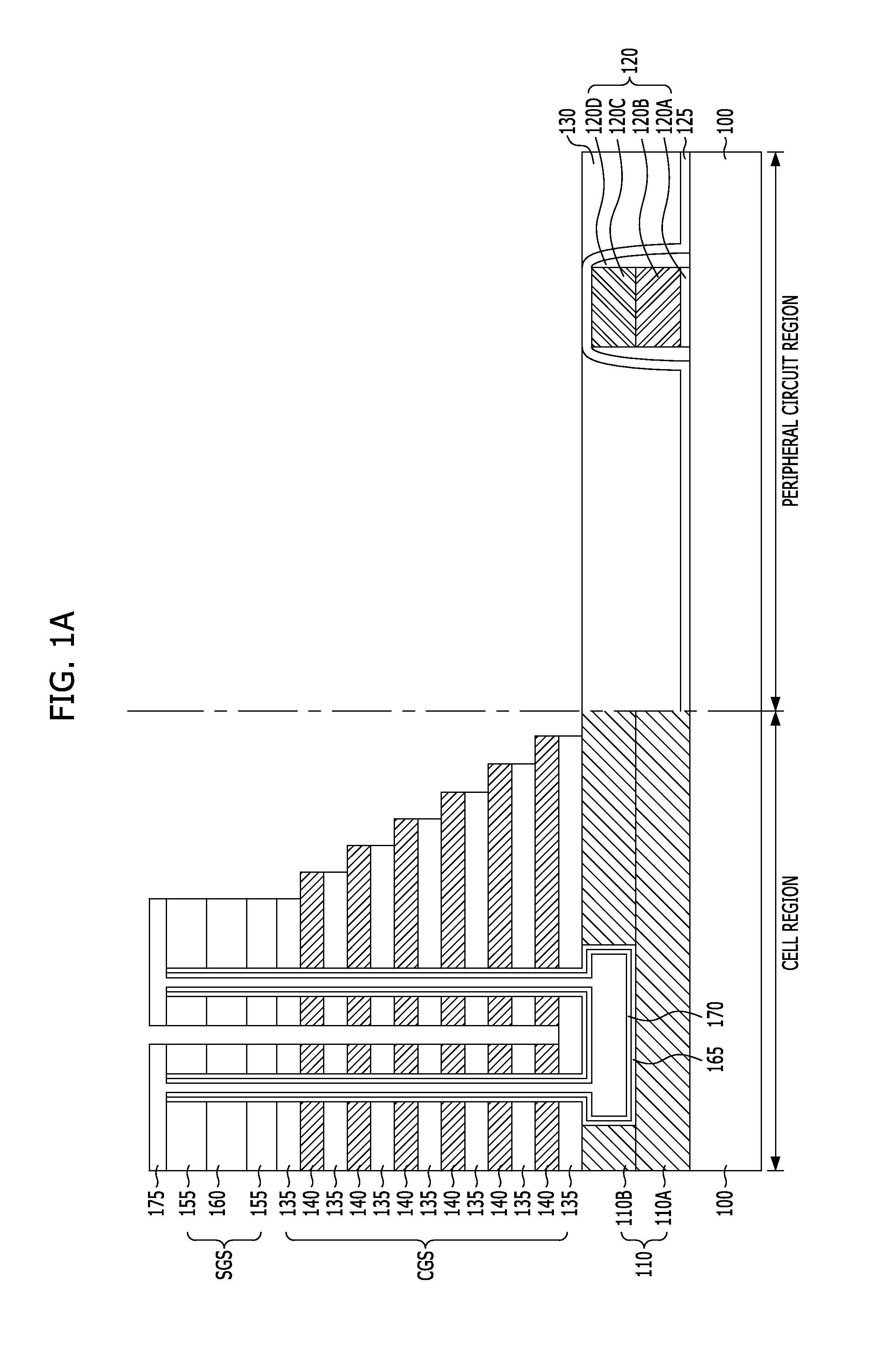
Non-volatile memory device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20120168858A1Reduce step heightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContact formationInter layer
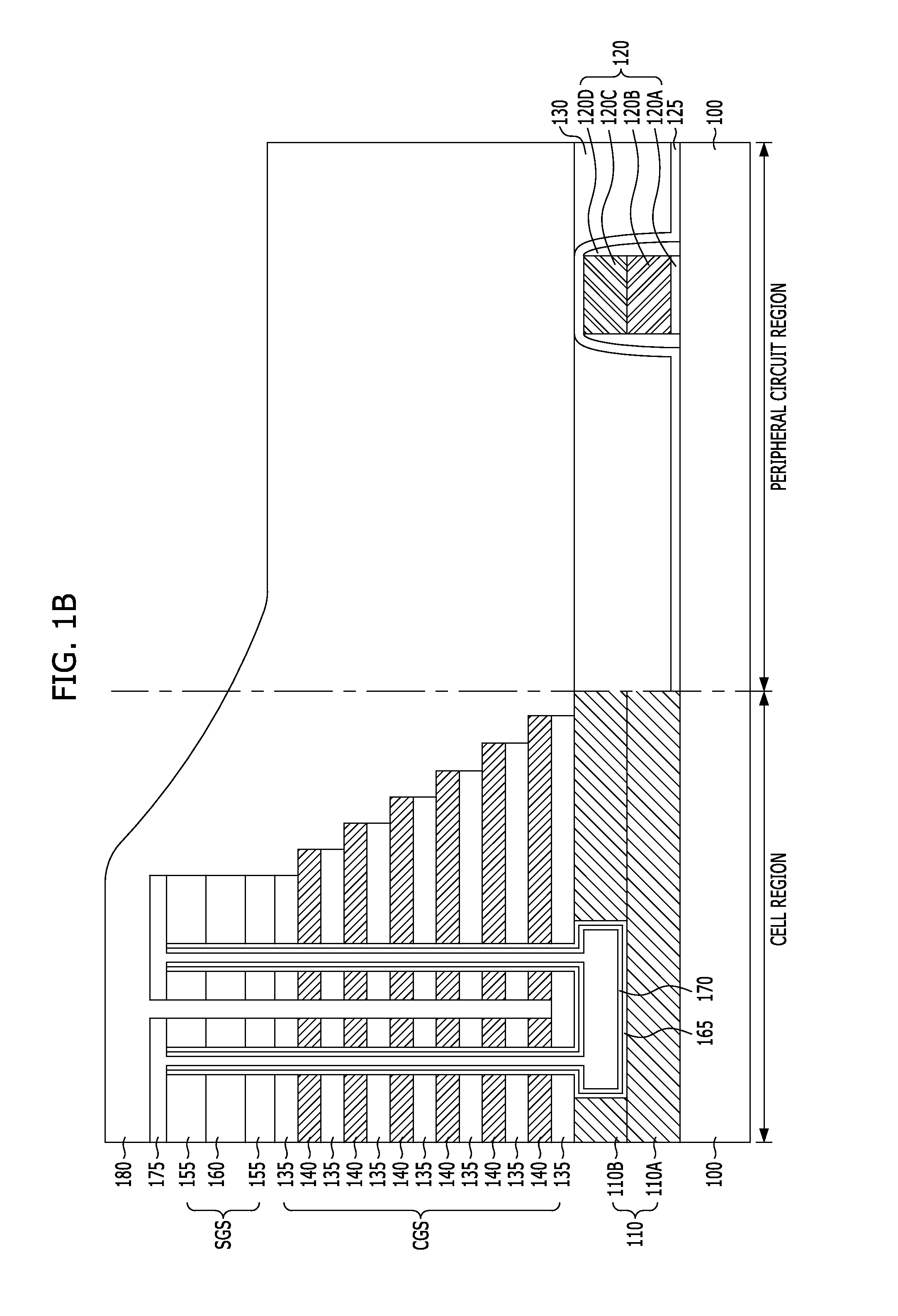
A method of fabricating a non-volatile memory device includes providing a substrate with a cell region where a plurality of memory cells that are stacked vertically are to be formed and a peripheral circuit region where a peripheral circuit device is to be formed. Forming a gate structure where an inter-layer dielectric layer and a gate electrode layer are alternately stacked over the substrate of the cell region and the peripheral circuit region. Forming a first trench that isolates the gate electrode layers in one direction by selectively etching the gate structure of the cell region and forming a trench by selectively etching the gate structure corresponding to a contact formation region of the peripheral circuit region.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Organic field effect transistor and method of manufacturing the same
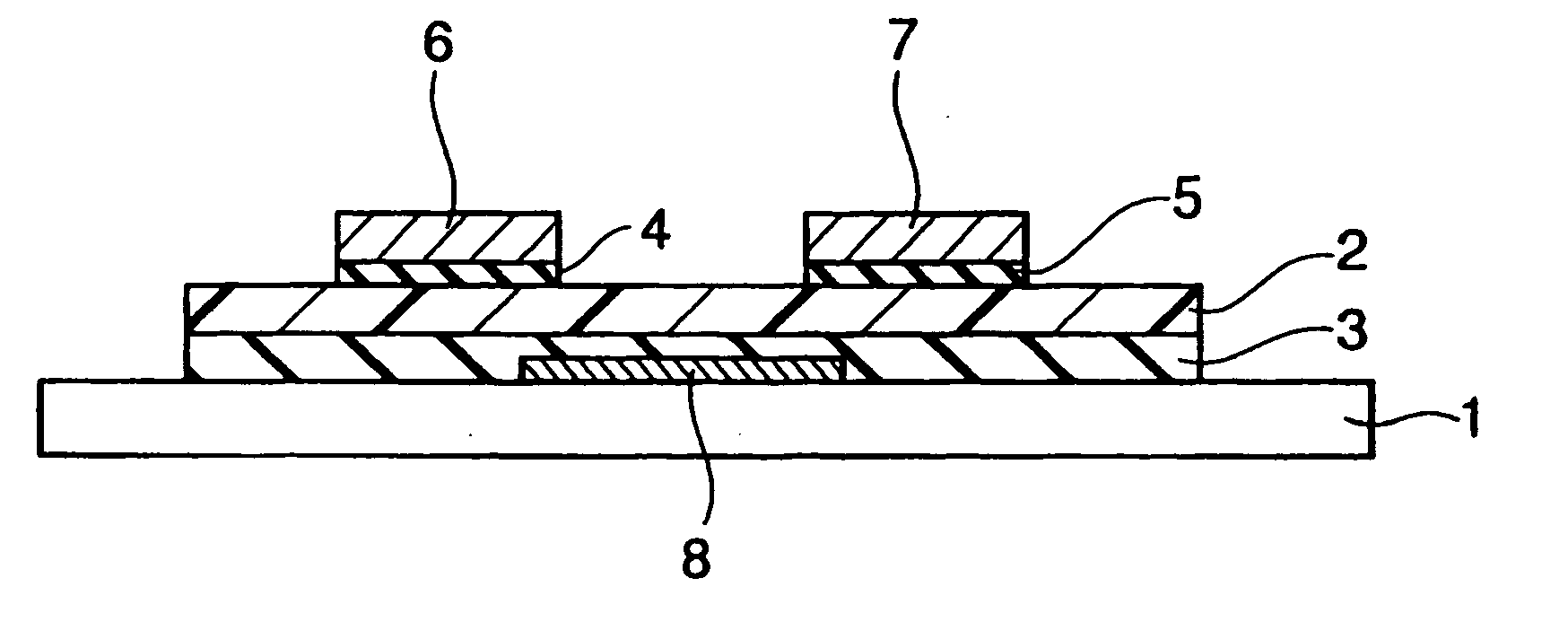
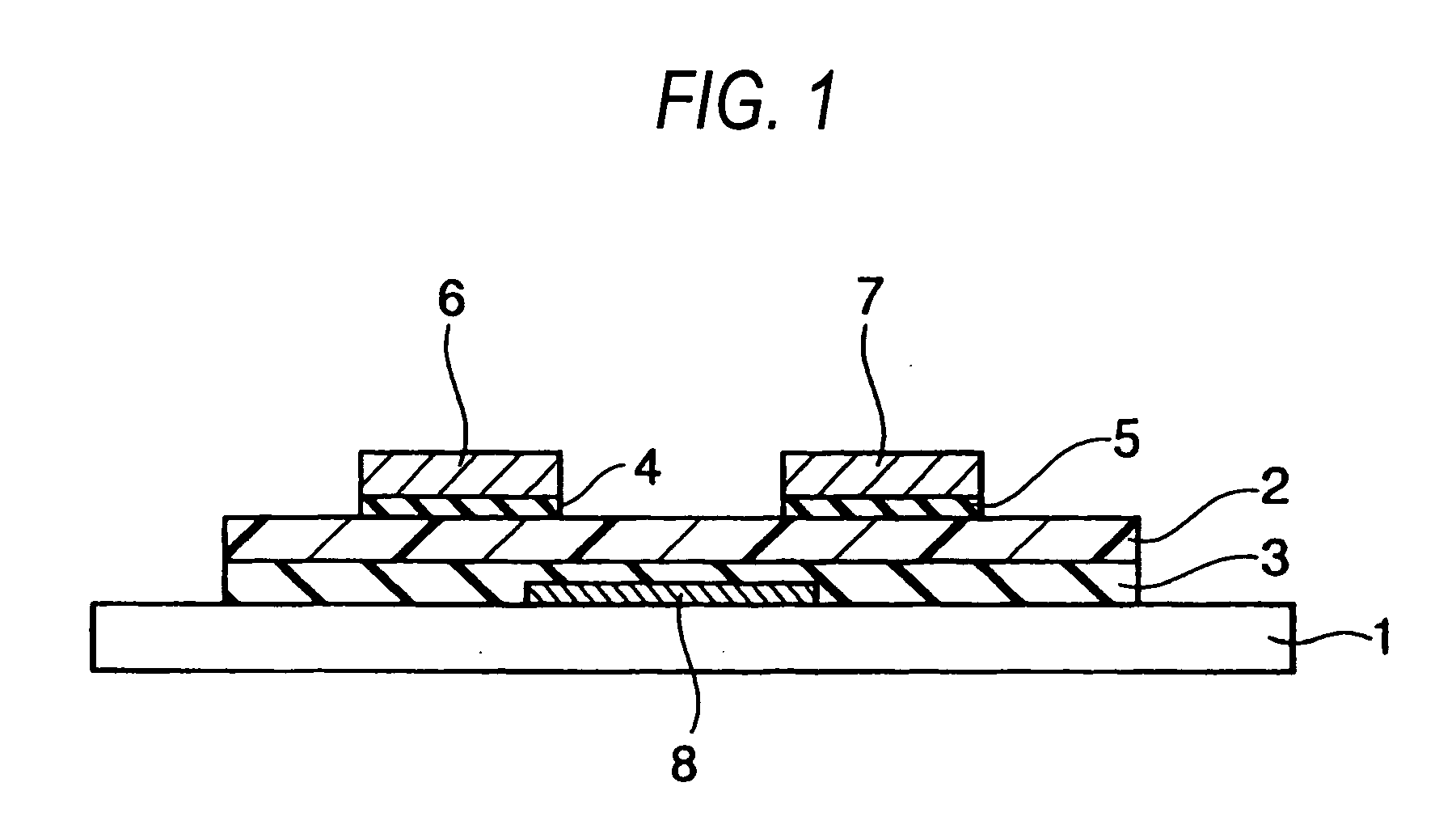
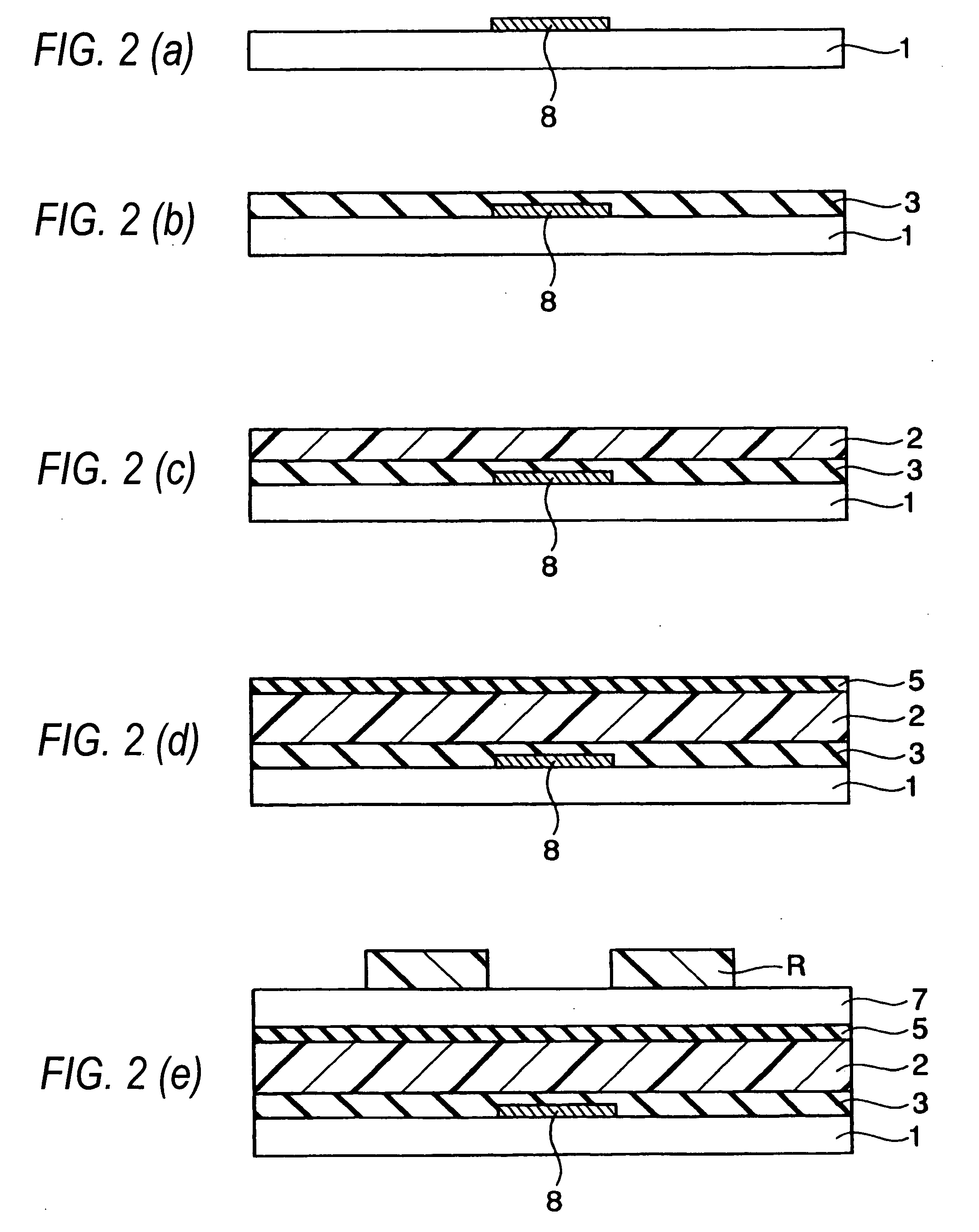
InactiveUS20050263756A1Characteristic changeExtend your lifeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge injectionContact formation
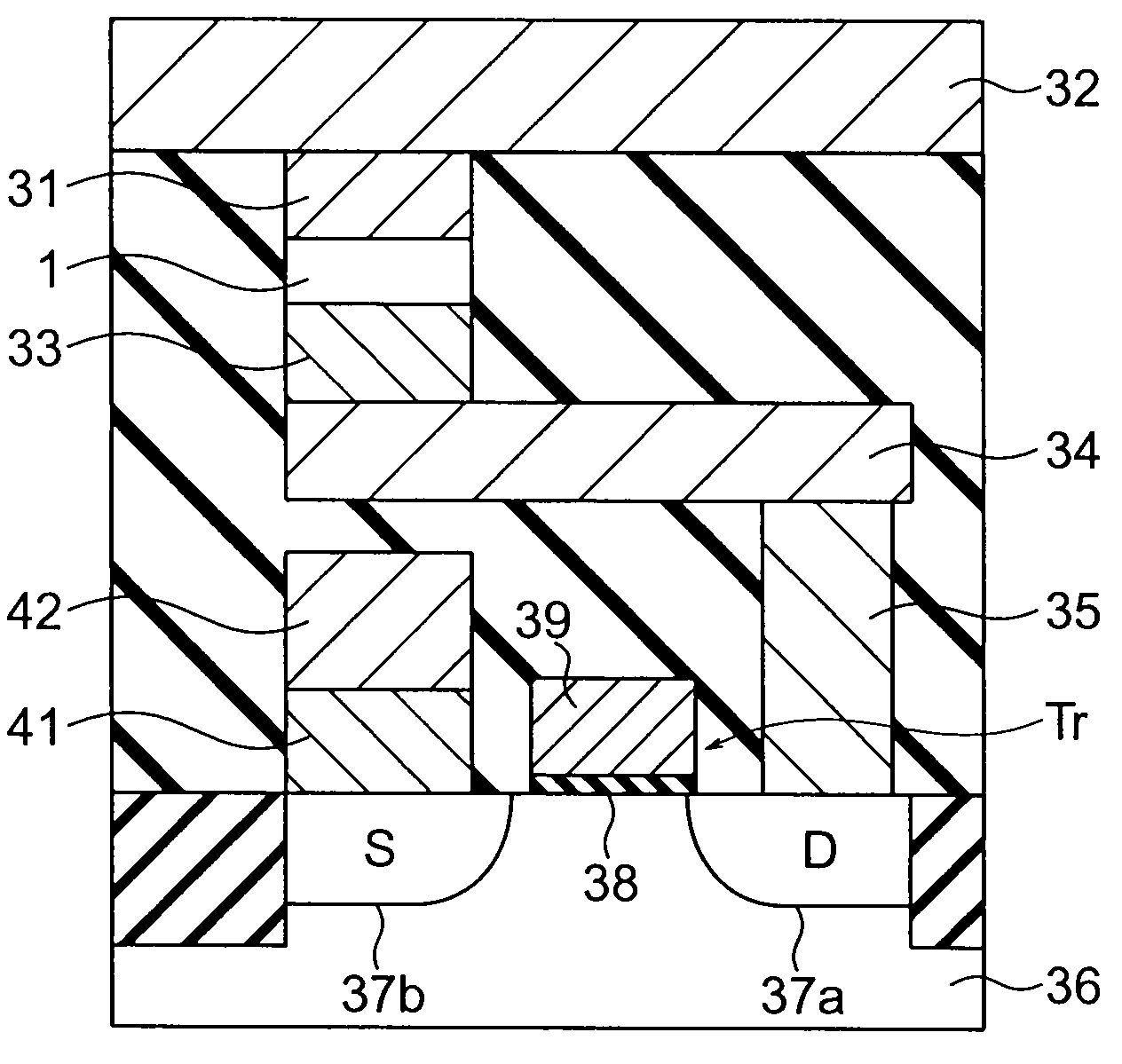
To provide an organic field effect transistor with stable characteristics and a long life span, an organic field effect transistor includes a gate electrode 8 formed on an organic semiconductor film 2 made of an organic semiconductor material with a gate insulating film 3 interposed therebetween; and a source electrode 6 and a drain electrode 7 provided so as to come in contacts with the organic semiconductor film with the gate electrode 8 interposed therebetween. At least one of the source electrode 6 and the drain electrode 7 is formed in contact with the organic semiconductor film 2 with charge injection layers 4 and 5 made of an inorganic material interposed therebetween.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Solar Cell Contact Formation Process Using A Patterned Etchant Material
InactiveUS20090142880A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationContact formationEtching
Embodiments of the invention contemplate the formation of a high efficiency solar cell using novel methods to form the active region(s) and the metal contact structure of a solar cell device. In one embodiment, the methods include the use of various etching and patterning processes that are used to define point contacts through a blanket dielectric layer covering a surface of a solar cell substrate. The method generally includes depositing an etchant material that enables formation of a desired pattern in a dielectric layer through which electrical contacts to the solar cell device can be formed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Vertical channel fin field-effect transistors having increased source/drain contact area and methods for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050186742A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContact formationEngineering
A fin field-effect transistor (FinFET) device includes a fin-shaped active region having first and second source / drain regions therein and a channel region therebetween vertically protruding from a semiconductor substrate. A gate electrode is formed on an upper surface and sidewalls of the channel region. First and second source / drain contacts are formed on respective upper surfaces and sidewalls of the first and second source / drain regions of the fin-shaped active region at opposite sides of the gate electrode. The channel region may be narrower than the first and second source / drain regions of the fin-shaped active region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070096183A1Easy to manufactureReduce contact resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesContact formationDevice material
In a semiconductor device including a MIS transistor with a FUSI gate electrode and a polysilicon resistor, a portion of the polysilicon resistor provided in a contact formation region is silicided simultaneously with the gate electrode or an impurity diffusion region.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and structure of in-situ wafer scale polymer stud grid array contact formation
InactiveUS20020121702A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact formationThermoplastic
Methods and structures of in-situ wafer scale polymer stud grid array (ISWS-PSGA) contact formation on integrated circuit devices, wherein a separate pre-manufactured PSGA substrate is not needed. The methods include injection molding of thermoplastics, transfer-molding of thermoset materials, lamination of polymer films with subsequent in-situ molding / embossing, and forming the PSGA structure directly on the semiconductor wafer. The ISWS-PSGA structure extends across the entire semiconductor wafer, with ISWS-PSGA metallized input / output studs disposed across each of the integrated circuit devices on the wafer. The polymer formed on the wafer surface to create the stud field is extended beyond the perimeter of the wafer, and the polymer film extension is used for temporary connection to an integrated circuit tester, or an integrated circuit test / burn-in system. The extension may further include studs for contacting the tester.
Owner:SIEMENS DEMATIC
Storage device
Owner:NIFCO INC
Vertical MOSFET reduced in cell size and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6888196B2Inhibition effectSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETContact formation
In a vertical MOSFET comprises: a semiconductor layer (1, 2, 9, 10) having first and second surfaces opposite to each other and trenches (6) formed on the first surface; trench gates (8) formed in the trenches; a unit cell formed in a region of the semiconductor layer surrounded by the trench gates, the unit cell comprising a base layer (9) and a source layer (10) formed on the base layer and having the first surface as a principal semiconductor surface, the unit cell having a contact hole (12) formed on a center of the principal semiconductor surface and extending from the principal semiconductor surface through the source layer to an inside of the base layer; a contact (17) formed in the contact hole; a source electrode (18) formed on the contact; and a drain electrode (19) formed on the second surface, the contact is formed to a depth different to a peak depth which is a position having a maximum impurity-concentration in a depth direction of the base layer. The unit call further comprises a base contact layer (14) formed within the base layer so as to enclose a bottom of the contact and to bring the base contact layer into contact with the bottom of the contact.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Methodology for the configuration and repair of unreliable switching elements
ActiveUS7599895B2NanoinformaticsDigital computer detailsContact formationElectrical resistance and conductance
A universal logic gate apparatus is disclosed, which include a plurality of self-assembling chains of nanoparticles having a plurality of resistive connections, wherein the plurality of self-assembling chains of nanoparticles comprise resistive elements. A plasticity mechanism is also provided, which is based on a plasticity rule for creating stable connections from the plurality of self-assembling chains of nanoparticles for use with the universal, reconfigurable logic gate. In addition, the universal logic gate can be configured with a cross-bar architecture, where nanoconnections are formed from a columbic-educed mechanical stress contact.
Owner:KNOWM TECH
Magnetoresistive element and magnetoresistive random access memory including the same
ActiveUS7768824B2Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesContact formationMagnetic reluctance
The present invention provides a low-resistance magnetoresistive element of a spin-injection write type. A crystallization promoting layer that promotes crystallization is formed in contact with an interfacial magnetic layer having an amorphous structure, so that crystallization is promoted from the side of a tunnel barrier layer, and the interface between the tunnel barrier layer and the interfacial magnetic layer is adjusted. With this arrangement, it is possible to form a magnetoresistive element that has a low resistance so as to obtain a desired current value, and has a high TMR ratio.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Electronic assembly with carbon nanotube contact formations or interconnections
InactiveUS20050285116A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsContact formationCarbon nanotube
According to one aspect of the invention, an electronic assembly is provided. The electronic assembly includes a microelectronic die having an integrated circuit formed therein. Carbon nanotubes are grown on the microelectronic die and are electrically connected to the integrated circuit. The carbon nanotubes form a plurality of contact formations to connect the die, and the integrated circuit therein, to a package substrate. The package substrate may then be attached to a printed circuit board and installed in a computing system. According to another aspect of the present invention, a first conductive layer is formed on a semiconductor substrate having a plurality of transistors formed thereon. Then a second conductive layer is formed on the first conductive layer. A hole is created at least partially through both the first and second conductive layers. Carbon nanotubes are grown within the hole to electrically interconnect the two conductive layers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
High-density phase change cell array and phase change memory device having the same
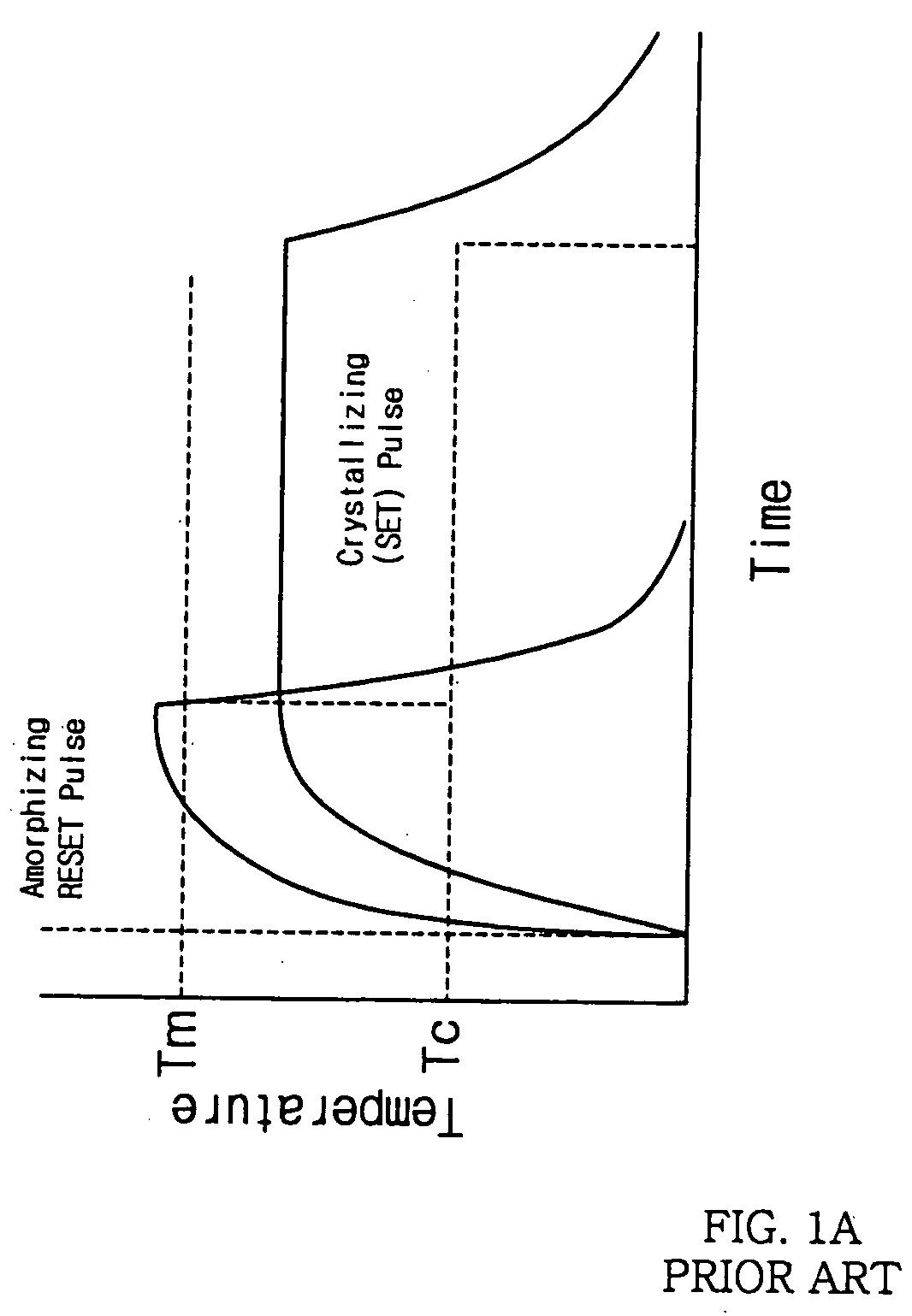
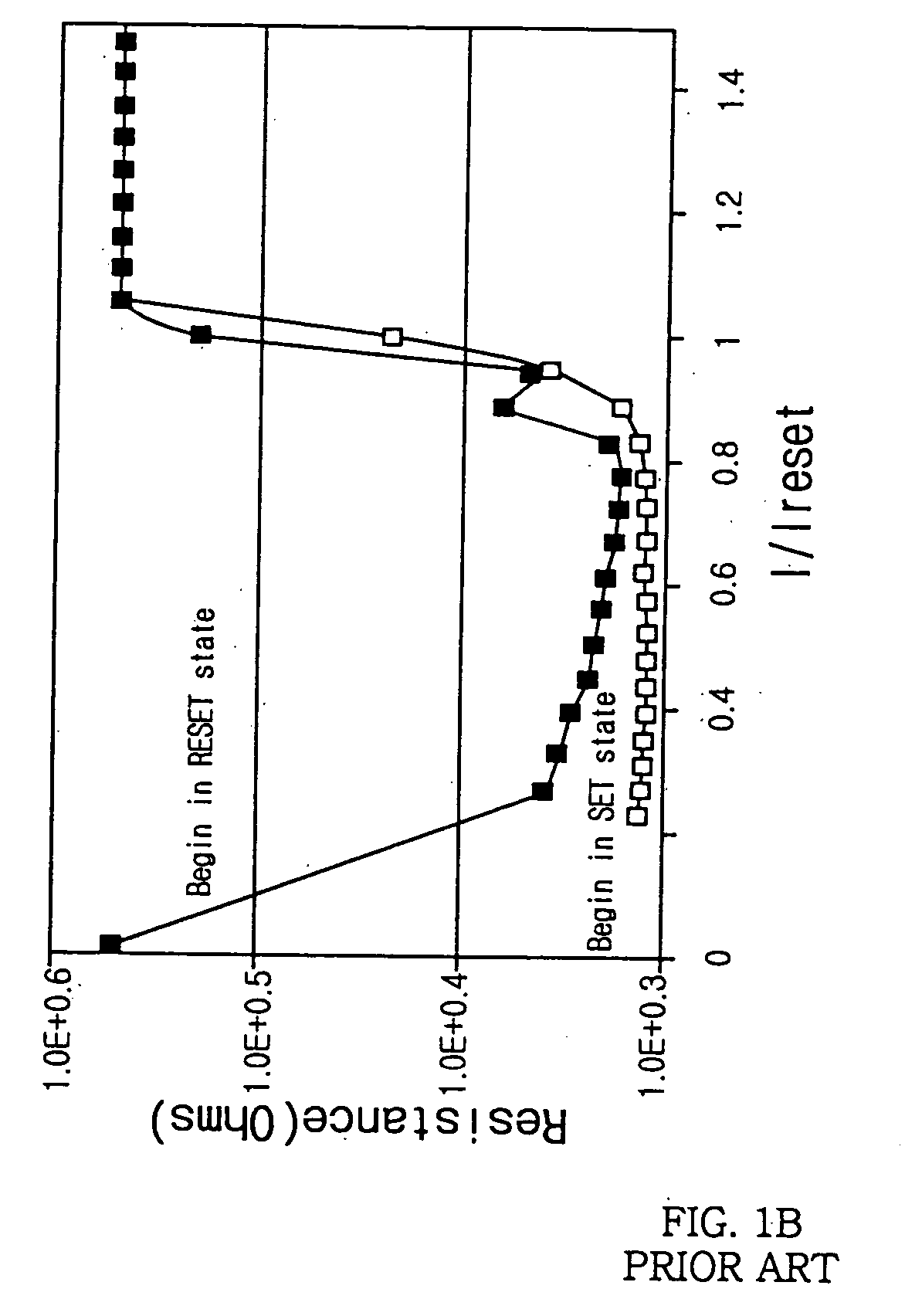
InactiveUS20050270832A1Suitable for implementationSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesContact formationPhase-change memory
The present invention relates generally to a phase change memory device and, more particularly, to a phase change memory cell array suitable for the implementation of a high-density memory device. The phase change memory cell array includes a first access transistor pair and a second access transistor pair formed on a semiconductor substrate to be adjacent to each other while each of the first and second access transistor pairs having a common drain, phase change resistance elements formed on source regions of the access transistors, respectively, and a semiconductor region formed on the same plane as the common drains to electrically connect the common drains of the first and second transistor pairs. The phase change memory cell array and the memory device of the present invention are suitable for the implementation of a high-density semiconductor device, and capable of improving the reliability of a contact forming process by securing a sufficient space for the contact forming process.
Owner:EROMTECH
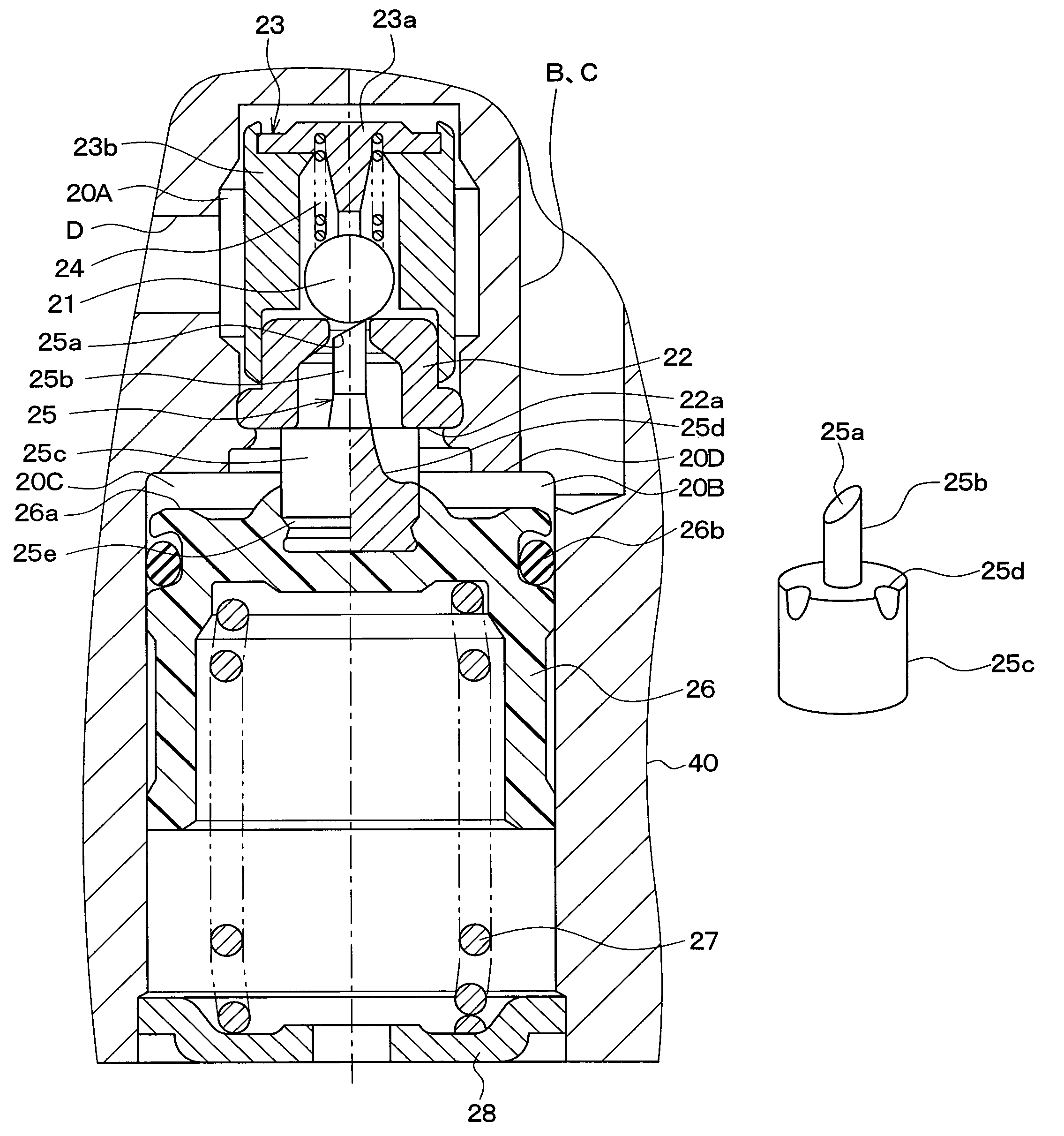
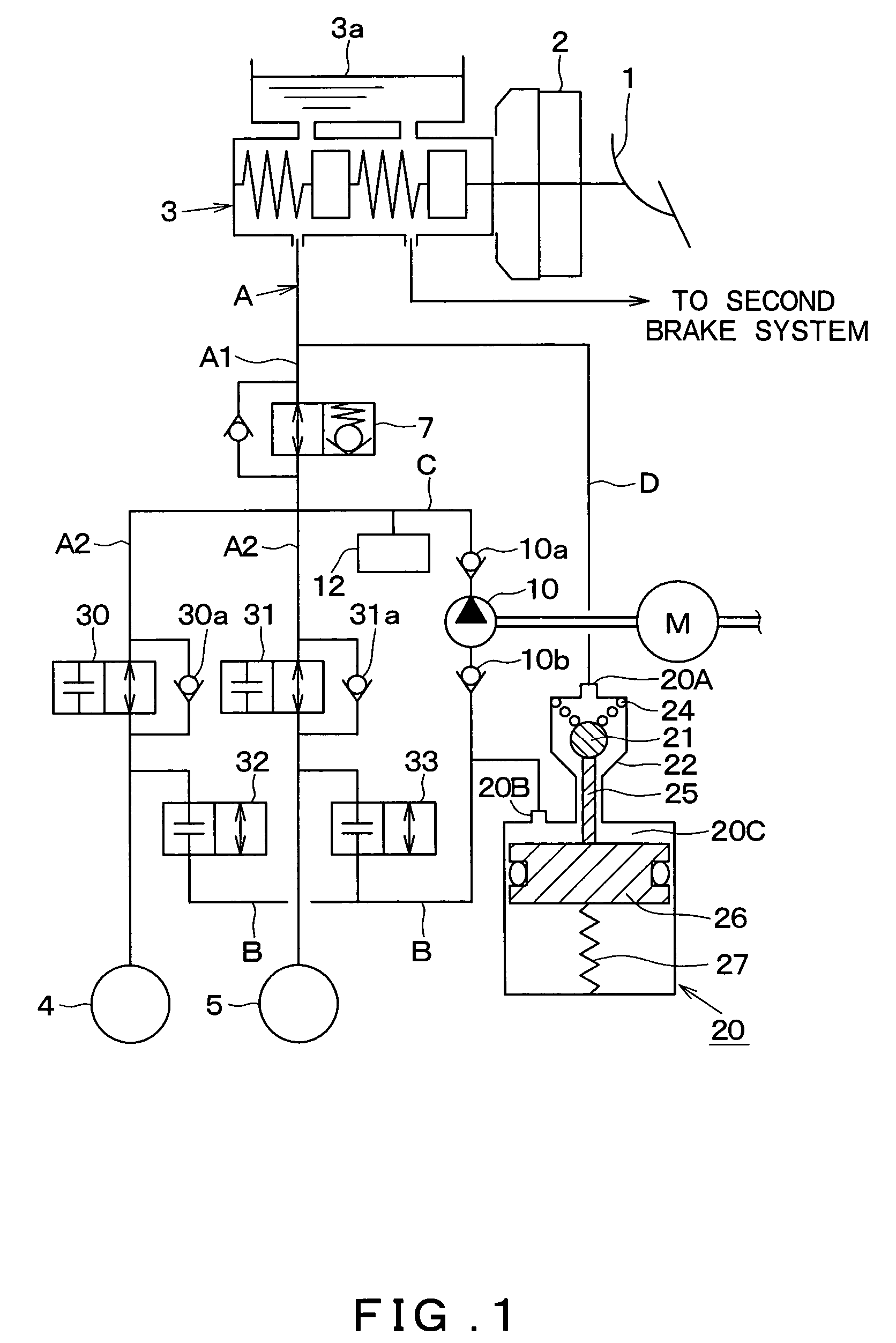
Pressure regulating reservoir and vehicular braking apparatus using it
A pressure regulating reservoir is structured such that a major diameter portion of a shaft contacts a bottom surface of a valve seat, whereas a top surface of a piston does not contact an upper end surface of a wall forming a reservoir chamber in a housing. Therefore, a lift amount of a ball valve can be set using a portion above the major diameter portion of the shaft that contacts the bottom surface of the valve seat. That is, the lift amount can be set using only a dimension in the axial direction of a minor diameter portion of the shaft.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device and method of making the same
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device according to the present invention includes a substrate; a first word-line provided above the substrate surface, the first word-line having a plate shape in an area where a memory cell is formed; a second word-line provided above the first word-line surface, the second word-line having a plate shape; a plurality of metal wirings connecting the first and second word-lines with a driver circuit; and a plurality of contacts connecting the first and second word-lines with the metal wirings. The contact of the first word-line is formed in a first word-line contact area. The contact of the second word-line is formed in a second word-line contact area. The first word-line contact area is provided on a surface of the first word-line that is drawn to the second word-line contact area.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
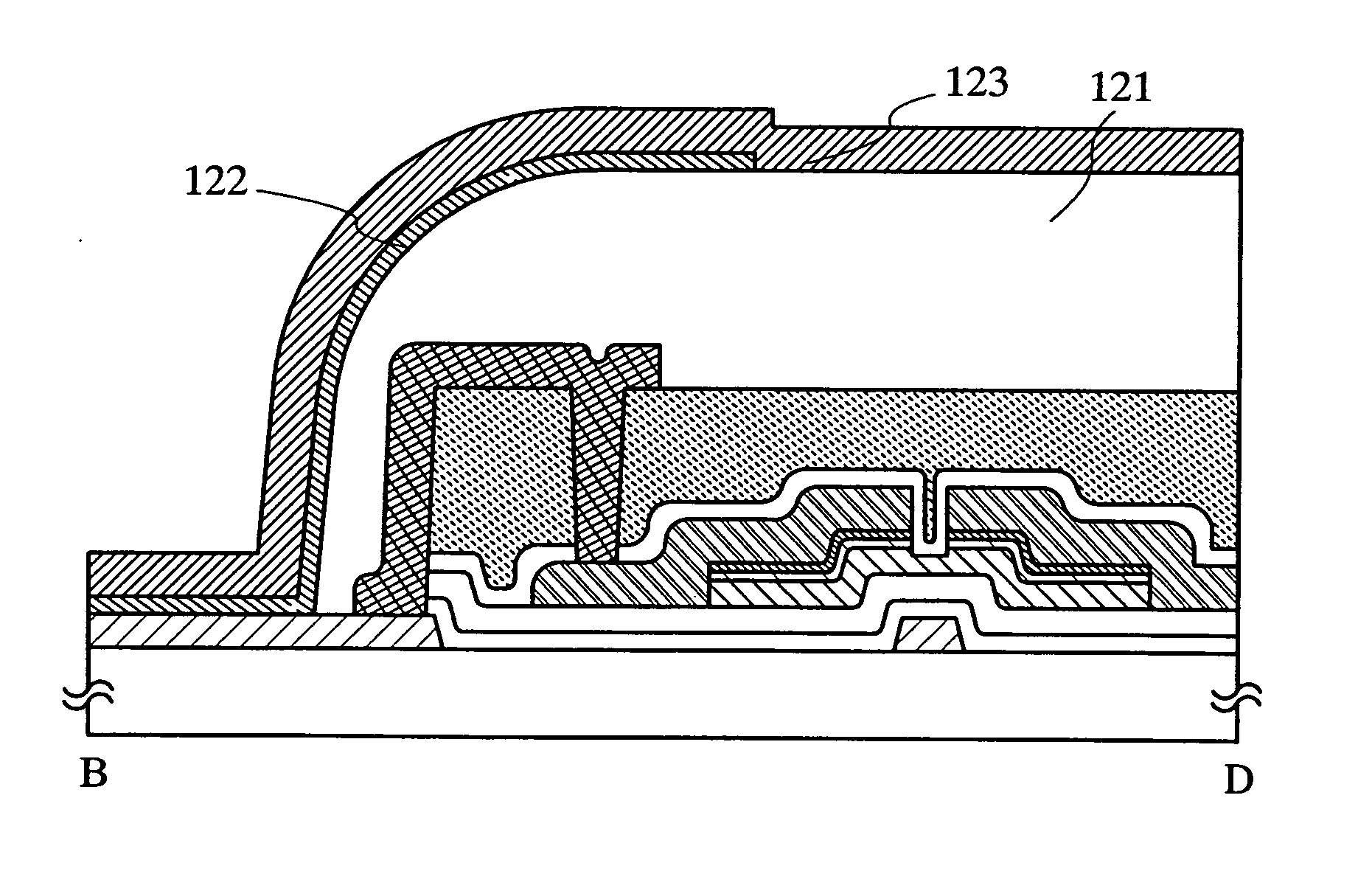
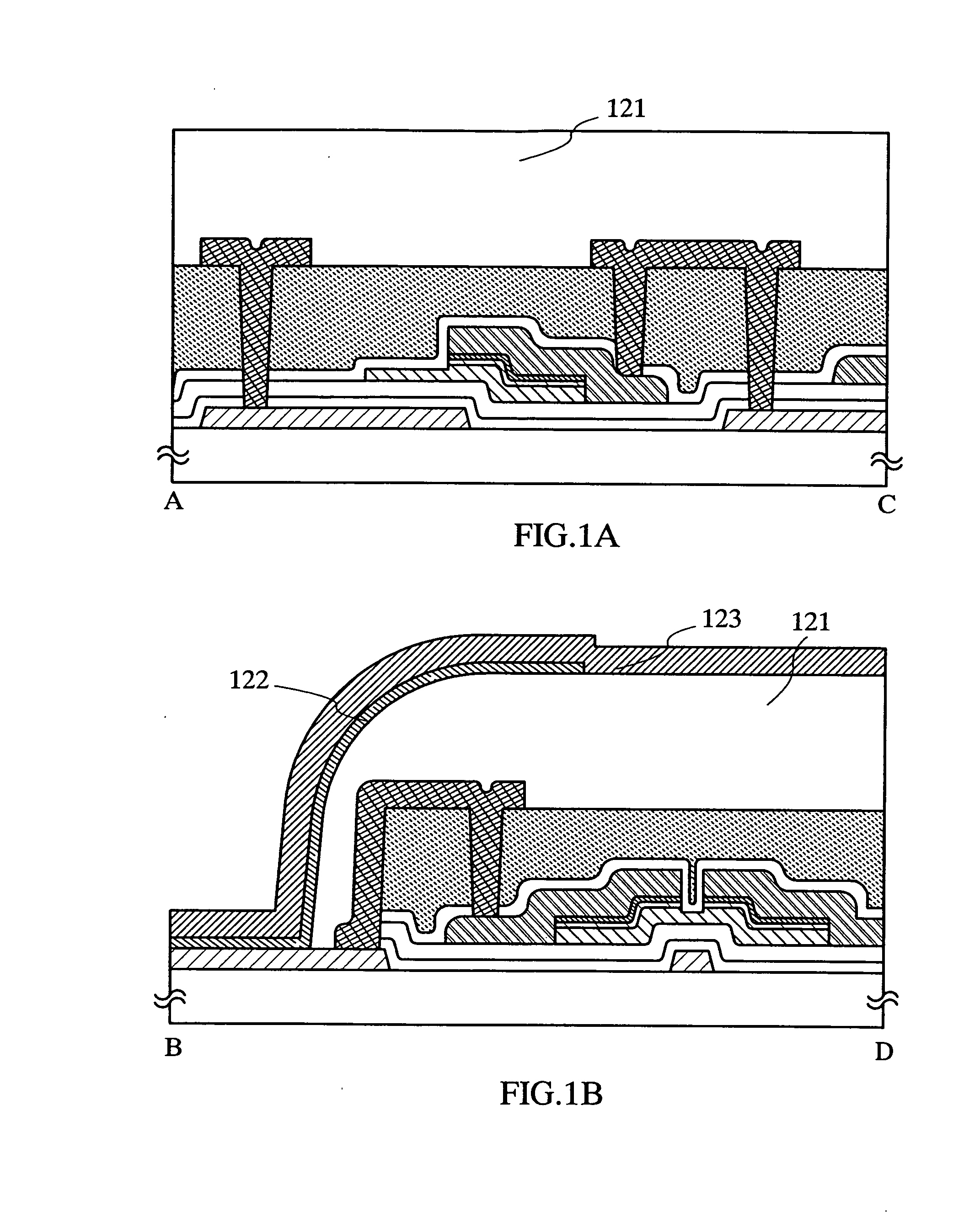
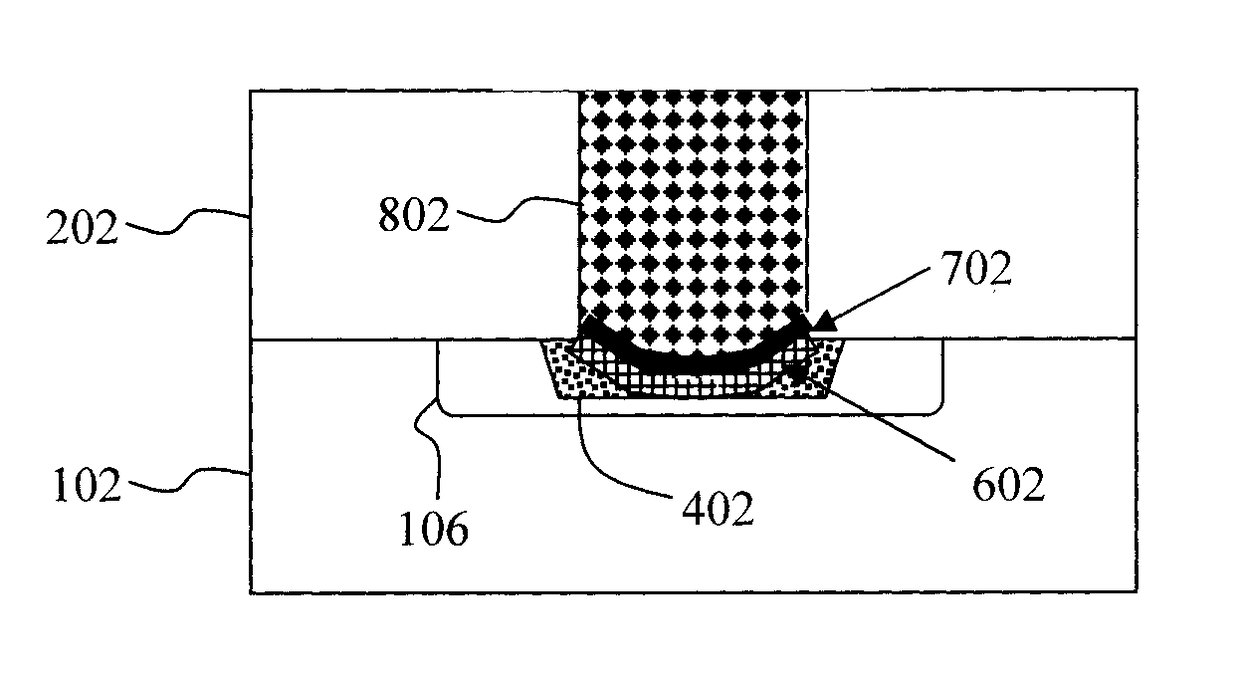
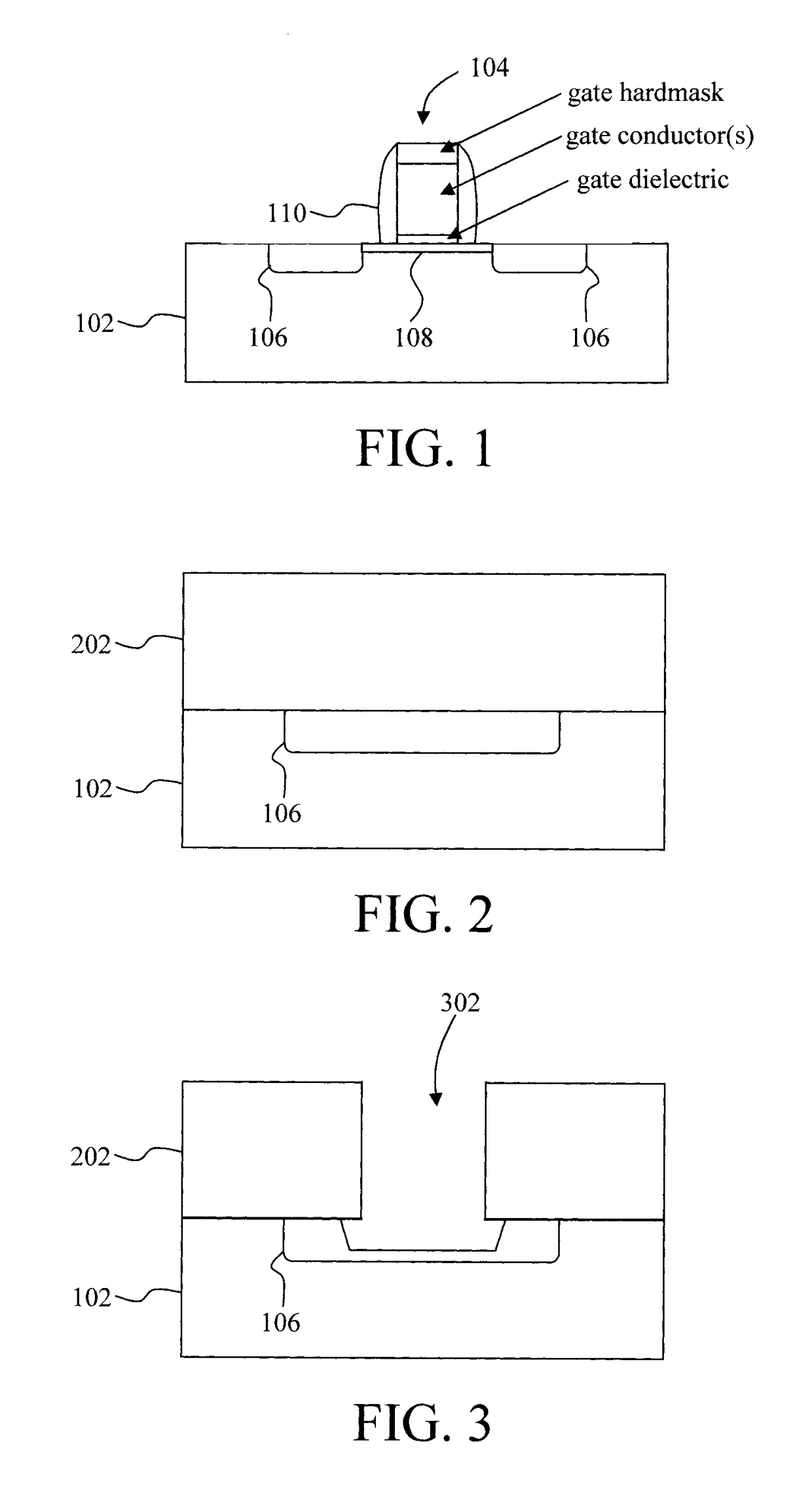
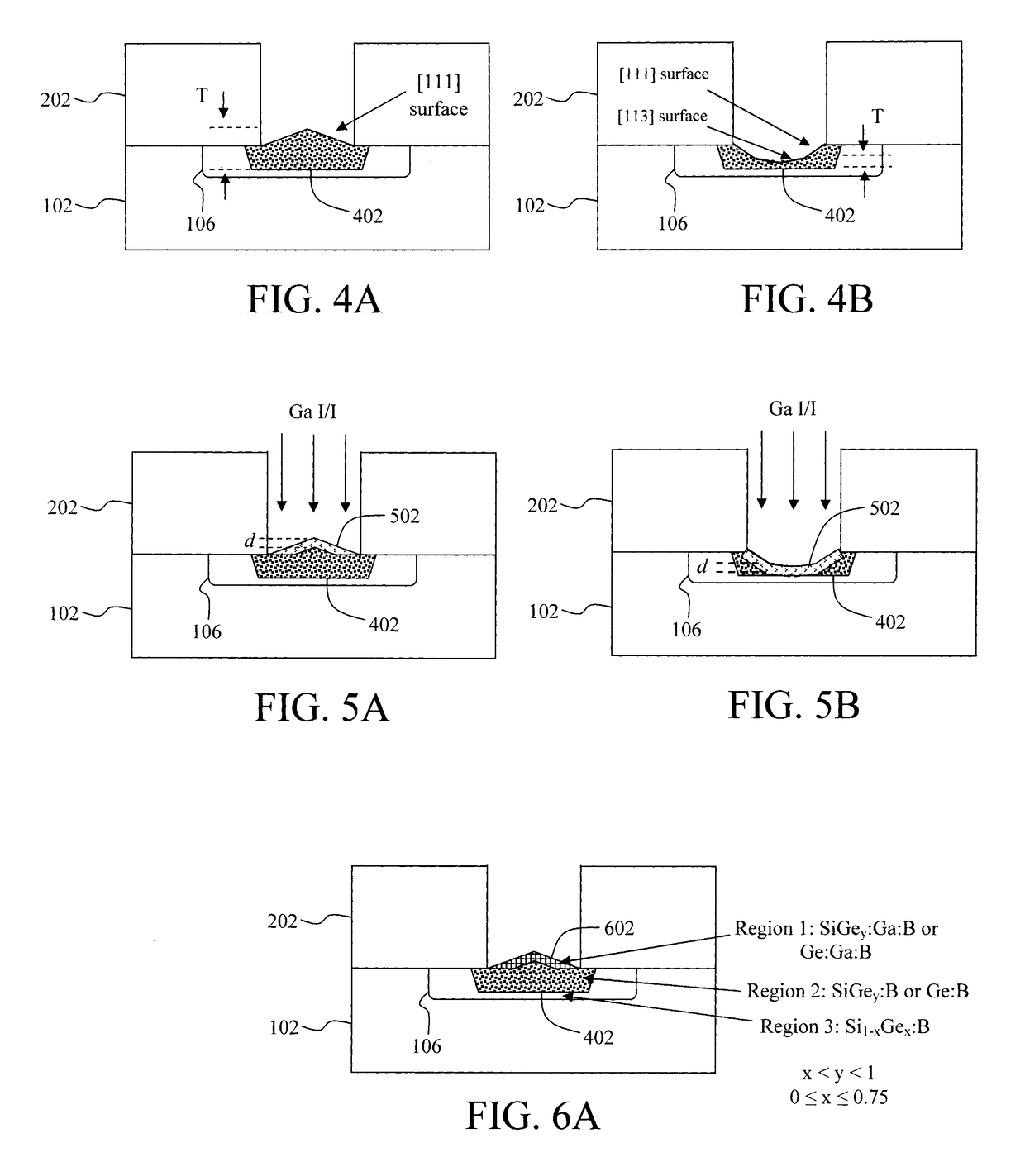
Low Resistance Source Drain Contact Formation
ActiveUS20170213889A1Reduce contact resistanceIncrease volumeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesContact formationDielectric
Techniques for forming Ga-doped source drain contacts in Ge-based transistors are provided. In one aspect, a method for forming Ga-doped source and drain contacts includes the steps of: depositing a dielectric over a transistor; depositing a dielectric over the transistor; forming contact trenches in the dielectric over, and extending down to, source and drain regions of the transistor; depositing an epitaxial material into the contact trenches; implanting gallium ions into the epitaxial material to form an amorphous gallium-doped layer; and annealing the amorphous gallium-doped layer under conditions sufficient to form a crystalline gallium-doped layer having a homogenous gallium concentration of greater than about 5×1020 at. / cm3. Transistor devices are also provided utilizing the present Ga-doped source and drain contacts.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Method for avoiding oxide undercut during pre-silicide clean for thin spacer FETs
InactiveUS6991979B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorGate dielectric
A method for forming a CMOS device in a manner so as to avoid dielectric layer undercut during a pre-silicide cleaning step is described. During formation of CMOS device comprising a gate stack on a semiconductor substrate surface, the patterned gate stack including gate dielectric below a conductor with vertical sidewalls, a dielectric layer is formed thereover and over the substrate surfaces. Respective nitride spacer elements overlying the dielectric layer are formed at each vertical sidewall. The dielectric layer on the substrate surface is removed using an etch process such that a portion of the dielectric layer underlying each spacer remains. Then, a nitride layer is deposited over the entire sample (the gate stack, the spacer elements at each gate sidewall, and substrate surfaces) and subsequently removed by an etch process such that only a portion of said nitride film (the “plug”) remains. The plug seals and encapsulates the dielectric layer underlying each said spacer, thus preventing the dielectric material from being undercut during the subsequent pre-silicide clean process. By preventing undercut, this invention also prevents the etch-stop film (deposited prior to contact formation) from coming into contact with the gate oxide. Thus, the integration of thin-spacer transistor geometries, which are required for improving transistor drive current, is enabled.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com