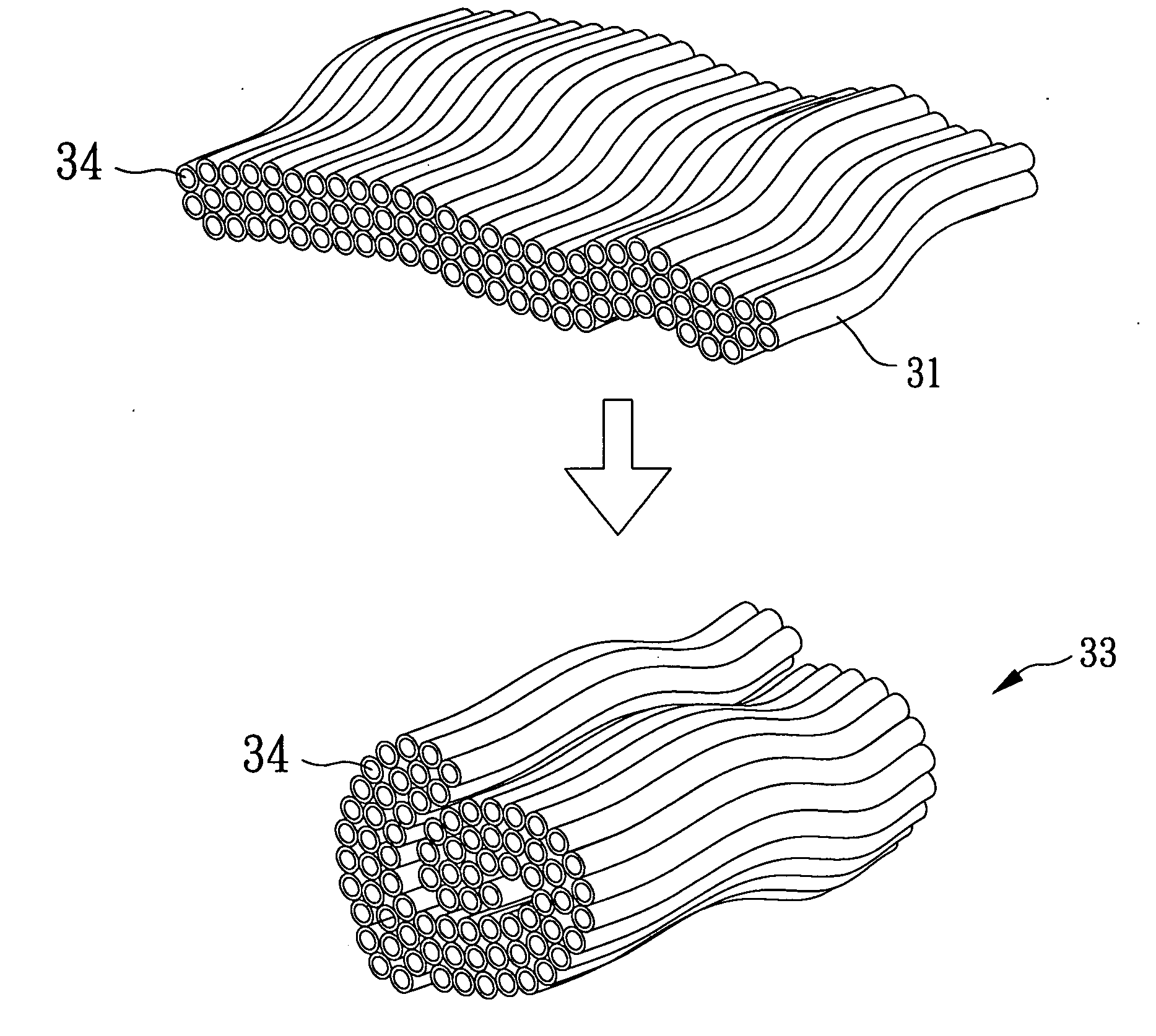
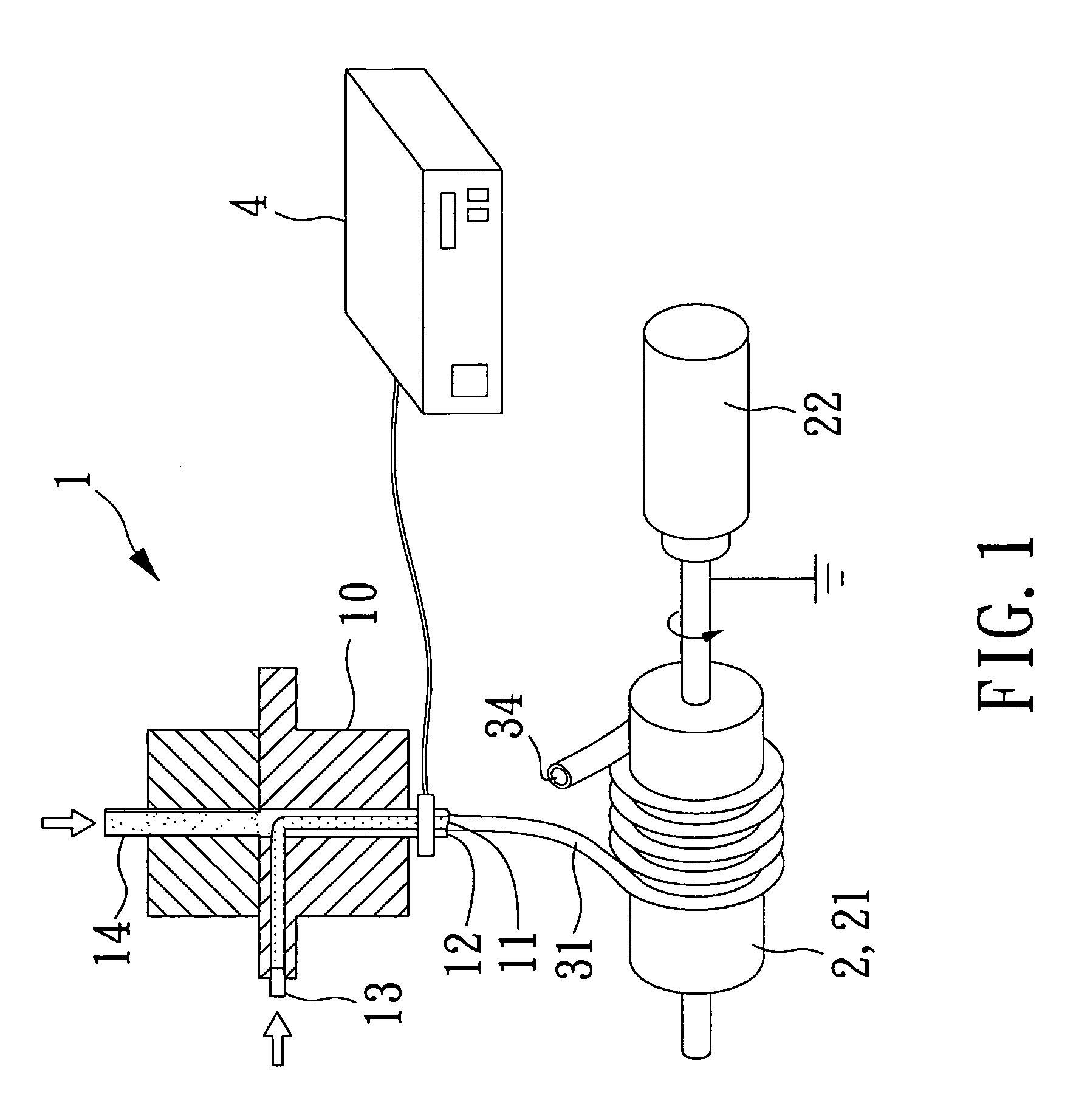
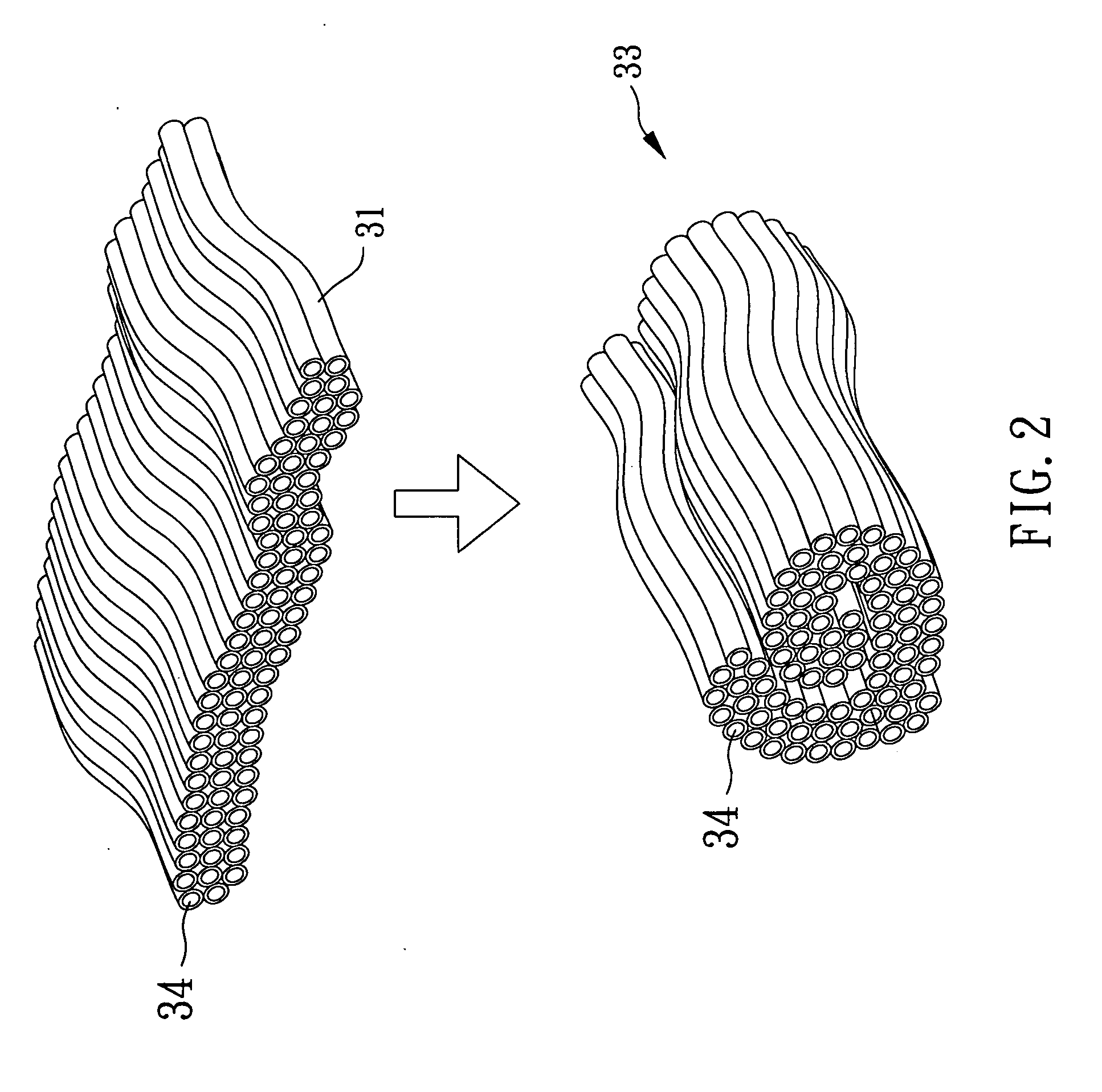
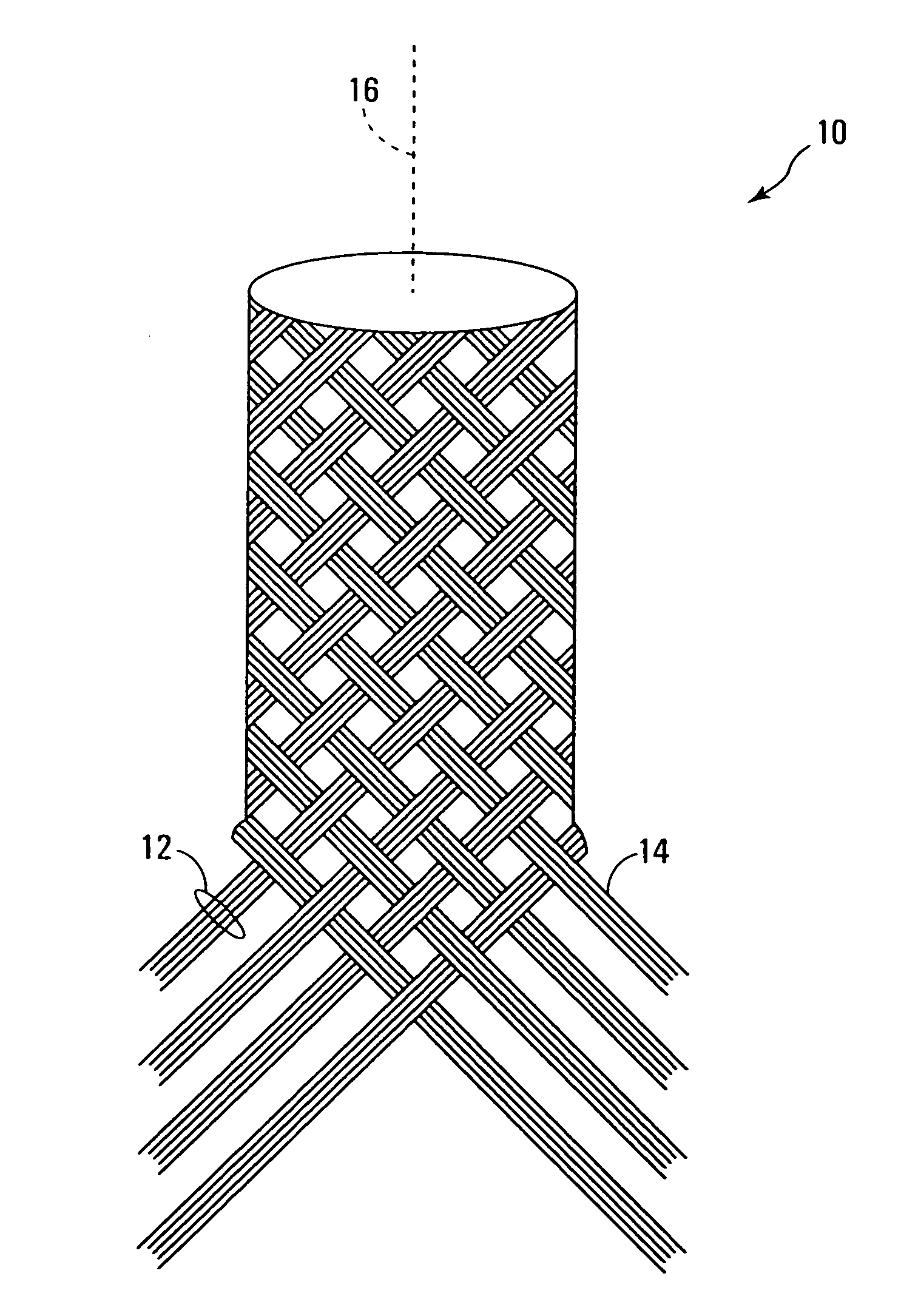
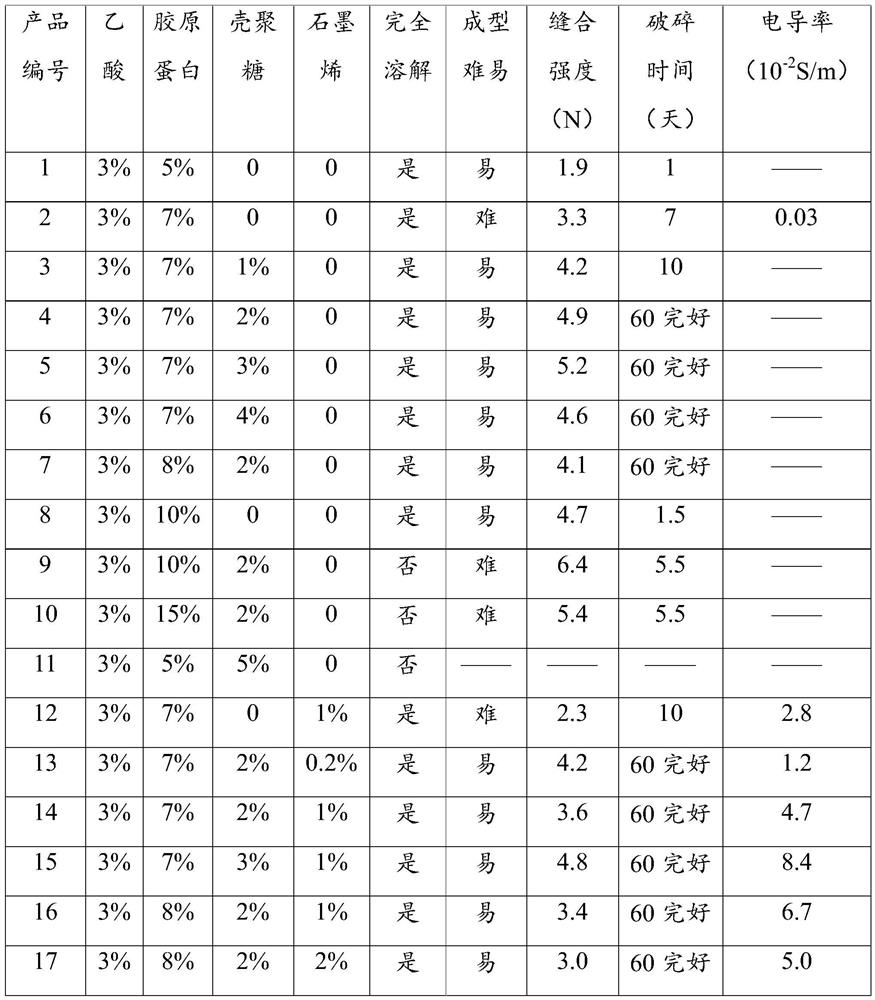
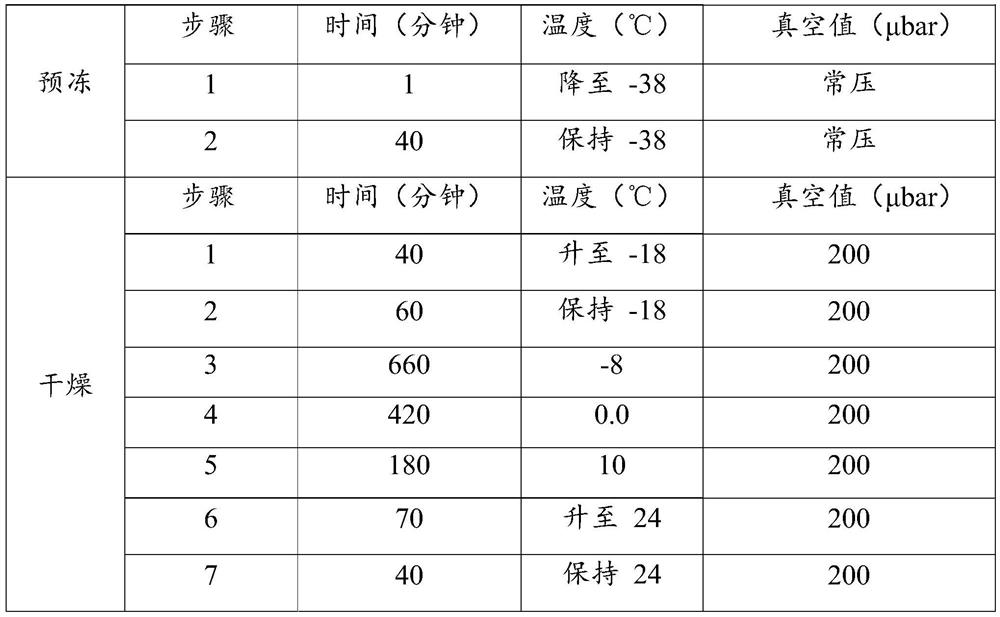
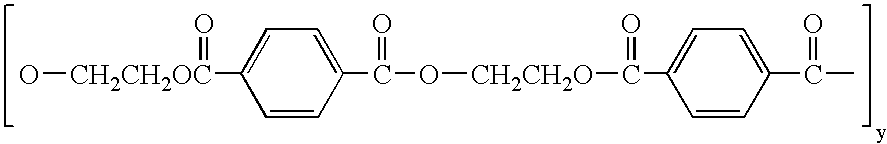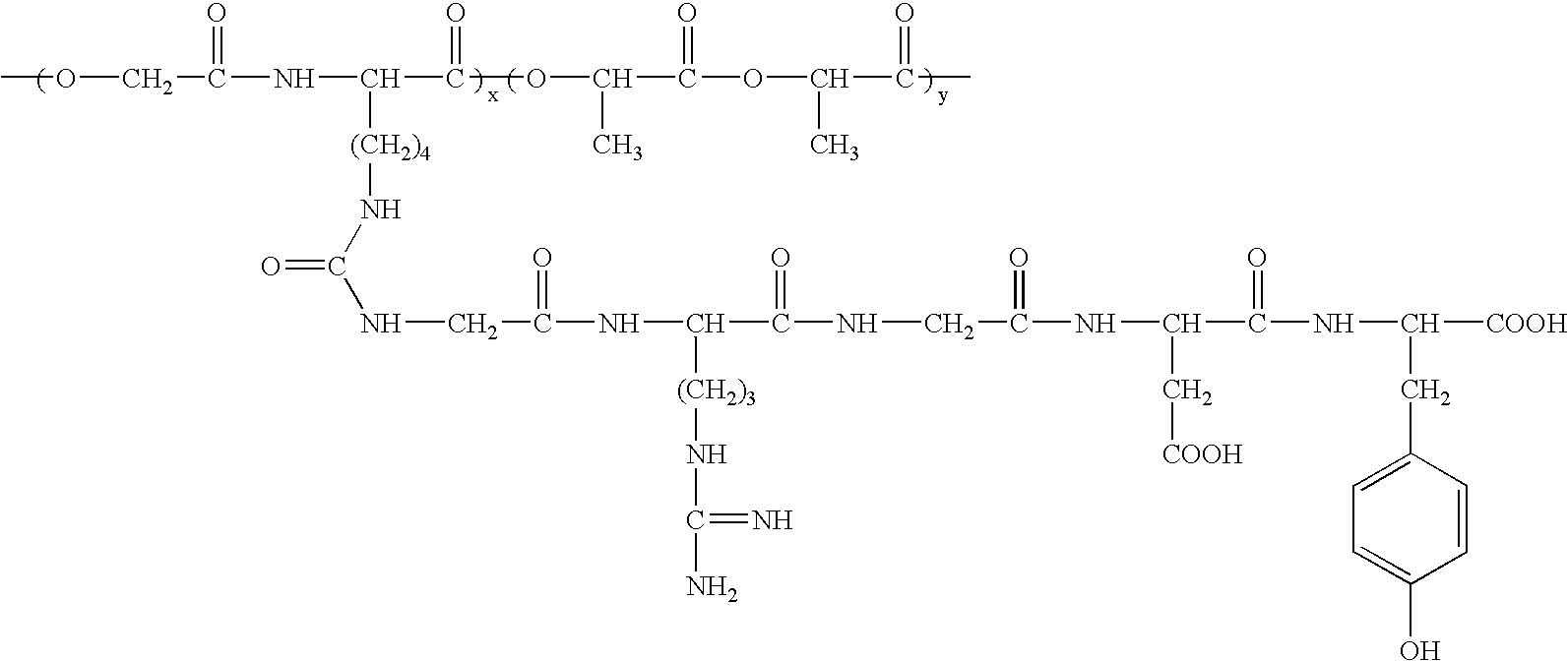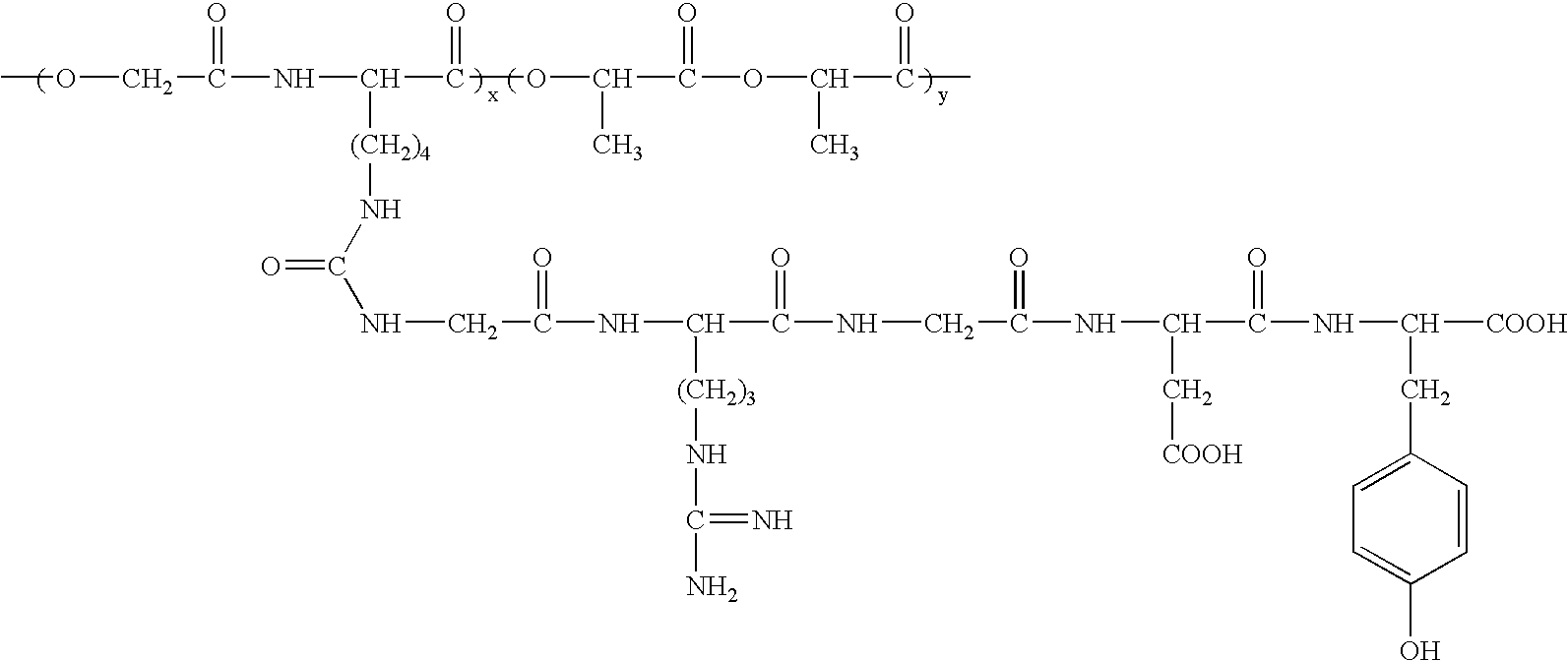Patents
Literature
39 results about "Nerve guide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
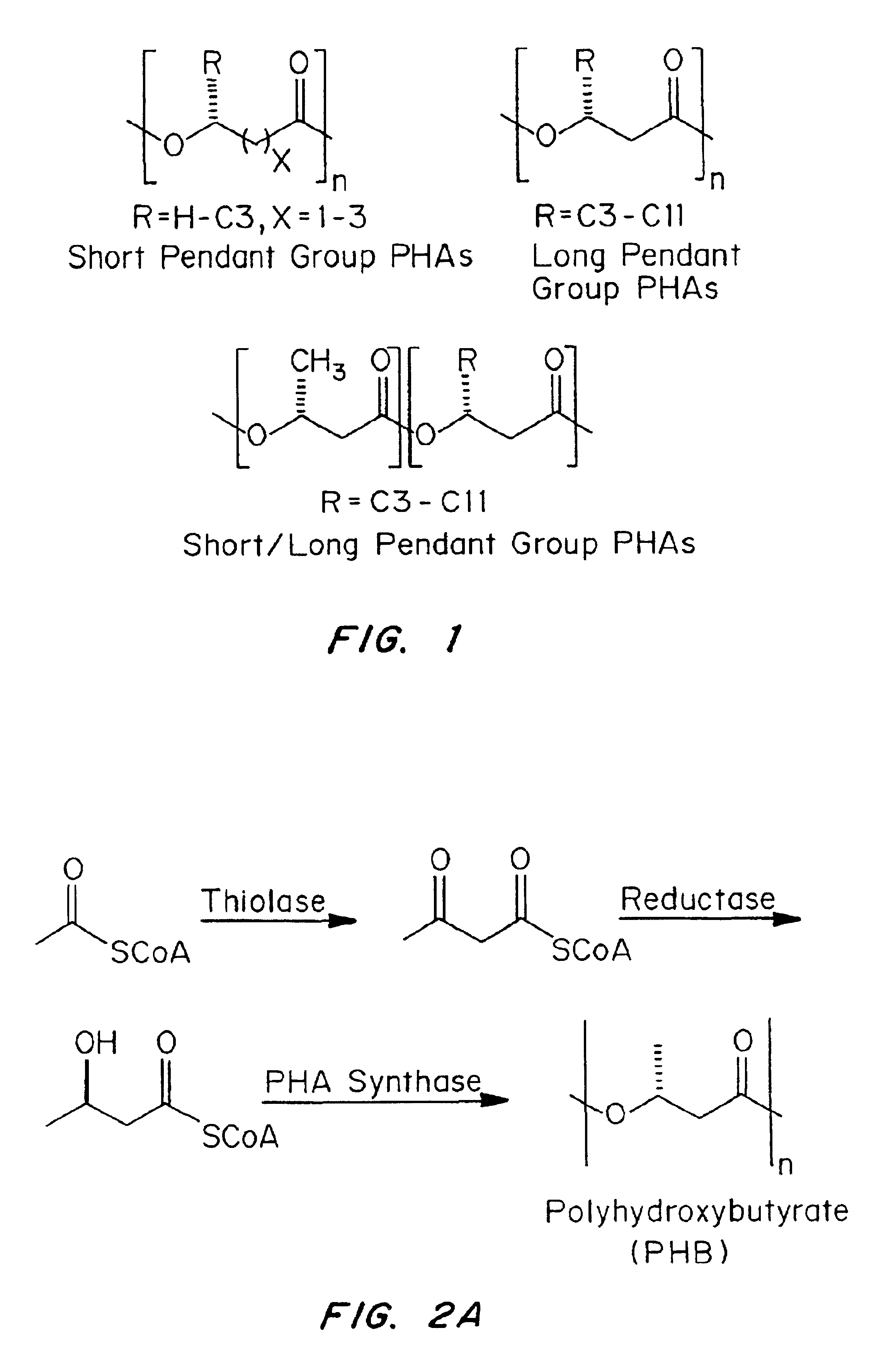
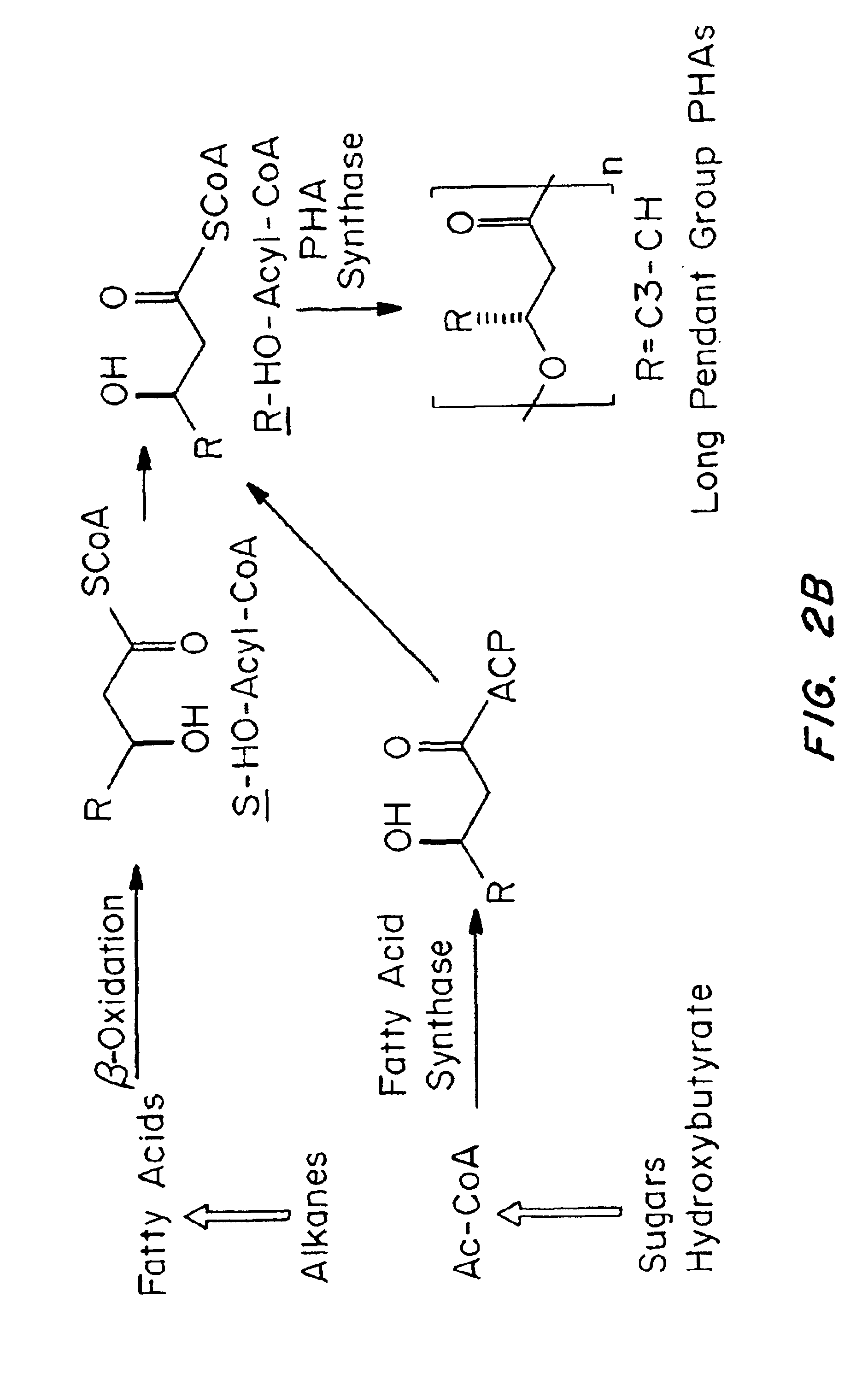
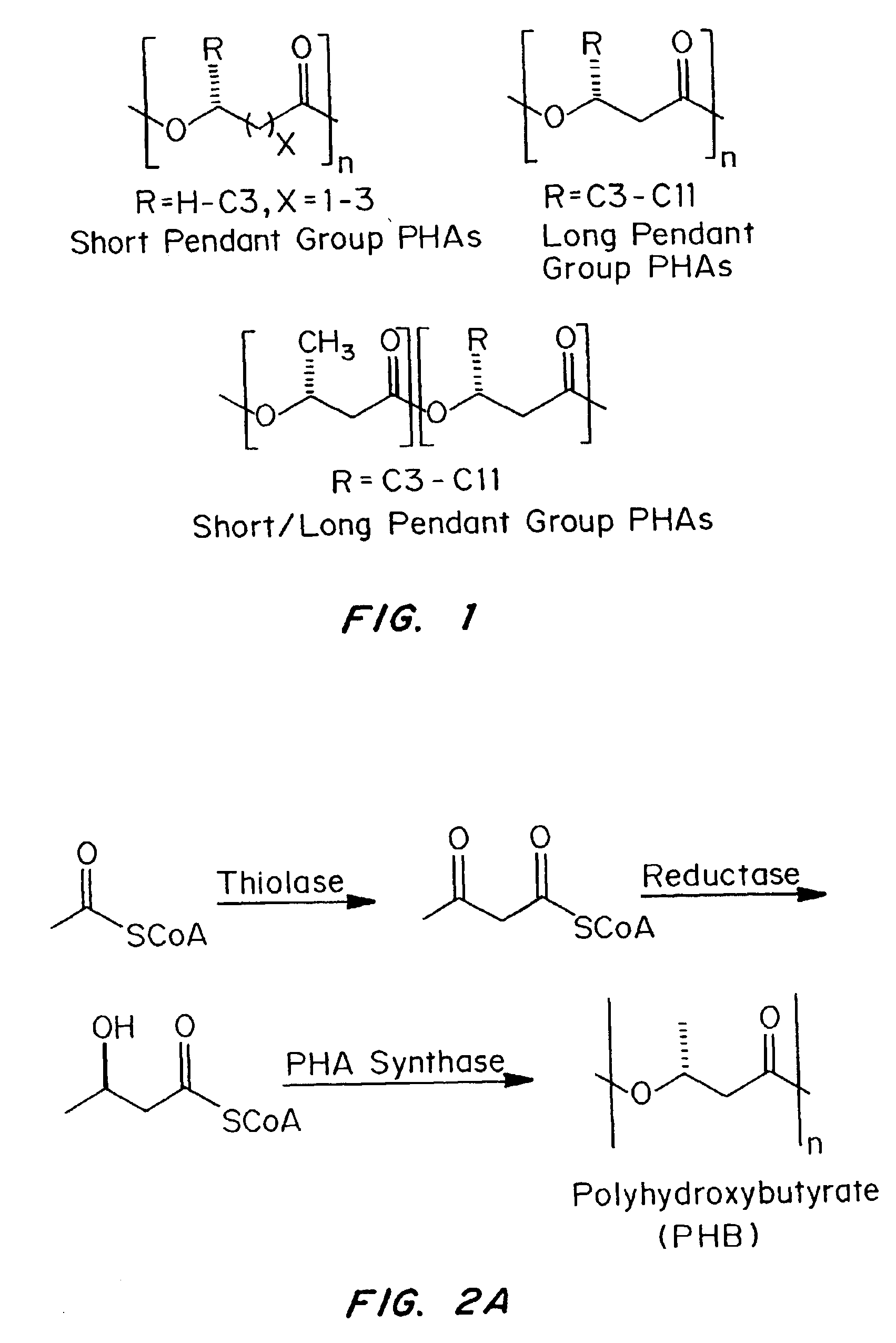
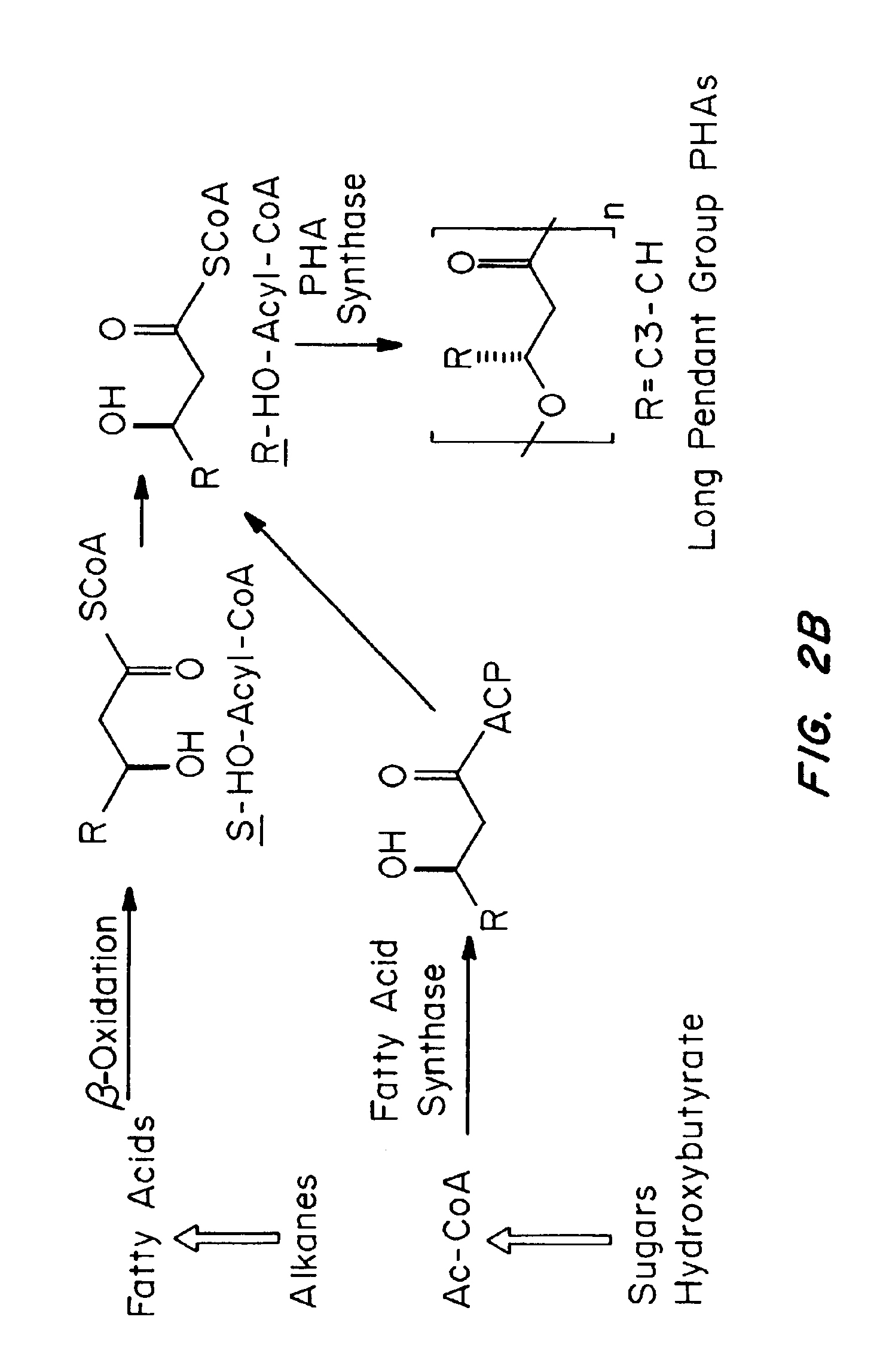
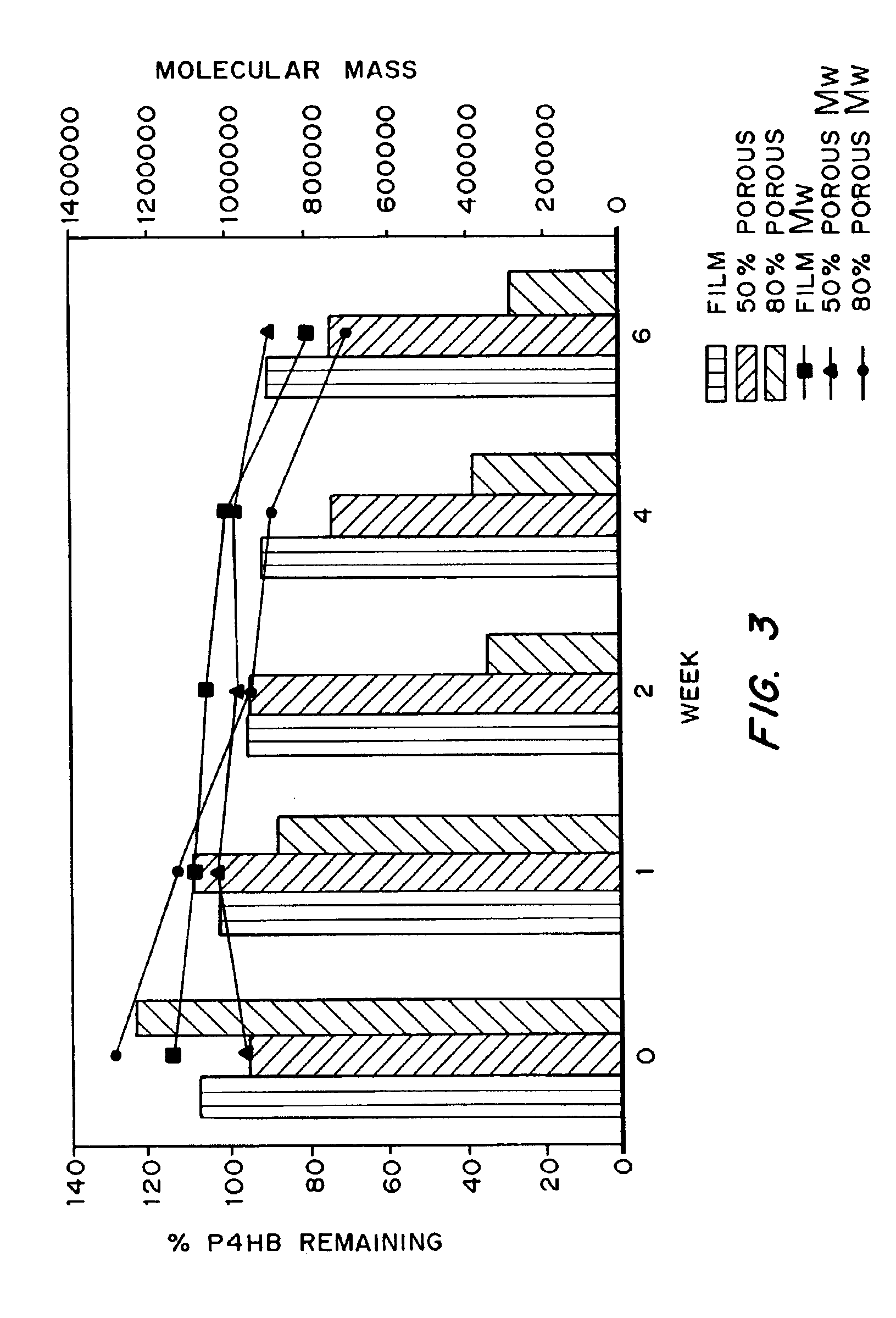
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6867247B2Reduce probabilityHigh porositySuture equipmentsStentsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Therapeutic Electrospun Fiber Compositions
InactiveUS20100303881A1Promote nerve growthEfficient releaseBiocideNervous disorderFiberActive agent
The instant invention provides electrospun fiber compositions comprising one or more polymers and one or more biologically active agents. In specific embodiments, the biologically active agents are nerve growth factors. In certain embodiments, the electrospun fiber compositions comprising one or more biologically active agents are on the surface of a film, or a tube. The tubes comprising the electrospun fiber compositions of the invention can be used, for example, as nerve guide conduits.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Bio-acceptable conduits and method providing the same
InactiveUS20100047310A1Reduced dimensionLow costElectric discharge heatingFilament/thread formingFiberFluorescence
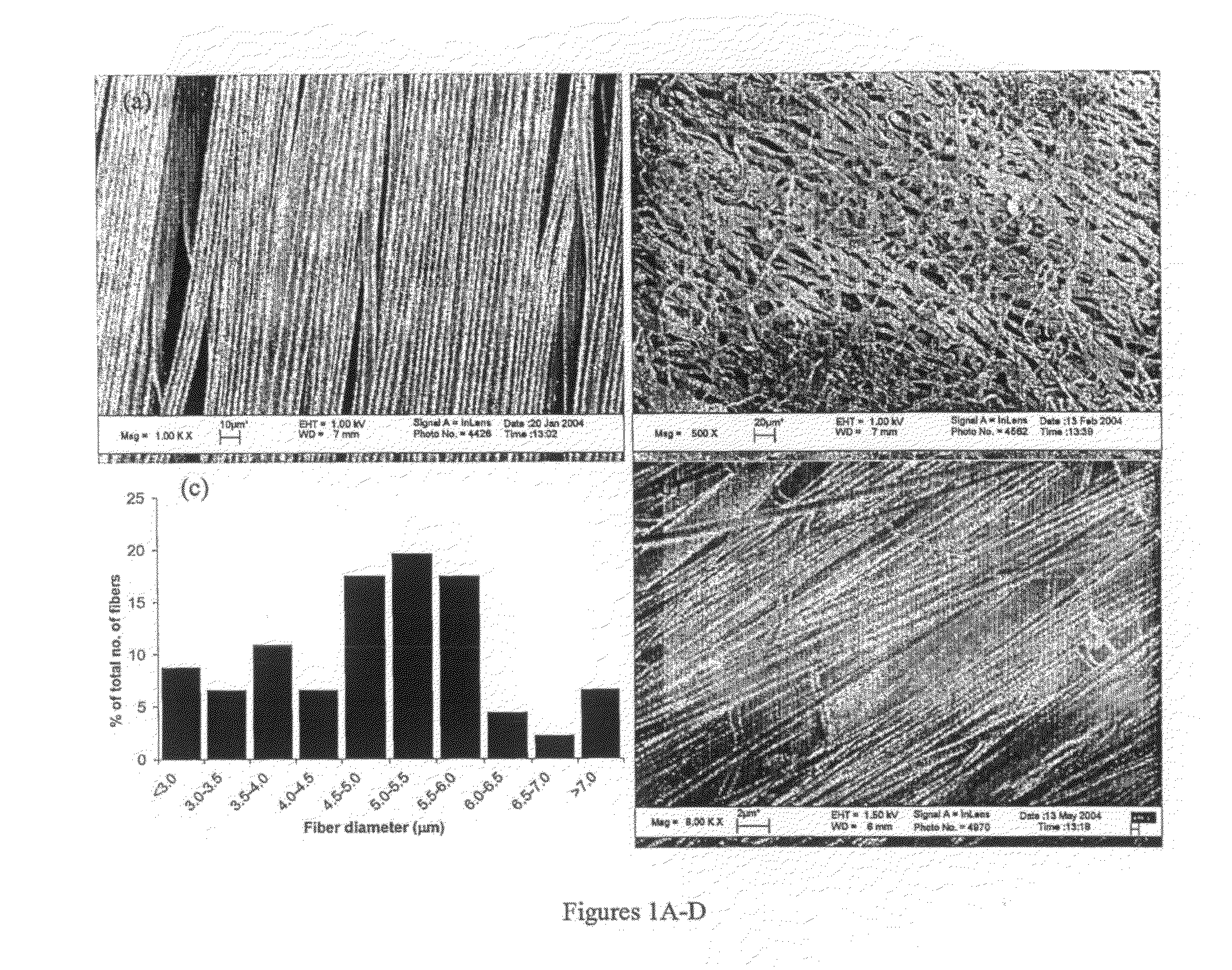
Disclosed is a bio-electrospinning technique for preparing a cell-containing, oriented, continuous tubular scaffold, made of biodegradable polymer, designed for use as a nerve guide conduit (NGC) in nerve regeneration. With a coaxial spinneret, the PC-12 cell medium solution was co-electrospun into a core of tubular fibers, with PLA on the outer shell. The resulted fibers' morphology was characterized via SEM and optical microscopy, and following structural characteristics were found: 1. the larger, hollow fibers had diameters in tenth of microns and wall thicknesses around few microns, 2. an orientation in a preferred direction with the aid of a high-rotating collection device. The fluorescent PC12 cells embedded within the scaffold were cultured and nerve growth factor was added. We observed cells could not only survive the process, but also sustain their viability by undergoing differentiation process, extending neurite along the micro tubular scaffold in the desired direction. All these results demonstrate its potential application for advanced NGC.
Owner:TAIPEI MEDICAL UNIV
Medical guide tubes
Polymeric fibers were microbraided around a mandrel to make a tubular guide tube for nerve regeneration. The polymer used for the fibers was one of poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide) (10:90 PLGA) and chitosan. These polymers are biodegradable and biocompatible. The tubes were studied for their surface morphology and swelling behavior. Biological performance of the tubes was examined in the rat sciatic nerve model with a 12 mm gap. One month after implantation nine out of ten rats showed successful nerve regeneration. Morphometric analysis of regenerated nerves confirmed the quality of the regeneration compatible with those offered by other types of biodegradable nerve guide tubes. The tubes were flexible, permeable and showed no swelling.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
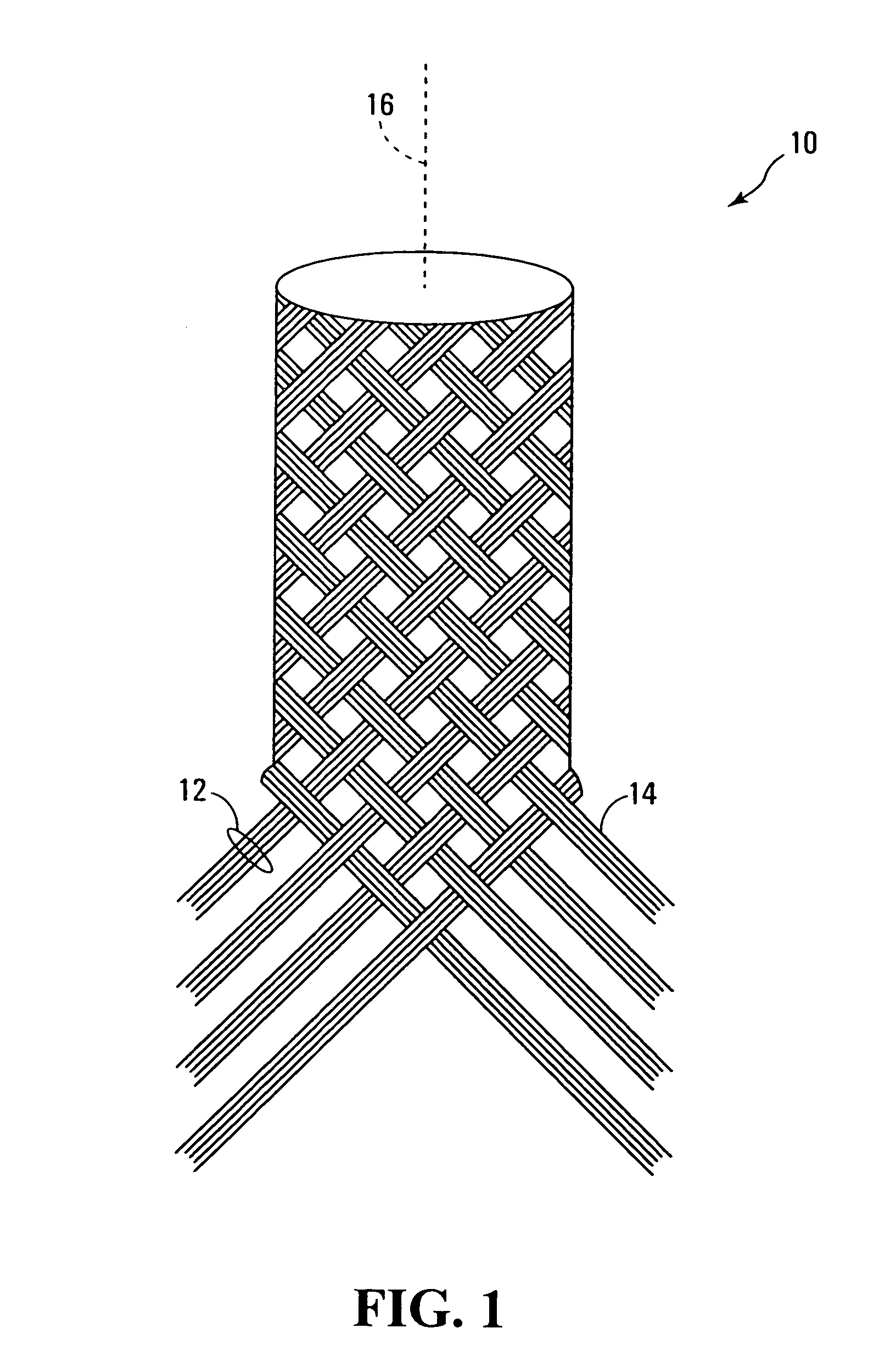
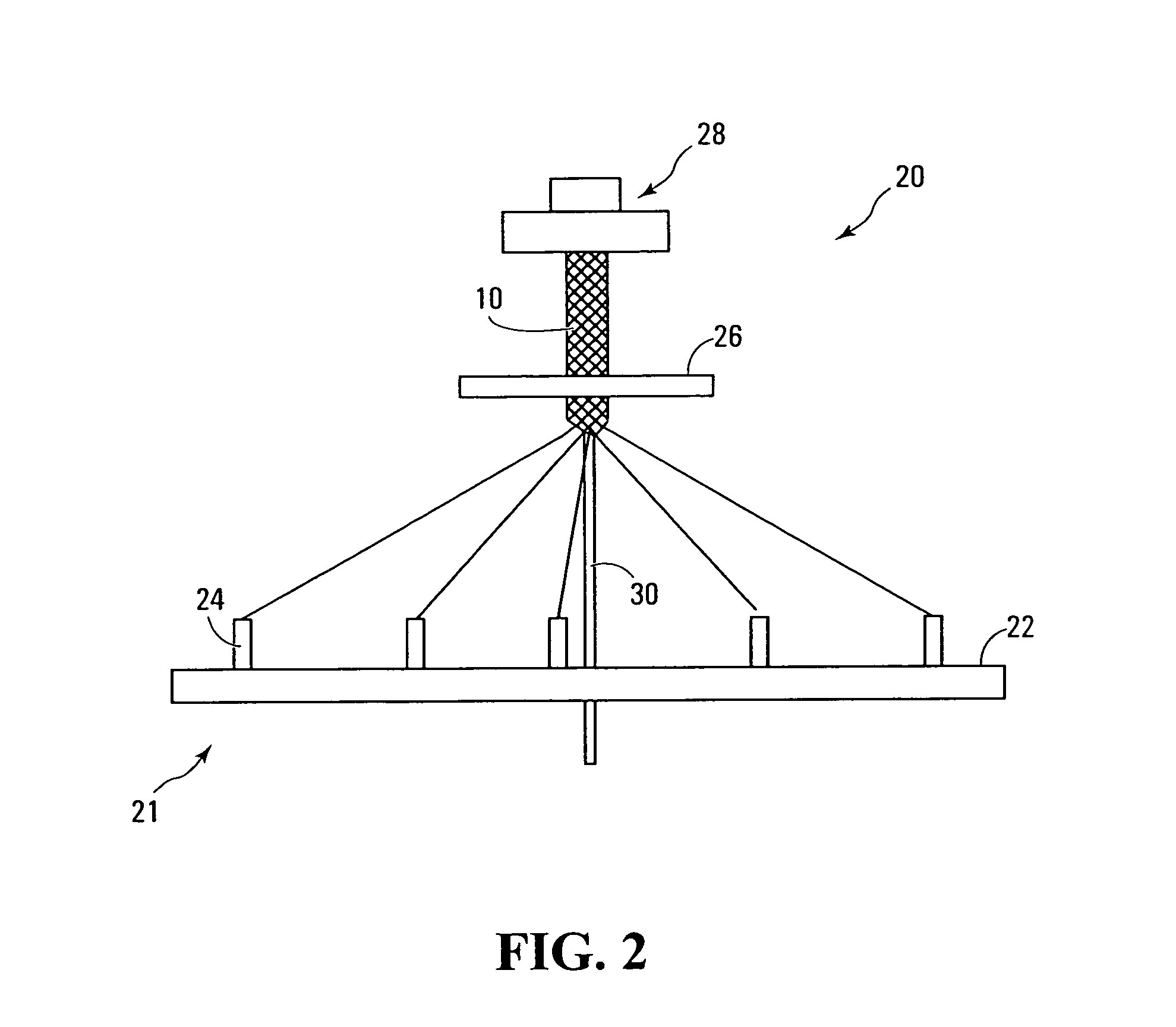
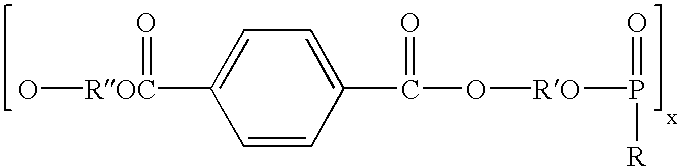
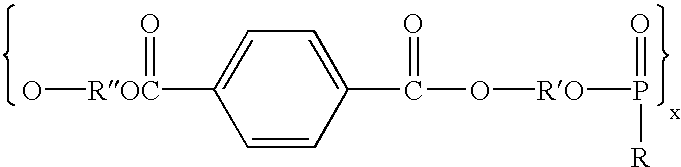
Polymer and nerve guide conduits formed thereof
Polymers comprising the subunit wherein R' is ethyl or butyl and R and R'' are any suitable side chain or cross link. Nerve guide conduits comprising this and other poly(phosphoesters) are also disclosed.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
Hydrogel-grafted degradable nerve guides
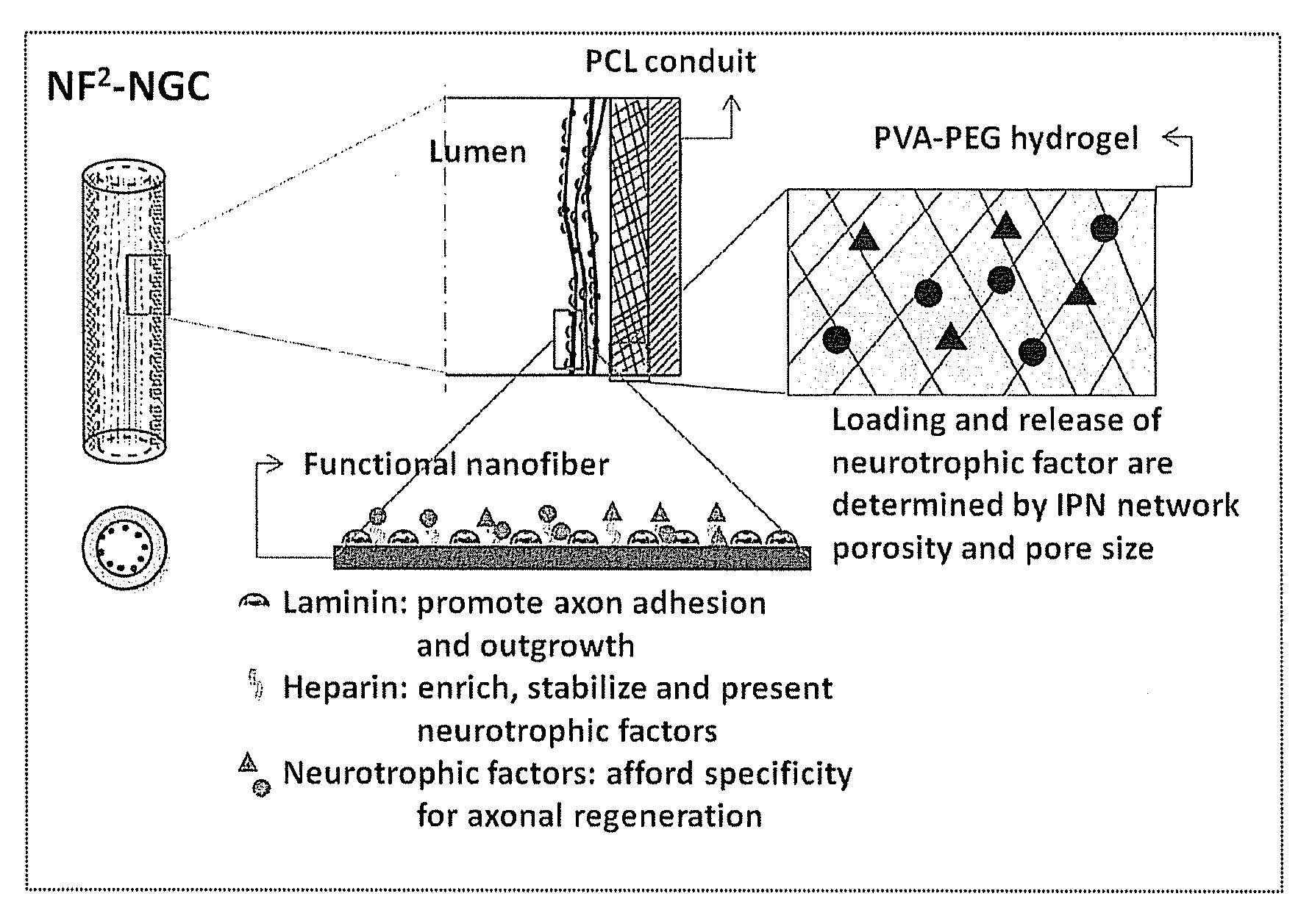
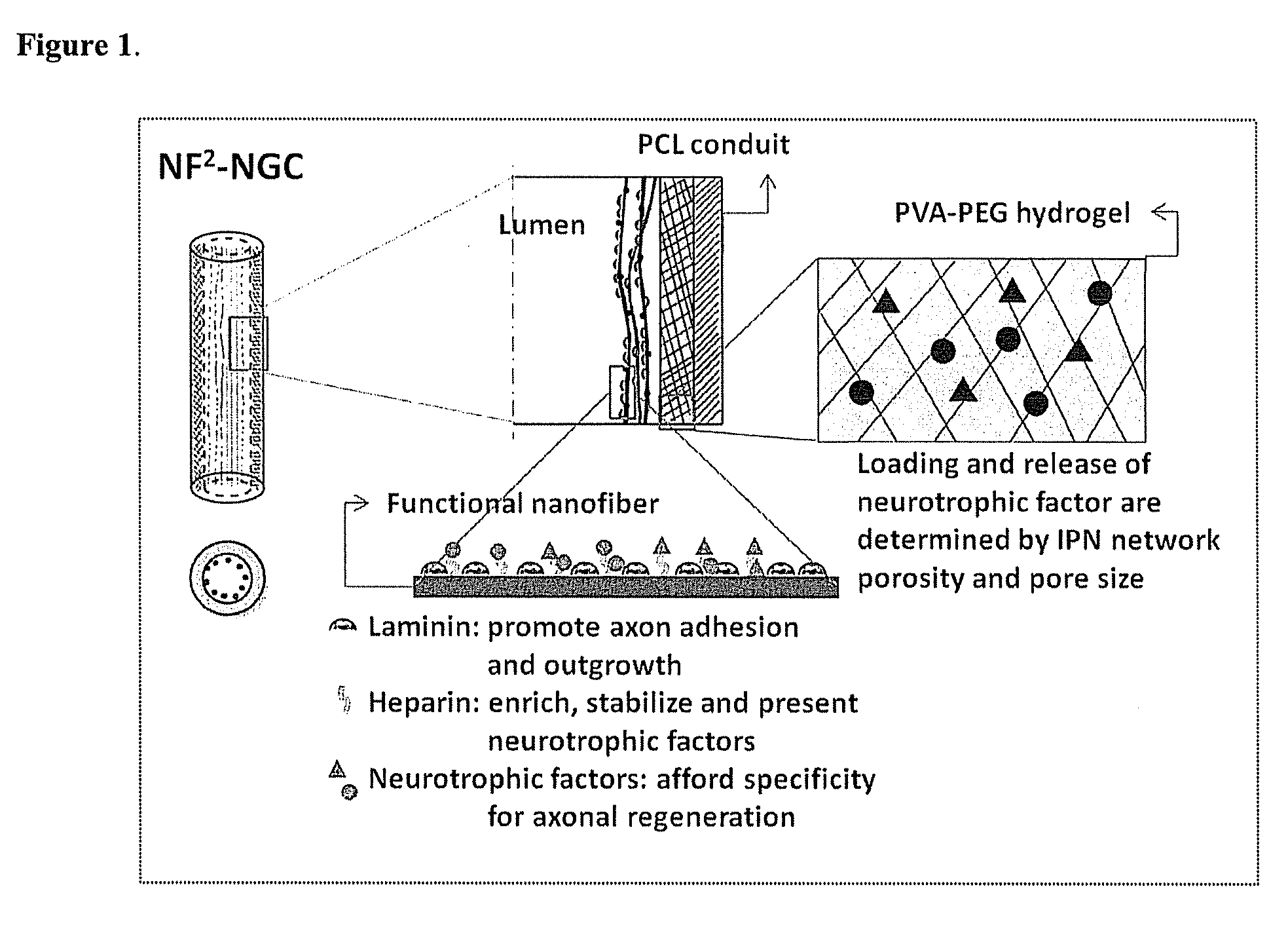
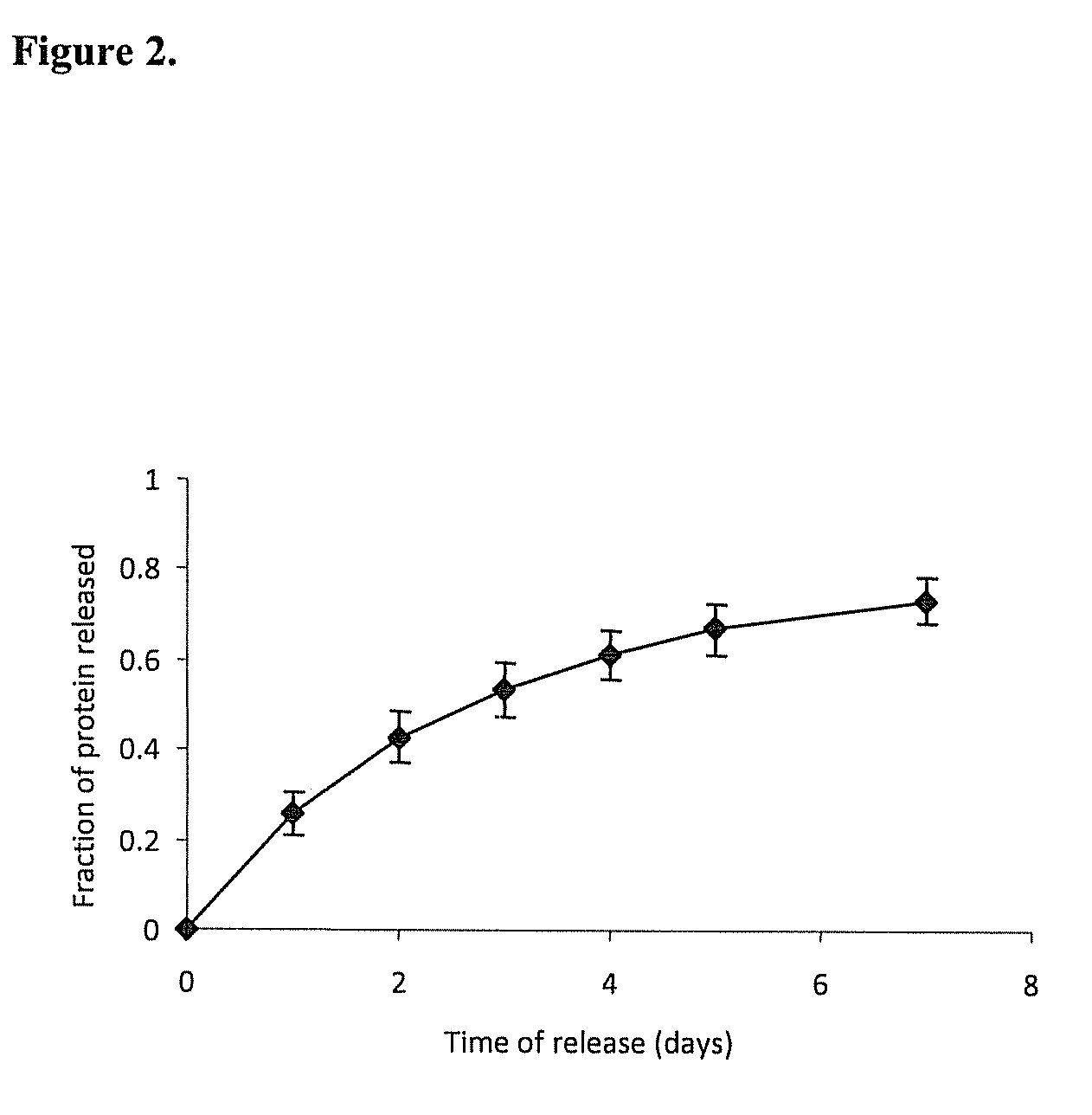
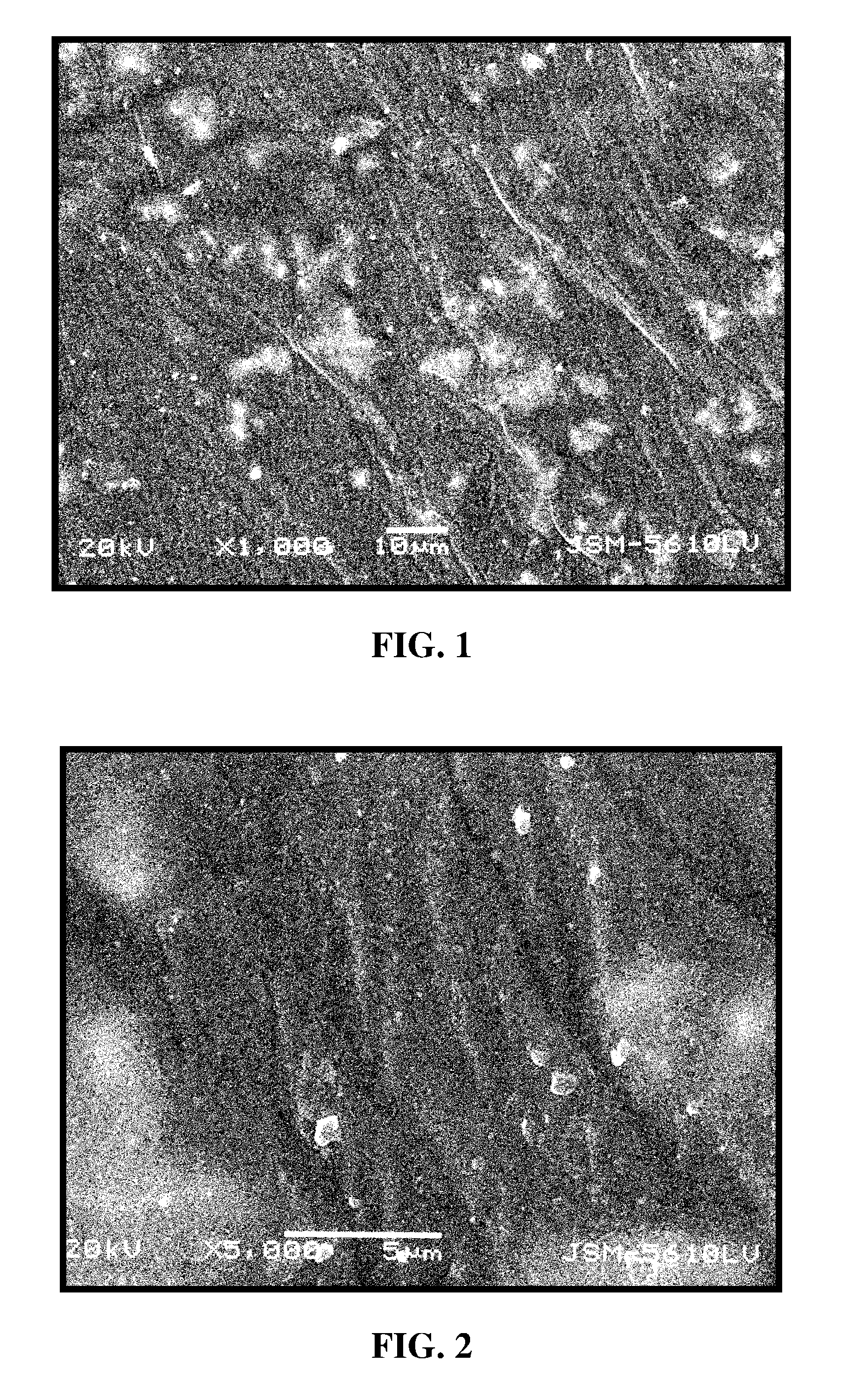
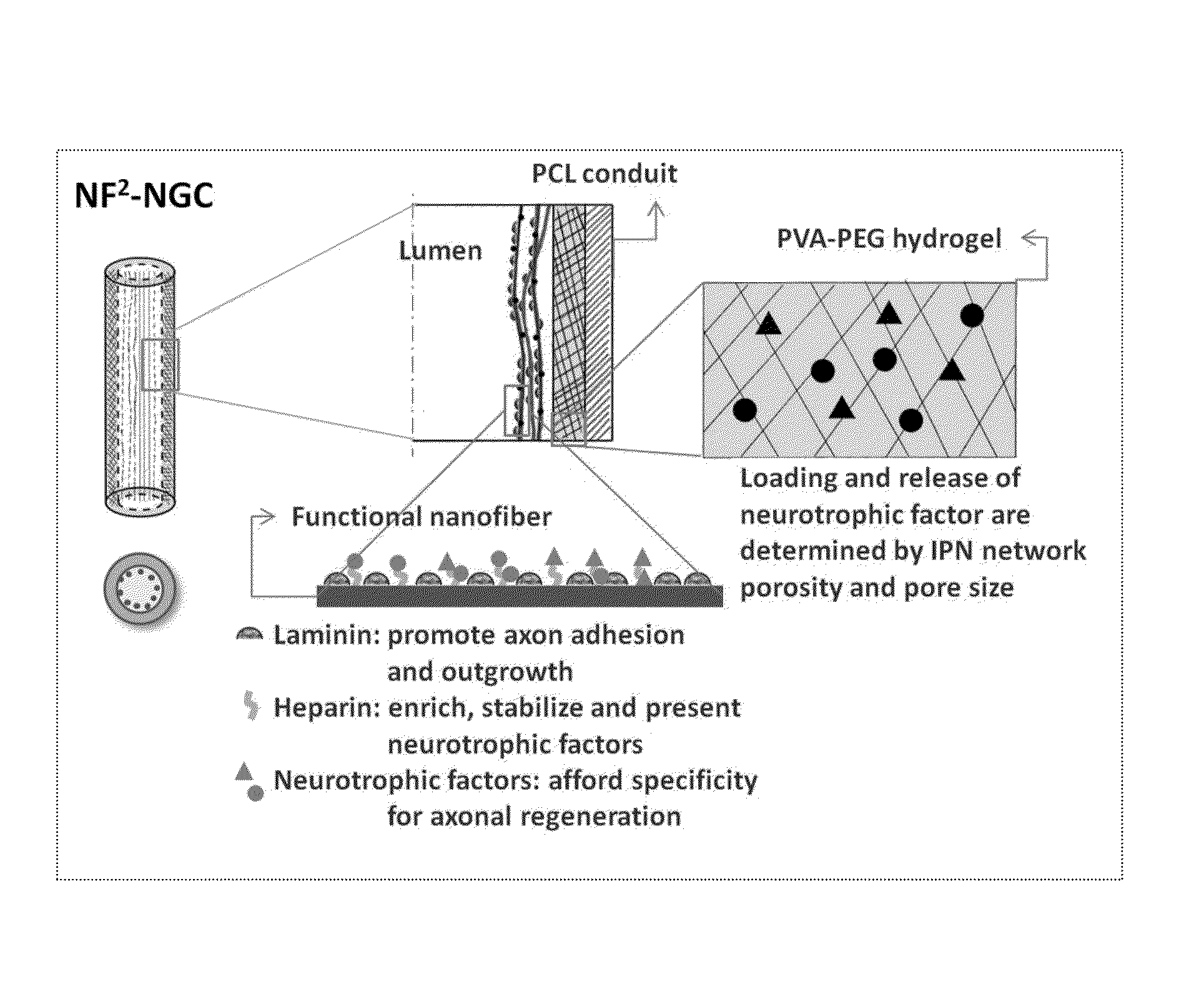
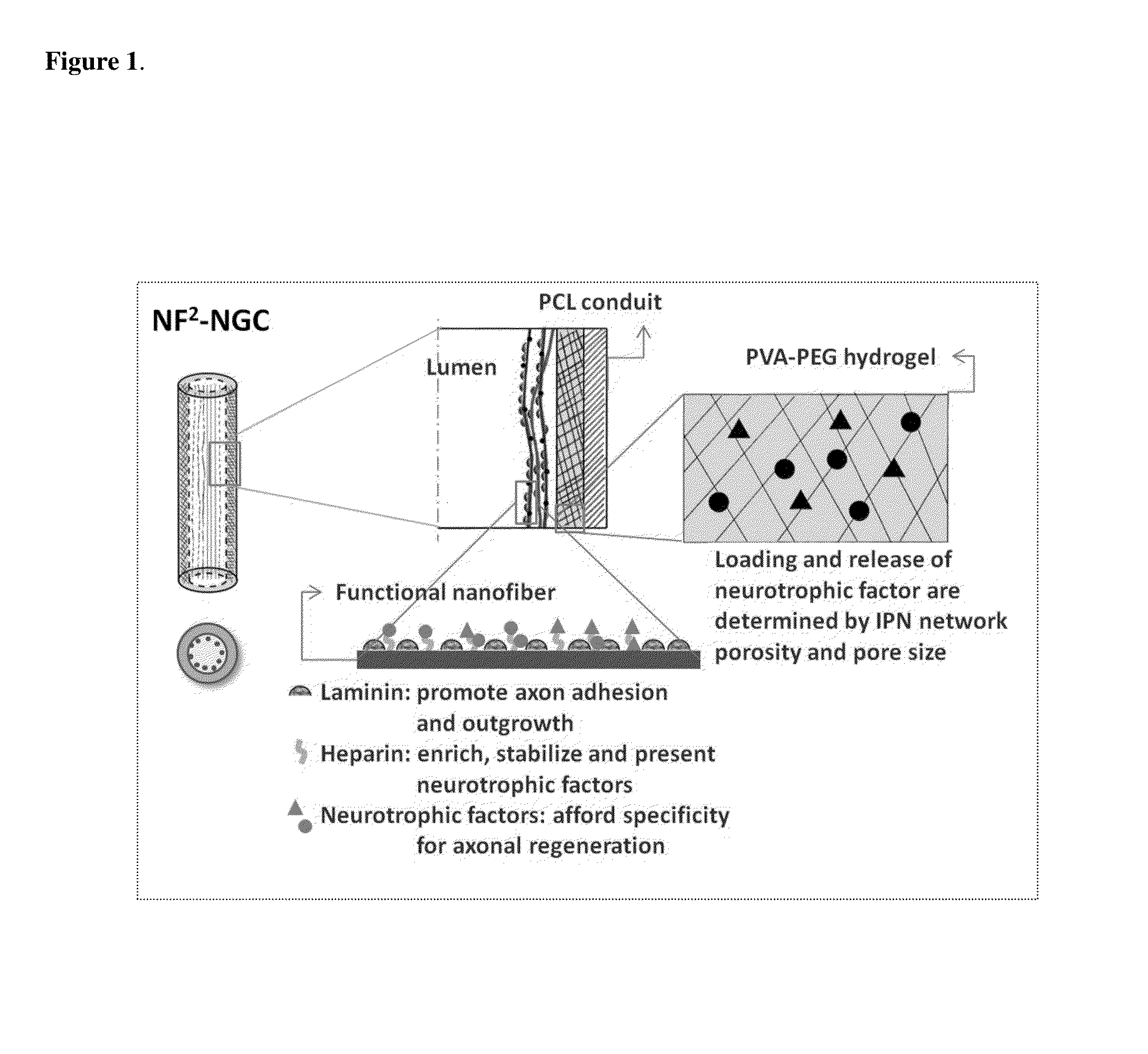
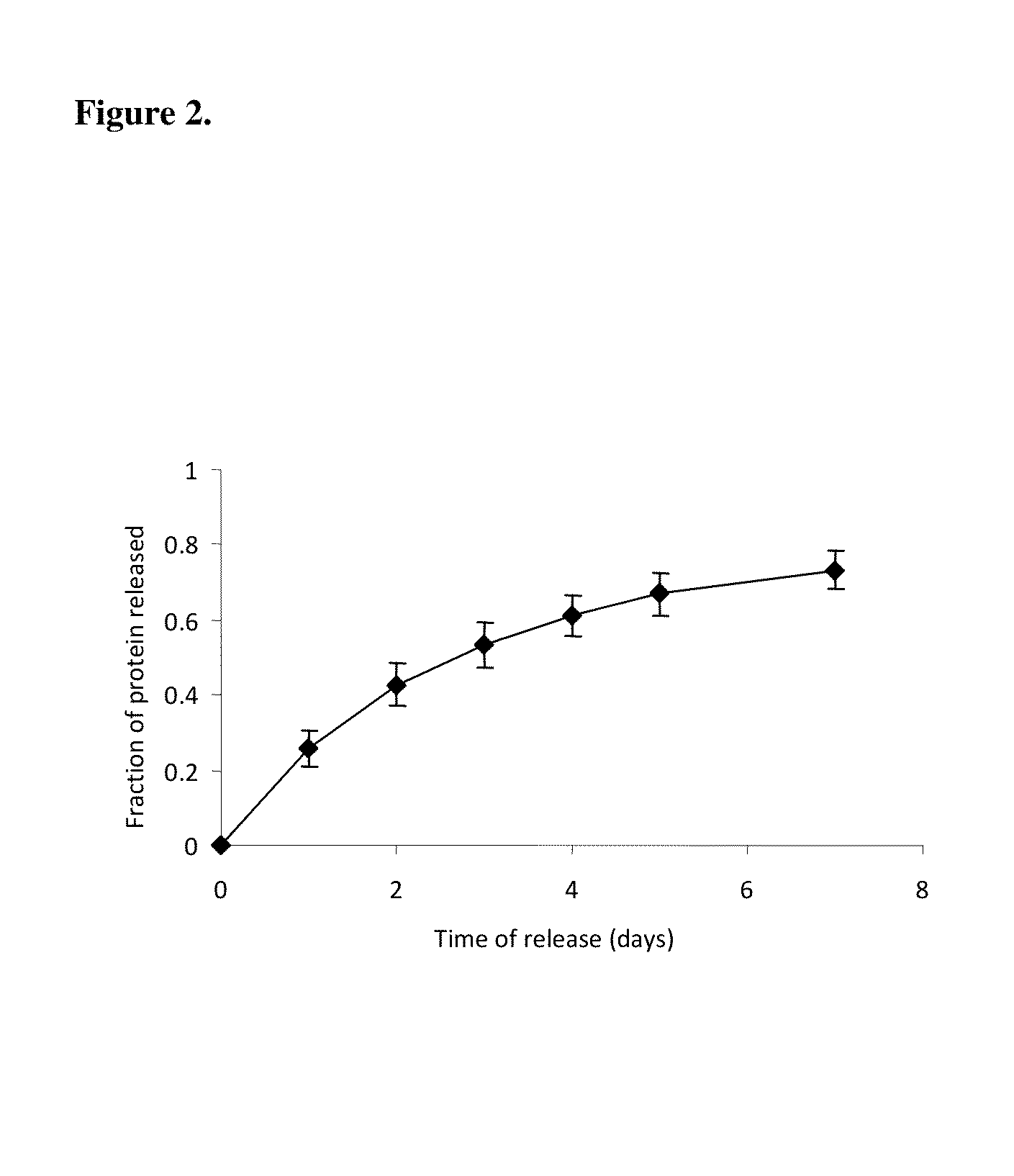
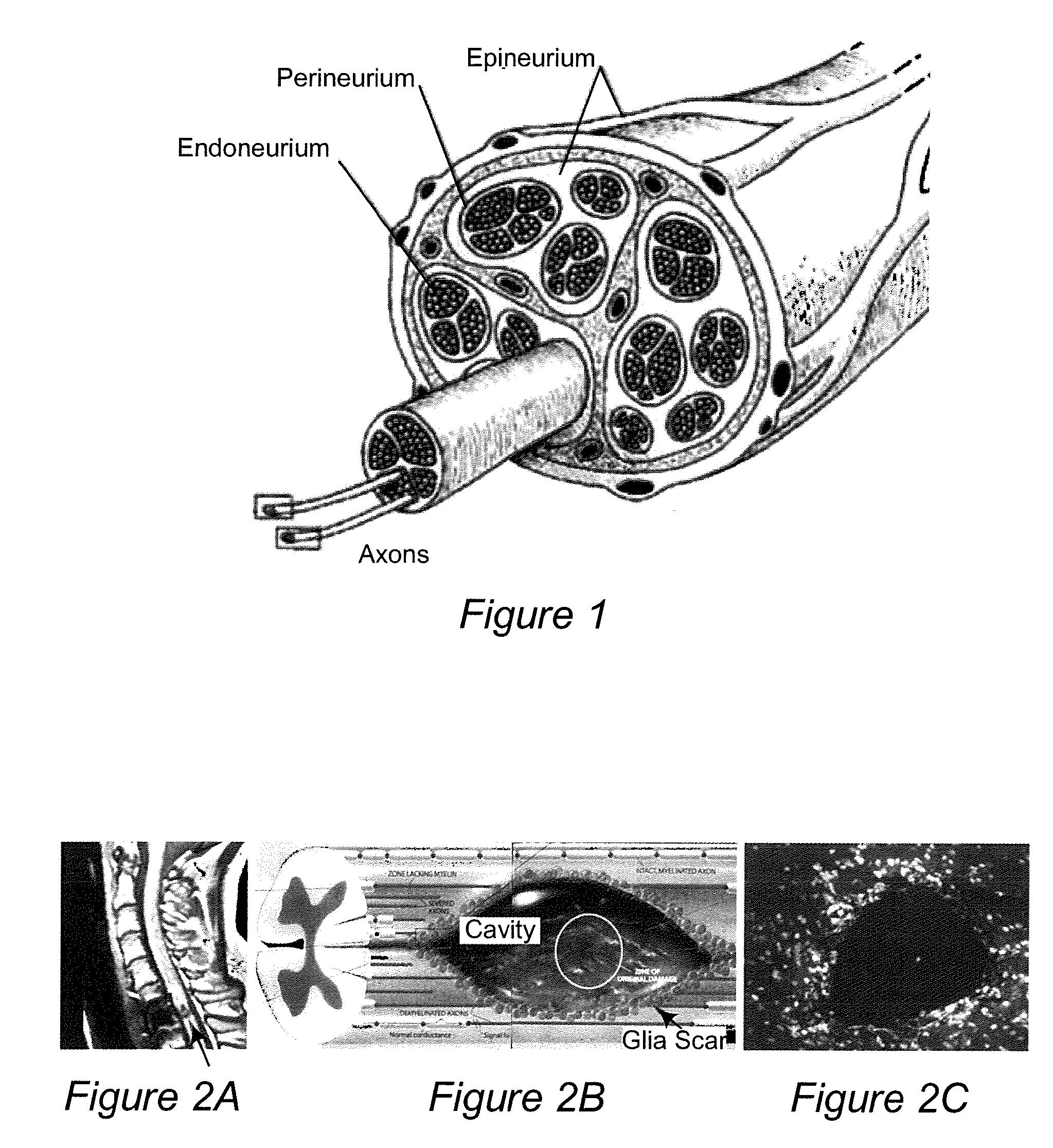
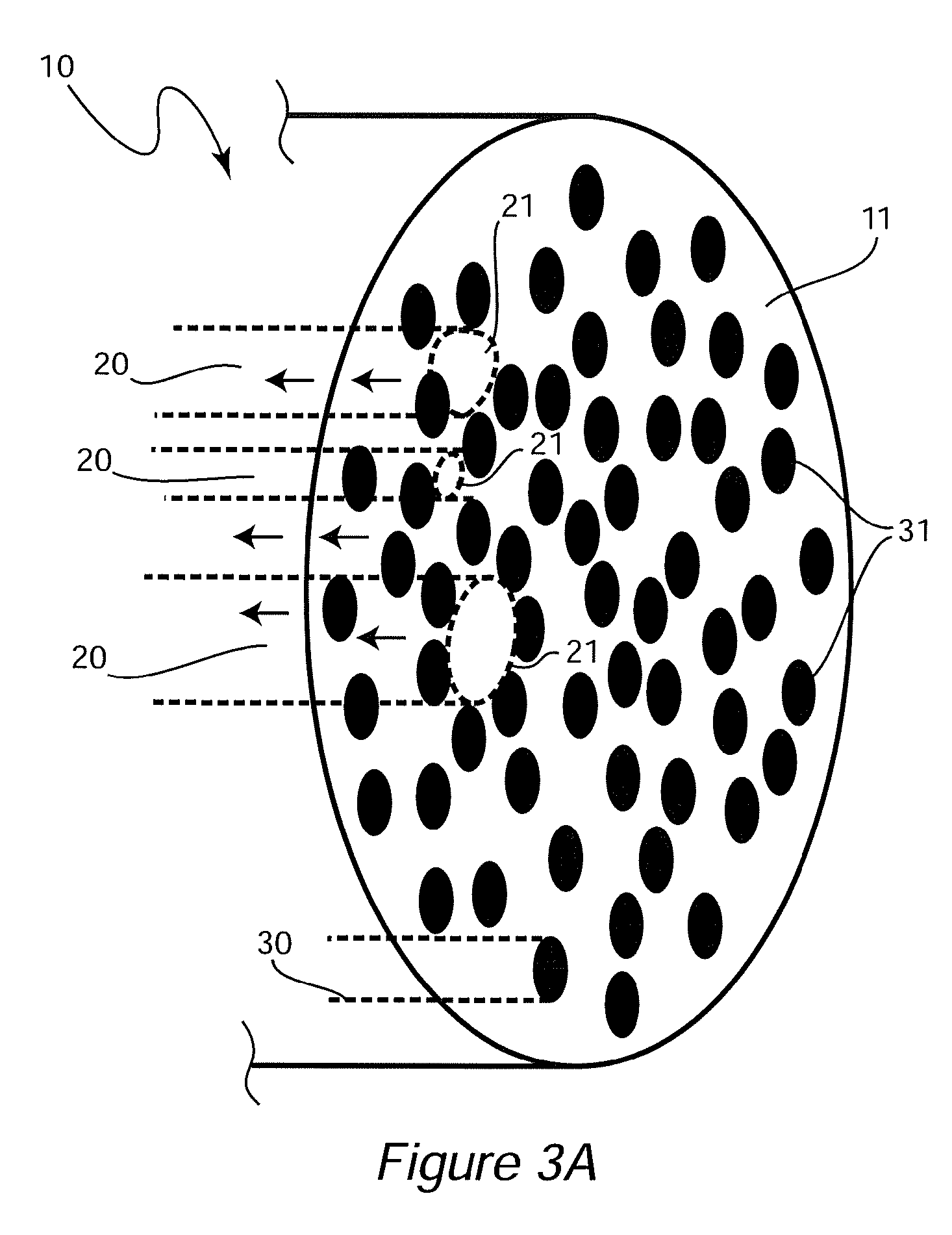
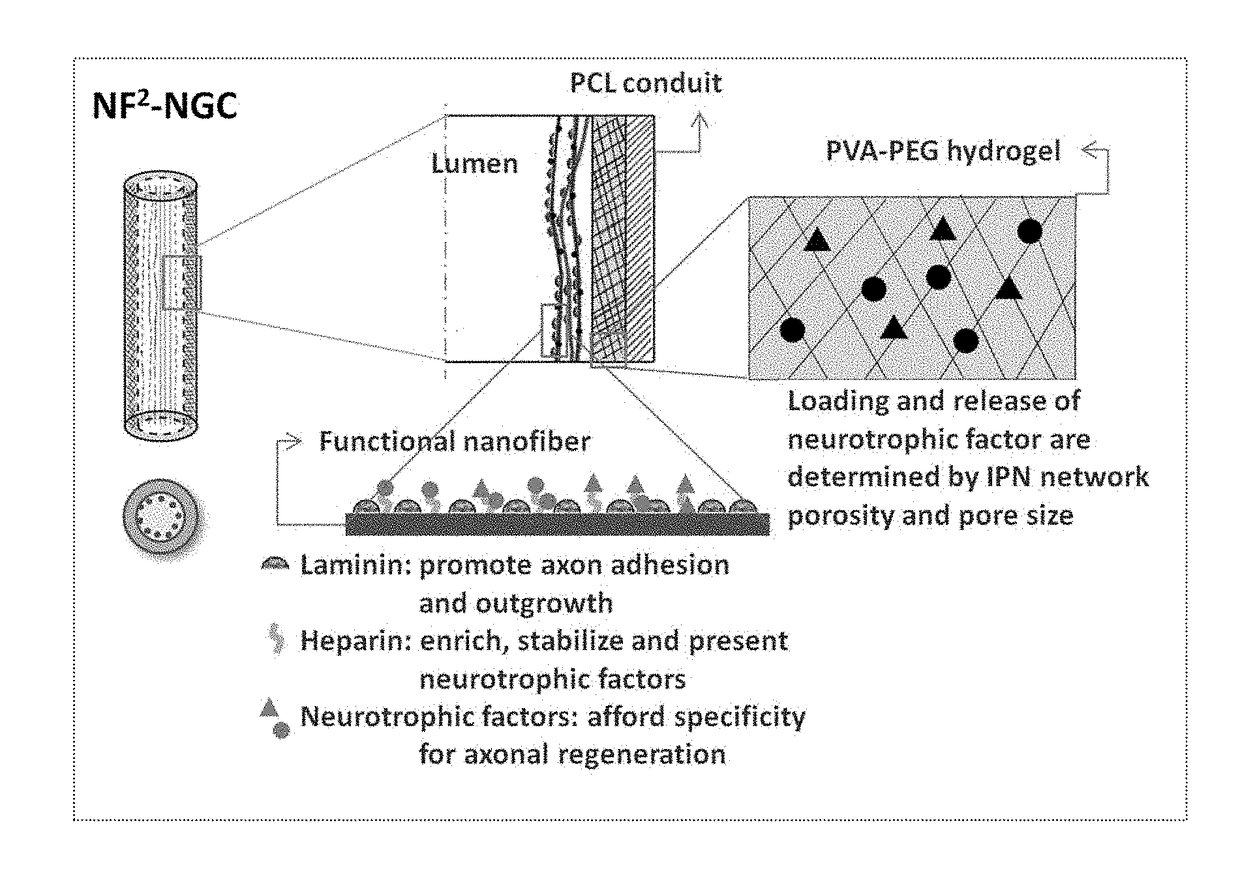
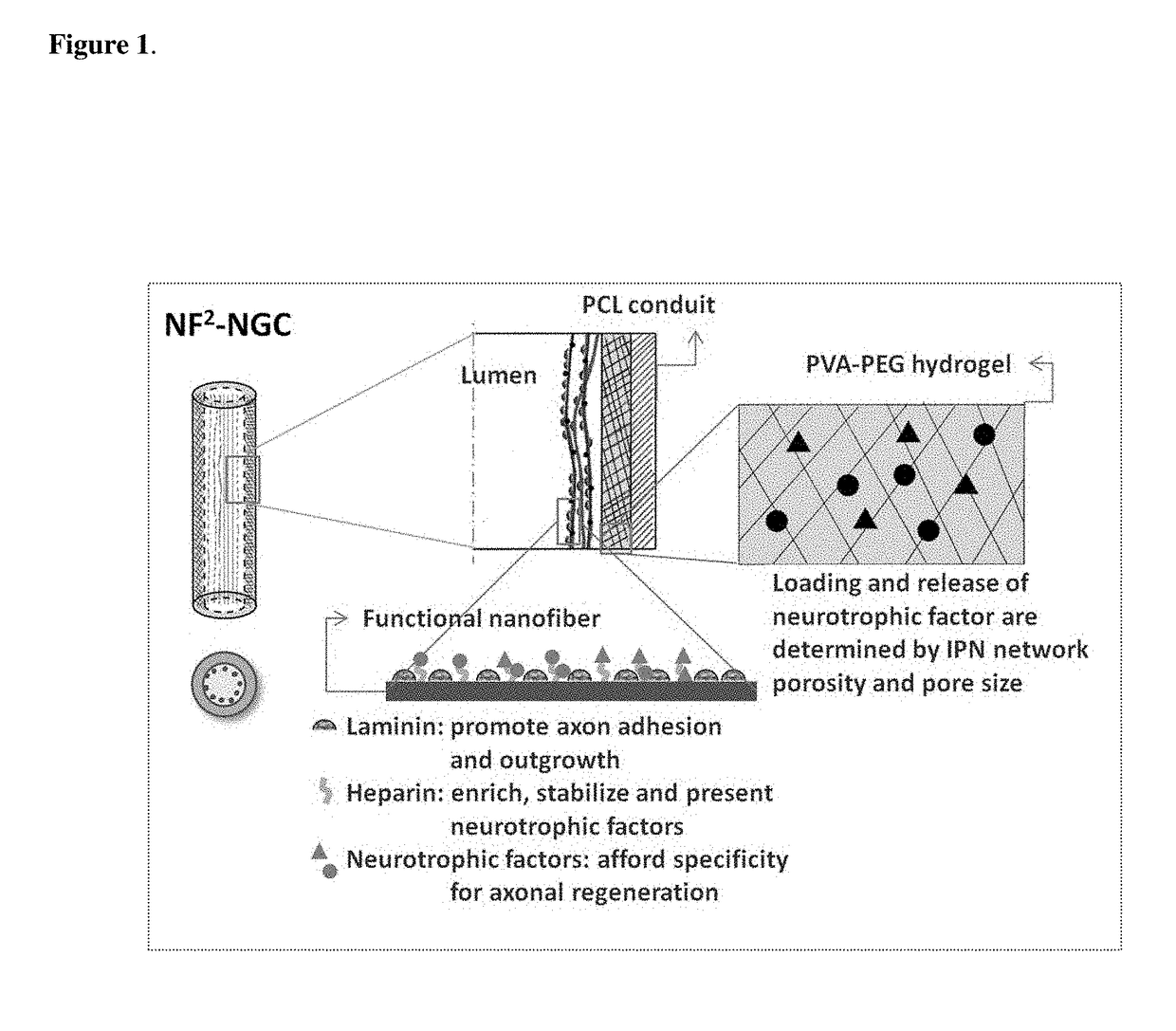
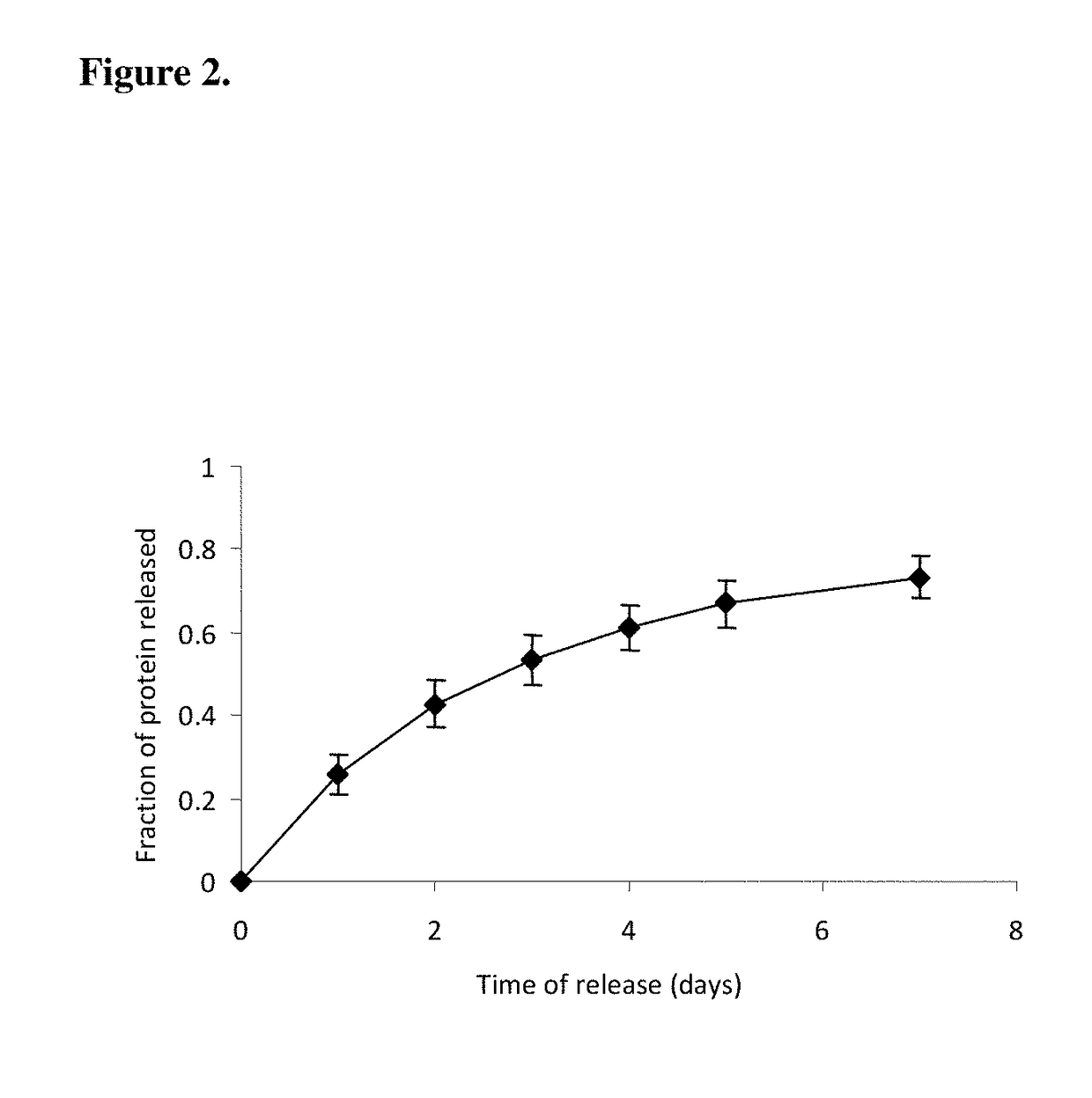
InactiveUS20110125170A1Mitigating burst releaseSustained releaseLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsNanofiberNeurotrophic factors
The present invention is directed to the compositions and methods of preparing hydrogel-grafted nerve guides for peripheral nerve regeneration. Particularly, the present invention describes the nerve guides and methods for preparation of hydrogel-grafted nerve guides with encapsulated neurotrophic factors and a nanofiber mesh lining the inner surface of the guide. The present invention also provides methods for peripheral nerve repair using these hydrogel-grafted nerve guides.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
RGD polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid) / β tricalcium phosphate composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS7989532B2Good biocompatibilityHigh affinityConnective tissue peptidesFibrinogenArginineTyrosine
An RGD polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid) / β-tricalcium phosphate composite material is composed of β-tricalcium phosphate particles and RGD polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid) with mass ratio of 1:10-1:100, in which the β-tricalcium phosphate particles are uniformly dispersed in the RGD polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid) matrix. The preparation method includes that poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid) is polymerized with GRGDY short peptide (glycin-arginine-glycin-aspartic acid-tyrosine sequence) to obtain RGD polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid), and then RGD polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid) is compounded with β-tricalcium phosphate particles. The composite material exhibits favorable biocompatibility, cellular affinity, biodegradability and mechanical behavior, and can avoid aseptic necrosis of tissues, which may be used as nerve guide or porous bone scaffold for repairing nerve tissue and bone tissue.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Biodegradable nerve guides
The present invention is directed to the compositions and methods of preparing hydrogel-grafted nerve guides for peripheral nerve regeneration. Particularly, the present invention describes the nerve guides and methods for preparation of hydrogel-grafted nerve guides with encapsulated neurotrophic factors and a nanofiber mesh lining the inner surface of the guide. The present invention also provides methods for peripheral nerve repair using these hydrogel-grafted nerve guides.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Electrospun nerve guides for nerve regeneration designed to modulate nerve architecture
InactiveUS9572909B2Recovery functionLevel of functional recoveryMovable spraying apparatusTissue regenerationFiberNerve structure
Nerve guides which are formed from three dimensional (3D) arrays of highly aligned electrospun fibers are provided. The electrospun fibers are oriented parallel to the long axis of the guide, and gaps and elongated spaces between the stacked fiber arrays provide channels for directed axonal growth. In some embodiments, the nerve guides also comprise high precision gradients of beneficial substances such as growth factors, which aid in nerve regeneration and growth along the guide.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Biological artificial nerve guide and method of making
InactiveUS20070141166A1Good biocompatibilityEnsure efficient flowPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesHuman bodyAntigen
A biological nerve guide for implantation into a human body is made by providing a natural animal tissue membrane, crosslinking and fixing the membrane, minimizing the antigens from the membrane, tanning the membrane, coupling an active layer to an inner surface of the membrane, cutting the membrane into a desired shape and size, positioning the cut membrane onto a rod-shaped mold so that the cut membrane assumes a cylindrical configuration, and attaching a spiral support to the outer surface of the cut membrane.
Owner:SUMMIT GD BIOTECH
Biodegradable nerve guides
The present invention is directed to the compositions and methods of preparing hydrogel-grafted nerve guides for peripheral nerve regeneration. Particularly, the present invention describes the nerve guides and methods for preparation of hydrogel-grafted nerve guides with encapsulated neurotrophic factors and a nanofiber mesh lining the inner surface of the guide. The present invention also provides methods for peripheral nerve repair using these hydrogel-grafted nerve guides.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Biological artificial nerve guide and method of making
InactiveUS7618653B2Good biocompatibilityEnsure efficient flowBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenCatheter
Owner:SUMMIT GD BIOTECH
Nerve guide
ActiveUS8216602B2Sufficient flexibilityMeet the requirementsPeptide/protein ingredientsCatheterCross-linkGuide tube
The aim of the invention is to provide a nerve guide that allows the axons to develop fairly freely during regeneration. For this purpose, the nerve guide is produced based on a shaped body from a cross-linked, resorbable, gelatin-based material. The shaped body is a tubular hollow body having a wall with an exterior surface and an interior surface, which wall defines a lumen. The nerve guide comprises a semipermeable layer surrounding the lumen.
Owner:GELITA AG
Method of delivery of nucleic acids to peripheral neurons
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Rgd polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-l-lysine-l-lactic acid) / beta tricalcium phosphate composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20080319114A1Good biocompatibilityHigh affinityConnective tissue peptidesFibrinogenArginineTyrosine
An RGD polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid) / β-tricalcium phosphate composite material is composed of β-tricalcium phosphate particles and RGD polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid) with mass ratio of 1:10-1:100, in which the β-tricalcium phosphate particles are uniformly dispersed in the RGD polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid) matrix. The preparation method includes that poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid) is polymerized with GRGDY short peptide (glycin-arginine-glycin-aspartic acid-tyrosine sequence) to obtain RGD polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid), and then RGD polypeptide grafted poly (glycolic acid-L-lysine-L-lactic acid) is compounded with β-tricalcium phosphate particles. The composite material exhibits favorable biocompatibility, cellular affinity, biodegradability and mechanical behavior, and can avoid aseptic necrosis of tissues, which may be used as nerve guide or porous bone scaffold for repairing nerve tissue and bone tissue.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
A kind of silk fibroin fiber hollow nerve guide and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110732038BEasy to prepareThe preparation method is simple and easyTissue regenerationProsthesisFiberBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a silk fibroin fiber hollow nerve guide and its preparation method and application, belonging to the technical field of biomedical materials. Using natural silk fibroin as raw material, it has good biocompatibility and biodegradability. The hollow nerve guide prepared by swelling the silk fibroin fiber with polydioxanone / formic acid solution has good compression resilience. The raw material price is low, the sources are wide, the operation method is simple and the process flow is short, the hollow nerve guide with different size requirements can be prepared quickly and conveniently, and it can be mass-produced. The prepared silk fibroin fiber hollow nerve guide has very good mechanical properties and compression resilience, is not easy to cause the collapse of the support material, and can ensure the normal growth of nerve cells. The scaffold material has high porosity and many connected pores, and nerve cells can adhere, proliferate, migrate and grow on the nerve conduit material, which can promote the regeneration and repair of damaged nerves.
Owner:XI'AN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
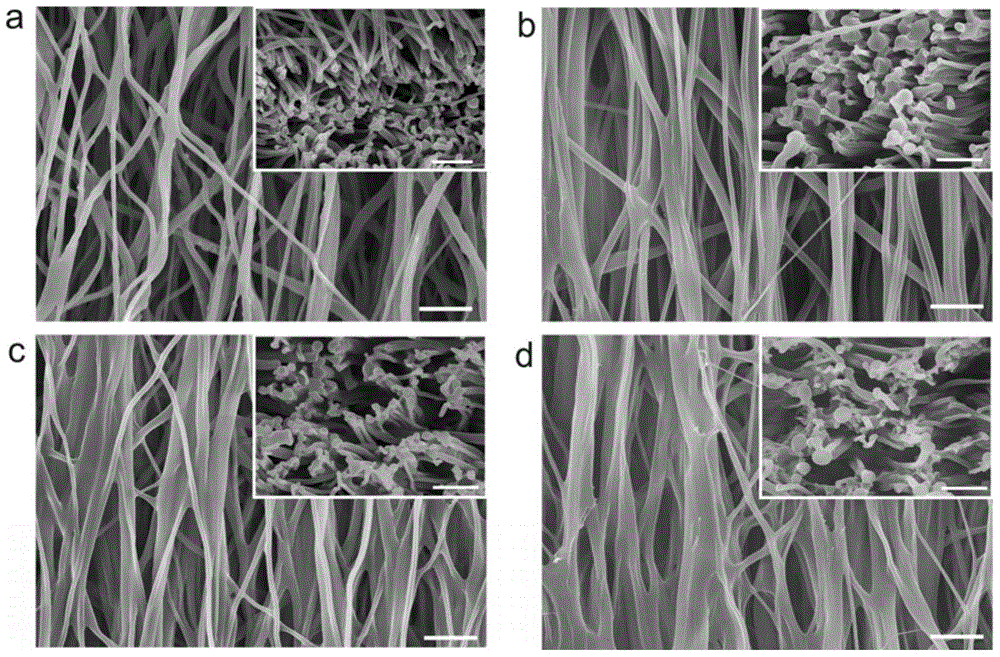
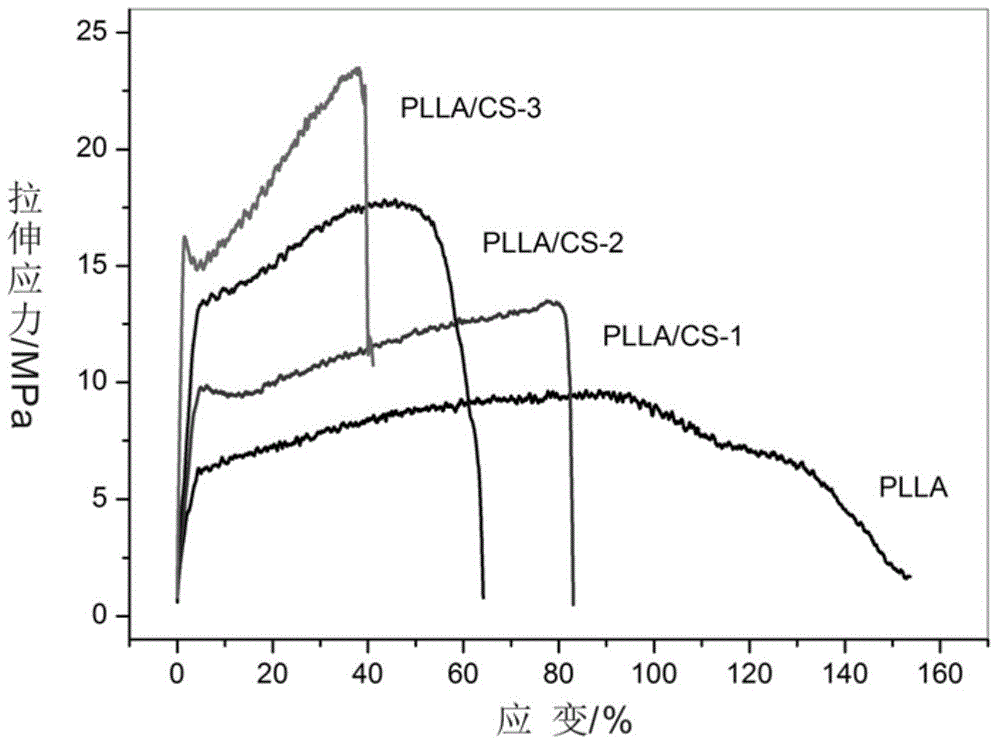
A kind of polylactic acid and chitosan composite nerve guide and its preparation method
InactiveCN103751839BKeep the clock throughHigh tensile strengthFibre typesProsthesisBiomechanicsPeripheral neuron
Belonging to the technical field of medical biomaterials, the invention in particular relates to a polylactic acid-chitosan composite nerve conduit. The composite nerve conduit is composed of oriented polylactic acid electrospun fiber and a chitosan layer wrapping the fiber. The invention also provides a preparation method of the polylactic acid / chitosan composite nerve conduit, and application of the nerve conduit in preparation of peripheral nerve defect repair materials. The polylactic acid-chitosan composite nerve conduit prepared by the invention has excellent biomechanical properties and superior hydrophilcity, also has good biological tissue compatibility, can significantly promote the attachment, migration and proliferation of Schwann cells, is easy to cut and preserve, and is simple to operate during clinical use, thus having good clinical application prospects in the peripheral nerve damage repair field.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Nerve conduit and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102688076BAddress barriers to developmentModerate intensitySurgeryCatheterNerves regenerationNerve repair
Owner:MEDPRIN REGENERATIVE MEDICAL TECH
DL-Lactide-Epsilon-Caprolactone Copolymers
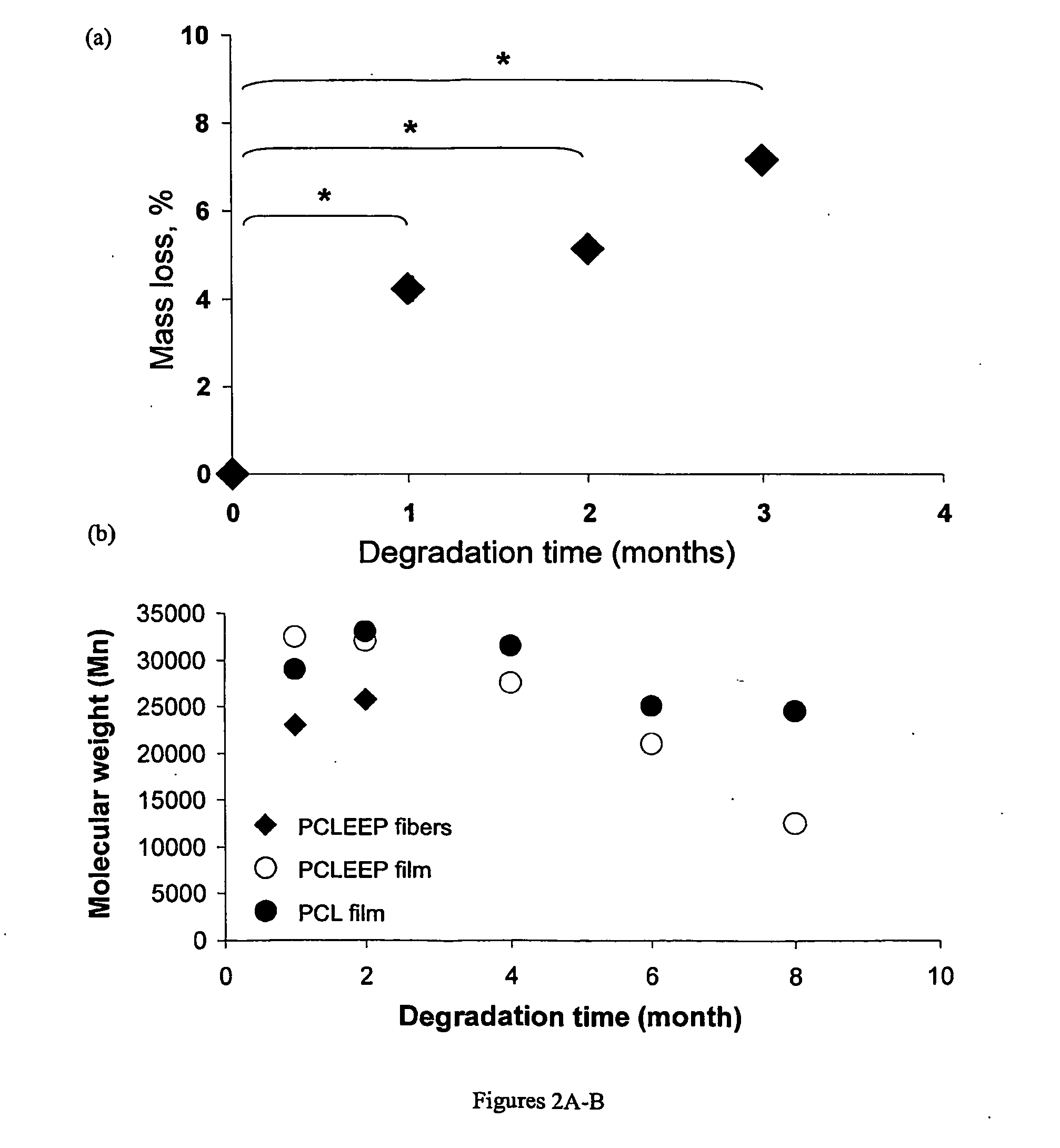
The present invention relates to specific DL-lactide-ε-caprolactone copolymers and the application of these polymers in the production of biodegradable medical applications. According to the present invention a polymeric material comprising poly(DL-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) is provided, which is obtained by the copolymerization of DL-lactide and ε-caprolactone, having a lactide content of 51-75 mol %, most preferably of 62-69 mol %.The materials of the present invention have excellent mechanical properties and may be used to provide articles for medical application, in particular nerve guides.
Owner:STRYKER EURO HLDG I LLC
Nerve graft capable of guiding nerve tracts to be regenerated accurately
The invention relates to a nerve graft capable of guiding nerve tracts to be regenerated accurately. The nerve graft comprises a plurality of nerve guide wires and an outer sleeve, and is prepared from a material with good nerve biocompatibility. The guide wires are inserted into the nerve tracts corresponding to two broken ends of a nerve trunk, so that a function of accurately guiding the nerve tracts to grow in an orientated manner is fulfilled, meanwhile, the two broken ends of the nerve trunk are fixedly connected through the outer sleeve, and the circumstance that the guide wires slip due to pulling of the nerve trunk in a moving process of limbs is prevented. The whole nerve graft is simple in structure, and is convenient and speedy in an implanting process, and meanwhile, the effect of nerve regeneration and repair can be improved.
Owner:邹玉华
Medicine compound preparation for treating osteoarthritis and preparation method of medicine compound preparation
ActiveCN110721308ARelieve symptomsPrevent or slow progressionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticHyaluronate InjectionClinical trial
The present invention discloses a medicine compound preparation for treating osteoarthritis. The compound preparation is preferably a compound injection and comprises a nerve guiding factor Sema and asodium hyaluronate injection. A concentration of the nerve guiding factor Sema in the sodium hyaluronate injection is 4-9 [mu]g / mL. In a preferred embodiment, the nerve guiding factor Sema is selected from Sema 3a protein. Results of clinical trials show that the injection prepared by combination of the nerve guiding factor Sema 3a protein and the sodium hyaluronate injection has a superior therapeutic effect for patients with early stage degenerative osteoarthritis than that of a sodium hyaluronate injection treatment alone.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
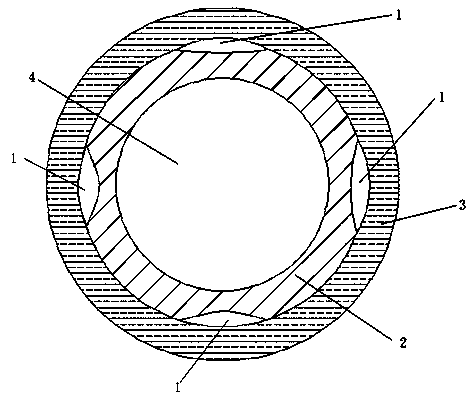
Method for preparing multi-channel antibacterial nerve guide by variable spindle braiding method
ActiveCN110786965BImprove mechanical propertiesHigh tensile strengthTissue regenerationProsthesisYarnExternal catheter
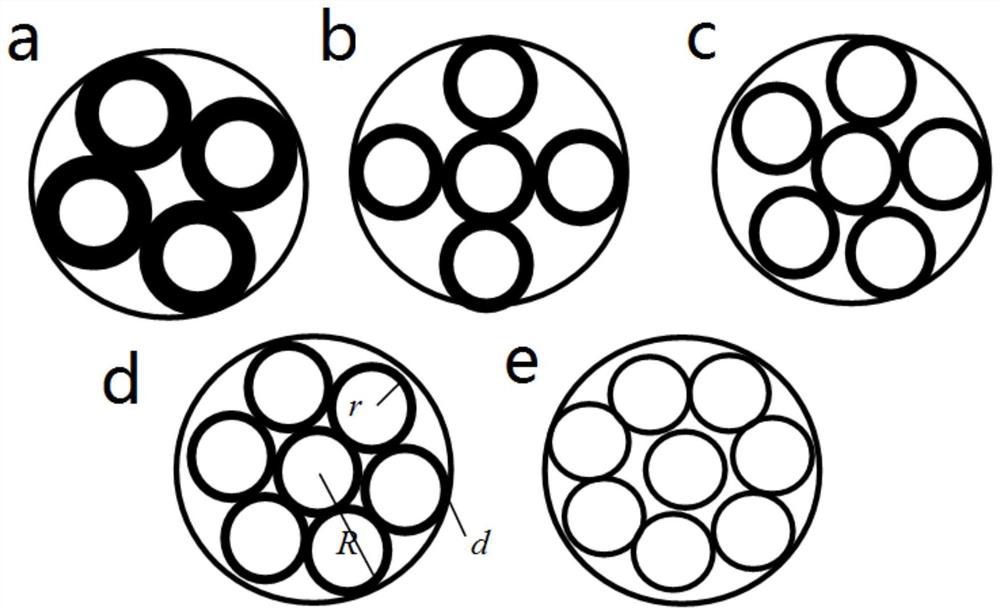
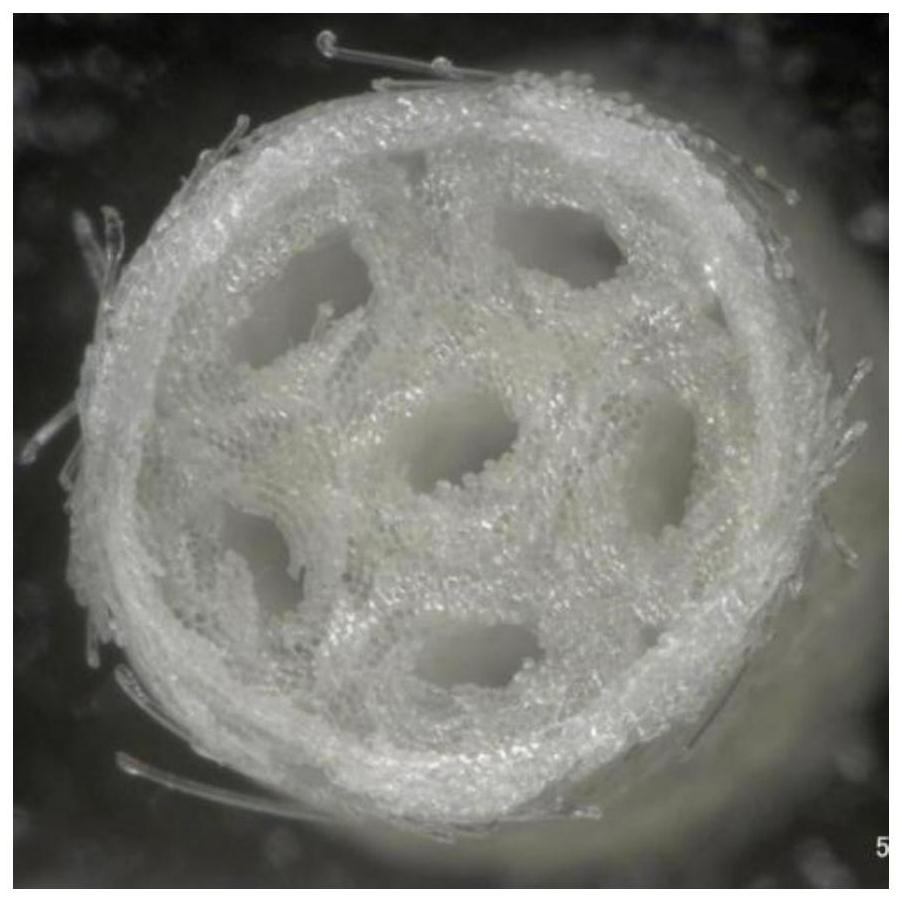
The invention relates to a method for preparing a multi-channel antibacterial nerve conduit by a variable-spindle weaving method, comprising the following steps: braiding a plurality of inner conduit braiding yarns on the outside of an inner core material to form a conduit, and the conduit includes an inner core material and an inner core material. The tube body is sleeved on the outside; the color difference between the braided yarn of the inner conduit and the inner core material is obvious, and the inner core material is in the shape of a solid cylinder with a smooth surface. The number of braided yarns in the inner conduit can be estimated by the following formula ; Among them, m represents the number of braided yarns in the inner conduit, and d y Represents the diameter of the braided yarn of the inner catheter, R represents the inner diameter of the outer catheter, n represents the number of inner catheters in the multi-channel antibacterial nerve guide, r represents the inner radius of the inner catheter; 0<k≤1, 0<λ≤1; The catheter is divided into n tubes, and the n tubes are arranged side by side as the core material, and the outer catheter braided yarn is woven on the outside of the core material to form an outer catheter outside the core material, and then the inner core material is removed to obtain a multi-channel antibacterial nerve guide.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
An axial gradient protein-loaded silk nerve conduit and its preparation and application
ActiveCN111317864BImprove biological activityPromote proliferationTissue regenerationProsthesisNerve repairNerve cells
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
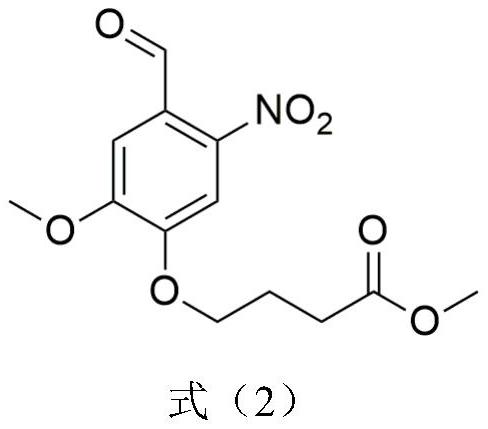
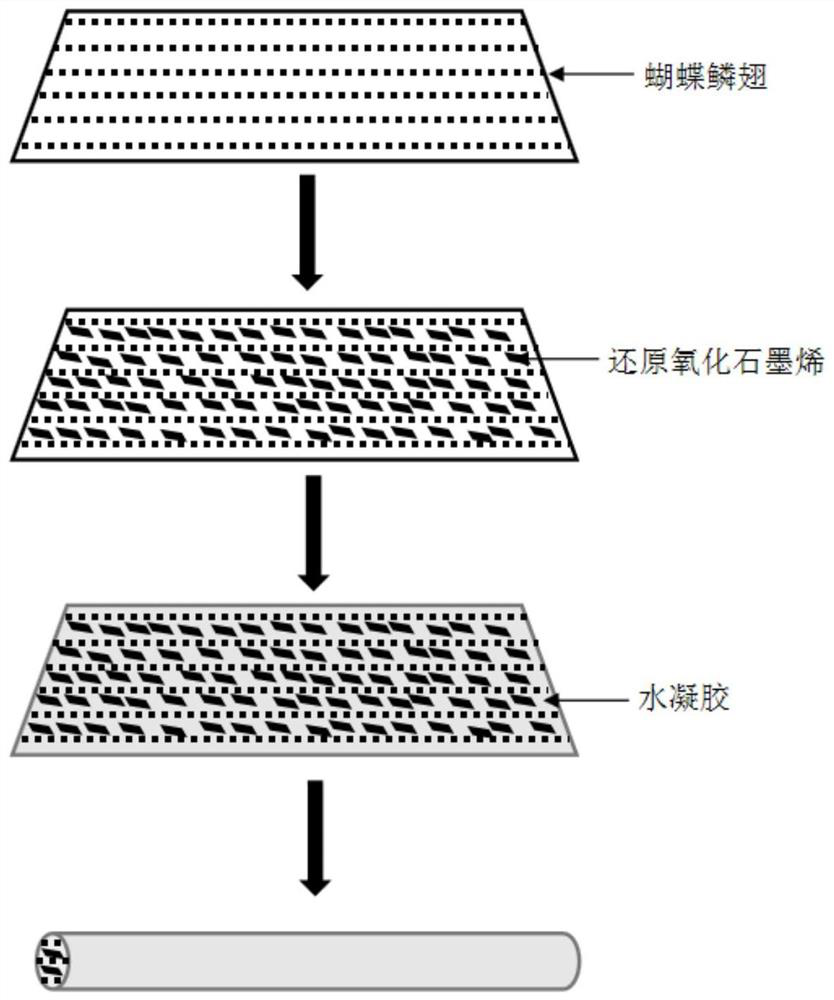
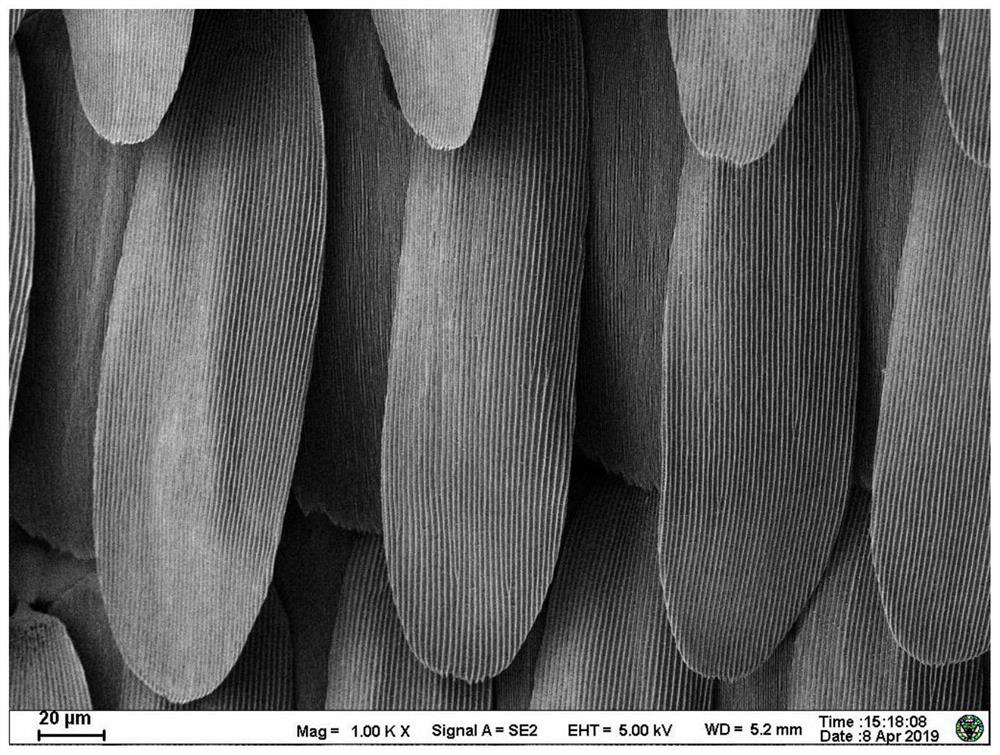
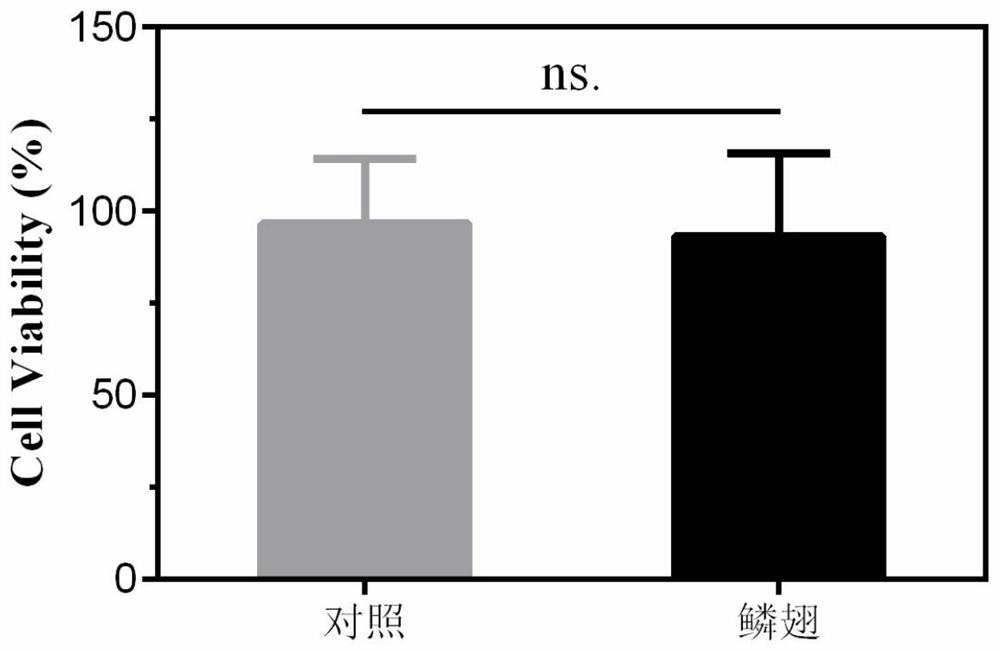
A kind of conductive nerve conduit based on butterfly lepidopteran and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114288470BHigh degree of orientation of micro-nano structureImprove adhesionCoatingsProsthesisNutritionNeurotrophic factors
The invention discloses a conductive nerve conduit based on butterfly lepidopteran and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises modifying reduced graphene oxide on the surface of butterfly lepidopteran and coating a layer of methacrylated gelatin solution containing neurotrophic factor BDNF, UV light cures it and then crimps it into a nerve guide. The micro-nano structures arranged in parallel on the inner surface of the prepared nerve conduit can guide the nerve cells to extend in the direction of the lepidopteran ridge, and the BDNF in the hydrogel can be slowly released, which can effectively promote nerve regeneration. This butterfly lepidopteran-based nerve conduit uses butterfly lepidoptery as a raw material, which is easy to obtain, low in cost, safe and non-toxic, and combines various factors that promote nerve regeneration, such as nano-bionics, directional induction, and sustained release of nutritional factors.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A kind of poly(l-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) nanofiber nerve conduit and preparation method
The invention discloses a poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) nanofiber nerve guide and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: (1) mixing poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) Caprolactone) dissolved in a mixed solvent of tetrahydrofuran and N,N-dimethylformamide; (2) Dip the nanofiber-receiving metal rod into the gelatin solution, take it out and dry it, and form a layer of gelatin film on the outer layer of the metal rod (3) Electrospinning of poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) / tetrahydrofuran / N,N-dimethylformamide solution to accept nano (4) After electrospinning, the metal rod is immersed in warm water to dissolve the gelatin, and the nerve guide can be removed. The nerve guide of the present invention has good biocompatibility and mechanical strength, and the tube wall has abundant micropores, which is beneficial to the exchange of nutrients, and the degradation time of the nerve guide matches the regeneration time of the autologous nerve; the preparation method of the present invention is simple and does not require Pollution environment, high economic benefit.
Owner:山东隽秀生物科技股份有限公司
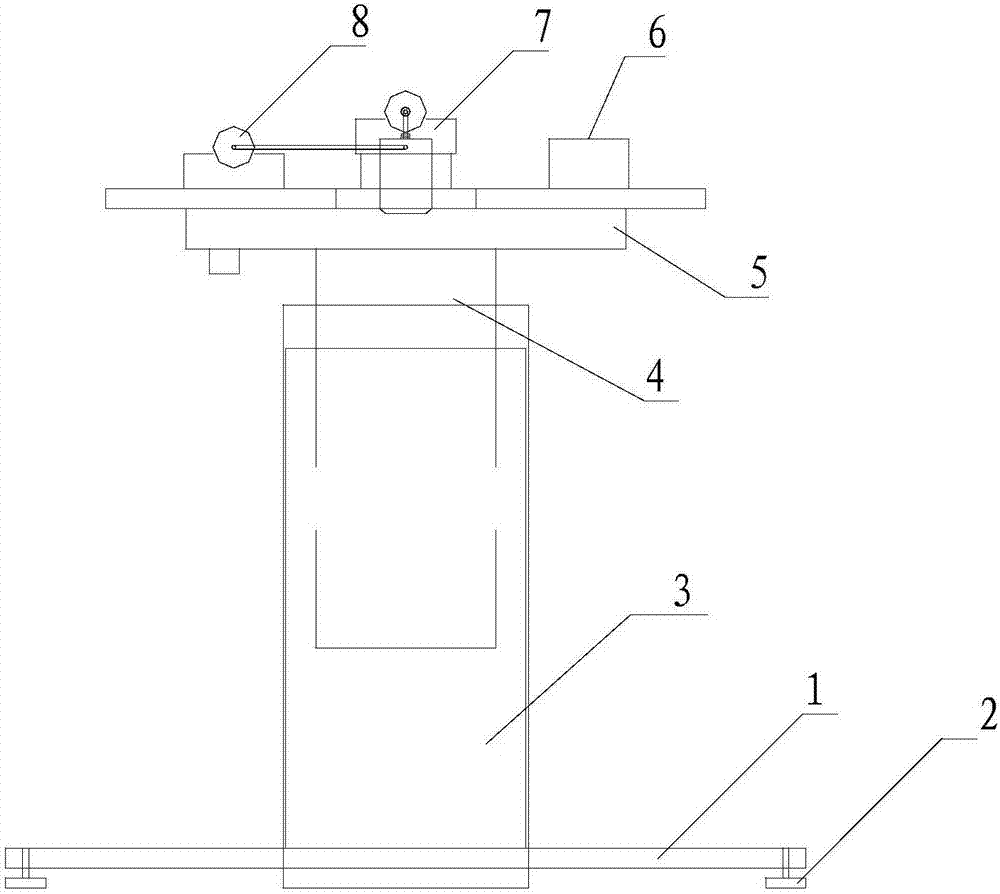
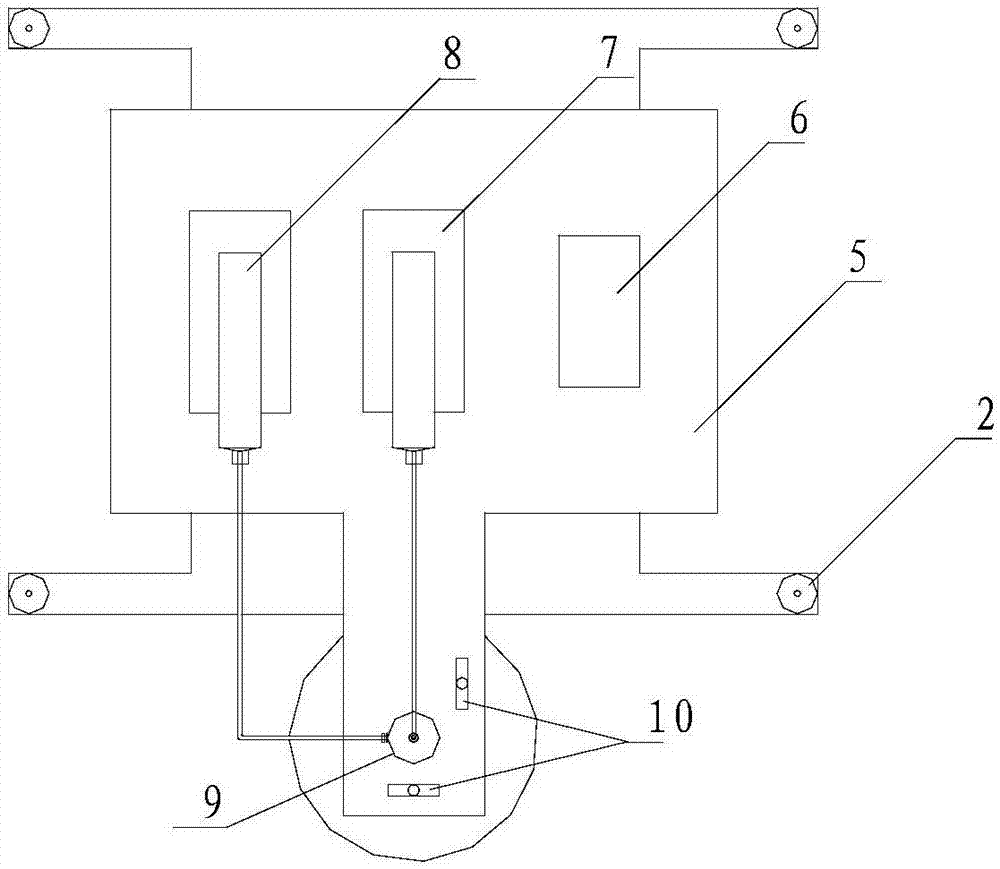
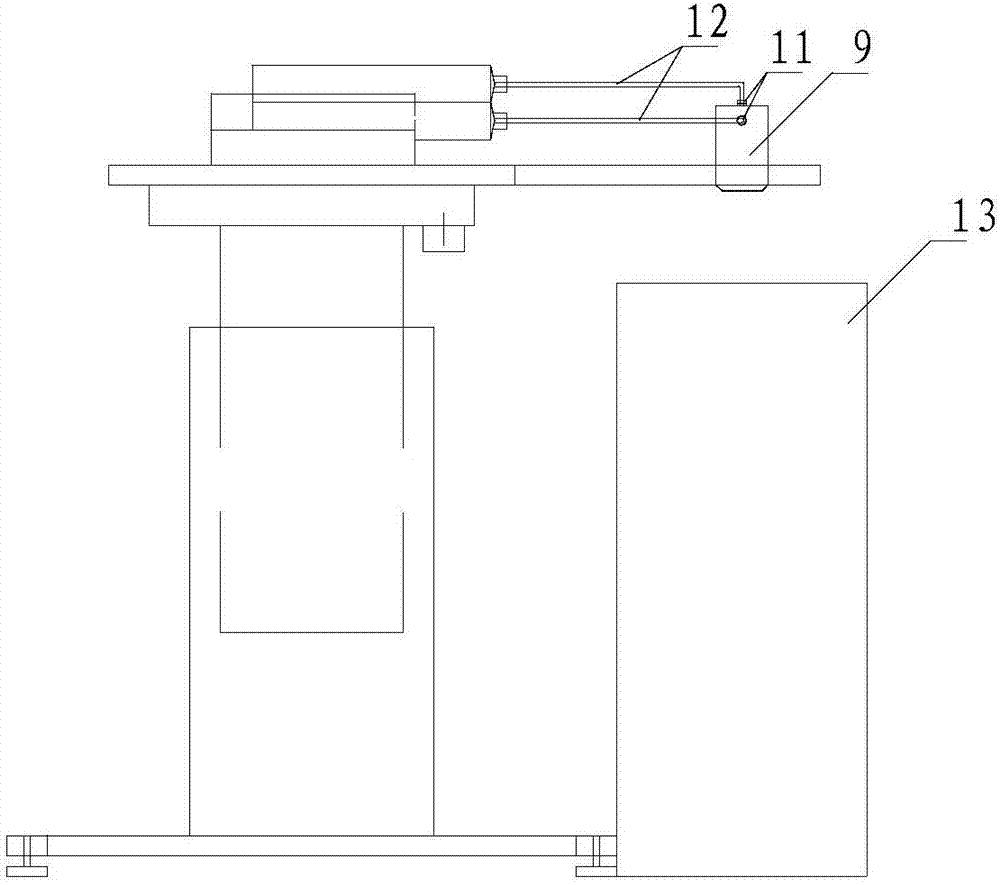
A nerve guide with contact guiding function and its preparation method and device
ActiveCN106236323BUniform and stable structural shapeAvoid secondary processingHollow filament manufactureFilament/thread formingEngineeringCatheter
The invention discloses a nerve conduit having a contact-type guiding function. The nerve conduit comprises a hollow thin-film tube body, wherein a longitudinal groove structure is formed in the inner wall of the hollow thin-film tube body; the invention also discloses a manufacturing device, which comprises a base, a lifting platform which is arranged on the base, two micro injection pumps and a spinning nozzle which are arranged on the top surface of the lifting platform, and a coagulation basin which is located below the spinning nozzle; the spinning nozzle comprises a spraying head and two layers of spraying holes in the spraying head; a spraying cavity, which is connected to one of the micro injection pumps, is formed in the spraying head; the top ends of the outer layer of spraying holes communicate with the spraying cavity; the top ends of the inner layer of spraying holes are externally connected to the other micro injection pump and the bottom ends extend out of the outer layer of spraying holes; and grooves, which extend in the axial direction of the inner layer of spraying holes, are formed in the outer walls of the inner layer of spraying holes. The invention also discloses a method for manufacturing the nerve conduit. The nerve conduit manufactured by the invention is simultaneously formed with the longitudinal groove structure in the inner wall of the nerve conduit in a manufacturing process; and the longitudinal groove structure is uniform and stable in shape, so that such additional processes as secondary processing are avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Bending fully degradable magnesium alloy nerve guide and its preparation method
ActiveCN104107096BUniform wall thicknessFlat surfaceTubular organ implantsCatheterUltimate tensile strength
The present invention provides a bendable and fully degradable magnesium alloy nerve guide for nerve defect repair, which forms an integrally formed round tubular structure through the braiding of multiple magnesium alloy wires, wherein the distance between each row of magnesium alloy wires and the shaft of the round tube is There is a 45-degree angle between them, and there is a gap between two adjacent rows of magnesium alloy wires in the same direction; meanwhile, a preparation method for the bendable fully degradable magnesium alloy nerve guide is provided. The bendable fully degradable magnesium alloy nerve guide provided by the invention has high radial support strength, good bending flexibility, and controllable uniform degradation performance. The prepared bendable fully degradable magnesium alloy nerve conduit for nerve defect repair has uniform wall thickness and smooth surface, and can be widely used to repair various defective nerves that need to be bent.
Owner:SHANGHAI INNOVATON MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
A kind of nerve injury repair material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111001039BNo residueSimple manufacturing processTissue regenerationProsthesisAnatomyCollagenan
The application discloses a nerve injury repairing material, its preparation method and application. The preparation method of the material comprises: solidifying and drying the following mixed solution: the solute of the mixed solution includes collagen and chitosan, and the solvent is an acid solution; the collagen in the mixed solution The concentration is 60-90mg / mL; the concentration of the chitosan in the mixed solution is 20-40mg / mL. The product of the present invention retains the advantages of the original collagen nerve repair product, has been significantly improved in suture performance and degradation performance, and can also increase the conductive function, which is more in line with the requirements of an ideal nerve guide. Repair, without adding new solvents, and without new chemical reagent residue problems.
Owner:TIANXINFU (BEIJING) MEDICAL APPLIANCE CO LTD
Nerve guiding device
ActiveCN113040840AEasy to manufactureReduce manufacturing costDiagnosticsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryMedicineAnatomy
The invention discloses a nerve guiding device. The nerve guiding device comprises an adsorption head used for wrapping nerve broken ends of nerves to be dragged, the adsorption head communicates with a guiding strip, and the guiding strip is used for guiding the adsorption head to move and penetrate through a soft tissue tunnel under the action of external force. The guiding strip communicates with a vacuumizing adsorption device, and the vacuumizing adsorption device is used for enabling the adsorption head to adsorb and wrap the nerve broken ends in vacuum through the guiding strip. The guiding strip communicates with a negative pressure regulator, and the negative pressure regulator is used for manually regulating the adsorption force of the adsorption head for vacuum adsorption of the nerve broken ends. According to the nerve guiding device, in the traction process, the nerve broken ends can be protected through wrapping of the adsorption head, the nerve broken ends are prevented from being bruised and collided, the situation that the nerves are damaged due to external force compression or tearing can be effectively avoided, the adsorption force of the adsorption head for vacuumizing and adsorbing the nerve broken ends can be adaptively adjusted through the negative pressure regulator, so that the traction requirements of various nerve broken ends are met, and the application range of the nerve guiding device is widened.
Owner:长沙众智医疗器械有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com