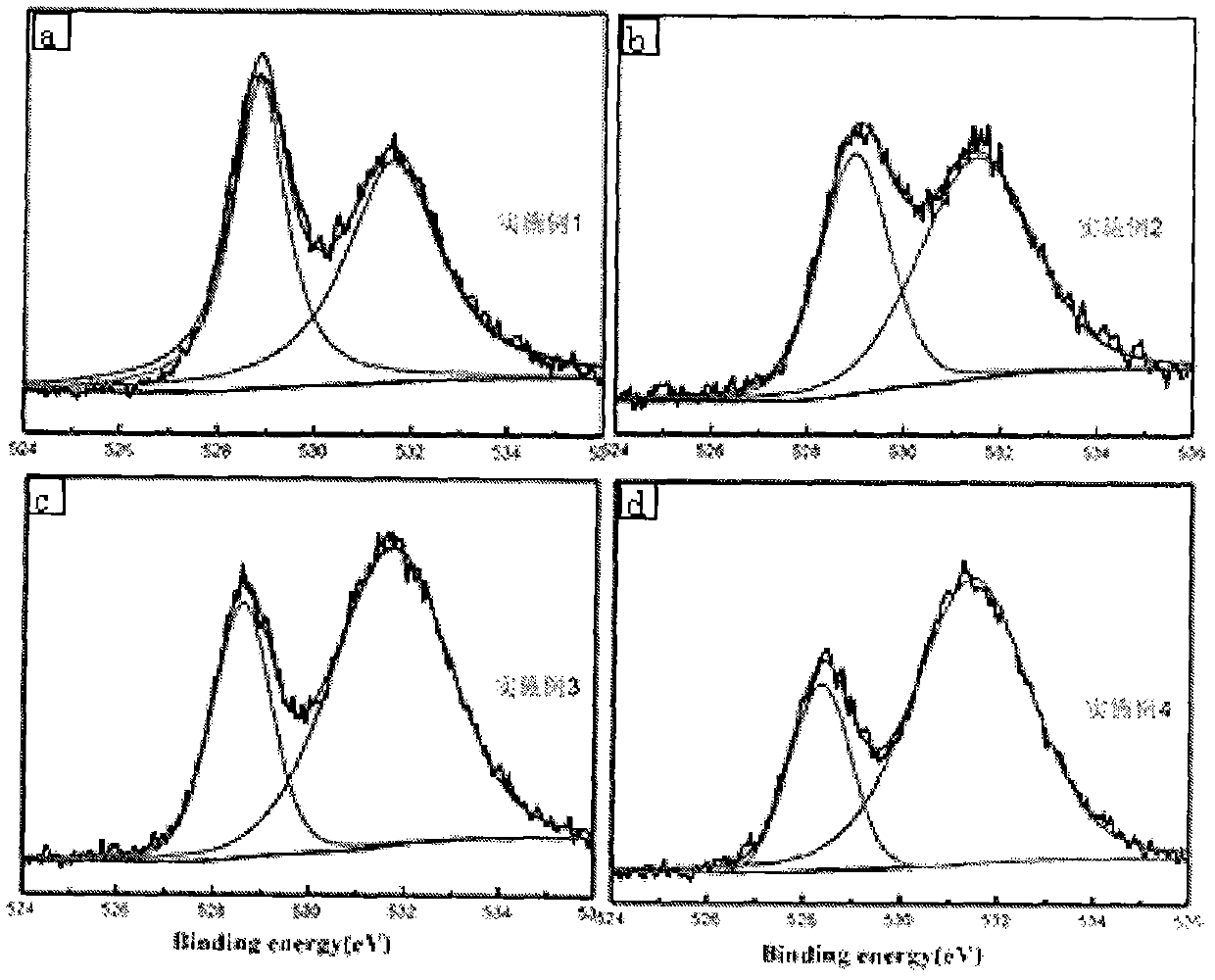
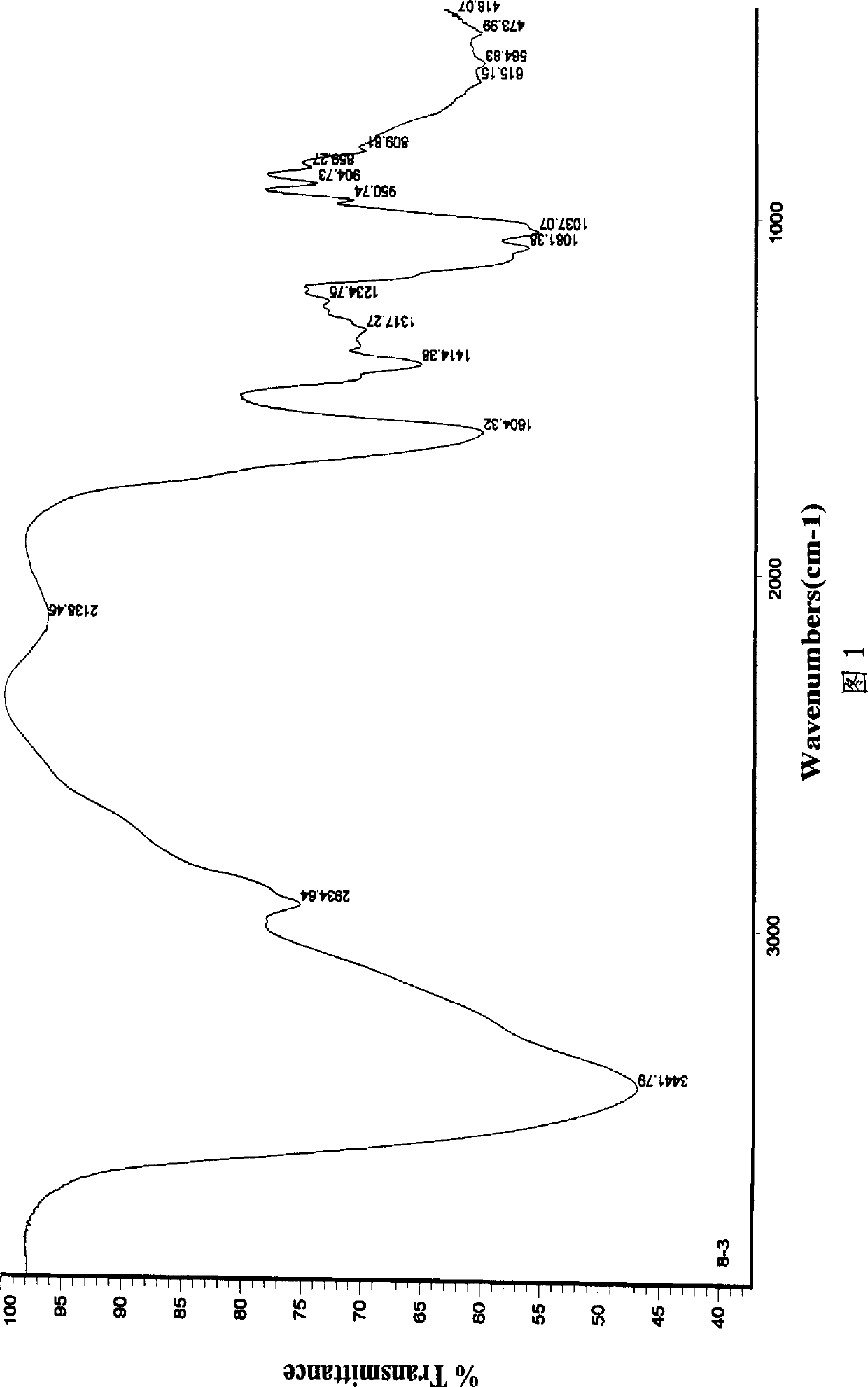
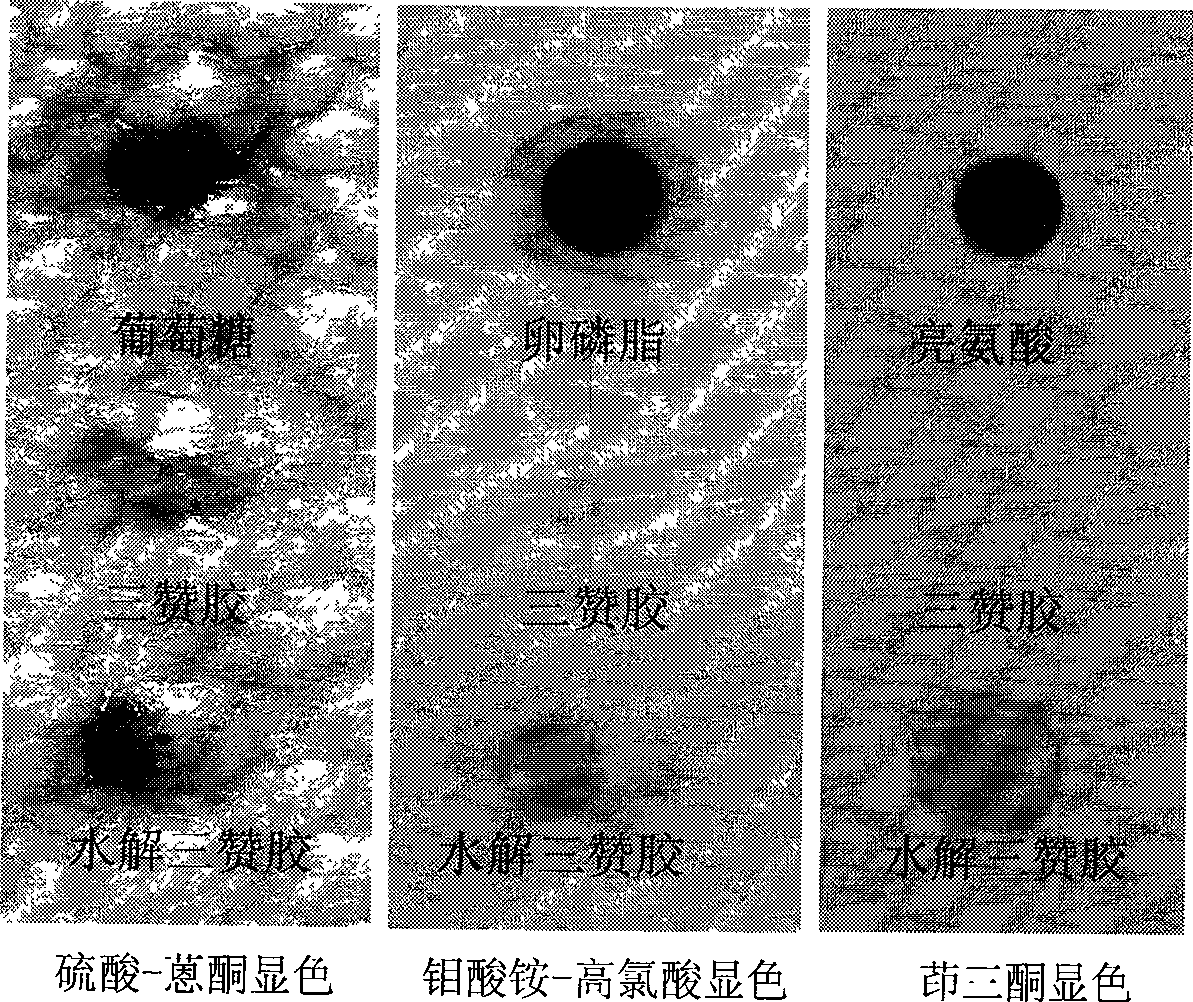
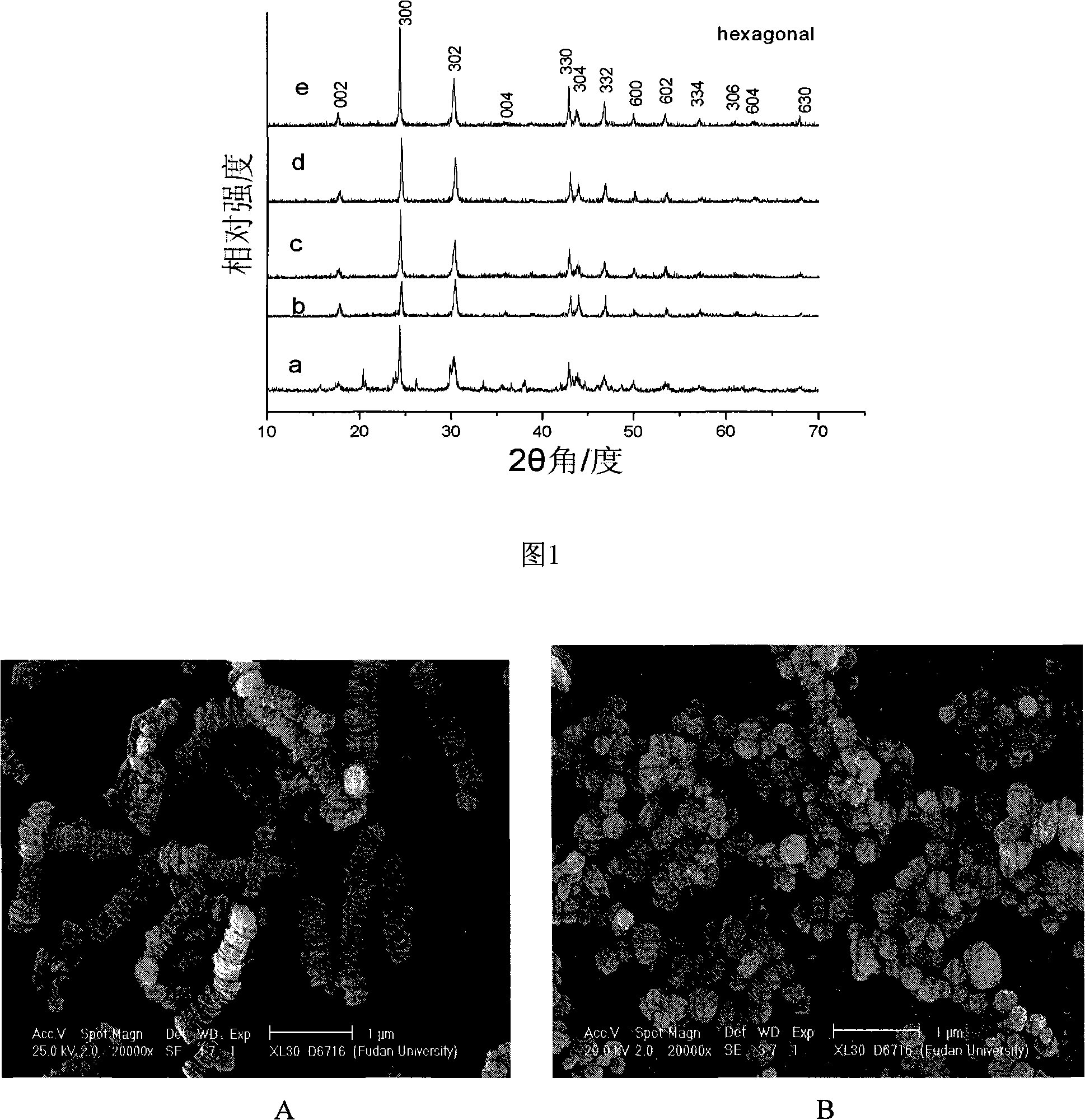
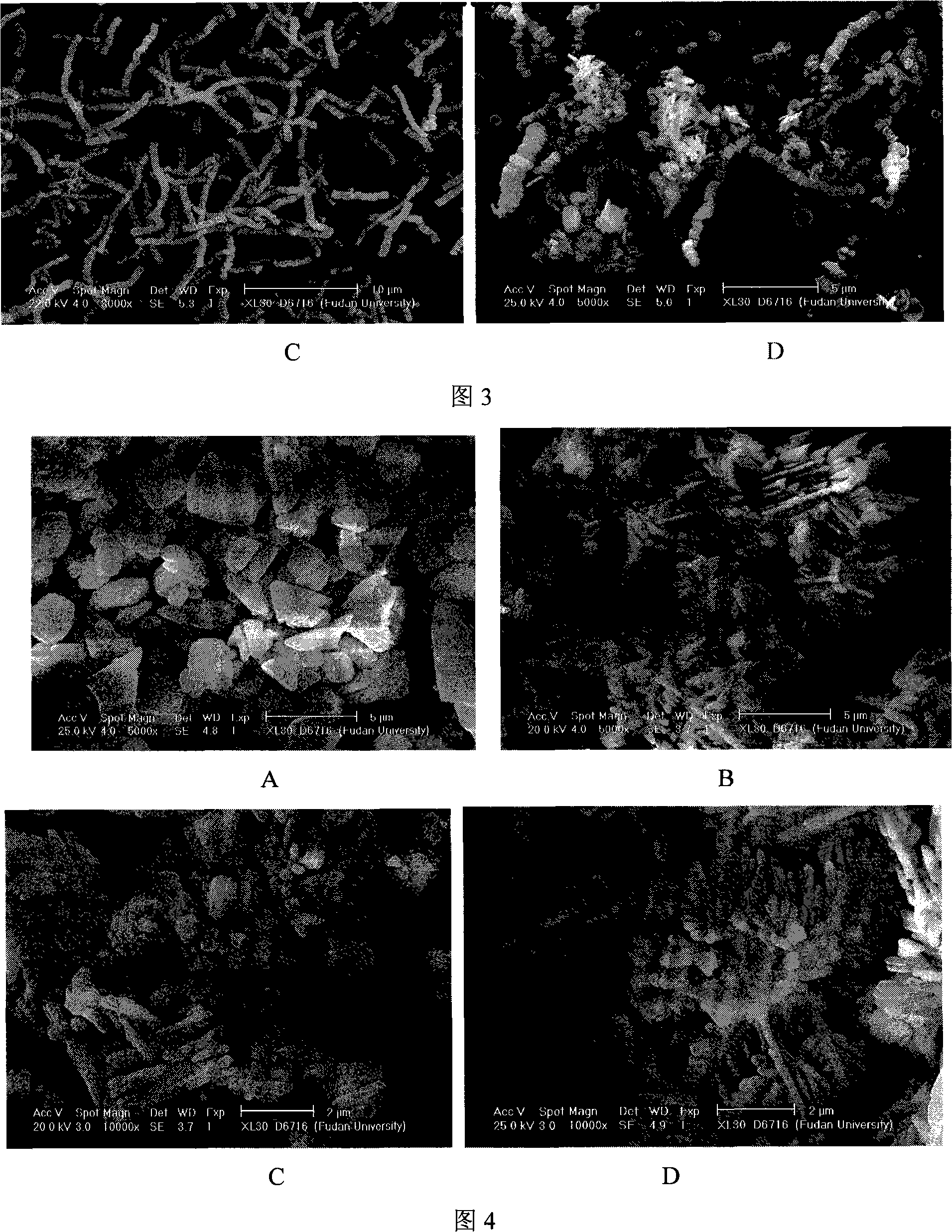
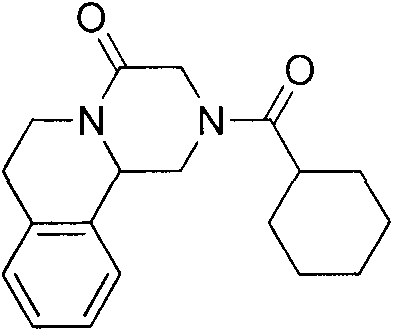
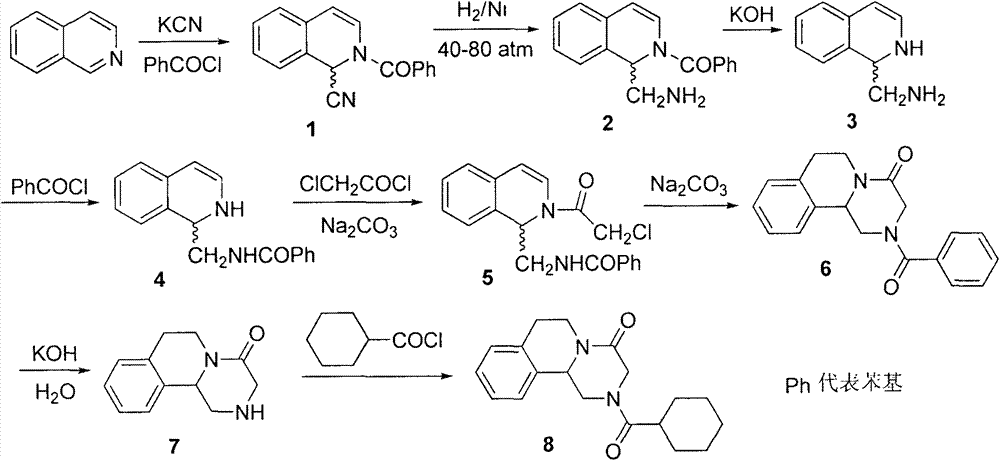
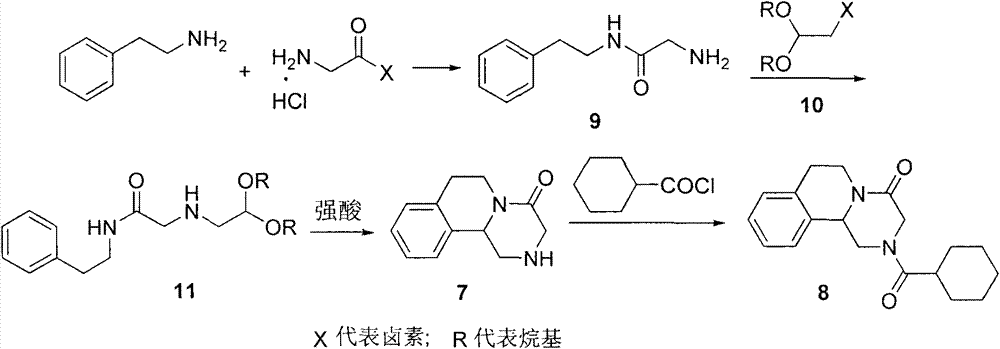
Patents
Literature
138 results about "Glycin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glycin, or N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)glycine, is N-substituted p-aminophenol. It is a photographic developing agent used in classic black-and-white developer solutions. It is unrelated to the amino acid glycine. It is typically characterized as thin plates of white or silvery powder, although aged samples appear brown. It is sparingly soluble in water and most organic solvents; it is readily soluble in alkalies and acids.
Catalyst for preparing carbon nanotube and its prepn
The catalyst for preparing carbon nanotube has perovskite or perovskite-like structure. Under heating condition, the catalyst is reduced with hydrogen to produce hydroxide of RE or alkali earth element. During its preparation, salt or oxide of corresponding element is used as main material, and one or several of citric acid, tartaric acid, glycin and EDTA is used as complexing agent and burning agent to prepare the catalyst via gel burning synthesis process in water or ethanol solution. If necessary, ammonia or ammonium compound as pore creating agent may be added in the preparation process to increase the specific surface area of the catalyst. The catalyst makes the prepared carbon nanotube possess even homogeneous tube diameter and even high yield.
Owner:CHENGDU ORGANIC CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing chicken flavor essence base material by using chicken framework
The invention relates to a method for producing a chicken flavor essence base material by using a chicken framework, which comprises the following steps: firstly, crushing the cleaned chicken framework by a bone crusher, grinding the crushed chicken framework into chicken bone cement of which diameter is 10 + / - 5mu m by a colloid grinder, directly delivering the chicken bone cement into a reaction kettle without high-temperature boiling, adding water into the chicken bone cement to make the solid content reach 8 percent, and adjusting the pH to 7.0 by using 10 percent NaOH solution; adding 0.5 to 1.5 percent of composite proteinase by mass of the chicken bone cement into the mixture, and carrying out enzymolysis for 3 to 5 hours at a temperature of 55 DEG C; adding a thermal reaction mixture into the reaction kettle; heating the reaction kettle to make the mixture react at a temperature of between 100 and 125 DEG C; and after reacting for 30 to 180 minutes, obtaining the essence base material with intense chicken flavor, wherein the thermal reaction mixture comprises: 5 to 15 percent of glucose, 5 to 10 percent of xylose, 1 to 3 percent of cysteine hydrochloride, 1 to 3 percent of glycin, 30 to 50 percent of enzymolysis liquid, 1 to 5 percent of chicken fat, 5 to 20 percent of yeast powder, and 0.5 to 1.5 percent of vitamin B1.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Acid soluble fish skin collagen and its preparing method
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Compound antibacterial agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101940225AIncrease lethalityWide range of sterilizationBiocideDisinfectantsEpsilon-PolylysineGlycin
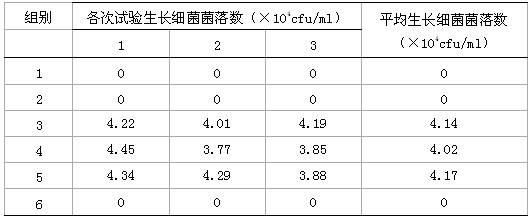
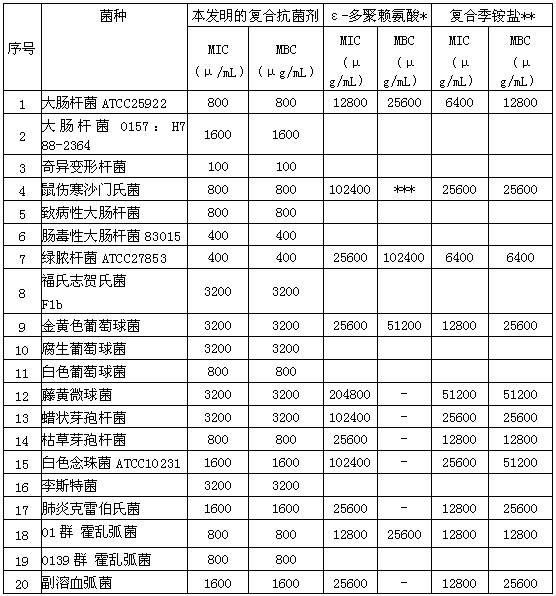
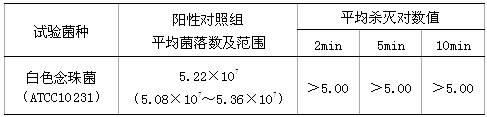
The invention provides a compound antibacterial agent and a preparation method thereof. The compound antibacterial agent comprises the following components in portions by weight: 100 portions of water, 0.5-10 portions of soybean extract, 0.5-2.5 portions of glycin, 0.005-3.0 portions of epsilon-polylysine, 0.1-5.0 portions of benzalkonium chloride and 0.1-6.0 portions of didecyl dimethyl ammoniumchloride. The preparation method comprises the following steps: diluting the soybean extract with water, and adding the glycin, the epsilon-polylysine, the benzalkonium chloride and the didecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride according to the ratio to obtain the compound antibacterial agent. The compound antibacterial agent is novel antibacterial agent having no harm to people and livestock and high sterilizing capability, can be used in various locations to be sterilized and disinfected, and has the advantages of low cost, wide application range, good sterilizing effect and the like.
Owner:福建圣德实业有限公司
Compound aquatic product feeding promoting agent
InactiveCN101611764AIncrease food intakeImprove bait efficiencyAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsPropanoic acidAquatic animal
The invention relates to a compound aquatic product feeding promoting agent used in feed for fish, shrimp and crabs, and belongs to a feed additive. The feeding promoting agent is characterized in that: the feeding promoting agent comprises the following compositions: 25 to 35 portions of dimethyl-beta-propionic acid thetine, 15 to 25 portions of taurine, 15 to 25 portions of alanine, 5 to 15 portions of glycin, 5 to 15 portions of glutamic acid and 5 to 15 portions of nucleotide; and the taurine, the alanine, the glycin, the glutamic acid and the nucleotide are crushed, sieved by a 40-mesh sieve, put into a mixer and added with the dimethyl-beta-propionic acid thetine for even mixing to prepare the compound aquatic product feeding promoting agent. The compound aquatic product feeding promoting agent can improve the food intake of aquatic animals, promote quick growth of the aquatic animals, improve the bait efficiency of the aquatic animals, reduce residual bait to a large extent, greatly reduce pollution to water body and contribute to environmental protection.
Owner:无锡华诺威动物保健品有限公司
Yeast extract, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101513246AFlavor coordinationTaste balanceFood preparationCaramel FlavorVegetable Proteins
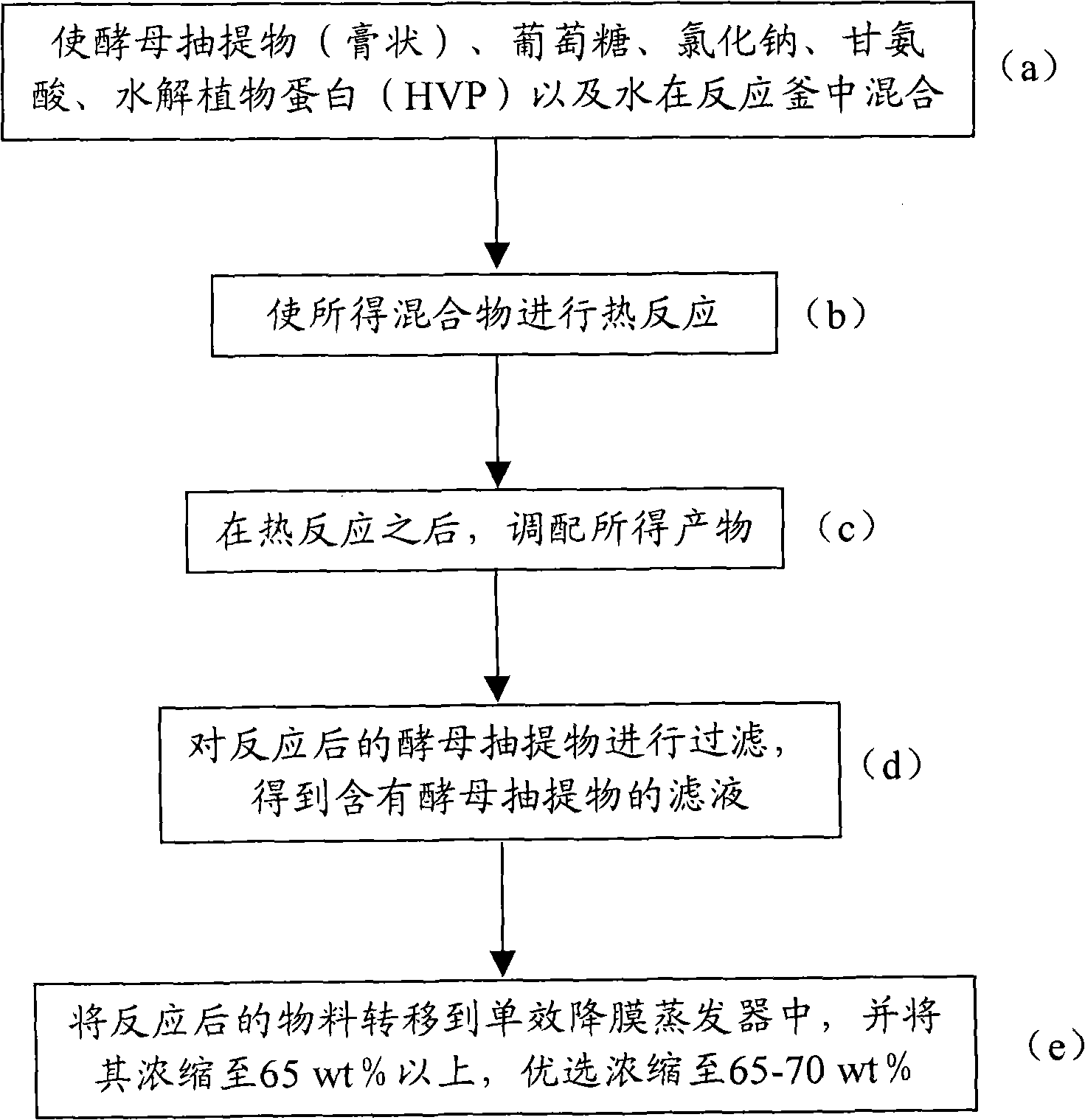
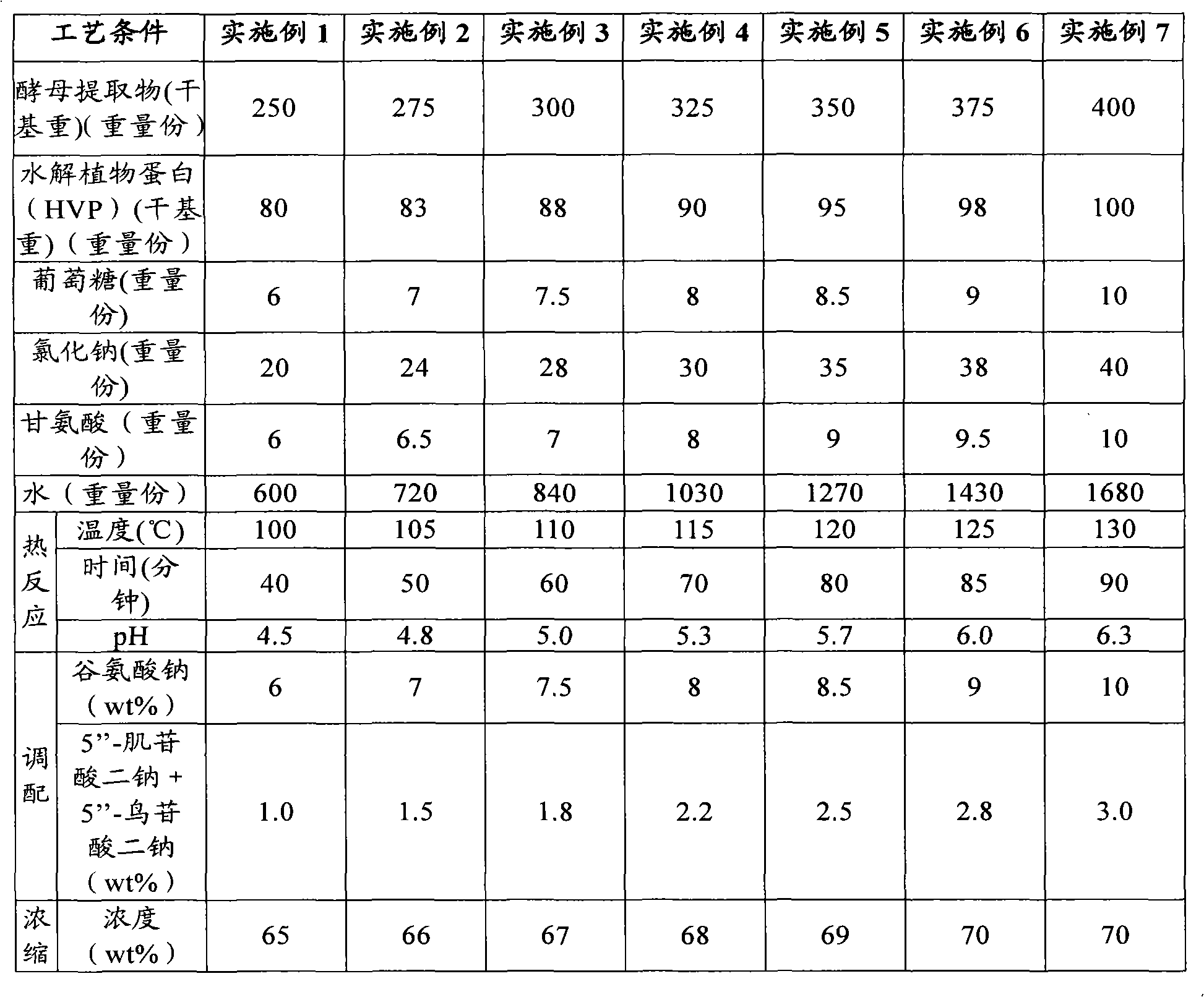
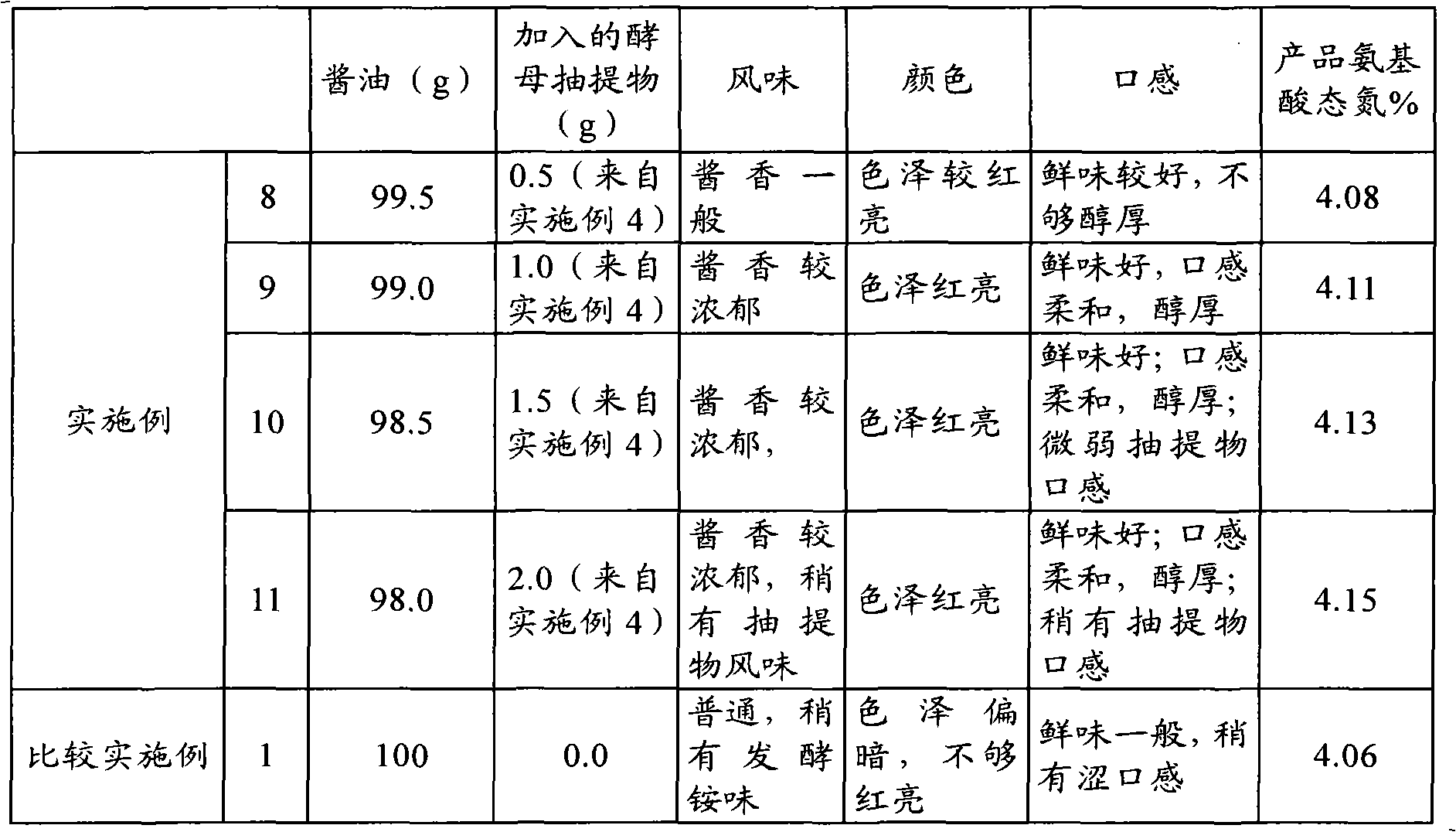
The invention provides a yeast extract, a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the yeast extract comprises the following steps: (a) mixing the yeast extract, glucose, sodium chloride, glycin, hydrolyzed vegetable protein and water in a reaction kettle; (b) performing heat reaction on the mixture in step (a) for 40 to 90 minutes at a temperature of between 100 and 130 DEG C and pH of between 4.5 and 6.3; (c) after the heat reaction, adding 6 to 10 weight percent of sodium glutamate and 1.0 to 3.0 weight percent of disodium inosinate and disodium guanylate into an obtained product for preparation; (d) filtering the yeast extract after the reaction to obtain filtrate containing the yeast extract; and optional (e) transferring materials after the reaction to a single effect falling film evaporator, and concentrating the materials to more than 65 weight percent and preferably concentrating the materials to between 65 and 70 weight percent. The yeast extract prepared by the method has sauce fragrance and caramel like deep bright red color, and a water solution of the yeast extract has transparent bright red color and fresh and salty mouthfeel.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
High-specific-surface-area perovskite catalyst LaCo0.9Mg0.1O3 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103372447AImprove flammabilityLow priceMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNitrateGlycin
The invention provides a perovskite catalyst for catalyzing oxidized combustion of methane and a preparation method thereof. The structural formula of the perovskite catalyst for the oxidized combustion of the methane is LaCo0.9Mg0.1O3. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing a solution with a raw material ratio of magnesium to lanthanum of 0.1 to 3 by taking lanthanum, cobalt and magnesium as raw materials, stirring the raw materials at the temperature of 80 DEG C until the solution is evaporated to gel, pre-sintering a precursor at the temperature of 400 DEG C, finally sintering the precursor at the temperature of 700 DEG C to obtain a preproduct, stirring the preproduct in acetum with the concentration of 0.4 mol / L for 1 hour, removing residual MgO from the product, centrifugating and washing the product by deionized water, and drying the product to obtain the catalyst LaCo0.9Mg0.1O3 with high specific surface area. The perovskite catalyst has the advantages of simple operation and low cost; the synthesized catalyst is higher in specific surface area and has extremely high activity on the catalytic combustion of the methane.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Bacillus adhaerens and its use in preparing health food having thrombolysis property
InactiveCN1464046AHigh activityStrong thrombolytic effectBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsAcid-fastSolubility
Bacilliis natto NLSSc with the preservation number CGMCC No. 0724 is Gram staining positive, non-acid fast, straight or near straight, (0.6-0.8)x(1.5-2.0) micron sized and aerobic; has mesial and un-swelled spore with the spore number inside one sporange cell not more than one, meso diamino heptane diacid and glycin contained in the cell wall, no characteristic saccharum and peripheral flagellum; and can be grown well in five kinds of natural organic culture medium and can form relatively thick mycoderm and butter fat colored colony with smooth edge in soybean cake powder culture medium. Bacilliis natto can be cultured in culture medium with nitrogen source to obtain thrombus dissolving matter natto kinase and the cultured matter may be extracted to obtain powdered matter as the additive for thrombolytic health food.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Meat quality flavor modifying agent for grass carp or carp and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101744145AIncrease attractivenessImprove immunityAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAquaculture industry
The invention relates to a feed additive of aquaculture industry, in particular to a meat quality flavor modifying agent for grass carp or carp and a preparation method thereof. Each kilogram of modifying agent comprises the following components: 30 to 50g of seaweed extract, 10 to 20g of combination of inosinic acid and guanylic acid, 20 to 30g of carnitine, 15 to 30g of glycin, 10 to 20g of alanine and the balance of zeolite powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, crushing solid materials in the seaweed extract, the combination of inosinic acid and guanylic acid, the carnitine, the glycin, the alanine and the zeolite powder materials and sieving the crushed solid materials through a sieve with 80 to 100 meshes for later use; and secondly, mixing and stirring the crushed solid materials in the proportion to ensure that the coefficient of variation CV of the uniformity is less than 5 percent to obtain the product. The modifying agent can effectively improve protein content, content of total amino acids, content of essential amino acids and content of delicious amino acid in muscles of the grass carp and the carp.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation process of intravenous injection human immunoglobulin
ActiveCN101972479AHigh yieldHigh purityAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsUltrafiltrationPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a preparation process of intravenous injection human immunoglobulin, belonging to the field of pharmaceuticals. On a basis of a traditional preparation process of intravenous injection human immunoglobulin with the low protein concentration of 5 percent, a filter pressing method is adopted instead of a centrifuging method in an extraction process. During hyperfiltration, the protein concentration is adjusted to 3-6 percent, a pH value is adjusted to 6.4-6.6 with 0.5 mol / L of NaOH; then, 1 mol / L phosphoric acid-NaOH buffer solution is added to adjust the electrical conductivity which is measured to be 0.175-0.205 s / m at a temperature T of 19 DEG C; and a chromatography method is adopted to carrying out column chromatography and purification by using upper ion exchange columns after the electrical conductivity is adjusted. The protein impurities can be effectively removed, the protein purify and the product yield are improved; maltose or glycin is used as a protector, which benefits the improvement of the stability of the intravenous injection human immunoglobulin; and the glycin is used as the protector, which satisfies the clinical use of diabetics. According to the invention, the intravenous injection human immunoglobulin with the protein concentration of 5-11 percent can be obtained.
Owner:华润博雅生物制药集团股份有限公司
Main field selenium-rich garlic pedicle, leaf, seed stalk and head cultivating method
The present invention discloses a planting method of the stem, leaf, bolt and head of field high-selenium garlic; the puke garlic of Cangshan is taken as the seed; people select field with more than 1.2 percent of organic material and implement disinsection treatment on soil seed before plantation; people strictly manage the field and apply selenium fertilizer made of aspartic acid, threonine, serine, glutamic acid, cysinic acid, glycin, arginine, total ammonia acid, nitrogen, phosphor, kalium, Na2SeO3, etc. on the leaf every other week. The selenium contents of the root, stem, leaf, bolt and head of the planted high-selenium garlic are separately between 21.75 and 35.83mg / kg, between 9.83and 20.12mg / kg, between 19.76 and 33.89mg / kg which are separately 311 times, 328 times and 725 times of that of the root, stem, leaf, bolt and head of garlic which are not added with selenium; the present invention is convenient for large-area field plantation and the root, stem, leaf, bolt and head of the planted high-selenium all contains active selenium which is beneficial to the health care of people; the raw material and extract can be used to make troche, capsule, injection, spray, oral liquid, health care food or commodity for hairdressing and skin protection integrating the functions of curing disease, health care and hairdressing.
Owner:蒋新东
Monoclonal antibodies to progastrin
The present invention provides progastrin-binding molecules specific for progastrin that do not bind gastrin-17(G17), gastrin-34(G34), glycine-extended gastrin-17(G17-Gly), or glycine-extended gastrin-34(G34-Gly). Further, the invention provides monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) selective for sequences at the N-terminus and the C-terminus of the gastrin precursor molecule, progastrin and the hybridomas that produce these MAbs. Also provided are panels of Mabs useful for the detection and quantitation of progastrin and gastrin hormone species in immuno-detection and quantitation assays. These assays are useful for diagnosing and monitoring a gastrin-promoted disease or condition, or for monitoring the progress of a course of therapy. The invention further provides solid phase assays including immunohistochemical (IHC) and immunofluorescence (IF) assays suitable for detection and visualization of gastrin species in solid samples, such as biopsy samples or tissue slices. The progastrin-binding molecules are useful therapeutically for passive immunization against progastrin in progastrin-promoted diseases or conditions. Also provided are surrogate reference standard (SRS) molecules that are peptide chains of from about 10 to about 35 amino acids, wherein the SRS molecule comprises at least two epitopes found in a protein of interest of greater than about 50 amino acids. Such SRS molecules are useful as standards in place of authentic proteins of interest.
Owner:CANCER ADVANCES INC
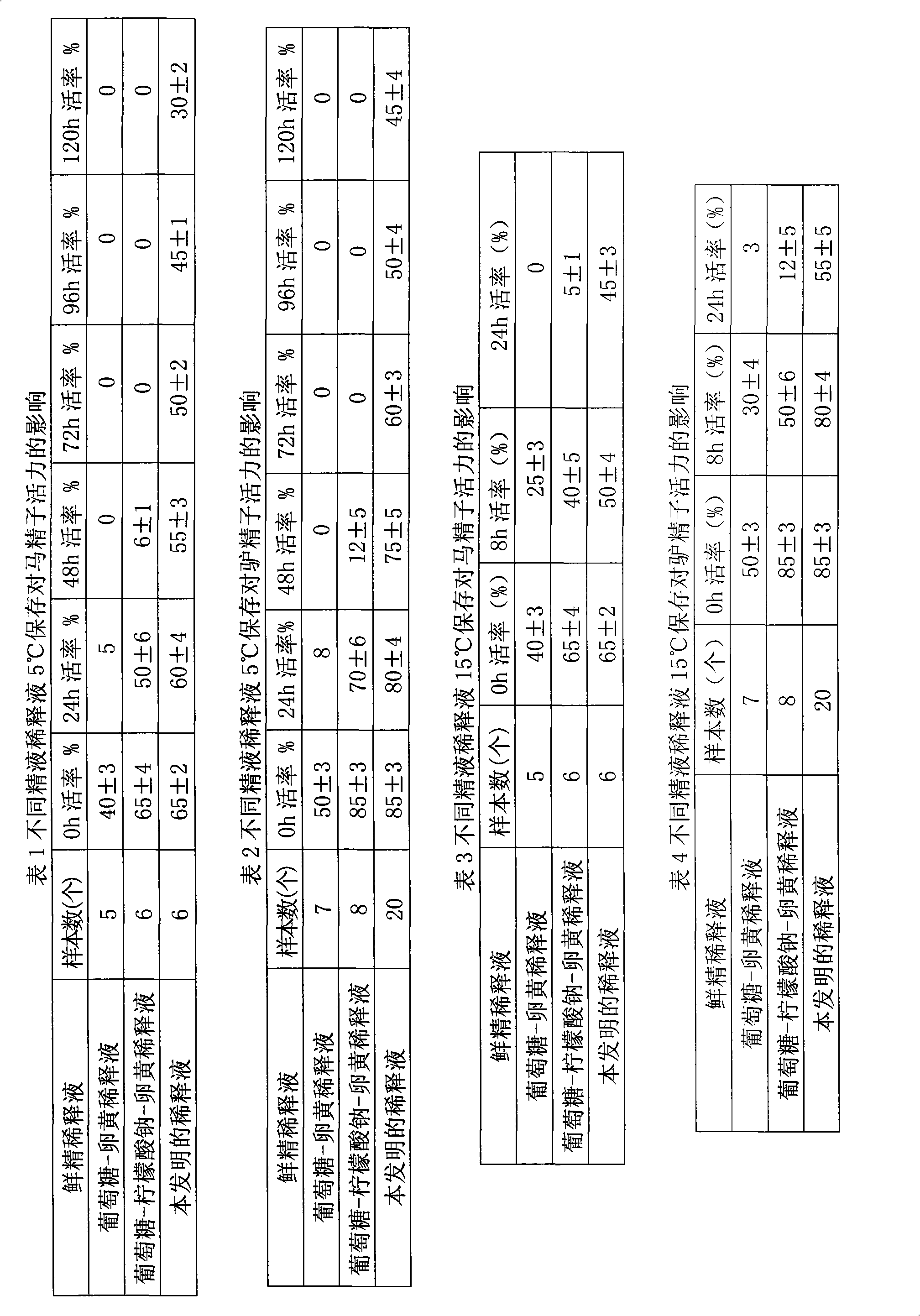
Equus semen storage diluter and preparing method and use method thereof
InactiveCN101647427AConducive to preservationReduce manufacturing costDead animal preservationYolkPenicillin
The invention relates to an equus semen storage diluter and a preparing method and a use method thereof, belonging to the technical field of animal semen storage. The equus semen storage diluter is prepared from double distilled water, glucose, glycin, penicillin, streptomycin and yolk. The equus semen storage diluter has a good effect of preserving the equus semen under the normal or low temperature, has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, easy mastery, and is suitable for popularization and application, which is beneficial to the development of the equus breeding.
Owner:TARIM UNIV
Skin externally-applied liquid state and solid state kreotoxin (liushengtai) composite nano emulsion and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101214200AAnti aging goodImprove scienceCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPolyethylene glycolExternal Liquid
The present invention relates to external liquid and solid kreotoxin (argireline) composite nanometer latex for skin and a preparation method thereof. The weight proportion of each raw material of liquid nanometer latex is 10g of isopropyl myristate, 2g of vitamin E, 0.8g of vitelline lecithin, 0.2g of ginseng saponin, 0.01g of rhodiola element, 0.005g of the argireline, 0.001g of superoxide dismutase, 0.5g of reduction type glutathione, 5g of fetal calf serum, 0.05g of hyaluronic acid, 0.05g of ceramide, 40g of distilled water, 36g of polyethylene glyceride glycol caprylic decanoate and 12g of polyglycerol fatty acid ester; the weight proportion of each raw material of solid nanometer latex is 10g of the isopropyl myristate, 2g of the vitamin E, 0.8g of the vitelline lecithin, 0.2g of the ginseng saponin, 0.01g of the rhodiola element, 0.005g of the argireline, 0.001g of the superoxide dismutase, 0.5g of the reduction type glutathione, 5g of the fetal calf serum, 0.05g of the hyaluronic acid, 0.05g of the ceramide, 40g of the distilled water, 36g of the polyethylene glyceride glycol caprylic decanoate, 12g of the polyglycerol fatty acid ester, 22g of mannitol and 3g of glycin.
Owner:丁克祥
Polymer and use thereof
InactiveCN101372515AHigh viscosityGood thickening effectDrilling compositionFood preparationArginineValine
The invention belongs to the field of energy technology and food technology, and more particularly relates to a polymer and the application thereof. The polymer is composed of 34.8% of sugar, 63.1% of fat and 1.5% of polypeptide; wherein, the sugar component contains glucose, rhamnose, seminose and glucuronic acid; fat component contains 6.2% of hexadecanoic acid methyl ester and 93.8% of methyl stearate; the polypeptide component respectively contains 11.6% of asparticacid, 6.1% of threonine, 4.8% of serine, 11.7% of glutamic acid, 6.7% of glycin, 9.8% of lactamine, 6.7% of valine, 1.8% of methionine , 4.6% of isoleucine, 9.8% of leucine, 3.4% of tyrosine, 5.9% of phenyl alanine, 3.1% of lysine, 1.3% of histidine, 7.6% of arginine and 5.2% of proline. Sanzanjiao can be taken as drilling mud conditioner and jelly glue polymer used for water shutoff profile control treatment in oil field to be applied to petroleum extraction, and the characteristics of jelling and thickening lead the polymer to be taken as food additive to be widely applied to the food production field.
Owner:张禹
Anti-acne jelly with pearl hydrolyzate liposome
ActiveCN101697956AEnhance metabolismInhibition of secretionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPlant sterolHamamelis virginiana
The invention discloses an anti-acne jelly with pearl hydrolyzate liposome. Acrylic acid (ester) / C10-30 alkanol acrylate crosslinked polymer, glycerol, 1,3-butanediol, witch-hazel extract, pearl hydrolyzate liposome, plant sterols, capryloyl glycin, allantoin, dipotassium glycyrrhizinate, diazolidinyl urea, methyl hydroxybenzoate, trolamine, disodium ethylene diamine tetraacetate and deionized water are evenly mixed to prepare the anti-acne jelly. In the invention, the pearl hydrolyzate liposome is added to the anti-acne jelly to effectively enhance the metabolism of skin cells, inhibit surplus lipid from secretion, dredge pores of skin cells, smoothly discharge impurities blocking the skin pores, such as dust, grease, bacteria, peeling, dead cells and the like, and promote the regeneration of surface cells, thereby effectively repairing impaired skin, accelerating the healing of impaired skin sores and pox marks, enabling the skin to be in a healthy state and smoothing the skin.
Owner:HAINAN JINGRUN PEARL BIOTECH
Method for preparing lanthanum subcarbonate nana-/micro-crystal by double hydrolysis regulation
InactiveCN101279757ANovel and uniformReduce generationRare earth metal compoundsCrystallinitySolvent
The invention belongs to the micron-nanometer material preparation technique and the hydro-thermal synthesis technique field, in particular relates to a process for preparing a basic sodium lanthanum carbonate / micron crystal by means of double-hydrolytic regulation. The process has the specific steps that: a lanthanum oxide and an ammonium bicarbonate or a glycin being taken as precursors and a deionized water as a solvent are positioned in a hydrothermal reaction kettle in proportion, the mole ratio of the lanthanum oxide and the glycin or the ammonium bicarbonate is 1:20 to 1:45, and the added quantity of the deionized water is between 50 and 80 percent of the volume of a container; the hydrothermal reaction kettle provided with mixtures is put into a box-type resistance furnace for being heated to the temperature of between 150 and 220 DEG C, and the container is taken out after the 8 to 48h heating at such a temperature and is cooled naturally to the room temperature; and the needed product is obtained after washing and centrifugal separation. The preparing process has advantages of simple process, easy building of the whole preparing system, simple and convenient operation, easy control of conditions, low cost, easy control of the appearance and size of the product, high purity, good crystallinity and convenient and brief product treatment, and is applied to the mass industrial production.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Feedstuff additive for improving flavor of marine fish
InactiveCN101326965AIncrease contentHigh activityAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsArginineFood flavor
The invention discloses feed additive which improves the flavor of sea water cultivating fish. The feed additive consists of four or more than four types in aspartic acid, glutamic acid, glycin, arginine, lycine and L-carnitine by proportion. 0.5 percent to 5 percent of the feed additive which improves the flavor of the seawater cultivating fish of the invention is added in seawater fish feed, so that the total contents of amino acid and flavor developing amino acid required in fish is obviously improved, the content of saturated fatty acid is obviously reduced and the contents of unsaturated fatty acid is obviously improved, wherein, EPA and DHA are obviously improved; the content of inosinic acid in the fish is obviously improved. The feed additive which improves the flavor of sea water cultivating fish of the invention can obviously improve the flavor of the seawater fish, such as large yellow croaker, weever, etc., improve the contents of the flavor developing amino acid and the inosinic acid in the fish, reduce the content of body fat, and improve the content of the unsaturated fatty acid. The additive is safe without public harm and residue; the seawater fish cultivated by the additive meet the green food sanitation requirements.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +2
Method for single-time measuring ten amino bioactivators in organism
InactiveCN101581703ALow costSave human effortComponent separationBiological testingOrganismBrains tissue
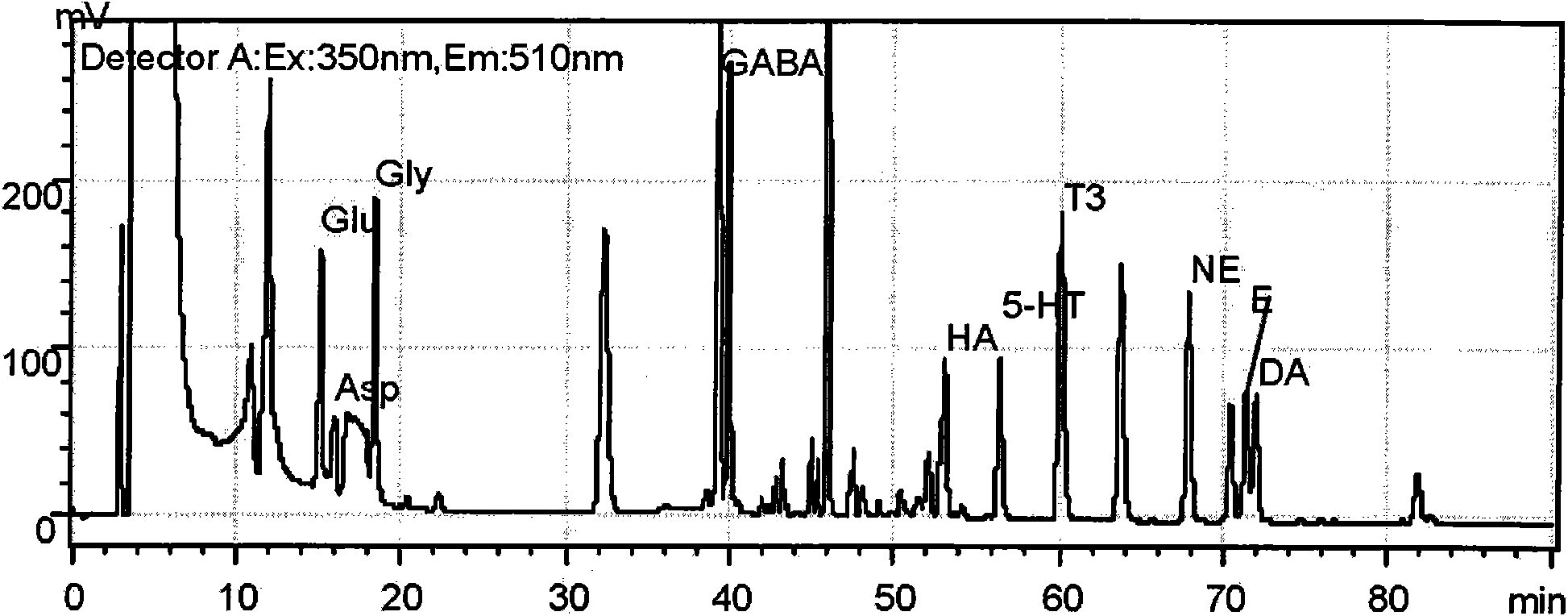
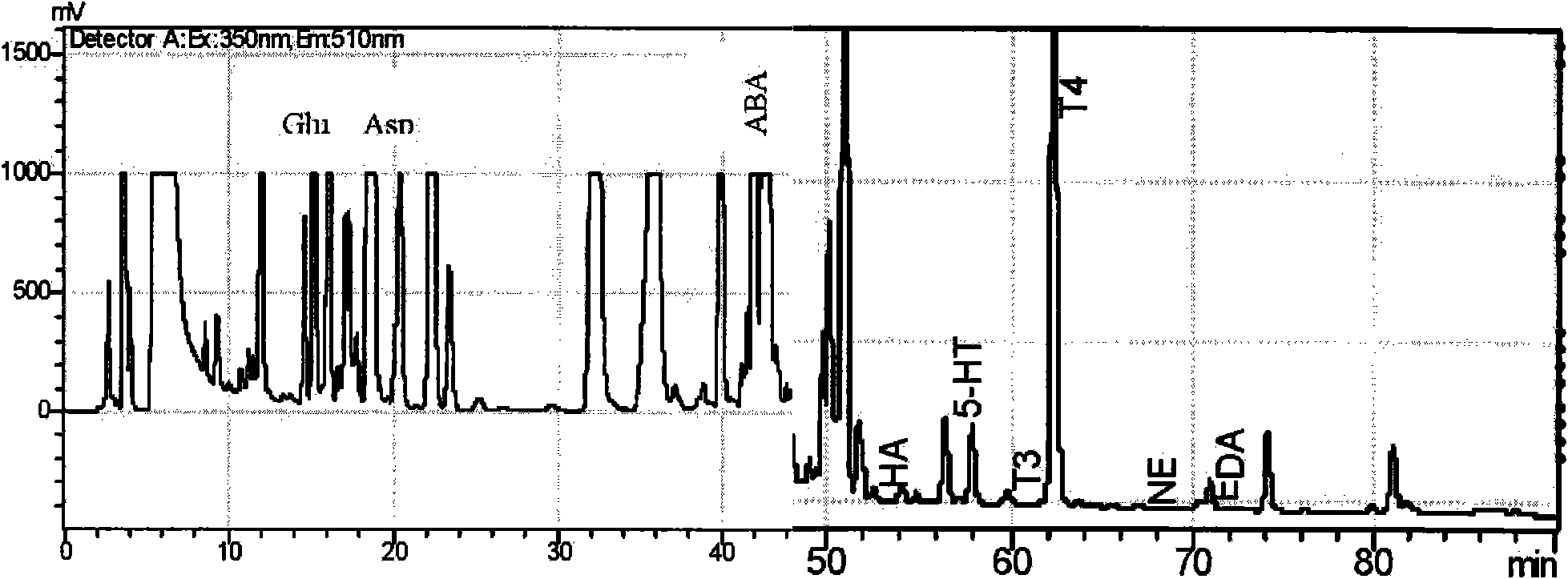
The invention belongs to the field of biochemistry detection, in particular to the measurement of bioactive molecules of neuroendocrine immunological network, particularly to a measurement method of amino bioactivators in organism (such as blood or brain tissue), in particular discloses a method for the single-time measuring of ten amino bioactivators in organism, which comprises: taking dansyl chloride as derivative reagent to perform single-time measuring on ten amino bioactivators such as epinephrine (E), noradrenalin (NE), dopamine (DA), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), histamine (HA), gluetamic acid (Glu), aspartic acid (Asp), Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycin (Gly) and trilute (T3) within 75min. The method is simple and rapid, can sensitively measure the concentrations of the ten amino bioactivators in organism fluid, and is suitable to the research requiring to completely analyze the ten amino bioactivators in the organism.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Fermentation-method theabrownin preparation method
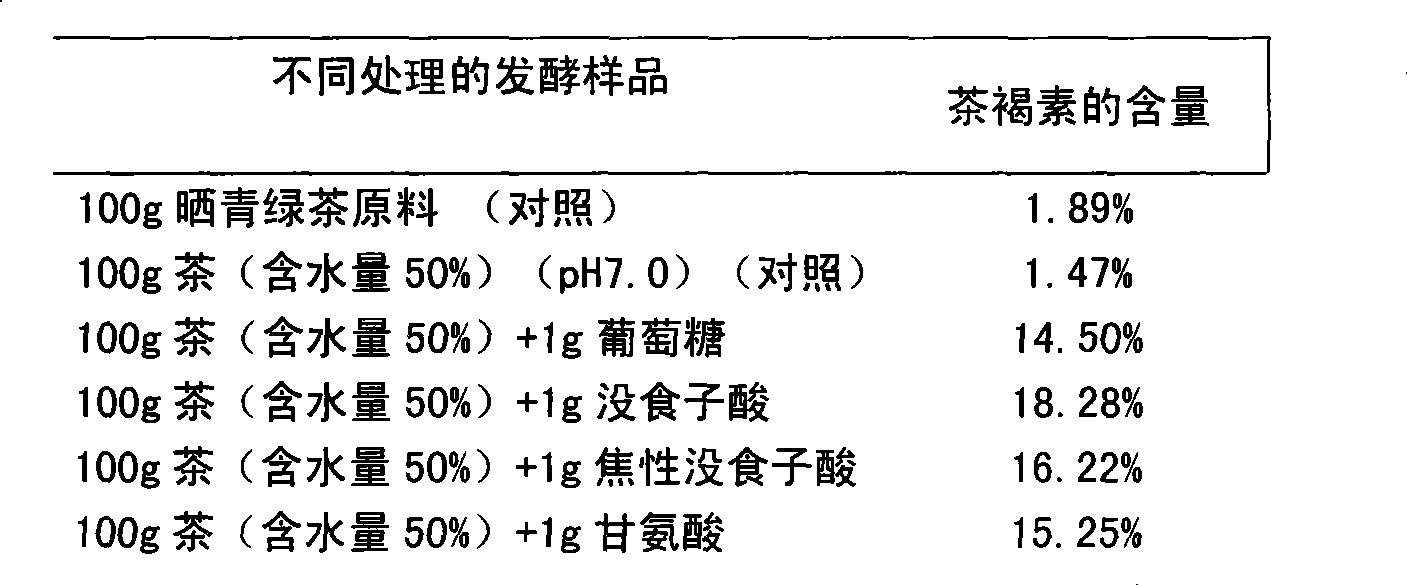
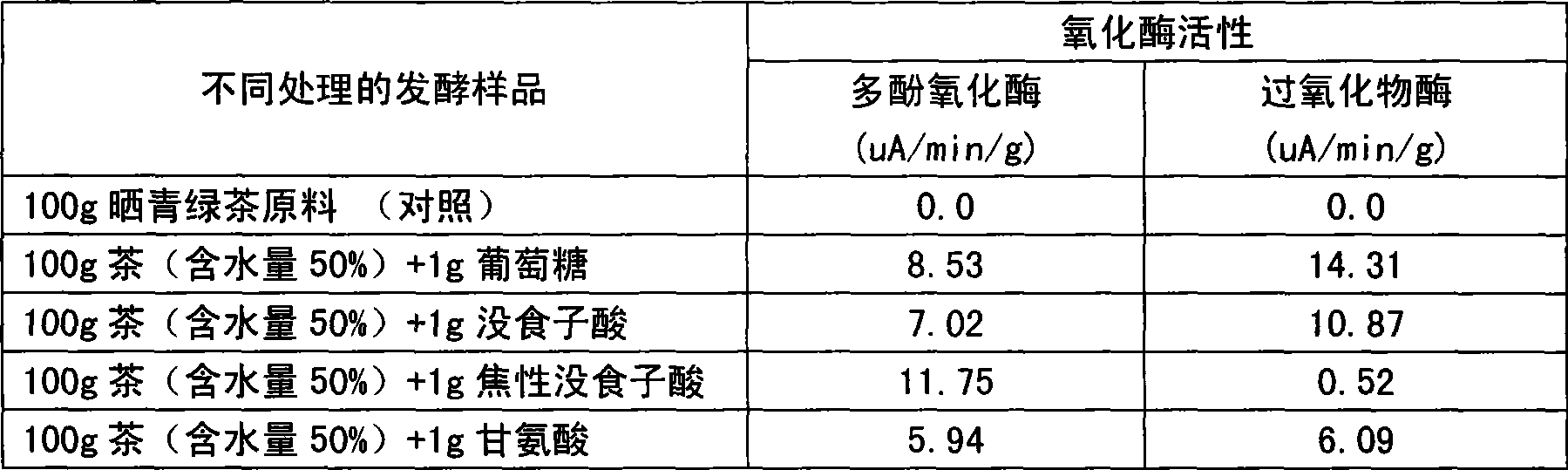
InactiveCN101455257ANot limited by production seasonEasy to controlTea extractionFood preparationGallic acid esterMoisture
A method for preparation of tea brown element using a fermentation method pertains to the field of processing technology. The method includes: A. comminuting the tea into 60-80 mesh, performing UV sterilization for 30min, adding deionized water, at the same time, adding saccharomycete or Aspergillus in the water, adding 1% of gallic acid or pyrogallic acid or glycin or glucose, standing for 60min, until using the food fresh keeping diaphragm to seal after the tea has fully absorbed the water; and then placing in the conditions of ventilation, temperature of 35-55 DEG C and humidity of 60-85%, for light-shading training for 20 days, to obtain the fermented tea with the tea brown element; B. the drying the fermented tea leaves dried at 60 DEG C to 10 percent moisture content, soaking for 30min in a solution with the feed liquid ratio of 1:50, filtering; extracting 100mL filtrate, adding 400mL edible alcohol, standing 3 hours after mixing, centrifugally filtrating, to obtain the crude extract of the tea brown element; and then using20% alcohol-water blend to dissolve the crude extract of the tea brown element, the obtained solution passing through the conventional concentrating and drying process to obtain the tea brown element. The present invention ahs advantages of easy control, fast velocity, high efficiency and no limitation of the producing seasons of tea leaves. efficient and not subject to seasonal restrictions on tea production advantages.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method of preparing hydroxyl acetonitrile in industrial scale from acrylonitrile apparatus by-product formonitrile
InactiveCN1907963AReduce manufacturing costSimple processPreparation by hydrogen cyanide additionAcrylonitrileGlycin
This invention involves an industrial scale preparation method for hydroxyacetonitrile by using acrylonitrile production byproduct hydrocyanic acid through a synthesis reaction with acetonitrile at the presence of catalyst. The method is characterized by (1) taking acrylonitrile production byproduct hydrocyanic acid as the raw material with content of 95% or above, (2) controlling a molar ratio of hydrocyanic acid : formaldehyde : catalyst at 1 : 1.0~1.5 : 0.001~ 0.015, (3) adding catalyst in formaldehyde while stirring, adding hydrocyanic acid at 0-20DEG C, and reacting at 0~40DEG C for 1~6 h, and (4) adjusting pH of 6 or below with inorganic acid to obtain hydroxyacetonitrile. The invention has the advantages of low cost, product content of 50% or above, simplified aftertreatment, no wastes discharge, and product with formaldehyde and hydrocyanic acid content less than 0.05%. Hydroxyacetonitrile can be used as the intermediates of glycin, malononitrile, and indigo dye to solve transport inconvenience of hydrocyanic acid and geographical limitation of production.
Owner:YINGKOU YINGXIN CHEM TECH CO LTD
Red luminous material for LED and producing process thereof
InactiveCN101402857ALow costEasy to operateGas discharge lamp usageLuminescent compositionsViscous liquidChemical formula
The invention discloses a red luminescent material used for an LED and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula thereof is Ca1-x-ySrxMgyAl12-zO19:Mn<4+>z; wherein, x is equal to or larger than 0 and less than 0.5; y is equal to or larger than 0 and less than 1; z is equal to 0.01 to 10 percent; the preparation method is as follows: materials like soluble metal acetate and nitrate are dissolved in water and uniformly mixed according to a stoichiometric ratio and are respectively added with one or a plurality of fuels like carbamide, citric acid, boric acid and glycin for forming a transparent viscous liquid; then the transparent viscous liquid is heated and condensed to be dry for obtaining a yellow or brown powder precursor. The precursor sintered in the air of 500 to 900 DEG C for 5 to 12 hours is cooled and ground and then sintered for 5 to 24 hours in the air of 1100 to 1300 DEG C and then is naturally cooled to the room temperature, thus obtaining the product. The material is used for a white light LED; and the preparation method is 200 to 400 DEG C lower than the traditional synthetic method.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of praziquantel
The invention belongs to the field of medicine, and relates to a preparation method of a veterinary drug praziquantel, in particular to a novel method for preparing praziquantel. Raw materials such as chloracetyl chloride and glycin used in the method are low in cost and easy to obtain; the reaction is conventional; the operation is simple; the method has no special requirements on equipment; one step that a key intermediate 14 is subjected to intramolecular cyclization to form a compound 15 is designed in a reaction route; the design is brand-new and is not reported previously; the reaction yield is higher in the whole route; the total yield can reach 50%; most solvents used in a reaction process can be recovered, so that the cost is saved, and the environmental pressure is reduced; the cost is lowered extremely; and the route has a very good industrial application prospect.
Owner:迪嘉药业集团股份有限公司
Novel process for preparing glyphosate by glycin method
ActiveCN101591352AIncrease production capacityHigh yieldGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHerbicides and algicidesDepolymerizationAlcohol
The invention relates to a method for preparing glyphosate, which comprises the following steps: according to certain mixture ratio, putting glycin and paraformaldehyde into a monacid alcohol / tertiary amine system together for depolymerization condensation; then, after the mixture and dialkyl phosphate in mixing amount undergo condensation reaction, directly reclaiming monacid alcohol and tertiary amine; then, controlling temperature for acidolysis; in the acidolysis or after the acidolysis, removing and oxidizing formaldehyde; and deacidifying and neutralizing the reactant to prepare the glyphosate. The method adopts a plurality of methods such as reduction of the mixture ratio of the paraformaldehyde, direct exsolution and application, low-temperature acidolysis after the exsolution and the like to remove the influence of the formaldehyde, reduce consumption and stabilize the yield and the quality of the glyphosate.
Owner:BEIJING ZIGUANG YINGLI CHEM TECH CO LTD
Nano-selenium compound fertilizer
The invention relates to a nano-selenium compound fertilizer which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: a, preparing glycine modified nano-selenium; and b, preparing the nano-selenium compound fertilizer. The nano-selenium compound fertilizer is prepared by nanoscale red zero-valent selenium by a biological or chemical method, and the nanoscale zero-valent selenium is dissolved in water so as to form bright red transparent solution. The nano-selenium has strong biological activity and very high safety; and compared with inorganic selenium salt, the nano-selenium has the characteristics of low toxicity and high efficiency for which people hope best of all.
Owner:湖北圣峰药业有限公司
Thymopentin dry powder formulation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101411864AEasy to degradeImprove solubilityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityCurative effect
The invention discloses a thymopeptide-5 powder preparation and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving excipient in water to produce solution I, and filtering the solution I to collect filtrate I; adding the thymopeptide-5 to the filtrate I to obtain solution II, and filtering solution II to collect filtrate II; and freezing and drying the filtrate II to obtain the thymopeptide-5 powder preparation. The excipient can be any one of mannite, lactose and glycin. Experiments prove that, in the thymopeptide-5 powder preparation, thymopeptide-5 is not easy to be degraded, and has good solubility; low content of 'related substances' which is below 1.0 percent, so that healing efficacy and safety of the thymopeptide-5 powder preparation can be greatly improved.
Owner:上海华源药业(宁夏)沙赛制药有限公司
Fundus disease laser photo-thermal treatment system based on gold nanorods
InactiveCN103083133ALarge internal cavityNon-immunogenicLaser surgeryEnergy modified materialsDiseaseArginine
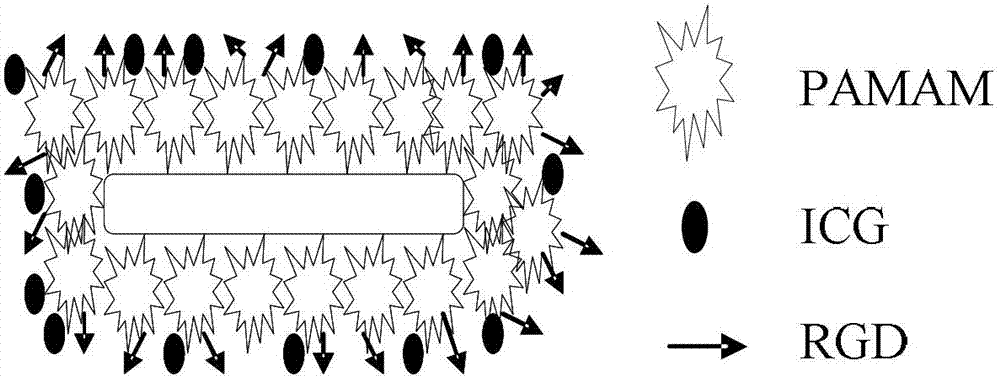
The invention discloses a fundus disease laser photo-thermal treatment system based on gold nanorods. The fundus disease laser photo-thermal treatment system based on the gold nanorods comprises the gold nanorods, a treatment laser source, a fundus imaging system and a personal computer (PC) control platform. The gold nanorods are combined by a gold seed method, and grows according to surface active agent hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide micelle shaped template in an orientated mode, silver ion concentration in solution is changed to control draw ratio of the gold nanorods, and after modification of polyamide-amine type arborization high polymer, vessel contrast agent indocyanine green is connected with pathology novel vascular endothelial cell peculiar arginine-glycine-aspartic acid polupeptide in a covalent mode to assist working.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Instant matched medical styptic anti-adhesive flush fluid
InactiveCN101259137AGood hemostasisGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsSurgical drugsMANNITOL/SORBITOLWater insoluble
The invention discloses a ready-to-prepare medical haemostatic and anti-adhesive flushing fluid used in perioperative period, which pertains to polymeric biological materials with anastalsis, antisepsis and anti-adhesive effect in the surgical perioperative period. Water for injection is adopted bythe invention as a carrier, water-insoluble chitosan, water-soluble chitosan or carboxymethyl chitosan is functioned as a main material, matched with osmotic pressure regulating substance NaCl or mannitol or glycin as auxiliary material. Chitosan and water for injection, or water for injection mixed and dissolved with osmotic pressure regulating substance are respectively sealed in two chambers with soft chamber bags made from PVC films, the two chambers are separated by a weak sealing layer made through thermal sealing or gluing, and can be used only by squeezing the liquid chambers to mix two liquids. The flushing liquid can be used immediately after being prepared, which is convenient for an employment and has long preservation period; the problem that the physical and chemical properties of chitosan is unstable and can not be preserved for a long term is solved.
Owner:XUZHOU HAIERZI BIOENG CHEM
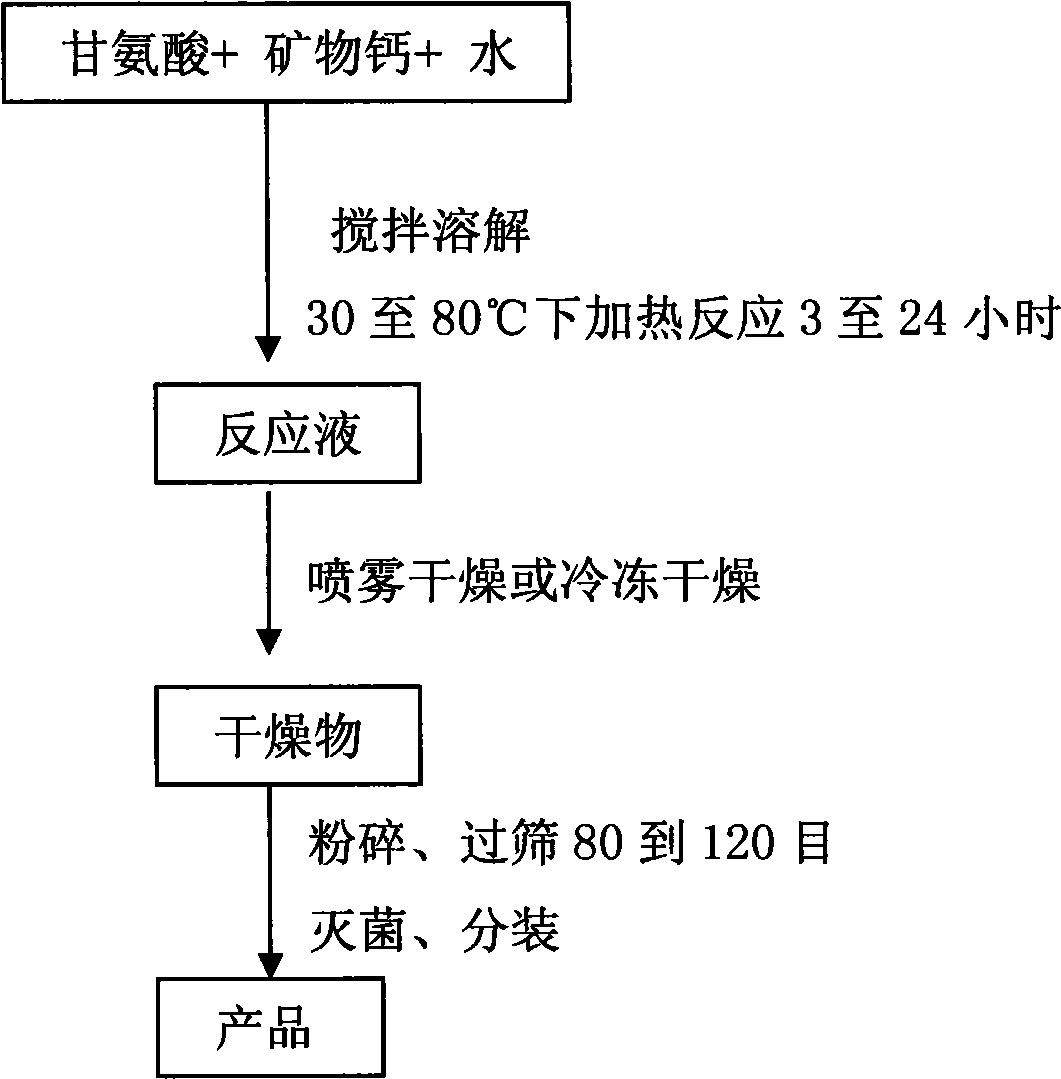
Method for preparing calcium glycine
InactiveCN101531609AHigh yieldLow costOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationGlycineFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for preparing calcium glycine, which comprises the following steps: respectively taking 15 to 30 weight percent of glycin, 0.8 to 15 weight percent of mineral calcium and 60 to 80 weight percent of water, mixing and stirring the raw materials in a reaction kettle to make the raw materials fully dissolved, performing reaction for 3 to 24 hours by heating at a temperature between 30 and 80 DEG C, and then standing for 6 to 24 hours; taking reaction solution, and performing spray drying or freeze drying to obtain a dry substance; and crushing the dry substance, passing through a 80 to 120-mesh sieve, performing sterilizing and split charging. The method for preparing the calcium glycine has easily obtained raw material used, scientific and reasonable mixture ratio of the raw materials, simple preparation process, high yield of the synthesized calcium glycine, low cost and suitability for industrial production.
Owner:WUXI ZUPING FOOD SCI & TECH
Glucagon-likepeptide1 derivatives and use thereof
ActiveCN102186881AChemically stableNot easy to degradeNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood plasmaBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a type of Glucagon-likepeptide1 and the use thereof. The structure of the Glucagon-likepeptide1 derivatives is presented in the following formula. The invention also provides a medical salt, a solvolyte, a chelate or a non-covalent complex formed by the compounds shown by the structure, a prodrug based on the compound, or any mix of the above form. The chemical property of the compounds provided in the invention is stable, unlikely to be degraded by IV (DPP-IV) in body. When used for decreasing blood glucose concentration in body, the compound or the drug adopting the compound as an active ingredient have relatively long plasma half-life (above 30 hours) and an significant effect in decreasing blood glucose concentration. X, in the formula, is selected from glycin or glycinamide.
Owner:BETTA PHARM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com