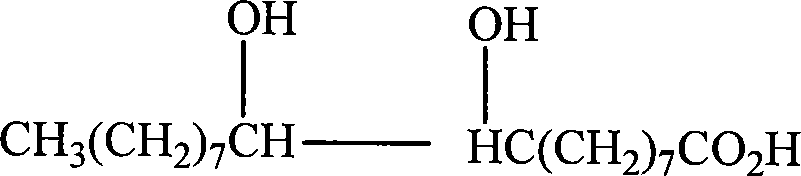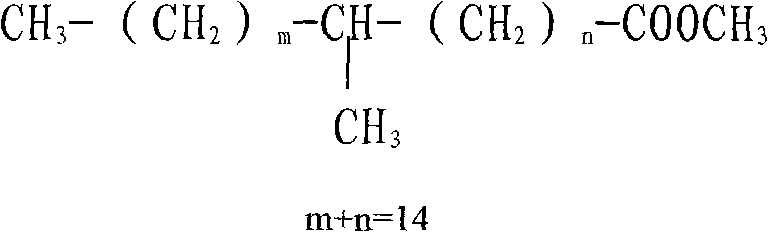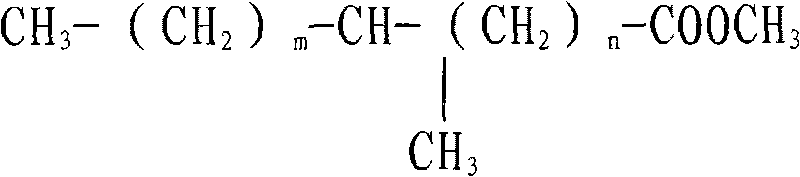Patents
Literature
163 results about "METHYL STEARATE" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
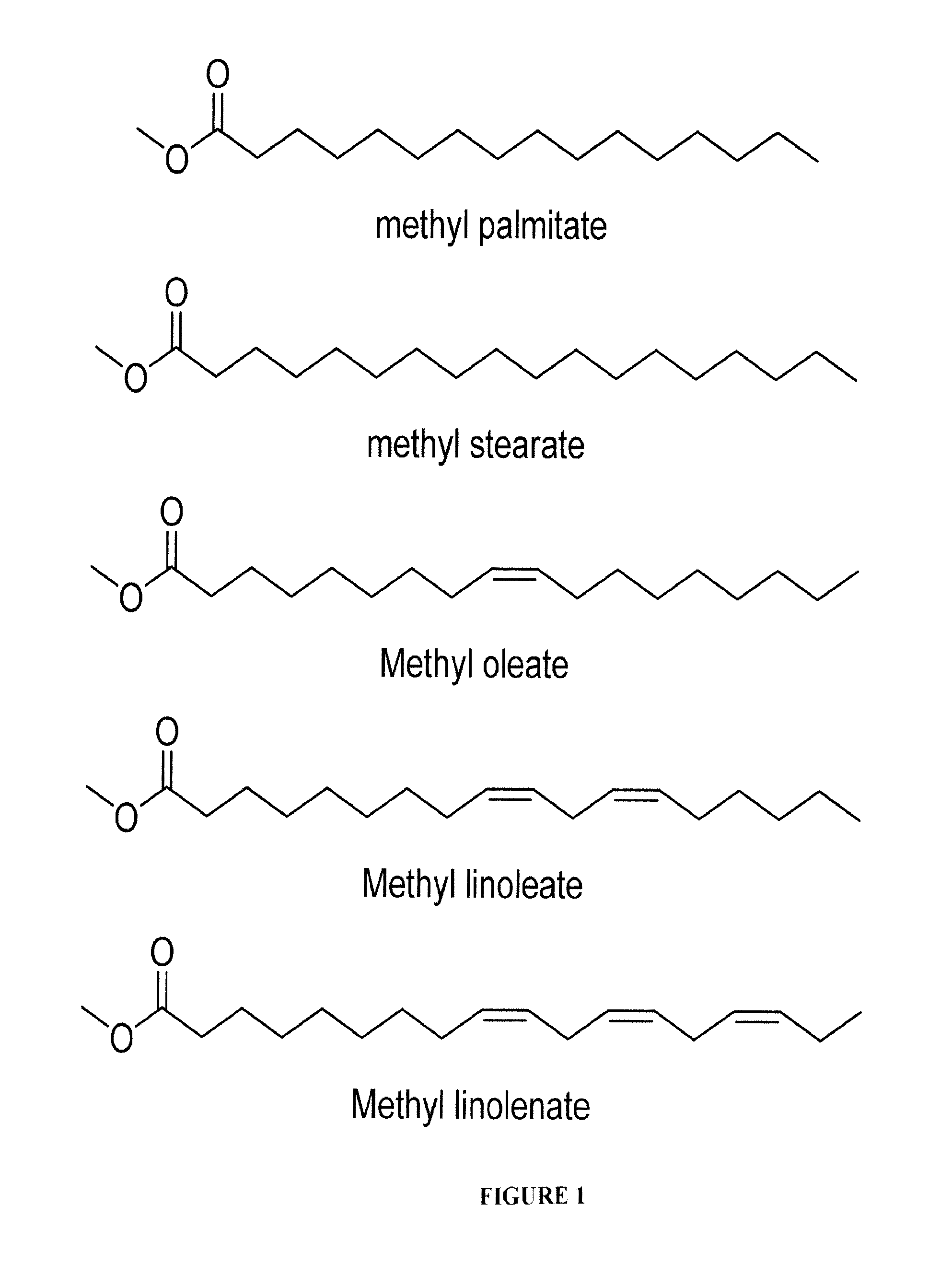
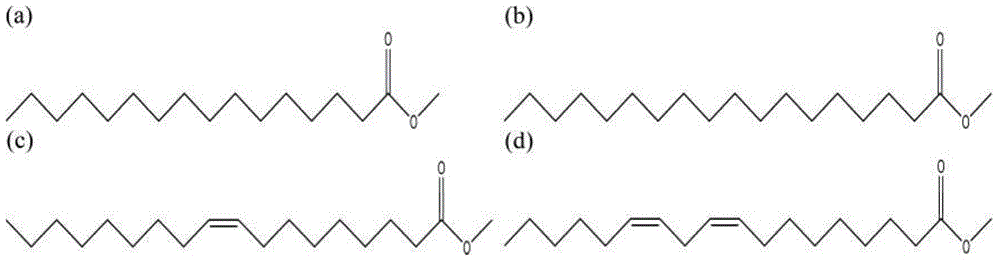
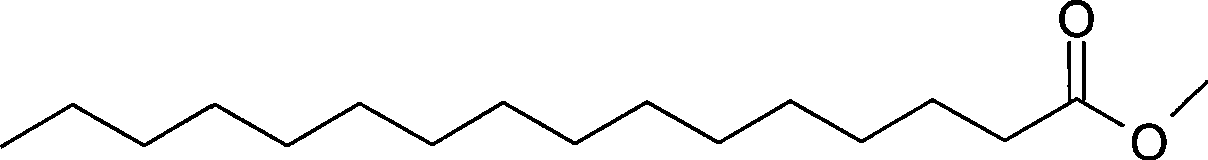
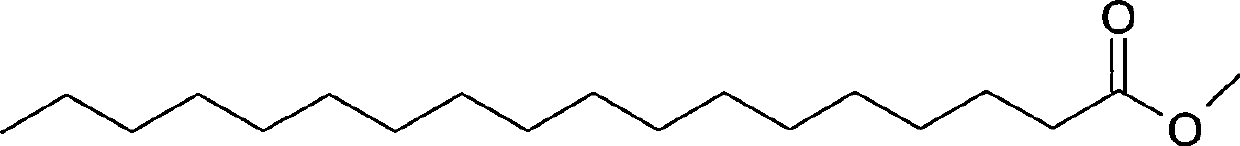
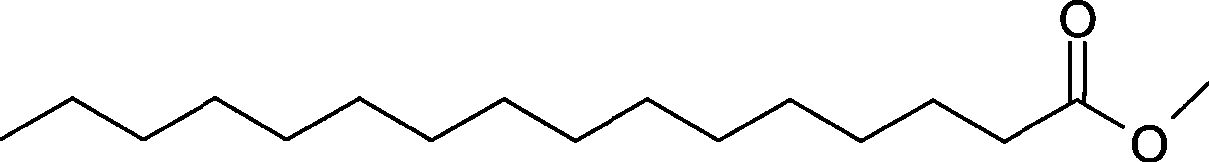
Methyl stearate. [′meth·əl ′stir‚āt] (organic chemistry) C17H35COOCH3 Colorless crystals melting at 39°C; soluble in alcohol and ether, insoluble in water; used as an intermediate for stearic acid manufacture.
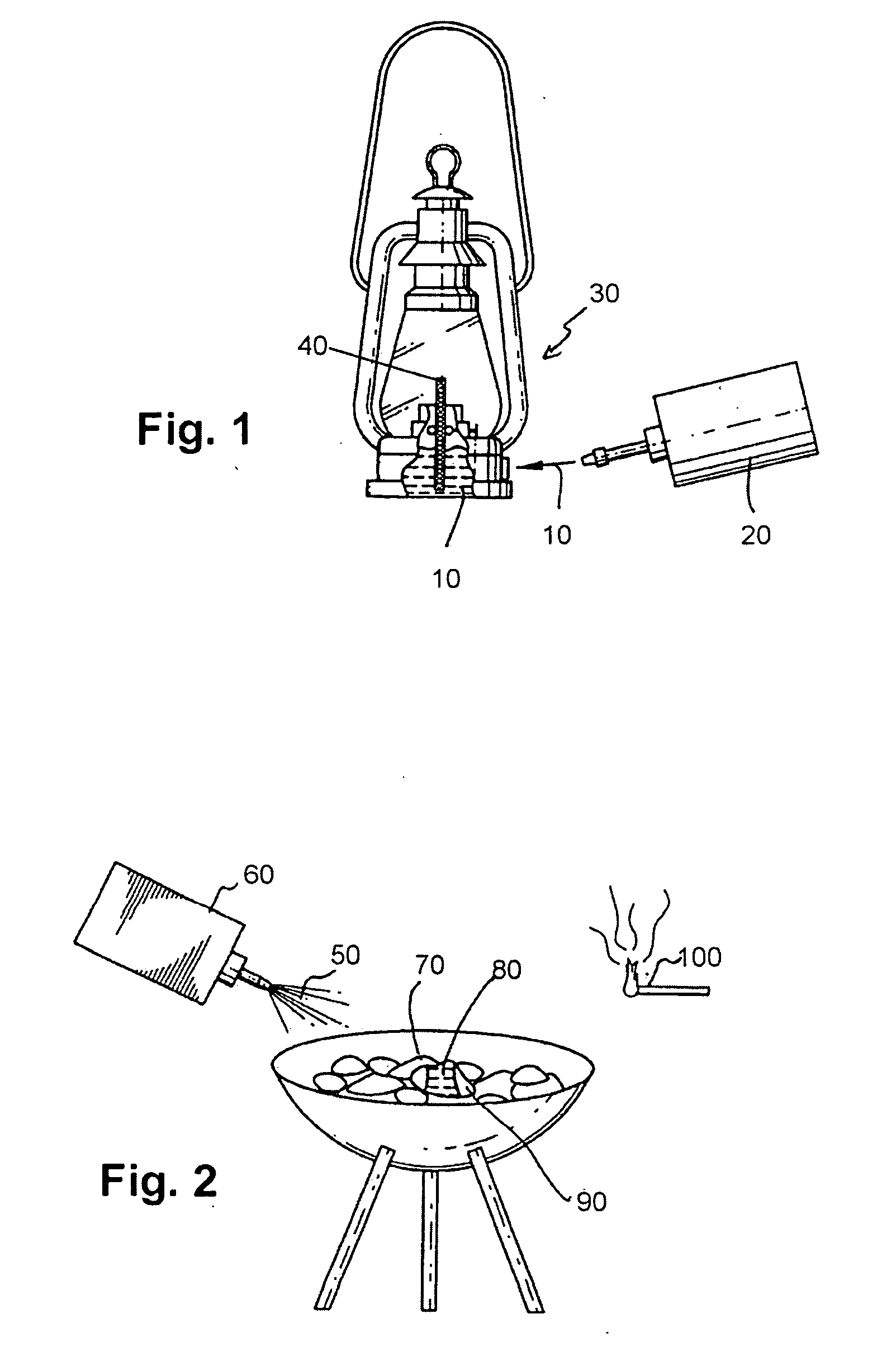
Lamp oil composition and lighter fluid composition
InactiveUS20050115145A1SaferEasy to manufactureCapillary burnersLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAlcoholLighter fuel
Lamp oil compositions including methyl palmitate, methyl stearate, myristyl alcohol, an alcohol with less than six carbons, preferably ethyl alcohol, and fragrance. Also disclosed herein are lighter fluid compositions which include methyl laurate, methyl stearate, ethyl alcohol and fragrance.
Owner:LUMETIQUE
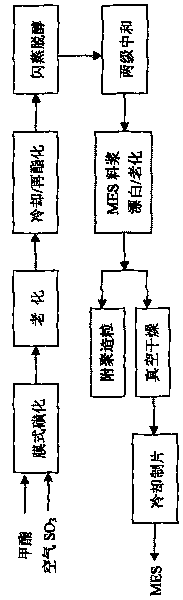
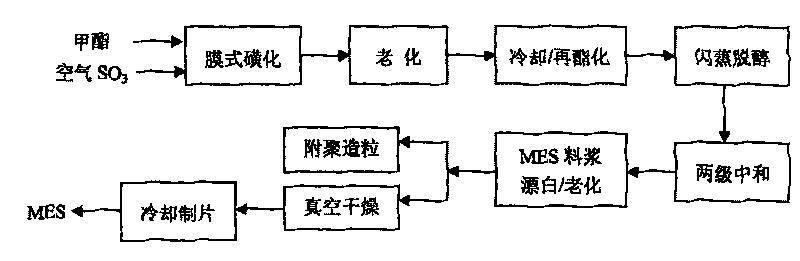
Method for producing sodium fatty acid methyl ester sulfonate
ActiveCN101759612AAvoid coexistenceReduce dosageSulfonic acids salts preparationSolventFatty acid methyl ester
The invention relates to a surfactant used in the production of washing powder, in particular to a method for producing sodium fatty acid methyl ester sulfonate, which solves the problem that the prior art cannot realize continuous, stable industrialized mass production. Hydrogenated palm-methyl stearate is adopted as material, and is sulfonated by SO3 gas on a multi-tube film reactor, steps, such as aging, reesterification, dealcoholization, neutralization, bleaching and vacuum drying, are then sequentially carried out, so that sodium fatty acid methyl ester sulfonate product is obtained, the content of MES is more than 80 percent, the content of disodium salt is less than 5 percent, the content of free oil is less than 2.5 percent, the content of sodium methyl sulfate is less than 8 percent, and color is less than 60 klett(5 percent A.M). Because highly selective catalyst is added in the aging process, the production of deep-colored by-product is reduced; because the reesterification reaction and the bleaching reaction are separately carried out, the safety of reaction is enhanced, and the consumption of methanol as solvent is greatly reduced; because vacuum dealcoholization is carried out before sulfoacid neutralization, industrialized operation can be easily carried out, and meanwhile, the safety problem of methanol in the subsequent bleaching step is eliminated.
Owner:南风化工(运城)集团有限公司
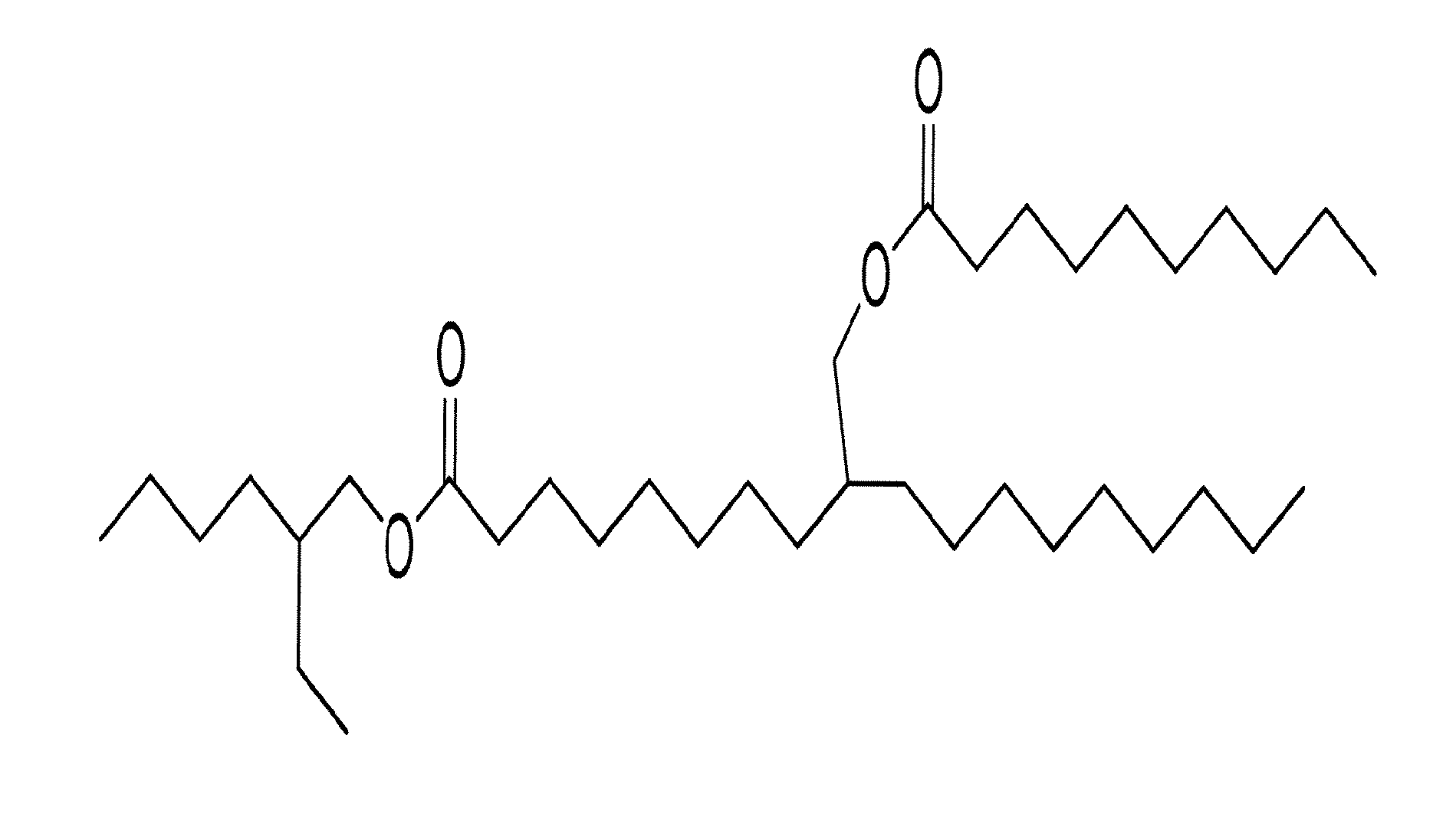
Synthetic ester-based dielectric fluid compositions for enhanced thermal management
ActiveUS20140252281A1Fatty acid chemical modificationFatty acids production/refiningPolymer scienceHydroxystearic Acid
A dielectric fluid composition for electrical apparatus comprises a functionalized methyl-12-carboxy methyl stearate having desirable properties including a pour point less than −30° C. and a fire point greater than 250° C. It may be prepared by a process wherein methyl-12-hydroxy methyl stearate is transesterified by reaction with a C3-C20 alcohol to form the hydroxy methyl ester, followed by reaction with a linear or branched C4-C20 carboxylic acid selected from free acid chlorides, fatty acids, carboxylic acid anhydrides, and combinations thereof. The second step serves to end-cap the hydroxyl groups, thereby producing the functionalized methyl-12-carboxy methyl stearate compound that exhibits improved thermoxidative stability and low temperature flowability, as well as increased fire point.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
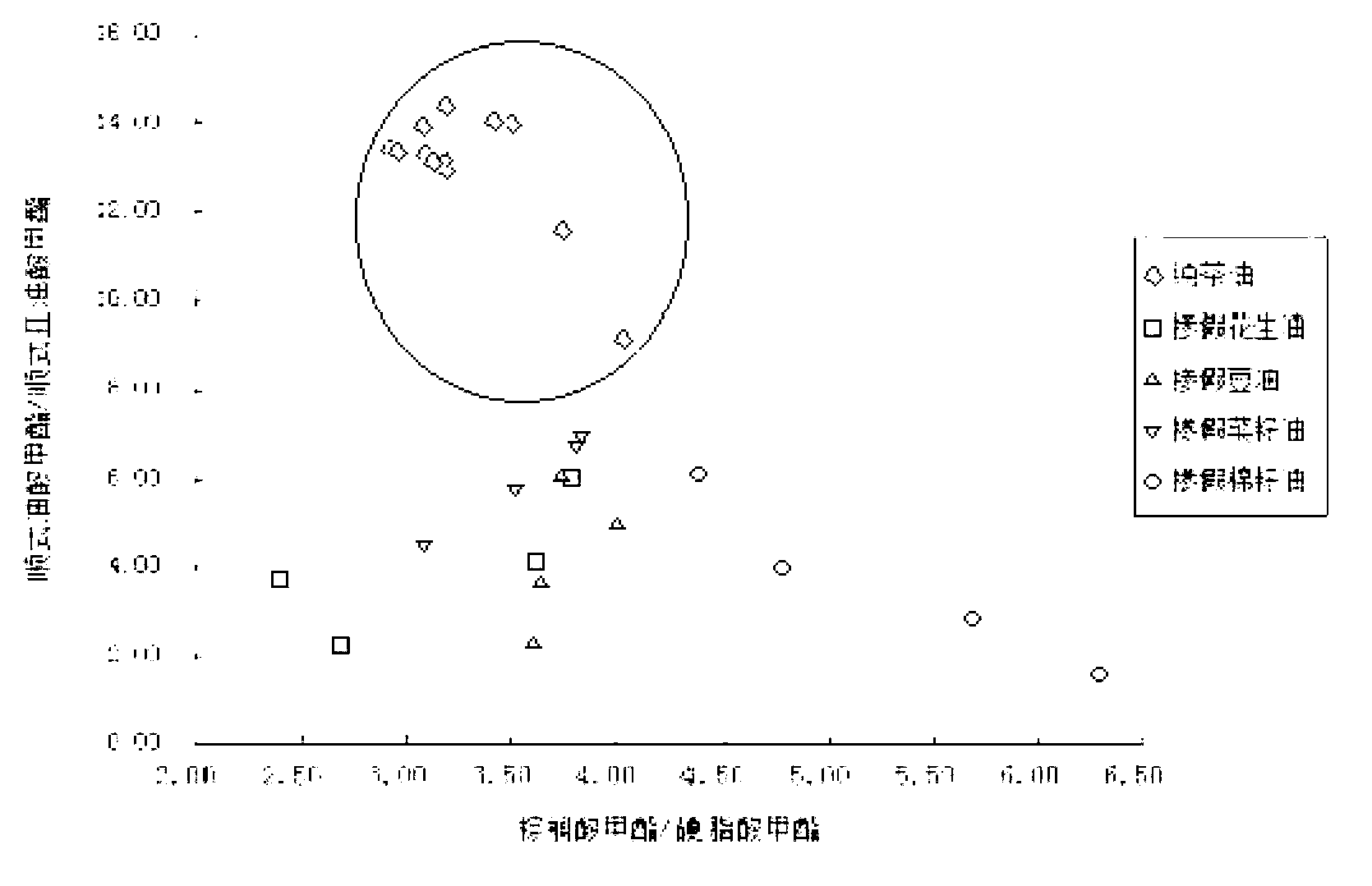
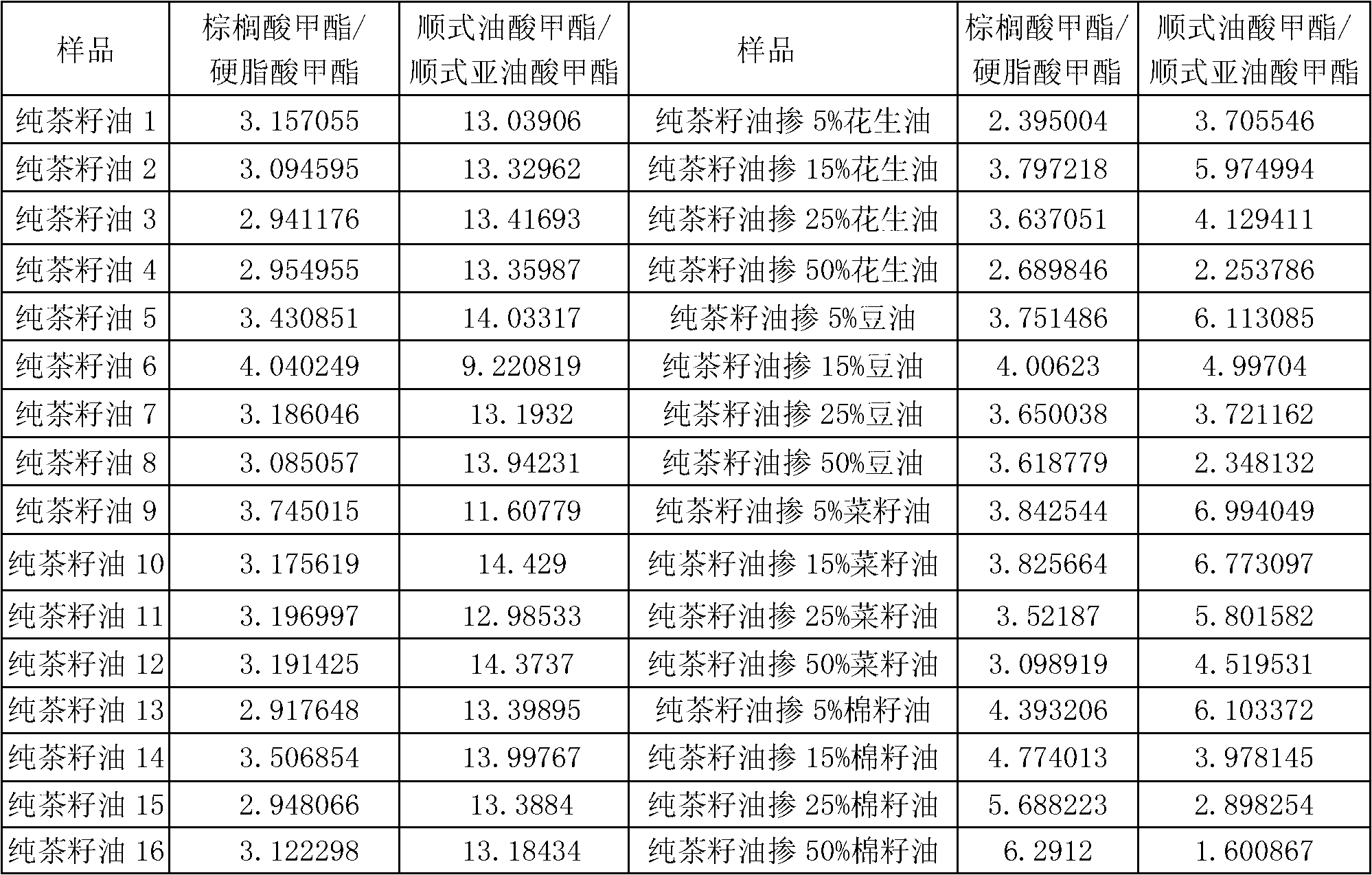
Detection method for tea seed oil adulteration based on ratio of main fatty acids
A detection method for tea seed oil adulteration based on ratio of main fatty acids obtains the contents of main fatty acids in pure tea seed oil and adulterated tea seed oil samples by applying gas chromatography and mass spectrometry technology (GC-MS technology), and intuitively presents the distribution characteristic of fatty acids of grease-adulterated pure tea oil by adopting a two-dimensional diagram of methyl cis-oleate / methyl cis-linoleate and methyl palmitate / methyl stearate, so as to qualitatively identify adulteration of tea oil.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Polymer and use thereof
InactiveCN101372515AHigh viscosityGood thickening effectDrilling compositionFood preparationArginineValine
The invention belongs to the field of energy technology and food technology, and more particularly relates to a polymer and the application thereof. The polymer is composed of 34.8% of sugar, 63.1% of fat and 1.5% of polypeptide; wherein, the sugar component contains glucose, rhamnose, seminose and glucuronic acid; fat component contains 6.2% of hexadecanoic acid methyl ester and 93.8% of methyl stearate; the polypeptide component respectively contains 11.6% of asparticacid, 6.1% of threonine, 4.8% of serine, 11.7% of glutamic acid, 6.7% of glycin, 9.8% of lactamine, 6.7% of valine, 1.8% of methionine , 4.6% of isoleucine, 9.8% of leucine, 3.4% of tyrosine, 5.9% of phenyl alanine, 3.1% of lysine, 1.3% of histidine, 7.6% of arginine and 5.2% of proline. Sanzanjiao can be taken as drilling mud conditioner and jelly glue polymer used for water shutoff profile control treatment in oil field to be applied to petroleum extraction, and the characteristics of jelling and thickening lead the polymer to be taken as food additive to be widely applied to the food production field.
Owner:张禹
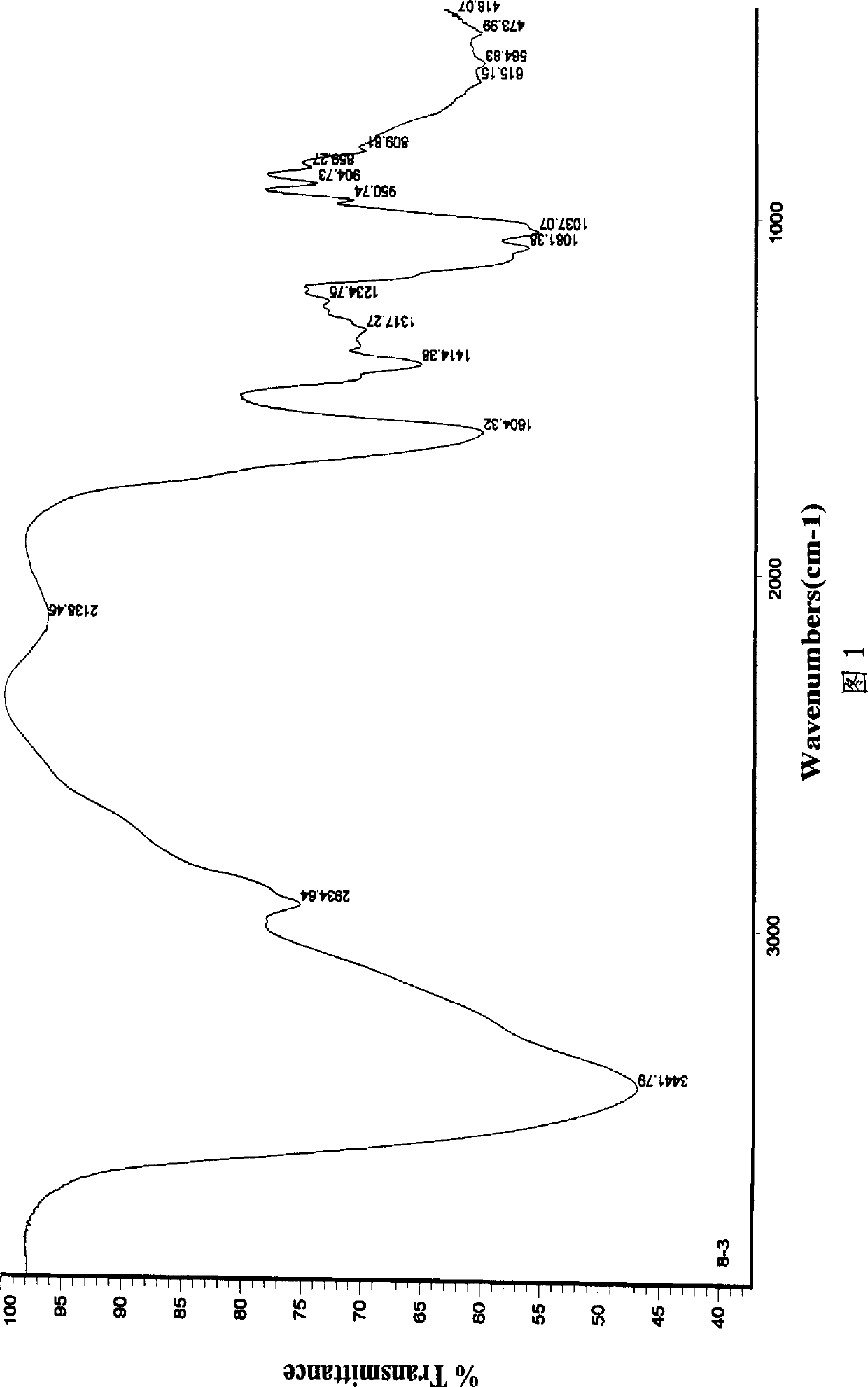
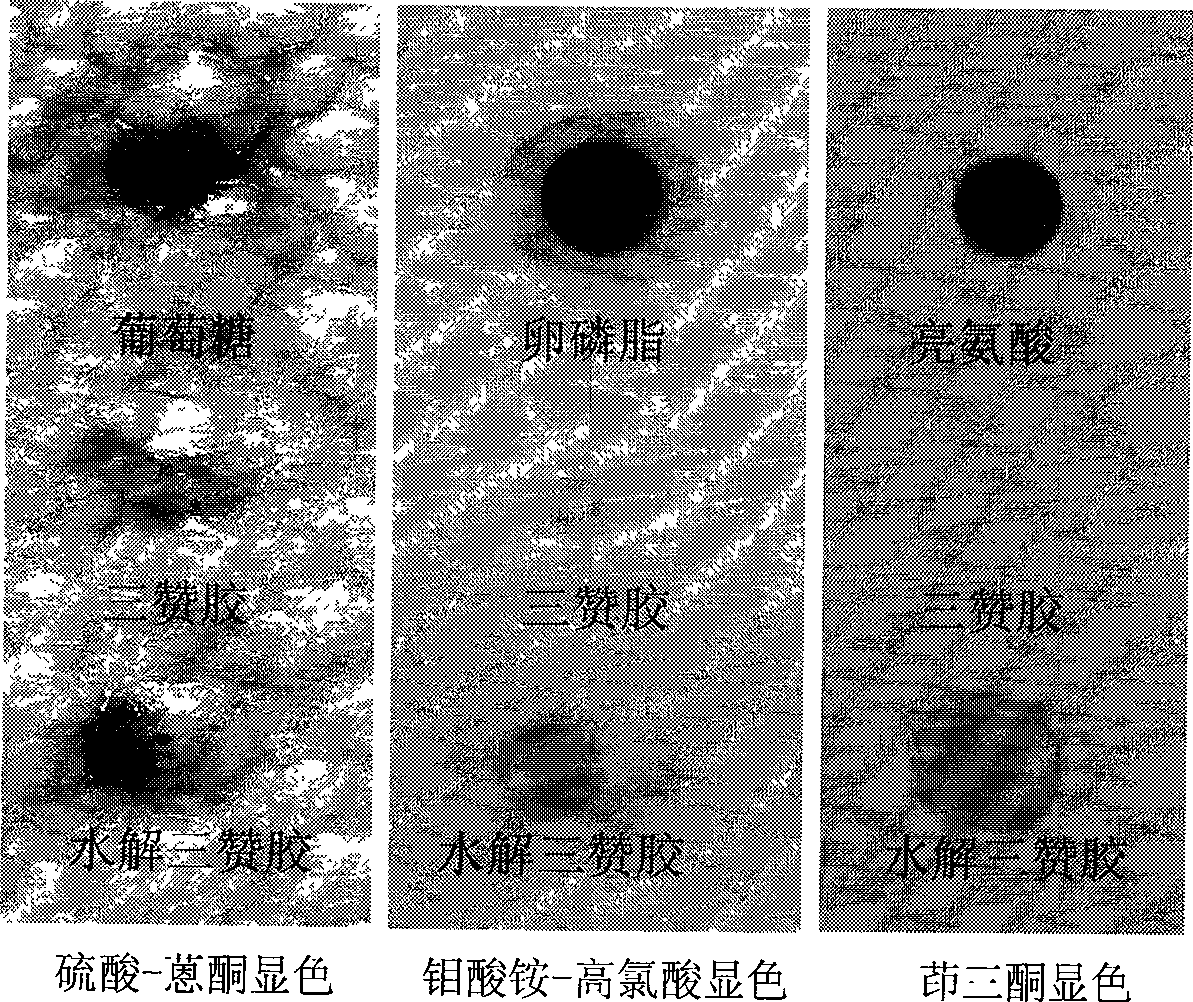
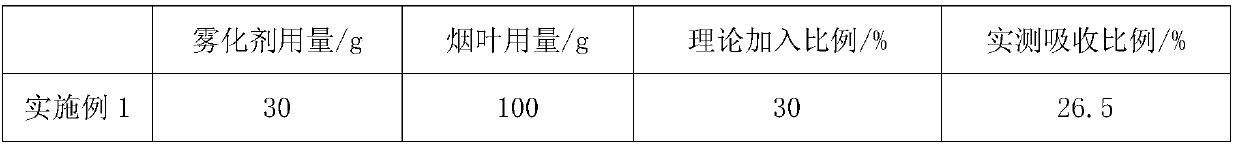
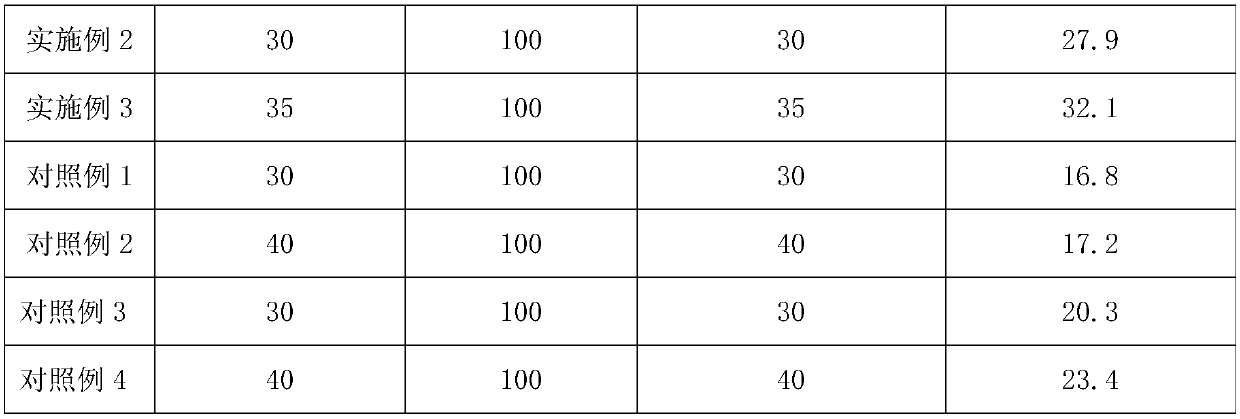
Atomizing agent for cigarettes and method for increasing atomizing agent absorbing amount of conventional tobacco leaves
InactiveCN109602074ALow viscosityPromote absorptionTobacco treatmentTriethylene glycol diacetateSteam pressure
The invention provides an atomizing agent for cigarettes and a method for increasing the atomizing agent absorbing amount of conventional tobacco leaves. The atomizing agent for the cigarettes is prepared by mixing sorbitol, glycerin, propanetriol, triethylene glycol diacetate, methyl stearate and dimethyl dodecanedioate according to a mass ratio of 1:(10-20):(10-20):(5-10):(2-6):(0.6-1.0). The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing formulated tobacco leaves, then performing steam explosion treatment under the conditions that the temperature is 30-50 DEG C, the steam explosiontime is shorter than 0.01 second, the steam pressure is 0.4-0.8 Mpa and the pressure retention time is 10-60 seconds, quickly spreading the prepared atomizing agent into the tobacco leaves after completion of the treatment, then sending to a leaf storage cabinet, balancing the moisture, thoroughly absorbing, and then taking out for shred preparation. By adopting the method, the atomizing agent adding amount of the conventional tobacco leaves can be greatly increased, and the atomizing agent can be applied to the cigarettes which are nonflammable after being heated.
Owner:HUBEI CHINA TOBACCO IND
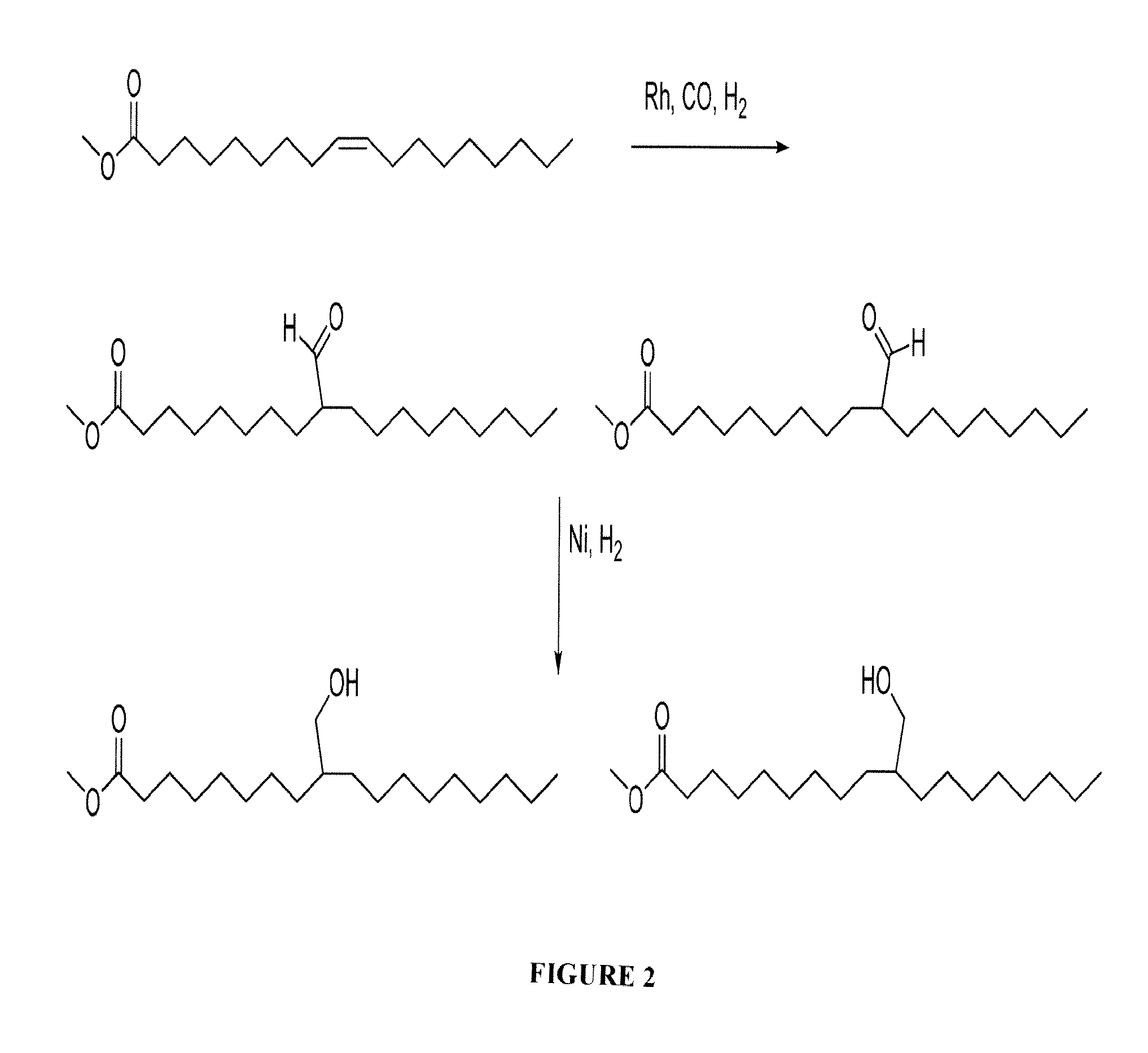
Method for preparing 9,10-dihydroxystearic acid and its methyl by hydrogen dioxide oxidation process
InactiveCN101177392AHigh yieldHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationDistillationCalcium formate
The invention relates to a preparation method for 9, 10-dihydroxy stearic acid and methyl ester, which is characterized in that the oleic acid and the formic acid are mixed uniformly in room temperature; the mixture is added with hydrogen peroxide, and warmed up and separated from water phase; the solvent is recycled through decompression and distillation; the generative reaction admixture is recrystallized with organic solvent, so that the product 9, 10-dihydroxy stearic acid is prepared. The recovered formic acid solution can generate ice-cream calcium formate salt separation by adding calcium oxide and calcium carbonate; subsequently the methyl alcohol and oil of vitriol is arranged into the product 9, 10-dihydroxy stearic acid for a reflux reaction, and then is rotated and vaporized out the water phase and oil phase for being washed to be neutral, thereby the 9, 10-dihydroxy stearic acid methyl ester product is generated through dehydration. The invention has the advantages of clean process, safe implementation, easy operation, full utilization of the reactant, reduced waste emission, effective utilization of the low-concentration hydrogen peroxide, and favorableness to large-scale production.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lamp oil composition and lighter fluid composition
InactiveUS7524339B2Not to damageTransportation safetyCapillary burnersLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAlcoholLighter fuel
Lamp oil compositions including methyl palmitate, methyl stearate, myristyl alcohol, an alcohol with less than six carbons, preferably ethyl alcohol, and fragrance. Also disclosed herein are lighter fluid compositions which include methyl laurate, methyl stearate, ethyl alcohol and fragrance.
Owner:LUMETIQUE
Hydroxyl compound type composite foaming agent and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a foaming agent, specifically to a hydroxyl compound type composite foaming agent and a preparation method thereof. The hydroxyl compound type composite foaming agent at leastcomprises the following preparation raw materials in parts by weight: 2 to 20 parts of a nonionic surfactant, 1 to 5 parts of an anionic surfactant, 0.1 to 5 parts of a foam stabilizer, 0.5 to 1 partof a thickening agent and 69 to 96.4 parts of water, wherein the nonionic surfactant is one ore more selected from the group consisting of polyether polyol and lignin polyether polyol; and the anionic surfactant is one or more selected from the group consisting of a dodecyl anionic surfactant, lauryl sulfate triethanolamine, secondary alkyl sodium sulfonate, fatty alcohol sodium hydroxyethyl sulfonate, N-sodium lauroyl sarcosine, amide polyoxyethylene ether magnesium sulfate, dodecanol polyoxyethylene ether disodium sulfosuccinate, sodium alpha-olefin sulfonate, sodium fatty alcohol ether sulfate, sulfonates of ethoxylated fatty acid methyl ester, alcohol ether carboxylate, methyl stearate polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfonate and isooctyl phosphate.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGRUI TECH CO LTD
Gas chromatography method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting soya fatty acid components
ActiveCN105044229AImprove extraction efficiencyImprove accuracyComponent separationGas phaseMethyl oleate
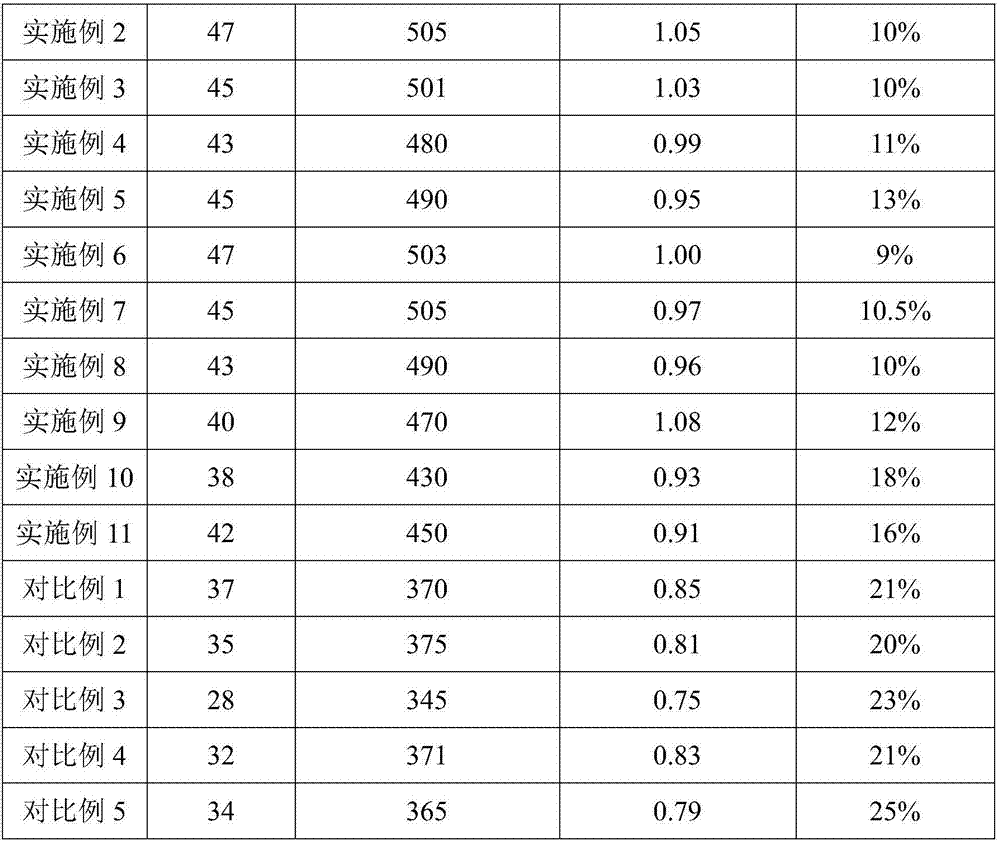
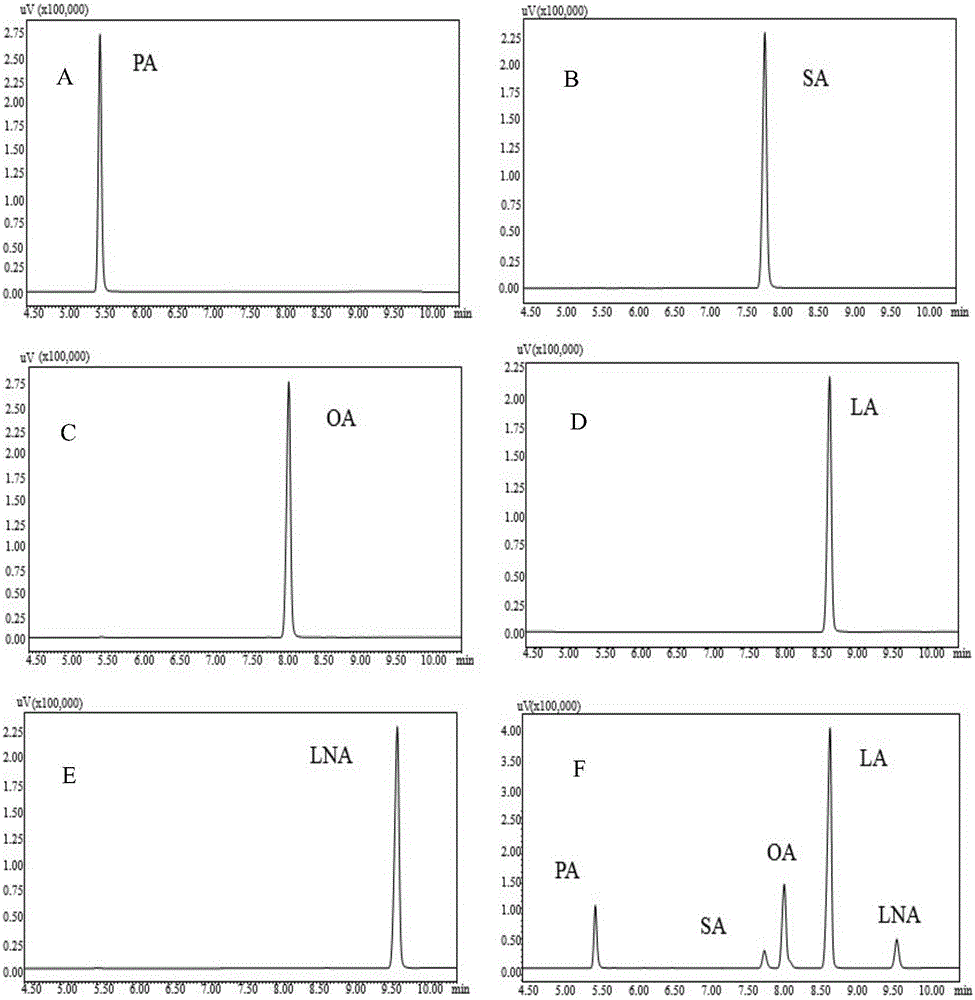
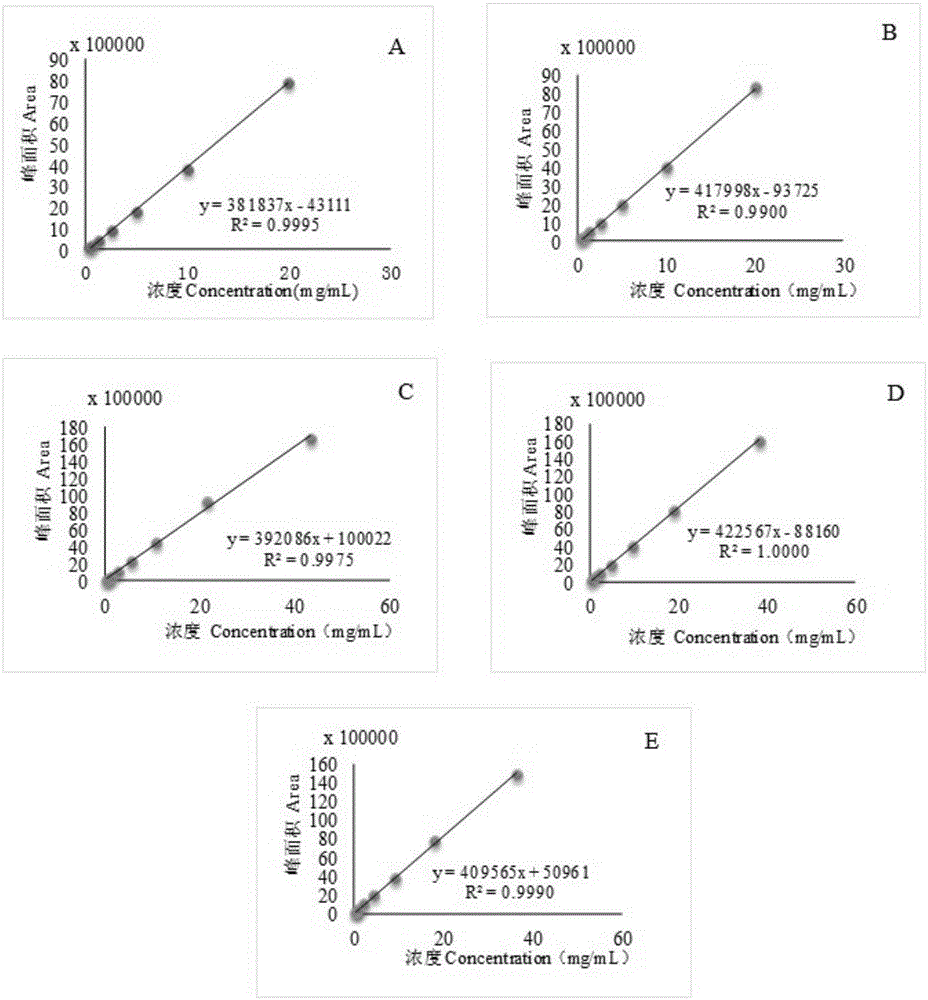
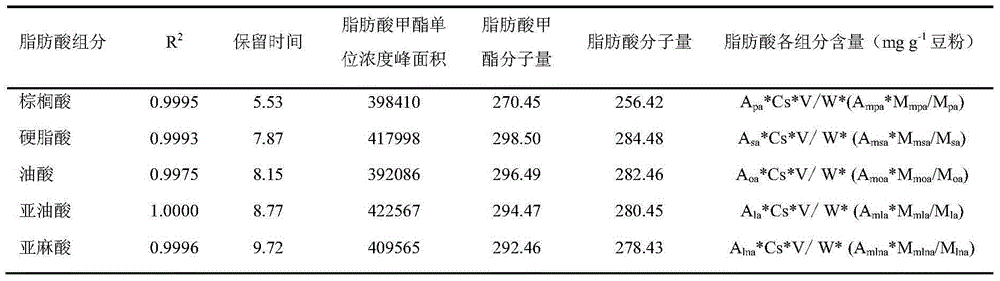
The invention relates to a gas chromatography method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting soya fatty acid components. The gas chromatography method is characterized in that fatty acids in soya seeds are extracted by adopting methods of heating and methylating and detected by adopting a gas chromatography, and the actual content of the fatty acid components in the soya seeds can be accurately detected according to a standard curve and a regression equation of standard samples of five fatty acid methyl esters (methyl palmitate, methyl stearate, methyl oleate, methyl linoleate and methyl linolenate). The method is applicable to qualitative and quantitative analysis of the fatty acid components of the soya seeds, is simple and convenient to operate, easy to control and easy to popularize, can be used for detecting relative percentage content of the five fatty acid components and accurately calculating the absolute content of each fatty acid component in the soya seeds, and has an important meaning in soya fatty acid detecting and breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Ultrathin nonwoven fabric
InactiveCN102505349AWith temperature control effectObvious temperature control effectConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsNon-woven fabricsVanadium dioxideInfrared
The invention relates to ultrathin nonwoven fabric, which is prepared by adopting an electrostatic spinning method. The ultrathin nonwoven fabric is monolayer, has the thickness of 60-136 mu m, and is prepared from the following spinning raw materials: a fiber main body raw material and phase-change temperature-adjusting microcapsules, wherein the fiber main body raw material comprises polyphenyl thioether and polyamide at a mass ratio of (50-55):(58-62); the phase-change temperature-adjusting microcapsules are contained in the fiber main body raw material, and are prepared by adopting an interfacial polymerization method with polyurea type resin as the capsule wall; and the phase-change material contained in the microcapsules is a mixture of capric acid, lauric acid, methyl stearate and C17-19 straight-chain alkanes. According to the invention, the ultrathin nonwoven fabric contains the phase-change temperature-adjusting microcapsules, thus the ultrathin nonwoven fabric has obvious adjusting effect on temperature; and at the same time, the ultrathin nonwoven fabric contains nano vanadium dioxide, which is an infrared-sensitive material and can project or reflect infrared according to the external infrared change, thus the ultrathin nonwoven fabric has a temperature controlling action.
Owner:江西半球家用品实业有限公司
Method for reducing freezing point of biodiesel
InactiveCN101760263AImprove Oxidation StabilityImprove stabilityBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsBiodieselMethyl stearic acid
The invention relates to a method for reducing the freezing point of biodiesel, which belongs to the technical field of fine chemical industry. In the method, mixture of branched methyl-based methyl stearate without any double bond is added in biodiesel according to a specific proportion, the methyl can be in various positions, and the biodiesel with a low freezing point can be obtained after complete mixing. The addition of methyl isostearate into the biodiesel enhances the stability and oxidation resistance of the biodiesel, and also improves the engine lubricating property. Moreover, the compounding process is simple and safe.
Owner:江苏永林油脂科技有限公司
Stearic acid 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidine ester of light stabilizer and production method thereof
InactiveCN101544595AReduce pollutionEasy to separate and purifyOrganic chemistryNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesStearic acidMETHYL STEARATE
The invention discloses a stearic acid 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidine ester of a light stabilizer and a production method thereof. Methyl stearate and 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-hydroxypiperidine are used as raw materials and react under the condition that a catalyst exists to obtain the stearic acid 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidine ester; and the catalyst is tetrabutylammonium bromide with the use amount being 0.8-4.8 percent of the methyl stearate. By utilizing the methyl stearate and the 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-hydroxypiperidine as raw materials to synthesize the stearic acid 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidine ester and adopting the tetrabutylammonium bromide as the catalyst, the invention simplifies the separation and purification processes and has short reaction time, high product yield which reaches over 95 percent, higher product purity, great reduction of energy consumption, little environment pollution and low cost, thereby being a relatively ideal process for realizing industrial production.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY +1
Preparation method of stearoylbenzoylmethane and application thereof to molding processing of thermoplastic resin
ActiveCN102503793AHigh cost of solutionThe condensation reaction cycle is longOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationKetoneStearic acid
The invention discloses a preparation method of stearoylbenzoylmethane and an application thereof to molding processing of thermoplastic resin, which belong to preparation of a compound which only contains a CO radical and is only connected with a carbon atom or a hydrogen atom, and particularly relate to preparation of beta-diketone. The stearoylbenzoylmethane is obtained by undergoing a condensation reaction on methyl stearate and acetophenone in an alkaline environment, wherein the methyl stearate is obtained by taking stearic acid and methanol as raw materials, taking sulfuric acid as a catalyst and undergoing an esterification reaction. The invention provides a preparation method of the stearoylbenzoylmethane, which has the advantages of low costs of major raw materials, short condensation reaction period, small quantity of byproducts, high yield of stearoylbenzoylmethane, complete recycling of a solvent, nontoxicity of a crystallization solvent and high crystal yield. The condensation yield is up to 88 percent, the solvent is completely recycled, the crystallization solvent is nontoxic and environmentally-friendly, the crystal yield is up to 95 percent, and the purity of a product, i.e., stearoylbenzoylmethane is up to 98 percent. The invention further provides a method for applying the stearoylbenzoylmethane to molding processing of thermoplastic resin.
Owner:SHANDONG RUIFENG CHEM
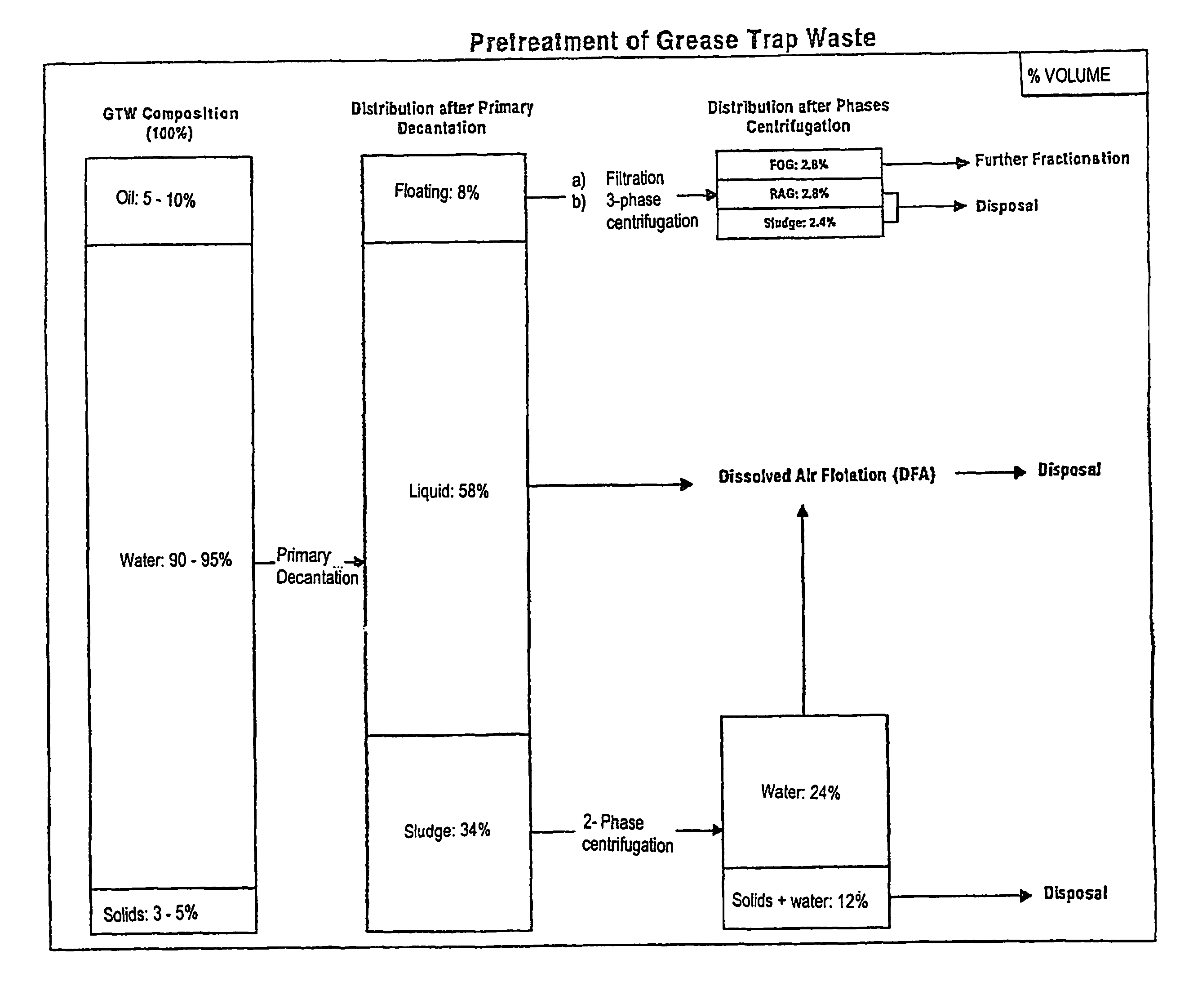
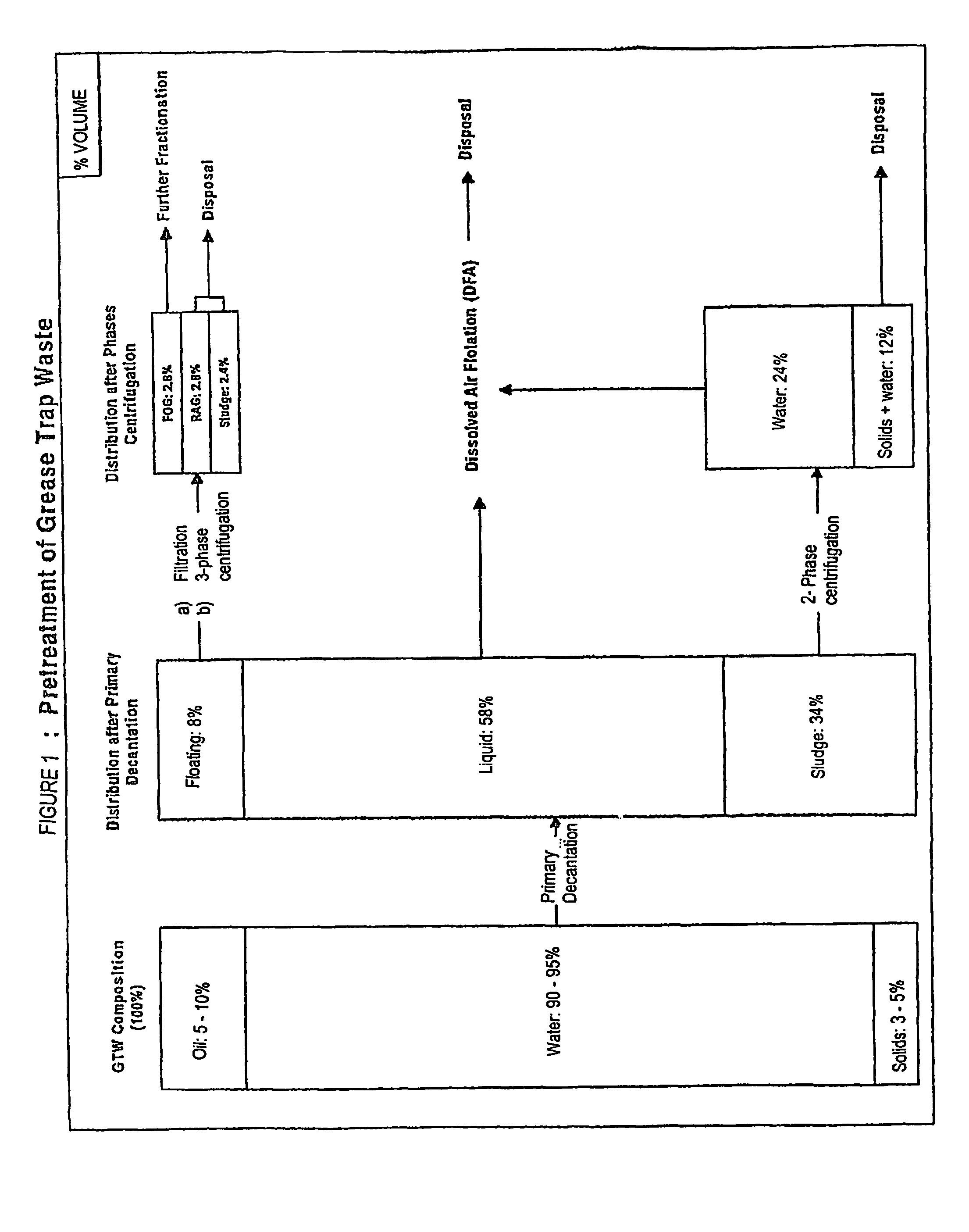
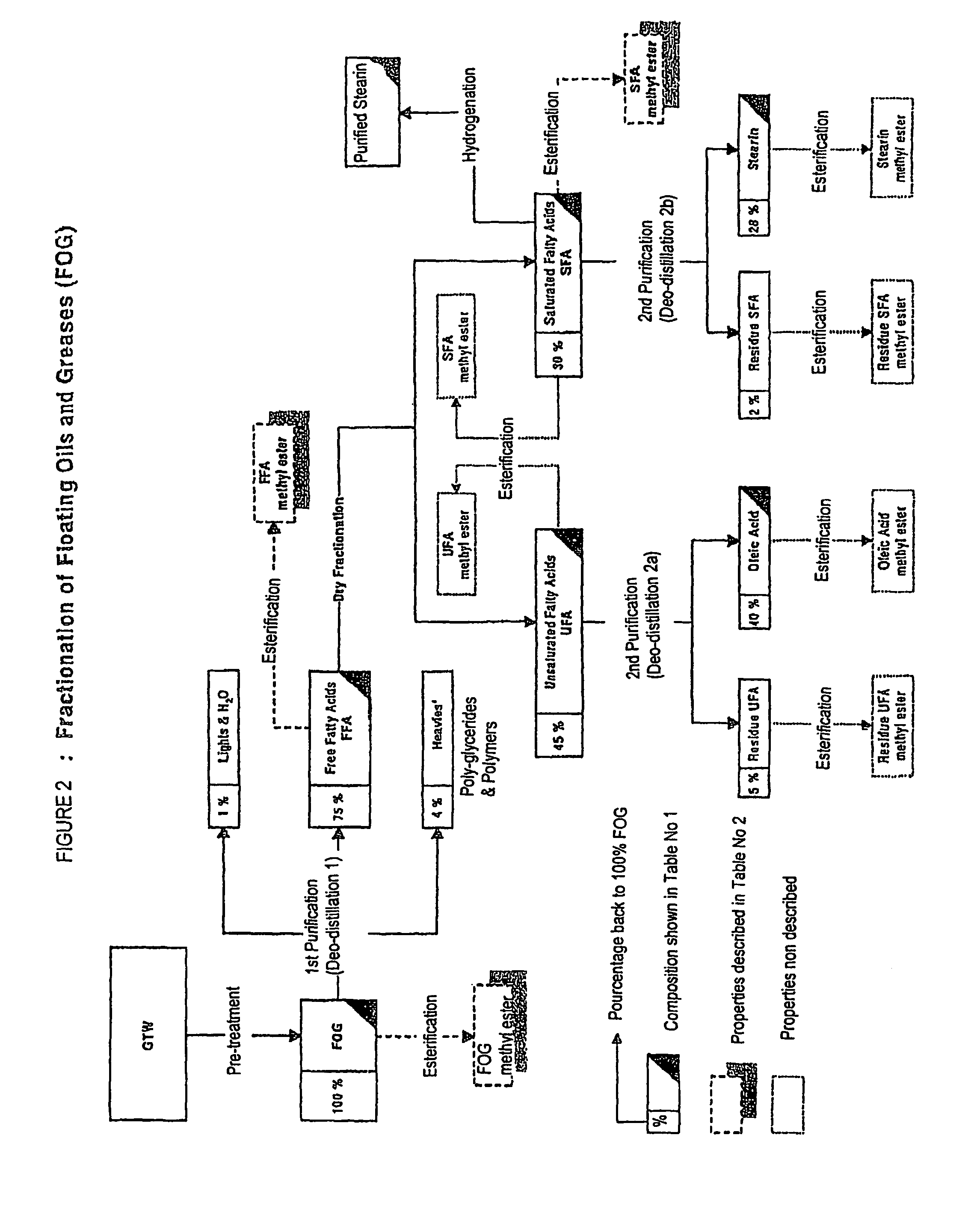
Method for fractionating grease trap waste and uses of fractions therefrom
InactiveUS7161017B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid hydrogenationStearic acidOleic Acid Triglyceride
Owner:PROLAB TECH
C18 series fatty acid and C20-C22 series fatty acid fine separation method
ActiveCN105062694AMild reaction conditionsSimple processFatty acid esterificationFatty-oils/fats refiningCarbon numberMethyl linoleate
The invention discloses a C18 series fatty acid and C20-C22 series fatty acid fine separation method. The method includes: pretreating the raw material animal and vegetable oil by a ionic liquid to obtain high-yield and low-acid value biodiesel, i.e. a mixture of a variety of fatty acid methyl esters, with the process being simple, green and environment-friendly; then placing the obtained biodiesel in a pressured reduced rectification tower kettle, taking the ionic liquid as an extraction agent to conduct extraction pressured reduced rectification, and collecting methyl stearate, methyl oleate and methyl linoleate or eicosapentaenoic acid methyl ester and docosahexaenoic acid methyl ester with mass percentage purity of over 98% at the tower top. The method provided by the invention makes up the blank of the prior art, has a convenient operation process, provides the operation process for separation of long-chain fatty-acid methyl esters with a same carbon number, different double-bond numbers and poor heat sensitivity, and lays the foundation for fine separation of fatty acid methyl ester.
Owner:天津领碳能源环保科技有限责任公司
Intra-tower pump suction type high vacuum distillation method and device for precise separation of C16-C22 fatty acids
ActiveCN105695104AIncrease the compression ratioFast pumping speedOrganic compound preparationFatty acids production/refiningOil and greaseMethyl linoleate
The invention discloses an intra-tower pump suction type high vacuum distillation method and device for precise separation of C16-C22 fatty acids. The high vacuum distillation method comprises the following steps: firstly taking heat sensitive materials with a high additional value, such as animal and vegetable oil, as raw materials, adopting plasma liquid and the like as an esterification and transesterification catalyst, and obtaining mixture of multiple fatty acid methyl esters with high yield in one step; secondly, in a distillation tower with almost zero pressure drop, carrying out high vacuum distillation operation on the formed multiple fatty acid methyl esters through catalysis; and finally separating and purifying, so that single fatty acid methyl esters such as timnodonic acid methyl ester, docosahexoenoic acid methyl ester, methyl palmitate, methyl stearate, methyl oleate and methyl linoleate with the mass fraction more than 98% respectively are obtained. The whole technological method is simple and clear, the operation is simple, the equipment cost is low, the energy is saved, and the enlargement can be easily realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Catalyst for glycerin monostearate synthesis and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103111297AHigh catalytic activityImprove conversion ratePreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsFerrocobaltLamellar structure
The invention discloses a hydrotalcite catalyst for preparing glycerin monostearate and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst has a magnetic core-shell structure and is specially used for exchange reaction between methyl stearate and glyceride to prepare glycerin monostearate. The magnetic core center of the catalyst is ferrocobalt spinel, the shell component is rehydrated bimetal hydrotalcite or trimetal hydrotalcite with a lamellar structure and the structure conforms to the general formula [M<2+>xAl<3+>y(OH)2] [OH<->]2x+3y-2.mH2O, wherein M<2+> is one or two of divalent metals such as magnesium, zinc, calcium, copper and nickel; x:y is (2:1)-(4:1); x is 3-8; and y is 1-3. The solid catalyst is efficient and nontoxic, is environment-friendly and has good effect of separation from the product after reaction.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Preparation method of low-calorie functional fat
ActiveCN102191285ADetermine the processDetermine parametersFermentationLipid formationReaction temperature
The invention relates to a preparation method of low-calorie functional fat, belonging to the research field of functional lipid. The method comprises the following steps: tributyrin and methyl stearate are used as raw materials and 1,3-specific Lipozyme RMIM is used as catalyst to perform ester exchange reaction under the conditions of reduced pressure, heating and rotating, cooling, dissolving and centrifuging are performed after some time to remove enzyme, and rotary steaming is performed to obtain the low-calorie functional fat. The conversion rate of methyl stearate in the reaction product, the content of low-calorie functional fat (SSL and LLS) and the content of the unexpected product glycol tristearate are used as indexes and the factors such as reaction time, substrate molar ratio, the additive amount of enzyme and reaction temperature are optimized to determine the preparation technology. The method lays foundations for the regulations of the short carbon chains and long-carbon-chain fatty acid of triglyceride and the construction of the low-calorie functional fat processing technology which can meet different demands on processability.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
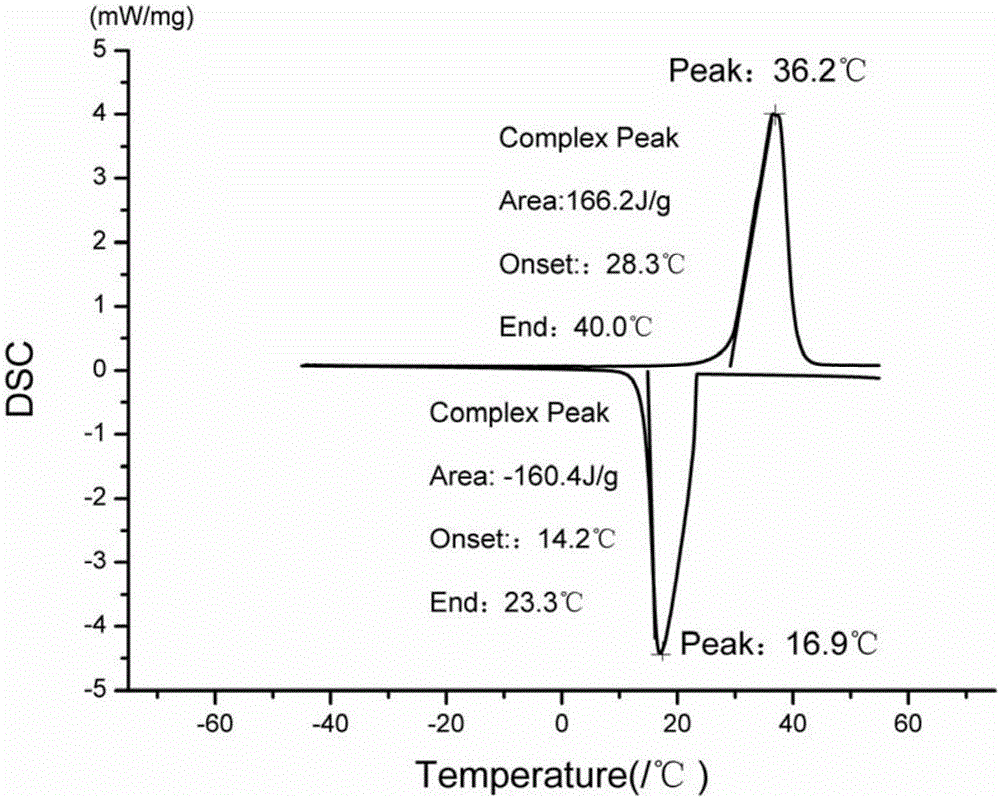
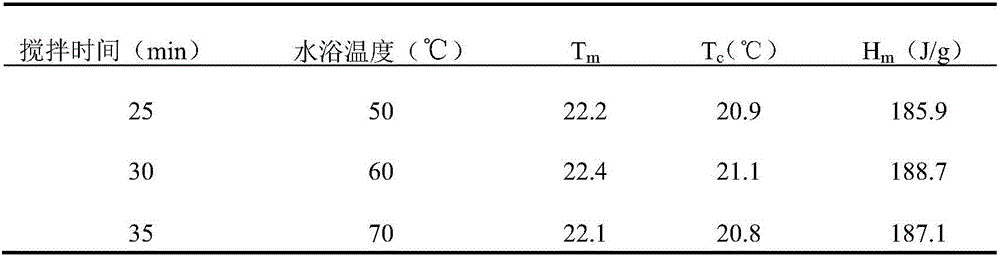
Methyl hexadecanoate-methyl stearate composite phase-change energy-storage material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of a methyl hexadecanoate-methyl stearate composite phase-change energy-storage material. The preparation method of the methyl hexadecanoate-methyl stearate composite phase-change energy-storage material comprises the following steps that methyl hexadecanoate and methyl stearate are added to a reaction container according to the mass ratio of one fourth to four, the mixture is heated in a thermostatic water bath and stirred for 25-35 min, the mixture is then cooled to the indoor temperature, and then the methyl hexadecanoate-methyl stearate composite phase-change energy-storage material is obtained, wherein the temperature of the thermostatic water bath is set to be 50-70 DEG C. According to the preparation method of the methyl hexadecanoate-methyl stearate composite phase-change energy-storage material, the phase change material has the advantages that the phase change latent heat is high, the volume change in the phase change process is small, the surface temperature fluctuation is low, the phase change material is well fused with a building material and low in cost, and the phase change temperature of the phase change material is closest to the indoor and outdoor optimum temperatures, and the advantages of the phase change material are utilized for synthesis of the composite phase-change energy-storage material; and the phase change temperature of the composite phase-change energy-storage material is obviously lower than a single phase change material, the comfortable state that the indoor temperature gradient is lowered to be smaller than 5 DEG C can be achieved, the service efficiency of an air conditioner is improved, and energy is saved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Temperature sensitive ink
The invention discloses temperature sensitive ink, which is suitable for offset printing or flexography on a rotary press. The temperature sensitive ink consists of following three parts by weight percent: totally about 48 percent of petroleum resin (large amount), paraffin (small amount) and pigment (trace amount), totally about 41 percent of methyl stearate (large amount), methyl palmitate (small amount) and 2, 6-ditertiary butyl-p-hydroxytoluene (trace amount), and totally about 11 percent of methylbenzene and dimethylbenzene. If necessary, about 3 percent of fluorescent powder can be added. By adopting the special formula, the ink is suitable for offset printing or flexography on the rotary press on which common temperature sensitive ink cannot be used. Moreover, the ink has the temperature sensitive color changing function or not only the temperature sensitive color changing function but also the fluorescence detection function.
Owner:吴月梅
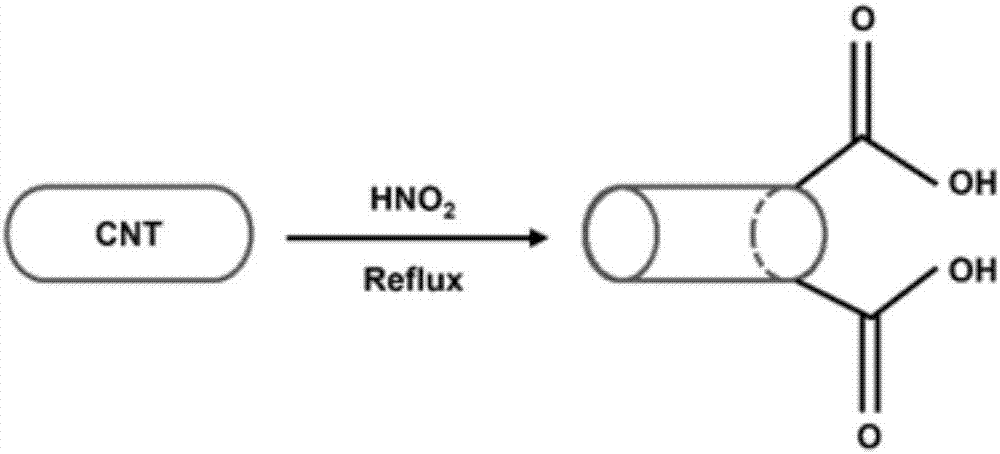
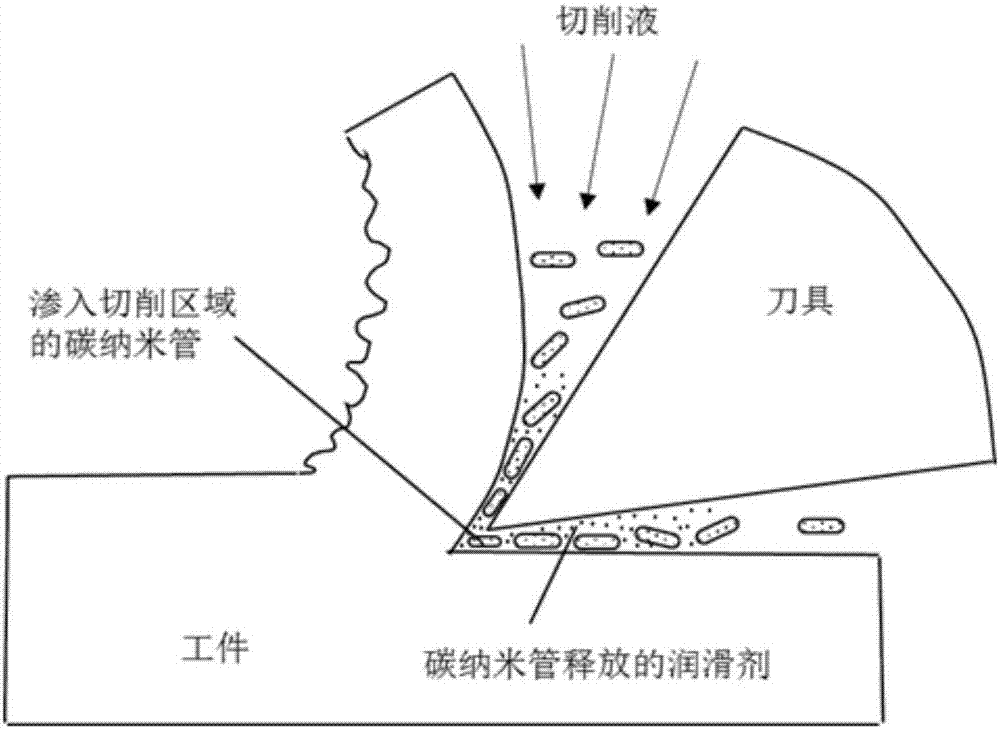
Water-based nano-fluid cutting fluid prepared via adding of carbon nanotube compound, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107353990AImprove thermal conductivityImprove dispersion stabilityLubricant compositionSolubilityWater based
The invention belongs to the technical field of cutting fluid, and discloses a water-based nano-fluid cutting fluid prepared via adding of a carbon nanotube compound, and a preparation method thereof. The water-based nano-fluid cutting fluid comprises, by mass, 0.5 to 2% of the carbon nanotube compound, 1 to 2% of methyl stearate, 0.5% of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, 0.5% of OP-10, 1 to 2% of sodium benzoate, 0.5% of 2-n-octy1-4-isothiazoline-3-one, 1% of triethanolamine, 0.1 to 0.5% of disodium ethylene diamine tetraacetate, and the balance deionized water. The carbon nanotube compound is a one-dimensional nanocomposite prepared via adding a lubricant additive into the cavity of carbon nanotube obtained via acidifying treatment. According to the preparation method, the carbon nanotube compound is taken as an additive of the water-based nano-fluid cutting fluid, so that cutting fluid thermal conductivity is improved; the carbon nanotube compound possesses certain dissolvability and excellent dispersibility in the cutting fluid, so that the lubrication performance of the water-based nano-fluid cutting fluid is improved. The water-based nano-fluid cutting fluid is used for processing, workpiece quality is improved at same working conditions, cutter wearing is reduced, and cutting fluid quality is increased.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF INDAL TECH
Biosynthesis of cocoa butter improver
A cocoa butter improver (CBI) is a specific heat-resistant cocoa butter equivalent (CBE), wherein glycerol-1,3-distearate-2-oleate (SOS) having higher melting point constitutes the main component in the triglyceride composition of the CBI. In the invention, the biosynthesis of the cocoa butter improver comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out transesterification reaction preferably among SOS with a high content, and glycerol-1,2-distearate-3-oleate (SSO) and tri-stearin (SSS) with a low content in the presence of 1,3-specific lipases as a catalyst under the optimized conditions of the transesterification reaction; carrying out molecular distillation on the product obtained from the optimized transesterification reaction to remove fatty acid from the product, wherein the optimization is carried out by targeting on the heavy-phase yield and acid value; and carrying out wet fractionation on the deacidified product by using acetone, n-hexane and other solvents, wherein the conditions of fractionation are optimized by targeting on the yield of SOS-rich stearin. A large amount of stearic acid (or low-grade alcohol ester thereof) obtained through the removal of fatty acid in the molecular distillation and the palmitic components of SOO and OOO as the main triglyceride composition obtained through the follow-up fractionation are recyclable as the raw materials for the transesterification, thus improving the utilization rate of raw materials. The CBI prepared through the biosynthesis of the invention is applicable as the raw material for the production of heat-resistant chocolate in the food industry.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for extracting methyl stearate from stearoylbenzoylmethane raffinate
InactiveCN102898303AReduce energy consumptionLow costOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationDistillationMETHYL STEARATE
The invention discloses a method for extracting methyl stearate from stearoylbenzoylmethane (SBM) raffinate. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the SBM raffinate with methanol according to a volume ratio of 1: 2-6; heating an obtained mixture to a temperature of 50 to 56 DEG C under stirring and maintaining for 20 min to ensure full extraction; then cooling the mixture to a temperature of 33 to 36 DEG C under stirring and standing the mixture for layering; carrying out separation to remove a lower layer; continuing to cool an upper layer to a temperature of 10 DEG C; carrying out vacuum filtration; heating and melting a filter cake, adding 2 times volume of methanol and repeating the above-mentioned procedures of extraction, layering, separation and vacuum filtration; rinsing the filter cake twice to three times; and heating the filter cake to a temperature of 100 DEG C to remove water so as to obtain methyl stearate. According to the invention, methyl stearate is extracted from SBM raffinate by using an extractive crystallization method, methanol used twice in the extraction process can be repeatedly used after distillation, the lower layer obtained after separation can be reused as raffinate, and the advantages of small energy consumption and low cost are obtained.
Owner:ANHUI JIAXIAN FUNCTIONAL AUXILIARY
Composite ultra-thin non-woven fabric
ActiveCN102433683AWith temperature control effectEasy to adjustNon-woven fabricsMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentVanadium dioxideInfrared
The invention relates to composite ultra-thin non-woven fabric which is prepared by adopting an electrostatic spinning method. The composite ultra-thin non-woven fabric comprises three layers, namely an intermediate layer and a first surface layer and a second surface layer which are respectively located at both sides of the intermediate layer, wherein the intermediate layer is made of polyester fiber with average diameter of 760-910 nm, the polyester fiber contains a phase-change temperature-adjusting microcapsule, the phase-change microcapsule is prepared by adopting an interfacial polymerization method and taking polyurea type resin as a capsule wall, and the phase-change material contained in the microcapsules is a mixture of capric acid, lauric acid, methyl stearate and C17-C19 straight-chain paraffins. In the composite ultra-thin non-woven fabric, because the intermediate layer is prepared from the polyester fiber containing the phase-change temperature-adjusting microcapsule, the composite ultra-thin non-woven fabric has a significant temperature adjusting effect; and at the same time, the fiber adopted by the first surface layer contains nanoscale vanadium dioxide, and vanadium dioxide is an infrared sensitive material and can project or reflect infrared according to the change of environment infrared, therefore, the composite ultra-thin non-woven fabric has a temperature control effect.
Owner:JIANGSU HAINA AIR CONDITIONER PURIFICATION EQUIP
Method for preparing cocoa butter equivalent by using chemical transesterification method
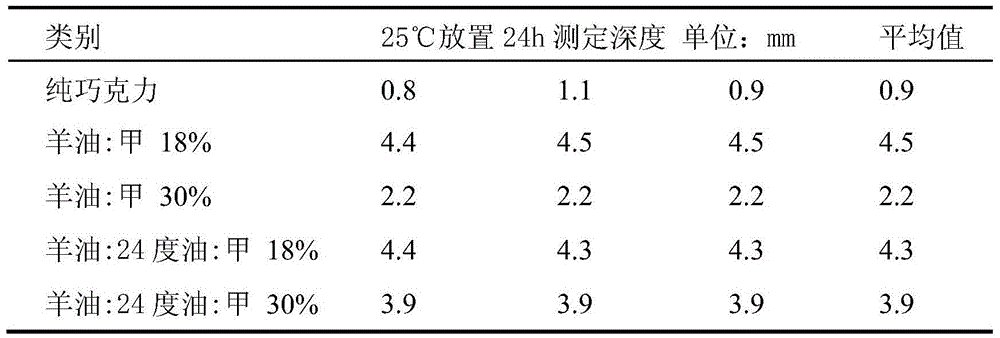
The invention discloses a method for preparing cocoa butter equivalent by using a chemical transesterification method. The method is characterized in that mutton fat and 24-degree palm oil are mixed with methyl stearate according to a certain mass ratio, and then an esterification reaction is conducted through a high-performance catalyst to prepare the cocoa butter equivalent. The cocoa butter equivalent, produced through the method, has high yield and is low in cost.
Owner:安徽康尔美油脂有限公司 +1
Cat appeasing pheromone
The present invention relates to a semiochemical composition comprising methyl palmitate, methyl linoleate, methyl oleate methyl stearate, methyl laurate, methyl myristate, salts thereof, derivatives thereof, isomers thereof and / or structural analogues thereof that have an appeasing effect in cats and / or also effects social facilitation in cats, and an acceptable vehicle. Solutions such as spot-on formulations of long duration are also encompassed. Methods to effect appeasing in a cat and / or social facilitation in cats are also disclosed.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION CHEM & APPLIED ANIMAL BEHAVIOR
Adjuvant composition with pesticide synergistic function
InactiveCN101371659AConvenient sourceNo pollution in the processBiocideAnimal repellantsOctadecadienoic AcidMETHYL STEARATE
The invention provides a additive combination with synergism function of pesticide, the combination comprises the following components by weight percentage: 10 to 20 percent of methyl hexadecanoate, 5 to 10 percent of methyl stearate, 20-40 percent of 9-cis-octadecenoic acid methyl ester, 20 to 40 percent of 9, 12-cis-octadecadienoic acid methyl ester, 10 to 20 percent of 9-cis-11-trans-13-trans-jecoric acid methyl ester, 10 to 20 percent of benzene ethylphenol polyoxyethylene ether, 1 to 5 percent of calcium alkyl benzene sulfonate. The additive combination with synergism function of pesticide has the advantages of convenient raw material source, no pollution to environment, convenient preparation and application, and herbicidal efficacy of herbicide can be improved significantly.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
Atrazine herbicidal composition containing pesticide builder
The invention discloses an atrazine weedicide composite containing effective adjuvant for farm insecticides, and the composite is formed by the components by volume proportion of 100 portions of atrazine aqueous suspending agent diluents and 0.05-0.5 portion of effective adjuvant, wherein, the atrazine aqueous suspending agent diluents are formed by diluting atrazine weedicide of 38% weight content in water into 200-300 times of volume; the effective adjuvant is composed of the following components by weight percentage: 10-20% of methyl hexadecanoate, 5-10% of methyl stearate, 20-40% of 9-cis-methyl-6-octadecenoate, 20-40% of 9-cis, 12-cis-octadecadienoic acid methyl ester, 10-20%of 9-cis-11-trans-13-trans-octadecadienoic acid methyl ester, 10-20% of benzene ethylphenol polyoxyethylene ether and 1-5% of calcium alkylbenzene sulfonate. The composite has the advantages of available raw materials, no environmental pollution, convenient preparation and easy application, can obviously enhance the efficacy of the atrazine weedicide, and has great application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
Nicosulfuron herbicidal composition containing pesticide builder
InactiveCN101371664AImprove efficacyConvenient sourceBiocideAnimal repellantsAdjuvantSuspending Agents
The invention relates to a nicosulfuron weedicide composite which contains effective adjuvant for farm insecticides and is prepared by the components by volume proportion of 100 portions of nicosulfuron suspending agent diluents and 0.05-0.5 portion of effective adjuvant, wherein, the nicosulfuron suspending agent diluents are formed by diluting nicosulfuron weedicide the mass content of which is 4% in water into 300-1500 times of volume; the effective adjuvant contains the following components by weight percentage: 10-20% of methyl hexadecanoate, 5-10% of methyl stearate, 20-40% of 9-cis-octadecenoic acid methyl ester, 20-40% of 9-cis, 12-cis-octadecadienoic acid methyl ester, 10-20% of 9-cis-11-trans-13-trans-ecoric acid methyl ester, 10-20% of benzene ethylphenol polyoxyethylene ether and 1-5% of calcium alkylbenzene sulfonate. The composite has the advantages of available raw materials, no environmental pollution, convenient preparation and easy application, can obviously enhance the efficacy of the nicosulfuron weedicide, and has great application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com