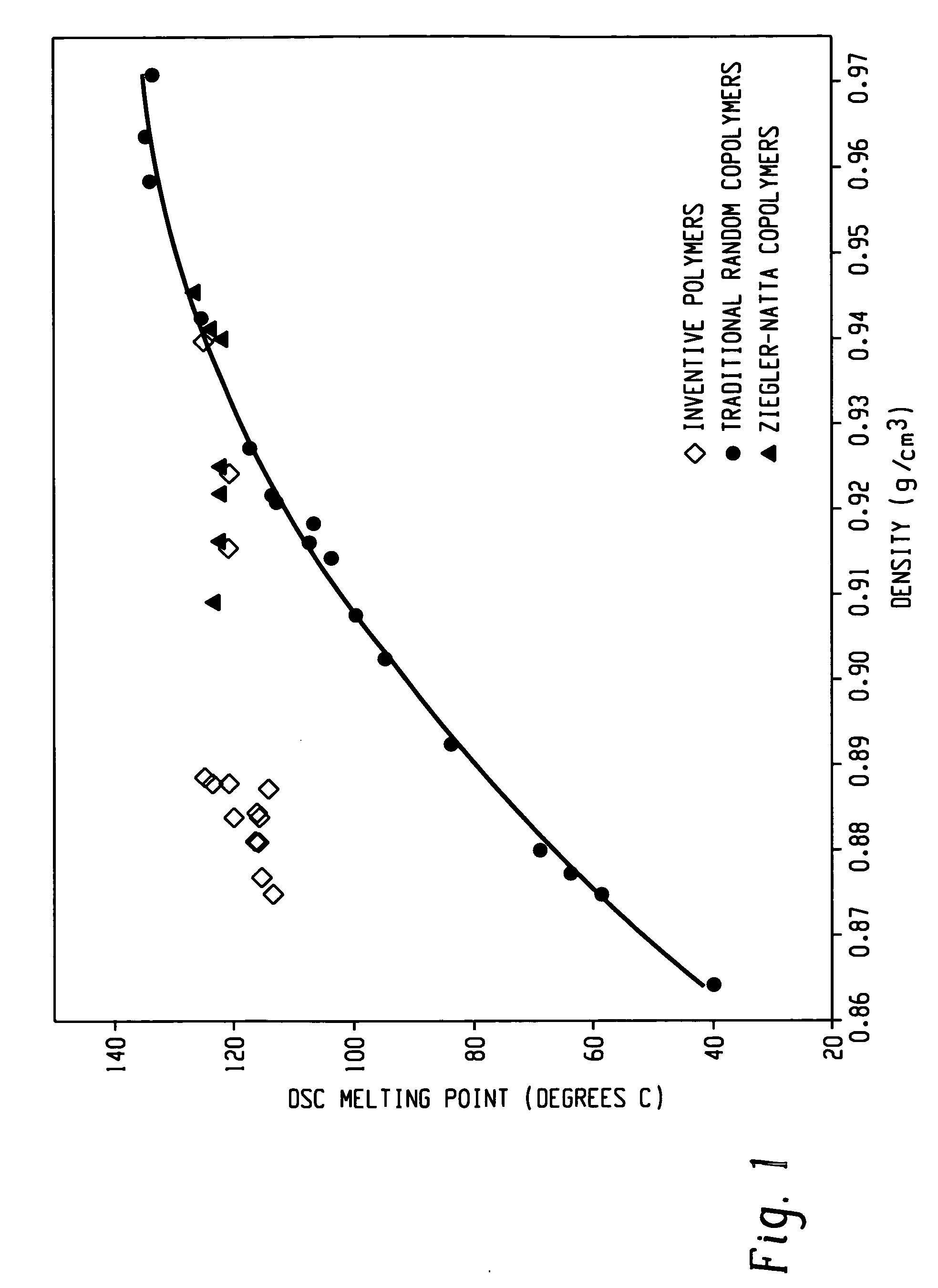
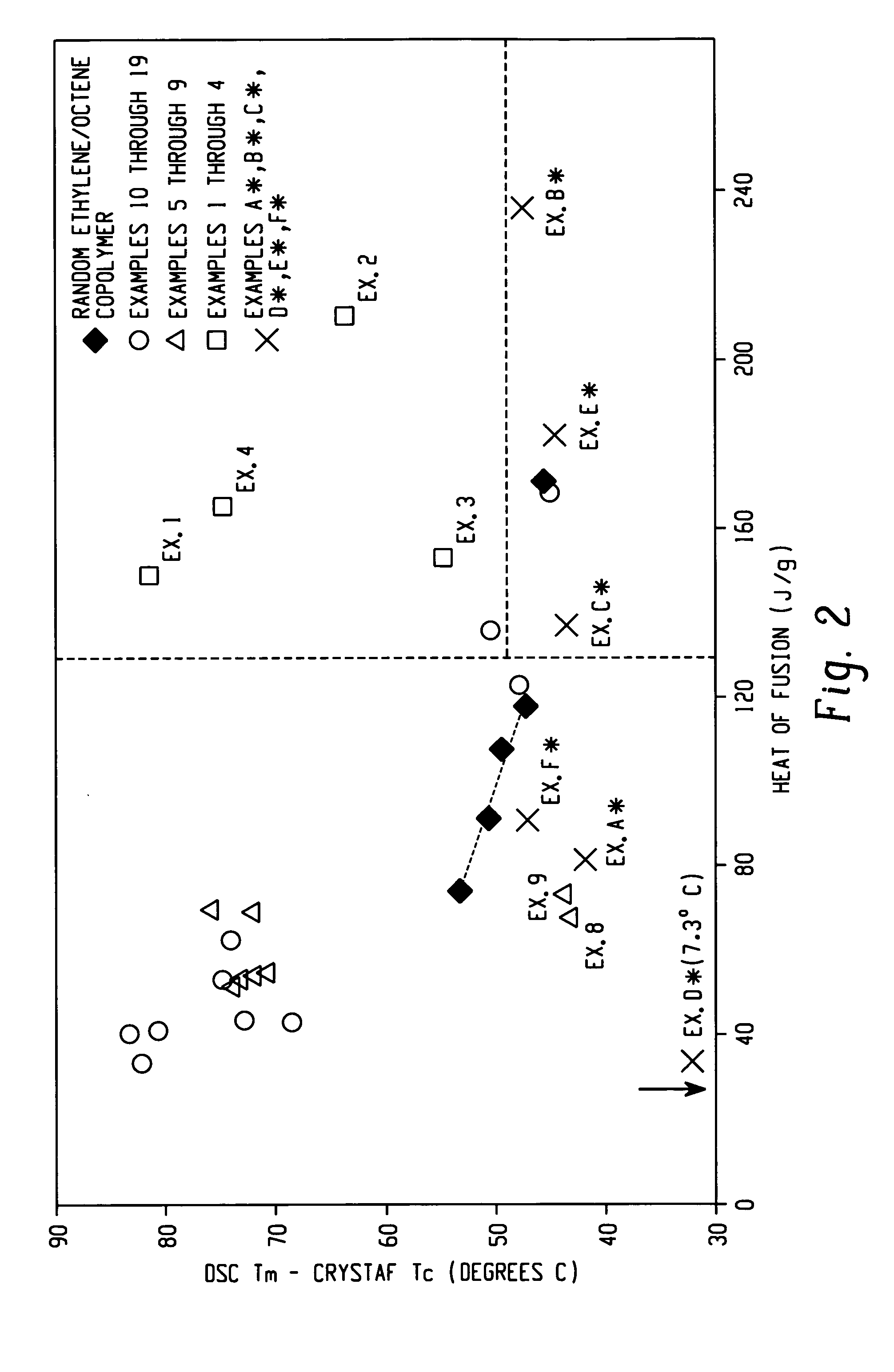
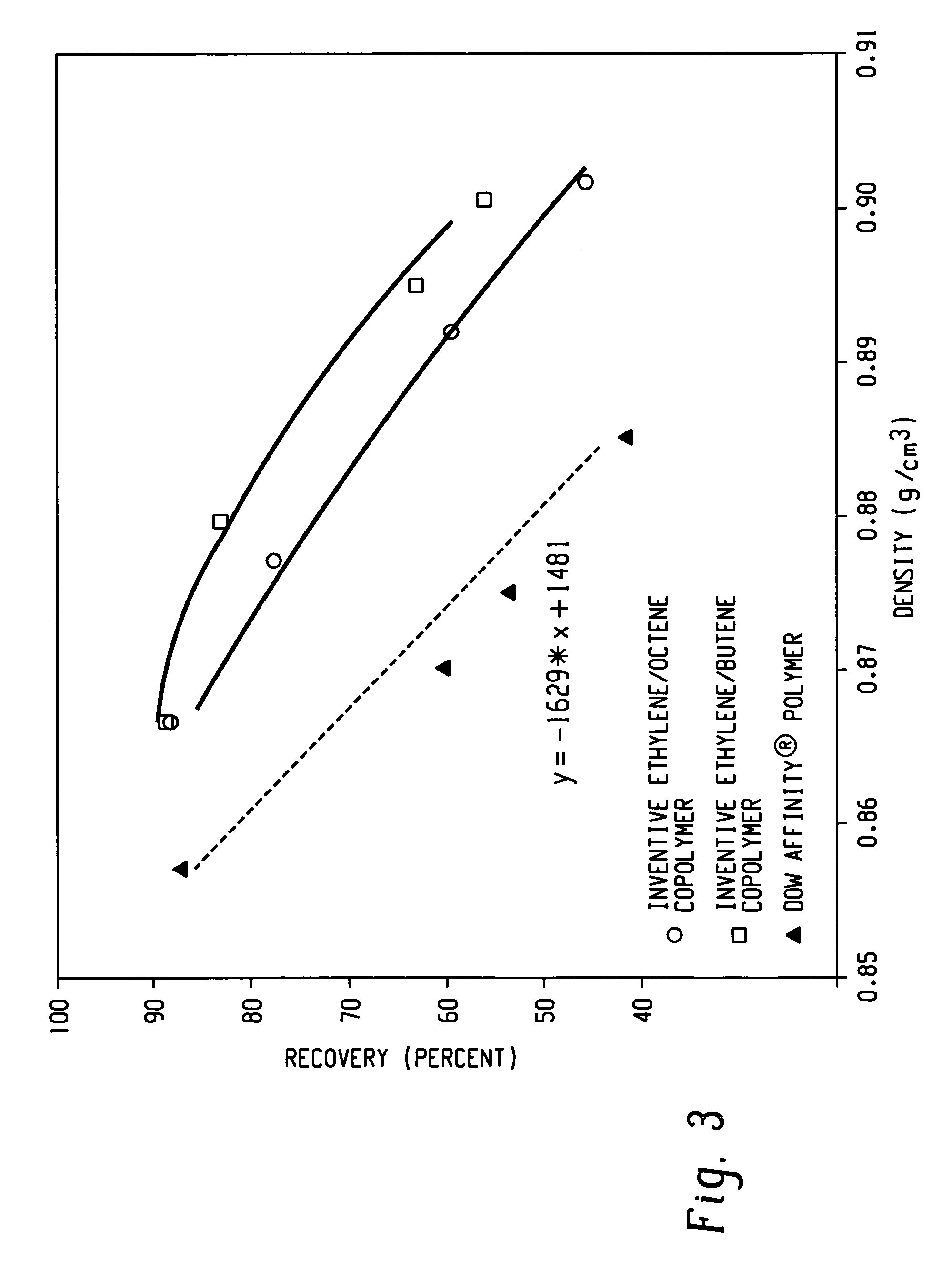
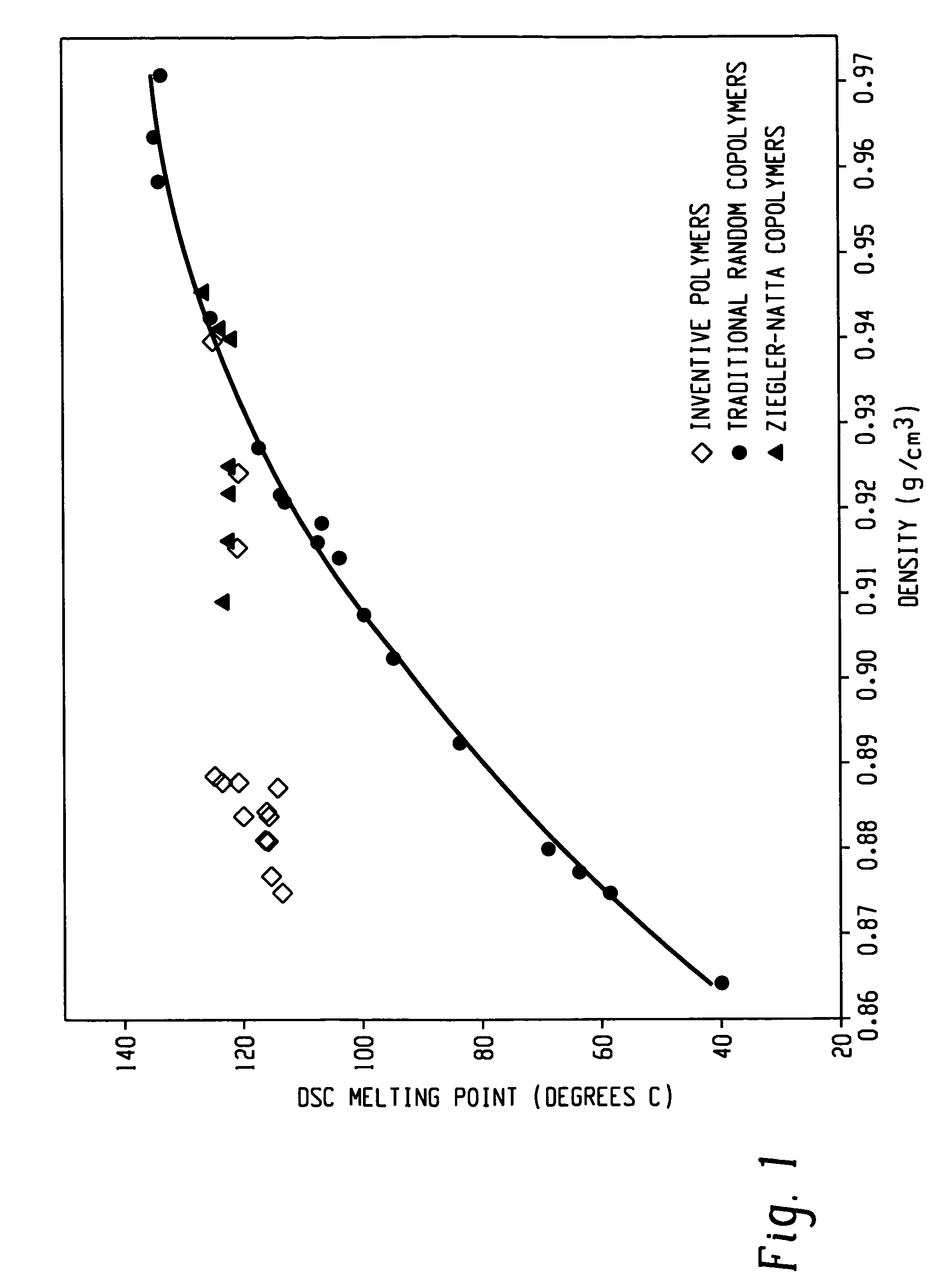
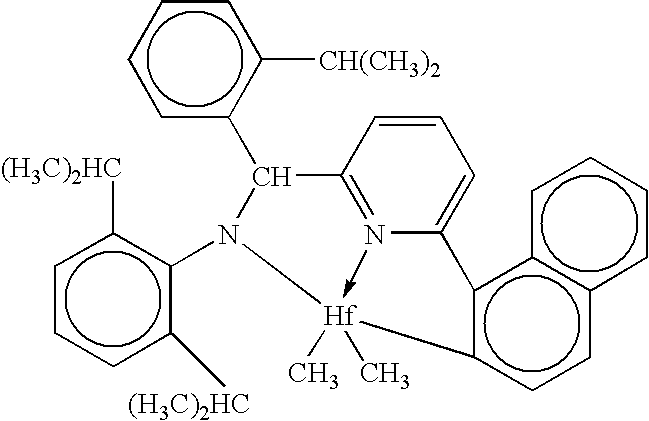
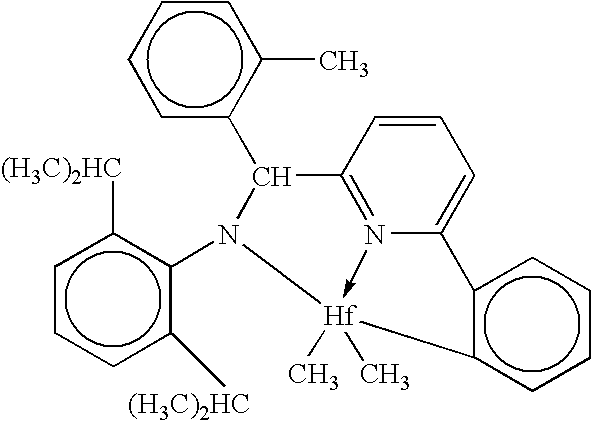
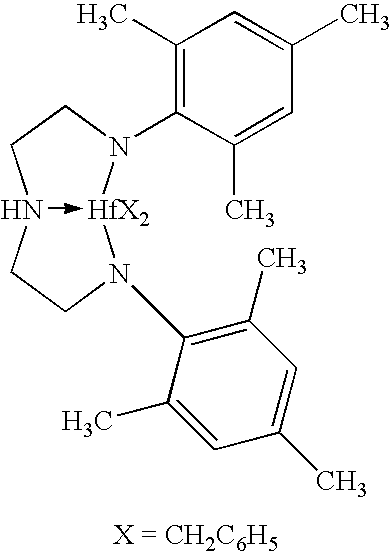
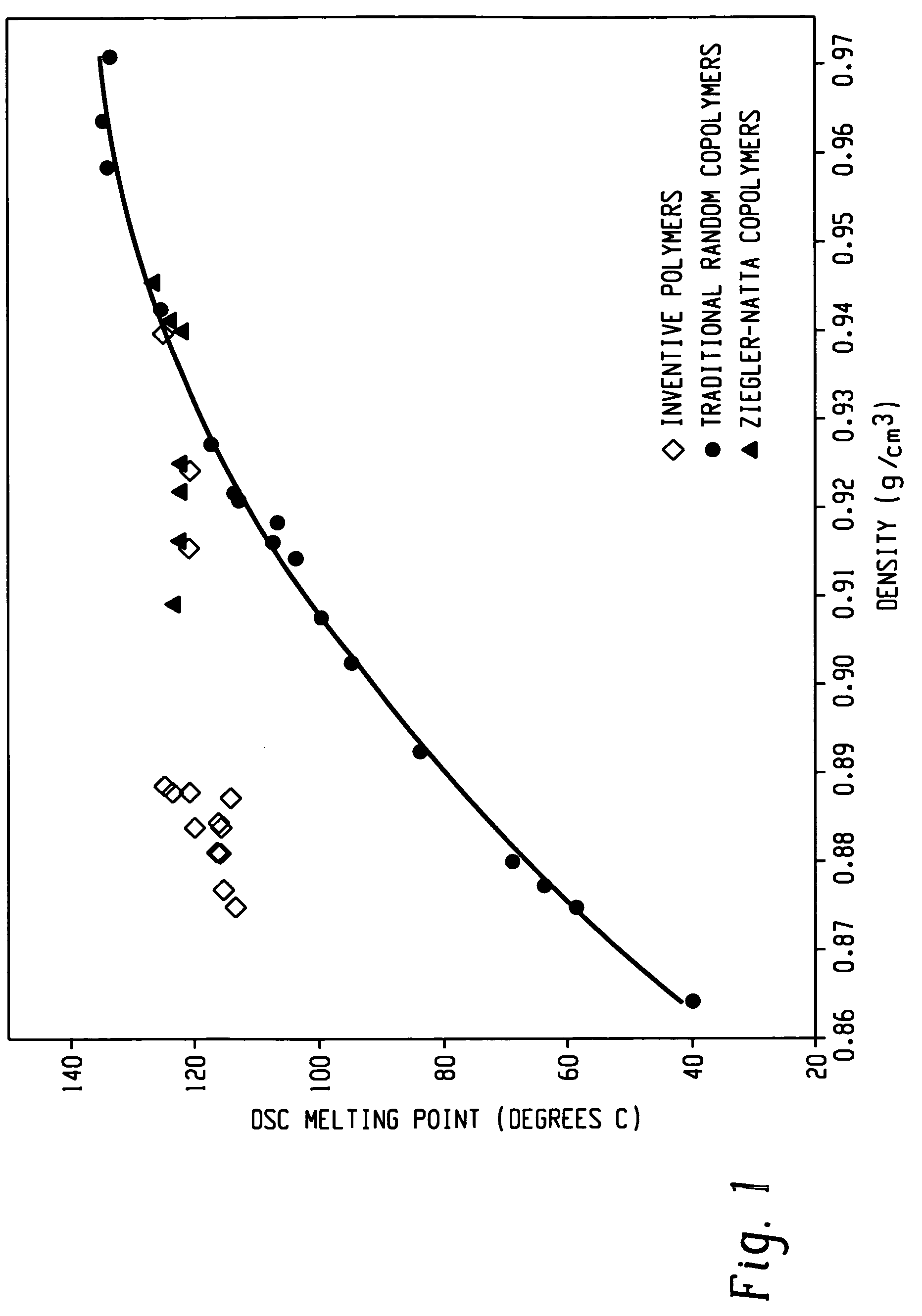
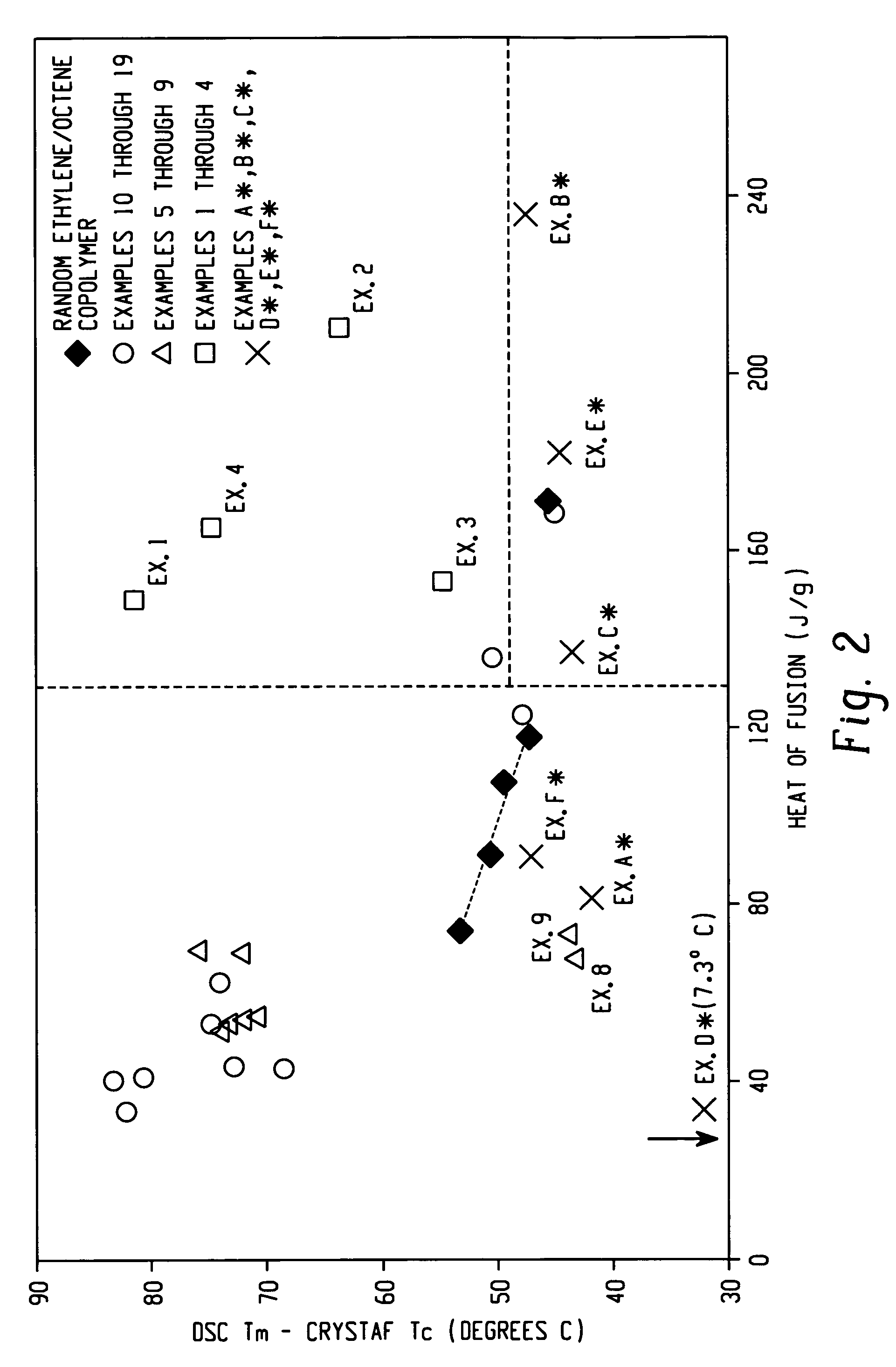
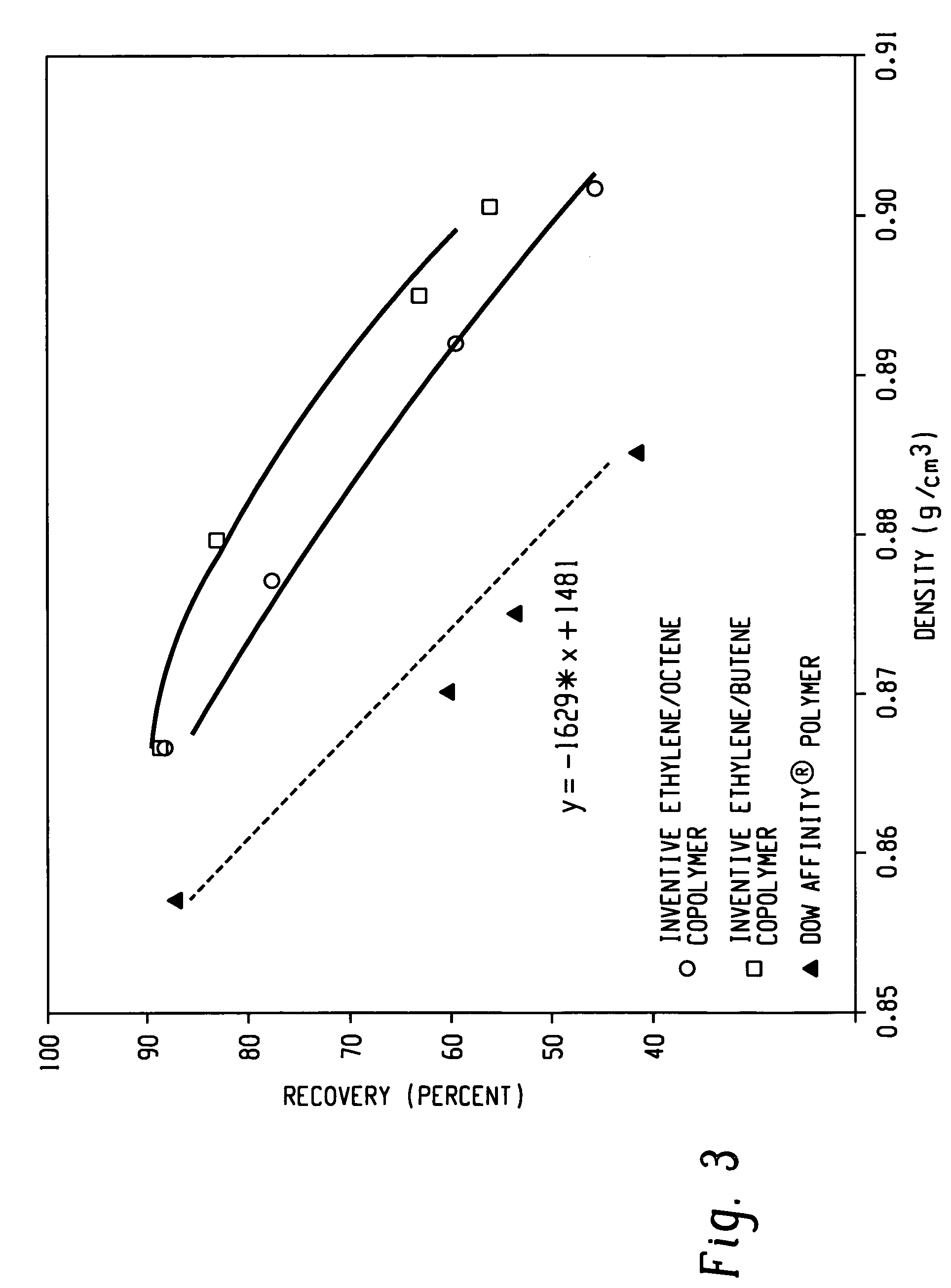
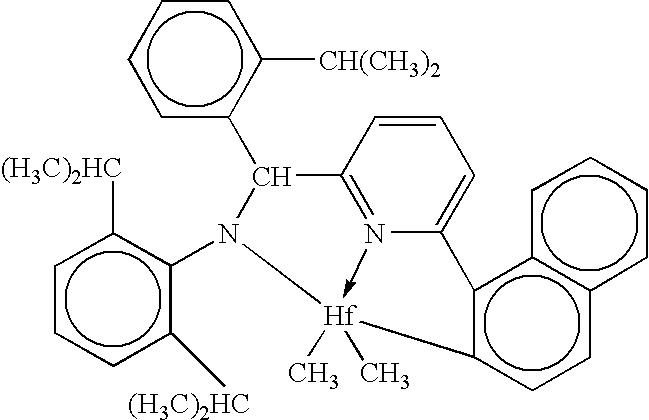
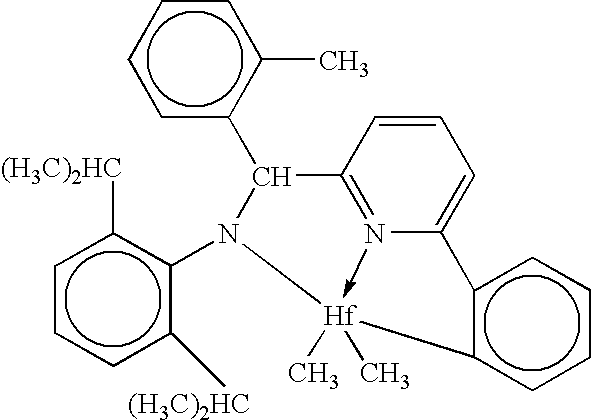
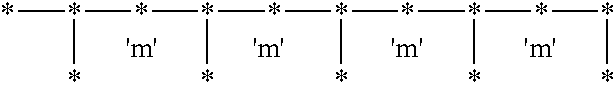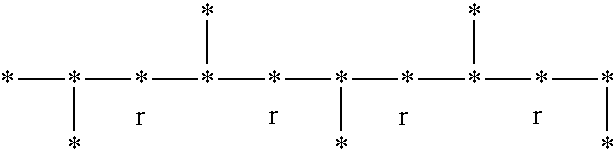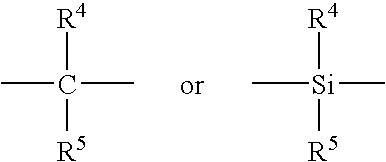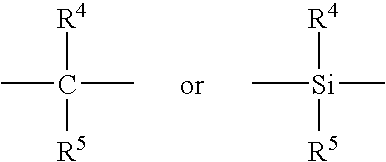Patents
Literature
4679 results about "Alpha-olefin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Alpha-olefins (or α-olefins) are a family of organic compounds which are alkenes (also known as olefins) with a chemical formula CₓH2x, distinguished by having a double bond at the primary or alpha (α) position. This location of a double bond enhances the reactivity of the compound and makes it useful for a number of applications.
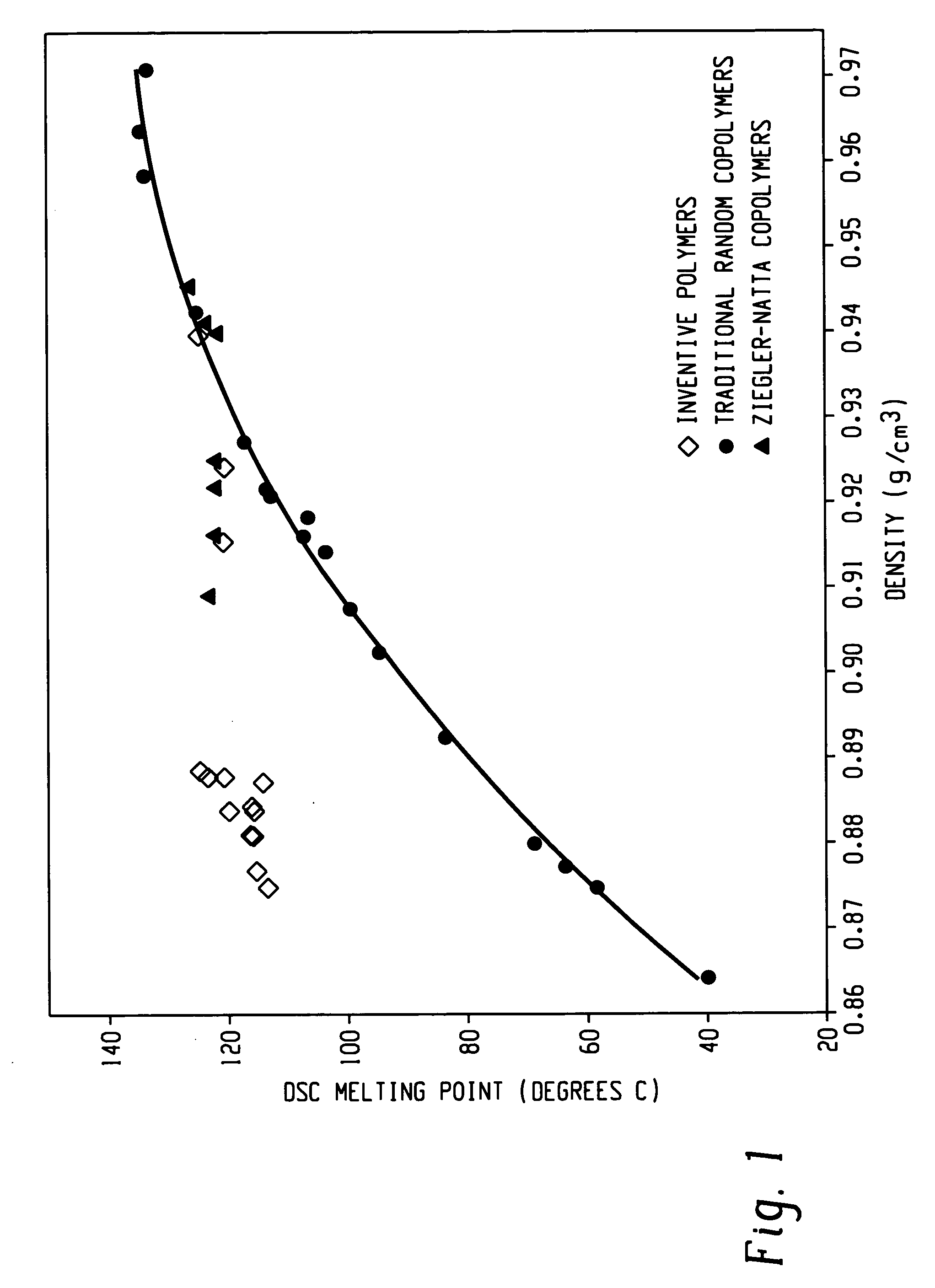
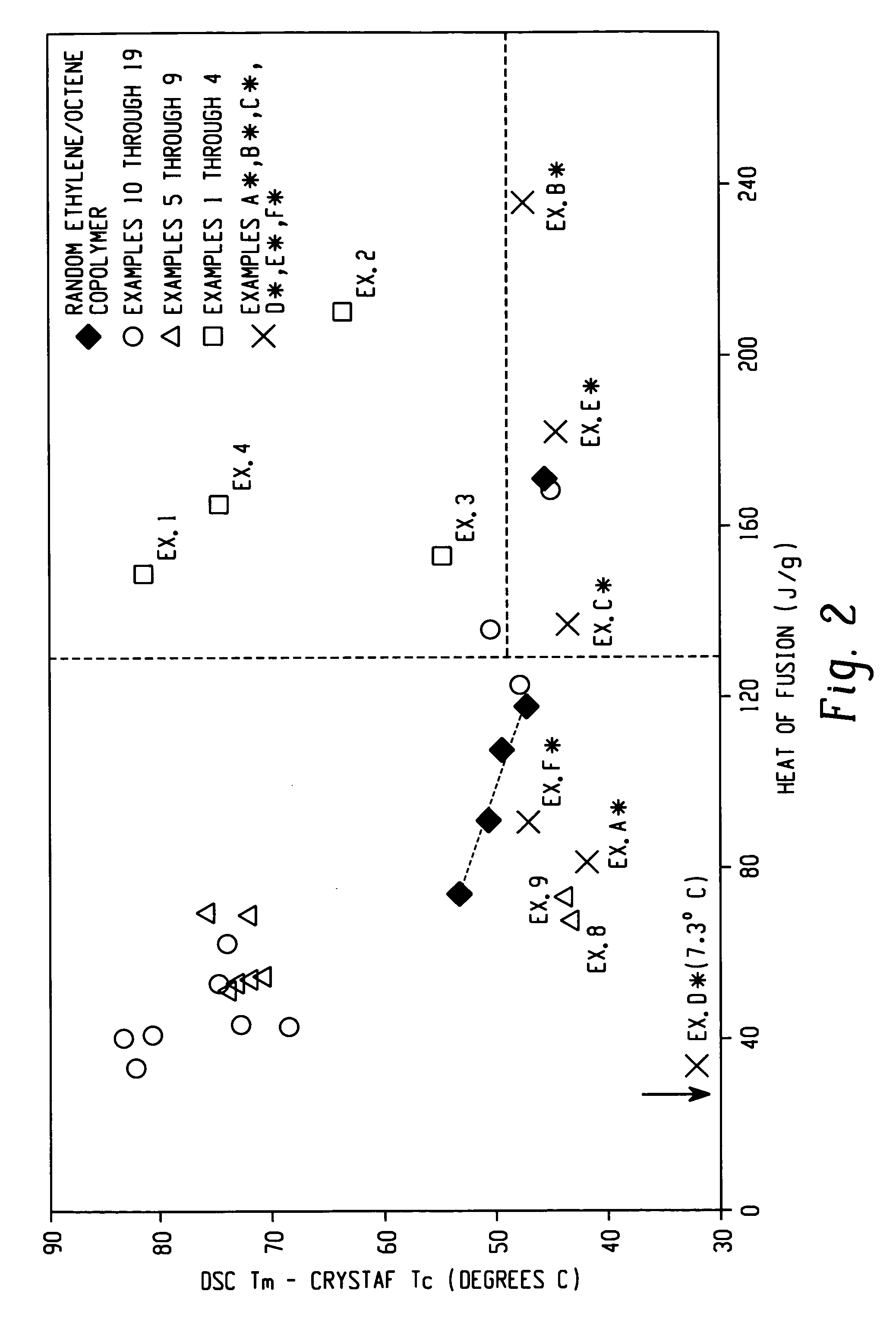
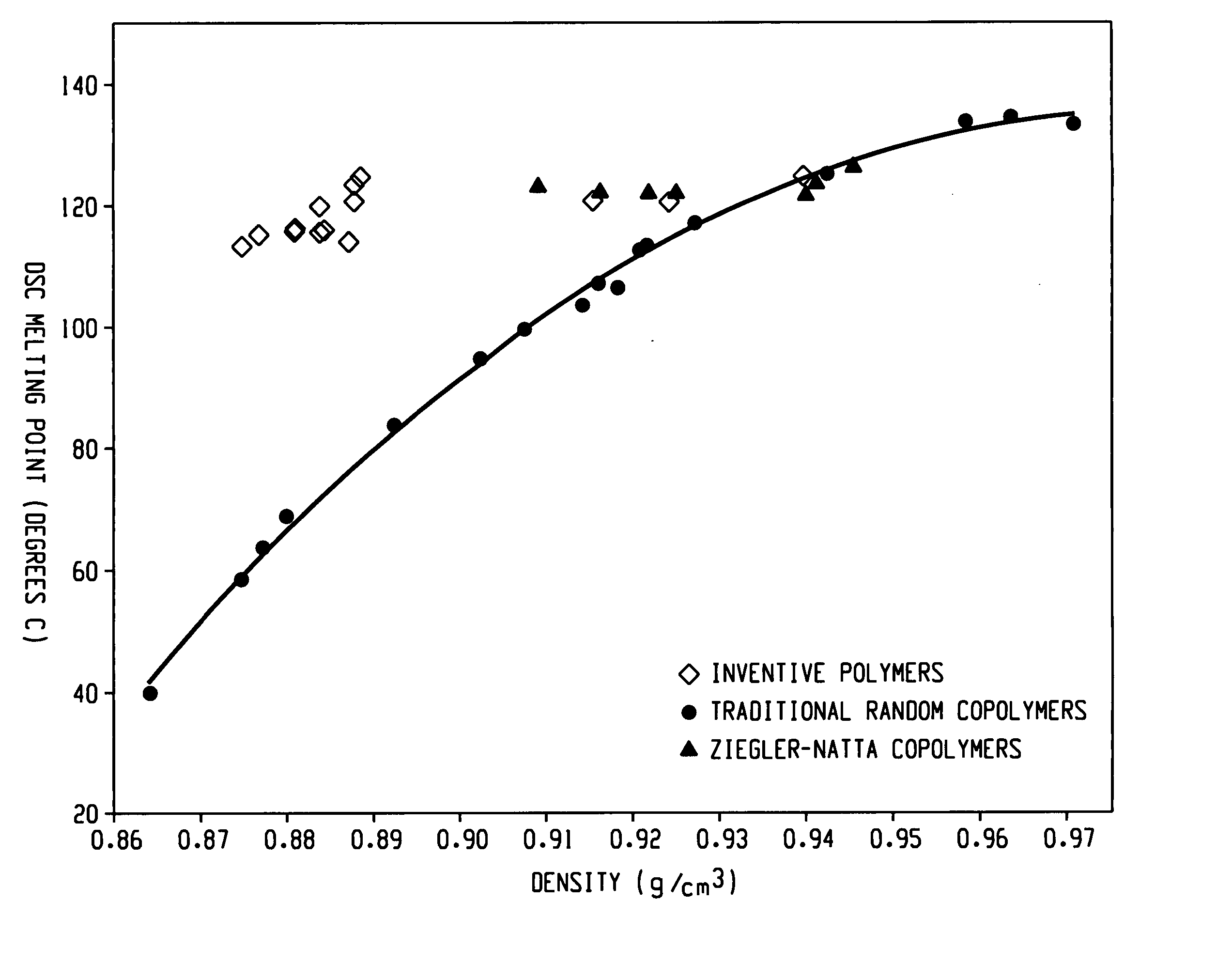
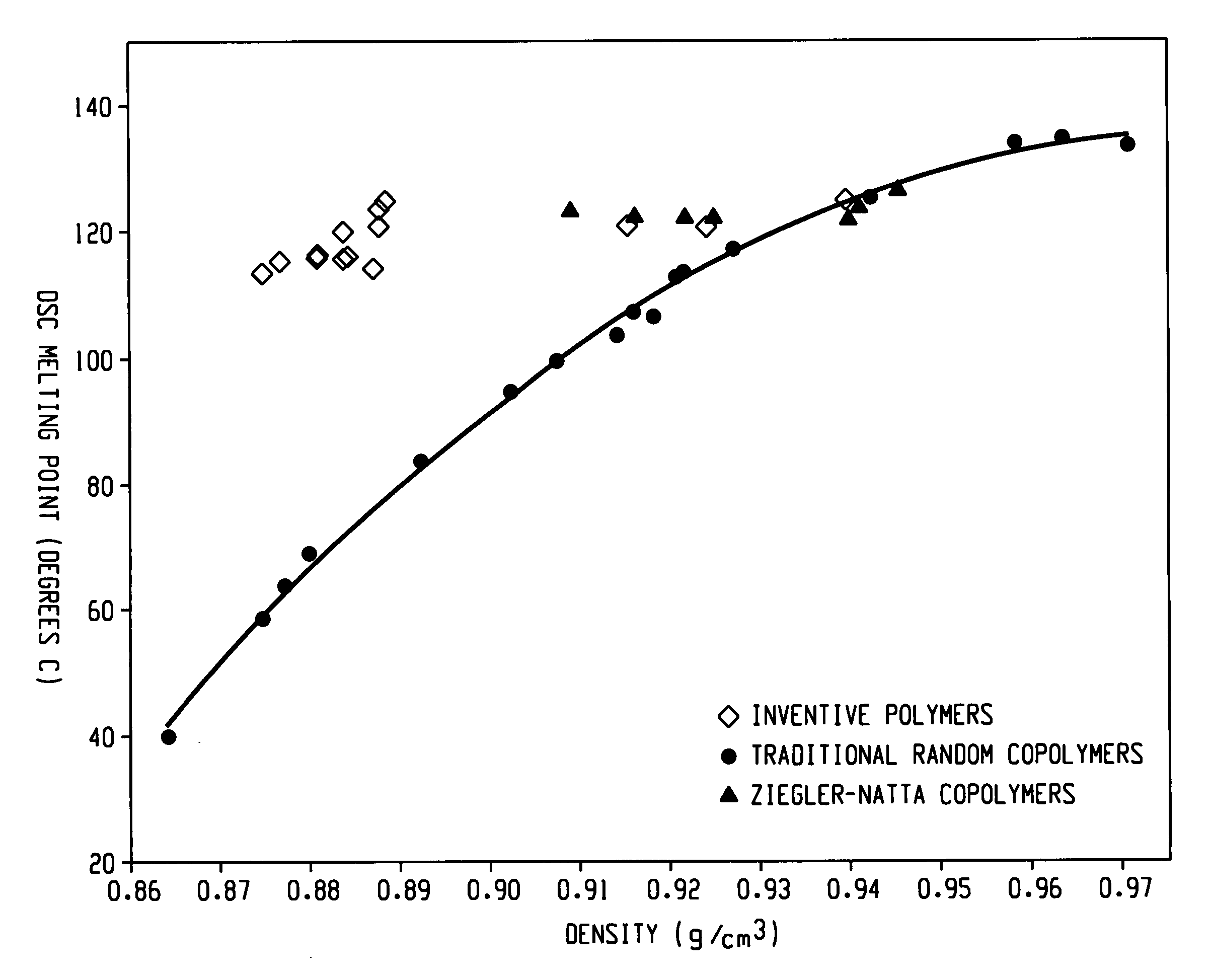
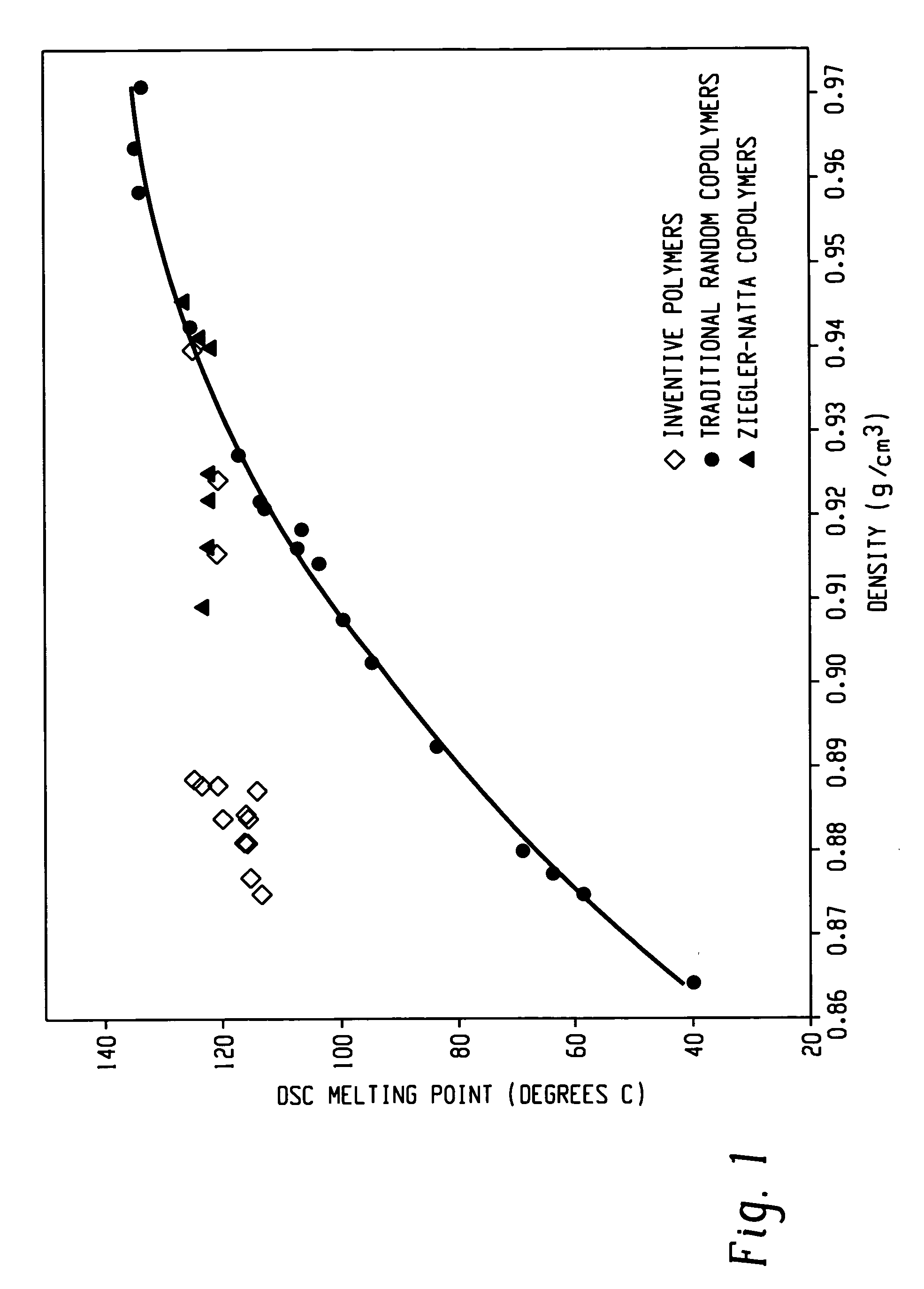
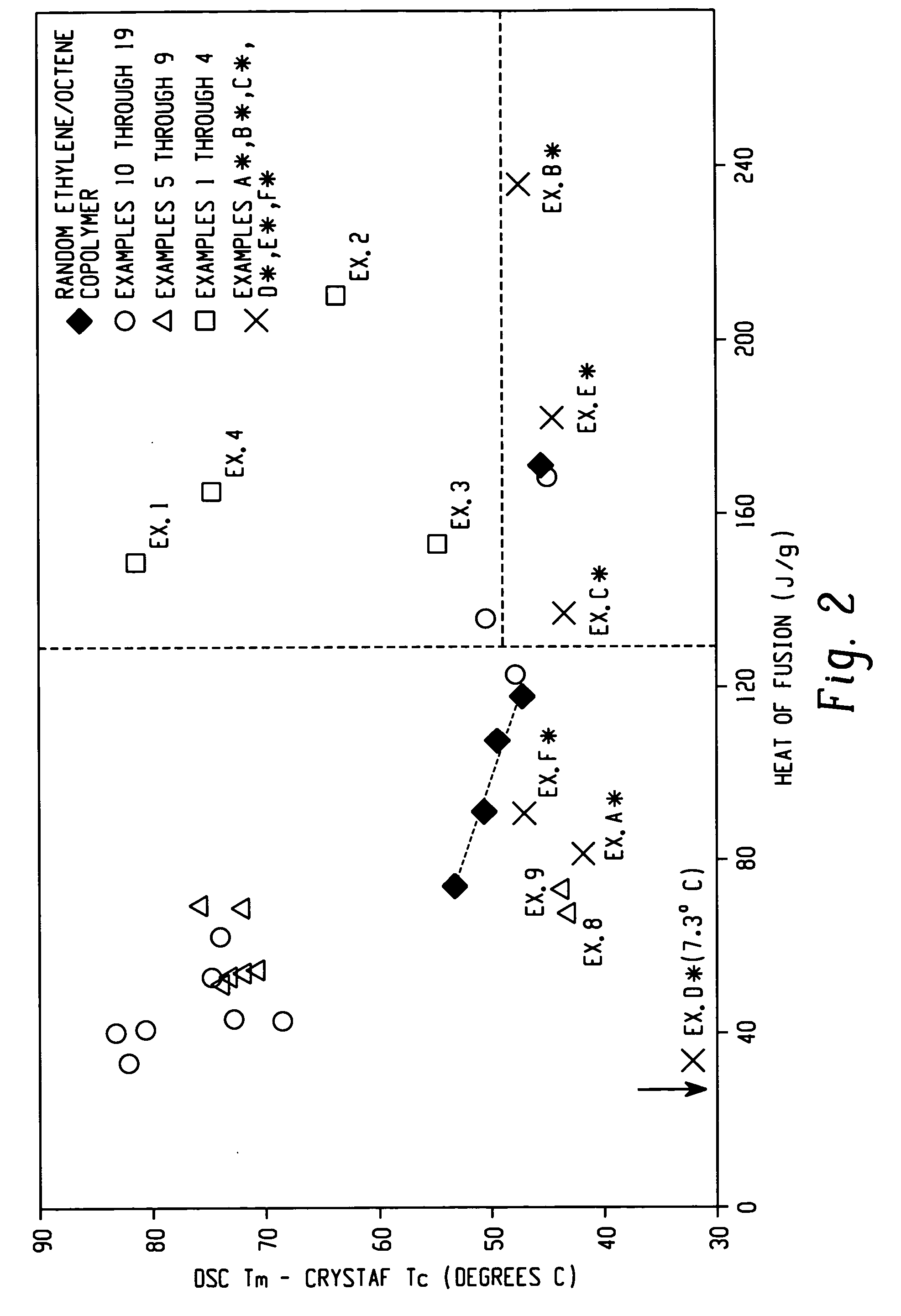
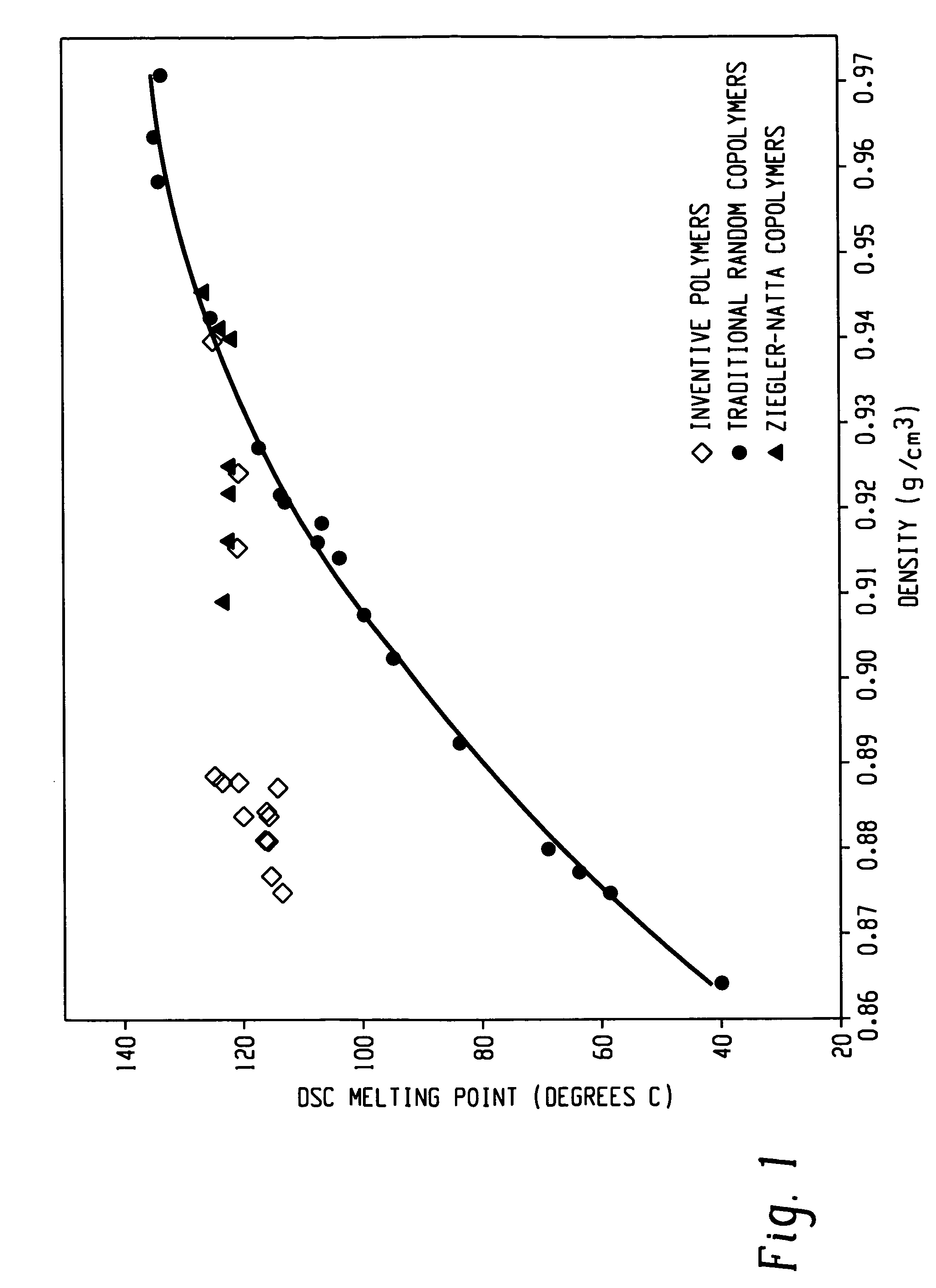
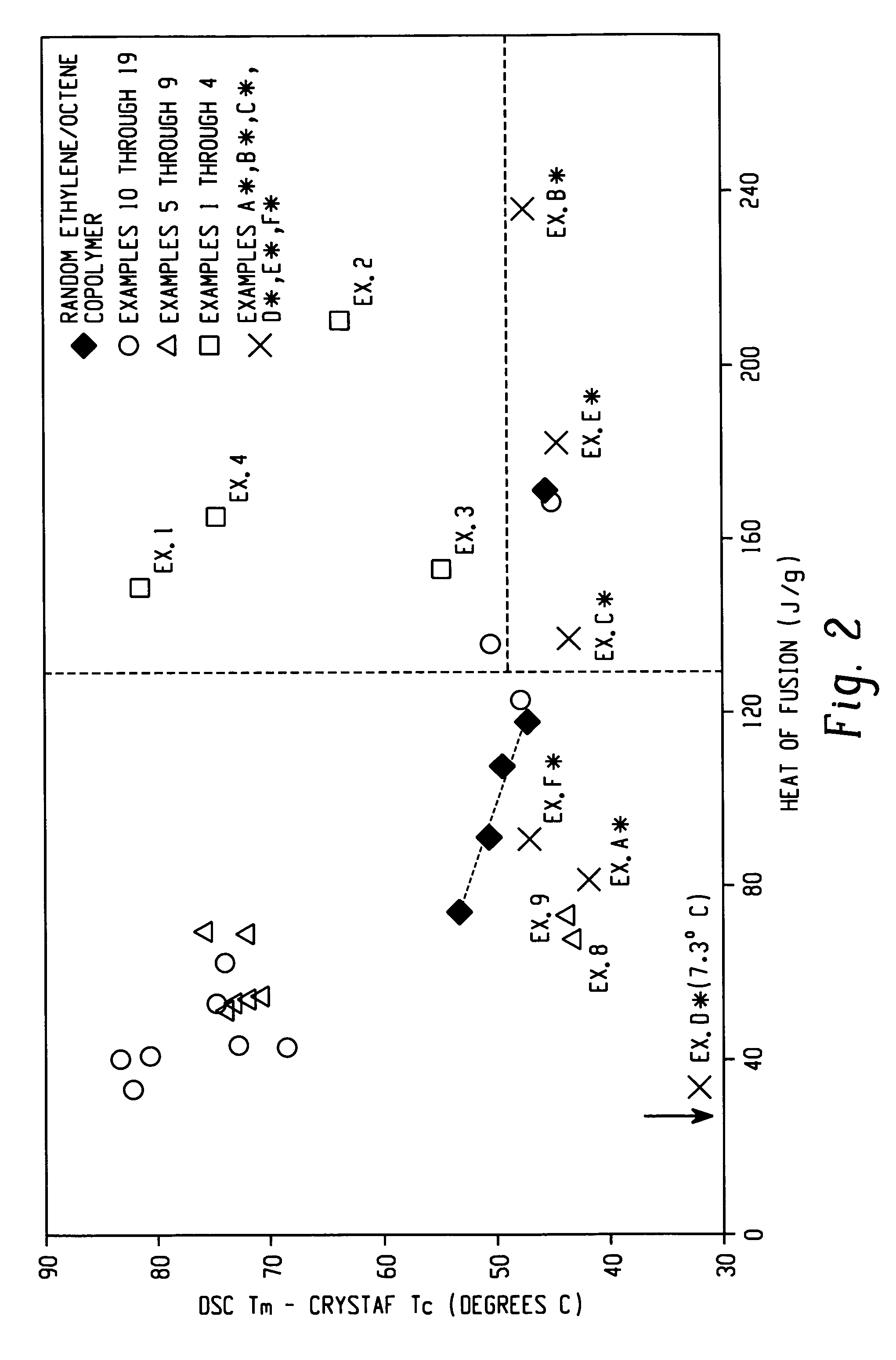
Ethylene/alpha-olefins block interpolymers
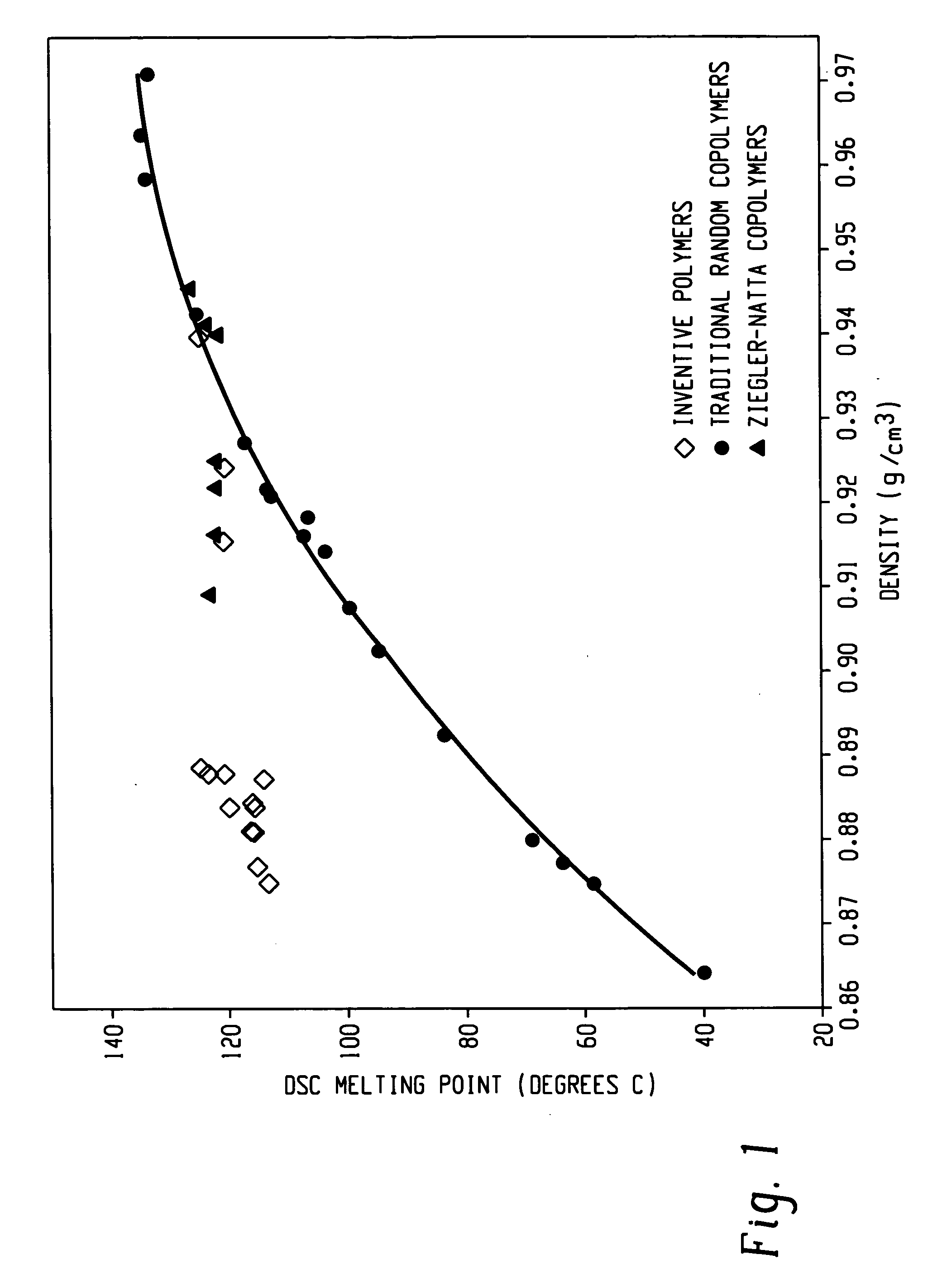
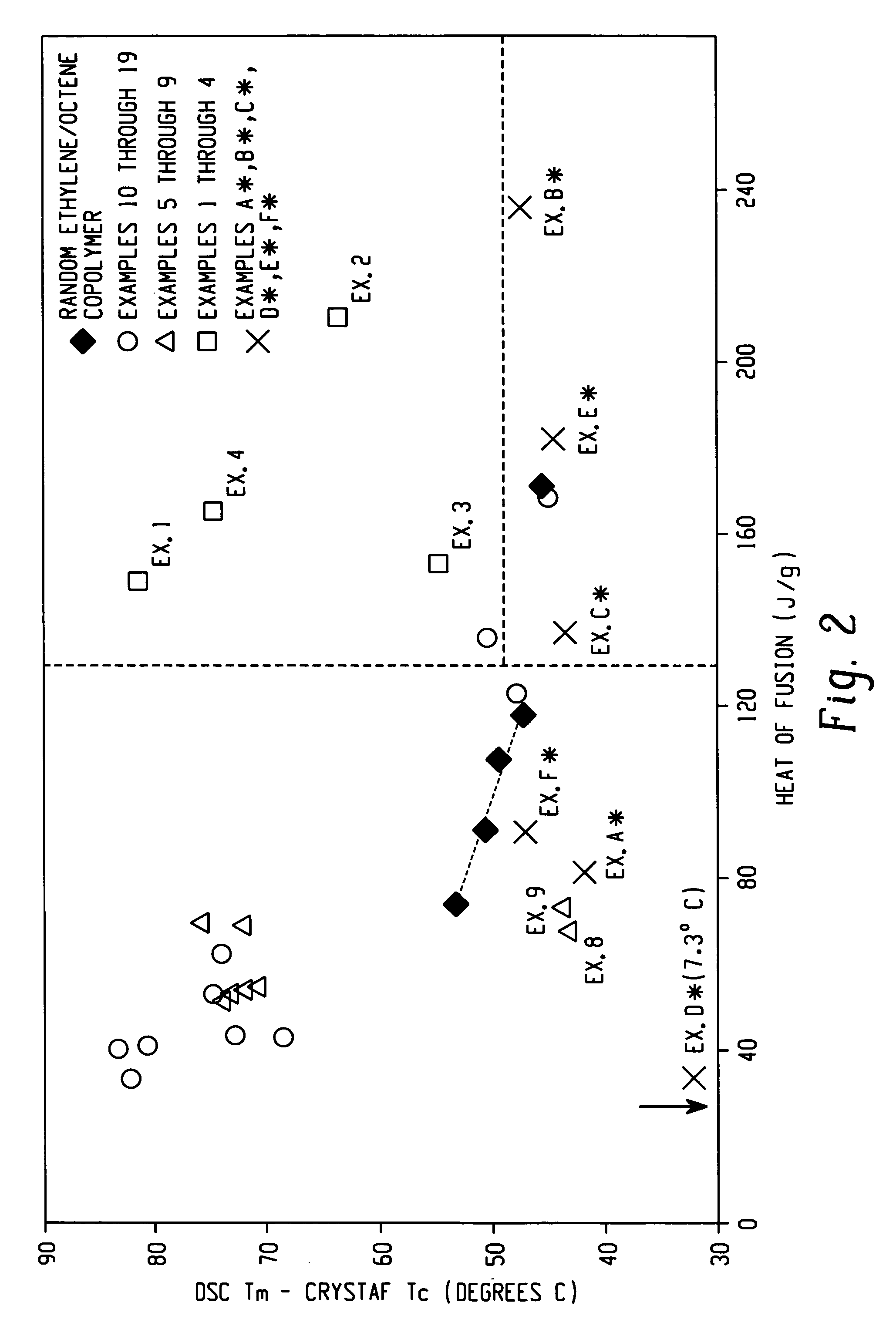
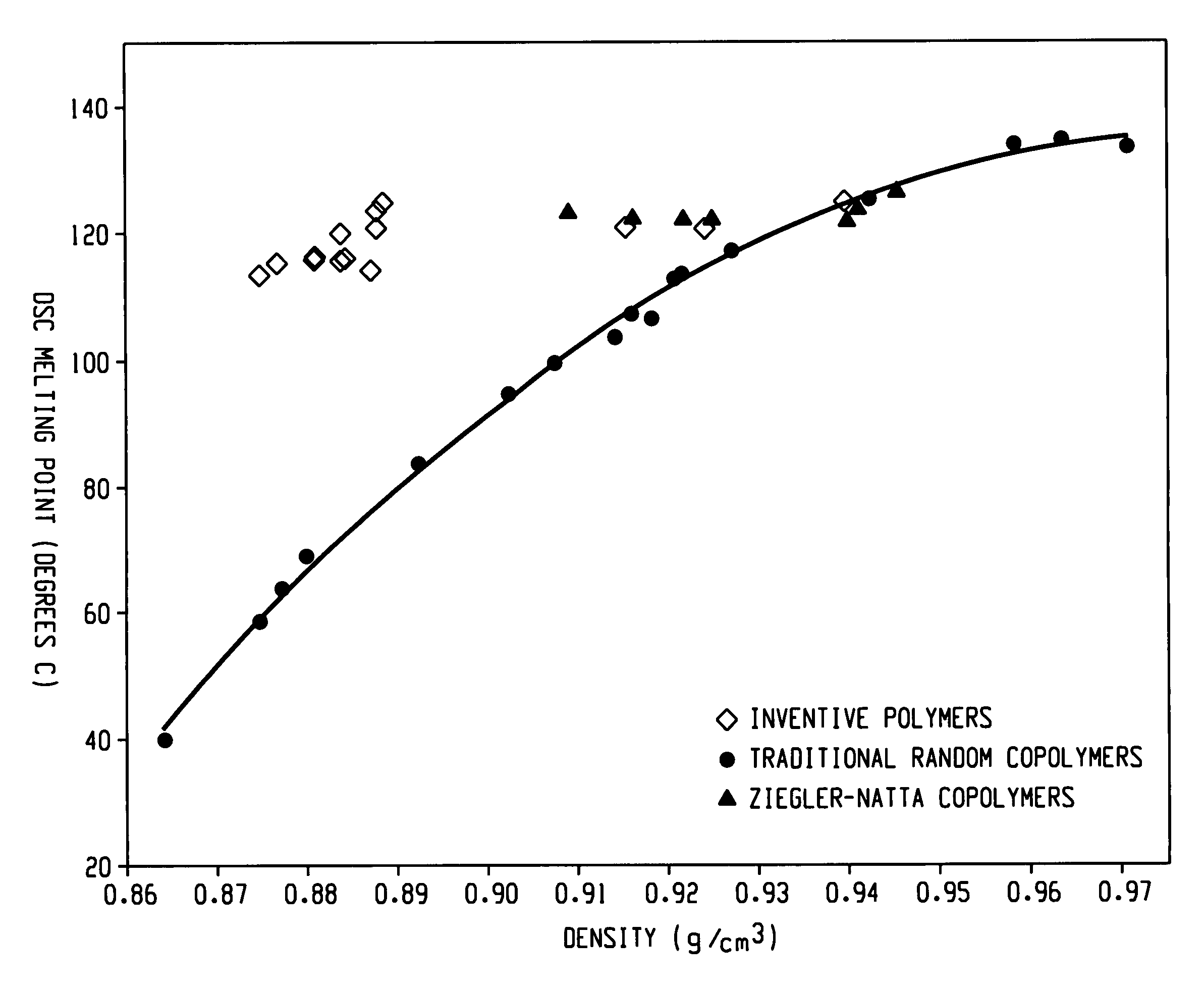
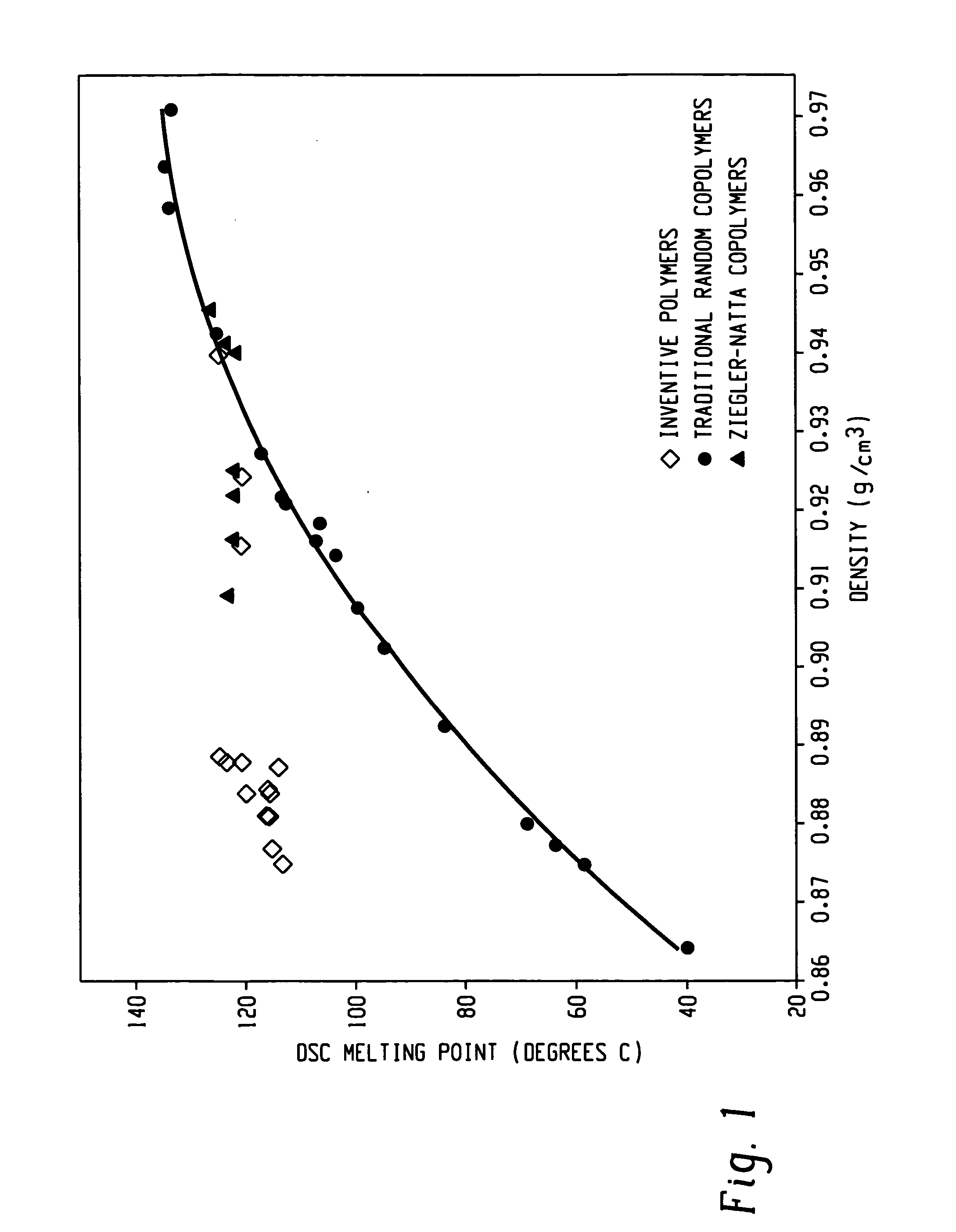
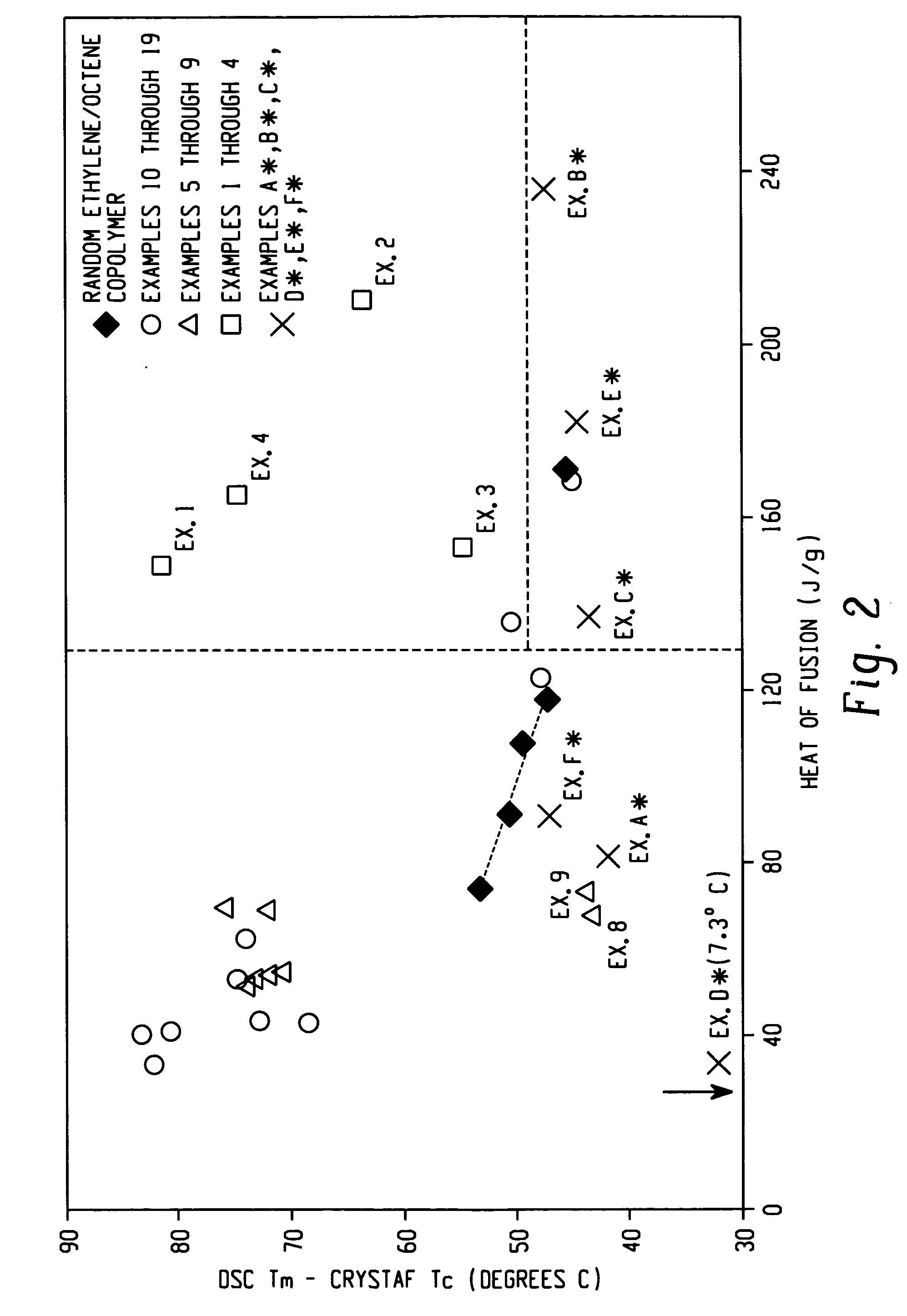
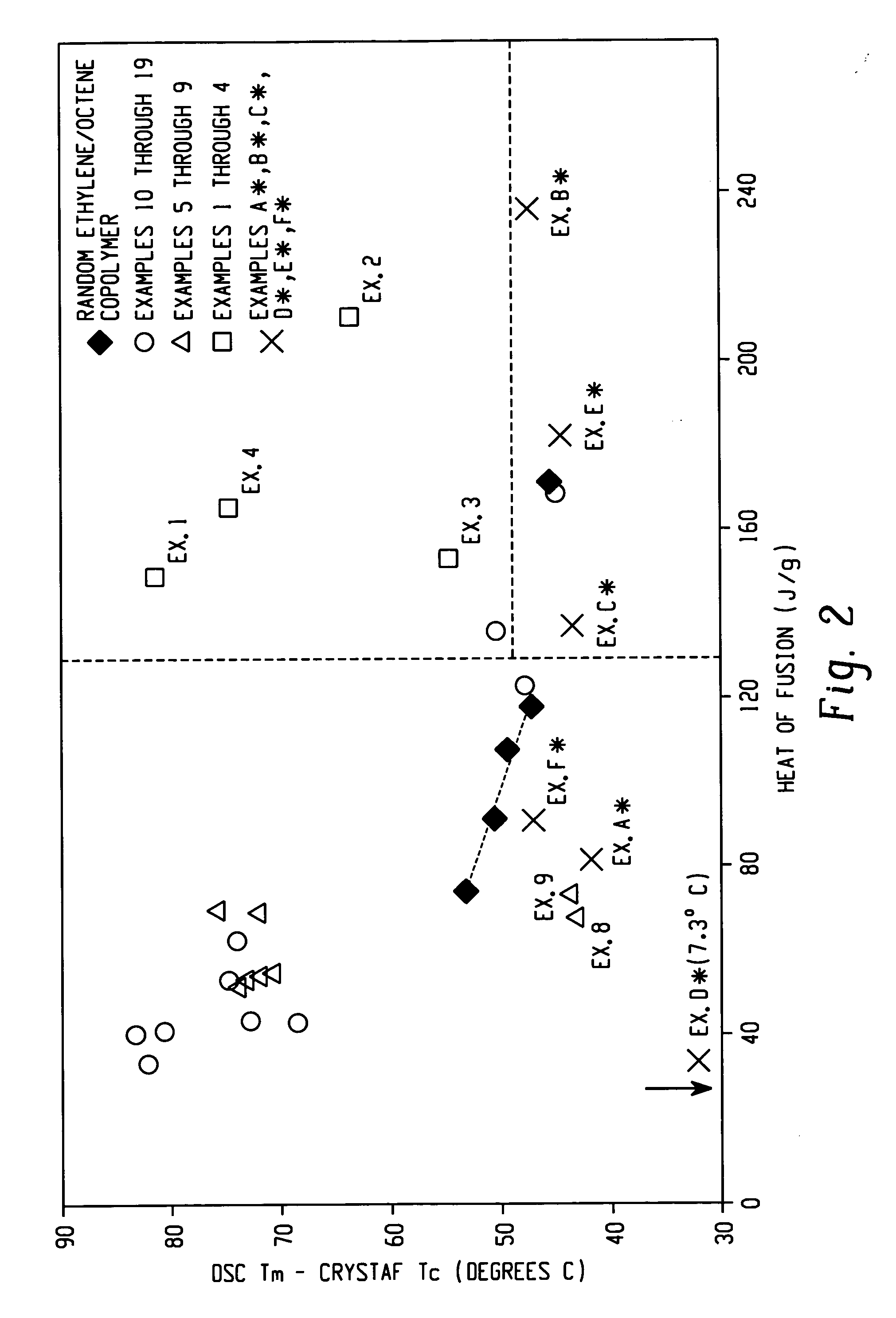
Embodiments of the invention provide a class of ethylene / α-olefin block interpolymers. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are characterized by an average block index, ABI, which is greater than zero and up to about 1.0 and a molecular weight distribution, Mw / Mn, greater than about 1.3. Preferably, the block index is from about 0.2 to about 1. In addition or alternatively, the block ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is characterized by having at least one fraction obtained by Temperature Rising Elution Fractionation (“TREF”), wherein the fraction has a block index greater than about 0.3 and up to about 1.0 and the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer has a molecular weight distribution, Mw / Mn, greater than about 1.3.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Compositions of ethylene/alpha-olefin multi-block interpolymer for elastic films and laminates
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Ethylene/alpha-olefins block interpolymers
Embodiments of the invention provide a class of ethylene / α-olefin block interpolymers. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are characterized by an average block index, ABI, which is greater than zero and up to about 1.0 and a molecular weight distribution, Mw / Mn, greater than about 1.3. Preferably, the block index is from about 0.2 to about 1. In addition or alternatively, the block ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is characterized by having at least one fraction obtained by Temperature Rising Elution Fractionation (“TREF”), wherein the fraction has a block index greater than about 0.3 and up to about 1.0 and the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer has a molecular weight distribution, Mw / Mn, greater than about 1.3.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Aqueous dispersion, its production method, and its use
ActiveUS20050100754A1Liquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsVolume averageAlpha-olefin
Aqueous dispersions including at least one thermoplastic resin; at least one dispersing agent; and water; wherein the dispersion has a pH of less than 12 are disclosed along with dispersions including at least one thermoplastic resin; at least one dispersing agent; and water wherein the dispersion has a volume average particle size of less than about 5 μm. Some dispersions include less than about 4 percent by weight of the dispersing agent based on the weight of the thermoplastic resin. Other dispersions include at least one propylene-rich alpha-olefin interpolymer; at least one dispersing agent; and water. Methods of making such dispersions are also described.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Ethylene/α-olefin block copolymers
Embodiments of the invention provide a class of ethylene / α-olefin block interpolymers. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are characterized by an average block index, ABI, which is greater than zero and up to about 1.0 and a molecular weight distribution, Mw / Mn, greater than about 1.3. Preferably, the block index is from about 0.2 to about 1. In addition or alternatively, the block ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is characterized by having at least one fraction obtained by Temperature Rising Elution Fractionation (‘TREF’), wherein the fraction has a block index greater than about 0.3 and up to about 1.0 and the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer has a molecular weight distribution, Mw / Mn, greater than about 1.4.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
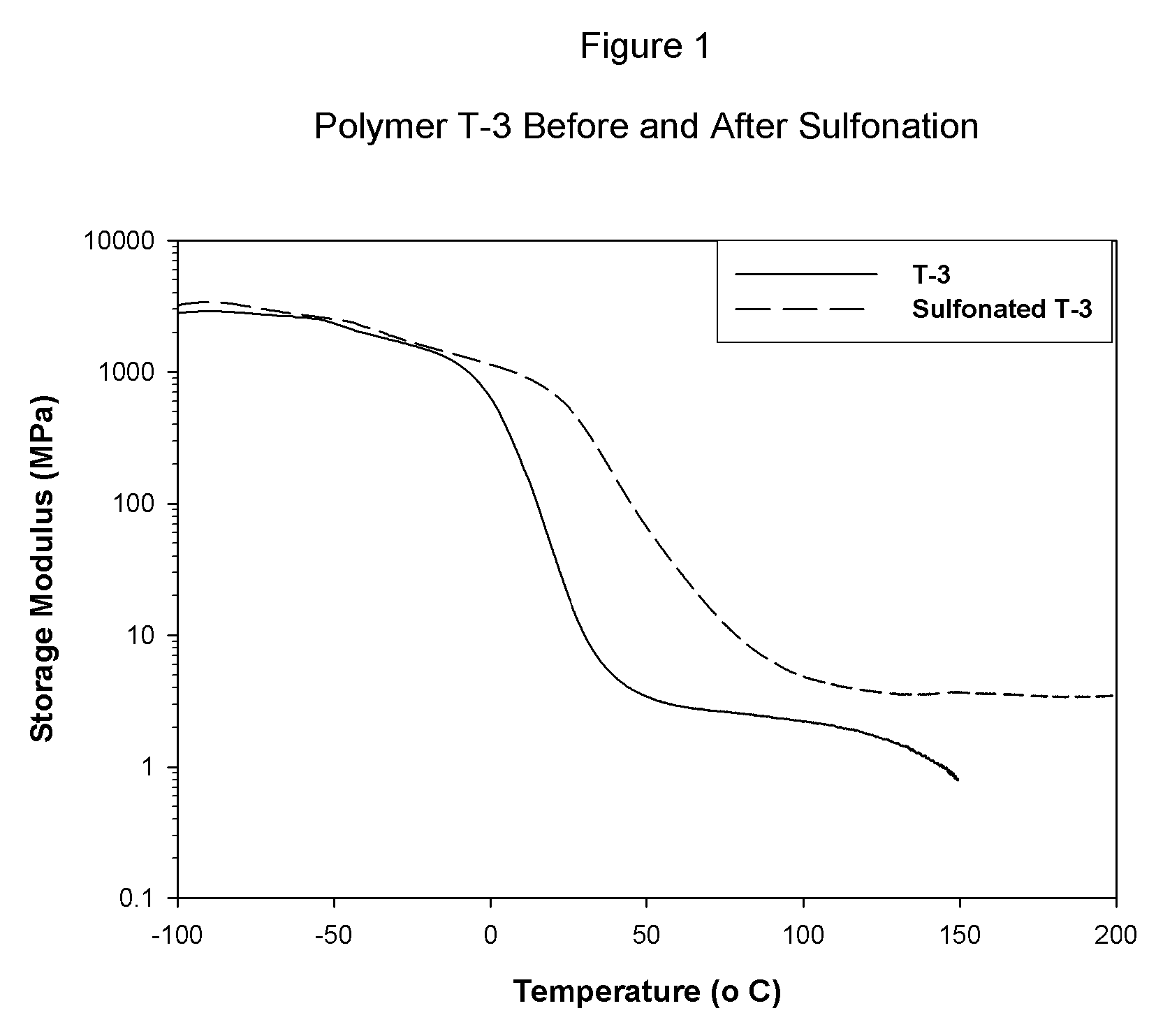
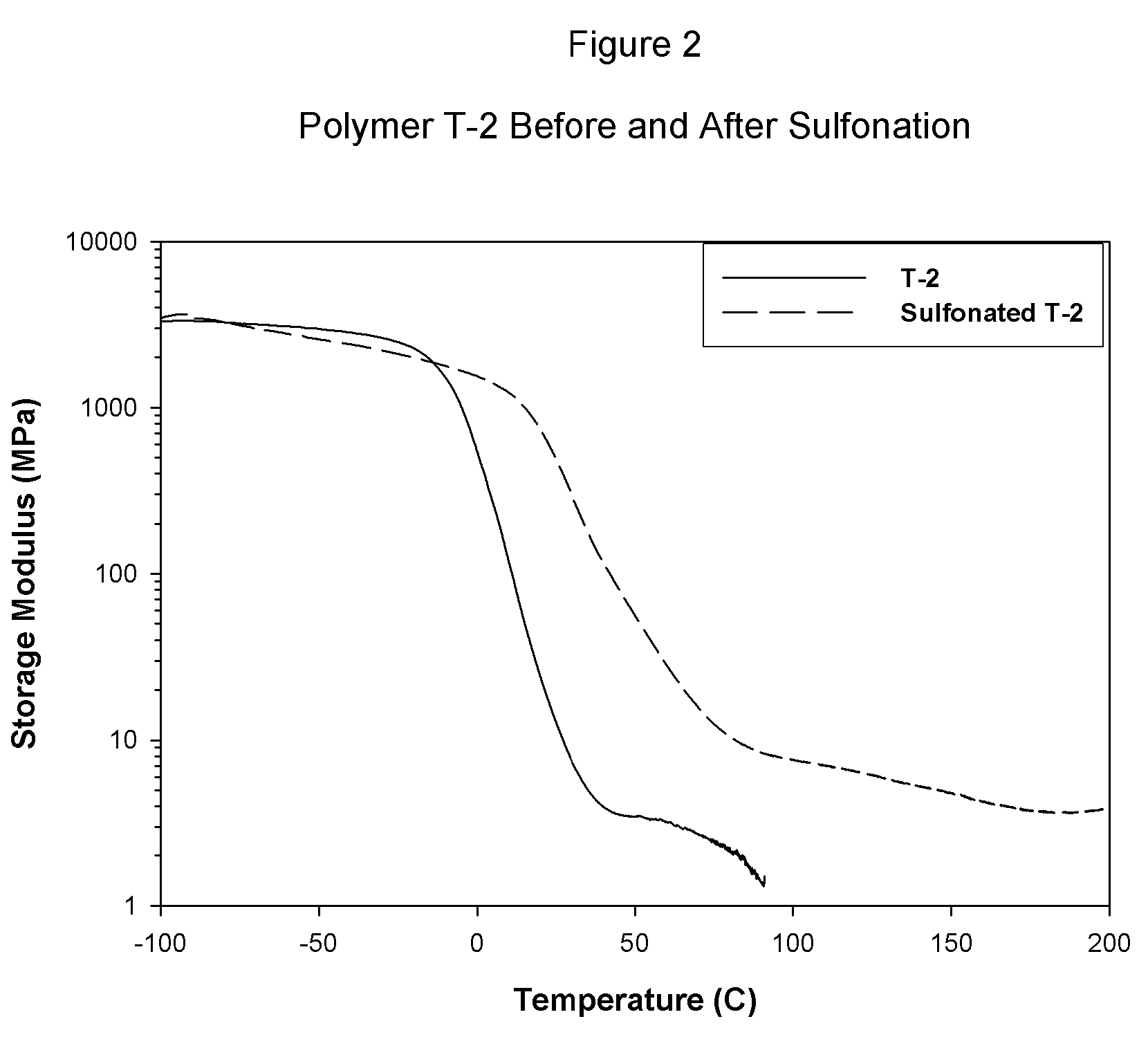
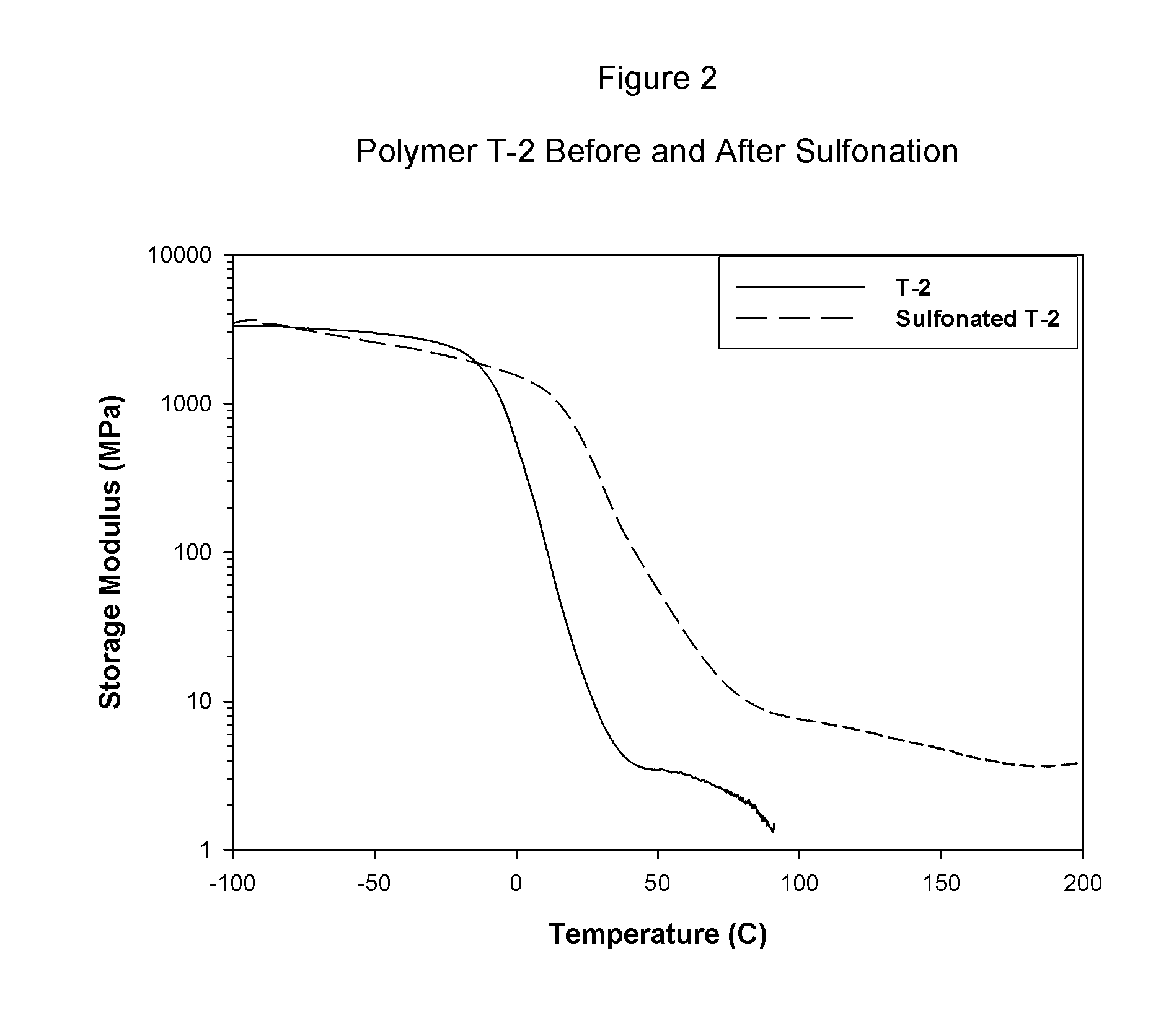
Sulfonated block copolymers, method for making same, and various uses for such block copolymers
ActiveUS7737224B2Reduced responseHigh propertySemi-permeable membranesNegative electrodesMethacrylatePolymer science
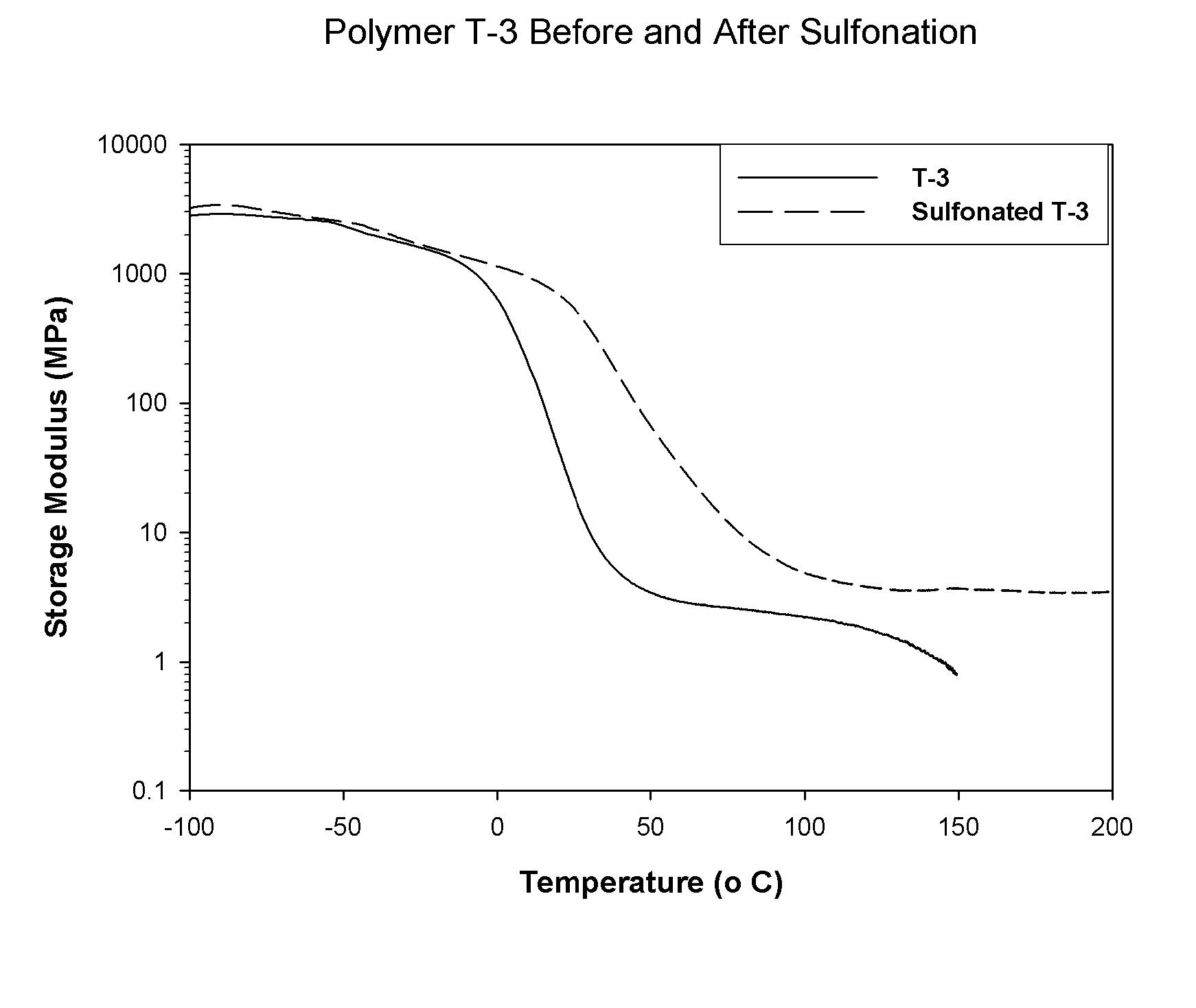
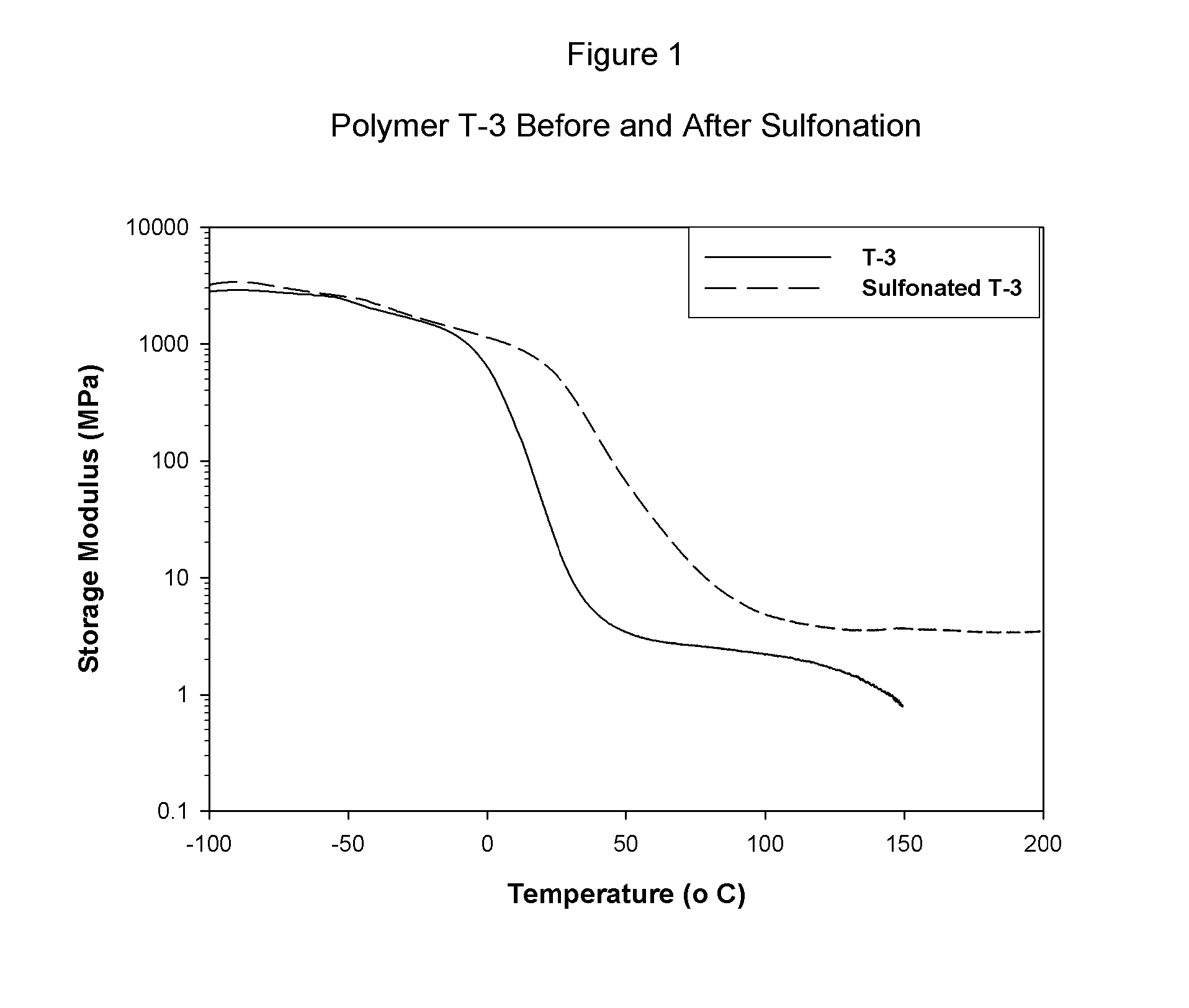
The present invention is a, solid block copolymer comprising at least two polymer end blocks A and at least one polymer interior block B wherein each A block is a polymer block resistant to sulfonation and each B block is a polymer block susceptible to sulfonation, and wherein said A and B blocks do not contain any significant levels of olefinic unsaturation. Preferably, each A block comprising one or more segments selected from polymerized (i) para-substituted styrene monomers, (ii) ethylene, (iii) alpha olefins of 3 to 18 carbon atoms; (iv) hydrogenated 1,3-cyclodiene monomers, (v) hydrogenated monomers of conjugated dienes having a vinyl content less than 35 mol percent prior to hydrogenation, (vi) acrylic esters, (vii) methacrylic esters, and (viii) mixtures thereof; and each B block comprising segments of one or more polymerized vinyl aromatic monomers selected from (i) unsubstituted styrene monomers, (ii) ortho-substituted styrene monomers, (iii) meta-substituted styrene monomers, (iv) alpha-methylstyrene, (v) 1,1-diphenylethylene, (vi) 1,2-diphenylethylene and (vii) mixtures thereof. Also claimed are processes for making such block copolymers, and the various end uses and applications for such block copolymers.
Owner:KRATON POLYMERS US LLC
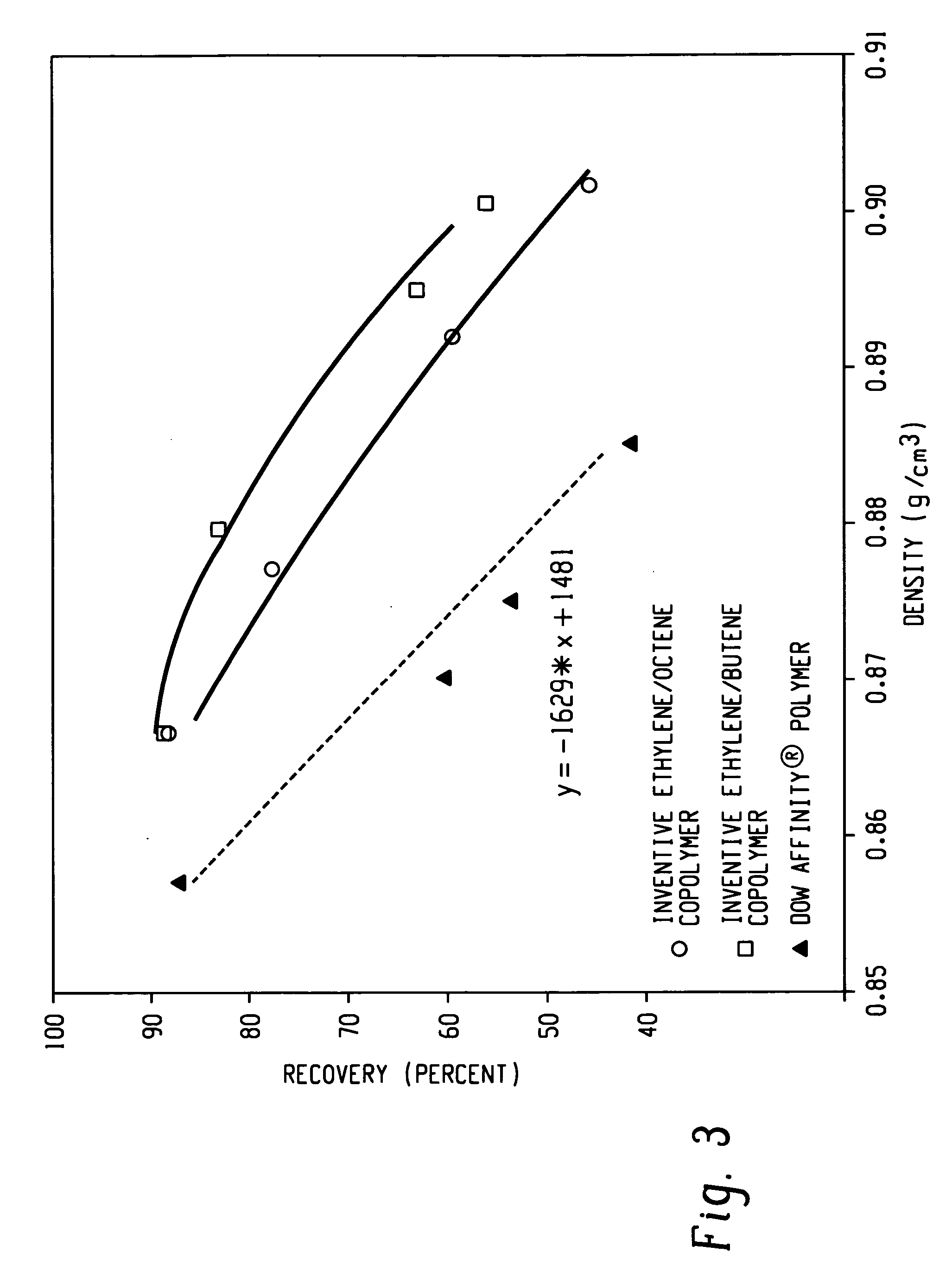
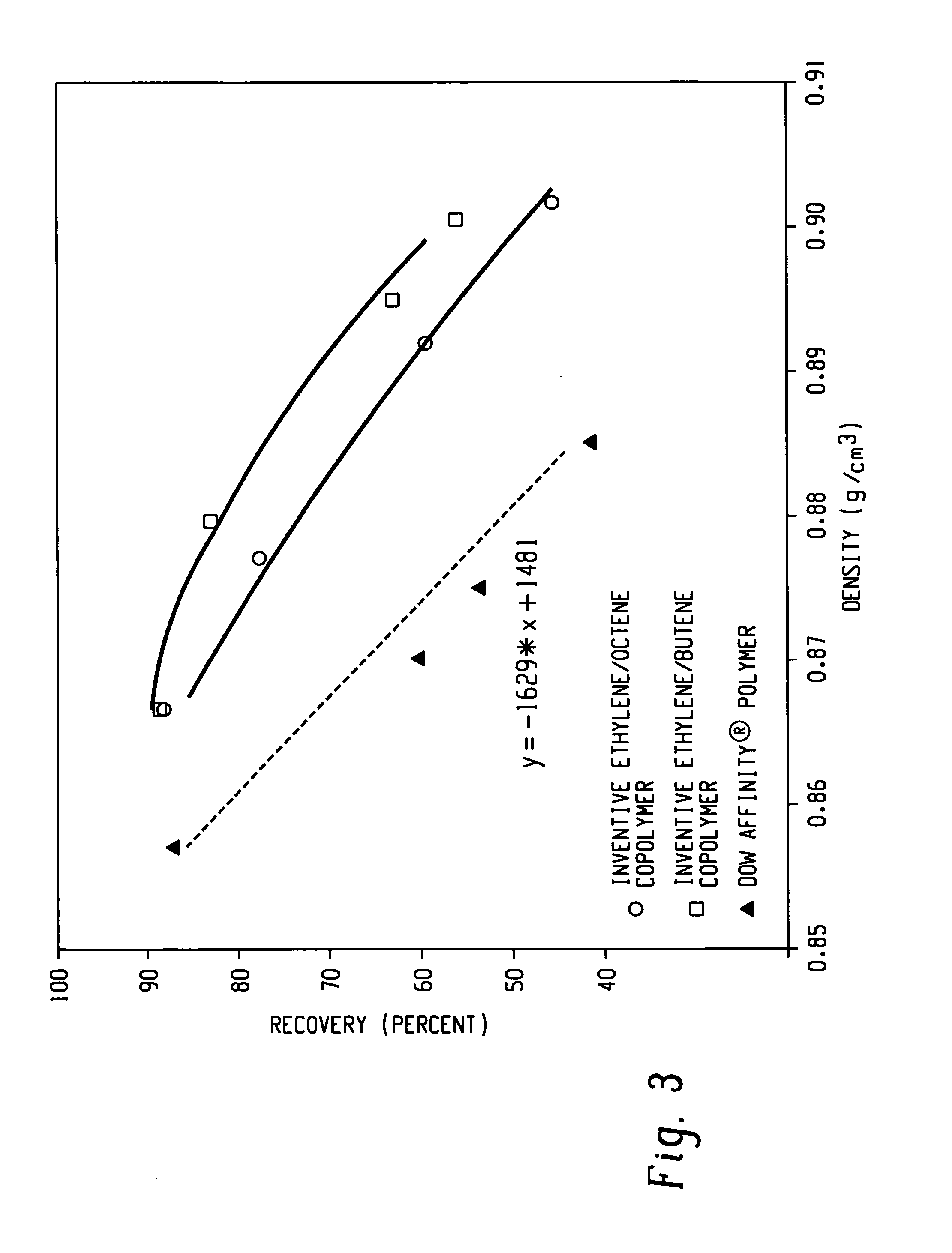
Fibers made from copolymers of propylene/alpha-olefins
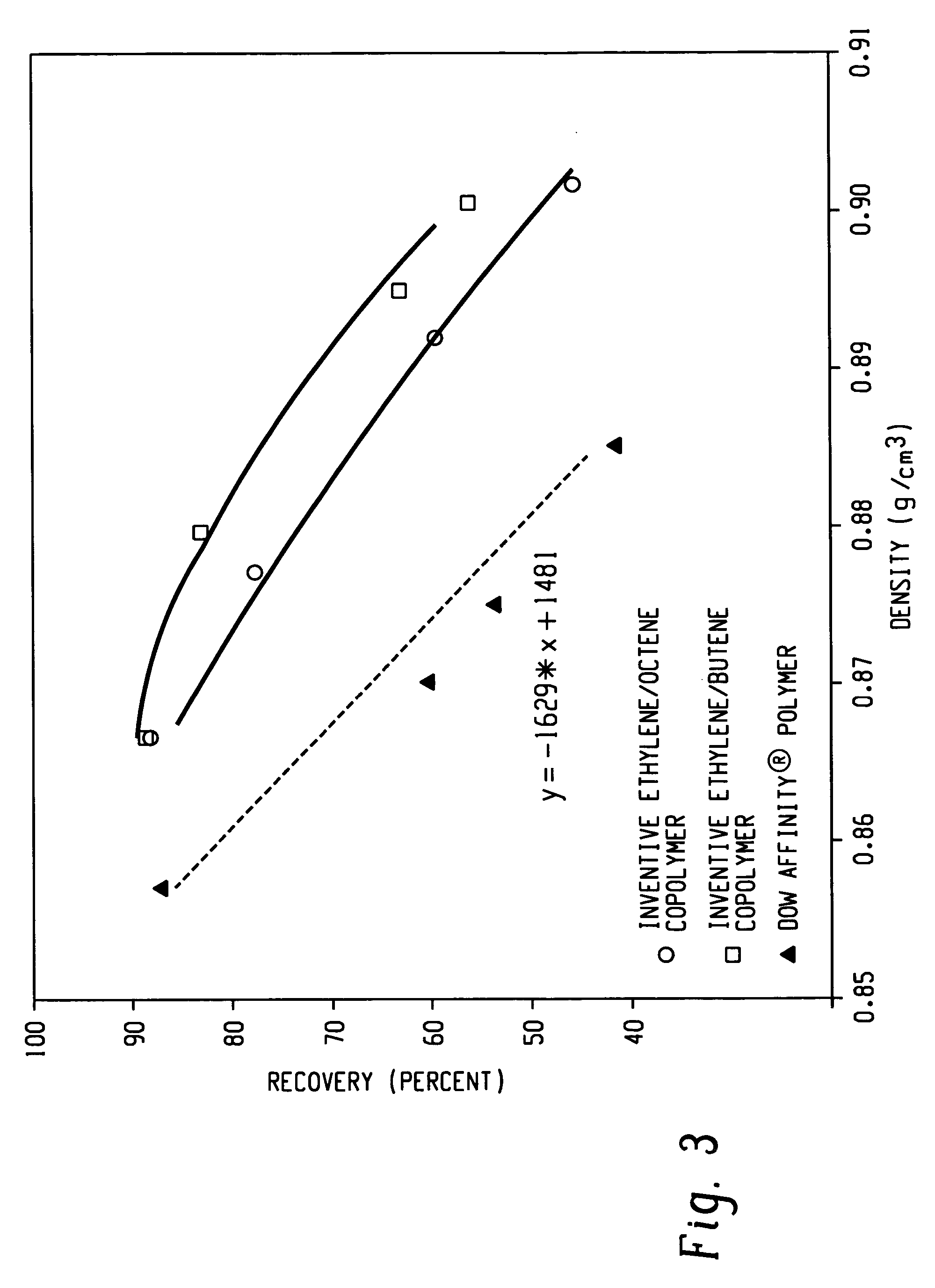
ActiveUS7504347B2Monocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentWoven fabricsFiberVolumetric Mass Density
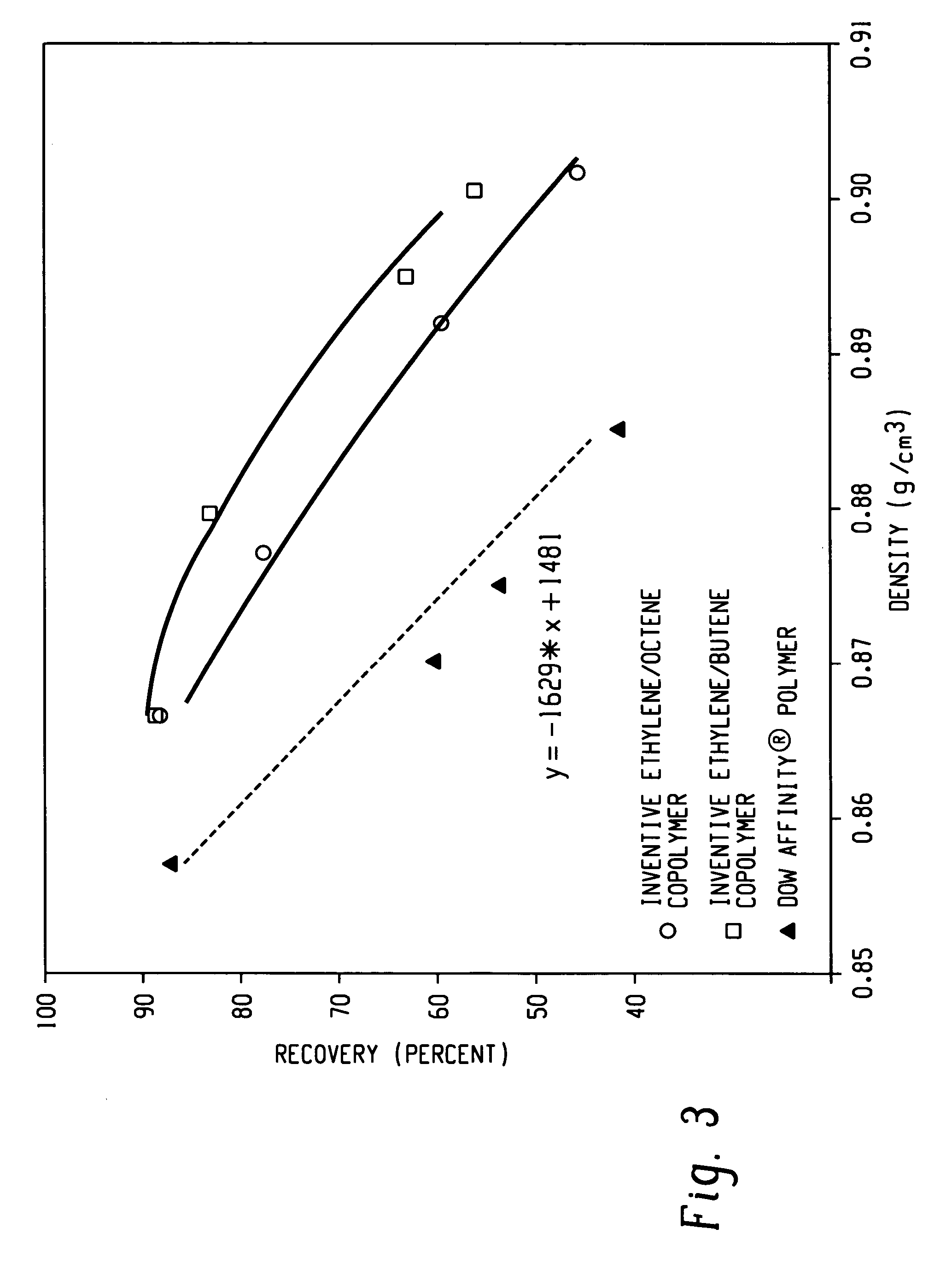
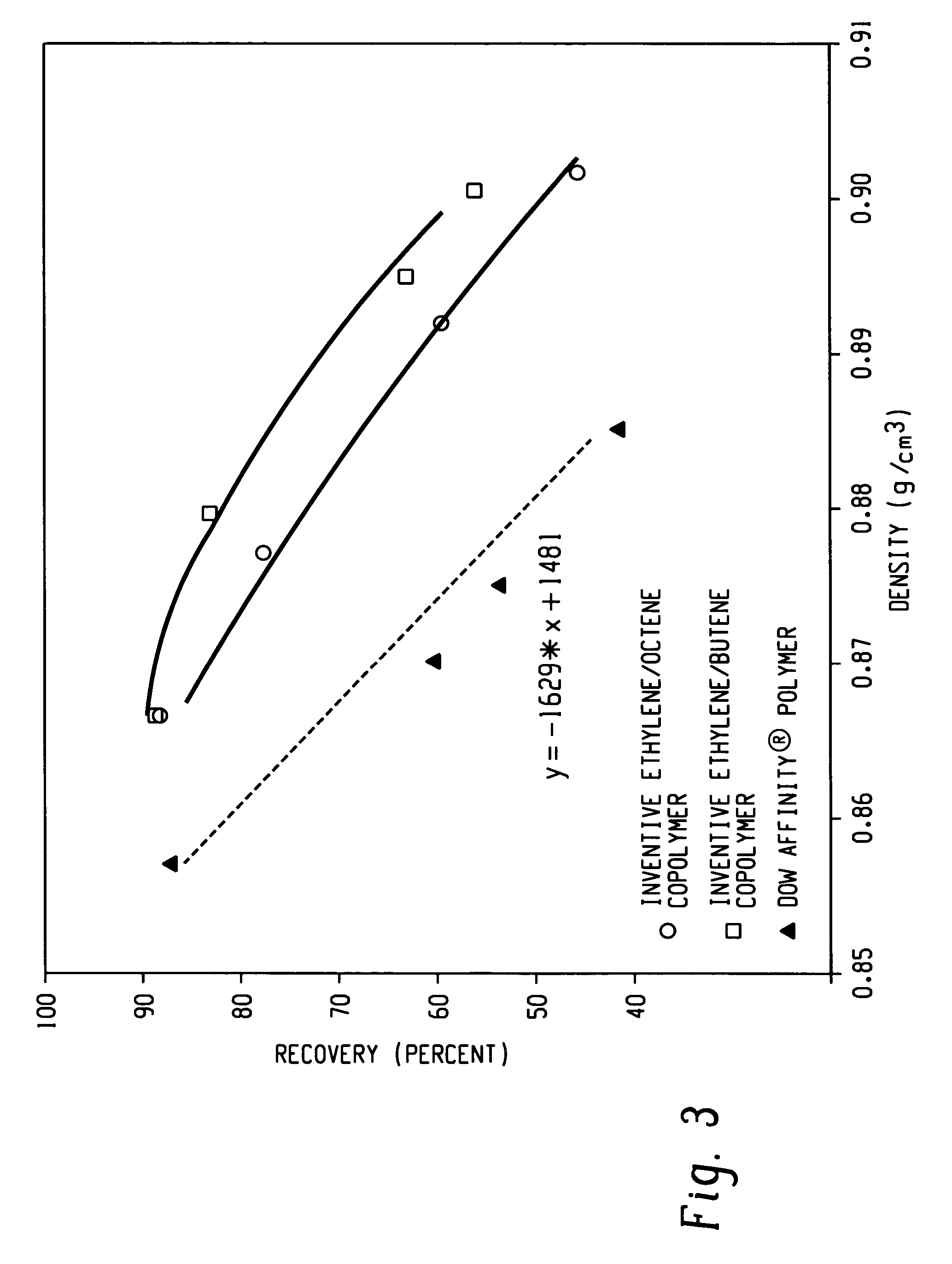
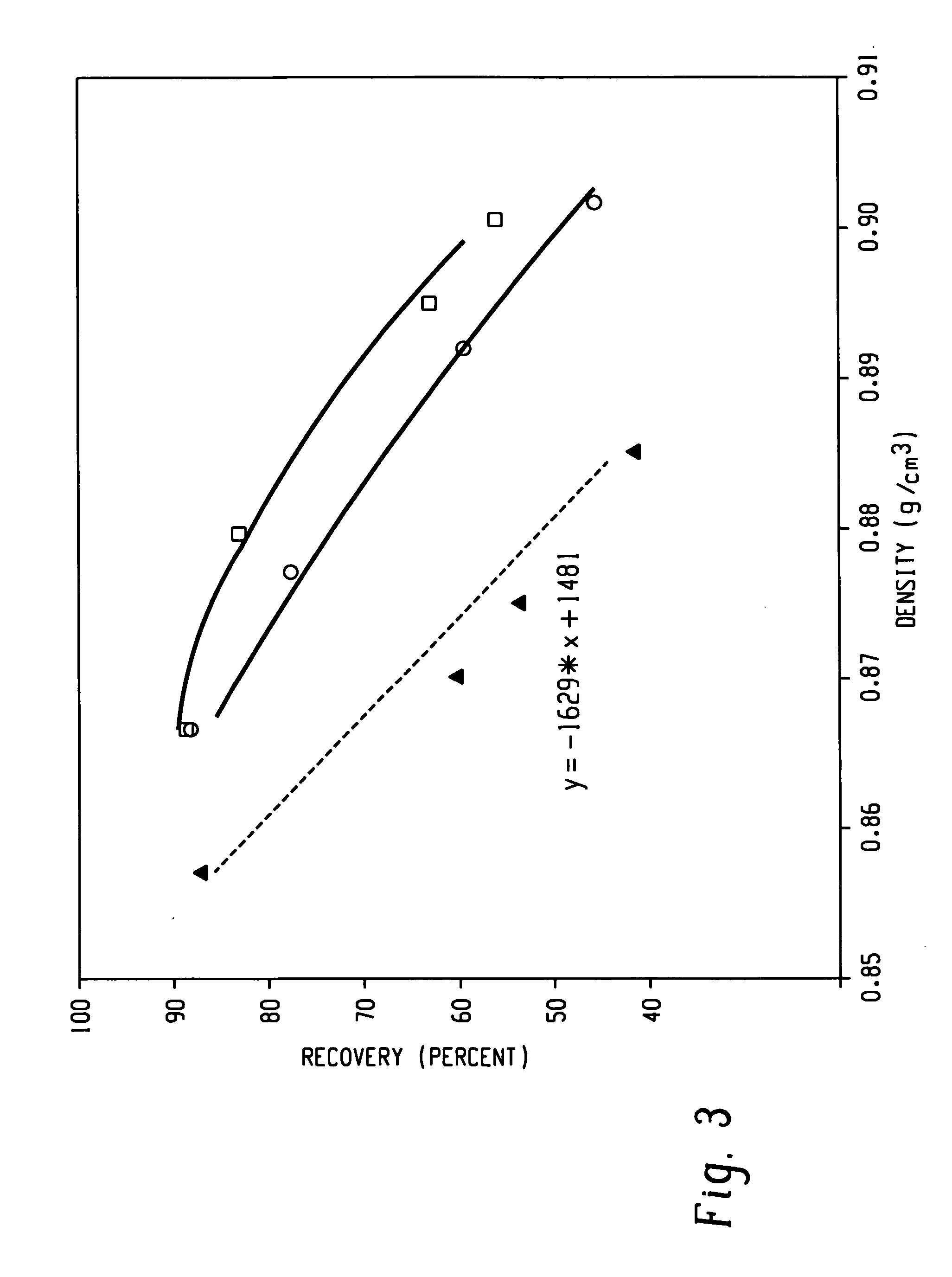
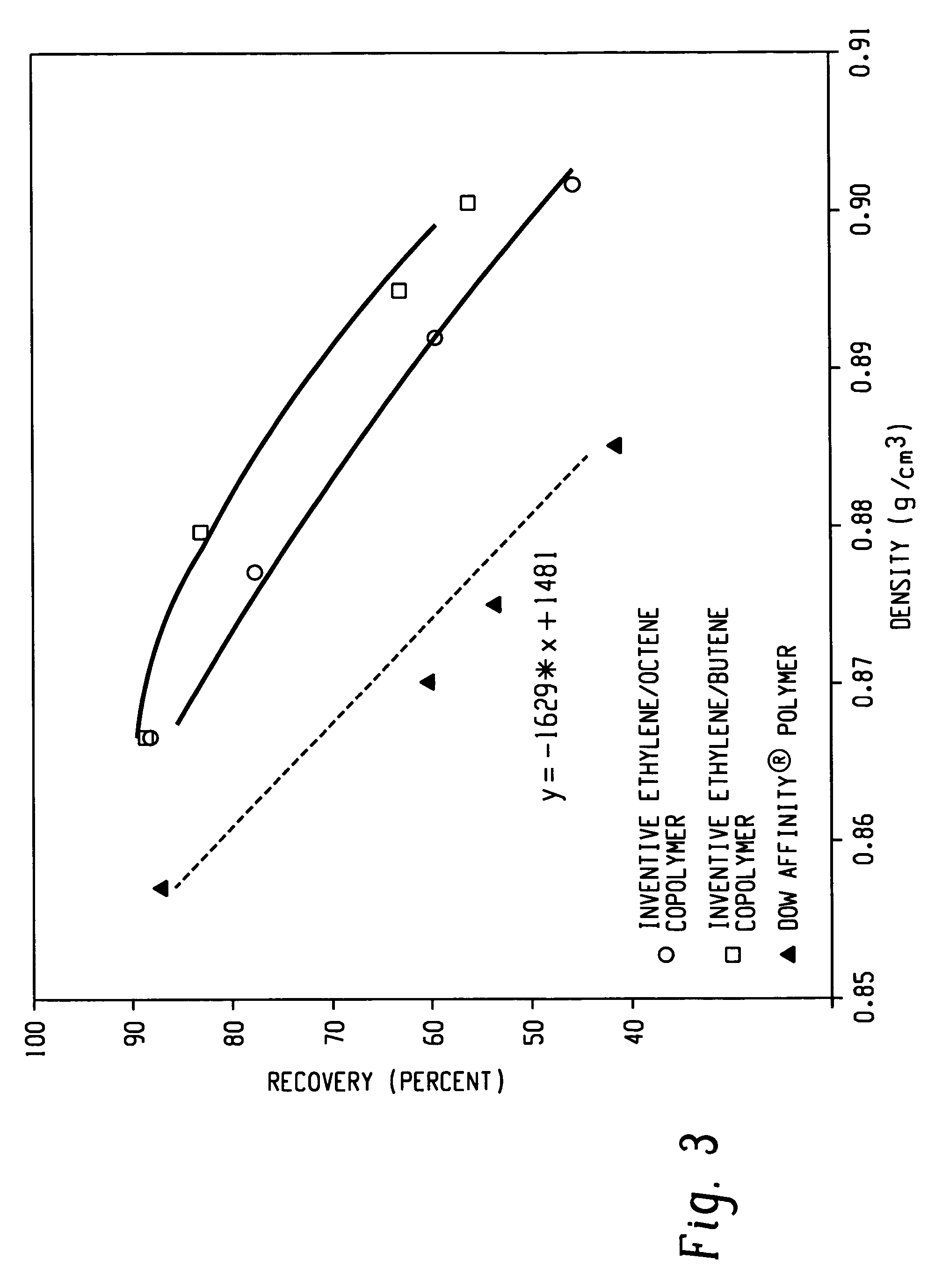
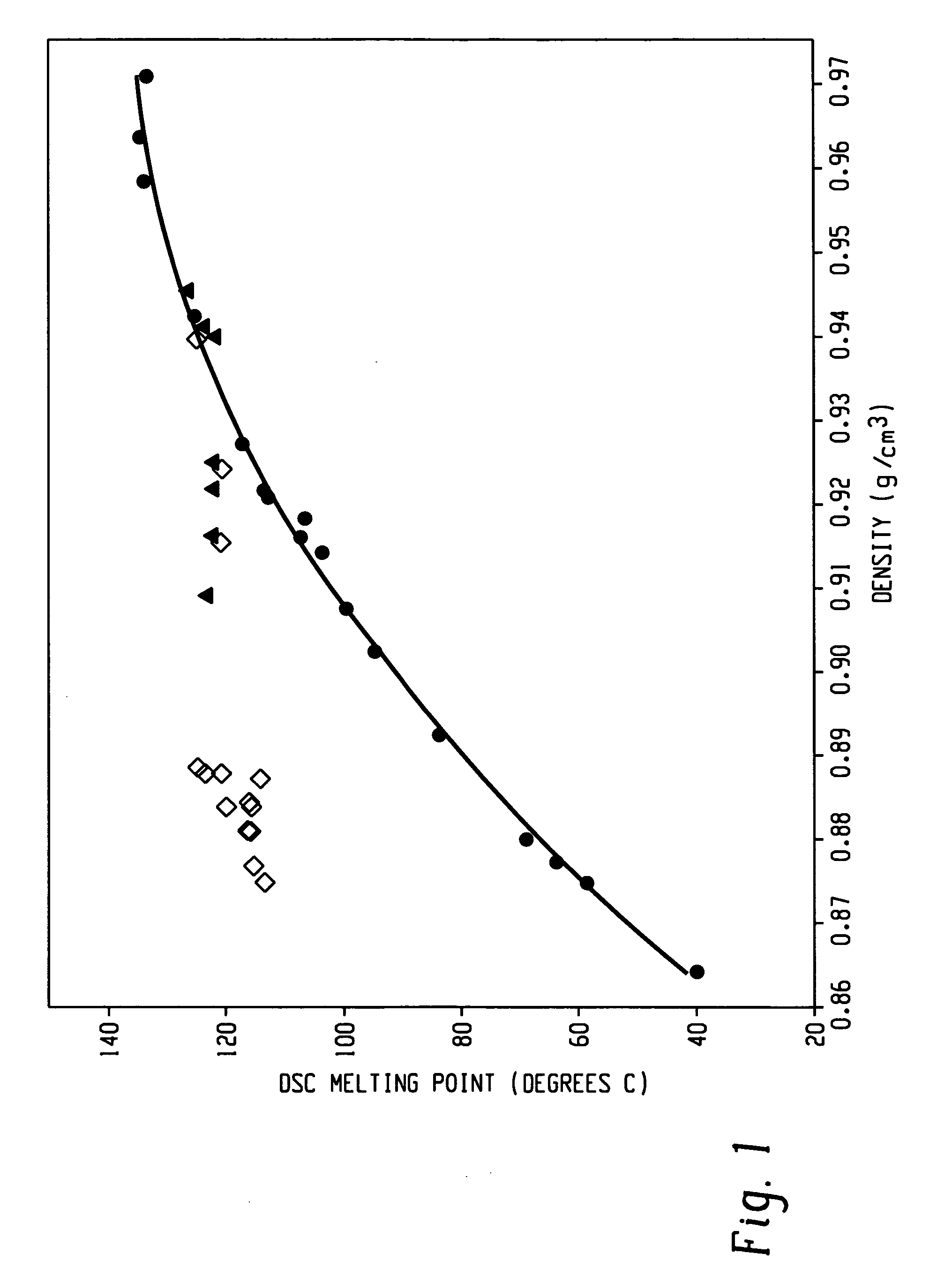
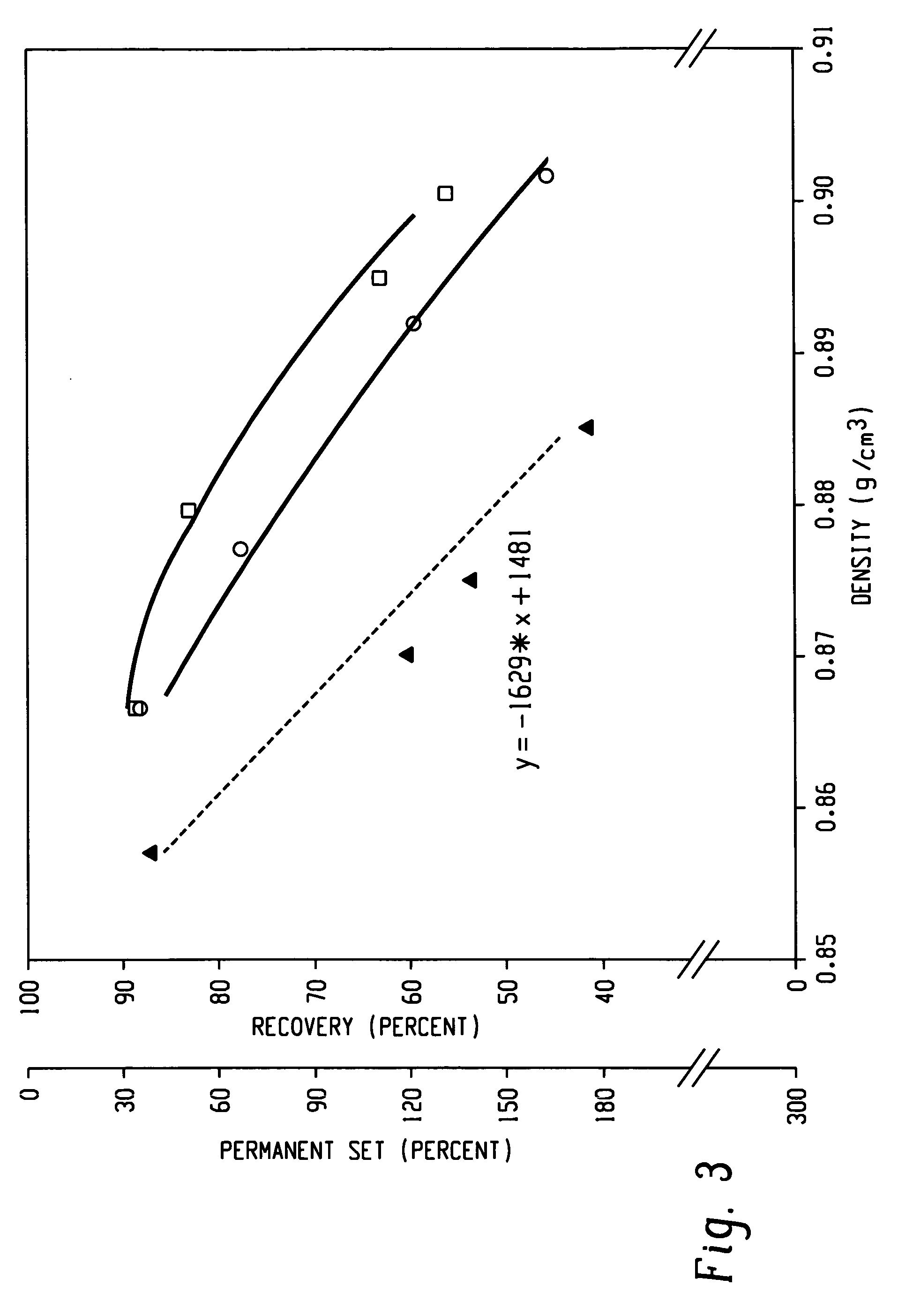
A fiber is obtainable from or comprises a propylene / α-olefin interpolymer characterized by an elastic recovery, Re, in percent at 300 percent strain and 1 cycle and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the elastic recovery and the density satisfy the following relationship: Re>1481-1629 (d). Such interpolymer can also be characterized by other properties. The fibers made therefrom have a relatively high elastic recovery and a relatively low coefficient of friction. The fibers can be cross-linked, if desired. Woven or non-woven fabrics can be made from such fibers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
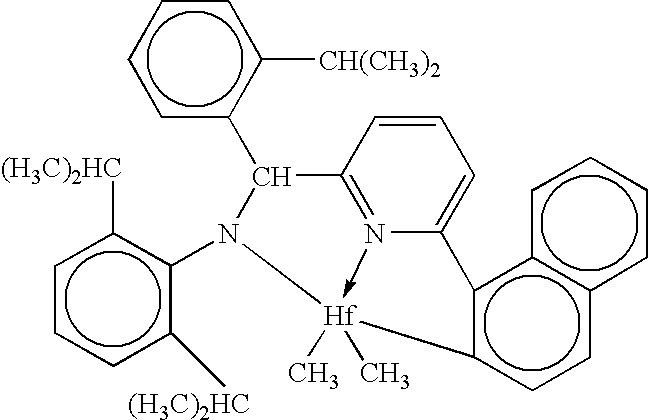
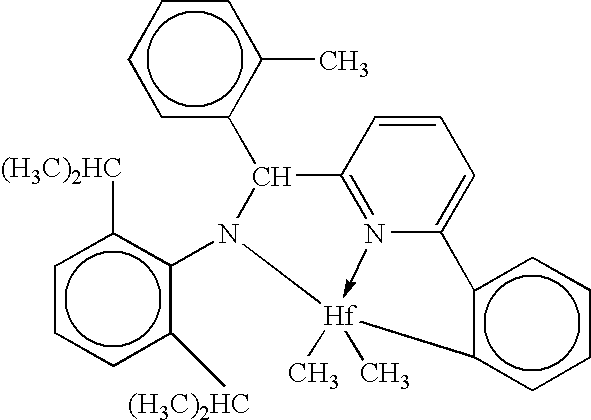
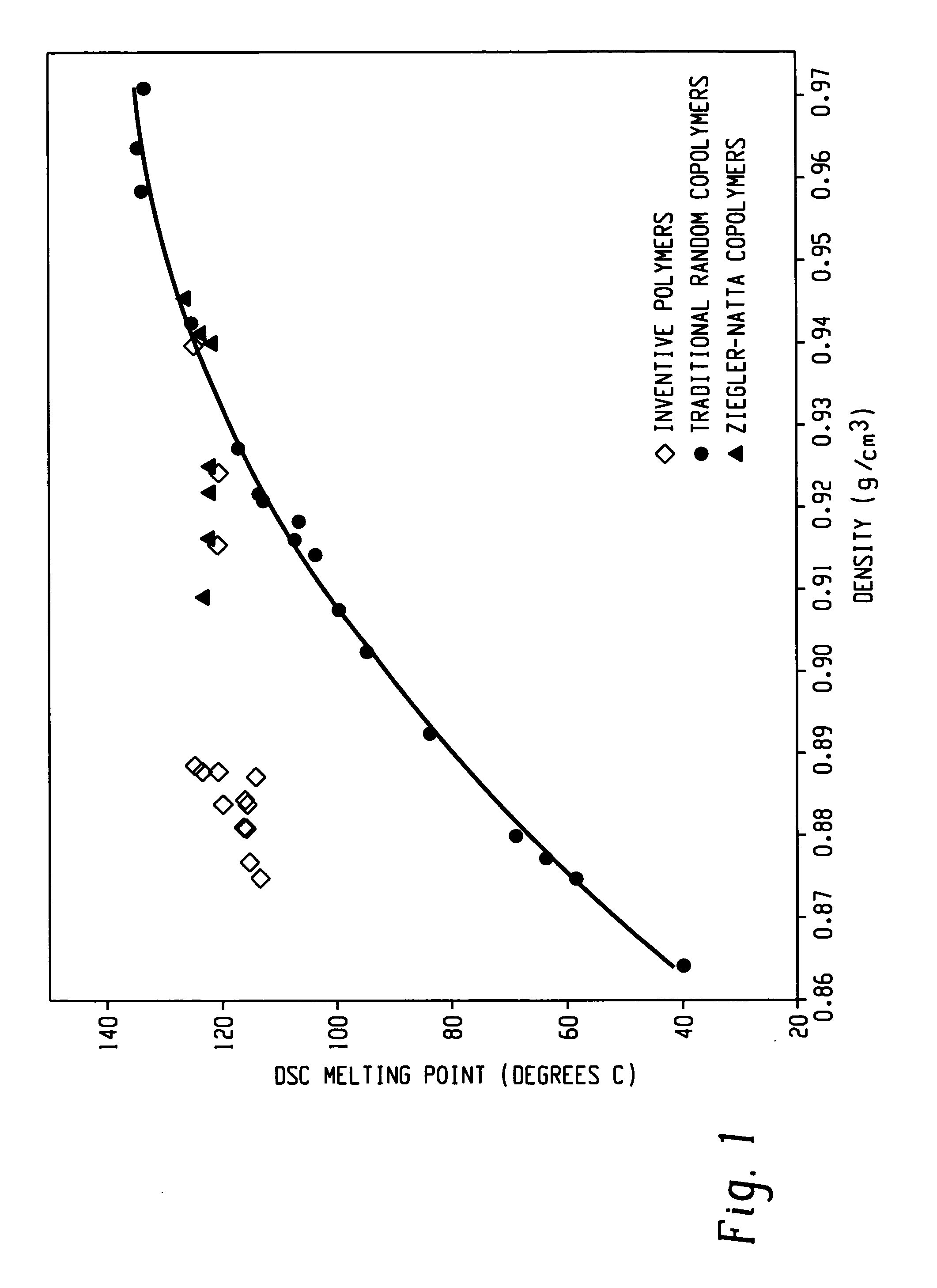
High melting thermoplastic elastomeric alpha-olefin polymers (PRE/EPE effect) and catalysts therefor
InactiveUS6559262B1Activity of fluxional unbridged metallocene polymerization catalystsHigh molecular weightGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsMetallocenesElastomerEthylene Homopolymers
This invention relates generally to low ethylene insertions into I-olefin polymers and processes for production of such polymers using unbridged fluxional metallocenes, primarily substituted aryl indenyl metallocenes, and more particularly to use of unbridged, fluxional, cyclopentadienyl or indenyl metallocene catalyst systems in methods of production of high melting point I-olefin homo- and co-polymers, particularly elastomeric crystalline and amorphous block homo- and co-polymers of I-olefins. The activity of fluxional unbridged metallocene polymerization catalysts containing at least one 2-arylindene ligand is increased 10x or more by the addition of small (typically 0.1-10 wt. %) amounts of ethylene to the polymerization system, which increase is termed the Polymerization Rate-Enhancement effect (PRE), which is measured in terms of an Ethylene Enhancement Factor (EEF) as a dimensionless ratio in the range of from about 1.1 to about 10 or above. The amount of ethylene included in the reaction system can be selected and controlled to be so small as to result in essentially minimal (<2 mole %) incorporation of ethylene units into the resulting elastomeric polymer and the molecular weight may be increased. Amounts of ethylene to generate the PRE effect may be greater than 0.1 wt. % and preferably range up to about 2 wt. %. However, if a polymer with more ethylene is desired, additional ethylene may be incorporated into the polymerization feed, including up to 10 to about 50 mole % based on olefin units. A second important aspect of this invention is the ability to use a PRE activity-enhancing amount of ethylene in an olefin polymerization without substantially affecting the physical properties of the elastomer. In a third important aspect of this invention, I-olefin elastomers are produced through incorporation of ethylene using unbridged fluxional catalyst systems which may not otherwise produce acceptable elastomeric homopolymers. This effect is termed the EPE effect, for Elastomeric Property-Enhancing effect. The EPE amount of ethylene required to produce such elastomers typically overlaps the PRE activity-enhancing amount. Incorporation of up to about 5 mole % or more of ethylene typically will produce an elastomeric polymer using such catalyst systems. Typical useful amounts of incorporated ethylene include about 1 to 3 mole %. Preferred polymers of this invention retain sufficient crystallinity to provide a high melting point (by DSC) of about 80° C., preferably above 100° C., including in the range of from about 120° C. to about 140° C. and above. Novel flexible alpha-olefin homo and copolymers having elongation in excess of 600% and substantially no retained force are disclosed.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Polymer blends from interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins and flexible molded articles made therefrom
Polymer blends comprises 1) at least one ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer and 2) at least one polyolefin, or at least one styrenic block copolymer, or a combination thereof. Such polyolefins include, but are not limited to, high melt strength high density polyethylene and high melt strength polypropylene. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are random block copolymers comprising at least a hard block and at least a soft block. The polyolefins can be homopolymers or interpolymers. The resulting polymer blends can be used to make flexible molded articles.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Polymer blends from interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefin with improved compatibility
Disclosed herein are polymer blends comprising at least one ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer and two different polyolefins which can be homopolymers. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are block copolymers comprising at least a hard block and at least a soft block. In some embodiments, the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer can function as a compatibilizer between the two polyolefins which may not be otherwise compatible. Methods of making the polymer blends and molded articles made from the polymer blends are also described.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
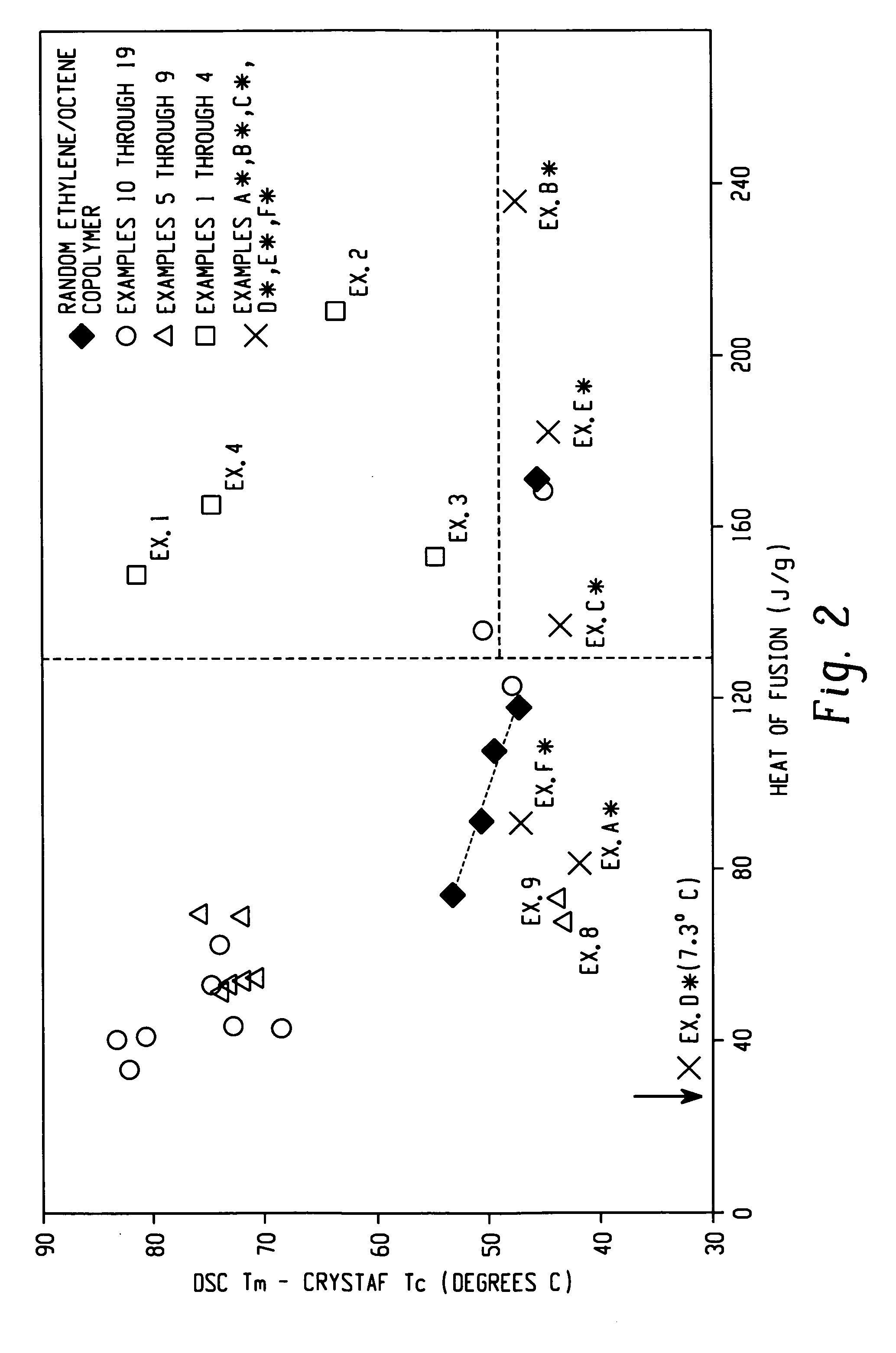
Compositions of ethylene/alpha-olefin multi-block interpolymer for blown films with high hot tack
InactiveUS20060199030A1Superior hot tack propertyWider process windowSynthetic resin layered productsBagsCelsius DegreeVolumetric Mass Density
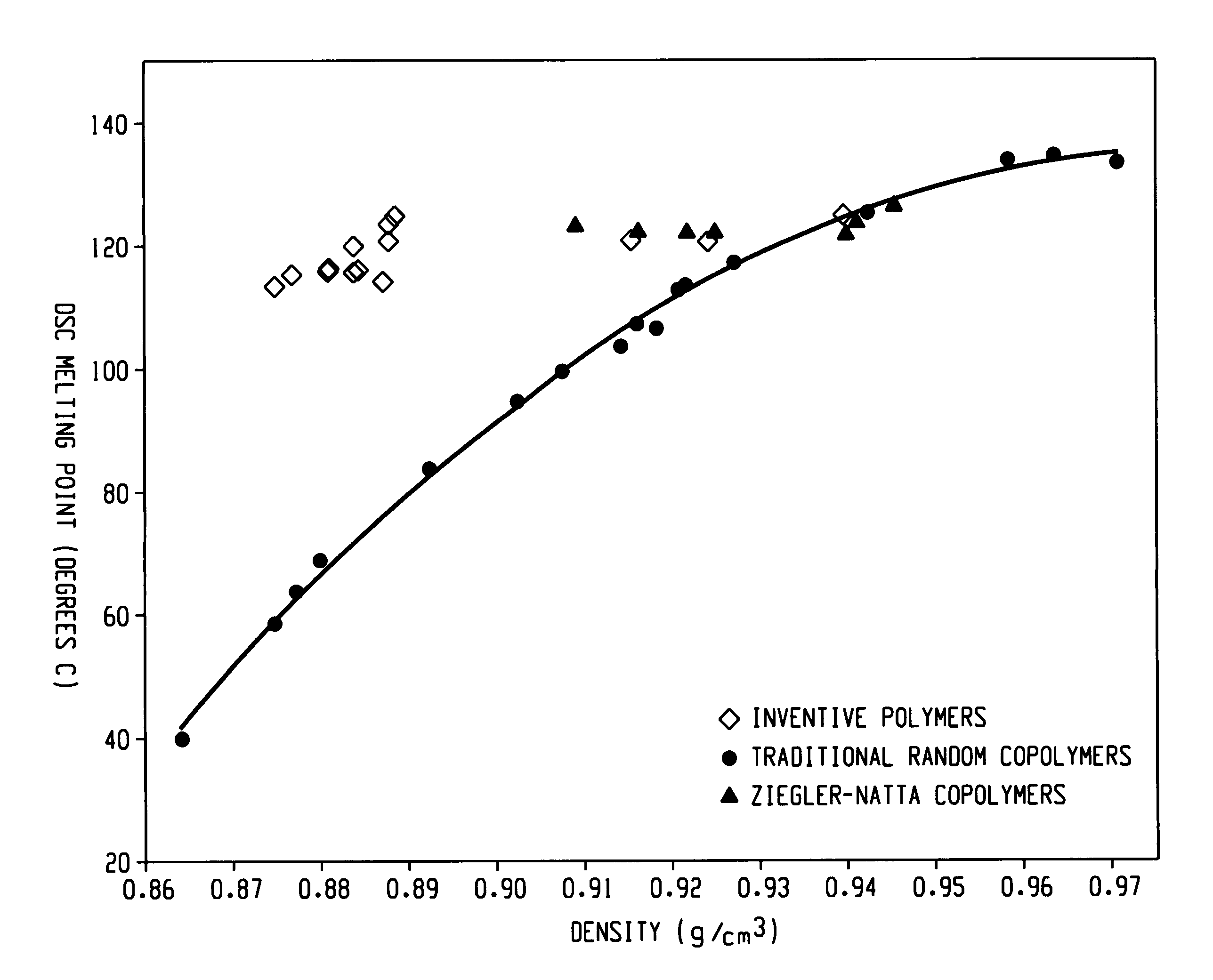
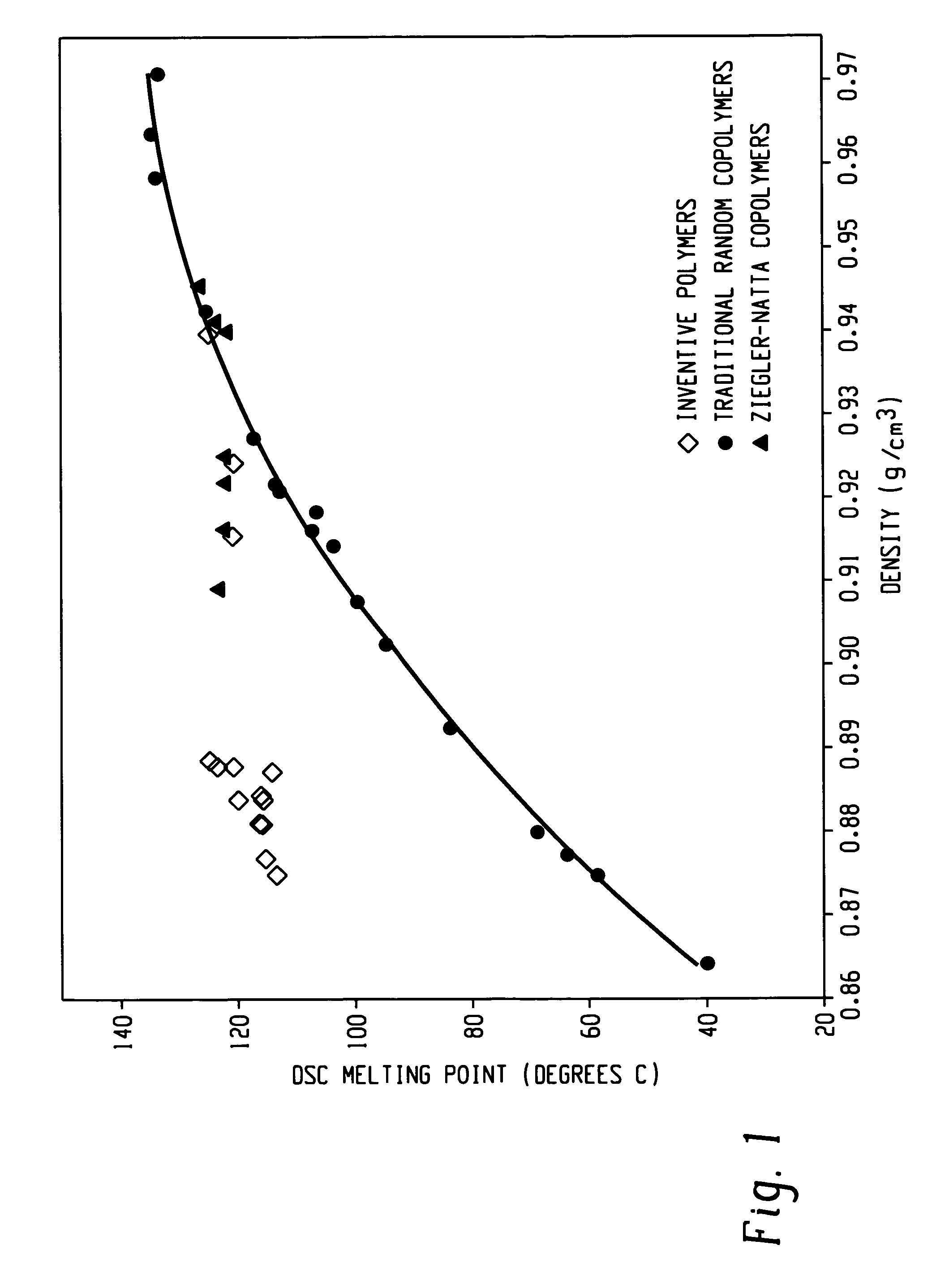
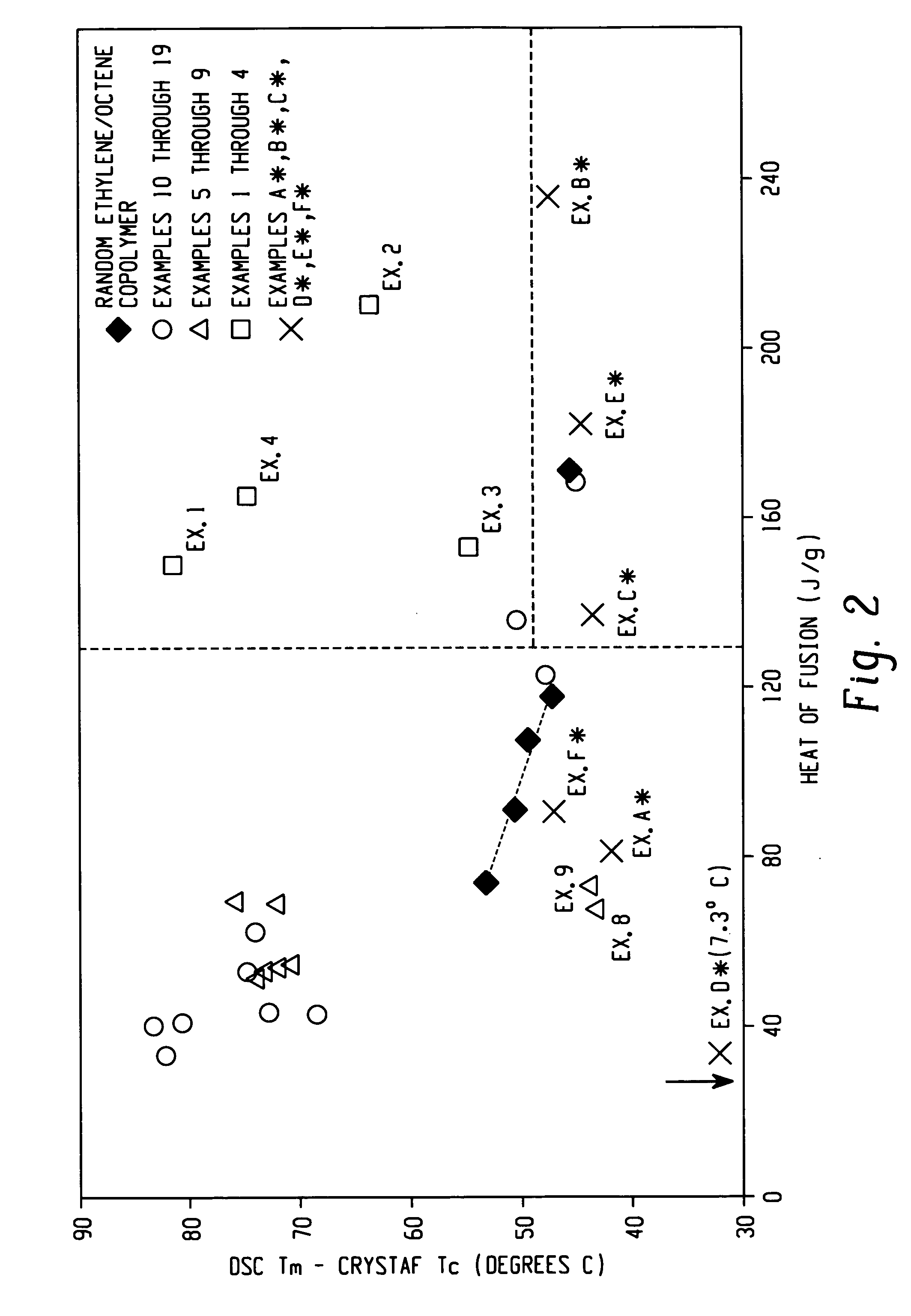
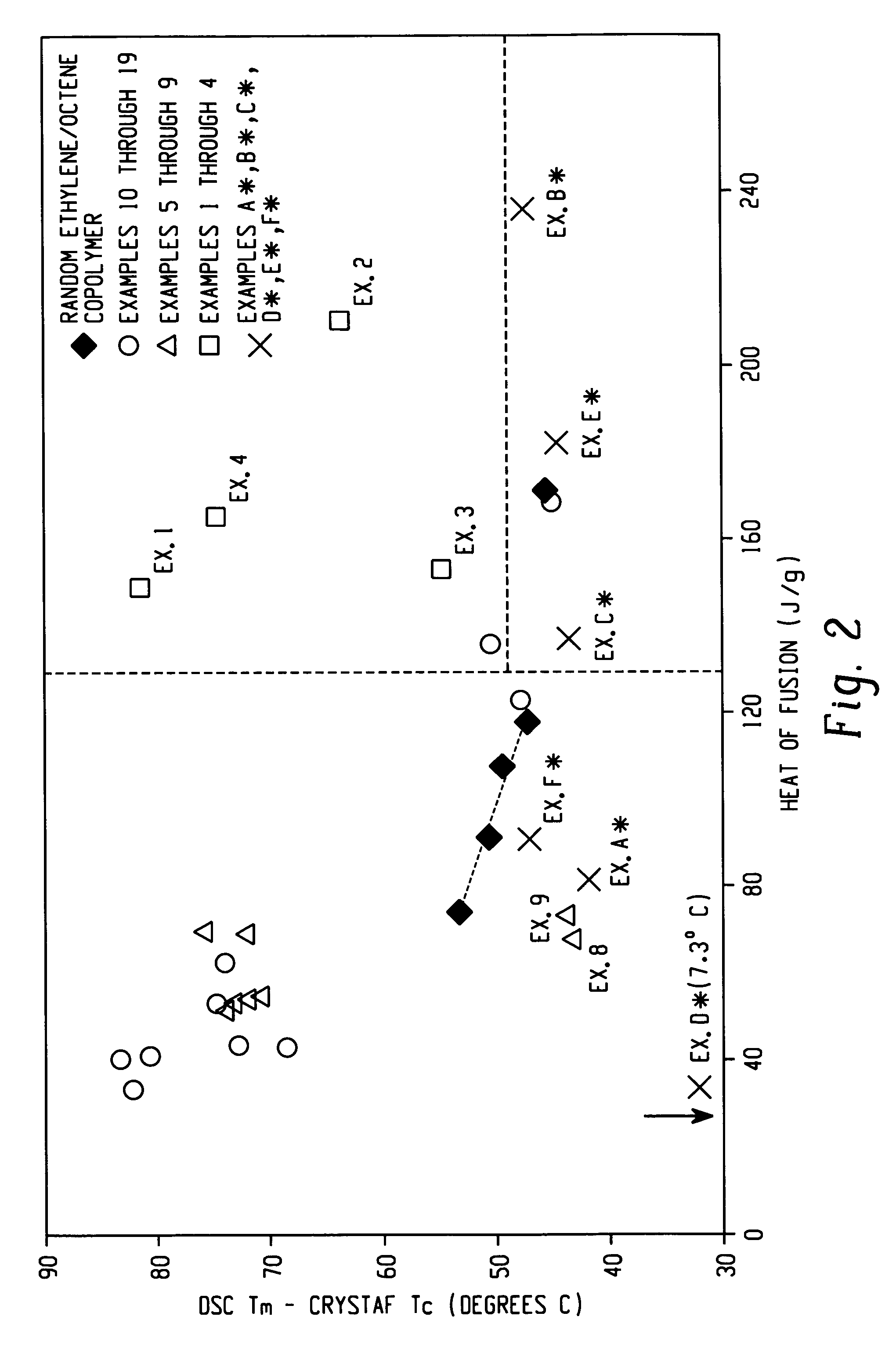
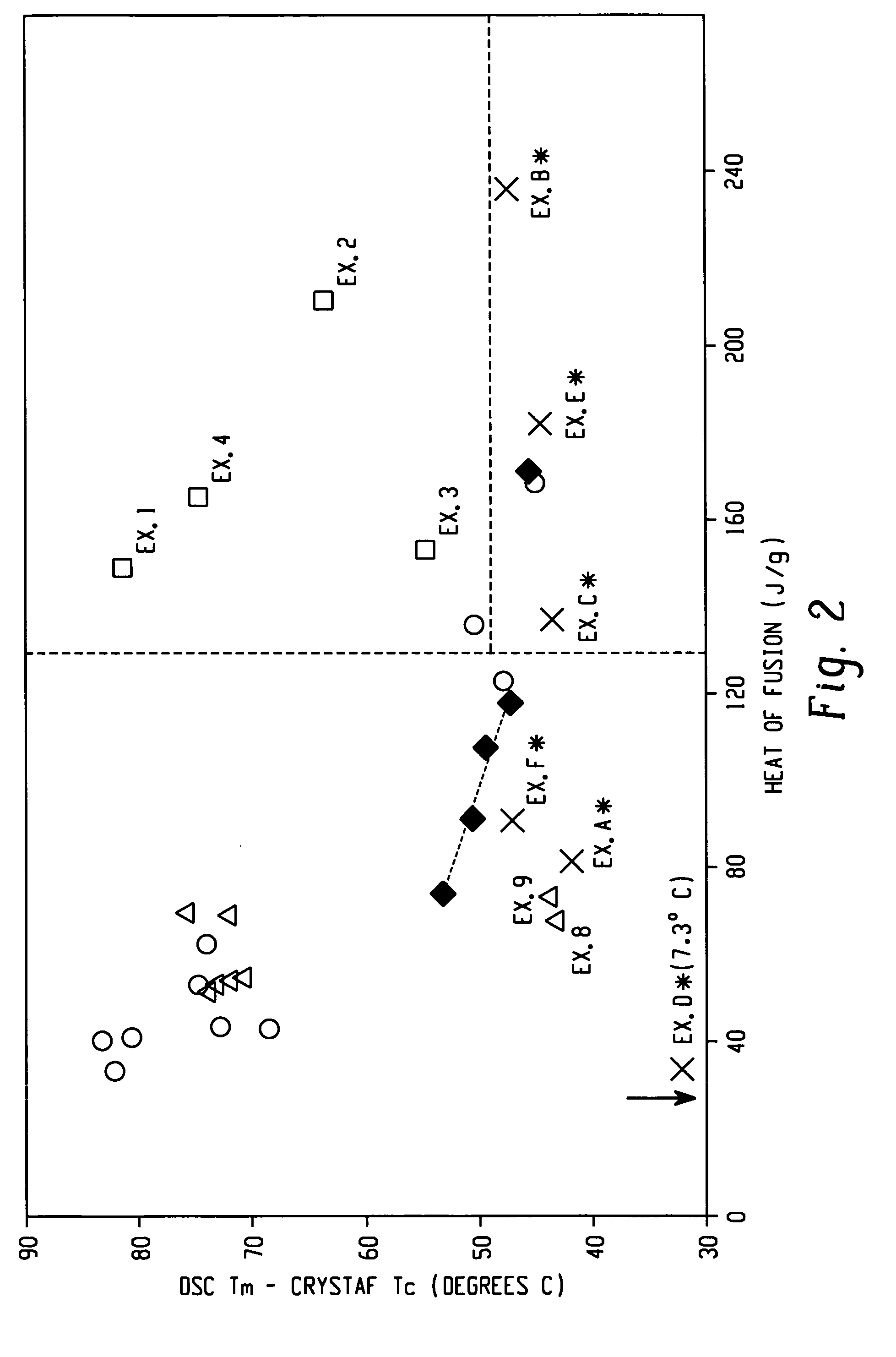
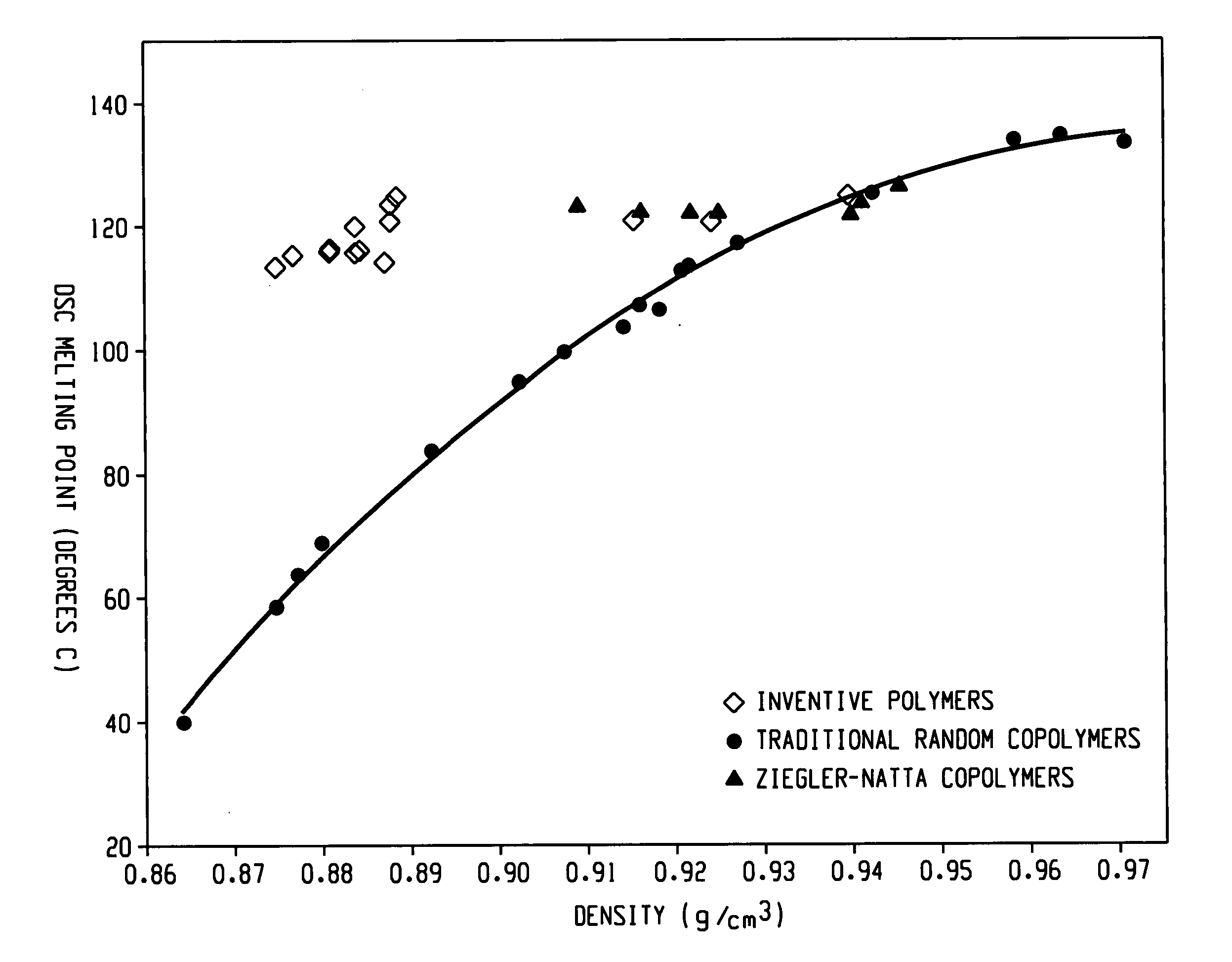
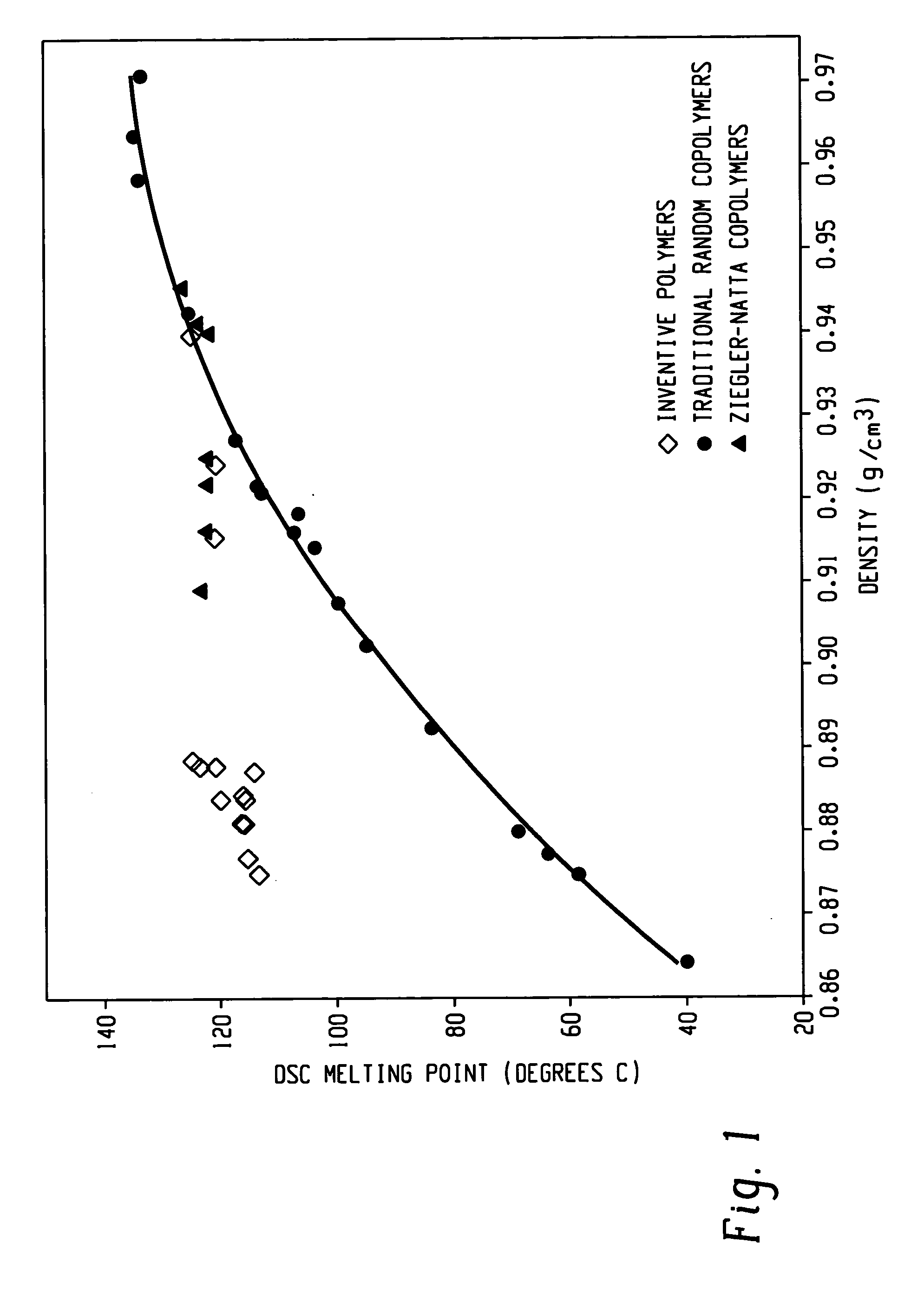
The present invention relates to film layers and compositions having improved hot tack properties. The compositions comprise at least one ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer, wherein the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer may have, for example, a Mw / Mn from about 1.7 to about 3.5, at least one melting point, Tm, in degrees Celsius, and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the numerical values of Tm and d correspond to the relationship: Tm>−2002.9+4538.5(d)−2422.2(d)2.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Anti-blocking compositions comprising interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Degradable ball sealers and methods for use in well treatment
Described is an oil-degradable ball sealer for use in the oil and gas industry. The ball seal comprises a particular composition including ethylene and one or more alpha-olefins, prepared by an injection molding technique to provide a ball sealer which will dissolve in stimulation or wellbore fluids after stimulation operations are complete. The composition, when dissolved into wellbore fluids, does not pose a hazard or problem to aqueous wellbore fluids or further wellbore stimulations.
Owner:FAIRMOUNT SANTROL
Fibers made from copolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins
A fiber is obtainable from or comprises an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer characterized by an elastic recovery, Re, in percent at 300 percent strain and 1 cycle and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the elastic recovery and the density satisfy the following relationship: Re>1481−1629(d). Such interpolymer can also be characterized by other properties. The fibers made therefrom have a relatively high elastic recovery and a relatively low coefficient of friction. The fibers can be cross-linked, if desired. Woven or non-woven fabrics can be made from such fibers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Foams made from interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins
Foamable compositions and foams comprise at least an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer. The foam has a density from greater than 150 to about 500 kg / m3. The foamable compositions further comprise a blowing agent and a crosslinking agent. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are a multi-block copolymer comprising at least one soft block and at least one hard block. Methods of making the foamable compositions and foams; and foamed articles made from the foams are also described.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Rheology modification of interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins and articles made therefrom
Rheology modification of an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is achieved by blending the interpolymer with at least one branched polyolefin. The polyolefins can be homopolymers or interpolymers and have a branching index of less than 1. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is a block copolymer having at least a hard block and at least a soft block. The soft block comprises a higher amount of comonomers than the hard block. The block interpolymer has a number of unique characteristics disclosed here. Rheology-modified ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer, i.e., the resulting polymer blends, can be extruded or molded into many useful articles, such as films, sheets, profiles, gaskets, foams, etc.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Manufacture of alpha -olefins
InactiveUS6103946AOrganic chemistry methodsIron group organic compounds without C-metal linkagesAlpha-olefinAlkene
Alpha-olefins are manufactured in high yield and with very high selectivity by contacting ethylene with an iron complex of a selected 2,6-pyridinedicarboxaldehyde bisimine or a selected 2,6-diacylpyridine bisimine, and in some cases a selected activator compound such as an alkyl aluminum compound. Novel bisimines and their iron complexes are also disclosed. The alpha -olefins are useful as monomers and chemical intermediates.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Sulfonated block copolymers, method for making same, and various uses for such block copolymers
ActiveUS20070021569A1High water transport propertyImprove wet strengthSemi-permeable membranesNegative electrodesMethacrylatePolymer science
The present invention is a, solid block copolymer comprising at least two polymer end blocks A and at least one polymer interior block B wherein each A block is a polymer block resistant to sulfonation and each B block is a polymer block susceptible to sulfonation, and wherein said A and B blocks do not contain any significant levels of olefinic unsaturation. Preferably, each A block comprising one or more segments selected from polymerized (i) para-substituted styrene monomers, (ii) ethylene, (iii) alpha olefins of 3 to 18 carbon atoms; (iv) hydrogenated 1,3-cyclodiene monomers, (v) hydrogenated monomers of conjugated dienes having a vinyl content less than 35 mol percent prior to hydrogenation, (vi) acrylic esters, (vii) methacrylic esters, and (viii) mixtures thereof; and each B block comprising segments of one or more polymerized vinyl aromatic monomers selected from (i) unsubstituted styrene monomers, (ii) ortho-substituted styrene monomers, (iii) meta-substituted styrene monomers, (iv) alpha-methylstyrene, (v) 1,1-diphenylethylene, (vi) 1,2-diphenylethylene and (vii) mixtures thereof. Also claimed are processes for making such block copolymers, and the various end uses and applications for such block copolymers.
Owner:KRATON POLYMERS US LLC
Interpolymers of ethylene/a-olefins blends and profiles and gaskets made therefrom
Polymer blends comprise at least an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers and at least one polyolefin. The polyolefins can be homopolymers or interpolymers and have a melt strength of at least about 6 cN. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is a block copolymer having at least a hard block and at least a soft block. The soft block comprises a higher amount of comonomers than the hard block. The block interpolymer has a number of unique characteristics disclosed here. The polymer blends can be profiled extruded to make profiles, gaskets, and other products.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Low molecular weight ethylene/alpha-olefin interpolymer as base lubricant oils
A lubricant composition comprises an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer having a number average molecular weight of less than 10,000 g / mol as a base oil and at least one oil additive. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer has at least one molecular fraction which elutes between 40° C. and 130° C. when fractionated using TREF, characterized in that the fraction has a molar comonomer content of at least 5 percent higher than that of a comparable random ethylene interpolymer fraction eluting between the same temperatures, wherein said comparable random ethylene interpolymer has the same comonomer(s) and has a melt index, density, and molar comonomer content (based on the whole polymer) within 10 percent of that of the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Catalyst components in use for polymerizing ethylene, and catalyst
This invention relates to a method for preparing catalyst for ethylene homopolymerization or copolymerization with other alpha-olefins. The catalyst comprises at least one Mg composite, at least one Ti compound, at least one organic alcohol compound, and at least one Si compound. The general formula of the Si compound is R1xR2ySi (OR3) z, where R1 and R2 are alkyl or halogen; R3 is alkyl; x is 0-2; y is 0-2; z is 0-4; x + y + z = 4. The catalyst has such advantages as high catalytic activity, high hydrogen sensitivity and narrow particle size distribution of polymer. The catalyst is suitable for slurry polymerization of ethylene, and combined polymerization process where catalyst with high activity is needed.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Compositions of ethylene/alpha-olefin multi-block interpolymer for blown films with high hot tack
InactiveUS7582716B2Less energyLess timeSynthetic resin layered productsBagsCelsius DegreeAlpha-olefin
The present invention relates to film layers and compositions having improved hot tack properties. The compositions comprise at least one ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer, wherein the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer may have, for example, a Mw / Mn from about 1.7 to about 3.5, at least one melting point, Tm, in degrees Celsius, and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the numerical values of Tm and d correspond to the relationship:Tm>−2002.9+4538.5(d)−2422.2(d)2.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Elastic blends comprising crystalline polymer and crystallizable polymers of propylene
Improved thermoplastic polymer blend compositions comprising an isotactic polypropylene component and an alpha-olefin and propylene copolymer component, said copolymer comprising crystallizable alpha-olefin sequences. In a preferred embodiment, improved thermoplastic polymer blends are provided comprising from about 35% to about 85% isotactic polypropylene and from about 30% to about 70% of an ethylene and propylene copolymer, wherein said copolymer comprises isotactically crystallizable propylene sequences and is predominately propylene. The resultant blends manifest unexpected compatibility characteristics, increased tensile strength, and improved process characteristics, e.g., a single melting point.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Fibers made from copolymers of propylene/alpha-olefins
ActiveUS20060199006A1Monocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentWoven fabricsFiberAlpha-olefin
A fiber is obtainable from or comprises a propylene / α-olefin interpolymer characterized by an elastic recovery, Re, in percent at 300 percent strain and 1 cycle and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the elastic recovery and the density satisfy the following relationship: Re>1481-1629(d). Such interpolymer can also be characterized by other properties. The fibers made therefrom have a relatively high elastic recovery and a relatively low coefficient of friction. The fibers can be cross-linked, if desired. Woven or non-woven fabrics can be made from such fibers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Process to produce low viscosity poly-alpha-olefins
ActiveUS20070043248A1Hydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionPolyolefinAlpha-olefin
This invention relates to a process to produce a polyalpha-olefin comprising: 1) contacting one or more alpha-olefin monomers having 3 to 24 carbon atoms with an unbridged substituted bis cyclopentadienyl transition metal compound having: 1) at least one non-isoolefin substitution on both cyclopentadientyl rings, or 2) at least two substitutions on at least one cyclopentadienyl ring, a non-coordinating anion activator, and optionally an alkyl-aluminum compound, where the molar ratio of transition metal compound to activator is 10:1 to 0.1:1, and if the alkyl aluminum compound is present then the molar ratio of alkyl aluminum compound to transition metal compound is 1:4 to 4000:1, under polymerization conditions wherein: i) hydrogen is present at a partial pressure of 0.1 to 50 psi, based upon the total pressure of the reactor or the concentration of the hydrogen is from 1 to 10,000 ppm or less by weight; ii) wherein the alpha-olefin monomer(s) having 3 to 24 carbon atoms are present at 10 volume % or more based upon the total volume of the catalyst / activator / alkylaluminum compound solutions, monomers, and any diluents or solvents present in the reaction; iii) the residence time of the reaction is at least 5 minutes; iv) the productivity of the process is at least 43,000 grams of total product per gram of transition metal compound; v) the process is continuous or semi-continuous, and vi) the temperature in the reaction zone does not rise by more than 10° C. during the reaction; and vii) ethylene is not present at more than 30 volume % of the monomers entering the reaction zone; and 2) obtaining a polyalpha-olefin (PAO), optionally hydrogenating the PAO, wherein the PAO comprises at least 50 mole % of a C3 to C24 alpha-olefin monomer, and wherein the PAO has a kinematic viscosity at 100° C. of 20 cSt or less.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Impact modification of thermoplastics with ethylene/alpha-olefin interpolymers
ActiveUS20070010616A1Improve and maintain and impact performanceImprove and maintain modulusThermoplasticPolymer science
Compositions having good impact performance can be made from a thermoplastic (e.g., a polyolefin such as polypropylene or HDPE) and an ethylene multi-block copolymer. The compositions are easily molded and often have particular utility in making, for example, automotive facia, parts and other household articles.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Syndiotactic rich polyolefins
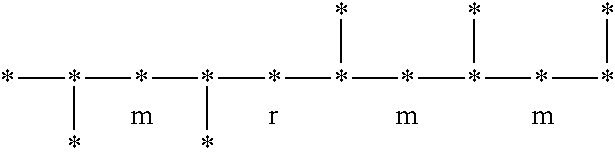
Disclosed herein is a polymer comprising an amorphous syndiotactic rich polyolefin comprising greater than about 50 wt % C3-C40 alpha olefins and having about 50% to less than about 80% r dyads, based on the total number of r and m dyads present in the polymer; a heat of fusion of 10 joules / g or less according to the procedure described in ASTM E 794-85; and an ash content of 1 wt % or less. A functionalized amorphous syndiotactic rich polyolefin is also disclosed, along with methods to produce and a method to use the inventive polymer.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for producing liquid polyalphaolefin polymer, metallocene catalyst therefor, the resulting polymer and lubricant containing same
InactiveUS6858767B1Eliminate needHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionHydrocarbonsPolymer scienceHydrogen
A liquid polyalphaolefin homo- or copolymer, preferably 1-decene, which is substantially amorphous is obtained by a polymerization process employing hydrogen and a particular type of metallocene catalyst. Additionally, liquid polyalphaolefin homo- or copolymer containing from 2 to about 12 carbon atoms possess a unique combination of properties, i.e., low molecular weight (Mw), low polydispersity index (Mw / Mn controllable kinematic viscosity (Kv100), low Iodine Number (I2) and low glass transition temperature (Tg) and are substantially amorphous. The liquid polyalphaolefin homo- or copolymers provided herein are useful for manufacturing a variety of products including lubricating oils in which the polyalphaolefin functions as a viscosity modifier.
Owner:DEUT BANK AG NEW YORK BRANCH
Compositions of ethylene/alpha-olefin multi-block interpolymer for elastic films and laminates
This invention relates to polyolefin compositions. In particular, the invention pertains to elastic polymer compositions that can be more easily processed on cast film lines, extrusion lamination or coating lines due to improved resistance to draw resonance. The compositions of the present invention preferably comprise an elastomeric polyolefin resin and a high pressure low density type resin.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Anti-blocking compositions comprising interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com