Patents
Literature
481results about "Artificial filament physical treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
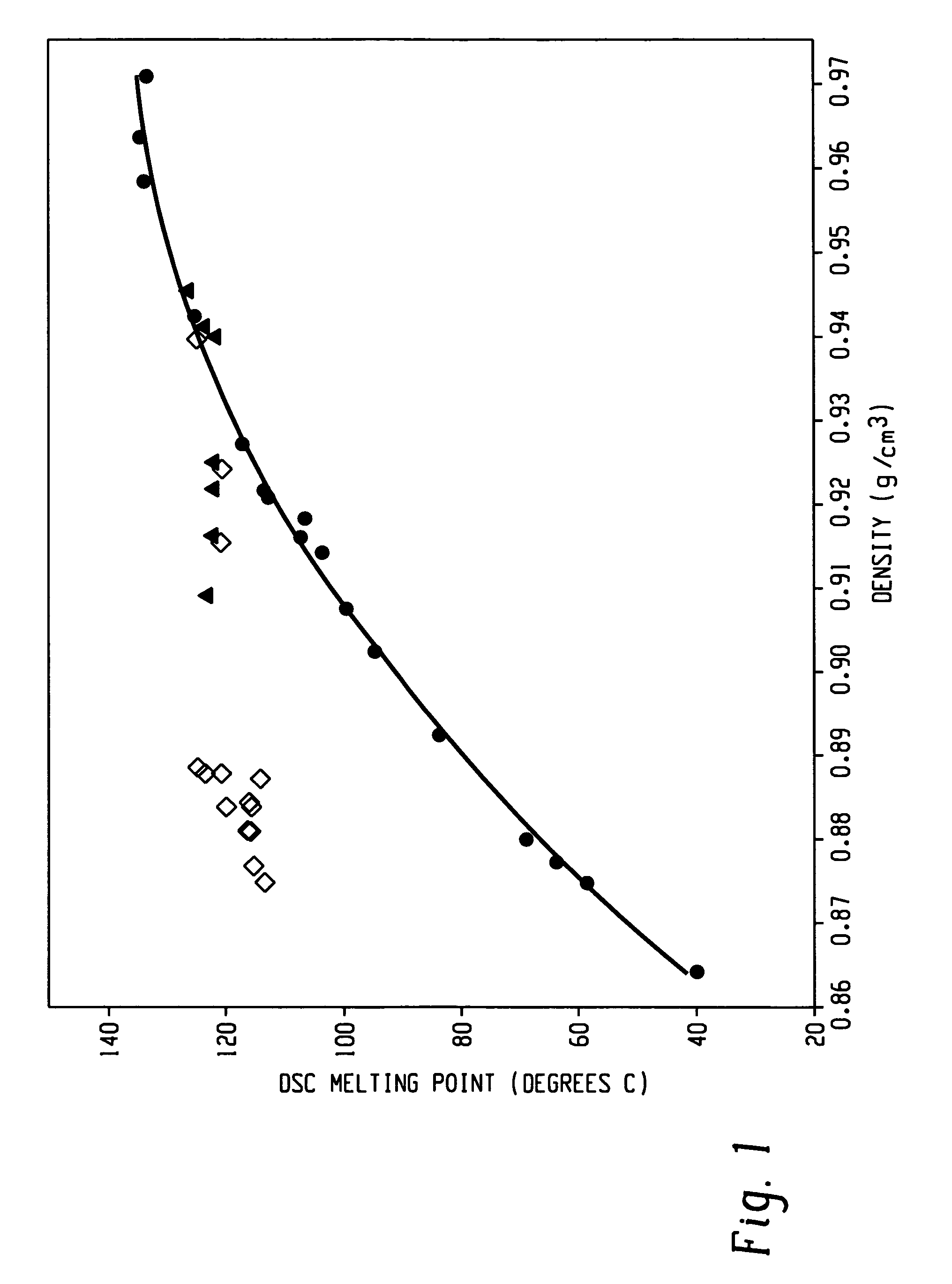
Fibers made from copolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins
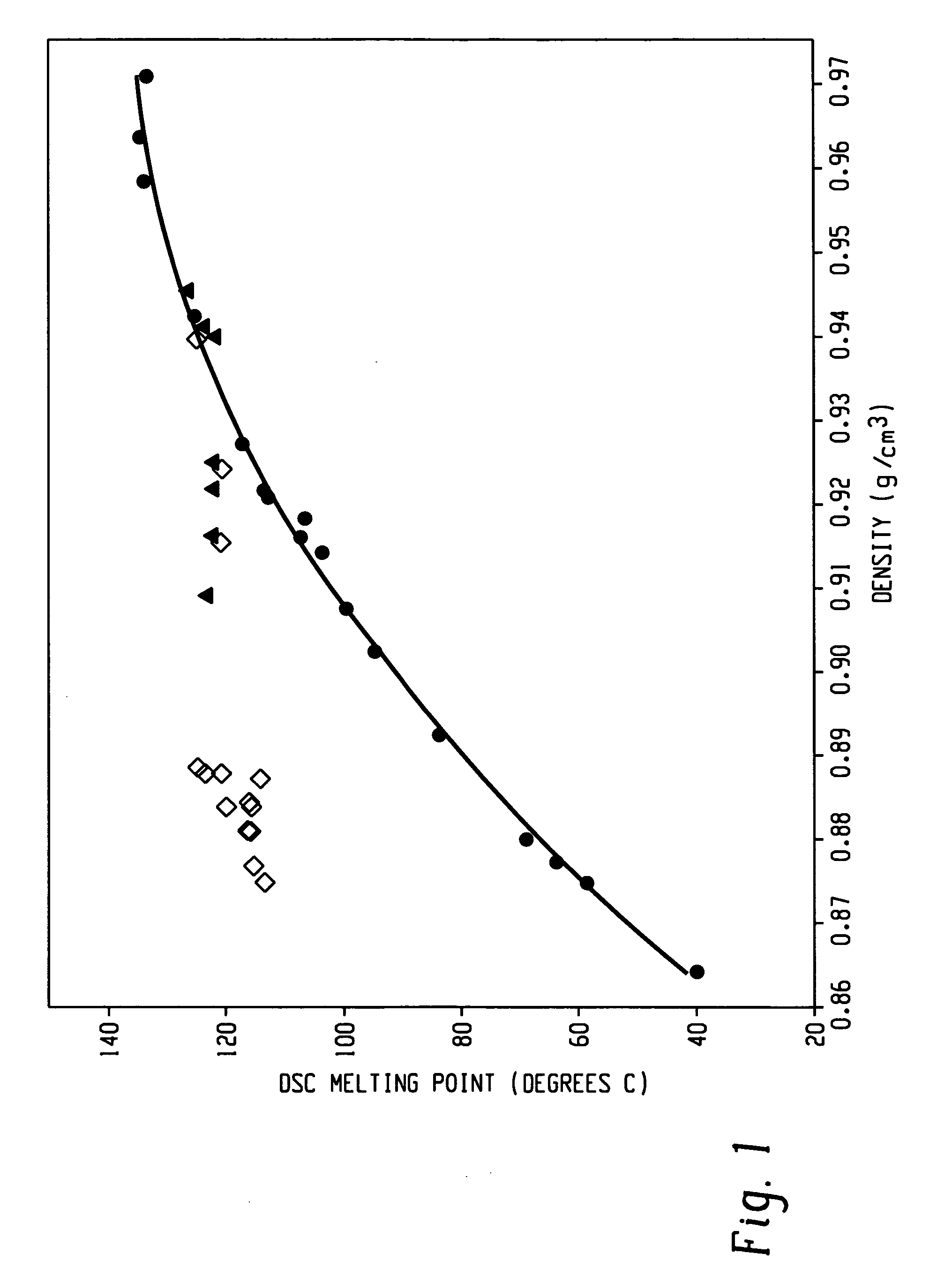
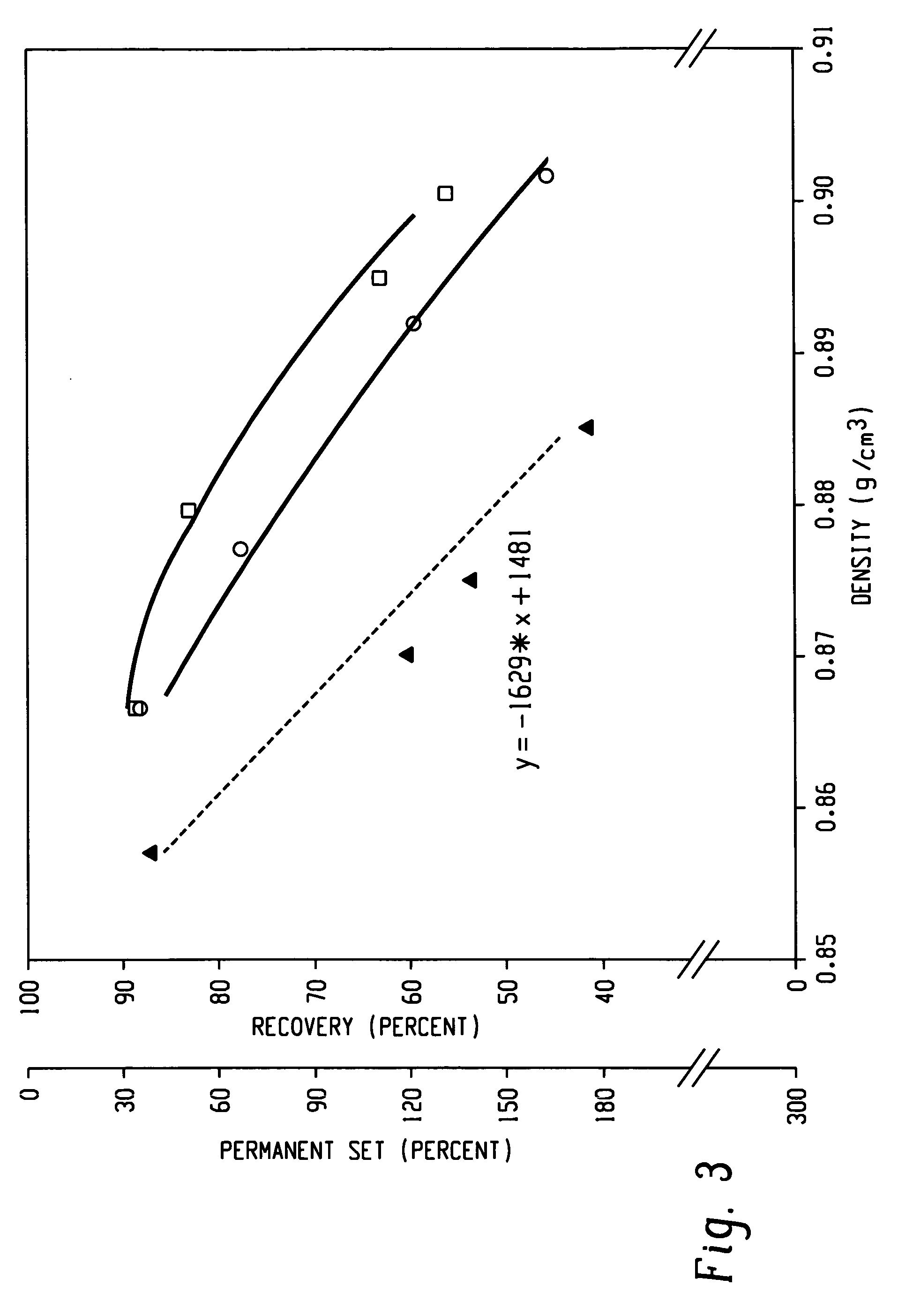
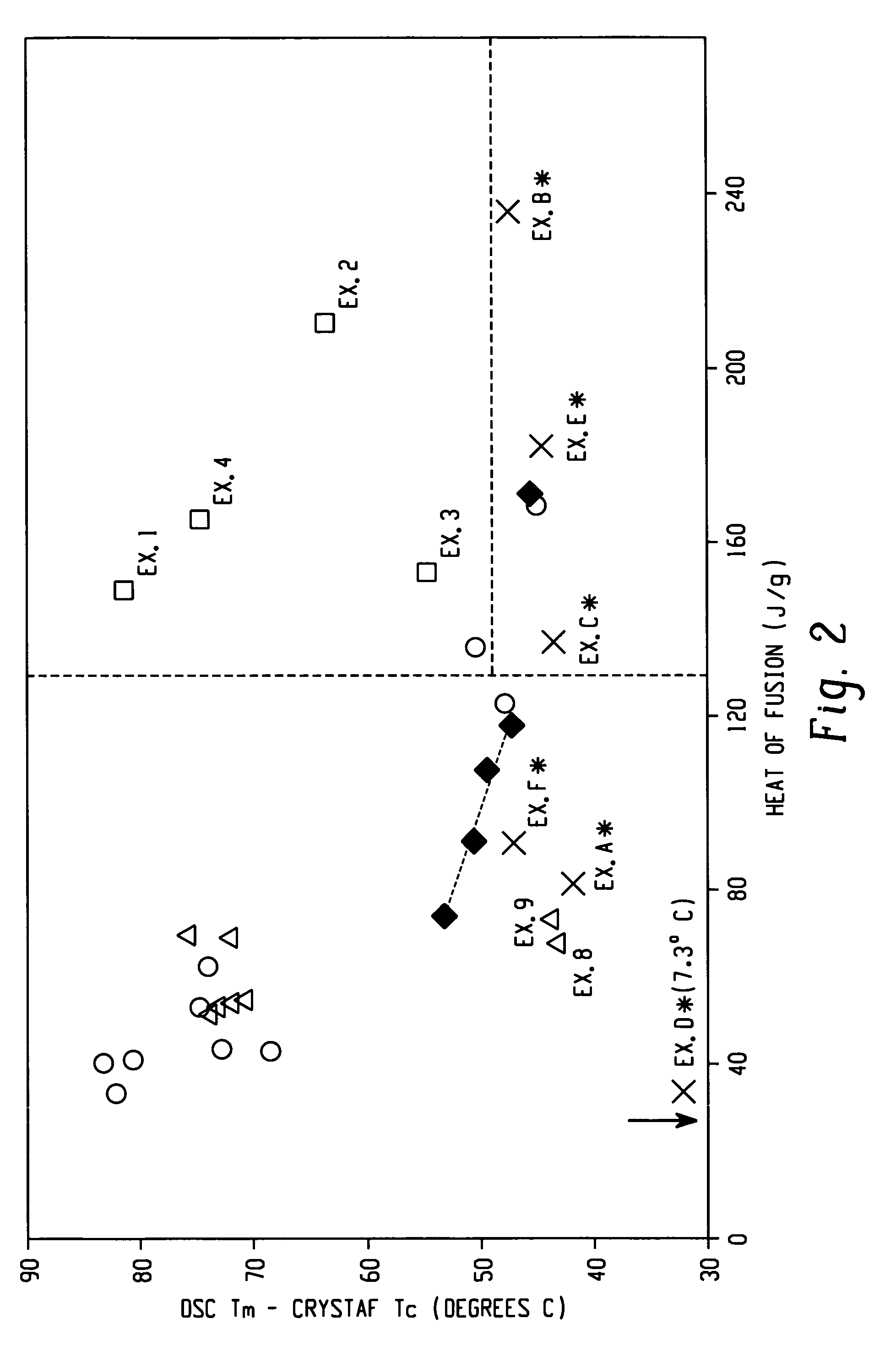
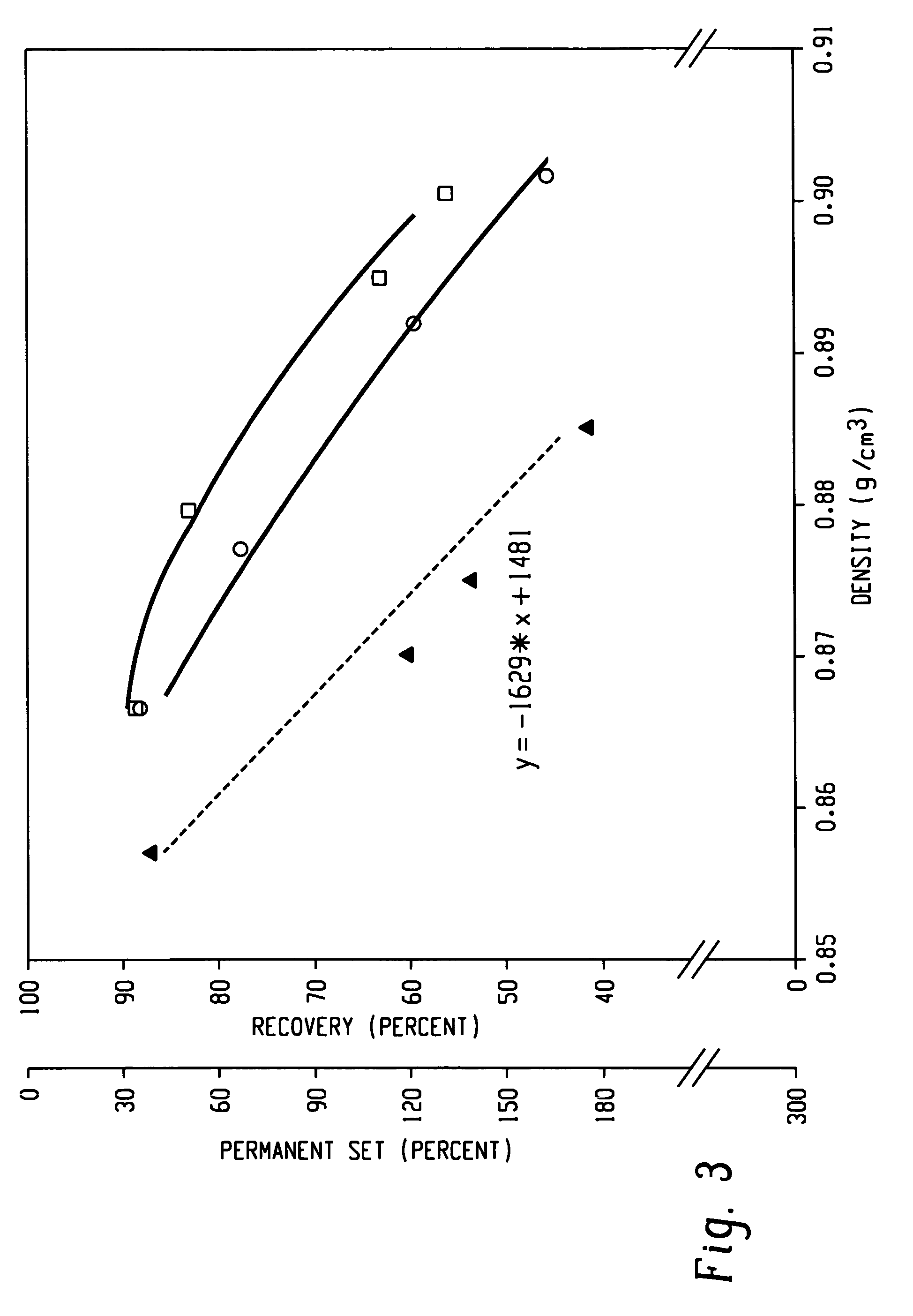
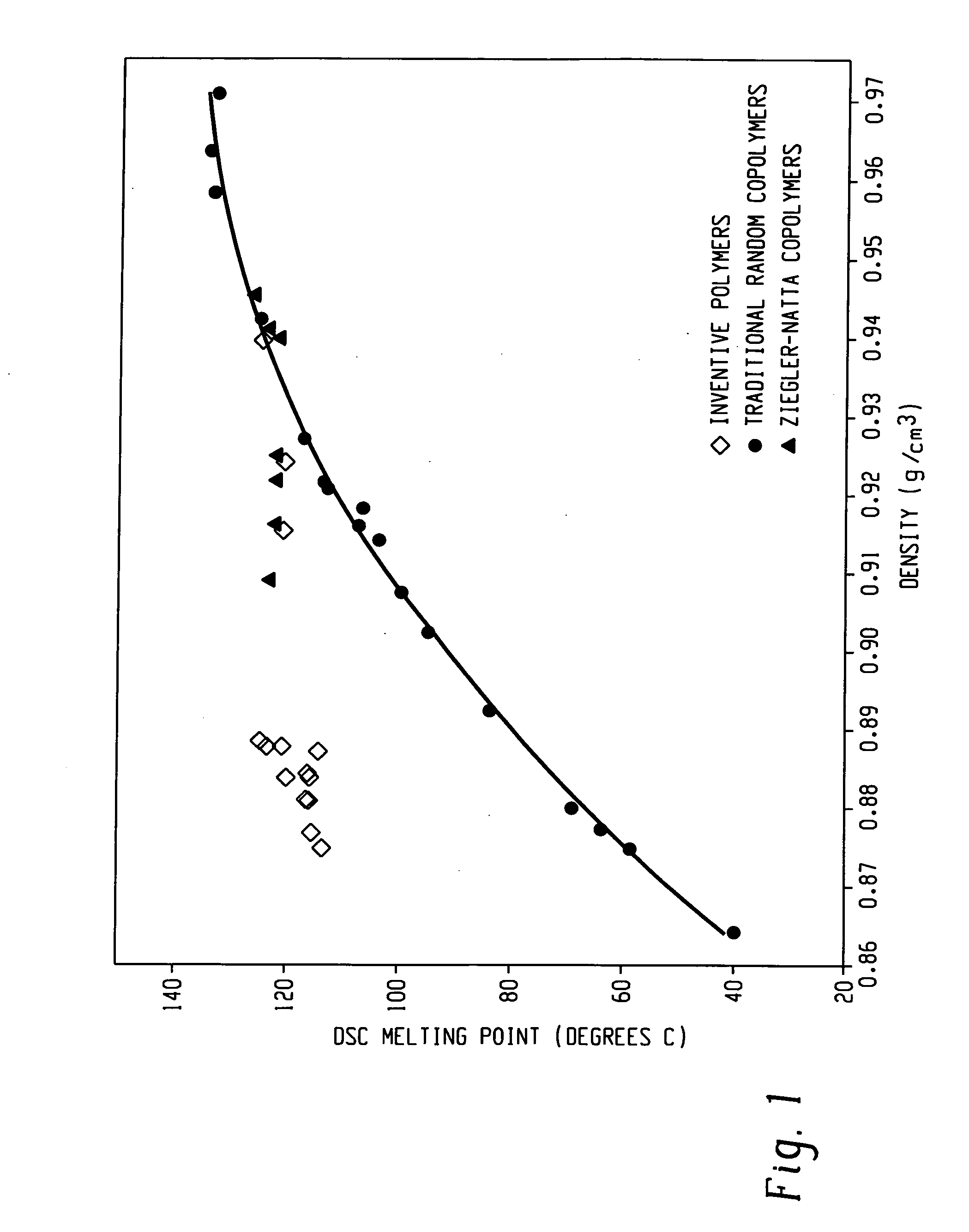
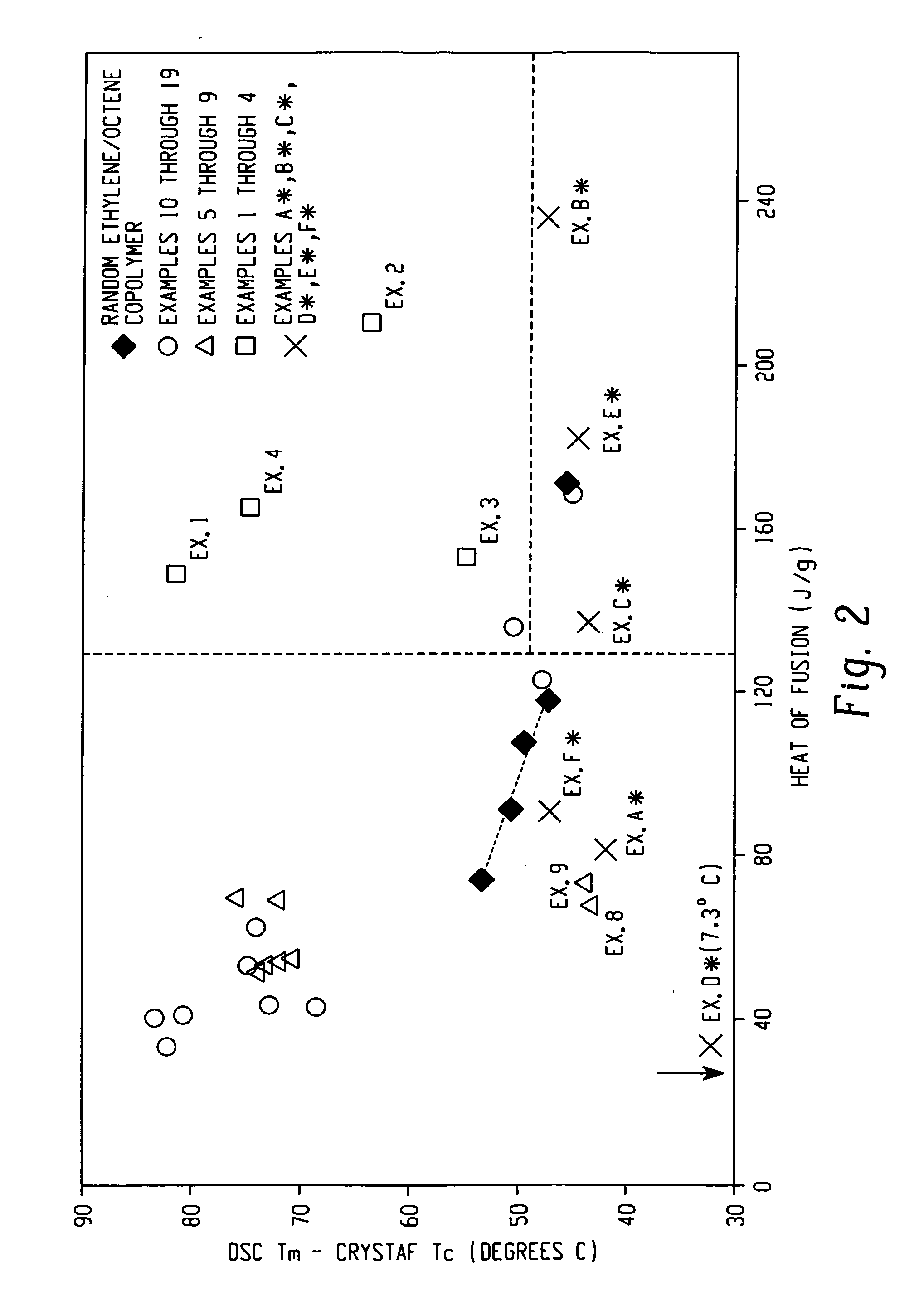
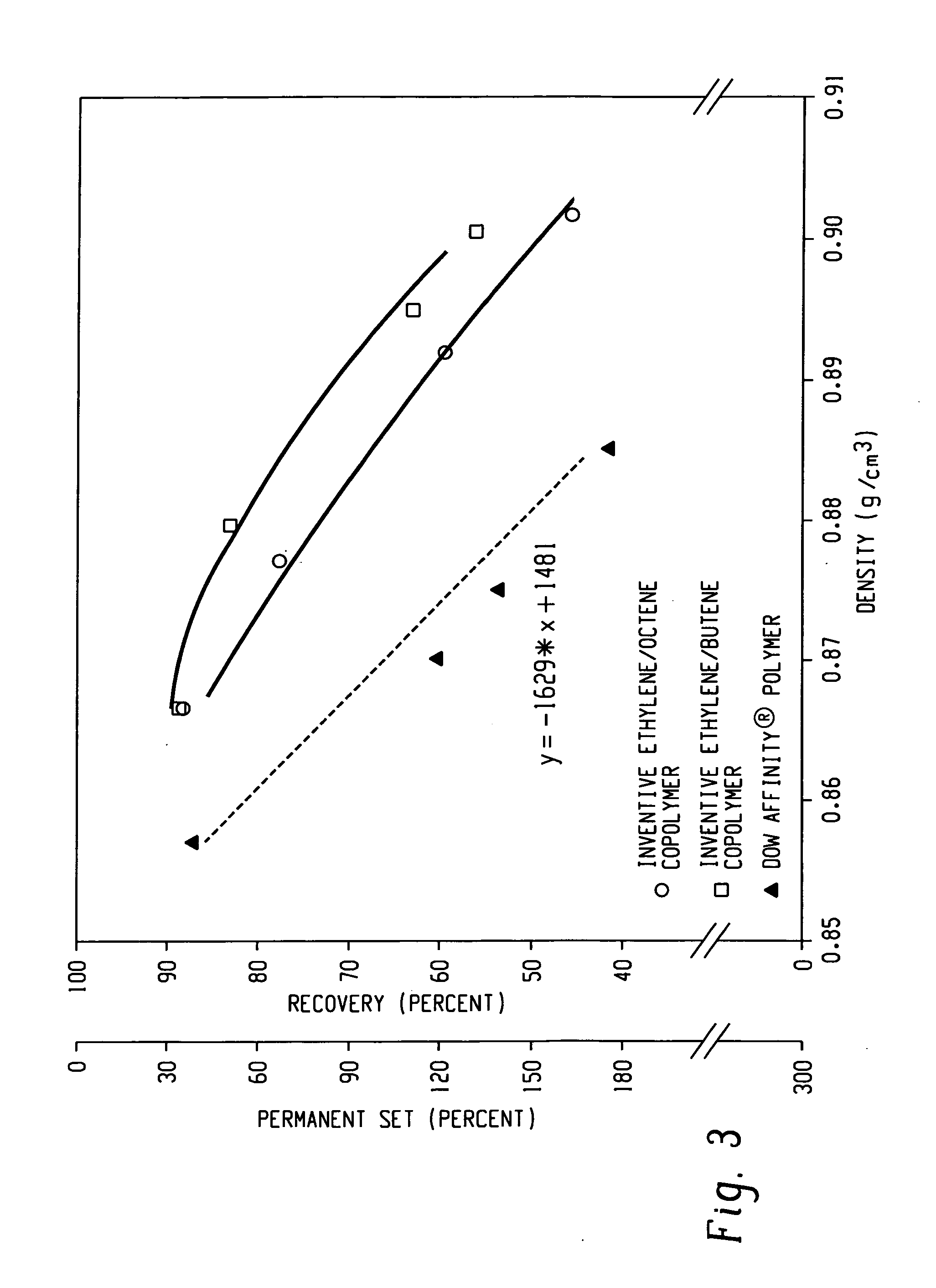
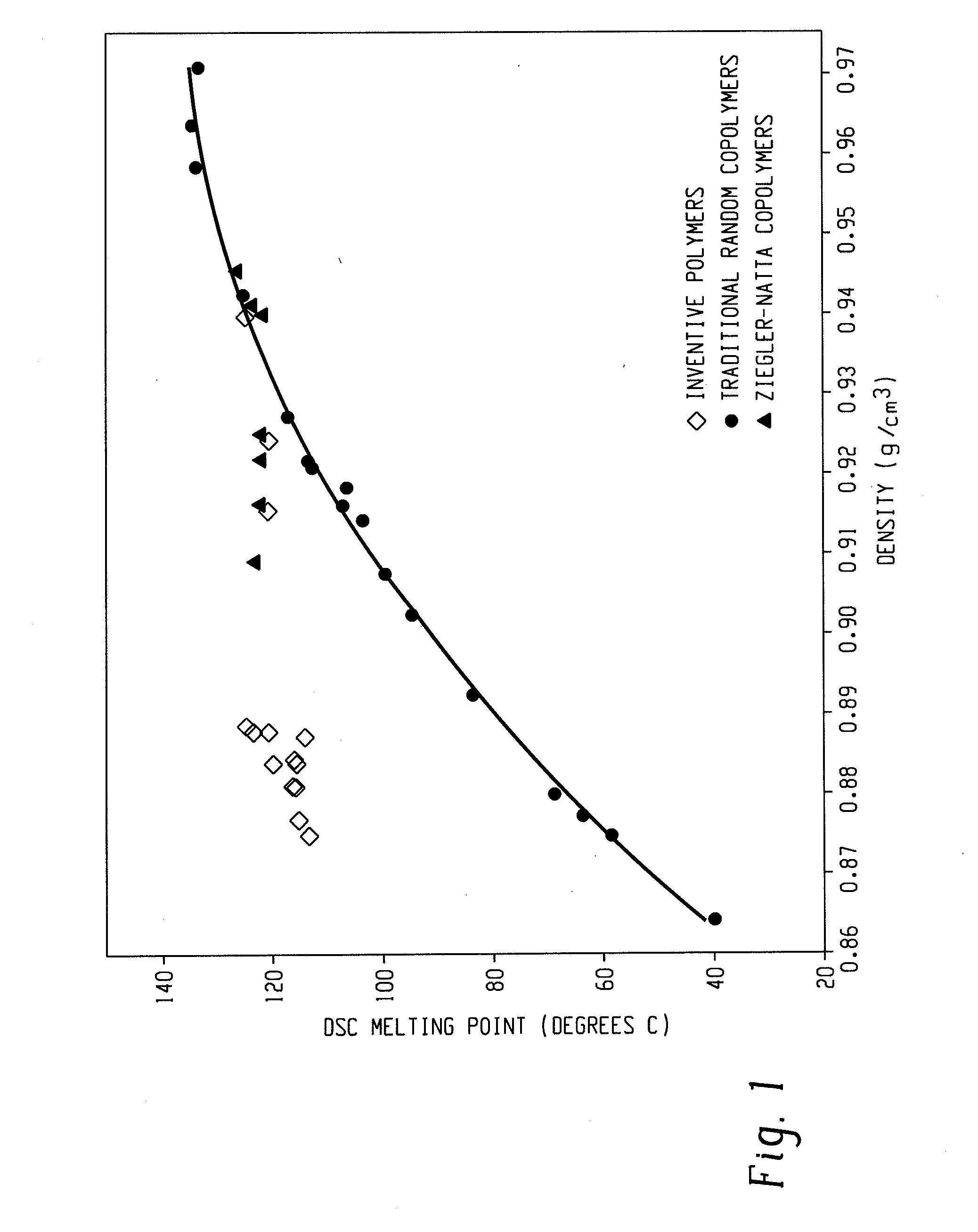
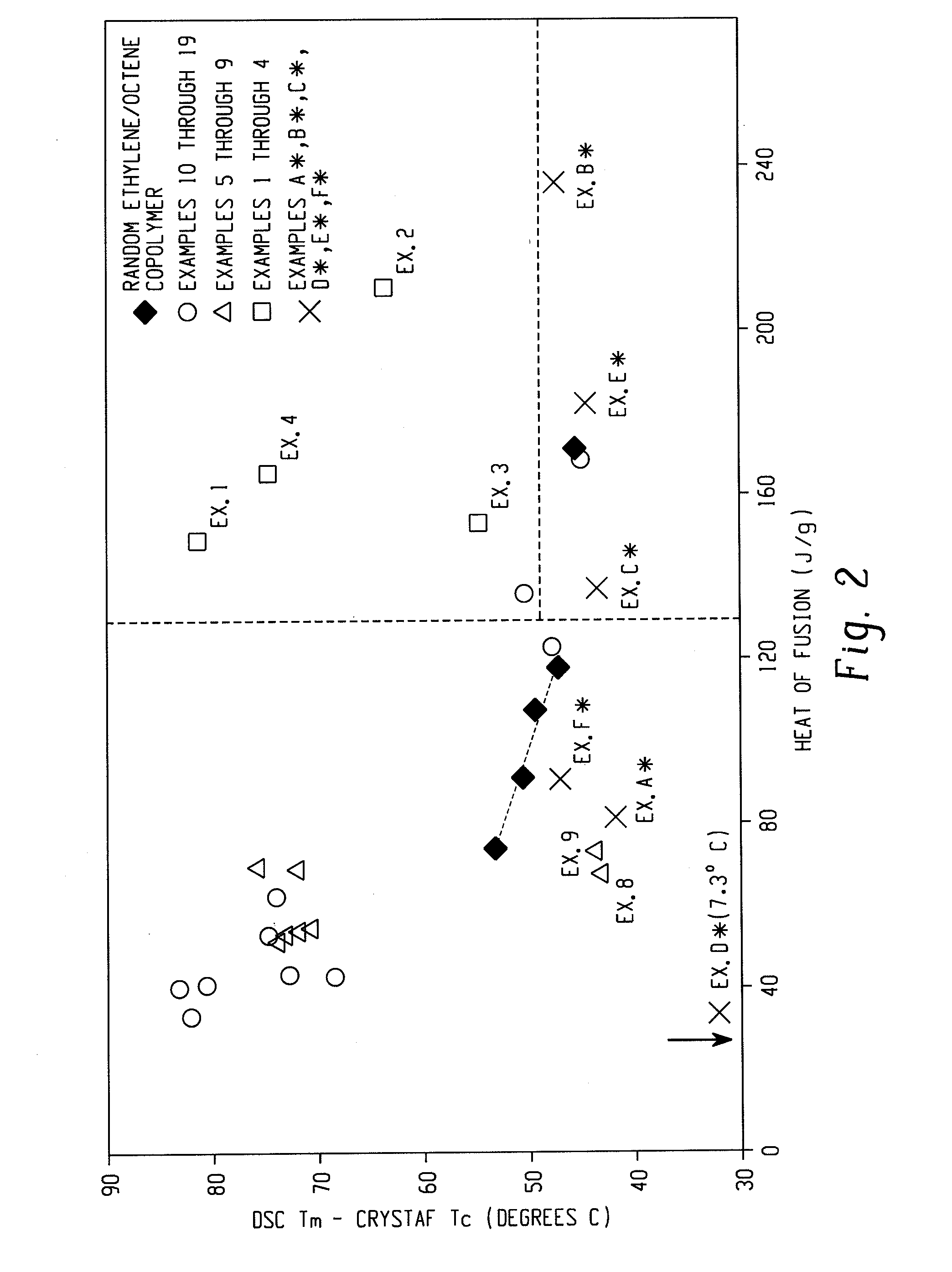
A fiber is obtainable from or comprises an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer characterized by an elastic recovery, Re, in percent at 300 percent strain and 1 cycle and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the elastic recovery and the density satisfy the following relationship: Re>1481−1629(d). Such interpolymer can also be characterized by other properties. The fibers made therefrom have a relatively high elastic recovery and a relatively low coefficient of friction. The fibers can be cross-linked, if desired. Woven or non-woven fabrics can be made from such fibers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
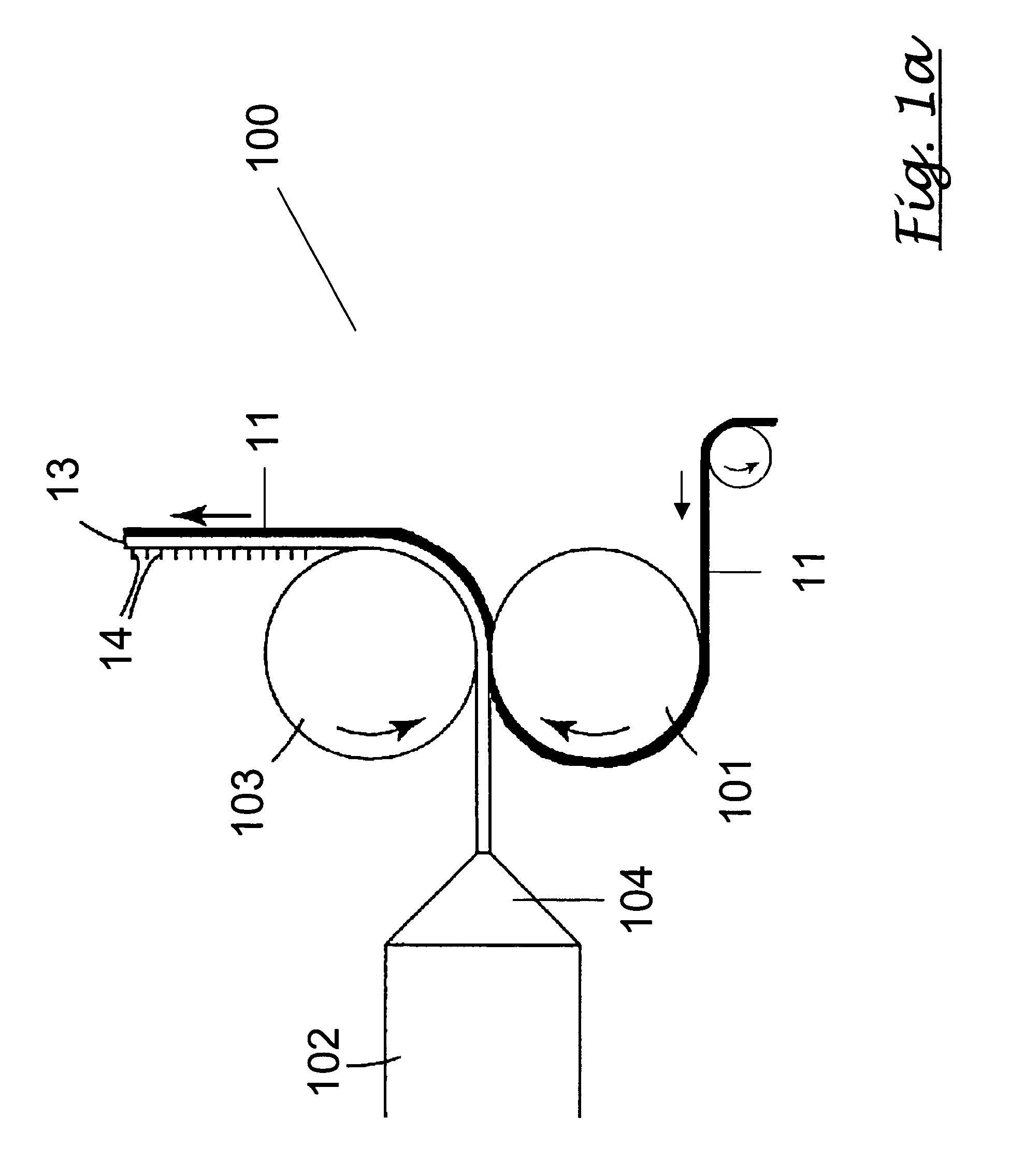
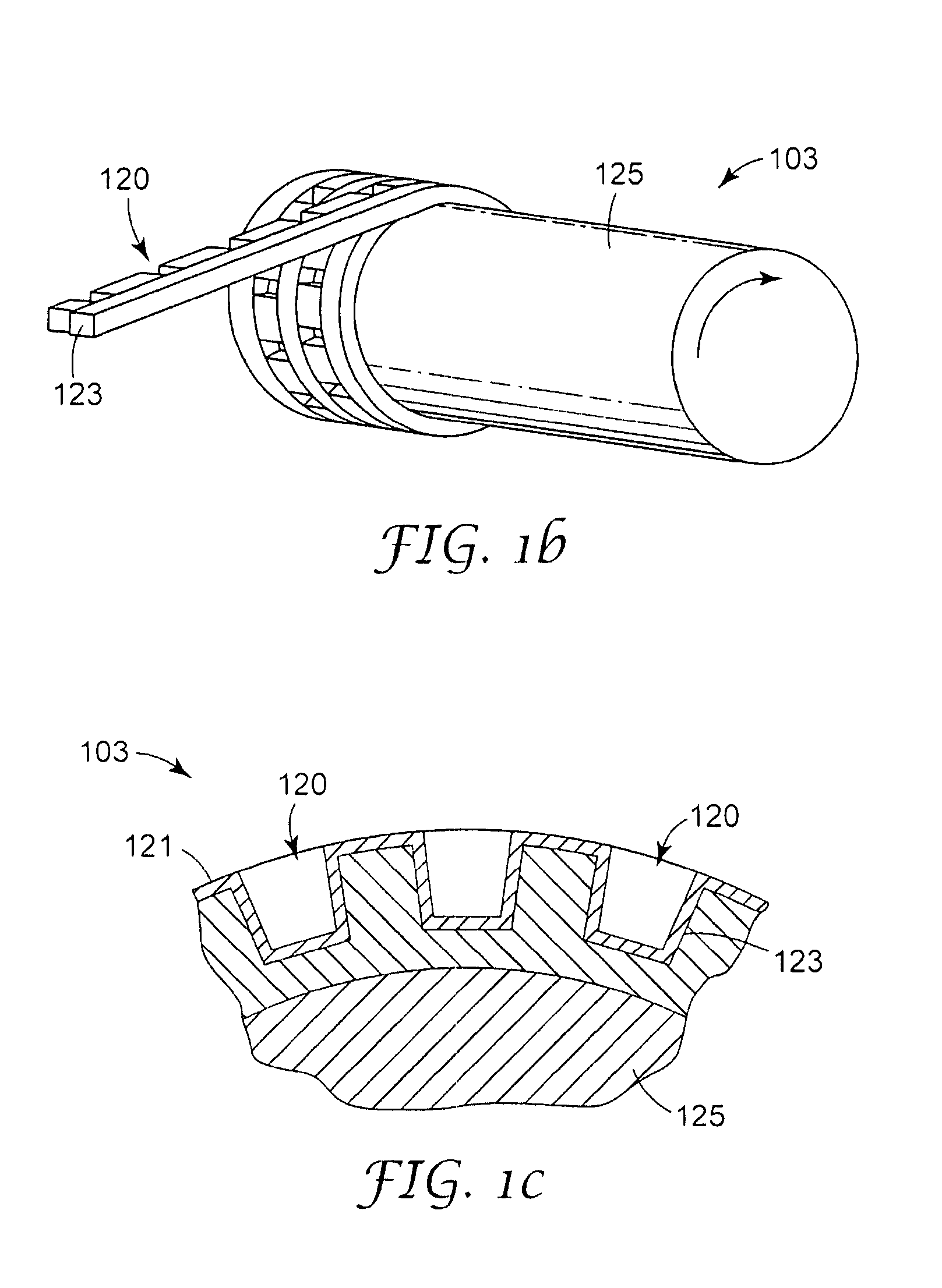
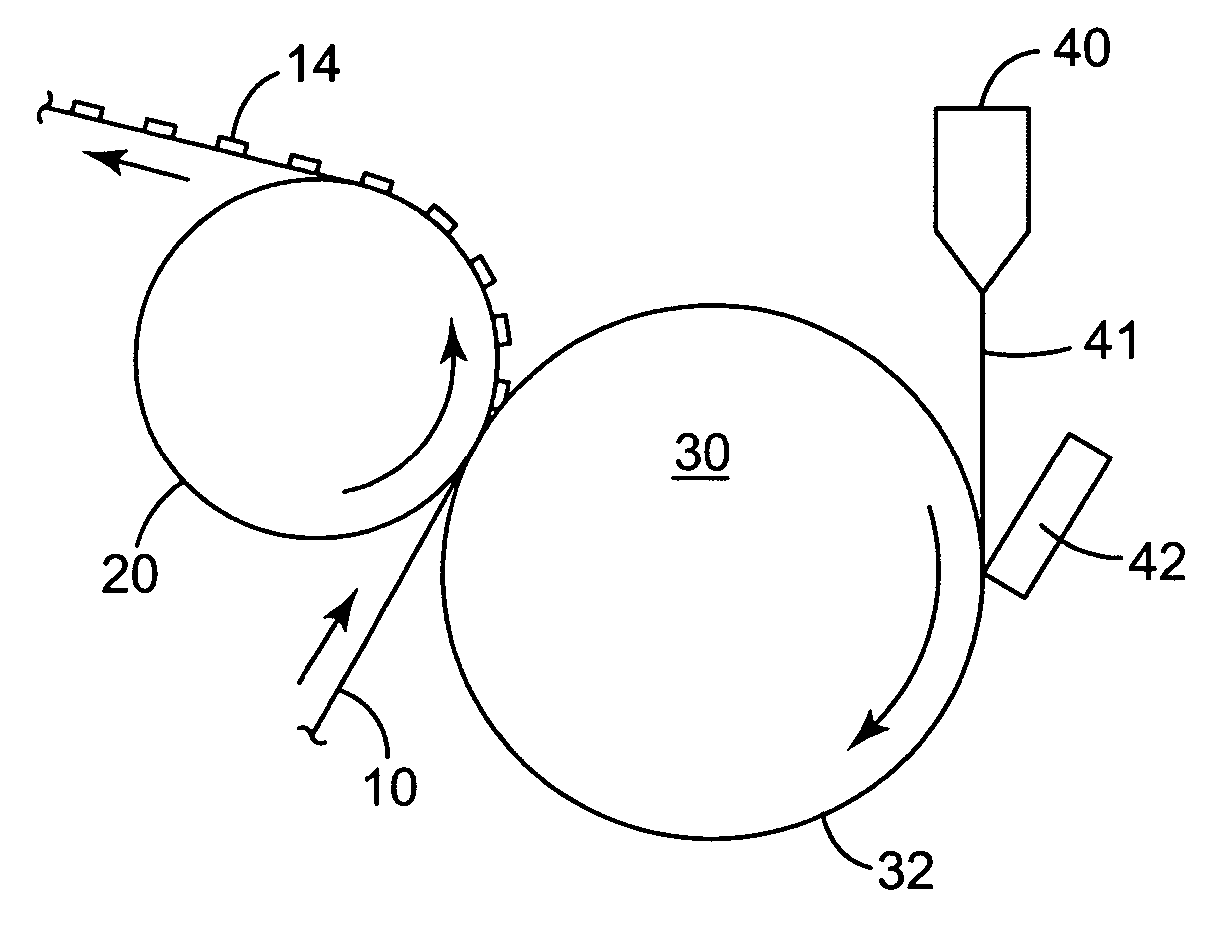
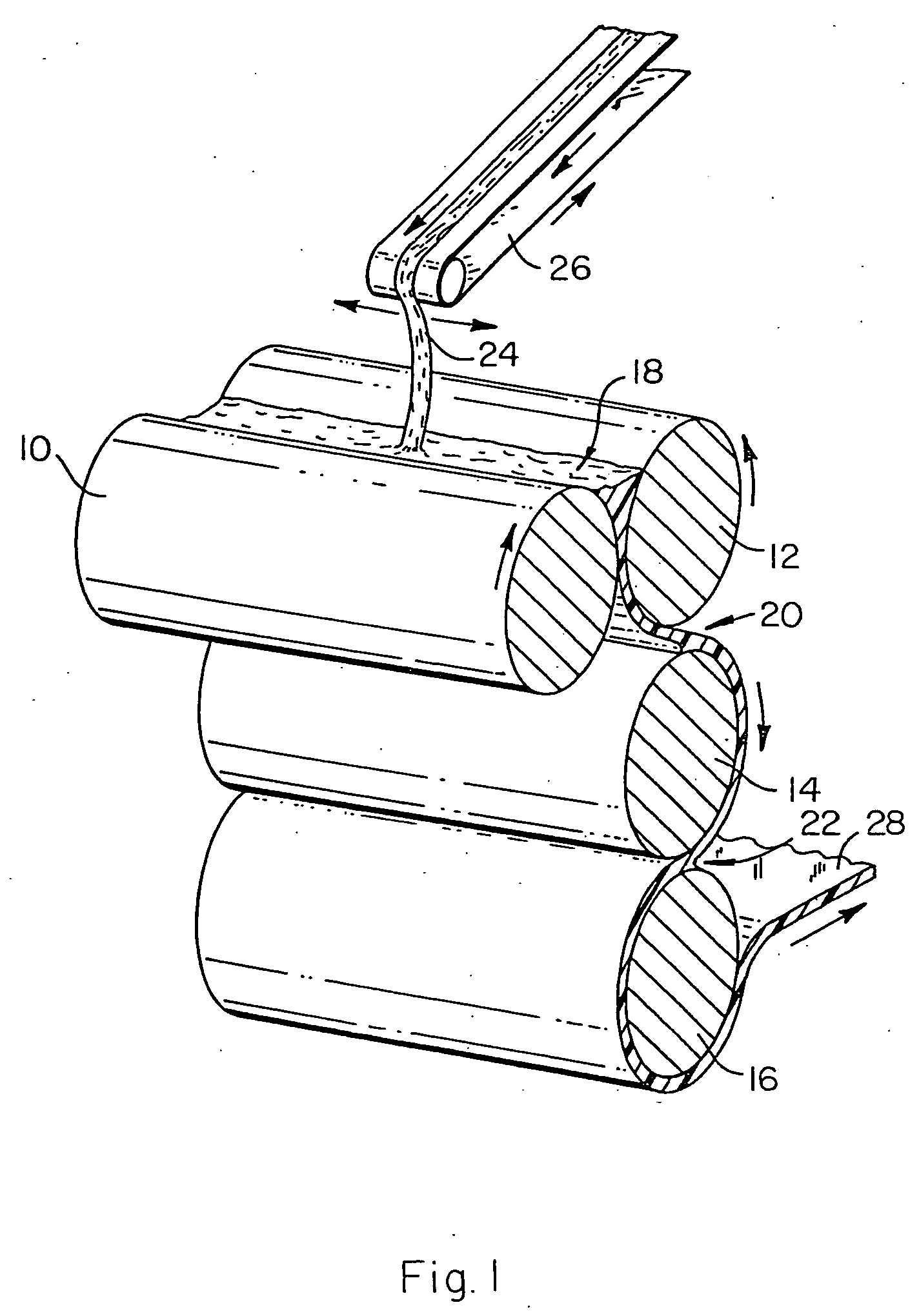
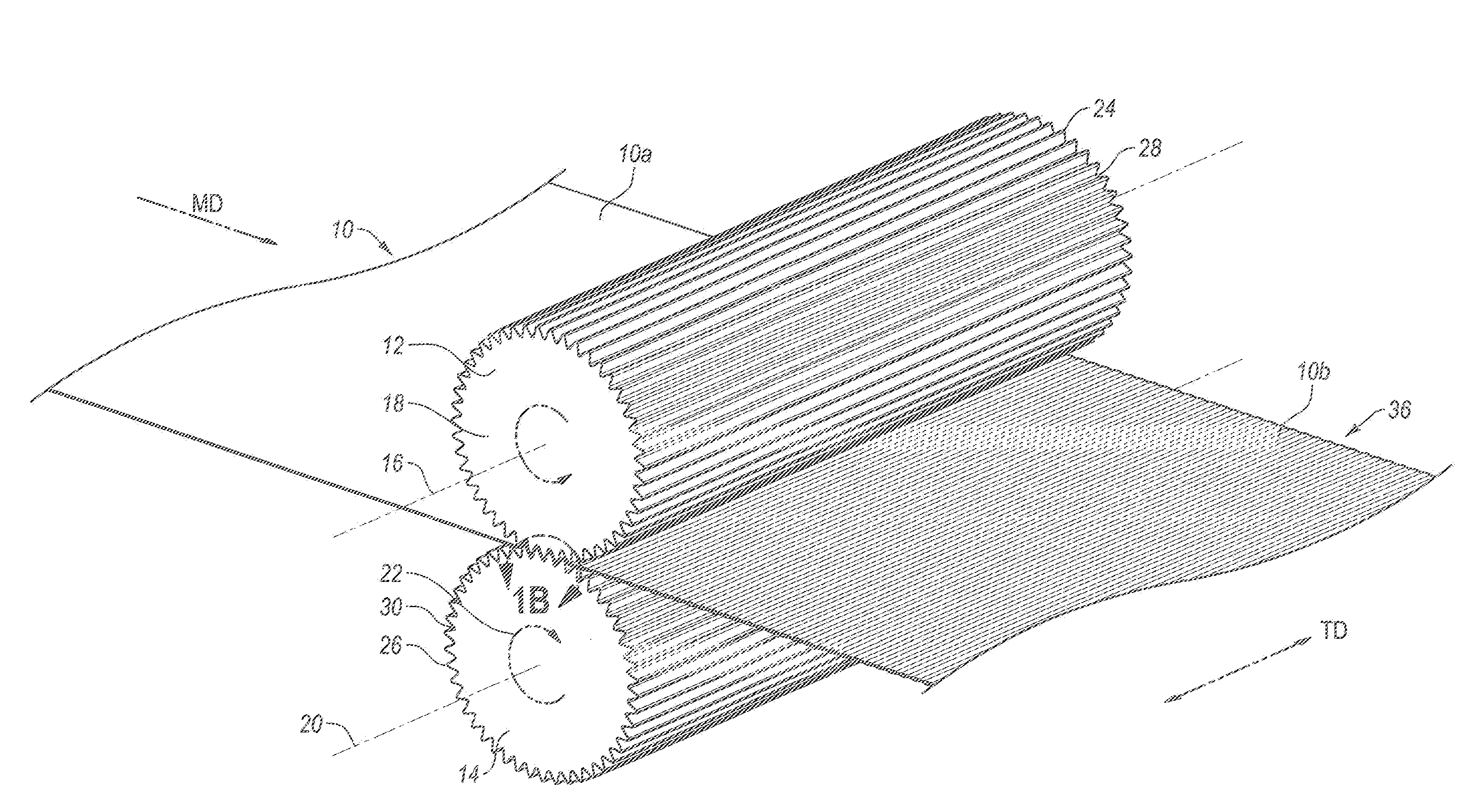
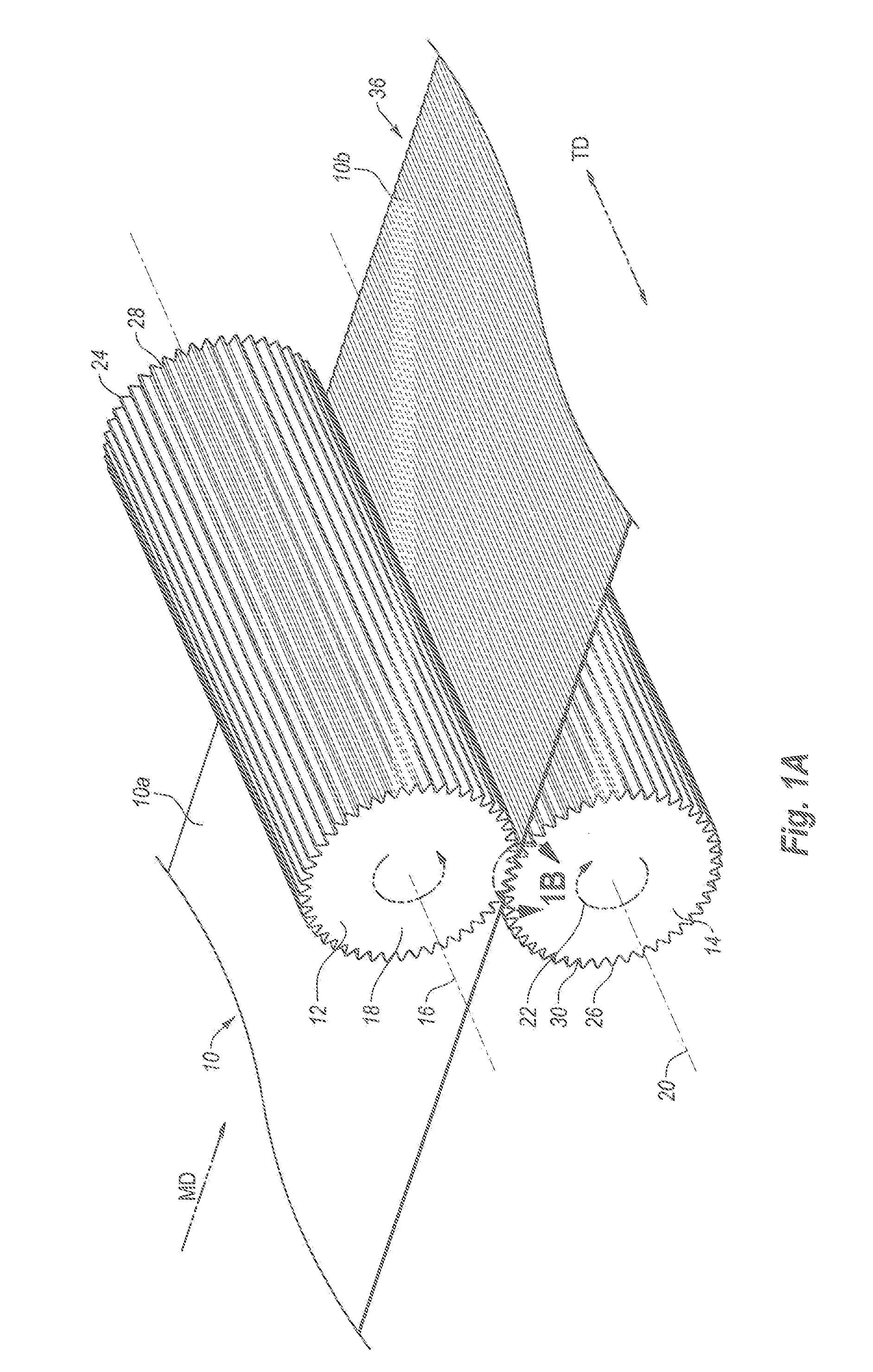
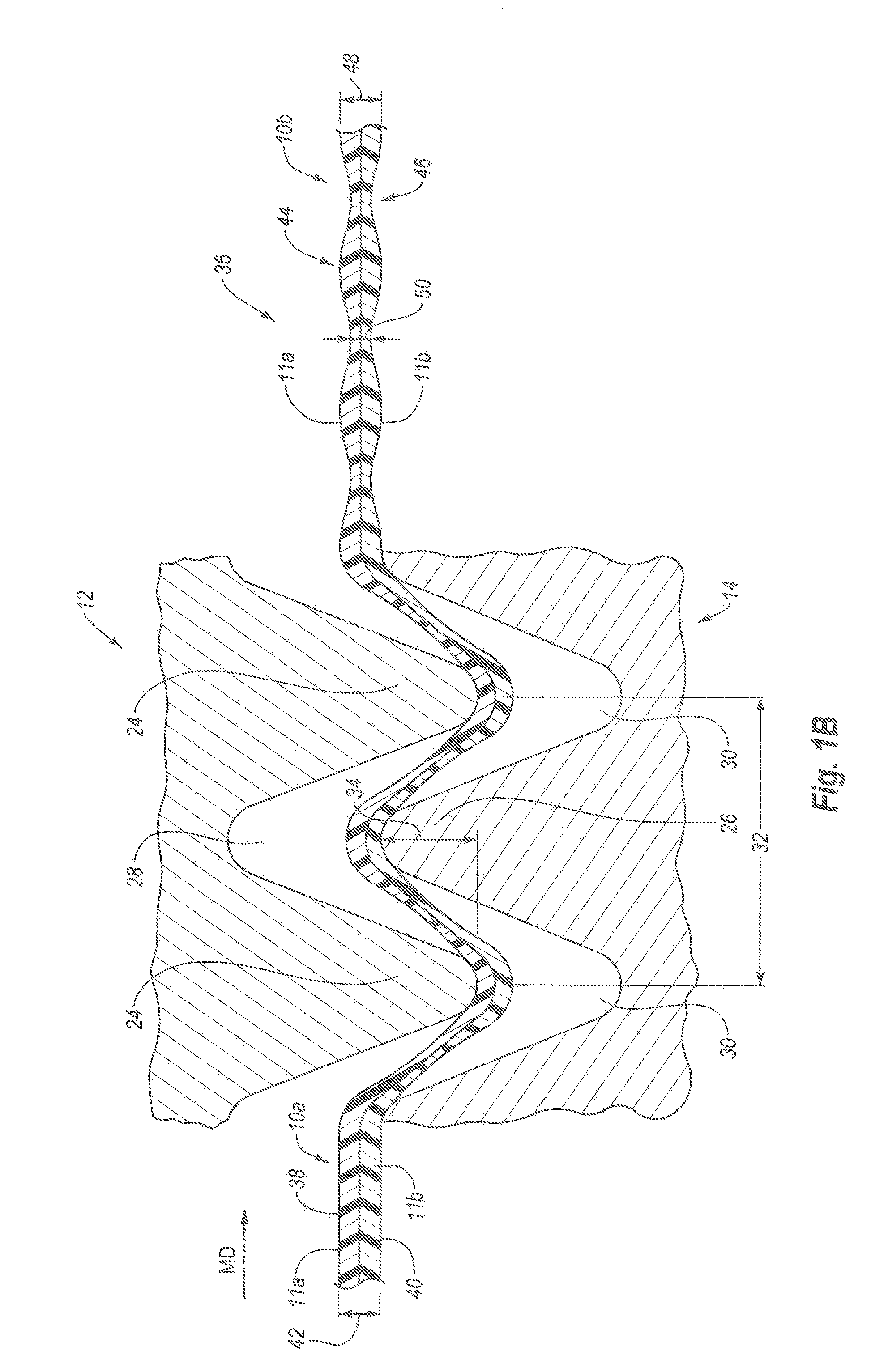
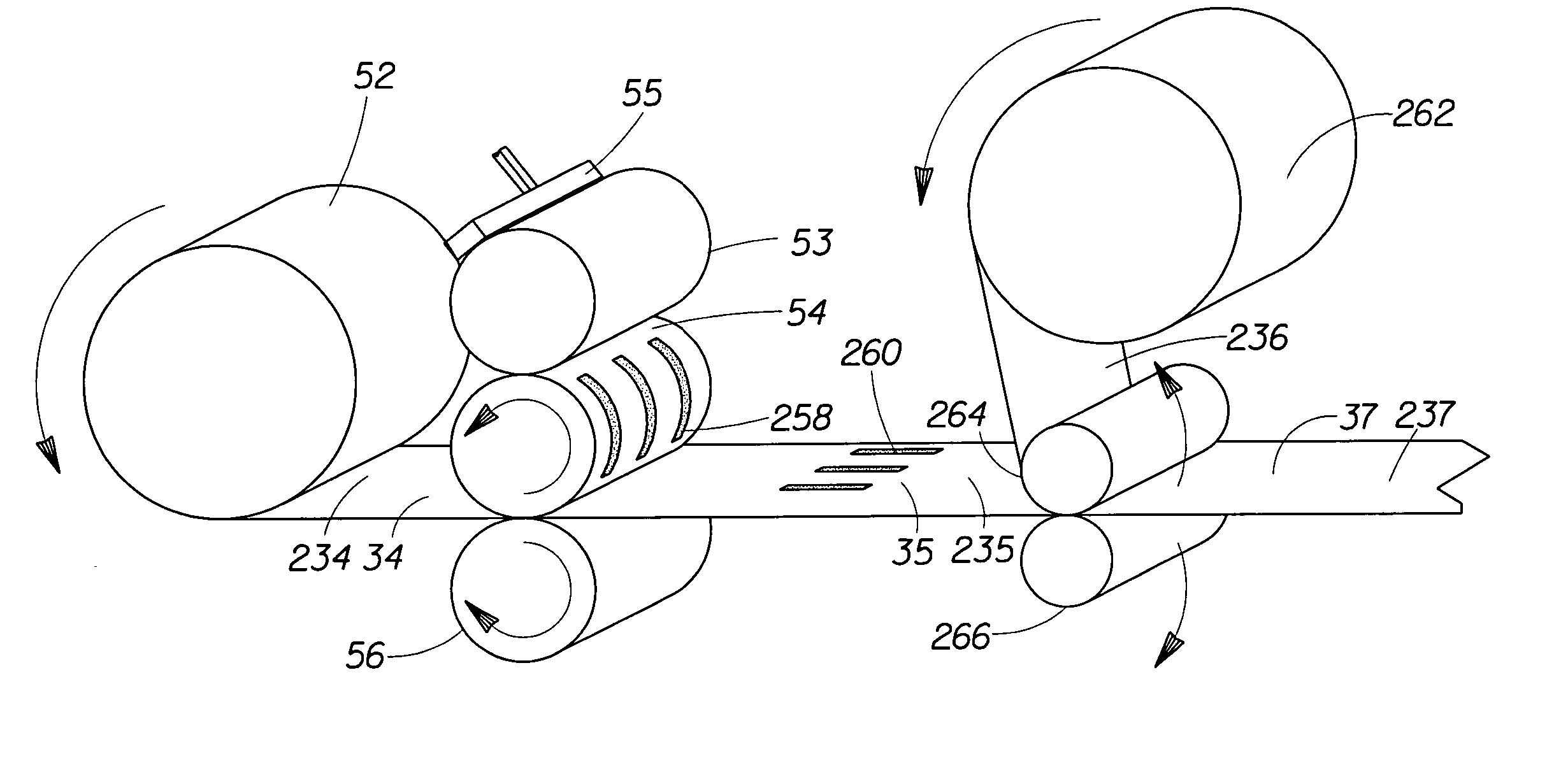
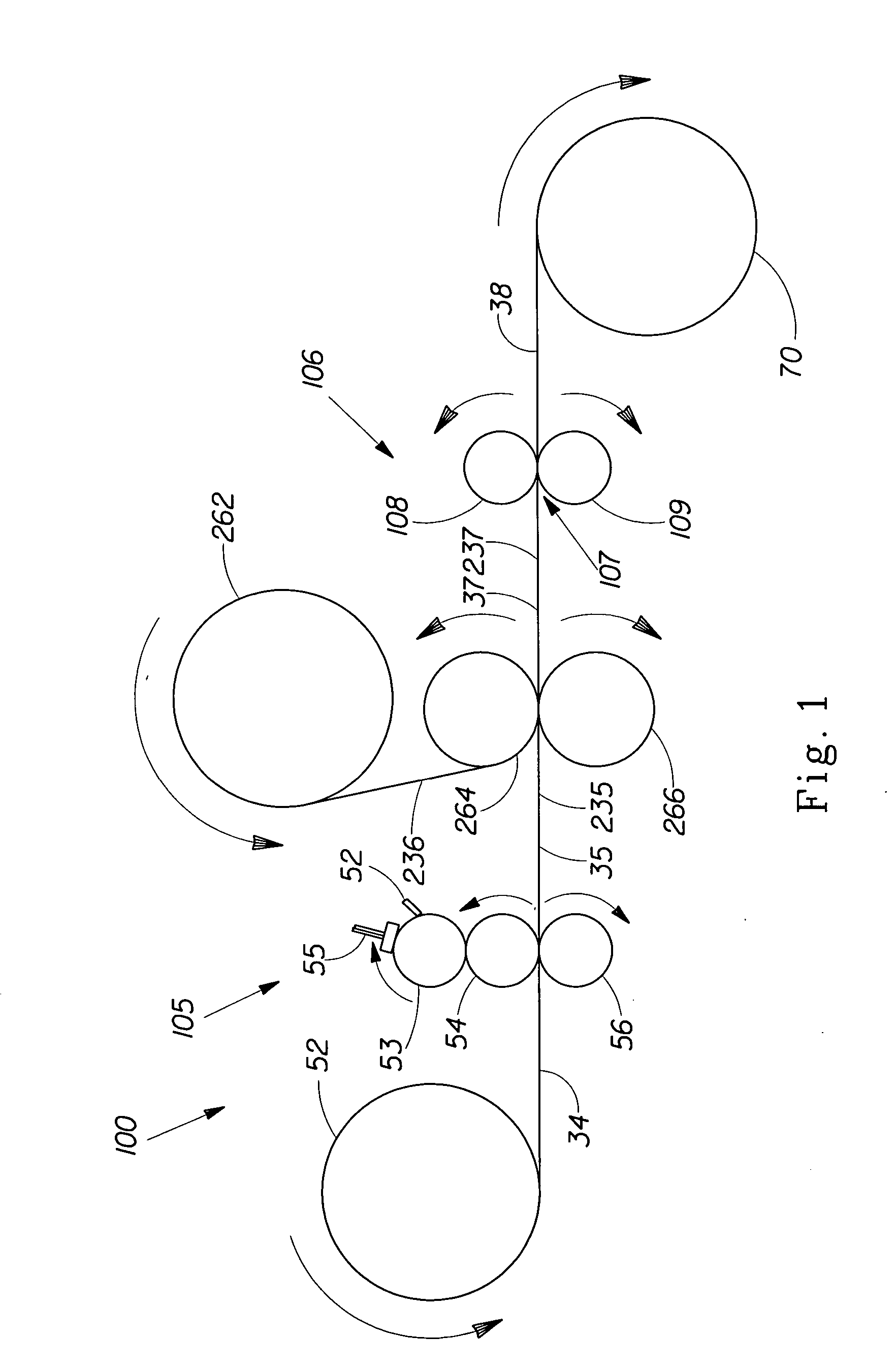
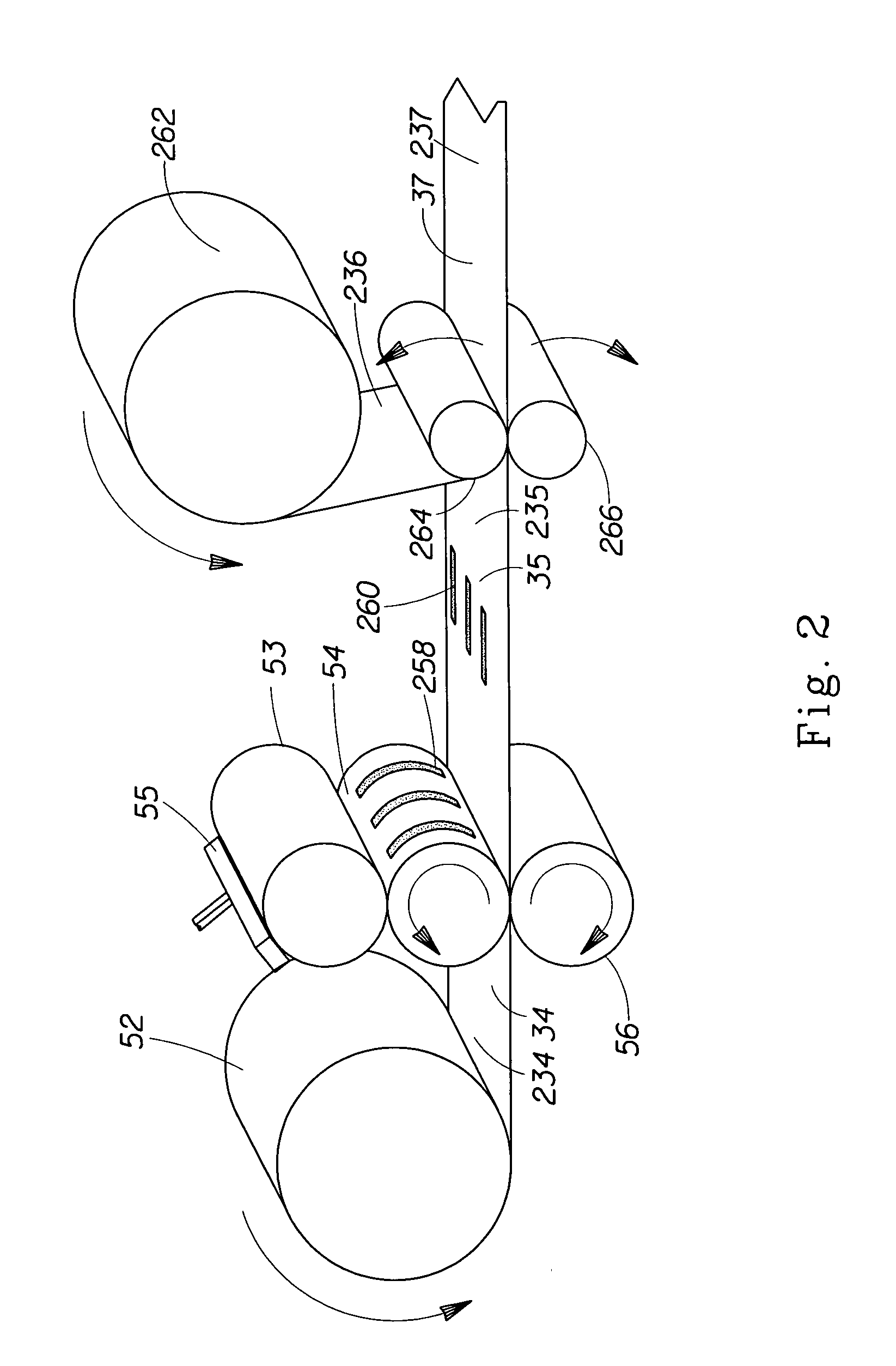
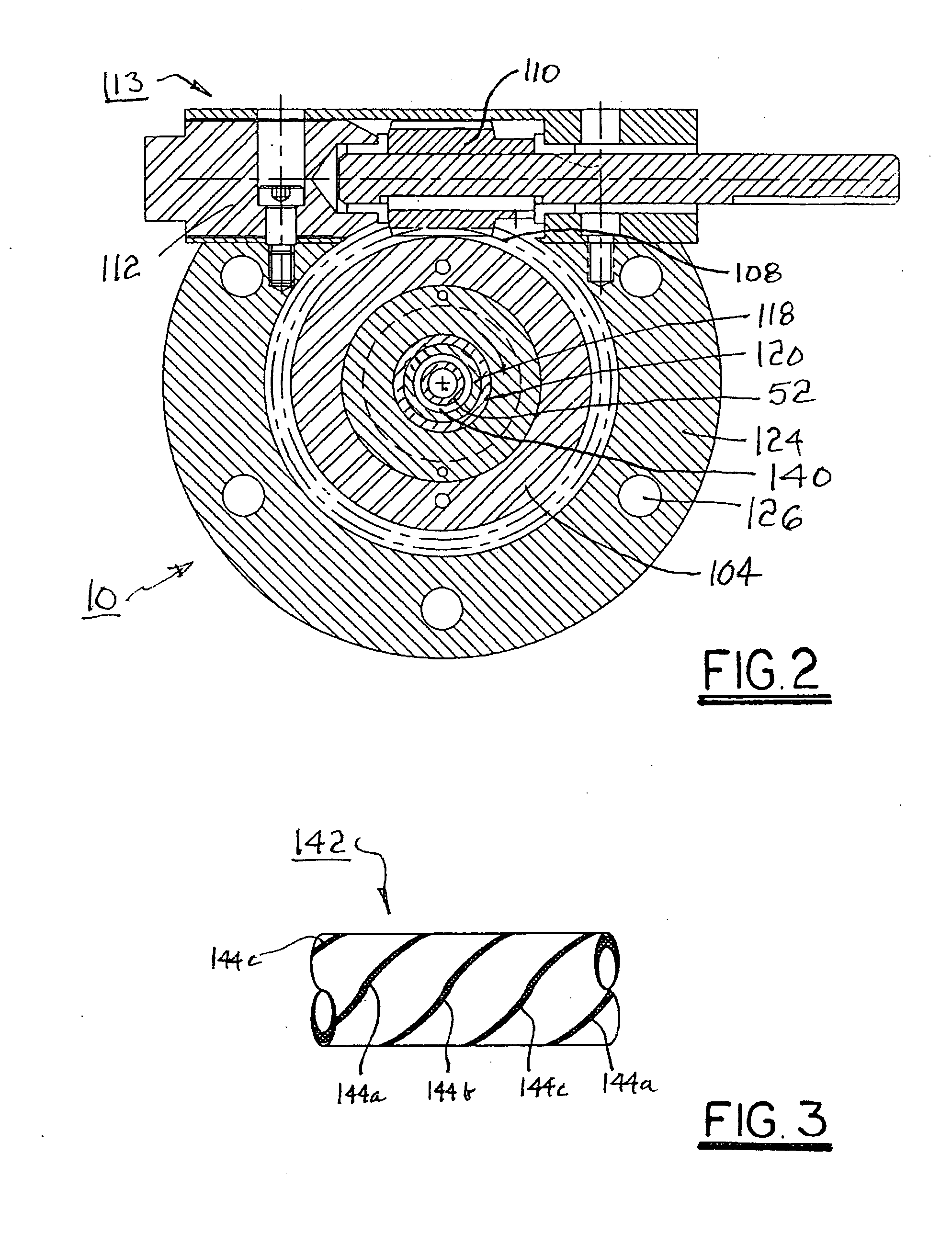
Methods of manufacturing a stretched mechanical fastening web laminate
InactiveUS7897078B2Reduce basis weightSnap fastenersWood working apparatusFiberVolumetric Mass Density
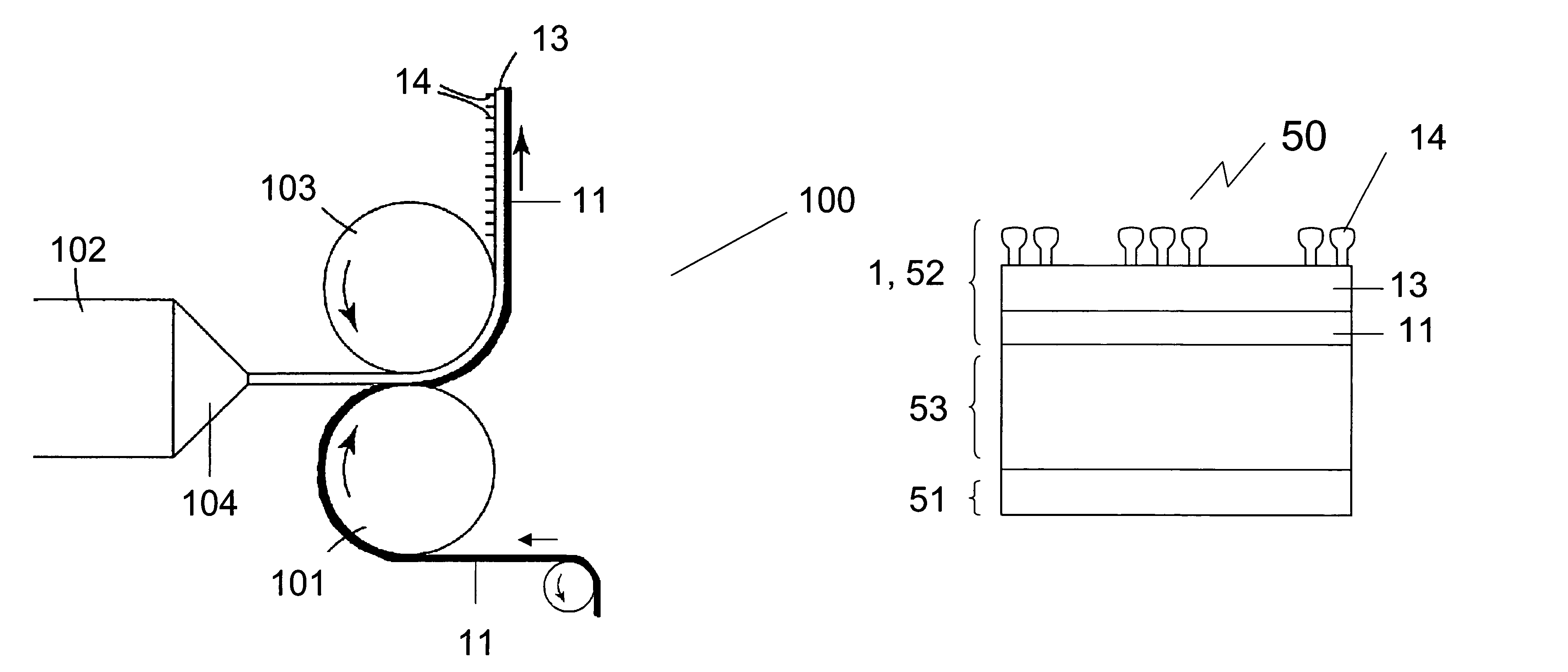
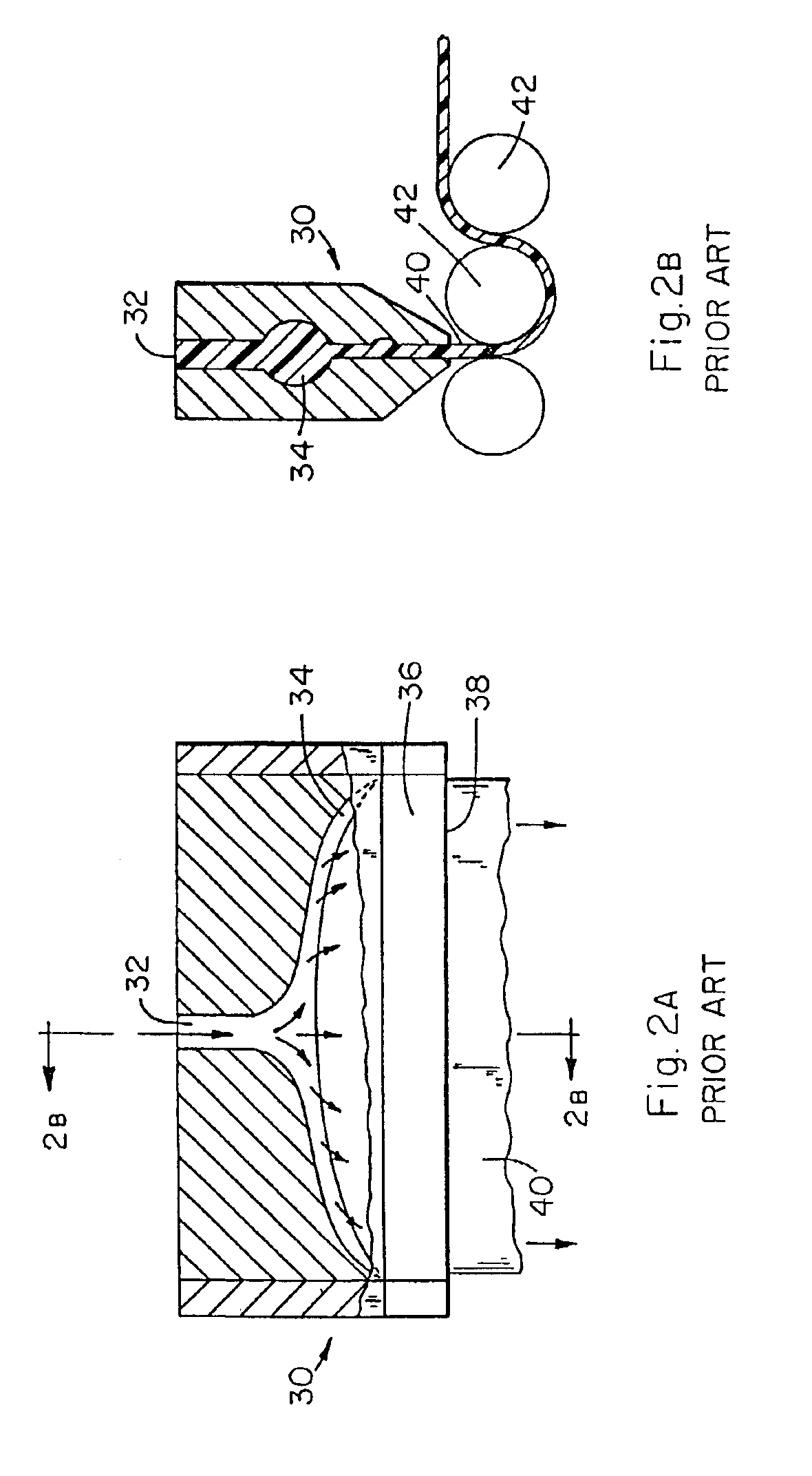
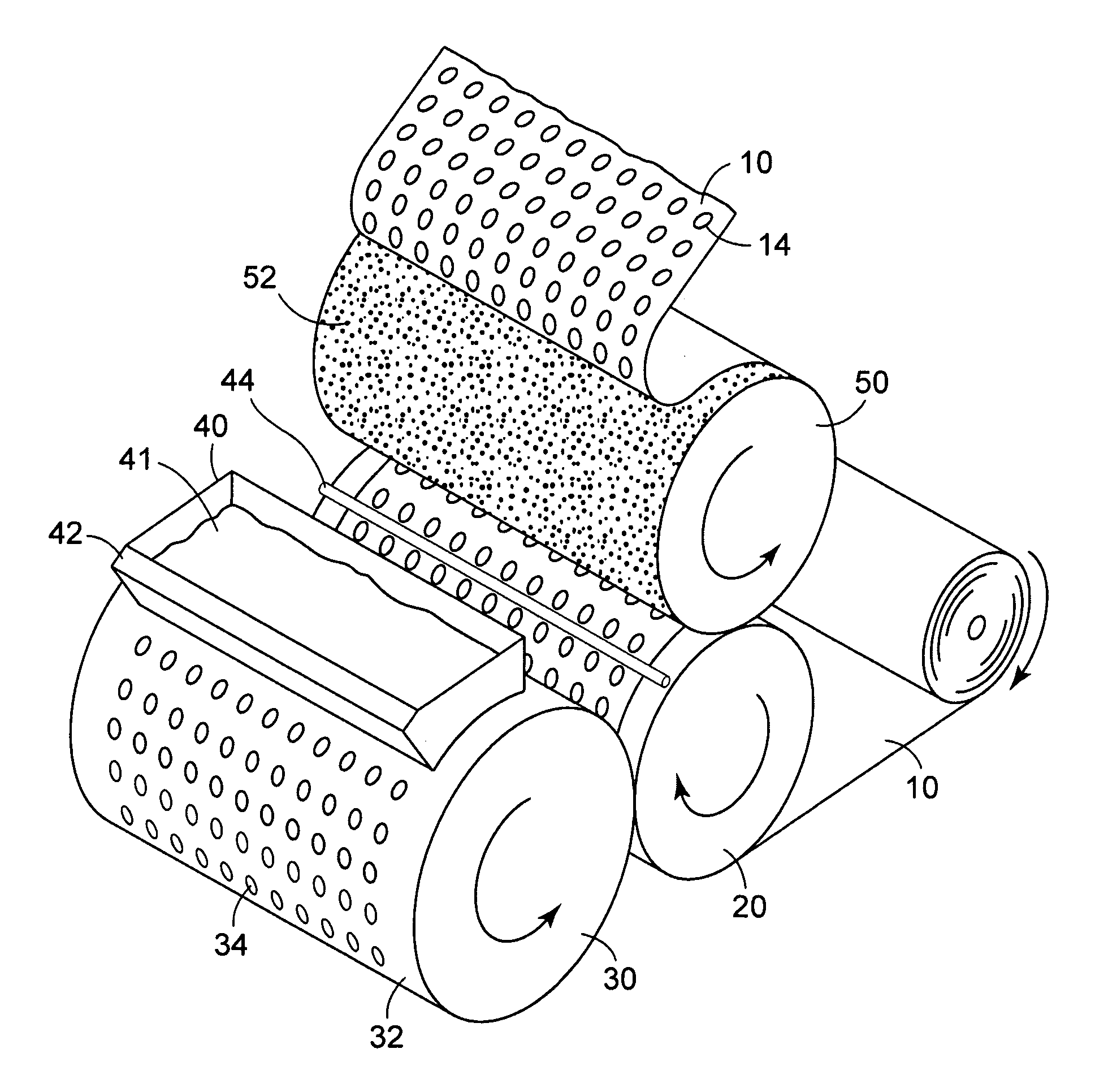
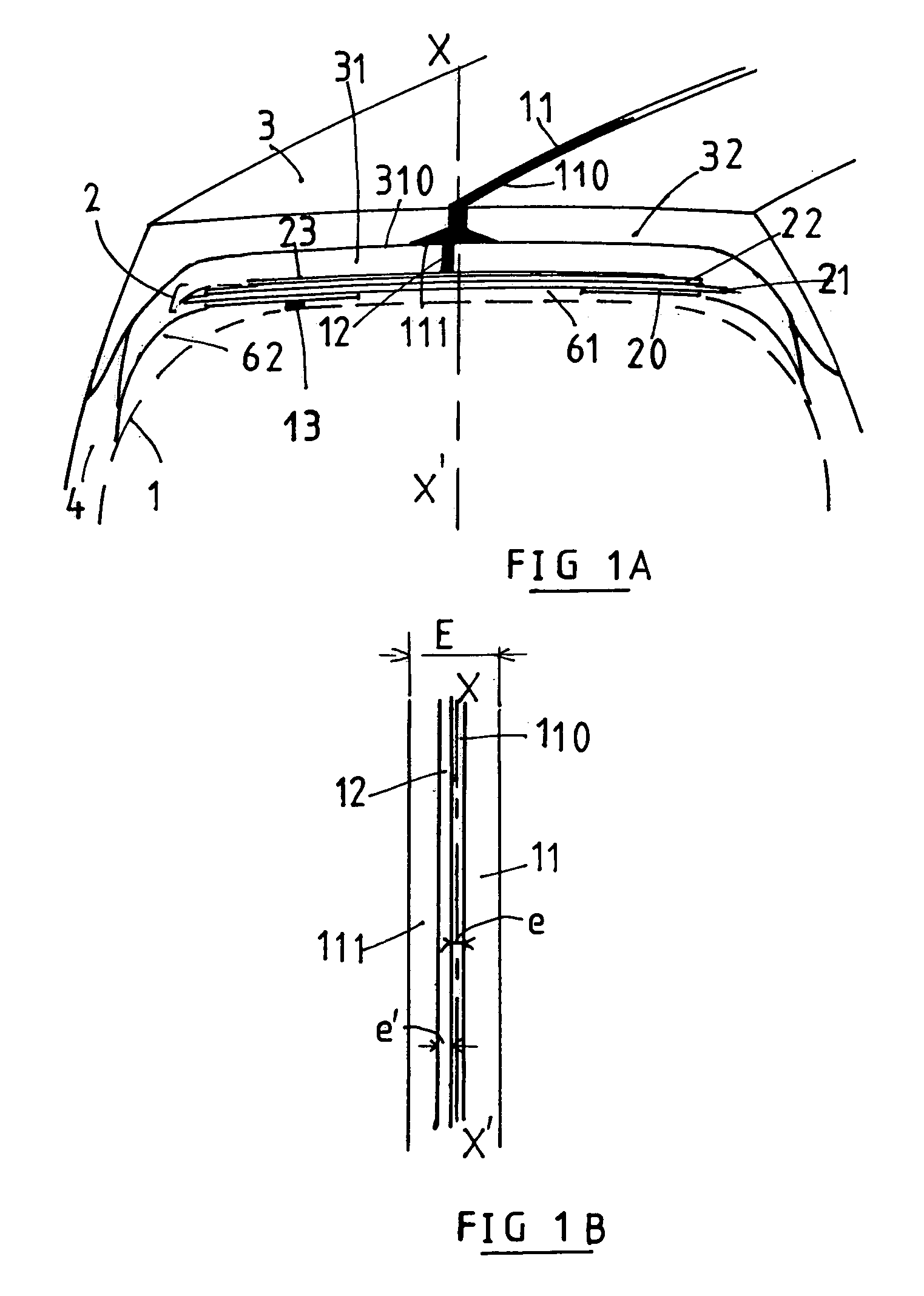
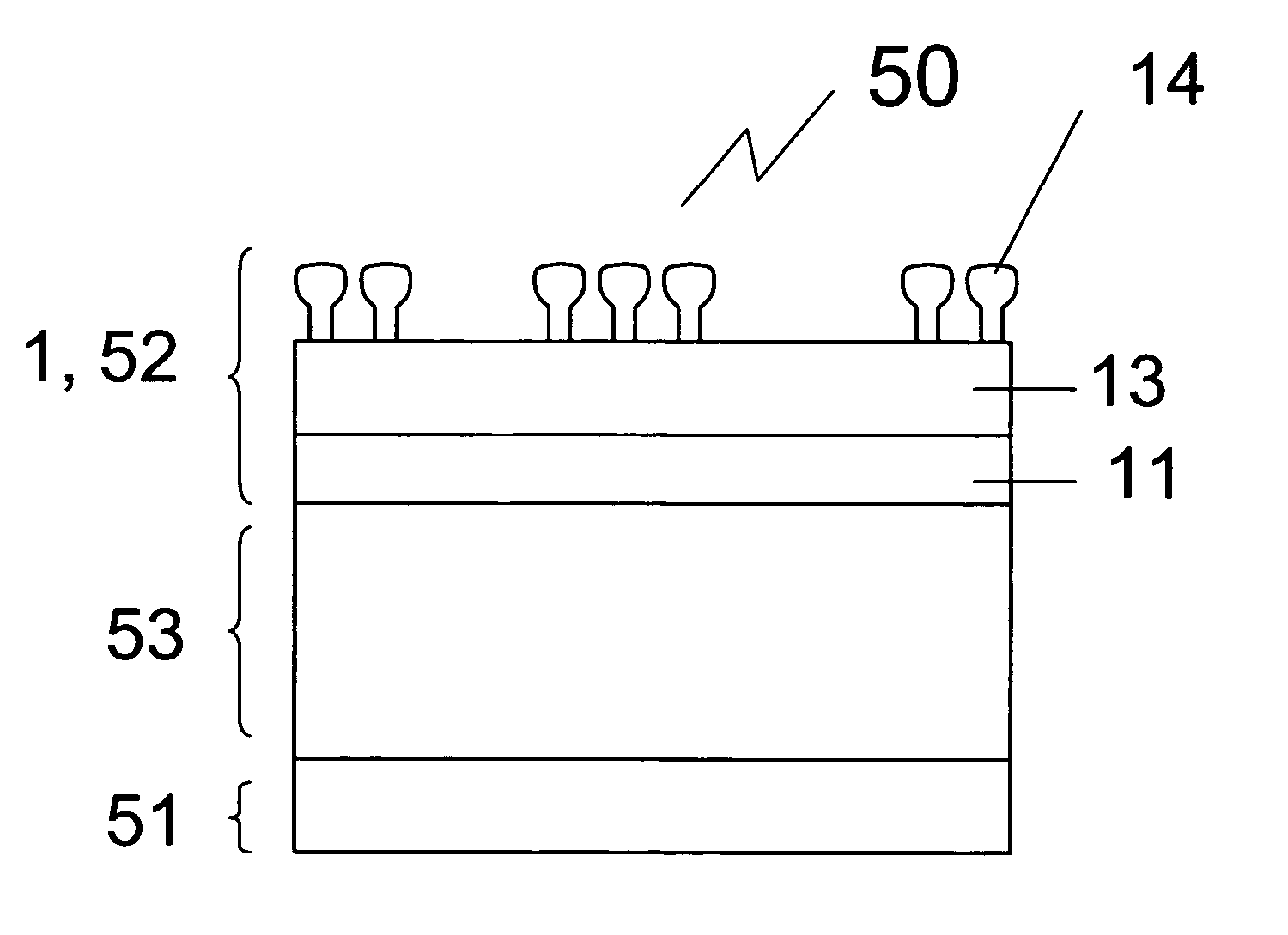
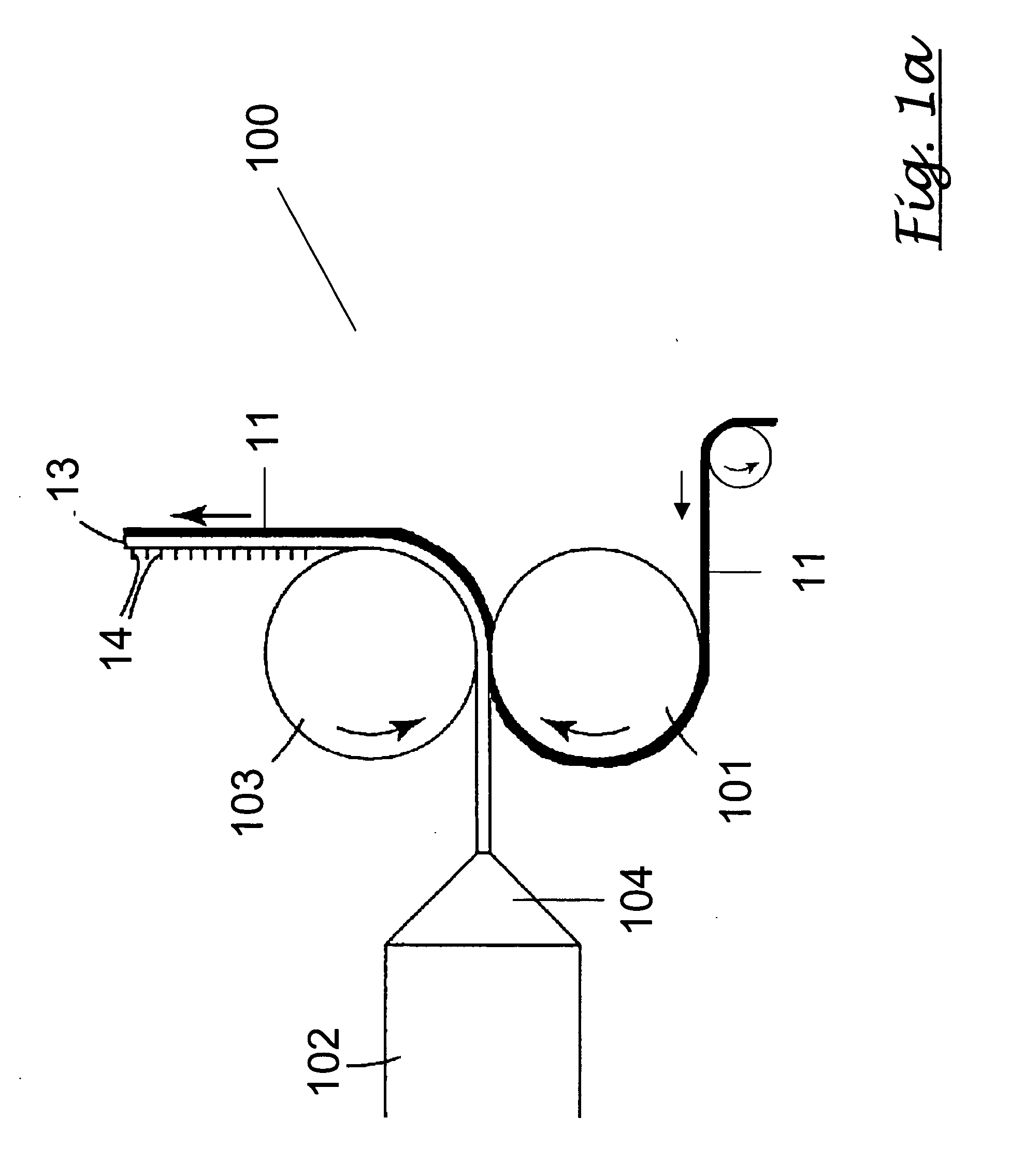
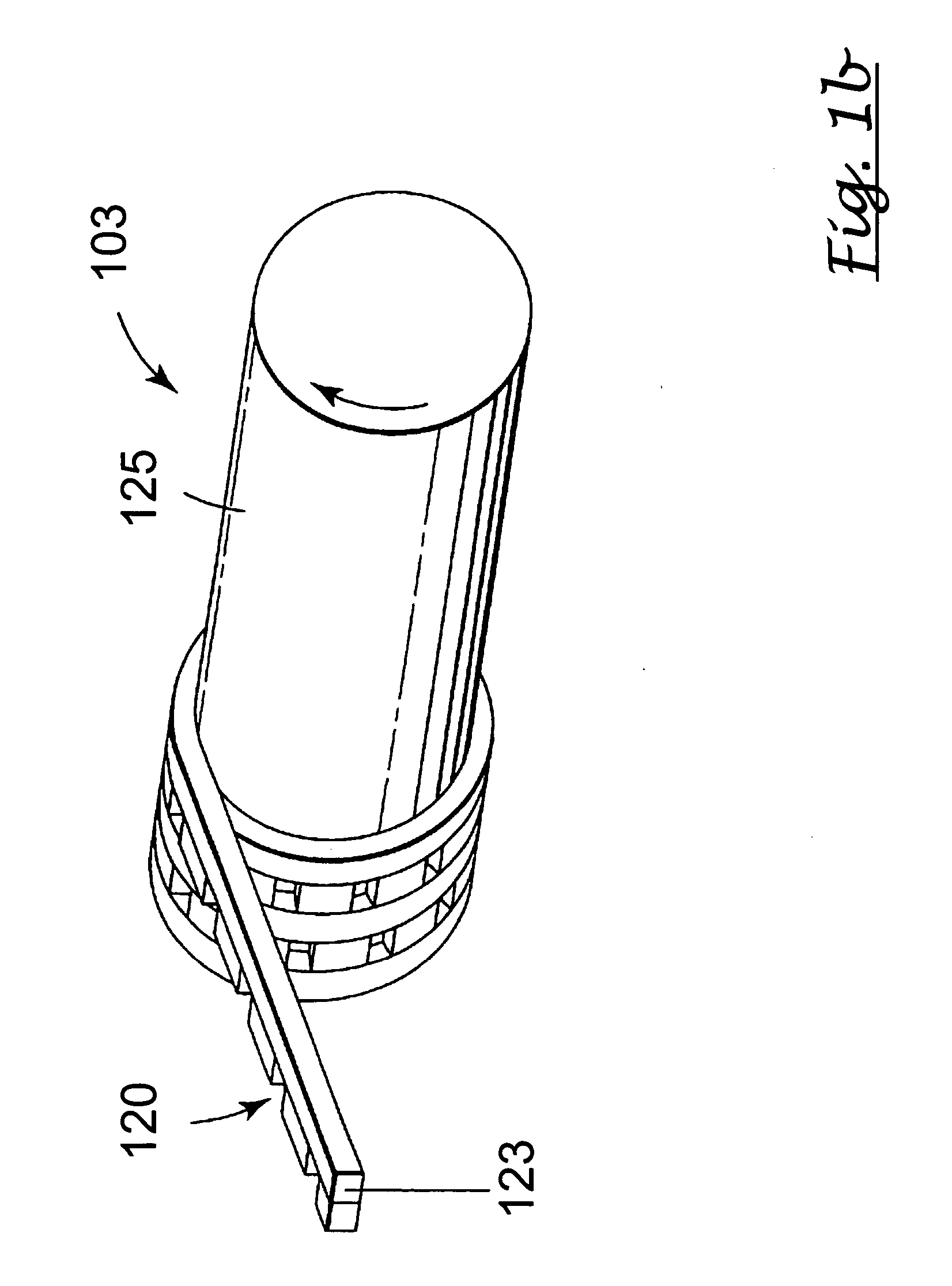
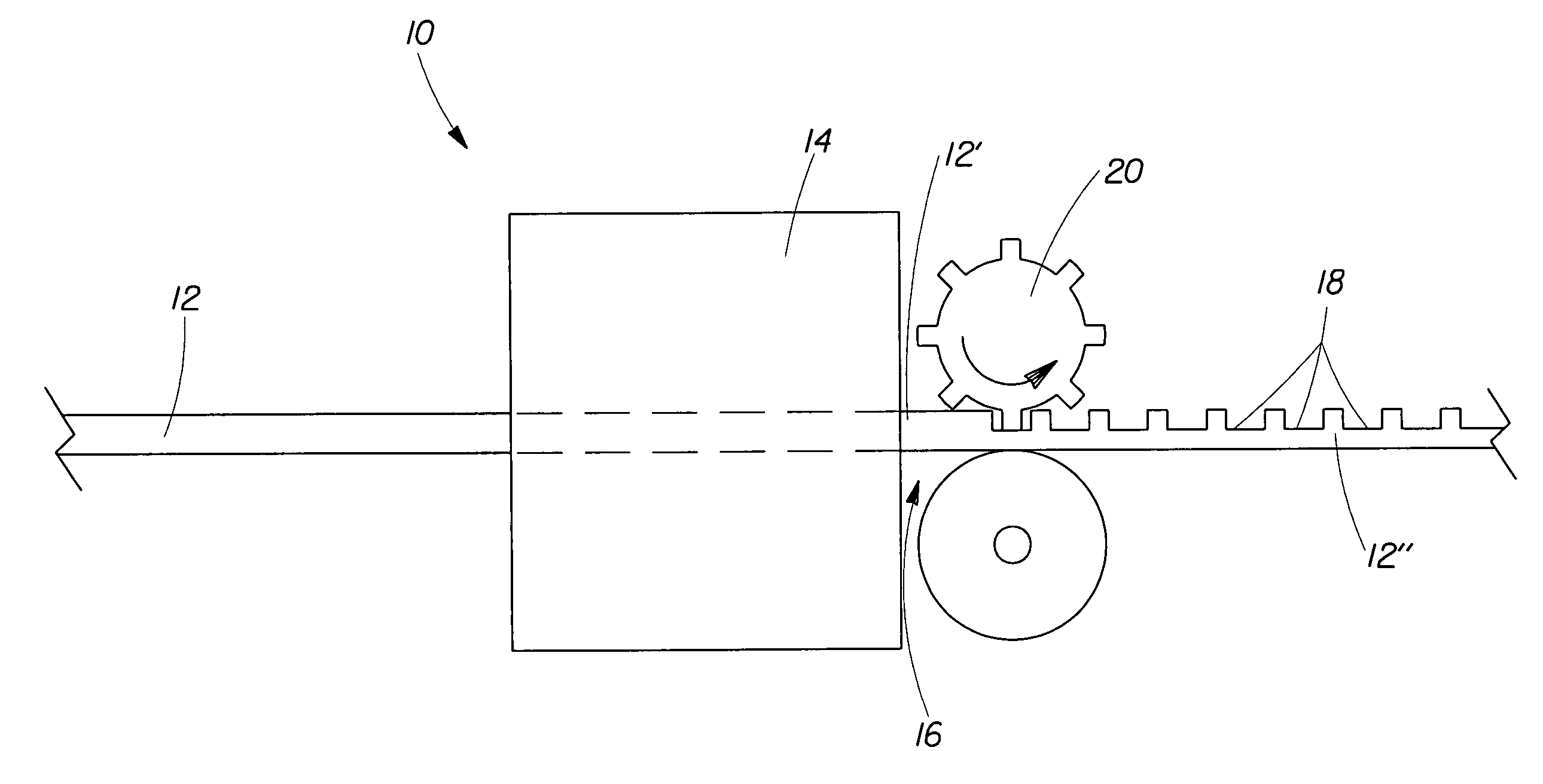
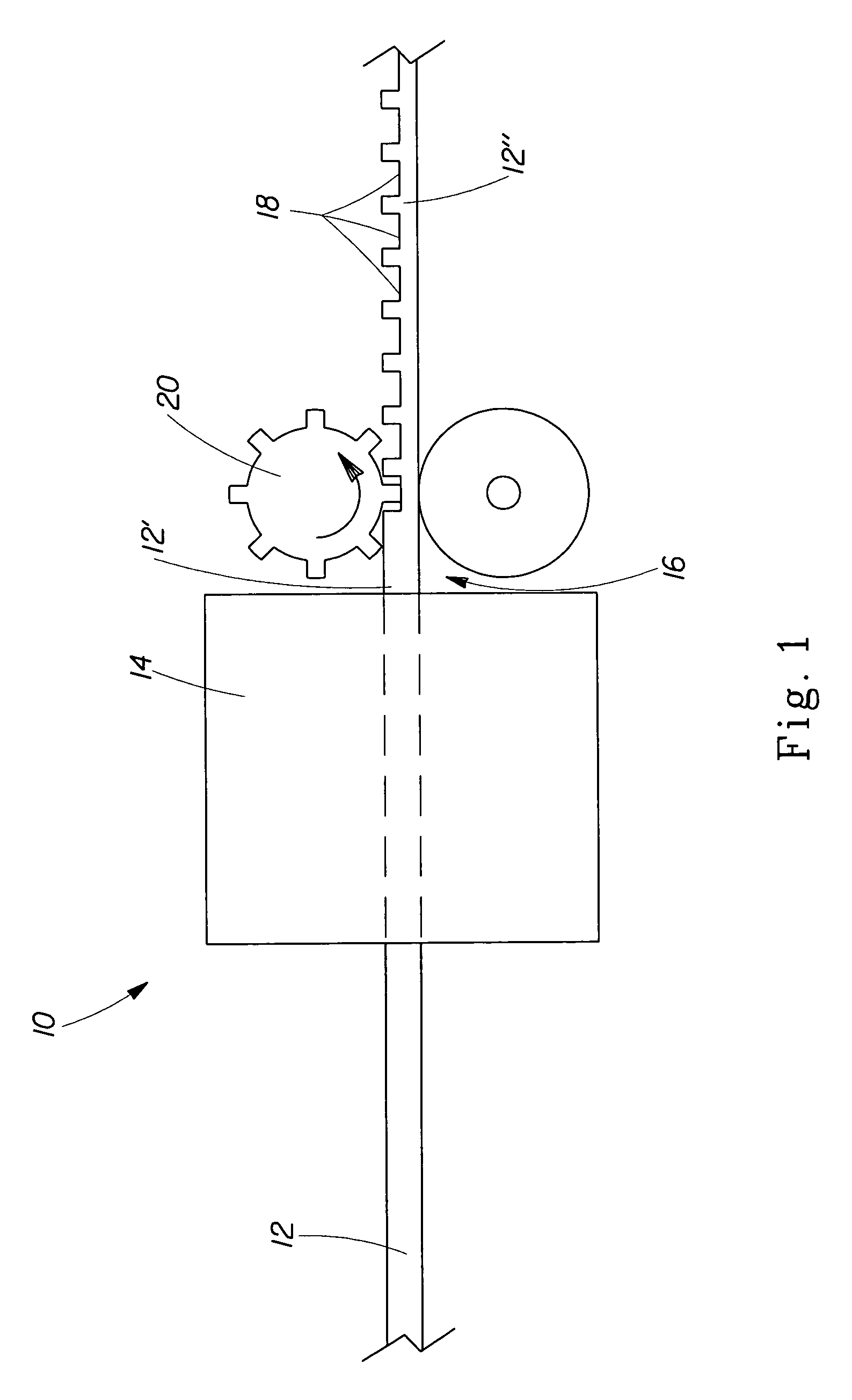
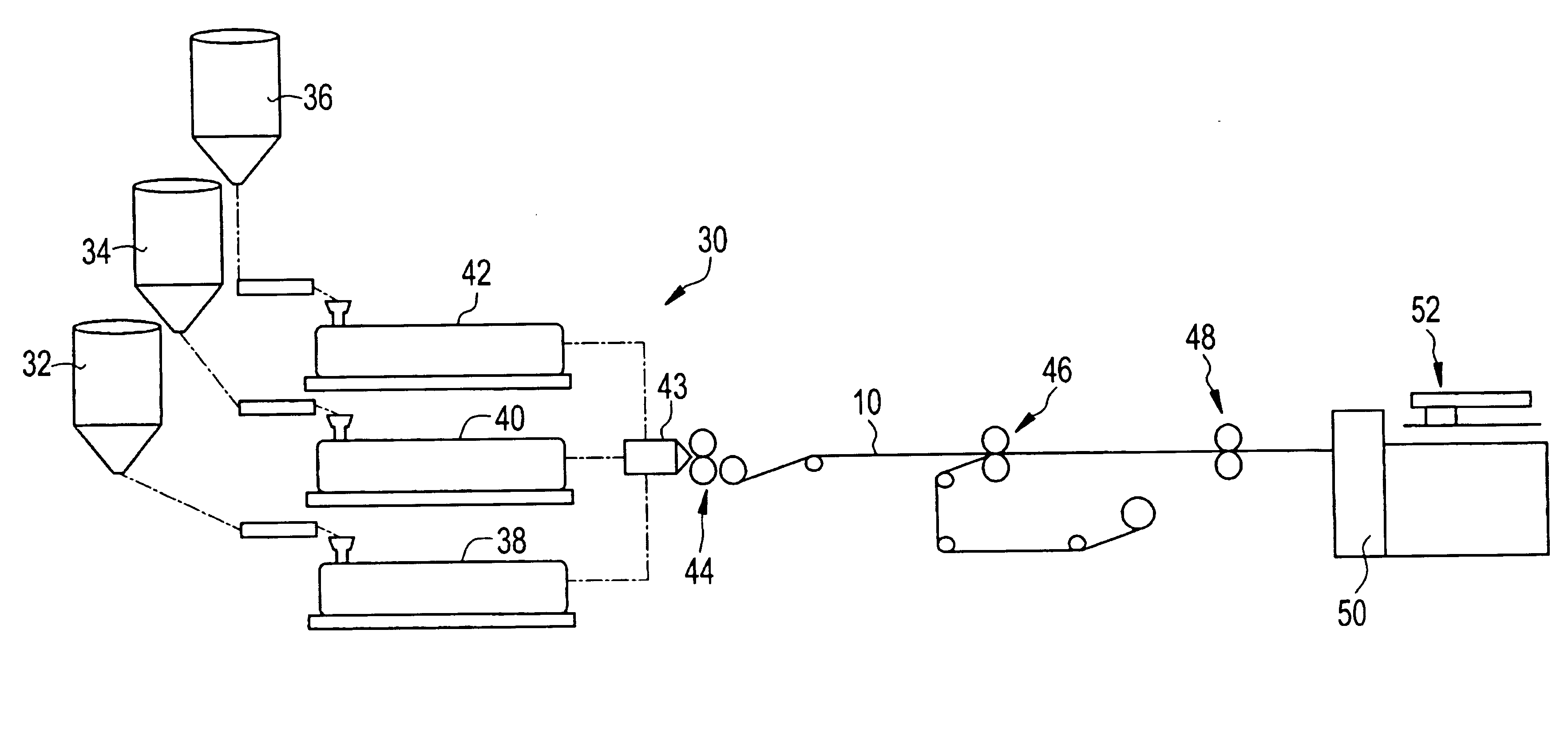
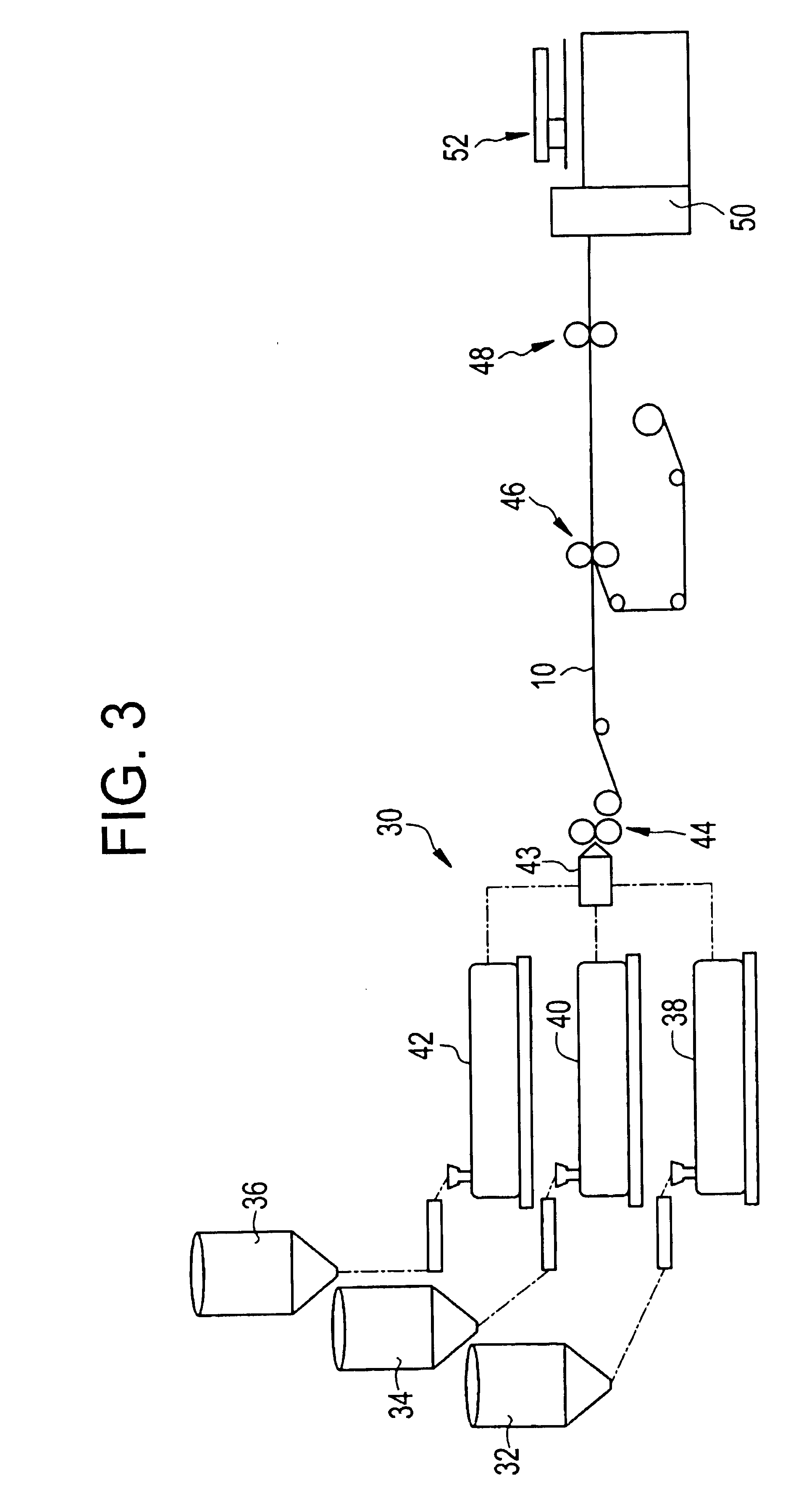
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a stretched mechanical fastening web laminate (1) comprising a thermoplastic web layer (13) having two major surfaces, one of the major surfaces bearing a multitude of male fastening elements (14) suitable for engagement with a corresponding female fastening material, and on its other major surface a fibrous web layer (11), said method comprising the steps of(i) providing the fibrous web layer (11) having an initial basis weight,(ii) passing the fibrous web layer (11) through a nip formed by two rolls (101), (103), one of them having cavities (120) that are the negatives of a plurality of male fastening elements (14), introducing a molten thermoplastic resin into the cavities (120) in excess of an amount that would fill the cavities (120) which excess forms the thermoplastic web layer (13), allowing the resin to at least partially solidify and stripping of a precursor web laminate (10) thus formed comprising the fibrous web layer (11) and the thermoplastic web layer (13) bearing a plurality of male fastening elements (14), from the cylindrical roll (103) having cavities (120) whereby the thermoplastic web layer (13) has an initial thickness and an initial hook density, and(iii) stretching the precursor web laminate (10) monoaxially or biaxially thereby decreasing the basis weight of the fibrous web layer (11) and the thickness of the thermoplastic web layer (13) from their respective initial values to provide a stretched mechanical fastening laminate (1) having a basis weight of less than 100 g·m−2.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Polyester resin compositions for calendering
InactiveUS6846440B2Avoid stickingArtificial filament physical treatmentWood working apparatusMolten statePolyester resin
A polyester resin composition is calendered to produce a film or a sheet. The polyester resin composition is a polyester having a crystallization half time from a molten state of at least 5 minutes combined with an additive for preventing sticking of the polyester to calendering rolls.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Method for producing an adhesive closing element
InactiveUS7198743B2Easy to demouldFavorable closing behaviorDischarging arrangementArtificial filament physical treatmentEngineeringHooking
A process for produces an adhesive closing element including a plurality of hook elements connected to a backing (10) forming a single piece with the hook elements and being disposed symmetrically thereon. The hook elements are provided in the form of a stem component (17) having a head piece (16). A deformable material is introduced into a forming zone in between a production master (3) and a forming tool (5). The opposite-lying defining walls, at least when seen in a longitudinal section of the respective forming cavity (12), are provided with a continuous convex trajectory. A continuous transition between the cross-sectional forms of the stem component (17) and the head piece (16) is provided for a hooking of the backing (10) resulting in seamless removal.
Owner:GOTTLIEB BINDER
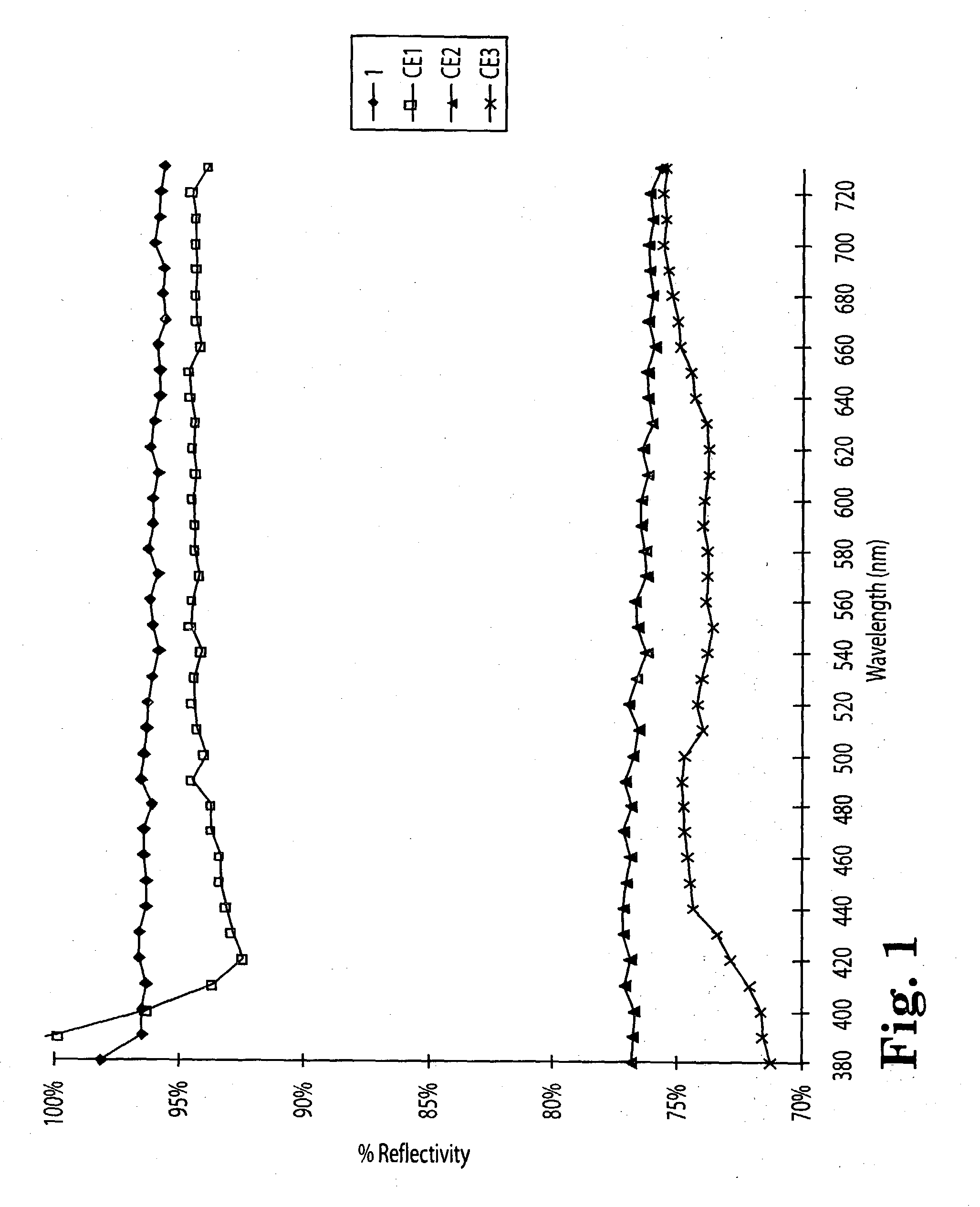
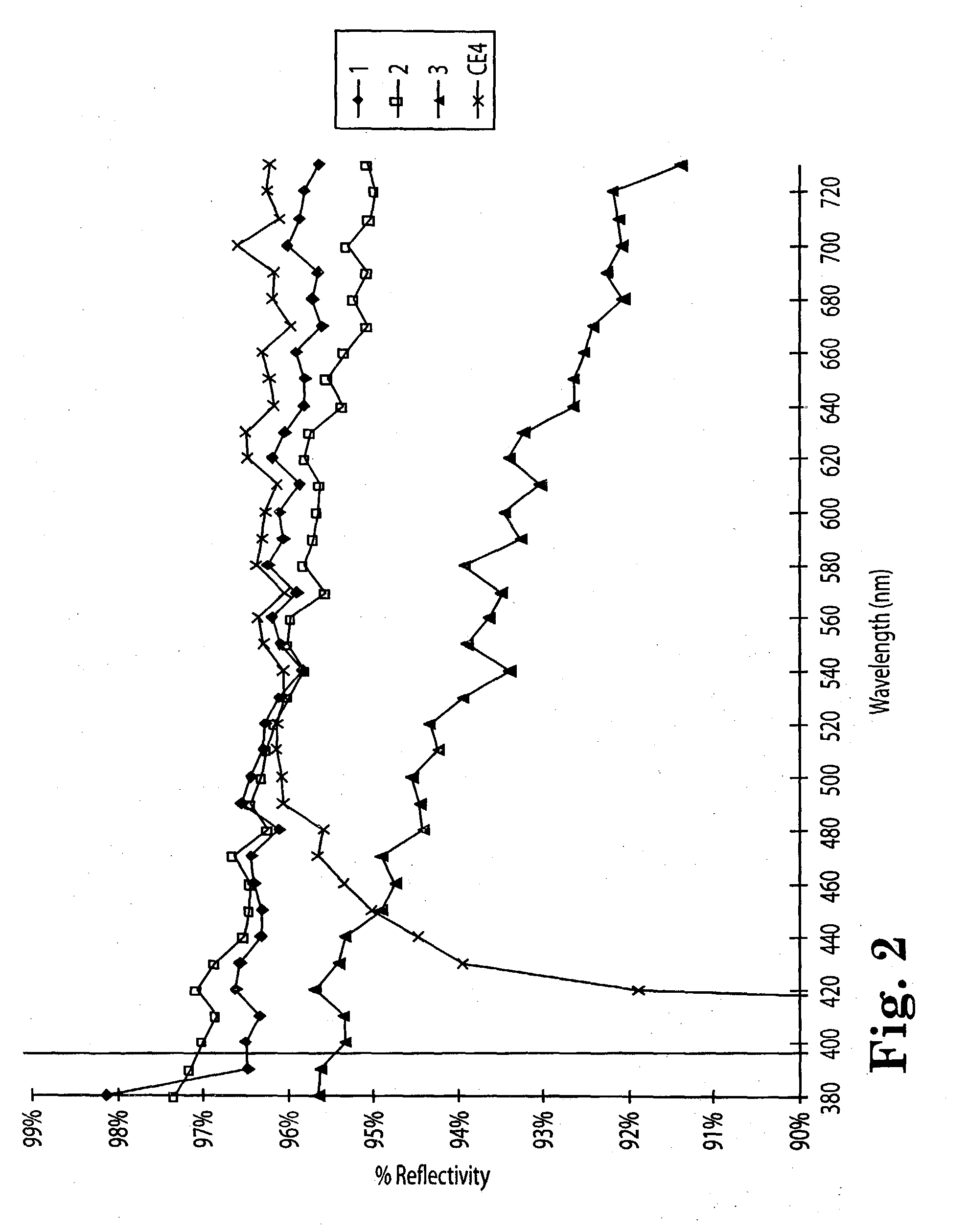
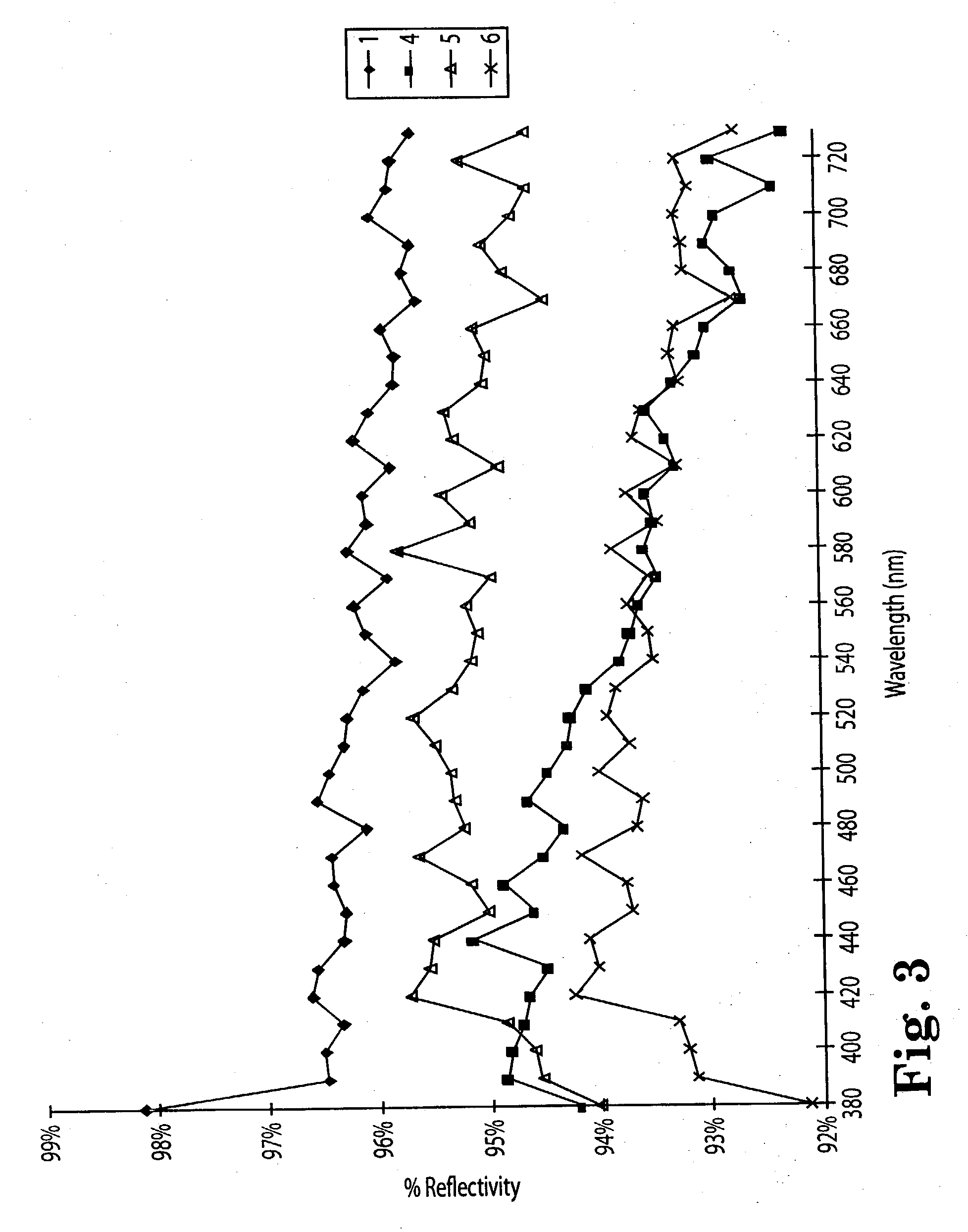
Diffuse reflective articles
InactiveUS20030118805A1Required thicknessImprove efficiencyMechanical apparatusVehicle headlampsLiquid-crystal displayDiluent
Diffuse reflective materials proximate to a structure formed by thermally induced phase separation of a thermoplastic polymer and a diluent providing enhanced flexibility and reflectivity especially in the visible wavelengths of 380-730 nanometers are described. Such materials find a wide variety of application among combinations with other reflective layers. The diffuse reflective articles are useful in backlight units of liquid crystal displays, lights, copy machines, projection system displays, facsimile apparatus, electronic blackboards, diffuse white standards, photographic lights and the like.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Composite webs and closure systems
InactiveUS7195729B2Increase the lengthDifferent compositionWood working apparatusCeramic layered productsMaterials sciencePolymer architecture
Composite webs having one or more polymeric structures located on a substrate, closure systems comprising composite webs, and methods of attaching articles are disclosed. The polymeric structures are formed using thermoplastic compositions and are attached to a surface of a substrate. The polymeric structures include an area that is attached to the substrate and a detached area that is not attached to a surface of a substrate.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
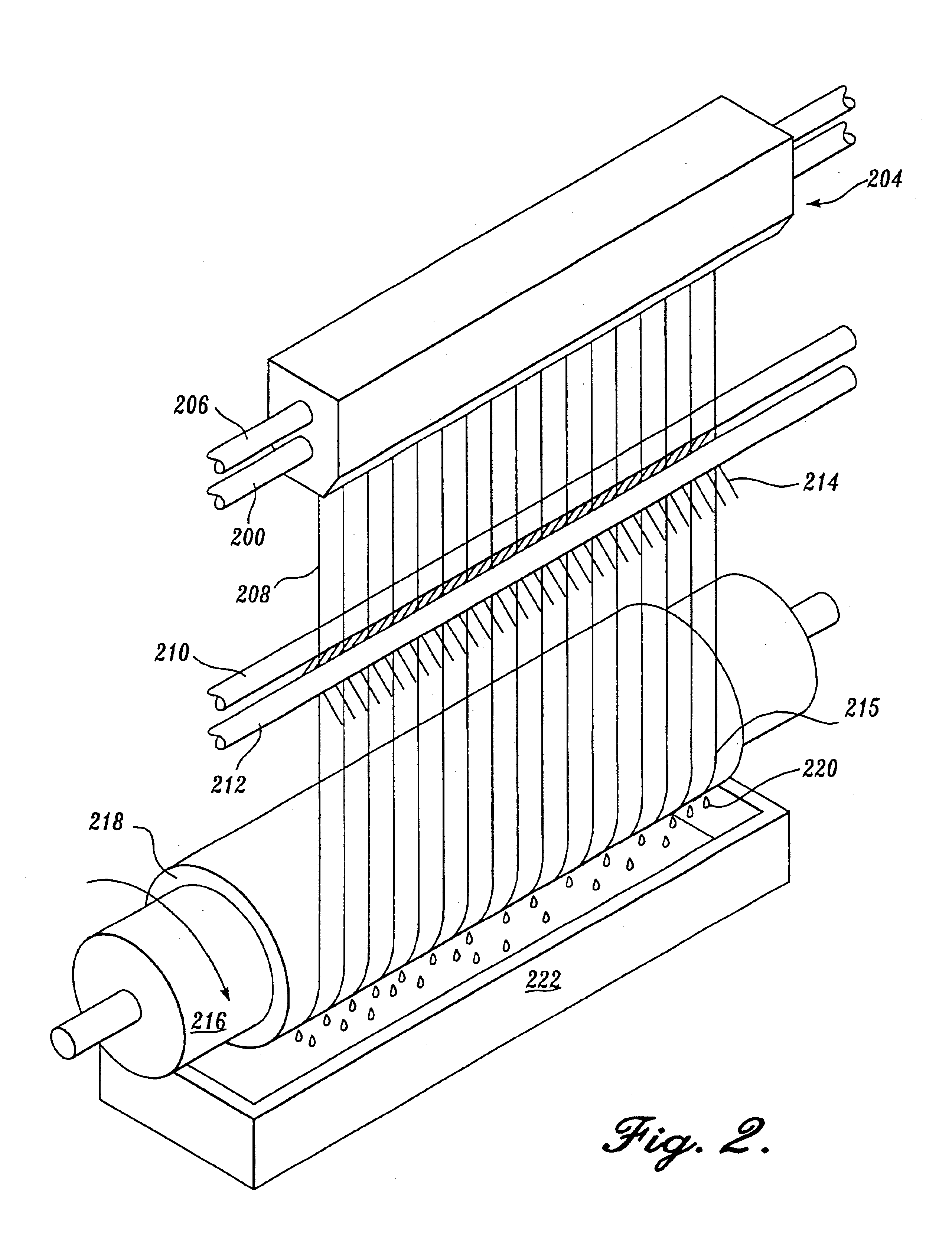
Meltblown process with mechanical attenuation
InactiveUS6773648B2High speed spinningImprove productivityPulp properties modificationArtificial filament physical treatmentCelluloseUltrasound attenuation
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
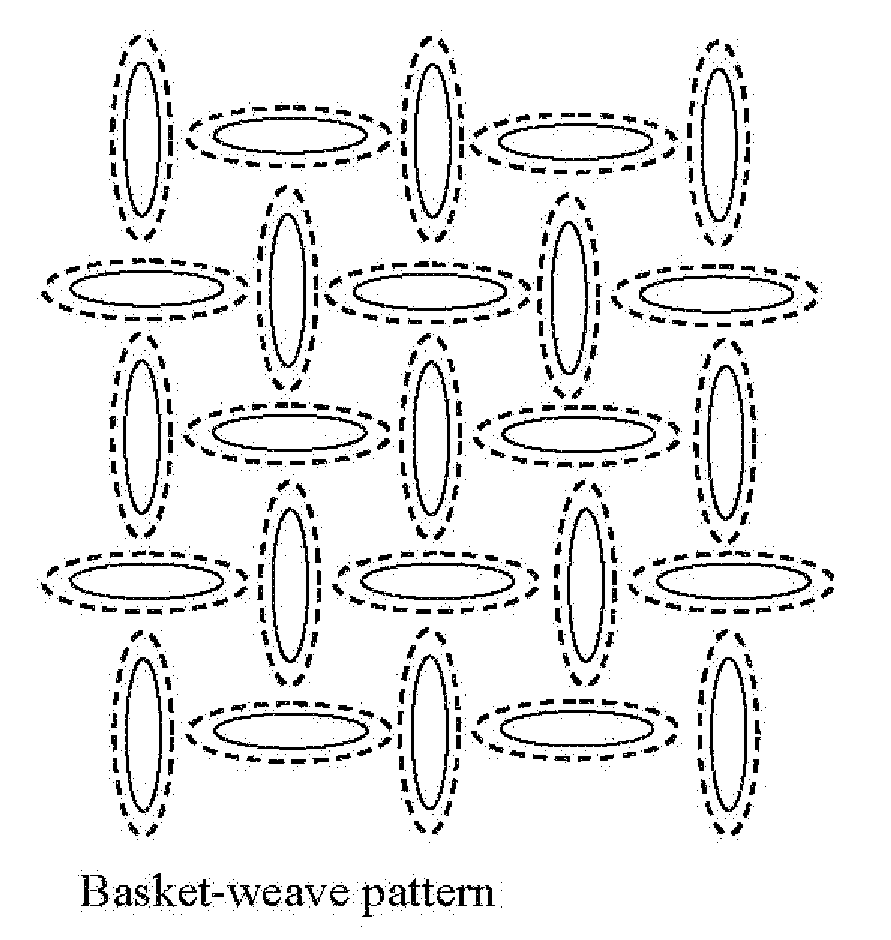
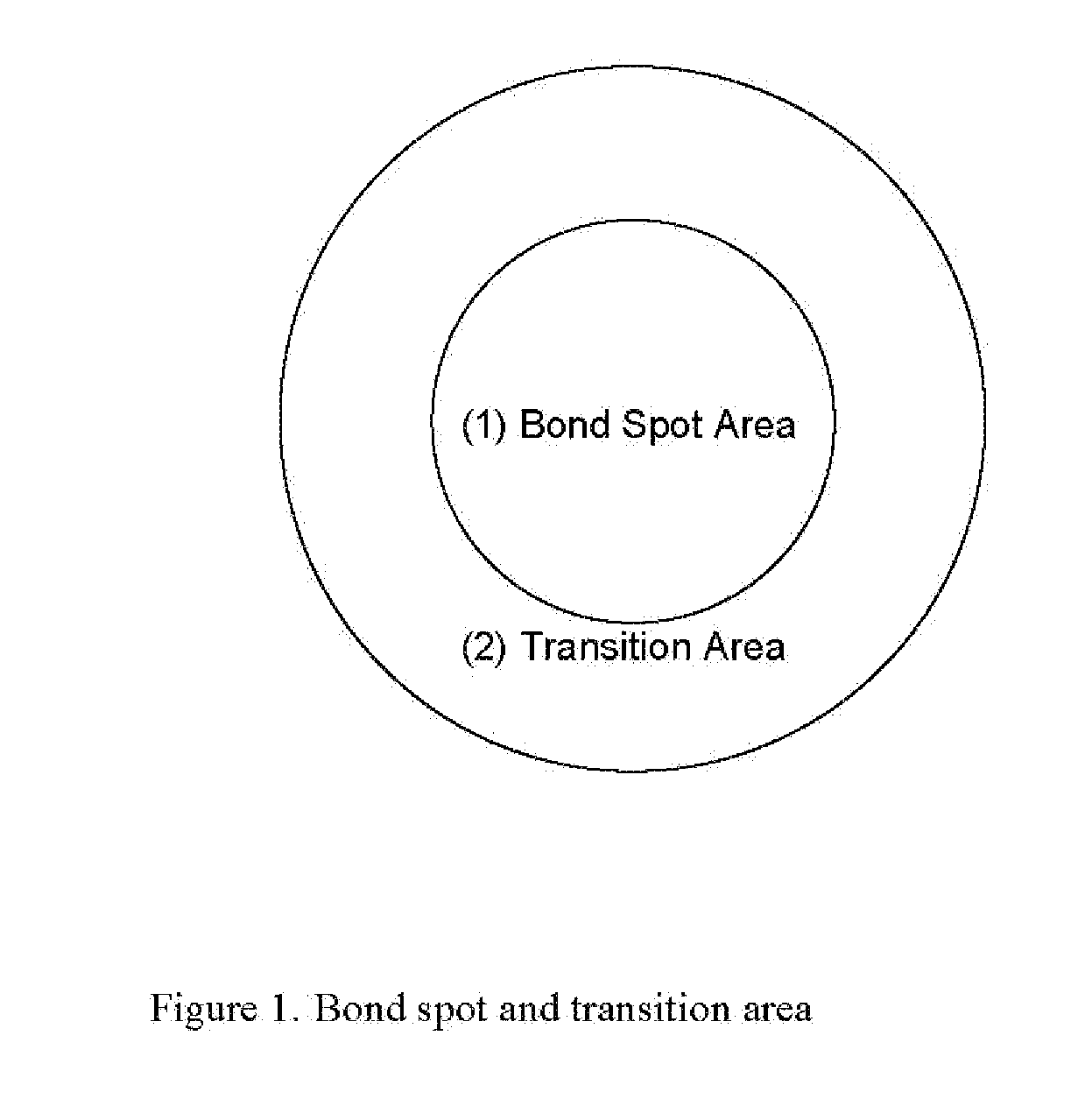
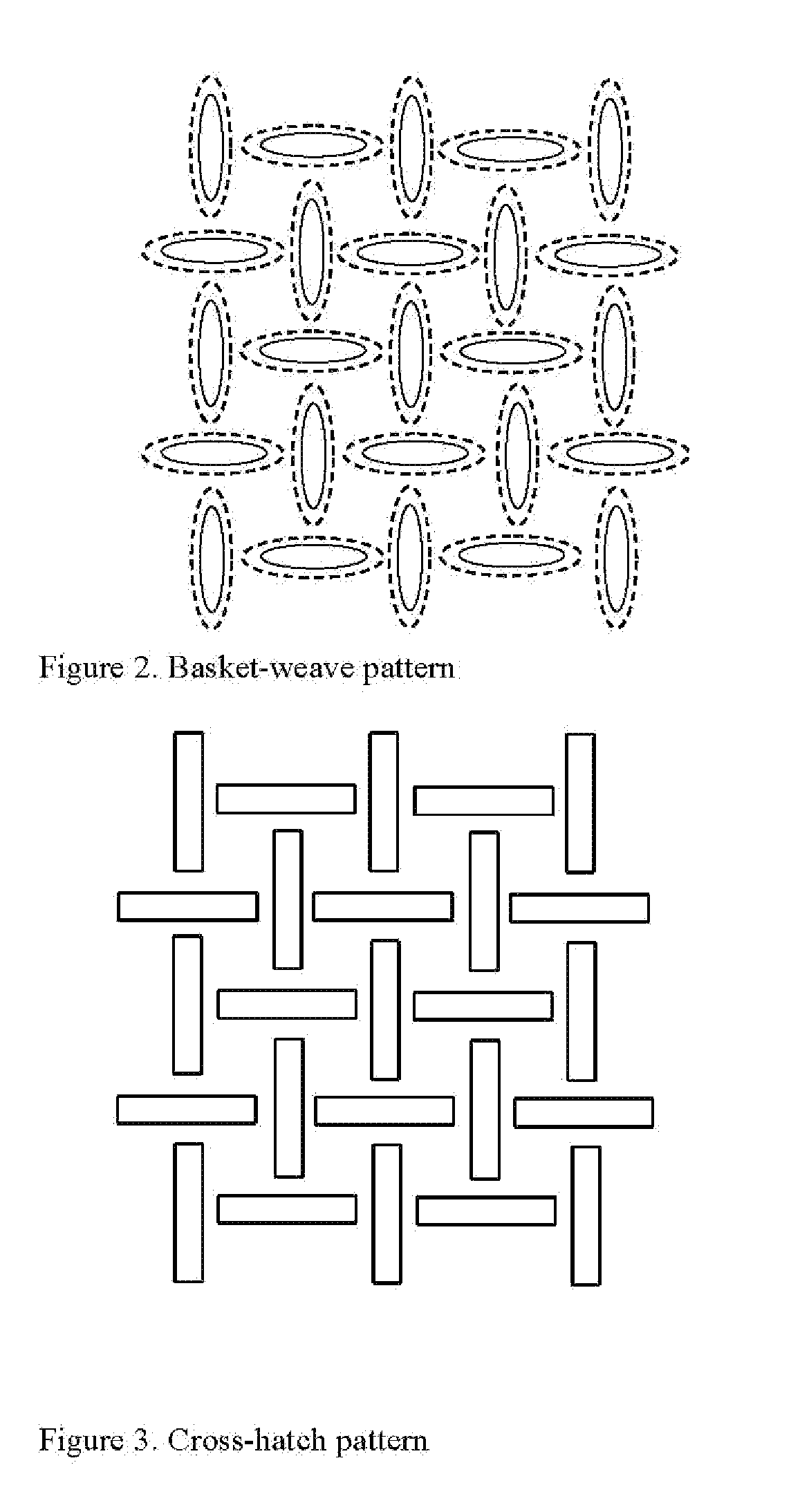
Nonwoven bonding patterns producing fabrics with improved abrasion resistance and softness
ActiveUS20080268194A1Excellent abrasion resistanceHigh strengthStampsWrappersEngineeringNonwoven fabric
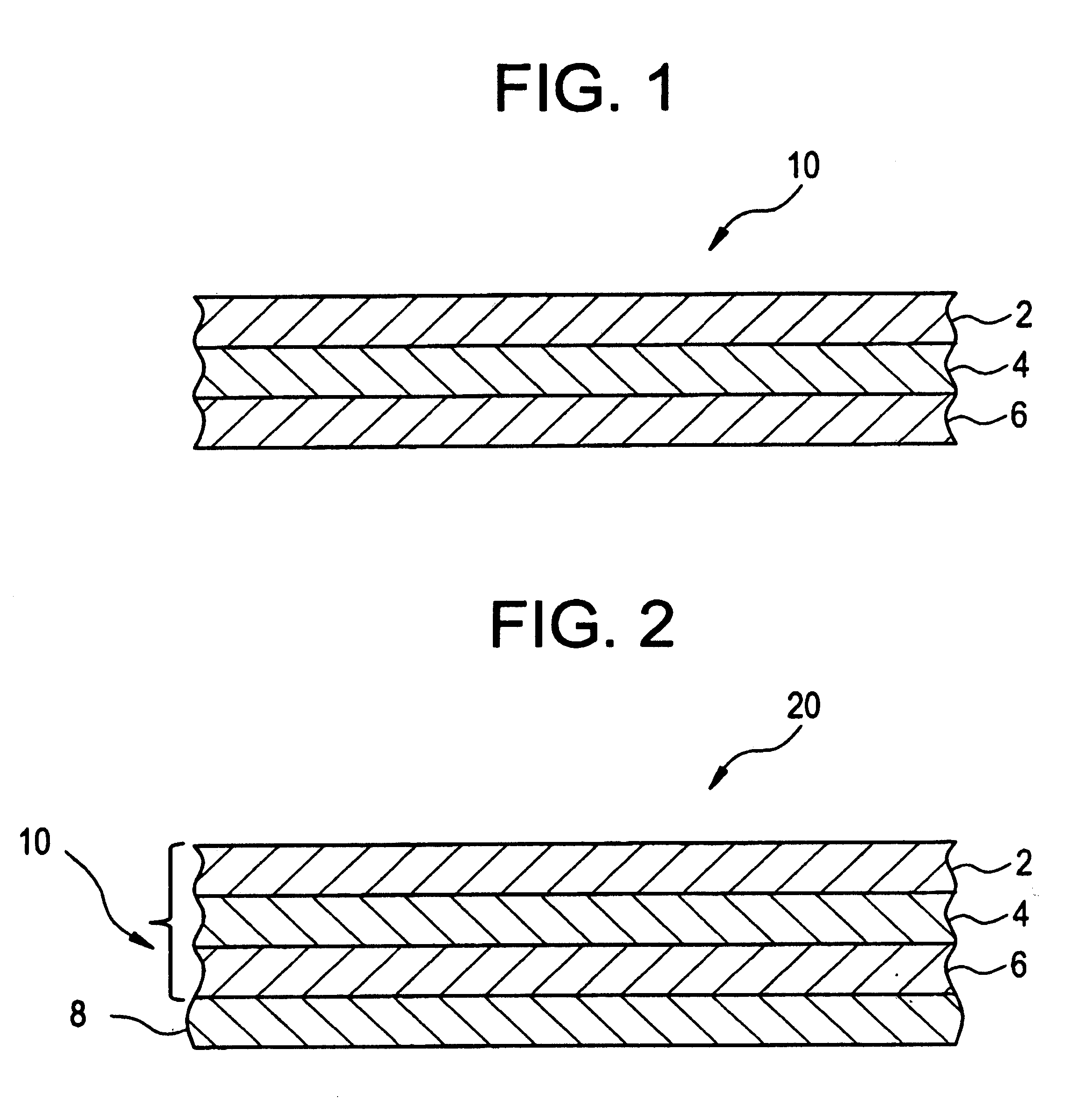
A thermal bonding pattern for nonwoven fabric possessing improved abrasion resistance while retaining softness, comprising a basket-weave pattern or other pattern having a transition area (2) equal to at least 10% of bonding spot area (1) in FIG. 1, more preferably a transition area (2) equal to at least 50% of bonding spot area (1), and most preferably a transition area (2) equal to at least 100% of bonding spot area.
Owner:A AHLSTROM CORP
Polyester resin compositions for calendering
InactiveUS20050096453A1Avoid stickingArtificial filament physical treatmentWood working apparatusPolymer sciencePolyester resin
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Fibers made from copolymers of ethylene/α-olefins
A fiber is obtainable from or comprises an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer characterized by an elastic recovery, Re, in percent at 300 percent strain and 1 cycle and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the elastic recovery and the density satisfy the following relationship: Re>1481−1629(d). Such interpolymer can also be characterized by other properties. The fibers made therefrom have a relatively high elastic recovery and a relatively low coefficient of friction. The fibers can be cross-linked, if desired. Woven or non-woven fabrics can be made from such fibers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Fibers made from copolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins
A fiber is obtainable from or comprises a blend of a propylene based polymer and an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer characterized by an elastic recovery, Re, in percent at 300 percent strain and 1 cycle and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the elastic recovery and the density satisfy the following relationship: Re>1481-1629(d). Such interpolymer can also be characterized by other properties. The fibers made therefrom have a relatively high elastic recovery and a relatively low coefficient of friction. The fibers can be cross-linked, if desired. Woven, knitted or non-woven fabrics can be made from such fibers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
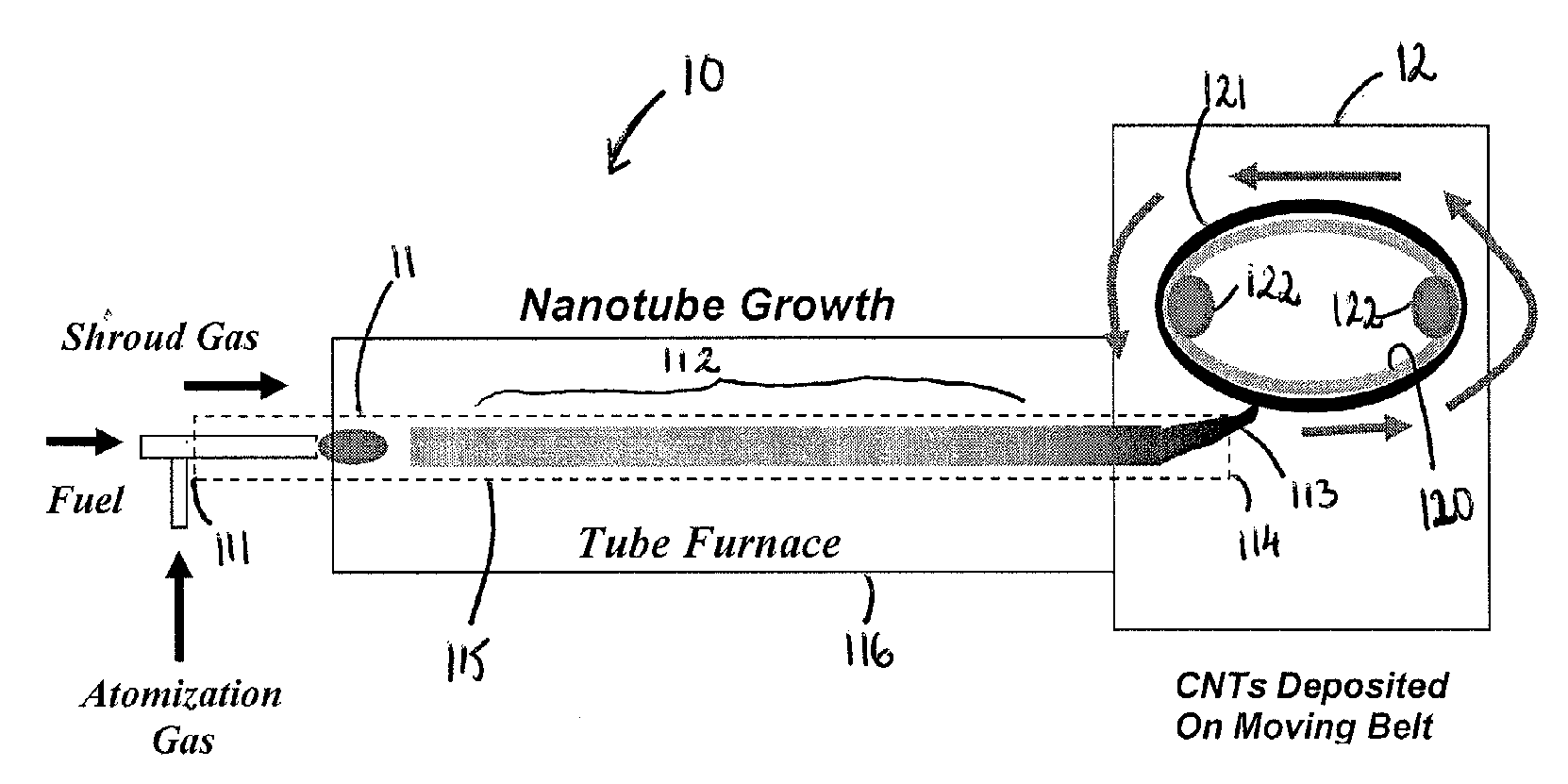
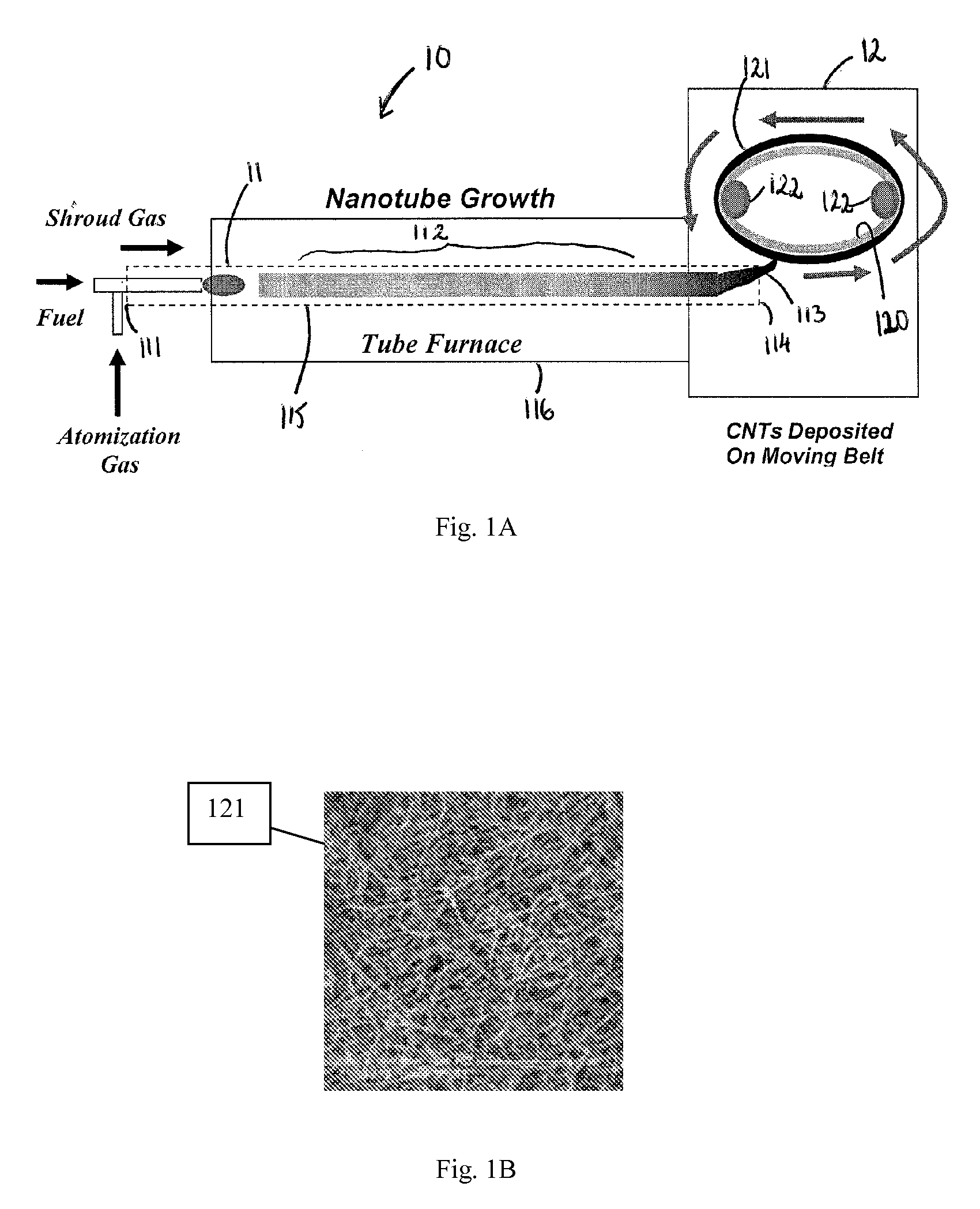
Chemically-Assisted Alignment of Nanotubes Within Extensible Structures
ActiveUS20090075545A1Smooth connectionImprove thermal conductivityArtificial filament physical treatmentHollow filament manufactureChemical mixturesYarn
A method and system for aligning nanotubes within an extensible structure such as a yarn or non-woven sheet. The method includes providing an extensible structure having non-aligned nanotubes, adding a chemical mixture to the extensible structure so as to wet the extensible structure, and stretching the extensible structure so as to substantially align the nanotubes within the extensible structure. The system can include opposing rollers around which an extensible structure may be wrapped, mechanisms to rotate the rollers independently or away from one another as they rotate to stretch the extensible structure, and a reservoir from which a chemical mixture may be dispensed to wet the extensible structure to help in the stretching process.
Owner:NANCOMP TECHNOLOGIES INC
Multi-Layered Films With Visually-Distinct Regions and Methods of Making The Same
Multi-layered thermoplastic films include intermittent stretched regions that are visually distinct from un-stretched regions. The stretched regions can be white, opaque, and non porous. The multi-layered thermoplastic films with visually-distinct stretched regions can be formed into bags for use as trash can liners or food storage. Additionally, methods of stretching thermoplastic films to create visually distinct stretched regions include incrementally stretching a plurality of film layers, at least one of which includes a thermoplastic material and a voiding agent.
Owner:THE GLAD PROD CO
Process of making cellulose acetate tow
ActiveUS7585441B2Artificial filament physical treatmentArtificial filaments from cellulose derivativesFiberPlasticizer
In the manufacture of a fiber tow, particularly cellulose acetate tow, the tow is plasticized prior to entry into the crimper. The preferred plasticizer is water.
Owner:DEUT BANK AG NEW YORK BRANCH AS COLLATERAL AGENT +1
Fibers Made From Copolymers of Ethylene/A-Olefins
A fiber is obtainable from or comprises an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer characterized by an elastic recovery, Re, in percent at 300 percent strain and 1 cycle and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the elastic recovery and the density satisfy the following relationship: Re>1481−1629(d). Such interpolymer can also be characterized by other properties. The fibers made therefrom have a relatively high elastic recovery and a relatively low coefficient of friction. The fibers can be cross-linked, if desired. Woven or non-woven fabrics can be made from such fibers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Systems and methods for composite webs with structured discrete polymeric regions
InactiveUS7037457B2Easy to attachExtensive controlLiquid surface applicatorsConfectioneryEngineeringMechanical engineering
Systems and methods for manufacturing composite webs including a substrate with one or more discrete polymeric regions located thereon are disclosed. The discrete polymeric regions are deposited by transferring molten thermoplastic composition from depressions on a transfer roll to a substrate. Each of the discrete polymeric regions is further formed to include multiple structures formed thereon. Those structures may include, for example, stems (capped or otherwise), hooks (as part of a hook and loop fastening system), pyramids, etc.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Electrically conductive tire and apparatus and process for extruding elements which have been made conductive
InactiveUS6951233B1Dissipate electrostatic chargeLow costConfectioneryCeramic shaping apparatusTreadElectrical and Electronics engineering
A tire having a tread composed of two non-conductive layers, each layer containing a circumferential insert of conductive mix, the inserts having a wider interface at the interface of the two layers. An apparatus for extruding a layer, provided with a conductive insert, including a main extruder for extruding a non-vulcanized, non-conductive layer, and a micro-extruder having an extrusion head, provided at its end with a nozzle, for extruding a conductive insert in the layer.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
Nonwovens produced from multicomponent fibers
InactiveUS20110168625A1Reduces blocking and fusionNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer scienceSlurry
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
FIBERS MADE FROM COPOLYMERS OF ETHYLENE/a-OLEFINS
ActiveUS20090247033A1Artificial filament physical treatmentWarp knittingFiberVolumetric Mass Density
A fiber is obtainable from or comprises a blend of a propylene based polymer and an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer characterized by an elastic recovery, Re, in percent at 300 percent strain and 1 cycle and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the elastic recovery and the density satisfy the following relationship: Re>1481−1629(d). Such interpolymer can also be characterized by other properties. The fibers made therefrom have a relatively high elastic recovery and a relatively low coefficient of friction. The fibers can be cross-linked, if desired. Woven, knitted or non-woven fabrics can be made from such fibers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Methods of manufacturing a stretched mechanical fastening web laminate
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a stretched mechanical fastening web laminate (1) comprising a thermoplastic web layer (13) having two major surfaces, one of the major surfaces bearing a multitude of male fastening elements (14) suitable for engagement with a corresponding female fastening material, and on its other major surface a fibrous web layer (11), said method comprising the steps of (i) providing the fibrous web layer (11) having an initial basis weight, (ii) passing the fibrous web layer (11) through a nip formed by two rolls (101), (103), one of them having cavities (120) that are the negatives of a plurality of male fastening elements (14), introducing a molten thermoplastic resin into the cavities (120) in excess of an amount that would fill the cavities (120) which excess forms the thermoplastic web layer (13), allowing the resin to at least partially solidify and stripping of a precursor web laminate (10) thus formed comprising the fibrous web layer (11) and the thermoplastic web layer (13) bearing a plurality of male fastening elements (14), from the cylindrical roll (103) having cavities (120) whereby the thermoplastic web layer (13) has an initial thickness and an initial hook density, and (iii) stretching the precursor web laminate (10) monoaxially or biaxially thereby decreasing the basis weight of the fibrous web layer (11) and the thickness of the thermoplastic web layer (13) from their respective initial values to provide a stretched mechanical fastening laminate (1) having a basis weight of less than 100 g·m−2.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
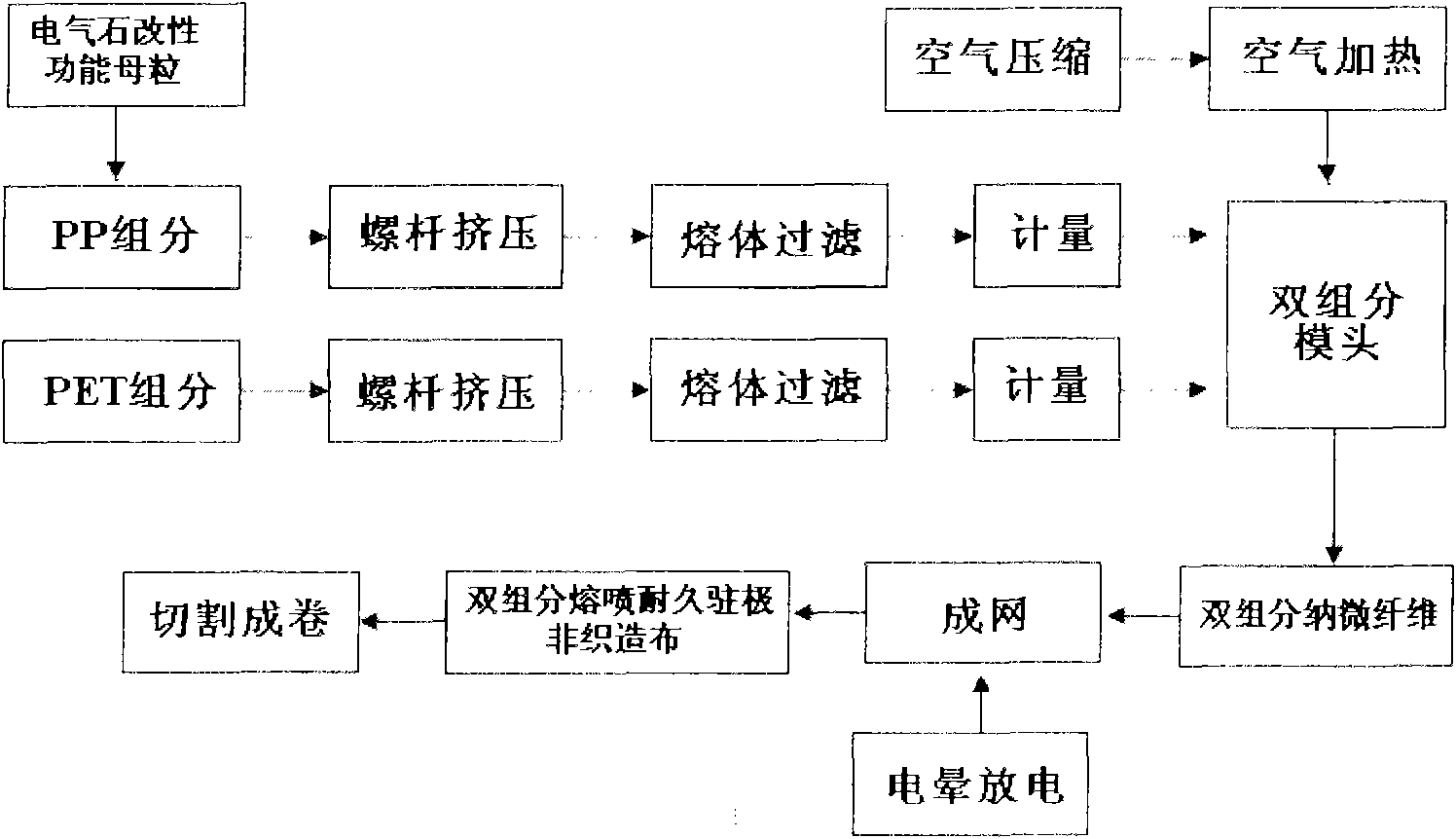
Double-component melt-blown durable electret non-woven fabric and manufacturing method thereof
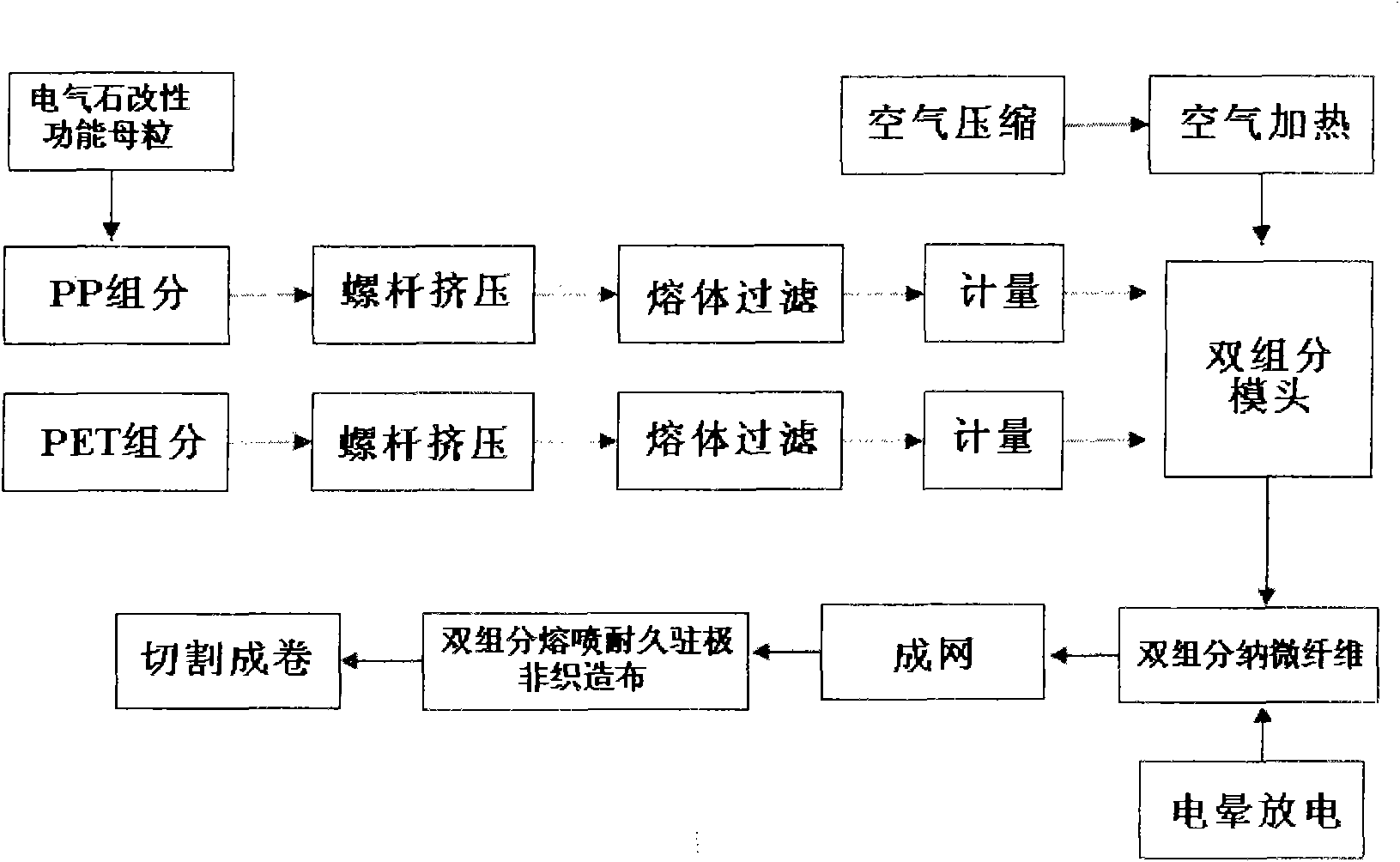
InactiveCN101591837ASoft touchImprove breathabilityElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureArtificial filament physical treatmentFiltrationThermal insulation
The invention relates to a double-component melt-blown durable electret non-woven fabric and a manufacturing method thereof. The non-woven fabric consists of tourmaline modified polypropylene / polyethylene glycol adipate (tourmaline modified PP / PET) parallel double-component melt-blown nano microfiber; and the fiber has the following components in percentage by mass: 20 to 80 percent of tourmaline modified PP, and 80 to 20 percent of PET. The method for manufacturing the non-woven fabric adopts the components in percentage by mass and the process steps of: (1) performing drying pre-treatment on the PET first; (2) then preparing a double-component melt-blown non-woven fabric by tourmaline modified PP / PET melt-blown composite spinning technology; and (3) finally obtaining the double-component melt-blown durable electret non-woven fabric by performing high-voltage corona discharge electret treatment on the non-woven fabric. The non-woven fabric can be used for durable high-efficiency filtration materials, and can also be applied to thermal insulation materials, antibacterial medical materials, oil absorption materials and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Polymeric structures and method for making same
ActiveUS6955850B1Artificial filament physical treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsFiberMaterials science
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
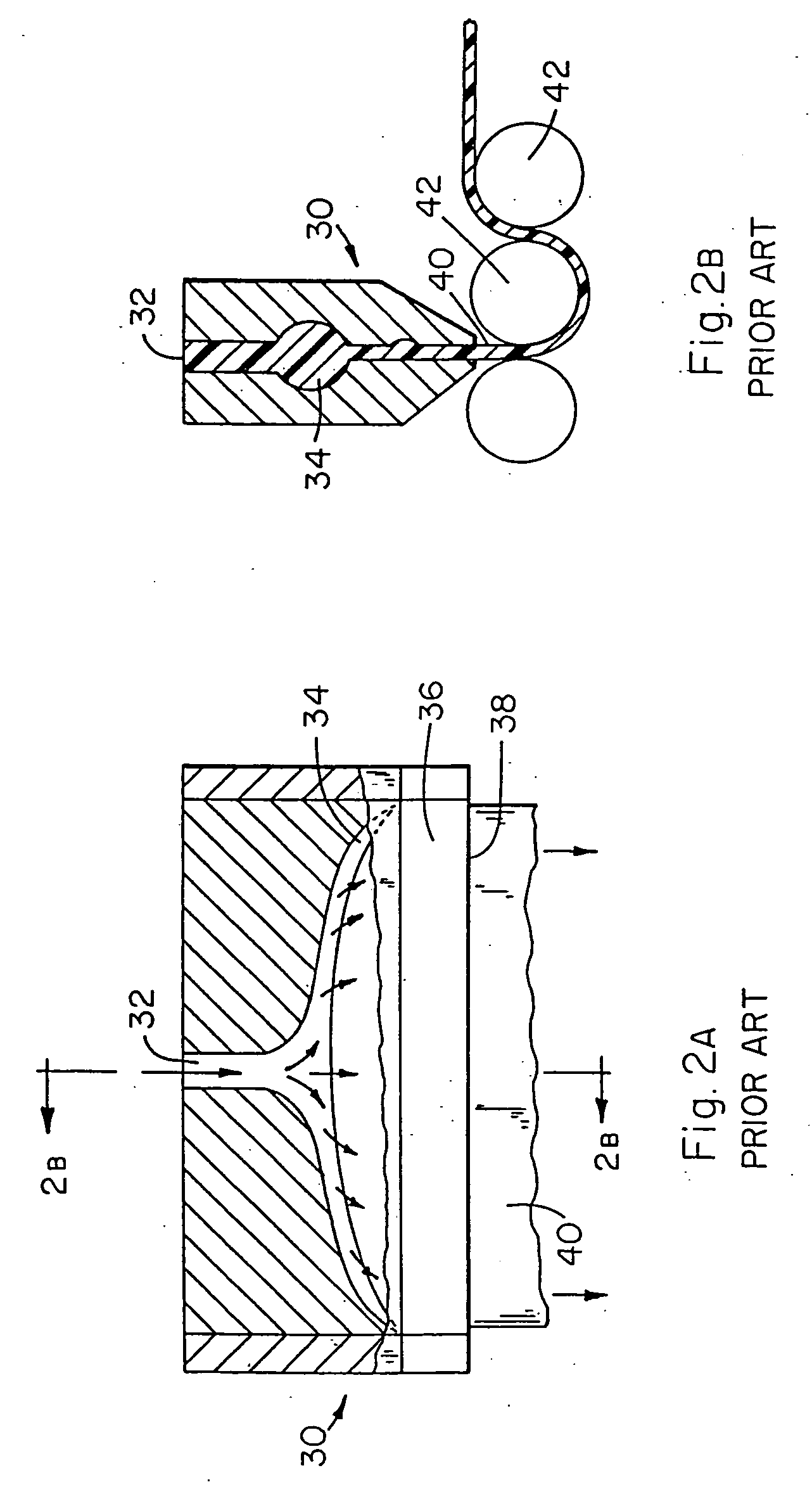
Letterpress application of elastomeric compositions
The invention provides a process to deliver an elastomeric composition to a substrate. The elastomeric composition is cooled. The cooling also results in substantially complete transfer of the elastomeric composition from the pattern roll to the substrate with a resulting reduction in elastomer degradation.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
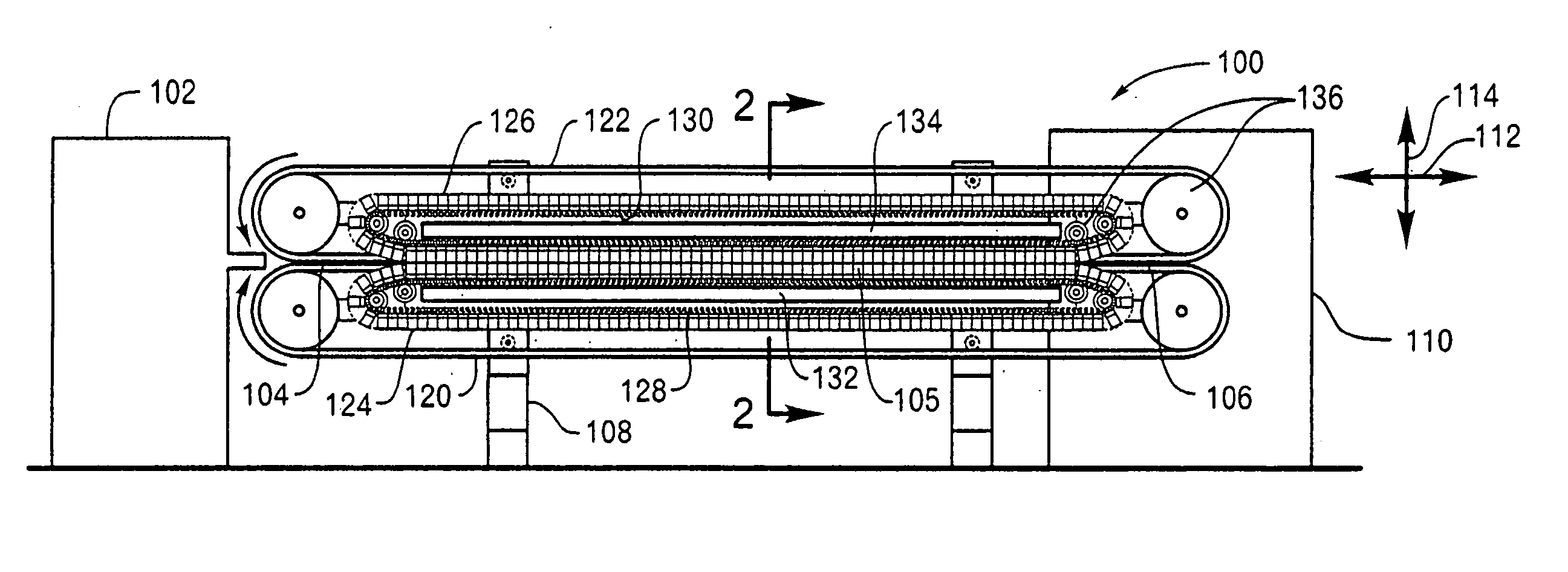
Method for molding three-dimensional foam products using a continuous forming apparatus
ActiveUS20070052128A1Reduce frictionAvoid cavitiesConfectioneryPress rollersEngineeringMotion transfer
A continuous forming apparatus for molding foam material into foam products that includes a first endless belt and a second endless belt that cooperates with the first endless belt to mold the foam material. The continuous forming apparatus may also include a first plurality of cleats and a second plurality of cleats opposed to the first plurality of cleats that support the first endless belt and the second endless belt respectively. The first plurality of cleats may include a three-dimensional abutment surface that provides transverse and lateral support to the first endless belt. Additionally, the continuous forming apparatus may include a first frame disposed to support the first plurality of cleats, a second frame disposed to support the second plurality of cleats, and a drive mechanism for imparting motion to the first endless belt, the second endless belt, the first plurality of cleats, and the second plurality of cleats.
Owner:CENTURY BOARD CORP +1
Method for preparing low-titer high-strength high-modulus polyethylene fibre
The present invention discloses a process for producing low-titer, high-strength and high-modulus polyethylene fibers, comprising the following steps: dissolving the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene into paraffin oil with a low viscosity to form a spinning solution with a concentration of 3ˆ¼15%; extruding the spinning solution through a thin spinneret with at least 10 orifices having a diameter ¦ of 0.7ˆ¼0.8mm and a length / diameter ratio of 10ˆ¼12, by applying a high pressure in the range of 2.5±1.0MPa to the spinning solution, such that the fluid in the orifices is extruded at a shear rate of 200ˆ¼3 500sec -1 ; and then performing a jet stretch at a deformation rate of 200ˆ¼5 000min -1 within an air-gap of 10ˆ¼15mm between the spinneret and the quench bath surface; feeding the jet-stretched fluid into the quench bath to form gel filaments; extracting and drying the gel filaments; and performing a multistage ultrahigh post stretch on the dried gel filaments with a stretch ratio of 15 or less. In this process, the solution is extruded at a high rate by using a spinneret with small orifice diameter, thereby achieving a high shear rate and a high deformation rate, so the present process is a novel and effective spinning process.
Owner:HUNAN ZHONGTAI SPECIAL EQUIP
Rotatable head for forming spiral extrusions
InactiveUS20050260408A1Increase sealing forceAvoid pollutionConfectioneryFilament/thread formingEngineeringCounterbore
A polymer extrusion crosshead assembly for forming a spirally-striped extrusion. The assembly includes conventional components for admitting, turning, and accelerating primary molten polymer toward a novel rotating die sub-assembly. A body element includes an axial counterbore for receiving a manifold supply block in communication with a source of secondary striping polymer. A wear plate is attached to the manifold block. The die sub-assembly includes a striping die having an annular passage for conveying the primary polymer to form an extruded tube or a core material coating. The die is loaded against the wear plate by a Belleville washer. The die includes one or more striping nozzles in communication with the manifold block for injecting secondary striping polymer into the annular stream of primary polymer flowing through the die, creating a longitudinal stripe of striping polymer. Rotating the die while extruding both polymers yields a helically striped (spiral) extrusion.
Owner:CANGEN HLDG
Method of manufacturing a wood-based board and such a wood-based board
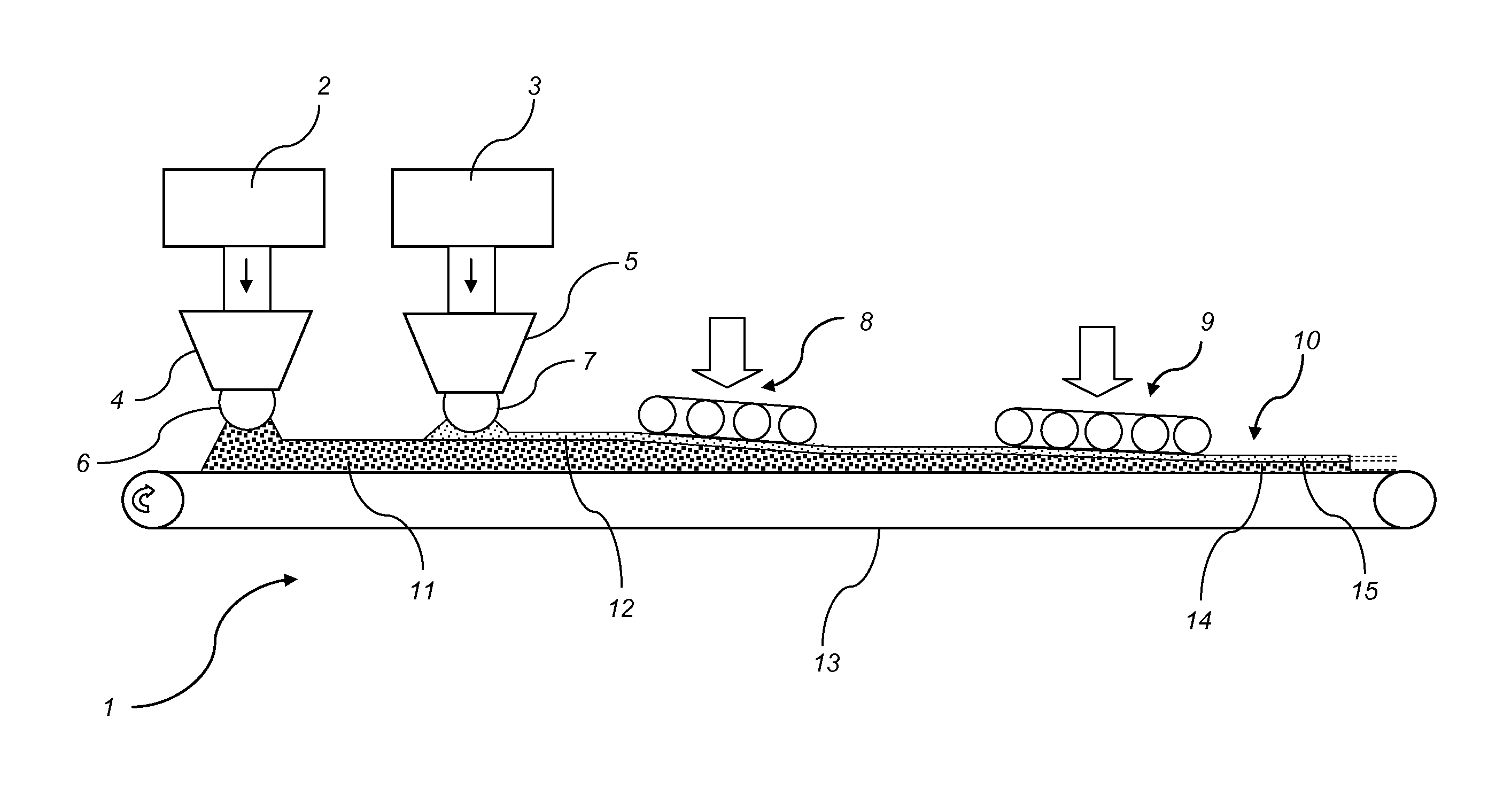
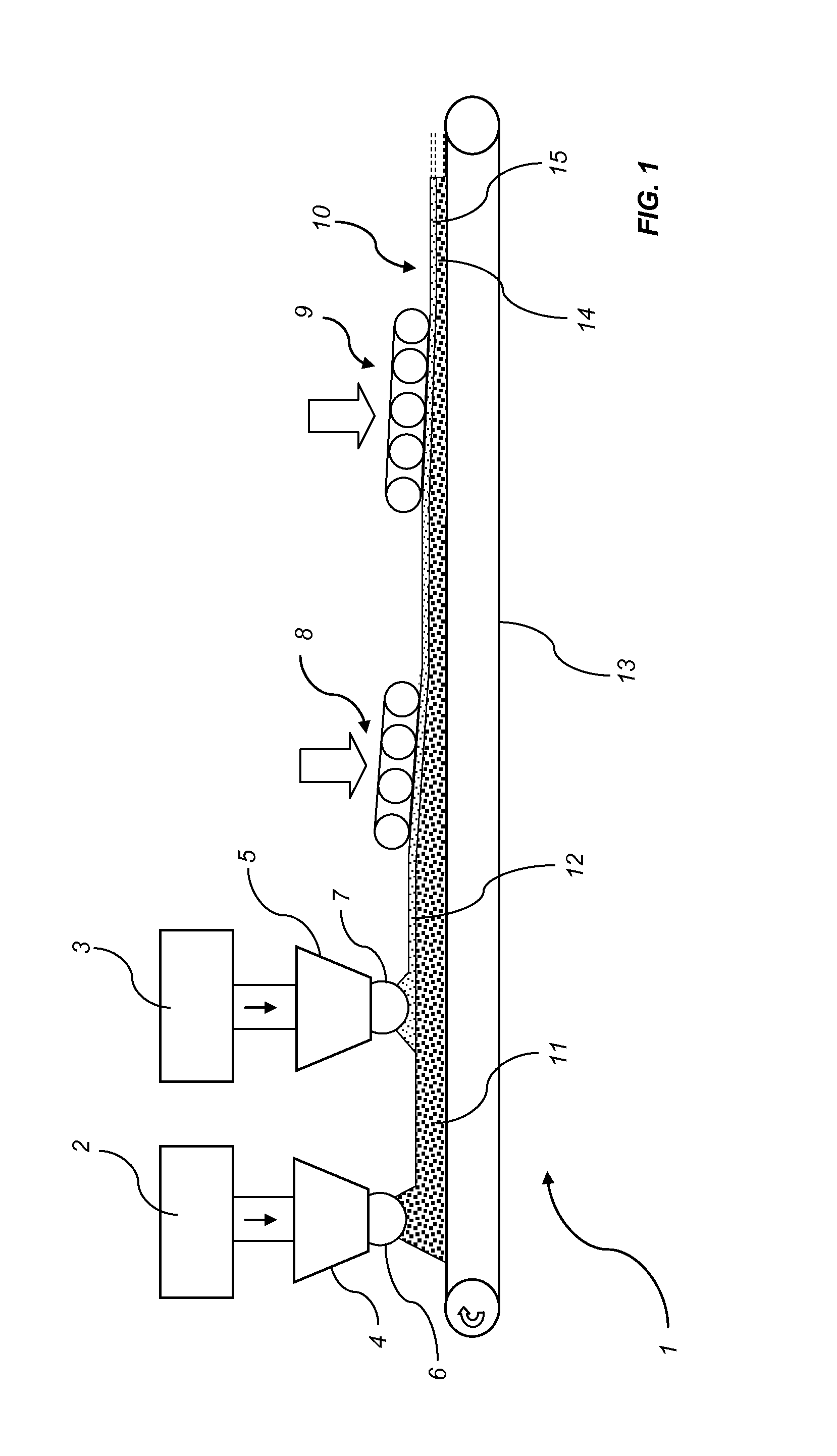
ActiveUS20140370319A1Low costConstruction materialArtificial filament physical treatmentFiberSurface layer
A method of manufacturing a wood-based board (10). The method includes applying at least one first fibre mat (11) including a first mix comprising lignocellulosic particles and a binder on a carrier (13), applying a second fibre mat (12) including a second mix including cellulosic particles and a binder on said at least one first fibre mat (11), and pressing said at least one first fibre mat (11) into a base layer (14) and the second fibre mat (12) into a surface layer (15) simultaneously, thereby forming a wood-based board (10). Also, to such a wood-based board (10).
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Dry-method spinning technique for preparing super high molecular weight polyethylene fibre
InactiveCN101148783AVolatileReduce manufacturing costFilament forming substance formingArtificial filament physical treatmentSolventCarbon dioxide
The present invention is dry spinning process for preparing ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber, and belongs to the field of polymer material preparing technology. The process includes: dissolving ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene powder and assistant in xylene solvent; filtering and debubbling the solution, extruding in a screw extruder, spraying through a metering pump, spinning manifold and spinneret and solidifying to form, hot air drying to eliminate xylene from fiber, hot drafting and final winding the product. The present invention includes also condensing and adsorbing to separate xylene from N2 or CO2, reusing the separated xylene and reusing the separated N2 or CO2.
Owner:BEIJING TEX STRONG NEW MATERIAL DEV
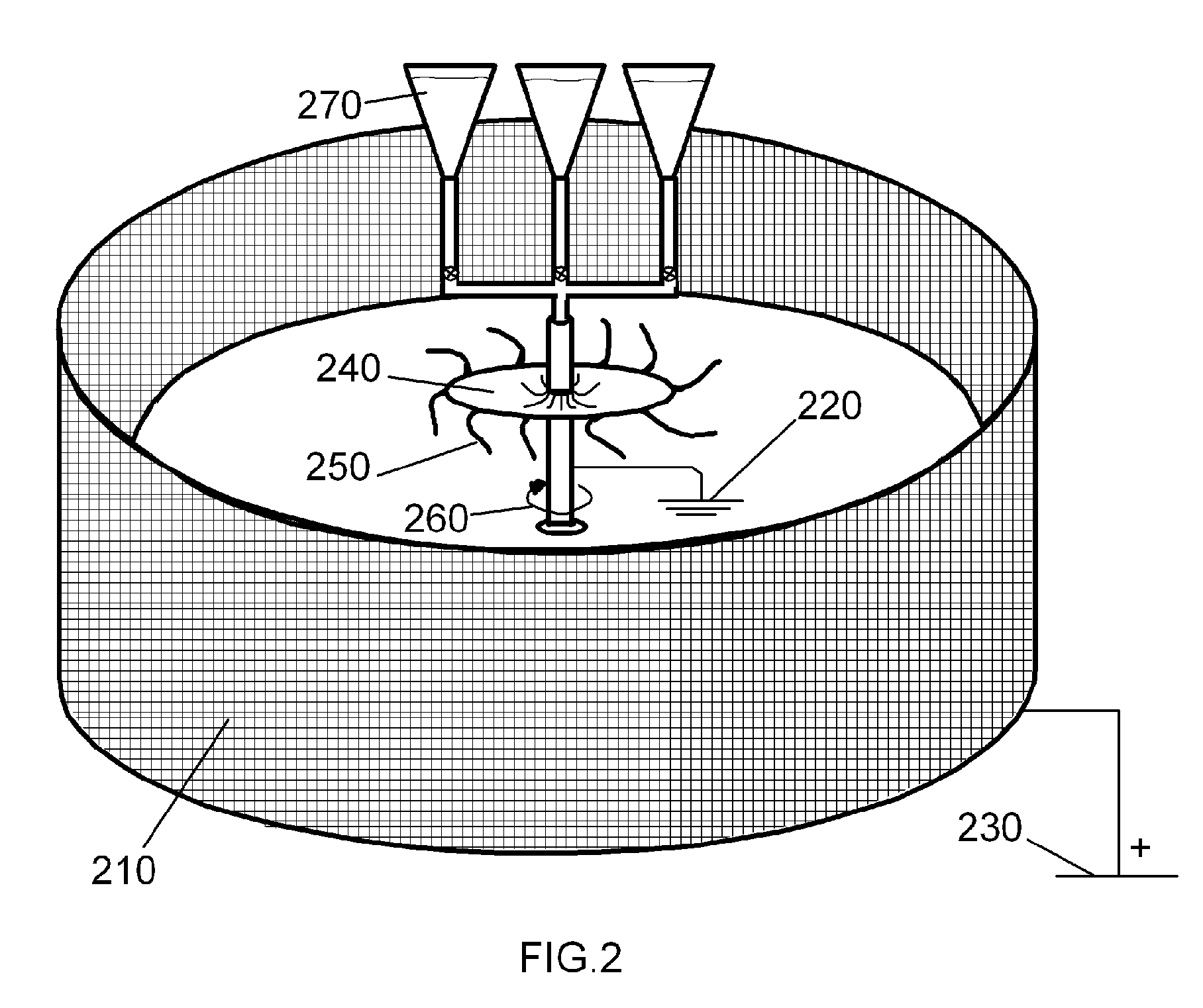
Method of Manufacturing Fibrous Hemostatic Bandages
InactiveUS20090136651A1Rapid customizationCreate redundancyPeptide/protein ingredientsArtificial filament physical treatmentEngineeringBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
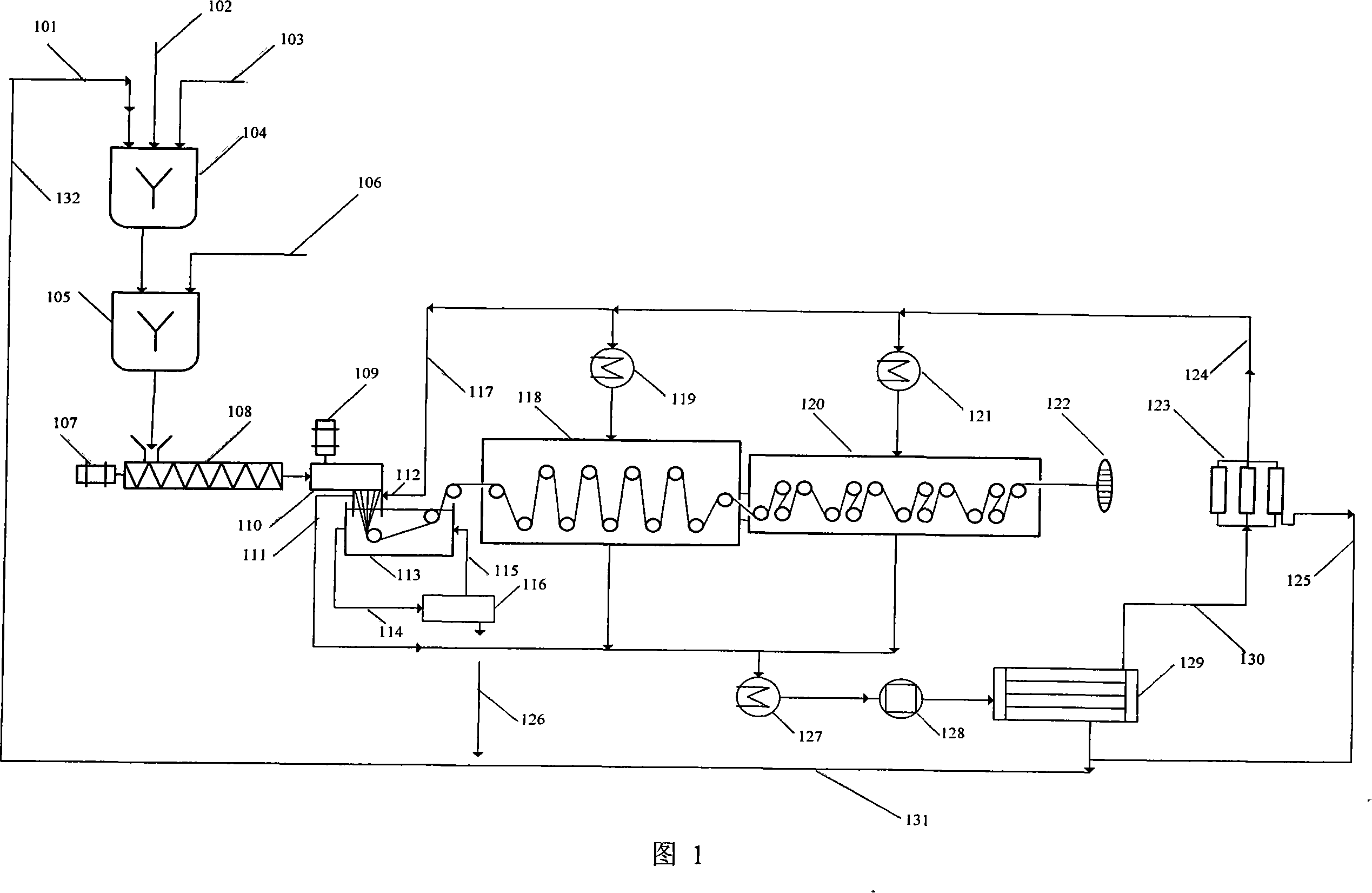
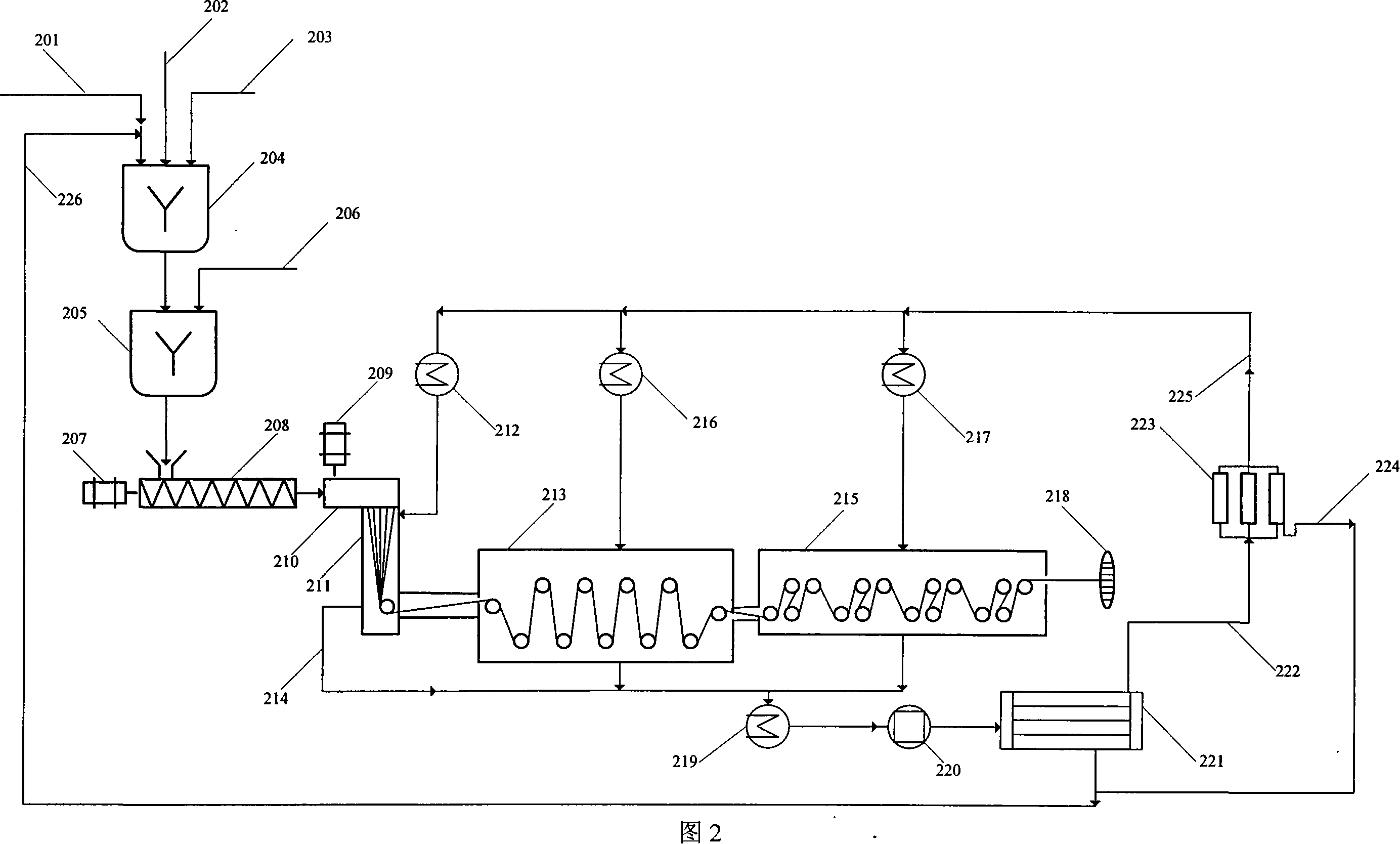
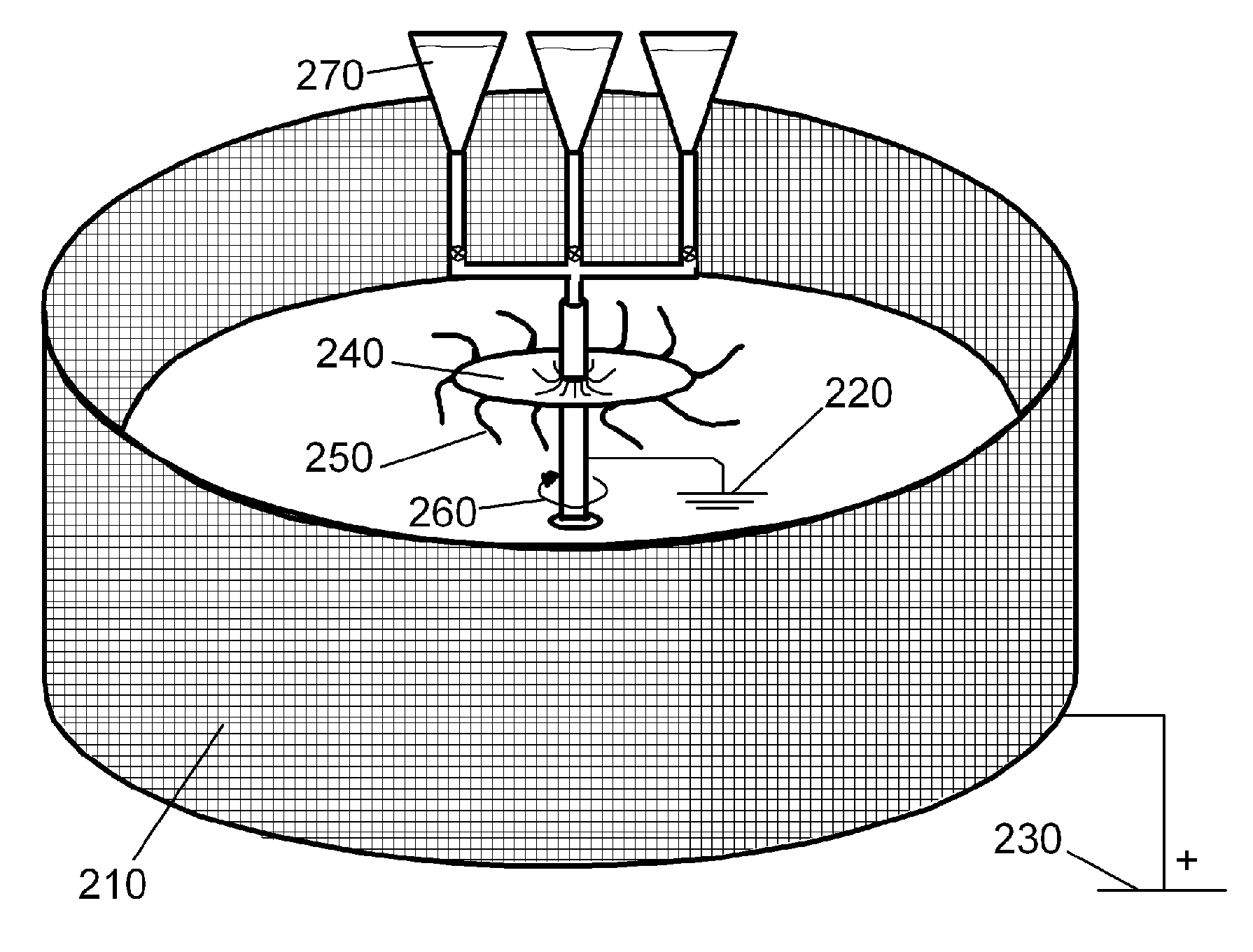
A method of manufacturing a sturdy and pliable fibrous hemostatic dressing by making fibers that maximally expose surface area per unit weight of active ingredients as a means for aiding in the clot forming process and as a means of minimizing waste of active ingredients. The method uses a rotating object to spin off a liquid biocompatible fiber precursor, which is added at its center. Fibers formed then deposit on a collector located at a distance from the rotating object creating a fiber layer on the collector. An electrical potential difference is maintained between the rotating disk and the collector. Then, a liquid procoagulation species is introduced at the center of the rotating disk such that it spins off the rotating disk and coats the fibers.
Owner:LNK CHEMSOLUTIONS
Method for manufacturing formable thermoplastic laminates
One method for making a laminate material comprising a first surface layer comprising resorcinol arylate polyester chain members and a second surface layer suitable for bonding to a substrate, comprises co-extruding a polymeric first surface layer material and a polymeric second surface layer material through a die and into the first nip of a calender roll stack comprising a first surface roll and a second surface roll that define the first nip, to form the laminate material. A nip load in the first nip of greater than or equal to about 400 N / cm can be applied to the laminate, and the laminate material can be collected from the roll stack. The first roll and the second roll can each have a surface smoothness of less than or equal to about 5 micrometers and temperatures of about 40° C. to about 150° C.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com