Patents
Literature
68results about How to "Reduce basis weight" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of manufacturing a stretched mechanical fastening web laminate
InactiveUS7897078B2Reduce basis weightSnap fastenersWood working apparatusFiberVolumetric Mass Density
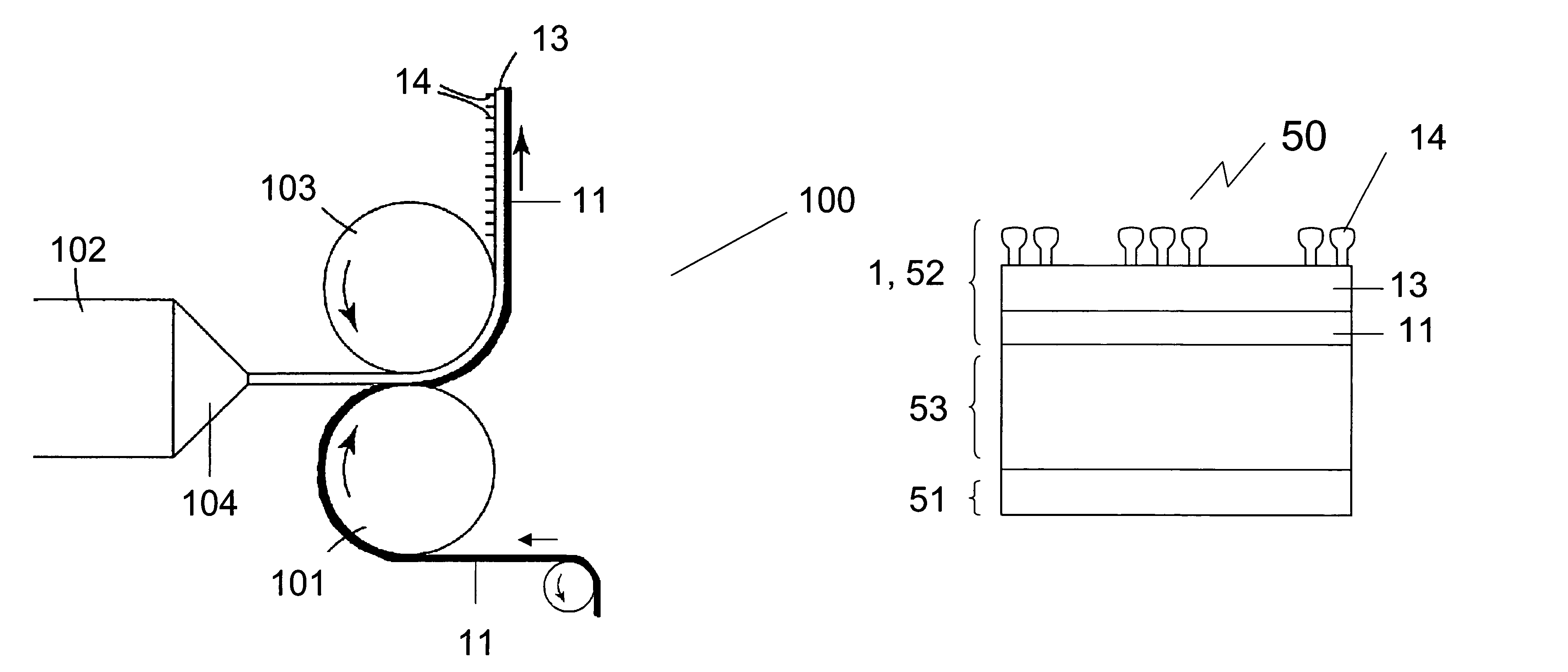
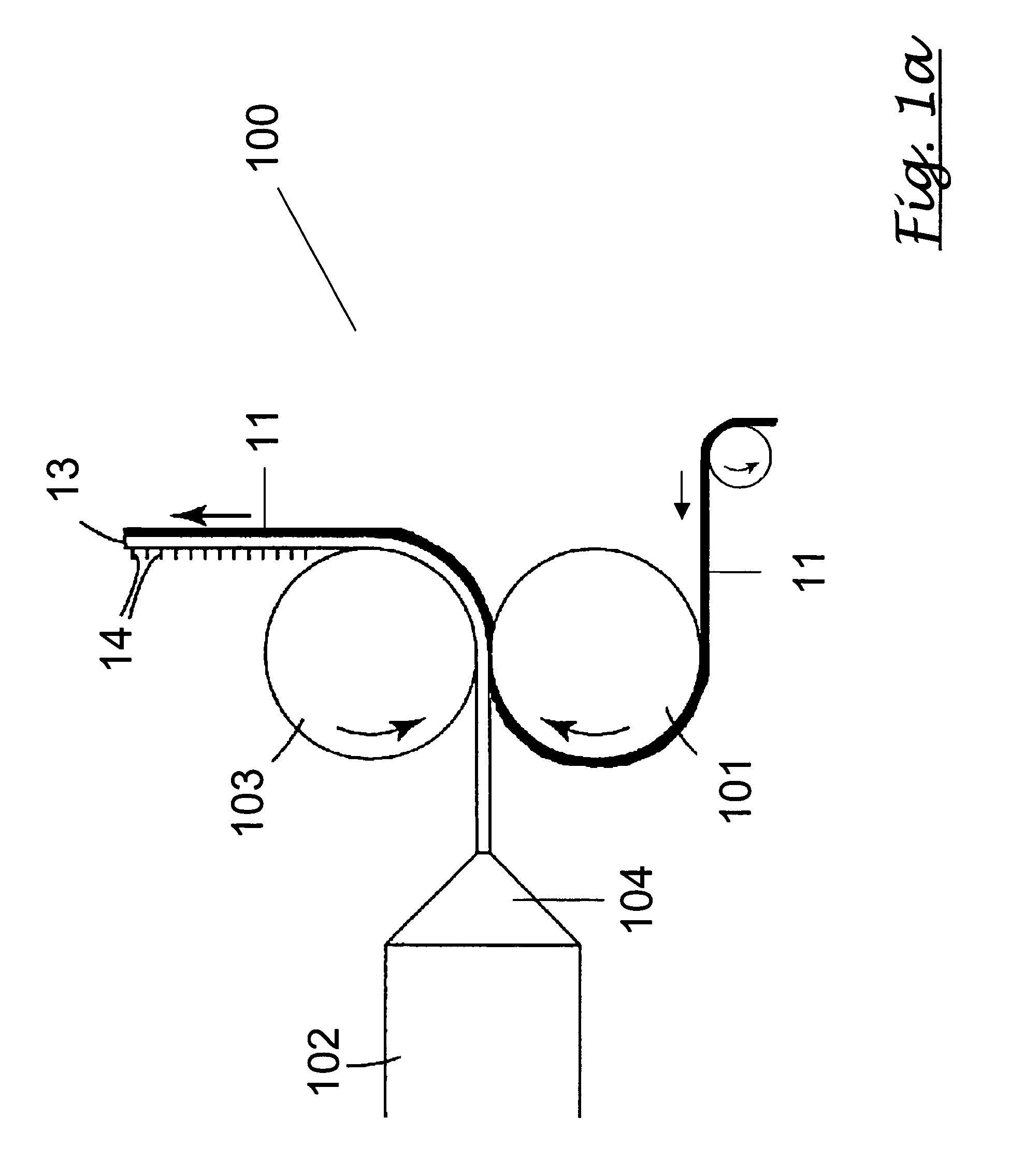
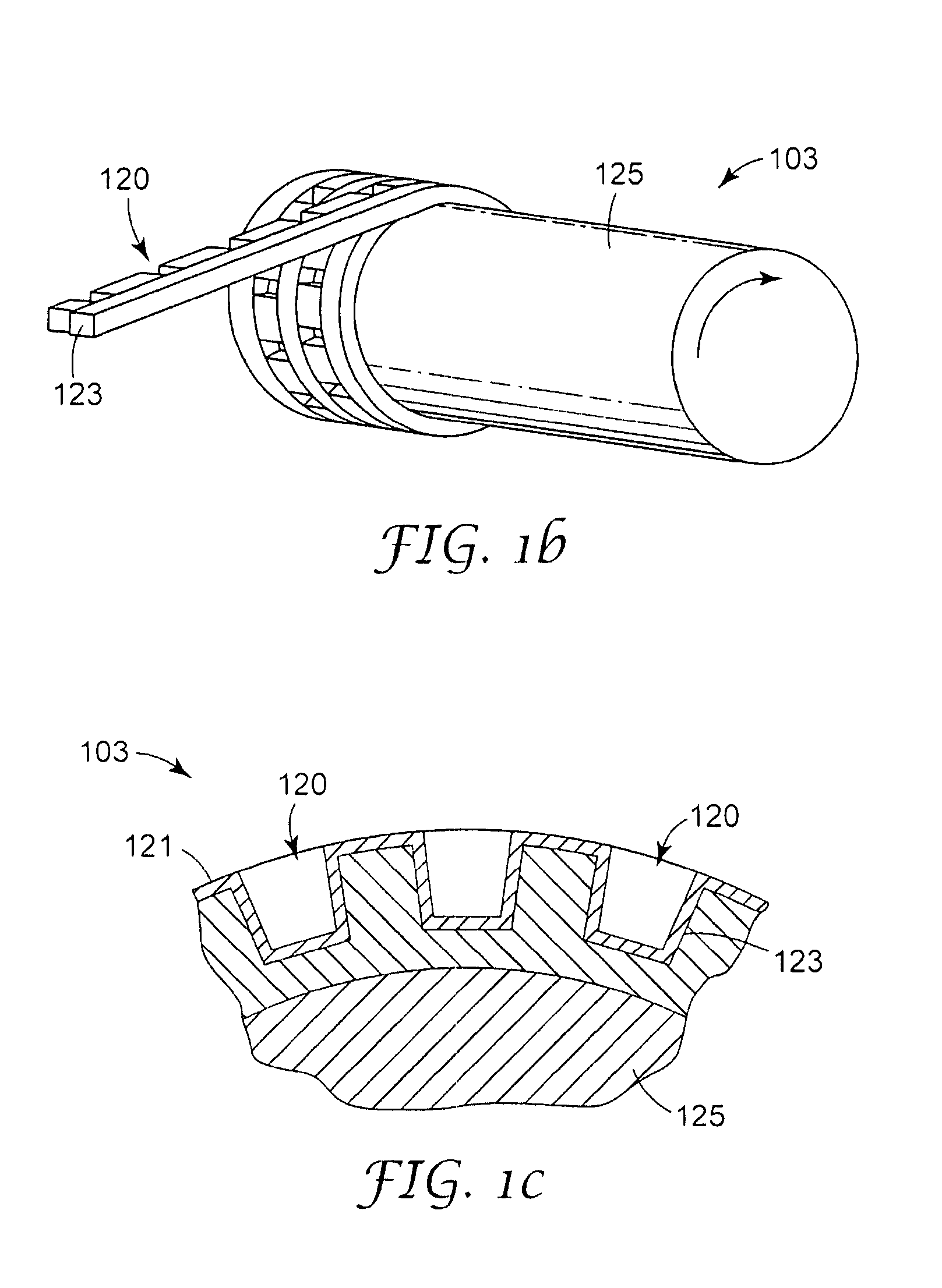
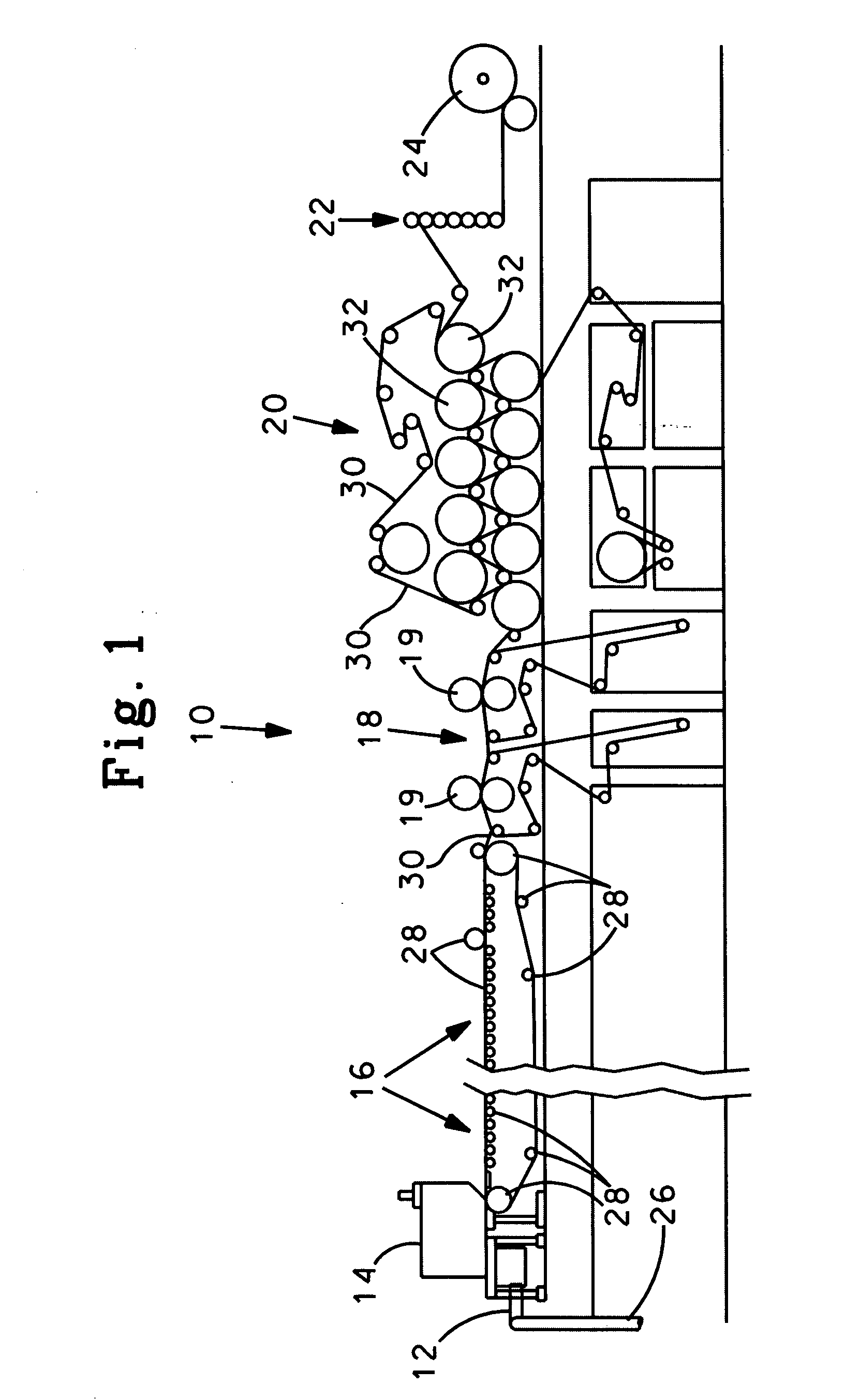
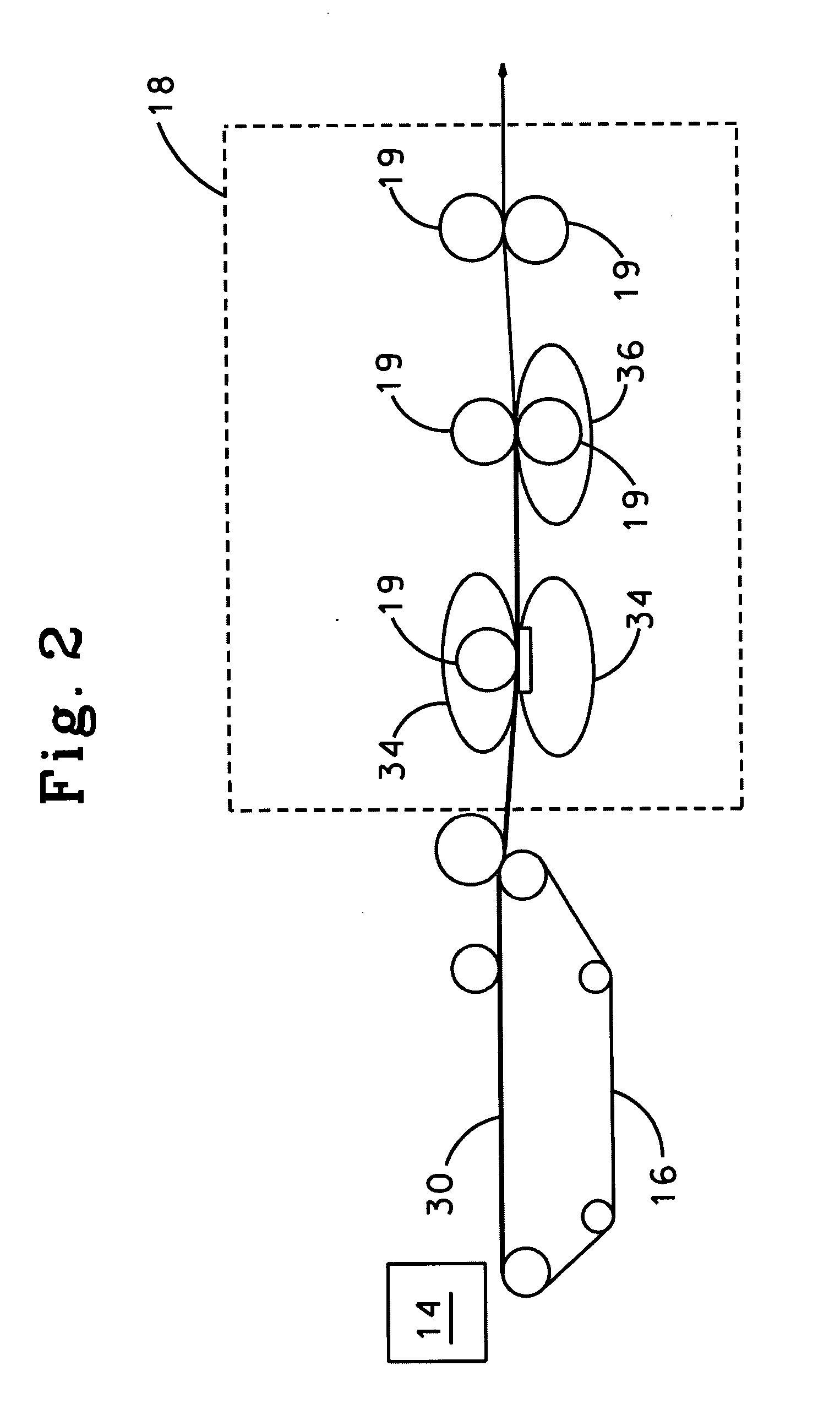
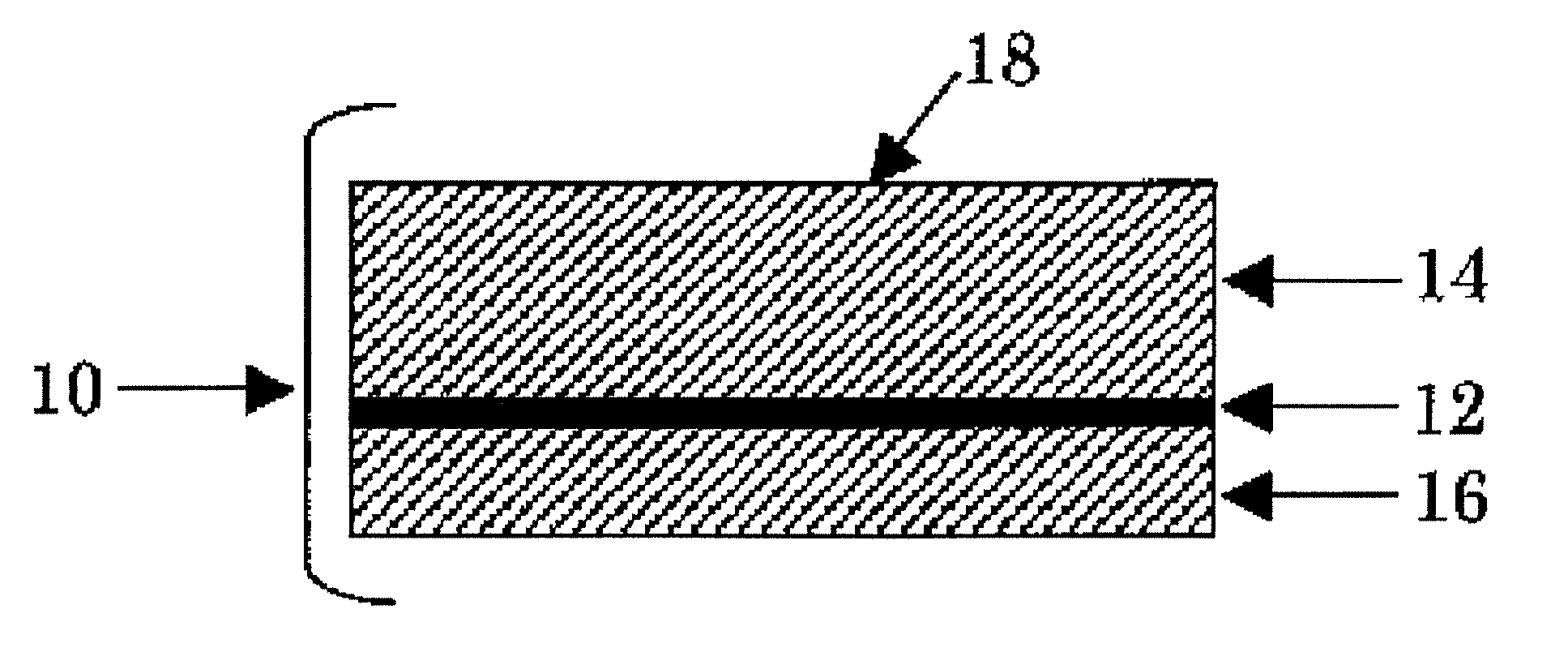
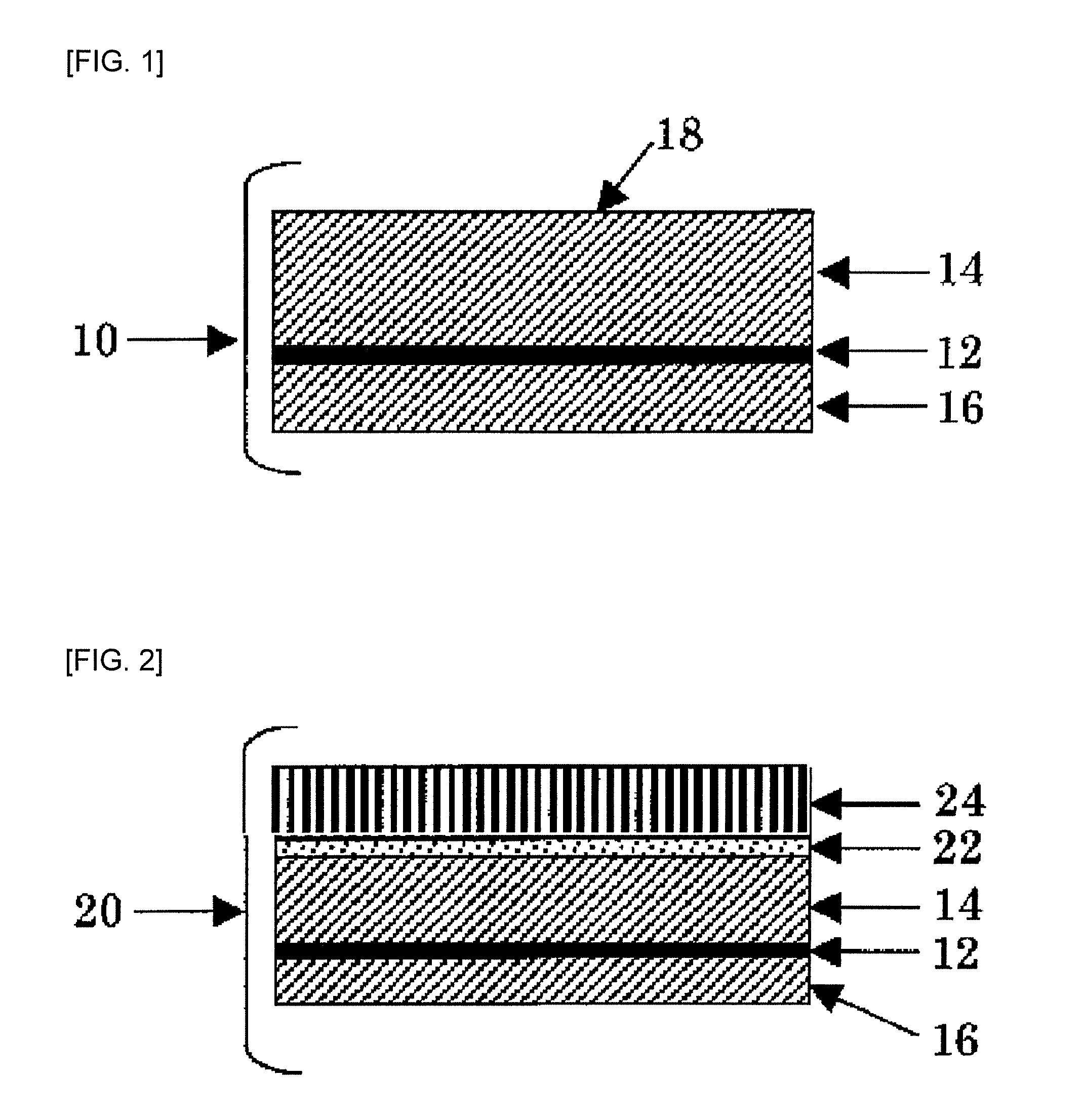
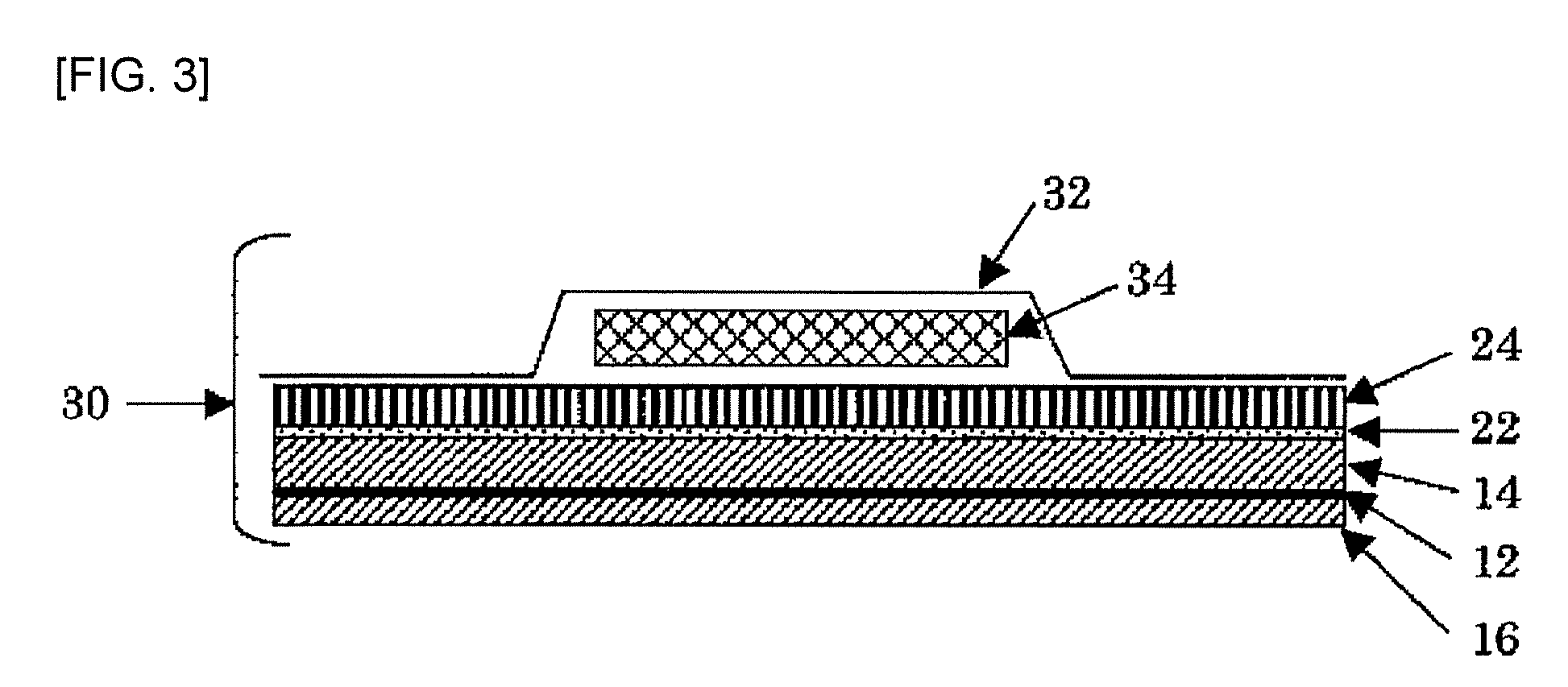
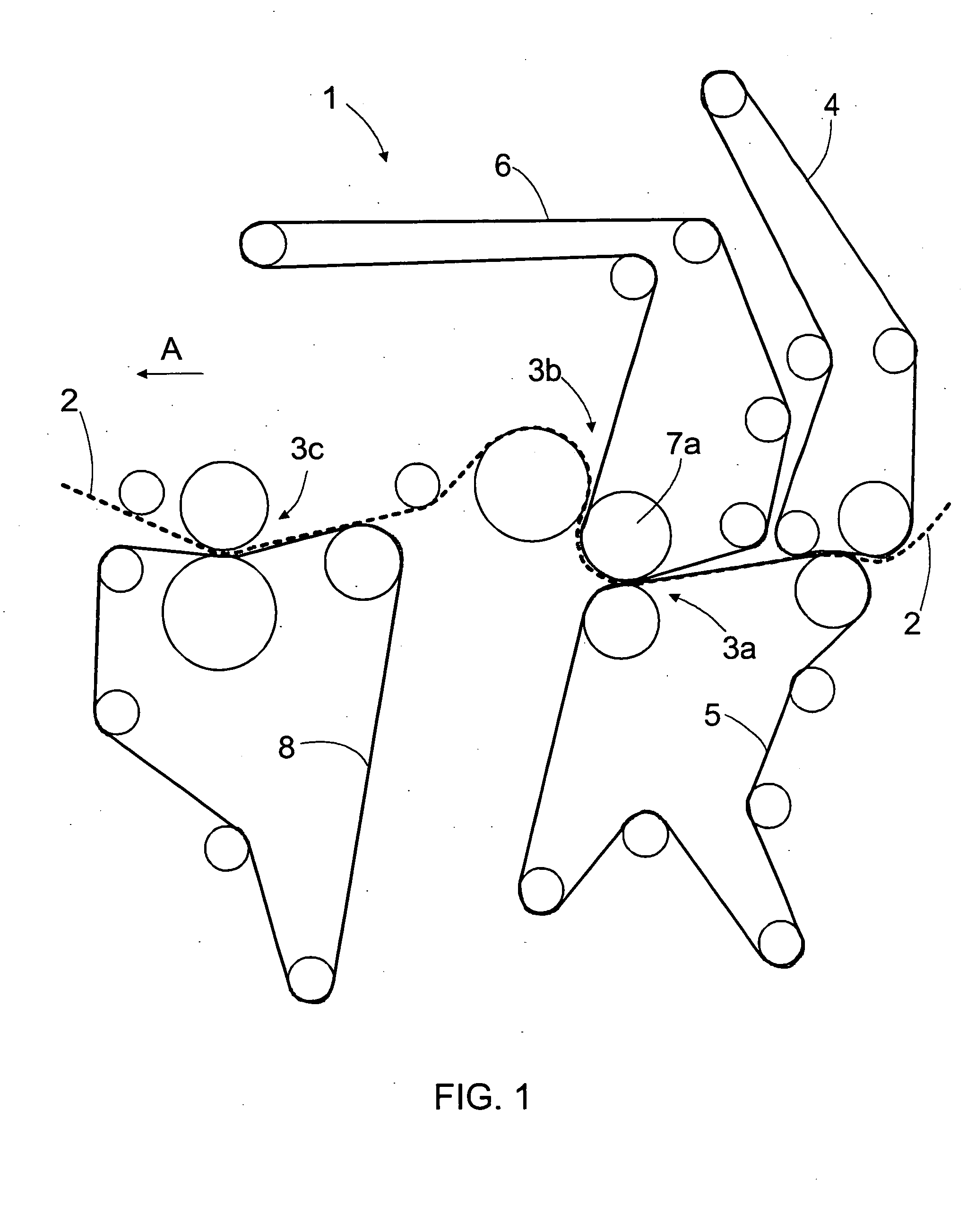
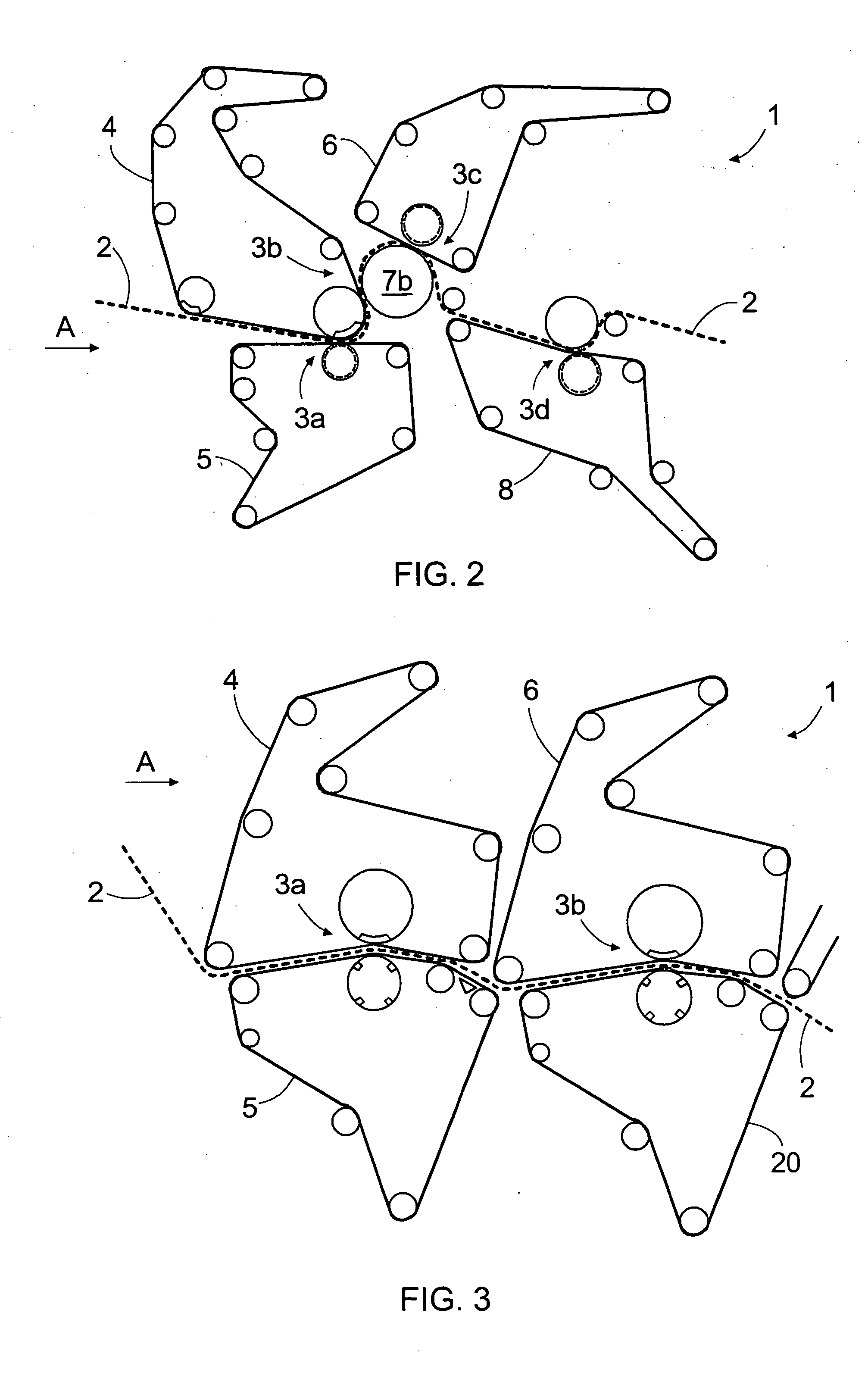
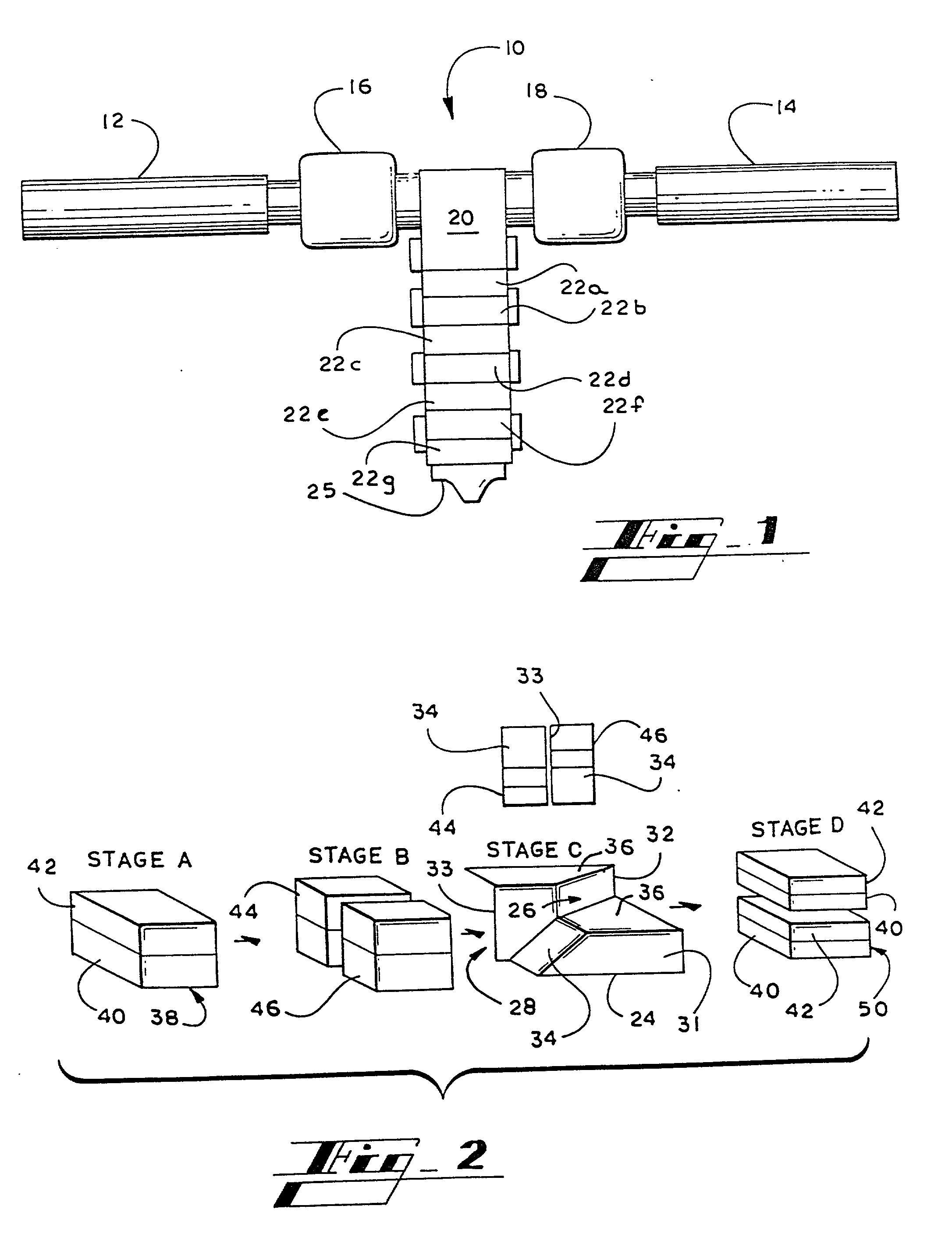
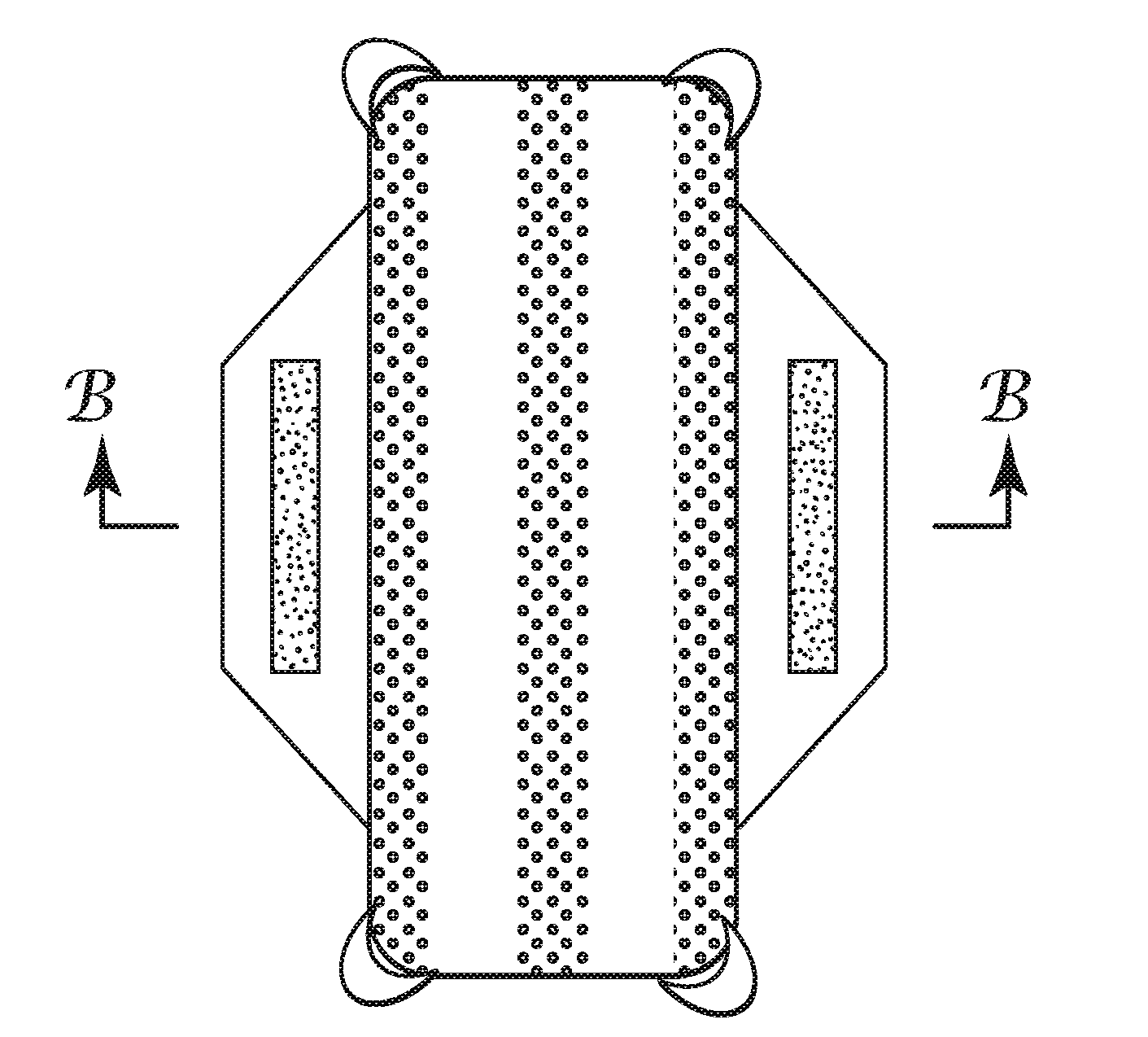
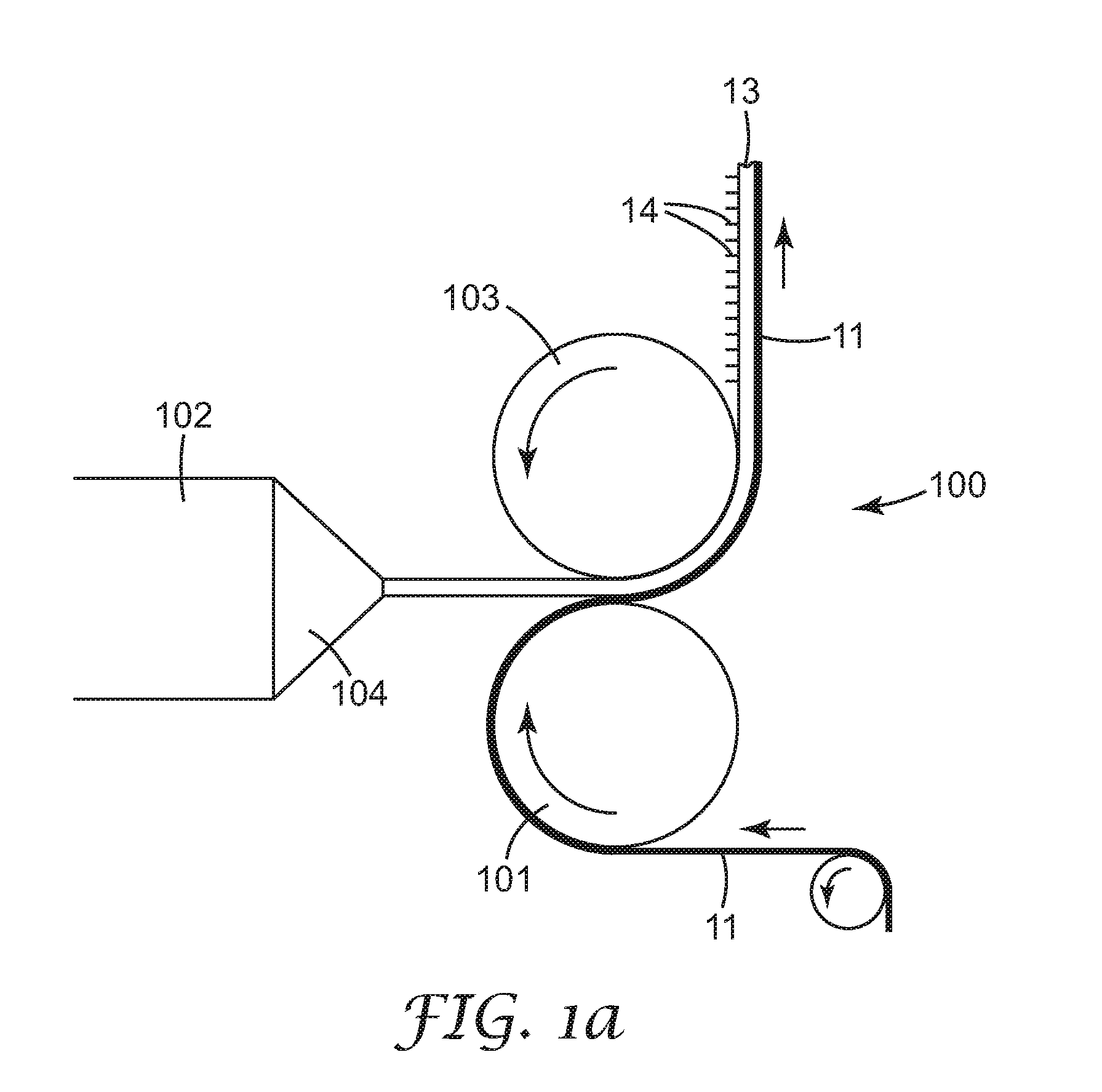
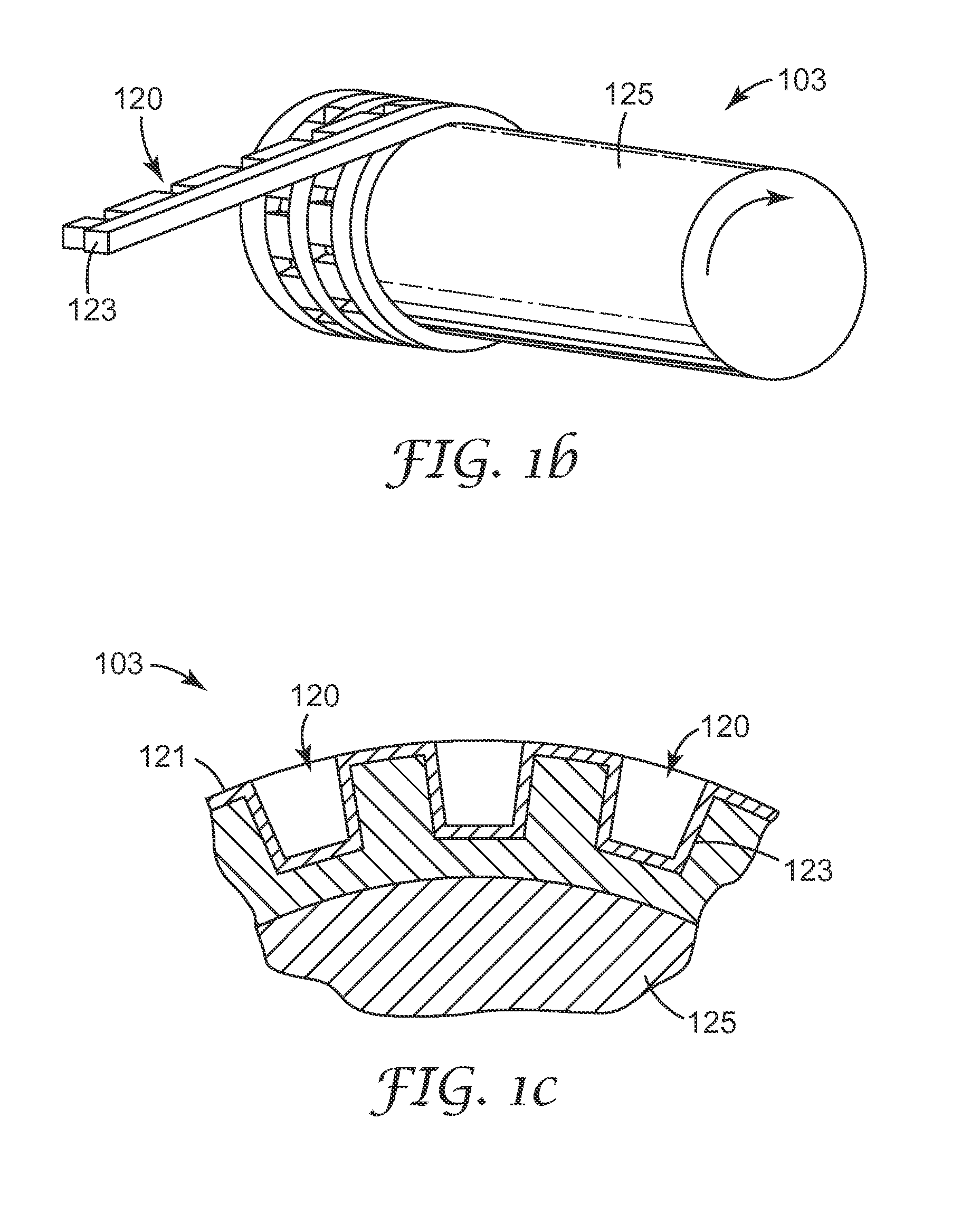
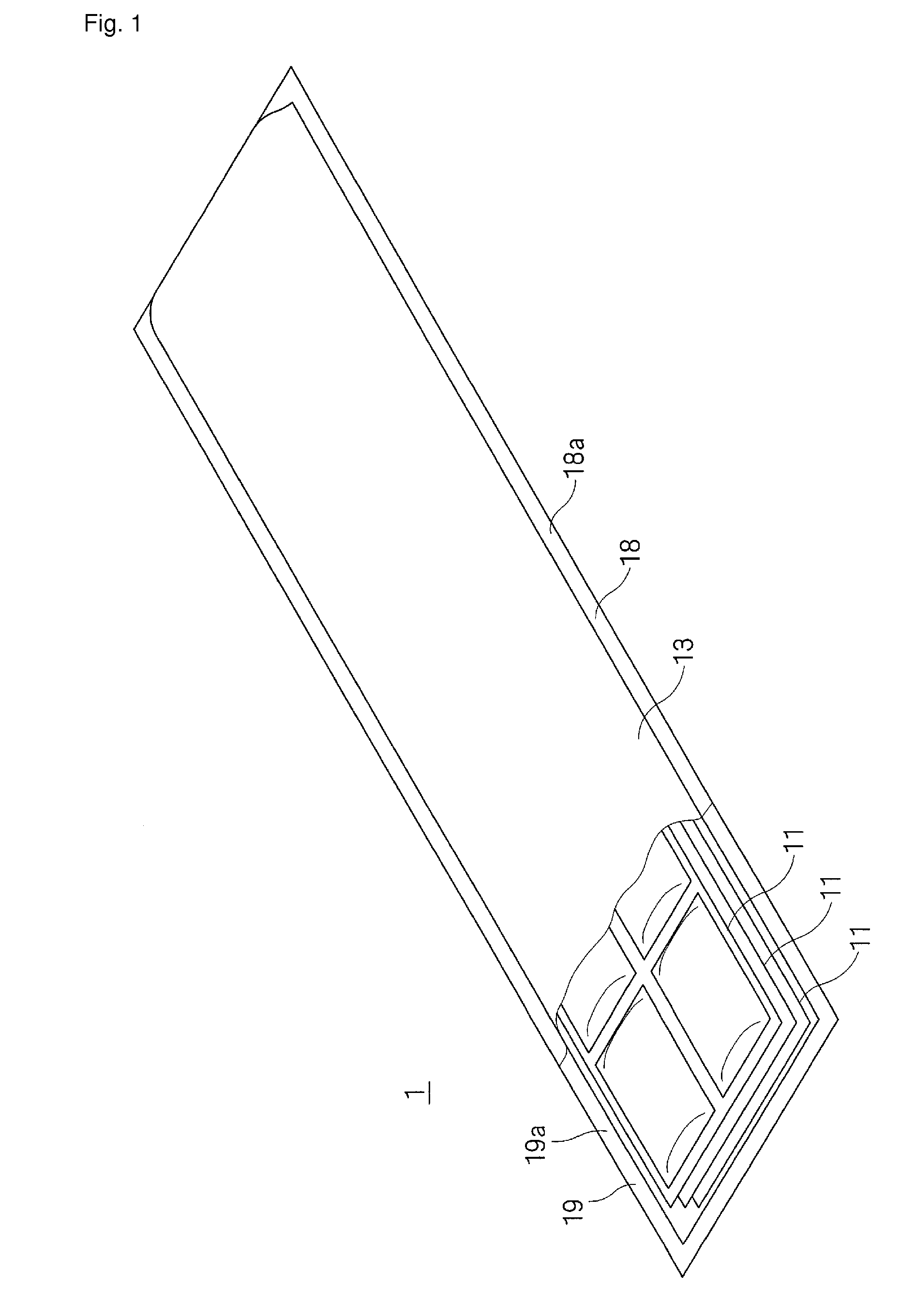
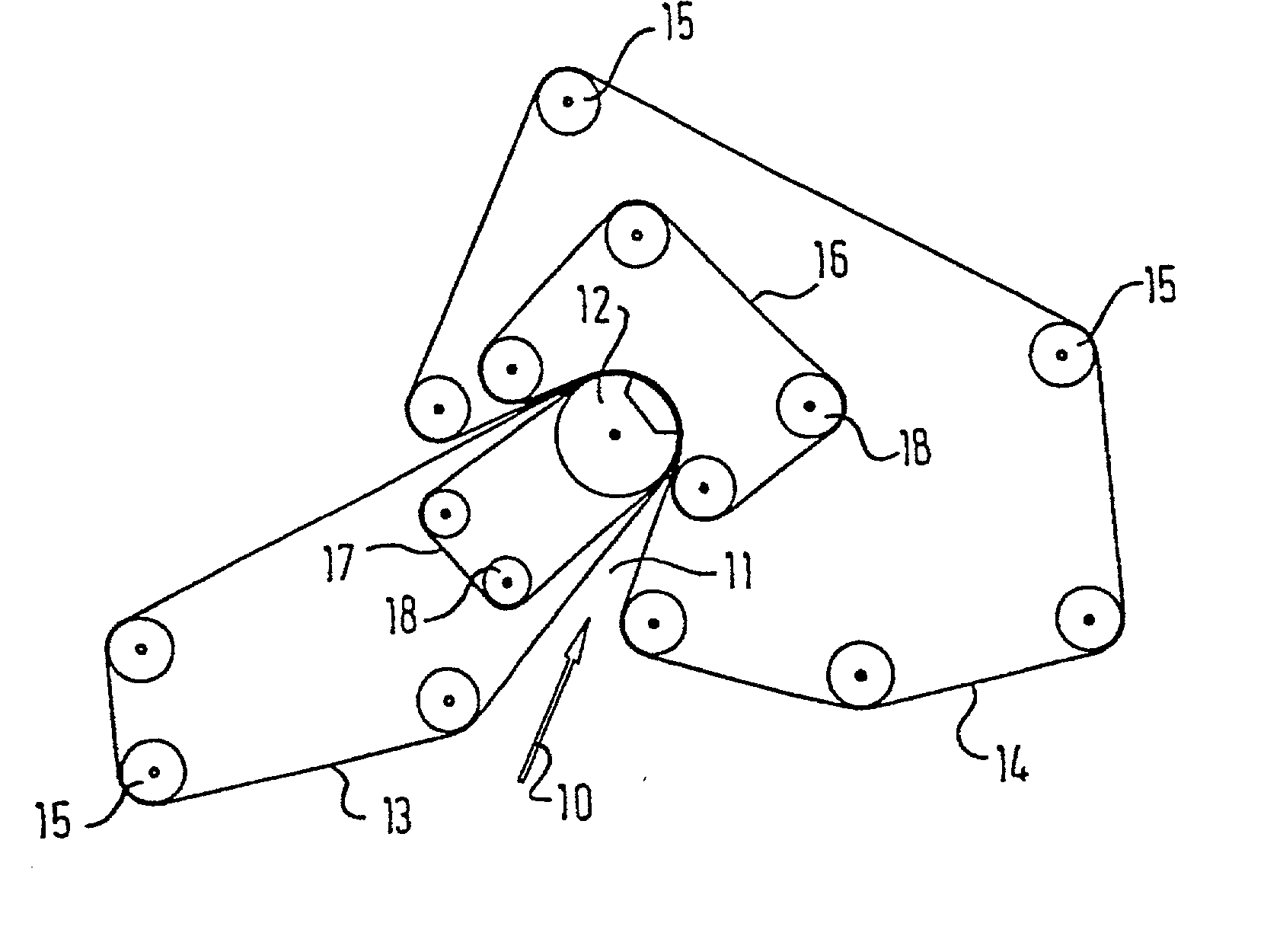
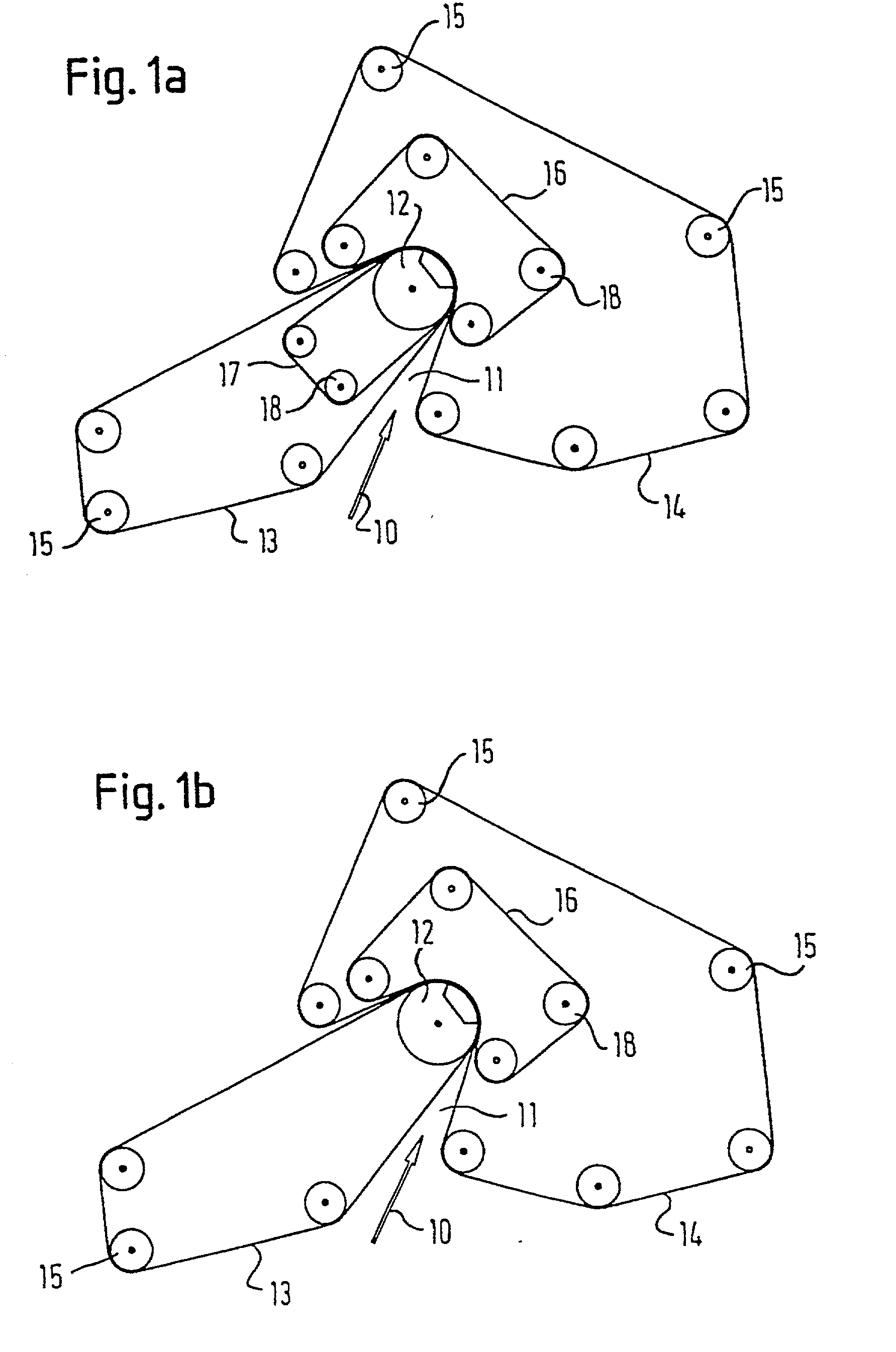
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a stretched mechanical fastening web laminate (1) comprising a thermoplastic web layer (13) having two major surfaces, one of the major surfaces bearing a multitude of male fastening elements (14) suitable for engagement with a corresponding female fastening material, and on its other major surface a fibrous web layer (11), said method comprising the steps of(i) providing the fibrous web layer (11) having an initial basis weight,(ii) passing the fibrous web layer (11) through a nip formed by two rolls (101), (103), one of them having cavities (120) that are the negatives of a plurality of male fastening elements (14), introducing a molten thermoplastic resin into the cavities (120) in excess of an amount that would fill the cavities (120) which excess forms the thermoplastic web layer (13), allowing the resin to at least partially solidify and stripping of a precursor web laminate (10) thus formed comprising the fibrous web layer (11) and the thermoplastic web layer (13) bearing a plurality of male fastening elements (14), from the cylindrical roll (103) having cavities (120) whereby the thermoplastic web layer (13) has an initial thickness and an initial hook density, and(iii) stretching the precursor web laminate (10) monoaxially or biaxially thereby decreasing the basis weight of the fibrous web layer (11) and the thickness of the thermoplastic web layer (13) from their respective initial values to provide a stretched mechanical fastening laminate (1) having a basis weight of less than 100 g·m−2.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
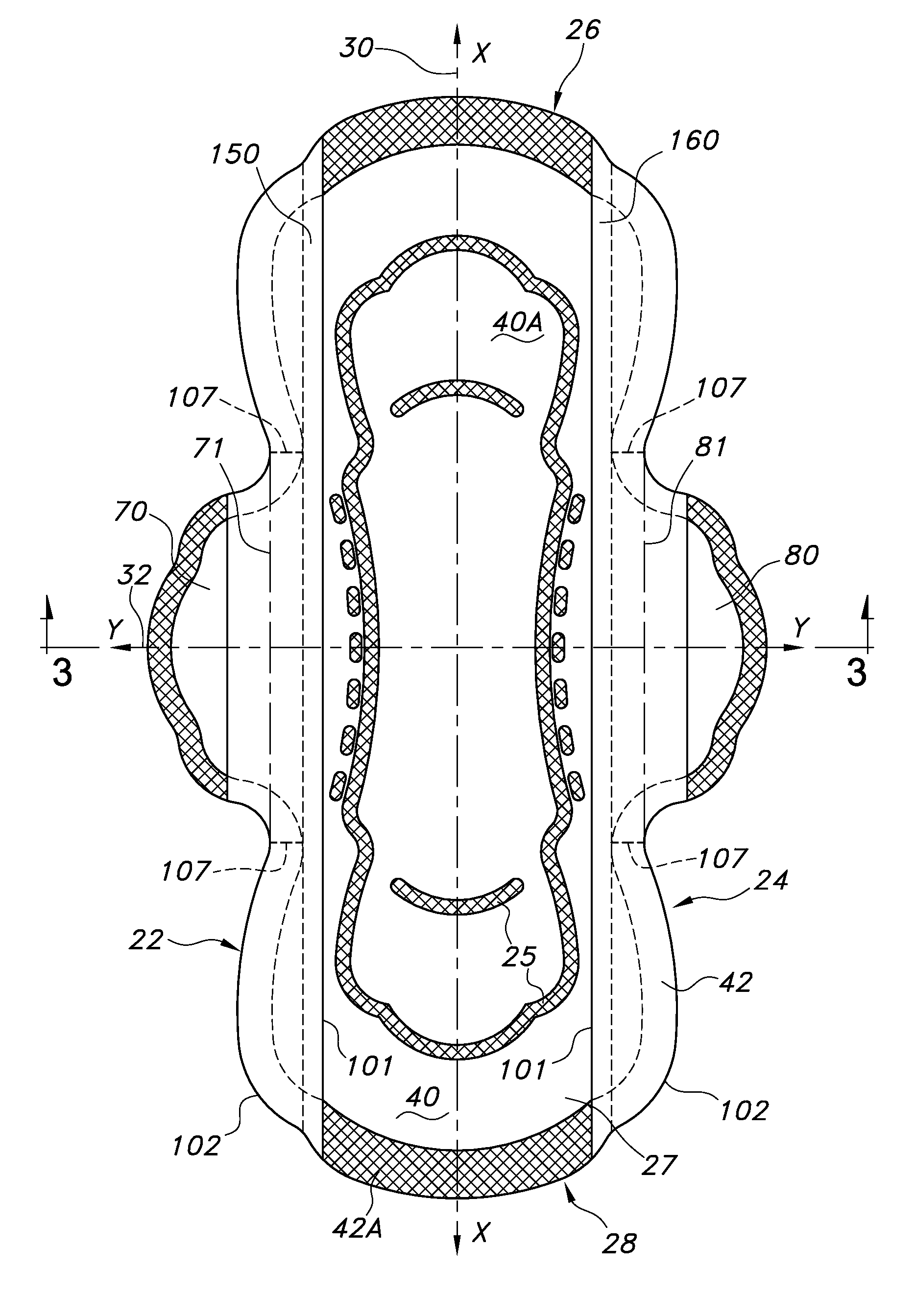
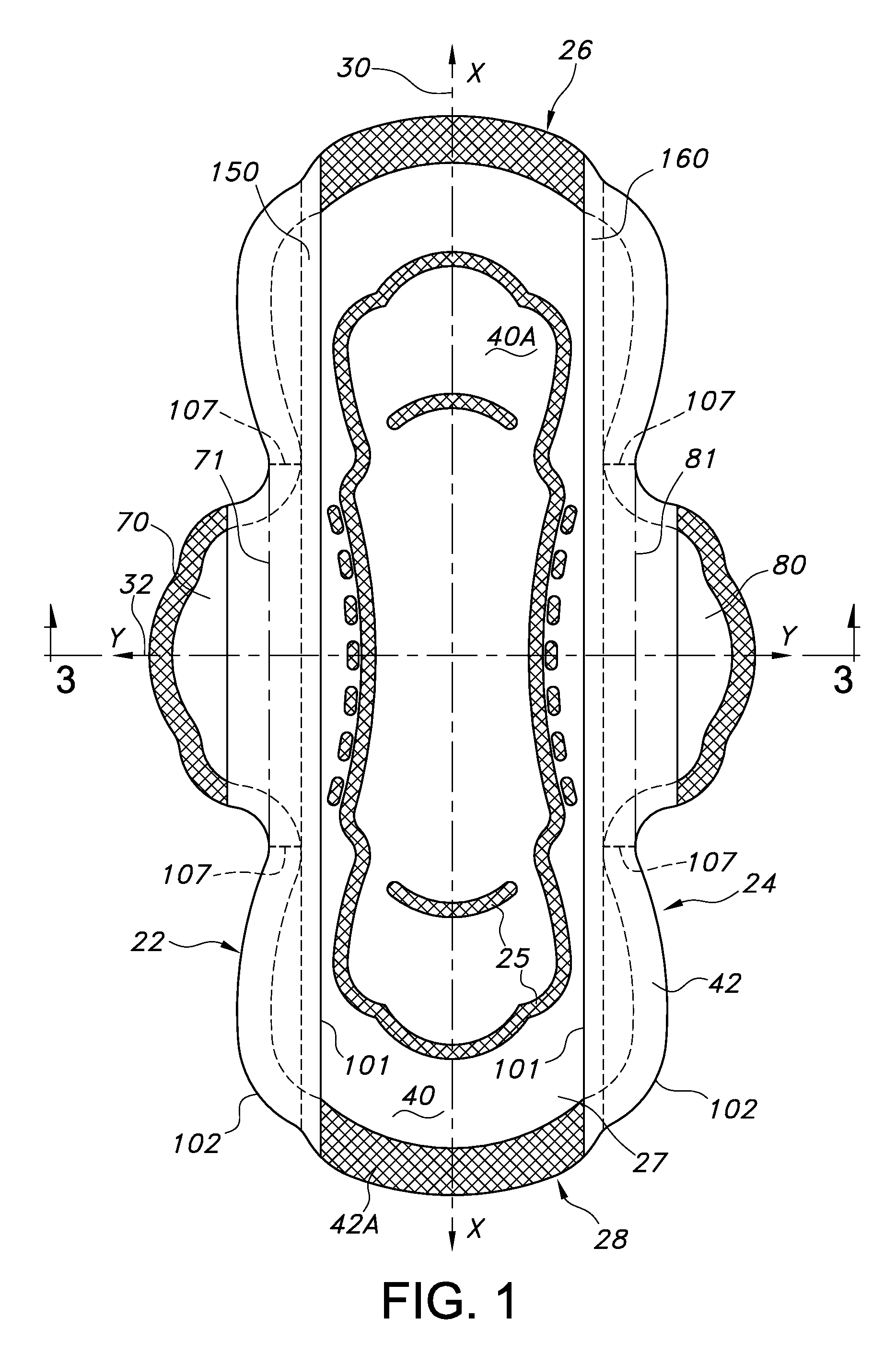
Absorbent personal care article having wings and protective strips
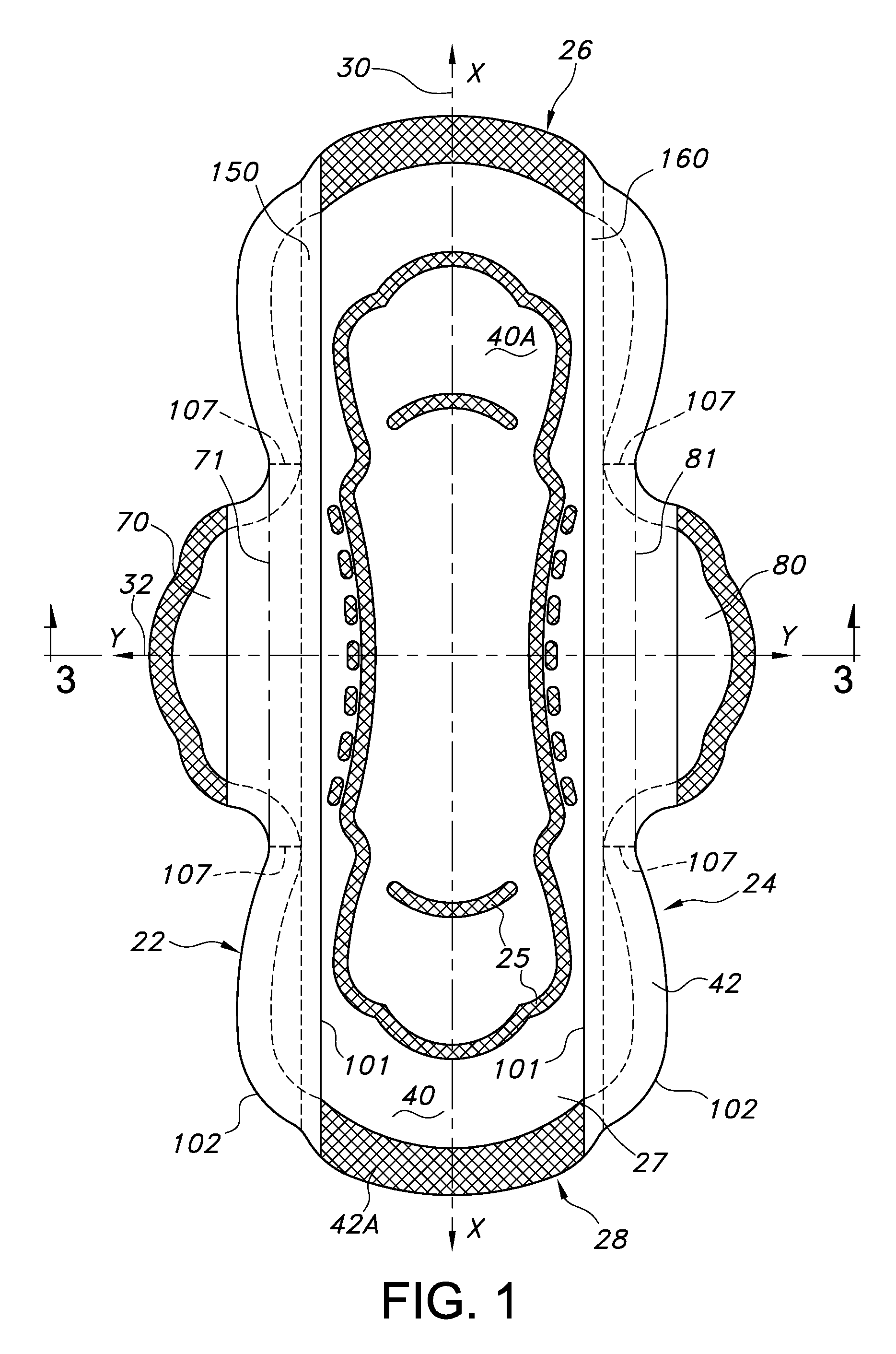
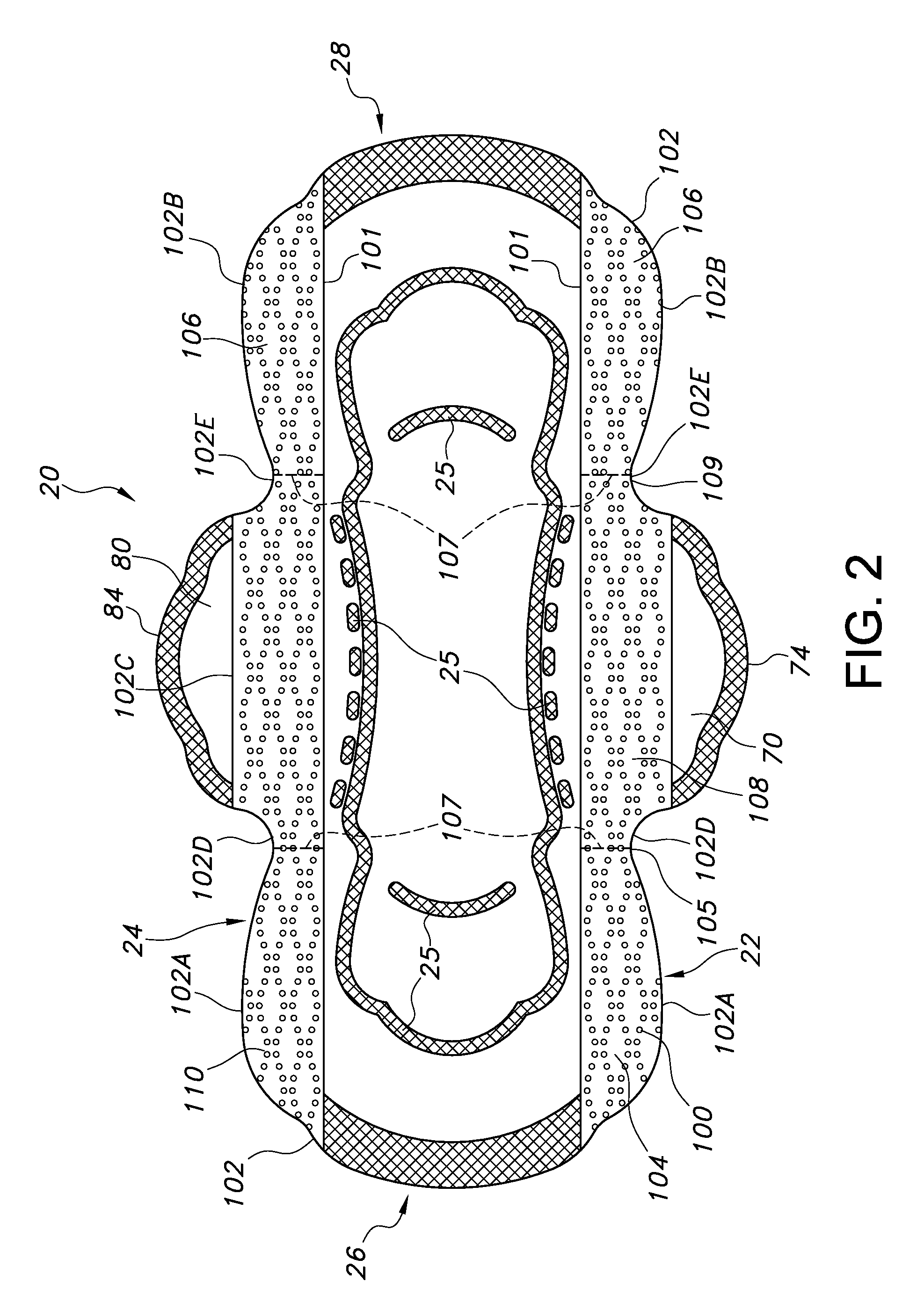
ActiveUS20140343525A1Reduce leakageFacilitate good fitSanitary towelsBaby linensPersonal careEngineering
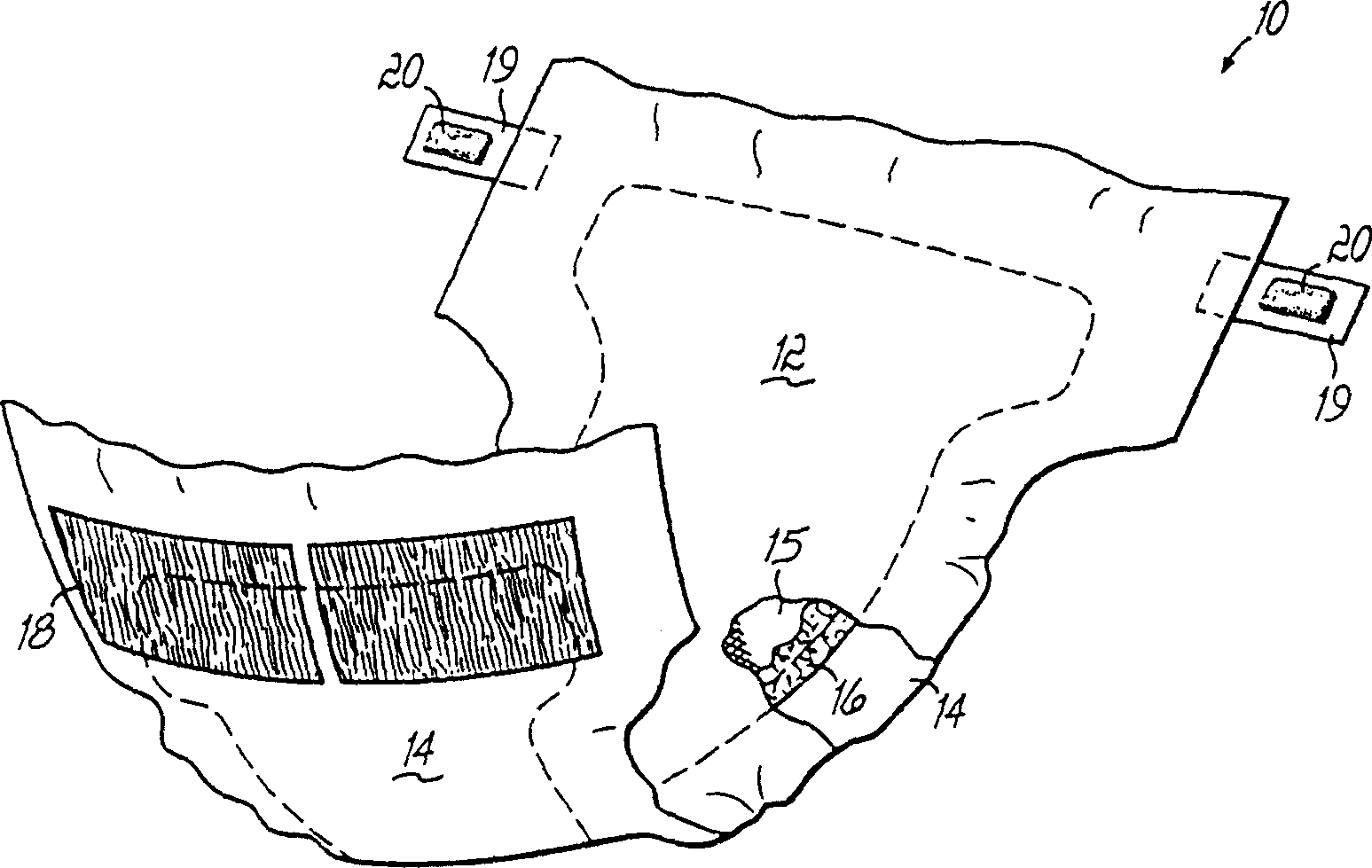
An absorbent personal care article, such as a sanitary napkin or incontinence pad is described having a longitudinal centerline and a transverse centerline and including a pair of opposed first and second wings extending along the longitudinal sides of the article. The article further includes first and second protective strips attached to the sides of the article such that when the wings are folded under the article and around the wearer's undergarment, the first and second protective strips extend laterally outboard of the article and the edges of the wearer's undergarment to provide additional protection against leakage of body fluids deposited onto the absorbent personal care article
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Coated multifilament dental devices overcoated with imbedded particulate
Disclosed are coated multifilament dental devices overcoated with biofilm-responsive, imbedded, particulate abrasives.
Owner:WHITEHILL ORAL TECH
Absorbent article
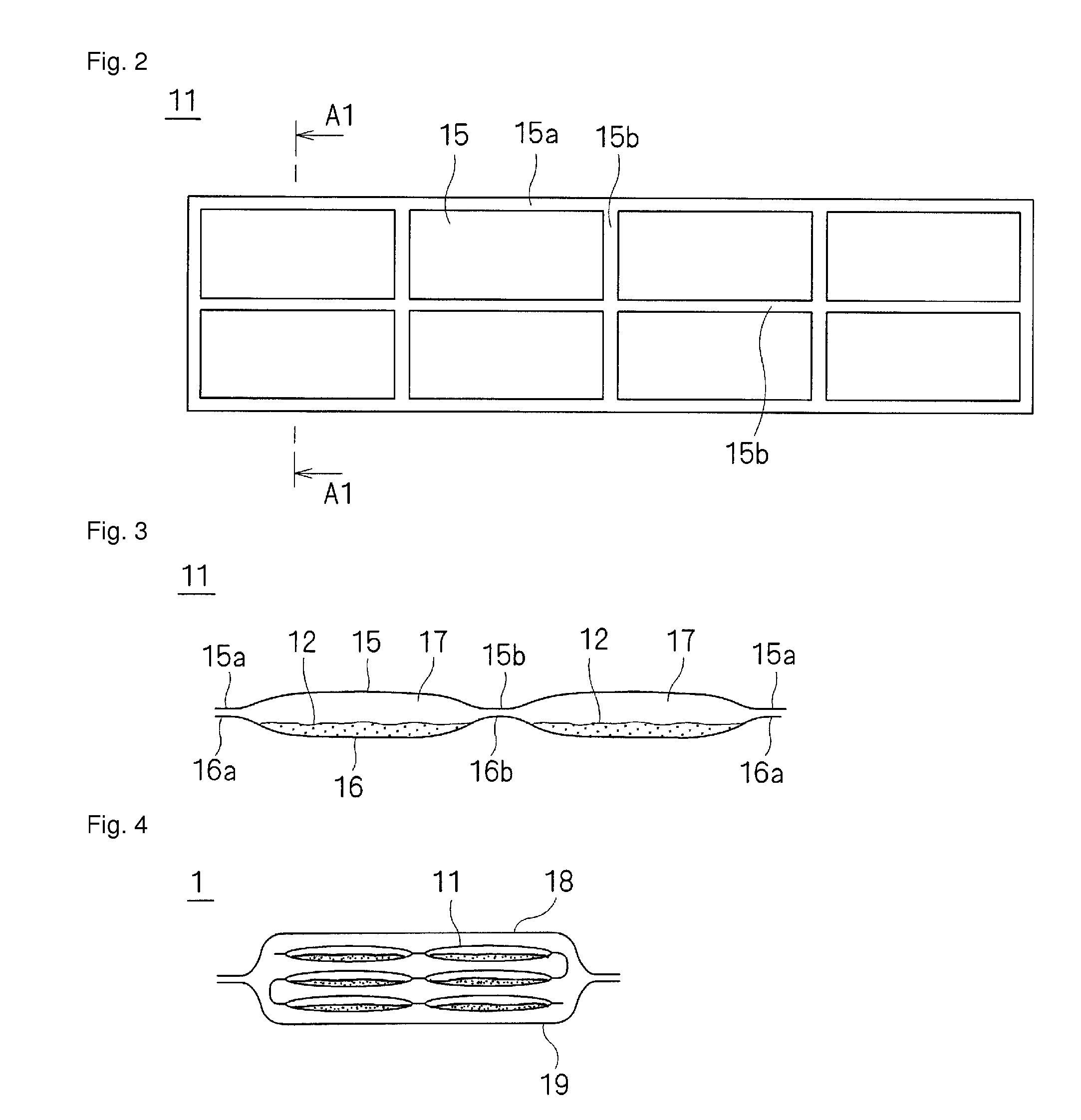
ActiveUS20080045915A1Improve permeabilityNot easy to collapseLayered productsBaby linensNonwoven fabricMechanical engineering
An absorbent article comprising nonwoven fabric having convex and concave surfaces, and that allows liquid such as excreta and the like to permeate quickly. A sanitary napkin has a plurality of raised ridge portions and groove portions in a top sheet member. The fiber density of the side edge portions of each of the plurality of raised ridge portions in the thickness direction of the nonwoven fabric is substantially uniform, and is higher than the average fiber density in the raised ridge portions. The fiber density of the central portion between both the side edge portions of each of the plurality of raised ridge portions is substantially uniform in the thickness direction of the nonwoven fabric, and is lower than the average fiber density in the raised ridge portions.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Absorbent article
ActiveUS8304600B2Not easy to collapseEasily passes liquidLayered productsBaby linensEngineeringNonwoven fabric
An absorbent article comprising nonwoven fabric having convex and concave surfaces, and that allows liquid such as excreta and the like to permeate quickly. A sanitary napkin has a plurality of raised ridge portions and groove portions in a top sheet member. The fiber density of the side edge portions of each of the plurality of raised ridge portions in the thickness direction of the nonwoven fabric is substantially uniform, and is higher than the average fiber density in the raised ridge portions. The fiber density of the central portion between both the side edge portions of each of the plurality of raised ridge portions is substantially uniform in the thickness direction of the nonwoven fabric, and is lower than the average fiber density in the raised ridge portions.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Lightweight glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic material
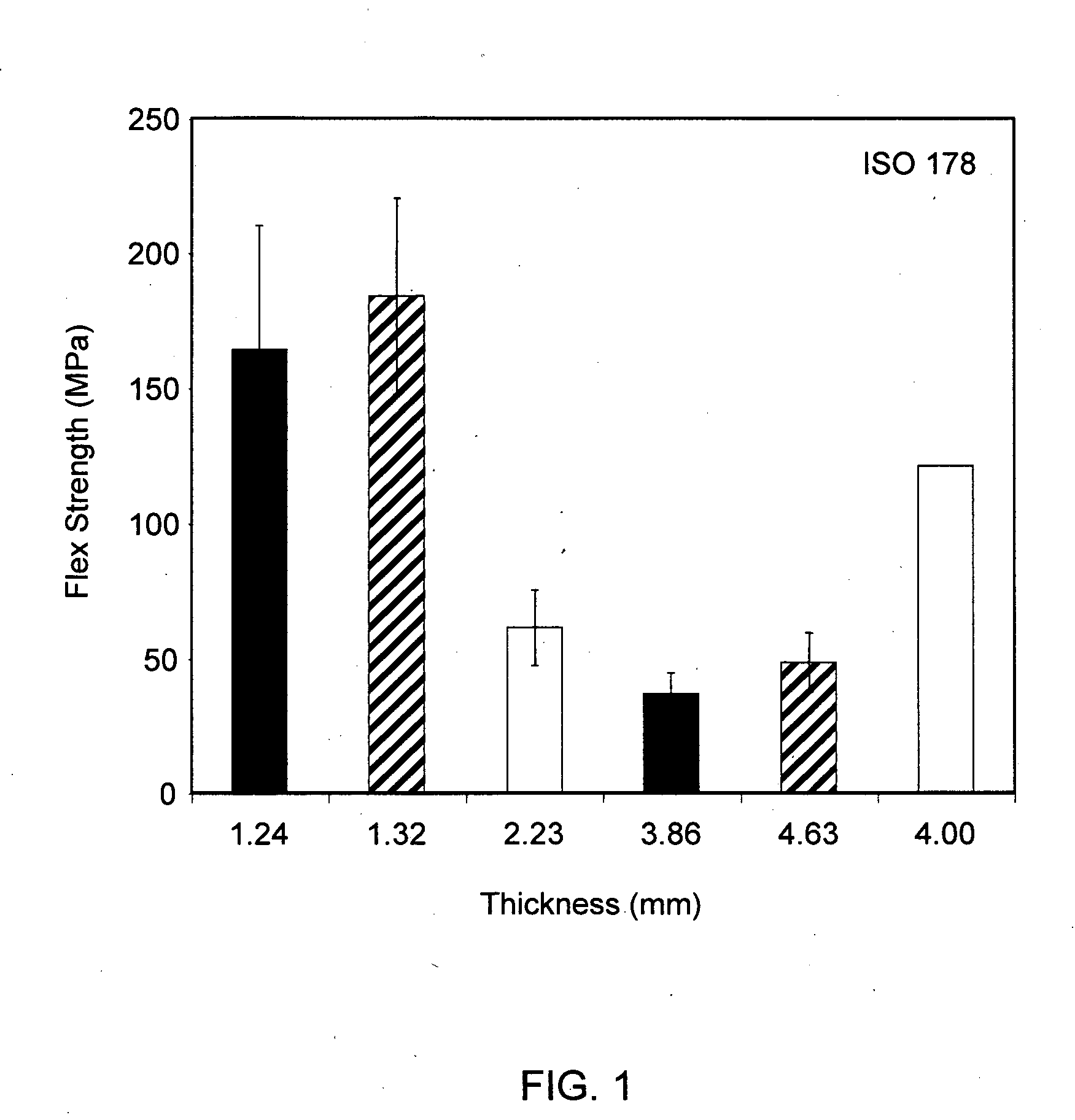
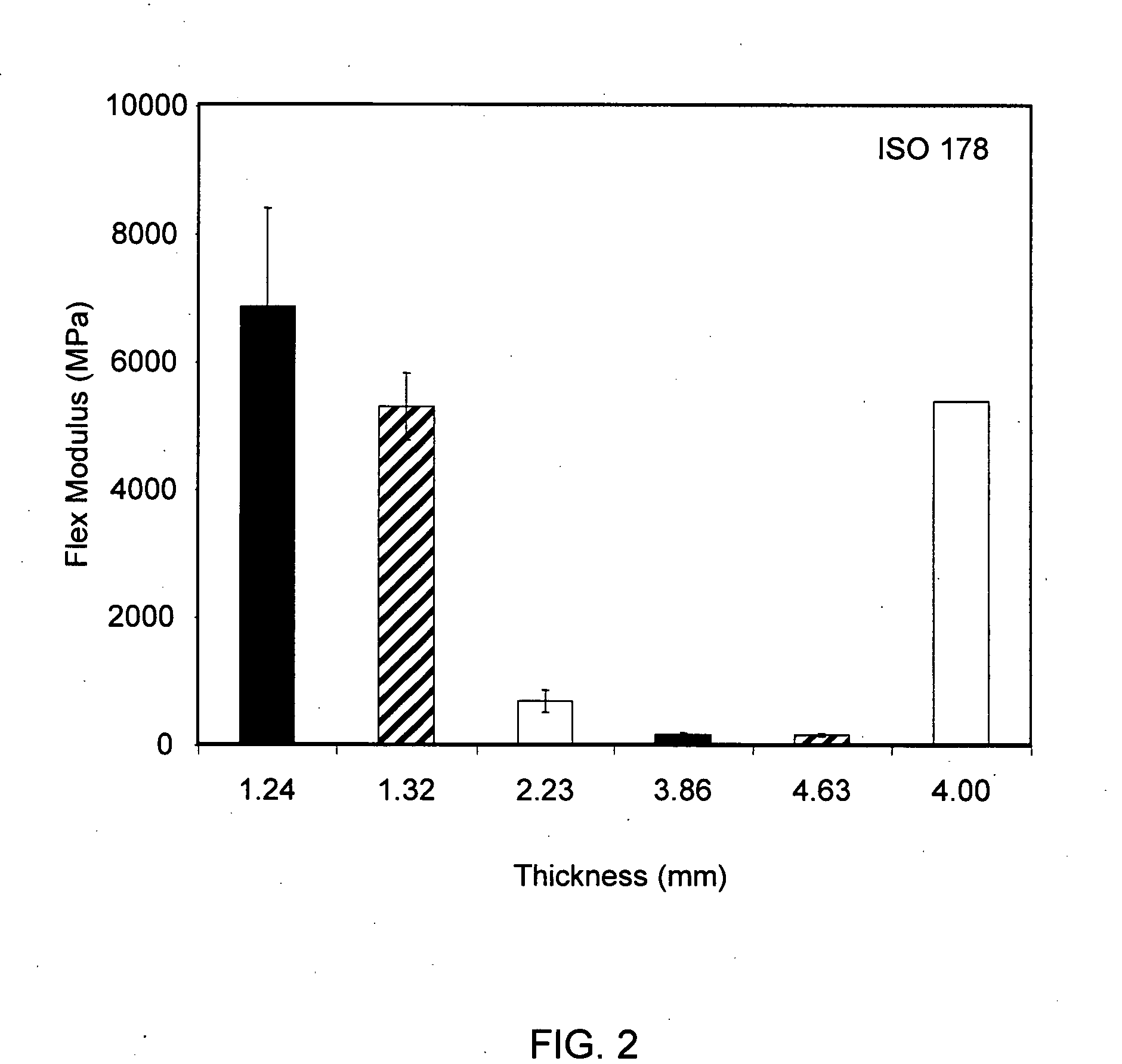
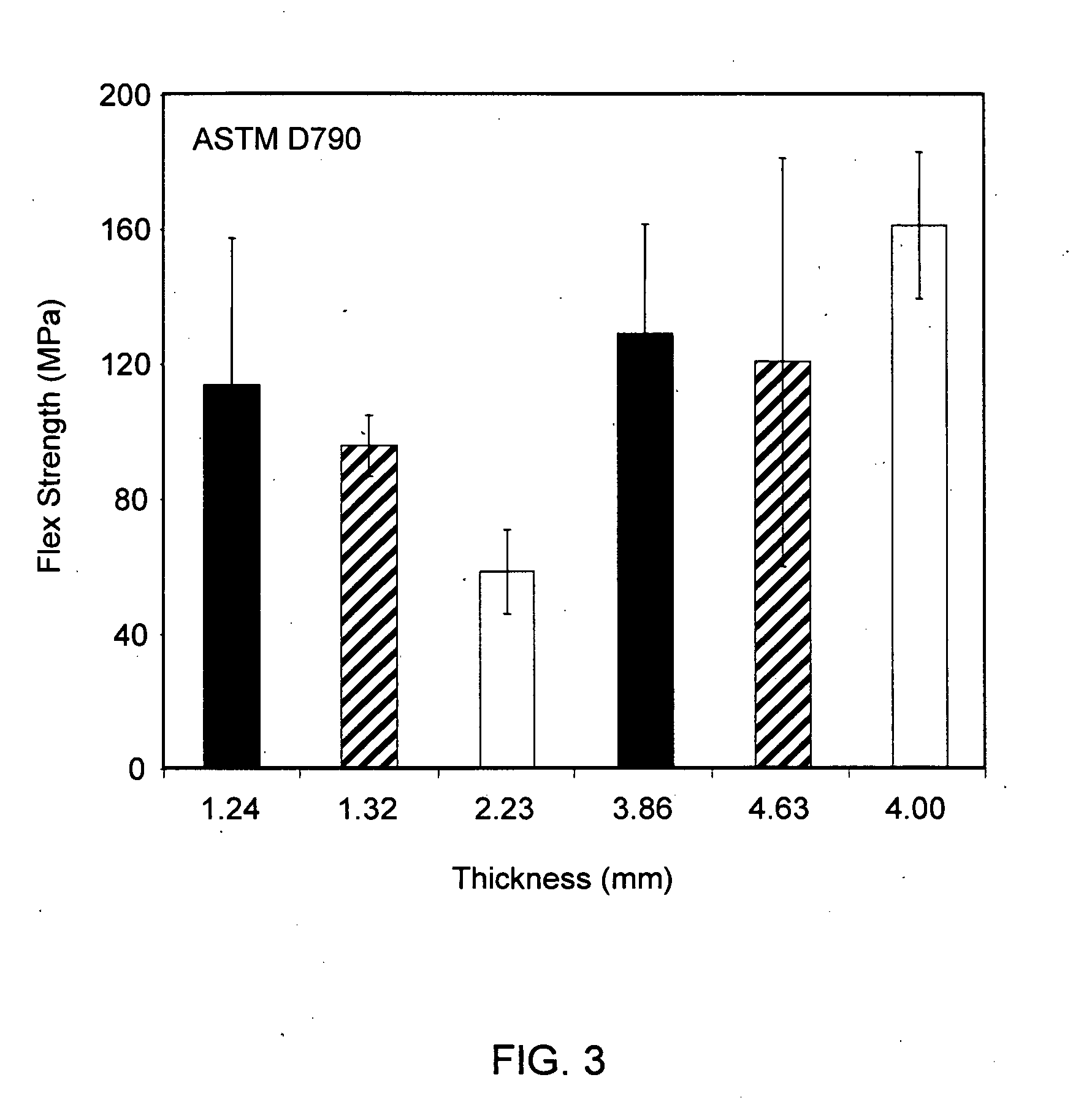
InactiveUS20090011210A1Improve flexural and tensile strength and modulus propertyReduce basis weightLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentFlexural strengthFiber
A glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic sheet material is provided in which certain properties, or combinations of properties, are improved relative to similar comparative sheet materials. The sheet material generally comprises a glass mat or glass fabric fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin in which the thermoplastic resin at least partially impregnates the glass mat or fabric. The thermoplastic sheet material contains about 15 wt. % to about 65 wt. % of the glass mat or fabric based on the weight of the thermoplastic sheet material and has a thickness in the range of about 0.4 mm to about 3.0 mm. By including glass mat or fabric and maintaining the sheet thickness in the aforementioned range, the present invention thermoplastic sheet material exhibits improved flexural and / or tensile strength and modulus properties at reduced basis weight compared to a comparative thermoplastic sheet materials. A method of providing the glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic sheet material having an improved combination of flexural strength and modulus and / or tensile strength and modulus properties is also described, in which a first layer of a first thermoplastic resin, a second layer of a second thermoplastic resin, and a layer of glass mat or glass fabric are provided; the first thermoplastic resin layer, the second thermoplastic resin layer and the glass mat or glass fabric layer are arranged such that the glass mat or glass fabric layer is interposed between the first and second thermoplastic resin layers; and heat and pressure are applied to substantially melt and compress the first thermoplastic resin and / or the second thermoplastic resin and to at least partially impregnate the glass mat or glass fabric layer with the molten first thermoplastic resin and / or the molten second thermoplastic resin.
Owner:AZDEL INC
Panel materials for vehicles and enclosures
InactiveUS20080001429A1Reduce basis weightImprove delaminationDomestic articlesFlat articlesPliabilityThermoplastic
A fiber reinforced polymer material having an improved combination of characteristics. The polymer material generally comprises a fiber reinforced polymer resin containing reinforcing fibers and having a porosity between about 0% to about 95% by volume of the polymer material. The fiber reinforced polymer material may form a panel or substrate material that helps resist impact and / or environmental loading. Typically, such a material includes a fiber reinforced thermoplastic or thermoset support layer that has a skin layer on one or both sides, which are joined to one another to form the substrate or panel material. The exterior skin layer typically includes a polymer resin that may also include a support structure, such as reinforcing fibers. The resulting material is typically lightweight and has a reduced basis weight, particularly as compared to current commercial products, in addition to a low thermal expansion such that it provides improved resistance to delamination, improved dimensional stability and flexibility, and decreased water absorption and retention.
Owner:WILLIS CHRISTOPHER D +2
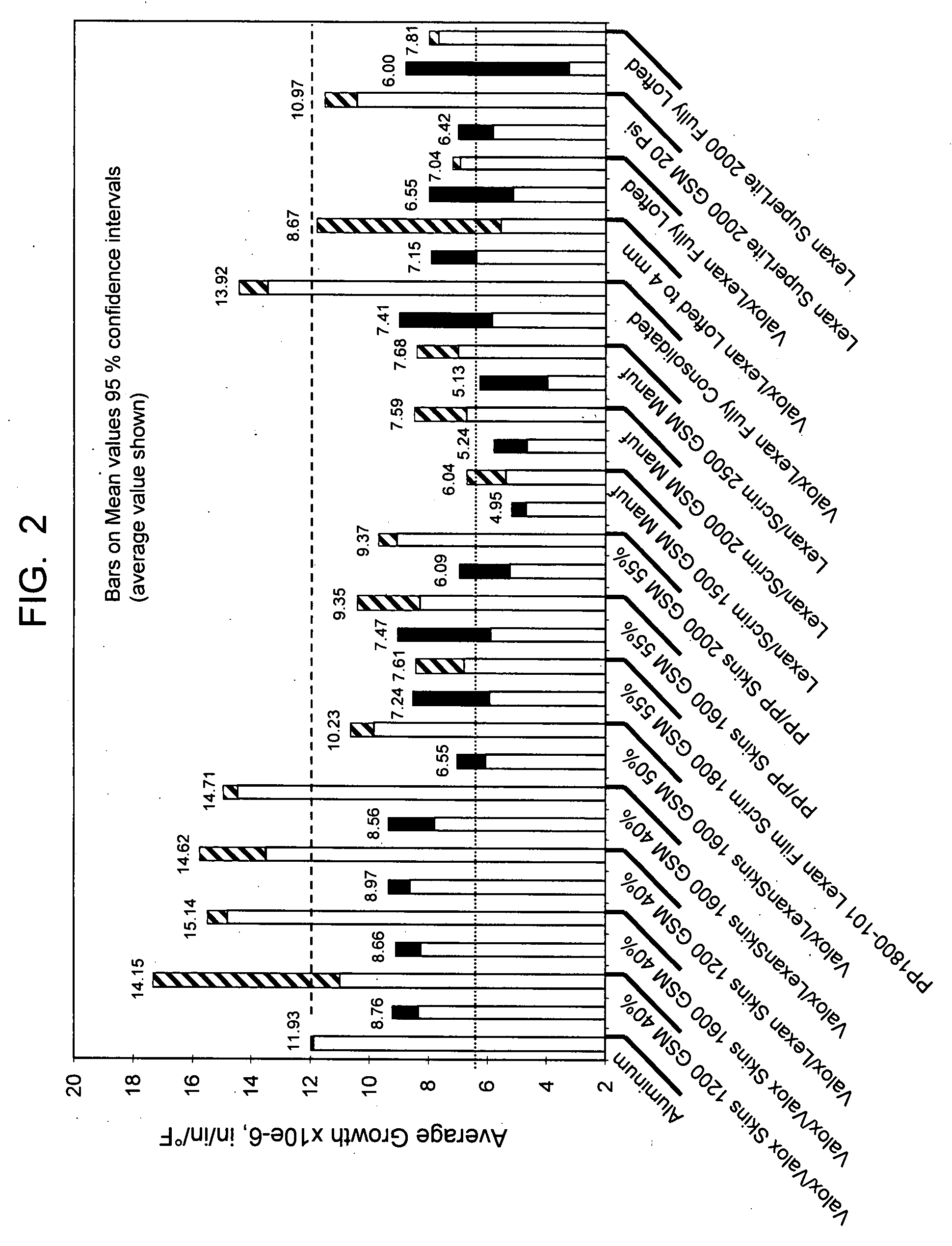
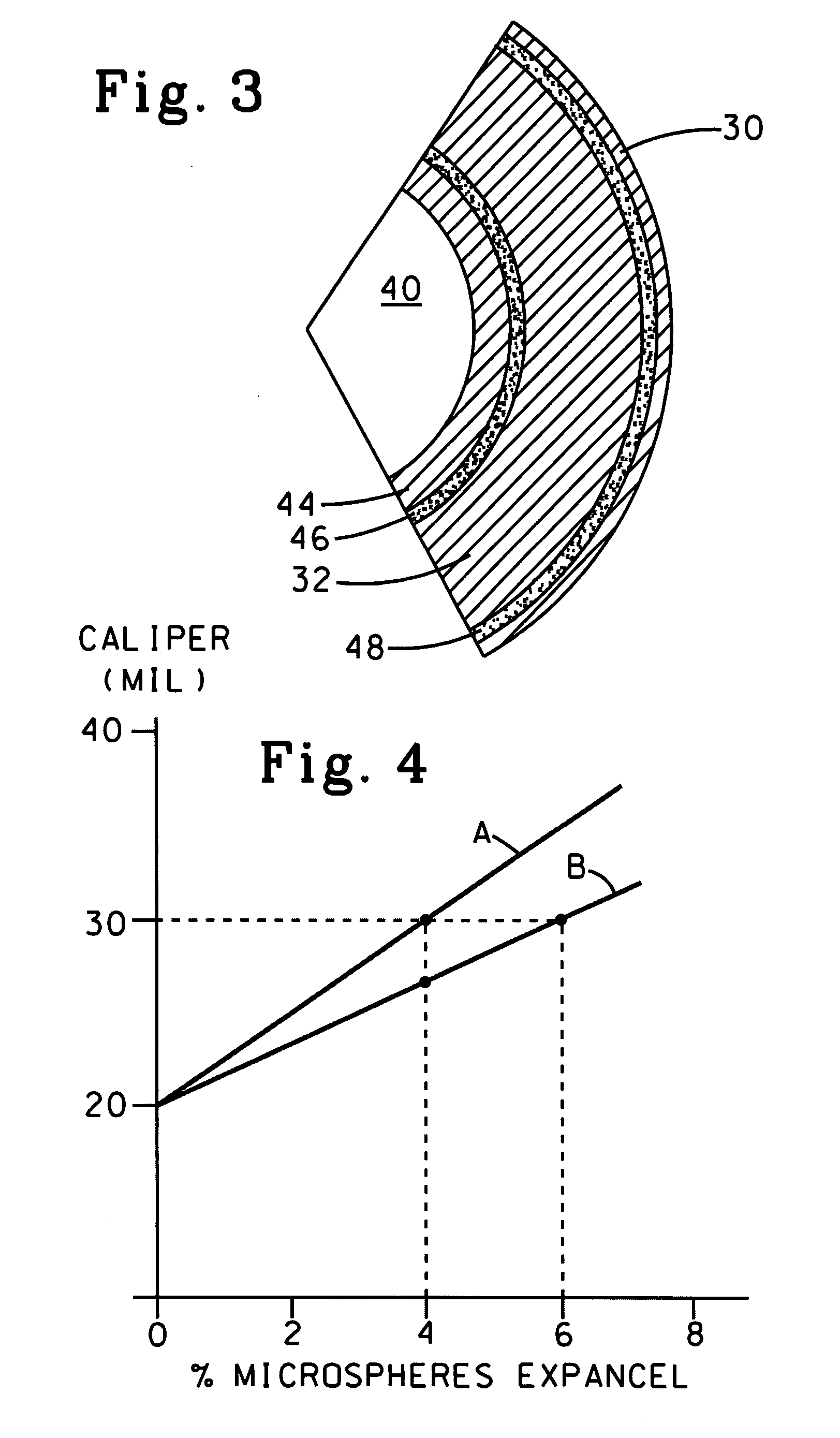
Paperboard material with expanded polymeric microspheres
InactiveUS20070256805A1Improve offset print performanceDecreased print mottle of printedNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCoated surfaceMicrosphere
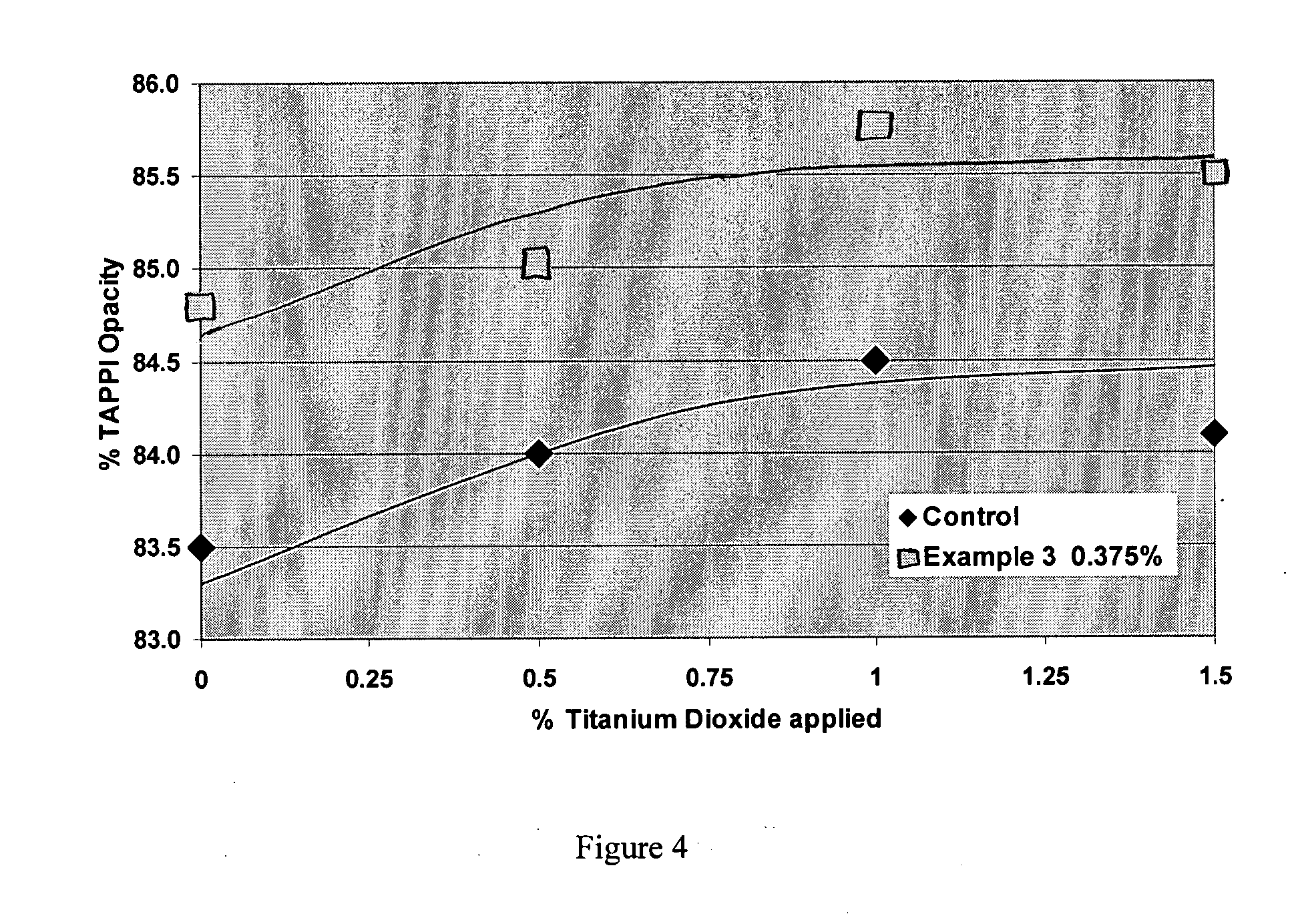
The present invention is related to a paperboard product having a basis weight in a range of 100 to 350 pounds per 3,000 square feet. The paperboard comprises at least one coated surface suitable for printing. The at least one coated surface comprising cellulosic fibers and from about 0.05 to about 0.5 wt. % dry basis expanded synthetic polymer microspheres based on total weight of the of cellulosic fiber dispersed thereof. The coated surface has a Parker smoothness less than about 2.0 and a Hagerty / Sheffield smoothness not less than about 20 Sheffield units.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Nonwoven fabric laminate, moisture-permeable nonwoven fabric laminated sheet using nonwoven fabric laminate, and sanitary products using them
InactiveUS20090061185A1Reduce in quantitySoft feeling in useSynthetic resin layered productsSanitary towelsMedicineNonwoven fabric
There is provided by the present invention a nonwoven fabric laminate which comprises a first spunbonded nonwoven fabric comprising a propylene-based polymer (first SB nonwoven fabric), a melt blown nonwoven fabric comprising a propylene-based polymer and laminated on the first spunbonded nonwoven fabric, and a second spunbonded nonwoven fabric (second SB nonwoven fabric) comprising a propylene-based polymer and laminated on the melt blown nonwoven fabric, and which has overall basis weight of not more than 30 g / m2, wherein the basis weight of the first SB nonwoven fabric is in the range of 3 to 25 g / m2, the basis weight of the second SB nonwoven fabric is in the range of 1 to 11 g / m2, the ratio of the basis weight of the first SB nonwoven fabric to the basis weight of the second SB nonwoven fabric is not less than 1.6, the ratio of a thickness of the first SB nonwoven fabric to a thickness of the second SB nonwoven fabric is not less than 1.4, the basis weight of the melt blown nonwoven fabric is less than 3 g / m2, and the compression bond area ratio is in the range of 6 to 25%.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
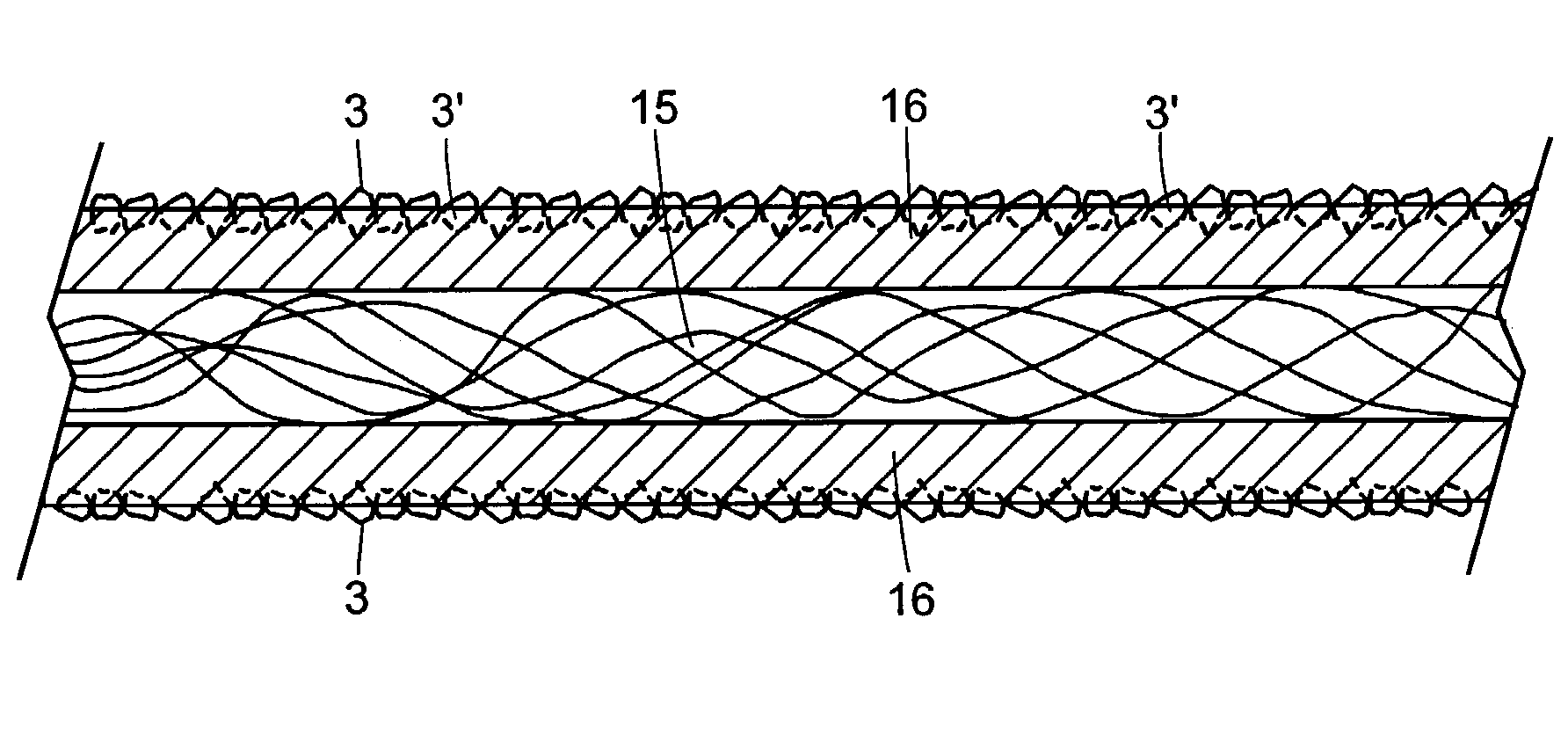
Press felt
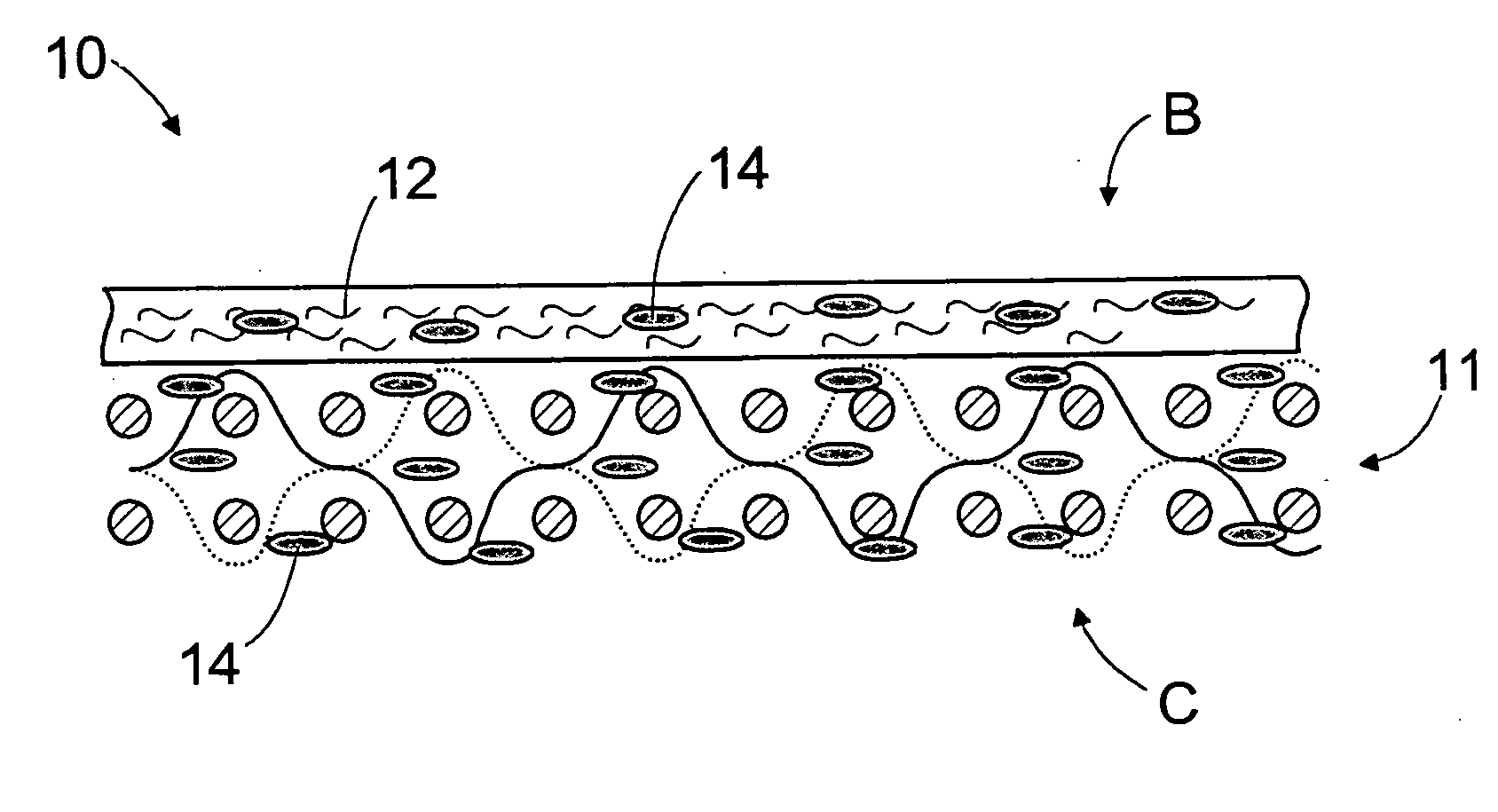
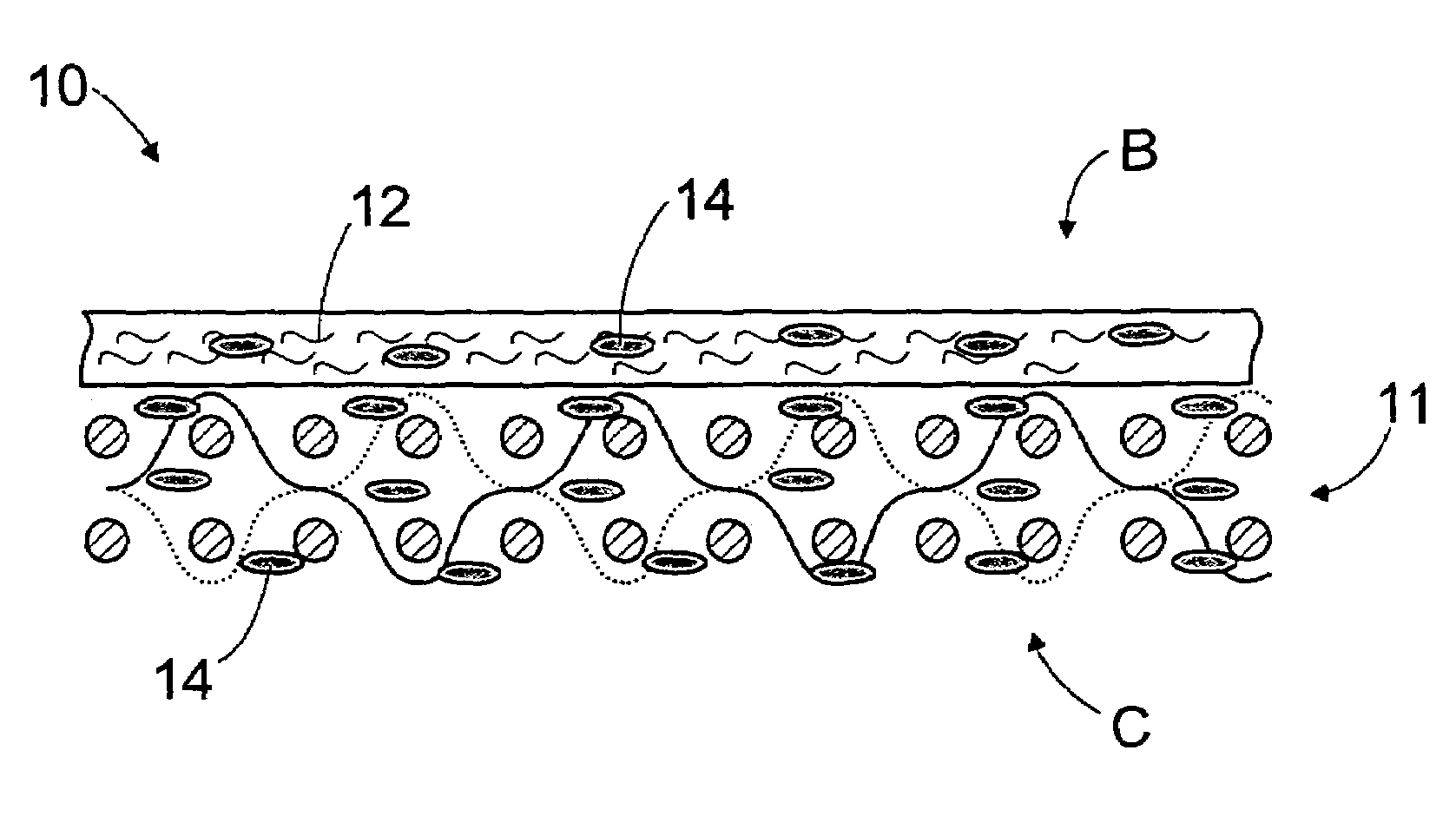
InactiveUS20050124248A1Reduce basis weightImprove efficiencyLayered productsPaper/cardboardFiberEngineering
A method of manufacturing a press felt, a press section, and a press felt. The press felt comprises a base structure (11), a batt fibre layer (12) being attached to a first, web-side surface (B) of the base structure. Further, the structure of the press felt is compacted by treating it with a polymer material at least on the side of the first felt surface (B). After the polymer treatment, the surface of the felt is ground smooth.
Owner:TAMFELT PMC OY
Coated dental devices with ablative abrasives
InactiveUS20090188520A1Easy to holdEasy to slideCosmetic preparationsGum massageDental EquipmentDental floss
Dental devices coated with substantially aqueous-free, saliva soluble, base coatings and ablative abrasives that break down during flossing; which combination creates the perception during flossing that said devices are working.
Owner:WHITEHILL ORAL TECH
Water degradable microlayer polymer film and articles including same
InactiveUS20020127385A1High strengthSufficient breathabilitySynthetic resin layered productsAbsorbent padsParticulatesLinear low-density polyethylene
A microlayer polymer film comprising a plurality of coextruded microlayers including a non-degradable layer comprising a non-water degradable, melt-extrudable polymer and degradable layer comprising a water degradable, melt-extrudable polymer. The microlayer polymer film degrades when soaked in water and is suitable as a covering material for disposal items such as flushable diapers. The microlayer polymer film is also breathable and is a barrier to small amounts of water. A suitable non-water degradable, melt-extrudable polymer is linear low density polyethylene filled with a particulate filler. A suitable water degradable, melt-extrudable polymer is polyethylene oxide.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
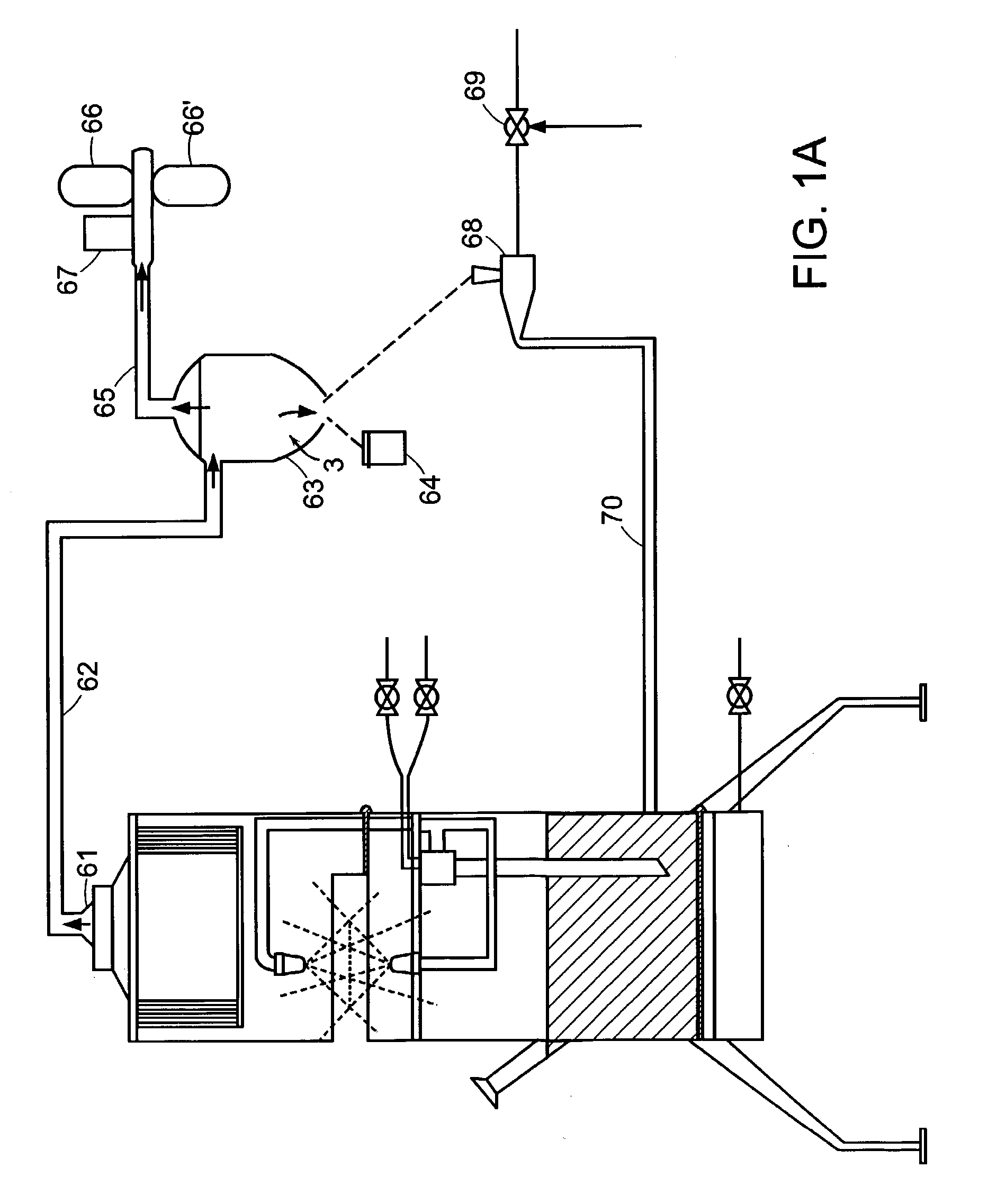
Method in connection with the production of mechanical pulp
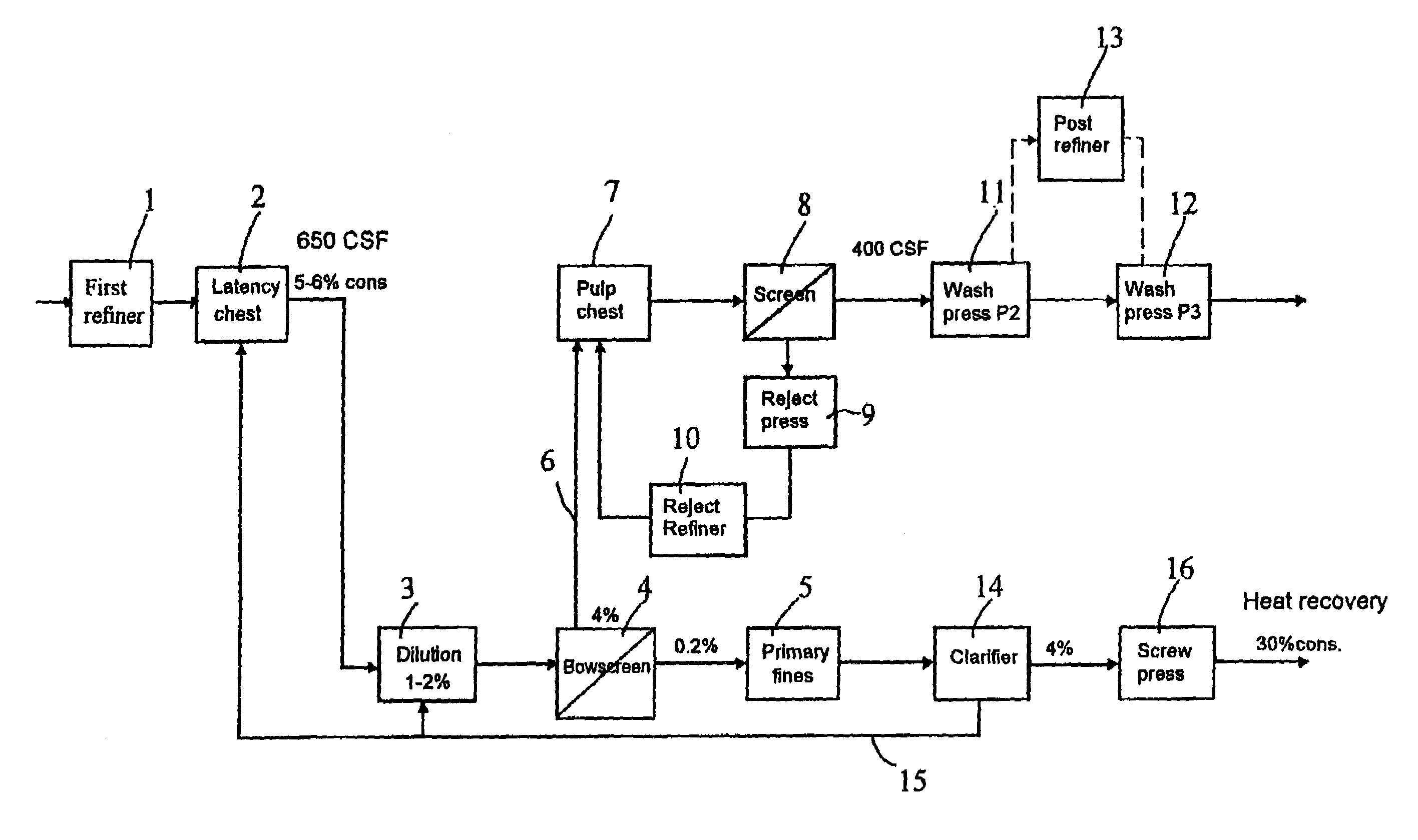
InactiveUS7005034B1Reduce consumptionGood removal effectFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpDigestersCellulosePaperboard
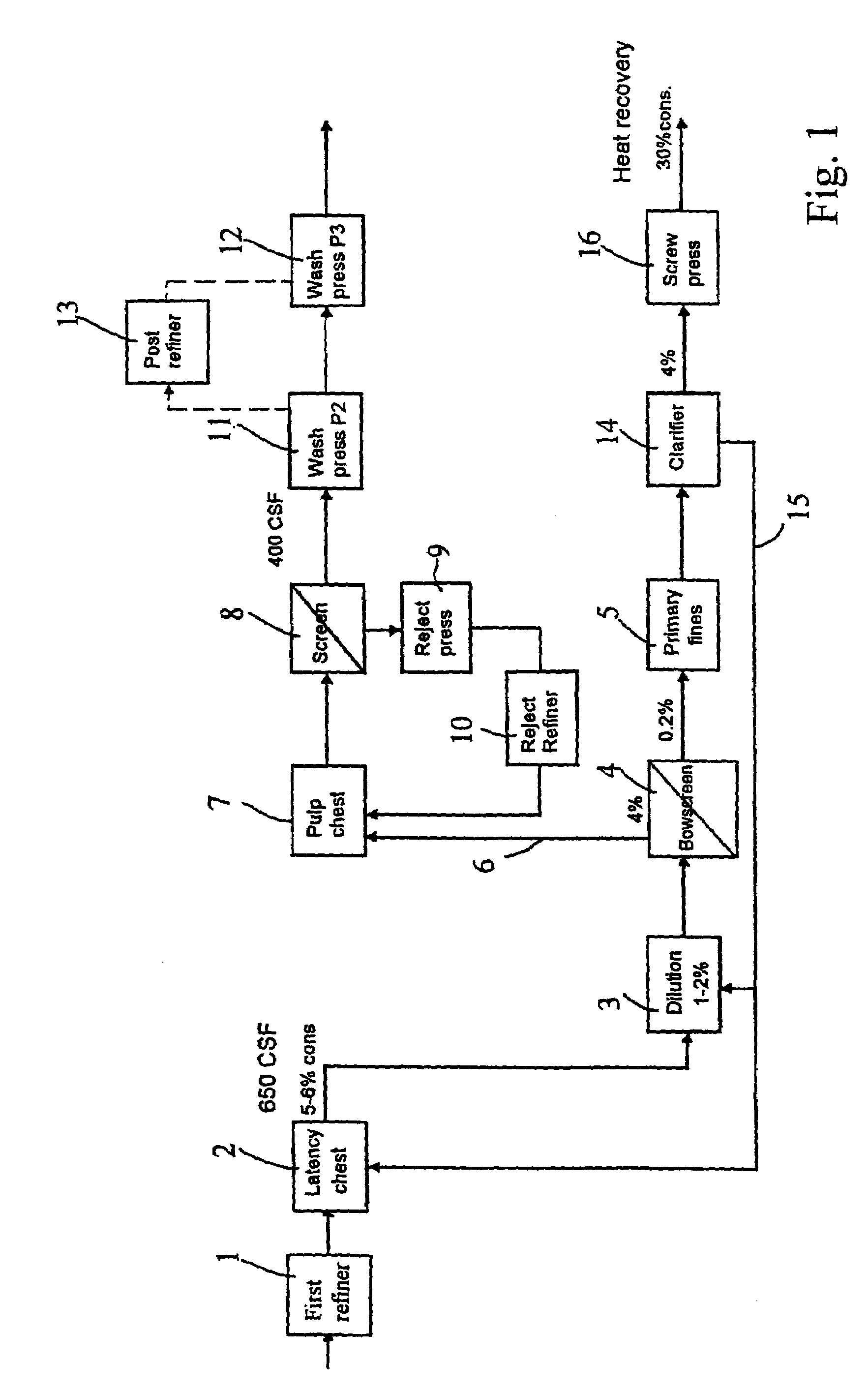
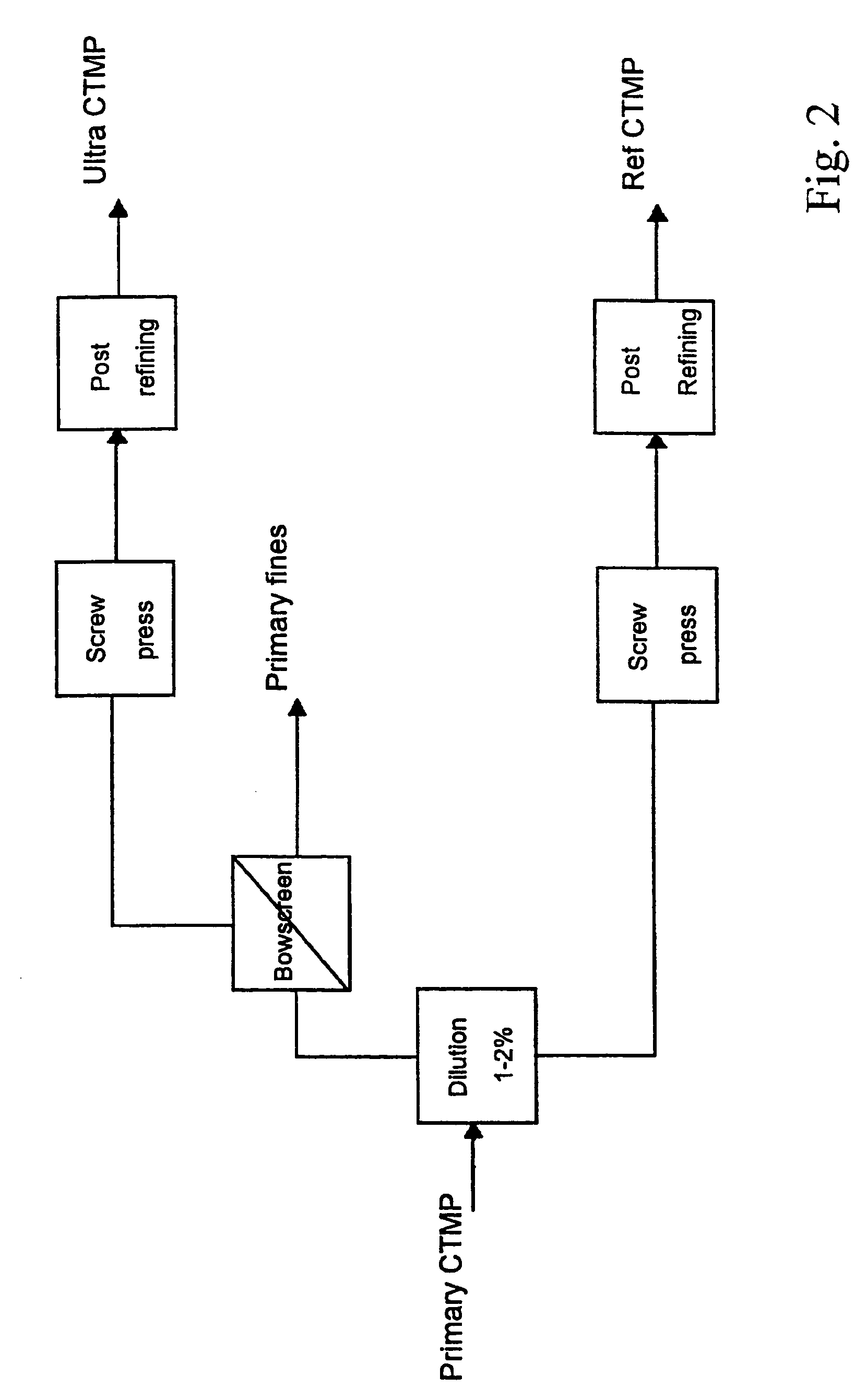
A method in connection with the production of mechanical pulp from a cellulose containing material wherein the material is processed in at least one refining step to produce pulp. According to the invention, the pulp is fractionated (4), after a first refining step (1), in order to separate primary fines (5) from the pulp. The invention also relates to a mechanical pulp, produced by the method, and to a paperboard, which at least partly consists of such mechanical pulp.
Owner:STORA ENSO AB
Waterborne adhesives for reduced basis weight multilayer substrates and use thereof
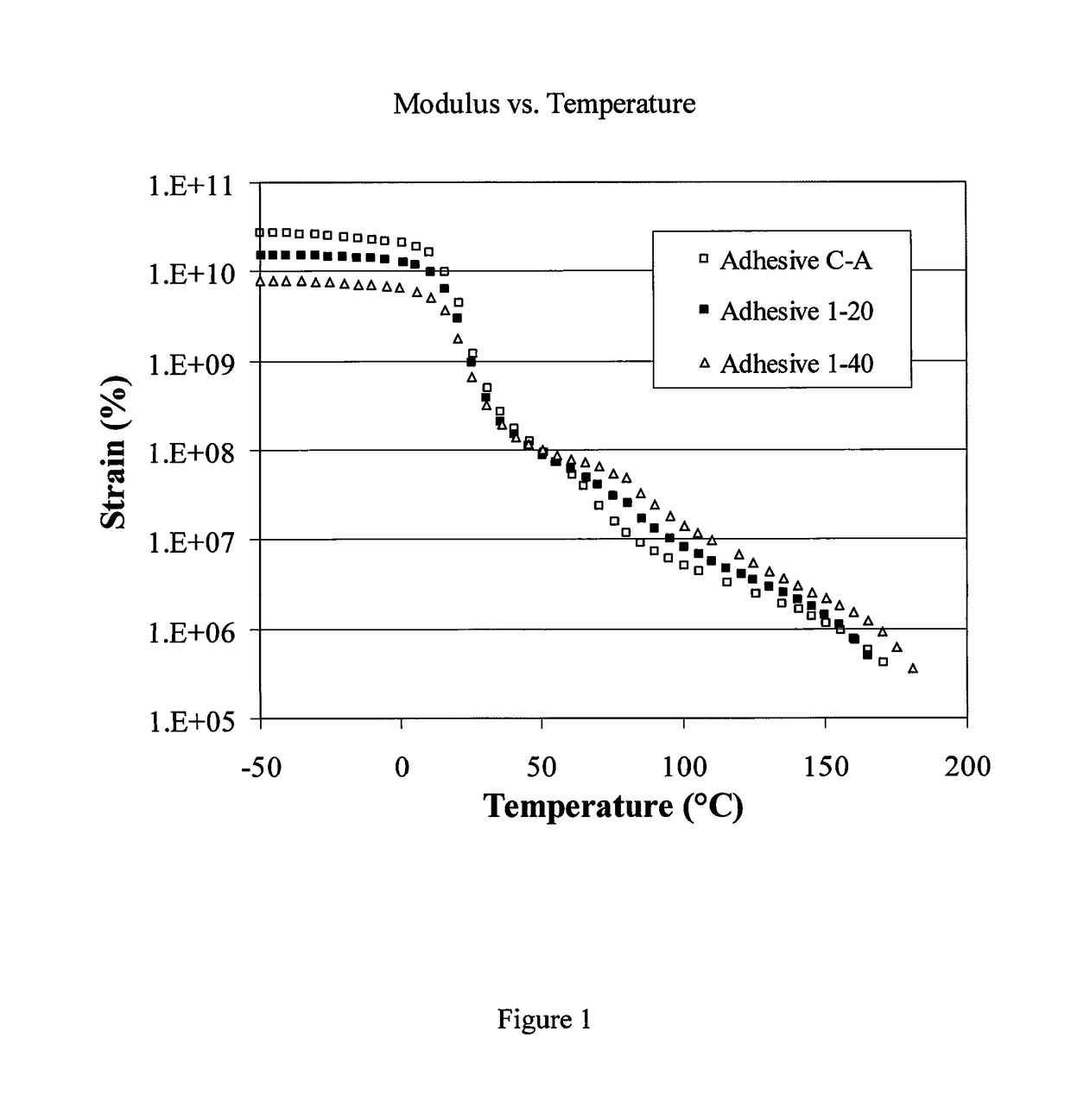
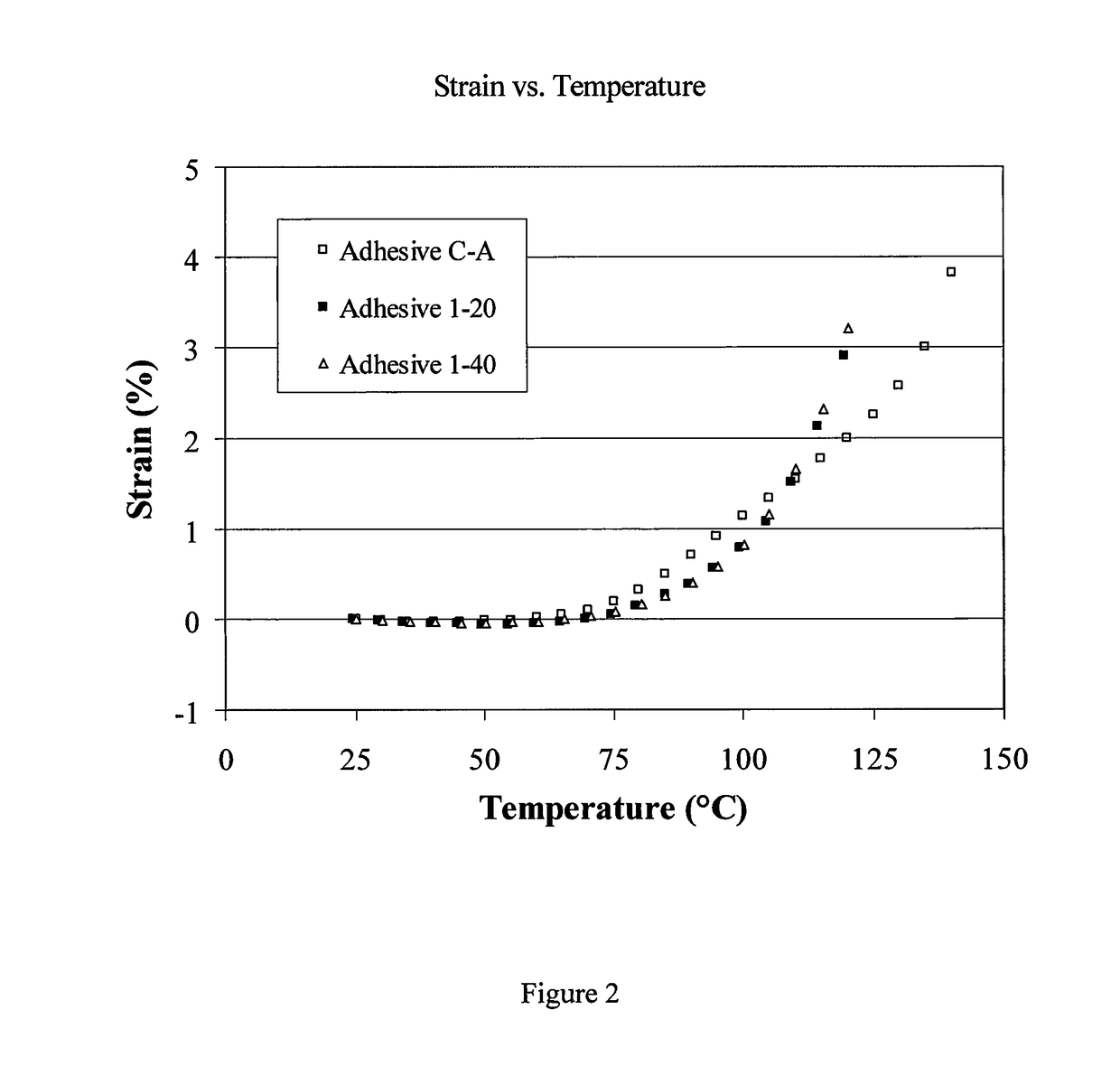
ActiveUS9657200B2Reduce basis weightHigh strengthMonocarboxylic acid ester polymer adhesivesNon-fibrous pulp additionEmulsionPolymer science
The adhesive composition comprising emulsion polymers and microspheres and articles made therefrom are provided. The adhesive is particularly suitable for packages for consumer products that provide sufficient strength and thermal insulation while reducing the overall basis weight of the substrates.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Press felt
InactiveUS7306704B2Reduce basis weightImprove efficiencyLayered productsPaper/cardboardFiberEngineering
A method of manufacturing a press felt, a press section, and a press felt. The press felt comprises a base structure (11), a batt fibre layer (12) being attached to a first, web-side surface (B) of the base structure. Further, the structure of the press felt is compacted by treating it with a polymer material at least on the side of the first felt surface (B). After the polymer treatment, the surface of the felt is ground smooth.
Owner:TAMFELT PMC OY
Increased ballistic performance of fabrics coated with polymer stripes
InactiveUS20060286880A1Reduce basis weightImprove permeabilityArmourProtective equipmentMedicinePolymer
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Papermaking method using opacification aid, and paper product made thereby
InactiveUS20060196624A1Reduce weightImprove strength propertiesNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperOptical propertyPaperboard
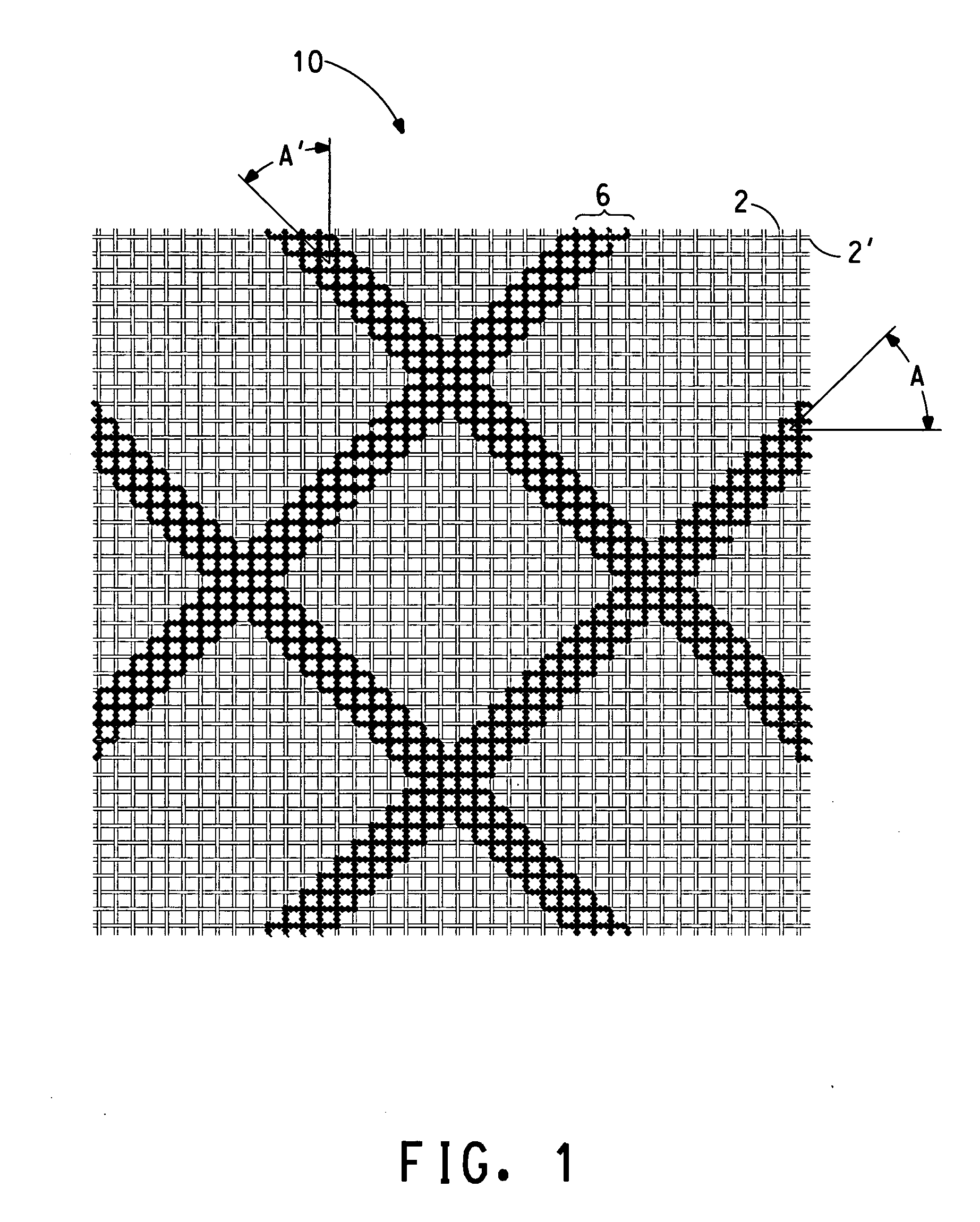
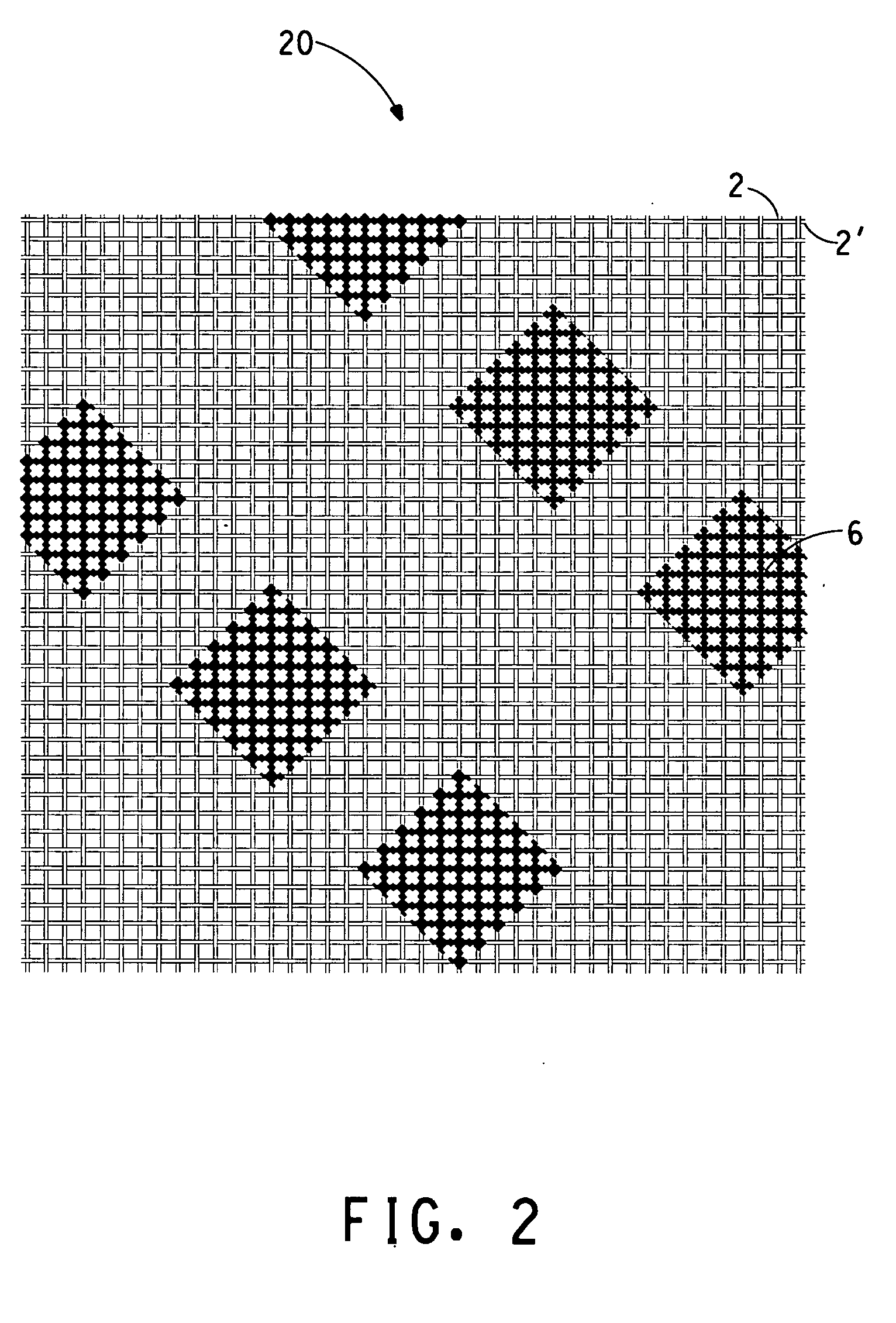
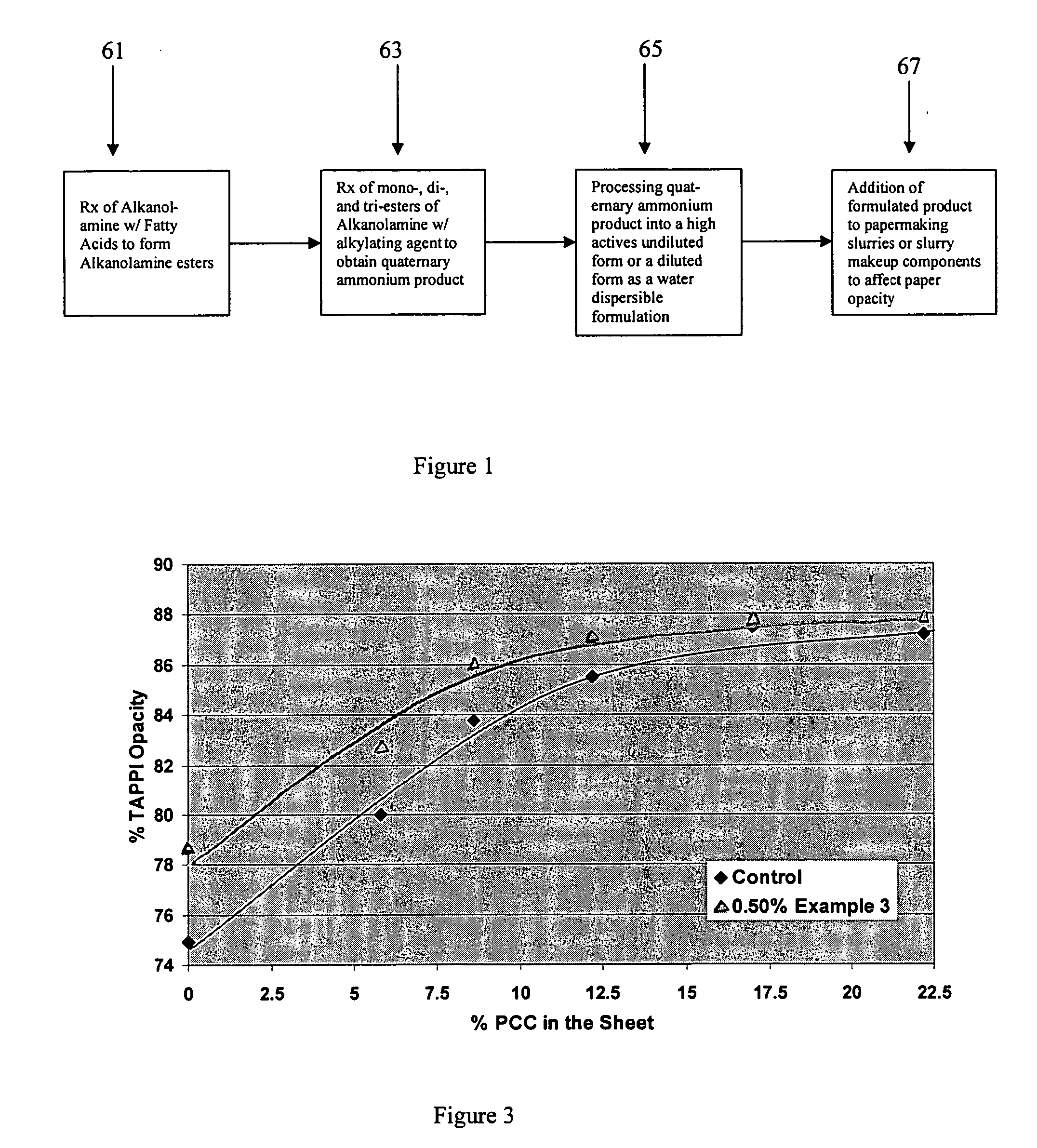
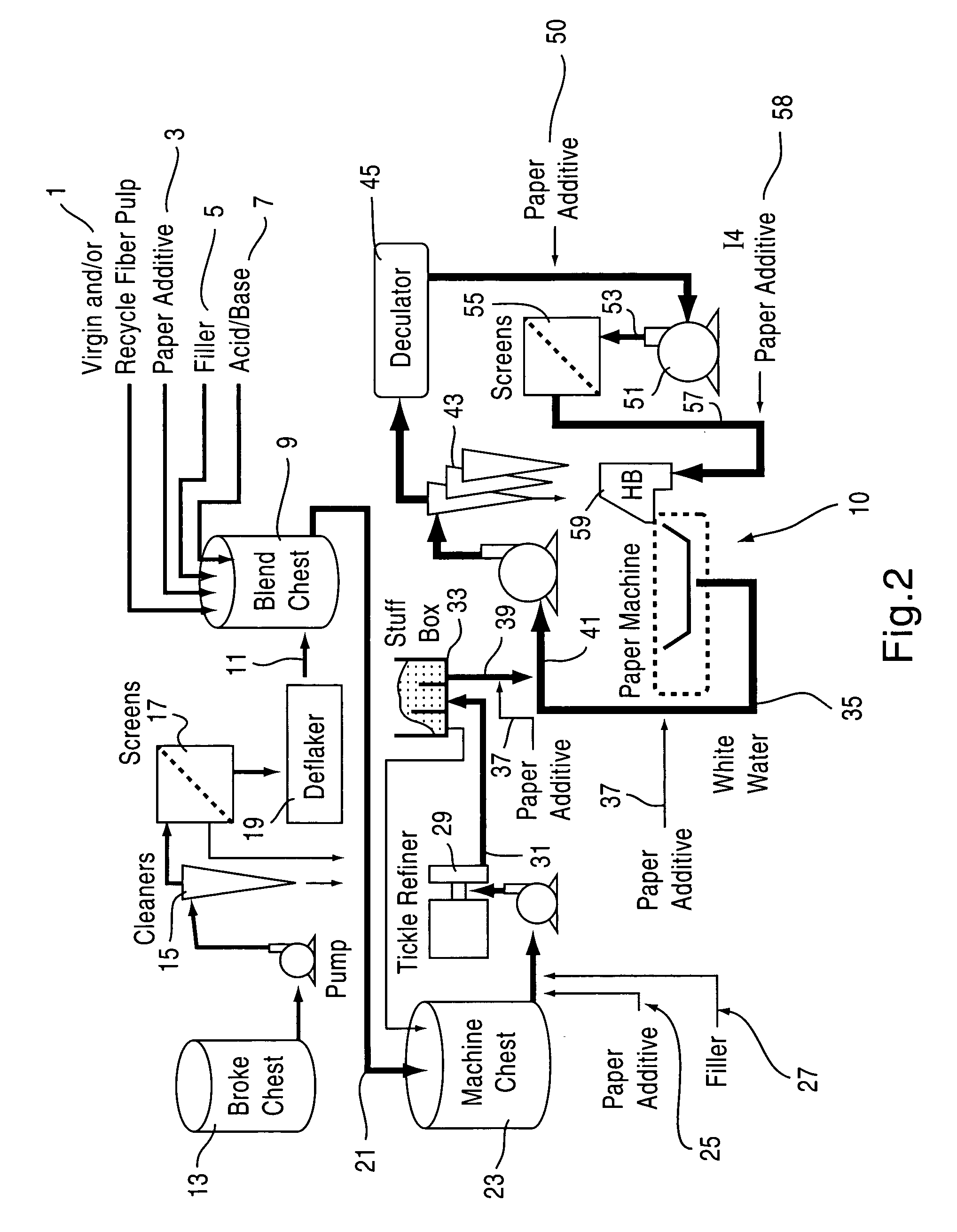
A method for making an opacity relevant grade paper or paperboard product, such as a communication type paper used for printing and writing applications, utilizes an effective amount of quaternized alkanolamine fatty acid ester compounds as an opacification aid to control the optical properties of the paper or paperboard product as a wet-end additive to a papermaking operation. Using the quaternized alkanolamine fatty acid ester compound can improve the opacity of the paper or paperboard product, maintain the opacity of the paper while reducing the use of other opacification aids, such as inorganic fillers and / or pigments, and allow for a reduction in paper grammage without a compromise in opacity. The improvements in paper optical properties are achieved without adversely affecting other characteristics of the paper product such as bulk value, tensile strength, tear index, and the like.
Owner:KEMIRA CHEM
Paperboard material with expanded polymeric microspheres
InactiveUS7943011B2Improve offset print performanceDecreased print mottle of printedNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCoated surfaceMicrosphere
The present invention is related to a paperboard product having a basis weight in a range of 100 to 350 pounds per 3,000 square feet. The paperboard comprises at least one coated surface suitable for printing. The at least one coated surface comprising cellulosic fibers and from about 0.05 to about 0.5 wt. % dry basis expanded synthetic polymer microspheres based on total weight of the of cellulosic fiber dispersed thereof. The coated surface has a Parker smoothness less than about 2.0 and a Hagerty / Sheffield smoothness not less than about 20 Sheffield units.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Stretched mechanical fastening web laminate
A stretched mechanical fastening web laminate having a thermoplastic web layer with two major surfaces is disclosed. One of the major surfaces bears a multitude of male fastening elements suitable for engagement with a corresponding female fastening material, and on its other major surface is a fibrous nonwoven web layer. The stretched mechanical fastening web laminate is stretched to provide a basis weight of less than 100 g / m2.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Absorbent article
The present invention provides an absorbent article that allows full use of the absorption performance of an absorbent polymer without inhibiting the swelling of the absorbent polymer due to the absorption of excreted body fluids, and that can be biodegraded with efficiency when it is disposed after use by burial in the soil or the like. The absorbent article includes at least one inner bag-like member, an absorbent polymer, and an outer bag-like member. The inner bag-like member is formed into a thin and substantially sheet-like form of a sheet having biodegradability and fluid permeability, and includes multiple accommodation spaces that are detached from the outside and separated from one another. The absorbent polymer has biodegradability and a substantially granular or powder form and is contained in each of the accommodation spaces in the inner bag-like member so as to be freely movable within the accommodation spaces.
Owner:LIVEDO CORP
Method of forming high-loft spunbond non-woven webs and product formed thereby
InactiveCN1550603AImprove performanceReduce basis weightHeating/cooling textile fabricsWoven fabricsEngineeringPolymer
A method of forming a plurality of substantially-continuous and uninterrupted multi-component filaments for use as a high-loft non-woven web. The multi-component filaments include at least two polymers of different melt flow rates, which imparts latent crimp in each filament. After collection, the latent crimp of the filaments is activated either thermally or by applying tension to the non-woven web.
Owner:NORDSON CORP
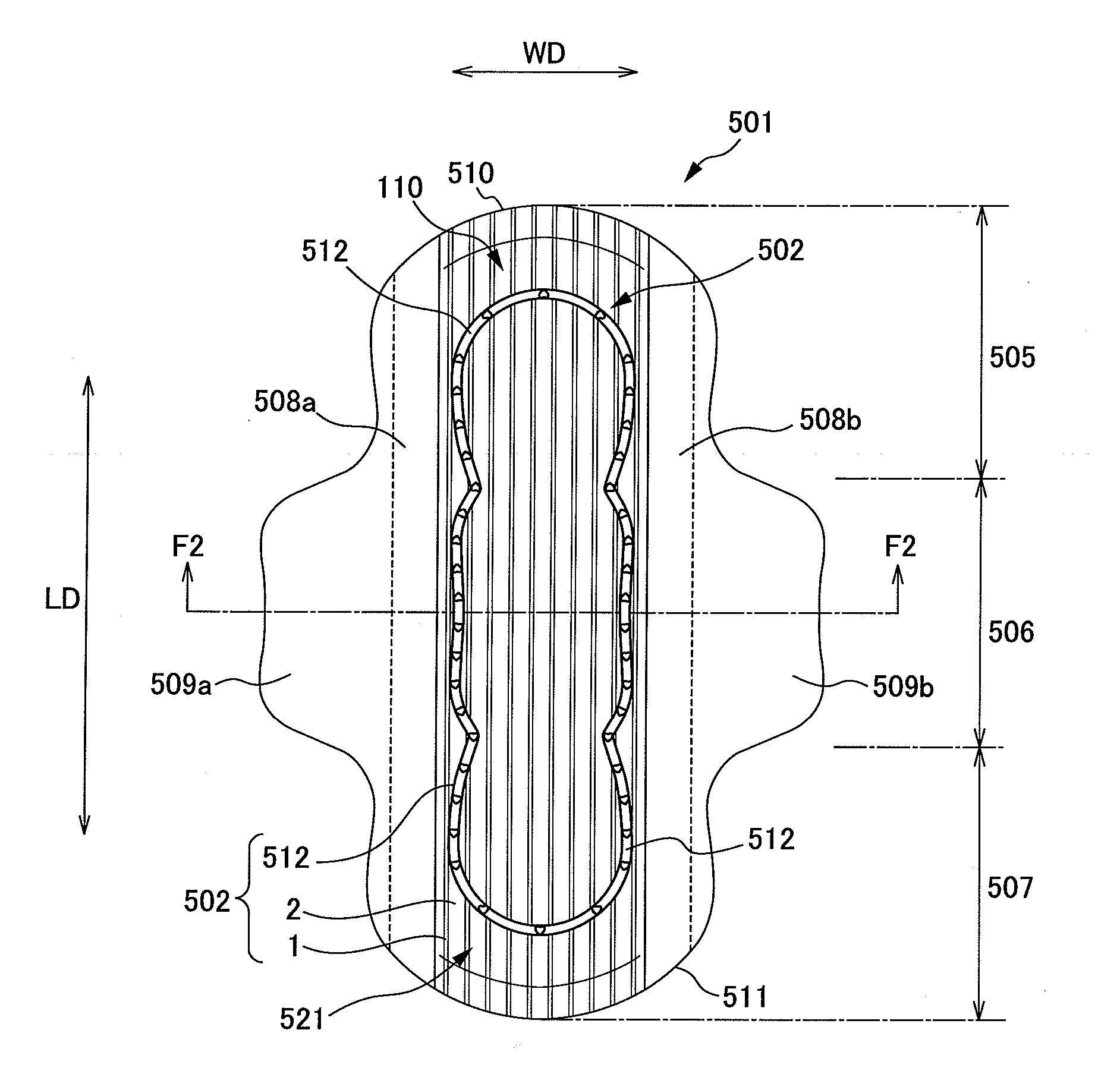
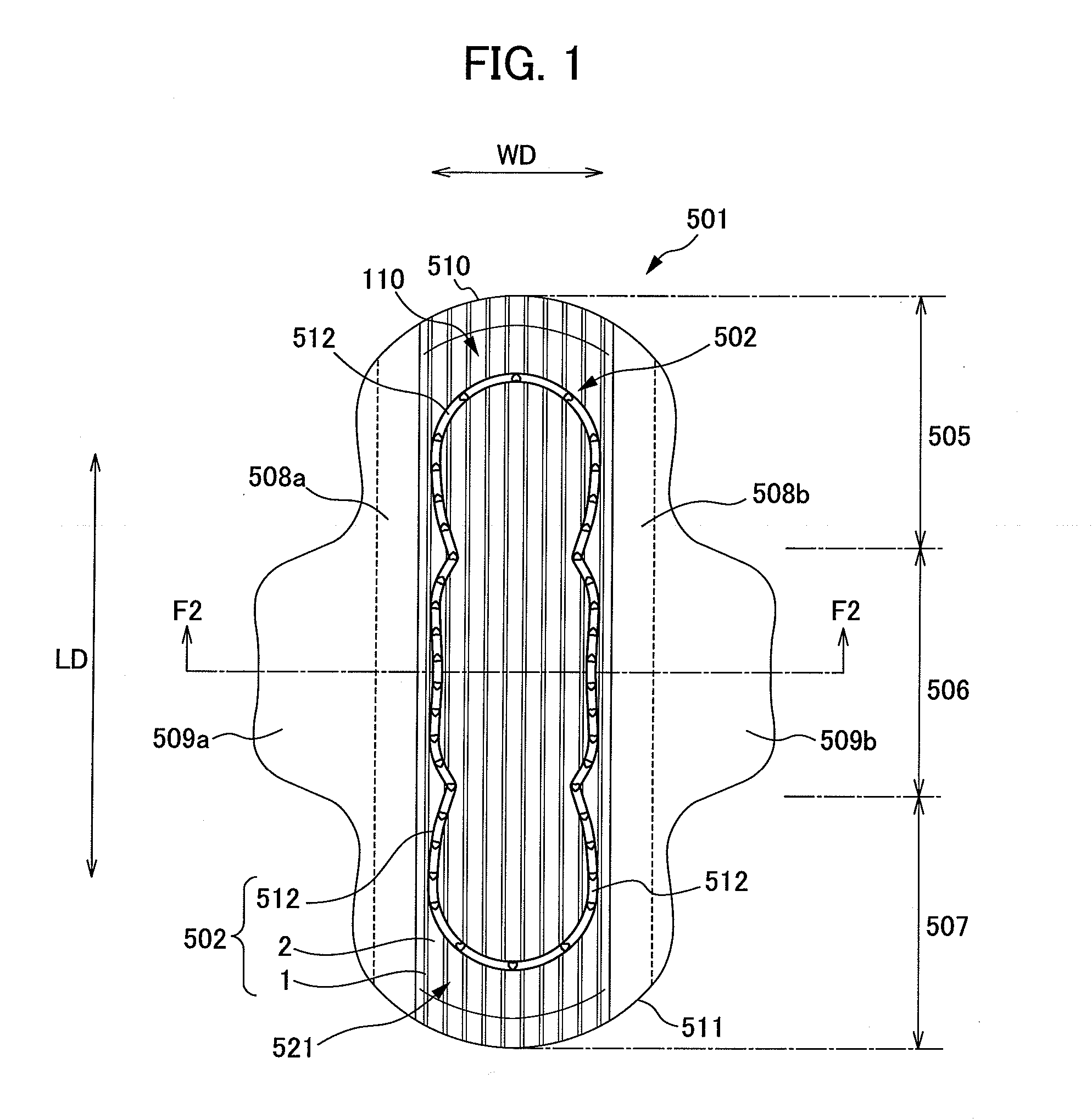
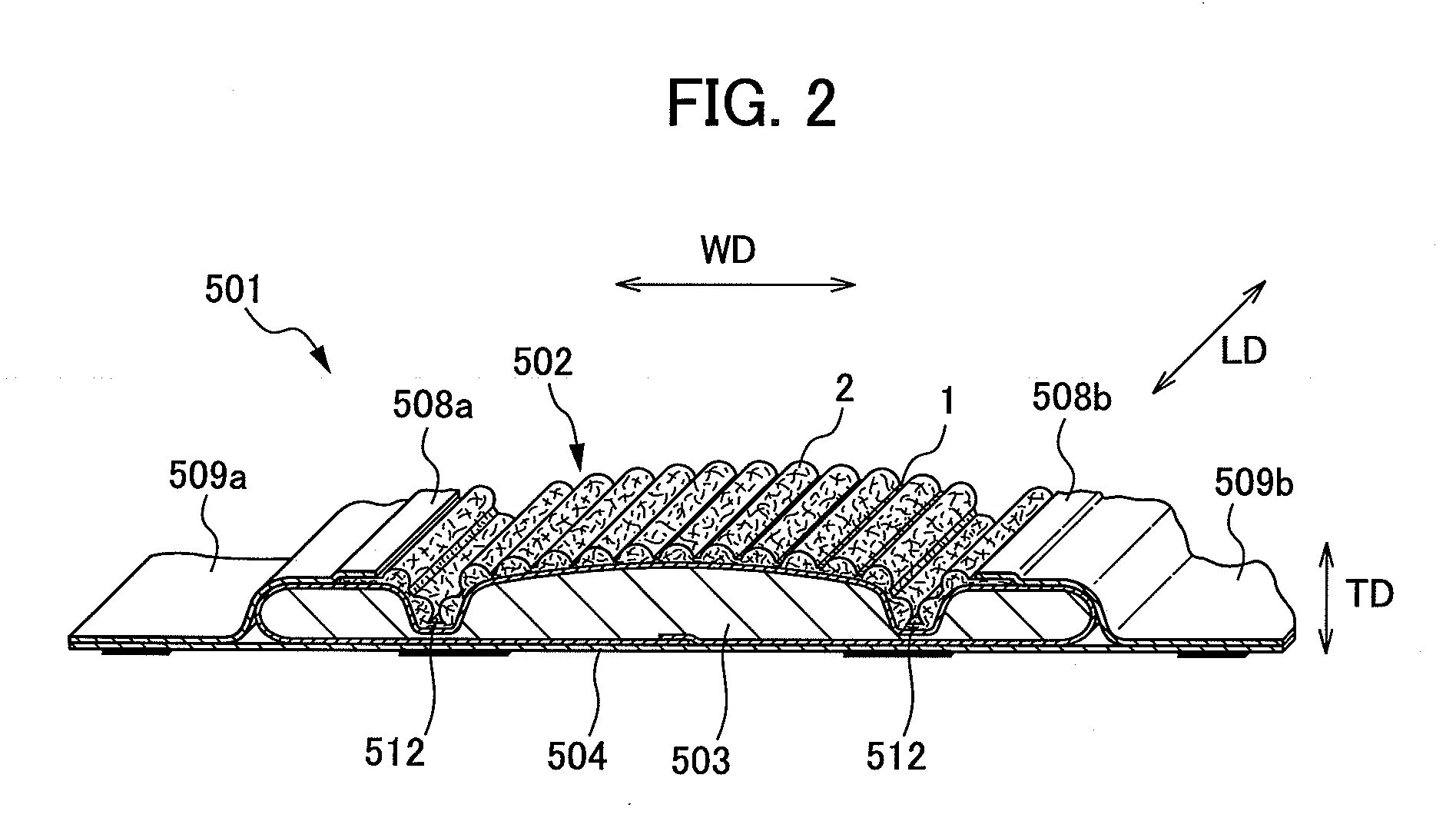
Composite sheet and absorbent article comprising composite sheet
ActiveCN101541526APrevent seepageReduce basis weightLayered productsAbsorbent padsAdhesiveEngineering
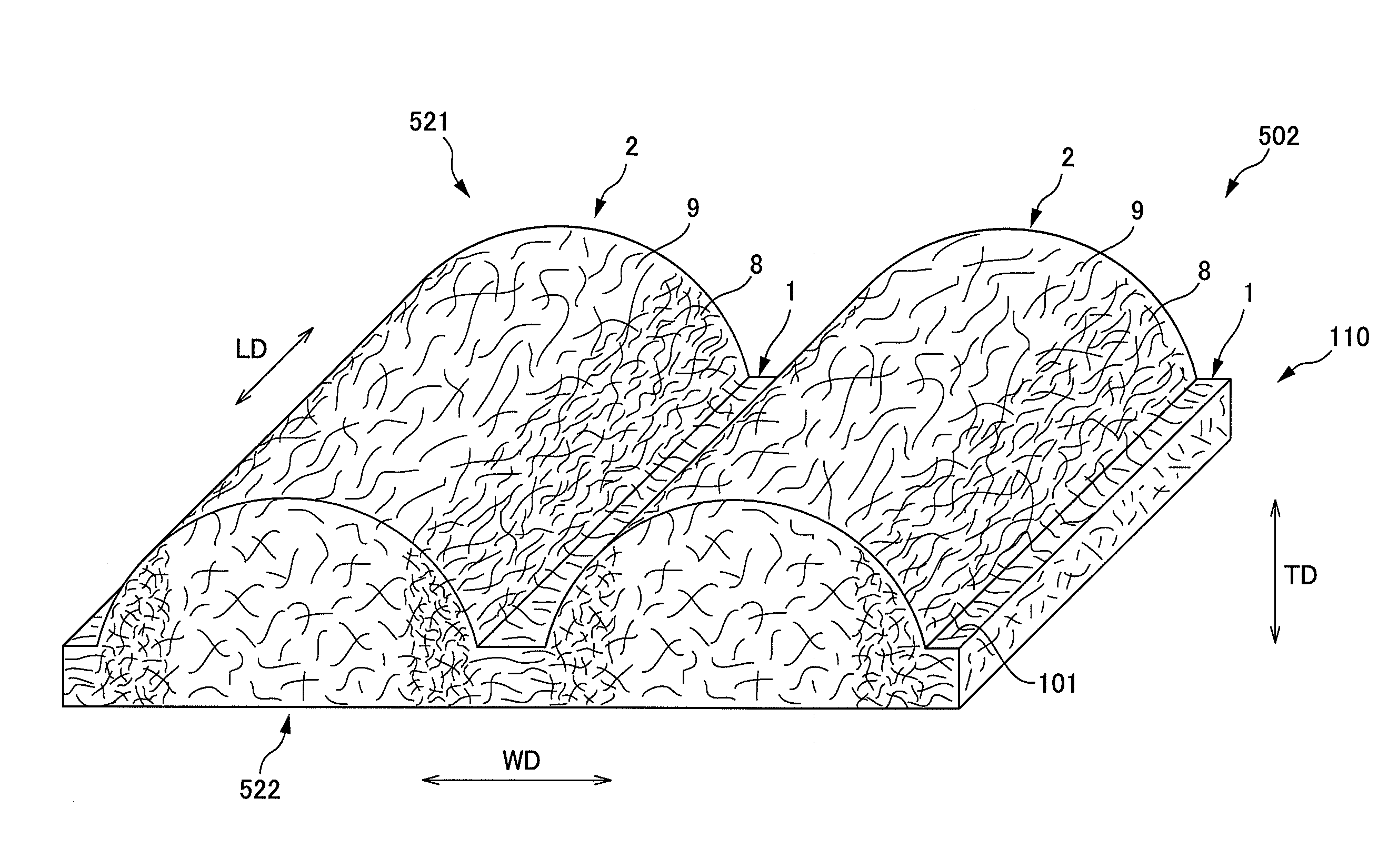
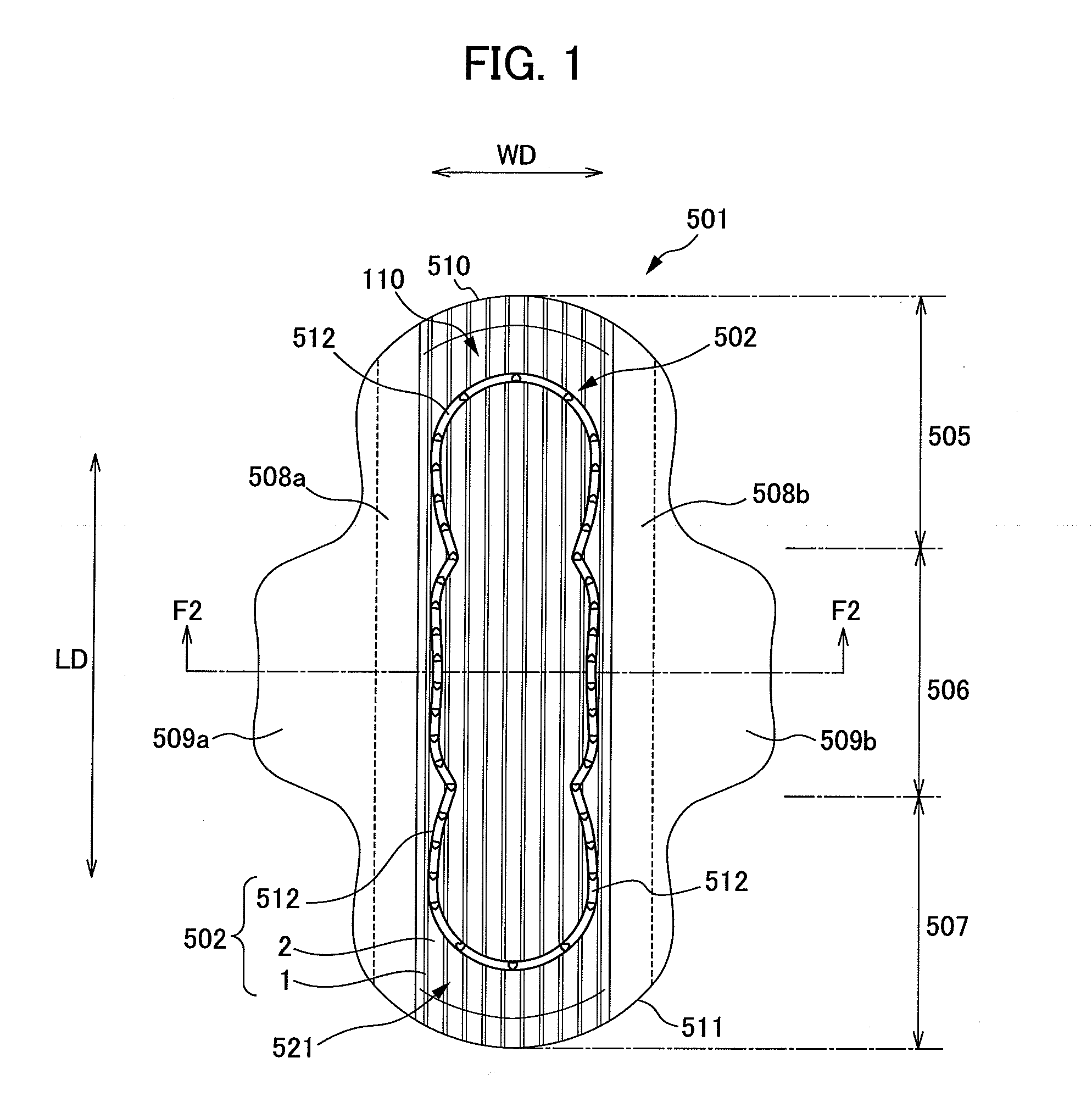
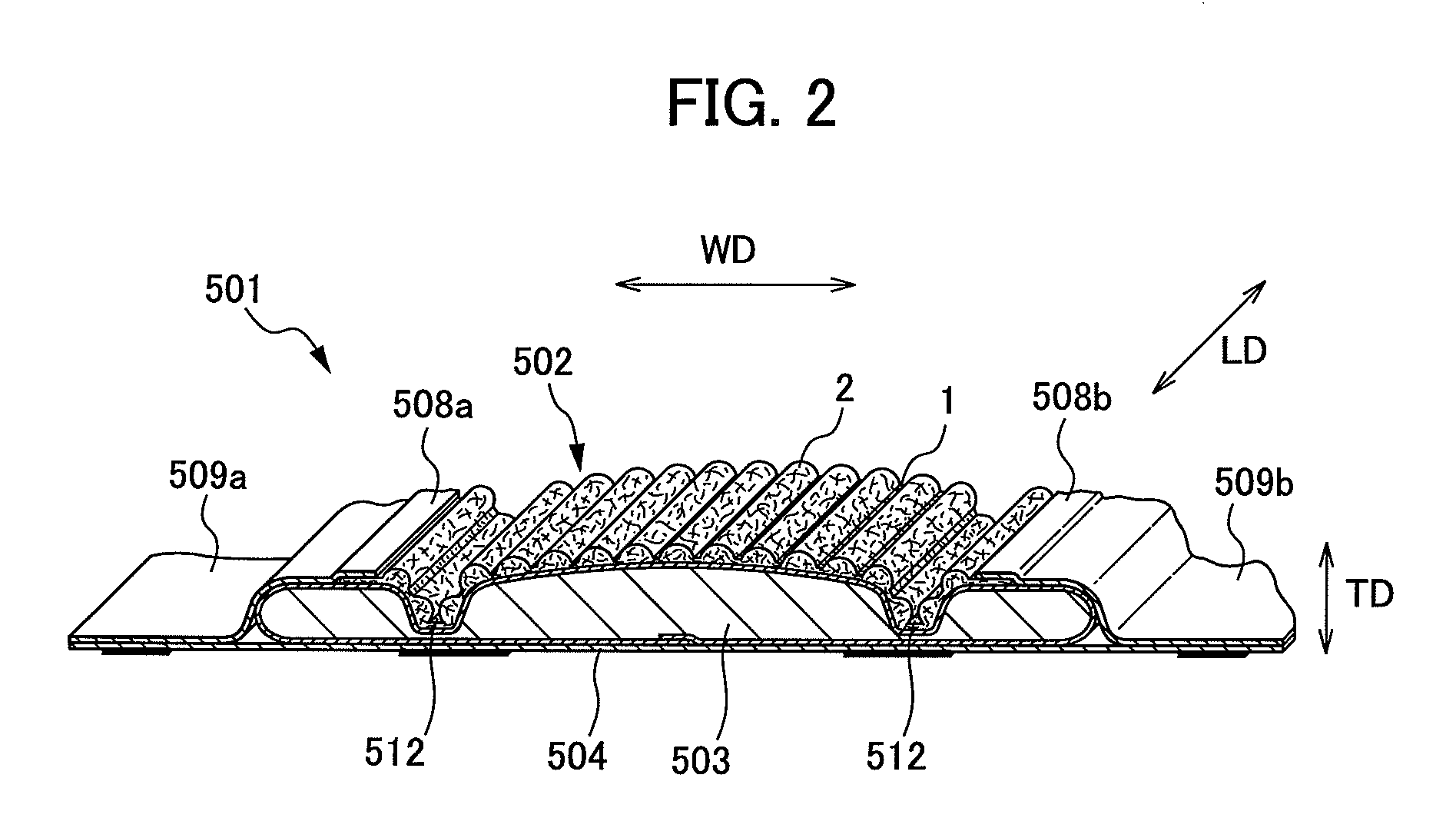
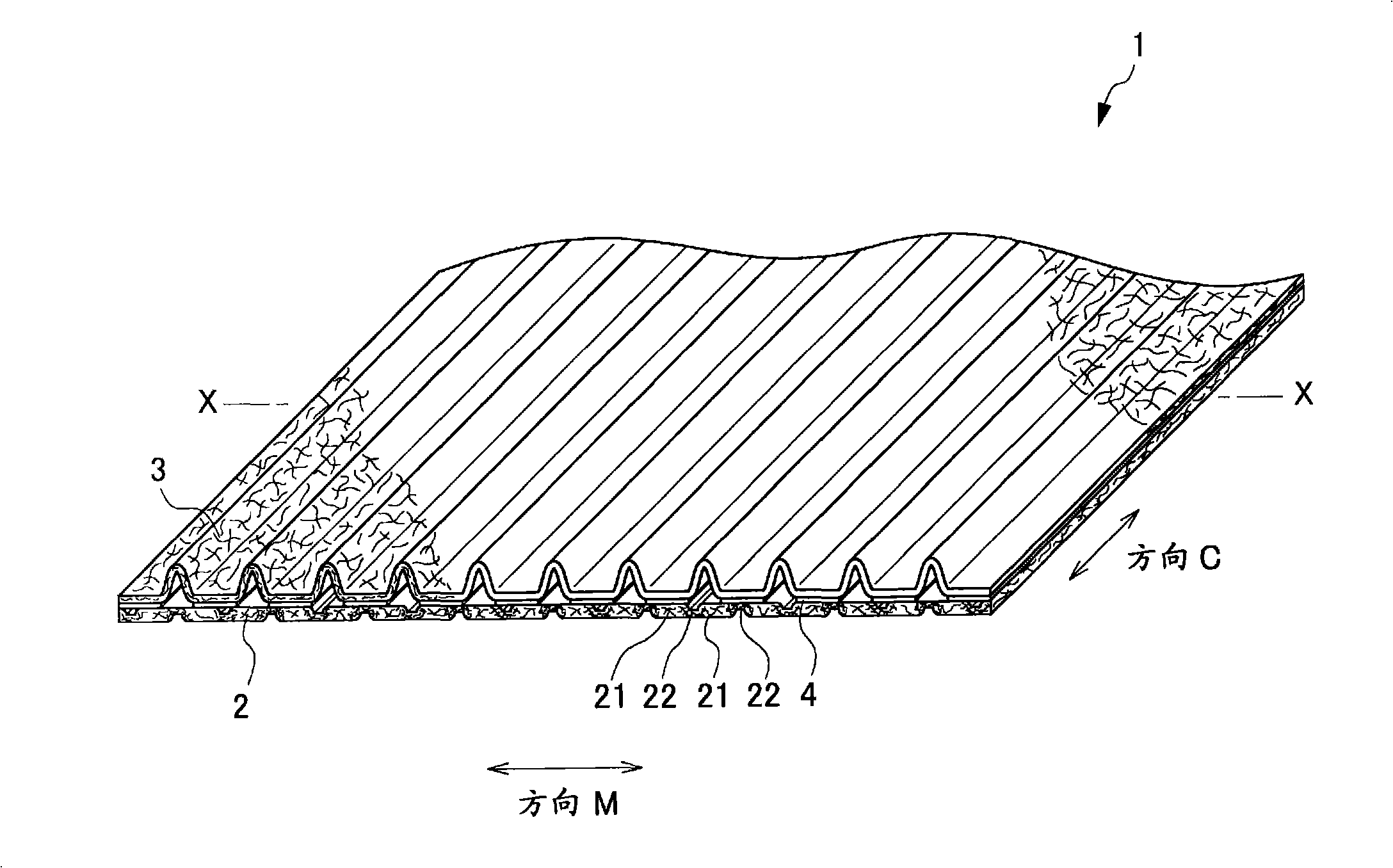
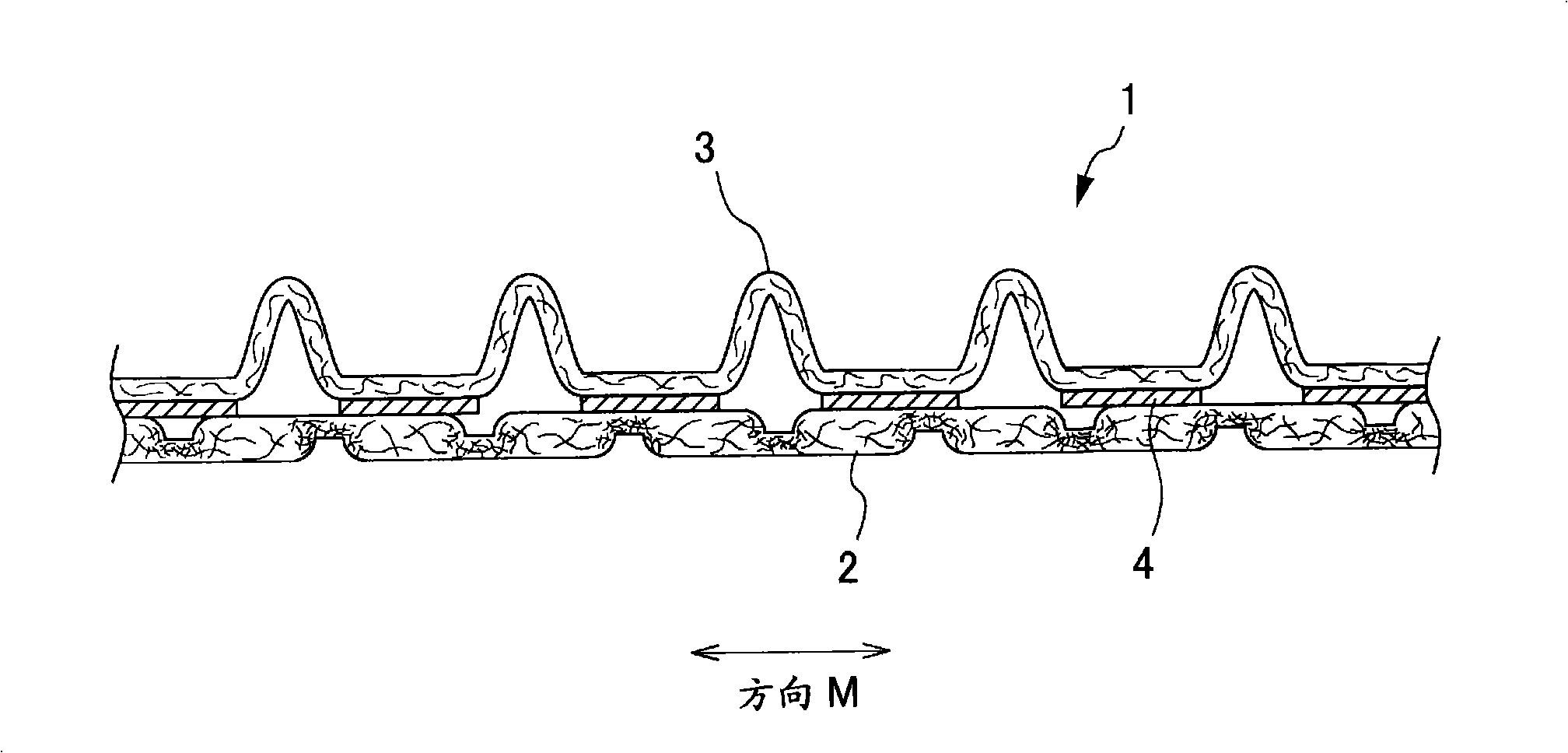
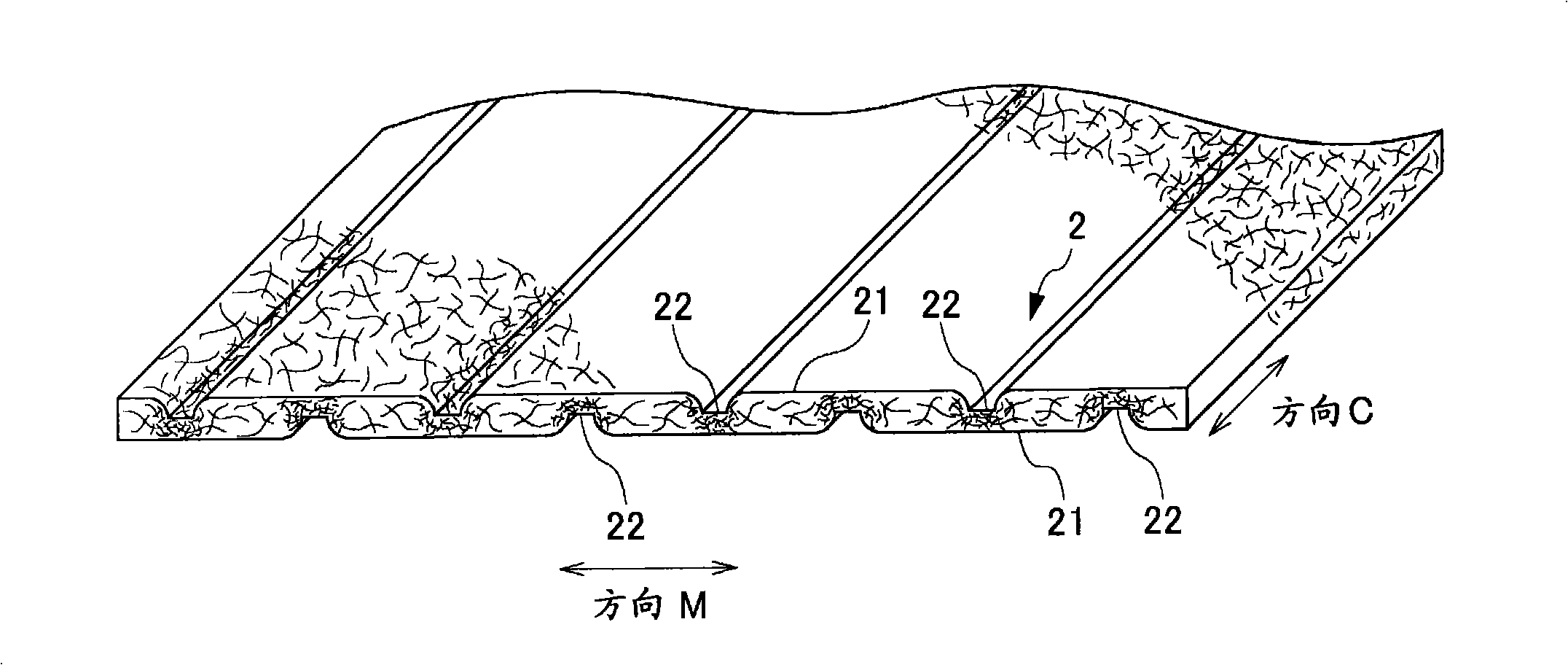
A composite sheet that has a low basis weight and can inhibit adhesives from flowing out is provided. The composite sheet 1 according to the present invention is formed by bonding a stretchable nonwoven fabric 2 and a non-stretchable nonwoven fabric 3 to each other with adhesives 4 . The stretchable nonwoven fabric 2 in an extended state is bonded to the non-stretchable sheet. The stretchable nonwoven fabric 2 has a plurality of strip-shaped non-dense regions 21 and a plurality of strip-shaped dense regions 22 formed on both its surfaces alternately and alternately in the transverse directionsuch that the dense regions 22 on one of the surfaces and the dense regions 22 on the other surface are not overlapped with each other. The stretchable nonwoven fabric 2 includes thermoplastic fibersthat have been stretched at least partially and elastomer fibers.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
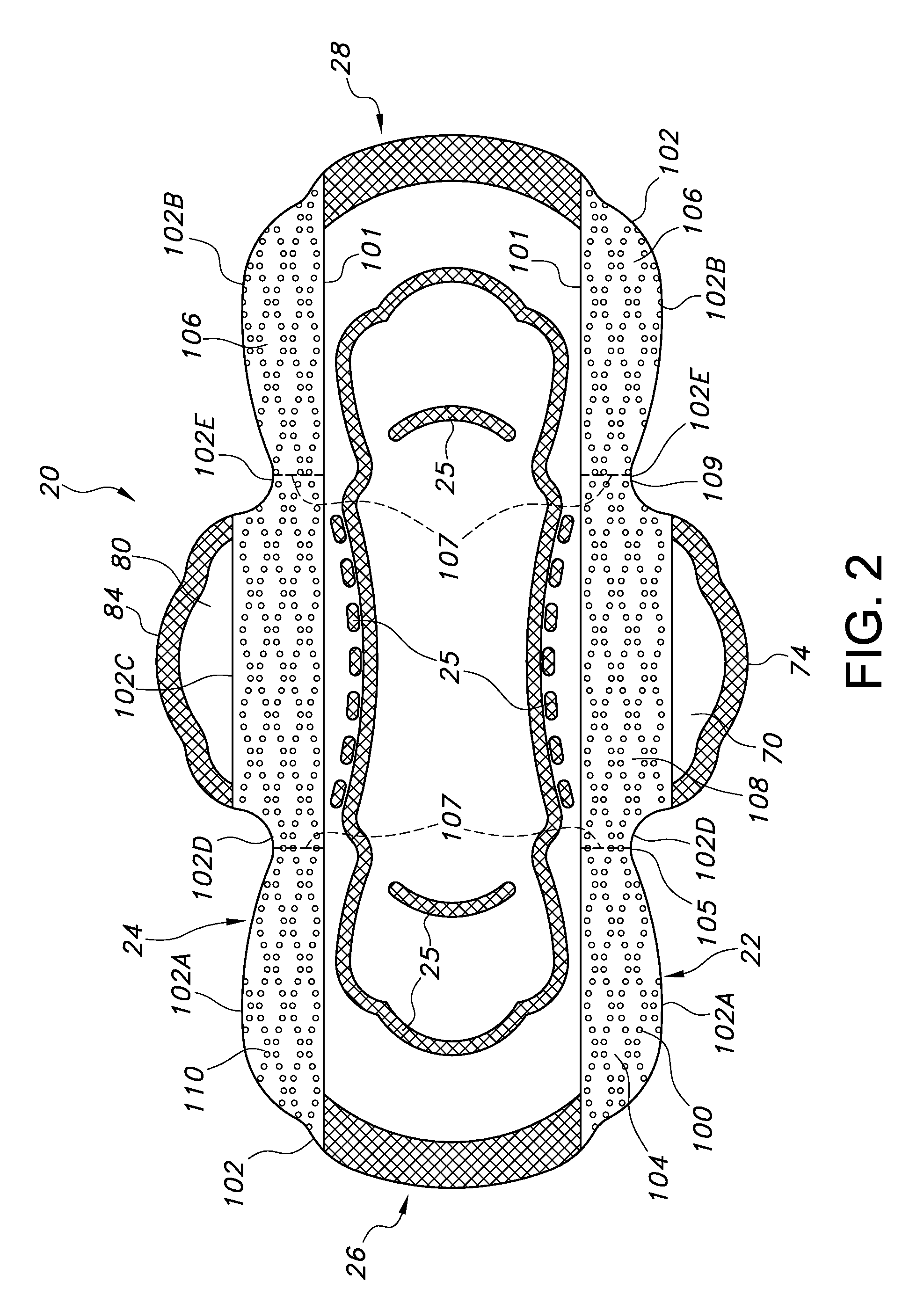
Absorbent personal care article having wings and protective strips
An absorbent personal care article, such as a sanitary napkin or incontinence pad is described having a longitudinal centerline and a transverse centerline and including a pair of opposed first and second wings extending along the longitudinal sides of the article. The article further includes first and second protective strips attached to the sides of the article such that when the wings are folded under the article and around the wearer's undergarment, the first and second protective strips extend laterally outboard of the article and the edges of the wearer's undergarment to provide additional protection against leakage of body fluids deposited onto the absorbent personal care article.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Cleansing sheets, manufacturing process and use thereof
InactiveUS20060205310A1Simple manufacturing processWell mixedPersonal careLayered productsFiberPersonal care
Disclosed are liquid impregnated sheets containing a combination of split-fibres and / or meltblown fibres with regular fibres of thermoplastic polymers. The sheets can be monolayers or multilayers with non-wovens of split-fibres on the outer portions of the multilayered sheets. The sheets possess good storage and release characteristics for a liquid and can be used as cleansing sheets for personal care or for polishing purposes.
Owner:CARL FREUDENBERG KG +1
Nonwoven Web With Enhanced Barrier Properties
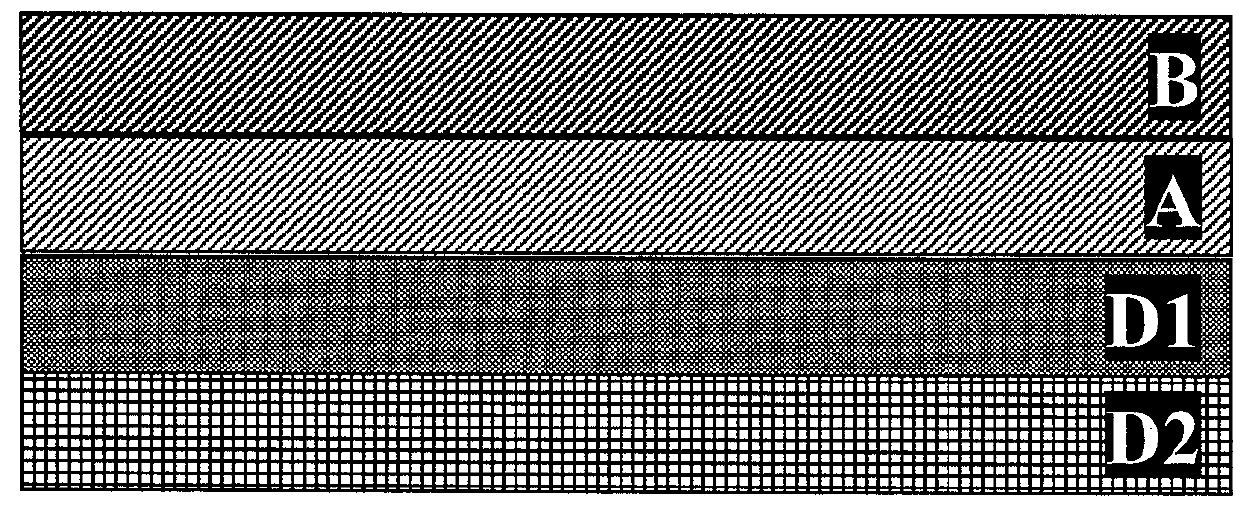
InactiveUS20180178486A1Barrier capacity can be increasedSmall spreadPersonal careProtective equipmentFiberTextile
This invention relates to nonwoven textile with barrier properties containing a first barrier layer A with a theoretical cover coefficient TCC A, and consisting of fibres having a median fibre diameter in the layer of dAm, and a second barrier layer B with a theoretical cover coefficient TCC B, and consisting of fibres having a median fibre diameter in the layer of dBm; while the first barrier layer A and the second barrier layer B are together in direct contact. The median diameters of fibres in the first and second layer have a theoretical fibre diameter coefficient x=(dBm−dAm) / dAm, where the theoretical fibre diameter coefficient x is less than or equal to 1 and where the theoretical fibre diameter coefficient x is greater than or equal to 0.25, and the sum of the theoretical cover coefficient TCC A and TCC B is greater than or equal to 50%.
Owner:PFNONWOVENS CZECH SRO
Meltblown nonwoven fabric and uses thereof
InactiveUS20150233030A1Low bulk densitySatisfactory sound absorption performanceLayered productsFilament/thread formingPolymer scienceFiltration
A meltblown nonwoven fabric is provided having thermoplastic resin fibers having an average fiber diameter of 0.1 to 10 μm, a bulk density of not more than 36 kg / m3 and an air permeability, as measured by a Frazier type method at basis weight of 200 g / m2, of 3 to 100 cc / cm2 / sec. The meltblown nonwoven fabric has a low bulk density and is excellent in sound absorption performance, oil adsorption performance, heat insulation performance, dust collection performance and filtration performance. Since the meltblown nonwoven fabric can be formed from one kind of a resin composition, it can be simply and easily produced as compared with the case of using mixed fibers or conjugated fibers formed from many kinds of resins, and the resulting meltblown nonwoven fabric can have uniformity and no variability of properties.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Cleansing Sheets, Manufacturing Process And Use Thereof
InactiveUS20090176063A1Well mixedSufficient absorbencyPersonal carePattern makingPersonal careEngineering
Disclosed are liquid impregnated sheets containing a combination of split-fibres and / or meltblown fibres with regular fibres of thermoplastic polymers. The sheets can be monolayers or multilayers with non-wovens of split-fibres on the outer portions of the multilayered sheets.The sheets possess good storage and release characteristics for a liquid and can be used as cleansing sheets for personal care or for polishing purposes.
Owner:CARL FREUDENBERG KG +1
Tissue paper making machine, tissue paper produced therewith and method for producing such a tissue paper
InactiveUS20020112829A1Lower resistanceShorten the lengthNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperTissue paperDewatering
A tissue paper making machine, a tissue paper product, and a method for producing such a tissue paper product. According to the invention, a dewatering and sheet-forming wire (13;14) is deposited in the pulp flow area by a texturing wire (16;17) that is provided with a texture comprised of closed wire zones. This results in the production of a tissue paper product having improved optical and haptic properties.
Owner:SCA HYGIENE PROD AB
Sheet feeding apparatus and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20170068199A1Reduce basis weightElectrographic process apparatusArticle feedersEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:CANON KK
Charged filter medium and method for manufacturing charged filter medium
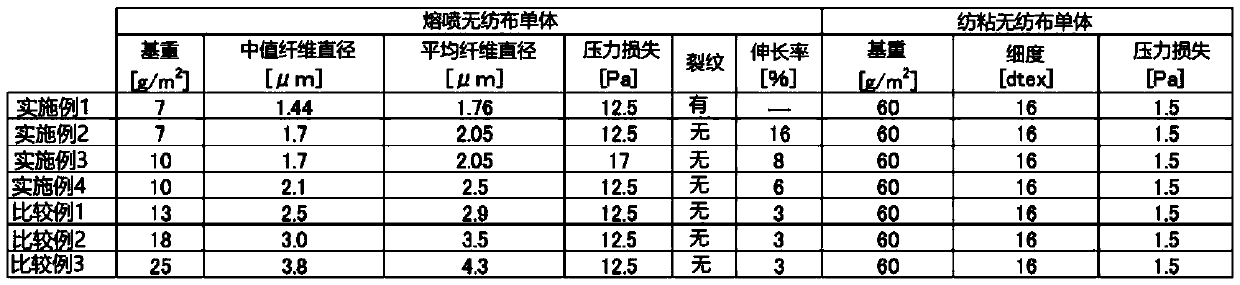
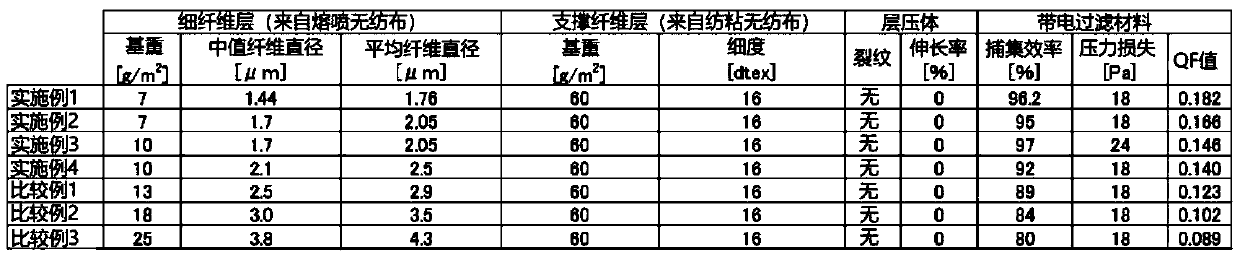
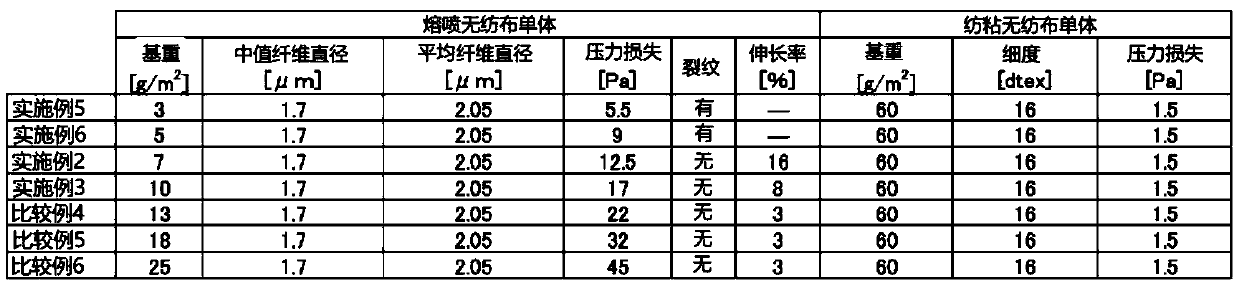
InactiveCN110430931AReduce basis weightIncreased pressure lossElectrostatic separationLayered productsFiberElectrical polarity
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a charged filter medium having superior filtration performance and a method for manufacturing a charged filter medium. The present invention is a charged filter medium having both superior pressure loss and collection efficiency in excellent balance such that the pressure loss is 24 Pa or less with an air flow of 10 cm / s and the collection efficiency for particles with a particle size of 0.3 - 0.5 [mu]m at an air flow of 10 cm / s is 76% or greater, even being a charged filter medium provided with a fine fiber layer with a median fiber diameterfor constituent fibers smaller than 2.1 [mu]m and a mesh smaller than 10 g / m2 and a charged laminate wherein a support fiber layer is integrated by lamination. In addition, a method for manufacturingthe charged filter medium has a step for preparing a laminate by integration of a fine fiber fabric and a support fabric by lamination, thereby being able to provide the same to a polarized fluid charging method in a state where the fine fiber fabric is reinforced by the support fabric. As a result, it is possible to manufacture a charged filter medium having both superior pressure loss and collection efficiency in excellent balance.
Owner:NIPPON BAIRIIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com