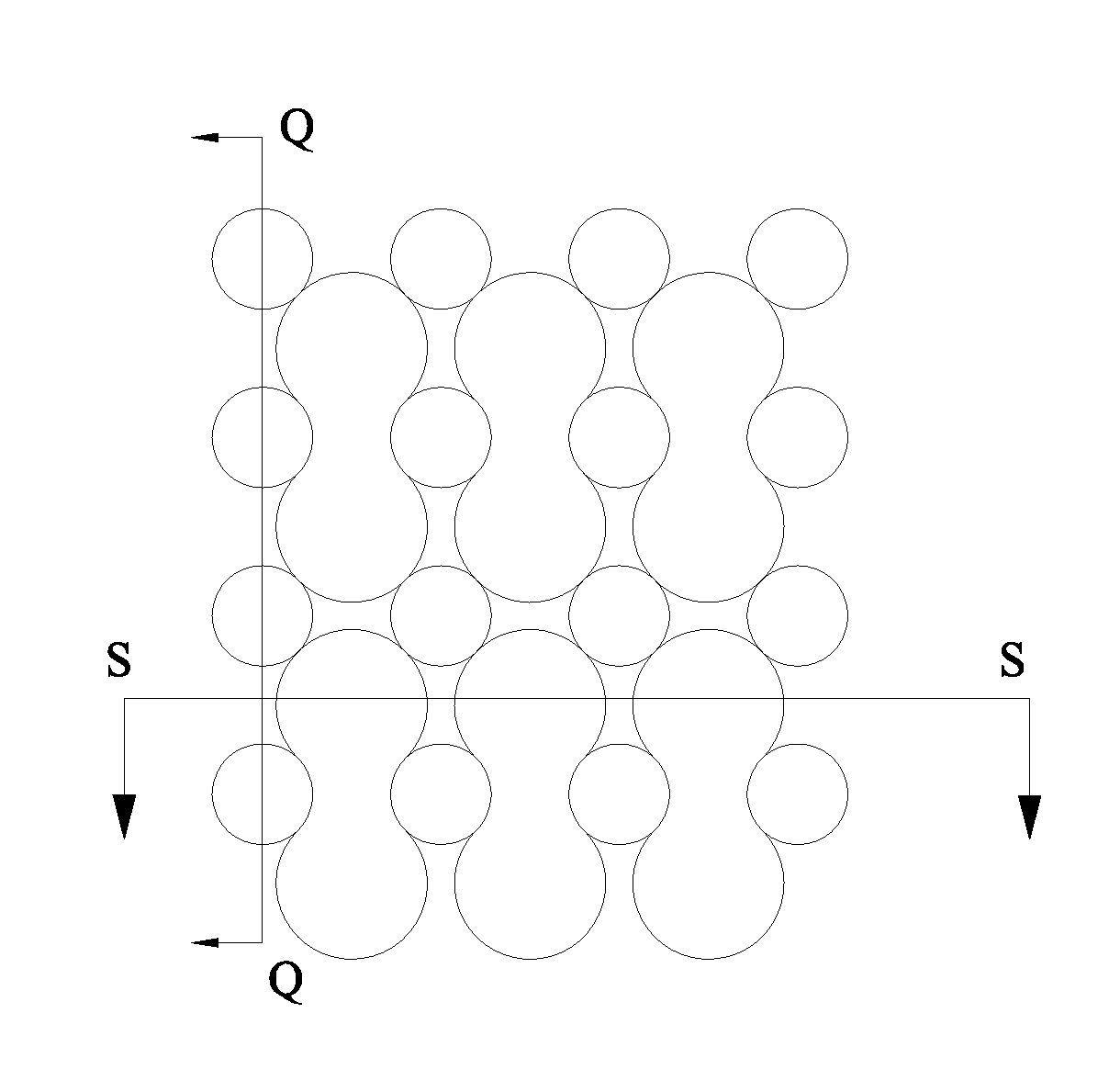Patents
Literature
300 results about "Fiber density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
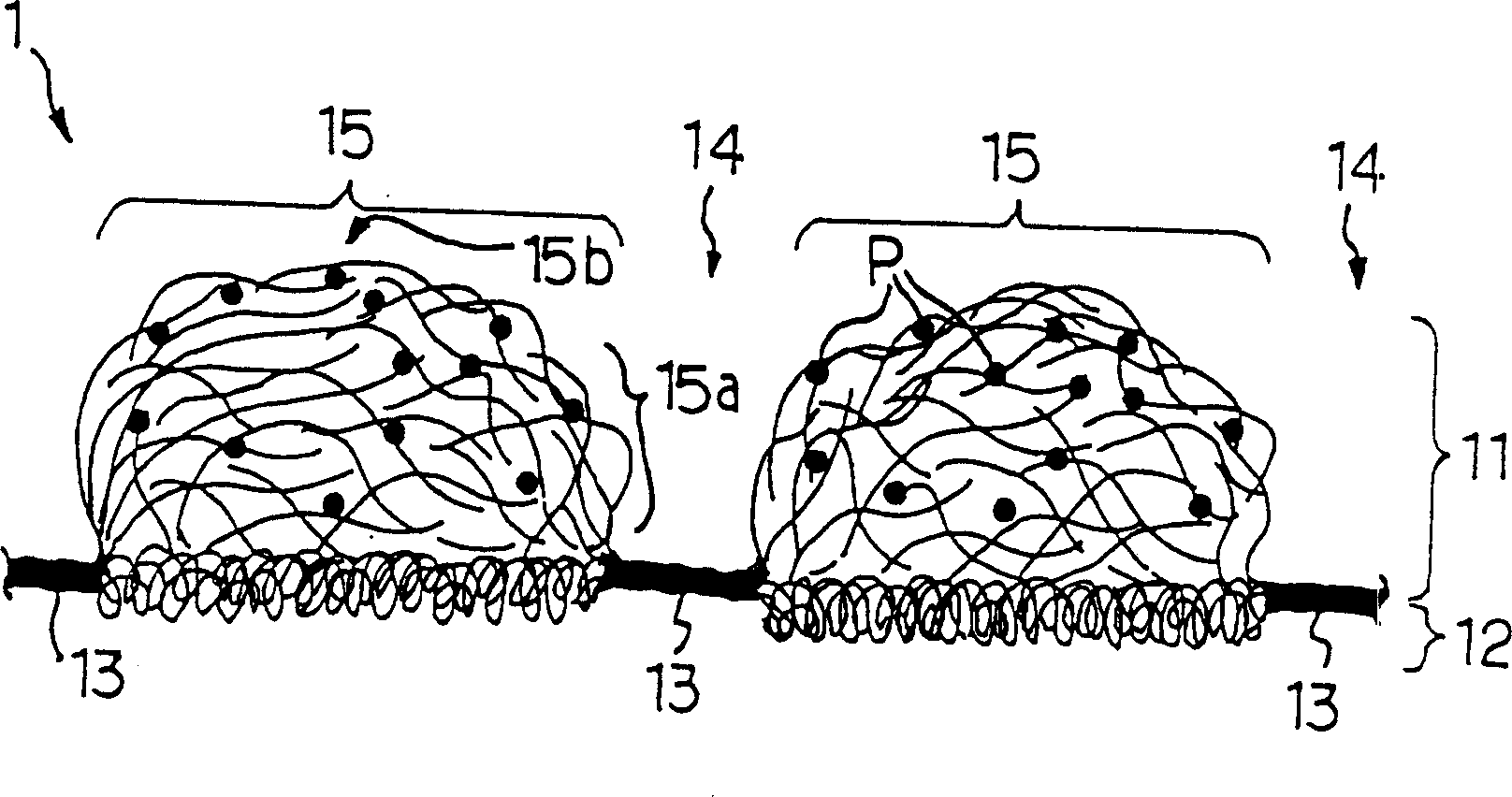
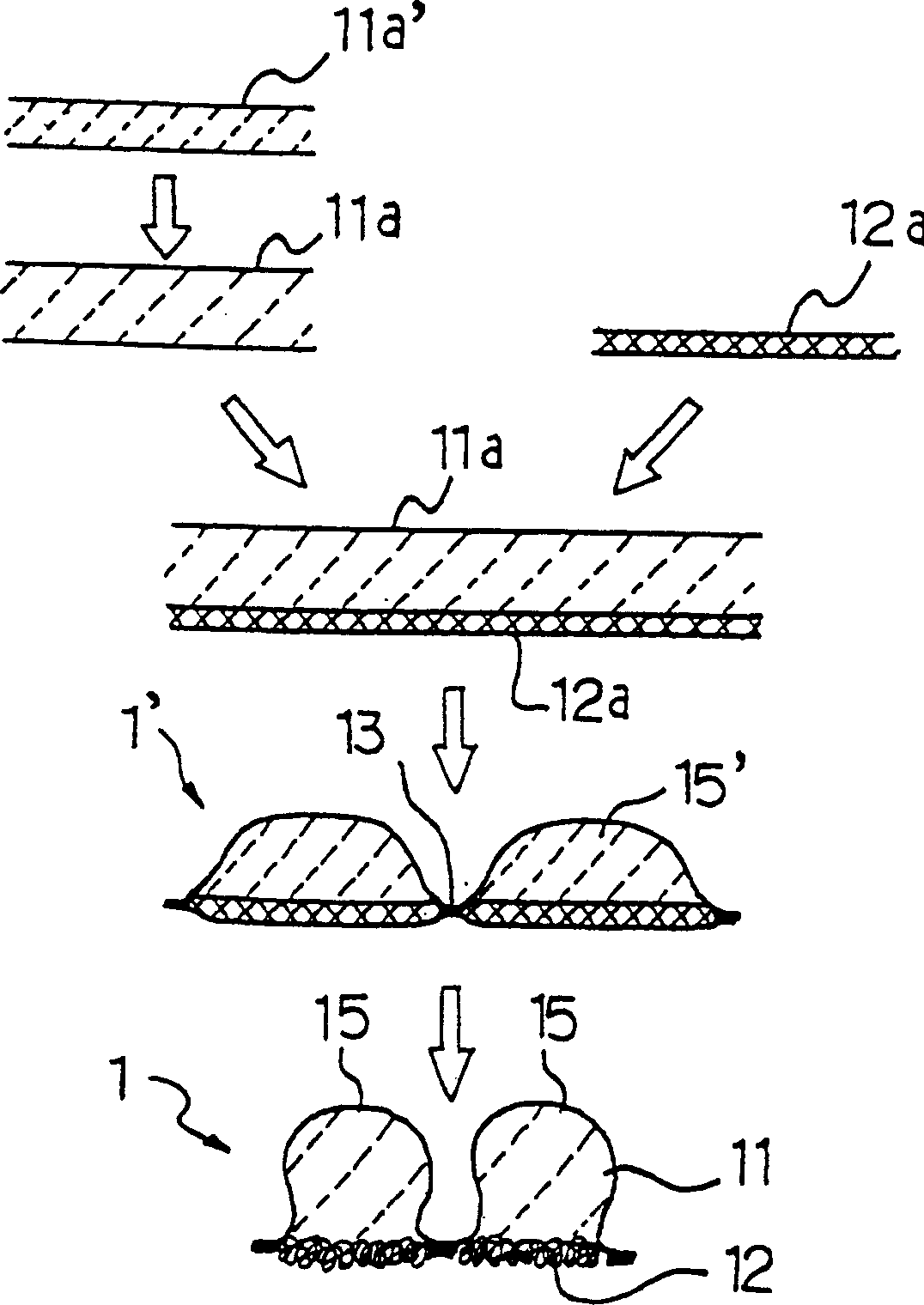
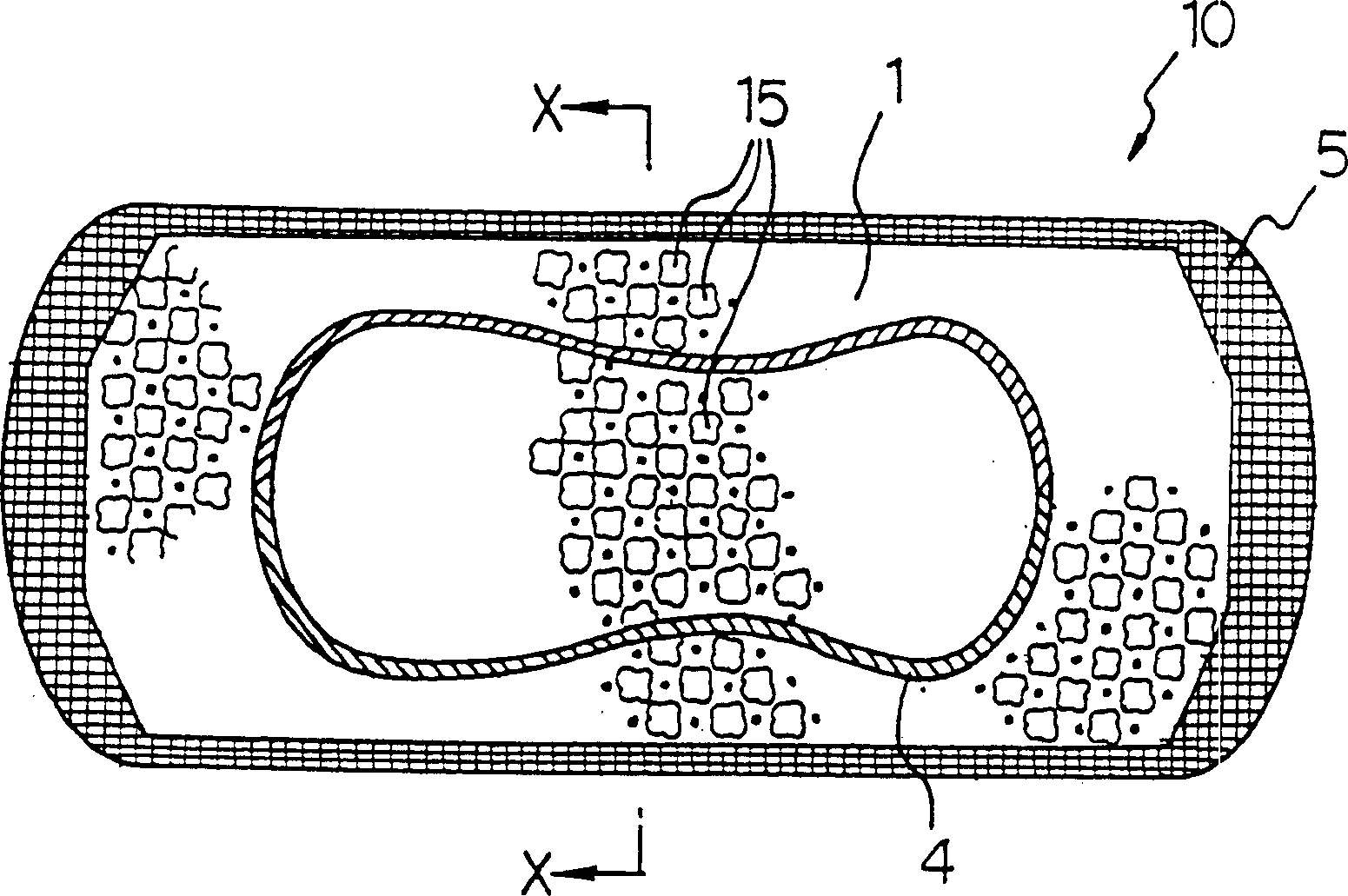
Bulk enhanced paperboard and shaped products made therefrom
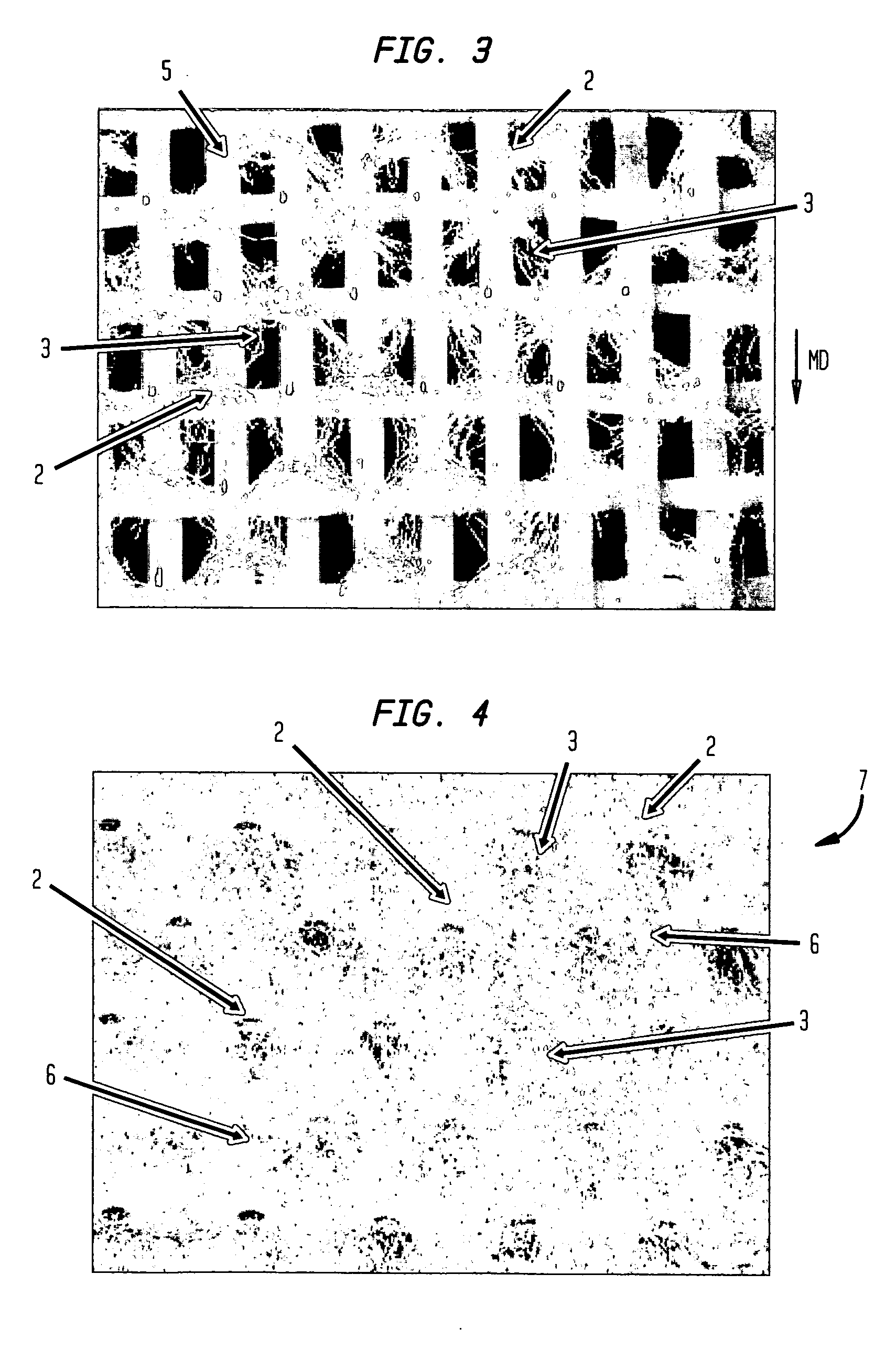
An improved paperboard has been bulk enhanced by retaining a substantial portion of bulk-enhanced additives including expandable microspheres in a suitable distribution within the paperboard. The cellulosic paperboard web has an overall fiber weight (w) of at least 40 lbs. / 3000 square feet and at a fiber density of 3, 4.5, 6.5, 7, 8.3, and 9 pounds per 3000 square foot ream at a fiberboard thickness of 0.001 inch respectively, has a GM Taber stiffness of at least about 0.00716 w2.63 grams-centimeter / fiber mat density1.63 pounds per 3000 square foot ream at a fiberboard thickness of 0.001 inch, and a GM tensile stiffness of at least about 1890+24.2 w pounds per inch. The high retention of the bulk enhancing additives is believed to result from the incorporation of suitable retention aids. The resulting paperboard has better GM Taber stiffness values and GM tensile stiffness than prior art paperboards. The paperboard also has increased strain to failure and is able to be formed into suitable paperboard containers without loss of integrity. The resulting containers have increased hold times when they contain hot or cold food or drink.
Owner:DIXIE CONSUMER PROD
Multi-ply paper towel with absorbent core
ActiveUS7662257B2VariationImprove performanceNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCellulosePaper towel
A multi-ply absorbent sheet of cellulosic fiber with continuous outer surfaces is provided an absorbent core between the outer surfaces. The absorbent core includes a non-woven fiber network having: (i) a plurality of pileated fiber enriched of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by way of (ii) a plurality of lower local basis weight linking whose fiber orientation is biased along the direction between pileated interconnected thereby, and (iii) a plurality of fiber-deprived cellules between the fiber enriched and linking regions, also being characterized by a local basis weight lower than the fiber enriched regions. The cellules provide a sponge-like internal structure of low fiber density regions.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Coated paperboards and paperboard containers having improved tactile and bulk insulation properties
InactiveUS6919111B2Quality improvementImprove insulation performanceNon-fibrous pulp additionWrappersPaperboardEngineering
An improved paperboard has been bulk enhanced by retaining a substantial portion of bulk-enhanced additives including expandable microspheres in a suitable distribution within the paperboard. The cellulosic paperboard web has an overall fiber weight (w) of at least 40 lbs. per 3000 square feet and, at a fiber density of 3, 4.5, 6.5, 7, 8.3, and 9 pounds per 3000 square foot ream at a fiberboard thickness of 0.001 inches, has a GM Taber stiffness of at least about 0.00246 w2.63 grams-centimeter / fiber mat density1.63, and a GM tensile stiffness of at least about 615+13.18 w pounds per inch. The high retention of the bulk enhancing additives is believed to result from the incorporation of suitable retention aids. The resulting paperboard has better GM Taber stiffness values and GM tensile stiffness than prior art paperboards. The paperboard also has increased strain to failure and is able to be formed into suitable paperboard containers without loss of integrity. The resulting containers have increased hold times when they contain hot or cold food or drink.
Owner:DIXIE CONSUMER PROD
Optical fiber management system and method and fiber bender thereof
InactiveUS20040165852A1Coupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresInformation processingEngineering
Owner:CIENA
Nonwoven fabric, nonwoven fabric manufacturing method, and nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus
The present invention provides a nonwoven fabric of which at least one of fiber orientation, fiber density, and basis weight is adjusted, and in which at least one of a predetermined groove portion, an opening, and a protrusion is formed, a manufacturing method for the nonwoven fabric, and a nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus. The nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus of the present invention manufactures a nonwoven fabric of which at least one of fiber orientation, fiber density, and basis weight is adjusted, or in which at least one of a predetermined groove portion, an opening, and a protrusion is formed by blowing fluid mainly containing gas onto a fiber web which is formed in a sheet shape, and which is in a state where at least a portion of the fibers constituting the fiber aggregate has a degree of freedom.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
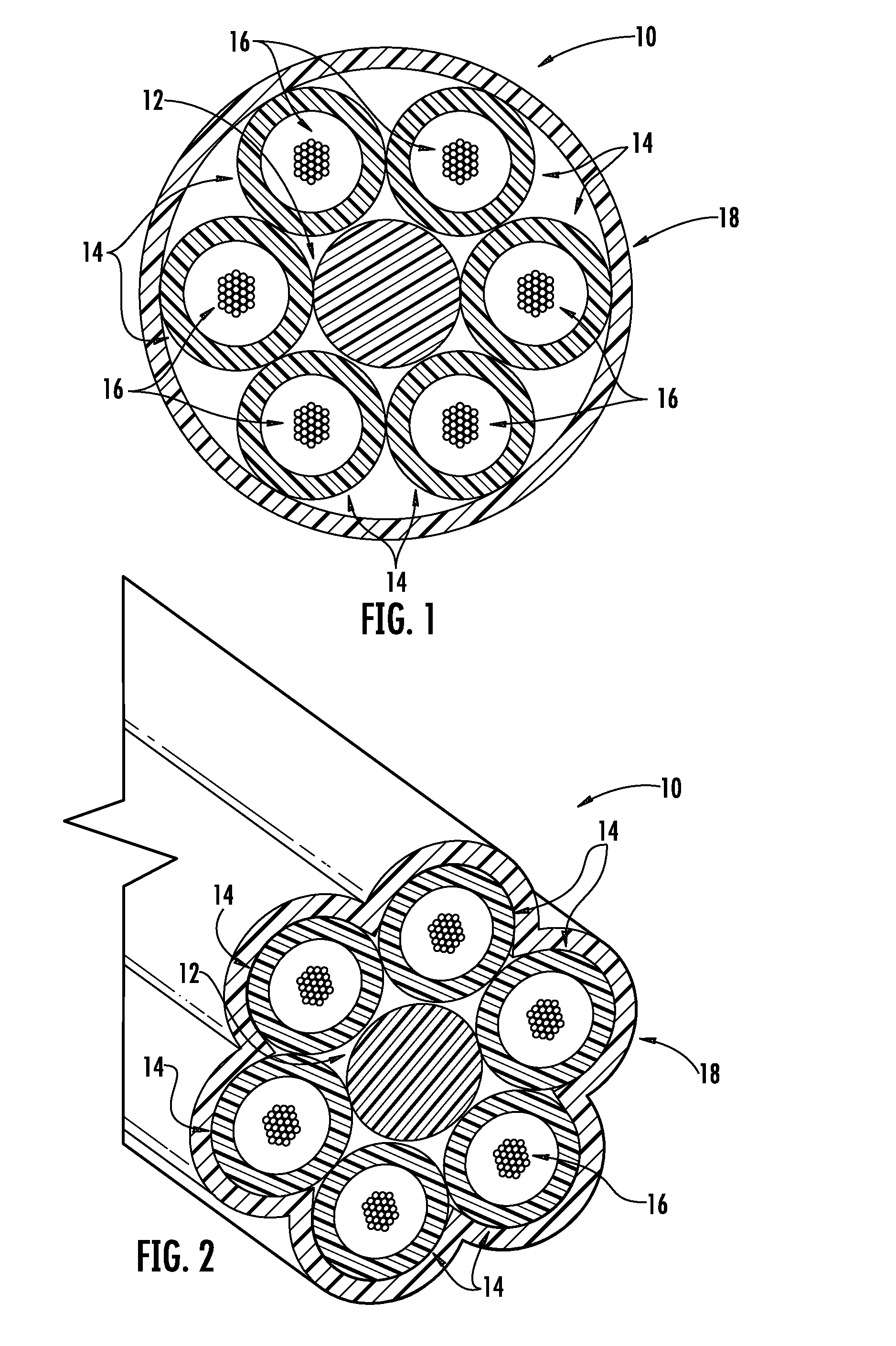
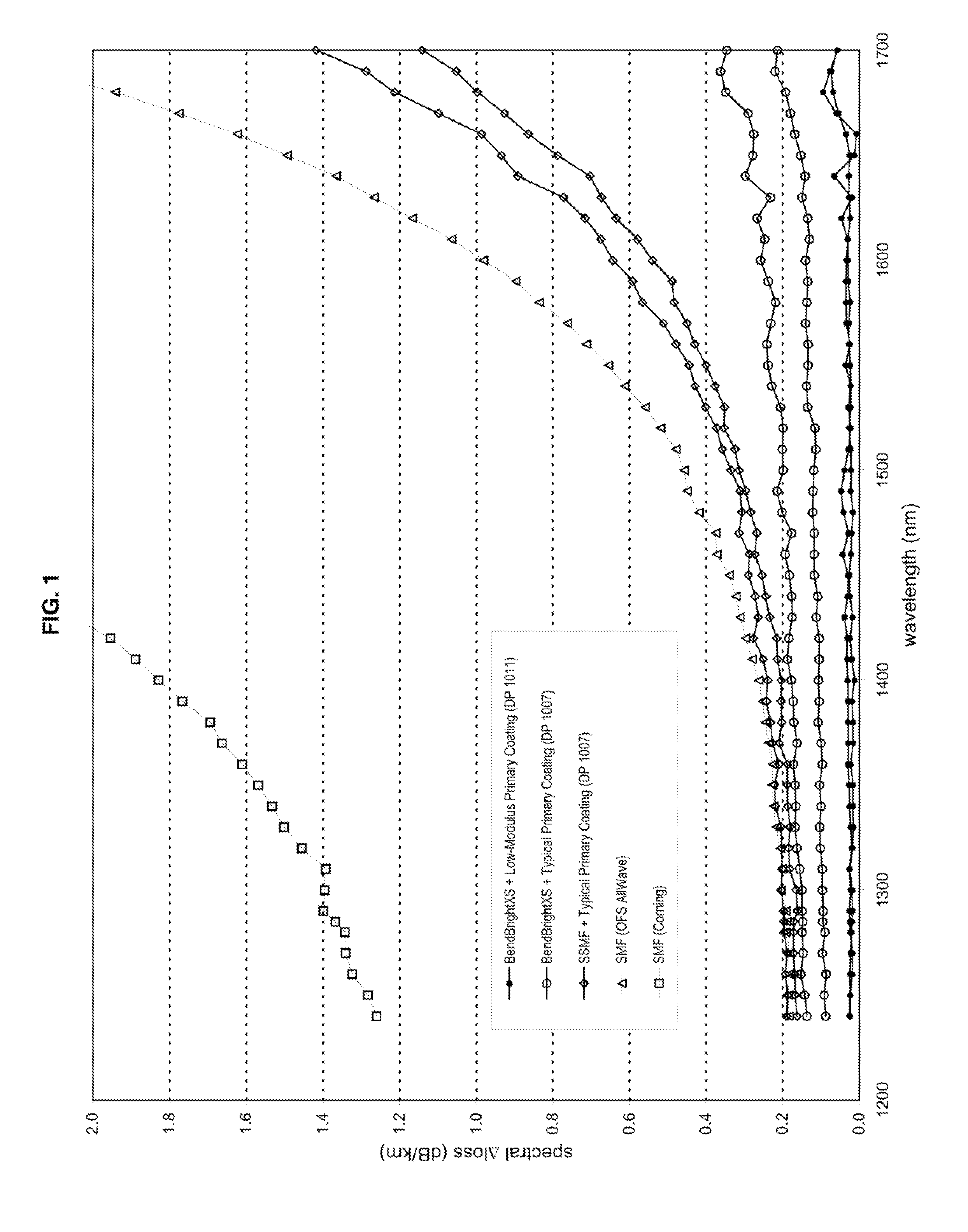
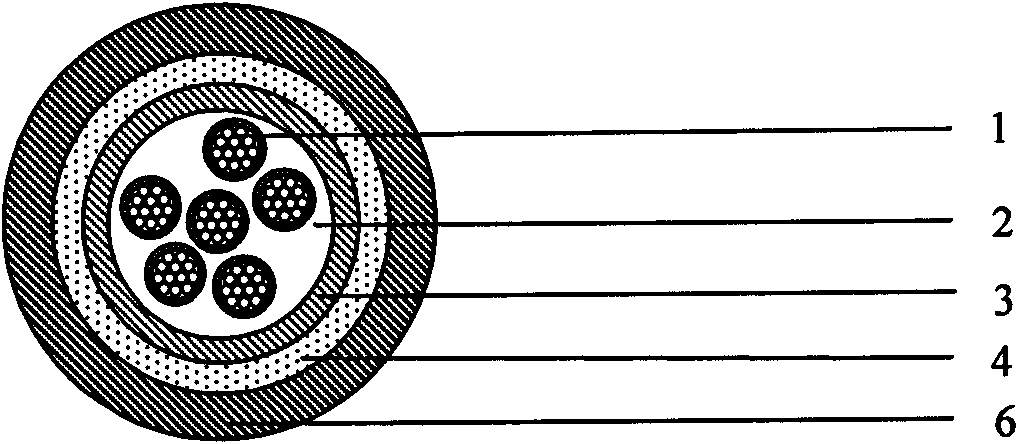
High-Fiber-Density Optical Fiber Cable
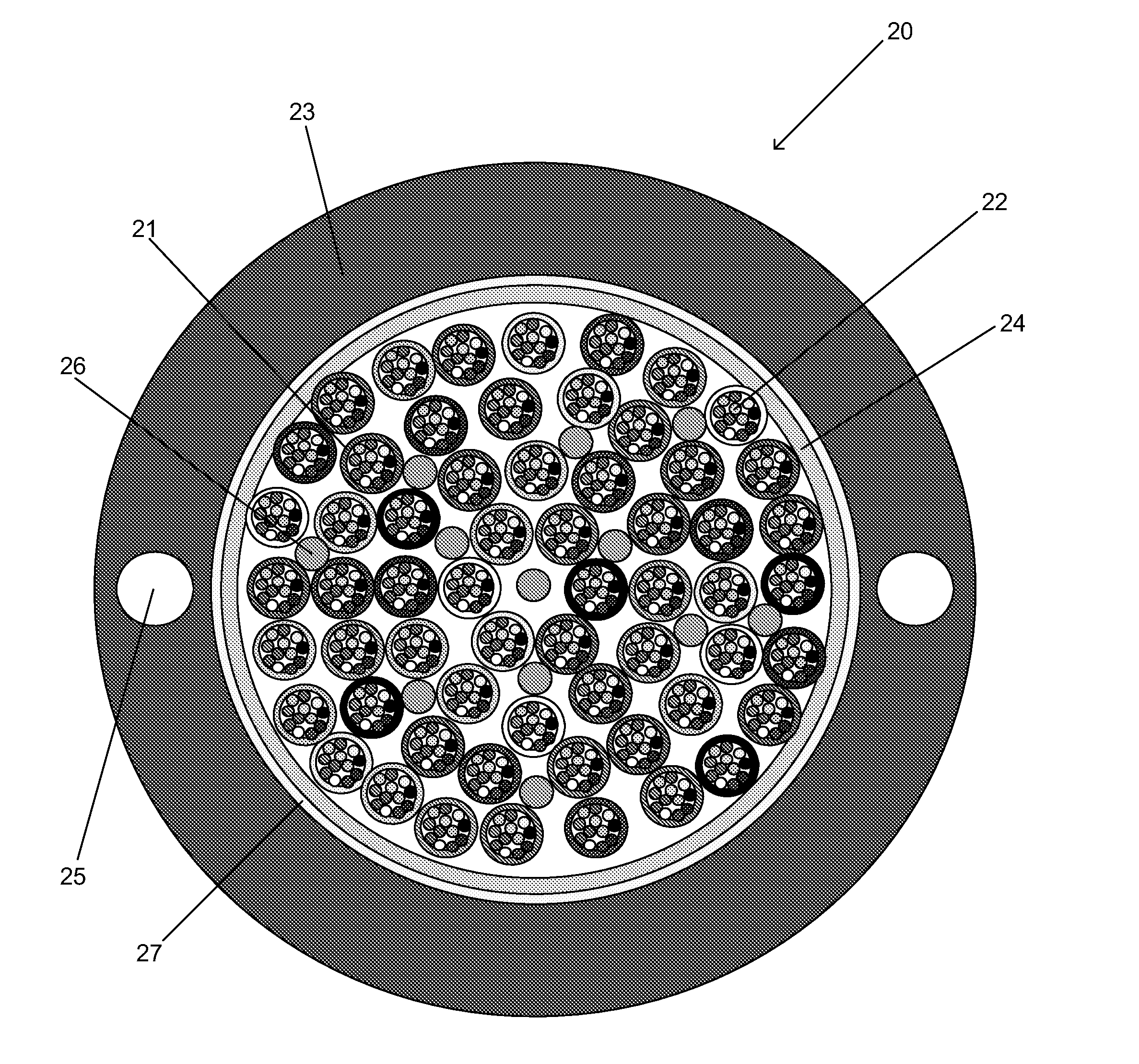
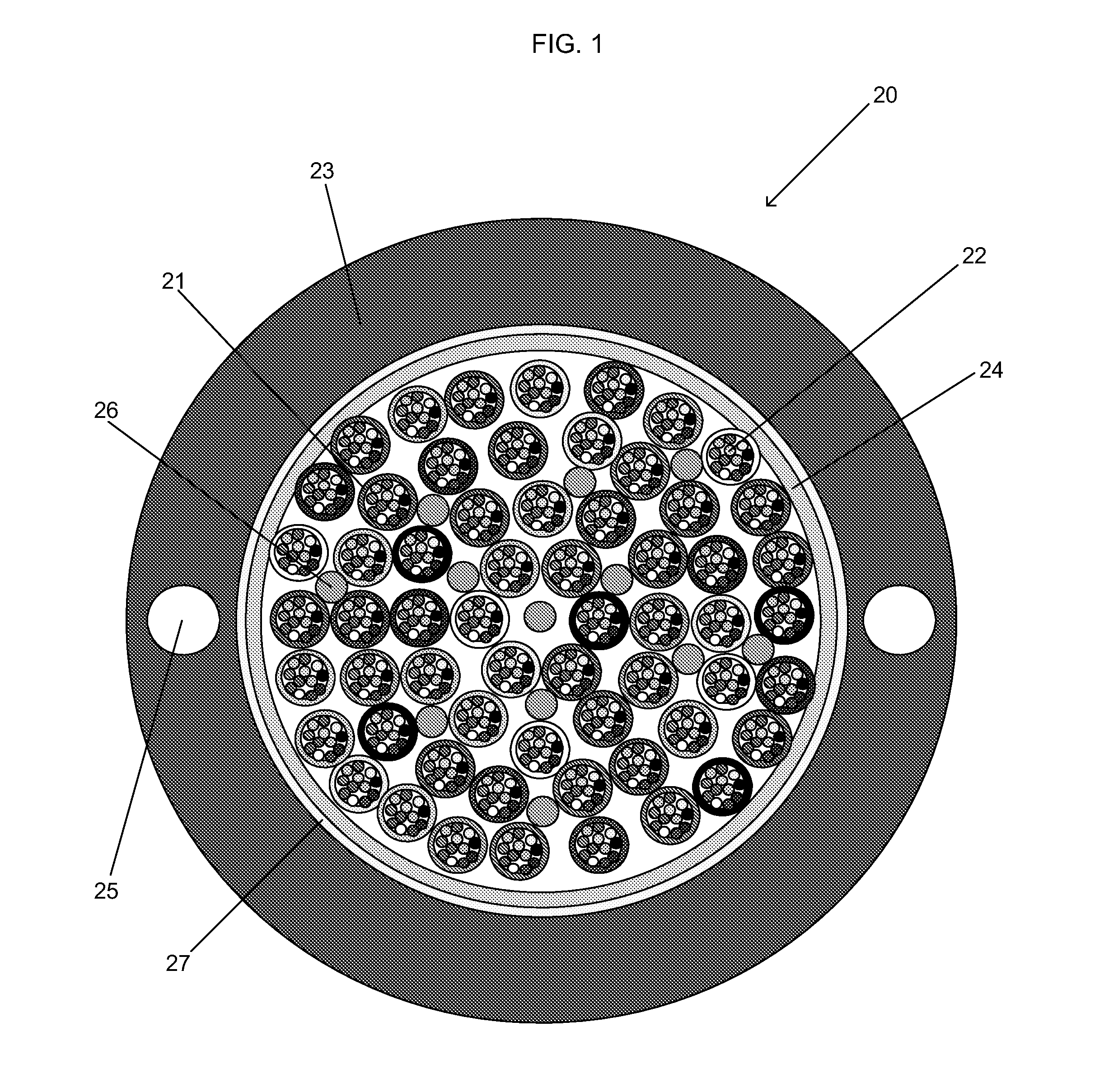
ActiveUS20100067857A1High cable fiber densityImprove the attenuation effectOptical fibre/cable installationFibre mechanical structuresUltrasound attenuationElectric cables
Disclosed is a fiber-optic cable that possesses a high cable filling coefficient (and / or a high cable fiber density) yet ensures that its enclosed optical fibers demonstrate improved attenuation performance when subjected to temperature variations between about −40° C. and 70° C. The fiber-optic cable is suitable for efficient installation into ducts, such as via blowing.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Molded wet-pressed tissue
ActiveUS7563344B2Lose weightIncrease speedNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperBiomedical engineeringSupport surface
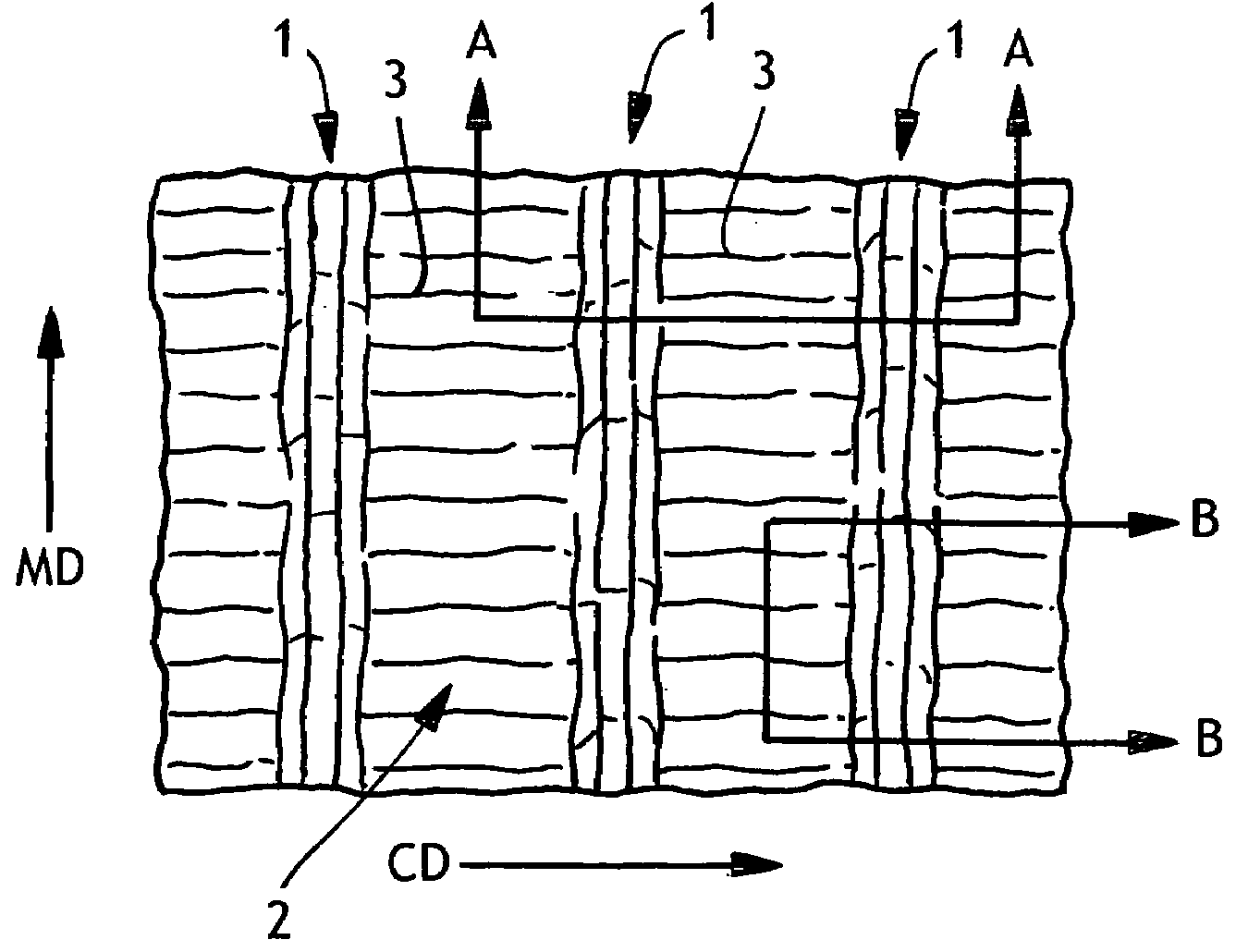
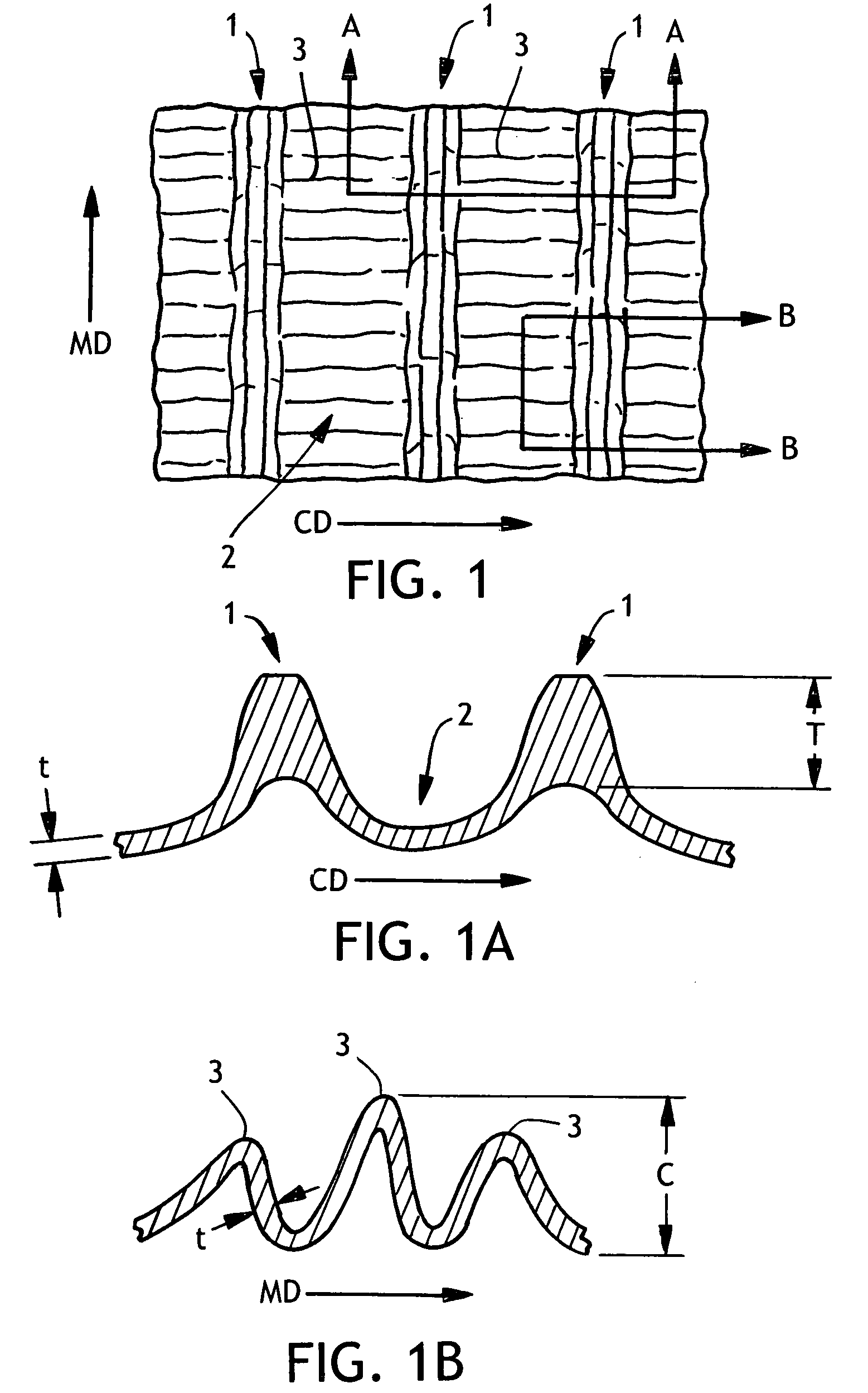
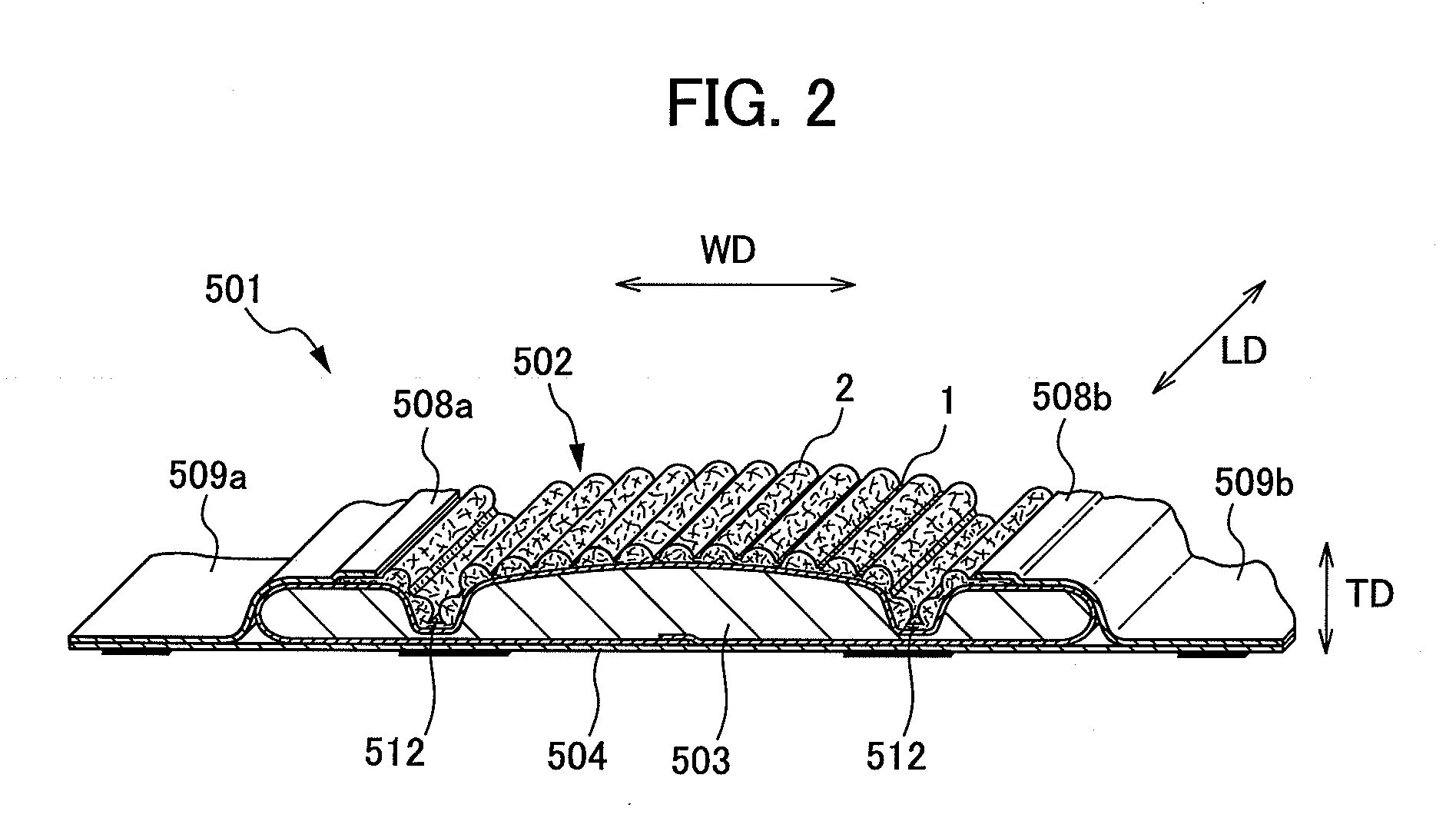
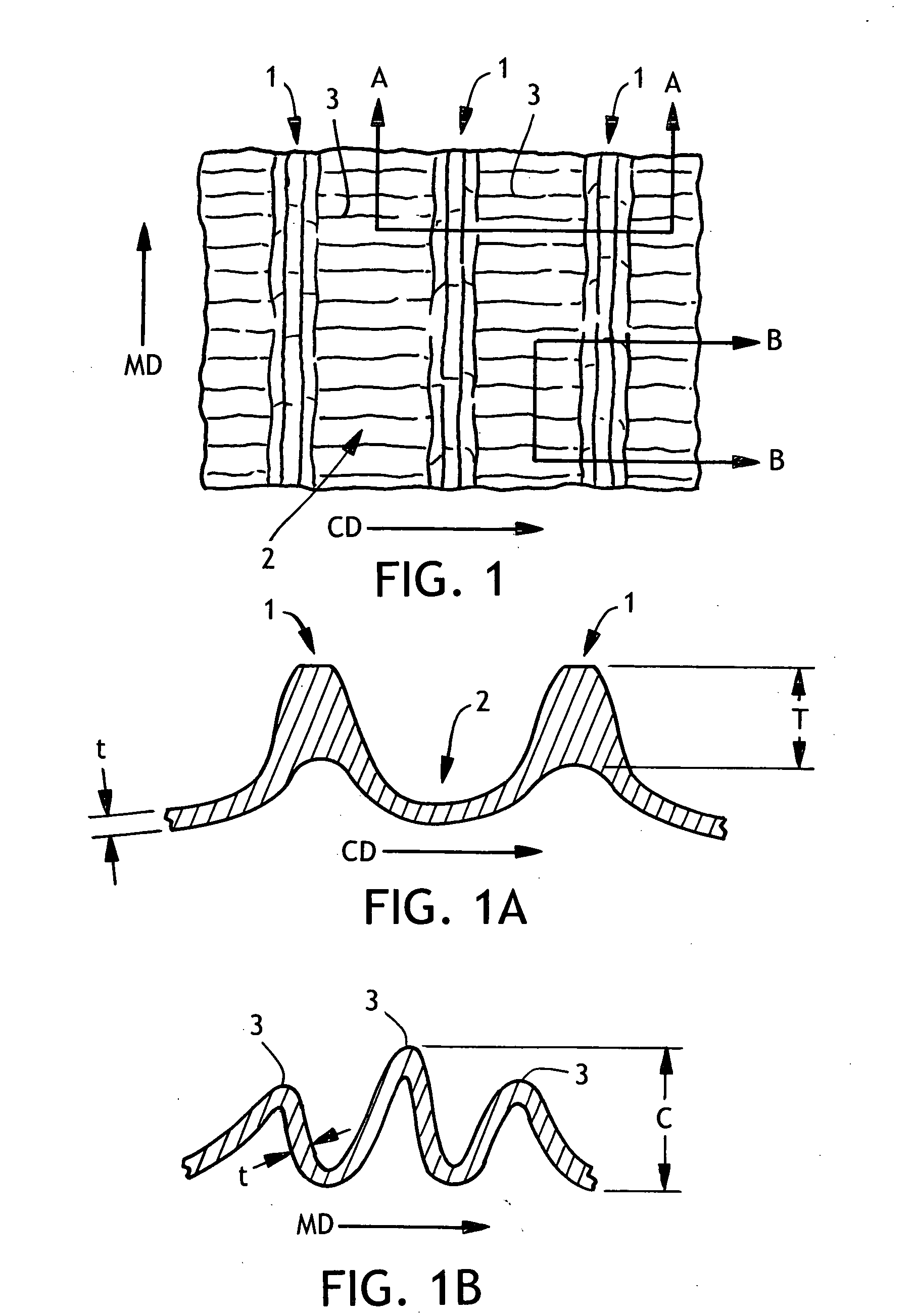
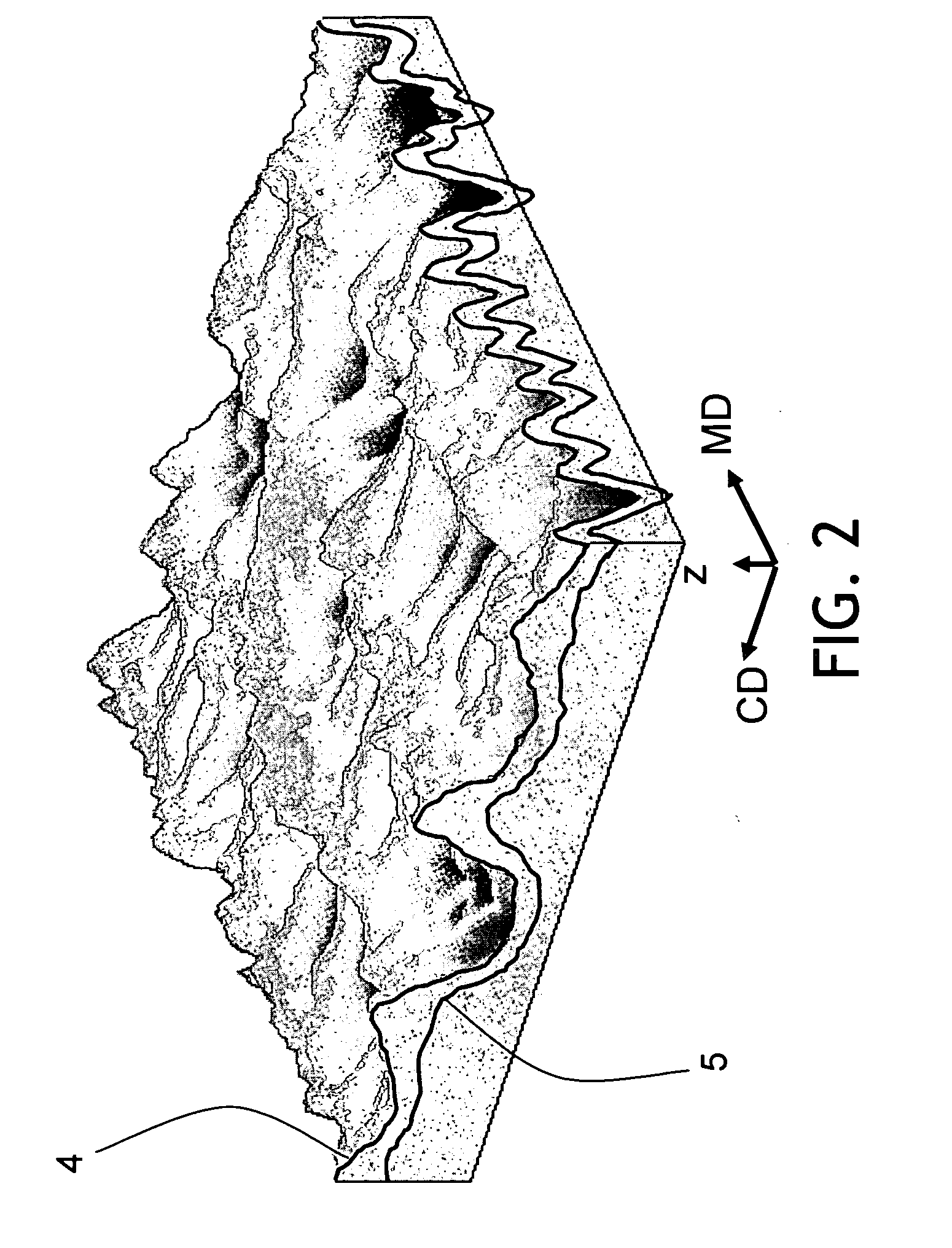
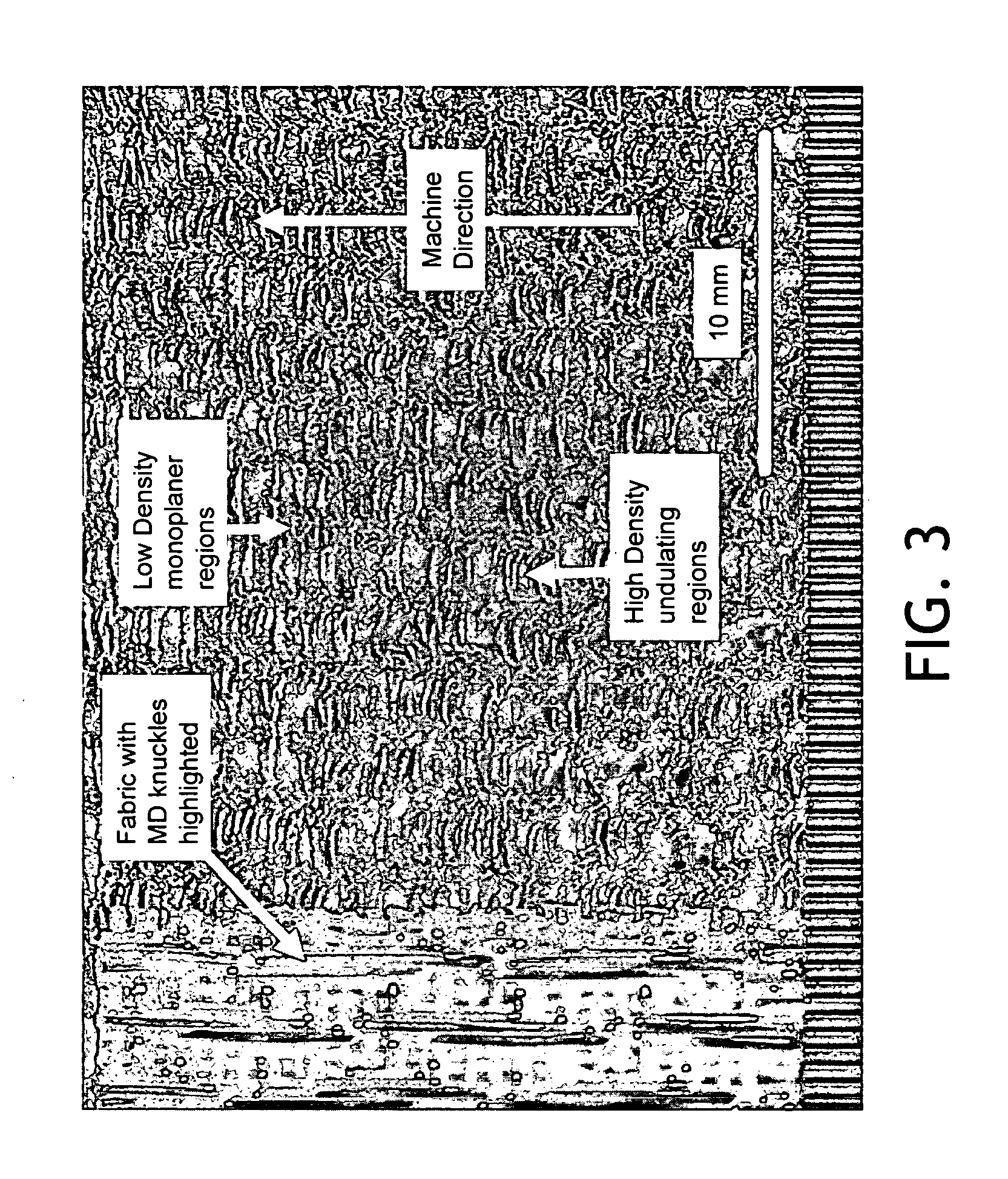
Wet-pressed creped tissue sheets exhibit continuous undulating valleys separated by continuous mono-planar macro-ridges running in the machine direction of the sheet, the macro-ridges being of a lower fiber density relative to the fiber density of the undulating valleys. The tissue structure can be created by pressing a densified tissue web against the surface of a Yankee dryer while the web is supported by a texturizing (molding) fabric having a web-supporting surface having highly topographic continuous or substantially continuous ridges and valleys and thereafter creping the web.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
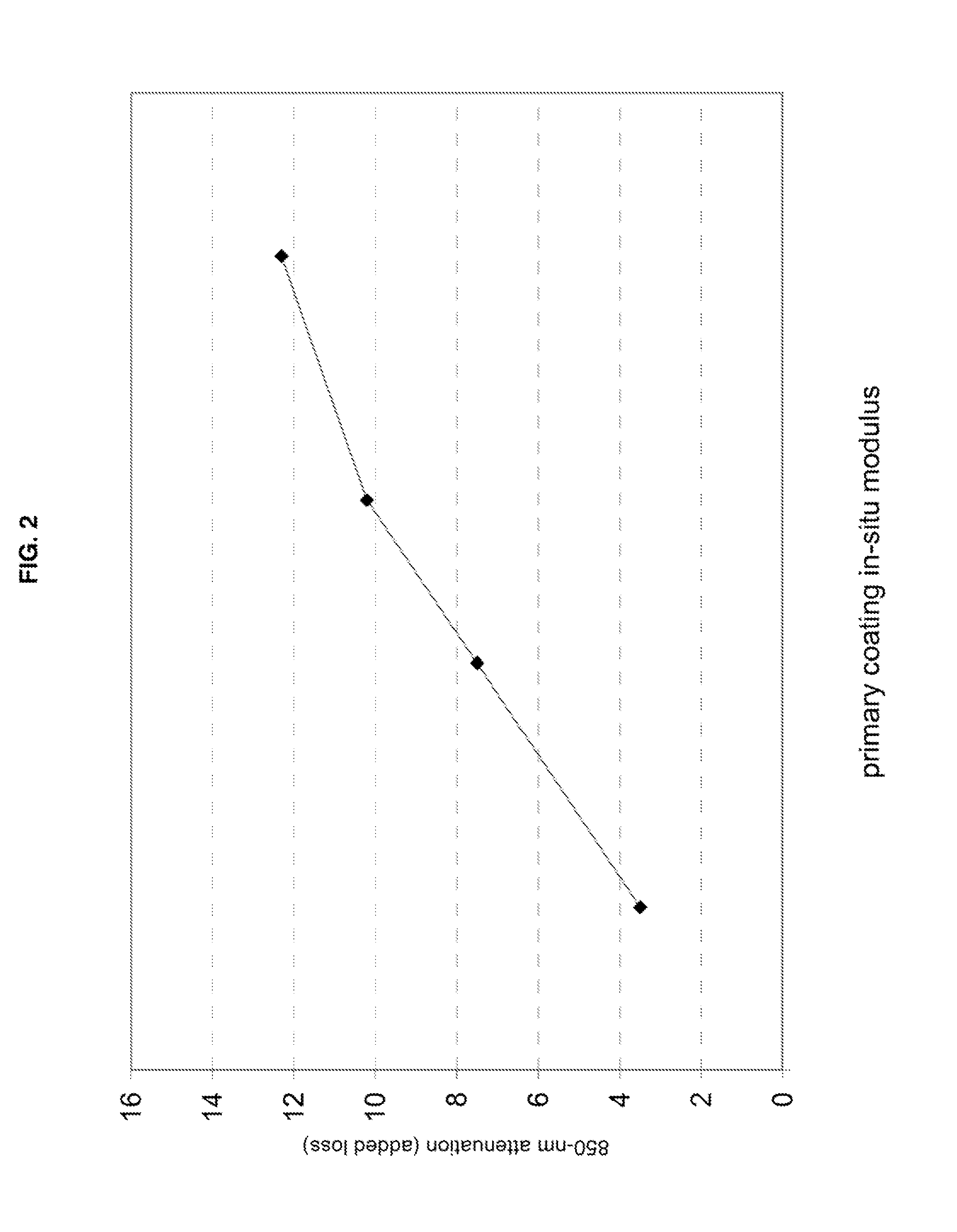
High-Fiber-Density Optical-Fiber Cable
ActiveUS20110069932A1Improve protectionGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingUltrasound attenuationGlass fiber
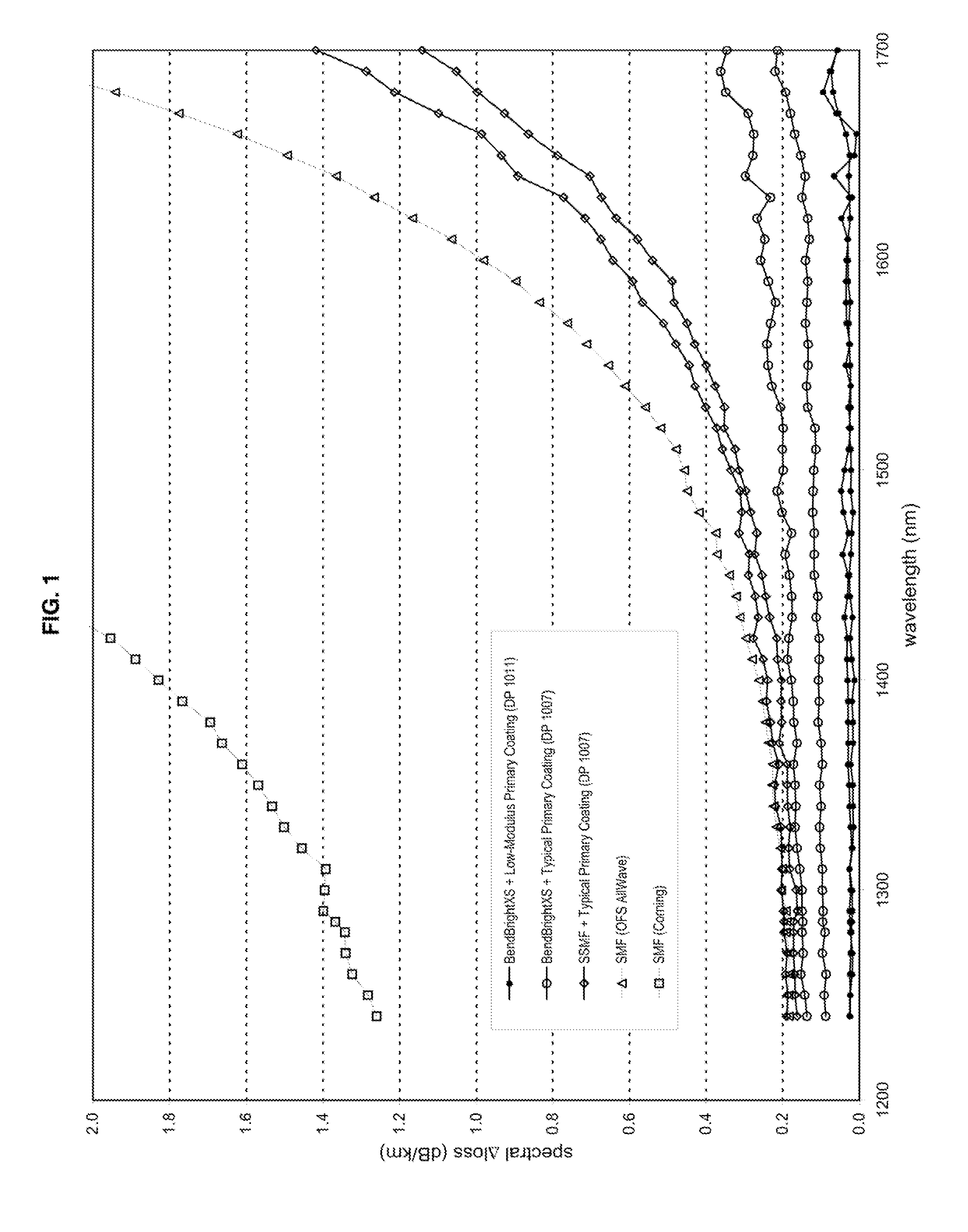
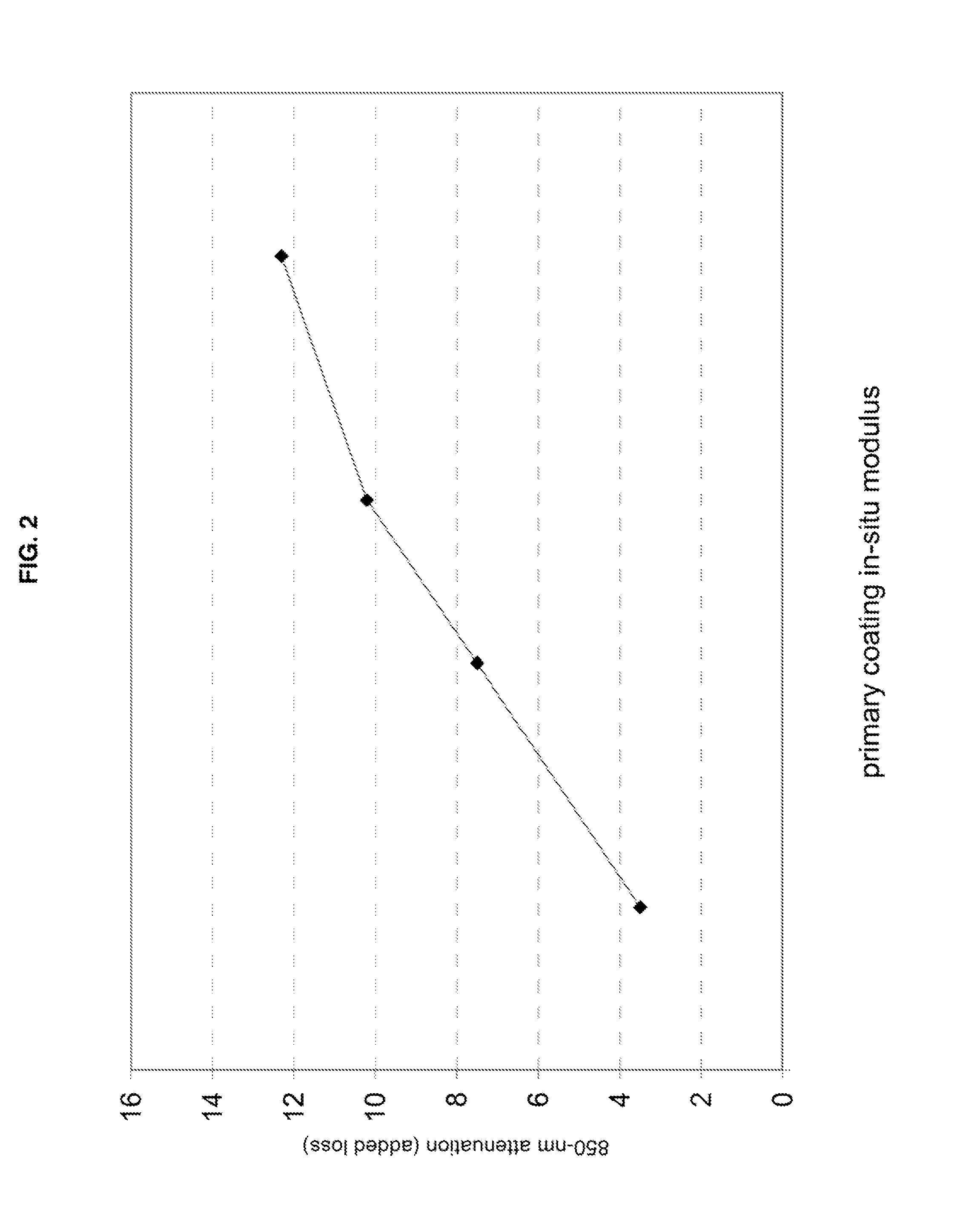
Disclosed is an improved optical fiber possessing a novel coating system. When combined with a bend-insensitive glass fiber, the novel coating system according to the present invention yields an optical fiber having exceptionally low losses.The coating system features (i) a softer primary coating with excellent low-temperature characteristics to protect against microbending in any environment and in the toughest physical situations and, optionally, (ii) a colored secondary coating possessing enhanced color strength and vividness. The secondary coating provides improved ribbon characteristics for structures that are robust, yet easily entered (i.e., separated and stripped).The optical fibers in accordance in the present invention may be incorporated into a reduced-diameter optical-fiber cable that possesses a high fiber count and a high cable fiber density. The high-fiber-density optical-fiber cable, which is suitable for deployments in ducts, is capable of achieving outstanding attenuation performance when subjected to temperature variations of between about −40° C. and 70° C.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
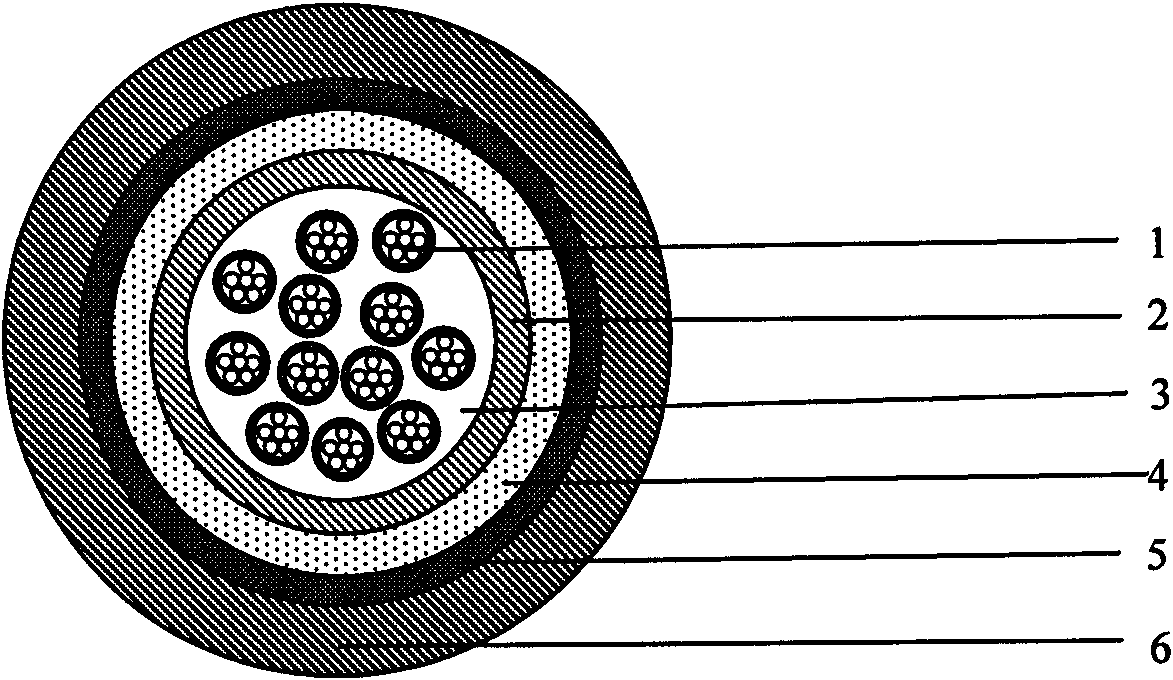
Optical-Fiber Cable Having High Fiber Count and High Fiber Density
ActiveUS20110091171A1Raise countHigh fiber densityFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringOptical fiber cable
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Three-dimensional nonwoven fabric with pore structure
InactiveUS20170014281A1Soft and comfortableGood compressibilityNon-woven fabricsBandagesHigh densityEngineering
A three-dimensional nonwoven fabric with a pore structure includes raised regions, recessed regions, and the pore structure. Fiber densities from the raised regions to the recessed regions are gradient. That is, the fiber density of the edges transiting from the raised regions to the recessed regions is higher than that of the tops of the raised regions. Pressure resistance performance of the high-density fiber regions keeps the three-dimensional nonwoven fabric significantly uneven, and quickens liquid permeation and reduces residues, and the three-dimensional nonwoven fabric has a high permeating speed and is dry and comfortable.
Owner:XIAMEN YANJAN NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
High-fiber-density optical fiber cable
InactiveUS7974507B2High cable fiber densityImprove the attenuation effectOptical fibre/cable installationFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringOptical fiber cable
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
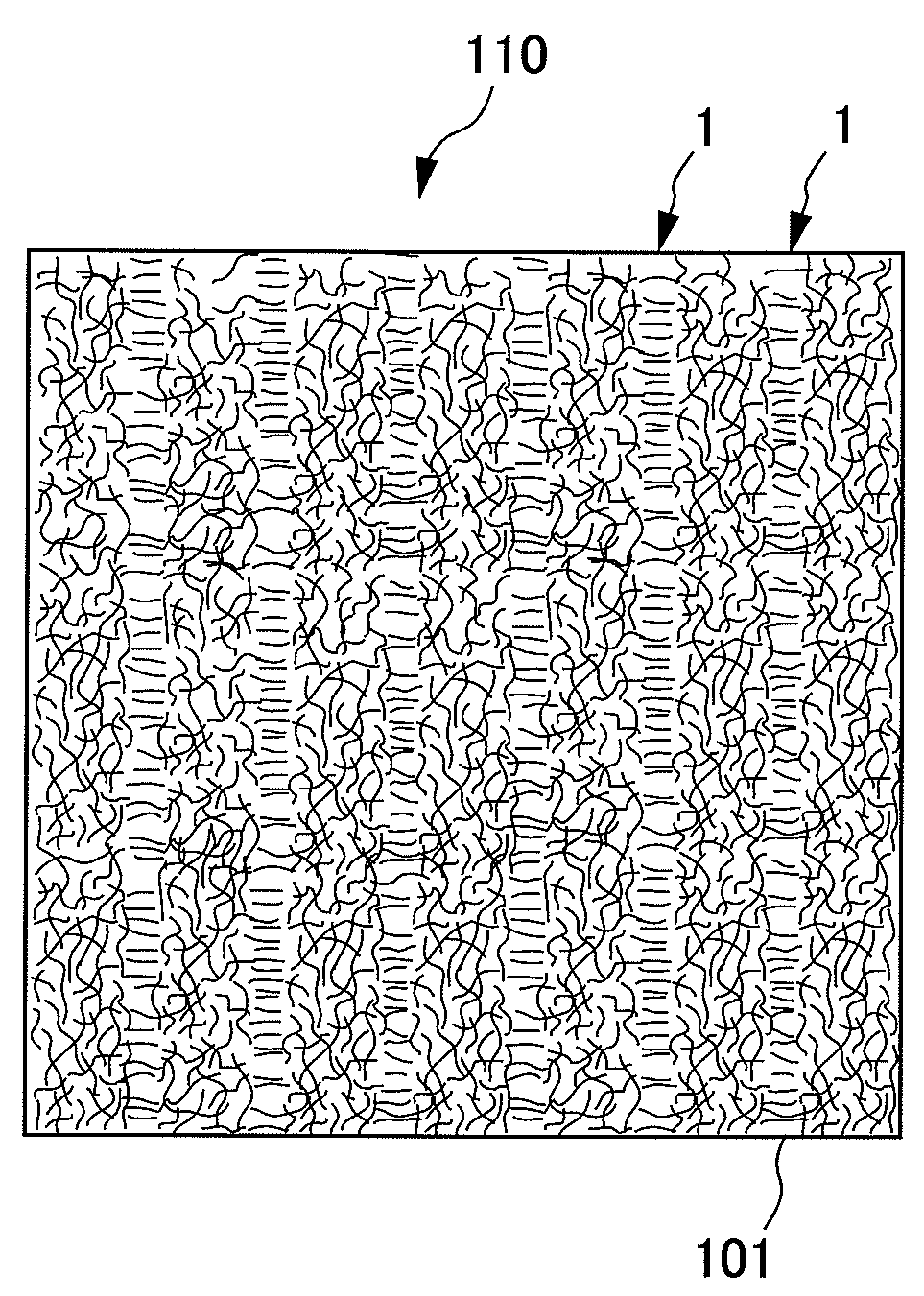
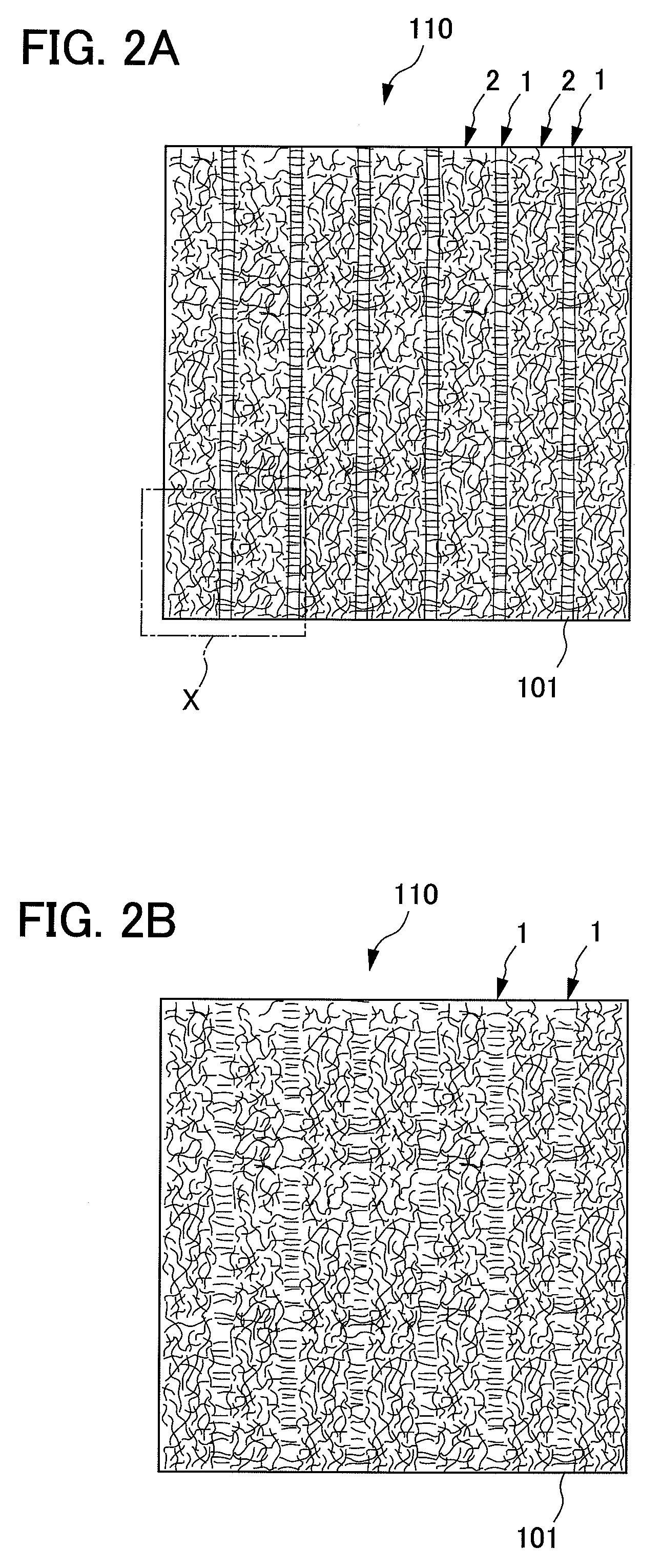
Nonwoven fabric
InactiveUS8143177B2Poor quick penetration characteristicHigh densitySynthetic resin layered productsAbsorbent padsEngineeringNonwoven fabric
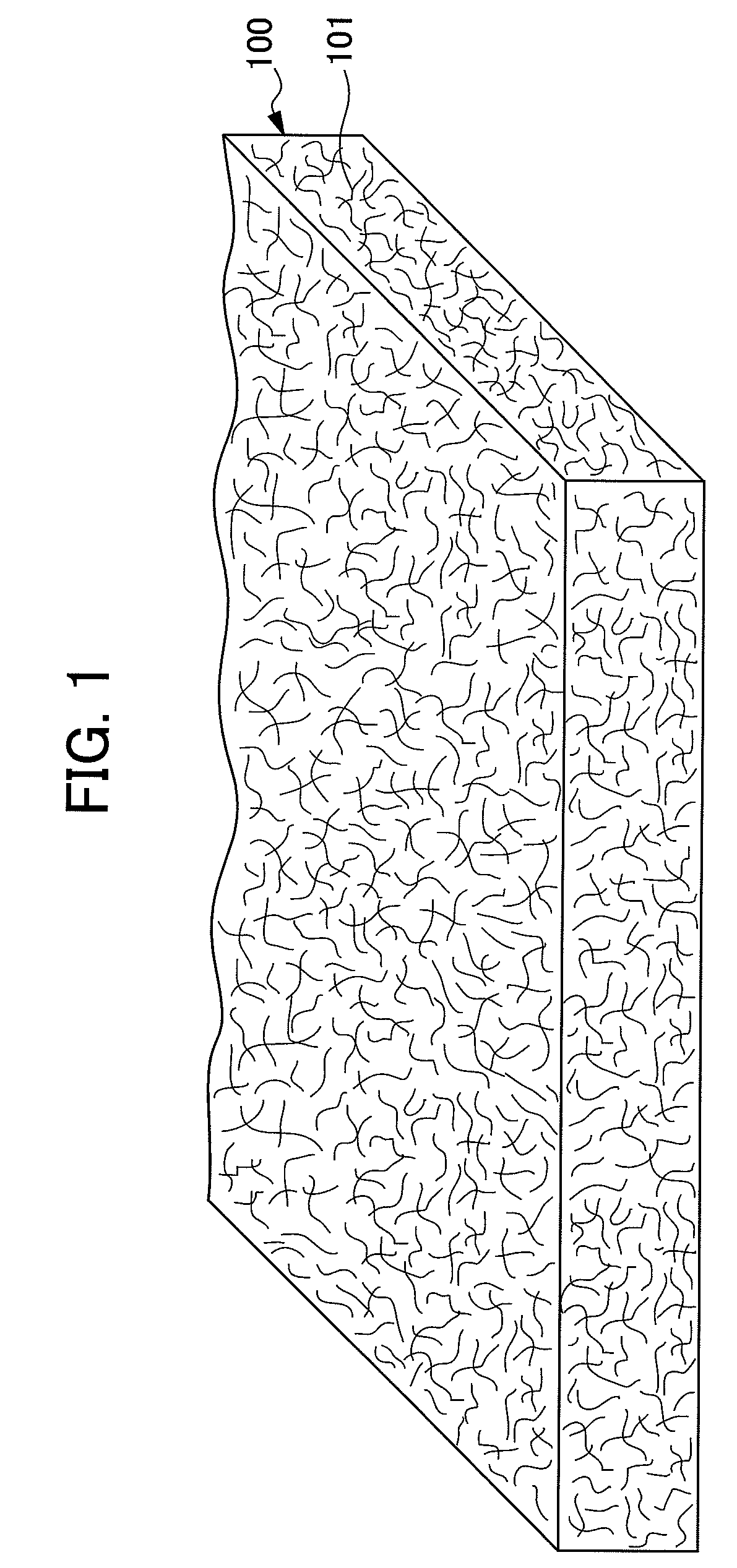
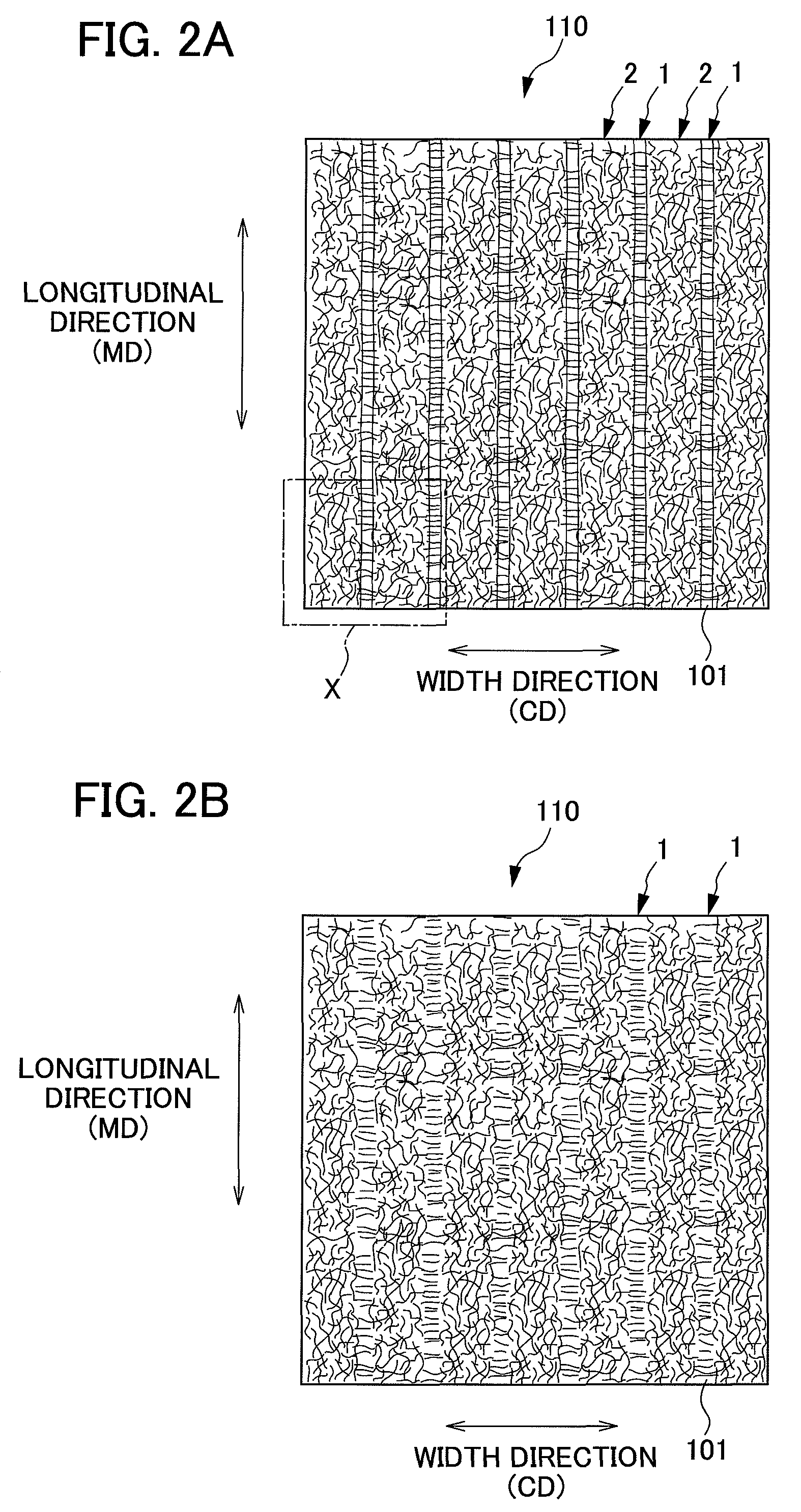
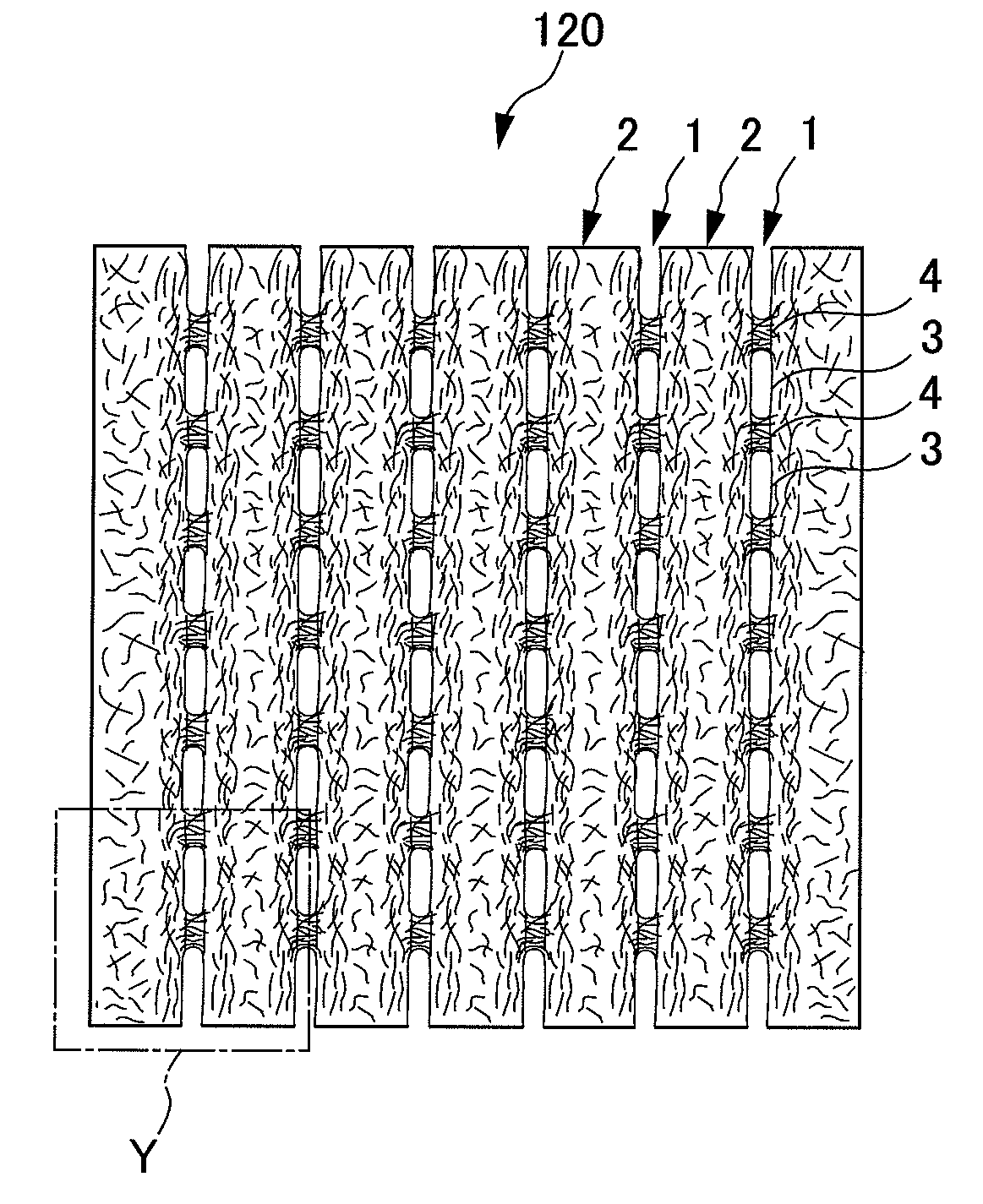
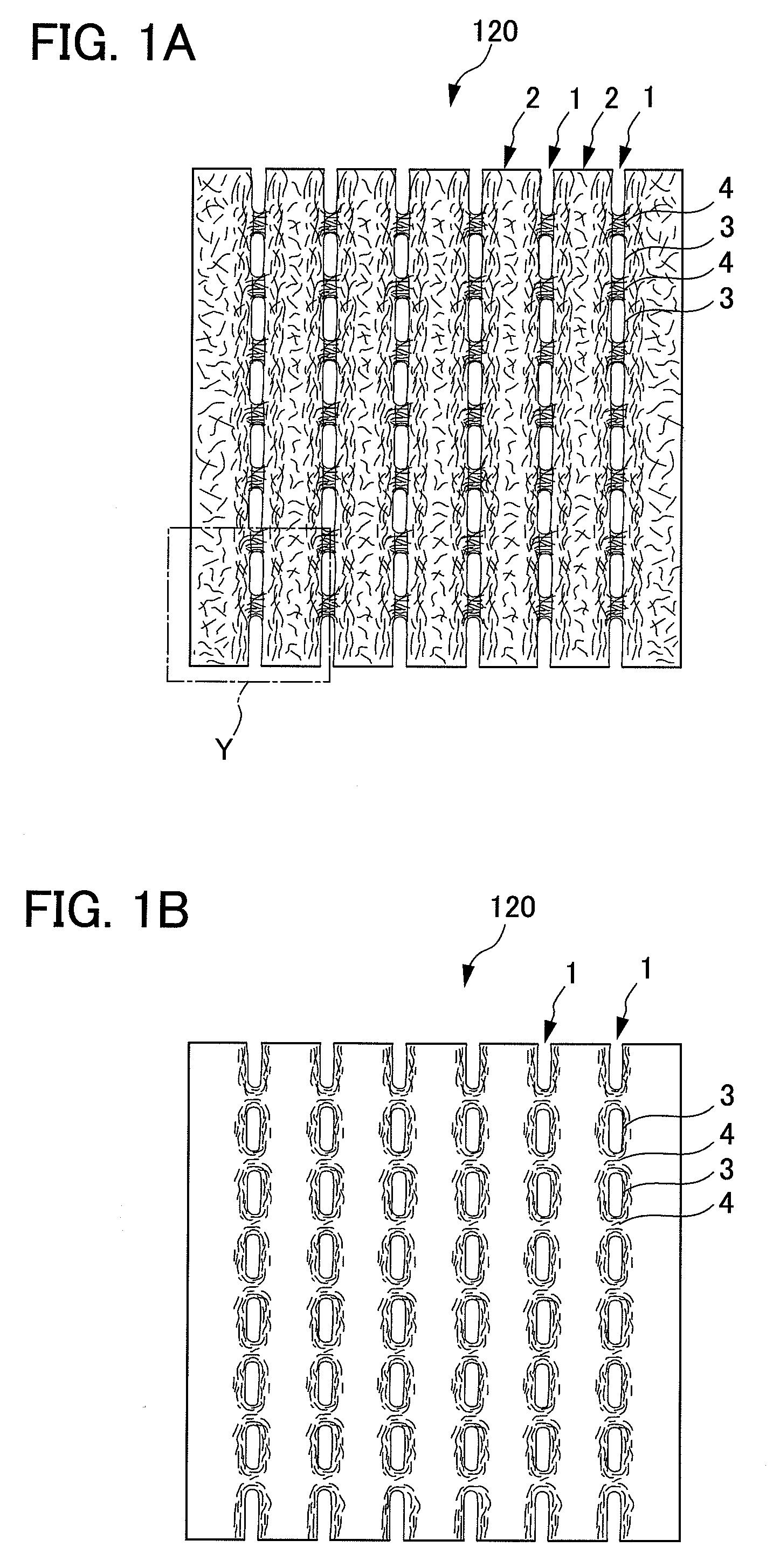
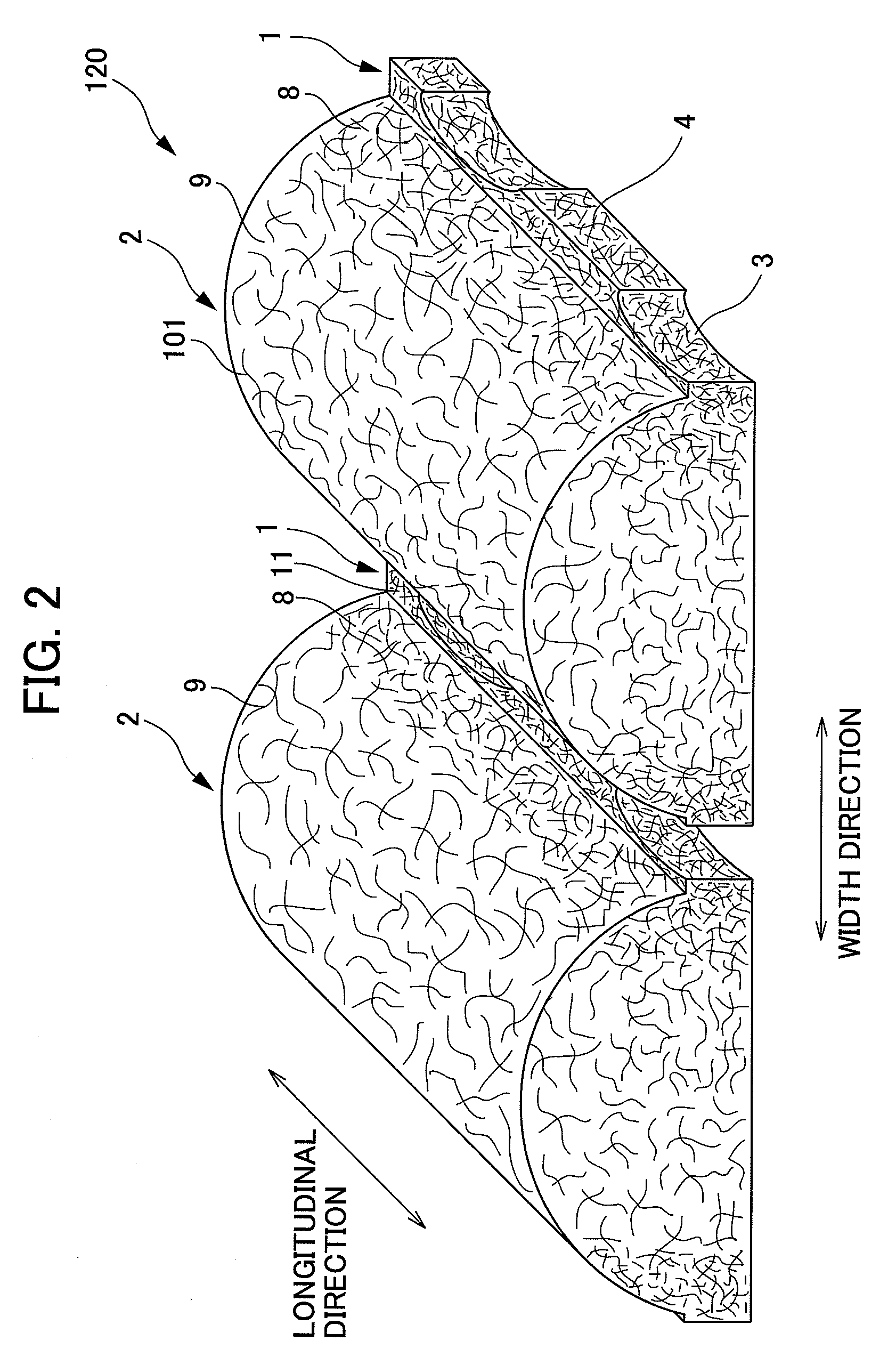
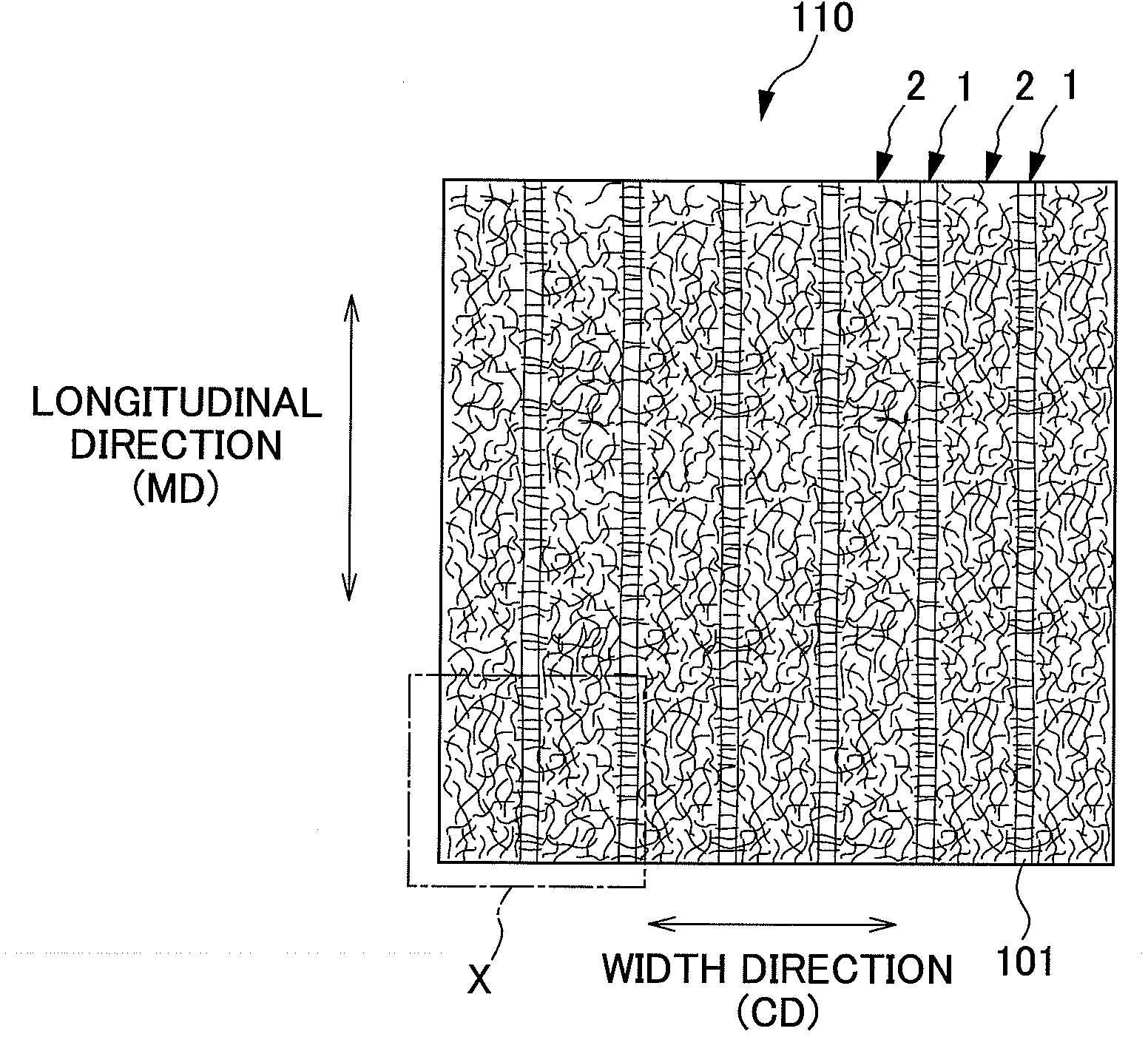
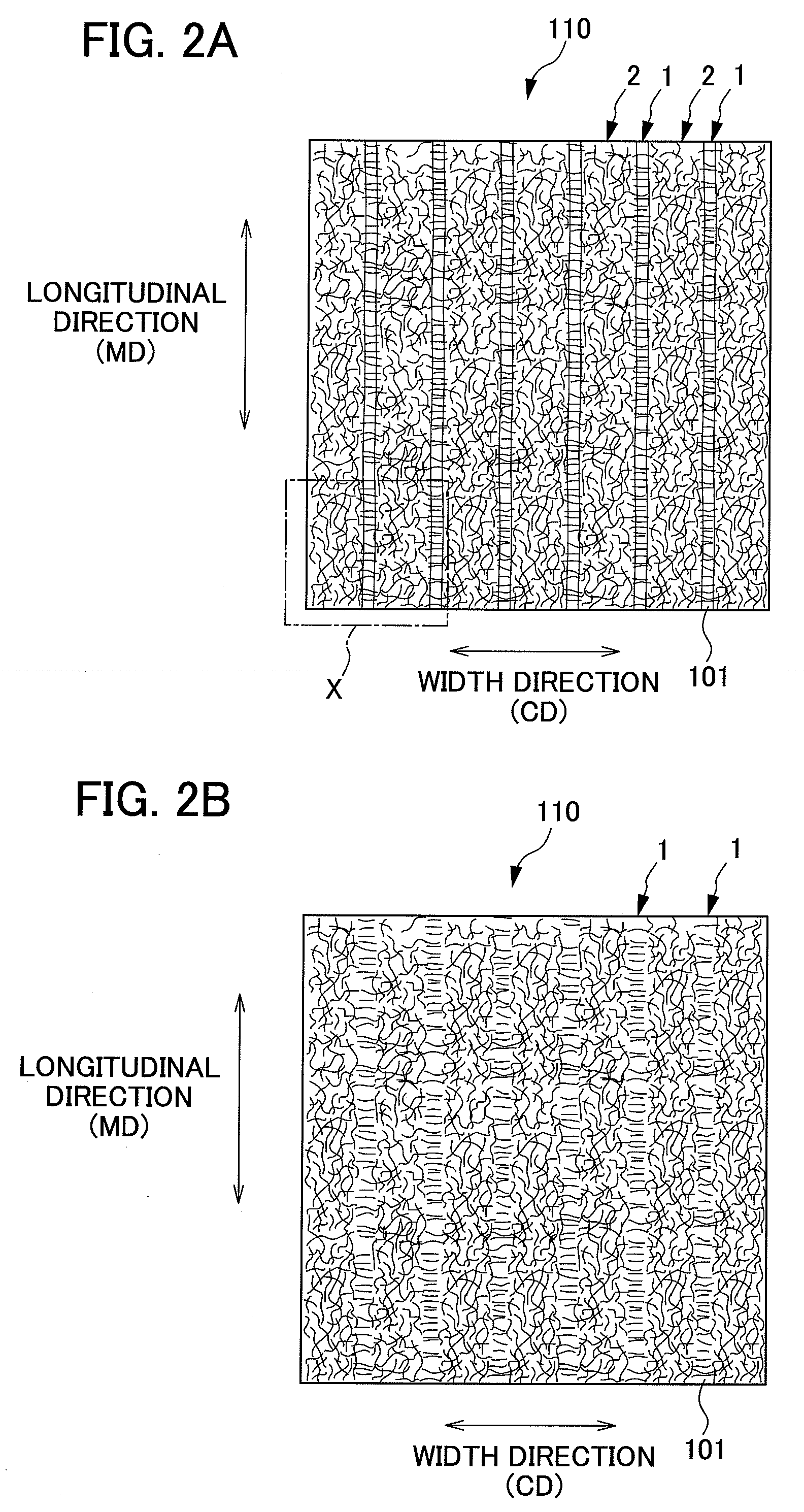
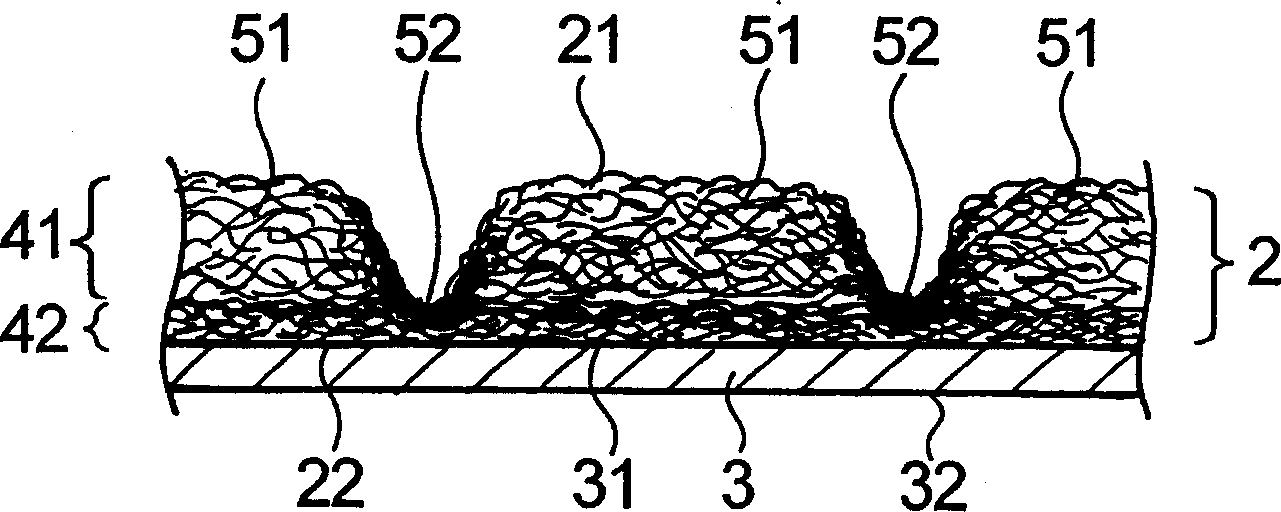
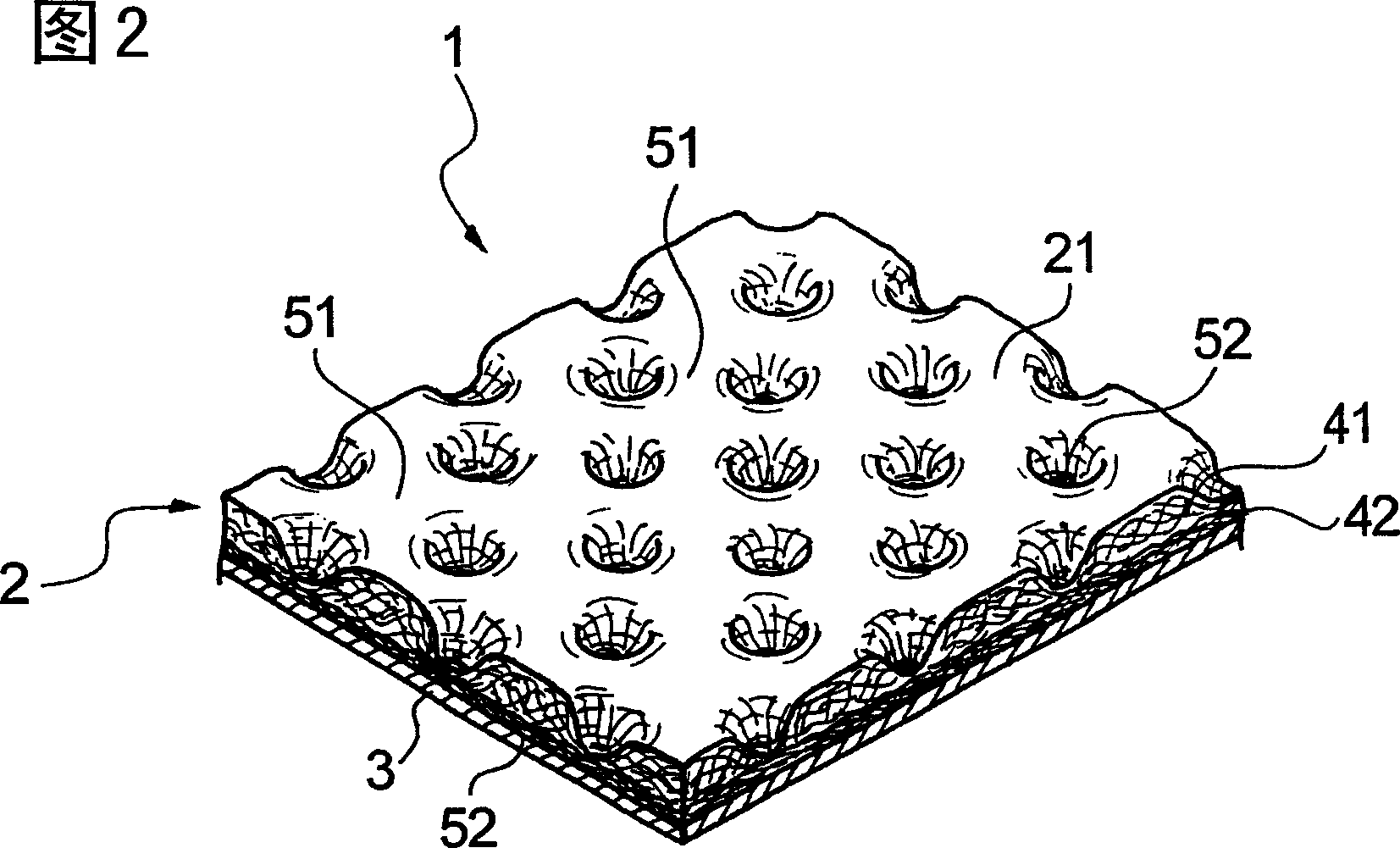
It is an objective of the present invention to provide a nonwoven fabric prepared so as to be able to rapidly transfer a predefined liquid. The nonwoven fabric is formed by jetting a fluid, which consists mainly of gaseous matter, to a fiber web 100 supported from beneath by a predefined breathable support member, from an upper surface side in order to move fibers in the fiber web 100. A number of groove portions 1 and a number of convex portions 2 are formed on a jetted area of the nonwoven fabric in the direction in which the area is extended, and the fiber density of the groove portions 1 is less than the fiber density of the convex portions 2.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Nonwoven fabric
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Absorbent article
ActiveUS8304600B2Not easy to collapseEasily passes liquidLayered productsBaby linensEngineeringNonwoven fabric
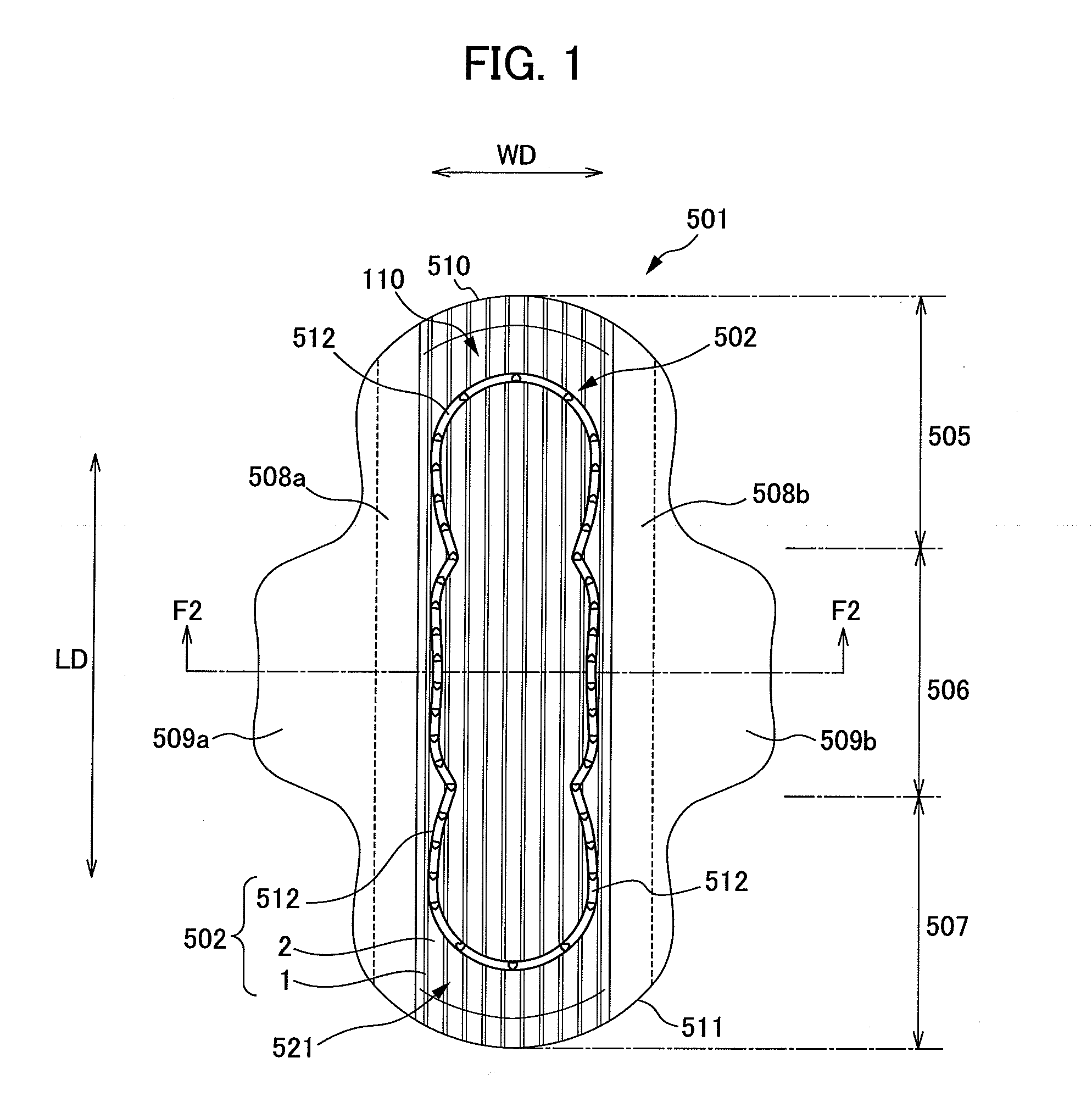
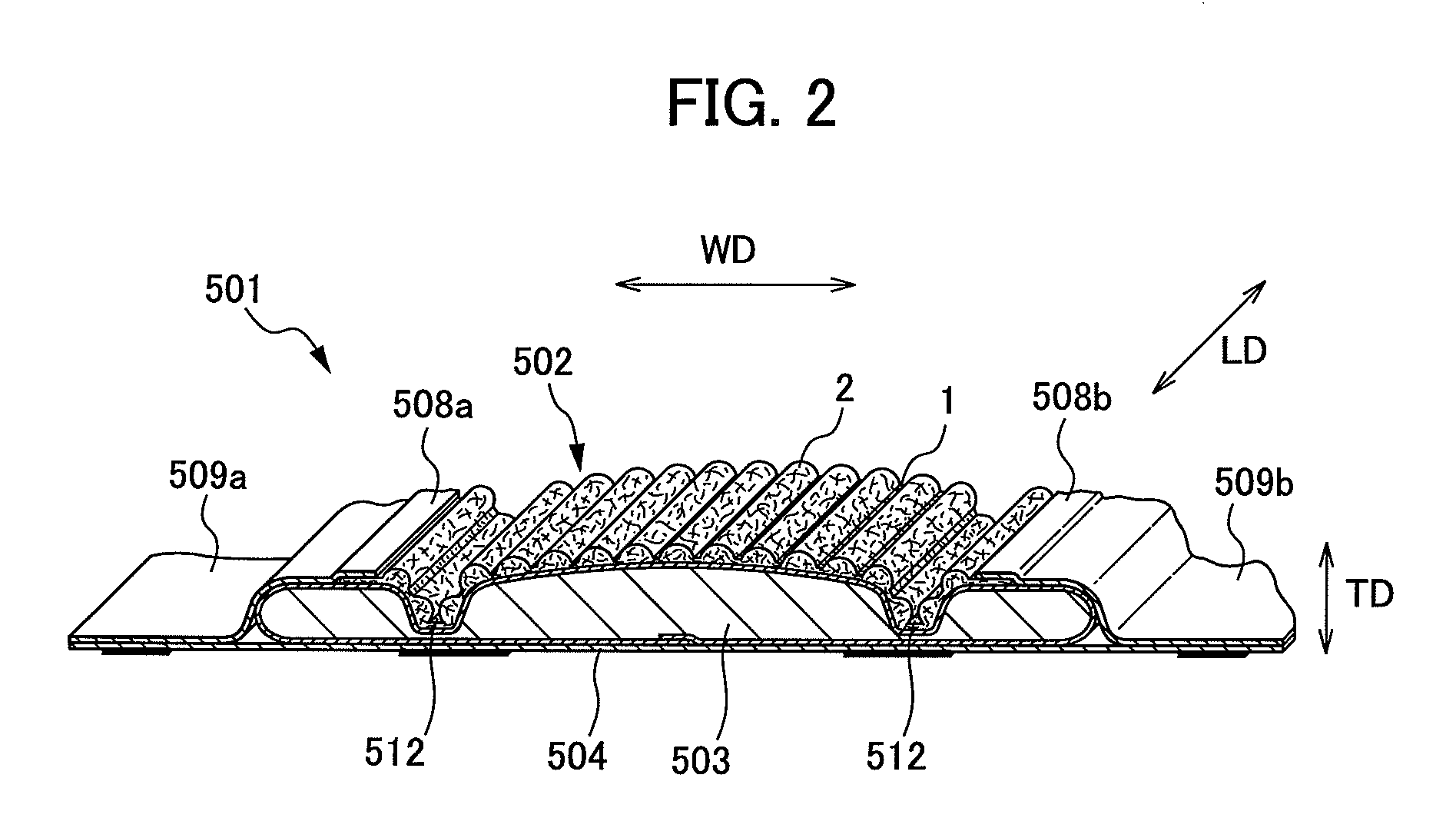
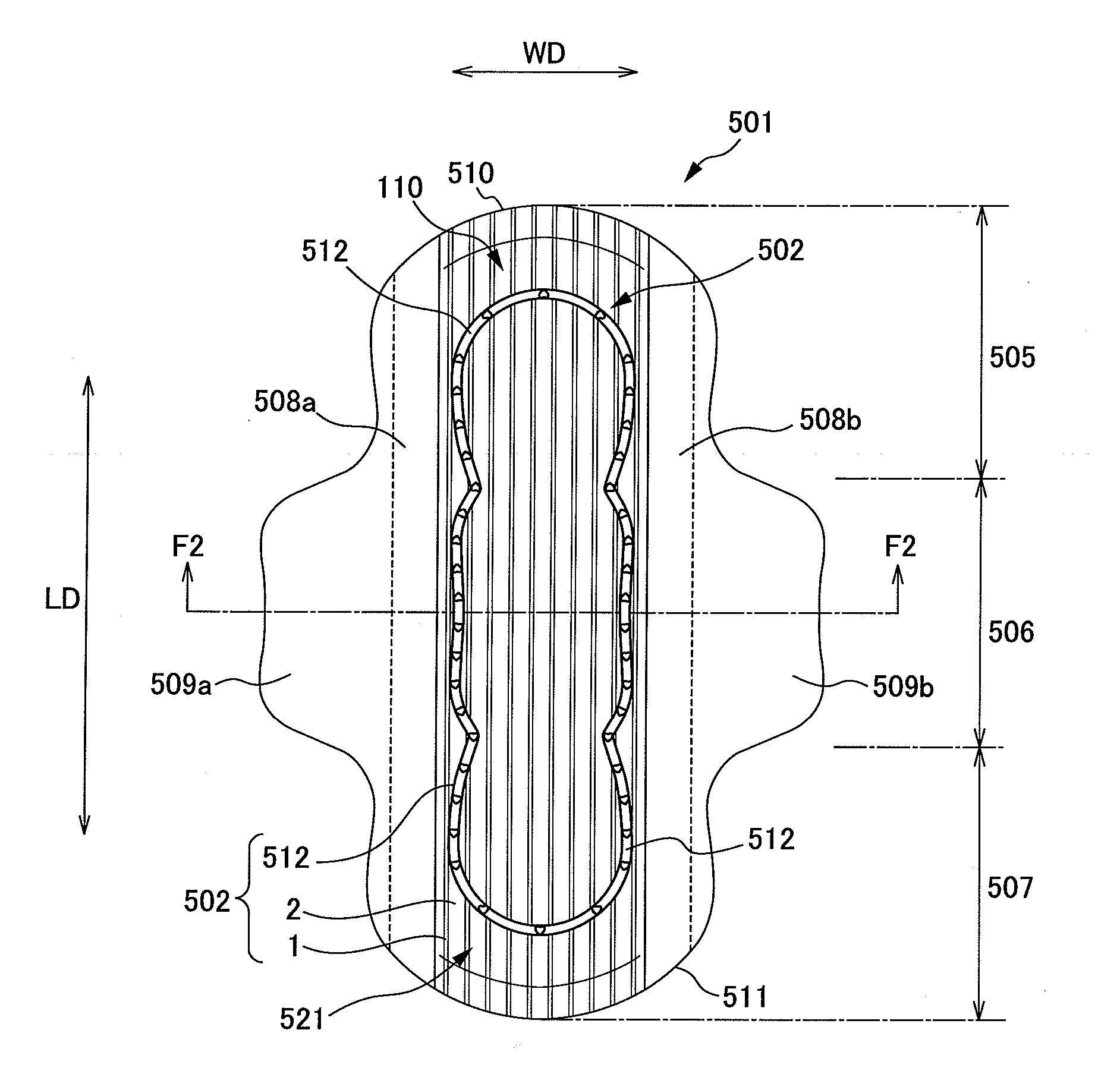
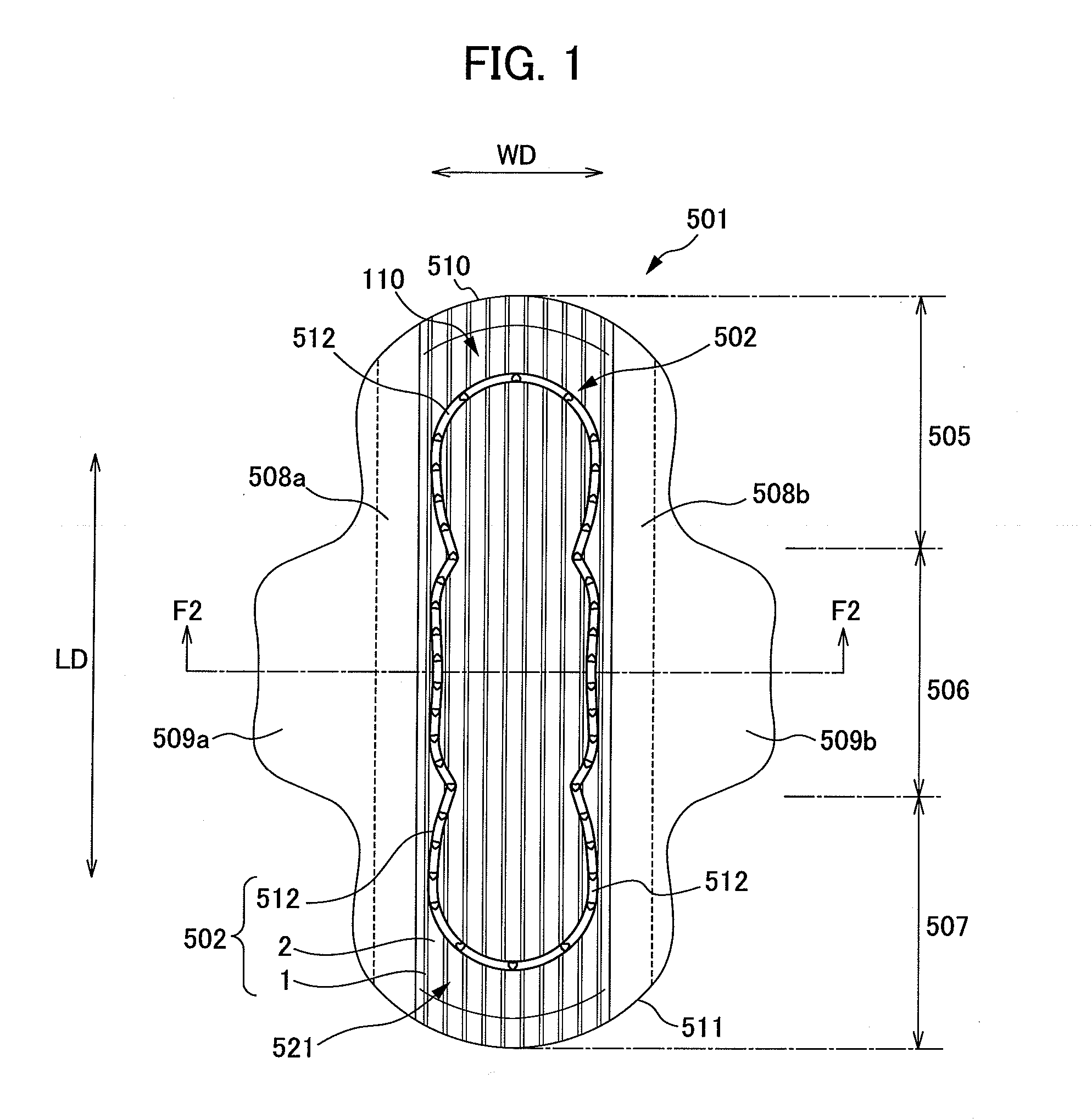
An absorbent article comprising nonwoven fabric having convex and concave surfaces, and that allows liquid such as excreta and the like to permeate quickly. A sanitary napkin has a plurality of raised ridge portions and groove portions in a top sheet member. The fiber density of the side edge portions of each of the plurality of raised ridge portions in the thickness direction of the nonwoven fabric is substantially uniform, and is higher than the average fiber density in the raised ridge portions. The fiber density of the central portion between both the side edge portions of each of the plurality of raised ridge portions is substantially uniform in the thickness direction of the nonwoven fabric, and is lower than the average fiber density in the raised ridge portions.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Absorbent article
ActiveUS20080045915A1Improve permeabilityNot easy to collapseLayered productsBaby linensNonwoven fabricMechanical engineering
An absorbent article comprising nonwoven fabric having convex and concave surfaces, and that allows liquid such as excreta and the like to permeate quickly. A sanitary napkin has a plurality of raised ridge portions and groove portions in a top sheet member. The fiber density of the side edge portions of each of the plurality of raised ridge portions in the thickness direction of the nonwoven fabric is substantially uniform, and is higher than the average fiber density in the raised ridge portions. The fiber density of the central portion between both the side edge portions of each of the plurality of raised ridge portions is substantially uniform in the thickness direction of the nonwoven fabric, and is lower than the average fiber density in the raised ridge portions.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Molded wet-pressed tissue
ActiveUS20080099169A1Lose weightIncrease speedNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperBiomedical engineeringPaper sheet
Wet-pressed creped tissue sheets exhibit continuous undulating valleys separated by continuous mono-planar macro-ridges running in the machine direction of the sheet, the macro-ridges being of a lower fiber density relative to the fiber density of the undulating valleys. The tissue structure can be created by pressing a densified tissue web against the surface of a Yankee dryer while the web is supported by a texturizing (molding) fabric having a web-supporting surface having highly topographic continuous or substantially continuous ridges and valleys and thereafter creping the web.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Nonwoven fabric
A nonwoven fabric adjusted so that the fiber densities of convex portions and recessed portions are not excessively high. A plurality of open portions is formed by blowing fluid mainly composed of gas from the top side of a fiber web onto the fiber web supported from the bottom side thereof by a supporting member, and moving fiber constituting the fiber web. The nonwoven fabric is formed with the plurality of open portions continuously formed at predetermined intervals along a predetermined direction and a plurality of joining portions formed between the open portions adjacent thereto in a predetermined direction.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Nonwoven fabric, nonwoven fabric manufacturing method, and nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus
The present invention provides a nonwoven fabric of which at least one of fiber orientation, fiber density, and basis weight is adjusted, and in which at least one of a predetermined groove portion, an opening, and a protrusion is formed, a manufacturing method for the nonwoven fabric, and a nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus. The nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus of the present invention manufactures a nonwoven fabric of which at least one of fiber orientation, fiber density, and basis weight is adjusted, or in which at least one of a predetermined groove portion, an opening, and a protrusion is formed by blowing fluid mainly containing gas onto a fiber web which is formed in a sheet shape, and which is in a state where at least a portion of the fibers constituting the fiber aggregate has a degree of freedom.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
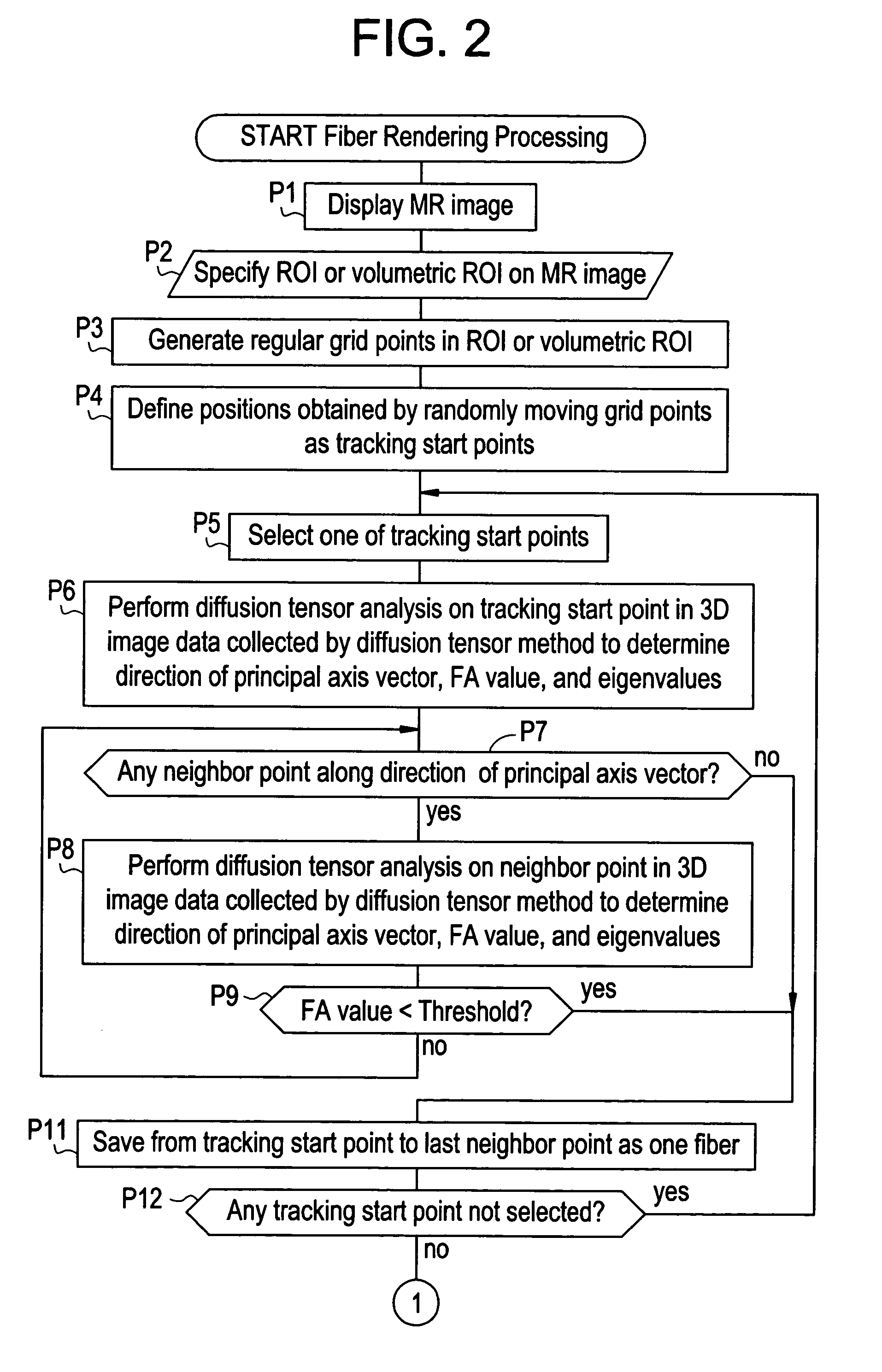
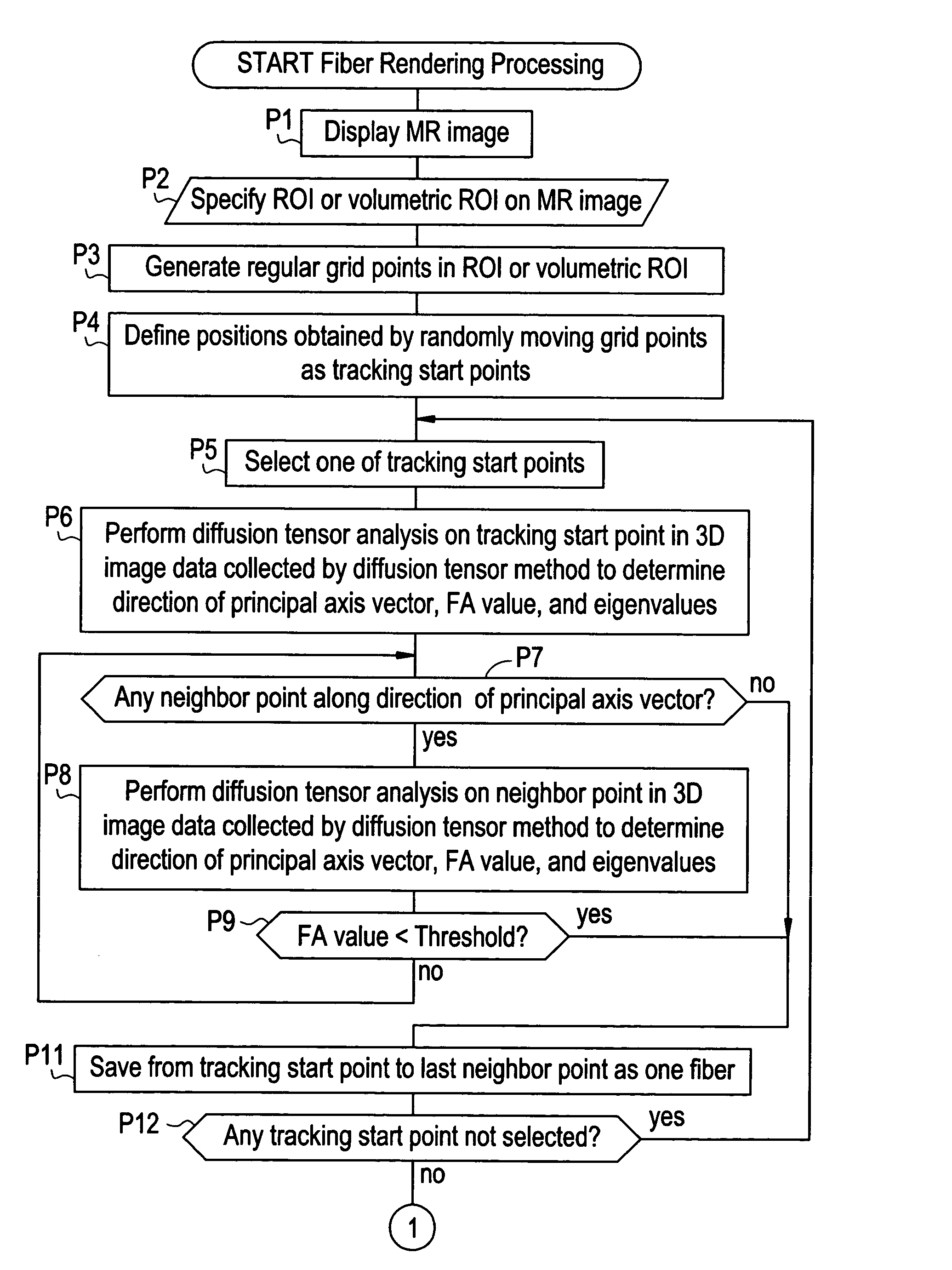
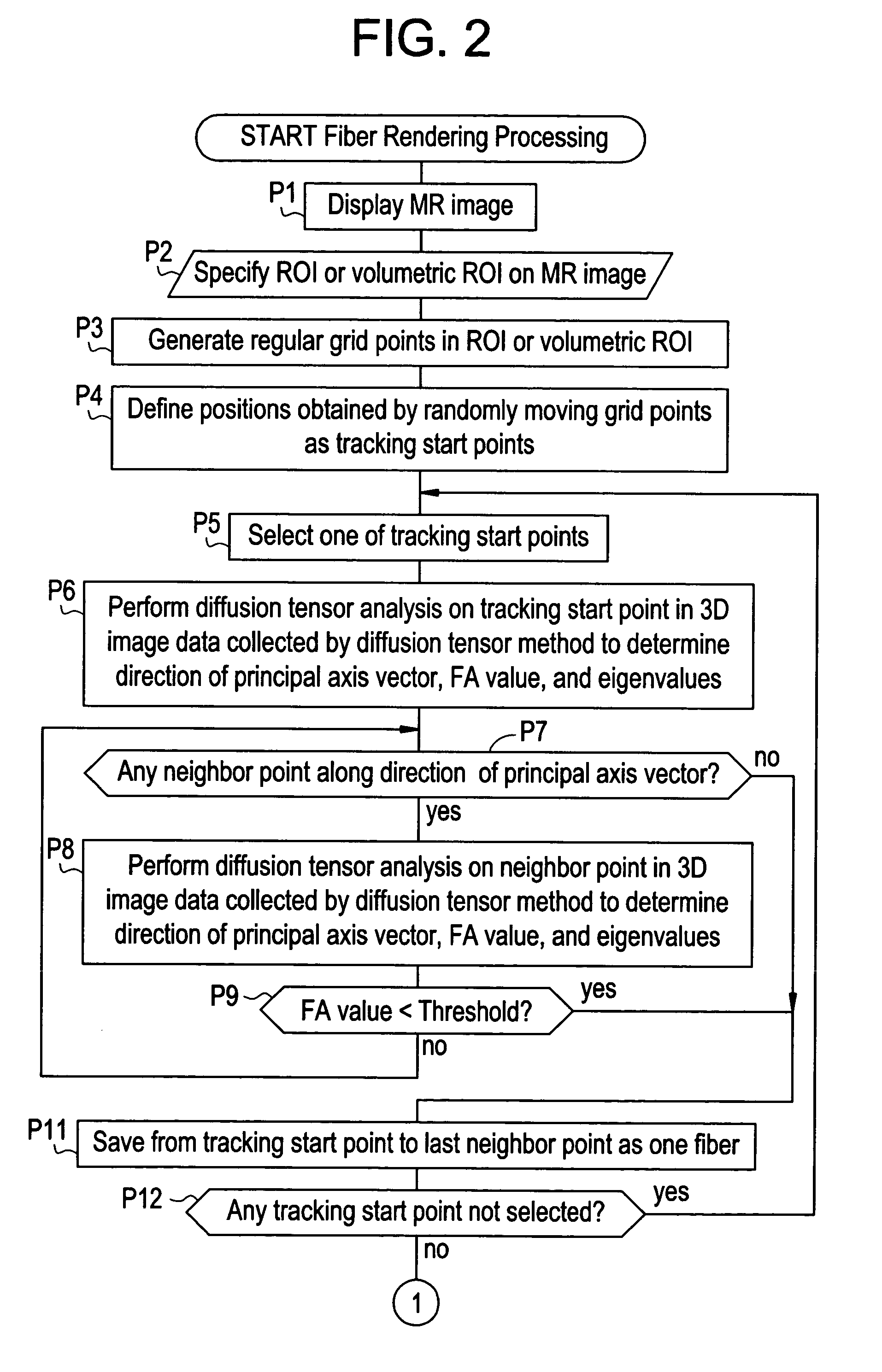
Fiber rendering apparatus
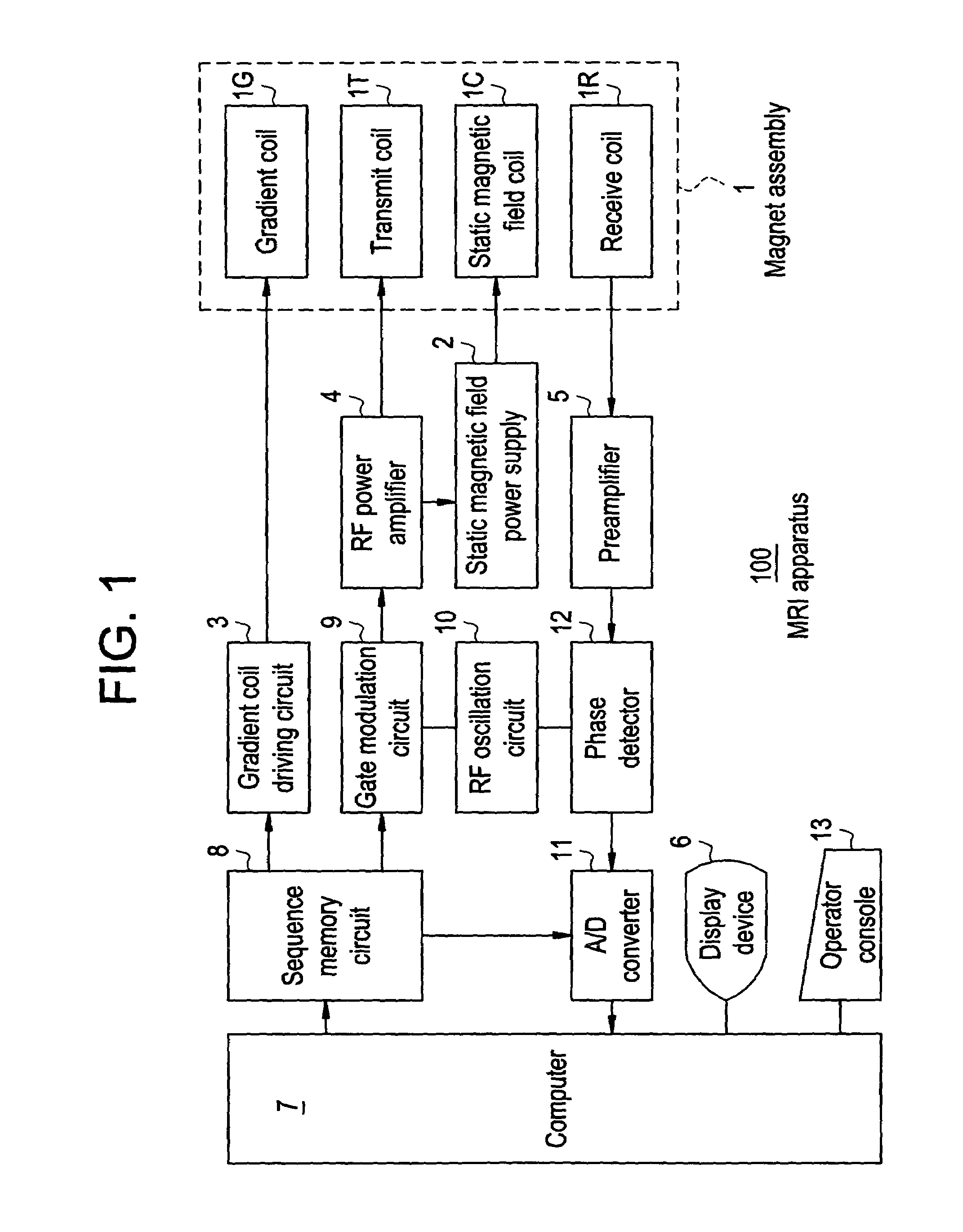
ActiveUS7505806B2Low transparencyHigh fiber tracking reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusionRegular grid
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
High-fiber-density optical-fiber cable
ActiveUS8467650B2Improve protectionGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoating systemEngineering
Disclosed is an improved optical fiber possessing a novel coating system. When combined with a bend-insensitive glass fiber, the novel coating system according to the present invention yields an optical fiber having exceptionally low losses. The coating system features (i) a softer primary coating with excellent low-temperature characteristics to protect against microbending in any environment and in the toughest physical situations and, optionally, (ii) a colored secondary coating possessing enhanced color strength and vividness. The secondary coating provides improved ribbon characteristics for structures that are robust, yet easily entered (i.e., separated and stripped). The optical fibers in accordance in the present invention may be incorporated into a reduced-diameter optical-fiber cable that possesses a high fiber count and a high cable fiber density. The high-fiber-density optical-fiber cable, which is suitable for deployments in ducts, is capable of achieving outstanding attenuation performance when subjected to temperature variations of between about −40° C. and 70° C.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Topsheet for absorbent article
InactiveUS7569264B2Sufficient absorbing performanceGood flexibilitySynthetic resin layered productsSanitary towelsMedicineSkin irritation
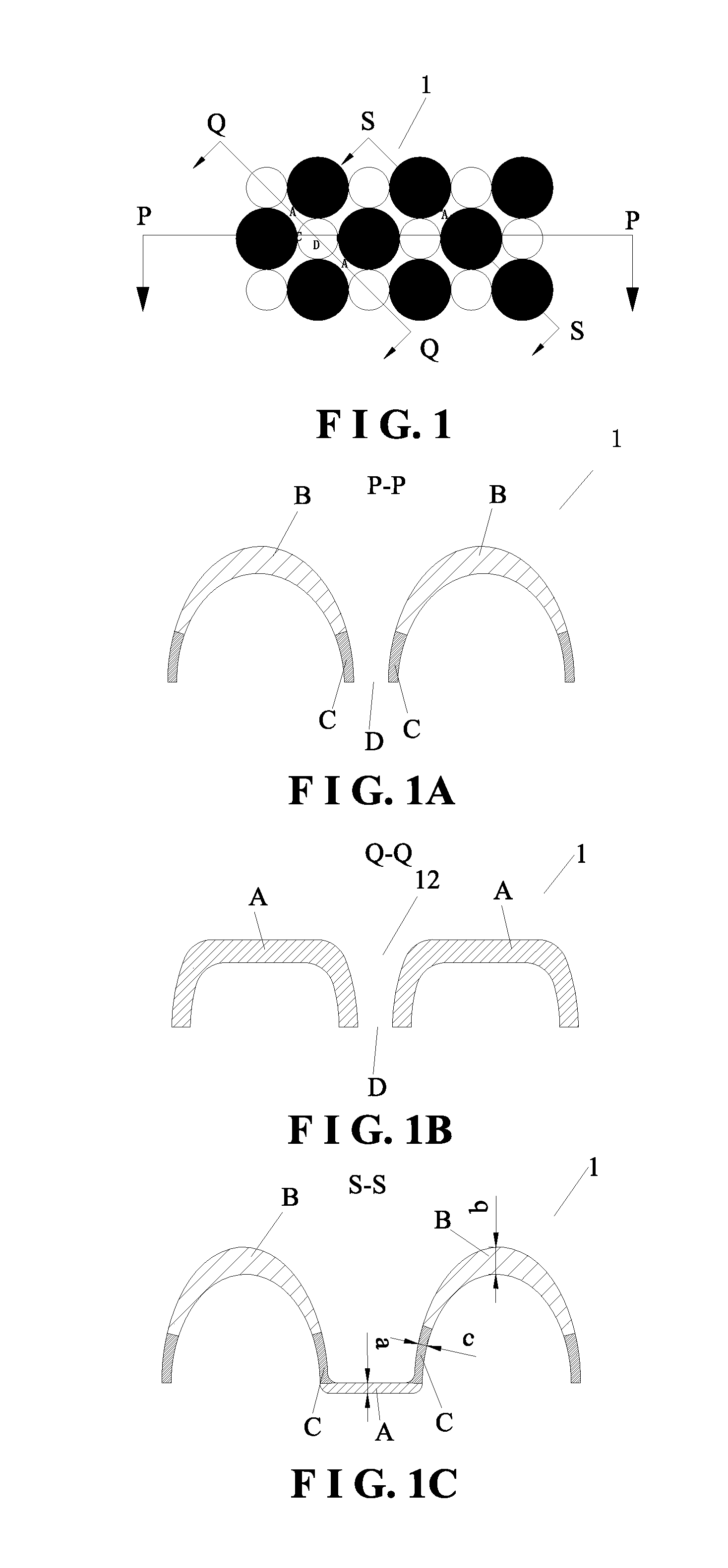
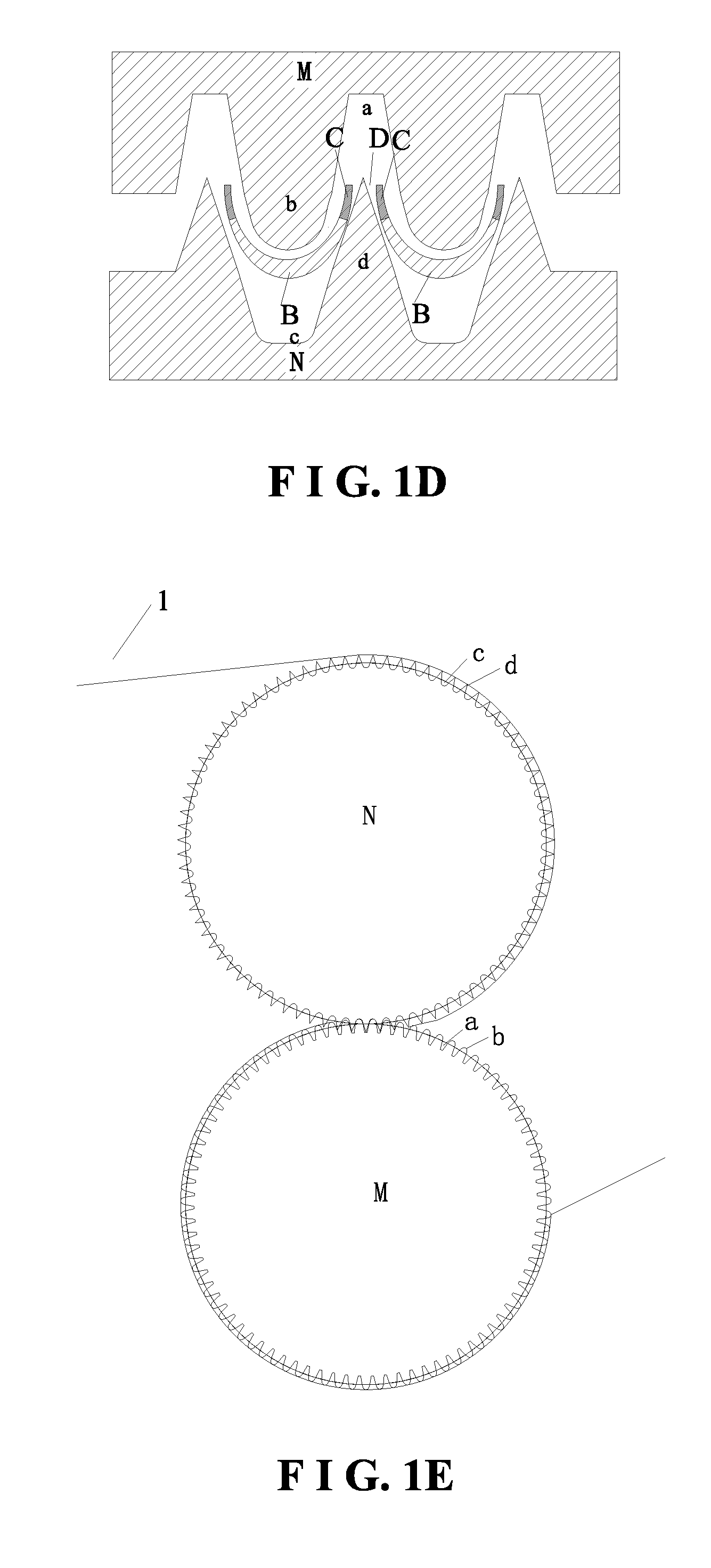
A topsheet for absorbent articles having absorbing performance for smoothly transferring liquid body waste, e.g., menstrual blood or urine, to an underlying absorbent member and surface characteristics such that the surface thereof in contact with wearer's skin is soft enough not to cause skin irritation. The topsheet 1 comprises a first layer 11 disposed on the side of a wearer and a second layer 12 disposed on the side of an absorbent member, the first layer and the second layer being partly joined together, and having protrusions and depressions on the side of a wearer, wherein the first and second layers each comprise a fiber aggregate, the first layer has fusion-bonded fiber intersections, the first layer has an apparent thickness (t1) of 0.1 to 5 mm, the second layer has an apparent thickness (t2) of 0.2 to 3 mm, the apparent thickness ratio of the first layer to the second layer (t1 / t2) is 0.5 to 8, the first layer has a fiber density (d1) of 0.001 to 0.05 g / cm3, the second layer has a fiber density (d2) of 0.03 to 0.2 g / cm3, and the fiber density (d2) of the second layer is higher than that (d1) of the first layer.
Owner:KAO CORP
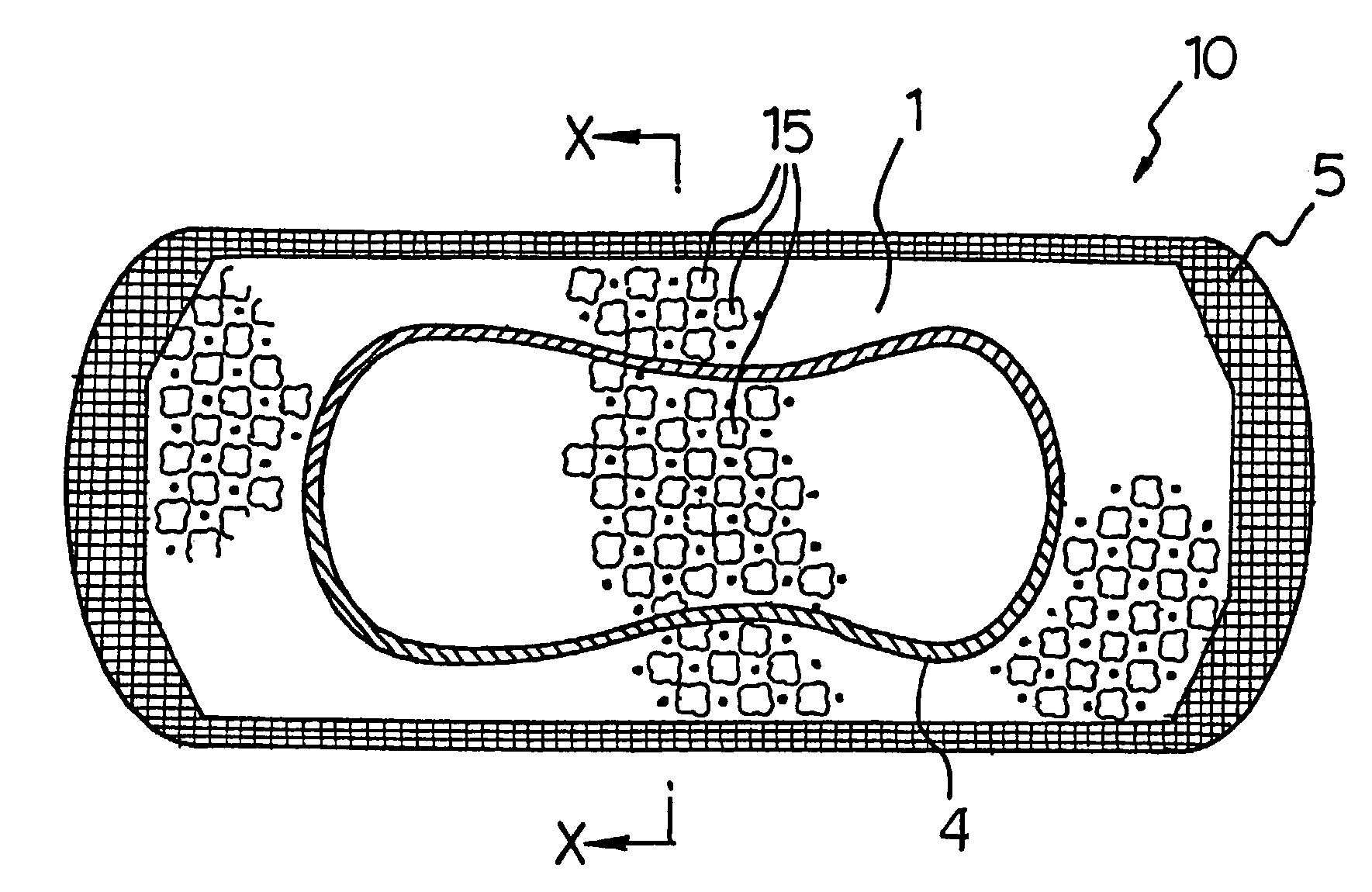
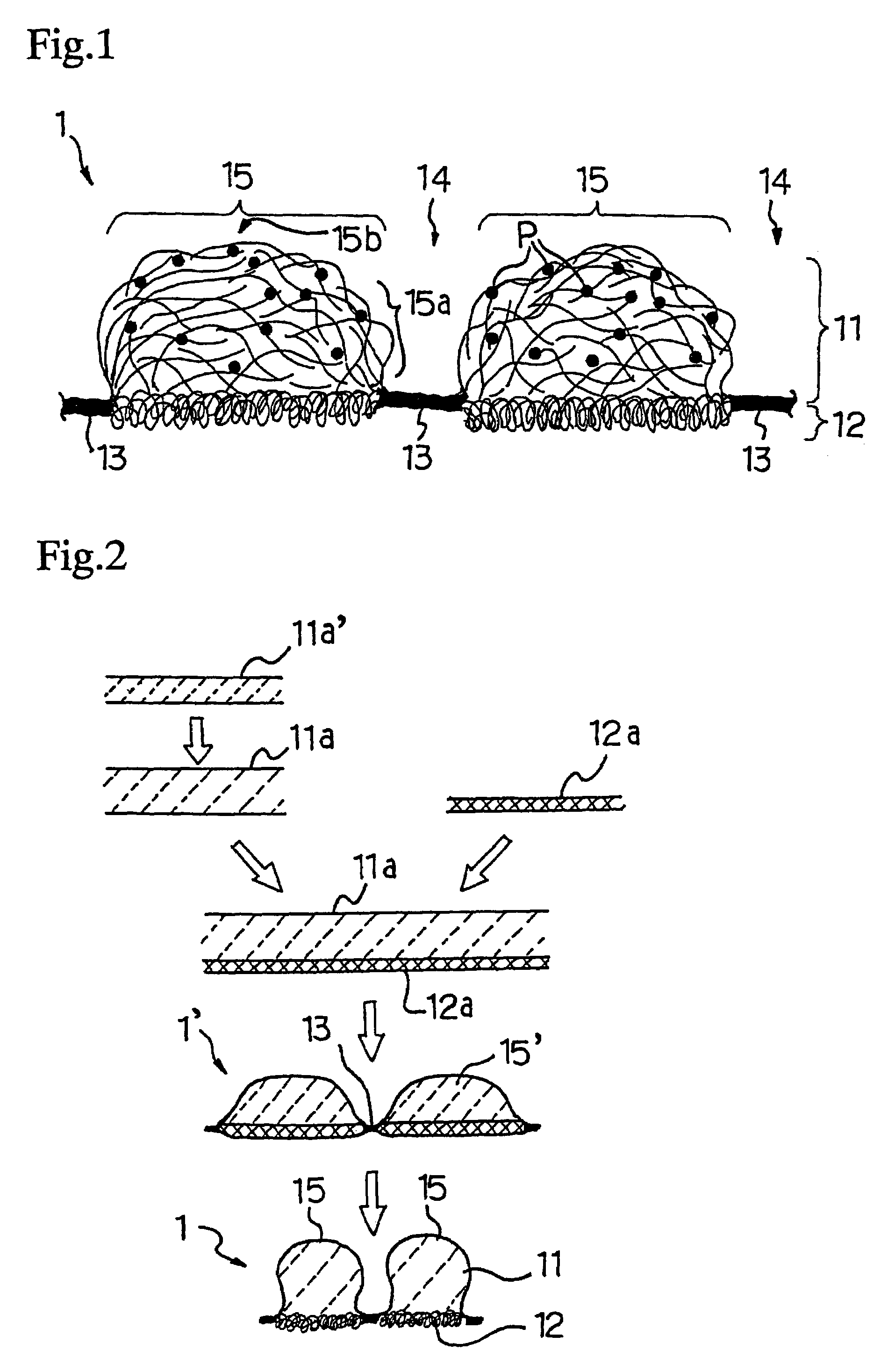
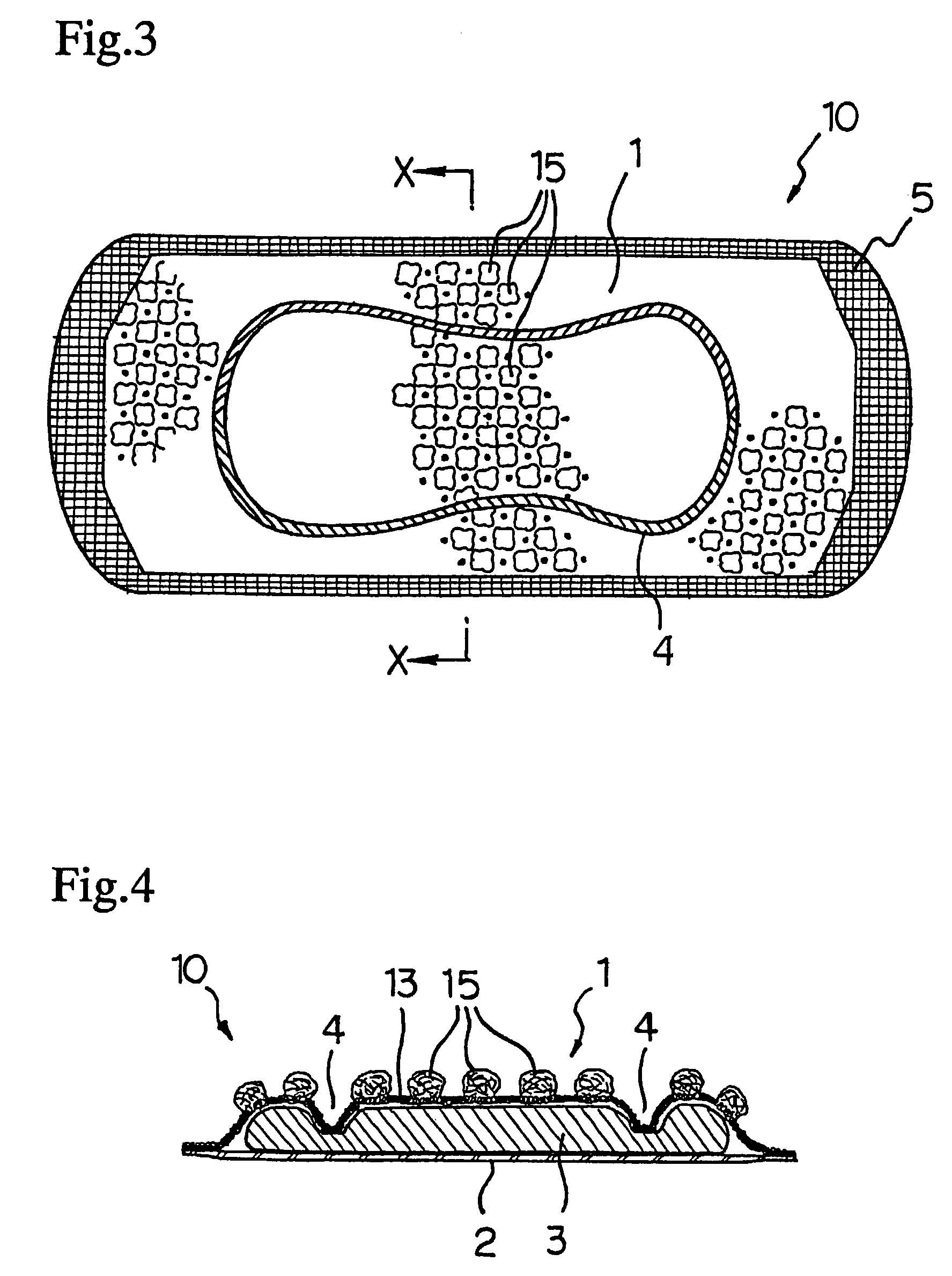
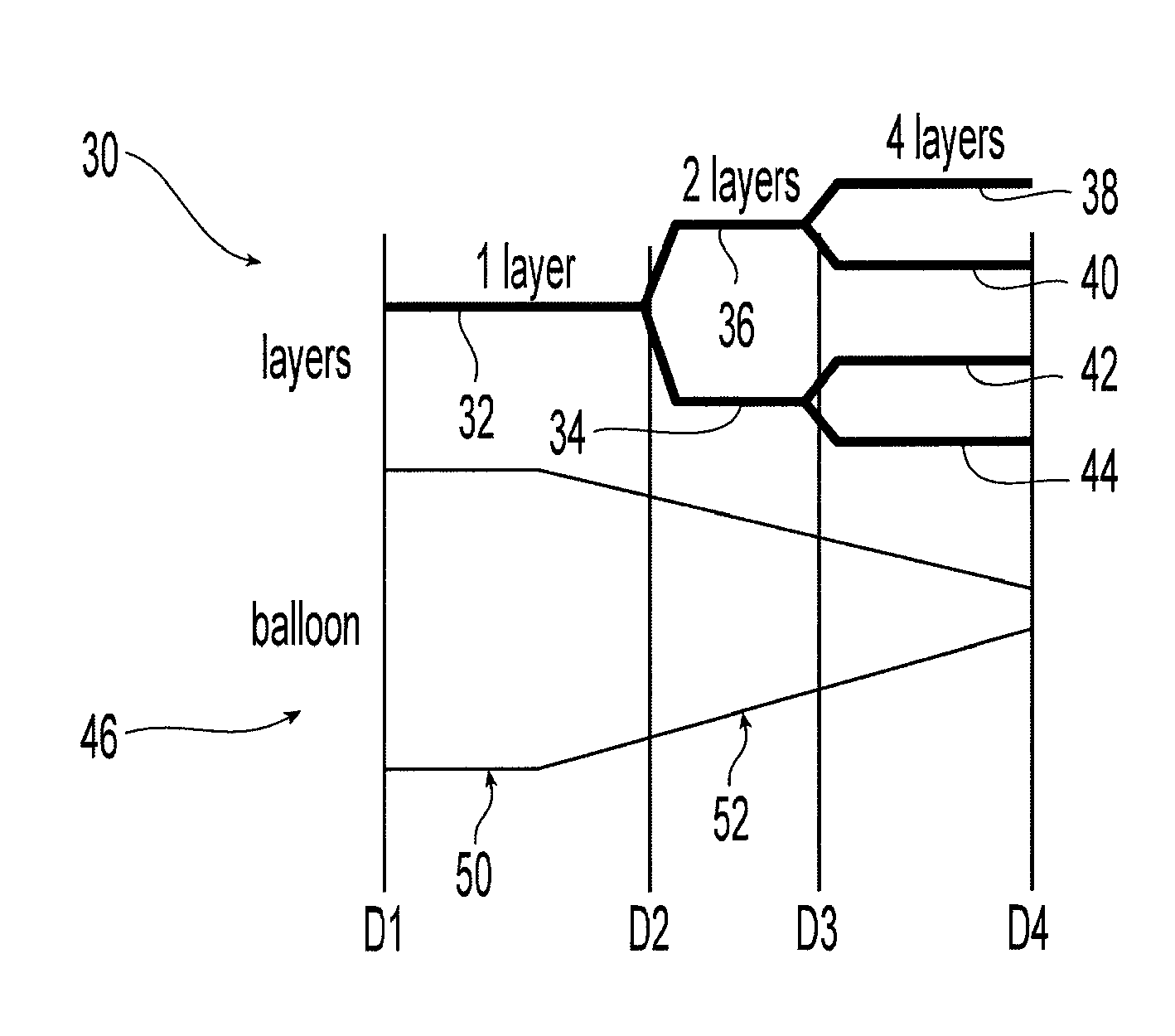
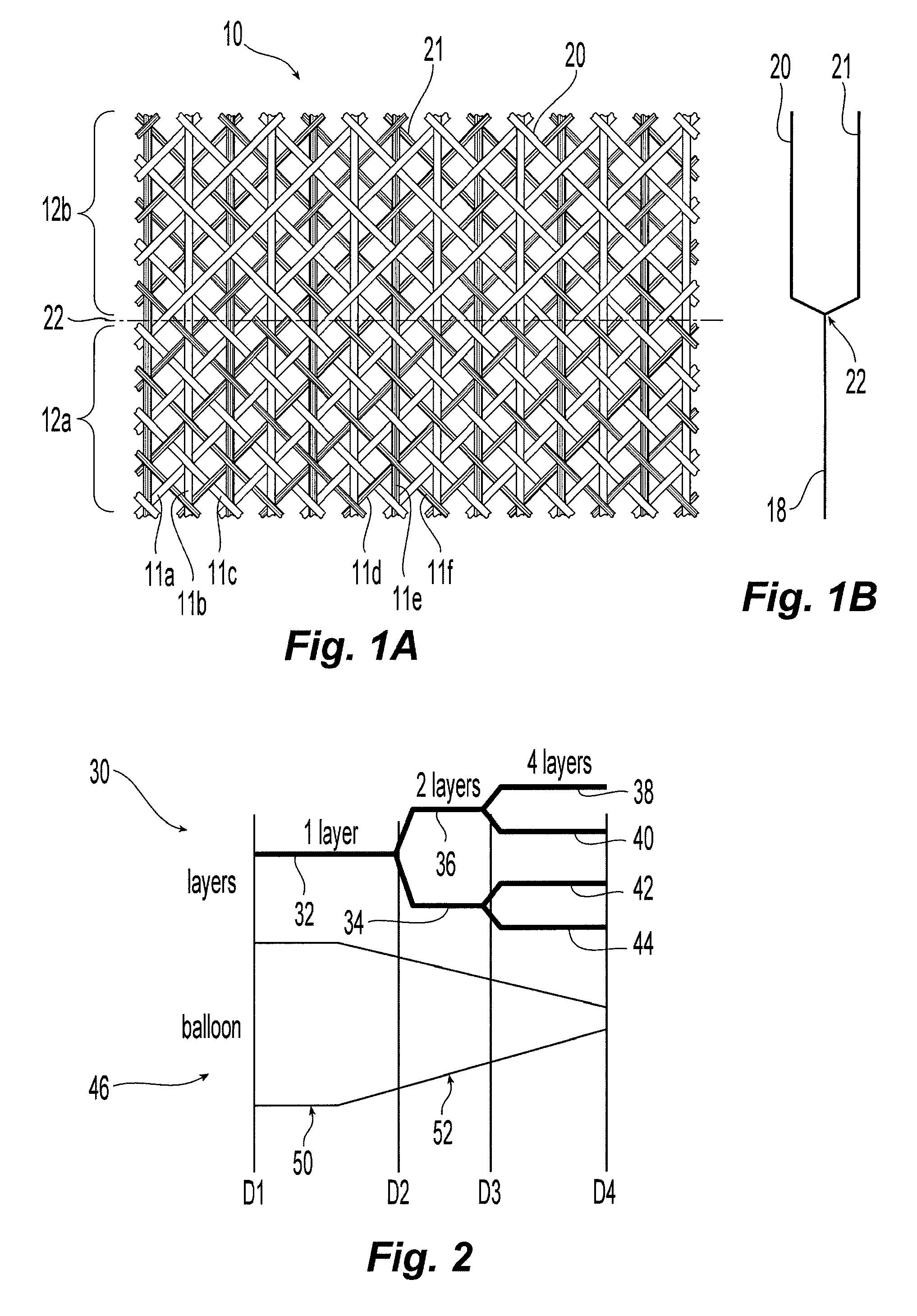
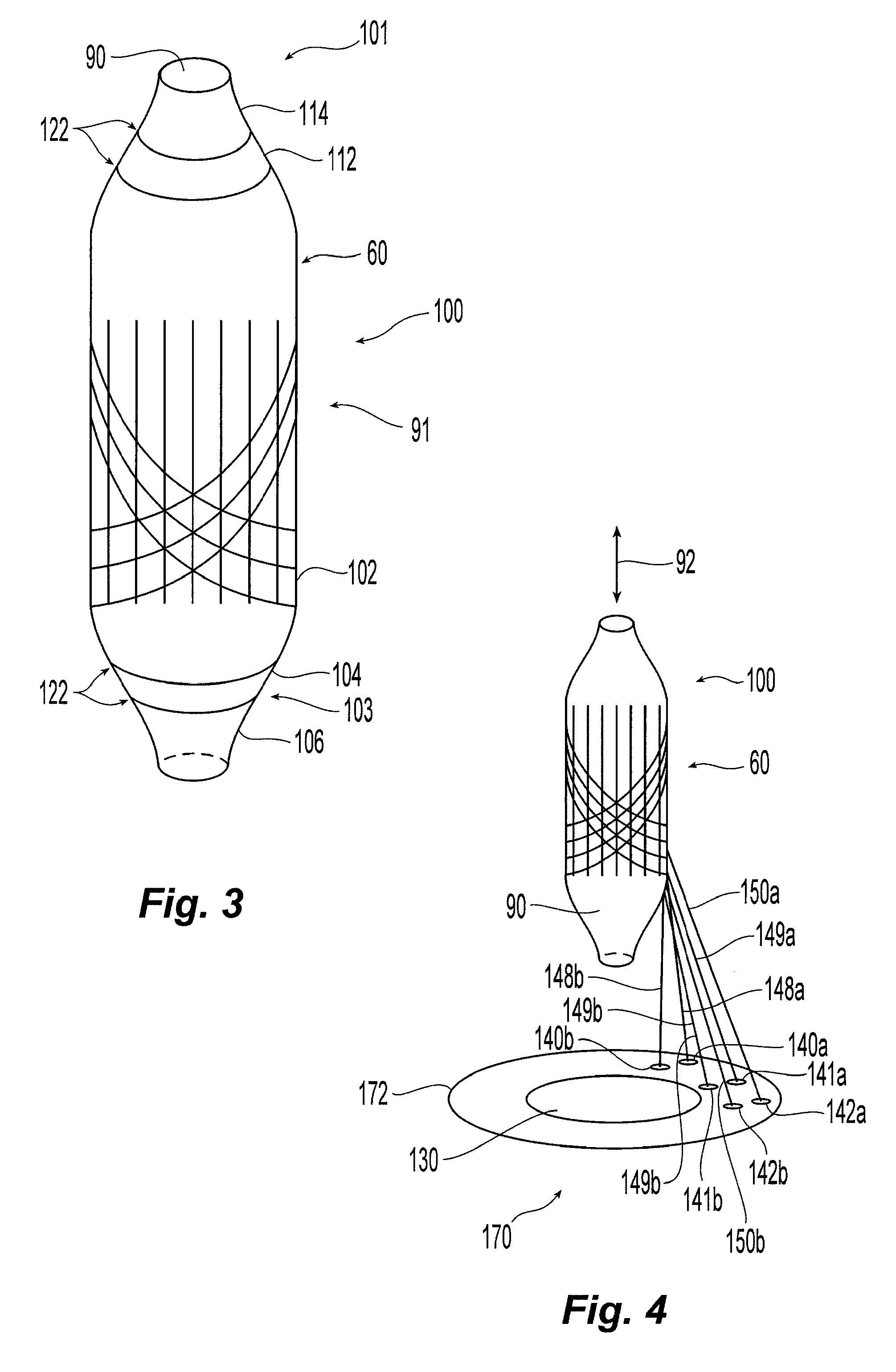
Balloon with dividing fabric layers and method for braiding over three-dimensional forms
ActiveUS8122809B2Minimize jammingMinimize jamming and bunchingStentsBalloon catheterEngineeringMultiple layer
A medical balloon with a variable diameter that is reinforced with continuous fibers woven to form a fabric with a varying number of layers and fiber densities. Portions of the balloon having a relatively smaller diameter are reinforced with a fabric having a reduced fiber density and an increased number of layers to facilitate the placement of the layers. The fabric also includes a braiding pattern that facilitates the transition from a single layer fabric to a multiple layer fabric. Also described is a manufacturing method for the braiding and layering.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Fiber rendering apparatus
ActiveUS20050101857A1Low transparencyHigh fiber tracking reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisRegular gridDiffusion
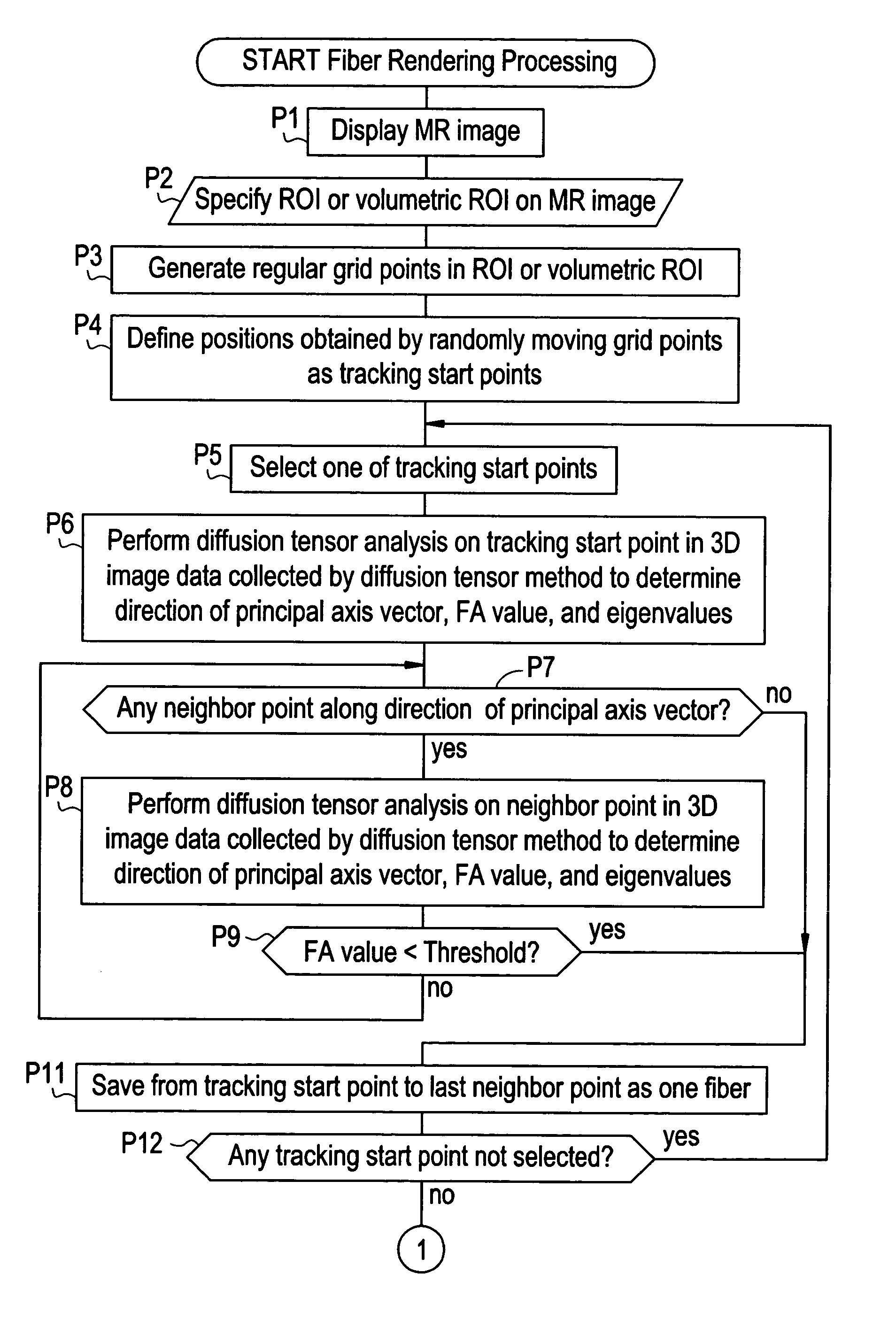
For the purpose of preventing a situation in which the fiber density looks as if it suddenly decreases in a specific view direction, a method comprises: specifying a region of interest R1 in MR image data collected by a diffusion tensor method; defining regular grid points in the region of interest R1; defining points obtained by randomly moving the grid points as tracking start points S1, S2, . . . ; performing diffusion tensor analysis on each tracking start point S1, S2, . . . in the image data to determine a direction of a principal axis vector; tracking a fiber by repeatedly selecting a neighbor point along the direction of the principal axis vector and performing diffusion tensor analysis on the neighbor point to determine the direction of the principal axis vector; and producing and displaying an image of the tracked fibers as viewed in a desired view direction.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Stereoscopic nonwoven fabric with pore structure
InactiveCN103908376AKeep 3D Visual EffectsImprove stress resistanceBandagesPolymer scienceHigh density
The invention discloses stereoscopic nonwoven fabric with a pore structure, comprising protrusion areas, recess areas and the pore structure. The protrusion areas and the recess areas are defined on the basis of a nonwoven application surface; fiber density from the protrusion areas to the recess areas is gradient, namely the fiber density of the edges from the protrusion areas to the recess areas is higher than that of the tops of the protrusion areas; the edge fiber density is 1.5-30 times of the top fiber density of the protrusion areas; the fiber density of the recess area is 1.5-20 times of the top fiber density of the protrusion areas; a height difference between the protrusion areas and the recess areas is larger than 0.2mm; the average area of each single pore of the pore structure is smaller than 20mm<2>, with smaller than 50% of porosity; the area of the protrusion areas accounts for 20-80% of total area of the stereoscopic nonwoven fabric. Pressure resistance of the high-density fiber areas keeps the stereoscopic nonwoven fabric significantly uneven, liquid permeation is quickened, residue is reduced, and the stereoscopic nonwoven fabric is high in permeating speed and is dry, cool and comfortable.
Owner:XIAMEN YANJAN NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
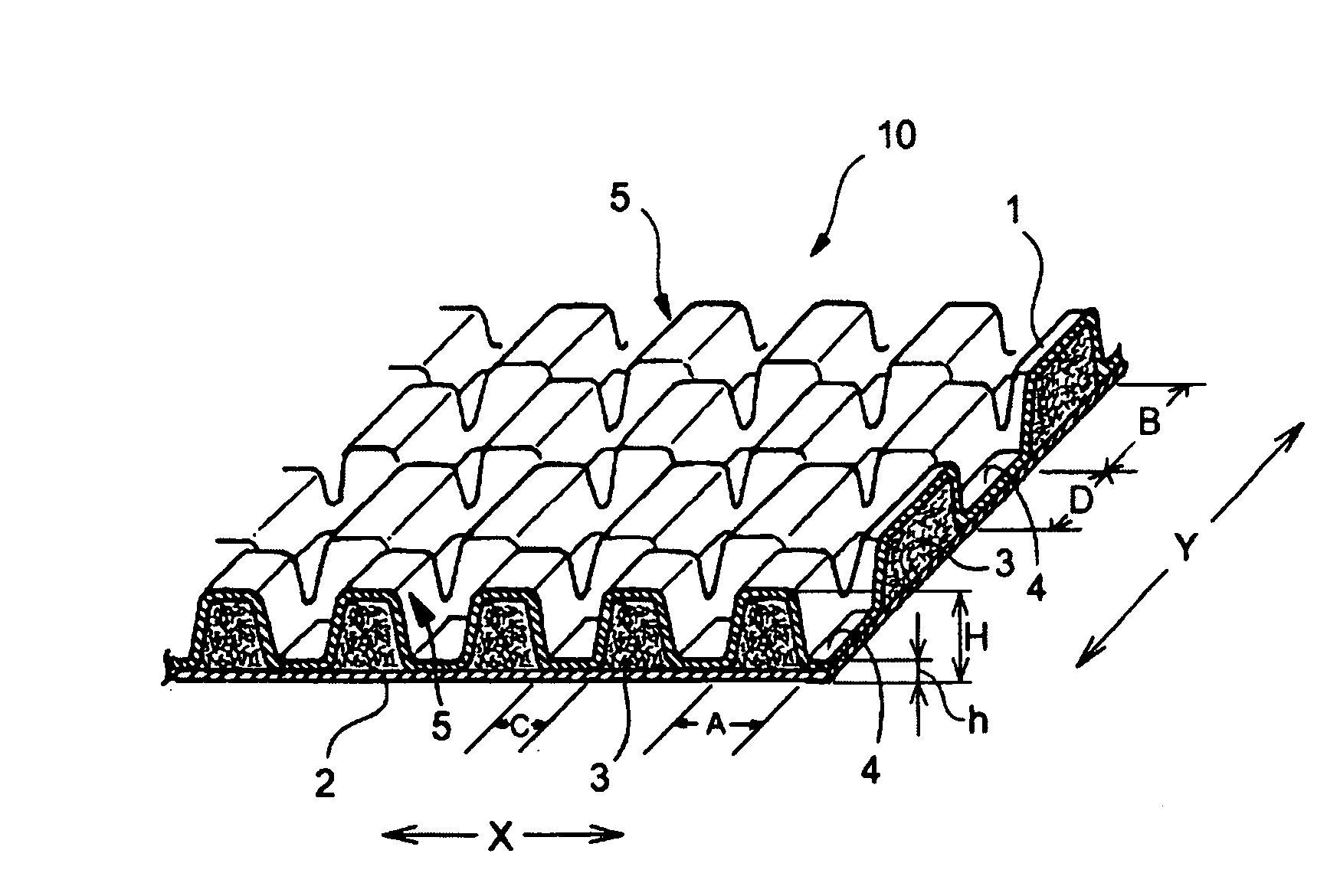
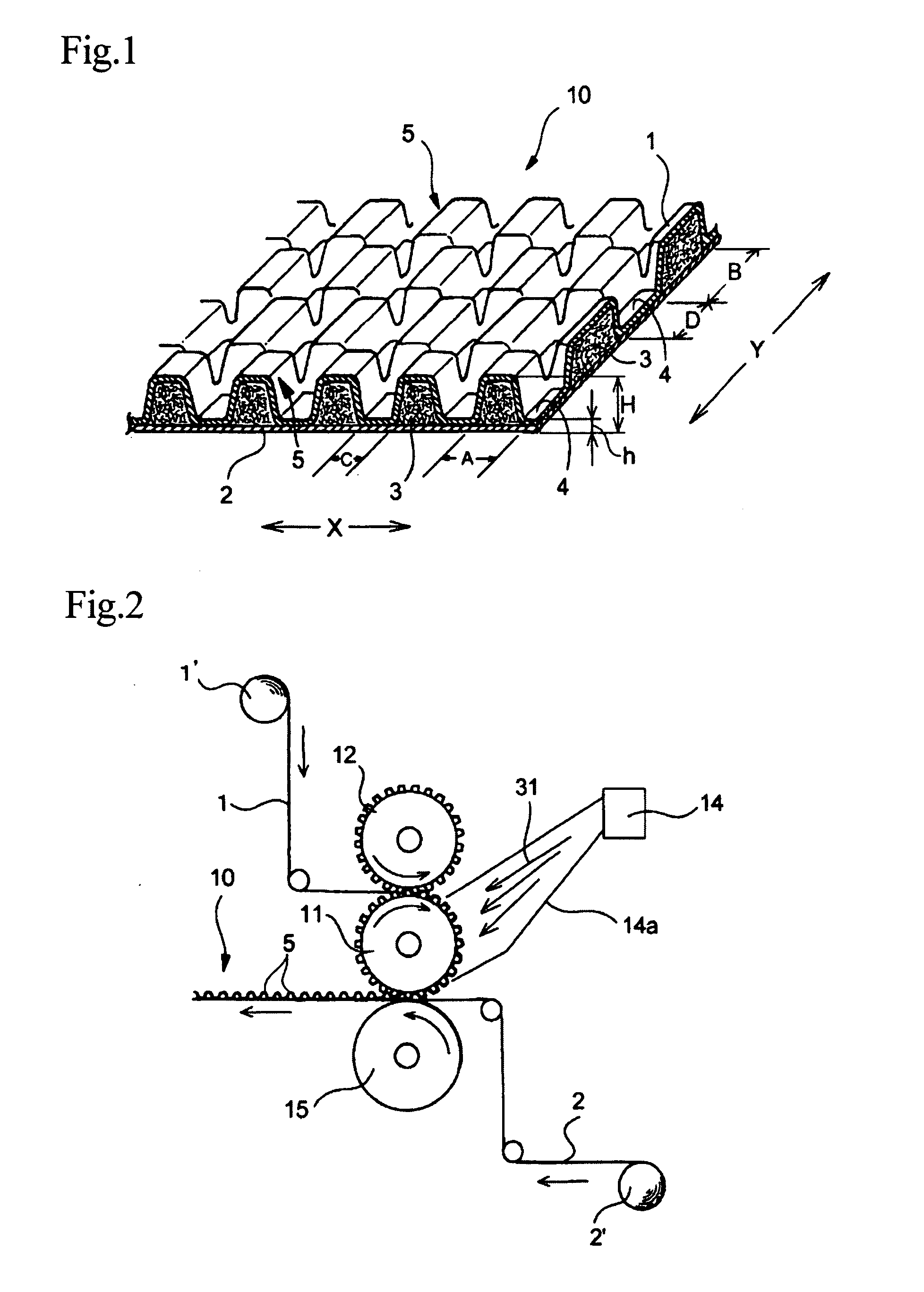
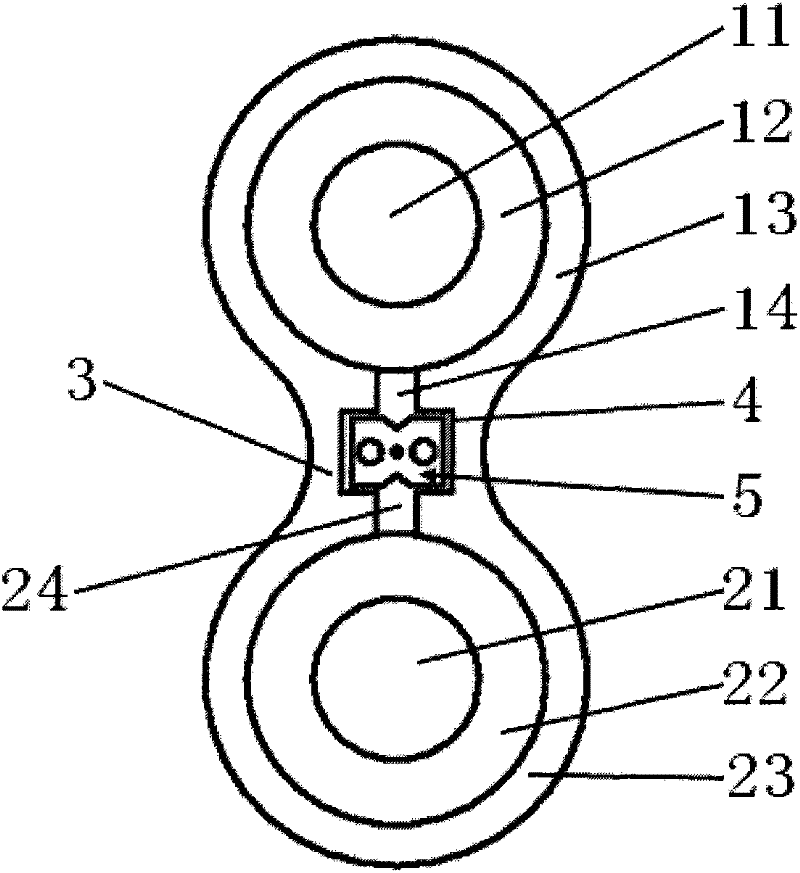
Topsheet For Absorbent Articles
A topsheet for use on the skin facing side of an absorbent article. The topsheet includes a first nonwoven fabric layer 1 and a second nonwoven fabric layer 2 laminated and partly joined together by heat fusion bonding, forming fusion bonds 4. The first nonwoven fabric layer 1 forms a large number of projections 5 projecting toward the skin of a wearer in portions other than the fusion bonds 4. The projections 5 are arranged discretely in both a first planar direction (direction X) and a second planar direction perpendicular to the first planar direction (direction Y). The individual projections 5 are filled with staple fiber 3. The staple fiber 3 is substantially absent in the fusion bonds 4. The individual projections 5 of the topsheet have fiber densities in the following relationship: first nonwoven fabric layer 1<the staple fiber 3<the second nonwoven fabric layer 2.
Owner:KAO CORP
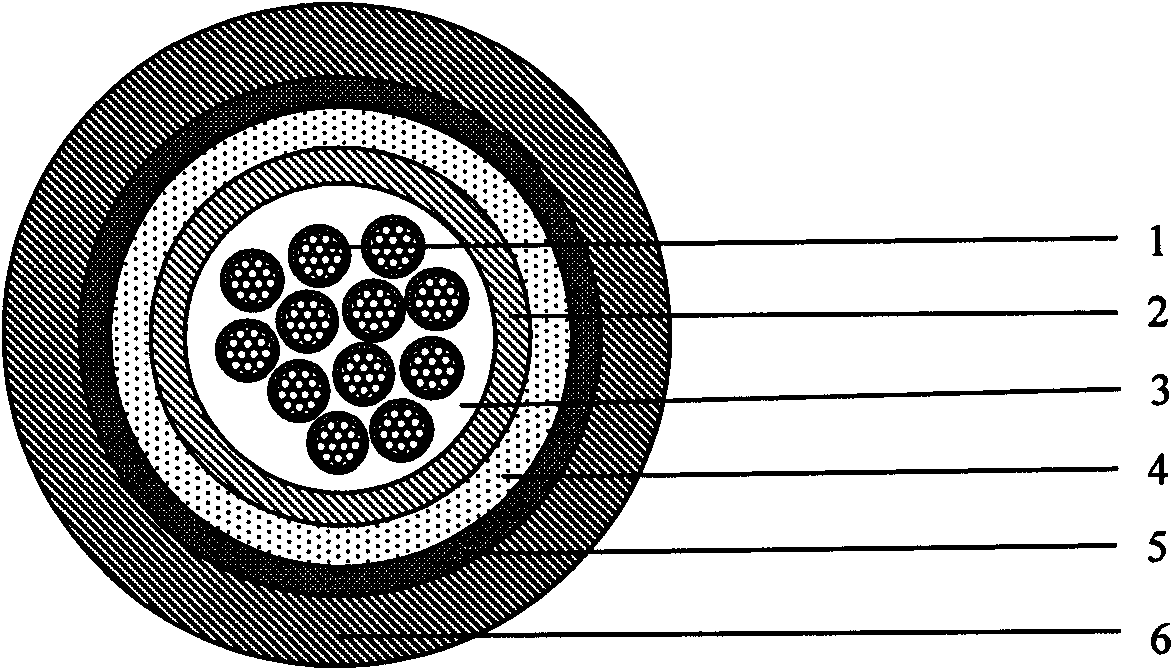
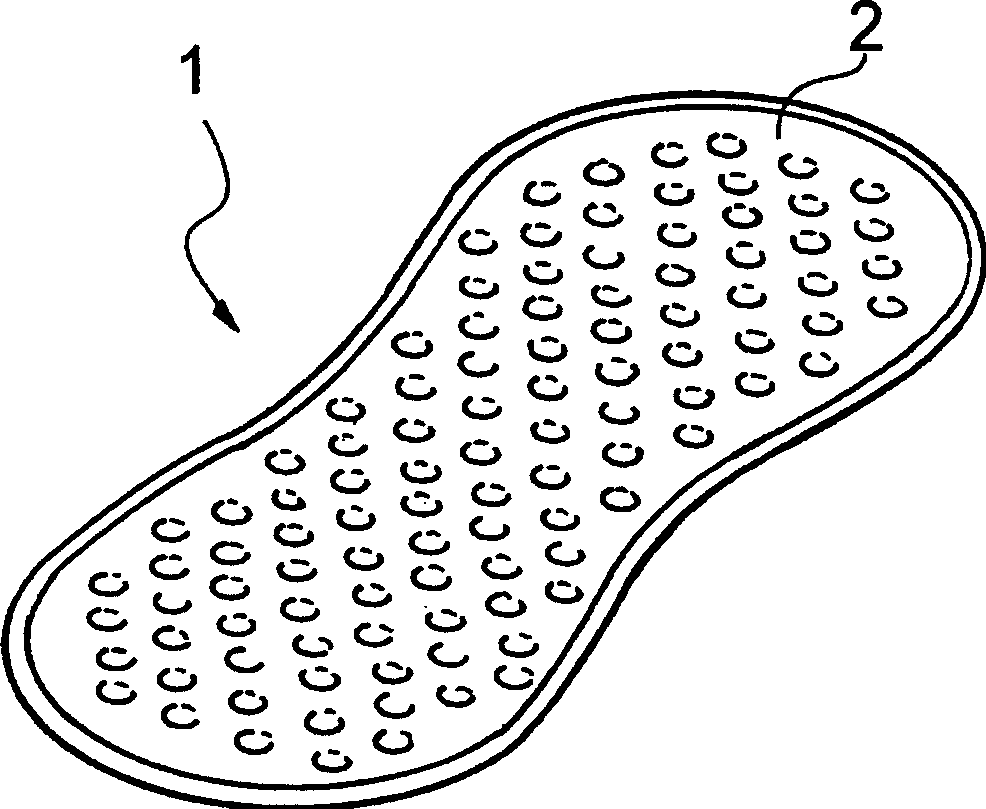
Novel fiber bundle central tube type optical cable
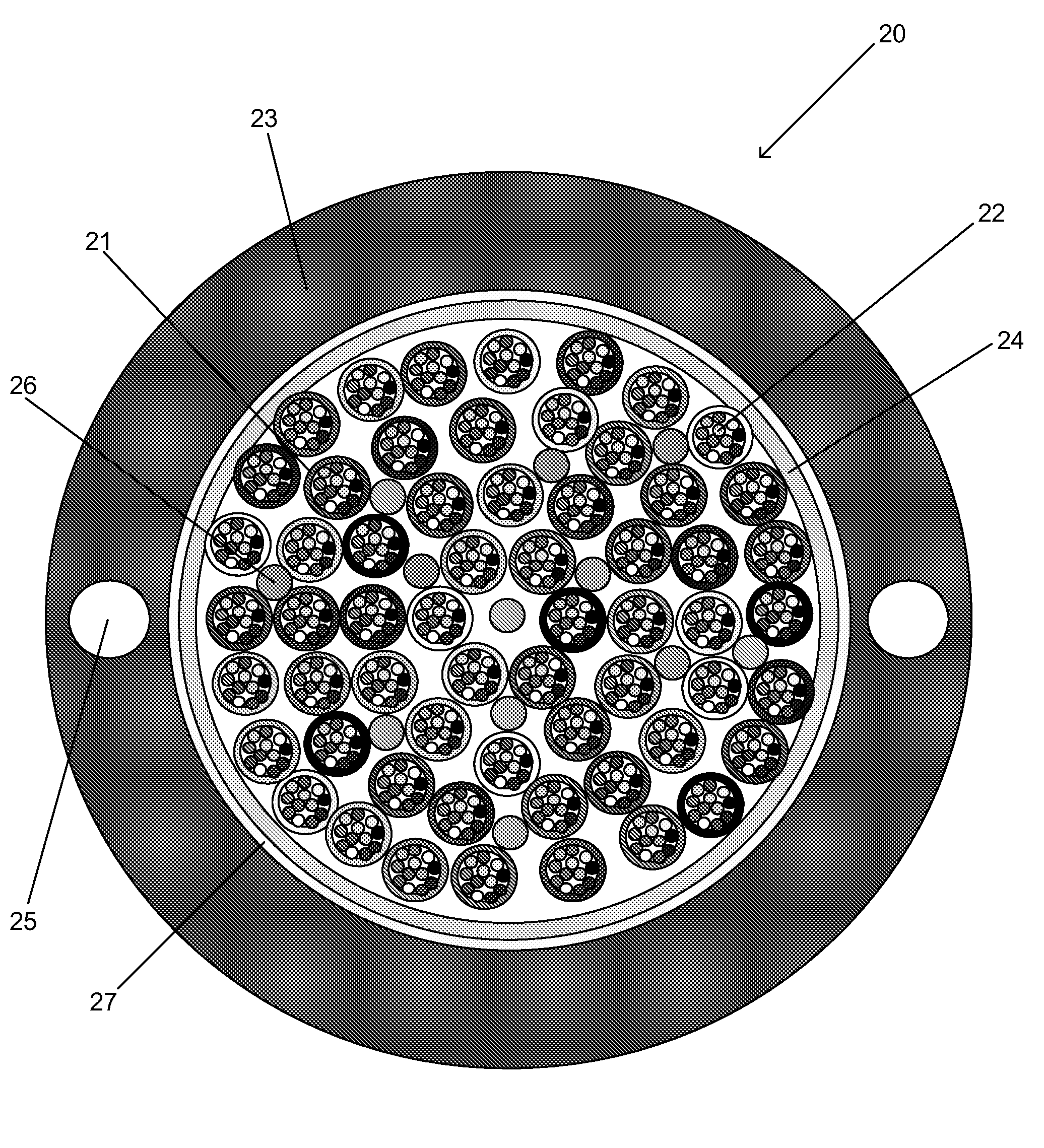
InactiveCN101840044AHigh fiber densityReduce volumeFibre mechanical structuresUltrasound attenuationHigh rate
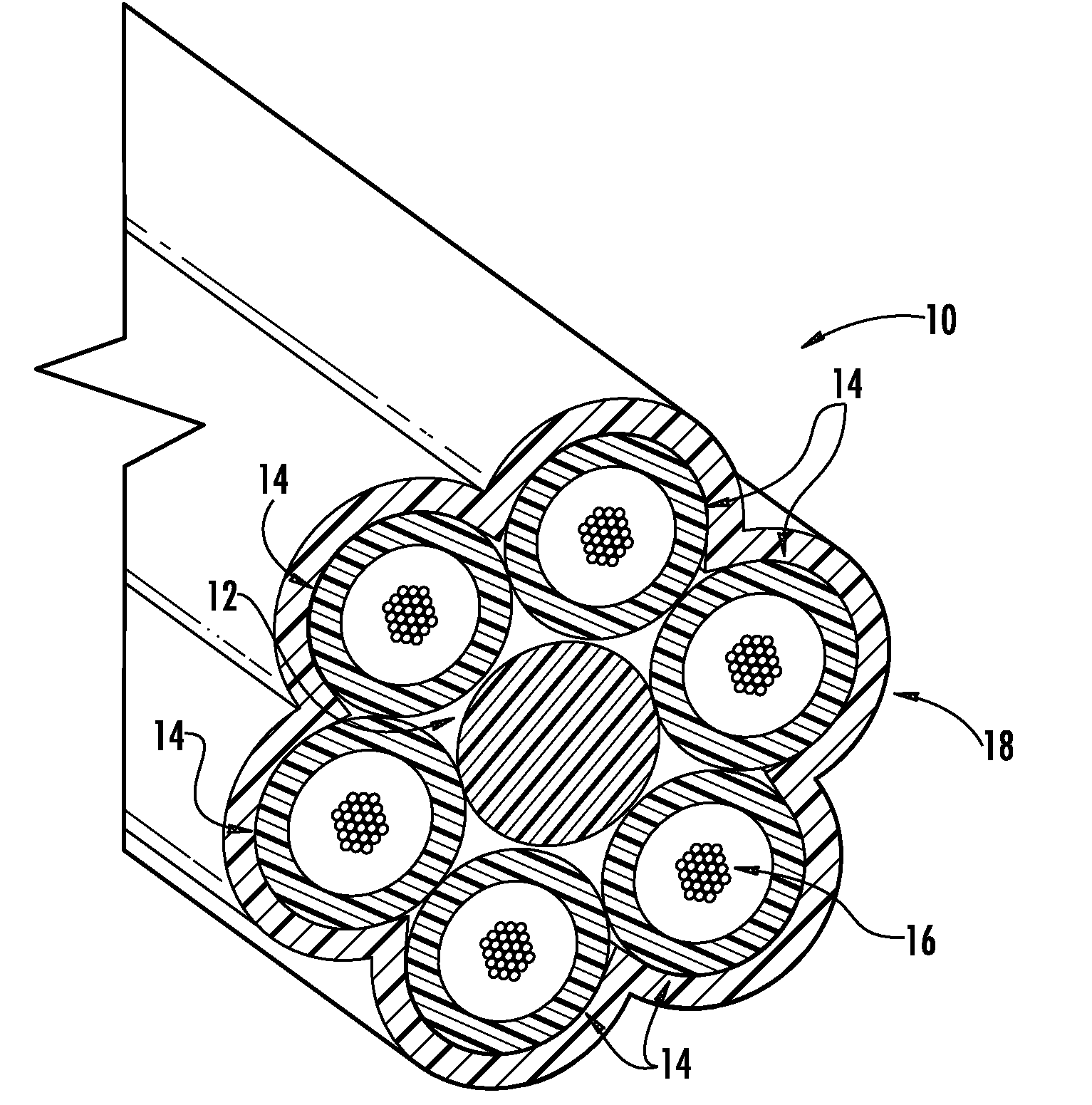
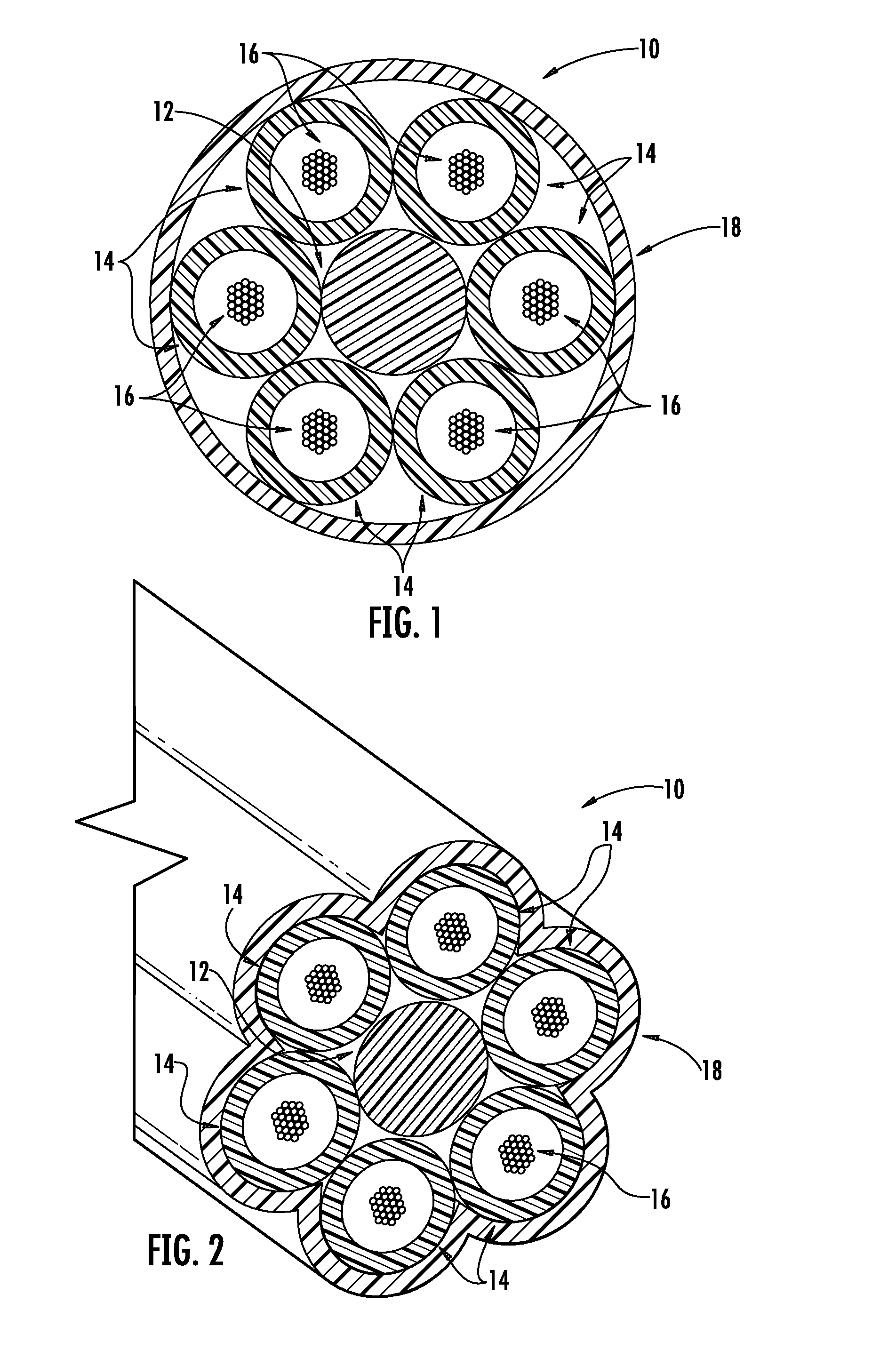
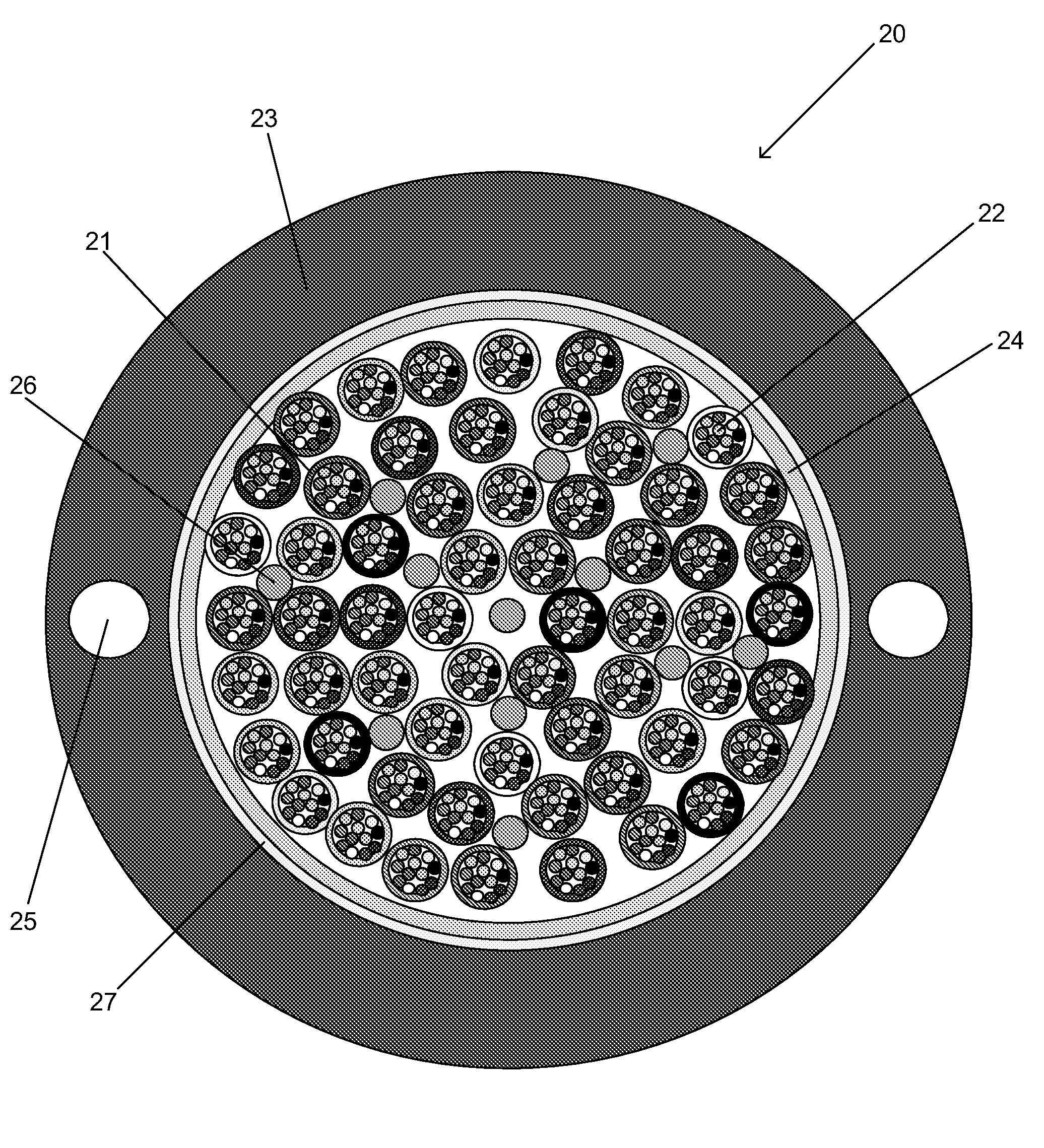
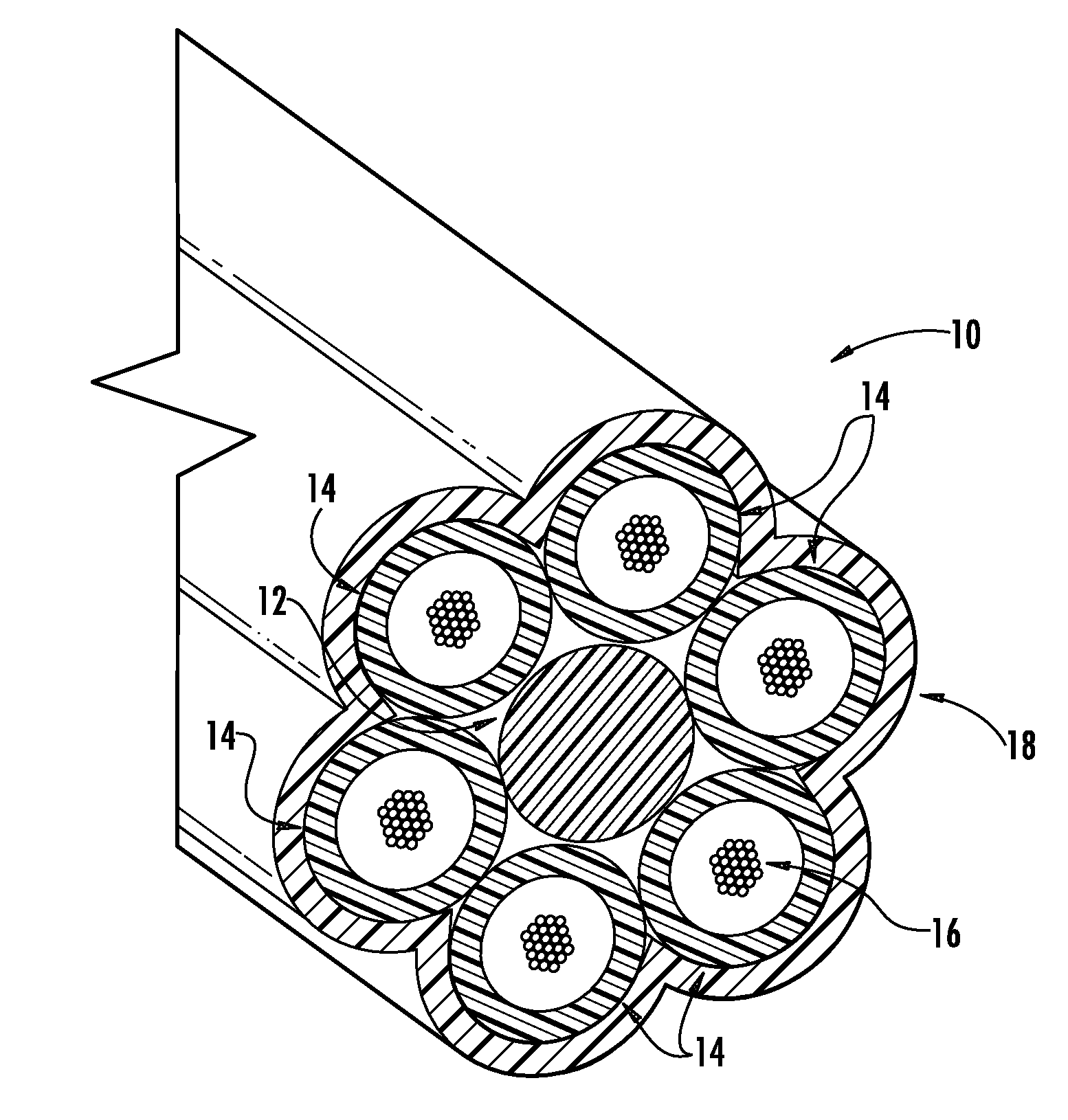
The invention relates to an optical cable for a communication network, in particular to a novel fiber bundle central tube type optical cable. The while cross section of the optical cable is round, and the optical cable comprises an outer sheath (6), a reinforcing piece (4) and a loose sleeve (2) in turn from outside to inside, wherein a plurality of fiber bundles (1) are arranged in the loose sleeve (2); a water-blocking ointment (3) is filled among the fiber bundles (1); the fiber bundles (1) are made of a plurality of optical fibers (12) by adopting an ultraviolet light curing process; a layer of ultraviolet light cured resin is formed outside the fiber bundles; and an optical fiber water-blocking ointment (11) is filed among the optical fibers. For the novel fiber bundle central tube type optical cable, a plurality of the fiber bundles which are produced by the ultraviolet light curing process and are filled with the water-blocking ointment are placed in the loose sleeve, and compared with the traditional central tube type optical fiber ribbon optical cable, the novel fiber bundle central tube type optical cable has a series of advantages of high fiber density, small volume, light weight, high rate of finished products and the like. The novel fiber bundle central tube type optical cable solves the problems that optical fiber ribbons are scattered easily and are distorted extensively in production or can make the optical fibers on the extreme edge generate large attenuations.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Absorbent article
InactiveCN1839776AKeep dryComfortable to useAbsorbent padsBaby linensMoisture permeabilityEngineering
This absorbent article comprises a liquid-permeable layer 2 formed of a plurality of layers of fiber assemblies and a leakproof layer 3 with moisture permeability, the liquid-permeable layer 2 is stuck to the leakproof layer 3 via adhesive with its bottom face 22 facing the leakproof layer 3, and the plurality of layers of liquid-permeable layer 2 is so formed that the fiber density of the layer 42 facing the leakproof layer 3 is denser than that of the layer 41 abutting on the skin.
Owner:KAO CORP
Catalyzed reinforced polymer composites
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Top layer for absorption products
InactiveCN1428135ADoes not cause irritationAbsorbent enoughSanitary towelsBaby linensEngineeringSkin exposure
A topsheet for absorbent articles having absorbing performance for smoothly transferring liquid body waste, e.g., menstrual blood or urine, to an underlying absorbent member and surface characteristics such that the surface thereof in contact with wearer's skin is soft enough not to cause skin irritation. The topsheet 1 comprises a first layer 11 disposed on the side of a wearer and a second layer 12 disposed on the side of an absorbent member, the first layer and the second layer being partly joined together, and having protrusions and depressions on the side of a wearer, wherein the first and second layers each comprise a fiber aggregate, the first layer has fusion-bonded fiber intersections, the first layer has an apparent thickness (t1) of 0.1 to 5 mm, the second layer has an apparent thickness (t2) of 0.2 to 3 mm, the apparent thickness ratio of the first layer to the second layer (t1 / t2) is 0.5 to 8, the first layer has a fiber density (d1) of 0.001 to 0.05 g / cm<3>, the second layer has a fiber density (d2) of 0.03 to 0.2 g / cm<3>, and the fiber density (d2) of the second layer is higher than that (d1) of the first layer.
Owner:KAO CORP
PFTTH (power fiber to the home) cable
InactiveCN102314968AReduce academic performanceReduced direct impact on academic performanceInsulated cablesPower cablesElectrical conductorProtection layer
The invention belongs to the technical field of combination of wire cables and electric power and provides a PFTTH (power fiber to the home) cable. The PFTTH cable is characterized by comprising a first insulated conducting wire, a second insulated conducting wire, a butterfly optical cable, a first outer protection layer, a second outer protection layer, a third outer protection layer and a cavity, wherein the first outer protection layer covers the first insulated conducting wire; the second outer protection layer covers the second insulated conducting wire; the third outer protection layercovers the butterfly optical cable; the cavity is arranged in the third outer protection layer and can accommodate the butterfly optical cable; the first insulated conducting wire and the second insulated conducting wire are respectively arranged at the two sides of the butterfly optical cable; the first outer protection layer, the second outer protection layer and the third outer protection layer are in a one-body shape; and on any plane which is vertical to the axis of a first conductor, the outer edge of the third protection layer protrudes towards the cavity. According to the invention, the problems in the prior art that the cable is difficult to lay and tear out and the fiber density is low can be solved; and the PFTTH cable provided by the invention has the beneficial effects of stable heating performance, modularization, easiness for laying, producing, laying and constructing and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com