Patents
Literature
972 results about "Fiber orientation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A muscle fiber orientation in which the component skeletal muscle cell is an equal distance apart for the entire length of the fibers everywhere; this fiber orientation provides more range of motion but less power for contraction.
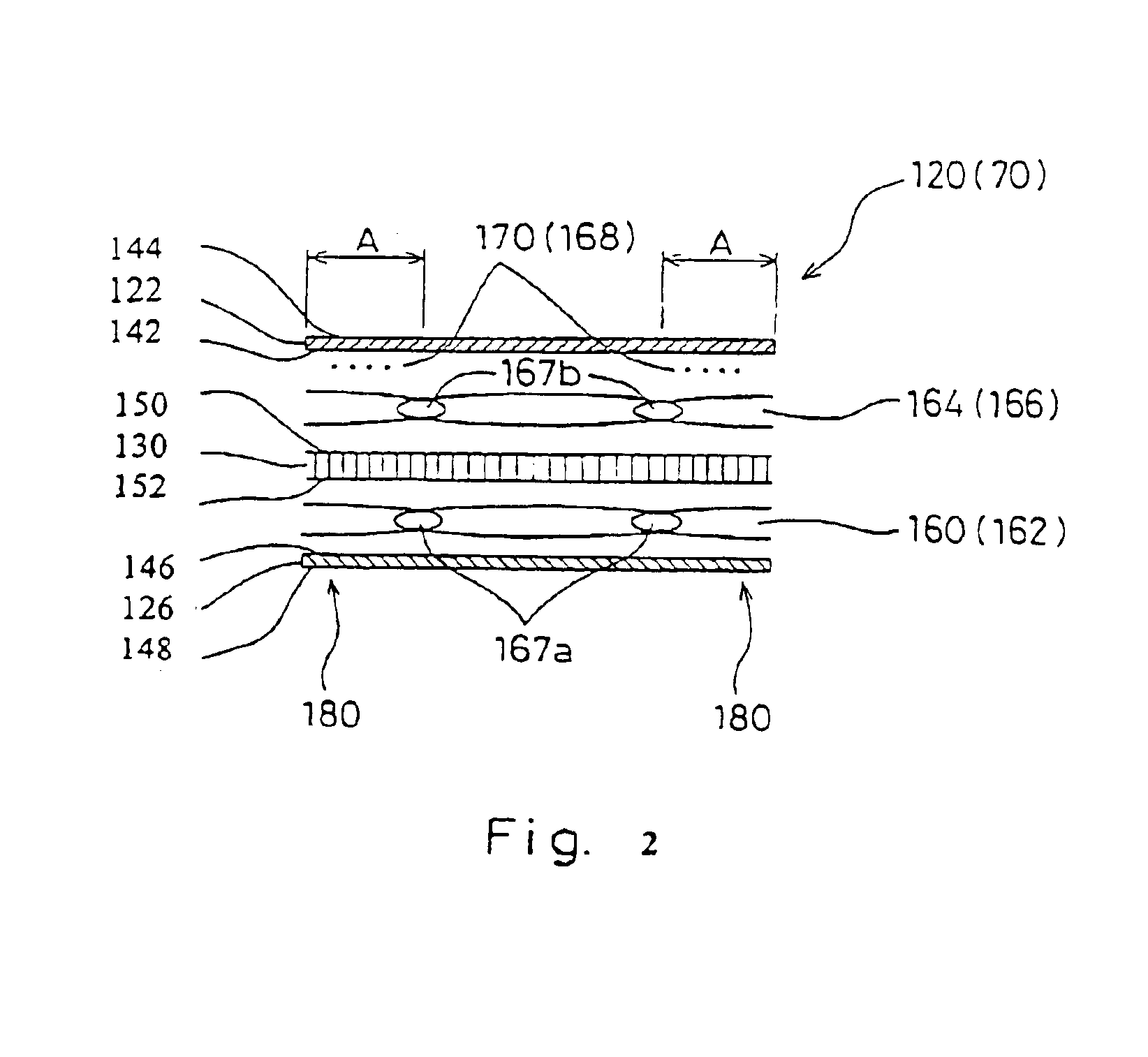
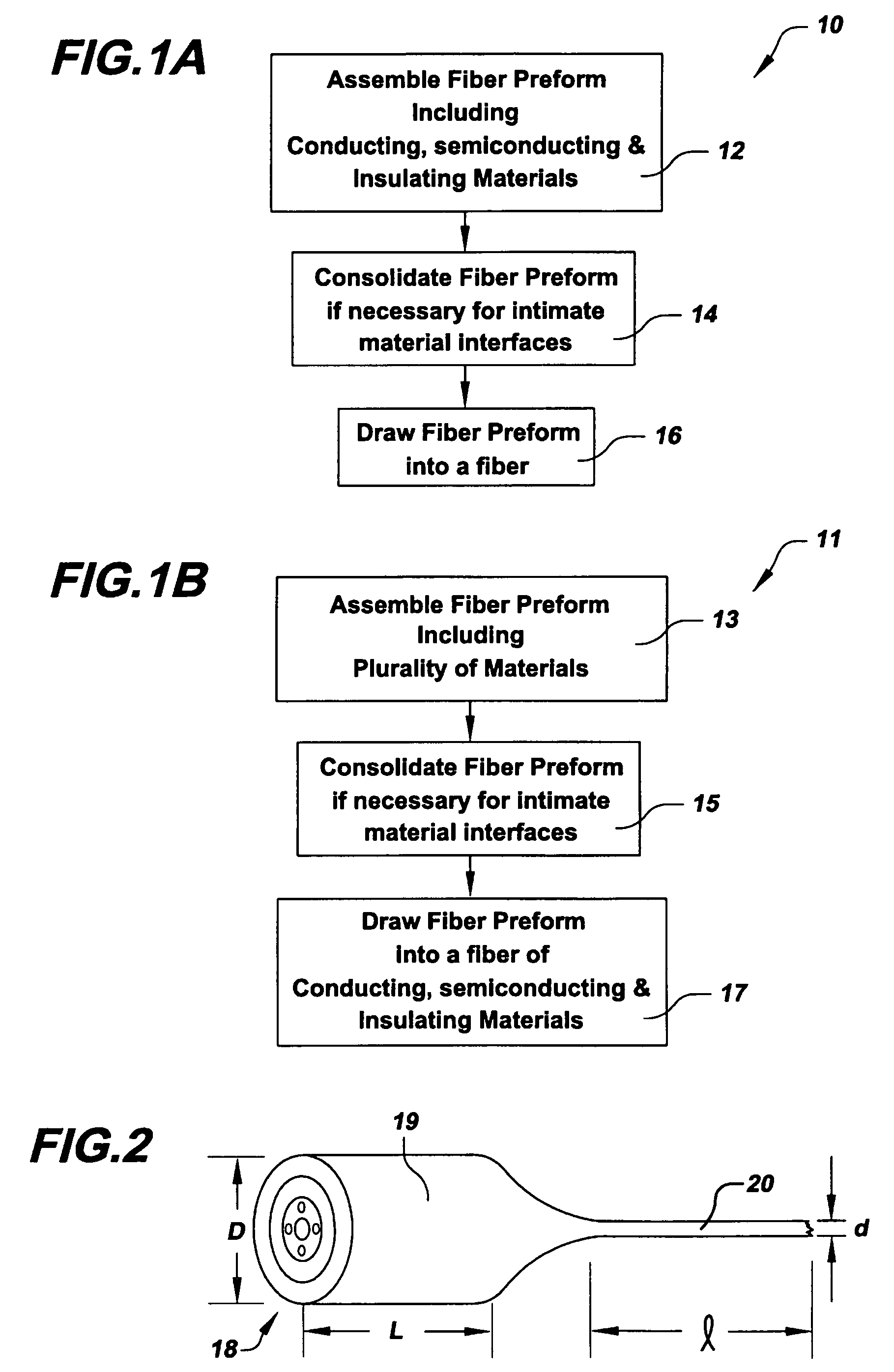
Laminate web
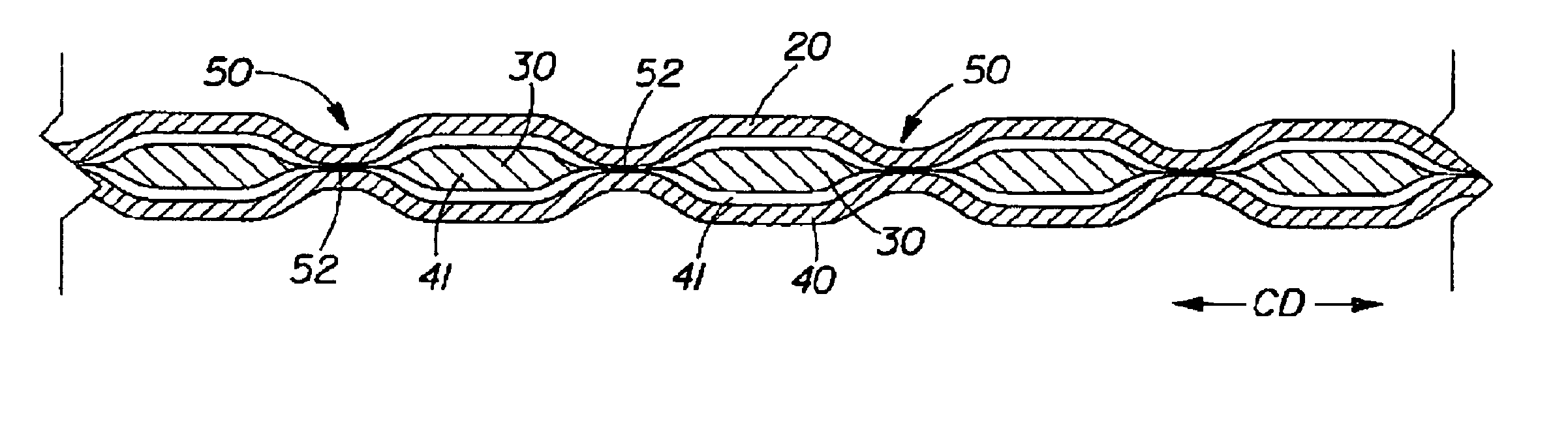
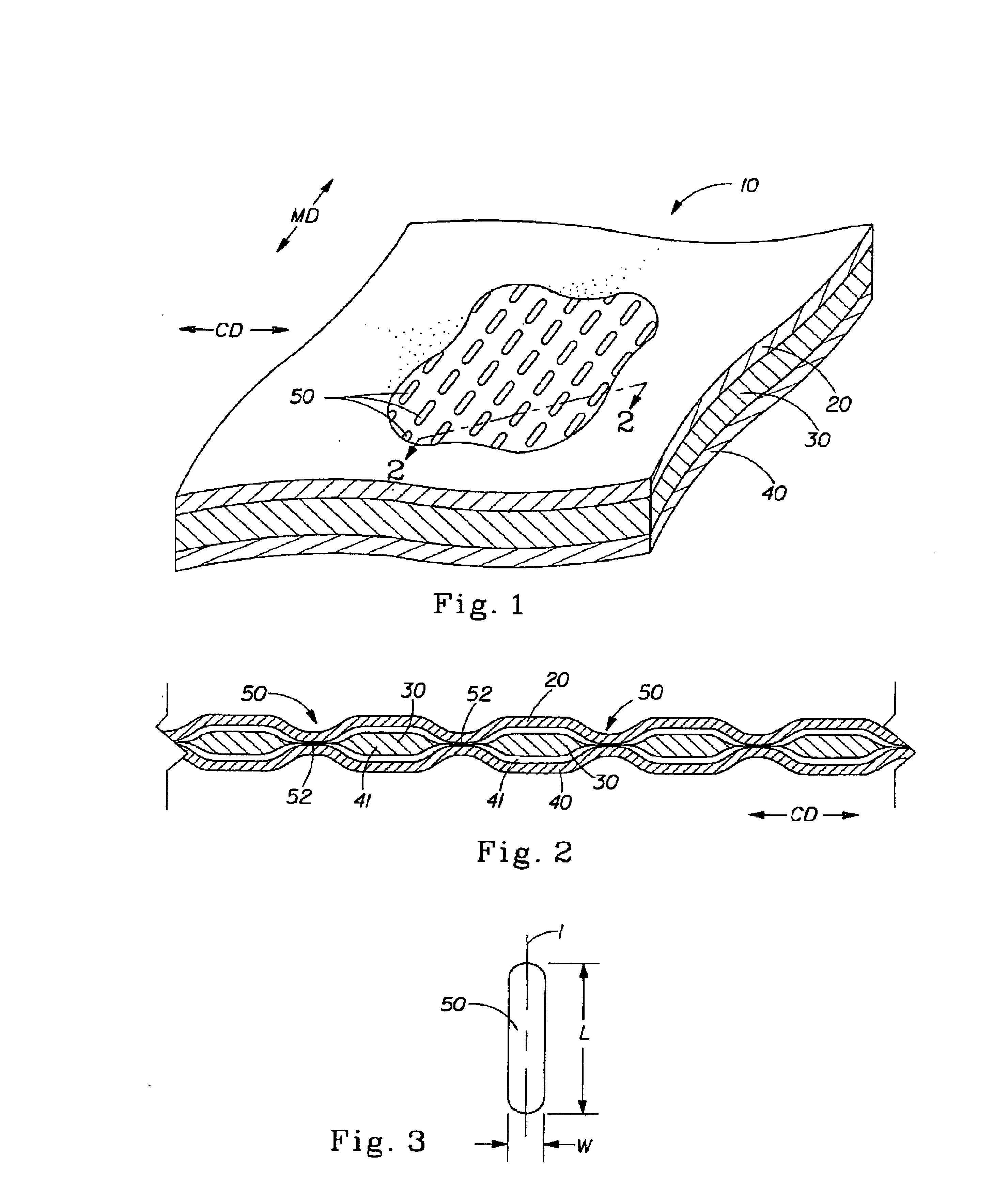
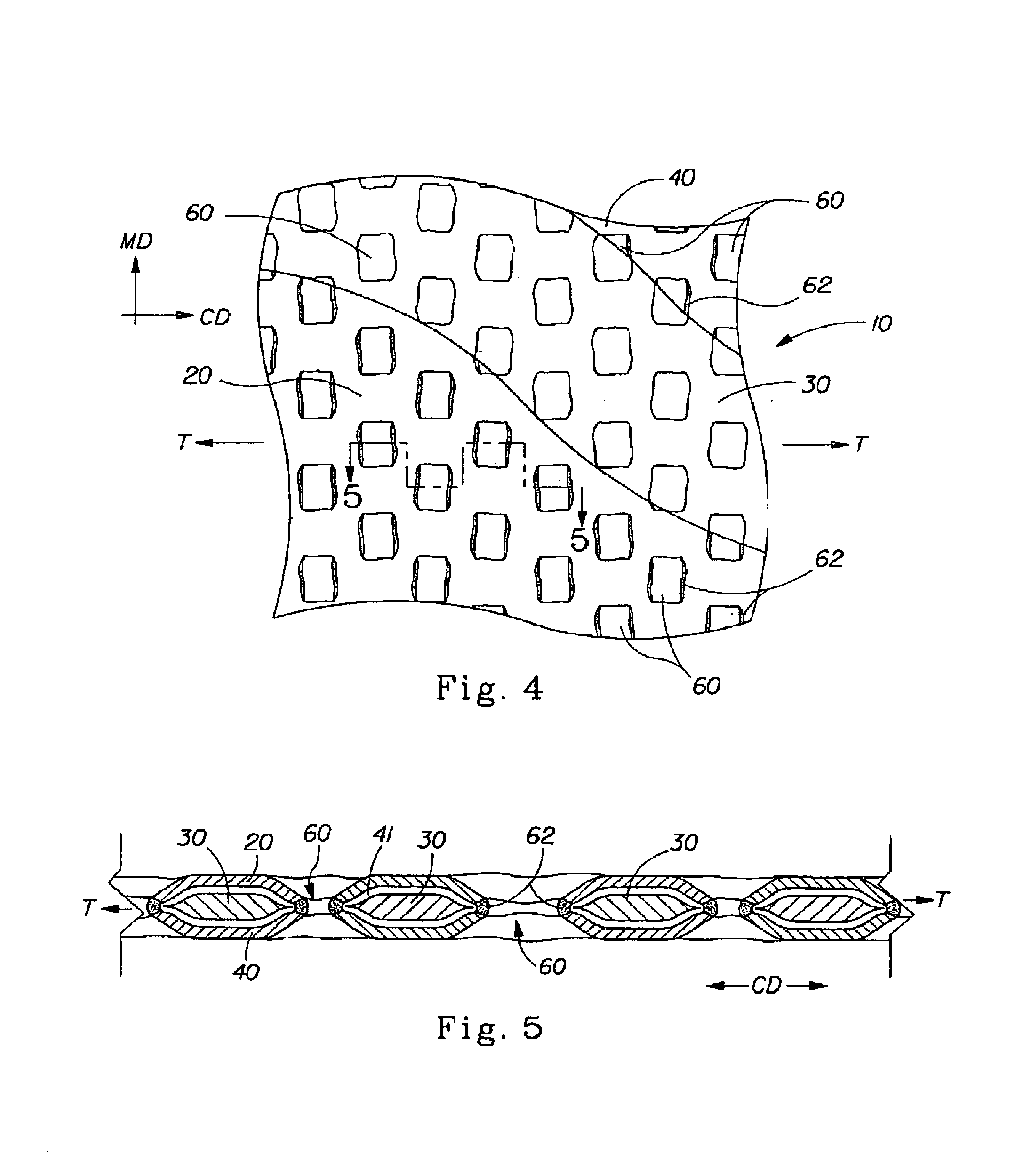
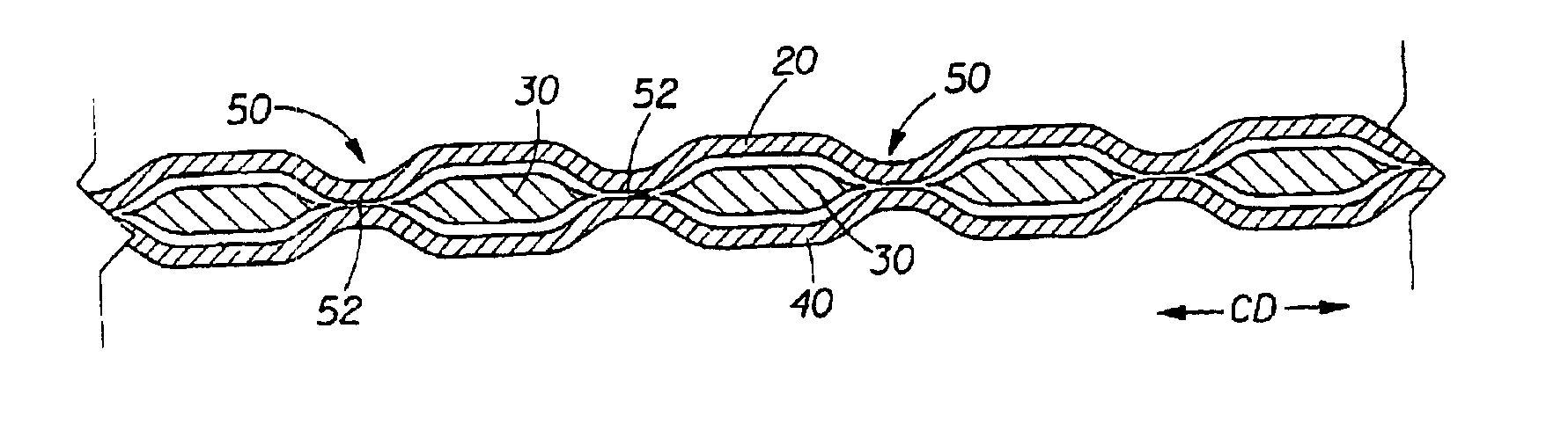
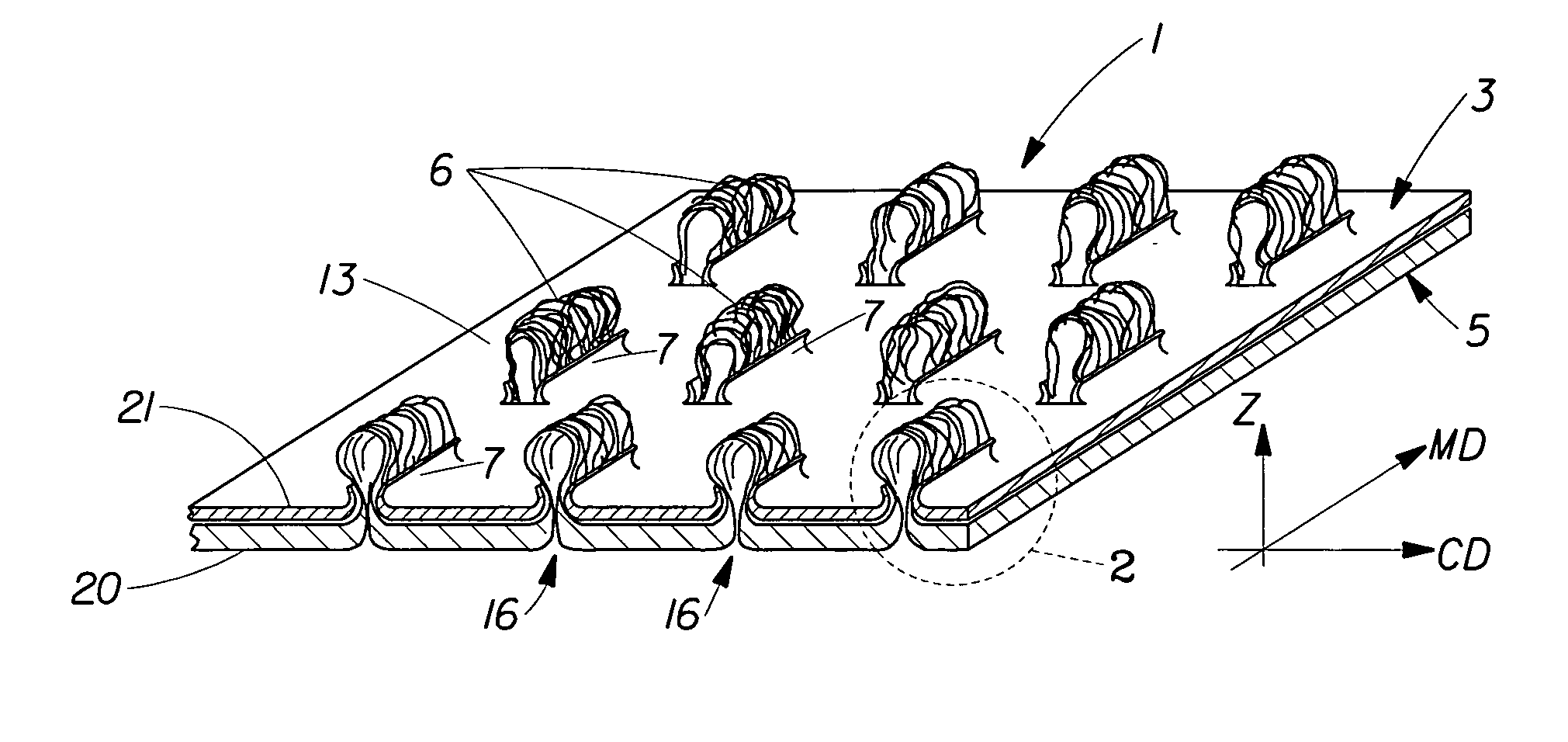
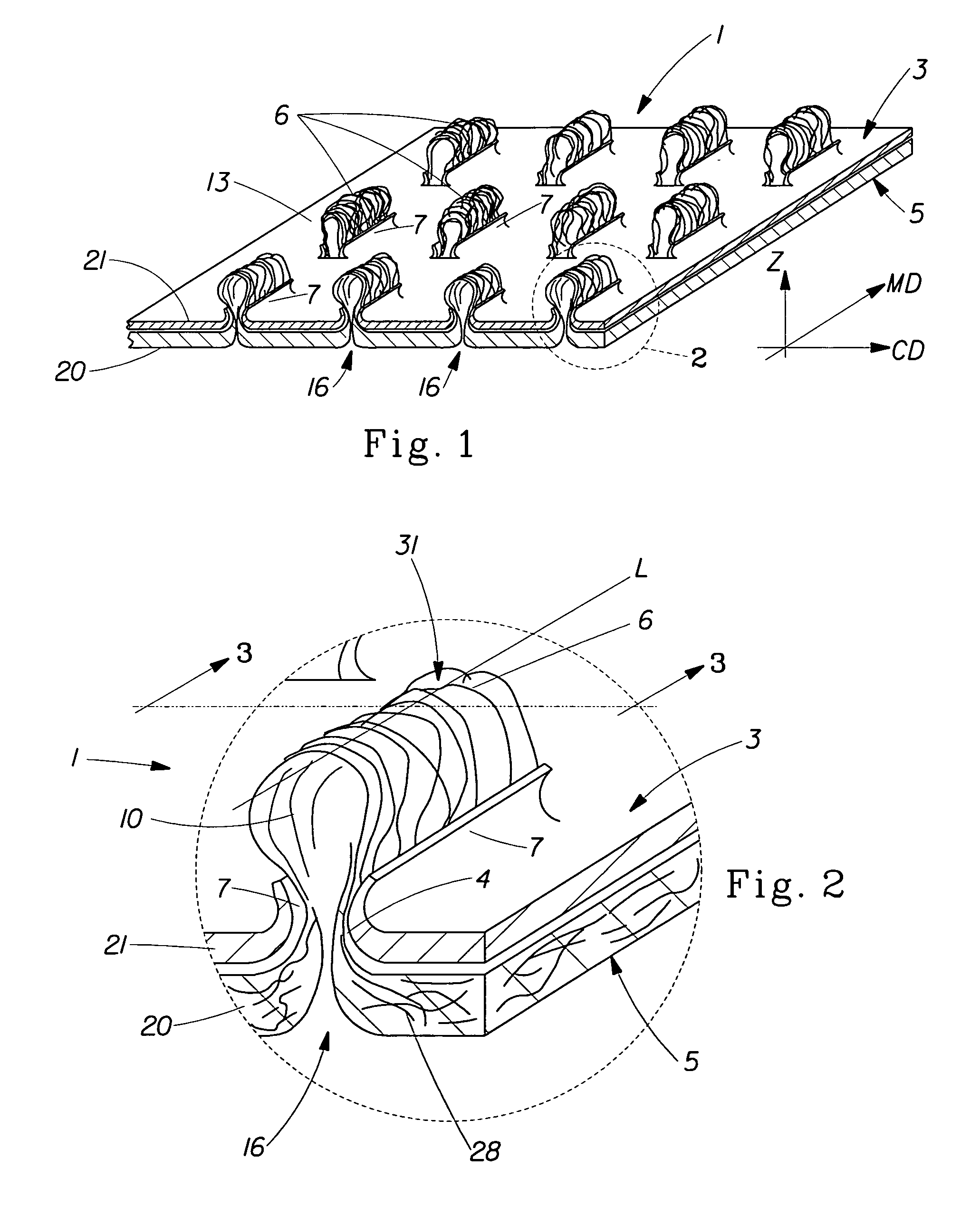
A laminate web is disclose, the laminate web comprising a first web, a second web joined to the first web at a plurality of discrete bond sites; and a third material disposed between at least a portion of the first and second nonwovens. The third material is apertured in regions adjacent the bond sites, such that the first and second nonwoven webs are joined through the apertures. In one embodiment an apertured laminate web is disclosed, having a first extensible web having a first elongation to break, and a second extensible web joined to the first extensible web at a plurality of bond sites, the second extensible web having a second elongation to break A third web material is disposed between the first and second nonwovens, the third web material having a third elongation to break which is less than both of the first or second elongations to break. In a further embodiment, an apertured laminate web is disclose, having first and second extensible webs being joined at a plurality of discrete bond sites and a third material disposed between the first and second nonwoven webs. The first and second nonwoven webs are in fluid communication via the apertures and have distinct regions being differentiated by at least one property selected from the group consisting of basis weight, fiber orientation, thickness, and density.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Laminate web comprising an apertured layer and method for manufacturing thereof
A laminate web comprising a first web, a second web joined to the first web at a plurality of discrete bond sites; and a third material disposed between at least a portion of the first and second nonwovens. The third material is apertured in regions adjacent the bond sites, such that the first and second nonwoven webs are joined through the apertures. In one embodiment an apertured laminate web is disclosed, having a first extensible web having a first elongation to break, and a second extensible web joined to the first extensible web at a plurality of bond sites, the second extensible web having elongation to break. A third web material is disposed between the first and second nonwovens, the third web material having a third elongation to break which is less than both of the first or second elongations to break. In a further embodiment, an apertured laminate web is disclosed, having first and second extensible webs being joined at a plurality of discrete bond sites and a third material disposed between the first and second nonwoven webs. The first and second nonwoven webs are in fluid communication via the apertures and have distinct regions being differentiated by at least one property selected from the group consisting of basis weight, fiber orientation, thickness, and density.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
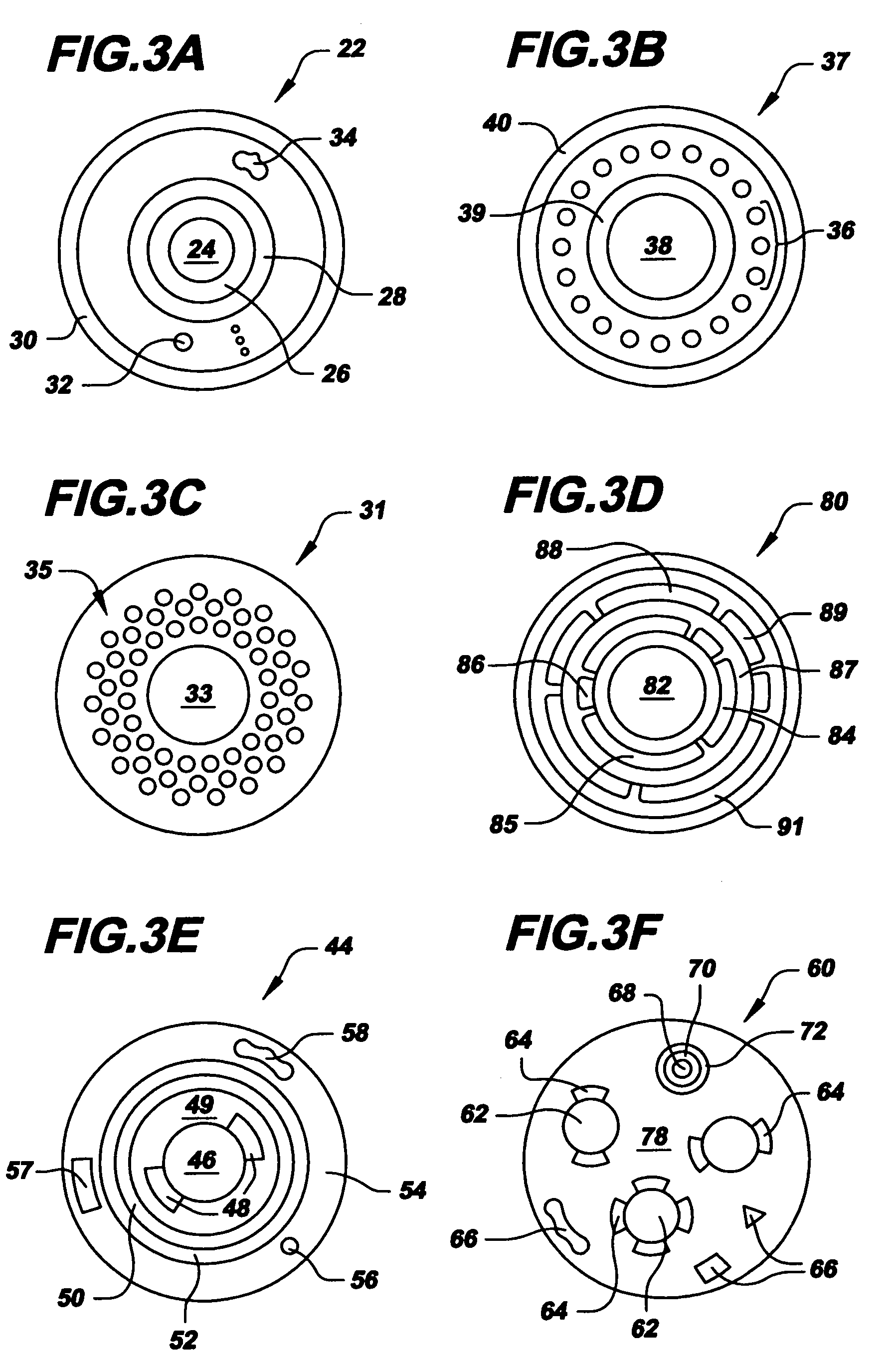
Elastic laminate including nonwoven layer formed from highly-oriented-component fibers and disposable garment employing the same
The present invention is directed to an elastic laminate which is elastically extensible in at least one direction. The elastic laminate includes an elastomeric material having a first surface and a second surface opposing the first surface; and a first nonwoven layer joined to the first surface of the elastomeric material. The first nonwoven layer is formed from component fibers having a primary fiber direction. The first nonwoven layer has a Fiber Orientation Ratio within about ±20 degrees from a primary fiber direction of at least about 65%. The present invention is also directed to a disposable garment employing such an elastic laminate.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
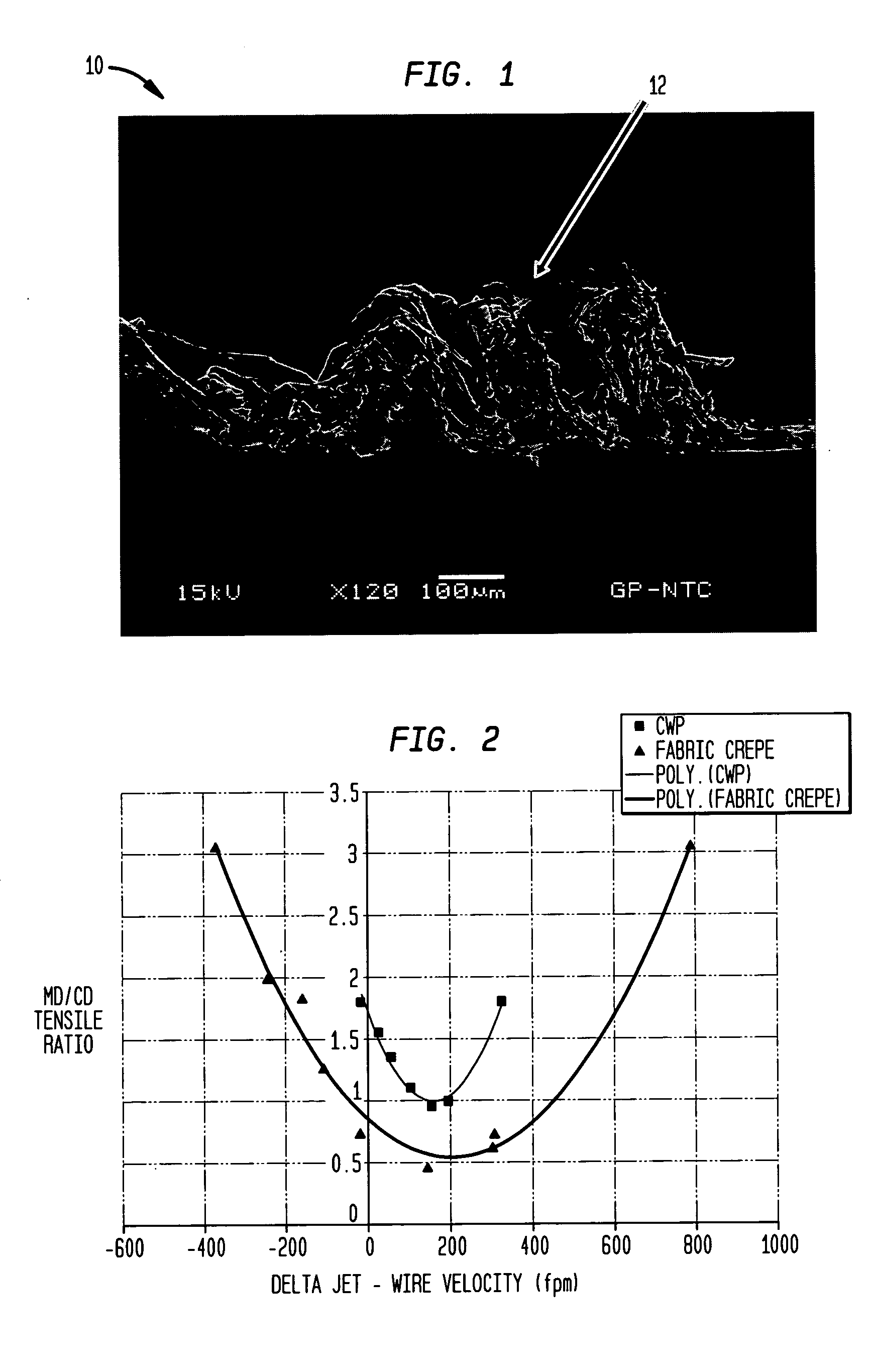
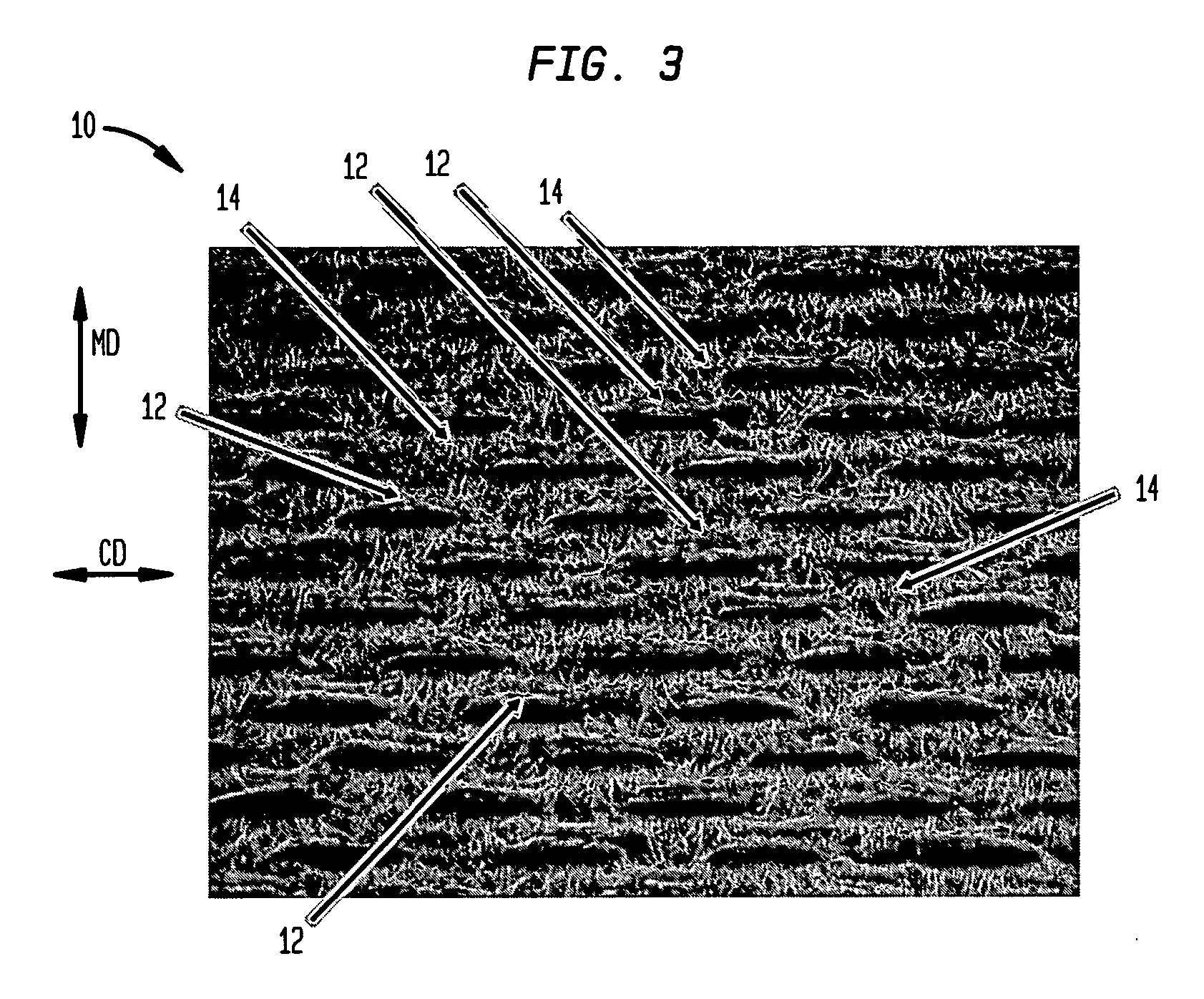
Wet-pressed tissue and towel products with elevated CD stretch and low tensile ratios made with a high solids fabric crepe process
ActiveUS20050241786A1The implementation process is simpleNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationMedicineCellulose fiber
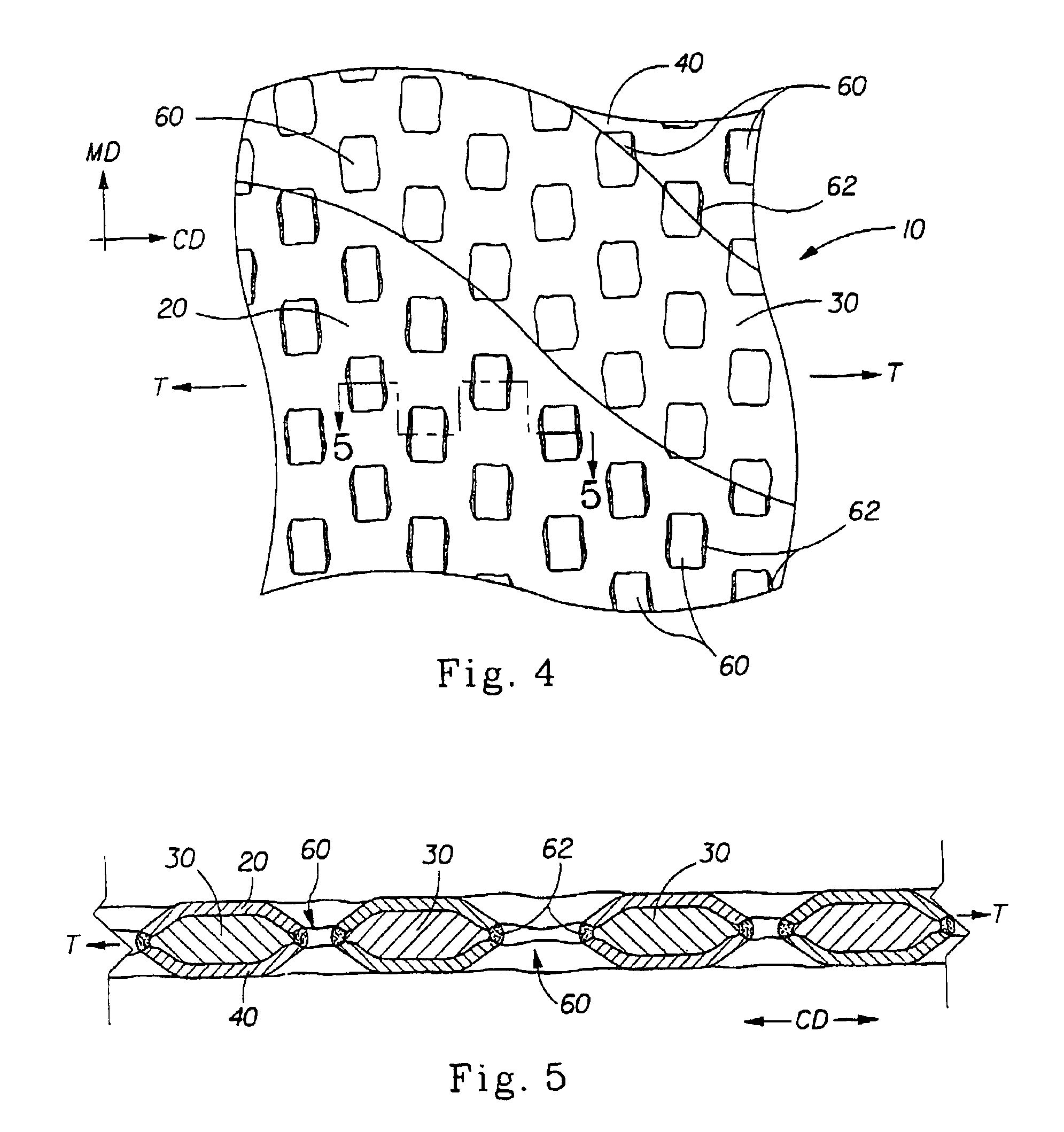
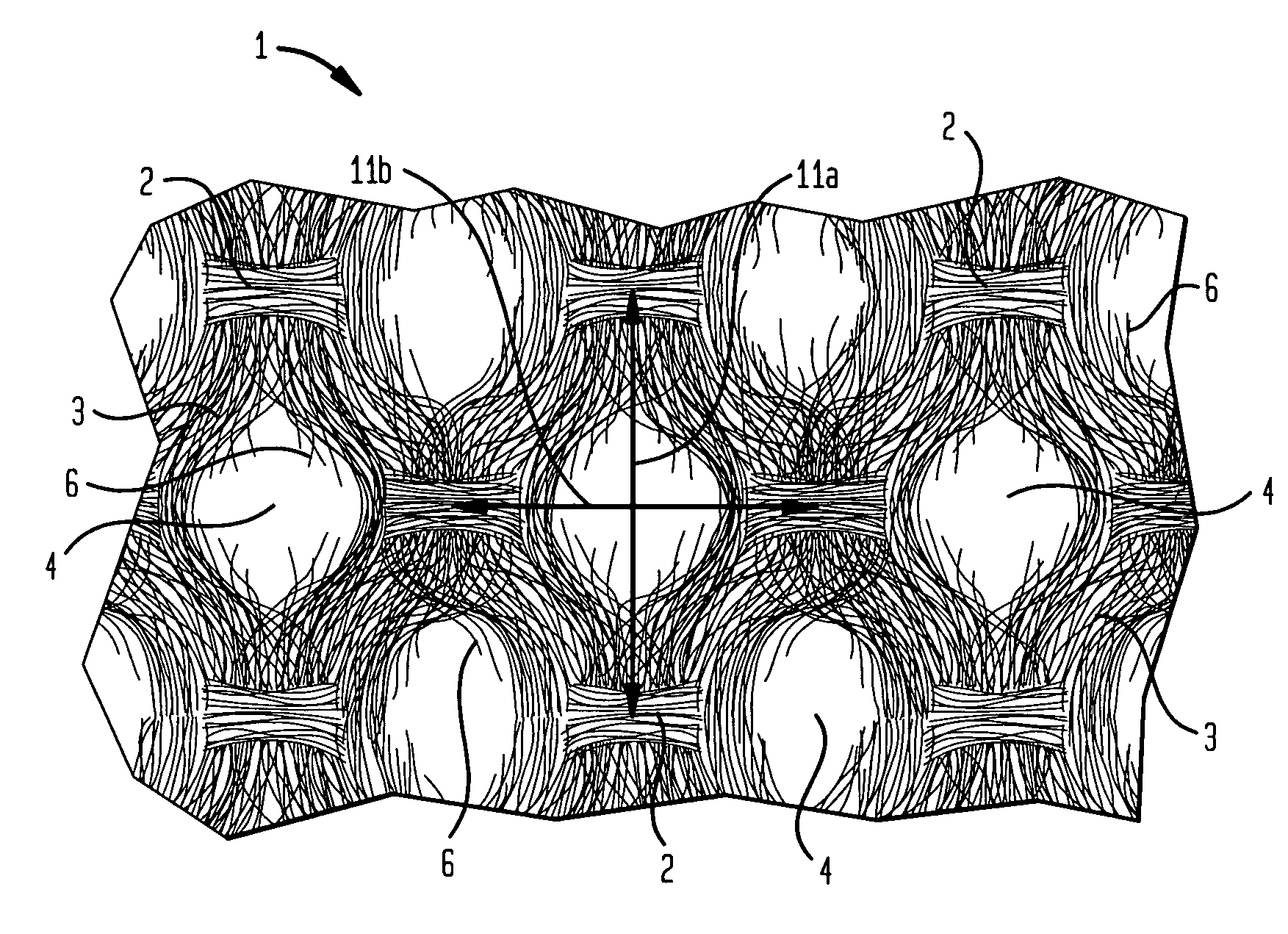
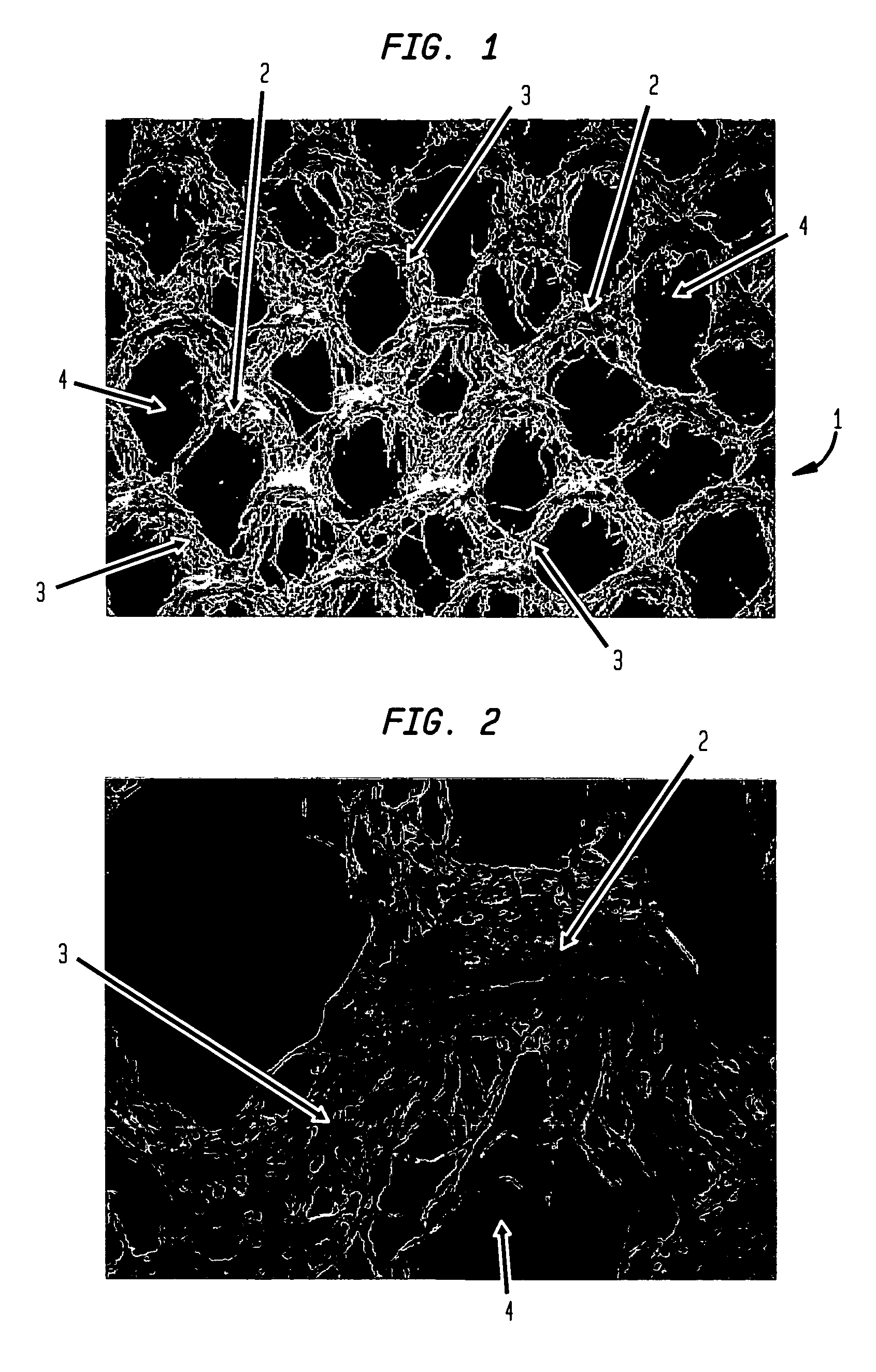
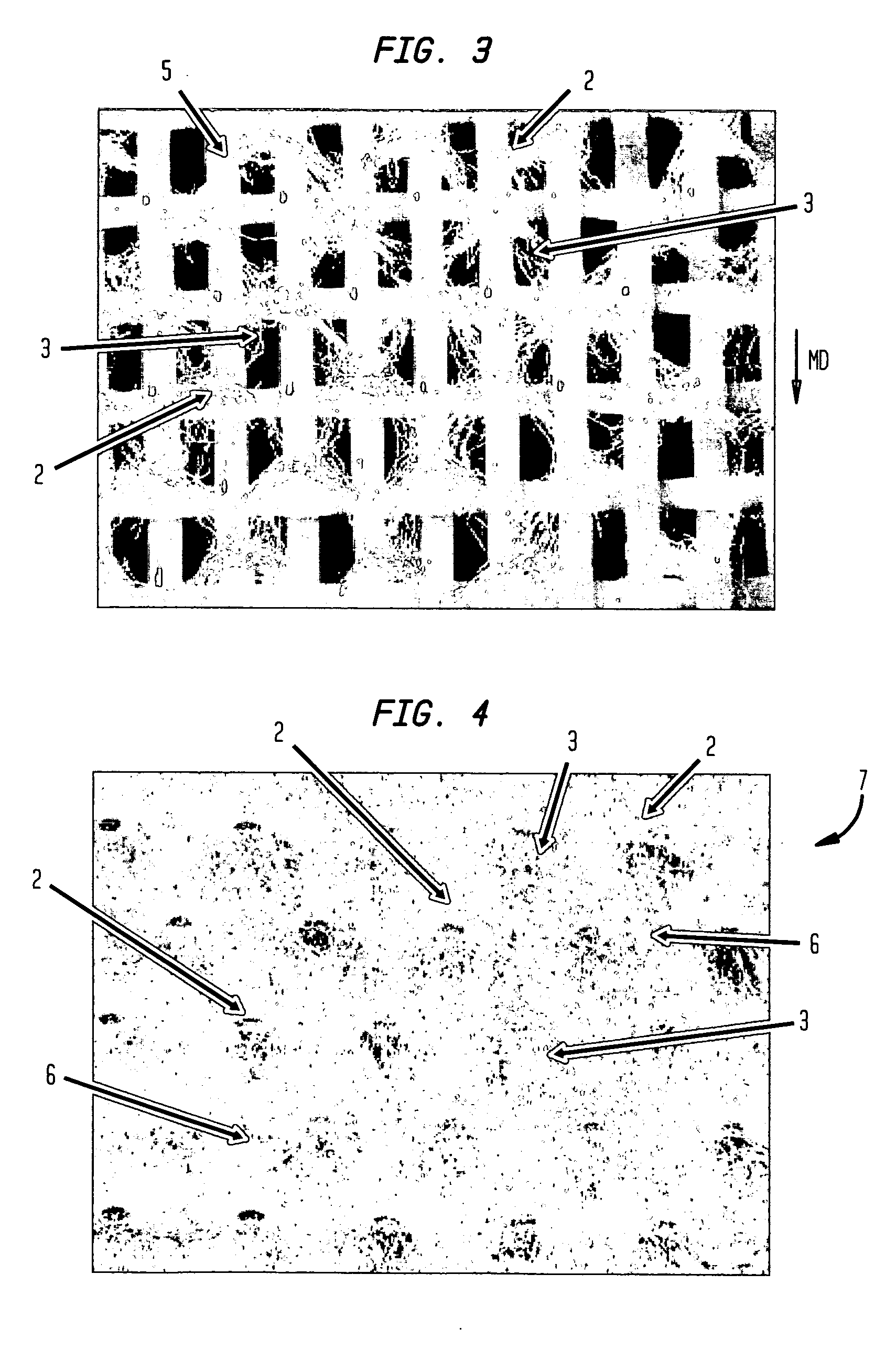
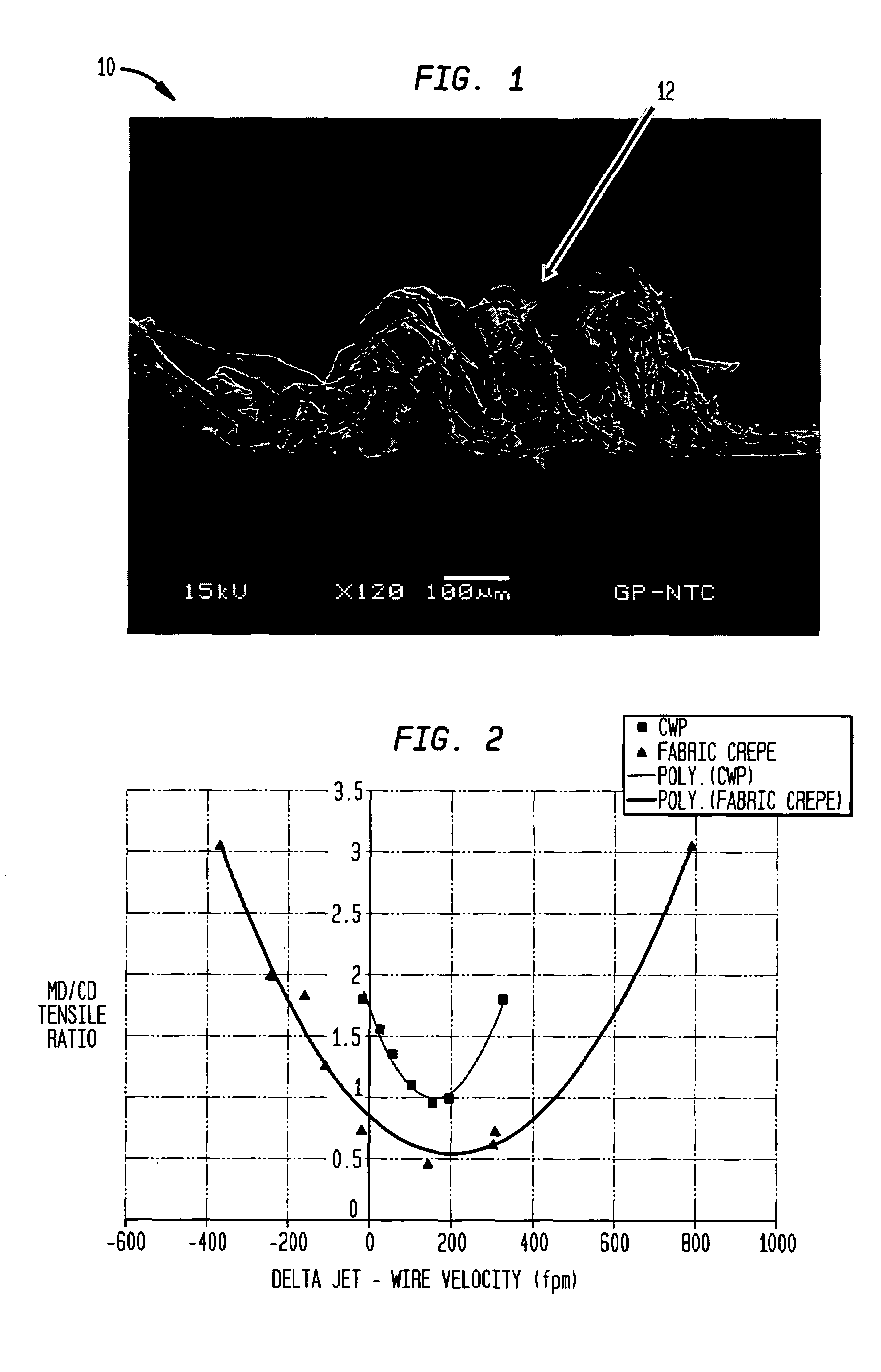
An absorbent sheet of cellulosic fibers includes a mixture of hardwood fibers and softwood fibers arranged in a reticulum having: (i) a plurality of pileated fiber enriched regions of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by way of (ii) a plurality of lower local basis weight linking regions whose fiber orientation is biased along the machine direction between pileated regions interconnected thereby, wherein the sheet exhibits a % CD stretch which is at least about 2.75 times the dry tensile ratio of the sheet. Tensile ratios of from about 0.4 to about 4 are readily achieved.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Multi-ply paper towel with absorbent core
ActiveUS7662257B2VariationImprove performanceNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCellulosePaper towel
A multi-ply absorbent sheet of cellulosic fiber with continuous outer surfaces is provided an absorbent core between the outer surfaces. The absorbent core includes a non-woven fiber network having: (i) a plurality of pileated fiber enriched of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by way of (ii) a plurality of lower local basis weight linking whose fiber orientation is biased along the direction between pileated interconnected thereby, and (iii) a plurality of fiber-deprived cellules between the fiber enriched and linking regions, also being characterized by a local basis weight lower than the fiber enriched regions. The cellules provide a sponge-like internal structure of low fiber density regions.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Wet-pressed tissue and towel products with elevated CD stretch and low tensile ratios made with a high solids fabric crepe process
An absorbent sheet of cellulosic fibers includes a mixture of hardwood fibers and softwood fibers arranged in a reticulum having: (i) a plurality of pileated fiber enriched regions of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by way of (ii) a plurality of lower local basis weight linking regions whose fiber orientation is biased along the machine direction between pileated regions interconnected thereby, wherein the sheet exhibits a % CD stretch which is at least about 2.75 times the dry tensile ratio of the sheet. Tensile ratios of from about 0.4 to about 4 are readily achieved.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Method of manufacturing curved composite structural elements
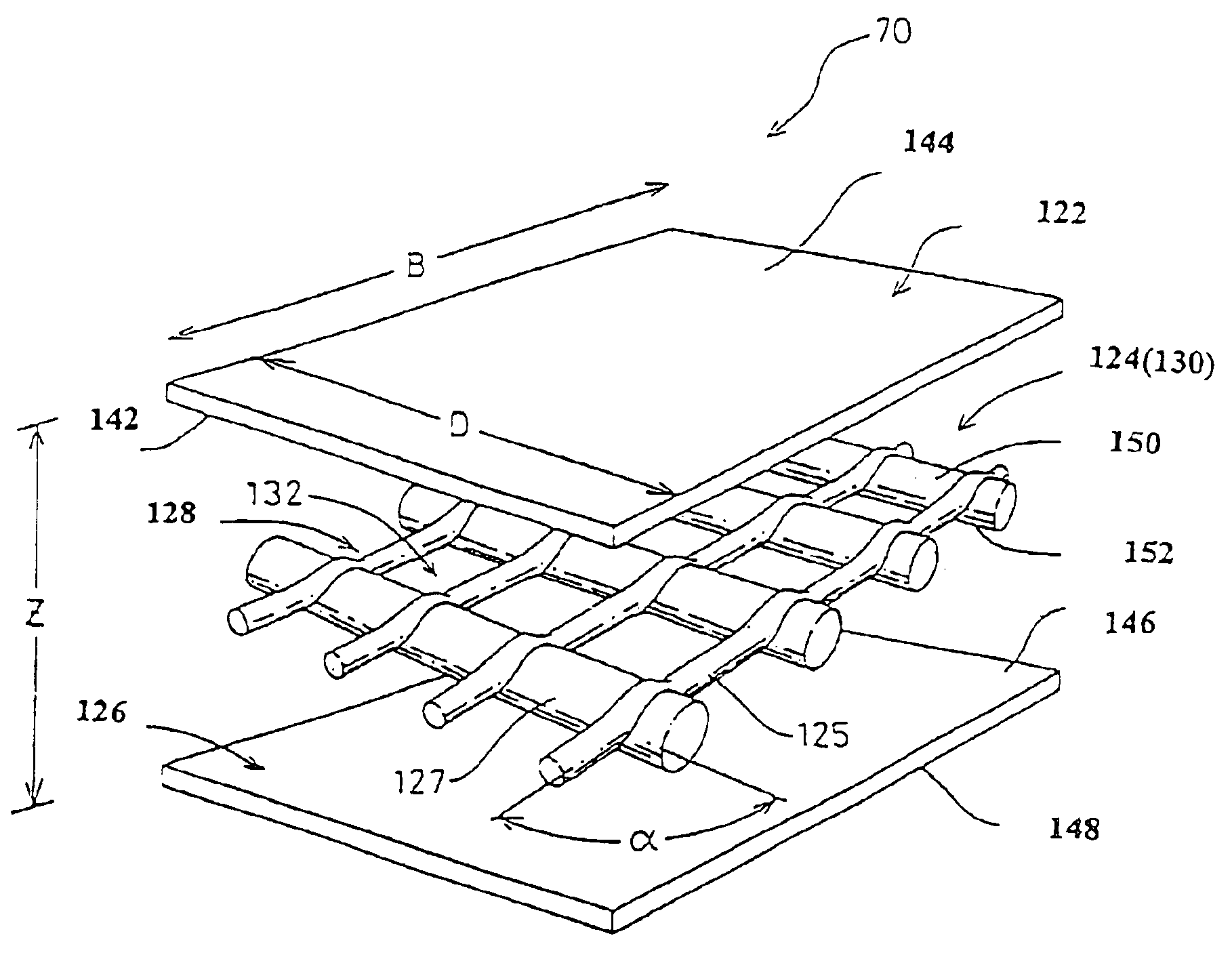
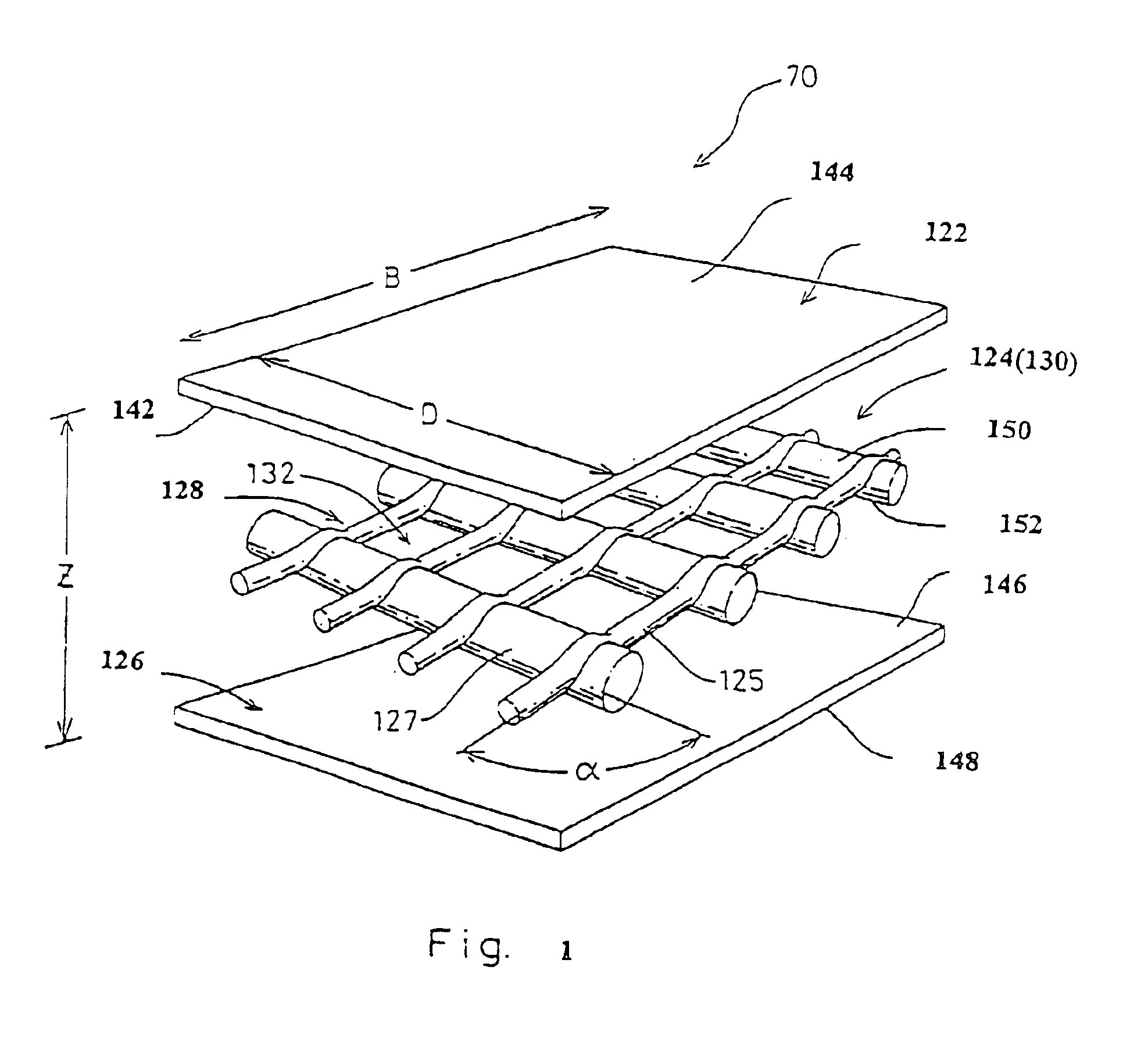
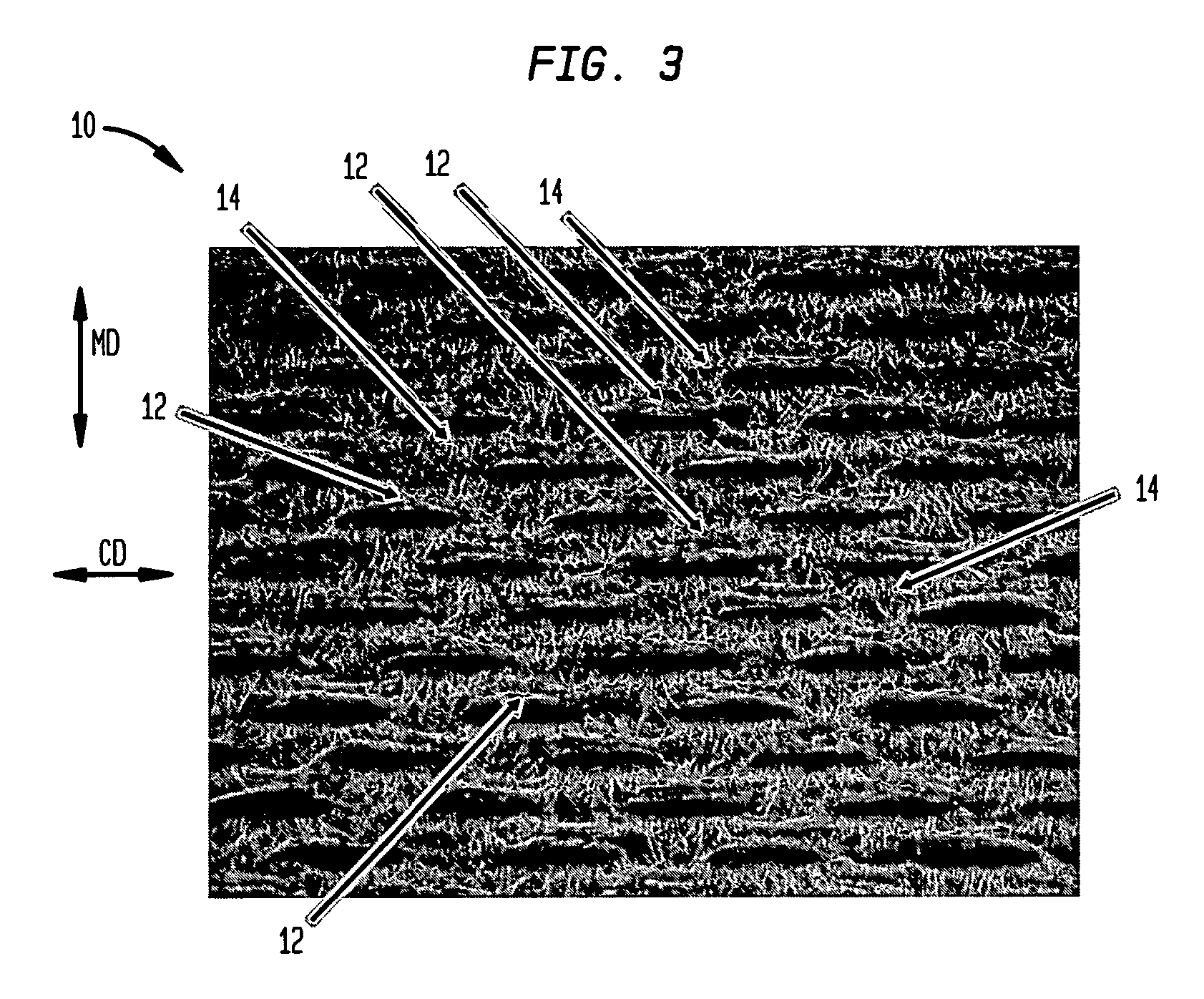
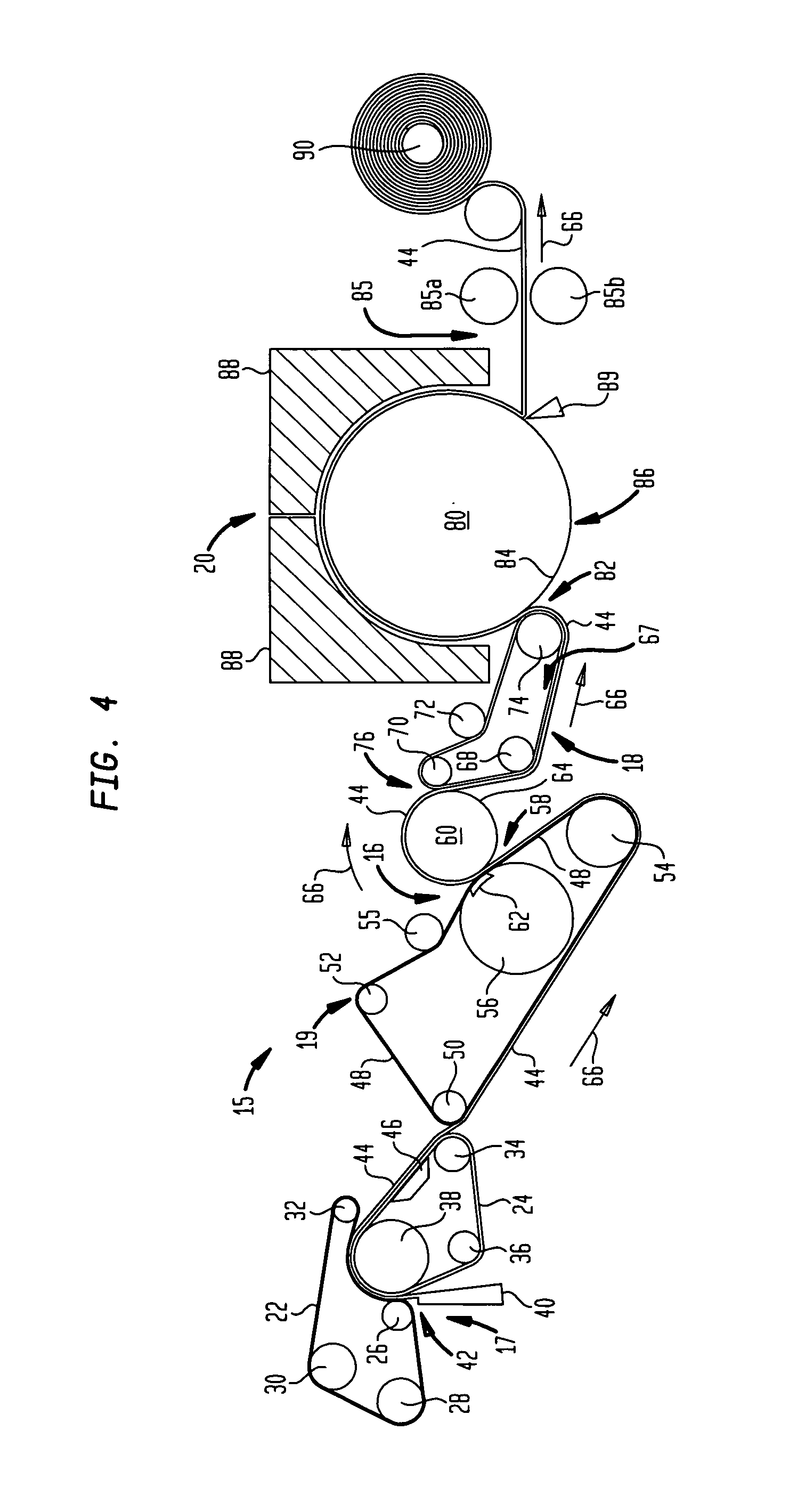
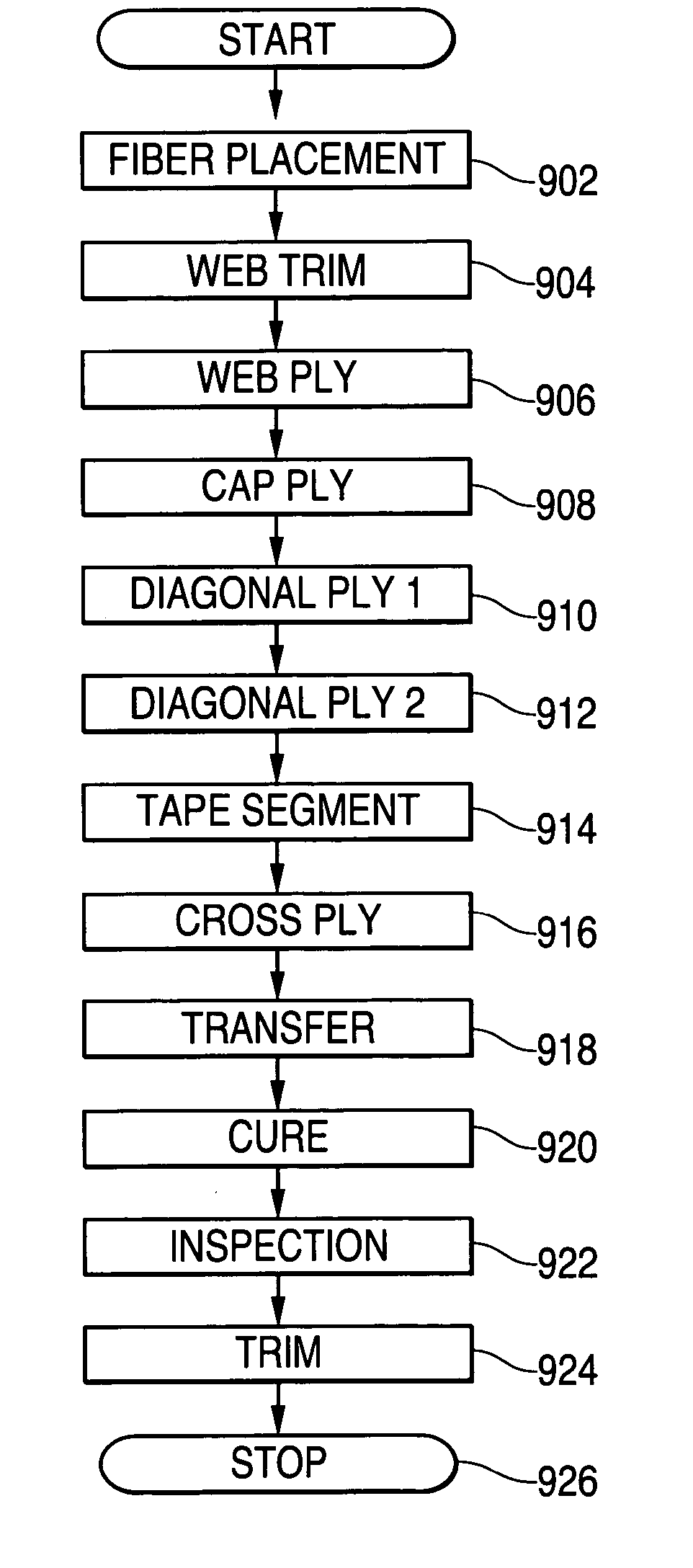
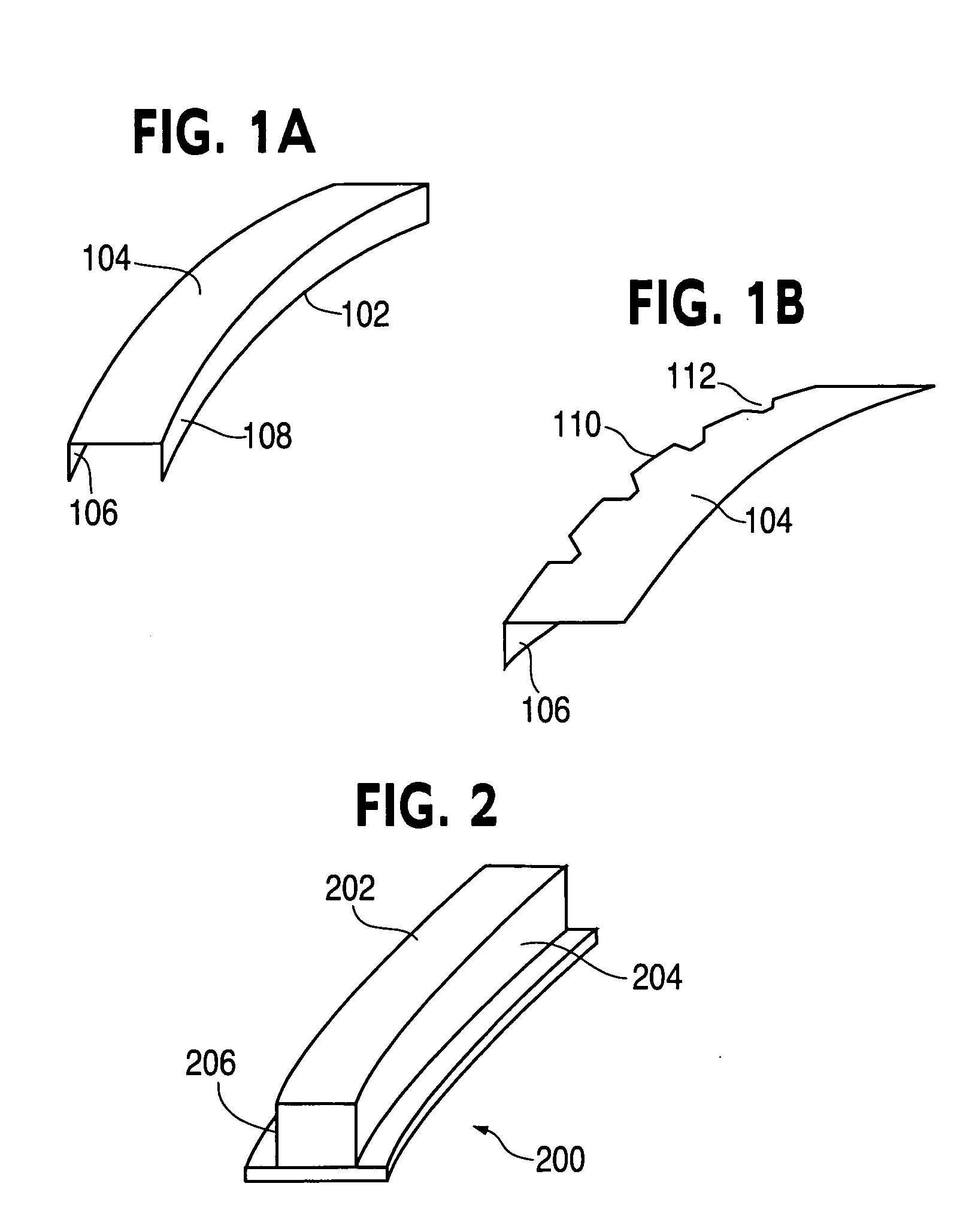
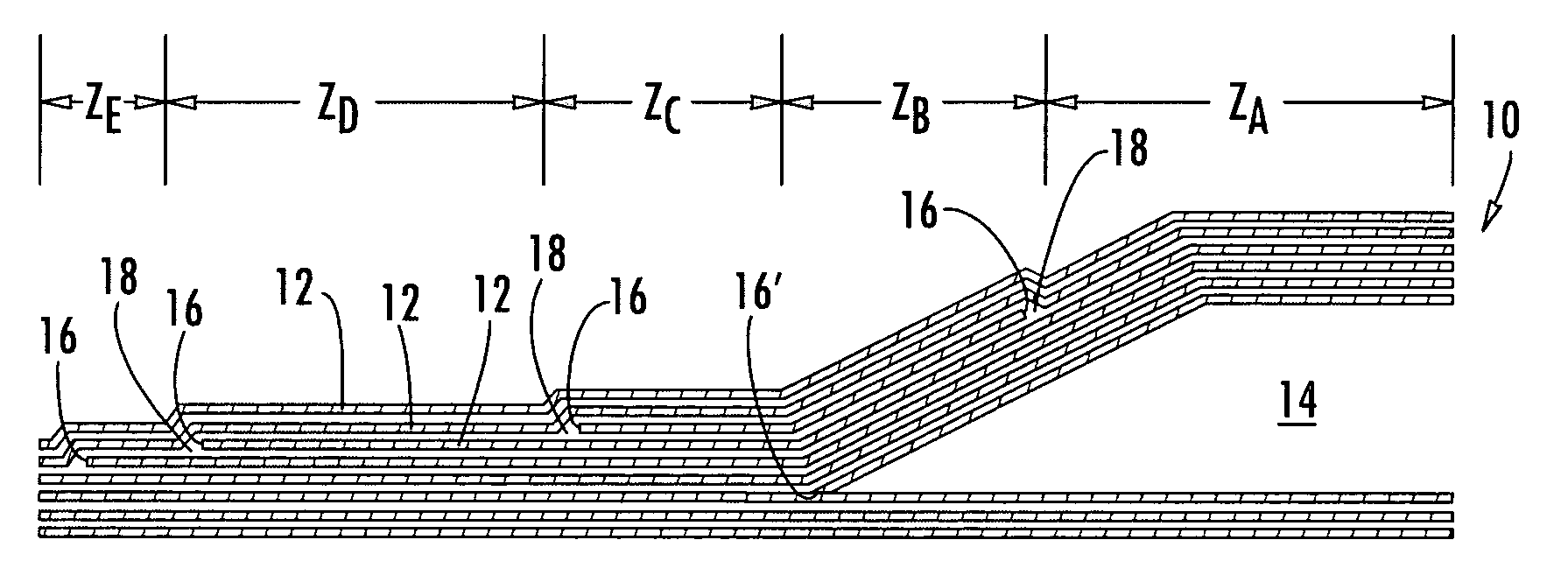
A method of manufacturing curved composite structural elements can include fabricating a web ply in a flat curve over a removable substrate and laying up the ply on a curved web surface of a manufacturing tool. The method also can include laying up a diagonal ply with fibers oriented at + / −45° from the centerline of the web surface. The method further can include cutting a unidirectional composite tape into segments and laying up the tape segments to form a cross ply with a fiber orientation normal to the centerline of the web surface. One or both edges of the diagonal and cross plies may be folded over one or two sides of the manufacturing tool to form one or two flange surfaces. Additionally, a cap ply can be laid up on one or both flange surfaces using composite tape. The structural element layup can then be inspected and any excess composite material can be trimmed away.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Nonwoven fabric, nonwoven fabric manufacturing method, and nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus
The present invention provides a nonwoven fabric of which at least one of fiber orientation, fiber density, and basis weight is adjusted, and in which at least one of a predetermined groove portion, an opening, and a protrusion is formed, a manufacturing method for the nonwoven fabric, and a nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus. The nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus of the present invention manufactures a nonwoven fabric of which at least one of fiber orientation, fiber density, and basis weight is adjusted, or in which at least one of a predetermined groove portion, an opening, and a protrusion is formed by blowing fluid mainly containing gas onto a fiber web which is formed in a sheet shape, and which is in a state where at least a portion of the fibers constituting the fiber aggregate has a degree of freedom.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Undirectionally cold stretched nonwoven webs of multipolymer fibers for stretch fabrics and disposable absorbent articles containing them
InactiveUS6849324B2High elongationPeak load will increaseDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsElastomerEthylene Homopolymers
A nonwoven web of multipolymer fibers is described that is unidirectionally stretched and permanently elongated at ambient conditions and exhibits a substantial increase in tensile strength in the stretch direction. The ratio of tensile strength of the web in the direction of fiber orientation to the tensile strength in the other direction is at least about 10:1. The ratio of elongation at peak load in a direction transverse to the direction of fiber orientation is at least about 6:1. The multipolymer fibers normally are a blend of polyethylene and a polypropylene homopolymer or copolymer, one of which is a dominant phase and one of which is a dispersed phase. A third component having elastomeric properties that is at least partially miscible with one or both of the other components is included in some blends. The nonwoven webs are stretchable well beyond their initial dimensions in the direction perpendicular to the stretch direction and are especially useful in laminates with elastomeric members for use in disposable absorbent articles to impart elasticity thereto.
Owner:BBA NONWOVENS SIMPSONVILLE
Cleaning device and process for producing the same
InactiveUS8146197B2Long operating timeLow costBoard cleaning devicesCarpet cleanersFiber bundleAdhesive
Owner:YAMADA KIKUO
High pressure molding of composite parts
ActiveUS20130101406A1Avoid distortionReduce weightPump componentsReaction enginesJet engineShell molding
Composite pre-forms are molded at high pressure to form composite parts that can be used in place of metal-based high performance parts, such as the outlet guide vanes found in turbofan jet engines. The composite pre-forms include two different fiber orientations that are co-molded in a resin matrix at high pressures to provide composite outlet guide vanes and other high performance parts. Chambers within the composite part are optionally formed during molding of the pre-form at high pressures.
Owner:HEXCEL
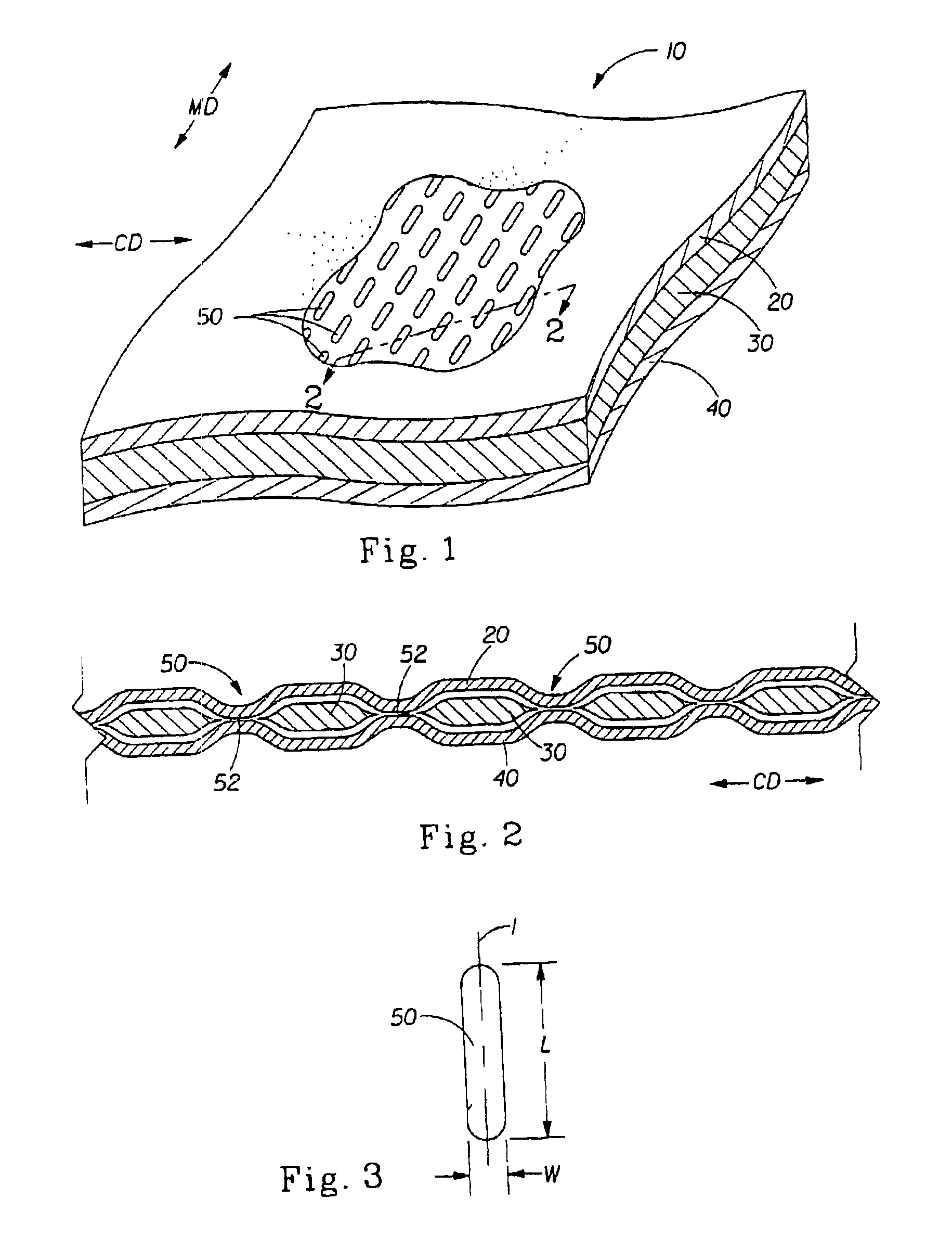
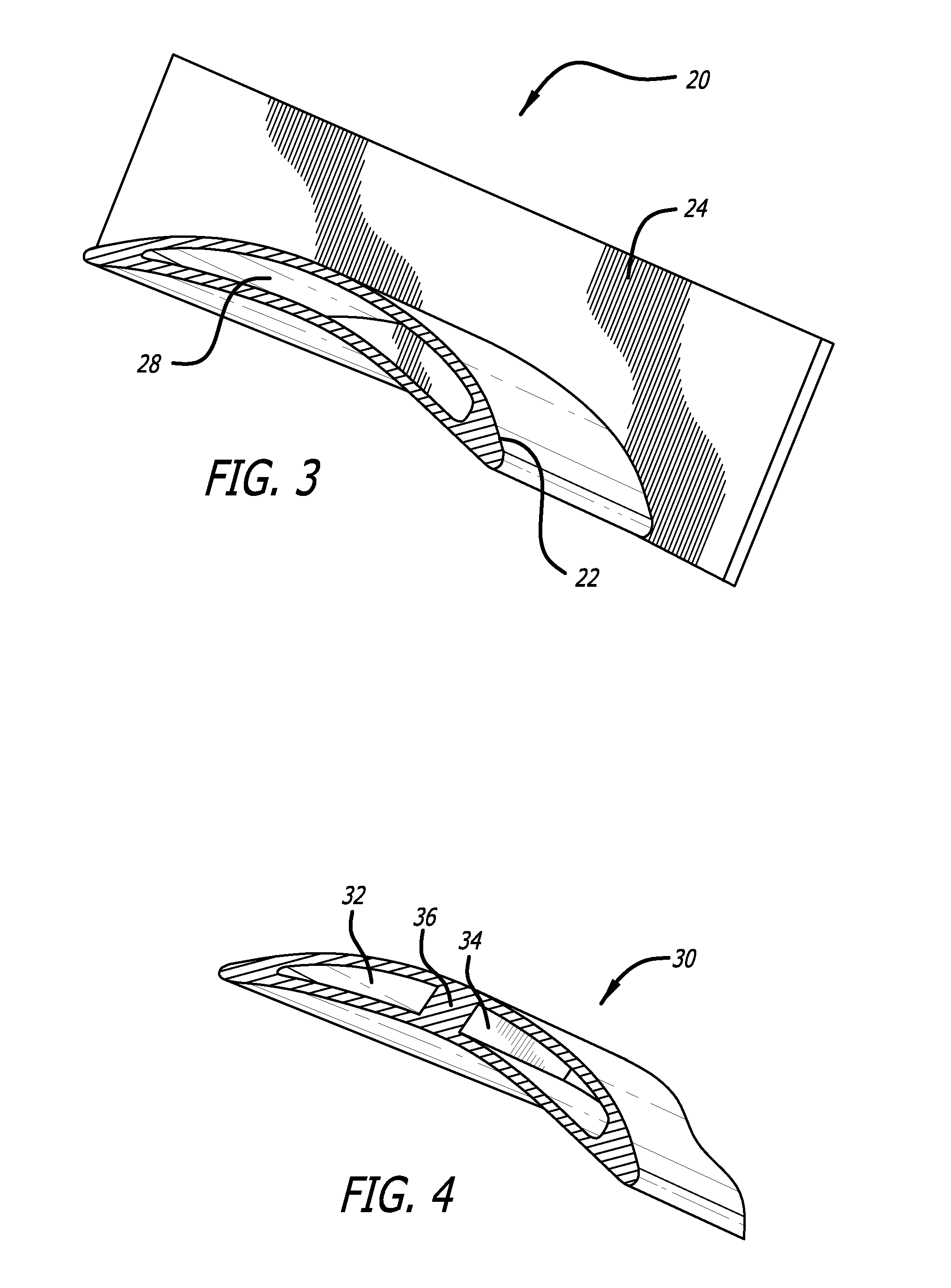
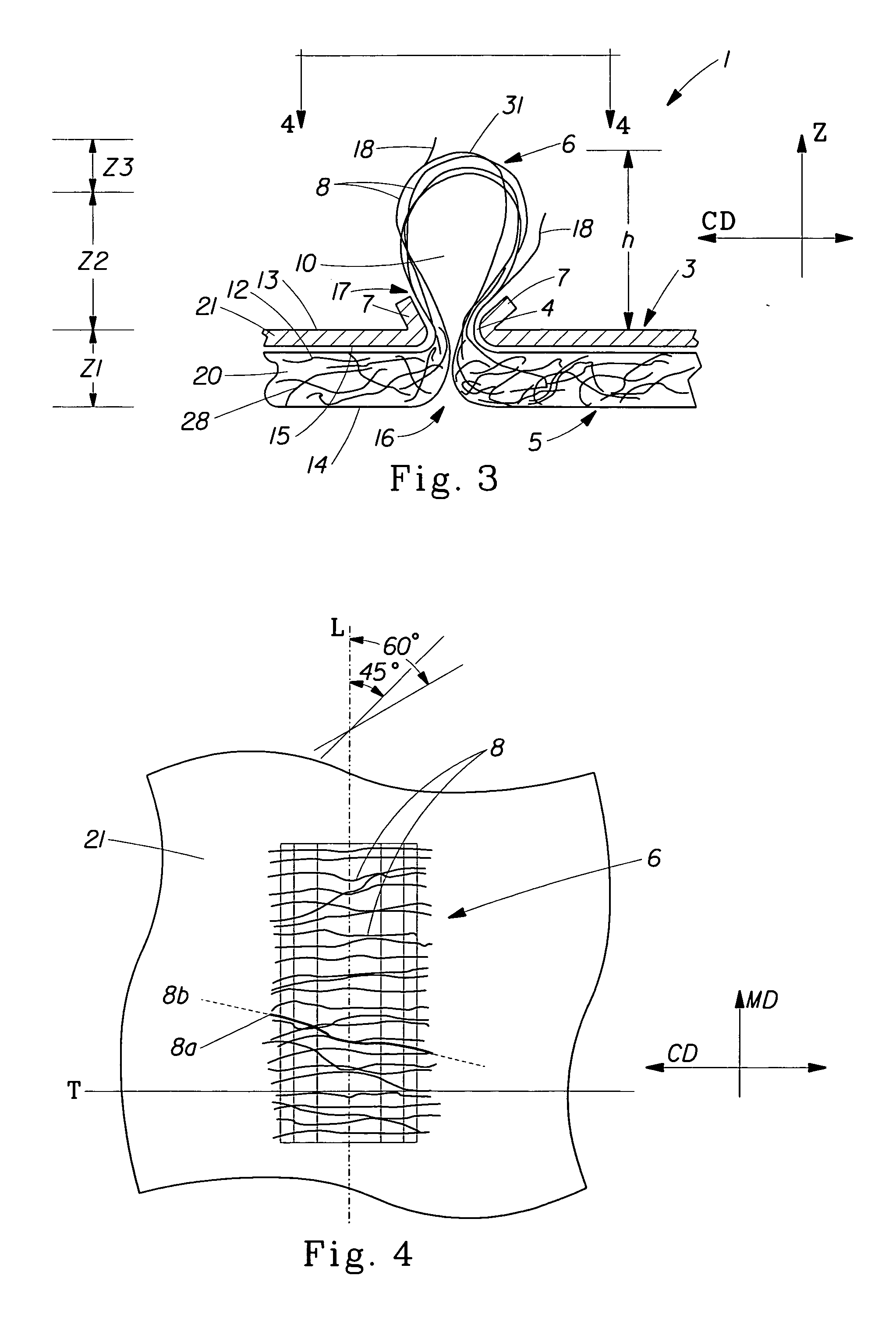
Tufted laminate web
InactiveUS20070116926A1Cosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFiber orientationMechanical engineering
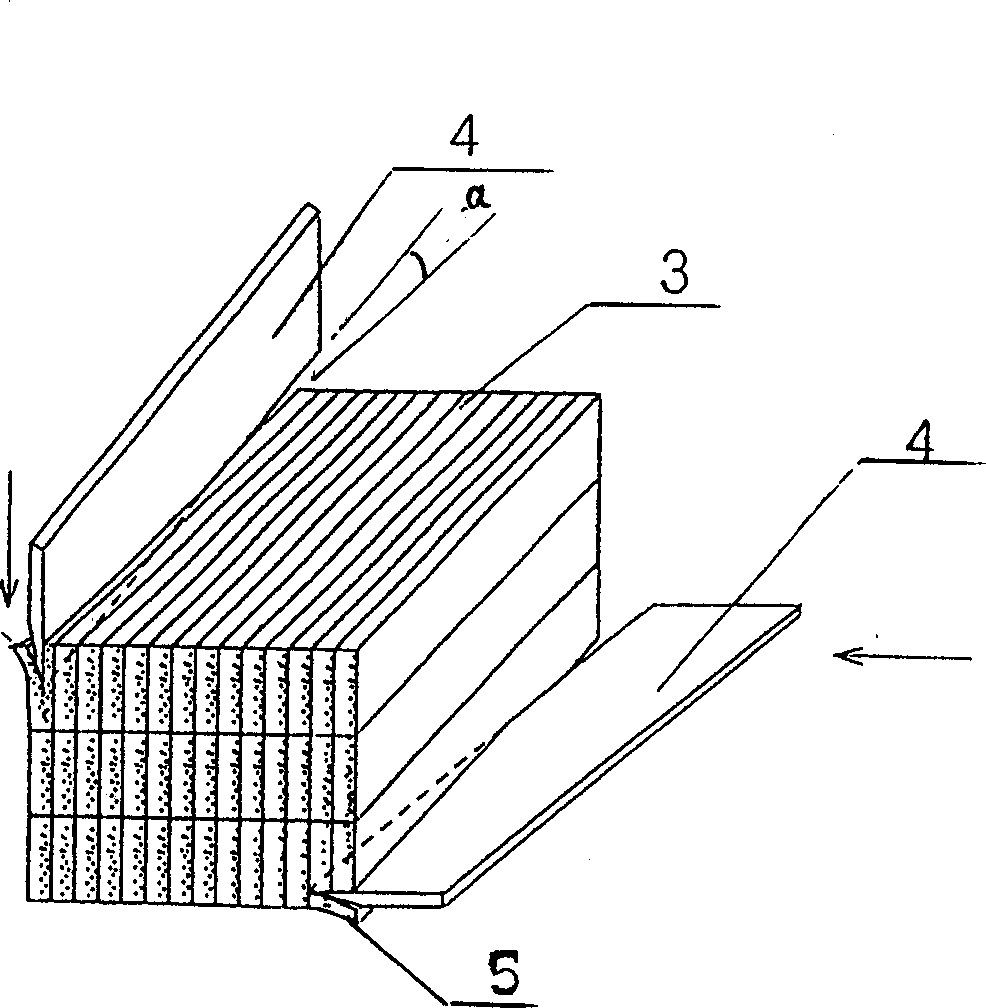
An absorbent article having a topsheet, a backsheet, and an absorbent core disposed between the topsheet and the backsheet. The topsheet has a first side and a second side, the first side being a body-facing side. The topsheet defines a CD-MD plane and includes a fibrous nonwoven web and tufts, the tufts having fibers of the fibrous nonwoven web. The topsheet further includes first, second and third zones, each zone being characterized in a Z-direction by the zone fiber orientation, wherein the first and third zones are displaced relative to each other and each include fibers having portions orientated substantially parallel to said CD-MD plane of the topsheet. The second zone is intermediate and adjacent to the first and third zones, the second zone including substantially reoriented fibers that are substantially vertically oriented with respect to the CD-MD plane of said topsheet.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
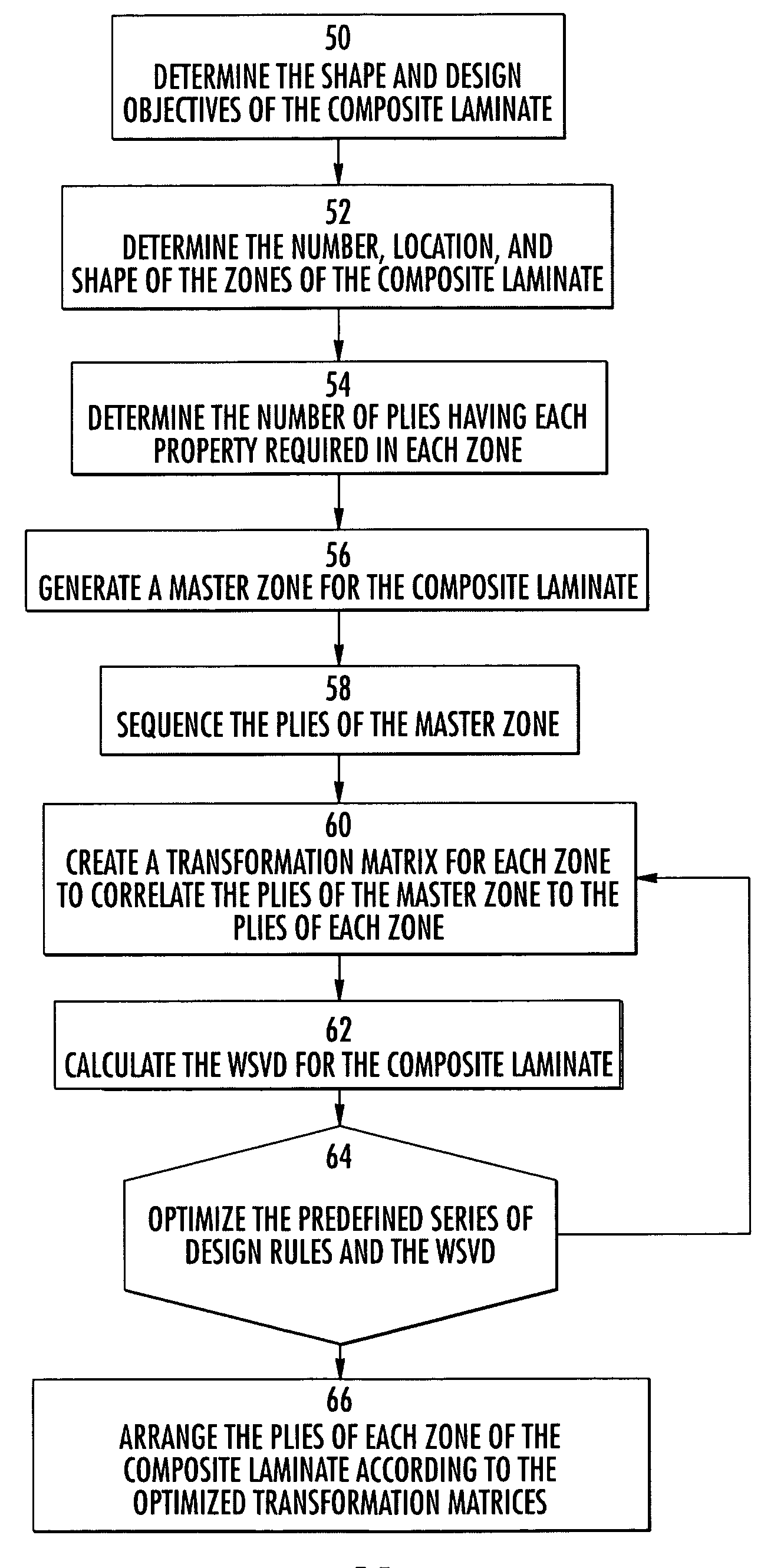
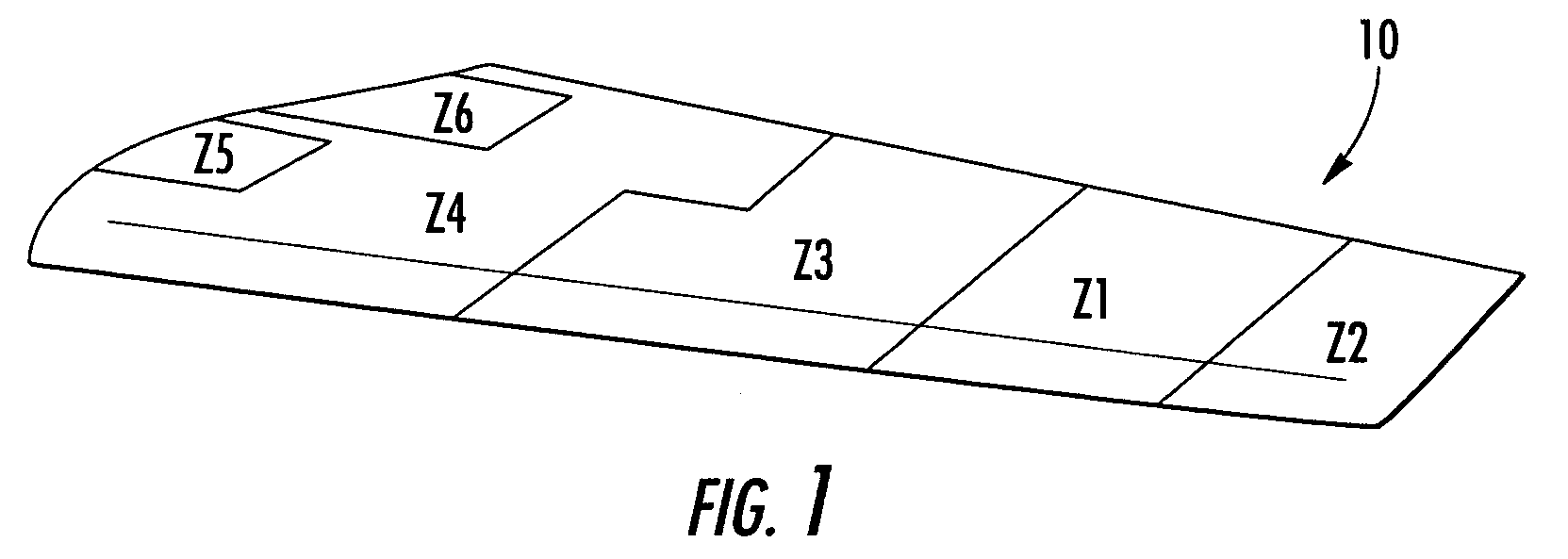
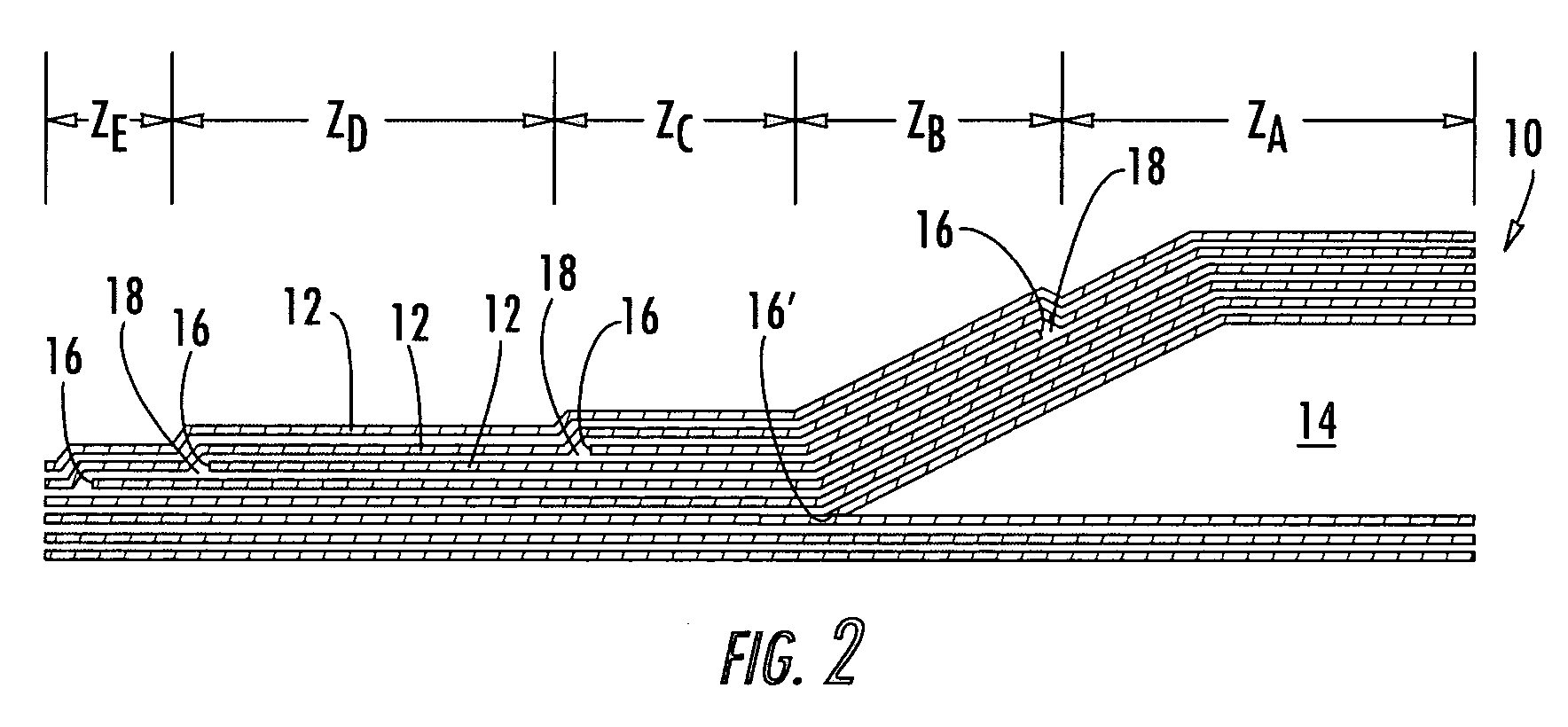
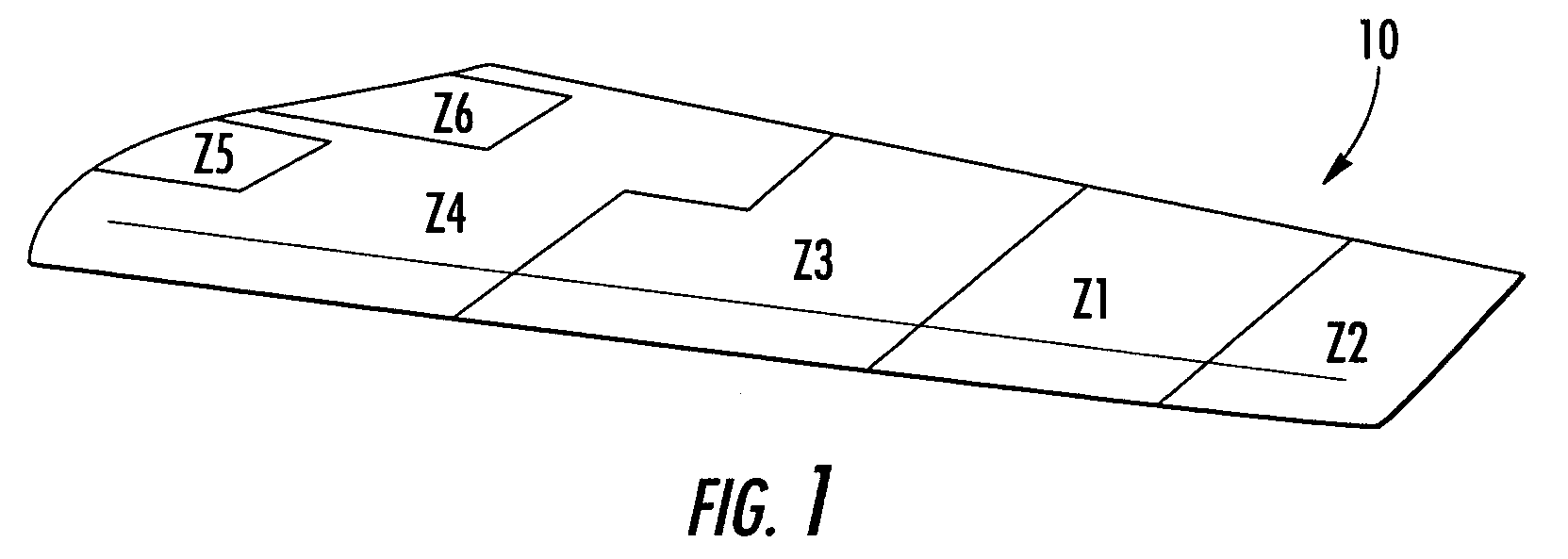
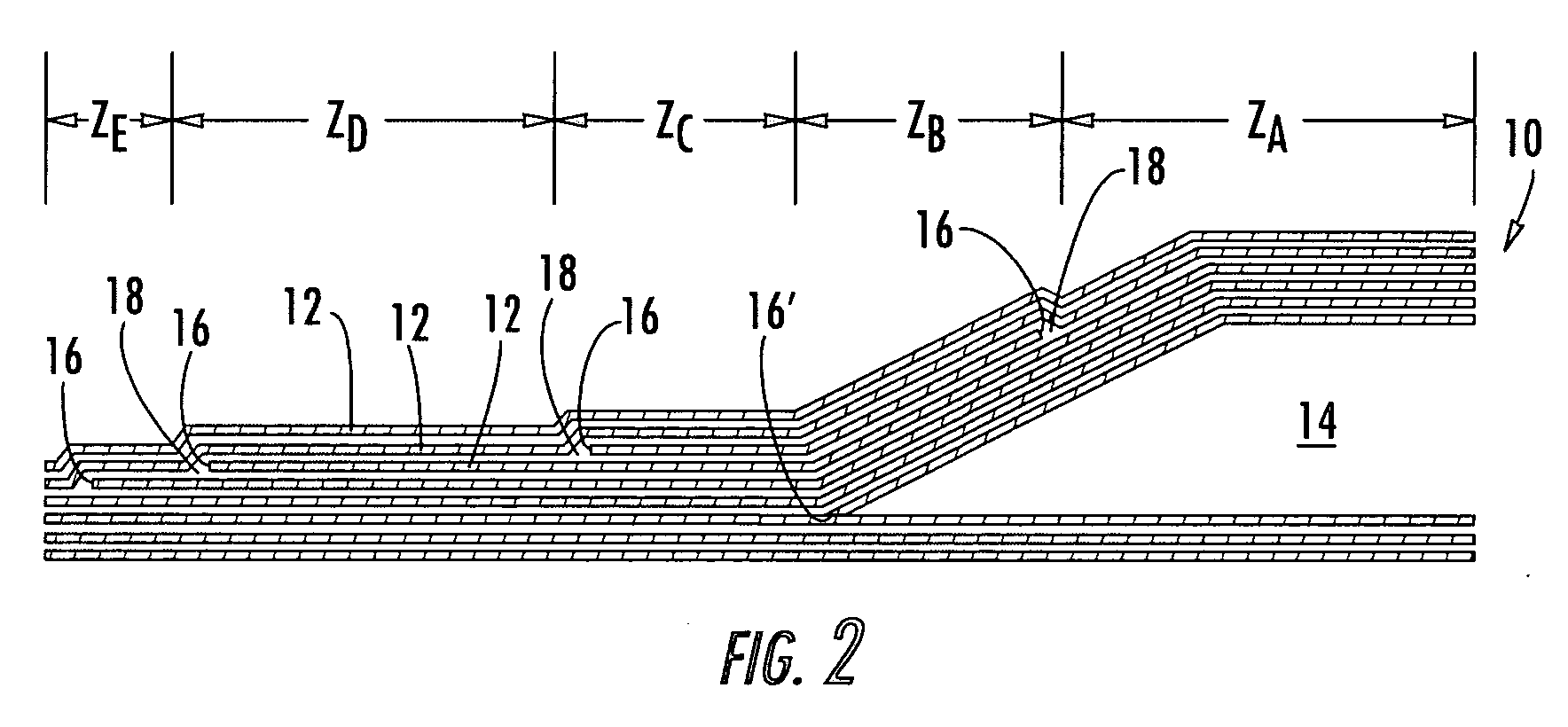
Composite stacking sequence optimization for multi-zoned composites
ActiveUS7243055B2Shorten the lengthReduce the numberCellulosic plastic layered productsComputation using non-denominational number representationComposite laminatesStructural engineering
Method, apparatus, and computer program products are provided for optimizing a stacking sequence for a composite laminate having multiple zones to reduce the number or length of internal ply edges in the composite laminate with the most design rule compliant sequences. Once the number and location of the zones and the number of plies having different properties required for each zone have been determined for the composite laminate, a master zone is generated. Advantageously, the property of the plies may be fiber orientation, though alternative properties such as material may be considered when determining the number of required plies. The master zone notionally includes the maximum number of plies having a respective property required by any one zone, and the plies of the master zone are sequenced using a predefined series of design rules. The plies of each zone are then arranged based upon the stacking sequence of the master zone. A transformation matrix, a second predefined series of design rules, and a weighted solid / void differential may be used when arranging the plies of each zone based upon the stacking sequence of the master zone.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for fabricating a curved beam from composite material
InactiveUS7670525B2Avoid huge wasteGood strength performanceMouldsWood working apparatusComposite laminatesEngineering
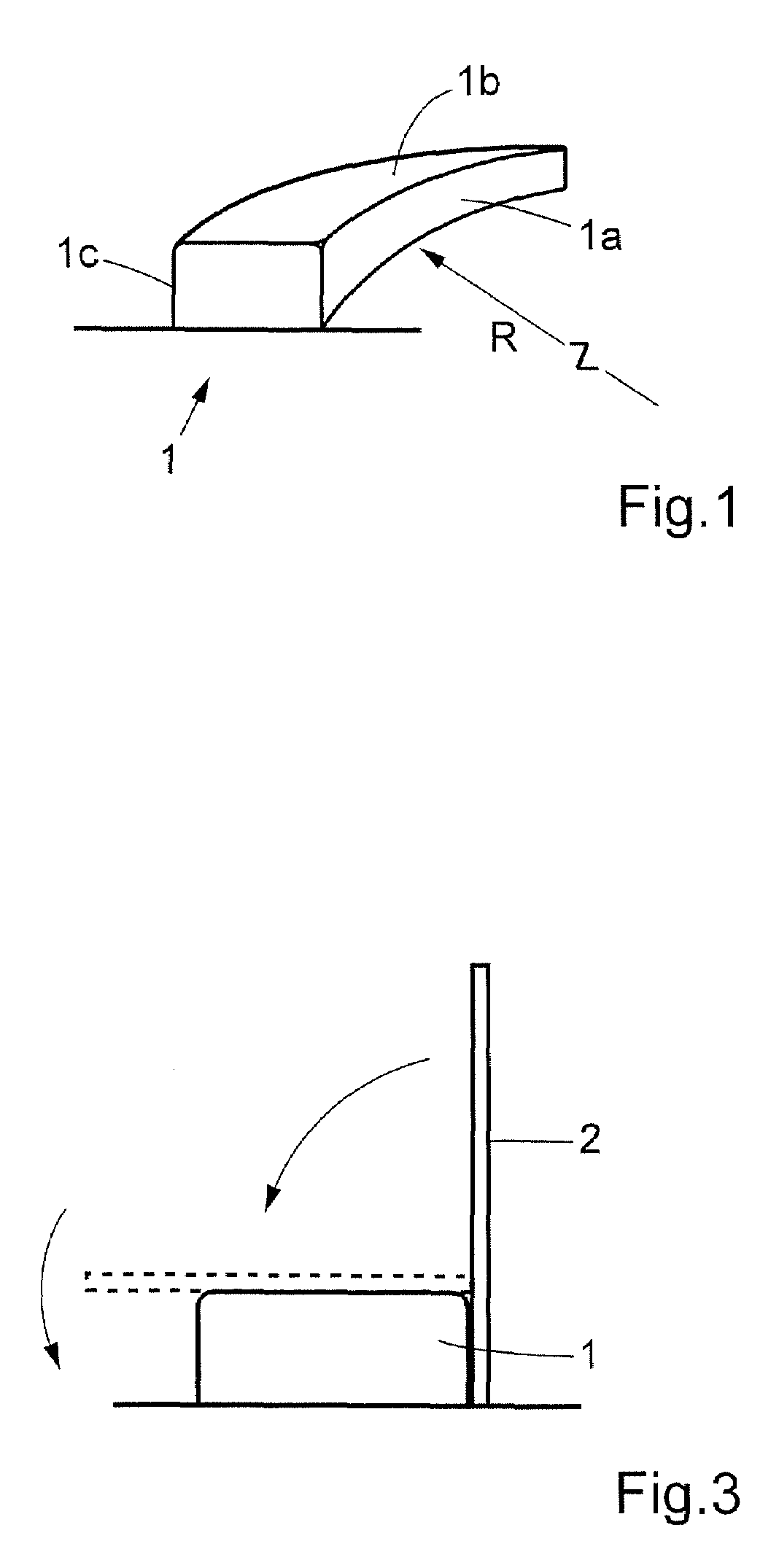
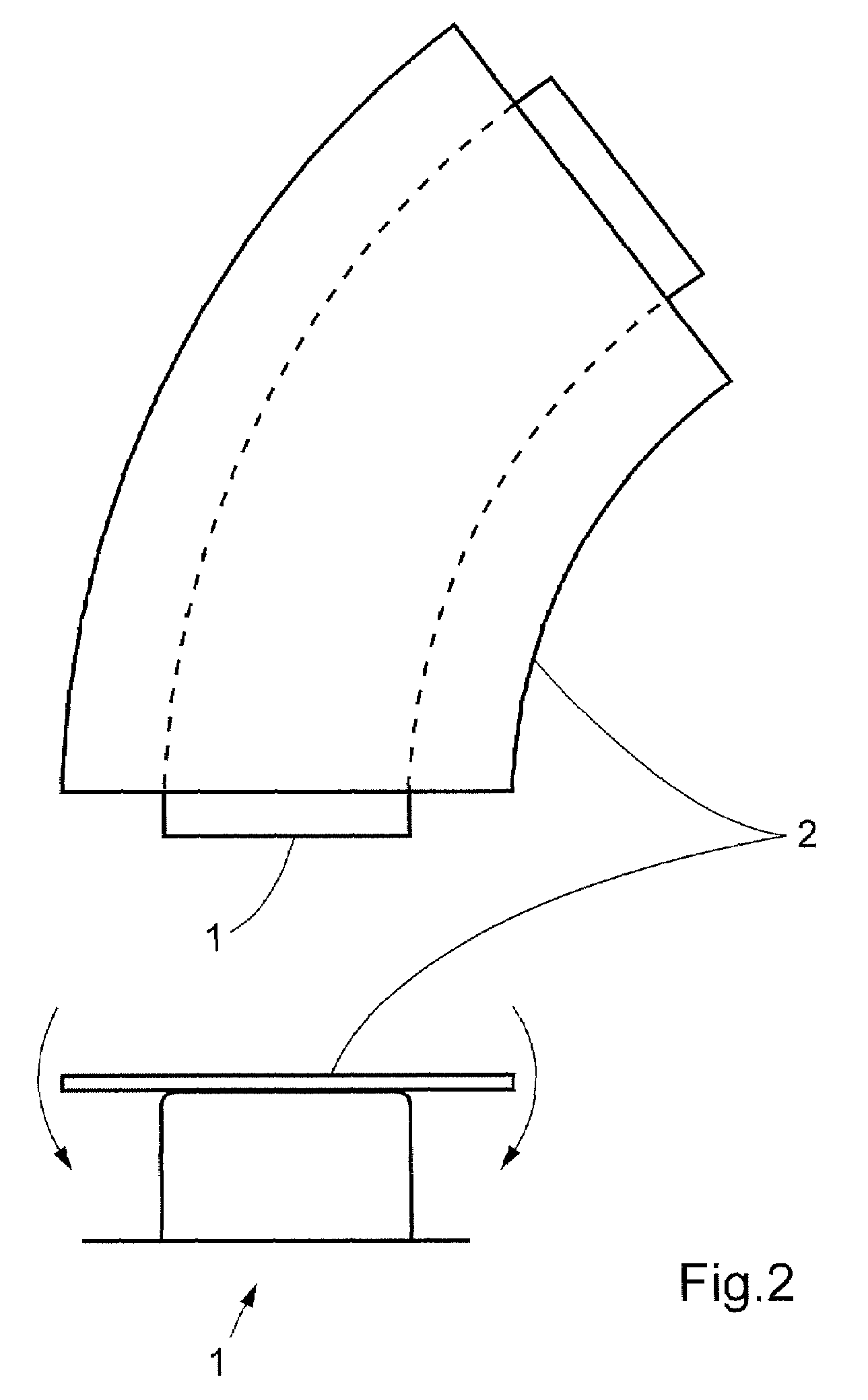
A method for fabricating a curved beam from fiber composite material. A flat fiber composite laminate including a plurality of layers and at least two different fiber directions is formed. The fiber composite laminate is disposed in contact with a male tool includes a first flange, a second flange and an intermediate web. The male tool is curved in its longitudinal direction with a radius of curvature in such a way that the first flange has a shorter longitudinal extent than the second flange. The fiber composite laminate is brought into contact with and secured to the first flange of the male tool. The male tool and the fiber composite laminate are then rotated relative to one another so that the fiber composite laminate is brought into contact with the intermediate web of the male tool in a first rotational movement, and brought into contact with the second flange of the male tool in a second rotational movement. The fiber composite laminate hardens on the male tool, and the finished beam is separated from the tool. Also a beam of fiber composite material fabricated according to the method.
Owner:SAAB AB
Absorbent body, multilayer absorbent body and absorbent article
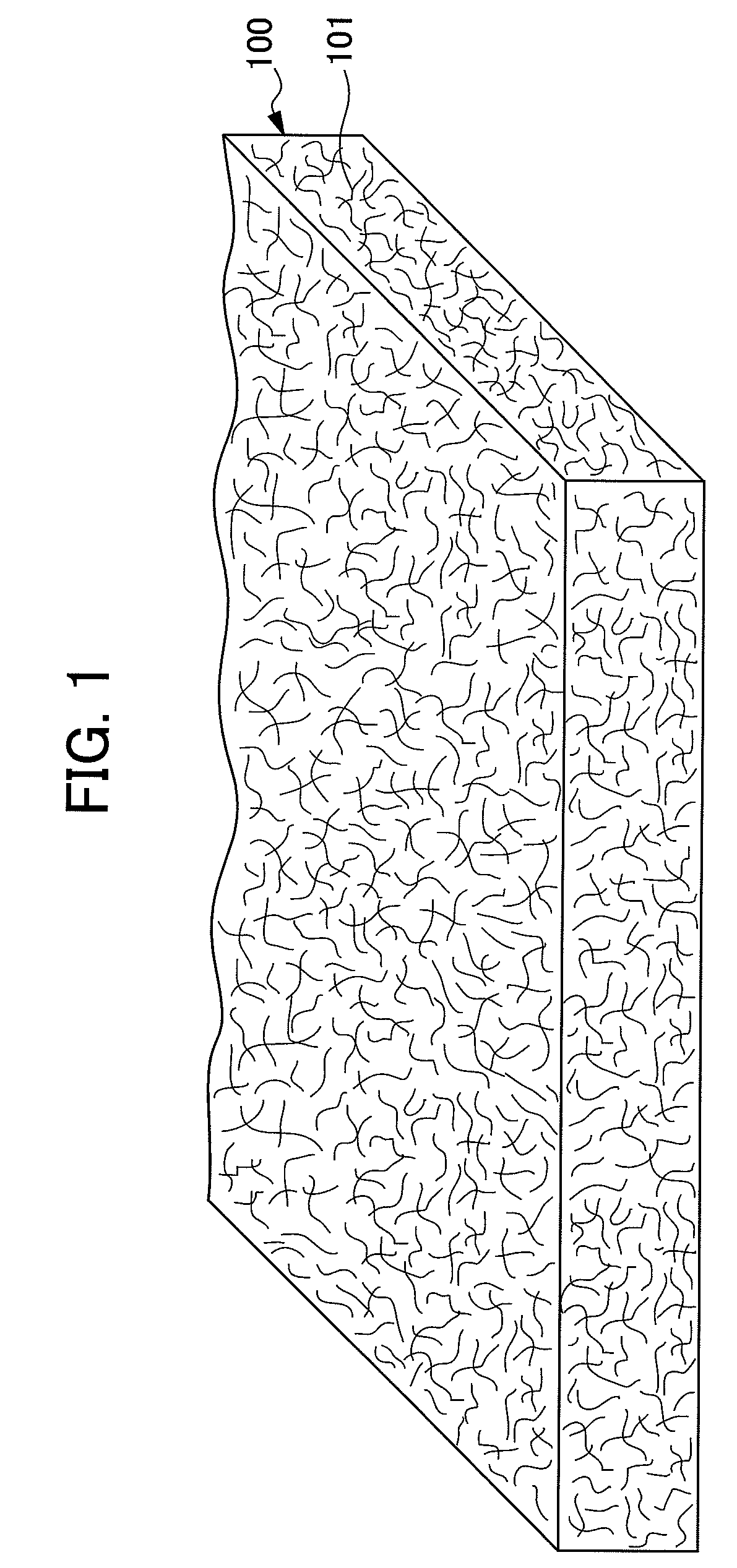
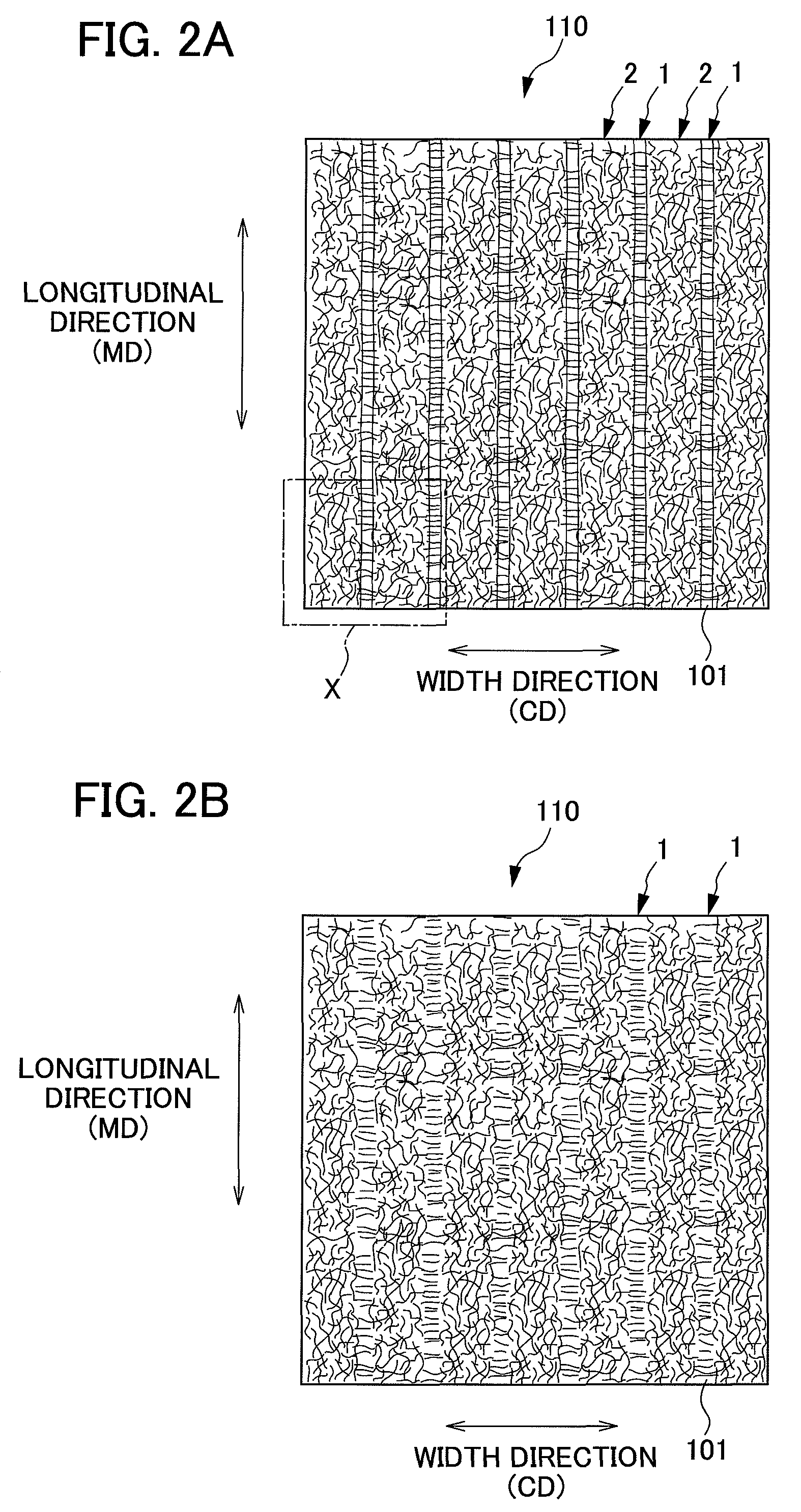
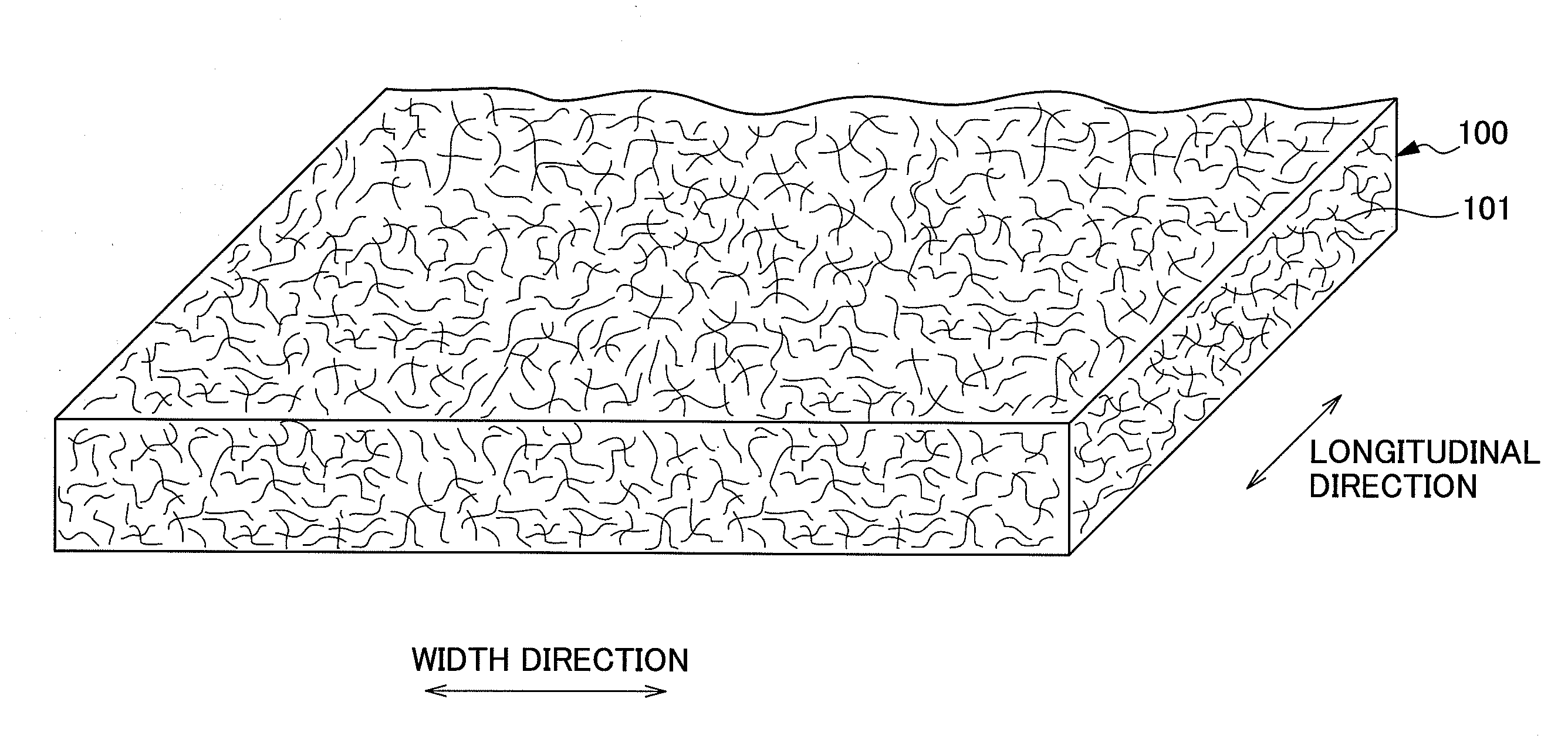
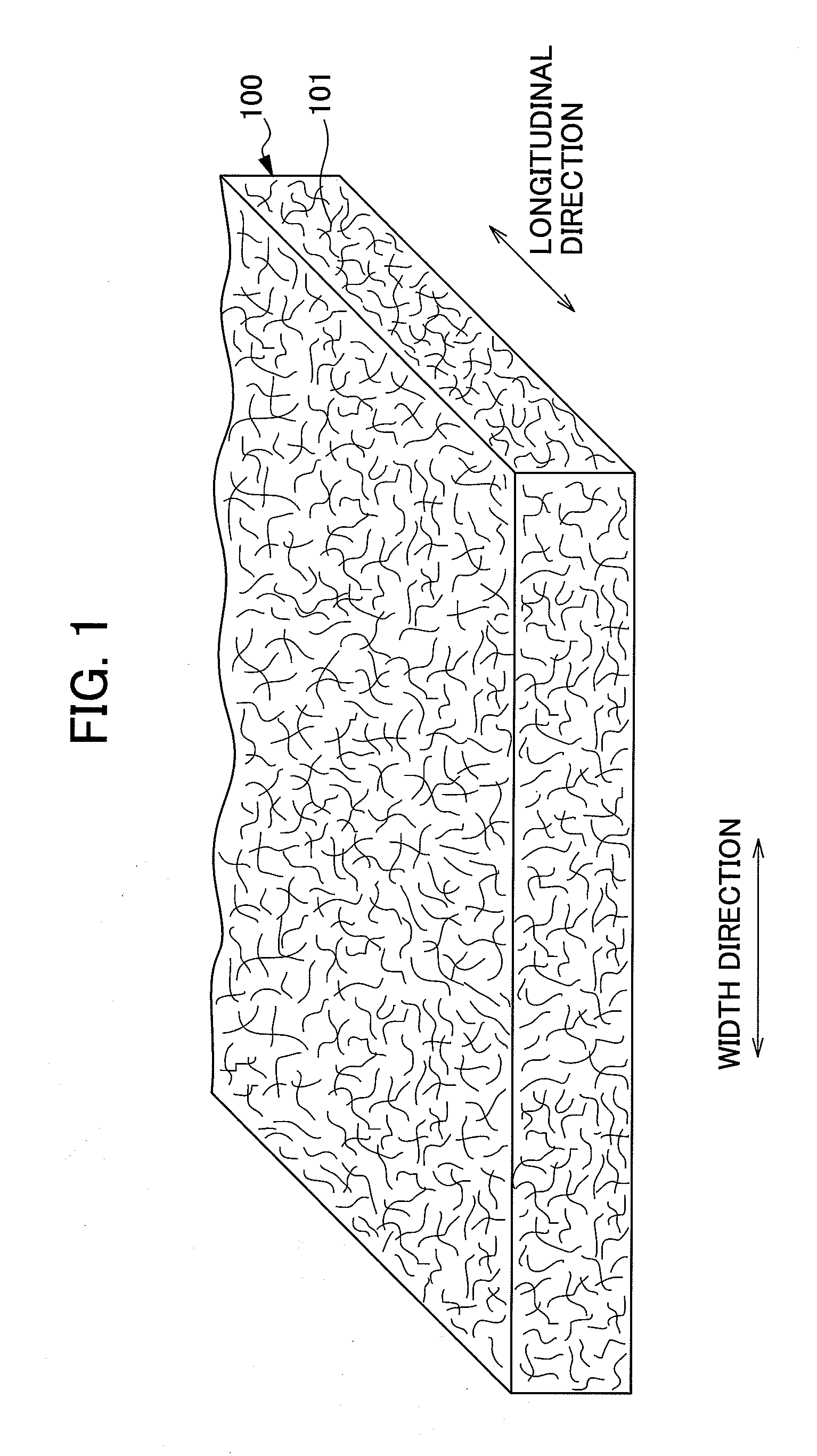
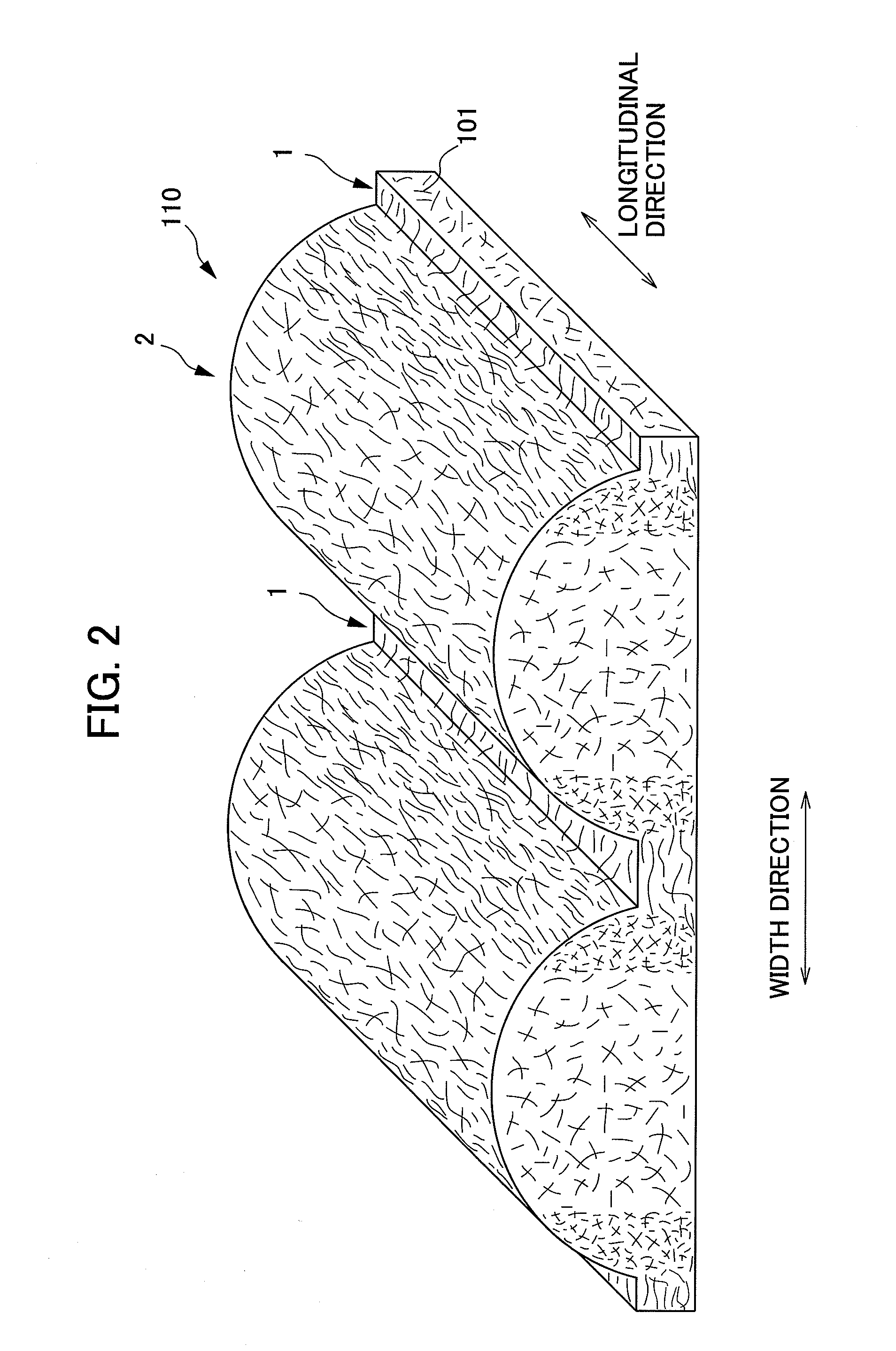
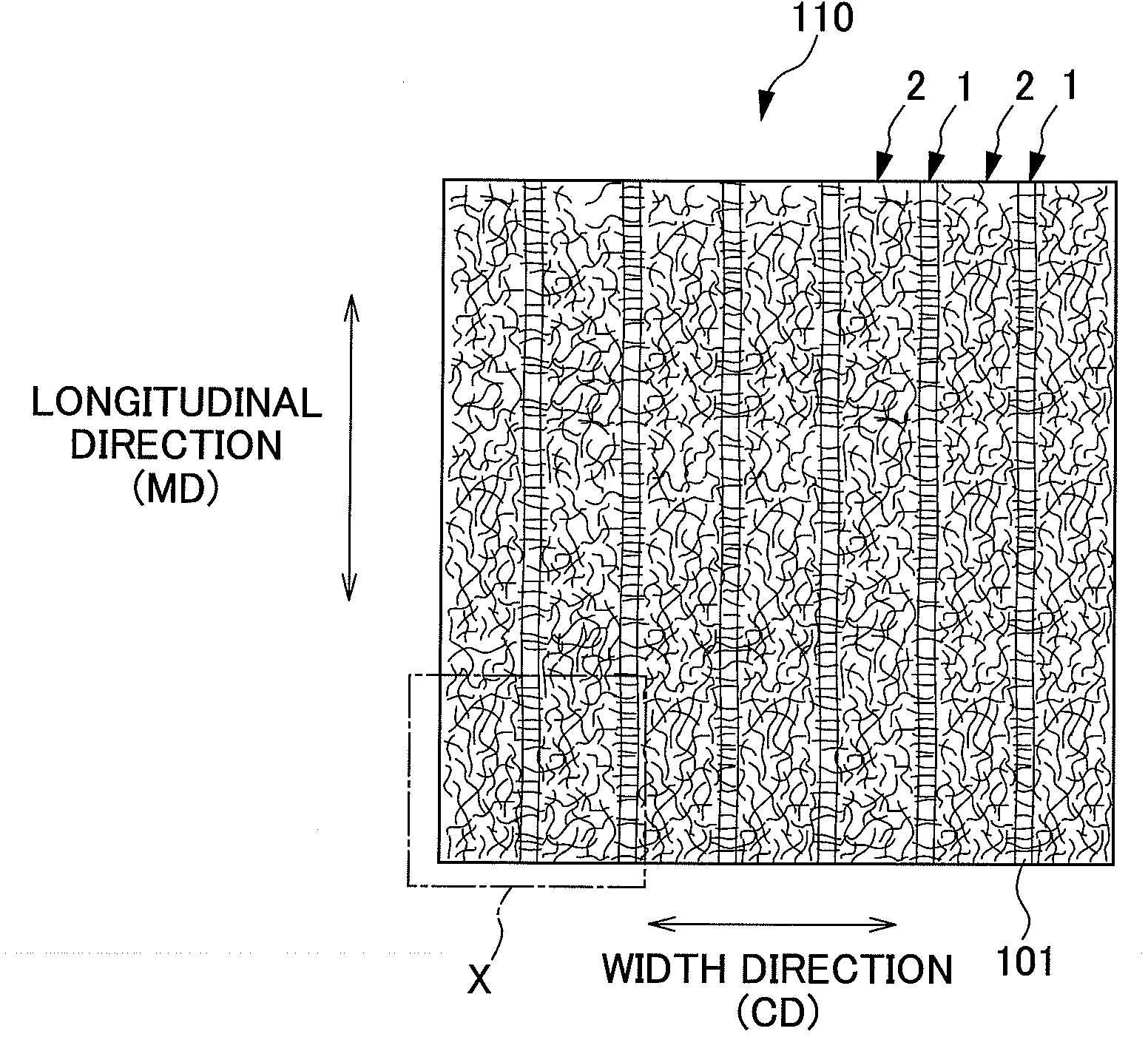
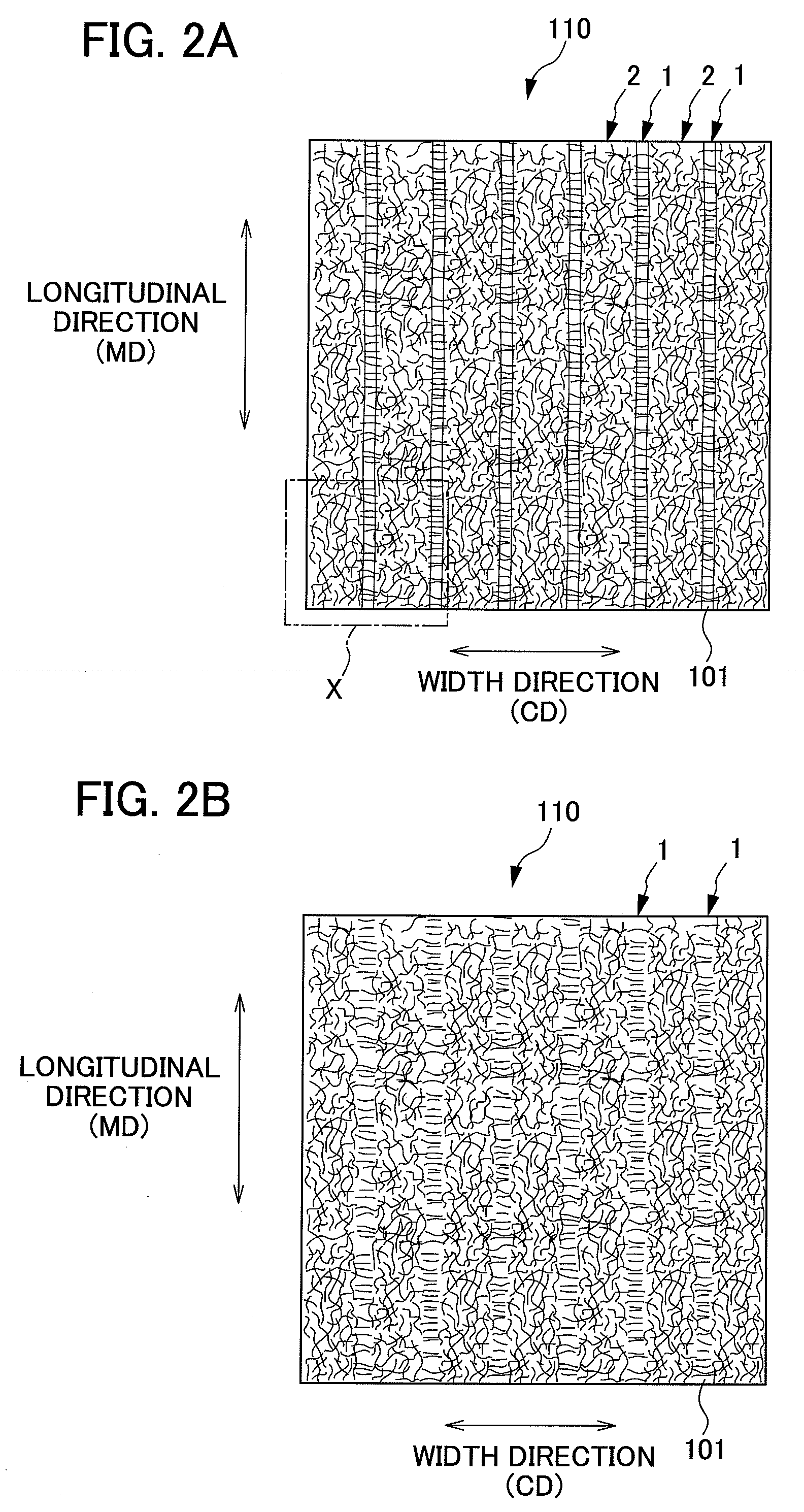
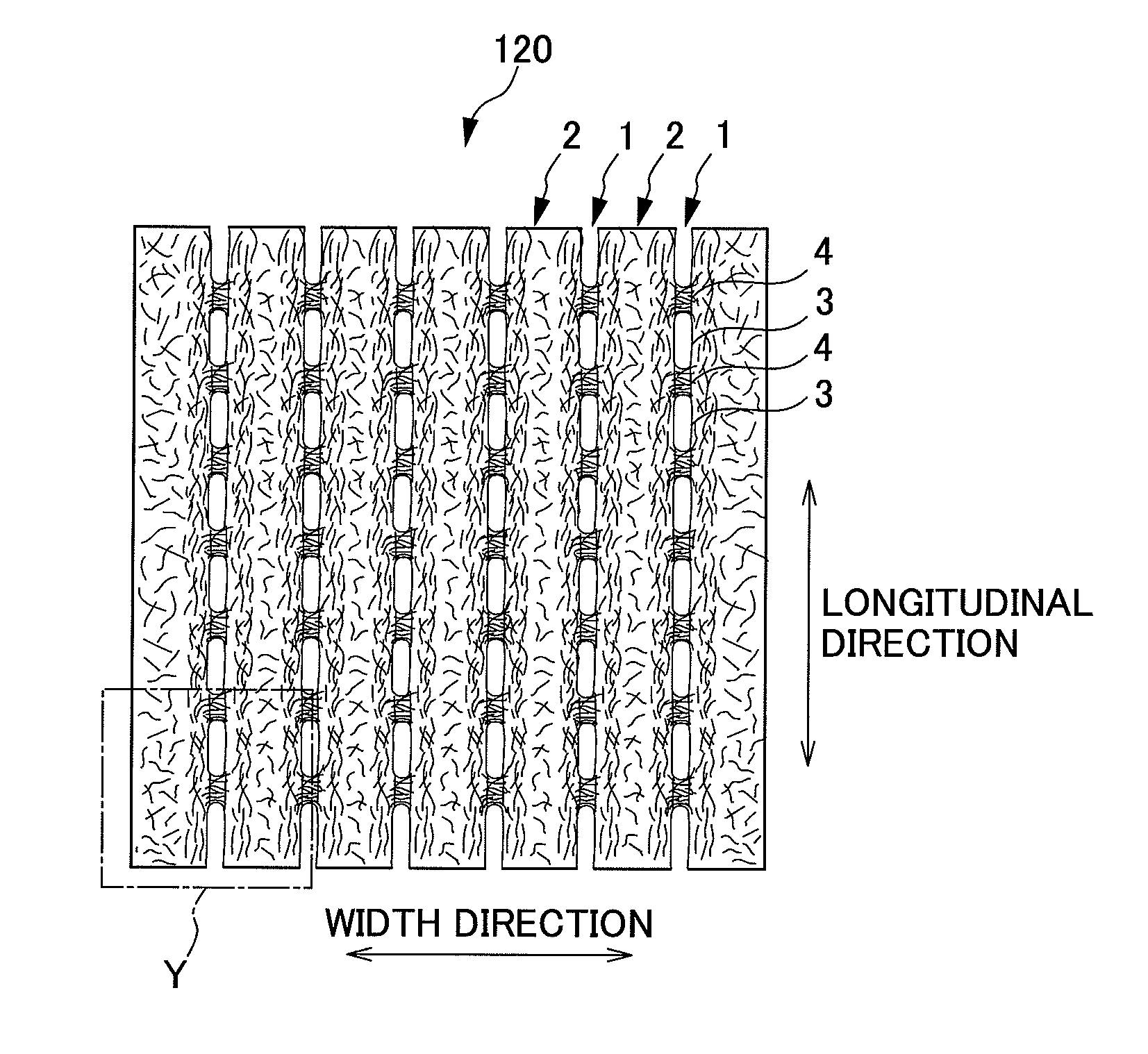
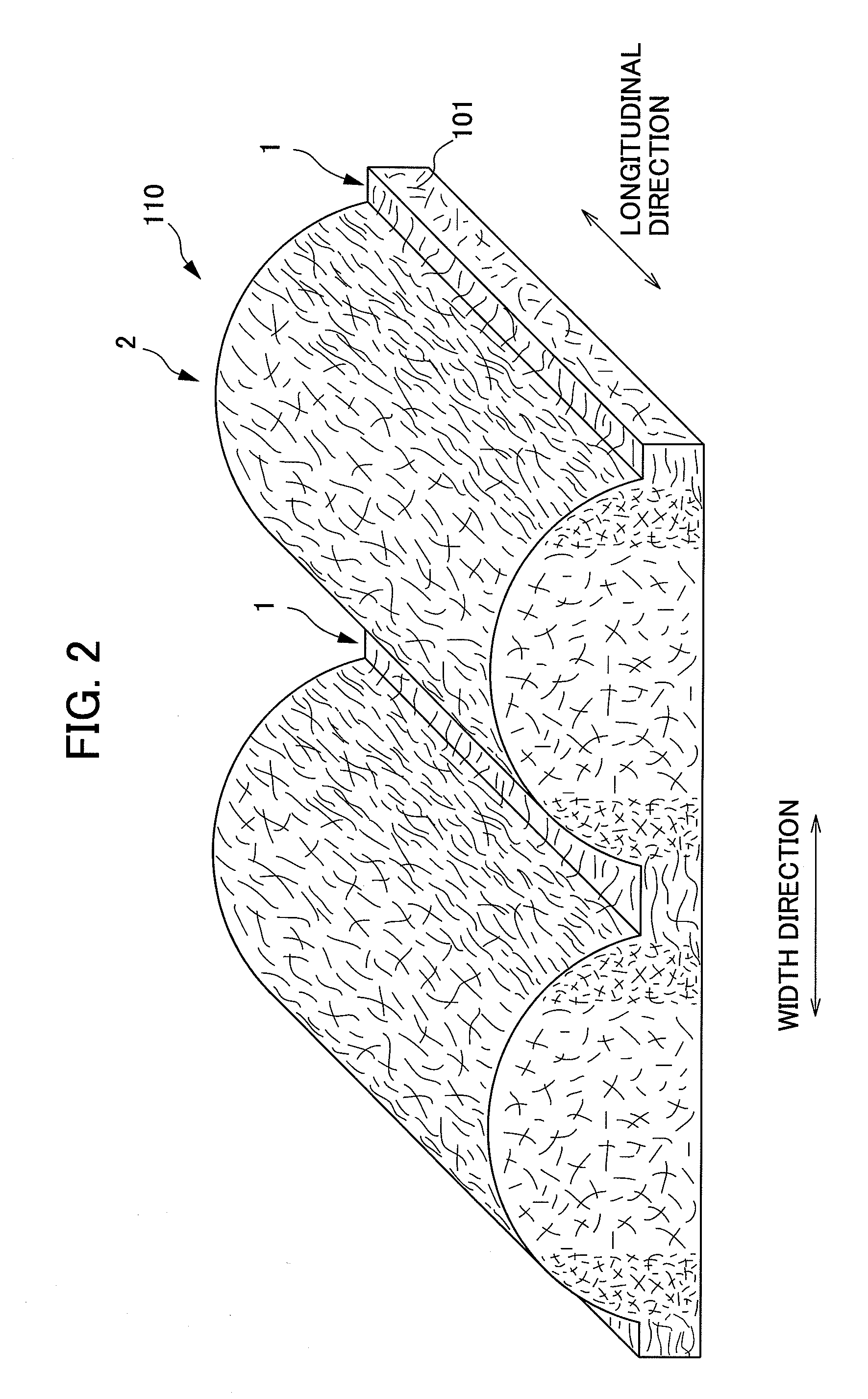
The present invention provides an absorbent body containing absorbent fibers in which fiber orientation is mainly adjusted, and fiber basis weight and shape are additionally adjusted. The absorbent body 110 of the present invention is an absorbent body containing absorbent fibers, a plurality of low fiber basis weight regions formed continuously in the first direction with a fiber basis weight that is less than an average fiber basis weight of the absorbent body 110, and a plurality of high fiber basis weight regions, formed along and on both sides of the low fiber basis weight regions in relation to the second direction perpendicular to the first direction, with a fiber basis weight that is greater than the average fiber basis weight of the absorbent body 110. The content of longitudinally oriented fibers in the fibers 101 making up the high fiber basis weight regions is greater than that of laterally oriented fibers, and the content of longitudinally oriented fibers in the fibers 101 making up the low fiber basis weight regions is greater than that of laterally oriented fibers.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Nonwoven fabric, nonwoven fabric manufacturing method, and nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus
The present invention provides a nonwoven fabric of which at least one of fiber orientation, fiber density, and basis weight is adjusted, and in which at least one of a predetermined groove portion, an opening, and a protrusion is formed, a manufacturing method for the nonwoven fabric, and a nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus. The nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus of the present invention manufactures a nonwoven fabric of which at least one of fiber orientation, fiber density, and basis weight is adjusted, or in which at least one of a predetermined groove portion, an opening, and a protrusion is formed by blowing fluid mainly containing gas onto a fiber web which is formed in a sheet shape, and which is in a state where at least a portion of the fibers constituting the fiber aggregate has a degree of freedom.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
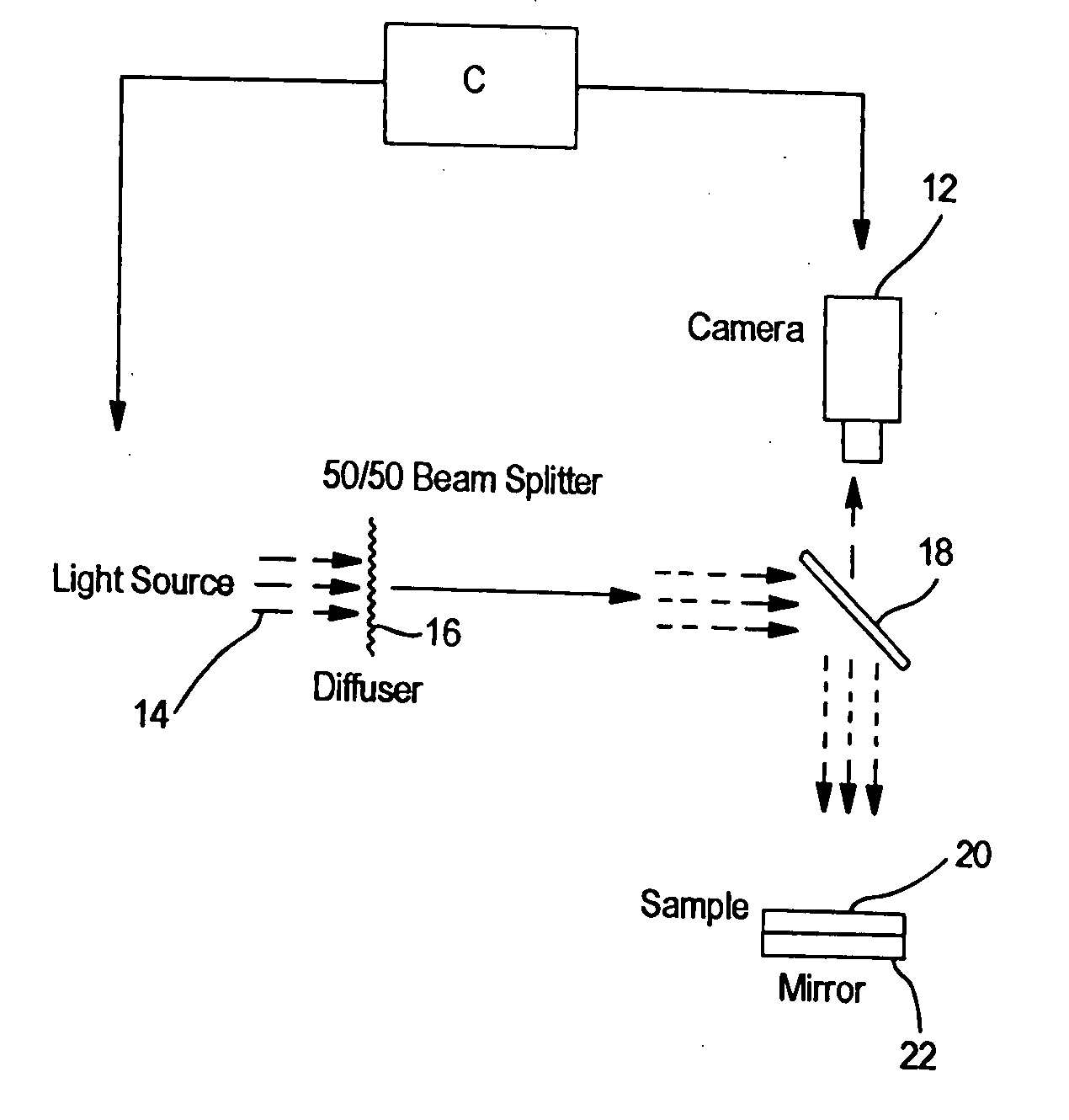
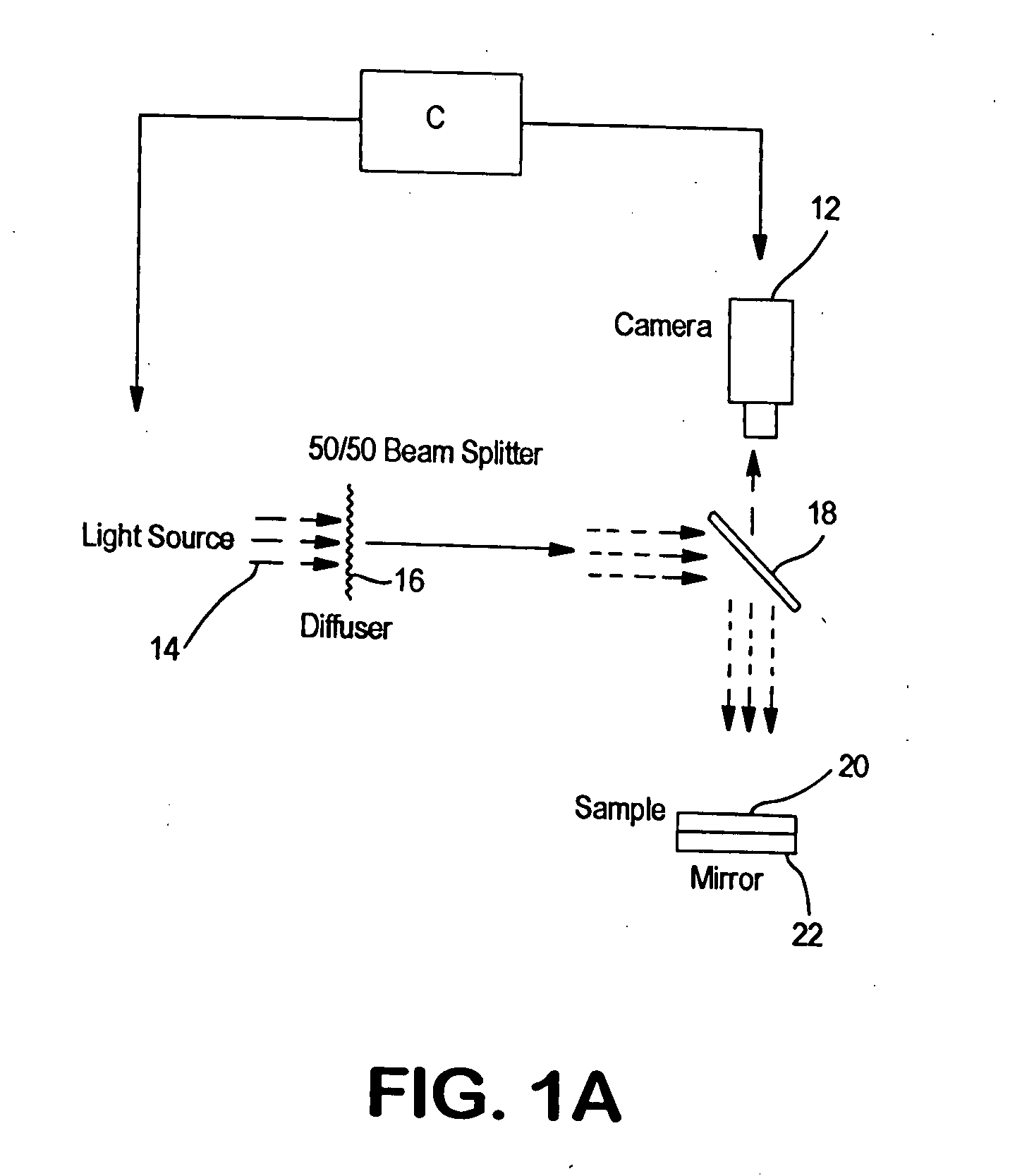
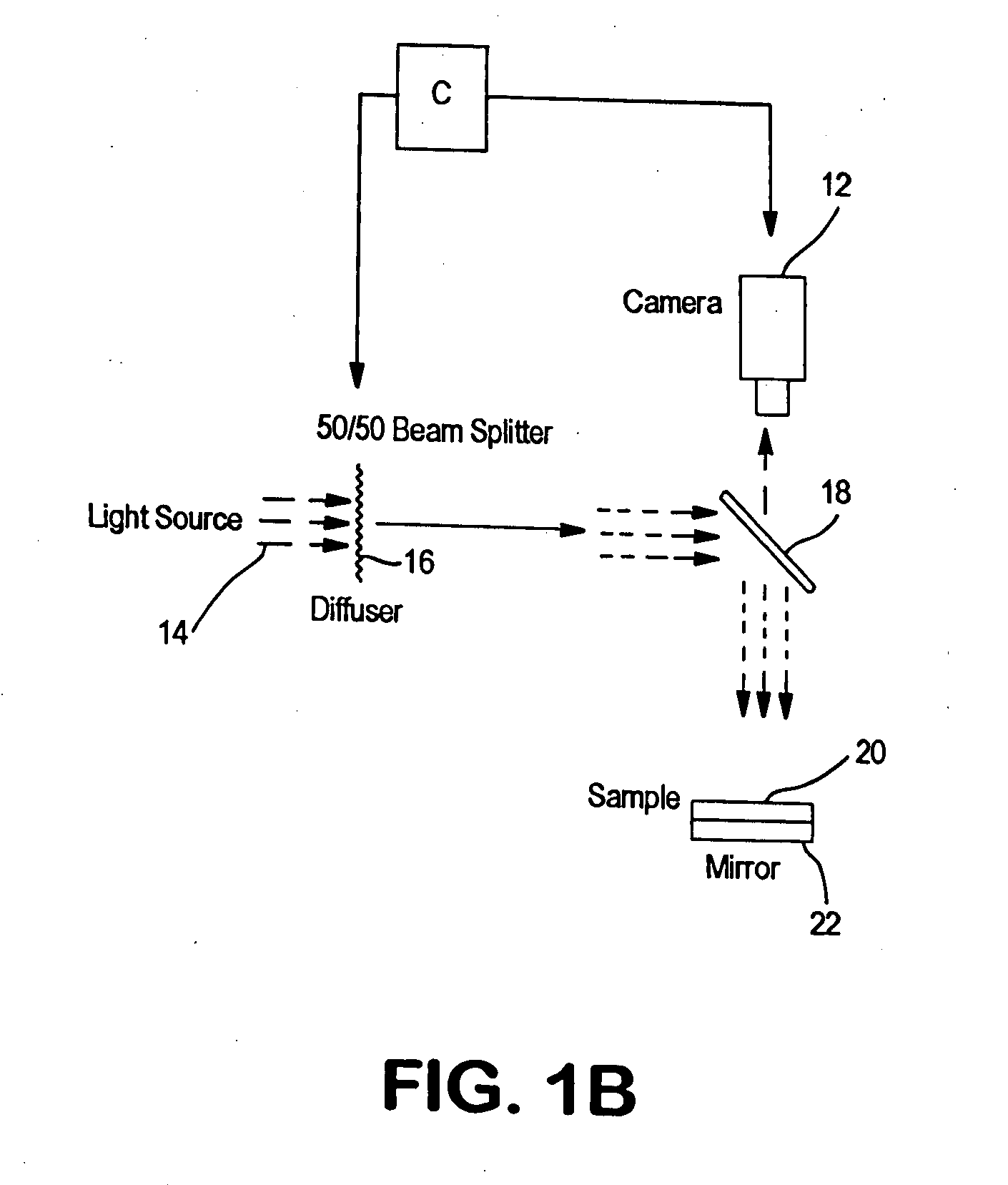
Optical method for evaluating surface and physical properties of structures made wholly or partially from fibers, films, polymers or a combination thereof
Optical methods for evaluating various surface and physical optical properties of structures made wholly or partially from fibers, polymers, films or a combination thereof. Such methods are comprised of special illumination, special software algorithms and controls that provide a unique solution for evaluating such properties as fiber orientation distribution function, basis weight uniformity, fuzz and pilling, texture, and other physical and surface properties.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Composite stacking sequence optimization for multi-zoned composites
ActiveUS20050163975A1Shorten the lengthReduce the numberCellulosic plastic layered productsComputation using non-denominational number representationComposite laminatesEngineering
Method, apparatus, and computer program products are provided for optimizing a stacking sequence for a composite laminate having multiple zones to reduce the number or length of internal ply edges in the composite laminate with the most design rule compliant sequences. Once the number and location of the zones and the number of plies having different properties required for each zone have been determined for the composite laminate, a master zone is generated. Advantageously, the property of the plies may be fiber orientation, though alternative properties such as material may be considered when determining the number of required plies. The master zone notionally includes the maximum number of plies having a respective property required by any one zone, and the plies of the master zone are sequenced using a predefined series of design rules. The plies of each zone are then arranged based upon the stacking sequence of the master zone. A transformation matrix, a second predefined series of design rules, and a weighted solid / void differential may be used when arranging the plies of each zone based upon the stacking sequence of the master zone.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Improved planed thin bamboo and productive method thereof
The present invention relates to an improved planed and cut thin bamboo and its production method. Said invention method includes the following steps: pretreating natural colour or carbonized bamboo sheets, applying glue, pressing, overlapping to obtain bamboo block, pressing and impregnating the integrated bamboo block, drying, applying glue, pressing to obtain bamboo squared timber, then planing and cutting said bamboo squared timber, drying so as to obtain the invented bamboo thin sheet whose thickness is 0.15-2.00 mm, then applying glue layer and technological layer on the thin bamboo sheet.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Absorbent body, multilayer absorbent body and absorbent article
The present invention provides an absorbent body containing absorbent fibers in which fiber orientation is mainly adjusted, and fiber basis weight and shape are additionally adjusted. The absorbent body 110 of the present invention is an absorbent body containing absorbent fibers, a plurality of low fiber basis weight regions formed continuously in the first direction with a fiber basis weight that is less than an average fiber basis weight of the absorbent body 110, and a plurality of high fiber basis weight regions, formed along and on both sides of the low fiber basis weight regions in relation to the second direction perpendicular to the first direction, with a fiber basis weight that is greater than the average fiber basis weight of the absorbent body 110. The content of longitudinally oriented fibers in the fibers 101 making up the high fiber basis weight regions is greater than that of laterally oriented fibers, and the content of longitudinally oriented fibers in the fibers 101 making up the low fiber basis weight regions is greater than that of laterally oriented fibers.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Method and apparatus for measuring fiber orientation of a moving web
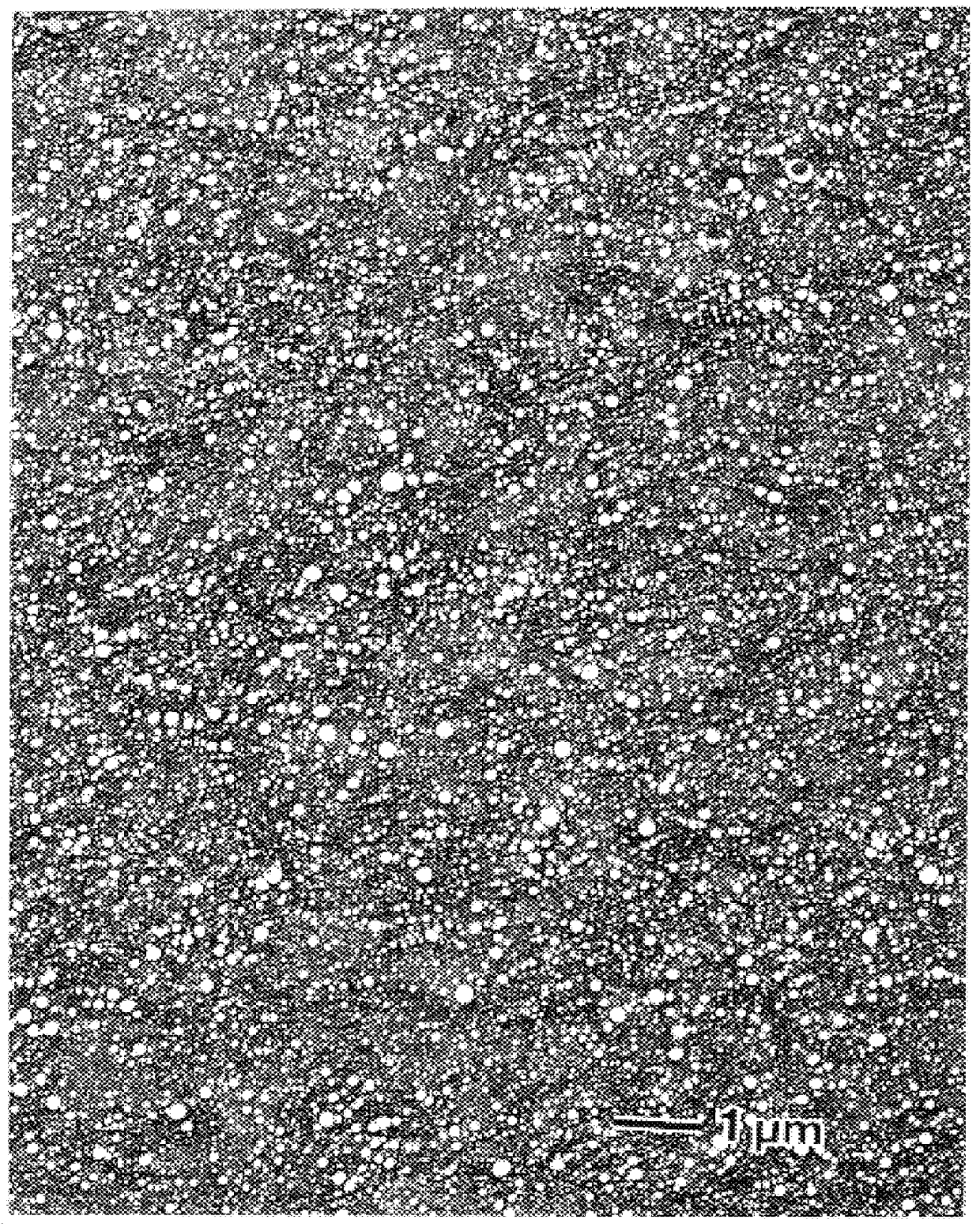
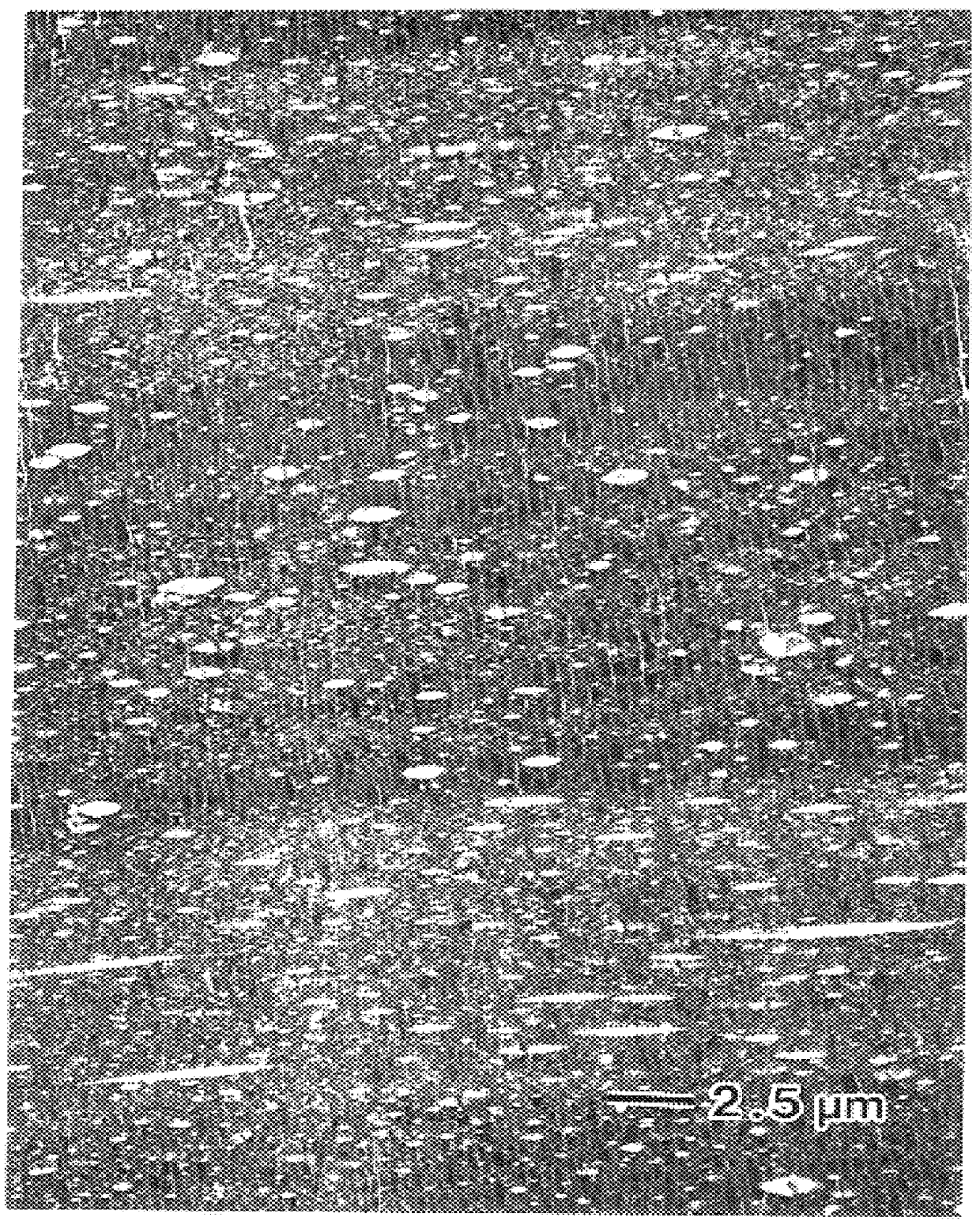
ActiveUS20060237156A1Substantial measureRobust estimate of the statistical distribution of fibersImage enhancementImage analysisGradient operatorsEngineering
An image-based measurement technique that directly measures the orientation of fibers in a moving web that comprises nonwoven material measures the orientation angles of the individual fibers so that a more robust estimate of the statistical distribution of fibers is obtained. The technique includes the steps of: (a) illuminating an area on at least one side of the web with radiation; (b) obtaining at least one digital image of the illuminated area; and (c) calculating the fiber orientation of the web by processing the at least one digital image with a gradient operator thereby analyzing the distribution of observed fiber orientation angles within the image. The gradient operator is preferably of a non-integer order between ⅓ and ⅔ and particularly between ¼ and ¾. The use of fractional-gradient operators yields more reliable results than when integer order gradients are employed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Optoelectronic fiber photodetector
ActiveUS7292758B2Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The invention provides an optical fiber photodetector including a photoconductive element, such as a semiconducting element, having a fiber length. The semiconducting element is characterized as a non-composite material in at least one fiber direction. At least one pair of conducting electrodes is in contact with the semiconducting element along the fiber length, and an insulator is provided along the fiber length. An optical resonator can be disposed along the fiber length and along a path of illumination to the semiconducting element. The resonator is dimensioned to substantially reflect all illumination wavelengths except for a prescribed range of wavelengths transmitted to the semiconducting element. The fiber photodetector can be arranged in a photodetecting fiber grid, photodetecting fiber fabric, or other configuration for detecting incident illumination.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for producing a three-dimensional fiber reinforced ring frame component
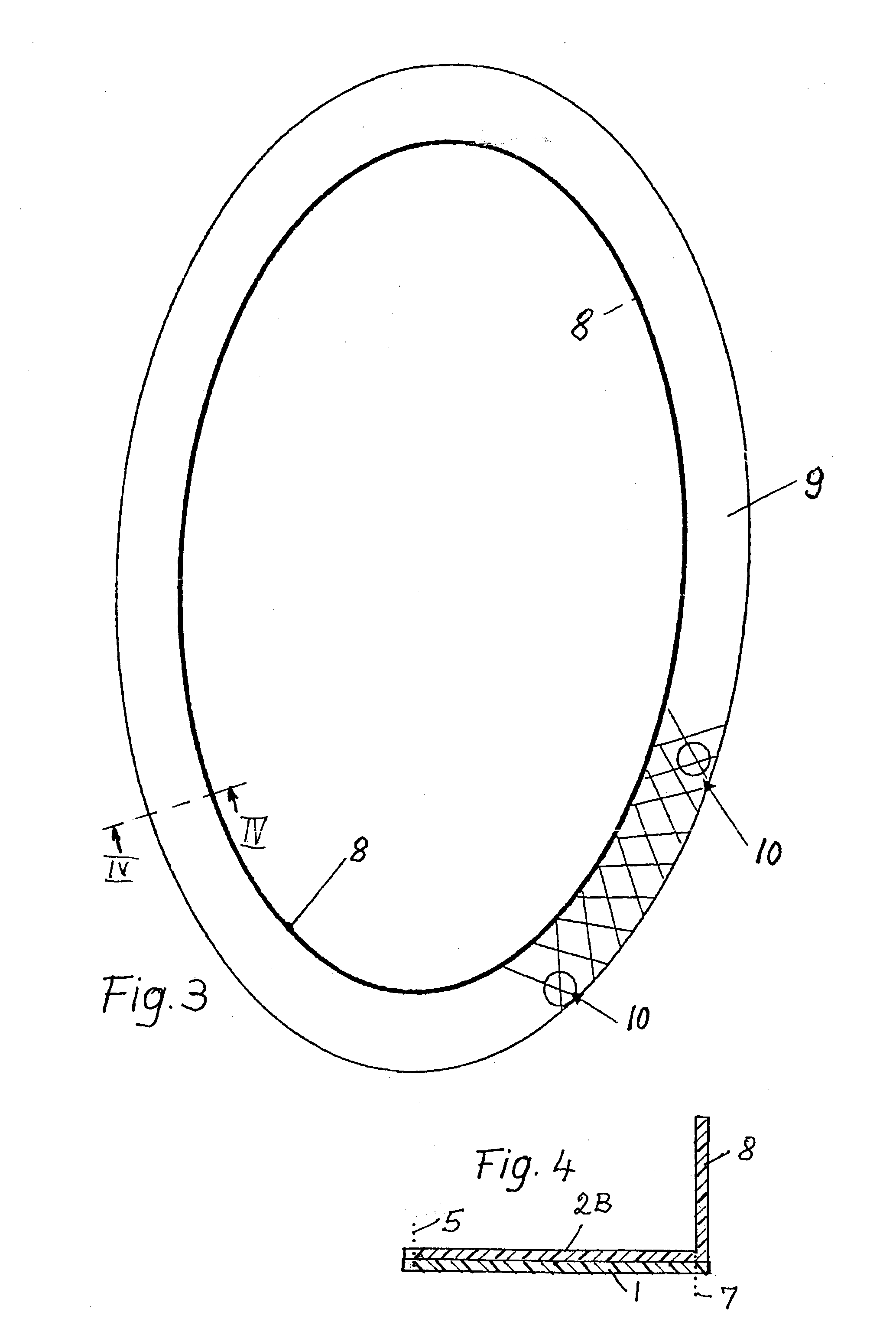
InactiveUS20030222371A1Produced economicallyAccurate materialsAircraft accessoriesLaminationRing fibersBand shape
A closed ring fiber reinforced frame structure is produced by first preparing a prepreg. A section of the prepreg is formed into a flange preferably after impregnation by folding the flange section along a folding line. The folding line is formed by securing a deformable or drapable fiber ribbon material, for example by sewing or stitching to a carrier substrate which is preferably also a fiber material. The sewing seam or stitching line becomes the folding line. The ribbon material is so secured to the carrier substrate that the fiber orientation of the ribbon material is uniformly distributed all around a ring component that is formed of the ribbon material on the substrate. The impregnated ring component with its substrate is then cured after the folding of the flange to complete the ring frame structure.
Owner:INST FUER VERBUNDWERKSTOFFE GMBH +1
System and method for characterizing fibrous materials using stokes parameters
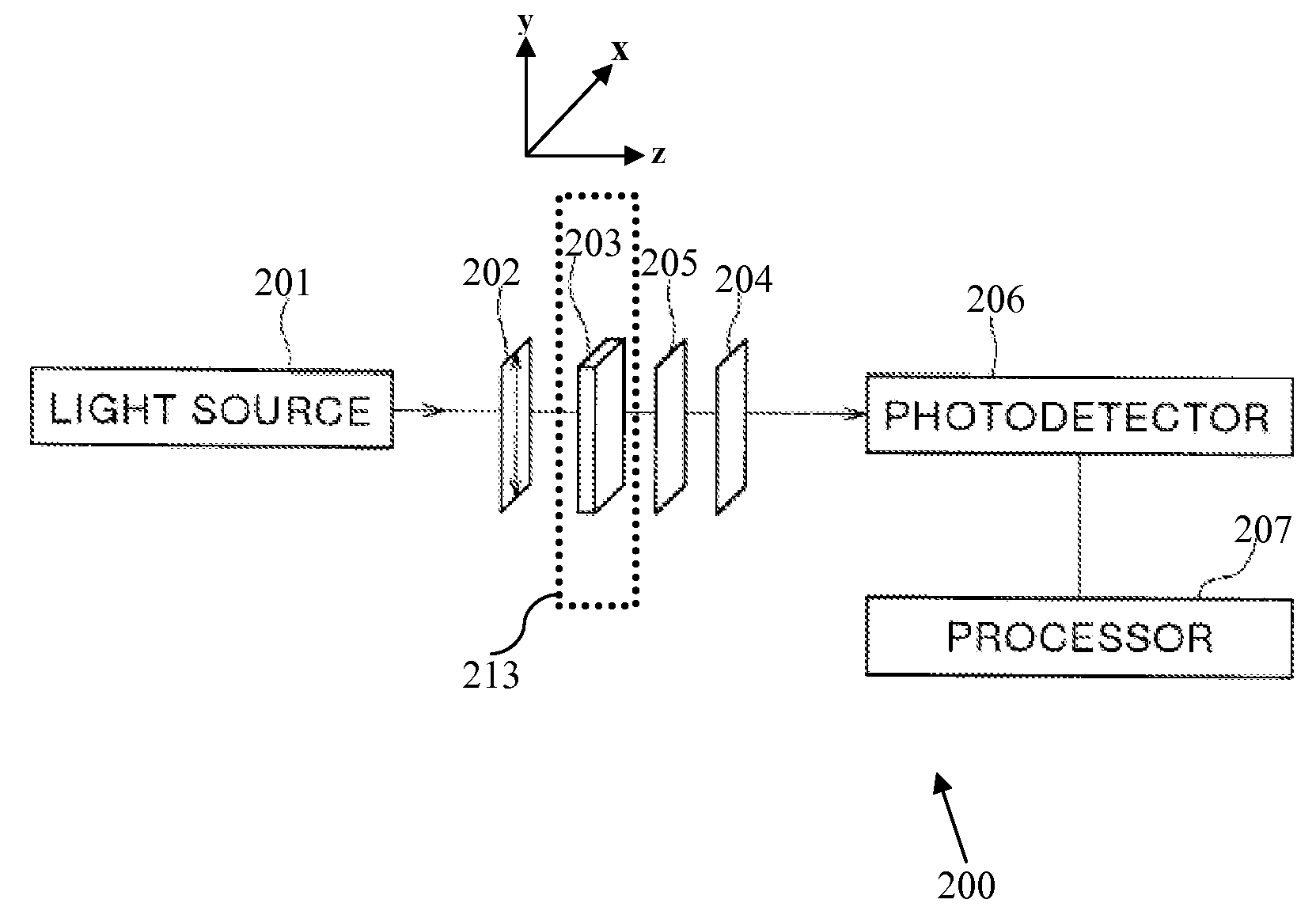
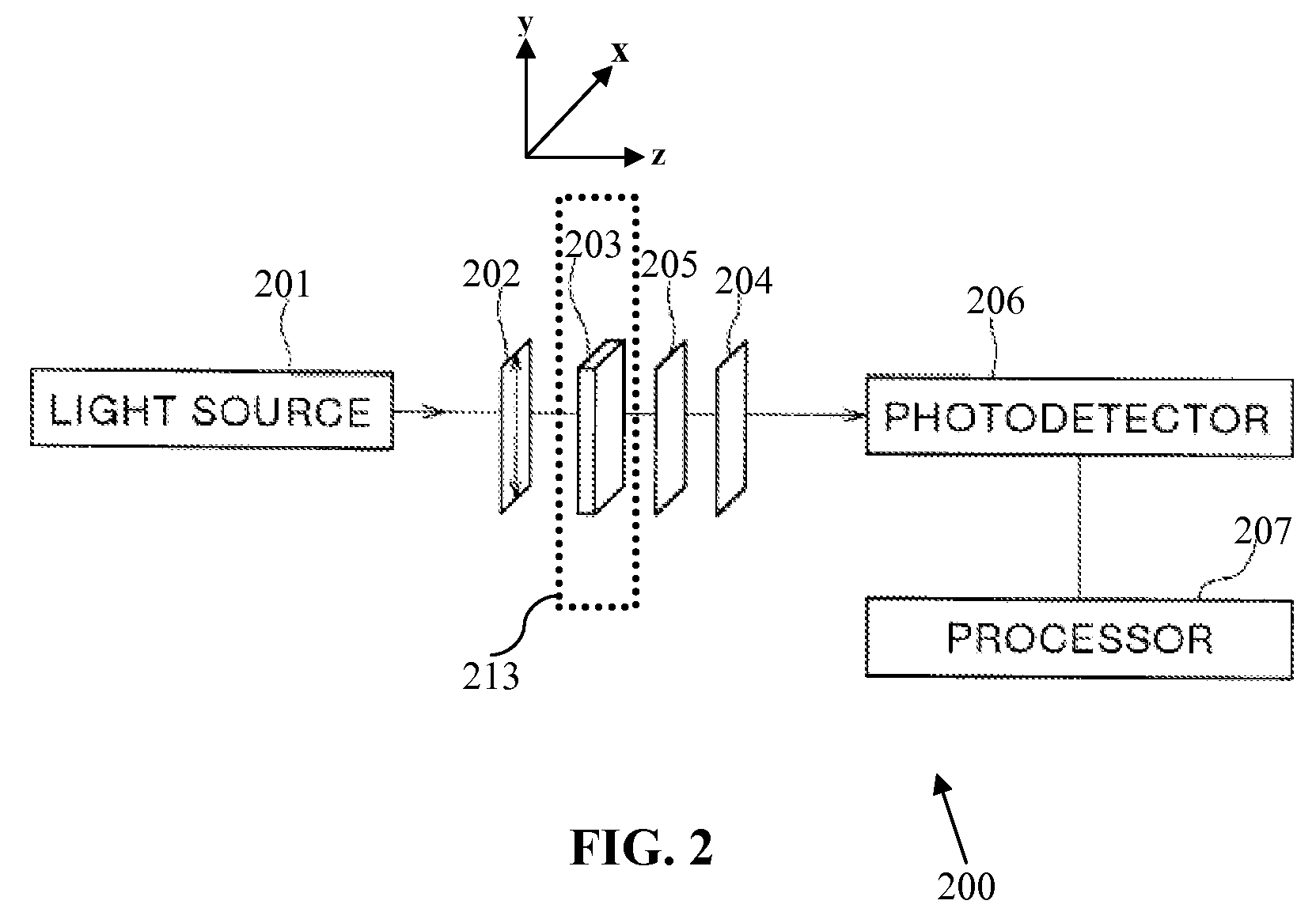
ActiveUS20090101297A1Material analysis using microwave meansInvestigating moving sheetsPhotodetectorPolarimeter
An apparatus (200) for determining fiber orientation parameters of a sheet of material during a production process includes a polarized radiation generating system (201, 202) operable for providing polarized radiation having a frequency of at least 1×108 Hz. The radiation is aligned to be incident on a sheet of material to be characterized (203). A polarimeter (204, 205) is aligned to receive the radiation transmitted by the sheet of material (203). A photodetector (206) is provided for measuring radiation received after polarization processing by the polarimeter. A processor (207) is coupled to the photodetector (206) for calculating Stokes parameters of the moving sheet (203) based upon intensities of the radiation received and determines at least one parameter relating to fiber orientation of the moving sheet based upon the Stokes parameters.
Owner:HONEYWELL ASCA INC +1
Building panels of solid wood
Building panels each comprise an upper first element of solid wood fixed to a lower second element of solid wood. The first and the lower second element are of different wood species. The building panels are provided with a mechanical locking system which comprises a locking strip at a first edge of a first building panel. The locking strip is provided with a locking element configured to cooperate with a locking groove at a second edge of a second building panel for horizontal locking of the first and the second building panels when a tension force is applied. The fibre direction of the first and the lower second elements is essentially along the first and the second edges. The lower second element has about the same or higher moisture shrinkage value than the first element. The locking strip comprises material of the lower second element.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Multi-colored fabrics made from a single dye formula, and methods of making same
A process for making multi-colored fabrics from a single dye formula is described. The process involves providing a substrate including synthetic fibers, with the substrate having defined regions where the synthetic fibers have differing levels of fiber orientation, and dyeing the substrate with a dye bath containing at least one dye from at least two of the categories of a) high contrast dyes, 2) medium contrast dyes and c) low contrast dyes, to thereby produce a multi-colored substrate from a single dye formula. The substrates are characterized by having a base of a first color and patterned regions of a different color, with the regions of different colors corresponding to regions of different levels of fiber orientation.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
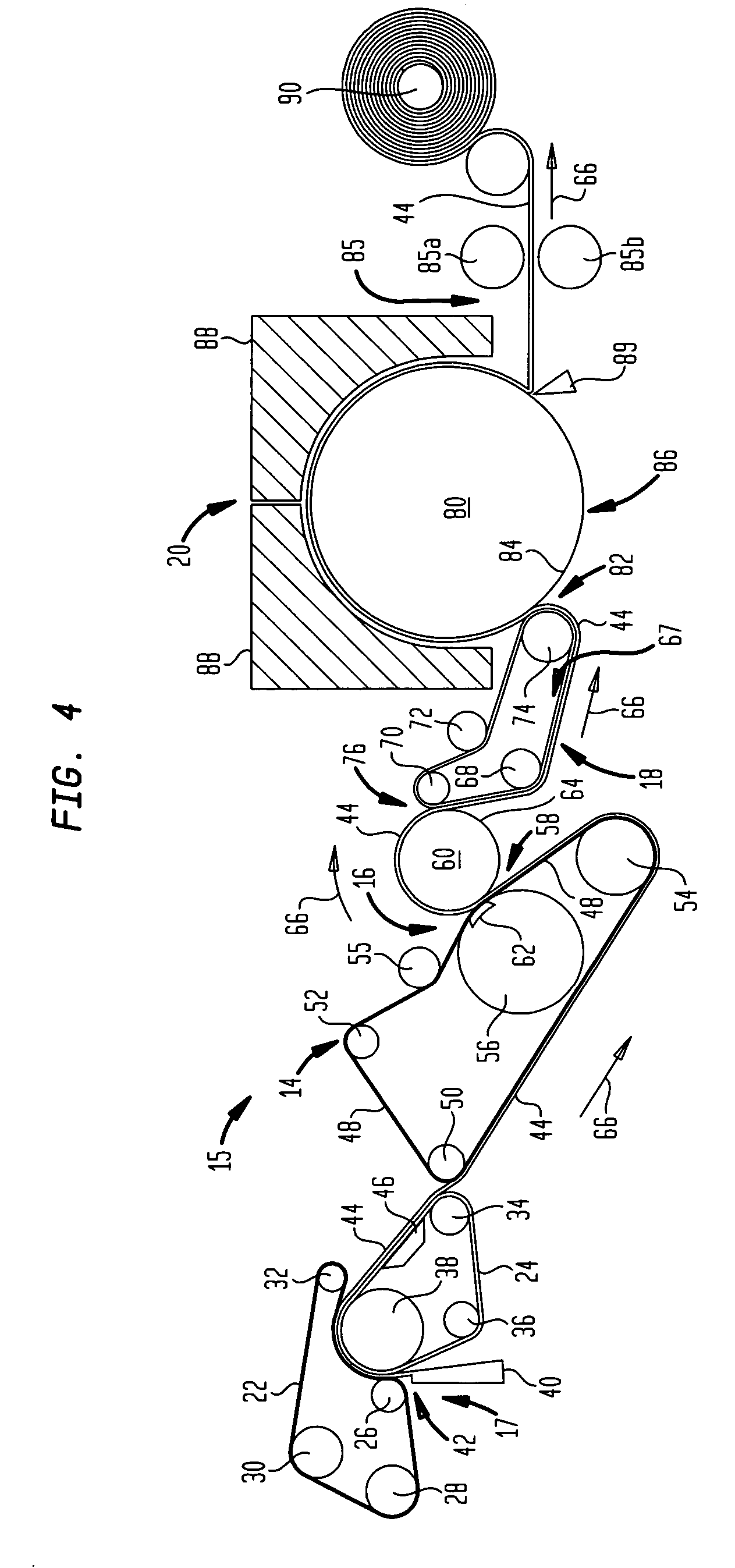
Methods of Making a Belt-Creped Absorbent Cellulosic Sheet Prepared with a Perforated Polymeric Belt
InactiveUS20120241113A1High local basis weightImprove firmnessNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCellulosePolymer science
A method of making a belt-creped absorbent cellulosic sheet. A paper making furnish is compactively dewatered to form a dewatered web having an apparently random distribution of papermaking fiber orientation. The dewatered web is applied to a translating transfer surface that is moving at a transfer surface speed. The web is belt-creped from the transfer surface at a consistency of from about 30% to about 60% utilizing a generally planar polymeric creping belt having a plurality of perforations, under pressure, in a belt creping nip defined between the transfer surface and the creping belt. The belt travels at a belt speed that is slower than the speed of the transfer surface. The web is creped from the transfer surface and redistributed on the creping belt to form a web having a plurality of interconnected regions of different local basis weights. The web is then dried.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Degradable monofilament and preparation process thereof
InactiveUS6090910AHigh strengthSlow hydrolysis velocitySuture equipmentsCosmetic preparationsAbsorbable sutureYoung's modulus
A degradable copolymer filament comprising an internal structure having the following separate phases: (a) a matrix phase comprised as a primary component of a polymer segment which exhibits a tensile Young's modulus of 2 GPa or less and a strength retention of 50% or more after two weeks in water at 37 DEG C., pH 7.3, and (b) a micro-dispersed phase comprised as a primary component of a polymer segment which exhibits a tensile strength of 200 MPa or more and a strength reduction greater than the matrix phase in water at 37 DEG C., pH 7.3. The weight ratio of each component in the matrix phase and dispersed phase is 50:50 to 95:5, respectively, and the dispersed phase a needle structure oriented by stretching in the fiber direction. A degradable monofilament having an excellent mechanical strength and flexibility, moderate hydrolyzability, high ligature stability and being suitable as a material of surgical absorbable suture can be obtained. A preparation process is also provided.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
AgNi electrical contact material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101608272AExtended service lifeImprove welding resistanceContact materialsElectricityHardness
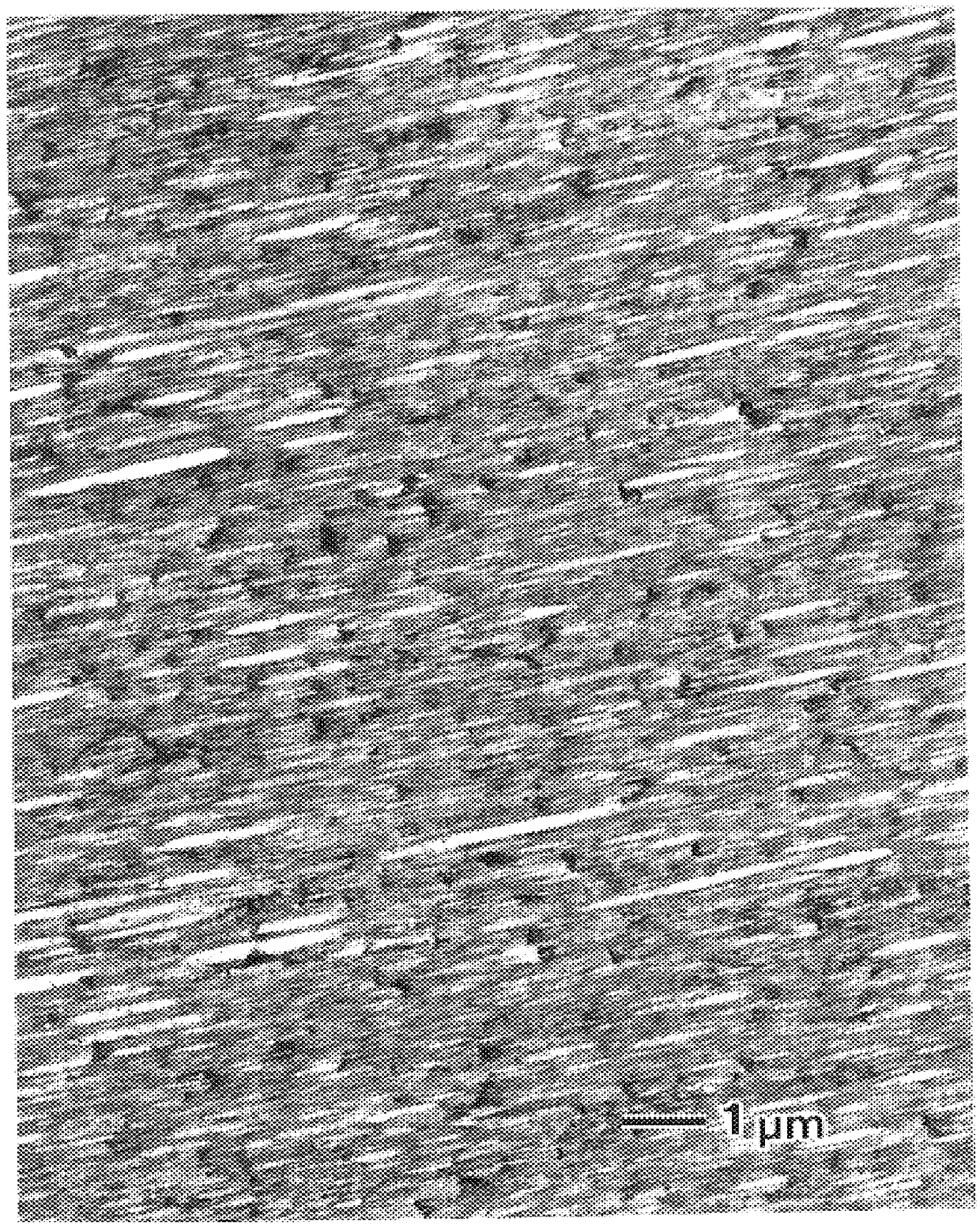
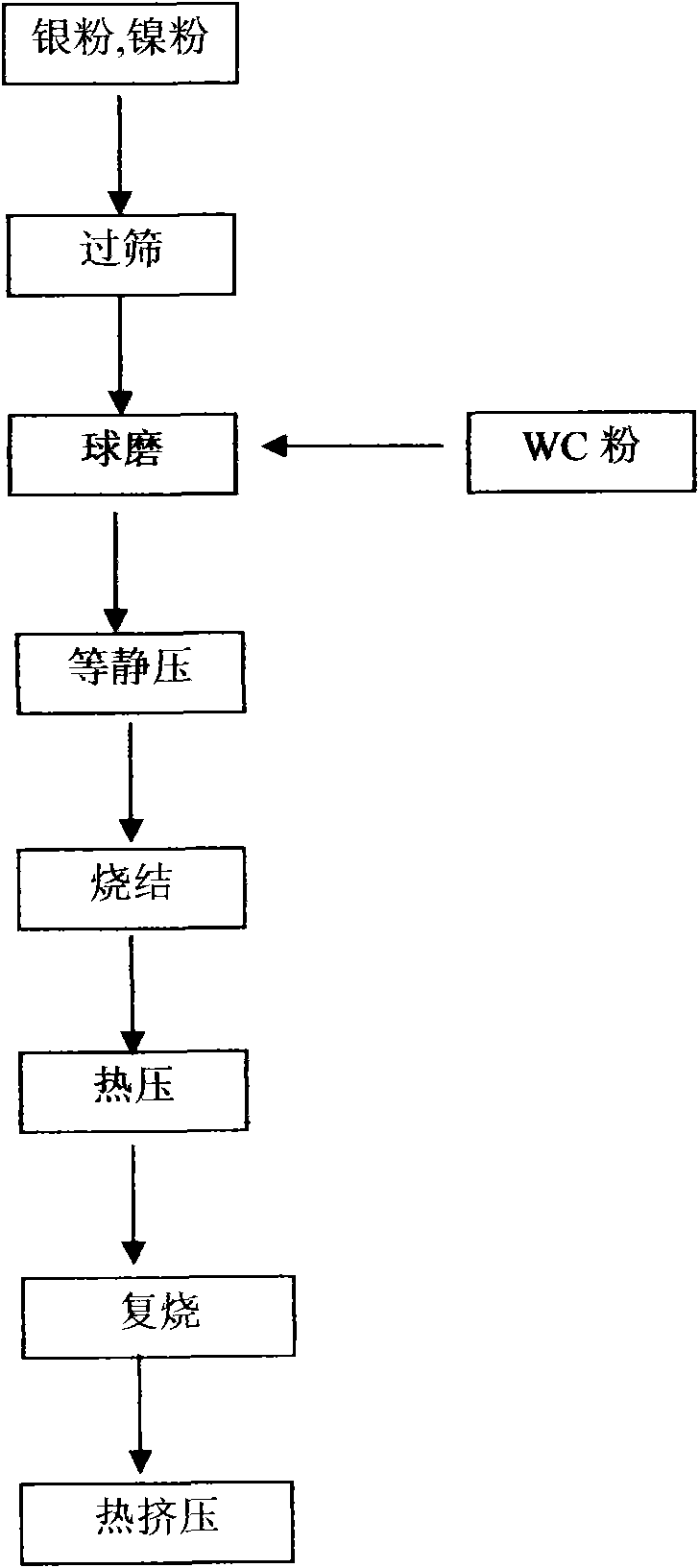
The invention discloses an AgNi-base electrical contact material and a preparation method thereof and the electrical contact material comprises nickel, tungsten carbide and silver; wherein, the weight percent of nickel is not less than 5% and not more than 10%, the weight percent of tungsten carbide is not less than 0.1% and not more than 5% and the allowance is silver. In the invention, the distribution of nickel particles and the fiber orientation are considered; the manufacturing process adopts the processes of ball-milling, pressing, sintering and extruding. Owning to the high hardness, high strength and high melting point of tungsten carbide, tungsten carbide / silver bonding strength is better; comprised with the traditional AgNi electrical contact material, the AgNi electrical contact material prepared by the method of the invention has higher welding resistance and arc deterioration resistance and longer electrical life.
Owner:WENZHOU HONGFENG ELECTRICAL ALLOY
Three-dimensional deep molded structures with enhanced properties
ActiveUS7060344B2Increase stiffnessImprove propertiesLayered productsWoven fabricsPolymer scienceFiber diameter
A three-dimensional deep molded structure made from planar knits or wovens composed of homo-component, bicomponent or multi-component fibers having a fiber diameter of less than 100 microns and nonwovens composed of fibers or filaments of any size. Most suitably, nonwovens with a random fiber orientation distribution and a high degree of crimp with partially oriented fibers are preferred for use in forming the deep molded structure.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com