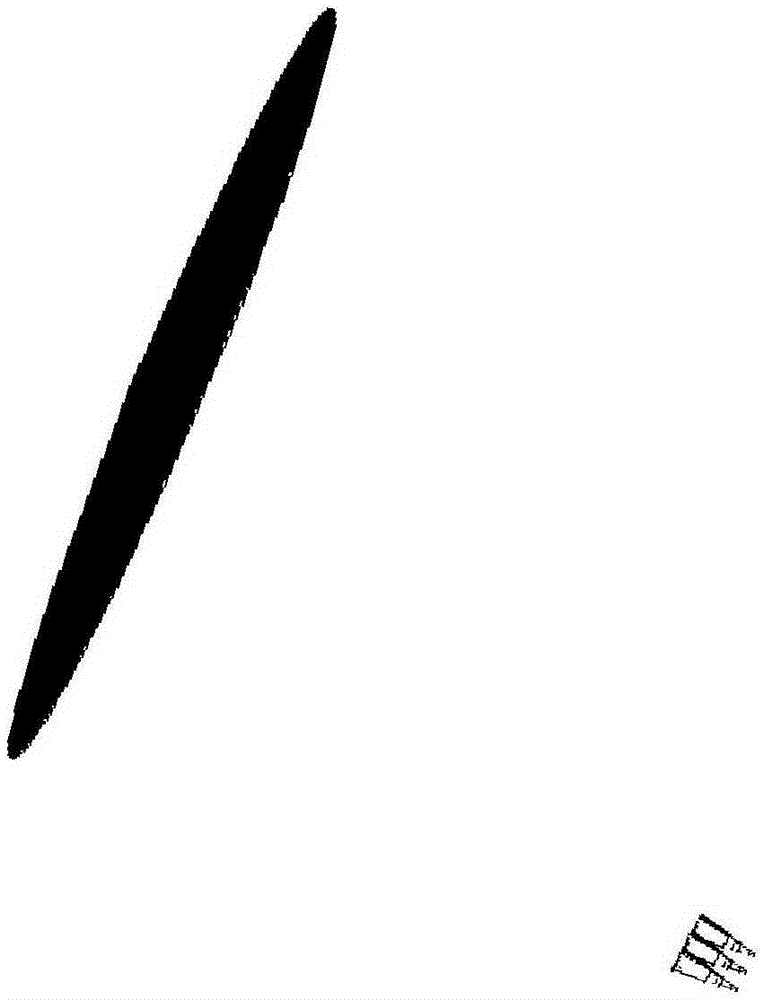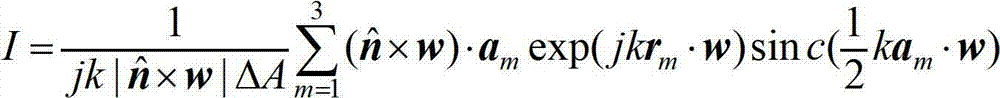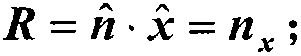Patents
Literature
170 results about "Physical optics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, physical optics, or wave optics, is the branch of optics that studies interference, diffraction, polarization, and other phenomena for which the ray approximation of geometric optics is not valid. This usage tends not to include effects such as quantum noise in optical communication, which is studied in the sub-branch of coherence theory.
Processes For Forming Multi-Layered Pet Treats
ActiveUS20070264415A1Improving coatImprove skinConfectioneryAnimal feeding stuffPhysical opticsMaterials science
A process for manufacturing a multi-layer pet treat or animal chew comprising the indexing of a moveable mold portion into alignment with the first of a plurality of stationary mold portions fed a first composition by a first injection molding unit to form a first layer in a cavity space formed by the aligned mold portions. The moveable mold portion and the first layer may be indexed to align with a second of a plurality of stationary mold portions fed a second composition by a second injection molding unit to form a second layer over said first in the cavity space formed by the aligned mold portion. The compositions fed by the first and second injection molding units may both be edible. In a further aspect, multi-component pet treats may be provided formed from two materials which may be different in physical, optical, sensual, nutritional or compositional properties. One of the materials may specifically include textured vegetable protein.
Owner:T F H PUBLICATIONS
Optical method for evaluating surface and physical properties of structures made wholly or partially from fibers, films, polymers or a combination thereof
Optical methods for evaluating various surface and physical optical properties of structures made wholly or partially from fibers, polymers, films or a combination thereof. Such methods are comprised of special illumination, special software algorithms and controls that provide a unique solution for evaluating such properties as fiber orientation distribution function, basis weight uniformity, fuzz and pilling, texture, and other physical and surface properties.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on parallel moment method and physical optics mixing
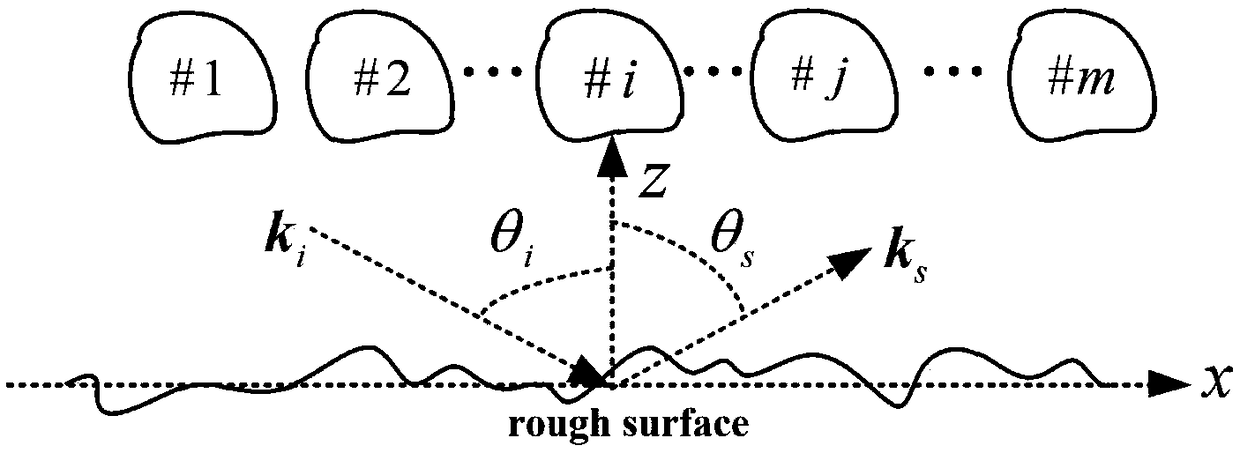
InactiveCN103870654AImprove accuracyAvoid artificial reflexesSpecial data processing applicationsRough surfacePhysical optics
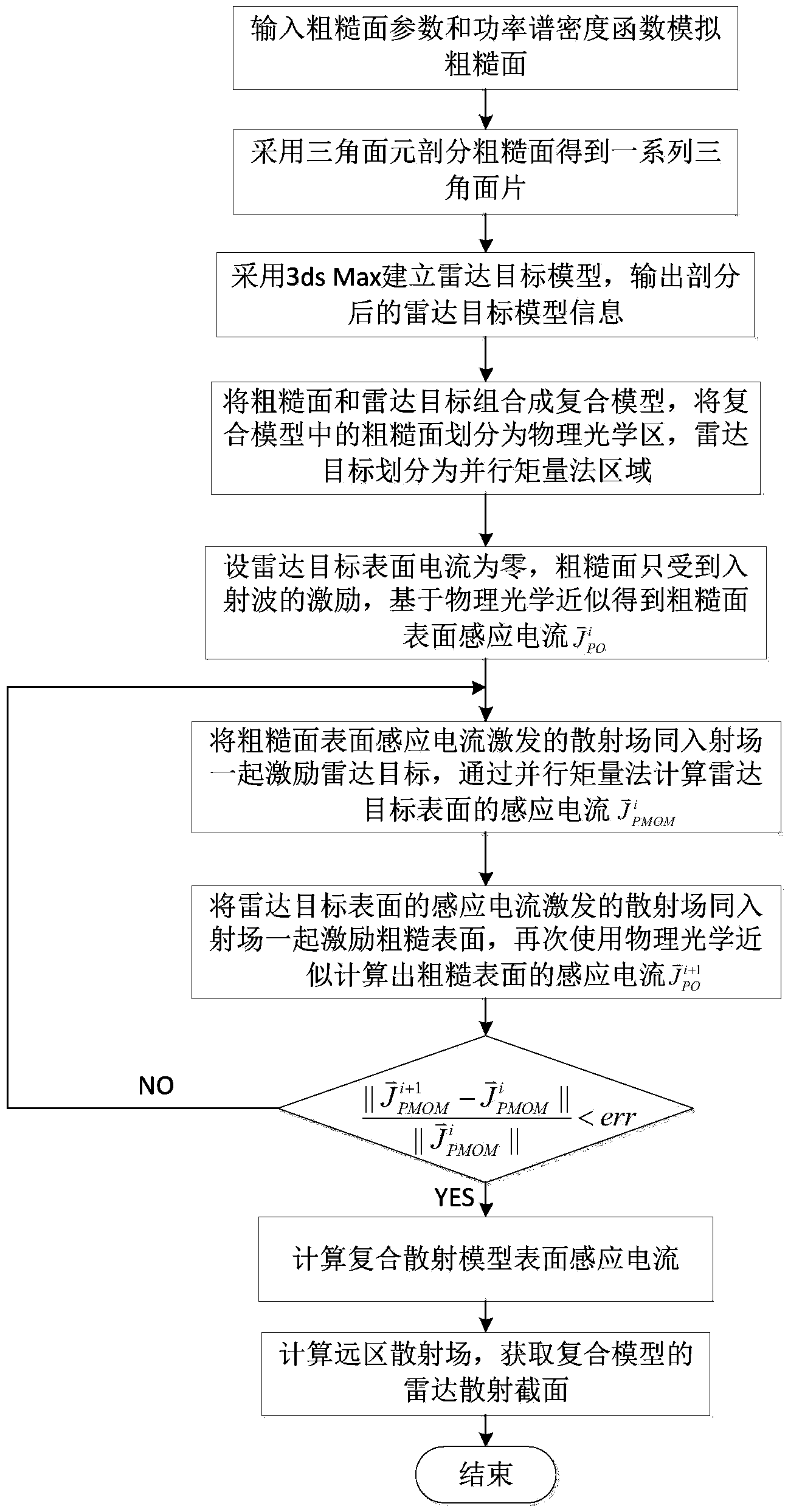
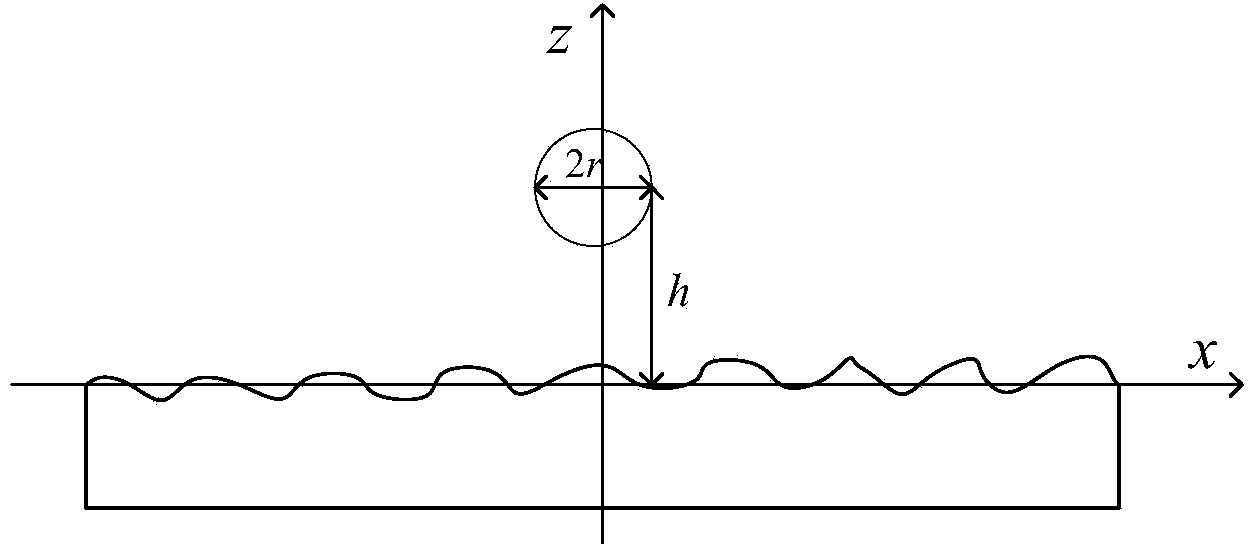
The invention discloses an electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on parallel moment method and physical optics mixing to mainly solve the problem that when electrically large models are processed in the prior art, the simulation efficiency of electromagnetic scattering and the precision are low. The electromagnetic scattering simulation method comprises the steps that a rough surface power spectrum and rough surface parameters are input, and a rough surface is simulated based on the Monte Carlo method; geometric modeling is carried out on a radar target through 3dsMax software, and the subdivided radar target is output; a combined model is formed by combining the rough surface and the radar target, the rough surface is divided into a physical optics area, and the radar target is divided into a parallel moment method area; induced currents on the rough surface and induced currents on the surface of the radar target are obtained; a far scattered field of the combined model is calculated based on the induced currents on the surface of the combined model, a radar cross section of the combined model is obtained, and simulation between the rough surface and the combined electromagnetic scattering of the radar target is achieved. According to the electromagnetic scattering simulation method, the memory consumption is little, the simulation efficiency is high, and the electromagnetic scattering simulation method can be used in the study on the rough surface and the radar target combined electromagnetic scattering character in the field of national defense and the civil using.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
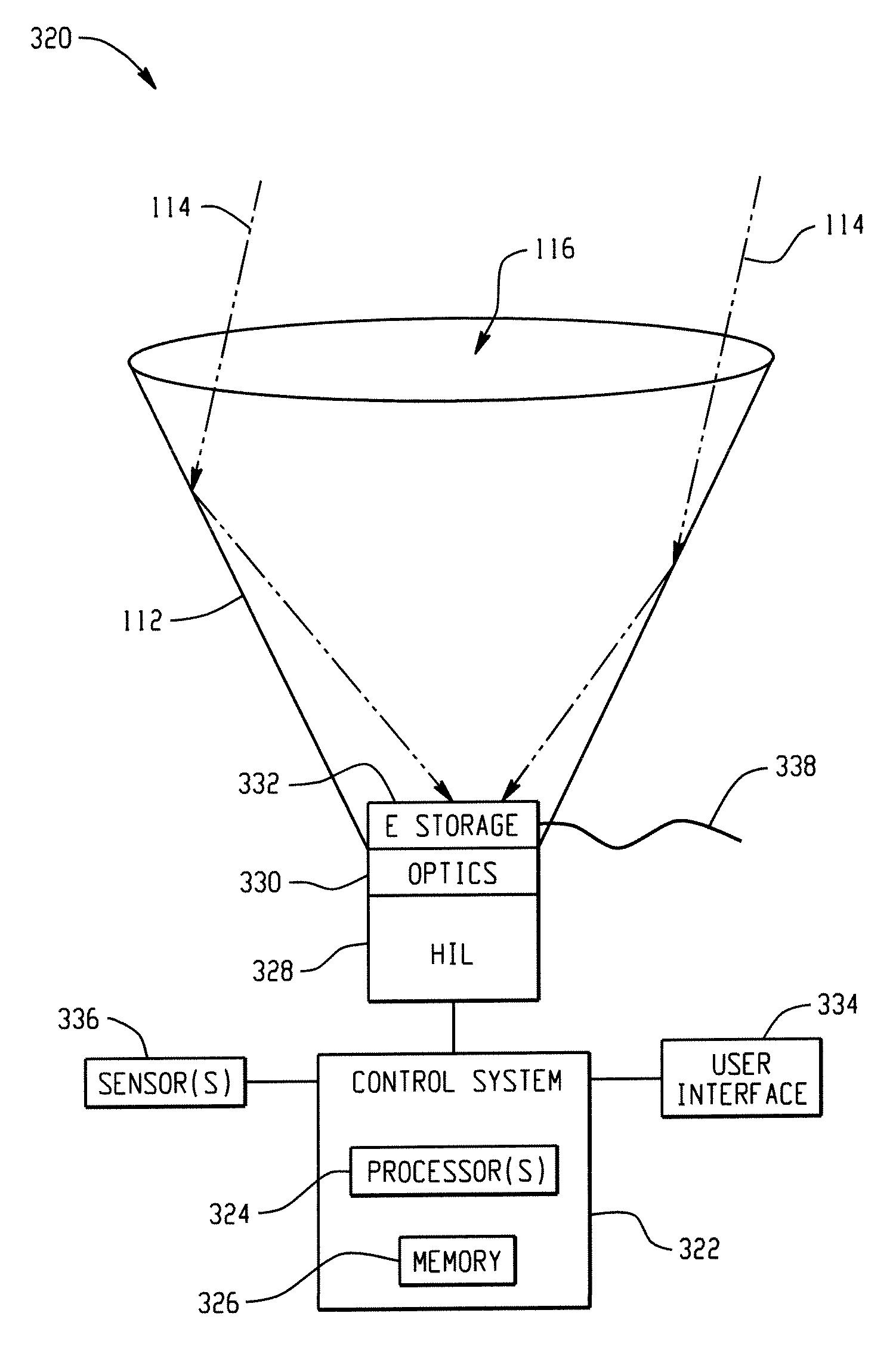
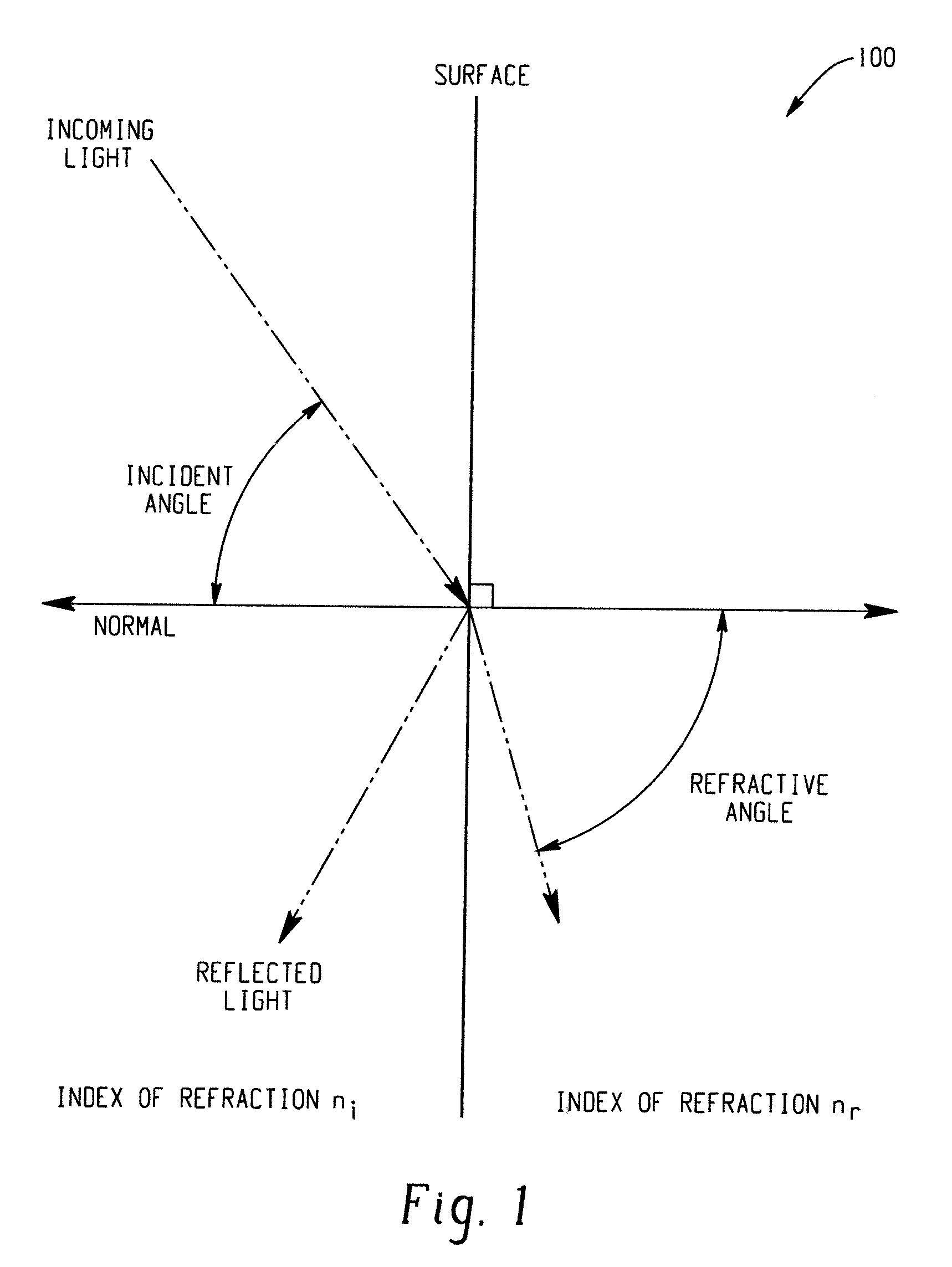
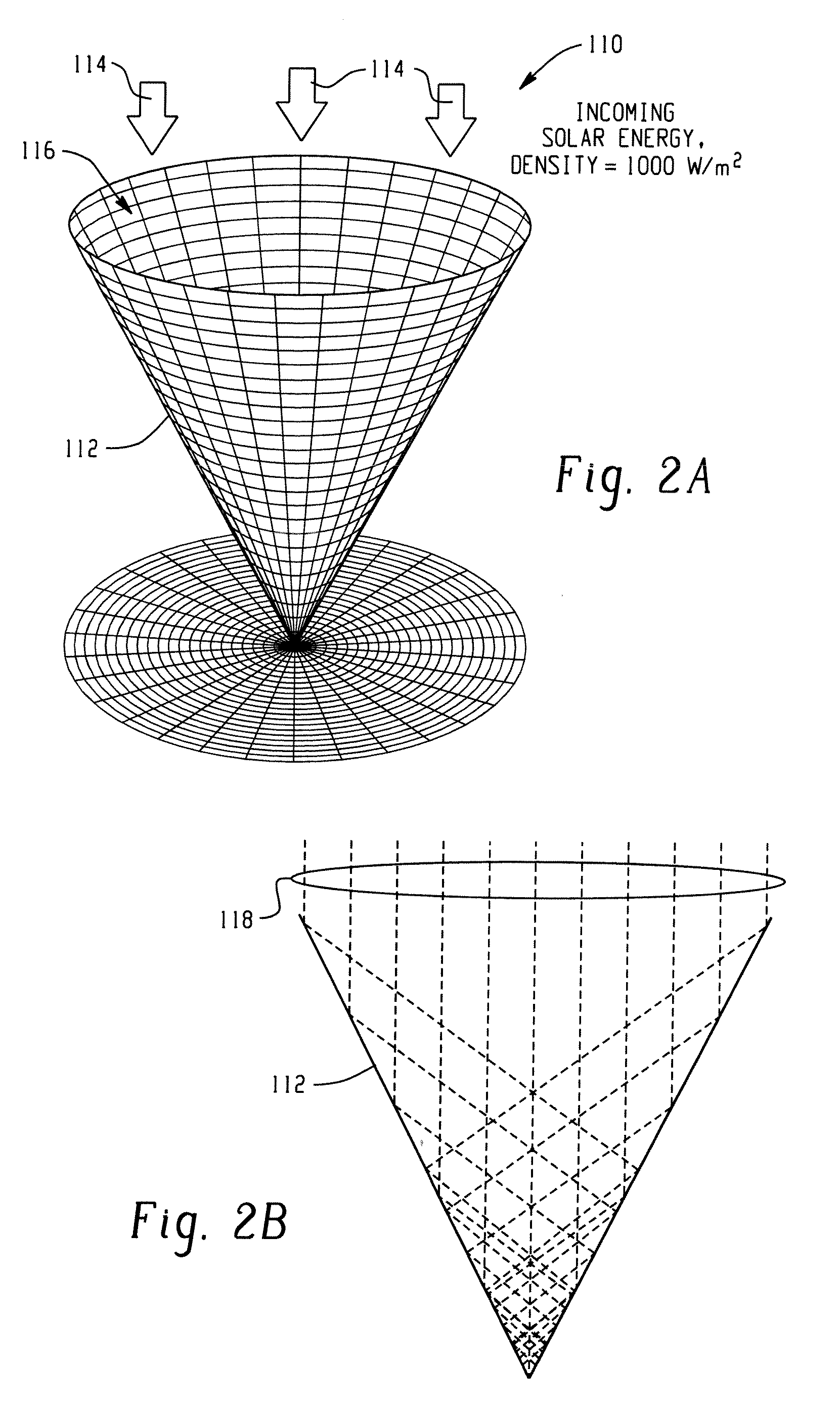
Laser generated synthetic mega scale aperture for solar energy concentration and harnessing
InactiveUS20090171477A1Reducing laser power levelSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersPhysical opticsAtmospheric air
Systems and methods are described that employ high-intensity lasers to set up a thin plasma sheet, also called a waveguide or “hot shell”, in the atmosphere as a function of beam intensity and geometry. A laser beam can be spread and directed with physical optics (e.g., lenses, mirrors, other optical elements, etc.) to generate a thin inverted cone-shaped hot shell waveguide in the atmosphere. The hot shell of the waveguide has a different index of refraction (n) from that of the surrounding air layers and as such serves to internally reflect portions of the entering solar rays entering an aperture in the hot shell, toward the tip of the cone and a solar energy storage component positioned there, thus providing a virtual solar energy concentration system. In another embodiment, the solar energy storage component shuts down or otherwise rejects incoming solar energy when fully charged, to mitigate damage to system components.
Owner:CLEVELAND STATE UNIVERSITY
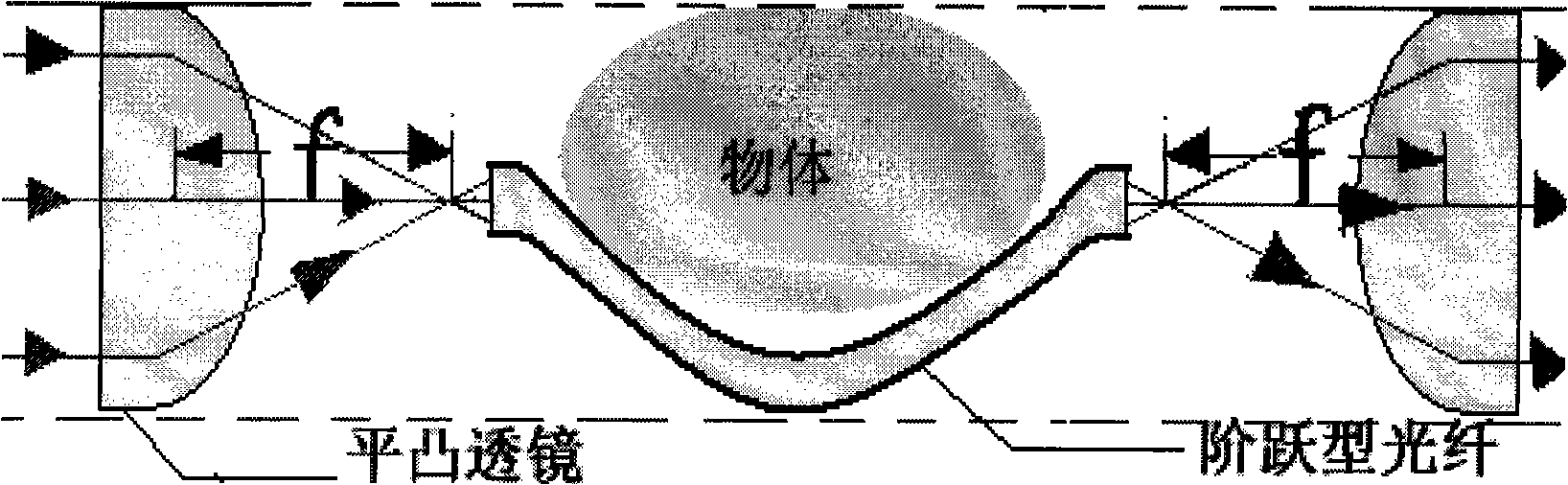
Invisible apparatus and design based on geometrical optics
InactiveCN101299079AAchieve optical invisibilitySimple structureBundled fibre light guidePhysical opticsImage transfer
The present invention provides a concealing device which is based on geometric optics and a design thereof, and relates to the field of optical concealing technique. According to the principle of physical optics, the light beams are converged with a convex lens. The cross-sectional area of the light beam is changed. The incidence light at the front of the object can be converged through the convex lens and transferred to the backside of the object through an image transferring channel, and is changed to the former incidence ray through radiation. The effect of concealing the visible light is obtained. The core of the device is that the concealing device is composed of at least one group of object group 1 which can be permeated with light and focus the light, a light beam transmission component 2 which is provided between the focusing object group 1 and a concealing area 3. The device is designed with an imaging formula of the convex lens to obtain the effect of optical concealing the visible light. The concealing state of the device is sustained without exterior power. The exterior exposed part of the device is fewer. Compared with the optical physical concealing device, the concealing device according to the invention has the characteristics of simple structure, easy manufacture, low cost and wide application area.
Owner:上海市第二中学
Radar target identification method on basis of biomimetic pattern identification theory
ActiveCN102608589AImprove the correct recognition rateHigh coverage accuracyWave based measurement systemsFeature vectorPhysical optics
The invention discloses a radar target identification method on the basis of the biomimetic pattern identification theory, which includes steps of calculating echo data corresponding to a radar target by the physical optic method, analyzing the radar echo data and building one-dimension range profile of the radar target, preprocessing the one-dimension range profile of the radar target into characteristic vectors, and then identifying different targets by the biomimetic pattern identification theory. As a new pattern identification method, the radar target identification method on the basis of the biomimetic pattern identification theory is characterized by being based on 'understanding' rather than 'dividing'. Particularly, the targets are 'understood' by covering feature samples of each type of targets in high-dimensional space by the aid of a hyper-sausage model, so that correct recognition rate is increased effectively, while defects that conventional radar target identification methods are poor in identification capacity and original data are required to be retrained once a new type targets are added are avoided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
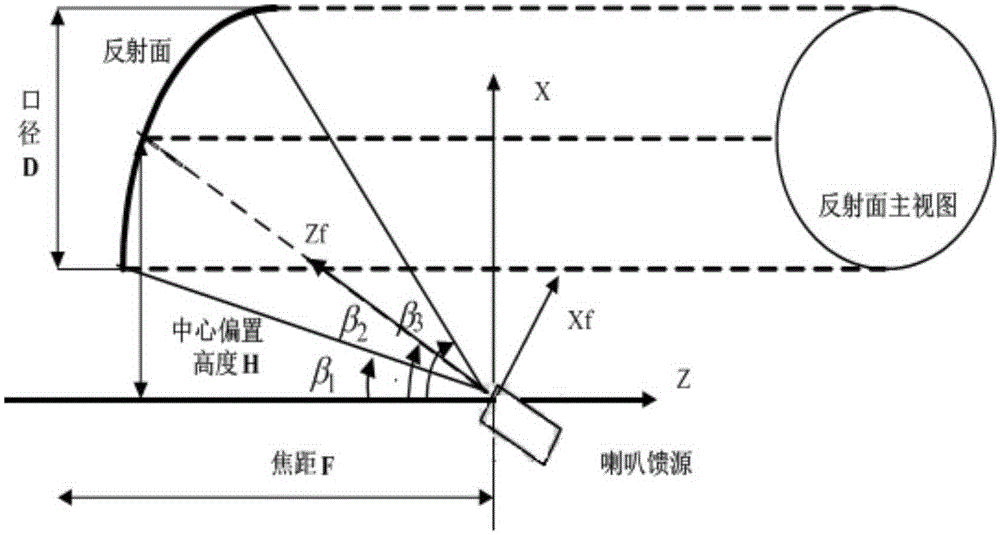
Satellite-borne multi-beam reflector antenna forming method based on bat algorithm
The invention discloses a satellite-borne multi-beam reflector antenna forming method based on a bat algorithm, comprising the steps as follows: selecting the reflector size and feed source position according to the shape of a multi-beam coverage area; deploying a reflector antenna based on a multi-focus reflector equation; and introducing a bat algorithm to optimize the parameters of the multi-focus reflector equation, and accelerating a physical optics method through a GPU to calculate the pattern of the reflector antenna. According to the invention, the designed parameters are all optimized, and the computation time is reduced on the premise of guarantee accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
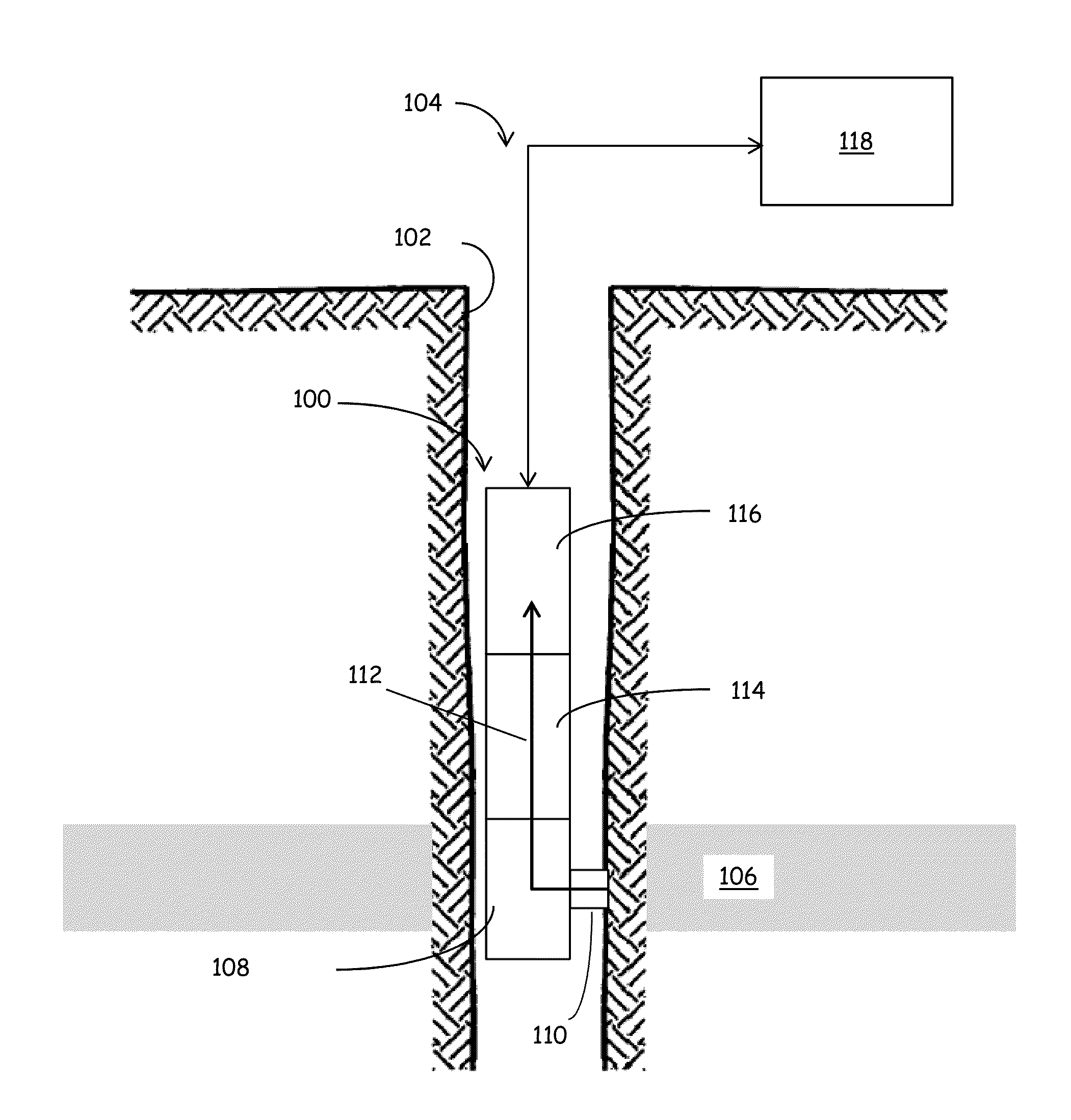
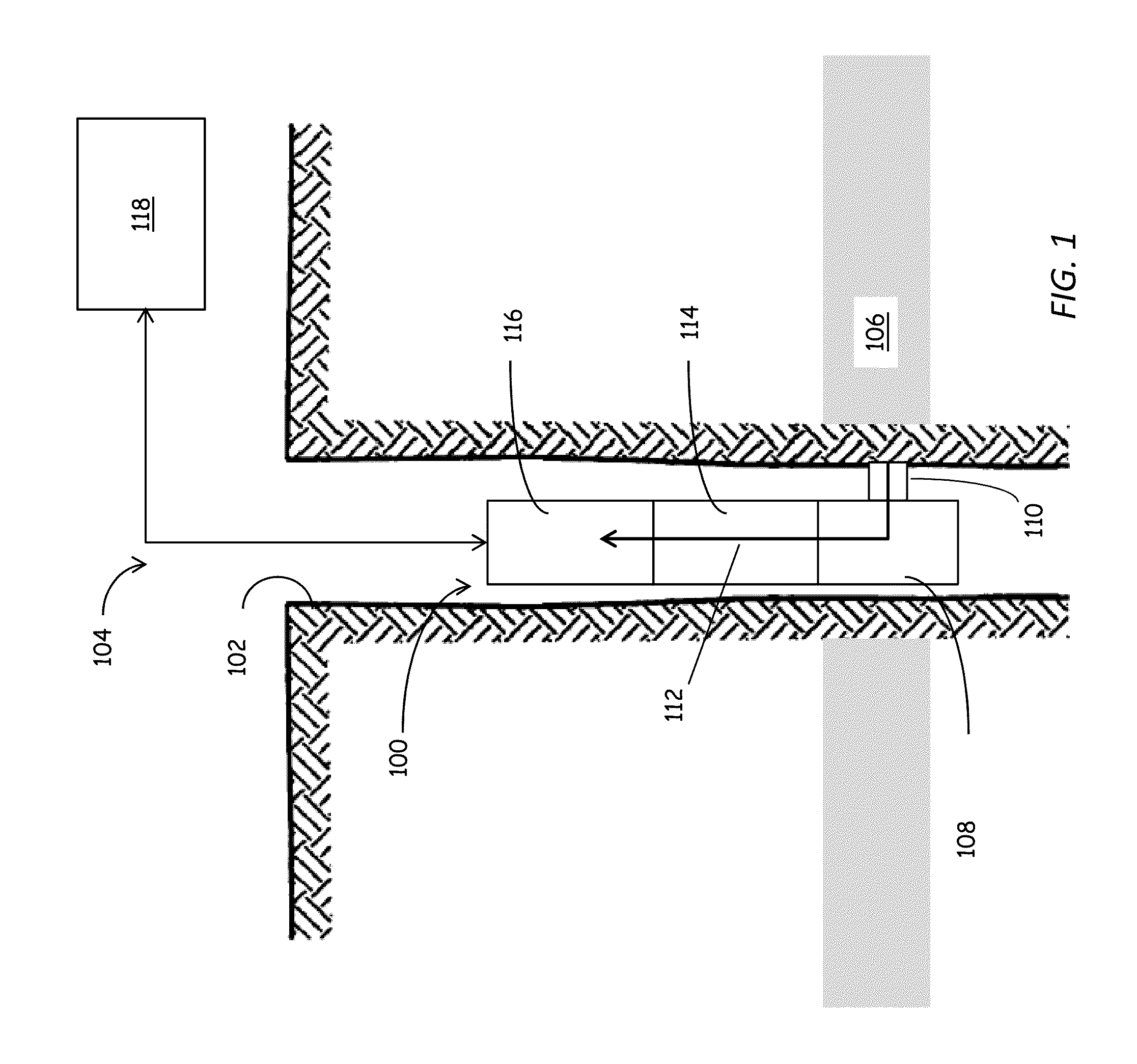
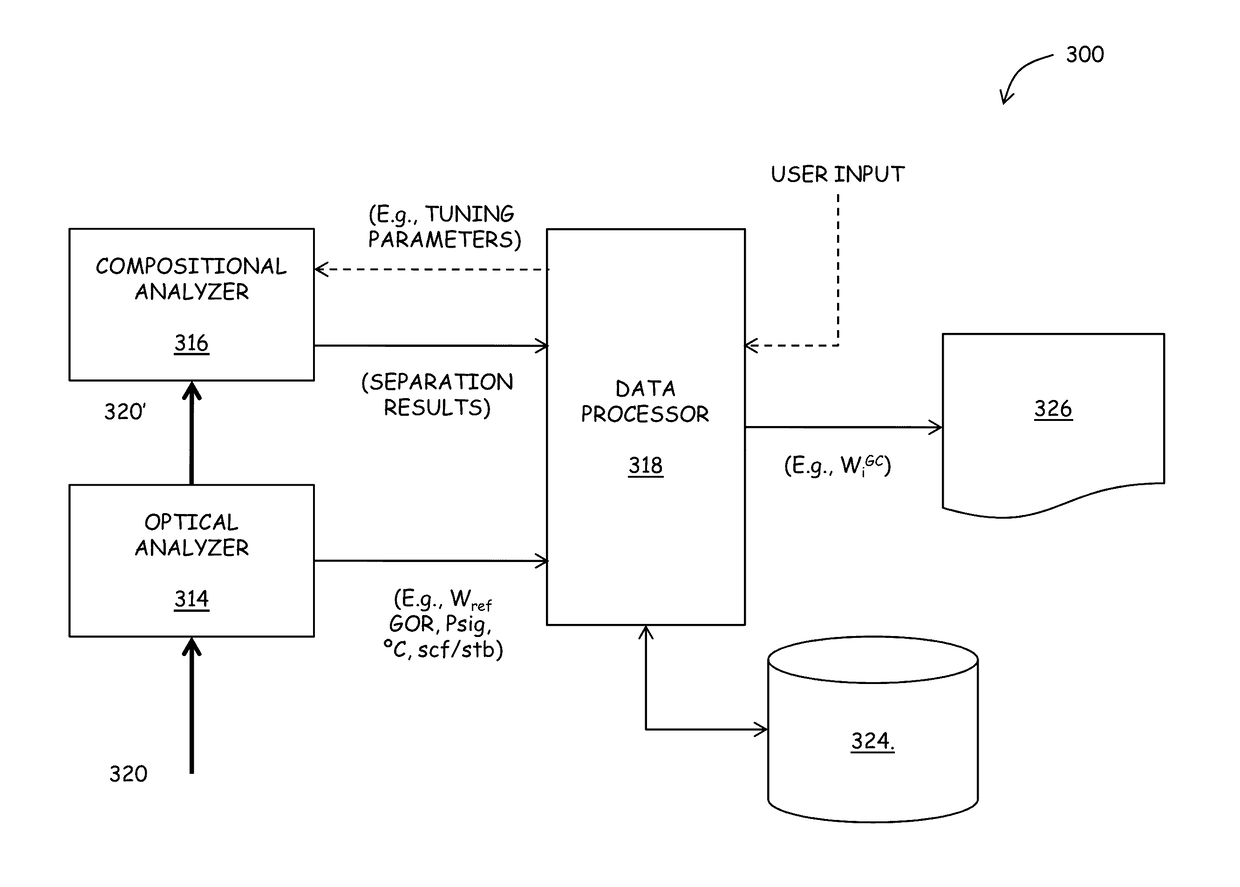
Real-time compositional analysis of hydrocarbon based fluid samples
ActiveUS20130085674A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComponent separationElemental compositionQuality control
Accurate, real-time formation fluids analysis can be accomplished using the systems and techniques described herein. A fluid analyzer includes a first mode of analysis, such as an optical analyzer, configured to determine a physical (optical) property of a fluid sample. The fluid analyzer also includes another mode of analysis, such as a composition analyzer, such as a gas chromatographer, configured to determine an elemental composition of the fluid sample. A data processor is configured to determine a quantity, such as a weight percentage, of a target component of the fluid sample in response results obtained from the first and second modes of analysis. Beneficially, the results are obtained at least in near real-time, allowing for interim results, such as results from the first analyzer to be used for one or more of tuning the compositional analyzer and for implementing quality control.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
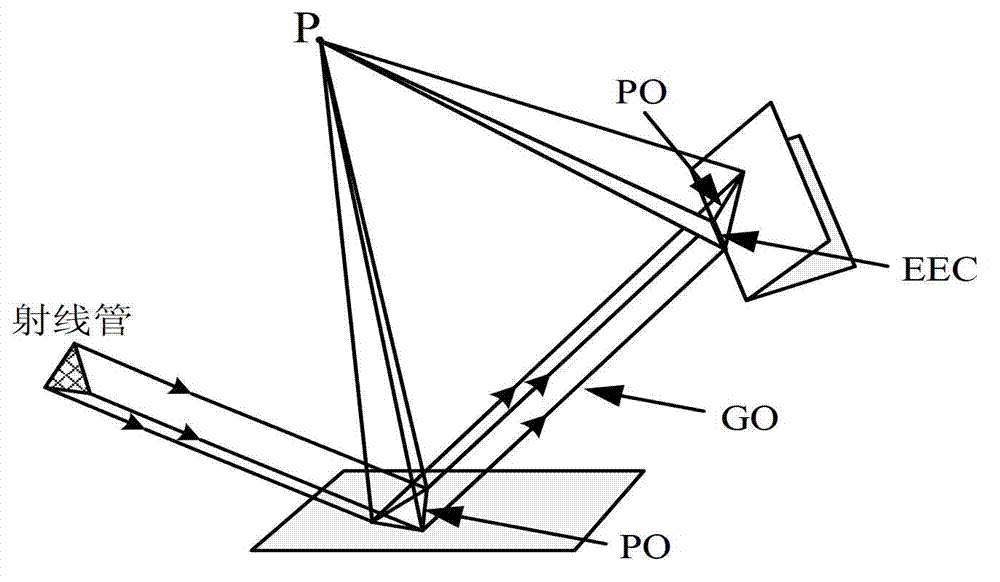
Rapid calculation method for electromagnetic scattering of ultra-high-speed target in thin atmosphere
ActiveCN107942309AEnabling Electromagnetic Scattering CalculationsWave based measurement systemsPhysical opticsStream flow
The invention discloses a rapid calculation method for electromagnetic scattering of an ultra-high-speed target in a thin atmosphere. The rapid calculation method comprises the steps of: plasma equivalent layered medium model modeling, which is implemented by analyzing streaming flow field data f a hypersonic speed target by utilizing an isotimic-surface extraction algorithm, and establishing a plasma equivalent layered medium model; ray tracing and field intensity tracing in layered media, wherein the tracking is implemented by simulating the propagation process of electromagnetic waves in the layered media by utilizing rays, performing field intensity tracing along propagation paths of the rays, and acquiring electric field information of the rays at intersection points in the layered media; and modeling of a far-region scattering field for a layered media coated target, wherein the modeling is implemented by modeling electromagnetic scattering features of a multilayer-medium-coatedtarget by adopting an shooting and bouncing ray method in the case of high-frequency electromagnetic wave incidence, calculating scattering contributions of emergent rays in the direction of a radar receiver by utilizing a physical optics method for the emergent rays, and acquiring a total scattering field and RCS information. The rapid calculation method has the advantage of expanding the range of applicability.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
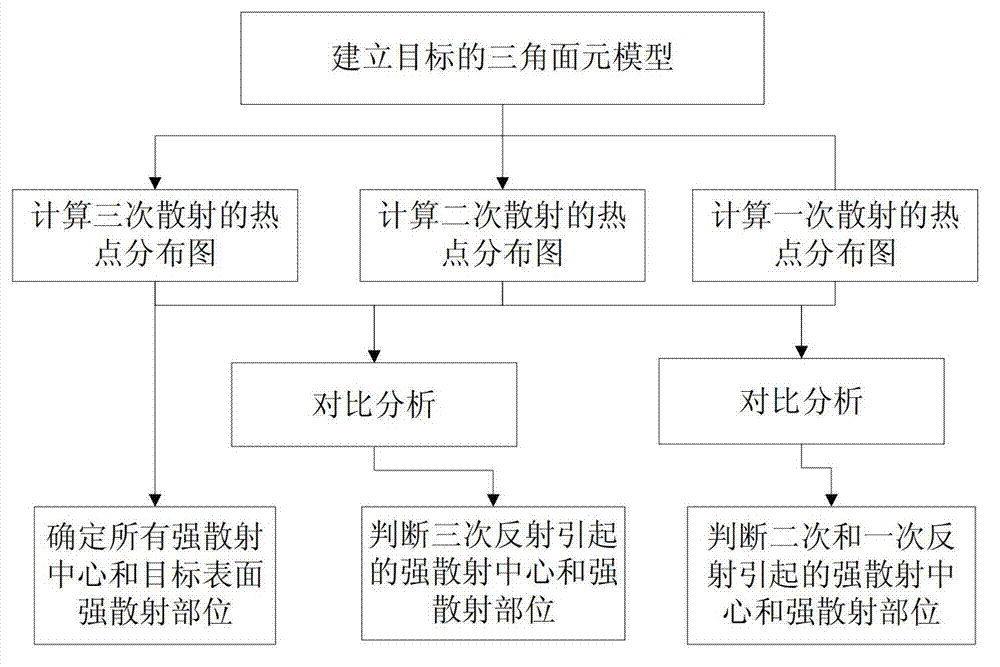
SBR and PO technology-based strong scattering center calculation method
InactiveCN103713284AImprove efficiencyEasy to analyzeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTarget surfacePhysical optics
The invention belongs to the signal characteristic control technical field and relates to an SBR and PO technology-based strong scattering center calculation method. The calculation method comprises the following steps that: hotspot calculation is performed through ray tracing and physical optics; a distribution diagram which can indicate the radar cross section (RCS) contribution of each surface element of a target surface is obtained; and strong scattering parts can be located through comparing hotspot diagrams. Compared with a low-frequency method, and according to the SBR and PO technology-based strong scattering center calculation method, SBR and PO methods are adopted to calculate target hotspots, and therefore, high efficiency can be realized; hotspot contribution is attached to the surface of a 3D model, and therefore, the strong scattering contribution parts can be analyzed intuitively. The SBR and PO technology-based strong scattering center calculation method of the invention can trace separated two-times and three-times strong coupling structures. Strong multiple-times scattering which is generated through the coupling of separated parts on a target is usually difficult to discover, while, hidden strong scattering structures can be found out through the hotspot diagrams.
Owner:中国航天科工集团第二研究院二〇七所
Method for calculating near-field radar echo characteristics of moving object based on beam decomposition and local irradiation
InactiveCN103777186ASolve the major technical problems of near-field radar echoRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumRadar equation
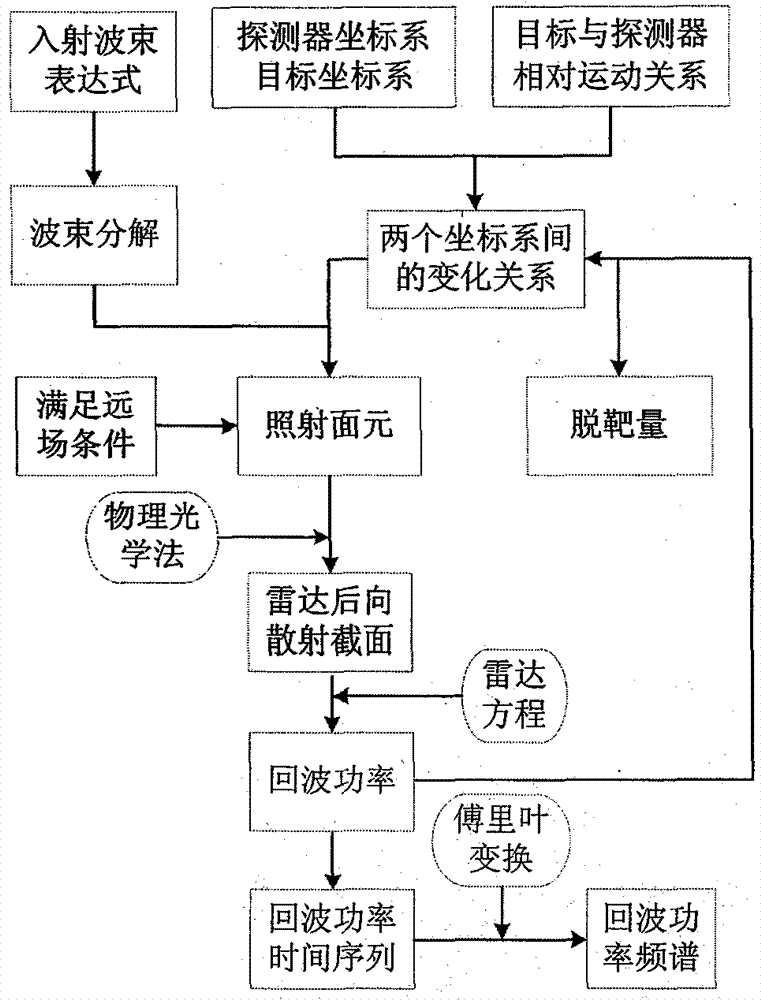
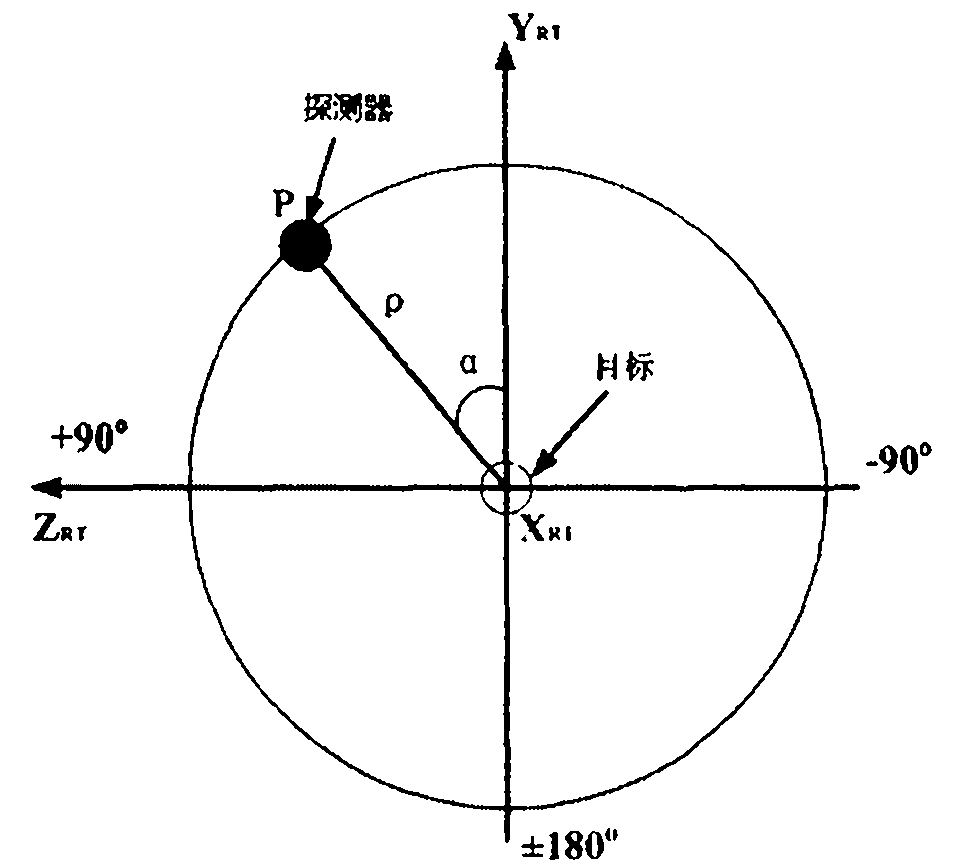
The invention discloses a method for calculating near-field radar echo characteristics of a moving object based on beam decomposition and local irradiation. The method comprises the steps of determining a coordinate system of radar or a detector, a coordinate system of the moving object and transformation relation between the coordinate systems; determining a relative speed coordinate system of the detector and the object, thereby acquiring a miss distance; providing radar beam description so as to decompose an incident beam, carrying out surface element subdivision on the object, determining the local irradiation area, and judging surface element shielding; meeting a far-field condition by a sub-beam irradiation surface element, and superimposing by using a physical optics method to acquire a backward radar cross section; and acquiring a time series of the power of near-field radar echoes by using a radar equation and the corresponding spectral characteristics. A far-field calculation method is expanded to near-field calculation by using the characteristic that beam decomposition and physical optics are similar to each other locally, and the time series of the power of the near-field radar echoes and the corresponding spectral characteristics. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the far-field calculation method is expanded to the near-field calculation by using the characteristic that the beam decomposition and the physical optics are similar to each other locally, and the time series of the power of the near-field echoes and the corresponding frequency spectrum are calculated by the radar equation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
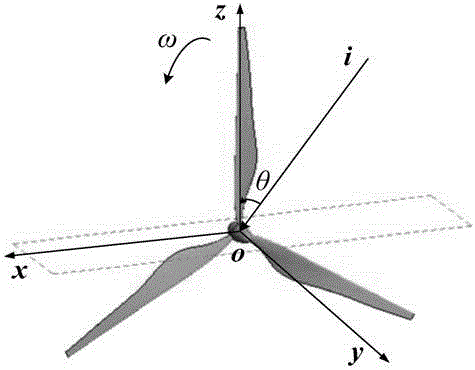
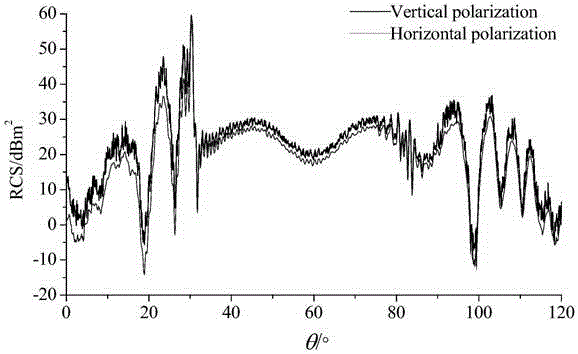
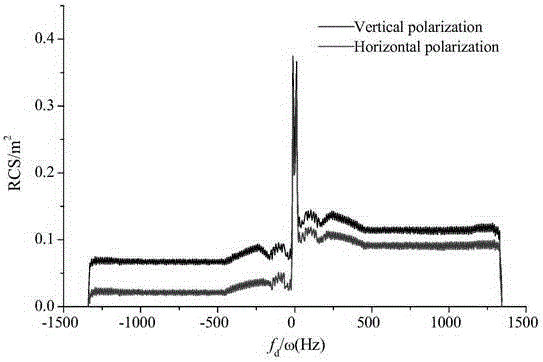
Wind turbine fan radar echo signal Doppler spectrum solving method
The invention discloses a wind turbine fan radar echo signal Doppler spectrum solving method. The wind turbine fan radar echo signal Doppler spectrum solving method comprises the following steps: first, determining a rotating angle interval for calculating a blade static RCS by utilizing the 'Nyquist sampling theorem' according to the derived equivalence relation between blade dynamic radar cross section fluctuation frequency and blade radar echo signal Doppler frequency; then, respectively calculating the RCS of a wind turbine blade at various sampling angles by utilizing a mixed algorithm consisting of a physical optics method and an equivalent electromagnetic current method, so that a blade dynamic RCS is obtained based on a 'quasi-static method'; finally, performing discrete short time Fourier transform on the obtained blade dynamic RCS, and solving to obtain the Doppler spectrum of the blade dynamic RCS, namely, the Doppler spectrum of the blade radar echo signal. According to the wind turbine fan radar echo signal Doppler spectrum solving method, a new method and a new way can be provided for effectively identifying a wind turbine target by a radar station, and theoretical basis can also be provided for the aspects, such as electromagnetic scattering reduction of a wind power plant, and wind power plant clutter extraction and inhabitation of the radar station.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
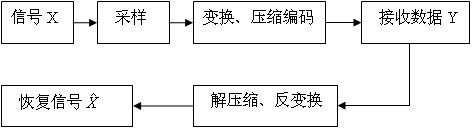
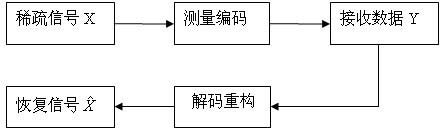
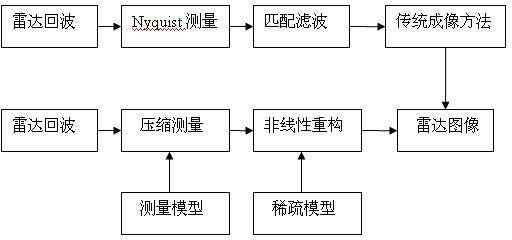
Compressive sensing radar imaging algorithm based on subspace tracking
ActiveCN102495393AGood effectDownsamplingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsPhysical optics
The invention discloses a compressive sensing radar imaging algorithm based on subspace tracking. By using a physical optical method, corresponding echo data are calculated, radar echo data are analyzed, a sparse model of a signal is established, and echo reconstruction is realized by using an effective and steady subspace tracking algorithm, so that synthetic aperture radar imaging is realized. The signal is subjected to non-adaptive sampling by using a compressive sensing theory at the speed rate which is much lower than Nyquist sampling rate. Therefore, the compressive sensing theory is applicable to synthetic aperture radar imaging, an imaging effect can be achieved, and the aim of reducing the sampling rate of the echo data is fulfilled, so that simulation time is shortened, and the cost of a radar system can be reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
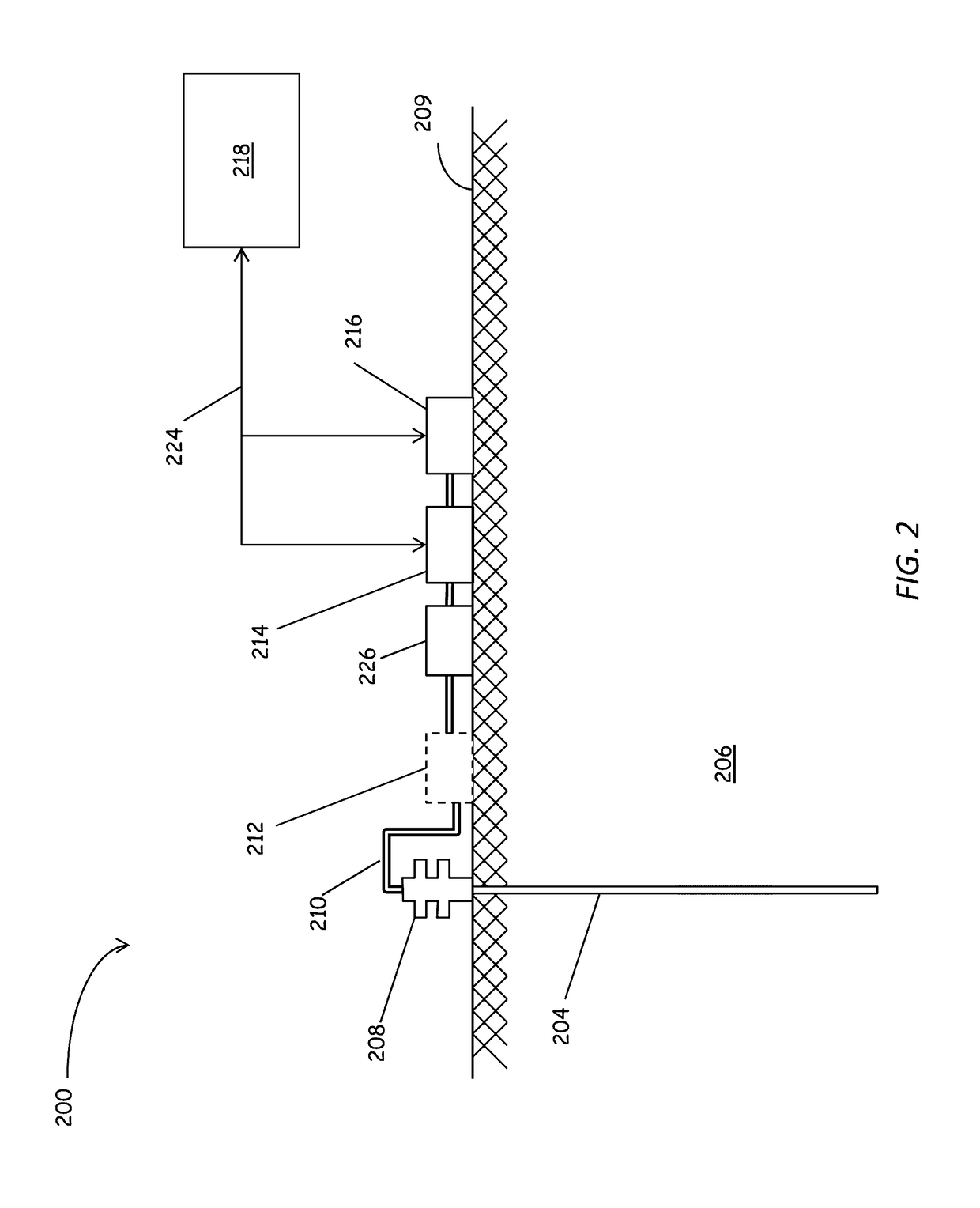
Foldable electronic device comprising flexible display
ActiveUS20190361501A1Avoid spaceDetails for portable computersCamera diaphragmsPhysical opticsOptical axis
An electronic device according to various embodiments can provide a structure capable of imparting a physical optical effect to a camera unit of a foldable electronic device to which a flexible display is applied. An electronic device according to various embodiments may comprise: a lens unit placed in a partial area of a first side, which does not include a flexible display, through the first side and a second side; a first imaging unit which, when the first side is divided into a first area and a second area on the basis of an axis, is placed adjacent to the first area in which the lens unit is placed; and a second imaging unit which is placed in at least a partial area of the second side and is configured to be combined on the same optical axis with the lens unit when the electronic device is folded on the basis of the axis. In addition, other embodiments are possible.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Warship-targeted radar scattering cross section detecting method
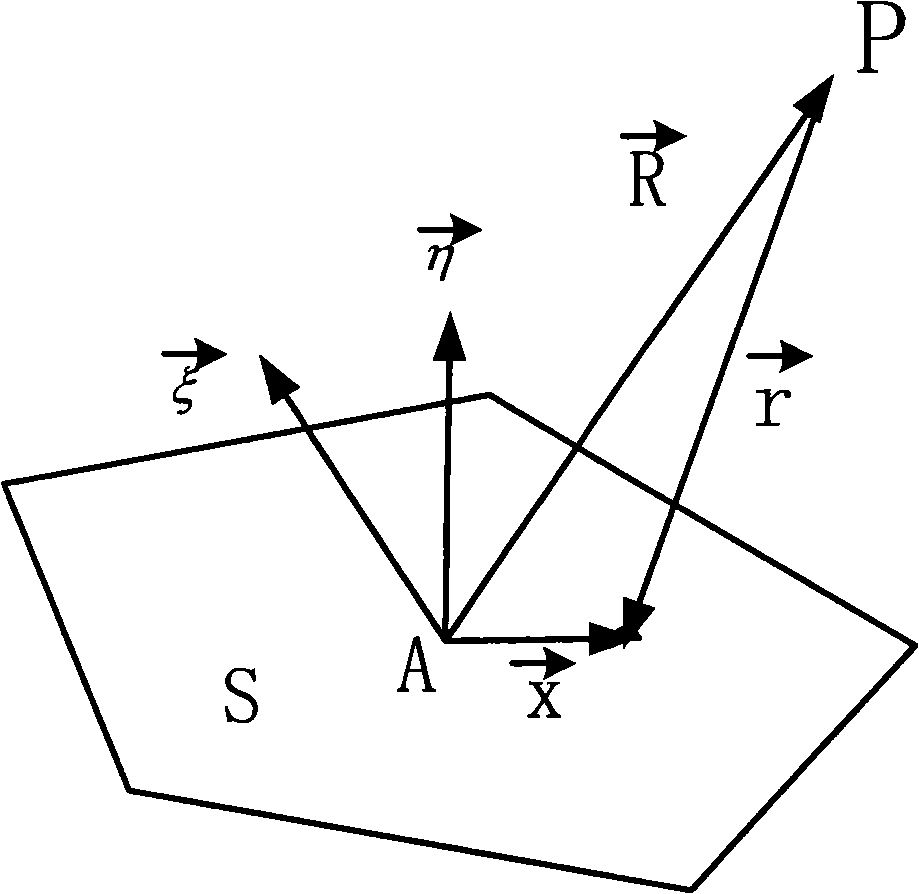
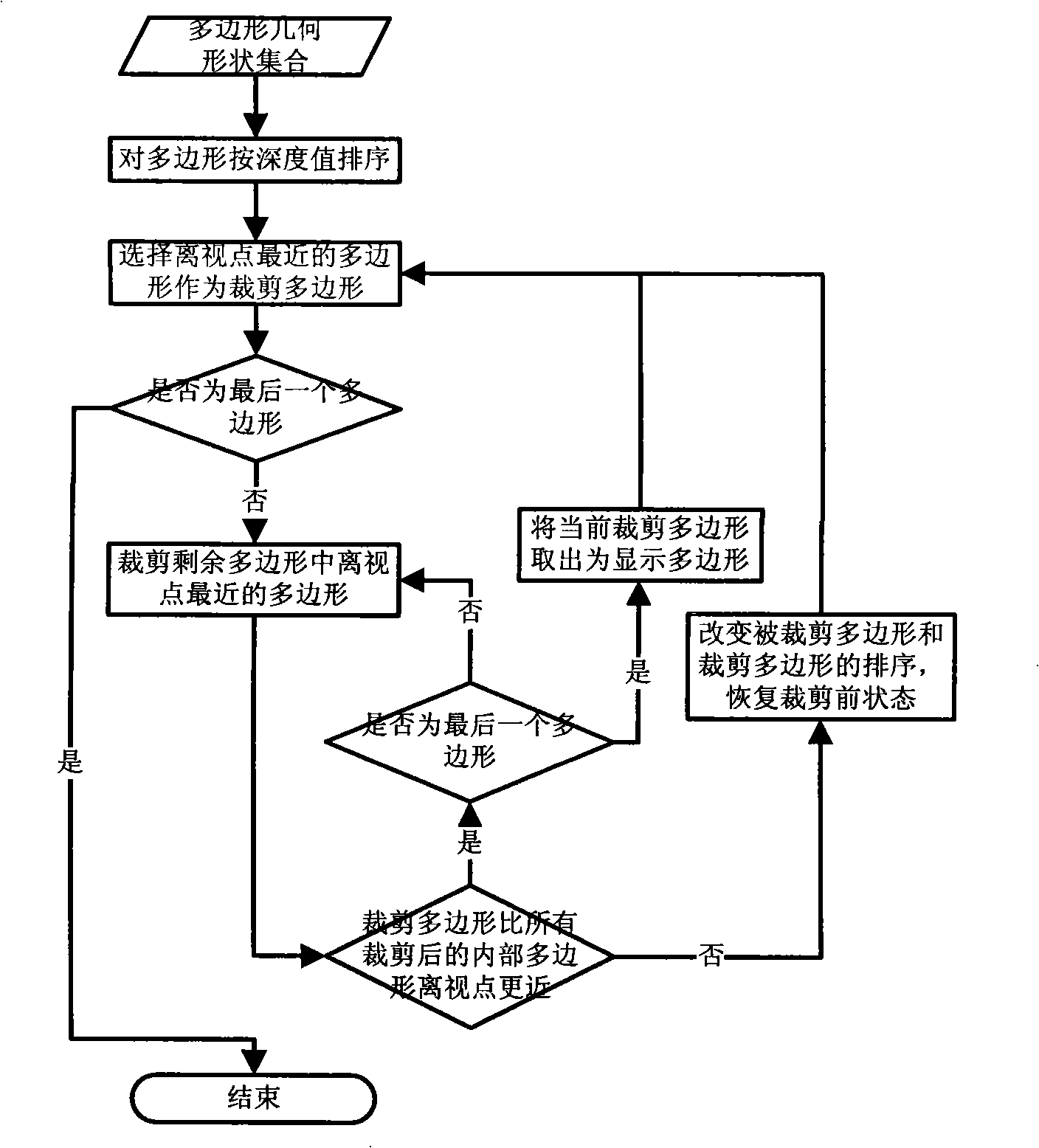
The invention provides a warship-targeted radar scattering cross section detecting method, belonging to the field where the radar scattering cross section (RCS) of a target object is analyzed in high speed by using graphic electromagnetic computing (GRECO) technology. The detecting method is characterized in that a model expressed by a polygon is made for the target object. And a physical optical scattering equation is used to be combined with the blanking technology of computer graphics to improve the calculation of RCS. The subdivision is no longer required for the object. Therefore, the calculation cost has no relation with frequency. The introduction of blanking also solves defects in precision during the calculation, thus the high frequency radar scattering cross section can be calculated precisely in high speed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
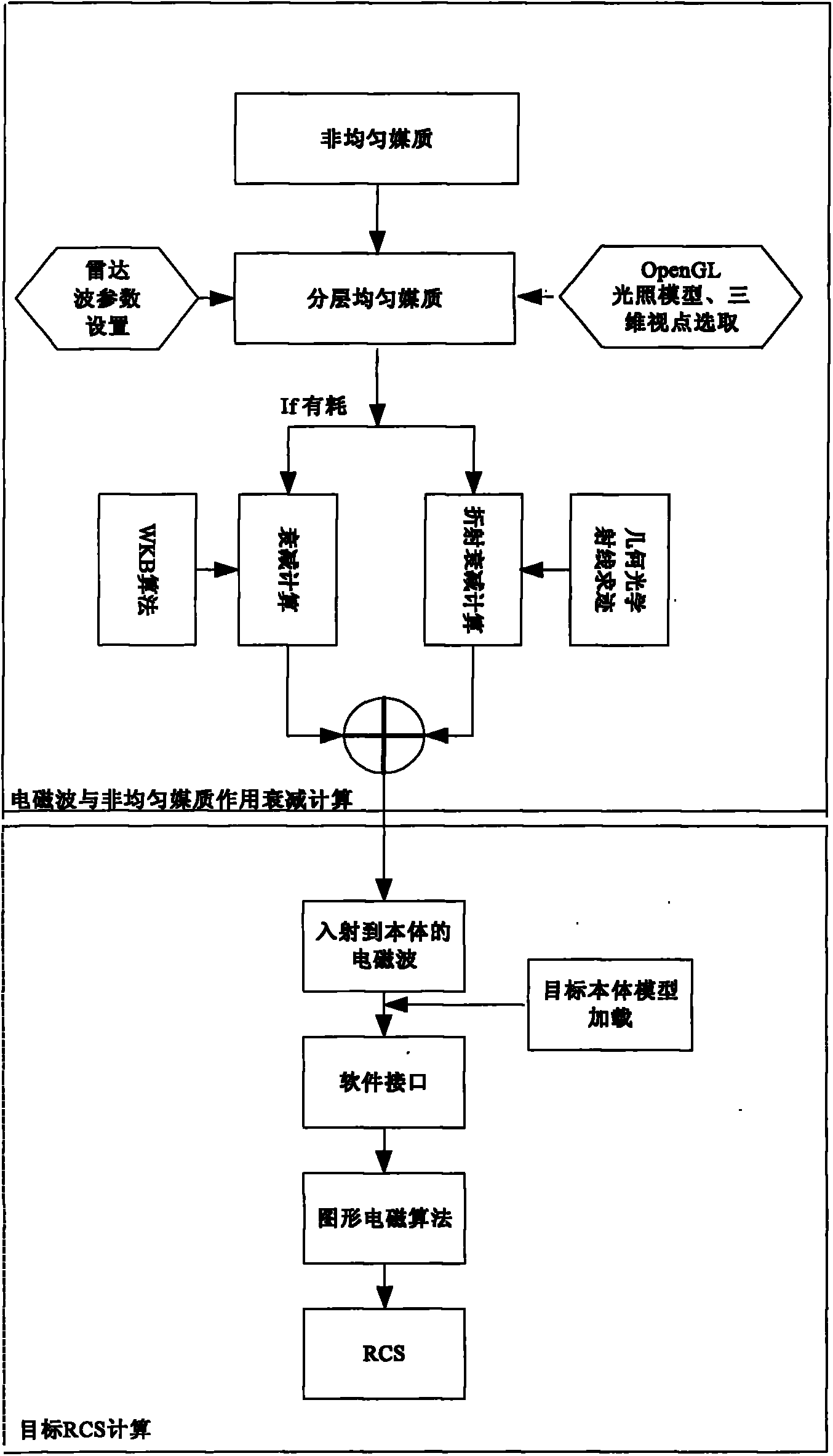
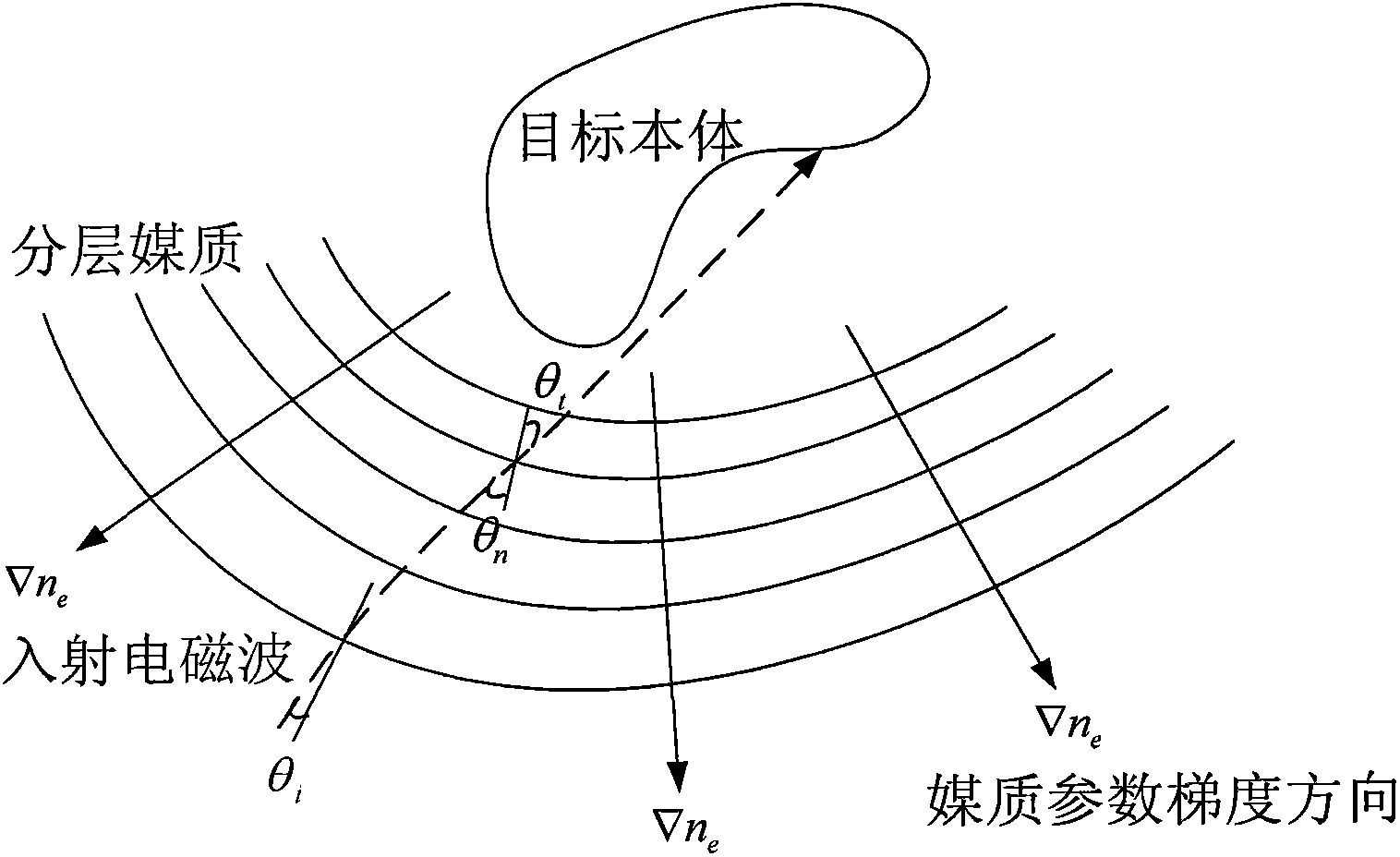
Visual tracing scattering analysis method of inhomogeneous medium
InactiveCN102880773AComputationally efficientSpecial data processing applicationsScattering cross-sectionPhysical optics
The invention discloses an efficient calculation method of a radar scattering cross section of an inhomogeneous medium wrapped target. The method comprises the following steps: firstly equalizing the inhomogeneous medium into a layered homogeneous medium according to electromagnetic parameters; setting up a lighting model and selecting a three-dimensional viewpoint in an OpenGL (open graphics library) and inputting the three parts of information into a graph hardware processor; accomplishing the automatic shielding of a three-dimensional target by using the graph hardware processor; outputting a real-time target image and visible pixel information displayed on a computer screen after the automatic shielding, wherein the visible pixel information includes brightness values (R,G,B) and three-dimensional coordinates (x,y,z) of pixels; displaying medium interfaces at which rays arrive layer by layer in the OpenGL according to the direction of incident electromagnetic waves; extracting the brightness and the coordinate information of the pixels; determining the reflection and refraction of the rays by combination of the electromagnetic parameters at two sides of the interface, so as to trace the direction of the rays and determine the incidence direction of incidence electromagnetic waves of the pixels of the target when the rays arrives at a target body; in a loss medium, synchronously calculating the attenuation of each ray on a transmission journey; and finally, calculating the radar scattering cross section of the inhomogeneous medium wrapped target according to integrals of a physical optical field and a boundary diffraction field. The method has the advantages that a novel method for calculating radar scattering characteristics of the inhomogeneous medium based on graphic display is provided, so that the defects that in a traditional calculation method, a large-sized medium cannot be calculated, and control in manual mode is difficulty are overcome.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ENG
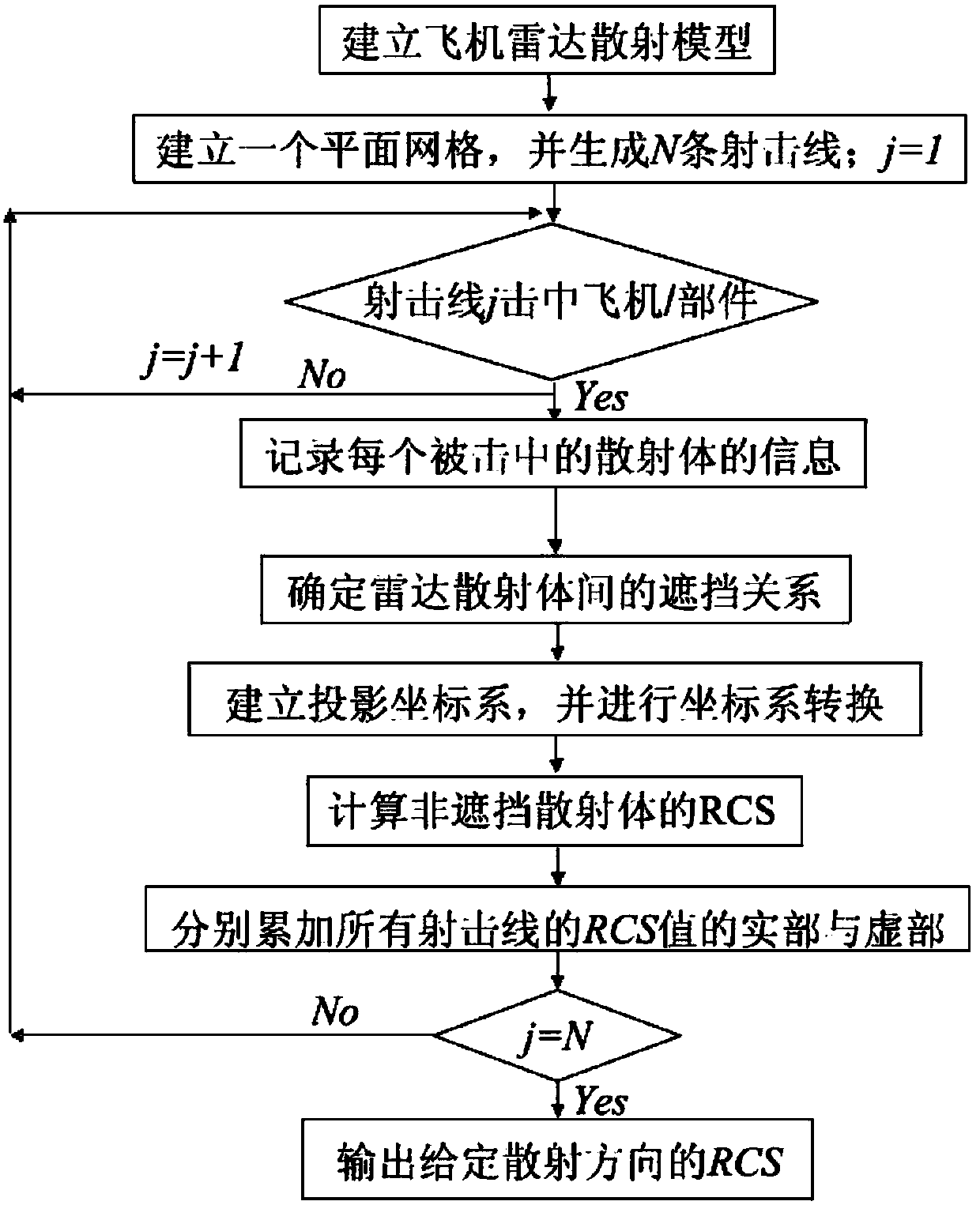
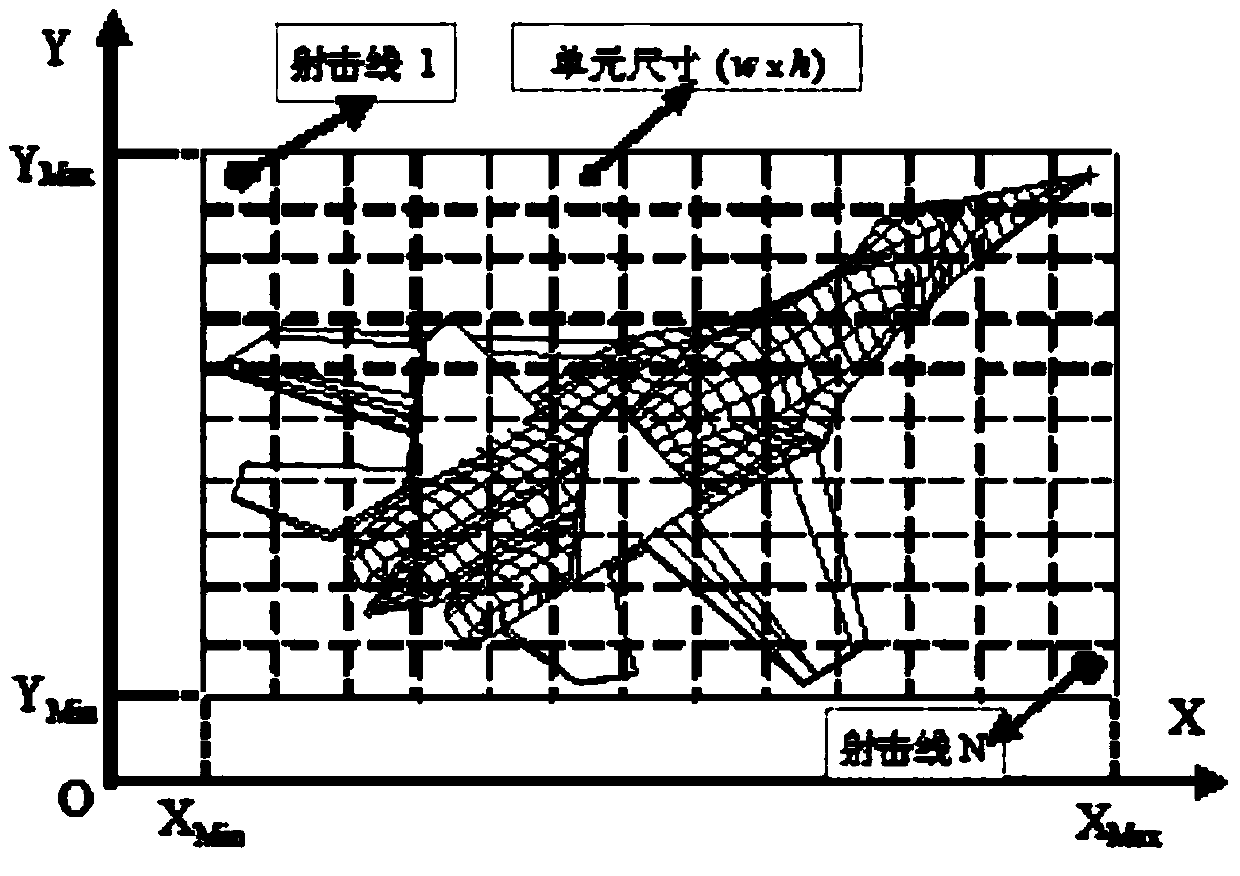
Method for obtaining radar scattering area
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a radar scattering area. The method is used for resolving the technical problem that an existing method for obtaining the radar scattering area is low in speed. According to the technical scheme, firstly, a radar scattering model is set up, a firing line is used for simulating an attack direction, association attributes of components are defined, and related data of firing line meshes and the like of the components are obtained; secondly, a projected coordinate system is set up, the data are converted into the projected coordinate system, and RCS calculation is carried out on the related data; at last, real parts and imaginary parts are respectively accumulated to obtain the radar scattering area. Due to the fact that the radar scattering area is obtained by means of a physical optical method and a planar firing line method, the planar meshes are laid on a quadrilateral finite element projected model, 1-N firing lines are produced randomly in units of the planar meshes, and surfaces of the components are scanned through the 1-N firing lines to obtain geometric description data of the radar scattering area. Step sizes of the meshes are regulated according to different precision requirements, radar scattering areas of different precisions are obtained, and the speed for obtaining the radar scattering area is increased.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Time domain physical optics algorithm based on CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) hybrid asynchronous parallel way
ActiveCN105243280AReduce development and writing costsShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsArray data structurePhysical optics
The invention discloses a time domain physical optics algorithm based on a CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) hybrid asynchronous parallel way. The time domain physical optics algorithm comprises the following steps: 1, performing modeling through 3Dmax, and performing subdivision through triangular surface elements, wherein a derived model is in an OBJ format; 2, synchronously reading usable information such as vertex coordinates and a vertex quantity of the triangular surface elements in a model file (1), vertex numbers and a surface element quantity of the surface elements in the model file (2) and an incident electric field (3) respectively on three threads in an MPI parallel way; 3, accelerating the whole process in parallel through OpenMP; 4, transmitting data such as a Gaussian node array and a triangular surface element array into a GPU, accelerating a Gaussian integral value operation by the GPU to obtain a scattered field, and transmitting the scattered field into a CPU; and 5, transforming a scattered field time domain into a frequency domain through a Fourier transform, and dividing the frequency domain by an incident electric field frequency domain to obtain an RCS (Radar Cross Section) array. Through adoption of the time domain physical optics algorithm, time is saved greatly when a transient scattering calculation amount of an electrically large object is large.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
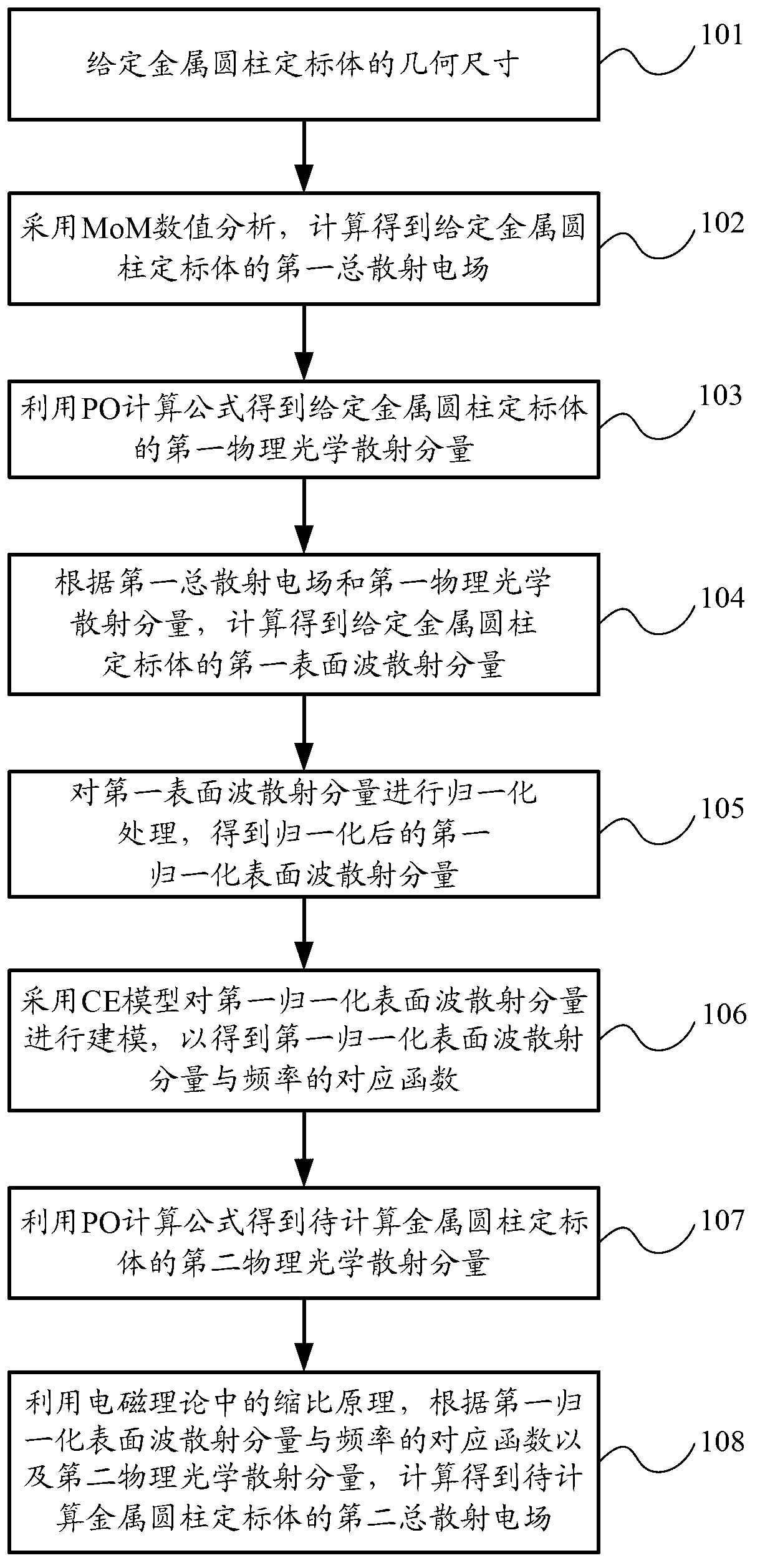
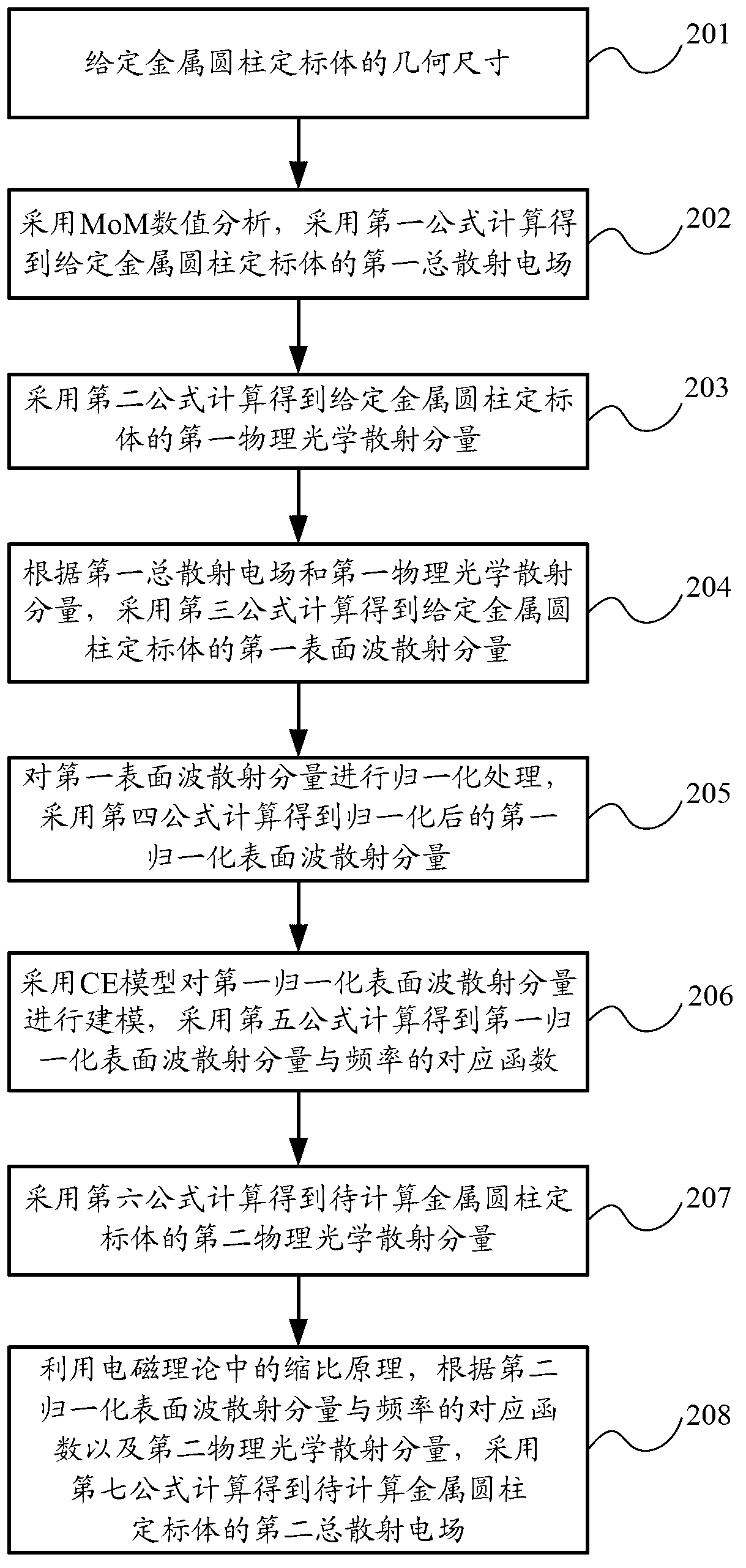
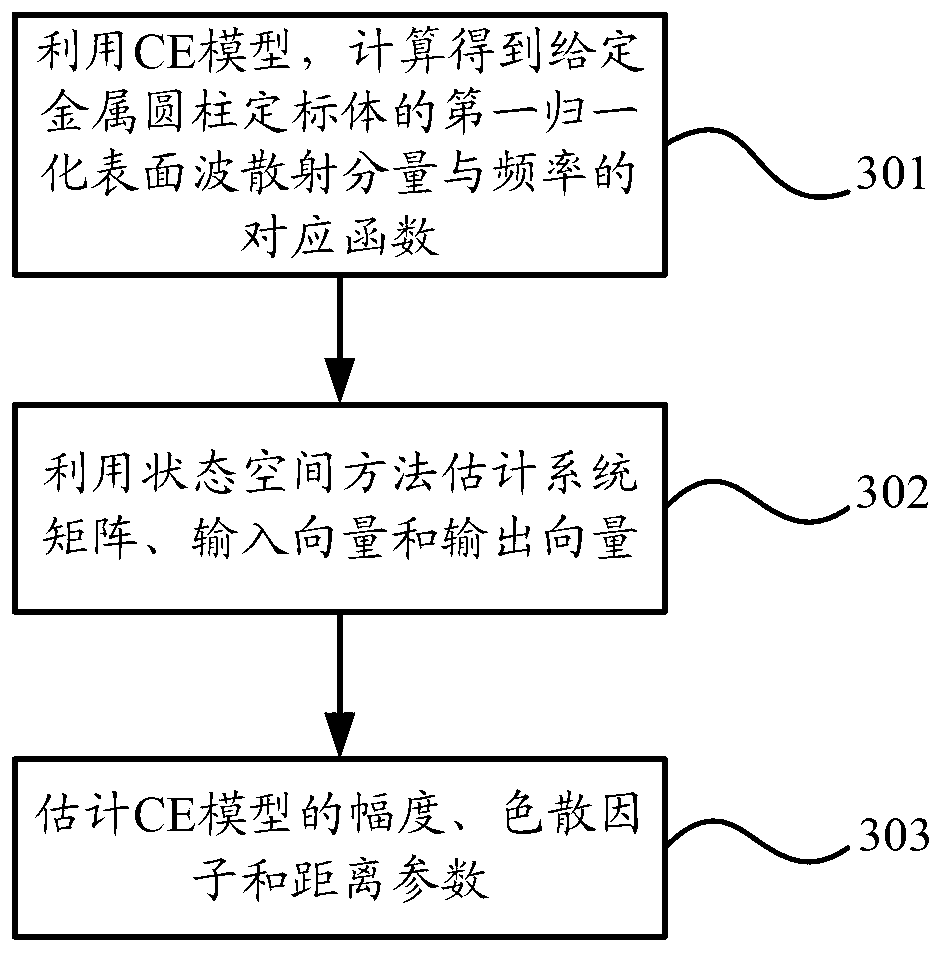
Method for calculating radar scattering cross section of metal cylindrical calibration body
The invention provides a method for calculating a radar scattering cross section of a metal cylindrical calibration body, which comprises the following steps of: pre-setting the size of the metal cylindrical calibration body; calculating a first total scattering electric field of the pre-set metal cylindrical calibration body by adopting MoM numerical value analysis; obtaining a first physical optical scattering component of the pre-set metal cylindrical calibration body by utilizing a PO formula; calculating a first surface wave scattering component of the pre-set metal cylindrical calibration body according to the first total scattering electric field and the first physical optical scattering component, and carrying out normalization processing of the first surface wave scattering component to obtain a first normalized surface wave scattering component; modelling the first normalized surface wave scattering component by adopting a CE model to obtain corresponding functions of the first normalized surface wave scattering component and frequency; obtaining a second physical optical scattering component of the metal cylindrical calibration body to be calculated by utilizing the PO formula; and calculating to obtain a second total scattering electric field of the metal cylindrical calibration body to be calculated by utilizing the shrinkage ratio principle according to the corresponding functions and the second physical optical scattering component.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for detecting micro lens fixed focus based on grating shear interference detection system
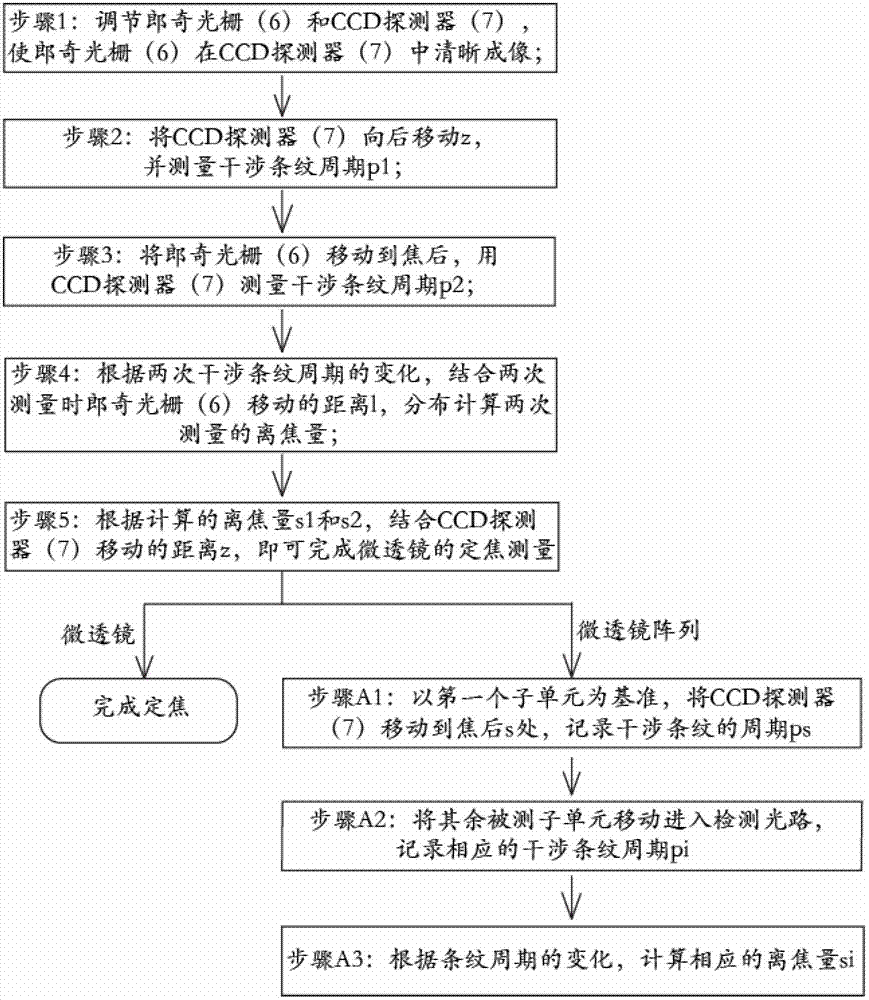
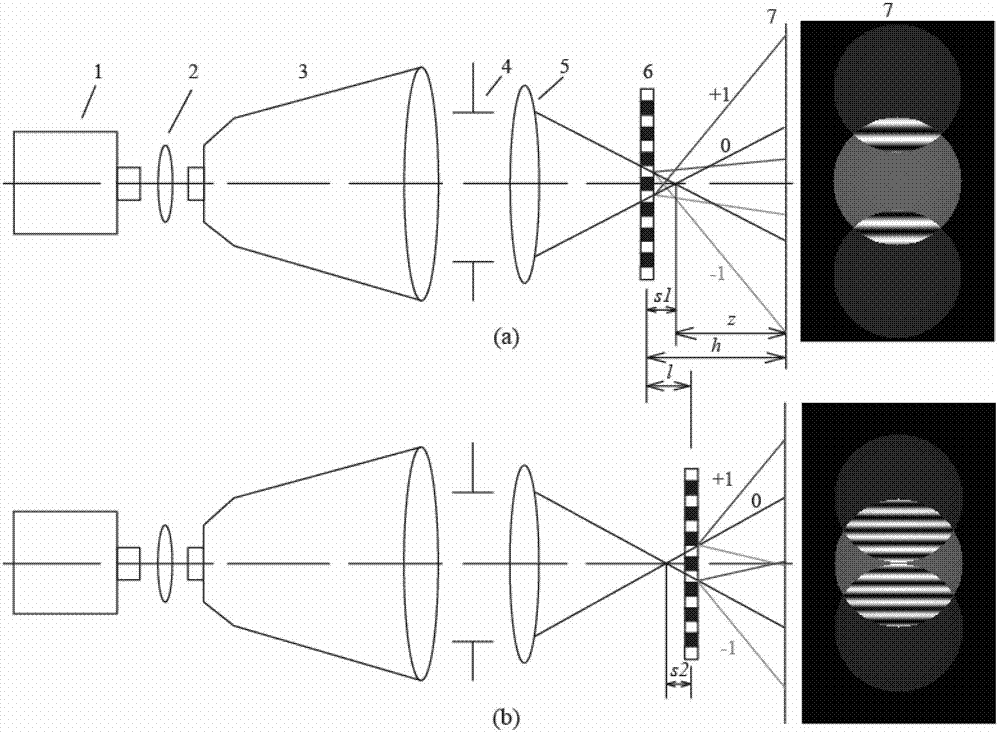
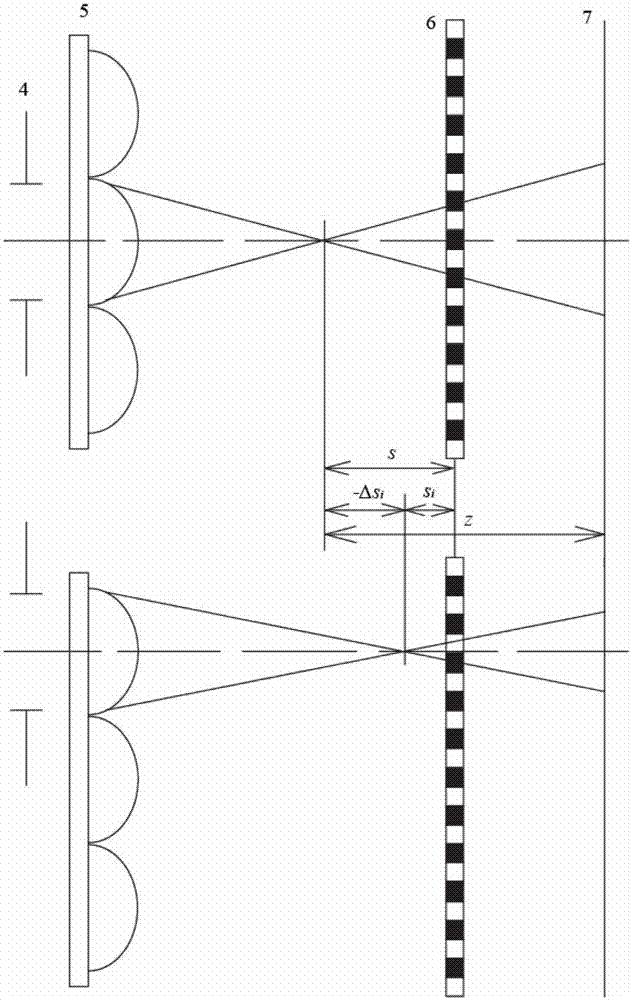
InactiveCN102889980AEasy to operateImprove detection efficiencyTesting optical propertiesDiffraction effectGrating
The invention relates to a method for detecting micro lens fixed focus based on a grating shear interference detection system. The method belongs to the technical field of optical detection. The method achieves fixed focus measurement of a micro lens by use of fringes generated by zero-grade and first-grade diffraction light interference of Ronchi grating: when a parallel light passes through the Ronchi grating, zero-grade and first-grade diffraction light spots are generated due to a diffraction effect of the grating; according to a phase change in front of a diffraction light wave, when the grating is arranged on a micro lens focal plane, interference fringes in a light spot overlapping region can be avoided; when the grating is arranged at an out-of-focus position, the light spot overlapping region generates the interference fringes due to phase difference; defocusing amount of the grating can be calculated by a fringe periodic change at different defocusing positions, and thus the fixed focus measurement of the micro lens can be achieved. According to a physical optical theory, the method analyzes the relation between grating defocusing amount and a fringe cycle quantitatively, calculates the defocusing amount twice through difference of fringe cycles when the grating defocuses twice before and after focusing, thereby achieving fixed focus of the micro lens and array elements.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wide-spectrum white-light LED
InactiveCN101572262AIncrease widthChange color temperatureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPhysical opticsElectric light
The invention discloses a wide-spectrum white-light LED electric light source formed by combining a metal or ceramic basal plate, a chip array layer, a fluorescent powder coating array layer and a transparent material mixed-light capsule. The wide-spectrum white-light LED electric light source is characterized in that the chip array layer comprises chip arrays formed by combining chips with different emission wavelengths, each array at least comprises a chip, and the fluorescent powder coating array layer comprises fluorescent powder arrays comprising different emission spectrums. The invention has the advantages that an LED encapsulation technology commonly used at present can be used in the same capsule to select low-cost and high-efficiency LED chips so as to be convenient to optimize various permutations and combinations according to a physical optical white light mixed-light theory and be fixed on the metal or ceramic basal plate. The wide-spectrum white-light LED electric light source can be also a favorable white-light mixed-light luminescence system.
Owner:HANGZHOU HANGKE OPTOELECTRONICS
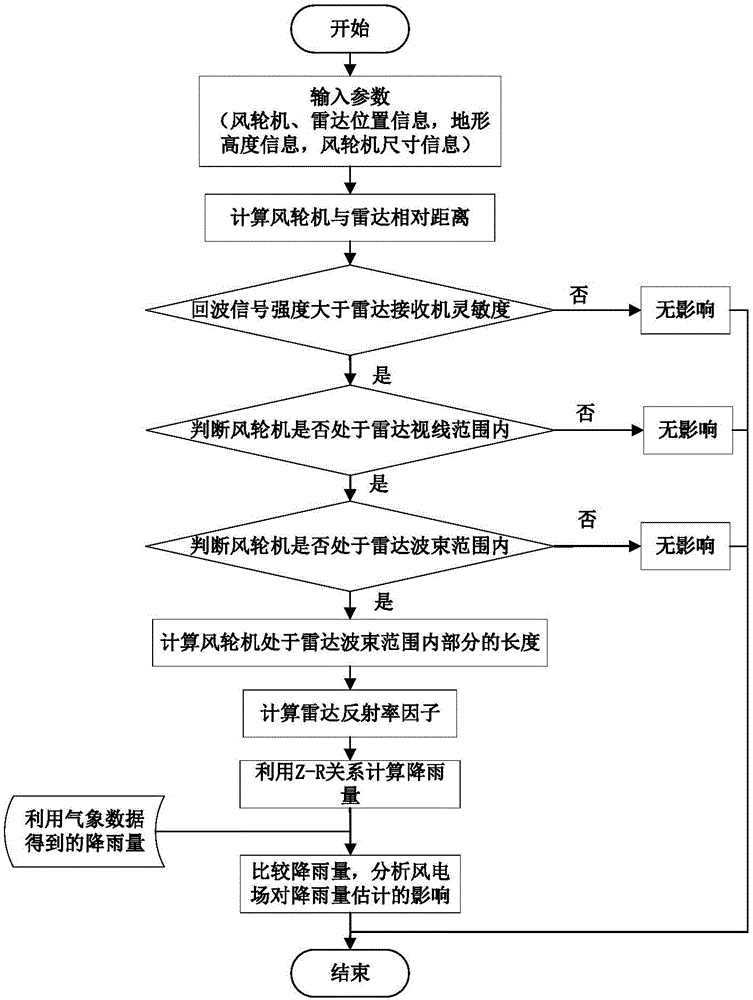
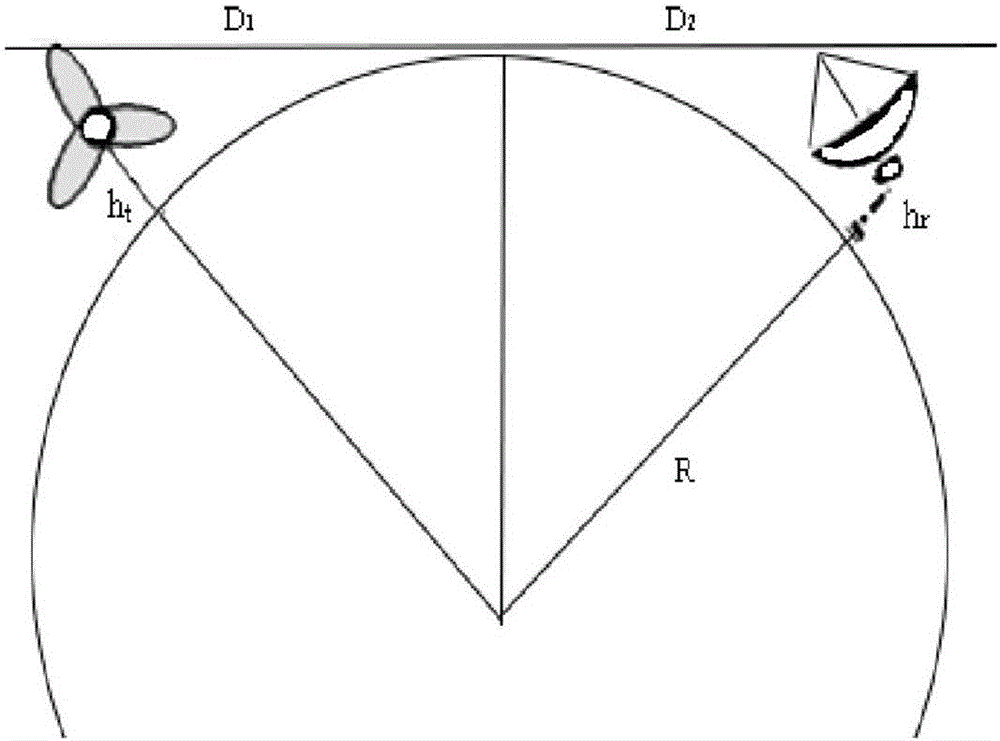
Method for analyzing and quantitatively estimating influence of wind farm on weather radar based rainfall
ActiveCN106845018ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTerrainWeather radar
The invention provides a method for analyzing and quantitatively estimating influence of a wind farm on weather radar based rainfall. The method comprises the following steps: the relative distance between the wind farm and the radar is calculated on the basis of longitude and latitude position information of the radar and the wind farm and compared with a line-of-sight distance of the radar; echo signal intensity of wind turbines is calculated and compared with sensitivity of a radar receiver; the irradiation range of radar beams is calculated by means of terrain height of an area where the wind farm and the radar are located and in combination with parameters such as radar elevation, beam width and the like; the length of the wind turbine in the radar irradiation range is calculated, RCS of the wind turbine is calculated with an analytical model based on a physical optics method, and then radar reflectivity is obtained; influence of a wind turbine model and a wind turbine distribution mode on the radar reflectivity is analyzed; the rainfall of the wind farm area is calculated according to the relation between the radar reflectivity and the rainfall. The method is completed with the analytical model based on the physical optics method and has the advantages of high calculation speed, relatively simple processing steps and the like.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
RCS conversion method based on scattering center matrix
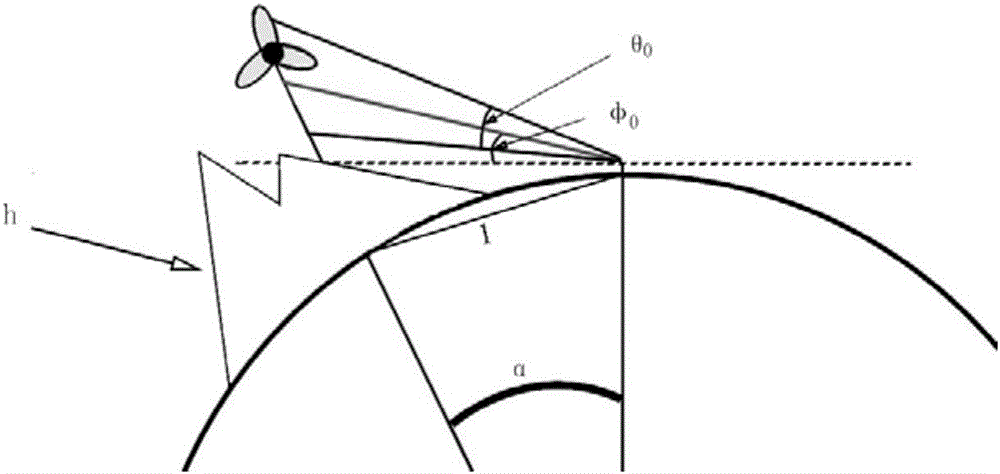
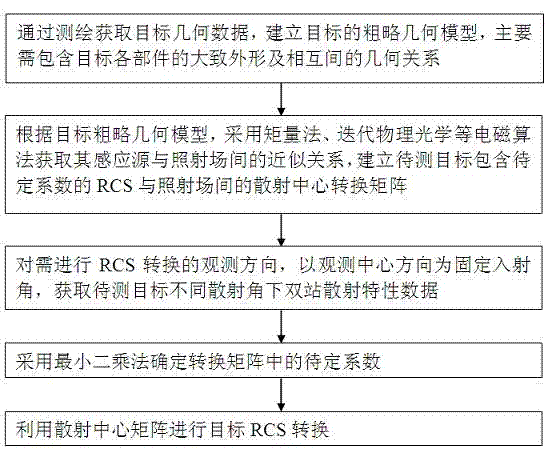
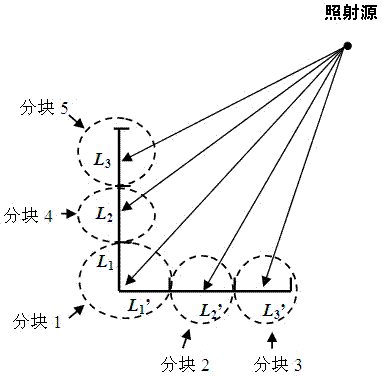
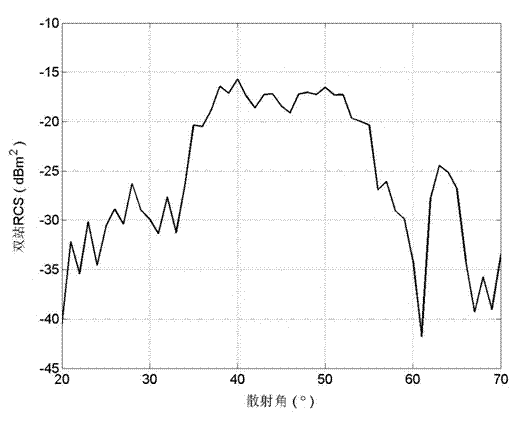
InactiveCN103487791ALarge applicable angle rangeReduce data volumeWave based measurement systemsPhysical opticsCentering matrix
The invention relates to an RCS conversion method based on a scattering center matrix. The method comprises the steps of adopting a moment method or an iterative physical optical method to obtain the approximation relation between an induction source and an exposure field according to a set target rough geometric model, and setting the scattering center conversion matrix between the exposure field and the RCS with a target to be measured comprising an undetermined coefficient; according to the observation direction required to conduct RCS conversion, using the direction of an observation center as a fixed incident angle, and obtaining double-station scattering performance data under the different scattering angles of the target to be measured; adopting the least square method to determine the undetermined coefficient in the conversion matrix; achieving the RCS conversion of the target. The method is not limited in the high-frequency area, the suitable angle range is larger, the required data size is small, and engineering realization is easy.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Method of measuring influence of radome on antenna array direction-finding performance
InactiveCN105388449AReduce complexityReduce workloadRadio wave finder monitoring/testingElectricityPhysical optics
The invention discloses a method of measuring the influence of a radome on the antenna array direction-finding performance. The method comprises the steps of determining various parameters in an antenna array, including antenna coordinates, antenna equivalent aperture data and radome geometry and the like; calculating the amplitude and phase of an electric field generated by each antenna at a far region outside the radome by using a physical optics method; calculating the insertion phase delay of an arbitrary antenna unit in the antenna array; calculating the phase error, that is the difference of the insertion phase delay between two antennas; and calculating an average value of the phase errors of any two antennas in the antenna array system, and finally calculating the difference between the phase error of the two antennas and the average value, that is the phase inconsistency of the radome, for measuring the influence of the radome on the antenna array electrical performance. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages of requiring no knowledge of the working pattern or radiation characteristics of the antenna array in the radome, reducing the complexity and amount of calculation, facilitating requirements of special systems and so forth.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
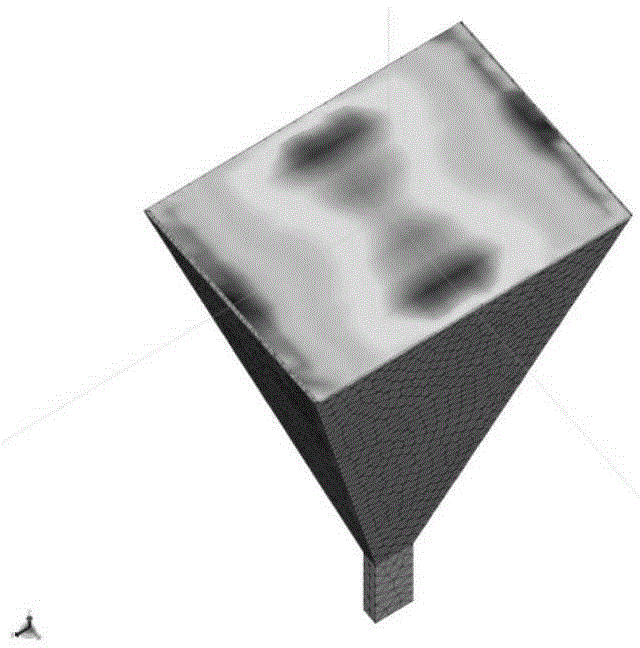
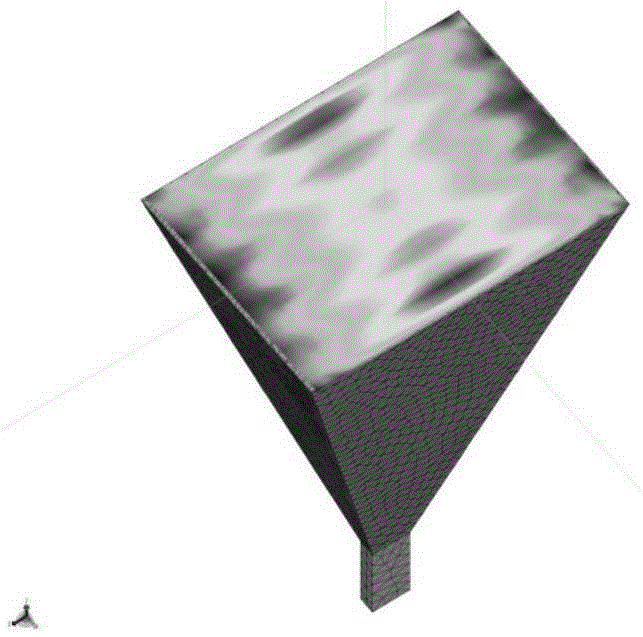
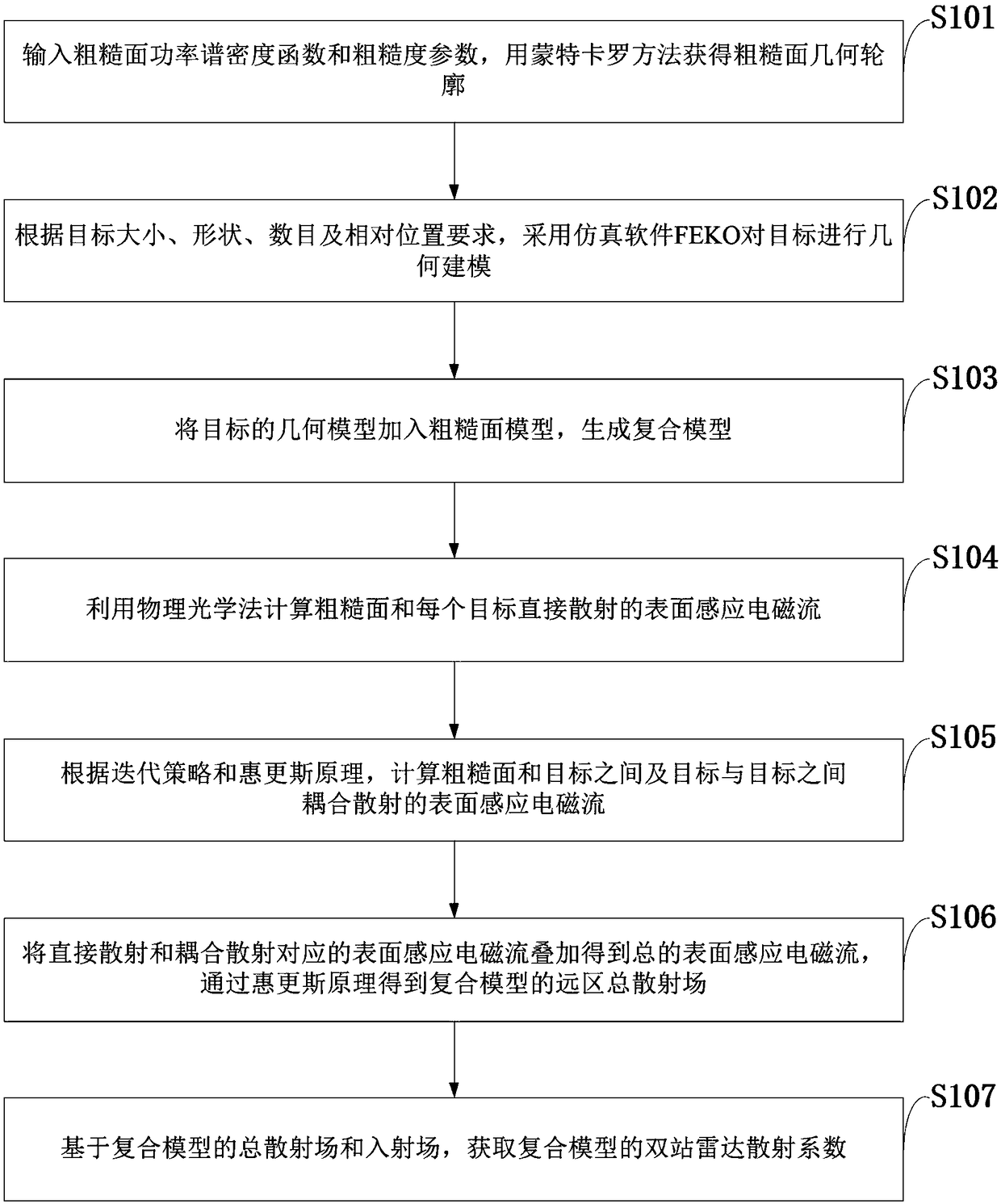
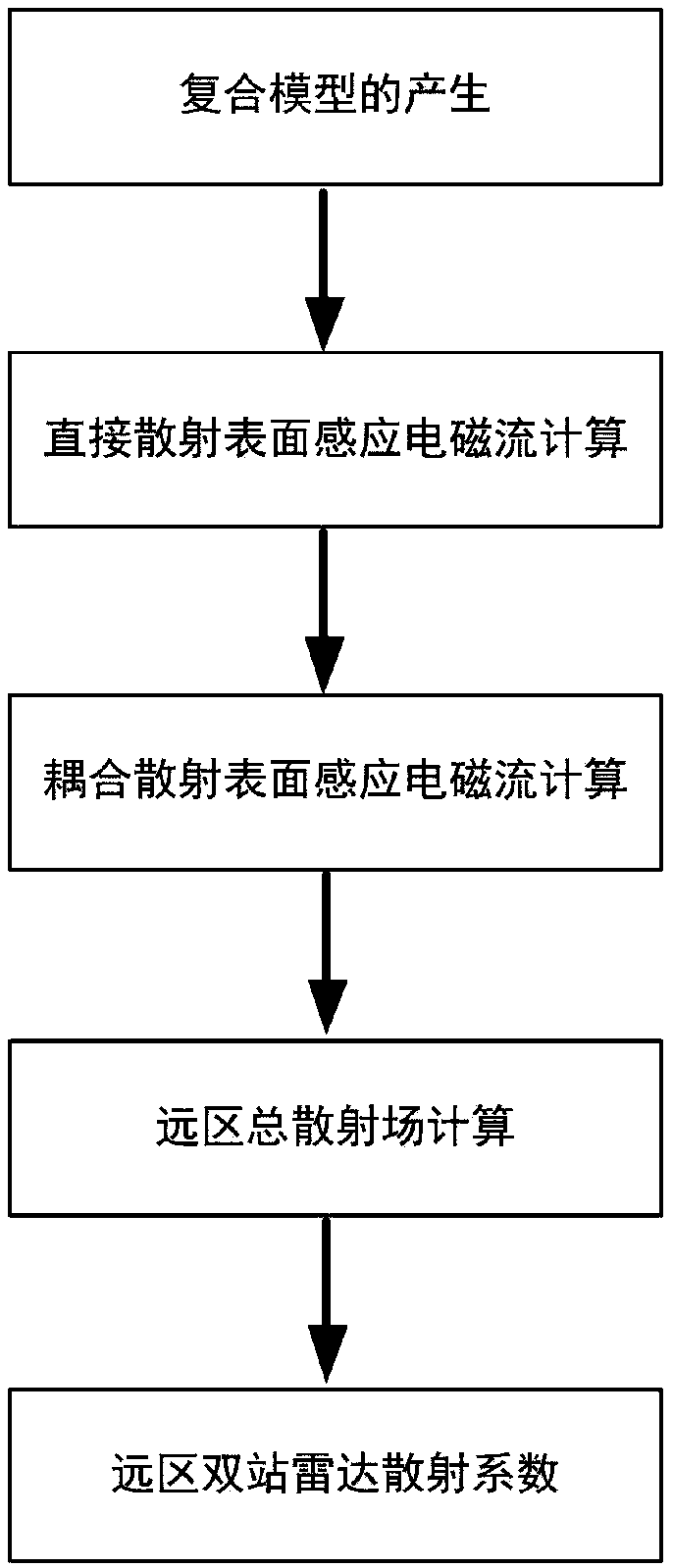
Rough surface and multi-target composite scattering simulation method based on iterative physical optics
ActiveCN109100692AAvoid artificial reflexesImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsICT adaptationPhysical opticsSimulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar electromagnetic simulation, and discloses a rough surface and multi-target composite scattering simulation method based on iterative physical optics. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a rough surface power spectral density function and a roughness parameter, obtaining a rough surface geometric contour by the Monte Carlo method; using the simulation software FEKO to geometrically model the targets; adding the geometric models of the targets to the rough surface model to generate a composite model; using the physical opticsmethod to calculate the surface induced electromagnetic current directly scattered by the rough surface and each target; calculating the surface-induced electromagnetic current between the rough surface and the targets and between the targets according to the iterative strategy and Huygens principle; obtaining a far-field total scattering field of the composite model by the Huygens principle; andobtaining a two-station radar scattering coefficient of the composite model based on the total scattering field and the incident field of the composite model. The rough surface and multi-target composite scattering simulation method based on iterative physical optics has the advantages such as low memory requirement, high simulation efficiency and strong versatility of the simulation method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
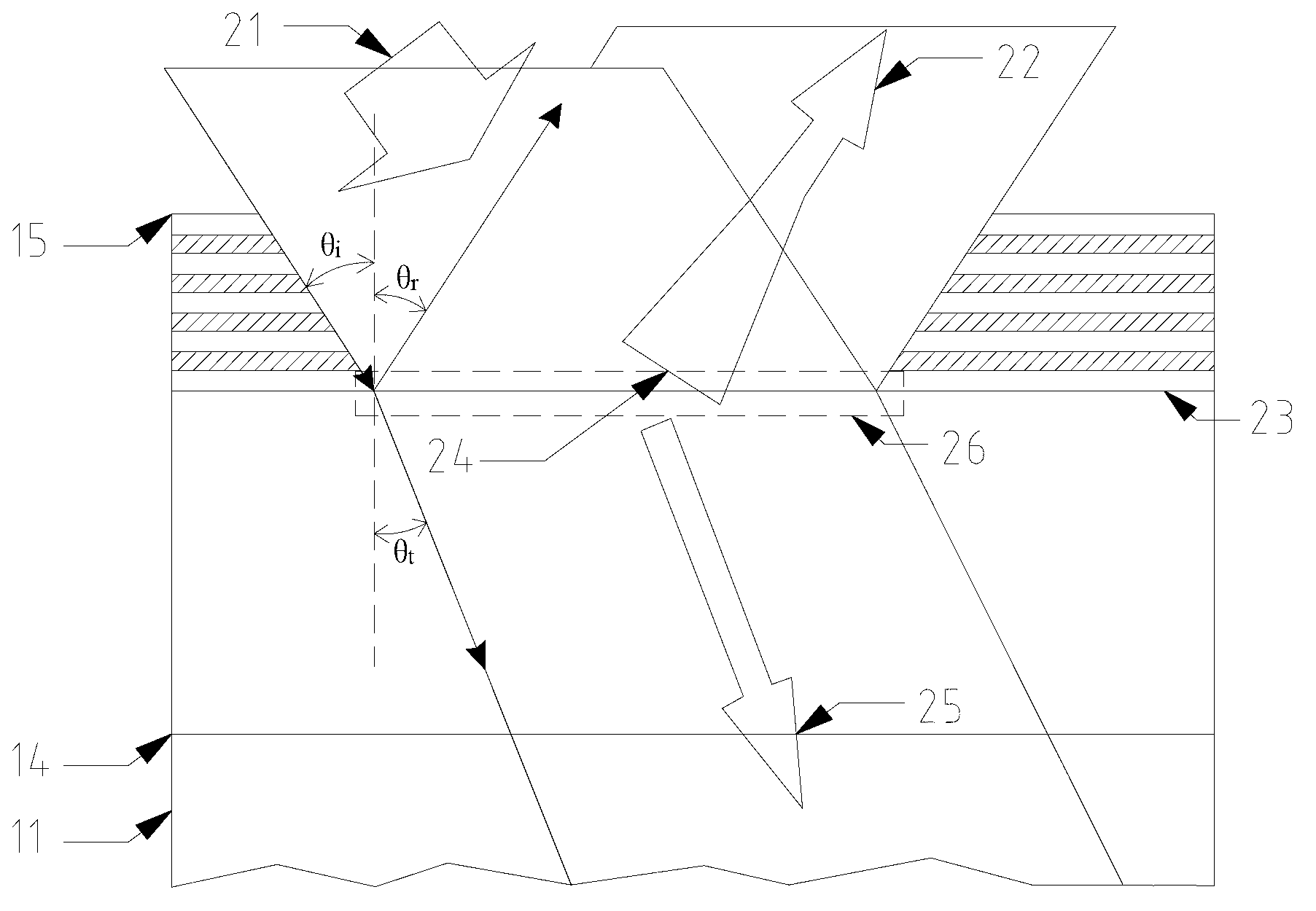
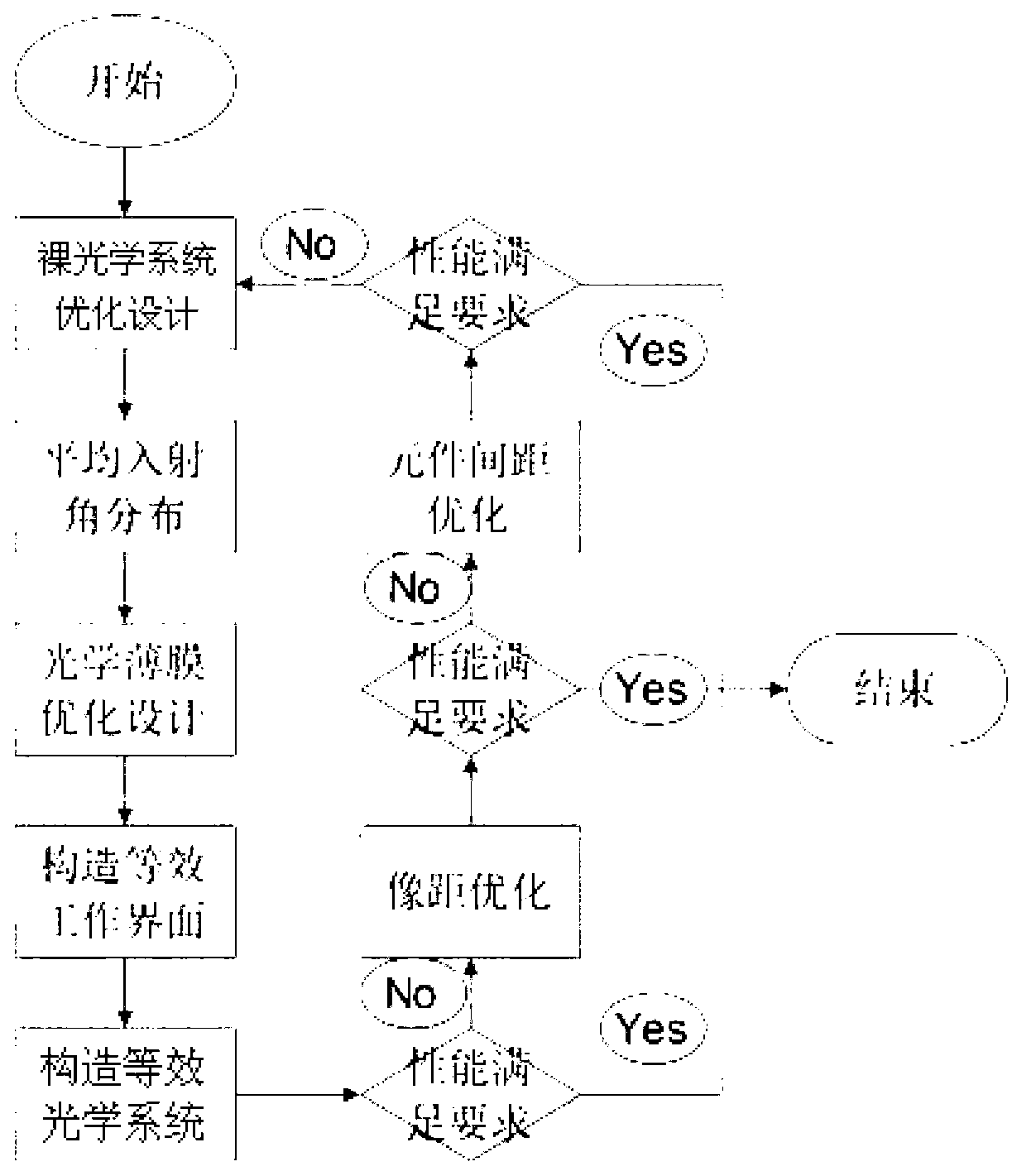
Optical system analysis design method based on energy conservation law
InactiveCN103226241AExplanationRapid Evaluation AnalysisPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPhysical opticsImaging quality
The invention provides an optical system analysis design method based on an energy conservation law and belongs to the field of optical design. The method solves the problems that a processing mode of the existing optical design software for an optical thin film cannot predict the imaging quality of the optical system additionally provided with the optical thin film reasonably, so that the designed and processed optical system is not compatible with the optical thin film. The method establishes an equivalent working interface from energy modulation by taking a strict electromagnetic field theory as a starting point, constructs the equivalent optical system additionally provided with the optical thin film according to bare optical system parameters, and evaluates and analyzes the system. The method overcomes defects in processing the optical thin film with the existing optical design software, a complicated physical optic course in the optical thin film is equivalent to a geometrical optic course, and the time and cost are saved in comparison with the existing optical software.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dust removal device of physical optical experimental instrument
InactiveCN108283846APrevent outflowPrevent inflowAuxillary pretreatmentDispersed particle filtrationBristlePhysical optics
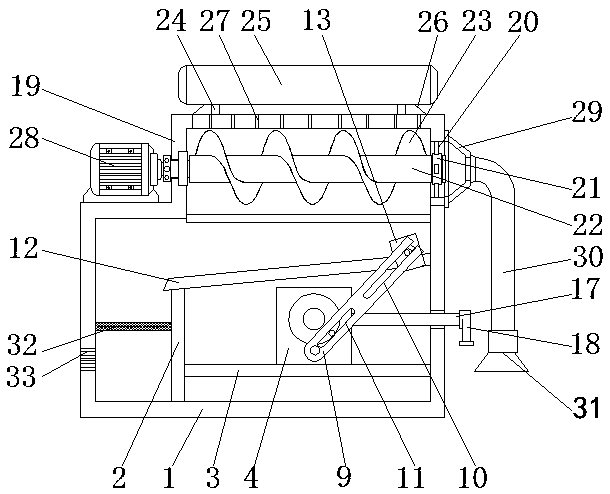
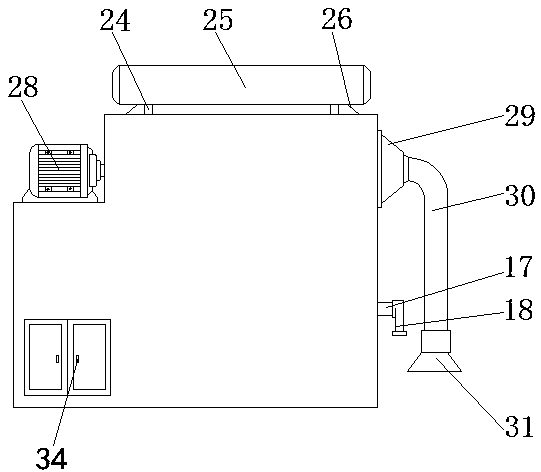
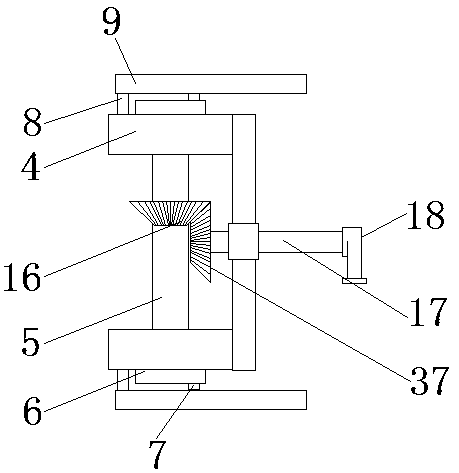
The invention discloses a dust removal device of a physical optical experimental instrument, and relates to the technical field of dust removal devices. A clapboard is fixedly connected to the bottomof an inner cavity of a dust removal box, a supporting plate is fixedly connected between the right side of the clapboard and the inner wall of the dust removal box, and two supporting bases are fixedly connected with the top of the supporting plate; a first rotating shaft penetrates through the space between the two supporting bases, the two ends of the first rotating shaft are fixedly connectedwith rotating blocks, a first bump is fixedly connected to the surface of each rotating block, swing rods are rotatably connected with the portions, located below the rotating blocks, of the surfacesof the supporting bases through rotating shafts, and one end of each swing rod is slidingly connected with the corresponding first bump through a second sliding groove. According to the dust removal device of the physical optical experimental instrument, sliding blocks can be controlled to swing left and right by utilizing the sliding connection between second bumps on the surfaces of the slidingblocks and the swing rods through the first sliding grooves, the sliding blocks drive a bristle brush plate, and dust particles falling on an inclined plate can be pushed to a filter plate.
Owner:杨曙铭
Method for rapidly extracting electrical property parameter of metal truss-type radome
ActiveCN104750960AReduce calculationSpecial data processing applicationsMagnetic currentPhysical optics
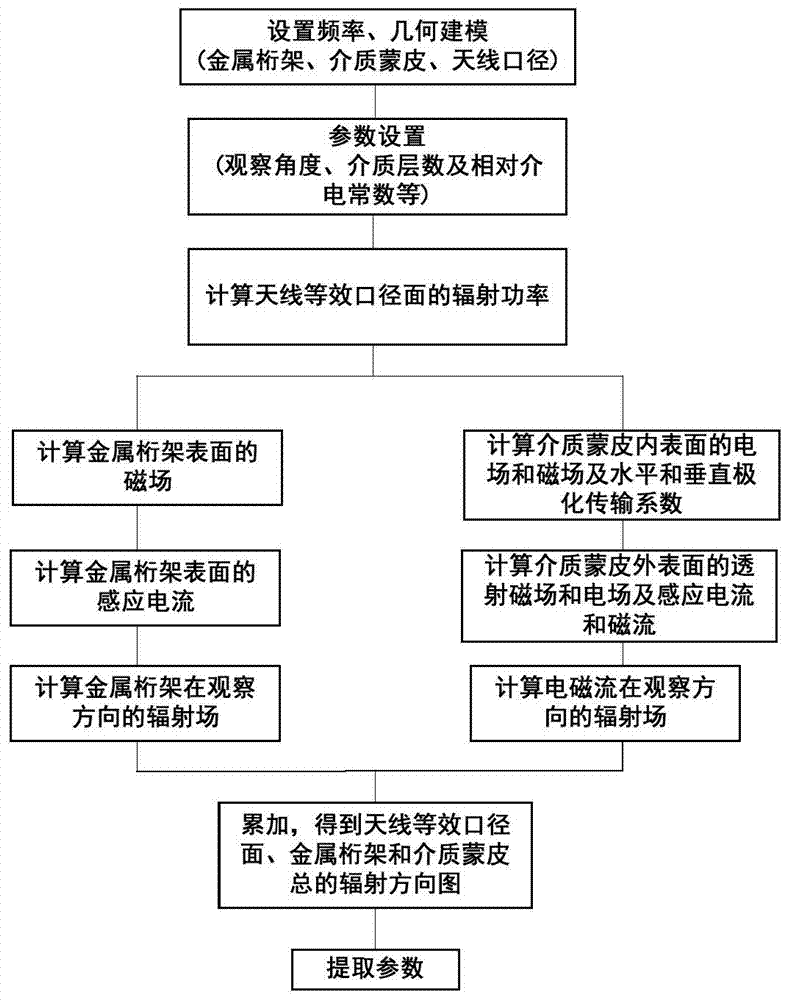
The invention discloses a method for rapidly extracting the electrical property parameter of a metal truss-type radome. The method includes: building geometric models of the antenna equivalent aperture, the metal truss and the medium skin firstly; then calculating the magnetic field of the metal truss surface through the formula of Stratton-Chu and the induced current of the metal truss light area through the physical optical method; calculating the incident electric field and the magnetic field of any point on the medium skin inner surface through the formula of the Stratton-Chu and the transmission coefficient of the point, obtaining the electric field and the magnetic field of the skin outer surface according to the incident electric field and the magnetic field, and calculating the equivalent current and magnetic current of the outer surface; and respectively calculating the induced current of the metal truss and the far field of the induction electromagnetic current on the medium skin outer surface in the observing direction, calculating the gain pattern and obtaining the electrical property parameter of the metal truss-type radome. Compare with the prior art, the method for rapidly extracting the electric property parameter of the metal truss-type radome has the advantages of being high in precision and calculating speed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Real-time compositional analysis of hydrocarbon based fluid samples
ActiveUS9638681B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComponent separationQuality controlVapor phase chromatography
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
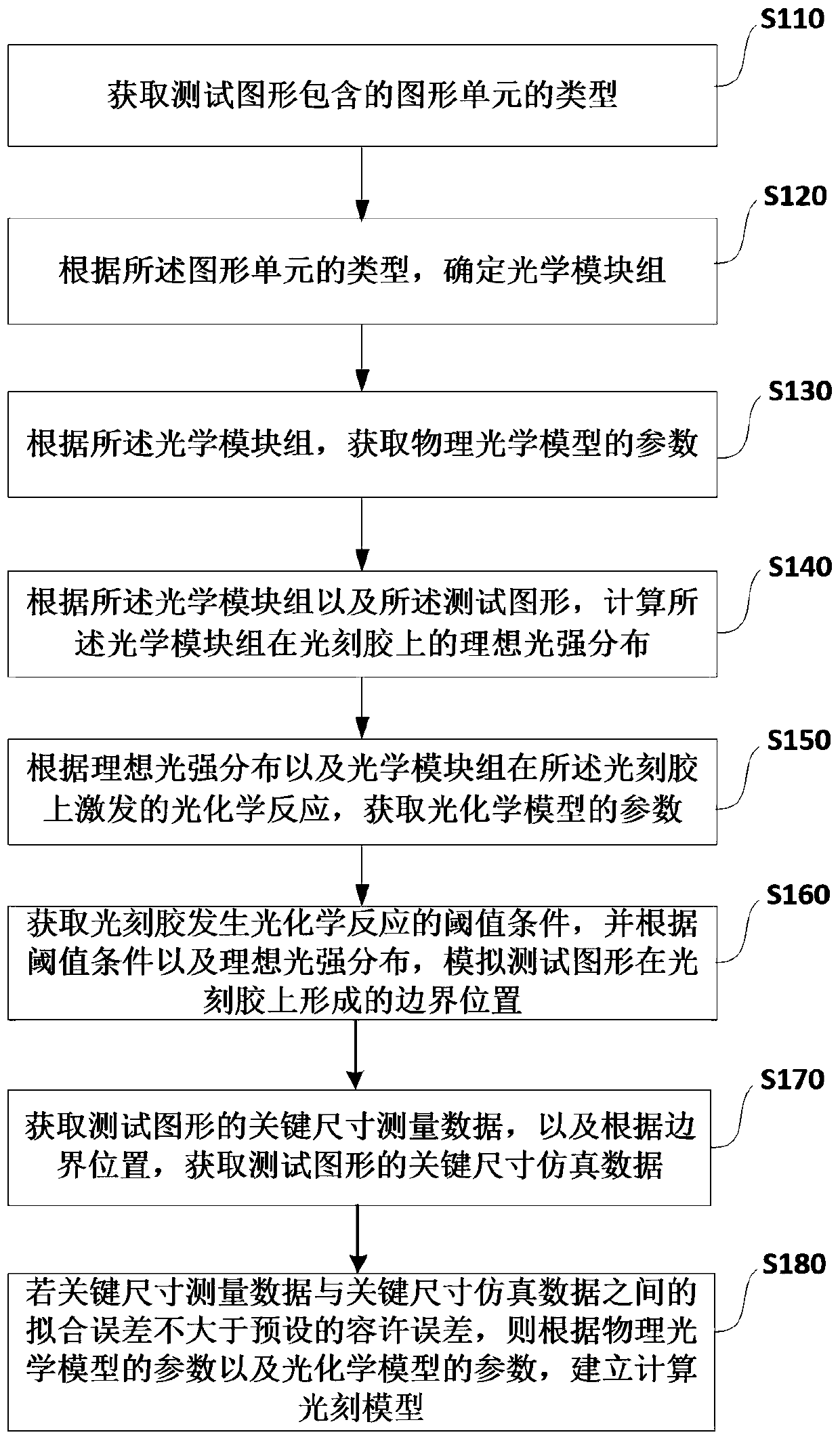
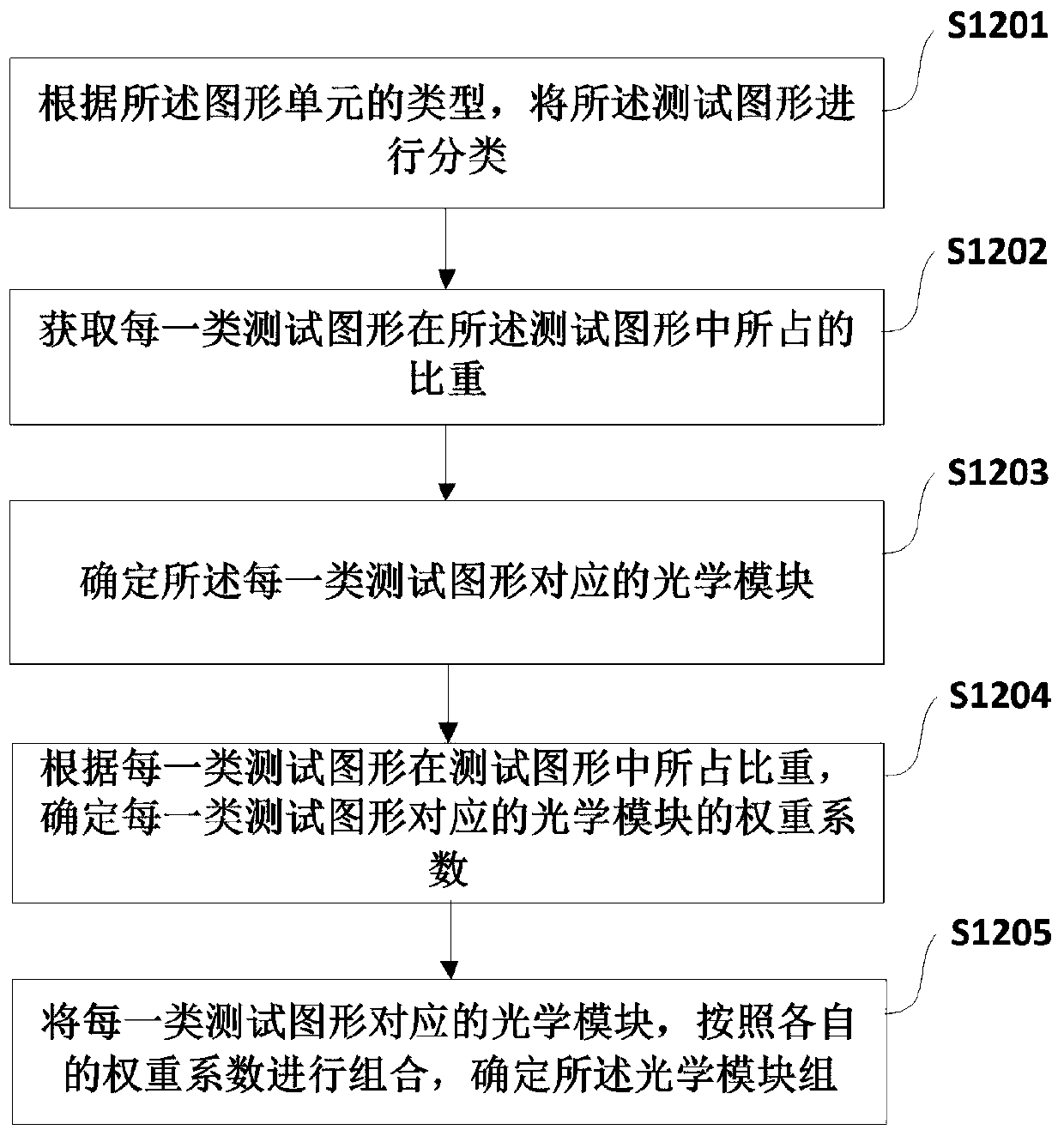
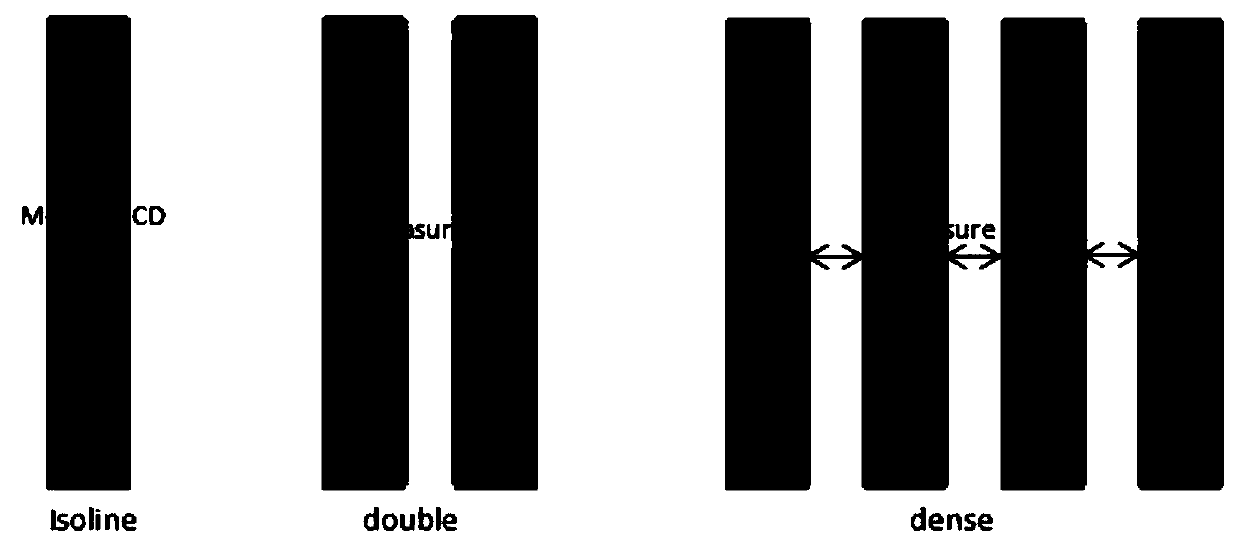
Computational lithography modeling method and device
ActiveCN110262191AHigh precisionGuaranteed accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusGraphicsIntegrated circuit manufacturing
The application relates to the technical field of integrated circuit manufacturing and discloses a computational lithography modeling method and device. The method comprises the steps of determining an optical module group by acquiring the type of a graphic unit included in a test pattern, and then acquiring the parameters of a physical optical model according to the optical module group; calculating the ideal light intensity distribution of the optical module group on the photoresist, and acquiring the parameters of a photochemical model according to the ideal light intensity distribution and a photochemical reaction excited by the optical module group on the photoresist; then simulating a boundary position formed by the test pattern on the photoresist, acquiring the key dimension simulation data of the test pattern, and establishing a computational lithography model if a fitting error between the key dimension measurement data and the key dimension simulation data is not greater than a preset allowable tolerance. The computational lithography modeling method disclosed in the application improves the precision of a lithography model by establishing different optical modules to simulate different graphic units.
Owner:MOYAN COMPUTATIONAL SCI NANJING PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com