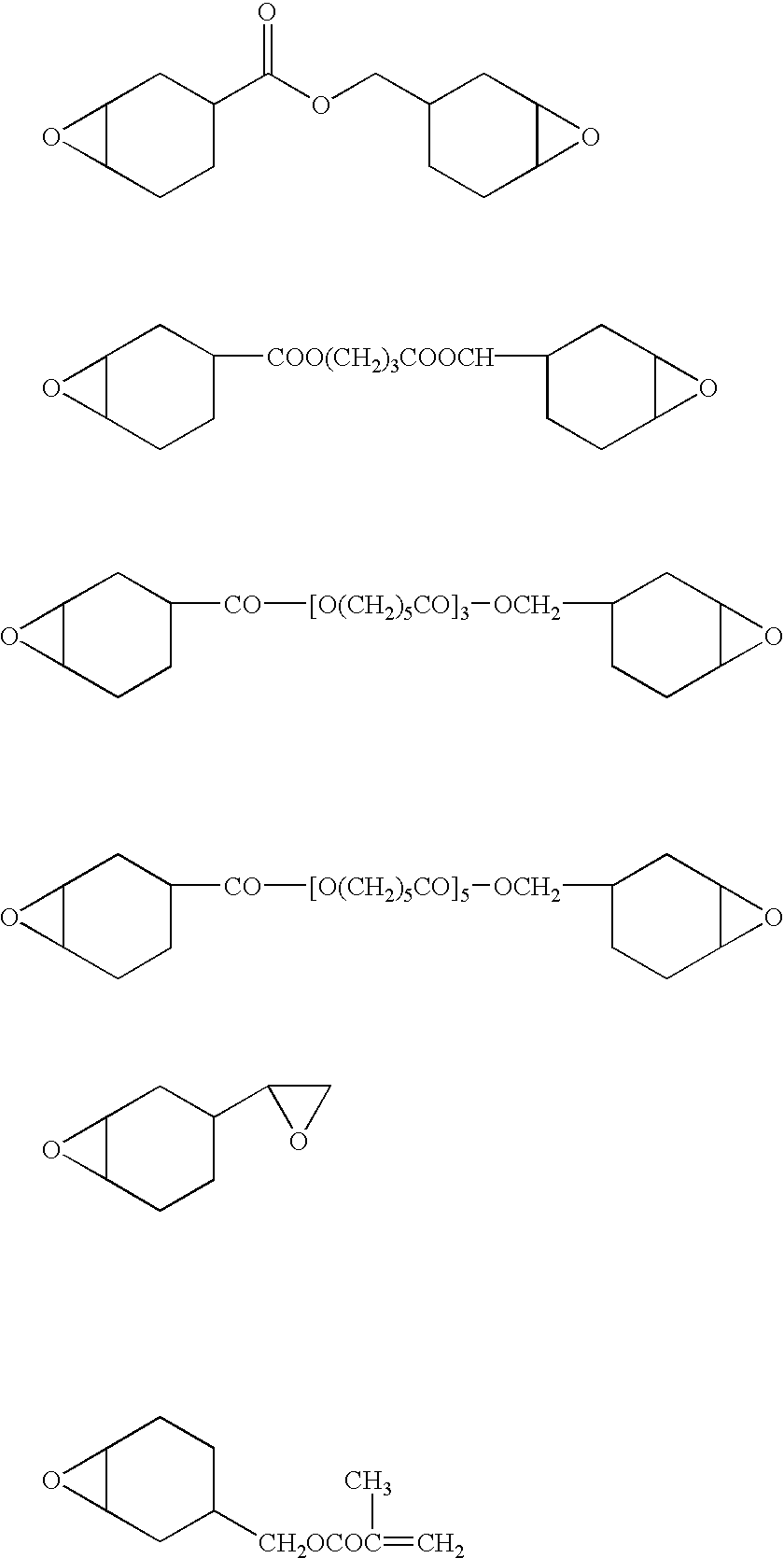
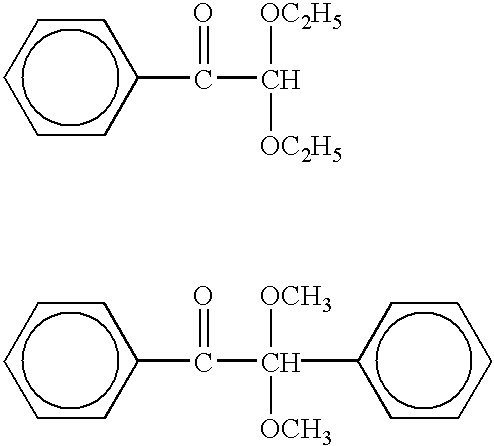
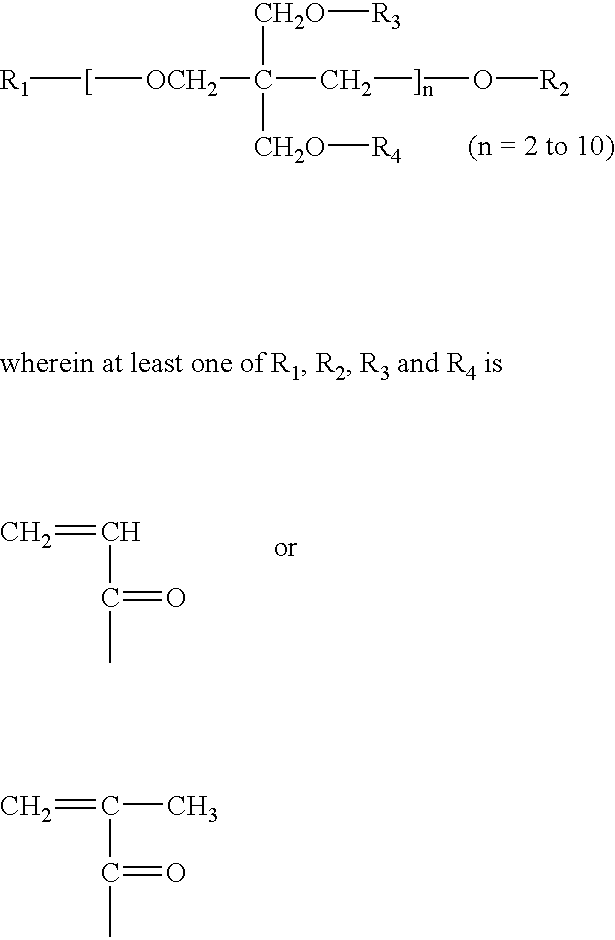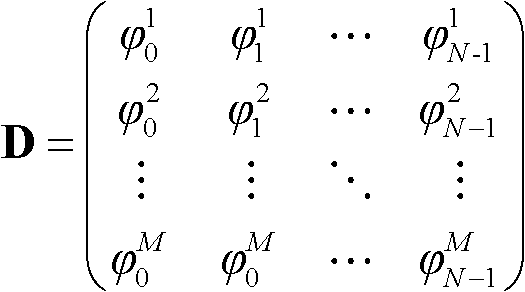Patents
Literature
612 results about "Scattering coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Scattering coefficient. noun. : the fractional rate in the transmission of radiation through a scattering medium (as of light through fog) at which the flux density of radiation decreases by scattering in respect to the thickness of the medium traversed.
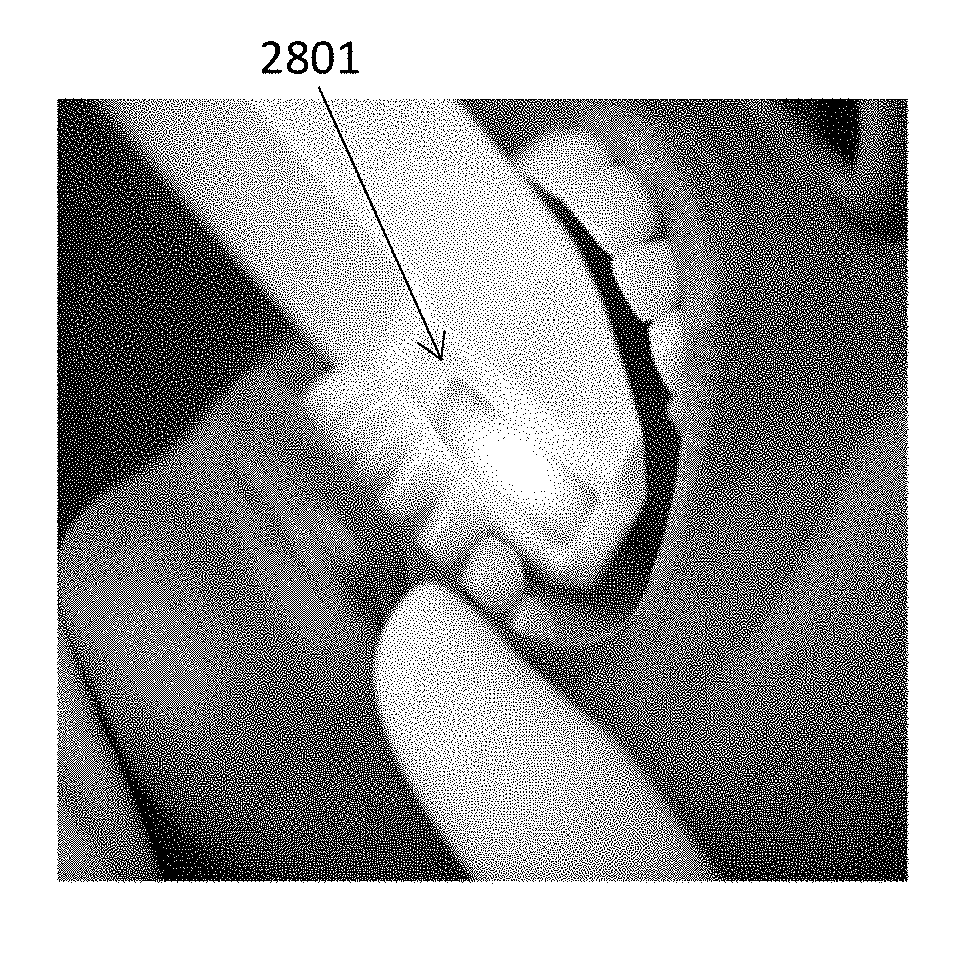
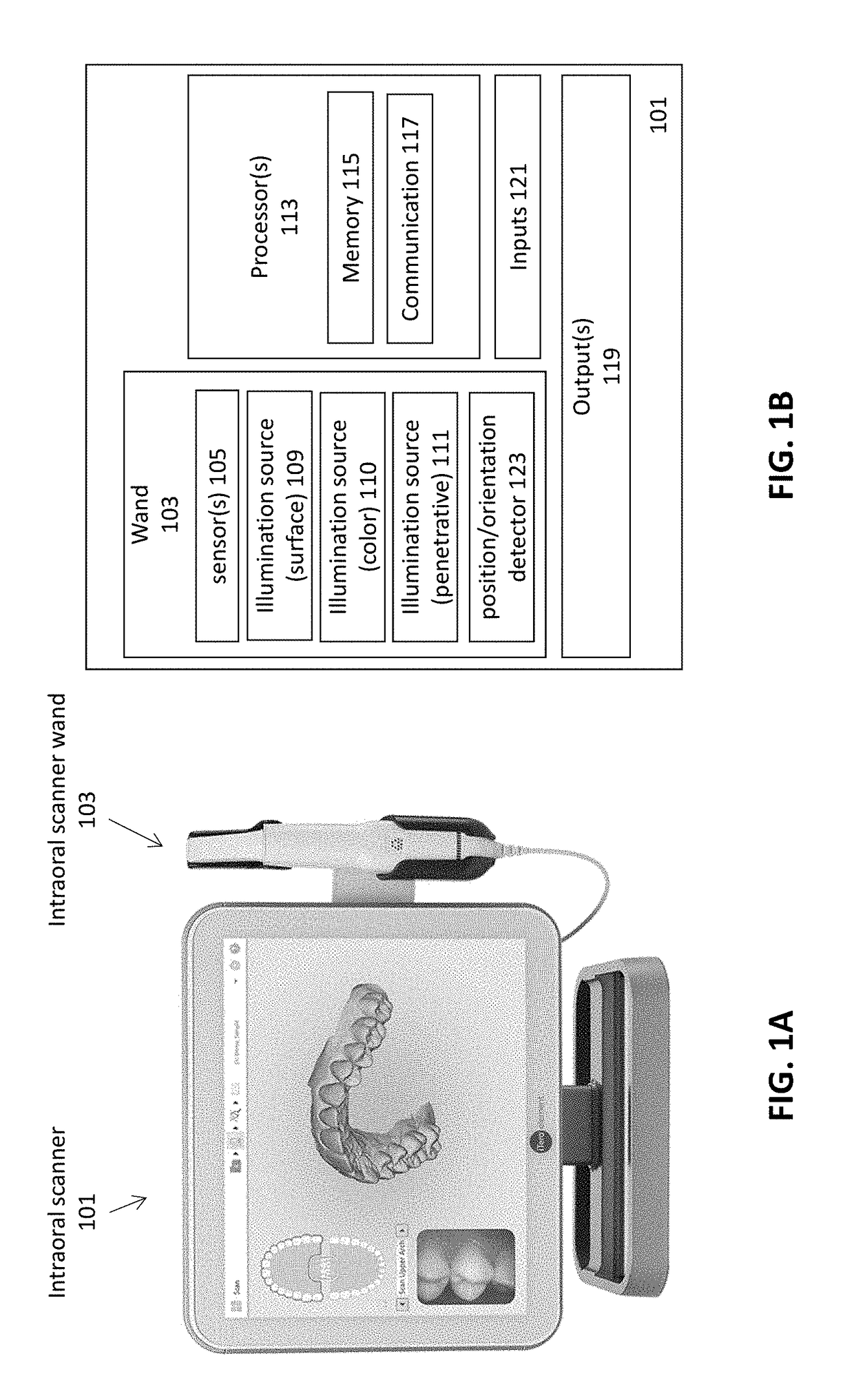
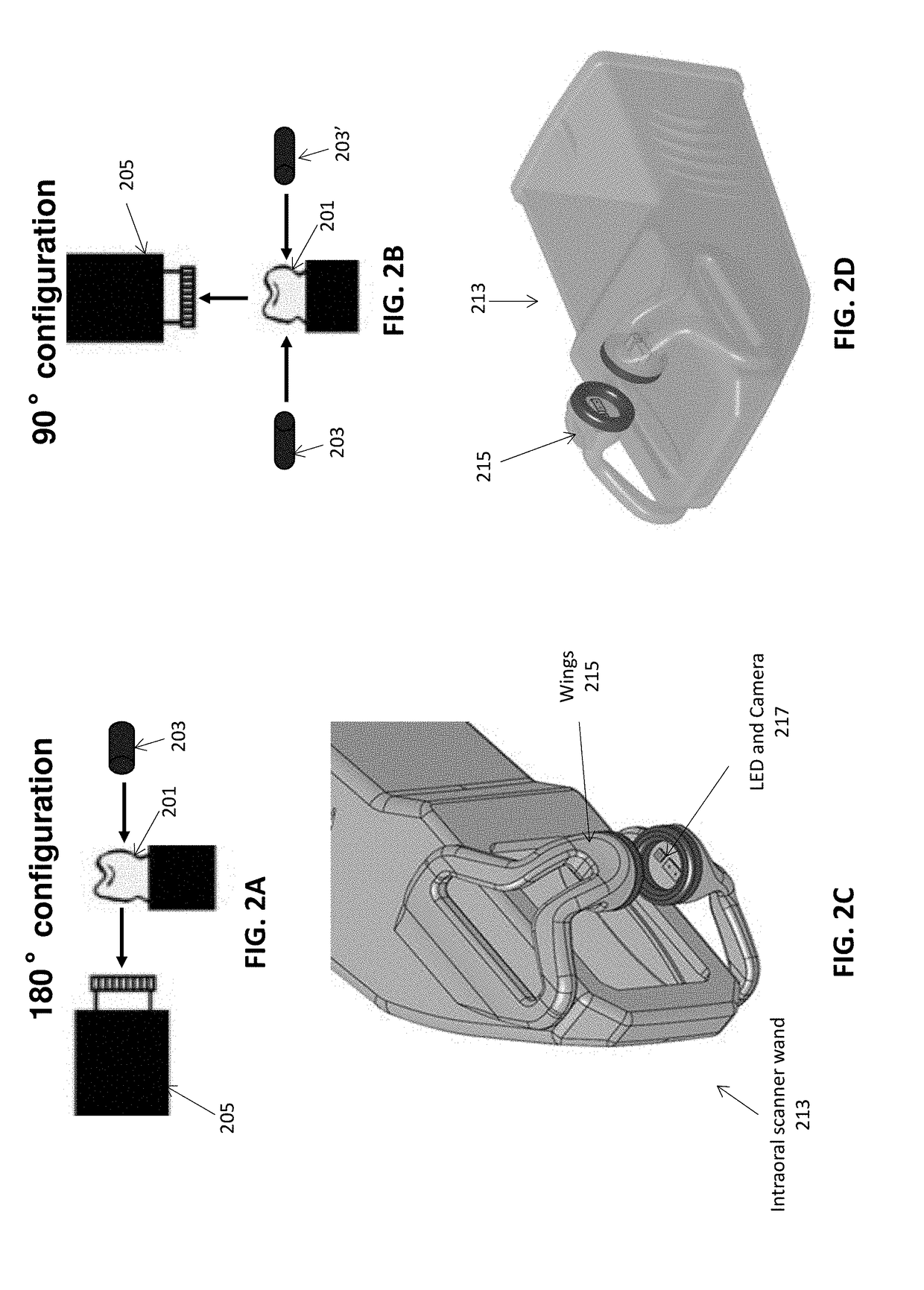
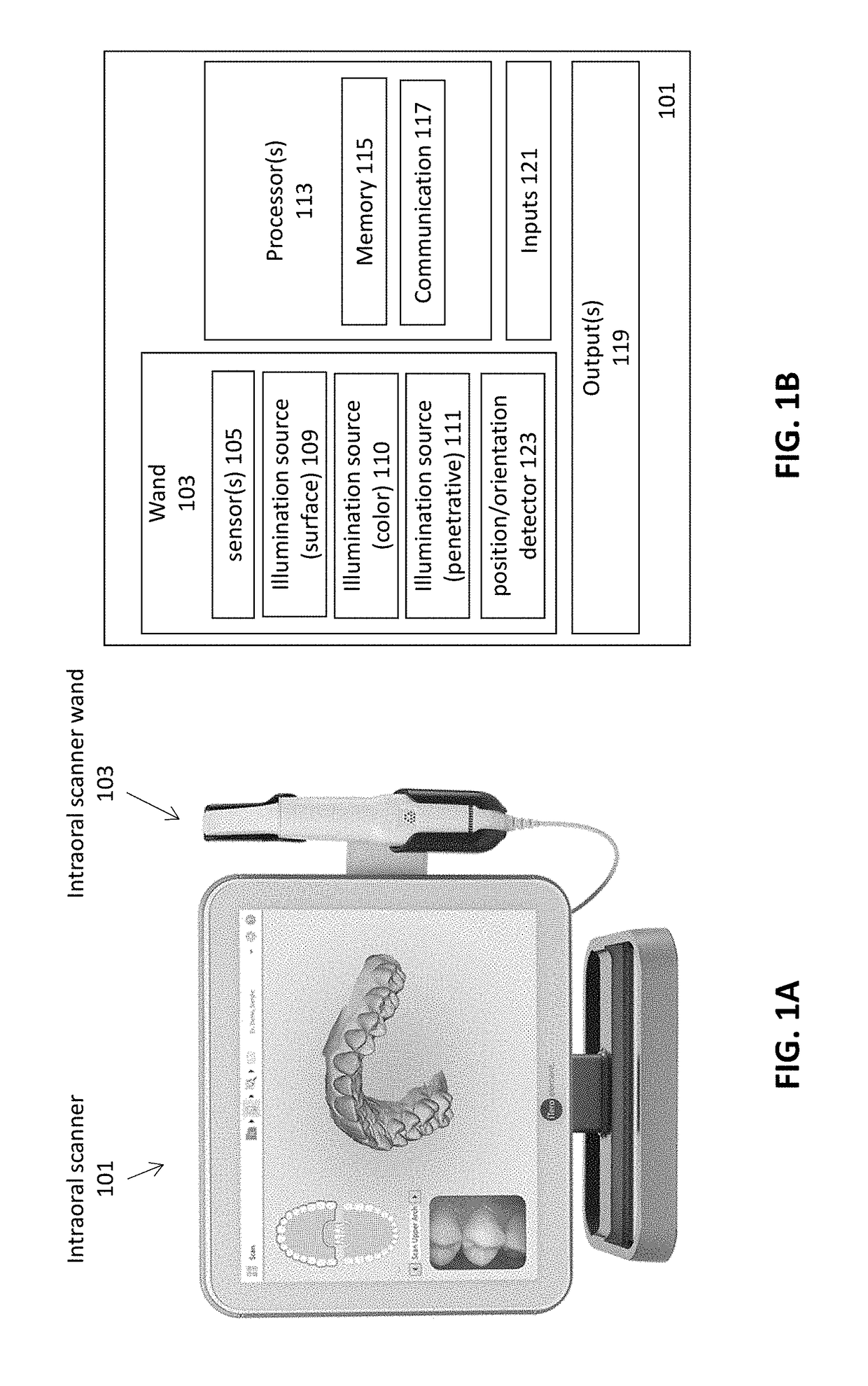
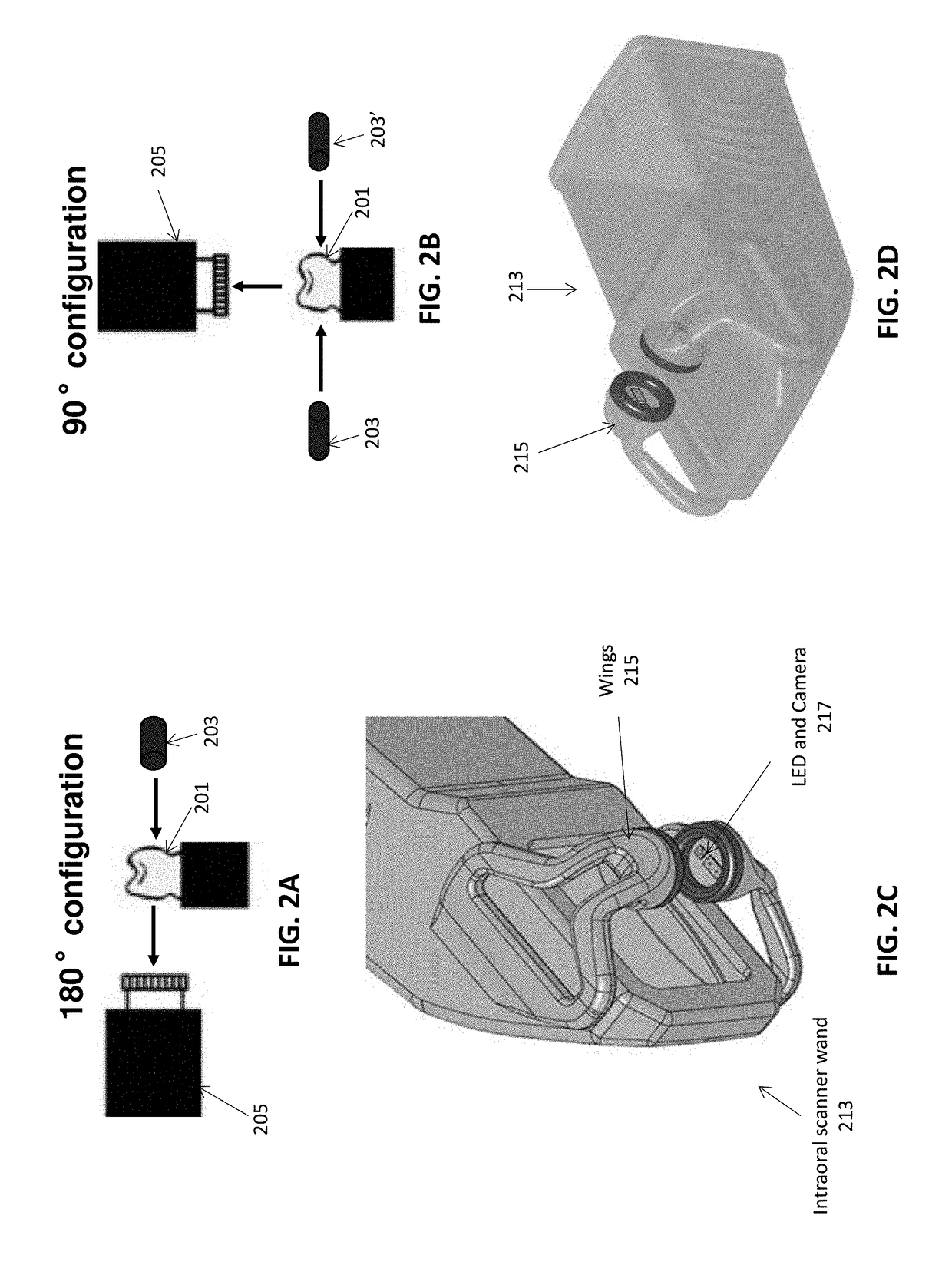
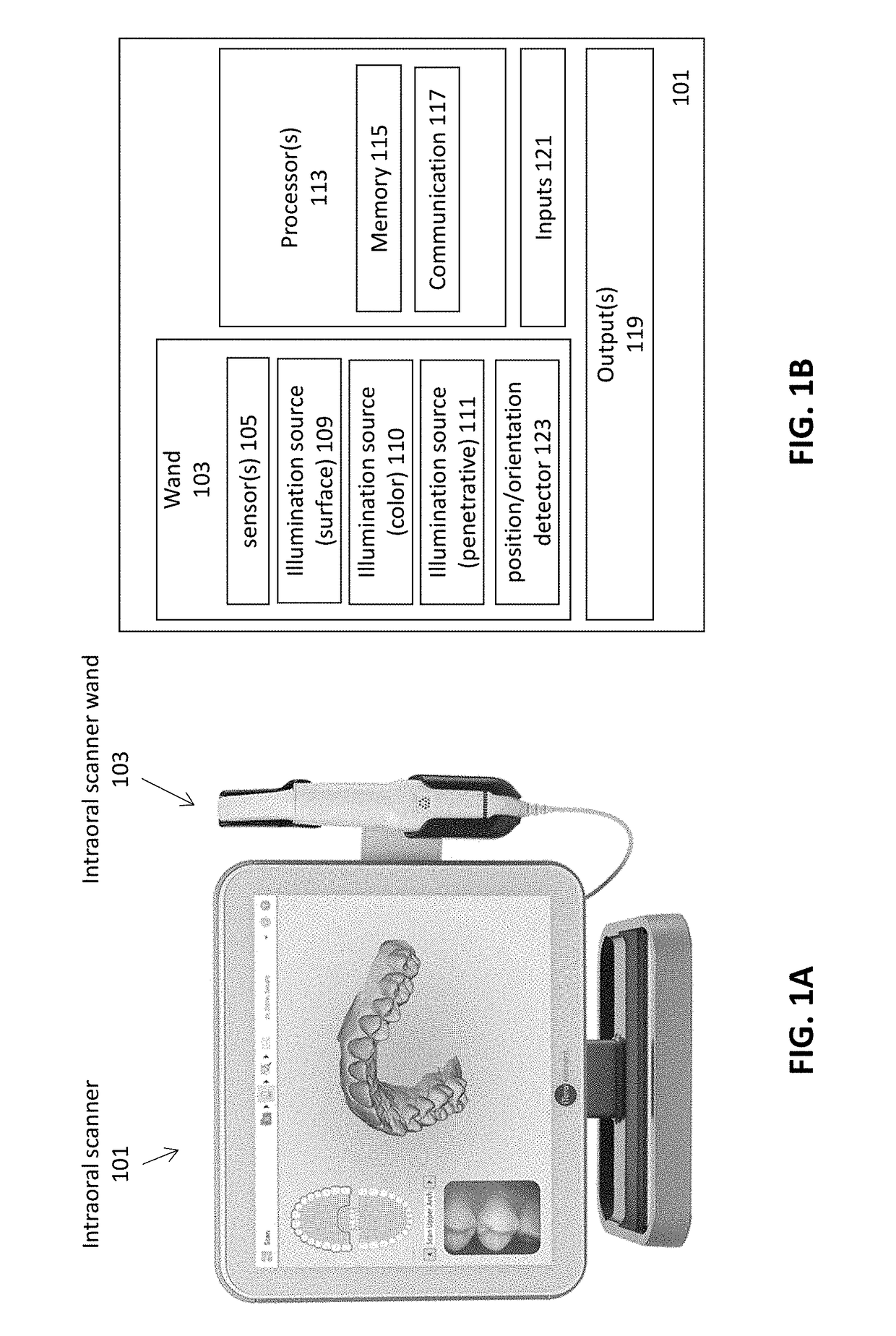
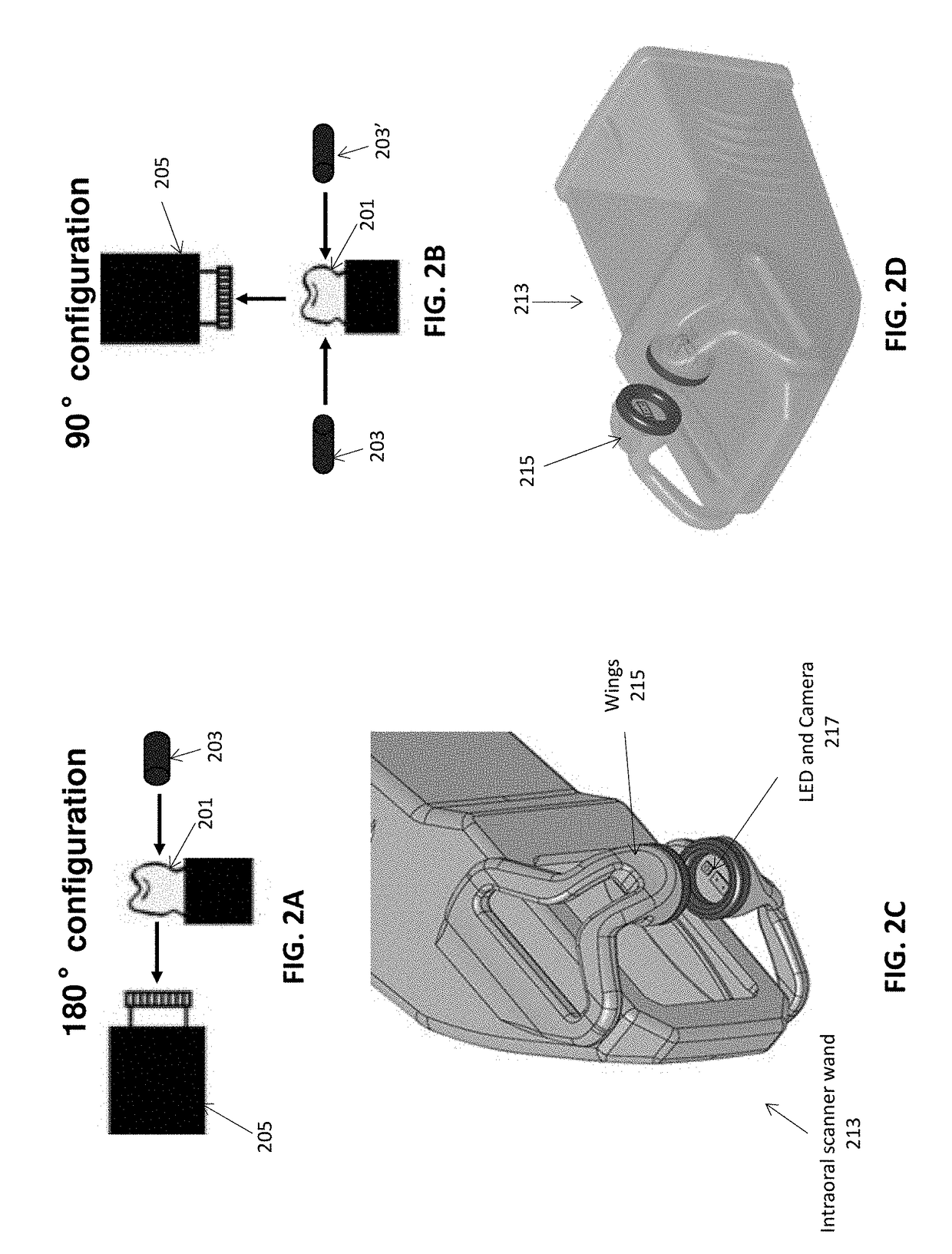
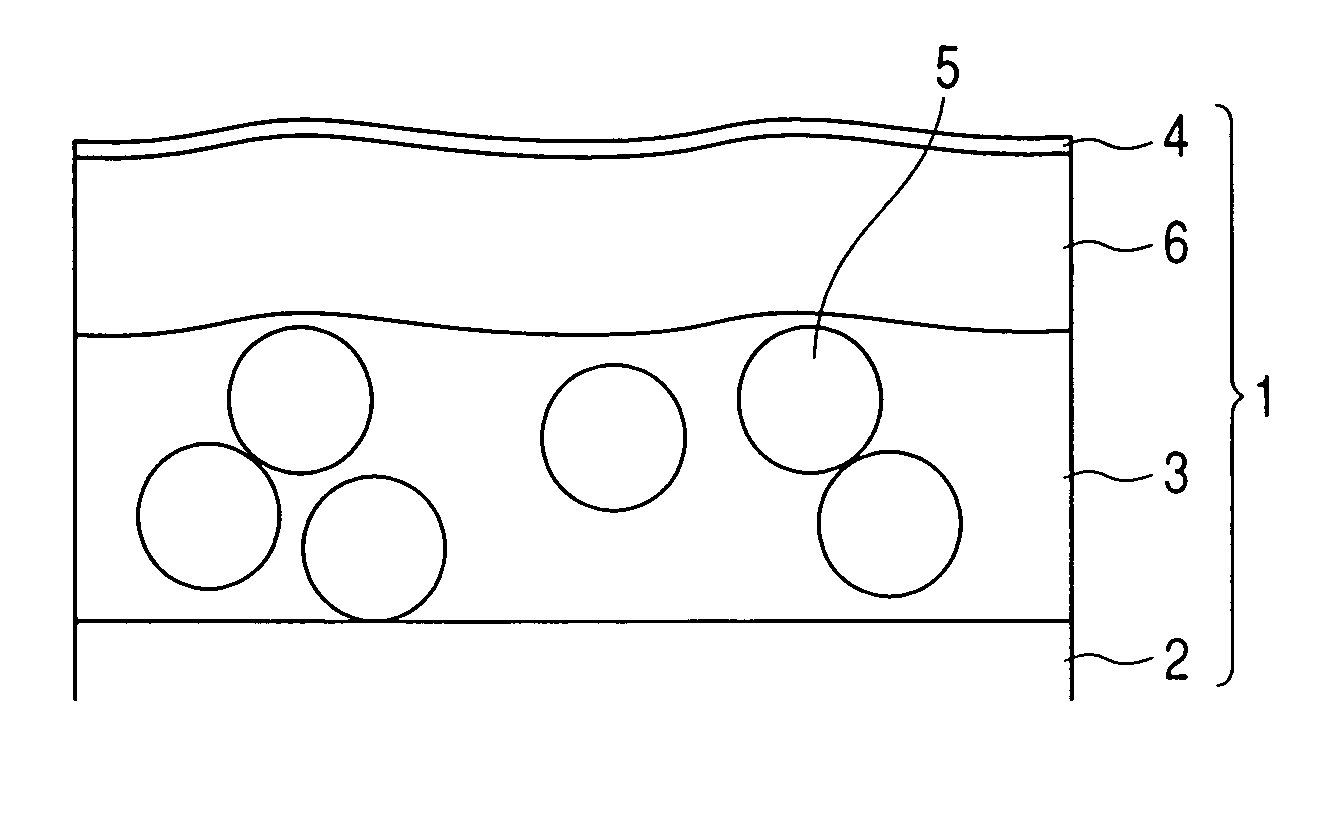
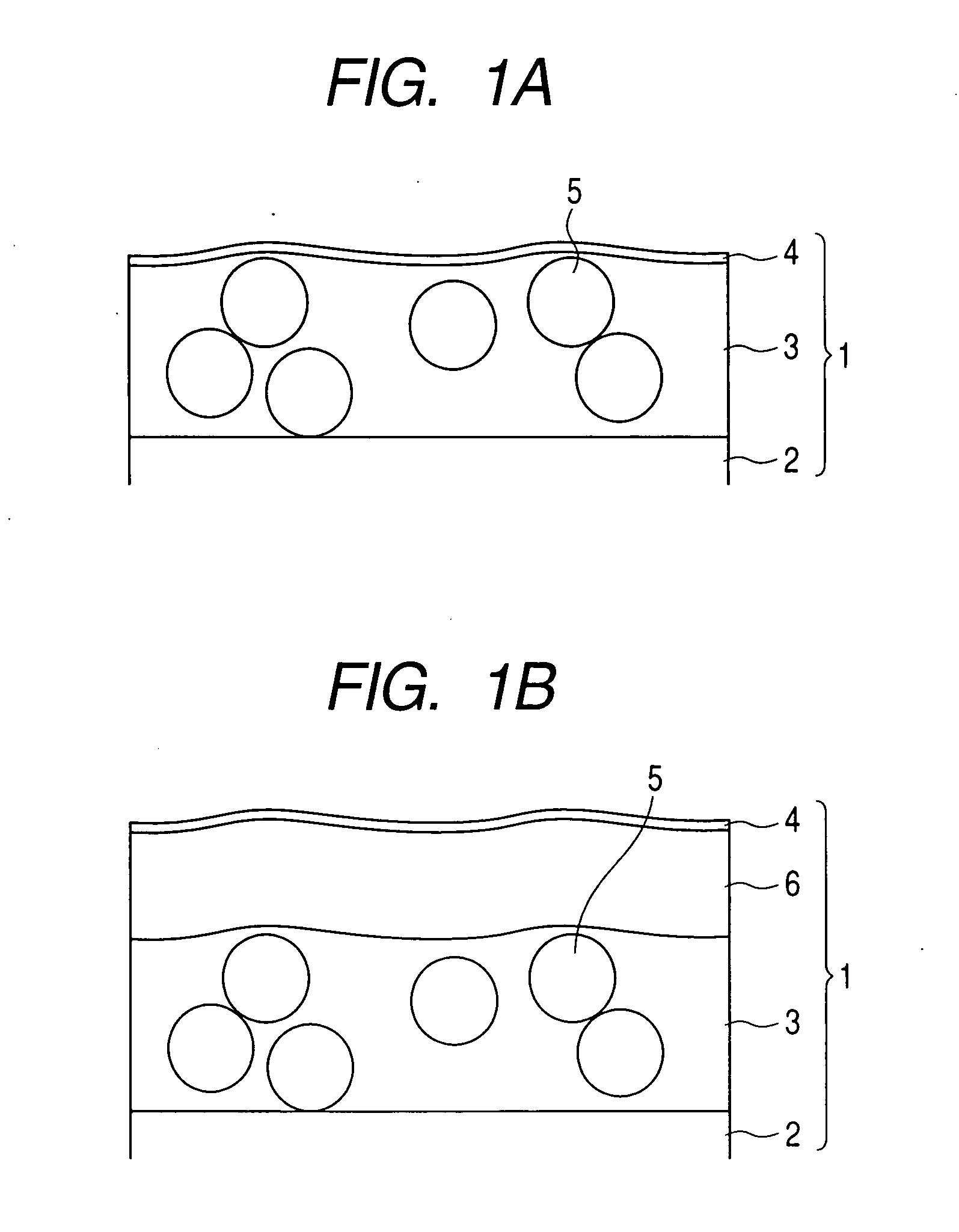
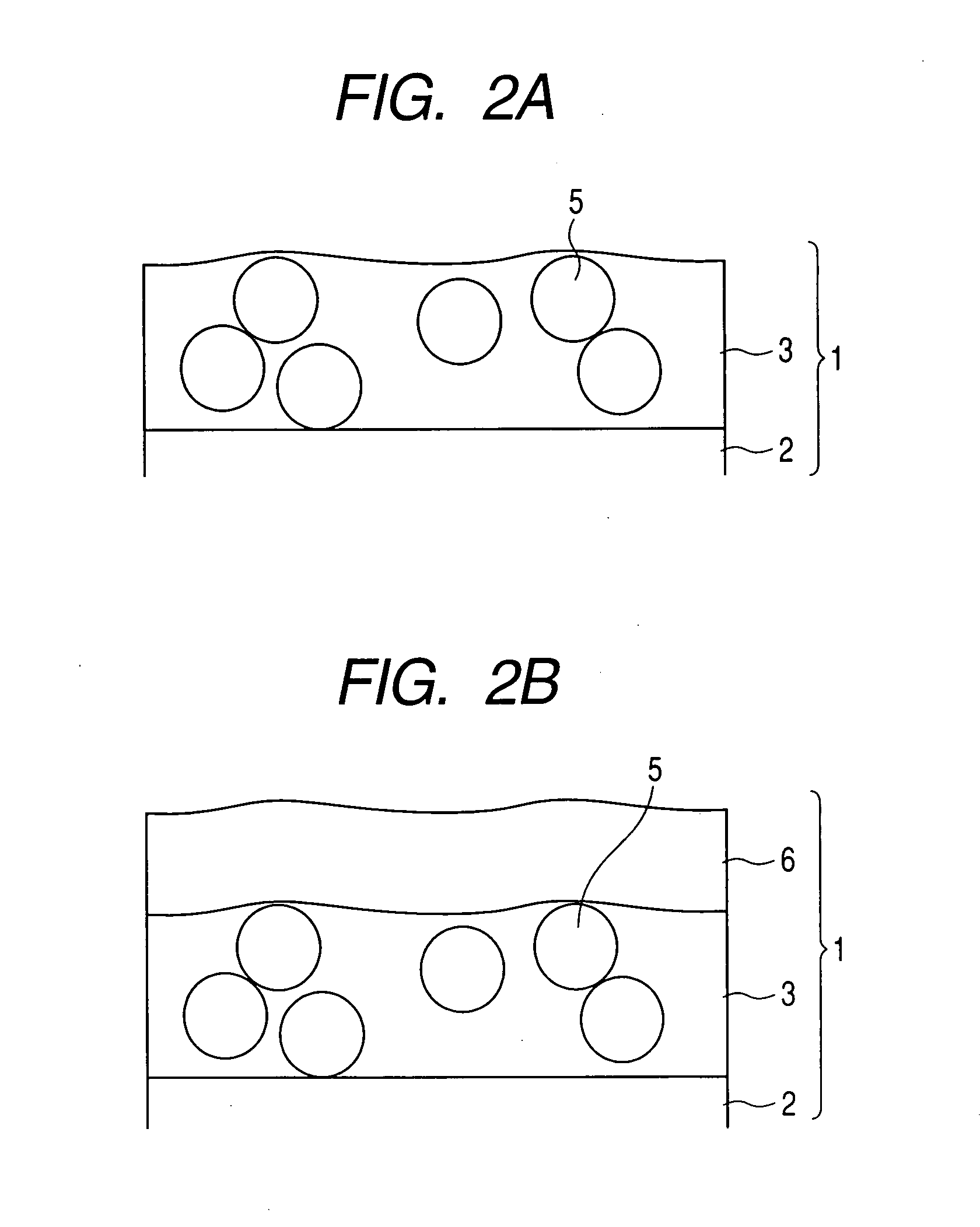
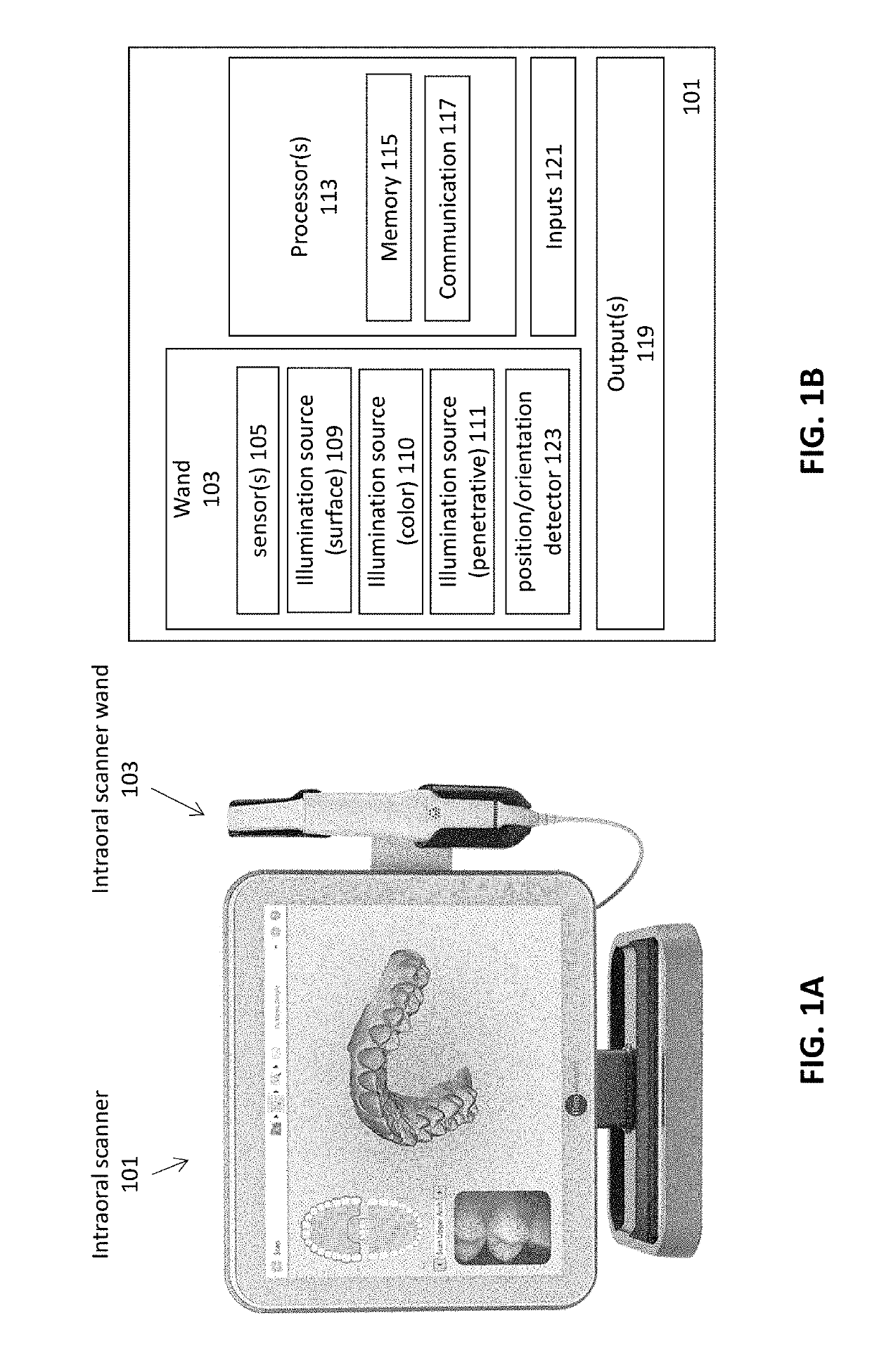
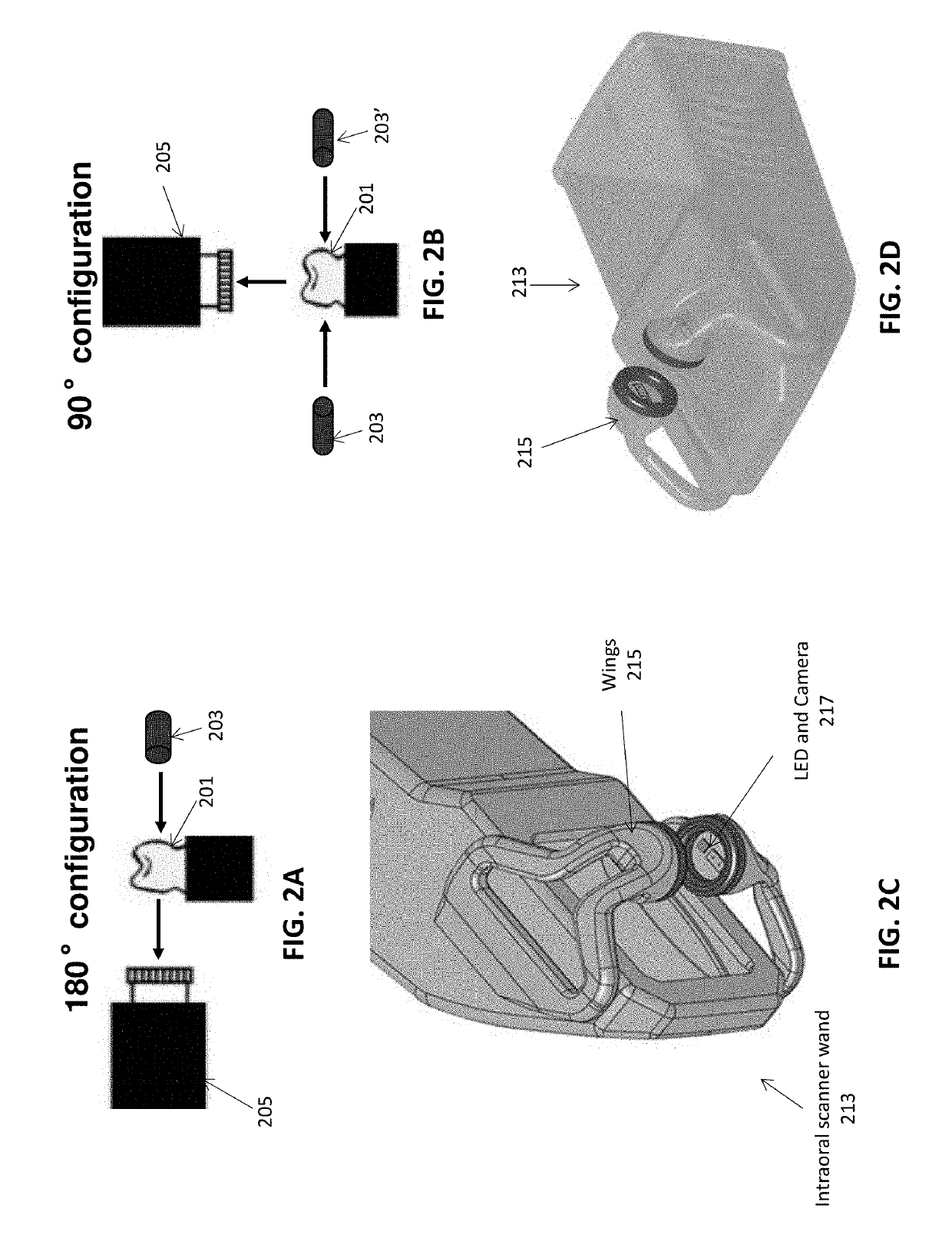
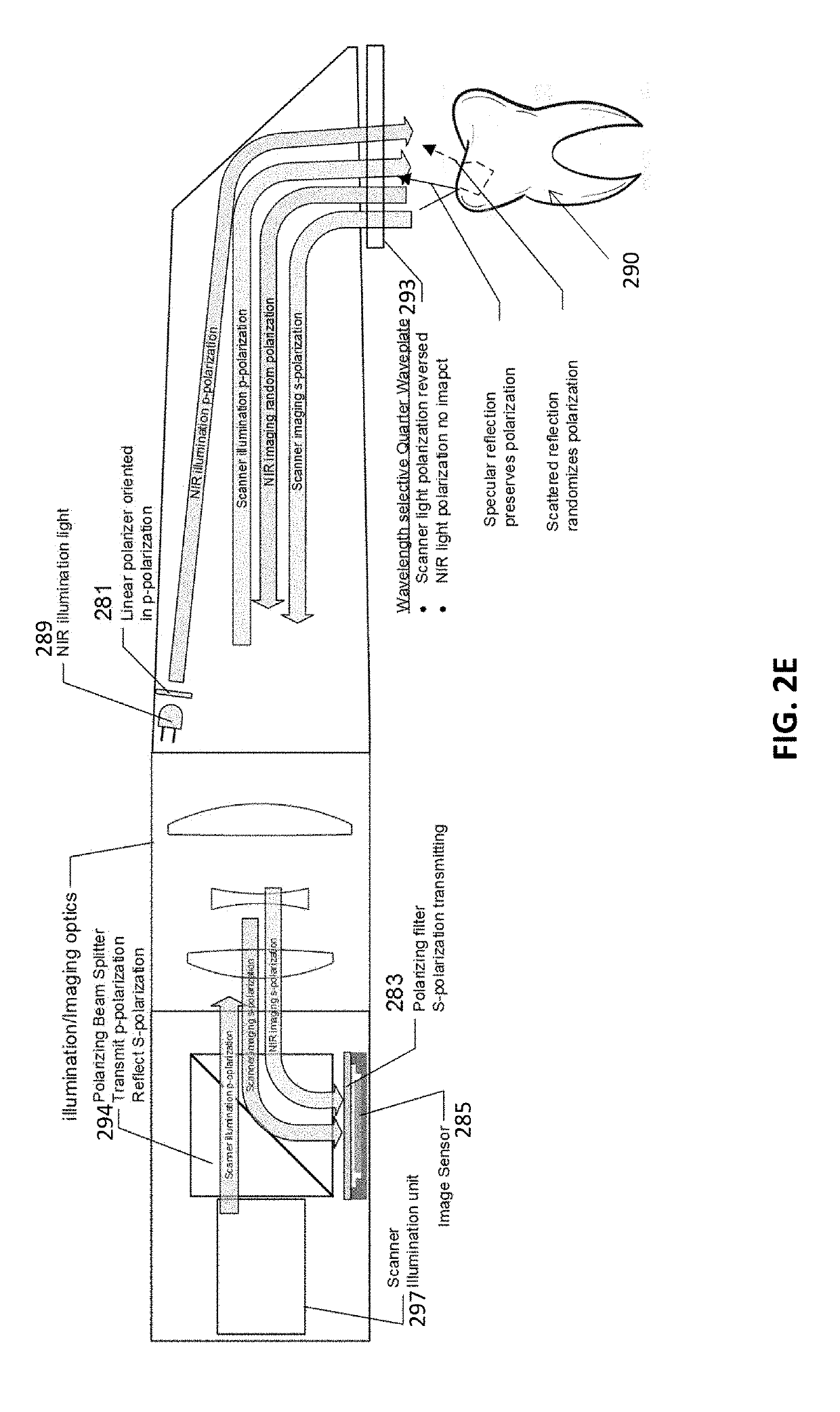
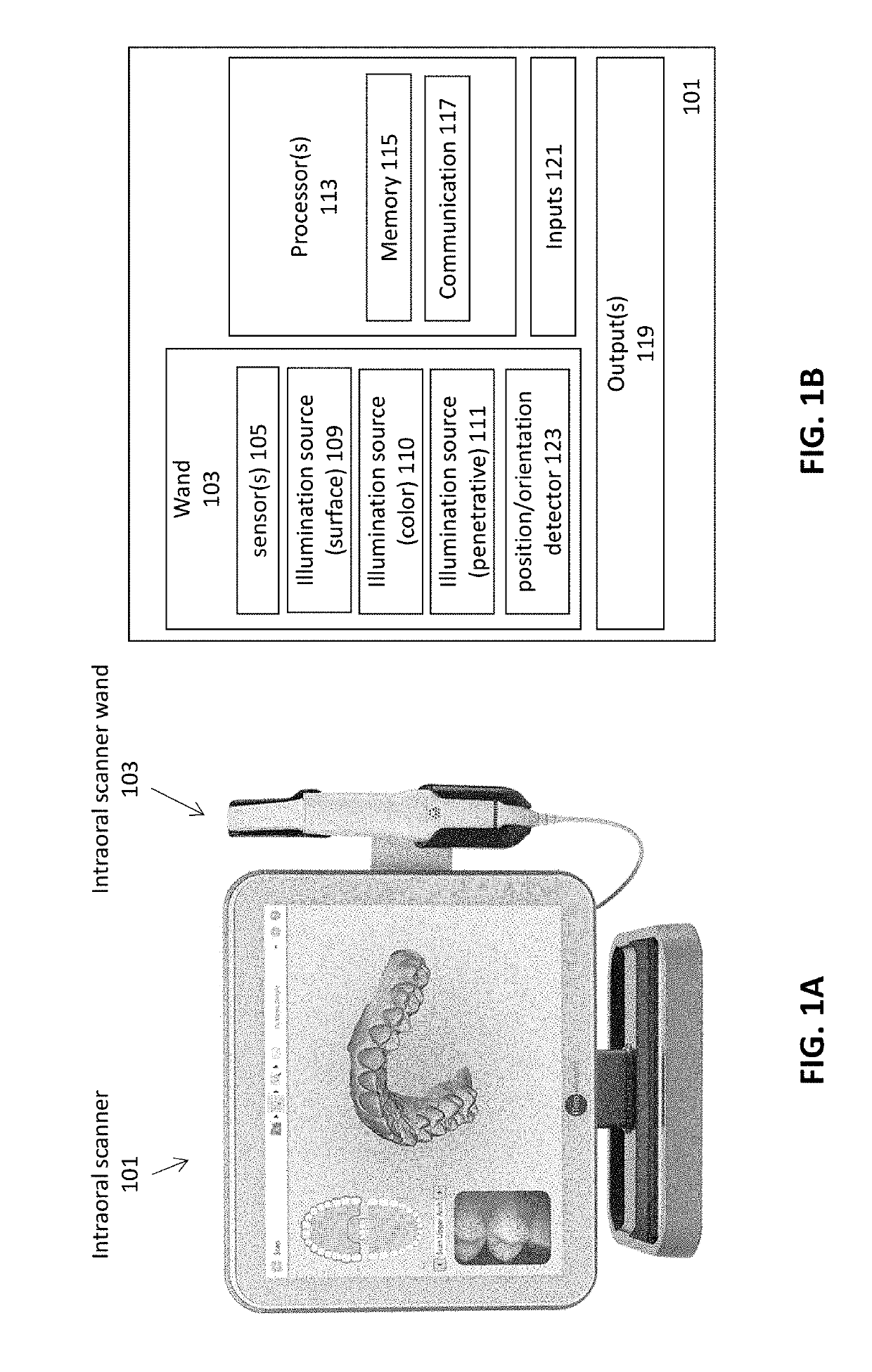
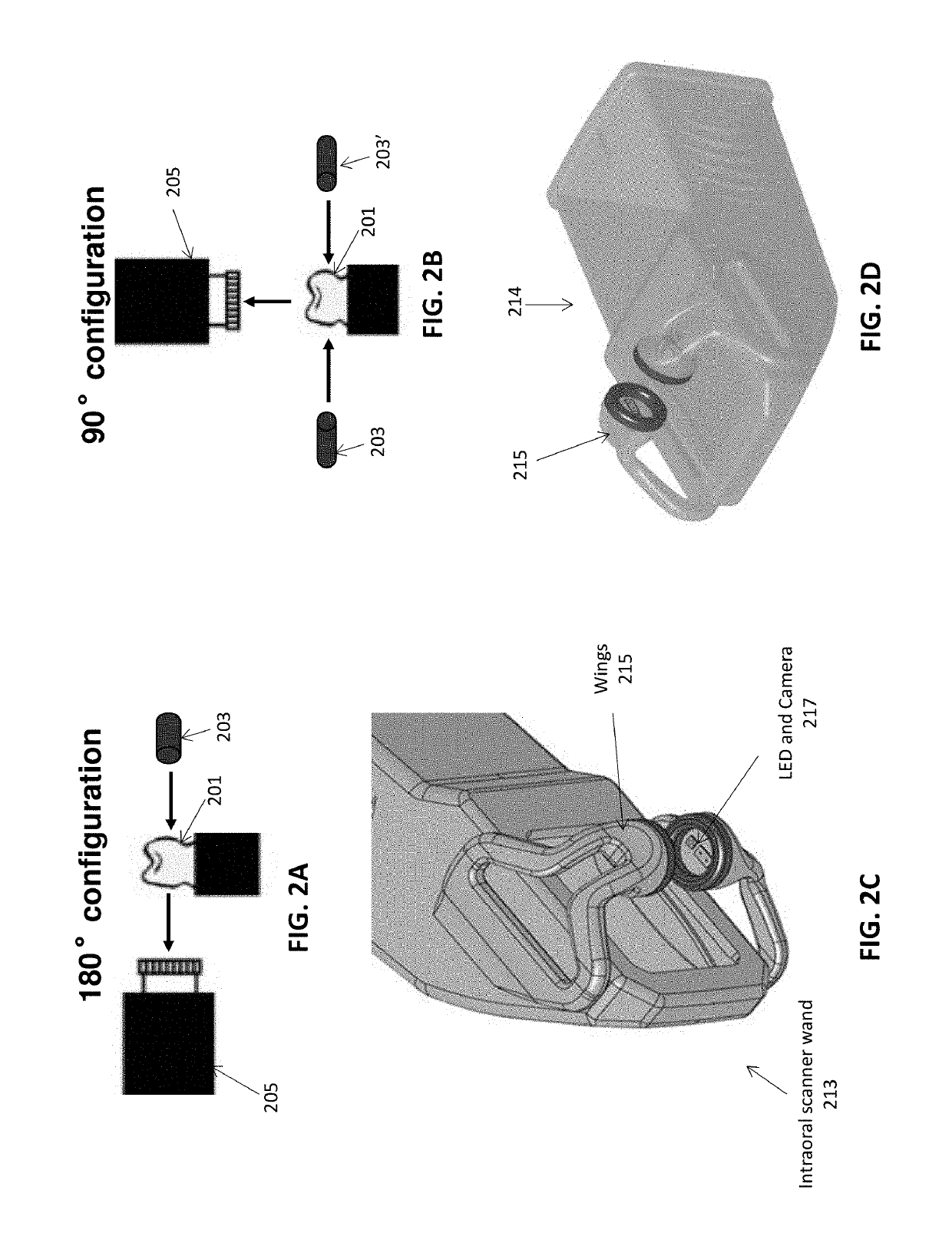
Methods and apparatuses for forming a three-dimensional volumetric model of a subject's teeth
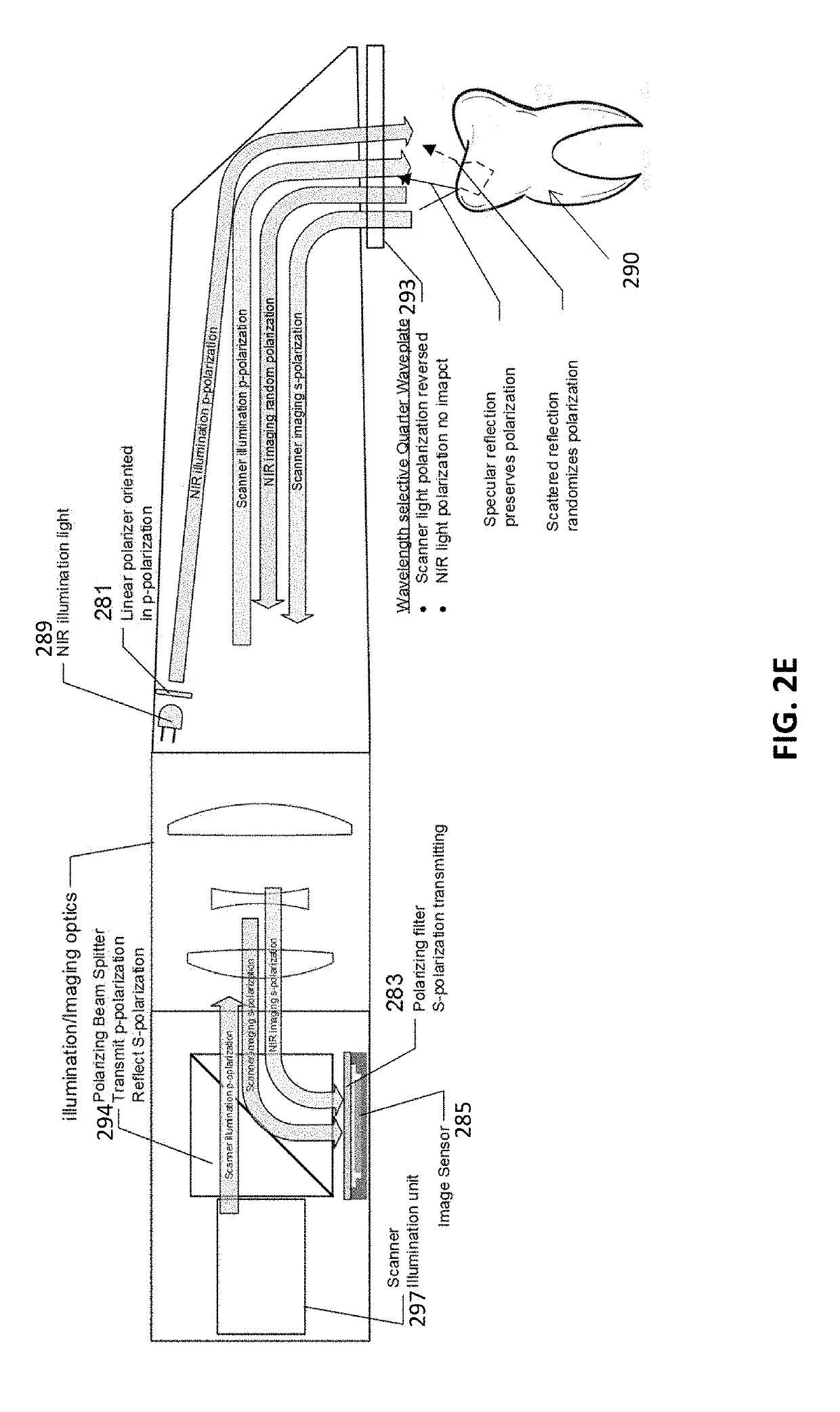
Methods and apparatuses for generating a model of a subject's teeth. Described herein are intraoral scanning methods and apparatuses for generating a three-dimensional model of a subject's intraoral region (e.g., teeth) including both surface features and internal features. These methods and apparatuses may be used for identifying and evaluating lesions, caries and cracks in the teeth. Any of these methods and apparatuses may use minimum scattering coefficients and / or segmentation to form a volumetric model of the teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Intraoral scanner with dental diagnostics capabilities
Methods and apparatuses for generating a model of a subject's teeth. Described herein are intraoral scanning methods and apparatuses for generating a three-dimensional model of a subject's intraoral region (e.g., teeth) including both surface features and internal features. These methods and apparatuses may be used for identifying and evaluating lesions, caries and cracks in the teeth. Any of these methods and apparatuses may use minimum scattering coefficients and / or segmentation to form a volumetric model of the teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
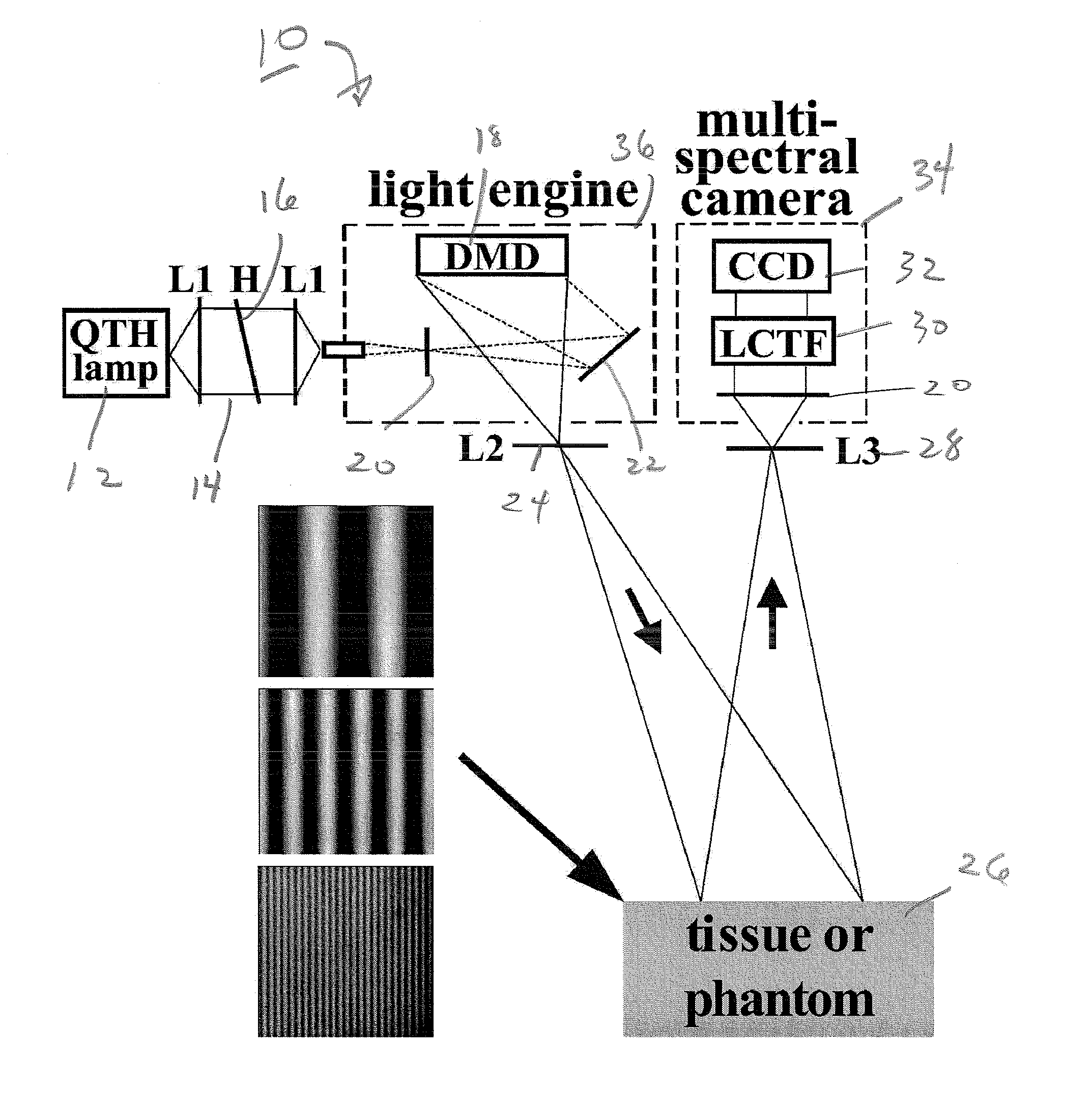
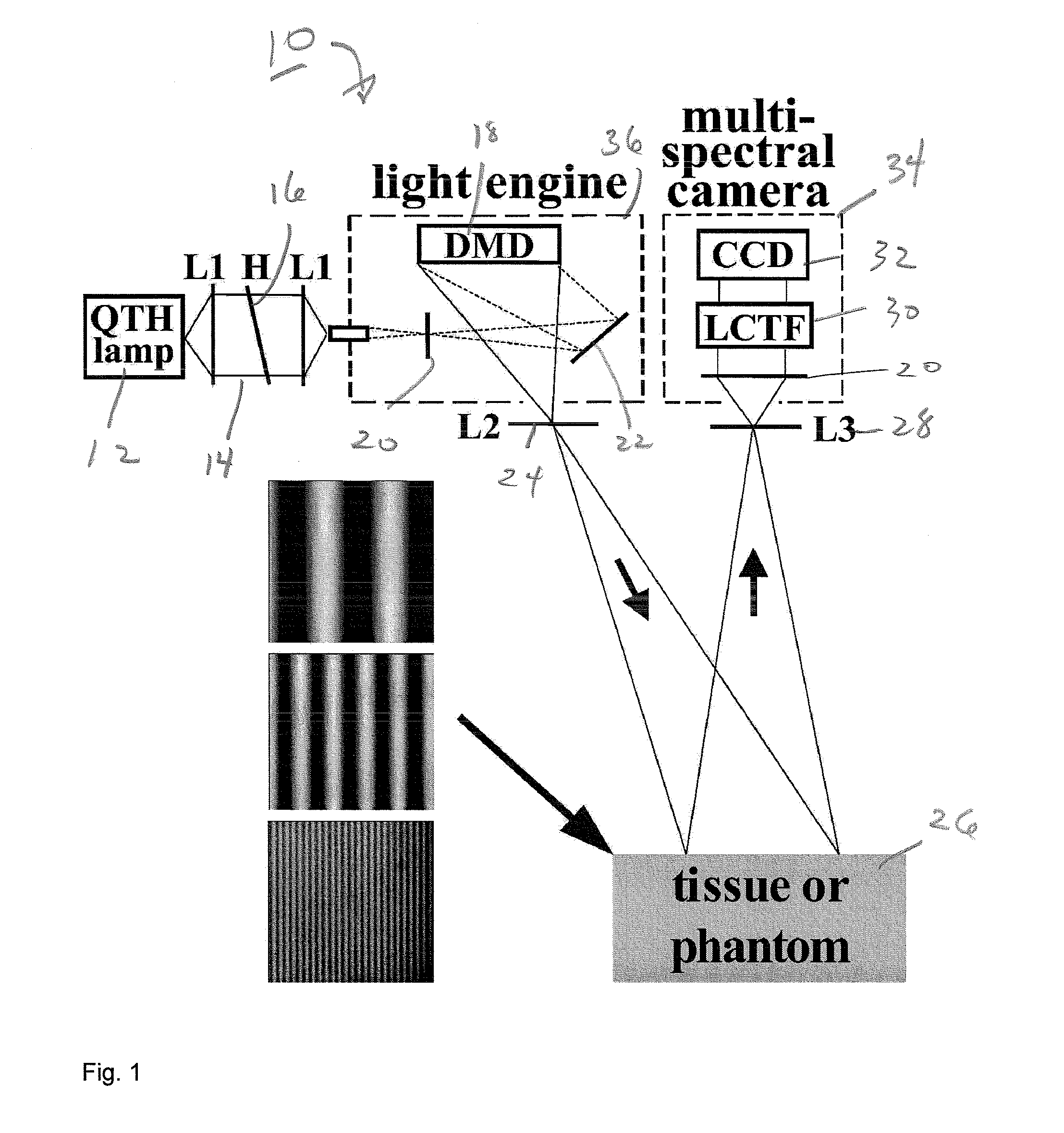
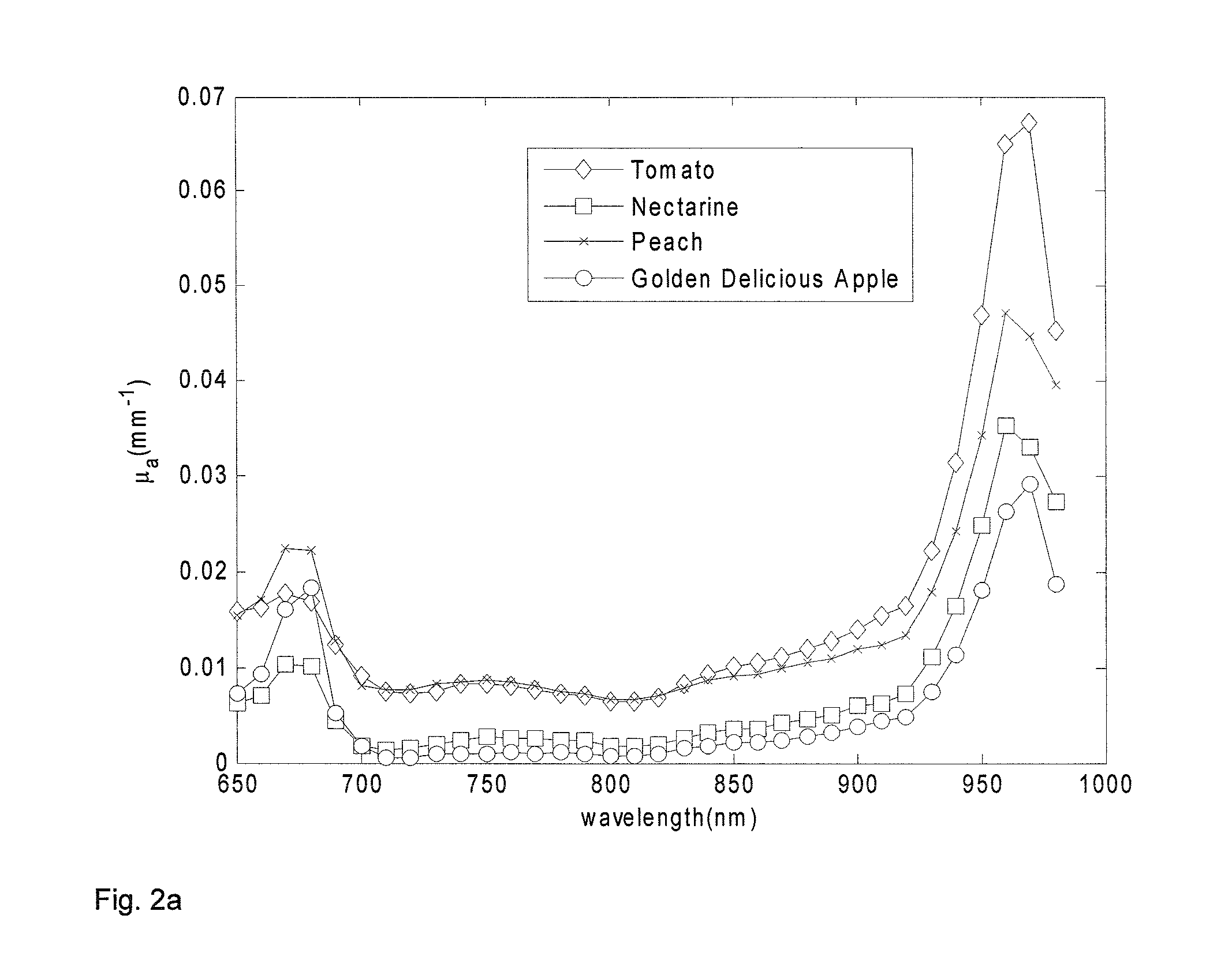
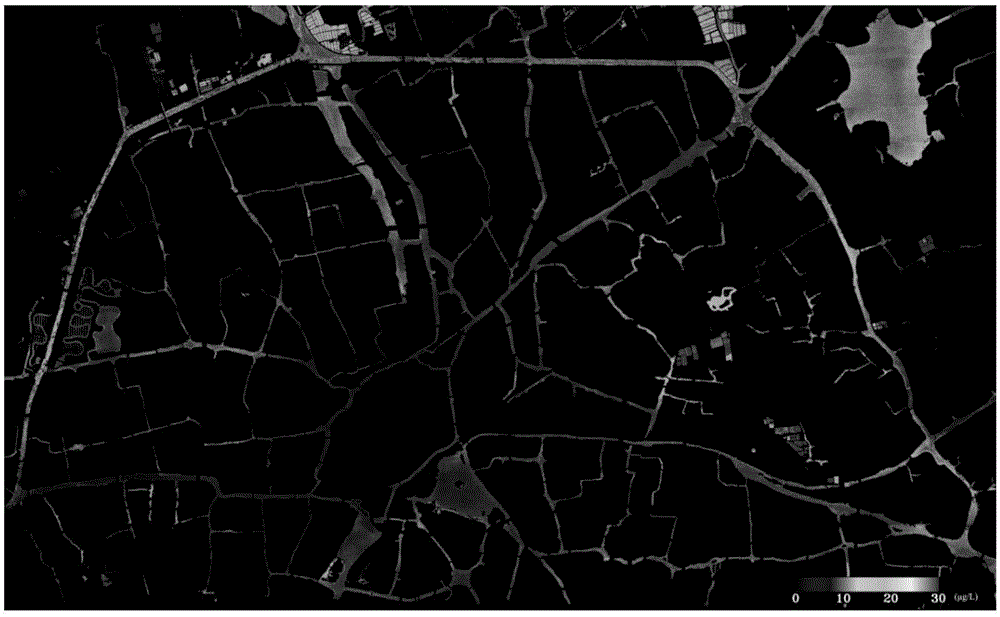
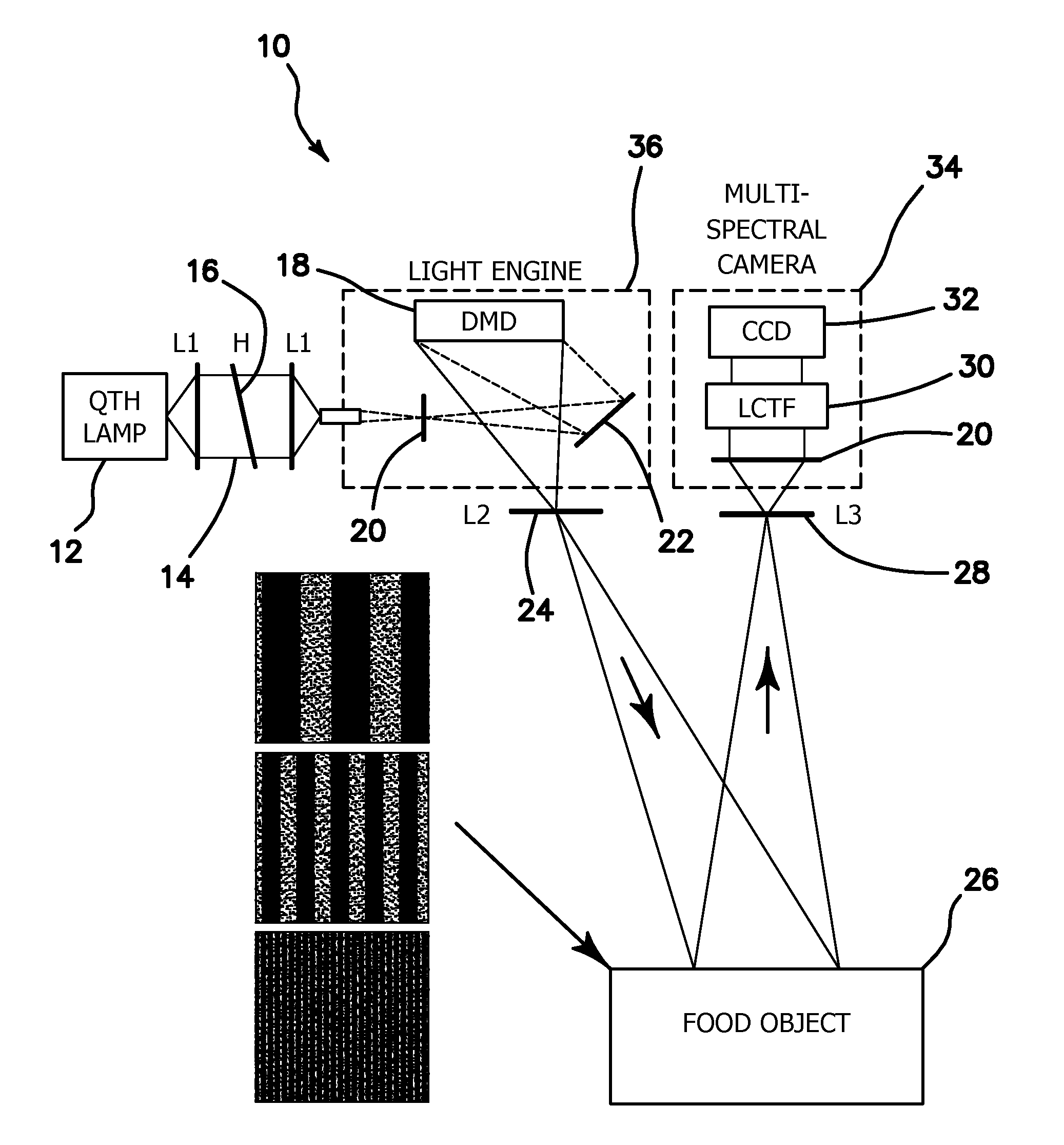
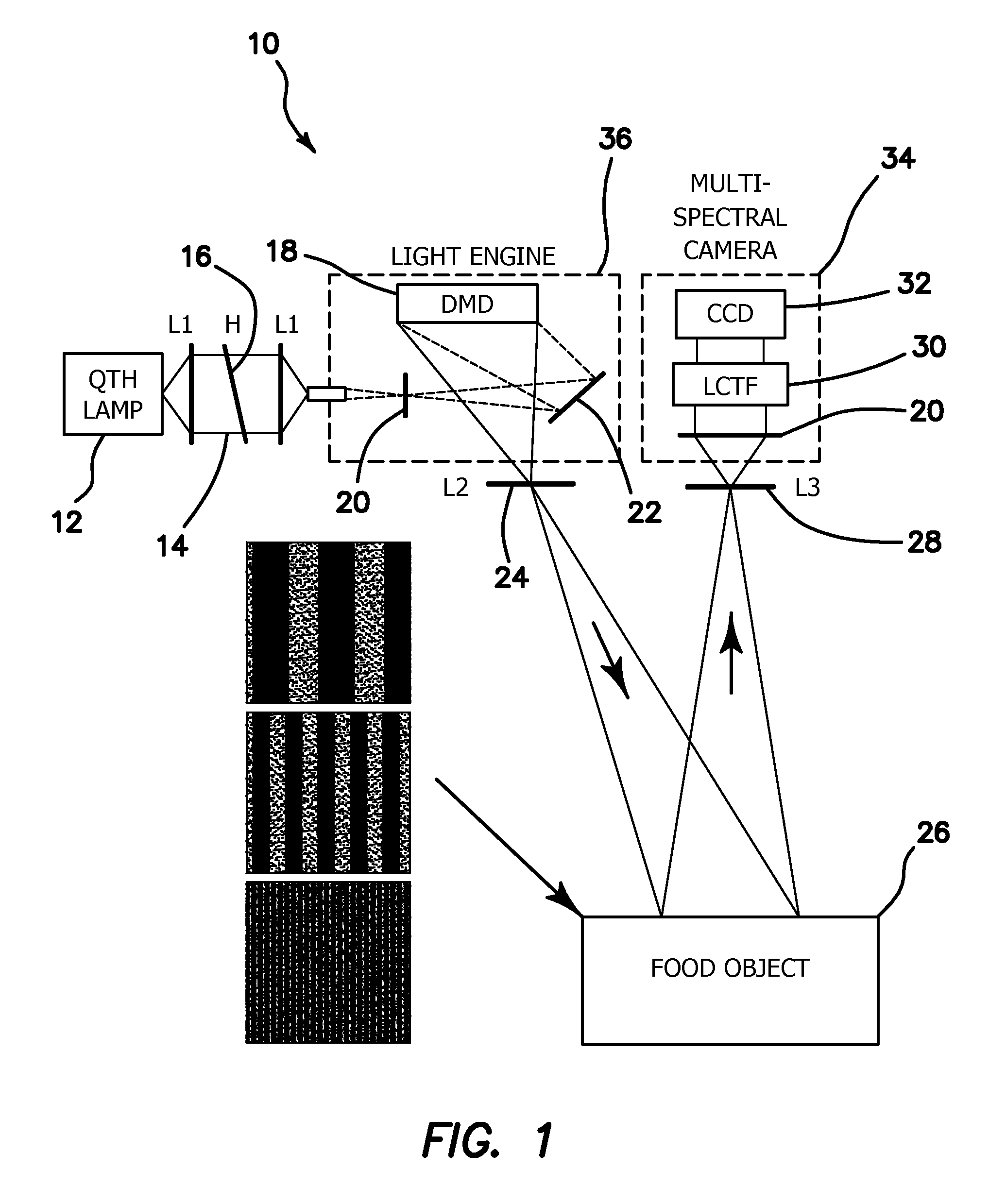
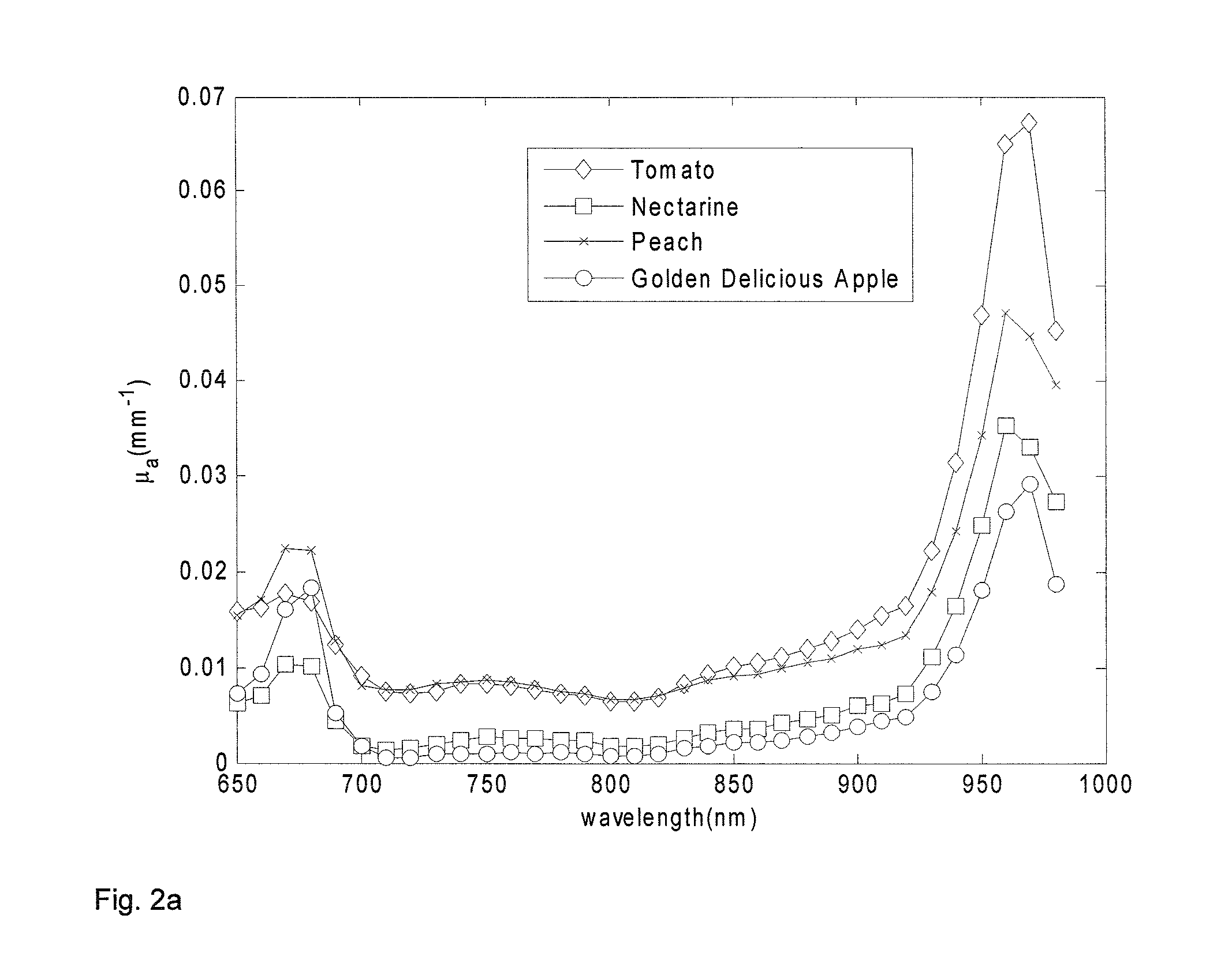
Method and apparatus for performing qualitative and quantitative analysis of produce (fruit, vegetables) using spatially structured illumination
ActiveUS20080101657A1Reduction factorEnhance the imageRaman/scattering spectroscopyCharacter and pattern recognitionDomain imagingSpatial frequency
A method and an apparatus for noninvasively and quantitatively determining spatially resolved absorption and reduced scattering coefficients over a wide field-of-view of a food object, including fruit or produce, uses spatial-frequency-domain imaging (SFDI). A single modulated imaging platform is employed. It includes a broadband light source, a digital micromirror optically coupled to the light source to control a modulated light pattern directed onto the food object at a plurality of selected spatial frequencies, a multispectral camera for taking a spectral image of a reflected modulated light pattern from the food object, a spectrally variable filter optically coupled between the food object and the multispectral camera to select a discrete number of wavelengths for image capture, and a computer coupled to the digital micromirror, camera and variable filter to enable acquisition of the reflected modulated light pattern at the selected spatial frequencies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
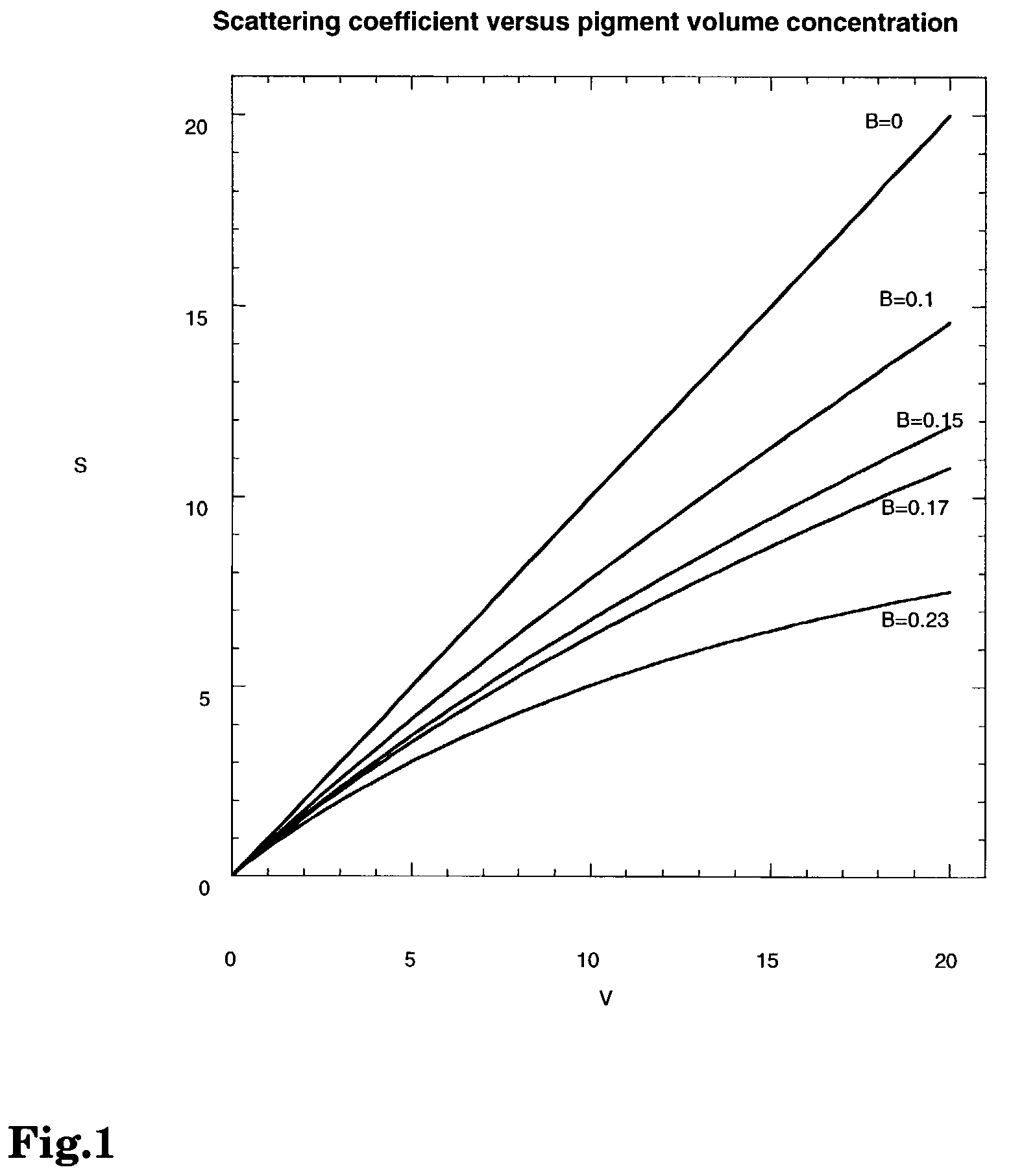
Coating with improved hiding, compositions prepared therewith, and processes for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS7081488B2Low levelIncreased hiding levelMaterial nanotechnologyConductive materialLinear relationshipVolume concentration
A coating containing pigment particles and a polymer matrix is provided. The coating contains pigment particles that have a scattering coefficient with a linear or quasi-linear relationship to the pigment volume concentration of those pigment particles. The coating has improved hiding and is useful as a protective coating or an aesthetic coating on an underlying substrate. Also provided are compositions useful for preparing the coating, including covalently bonded composite particles and aqueous dispersions containing composite particles. The composite particles each contain a pigment particle with a plurality of polymer particles attached by adsorption on the outer surface of the pigment particle or by covalent bonding to the pigment particle through a coupling agent. Methods to prepare the composite particles and coating compositions containing the composite particles are also provided.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
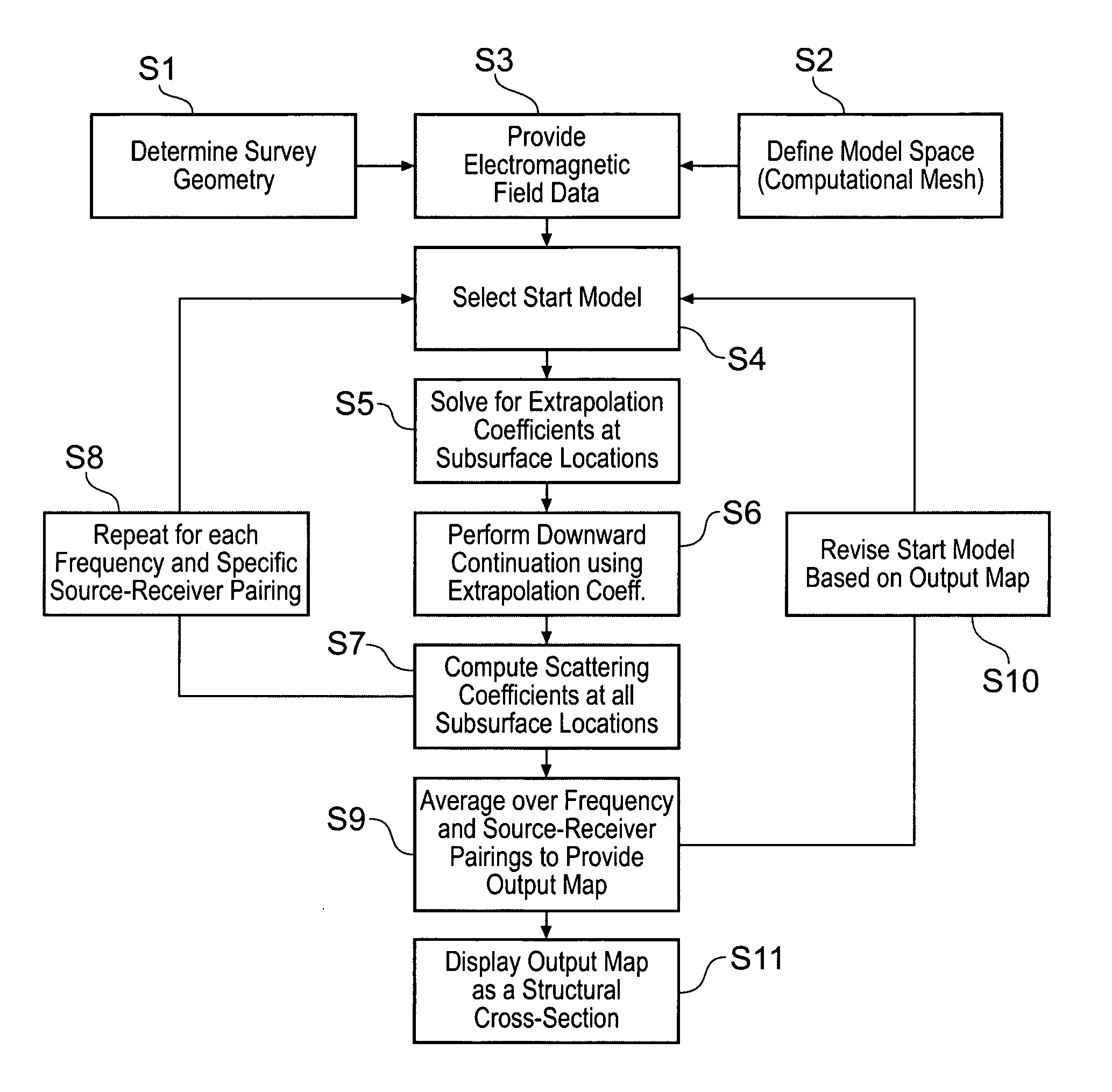
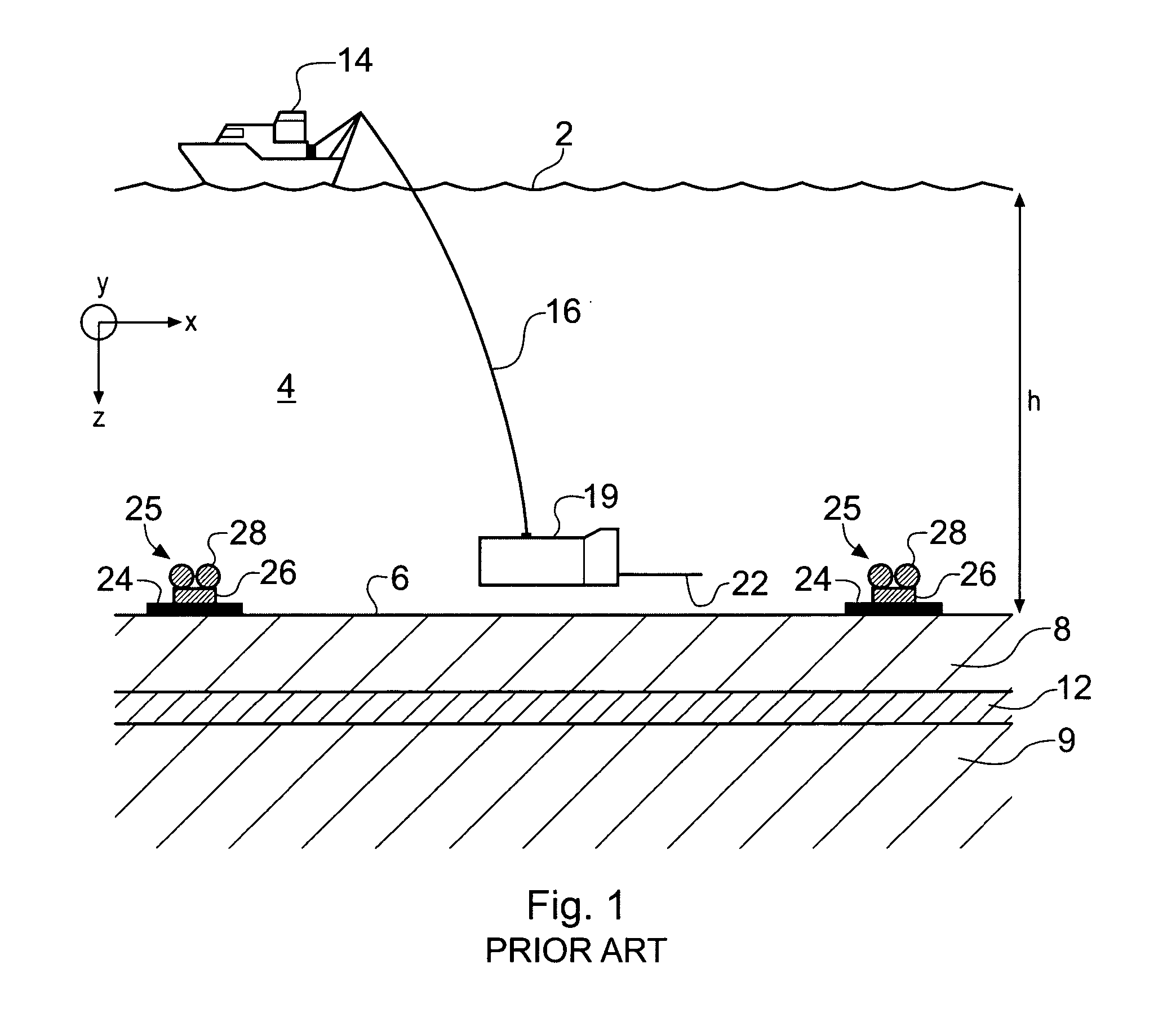
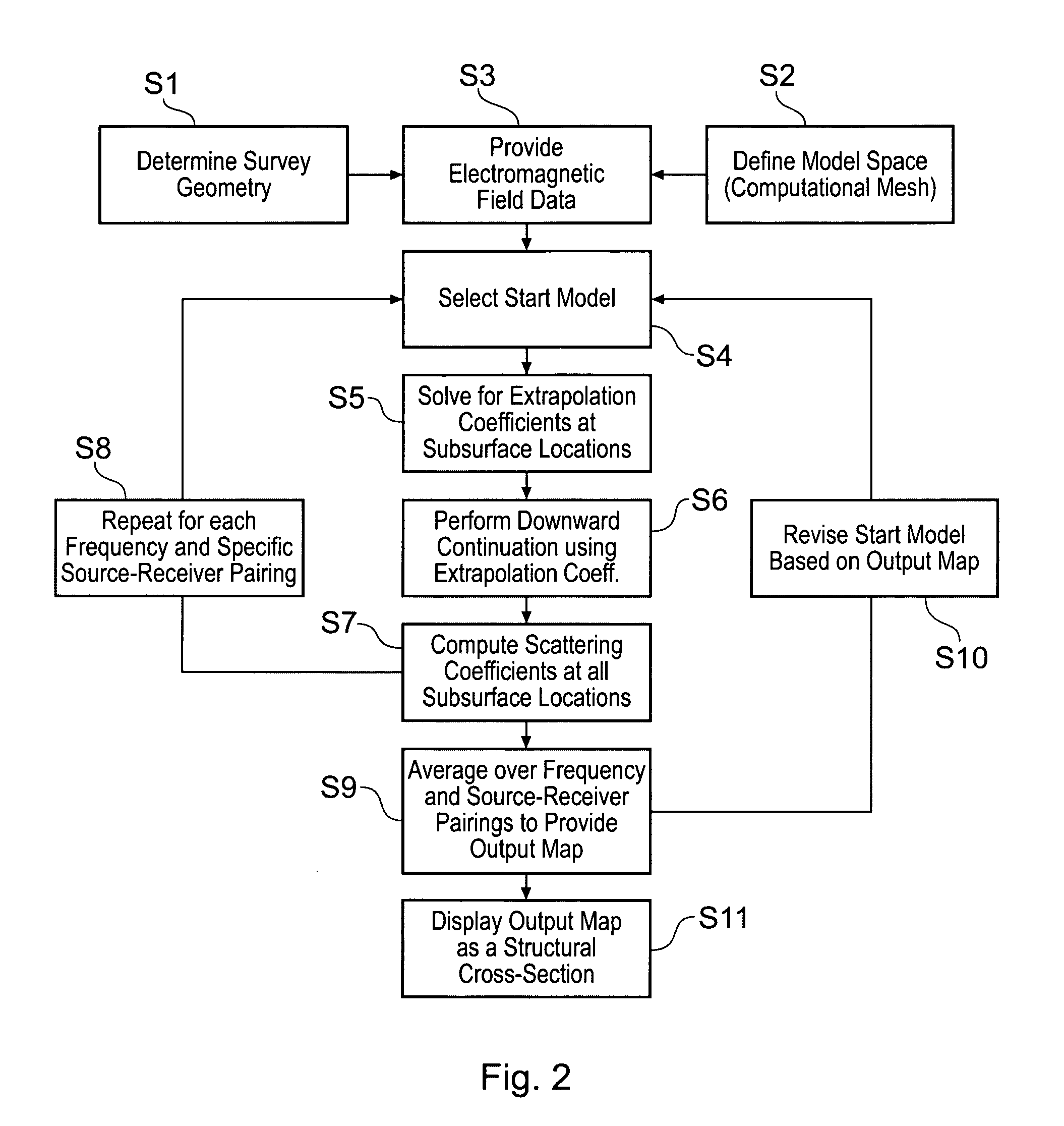
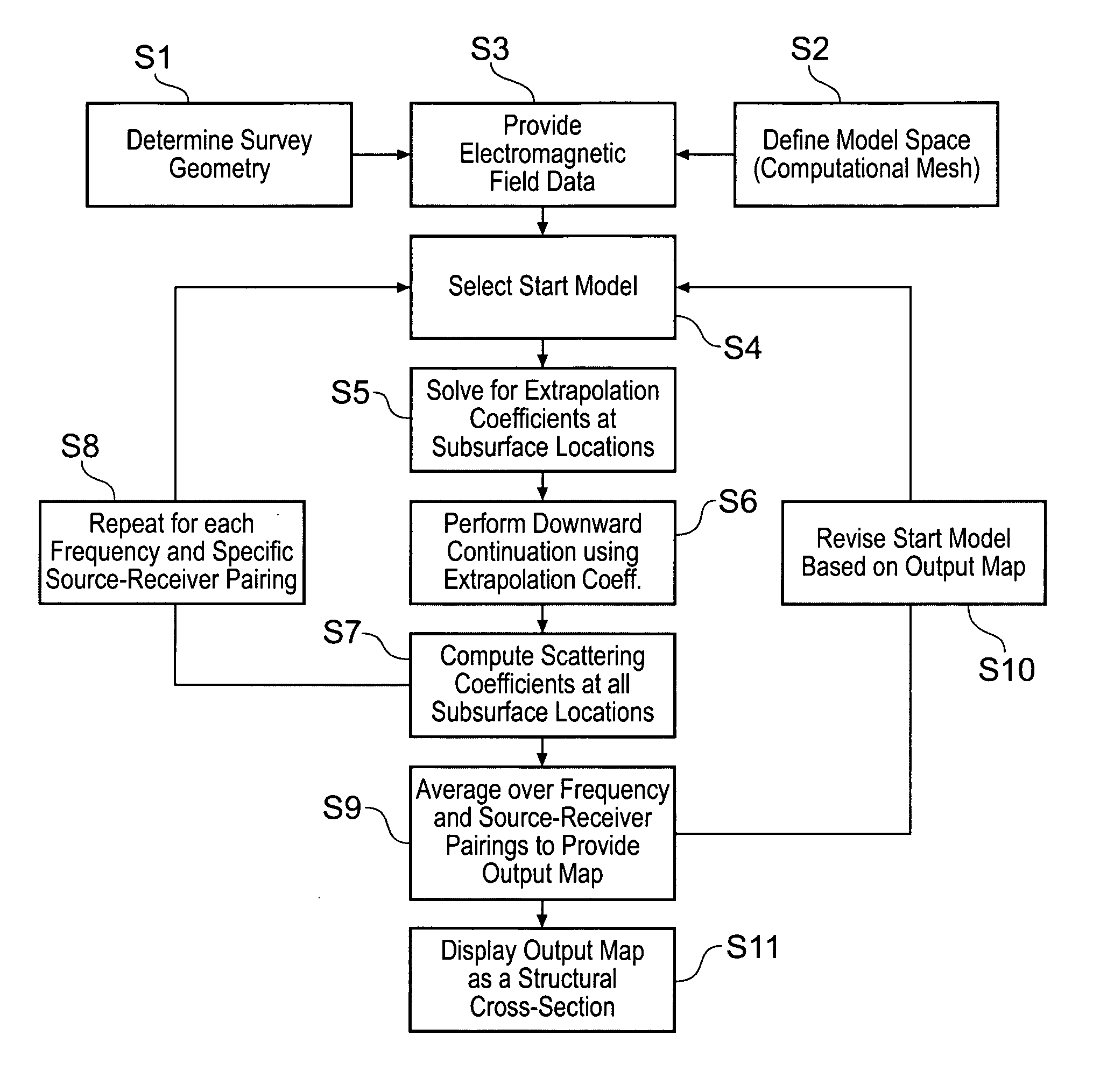
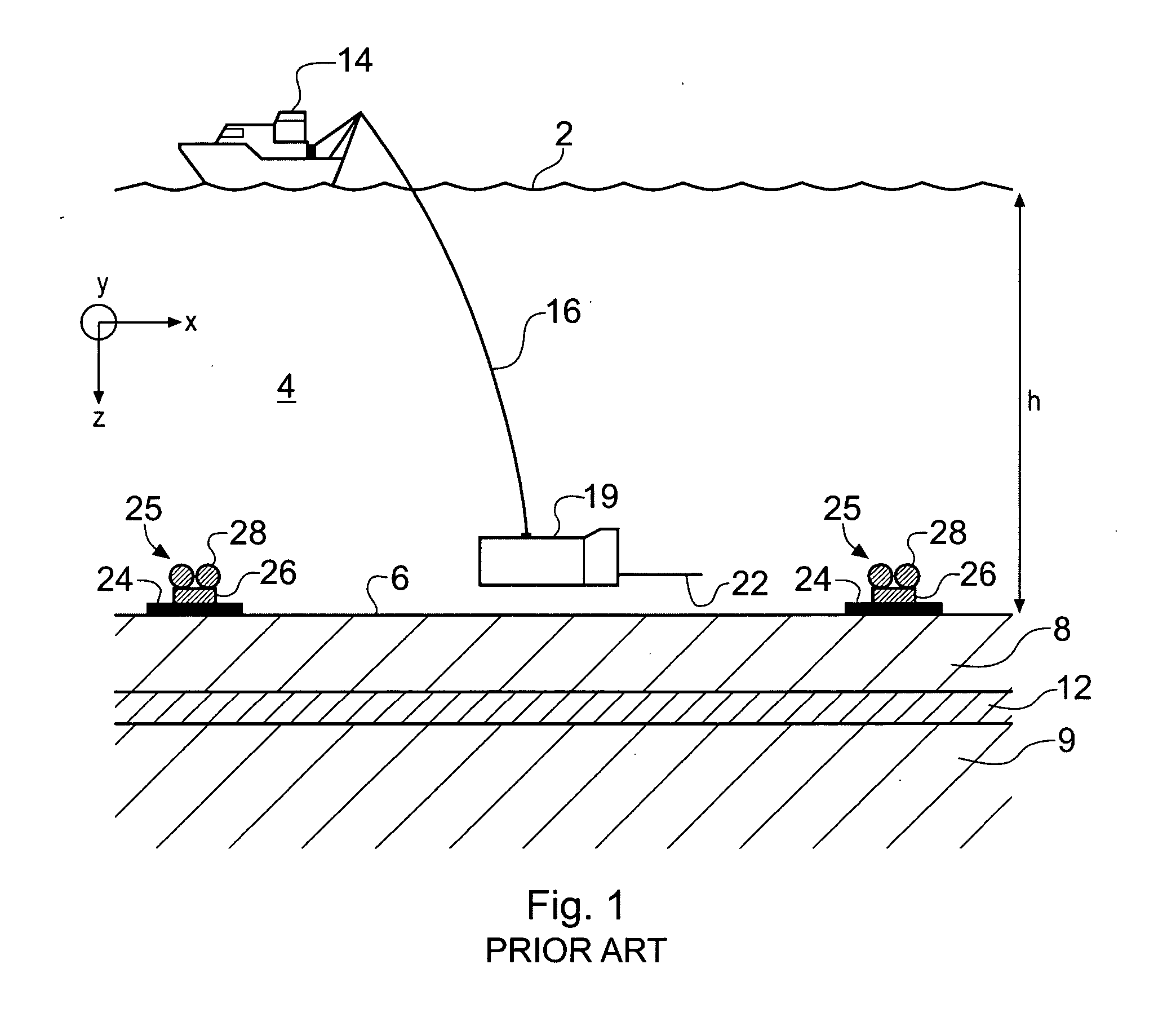
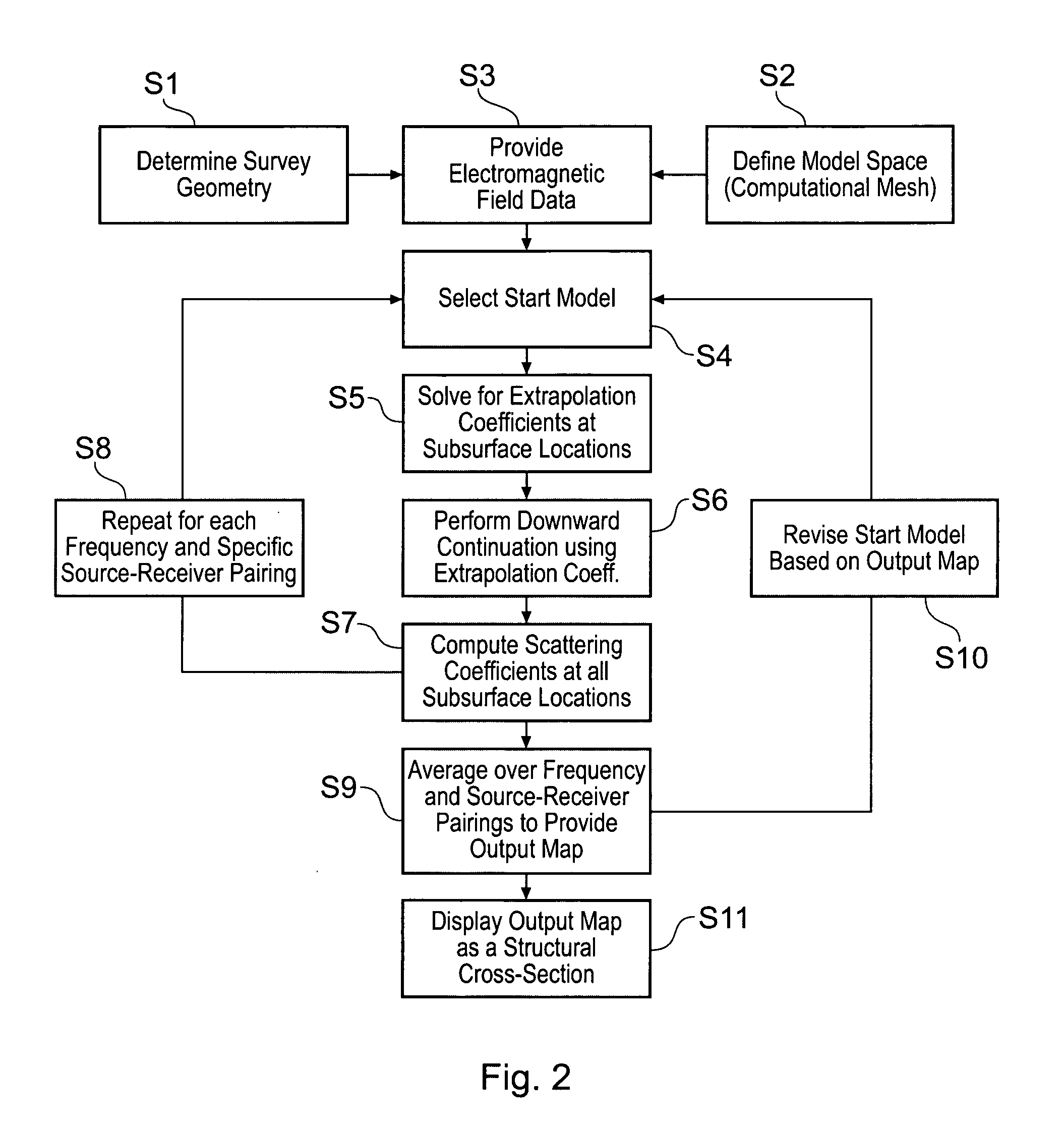
Electromagnetic surveying for hydrocarbon reservoirs
ActiveUS7191063B2Correction for variationEasy to explainElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisUnderwaterElectromagnetic field
A method of analyzing results from an underwater controlled source electromagnetic (CSEM) survey of an area that is thought or known to contain a subterranean hydrocarbon reservoir is described. The method is based on a wavefield extrapolation of narrow-band electromagnetic field data obtained from pairs of source and receiver locations. The data comprise a plurality of discrete frequencies between 0.01 Hz and 60 Hz. The wavefield extrapolation is performed for each of these discrete frequencies to provide distributions of electromagnetic scattering coefficient as a function of position and depth beneath the survey area. These distributions may then be combined to provide a displayable image of electromagnetic scattering coefficient. The method is able to quickly provide a displayable image that is readily interpretable.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Intraoral scanner with dental diagnostics capabilities
Methods and apparatuses for generating a model of a subject's teeth. Described herein are intraoral scanning methods and apparatuses for generating a three-dimensional model of a subject's intraoral region (e.g., teeth) including both surface features and internal features. These methods and apparatuses may be used for identifying and evaluating lesions, caries and cracks in the teeth. Any of these methods and apparatuses may use minimum scattering coefficients and / or segmentation to form a volumetric model of the teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
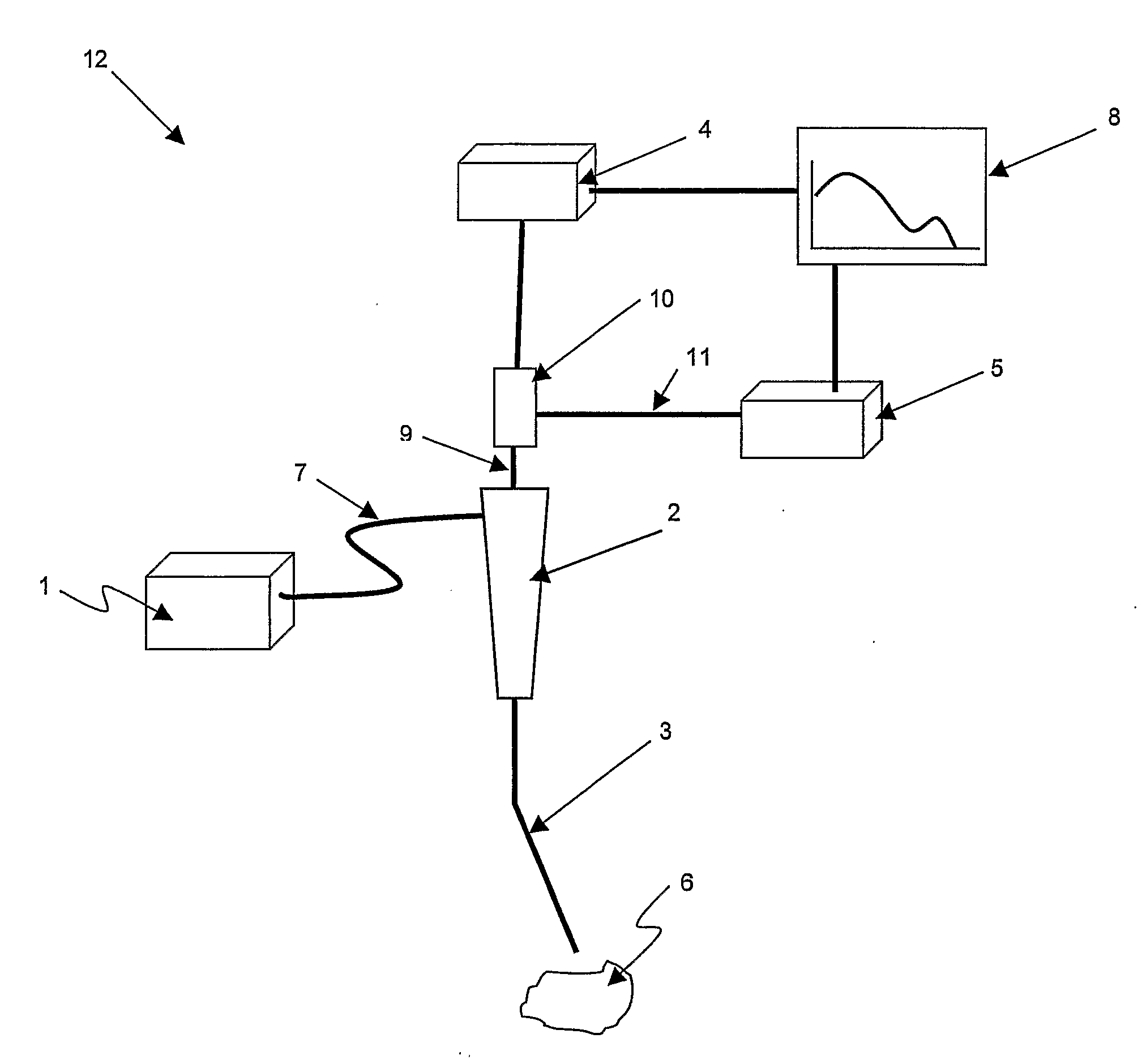
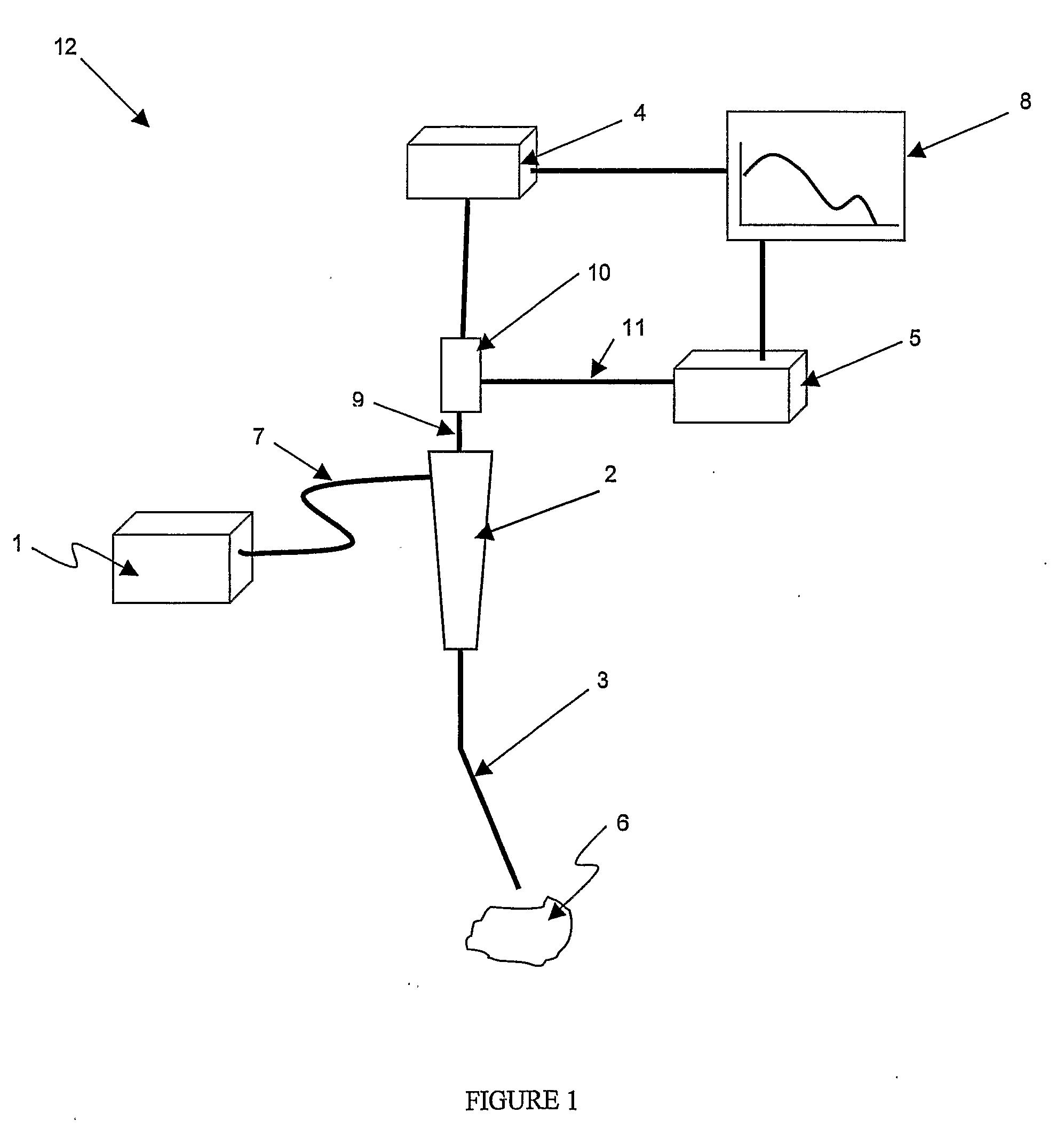
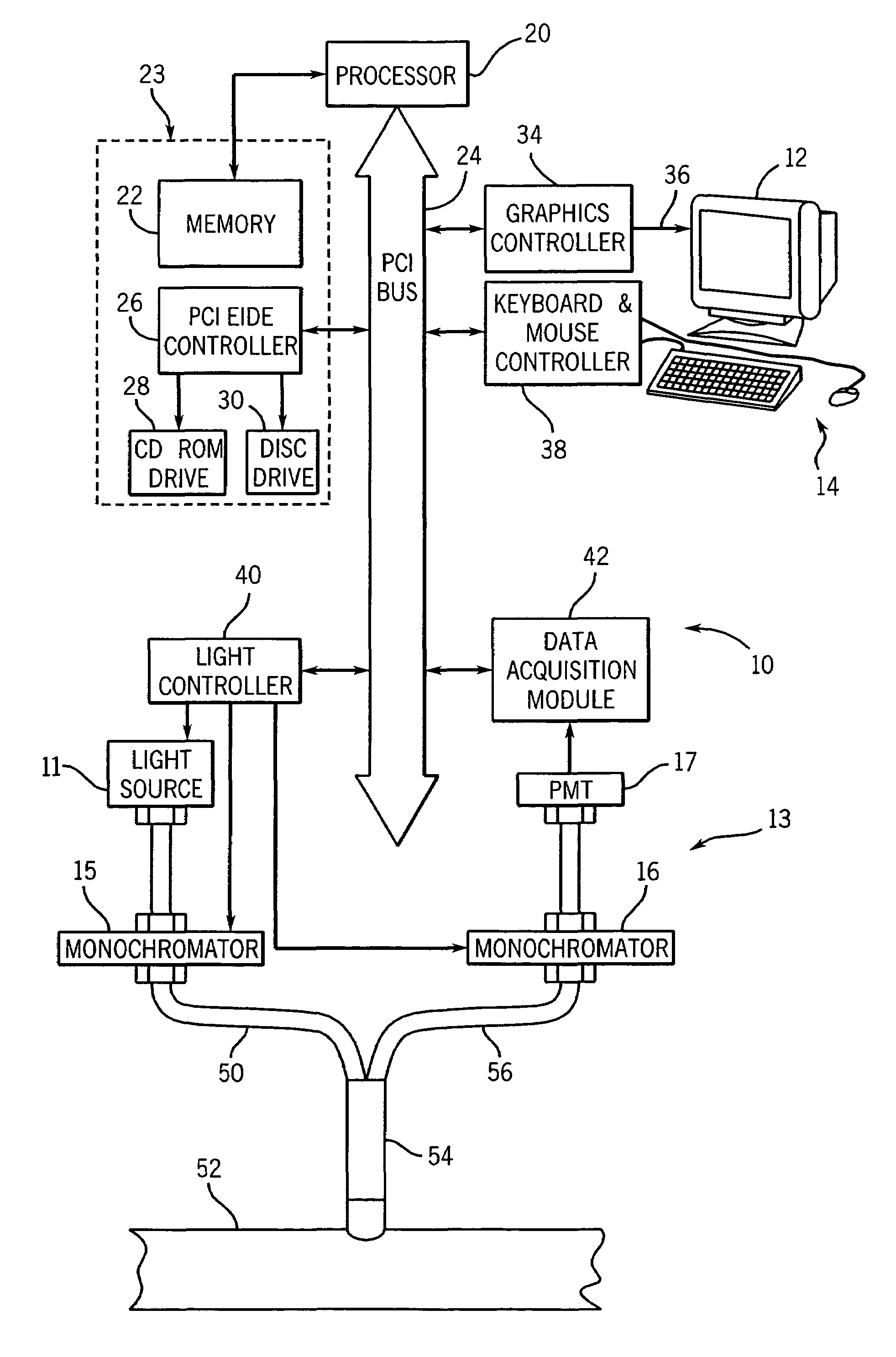
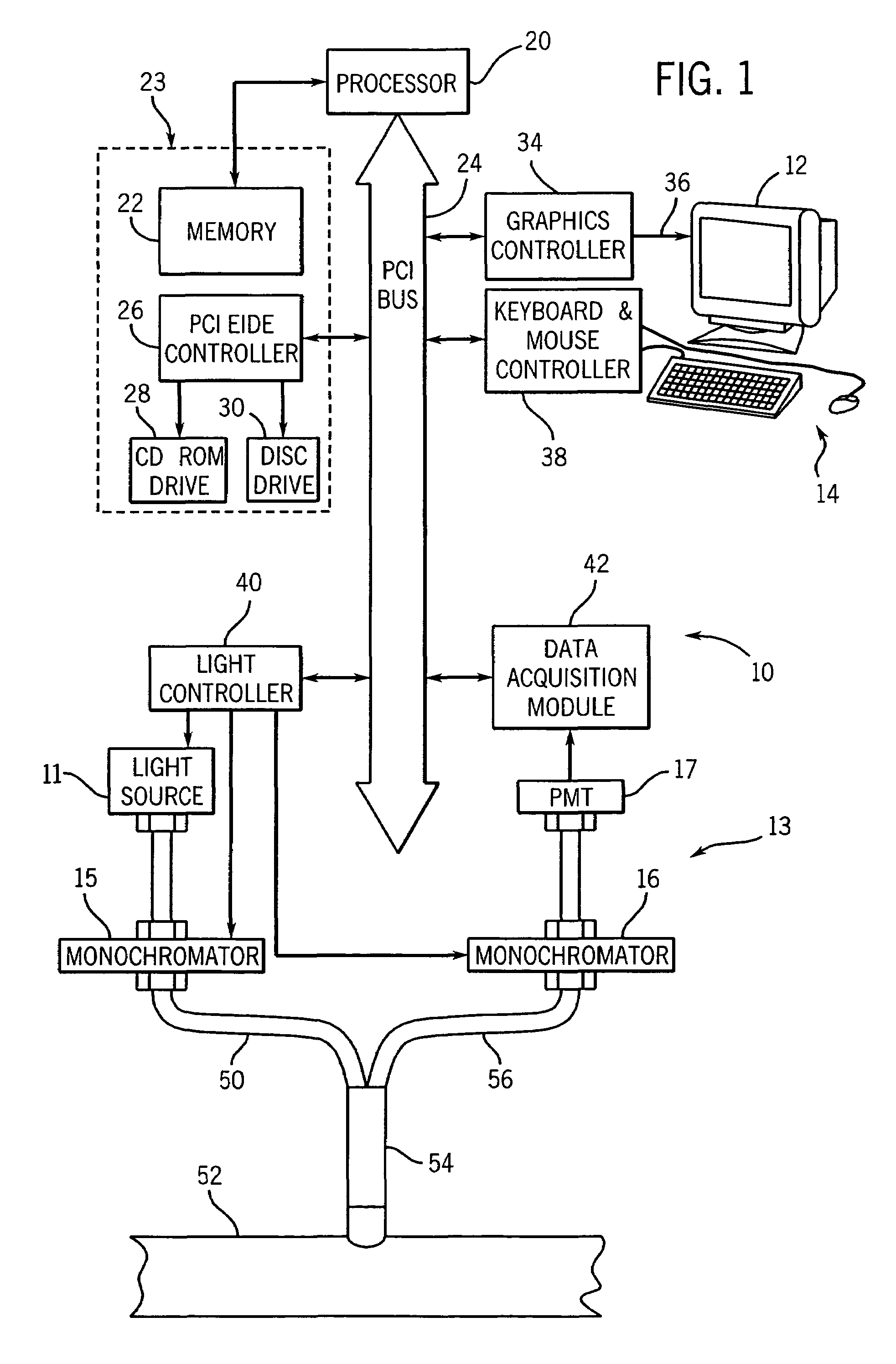
Method and apparatus for measuring cancerous changes from reflectance spectral measurements obtained during endoscopic imaging
The present invention provides a new method and device for disease detection, more particularly cancer detection, from the analysis of diffuse reflectance spectra measured in vivo during endoscopic imaging. The measured diffuse reflectance spectra are analyzed using a specially developed light-transport model and numerical method to derive quantitative parameters related to tissue physiology and morphology. The method also corrects the effects of the specular reflection and the varying distance between endoscope tip and tissue surface on the clinical reflectance measurements. The model allows us to obtain the absorption coefficient (μa) and further to derive the tissue micro-vascular blood volume fraction and the tissue blood oxygen saturation parameters. It also allows us to obtain the scattering coefficients (μs and g) and further to derive the tissue micro-particles volume fraction and size distribution parameters.
Owner:PERCEPTRONIX MEDICAL +1
Electromagnetic surveying for hydrocarbon reservoirs
ActiveUS20050251340A1Promote generationCorrection for variationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisUnderwaterElectromagnetic field
A method of analyzing results from an underwater controlled source electromagnetic (CSEM) survey of an area that is thought or known to contain a subterranean hydrocarbon reservoir is described. The method is based on a wavefield extrapolation of narrow-band electromagnetic field data obtained from pairs of source and receiver locations. The data comprise a plurality of discrete frequencies between 0.01 Hz and 60 Hz. The wavefield extrapolation is performed for each of these discrete frequencies to provide distributions of electromagnetic scattering coefficient as a function of position and depth beneath the survey area. These distributions may then be combined to provide a displayable image of electromagnetic scattering coefficient. The method is able to quickly provide a displayable image that is readily interpretable.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
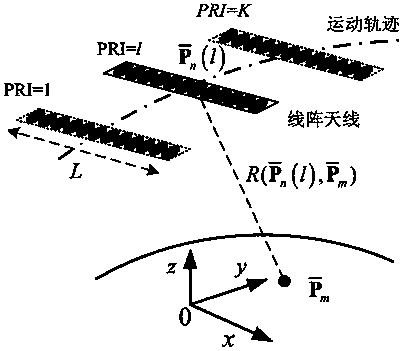
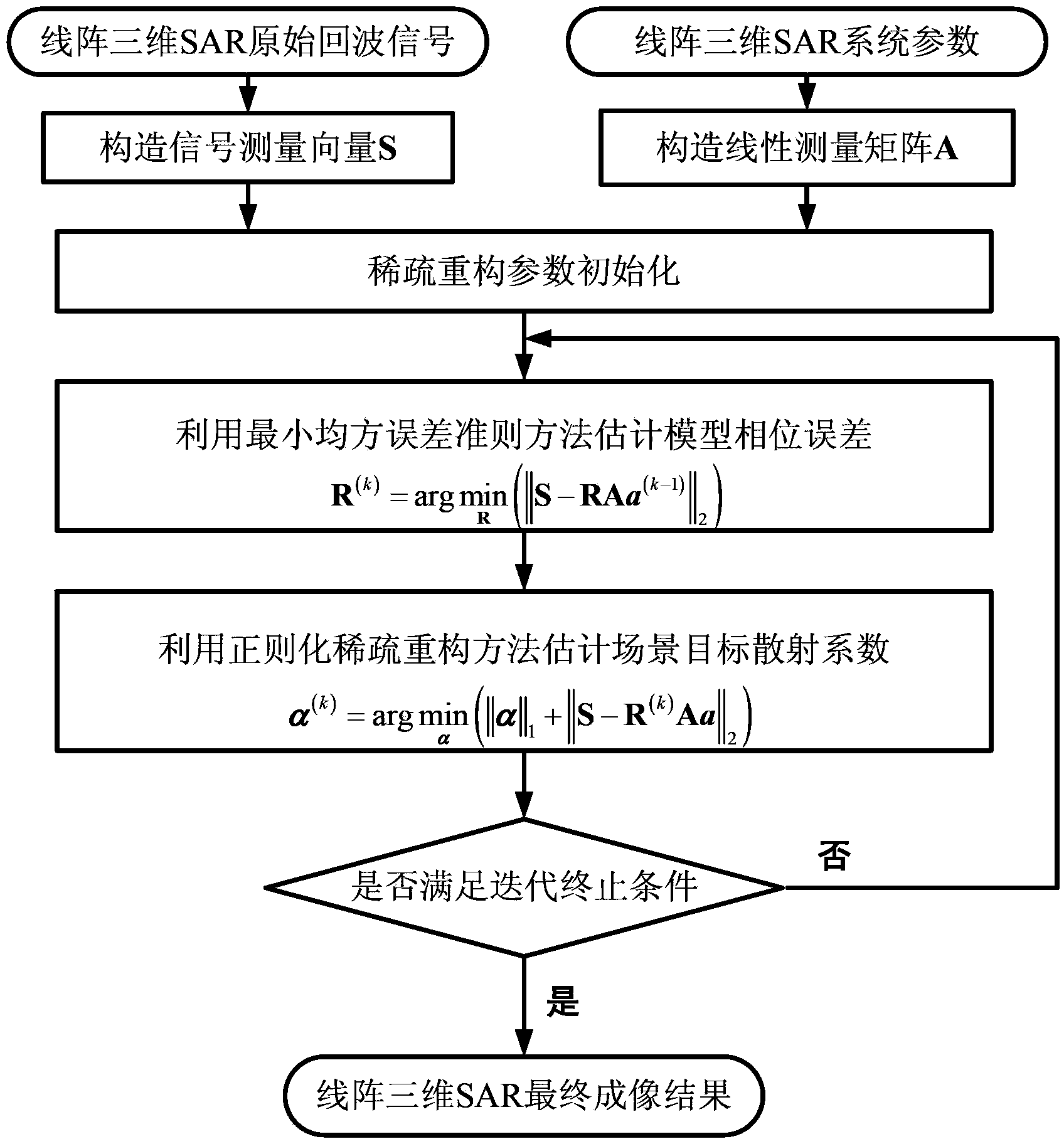
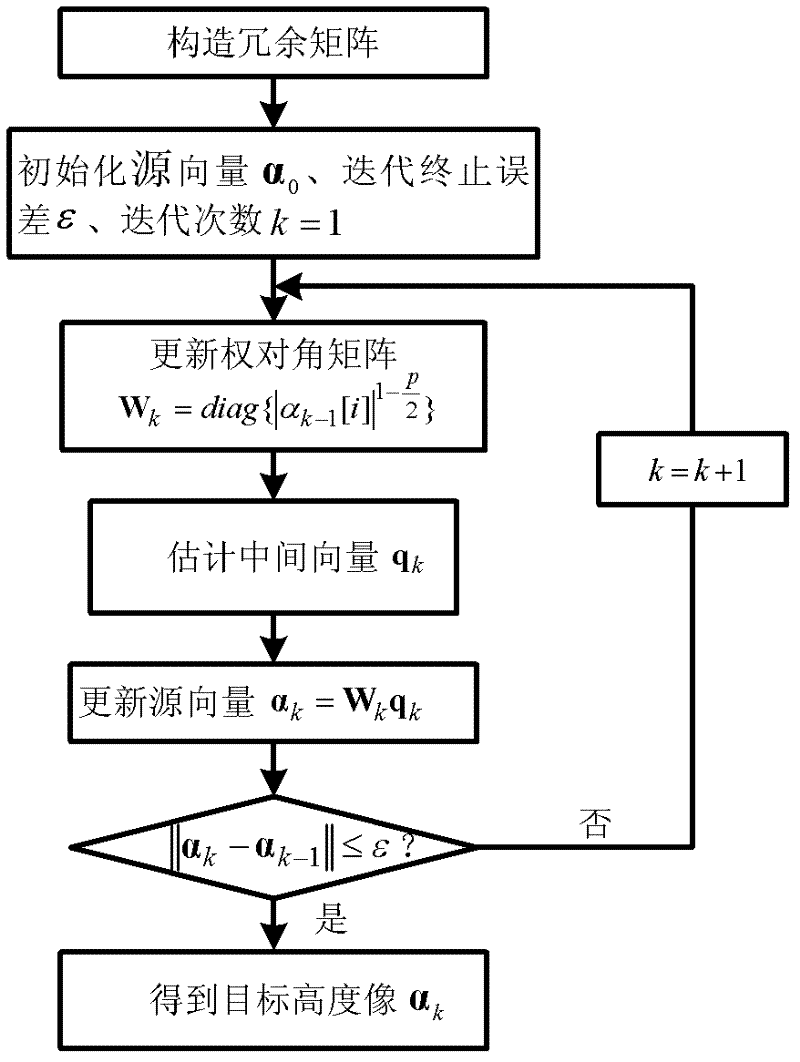
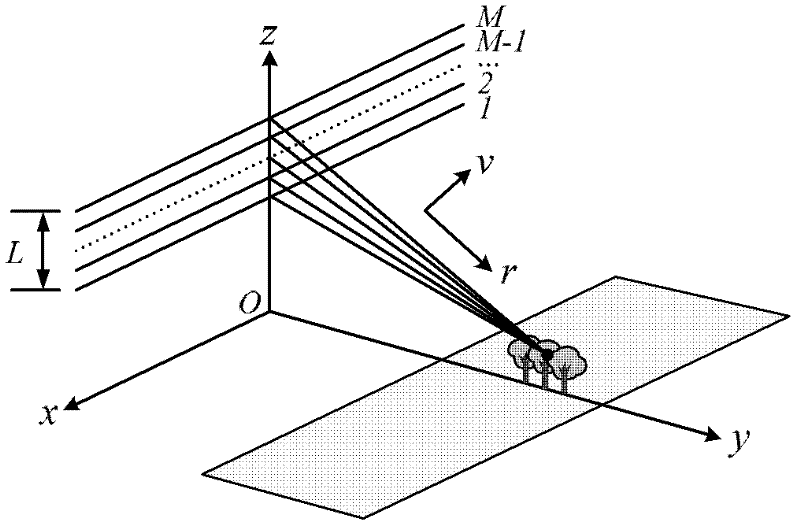
Linear array SAR sparse reconstitution imaging and phase error correction method
ActiveCN103439693ASparse imaging suppressionImproving Sparse Reconstruction Imaging PerformanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarCorrection method
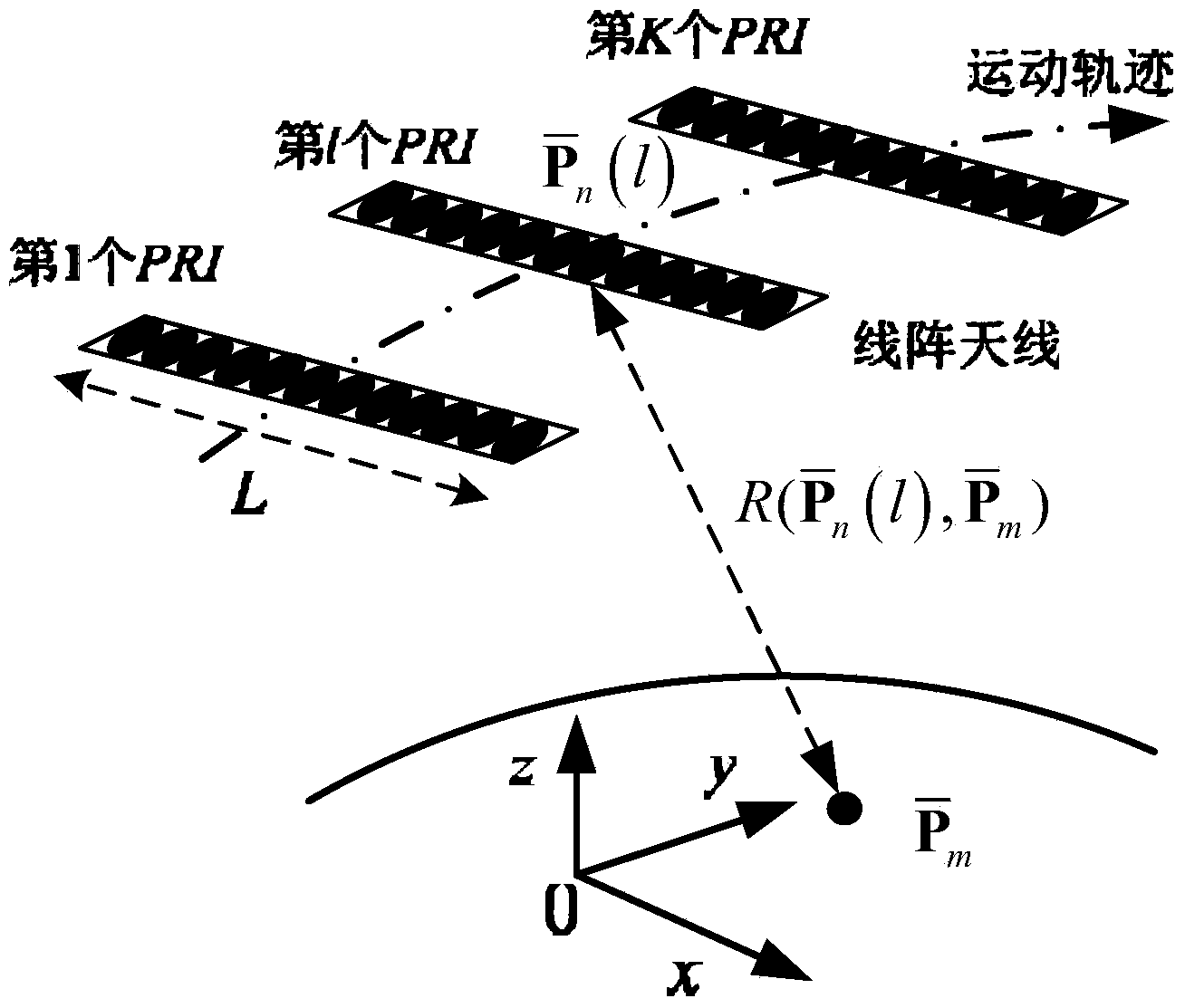
The invention discloses a linear array SAR sparse reconstitution imaging and model phase error correction method. According to the characteristic that scattering targets are sparse in an actual linear array three-dimensional SAR imaging scene space, the linear array SAR sparse reconstitution imaging and model phase error correction method establishes a linear measurement matrix of linear array SAR original echo signals and scattering coefficients in a scene target space, phase error factors existing in the linear array three-dimensional SAR actual measurement are also taken into account, a scattering phase vector between a phase error matrix and a scene target is estimated through iterative optimization, imaging processing of the sparse targets in a linear array SAR three-dimensional space is realized, the effect on imaging by phase errors is restrained, and the stability of linear array SAR sparse reconstitution imaging and the imaging precision of a linear array SAR are improved. The linear array SAR sparse reconstitution imaging and model phase error correction method can be applied to synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging, earth remote sensing and other fields.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
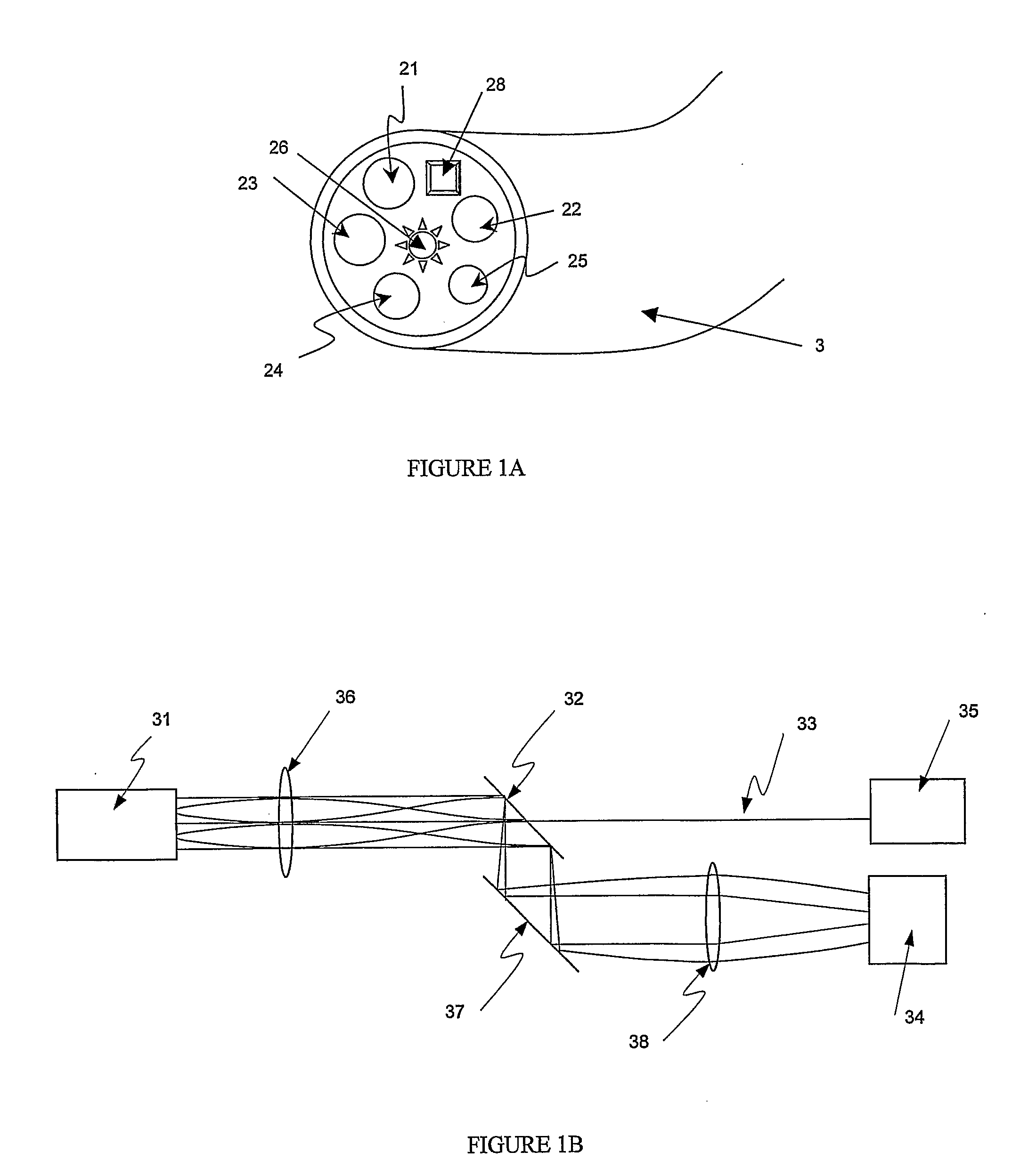
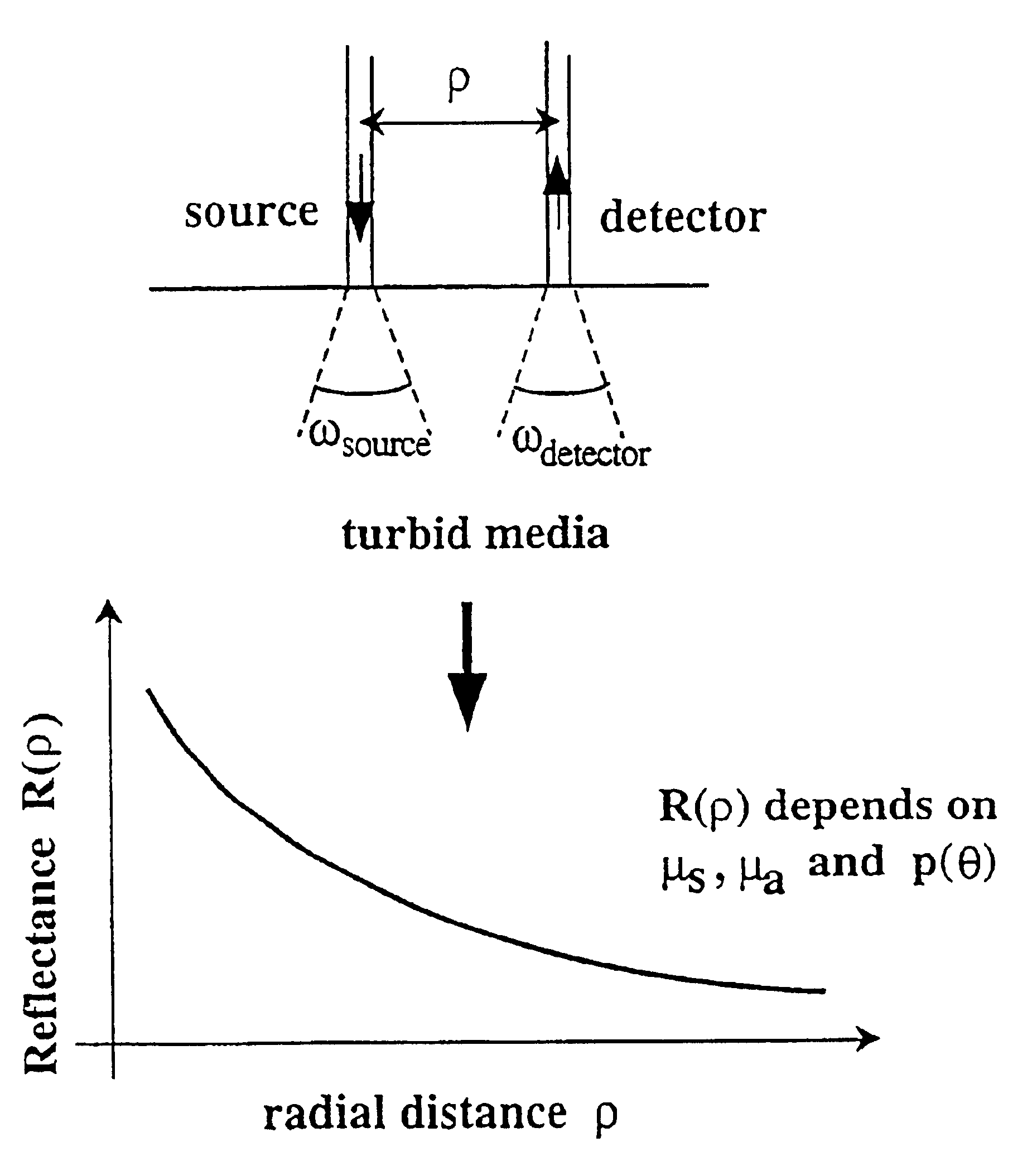
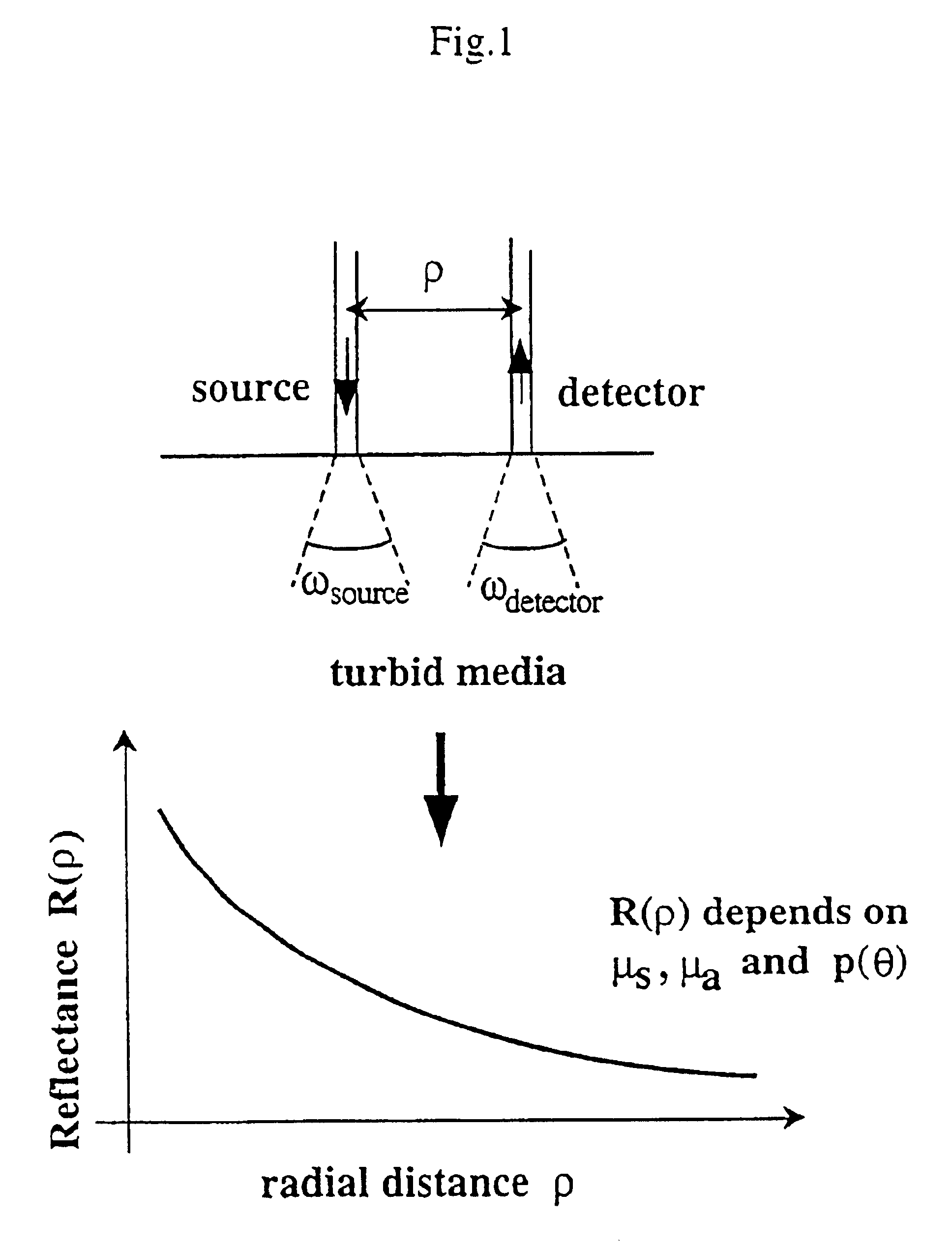
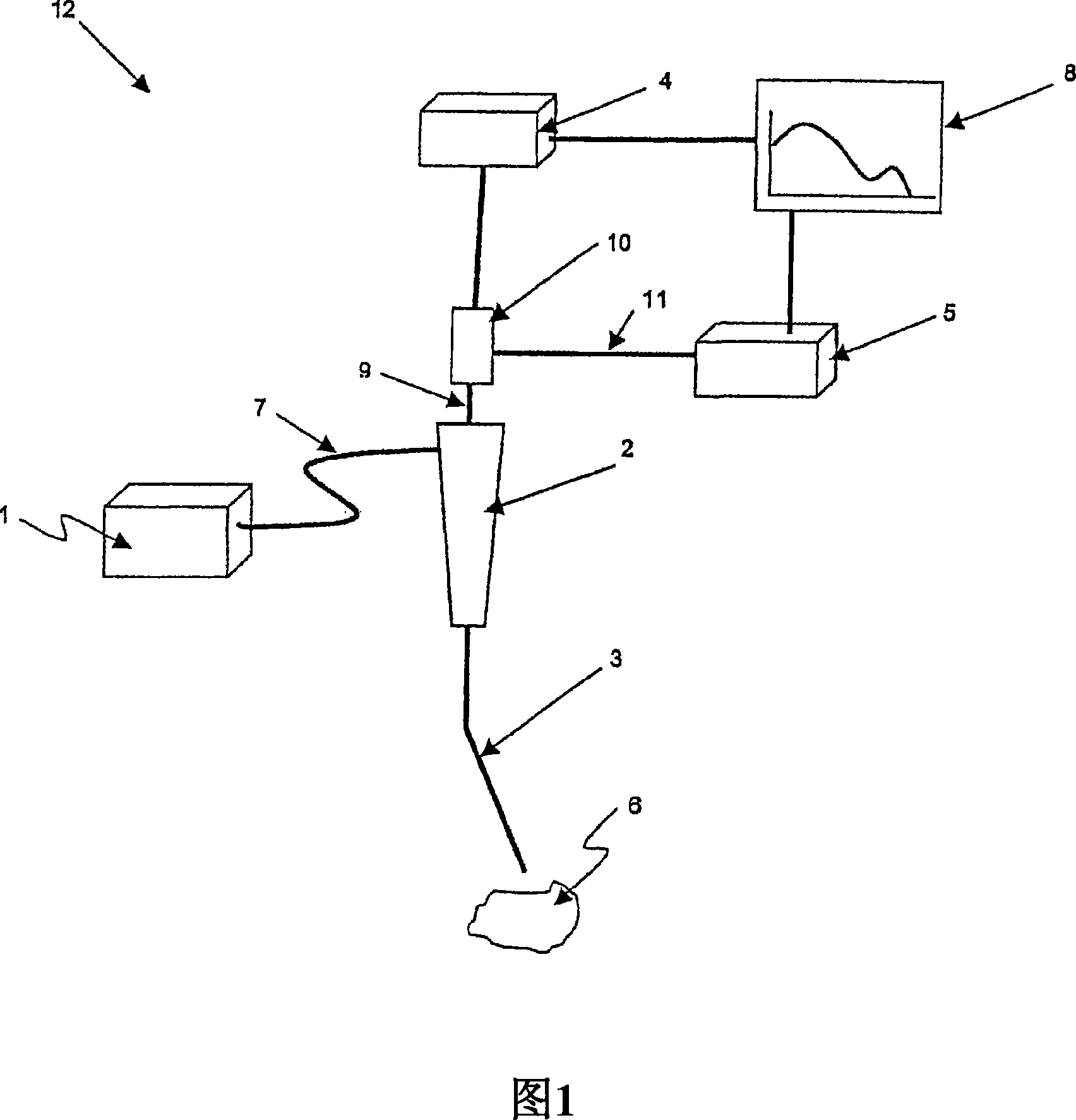
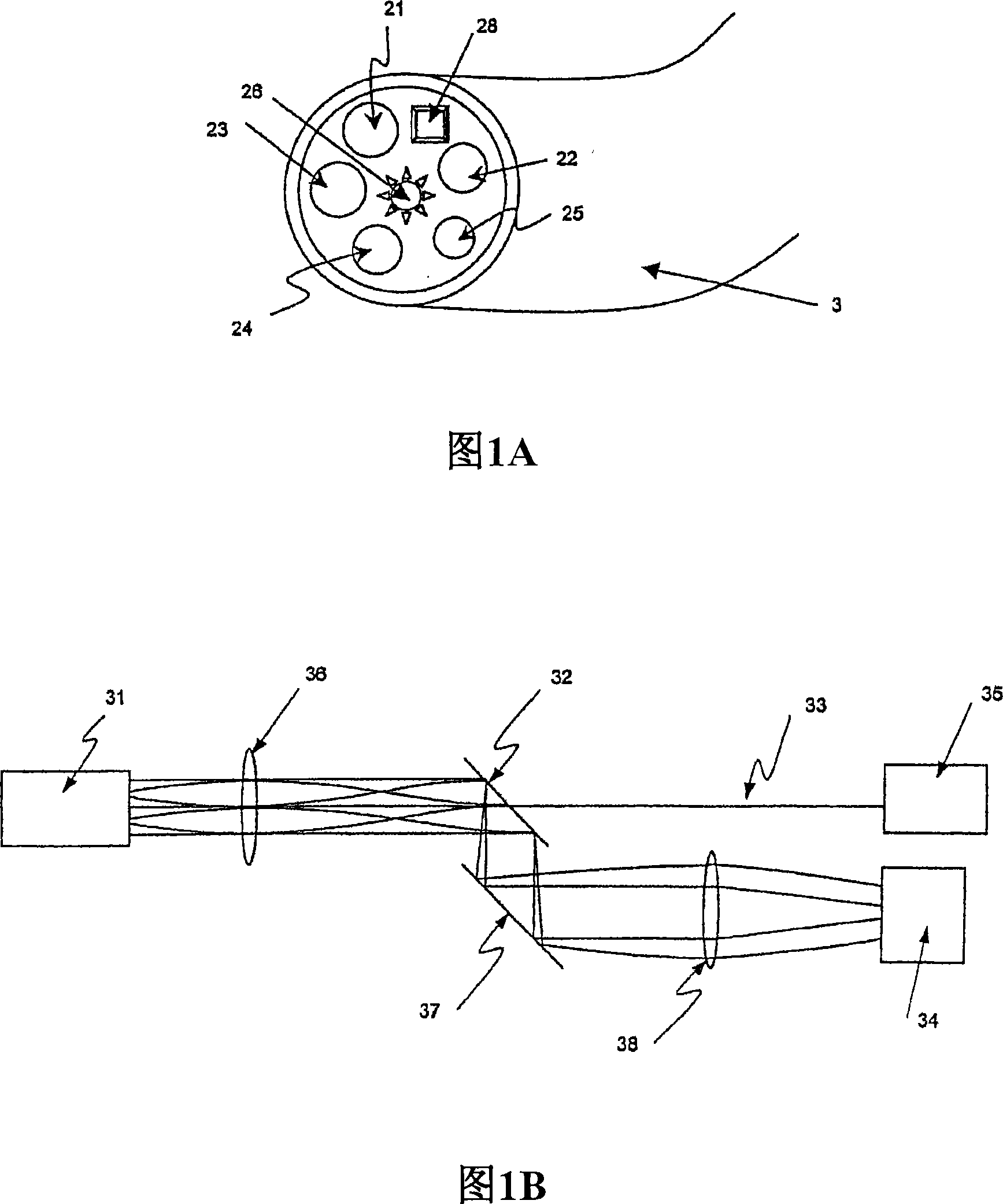
Method and apparatus for measuring locally and superficially the scattering and absorption properties of turbid media
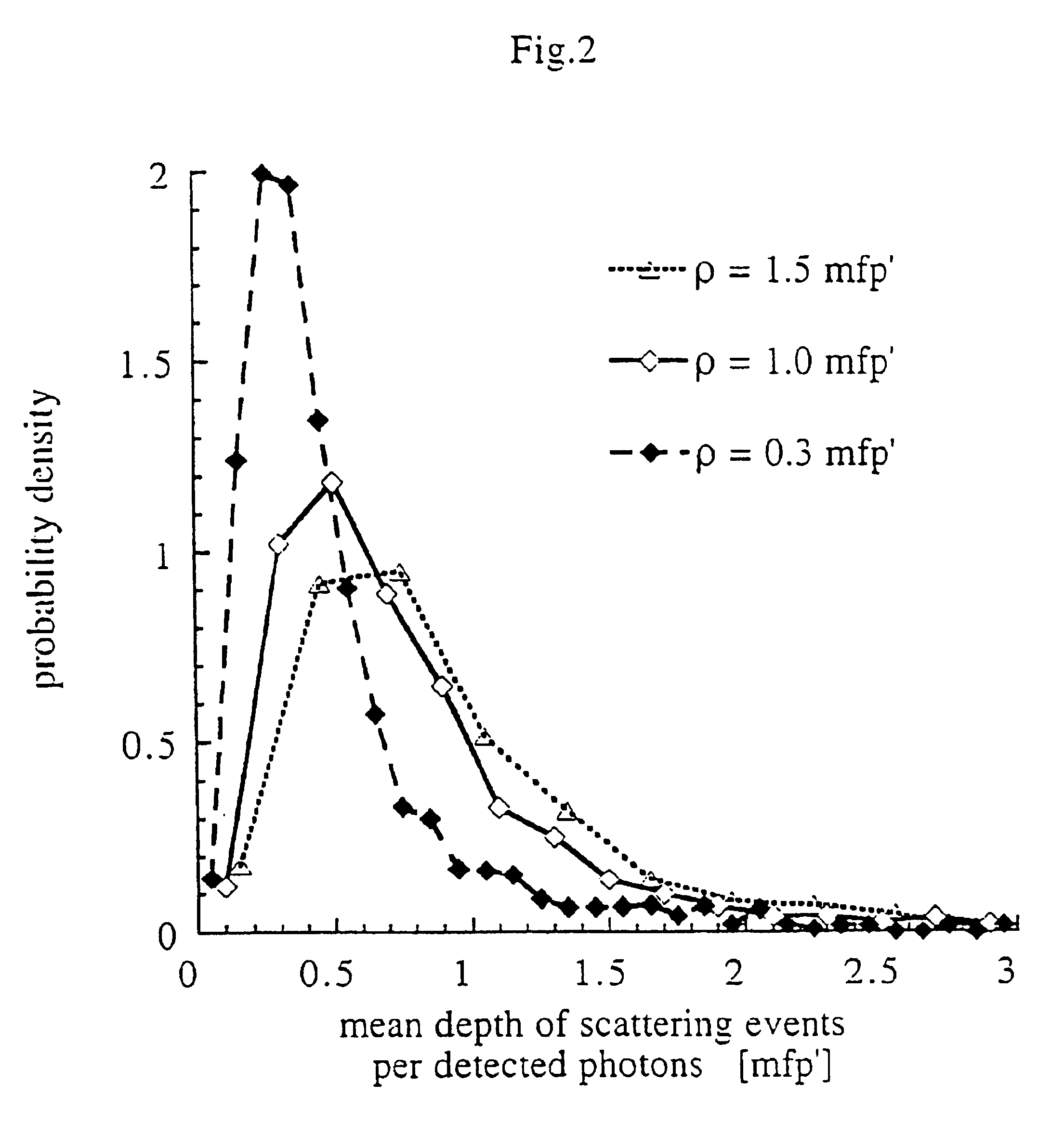
We present a method and apparatus for local and superficial measurement of the optical properties of turbid media. The depth probed is on the order of 1 transport mean free path of the photon. The absorption coefficient, reduced scattering coefficient and the phase function parameter γ=(1−g2) / (1−g1) are optical parameters computed from a single measurement of the spatially resolved reflectance close to the source. Images of superficial structures of the medium can be obtained by performing multi-site measurements. An important application of this technique is the characterization of biological tissues, for example for medical diagnostic purposes. Measurements on biological tissues can be achieved using a probe of diameter less than 2 mm, and the average volume probed is on the order of 1 mm3. Separate images of absorption and tissue structure can be achieved with a resolution of approximately one transport mean free path of the considered tissue.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Linear array SAR imaging method based on iterative minimization sparse Bayesian reconstitution
InactiveCN103713288AImproving Performance for Sparse ImagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHypothesisRadar
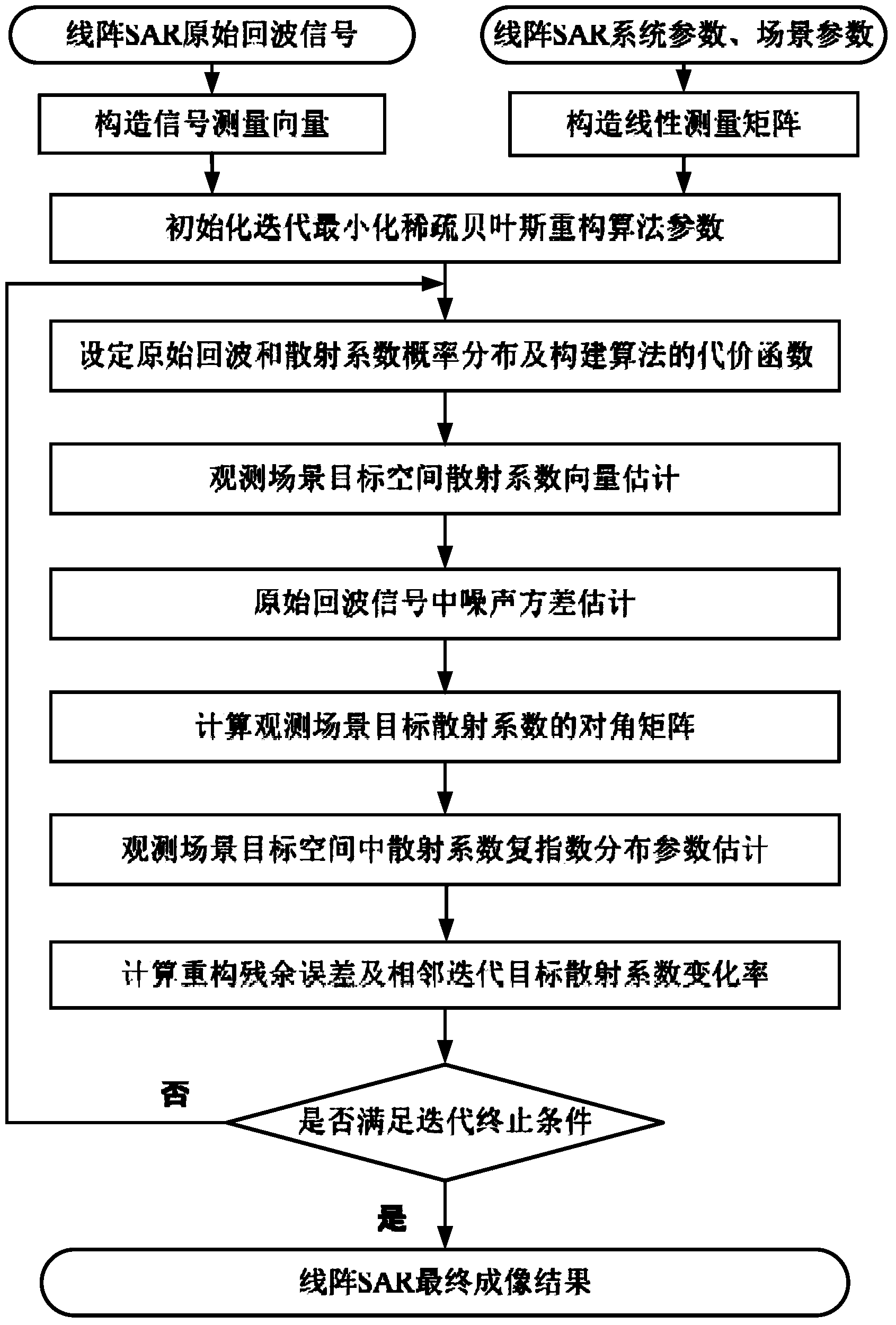
The invention provides a linear array SAR imaging method based on iterative minimization sparse Bayesian reconstitution. The method is prior distributional hypothesis based on a linear array SAR original echo signal measurement model, it is assumed that a prior probability density function of a scattering coefficient in a linear array SAR observation scene target space complies with complex exponential prior distribution, it is also assumed that a posterior probability density function of a linear array SAR original echo signal complies with Gaussian stochastic distribution, a reconstitution cost function of the scattering coefficient in the linear array SAR observation scene target space is set up through the Bayesian criterion, sparse reconstitution of the scattering coefficient in the linear array SAR observation scene target space is achieved through complex exponential distribution parametric optimization estimation and the iterative minimization constitution cost function, and therefore performance of linear array SAR sparse imaging is improved. The linear array SAR imaging method can be applied to the synthetic aperture radar imaging field, the global remote sensing field and other fields.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Light-scattering film, polarizing plate and image display
ActiveUS20070229804A1Reduce reflectionReduction of bright-room contrastDiffusing elementsPhotometryDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
A light-scattering film is provided and includes a transparent support having thereon at least a light-scattering layer. When substantially parallel light is incident on a surface of the film at an incident angle of 5°, the reflectance for an angle θ in the light-receiving part measured in a plane containing the film normal line and the incident direction is R(θ), the value obtained by normalizing R(θ) by the reflectance of regular reflection is Rrel(θ), and the value calculated from the maximum variation |dRrel(θ) / dθ|max for the angle θ is a scattering coefficient A (formula 1), the reflection coefficient B (formula 2) calculated from the scattering coefficient A and the 5° specular reflectance Rs is from 2.0 to 5.0.Scattering coefficient A=1 / (10×|dRrel(θ) / dθ|max) (Formula 1)Reflection coefficient B=2.2×log 10(Rs)−7.5×log 10(A)+5.9 (Formula 2)
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for generating three-dimensional imaging original echoed signals of chromatography synthetic aperture radars
InactiveCN101581779AProcesses that avoid coherent superpositionGenerate high precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRectangular coordinatesSynthetic aperture radar
The invention relates to a method for generating three-dimensional imaging original echoed signals of chromatography synthetic aperture radars, which comprises the following steps: taking a three-dimensional image containing backward plural scattering coefficients of imaging area targets in a rectangular coordinate system OXYZ as the input, carrying out three dimensional fourier transform on the three-dimensional image and converting an image signal to a rectangular coordinate system wave-number domain; converting signals in Kx, Ky and Kz domains to be signals in Kw, Ku and Kv domains according to the method of converting the rectangular coordinate system to a spherical coordinate system; introducing imaging geometrical relationships among same imaging area of chromatography synthetic aperture radars by multiplying three dimensional filter function H2 (Kw, Ku and Kv); introducing a transmission signal form by the multiplication of a two-dimensional inverse Fourier transform function and a reference phase function; and at last, by W direction process and other operations, obtaining the three-dimensional imaging original echoed signals of chromatography synthetic aperture radars, which contains a carrier frequency. The method can be used for generating three-dimensional imaging original echoed signals of side-looking, downward-looking, forward-looking, backward-looking and downward side-looking chromatography synthetic aperture radars, and has high echo generating efficiency and easy realization of modularization.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
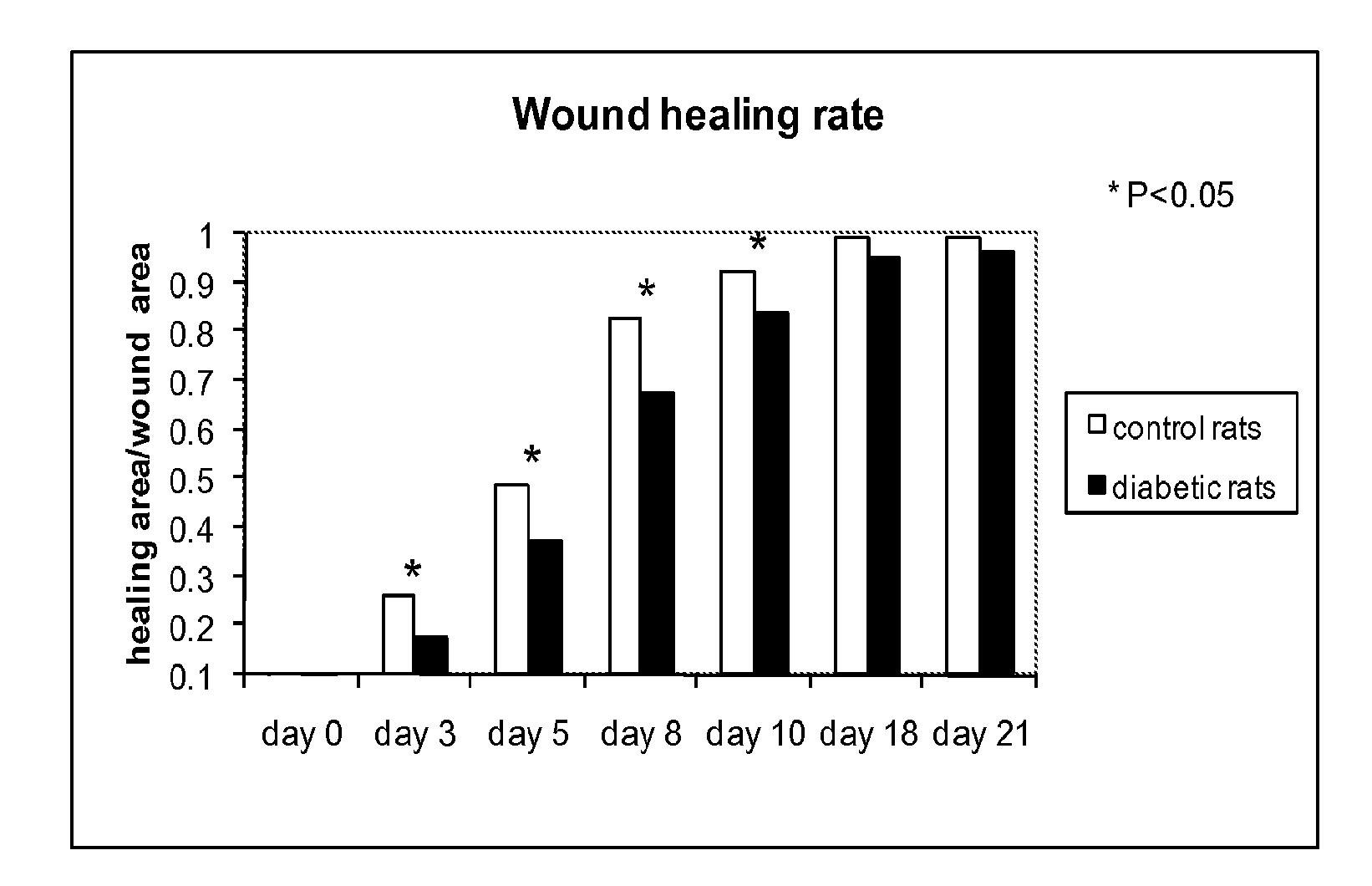
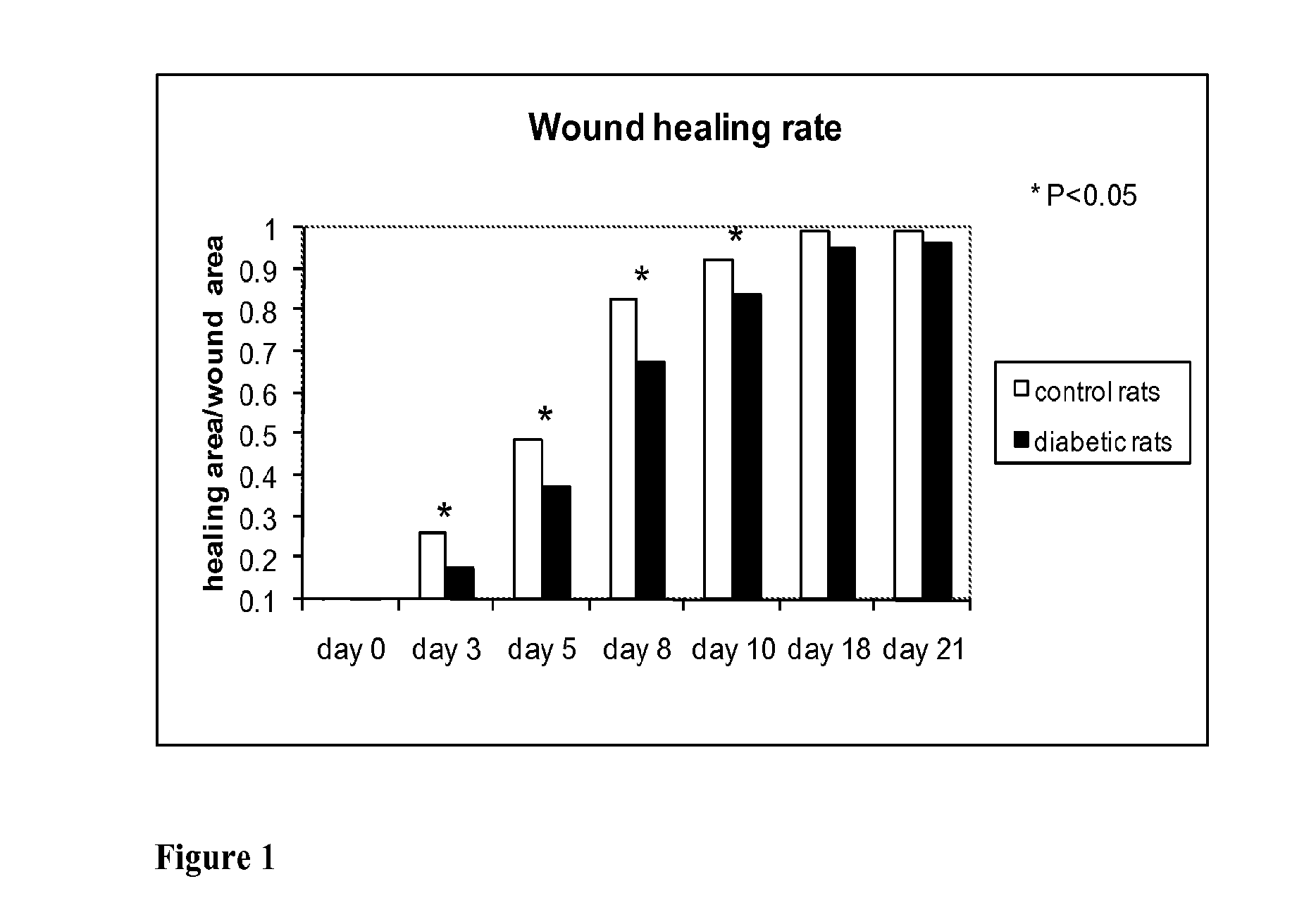
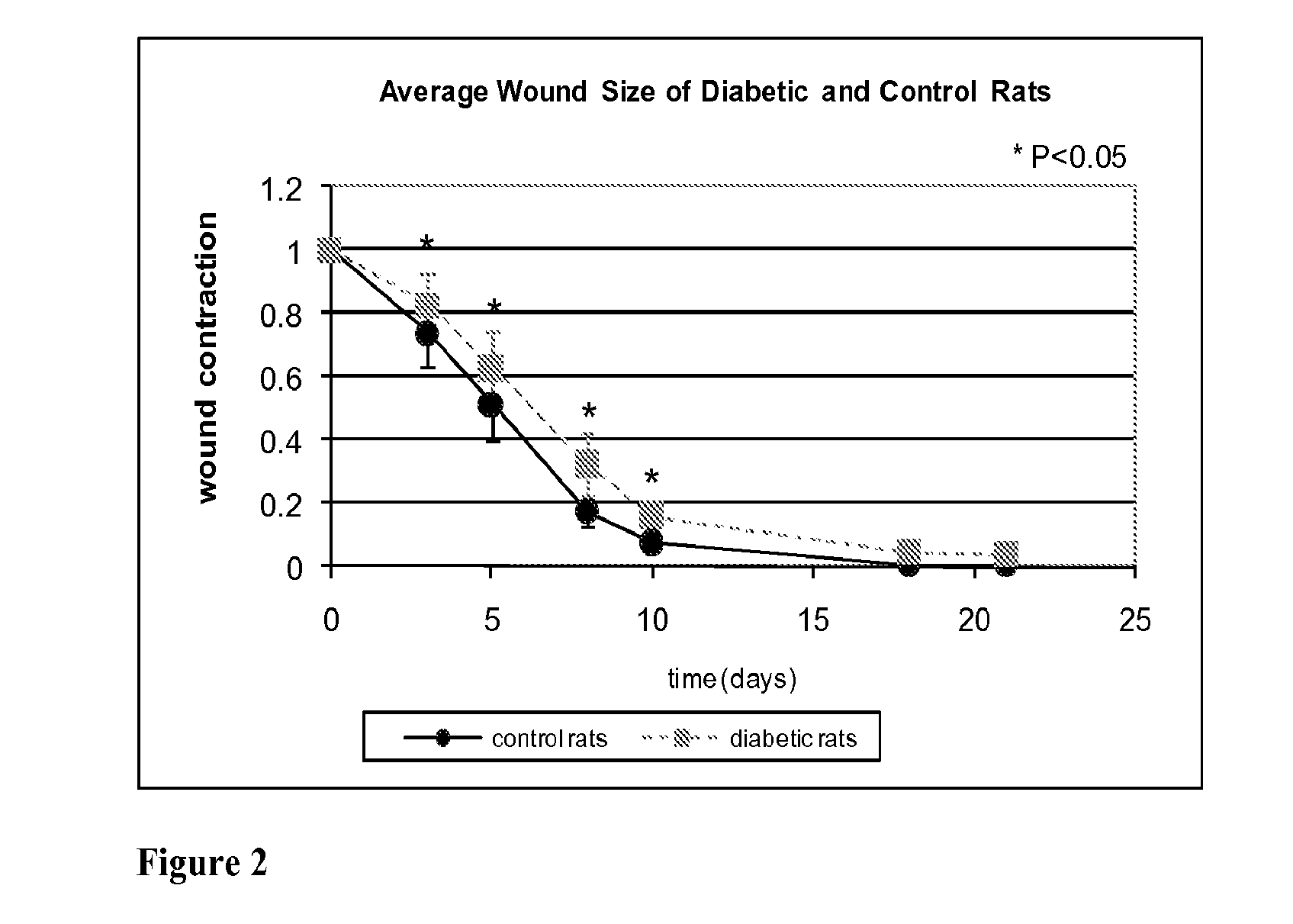
Methods for Measuring Changes in Optical Properties of Wound Tissue and Correlating Near Infrared Absorption (FNIR) and Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy Scattering (DRS) With Tissue Neovascularization and Collagen Concentration to Determine Whether Wound is Healing
ActiveUS20110124987A1Reduction factorDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyReflectance spectroscopyDiffusion equation
Optical changes of tissue during wound healing measured by Near Infrared and Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy are shown to correlate with histologic changes. Near Infrared absorption coefficient correlated with blood vessel in-growth over time, while Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS) data correlated with collagen concentration. Changes of optical properties of wound tissue at greater depths are also quantified by Diffuse Photon Density Wave (DPDW) methodology at near infrared wavelengths. The diffusion equation for semi-infinite media is used to calculate the absorption and scattering coefficients based on measurements of phase and amplitude with a frequency domain or time domain device. An increase in the absorption and scattering coefficients and a decrease in blood saturation of the wounds compared to the non wounded sites was observed. The changes correlated with the healing stage of the wound. The methodologies used to collect information regarding the healing state of a wound may be used to clinically assess the efficacy of wound healing agents in a patient (e.g., a diabetic) and as a non-invasive method
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Methods and apparatuses for forming a three-dimensional volumetric model of a subject's teeth
ActiveUS20190269485A1Change in positionImpression capsDiagnostics using lightCementum cariesSimulation
Methods and apparatuses for generating a model of a subject's teeth. Described herein are intraoral scanning methods and apparatuses for generating a three-dimensional model of a subject's intraoral region (e.g., teeth) including both surface features and internal features. These methods and apparatuses may be used for identifying and evaluating lesions, caries and cracks in the teeth. Any of these methods and apparatuses may use minimum scattering coefficients and / or segmentation to form a volumetric model of the teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Method and system for measuring kin physiology parameters and optical property parameters based on reflective spectral measurement
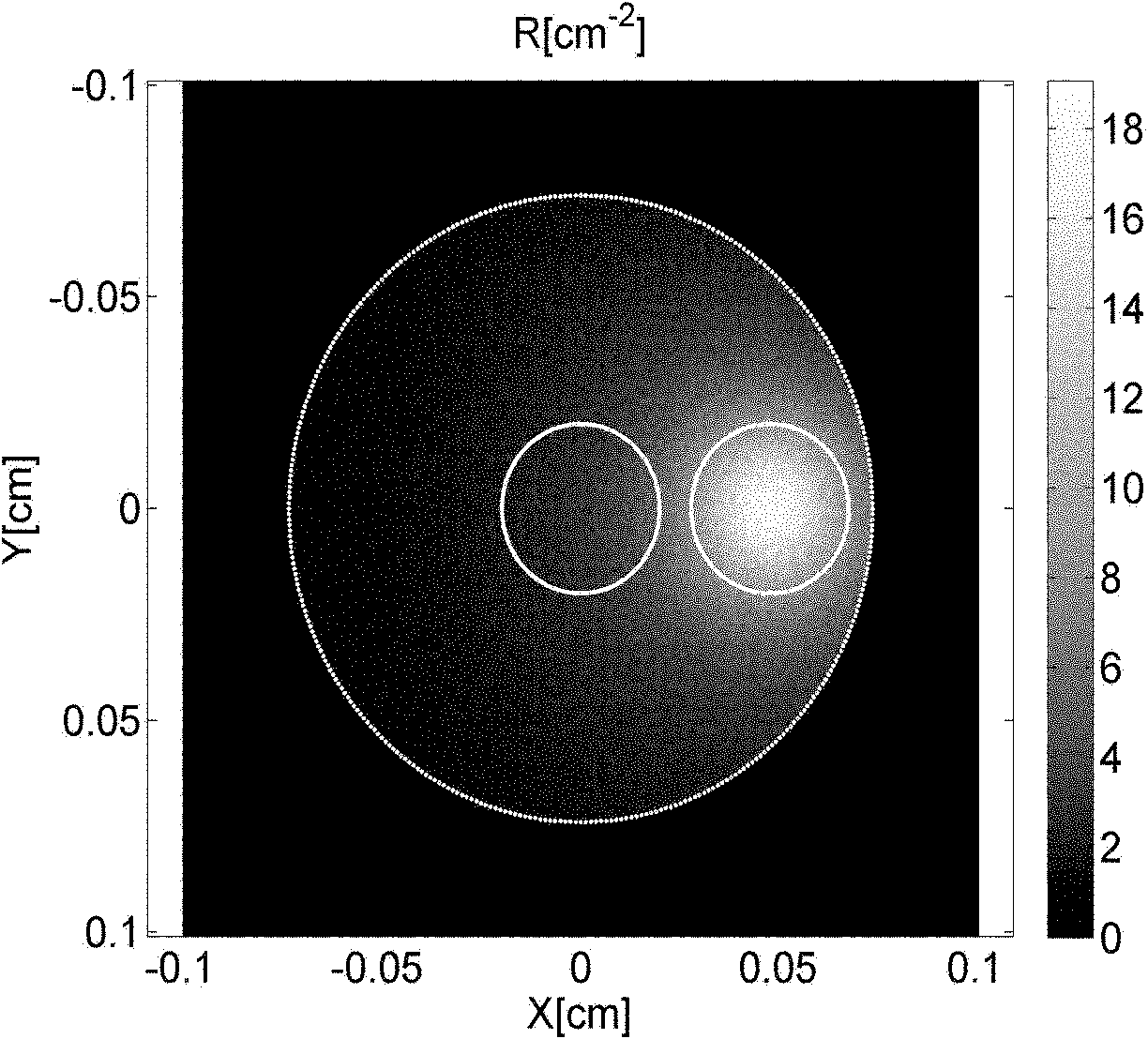
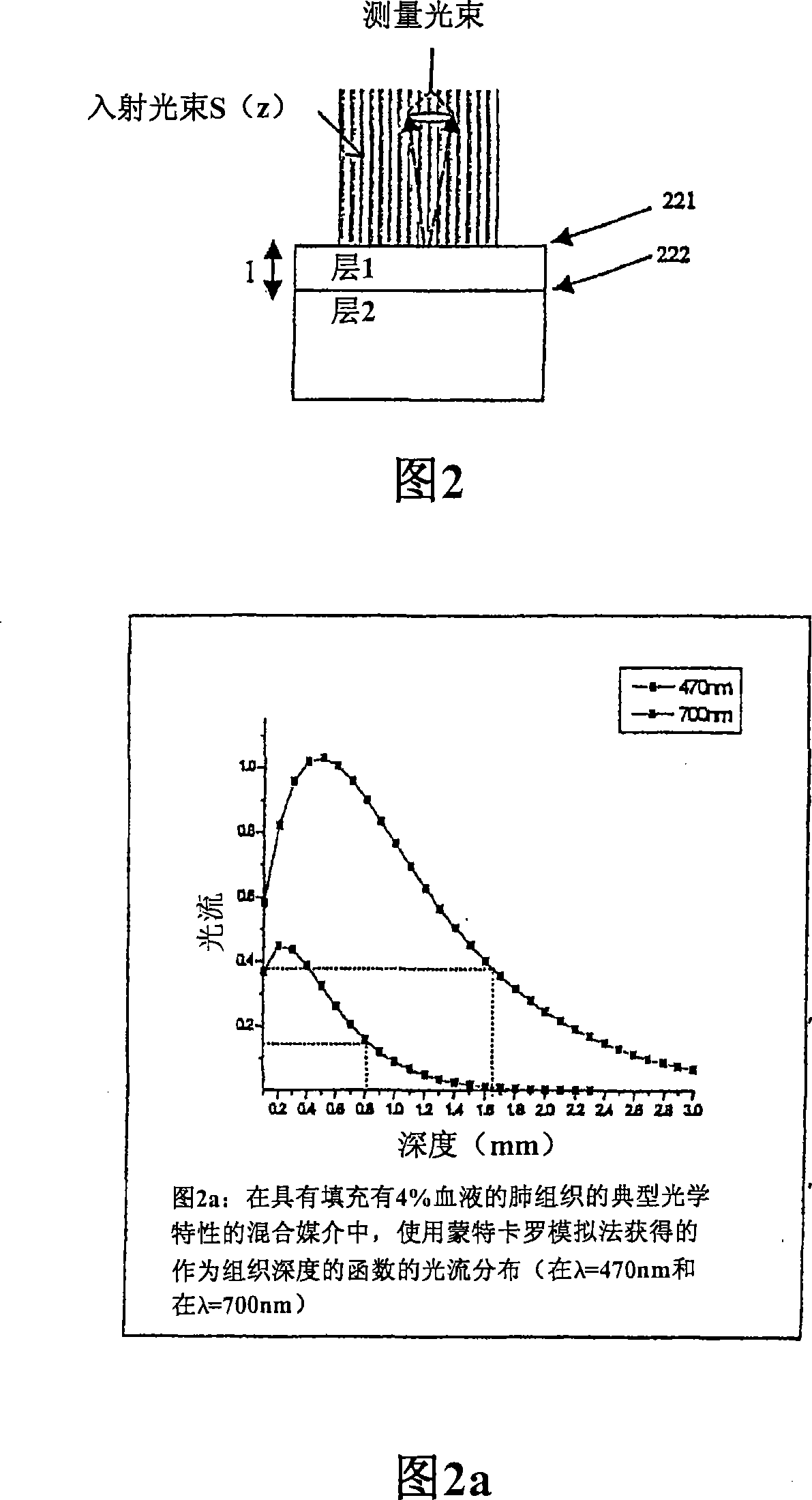
The invention provides a method and system for measuring skin physiology parameters and optical property parameters based on reflective spectral measurement. The measuring system is composed of measuring equipment for a skin reflection spectrum and a computation and display device. By utilizing an analysis method of combining experimental data with the Monte Carlo simulation, the measuring system provides more accurate corresponding data of reflection light intensity and skin optical property; during the practical measurement of sample skin, on the basis of a practically measured reflection spectrum, the data and more physiology parameters are calculated and fit to obtain the skin physiology parameters and the optical property parameters based on reflective spectral measurement; finally, the optical property parameters of the skin adsorption coefficient mu a, a reduction scattering coefficient mu s' and the like as well as physiological information, such as melanin content, deoxygenated haemoglobin content, oxygenated haemoglobin content, moisture content and the like are also measured are measured in real time in a non-invasive and lossless mode.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Apparatus and method for nondestructive optical constant imaging of dermatosis tissue of human body
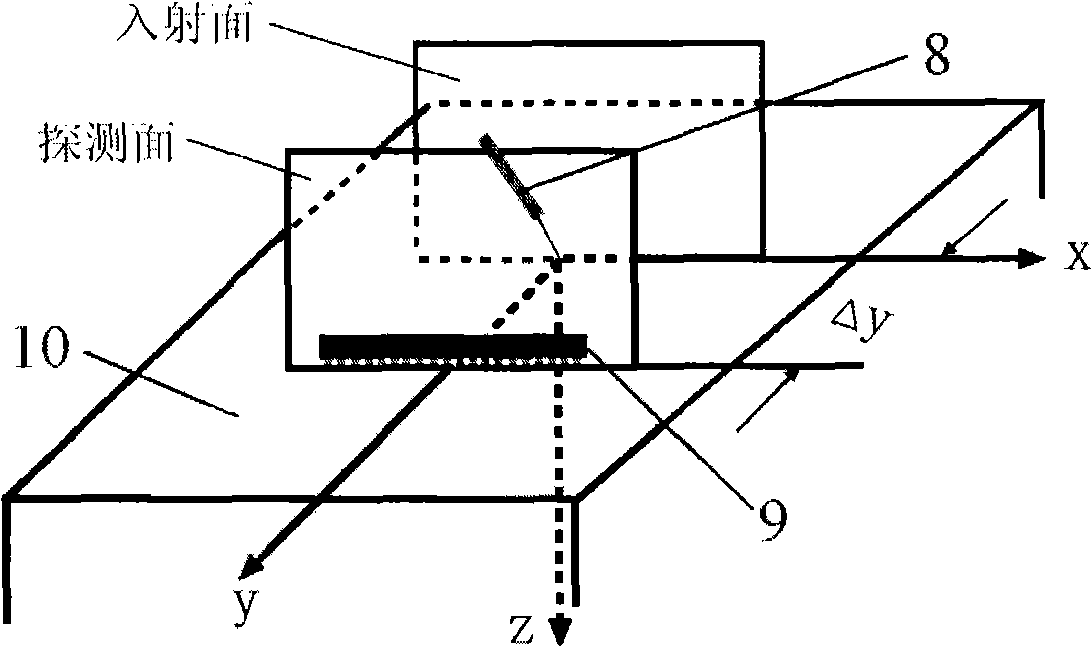
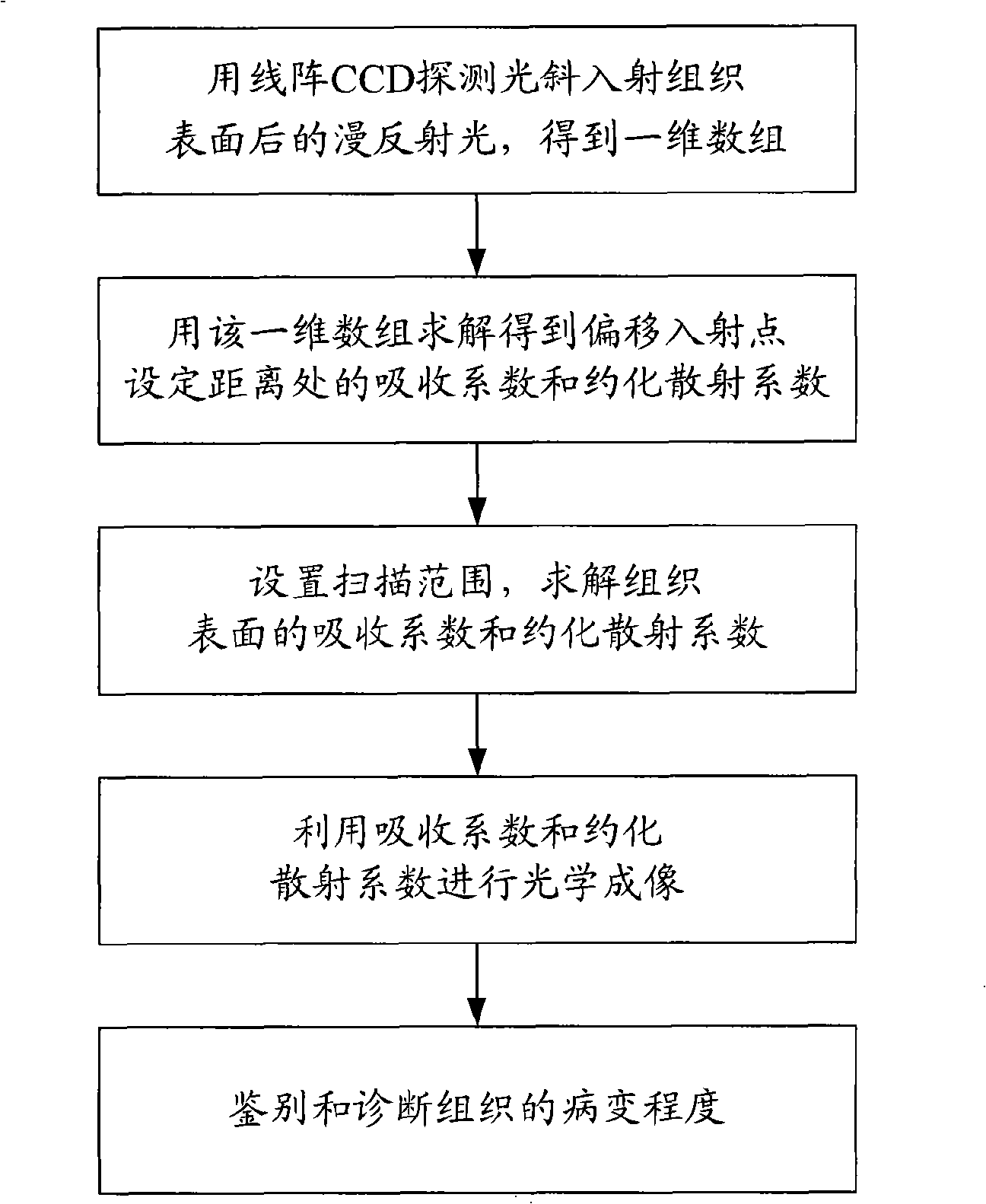
InactiveCN101313847AHigh resolutionImprove clarityScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyFiber
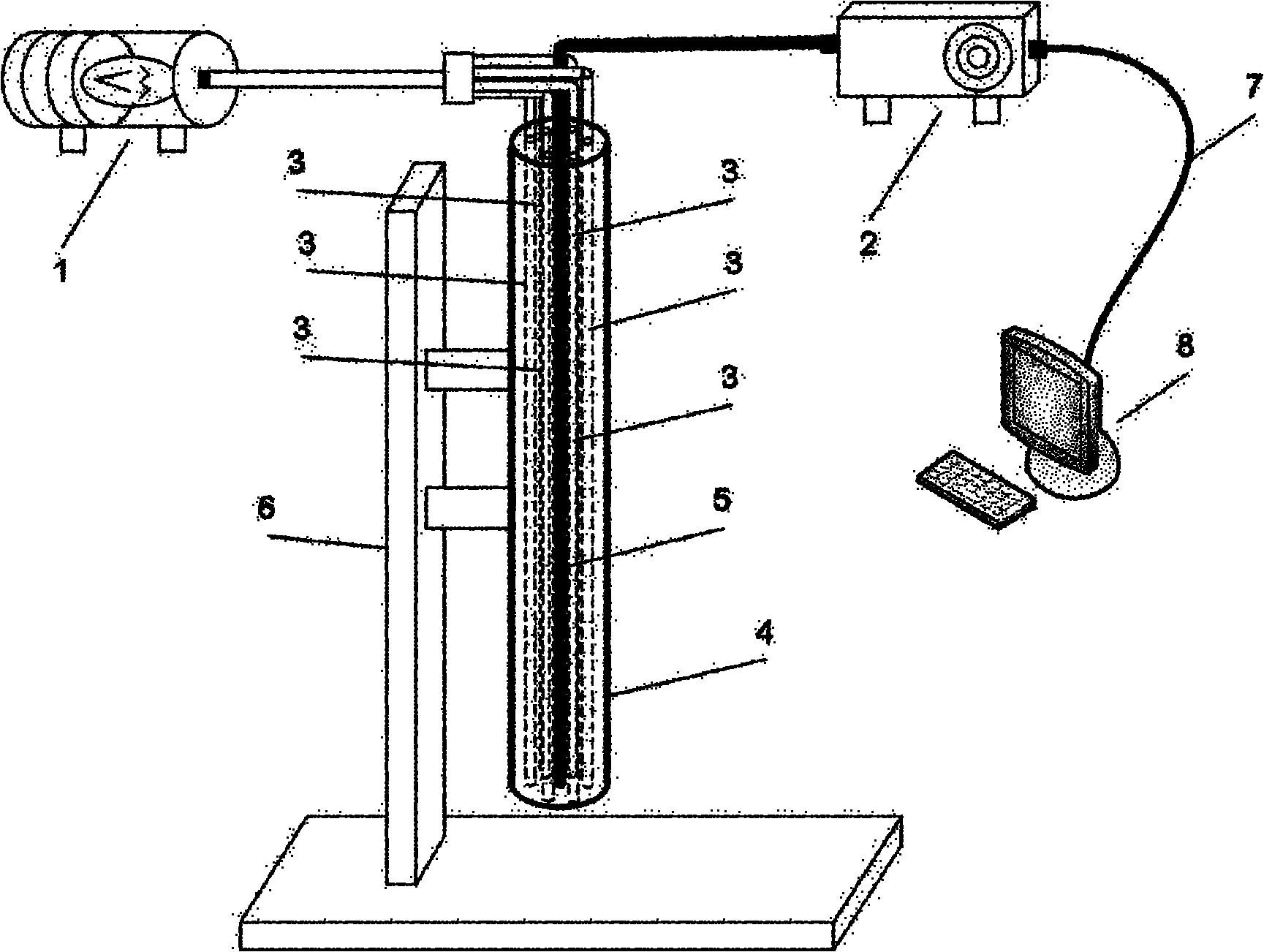
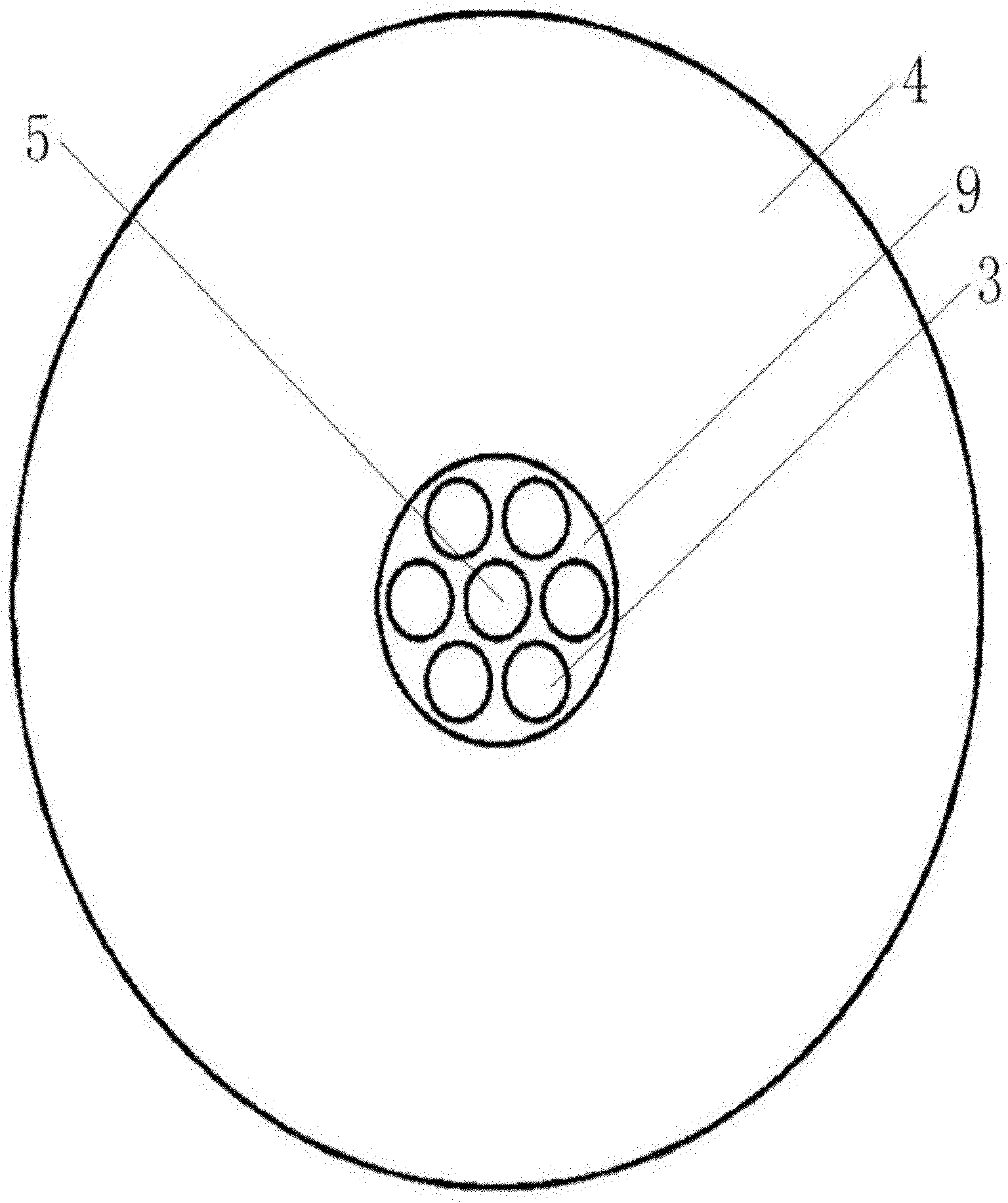
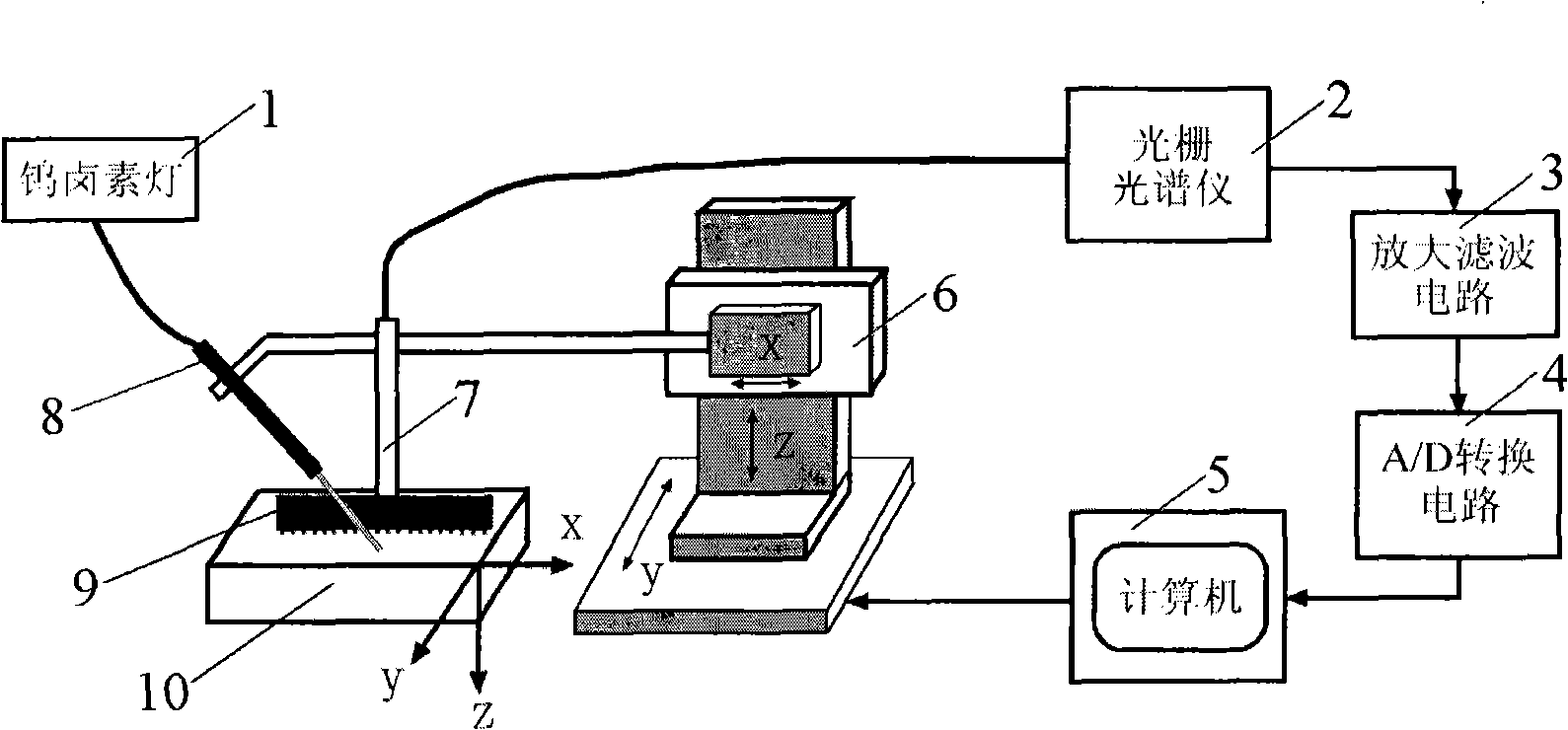
The invention relates to a device for carrying out the nondestructive optical constant imaging of a human body cutis pathologic tissue and a method thereof. The device comprises a tungsten halogen lamp, an incident fiber optic probe, a line array CCD for receiving diffused reflection light, and a grating spectrograph, an amplification filter circuit, an A / D conversion circuit, a computer and a computer-controlled three-dimensional traveling table which are connected in turn through an optical fiber. The invention uses the line array CCD optical measurement device detecting the obliquely incident diffused reflection light to detect the human body cutis tissue, uses a Monte Carlo statistical method limited by characteristic parameters to conversely compute the values of the absorption coefficient and the reduction scattering coefficient at each two-dimensional space coordinates of the detected cutis tissue, then uses the grating spectrograph to carry out spectrum, and respectively images through the absorption coefficient and the reduction scattering coefficient and simultaneously detects the detected human body pathologic tissue and a healthful tissue around the pathologic tissue. Then the optical constants of the pathologic tissue and the healthful tissue are compared to see difference or the optical constant of the pathologic tissue is compared with a healthful human body tissue sample, thereby carrying out the diagnosis and identification of diseases.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
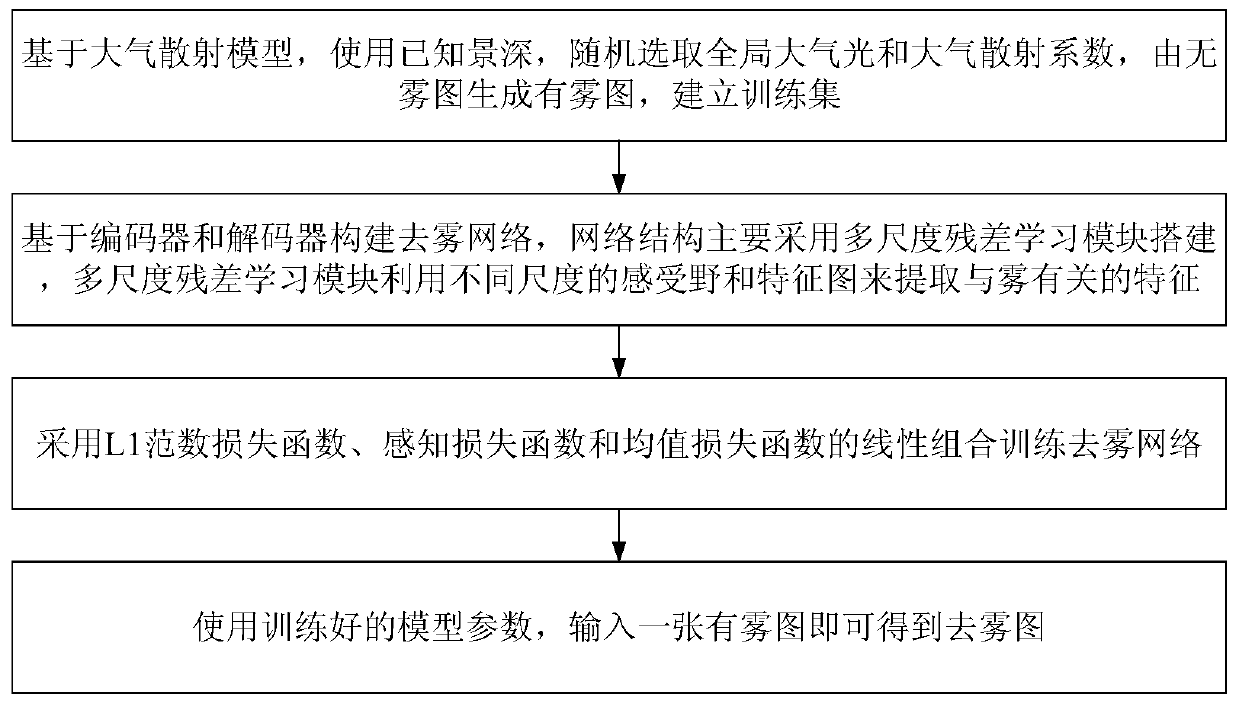
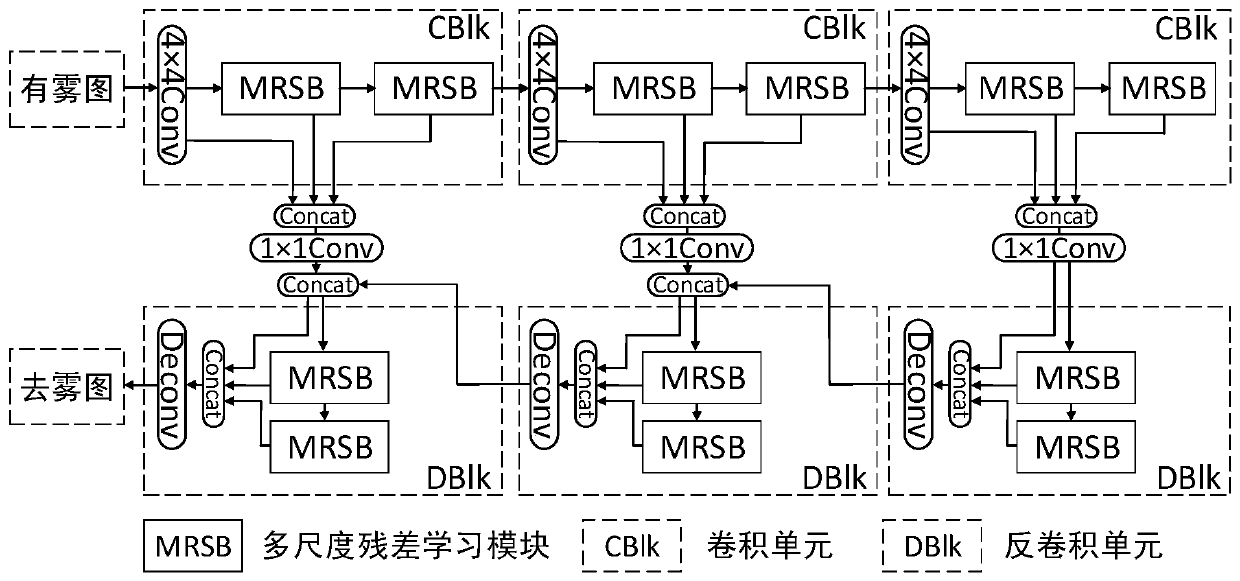
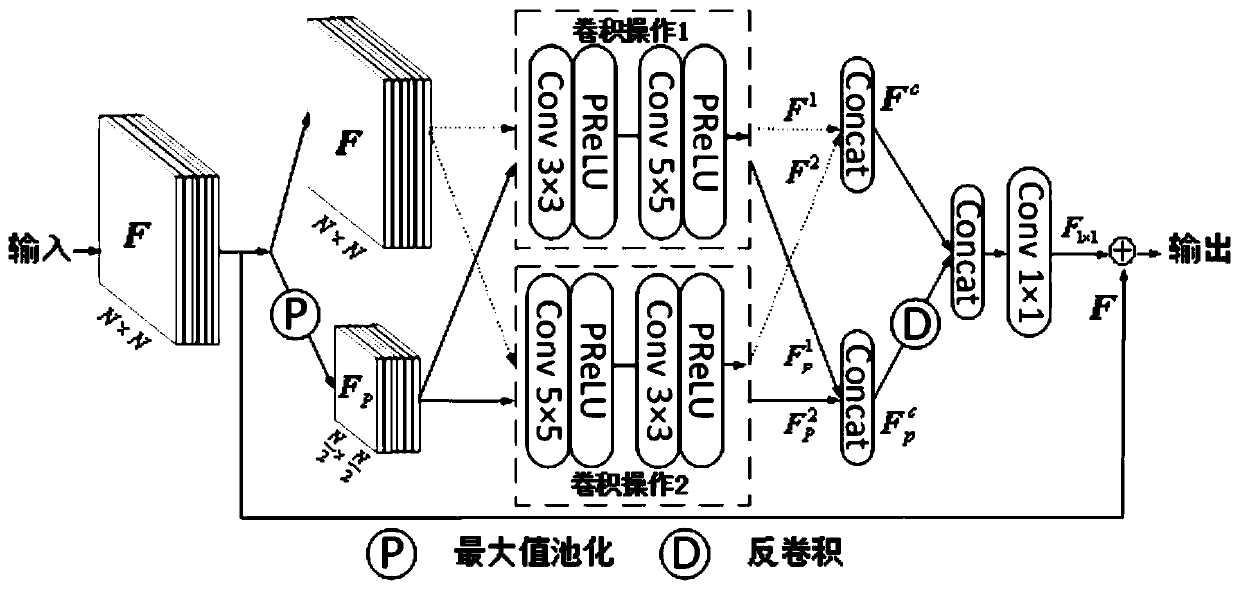
Image defogging method based on multi-scale residual learning
PendingCN110570371ARealistic Image DehazingEasy to implementImage enhancementImage analysisHypothesisNetwork structure
The invention discloses an image defogging method based on multi-scale residual learning, and the method comprises the steps: randomly selecting global atmospheric light and atmospheric scattering coefficients through a known depth of field based on an atmospheric scattering model, generating a foggy image through a fogless image, and building a training set; creating a defogging network based onan encoder and a decoder, creating a network structure by adopting a multi-scale residual learning module, and enabling a multi-scale residual learning module to extract features related to fog by utilizing receptive fields and feature maps of different scales; training a defogging network by adopting a linear combination of an L1 norm loss function, a perception loss function and a mean value loss function; and inputting a foggy image by using the trained model parameters to obtain a defogged image. Complex hypothesis and prior are not needed, the fogless image can be directly recovered fromone foggy image, and the method is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
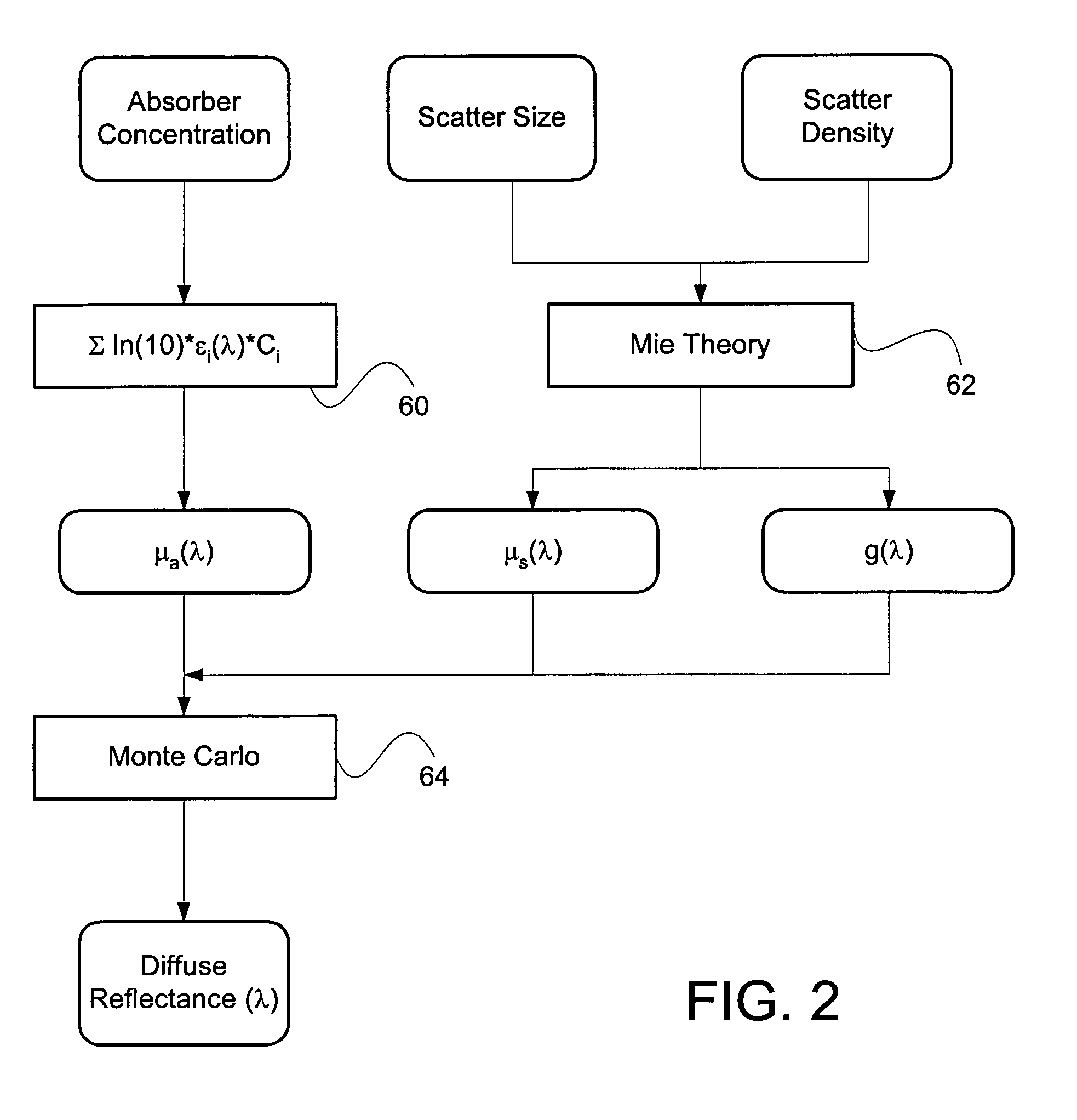
Method for extraction of optical properties from diffuse reflectance spectra
ActiveUS7570988B2Promote absorptionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical propertyOptical spectrometer
An iterative process calculates the absorption and scattering coefficients of tissue from a set of diffuse reflectance measurements made with an optical spectrometer operating in the UV-VIS spectral range. The relationship between measured diffuse reflectance and the absorption and scattering coefficients is modeled using a Monte Carlo simulation.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Infrared cutoff film
An infrared cut-off layer containing an ITO powder is formed on one surface of a base film, to form an infrared cut-off film. The ITO powder has a minimum value of a diffused-reflection-functional logarithm, logf(Rd), at a light wavelength of 470 nm or lower, which logarithm is measured on the basis of the following equation, f(Rd)=(1-Rd)2 / 2Rd=alpha / S (Rd: a relative reflectance to a standard sample, alpha: an absorption coefficient, S: a scattering coefficient, formulated for a diffused reflection light, and the minimum value of -0.1 or less. There is provided an infrared cut-off film having a hue of blue and sufficient transparency.
Owner:TOMOEGAWA PAPER CO LTD
Methods and apparatuses for forming a three-dimensional volumetric model of a subject's teeth
Methods and apparatuses for generating a model of a subject's teeth. Described herein are intraoral scanning methods and apparatuses for generating a three-dimensional model of a subject's intraoral region (e.g., teeth) including both surface features and internal features. These methods and apparatuses may be used for identifying and evaluating lesions, caries and cracks in the teeth. Any of these methods and apparatuses may use minimum scattering coefficients and / or segmentation to form a volumetric model of the teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
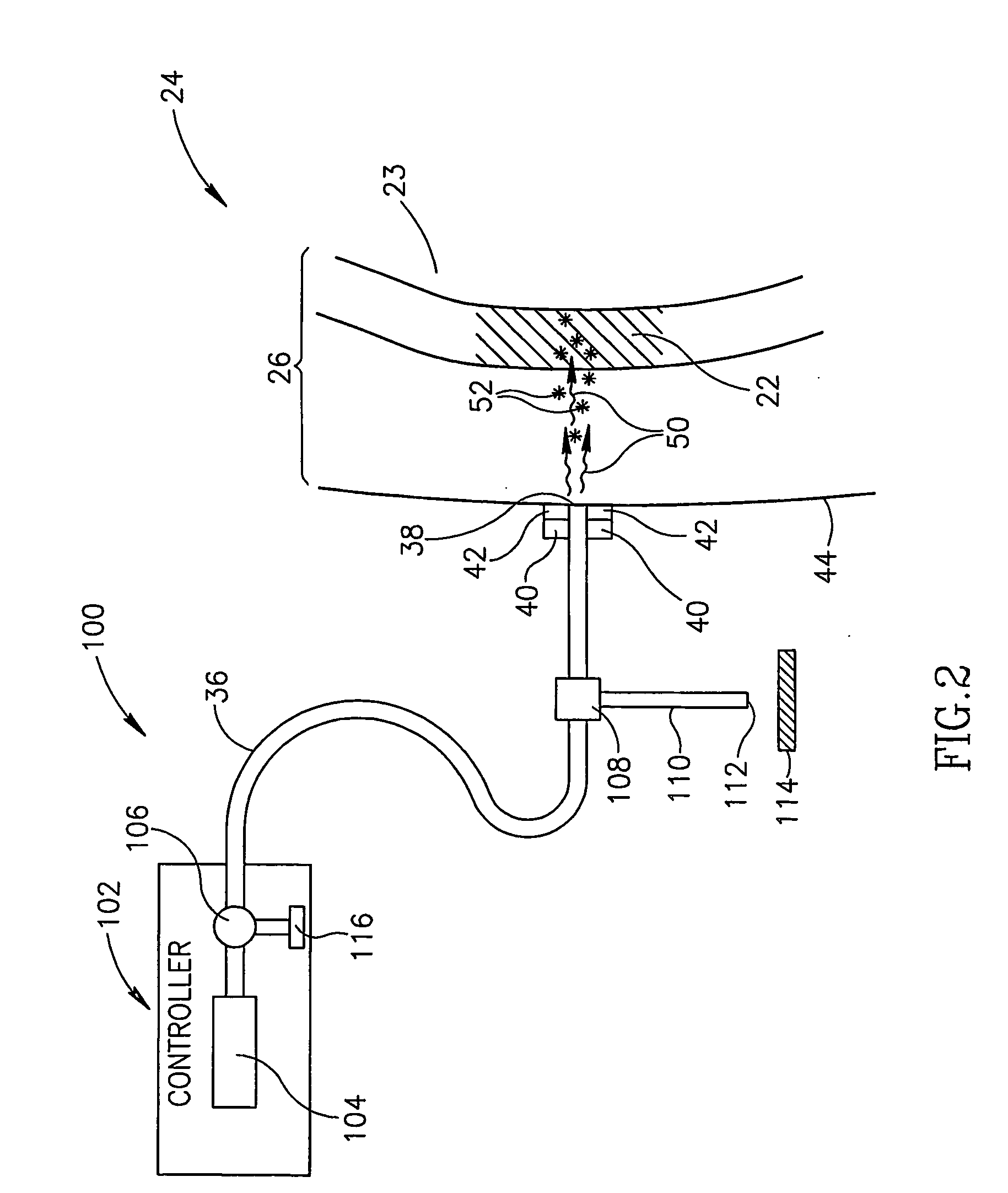
Photoacoustic Assay Method and Apparatus
Apparatus (20, 100) for assaying a target analyte in a localized tissue region (22) that may include the target and other analytes comprising: a light source (34, 104) that illuminates the region with light at each of a plurality of wavelengths at which light is absorbed and / or scattered by tissue in the region wherein light at a least one of the wavelengths is absorbed or scattered by the target analyte; a signal generator (40) that generates signals responsive to intensity of the light from the light source (34, 104) at different locations in the localized region (22); and a controller (32, 102) that: receives the generated signals; processes the signals to determine an extinction coefficient for light in the localized region at each wavelength; and determines the concentration of the target analyte responsive to a solution of a set of simultaneous equations having as unknown variables concentrations of a plurality of analytes in the region (22), one of which is the target analyte, wherein each equation in the set expresses a relationship between the extinction coefficient, the absorption coefficient and / or the reduced scattering coefficient for light at a different one of the plurality of wavelengths and at least one of the equations expresses a relationship between the extinction coefficient and the reduced scattering coefficient.
Owner:GLUCON
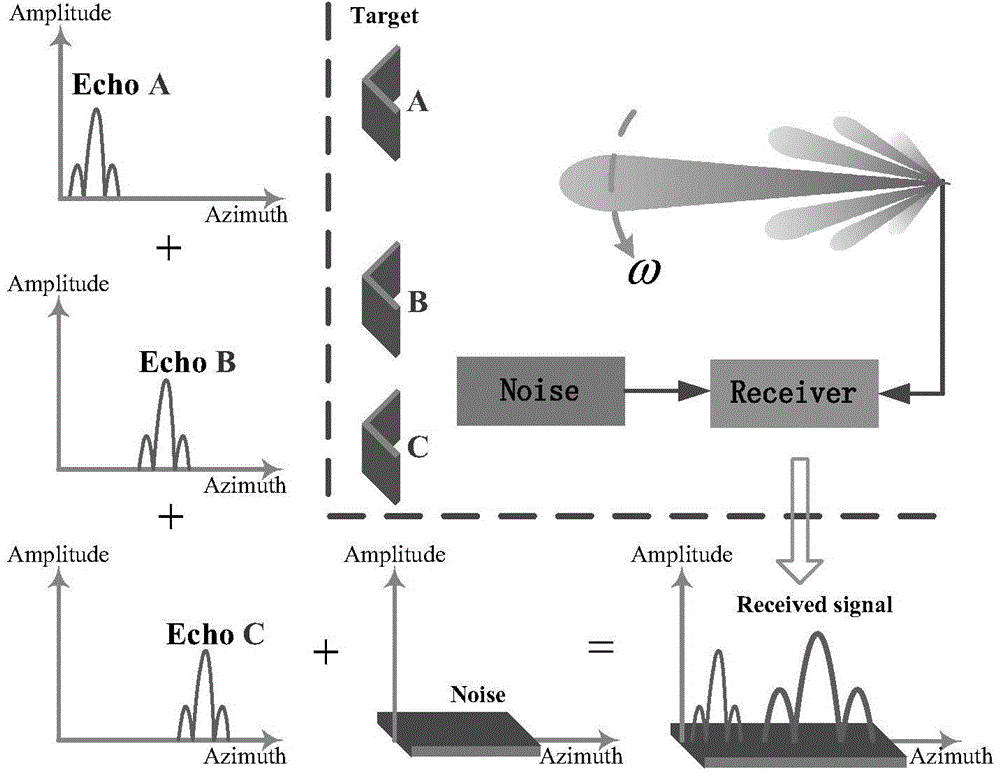
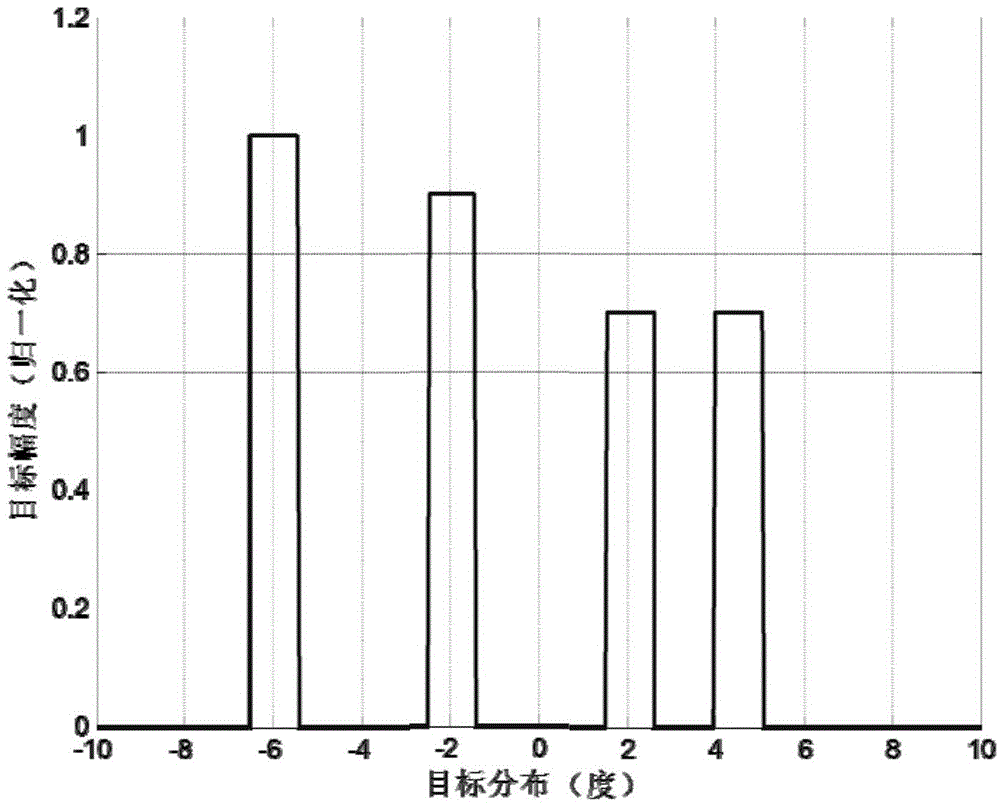
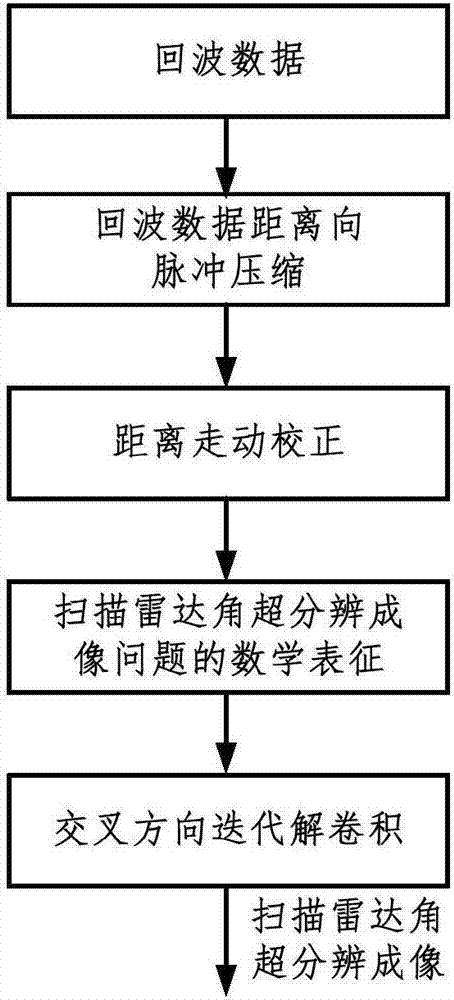
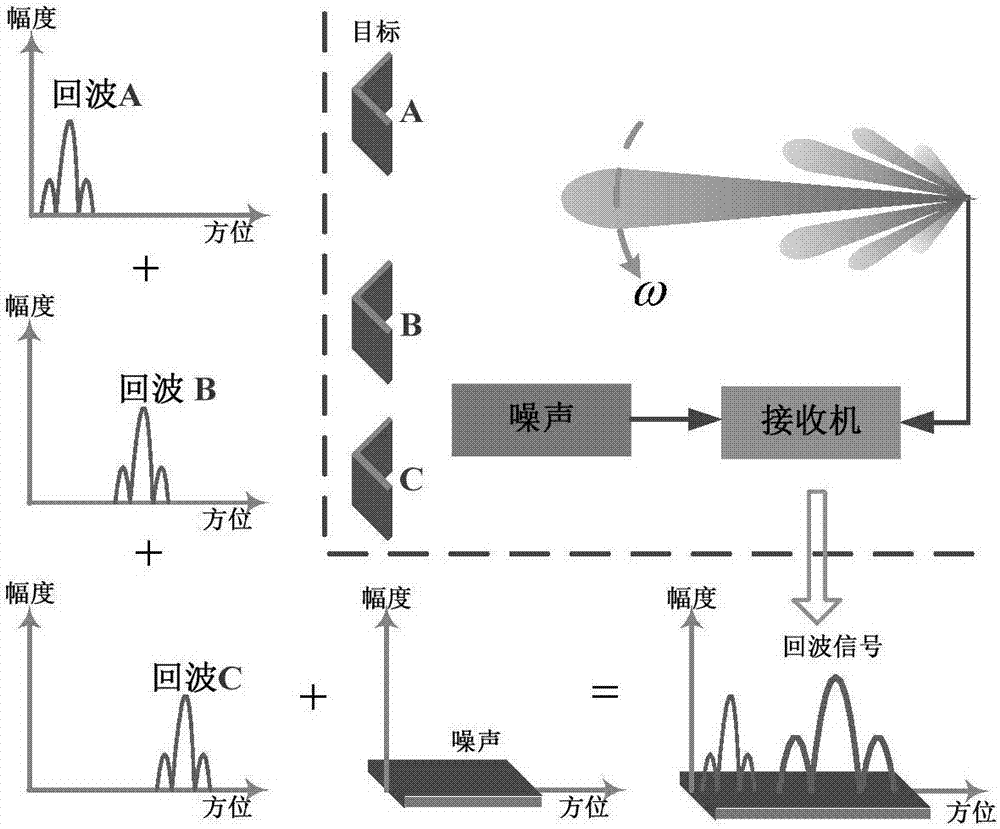
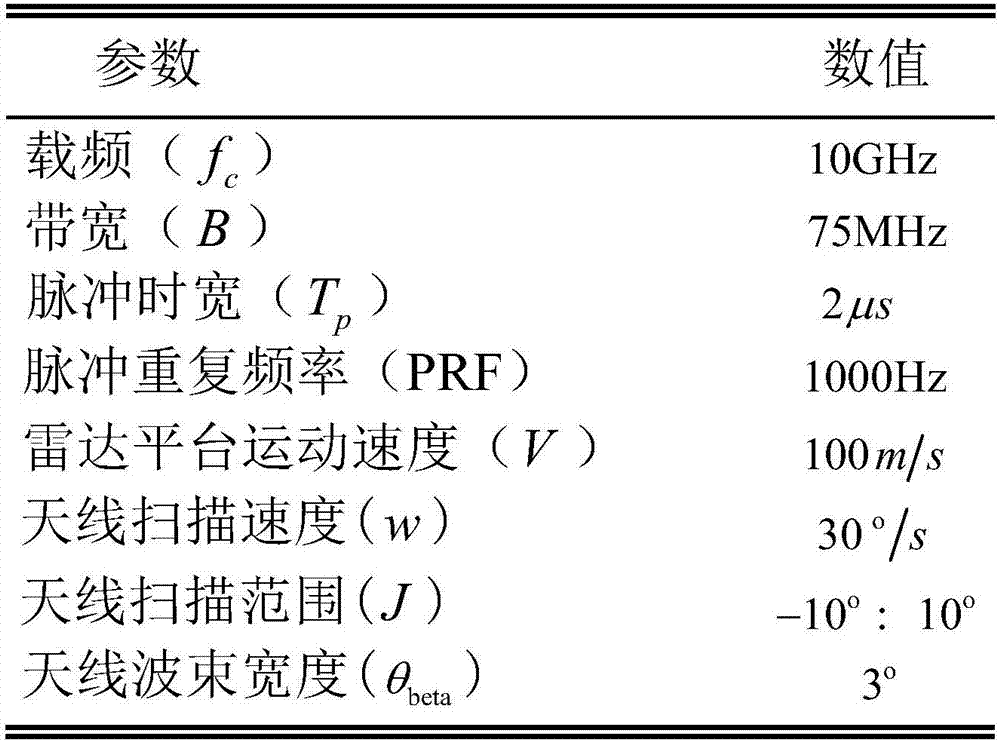
Real beam scanning radar corner super-resolution method
InactiveCN104536000AOvercoming Noise Amplification ProblemsHigh precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSingular value decompositionRadar
The invention discloses a convolution retrieval method based on the truncated singular value decomposition theory. According to an echo model of a scanning radar, scanning radar azimuth echoes are built into convolutions of an antenna directional diagram and a target scattering coefficient. Scanning radar corner super-resolution imaging is achieved by using the convolution retrieval method. According to noise amplification in the convolution retrieval process, firstly, the noise amplification reason is analyzed from the algebraical angle; secondly, singular value decomposition is carried out on a convolution matrix, and singular value components causing noise amplification are removed; finally, convolution retrieval and scanning radar corner super-resolution imaging are achieved through the adoption of an algebra inversion method. By means of the method, the problem of the noise amplification caused by a traditional deconvolution method in the convolution process is effectively solved, and the accuracy of scanning radar corner super-resolution imaging achieved according to the deconvolution method is accordingly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for measuring cancerous changes from reflectance spectral measurements obtained during endoscopic imaging
The present invention provides a new method and device for disease detection, more particularly cancer detection, from the analysis of diffuse reflectance spectra measured in vivo during endoscopic imaging. The measured diffuse reflectance spectra are analyzed using a specially developed light-transport model and numerical method to derive quantitative parameters related to tissue physiology and morphology. The method also corrects the effects of the specular reflection and the varying distance between endoscope tip and tissue surface on the clinical reflectance measurements. The model allows us to obtain the absorption coefficient ([mu]a) and further to derive the tissue micro-vascular blood volume fraction and the tissue blood oxygen saturation parameters. It also allows us to obtain the scattering coefficients ([mu]s and g) and further to derive the tissue micro-particles volume fraction and size distribution parameters.
Owner:维利桑特技术公司 +1
Real beam scanning radar front-view super-resolution imaging method
ActiveCN106908787AAchieving super-resolution imagingRealization of super-resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSample sequenceBeam scanning
The invention discloses a real beam scanning radar front-view super-resolution imaging method, which belongs to a method for realizing scanning radar front-view super-resolution imaging by using the total variation functional of the scattering coefficient of an imaging region as de-convolution of priori information. A scanning radar azimuth echo signal is modeled into a result obtained by superimposing noise onto the convolution of a sampling sequence of antenna beam along the azimuth and a sampling sequence of a target reflectance distribution function along the azimuth, and a problem of scanning radar front-view super-resolution imaging is converted into a de-convolution problem; then, the total variation functional of the scattering coefficient of an imaging region is integrated into priori information of the de-convolution problem, and the de-convolution problem is converted into a constrained optimization problem; and finally, a global optimal solution to the constrained optimization problem is obtained through a cross iteration method, and scanning radar front-view super-resolution imaging is realized.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
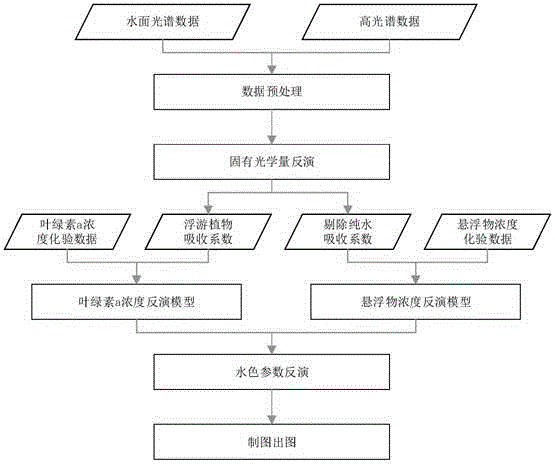
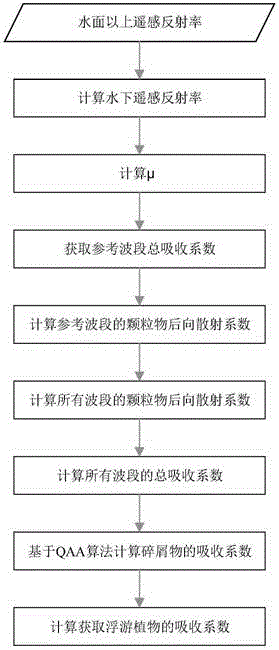
Analysis method of remote sensing inversion of water color parameters of inland class II water
InactiveCN105158172AHigh precisionRegionally applicableColor/spectral properties measurementsRemote sensing reflectancePhytoplankton absorption
The invention discloses an analysis method of remote sensing inversion of water color parameters of inland class II water. According to the method, inherent optical quantity of the class II water is inverted with an improved QAA (quasi-analytical algorithm), and concentration inversion of the water color parameters such as chlorophyll a and suspended matters is realized based on the inverted inherent optical quantity of the class II water. The method comprises specific steps as follows: (1), data of remote sensing reflectance above the surface of the water is input, parameter inversion of the inherent optical quantity of the water is realized based on the improved QAA, and absorption coefficients and scattering coefficients of the water and absorption coefficients of phytoplankton are acquired; (2), concentration data of the chlorophyll a and concentration data of the suspended matters of the water at a sampling point are input, a chlorophyll a concentration quantitative inversion model is established according to the concentration data of chlorophyll a and the absorption coefficients of the phytoplankton, and a suspended matter concentration quantitative inversion model is established according to the concentration data of the suspended matters and the absorption coefficients of the water after removal of pure water; (3), hyperspectral data finishing atmospheric correction are input, and concentration inversion of the water color parameters of the inland class II water in a monitoring area is realized according to the step (1) and the step (2).
Owner:中国城市科学研究会
Method and apparatus for performing qualitative and quantitative analysis of produce (fruit, vegetables) using spatially structured illumination
ActiveUS8014569B2Raman/scattering spectroscopyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatially resolvedWide field
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
SAR (synthetic aperture radar) tomography super-resolution imaging method
InactiveCN102645651ASolve the problem of fewLow number of solutionsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarImage resolution
The invention discloses an SAR (synthetic aperture radar) tomography super-resolution imaging method. The SAR tomography super-resolution imaging method includes registering obtained two-dimensional imaging results of various SAR tomography baselines, creating height-direction signals pixel by pixel according to the sequence of the baselines, realizing frequency modulation correction and constructing a redundancy matrix; and modeling a height-direction imaging problem into a sparse signal reconstruction problem according to the characteristic of sparsity of height-direction scattering coefficients, computing a sparse solution of the spares signal reconstruction problem by means of iteration by the aid of the constraint condition of the minimum weighted norm, and realizing height-dimensional imaging of an object. The method is applied to SAR tomography height-dimensional imaging, and problems that the quantity of two-dimensional SAR images in the same area and ( / or) trajectory distribution is uneven, and only a few parts of trajectory intervals (baselines) meet the Nyquist sampling theory are solved. In addition, by the aid of the method, energy of the object is more concentrated, namely, the resolution is improved, and the problem that the quantity of baselines is small is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
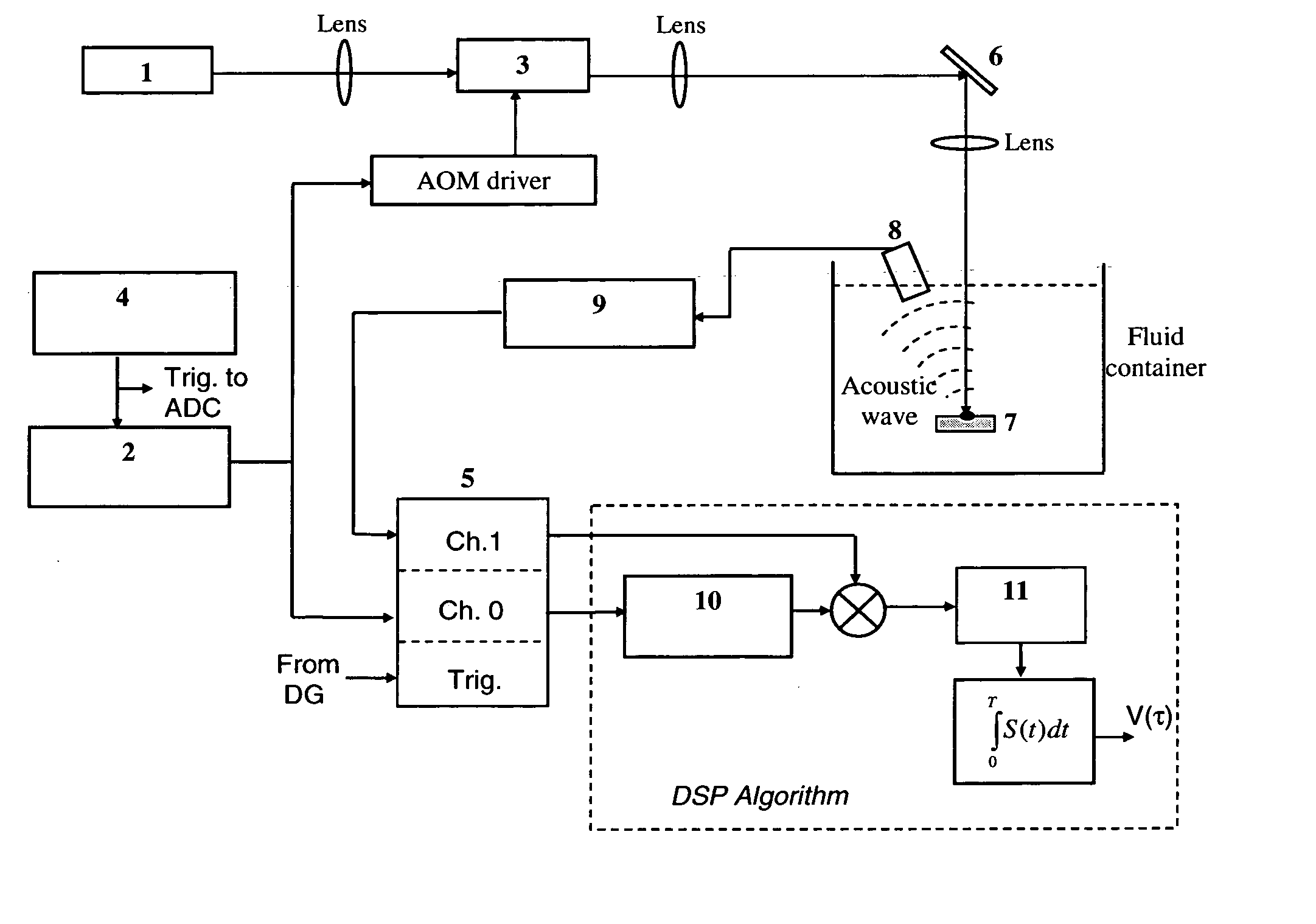
Laser photo-thermo-acoustic (PTA) frequency swept heterodyned lock-in depth profilometry imaging system
InactiveUS20050234319A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesScattering properties measurementsSubsurface imagingOptical absorption coefficient
A method and apparatus for biomedical subsurface imaging and measurement of thickness, elastic and optical properties of industrial and biomedical materials based on laser Photo-Thermo-Acoustic (PTA) frequency-swept heterodyne depth profilometry, In particular, the invention relates to biomedical imaging and measure of tissue and tumour thickness, L, speed of sound, cs, acoustic attenuation coefficient, γ, optical absorption coefficient, μa, and optical scattering coefficient, μs. The method and apparatus involves providing for a sample of the material to be characterized; irradiating the material for a selected period of time with an excitation waveform from a modulated optical excitation source wherein a photo-thermo-acoustic emission is responsively emitted from said solid; detecting said emitted photo-thermo-acoustic emission; processing the electronic signal to convert the frequency-domain signal into time-domain and perform depth profilometric imaging and determining thermoelastic and optical properties of the material sample;
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +3
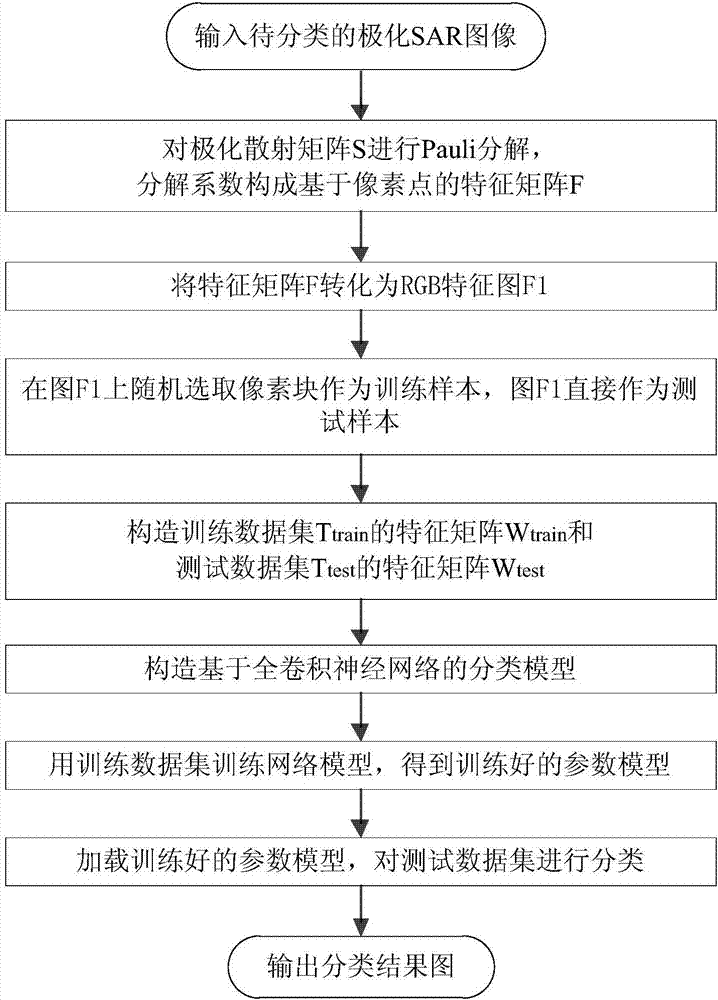
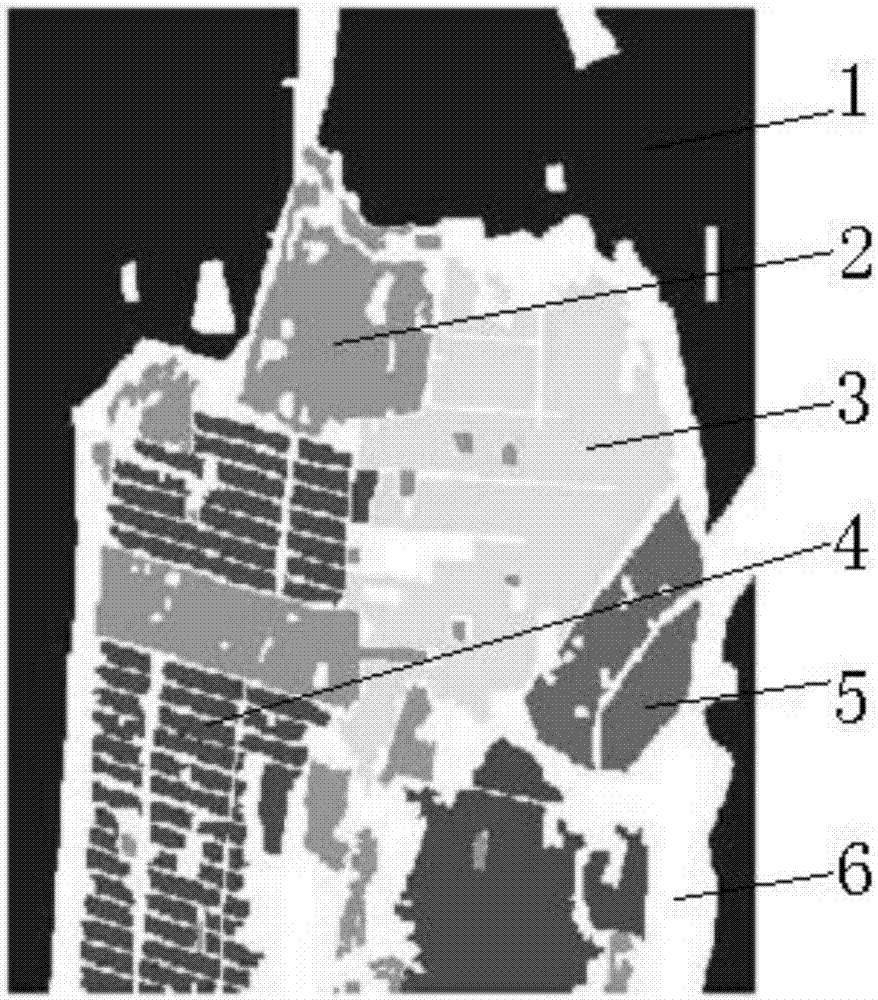
Polarized SAR land feature classification method based on full convolution neural network
InactiveCN107239797AImplement classificationReduce network parametersCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsDecompositionRgb image
The invention discloses a polarized SAR land feature classification method based on a full convolution neural network, comprising: performing Pauli decomposition on a to-be-classified polarized scattering matrix S to obtain the odd scattering coefficient, the even scattering coefficient and the volume scattering coefficient; using the odd scattering coefficient, the even scatter coefficient and the volume scattering coefficient as the three-dimensional image characteristics F of the polarized SAR image; then converting the obtained three-dimensional image characteristics matrix F into an RGB image F1; randomly selecting m x n pixel blocks in the RGB image F1 as training samples; using the whole RGB image F1 as a testing sample; re-constructing a full convolution neural network model; training the training samples through the full convolution neural network to obtain a trained model; and then, through the trained model, classifying the test set and obtaining the classification result. The method of the invention can solve the problem of low time efficiency in the prior art and shorten the running time under the condition of high classification accuracy.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com