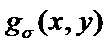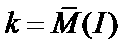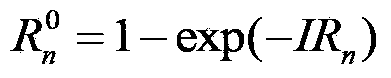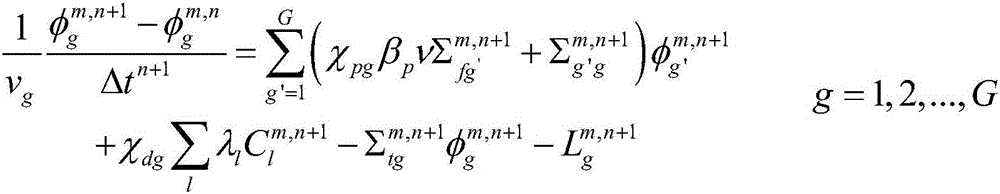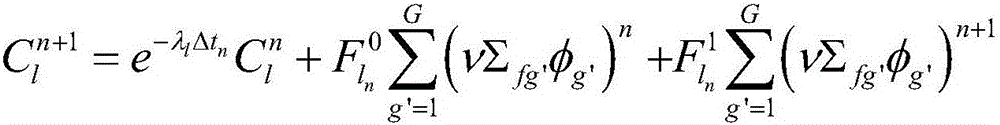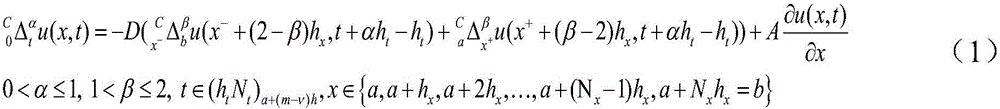Patents
Literature
163 results about "Diffusion equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The diffusion equation is a partial differential equation. In physics, it describes the behavior of the collective motion of micro-particles in a material resulting from the random movement of each micro-particle. In mathematics, it is applicable in common to a subject relevant to the Markov process as well as in various other fields, such as the materials sciences, information science, life science, social science, and so on. These subjects described by the diffusion equation are generally called Brown problems.
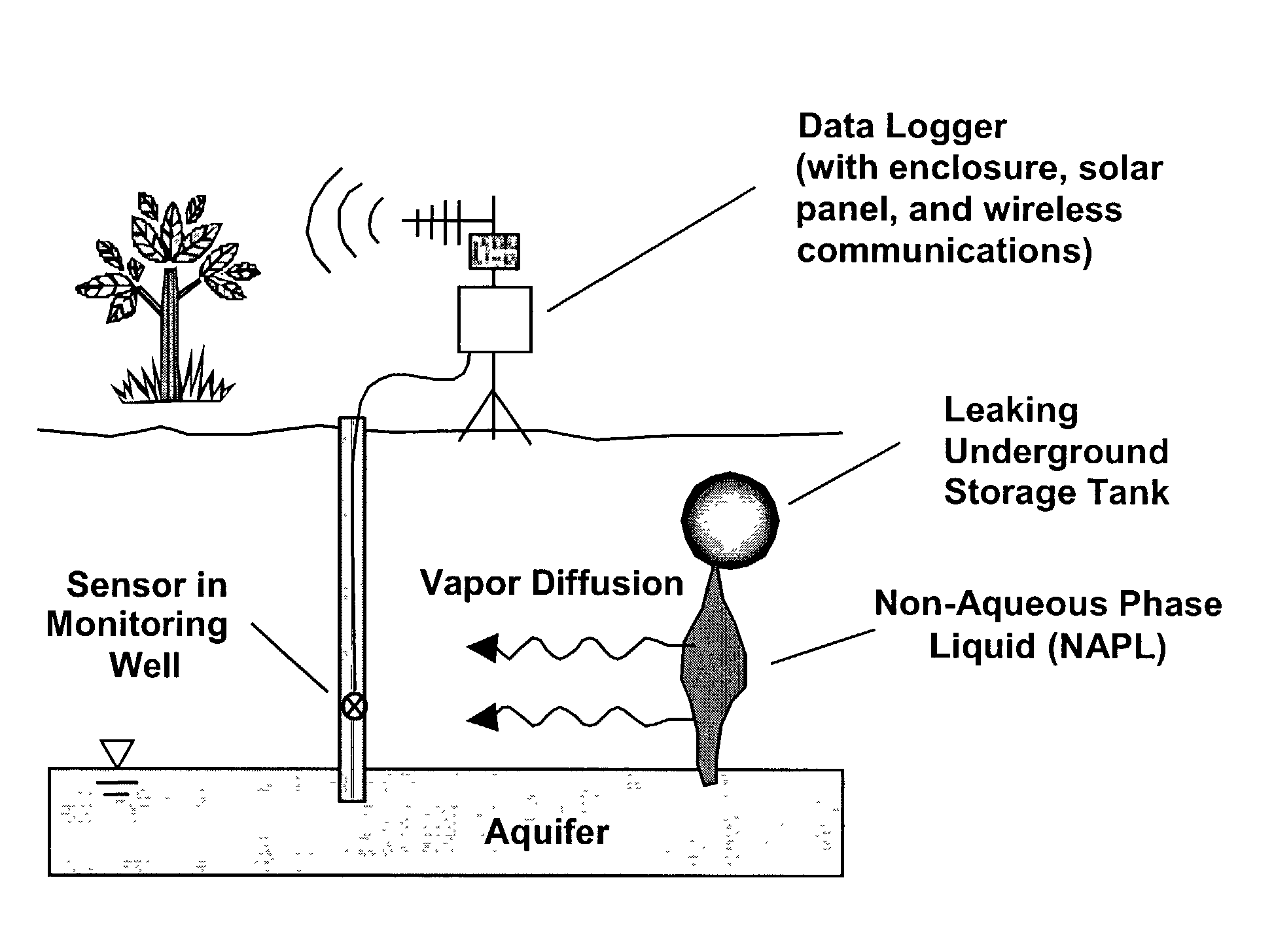
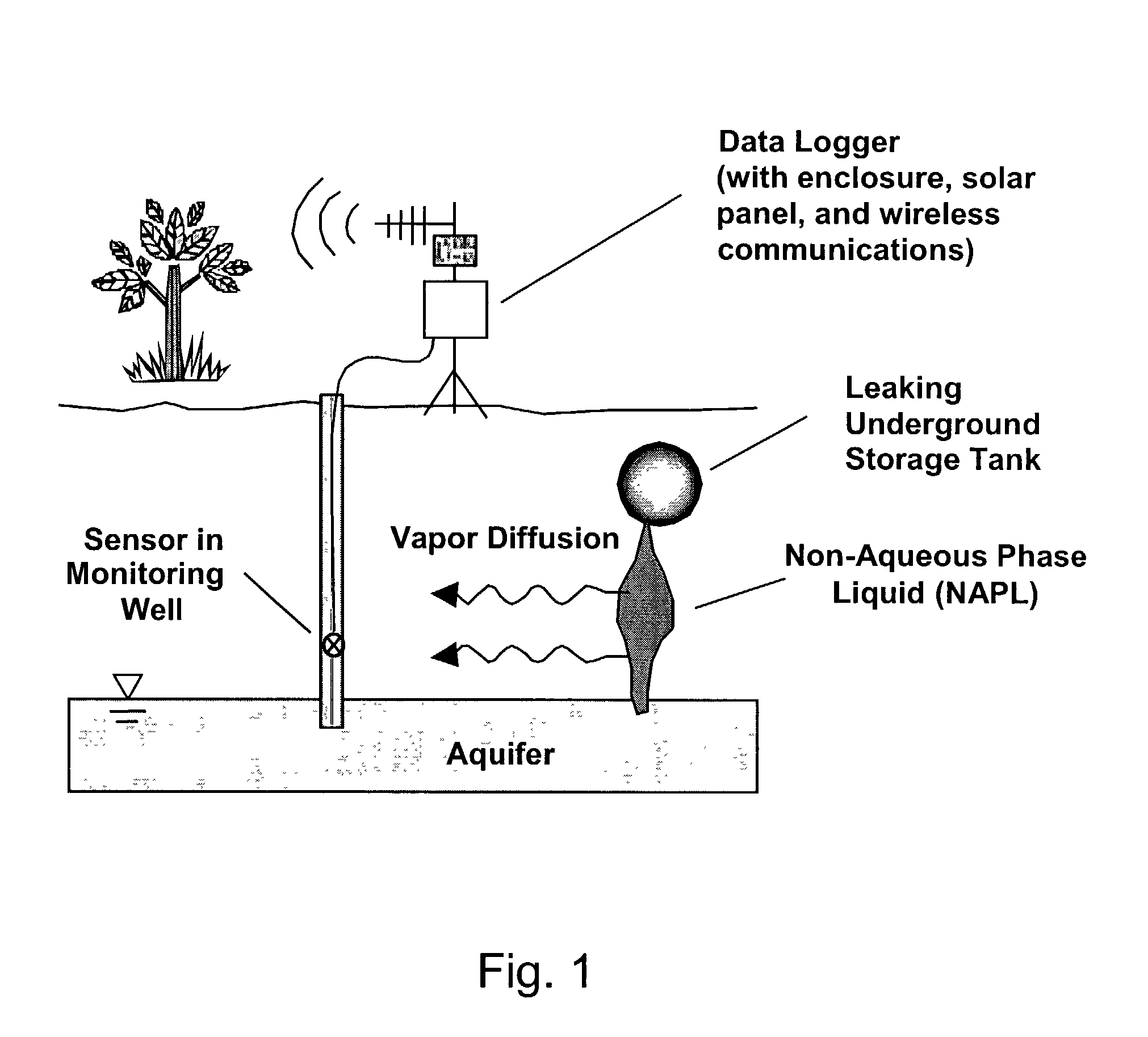
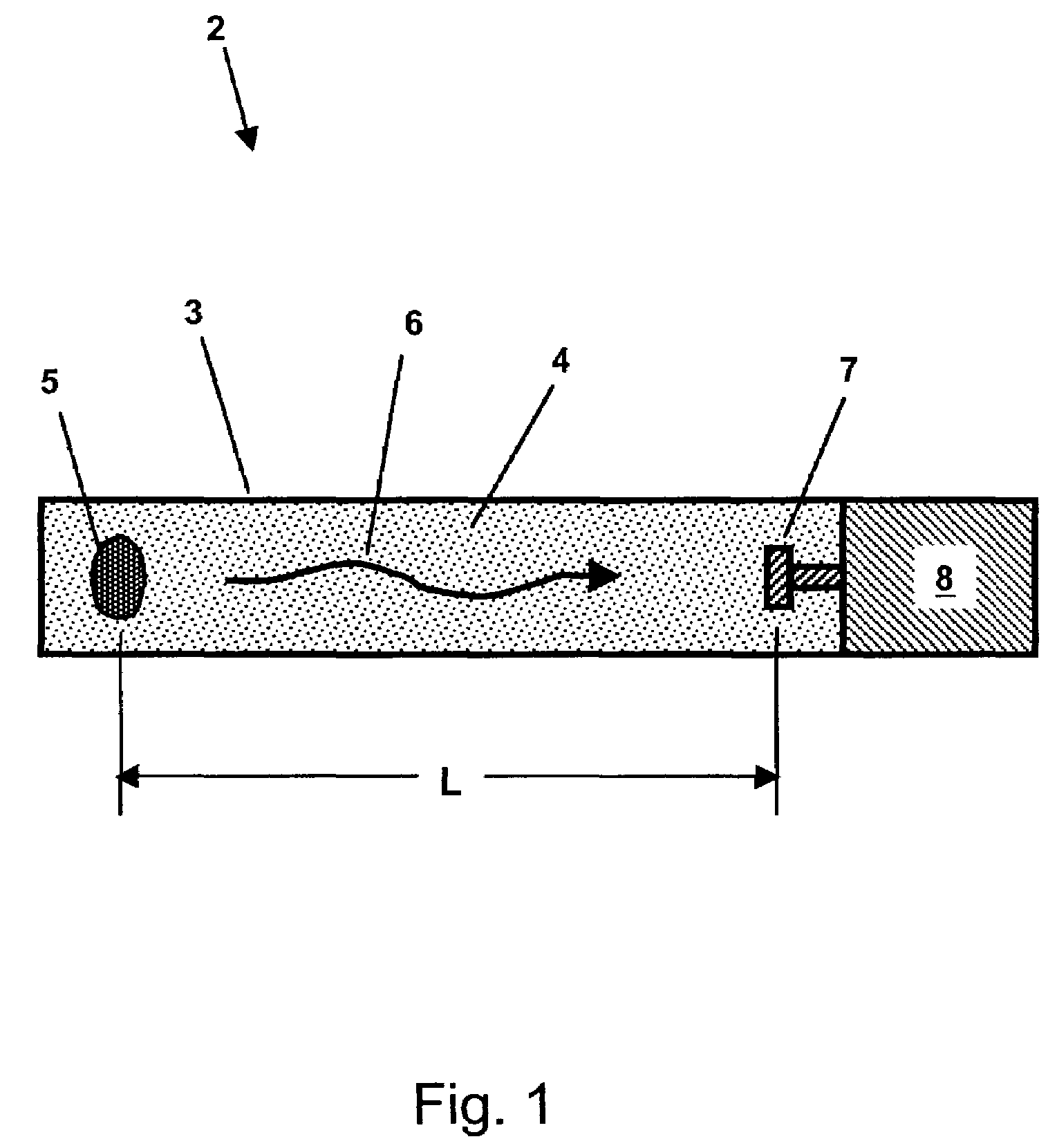
Methods for characterizing subsurface volatile contaminants using in-situ sensors
ActiveUS7003405B1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConcentration ResponseTriangulation
An inverse analysis method for characterizing diffusion of vapor from an underground source of volatile contaminant using data taken by an in-situ sensor. The method uses one-dimensional solutions to the diffusion equation in Cartesian, cylindrical, or spherical coordinates for isotropic and homogenous media. If the effective vapor diffusion coefficient is known, then the distance from the source to the in-situ sensor can be estimated by comparing the shape of the predicted time-dependent vapor concentration response curve to the measured response curve. Alternatively, if the source distance is known, then the effective vapor diffusion coefficient can be estimated using the same inverse analysis method. A triangulation technique can be used with multiple sensors to locate the source in two or three dimensions. The in-situ sensor can contain one or more chemiresistor elements housed in a waterproof enclosure with a gas permeable membrane.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
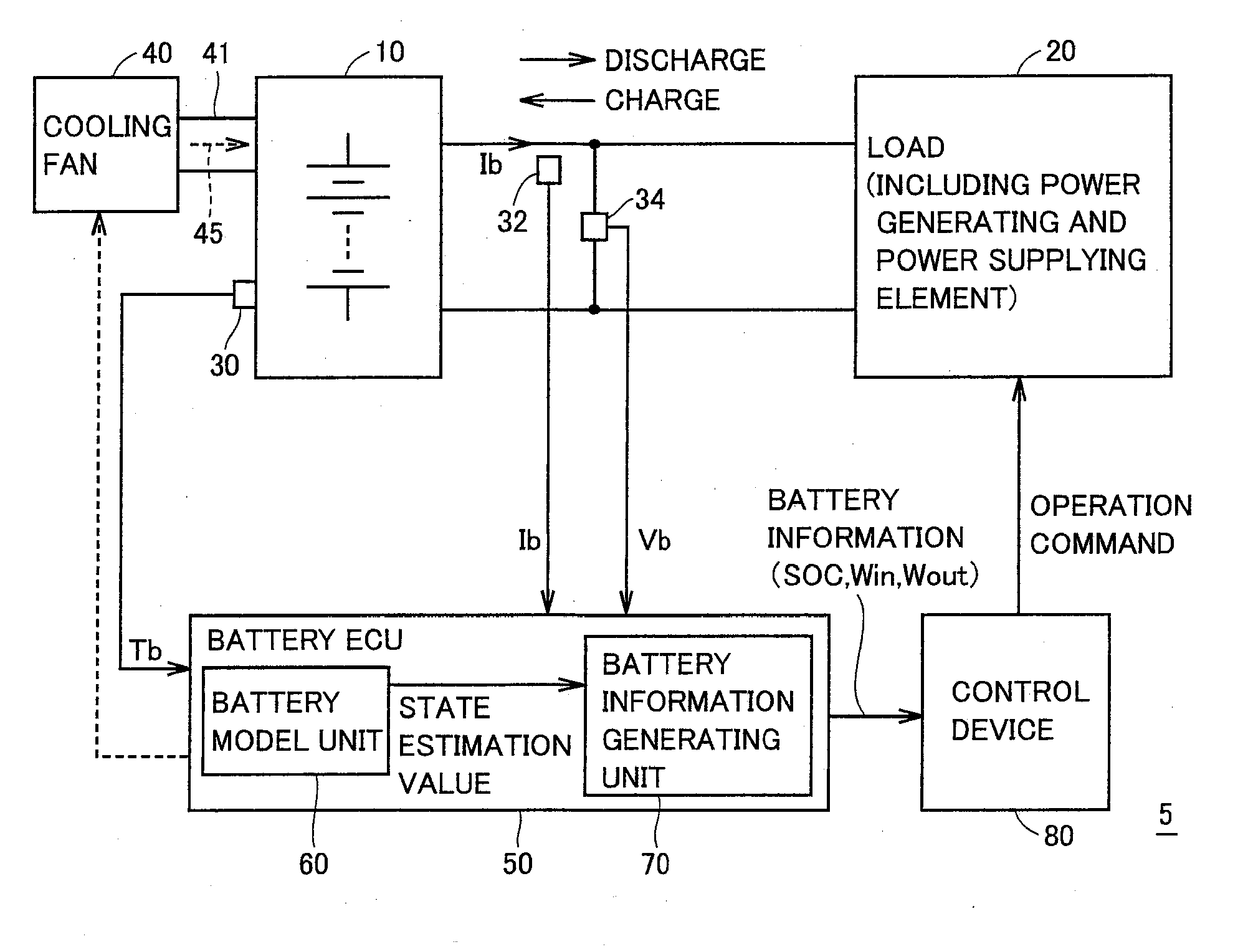
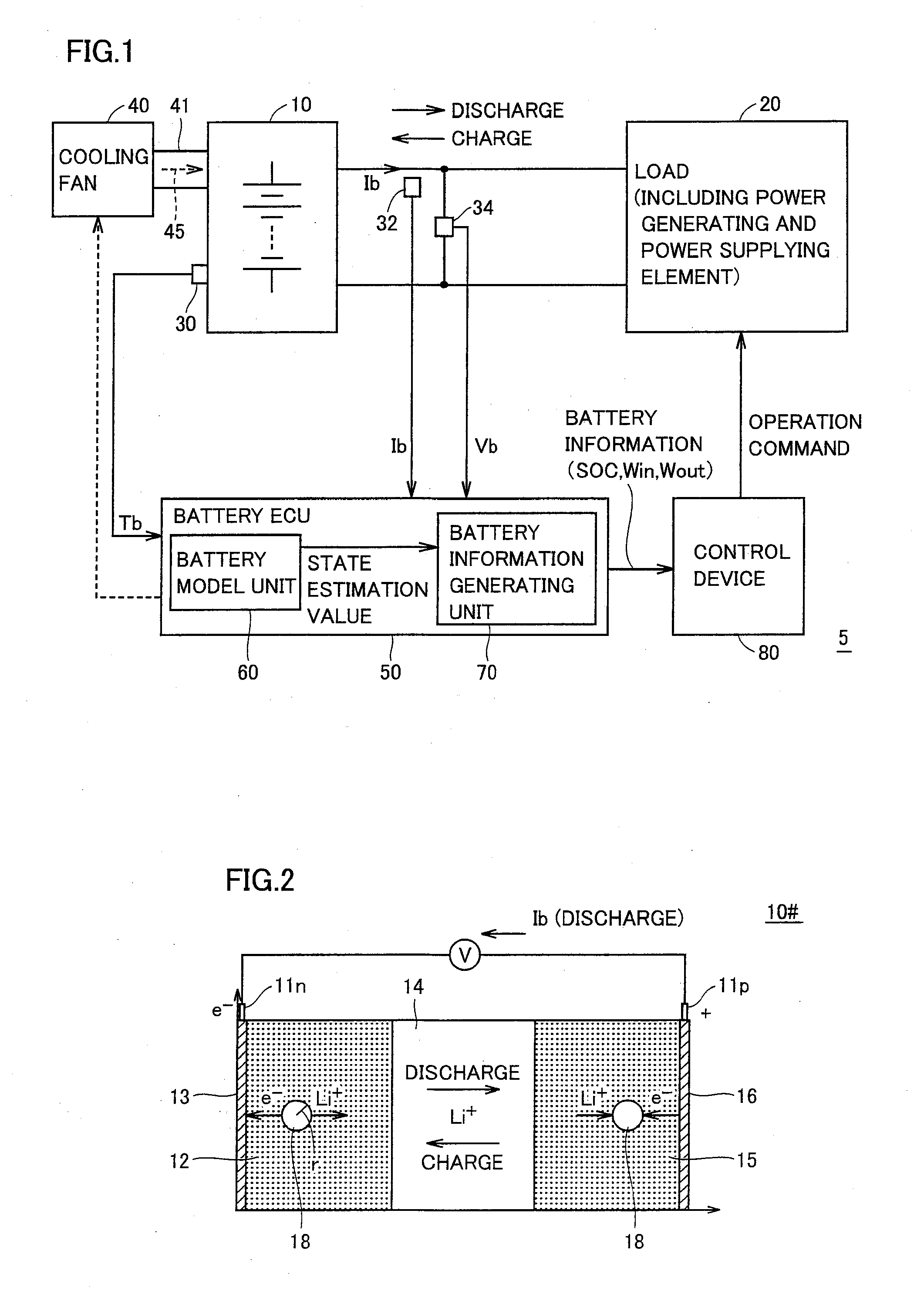
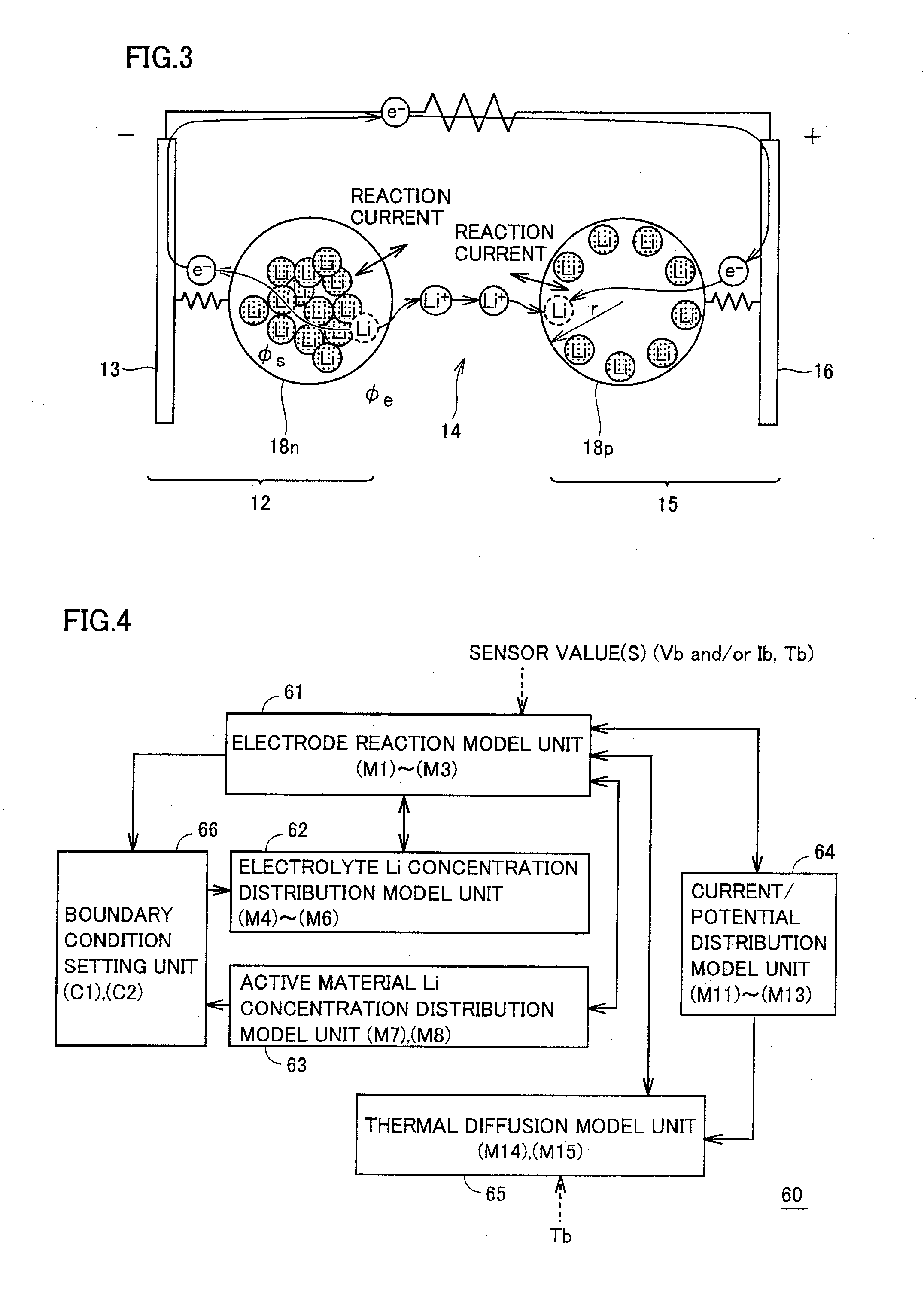
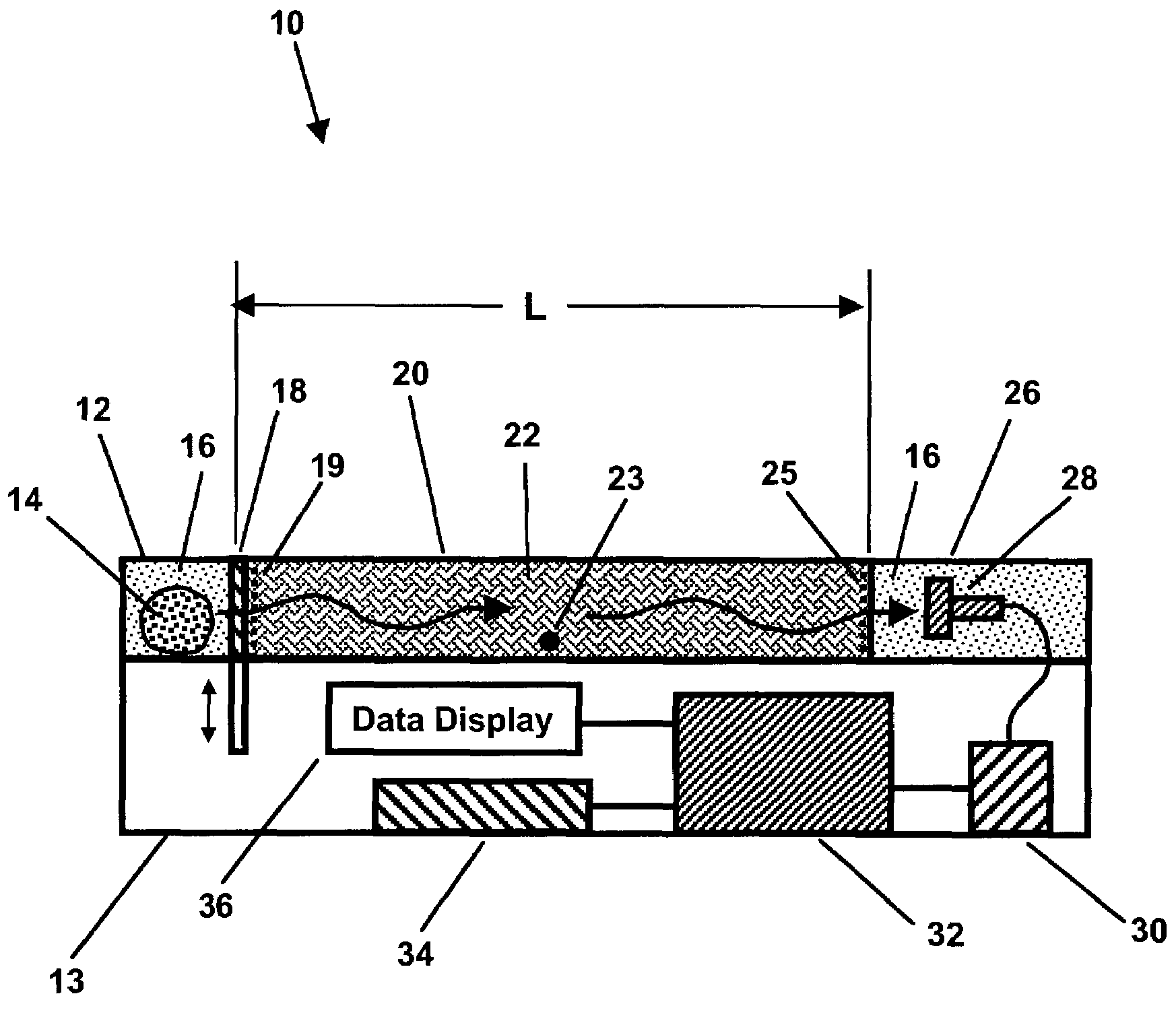
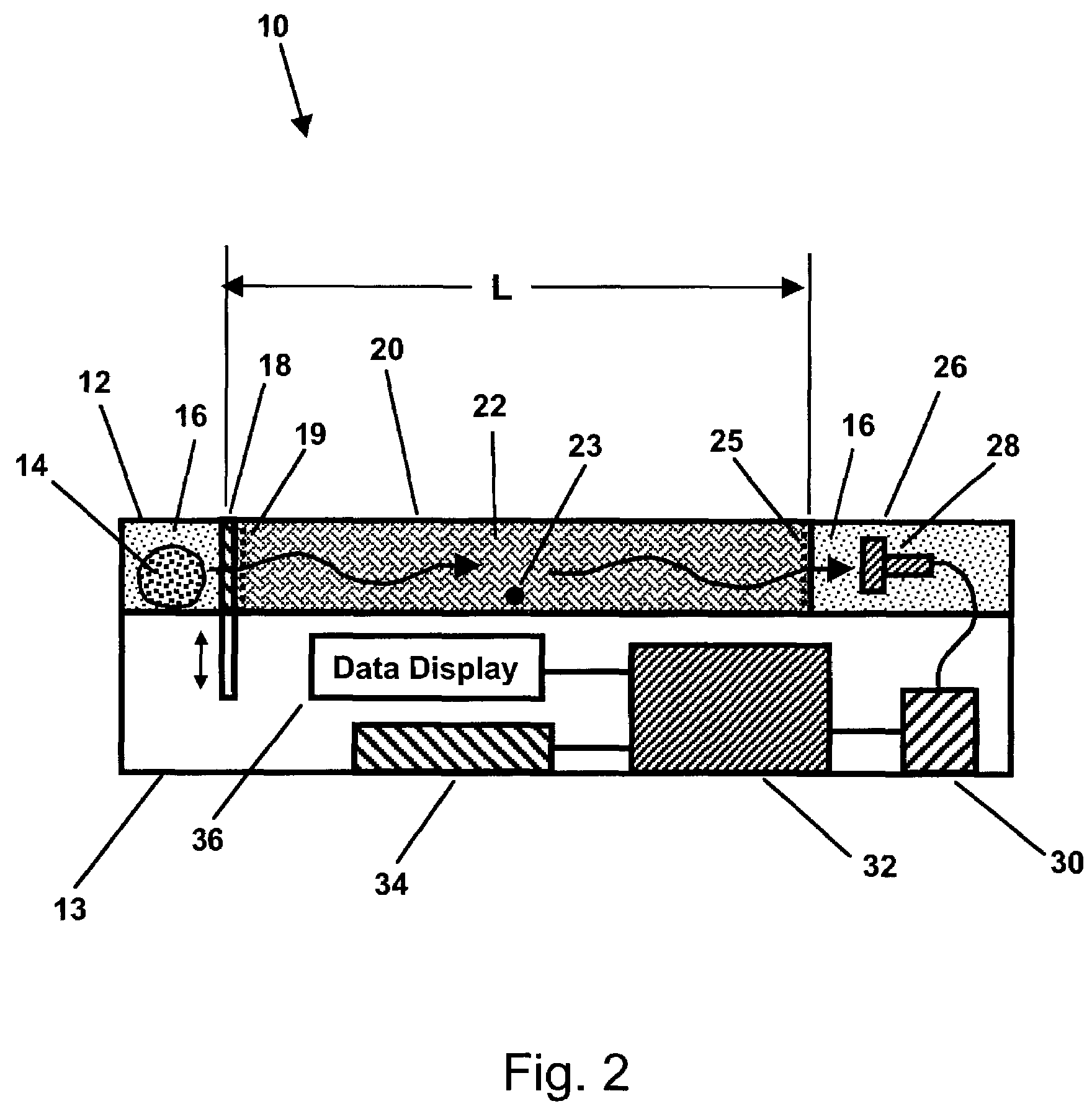
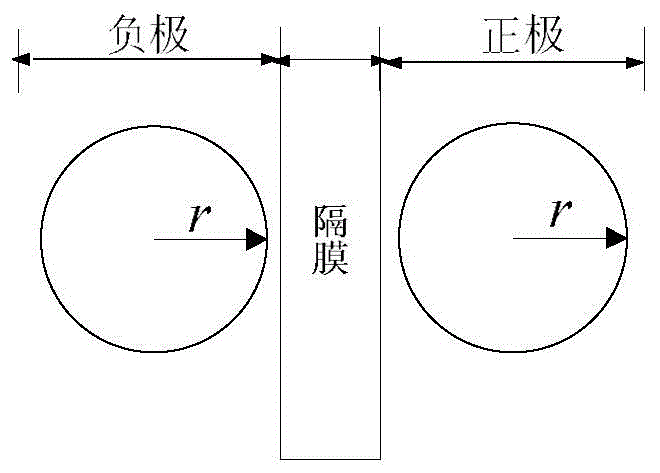
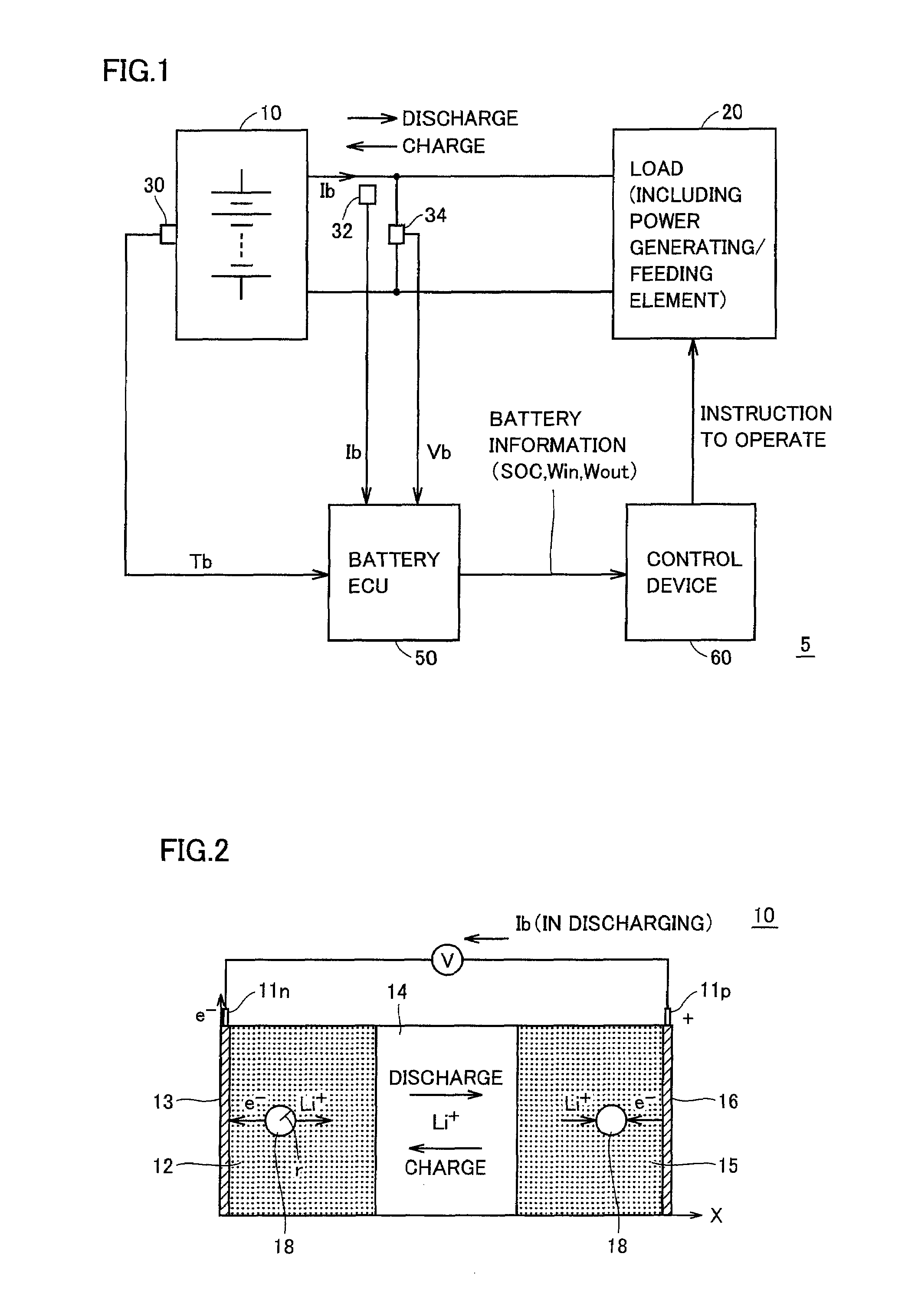
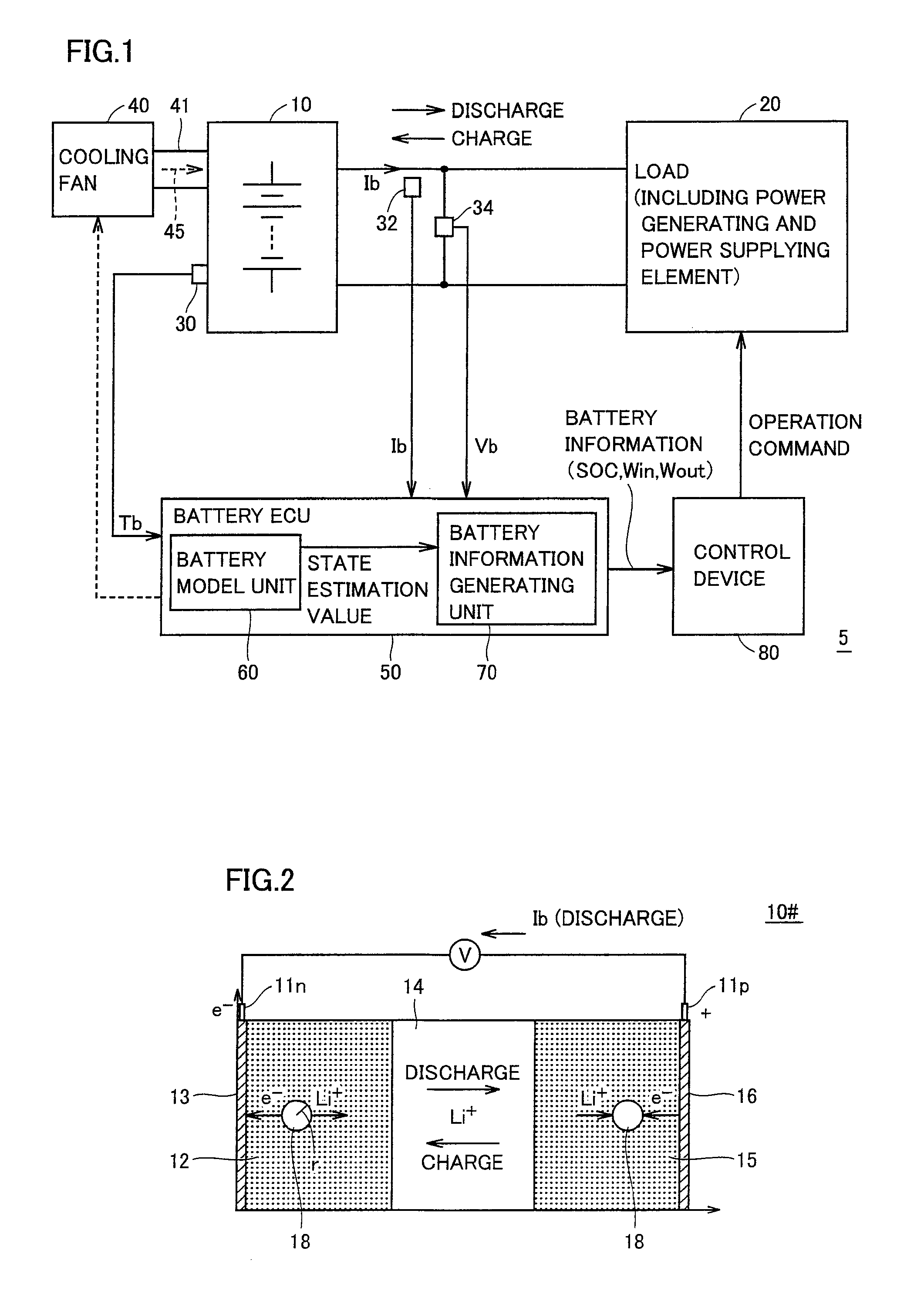
Control system of secondary battery and hybrid vehicle equipped with the same
ActiveUS20100033132A1Rapid deteriorationPreventing overchargeHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesElectrical batteryEngineering
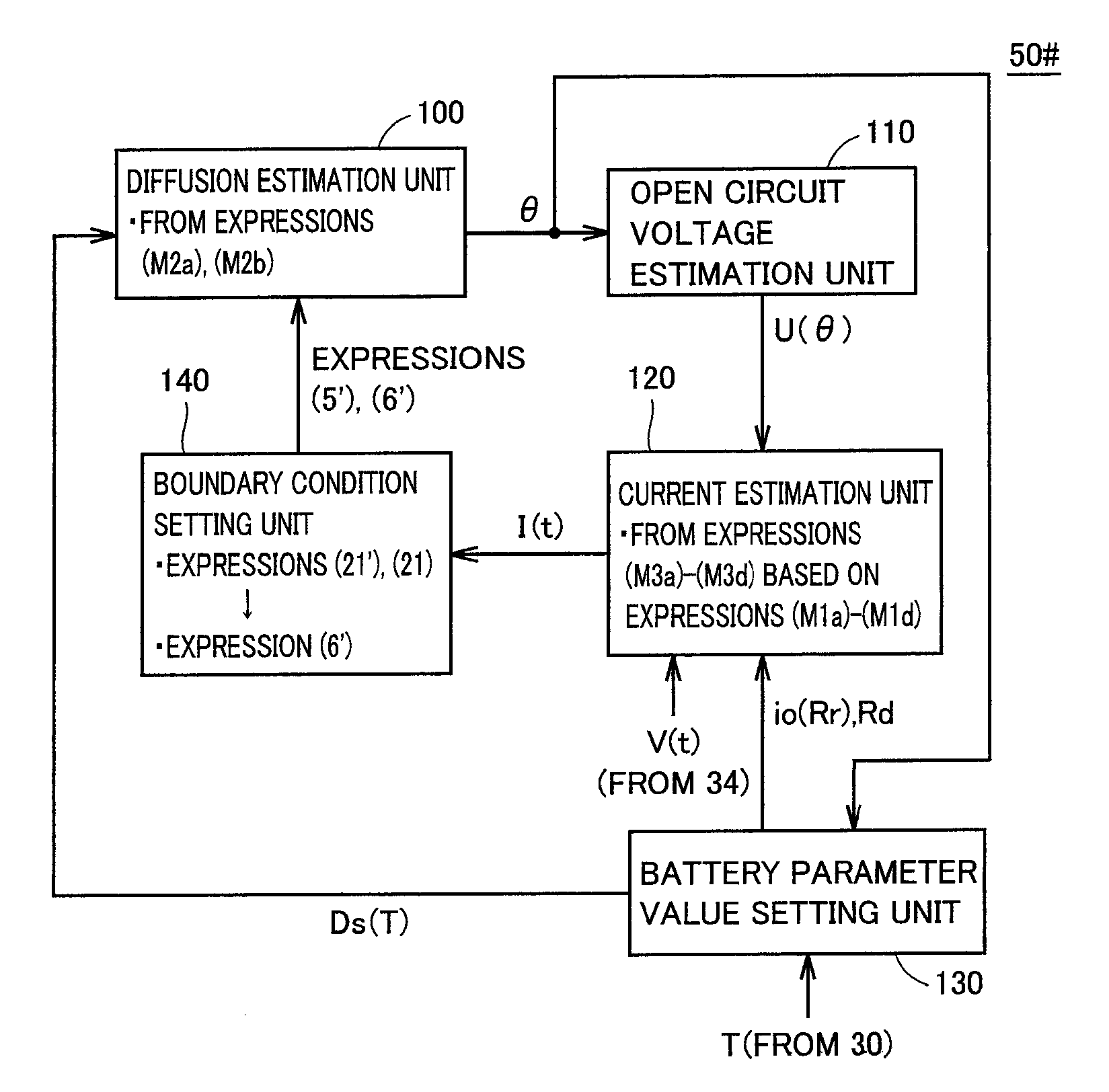
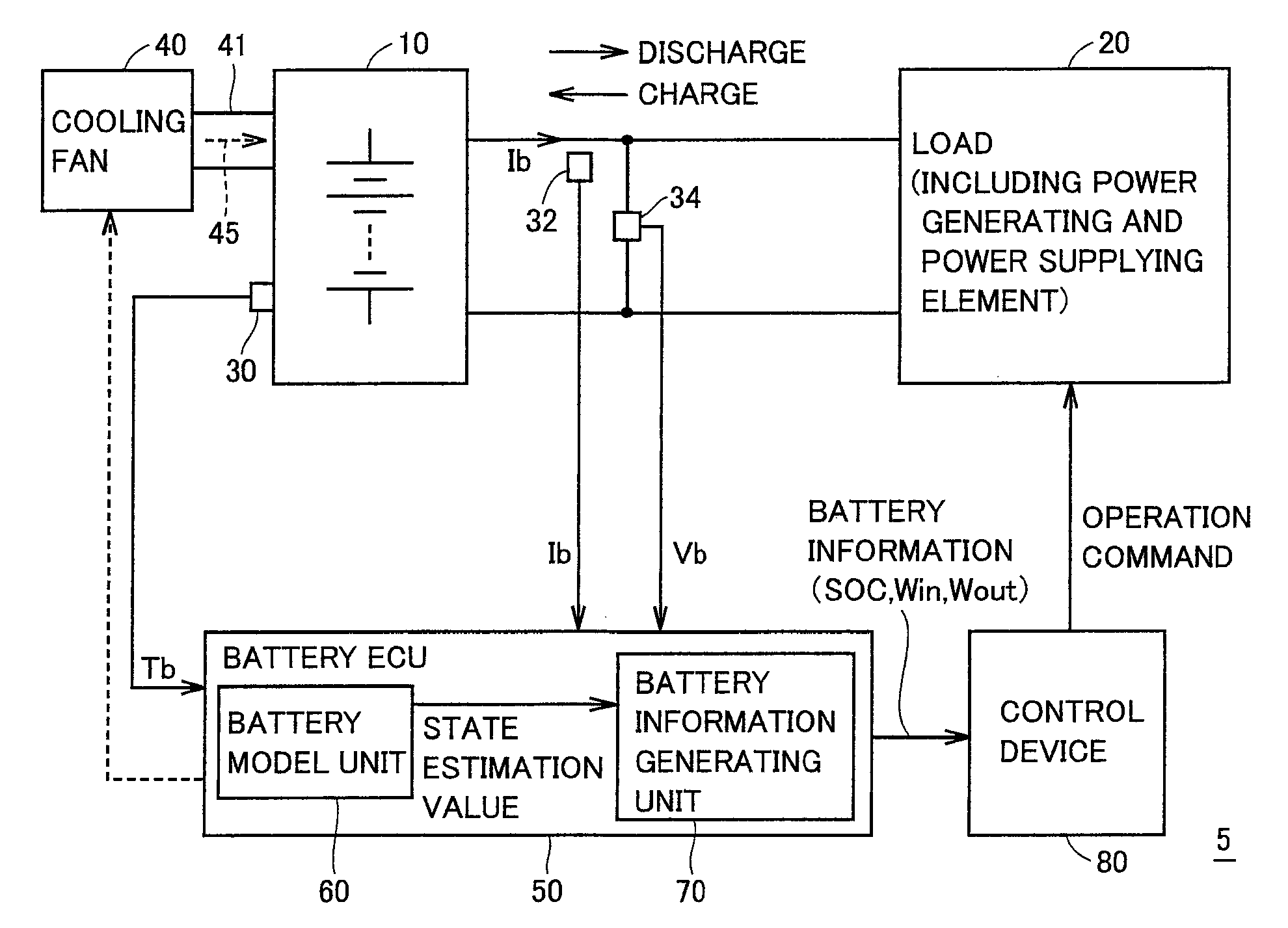
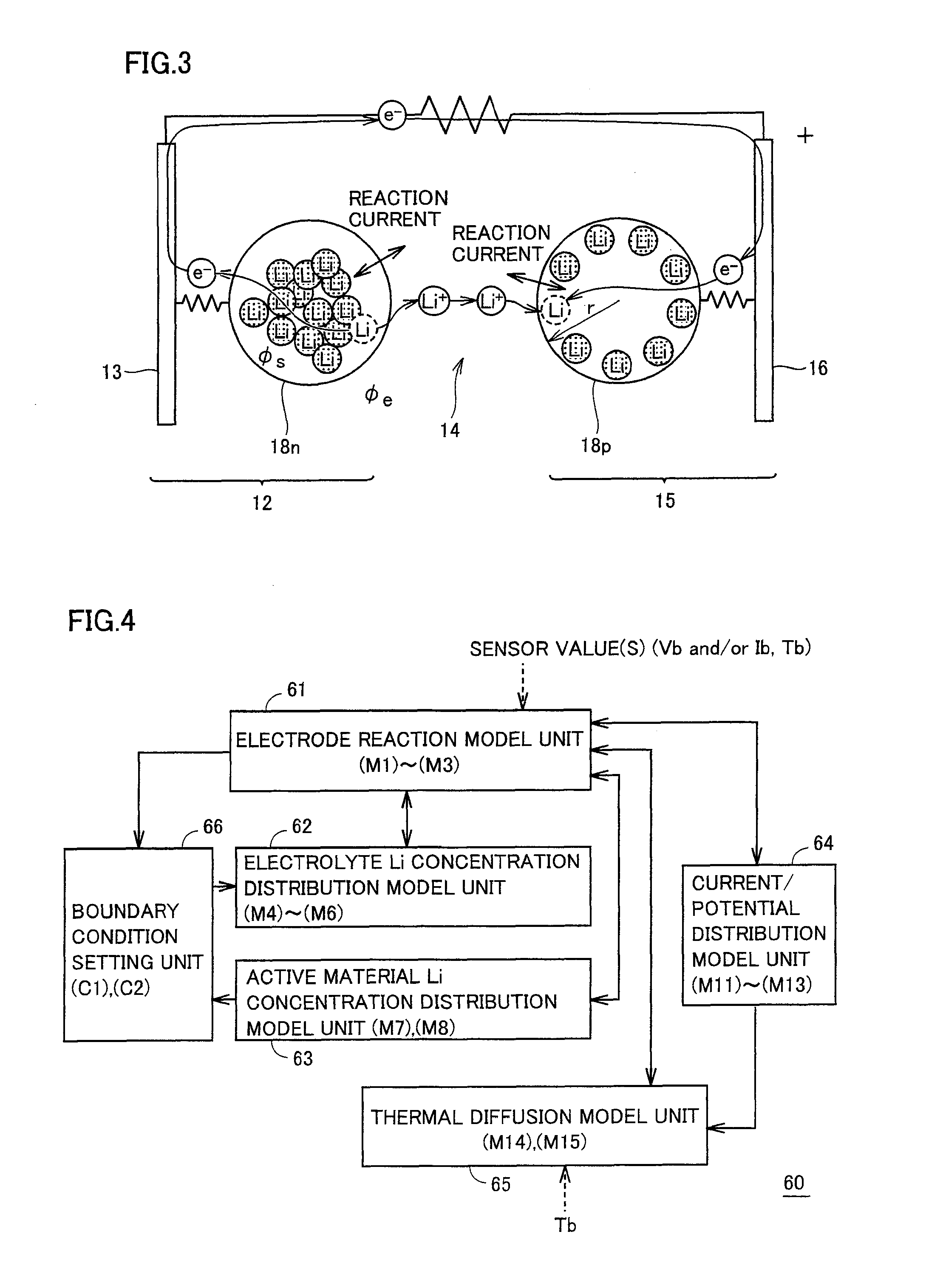
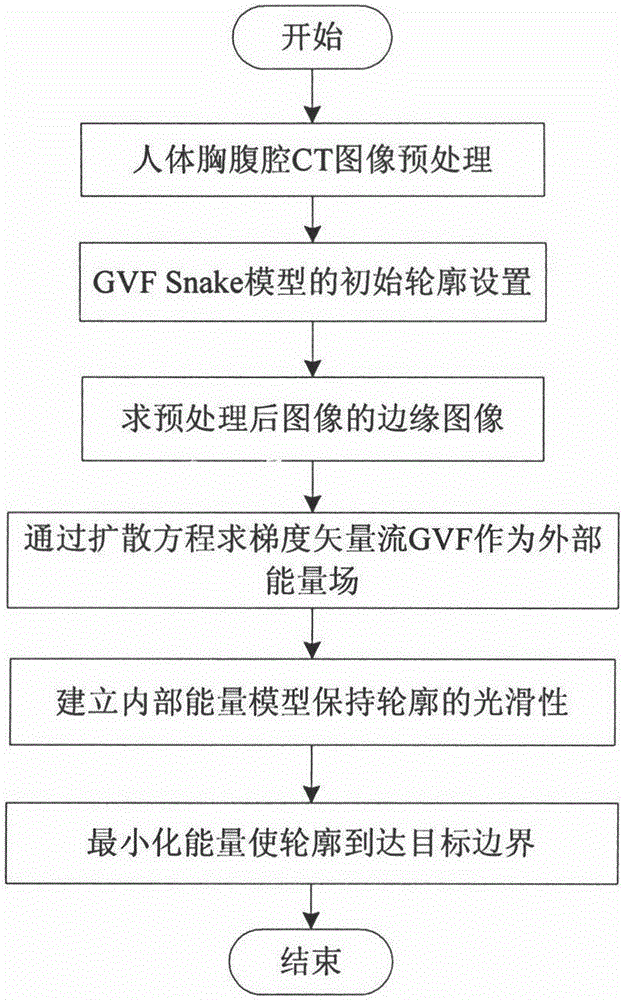
A battery model unit includes an electrode reaction model unit based on the Butler_Volmer equation, an electrolyte lithium concentration distribution model unit analyzing a lithium ion concentration distribution in an electrolyte solution by a diffusion equation, an active material lithium concentration distribution model unit analyzing an ion concentration distribution in a solid state of an active material by a diffusion equation, a current / potential distribution model unit for obtaining a potential distribution according to the charge conservation law, a thermal diffusion model unit and a boundary condition setting unit. The boundary condition setting unit (66) sets a boundary condition at an electrode interface such that a reacting weight at the electrode interface is not determined by a difference in material concentration between positions but a deviation from an electrochemically balanced state causes a change with time in lithium concentration at the interface and thus a (time-based) drive power for material transportation. Thereby, an appropriate charge / discharge control can be performed based on the battery model having the appropriately set battery condition.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Hybrid-dual-Fourier tomographic algorithm for a fast three-dimensional optical image reconstruction in turbid media
InactiveUS20040030255A1Reconstruction from projectionScattering properties measurementsDiffusionImaging algorithm
A method for imaging objects in a highly scattering turbid medium comprises: using a group of sources and detectors to generate a plurality of emergent energy waves from the medium, determining the intensity data of the emergent energy waves and processing the intensity data by using an image reconstruction algorithm. Arrangement of sources-detectors may be in parallel (transmission and / or backscattering) geometry or in cylinder geometry. The reconstruction algorithm is a novel hybrid dual Fourier tomographic algorithm for a fast 3D image reconstruction. The forward models are the radiative transfer model based on the cumulant solution of the radiative transfer equation or the diffusion model based on the approximate diffusion equation.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
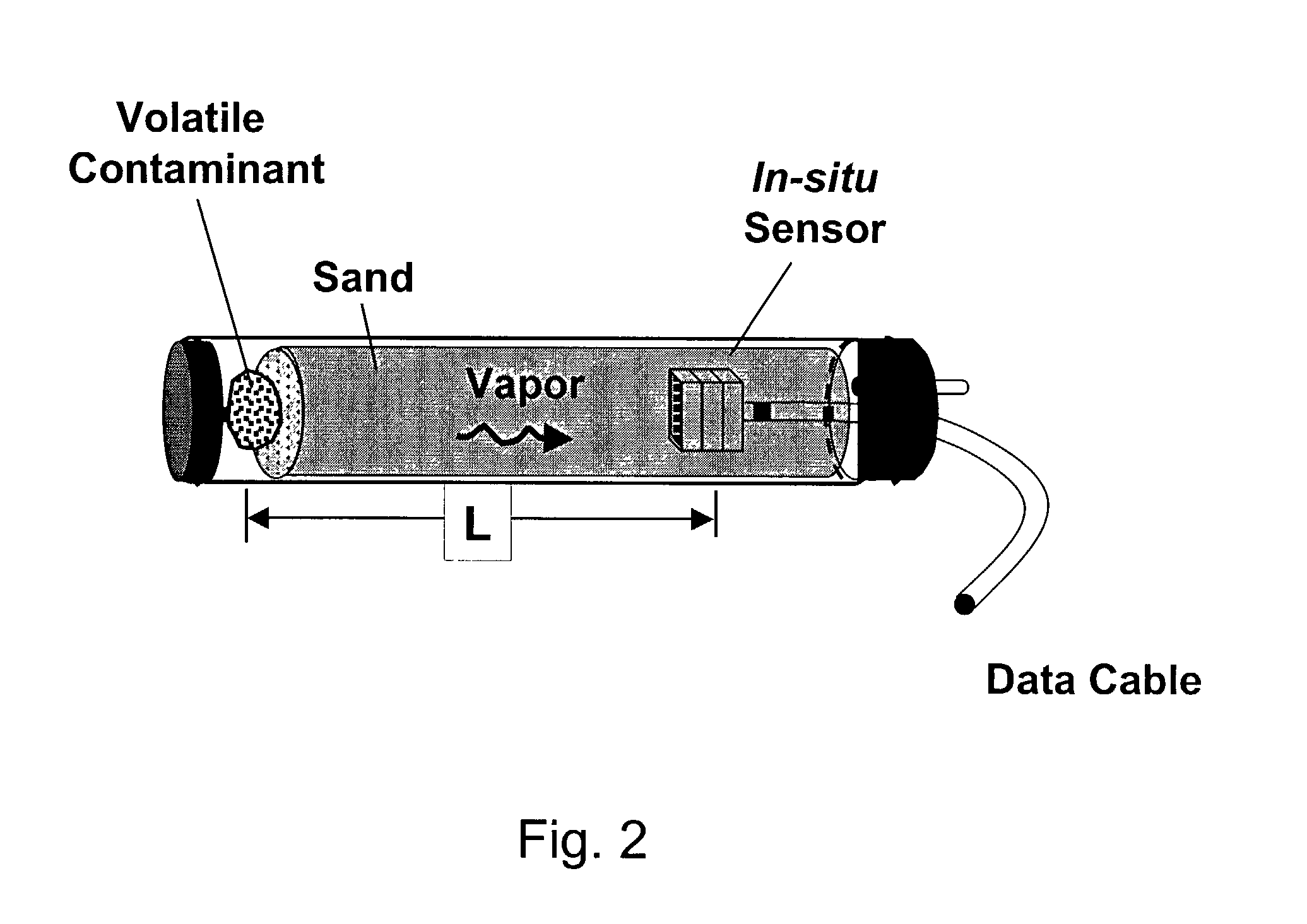
Portable vapor diffusion coefficient meter
ActiveUS7229593B1Minimize the differenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansDiffusionGas phase
An apparatus for measuring the effective vapor diffusion coefficient of a test vapor diffusing through a sample of porous media contained within a test chamber. A chemical sensor measures the time-varying concentration of vapor that has diffused a known distance through the porous media. A data processor contained within the apparatus compares the measured sensor data with analytical predictions of the response curve based on the transient diffusion equation using Fick's Law, iterating on the choice of an effective vapor diffusion coefficient until the difference between the predicted and measured curves is minimized. Optionally, a purge fluid can forced through the porous media, permitting the apparatus to also measure a gas-phase permeability. The apparatus can be made lightweight, self-powered, and portable for use in the field.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Simulating method of numerical value of sediment movement of silty and muddy coast
InactiveCN102359862ACalculation results are reasonable and credibleHydrodynamic testingShear stressMathematical model
The invention discloses a simulating method of numerical values of sediment movement of silty and muddy coast. The simulating method mainly comprises the following steps of: step one. establishing basic equations which comprise a water current continuity equation, a water current movement equation, a suspended load transporting and diffusing equation and a bed surface scouring and silting variation equation; step two. calculating the shearing stress of a bed surface under the combined action of settling velocity of suspended sediment, scouring and silting functions of sediment and wave currents; step three. establishing a sediment mathematical model and solving; step four. verifying the model, including water current verification and sand content verification; and step five. judging a settling velocity field of the suspended sediment according to the sediment mathematical model. According to the simulating method, the sediment mathematical model is established on the basis of considering the characteristics of muddy and silty sediment, and the movement of two different types of sediment can be simulated simultaneously; and more than that, the established sediment mathematical model also can be used for calculating the settling velocity field of the suspended sediment; and accordingly, the characteristics of a region and influence factors are analyzed and researched.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
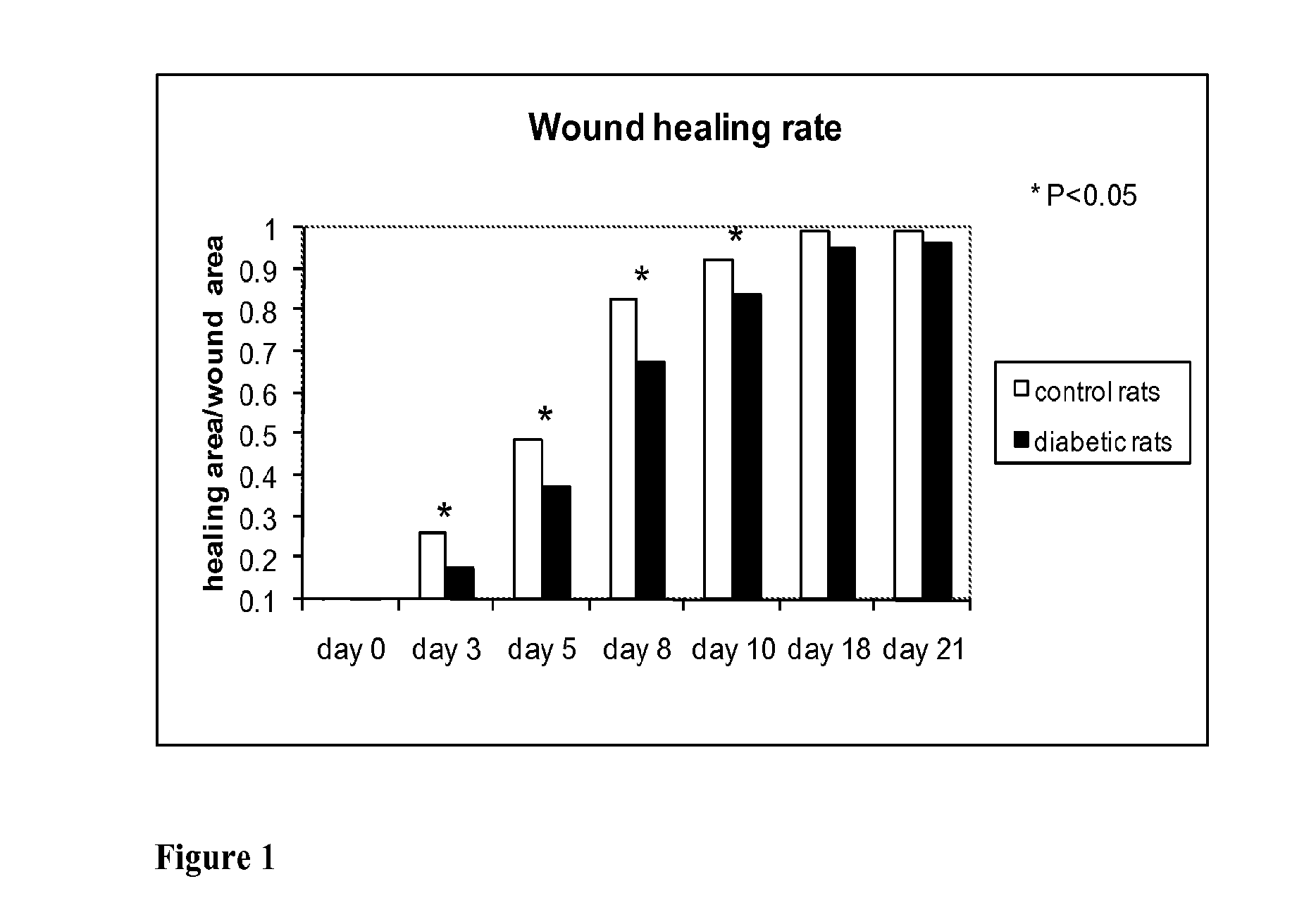
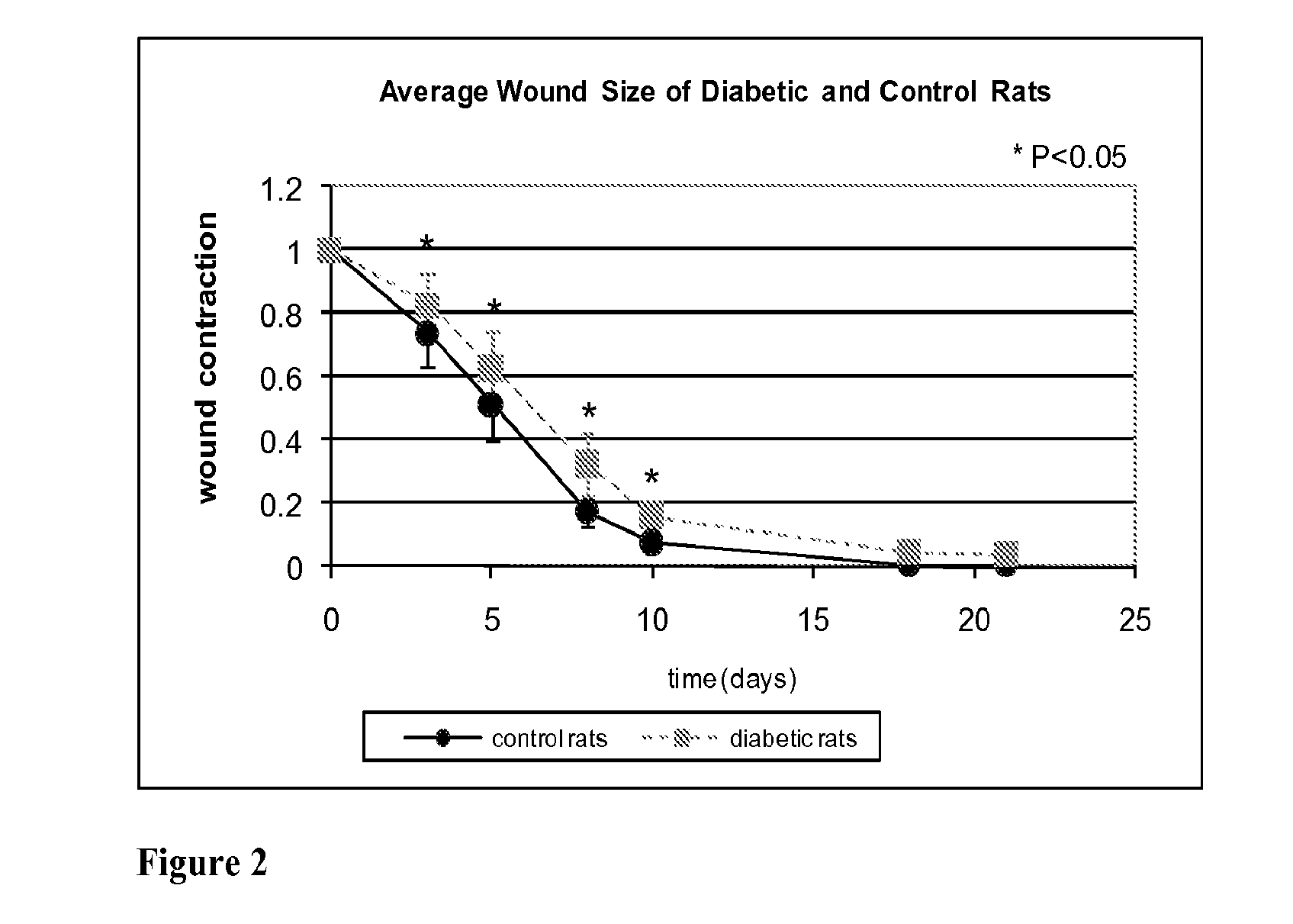
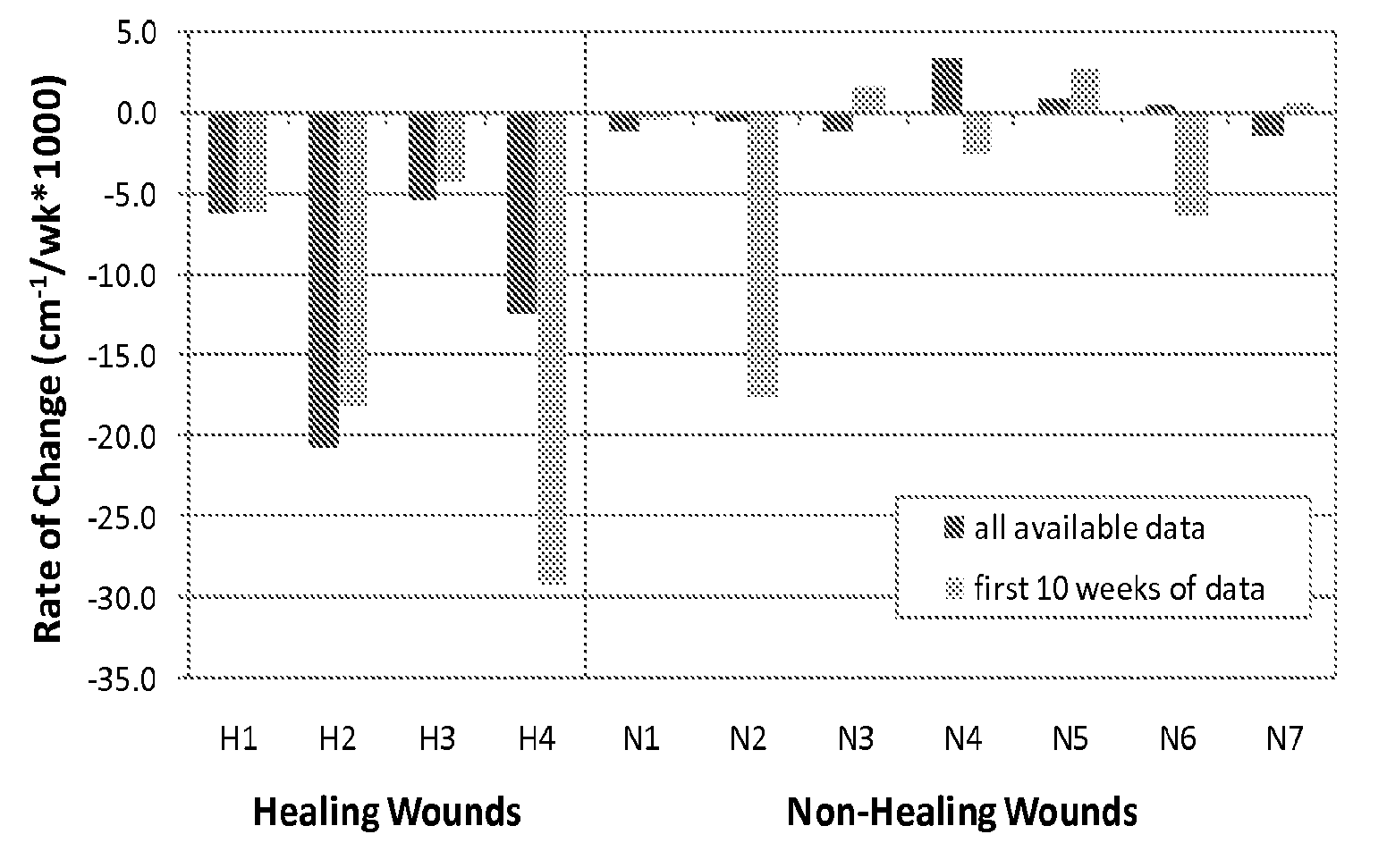
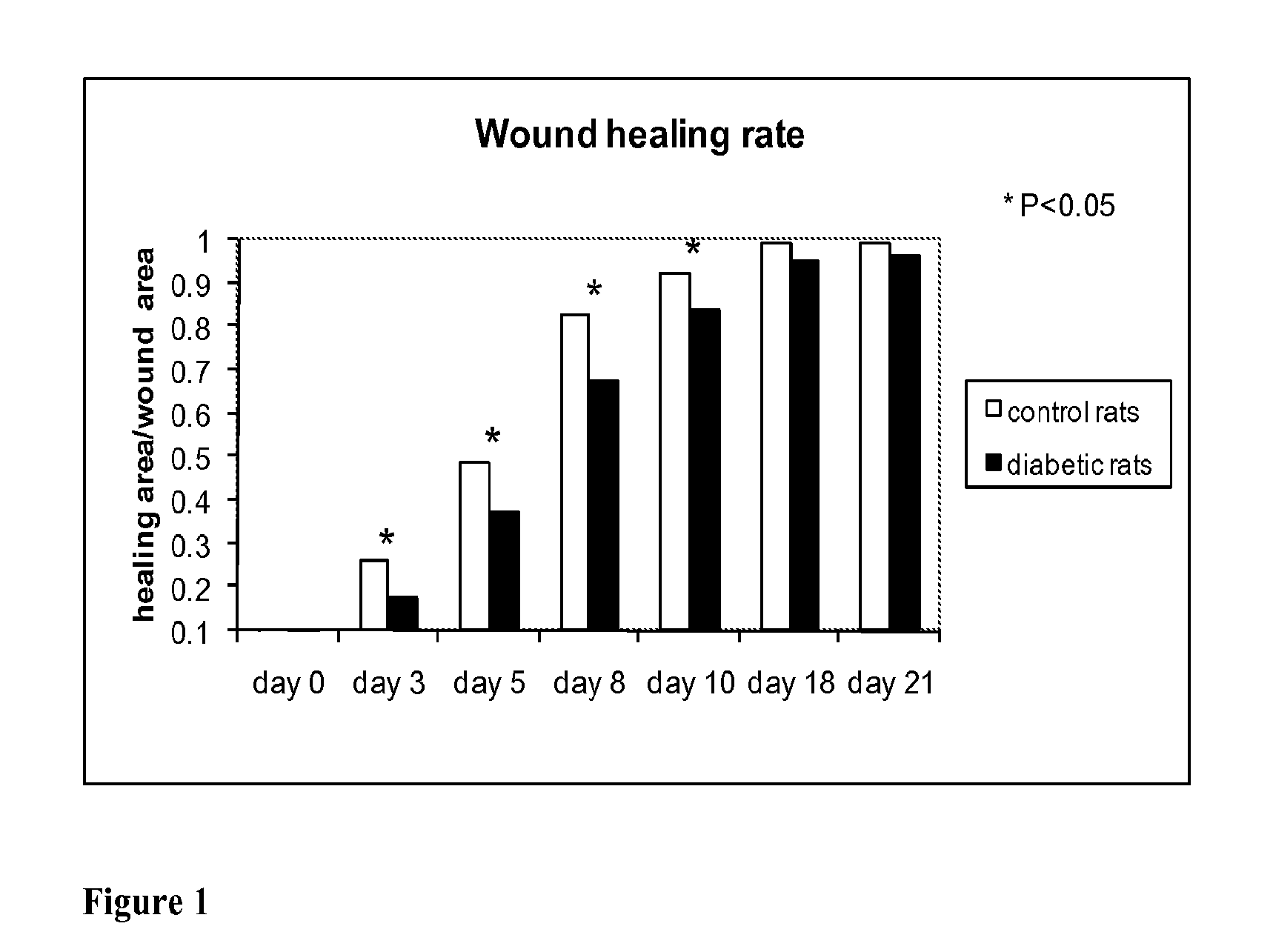
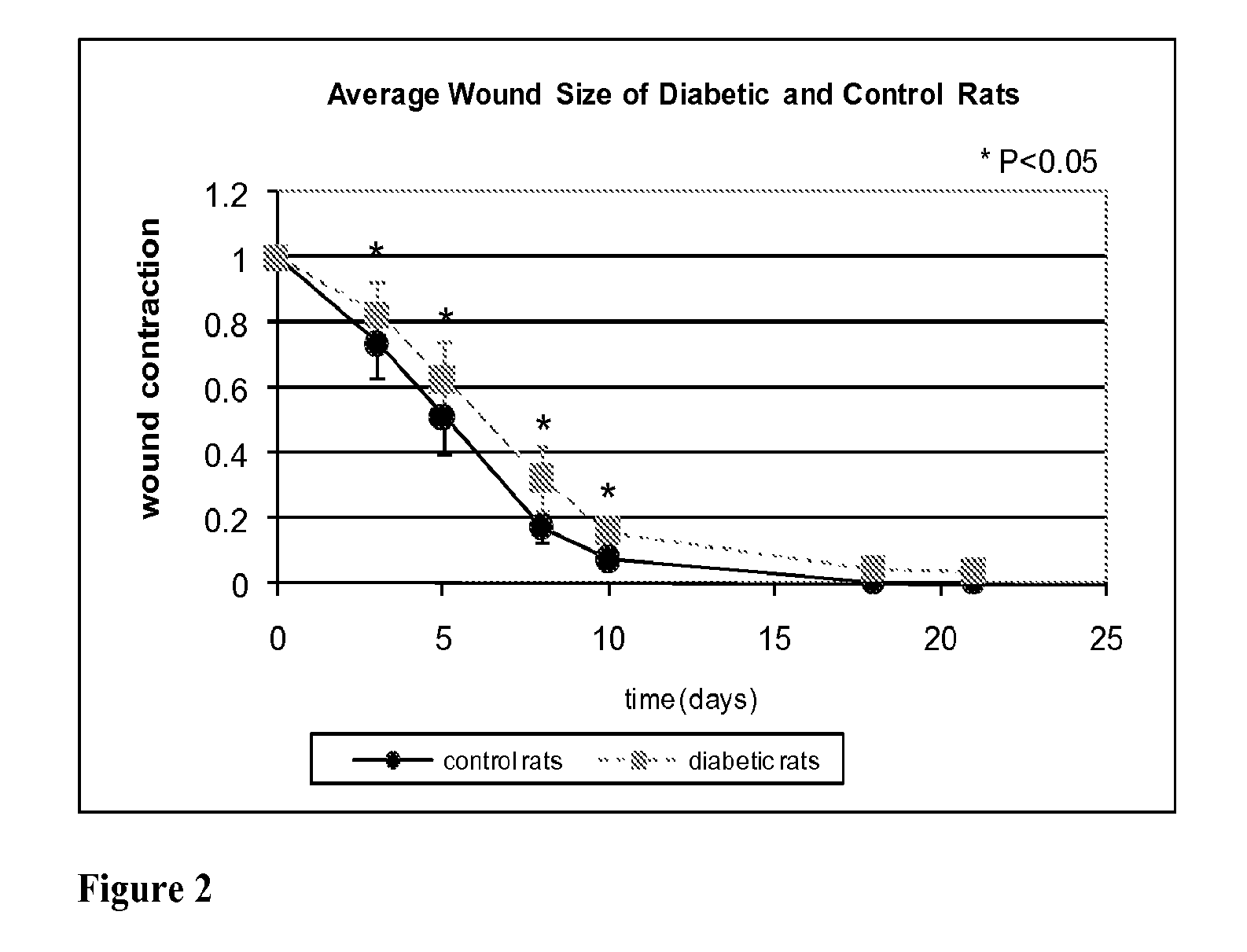
Methods for Measuring Changes in Optical Properties of Wound Tissue and Correlating Near Infrared Absorption (FNIR) and Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy Scattering (DRS) With Tissue Neovascularization and Collagen Concentration to Determine Whether Wound is Healing
ActiveUS20110124987A1Reduction factorDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyReflectance spectroscopyDiffusion equation
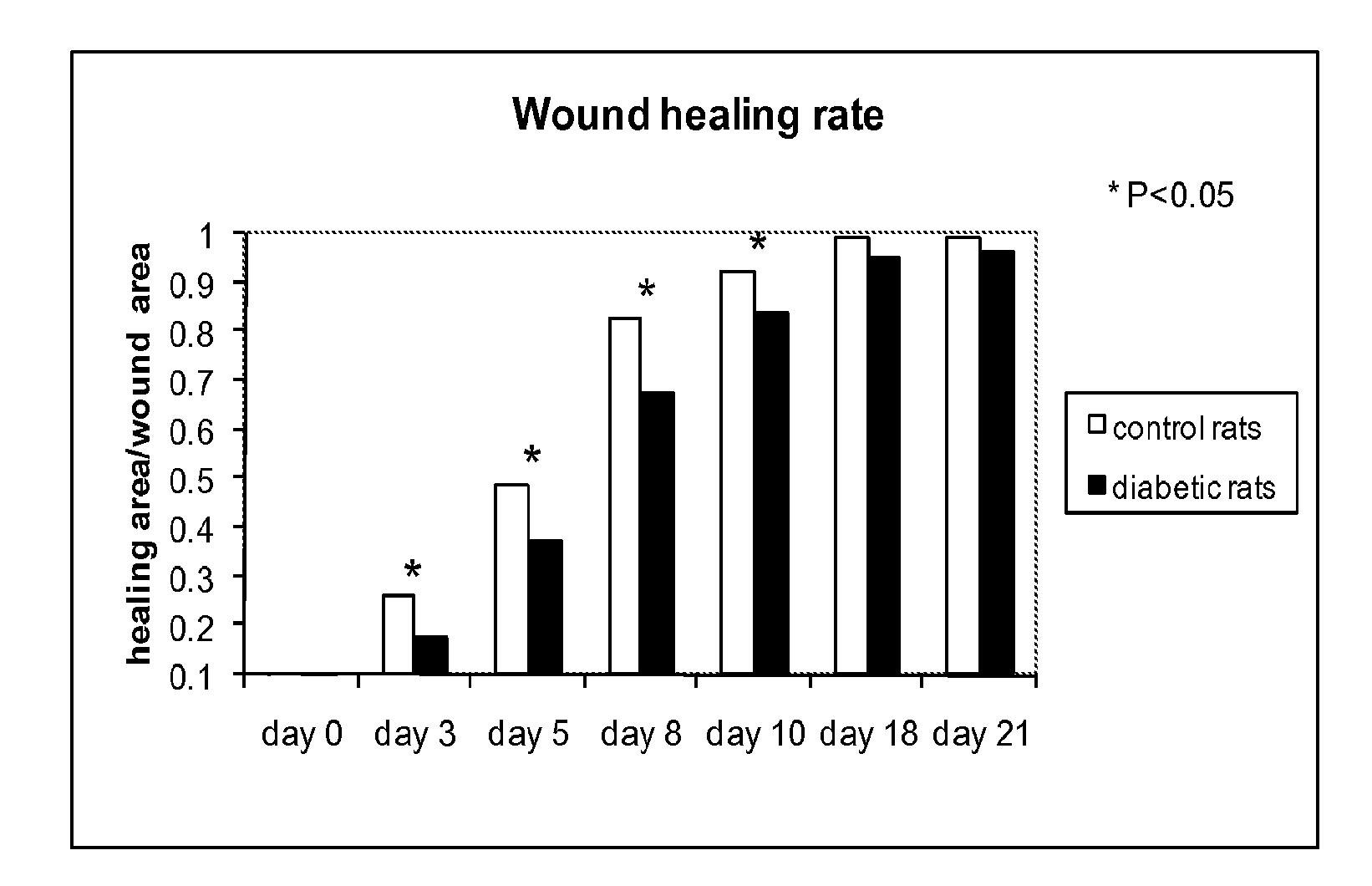
Optical changes of tissue during wound healing measured by Near Infrared and Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy are shown to correlate with histologic changes. Near Infrared absorption coefficient correlated with blood vessel in-growth over time, while Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS) data correlated with collagen concentration. Changes of optical properties of wound tissue at greater depths are also quantified by Diffuse Photon Density Wave (DPDW) methodology at near infrared wavelengths. The diffusion equation for semi-infinite media is used to calculate the absorption and scattering coefficients based on measurements of phase and amplitude with a frequency domain or time domain device. An increase in the absorption and scattering coefficients and a decrease in blood saturation of the wounds compared to the non wounded sites was observed. The changes correlated with the healing stage of the wound. The methodologies used to collect information regarding the healing state of a wound may be used to clinically assess the efficacy of wound healing agents in a patient (e.g., a diabetic) and as a non-invasive method
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
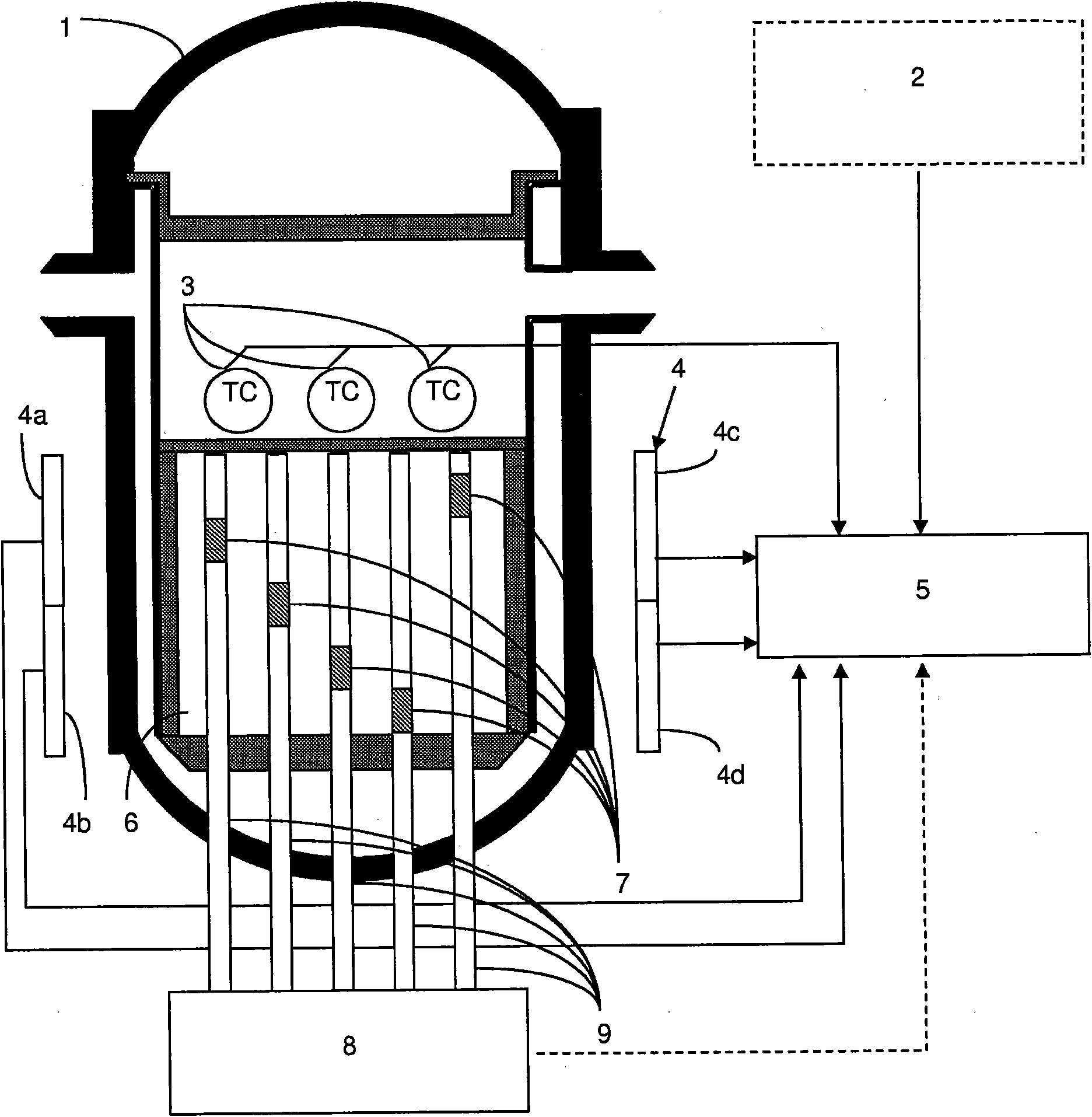
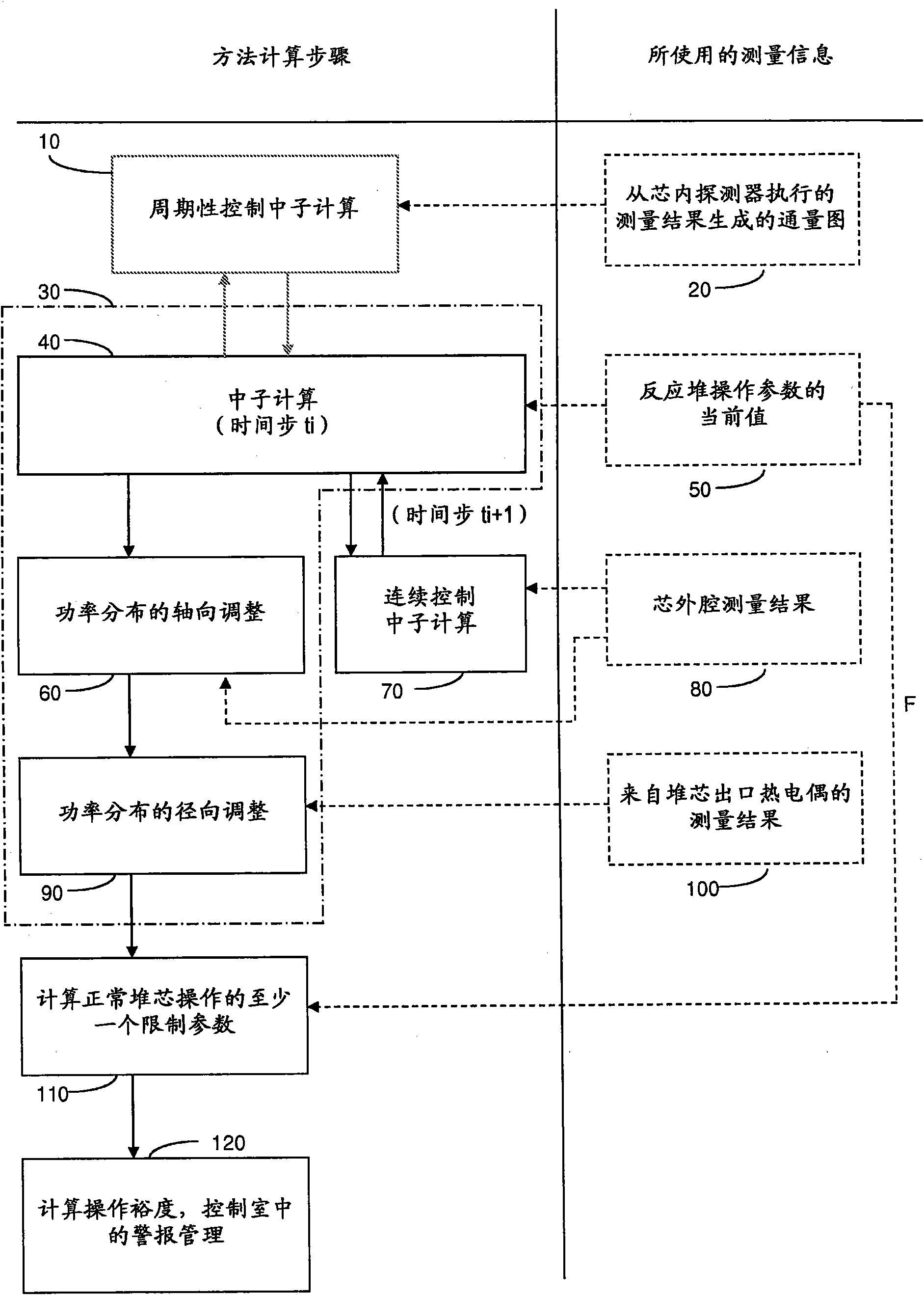
Method for determining the volumetric power distribution of the core of a nuclear reactor
ActiveCN101669176AAccurate and effective monitoringOptimizing TransientsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The invention relates to a method for determining (30) the volumetric power distribution of the core of a nuclear reactor using a set of detectors for measuring a neutronic flow provided outside the reactor vessel, and a set of probes for measuring the temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the fuel assemblies. The method (30) comprises the step of determining a first volumetric power distribution using a neutronic calculation code (40) instantaneously solving the diffusion equation and updating the isotopic balance of the core during the fuel depletion based on values of the core operation parameters, and the step of determining a new volumetric power distribution by adjusting (60 and 90) the first volumetric power distribution using the measures provided by the sensors for measuringthe neutronic flow and provided outside the reactor vessel (80) and by the temperature measuring probes (100).
Owner:FRAMATOME ANP
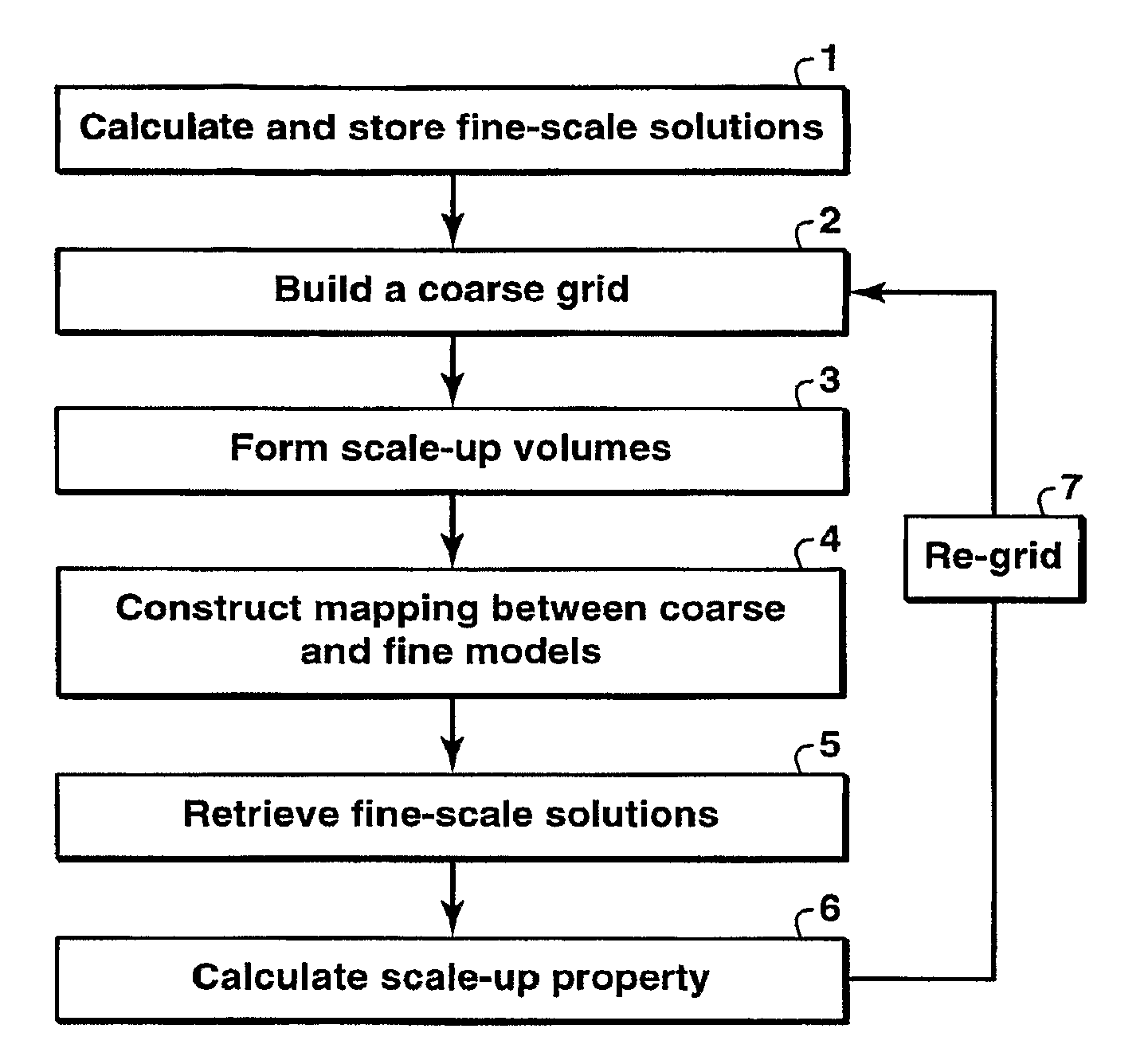
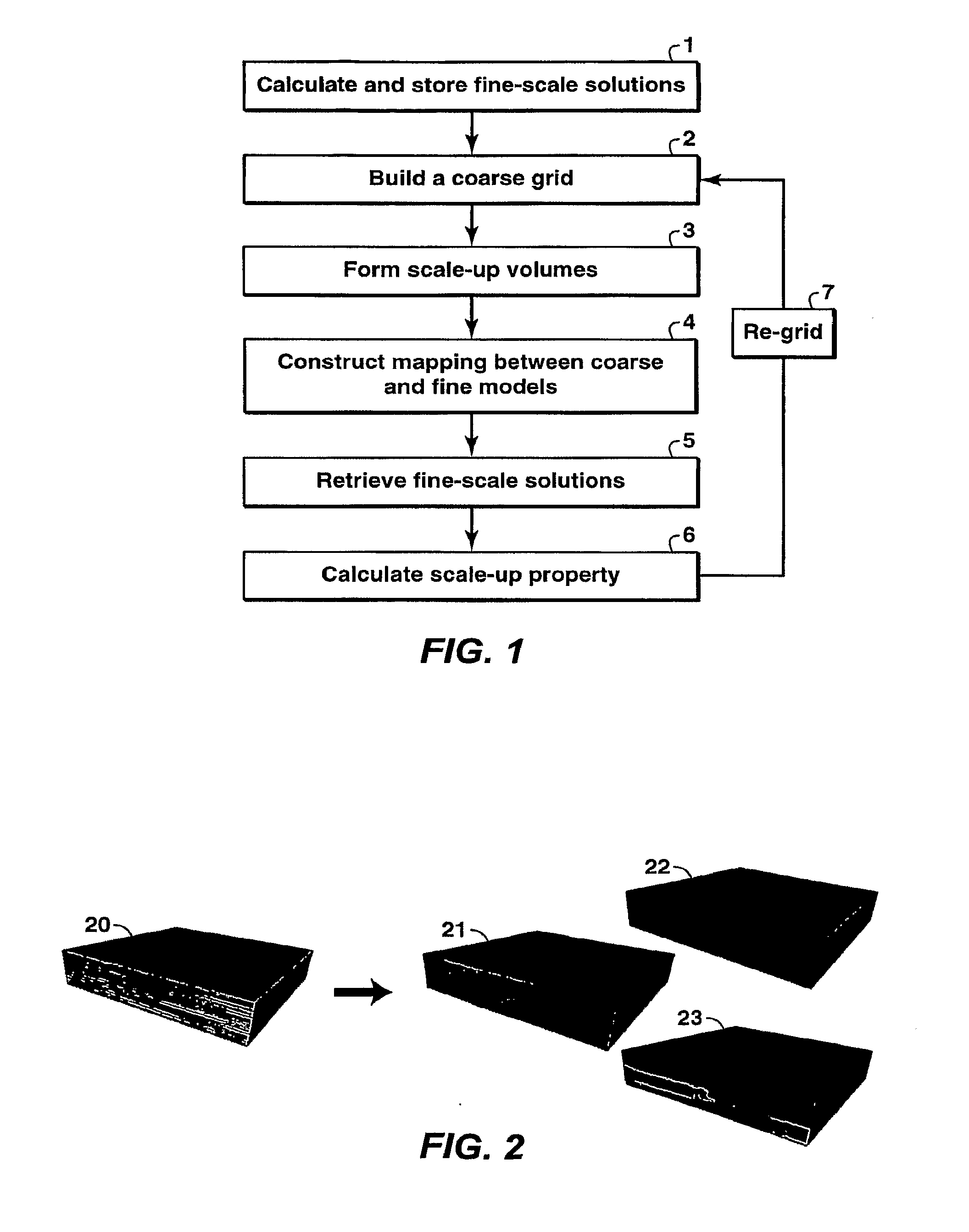
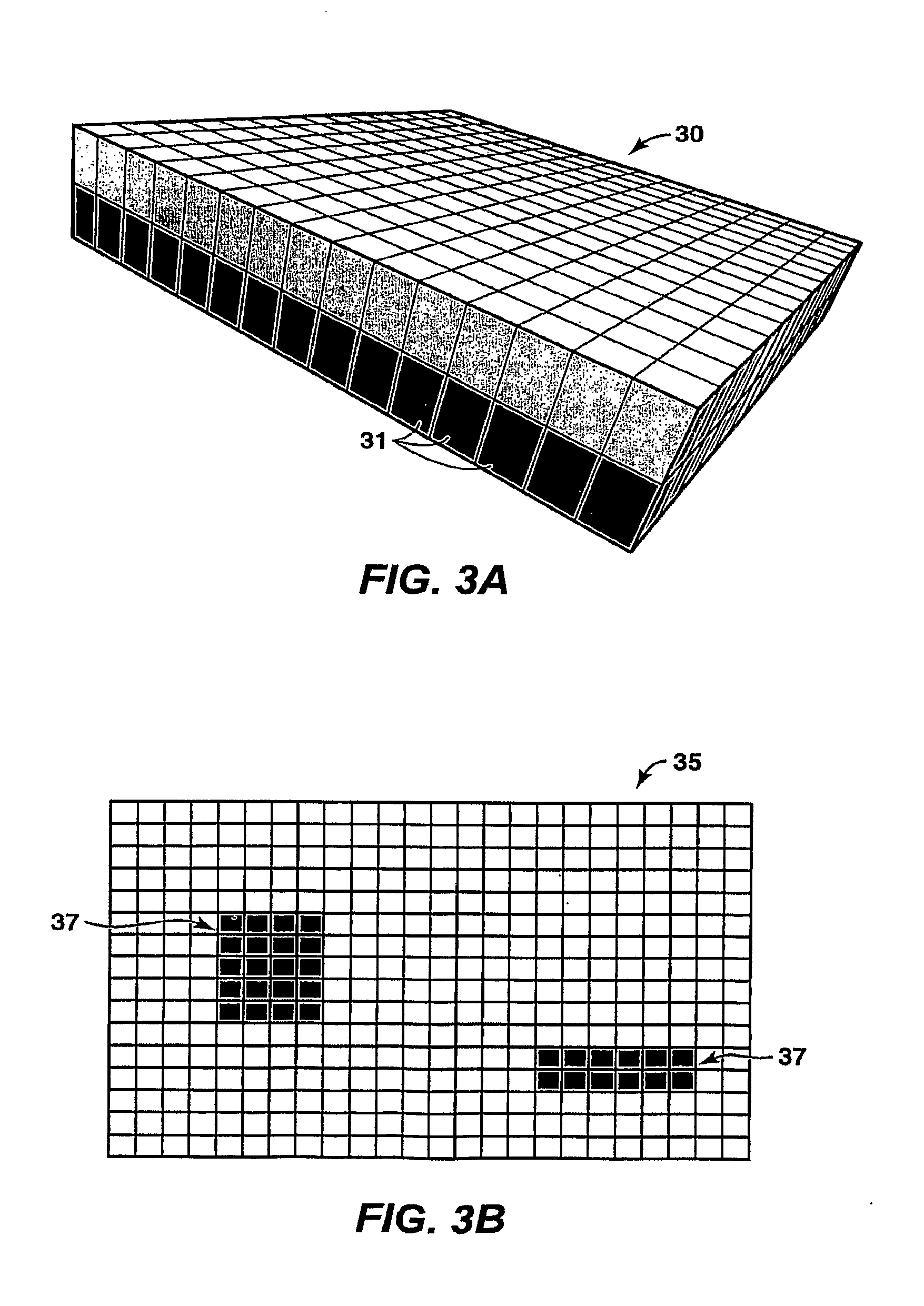
Upscaling Reservoir Models By Reusing Flow Solutions From Geologic Models
ActiveUS20090306945A1Faster and cost grid optimizationEfficient executionComputation using non-denominational number representationAnalogue computers for heat flowModel methodPorous medium
Method is provided for simulating a physical process such as fluid flow in porous media by performing a fine-grid calculation of the process in a medium and re-using the fine grid solution in subsequent coarse-grid calculations. For fluid flow in subsurface formations, the method may be applied to optimize upscaled calculation grids formed from geologic models. The method decreases the cost of optimizing a grid to simulate a physical process that is mathematically described by the diffusion equation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
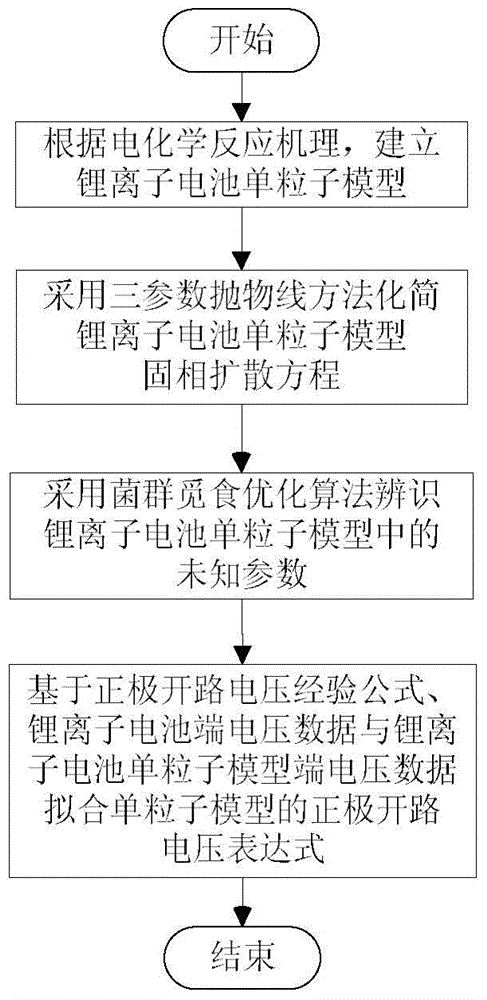
Mechanism modeling method for lithium ion battery
ActiveCN104899439ASimple structureRecognition speed is fastSecondary cellsSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringElectric vehicle
The invention belongs to the technical field of a lithium ion power battery of an electric vehicle, relates to a mechanism modeling method for the lithium ion battery and overcomes the defects that the electrochemical model of the lithium ion battery is complex in structure, parameters are difficult to identify and the experimental model precision is low. The mechanism modeling method comprises the following steps of: (1) building a single-particle model of the lithium ion battery; (2) simplifying a solid-phase diffusion equation in the single-particle model of the lithium ion battery by adopting a three-parameter parabola method; (3) identifying unknown parameters in the single-particle model of the lithium ion battery by adopting a bacteria foraging optimization algorithm; and (4) fitting an anode open-circuit voltage expression of the single-particle model of the lithium ion battery. According to the invention, by adopting the three-parameter parabola method, the structure of the single-particle model of the lithium ion battery is simplified; the unknown parameters in the single-particle model of the lithium ion battery are identified by adopting the bacteria foraging optimization algorithm, the identification speed is high, and the globally optimal solution is obtained; and the mechanism modeling method provides theoretical support for the state estimation, life prediction and characteristic analysis of the lithium ion battery.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
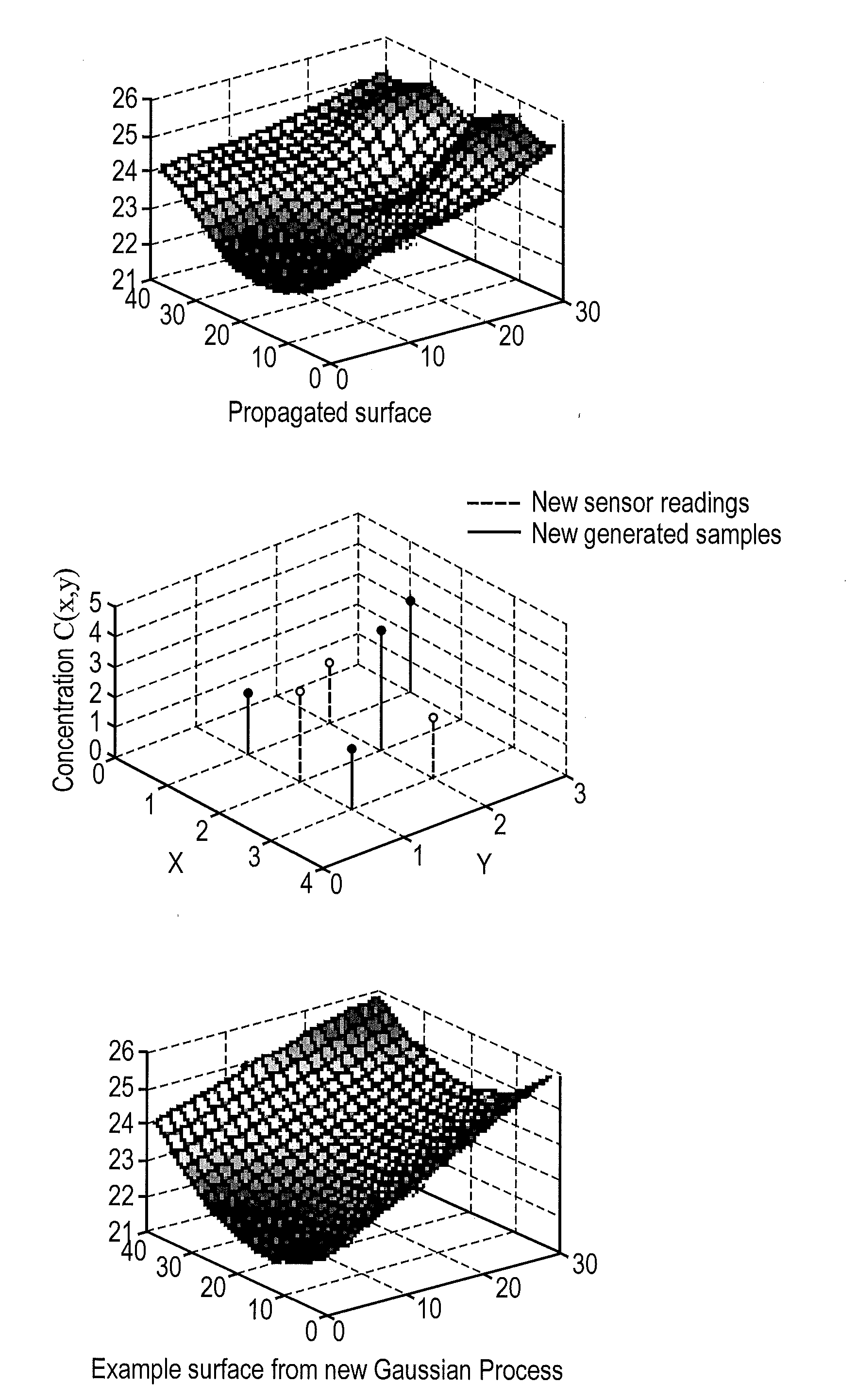
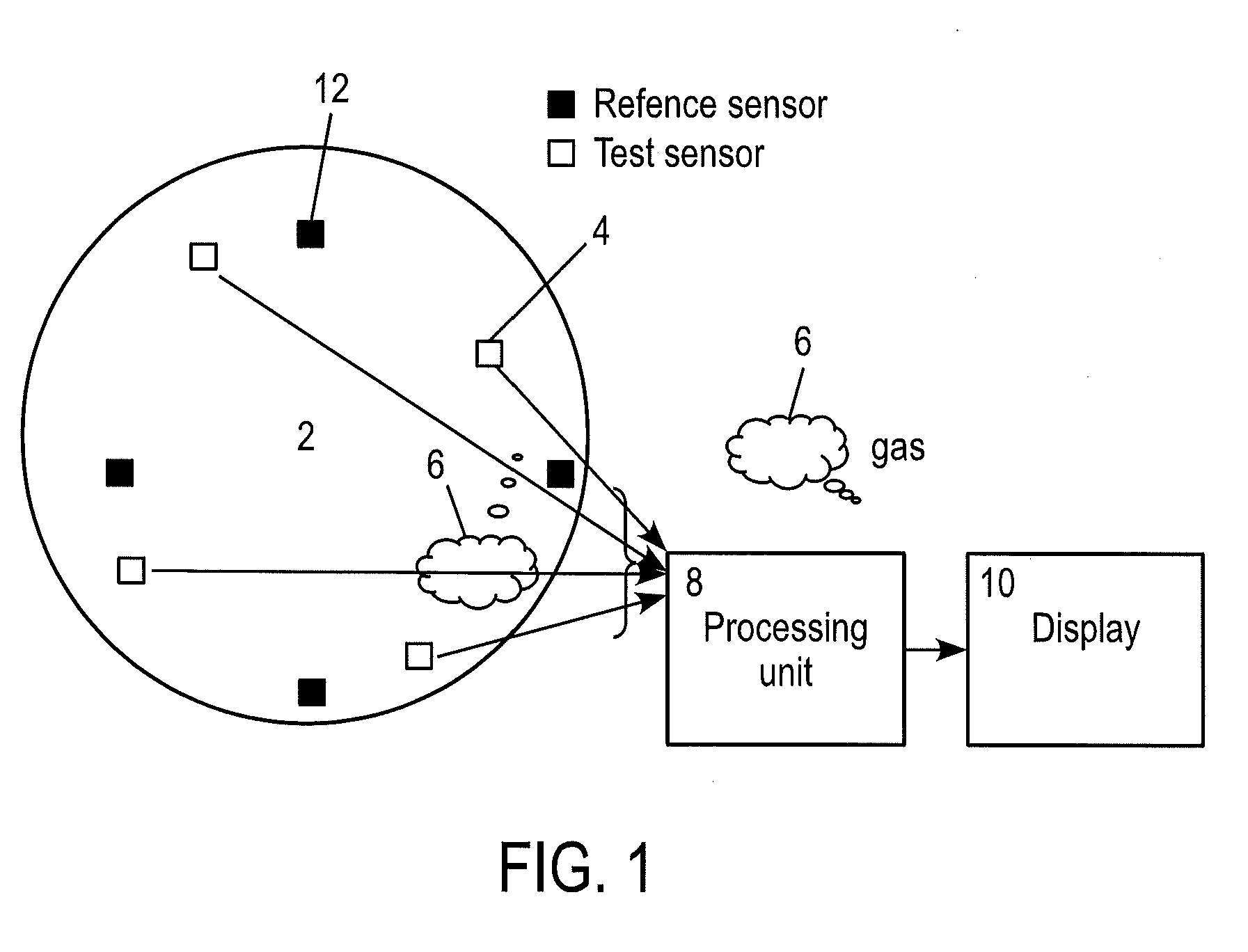
Sensor systems for estimating field
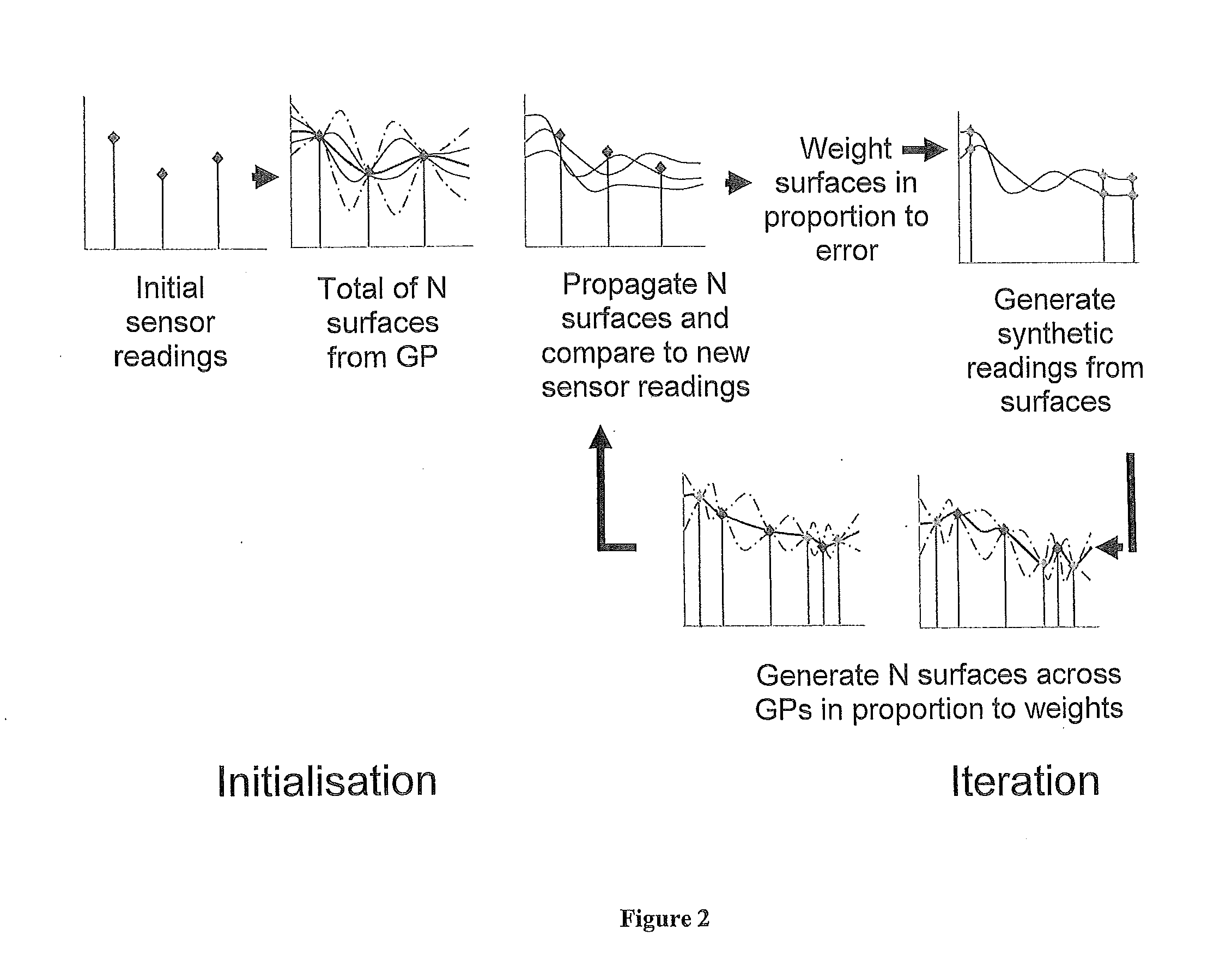
InactiveUS20120072189A1SamplingComputation using non-denominational number representationSensor arraySampling instant
In a sparse sensor array for detecting the progression of a cloud of gas within a confined space, a method is disclosed for estimating a distribution of the cloud of gas throughout the confined space. The method includes determining at each interval a plurality of functions representing possible distributions of the gas cloud by a Gaussian process, employing a particle filtering process to predict the progression of each such function at a subsequent sampling instant, using a diffusion equation for the gas cloud, attaching a likelihood value to each function at the subsequent sampling instant, and determining a revised set of functions with associated likelihood values, and repeating the above steps.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Detection method and test device for catalytic properties of heatproof material based on emission spectrum
ActiveCN103411940AObtain Surface Catalytic CoefficientEasy to operateFluorescence/phosphorescenceGas phaseInlet valve
The invention provides a detection method and a test device for catalytic properties of a heatproof material based on an emission spectrum. The test device comprises a plasma power supply, an air inlet valve, an infrared temperature measurement window, a double-colorimetric thermodetector, an emission piston, an induction heating power supply, a reaction cavity, a resistance vacuum gauge, a vacuum flange, an induction coil, a zirconium oxide support frame, a single-shaft electric stepping machine, a long-focus focusing lens and a short-focus focusing lens. According to an 'atom-dissipation' laboratory representation method based on emission spectrum diagnosis disclosed by the invention, the disturbance of the surface of the material to gas-phase atoms is quantitatively analyzed by an actinic ray strength method, and the recombination coefficient of the gas-phase atoms at the surface of the material is calculated according to mathematic models of gas-phase diffusion and object surface atomic mass conservation conditions. The test device has the advantages that the operation is simple; based on a catalytic mechanism and by virtue of an emission spectrum diagnosis technique, the surface catalysis coefficients of conductive heatproof materials in a temperature range of 600-3000 DEG C can be obtained through measuring the concentration change of oxygen atoms at the surfaces of the materials to represent the surface catalytic properties of the materials based on catalysis principles and diffusion equations.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
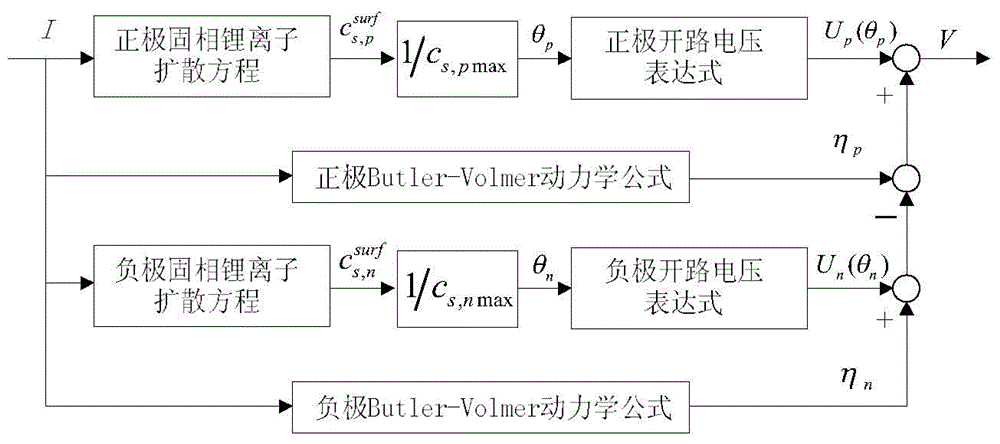
Device estimating a state of a secondary battery
ActiveUS8093902B2Reduce operating loadBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical responseChemical reaction
A diffusion estimation unit follows a diffusion equation in an active material that is represented by a polar coordinate to estimate a distribution in concentration of lithium in the active material. An open circuit voltage estimation unit obtains an open circuit voltage in accordance with a local SOC(θ) based on a concentration of lithium obtained at an interface of the active material as estimated by the diffusion estimation unit. A current estimation unit uses a battery's voltage measured by a voltage sensor, the estimated open circuit voltage, and a parameter value that is set for the battery by a battery parameter value setting unit, and follows a voltage-current relationship model expression simplified from an electrochemical reaction expression to estimate the battery's current density. A boundary condition setting unit sequentially sets a boundary condition for the diffusion equation of the diffusion estimation unit for the active material's interface, as based on the battery's estimated current density. Thus a battery model that allows an internal state to be estimated based on an electrochemical reaction dynamically and can also achieve an alleviated operating load can be used to estimate a state of a secondary battery.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
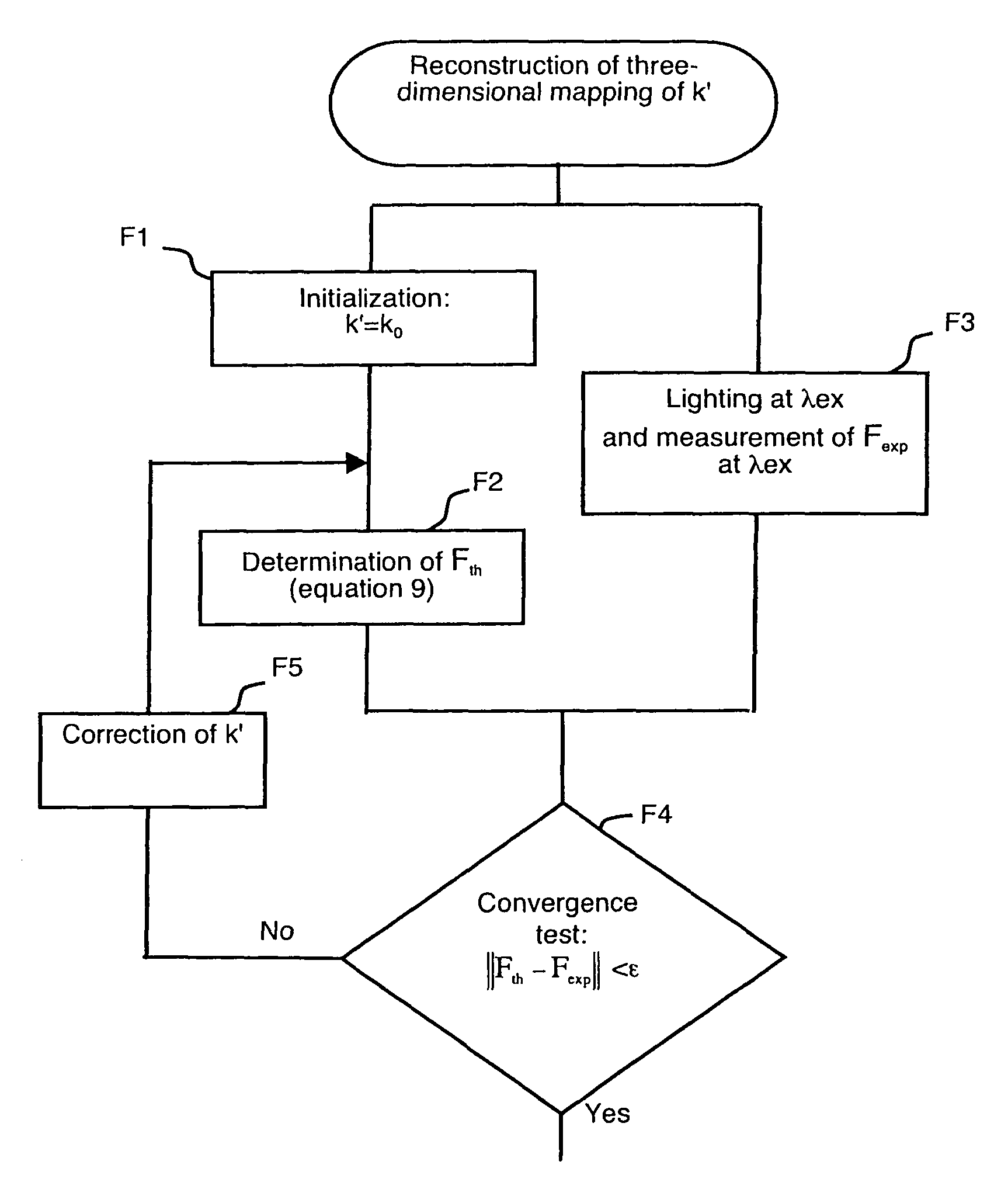
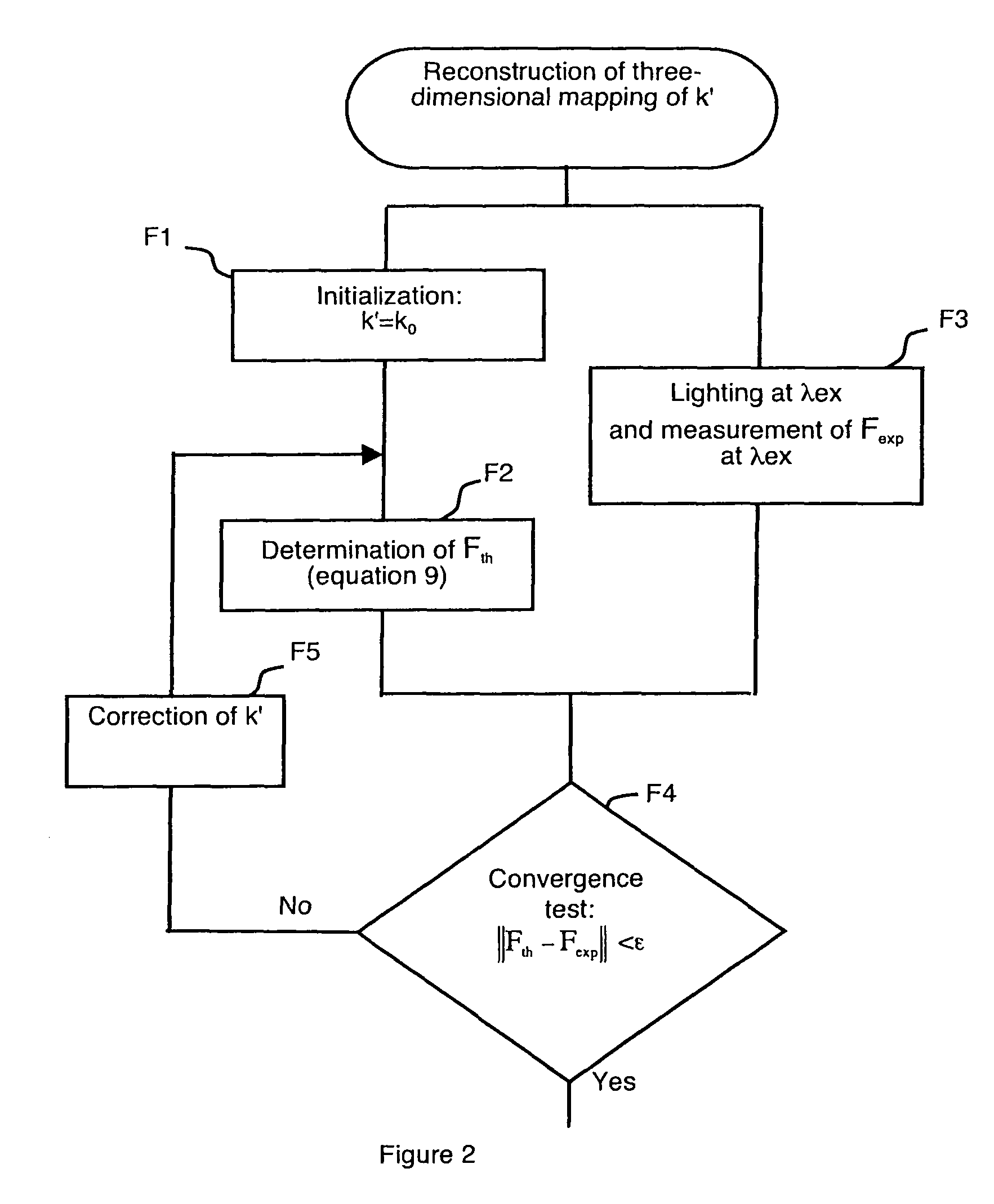
Method for reconstructing the distribution of fluorophores in a non-homogeneous medium by optical tomography in continuous mode
ActiveUS7965389B2Reconstruction from projectionRadiation pyrometryContinuous lightUltrasound attenuation
The method enables a non-homogeneous diffusing object to be examined by illuminating the object with a continuous light by means of a light source. It previously comprises reconstruction of the three-dimensional spatial mapping of an attenuation variable representative of the diffusion and absorption non-homogeneities of the object, by resolving a diffusion equation∇2F({right arrow over (r)}S, {right arrow over (r)})−k′2({right arrow over (r)})F({right arrow over (r)}S, {right arrow over (r)})=ASδ({right arrow over (r)}−{right arrow over (r)}S).In the diffusion equation, AS is a constant, {right arrow over (r)} the spatial coordinate of any point of the mesh of a volume at least partially containing the object, and {right arrow over (r)}S the spatial coordinate of the light source. The transfer functions of an equation used for reconstructing the distribution of fluorophores integrate the attenuation variable reconstituted in this way.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
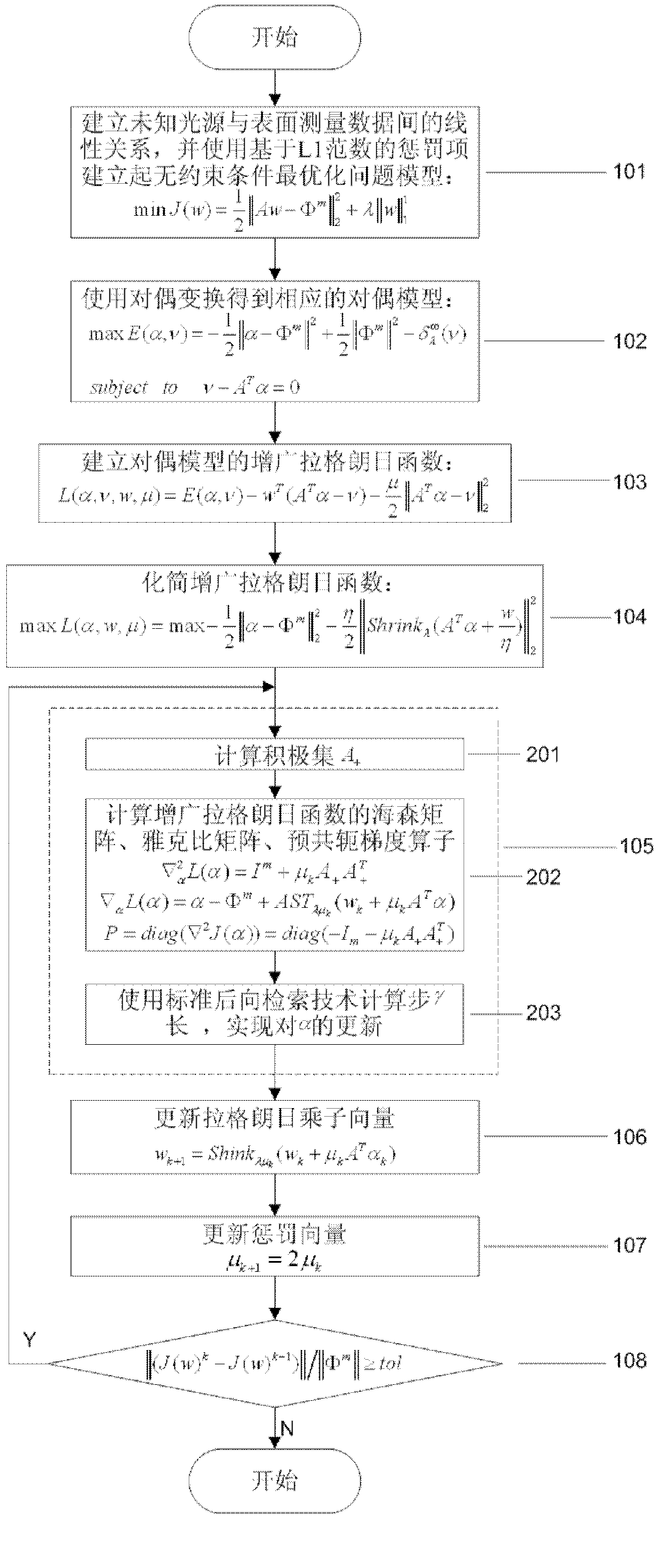
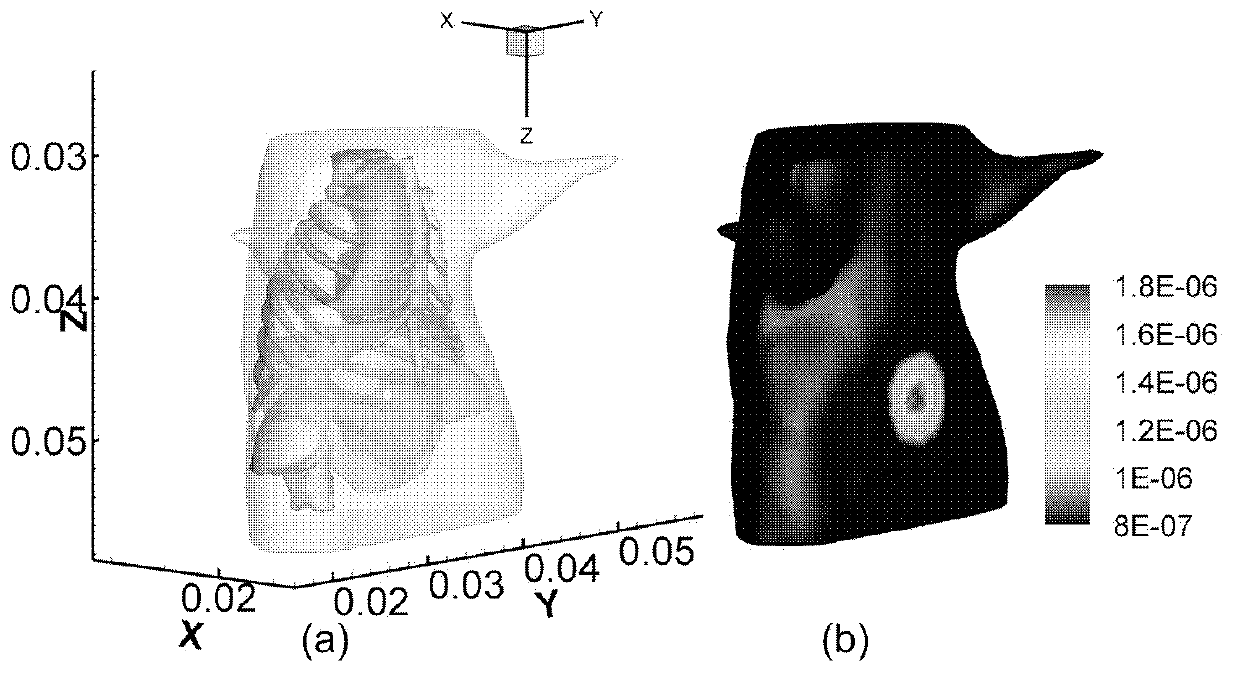
Auto-fluorescence tomography re-establishing method based on multiplier method
ActiveCN102988026AImprove robustnessAccurate and reliable light source distribution informationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSteep descentDescent direction
The invention discloses an auto-fluorescence tomography re-establishing method based on a multiplier method. The auto-fluorescence tomography re-establishing method based on the multiplier method comprises the following steps of: carrying out discretization by using a finite element method diffusion equation, and establishing an optimization problem model without constraint conditions based on a penalty term of an L1 norm; obtaining a dual model of the optimization problem model without constraint conditions; establishing an augmentation lagrange function of the dual model; simplifying the maximum function of the augmentation lagrange function; solving the maximum value of the augmentation lagrange function by using a truncated-Newton algorithm; upgrading the target vector by using the gradient of the augmentation lagrange function as the steepest descent direction of a target vector; upgrading a penalty vector; and calculating an objective function value J(w), calculating k=k+1 if the ratio of the norm of J(w)k-J(w)(k-1) to the norm of Pai m being not smaller than t0l is real, and jumping to the step S4, otherwise, ending the calculation, wherein t0l is the convergence efficiency threshold value of the target function. The auto-fluorescence tomography re-establishing method provided by the invention can quickly obtain accurate and reliable light source distribution information within a large image-forming region, so that other parameters except from the regularization parameter can realize self-adaptive adjustment for improving the image-forming robustness.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fractal derivative simulation method of anomalous diffusion dynamic data reconstruction of data in concreate
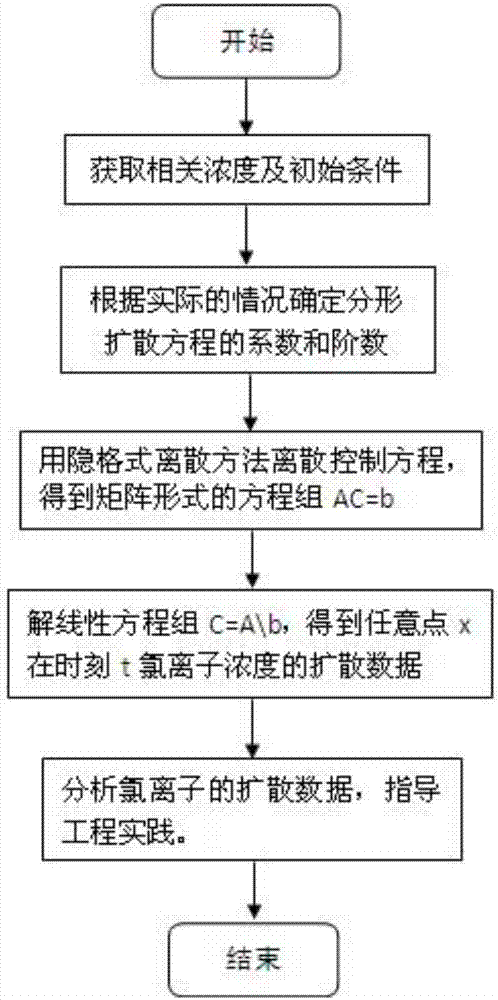
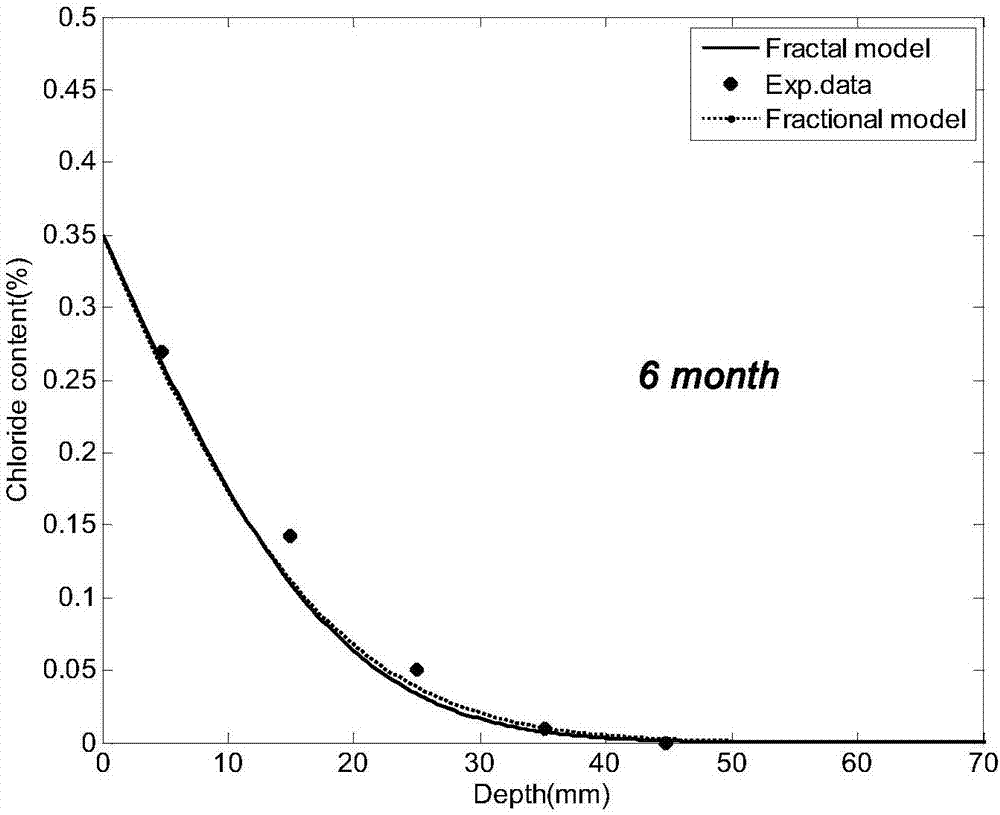
ActiveCN106951617AClear structureSimple calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPeak valueDiffusion equation
The invention discloses a fractal derivative simulation method of the anomalous diffusion dynamic data reconstruction of data in concreate. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) determining an initial boundary condition; (2) determining the parameter of a diffusion equation; (3) adopting a difference method to enable a control equation to be discrete, adopting implicit scheme dispersing on an aspect of space, and determining a mesh point number according to a distribution scale of substances which need to be subjected to numerical simulation, and tidying the discrete control equation to obtain an equation set AC=b of a matrix form, wherein a time point number is Nt+1, and a space point number is Nx+1; (4) solving a linear equation set C=A / b to obtain the diffusion data of chloride ion concentration of any point x at a moment t; and (5) analyzing the diffusion data of chloride, and guiding engineering practice. By use of the method, the anomalous diffusion process and the time evolution characteristics of the condition in the concrete can be accurately simulated, peak value arrival time and advance speed in a chloride diffusion process are predicted, and a reliable guidance is provided for engineering structure design and prevention
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Control system of secondary battery and hybrid vehicle equipped with the same
ActiveUS8018203B2High precisionHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringDiffusion equation
A battery model unit includes an electrode reaction model unit based on the Butler_Volmer equation, an electrolyte lithium concentration distribution model unit analyzing a lithium ion concentration distribution in an electrolyte solution by a diffusion equation, an active material lithium concentration distribution model unit analyzing an ion concentration distribution in a solid state of an active material by a diffusion equation, a current / potential distribution model unit for obtaining a potential distribution according to the charge conservation law, a thermal diffusion model unit and a boundary condition setting unit. The boundary condition setting unit (66) sets a boundary condition at an electrode interface such that a reacting weight at the electrode interface is not determined by a difference in material concentration between positions but a deviation from an electrochemically balanced state causes a change with time in lithium concentration at the interface and thus a (time-based) drive power for material transportation. Thereby, an appropriate charge / discharge control can be performed based on the battery model having the appropriately set battery condition.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
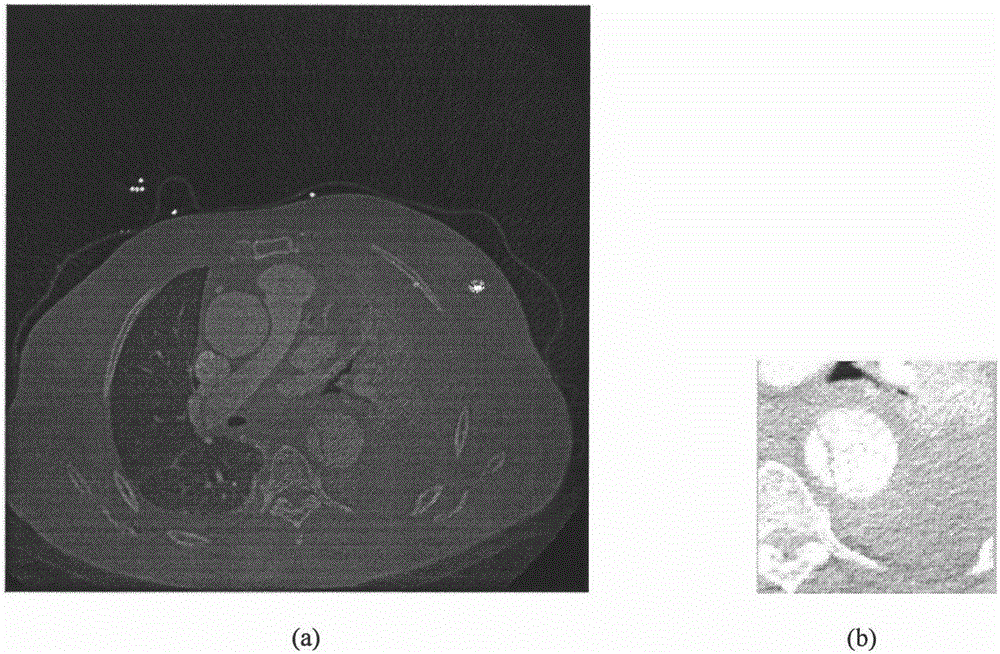
Human body thoracic and abdominal cavity CT image aorta segmentation method based on GVF Snake model
InactiveCN105976384AAvoid the disadvantages of heavy workload and long time consumptionGood repeatabilityImage enhancementImage analysisExternal energyDiffusion equation
The invention discloses a human body thoracic and abdominal cavity CT image aorta segmentation method based on a GVF Snake model. The method overcomes the shortcomings of the heavy workload and long time consuming of the traditional manual and semi-automatic segmentation, the repeatability of the method is good, and the uncertainty caused by artificial segmentation is prevented. The method includes (1) reading a CT image and performing image preprocessing; (2) performing the initial profile setting of the GVF Snake model on the image obtained after the preprocessing; (3) obtaining the edge image of the image after the preprocessing; (4) obtaining gradient vector flow GVF as the external energy field by the diffusion equation based on the obtained edge image; (5) establishing an internal energy model to maintain the smoothness of the profile; and (6) constructing an energy function E by means of internal energy and external energy, obtaining the minimum value of energy E by means of iteration operation, and the target boundary of the profile can be obtained at the end. The method has important application values in the field of human body thoracic and abdominal cavity aorta interlayer segmentation diagnosis treatment.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Anisotropy diffusion image noise reduction method based on McIlhagga edge detection operator
The invention discloses an anisotropy diffusion image noise reduction method based on a McIlhagga edge detection operator and belongs to the field of digital image noise reduction. The anisotropy diffusion image noise reduction method based on the McIlhagga edge detection operator is used for restraining speckle noise in an ultrasound image. The anisotropy diffusion image noise reduction method based on the McIlhagga edge detection operator comprises the steps that the McIlhagga edge detection operator with high robustness to noise is used for conducting edge detection on the ultrasound image so that a two-value edge image can be obtained; the two-value edge image is converted into a gradually-varied gray-level edge image through a distance mapping function; the gradually-varied edge image serves as the edge detection operator in an anisotropy diffusion equation, and noise reduction of the ultrasound image is achieved through a numerical solution method with a finite difference in an iterative mode. The method is capable of effectively reducing noise and maintaining the edge and high in robustness under the condition of large noise.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
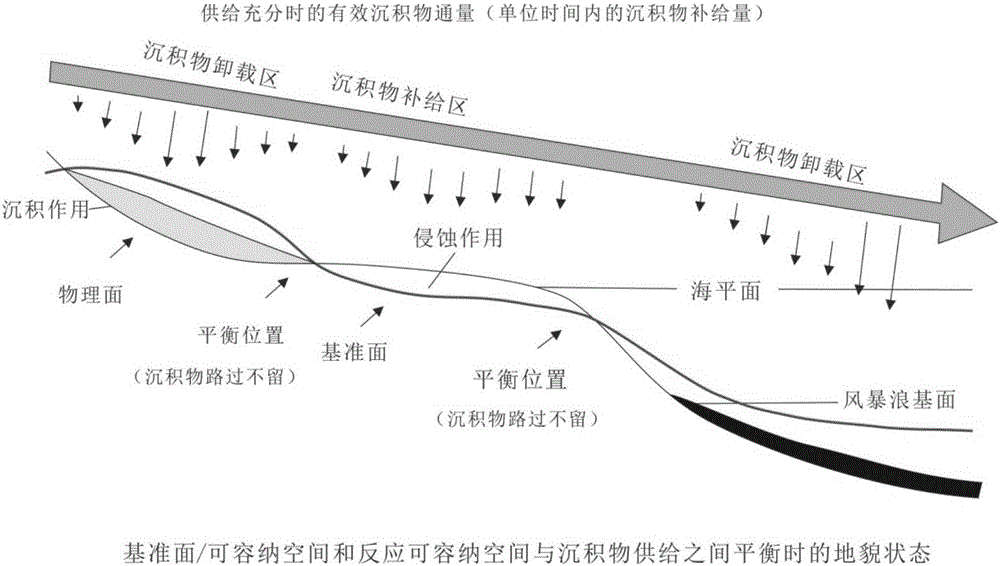
Method for simulating deposition on basis of deposition process control of reference planes
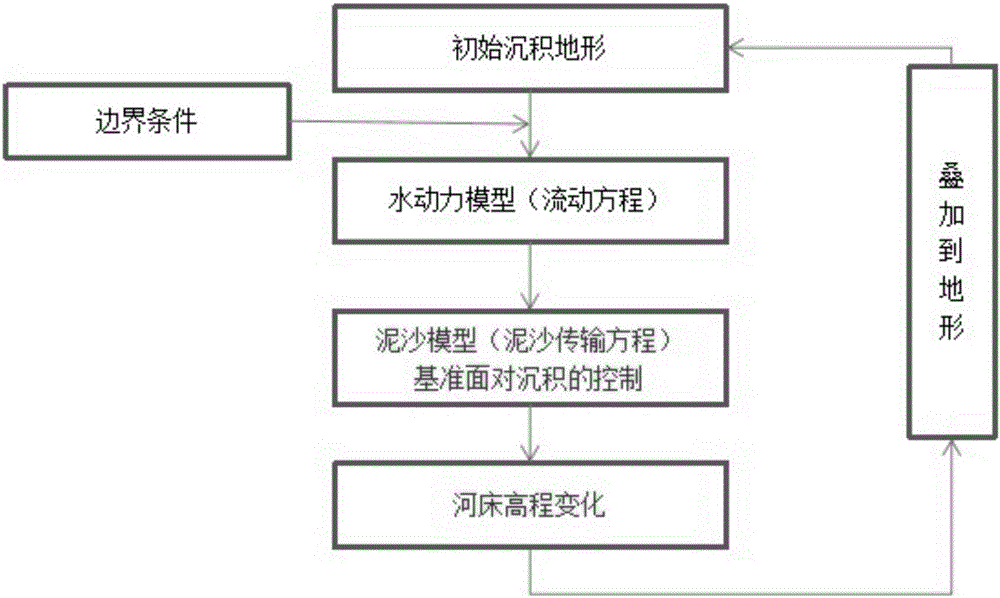
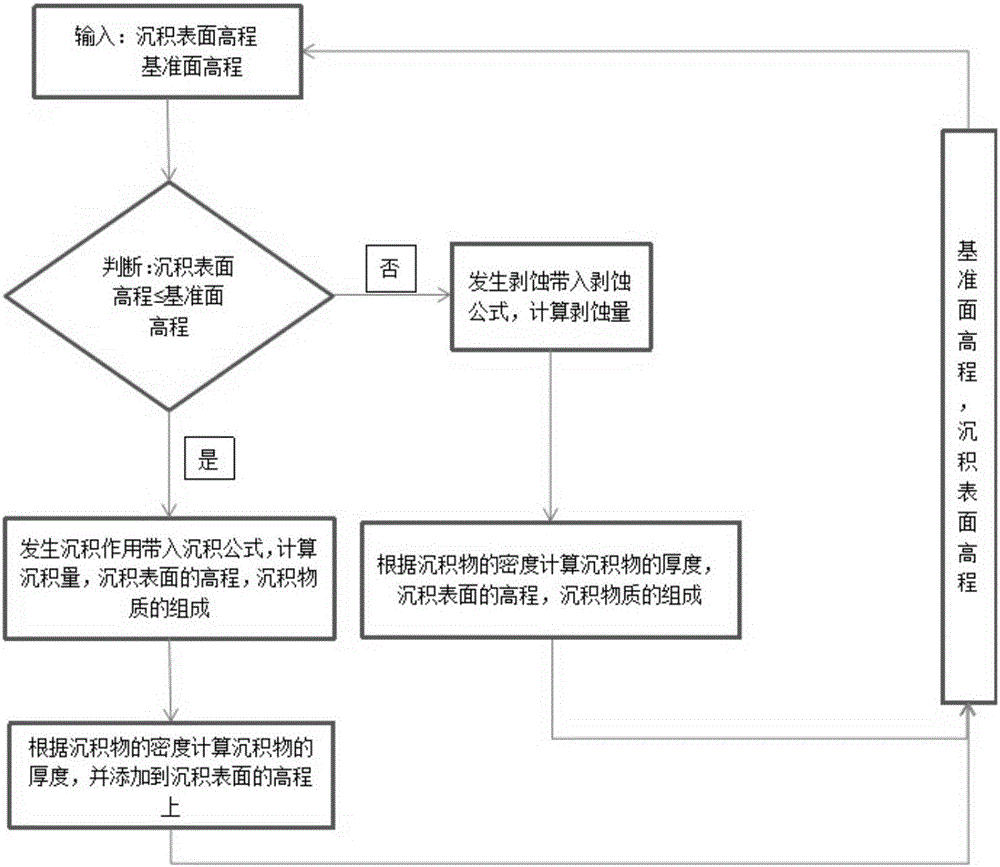
ActiveCN106202749AConsider the effects of sedimentationShort simulation timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCyclic processDiffusion
The invention discloses a method for simulating deposition on the basis of deposition process control of reference planes. The method includes analyzing deposition environments of deposition zones by the aid of well logging, mud logging and rock core information and determining change conditions of the reference planes and ancient landform conditions by the aid of burial history information; inputting ancient landforms into hydrodynamic models as initial landforms according to ancient landform analysis, simulating and reconstructing hydrodynamic characteristics of research zones, simulating and reconstructing transportation and deposition of sediment on the basis of hydrodynamic research according to sediment transport and diffusion equations, constraining deposition and denudation of deposits by the aid of the reference planes on the basis of transportation and deposition of the sediment, superposing deposition and denudation of the deposits on the initial landforms to be used as landforms for next simulation so as to carry out cyclic processes for simulating and reconstructing deposition. The method has the advantages that conditions of conditions of the reference planes are considered in simulation processes, and accordingly deposition at basin level can be simulated; the method is short in simulation time, and correction can be repeatedly carried out until requirements of geological characteristics are met.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
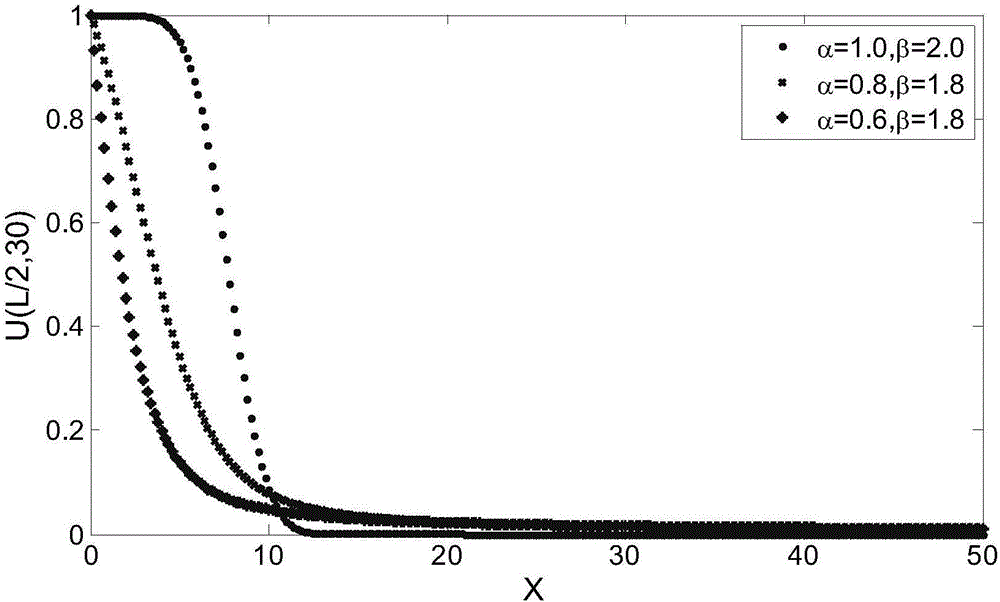
Anomalous diffusion simulation method based on discrete fraction order difference
InactiveCN104392127AKeep discrete memory effectsHigh expressionComplex mathematical operationsDiffusionMemory effect
The invention discloses an anomalous diffusion simulation method based on a discrete fraction order difference. The anomalous diffusion simulation method based on the discrete fraction order difference includes: using a one dimension classical diffusion equation for describing a diffusion phenomenon; defining the discrete fraction order difference, using the discrete fraction order difference to discretize the one dimension classical diffusion equation, and performing numerical simulation according to initial boundary conditions. Compared with a diffusion model built by using a classical fraction order diffusion equation, a diffusion model built by using the anomalous diffusion simulation method based on the discrete fraction order difference is concise in expression, and convenient and fast in numerical simulation on the premise of maintaining discrete memory effects.
Owner:NEIJIANG NORMAL UNIV
Rapid sparse reconstruction method and equipment for exciting tomography fluorescence imaging
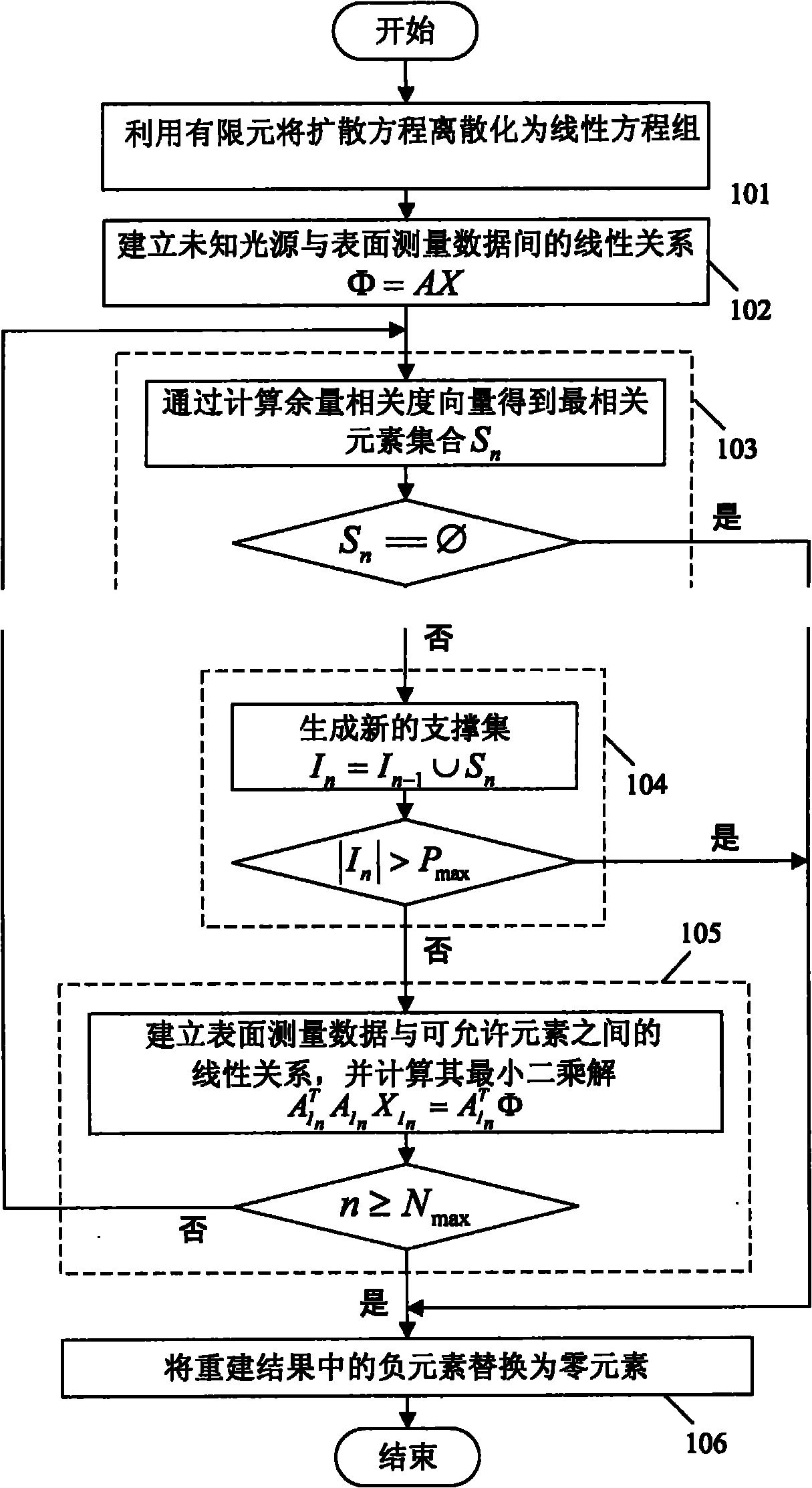
ActiveCN102034266AImprove rebuild speedAvoid oversmoothingImage analysis3D modellingDiffusionSparse constraint
The invention discloses a rapid sparse reconstruction method for exciting tomography fluorescence imaging (TFI), which comprises the following steps of: representing a diffusion equation into a linear equation by using a finite element theory; establishing a linear relation between unknown fluorescent light source distribution and boundary measuring data; calculating a surplus correlation vector to obtain the most relevant element set; merging the most relevant element set and a current support set to generate a new support set; dividing the discrete imaging space into an allowed area and a prohibited area by using the support set, and establishing a linear relation between surface fluorescence data and the allowed area; and substituting 0 for a negative element in a finally obtained solution vector. Heterogeneous characteristics of biological tissues are fully considered on the basis of a diffusion approximation model. In the process of reconstructing a light source, on the basis of sparse constraint of L1 norm, by regarding a TFI problem as a compressed sensing problem and positioning the light source by using a support set-based reconstruction method, the over-smooth phenomenonof a reconstruction result is effectively avoided, and the accuracy of TFI imaging is improved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adaptive tomographic fluorescence imaging (TFI) reconstructing method
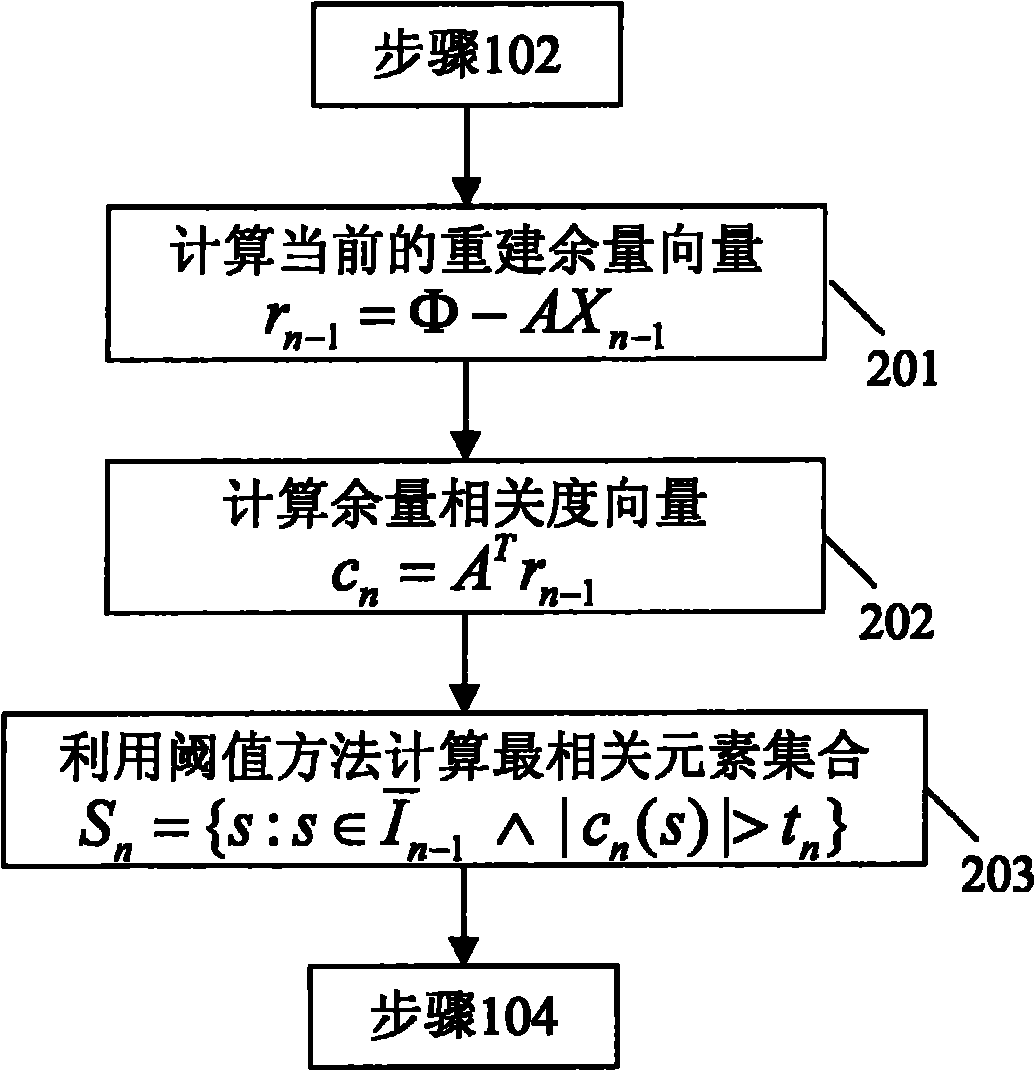
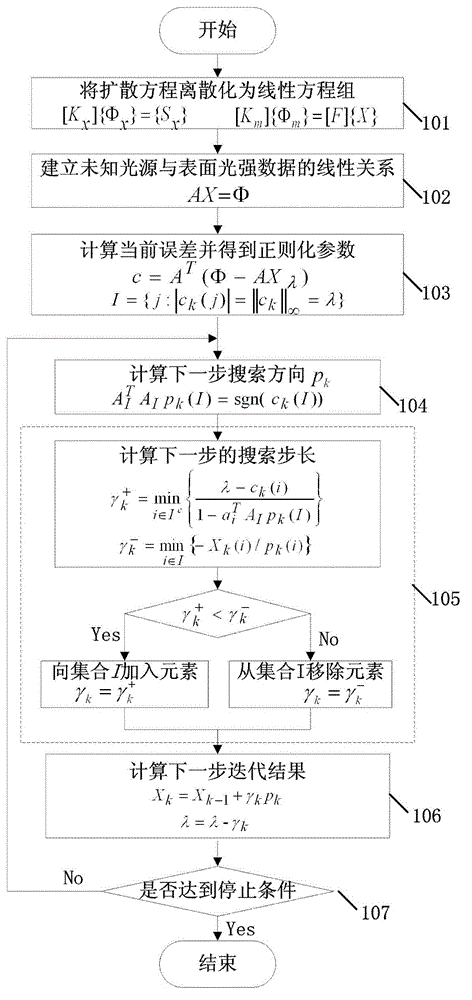
ActiveCN102940482AImprove robustnessImprove rebuild efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCorrelation coefficientCurrent element
An adaptive TFI reconstructing method includes converting a diffusion equation into a linear equation through a finite element method; constructing a linear relation between unknown fluorescent light source distribution and a surface fluorescence measurement value; calculating a current regularization parameter and selecting an element with the largest absolute value in a difference correlation coefficient into a support set I; extracting all the current elements in the updated support set from corresponding lines in a matrix A, constituting a matrix, and obtaining a next-step searching direction; calculating the length of the next step and updating the support set; obtaining a next-step result according to the solved searching direction and step length iteration, and updating the regularization parameter; and determining whether stopping requirements are satisfied, if yes, finishing the reconstructing process, or otherwise, turning to the fourth step. According to the method, the regularization parameter is not needed to predict but determined adaptively during the reconstructing method, the reconstructing robustness is improved through adaptive regularization parameter selection, and the reconstructing efficiency is improved greatly.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Transportation hazard prediction method for hazardous chemicals
ActiveCN103390201AHazard prediction results are accurateSimple calculationForecastingTerrainDiffusion
The invention discloses a transportation hazard prediction method for hazardous chemicals. The transportation hazard prediction method comprises four steps of forecast of near meteorological fields, calculation of condensation and dose fields, prediction of transportation hazards and selection of transportation routes. According to the transportation hazard prediction method, factors such as the accident liability of hazardous article, the transportation season, transportation time and inherent features of roads are comprehensively considered, an adjoint mode is adopted, effects of meteorological factors and terrain factors are considered, and the actual diffusion is accorded with, the hazard prediction efficiency is high, relatively accurate prediction results can be obtained through traditional evaluation methods of successive solution of diffusion equations, but selections of positions of accidents are multiple, roads are long usually, so that long time is certainly required for successive solution. Starting from protected objects, the adjoint mode can obtain hazard values through solving adjoint equations once, time for solving the adjoint equations is equal to that for solving diffusion equations.
Owner:中国人民解放军防化学院
Methods of optically monitoring wound healing
ActiveUS8812083B2Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyReflectance spectroscopyDiffusion equation
Optical changes of tissue during wound healing measured by Near Infrared and Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy are shown to correlate with histologic changes. Near Infrared absorption coefficient correlated with blood vessel in-growth over time, while Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS) data correlated with collagen concentration. Changes of optical properties of wound tissue at greater depths are also quantified by Diffuse Photon Density Wave (DPDW) methodology at near infrared wavelengths. The diffusion equation for semi-infinite media is used to calculate the absorption and scattering coefficients based on measurements of phase and amplitude with a frequency domain or time domain device. An increase in the absorption and scattering coefficients and a decrease in blood saturation of the wounds compared to the non wounded sites was observed. The changes correlated with the healing stage of the wound. The methodologies used to collect information regarding the healing state of a wound may be used to clinically assess the efficacy of wound healing agents in a patient (e.g., a diabetic) and as a non-invasive method to detect the progress of wound healing, particularly chronic wounds due to diabetes. The methodology applies to ischemic environments, impaired healing states, and emerging subsurface tissue deterioration, such as in pressure ulcers, venous ulcers, and ubiquitous ulcers.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
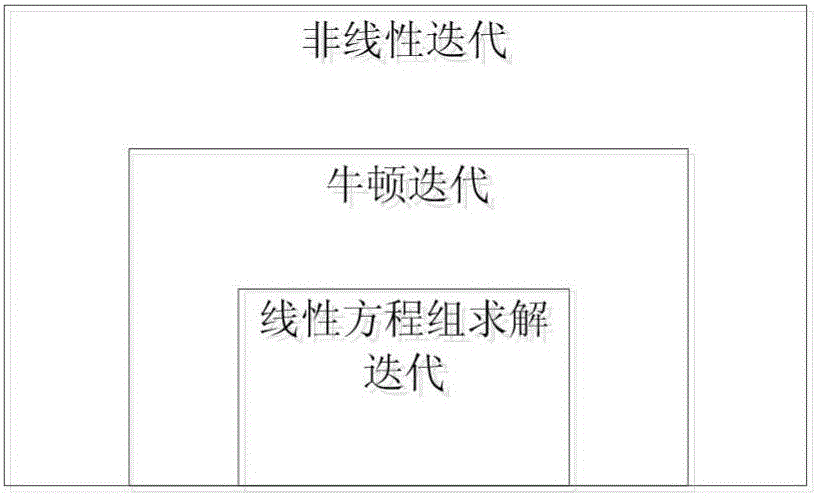
Stable and accurate reactor physics thermotechnical coupling calculating method
ActiveCN106202866AAvoid the effects of iterative convergenceGuaranteed accuracySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsNumerical stabilityApproximate computing
A stable and accurate reactor physics thermotechnical coupling calculating method can simultaneously obtain statuses of a neutronics field, a fluid field and a heat transfer field; all variables are simultaneously updated in an iteration process, so the method has better value stability when compared with a conventional coupling method; the method uses a simultaneous time-space neutron diffusion equation and a thermotechnical equation discrete equation to obtain a novel nonlinear equation group with larger scale; using a Newton iterative method to resolve values of the novel nonlinear equation group, wherein the Newton iterative method needs to calculate a Jacobian matrix of the equation group in each iteration step, so physics thermotechnical coupling calculation is difficult. The novel method builds a value relation between the diffusion equation and thermotechnical equation, and explicit calculation can provide the Jacobian matrix, so problems caused by approximation calculation f the Jacobian matrix can be prevented; in addition, the novel method inherits Newton method characteristics, and hopes to provide faster convergence speed.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
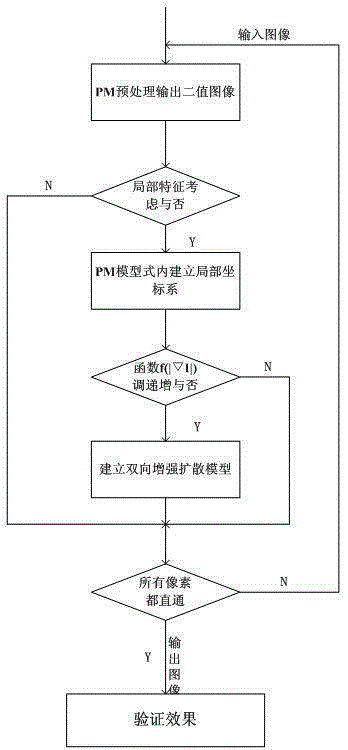
Image de-noising method based on bidirectional enhanced diffusion filtering
InactiveCN105427262AImprove contourWeaken texture detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionAutomatic control
The invention discloses an image de-noising method based on bidirectional enhanced diffusion filtering, which simplifies a diffusion equation. The method comprises the steps of establishing a bidirectional diffusion coefficient so that a model can implement a bidirectional process of smoothing and sharpening in the diffusion process, enhancing an image in order to further improve the smoothing and sharpening strength, performing wavelet transform to enhance the overall outline of the image and weaken texture details of the image, then adaptively designing and improving a gradient threshold to automatically control the gradient threshold according to the maximum gray value and the iterative times of the image and further retain edge and detail features of the image, finally, simulating the purposed model, and performing simulation verification on the method by using MATLAB software. The method can be used for removing image noise and protecting detail information of edge, texture and the like, greatly improves the peak signal to noise ratio, has more excellent de-noising performance, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
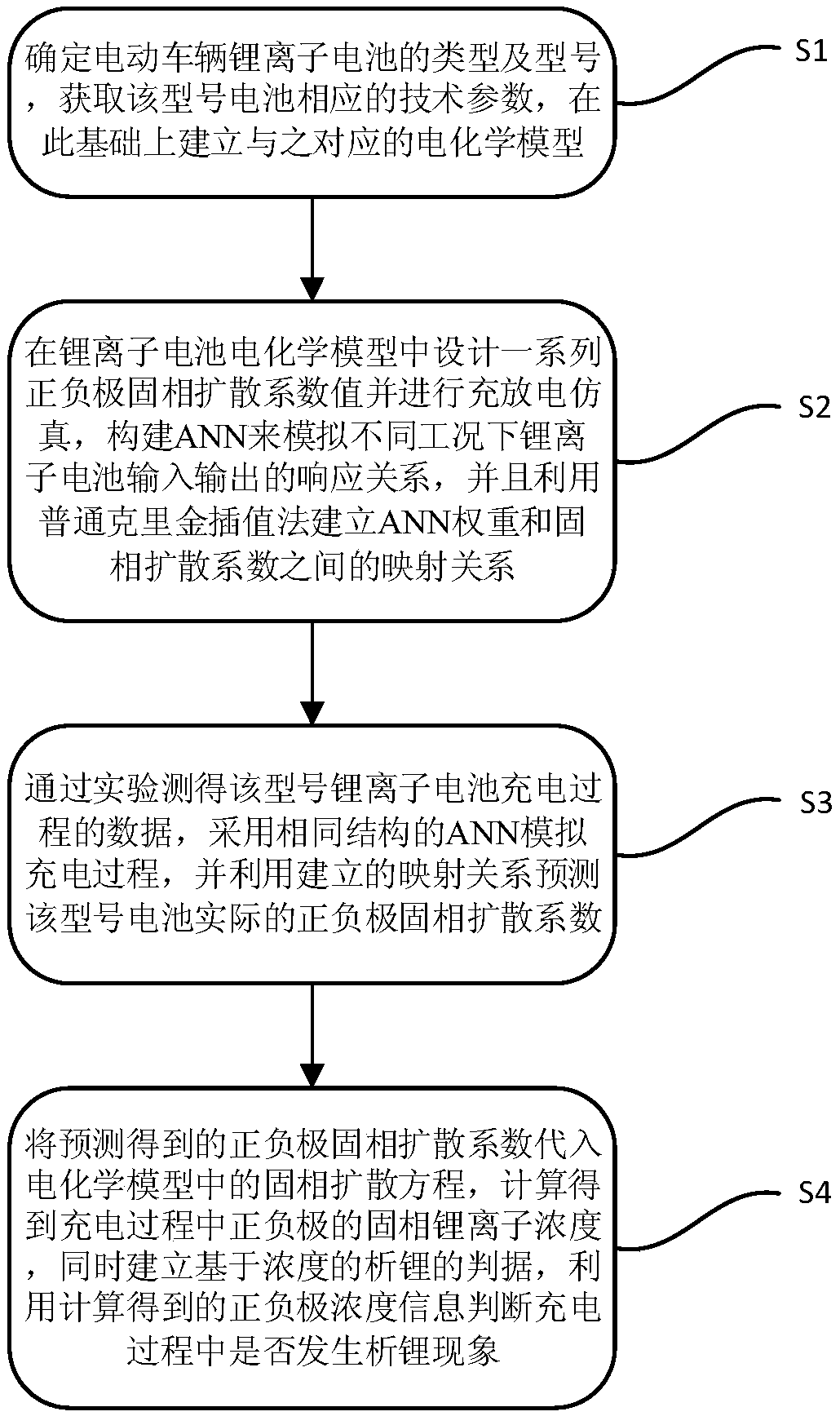
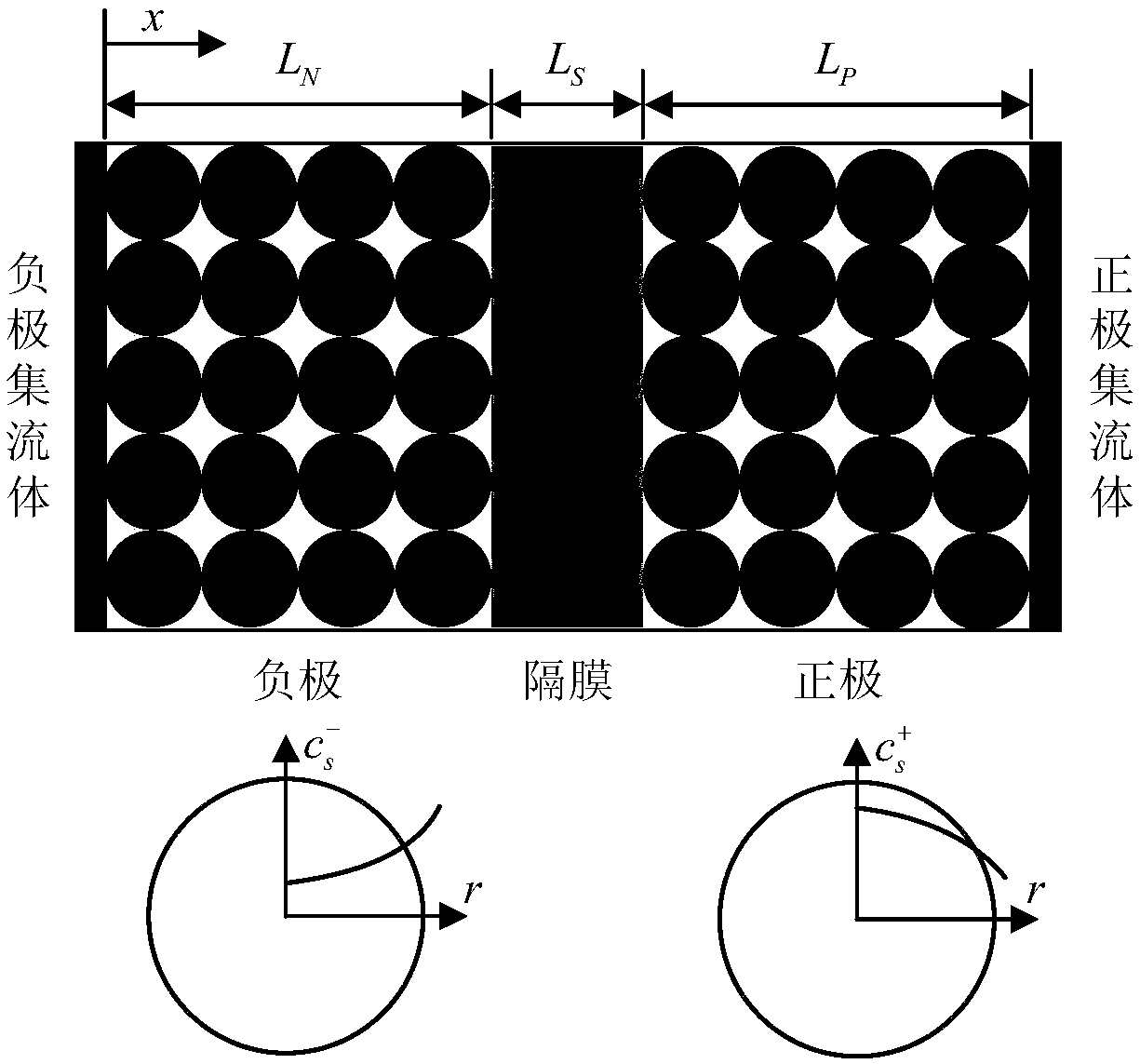
Electric vehicle lithium ion battery lithium precipitation diagnostic method with data drive
ActiveCN109143083AReduce dependencySolid phase diffusion coefficient predictionElectrical testingElectrical batteryEngineering
The present invention relates to an electric vehicle lithium ion battery lithium precipitation diagnostic method with data drive, belonging to the technical field of battery management. The method comprises the steps of: S1: establishing an electrochemical model of a lithium ion battery; S2: in an offline phase, constructing ANN to simulate a response relation of input and output of the lithium ion battery in different conditions, and employing a Kriging model to establish a mapping relation between the ANN weight and a solid phase diffusion coefficient; S3: in an online phase, measuring datain the battery charging process through an experiment, and predicting the actual solid phase diffusion coefficients of positive and negative poles of the battery; and S4: substituting the solid phasediffusion coefficients into a solid phase diffusion equation to calculate and obtain the solid phase lithium ion concentrations of the positive and negative poles in the charging process, establish the criterion of the lithium precipitation based on the concentrations and determine whether a lithium precipitation phenomenon is generated or not in the charging process through adoption of the calculated and obtained concentrations of the positive and negative poles. In a condition of ensuring the integration of the lithium ion battery, the dependence degree of the lithium precipitation phenomenon detection process on the mechanism model is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
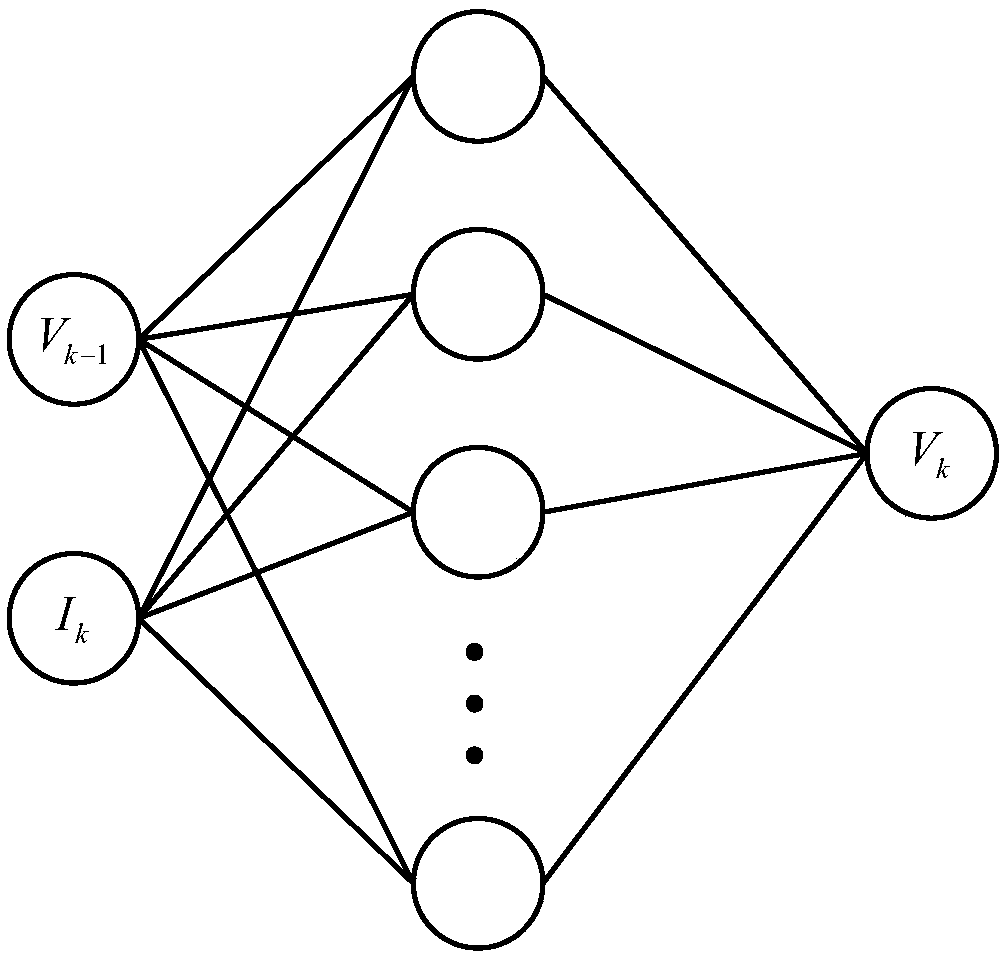
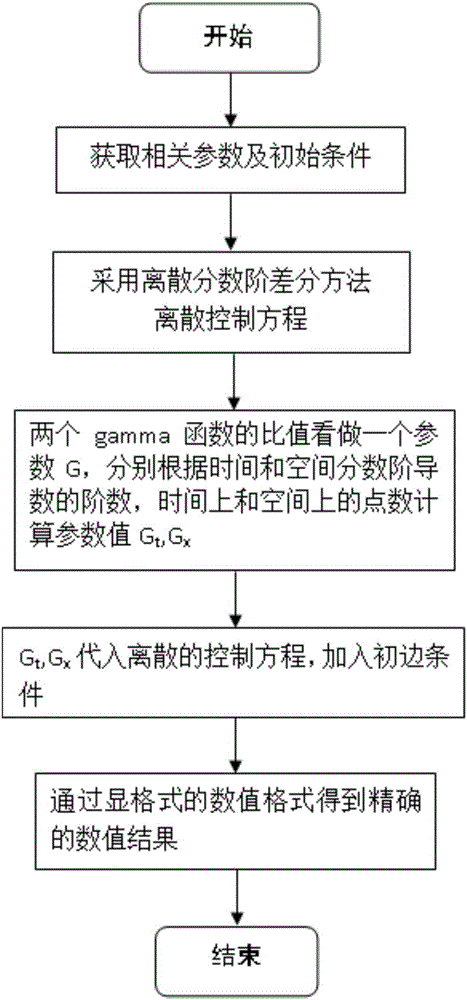
Discrete fractional order differencing method in anomalous diffusion and based on step-by-step calculation
InactiveCN106776478AReduce computational constraintsIncrease pointsComplex mathematical operationsDiffusionAnomalous diffusion
The invention discloses a discrete fractional order differencing method in anomalous diffusion and based on step-by-step calculation. The method includes following steps: acquiring related parameters and initial-boundary conditions; adopting the discrete fractional order differencing method to discretize a control equation, and simulating distribution size of substance according to needed numerical value to determine grid point number; determining a time-space fractional order anomalous diffusion equation of anomalous diffusion, and acquiring a discrete format of the time-space anomalous diffusion equation; taking a specific value of two gamma functions in the time-space anomalous diffusion equation as a parameter, utilizing recursive relation of the gamma functions, combining concept of distributed calculation and idea of overall consideration in numerical value simulation, converting a problem of the specific value of the gamma functions into a form of product of multiple decimals, and substituting into a discrete control equation to acquire a numerical value result of diffusion concentration. The discrete fractional order differencing method has the advantages that limitation on calculation of the gamma functions is reduced, point number of simulation is expanded, and simulation efficiency is improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Biological autofluorescence tomography method based on iteration reweighting
ActiveCN103300829ARealize 3D reconstructionImprove robustnessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnatomical structuresDiffusion equation
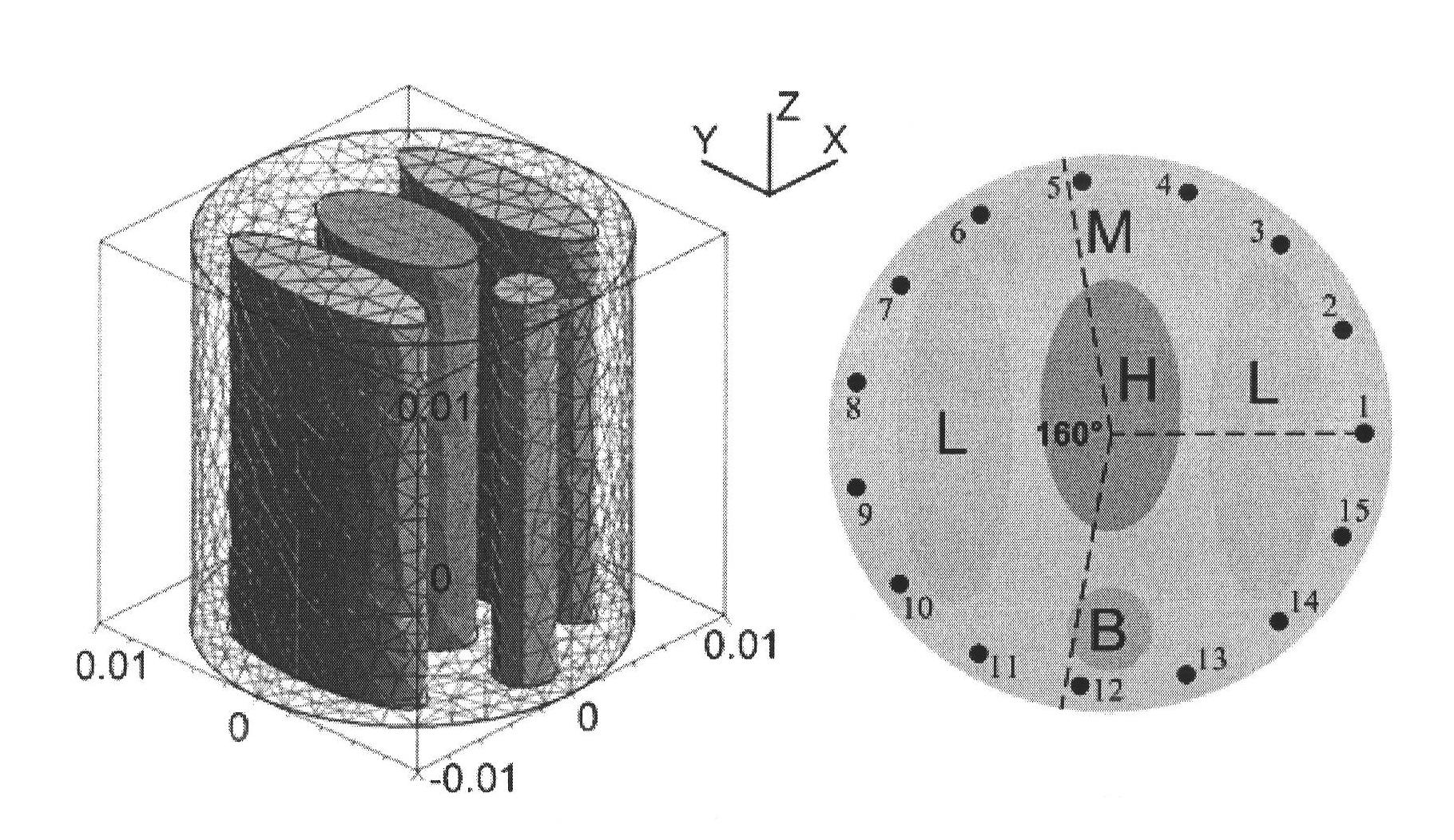
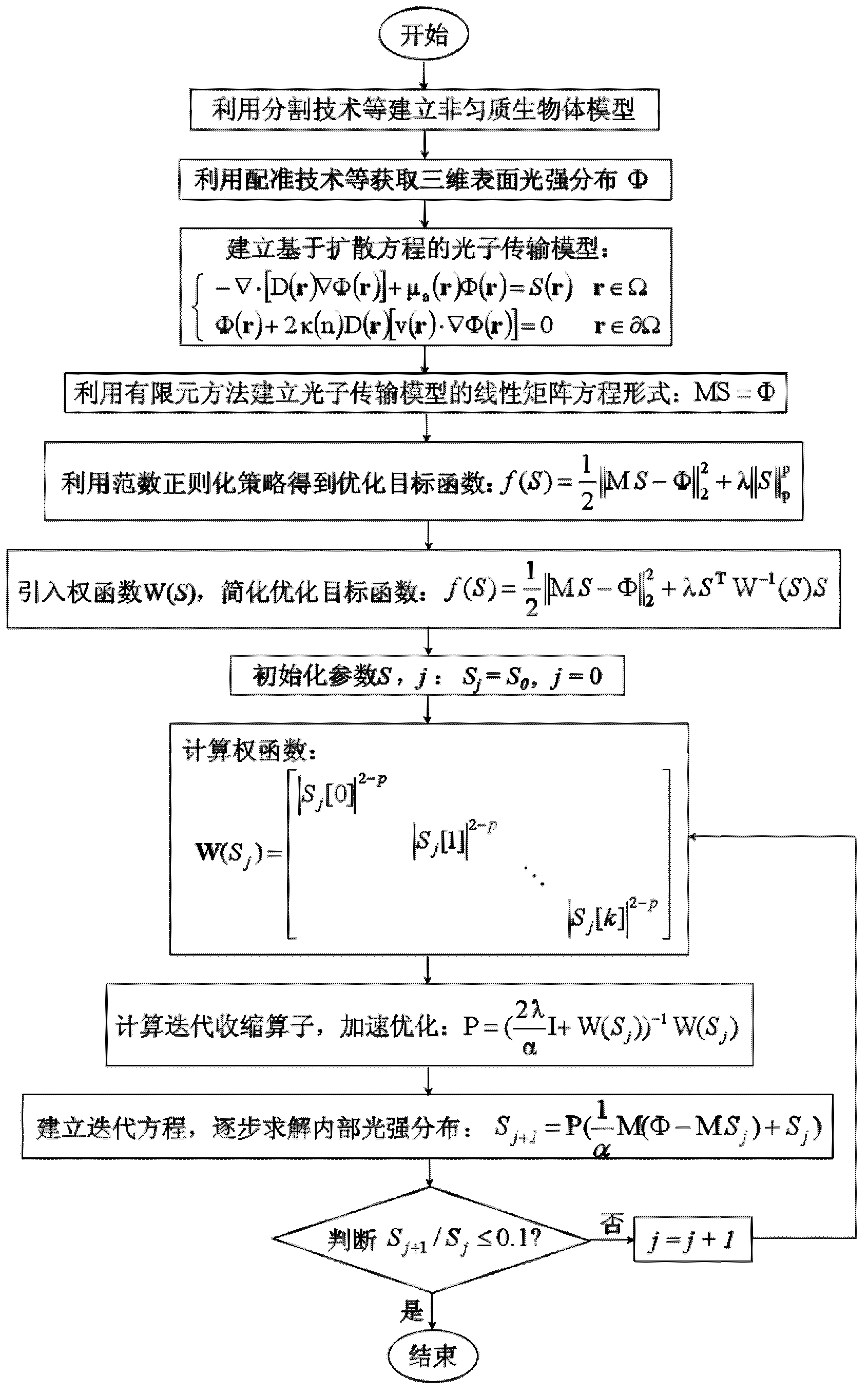
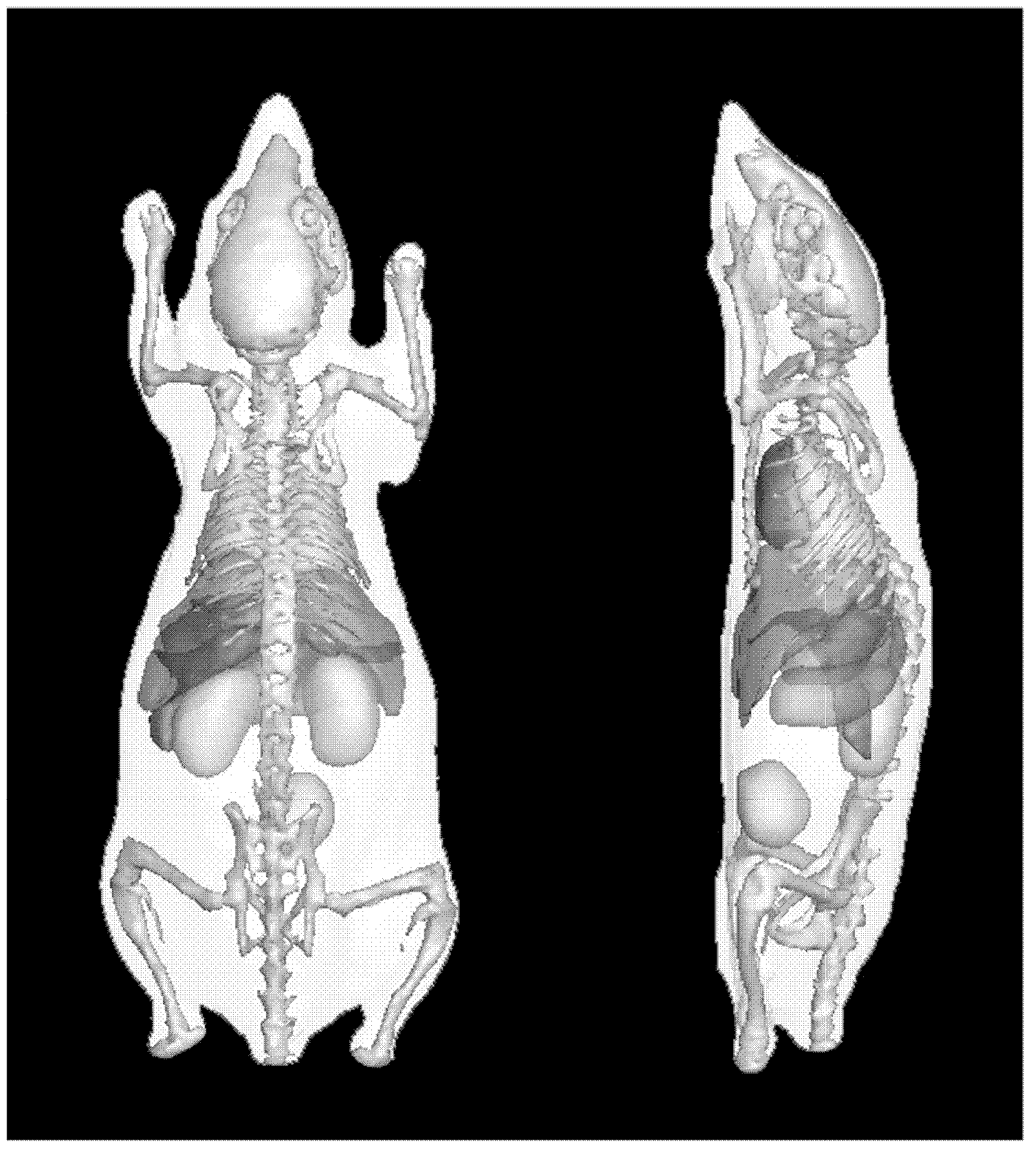
The invention relates to a biological autofluorescence tomography method and a device based on iteration reweighting. The method adopts the scheme that by capturing photon signals emitted by tumor cells of a fluorescent protein gene, a size of a tumor focal zone in an organism can be reconstructed three-dimensionally, and positioning analysis can be performed on the focal zone by fusing organism anatomical structure information provided by Micro-CT (Micro-Computed Tomography). According to the method and the device, a non-homogeneous organism model and a photon transmission model based on a diffusion equation are established by combining function information provided by autofluorescence imaging and the structure information provided by Micro-CT imaging, and three-dimensional reconstruction of an illuminant in the organism is achieved by using a norm regularization and iteration reweighting combined optimization strategy. With the adoption of the scheme, a result closer to an actual solution can be reconstructed by less observation quantity; the computational efficiency of solving can be improved effectively; the robustness of a reconstruction algorithm can be improved; and the method and the device are suitable for practical three-dimensional detection and quantitative analysis of a tumor in the practical organism.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-spectral reconstruction method based on adaptive finite element
ActiveUS20080259074A1Less discomfortQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostics using tomographyRegion selectionPrior information
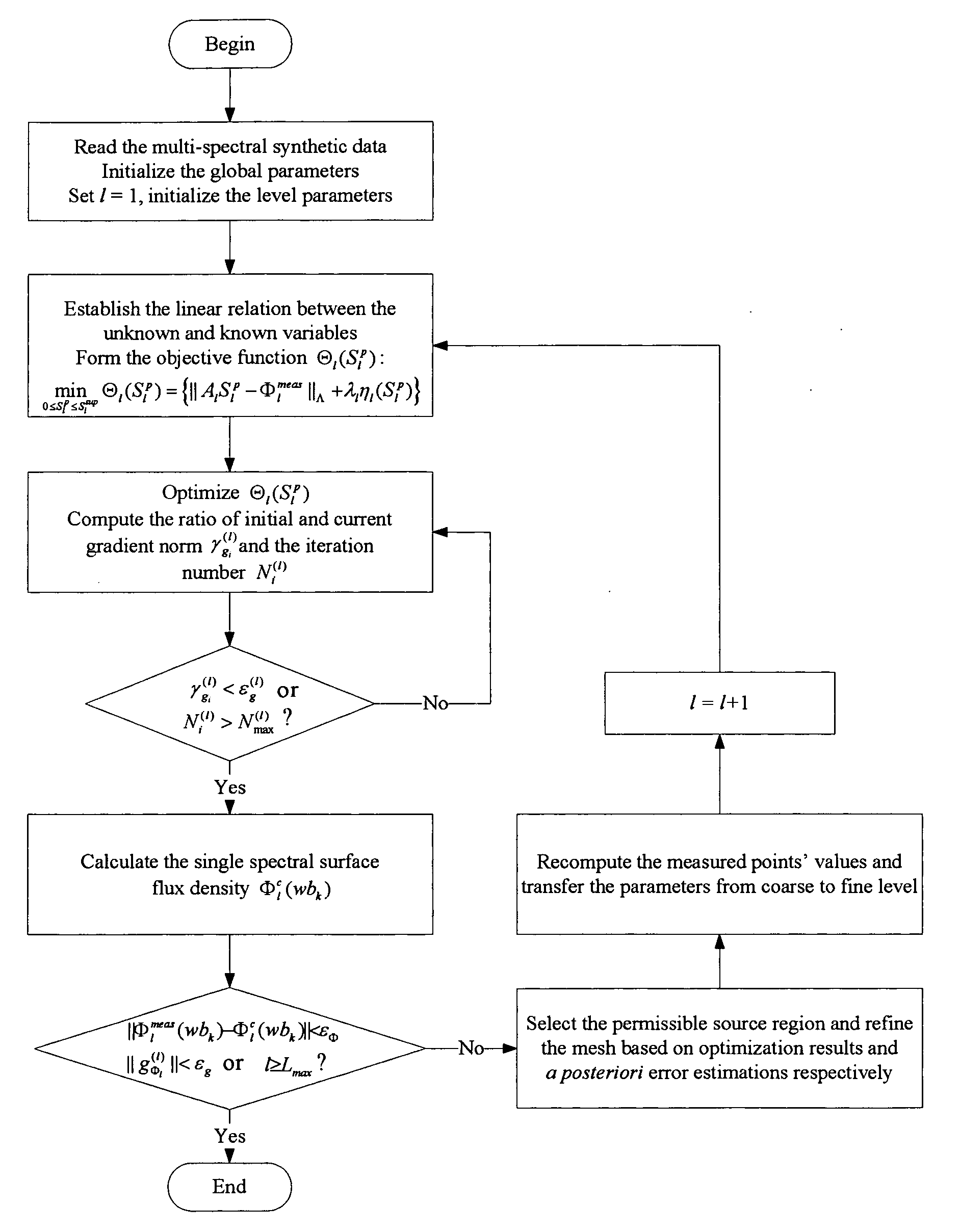
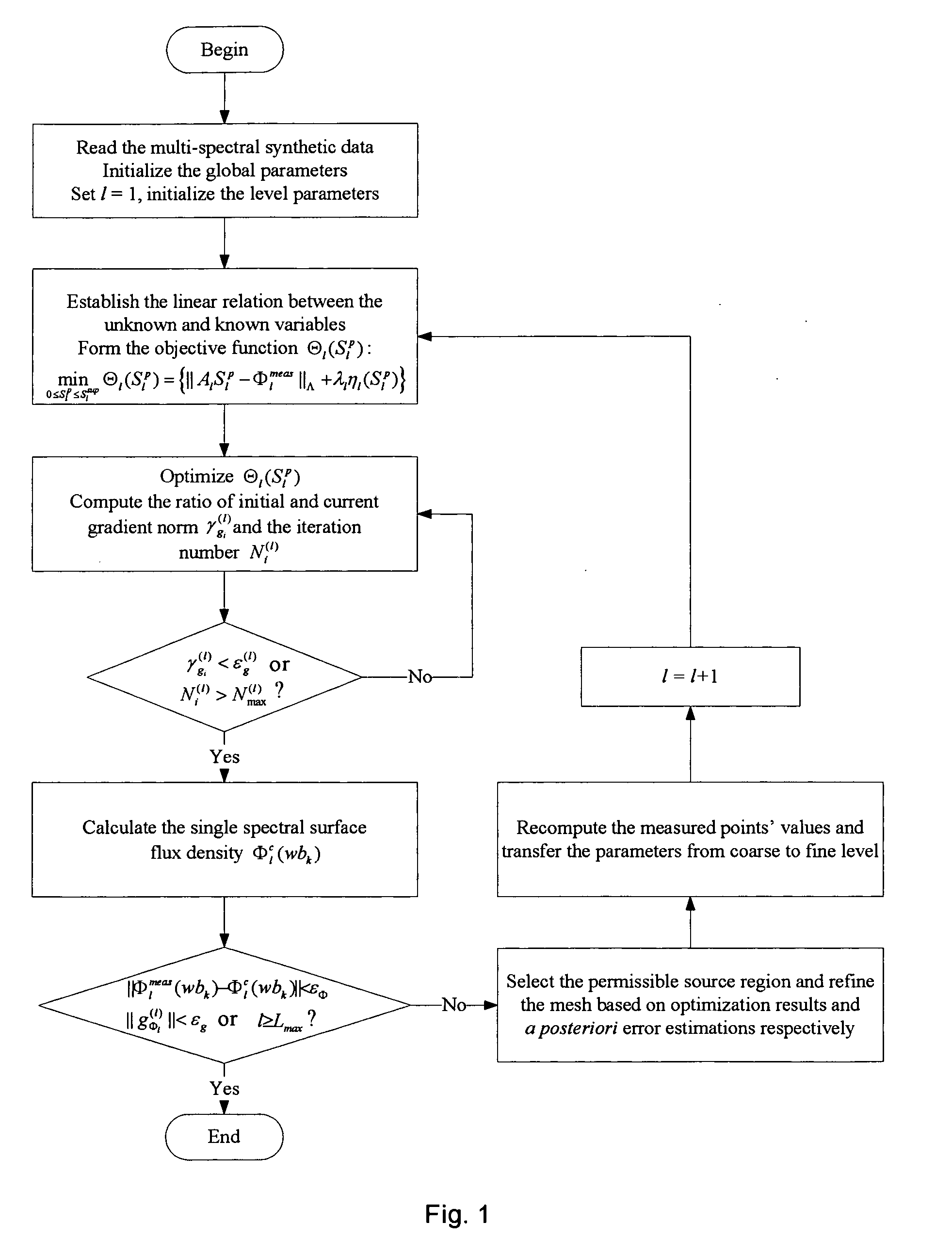
A multi-spectral reconstruction method based on adaptive finite element comprising the following steps: discretizing the diffusion equation in the object domain on the single spectral; establishing the relationship between the boundary measurement data and the unknown source variables on single spectral based on a posteriori permissible source region selection method, and forming the objective function based on the multi-spectral characteristics and the regularization method; optimizing the objective function and determining if the reconstruction shall be stopped or not; and if the reconstruction shall not be stopped, refining the mesh adaptively by using a posteriori measure method, and then returning to the first step to continue the reconstruction process. This method uses kinds of a priori information and the multi-spectral information, combined with the adaptive finite element method, proposes a posteriori permissible source region strategy, improves the reconstruction quality and speed of BLT availably, and reduces the ill-posedness of this imaging modality.
Owner:ZHUHAI DI PU MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com