Patents
Literature
110 results about "Radiative transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radiative transfer is the physical phenomenon of energy transfer in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The propagation of radiation through a medium is affected by absorption, emission, and scattering processes. The equation of radiative transfer describes these interactions mathematically. Equations of radiative transfer have application in a wide variety of subjects including optics, astrophysics, atmospheric science, and remote sensing. Analytic solutions to the radiative transfer equation (RTE) exist for simple cases but for more realistic media, with complex multiple scattering effects, numerical methods are required. The present article is largely focused on the condition of radiative equilibrium.
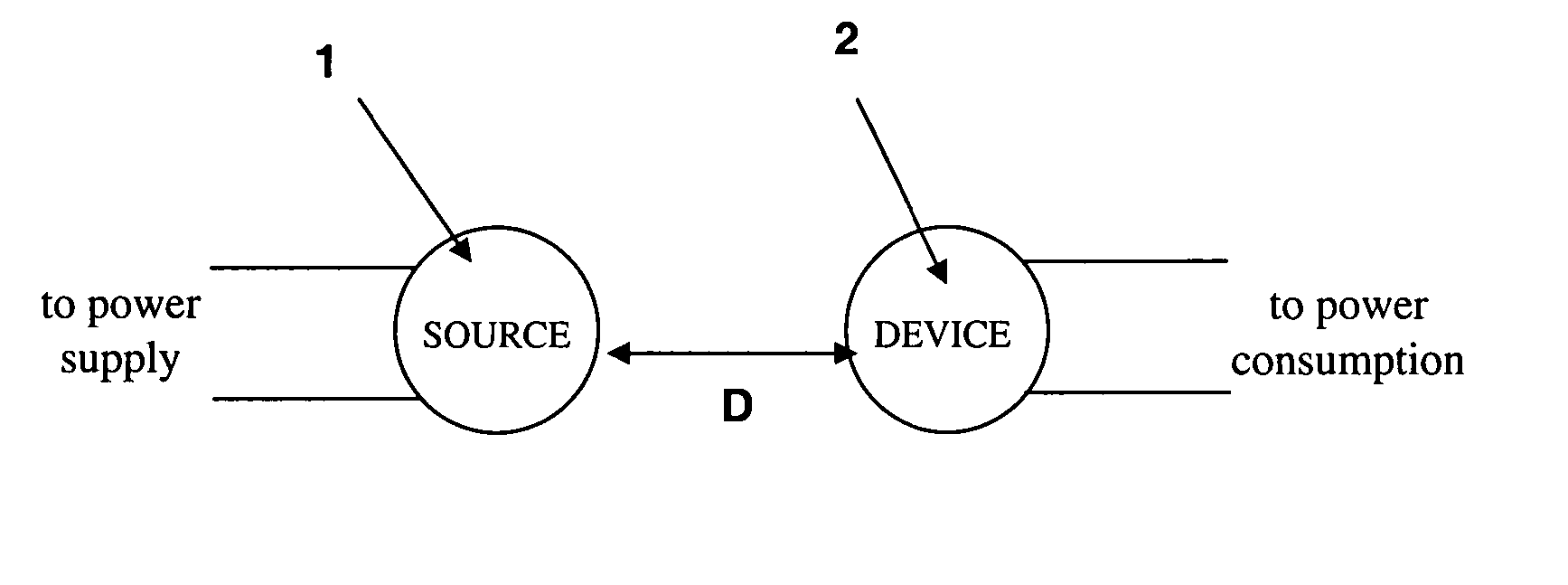
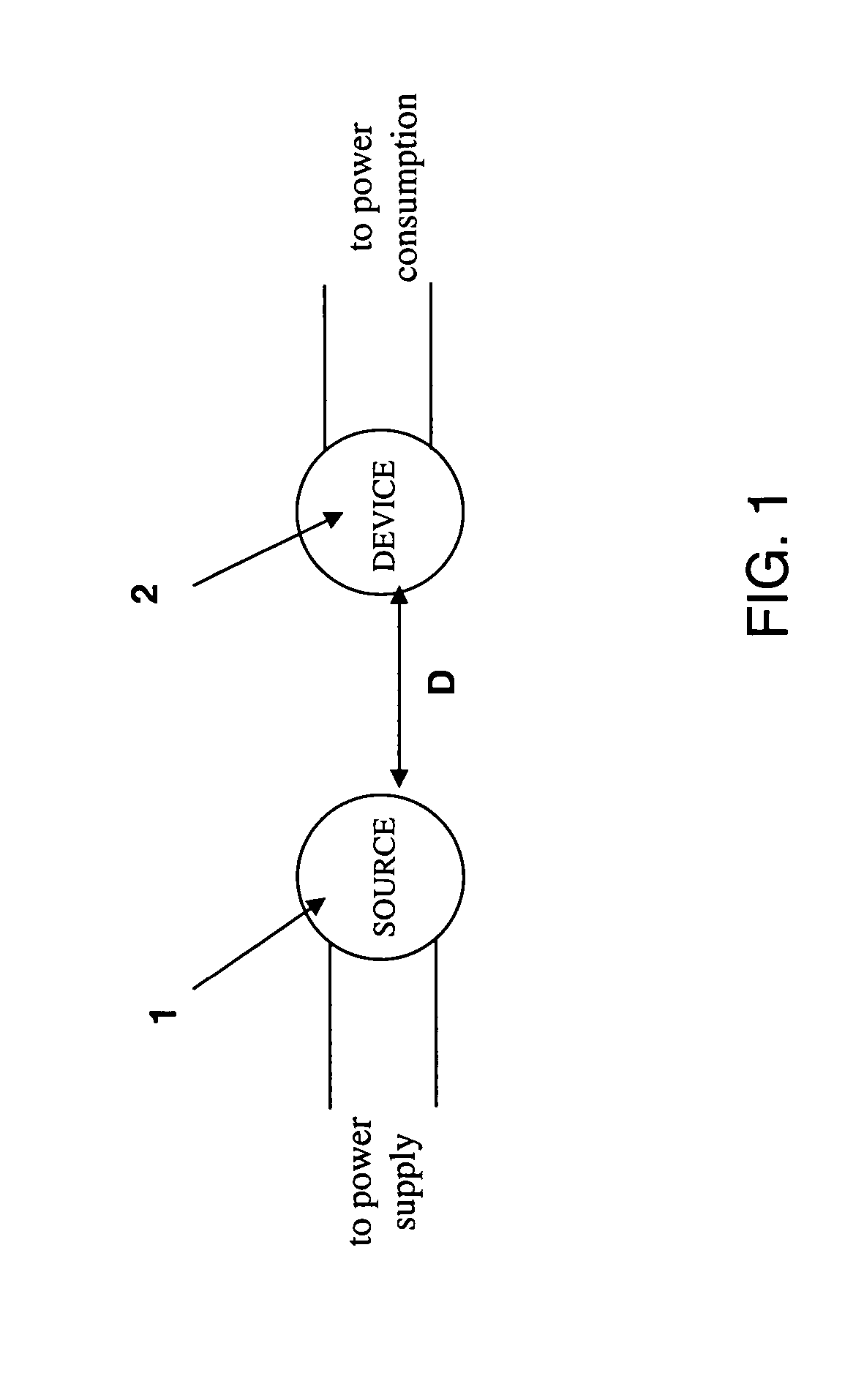
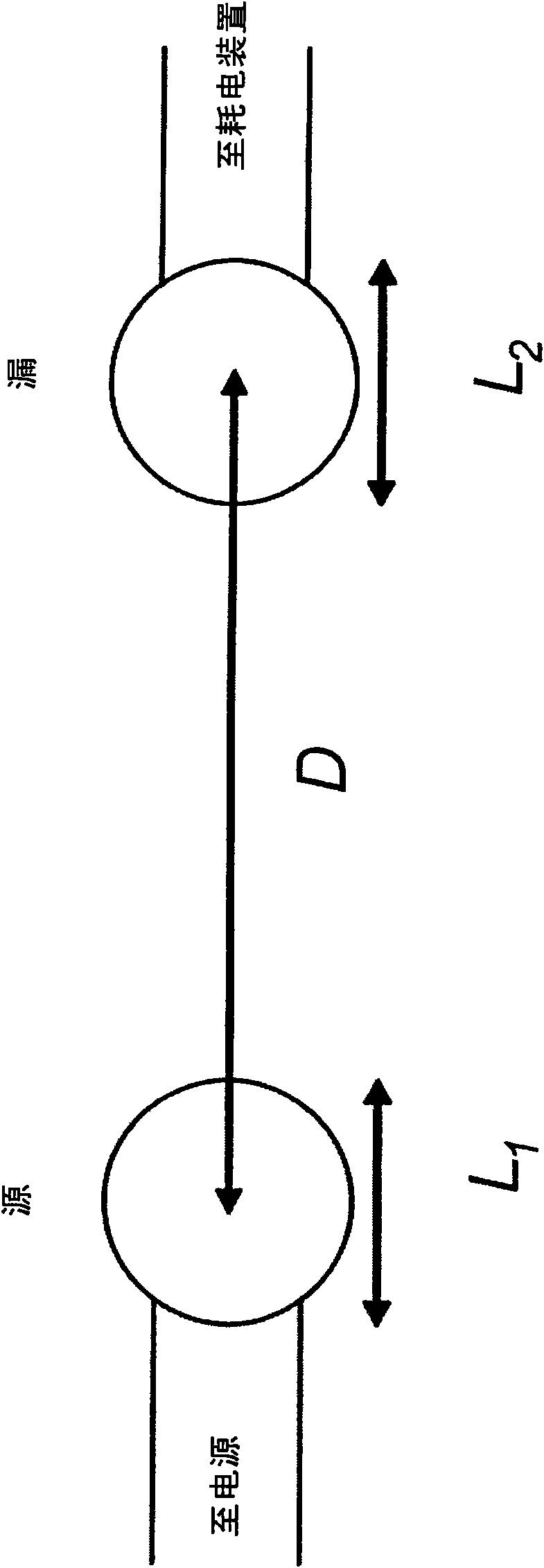
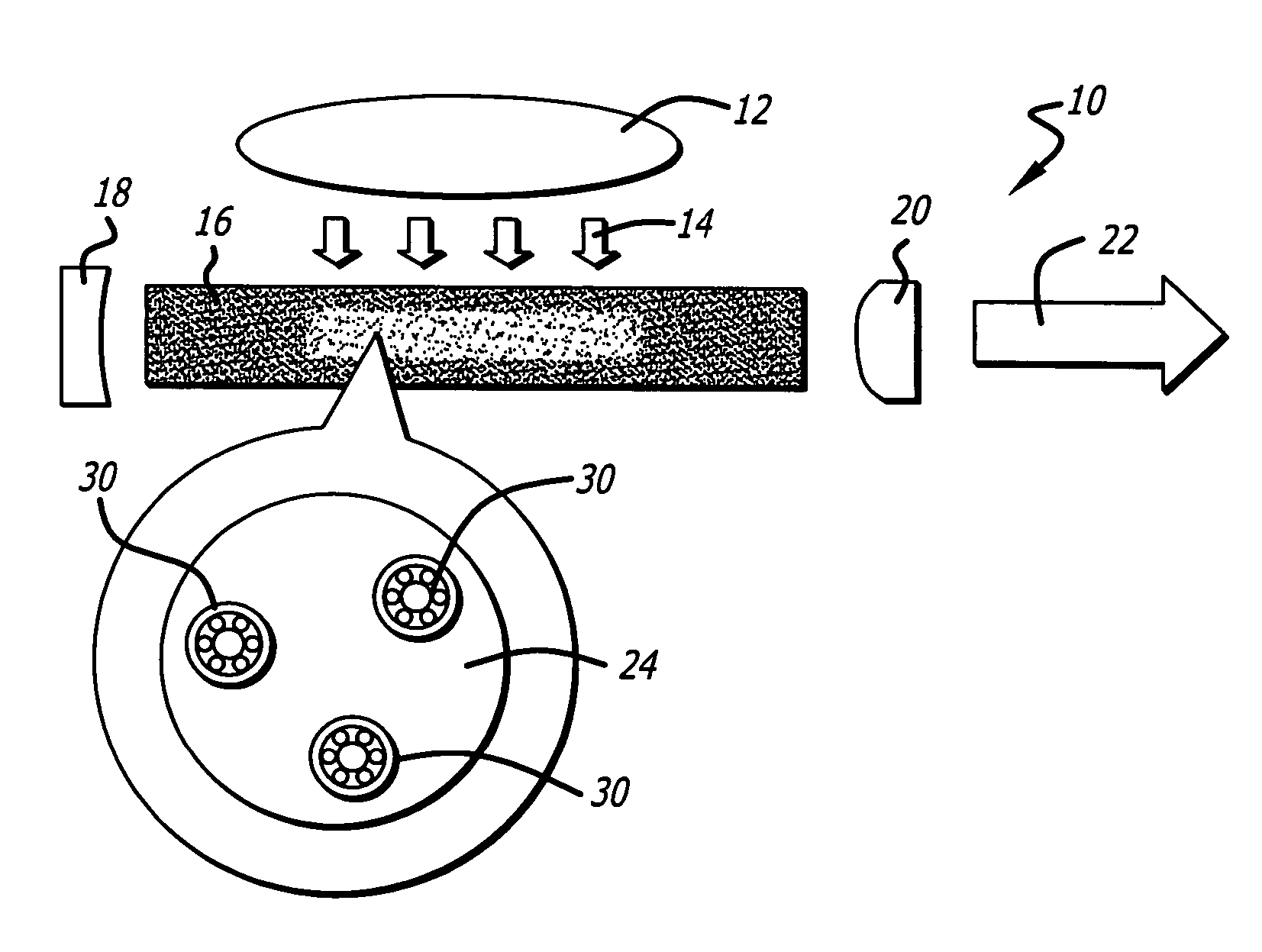
Wireless non-radiative energy transfer
The electromagnetic energy transfer device includes a first resonator structure receiving energy from an external power supply. The first resonator structure has a first Q-factor. A second resonator structure is positioned distal from the first resonator structure, and supplies useful working power to an external load. The second resonator structure has a second Q-factor. The distance between the two resonators can be larger than the characteristic size of each resonator. Non-radiative energy transfer between the first resonator structure and the second resonator structure is mediated through coupling of their resonant-field evanescent tails.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
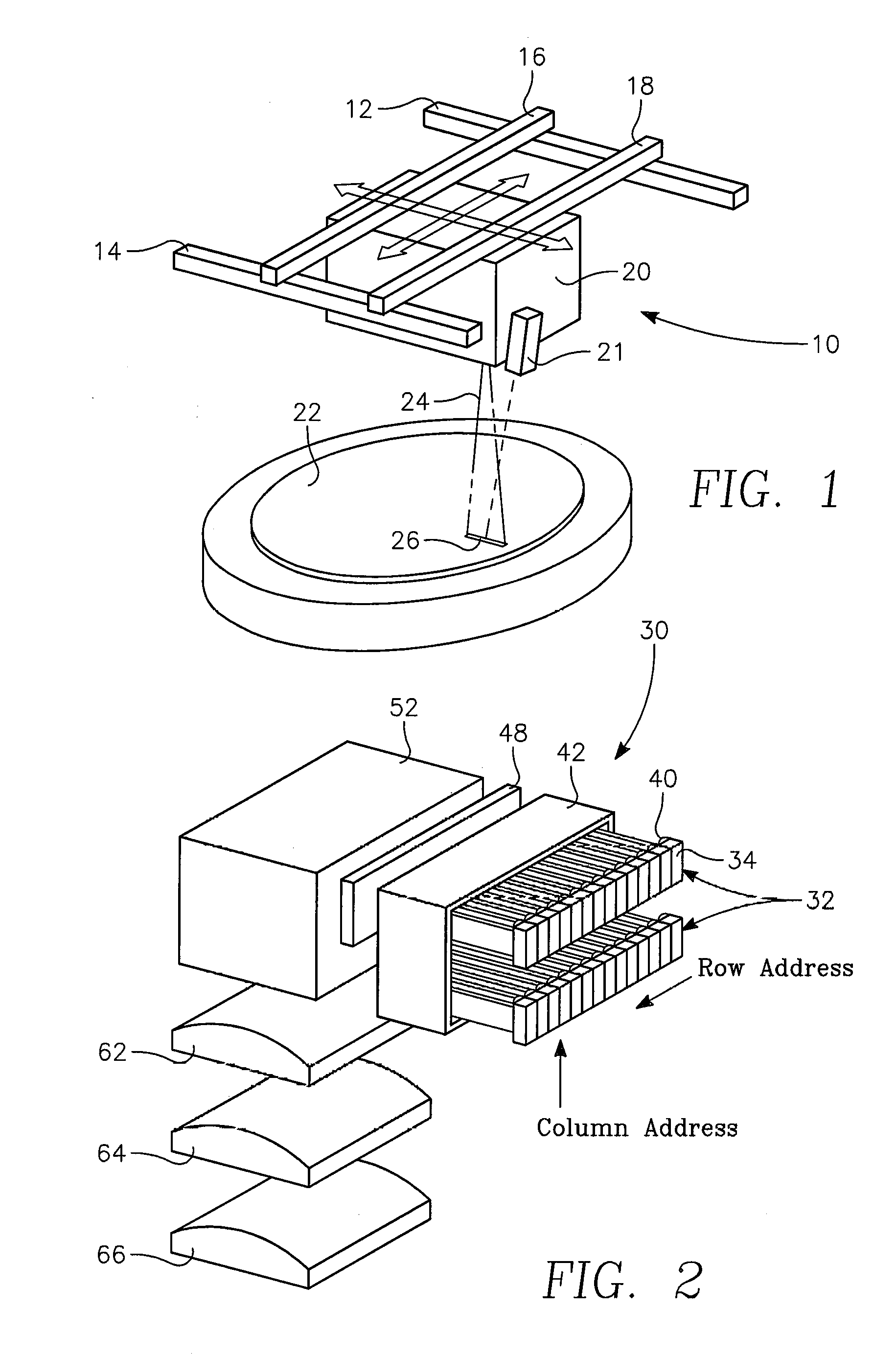
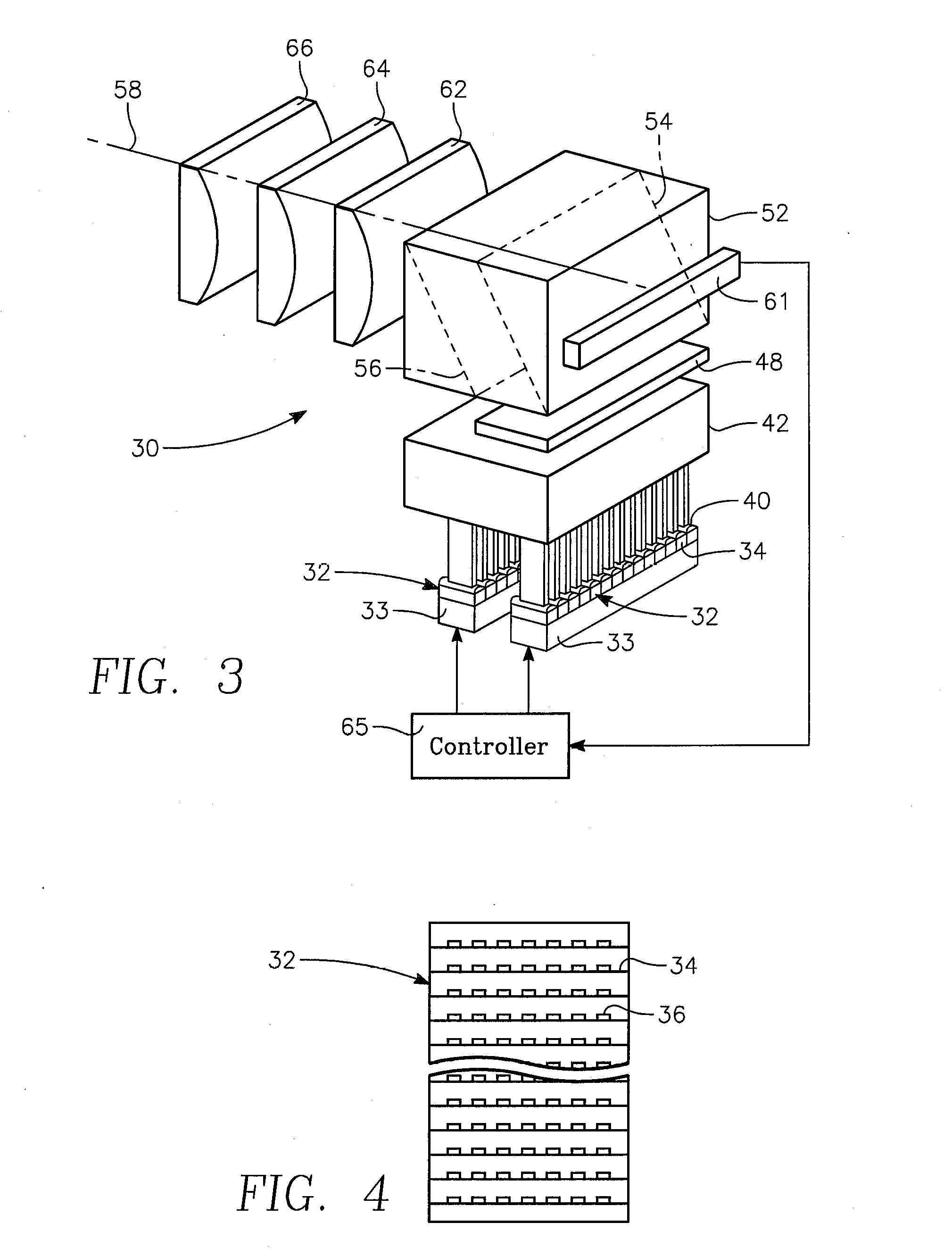
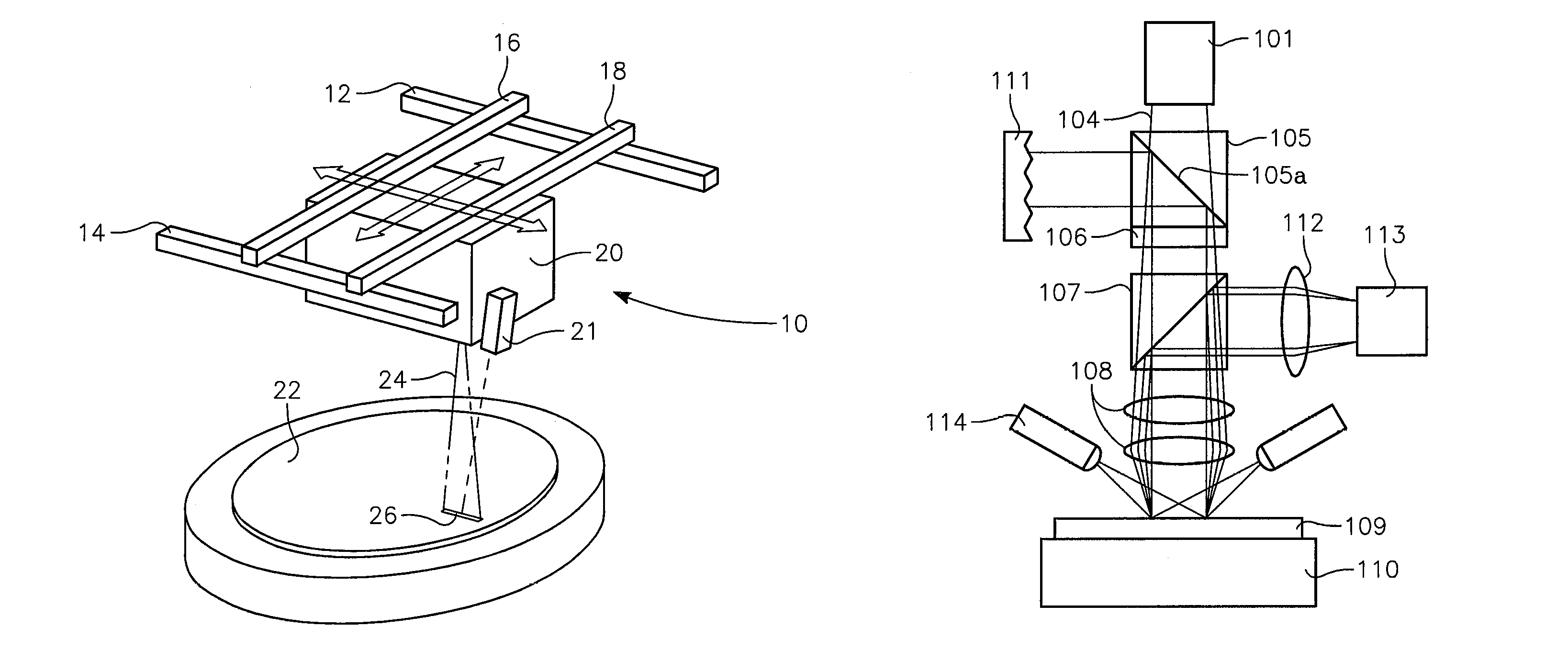
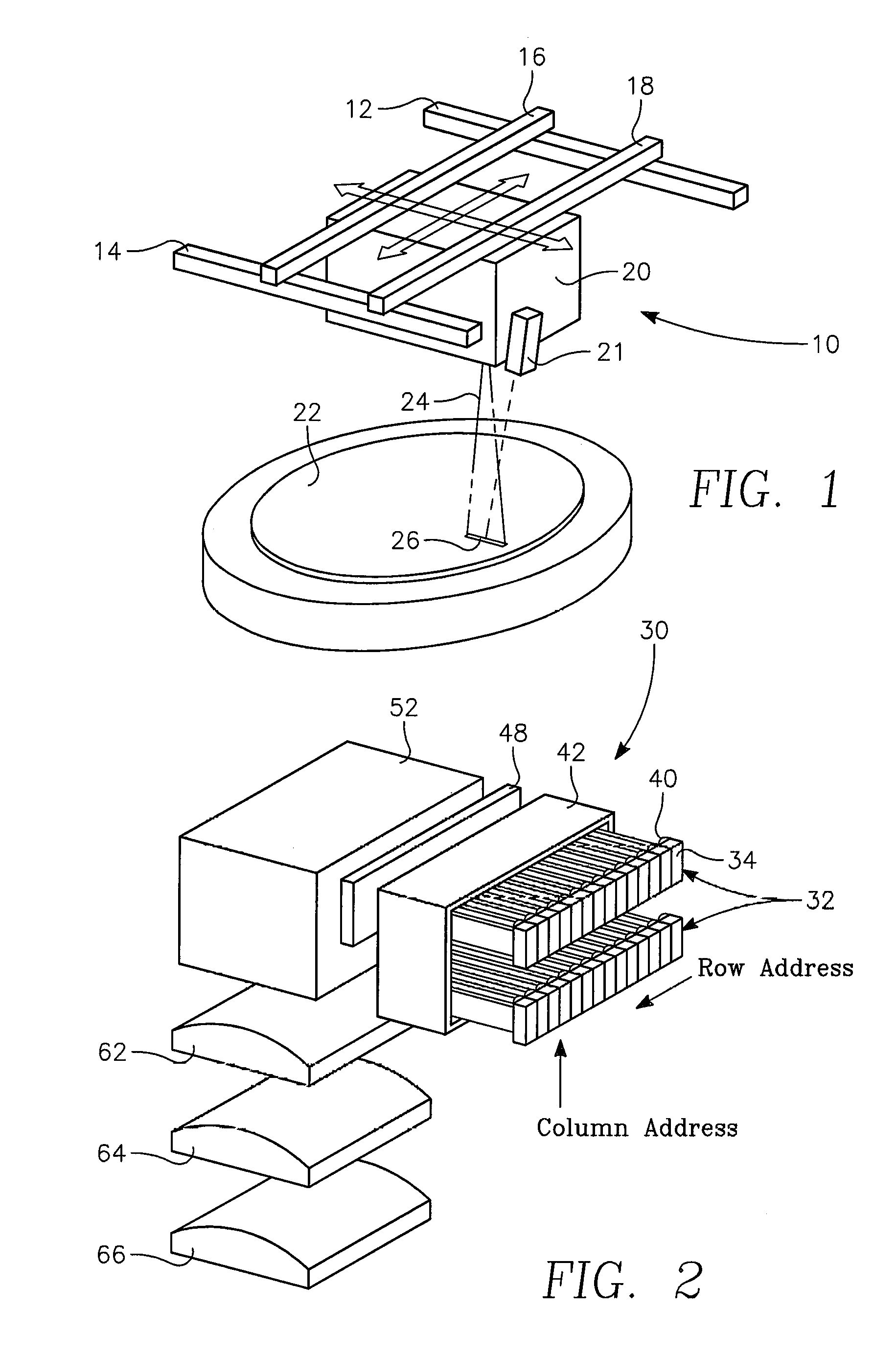
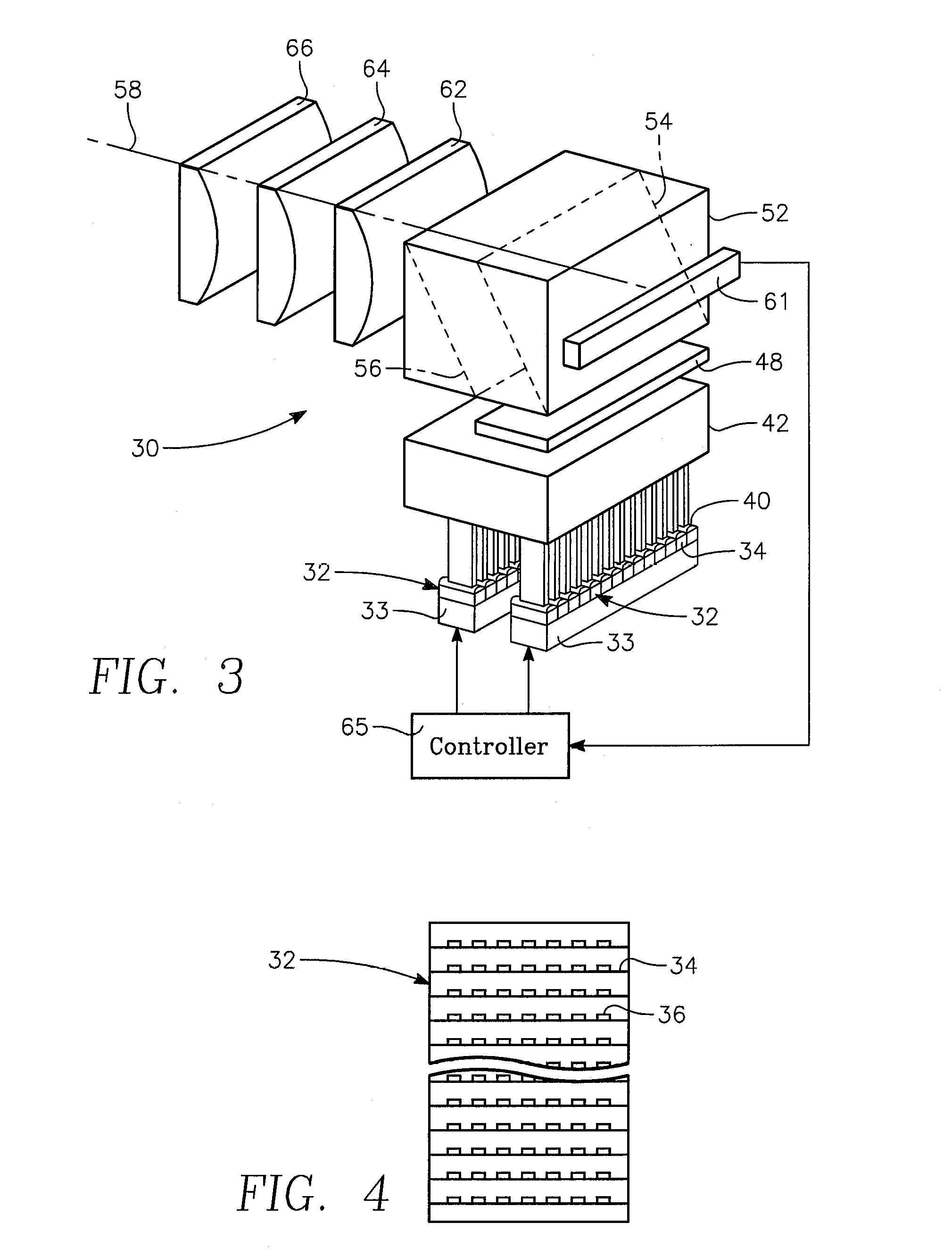
Dynamic surface annealing using addressable laser array with pyrometry feedback
Apparatus for dynamic surface annealing of a semiconductor wafer includes a source of laser radiation emitting at a laser wavelength and comprising an array of lasers arranged in rows and columns, the optical power of each the laser being individual adjustable and optics for focusing the radiation from the array of lasers into a narrow line beam in a workpiece plane corresponding to a workpiece surface, whereby the optics images respective columns of the laser array onto respective sections of the narrow line beam. A pyrometer sensor is provided that is sensitive to a pyrometer wavelength. An optical element in an optical path of the optics is tuned to divert radiation emanating from the workpiece plane to the pyrometry sensor. As a result, the optics images each of the respective section of the narrow line beam onto a corresponding portion of the pyrometer sensor. The apparatus further includes a controller responsive to the pyrometry sensor and coupled to adjust individual optical outputs of respective columns of the laser array in accordance with outputs of corresponding portions of the pyrometry sensor.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Wireless energy transfer
Disclosed is an apparatus for use in wireless energy transfer, which includes a first resonator structure configured to transfer energy non-radiatively with a second resonator structure over a distance greater than a characteristic size of the second resonator structure. The non-radiative energy transfer is mediated by a coupling of a resonant field evanescent tail of the first resonator structure and a resonant field evanescent tail of the second resonator structure.
Processes for the production of electro-optic displays, and color filters for use therein
ActiveUS20090004442A1Decorative surface effectsPhotomechanical apparatusRadiative transferEngineering
Processes are provided for depositing multiple color filter materials on a substrate to form color filters. In a first process, the surface characteristic of a substrate is modified by radiation so that a flowable form of a first color filter material will be deposited on a first area, and converted to a non-flowable form. A second color filter material can then be deposited on a second area of the substrate. In a second process, first and second color filter materials are deposited on separate donor sheets and transferred by radiation to separate areas of the substrate. A third process uses flexographic printing to transfer the first and second color filter materials to the substrate.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Processes for the production of electro-optic displays, and color filters for use therein
ActiveUS9199441B2Lamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentRadiative transferEngineering
Processes are provided for depositing multiple color filter materials on a substrate to form color filters. In a first process, the surface characteristic of a substrate is modified by radiation so that a flowable form of a first color filter material will be deposited on a first area, and converted to a non-flowable form. A second color filter material can then be deposited on a second area of the substrate. In a second process, first and second color filter materials are deposited on separate donor sheets and transferred by radiation to separate areas of the substrate. A third process uses flexographic printing to transfer the first and second color filter materials to the substrate.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
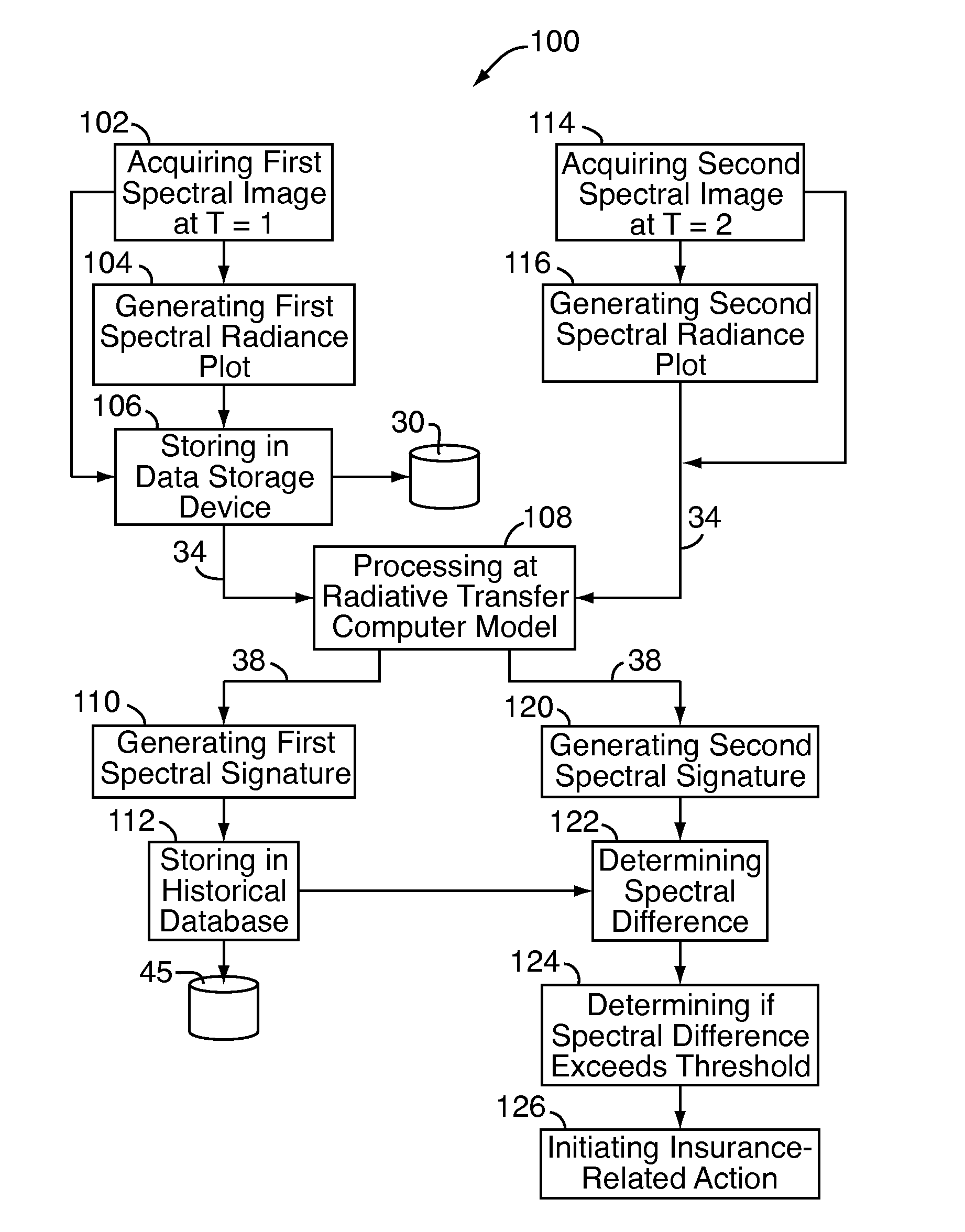
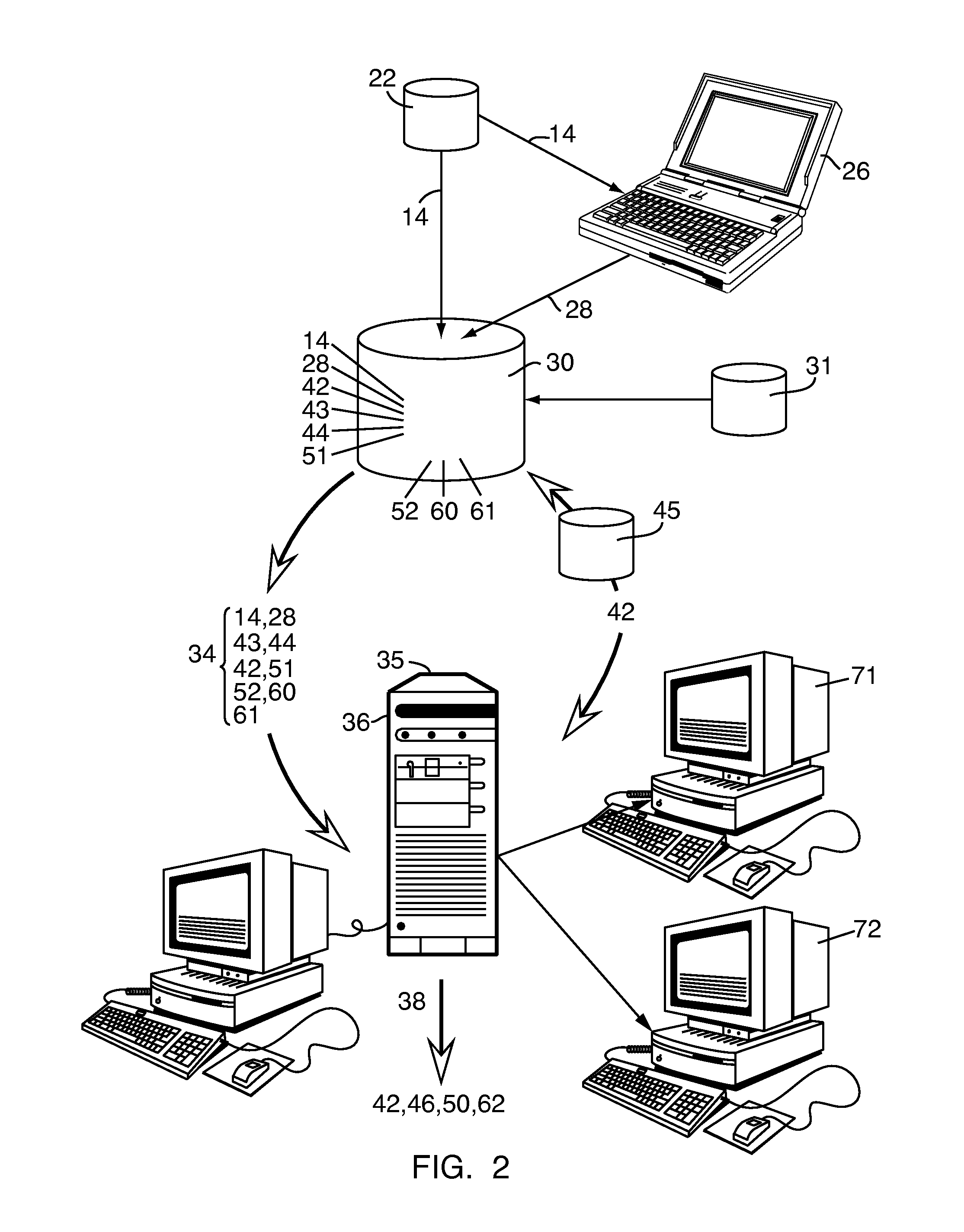
System and method for assessing a condition of property
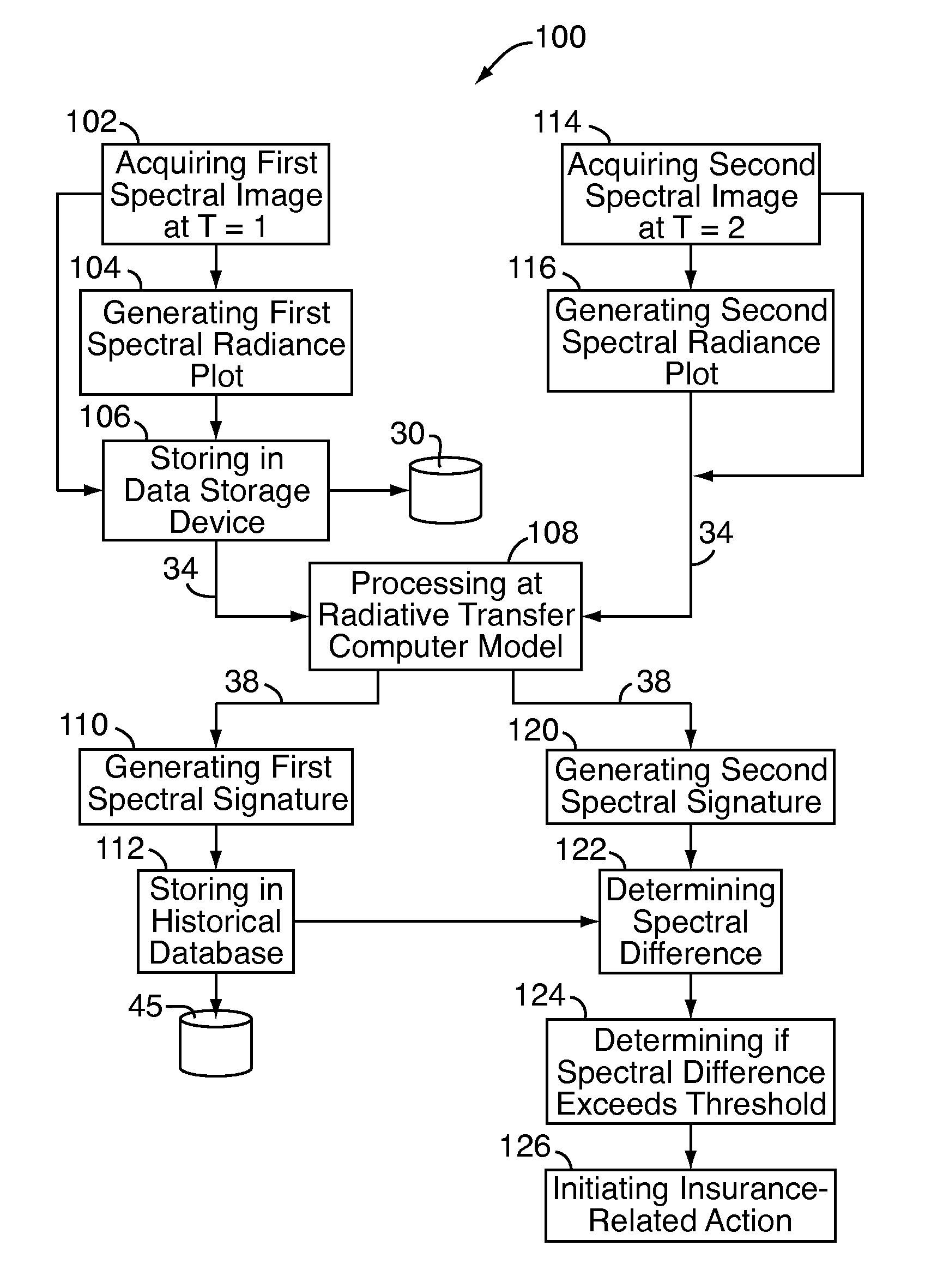
A system and method for assessing a condition of property for insurance purposes includes a sensor for acquiring a spectral image. In a preferred embodiment, the spectral image is post-processed to generate at least one spectral radiance plot, the plot used as input to a radiative transfer computer model. The output of the model establishes a spectral signature for the property. Over a period of time, spectral signatures can be compared to generate a spectral difference, the difference attributed to a change in the condition of the property, such as a fire or flood. In response to the change, an insurance company initiates an insurance-related action such as processing a claim.
Owner:HARTFORD FIRE INSURANCE
Device capable of extracting heat of phase transformation of compressed steam for radiative heat transfer
InactiveCN102445096AReduce power consumptionPrevent frost crackingIndirect heat exchangersFrostRadiative transfer
A device capable of extracting heat of phase transformation of compressed steam for radiative heat transfer adopts the structure that each group of heat pipe component is composed of a heat pipe and a sleeve; each heat pipe comprises a heating section and a condensation section, one end of the condensation section is sealed, the other end of the condensation section is communicated with one end of the heating section, and an end cover is arranged at the other end of the heating section; one end of each sleeve is welded at the joint of the heating section and the condensation section of the corresponding heat pipe, and the other end is welded together with an air-in communicating pipe; a hydrops baffle, as well as a liquid discharge pipe interface, is arranged in each air-in communicating pipe; and one end of each air-in communicating pipe is connected with the corresponding end cover, and an interface connected with a compressed steam delivery pipe is arranged at the other end. In theinvention, water or other liquid transportation can be avoided, so a huge heat exchange system and a delivery pipe net for heating liquid are prevented, the power consumption during the liquid transportation is also avoided, waterway frost cracking can also be prevented, and the maintenance cost is reduced.
Owner:陈万仁
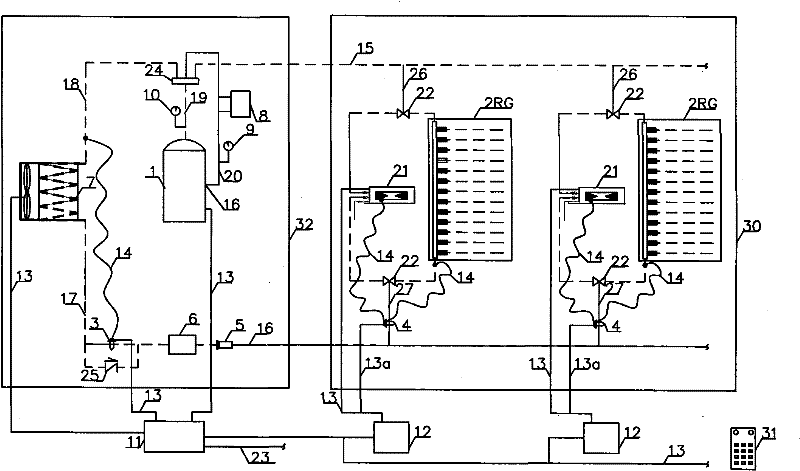
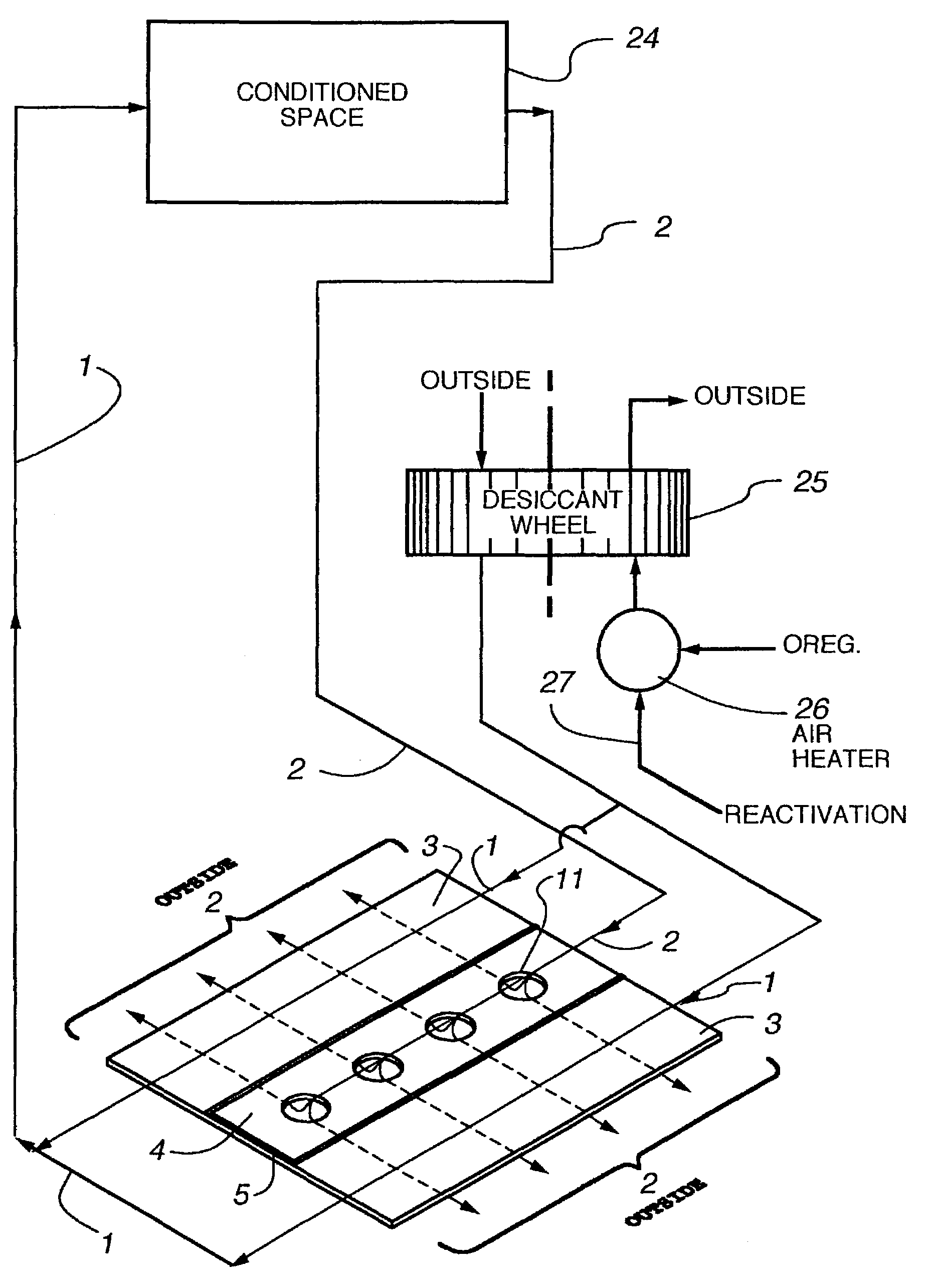
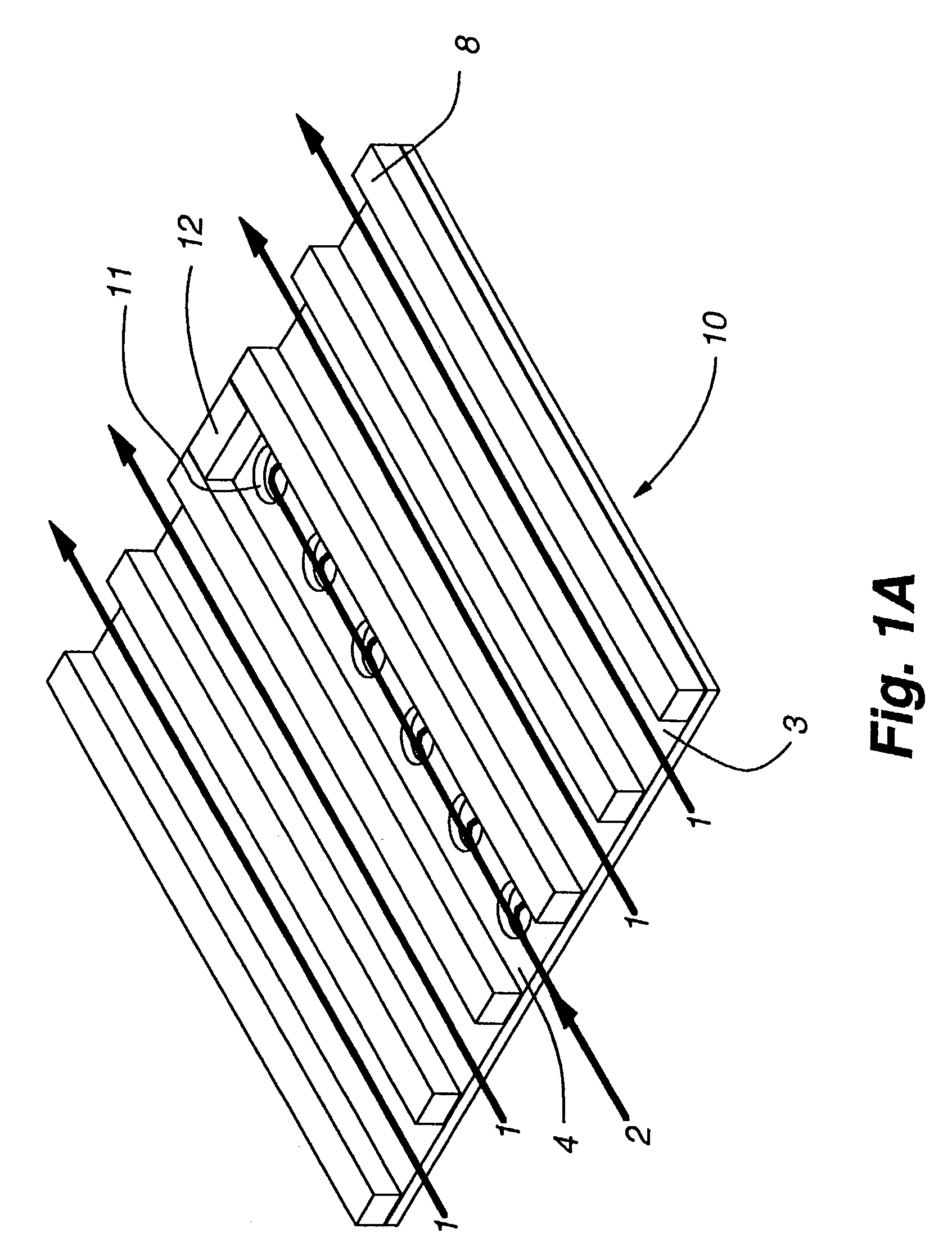
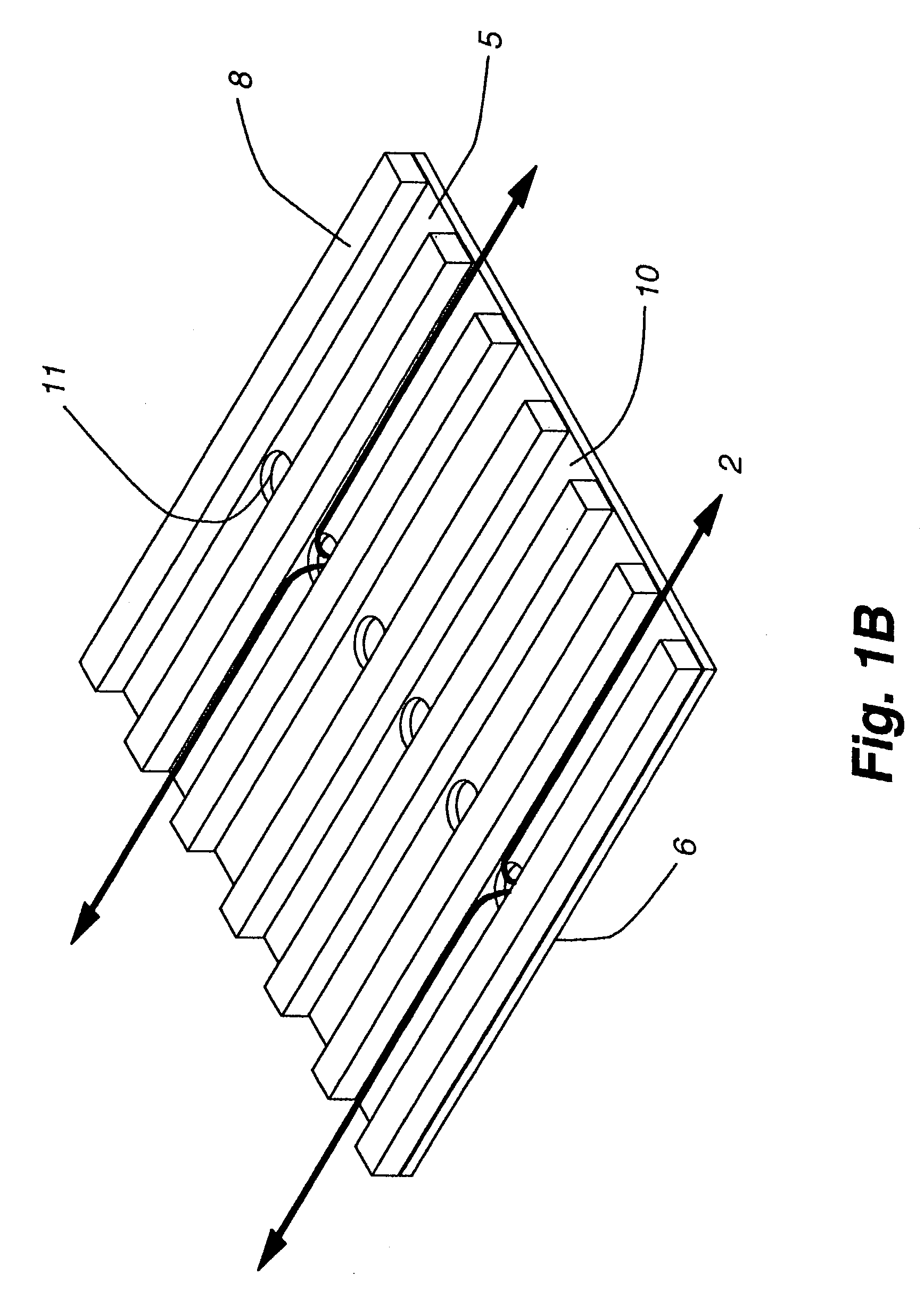
Method and plate apparatus for dew point evaporative cooler
InactiveUS7197887B2Small pressure dropReduce temperature differenceAir treatment detailsFree-cooling systemsEvaporative coolerFiber
An improved method and apparatus for indirect evaporative cooling of a fluid stream to substantially its dew point temperature. Plate heat exchanger has perforations 11 and channels 3, 4 and 5 for gas or a low temperature for liquids on a dry side and wet side. Fluid streams 1 flow across the dry side 9, transferring heat to the plate. Gas stream 2 flows across the dry side and through perforations to channels 5 on wet side 10, which it then cools by evaporative cooling as well as conductive and radiative transfer of heat from plate. A wicking material provides wetting of wet side. In other embodiments, a desiccant wheel may be used to dehumidify the gas, air streams may be recirculated, feeder wicks 13 and a pump may be used to bring water from a water reservoir, and fans may be used to either force or induce a draft. The wicking material may be cellulose, organic fibers, organic based fibers, polyester, polypropylene, carbon-based fibers, silicon based fibers, fiberglass, or combinations of them. The device may be operated in winter months to scavenge heat from exhaust gases of a space and thus pre-heat fresh air, while simultaneously humidifying the fresh air.
Owner:F F SEELEY NOMINEES
System and method for assessing a condition of property
A system and method for assessing a condition of property for insurance purposes includes a sensor for acquiring a spectral image. In a preferred embodiment, the spectral image is post-processed to generate at least one spectral radiance plot, the plot used as input to a radiative transfer computer model. The output of the model establishes a spectral signature for the property. Over a period of time, spectral signatures can be compared to generate a spectral difference, the difference attributed to a change in the condition of the property, such as a fire or flood. In response to the change, an insurance company initiates an insurance-related action such as processing a claim.
Owner:HARTFORD FIRE INSURANCE
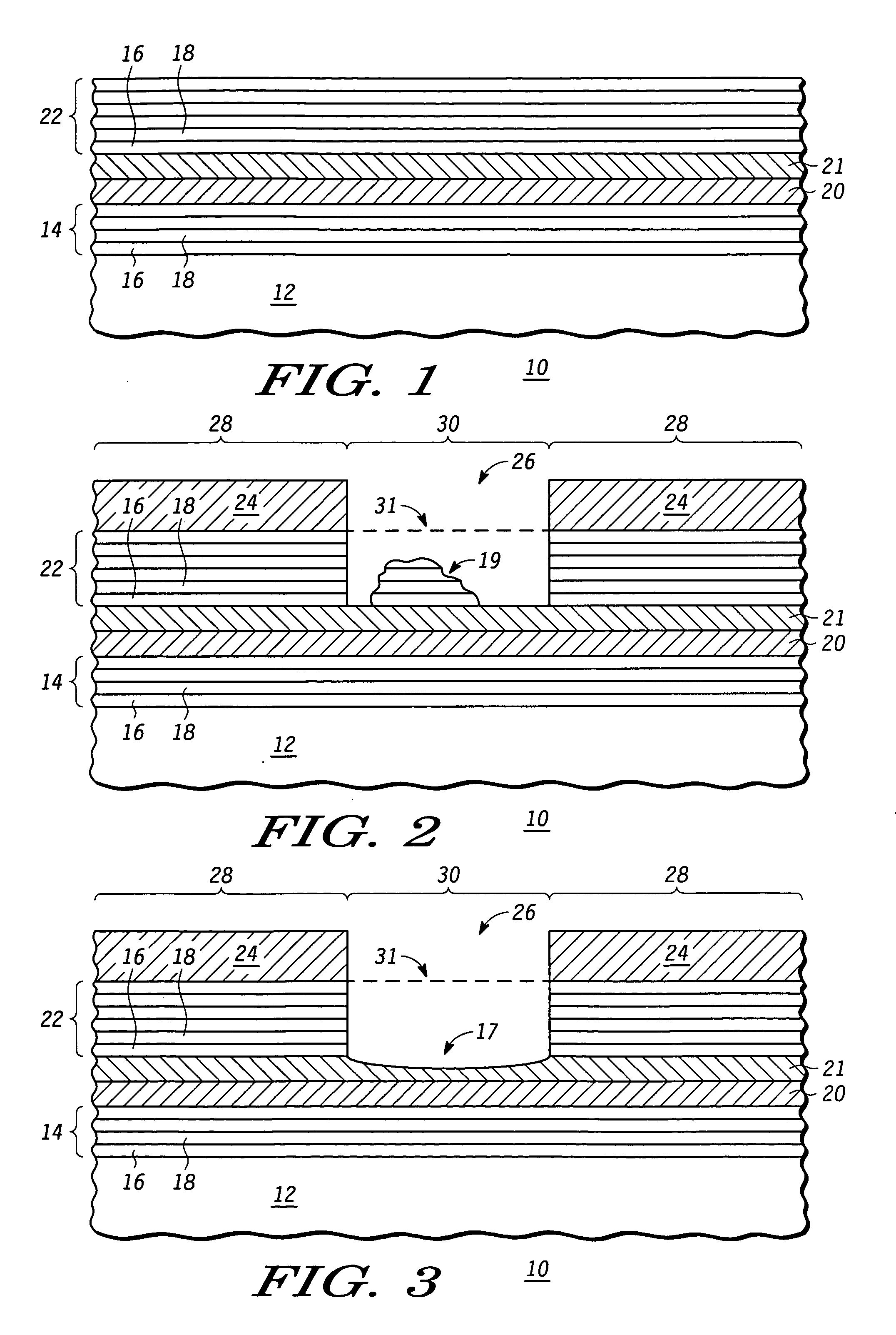
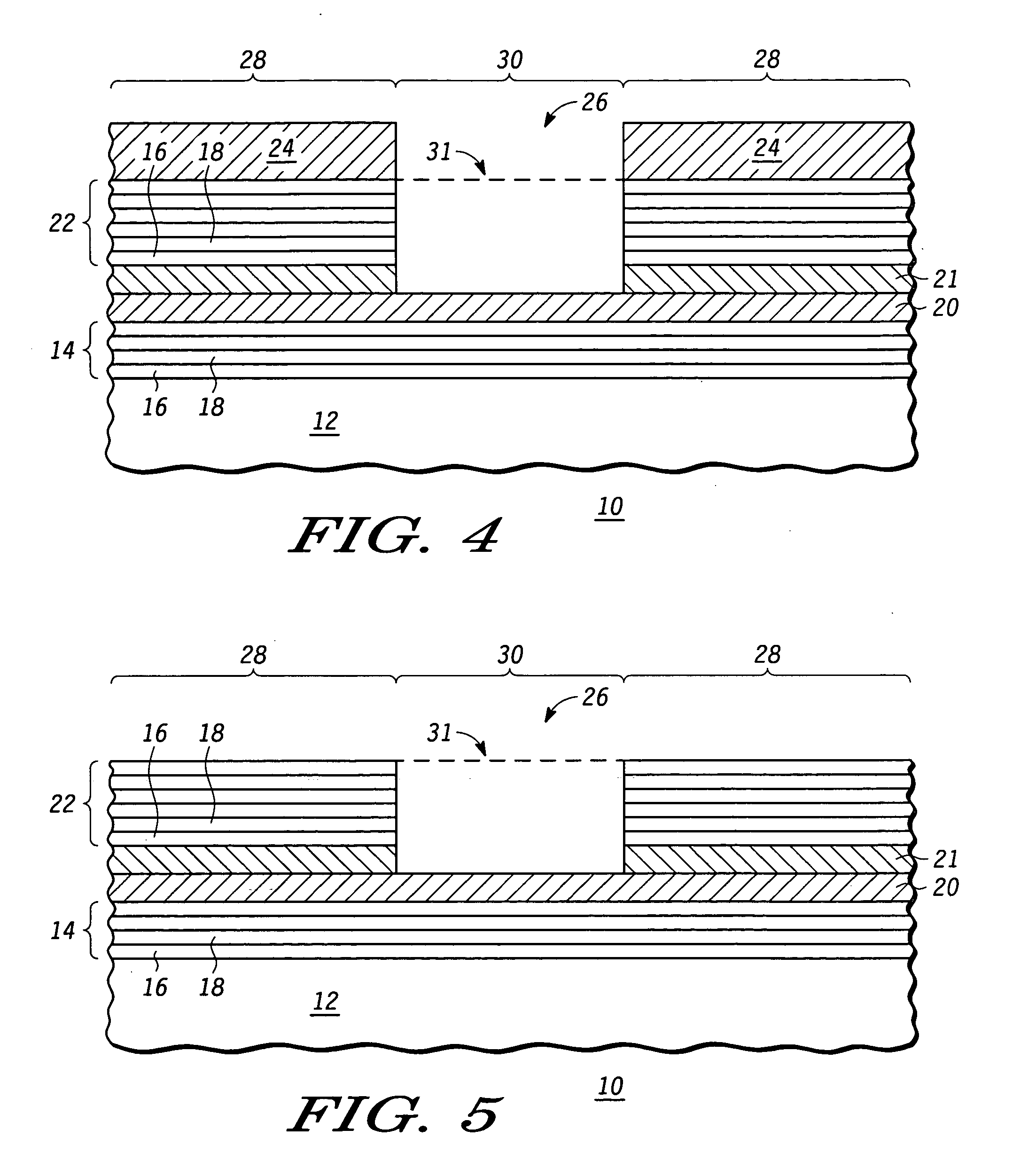
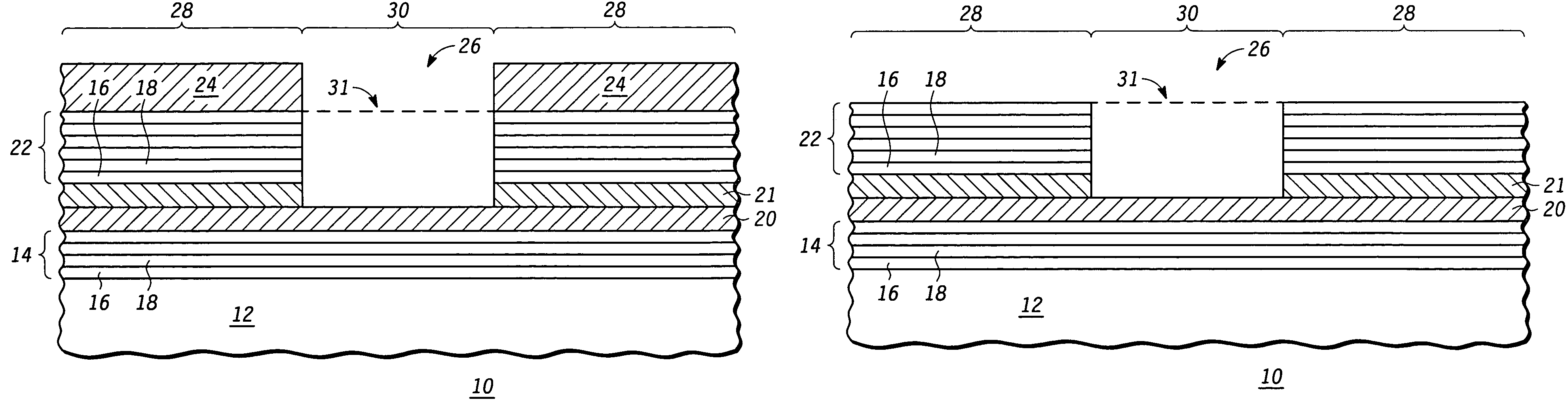
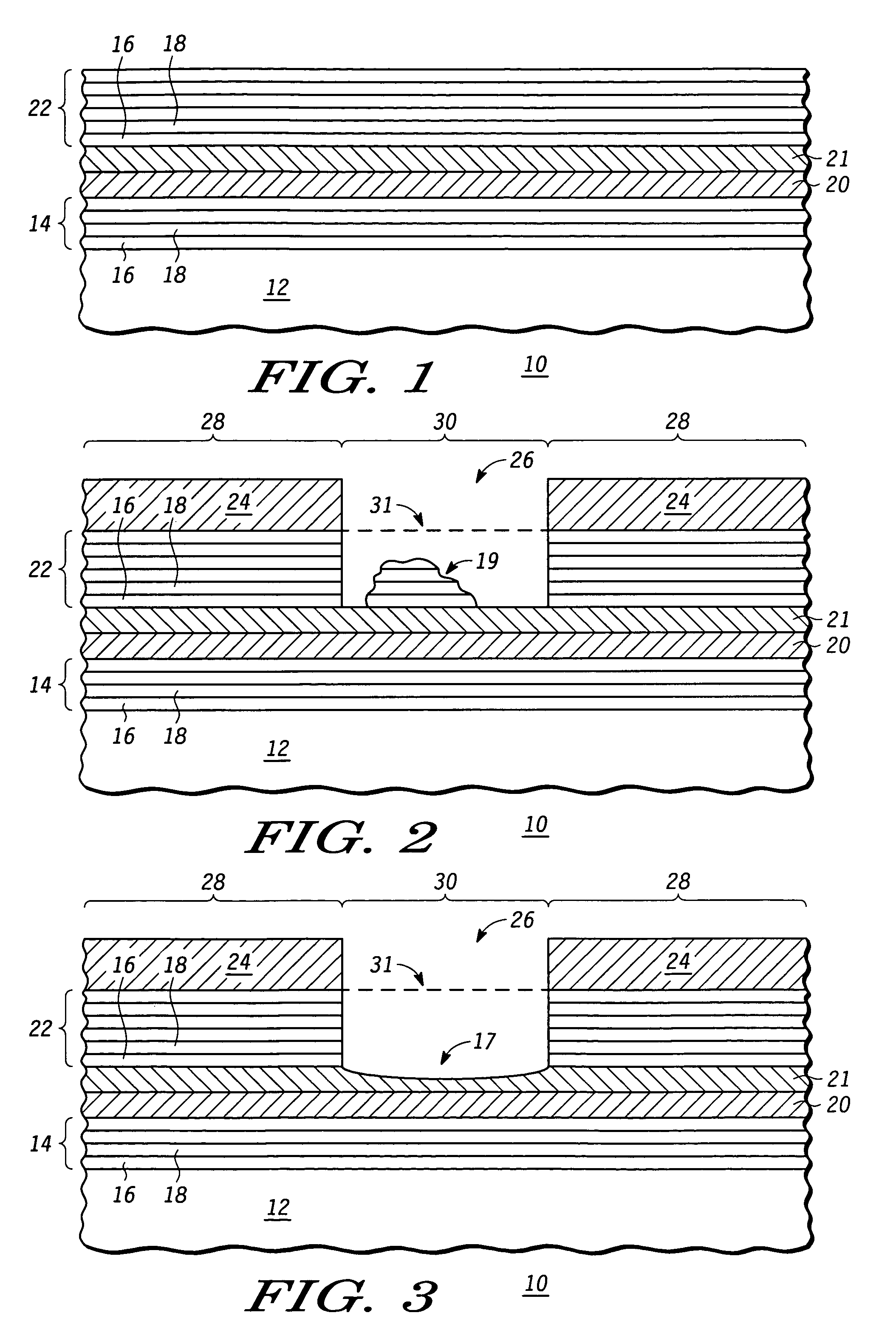
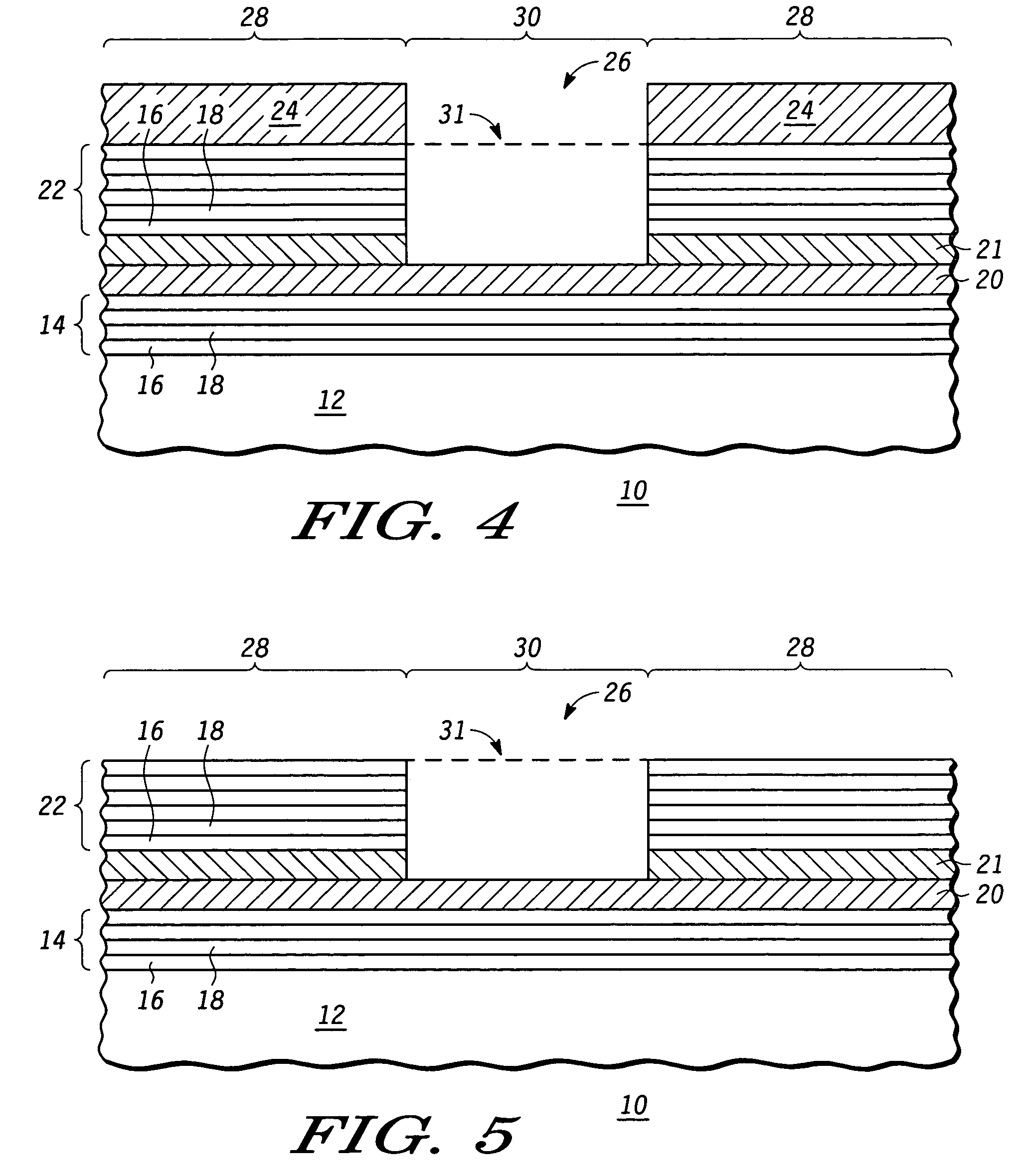
Reflective mask useful for transferring a pattern using extreme ultra violet (EUV) radiation and method of making the same
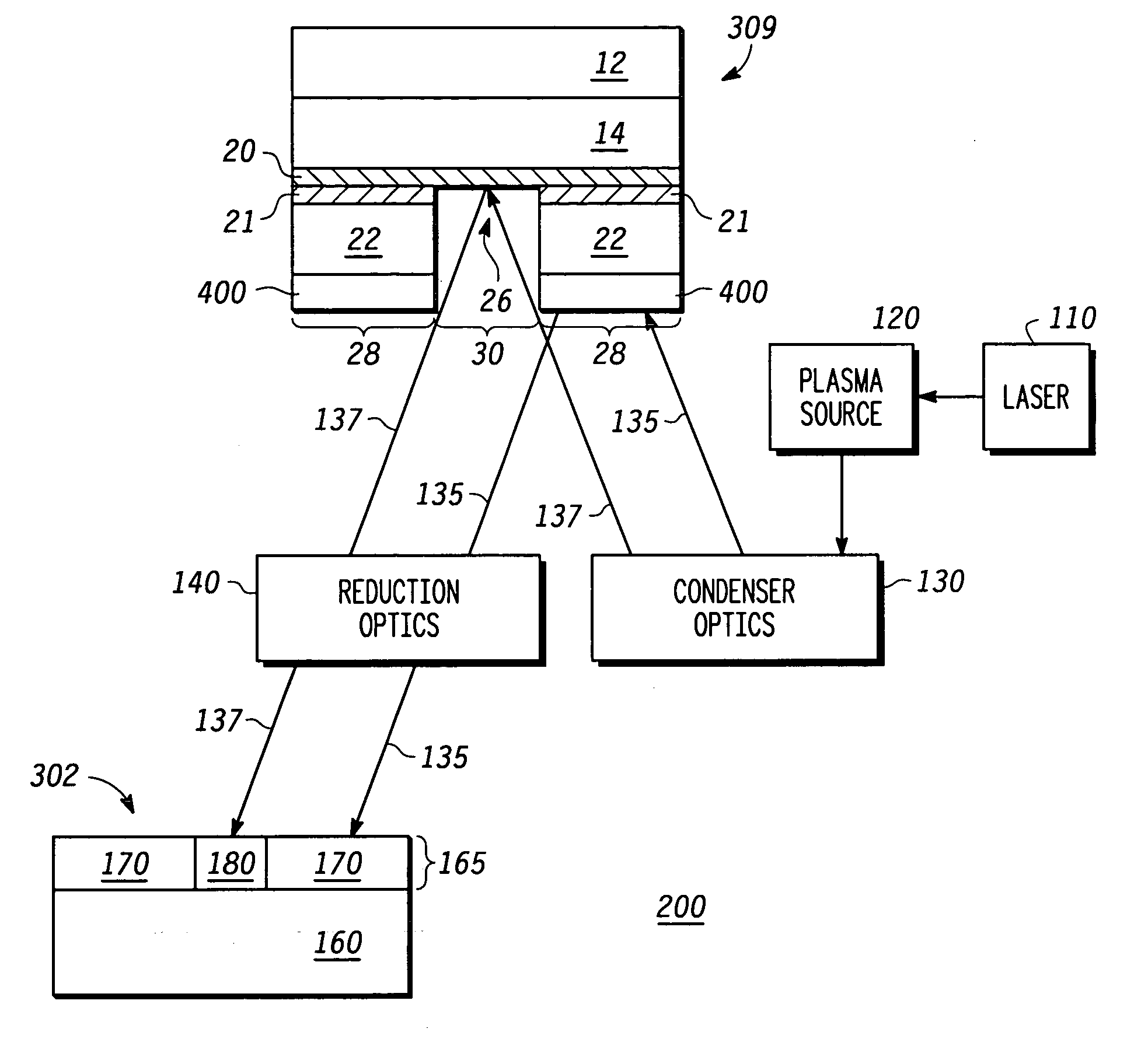
An EUV mask (10, 309) includes an opening (26) that helps to attenuate and phase shift extreme ultraviolet radiation using a subtractive rather than additive method. A first embedded layer (20) and a second embedded layer (21) may be provided between a lower multilayer reflective stack (14) and an upper multilayer reflective stack (22) to ensure an appropriate and accurate depth of the opening (26), while allowing for defect inspection of the EUV mask (10, 309) and optional defect repair. An optional ARC layer (400) may be deposited in region (28) to reduce the amount of reflection within dark region (28). Alternately, a single embedded layer of hafnium oxide, zirconium oxide, tantalum silicon oxide, tantalum oxide, or the like, may be used in place of embedded layers (20, 21). Optimal thicknesses and locations of the various layers are described.
Owner:NXP USA INC
System and method for detecting potential property insurance fraud
A system and method for assessing a condition of property for insurance purposes includes a sensor for acquiring a spectral image. In a preferred embodiment, the spectral image is post-processed to generate at least one spectral radiance plot, the plot used as input to a radiative transfer computer model. The output of the model establishes a spectral signature for the property. Over a period of time, spectral signatures can be compared to generate a spectral difference, the spectral difference can be used to determine whether a change in the condition of the property was potentially fraudulently caused.
Owner:HARTFORD FIRE INSURANCE
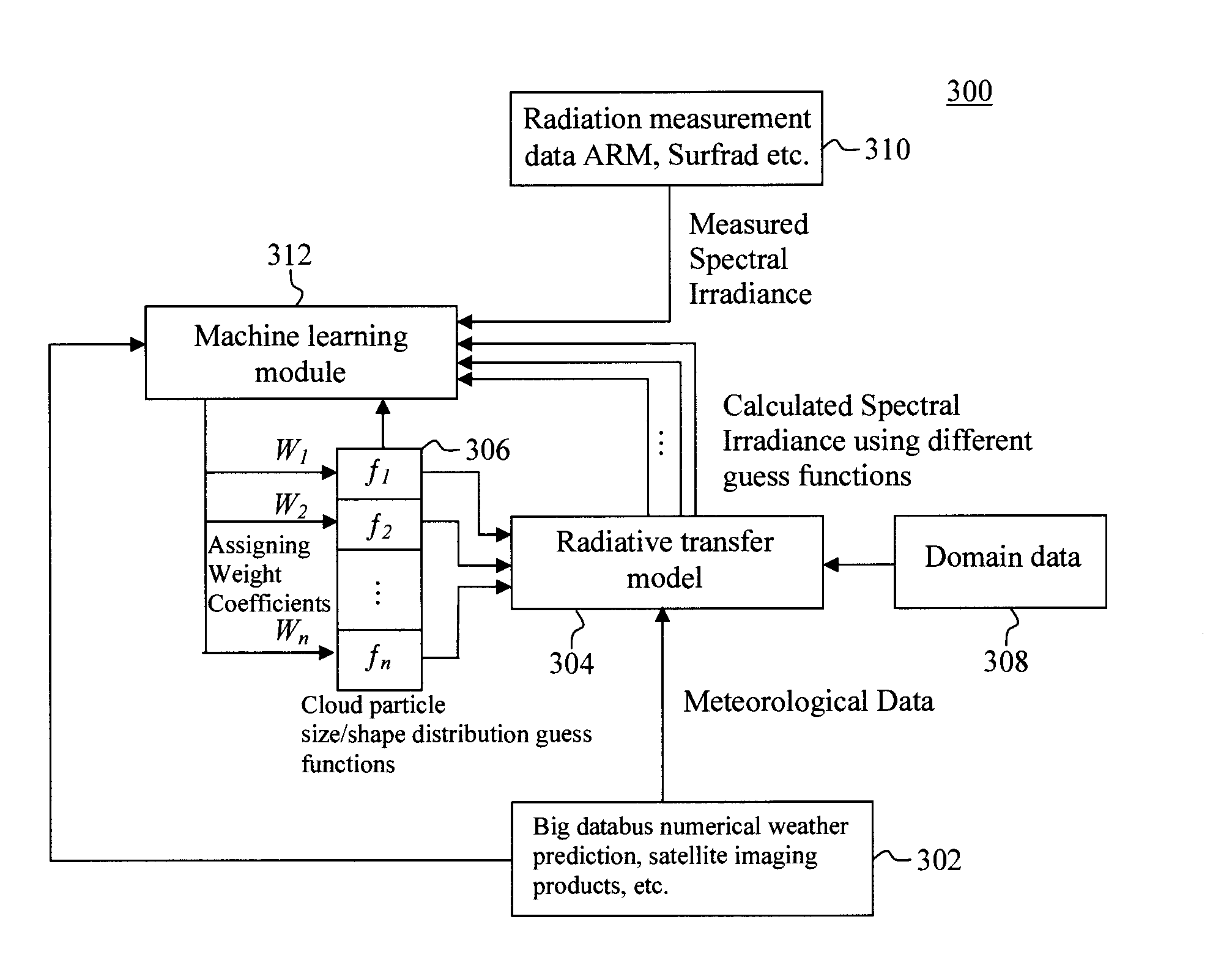
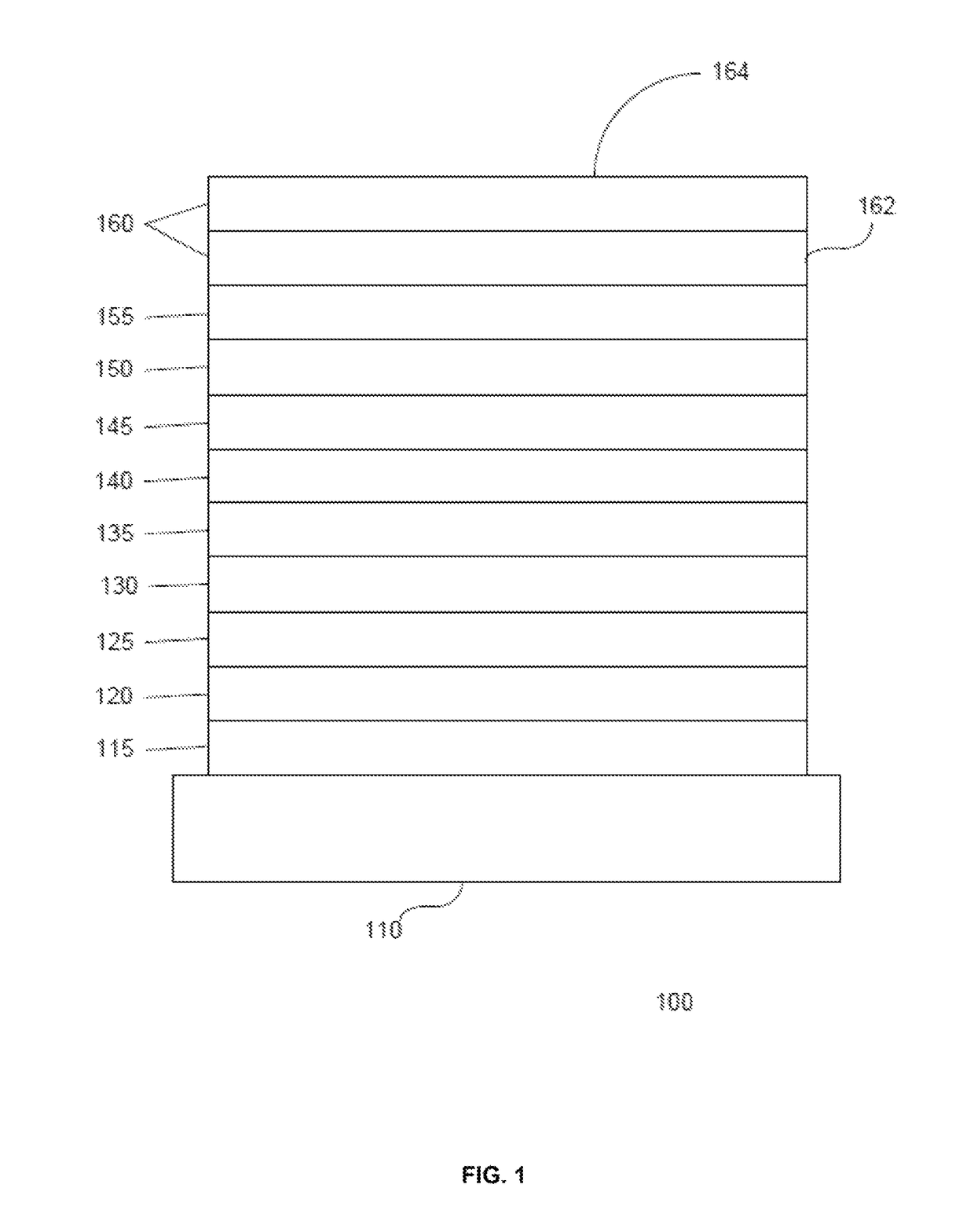
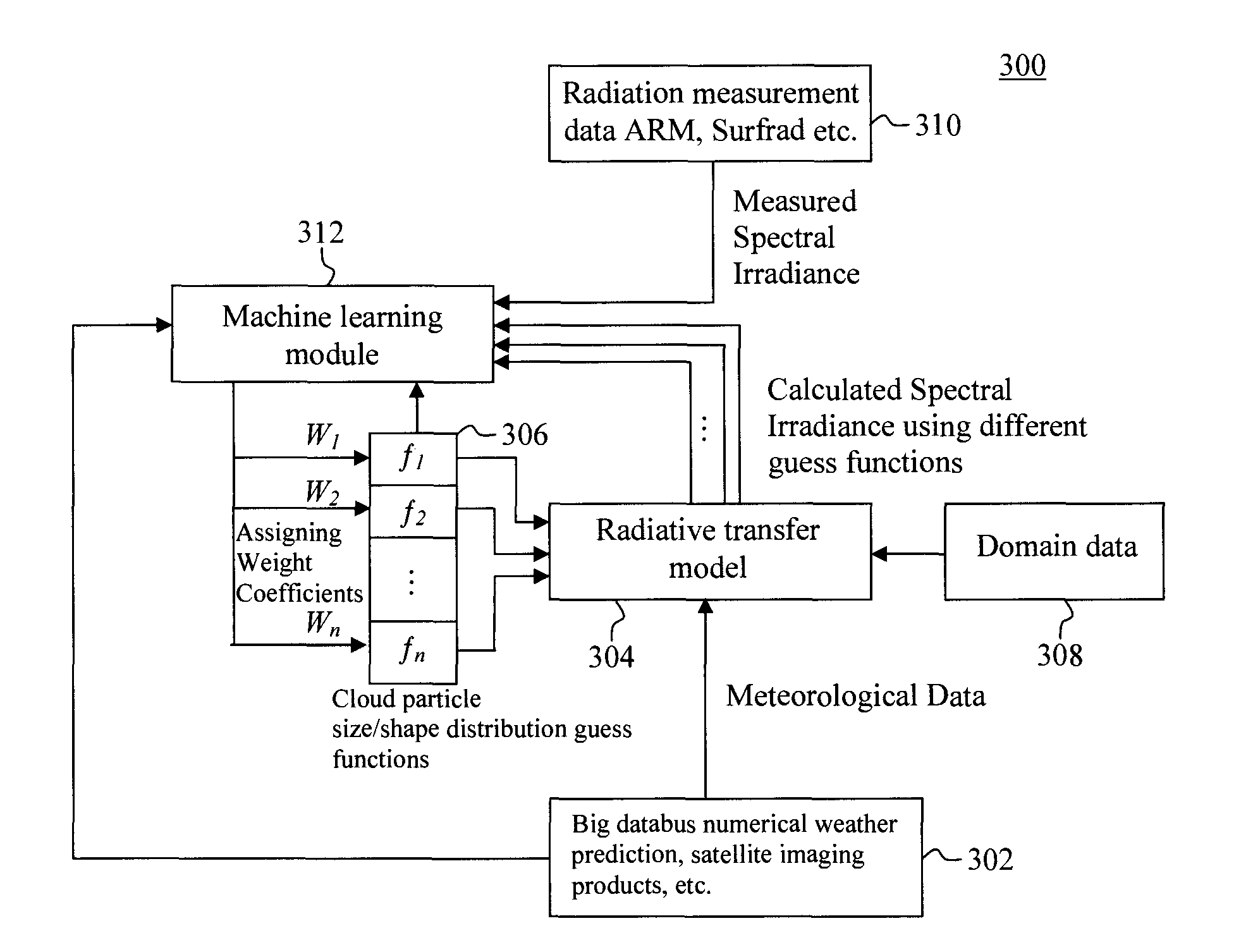
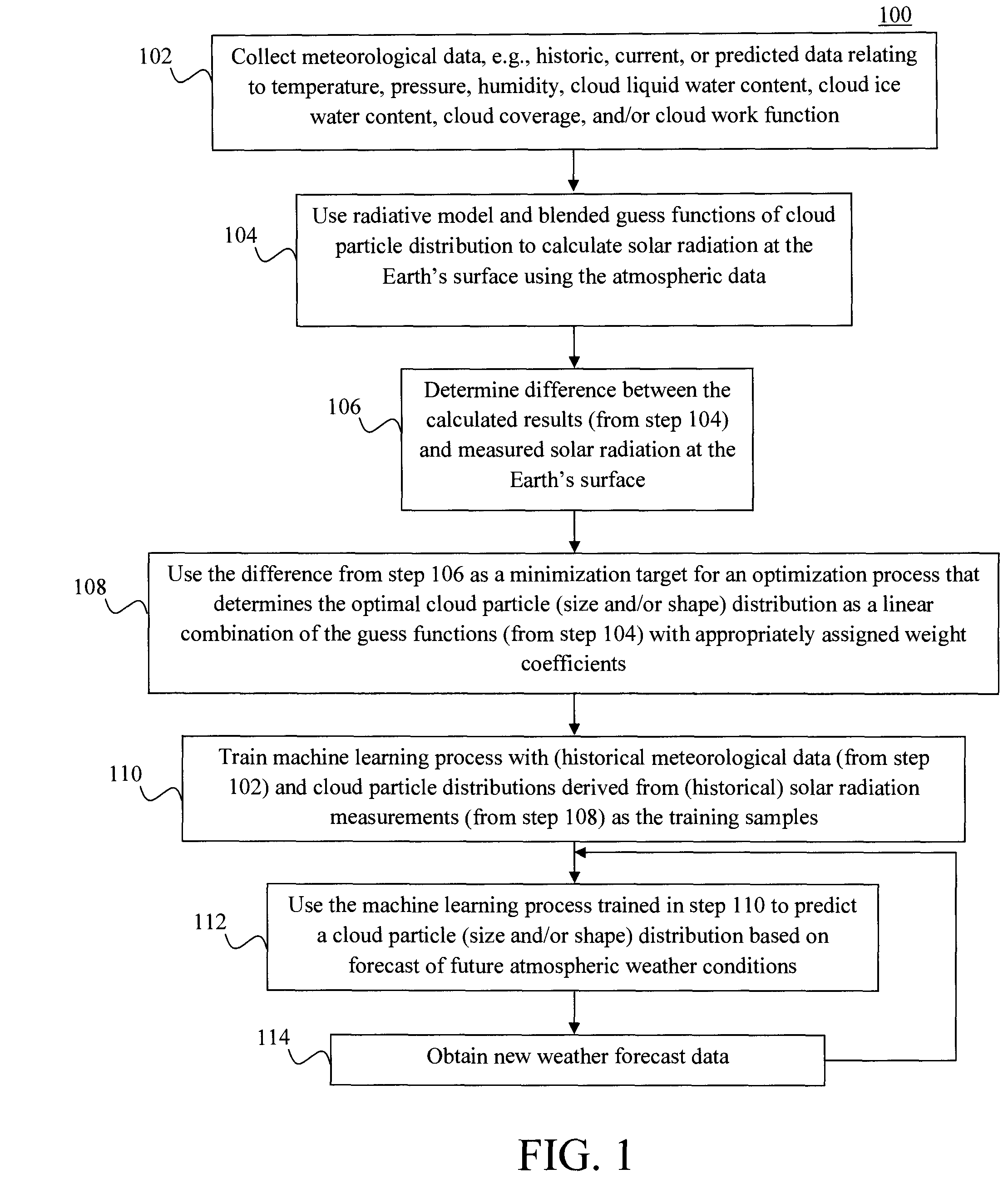
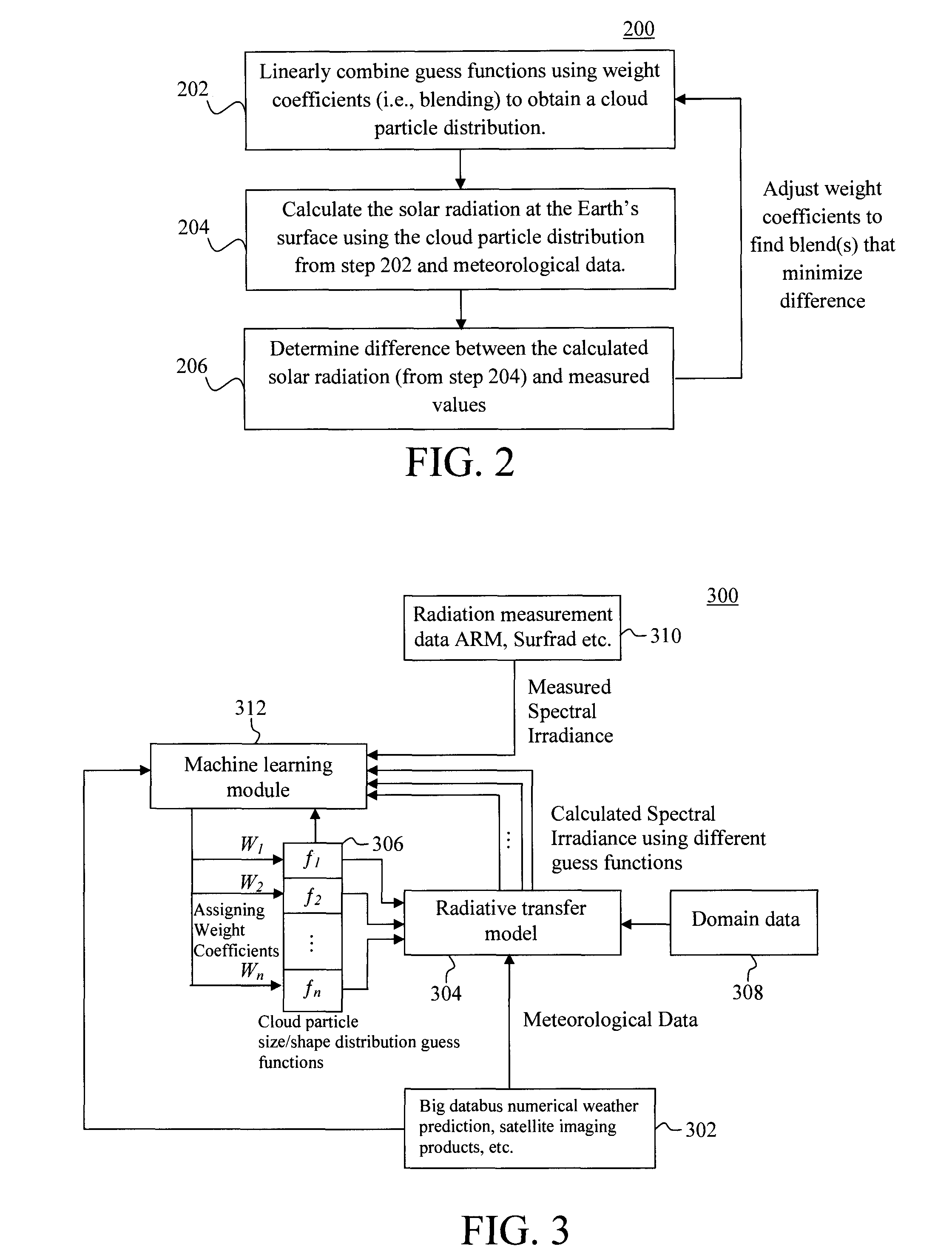
Machine Learning Approach for Analysis and Prediction of Cloud Particle Size and Shape Distribution
InactiveUS20140324352A1Weather condition predictionSpecial data processing applicationsRadiative transferWeight coefficient
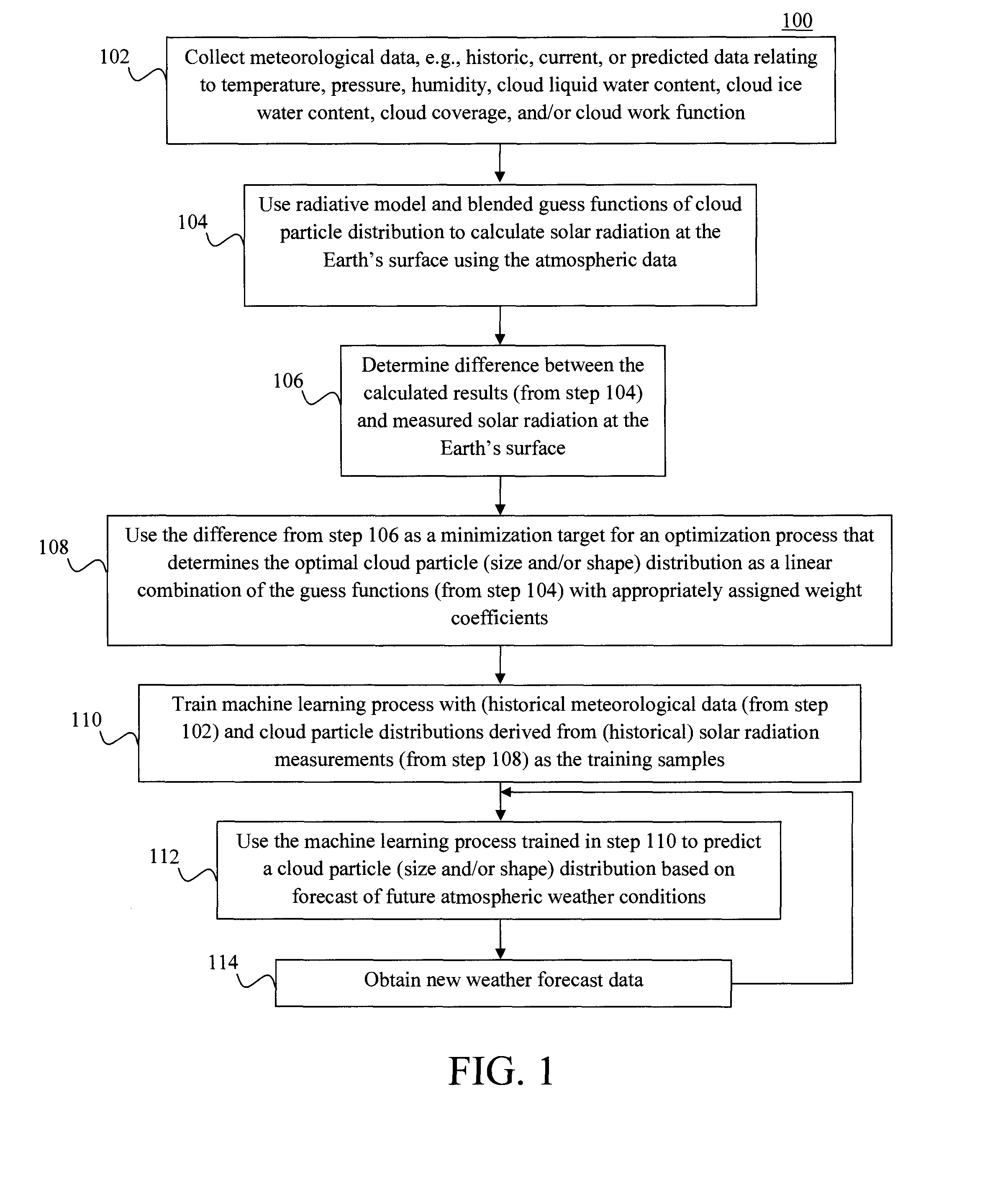
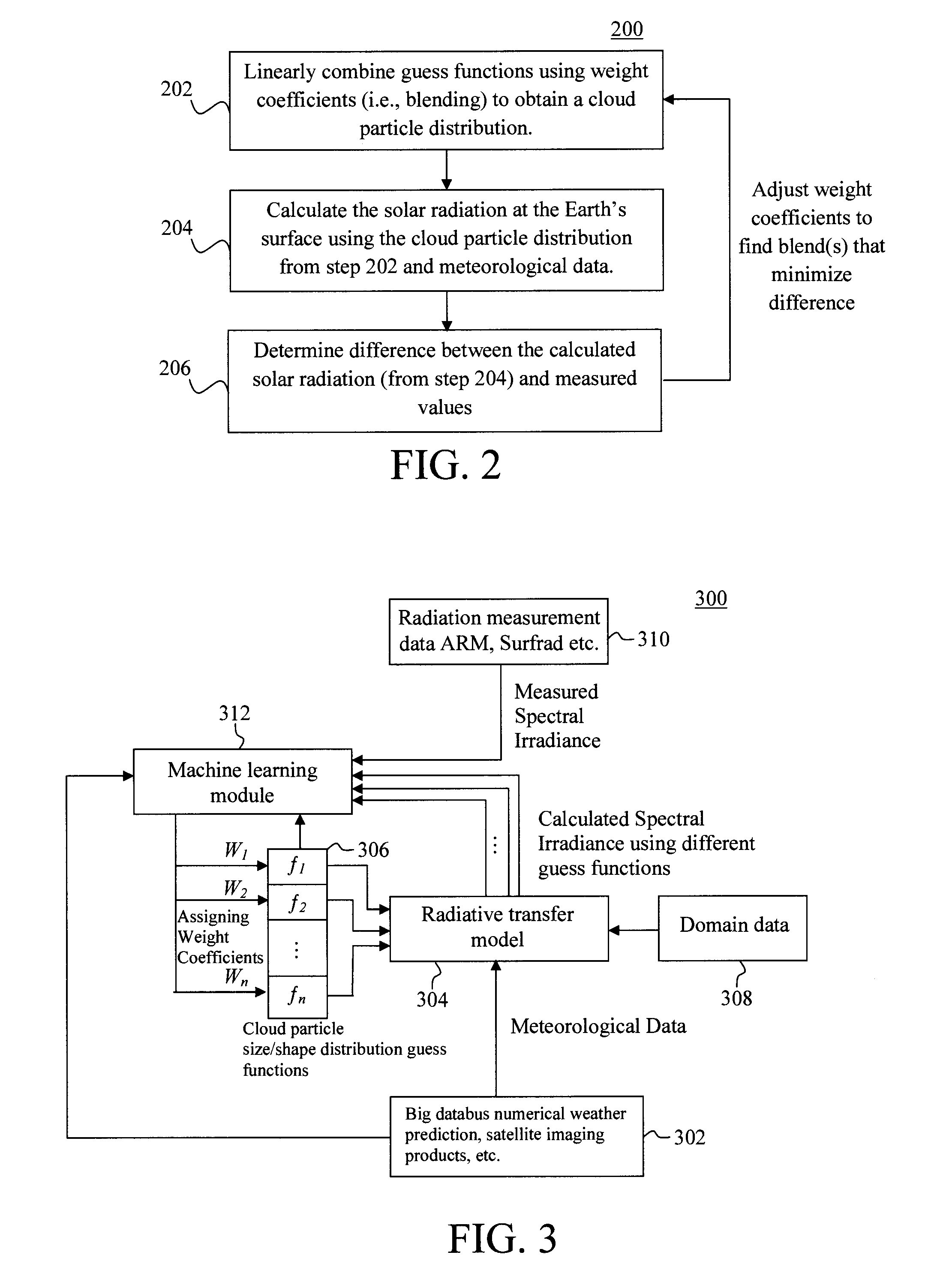
Techniques for analysis and prediction of cloud particle distribution and solar radiation are provided. In one aspect, a method for analyzing cloud particle characteristics includes the steps of: (a) collecting meteorological data; (b) calculating solar radiation values using a radiative transfer model based on the meteorological data and blended guess functions of a cloud particle distribution (c) optimizing the cloud particle distribution by optimizing the weight coefficients used for the blended guess functions of the cloud particle distribution based on the solar radiation values calculated in step (b) and measured solar radiation values; (d) training a machine-learning process using the meteorological data collected in step (a) and the cloud particle distribution optimized in step (c) as training samples; and (e) predicting future solar radiation values using forecasted meteorological data and the machine-learning process trained in step (d).
Owner:IBM CORP
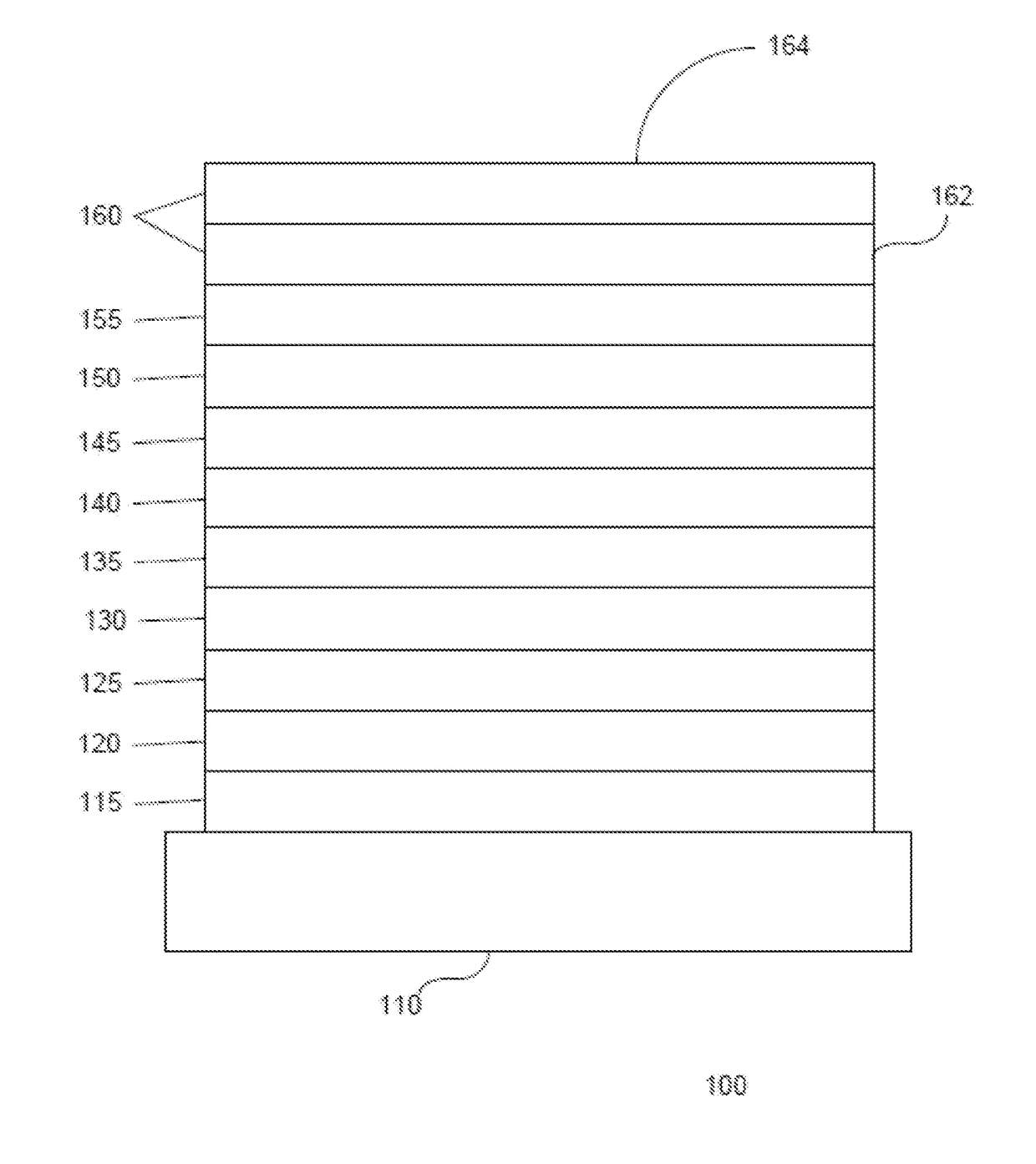
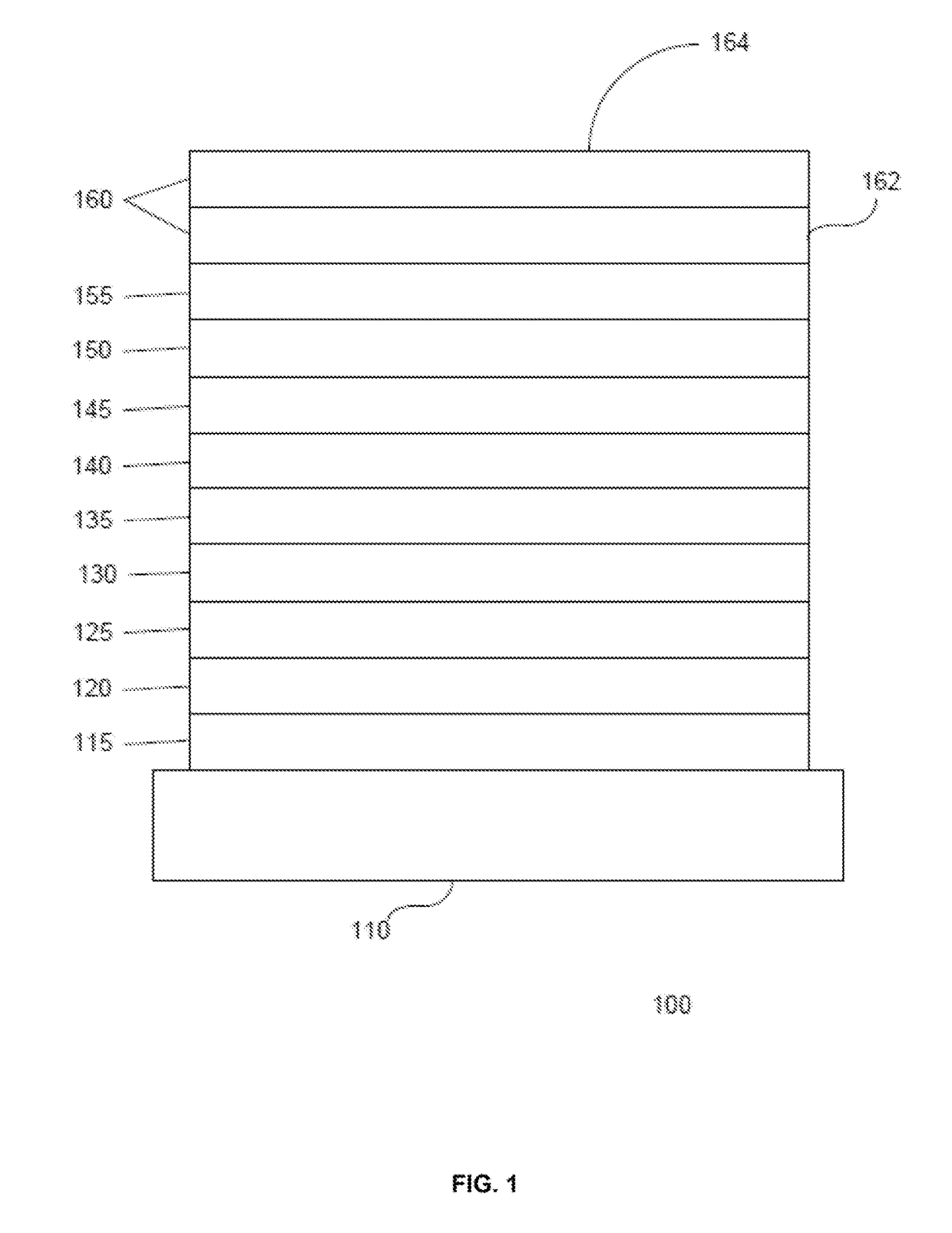
OLED device having enhancement layer(s)
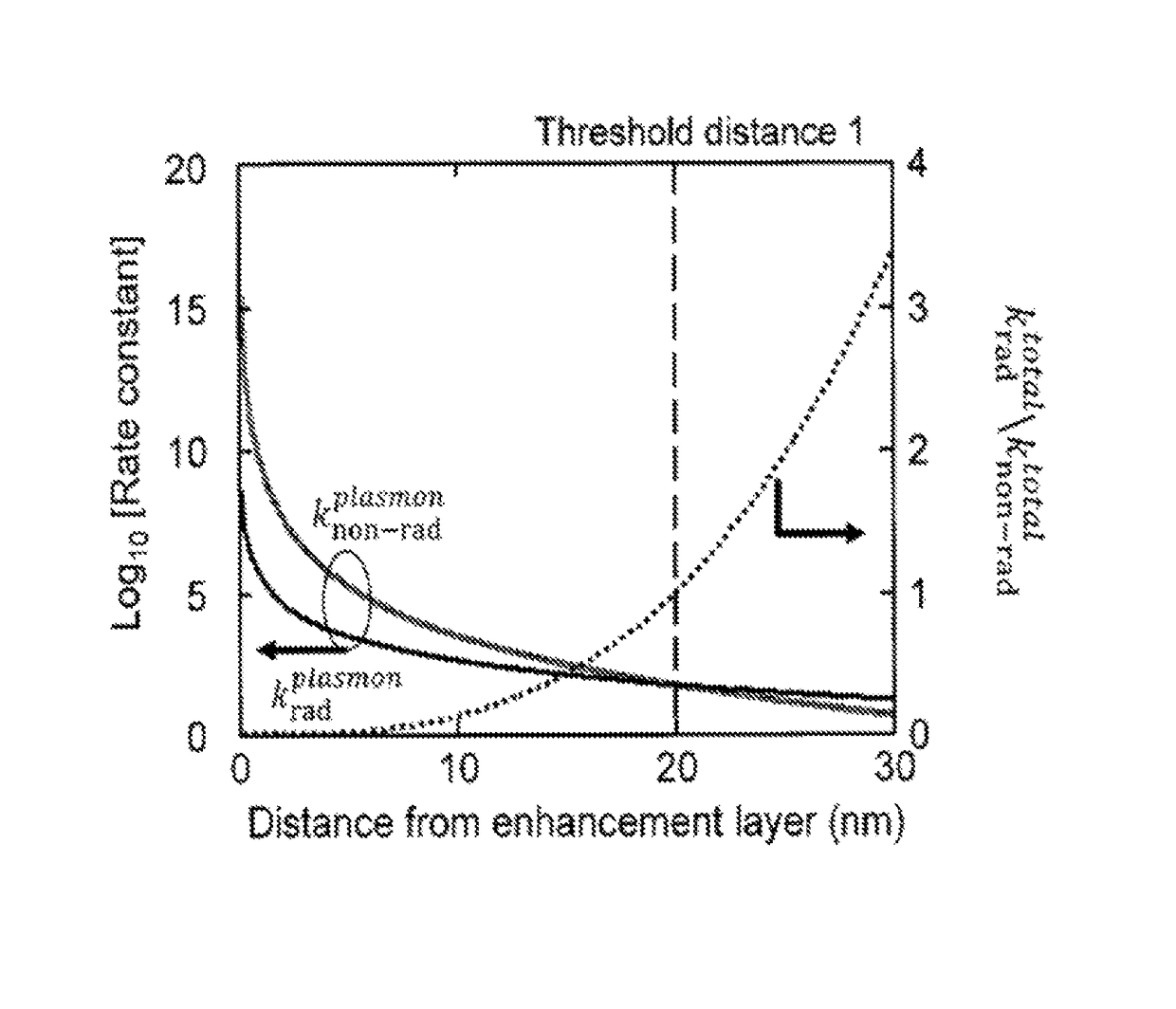
ActiveUS20170133631A1Lower emission rateLow efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadiative transferExcited state
A method for improving the operation of an OLED includes maximizing on-radiative transfer of excited state energy from the OLED's organic emissive material to surface plasmon polaritons in an enhancement layer by providing the enhancement layer no more than a threshold distance away from the organic emissive layer; and emitting light into free space from the enhancement layer by scattering the energy from the surface plasmon polaritons through an outcoupling layer that is provided proximate to the enhancement layer but opposite from the organic emissive layer.
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
OLED device having enhancement layer(s)
ActiveUS9960386B2Easy to operateMaximizing non-radiative transferSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExcited stateRadiative transfer
A method for improving the operation of an OLED includes maximizing on-radiative transfer of excited state energy from the OLED's organic emissive material to surface plasmon polaritons in an enhancement layer by providing the enhancement layer no more than a threshold distance away from the organic emissive layer; and emitting light into free space from the enhancement layer by scattering the energy from the surface plasmon polaritons through an outcoupling layer that is provided proximate to the enhancement layer but opposite from the organic emissive layer.
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
Machine Learning Approach for Analysis and Prediction of Cloud Particle Size and Shape Distribution
Techniques for analysis and prediction of cloud particle distribution and solar radiation are provided. In one aspect, a method for analyzing cloud particle characteristics includes the steps of: (a) collecting meteorological data; (b) calculating solar radiation values using a radiative transfer model based on the meteorological data and blended guess functions of a cloud particle distribution (c) optimizing the cloud particle distribution by optimizing the weight coefficients used for the blended guess functions of the cloud particle distribution based on the solar radiation values calculated in step (b) and measured solar radiation values; (d) training a machine-learning process using the meteorological data collected in step (a) and the cloud particle distribution optimized in step (c) as training samples; and (e) predicting future solar radiation values using forecasted meteorological data and the machine-learning process trained in step (d).
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic surface annealing using addressable laser array with pyrometry feedback
Apparatus for dynamic surface annealing of a semiconductor wafer includes a source of laser radiation emitting at a laser wavelength and comprising an array of lasers arranged in rows and columns, the optical power of each the laser being individual adjustable and optics for focusing the radiation from the array of lasers into a narrow line beam in a workpiece plane corresponding to a workpiece surface, whereby the optics images respective columns of the laser array onto respective sections of the narrow line beam. A pyrometer sensor is provided that is sensitive to a pyrometer wavelength. An optical element in an optical path of the optics is tuned to divert radiation emanating from the workpiece plane to the pyrometry sensor. As a result, the optics images each of the respective section of the narrow line beam onto a corresponding portion of the pyrometer sensor. The apparatus further includes a controller responsive to the pyrometry sensor and coupled to adjust individual optical outputs of respective columns of the laser array in accordance with outputs of corresponding portions of the pyrometry sensor.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Hybrid-dual-fourier tomographic algorithm for a fast three-dimensionial optical image reconstruction in turbid media
InactiveUS7218959B2Accurate solutionEasy to implementReconstruction from projectionScattering properties measurementsRadiative transfer3d image
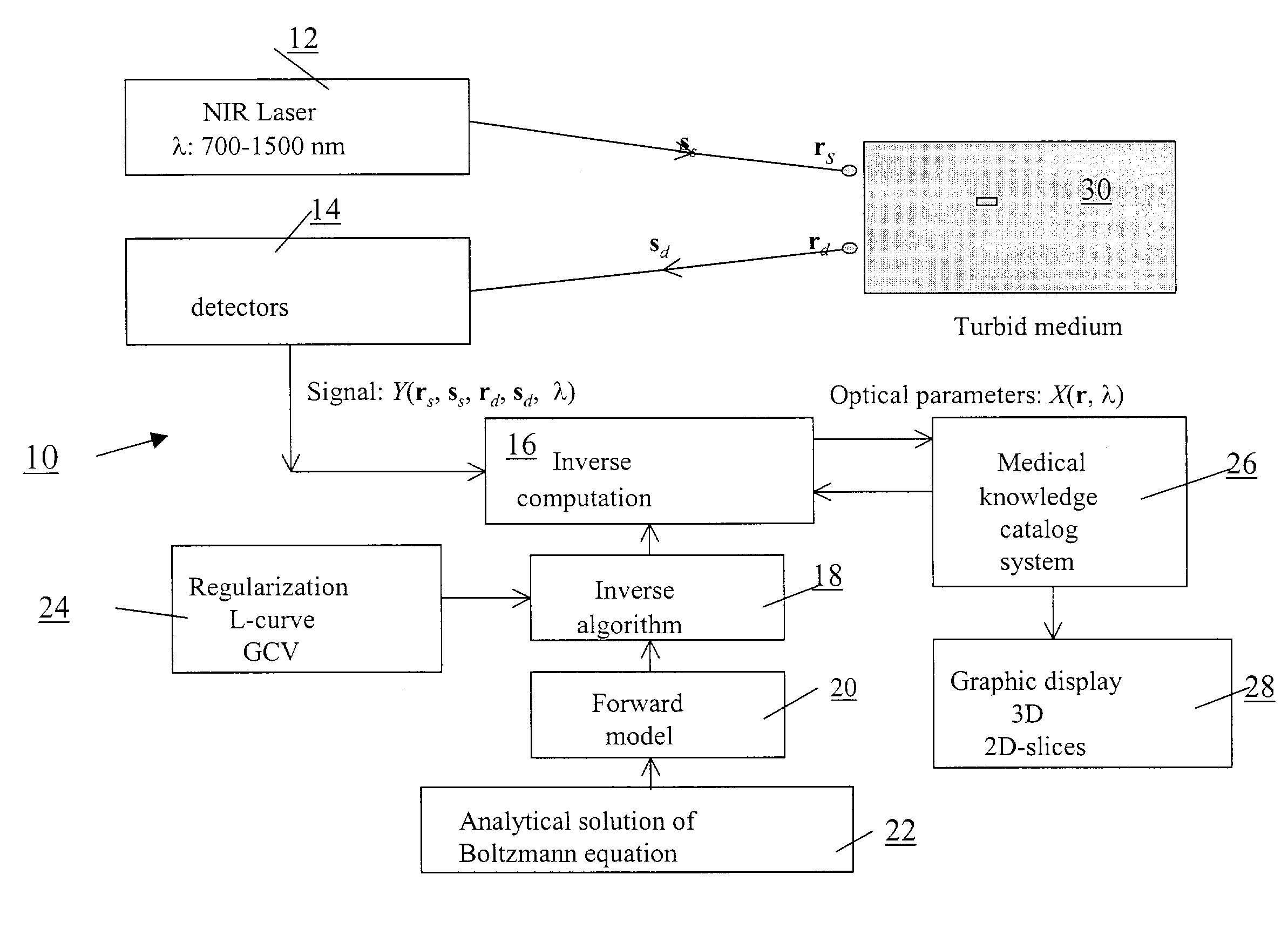
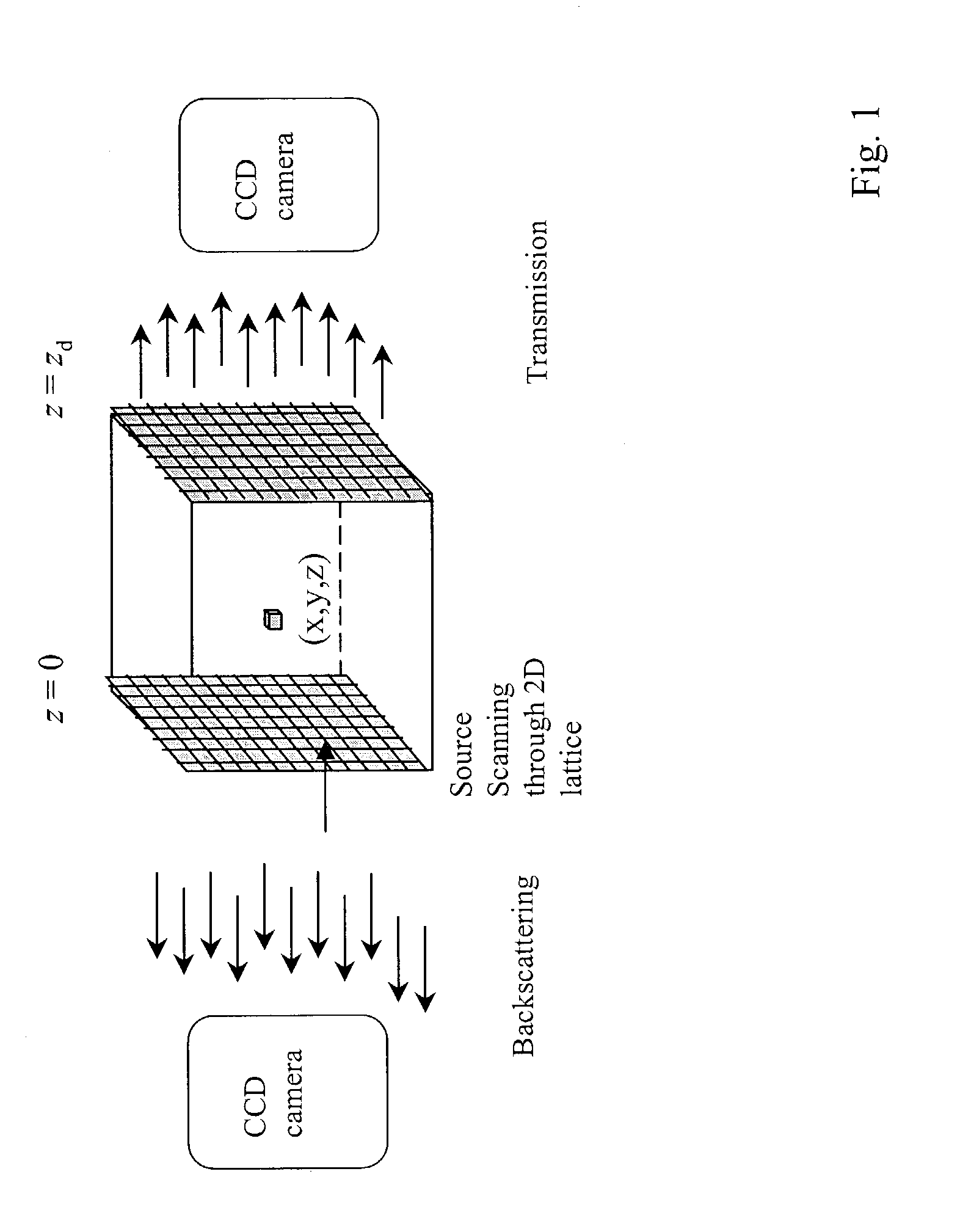
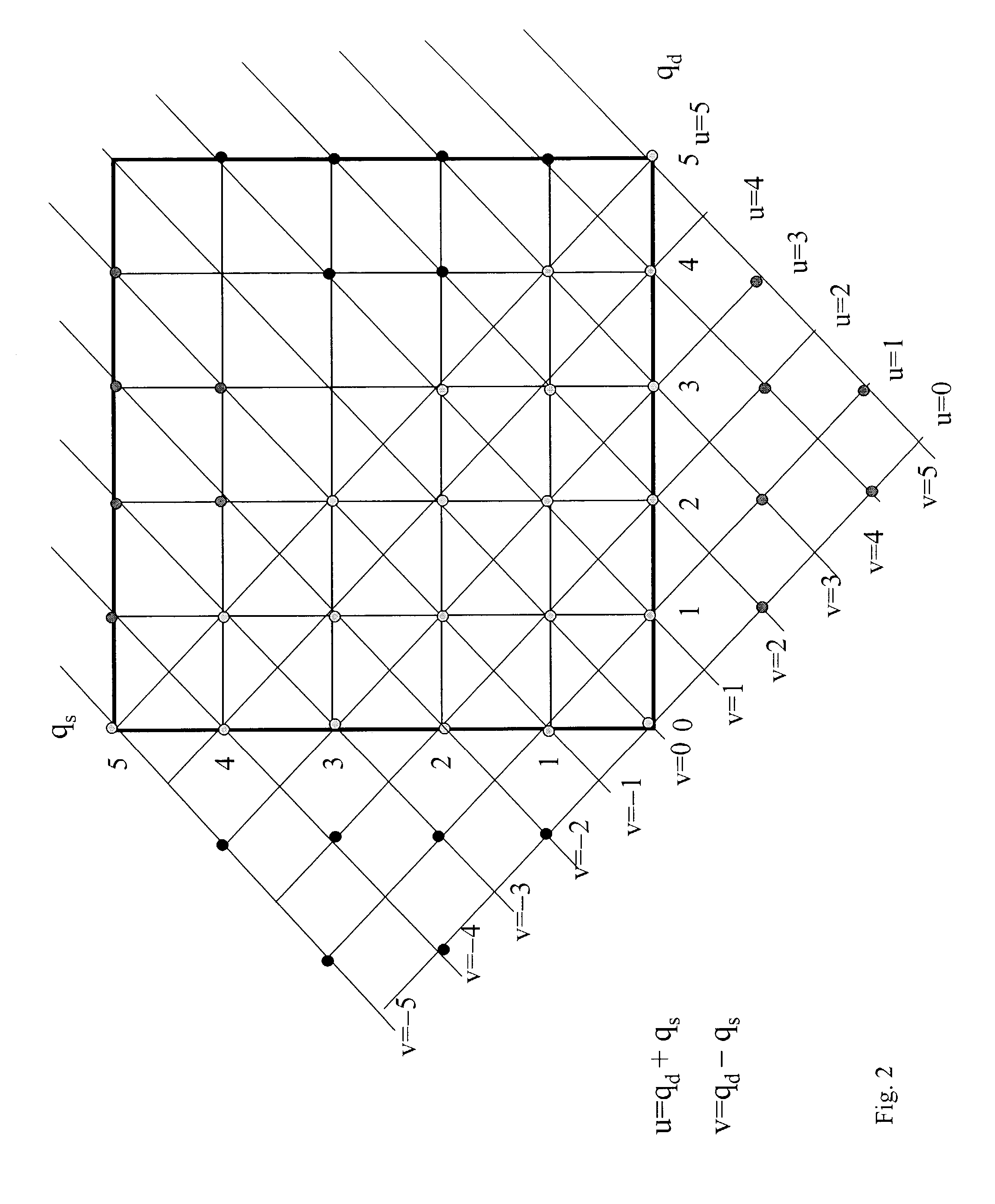
A reconstruction technique for reducing computation burden in the 3D image processes, wherein the reconstruction procedure comprises an inverse and a forward model. The inverse model uses a hybrid dual Fourier algorithm that combines a 2D Fourier inversion with a 1D matrix inversion to thereby provide high-speed inverse computations. The inverse algorithm uses a hybrid transfer to provide fast Fourier inversion for data of multiple sources and multiple detectors. The forward model is based on an analytical cumulant solution of a radiative transfer equation. The accurate analytical form of the solution to the radiative transfer equation provides an efficient formalism for fast computation of the forward model.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Reflective mask useful for transferring a pattern using extreme ultra violet (EUV) radiation and method of making the same
An EUV mask (10, 309) includes an opening (26) that helps to attenuate and phase shift extreme ultraviolet radiation using a subtractive rather than additive method. A first embedded layer (20) and a second embedded layer (21) may be provided between a lower multilayer reflective stack (14) and an upper multilayer reflective stack (22) to ensure an appropriate and accurate depth of the opening (26), while allowing for defect inspection of the EUV mask (10, 309) and optional defect repair. An optional ARC layer (400) may be deposited in region (28) to reduce the amount of reflection within dark region (28). Alternately, a single embedded layer of hafnium oxide, zirconium oxide, tantalum silicon oxide, tantalum oxide, or the like, may be used in place of embedded layers (20, 21). Optimal thicknesses and locations of the various layers are described.
Owner:NXP USA INC
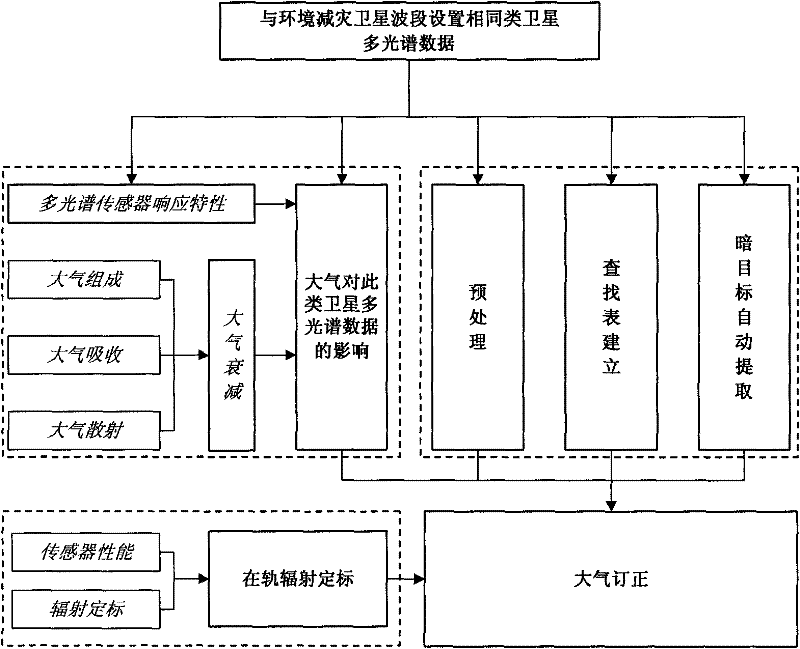
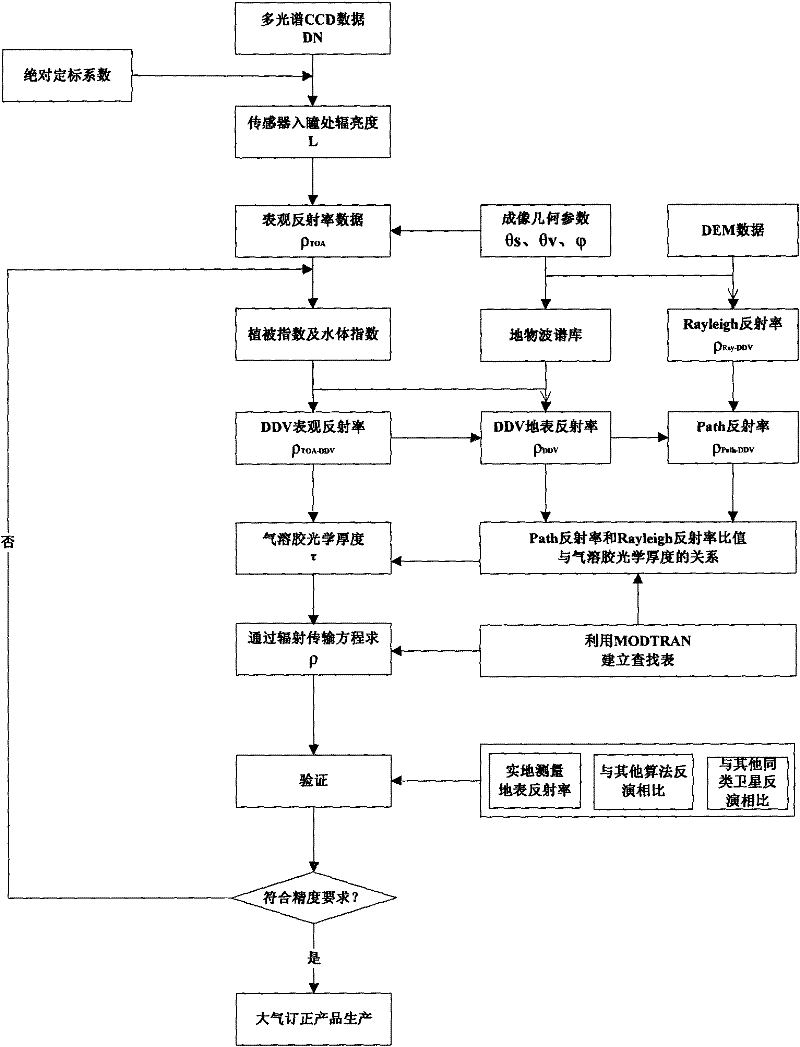
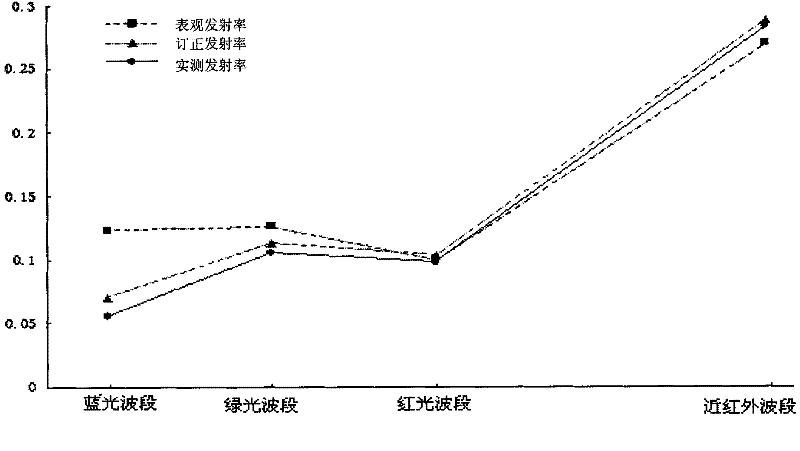
An Atmospheric Correction Method for Remote Sensing Satellite Multispectral Data
ActiveCN102288956AThe method is completeHigh precisionWave based measurement systemsRayleigh scatteringAtmospheric correction
The invention discloses an atmospheric correction method for multispectral data of a remote sensing satellite. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) reading data, and converting the data into apparent radiance data and apparent reflectivity data; (2) calculating decision factors, i.e. a ratio vegetation index, a soil adjustable vegetation index and a normalization water body index in adecision tree method according to the apparent reflectivity data; (3) acquiring apparent reflectivity data in a dark target area according to the apparent reflectivity data, and calculating air path reflectivity; (4) determining the aerosol optical depth of each multispectral waveband according to the relation among the air path reflectivity, a Rayleigh reflectivity ratio and the aerosol optical depth, and determining the total optical depth of a position of 550 nanometers according to the aerosol optical depth and the Rayleigh scatting optical depth of each multispectral waveband; and (5) acquiring an inversion parameter from a lookup table according to the total optical depth of the position of 550 nanometers, and solving land surface reflectivity through a radiative transfer equation to finish atmospheric correction.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
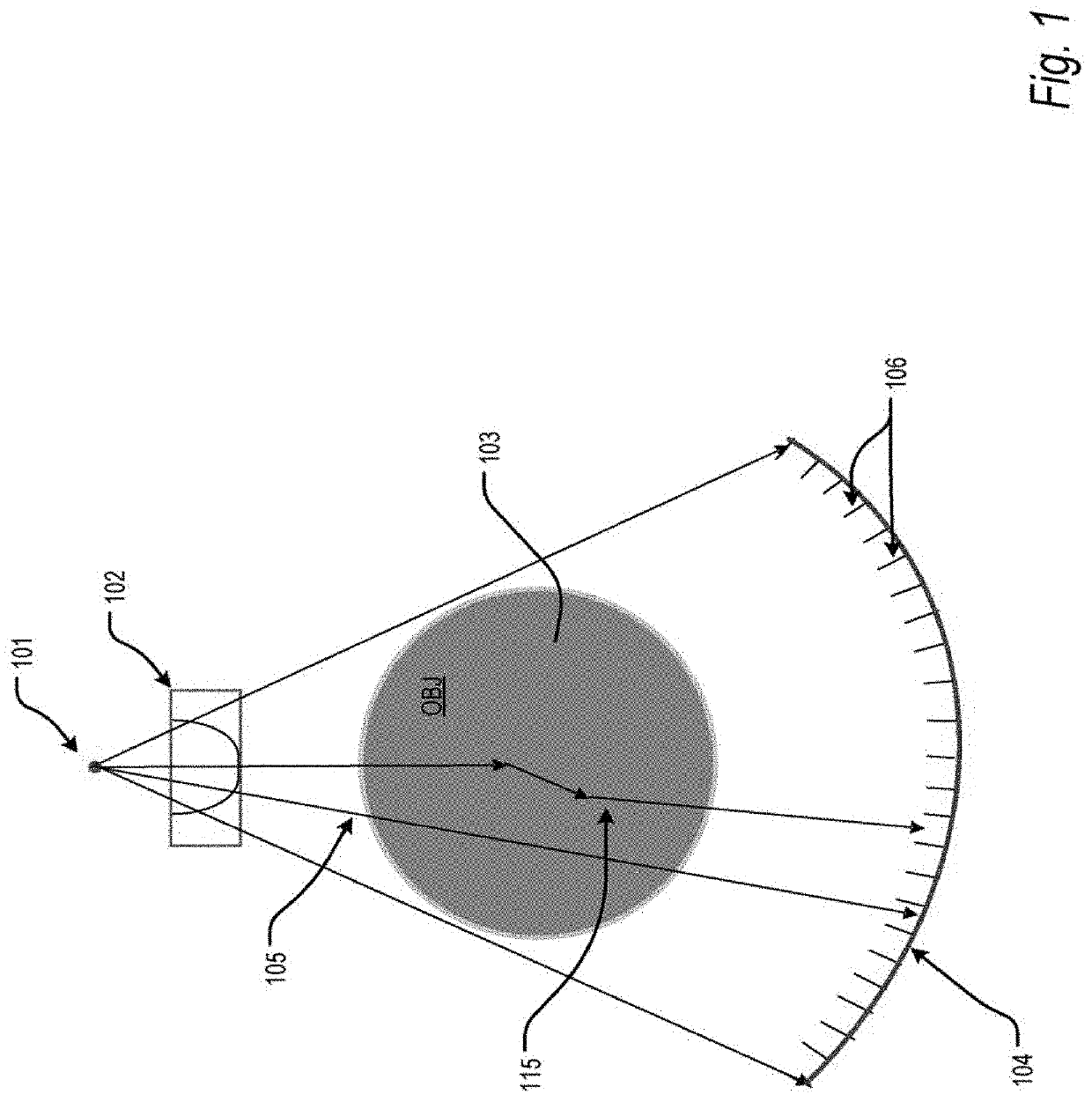
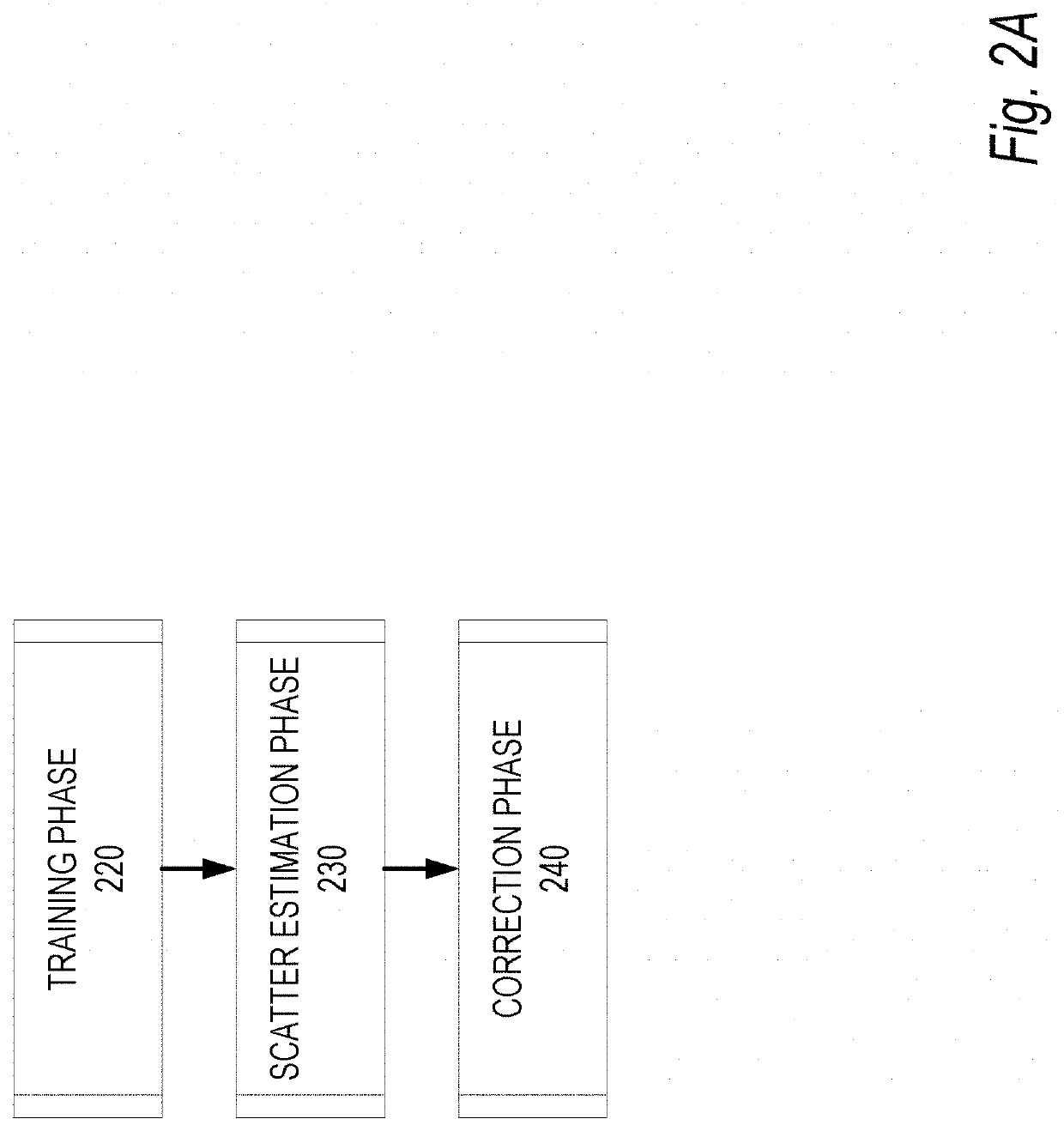
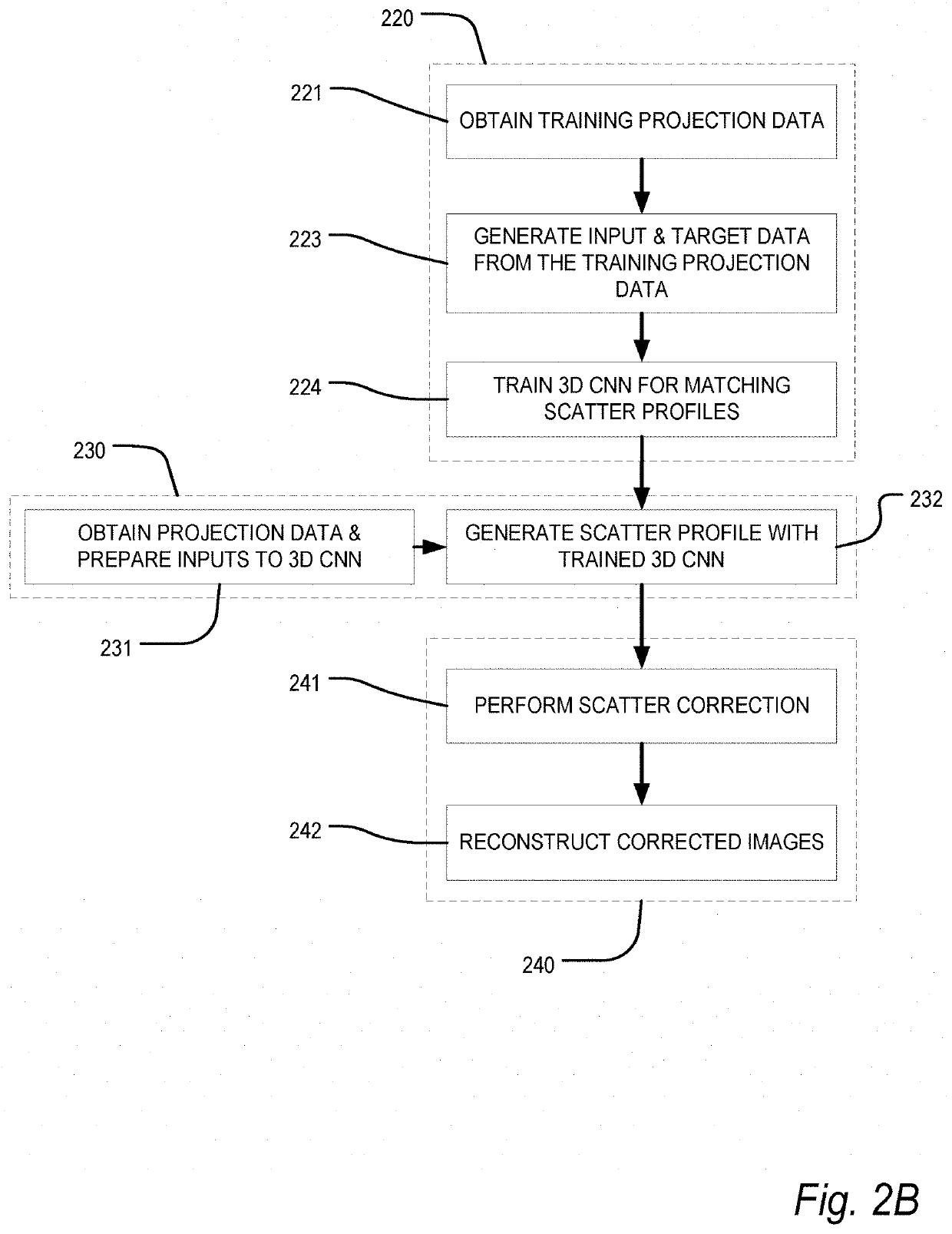
Deep-learning-based scatter estimation and correction for x-ray projection data and computer tomography (CT)
A method and apparatus are provided for using a neural network to estimate scatter in X-ray projection images and then correct for the X-ray scatter. For example, the neural network is a three-dimensional convolutional neural network 3D-CNN to which are applied projection images, at a given view, for respective energy bins and / or material components. The projection images can be obtained by material decomposing spectral projection data, or by segmenting a reconstructed CT image into material-component images, which are then forward projected to generate energy-resolved material-component projections. The result generated by the 3D-CNN is an estimated scatter flux. To train the 3D-CNN, the target scatter flux in the training data can be simulated using a radiative transfer equation method.
Owner:CANON MEDICAL SYST COPRPORATION
Method and system for determining atmospheric profiles using a physical retrieval algorithm
ActiveUS7558673B1Indication of weather conditions using multiple variablesThermometerFrequency spectrumNoise level
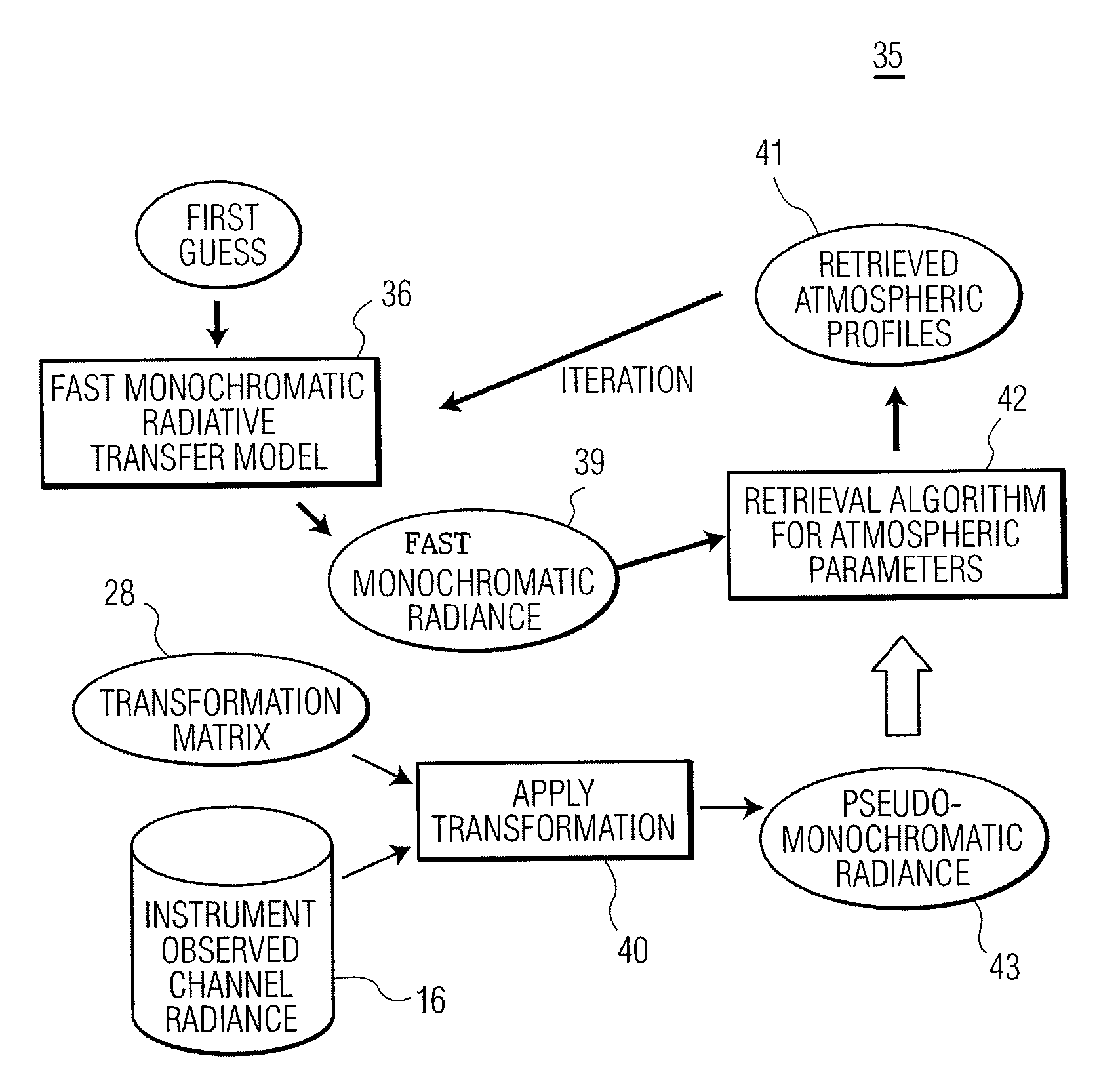
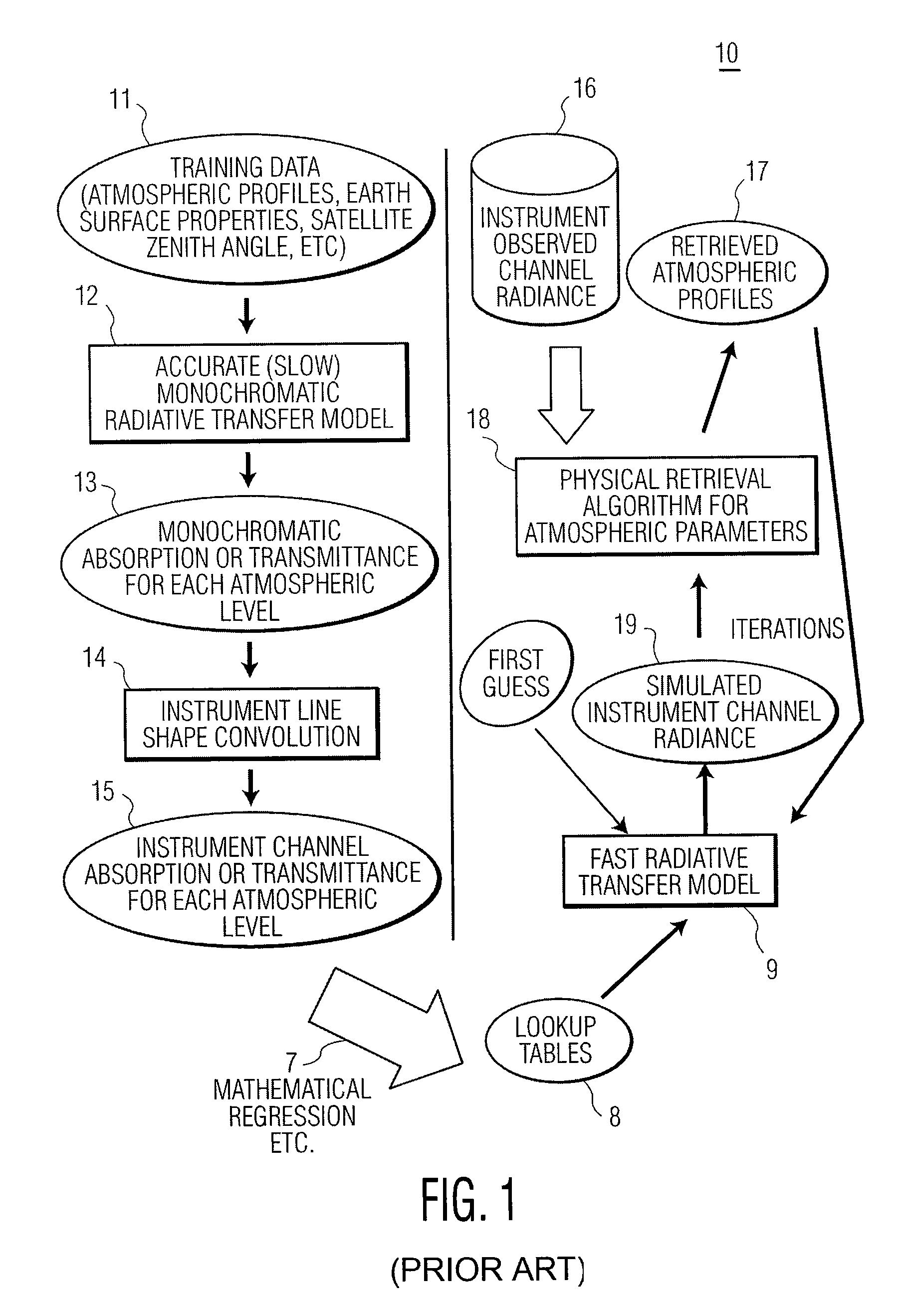
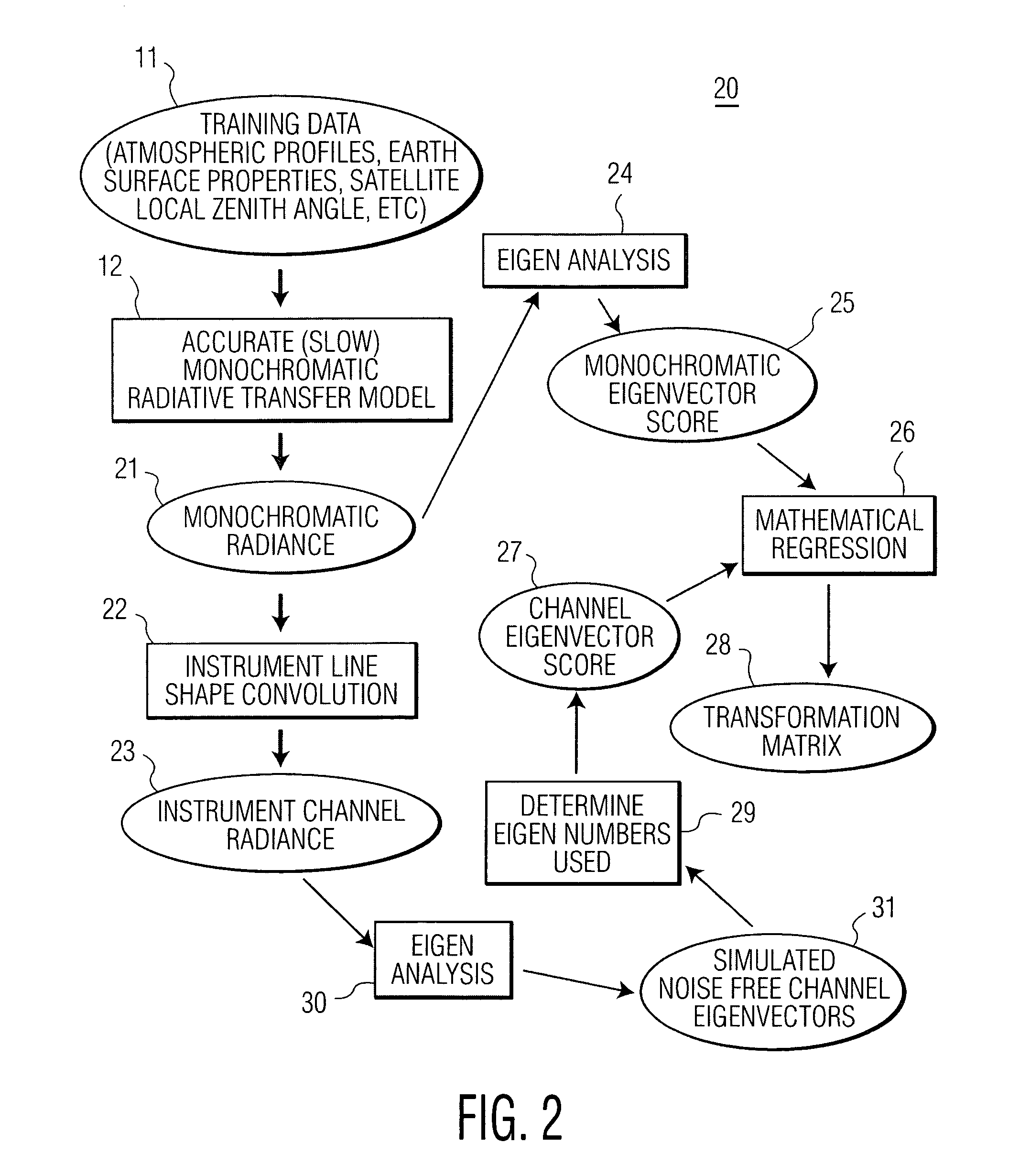
The present invention provides a new approach for processing hyper-spectral radiance data. It uses a transformation matrix to convert an instrument radiance spectrum into a pseudo-monochromatic radiance spectrum. The pseudo-monochromatic radiance spectrum is produced by an empirical transform of the instrument channel spectrum to a monochromatic equivalent spectrum (i.e., a pseudo-monochromatic spectrum). Eigenvector regression is used to produce the empirical transformation. Although the transformation does not produce the monochromatic radiance spectrum without error, the transformation error is generally well below nominal instrument noise levels for most spectral channels. The reduction in instrument noise results from a noise filtering effect of the eigenvector transformation. One of the advantages of the present invention is that it eliminates the need to build different fast radiative transfer models (RTMs) for different observing instruments, since the retrieval of geophysical parameters is based on an inversion of the monochromatic radiative transfer model. Although a different transformation matrix is required for different instrument spectral channel characteristics, the production of this transformation matrix is straightforward and simpler than the production of an accurate channel radiance fast model.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
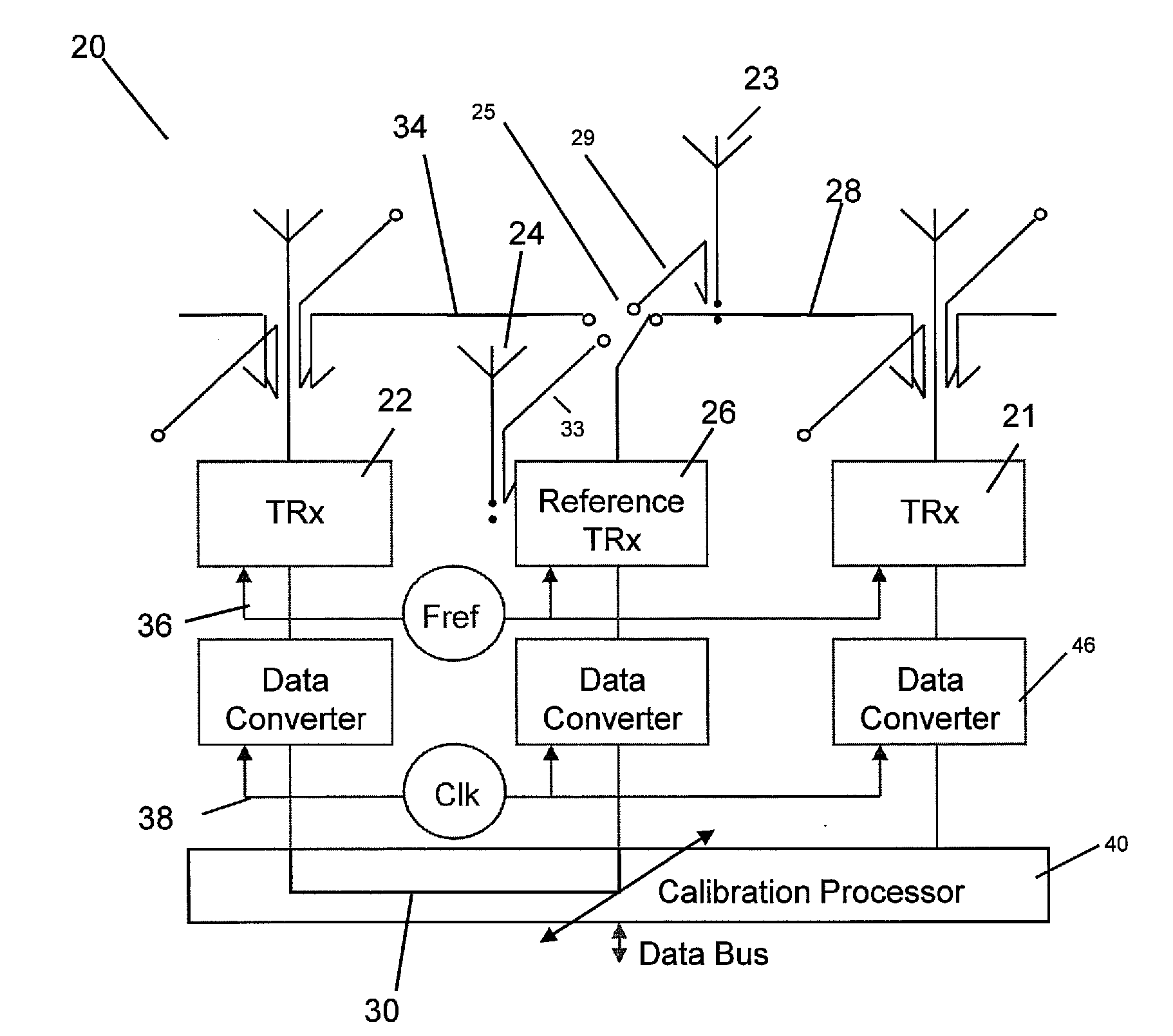
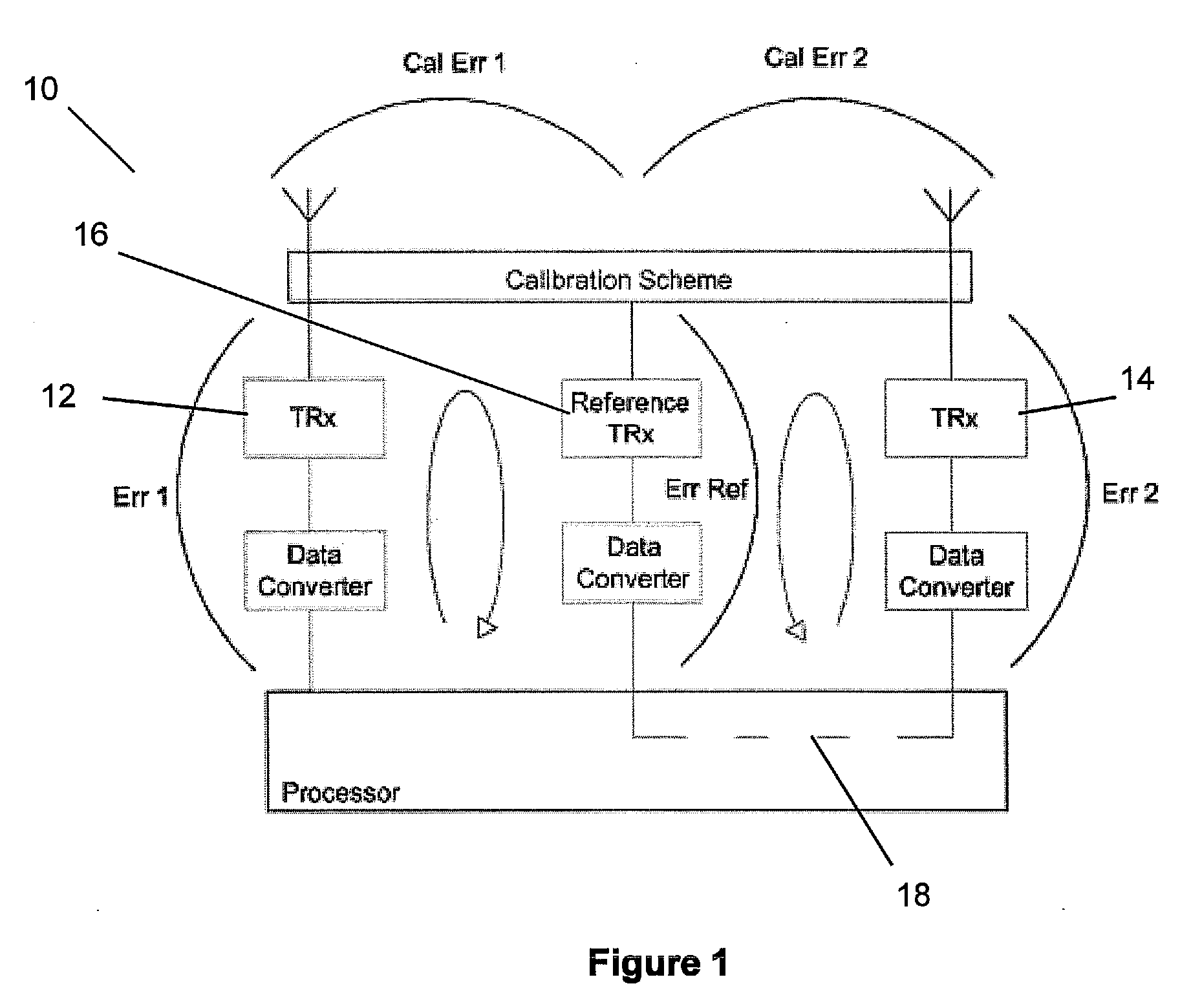
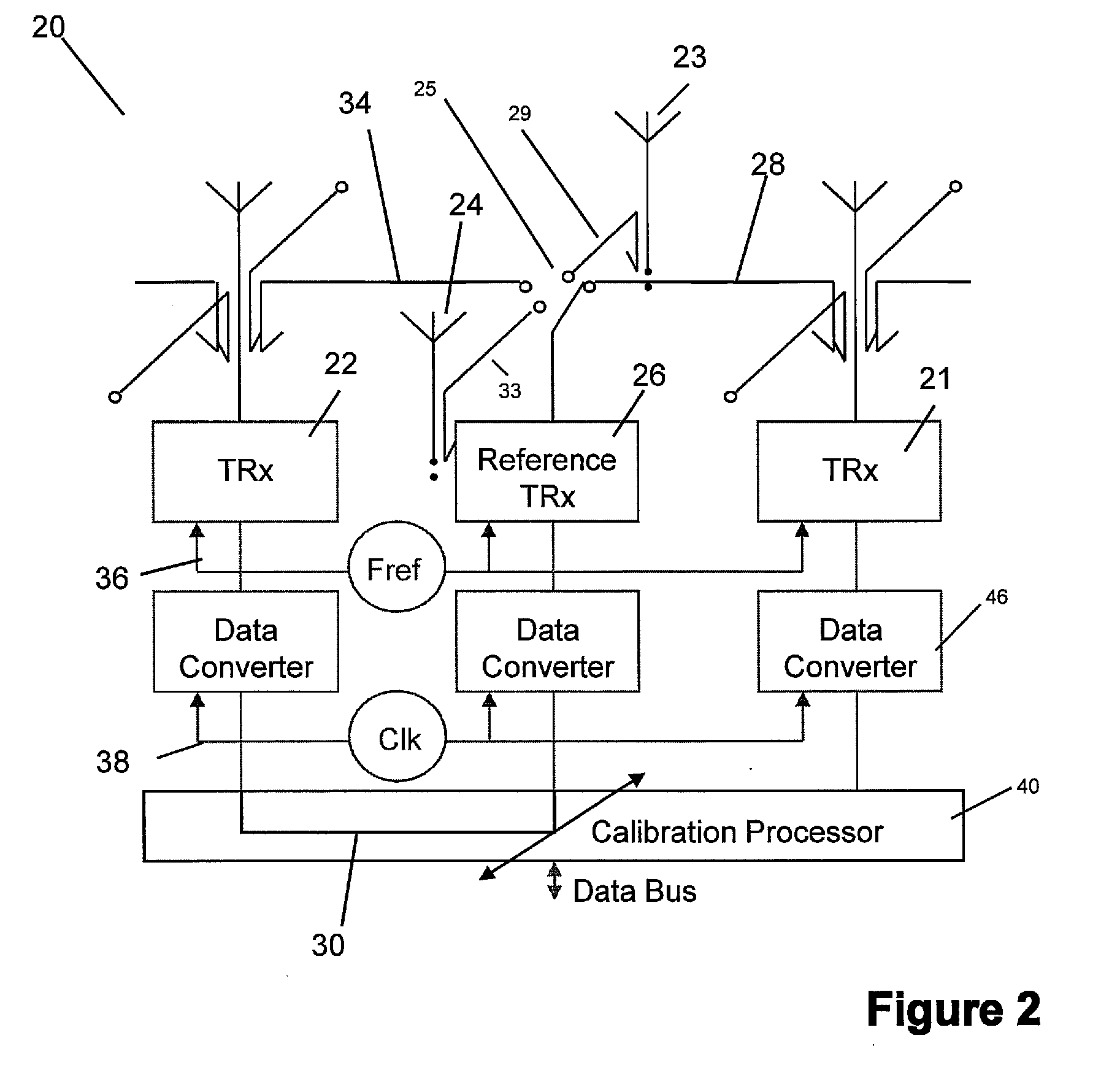
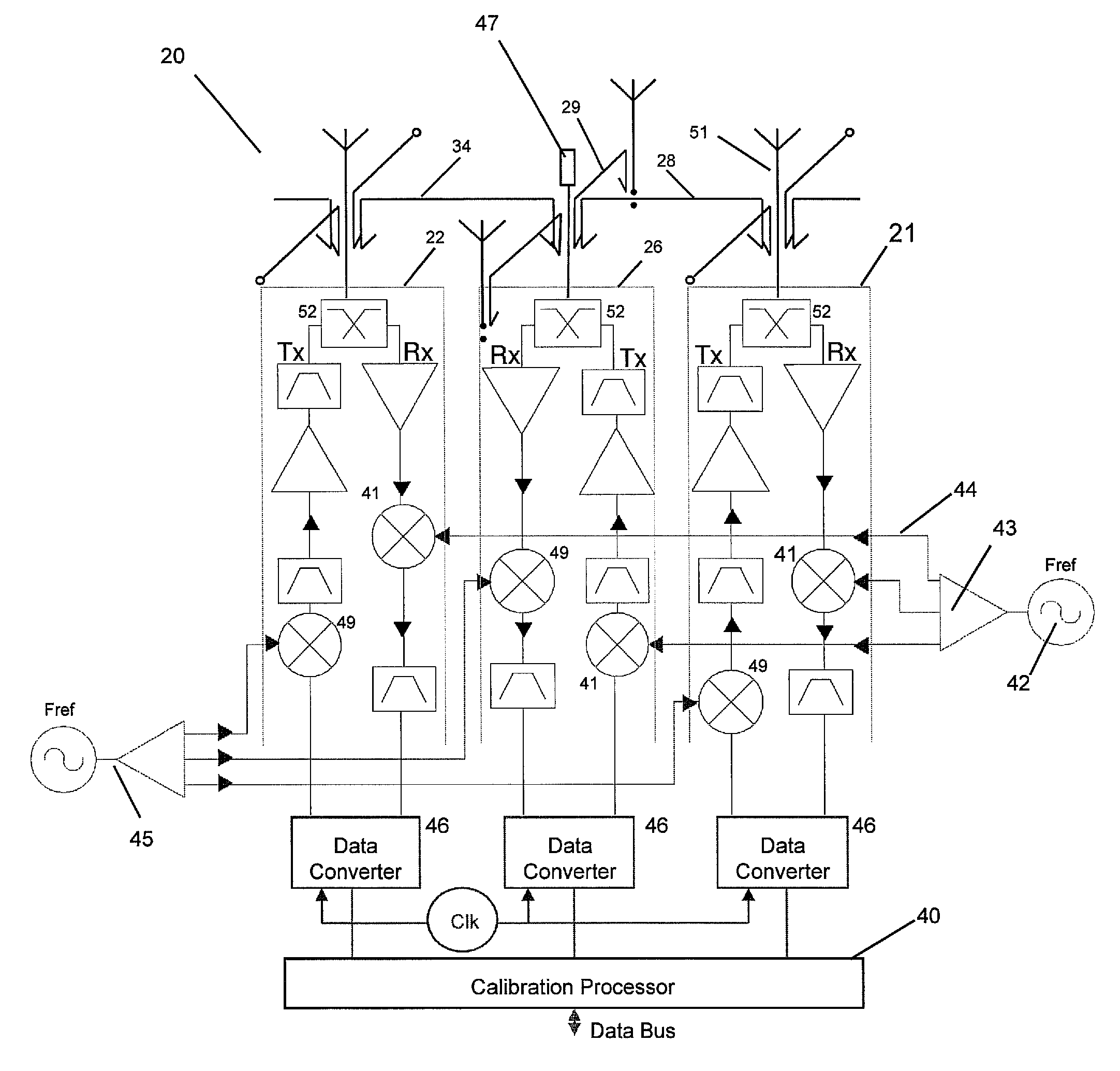
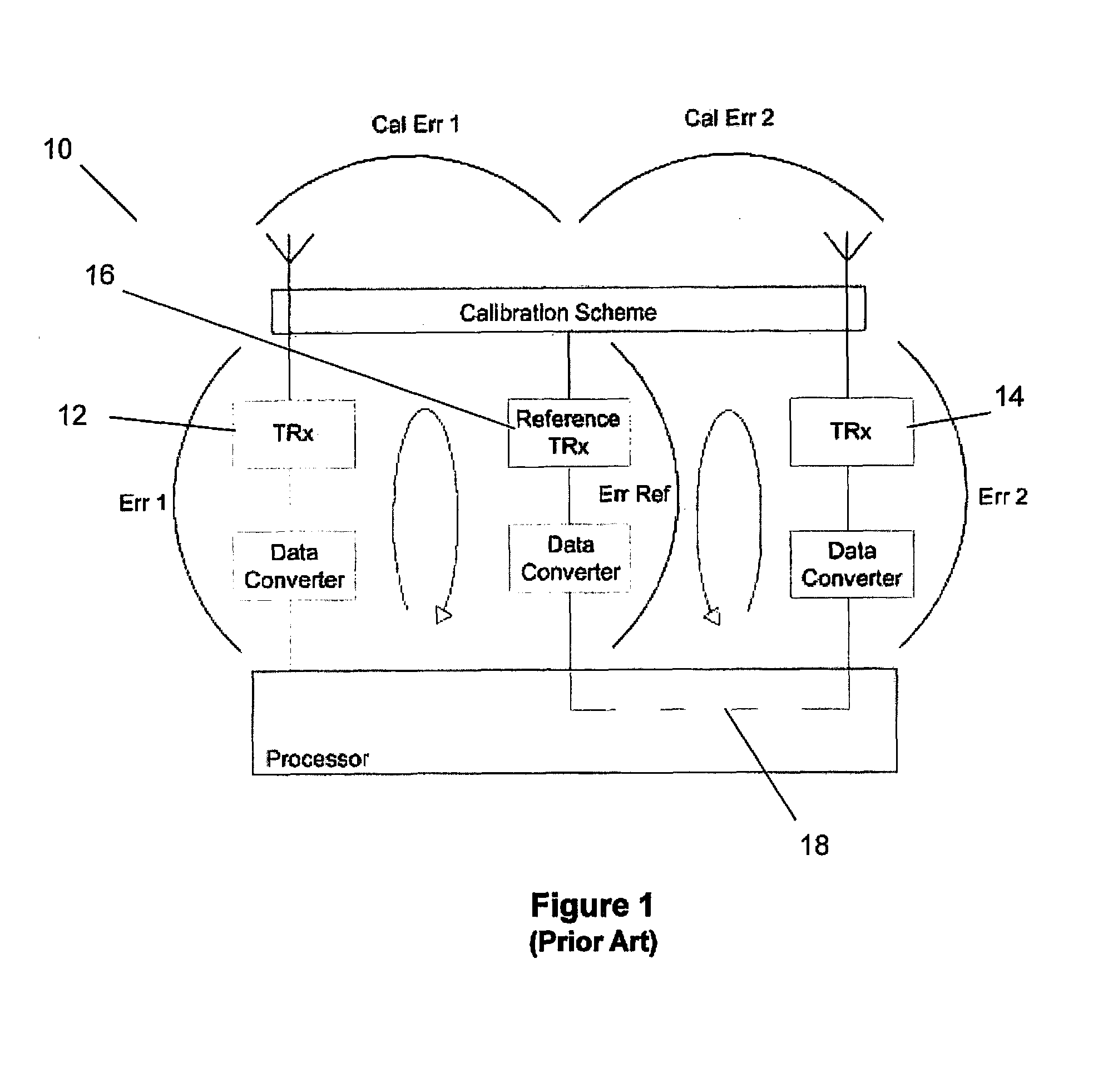
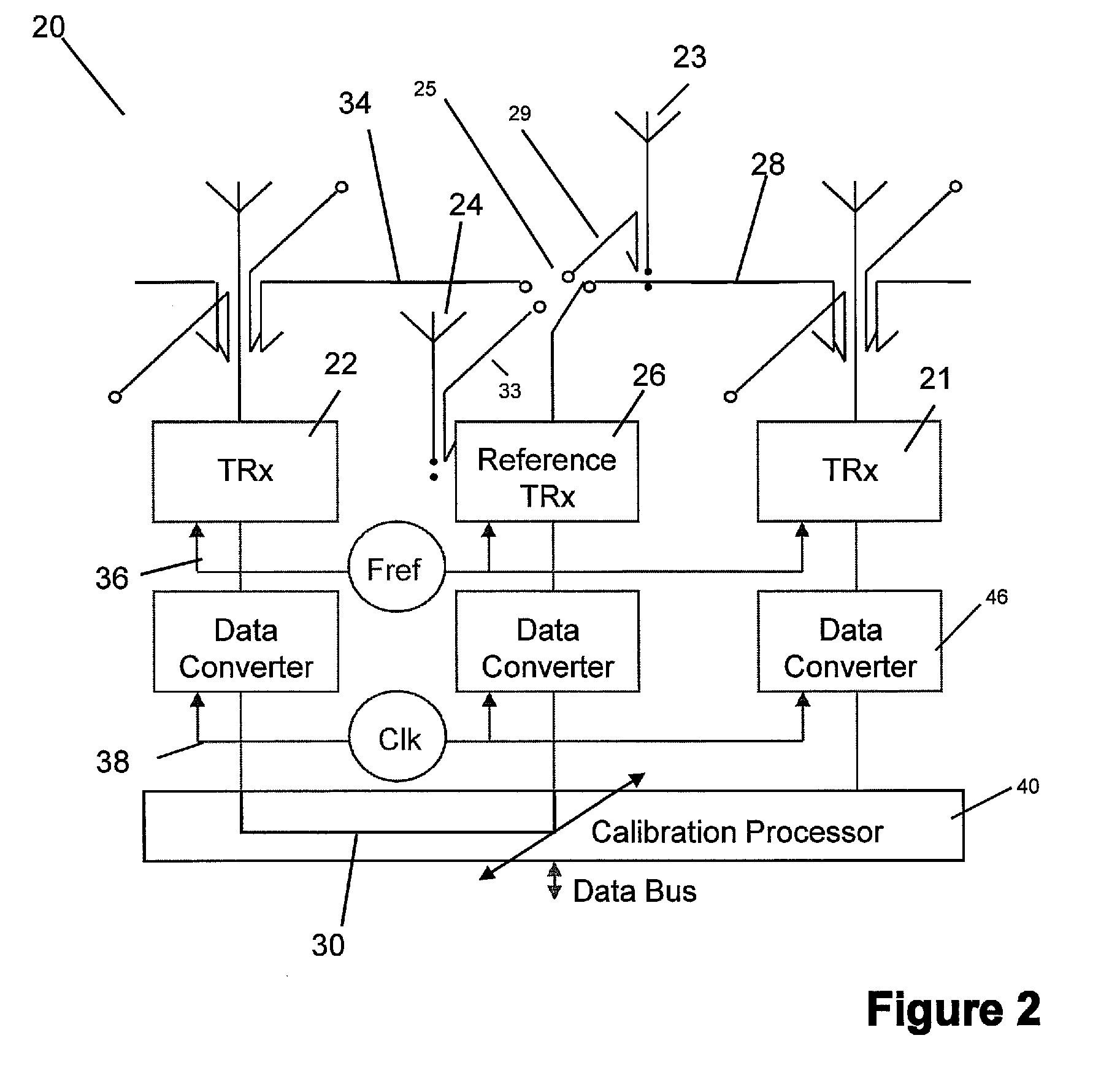
Antenna array calibration
ActiveUS20090267824A1Easy to copyAvoid complex processTransmitters monitoringWave based measurement systemsRadiative transferTransceiver
An antenna array comprises a surface comprising a replicated pattern of conductive tracks, the tracks defining a plurality of ports. A plurality of antennae are located at ports distributed about the surface. A plurality of radiative transceivers are electrically connected to a respective antenna. A plurality of reference transceivers are electrically connected to a non-radiative impedance located at a respective port so that each reference transceiver is surrounded by a group of antennae and electrically coupled to the group of antennae by the tracks. At least one antenna from at least one group of antennae belongs to one other group of antennae. Calibration circuitry includes a controller associated with each reference transceiver, each controller being arranged to transmit a calibration signal through an associated reference transceiver and to receive and store a received calibration signal from a selected transceiver for the group of antennae coupled to the reference transceiver. Each controller is further arranged to receive and store a calibration signal from the selected transceiver for the group of antennae coupled to the reference transceiver. The calibration circuitry further includes for each other transceiver for the group of antenna, circuitry for adjusting the phase and amplitude of signals transmitted and received by the radiative transceivers relative to the stored calibration signals for the selected radiative transceiver.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF IRELAND MAYNOOTH
Reconstruction method for hearth three-dimensional temperature field
InactiveCN102393027ADesign scienceCompact structureChamber safety arrangementReconstruction methodHearth
The invention relates to a reconstruction method for a hearth three-dimensional temperature field. The method comprises the following steps that: a burning flame colorized image can be obtained through a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) image pickup system and a computer processing system, based on R,G and B pixels of a flame image, two-dimensional temperature of a burning flame image can be obtained through a neural network BP algorithm, an inverse solution of a radiative transfer equation can be combined, and three-dimensional temperature distribution of a burning flame in a hearth can be further obtained. The reconstruction method has the advantages of scientific design and creativeness, three-dimensional characteristic of coal dust in a large-scale boiler can be fully embodied, and the reconstruction method is significant to safety, economic benefit, clean operation and the like of the boiler. The system disclosed by the invention has the advantages of compact structure, less material consumption, long service life, stable and reliable performance, convenient for maintenance and high measurement precision of three-dimensional temperature, and flame combustion condition in the boiler can be controlled in time.
Owner:SHENYANG LIGONG UNIV
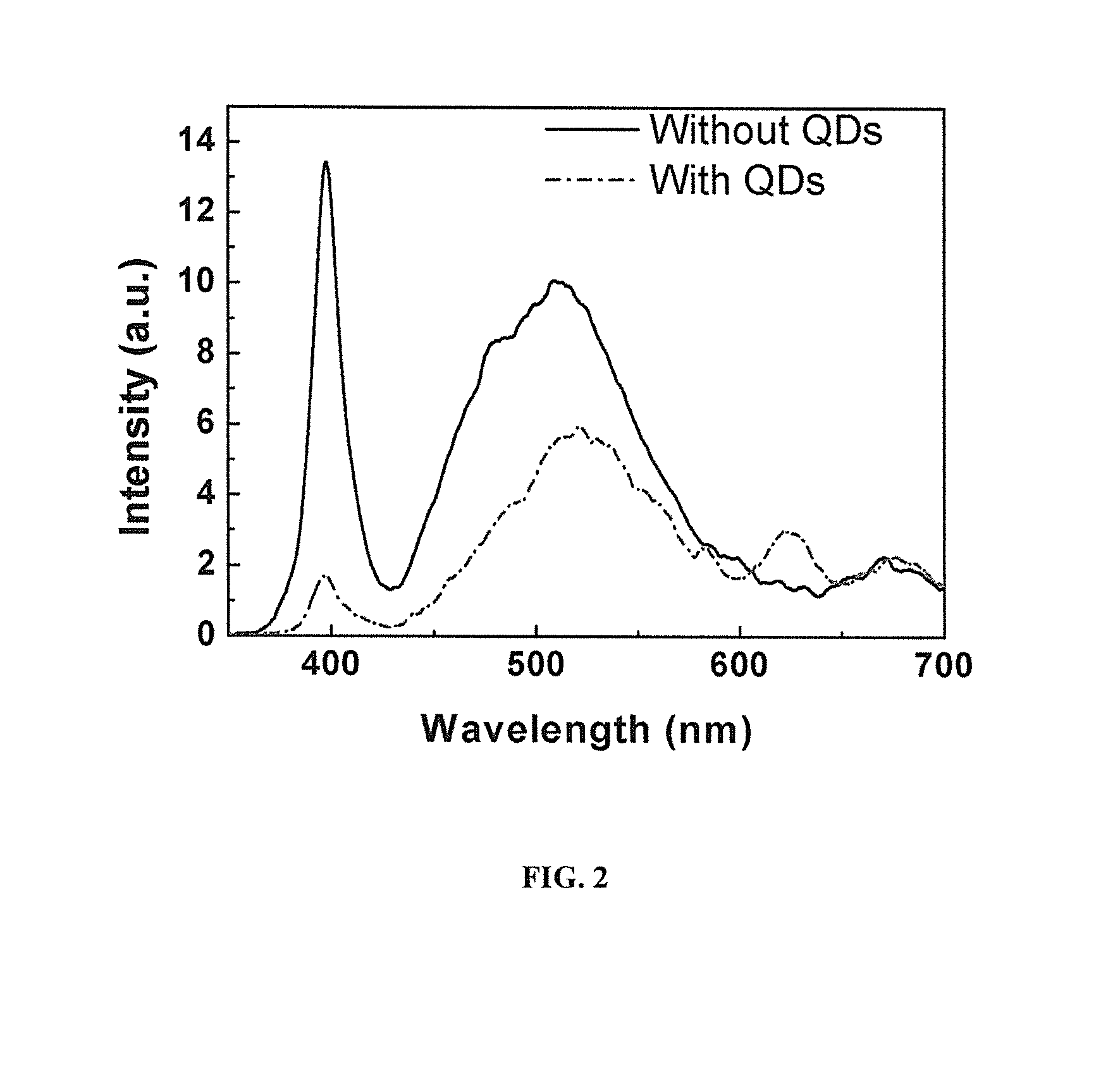
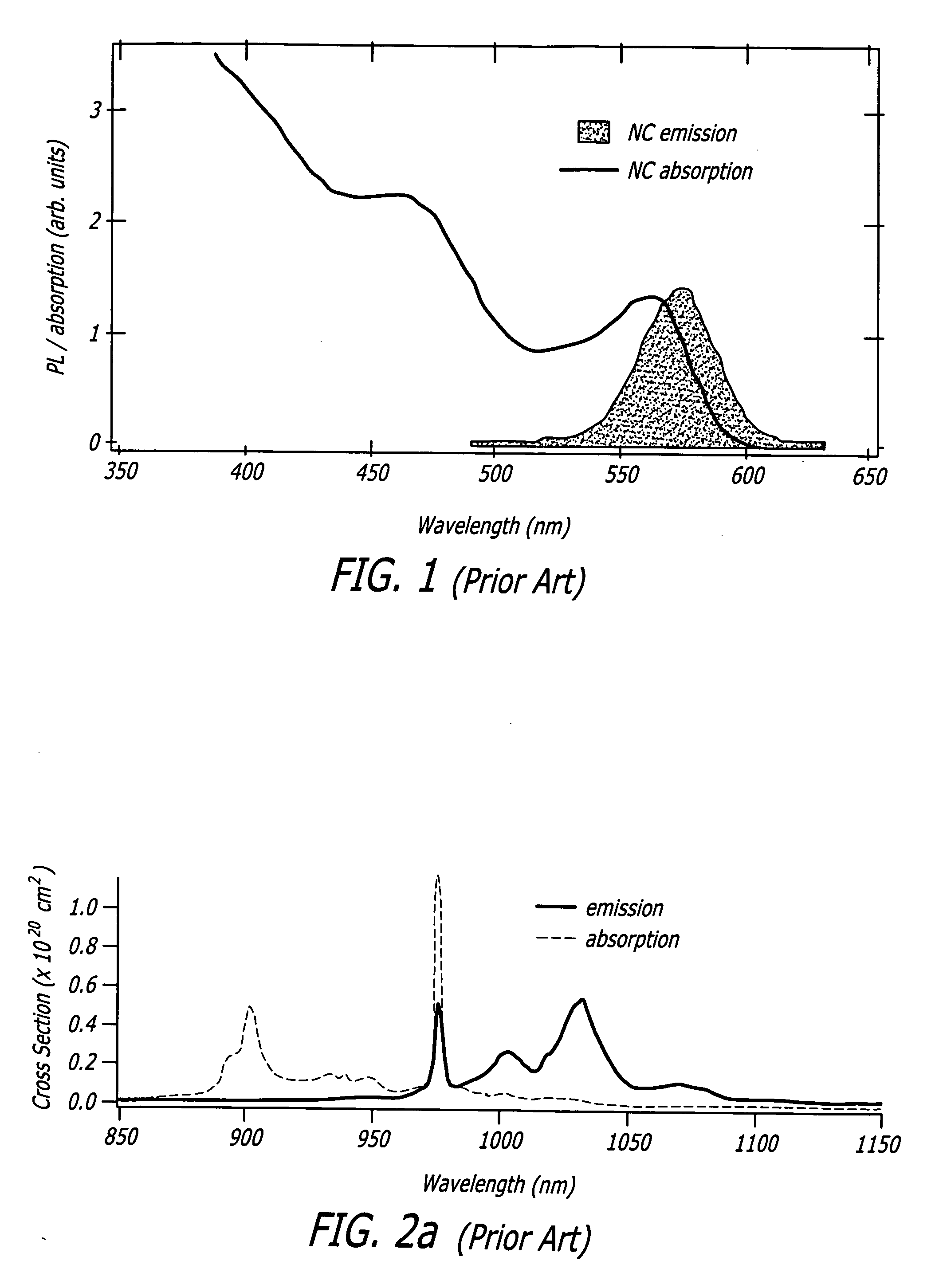
Light emitting diodes with quantum dot phosphors
InactiveUS20150021549A1Efficient non-radiative transferImprove efficiencyNanoinformaticsNanoopticsNanopillarFluorescence
A quantum well-based p-i-n light emitting diode is provided that includes nanopillars with an average linear dimension of between 50 nanometers and 1 micron. The nanopillars include a laminar layer of quantum wells capable of non-radiative energy transfer to quantum dot nanocrystals. Quantum dot-Quantum well coupling through the side walls of the nanopillar-configured LED structure achieves a close proximity between quantum wells and quantum dots while retaining the overlying contact electrode structures. An white LED with attractive properties relative to conventional incandescent and fluorescence lighting devices is produced.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
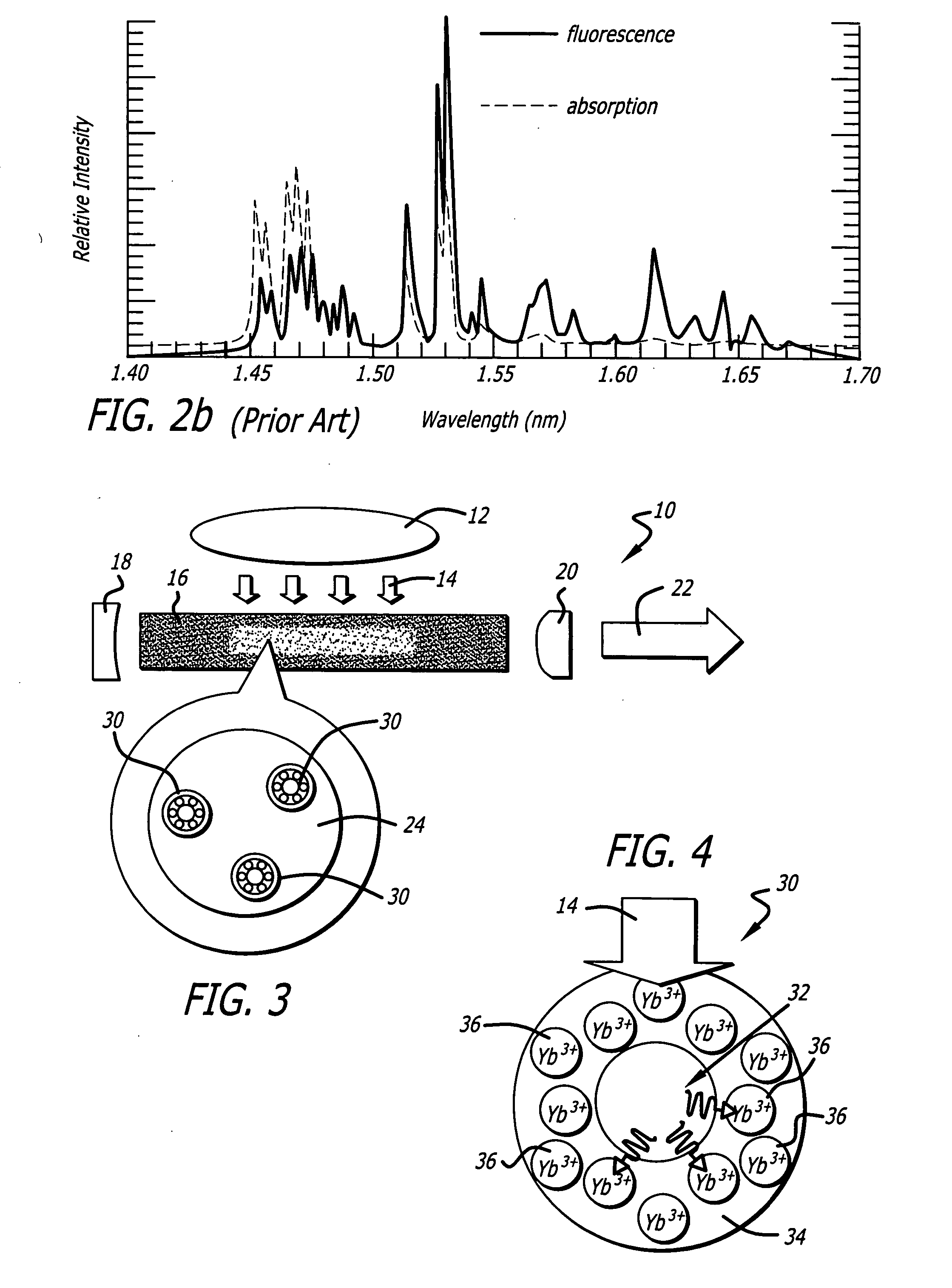
Laser based on quantum dot activated media with forster resonant energy transfer excitation
ActiveUS20070242713A1Active medium materialActive medium shape and constructionResonant energyRadiative transfer
A laser gain medium. The novel laser gain medium includes a host material, a plurality of quantum dots dispersed throughout the host material, and a plurality of laser active ions surrounding each of the quantum dots. The laser active ions are disposed in close proximity to the quantum dots such that energy absorbed by the quantum dots is non-radiatively transferred to the ions via a Forster resonant energy transfer, thereby exciting the ions to produce laser output. In an illustrative embodiment, each quantum dot is surrounded by an external shell doped with the laser active ions.
Owner:EVIDENT TECH +1
Method and program product for determining a radiance field in an optical environment
InactiveUS7286214B2Rapid of characteristicEfficient and finer processingScattering properties measurementsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsSpectral bandsUnderwater light field
A hybrid method is presented by which Monte Carlo techniques are combined with iterative relaxation techniques to solve the Radiative Transfer Equation in arbitrary one-, two- or three-dimensional optical environments. The optical environments are first divided into contiguous regions, or elements, with Monte Carlo techniques then being employed to determine the optical response function of each type of element. The elements are combined, and the iterative relaxation techniques are used to determine simultaneously the radiance field on the boundary and throughout the interior of the modeled environment. This hybrid model is capable of providing estimates of the under-water light field needed to expedite inspection of ship hulls and port facilities. It is also capable of providing estimates of the subaerial light field for structured, absorbing or non-absorbing environments such as shadows of mountain ranges within and without absorption spectral bands such as water vapor or CO2 bands.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Formulation of complex coating mixtures with effect pigments
ActiveUS20150127269A1Scattering properties measurementsMaterial testing goodsRadiative transferComputer science
A computer implemented method. The method includes obtaining, using a processor, reflectance data from a target coating and calculating, using the processor, a reflectance from the data, wherein calculating comprises performing a calculation using a radiative transfer equation. The method also includes generating, using the processor and based on the reflectance, a coating formulation that is the same or substantially similar in appearance to the target coating.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Technique for coupling meteorology to acoustics in forests
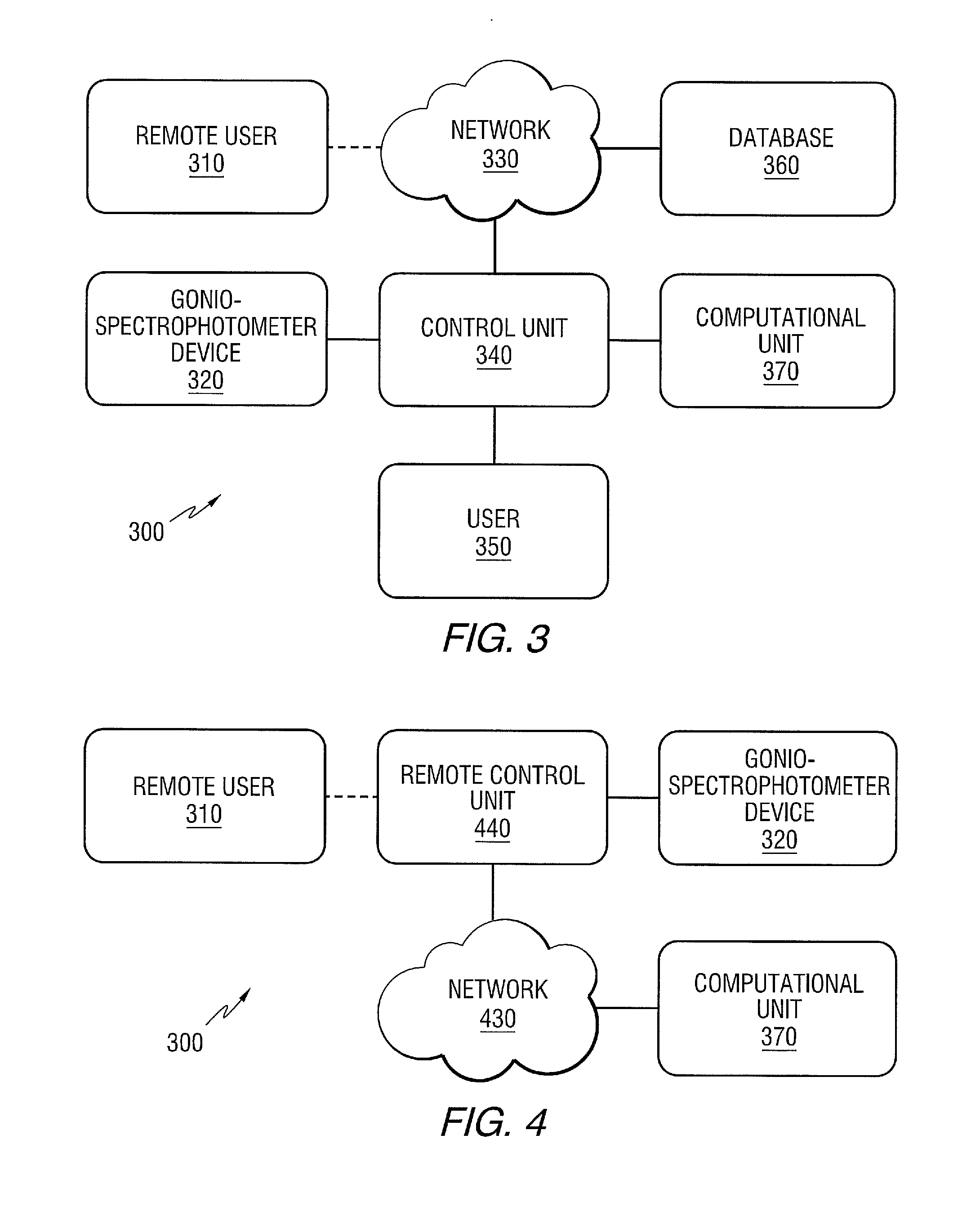
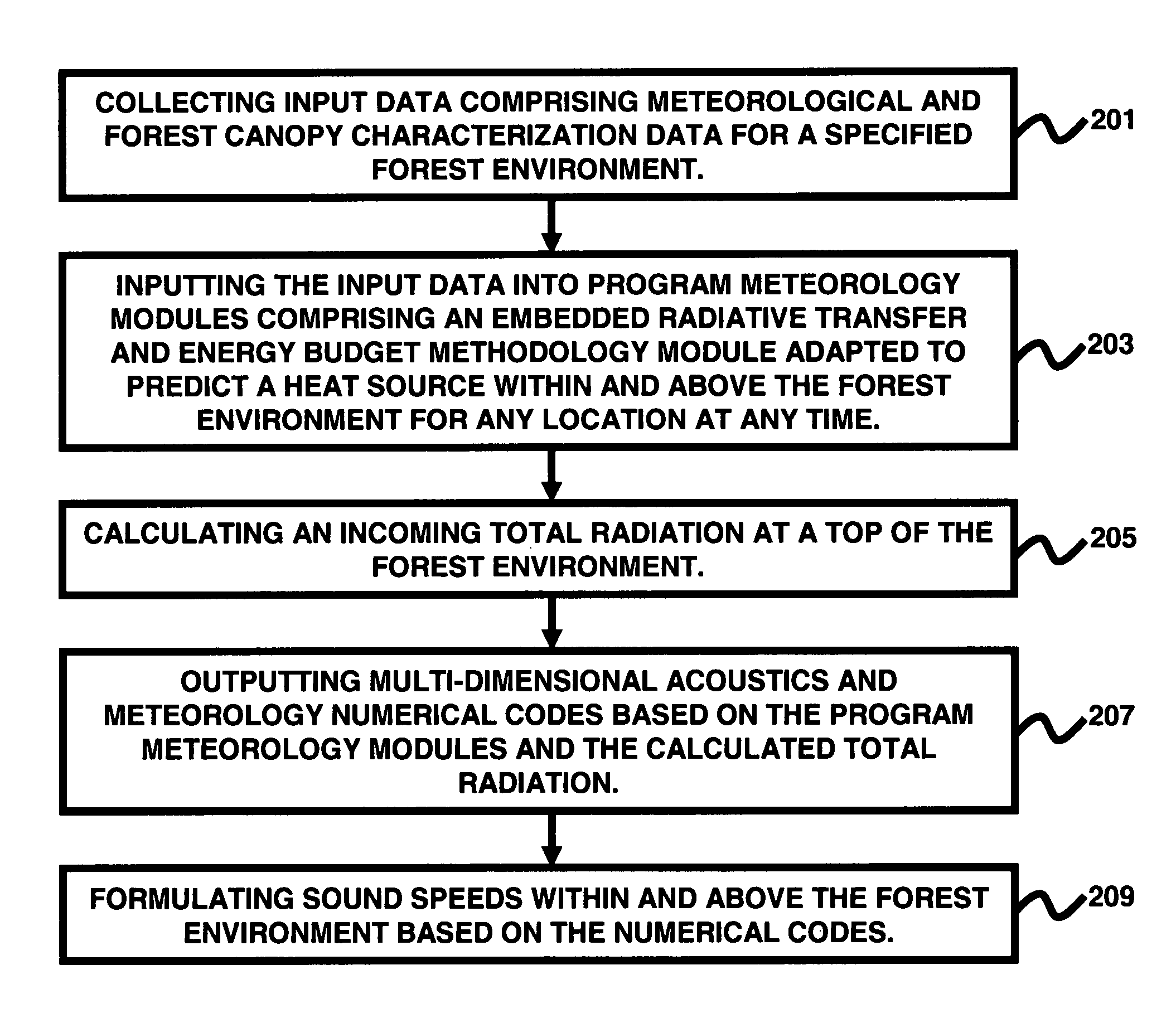
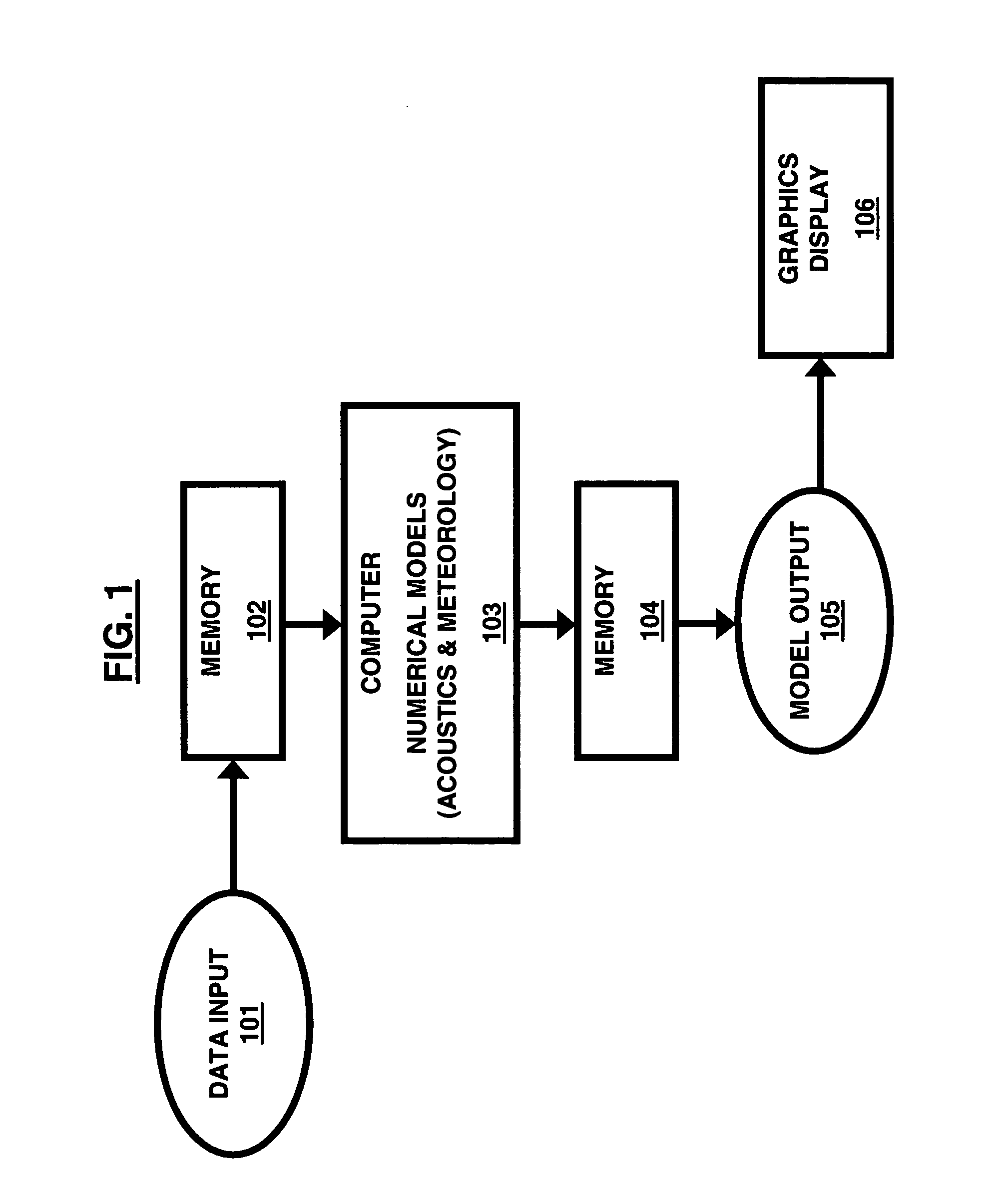
InactiveUS7634393B1Rapid and reliable predictionComputationally efficientWeather condition predictionComputation using non-denominational number representationEnergy budgetRadiative transfer
A system and method of predicting multi-dimensional meteorological and acoustic effects within and above a forest environment comprises collecting input data comprising meteorological and forest canopy characterization data for a specified forest environment; inputting the input data into program meteorology modules comprising an embedded radiative transfer and energy budget methodology module adapted to predict a heat source within and above the forest environment for any location at any time; calculating an incoming total radiation at a top of the forest environment; outputting multi-dimensional acoustics and meteorology numerical codes based on the program meteorology modules and the calculated total radiation; and formulating sound speeds within and above the forest environment based on the numerical codes.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Formulation of complex coating mixtures with effect pigments
ActiveUS9482657B2Scattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsRadiative transferComputer science
A computer implemented method. The method includes obtaining, using a processor, reflectance data from a target coating and calculating, using the processor, a reflectance from the data, wherein calculating comprises performing a calculation using a radiative transfer equation. The method also includes generating, using the processor and based on the reflectance, a coating formulation that is the same or substantially similar in appearance to the target coating.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Antenna array calibration
ActiveUS7714776B2Avoid complex processEasy to copyTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringTransceiverRadiative transfer
An antenna array comprises a surface comprising a replicated pattern of conductive tracks, the tracks defining a plurality of ports. A plurality of antennae are located at ports distributed about the surface. A plurality of radiative transceivers are electrically connected to a respective antenna. A plurality of reference transceivers are electrically connected to a non-radiative impedance located at a respective port so that each reference transceiver is surrounded by a group of antennae and electrically coupled to the group of antennae by the tracks. At least one antenna from at least one group of antennae belongs to one other group of antennae. Calibration circuitry includes a controller associated with each reference transceiver, each controller being arranged to transmit a calibration signal through an associated reference transceiver and to receive and store a received calibration signal from a selected transceiver for the group of antennae coupled to the reference transceiver. Each controller is further arranged to receive and store a calibration signal from the selected transceiver for the group of antennae coupled to the reference transceiver. The calibration circuitry further includes for each other transceiver for the group of antenna, circuitry for adjusting the phase and amplitude of signals transmitted and received by the radiative transceivers relative to the stored calibration signals for the selected radiative transceiver.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF IRELAND MAYNOOTH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com