Patents
Literature
689 results about "Q factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
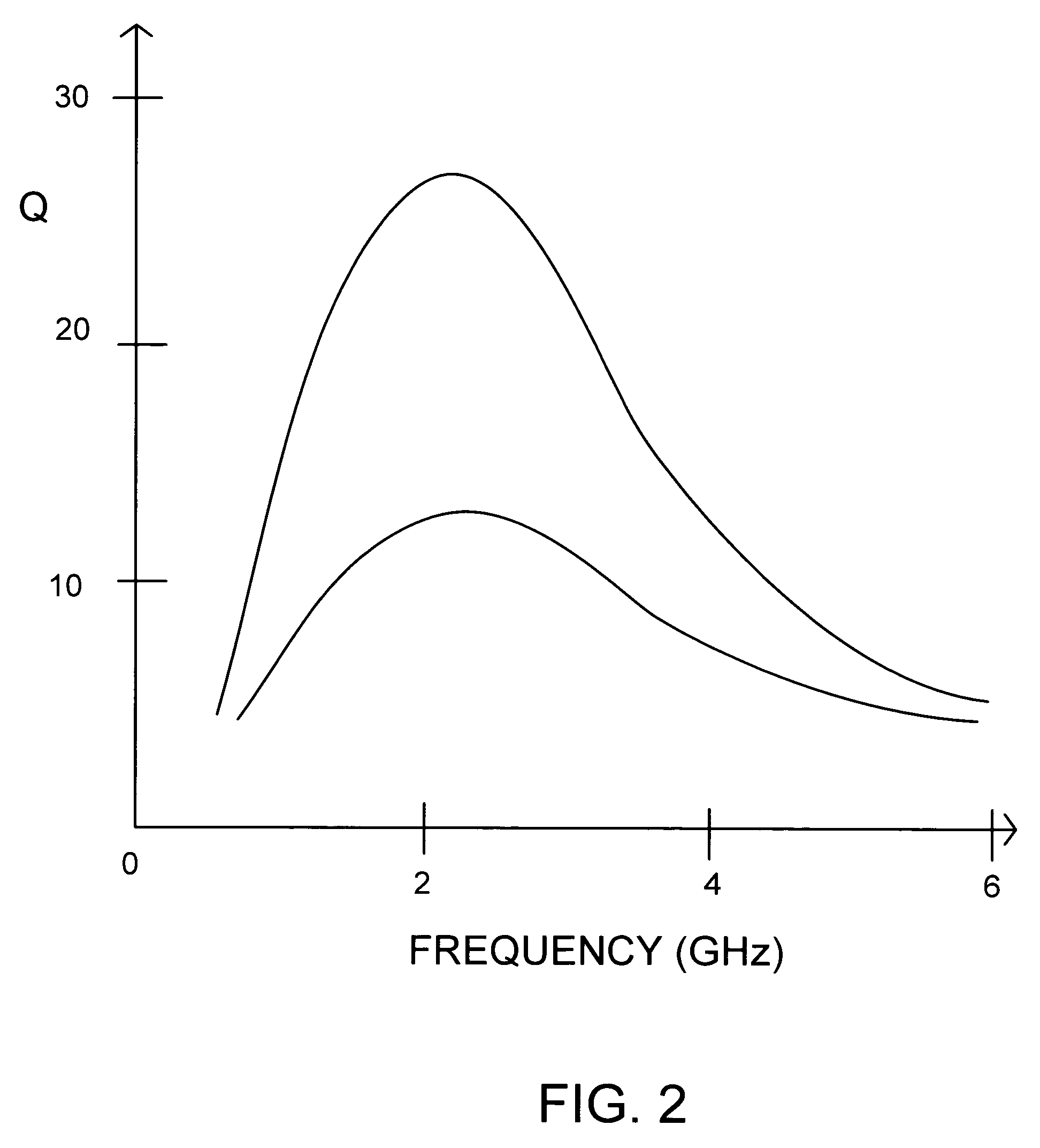
In physics and engineering the quality factor or Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how underdamped an oscillator or resonator is. It is defined as the ratio of the peak energy stored in the resonator in a cycle of oscillation to the energy lost per radian of the cycle. Q factor is alternatively defined as the ratio of a resonator's centre frequency to its bandwidth when subject to an oscillating driving force. These two definitions give numerically similar, but not identical, results. Higher Q indicates a lower rate of energy loss and the oscillations die out more slowly. A pendulum suspended from a high-quality bearing, oscillating in air, has a high Q, while a pendulum immersed in oil has a low one. Resonators with high quality factors have low damping, so that they ring or vibrate longer.
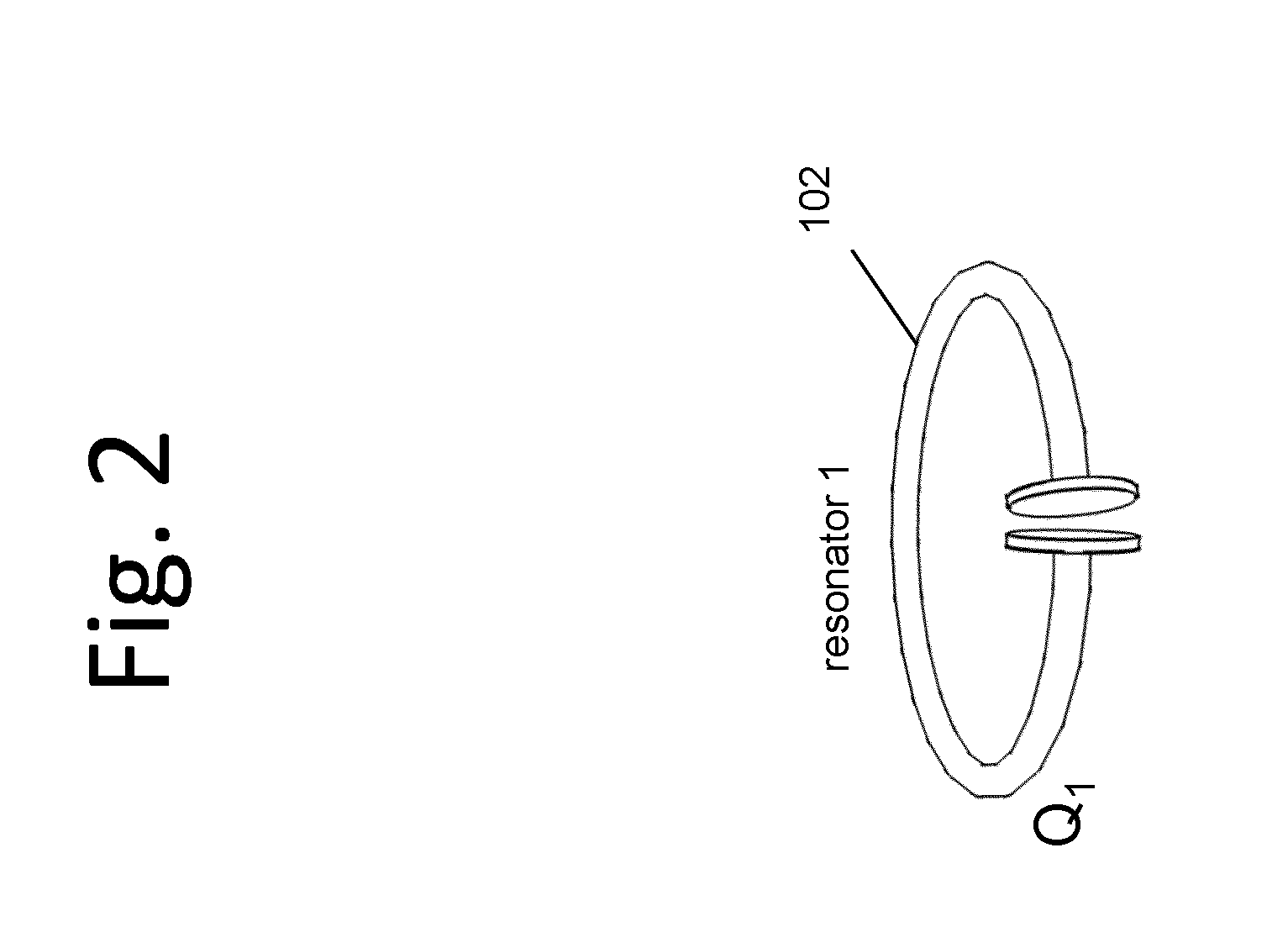
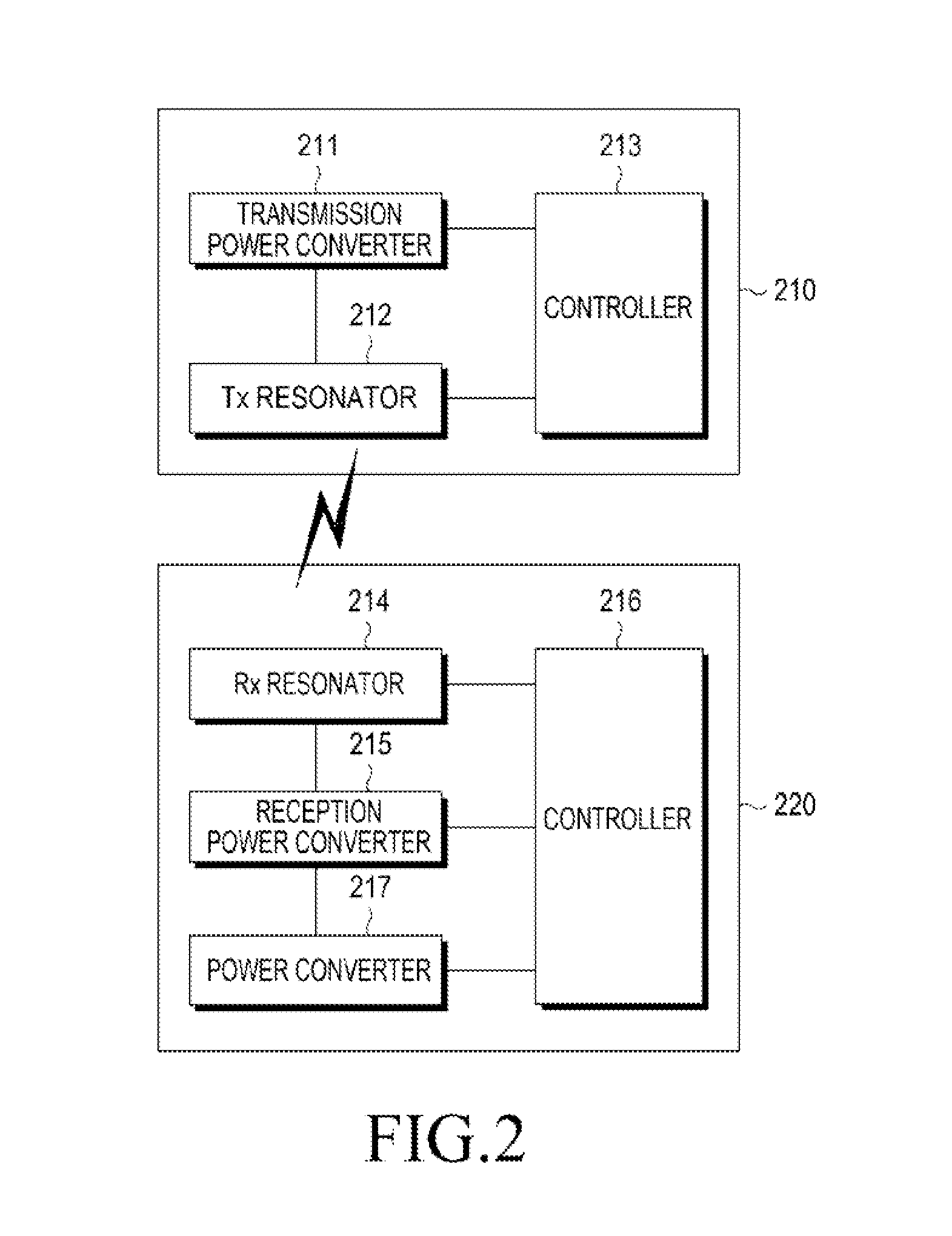
Wireless non-radiative energy transfer
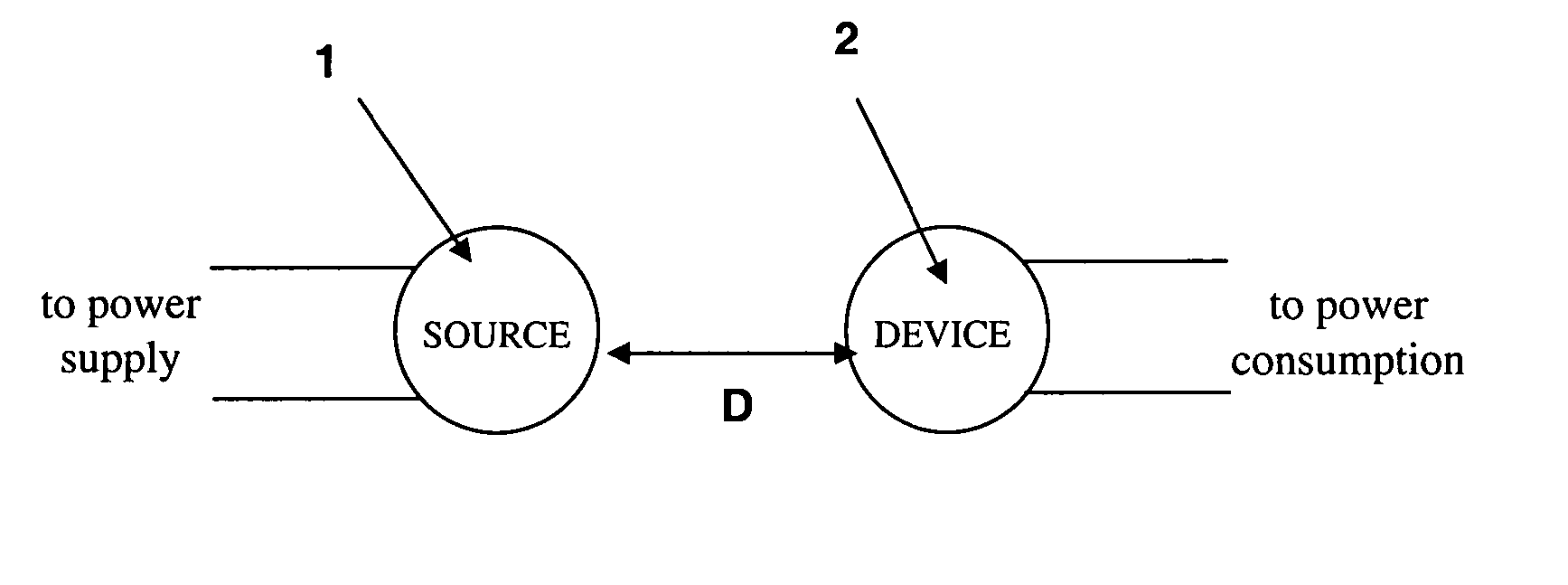
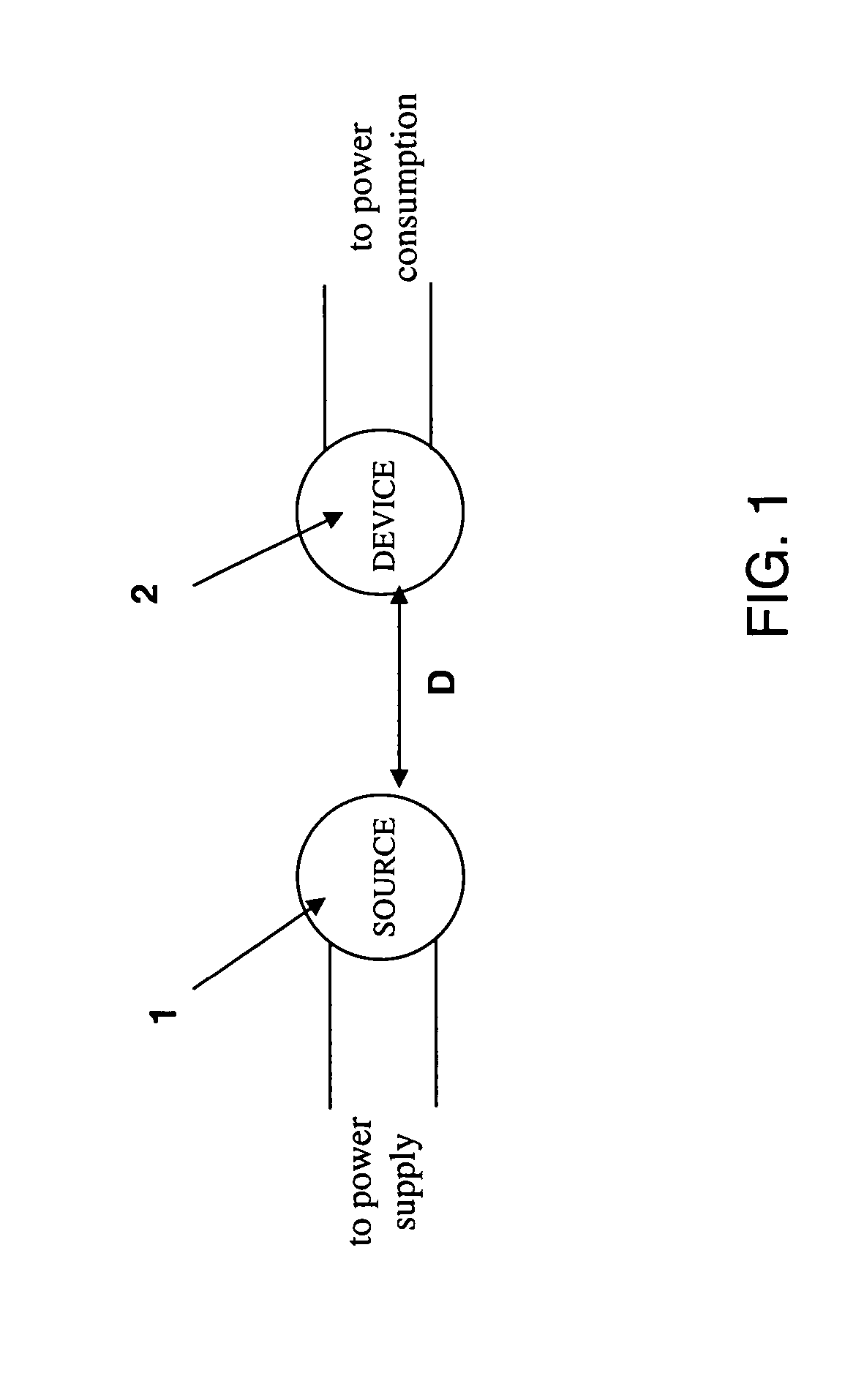
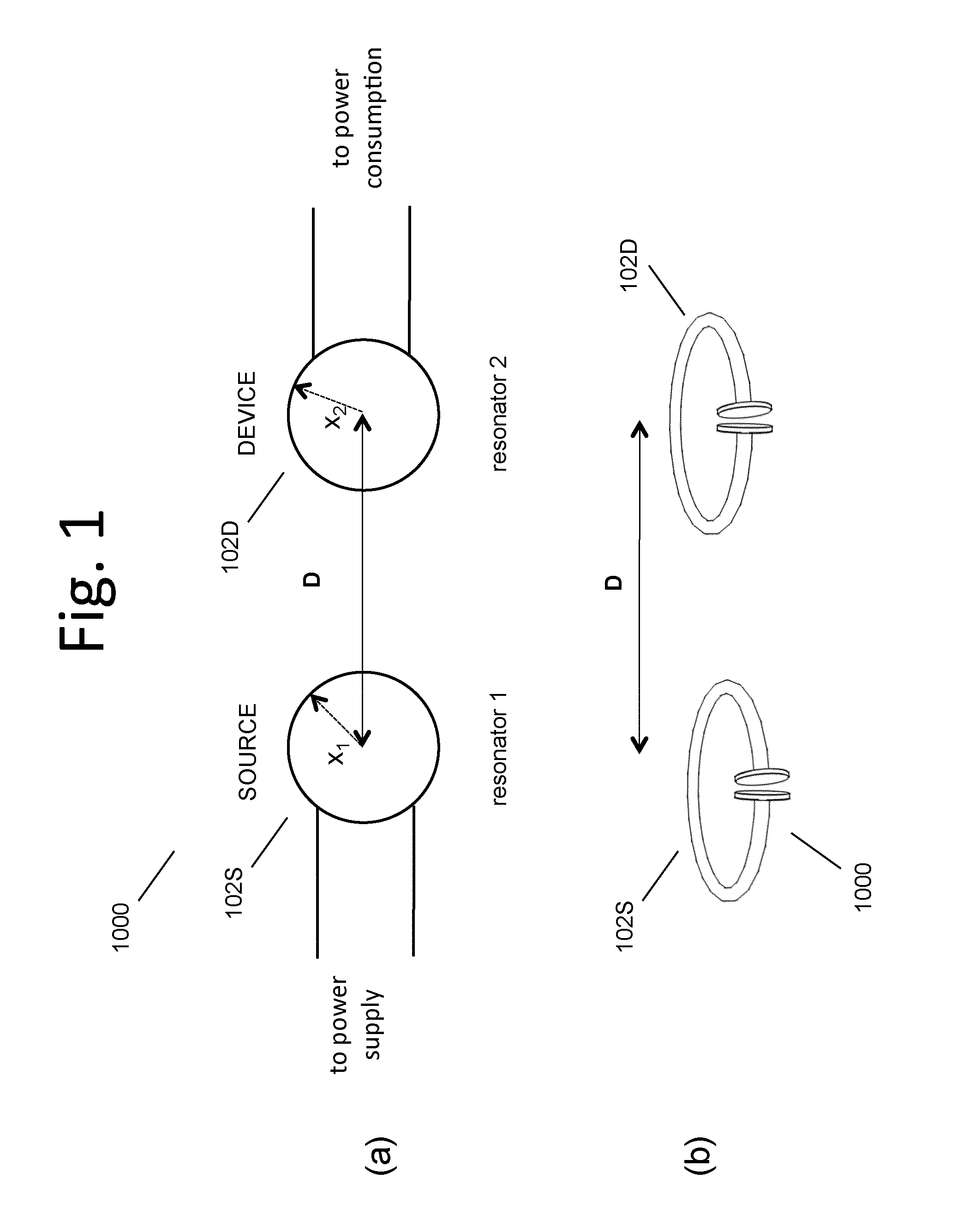
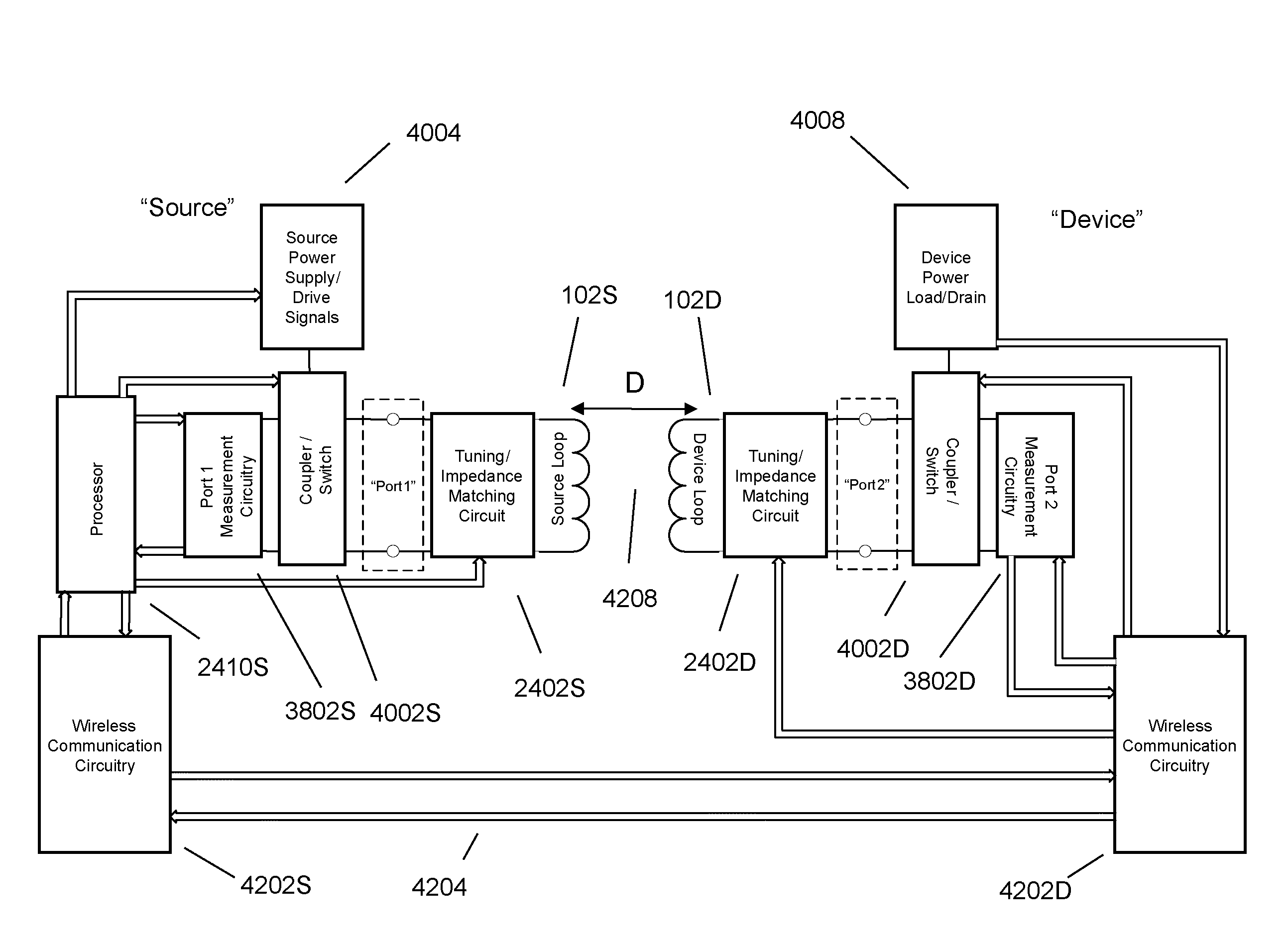
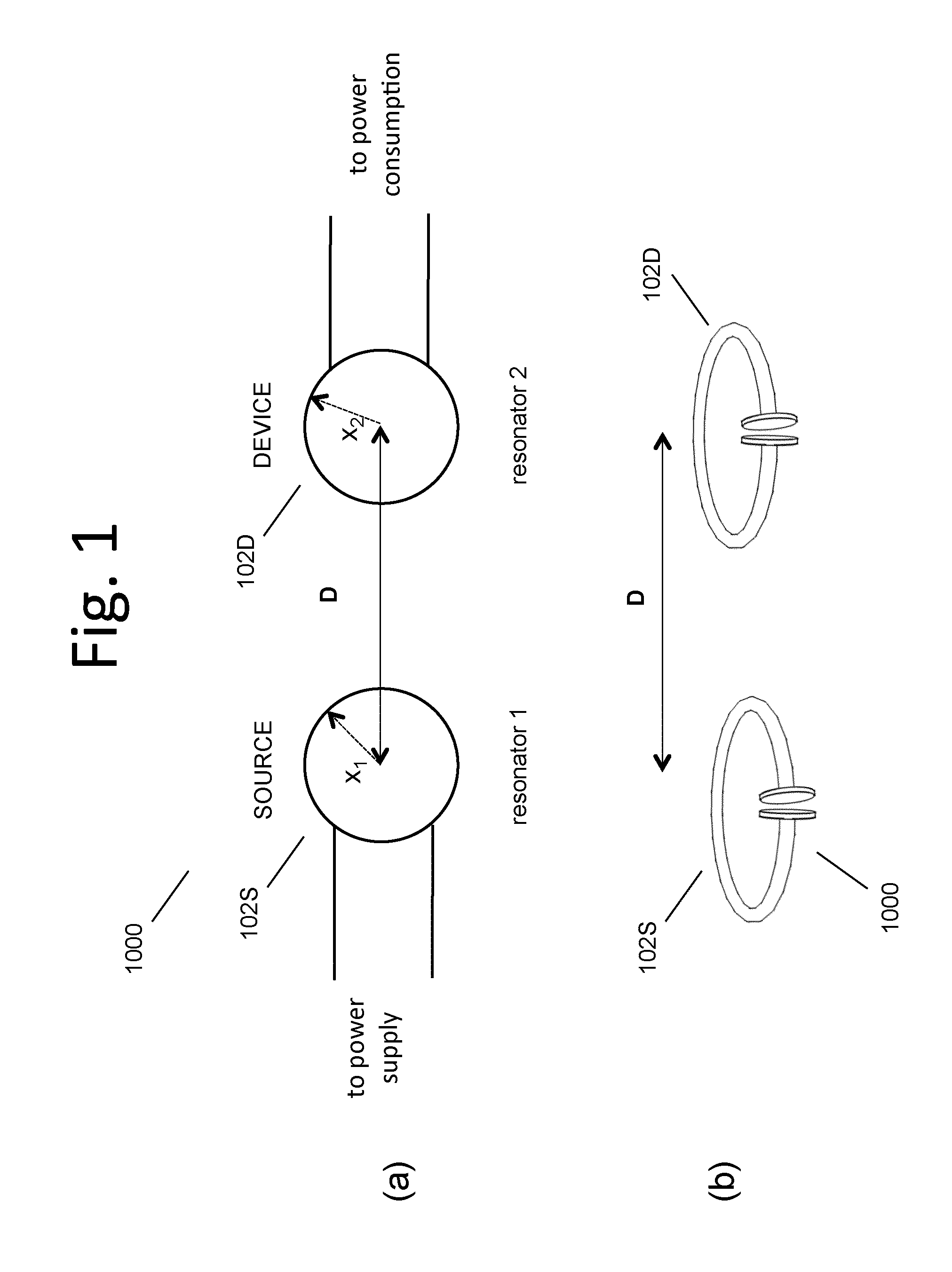
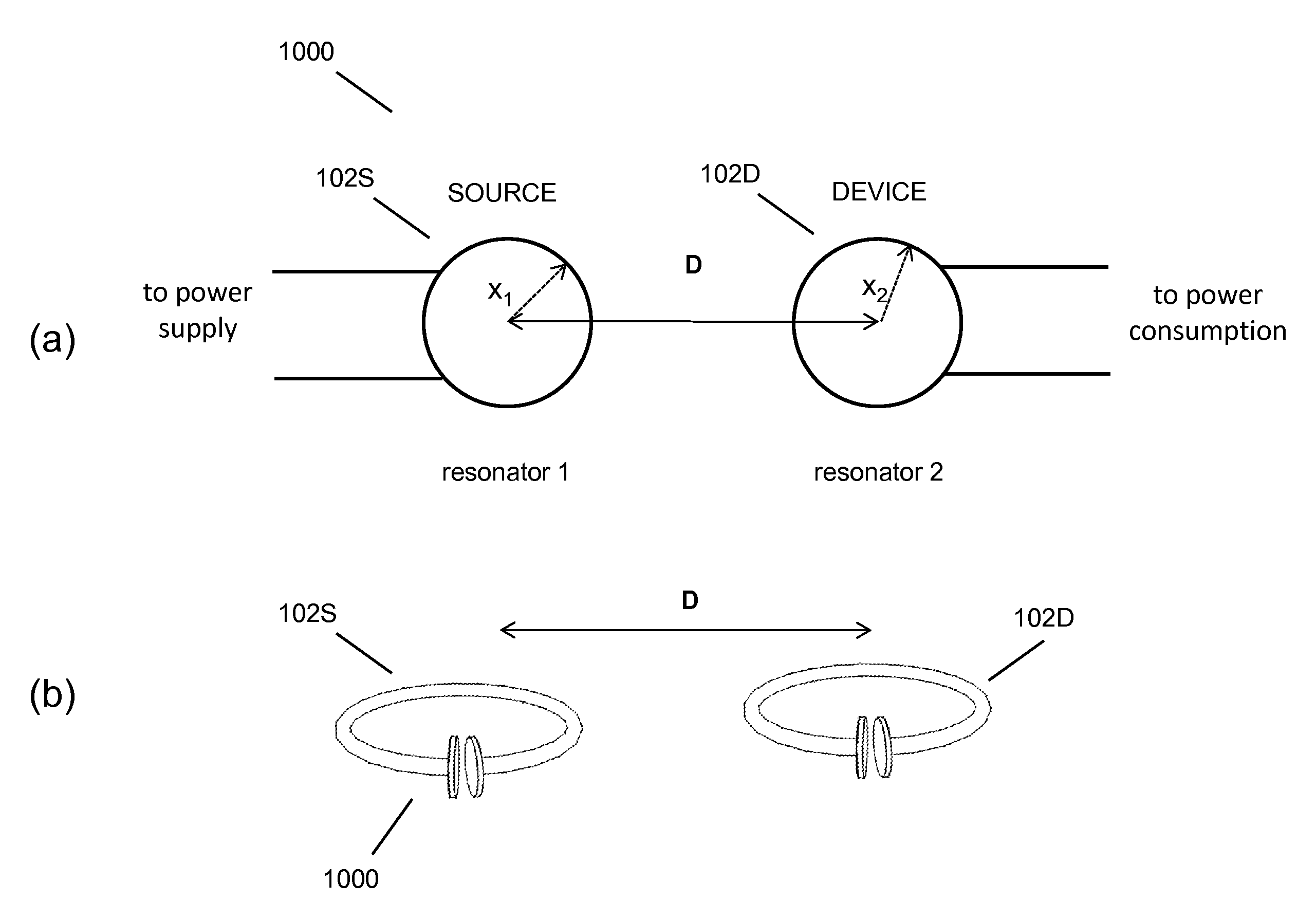
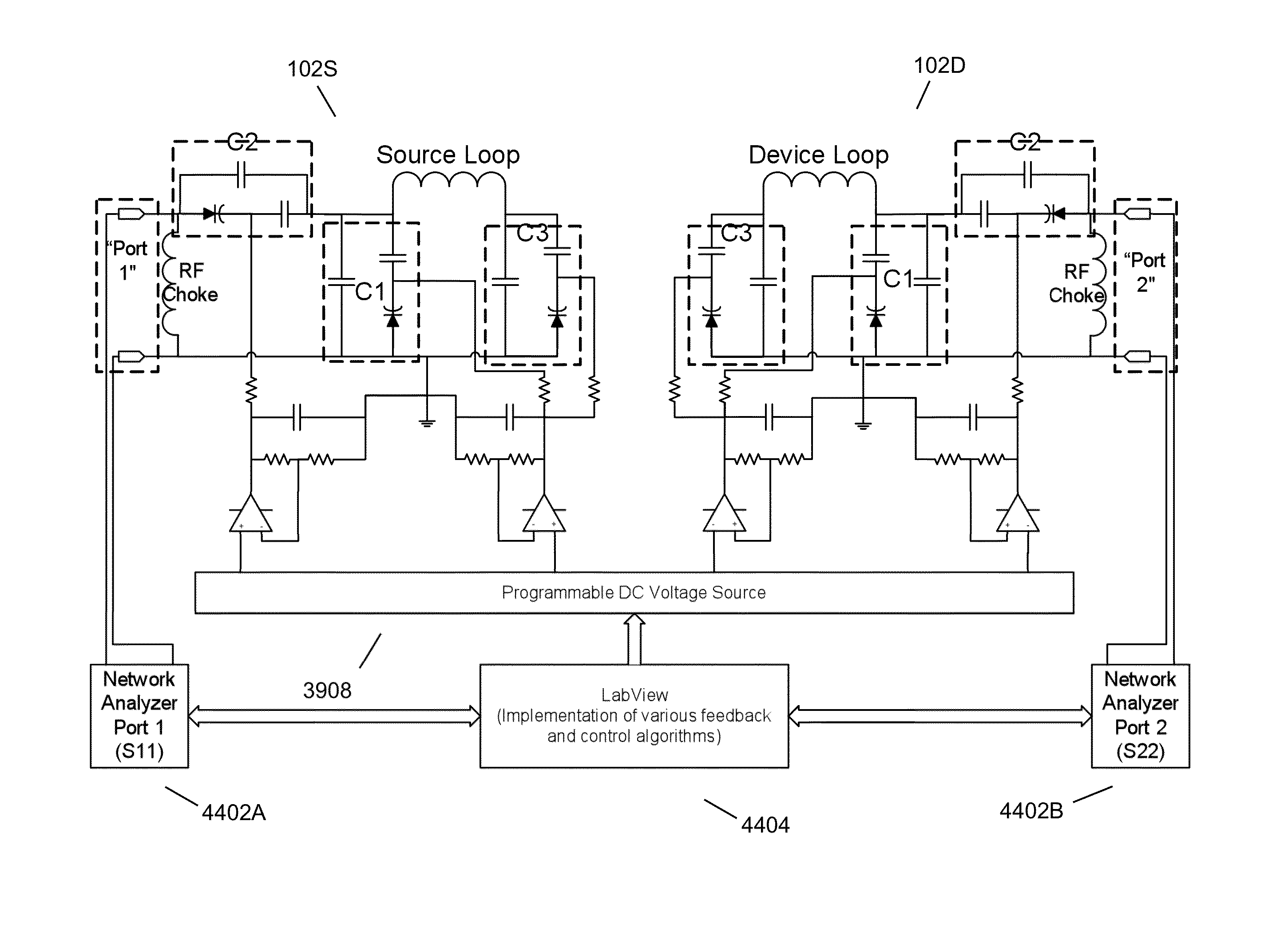
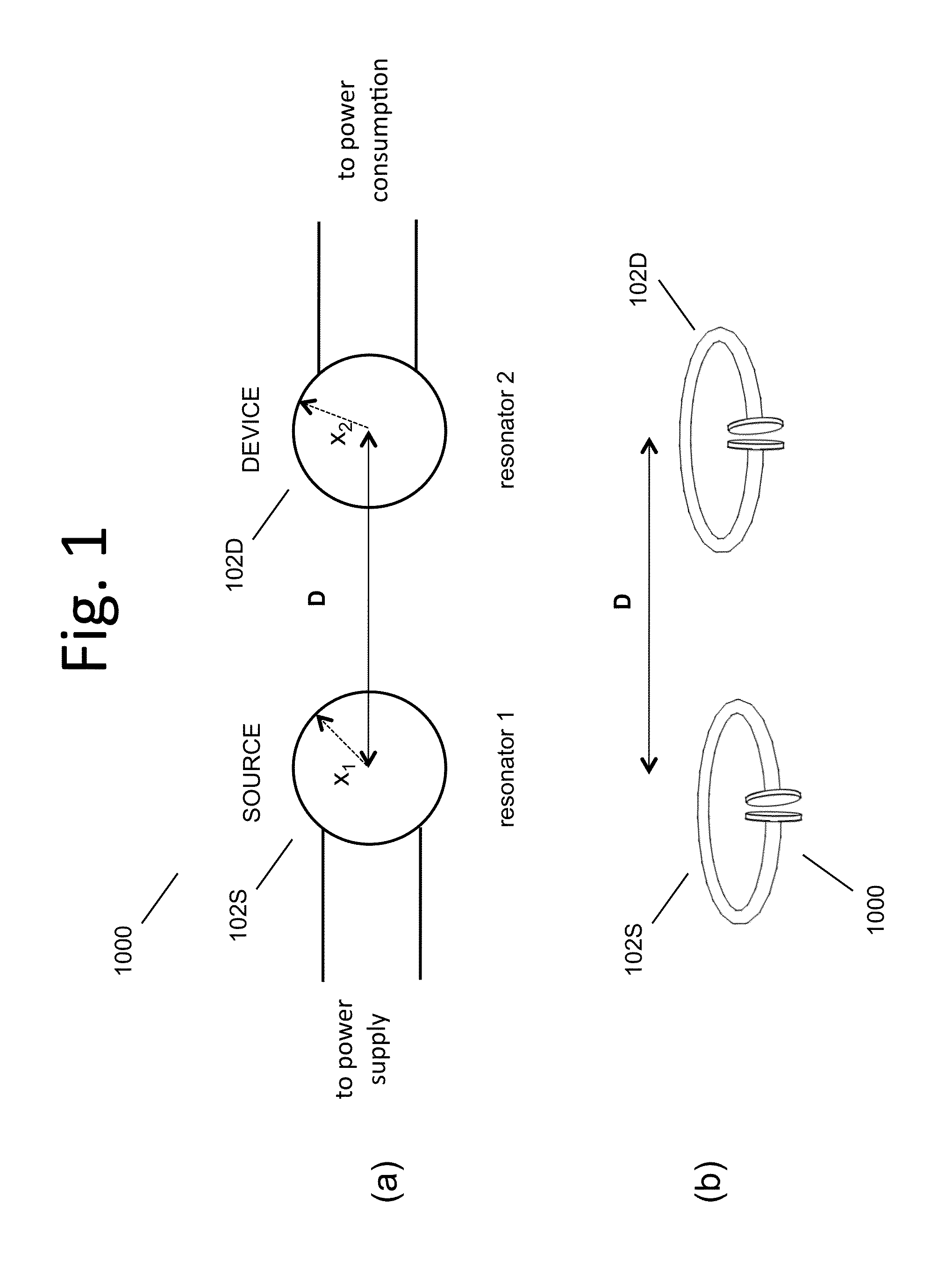
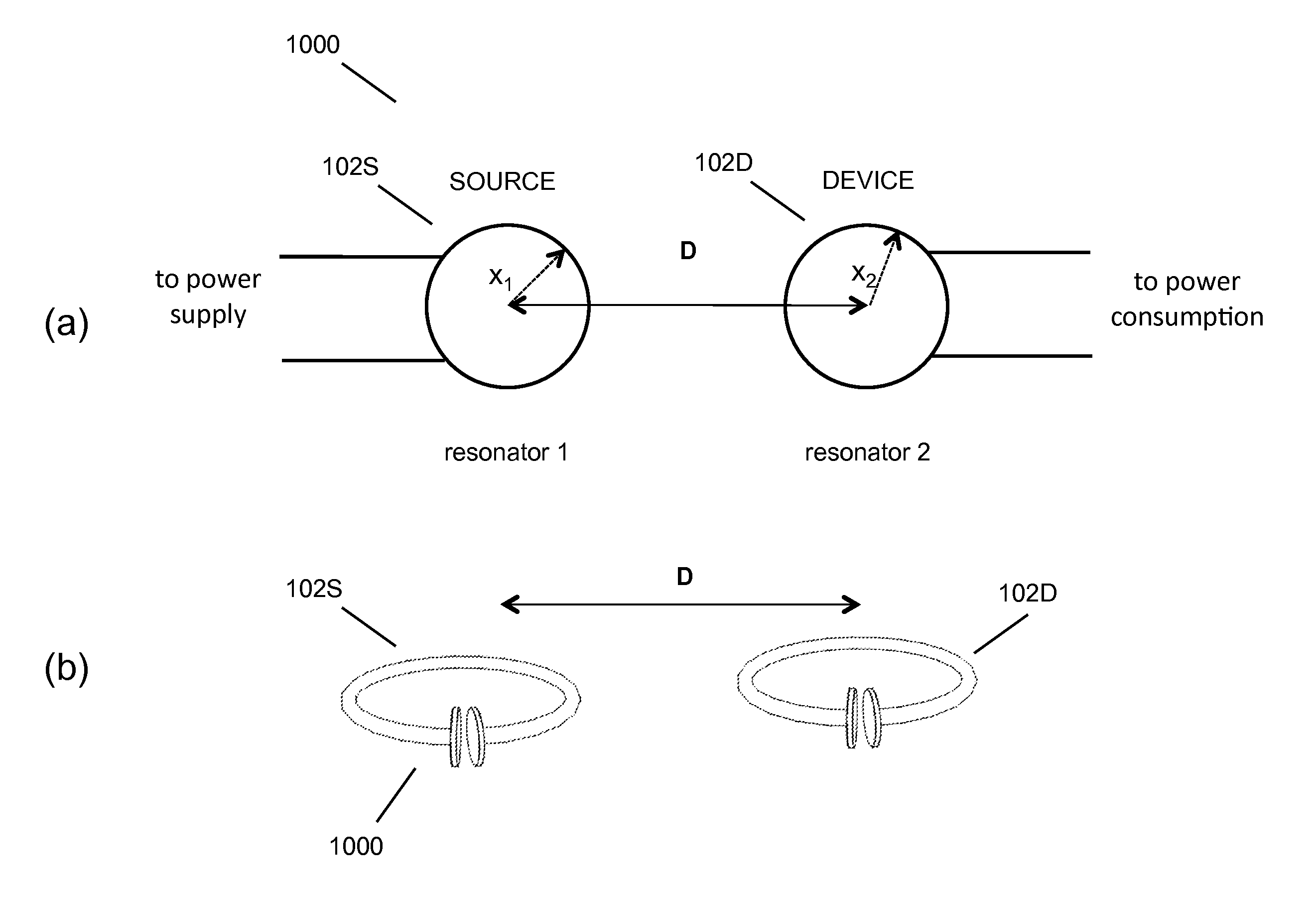
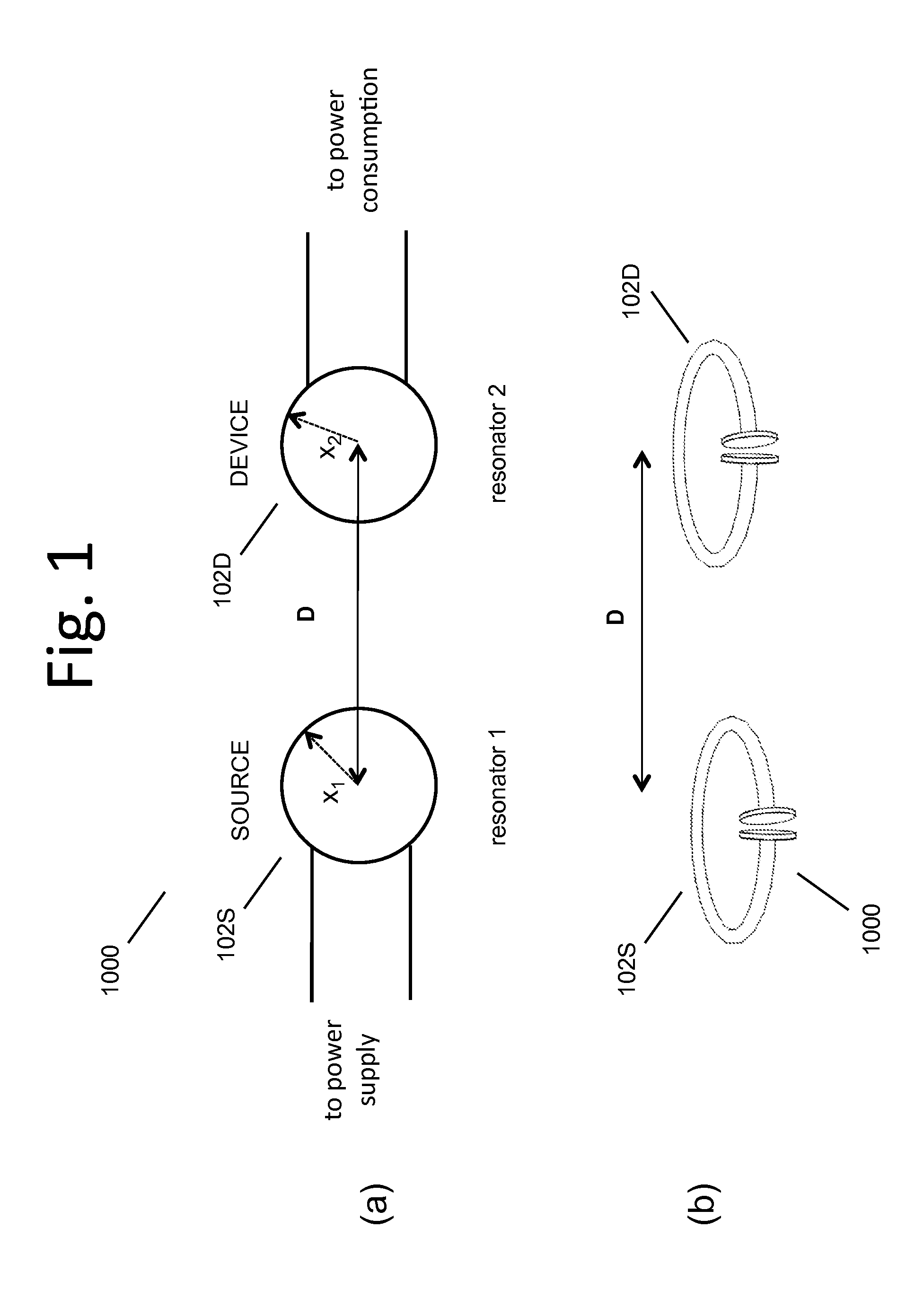
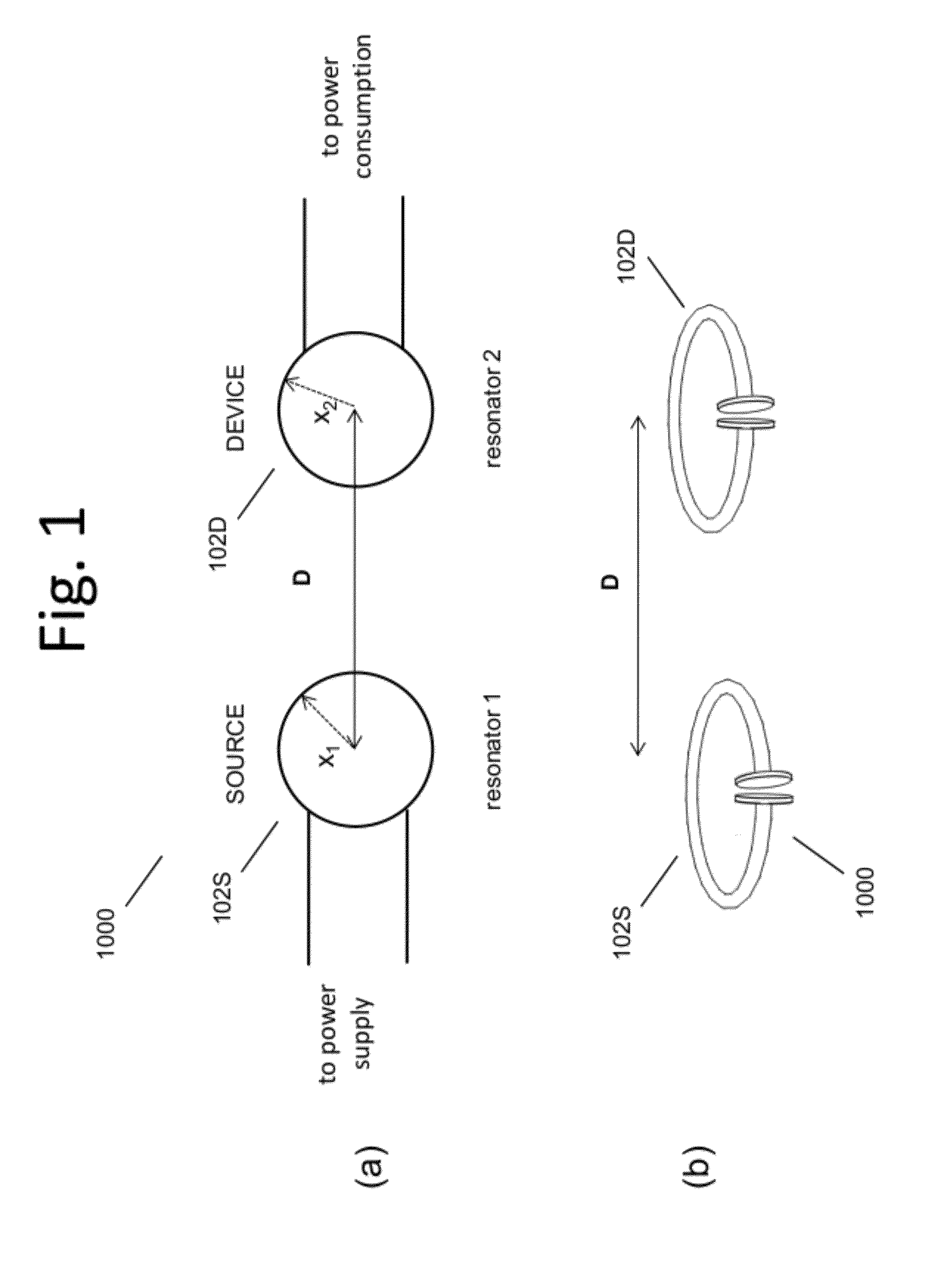
The electromagnetic energy transfer device includes a first resonator structure receiving energy from an external power supply. The first resonator structure has a first Q-factor. A second resonator structure is positioned distal from the first resonator structure, and supplies useful working power to an external load. The second resonator structure has a second Q-factor. The distance between the two resonators can be larger than the characteristic size of each resonator. Non-radiative energy transfer between the first resonator structure and the second resonator structure is mediated through coupling of their resonant-field evanescent tails.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
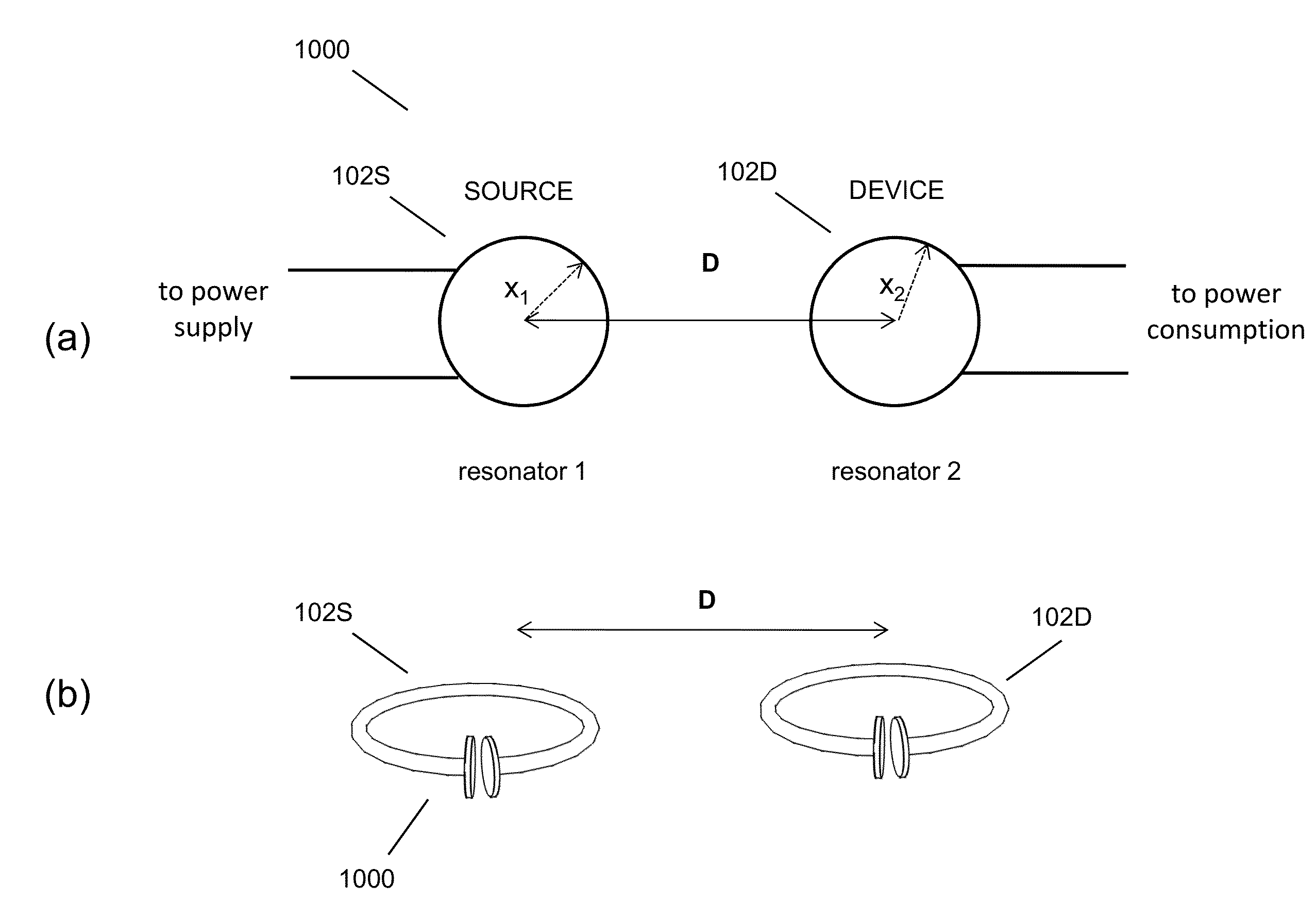
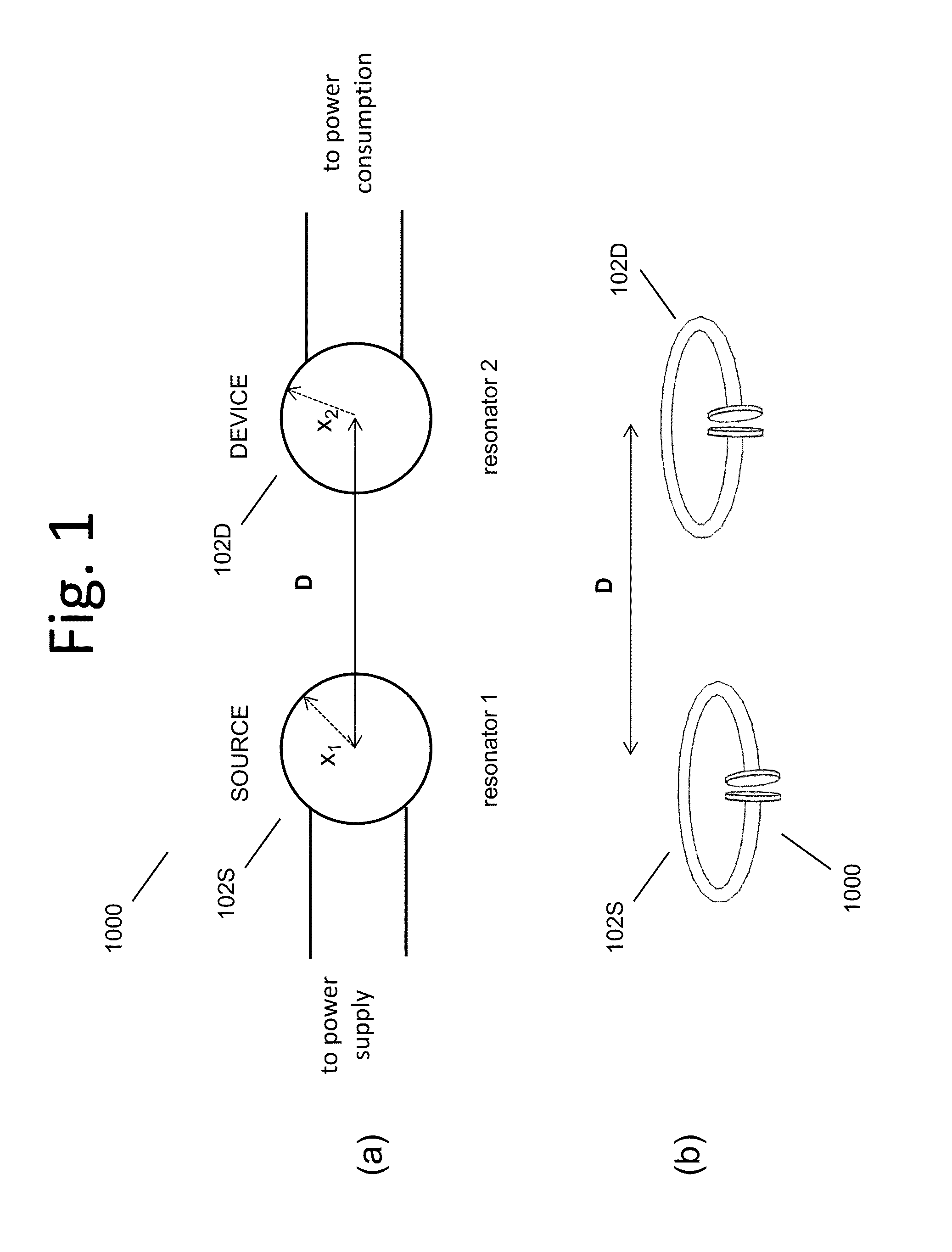
Wireless energy transfer systems
ActiveUS20100141042A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionEnergy transferCondensed matter physics
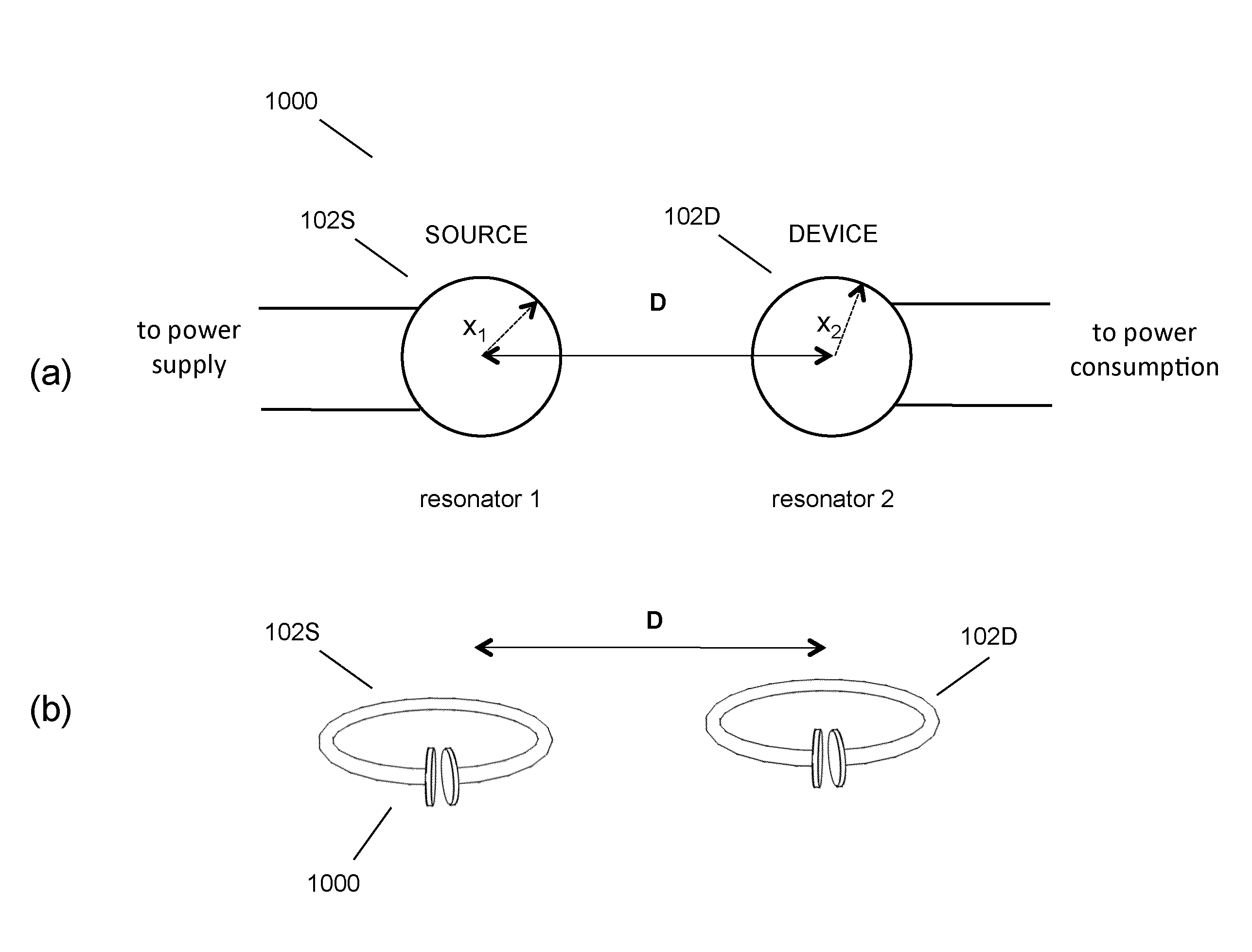
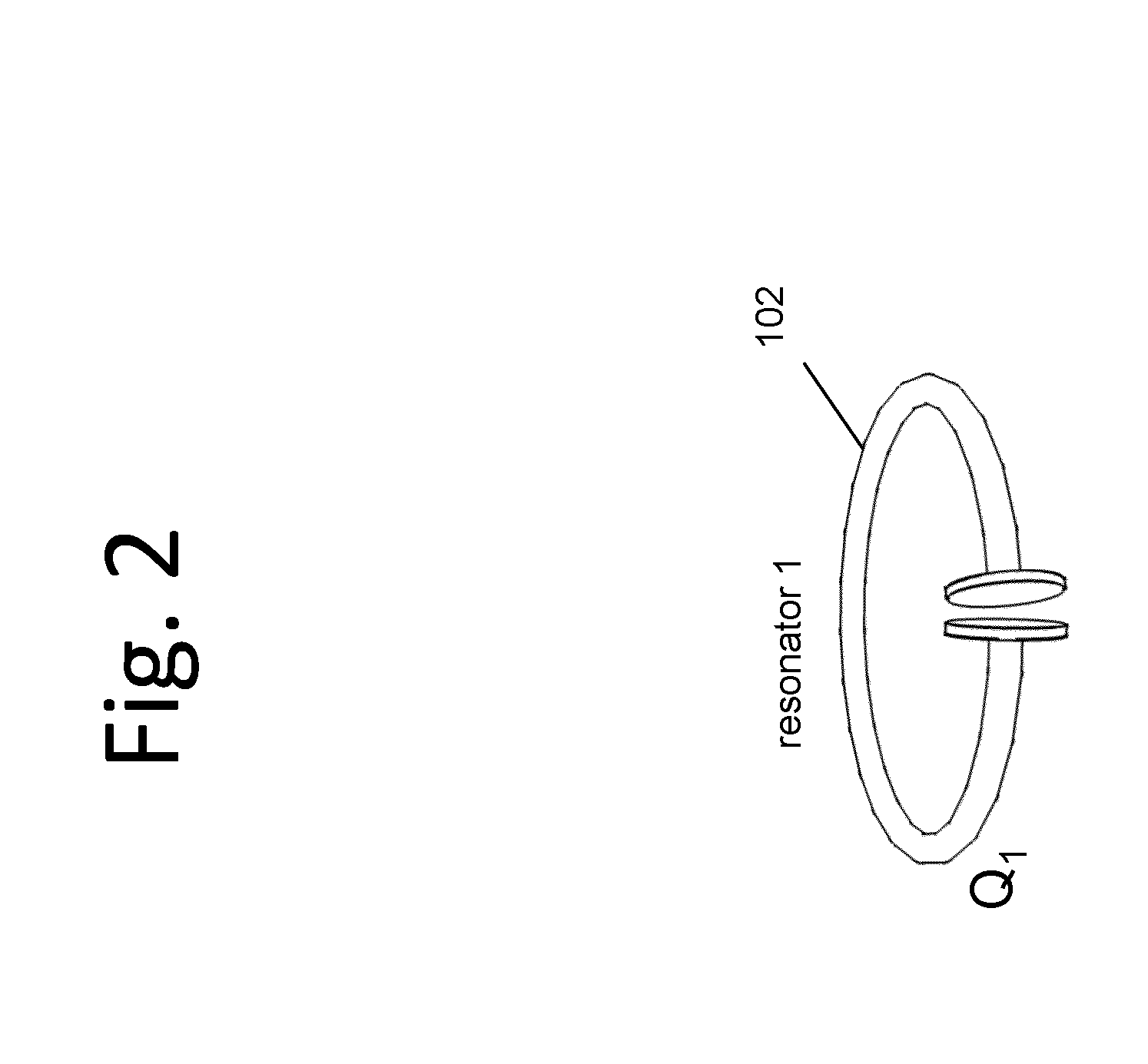
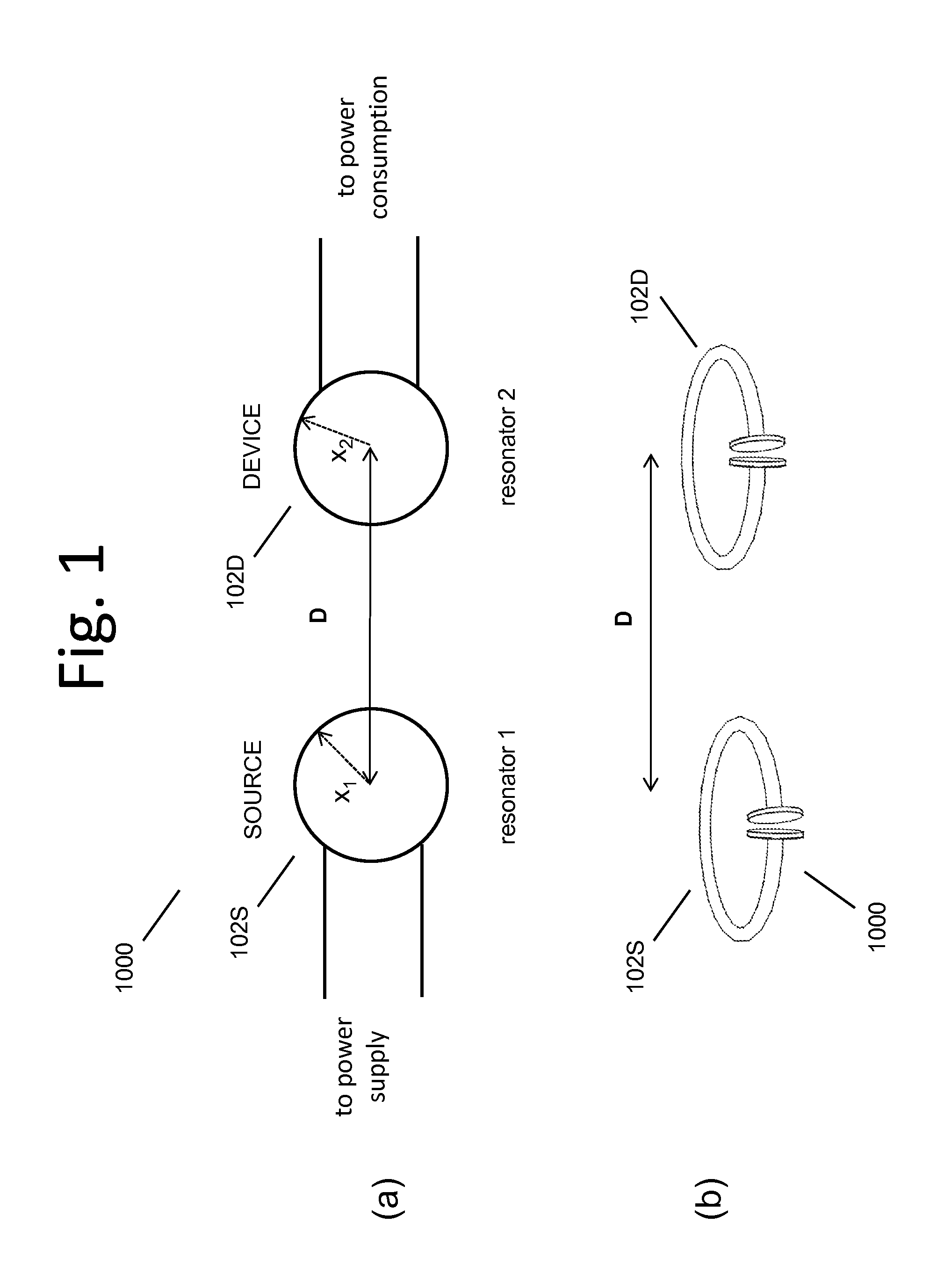
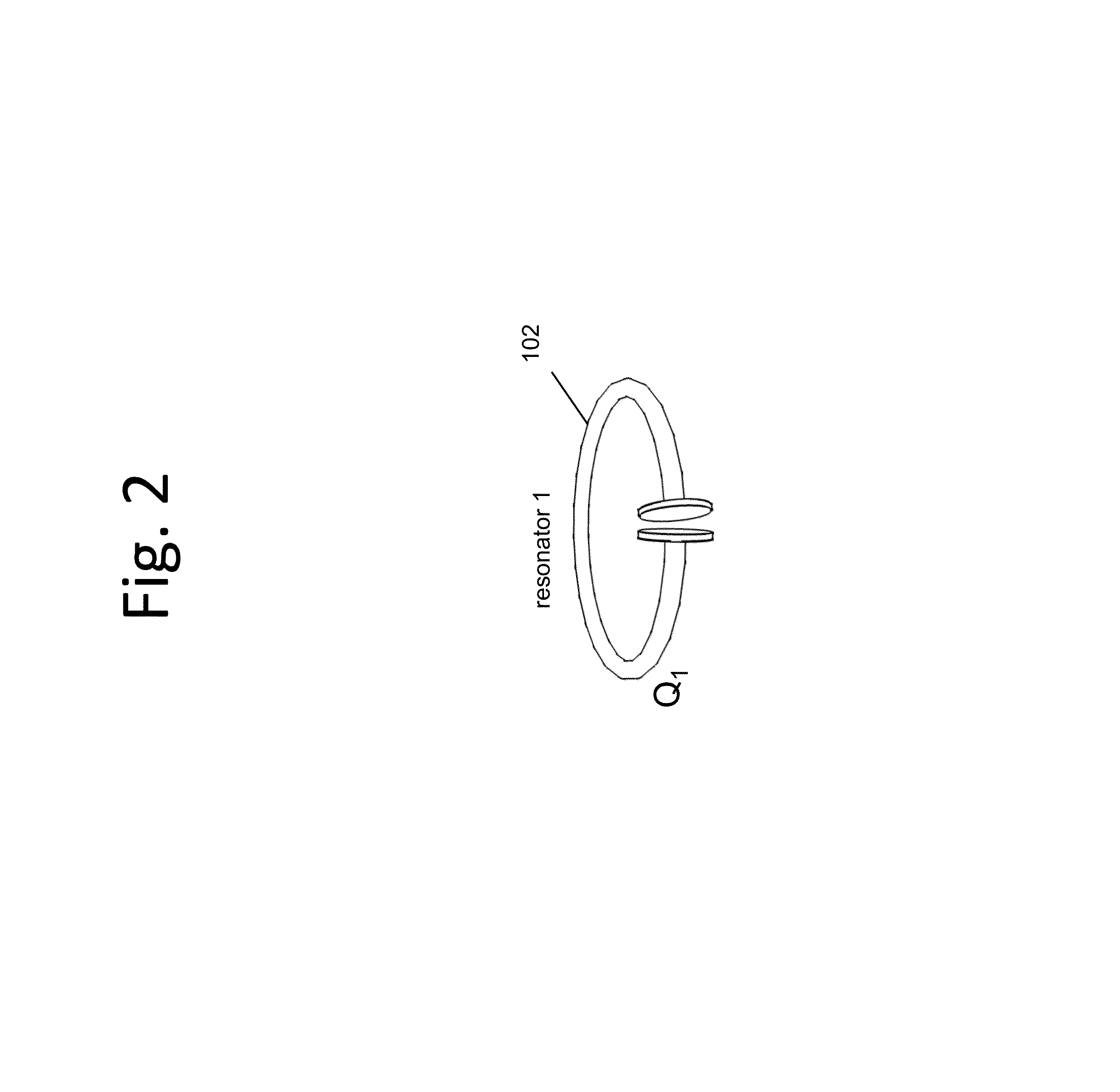
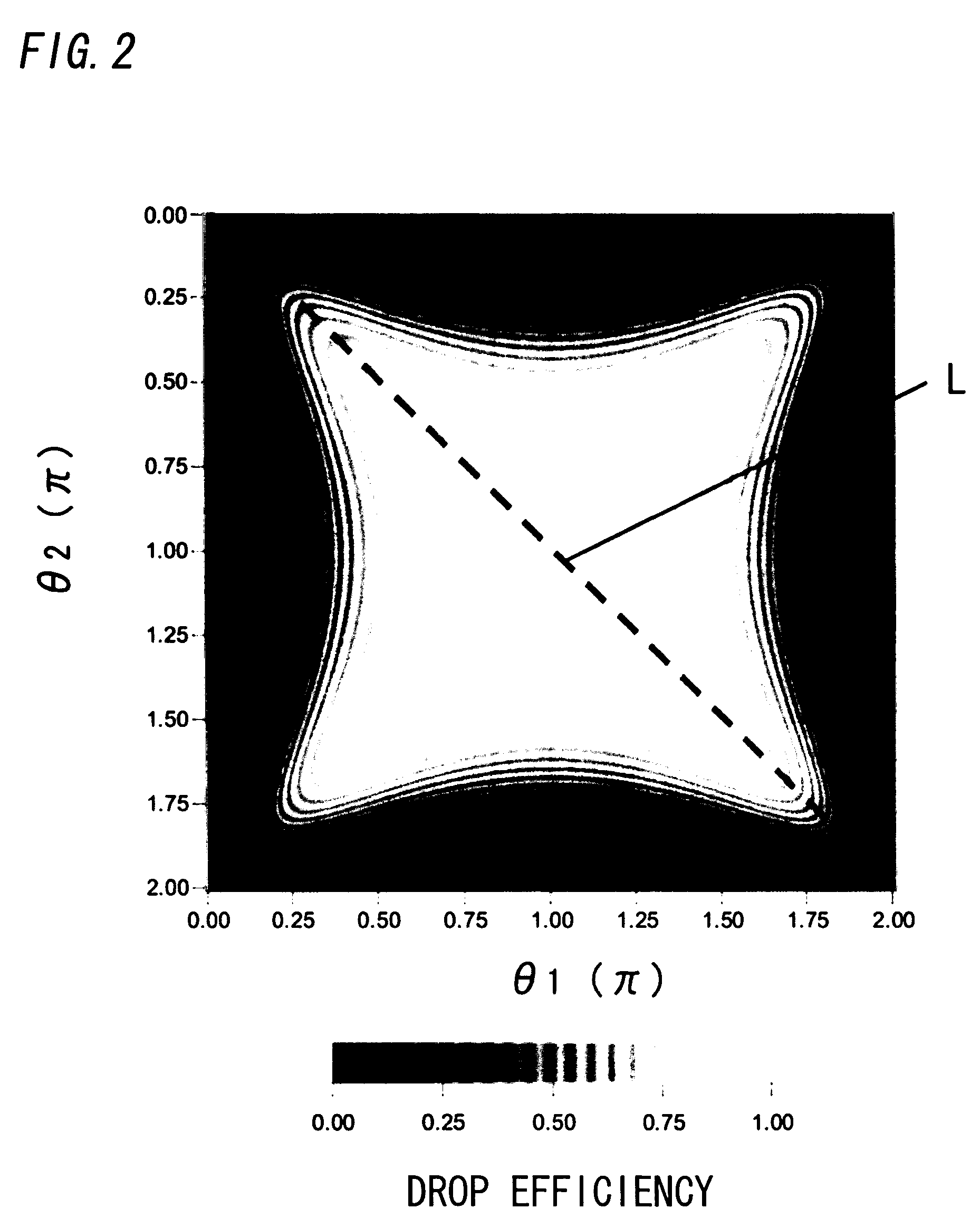
Described herein are improved capabilities for a source resonator having a Q-factor Q1>100 and a characteristic size x1 coupled to an energy source, and a second resonator having a Q-factor Q2>100 and a characteristic size x2 coupled to an energy drain located a distance D from the source resonator, where the source resonator and the second resonator are coupled to exchange energy wirelessly among the source resonator and the second resonator.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer systems
ActiveUS20100109445A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionEnergy transferCondensed matter physics
Described herein are improved capabilities for a source resonator having a Q-factor Q1>100 and a characteristic size x1 coupled to an energy source, and a second resonator having a Q-factor Q2>100 and a characteristic size x2 coupled to an energy drain located a distance D from the source resonator, where the source resonator and the second resonator are coupled to exchange energy wirelessly among the source resonator and the second resonator.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
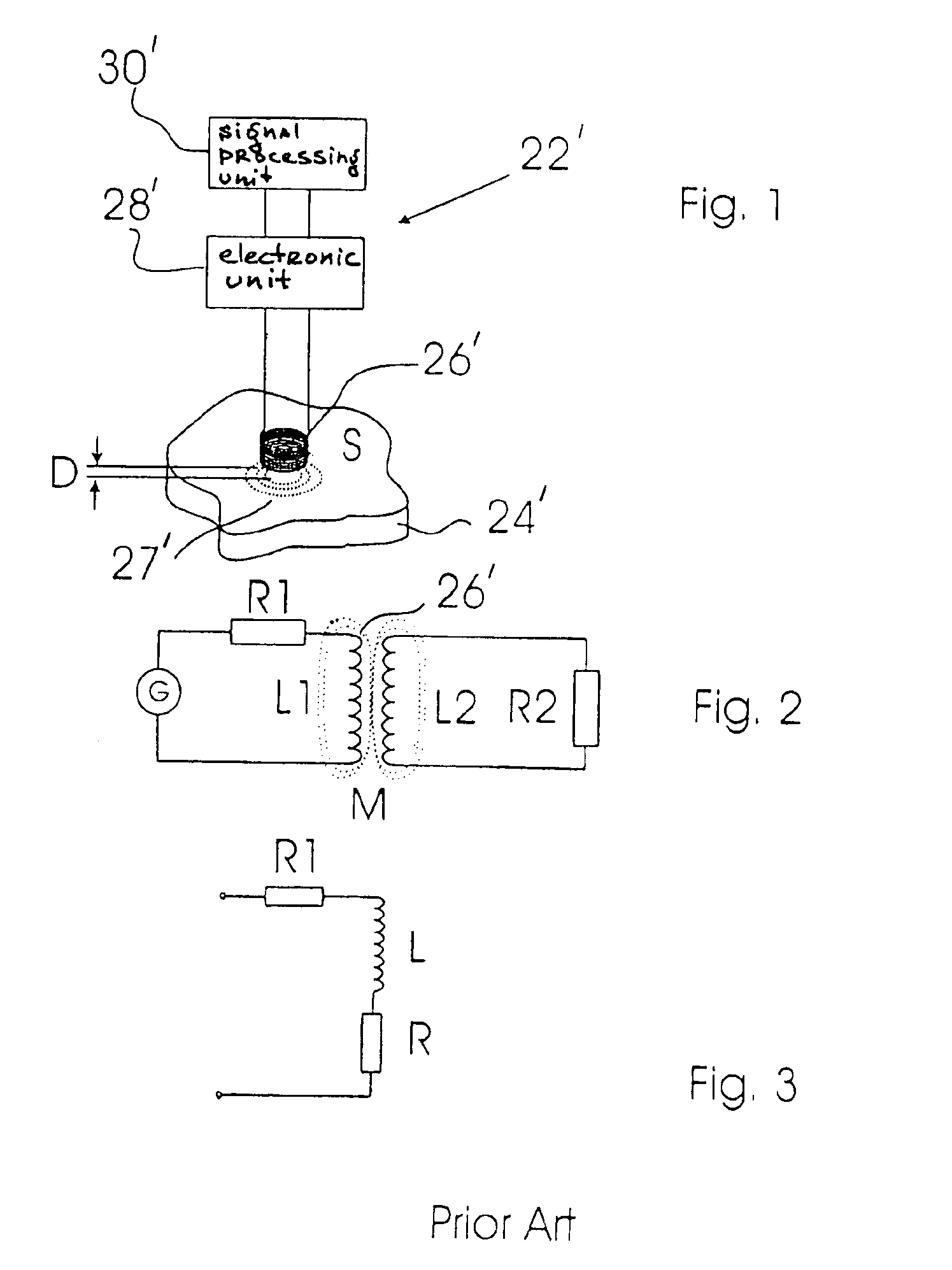
High Q factor sensor
ActiveUS7147604B1Measure easily and safely and inexpensively and accuratelySimple monitoring methodCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringPhysical propertyQ factor
A sensor for wirelessly determining a physical property within a defined space comprises an electrical resonance and has a high quality factor Q. The quality factor Q is sufficiently high that a signal generated by the sensor can be received outside the defined space. The sensor may optimally have a dielectric coating.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
Secure wireless energy transfer in medical applications
InactiveUS20120235503A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit monitoring/indicationEnergy transferAuthorization
A medical device-powering wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply includes a load configured to power the medical device using electrical power, and a second electromagnetic resonator adapted to be housed within the medical device and configured to be coupled to the load, wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator; wherein the square root of the product of the respective Q factors is greater than 100; and an authorization facility to confirm compatibility of the resonators and provide authorization for initiation of transfer of power.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer resonator kit
ActiveUS8487480B1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit arrangementsEnergy transferCondensed matter physics
Described herein are improved capabilities for a source resonator having a Q-factor Q1>100 and a characteristic size x1 coupled to an energy source, and a second resonator having a Q-factor Q2>100 and a characteristic size x2 coupled to an energy drain located a distance D from the source resonator, where the source resonator and the second resonator are coupled to exchange energy wirelessly among the source resonator and the second resonator.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Electromagnetic wave frequency filter
InactiveUS7321707B2Simple designEfficient extractionNanoopticsCoupling light guidesPhase shiftedFrequency matching
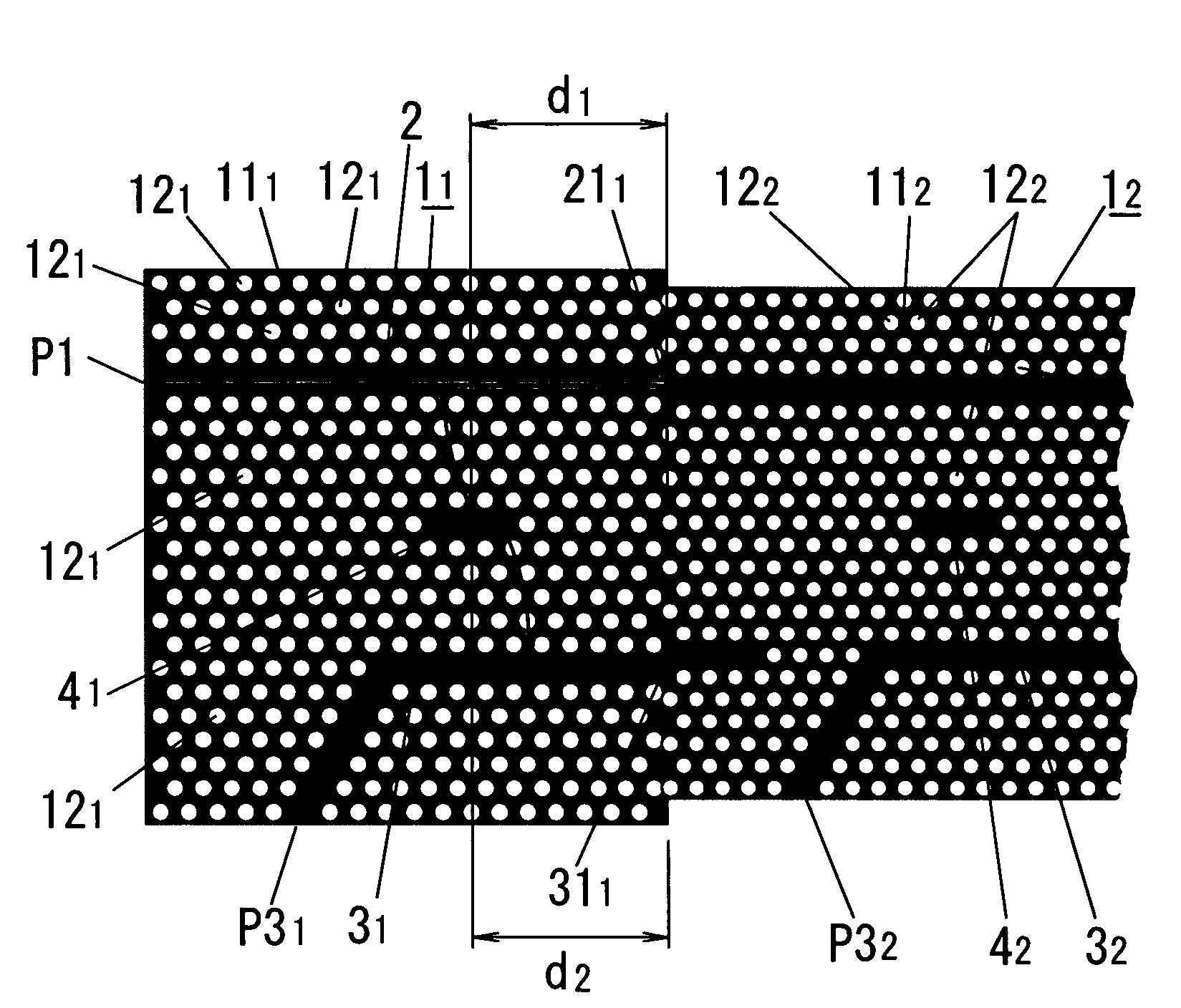
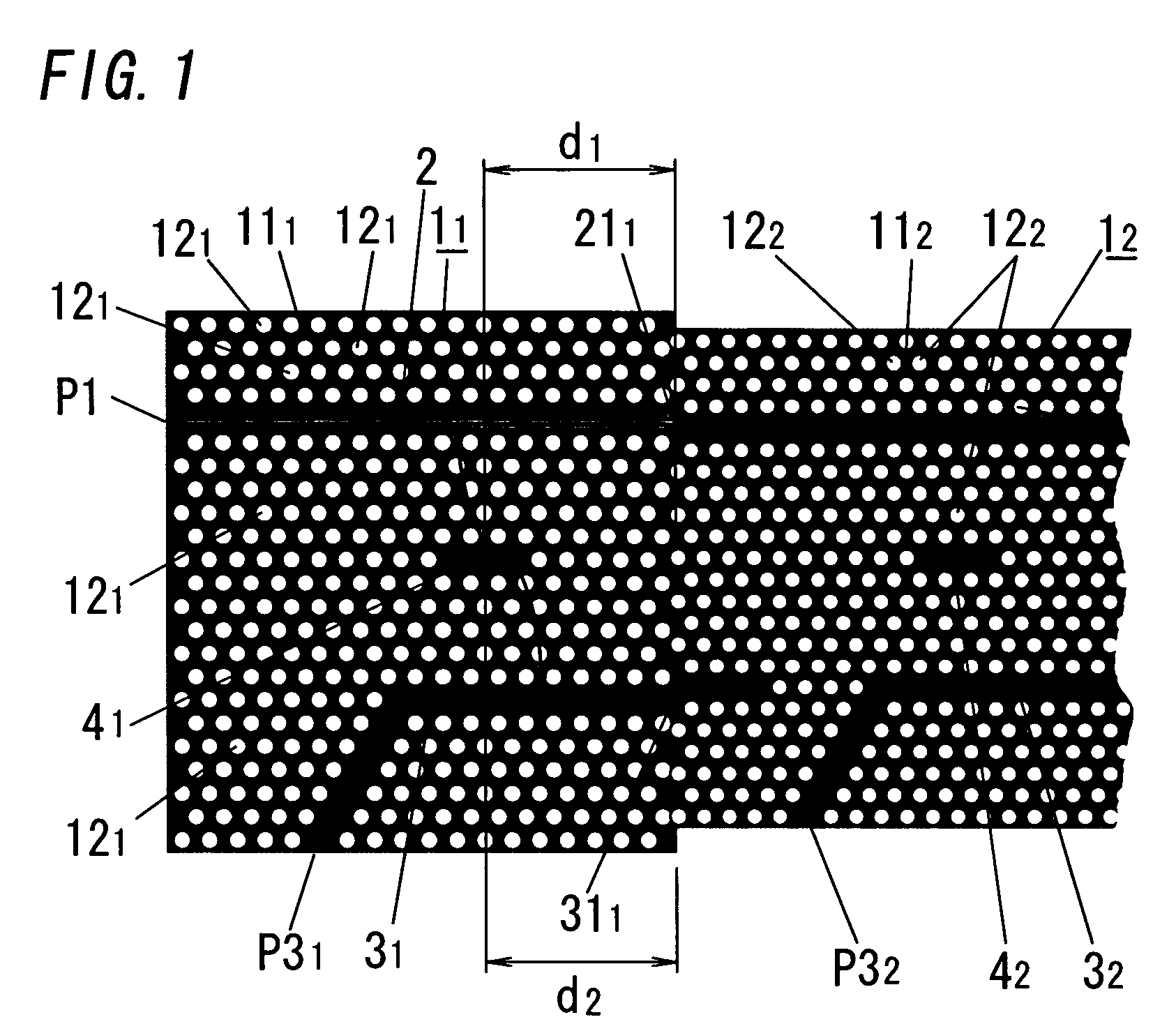
In this electromagnetic wave frequency filter, an electromagnetic wave of a predetermined frequency matching a resonant frequency of a resonator 41 is transmitted from an input waveguide 2 to an output waveguide 3 through the resonator 41, and is outputted from a drop port P31. This filter has an input-waveguide-side reflector 211 and an output-waveguide-side reflector 311, which reflect the electromagnetic wave of the predetermined frequency. The electromagnetic wave frequency filter satisfies the following relation:Qinb / (1−cos θ1)<<Qv,Qinb / (1−cos θ1)=Qinr / (1−cos θ2),θ1, θ2≠2Nπ(N=0, 1, . . . ),where θ1 is a phase shift amount of the electromagnetic wave reflected by the input-waveguide-side reflector 211, θ2 is a phase shift amount of the electromagnetic wave reflected by the output-waveguide-side reflector 311, Qinb is a Q-factor between the resonator 41 and the input waveguide 2, Qinr is a Q-factor between the resonator 41 and the output waveguide 31, and Qv is a Q-factor between the resonator 41 and free space.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Wireless energy transfer resonator kit
ActiveUS20130200716A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit arrangementsEnergy transferEnergy expenditure
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
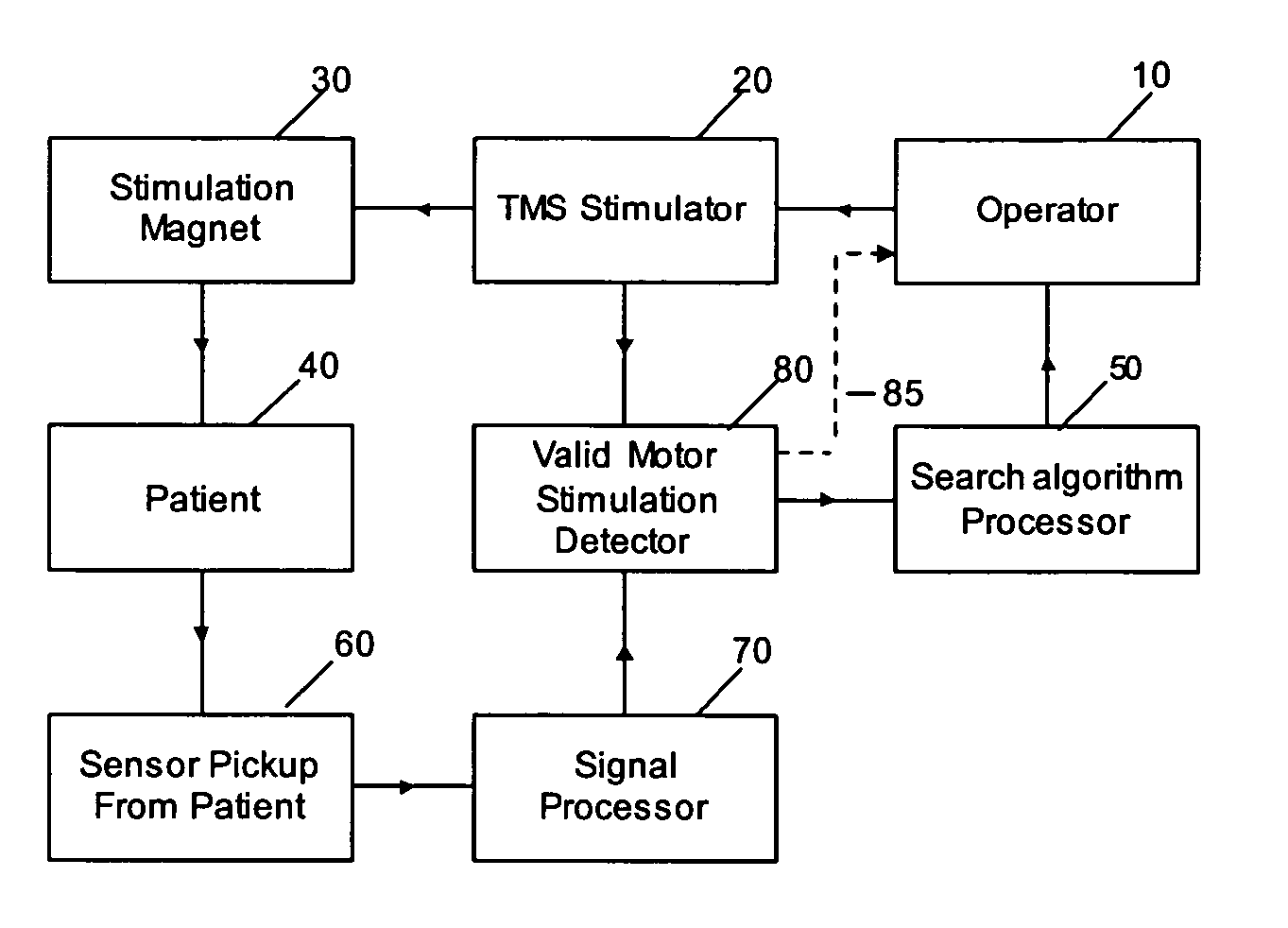
Determining stimulation levels for transcranial magnetic stimulation
ActiveUS7104947B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyMotion detectorREFLEX DECREASE
Owner:NEURONETICS
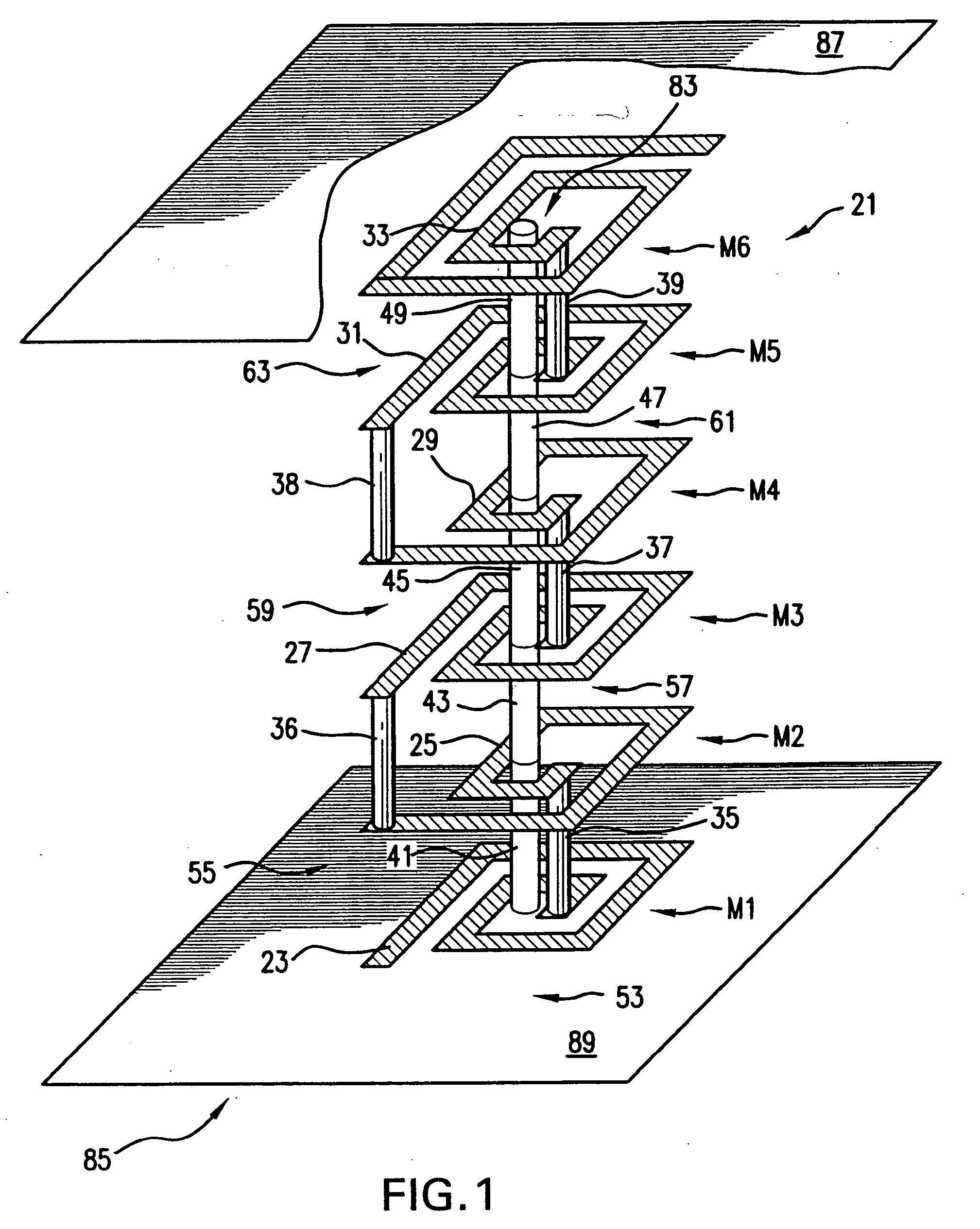
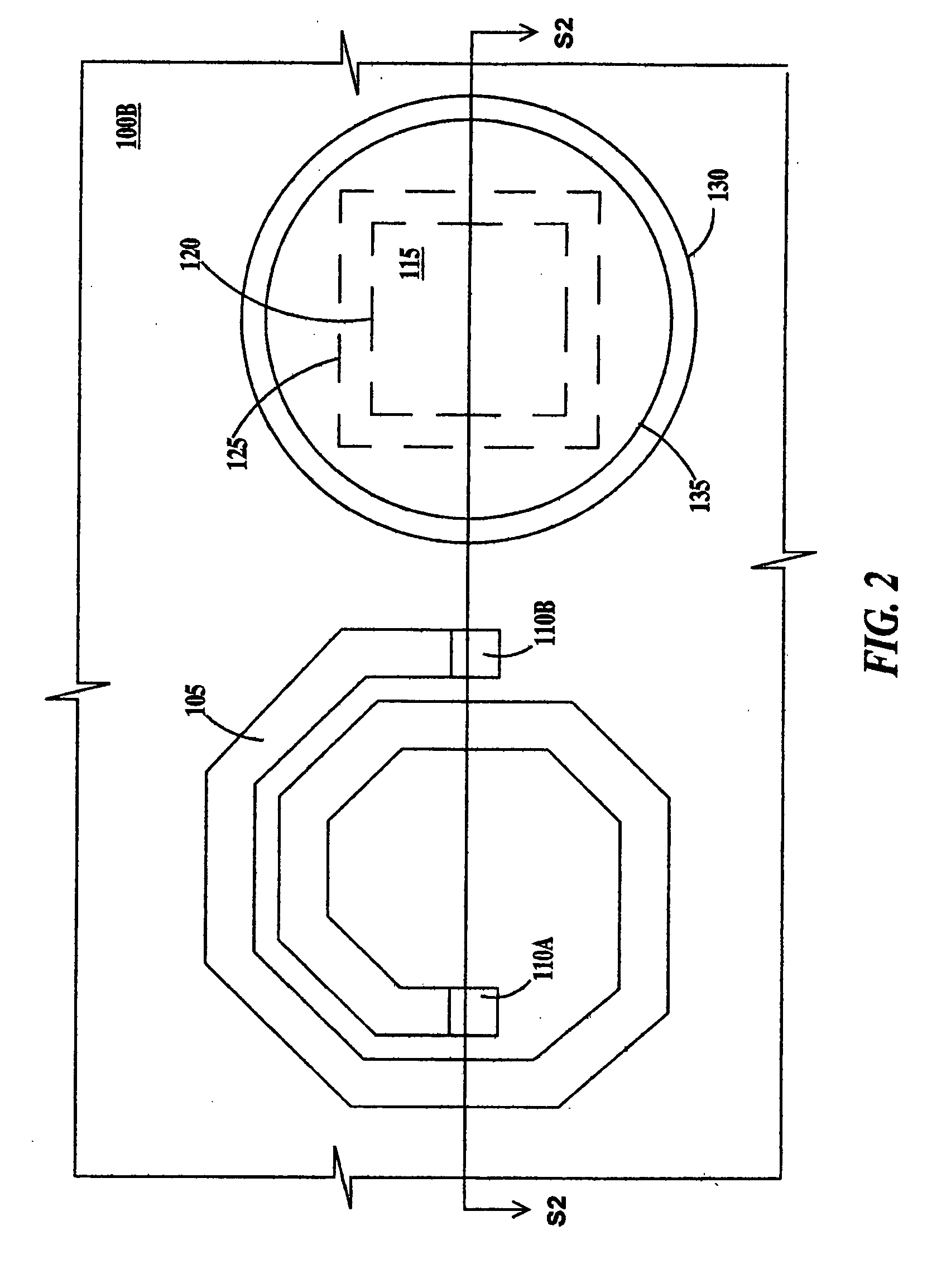
Compact inductor with stacked via magnetic cores for integrated circuits
InactiveUS7262680B2Small sizeReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuit designIntegrated circuit
An on-chip inductor device for Integrated Circuits utilizes coils on a plurality of metal layers of the IC with electrical connectors between the coils and a magnetic core for the inductor of stacked vias running between the coils. The magnetic core is made from a series of stacked vias which are deposited between each metal layer of the IC having a coil. The magnetic core desirably includes an array of magnetic bars comprising the magnetic core. The via material of the magnetic core may be both magnetic and electrically conductive. The magnetic and electrically conductive via material may also be used for the planar coil electrical connectors or other electrically conductive parts of the IC, or both, thereby lessening fabrication steps. Films of magnetic material may be formed at the ends of the inductor to provide a closed magnetic circuit for the inductor. A high Q factor inductor of small (e.g., transistor) size is thus obtained. The materials and processes which enable the on-chip inductor device are compatible with ordinary IC fabrication methods.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
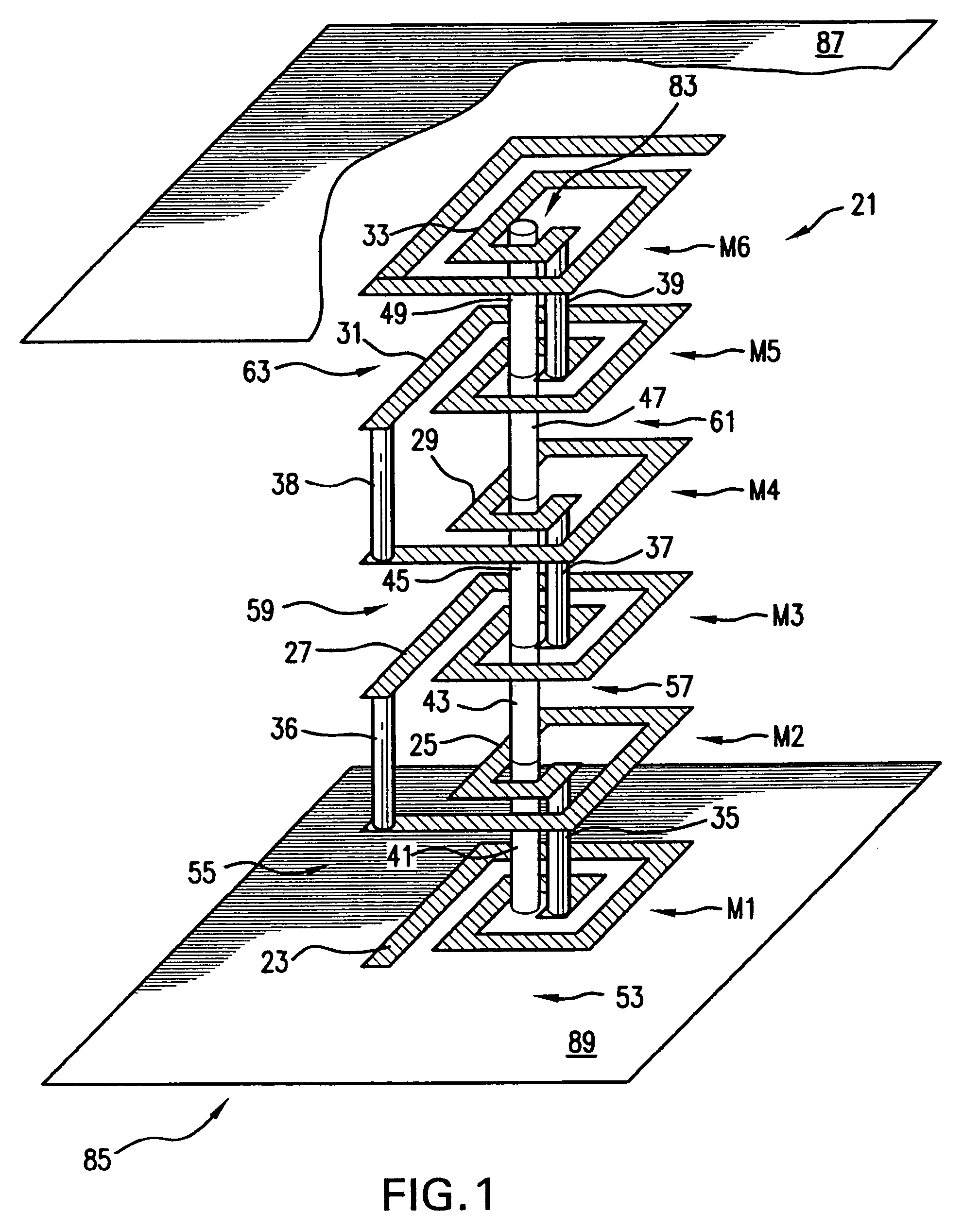
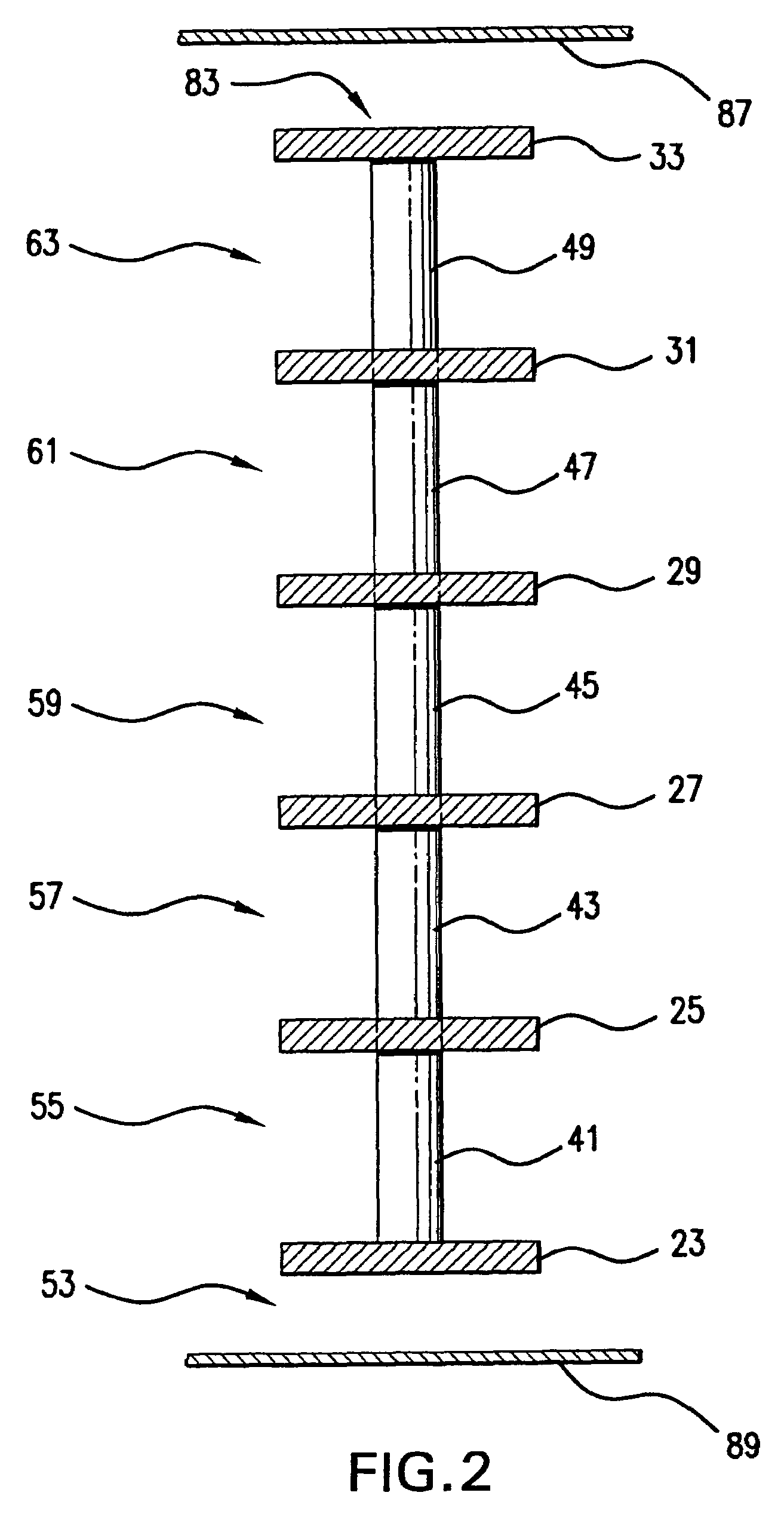
Ultrasonic impact machining of body surfaces to correct defects and strengthen work surfaces
InactiveUS6932876B1Improve power transfer efficiencyEfficient transferMechanical vibrations separationFurnace typesUltrasonic sensorPeriodic oscillation
Metallic workpieces of diverse shapes having work surfaces which are deformed at the surface and adjacent sub-surface layers by surface impact from ultrasonic transducers employing freely axially moving impacting elements propelled and energized by a transducer oscillating surface vibrating periodically at an ultrasonic frequency. The impacting elements are propelled in a random aperiodic and controlled impact mode at different phases of the periodic oscillation cycles. The transducer may be portable and provides a series of mechanically interconnected stages having mechanical resonances harmonically related as a multiple of the primary ultrasonic frequency and have matched stage resistances under instantaneous loading when the impact elements are driven by the transducer oscillating surface into the surface of the workpiece. This mode of operation produces Q-factor amplification of the input ultrasonic power oscillator energy at the impact needles and high propulsion velocities making it possible to machine metallic workpiece bodies to greater depths for compressing the metal to increase compressive strength of the workpiece work surfaces to substantially the ultimate material strength. The impact machining is done at ambient temperatures.
Owner:PROGRESS RAIL SERVICES
Mechanical resonator optimization using shear wave damping
ActiveUS8335356B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPrint image acquisitionEngineeringLength wave
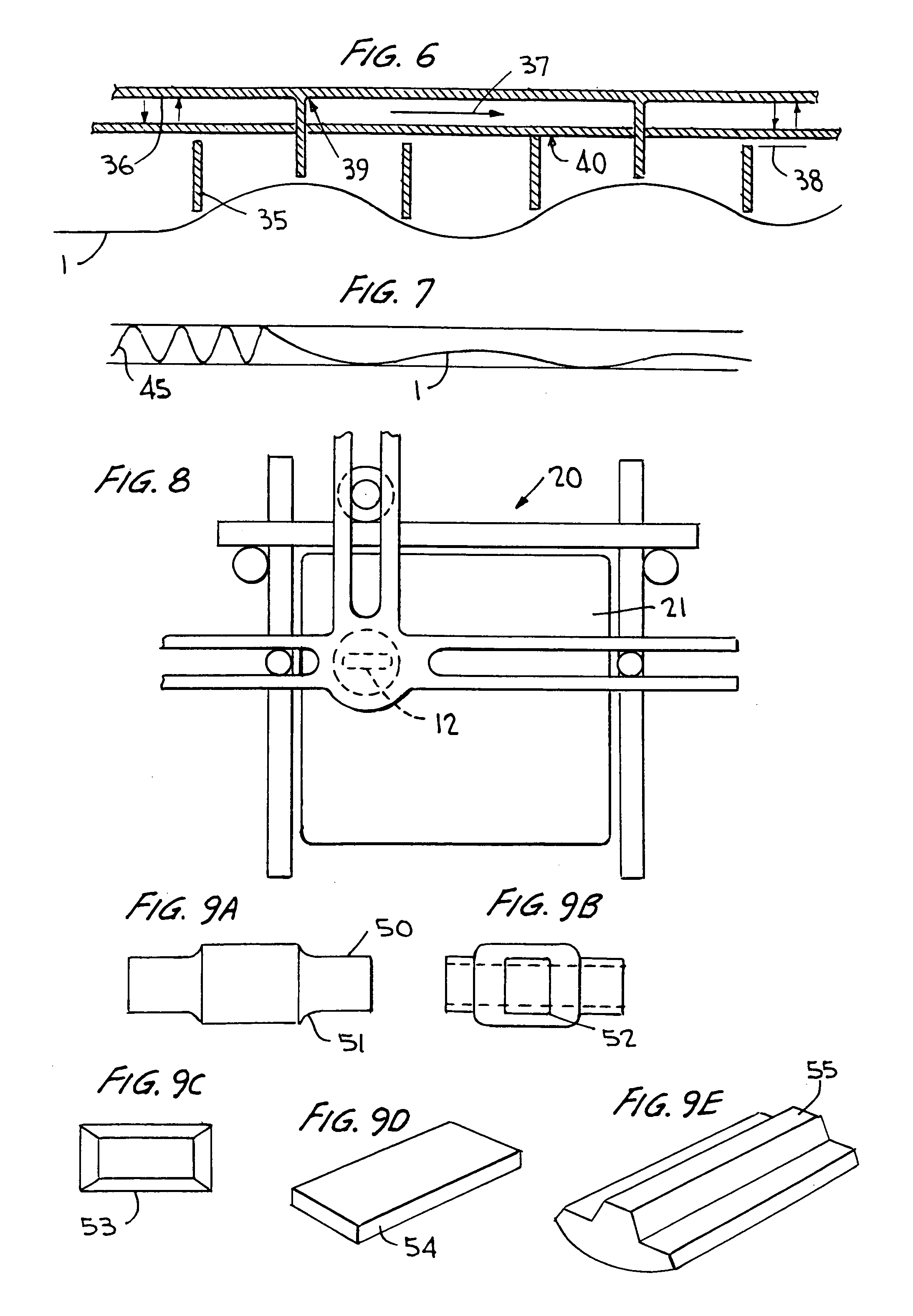
Provided is a fingerprint sensor including one or more mechanical devices for capturing the fingerprint. The mechanical devices include a matrix of pillars and are configured to be mechanically damped based upon an applied load. A q factor of the pillars is optimized by adjusting a distance between pillars within the matrix in accordance with a quarter shear wavelength at an operating wavelength.
Owner:SONAVATION INC
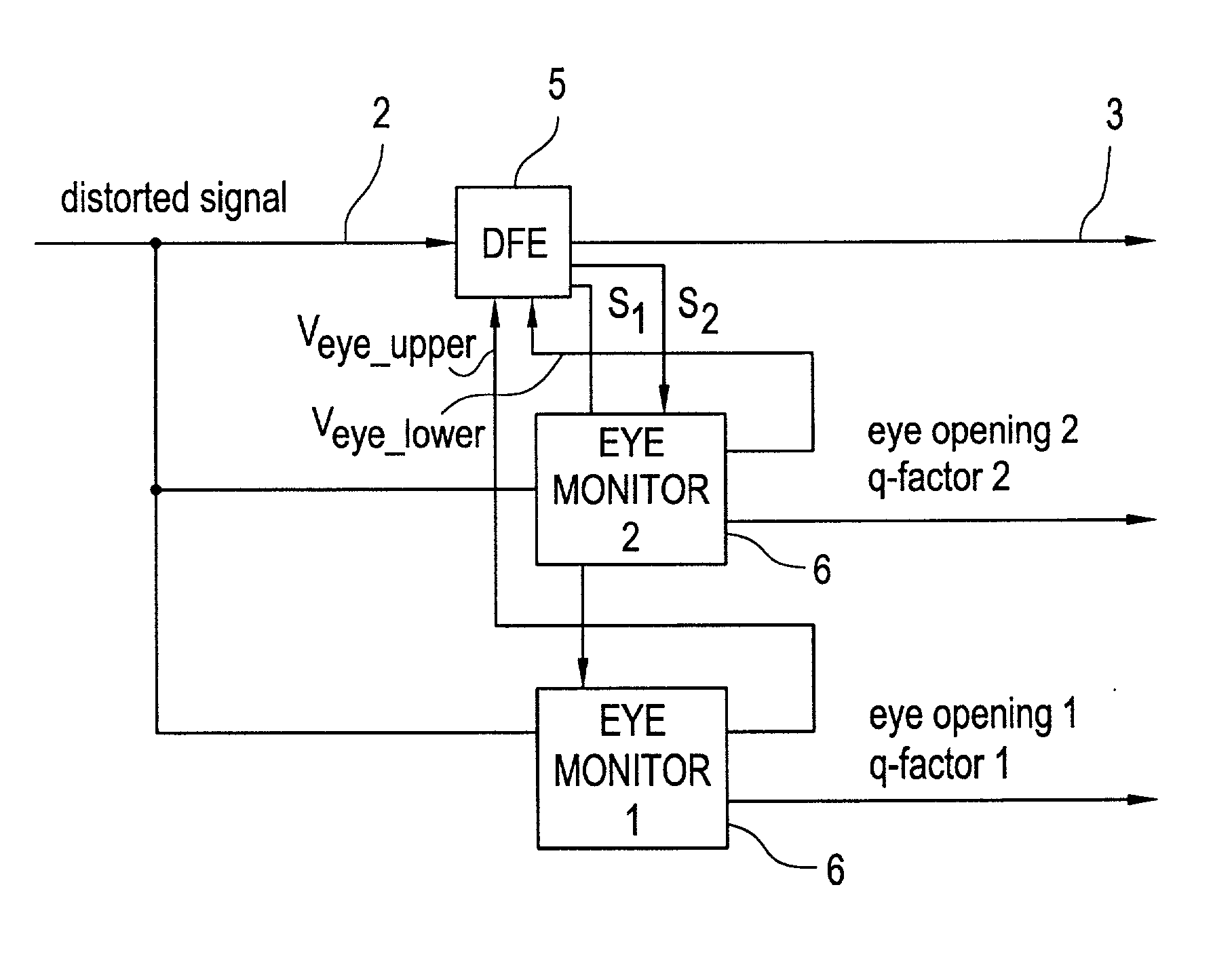
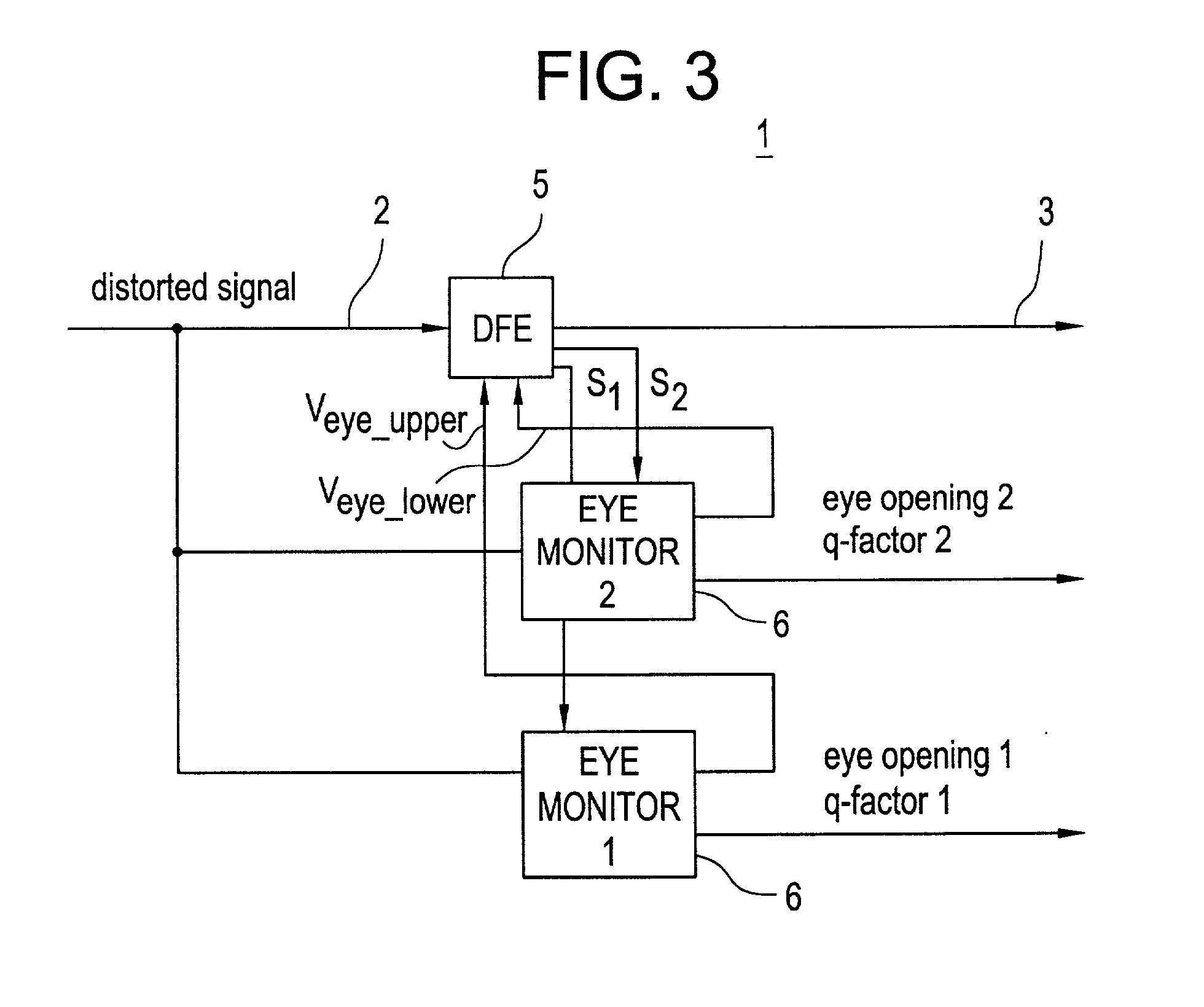
Receiver with feedback filter, and eye monitor for the feedback filter
An optical receiver with an electronic filter is described, the parameters of the filter being set by means of high-speed eye monitors. Also described is a high-speed eye monitor with threshold-value decision elements which are set close to the vertices of the eye of an eye diagram, the eye monitor being optimized through connection of a pseudo-error generator and comparison with setpoint values and outputting the eye opening and the Q-factor.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Compact inductor with stacked via magnetic cores for integrated circuits
InactiveUS20050190035A1Small sizeReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesQ factorPlanar coil
An on-chip inductor device for Integrated Circuits utilizes coils on a plurality of metal layers of the IC with electrical connectors between the coils and a magnetic core for the inductor of stacked vias running between the coils. The magnetic core is made from a series of stacked vias which are deposited between each metal layer of the IC having a coil. The magnetic core desirably includes an array of magnetic bars comprising the magnetic core. The via material of the magnetic core may be both magnetic and electrically conductive. The magnetic and electrically conductive via material may also be used for the planar coil electrical connectors or other electrically conductive parts of the IC, or both, thereby lessening fabrication steps. Films of magnetic material may be formed at the ends of the inductor to provide a closed magnetic circuit for the inductor. A high Q factor inductor of small (e.g., transistor) size is thus obtained. The materials and processes which enable the on-chip inductor device are compatible with ordinary IC fabrication methods.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Integrated repeaters for cell phone applications
ActiveUS8928276B2Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionInductorMobile device
A wireless power receiving system for a mobile electronic device that includes a high-Q repeater resonator comprising at least an inductor and a capacitor and having a Q-factor Q1. The inductor of the repeater resonator is enclosed in a removable sleeve of the mobile electronic. The system also includes a high-Q device resonator comprising at least an inductor and a capacitor and having a Q-factor Q2. The device resonator is integrated in the mobile device and electrically connected to the mobile electronic device, and the square root of the product Q1 and Q2 is greater than 100.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Noncontact communication apparatus and noncontact communication method
ActiveUS20100328045A1Without errorFast communication speedMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsElectromagnetic couplingResonance
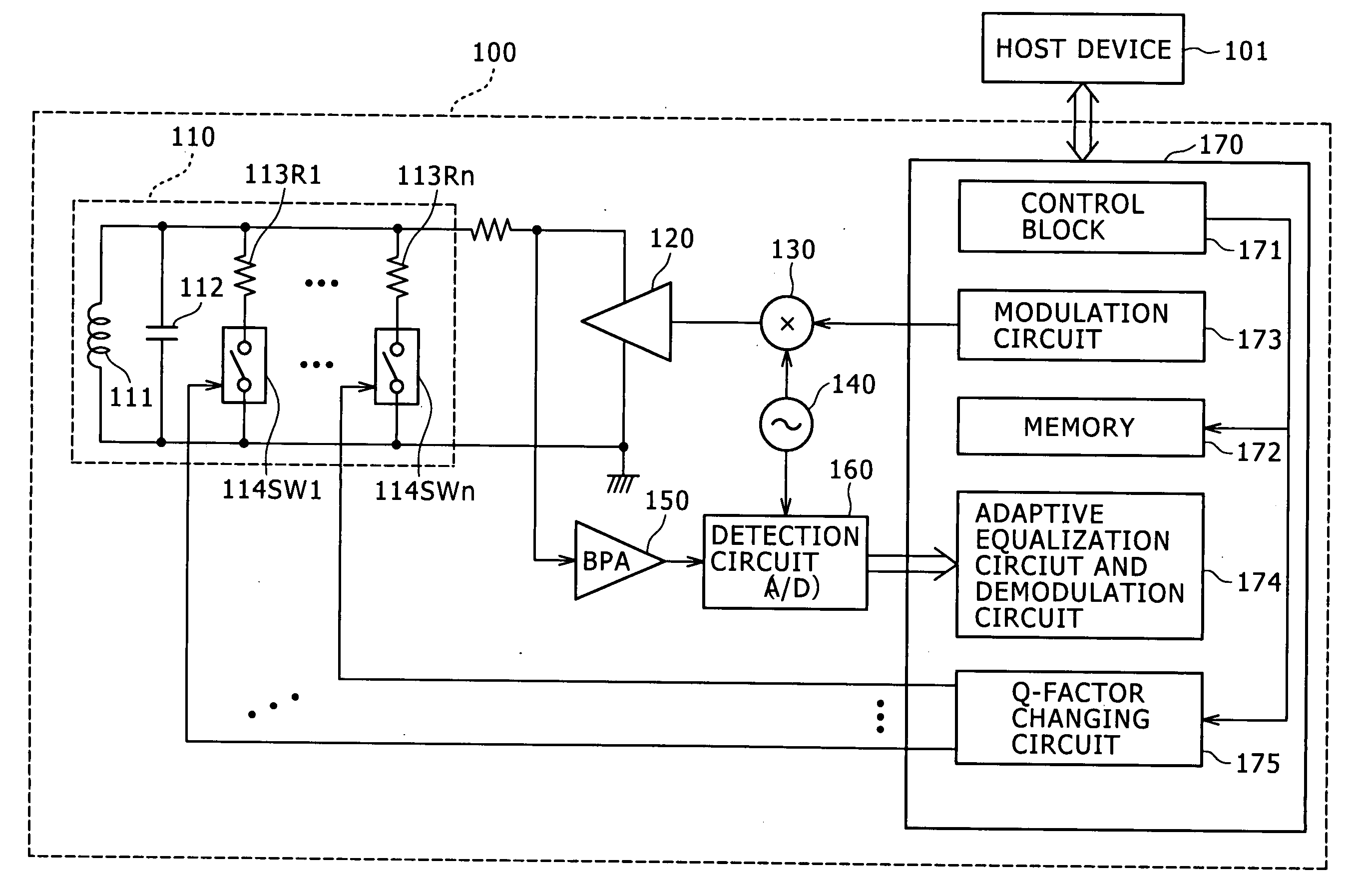
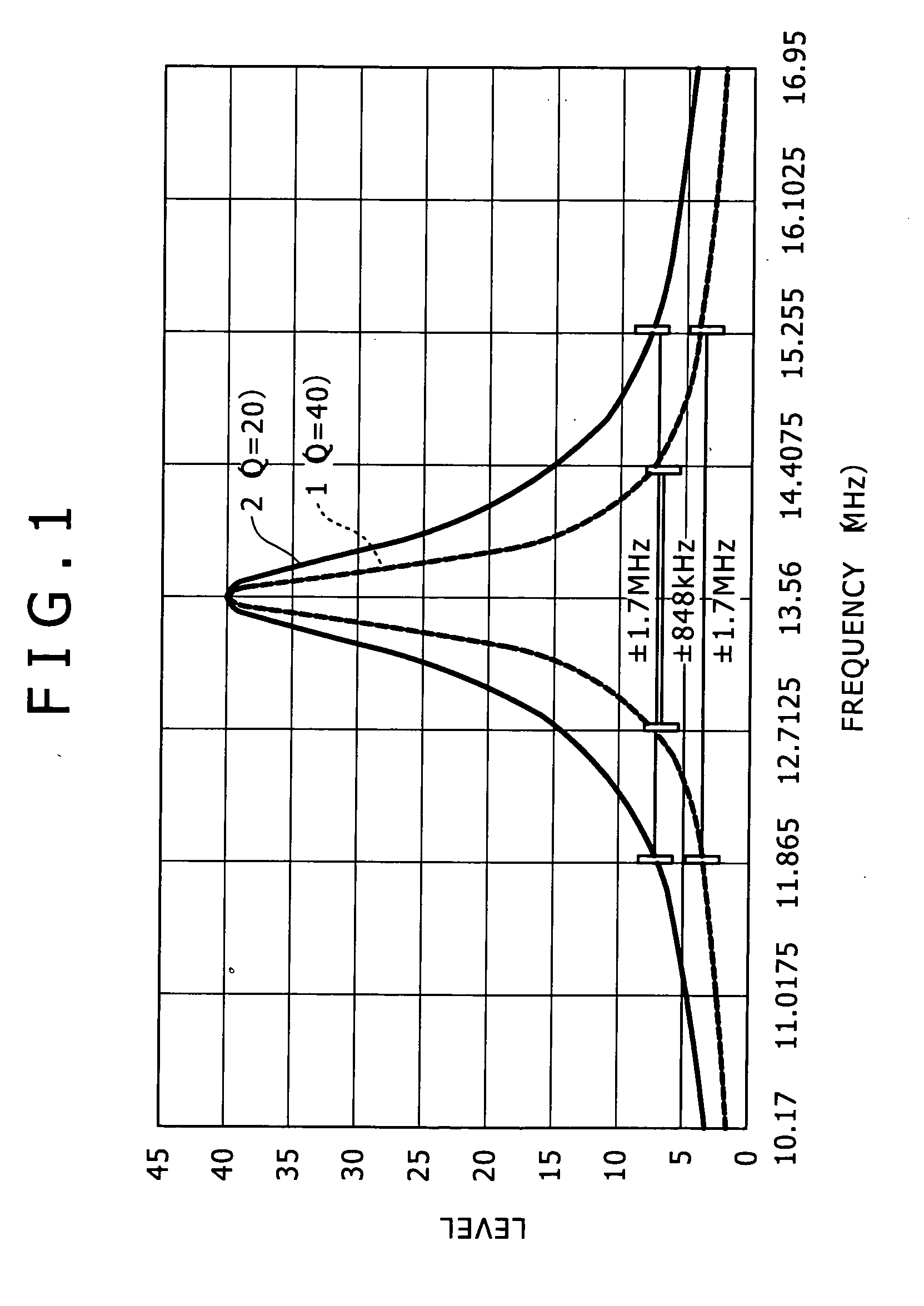
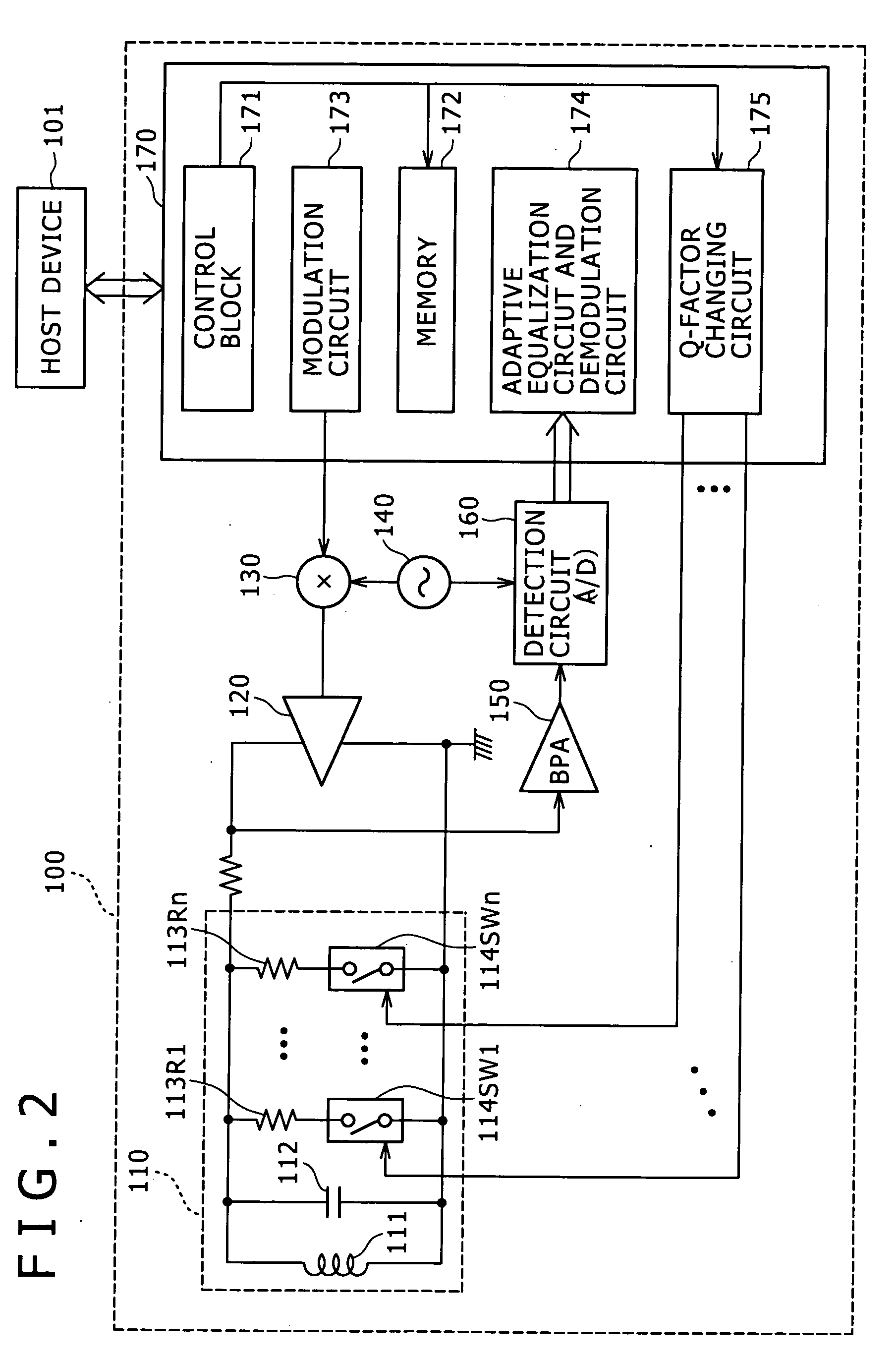
A noncontact communication apparatus is disclosed which includes: an antenna resonance circuit configured to have a coil for communicating with an opposite party through electromagnetic coupling; a changing block configured to change a Q-factor of the antenna resonance circuit; and a control block configured to control the antenna resonance circuit to transmit and receive data to and from the opposite party at one of a plurality of communication speeds prepared beforehand, the control block further controlling the changing block to reduce the Q-factor the higher the communication speed in use.
Owner:SONY CORP
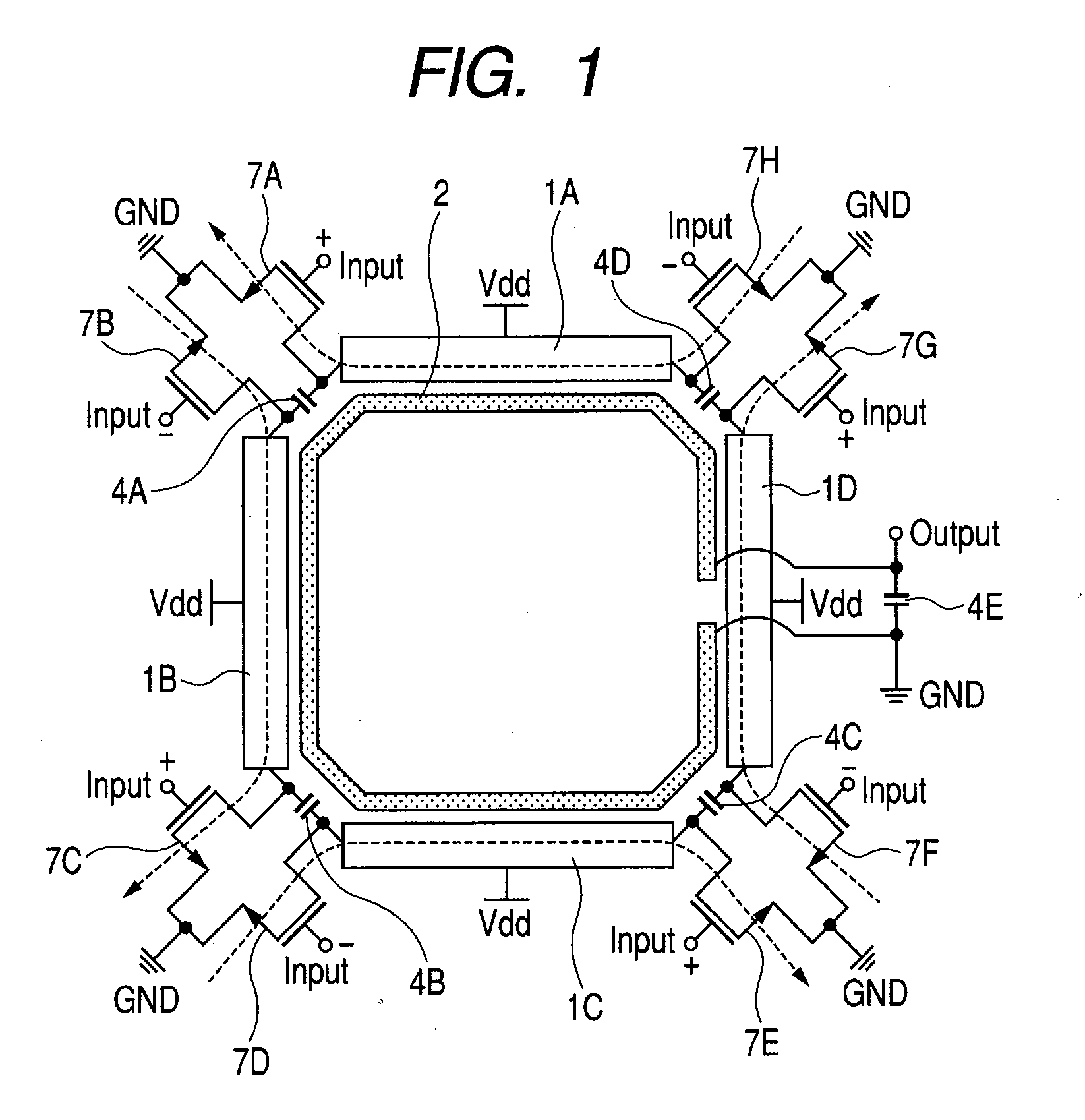
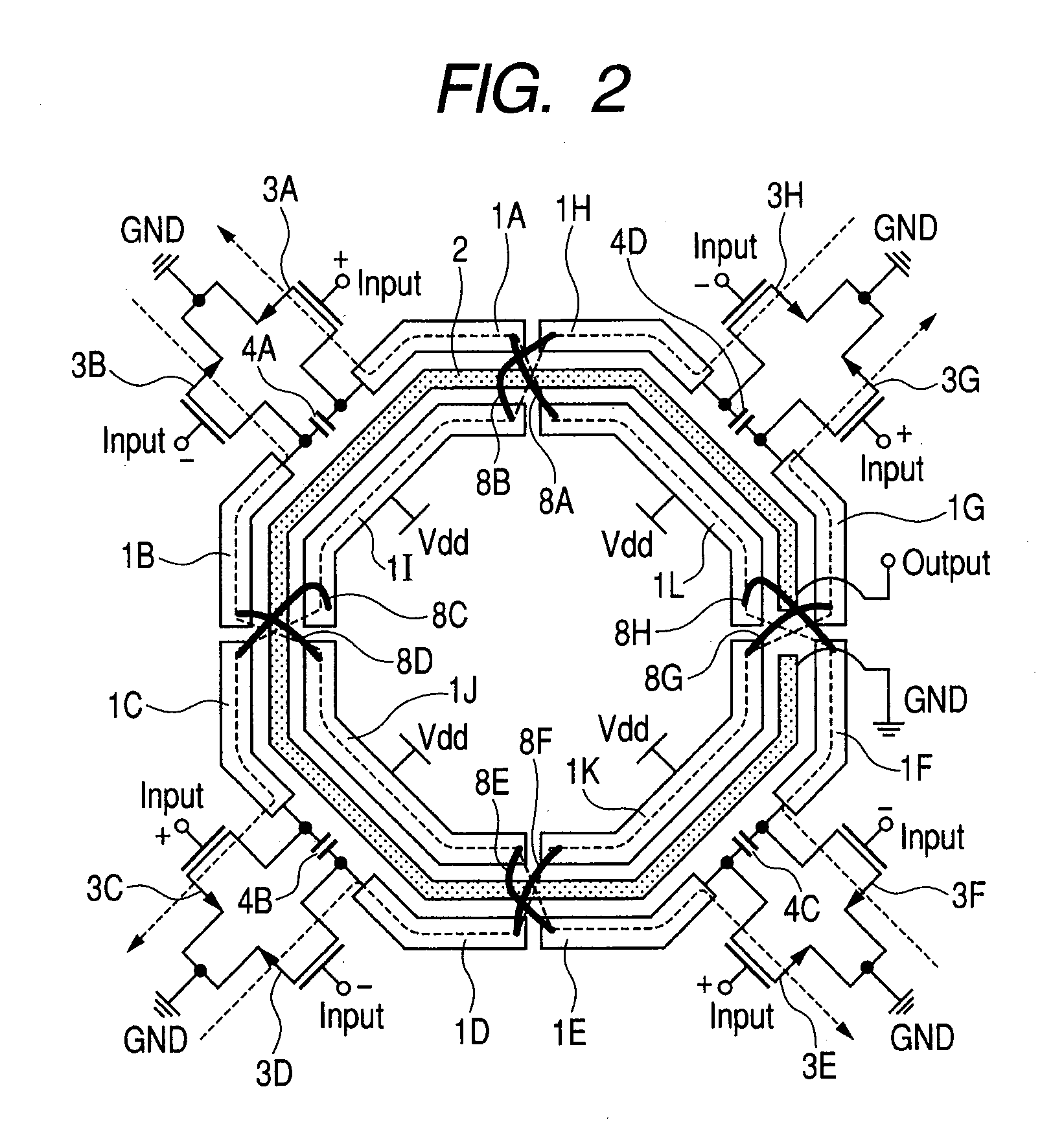
Apparatus and method for transmitting wireless power by using resonant coupling and system for the same
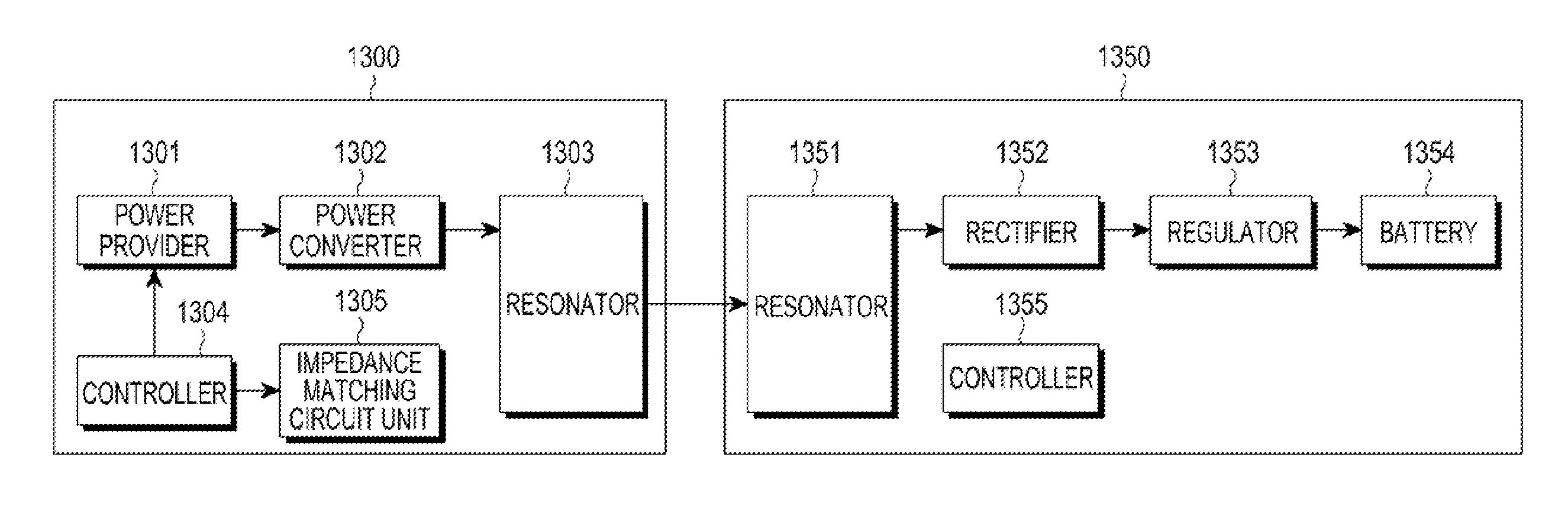
Disclosed are an apparatus and a method for charging power using a resonant coupling. The apparatus includes a transmission power converter for converting Direct Current (DC) power to Alternating Current (AC) power, a controller for adjusting a Q factor of a transmission resonator by using a frequency of the converted AC power and a resonant frequency of the transmission resonator and controlling adaptive impedance matching, and a transmission resonator for wirelessly transmitting the converted AC power to a receiver through the adjusted Q factor and the controlled adaptive impedance matching, the transmission resonator having a coil installed in the transmitter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
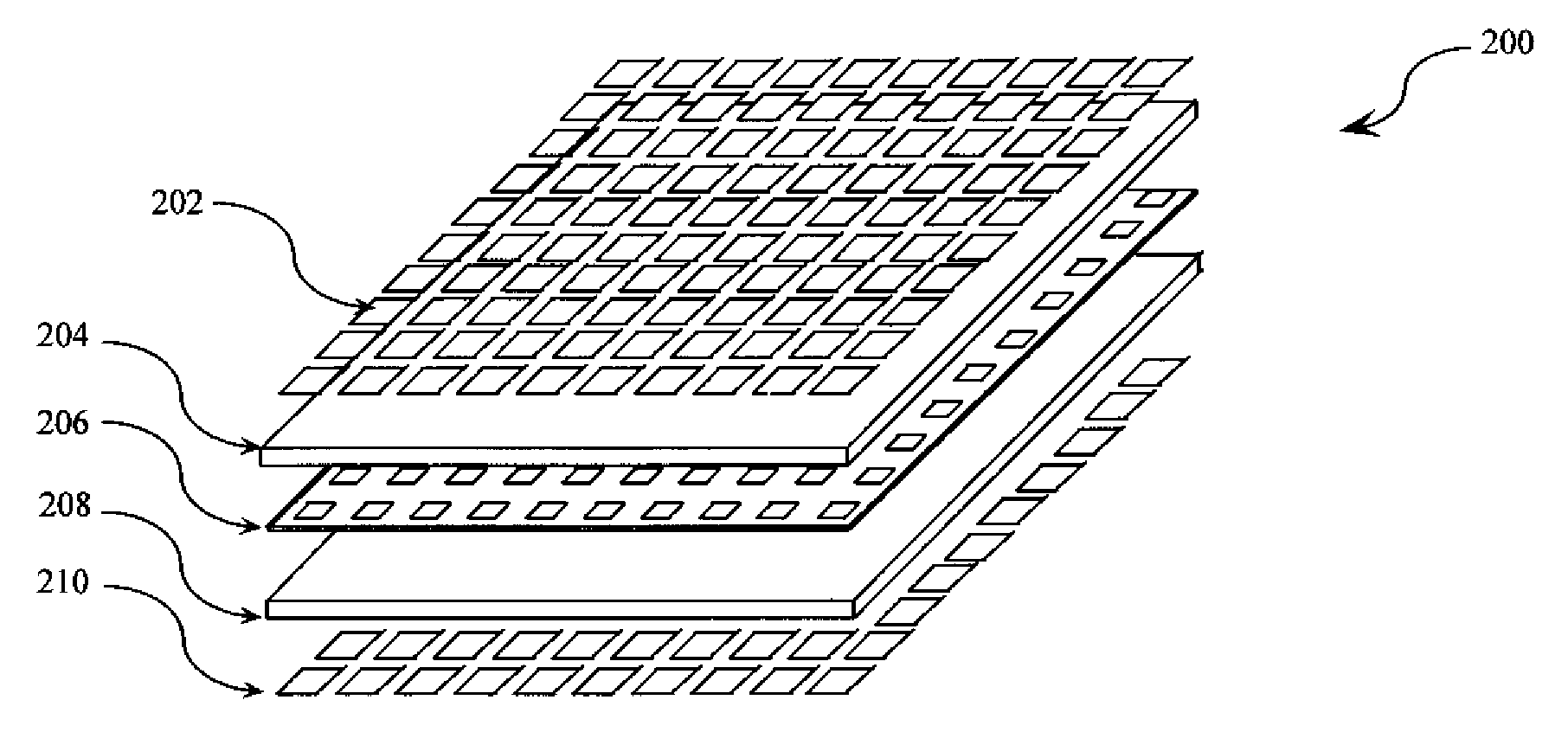
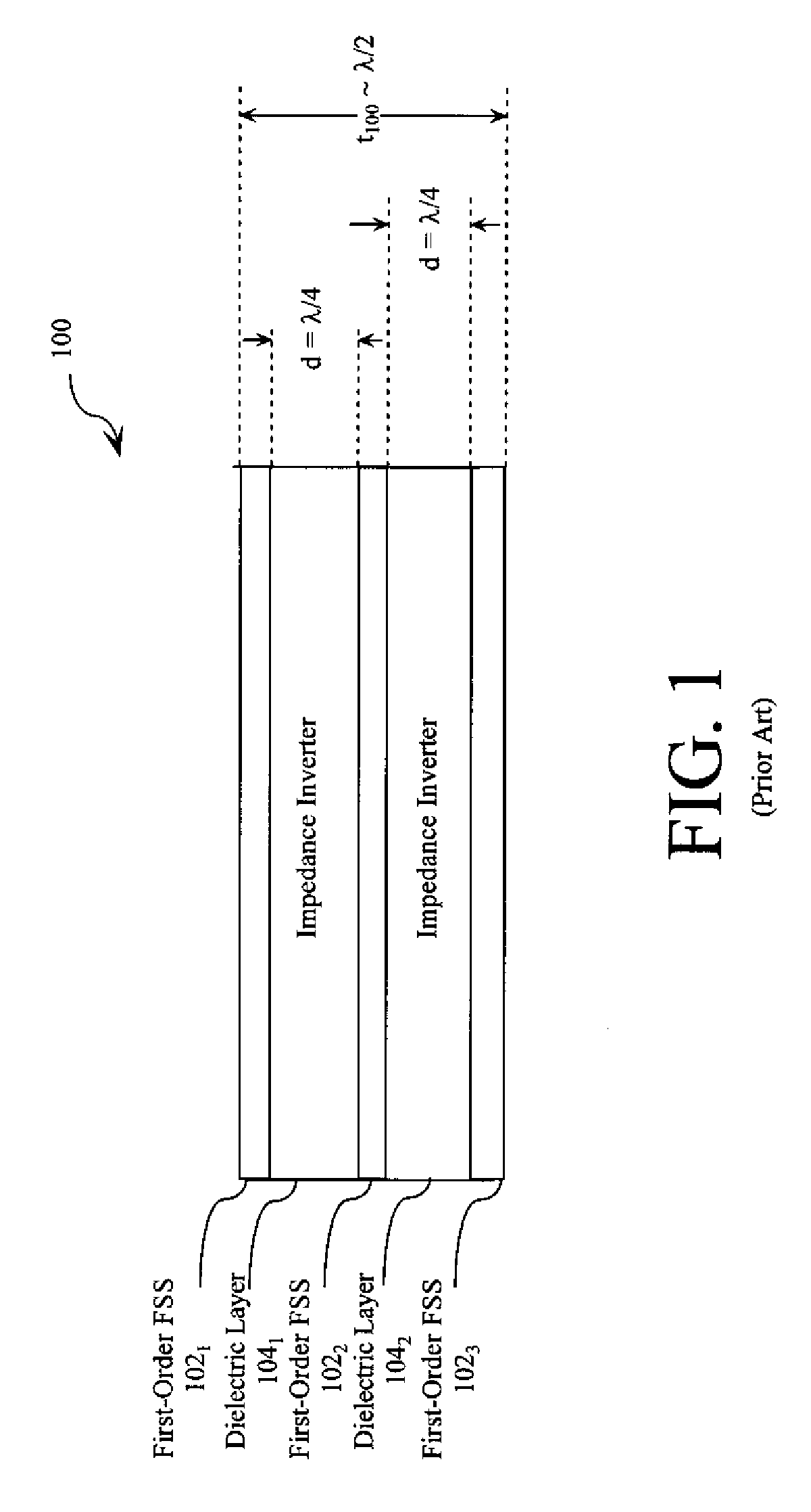
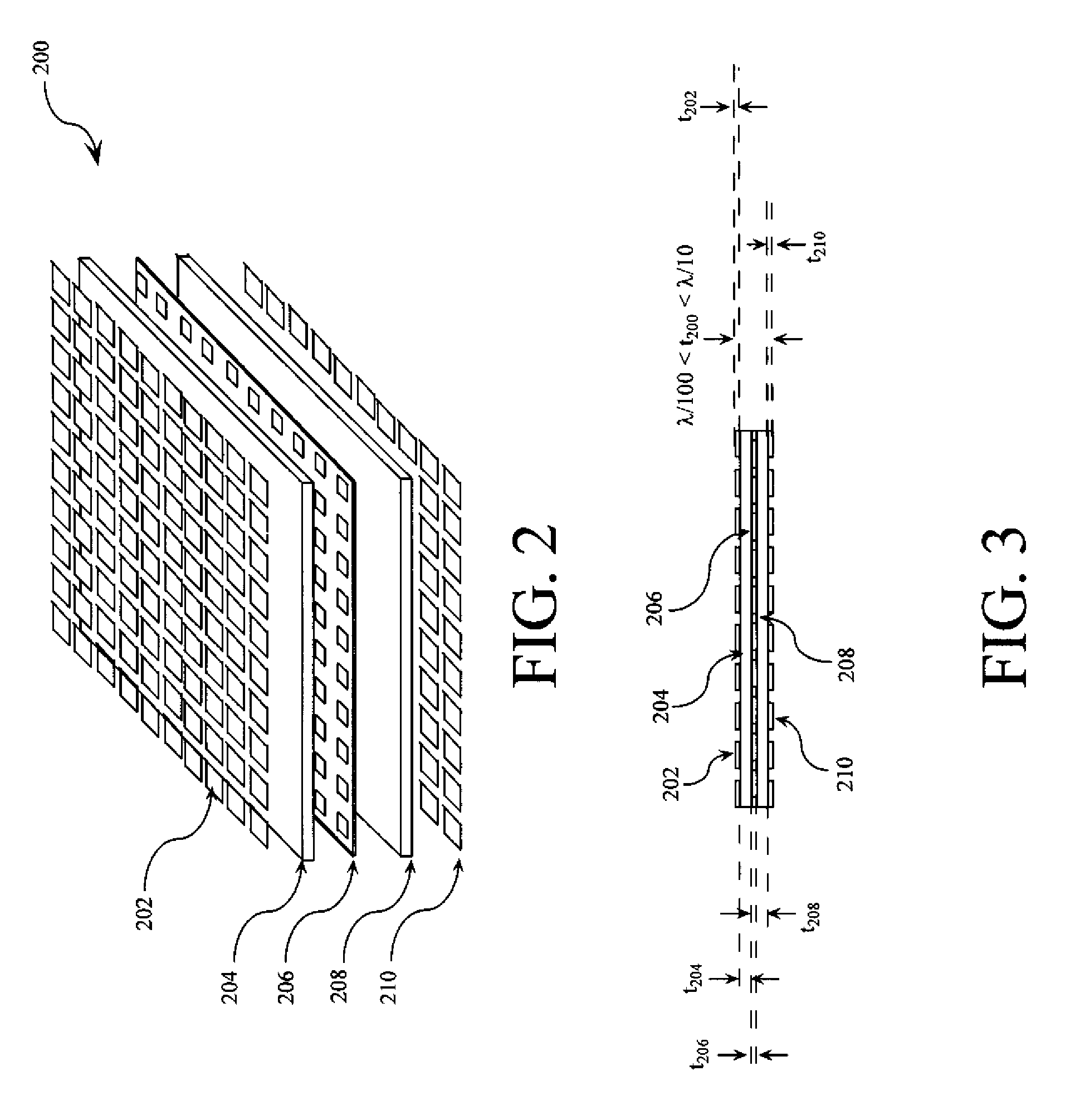
Low-profile frequency selective surface based device and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20090273527A1Antenna adaptation in movable bodiesPolarised antenna unit combinationsSelective surfaceQ factor
A frequency selective surface-based (FSS-based) device (200) for processing electromagnetic waves providing at least a third-order response. The FSS-based device includes a first FSS (202), a second FSS (210), and a high quality factor (Q) FSS (206) interposed between the first and second FSSs. A first dielectric layer (204) and a second dielectric layer (208) separate the respective FSS layers. The first and second FSSs have first and second primary resonant frequencies, respectively. The high Q FSS has a lower primary resonant frequency relative to the first and second primary resonant frequencies. The overall electrical thickness of the PSS device can be <λ / 10. The high Q FSS has a loaded quality factor of at least thirty at the lower primary resonant frequency.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
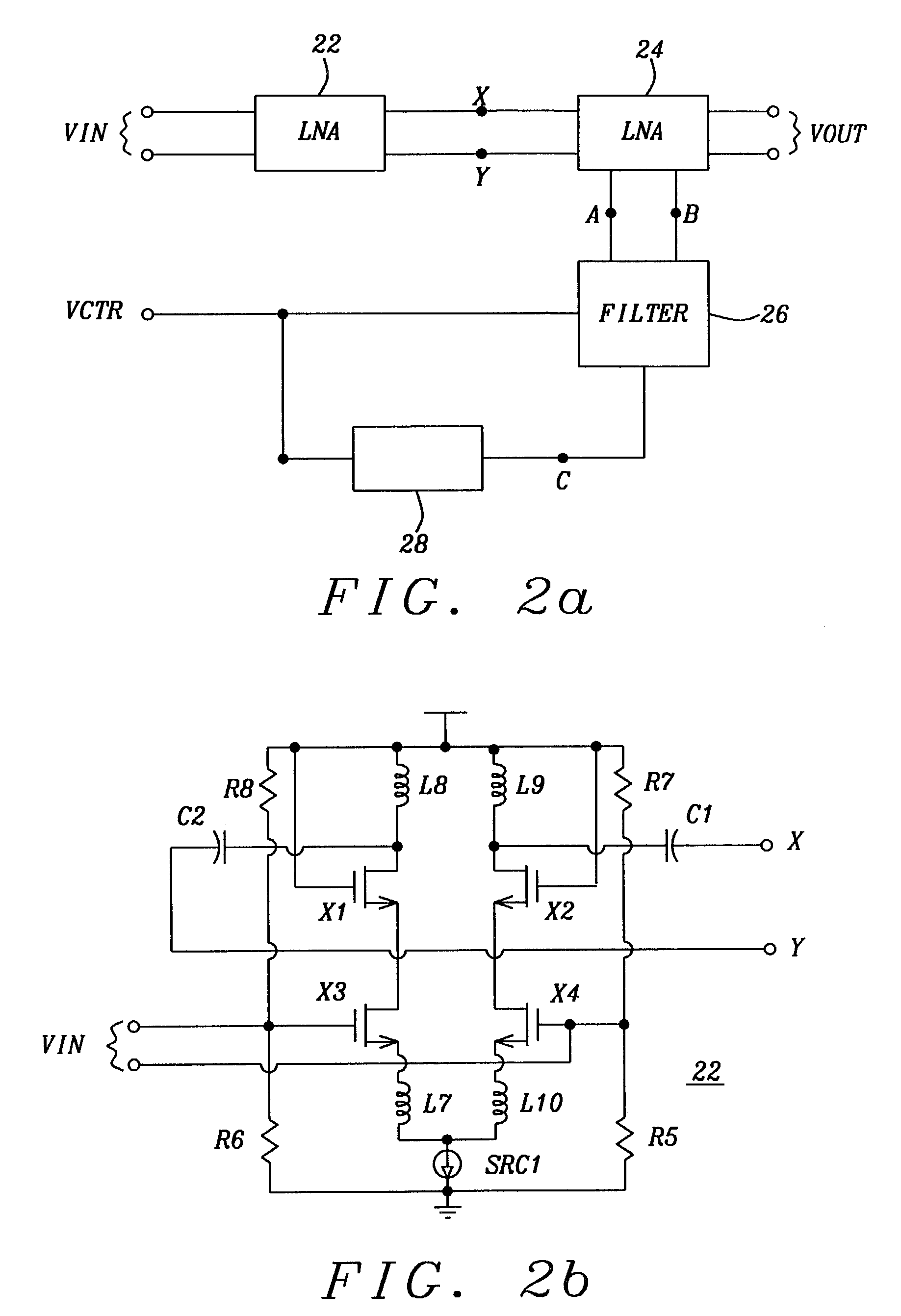
Wideband monolithic tunable high-Q notch filter for image rejection in RF application
InactiveUS6990327B2Good image rejectionWide tunable rangeMultiple-port networksTransmissionEngineeringInductor
A notch filter with a high Q factor, which is integrated with a first and a second cascoded LNA, is totally contained on an integrated chip. The notch filter, comprising two Q-enhancement circuits, is coupled to the second differential LNA. The two Q-enhancement circuits are combined to generate sufficient negative impedance to compensate for the loss in the on-chip low Q inductors. To improve the image rejection of the notch filter in a wide frequency band, the notch filter uses an automatic current tuning circuit which consists of an analog multiplier and fixed and voltage controlled current sources. Furthermore, by modifying the connection and location of the tunable varactor, another wideband tunable notch filter is implemented. The notch filter can be applied in all current wireless receiver systems.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Semiconductor chip and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20080258259A1Reduce in quantitySuppress noiseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh resistanceCapacitance
A semiconductor chip and a semiconductor device mounting the semiconductor chip capable of increasing a capacitance of a capacitor without reducing the number of signal bumps or power bumps of a package and the number of C4 solder balls of the semiconductor chip, and achieving a stable power supply with suppressing fluctuations of power at a resonance frequency without a limitation in a position to mount a capacitor for lowering noise of a signal transceiving interface block. In the semiconductor device, a via hole is provided to the semiconductor chip, a power-supply electrode connected to the via hole is provided to a back surface of the semiconductor chip, and a capacitor is mounted to the electrode on the back surface. And, a high-resistance material is used for a material of a power-supply via hole inside the semiconductor chip, thereby increasing the resistance and lowering the Q factor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
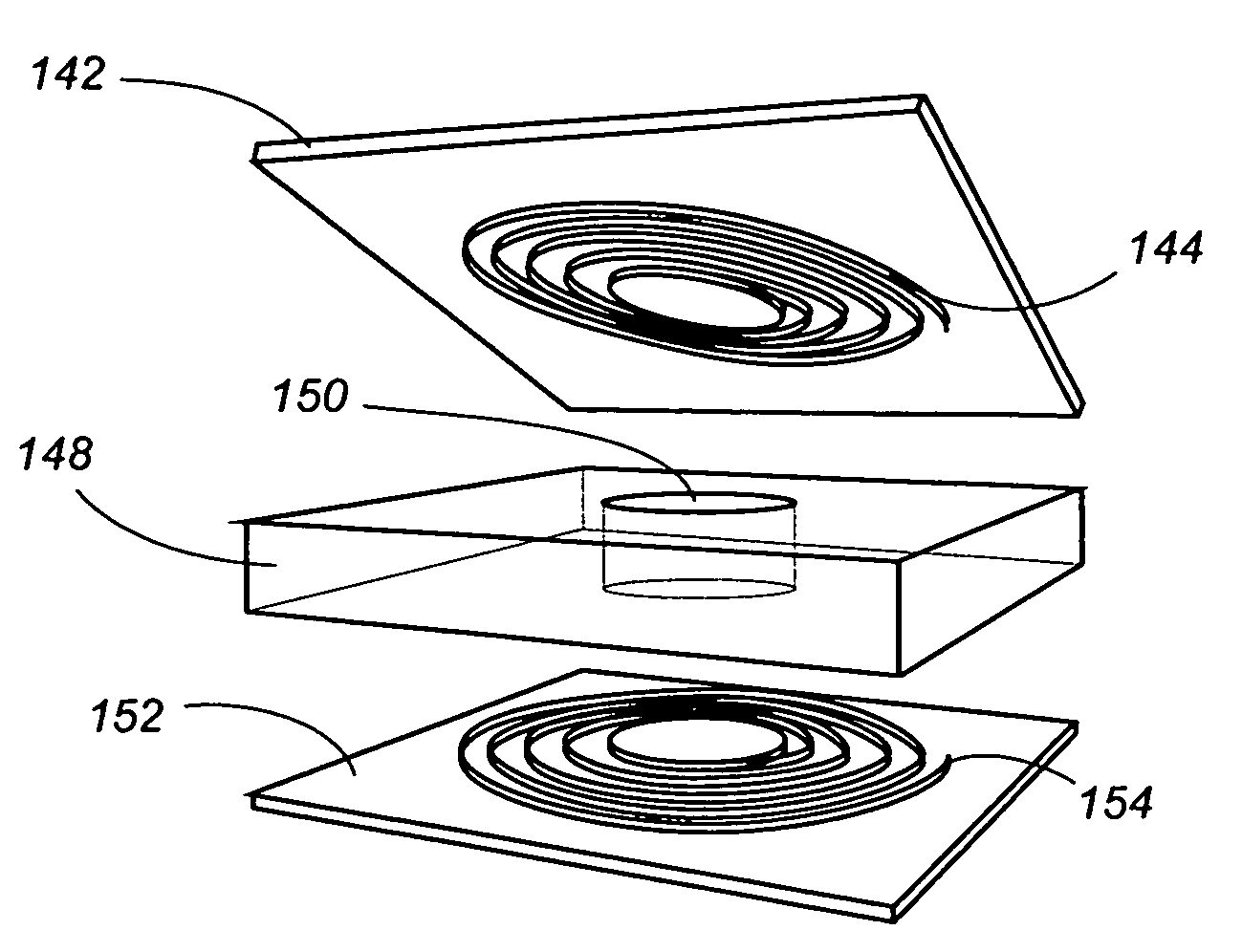
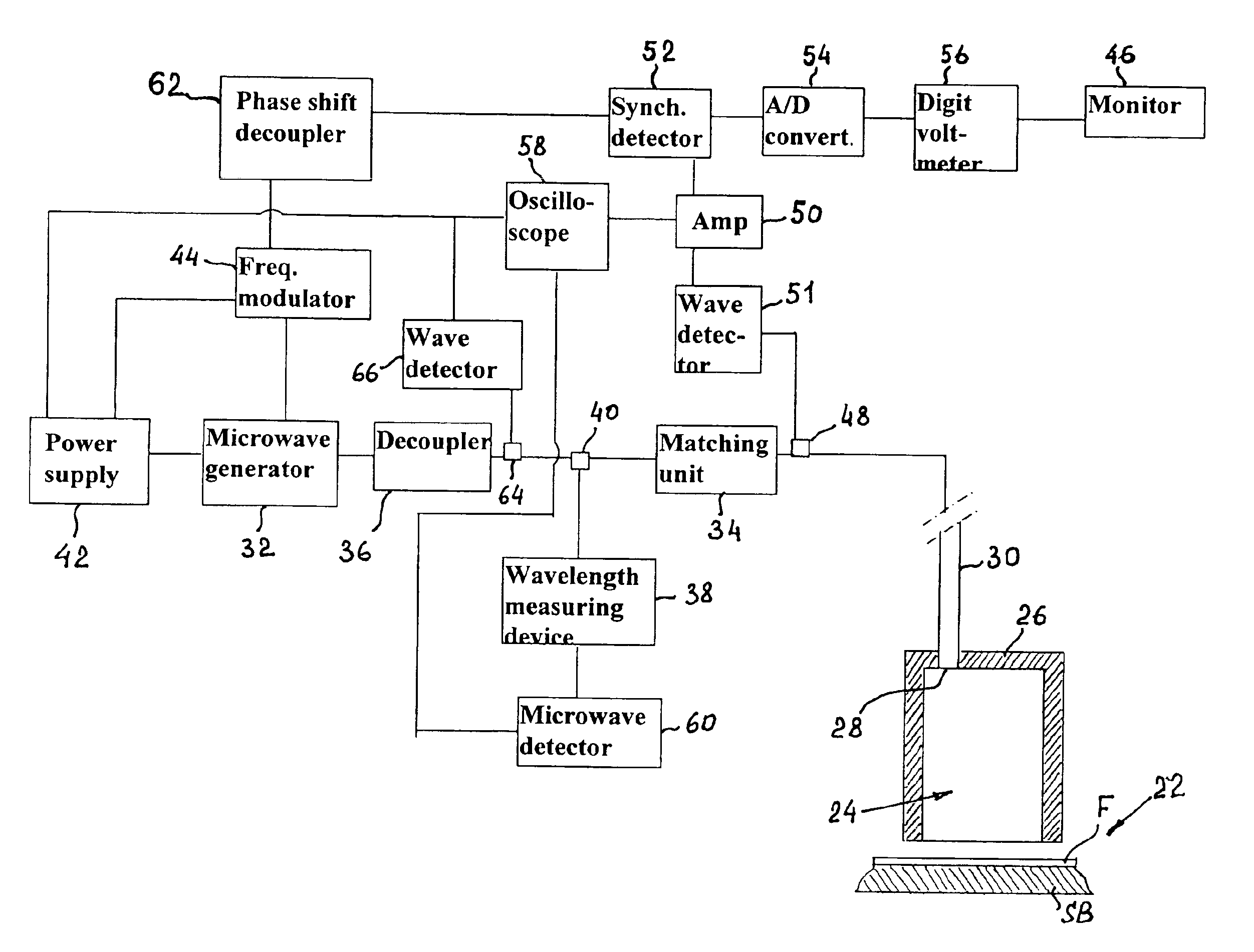
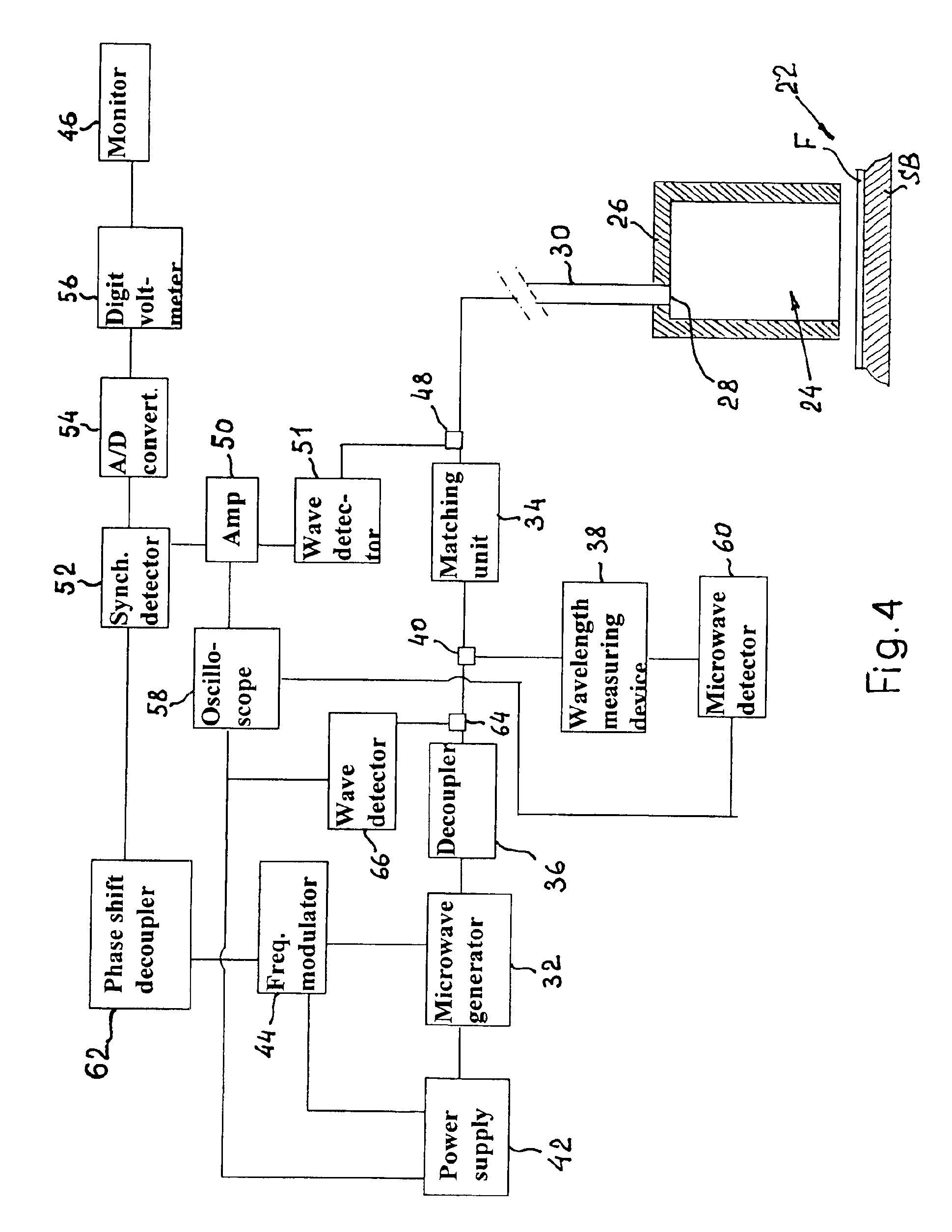
Method and apparatus for precision measurement of film thickness
InactiveUS6989675B2Inexpensive and simple and high-accurate and efficient contactless measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis by optical meansThin metalMicrowave
An apparatus for measuring thickness in super-thin films consists of a special resonator unit in the form of an open-bottom cylinder which is connected to a microwave swept frequency microwave source via a decoupler and a matching unit installed in a waveguide that connects the resonator unit with the microwave source. The apparatus operates on the principle that thin metal film F, the thickness of which is to be measured, does not contact the end face of the open bottom of the cylindrical resonator sensor unit and functions as a bottom of the cylindrical body. The design of the resonator excludes generation of modes other than the resonance mode and provides the highest possible Q-factor. As the conductivity directly related to the film thickness, it is understood that measurement of the film thickness is reduced to measurement of the resonance peak amplitudes. This means that superhigh accuracy inherent in measurement of the resonance peaks is directly applicable to the measurement of the film thickness or film thickness deviations.
Owner:MULTIMETRIXS
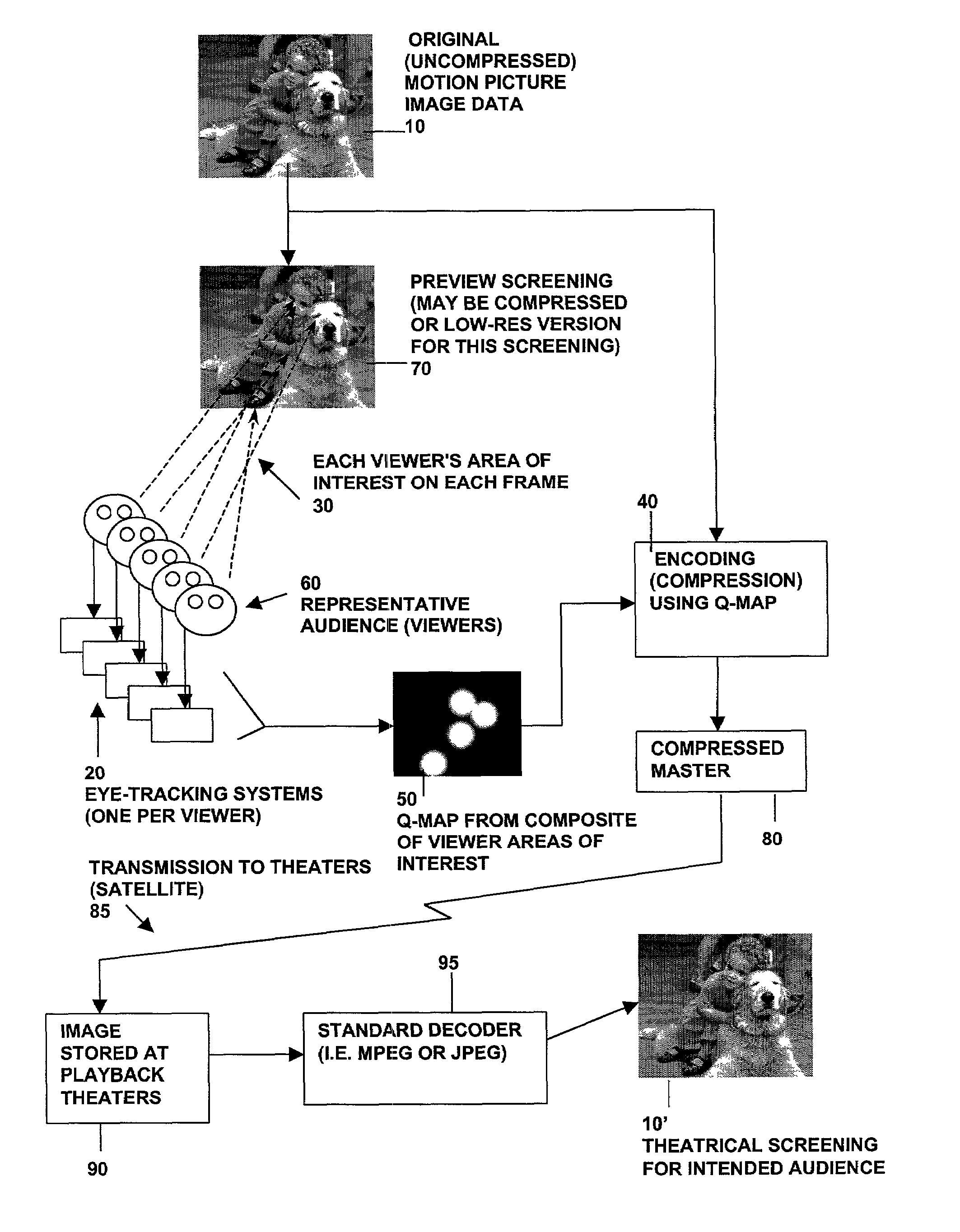
Digital image compression with spatially varying quality levels determined by identifying areas of interest
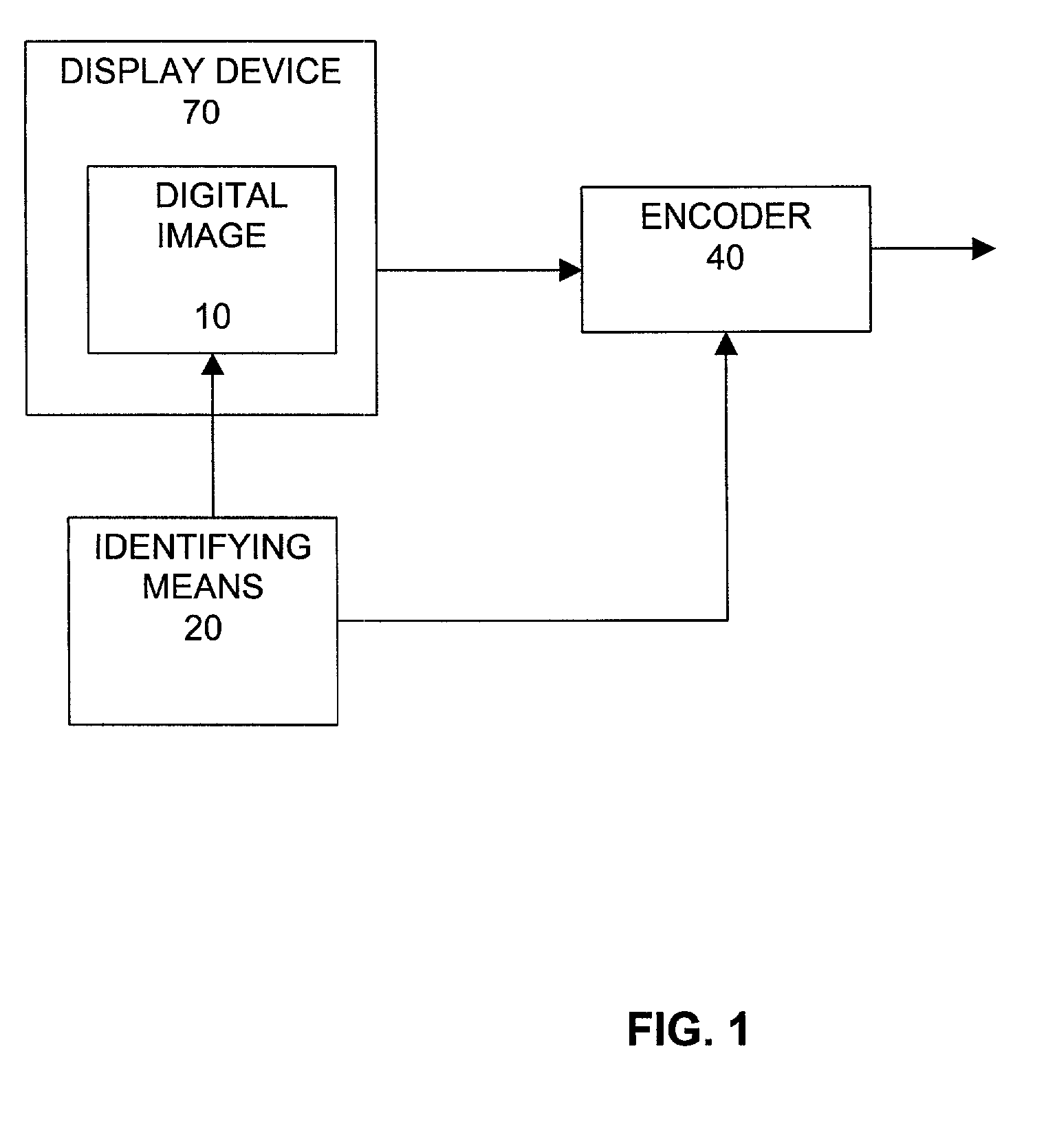
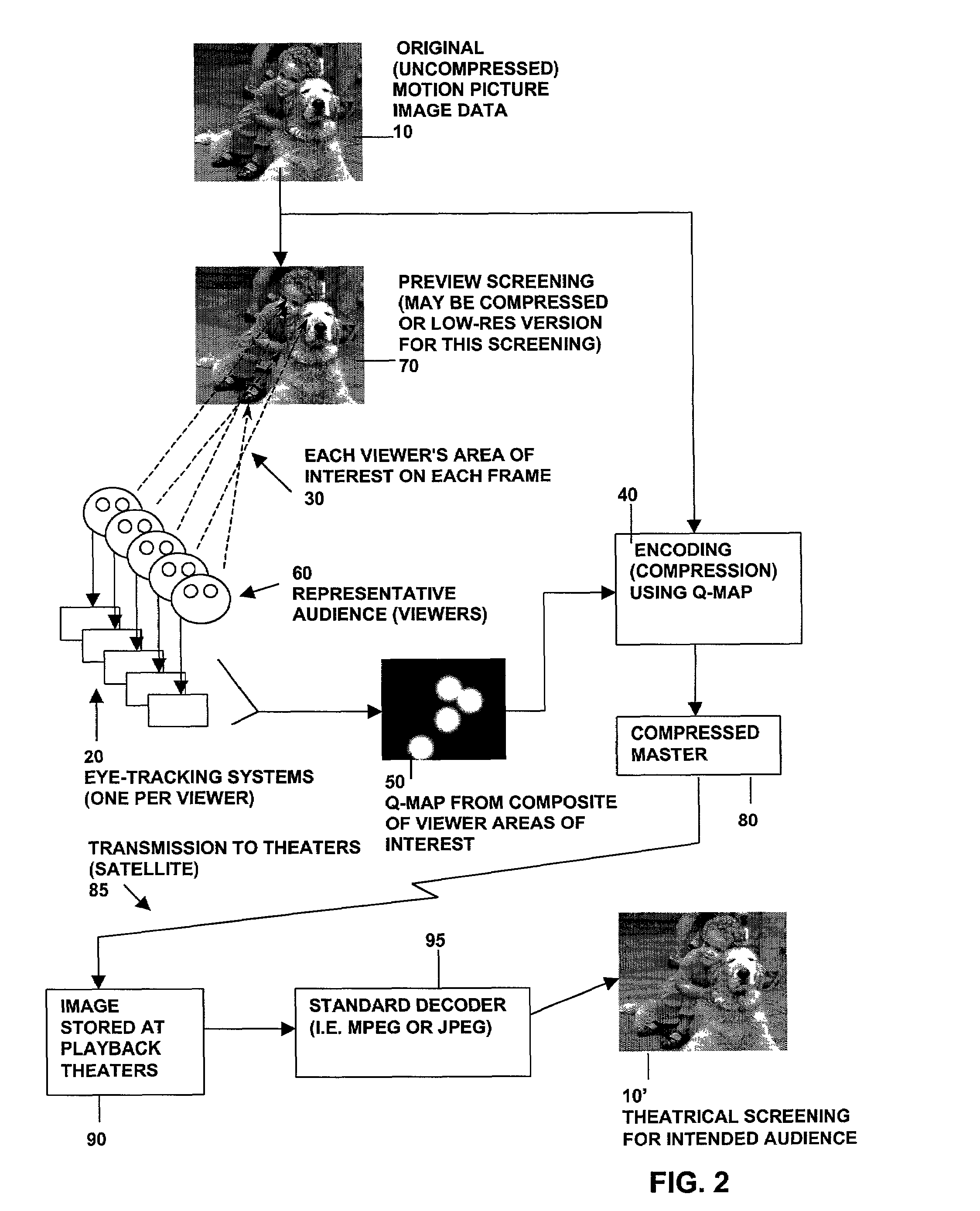
InactiveUS7027655B2Low bit rateLower quality factorAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionQuality levelDigital image compression
Methods and systems for compression of digital images (still or motion sequences) are provided wherein predetermined criteria may be used to identify a plurality of areas of interest in the image, and each area of interest is encoded with a corresponding quality level (Q-factor). In particular, the predetermined criteria may be derived from measurements of where a viewing audience is focusing their gaze (area of interest). In addition, the predetermined criteria may be used to create areas of interest in an image in order to focus an observer's attention to that area. Portions of the image outside of the areas of interest are encoded at a lower quality factor and bit rate. The result is higher compression ratios without adversely affecting a viewer's perception of the overall quality of the image.
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING
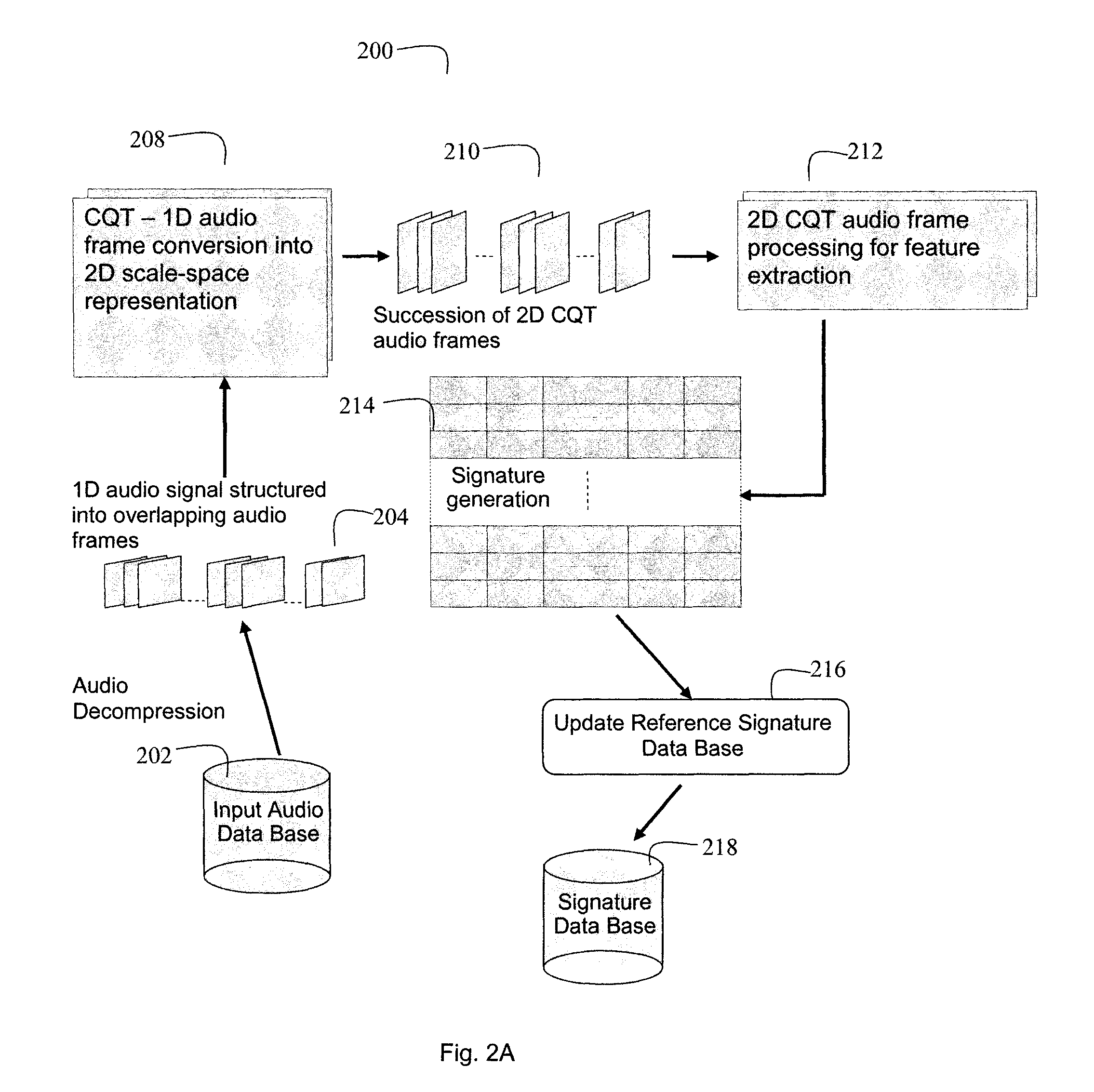
Audio content fingerprinting based on two-dimensional constant Q-factor transform representation and robust audio identification for time-aligned applications
ActiveUS9299364B1Speech analysisSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumSpectral bands
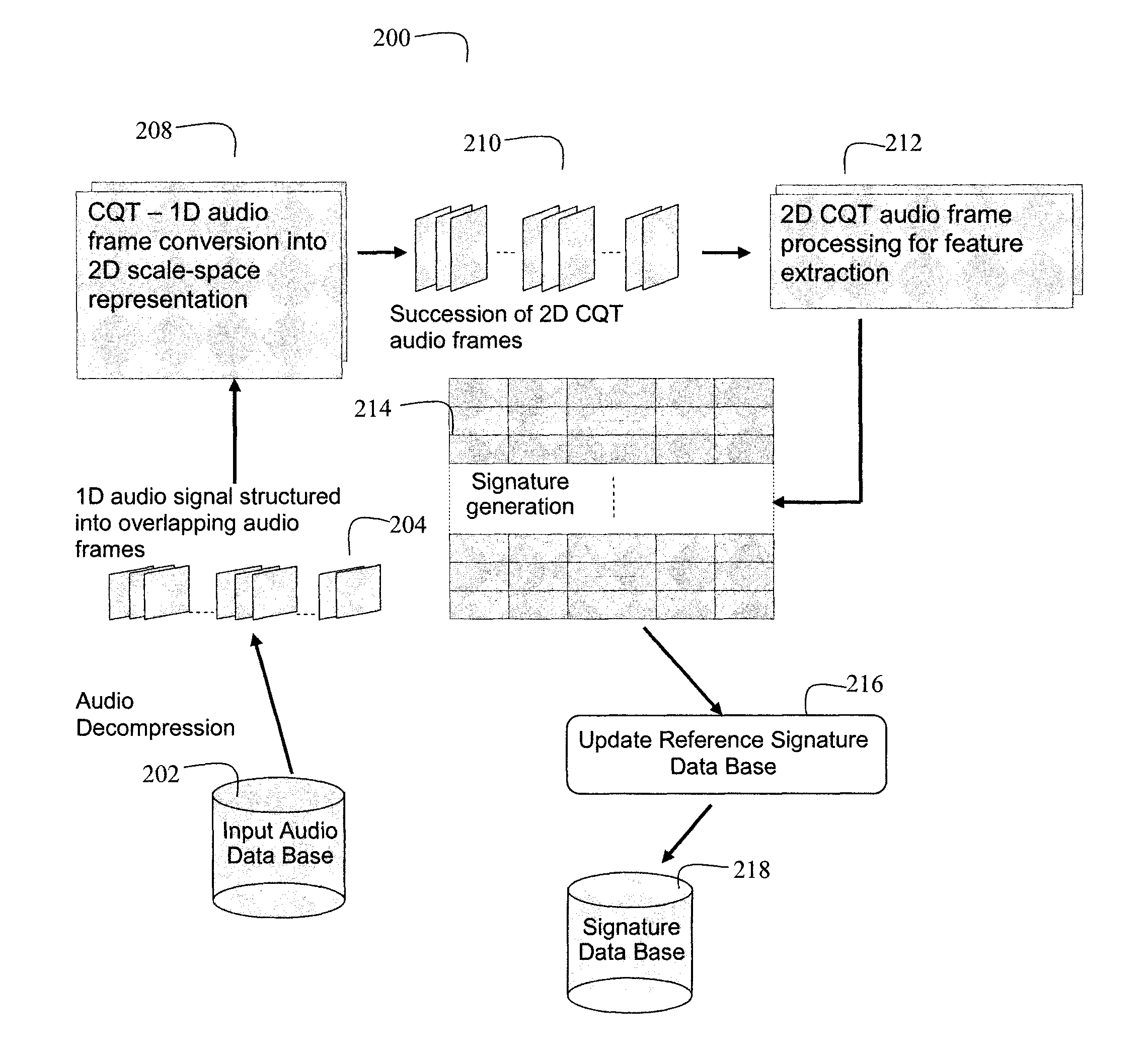
Content identification methods for consumer devices determine robust audio fingerprints that are resilient to audio distortions. One method generates signatures representing audio content based on a constant Q-factor transform (CQT). A 2D spectral representation of a 1D audio signal facilitates generation of region based signatures within frequency octaves and across the entire 2D signal representation. Also, points of interest are detected within the 2D audio signal representation and interest regions are determined around selected points of interest. Another method generates audio descriptors using an accumulating filter function on bands of the audio spectrum and generates audio transform coefficients. A response of each spectral band is computed and transform coefficients are determined by filtering, by accumulating derivatives with different lags, and computing second order derivatives. Additionally, time and frequency based onset detection determines audio descriptors at events and enhances descriptors with information related to an event.
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
Secure wireless energy transfer in medical applications
InactiveUS9106203B2Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit monitoring/indicationEnergy transferAuthorization
A medical device-powering wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply includes a load configured to power the medical device using electrical power, and a second electromagnetic resonator adapted to be housed within the medical device and configured to be coupled to the load, wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator; wherein the square root of the product of the respective Q factors is greater than 100; and an authorization facility to confirm compatibility of the resonators and provide authorization for initiation of transfer of power.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Dielectric filter, antenna duplexer
InactiveUS6965284B2Reduce lossSpeed up the descentMultiple-port networksResonatorsMetallic foilCoupling
A dielectric filter includes resonator electrodes, an inter-stage coupling capacitor electrode, and an input / output coupling capacitor electrode on dielectric substrates, respectively. The resonator electrodes are electro-magnetically coupled to each other to form a tri-plate structure, are made of a metallic foil embedded in a resonator dielectric substrate. Another dielectric filter includes an upper shield electrode dielectric substrate, an inter-stage coupling capacitor dielectric substrate, a resonator dielectric substrate, and an input / output coupling capacitor dielectric substrate which are made of a composite dielectric material including a high-dielectric-constant material and a low-dielectric-constant material. The above described arrangement provides the dielectric filter with an improved Q factor of a resonator, a low loss, and a high attenuation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
RF power amplifier
ActiveUS20100117737A1Lower input impedanceLow costPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersTransformerCoupling
A reduction is achieved in the primary-side input impedance of a transformer (voltage transformer) as an output matching circuit without involving a reduction in Q-factor. An RF power amplifier includes transistors, and a transformer as the output matching circuit. The transformer has a primary coil and a secondary coil which are magnetically coupled to each other. To the input terminals of the transistors, respective input signals are supplied. The primary coil is coupled to each of the output terminals of the transistors. From the secondary coil, an output signal is generated. The primary coil includes a first coil and a second coil which are coupled in parallel between the respective output terminals of the transistors, and each magnetically coupled to the secondary coil. By the parallel coupling of the first and second coils of the primary coil, the input impedance of the primary coil is reduced.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
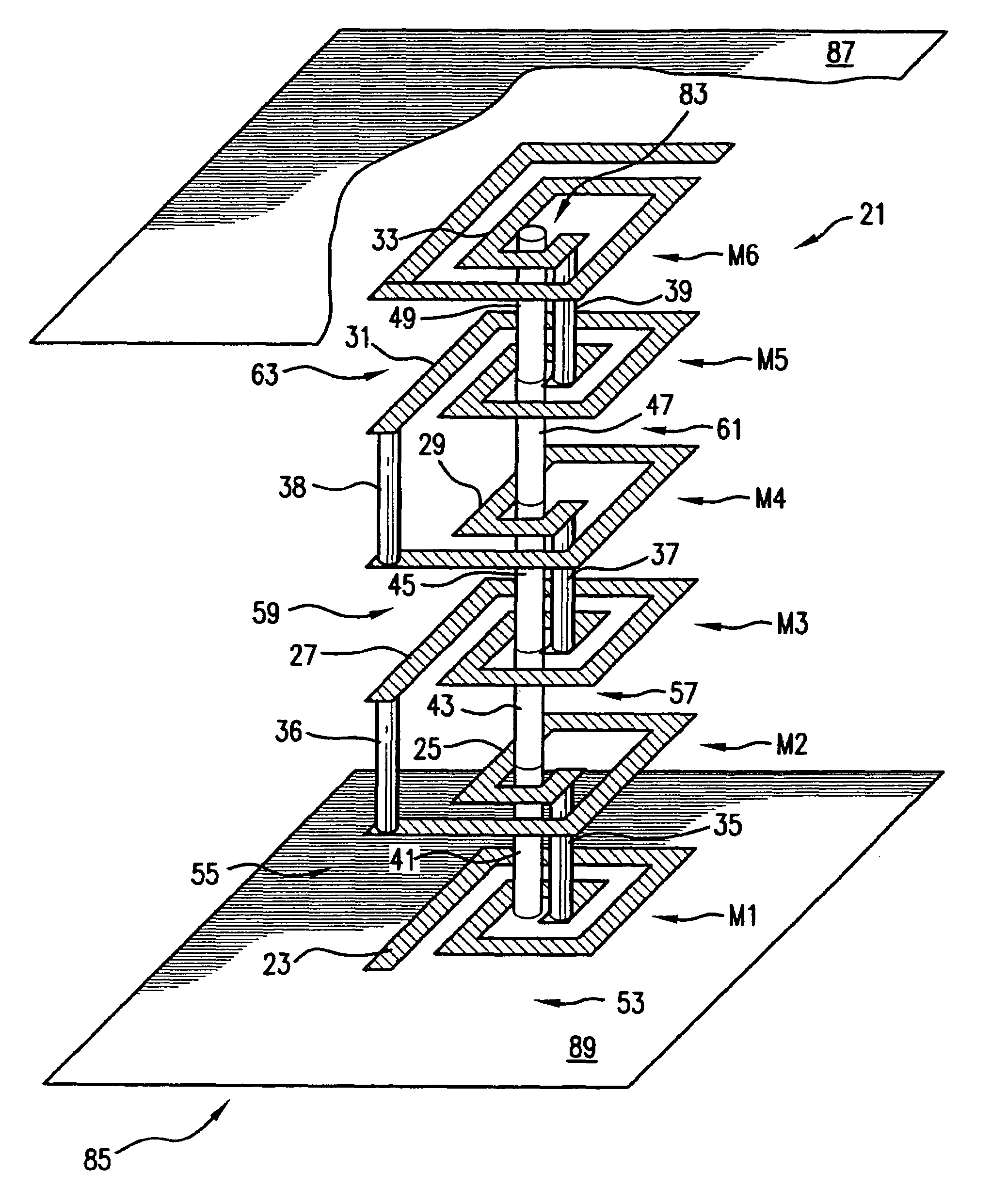
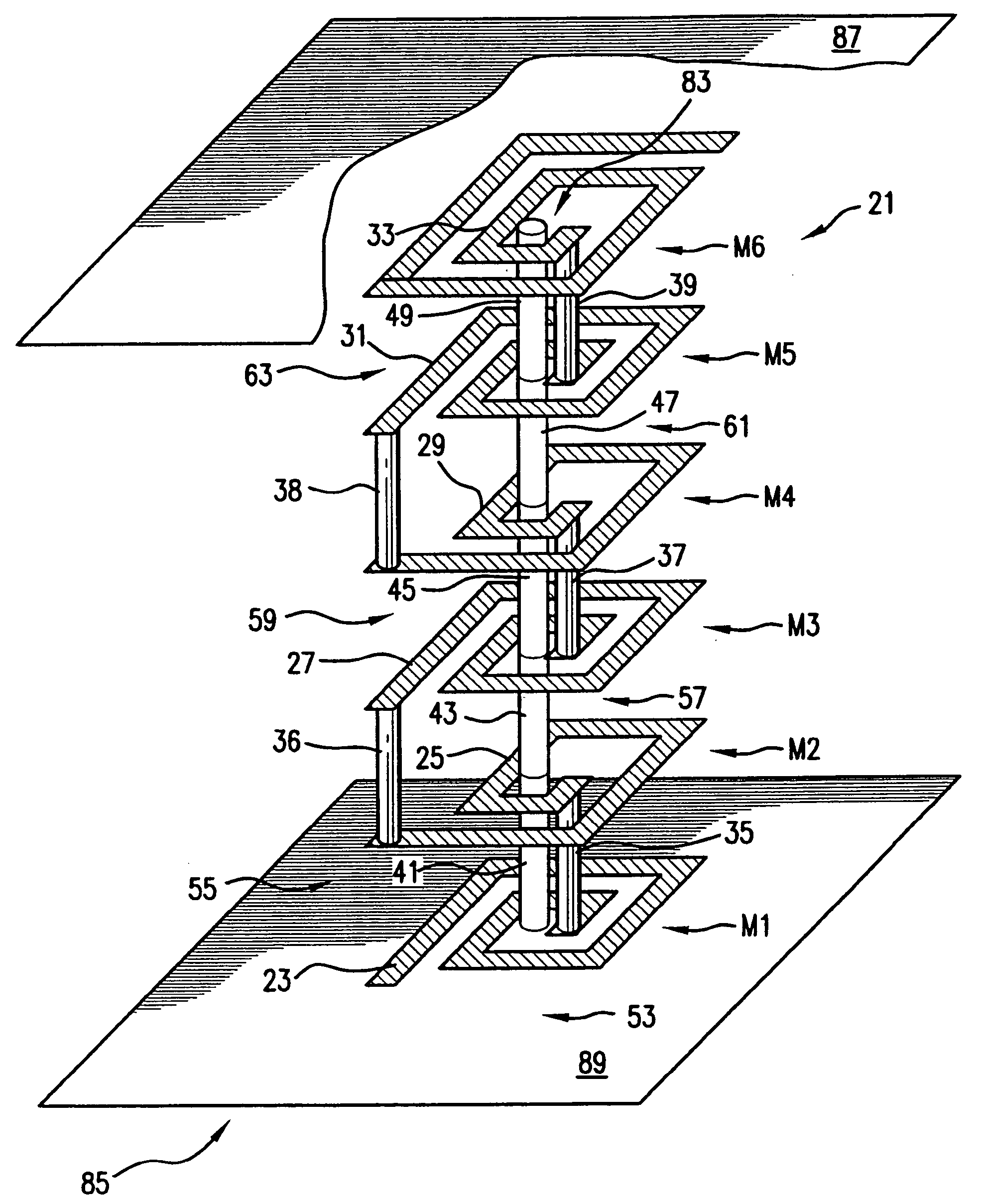
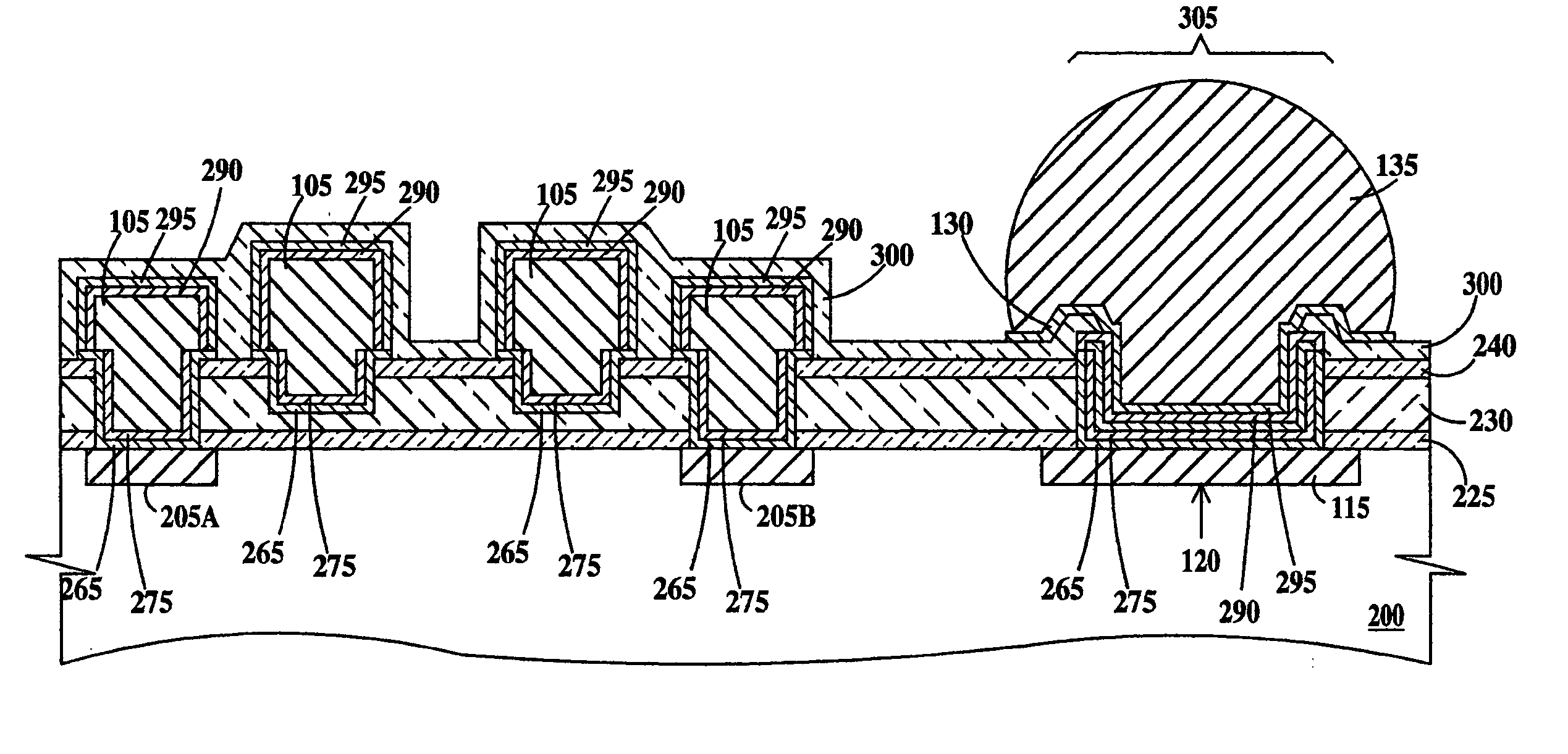
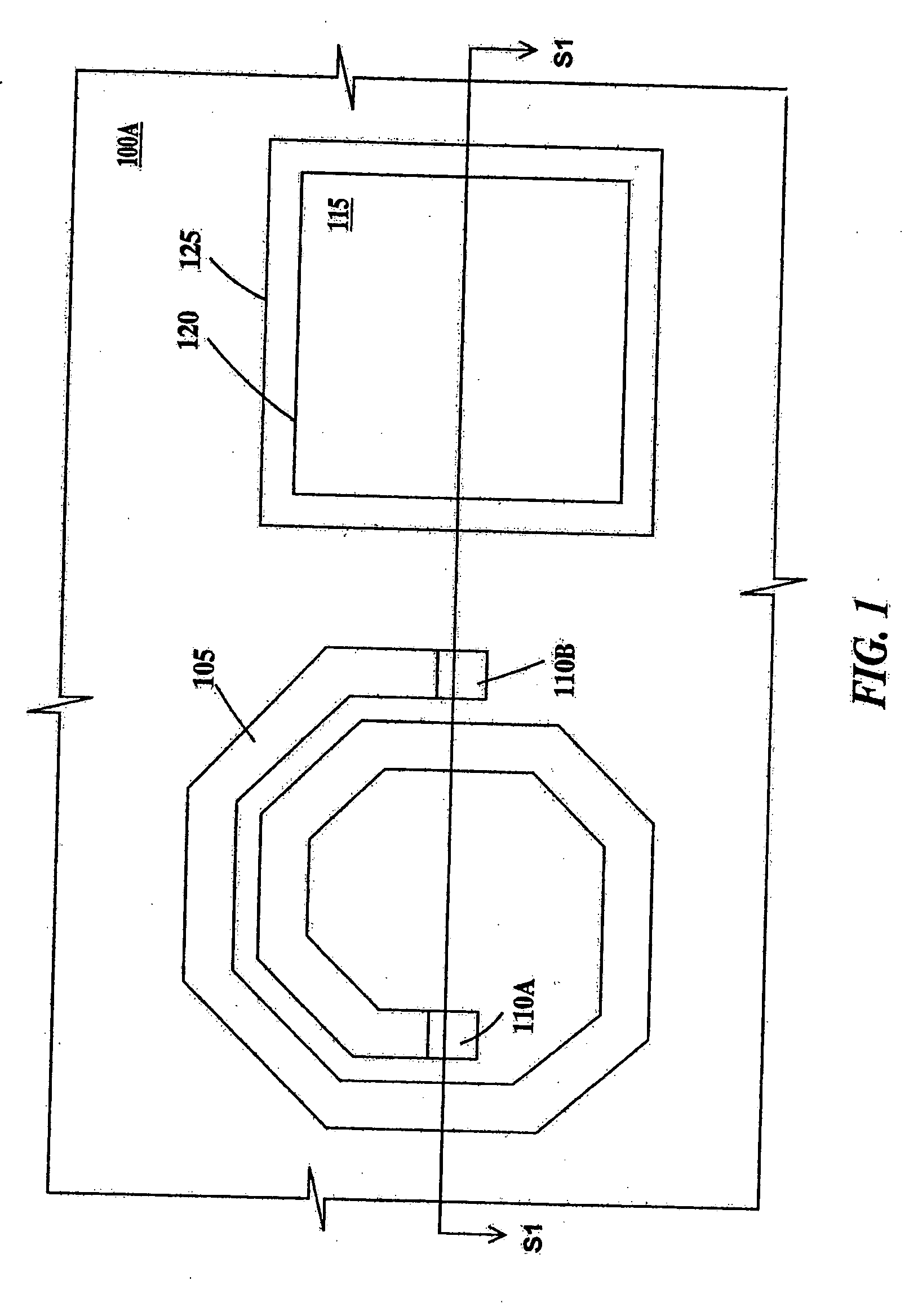
High Q factor integrated circuit inductor
ActiveUS20050167780A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsResistElectrical conductor
An inductor and a method of forming and the inductor, the method including: (a) providing a semiconductor substrate; (b) forming a dielectric layer on a top surface of the substrate; (c) forming a lower trench in the dielectric layer; (d) forming a resist layer on a top surface of the dielectric layer; (e) forming an upper trench in the resist layer, the upper trench aligned to the lower trench, a bottom of the upper trench open to the lower trench; and (f) completely filling the lower trench at least partially filling the upper trench with a conductor in order to form the inductor. The inductor including a top surface, a bottom surface and sidewalls, a lower portion of said inductor extending a fixed distance into a dielectric layer formed on a semiconductor substrate and an upper portion extending above said dielectric layer; and means to electrically contact said inductor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Integrated circuit inductors
InactiveUS7135951B1Q-factor of the integrated circuit may be enhancedLower on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsDielectricElectrical resistance and conductance
Integrated circuit inductors may be formed using a spiral layout on the surface of an interconnect dielectric stack. Conductive lines from two or more metal layers in the interconnect stack may be electrically connected using one or more via trenches. The via trench interconnection arrangement reduces the resistance of the inductor and increases the inductor's Q-factor. The Q-factor of the inductor may also be increased by placing a region of n-type and p-type wells or a metal plate region beneath the inductor to reduce power losses during operation. Shallow trench isolation may be used to reduce eddy currents and increase Q. The effects of copper dishing and trench blow-out may be used during inductor fabrication. A dual damascene fabrication process may be used.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
System and method for selecting transmission format using effective SNR
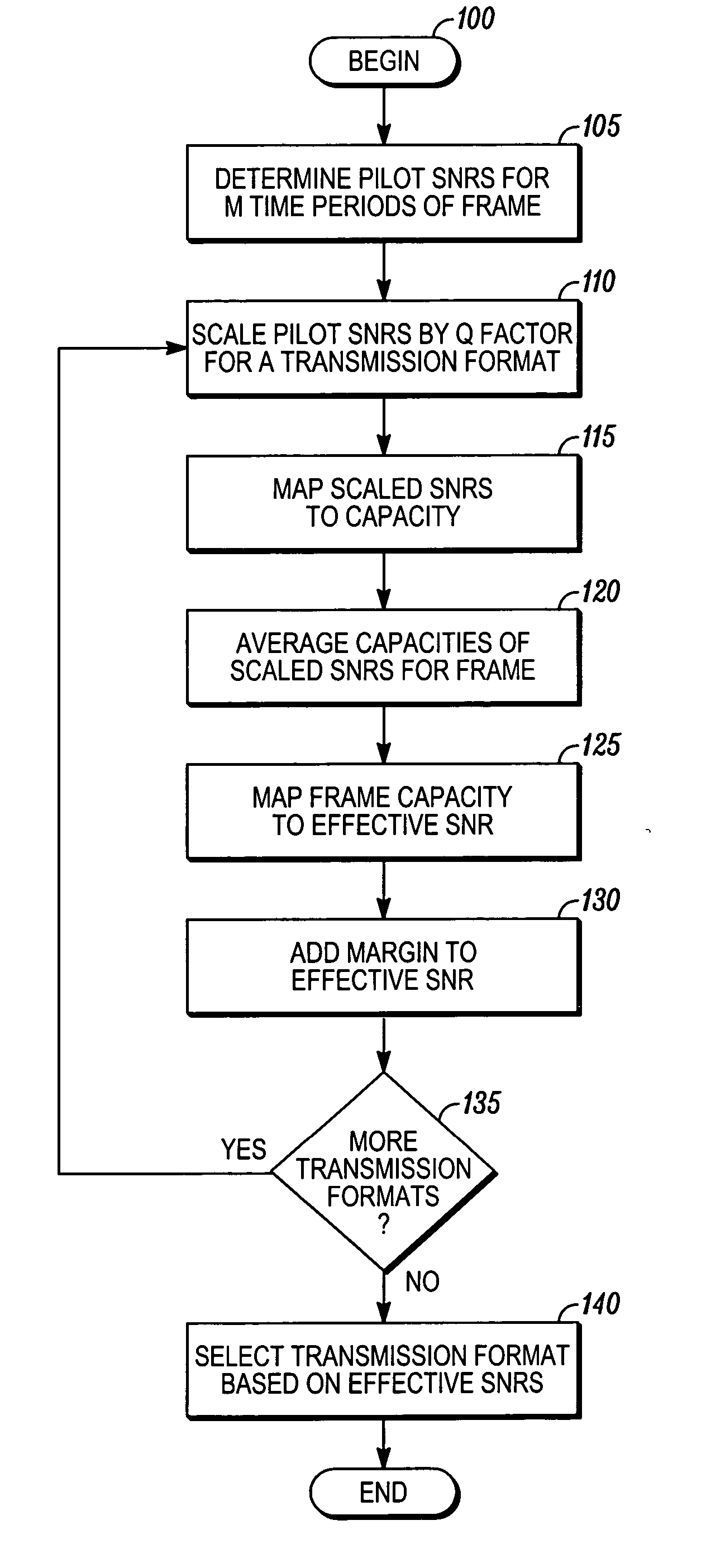
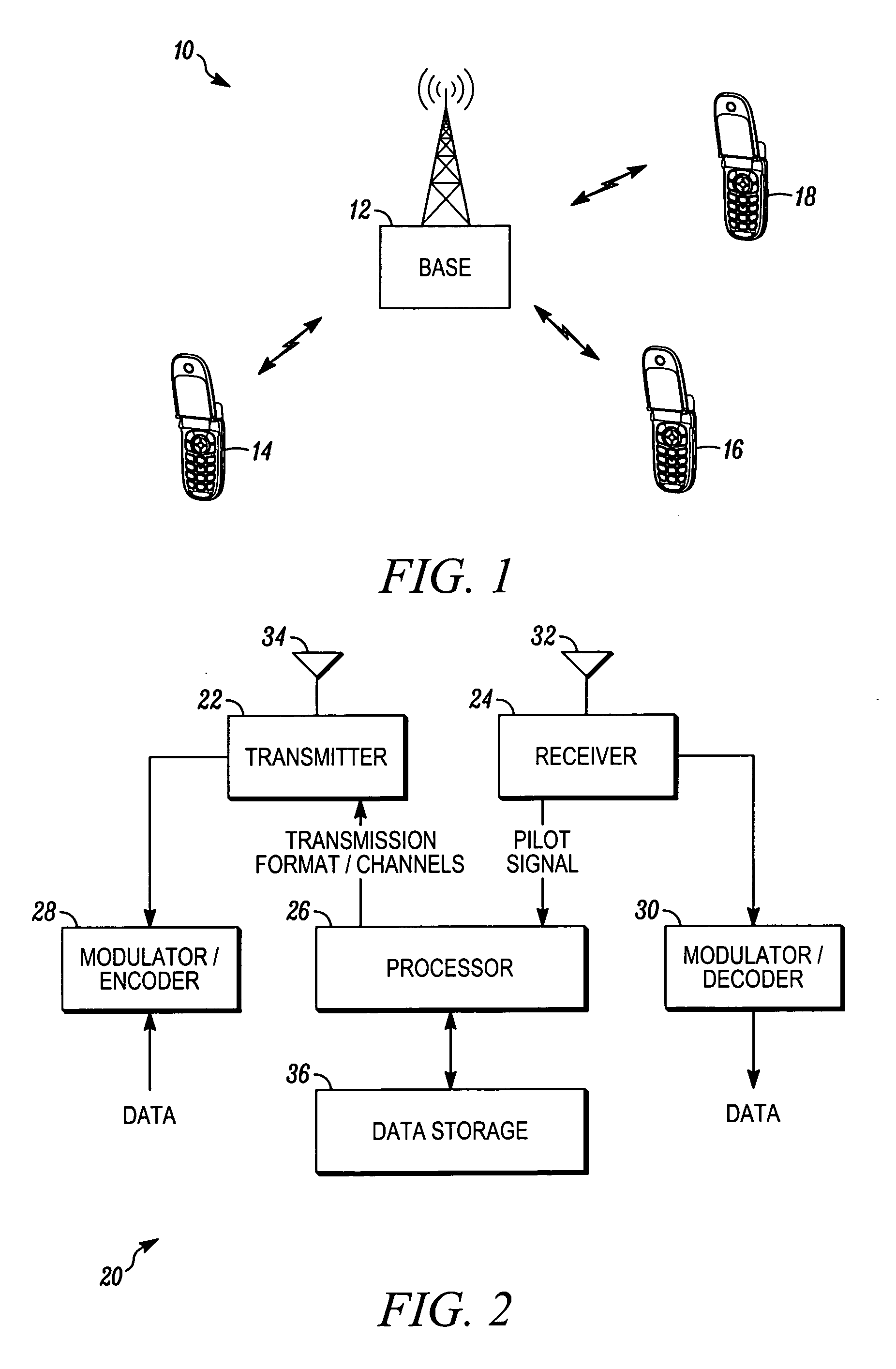
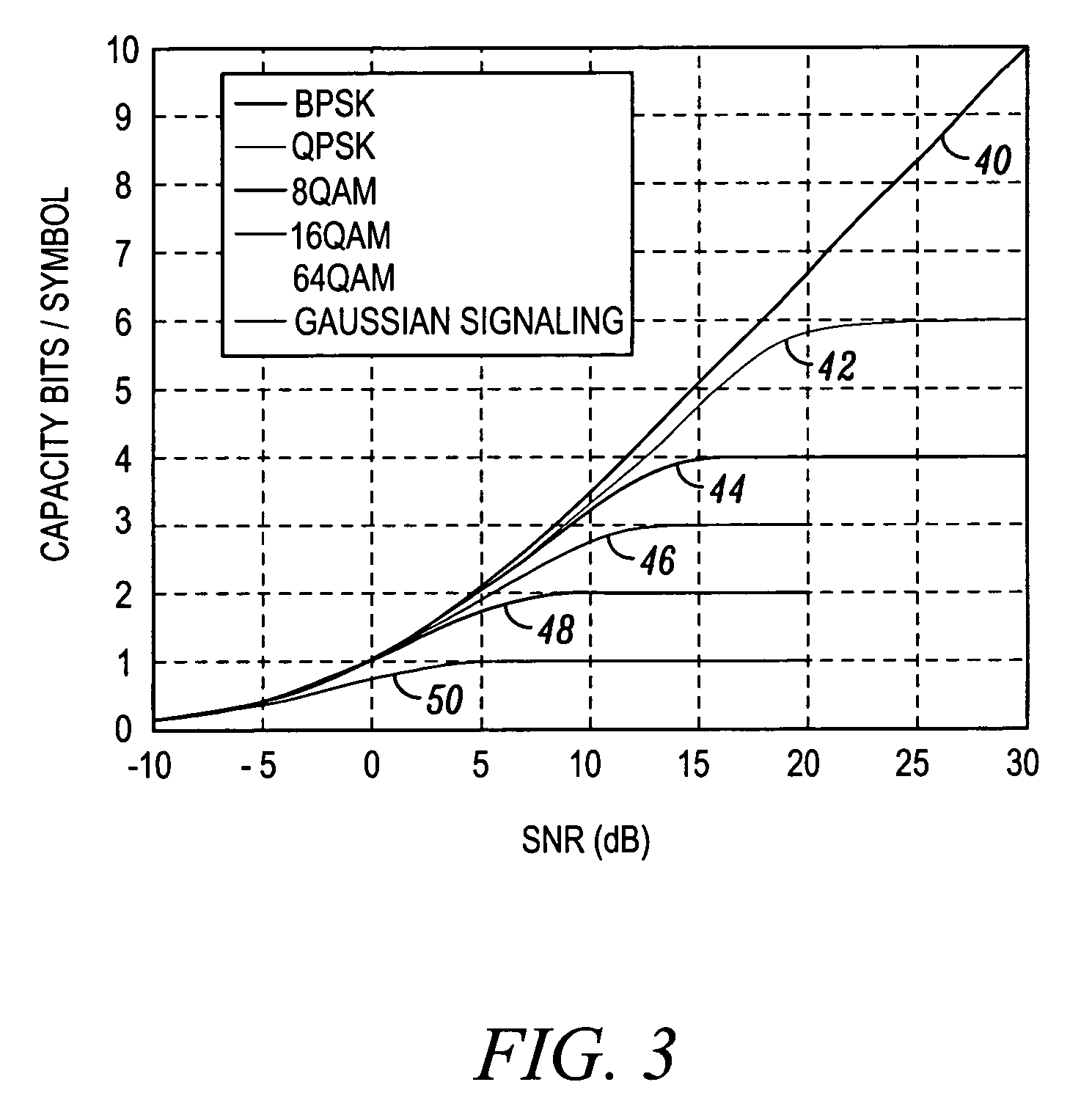
InactiveUS20070076810A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationTime segmentDistributed computing
Methods and systems are provided for determining a transmission format using an effective SNR. The method comprises determining (105) a pilot SNR for at least one time period in a frame, mapping (110, 115, 120, and 125) the scaled SNRs of the frame to a second SNR for at least one transmission format, and selecting (130) the transmission format based on the second SNRs. The system comprises a receiver (24) configured to detect pilot signals, a data storage (36), and a processor (26) coupled to the receiver and data storage. The data storage (36) comprises tables of capacity mapping functions and Q factors for each transmission format The processor (26) comprises a set of instructions to convert SNRs of different pilot signals to a second SNR using the tables and Q factors and select the transmission format based on the second SNR.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
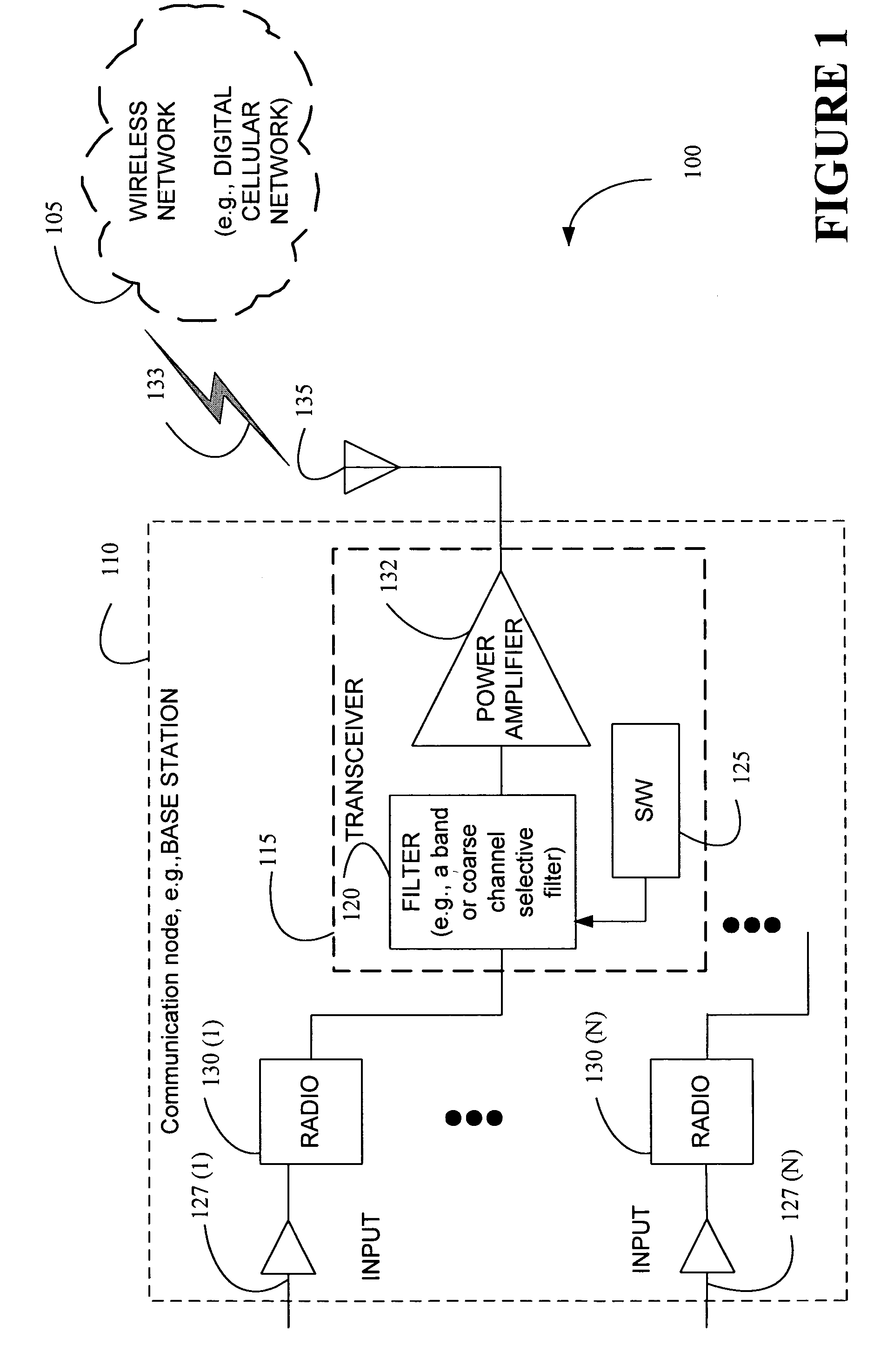
Controlling Q-factor of filters
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for controlling a Q-factor for a filter. The method comprises stabilizing an active feedback to provide a variable feedback in a filter, varying the active feedback based on an input signal to the filter, and producing a desired Q-factor for the filter at a first frequency band, in response to the variable feedback. The method further comprises reconfiguring a center frequency and a bandwidth of the filter based on a channel bandwidth of the input signal to the filter to adjust the Q-factor for the filter in response to a second frequency band different than the first frequency band. By reconfiguring a center frequency and a bandwidth of a filter, the Q-factor for the filter, such as a flexible or reconfigurable filter, may be controlled across a multiplicity of frequency band signals. Using software, for example, a common signal path may be provided for the multiplicity of frequency band signals within a frequency agile radio of a base station by tuning the radio based on a variable feedback through realization of a negative parallel resistance. Thus, tuneability of the Q-factor may provide frequency agile radios that include flexible or reconfigurable filters in a base station to serve different frequency bands without changing hardware. In this way, significant savings associated with frequency agility may be obtained.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com