Patents
Literature
108 results about "Spectral representation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
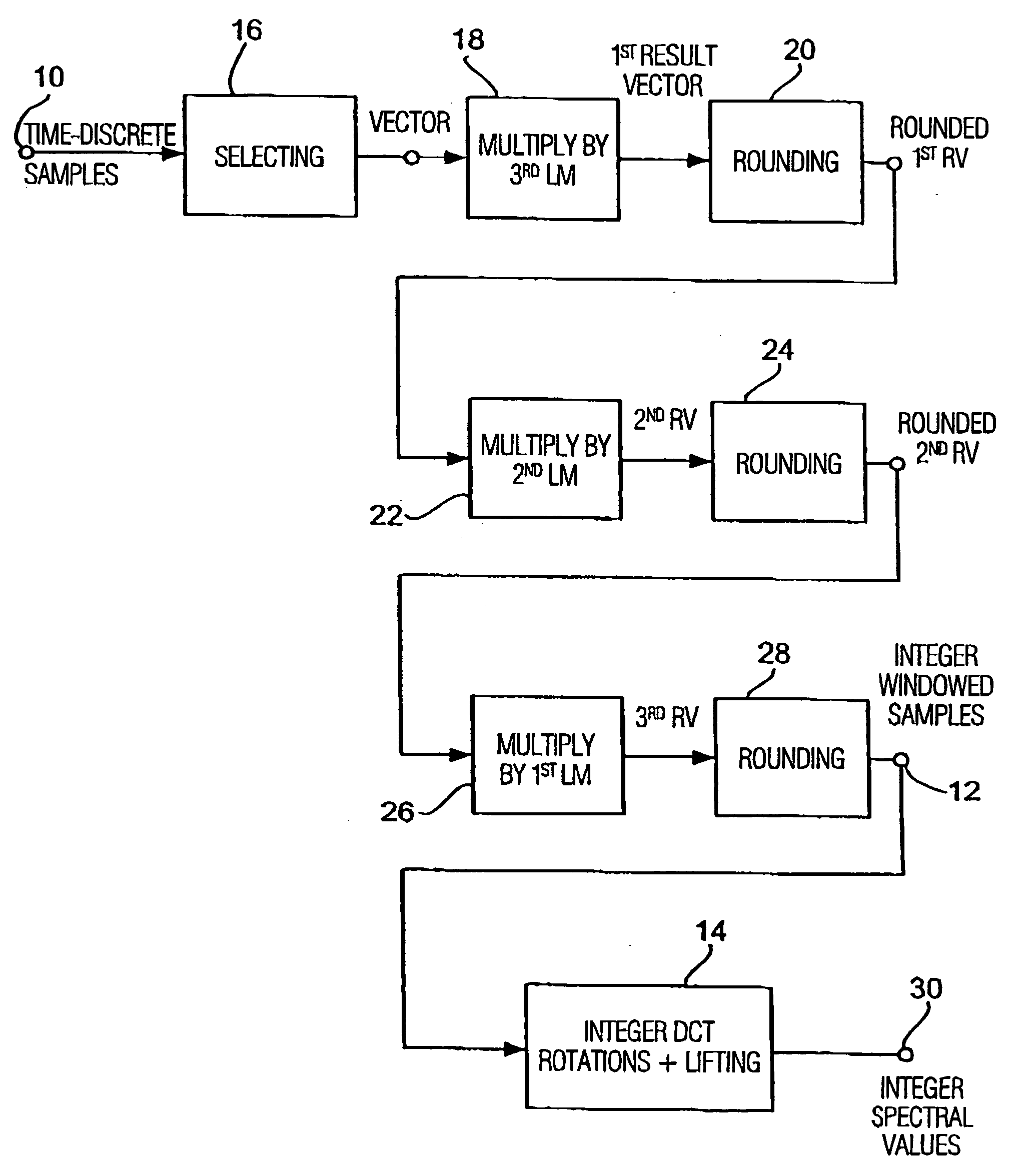
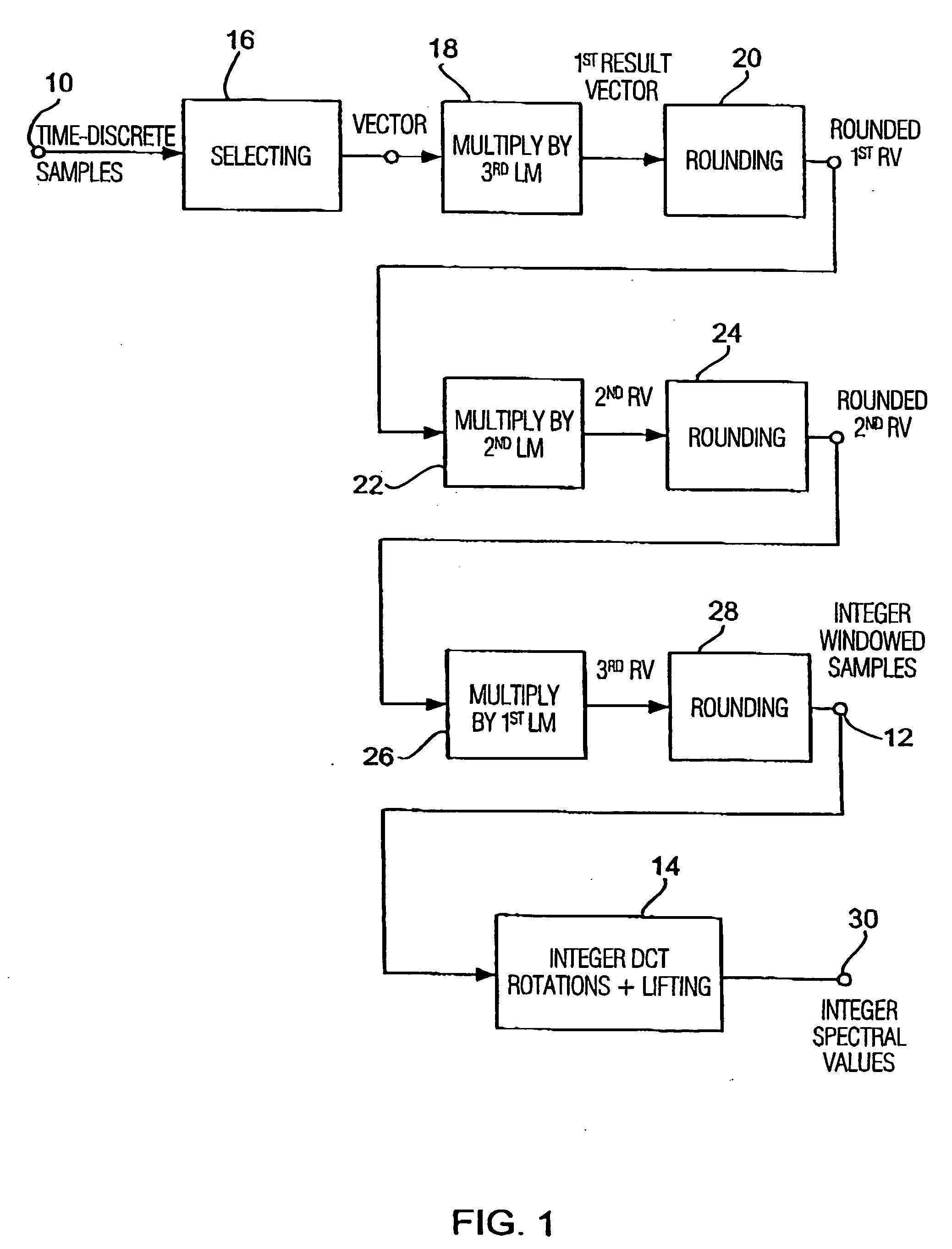
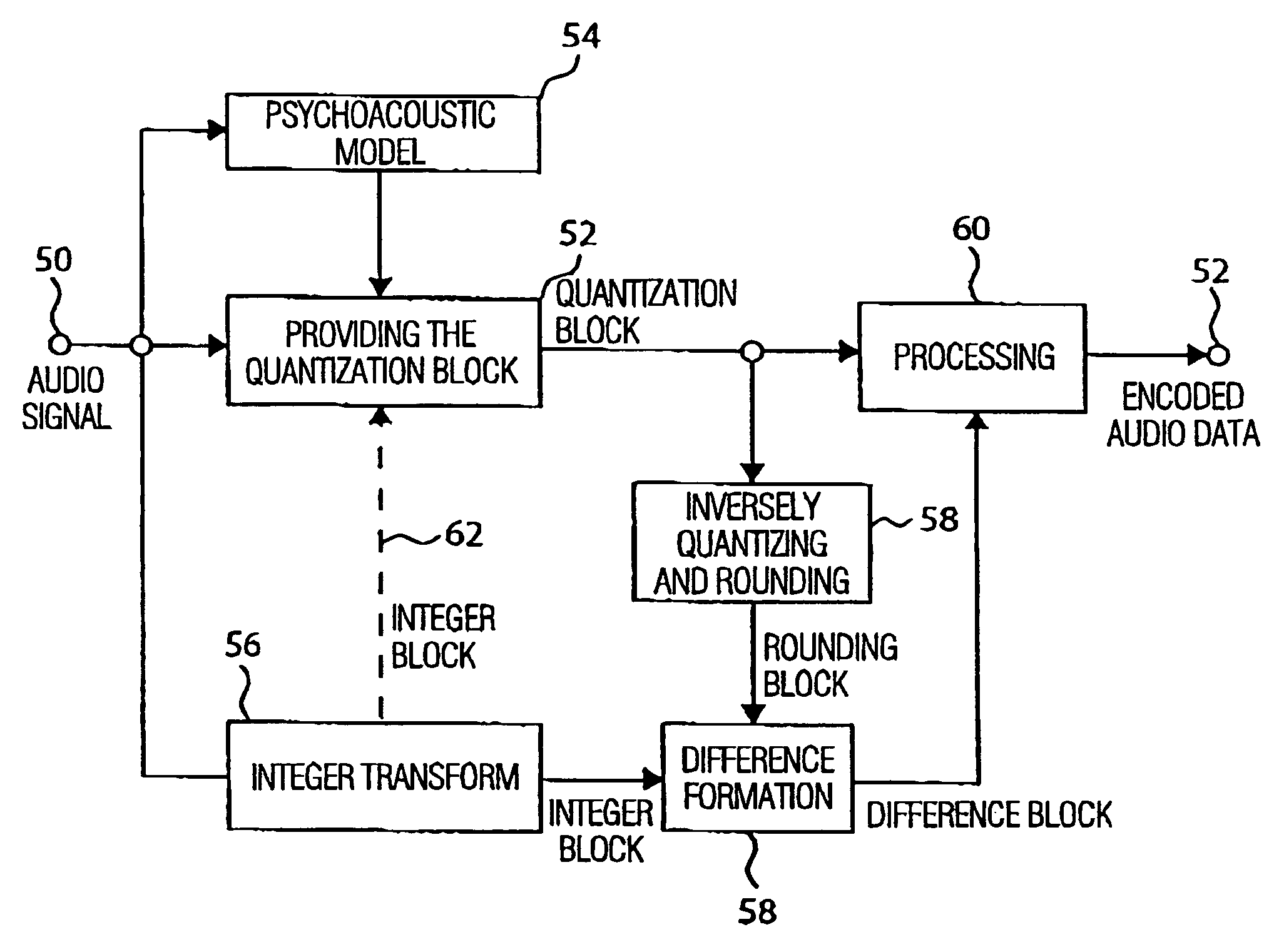
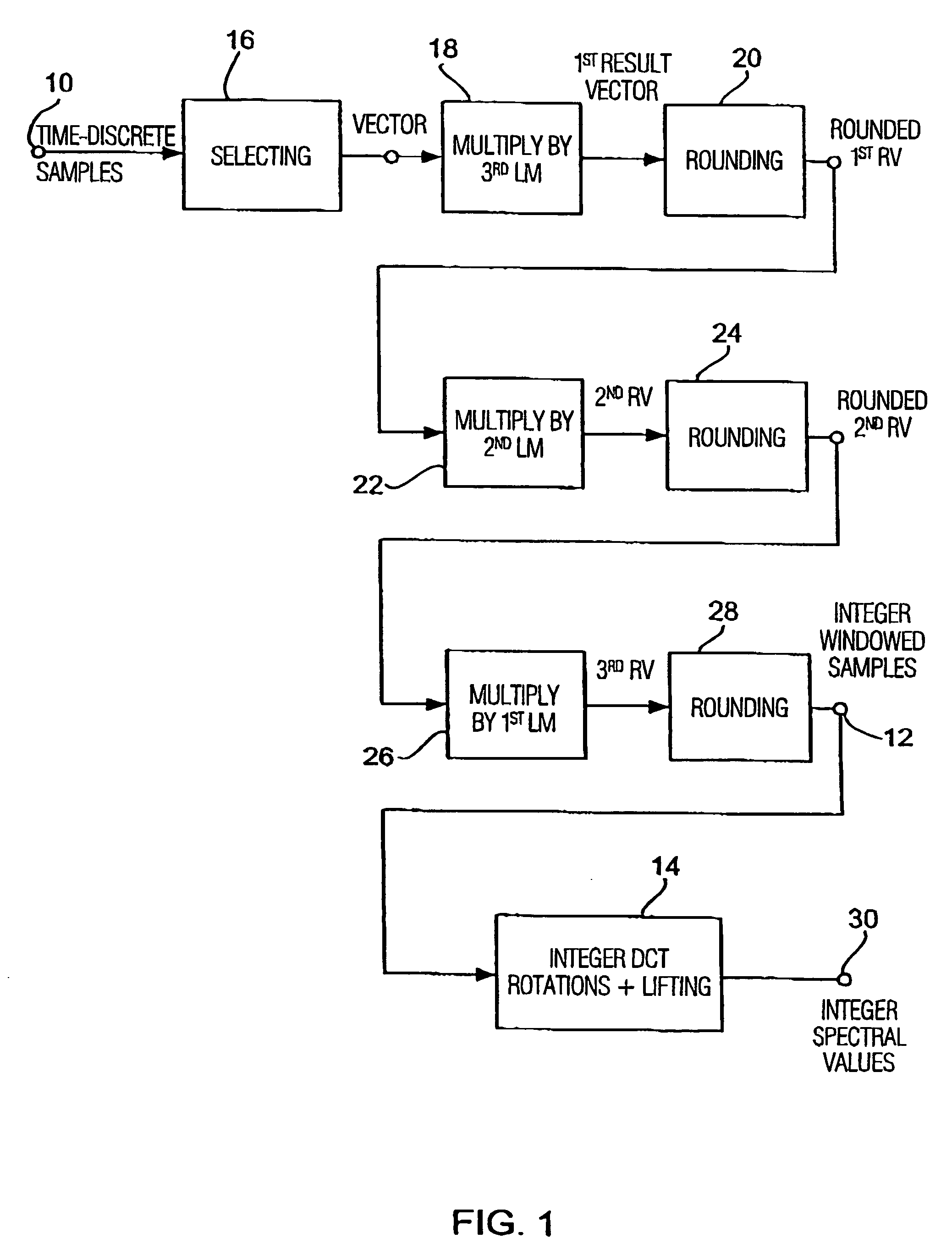
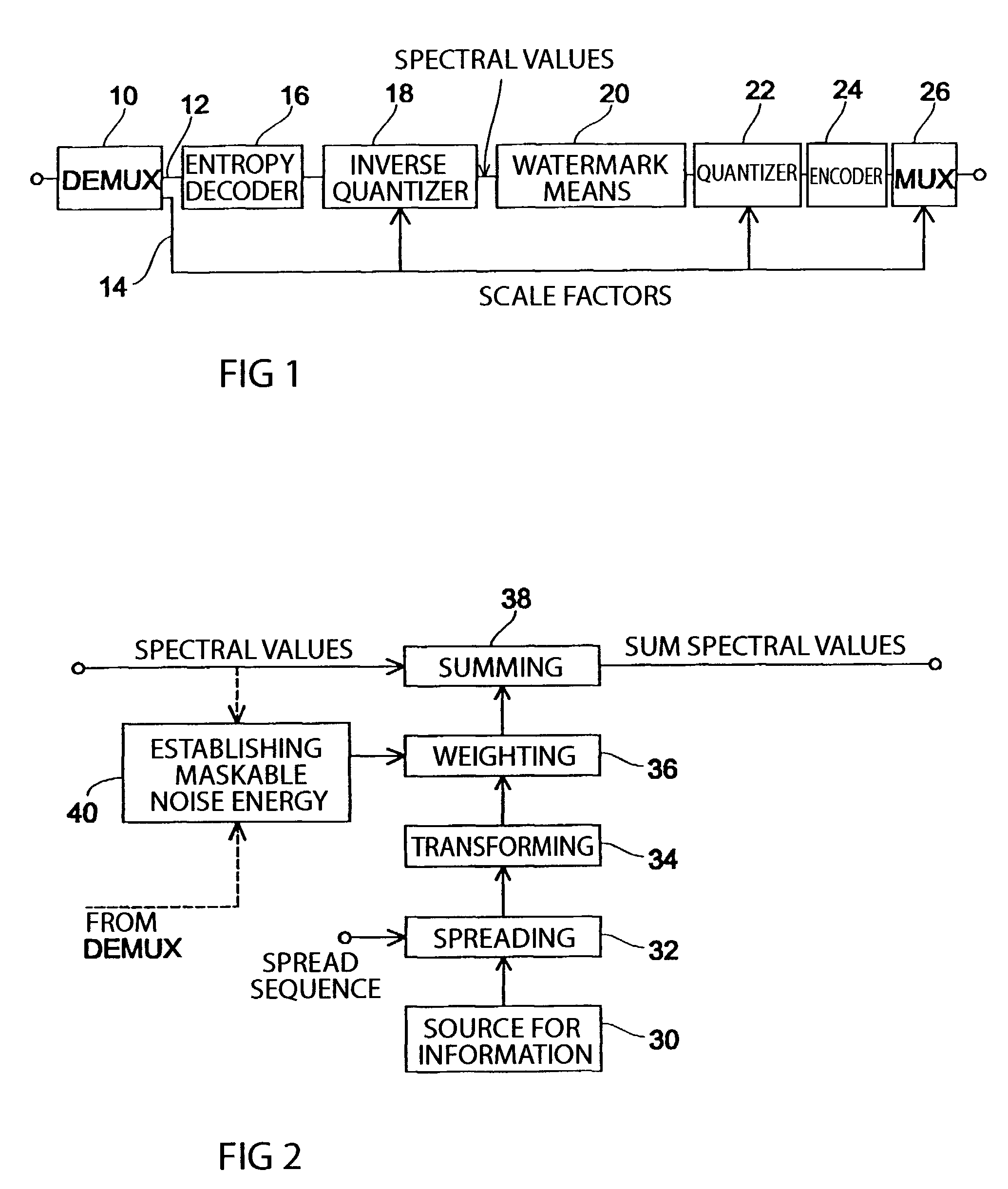
Apparatus and method for coding a time-discrete audio signal and apparatus and method for decoding coded audio data
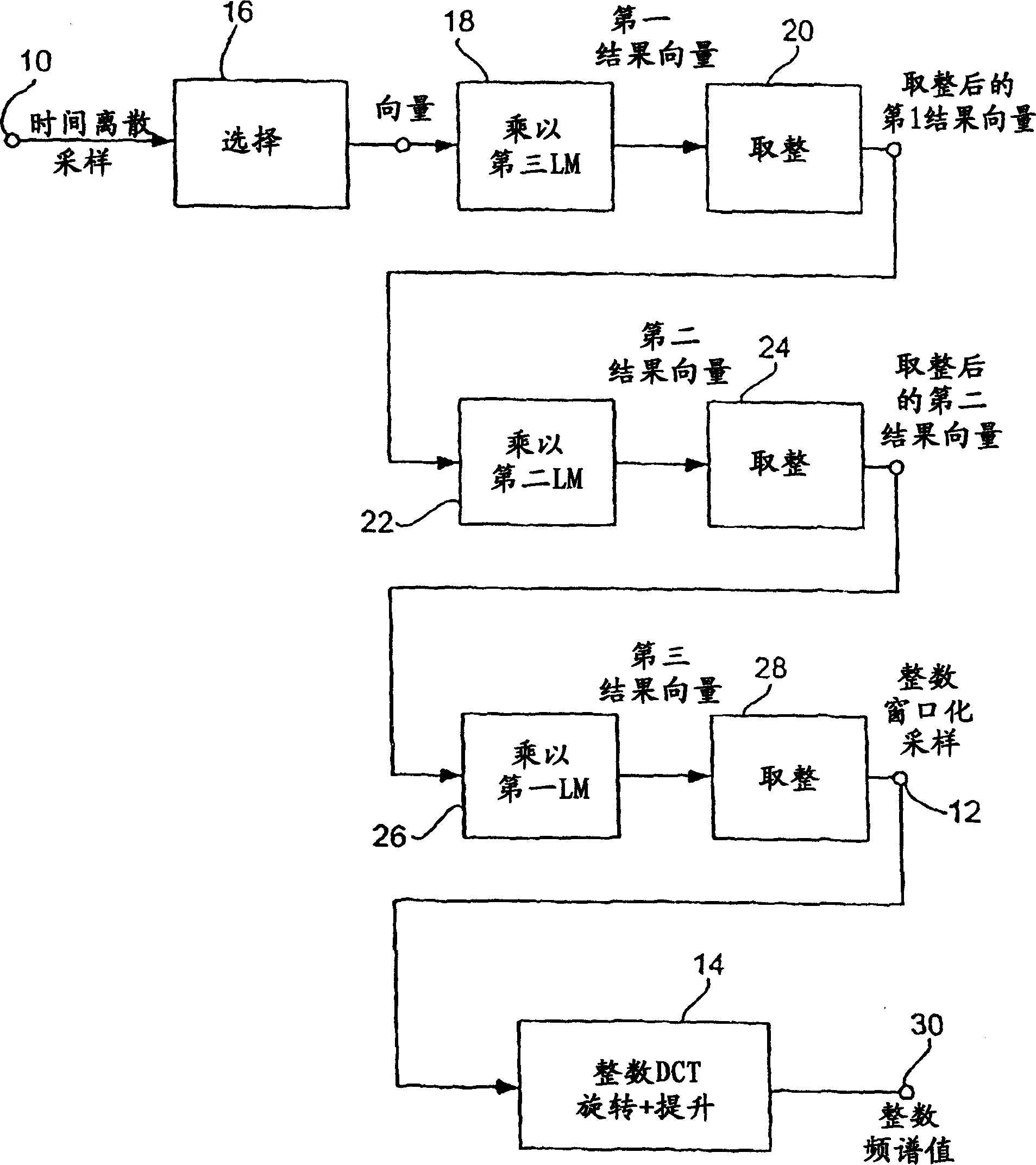
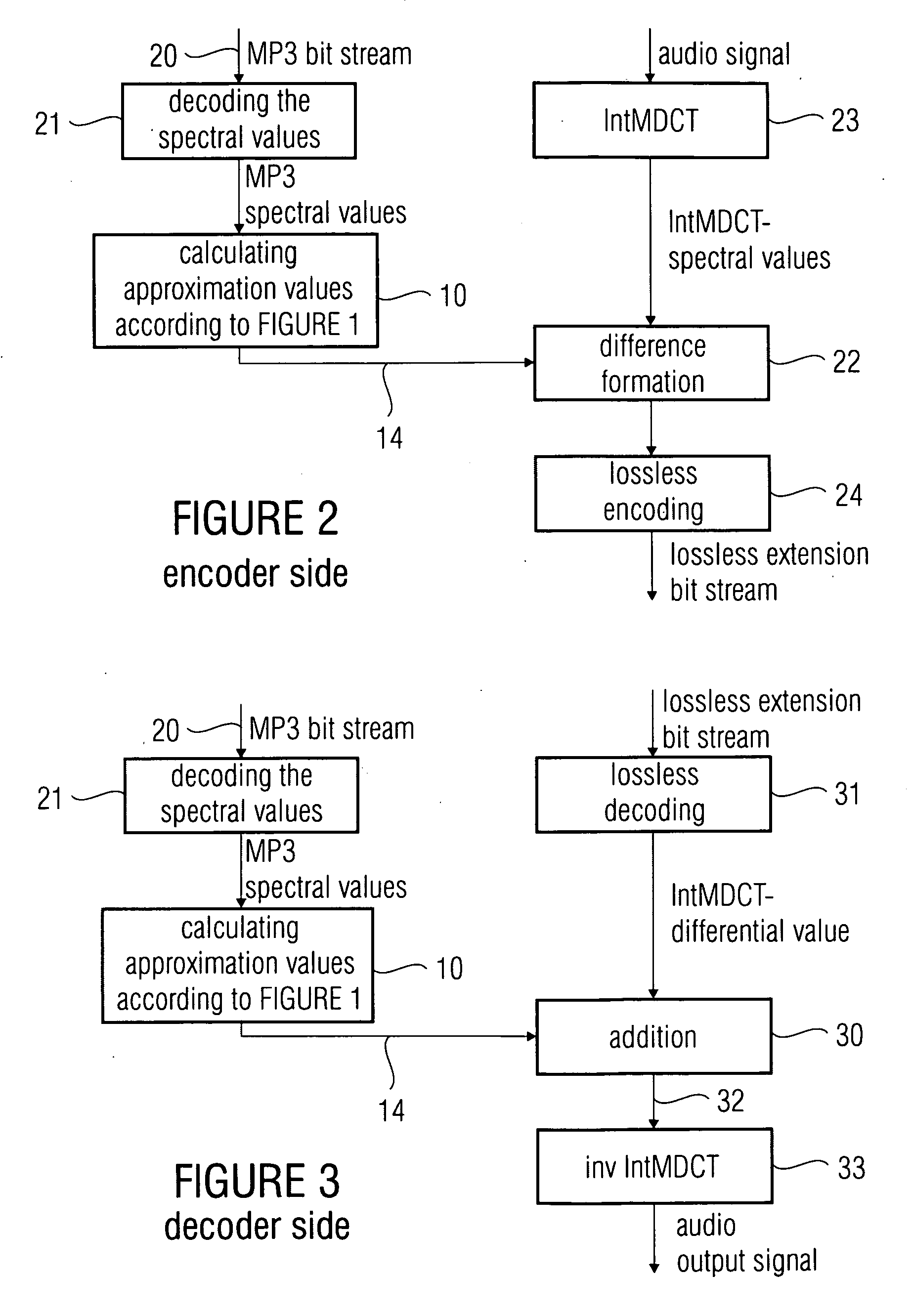
A time-discrete audio signal is processed to provide a quantization block with quantized spectral values. Furthermore, an integer spectral representation is generated from the time-discrete audio signal using an integer transform algorithm. The quantization block having been generated using a psychoacoustic model is inversely quantized and rounded to then form a difference between the integer spectral values and the inversely quantized rounded spectral values. The quantization block alone provides a lossy psychoacoustically coded / decoded audio signal after the decoding, whereas the quantization block, together with the combination block, provides a lossless or almost lossless coded and again decoded audio signal in the decoding. By generating the differential signal in the frequency domain, a simpler coder / decoder structure results.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
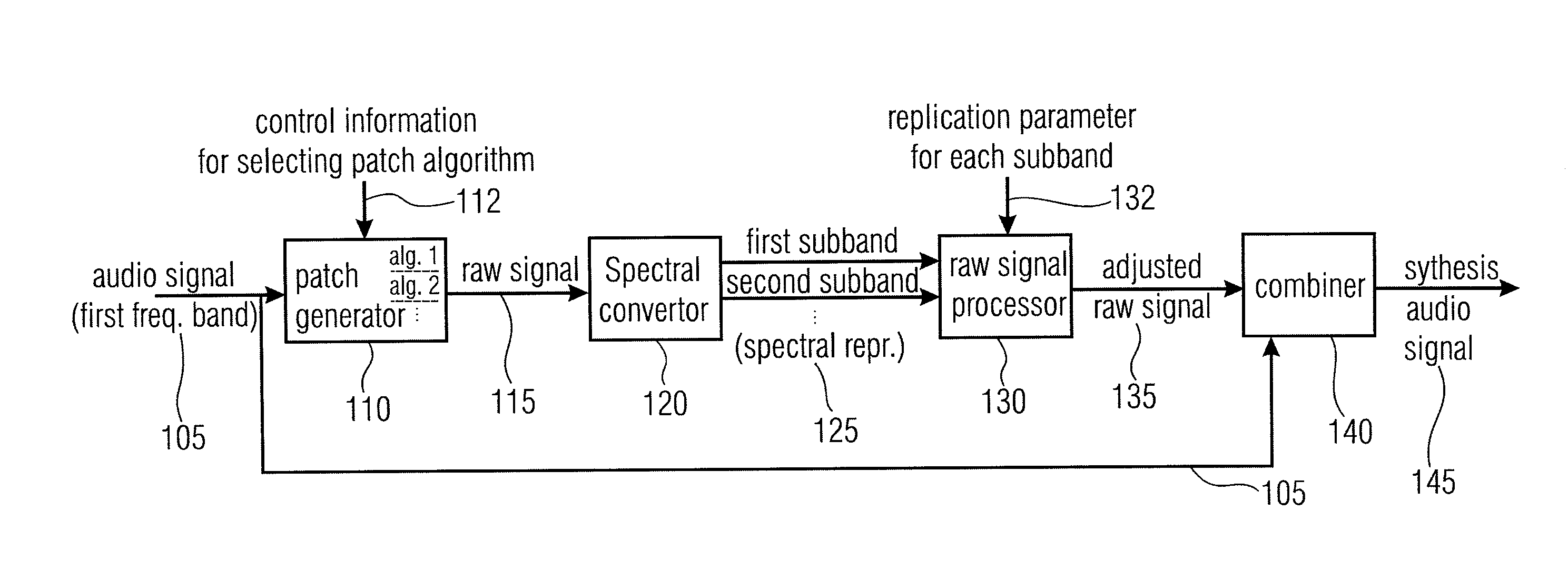
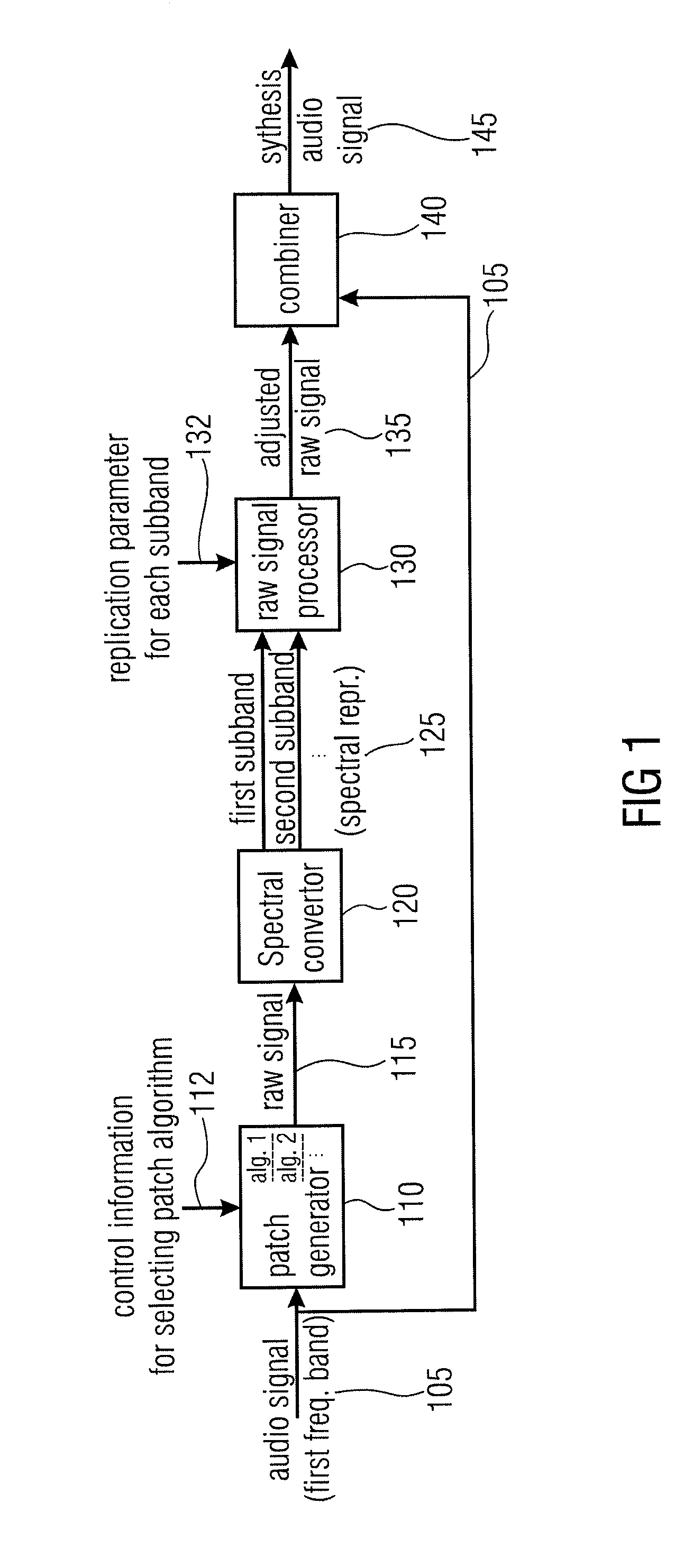
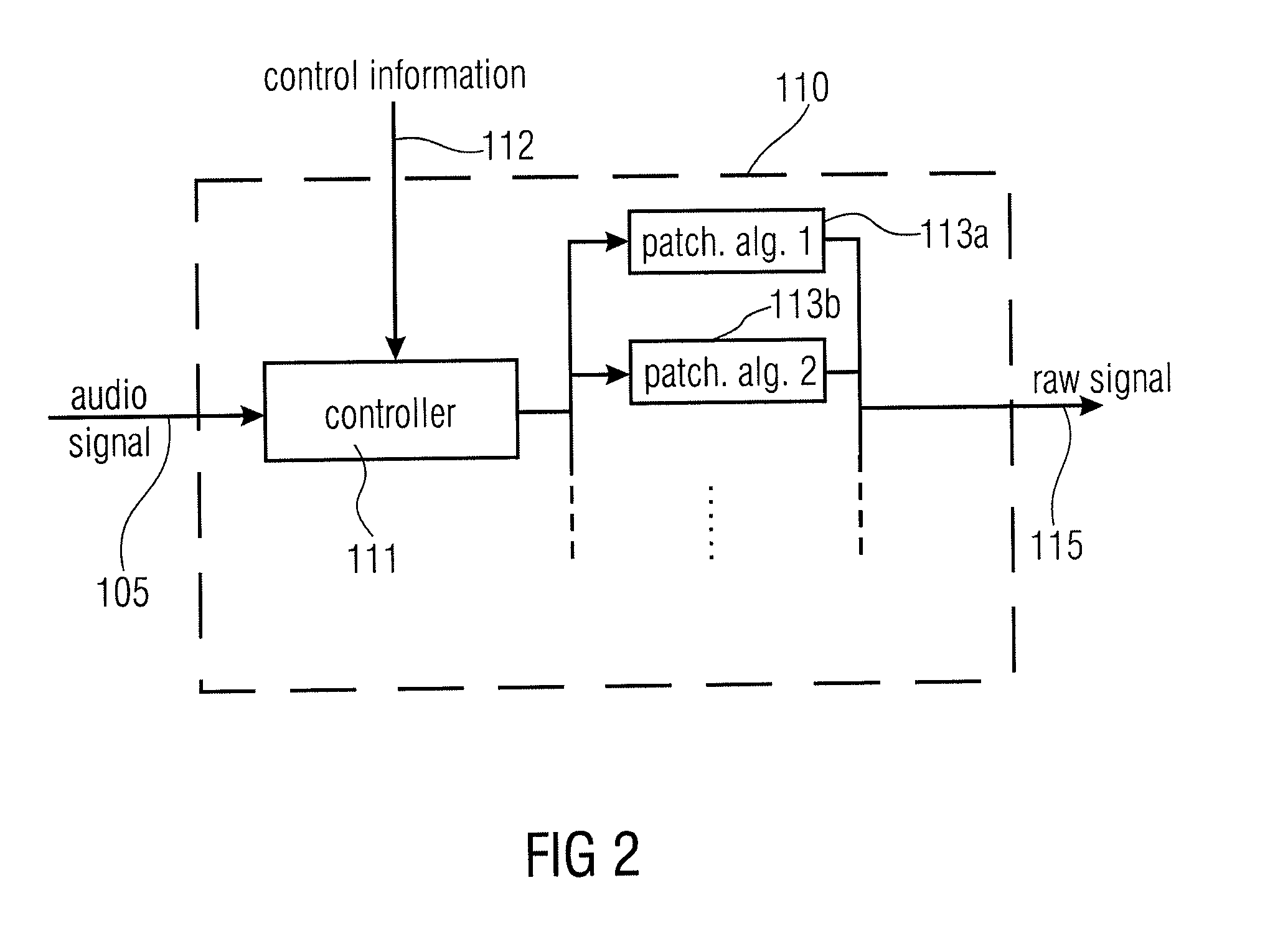
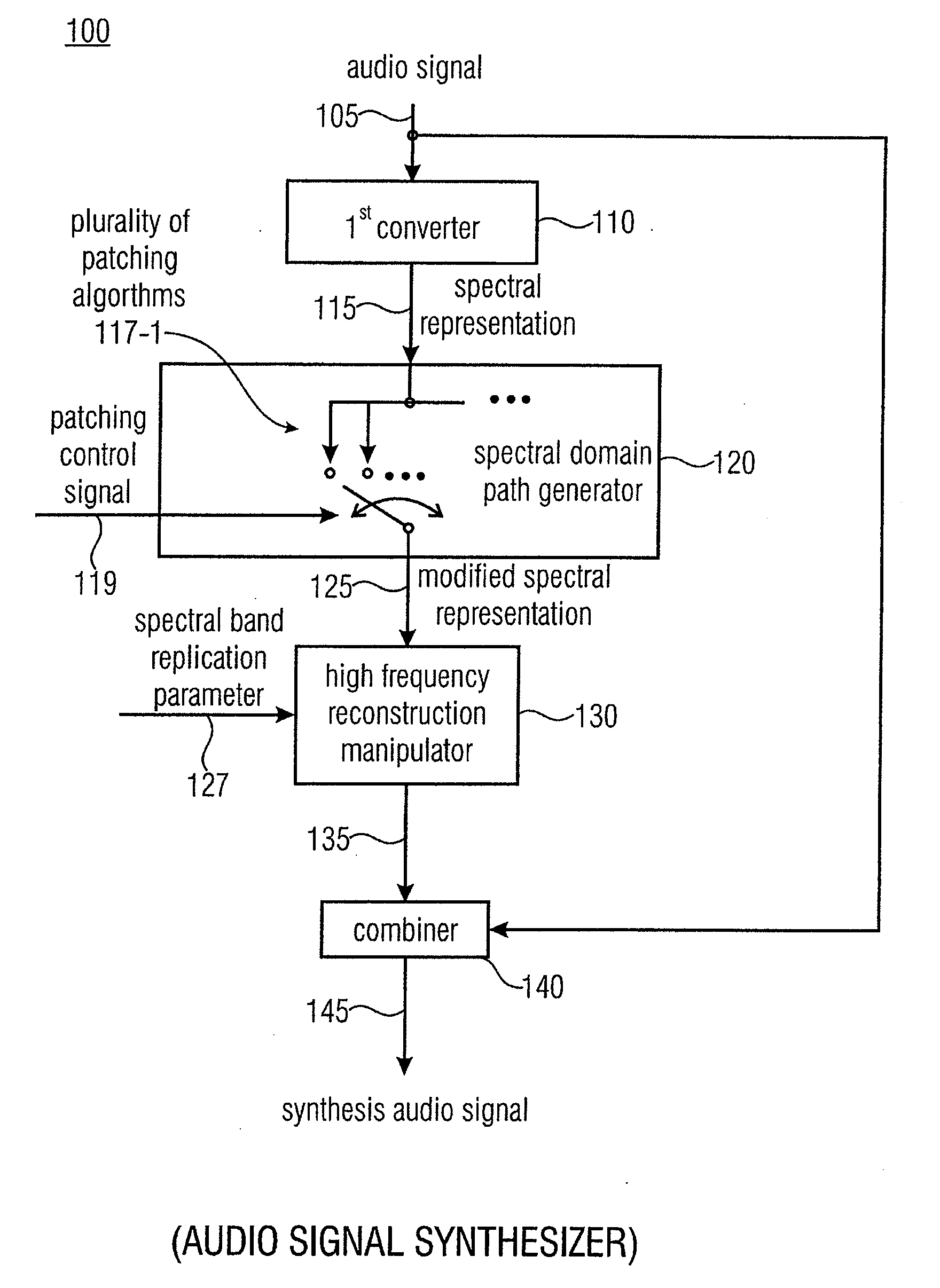
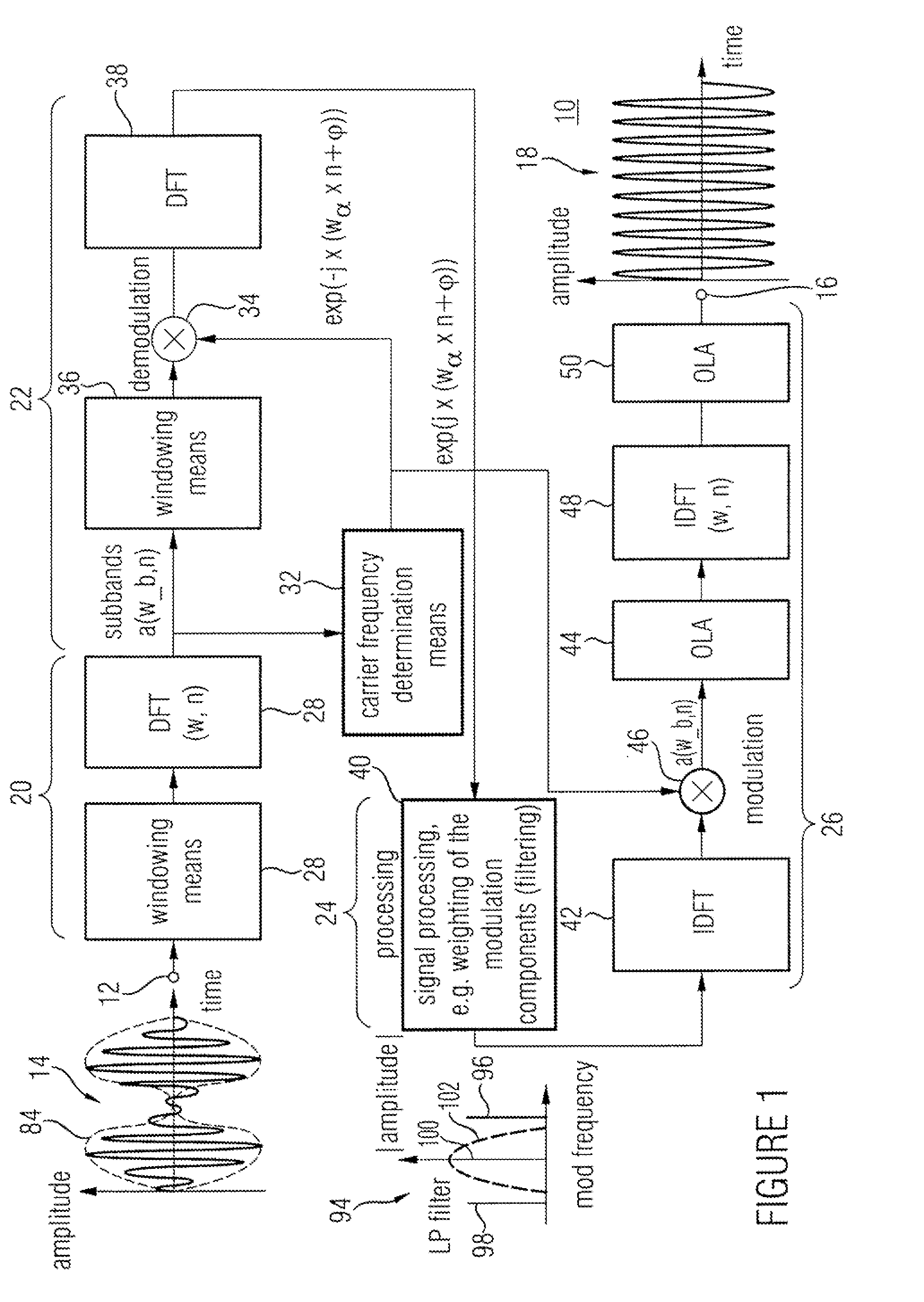
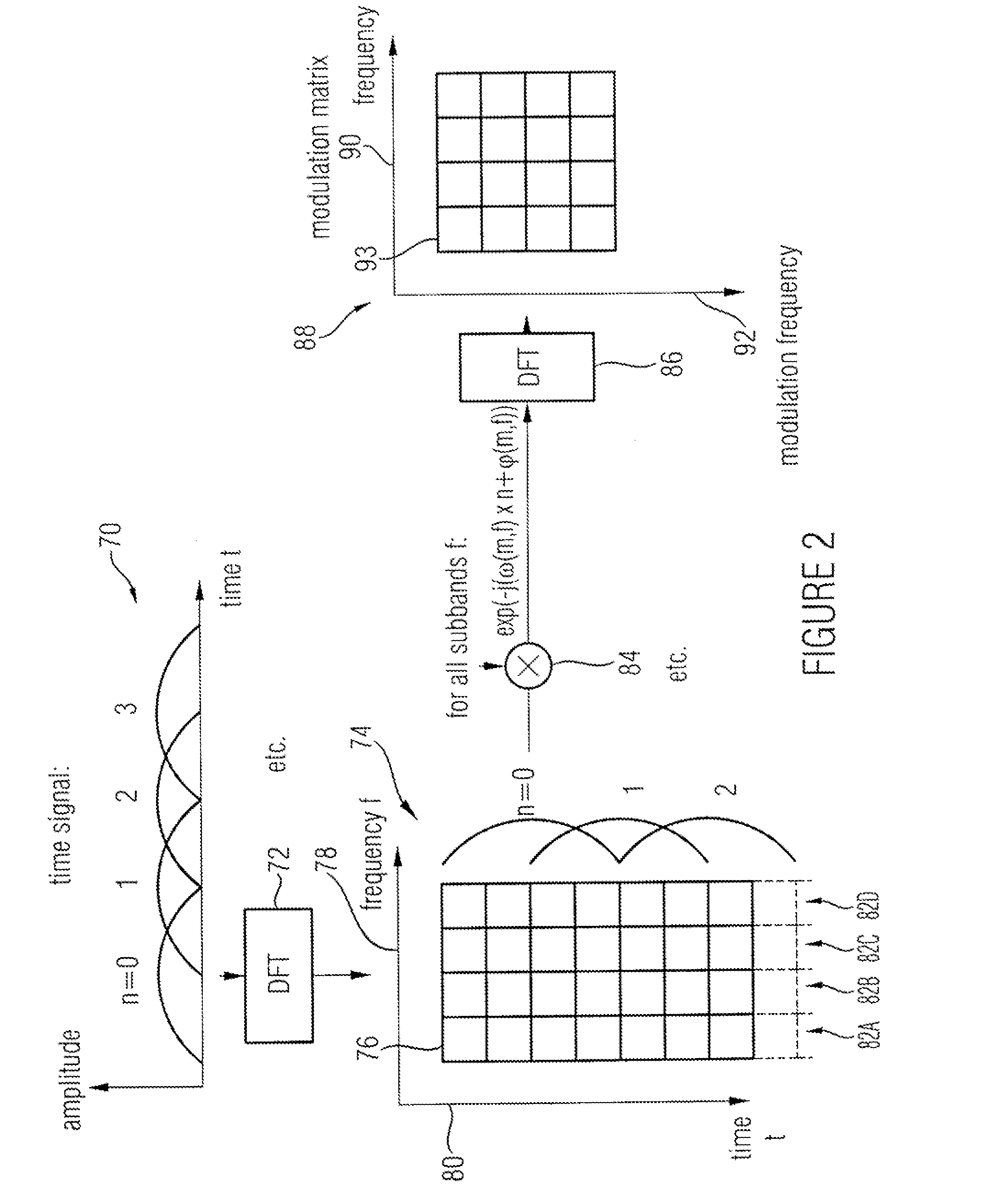
Audio Signal Synthesizer and Audio Signal Encoder
ActiveUS20110173006A1Quality improvementAvoid artifactsSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumSpectral domain
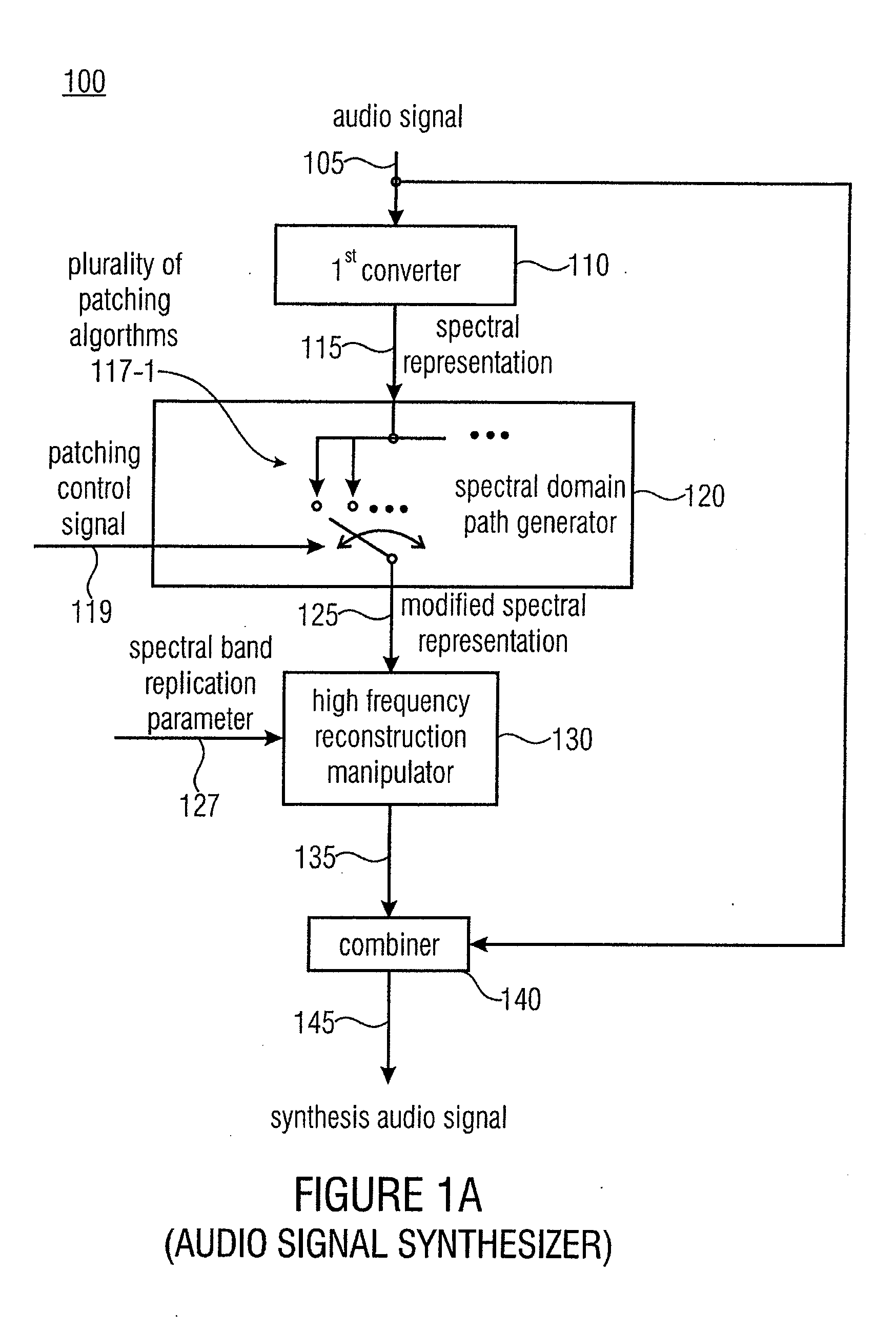
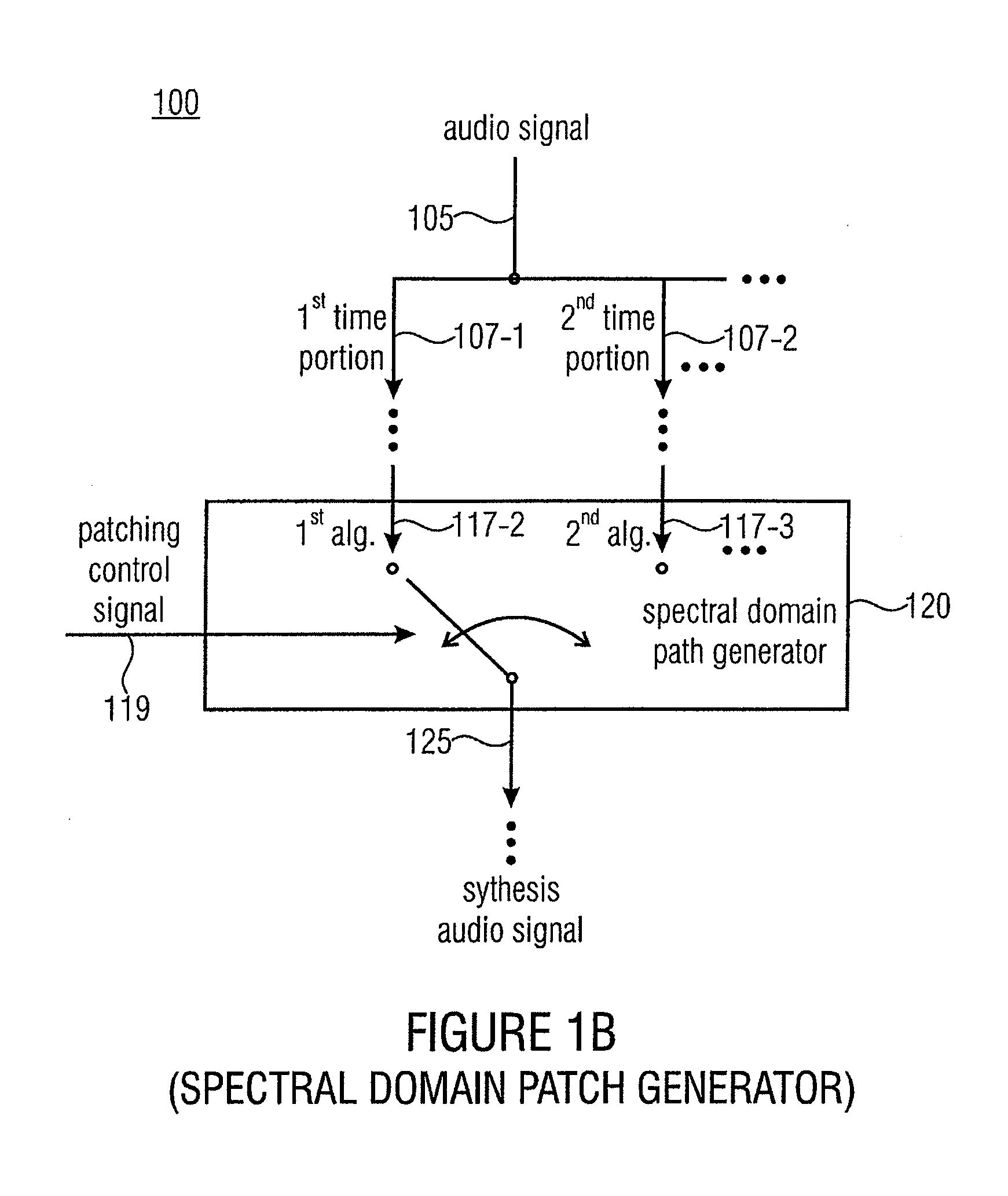
An audio signal synthesizer generates a synthesis audio signal having a first frequency band and a second synthesized frequency band derived from the first frequency band and comprises a patch generator, a spectral converter, a raw signal processor and a combiner. The patch generator performs at least two different patching algorithms, each patching algorithm generating a raw signal. The patch generator is adapted to select one of the at least two different patching algorithms in response to a control information. The spectral converter converts the raw signal into a raw signal spectral representation. The raw signal processor processes the raw signal spectral representation in response to spectral domain spectral band replication parameters to obtain an adjusted raw signal spectral representation.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
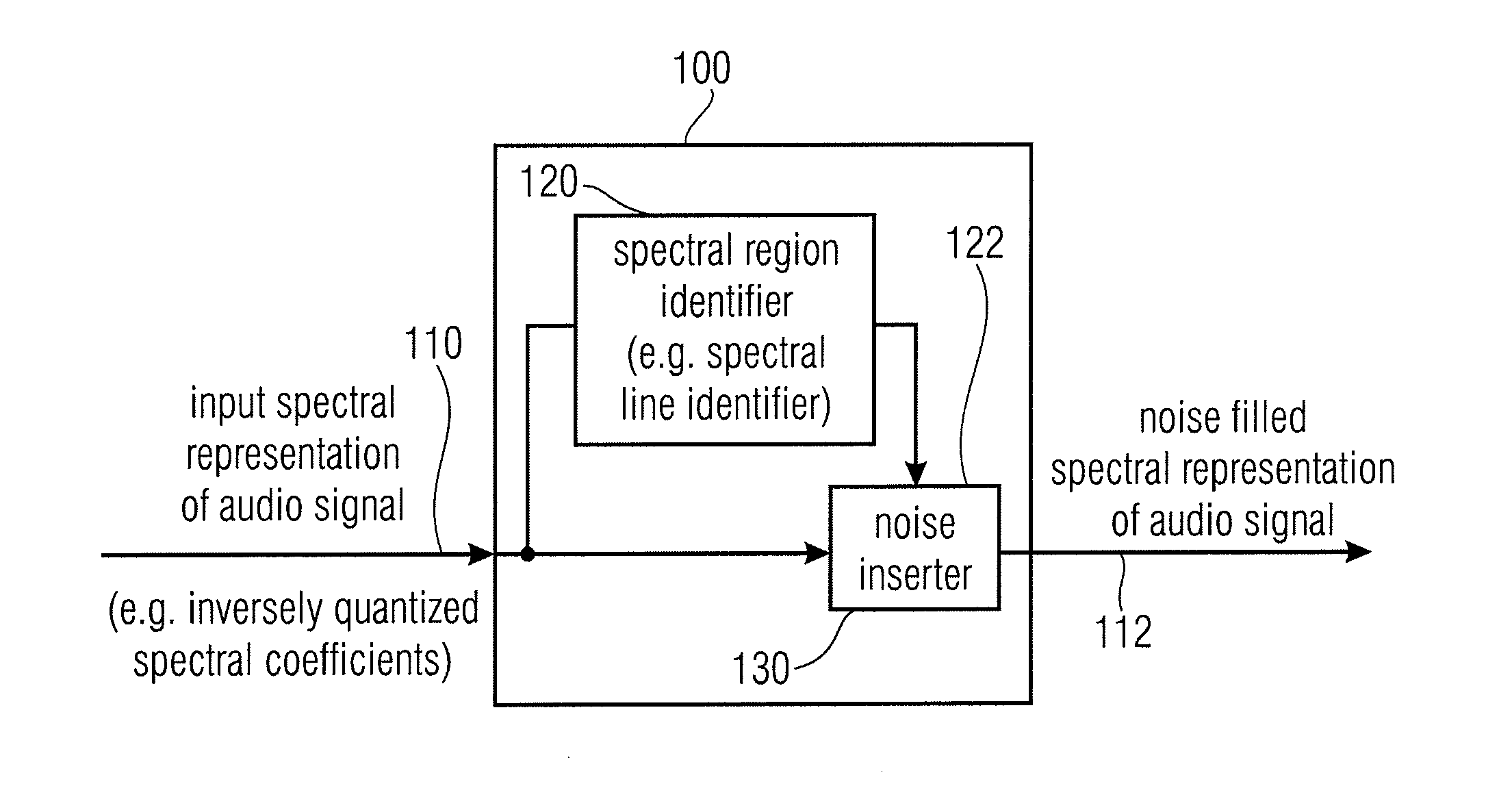
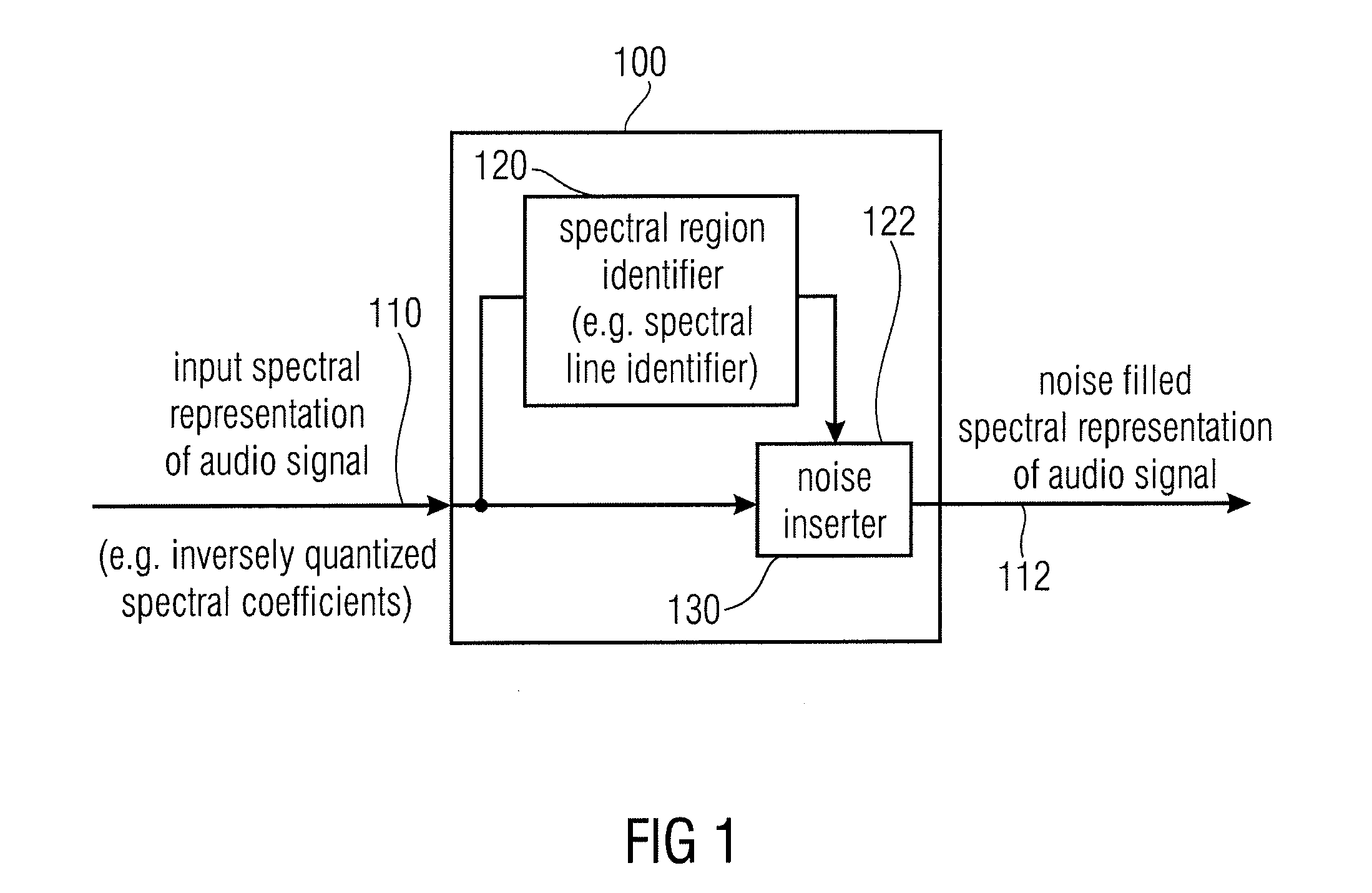
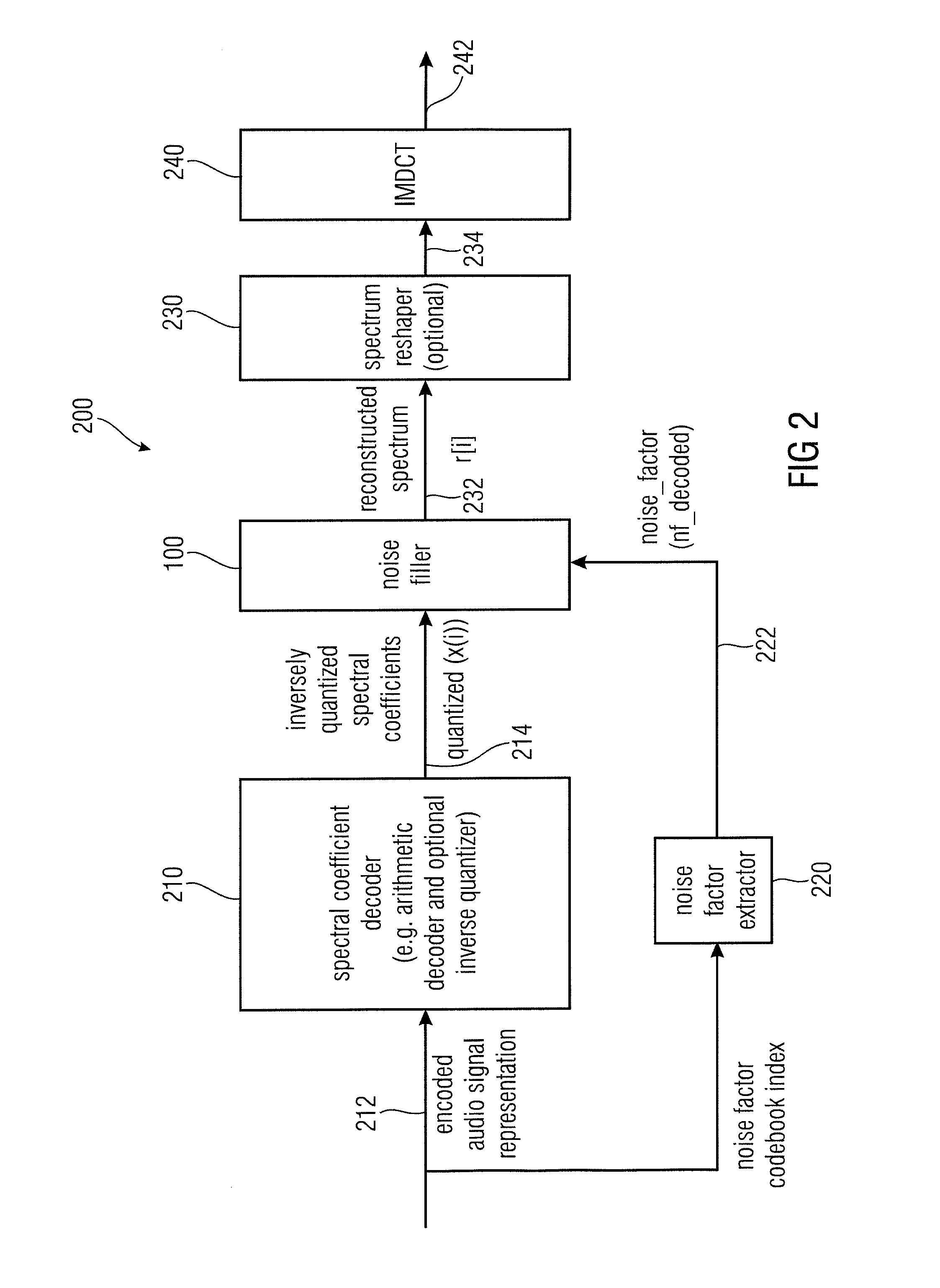
Noise Filler, Noise Filling Parameter Calculator Encoded Audio Signal Representation, Methods and Computer Program
ActiveUS20110173012A1Promote resultsRealistic sound reconstructionSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumSpectral representation
A noise filler for providing a noise-filled spectral representation of an audio signal on the basis of an input spectral representation of the audio signal has a spectral region identifier configured to identify spectral regions of the input spectral representation spaced from non-zero spectral regions of the input spectral representation by at least one intermediate spectral region, to obtain identified spectral regions, and a noise inserter configured to selectively introduce noise into the identified spectral regions to obtain the noise-filled spectral representation of the audio signal. A noise filling parameter calculator for providing a noise filling parameter on the basis of a quantized spectral representation of an audio signal has a spectral region identifier, as mentioned above, and a noise value calculator configured to selectively consider quantization errors of the identified spectral regions for a calculation of the noise filling parameter. Accordingly, an encoded audio signal representation representing the audio signal can be obtained.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
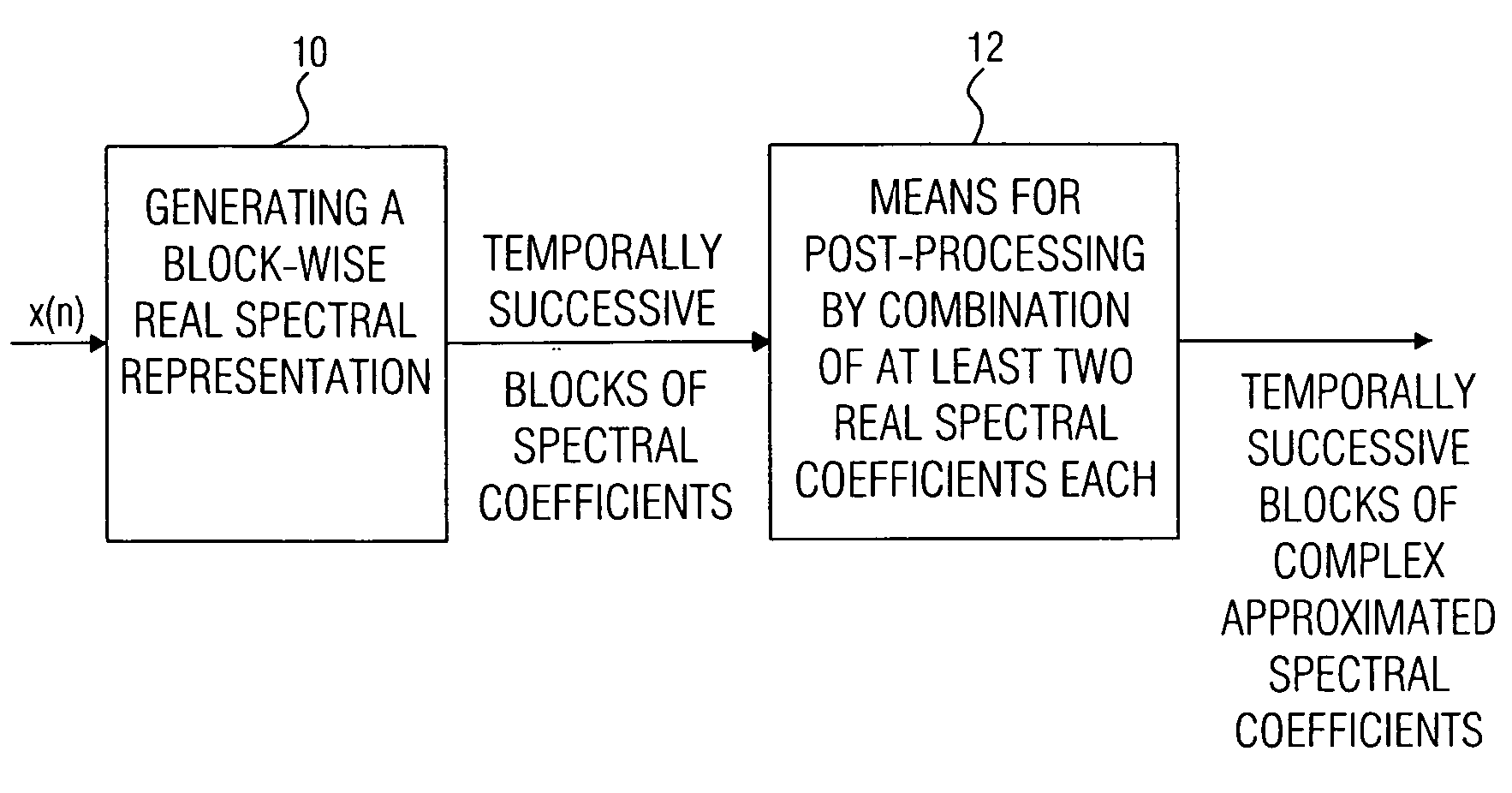
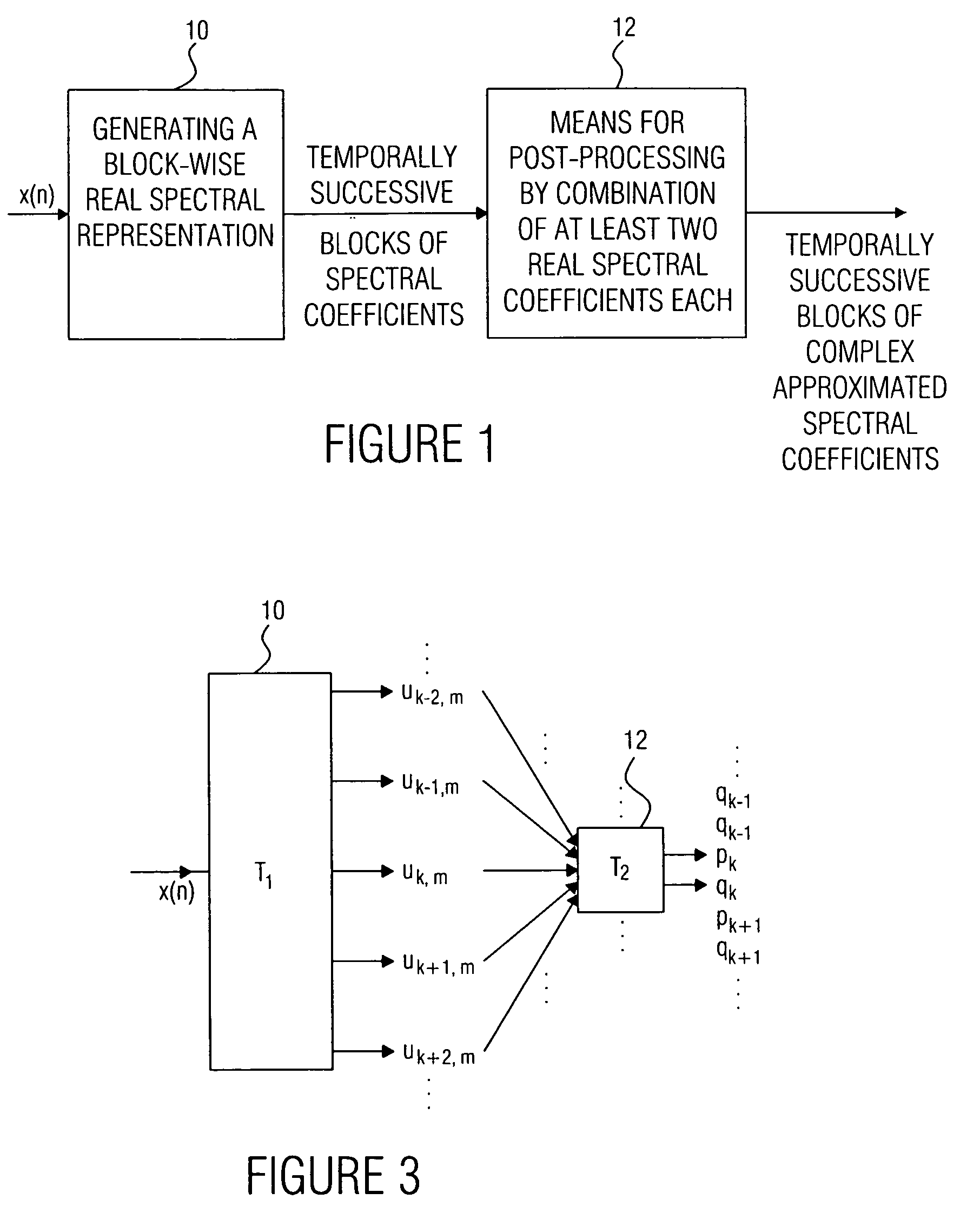
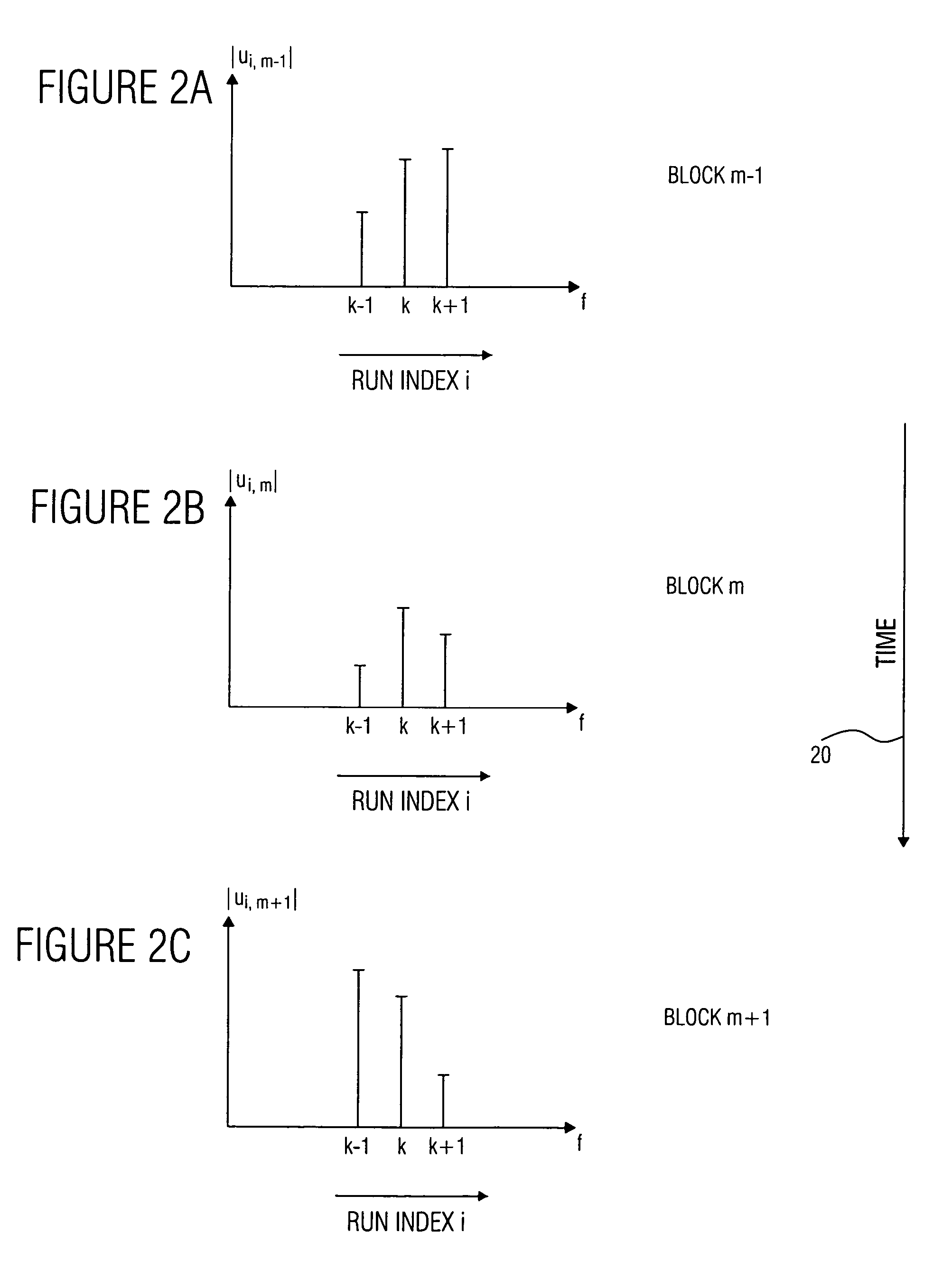
Device and method for generating a complex spectral representation of a discrete-time signal
ActiveUS20050197831A1Improve approximationSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumPost processor
A filter bank device for generating a complex spectral representation of a discrete-time signal includes a generator for generating a block-wise real spectral representation, which, for example, implements an MDCT, to obtain temporally successive blocks of real spectral coefficients. The output values of this spectral conversion device are fed to a post-processor for post-processing the block-wise real spectral representation to obtain an approximated complex spectral representation having successive blocks, each block having a set of complex approximated spectral coefficients, wherein a complex approximated spectral coefficient can be represented by a first partial spectral coefficient and by a second partial spectral coefficient, wherein at least one of the first and second partial spectral coefficients is determined by combining at least two real spectral coefficients. A good approximation for a complex spectral representation of the discrete-time signal is obtained by combining two real spectral coefficients, preferably by a weighted linear combination, wherein additionally more degrees of freedom for optimizing the entire system are available.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
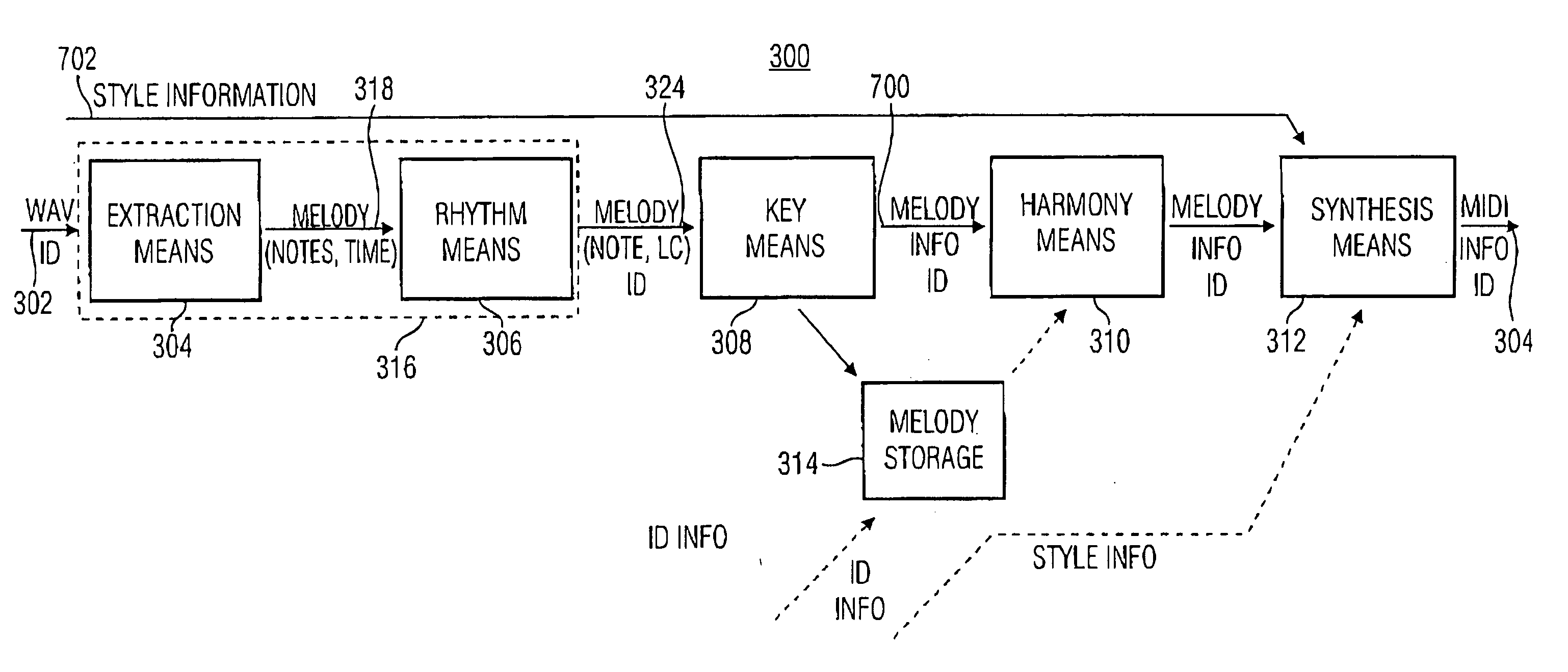
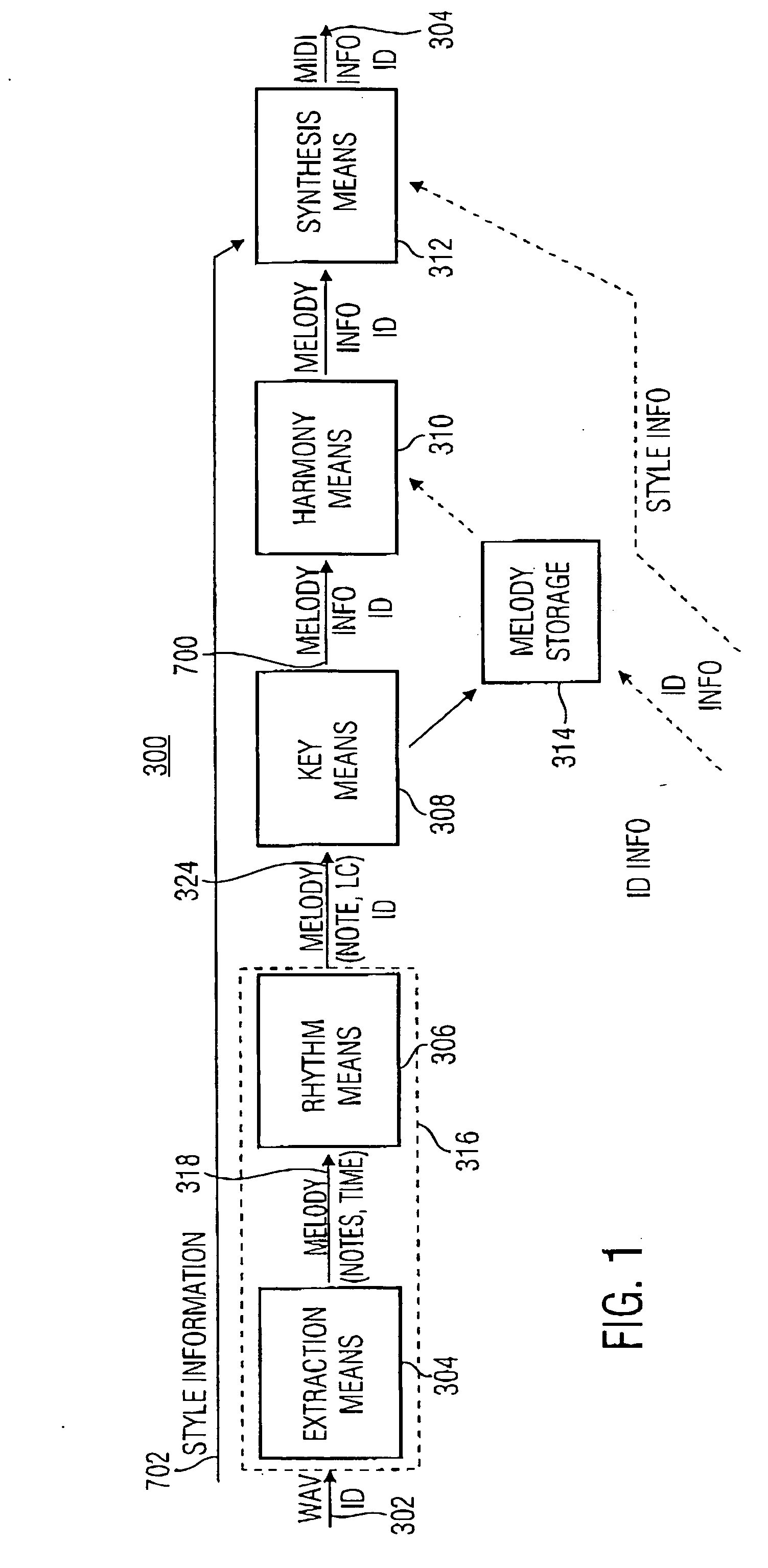
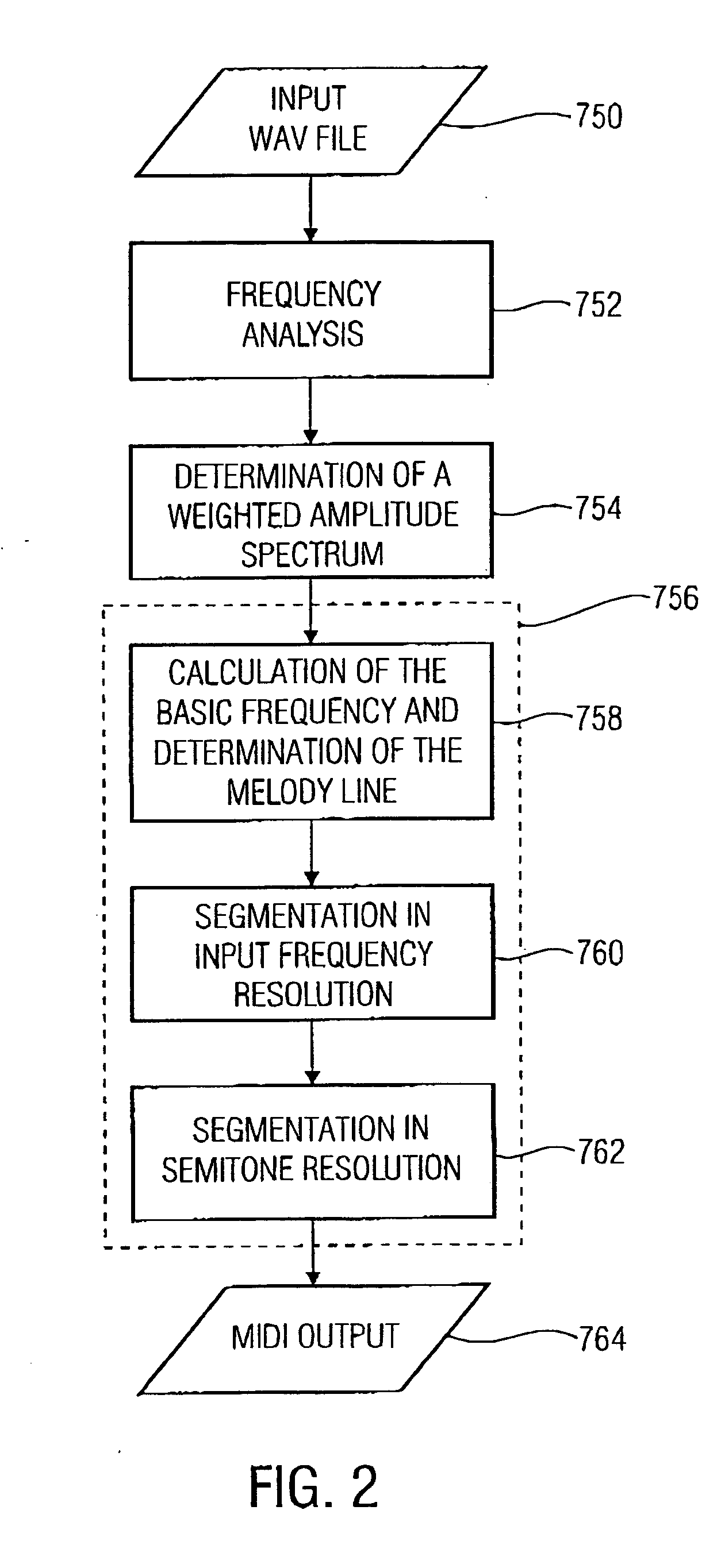
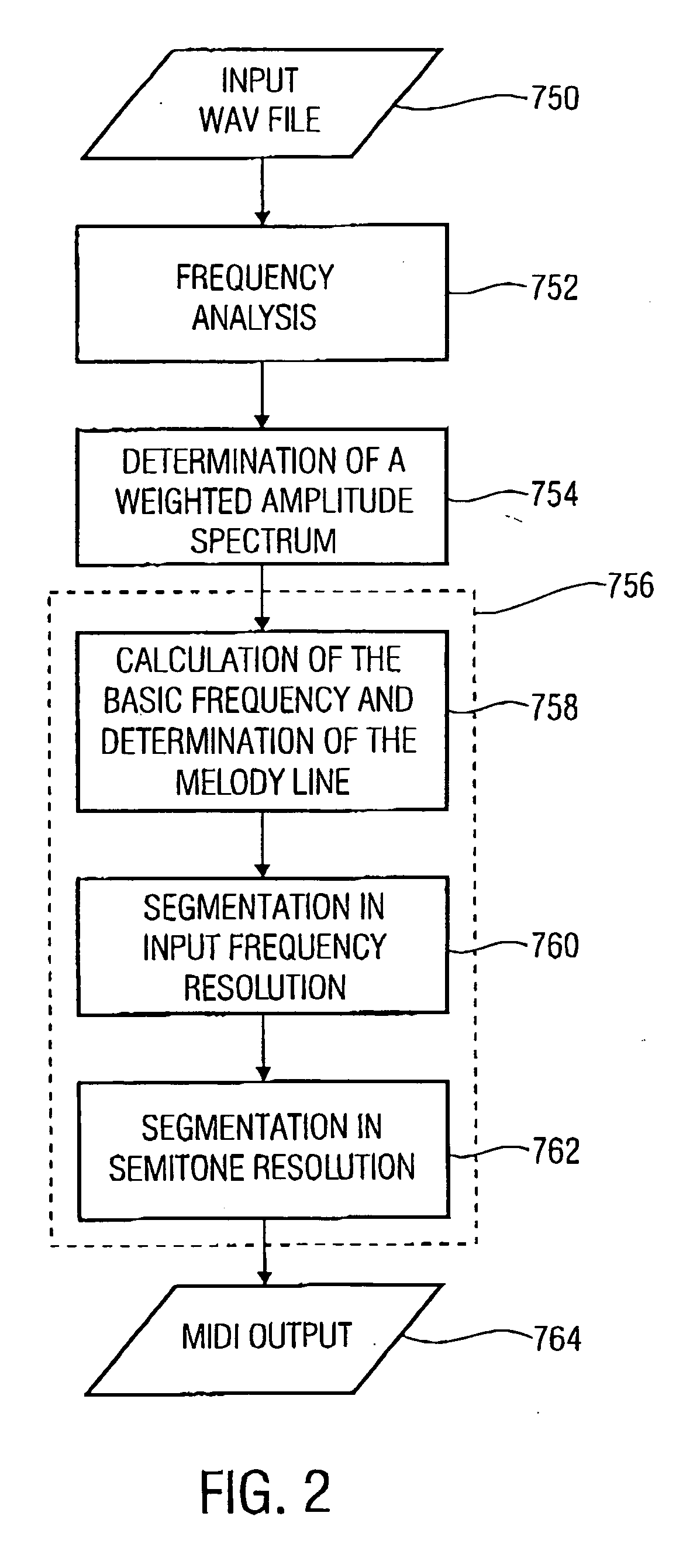
Method and device for extracting a melody underlying an audio signal
InactiveUS20060075884A1Stable extractionTranscription be stableElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumTime frequency spectrum
The finding of the present invention is that the melody extraction or automatic transcription may be implemented clearly more stable and if applicable even less expensive when the assumption is considered sufficiently that the main melody is the portion of a piece of music which man perceives the loudest and the most precise. Regarding this, according to the present invention the time / spectral representation or the spectrogram of an interesting audio signal is scaled using the curves of equal volume reflecting human volume perception in order to determine the melody of the audio signal on the basis of the resulting perception-related time / spectral representation.
Owner:GRACENOTE
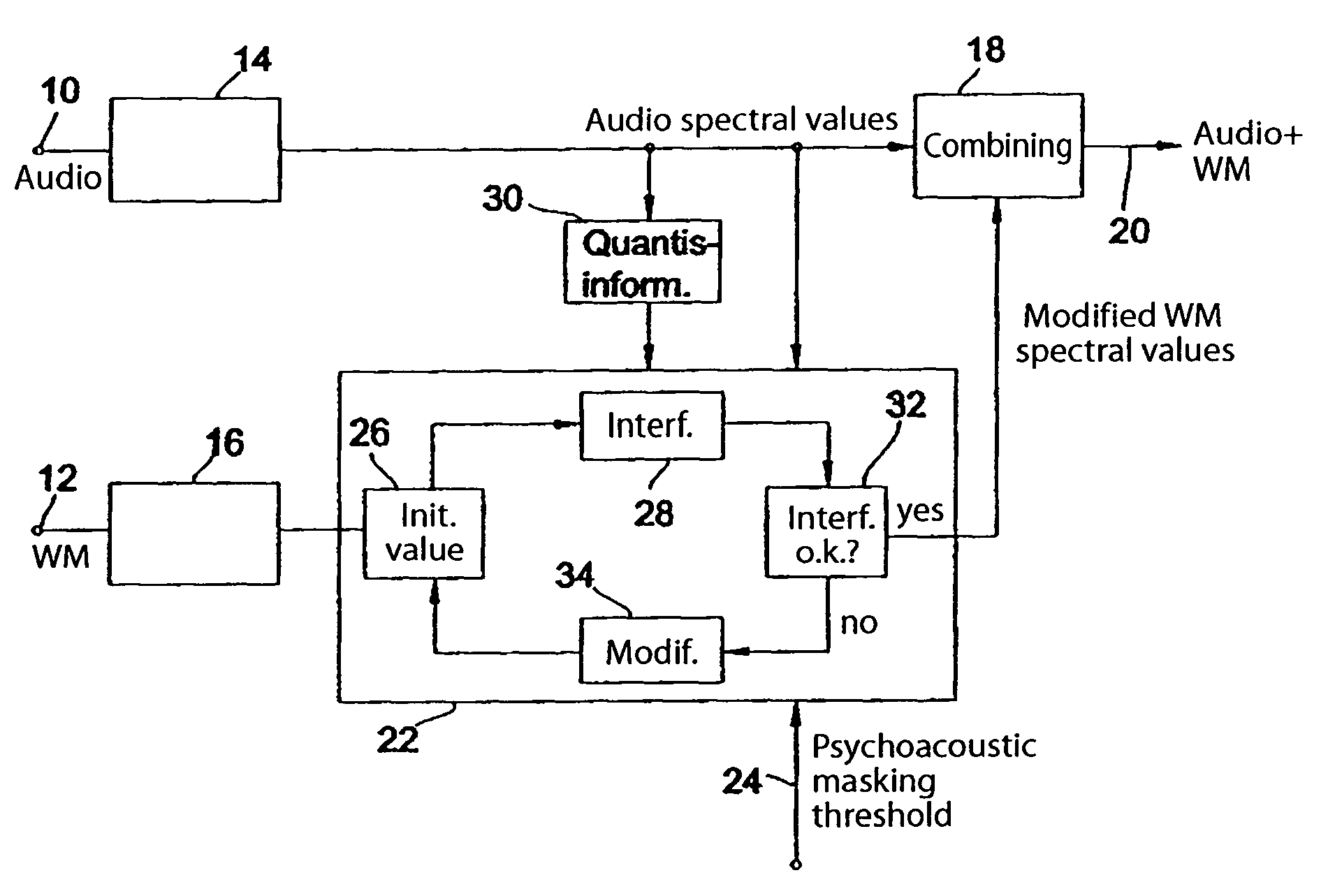
Device and method for embedding a watermark in an audio signal
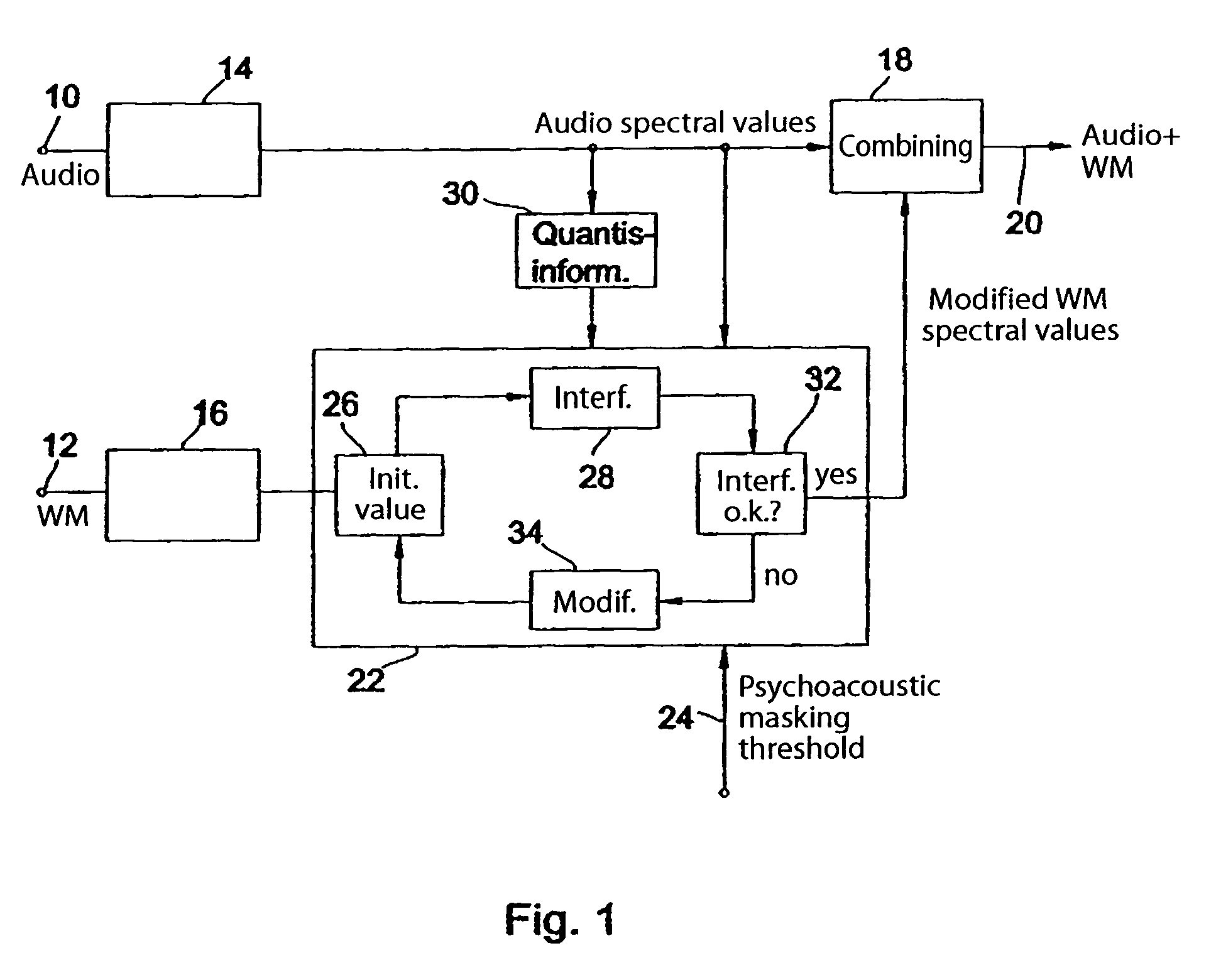
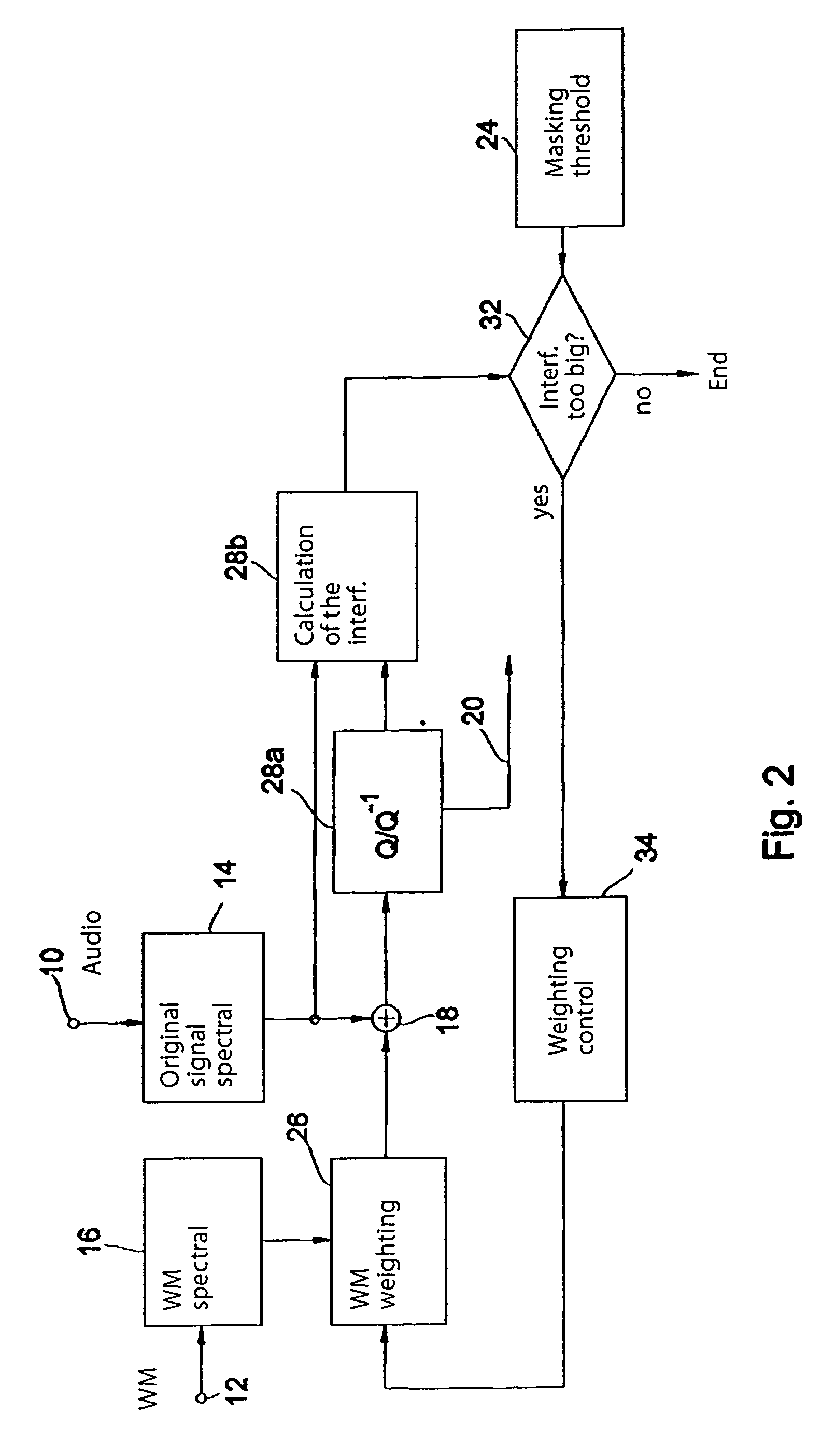
ActiveUS7346514B2Adequate watermark detectabilityEasy to detectFilamentary/web record carriersUser identity/authority verificationFrequency spectrumMasking threshold
Prior to embedding a watermark in an audio signal, a spectral representation of the audio signal and a spectral representation of the watermark signal are determined. The spectral representation of the watermark signal is then processed on the basis of a psychoacoustic masking threshold of the audio signal. The processed watermark signal is combined with the audio signal to obtain an audio signal bearing a watermark. The spectral representation of the watermark signal is processed iteratively as follows: first a predetermined watermark initial value is selected, then the interference introduced into the spectral representation of the audio signal after a quantization of the spectral representation of the audio signal is determined and then, if the interference introduced by the watermark initial value exceeds the predetermined interference threshold, the watermark initial value is modified progressively until the resulting interference introduced into the spectral representation of the audio signal after quantization is less than or equal to the predetermined interference threshold. The modified watermark initial value at the end of the iteration is used as the processed watermark signal to be combined with the audio signal. As a result it is no longer possible for a watermark to be quantized out. Instead, full control over the energy of the watermark is achieved. A watermark can therefore be embedded in an audio signal to provide either the best possible degree of watermark detectability or the best possible audio quality.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
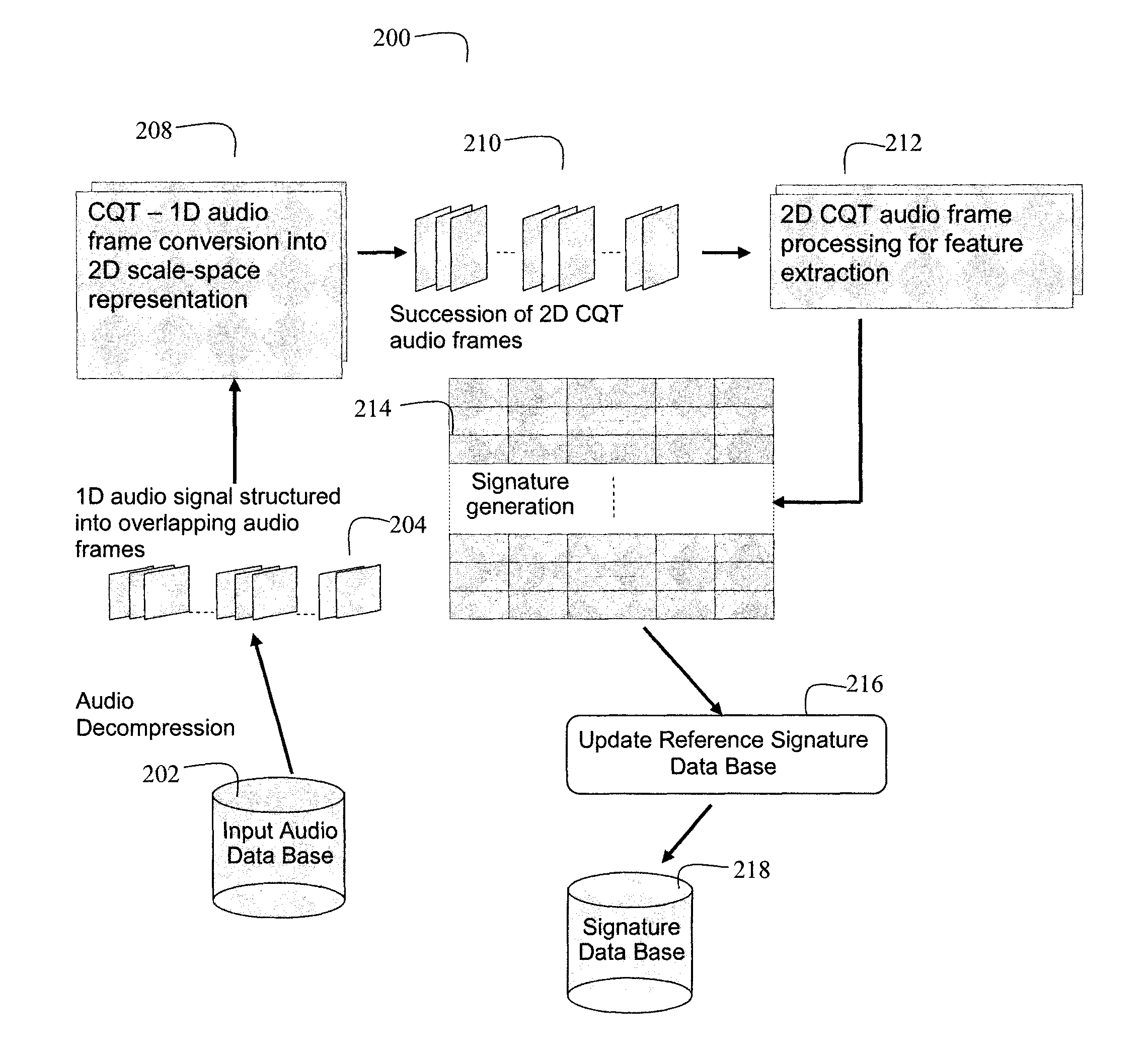
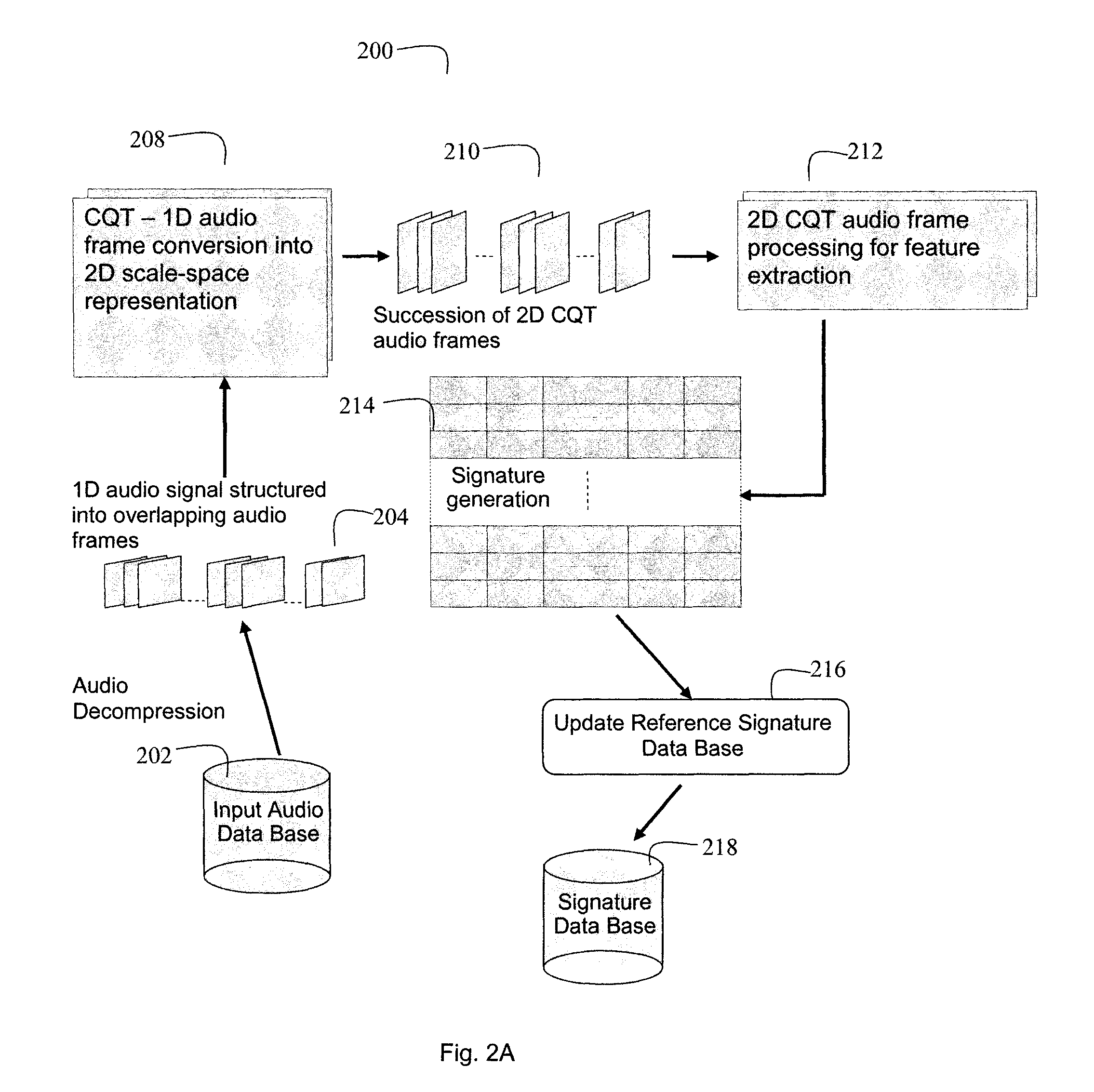
Audio content fingerprinting based on two-dimensional constant Q-factor transform representation and robust audio identification for time-aligned applications
ActiveUS9299364B1Speech analysisSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumSpectral bands
Content identification methods for consumer devices determine robust audio fingerprints that are resilient to audio distortions. One method generates signatures representing audio content based on a constant Q-factor transform (CQT). A 2D spectral representation of a 1D audio signal facilitates generation of region based signatures within frequency octaves and across the entire 2D signal representation. Also, points of interest are detected within the 2D audio signal representation and interest regions are determined around selected points of interest. Another method generates audio descriptors using an accumulating filter function on bands of the audio spectrum and generates audio transform coefficients. A response of each spectral band is computed and transform coefficients are determined by filtering, by accumulating derivatives with different lags, and computing second order derivatives. Additionally, time and frequency based onset detection determines audio descriptors at events and enhances descriptors with information related to an event.
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
Apparatus and method for coding a time-discrete audio signal to obtain coded audio data and for decoding coded audio data
A time-discrete audio signal is processed to provide a quantization block with quantized spectral values. Furthermore, an integer spectral representation is generated from the time-discrete audio signal using an integer transform algorithm. The quantization block having been generated using a psychoacoustic model is inversely quantized and rounded to then form a difference between the integer spectral values and the inversely quantized rounded spectral values. The quantization block alone provides a lossy psychoacoustically coded / decoded audio signal after the decoding, whereas the quantization block, together with the combination block, provides a lossless or almost lossless coded and again decoded audio signal in the decoding. By generating the differential signal in the frequency domain, a simpler coder / decoder structure results.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
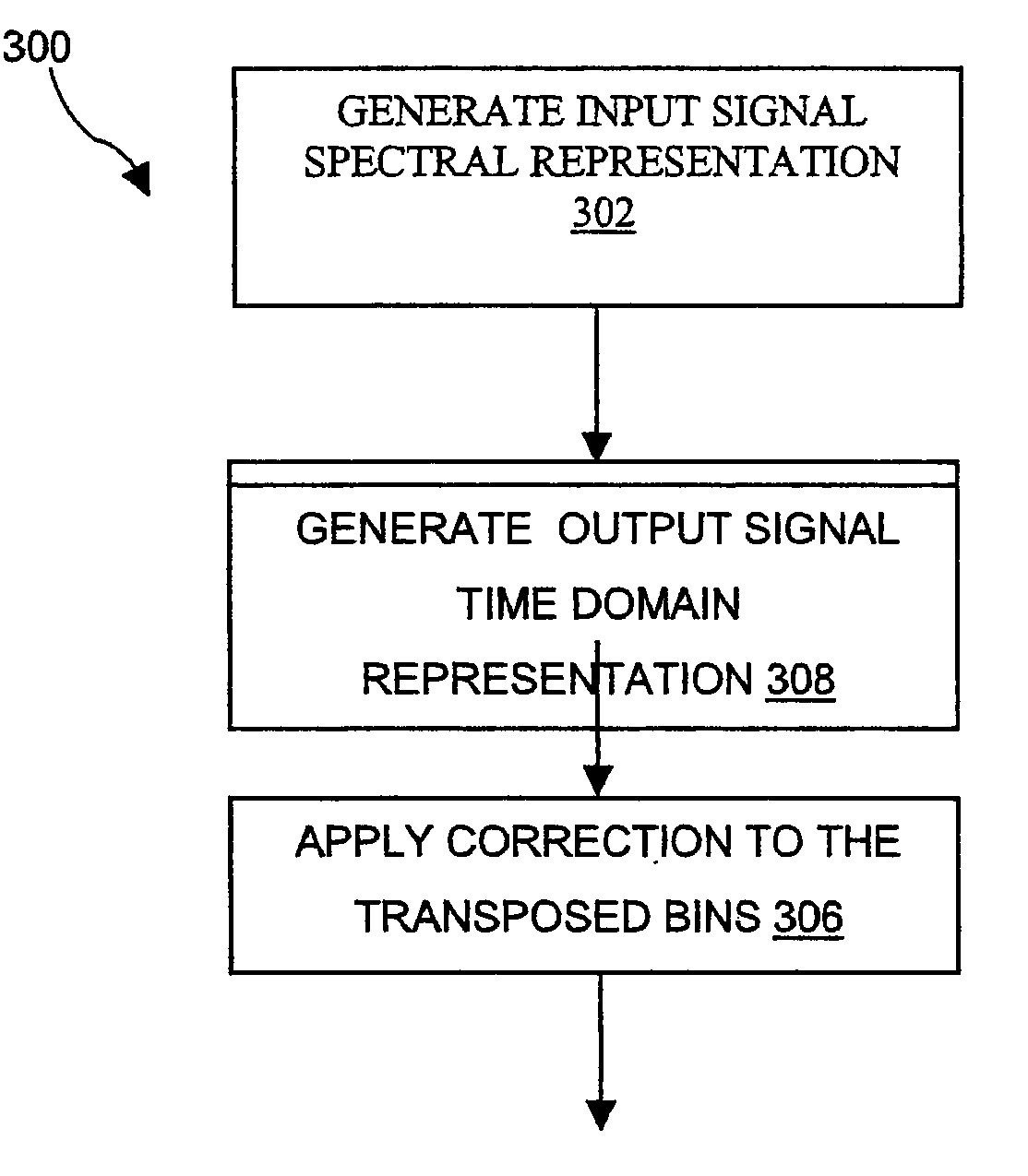
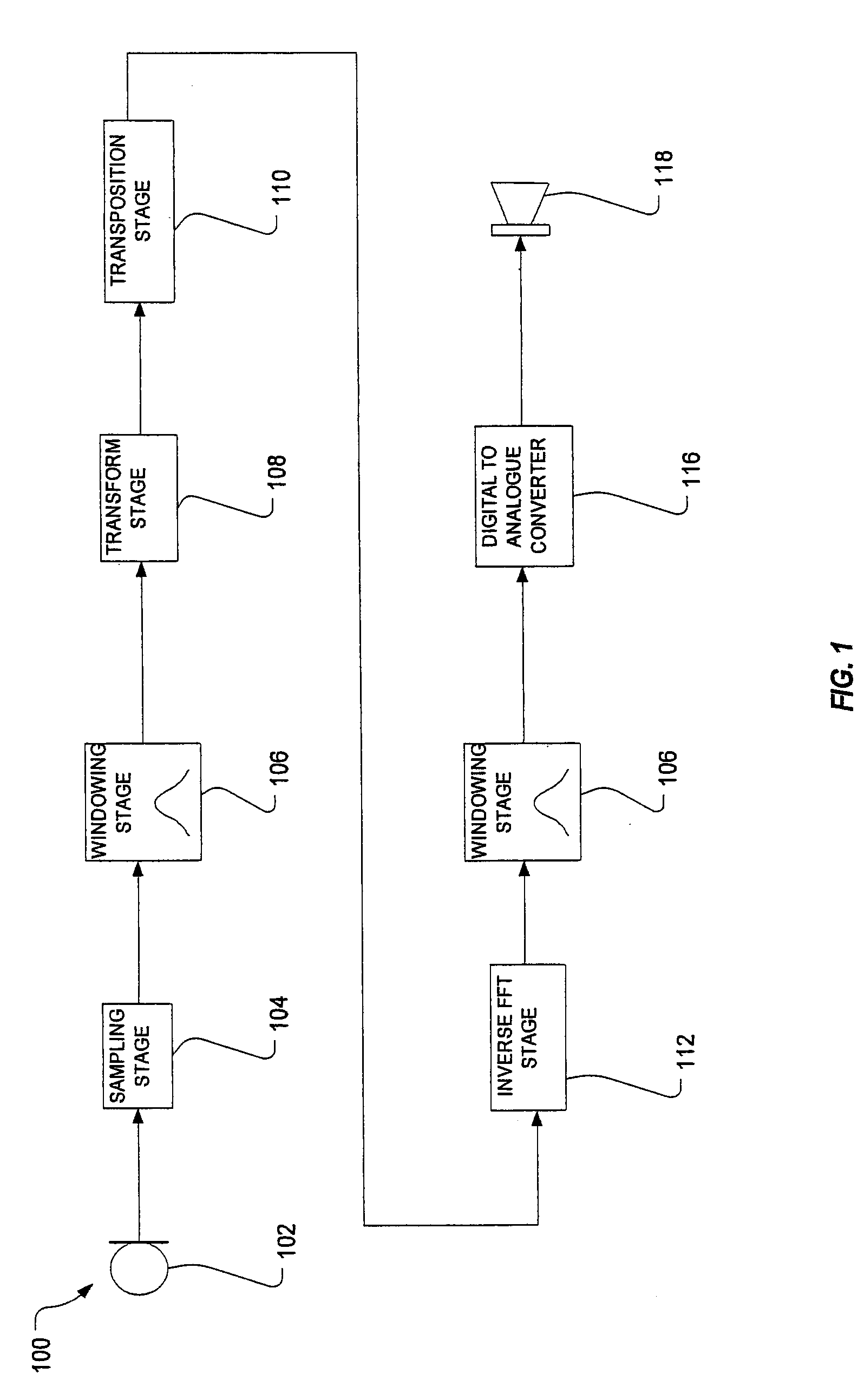
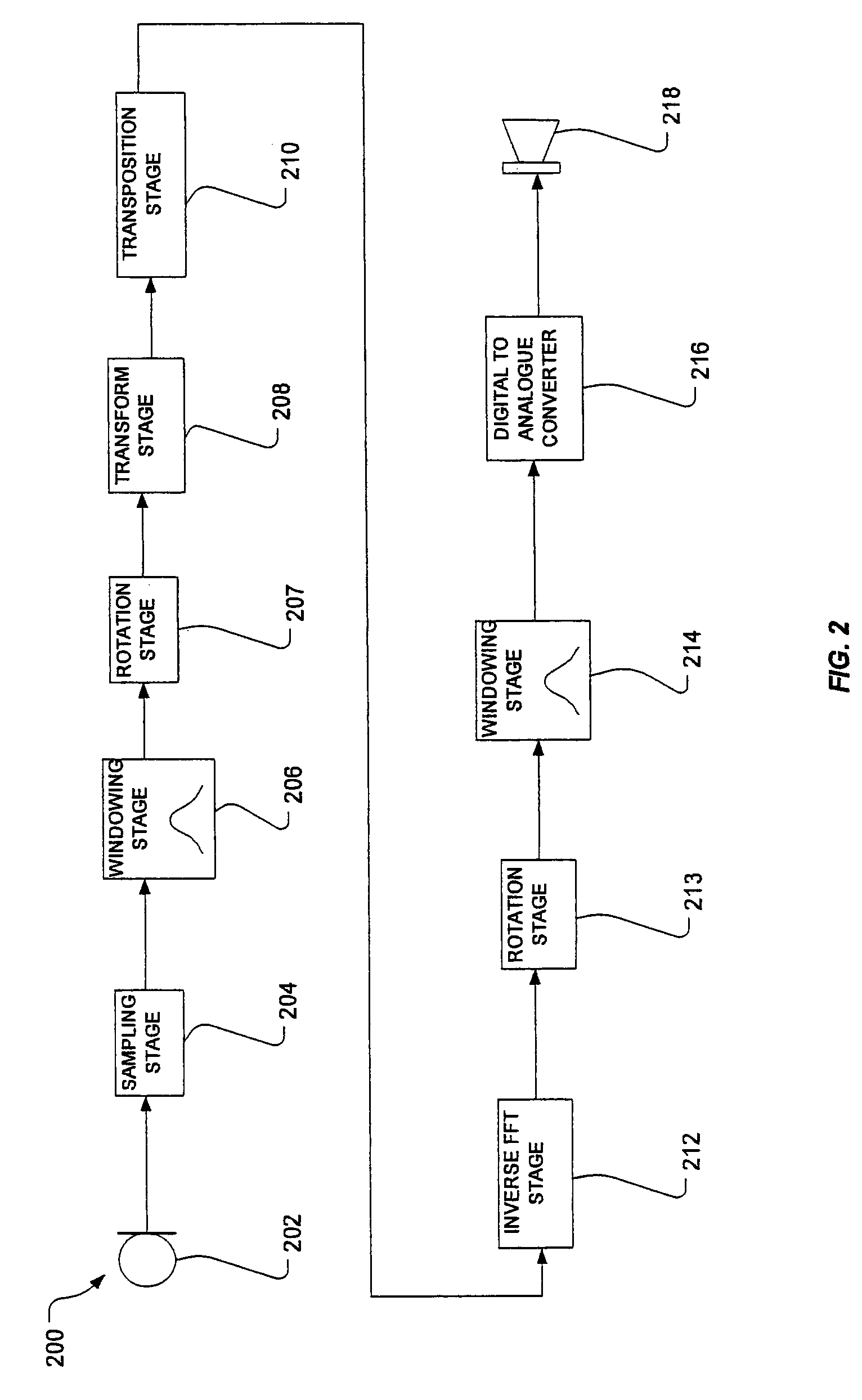
Sound processing with frequency transposition
InactiveUS20060253209A1Speech analysisHearing aids signal processingFrequency spectrumSpectral representation
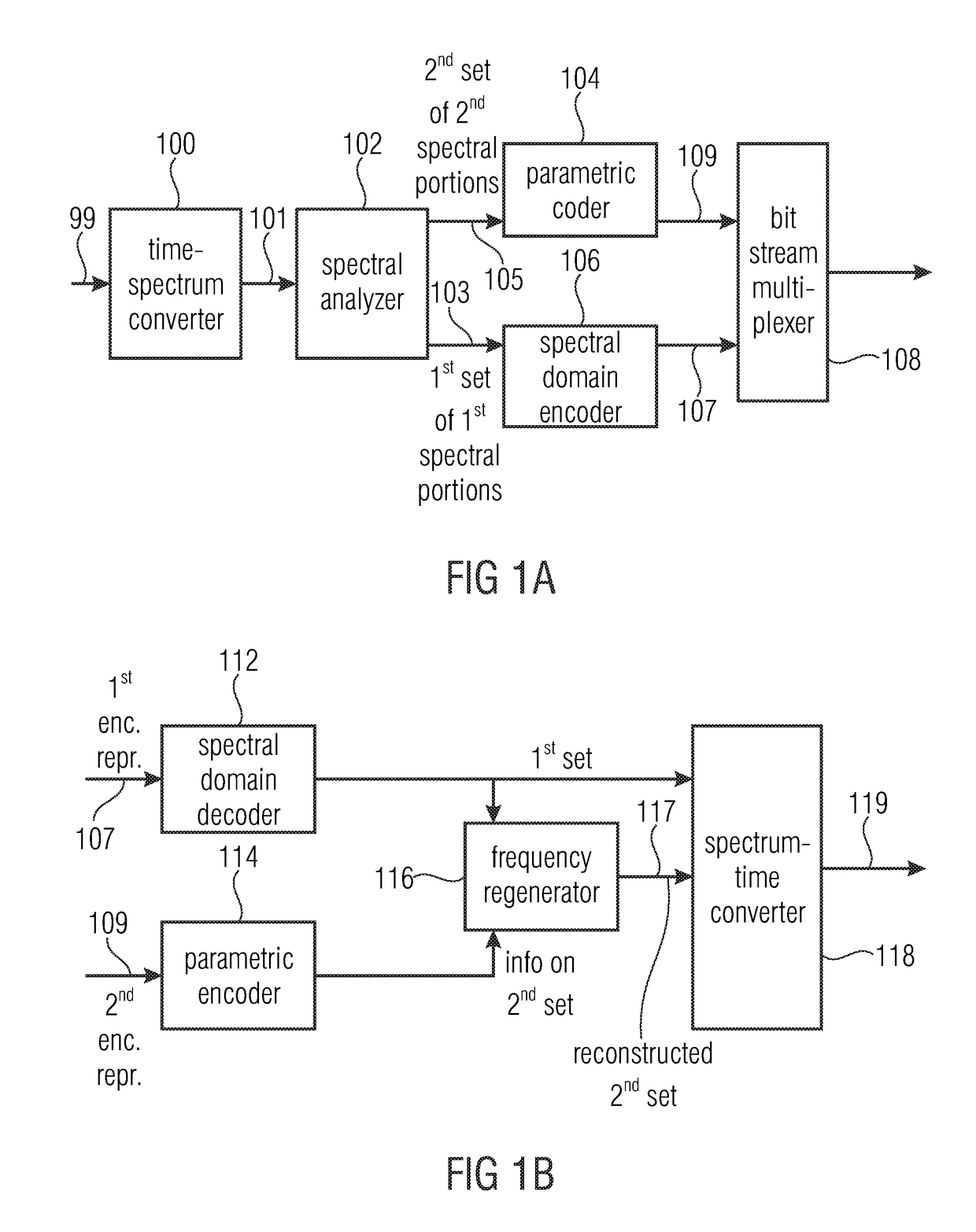
There is disclosed, in one aspect, a signal processing device (100) including: processing means (108) for generating a spectral representation of an input sound signal; frequency transposition means (110) for transposing at least part of the input signal's spectral representation to a transposed output frequency, said frequency transposition means (110) being configured to process the portion of the input signal spectral representation such that a phase relationship that existed in the input signal's spectral representation is substantially maintained in the transposed portion of the spectral representation; and synthesis means (112) for generating an output signal including the transposed portion of the input signal. Associated methods of processing a received sound signal are also disclosed.
Owner:PHONAK
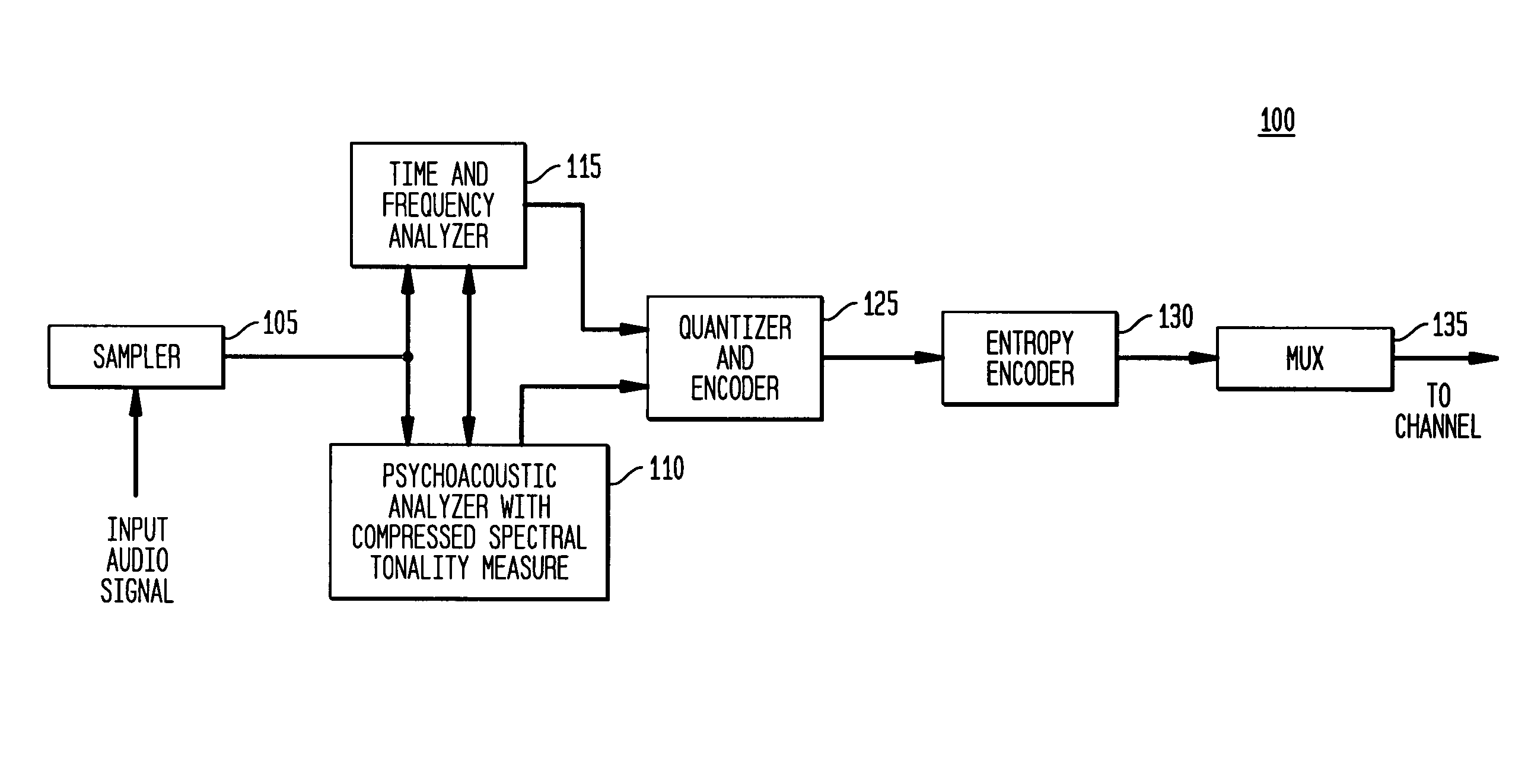
Tonal analysis for perceptual audio coding using a compressed spectral representation
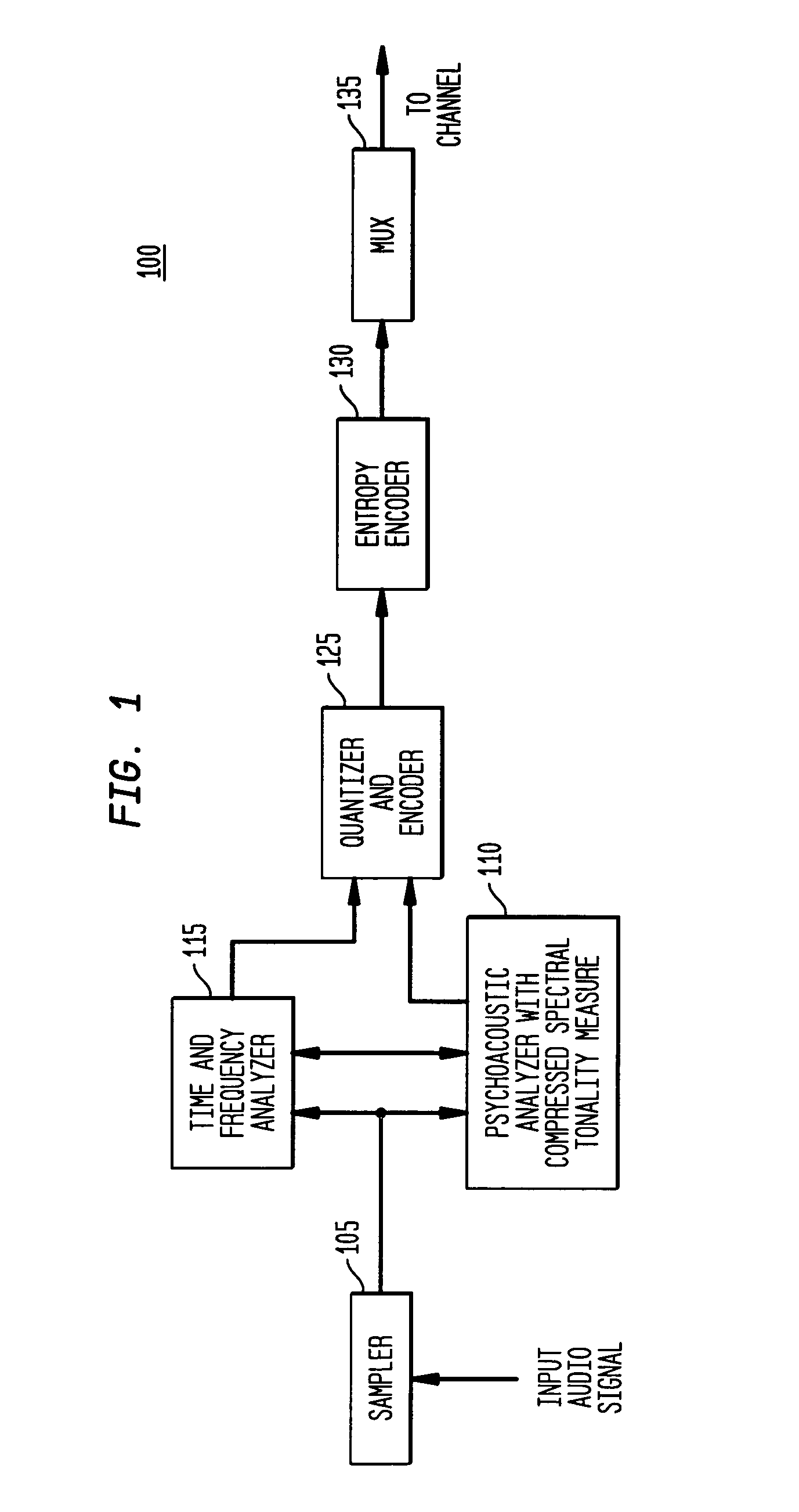
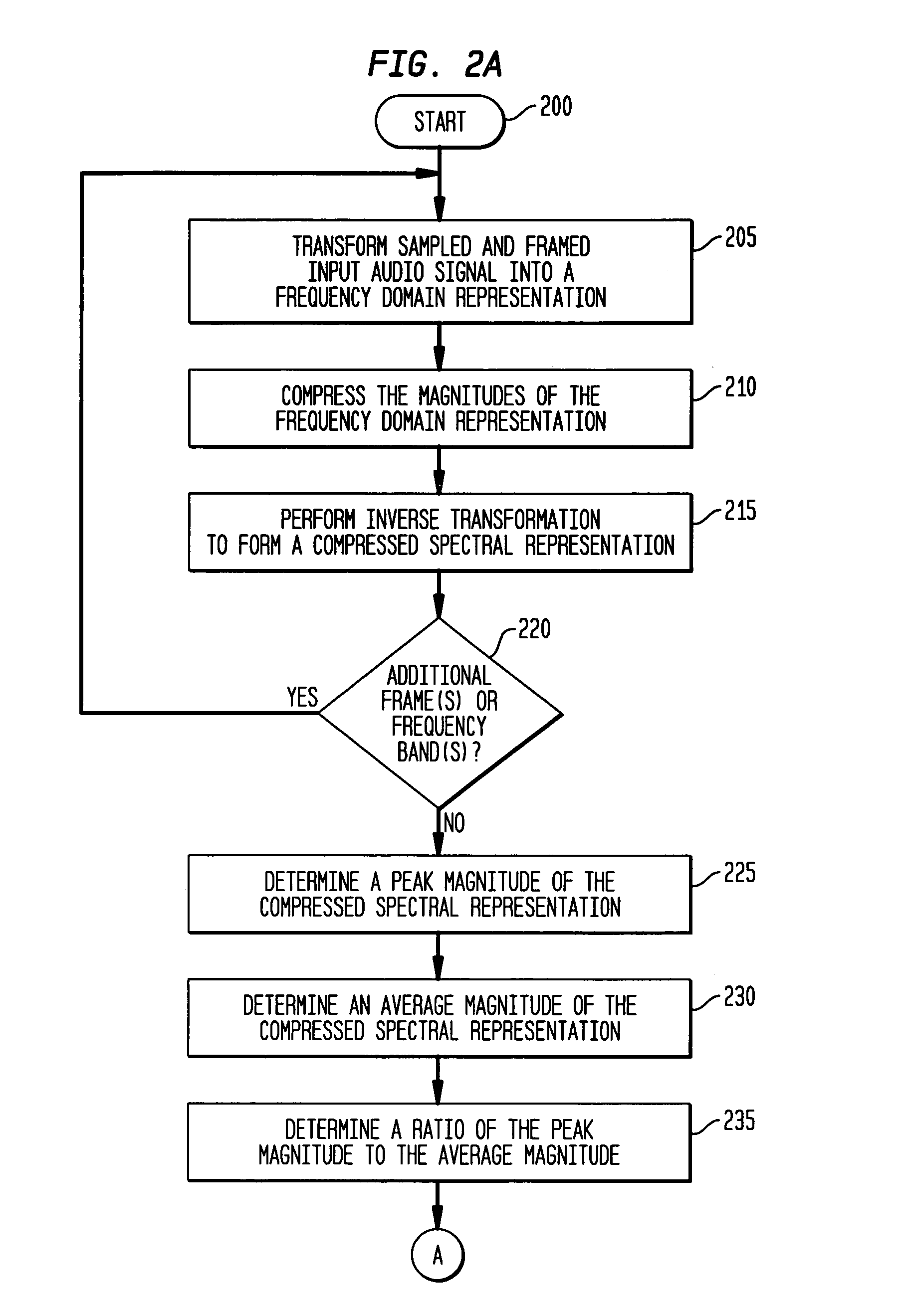
The present invention provides an apparatus, method and tangible medium storing instructions for determining tonality of an input audio signal, for selection of corresponding masked thresholds for use in perceptual audio coding. In the various embodiments, the input audio signal is sampled and transformed using a compressed spectral operation to form a compressed spectral representation, such as a cepstral representation. A peak magnitude and an average magnitude of the compressed spectral representation are determined. Depending upon the ratio of peak-to-average magnitudes, a masked threshold is selected having a corresponding degree of tonality, and is used to determine a plurality of quantization levels and a plurality of bit allocations to perceptually encode the input audio signal with a distortion spectrum beneath a level of just noticeable distortion (JND). The invention also includes other methods and variations for selecting substantially tone-like or substantially noise-like masked thresholds for perceptual encoding of the input audio signal.
Owner:MUCH SHELIST FREED DENENBERG ARNENT & RUBENSTEIN P C +1
Method and device for a harmonic rendering of a melody line
InactiveUS20060075881A1Promote resultsEliminate errorsGearworksMusical toysFrequency spectrumHarmonic
In order to implement the melody extraction or the automatic clearly more stable or to improve the transcription result, respectively, at the resulting segments or trajectories, respectively, of a melody line gained from a spectrogram of the audio signal a harmony mapping is performed such that a follower segment directly neighboring a reference segment in time direction is virtually shifted in the frequency direction by stages of octave, fifth and / or third in order to examine whether among the resulting lines of the octave, fifth and / or third there is one that fulfills a predetermined condition, like e.g. that the time / spectral representation along this line comprises a minimum which is larger by a certain factor than a minimum that it comprises along the reference segment line, and, if such a line exists, selects the same and actually performs the shifting of the follower segment. This way, errors in melody line determination may be corrected again. By a suitable selection of predetermined conditions for the lines of the octave, fifth and / or third, the direct neighborhood and further possible conditions, a faulty shifting may be prevented.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
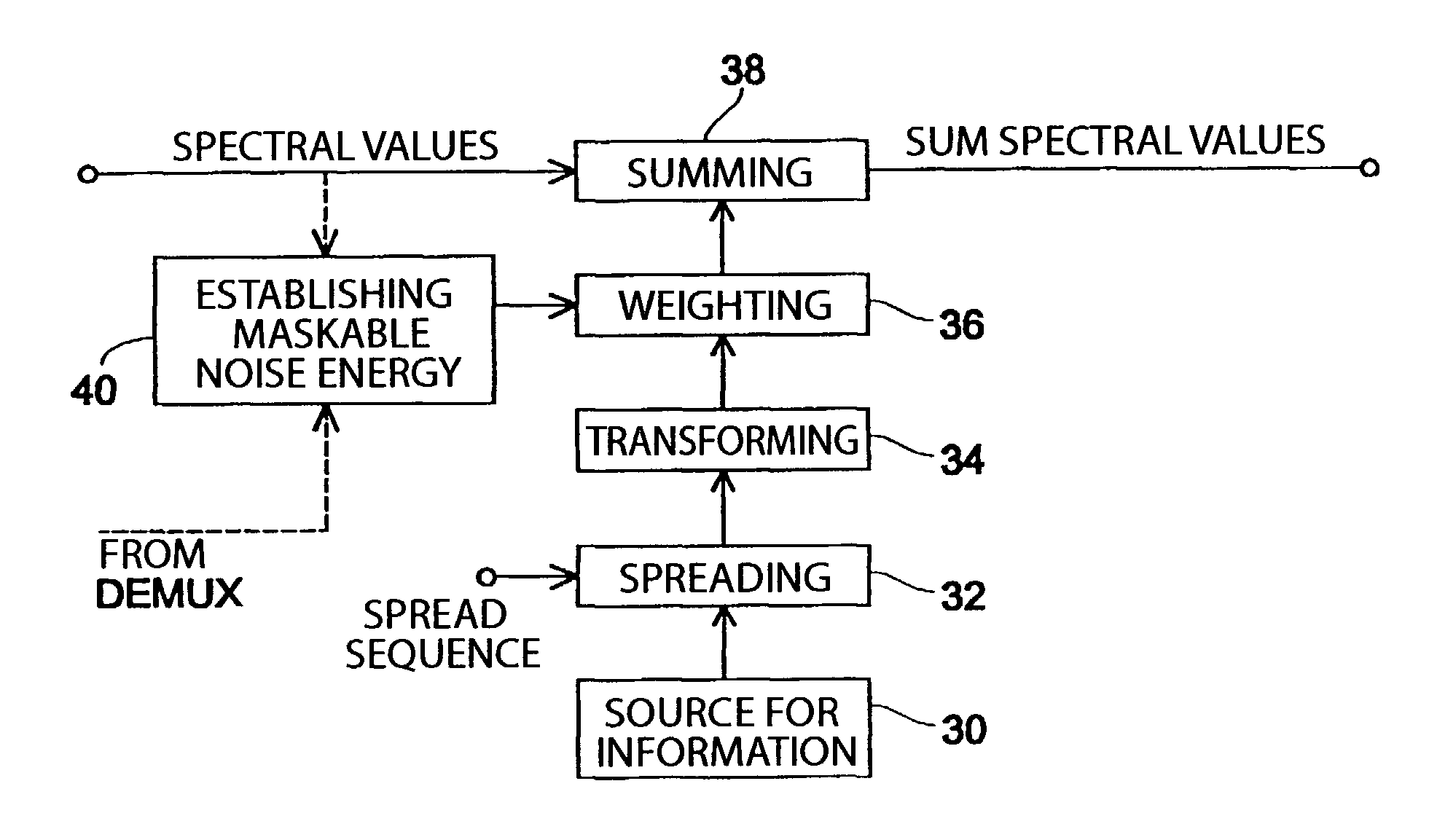
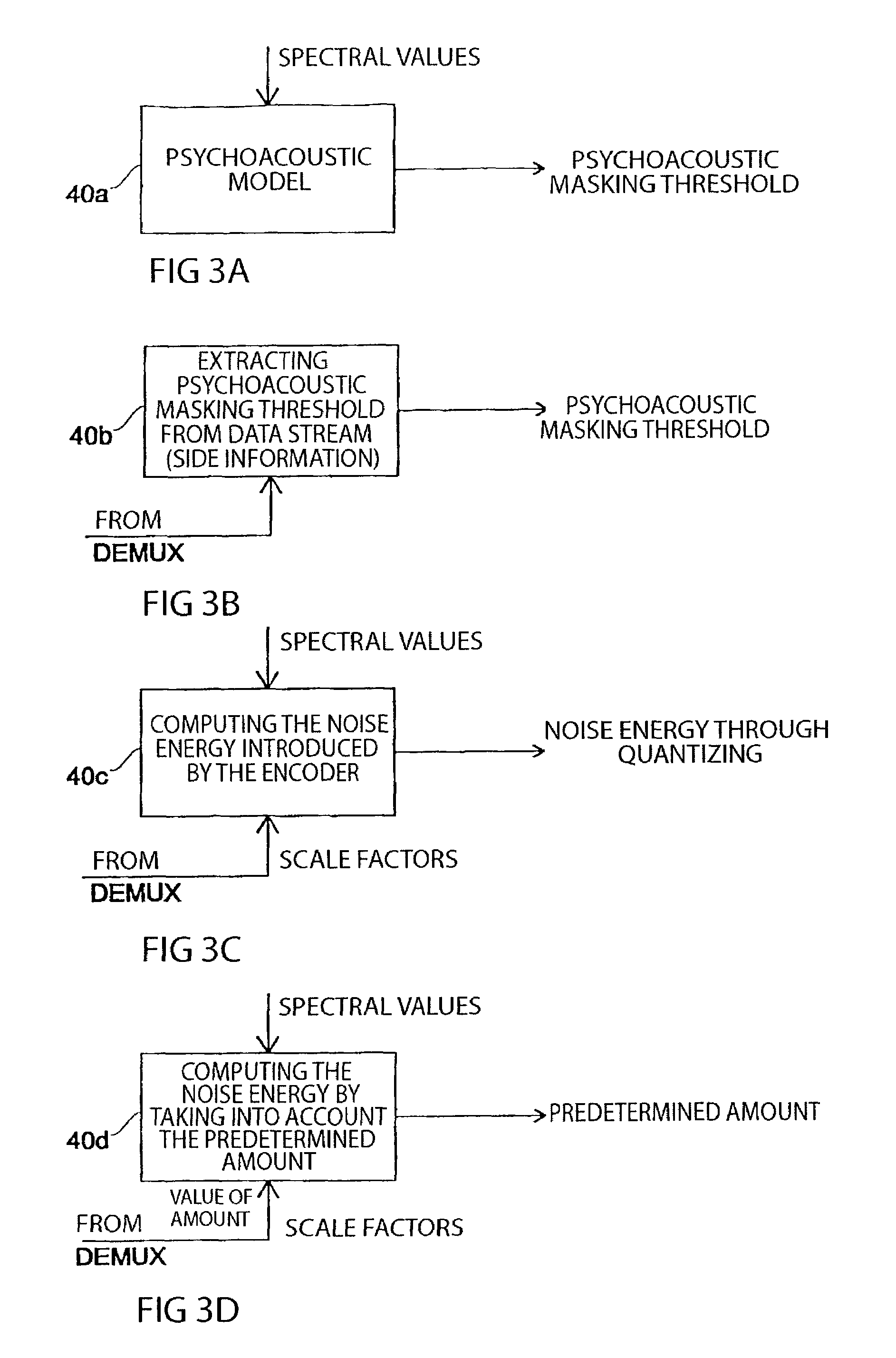
Method and apparatus for introducing information into a data stream and method and apparatus for encoding an audio signal
InactiveUS7454327B1Improve interoperabilityEasy to implementSpeech analysisPlural information simultaneous broadcastTime domainFrequency spectrum
An inventive method for introducing information into a data stream including data about spectral values representing a short-term spectrum of an audio signal first performs a processing of the data stream to obtain the spectral values of the short-term spectrum of the audio signal. Apart from that, the information to be introduced are combined with a spread sequence to obtain a spread information signal, whereupon a spectral representation of the spread information is generated which will then be weighted with an established psychoacoustic maskable noise energy to generate a weighted information signal, wherein the energy of the introduced information is substantially equal to or below the psychoacoustic masking threshold. The weighted information signal and the spectral values of the short-term spectrum of the audio signal will then be summed and afterwards processed again to obtain a processed data stream including both audio information and information to be introduced. By the fact that the information to be introduced are introduced into the data stream without changing to the time domain, the block rastering underlying the short-term spectrum will not be touched, so that introducing a watermark will not lead to tandem encoding effects.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
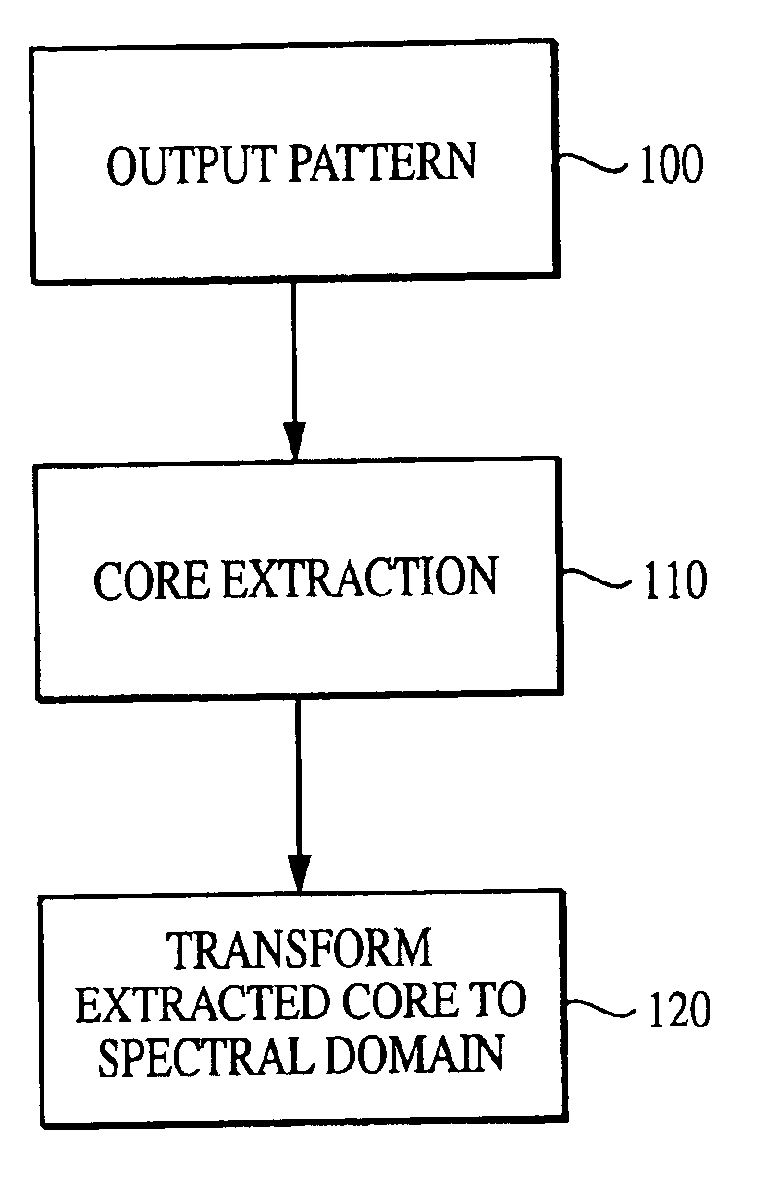
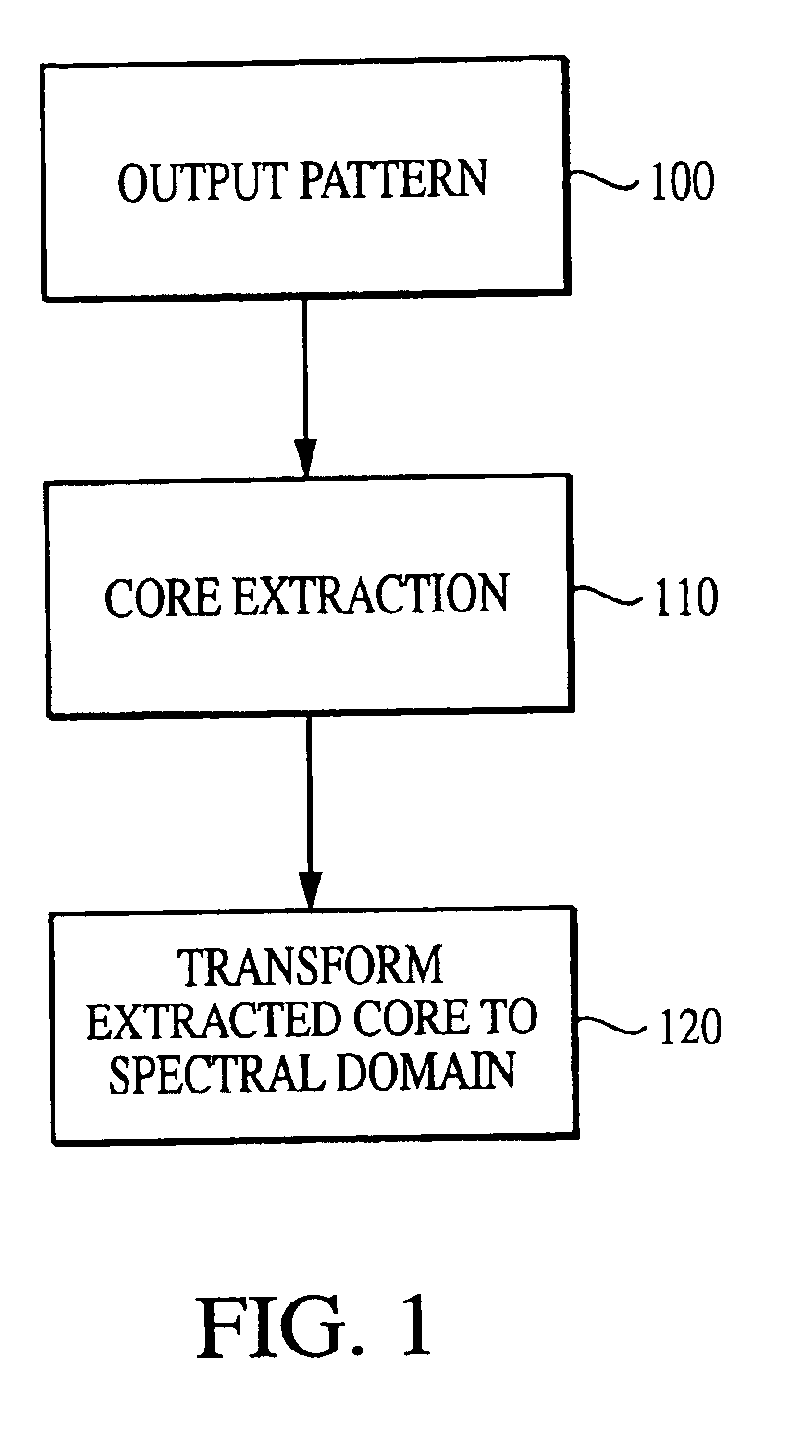
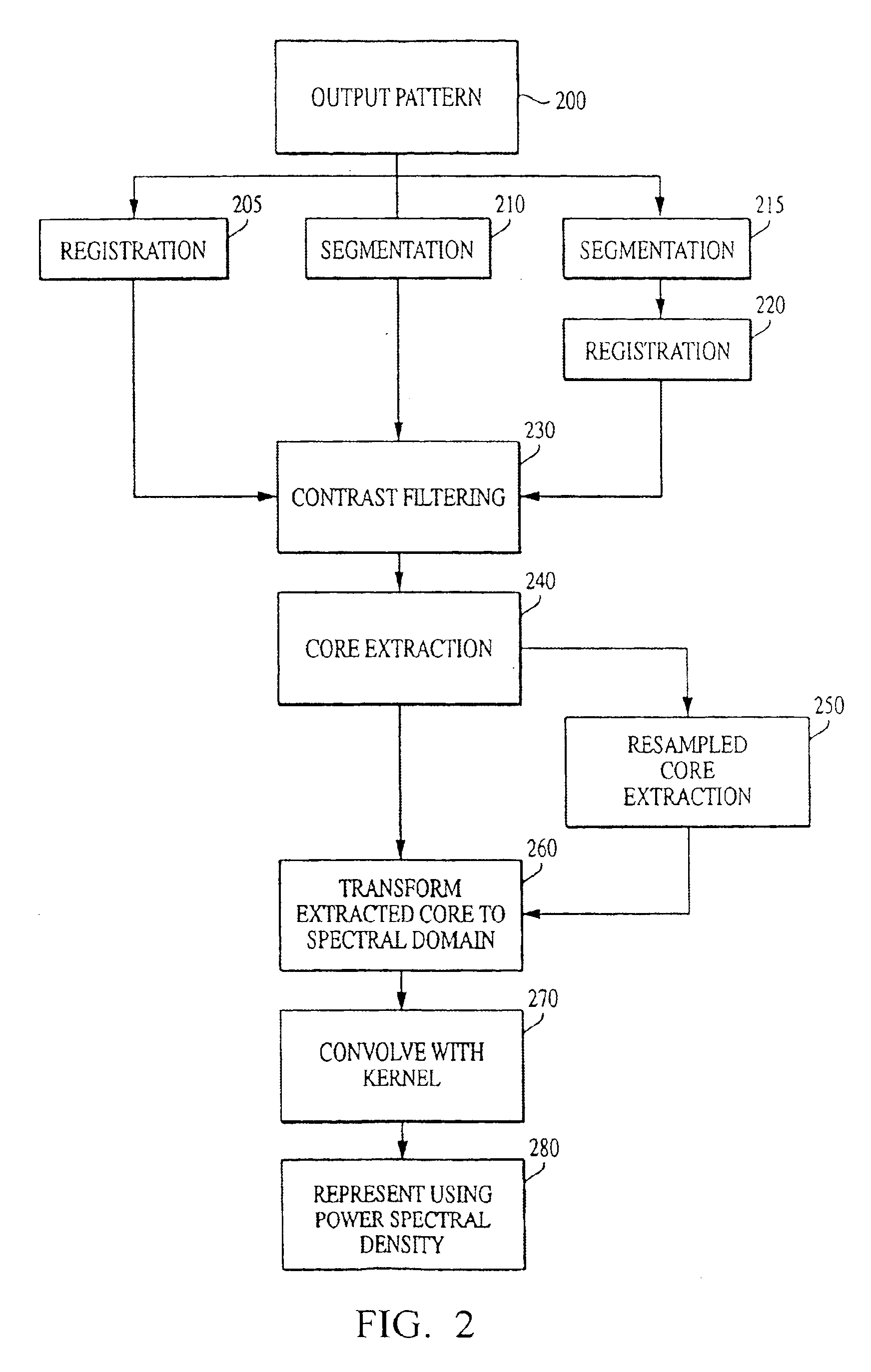
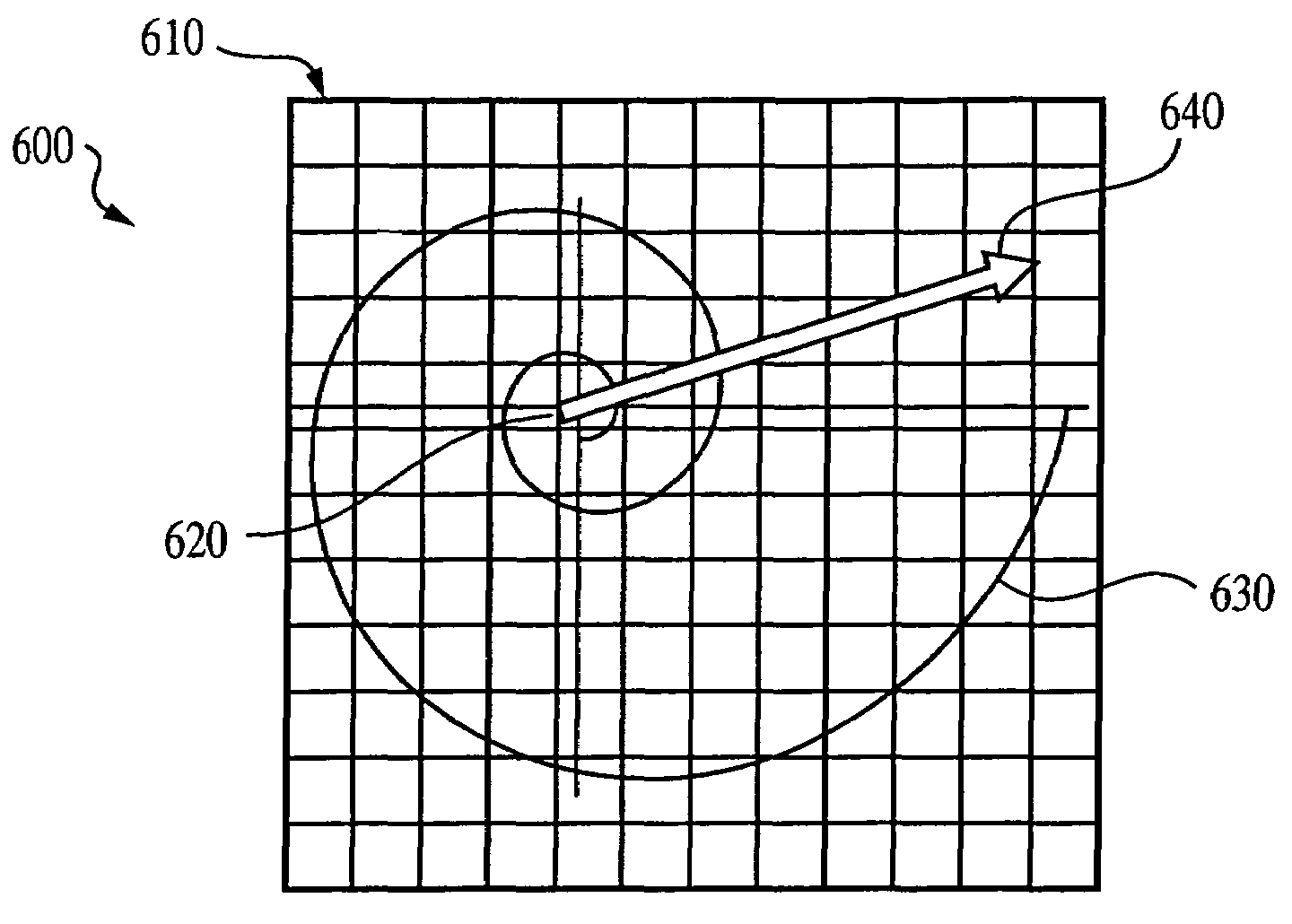
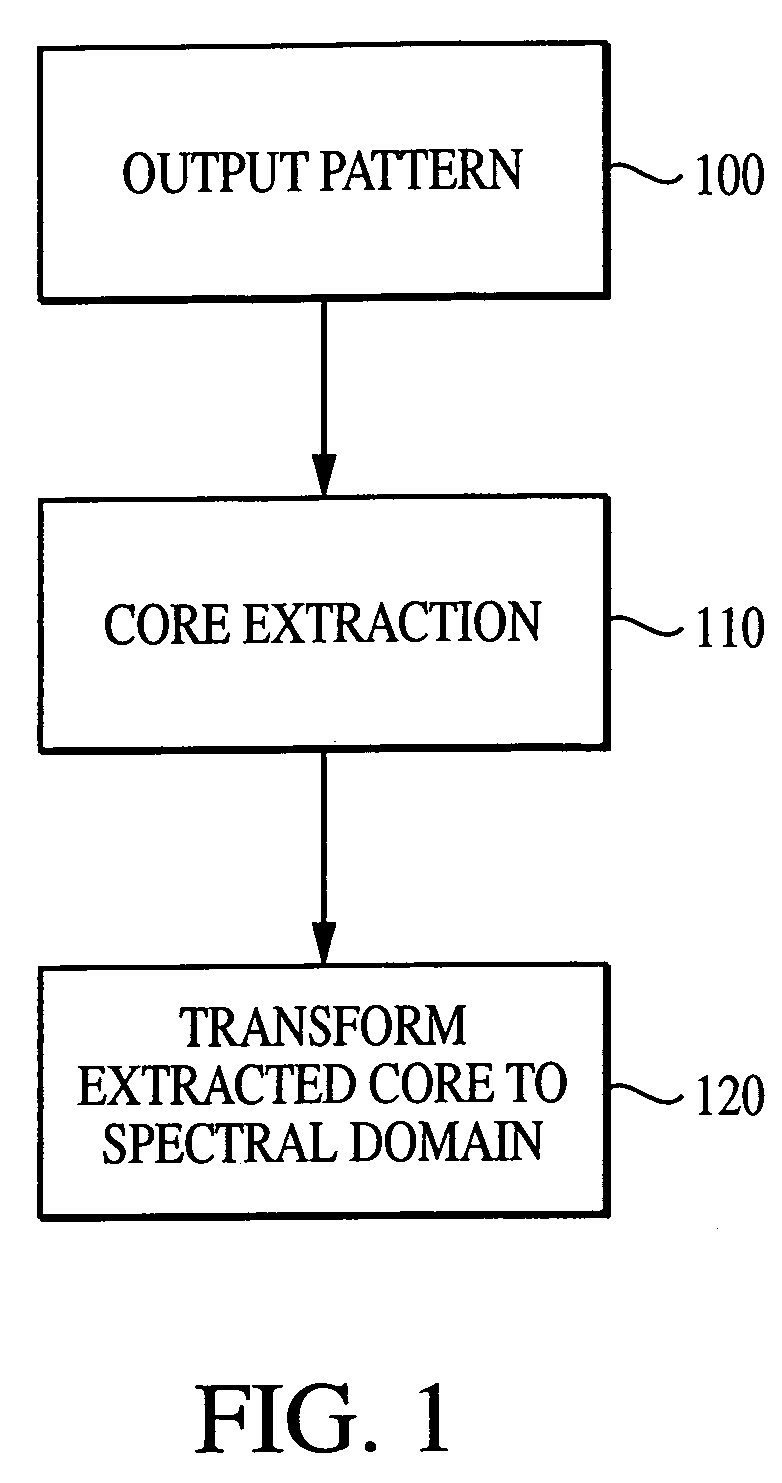
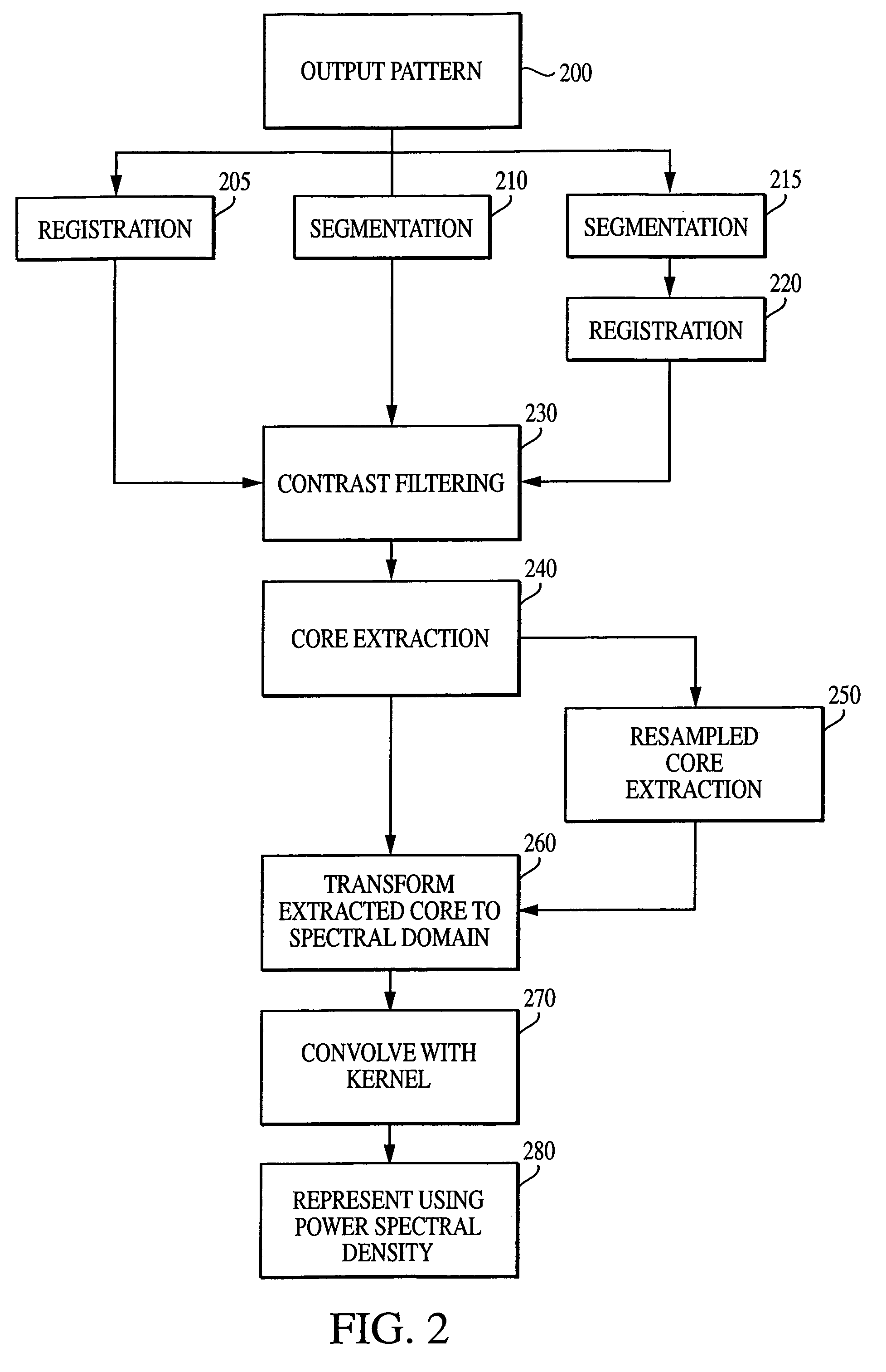
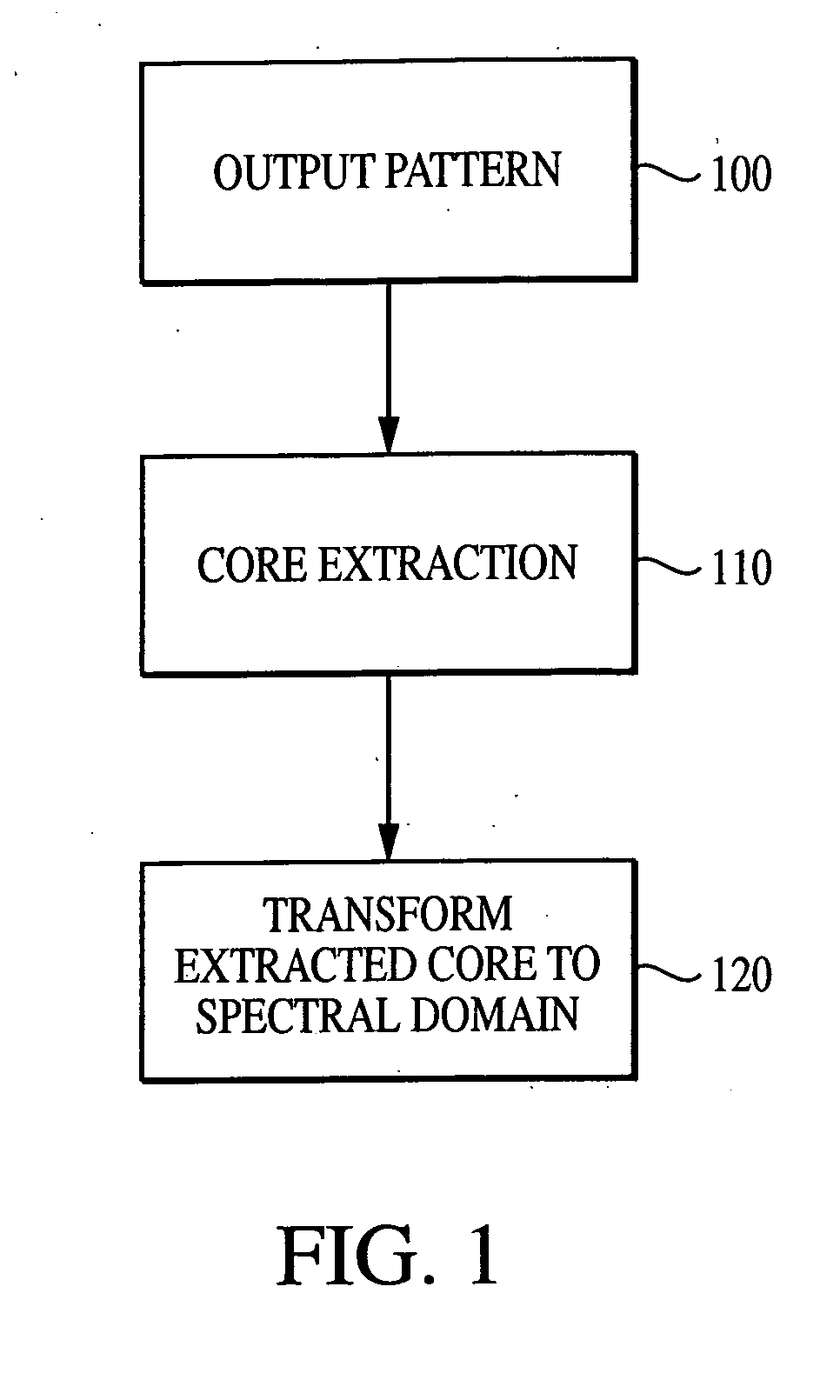
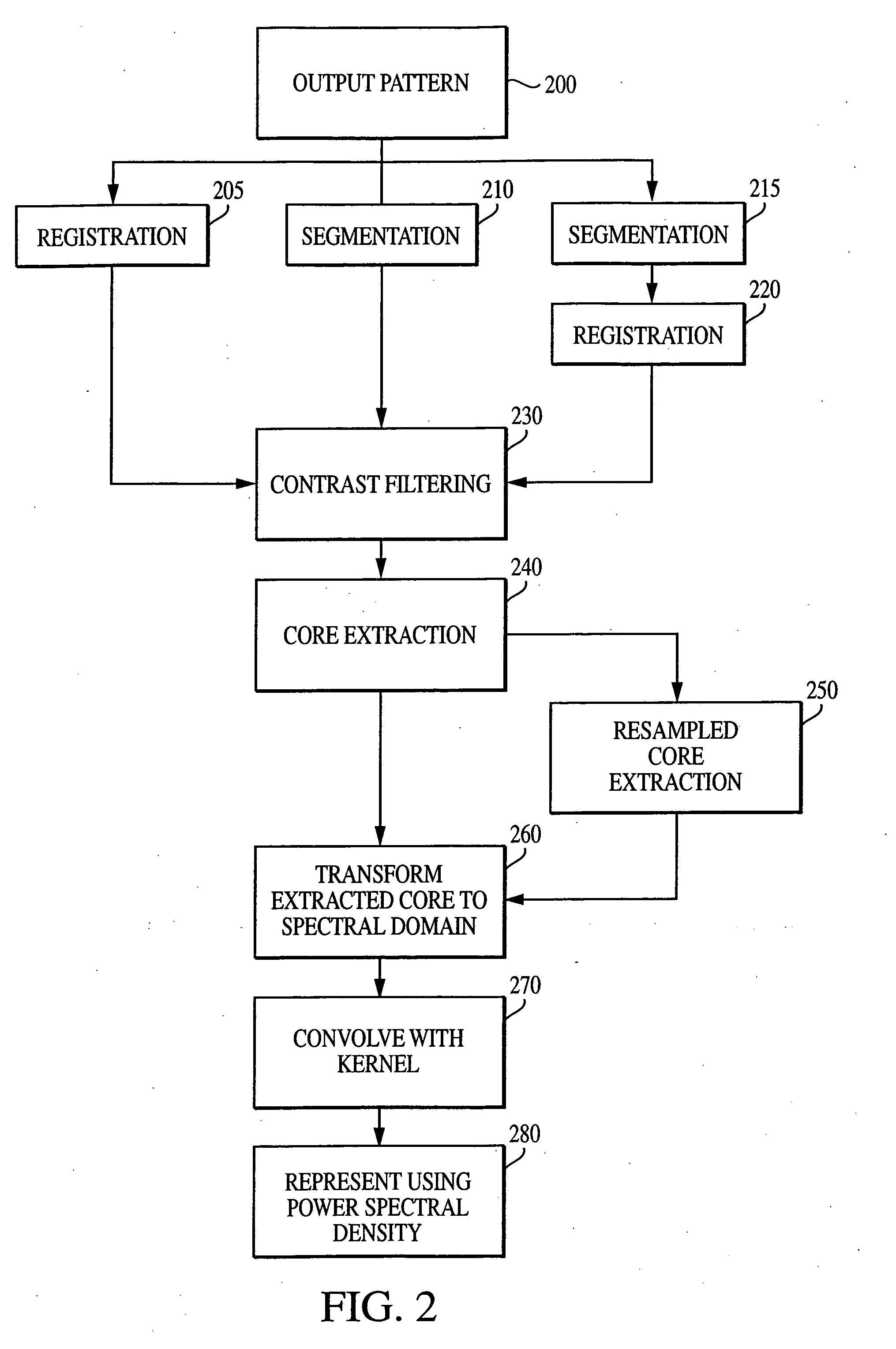
System and method for characterizing microarray output data
InactiveUS7006680B2Increase contrastImprove spatial resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisFrequency spectrumSpectral transformation
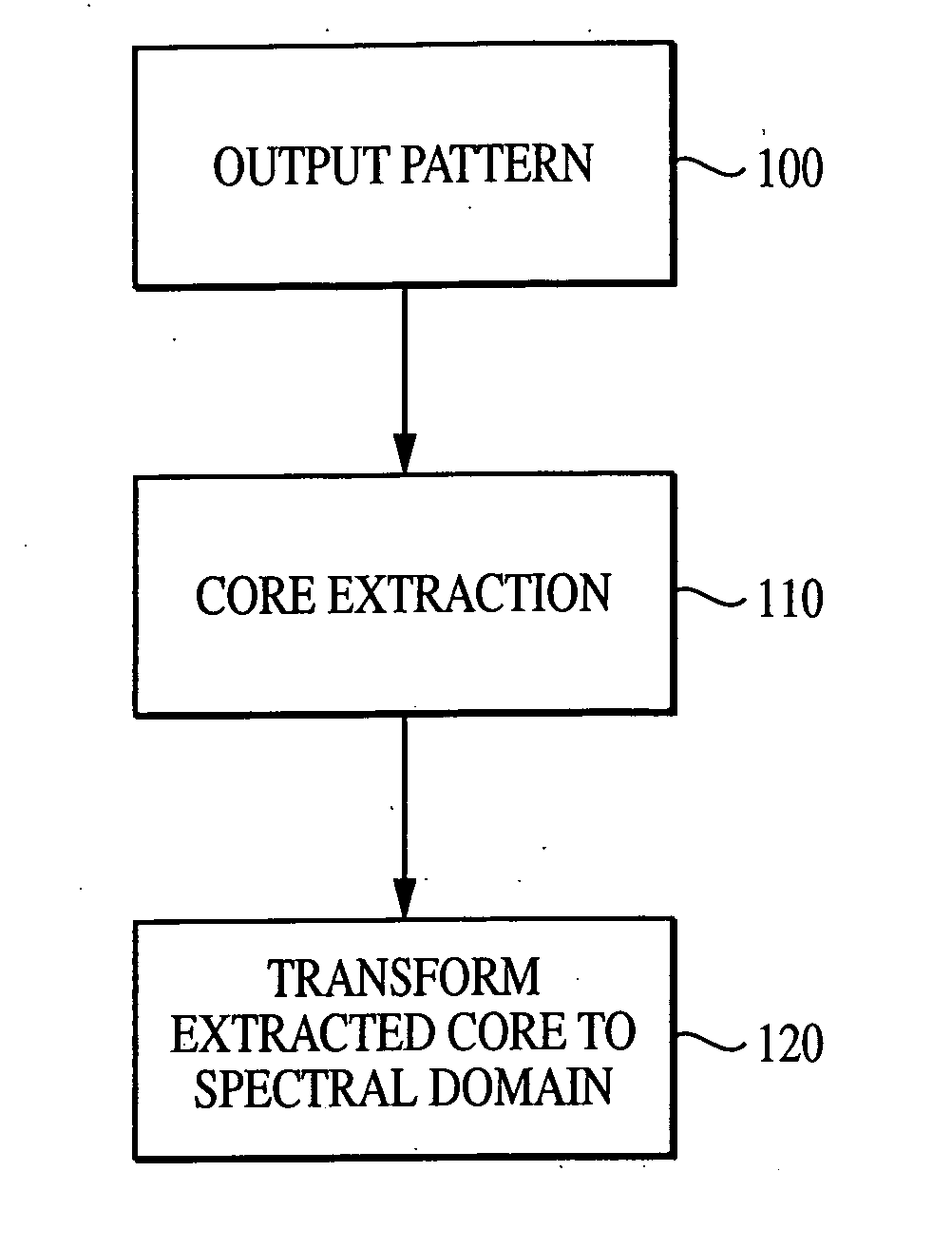
The current invention discloses a novel spectral transformation technique for characterizing digitized intensity output patterns from microarrays. This method yields improved sensitivity with reduced false positives and false negatives. Current microarray methods are overly sensitive to the detection of a visible distinction between pixels associated with probes and pixels associated with background. In one embodiment, a technique is disclosed that comprises the steps of: extracting pixels associated with an object of interest and transforming such pixels from an intensity representation to a spectral representation. In some embodiments, the extraction is based on a tessellated logarithmic spiral extraction that may yield a pixel core with a sampling of both foreground and background pixels. This core may then be computationally rescaled by 10×-10,000× to enhance spatial resolution. Once the extracted pixels are represented in the spectral regime, convolution with resolution-enhancement kernels may be used to accentuate morphological features capturing platform specific phenomenology.
Owner:VIALOGY
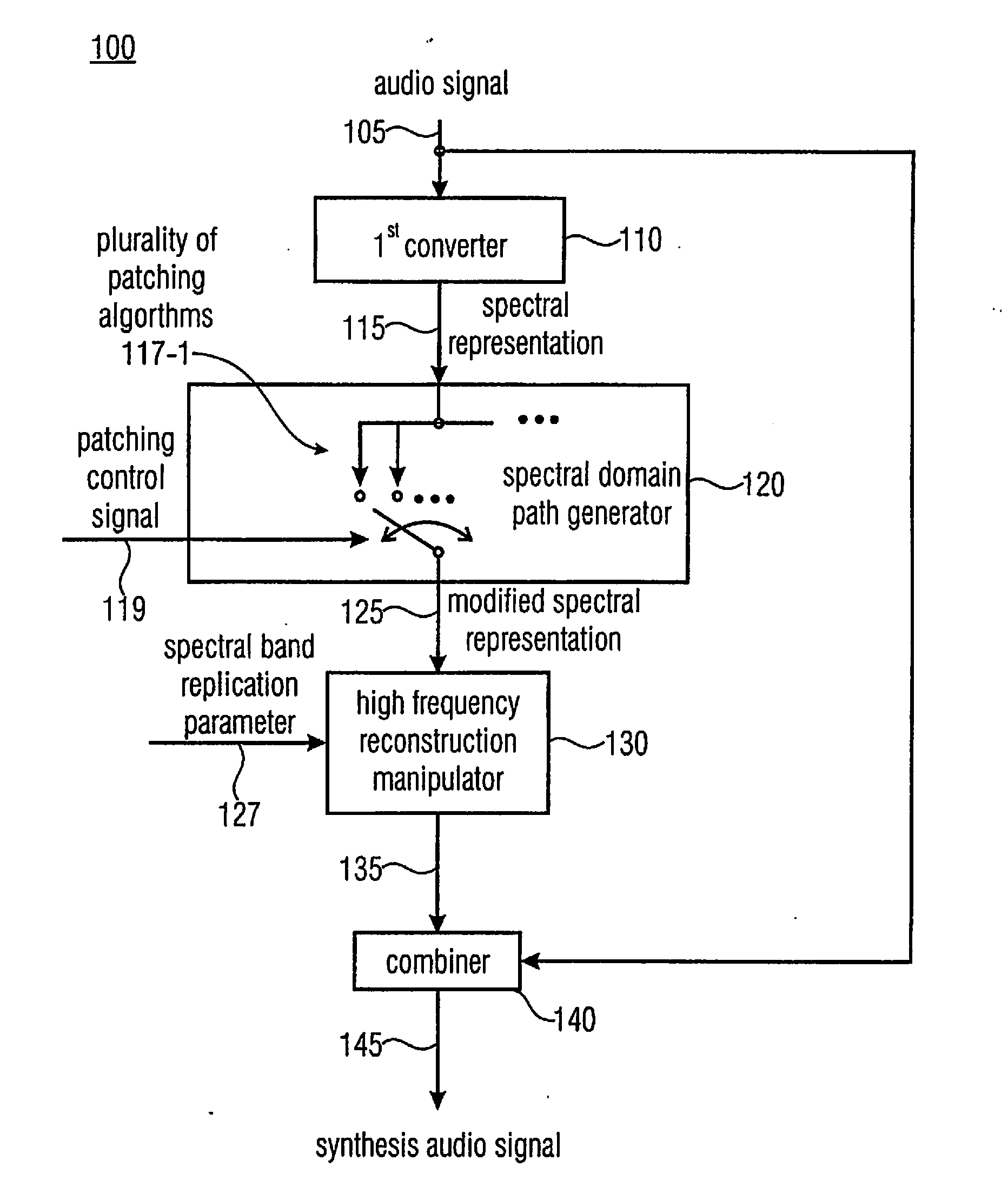
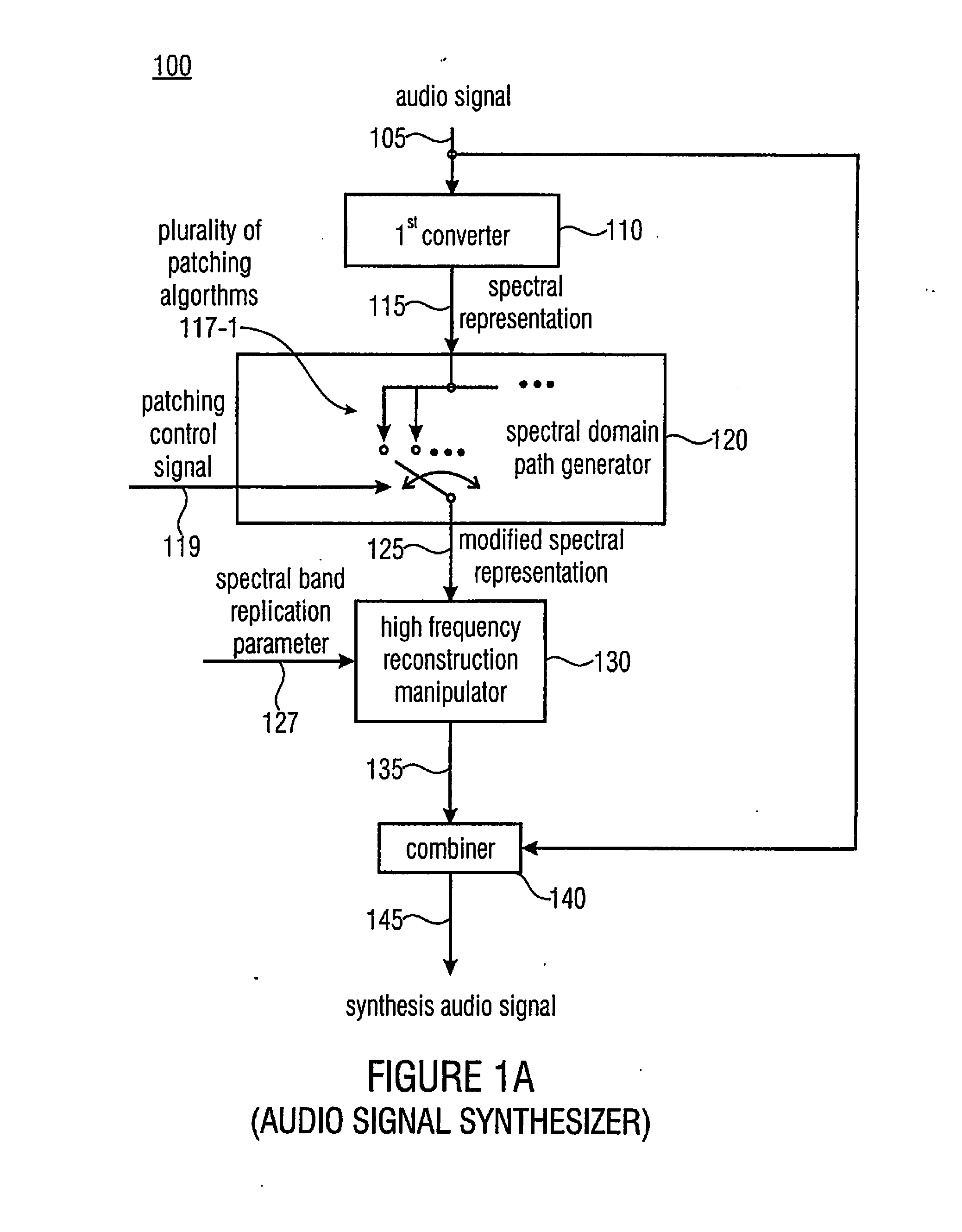
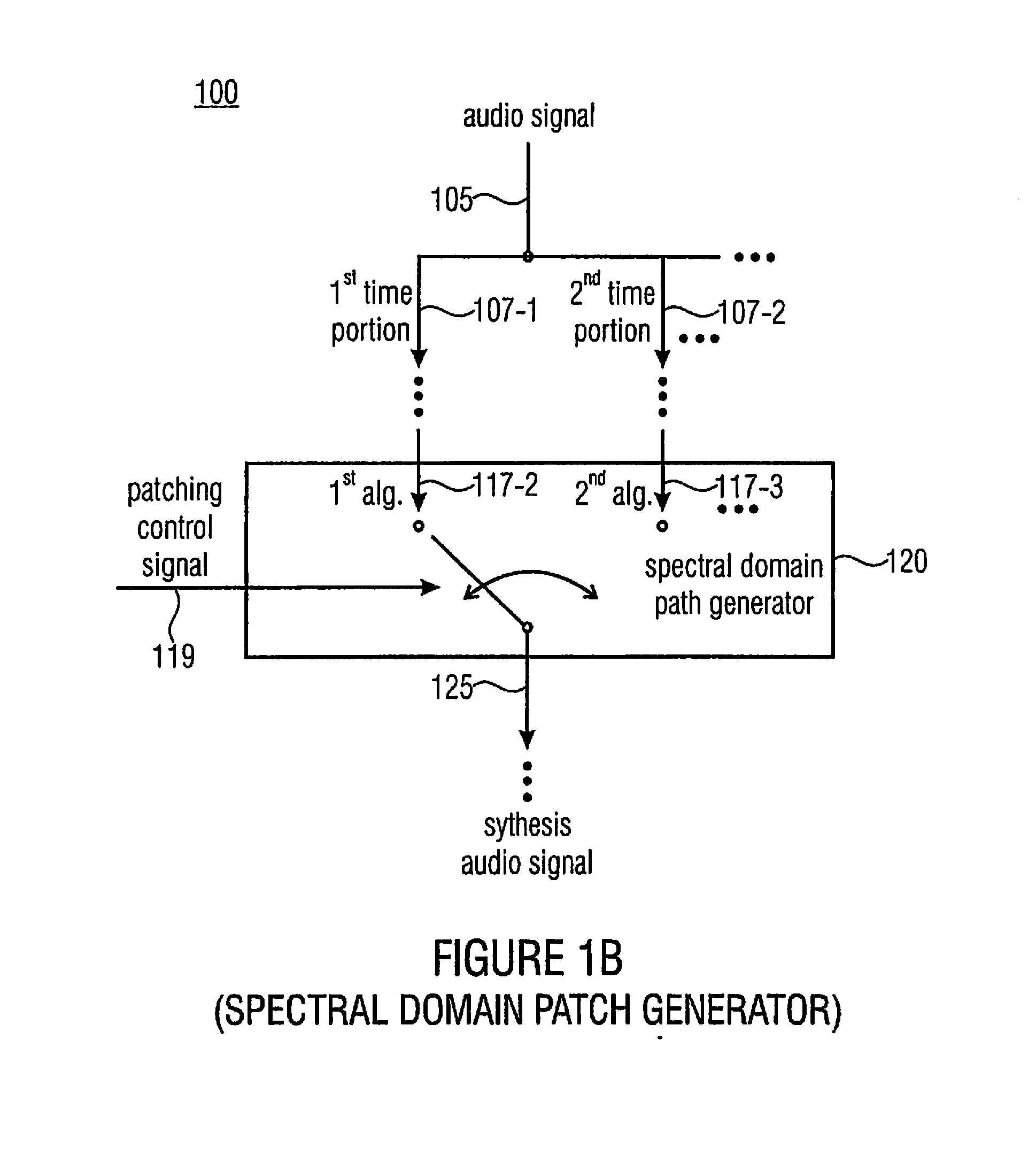
Apparatus and Method for Generating a Synthesis Audio Signal and for Encoding an Audio Signal
ActiveUS20110282675A1Reduced quality and flexibilityQuality improvementSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumControl signal
An apparatus for generating a synthesis audio signal using a patching control signal has a first converter, a spectral domain patch generator, a high frequency reconstruction manipulator and a combiner. The first converter is configured for converting a time portion of an audio signal into a spectral representation. The spectral domain patch generator is configured for performing a plurality of different spectral domain patching algorithms, wherein each patching algorithm generates a modified spectral representation having spectral components in an upper frequency band derived from corresponding spectral components in a core frequency band of the audio signal. The spectral domain patch generator is furthermore configured to select a first spectral domain patching algorithm from the plurality of patching algorithms for a first time portion and a second spectral domain patching algorithm from the plurality of patching algorithm for a second different time portion in accordance with the patching control signal to obtain the modified spectral representation.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Audio encoder and decoder using a frequency domain processor , a time domain processor, and a cross processing for continuous initialization
An audio encoder for encoding an audio signal, includes: a first encoding processor for encoding a first audio signal portion in a frequency domain, wherein the first encoding processor includes: a time frequency converter for converting the first audio signal portion into a frequency domain representation having spectral lines up to a maximum frequency of the first audio signal portion; a spectral encoder for encoding the frequency domain representation; a second encoding processor for encoding a second different audio signal portion in the time domain; a cross-processor for calculating, from the encoded spectral representation of the first audio signal portion, initialization data of the second encoding processor, so that the second encoding processing is initialized to encode the second audio signal portion immediately following the first audio signal portion in time in the audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Apparatus and method for generating a high frequency audio signal using adaptive oversampling
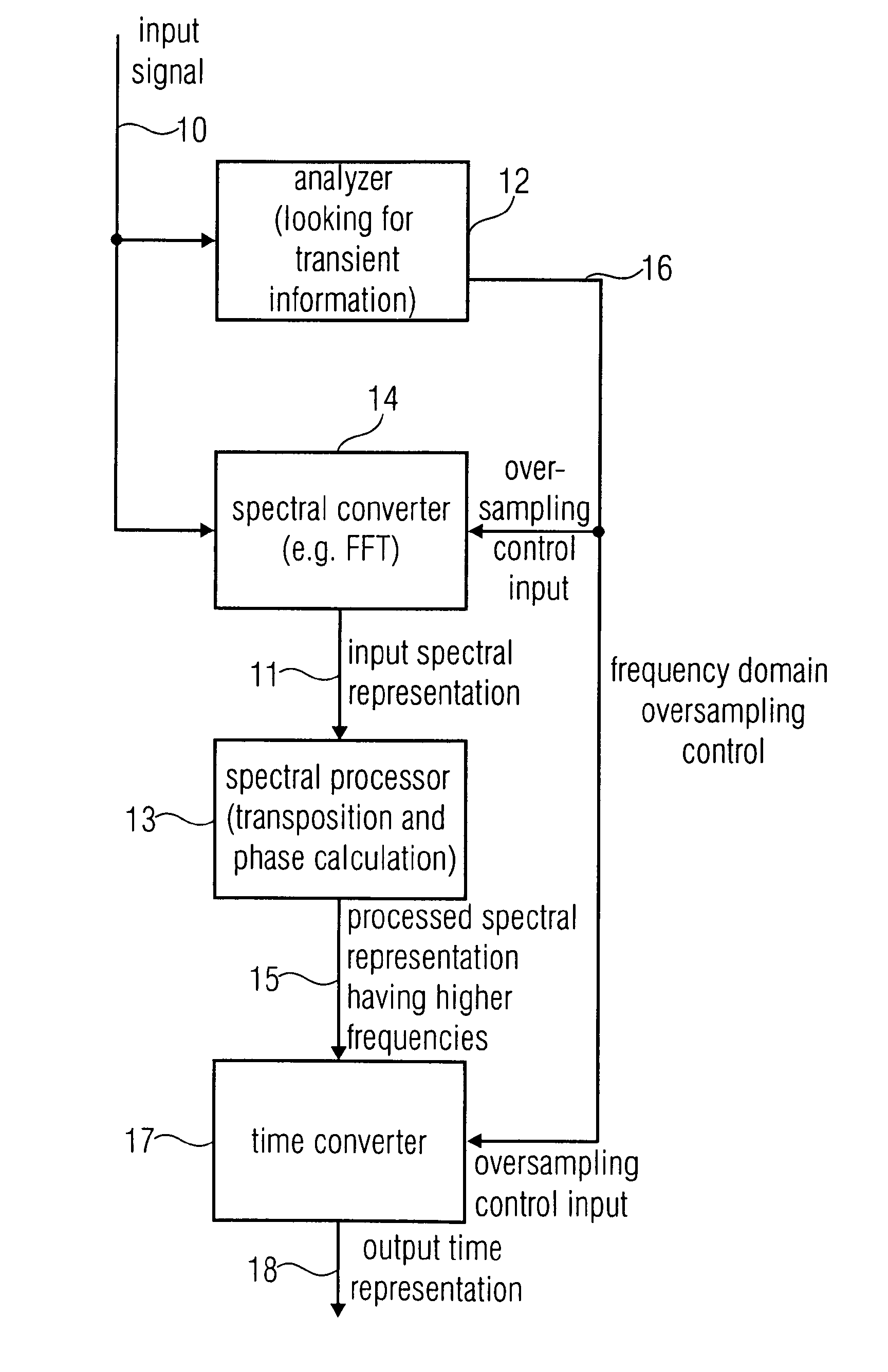
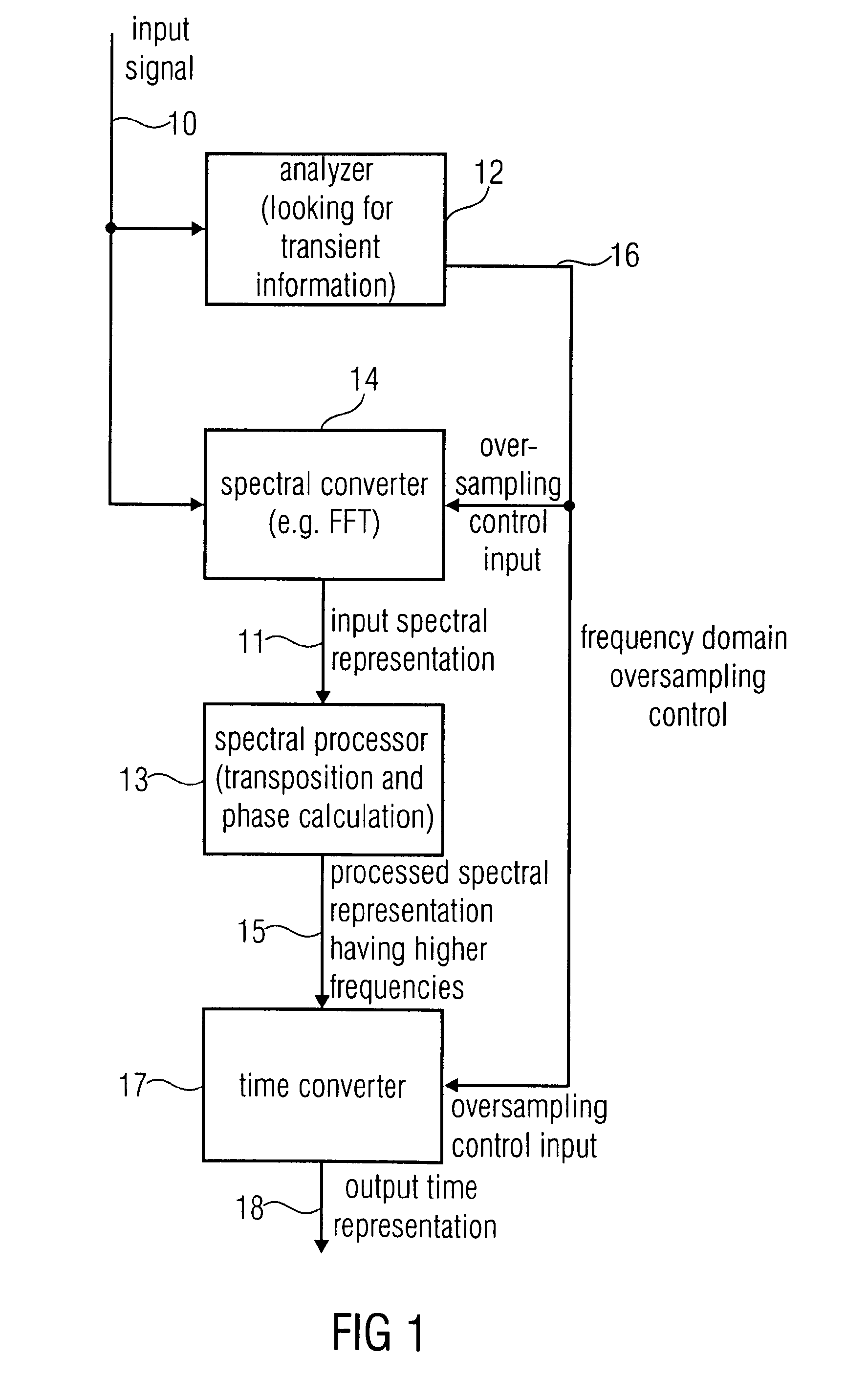
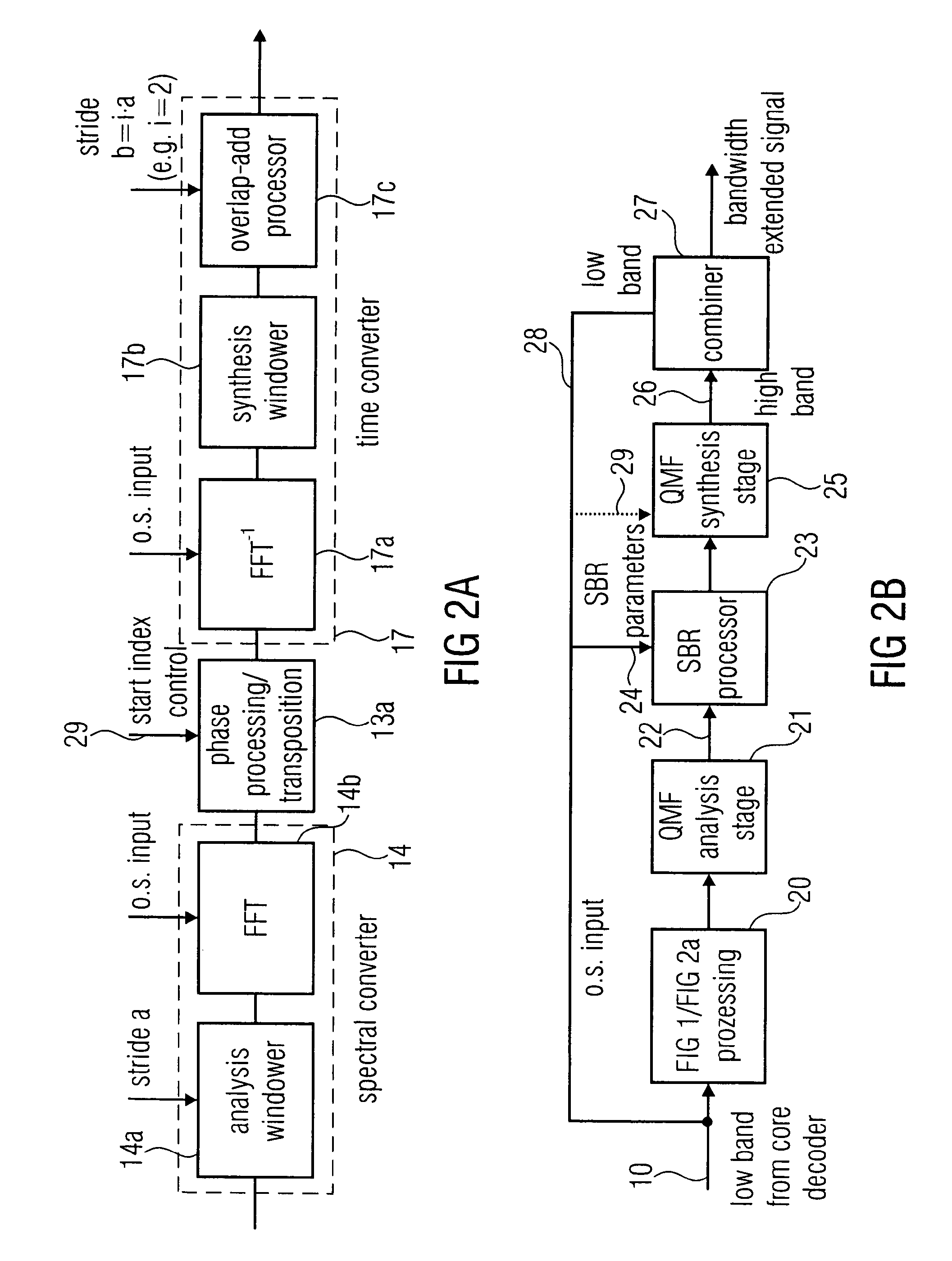
ActiveUS20120281859A1Reduce complexityImprove transient performanceSpeech analysisTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsFrequency spectrumOversampling
An apparatus for generating a high frequency audio signal that includes an analyzer for analyzing an input signal to determine a transient information adaptively. Additionally a spectral converter is provided for converting the input signal into an input spectral representation. A spectral processor processes the input spectral representation to generate a processed spectral representation including values for higher frequencies than the input spectral representation. A time converter is configured for converting the processed spectral representation to a time representation, wherein the spectral converter or the time converter are controllable to perform a frequency domain oversampling for the first portion of the input signal having the transient information associated and to not perform the frequency domain oversampling for the second portion of the input signal not having the associated transient information.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB +1
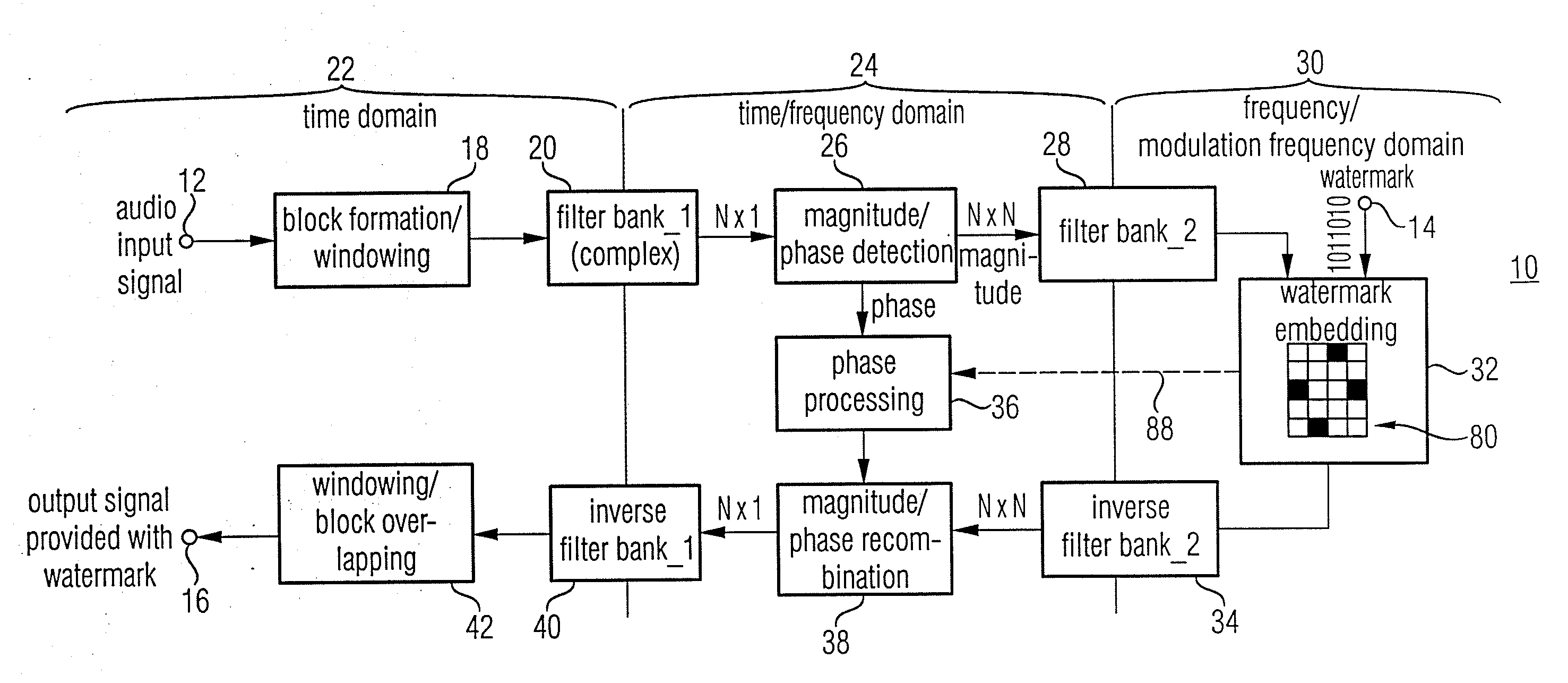
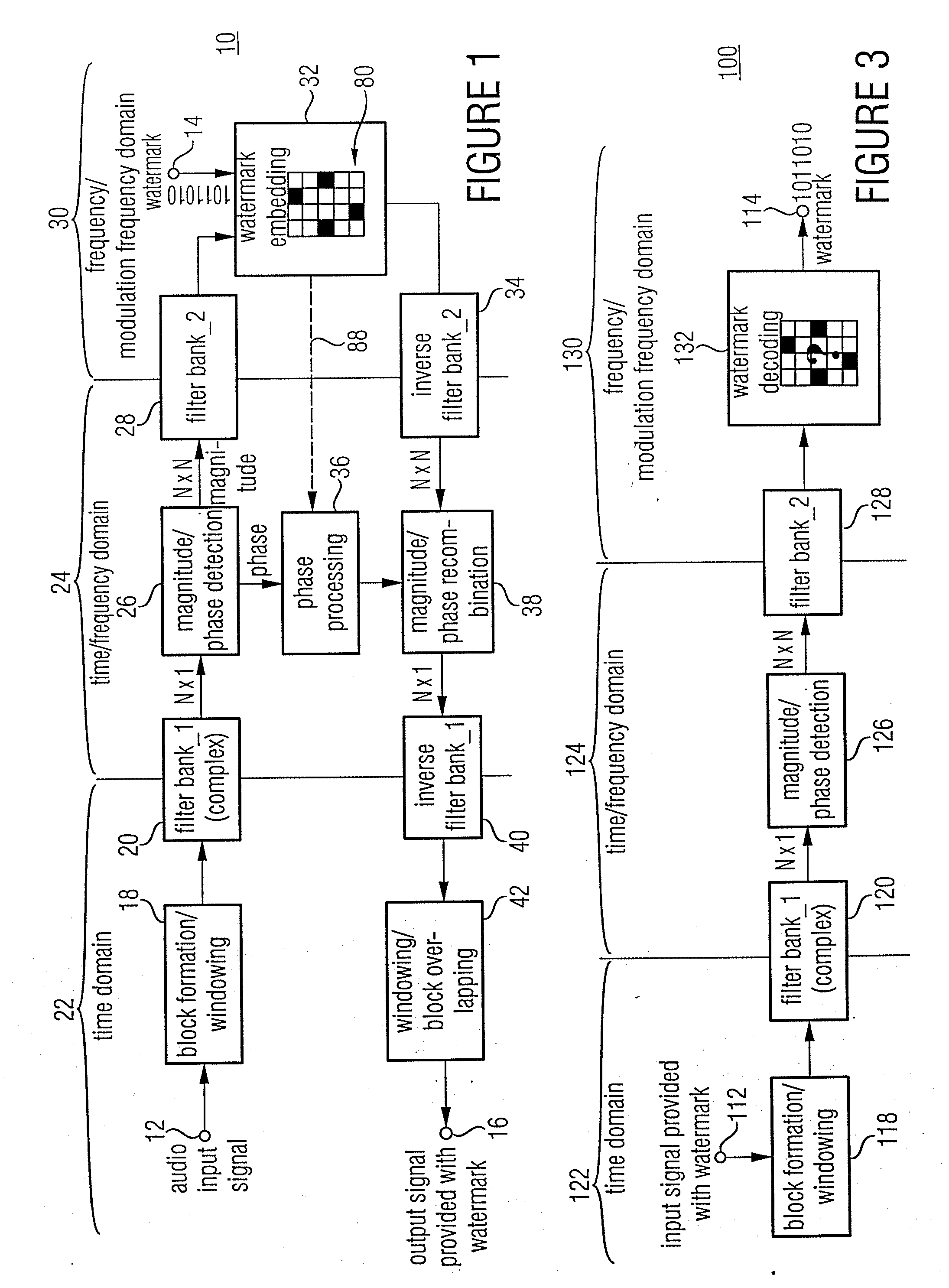
Watermark Embedding
ActiveUS20080027729A1Simple processSpectral/fourier analysisAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFrequency spectrumWatermark method
According to an inventive scheme for introducing a watermark into an information signal, the information signal is at first transferred from a time representation to a spectral / modulation spectral representation). The information signal is then manipulated in the spectral / modulation spectral representation in dependence on the watermark to be introduced to obtain a modified spectral / modulation spectral representation, and subsequently an information signal provided with a watermark is formed based on the modified spectral / modulation spectral representation. An advantage is that, due to the fact that the watermark is embedded and / or derived in the spectral / modulation spectral representation or range, traditional correlation attacks as are used in watermark methods based on a spread-band modulation cannot succeed easily.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
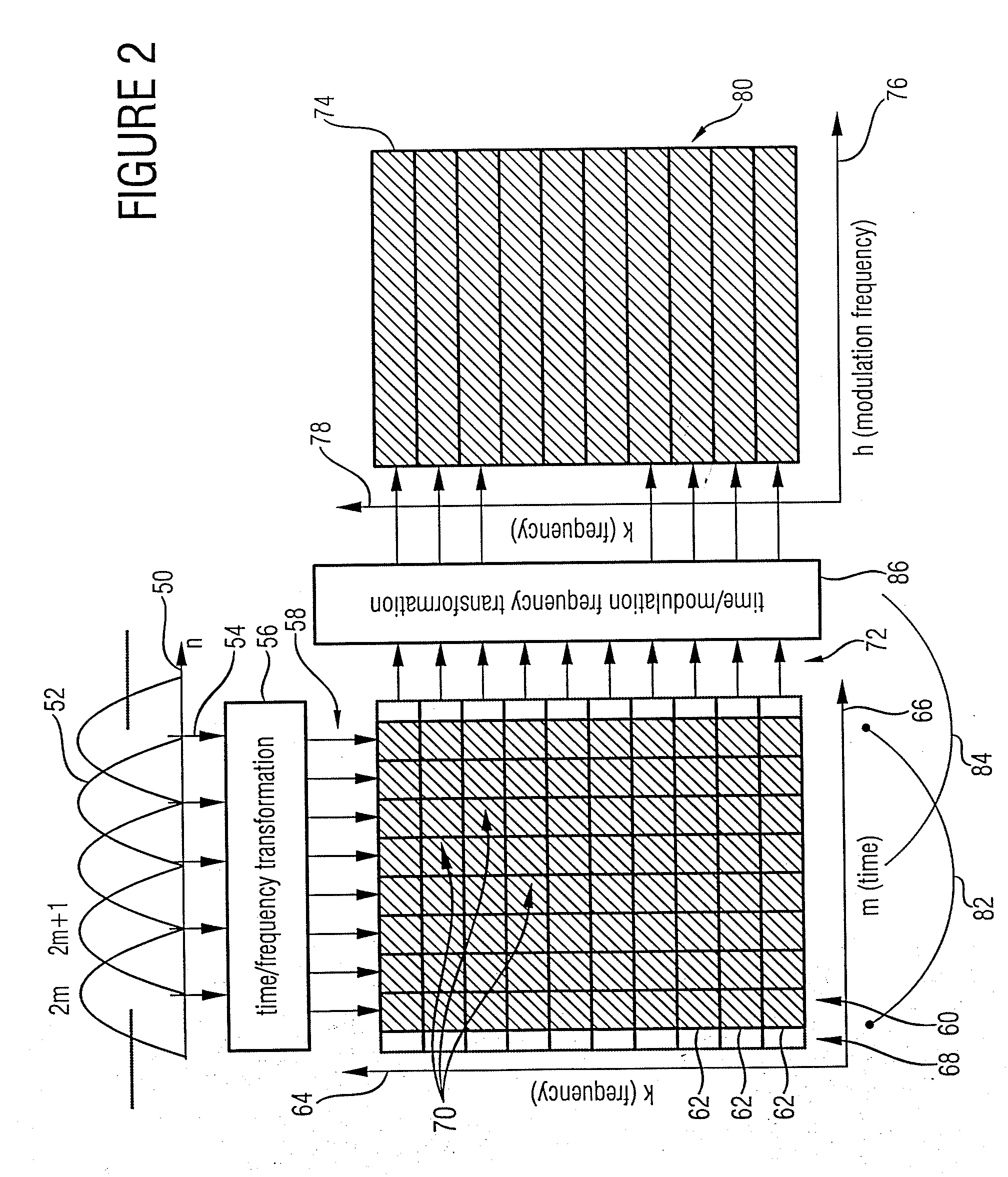
Information Signal Processing by Modification in the Spectral/Modulation Spectral Range Representation
ActiveUS20070100610A1Spectral/fourier analysisAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFrequency spectrumModulation spectrum
Processing of information signals separated according to modulation and carrier components in a more controlled way is made possible by a device for processing an information signal including a unit for converting the information signal to a time / spectral representation by block-wise transforming of the information signal and a unit for converting the information signal from the time / spectral representation to a spectral / modulation spectral representation, wherein the unit for converting is designed such that the spectral / modulation spectral representation depends on both a magnitude component and a phase component of the time / spectral representation of the information signal. A unit then performs a manipulation and / or modification of the information signal in the spectral / modulation spectral representation to obtain a modified spectral / modulation spectral representation. A further unit finally forms a processed information signal representing a processed version of the information signal based on the modified spectral / modulation spectral representation.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Apparatus and method for generating a synthesis audio signal and for encoding an audio signal
ActiveUS20130090934A1Reduced quality and flexibilityQuality improvementSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumControl signal
An apparatus for generating a synthesis audio signal using a patching control signal has a first converter, a spectral domain patch generator, a high frequency reconstruction manipulator and a combiner. The first converter is configured for converting a time portion of an audio signal into a spectral representation. The spectral domain patch generator is configured for performing a plurality of different spectral domain patching algorithms, wherein each patching algorithm generates a modified spectral representation having spectral components in an upper frequency band derived from corresponding spectral components in a core frequency band of the audio signal. The spectral domain patch generator is furthermore configured to select a first spectral domain patching algorithm from the plurality of patching algorithms for a first time portion and a second spectral domain patching algorithm from the plurality of patching algorithm for a second different time portion in accordance with the patching control signal to obtain the modified spectral representation.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Technique for extracting arrayed data
InactiveUS7466851B2Increase contrastImprove spatial resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisFrequency spectrumImage resolution
The current invention discloses a novel spectral transformation technique for characterizing digitized intensity output patterns from microarrays. This method yields improved sensitivity with reduced false positives and false negatives. Current microarray methods are overly sensitive to the detection of a visible distinction between pixels associated with probes and pixels associated with background. In one embodiment, a technique is disclosed that comprises the steps of: extracting pixels associated with an object of interest and transforming such pixels from an intensity representation to a spectral representation. In some embodiments, the extraction is based on a tessellated logarithmic spiral extraction that may yield a pixel core with a sampling of both foreground and background pixels. This core may then be computationally rescaled by 10×-10,000× to enhance spatial resolution. Once the extracted pixels are represented in the spectral regime, convolution with resolution-enhancement kernels may be used to accentuate morphological features capturing platform specific phenomenology.
Owner:VIALOGY
Device and method for encoding a time-discrete audio signal and method for decoding coded audio data
According to the invention, a time-discrete audio signal is processed (52) in order to provide a quantization block with quantized spectral values (52). In addition, a whole-number spectral representation is generated from a time-discrete audio signal, using a whole-number transformation algorithm (56). The quantization block, which has been generated using a psychoacoustic model (54), is inverse quantized and rounded (58) to form a differential between the whole-number spectral values and the inverse quantized rounded spectral values. The quantization block alone produces a psychoacoustic encoded / decoded audio signal affected by loss after the decoding process, whereas the quantization block together with the combination block provides a loss-free, or practically loss-free encoded and decoded audio signal during said decoding process. The generation of the differential signal in the frequency range allows a simpler encoder / decoder structure to be produced.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Technique for extracting arrayed data
InactiveUS20050105787A1Increase contrastImprove spatial resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisHigh spatial resolutionImage resolution
The current invention discloses a novel spectral transformation technique for characterizing digitized intensity output patterns from microarrays. This method yields improved sensitivity with reduced false positives and false negatives. Current microarray methods are overly sensitive to the detection of a visible distinction between pixels associated with probes and pixels associated with background. In one embodiment, a technique is disclosed that comprises the steps of: extracting pixels associated with an object of interest and transforming such pixels from an intensity representation to a spectral representation. In some embodiments, the extraction is based on a tessellated logarithmic spiral extraction that may yield a pixel core with a sampling of both foreground and background pixels. This core may then be computationally rescaled by 10×-10,000× to enhance spatial resolution. Once the extracted pixels are represented in the spectral regime, convolution with resolution-enhancement kernels may be used to accentuate morphological features capturing platform specific phenomenology.
Owner:VIALOGY
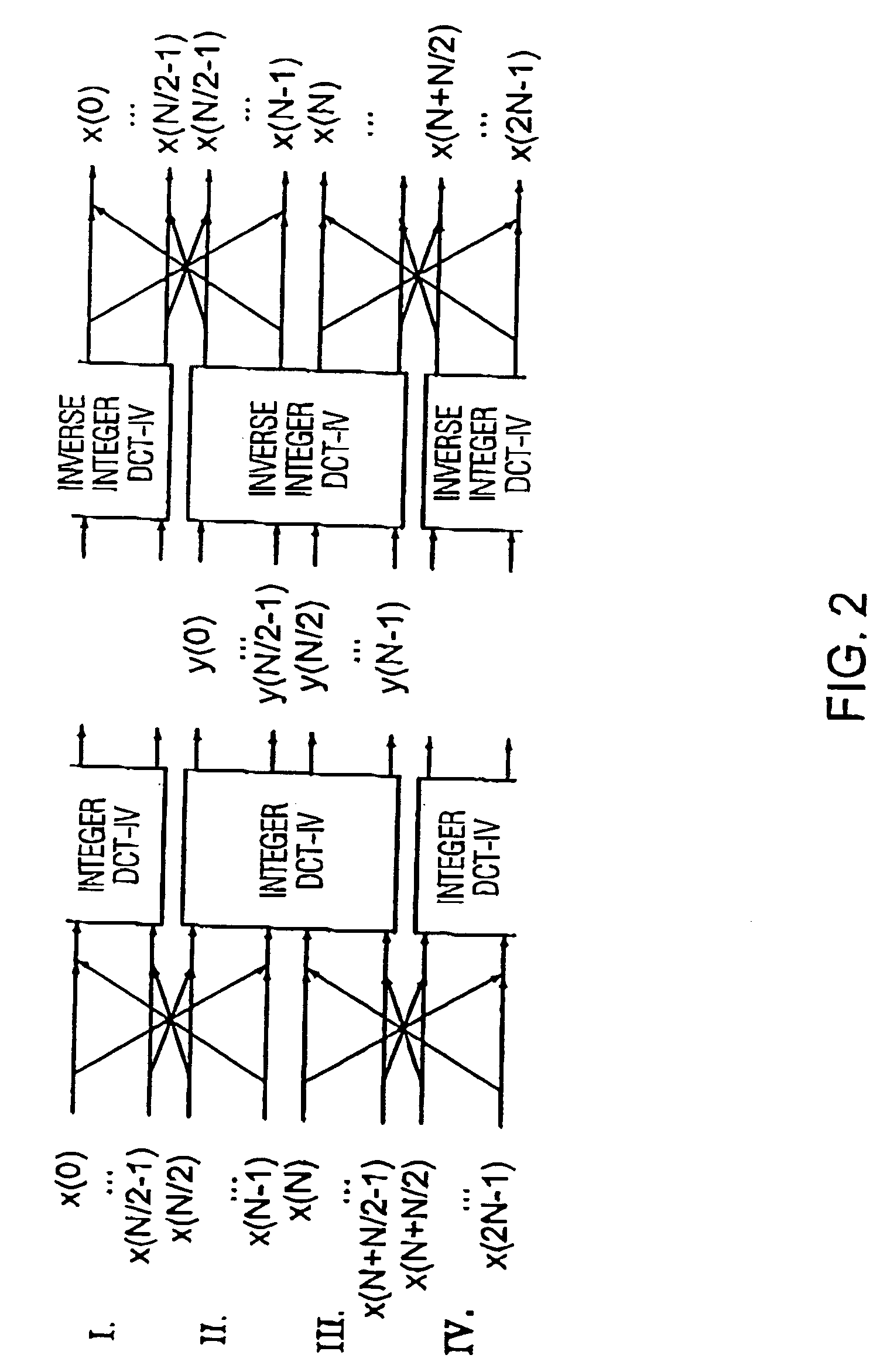
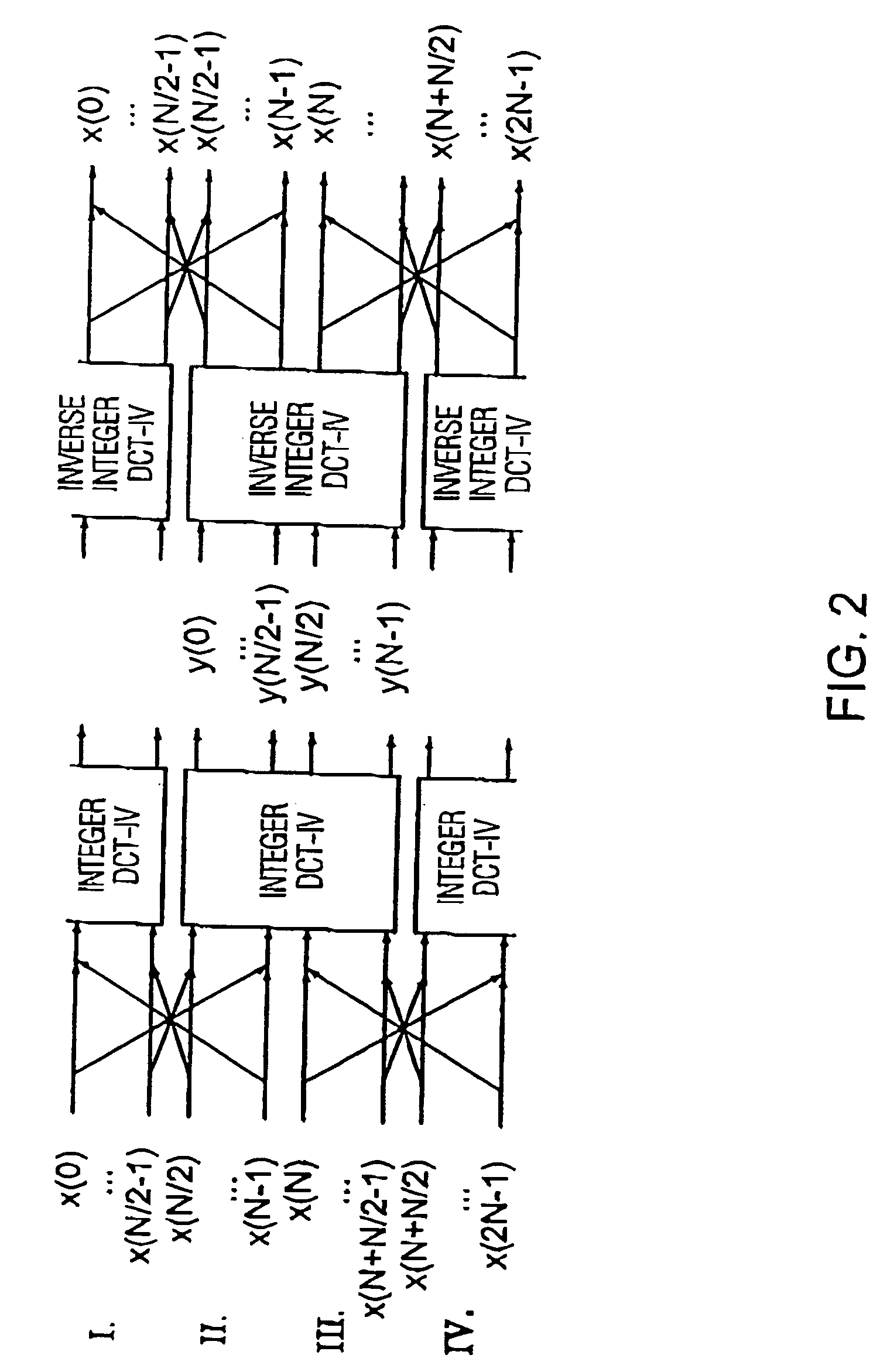
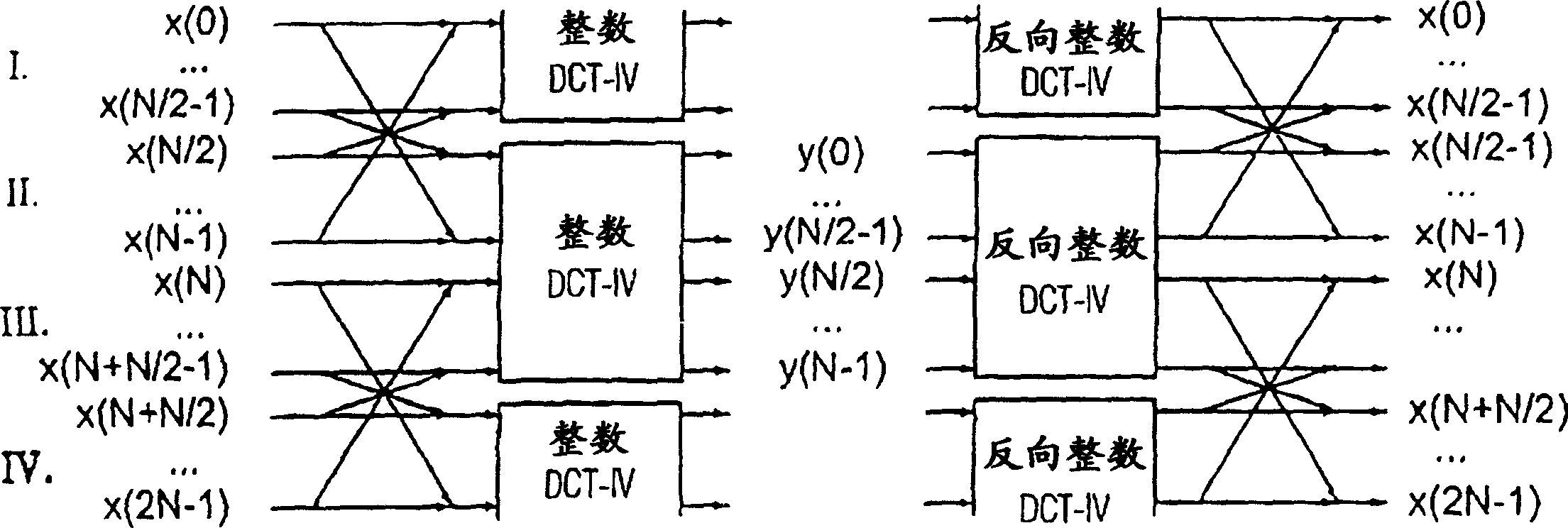
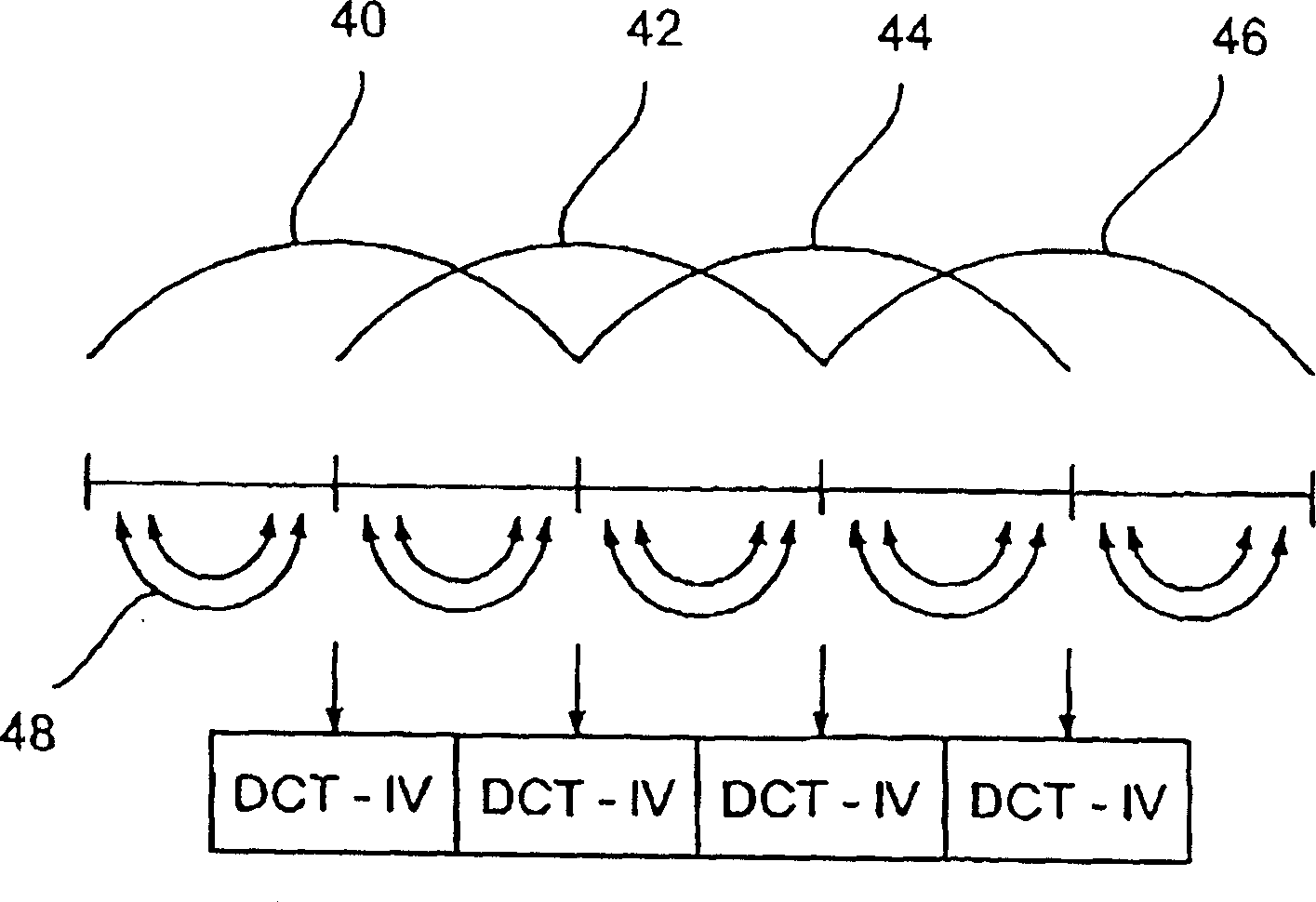
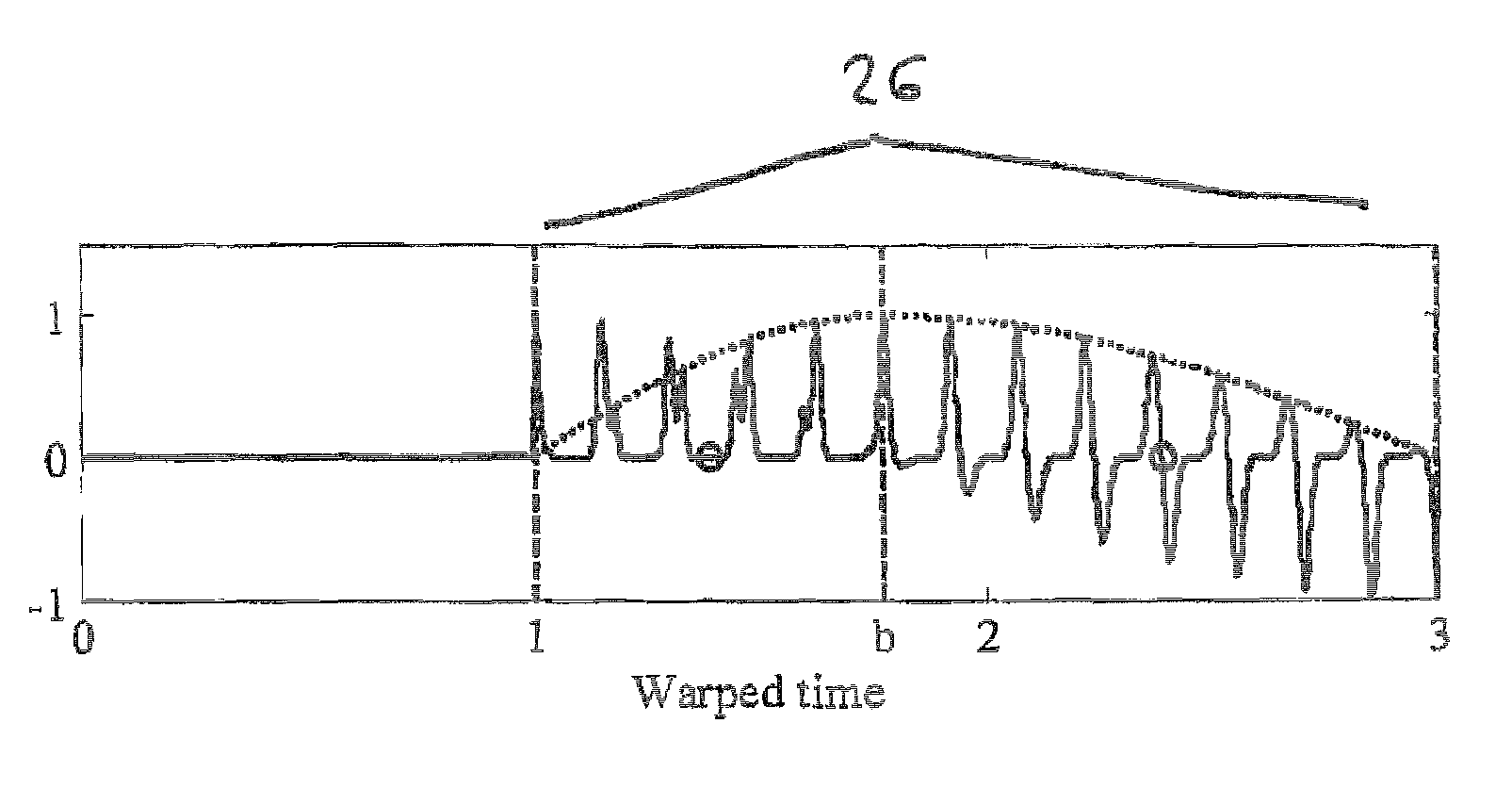
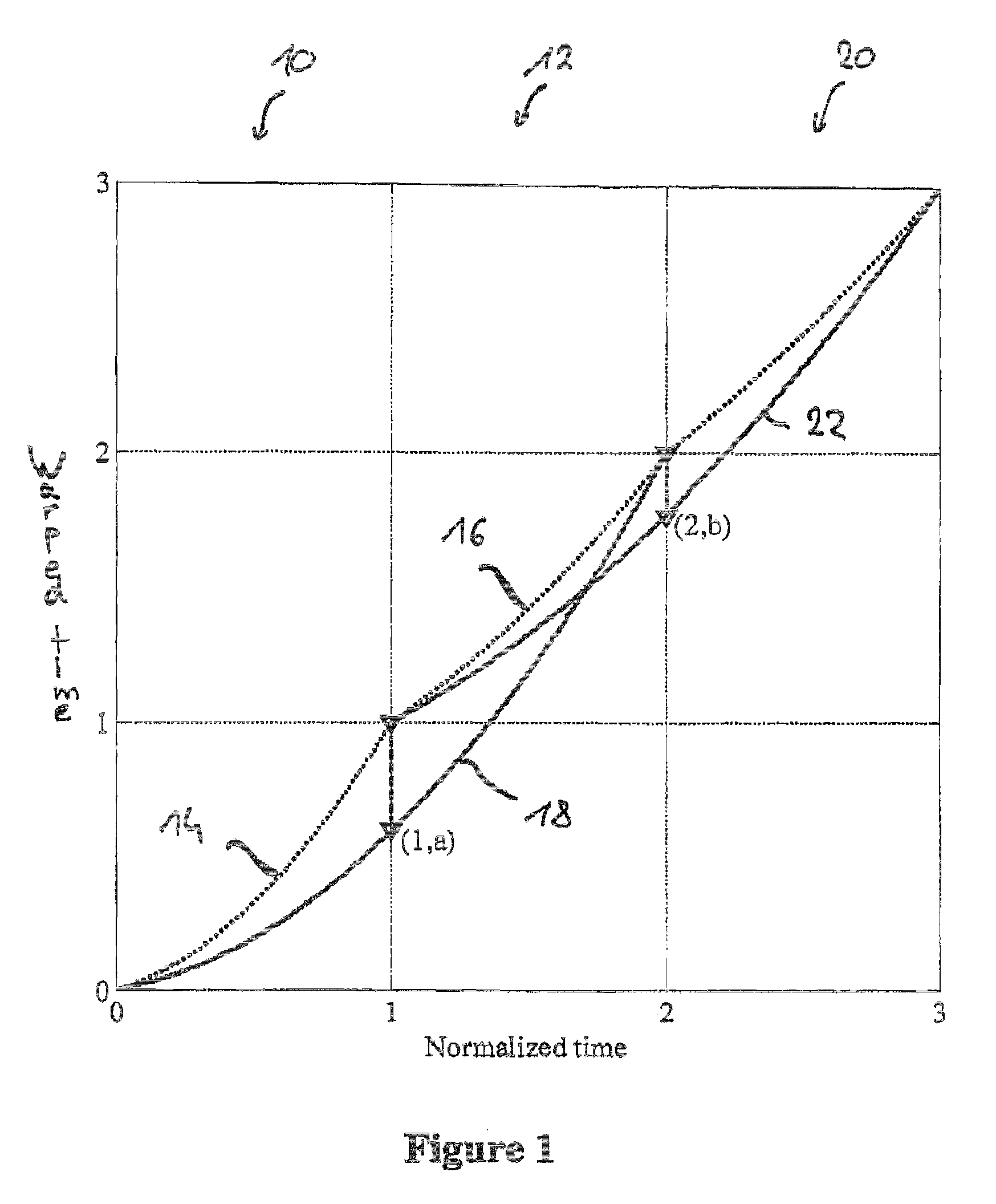
Time warped modified transform coding of audio signals
ActiveUS7720677B2Reduce rateHighly robustCode conversionSpeech recognitionComputer hardwareFrequency spectrum
A spectral representation of an audio signal having consecutive audio frames can be derived more efficiently, when a common time warp is estimated for any two neighboring frames, such that a following block transform can additionally use the warp information. Thus, window functions required for successful application of an overlap and add procedure during reconstruction can be derived and applied, the window functions already anticipating the re-sampling of the signal due to the time warping. Therefore, the increased efficiency of block-based transform coding of time-warped signals can be used without introducing audible discontinuities.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
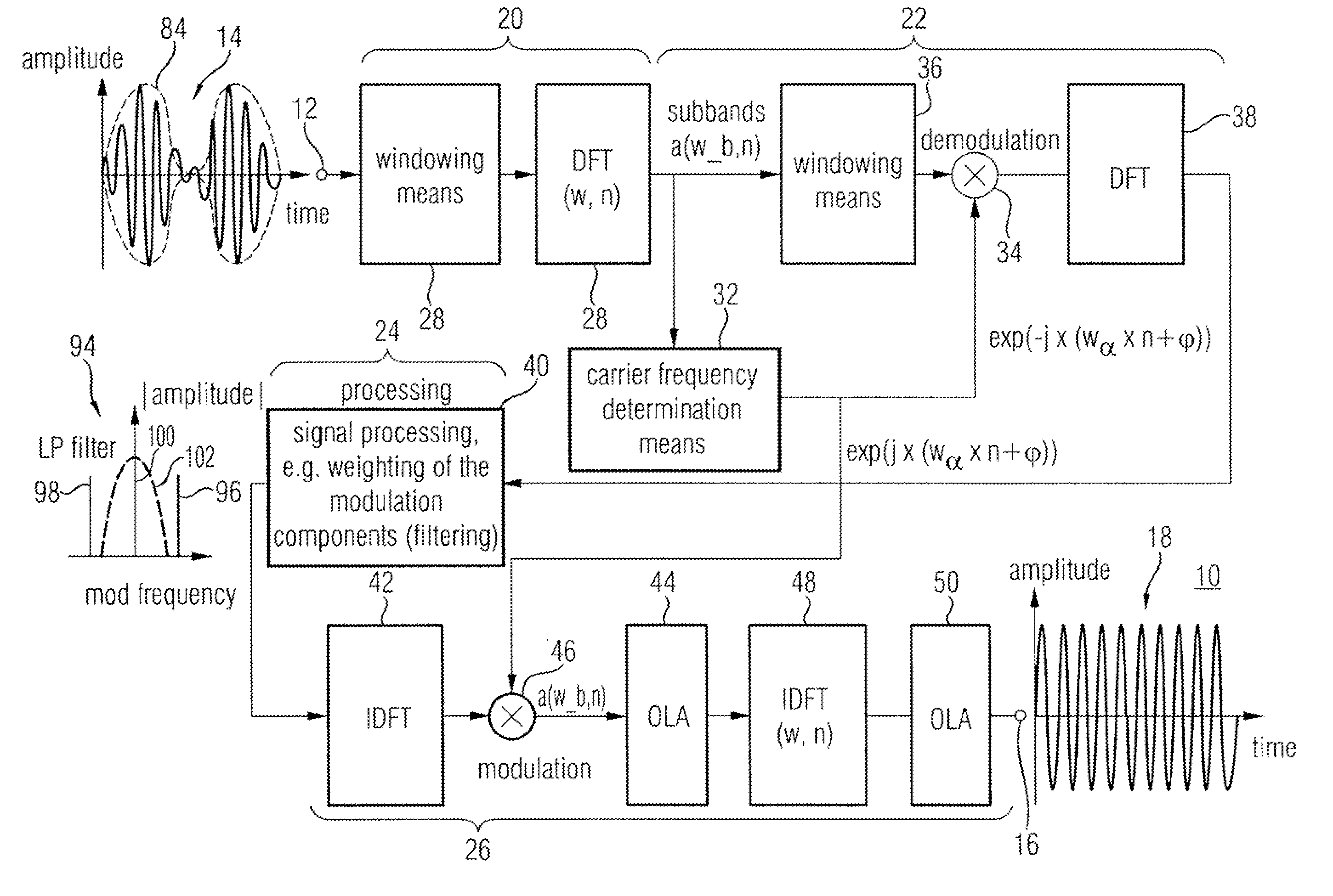
Device and Method for Manipulating an Audio Signal
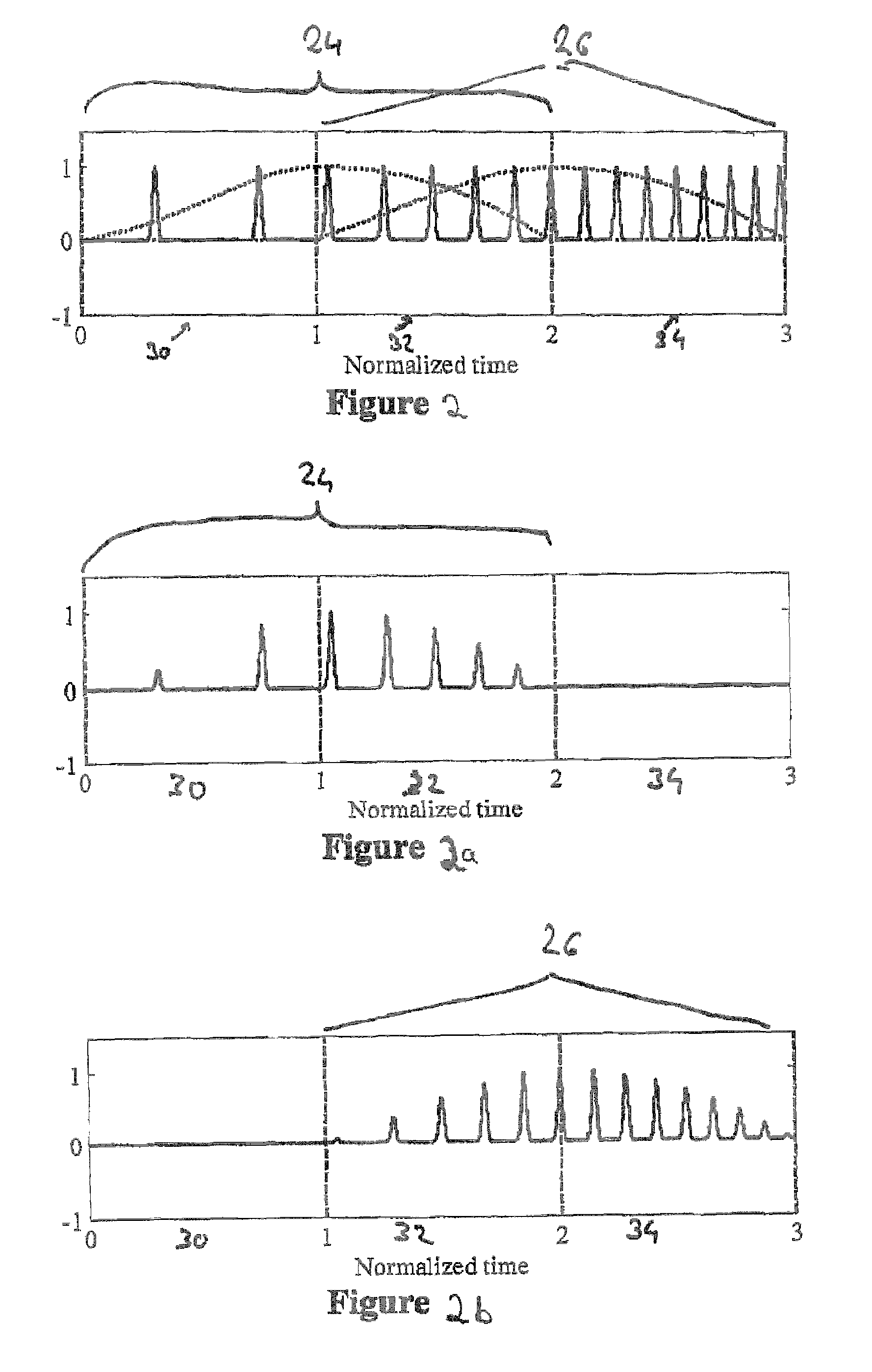
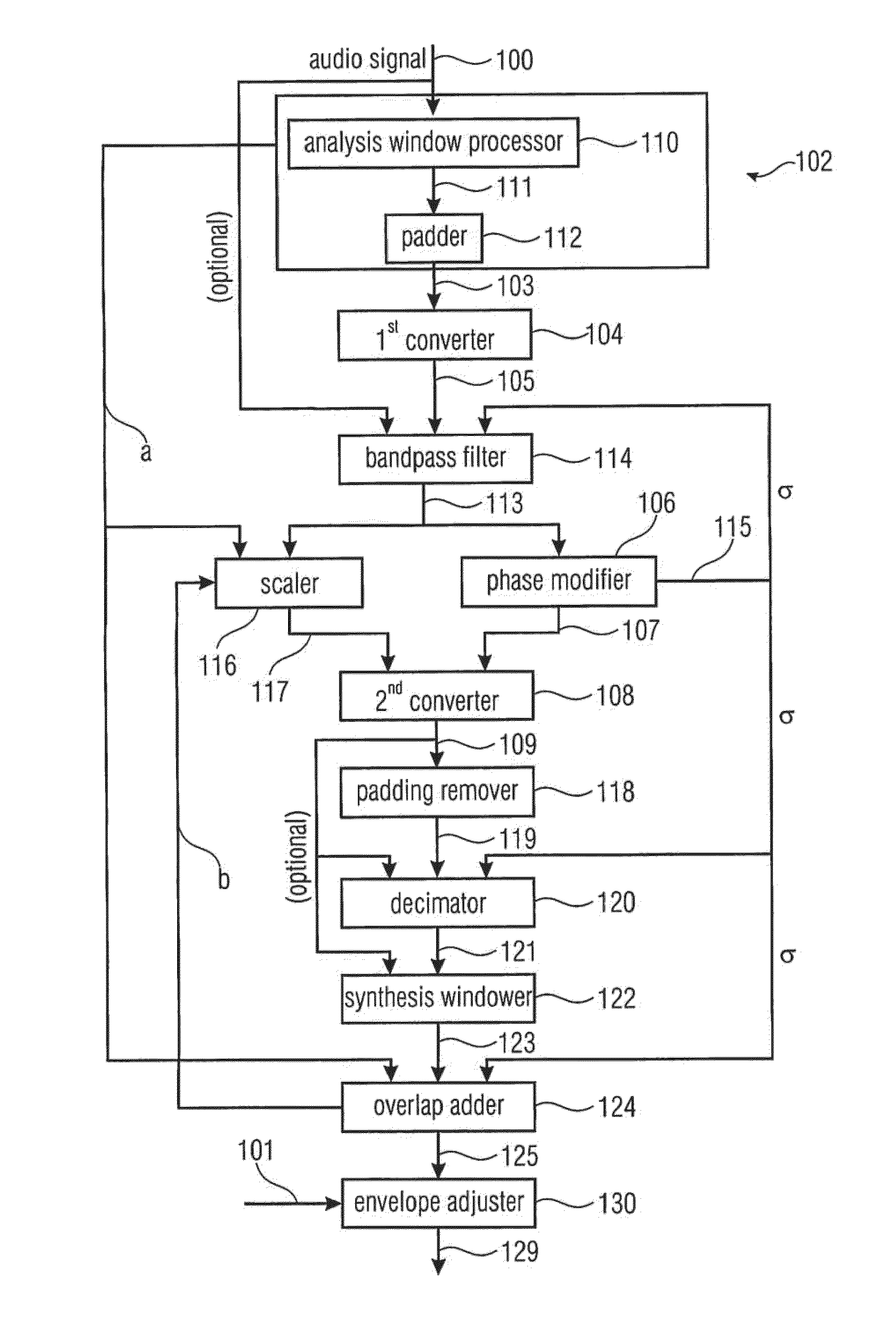
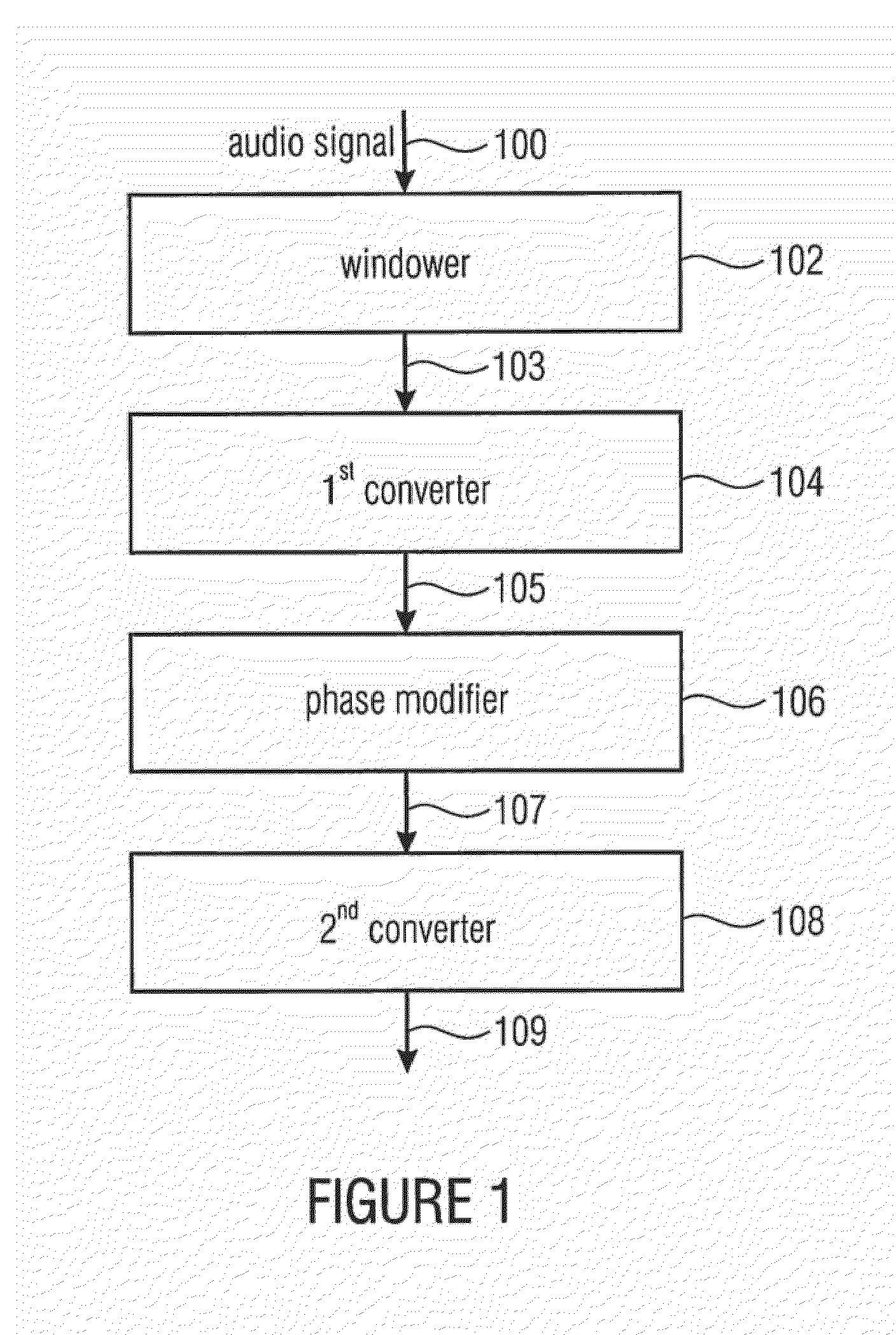
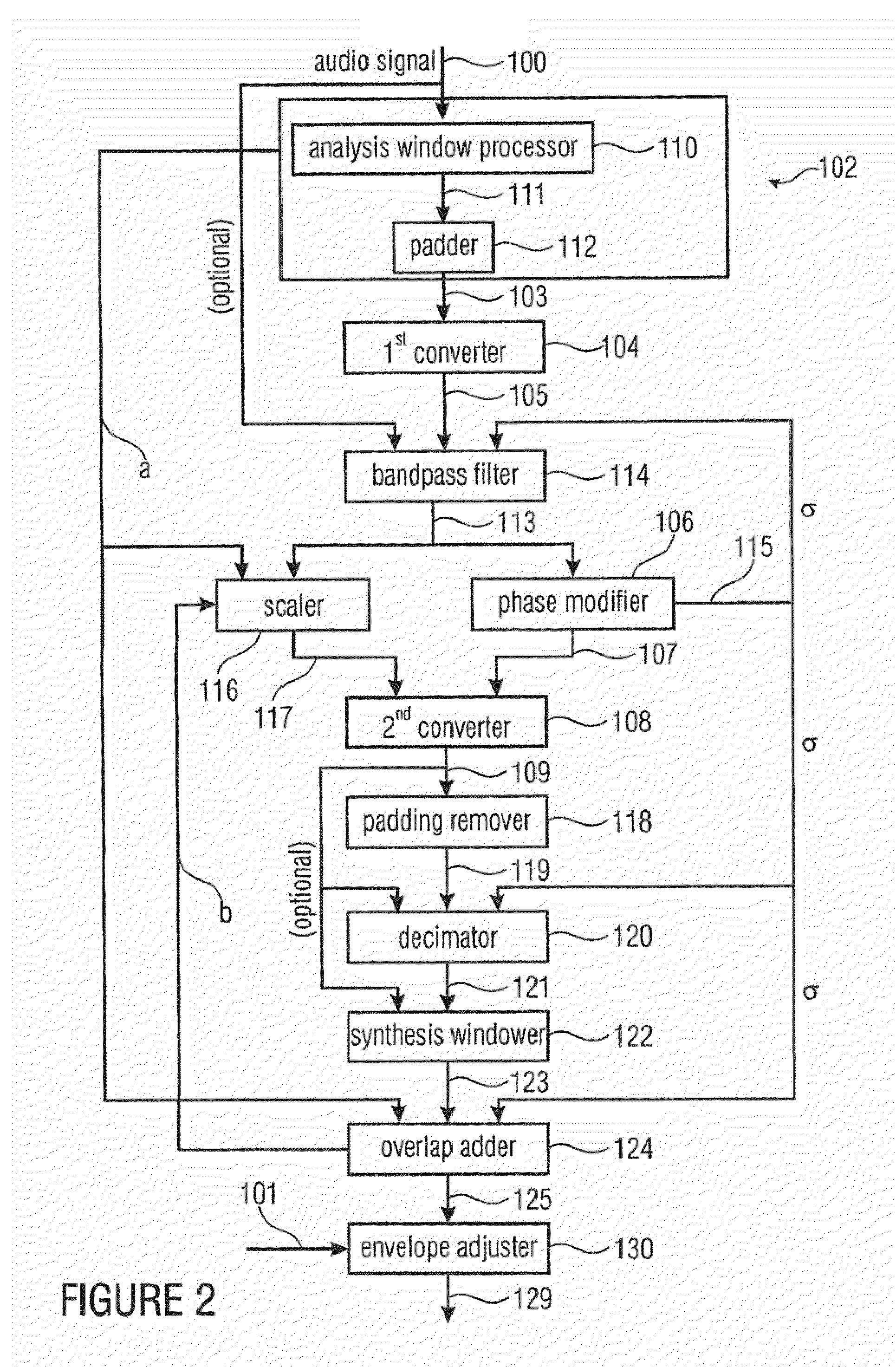
ActiveUS20120076323A1Restricting additional computational complexity overheadReduce effortSpeech analysisFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsTime domainFrequency spectrum
A device and method for manipulating an audio signal includes a windower for generating a plurality of consecutive blocks of audio samples, the plurality of consecutive blocks including at least one padded block of audio samples, the padded block having padded values and audio signal values, a first converter for converting the padded block into a spectral representation having spectral values, a phase modifier for modifying phases of the spectral values to obtain a modified spectral representation and a second converter for converting the modified spectral representation into a modified time domain audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Device and method for postprocessing spectral values and encoder and decoder for audio signals
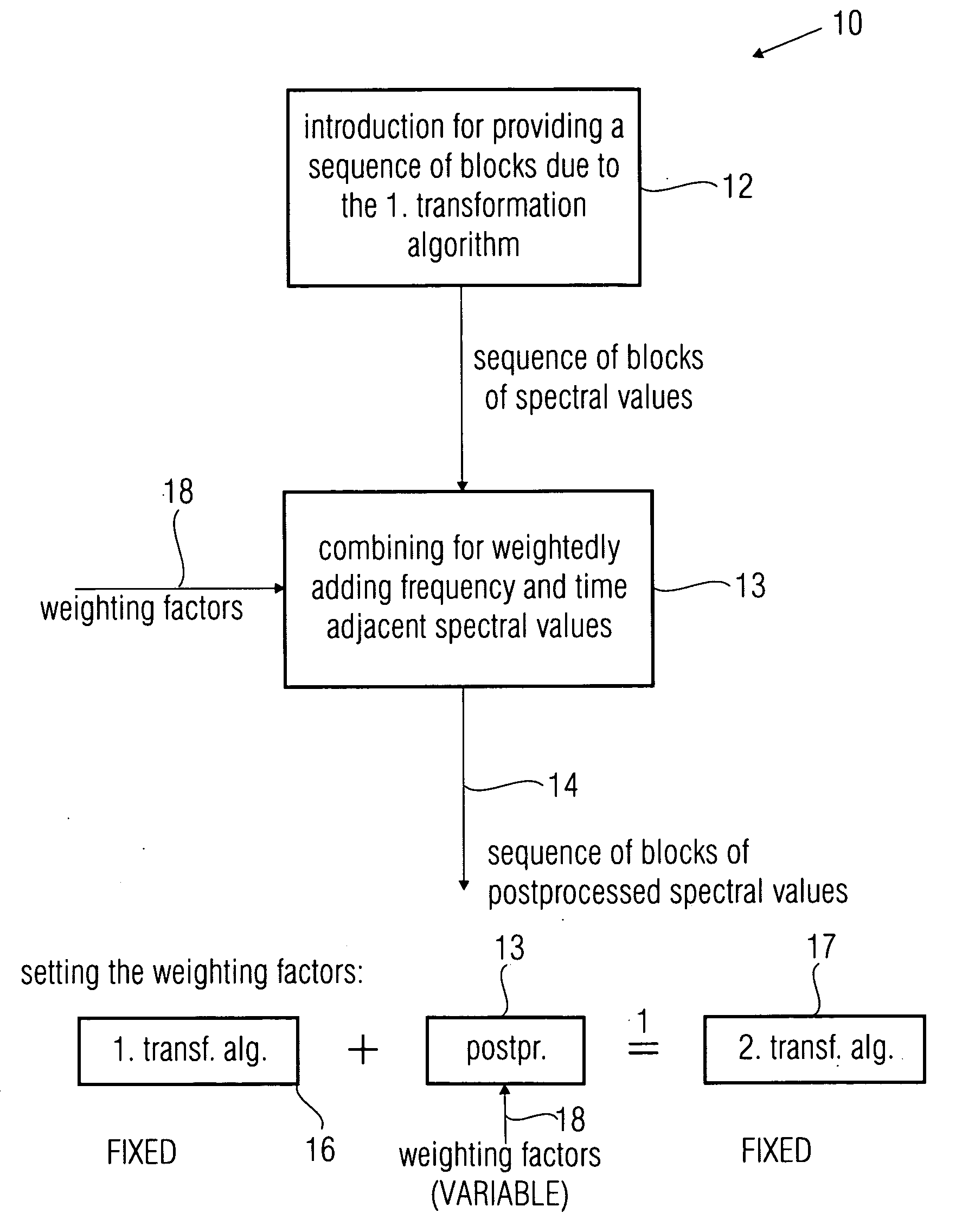
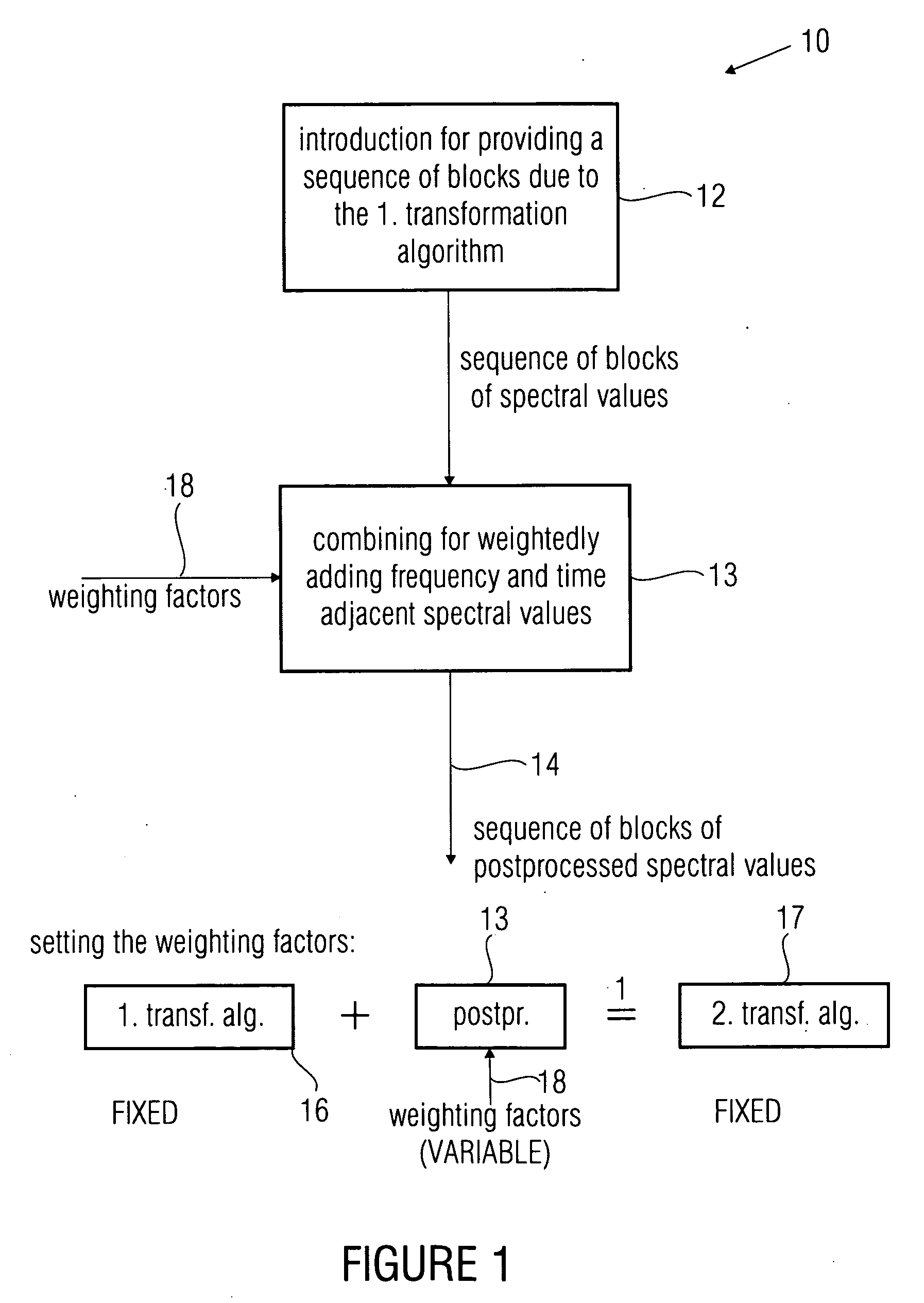
ActiveUS20100017213A1Quality improvementSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumTransformation algorithm
For postprocessing spectral values which are based on a first transformation algorithm for converting the audio signal into a spectral representation, first a sequence of blocks of the spectral values representing a sequence of blocks of samples of the audio signal are provided. Hereupon, a weighted addition of spectral values of the sequence of blocks of spectral values is performed in order to obtain a sequence of blocks of postprocessed spectral values, wherein the combination is performed such that for calculating a postprocessed spectral value for a frequency band and a time duration a spectral value of the sequence of blocks for the frequency band and the time duration and a spectral value for another frequency band or another time duration are used, wherein the combination is further performed such that such weighting factors are used that the postprocessed spectral values are an approximation to the spectral values as they are obtained by converting the audio signal into a spectral representation using a second transformation algorithm which is different from the first transformation algorithm. The postprocessed spectral values are in particular used for a difference formation within a scalable encoder or for an addition within a scalable decoder, respectively.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Fractional depletion estimation for battery condition metrics
ActiveUS20140266227A1Lower acquisition costsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFrequency spectrumEngineering
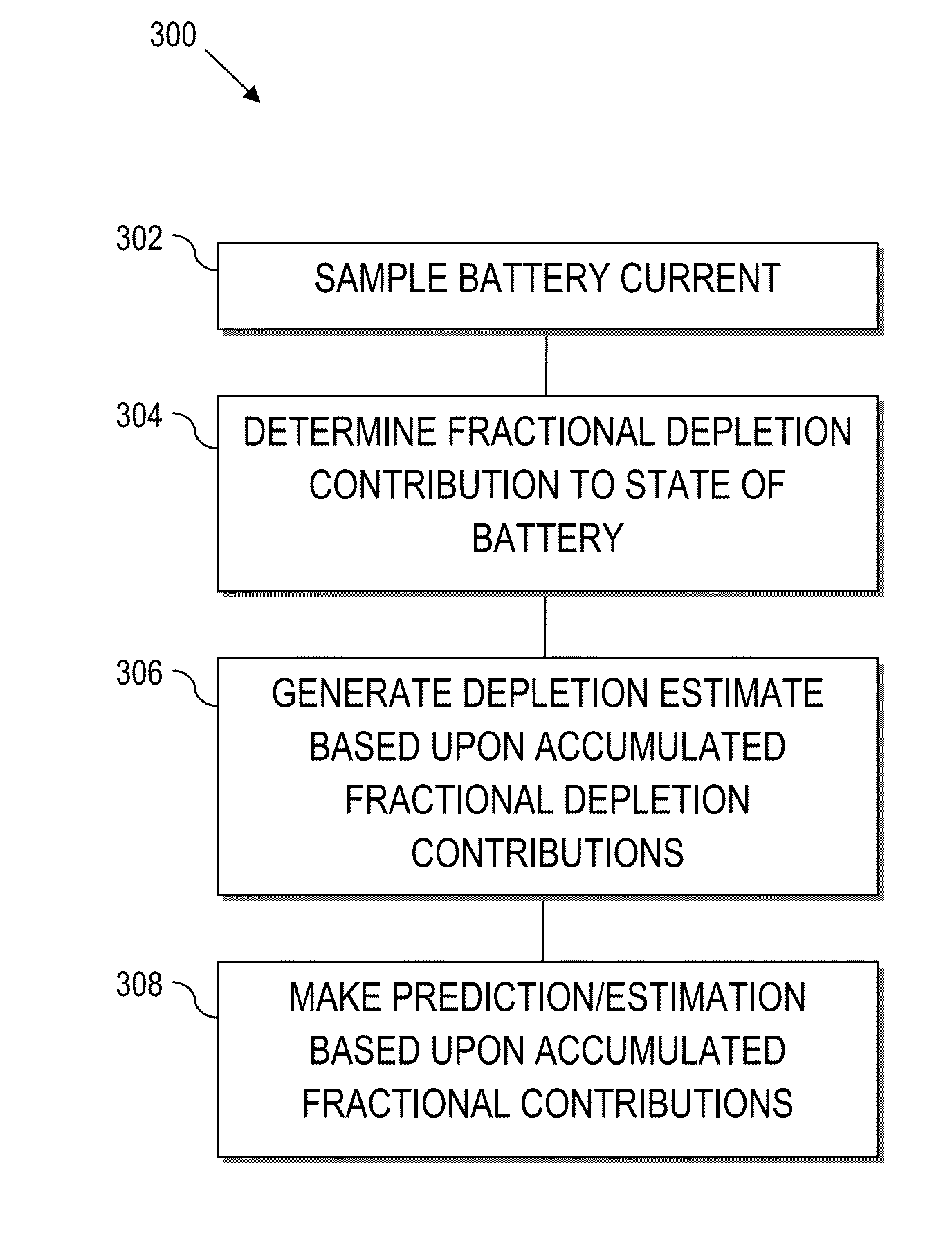
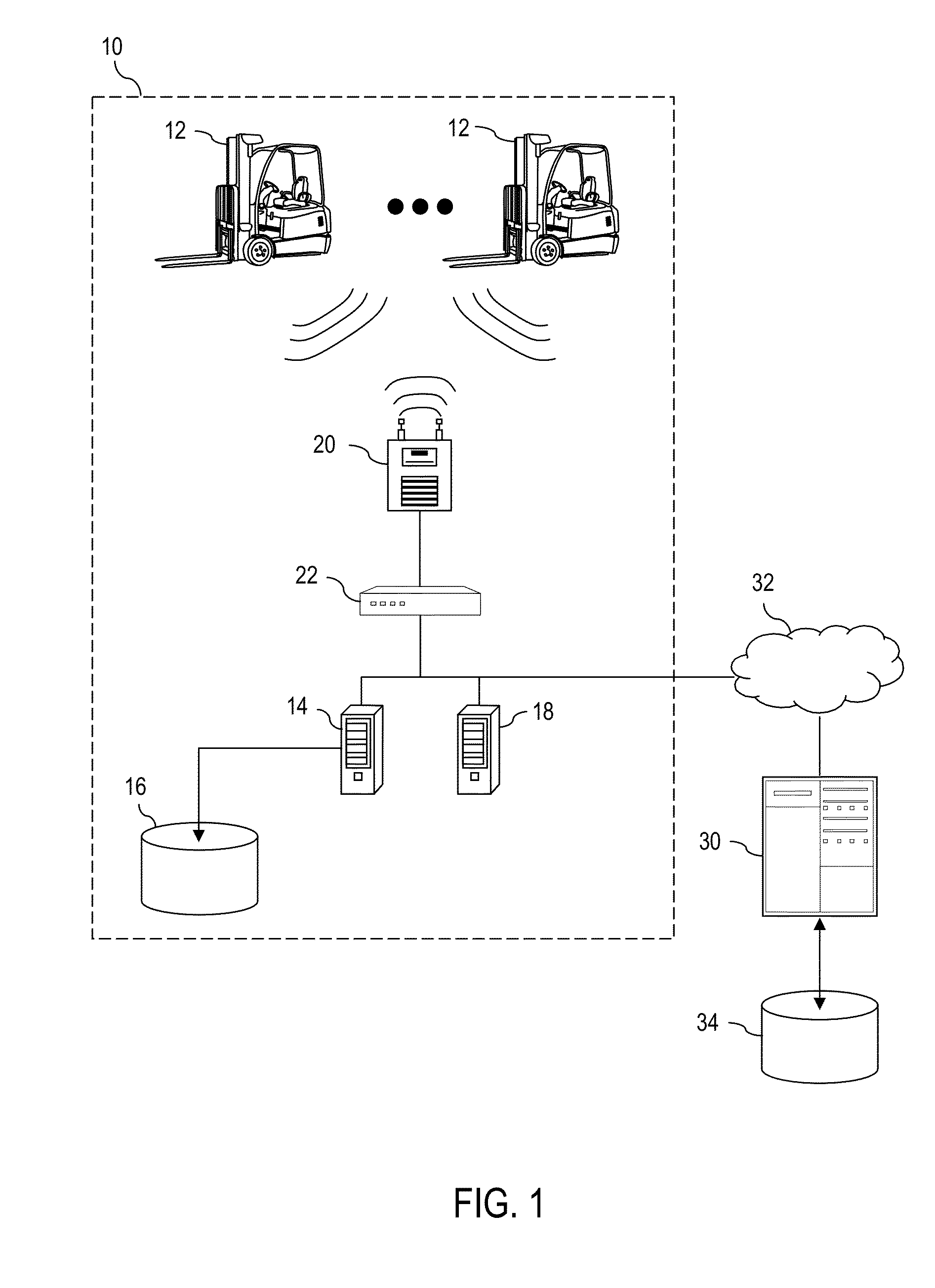
Evaluation of a battery state comprises transforming a time based history of the load on the battery into a spectral representation of that history in a load domain, e.g., the current domain. The method also comprises comparing the spectral representation to an expected battery capability for the load represented by each line in the spectra and calculating the fraction of the expected capability used at each spectral line. The method still further comprises aggregating the calculated fractions into a total fraction that represents the estimated fraction of the expected battery capability associated with that particular time history.
Owner:CROWN EQUIP CORP
Device and method for embedding binary payload in a carrier signal
ActiveUS20060095253A1Low priceIncrease data ratePulse modulation television signal transmissionSpeech analysisPattern recognitionTime domain
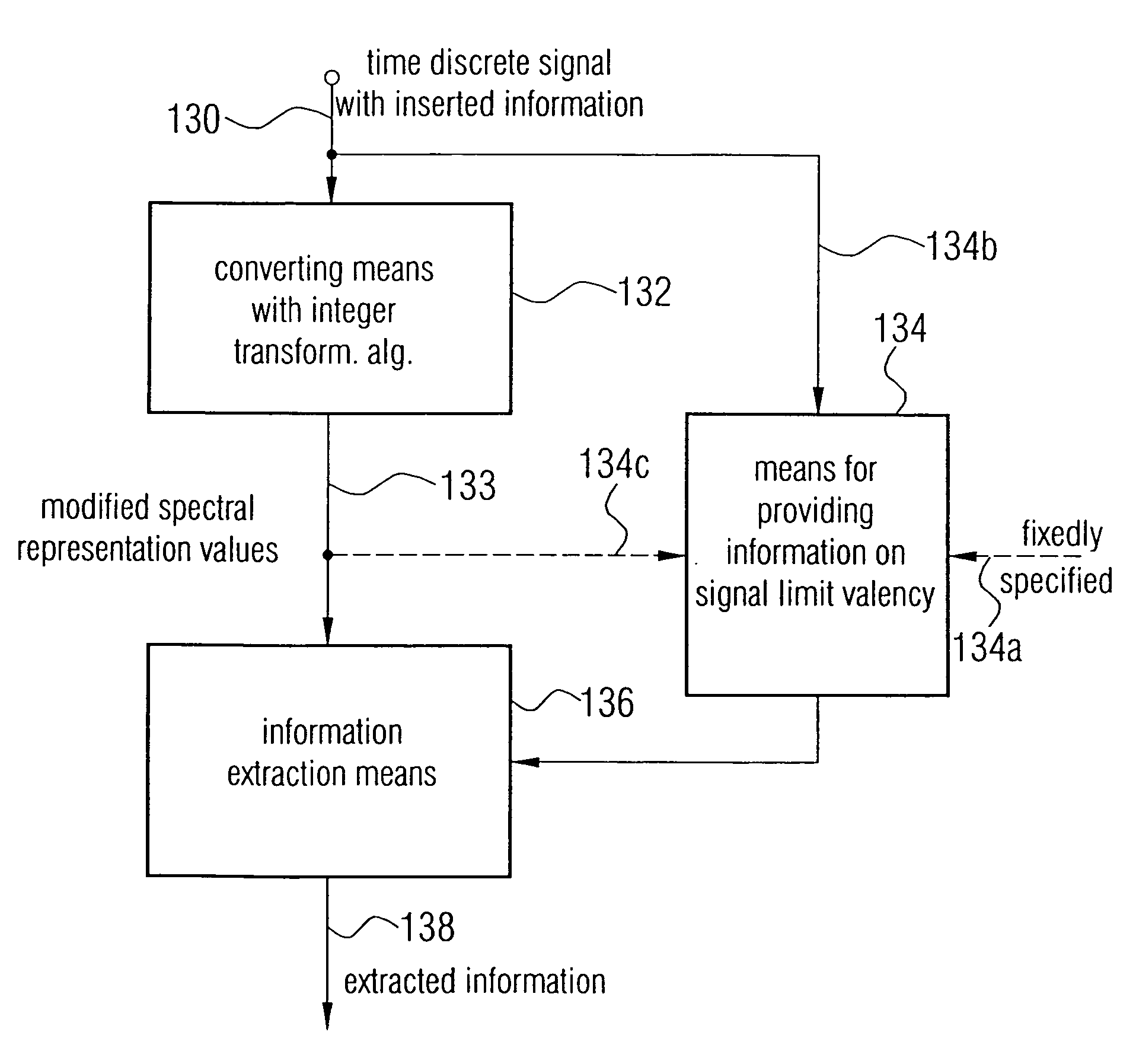
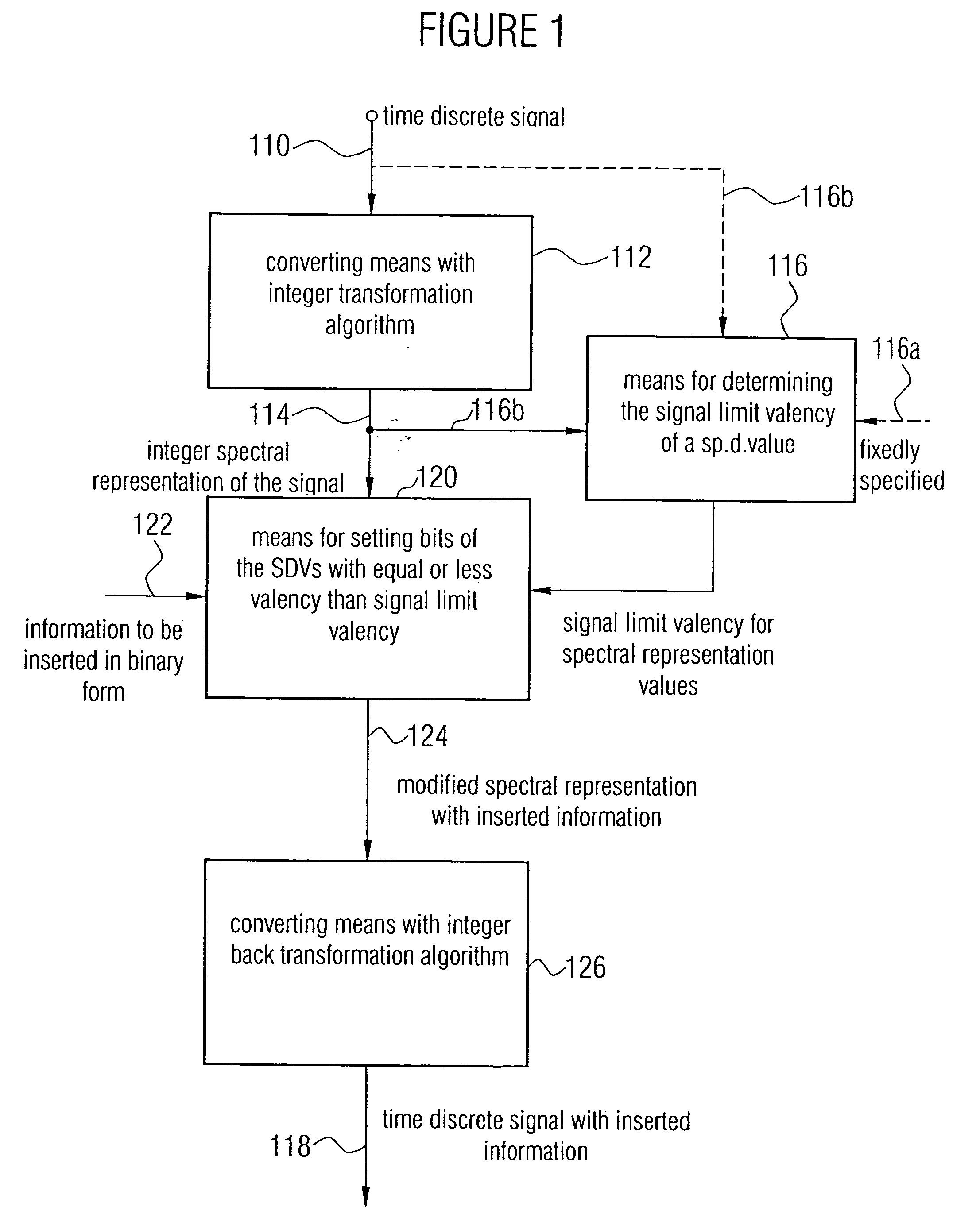
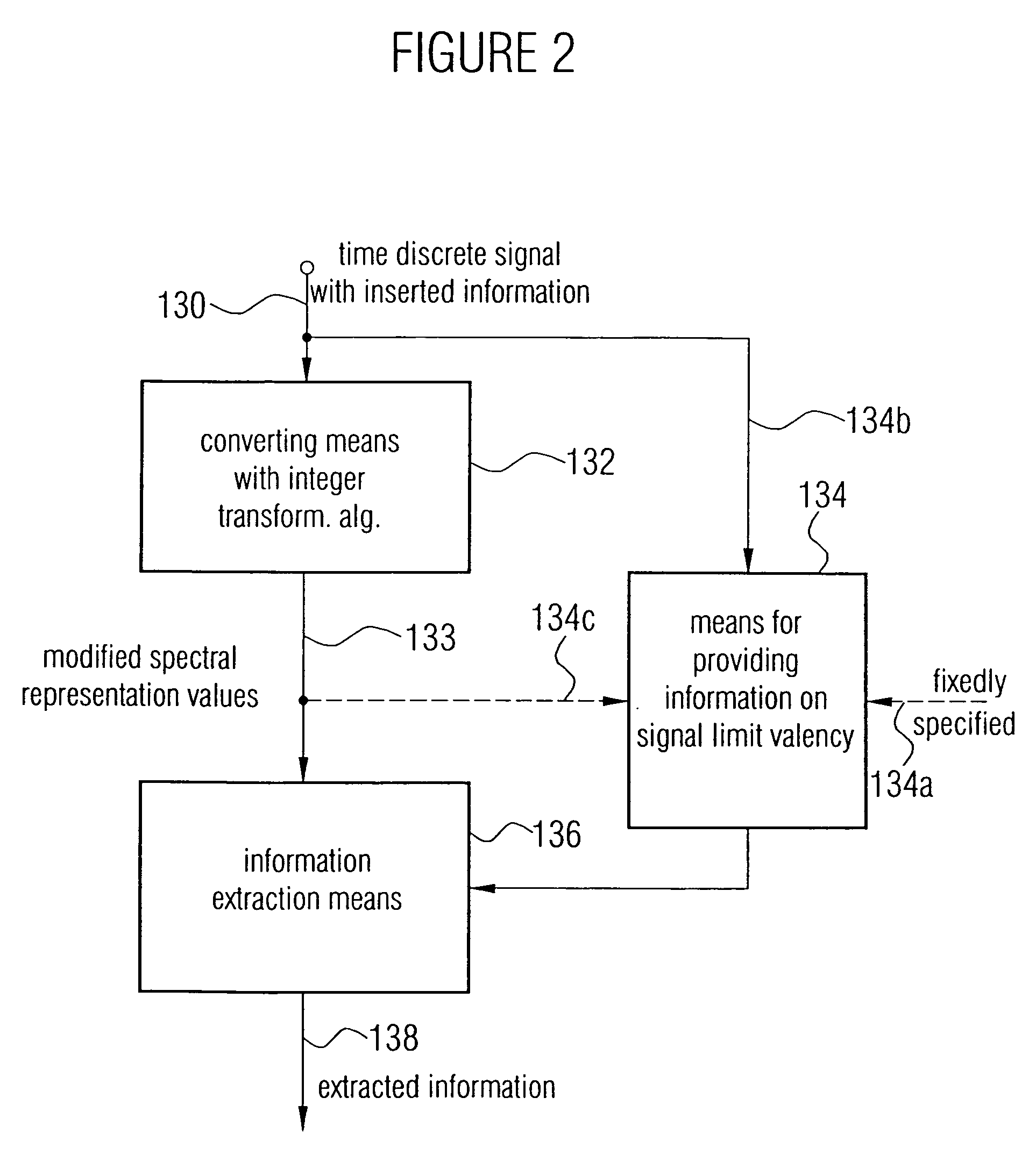
For embedding binary payload in a carrier signal, which, for example, is an audio signal, a sequence of time-discrete values of the carrier signal is converted to the frequency domain by means of an integer transform algorithm to obtain binary spectral representation values. Bits of the binary spectral representation values with a valency less than signal limit valency are determined and set according to the payload. The signal limit valency for a spectral representation value is less than the valency of the leading bit of this spectral representation value, so that, with adequate distance, a psychoacoustic transparent insertion of information is achieved. Thus a modified spectral representation with inserted information is generated which is finally converted back to the time domain using an integer back transform algorithm. For extracting the payload, the time-discrete signal with the inserted information is again converted to a spectral representation with the integer forward transform algorithm. Furthermore, signal limit valency information is determined to identify the bits of the binary spectral representation values containing no information regarding the carrier signal, but information regarding the payload signal, to extract these bits. The inventive concept is simple in its implementation and may be scaled with respect to the data rate of the information to be inserted.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
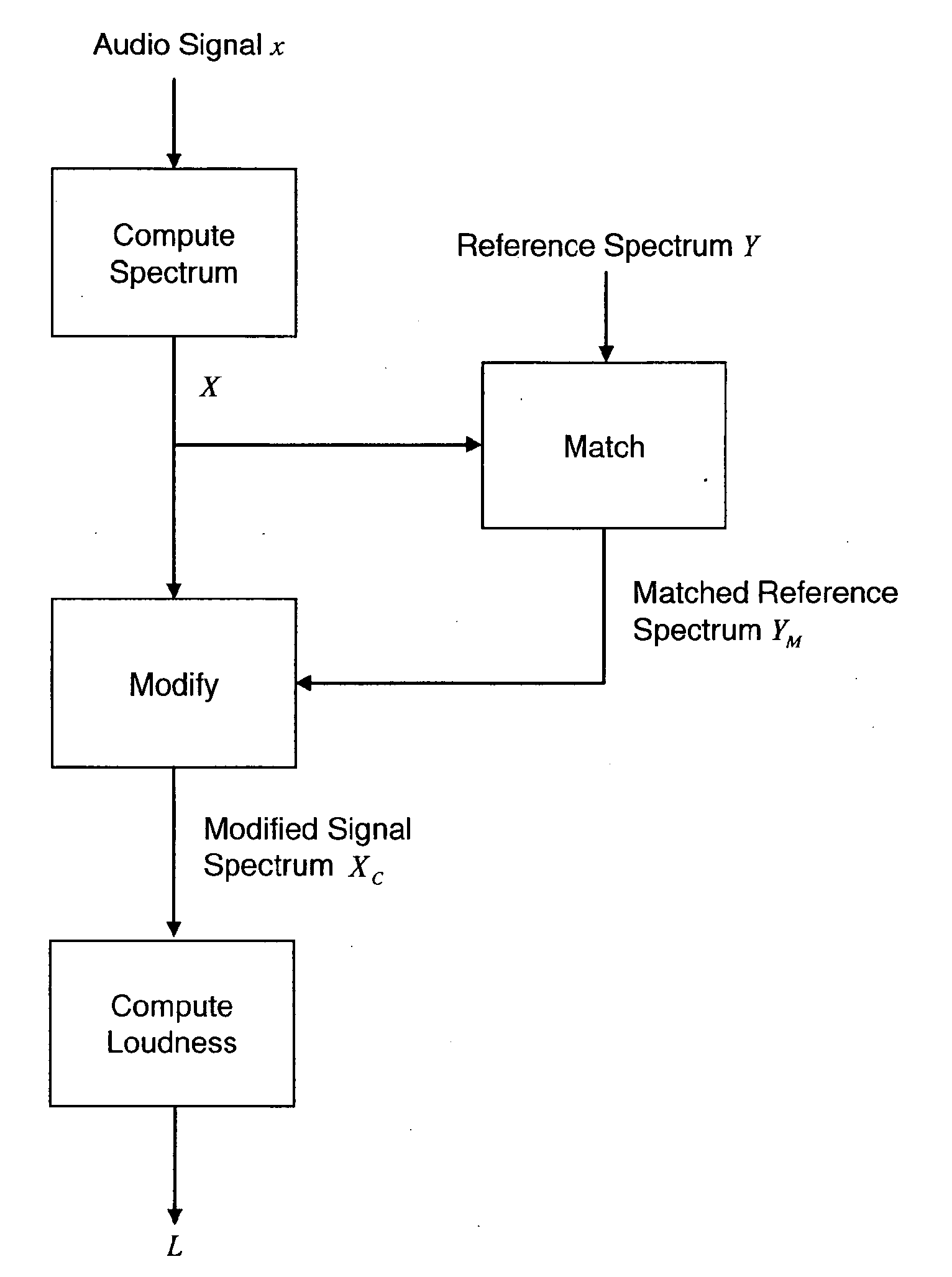
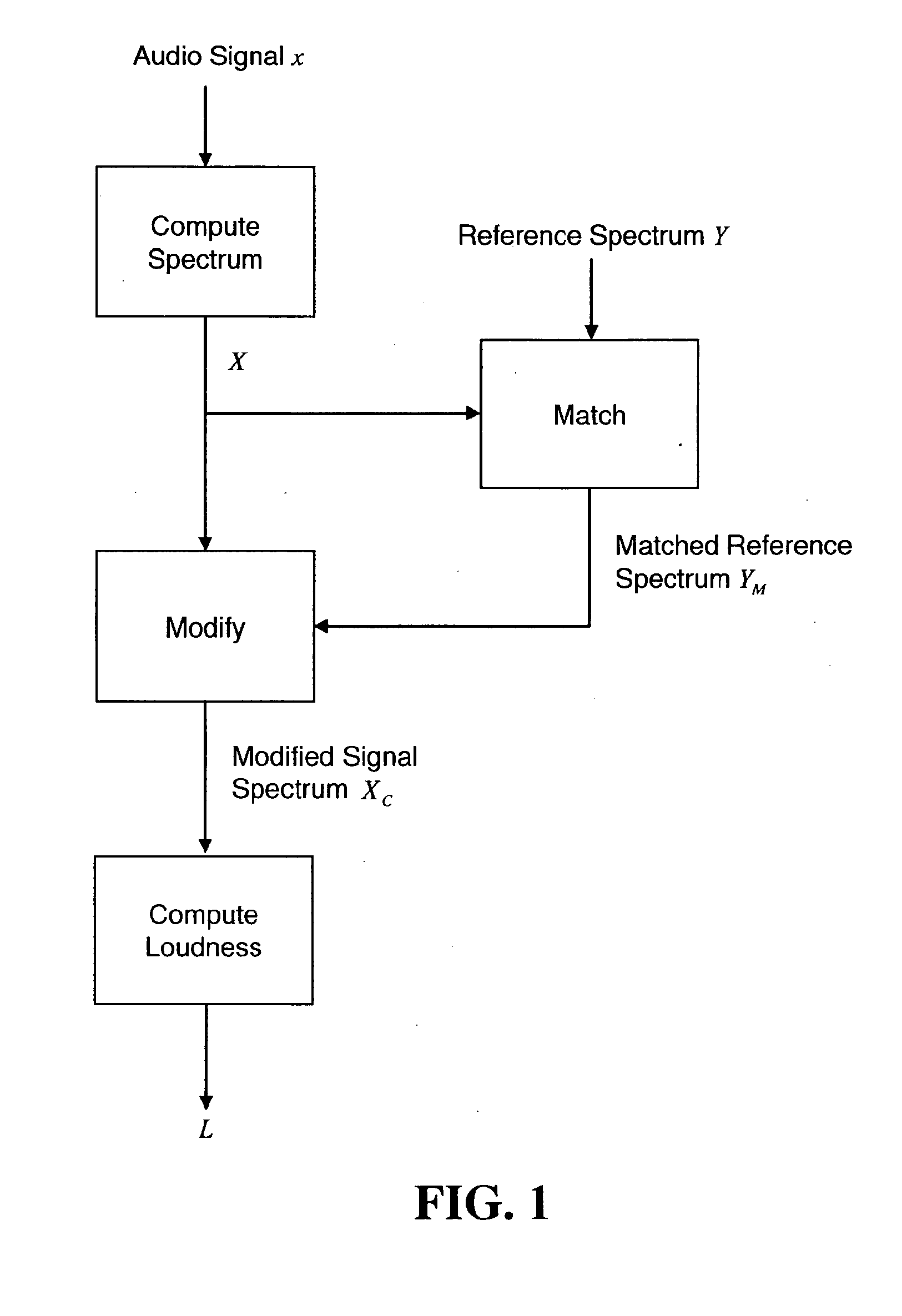
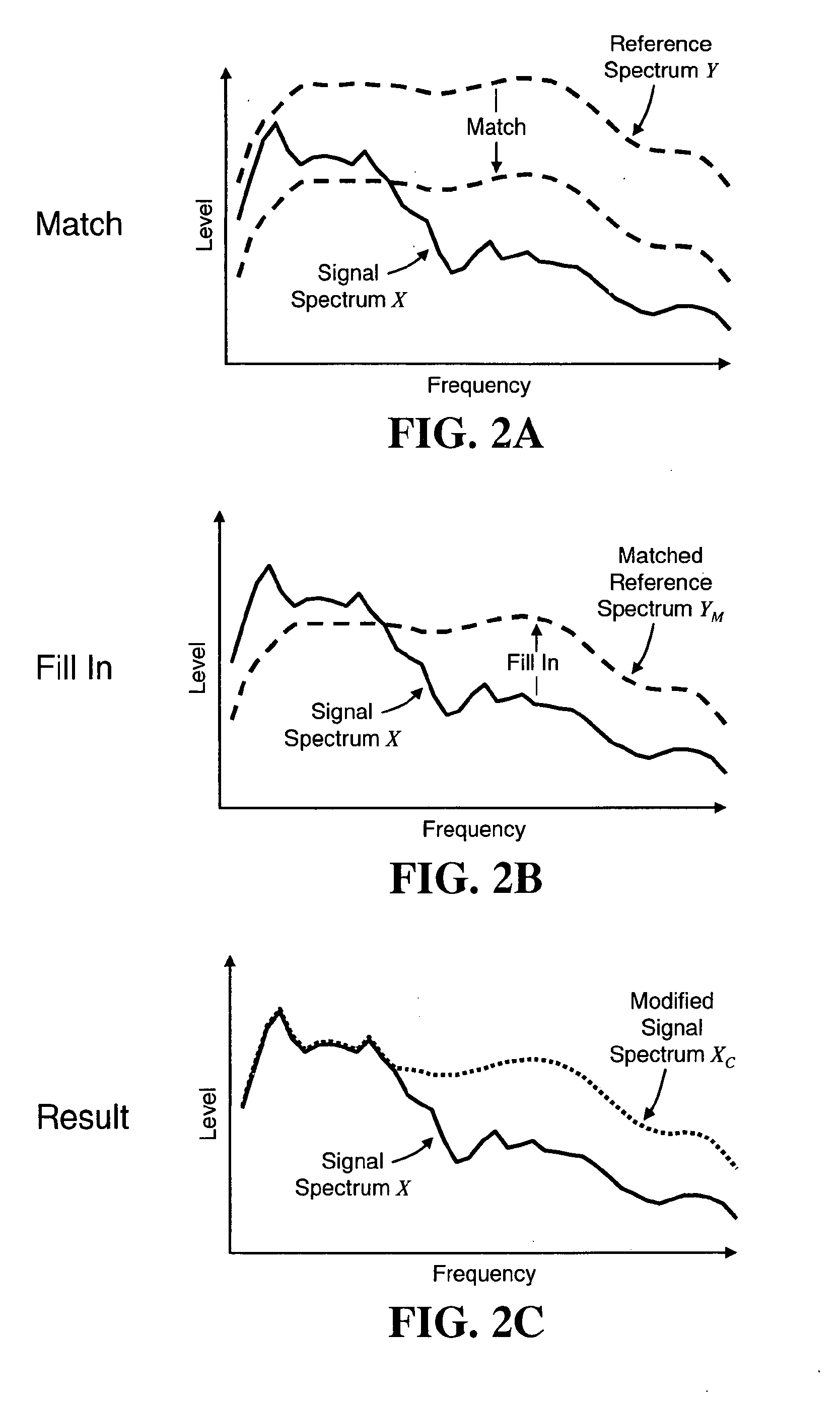
Loudness Measurement with Spectral Modifications
ActiveUS20100067709A1Minimizing functionImprove the level ofGain controlSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumSpectral representation
The perceived loudness of an audio signal is measured by modifying a spectral representation of an audio signal as a function of a reference spectral shape so that the spectral representation of the audio signal conforms more closely to the reference spectral shape, and determining the perceived loudness of the modified spectral representation of the audio signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
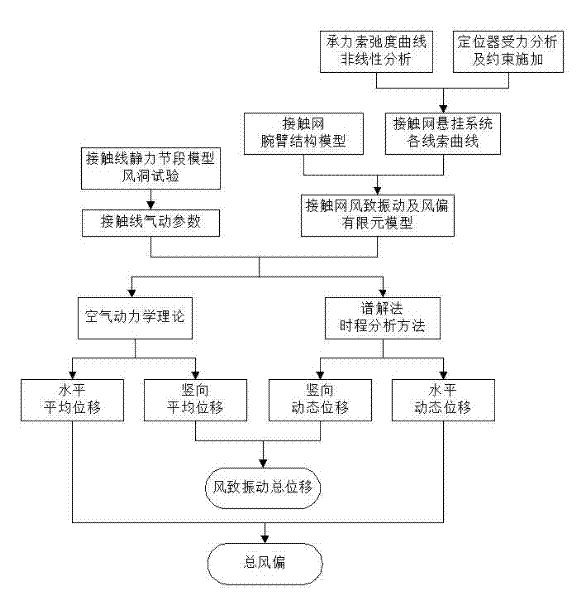
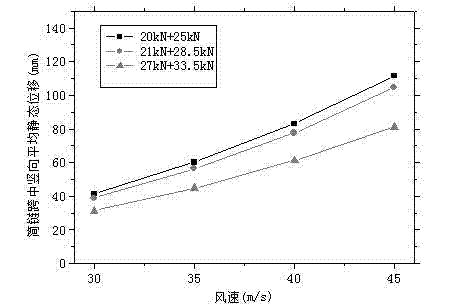
Dynamic calculating method of wind-caused vibration and windage yaw of contact net of electrified railway
InactiveCN102393184ARealize dynamic calculationImprove computing efficiencyAngle measurementElement modelEngineering
The invention relates to a dynamic calculating method of wind-caused vibration and windage yaw of a contact net of an electrified railway. With the development of a high-speed railway, an influence degree on security of train operation by wind becomes more obvious; and effects of strong wind at a wind field and a wind gap as well as an effect of wind caused by train operation will enable large and complex vibration and windage yaw to occur at a contact net, so that a dynamic quality of high speed operation of a bow net will be influenced and bow net contact security will be threatened. The method comprises the following steps that: a wind tunnel test of a contact wire static force segment model is utilized to test an aerodynamic force parameter of a contact wire; a finite element model of wind-caused vibration and windage yaw of a contact net is established; average displacement of a contact net thread is calculated; and a spectral representation method is employed to simulate a turbulent flow wind speed time history and a time history analysis method is employed to calculate dynamic displacement of the contact net thread; and vertical average displacement and vertical dynamic displacement are superposed to obtain total displacement of wind-caused vibration of the contact net thread; and horizontal average displacement and horizontal average displacement are superposed to obtain total windage yaw of the contact net thread. According to the invention, a method is provided for dynamic calculation of wind-caused vibration and windage yaw of a contact net; and moreover, the method is suitable for application to power transmission line route.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY FIRST SURVEY & DESIGN INST GRP
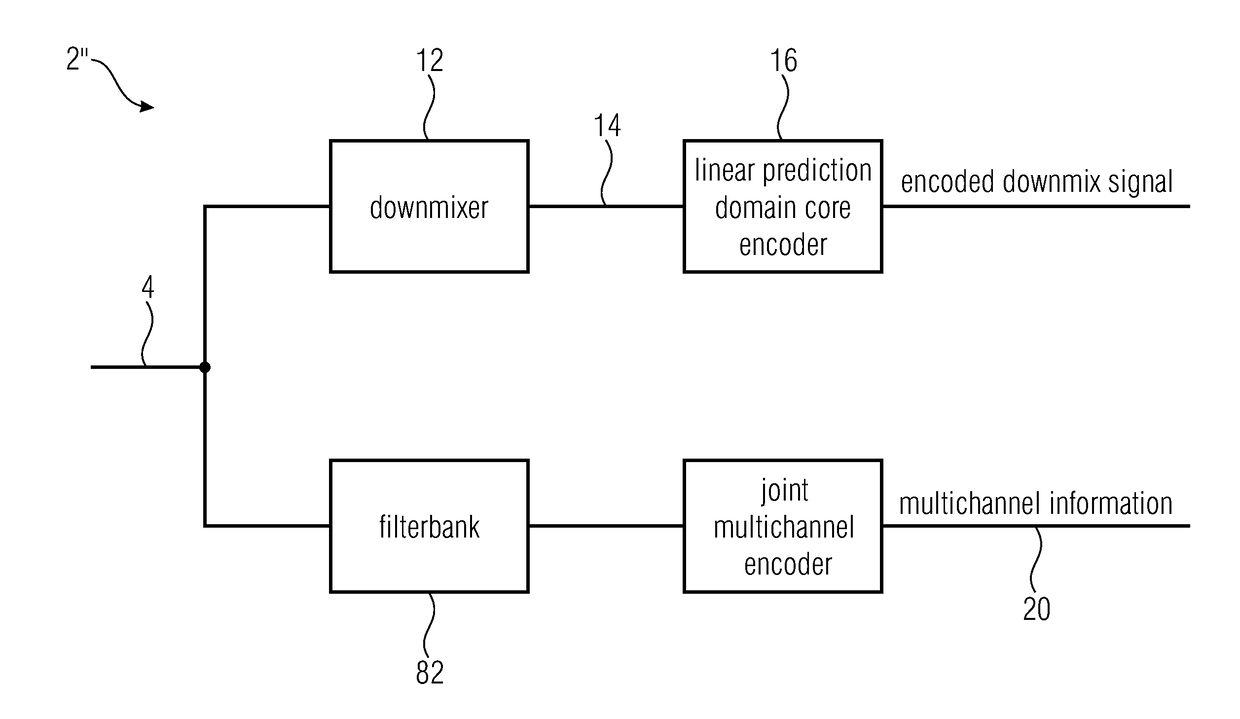
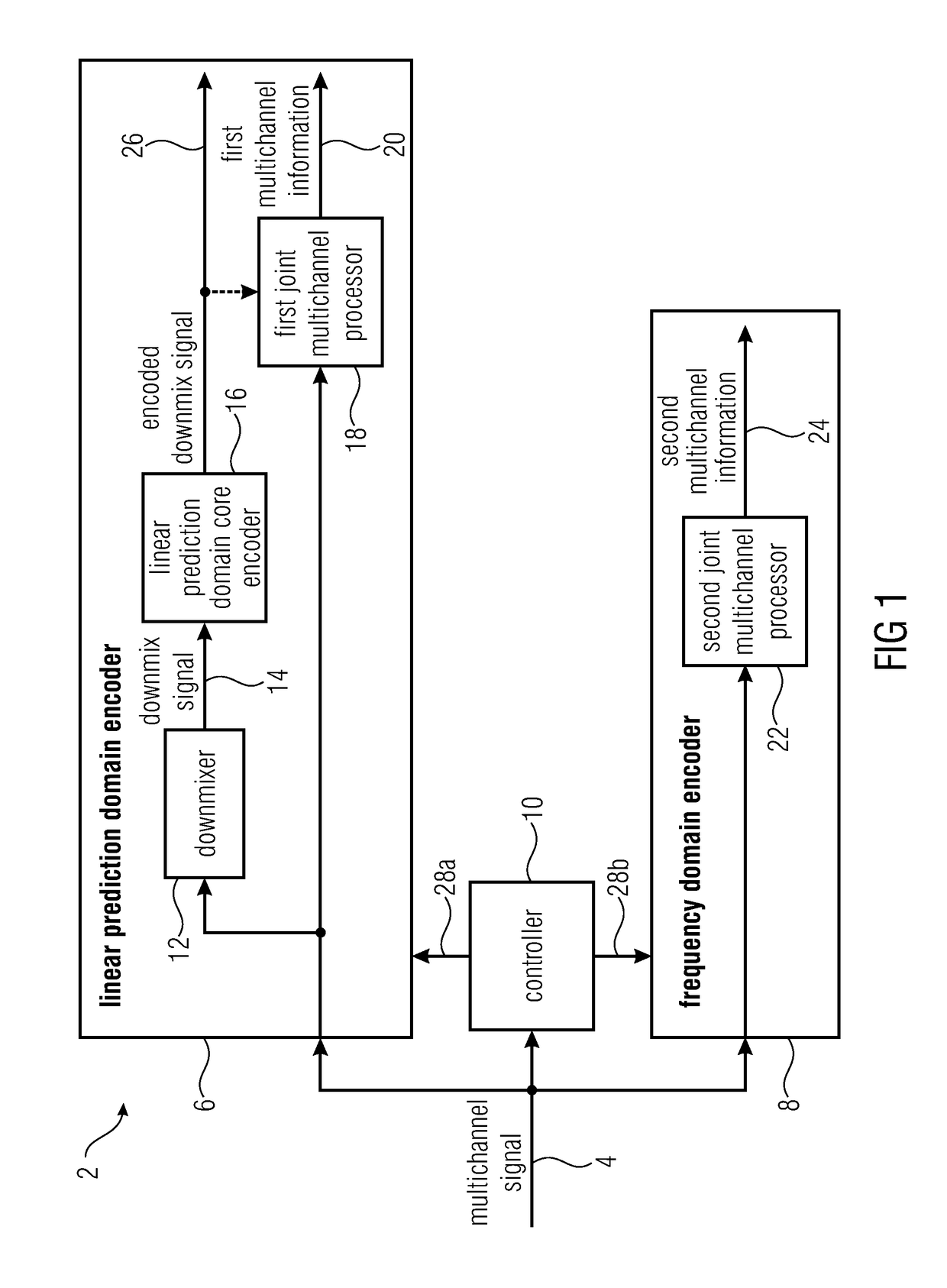
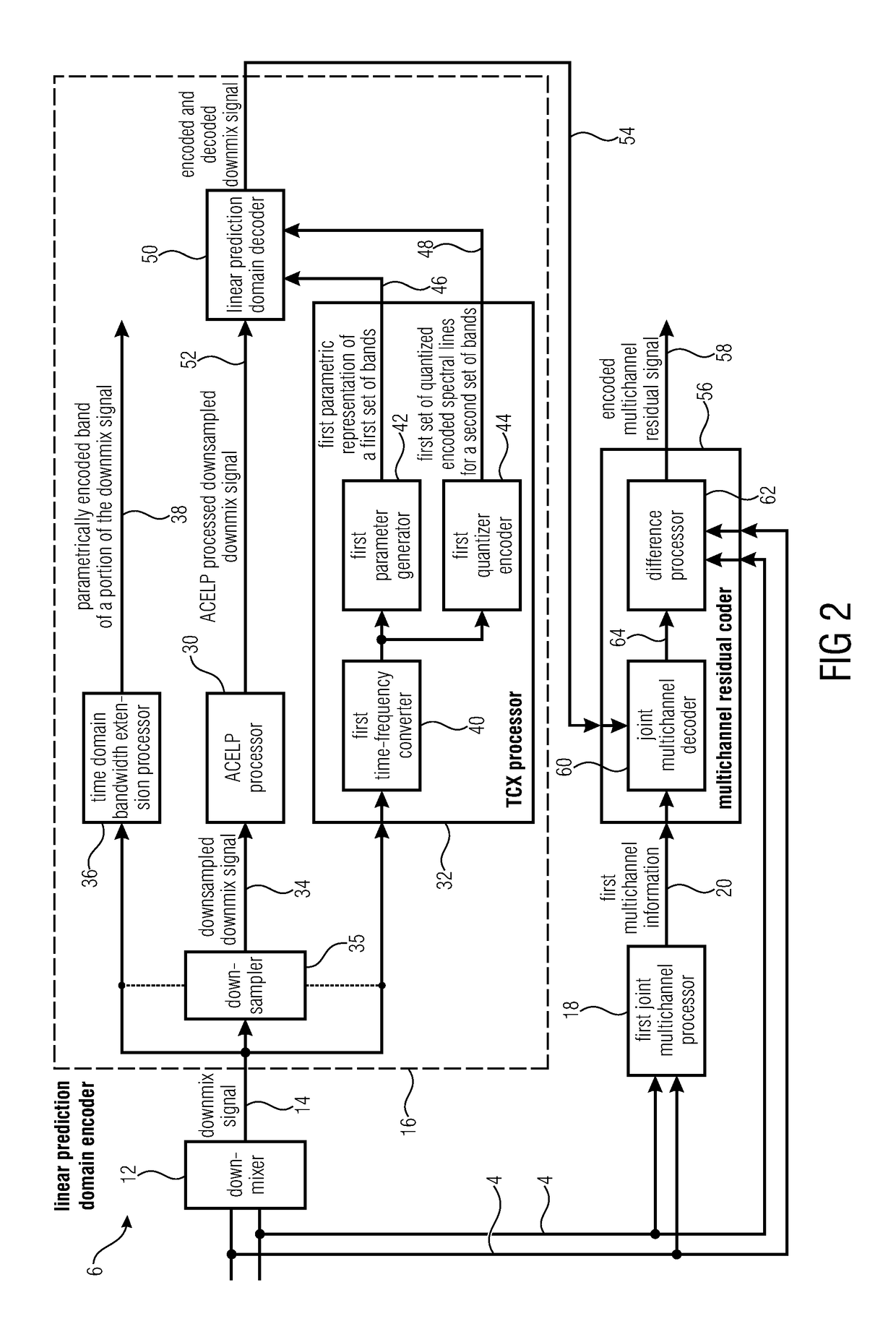
Audio encoder for encoding a multichannel signal and audio decoder for decoding an encoded audio signal
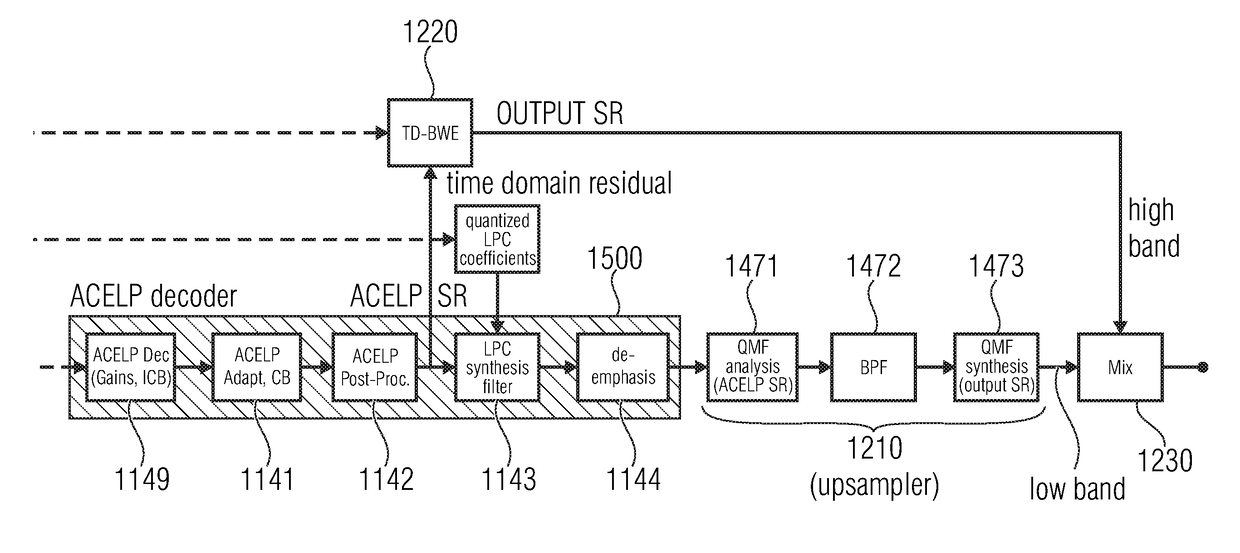
ActiveUS20170365264A1Attenuation bandwidthClosely matchedSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumBandwidth extension
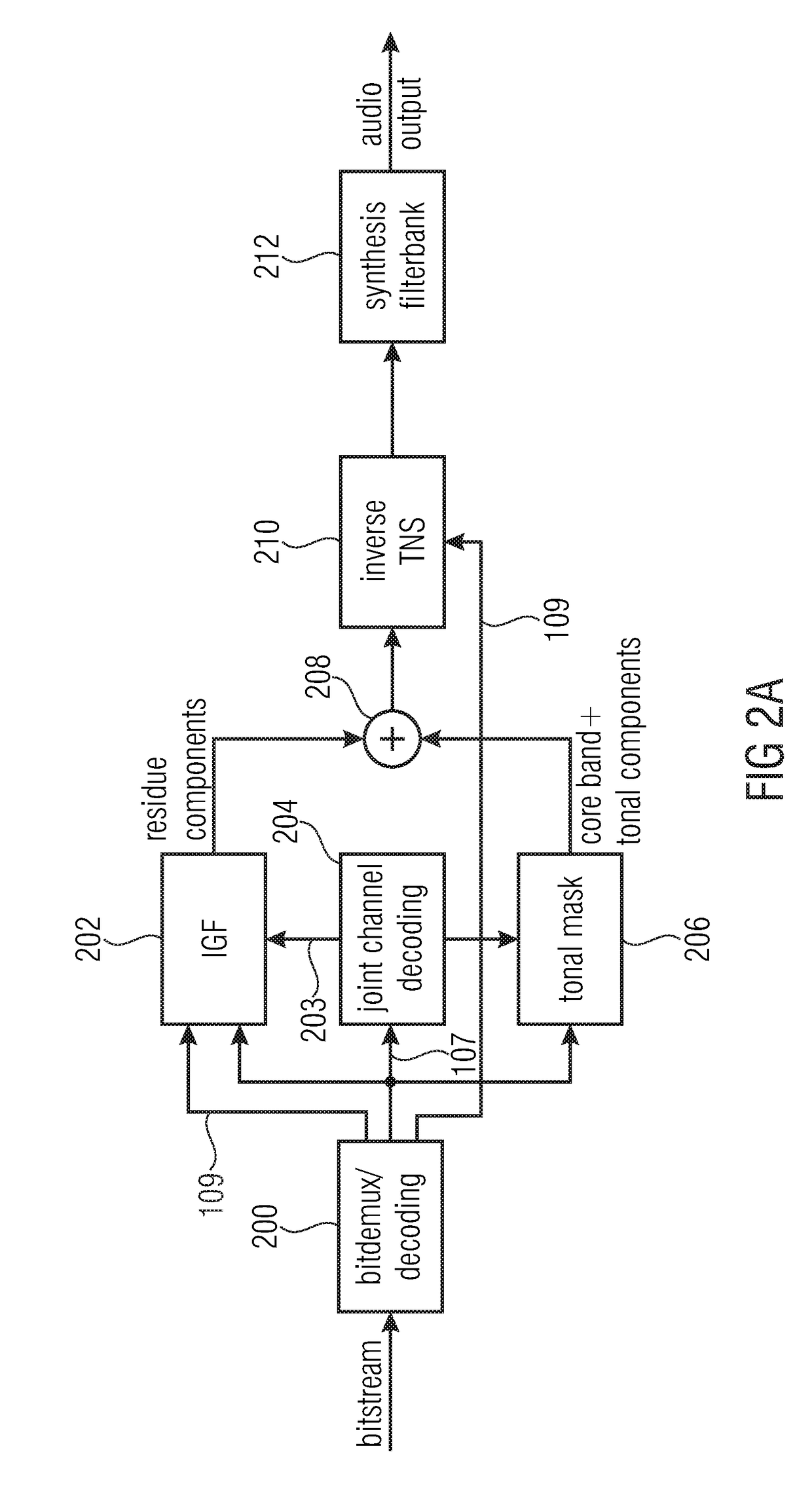
Audio encoder for encoding a multichannel signal is shown. The audio encoder includes a downmixer for downmixing the multichannel signal to obtain a downmix signal, a linear prediction domain core encoder for encoding the downmix signal, wherein the downmix signal has a low band and a high band, wherein the linear prediction domain core encoder is configured to apply a bandwidth extension processing for parametrically encoding the high band, a filterbank for generating a spectral representation of the multichannel signal, and a joint multichannel encoder configured to process the spectral representation including the low band and the high band of the multichannel signal to generate multichannel information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com