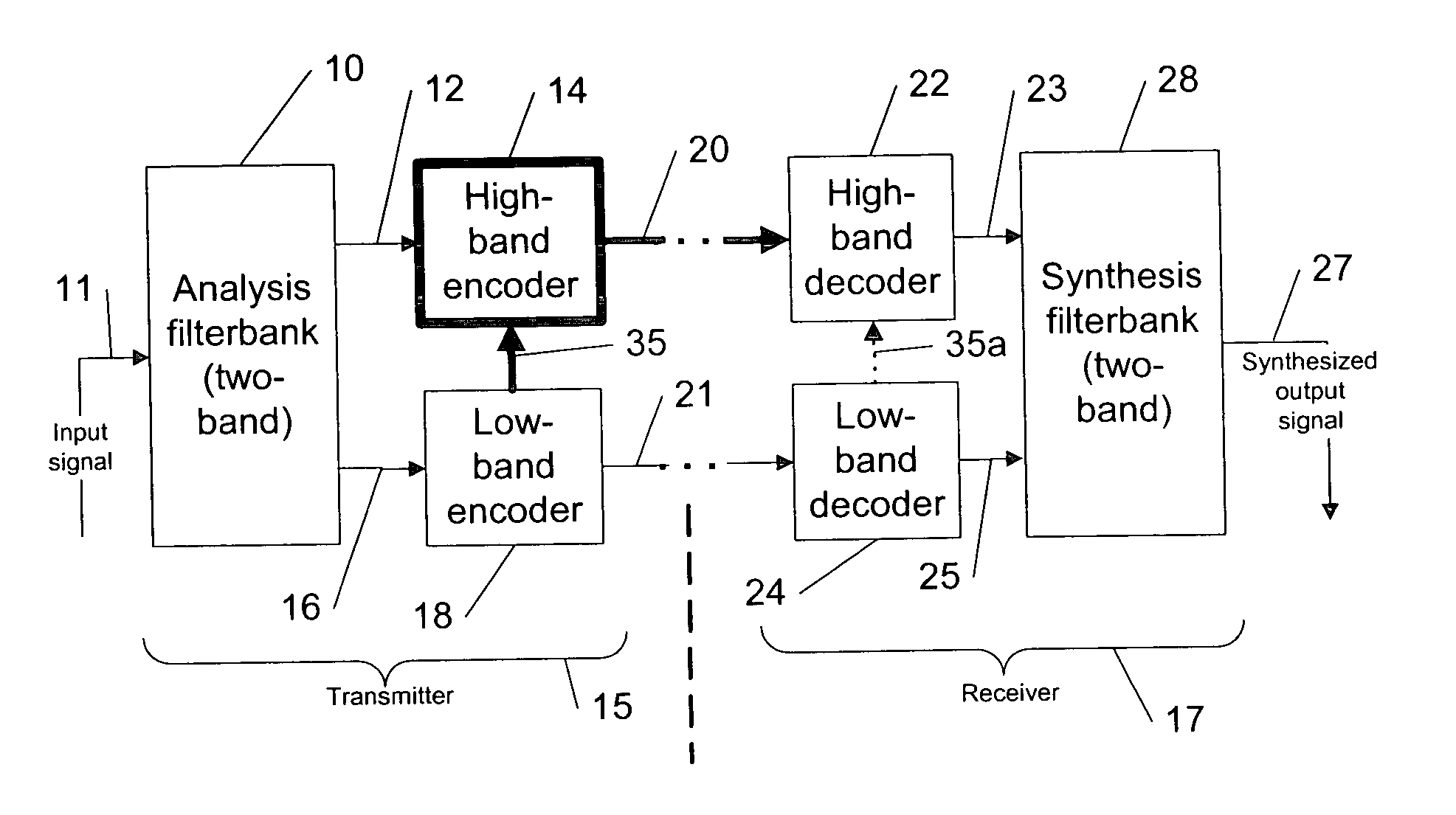
Patents
Literature
284 results about "Transform coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transform coding is a type of data compression for "natural" data like audio signals or photographic images. The transformation is typically lossless (perfectly reversible) on its own but is used to enable better (more targeted) quantization, which then results in a lower quality copy of the original input (lossy compression).
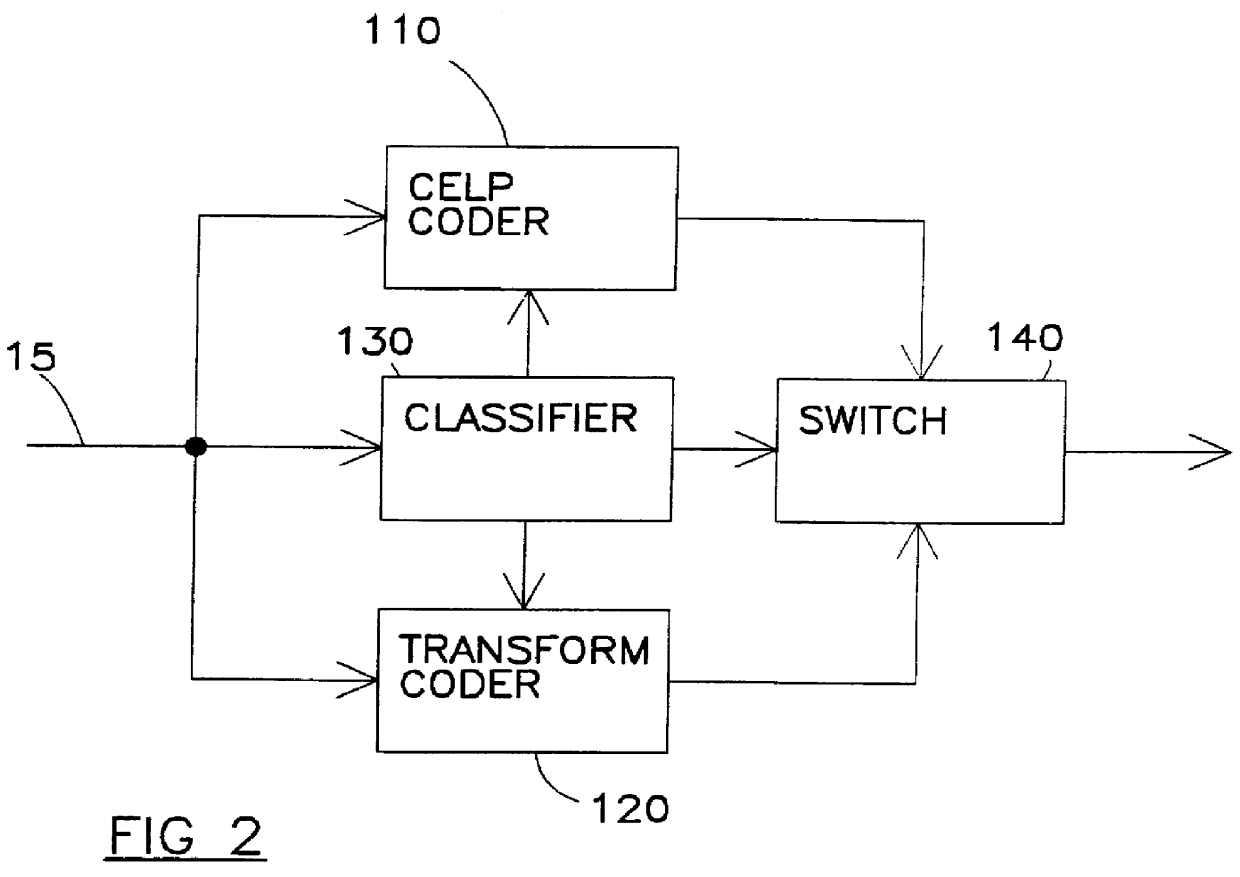
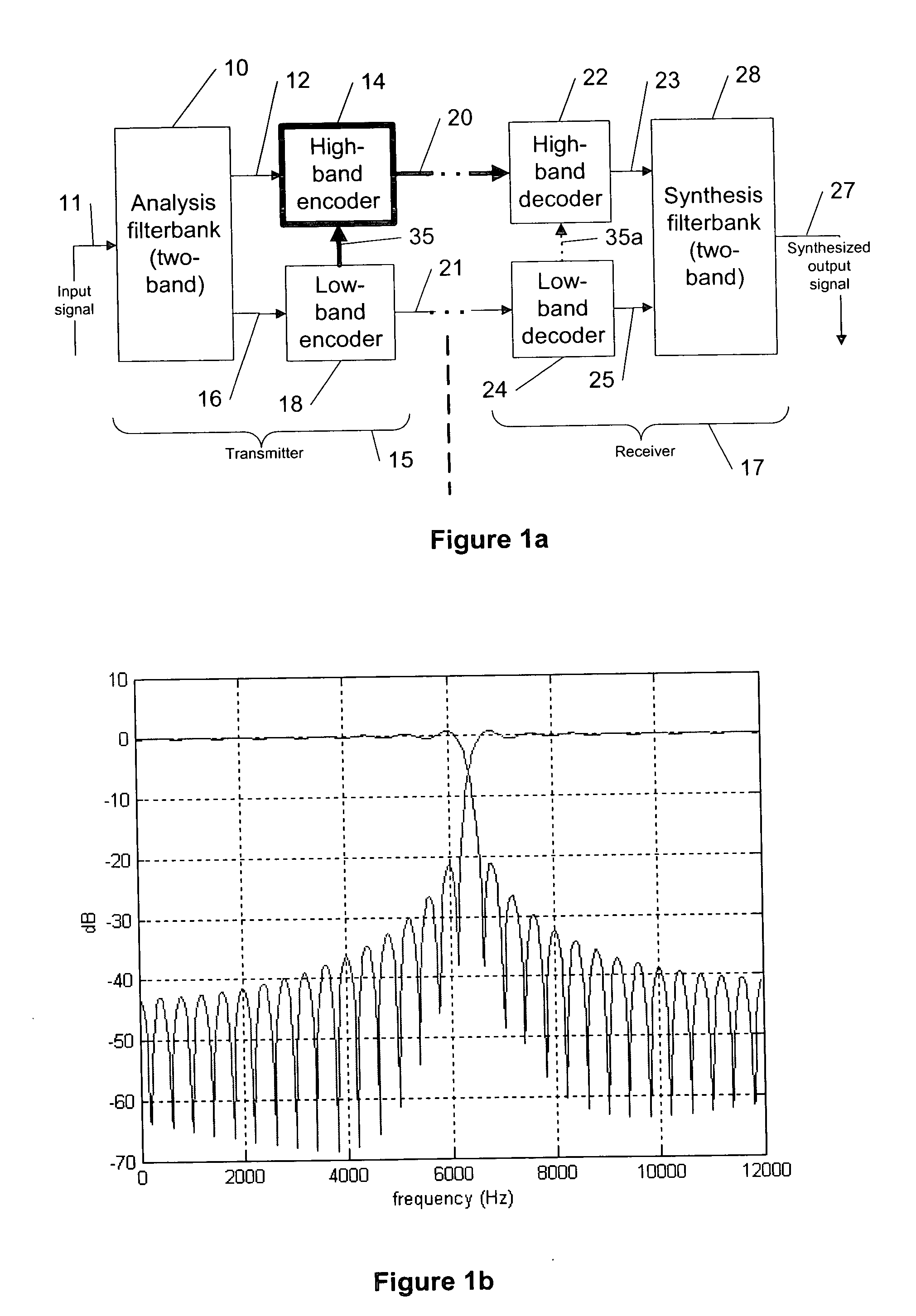
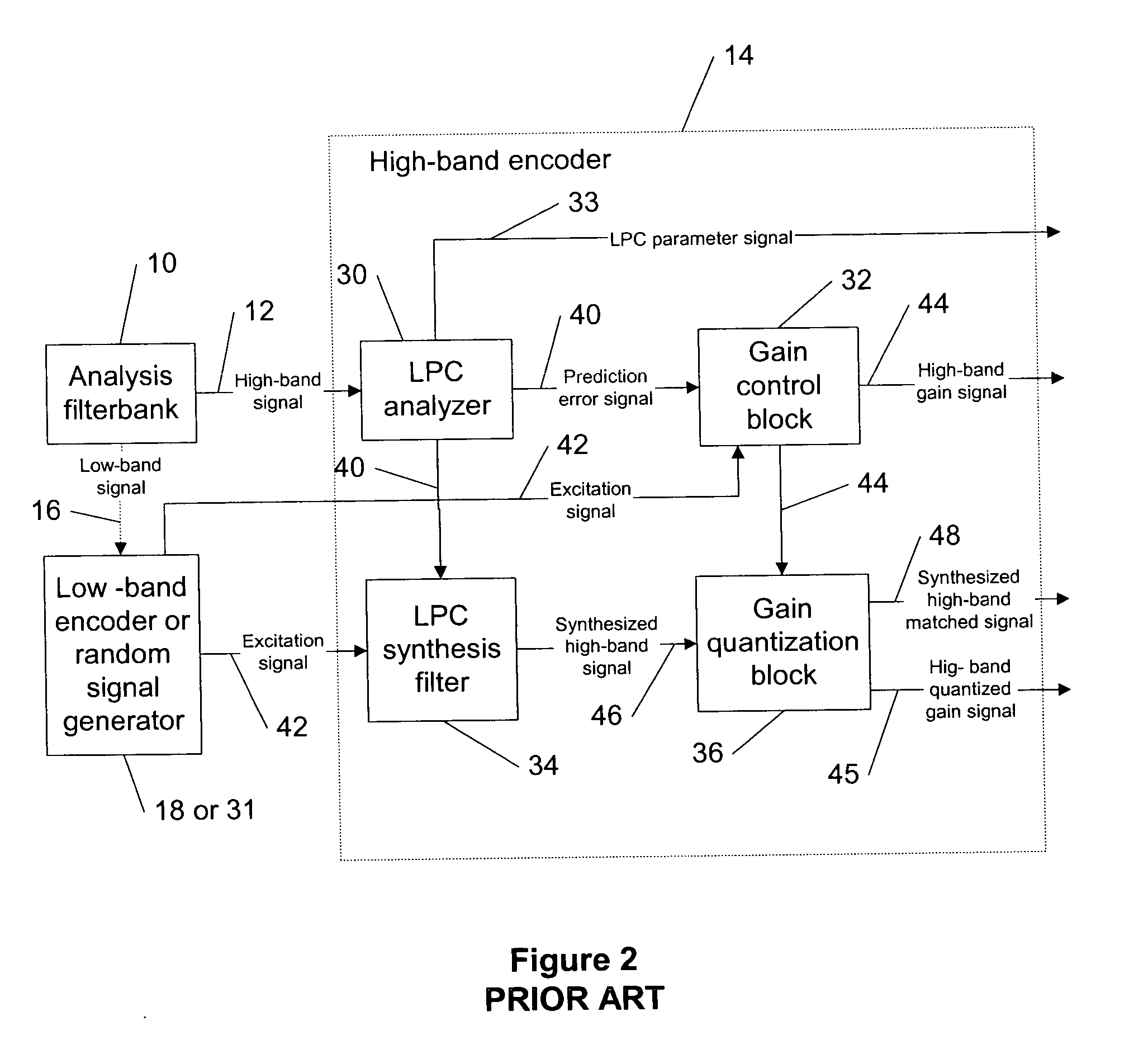
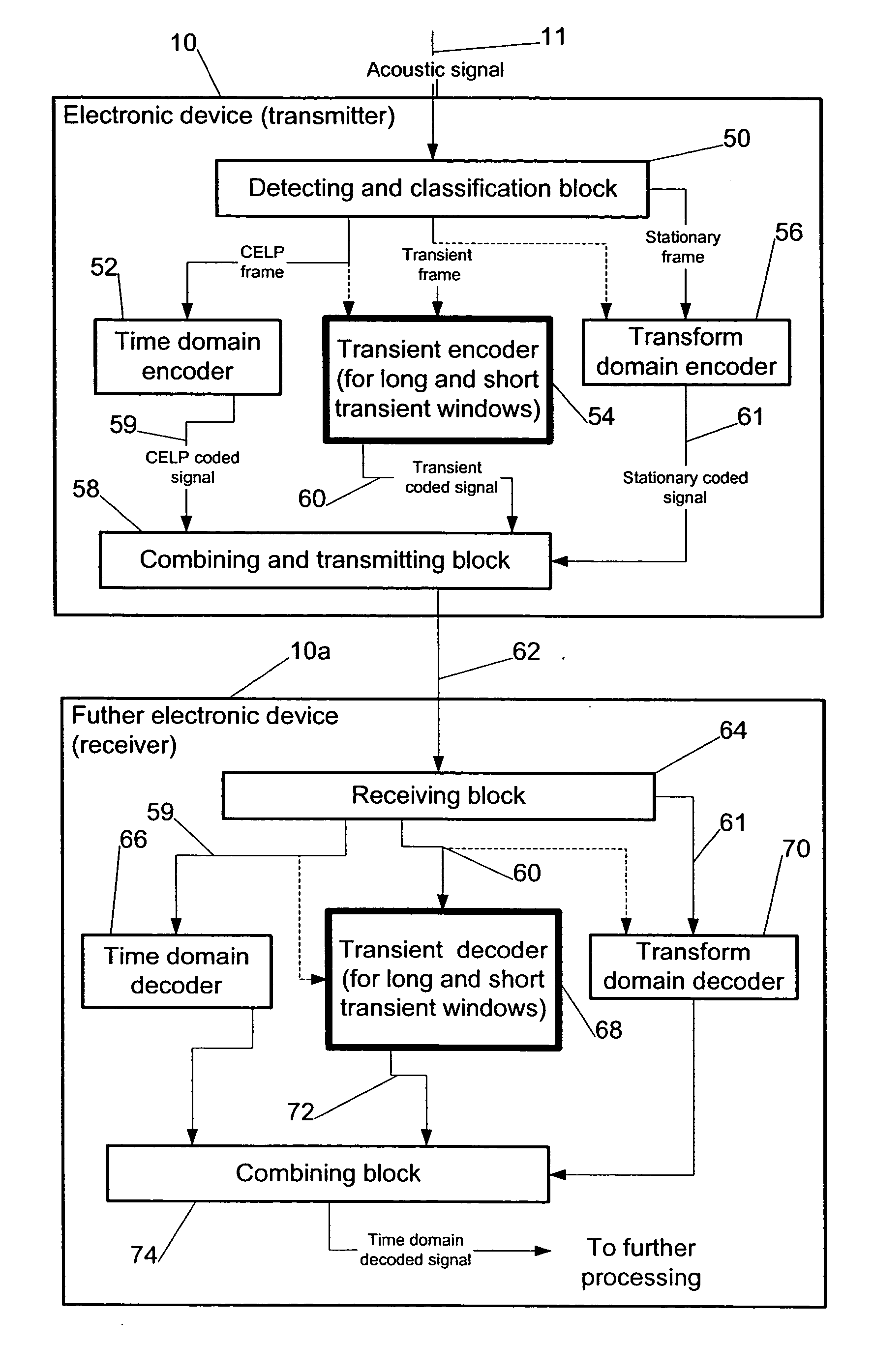
Digital audio signal coding using a CELP coder and a transform coder
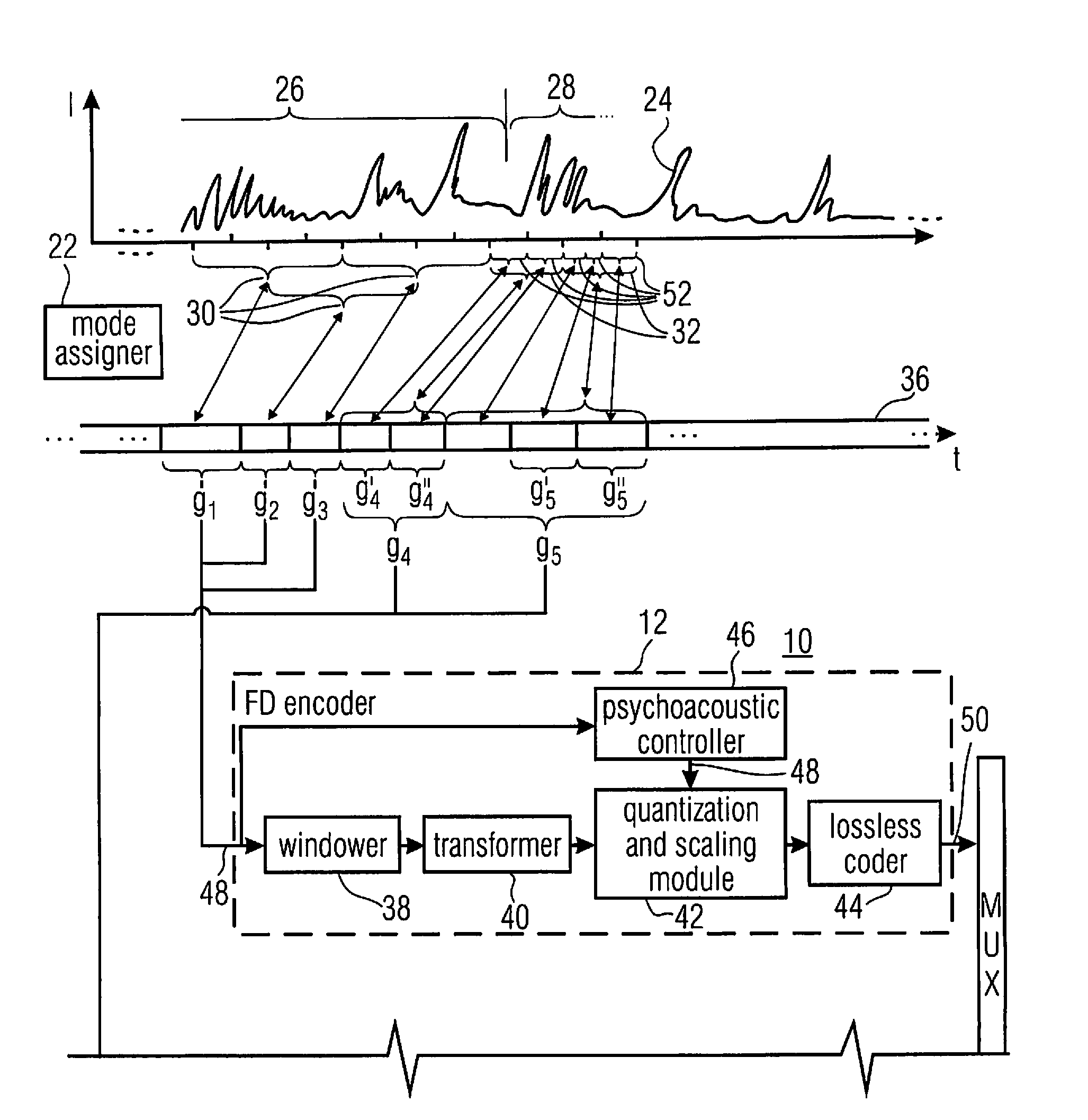
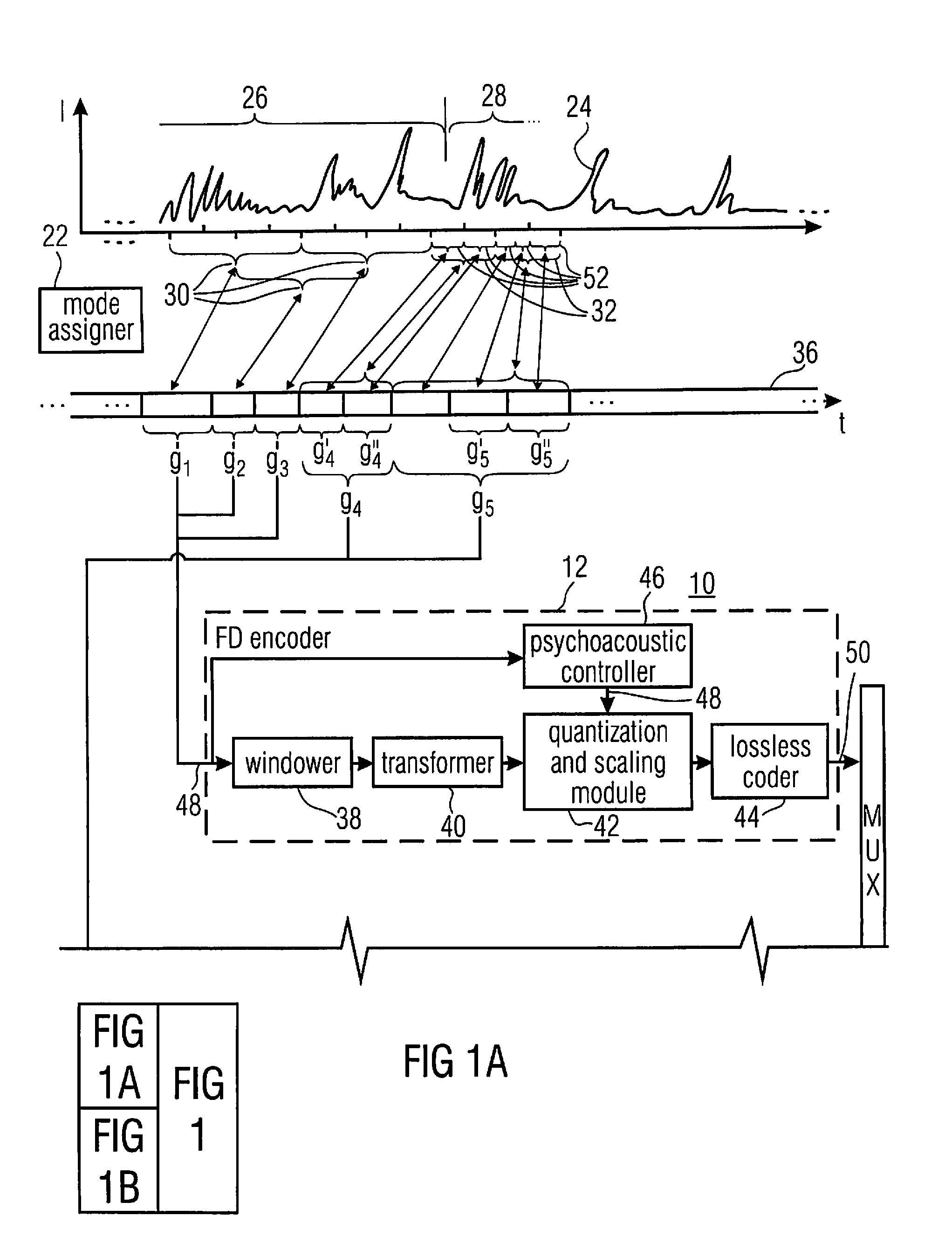
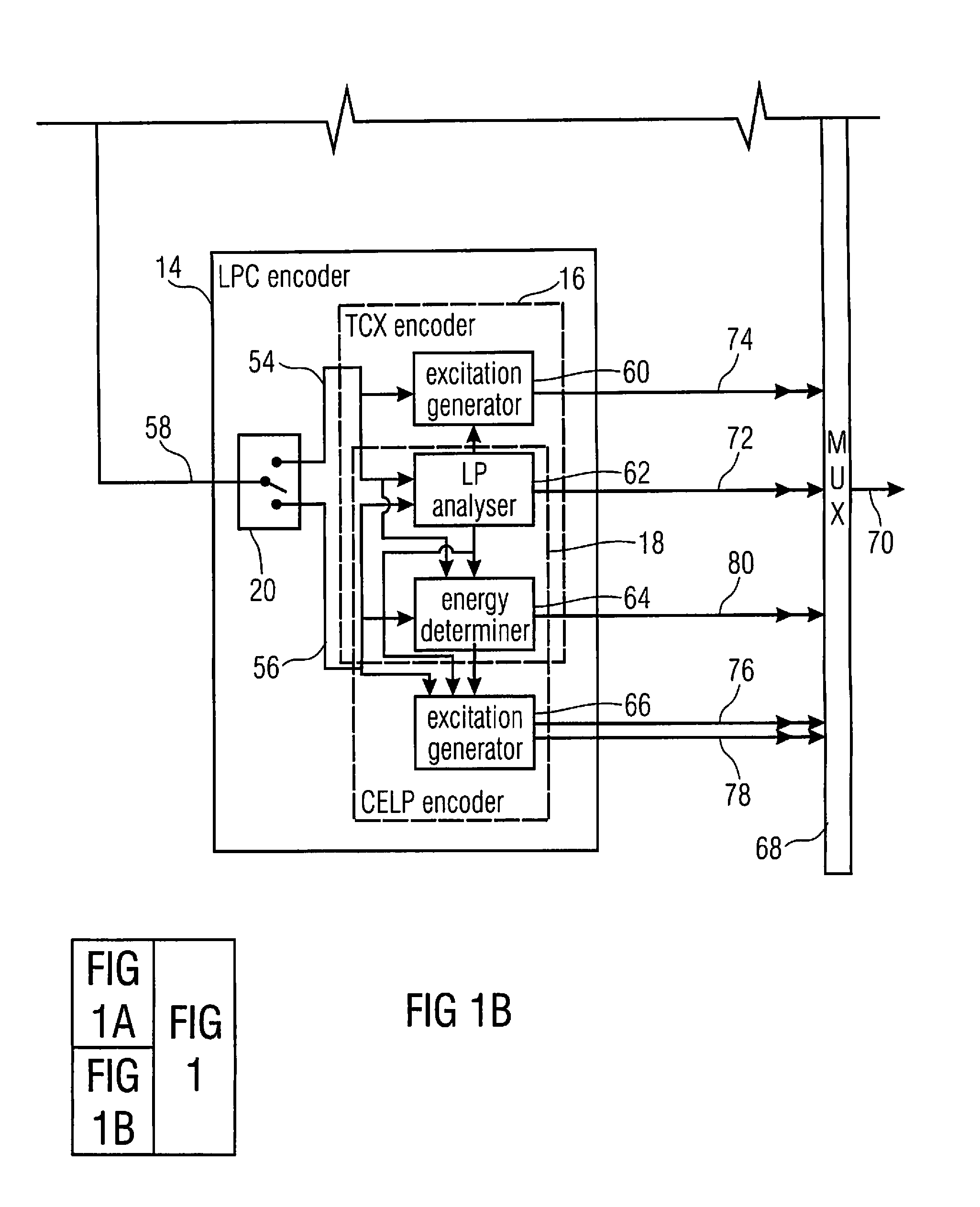
Apparatus is described for digitally encoding an input audio signal for storage or transmission. A distinguishing parameter is measure from the input signal. It is determined from the measured distinguishing parameter whether the input signal contains an audio signal of a first type or a second type. First and second coders are provided for digitally encoding the input signal using first and second coding methods respectively and a switching arrangement directs, at any particular time, the generation of an output signal by encoding the input signal using either the first or second coders according to whether the input signal contains an audio signal of the first type or the second type at that time. A method for adaptively switching between transform audio coder and CELP coder, is presented. In a preferred embodiment, the method makes use of the superior performance of CELP coders for speech signal coding, while enjoying the benefits of transform coder for other audio signals. The combined coder is designed to handle both speech and music and achieve an improved quality.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
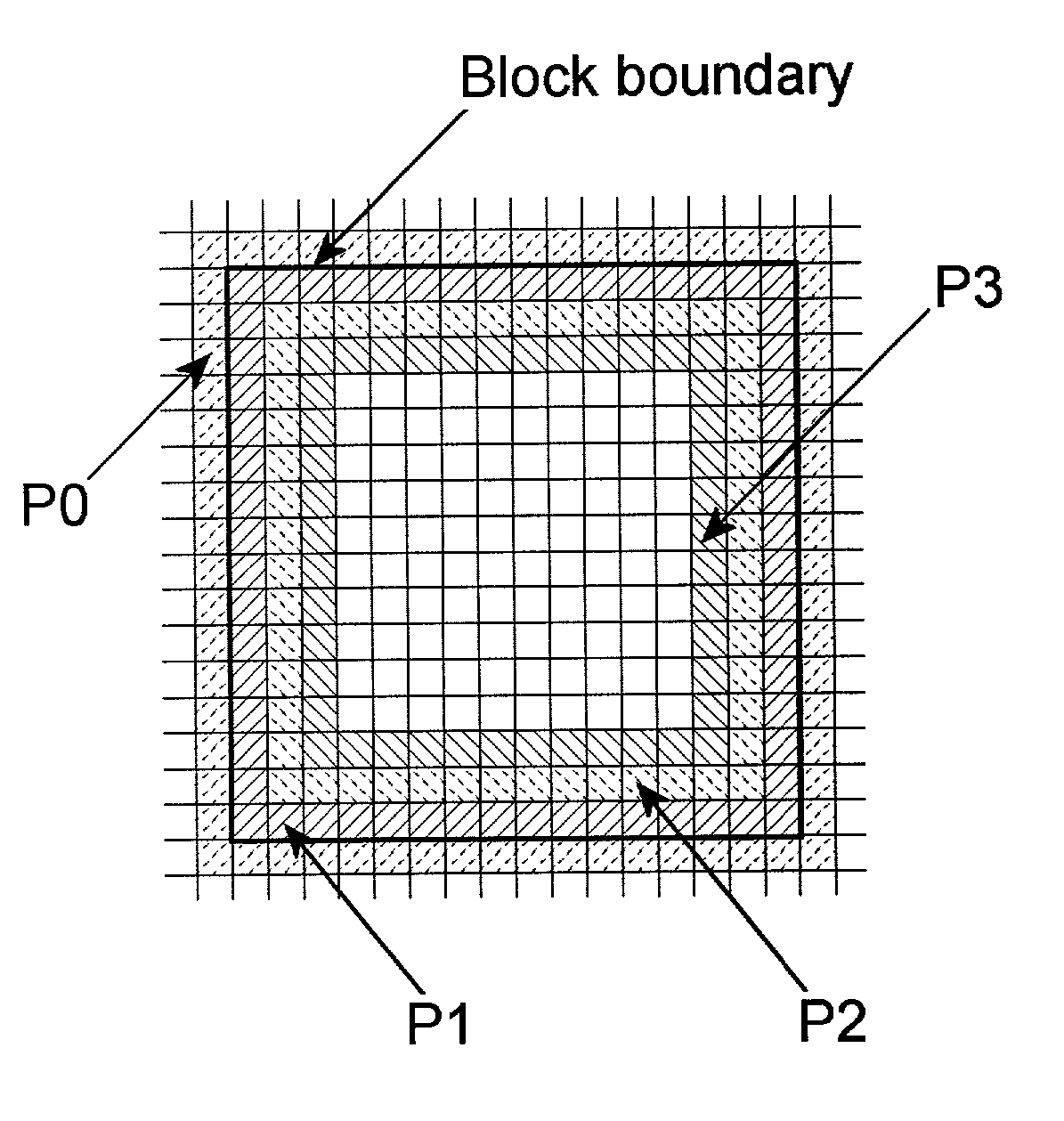
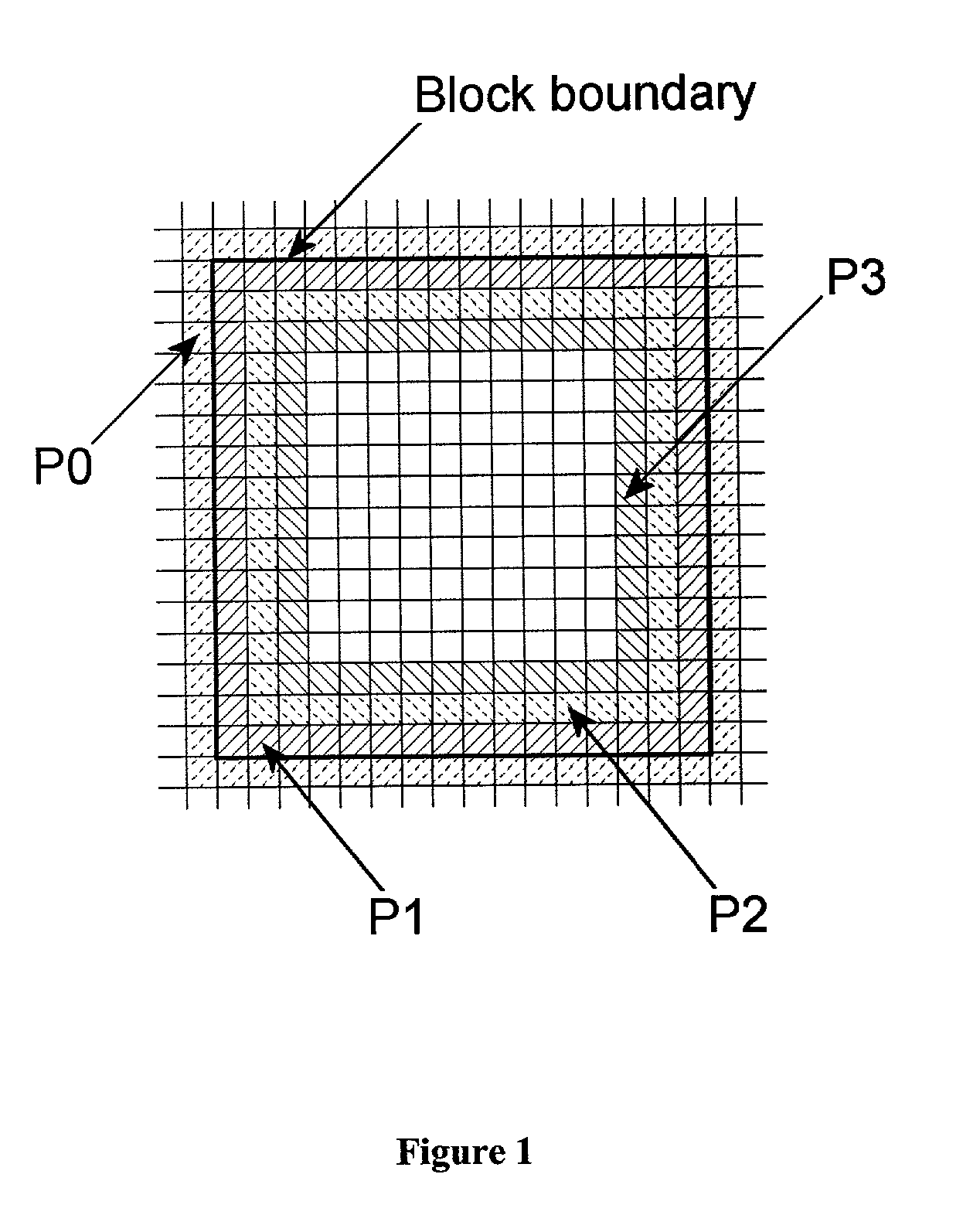
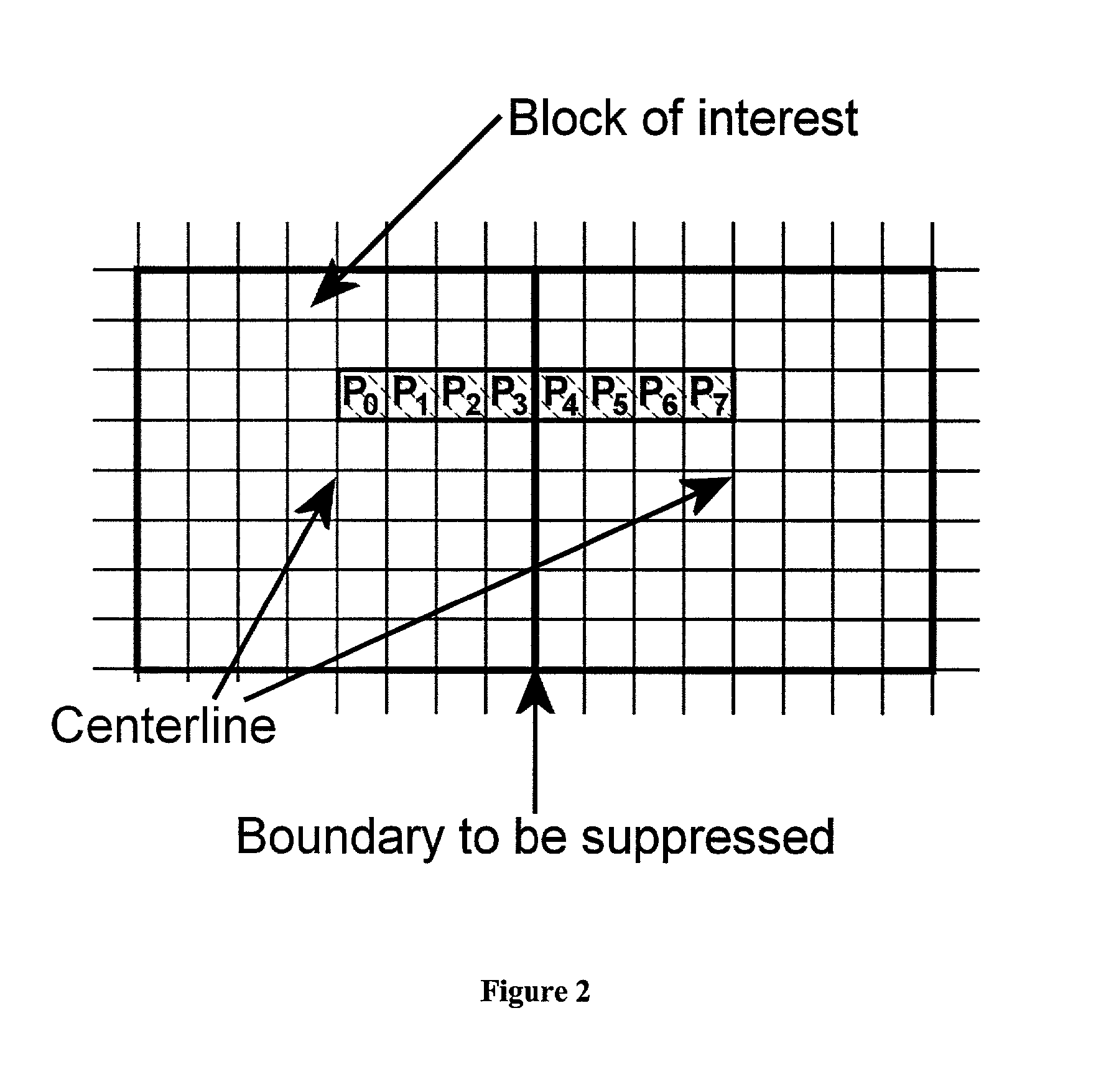
Removal of block encoding artifacts
InactiveUS7003174B2Reduce artifactsAccessImage enhancementPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVisibilityPattern recognition
A method of reducing artifacts in an image previously processed by block transform encoding may comprise the steps of:determining block boundaries;determining an approximate metric of artifact visibility;optionally interpolating across block boundaries;adaptively filtering luminance;optionally adaptively filtering chrominance;adaptively adjusting local saturation variation; andadaptively simulating high spatial frequency image detail;wherein the adaptive steps are executed to an extent or in an amount depending on the metric or standard or measurement of artifact visibility.
Owner:COREL CORP +1
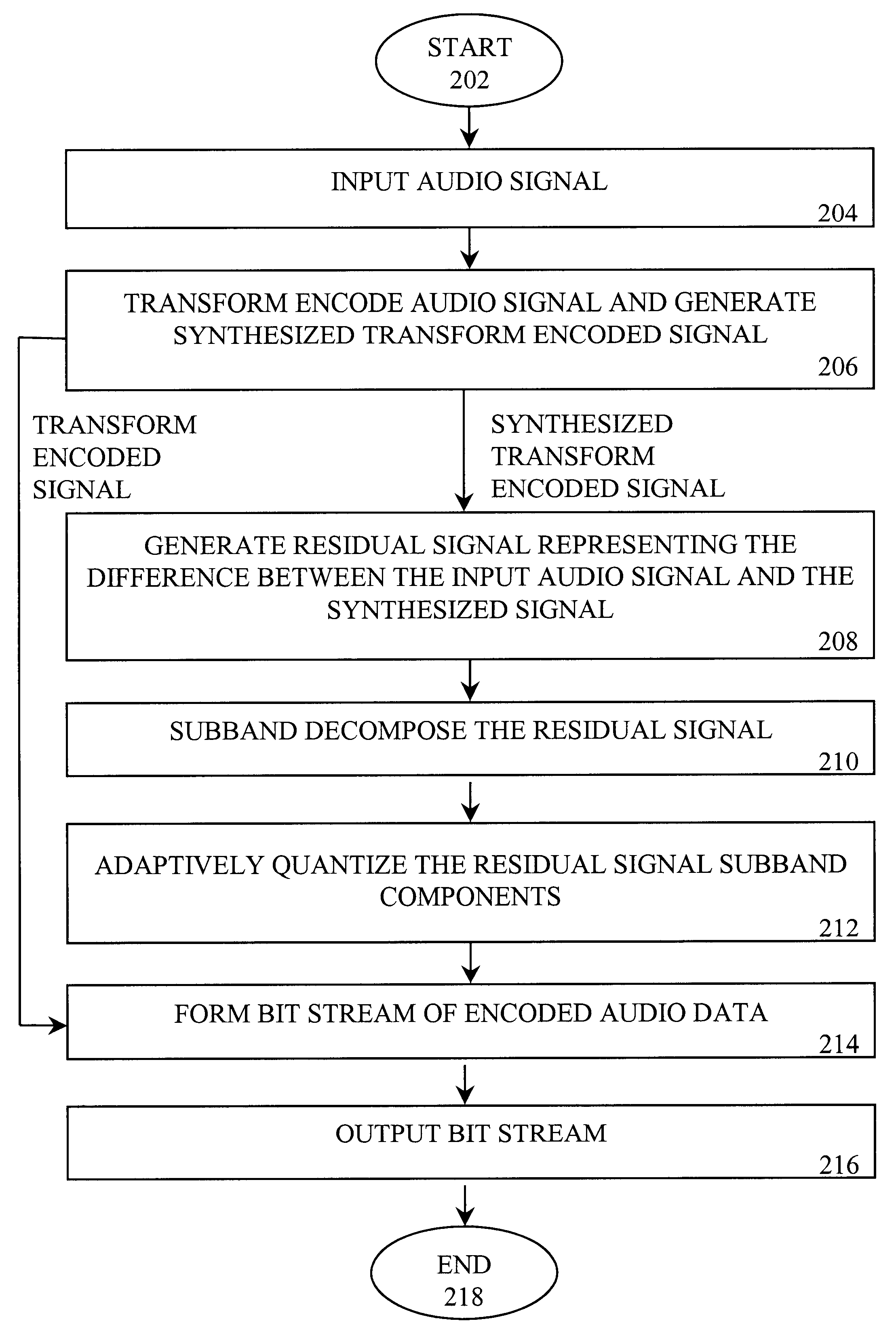
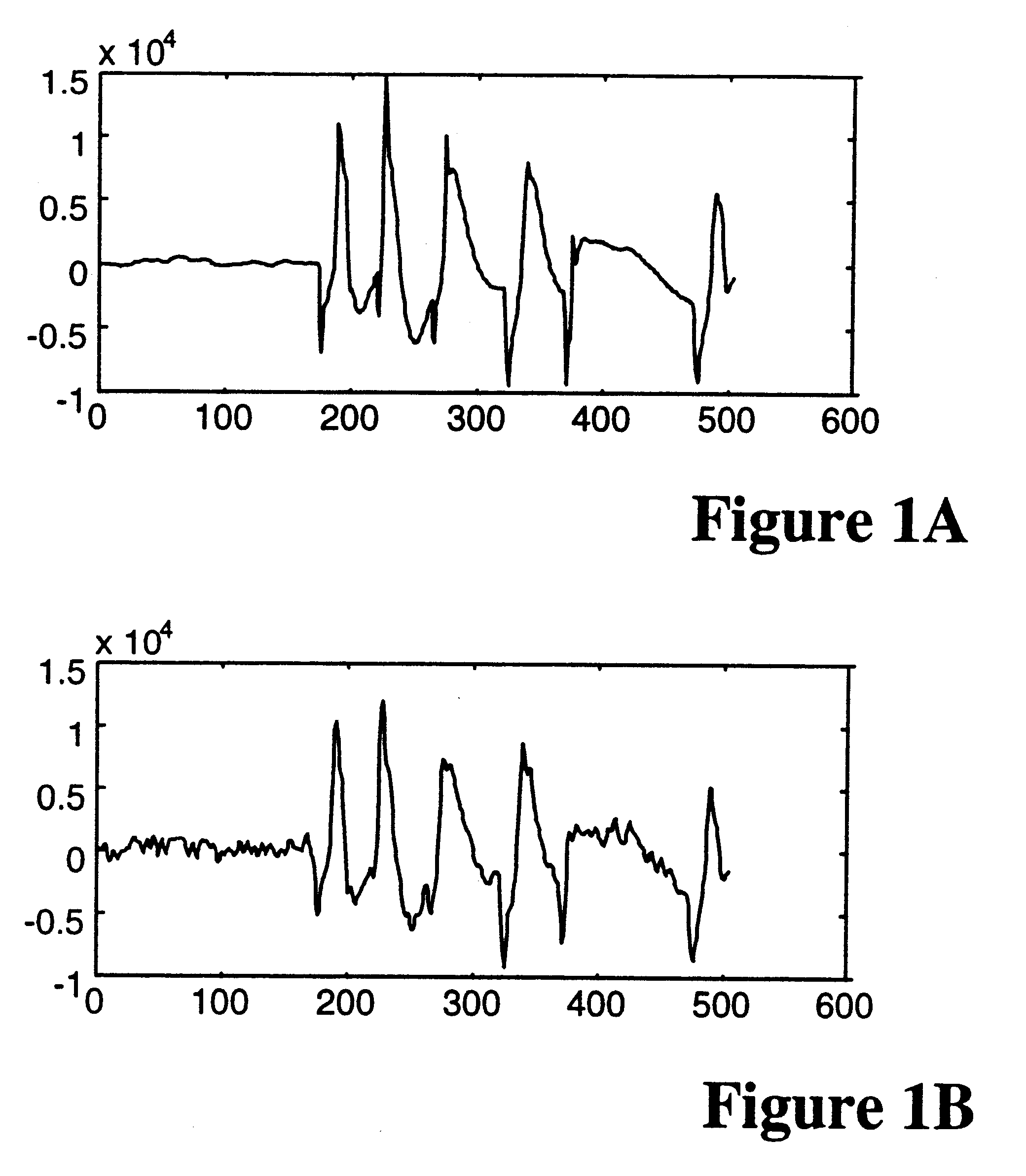
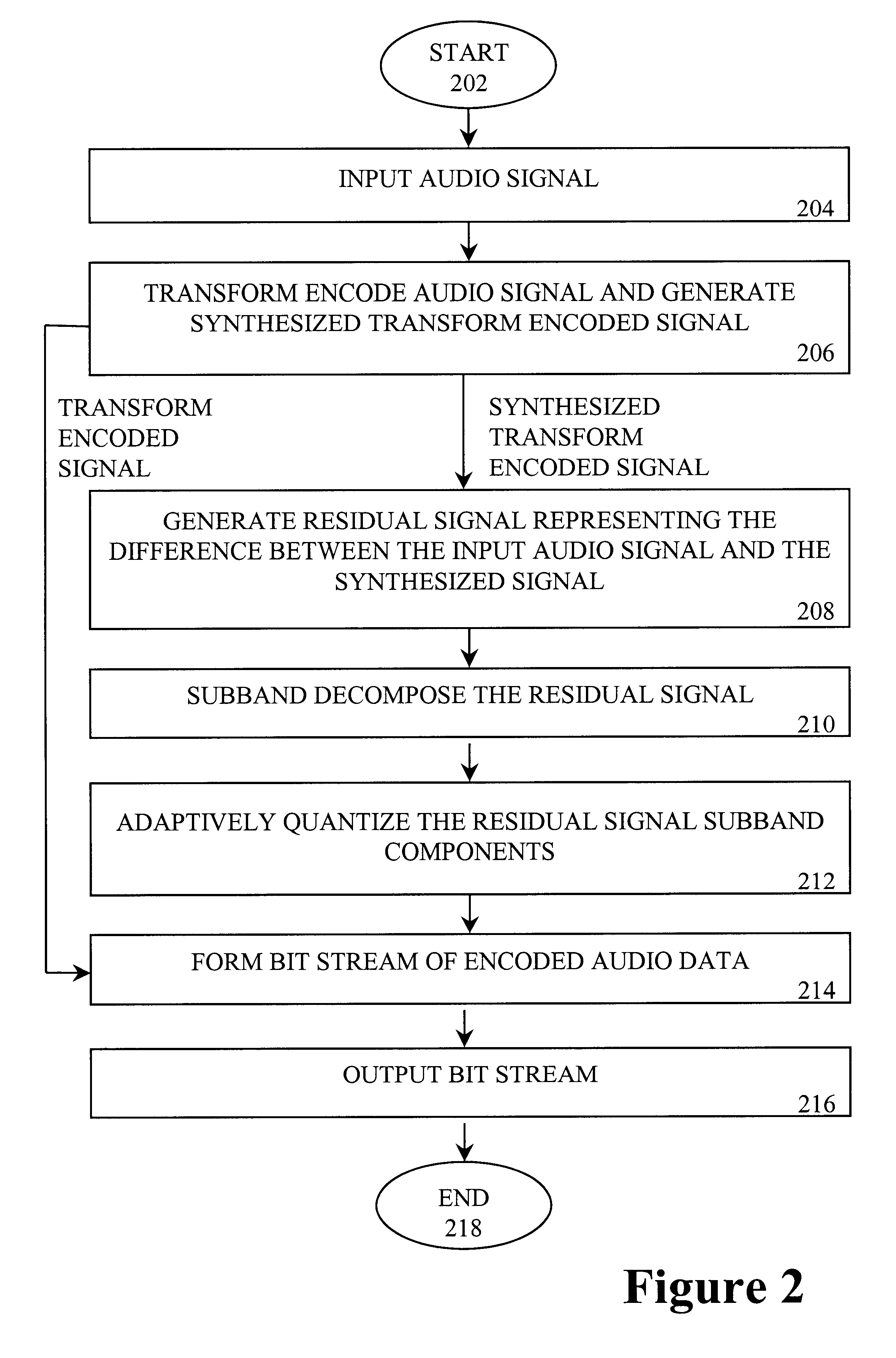
Audio compression and decompression employing subband decomposition of residual signal and distortion reduction
A method and apparatus to achieve relatively high quality audio data compression / decompression, while achieving relatively low bit rates (e.g., high compression ratios). According to one aspect of the invention, a residual signal is subband decomposed and adaptively quantized and encoded to capture frequency information that may provide higher quality compression and decompression relative to transform encoding techniques. According to a second aspect of the invention, an input audio signal is compared to an encoded signal based on the input audio signal to detect and reduce, as necessary, distortion in the encoded signal or portions thereof.
Owner:XVD TECH HLDG LTD IRELAND
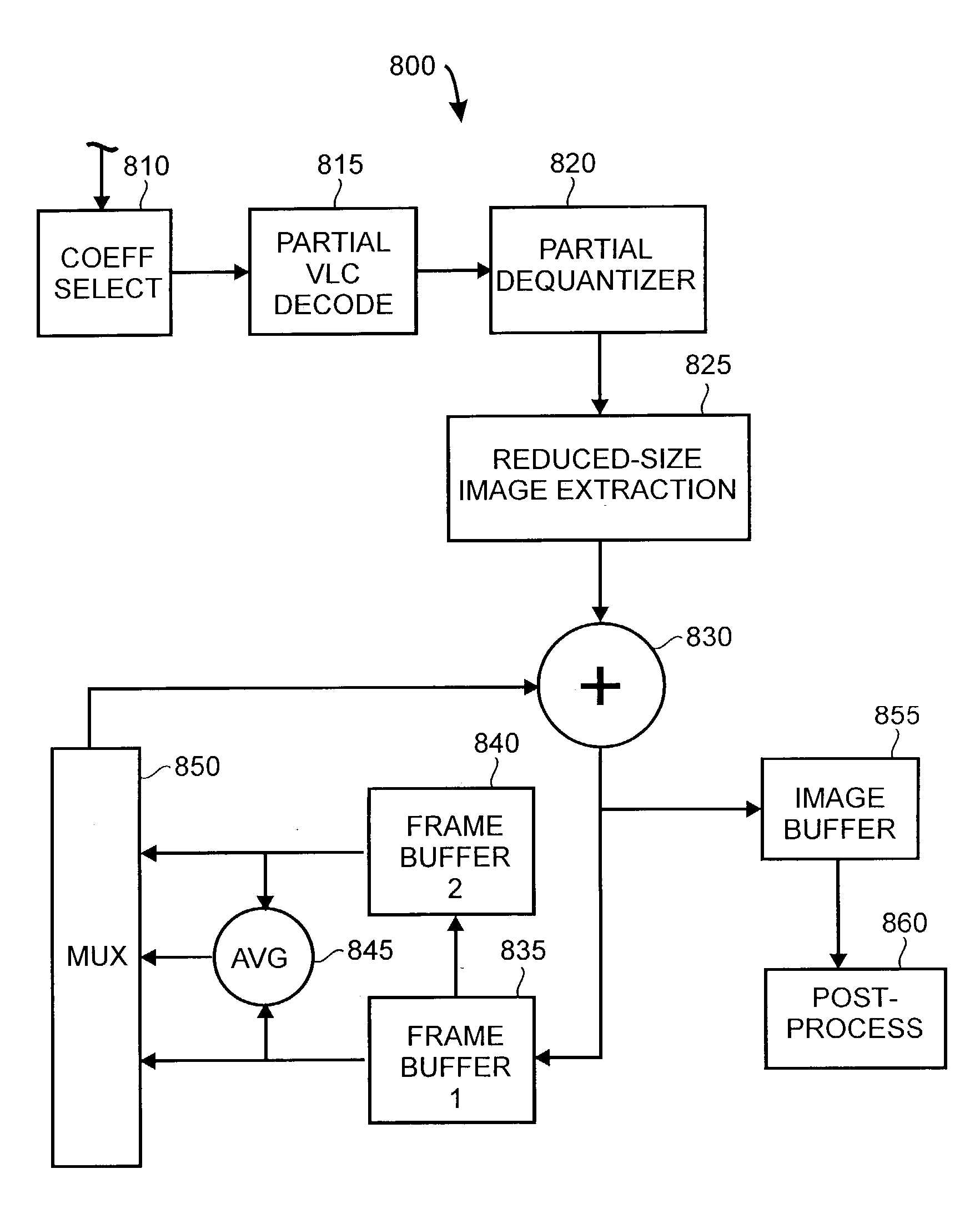
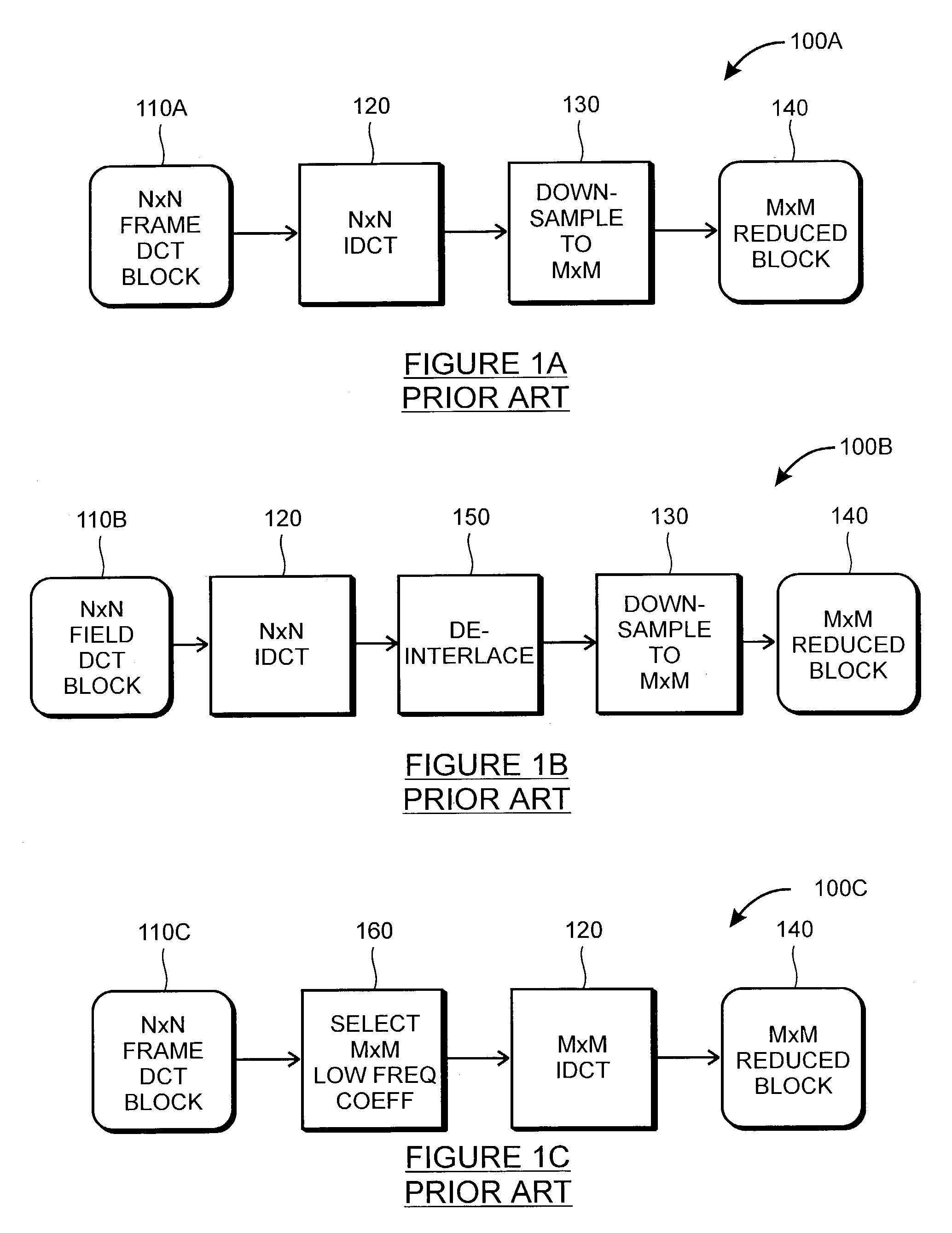
Rapid production of reduced-size images from compressed video streams
ActiveUS7471834B2Simple technologyRapid productionDisc-shaped record carriersFlat record carrier combinationsInterlaced videoReduced size
Methods for fast generating spatially reduced-size images directly from compressed video streams supporting the coding of interlaced frames through transform coding and motion compensation. A sequence of reduced-size images are rapidly generated from compressed video streams by efficiently combining the steps of inverse transform, down-sampling and construction of each field image. The construction of reduced-size field images also allows the efficient motion compensation. The fast generation of reduced-size images is applicable to a variety of low-cost applications such as video browsing, video summary, fast thumbnail playback and video indexing.
Owner:SCENERA INC
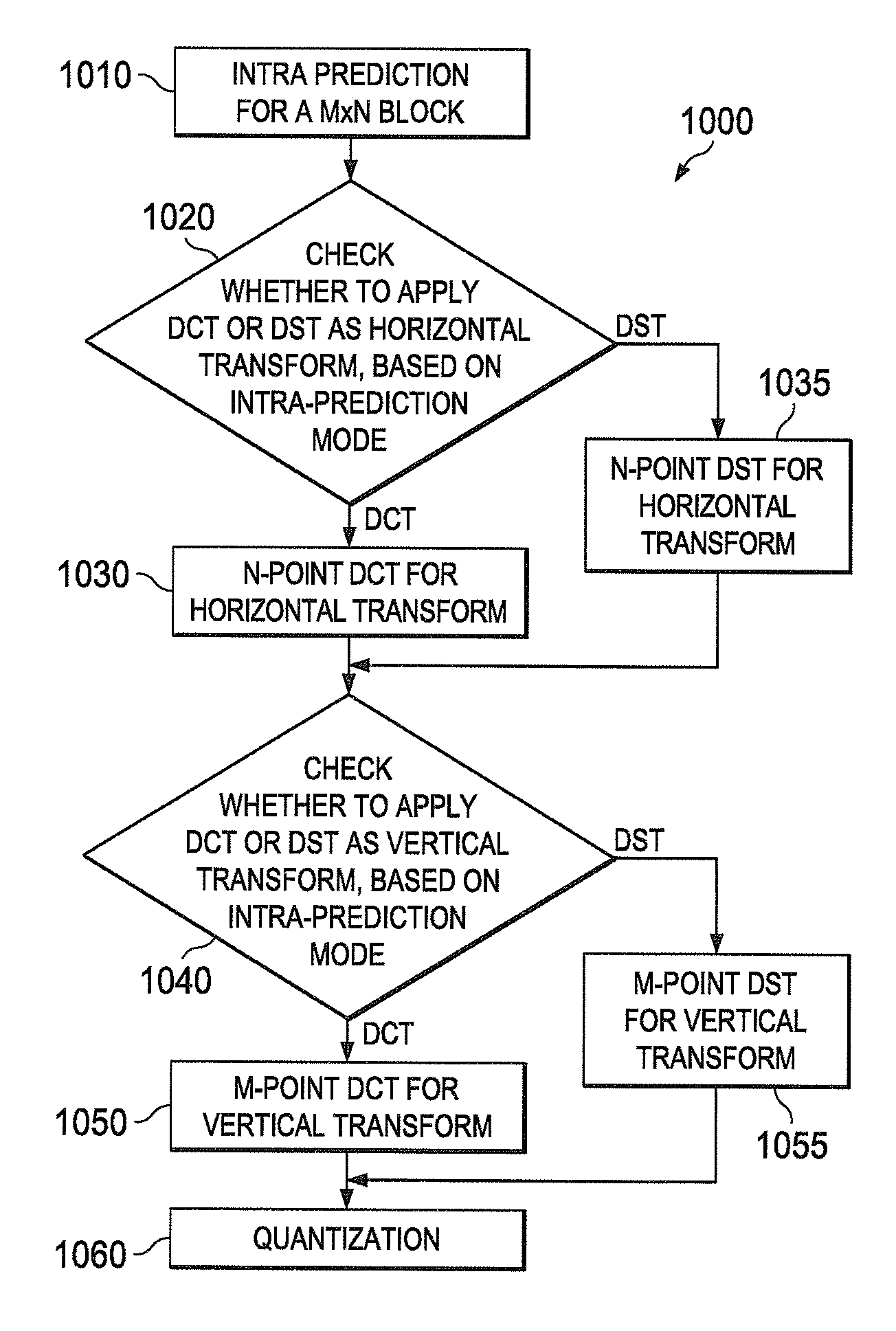
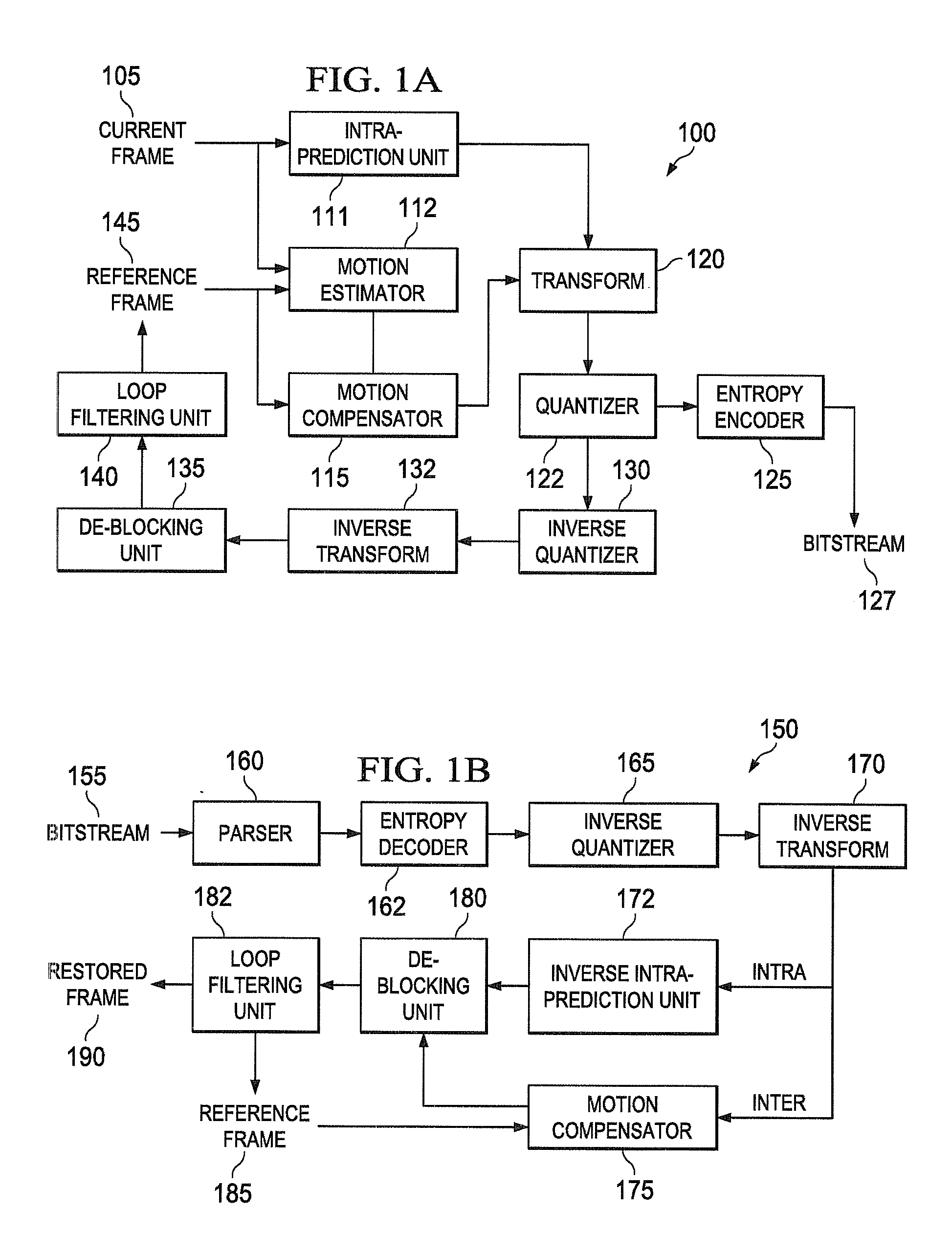
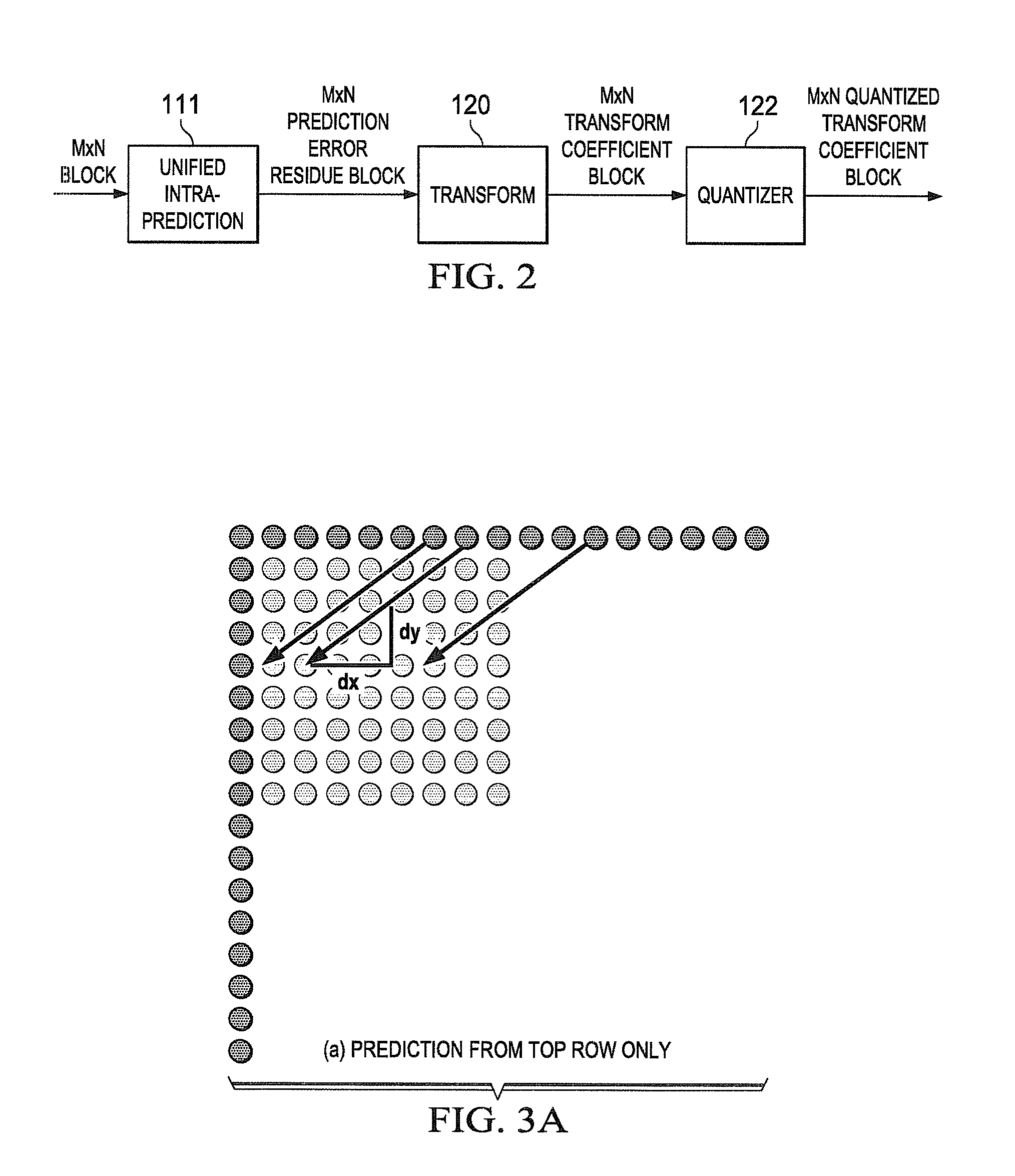
Low complexity transform coding using adaptive dct/dst for intra-prediction
InactiveUS20120057630A1Reduce complexityQuick implementationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo bitstreamSelf adaptive
A method and apparatus encode and decode video by determining whether to use discrete cosine transform (DCT) and DST for each of the horizontal and vertical transforms. During encoding, an intra-prediction is performed based on an intra-prediction mode determined for an M×N input image block to obtain an M×N intra-prediction residue matrix (E). Based on the intra-prediction mode, each of a horizontal transform and a vertical transform is performed using one of DCT and DST according to the intra-prediction mode. During decoding, the intra-prediction mode is determined from an incoming video bitstream. The M×N transformed coefficient matrix of the error residue is obtained from the video bitstream using an inverse quantizer. Based on the intra prediction mode, one of DCT and DST is performed for each of an inverse vertical transform and an inverse horizontal transform.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
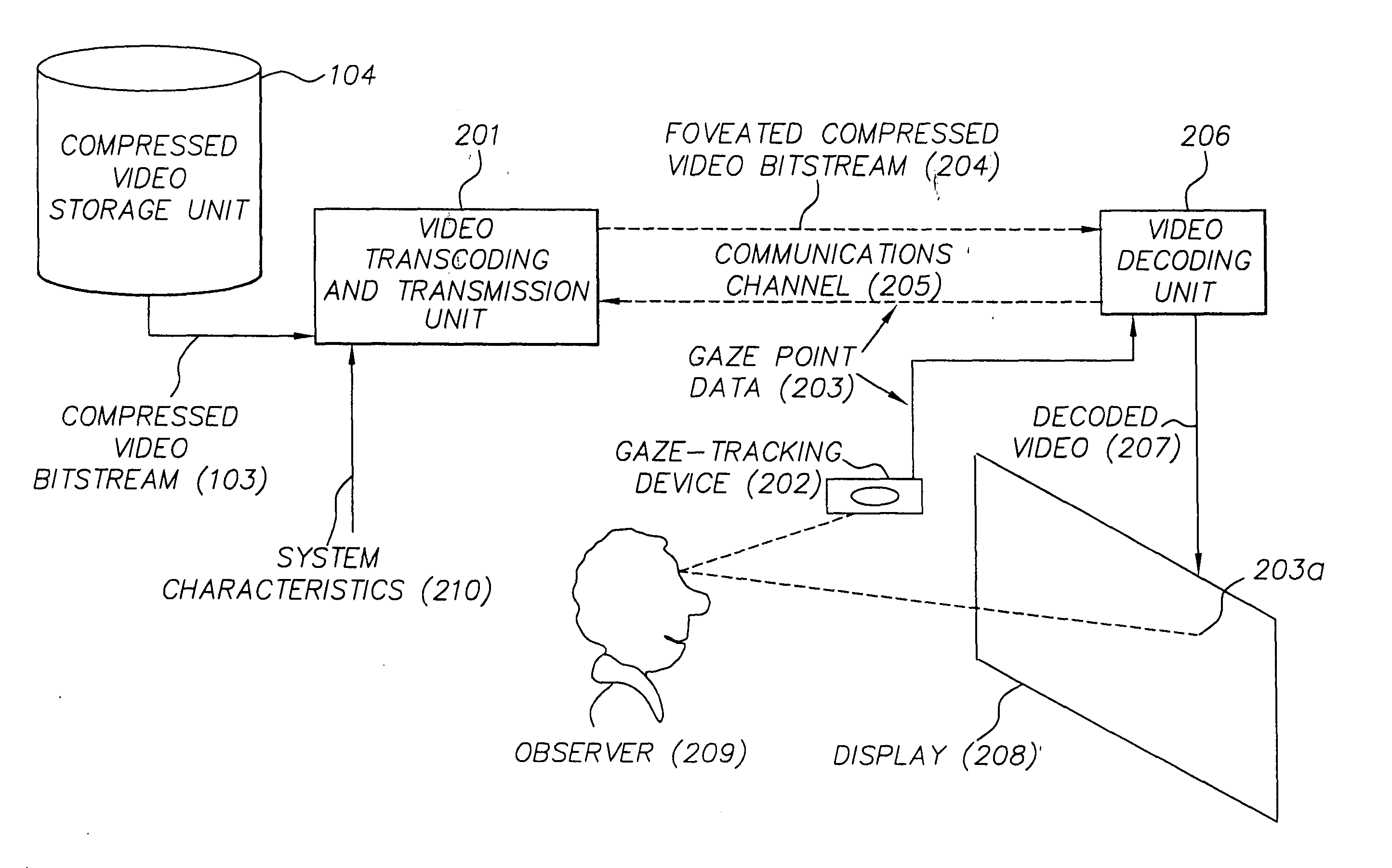
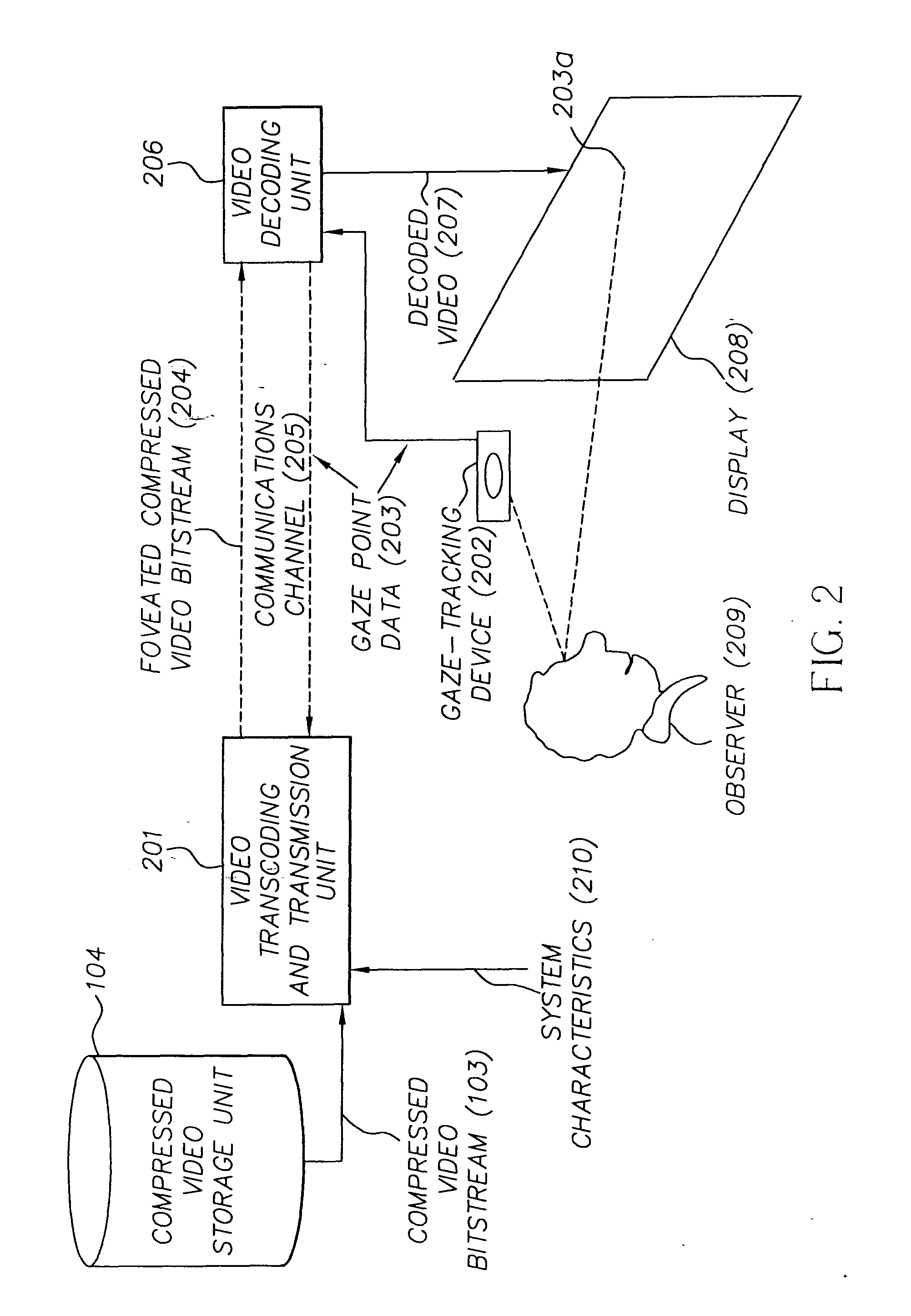
Foveated video coding system and method
InactiveUS20050018911A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsAttenuation bandwidthCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsDigital videoDisplay device
In transcoding a frequency transform-encoded digital video signal representing a sequence of video frames, a foveated, compressed digital video signal is produced and transmitted over a limited bandwidth communication channel to a display according to the following method: First, a frequency transform-encoded digital video signal having encoded frequency coefficients representing a sequence of video frames is provided, wherein the encoding removes temporal redundancies from the video signal and encodes the frequency coefficients as base layer frequency coefficients in a base layer and as residual frequency coefficients in an enhancement layer. Then, an observer's gaze point is identified on the display. The encoded digital video signal is partially decoded to recover the frequency coefficients, and the residual frequency coefficients are adjusted to reduce the high frequency content of the video signal in regions away from the gaze point. The frequency coefficients, including the adjusted residual frequency coefficients, are then recoded to produce a foveated, transcoded digital video signal, and the foveated, transcoded digital video signal is displayed to the observer.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
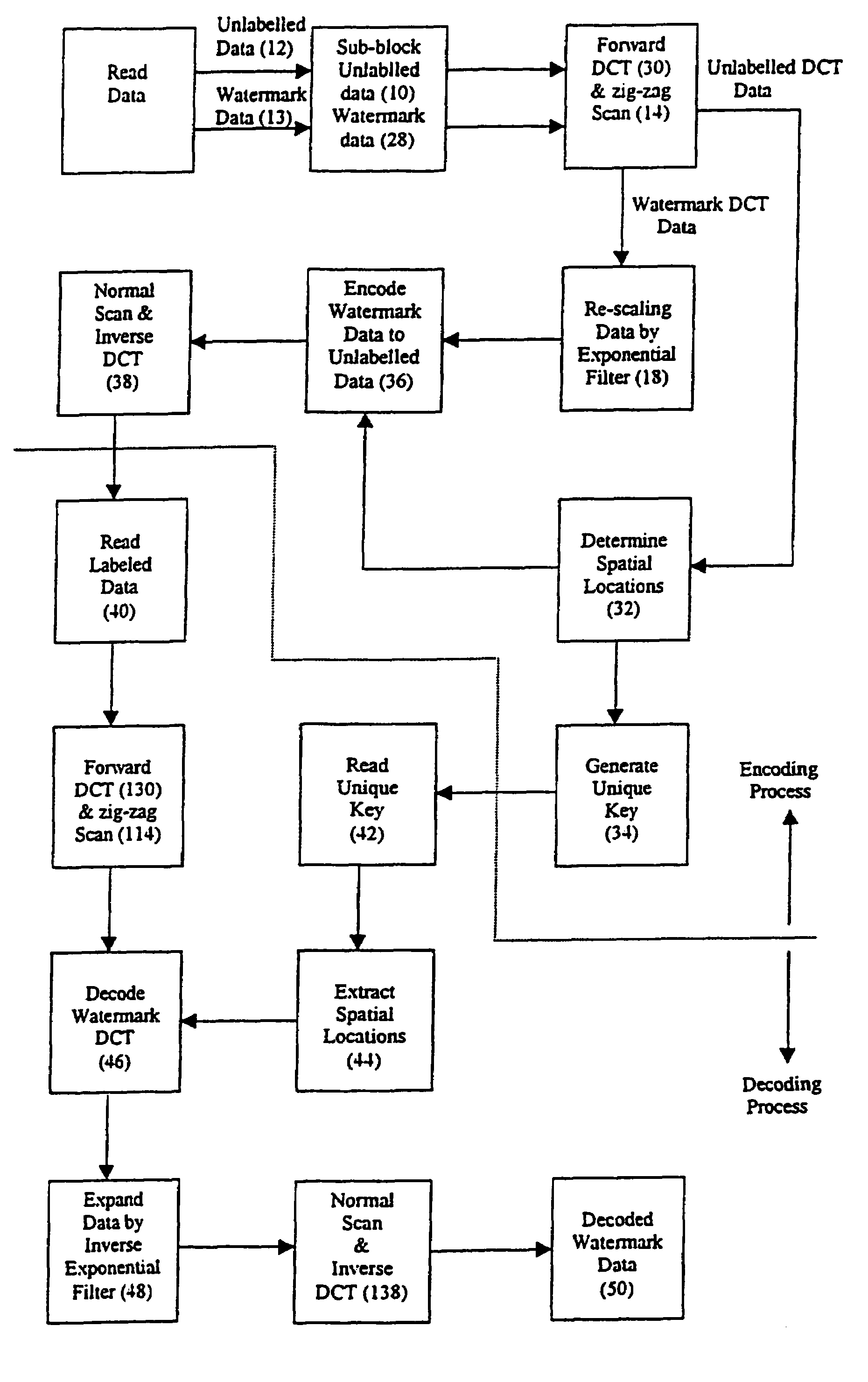
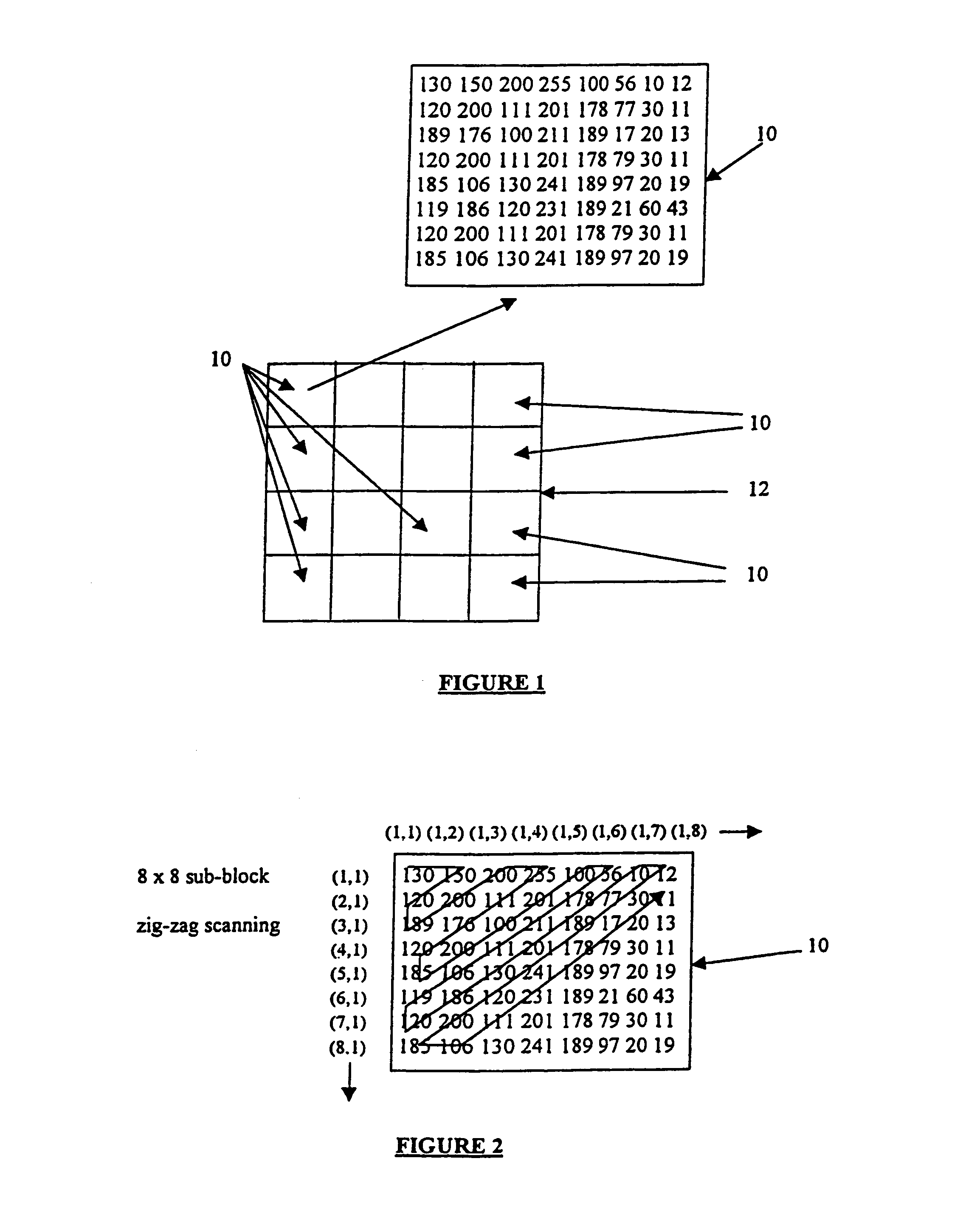
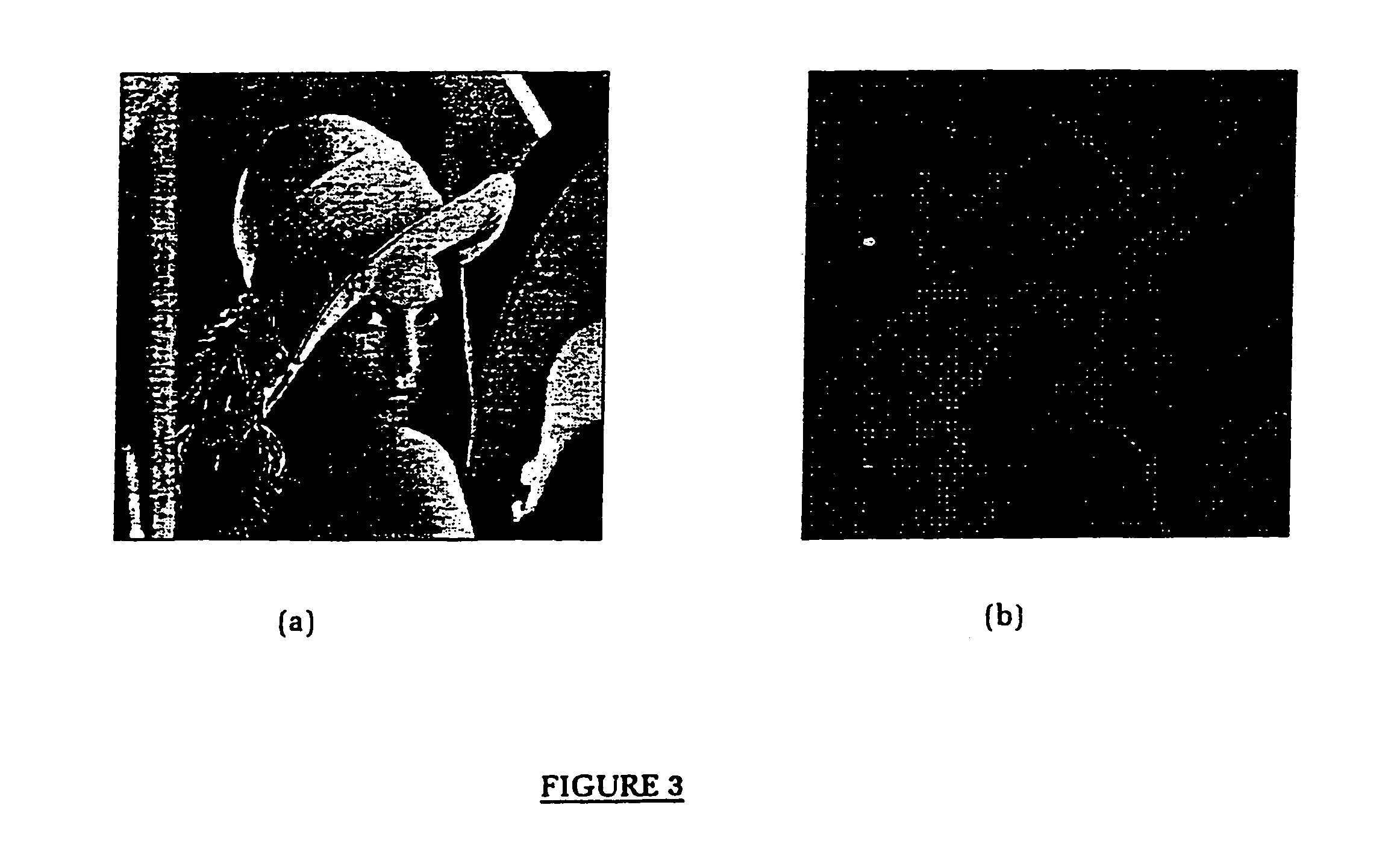
Methods for embedding image, audio and video watermarks in digital data
InactiveUS6983057B1Less coefficientTelevision system detailsRecord information storageDigital dataThe Internet
A method for embedding an entire image, audio or video watermark sequence within another image, audio or video data sequence with minimum loss of data quality is presented. The method exploits the de-correlation property of data coefficients in the orthogonal transform domain, similar to the application in data compression through transform coding. The present invention describes the usage of a Discrete Cosine Transform as the embedding domain. However, other orthogonal transforms such as Fourier, Walsh-Hadamard, Haar, Sine and Wavelet can also be used for this operation. A unique key derived adaptively from spatial locations registering the thresholds of the ac transform energies is used to unlock or de-watermark the embedded image or audio sequence. Moreover, an exponential filter has been developed to compress and expand the watermark coefficients prior to the embedding and retrieval process. The method can be used in resolving multimedia copyright protection issues arising on the Internet and in the music industry, such as the inclusion of a company's logo or an artist's recorded voice. The method can also be incorporated as a built-in feature for digital recording devices, such as still and video cameras, as well as more recent devices such as VCD and DVD players. Moreover, the method can be applied to the commercial and service sectors, where security in transmission and reception of private information in terms of speech or image is of the utmost importance.
Owner:ST ELECTRONICS INFO SECURITY
Interactive encoded content system including object models for viewing on a remote device
InactiveUS20080170622A1Input/output for user-computer interactionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesGraphicsUser input
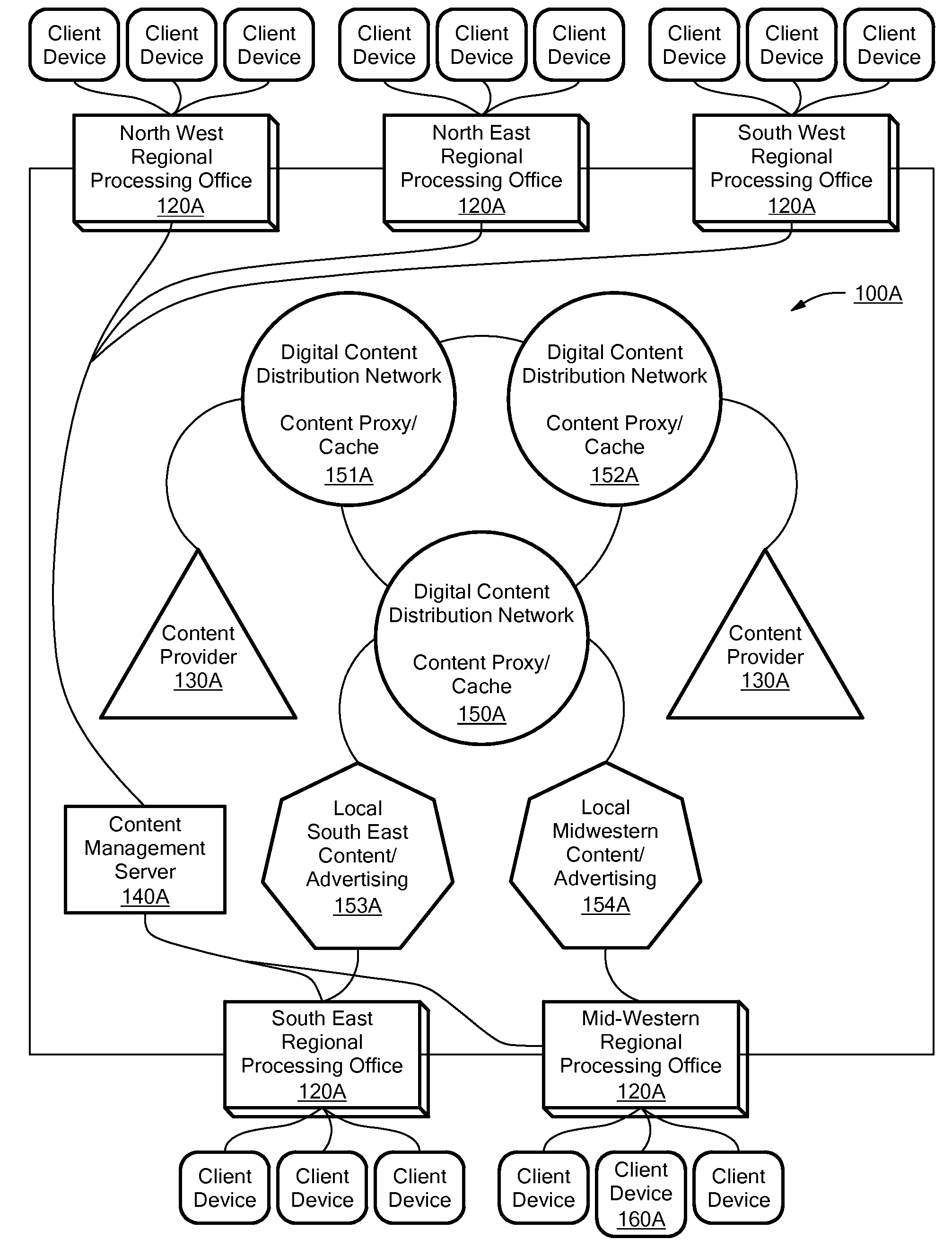
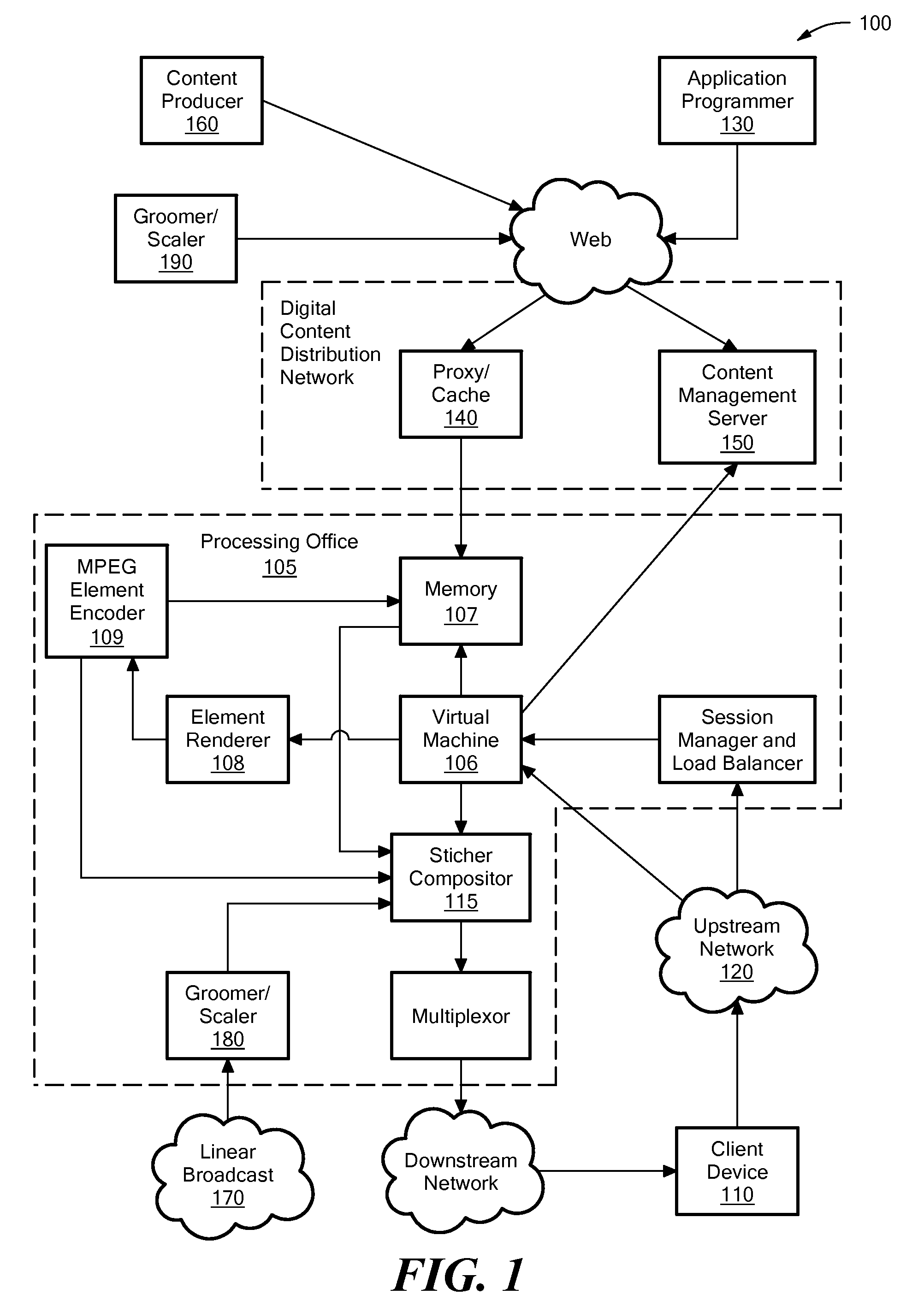
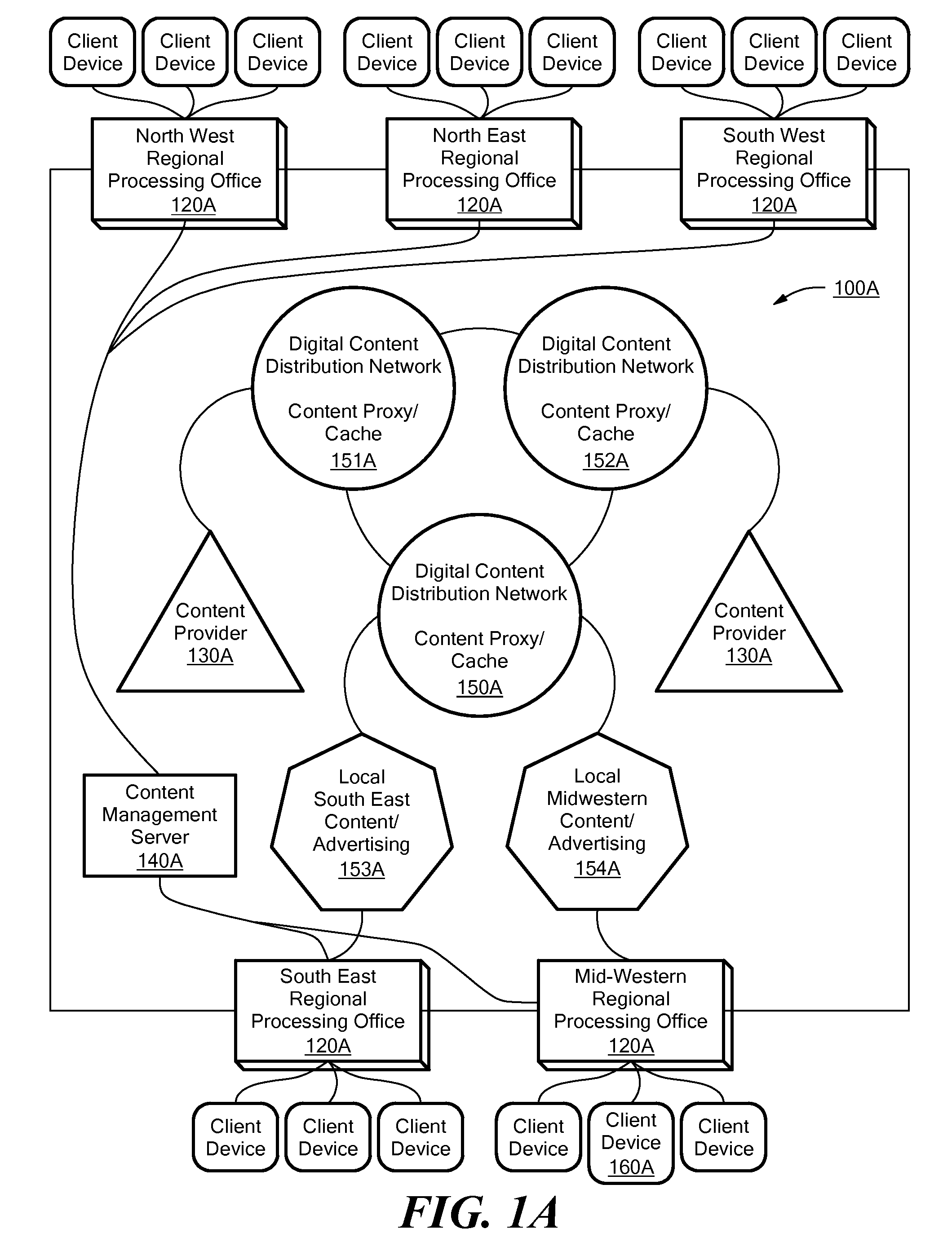
A system for creating composite encoded video from two or more encoded video sources in the encoded domain. In response to user input, a markup language-based graphical layout is retrieved. The graphical layout includes frame locations within a composite frame for at least a first encoded source and a second encoded source. The system either retrieves or receives the first and second encoded sources. The sources include block-based transform encoded data. The system also includes a stitcher module for stitching together the first encoded source and the second encoded source according to the frame locations of the graphical layout to form an encoded frame. The system outputs an encoded video stream that is transmitted to a client device associated with the user. In response to further user input, the system updates the state of an object model and replaces all or a portion of one or more frames of the encoded video stream. The system may be used with MPEG encoded video.
Owner:ACTIVE VIDEO NETWORKS INC
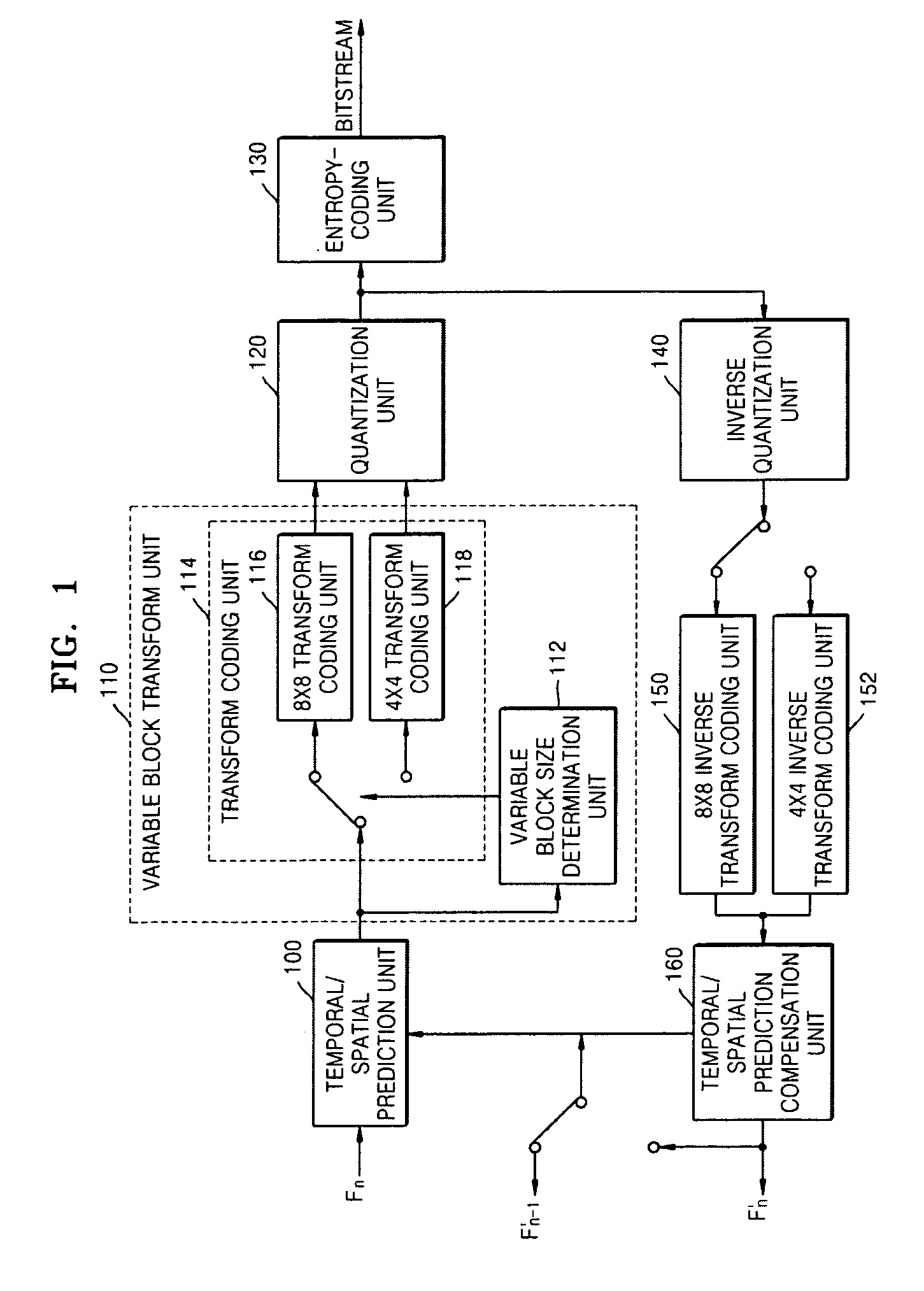
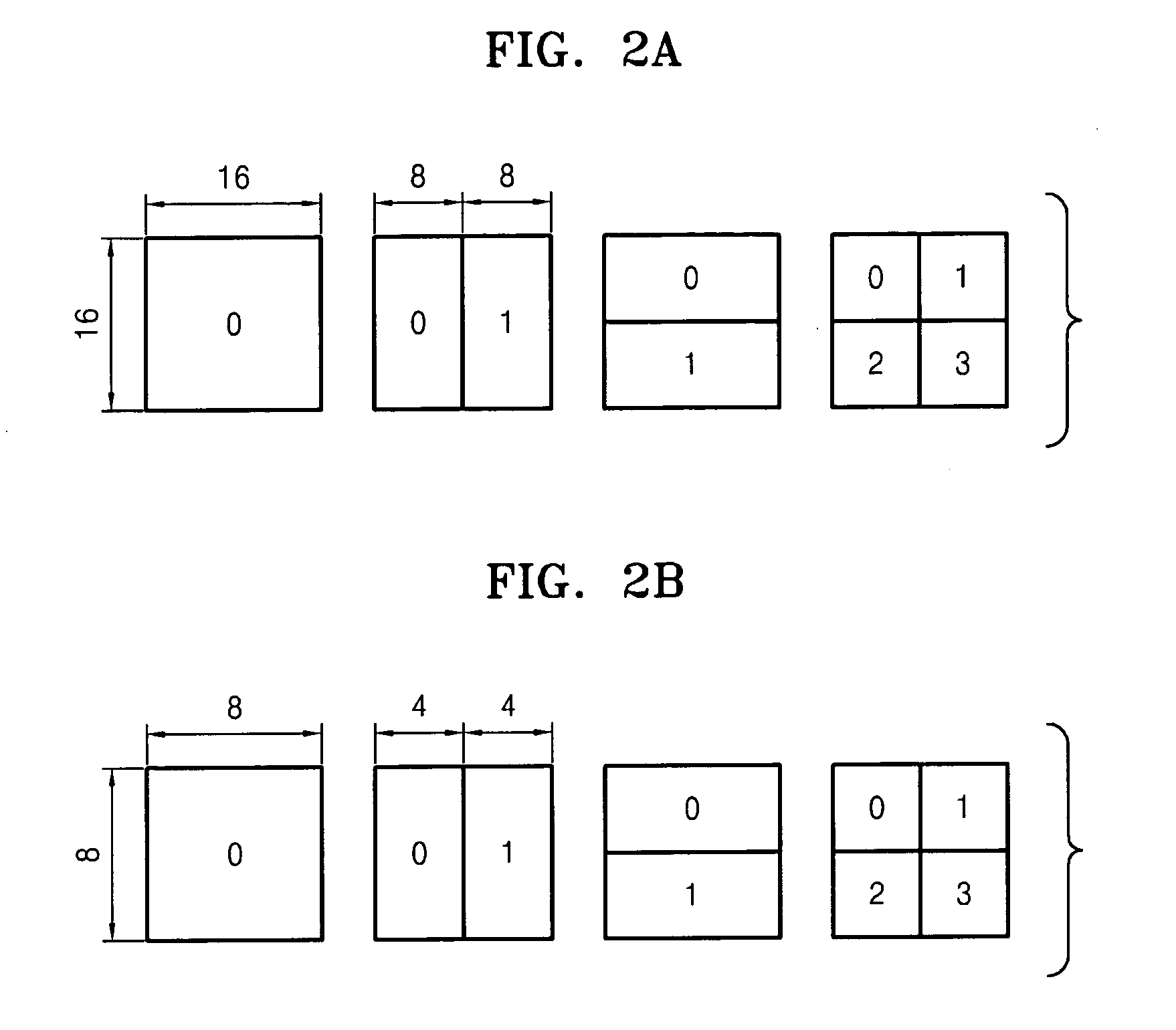
Adaptive variable block transform system, medium, and method
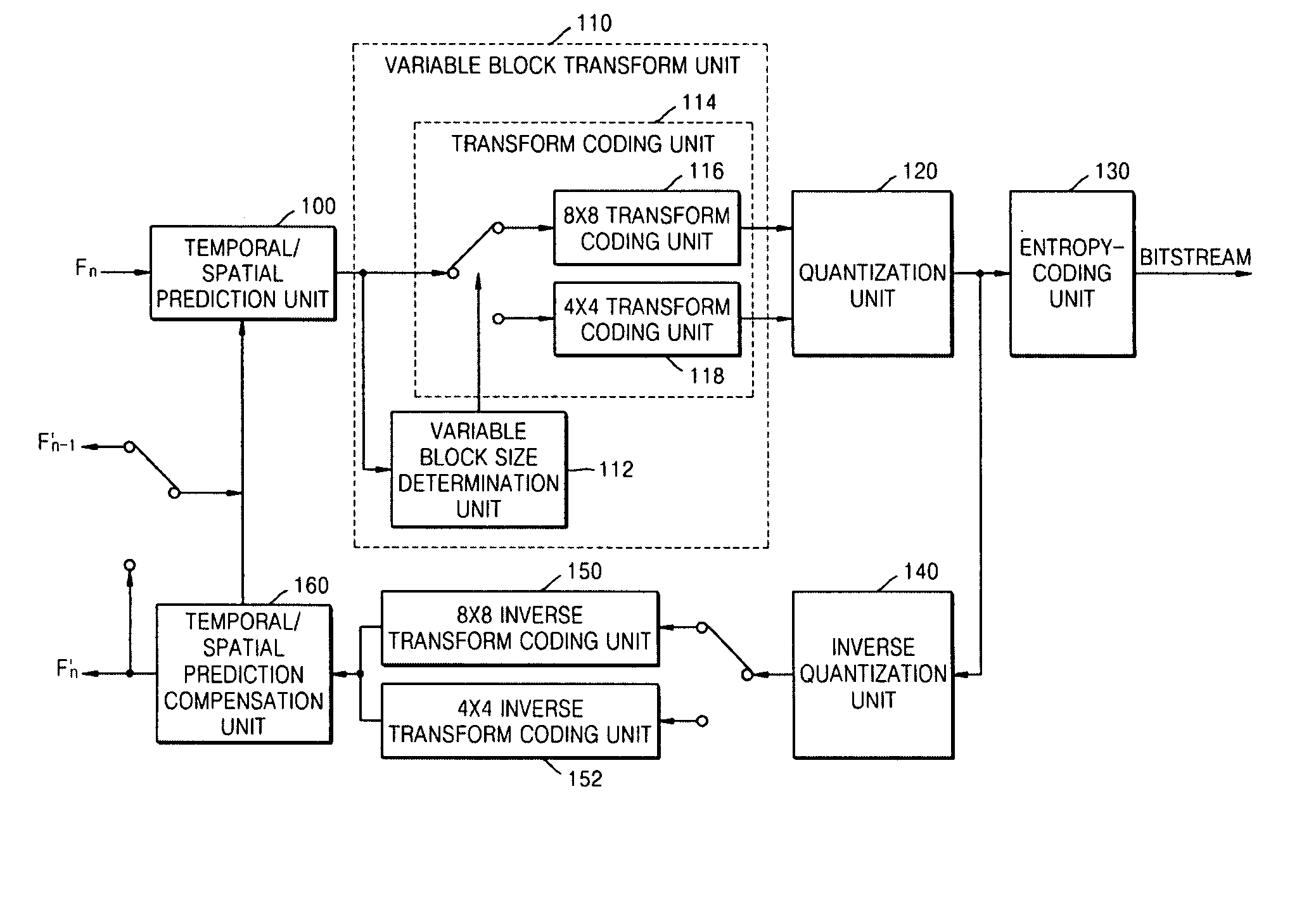
InactiveUS20070025631A1Improve compression efficiencyVaries in sizeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Video encoding
A variable block transform system, medium, and a system, medium, and method for video encoding / decoding using the variable block transform. The system includes a transform block size determination unit that determines the transform block size for components of an input video based on a format, defining the components, of the input video or characteristics of the components, and a transform coding unit that performs transform coding on each of the color components of the input video according to the determined transform block sizes and outputs transform coefficients.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Frame rate up-conversion coding mode with affine motion model
ActiveUS10778999B2Promote resultsIncreased complexityTelevision signal transmission by single/parallel channelsDigital video signal modificationAffine motionReference map
Methods, apparatuses, and computer-readable medium are provided for a frame rate up-conversion coding mode, in which an affine motion model is applied when conducting bilateral matching. The frame rate up-conversion coding mode can include generated additional frames from frames provided in a bitstream. In various implementations, bilateral matching includes, for a current block in a frame that is being generated, identifying a first block in a first reference picture a second block in a second reference picture. Affine (e.g., non-linear) motion information can be determined as between the first block and the second block. The current block can be predicted using the affine motion information.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Multi-mode audio codec and celp coding adapted therefore
In an embodiment, bitstream elements of sub-frames are encoded differentially to a global gain value so that a change of the global gain value results in an adjustment of an output level of the decoded representation of the audio content. Concurrently, the differential coding saves bits. Even further, the differential coding enables the lowering of the burden of globally adjusting the gain of an encoded bitstream. In another embodiment, a global gain control across CELP coded frames and transform coded frames is achieved by co-controlling the gain of the codebook excitation of the CELP codec, along with a level of the transform or inverse transform of the transform coded frames. In another embodiment, the gain value determination in CELP coding is performed in the weighted domain of the excitation signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Single-Shot Spectral Imager
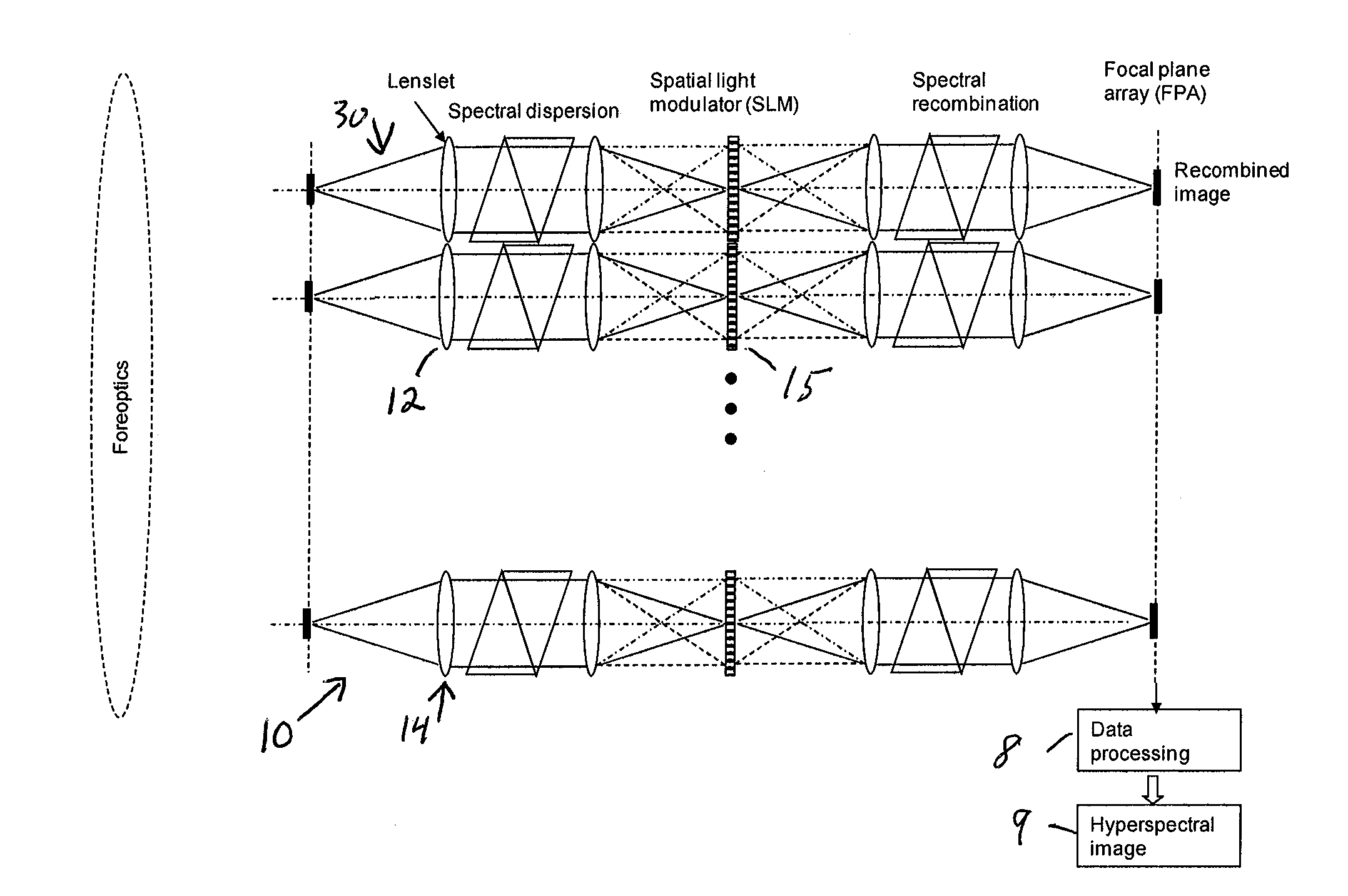
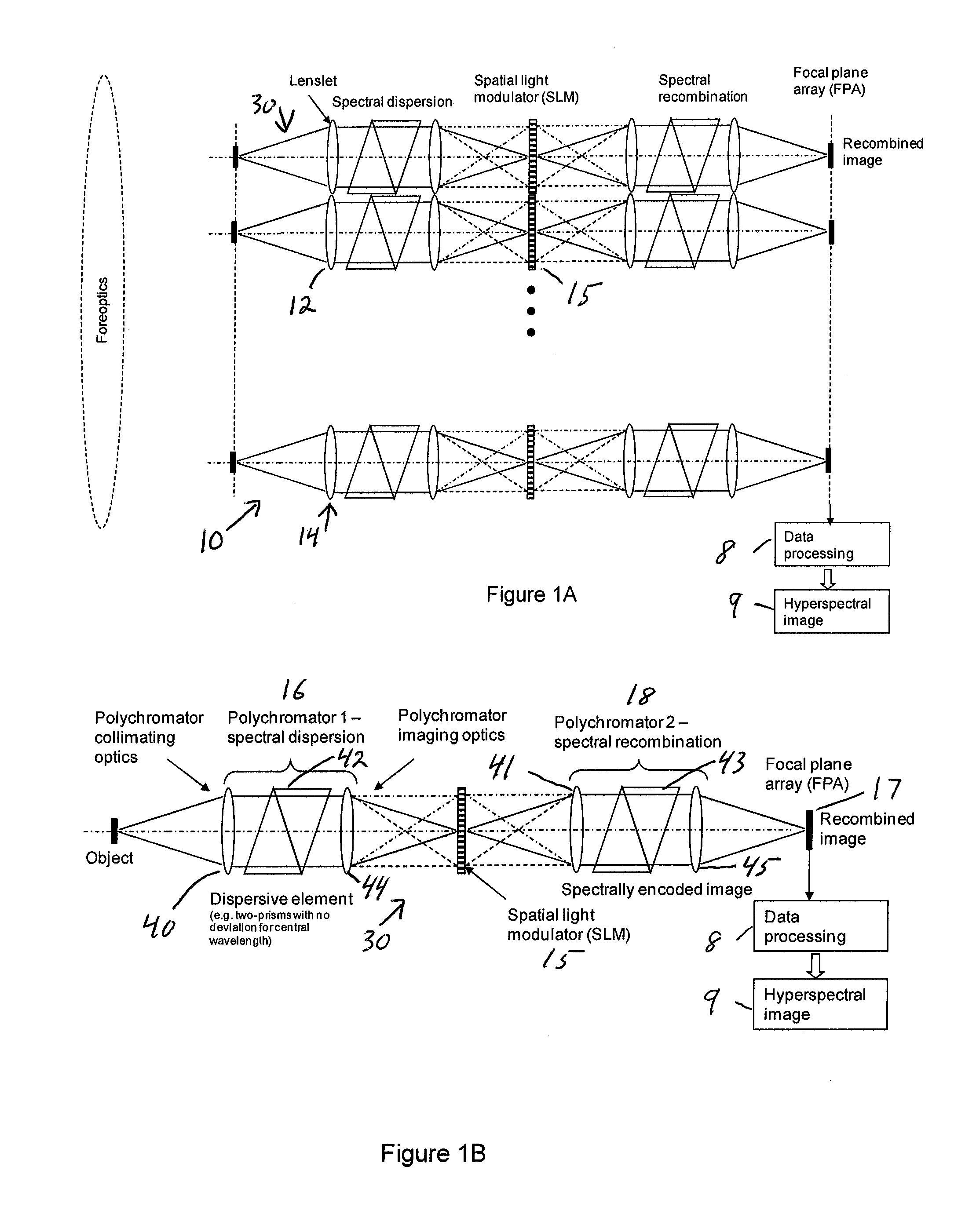
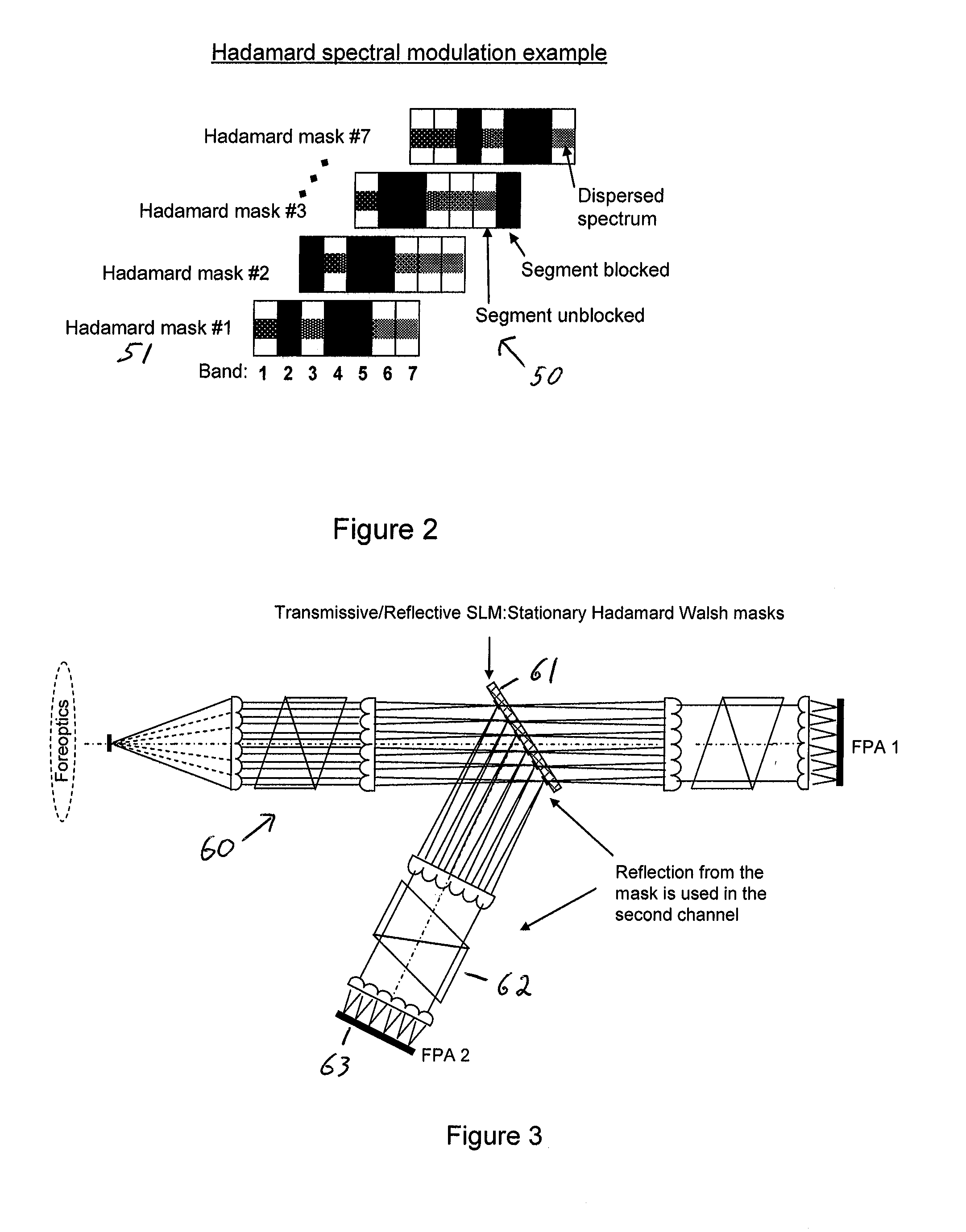
ActiveUS20100309467A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy to useRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using refracting elementsMultiplexingSpatial light modulator
A single-shot spectral imager or imaging system which acquires multiplexed spatial and spectral data in a single snapshot with high optical collection efficiency and with the speed limited only by the readout time of the detector circuitry. The imager uses dispersive optics together with spatial light modulators to encode a mathematical transform onto the acquired spatial-spectral data. A multitude of encoded images is recorded simultaneously on a focal plane array and subsequently decoded to produce a spectral / spatial hypercube.
Owner:SPECTRAL SCI
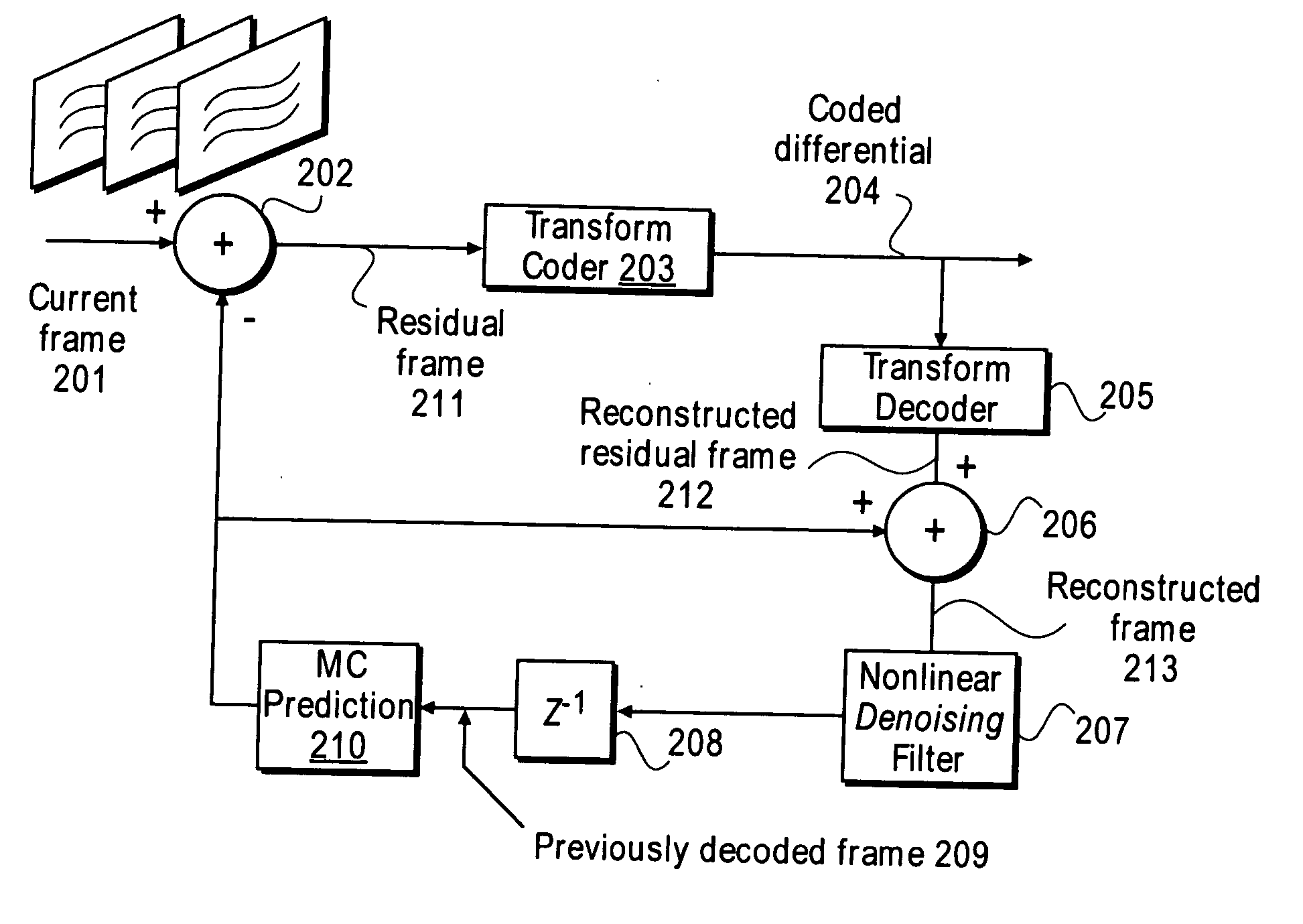
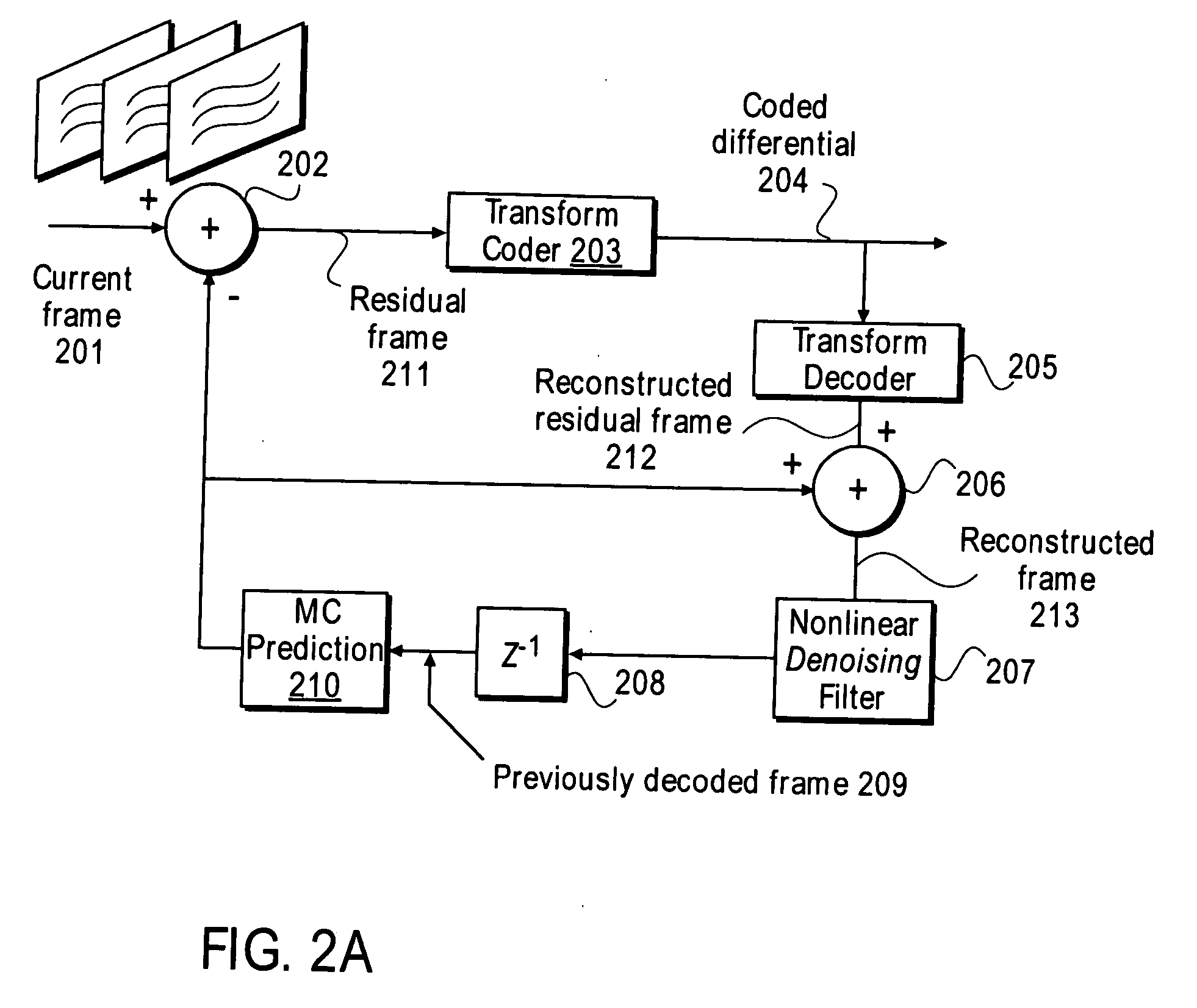
Nonlinear, in-the-loop, denoising filter for quantization noise removal for hybrid video compression
InactiveUS20060153301A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNoise removalComputer science
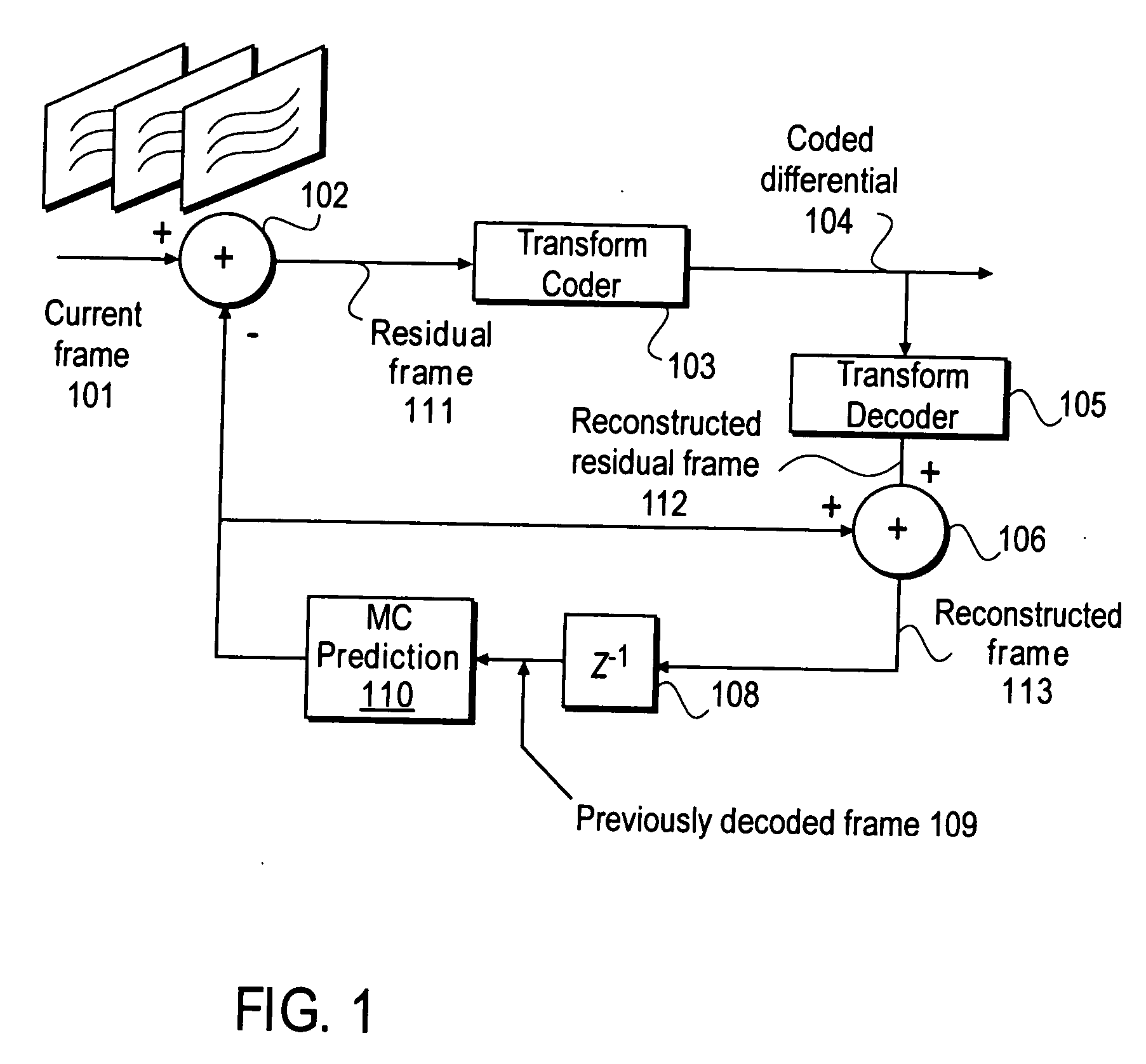
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for using an in-the-loop denoising filter for quantization noise removal for video compression. In one embodiment, the video encoder comprises a transform coder to apply a transform to a residual frame representing a difference between a current frame and a first prediction, the transform coder outputting a coded differential frame as an output of the video encoder; a transform decoder to generate a reconstructed residual frame in response to the coded differential frame; a first adder to create a reconstructed frame by adding the reconstructed residual frame to the first prediction; a non-linear denoising filter to filter the reconstructed frame by deriving expectations and performing denoising operations based on the expectations; and a prediction module to generate predictions, including the first prediction, based on previously decoded frames.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
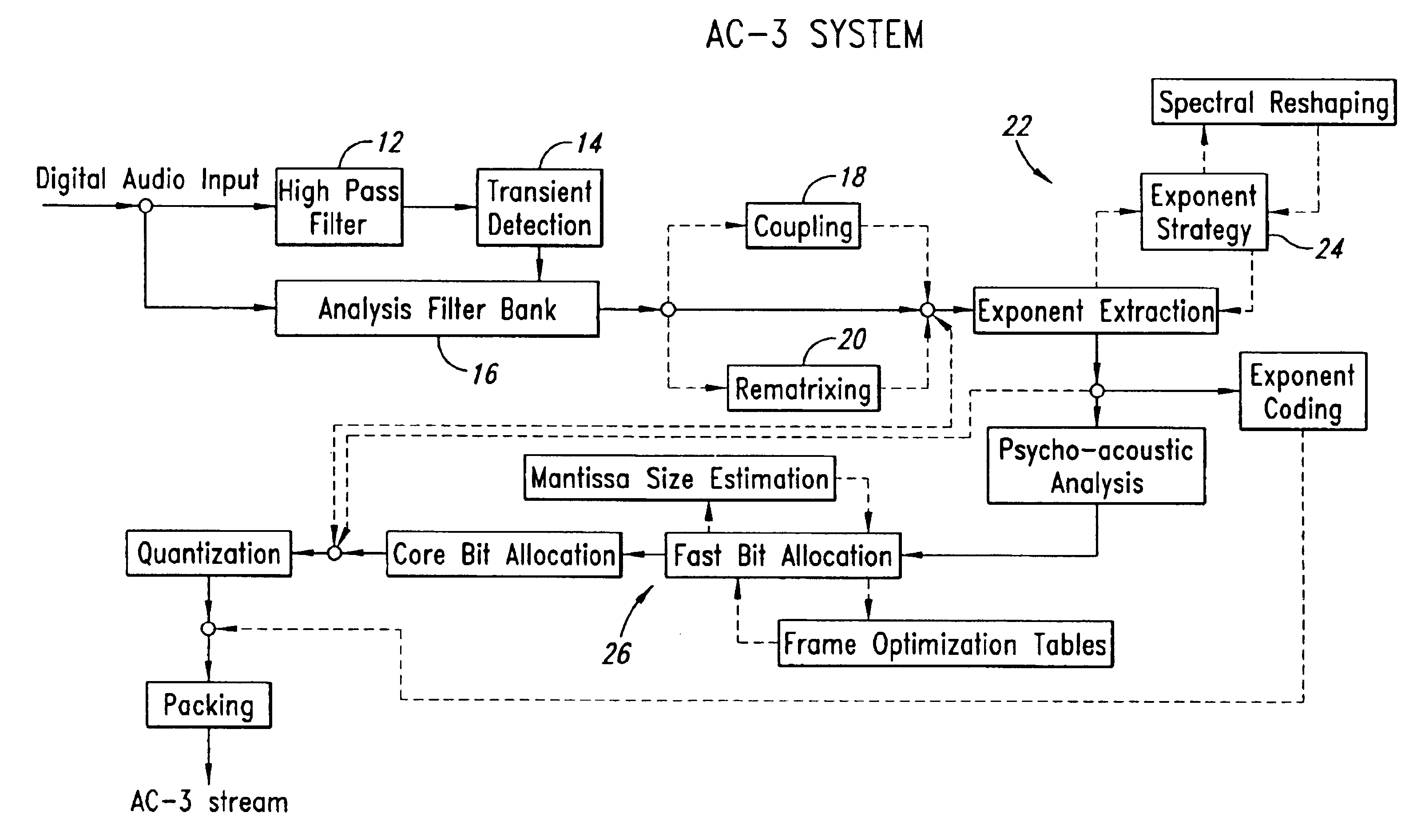
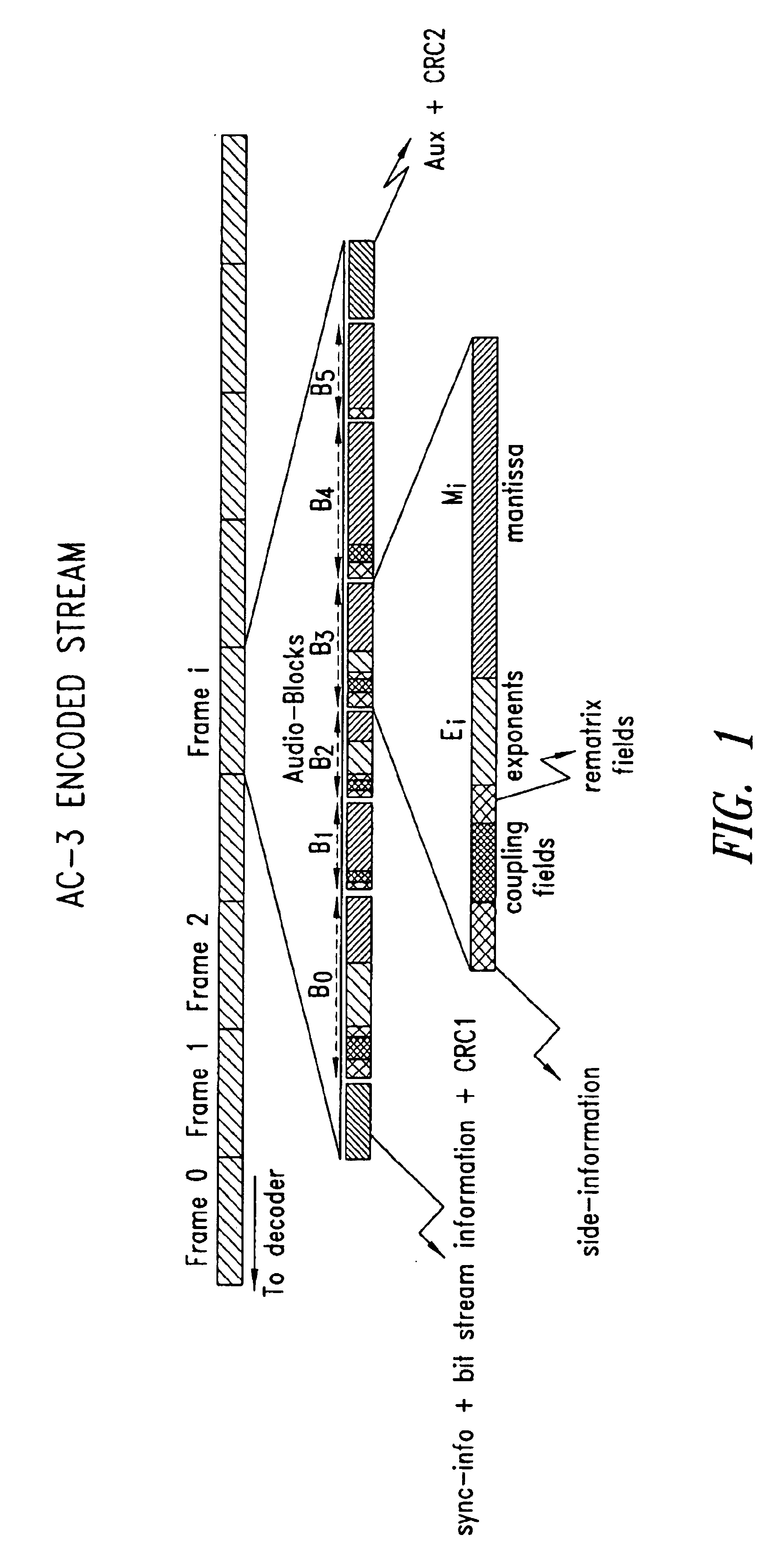
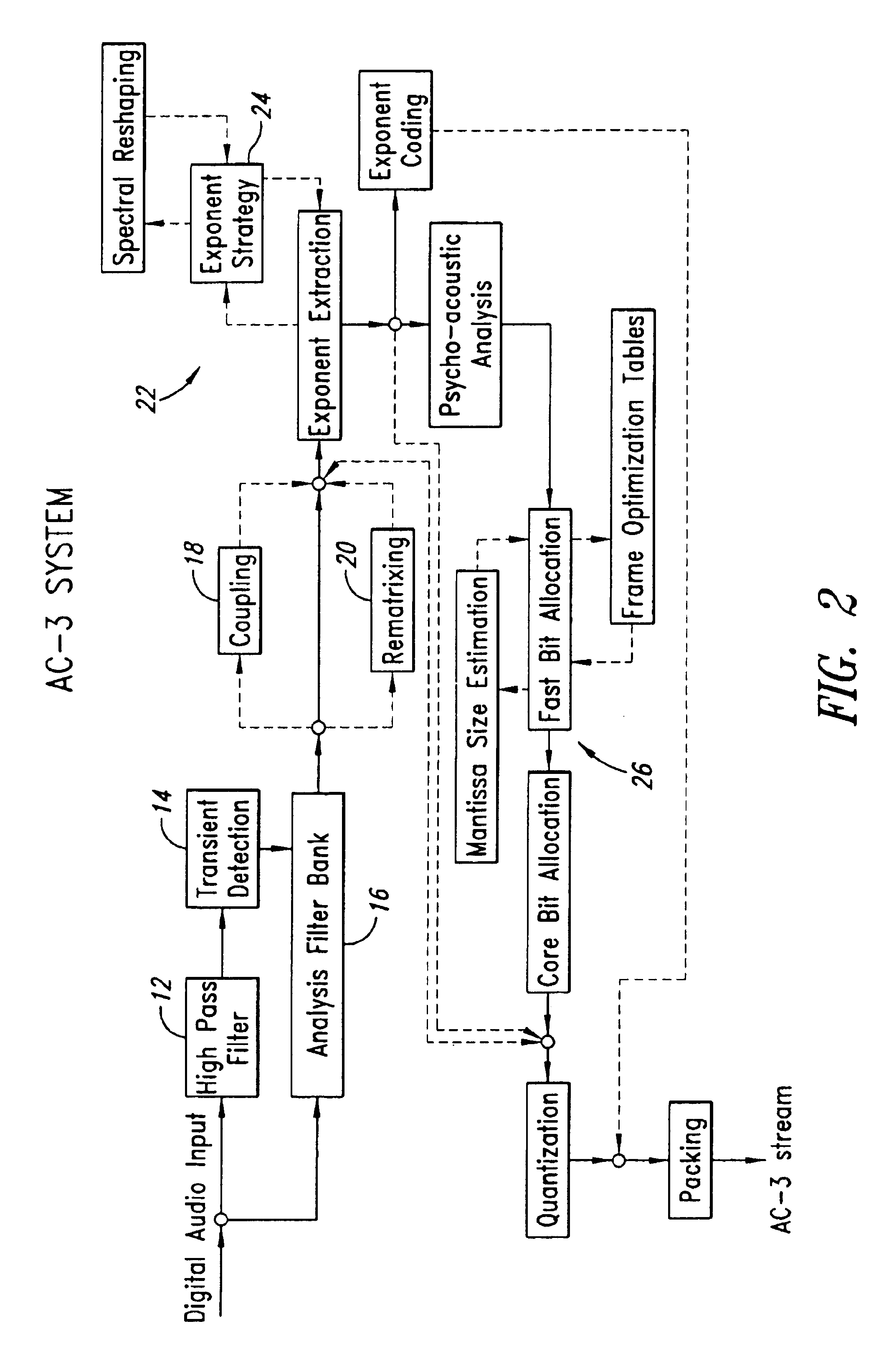
Fast frame optimization in an audio encoder
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
Method and device for encoding and decoding videos
ActiveUS20120201303A1Encoding efficiency can be improvedImprove efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo encoding
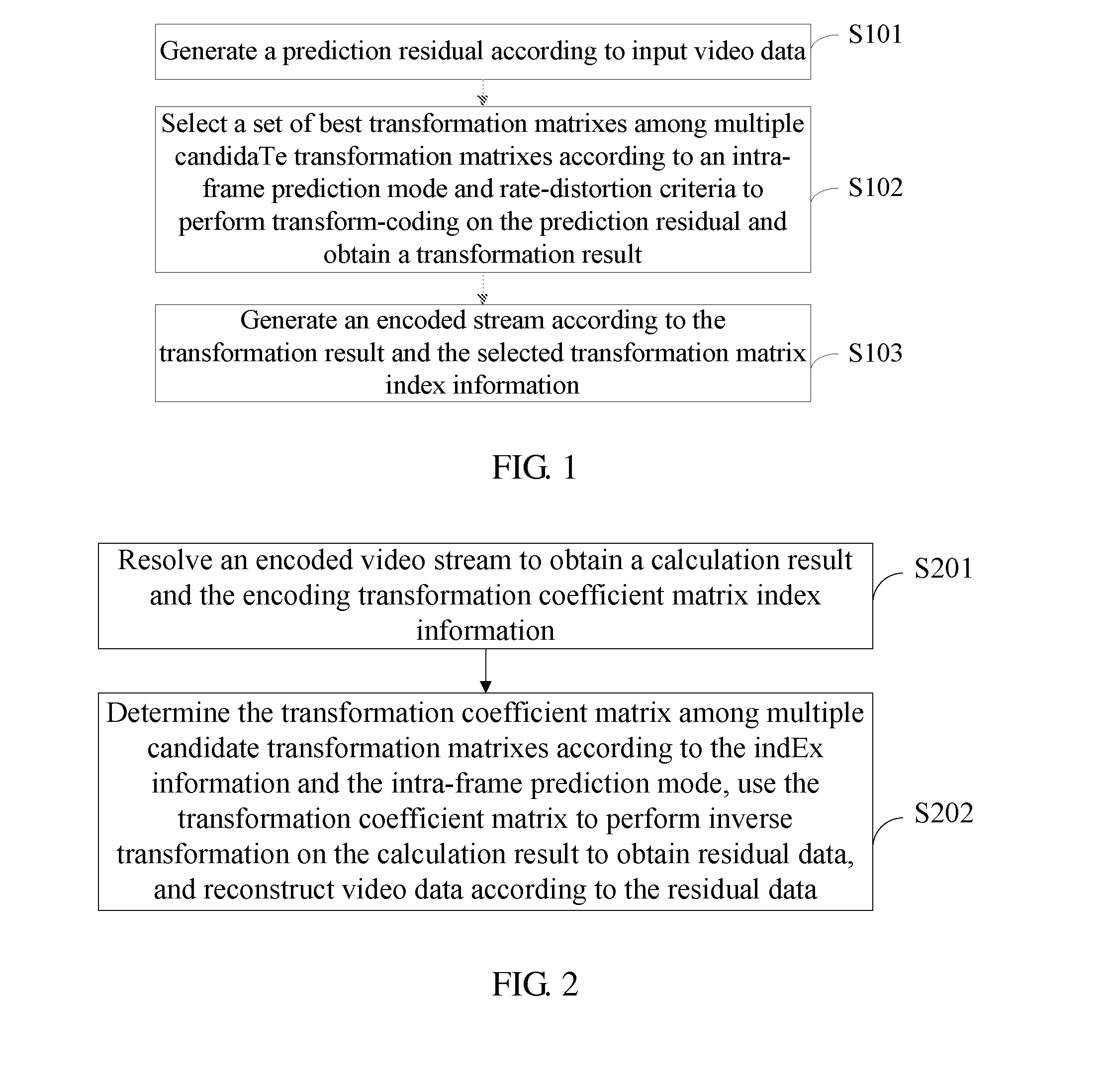
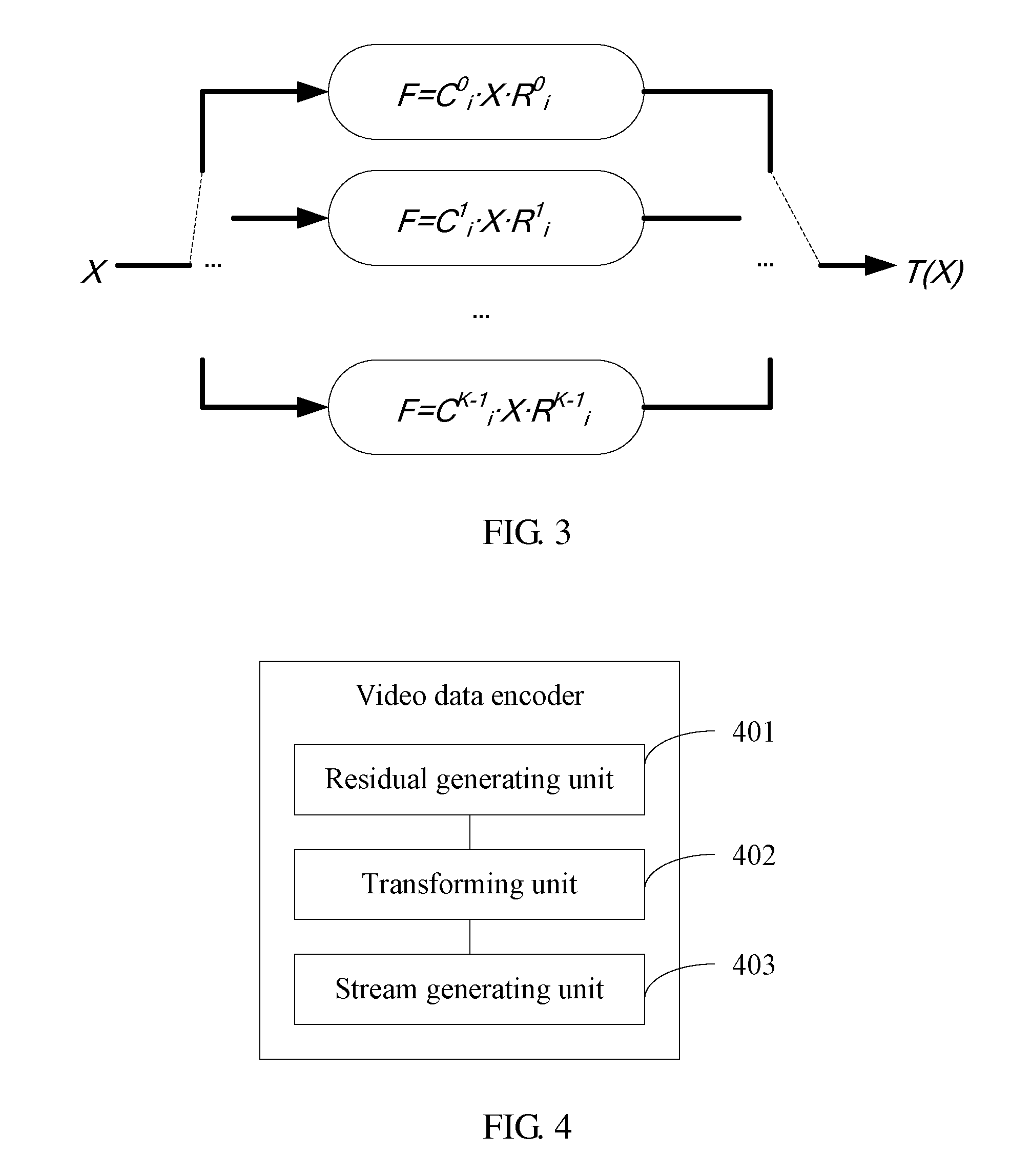
The embodiments of the present invention provide a method and a device for encoding and decoding videos, and relate to the communication field, and an efficient transformation matrix corresponding to features of each residual block is selected for transformation, which therefore improves encoding efficiency. The solution provided in an embodiment of the present invention is: generating a prediction residual according to input video data; selecting a set of best transformation matrixes among multiple candidate transformation matrixes according to an intra-frame prediction mode and rate-distortion criteria to perform transform-coding on the prediction residual and obtain a transformation result; and generating an encoded stream according to the transformation result and selected transformation matrix index information.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
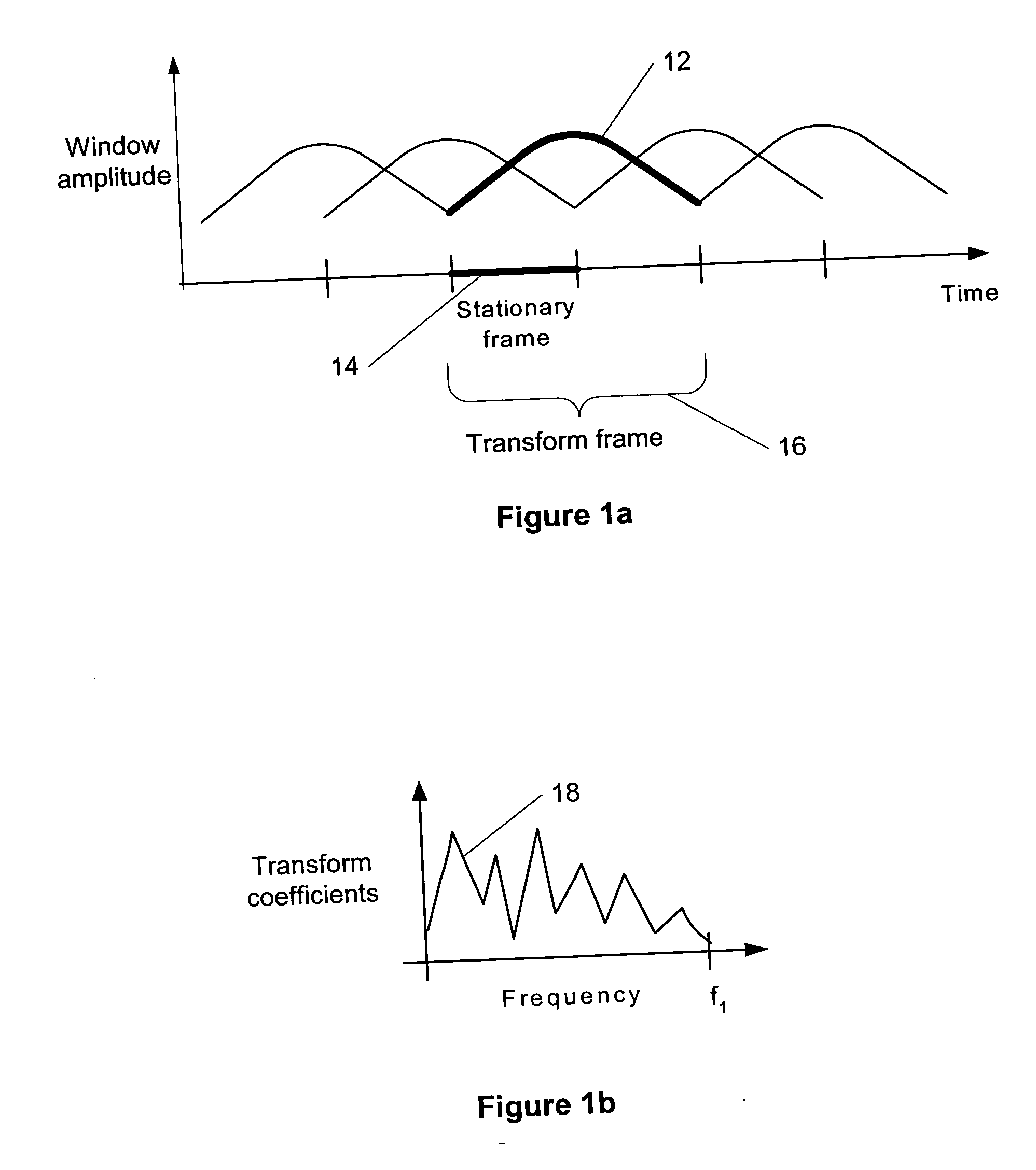
Adaptive window-size selection in transform coding
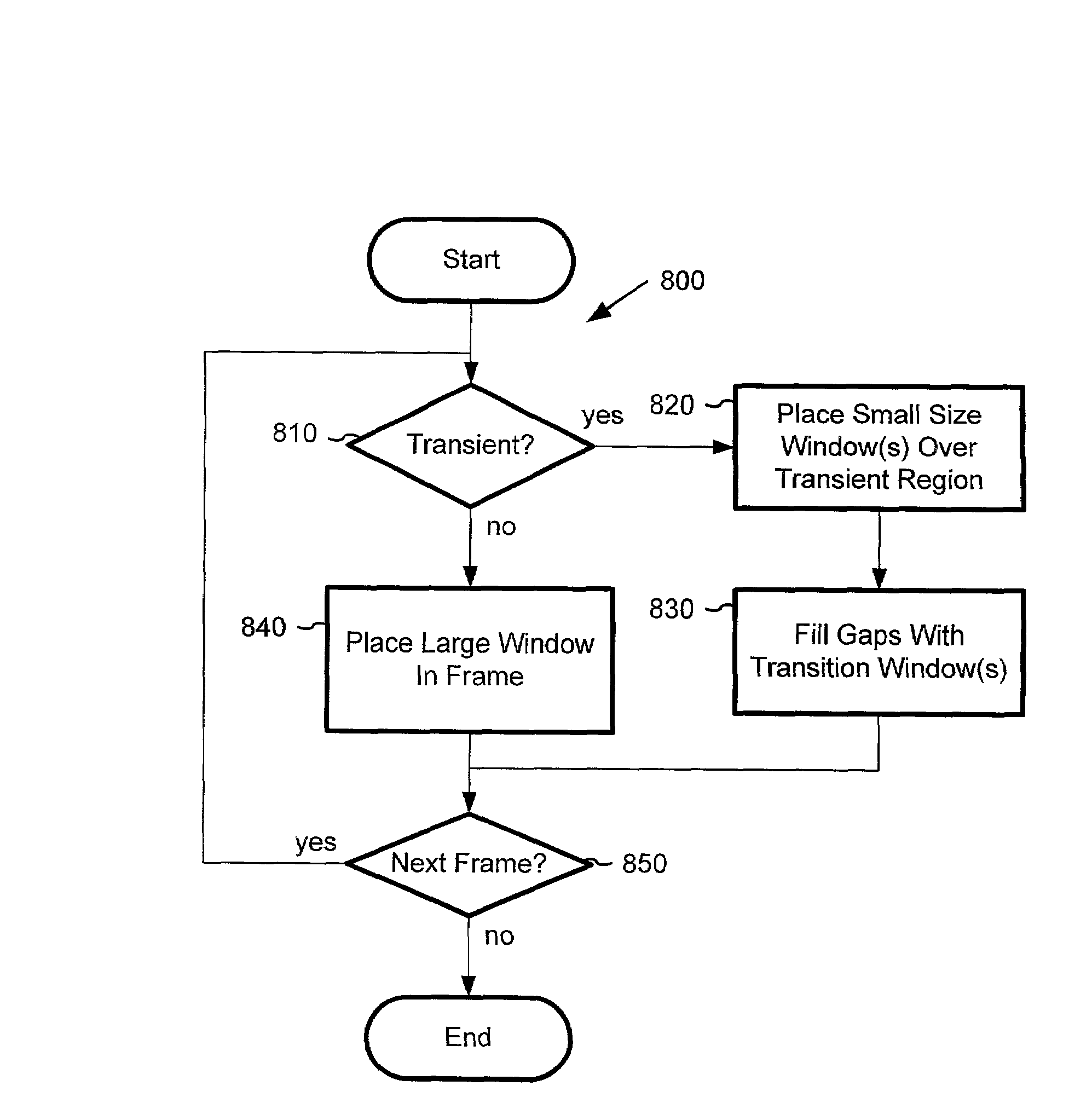
ActiveUS7460993B2Improve coding efficiencyQuality improvementSpeech analysisImage resolutionTransform coding
A transform coder adaptively configures window sizes for transform coding in a two-pass process to maximize coding efficiency, while achieving necessary time resolution to avoid pre-echo. In a first pass, the coder places small size windows over detected transient regions of an input signal in an open-loop window configuration process. In a second pass, the coder adjusts the window size configuration according to measurements of the achieved quality in a closed-loop window configuration process. Where quality measurement shows unacceptable quantization noise, the coder increases window size. Where pre-echo is detected, the coder reduces window size within coding bit rate constraints.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
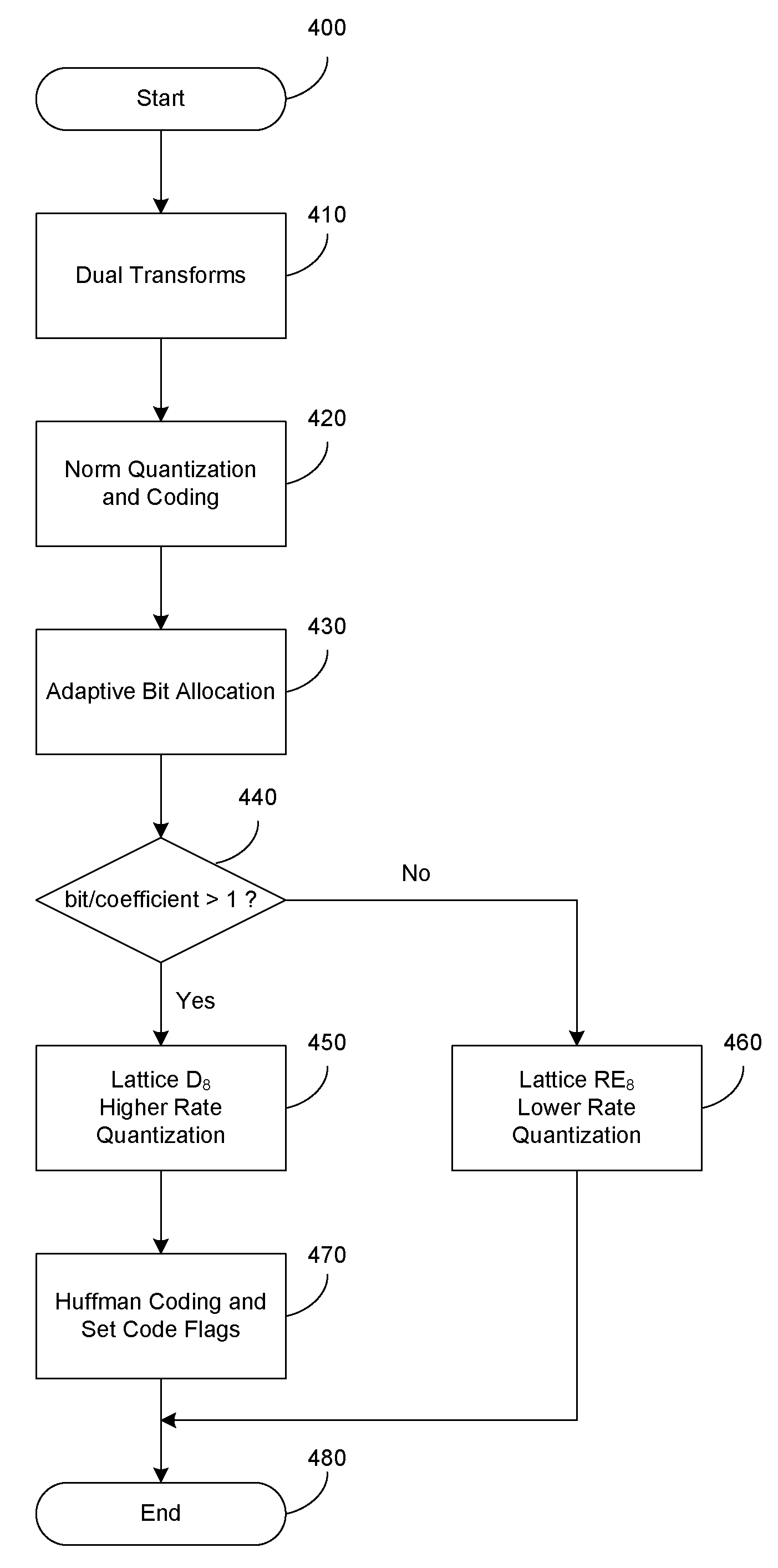
Dual-transform coding of audio signals
Methods, devices, and systems for coding and decoding audio are disclosed. At least two transforms are applied on an audio signal, each with different transform periods for better resolutions at both low and high frequencies. The transform coefficients are selected and combined such that the data rate remains similar as a single transform. The transform coefficients may be coded with a fast lattice vector quantizer. The quantizer has a high rate quantizer and a low rate quantizer. The high rate quantizer includes a scheme to truncate the lattice. The low rate quantizer includes a table based searching method. The low rate quantizer may also include a table based indexing scheme. The high rate quantizer may further include Huffman coding for the quantization indices of transform coefficients to improve the quantizing / coding efficiency.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
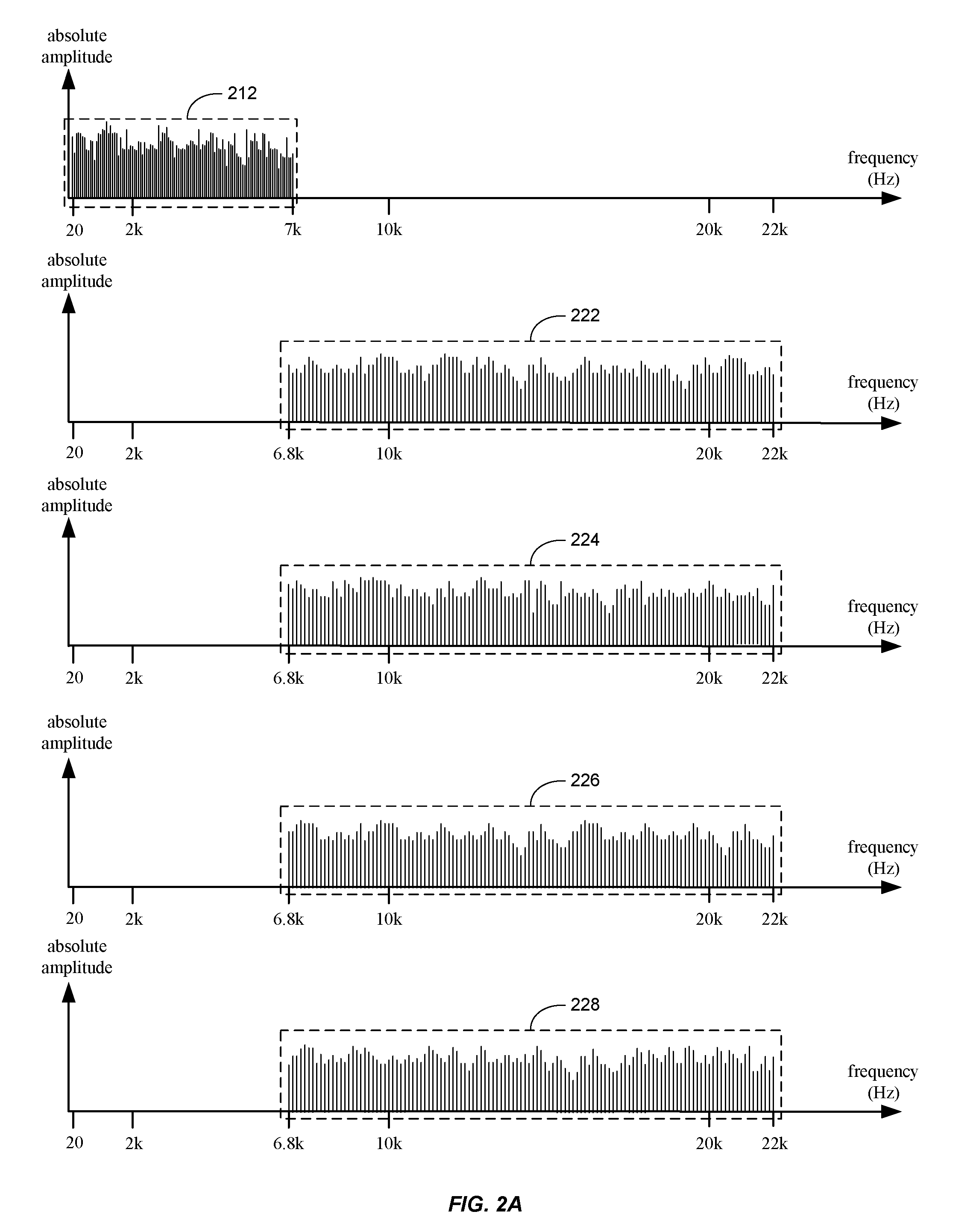
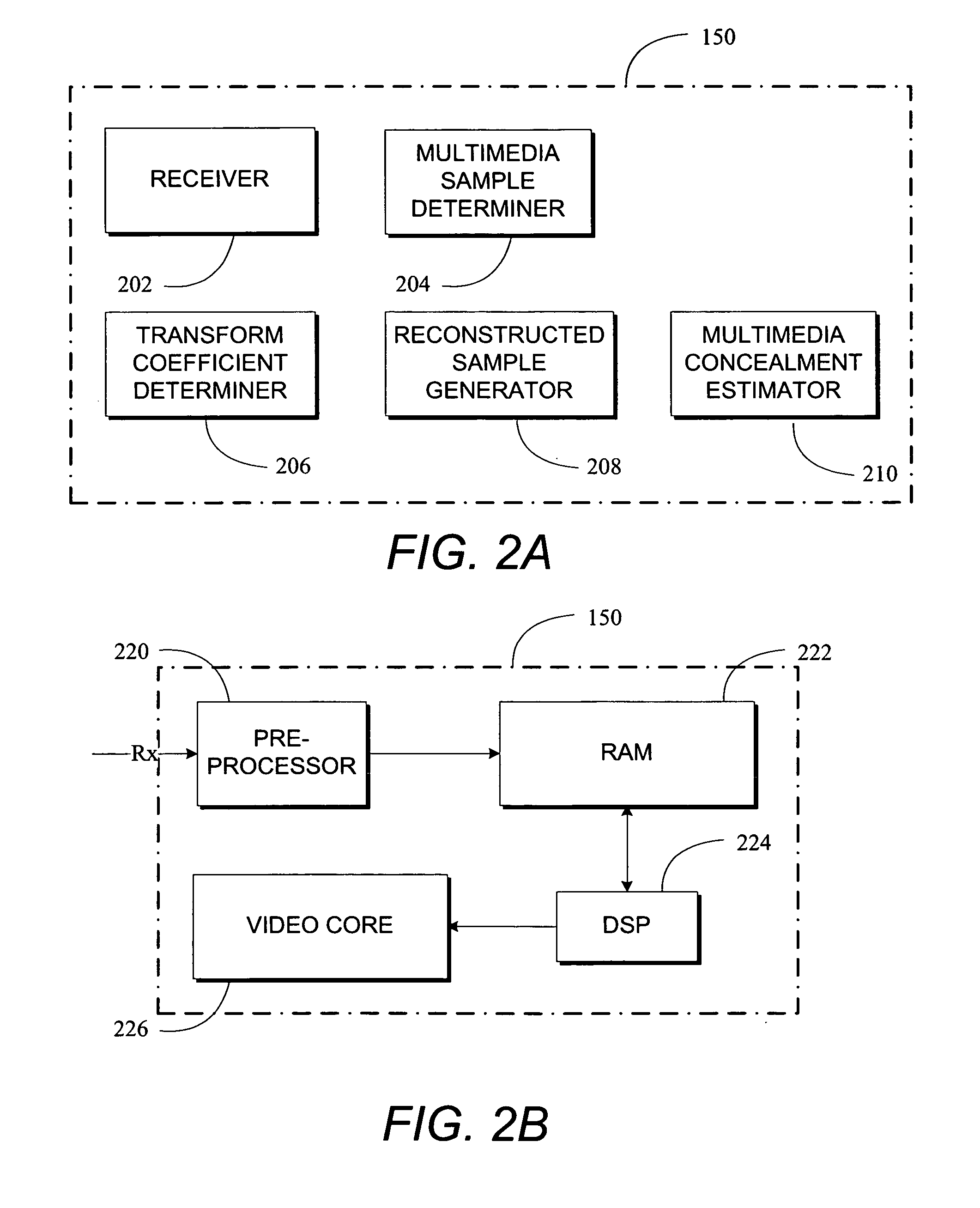
Video encoding method enabling highly efficient partial decoding of H.264 and other transform coded information
InactiveUS20070083578A1Improve errorImprove efficiencyDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsVideo encodingComputer vision
Methods and apparatus to process multimedia data enabling efficient partial decoding of transform coded data are described. A decoder device receives transform coefficients, where the transform coefficients are associated with multimedia data. The decoder device determines a set of multimedia samples to be reconstructed. In one aspect, the set of samples to be reconstructed is a subset of a matrix of transformed multimedia samples. The decoder device determines a set of transform coefficients to be used to reconstruct the multimedia samples. In one aspect, the transform coefficients are used to scale partial basis images associated with the encoding method used to generate the transform coefficients, resulting in reconstructed multimedia samples.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Frame rate up-conversion coding mode
ActiveUS20180098062A1Promote resultsIncreased complexityDigital video signal modificationAffine motionComputer science
Methods, apparatuses, and computer-readable medium are provided for a frame rate up-conversion coding mode, in which an affine motion model is applied when conducting bilateral matching. The frame rate up-conversion coding mode can include generated additional frames from frames provided in a bitstream. In various implementations, bilateral matching includes, for a current block in a frame that is being generated, identifying a first block in a first reference picture a second block in a second reference picture. Affine (e.g., non-linear) motion information can be determined as between the first block and the second block. The current block can be predicted using the affine motion information.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
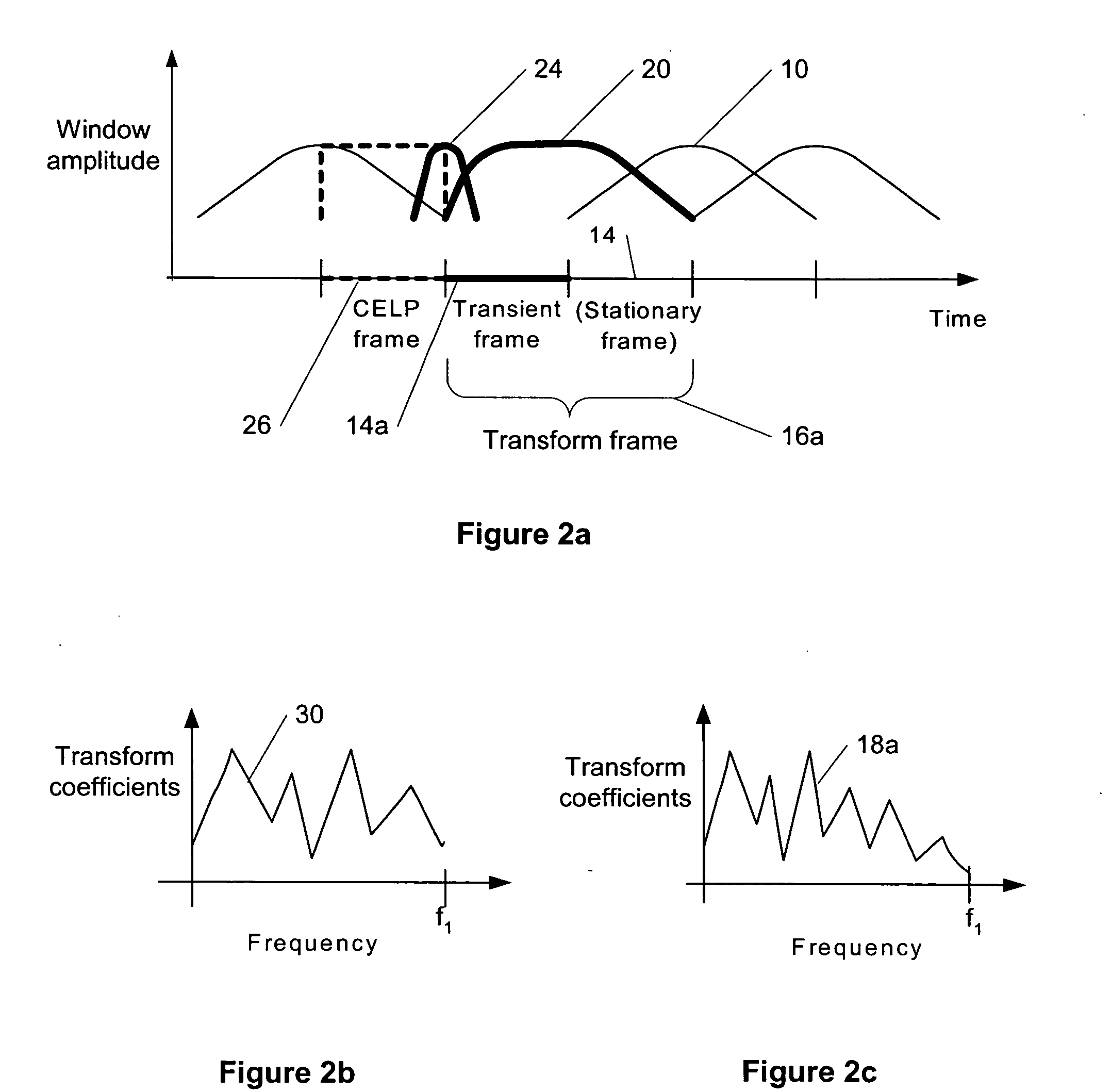
Compensation of transient effects in transform coding
The present invention provides a method for compensating transient effects in transform coding and decoding of a combined speech and audio in electronic devices by using a transform based time-frequency domain codec. The method can combine, e.g., a CELP (code excited linear prediction) type speech codec and a transform type audio codec. The invention describes a compensation method to handle the transient (e.g., from the CELP coding to the transform coding) in transform coding when the number of quantized transform coding coefficients is lower than in the output of the transform.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
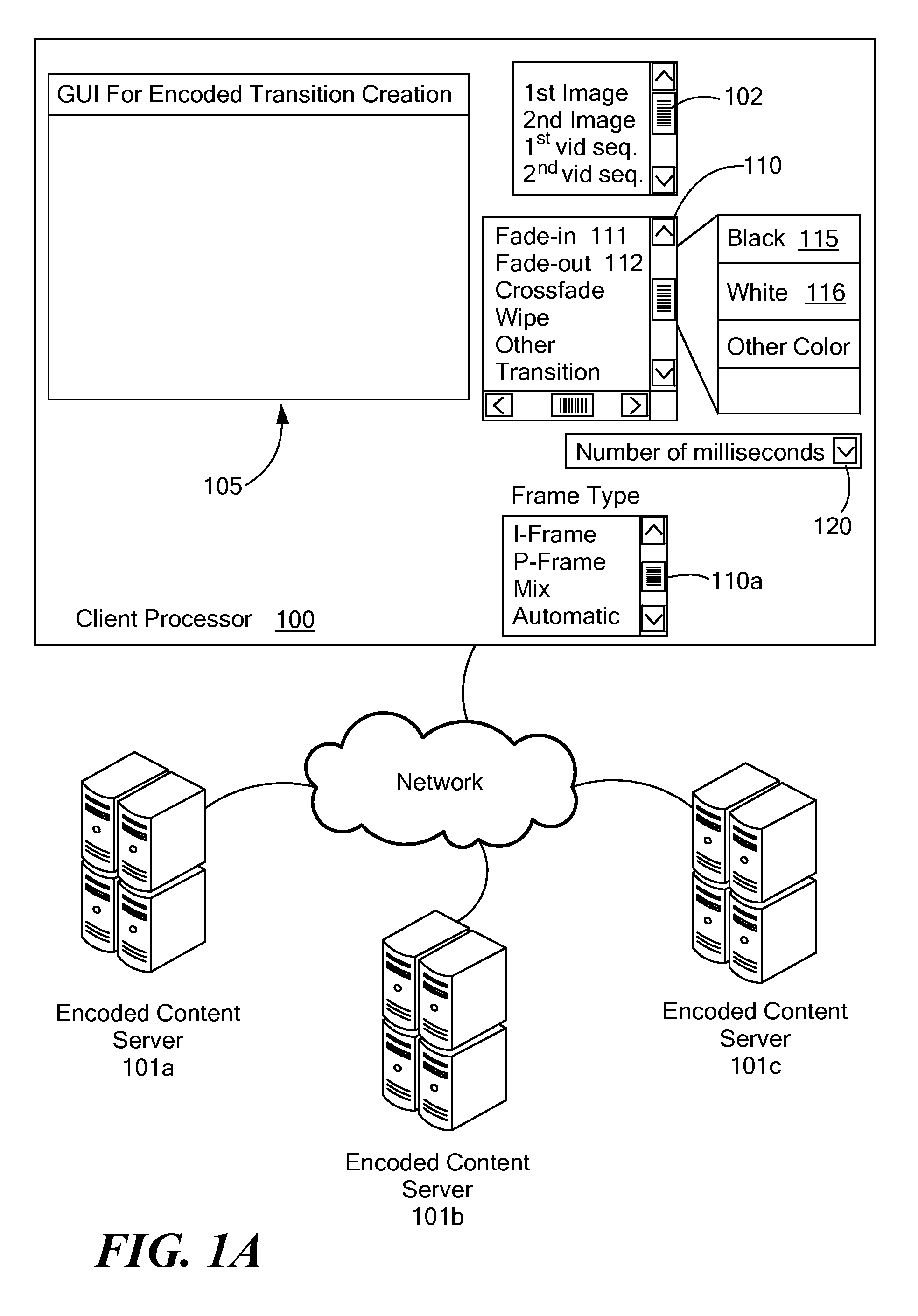
Transition Creation for Encoded Video in the Transform Domain
InactiveUS20090196346A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo sequenceTransform coding
A system and method for calculating data representative of at least one intermediary transition image between a first image and a second image in the encoded domain is disclosed. Cinematic transitions can be created between encoded still images and frames from video sequences. For each corresponding location within the first and second image, a transform coded value is calculated for the at least one intermediary image using the transform encoded data of the first and second images without transform decoding the transform encoded data. The transform coded values can be fully encoded using a compression protocol and transmitted to a device for decoding and display of the cinematic transition.
Owner:ACTIVE VIDEO NETWORKS INC
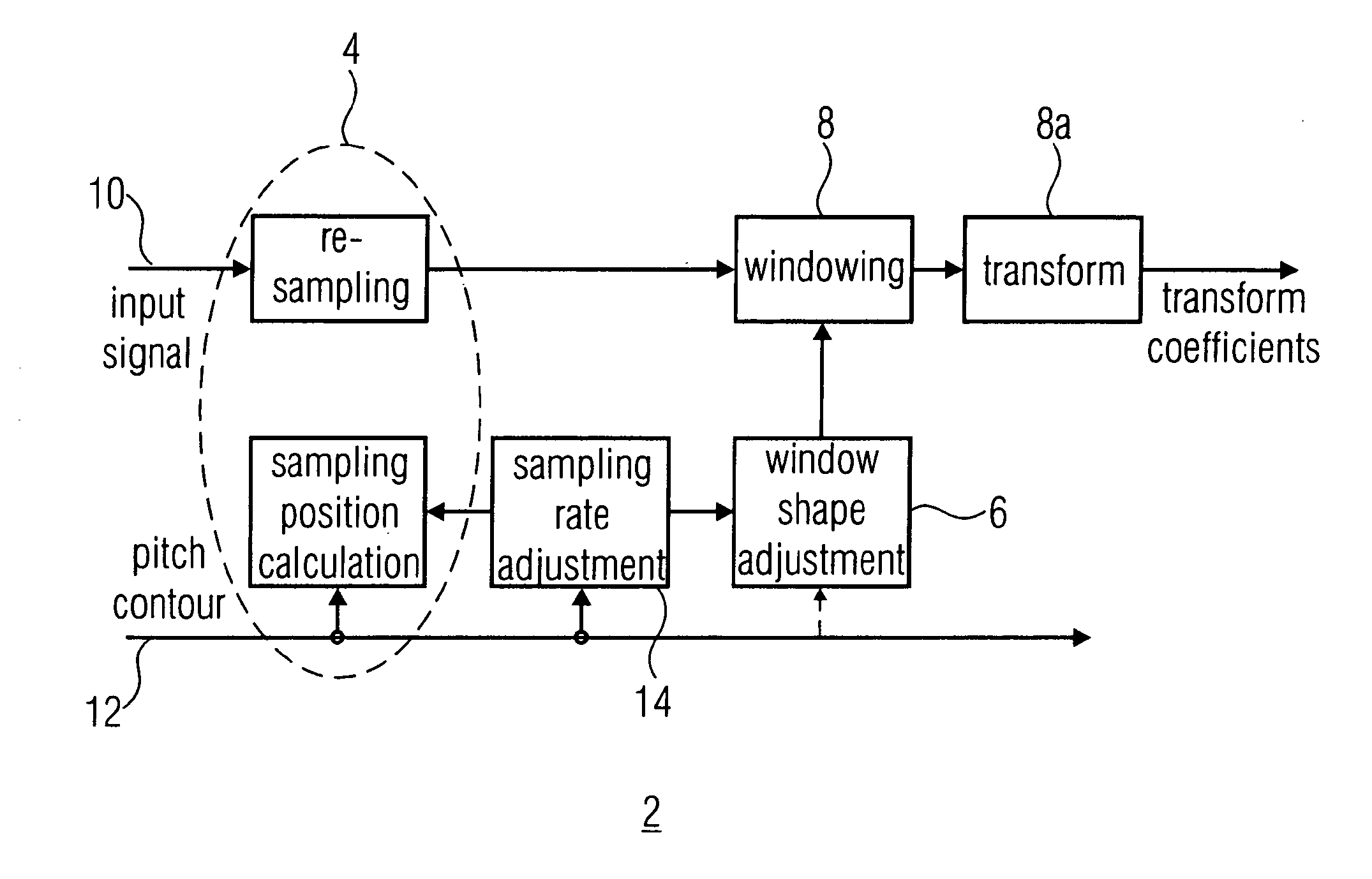
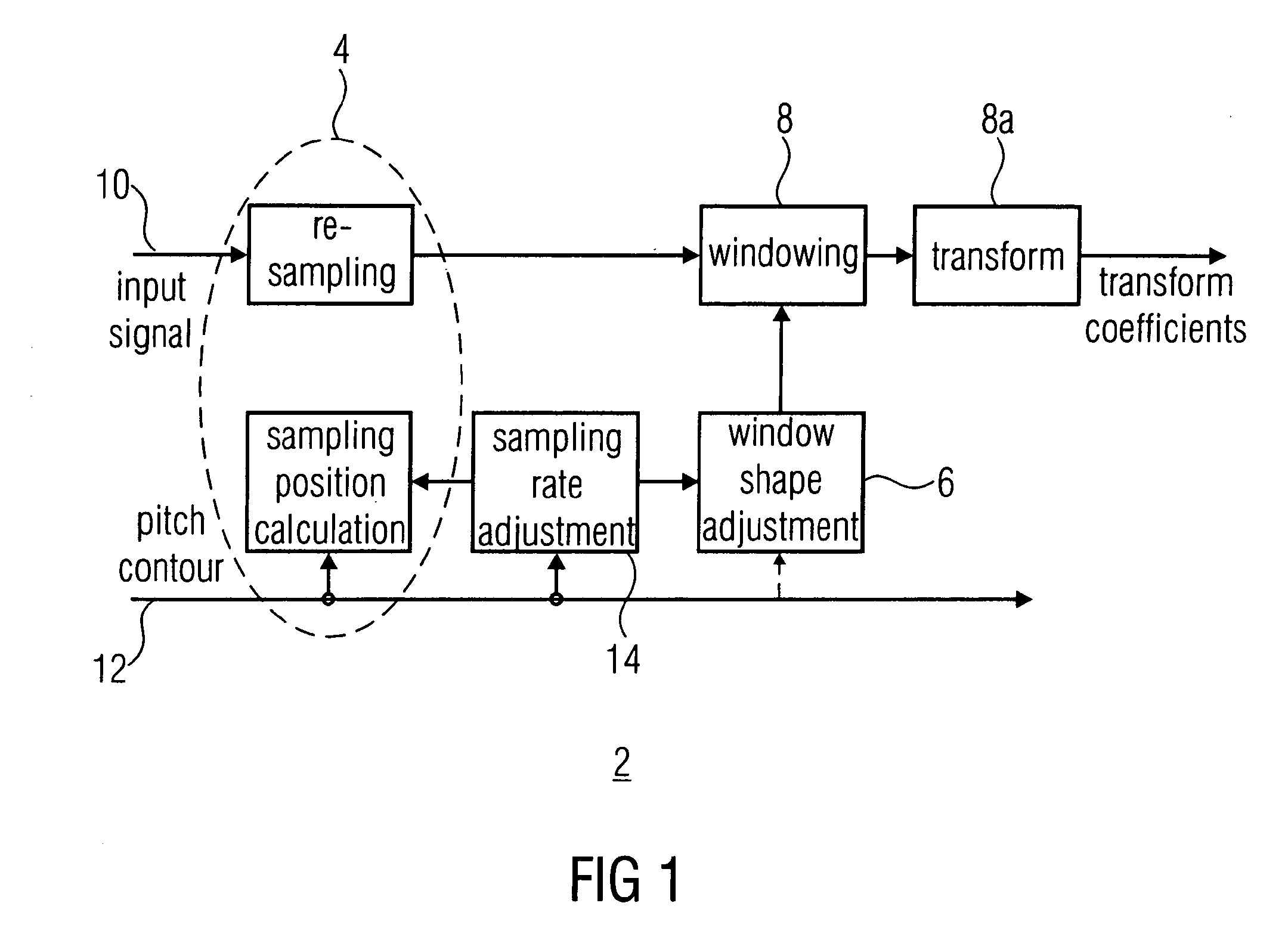
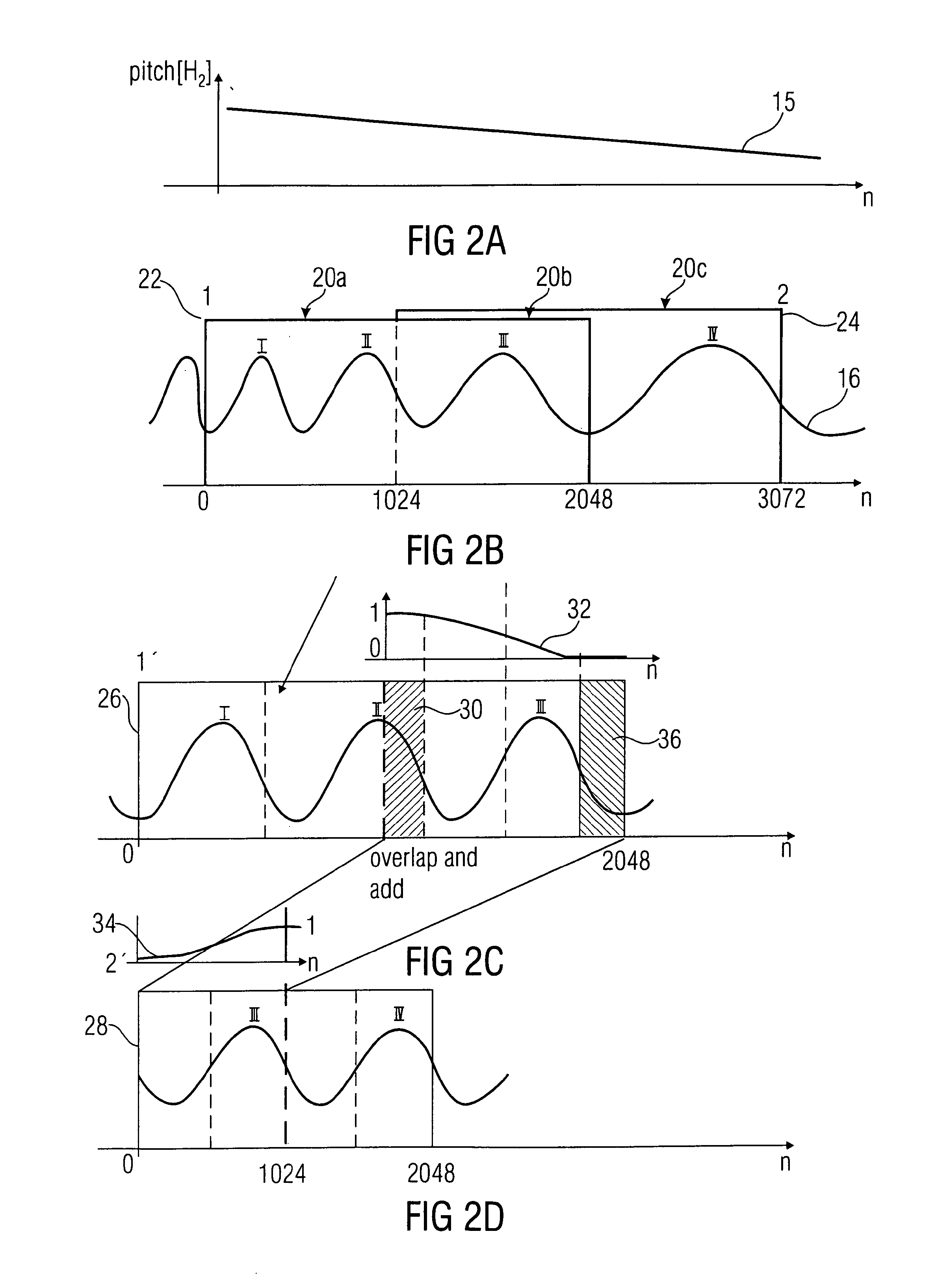
Audio transform coding using pitch correction
ActiveUS20100198586A1Reducing transition lengthEfficient codingSpeech analysisPitch contourTransform coding
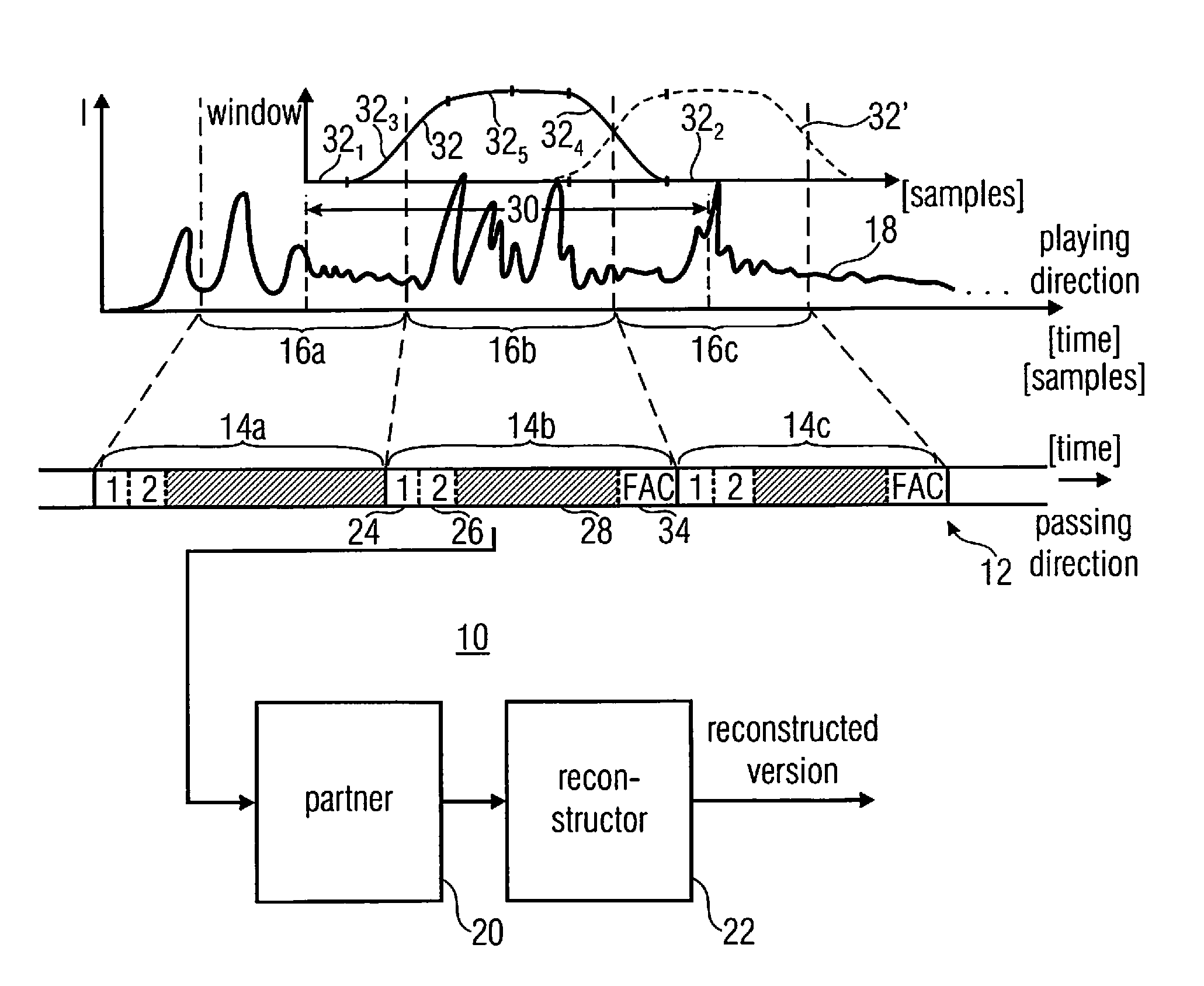
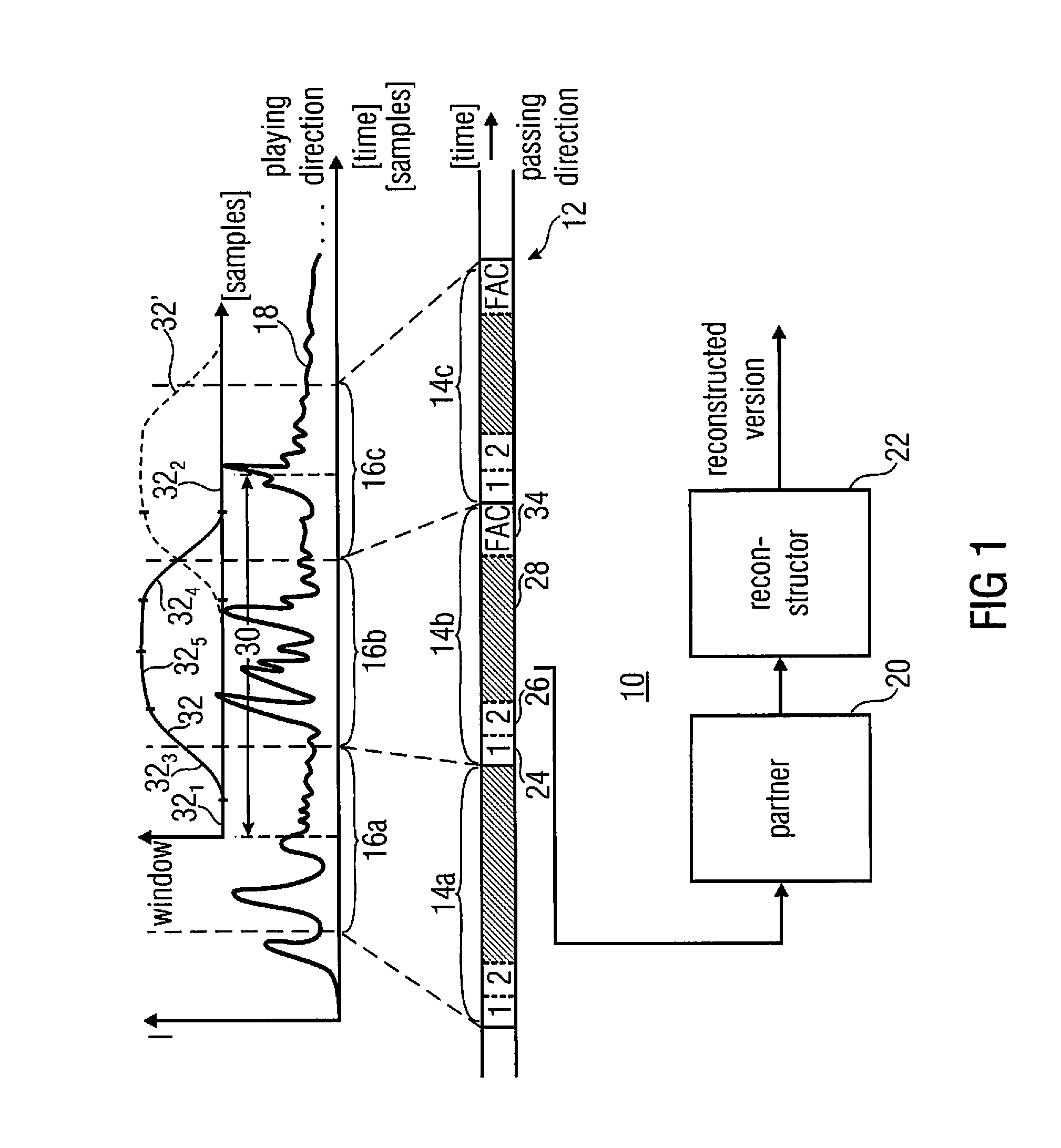
A processed representation of an audio signal having a sequence of frames is generated by sampling the audio signal within first and second frames of the sequence of frames, the second frame following the first frame, the sampling using information on a pitch contour of the first and second frames to derive a first sampled representation. The audio signal is sampled within the second and third frames, the third frame following the second frame in the sequence of frames. The sampling uses the information on the pitch contour of the second frame and information on a pitch contour of the third frame to derive a second sampled representation. A first scaling window is derived for the first sampled representation, and a second scaling window is derived for the second sampled representation, the scaling windows depending on the samplings applied to derive the first sampled representations or the second sampled representation.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
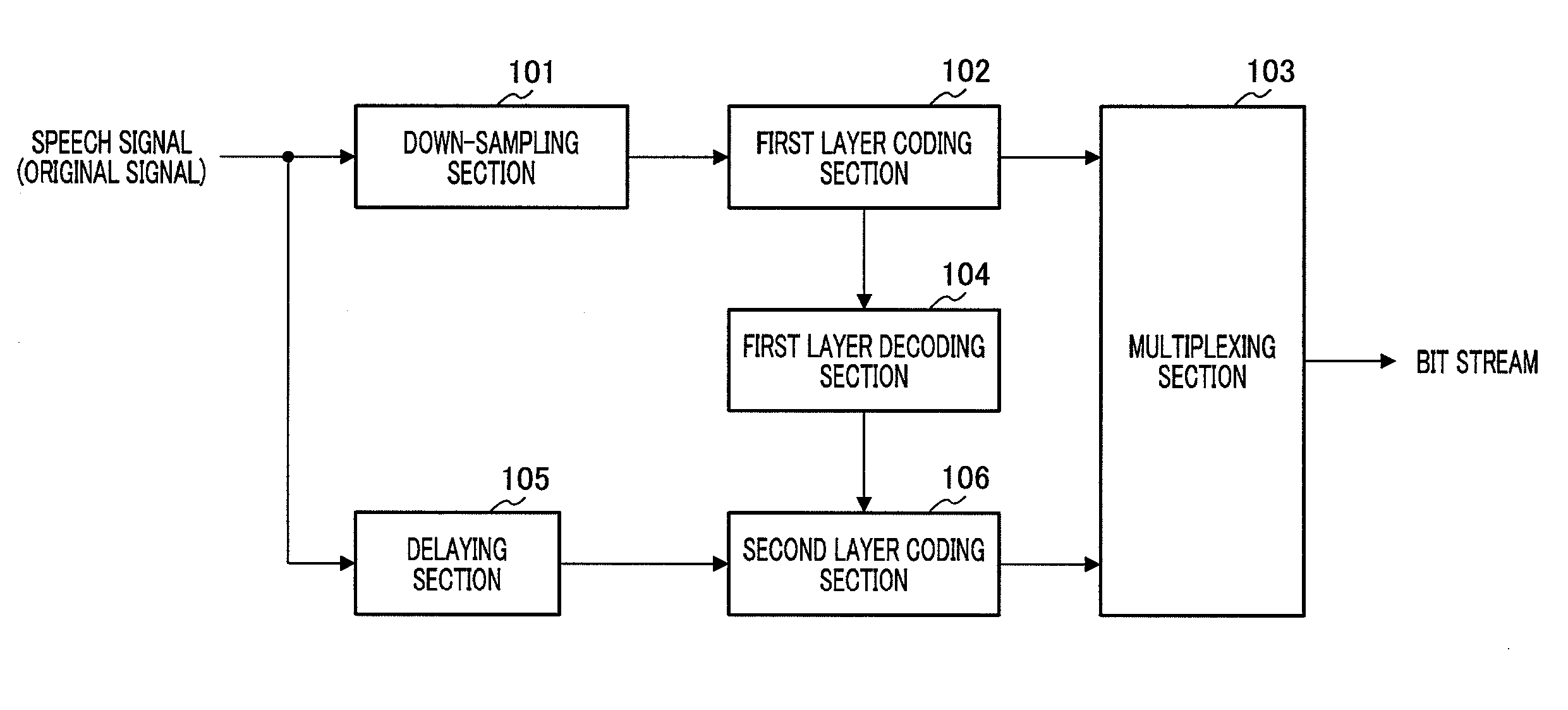
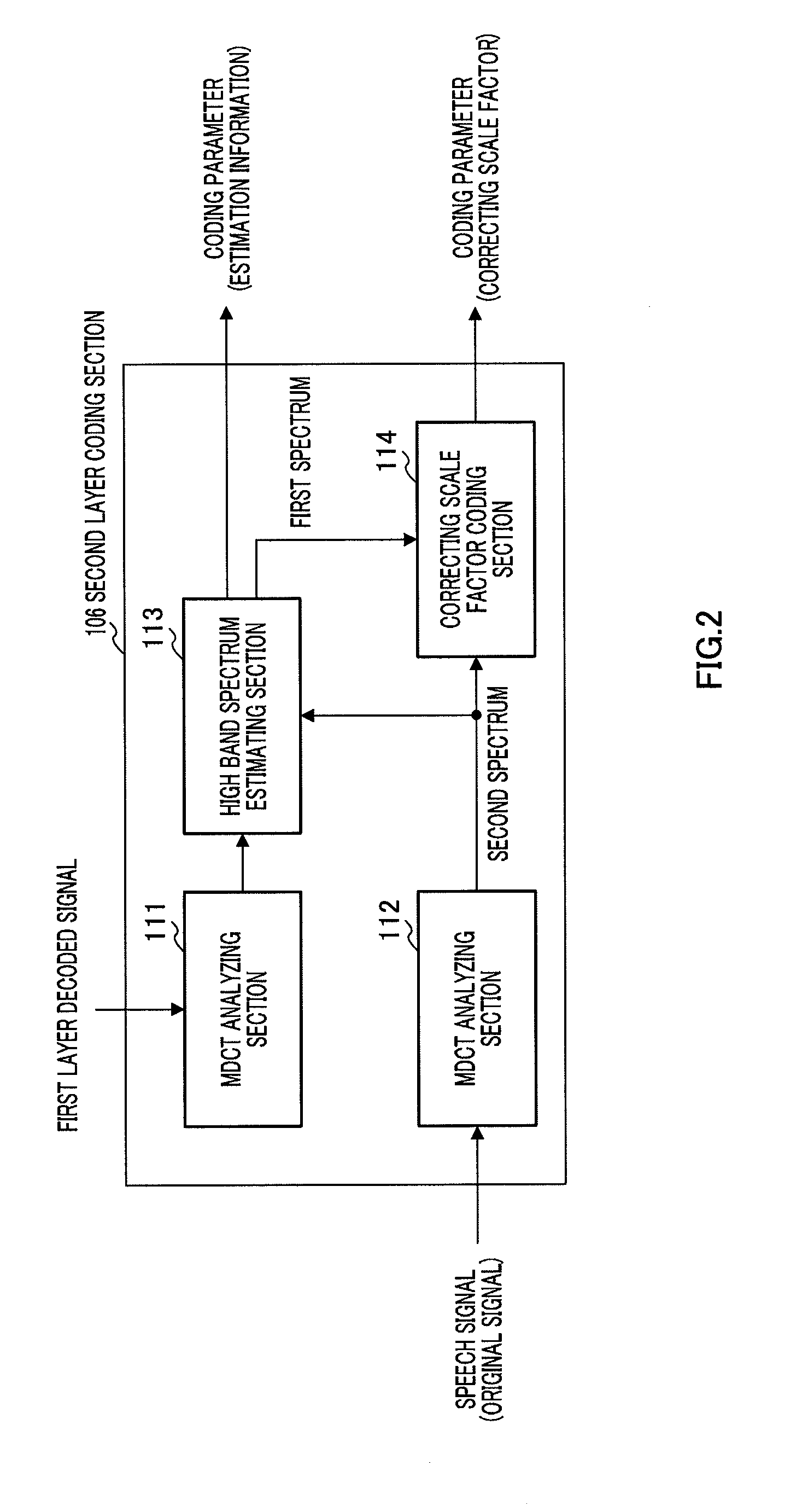
Transform coder and transform coding method
ActiveUS20090281811A1Reduce perceptual speech quality deteriorationQuality improvementSpeech analysisClosed loopSound quality
A transform coder leading to reduction of degradation of perceptual sound quality even if an adequate number of bits is not assigned. Candidates of a correction scale factor stored in a correction scale factor codebook (123) are outputted one by one, and an error signal is generated by subjecting the candidate and scale factors outputted from scale factor computing sections (121, 122) to a predetermined operation. A judging section (126) determines a weight vector given to a weighted error computing section (127) depending on the sign of the error signal. The weighted error computing section (127) computes the square of the error signal, multiplies the square of the error signal by the weight vector given from the judging section (126), and computes a weighted squared error E. A search section (128) determines the candidates of the correction scale factor which minimizes the weighted squared error E by a closed loop processing.
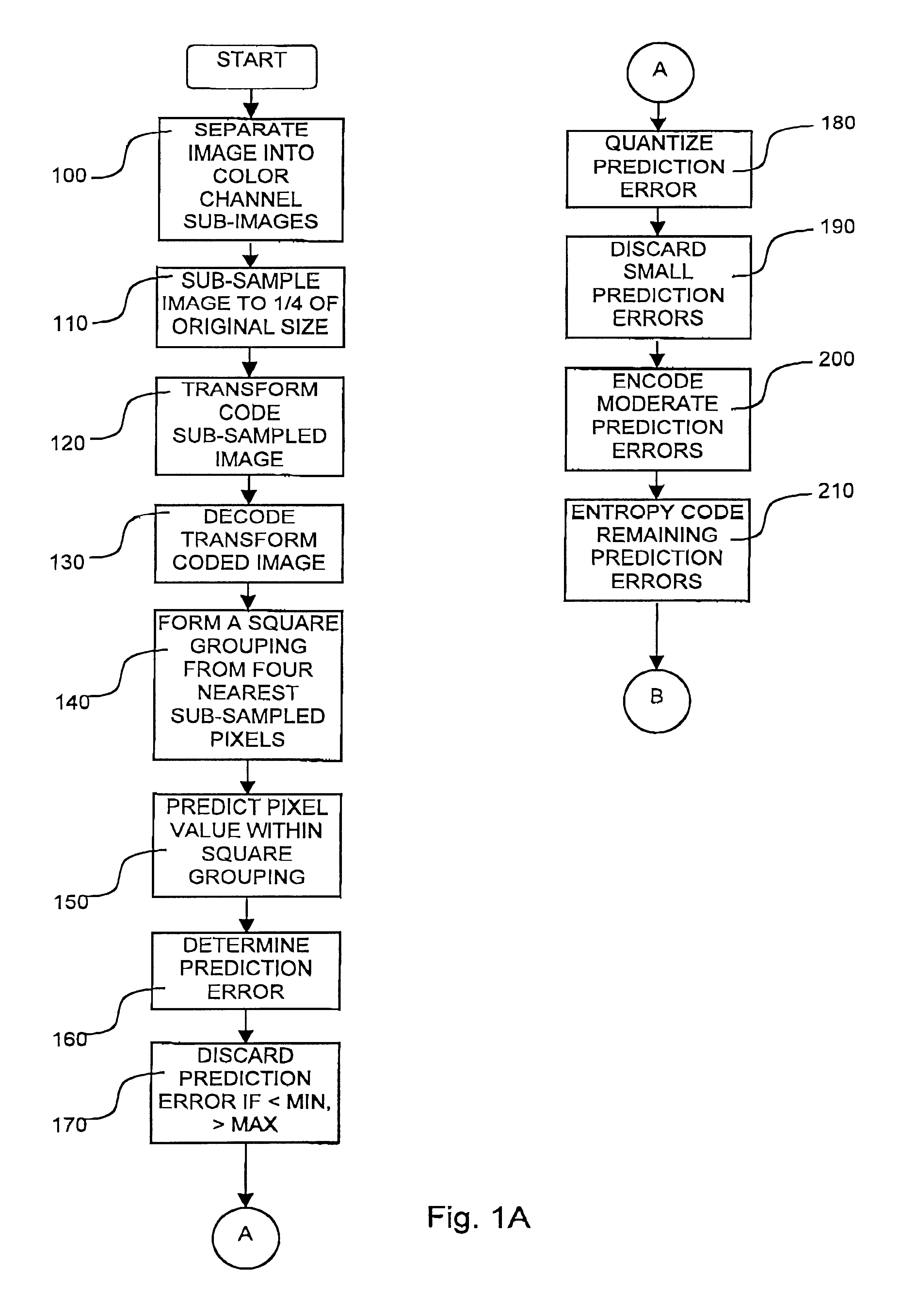
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
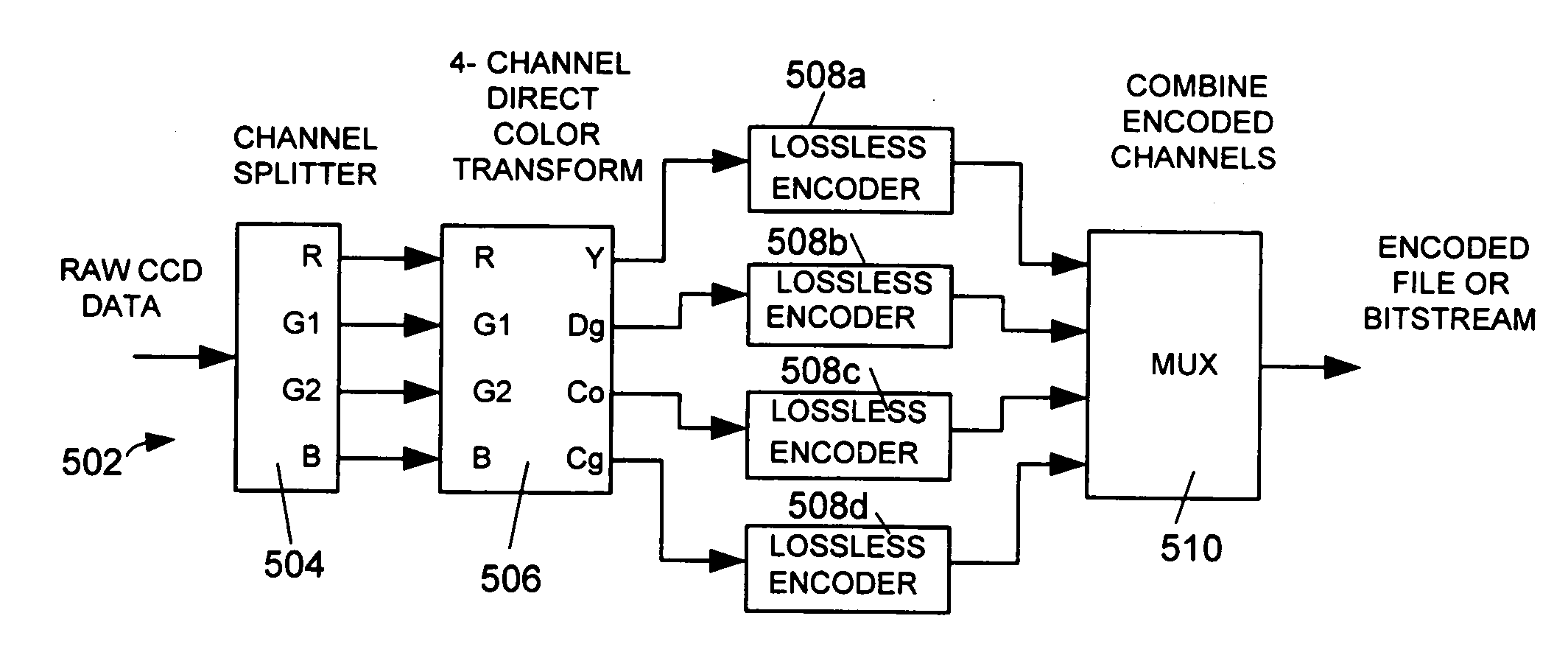
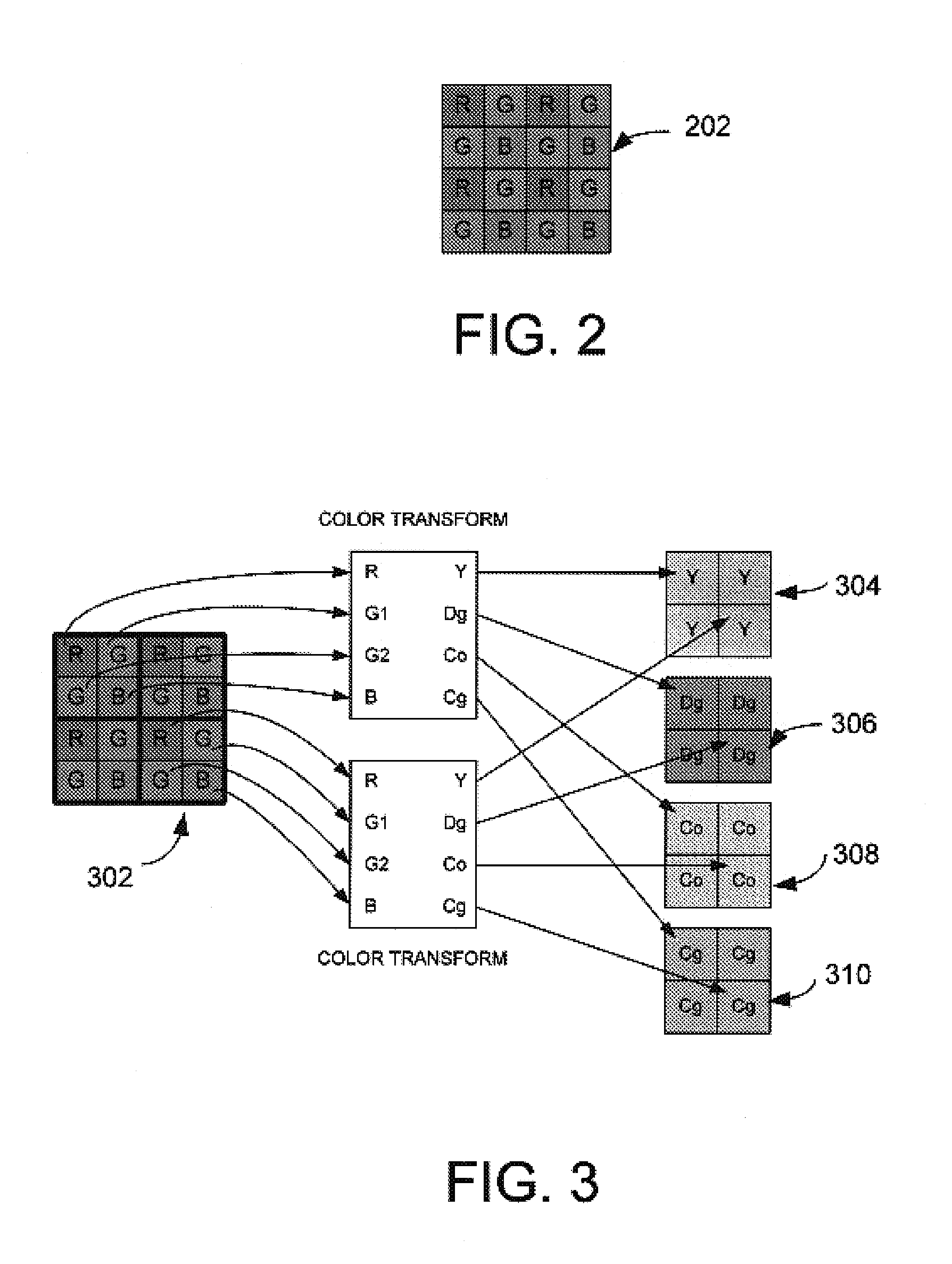
System and method for encoding mosaiced image data employing a reversible color transform
InactiveUS7480417B2Reduce complexityCompression can be losslessColor television with pulse code modulationCharacter and pattern recognitionImage compressionColor filter array
A new color space that maps image pixel values in a mosaiced sampling pattern (such as that generated by a Bayer color filter array) into four color channels that correspond to rectangular sampling patterns. Because these new channels correspond to a rectangular sampling grid, they are much more amenable to processing steps such as compression. In one embodiment, the transformation from the original mosaic-patterned pixels into the new four-channel color space can be made reversible in integer arithmetic. That allows for the implementation of efficient lossless image compression systems for mosaiced (e.g., raw, or raw Charged Couple Device (CCD)) images.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for context-based adaptive binary arithmetic coding
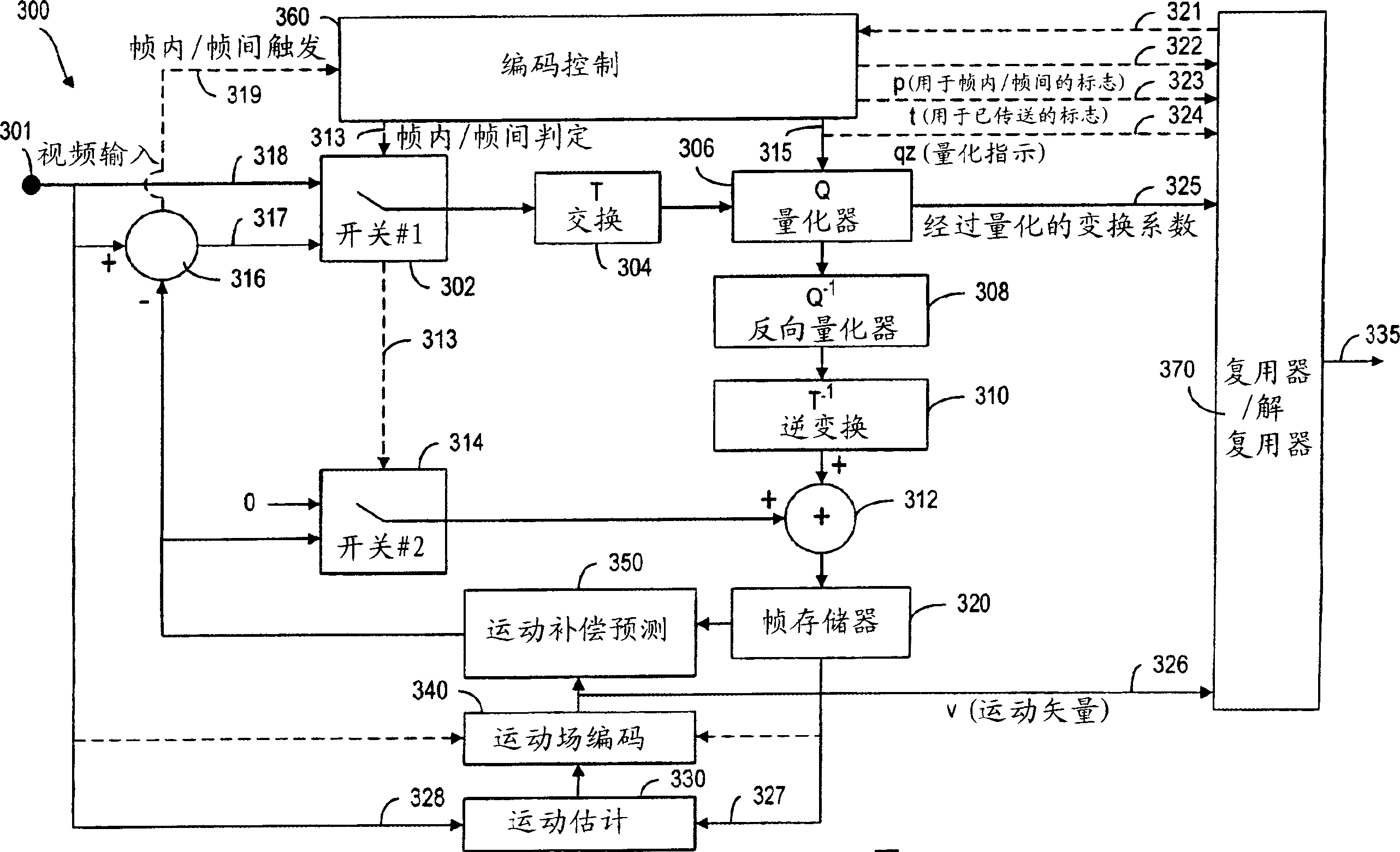
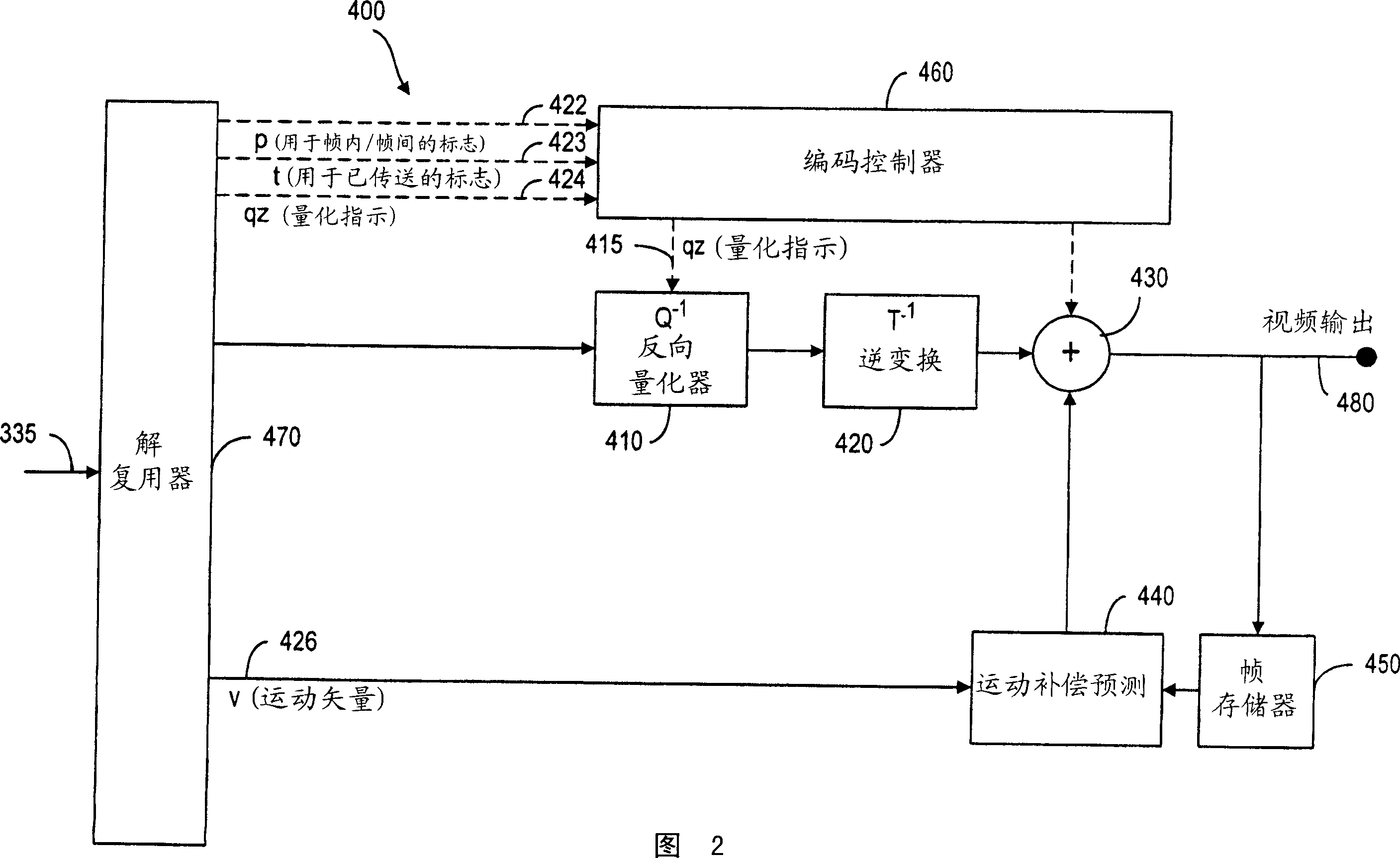
InactiveCN1874509APulse modulation television signal transmissionImage codingMultiple contextNonzero coefficients
A method of image coding wherein an image is divided into blocks having a plurality of pixels. A transform coding operation is performed on a block of pixels to produce a corresponding block of transform coefficient values, which is scanned to produce a scanned array of coefficient values represented by a plurality of number pairs having a first and a second number. The first and second numbers are assigned to one of a plurality of contexts (14) representative of the number pairs. The first number of a number pair is assigned to a context based on a first number of another number pair. Alternatively, the second number of a number pair is assigned to a context based on the first number of the number pair (16). Furthermore, a number indicative of the number of non-zero coefficient values in the block of transform coefficient values is determined and assigned to a context.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
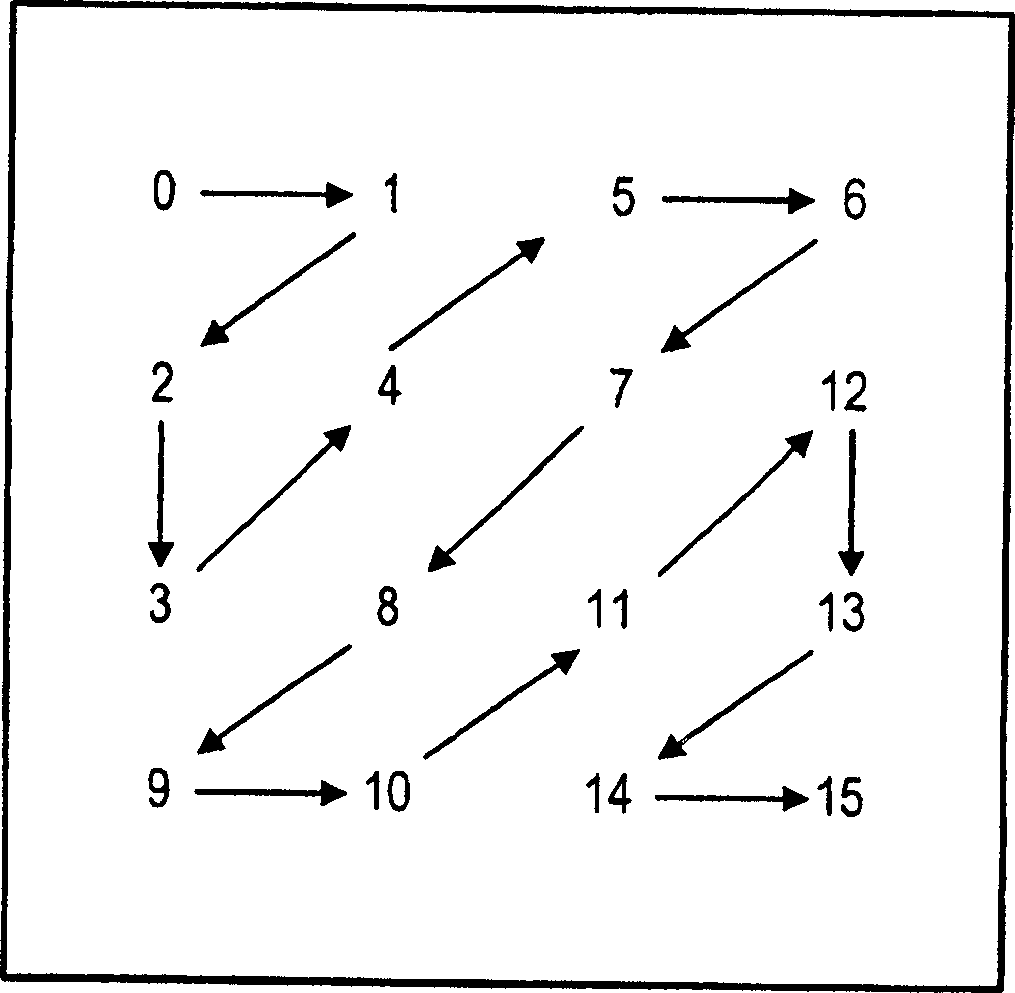
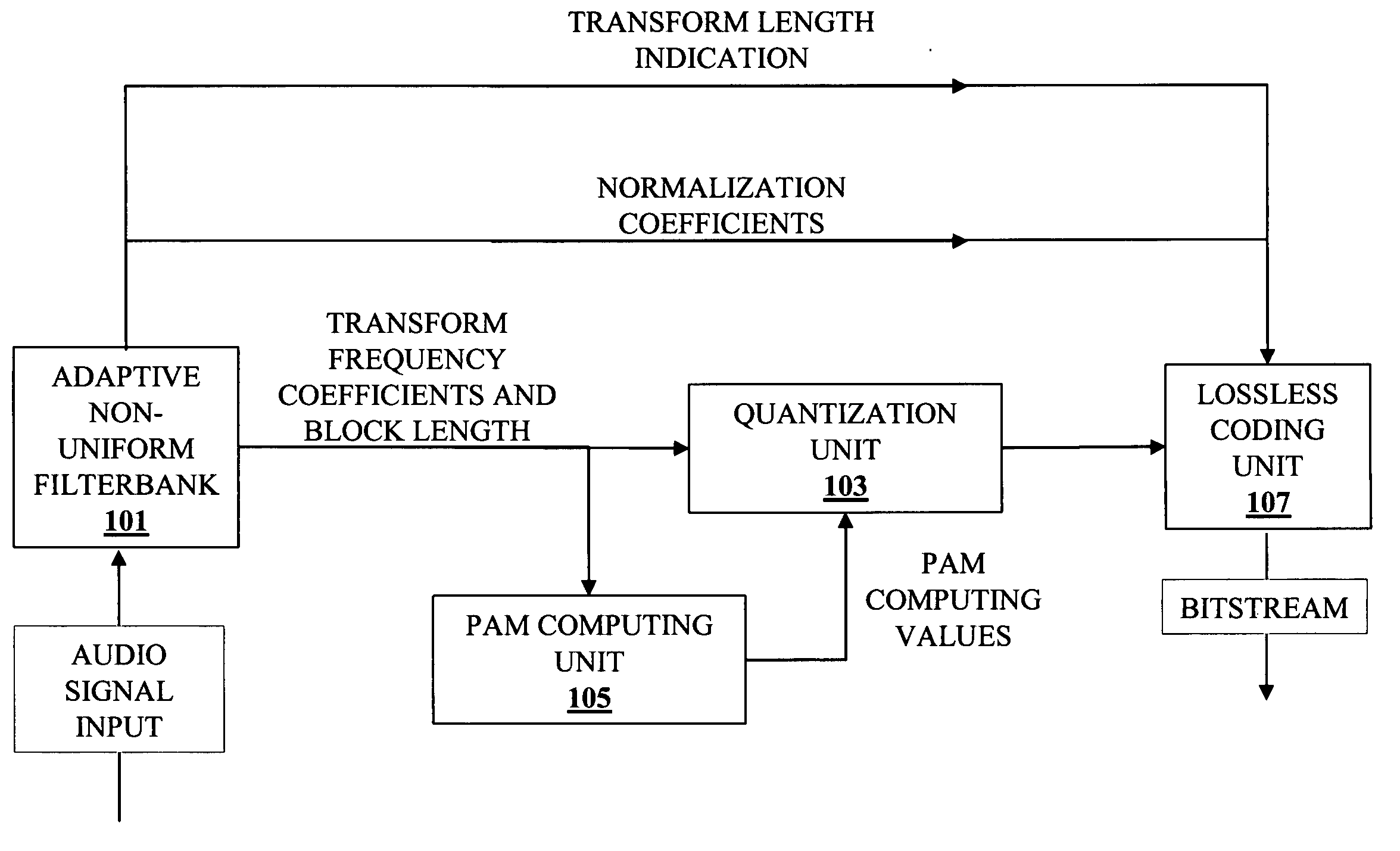
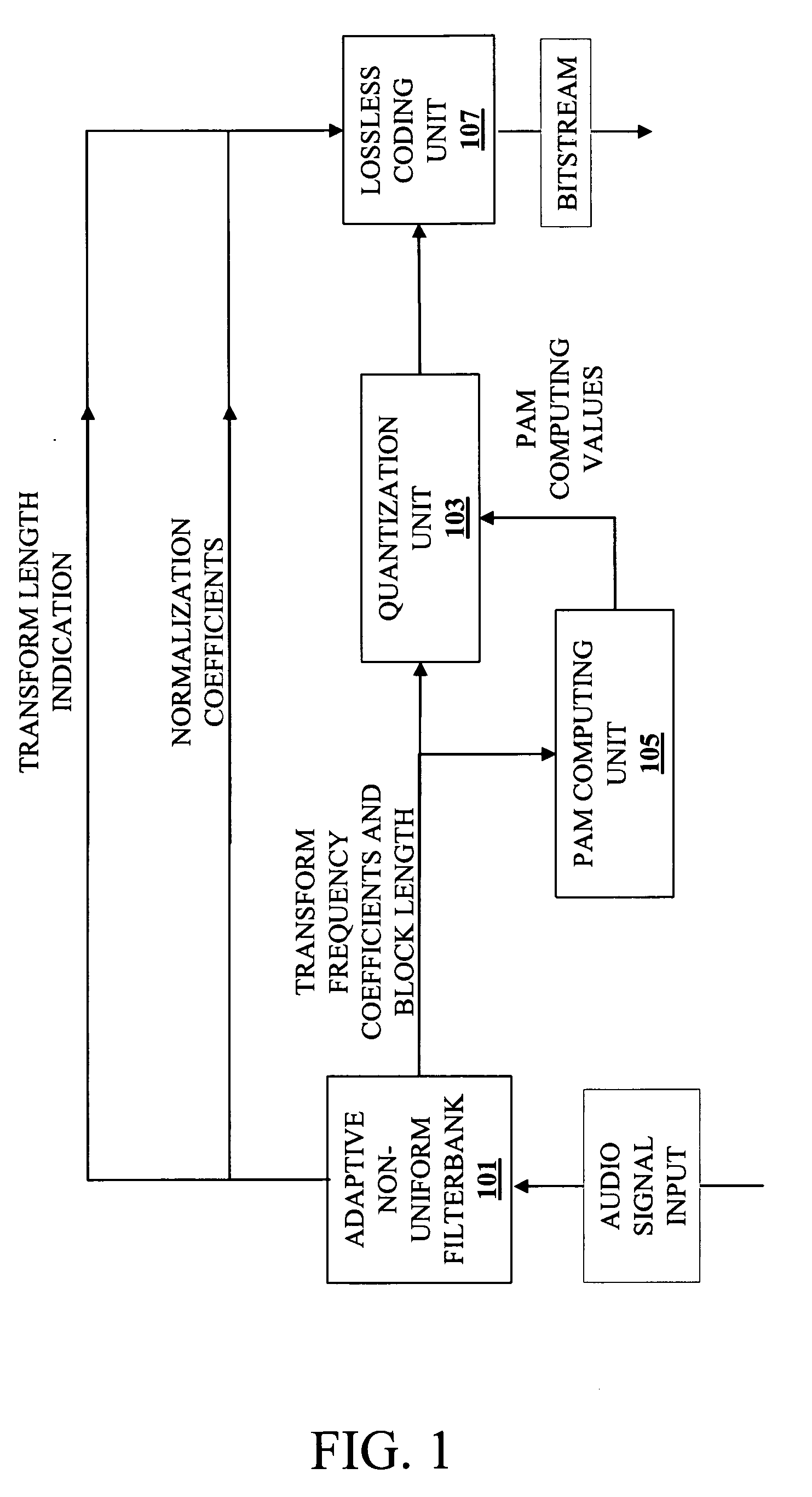
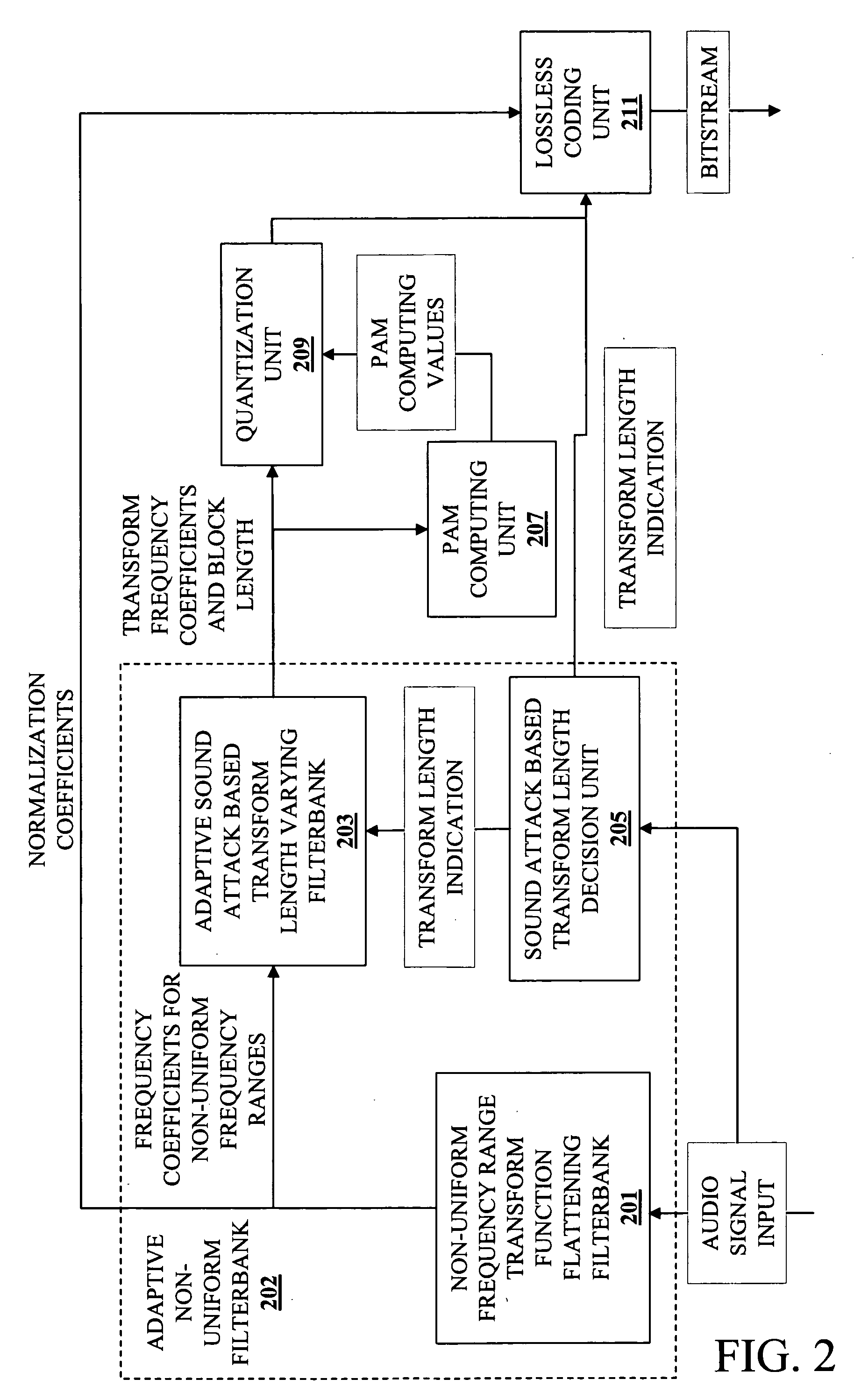
Method and apparatus for audio compression
A method and apparatus for audio compression receives an audio signal. Transform coding is applied to the audio signal to generate a sequence of transform frequency coefficients. The sequence of transform frequency coefficients is partitioned into a plurality of non-uniform width frequency ranges and then zero value frequency coefficients are inserted at the boundaries of the non-uniform width frequency ranges. As a result, certain of the transform frequency coefficients that represent high frequencies are dropped.
Owner:XVD TECH HLDG LTD IRELAND
Visual lossless image compression
InactiveUS6868186B1Color television with pulse code modulationCode conversionPattern recognitionImage compression
An image compression method is provided including separating an image into a plurality of color channel sub-images processing each of the color channel sub-images by sub-sampling the sub-image transform coding the sub-sampled sub-image decoding the transform-coded image forming a plurality of square groupings of pixels in the decoded image predicting a value for a pixel within each of the x-shaped groupings determining a prediction error for each predicted pixel value within each of the square groupings coding the prediction error forming a plurality of at least partly diamond-shaped groupings of pixels in the decoded image predicting a value for a pixel within each of the diamond-shaped groupings and combining each of the processed color channel sub-images with the coded prediction errors, thereby forming a compressed image.
Owner:MEICOM +1
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding image
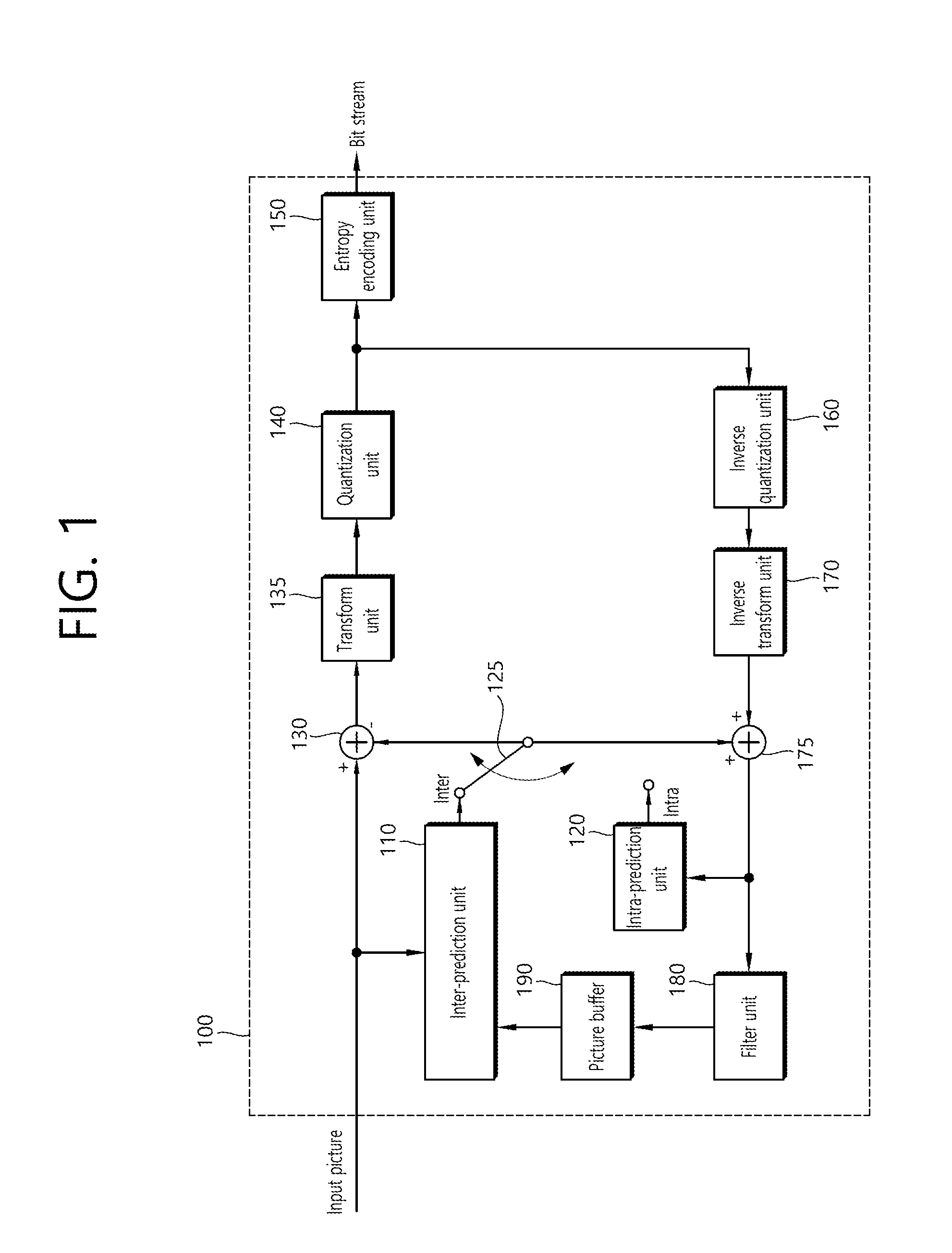
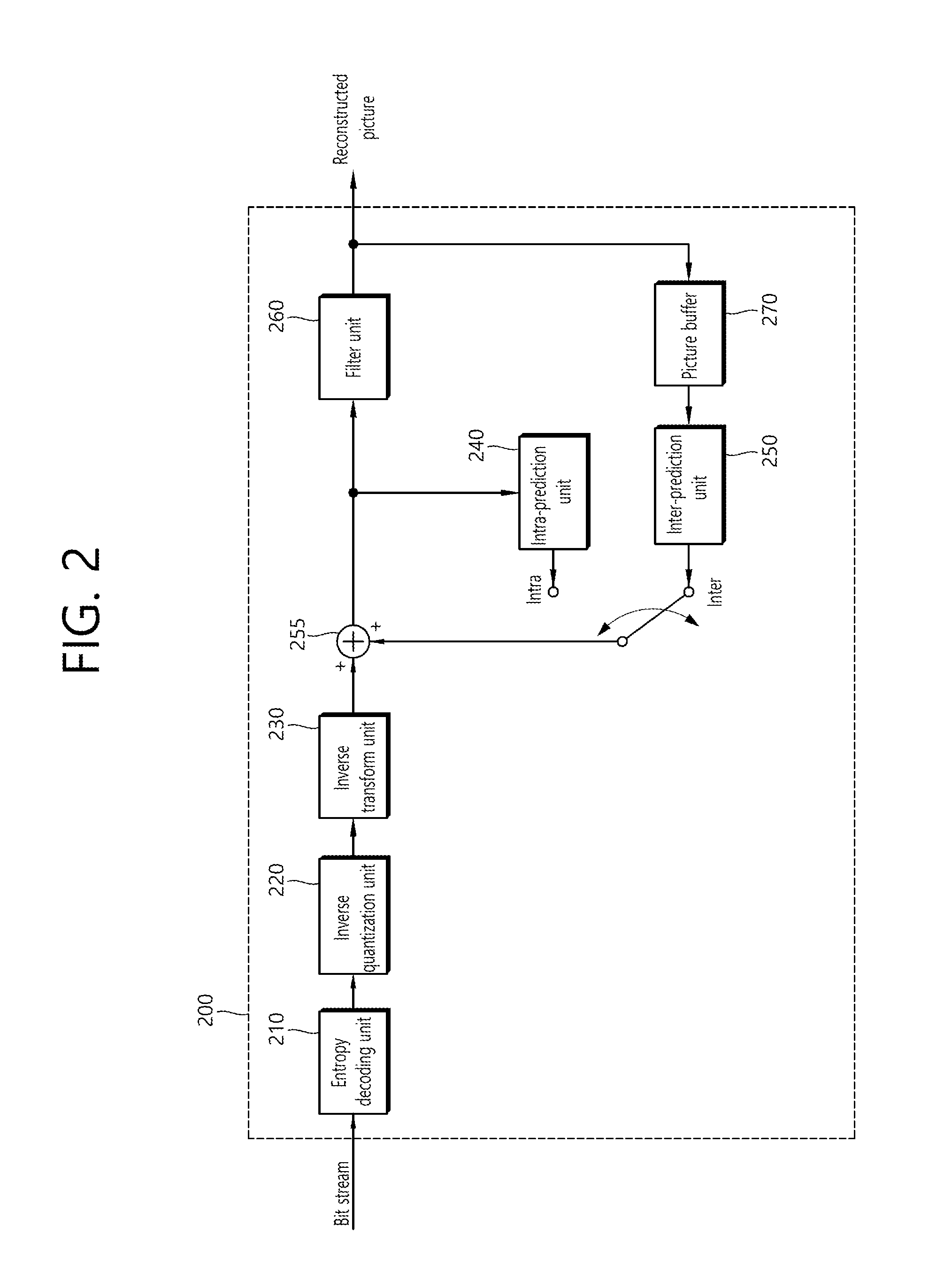
ActiveUS20160269730A1Improve coding efficiencyImprove picture qualityDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Computer image
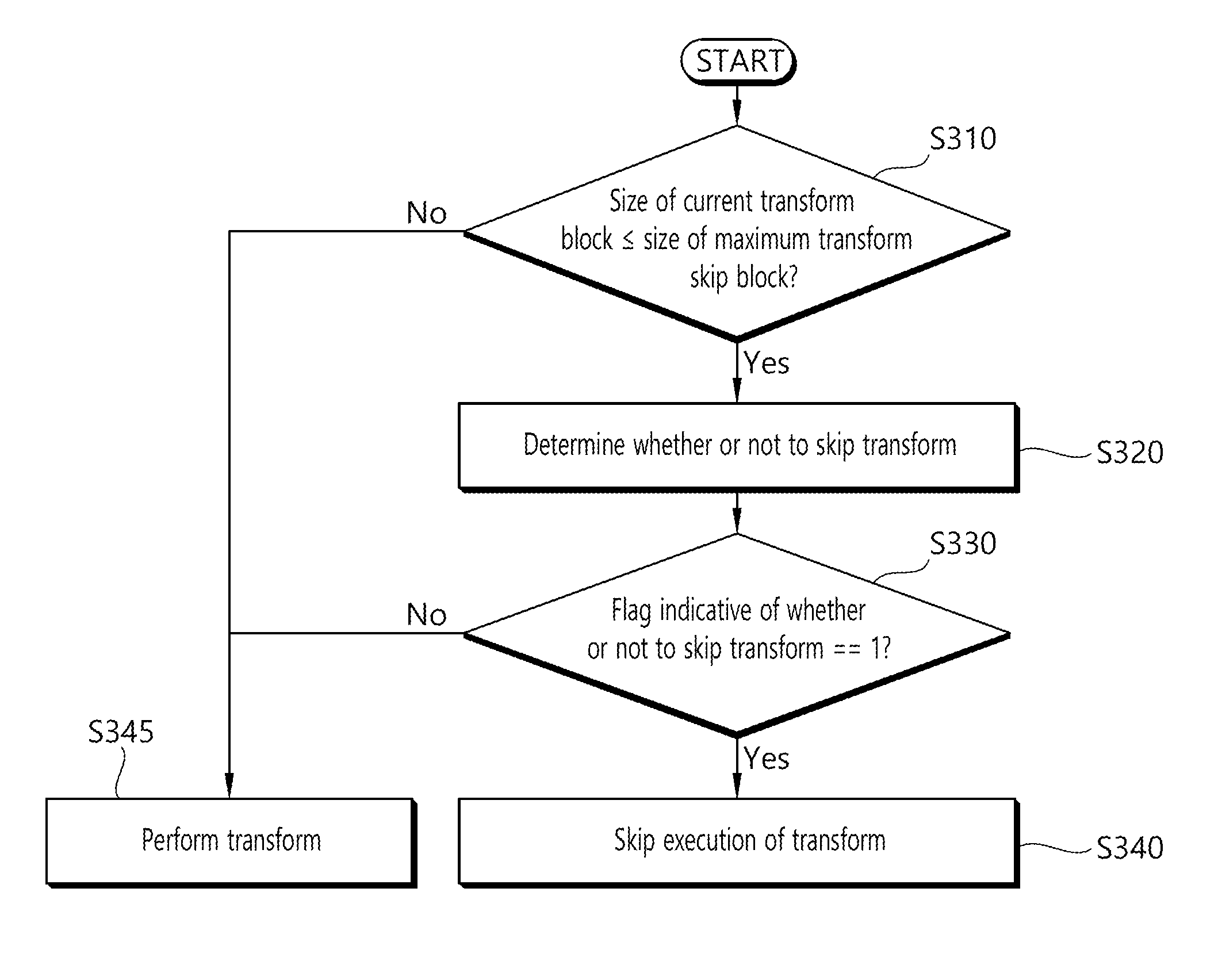
The present invention relates to a method which can selectively skip a transform to alleviate problems of deterioration in compression rate and image quality which are mainly generated when applying the motion compensation-transform encoding image compression technique which is mainly used currently, to an image having a drastic spatial change in a pixel value such as a computer image, and can skip the transform by comparing a transform size of a current block and the size of a maximum transform skip block with each other, and provides an efficient signaling technique therefor. The method includes the steps of: comparing the size of a current transform unit (TU) with the size of a maximum transform skip block when determining whether to transform a residual signal corresponding to difference between the current block and a prediction block; and determining whether to perform the transform on the basis of the comparison information on the size of the TU and the size of the maximum transform skip block.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Coder using forward aliasing cancellation
A codec supporting switching between time-domain aliasing cancellation transform coding mode and time-domain coding mode is made less liable to frame loss by adding a further syntax portion to the frames, depending on which the parser of the decoder may select between a first action of expecting the current frame to have, and thus reading forward aliasing cancellation data from the current frame and a second action of not-expecting the current frame to have, and thus not reading forward aliasing cancellation data from the current frame. In other words, while a bit of coding efficiency is lost due to the provision of the new syntax portion, it is merely the new syntax portion which provides for the ability to use the codec in case of a communication channel with frame loss. Without the new syntax portion, the decoder would not be capable of decoding any data stream portion after a loss and will crash in trying to resume parsing. Thus, in an error prone environment, the coding efficiency is prevented from vanishing by the introduction of the new syntax portion.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com