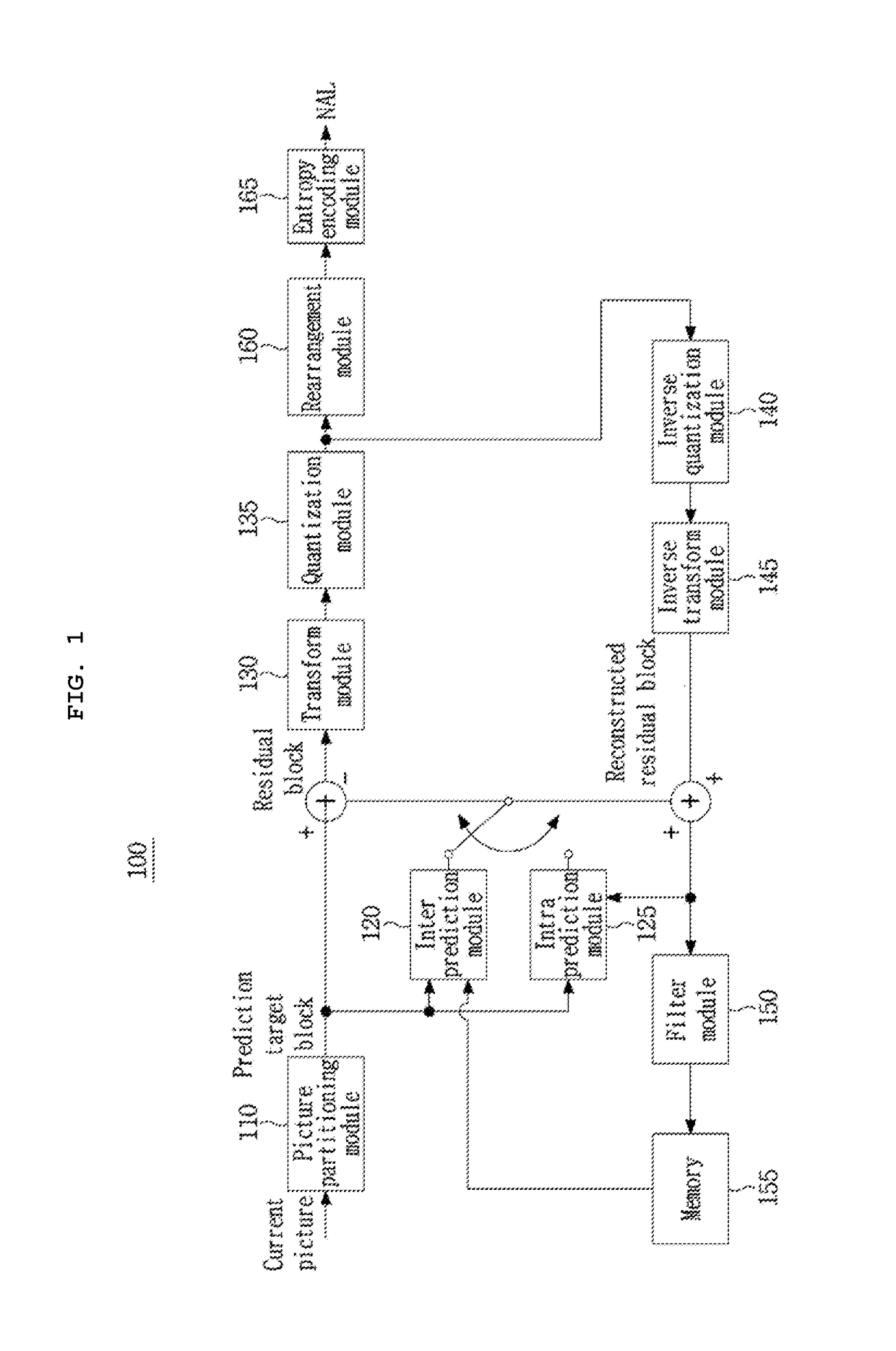
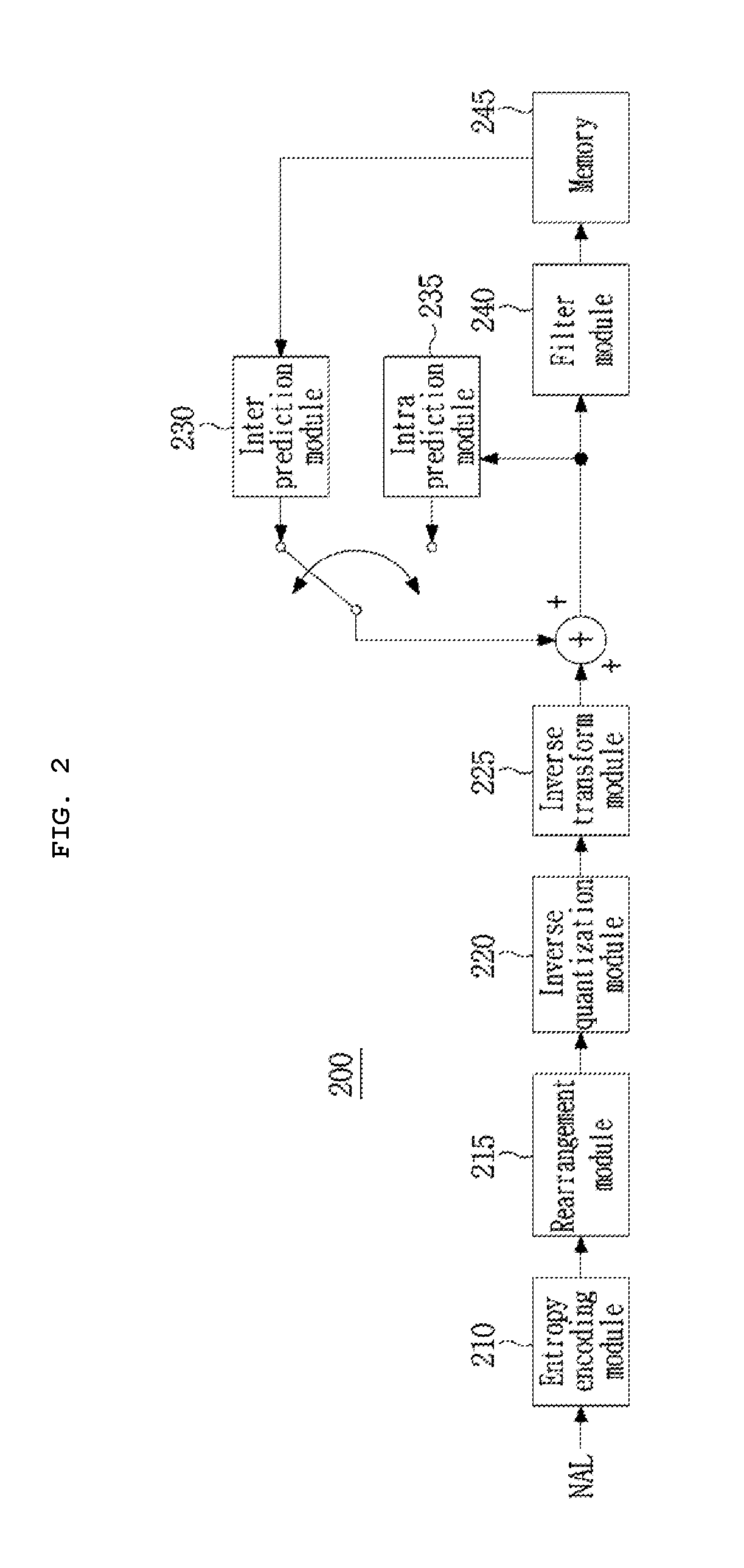
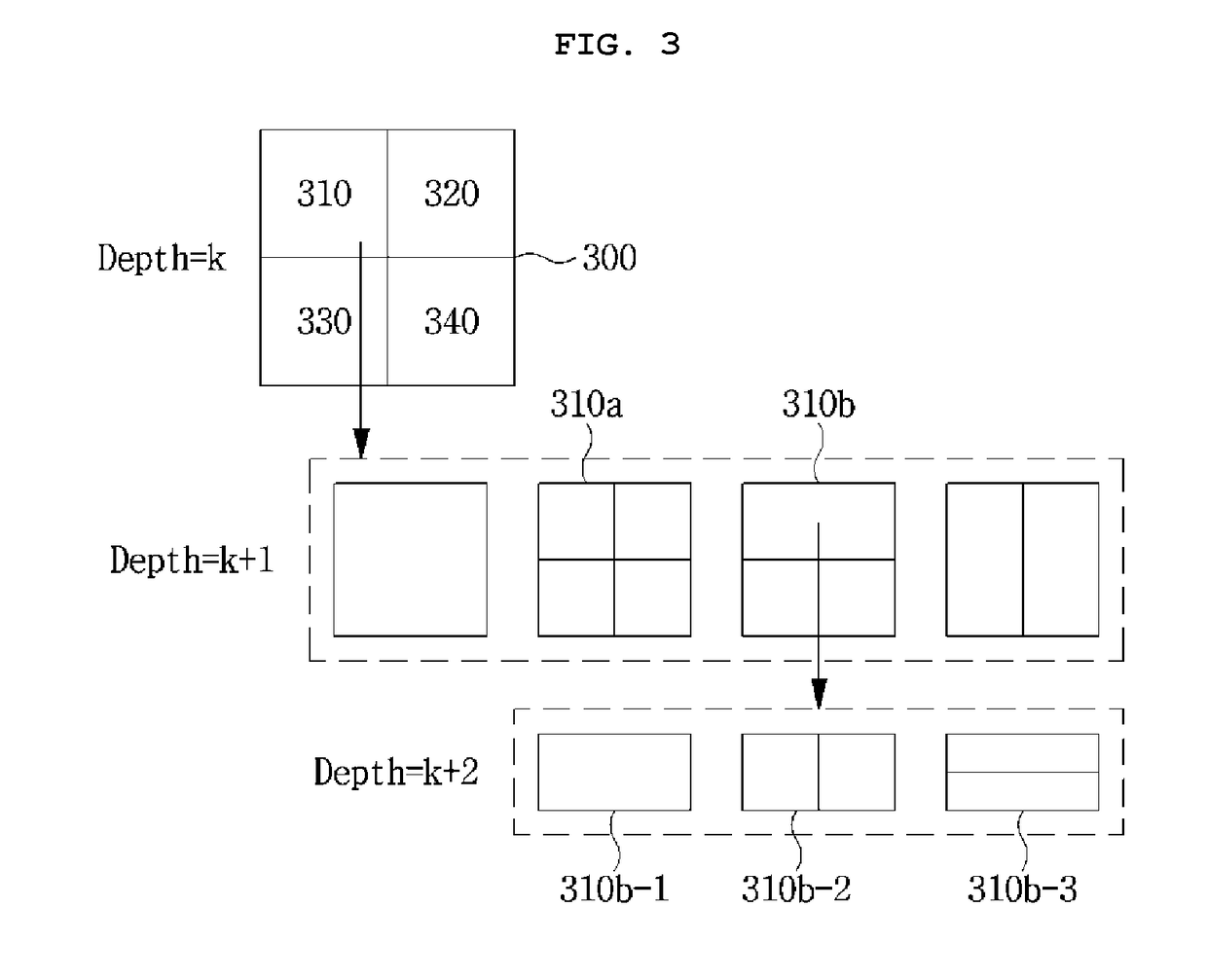
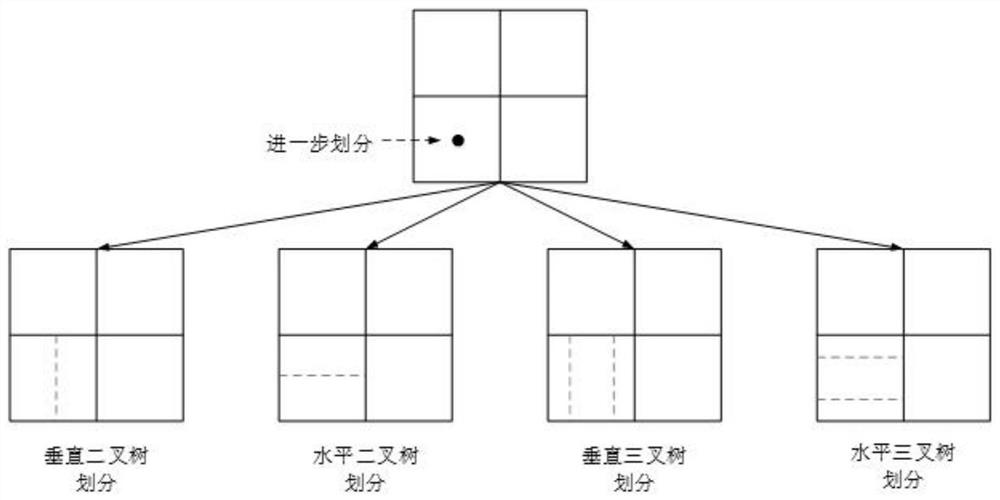
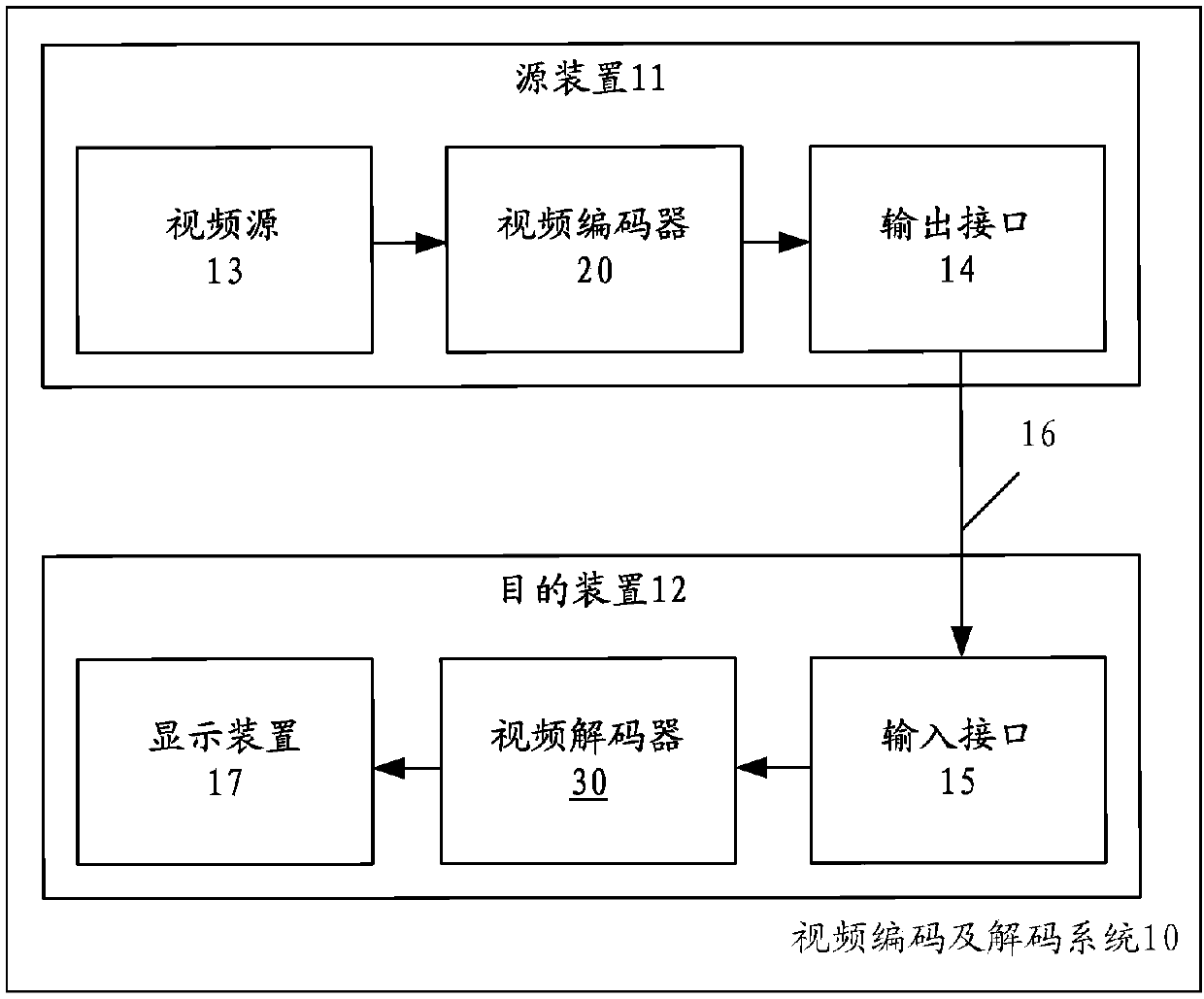
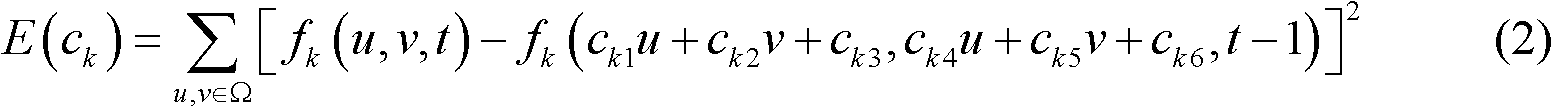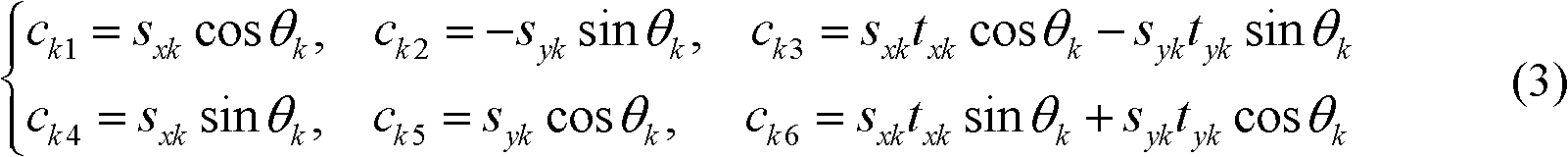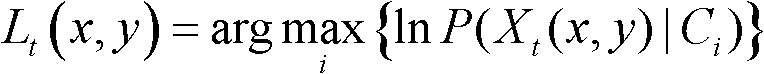Patents
Literature
94 results about "Affine motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
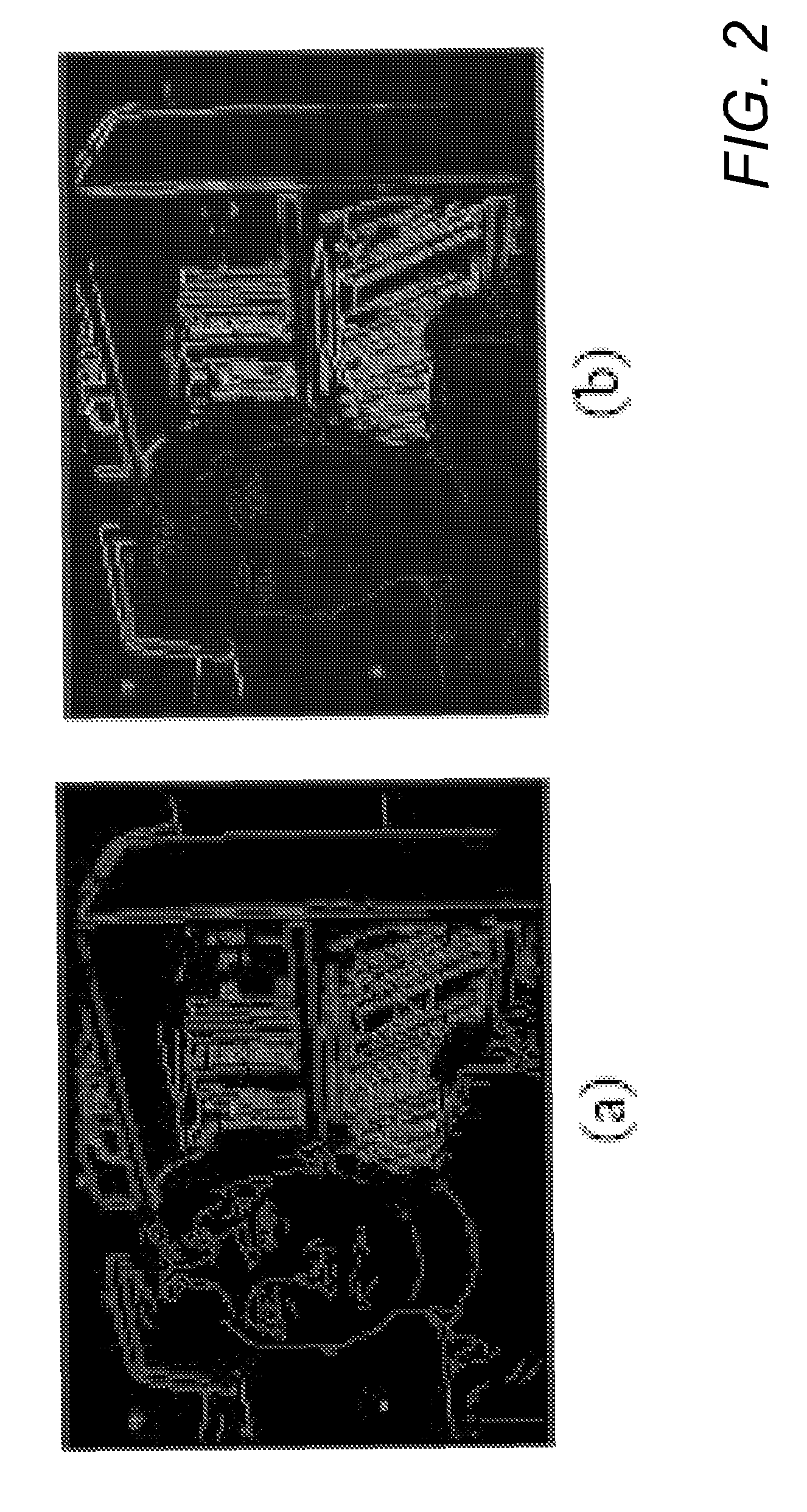
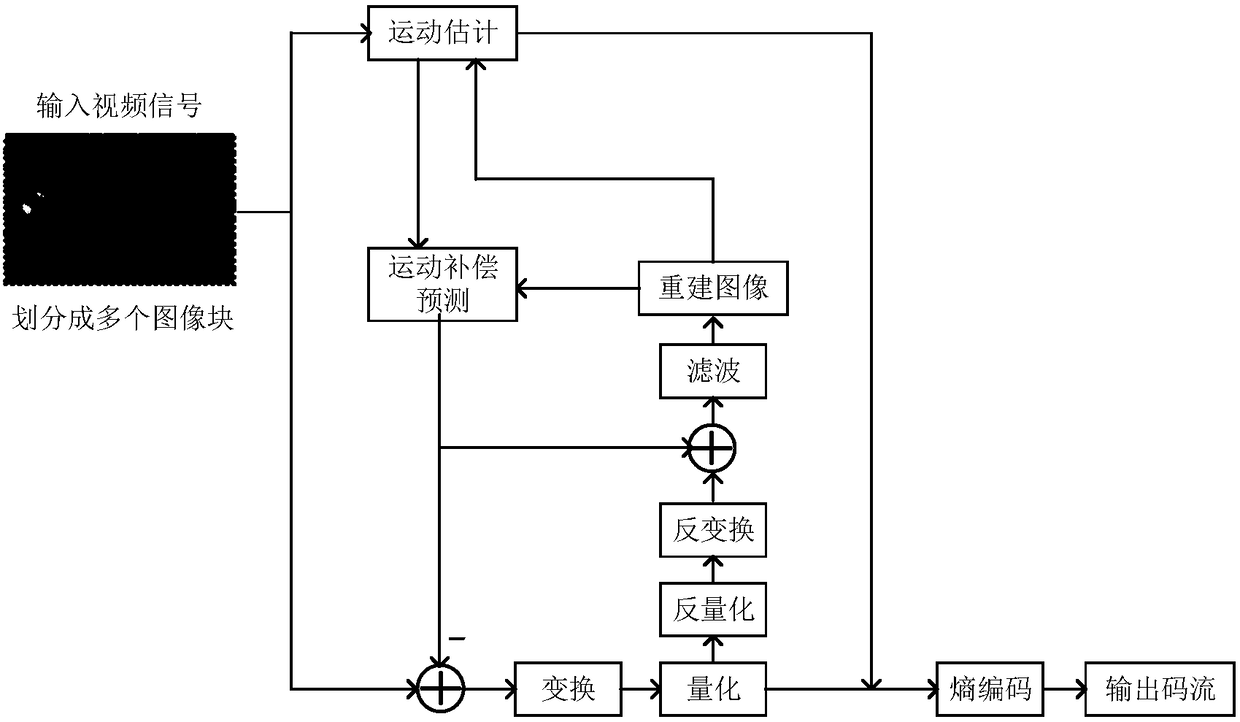
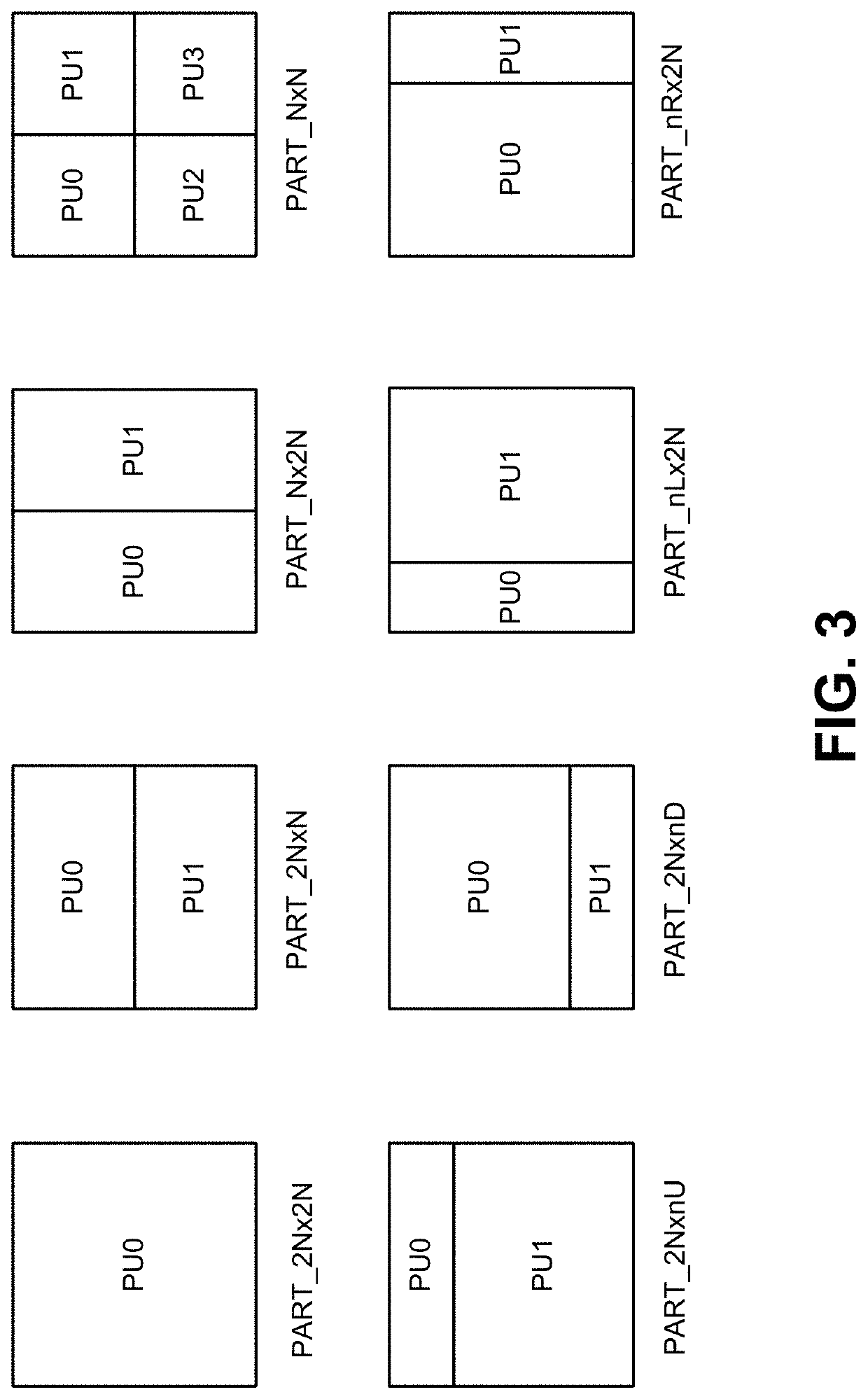
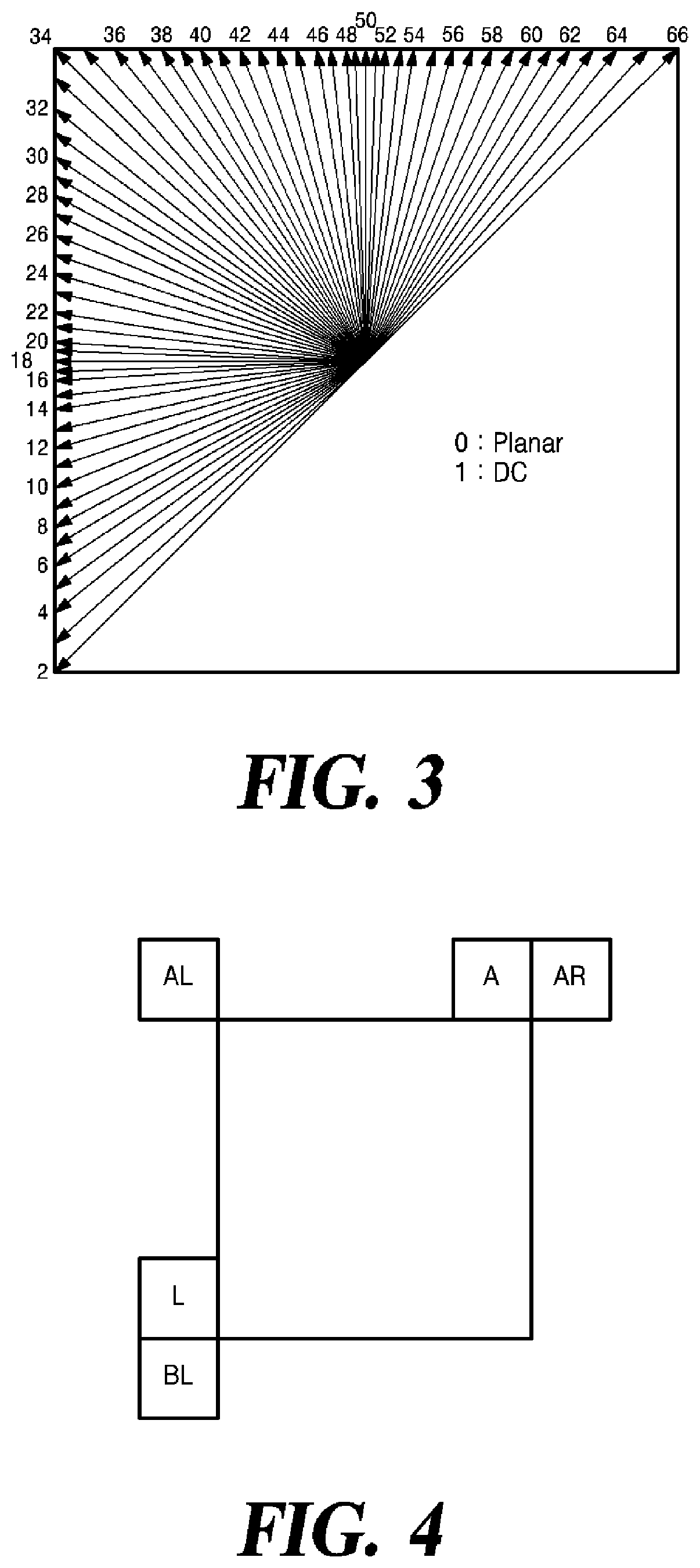
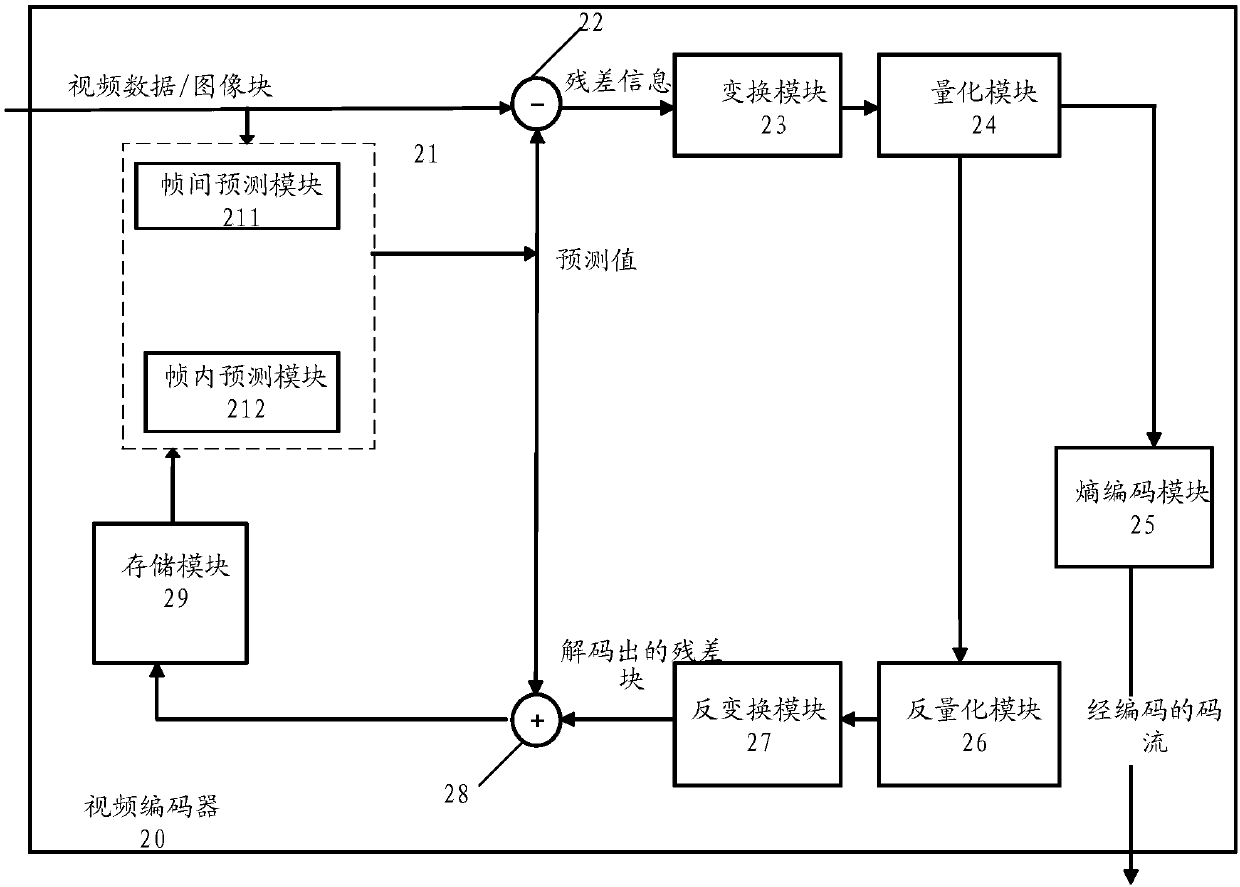
Affine motion information derivation
ActiveUS20180270500A1Error minimizationDigital video signal modificationTemplate matchingAffine motion
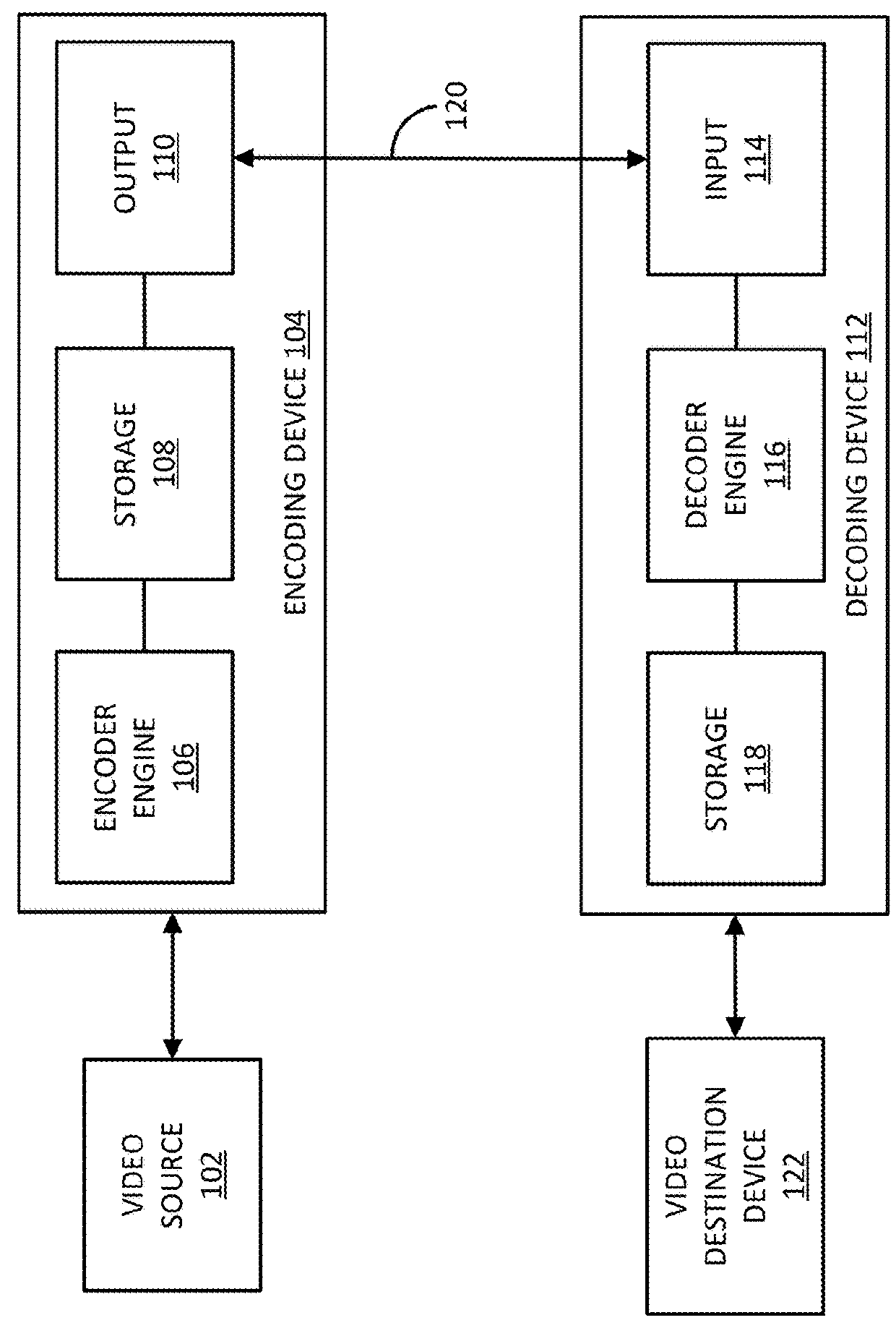
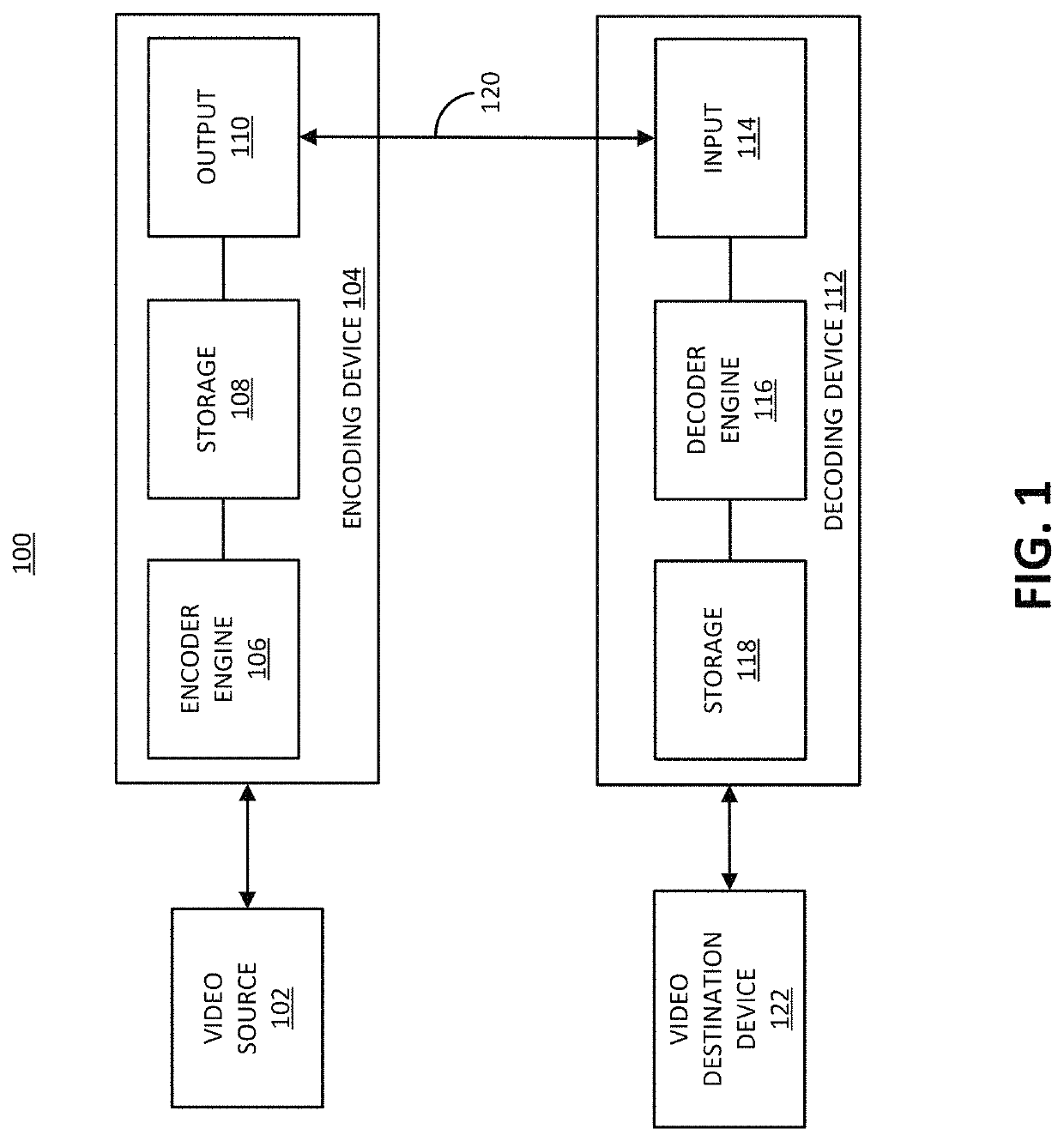
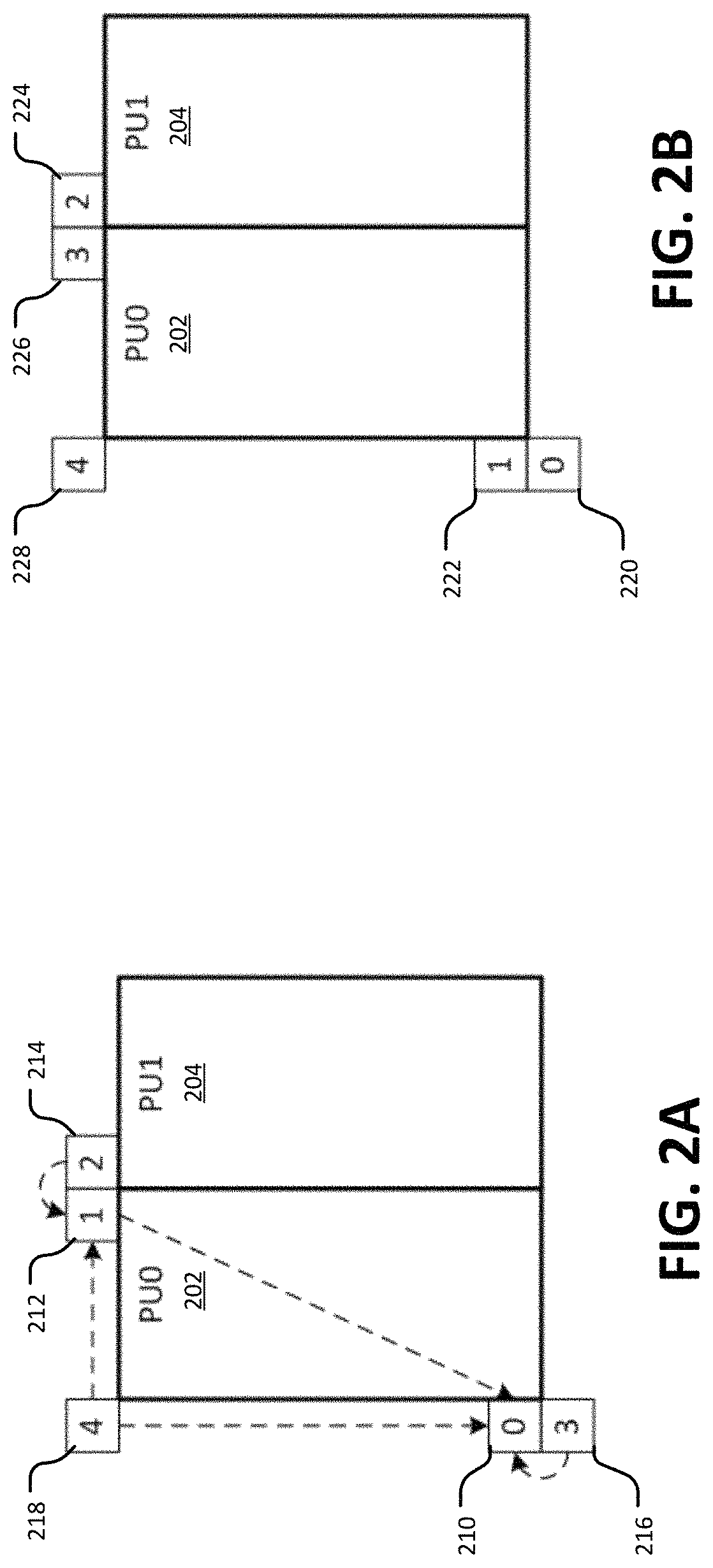
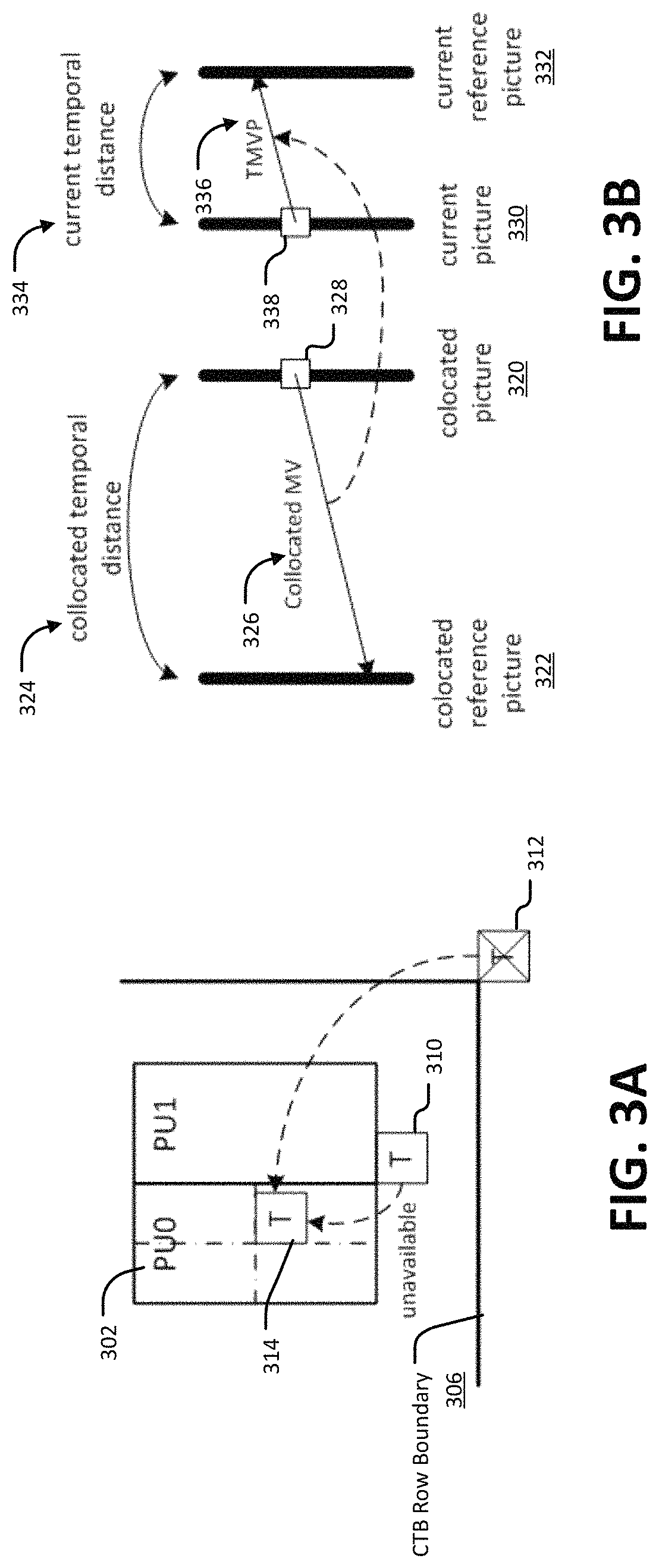
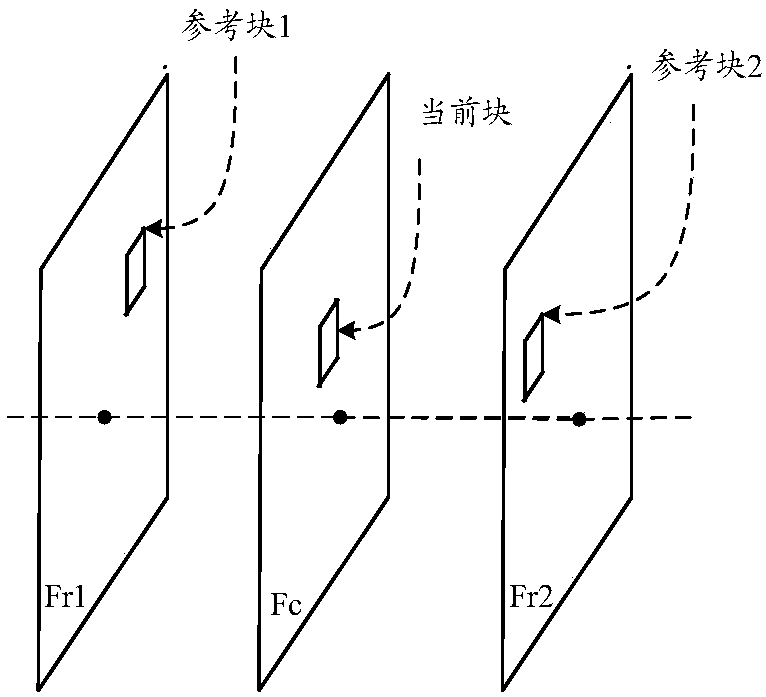
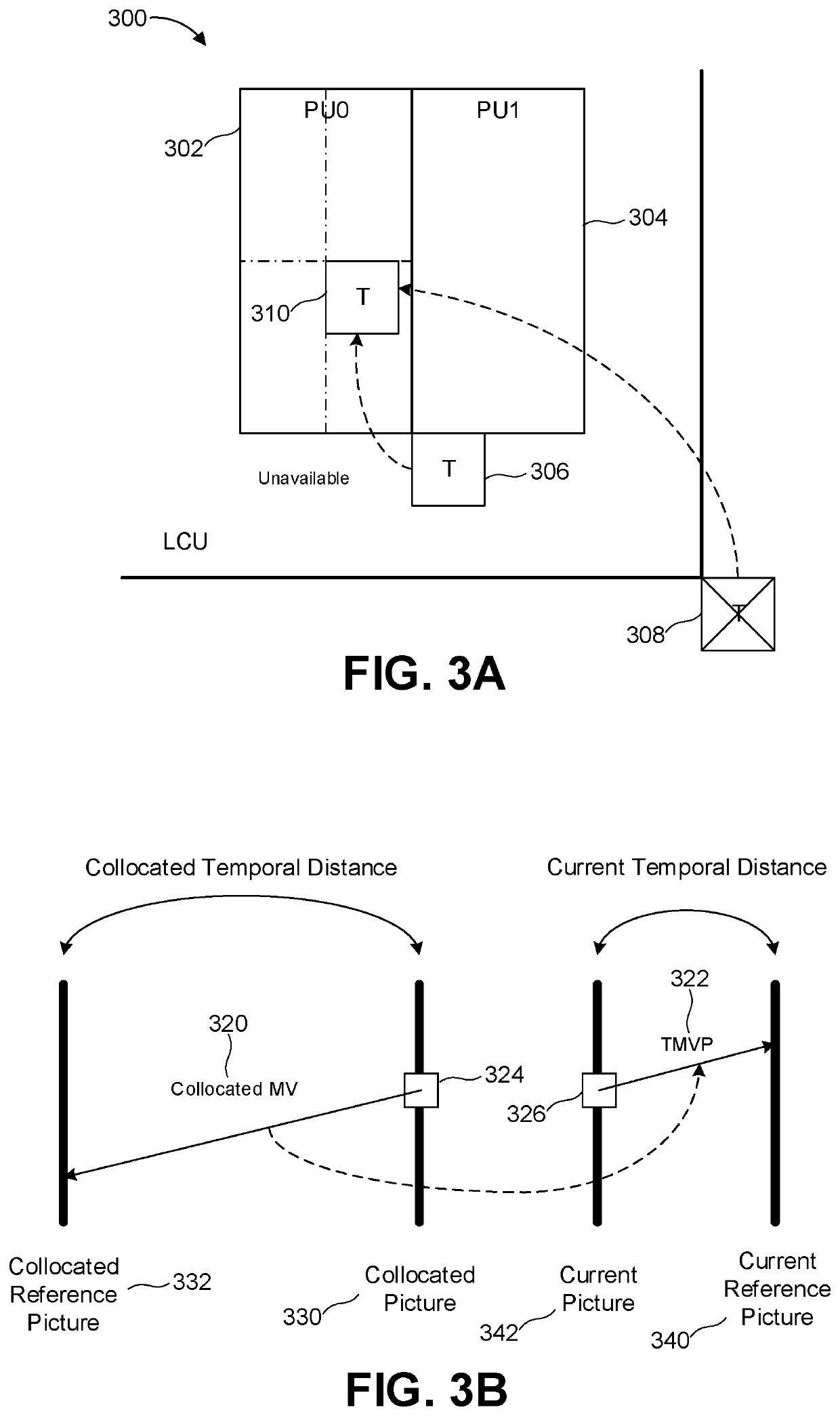
Techniques and systems are provided for deriving one or more sets of affine motion parameters at a decoder. For example, the decoder can obtain video data from an encoded video bitstream. The video data includes at least a current picture and a reference picture. The decoder can determine a set of affine motion parameters for a current block of the current picture. The set of affine motion parameters can be used for performing motion compensation prediction for the current block. The set of affine motion parameters can be determined using a current affine template of the current block and a reference affine template of the reference picture. In some cases, an encoder can determine a set of affine motion parameters for a current block using a current affine template of the current block and a reference affine template of the reference picture, and can generate an encoded video bitstream that includes a syntax item indicating template matching based affine motion derivation mode is to be used by a decoder for the current block. The encoded video bitstream may not include any affine motion parameters for determining the set of affine motion parameters.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Frame rate up-conversion coding mode with affine motion model
ActiveUS10778999B2Promote resultsIncreased complexityTelevision signal transmission by single/parallel channelsDigital video signal modificationAffine motionReference map
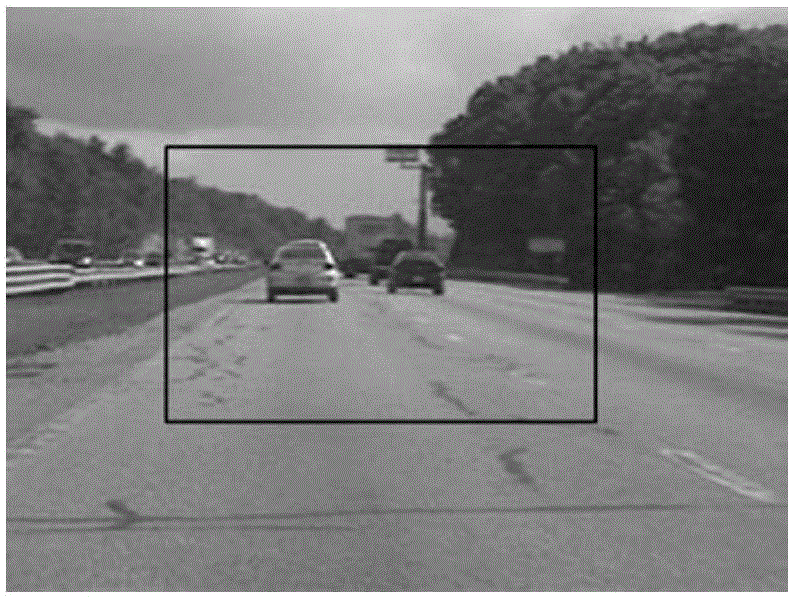
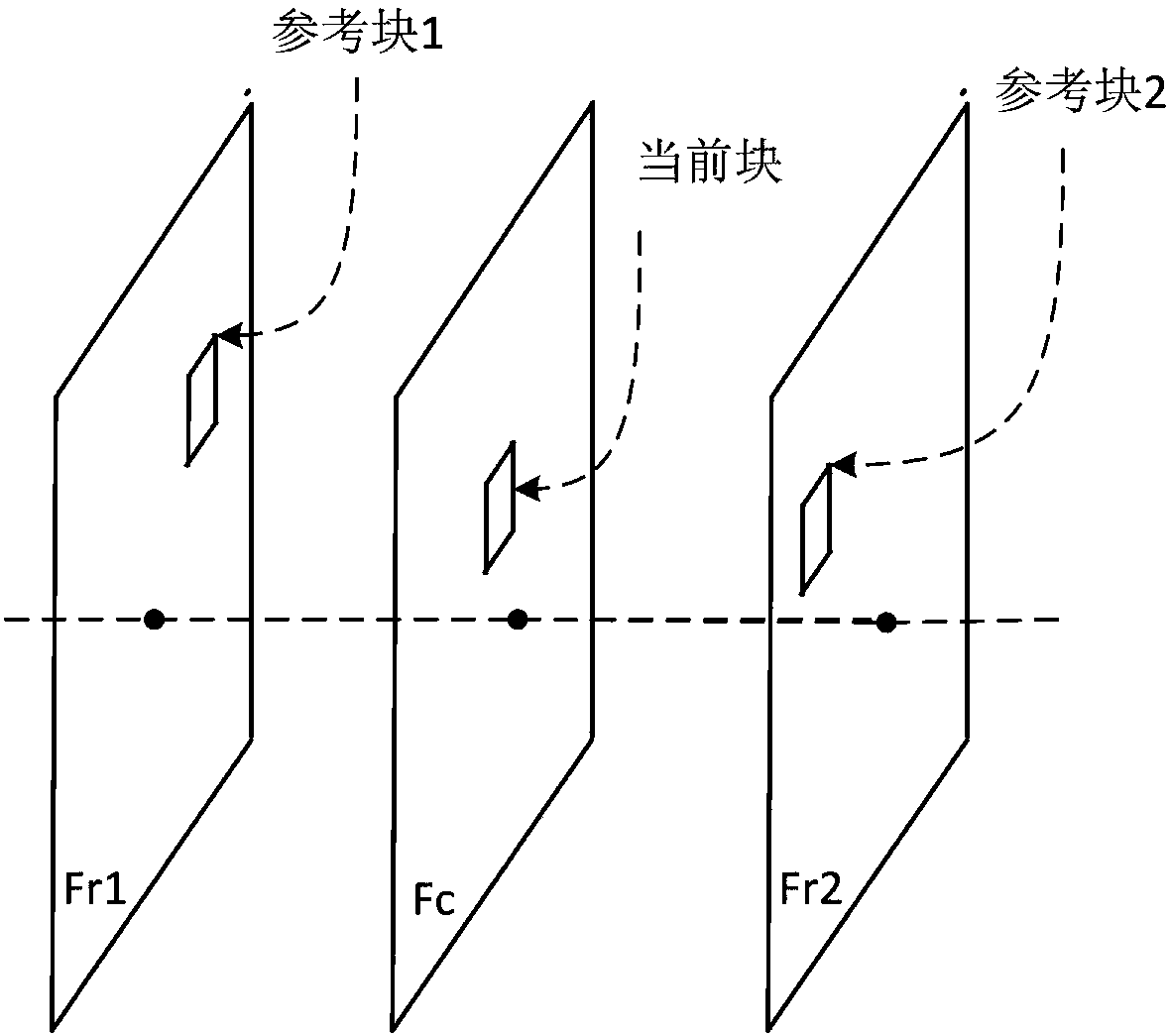
Methods, apparatuses, and computer-readable medium are provided for a frame rate up-conversion coding mode, in which an affine motion model is applied when conducting bilateral matching. The frame rate up-conversion coding mode can include generated additional frames from frames provided in a bitstream. In various implementations, bilateral matching includes, for a current block in a frame that is being generated, identifying a first block in a first reference picture a second block in a second reference picture. Affine (e.g., non-linear) motion information can be determined as between the first block and the second block. The current block can be predicted using the affine motion information.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
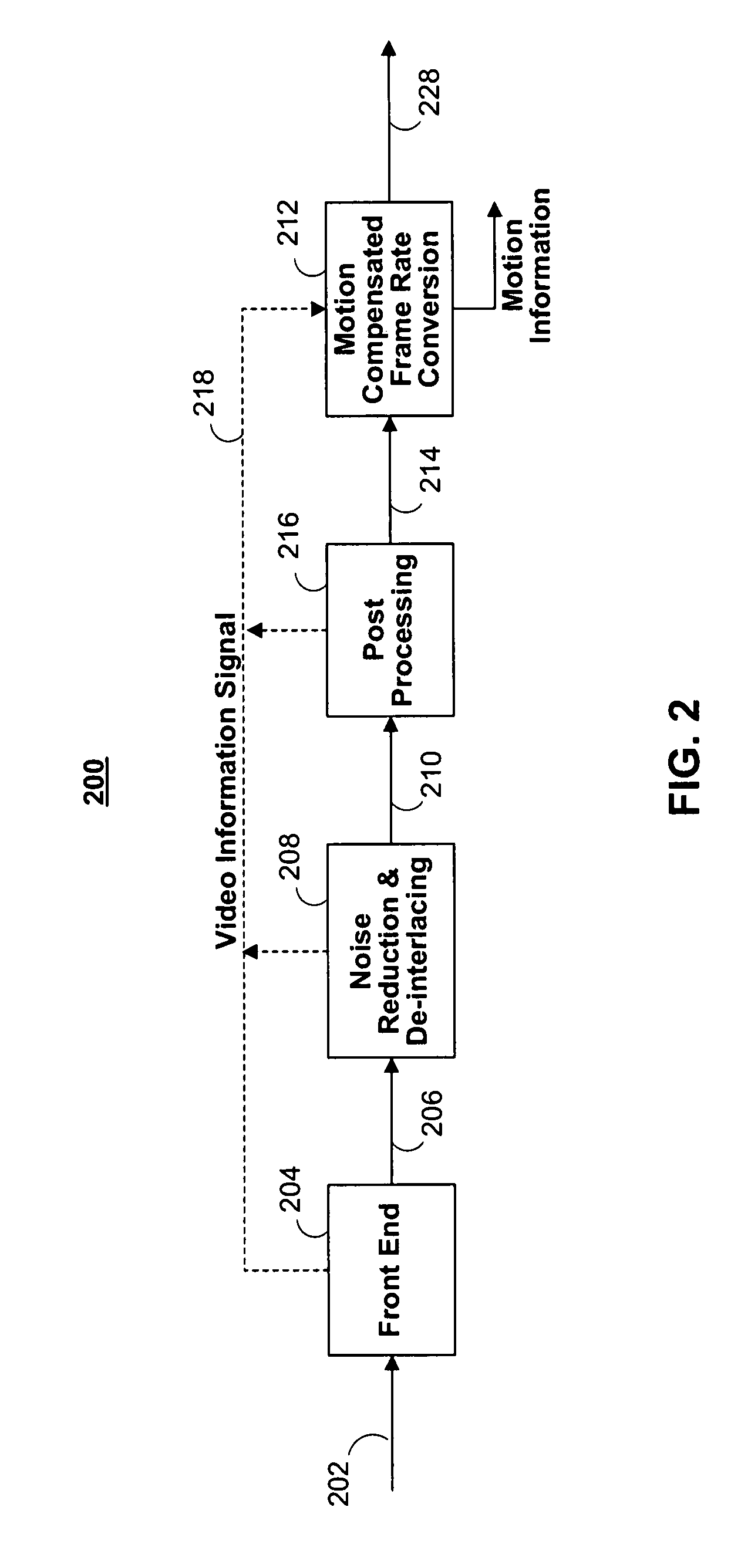
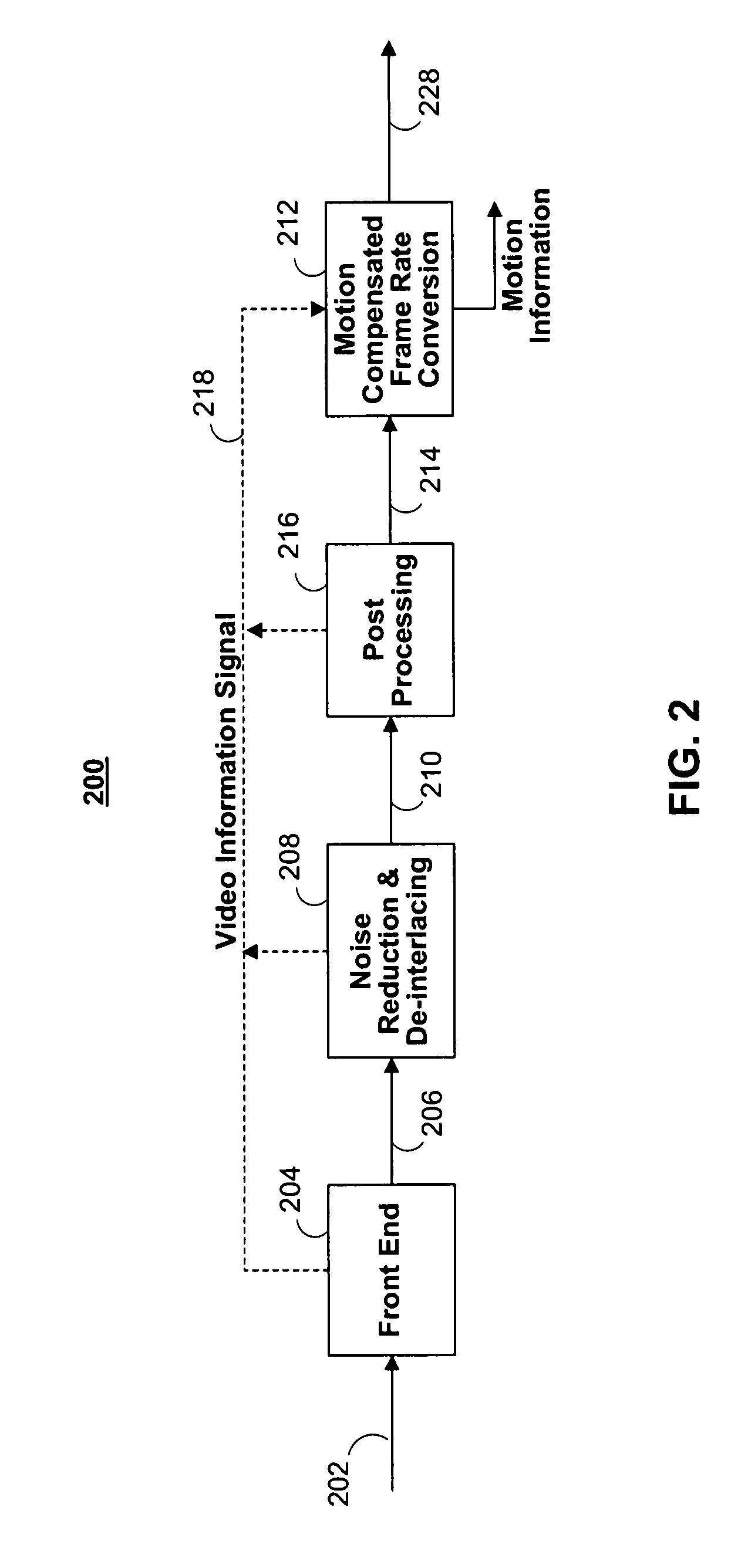
Systems and methods for a motion compensated picture rate converter
ActiveUS20070297513A1Minimize the differenceTelevision system detailsImage analysisAffine motionMotion vector
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for estimating global and local motions between a pair of temporally adjacent frames of an input signal and for applying these motion vectors to produce at least one interpolated, motion-compensated frame between the adjacent frames. In particular, the systems and methods comprise designs for a motion compensated frame rate converter including a global affine motion estimation engine, a global translation motion estimation engine, a segmentation mask generator, an object edge strength map generator and a local motion estimation engine. Combinations of these features are implemented in a motion compensated picture rate converter to accurately and efficiently provide motion estimation and compensation for a sequence of frames.
Owner:MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD +2
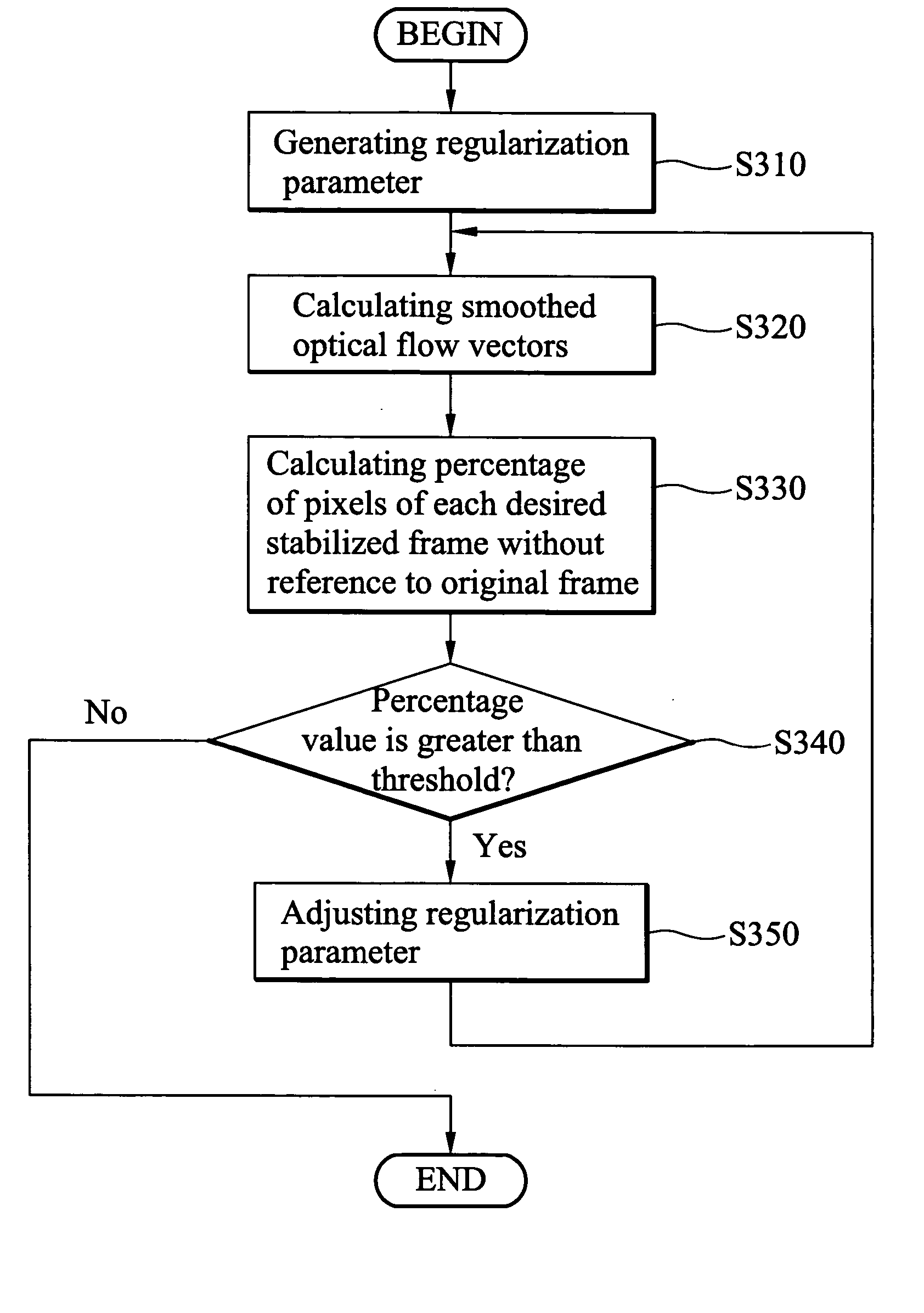
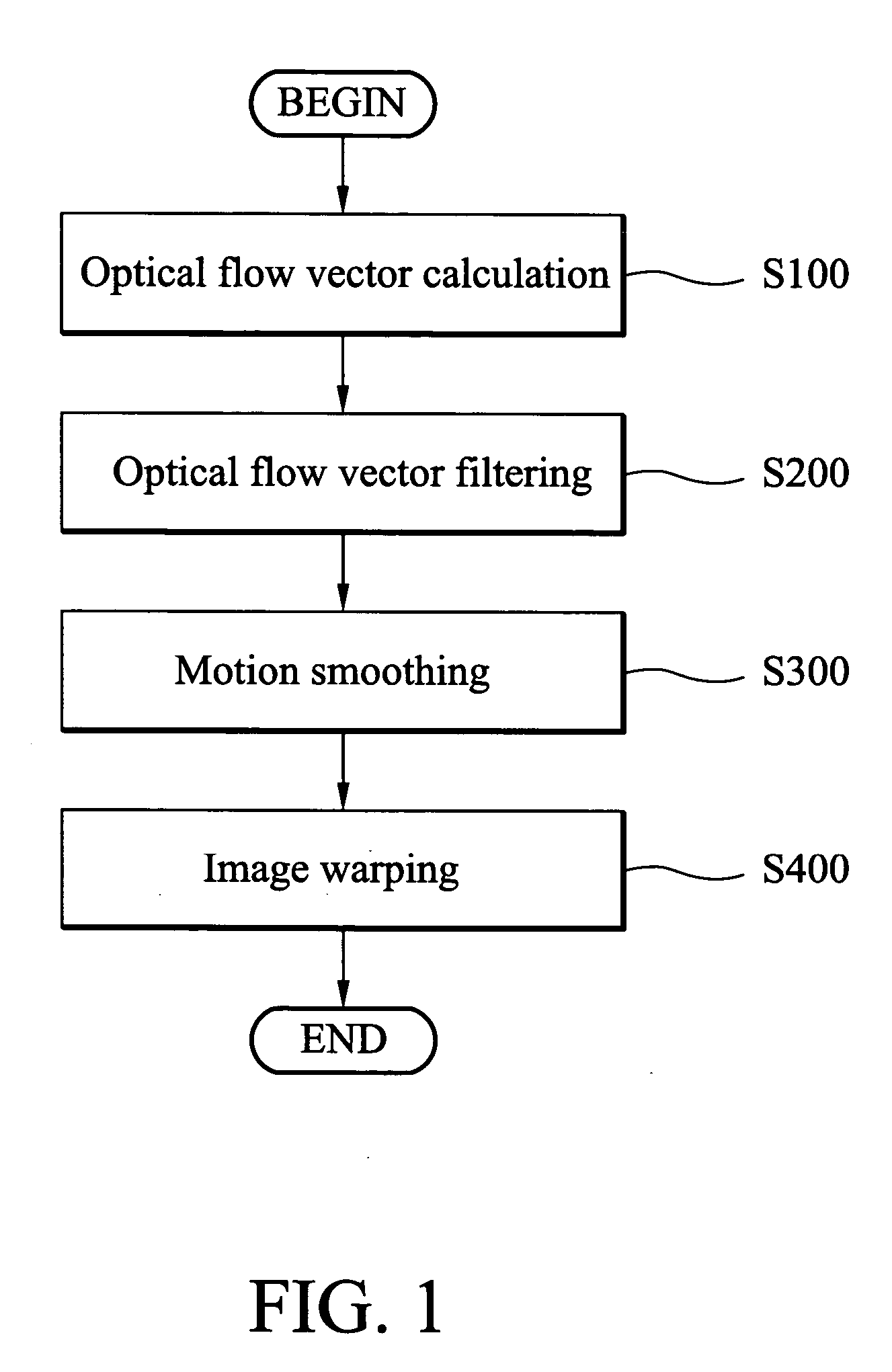
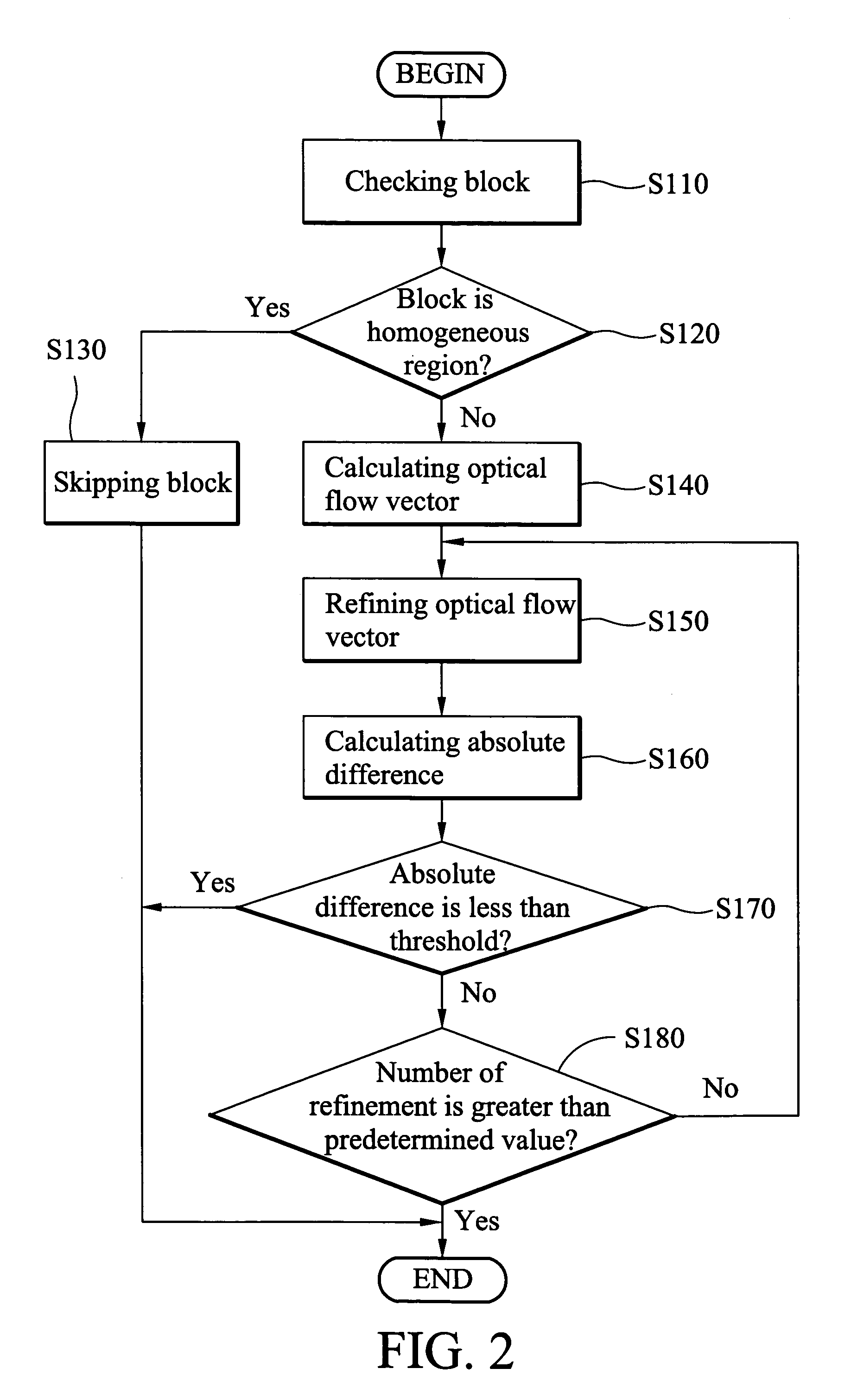
Video stabilization method
A video stabilization method. First, optical flows between successive frames are calculated. The camera motion is then estimated by fitting the computed optical flow field to a simplified affine motion model with a trimmed least square method. Then, the computed camera motions are smoothed to reduce the motion vibrations by using a regularization method. Finally, all frames of the video are transformed based on the original and smoothed motions to obtain a stabilized video.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Video foreground segmentation method
A fully automatic, computationally efficient segmentation method of video employing sequential clustering of sparse image features. Both edge and corner features of a video scene are employed to capture an outline of foreground objects and the feature clustering is built on motion models which work on any type of object and moving / static camera in which two motion layers are assumed due to camera and / or foreground and the depth difference between the foreground and background. Sequential linear regression is applied to the sequences and the instantaneous replacements of image features in order to compute affine motion parameters for foreground and background layers and consider temporal smoothness simultaneously. The Foreground layer is then extracted based upon sparse feature clustering which is time efficient and refined incrementally using Kalman filtering.
Owner:NEC CORP
Frame rate up-conversion coding mode
ActiveUS20180098062A1Promote resultsIncreased complexityDigital video signal modificationAffine motionComputer science
Methods, apparatuses, and computer-readable medium are provided for a frame rate up-conversion coding mode, in which an affine motion model is applied when conducting bilateral matching. The frame rate up-conversion coding mode can include generated additional frames from frames provided in a bitstream. In various implementations, bilateral matching includes, for a current block in a frame that is being generated, identifying a first block in a first reference picture a second block in a second reference picture. Affine (e.g., non-linear) motion information can be determined as between the first block and the second block. The current block can be predicted using the affine motion information.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Video foreground segmentation method
A fully automatic, computationally efficient segmentation method of video employing sequential clustering of sparse image features. Both edge and corner features of a video scene are employed to capture an outline of foreground objects and the feature clustering is built on motion models which work on any type of object and moving / static camera in which two motion layers are assumed due to camera and / or foreground and the depth difference between the foreground and background. Sequential linear regression is applied to the sequences and the instantaneous replacements of image features in order to compute affine motion parameters for foreground and background layers and consider temporal smoothness simultaneously. The Foreground layer is then extracted based upon sparse feature clustering which is time efficient and refined incrementally using Kalman filtering.
Owner:NEC CORP
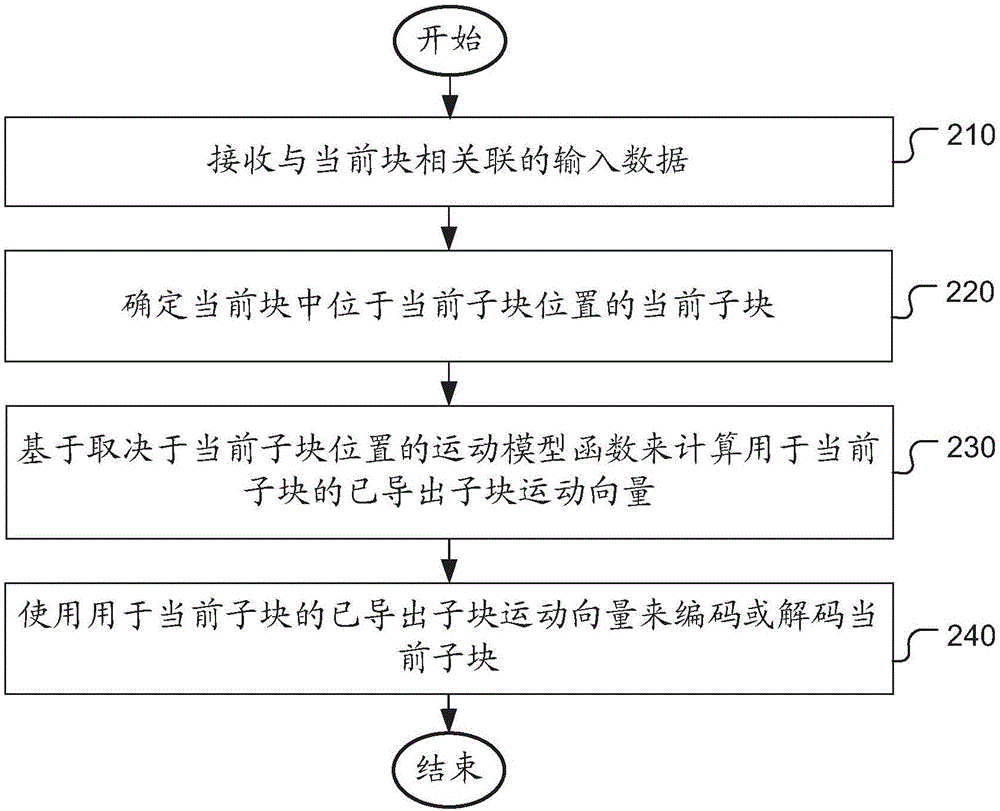
Method of motion vector derivation for video coding
A method and apparatus for deriving a sub-block motion vector for the current sub-block based on a motion-model function depending on the current sub-block location are disclosed. The derived sub-block motion vector is then used for encoding or decoding the sub-block. The motion-model function may correspond to an affine motion-model function or a bilinear motion-model function. In one embodiment, a new Merge mode can be used to apply prediction of a current block by applying prediction on the sub-block basis using the sub-block motion vector derived from the motion-model function. In another embodiment, an additional inter prediction mode can be used to apply prediction of a current block by applying prediction on the sub-block basis using the sub-block motion vector derived from the motion-model function.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
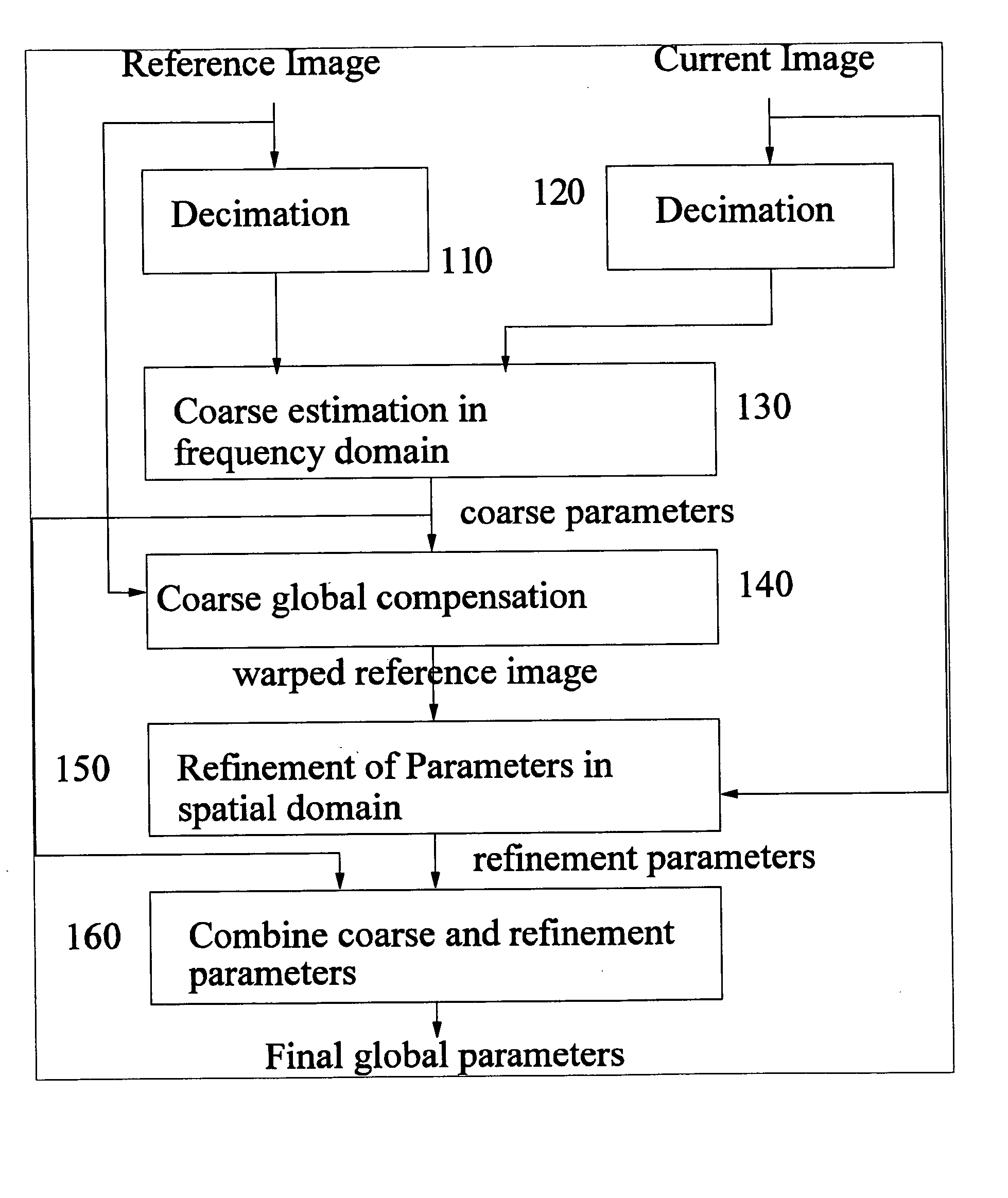
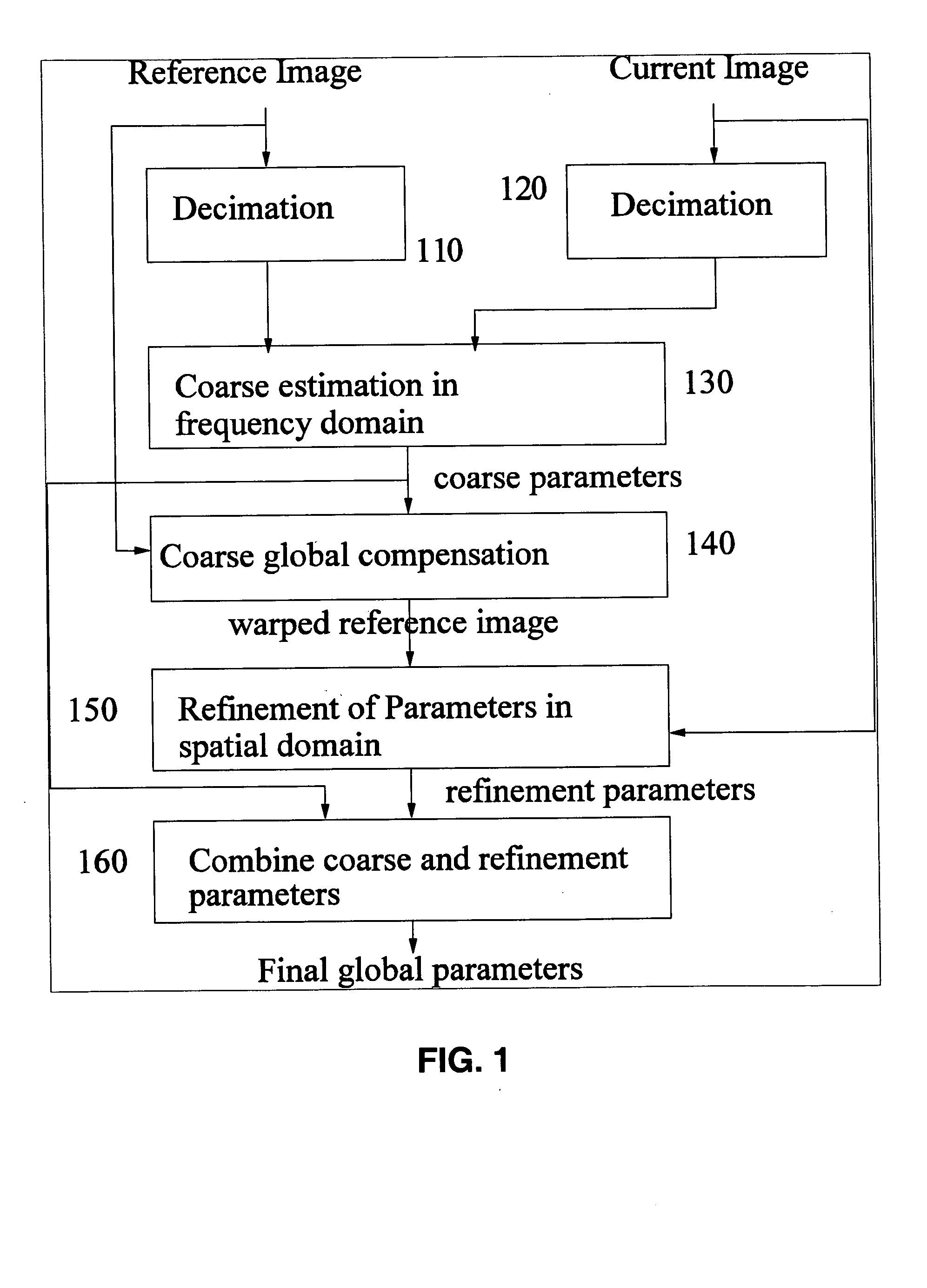
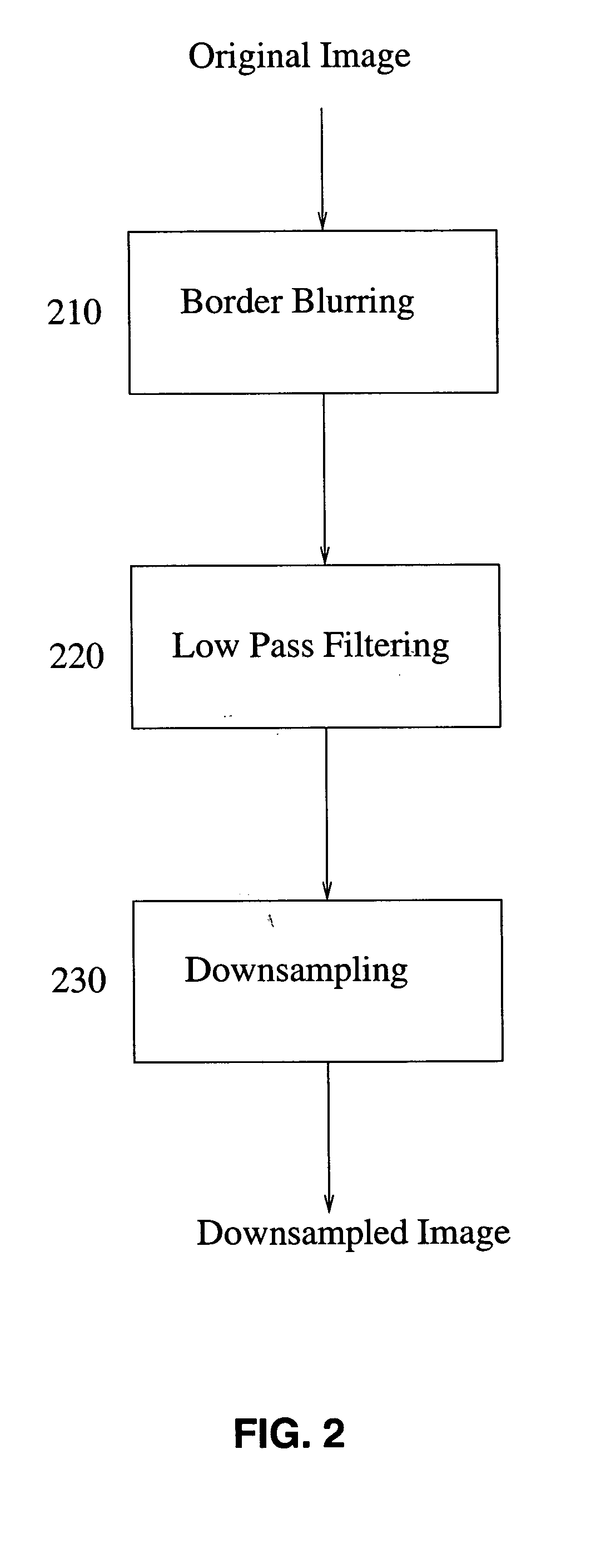
Global motion estimation image coding and processing
ActiveUS20050094852A1Fast and robust global motion estimationTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsAffine motionMotion estimate
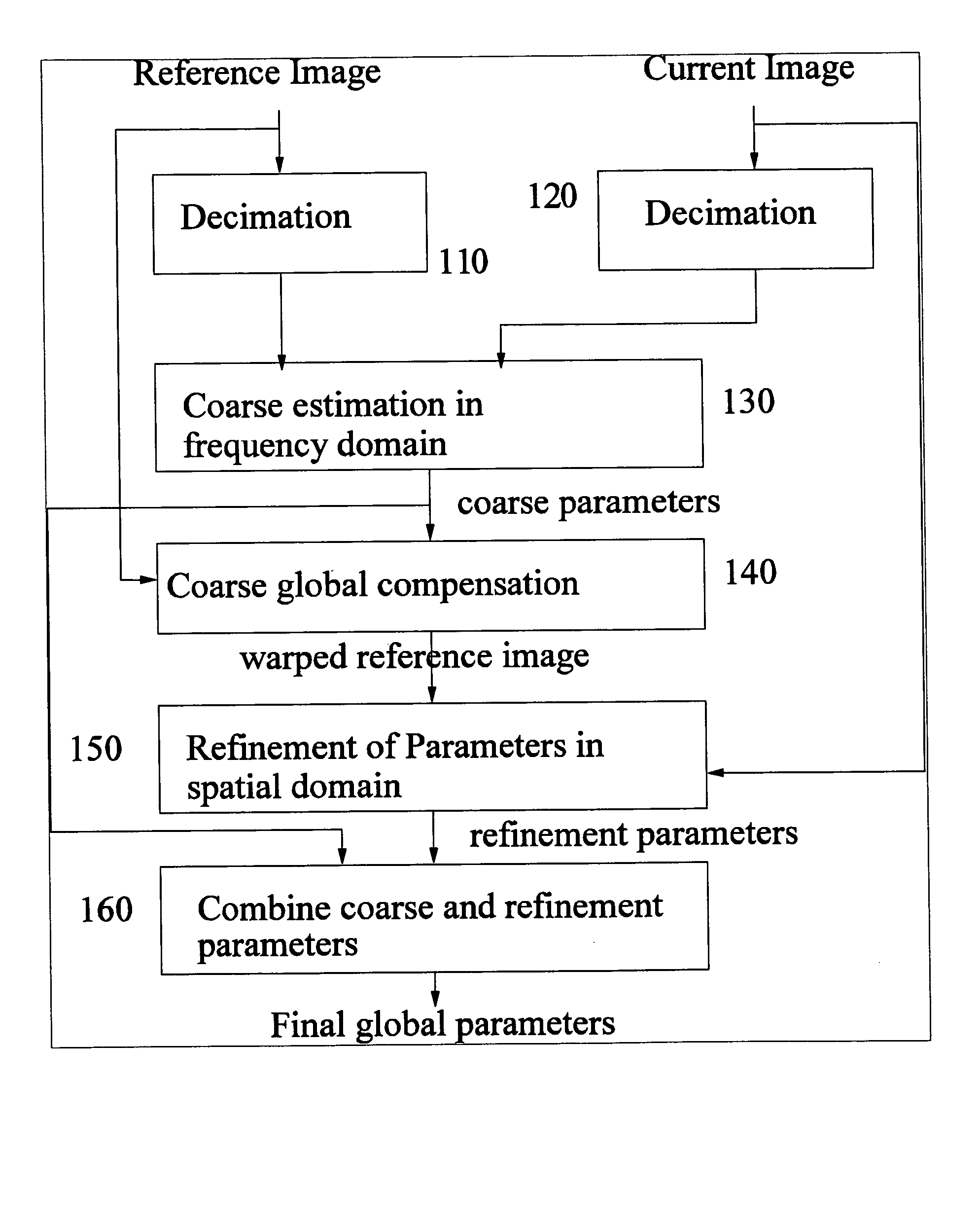
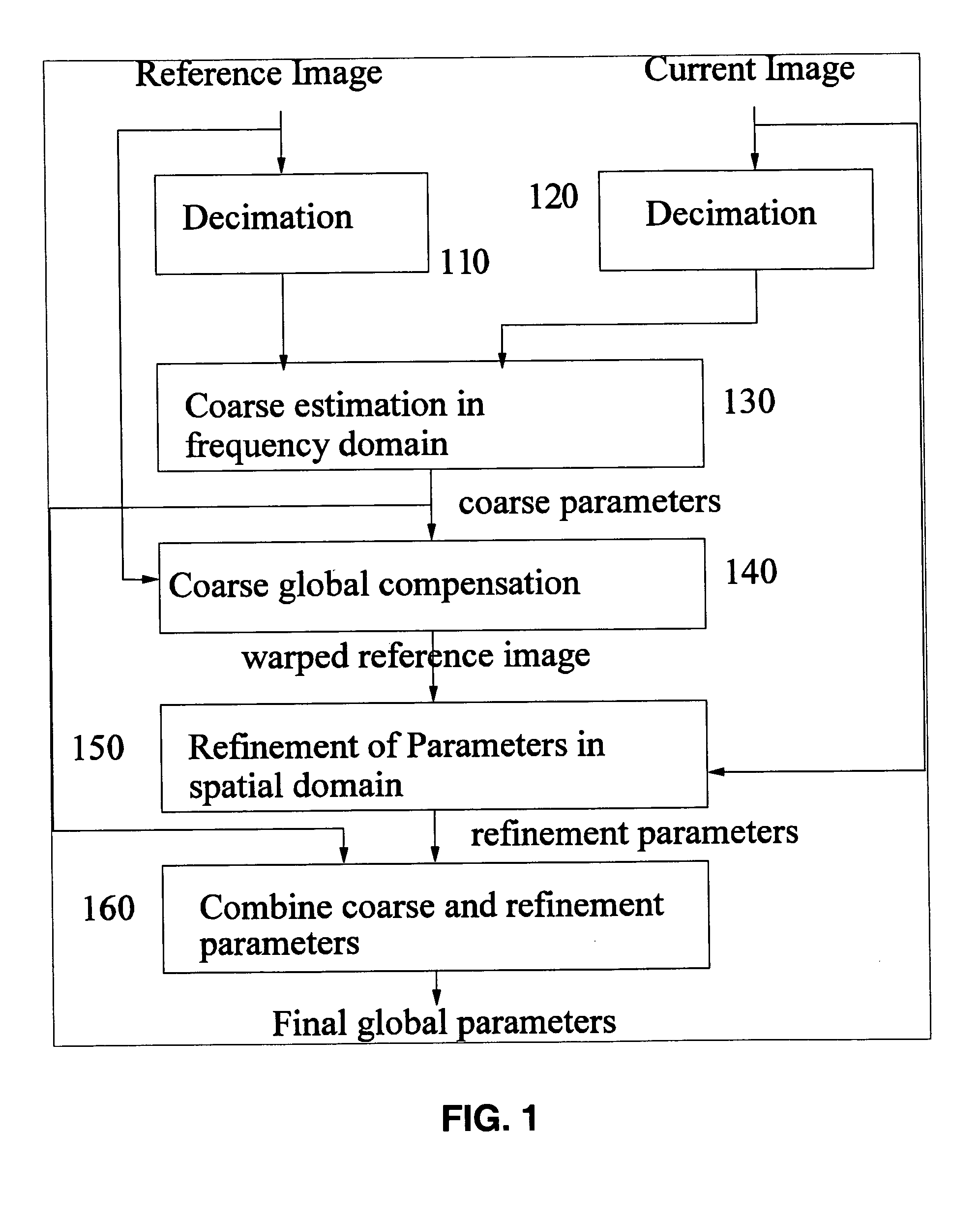
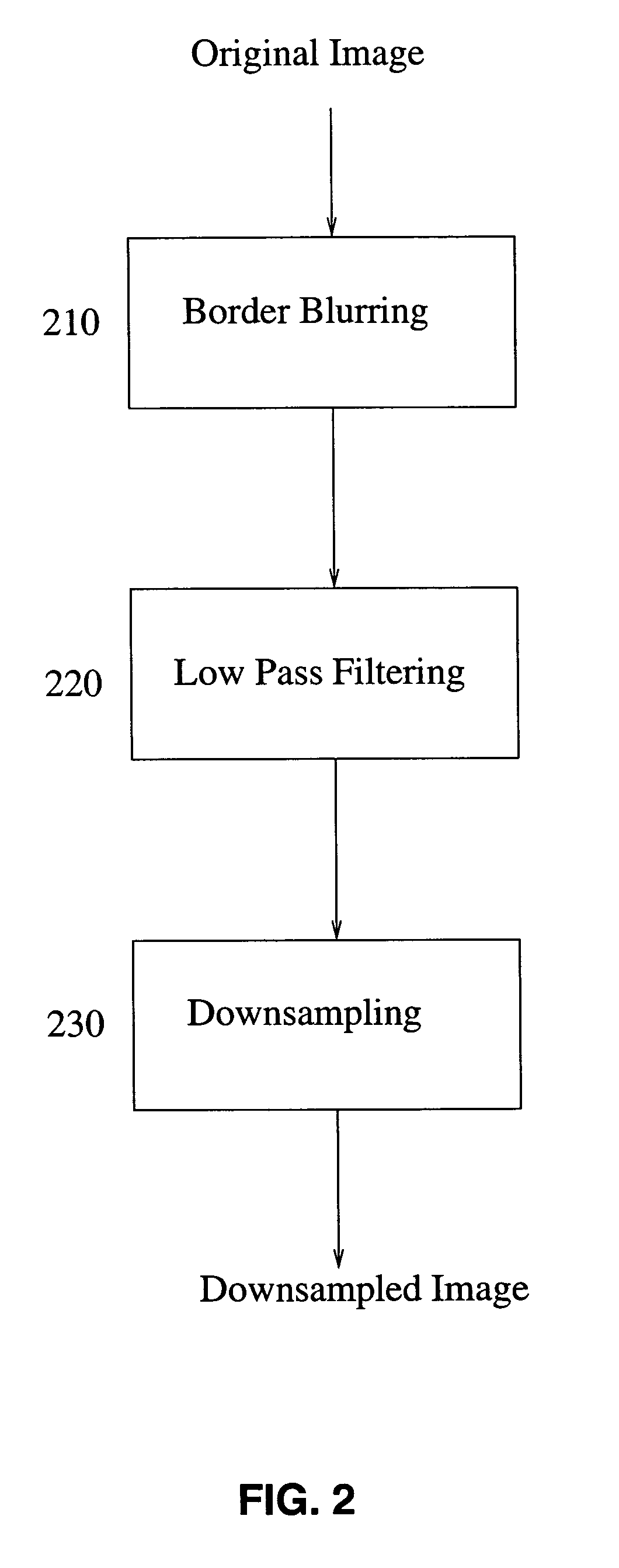
The invention provides methods for global motion estimation, determining a coarse estimation, and refining a coarse estimation. Embodiments of the invention provide a fast and robust global motion estimation algorithm based on two-stage coarse-to-fine refinement strategy, which is capable of measuring large motions. An embodiment of the invention may be applied as a modification of any standard, e.g. MPEG-4 that uses the affine model of motion estimation. Embodiments of the invention may be used in the six parameter affine motion model, and other embodiments of the invention are applicable to the two parameter translation model, the four parameter RST model, and the eight parameter projective model. In a preferred embodiment, a coarse estimation is developed in a translation invariant domain, and then is refined in the spatial domain.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Global motion estimation image coding and processing
ActiveUS7349583B2Fast and robust global motion estimationTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsAffine motionRST model
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Affine motion target tracing algorithm based on fast robust feature matching
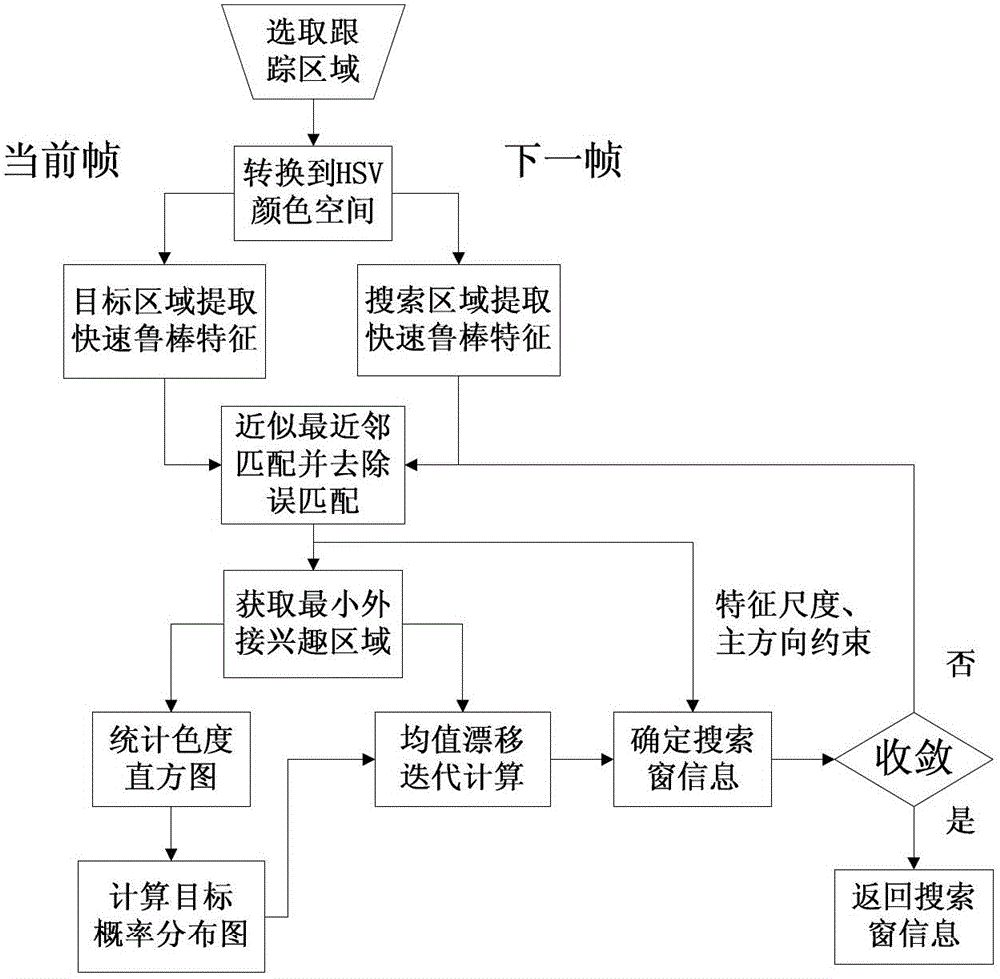
The invention belongs to the field of computer vision and aims at solving the problem that the continuous self-adapting mean shift algorithm is apt to be interfered by color close backgrounds and achieving real-time steady tracing of affine motion targets in complex backgrounds. The technical scheme is that an affine motion target tracing algorithm based on fast robust feature matching includes the following steps: (1) enabling a target area determined in video flowing to be switched from a red, green and blue (RGB) color space to a hue, saturation and value (HSV) color space; (2) detecting fast robust feature points of an H channel, an S channel and a V channel of a current frame target area; (3) obtaining a minimum external interesting area through the position of matched and purified feature points; (4) determining the mass center of a target probability distribution map, namely the search window position, by aid of the mean shift iterative algorithm; (5) performing updating and restraining; and (6) finishing single-step tracing if iteration is converged and entering the step 2 for continuing operating otherwise. The affine motion target tracing algorithm is mainly applied to image processing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method and apparatus of video coding with affine motion compensation
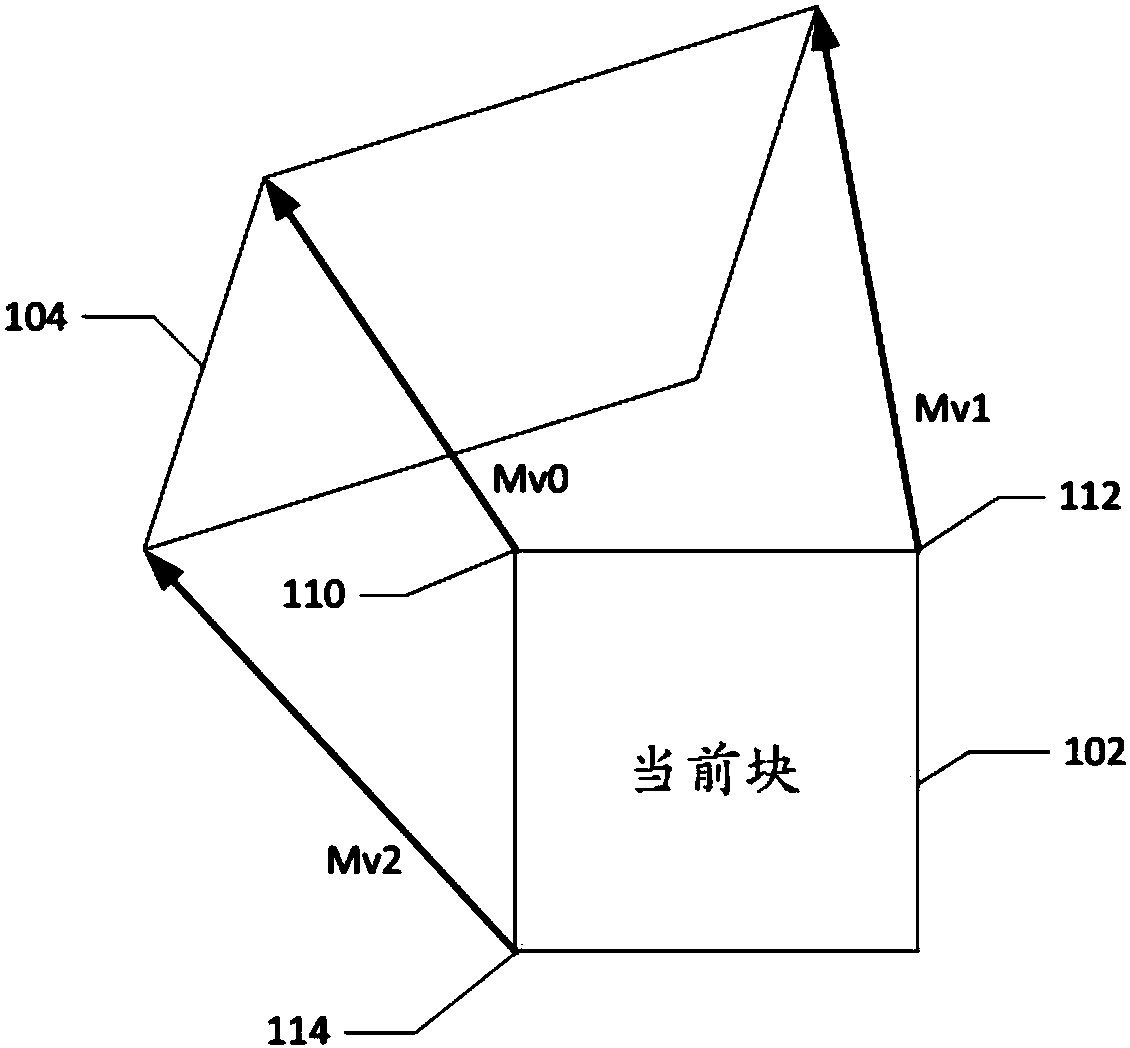
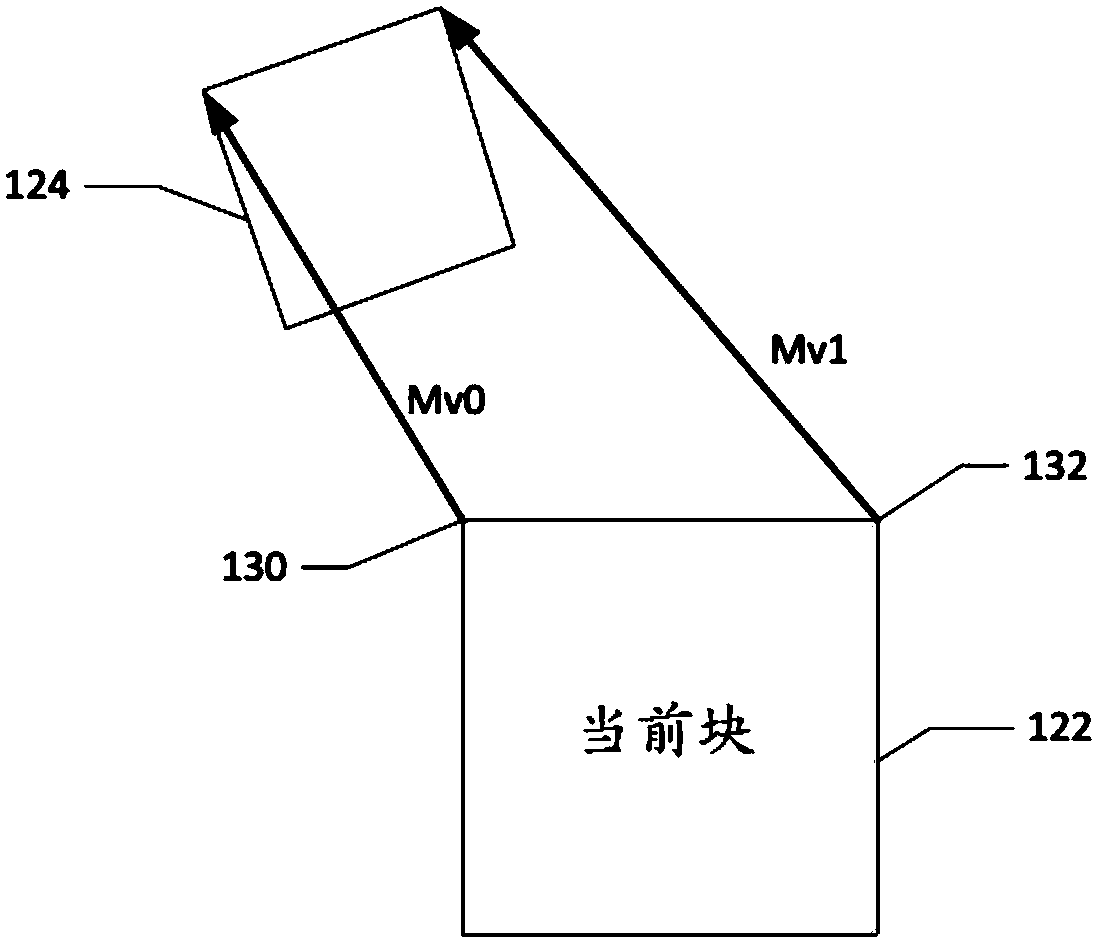
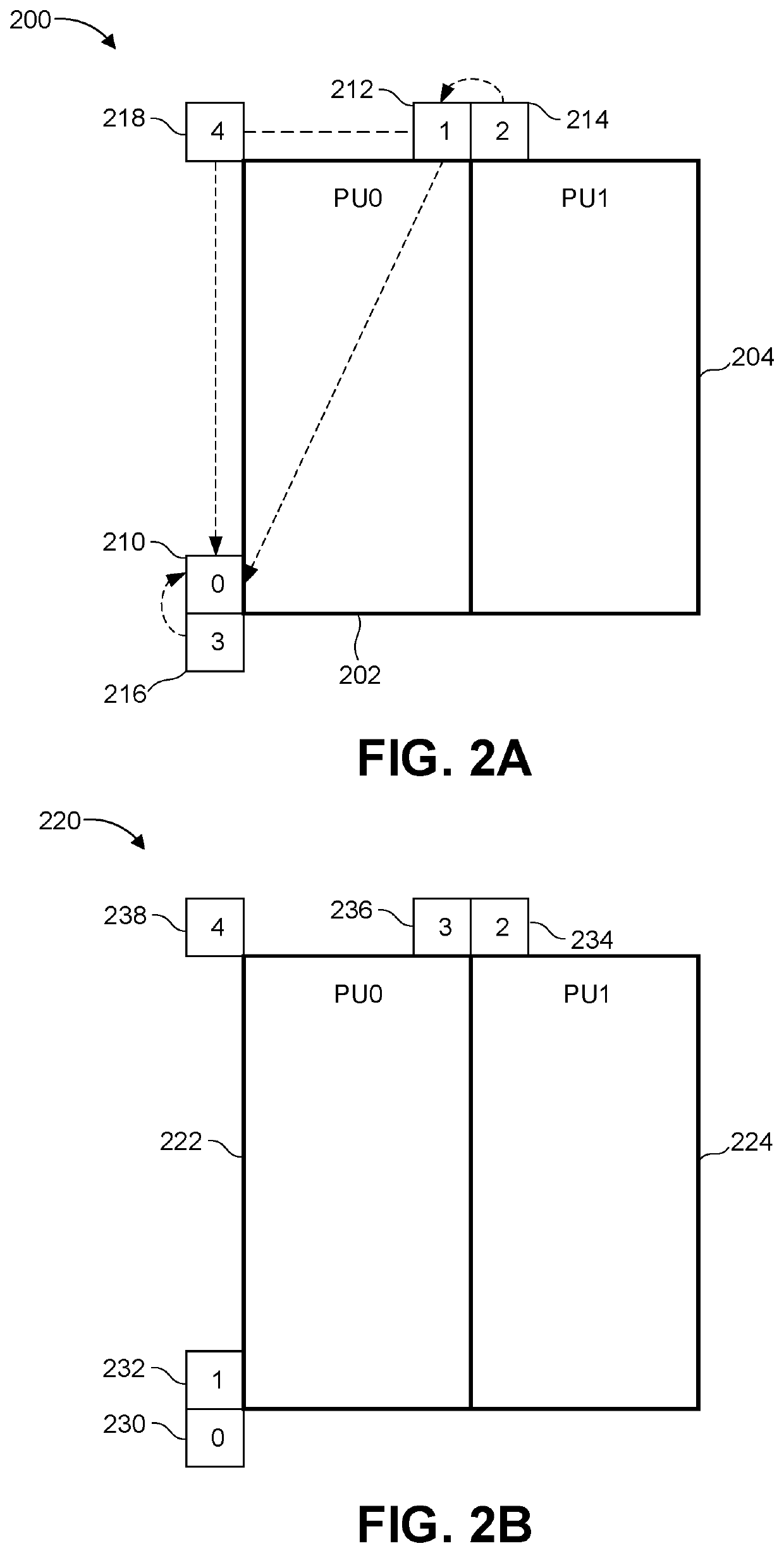
An encoding or decoding method with affine motion compensation includes receiving input data associated with a current block in a current picture, and deriving a first affine candidate for the currentblock including three affine motion vectors for predicting motion vectors at control points of the current block if the current block is coded or to be coded in affine Merge mode. The affine motion vectors are derived from three different neighboring coded blocks of the current block. An affine motion model is derived according to the affine motion vectors if the first affine candidate is selected. Moreover, the method includes encoding or decoding the current block by locating a reference block in a reference picture according to the affine motion model. The current block is restricted to becoded in uni-directional prediction if the current block is coded or to be coded in affine Inter mode.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Video signal processing method and device
ActiveCN108702509AImprove coding efficiencyEfficient determinationDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionAffine motion
The present invention relates to a video signal processing method and device for increasing prediction accuracy and improving encoding efficiency by using a simplified affine motion model. The video signal processing method according to the present invention induces an affine motion vector by using a plurality of motion vectors related to a current block and performs motion compensation on the basis of the affine motion vector and a location of a current sample.
Owner:KT CORP
Video signal processing method and device
InactiveUS20190068989A1Encoding efficiency can be improvedImprove accuracyDigital video signal modificationAffine motionCurrent sample
A method of processing video signal according to a present invention comprises deriving an affine motion vector using a plurality of motion vectors related to a current block, and performing a motion compensation based on the derived affine motion vector and a position of a current sample.
Owner:KT CORP
Image prediction method and related device
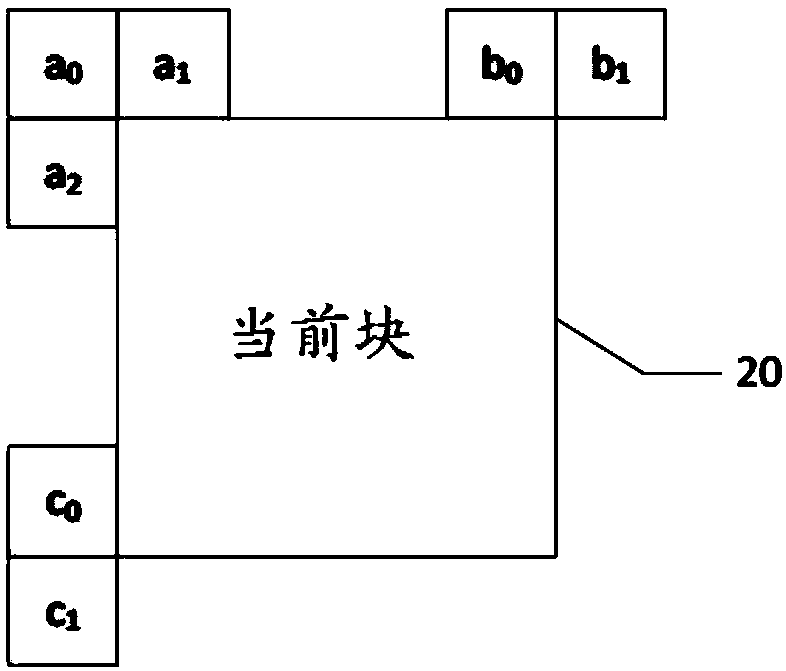
The embodiment of the invention provides an image prediction method and a related device. The image prediction method comprises steps: a reference block of a current block is determined, wherein the reference block is adjacent to the current block in space, and the reference block is predicted by using an affine motion model; position information and motion information of at least two feature points in the reference block are acquired, wherein the at least two feature points are located at a subblock where at least two control points of the reference block are located, and the at least two control points are control points used by the affine motion model used for predicting the reference block, and the motion information of the subblock where the feature points are located is obtained based on motion information of the corresponding feature points; motion information of each subblock in the current block is computed according to the position information and the motion information of the at least two feature points in the reference block; and motion compensation prediction is carried out on each subblock of the current block according to the motion information of each subblock in the current block, so as to obtain a prediction block of the current block. The embodiments of the invention help to improve the prediction accuracy of the current block.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for a motion compensated picture rate converter
ActiveUS8340185B2Minimize the differenceTelevision system detailsImage analysisAffine motionMotion vector
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for estimating global and local motions between a pair of temporally adjacent frames of an input signal and for applying these motion vectors to produce at least one interpolated, motion-compensated frame between the adjacent frames. In particular, the systems and methods comprise designs for a motion compensated frame rate converter including a global affine motion estimation engine, a global translation motion estimation engine, a segmentation mask generator, an object edge strength map generator and a local motion estimation engine. Combinations of these features are implemented in a motion compensated picture rate converter to accurately and efficiently provide motion estimation and compensation for a sequence of frames.
Owner:MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD +2
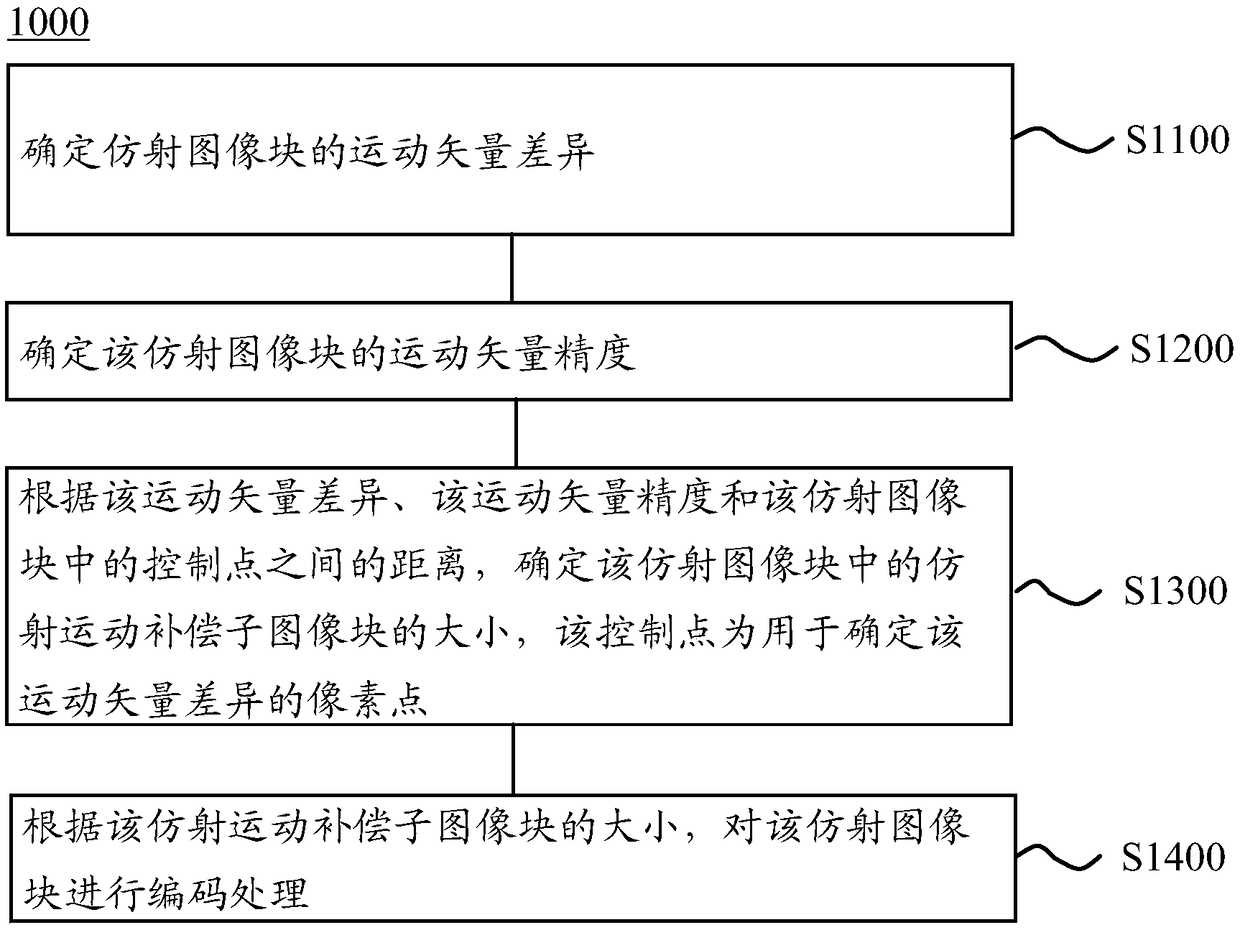
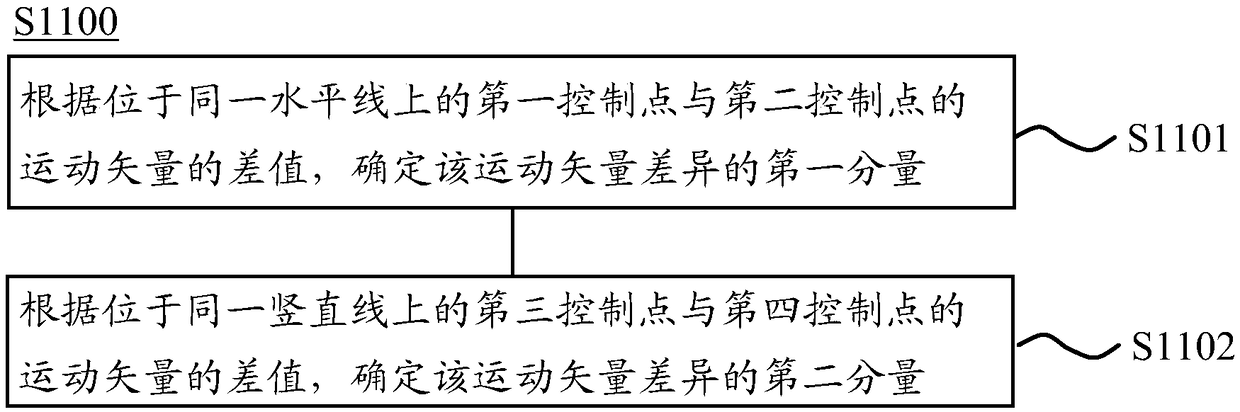
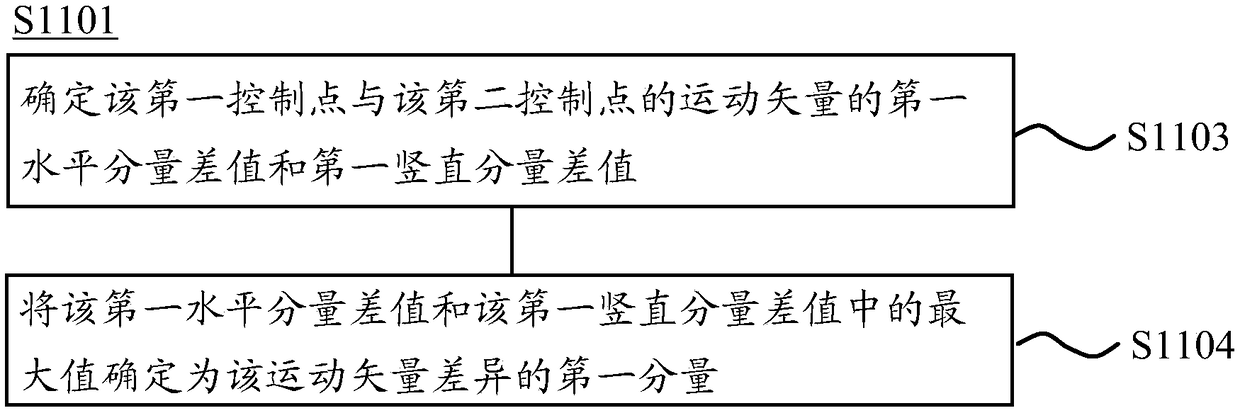
Video image encoding and decoding method, encoding device, and decoding device
ActiveCN109005407AReduce complexityImprove codec performanceImage analysisImage codingDecoding methodsAffine motion
The invention provides a video image encoding and decoding method, an encoding device and a decoding device. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a motion vector difference of affine image blocks; determining a motion vector accuracy of the affine image block; determining a size of an affine motion compensation sub-image block in the affine image block according to the motion vector difference, the motion vector accuracy and a distance between control points in the affine image block, the control points being pixel points for determining the motion vector difference; according to the size of the affine motion compensation sub-image block, encoding the affine image block. Thus, the coding complexity can be reduced and the coding performance can be improved by selecting asub-image block with an appropriate size.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Blind reconstruction method for video sequence
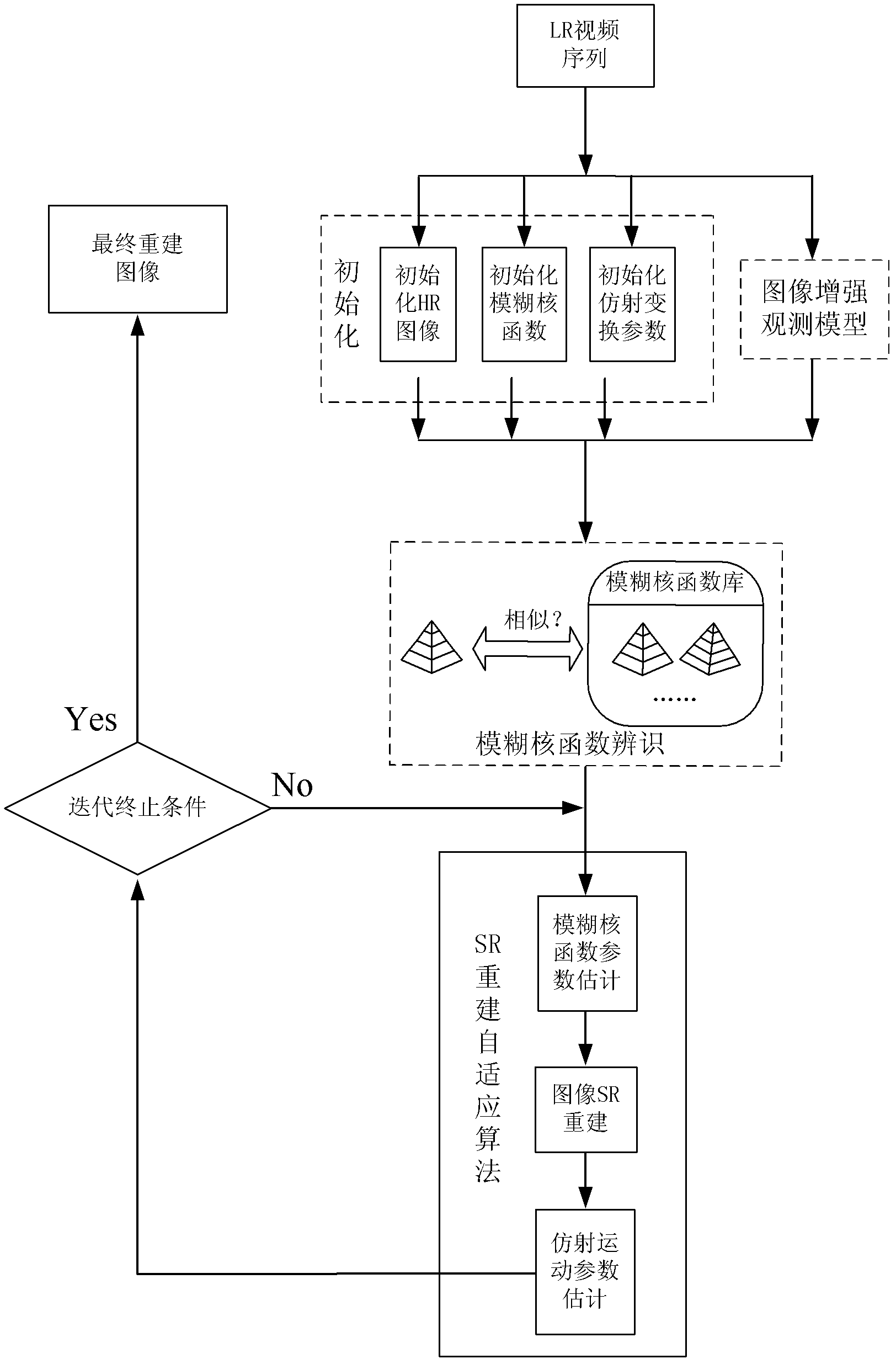
The invention discloses a blind reconstruction method for a video sequence. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) initializing an algorithm, including initializing an affine motion initial parameter, a fuzzy kernel function and a high-resolution video sequence image; (2) establishing an image enhancement observation model; (3) performing the following iterative algorithms: 1, identifying the fuzzy kernel function; 2, performing super-resolution reconstruction on the video sequence image to obtain a high-resolution image; 3, estimating an affine motion parameter; and 4, judging whether results obtained in the steps 2 and 3 satisfy an iteration ending condition, and otherwise, returning to the step 1 until the condition is satisfied; and (4) obtaining a final video sequence reconstruction image. According to the method, the quality of a reconstructed video can be enhanced effectively, blind reconstruction can be performed on any group of low-resolution video sequences according to the characteristics of the video sequences, and the image display effect is enhanced; and the method plays an important theoretical and practical role in processing random remote sensing images, processing medical videos, developing military safety monitoring systems and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method, device and equipment for encoding and decoding a video image
ActiveCN109391814AReduce complexityImprove codec performanceDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsAffine motion
The present invention provides a video image decoding method, and the method comprises the steps: determining the size of an affine movement compensation sub-image block in an affine image block according to the motion vector differences, motion vector accuracy, the distance between control points in the affine image block, and the size of the affine image block, wherein the size includes a lengthin the horizontal direction and a length in the vertical direction so that the length of the affine image block in the horizontal / vertical direction is integer multiples of the length of an affine motion compensation sub-image block; finally, decoding the affine image block according to the size of the affine motion compensation sub-image block. The method can adaptively adjust the size of the affine motion compensation sub-image block to the optimal size according to the attribute of the affine image block itself, thereby guaranteeing the quality of the decoding, reducing the decoding complexity and effectively improving the decoding efficiency.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Affine motion information derivation
ActiveUS10701390B2Error minimizationDigital video signal modificationVideo bitstreamTemplate matching
Techniques and systems are provided for deriving one or more sets of affine motion parameters at a decoder. For example, the decoder can obtain video data from an encoded video bitstream. The video data includes at least a current picture and a reference picture. The decoder can determine a set of affine motion parameters for a current block of the current picture. The set of affine motion parameters can be used for performing motion compensation prediction for the current block. The set of affine motion parameters can be determined using a current affine template of the current block and a reference affine template of the reference picture. In some cases, an encoder can determine a set of affine motion parameters for a current block using a current affine template of the current block and a reference affine template of the reference picture, and can generate an encoded video bitstream that includes a syntax item indicating template matching based affine motion derivation mode is to be used by a decoder for the current block. The encoded video bitstream may not include any affine motion parameters for determining the set of affine motion parameters.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Encoding method and device therefor and decoding method and device therefor
A video decoding method includes: obtaining two or more base motion vectors from an adjacent block of a current block; obtaining correction information for correcting the two or more base motion vectors; determining two or more affine motion vectors by correcting the two or more base motion vectors according to the correction information; obtaining a plurality of affine parameters of the current block according to the two or more affine motion vectors; and predicting the current block according to the plurality of affine parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
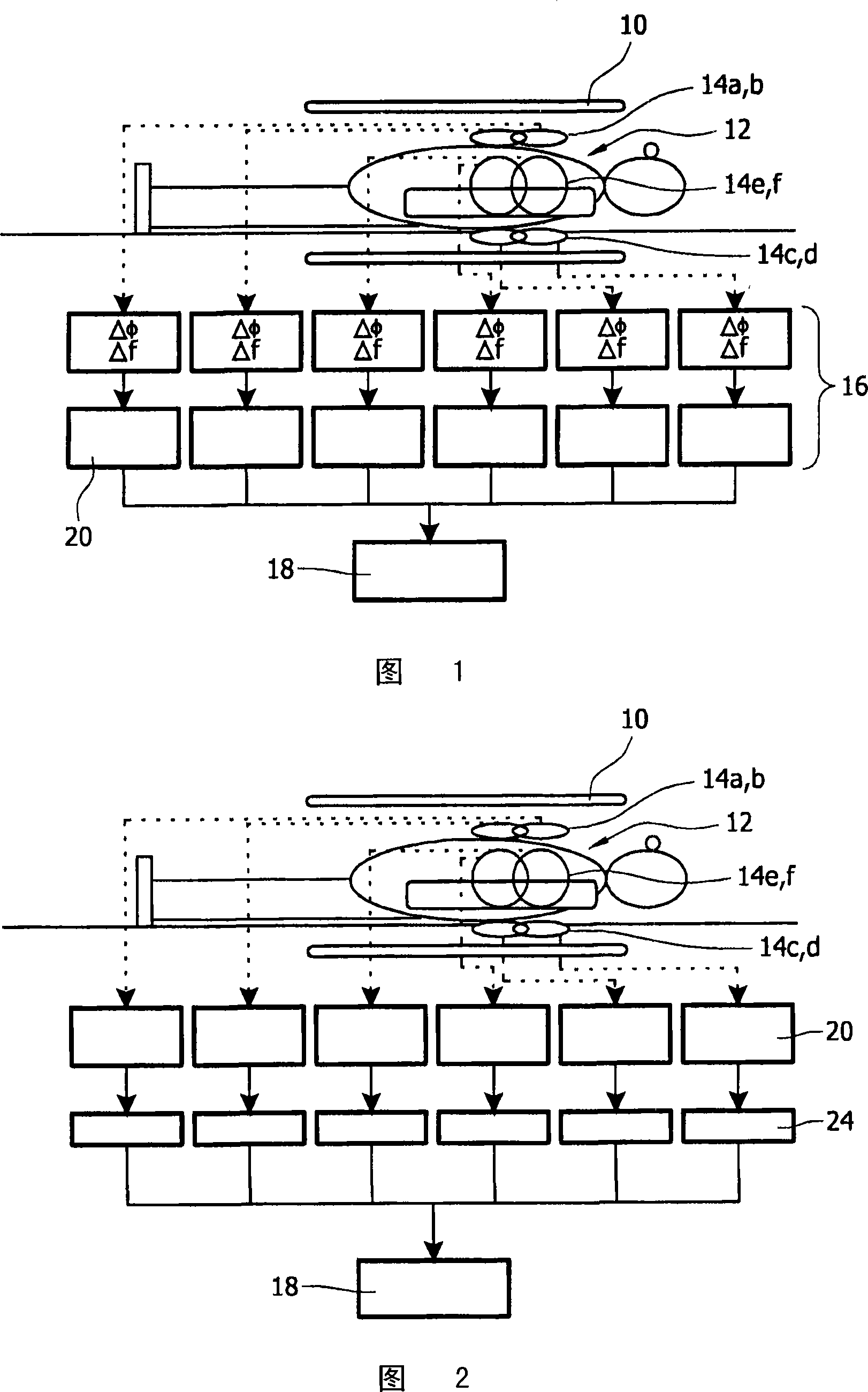
Independent motion correction in respective signal channels of a magnetic resonance imaging system
InactiveCN101171527ALarge amount of processingPrecision Motion CorrectionMagnetic measurementsIndependent motionAffine motion
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, wherein a plurality of independent signal acquisition channels, defined by spatially separated coil elements (14a, 14b, 14c, 14d, 14e, 14f) is provided. The signals received by each of the channels are individually motion corrected before image reconstruction, so that non-uniform, non-affine motion across the imaging volume can be corrected locally. Motion correction may be prospective or retrospective.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
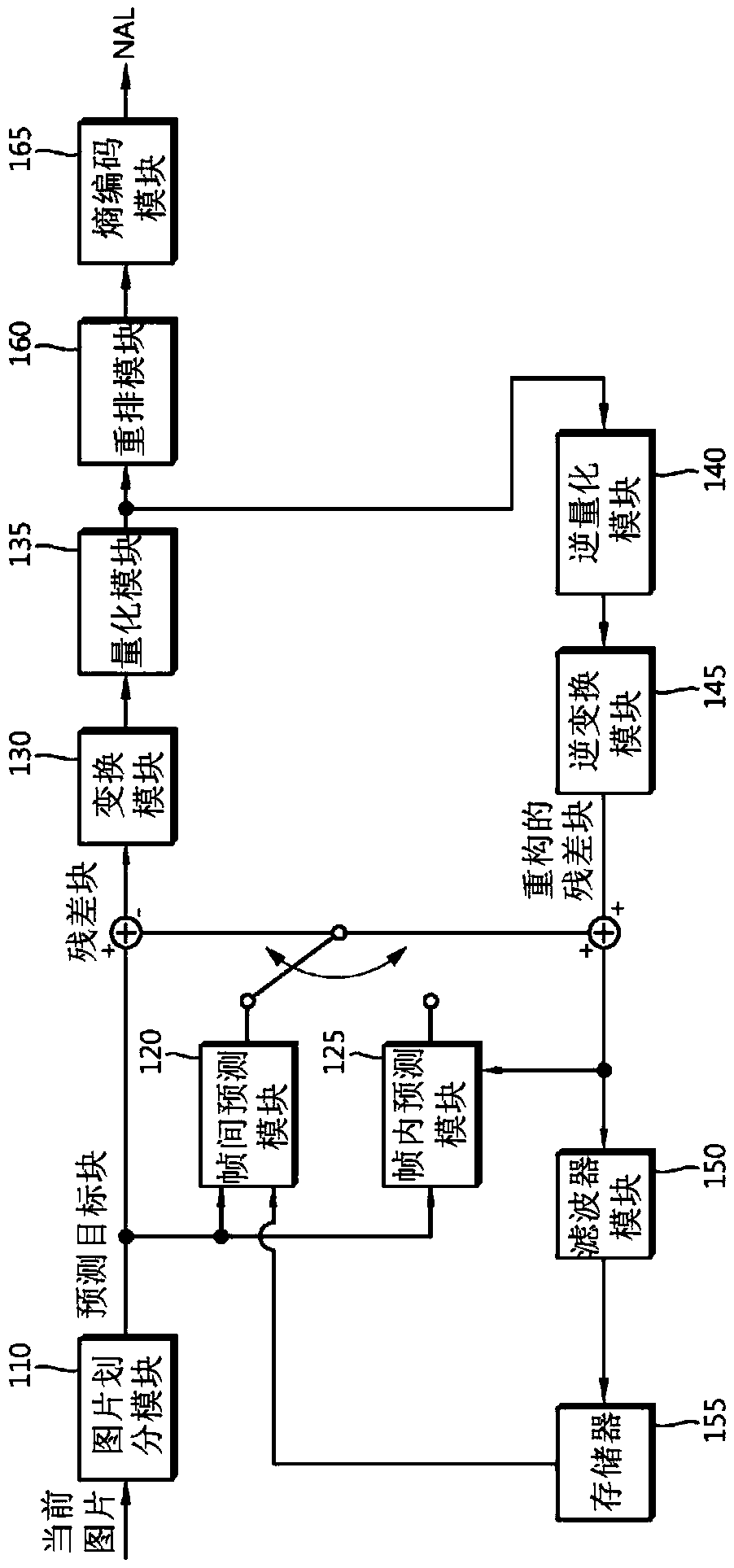
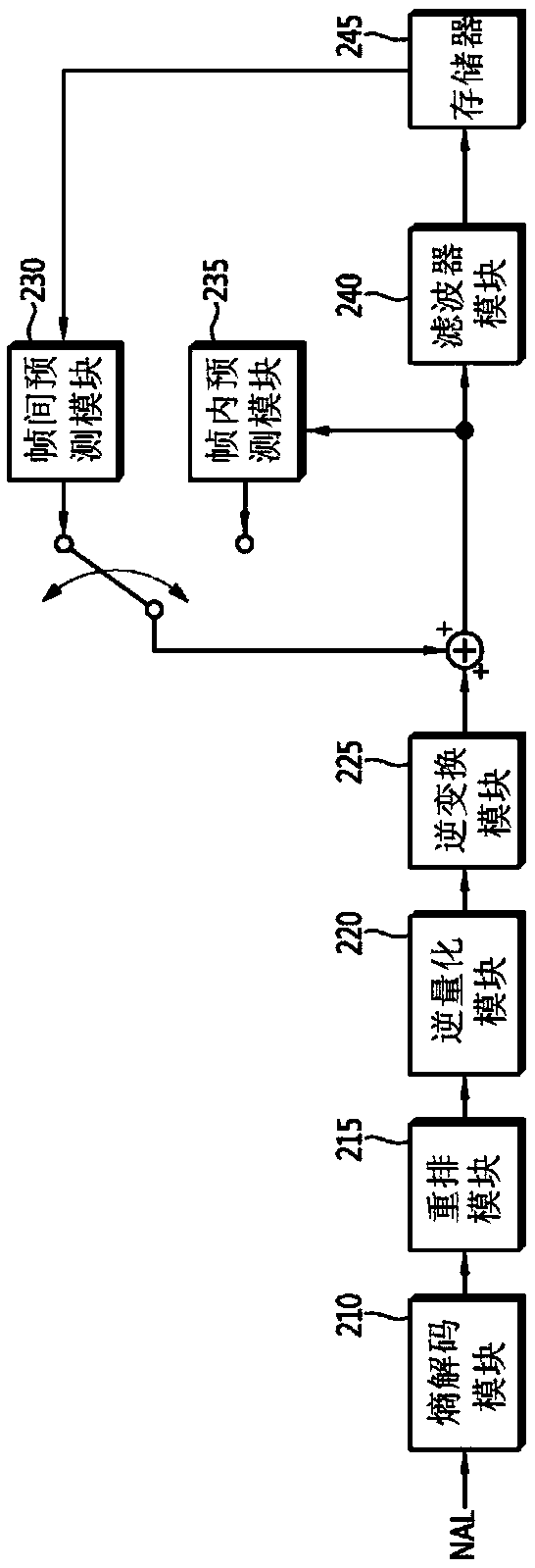
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding video using inter-prediction
Image decoding of decoding a sequence of coded pictures on a block-by-block basis is provided. The image decoding incudes decoding a first high-level syntax element from a bitstream to determine, at a sequence level, whether affine motion prediction is allowed. A second high-level syntax element is extracted for each of at least one coding tool from the bitstream depending on the first high-level syntax element. At a picture level, the method determines whether each of the at least one coding tool is allowed. The coding tool includes sample-by-sample adjustment of affine motion prediction samples.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +2
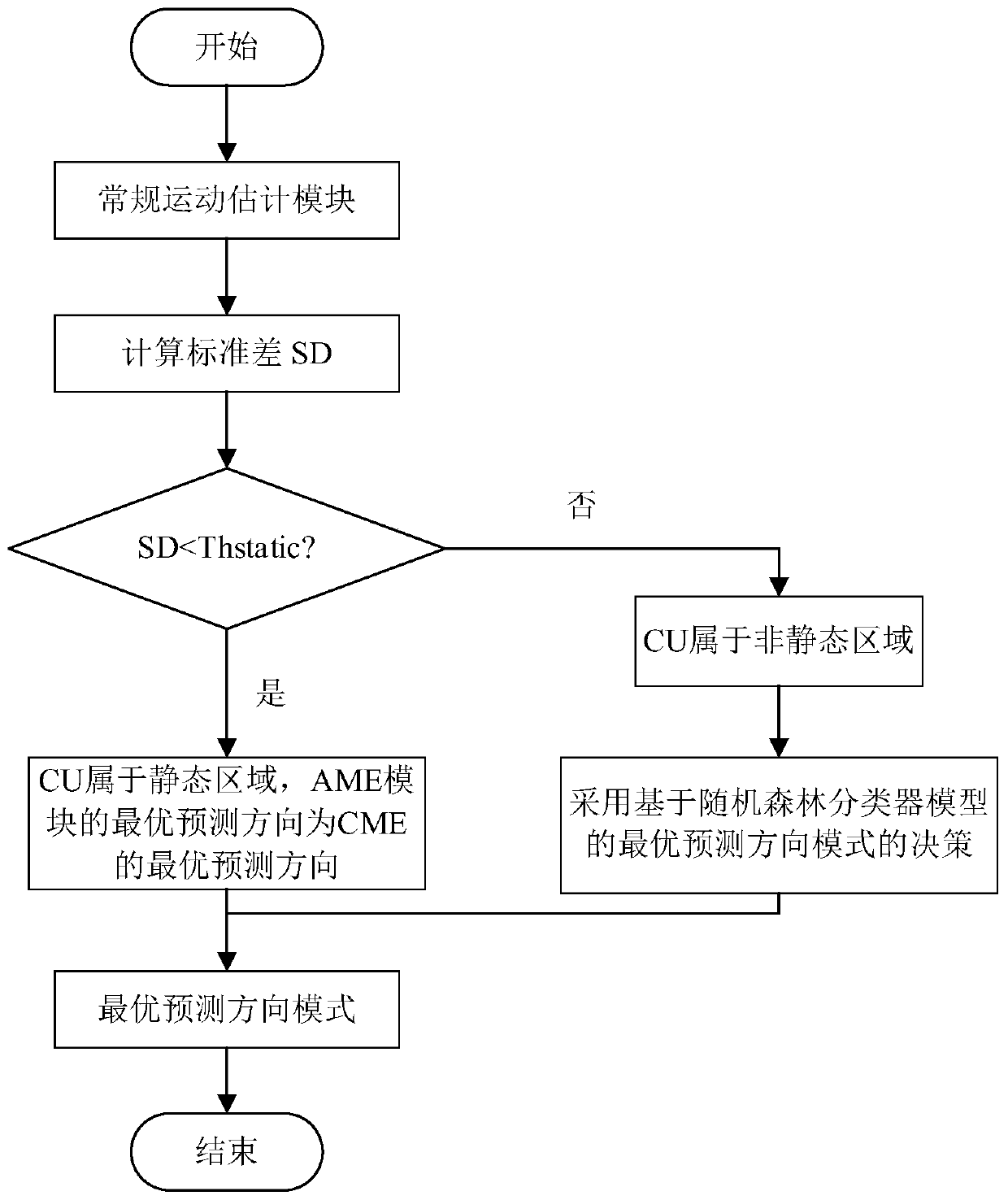
Rapid affine motion estimation method for H.266/VVC
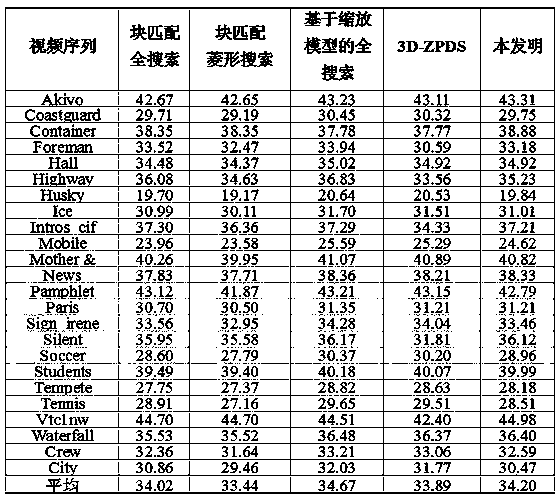
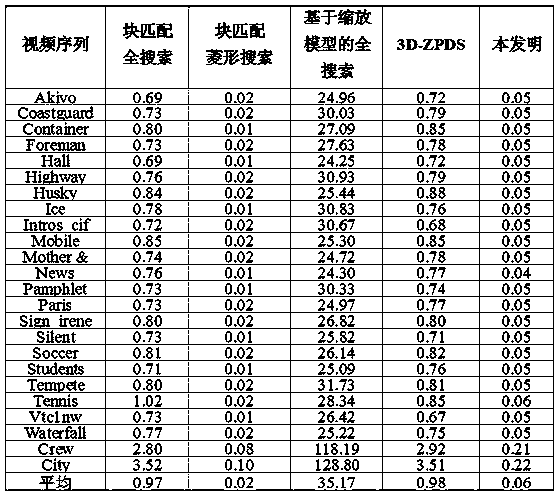
ActiveCN111479110AReduce coding timeQuick codingDigital video signal modificationAffine motionComputation complexity
The invention provides a rapid affine motion estimation method for H.266 / VVC, and the method comprises the steps: calculating the texture complexity of a current CU through adoption of a standard deviation, and dividing the current CU into a static region or a non-static region according to the texture complexity; for the CU of the static region, skipping affine motion estimation, directly utilizing motion estimation to predict the current CU, and selecting an optimal prediction direction mode through adoption of a rate distortion optimization method; and for the CU in the non-static region, classifying the current CU by using the trained random forest classifier RFC model, and outputting an optimal prediction direction mode. For a CU in the static region, affine motion estimation is skipped, and the calculation complexity is reduced; for a CU in the non-static region, prediction of a prediction direction mode is directly carried out through a model trained in advance, calculation of affine motion estimation is avoided, and therefore the complexity of an affine motion estimation module is reduced.
Owner:郑州轻大产业技术研究院有限公司 +1
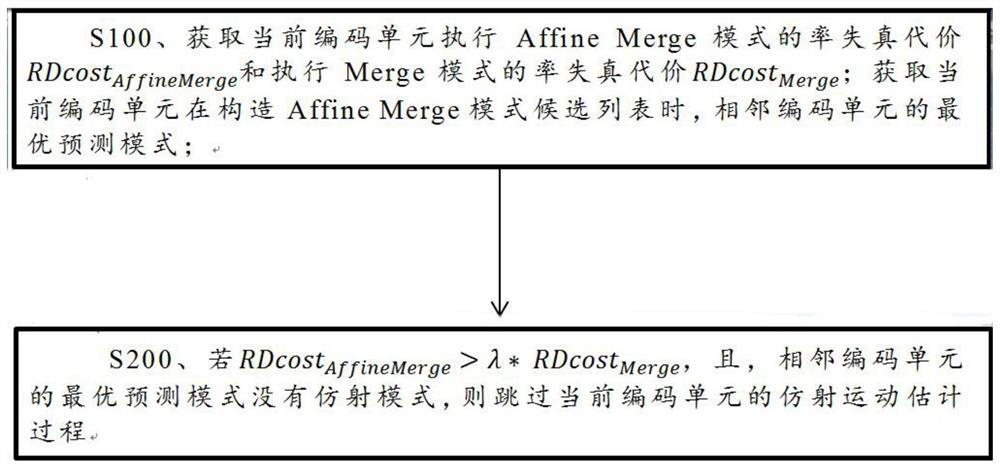
Affine motion estimation acceleration method and device based on VVC coding, and storage medium
InactiveCN111698502AReduce time complexityImprove efficiencyDigital video signal modificationAffine motionRound complexity
The invention discloses an affine motion estimation acceleration method and device based on VVC coding and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: if RDcostAffineMerge>[lambda]*RDcostMerge is satisfied, or when the current coding unit constructs an Affine Merge mode candidate list, the optimal prediction mode of the adjacent coding units has no affine mode, the affine motion estimation process of the current coding unit is skipped; otherwise, the current coding unit continues to carry out affine motion estimation, whereinRDcostAffine Merge represents the rate distortion cost of the current coding unit for executing the Affine Merge mode, RDcostMerge represents the rate-distortion cost of executing the Merge mode by the current coding unit, [lambda] is a threshold value,and [lambda] is greater than or equal to 1. According to the method, unnecessary affine motion estimation is skipped according to the Affine Merge mode information executed by the current coding unit, so that the time complexity of the encoder can be reduced, the efficiency of the encoder is effectively improved, and the method is beneficial to being put into practical application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Video image prediction method and device
The invention provides a video image prediction method and a video image prediction device, which are used for solving the problem that the length of a coded video sequence is increased in the prior art. Some video images do not have affine characteristics; some video images are not all stripes and have affine characteristics, therefore, a first identifier and / or a second identifier can be added in the code stream, the first identifier is used for indicating whether the video image can adopt the inter-frame prediction mode of the affine motion model, and the second identifier is used for indicating whether the strip in the video image can adopt the inter-frame prediction mode of the affine motion model. For video images or image blocks included in stripes that do not require an affine motion model, transmission of parameters related to the affine motion model for the image blocks may not be required. On the decoding side, when the image block is decoded, parameters related to the affine motion model do not need to be analyzed, the load of a decoder can be reduced, the processing speed can be increased, and the processing time can be shortened.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
History-based motion vector prediction
Systems, methods, and computer-readable media are provided for updating history-based motion vector tables. In some examples, a method can include obtaining one or more blocks of video data; determining a first motion vector derived from a first control point of a block of the one or more blocks, the block being coded using an affine motion mode; determining a second motion vector derived from a second control point of the block; based on the first motion vector and the second motion vector, estimating a third motion vector for a predetermined location within the block; and populating a history-based motion vector predictor (HMVP) table with the third motion vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Video affine motion estimation method of adaptive factors
ActiveCN109640097AQuality improvementImprove the efficiency of motion estimationDigital video signal modificationAffine motionParametric search
The invention discloses a video affine motion estimation method of adaptive factors. The method comprises the following steps: judging a zoom factor of a current to-be-predicted macro block by using alinear weighting prediction error corresponding to a translational motion vector and 2D weighting autocorrelation of a reference frame; and secondly, keeping the zoom factor unchanged, expressing anaffine motion compensation error as a quadratic function about a rotation angle, calculating an adaptive rotation angle under the affine motion through the Vieta theorem, and then obtaining an affinemotion vector of the current to-be-predicted macro block. By adoption of the video affine motion estimation method disclosed by the invention, the "violent" parameter search or iterative solution of the traditional affine motion estimation method is avoided, the optimal zoom factor and rotation angle can be directly calculated, and the number of sub-pixel interpolation operations is significantlyreduced, thereby improving the compensation quality of the traditional block matching motion estimation method while ensuring the instantaneity.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
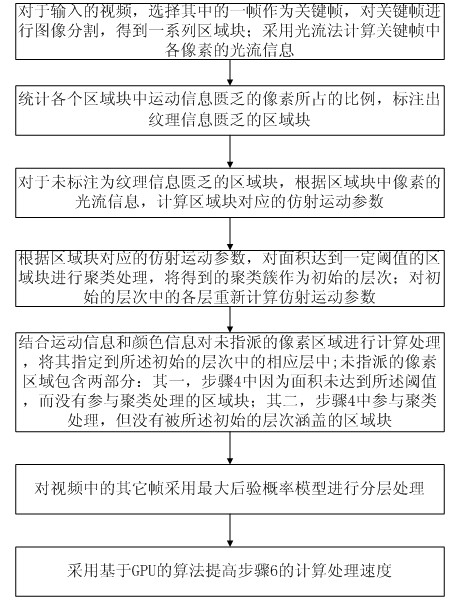
Ground power unit (GPU)-based video layering method
ActiveCN101964911AQuickly process resultsEasy maintenanceImage analysisTelevision systemsAffine motionMaximum a posteriori estimation
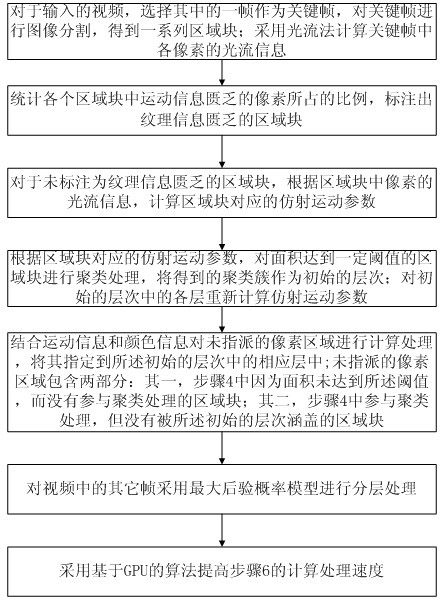
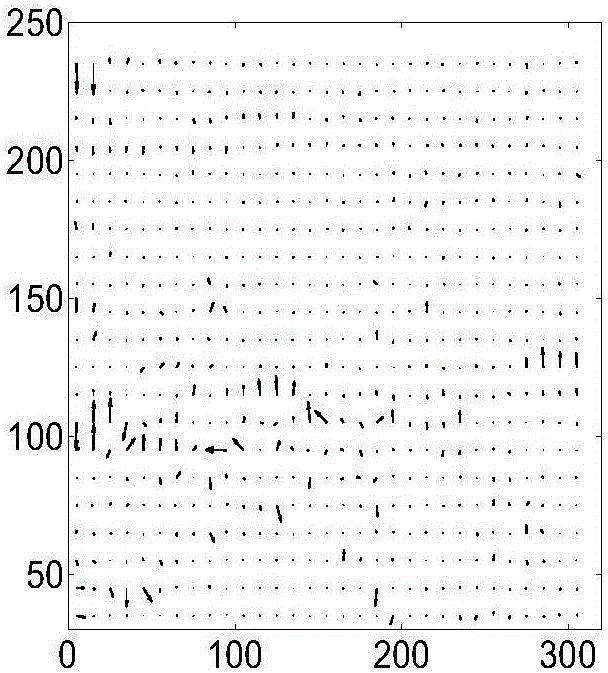
The invention provides a GPU-based video layering method, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, selecting a key frame from an input video and performing image over-division treatment on an image by using a man-shift image dividing method to obtain a series of region blocks; secondly, marking region blocks lacking texture information by computing the rate of pixels lacking motion information in each region block; thirdly, computing affine motion parameters of regions which are not marked and clustering the regions of which the areas reach a threshold to obtain an initial layer; and finally, computing non-appointed pixel regions by combining the motion information and color information and appointing the pixel regions into a corresponding layer in the initial layer to complete the layering processing operation of the key frame. The other frames in the video are layered by mainly combining the layering result of a former frame and the information of the current frame and using a maximal posterior probability model and accelerated by using a GPU, so that the processing efficiency of each frame of the video is greatly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Image stabilizing method capable of accurate detection of complex jittering in video sequence
InactiveCN105100618AOvercome the disadvantage of large estimation errorIncrease computing speedTelevision system detailsImage analysisAffine motionDecomposition
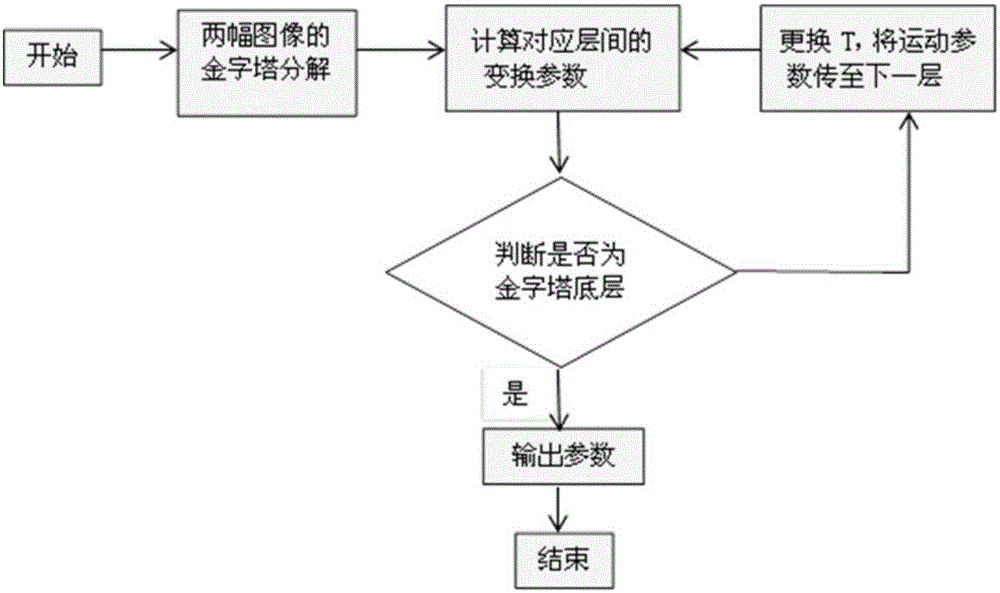
The invention discloses an image stabilizing method capable of accurate detection of complex jittering in a video sequence. According to the method, first of all, pyramid decomposition is carried out on an image, through performing sampling on an original 0-th layer in an interlacing inter-row and inter-column mode after smoothing, a high layer with quite low resolution is obtained, then from the top layer, affine motion parameters between corresponding layers of two frames of images are calculated, afterwards, the calculated affine motion parameters are transmitted to a layer with quite high resolution, parameter iteration is performed, and accurate affine motion parameters can be solved through iteration calculation to the bottom of a pyramid. According to the invention, a good image stabilizing effect can be obtained through performing compensation on a jittering video according to the solved accurate affine motion parameters. Experiments show that an optical flow algorithm combining a pyramid multi-resolution layered technology solves the problem of quite large errors caused by motion estimation by use of a conventional gradient optical flow method under the condition of discontinuous motion between video sequences, and the method can obtain the good image stabilizing effect for the motion sequences comprising such complex motion as rotation, zooming, translation and the like.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com