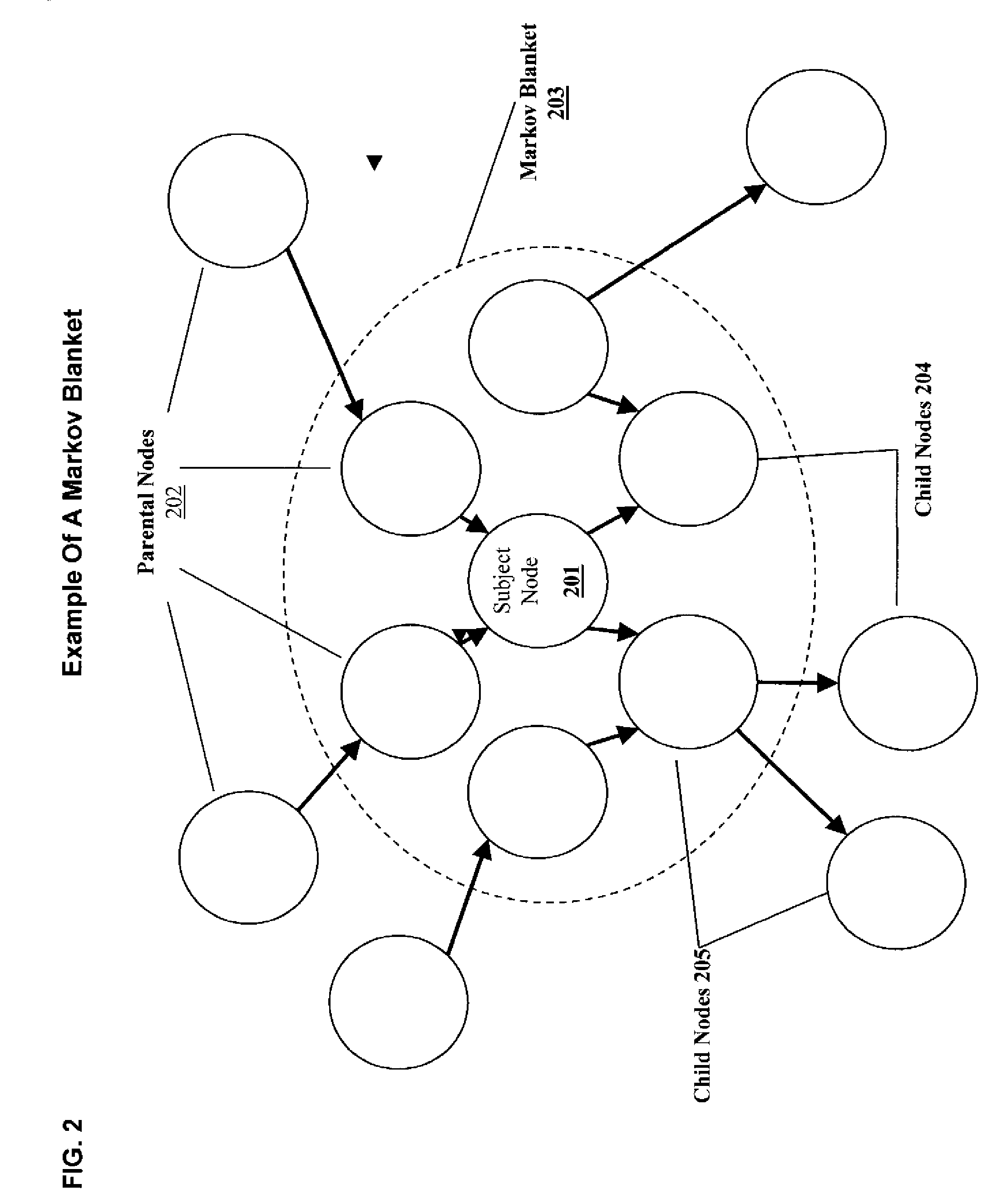
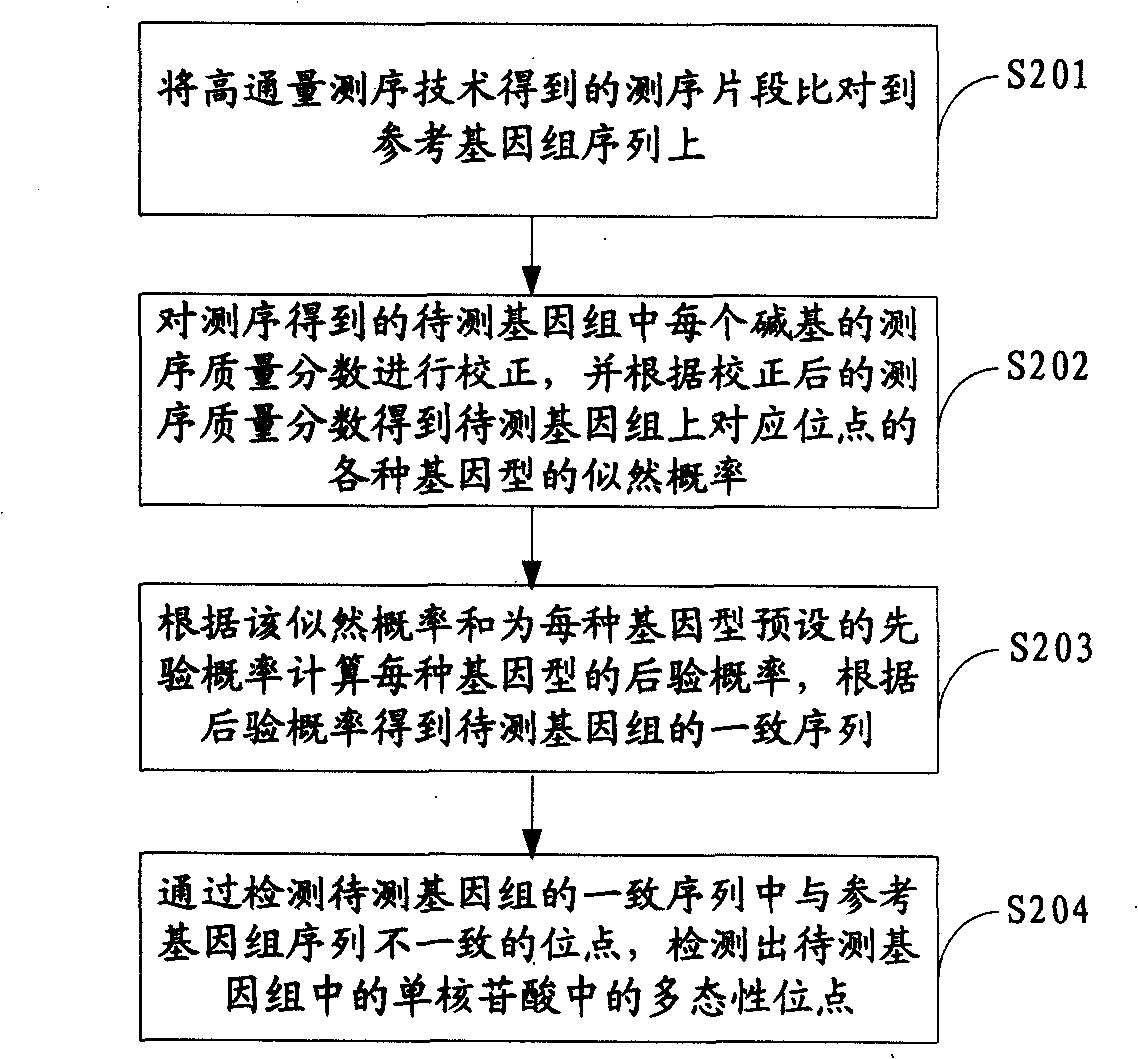
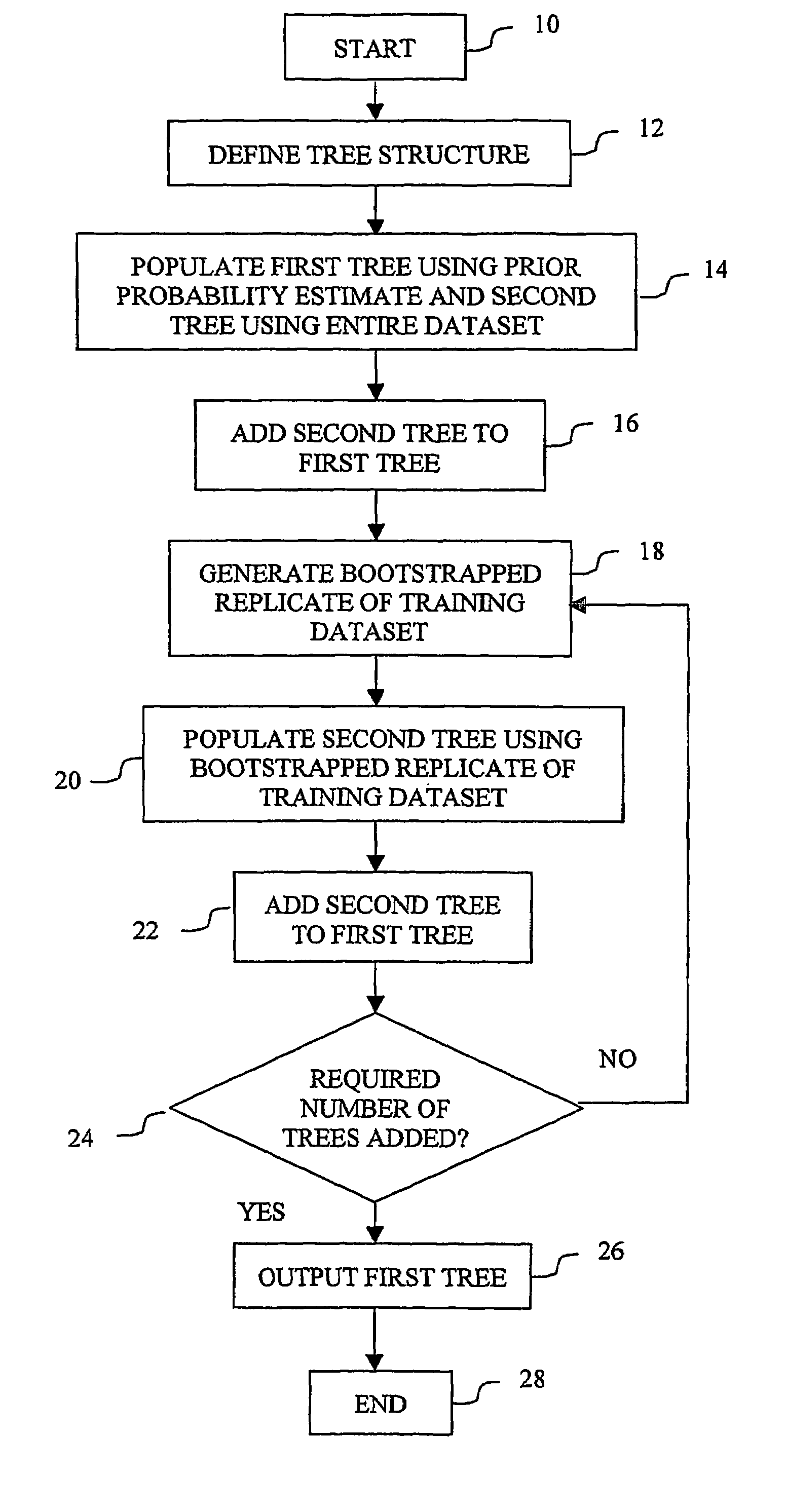
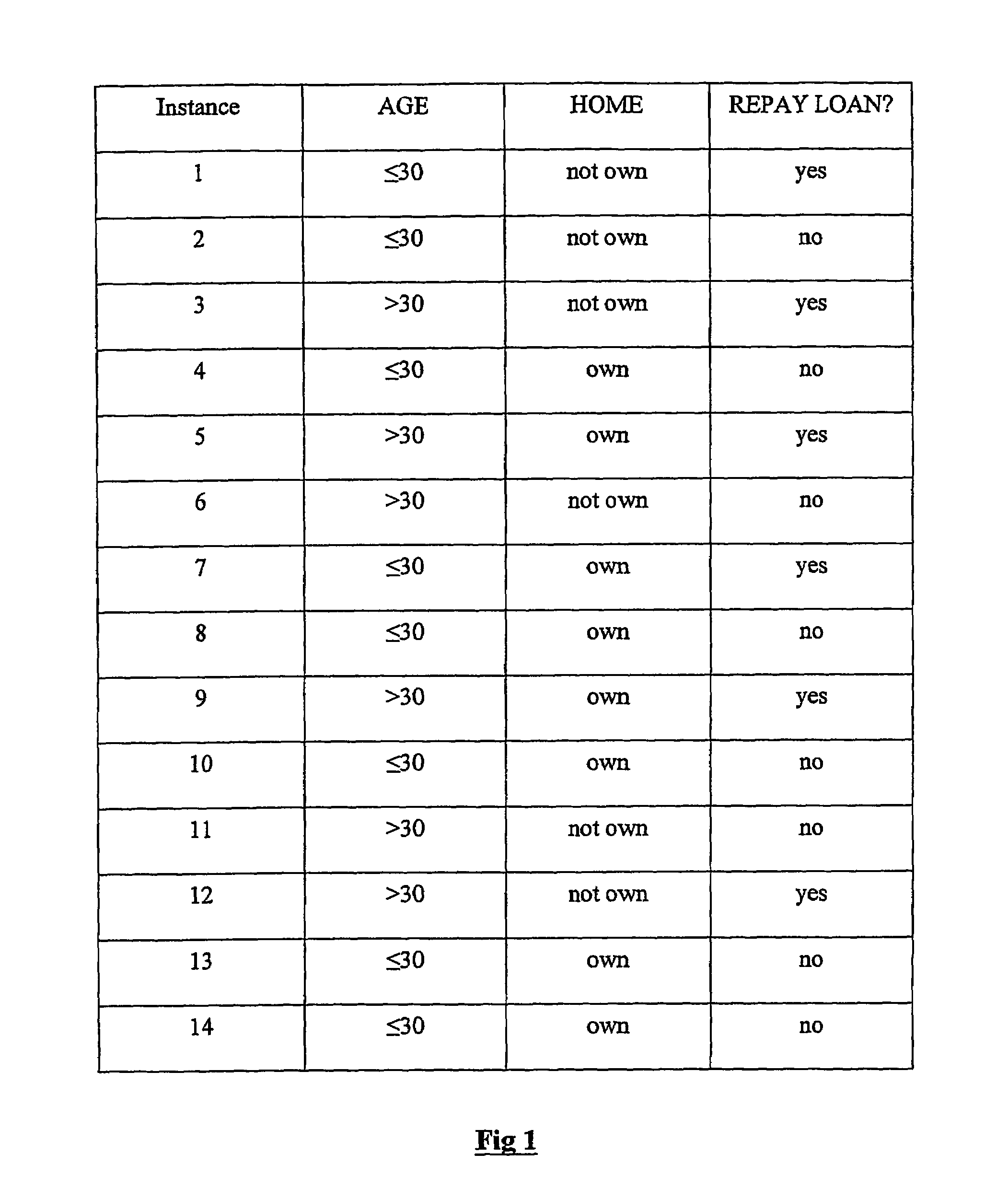
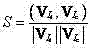Patents
Literature
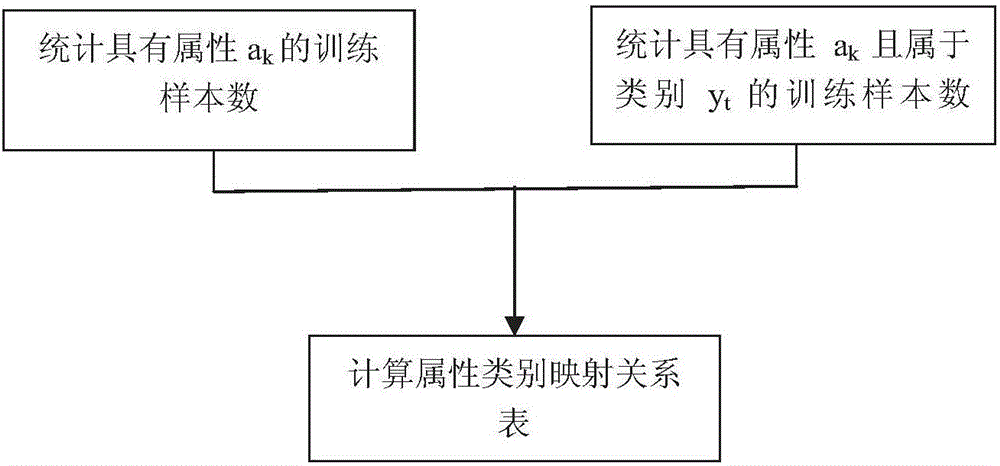
1061 results about "Posterior probability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In Bayesian statistics, the posterior probability of a random event or an uncertain proposition is the conditional probability that is assigned after the relevant evidence or background is taken into account. Similarly, the posterior probability distribution is the probability distribution of an unknown quantity, treated as a random variable, conditional on the evidence obtained from an experiment or survey. "Posterior", in this context, means after taking into account the relevant evidence related to the particular case being examined. For instance, there is a ("non-posterior") probability of a person finding buried treasure if they dig in a random spot, and a posterior probability of finding buried treasure if they dig in a spot where their metal detector rings.
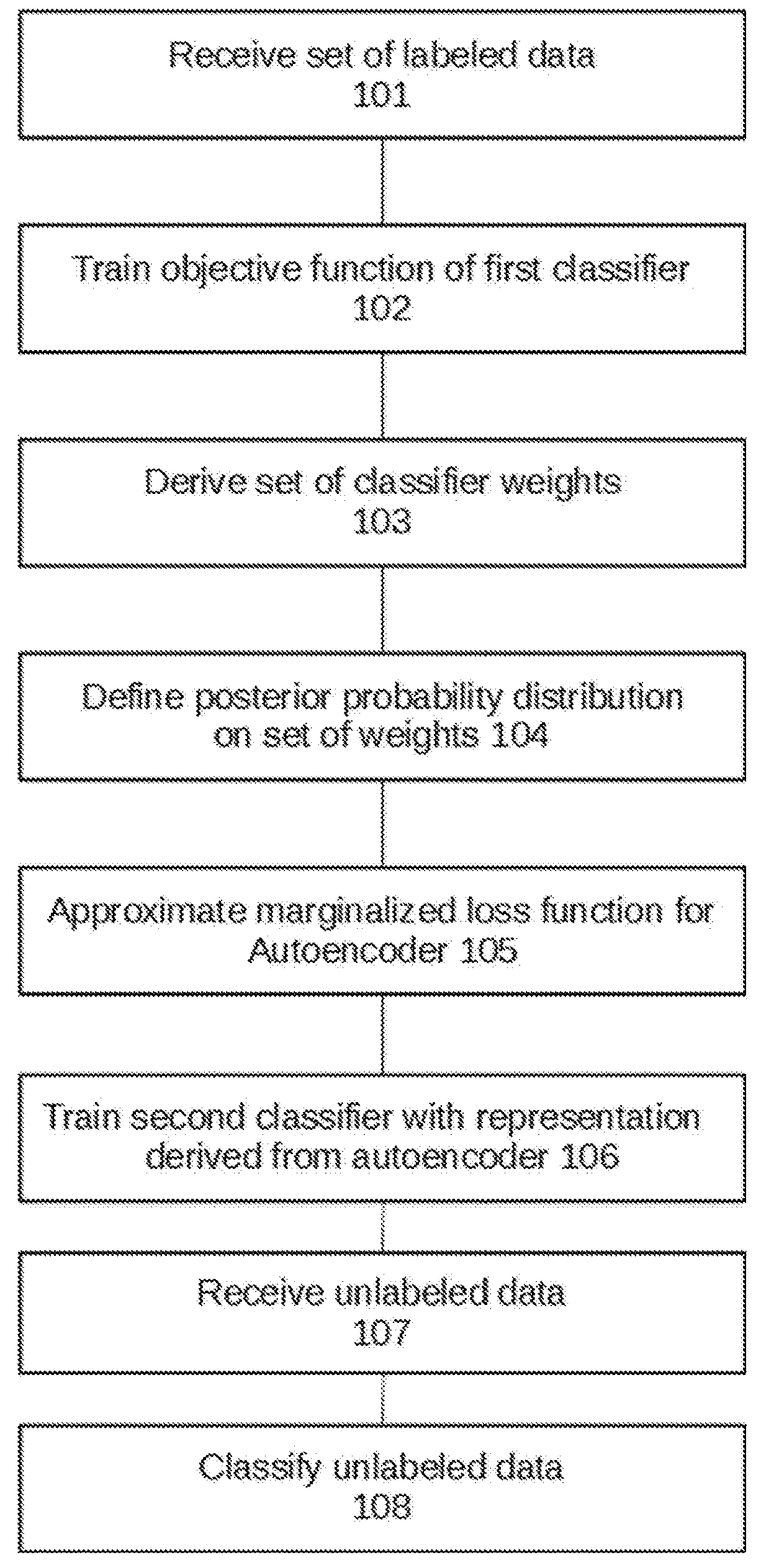
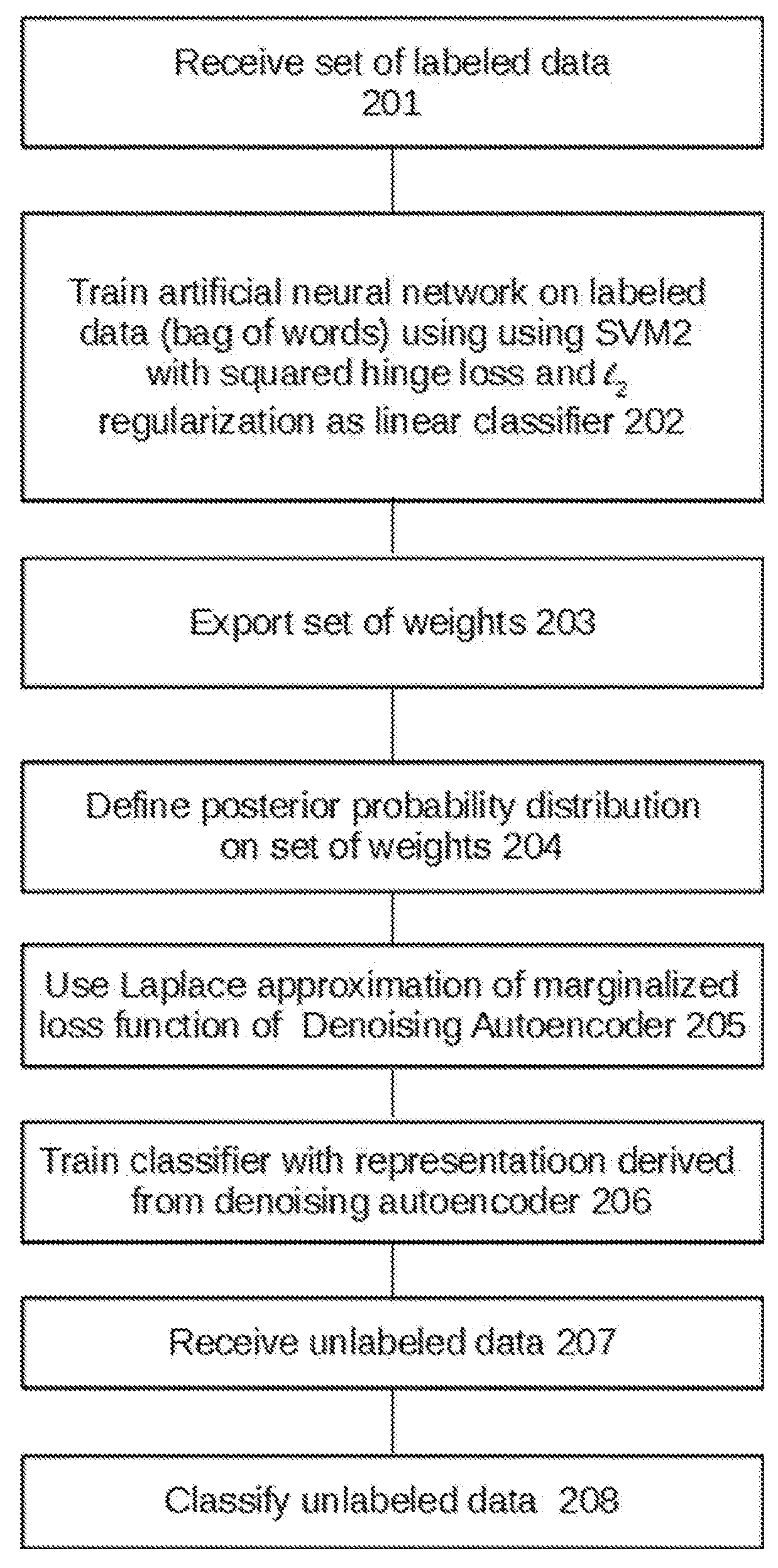
Semisupervised autoencoder for sentiment analysis
ActiveUS20180165554A1Reduce biasImprove performanceMathematical modelsKernel methodsLabeled dataComputer science
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
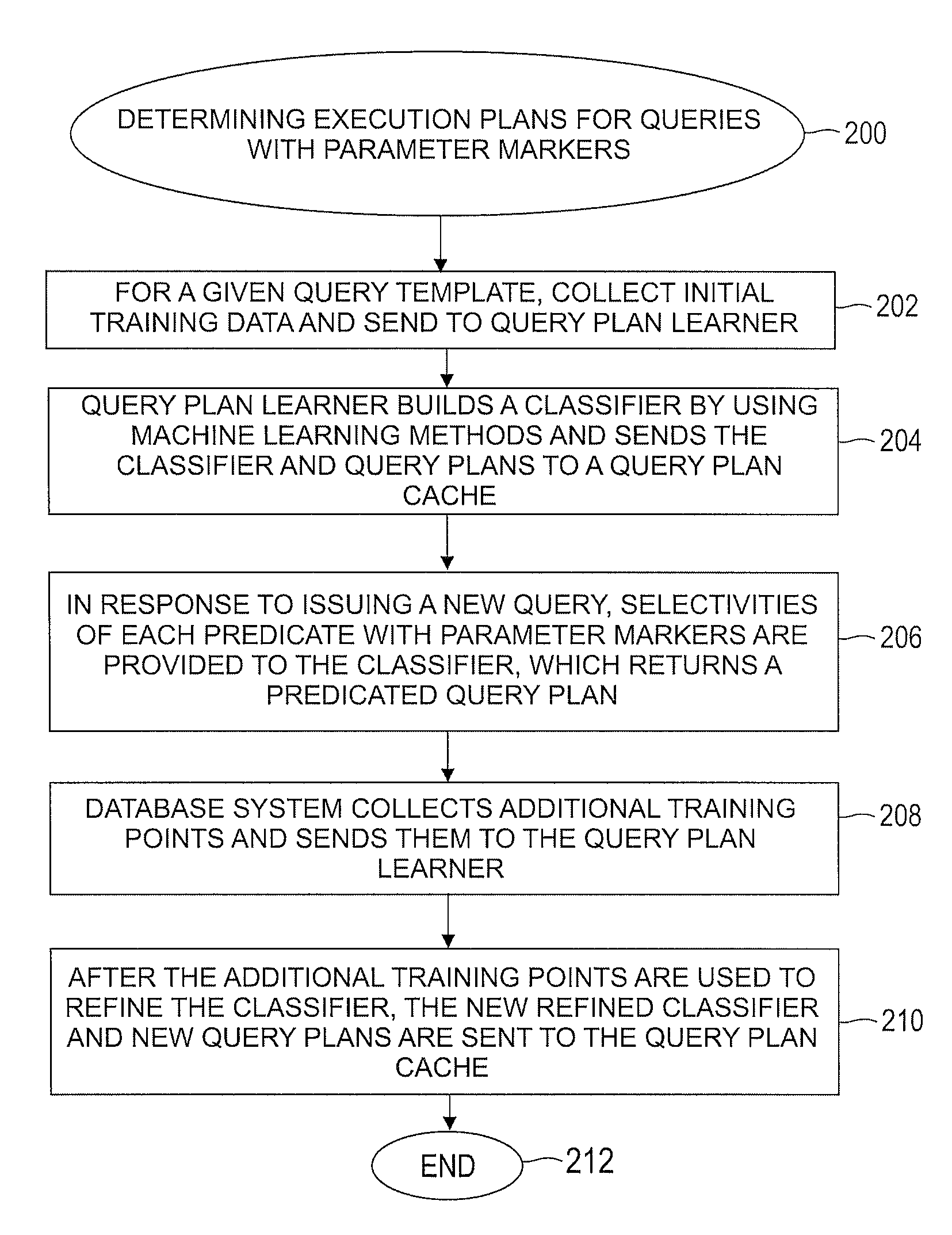
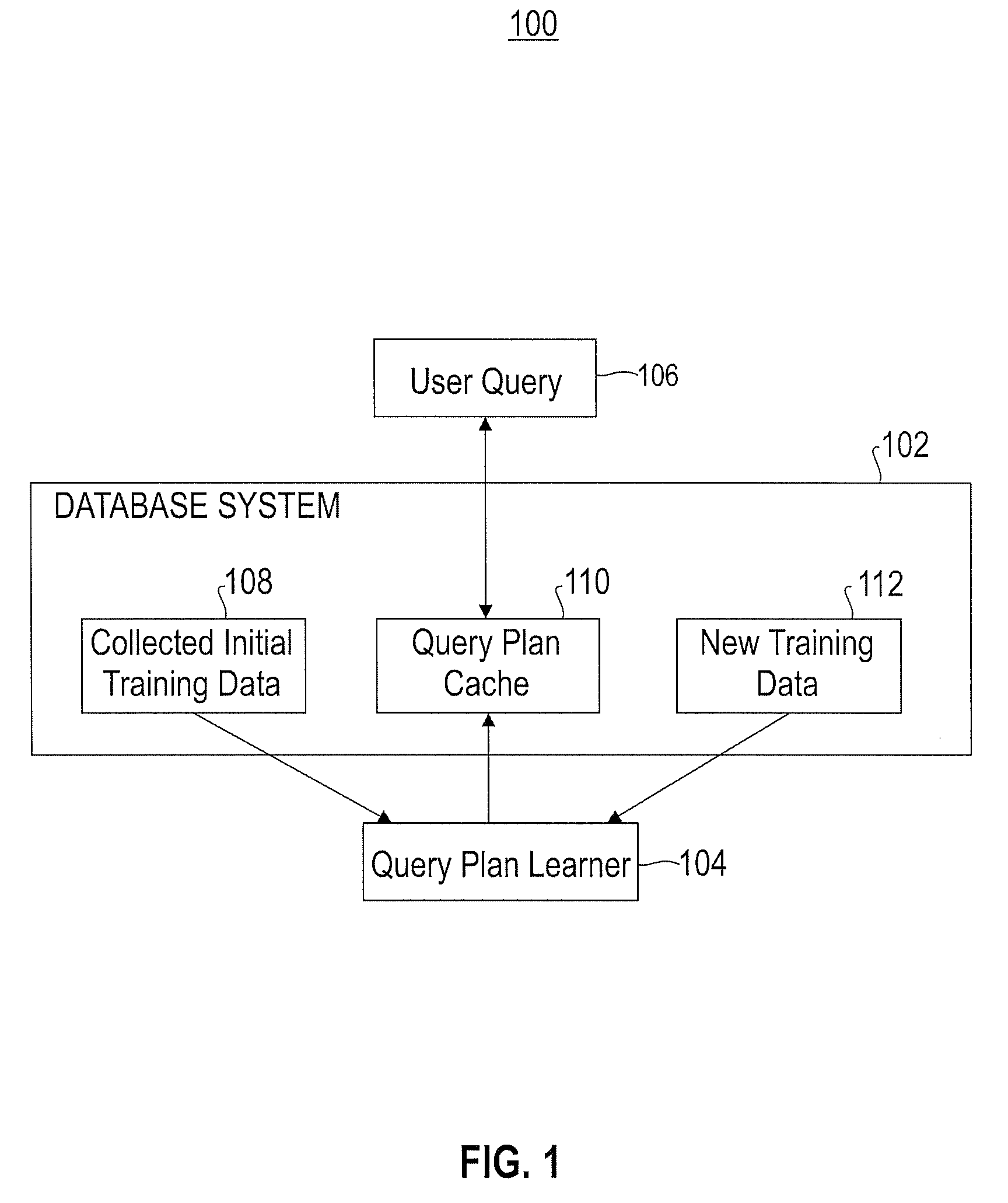
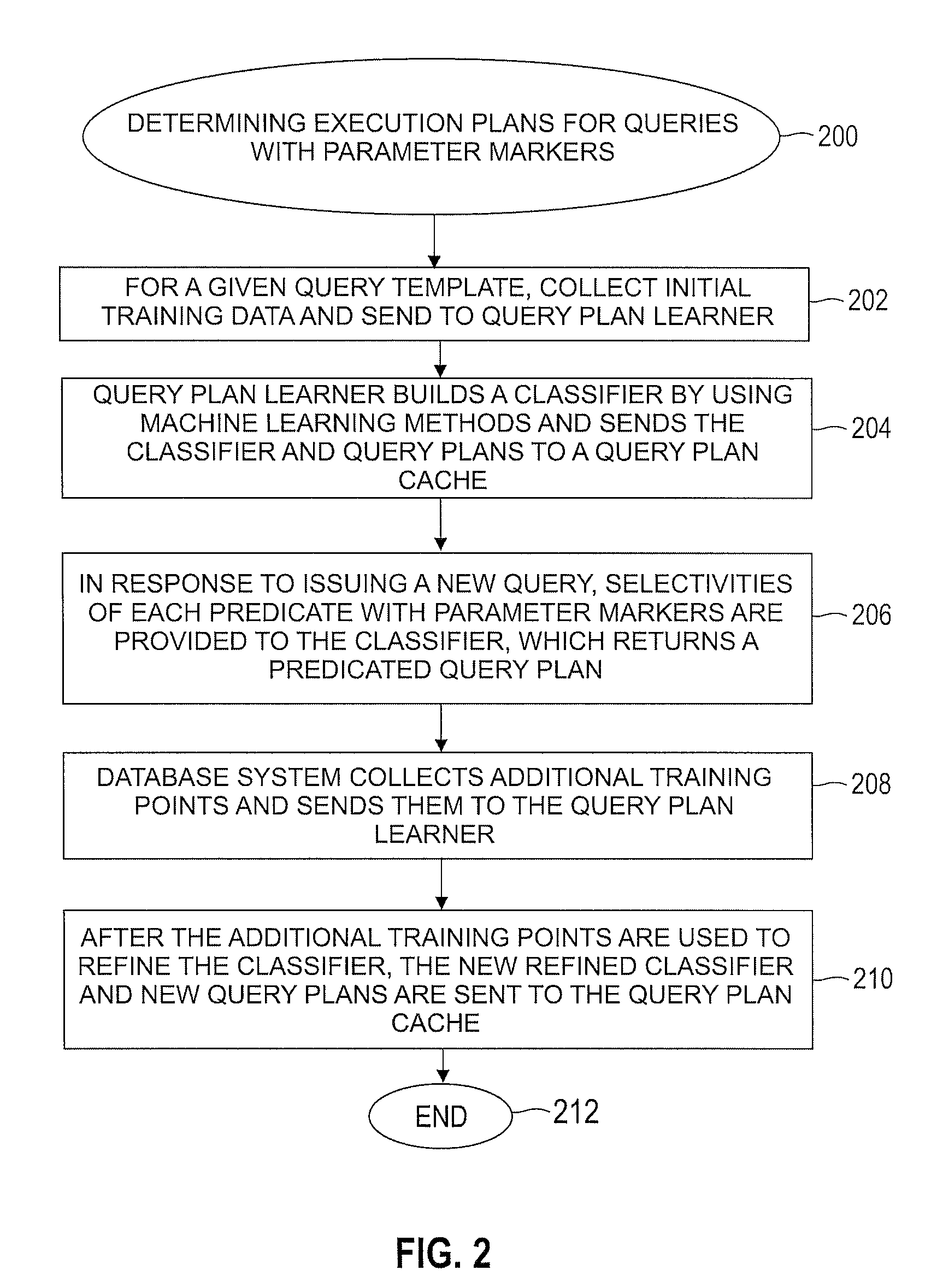
Automatically and adaptively determining execution plans for queries with parameter markers
InactiveUS20080195577A1Accurate modelingImprove forecast accuracyDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsExecution planWorkload
A method for automatically and adaptively determining query execution plans for parametric queries. A first classifier trained by an initial set of training points is generated using a set of random decision trees (RDTs). A query workload and / or database statistics are dynamically updated. A new set of training points collected off-line is used to modify the first classifier into a second classifier. A database query is received at a runtime subsequent to the off line phase. The query includes predicates having parameter markers bound to actual values. The predicates are associated with selectivities. The query execution plan is determined by identifying an optimal average of posterior probabilities obtained across a set of RDTs and mapping the selectivities to a plan. The determined query execution plan is included in an augmented set of training points that includes the initial set and the new set.
Owner:IBM CORP
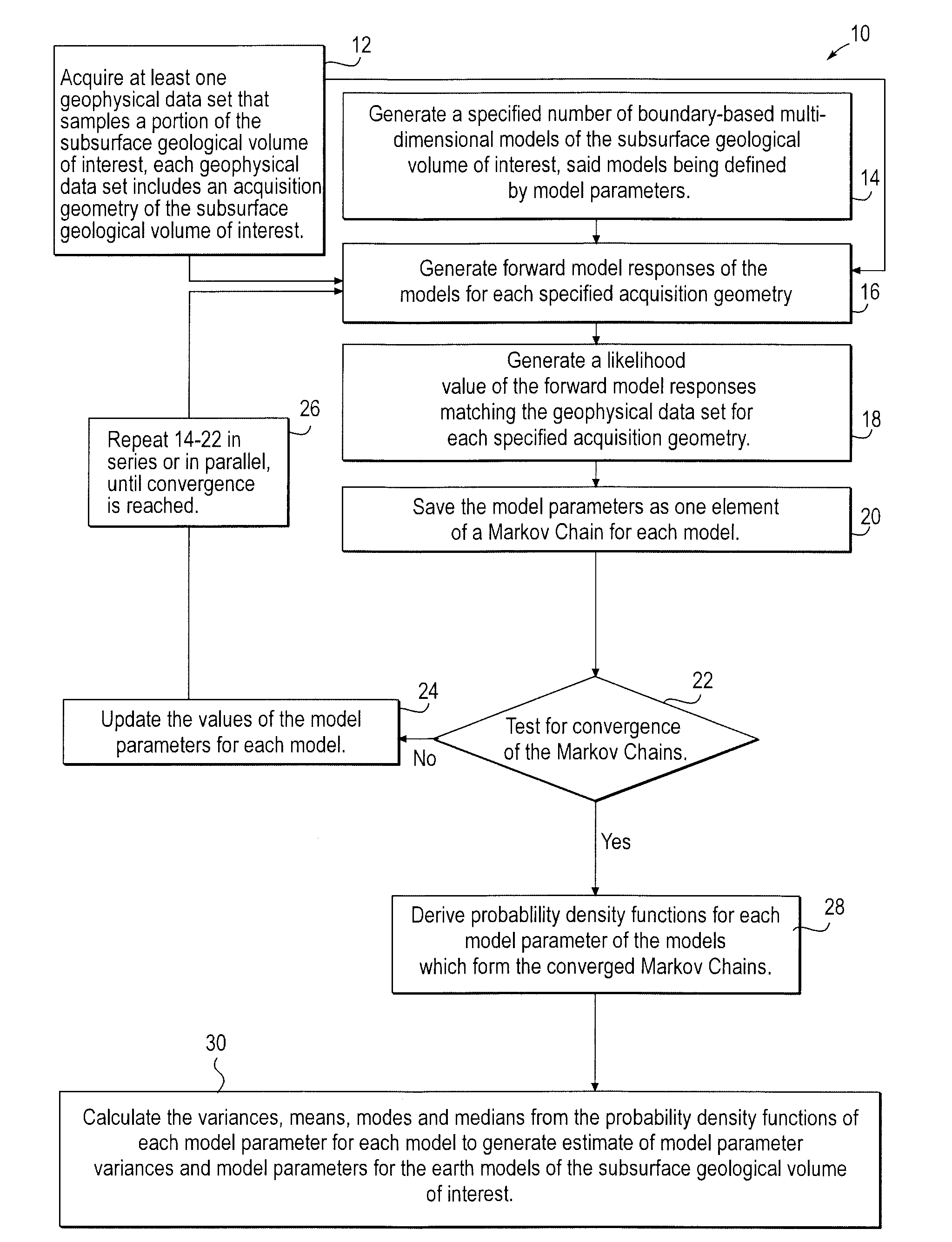
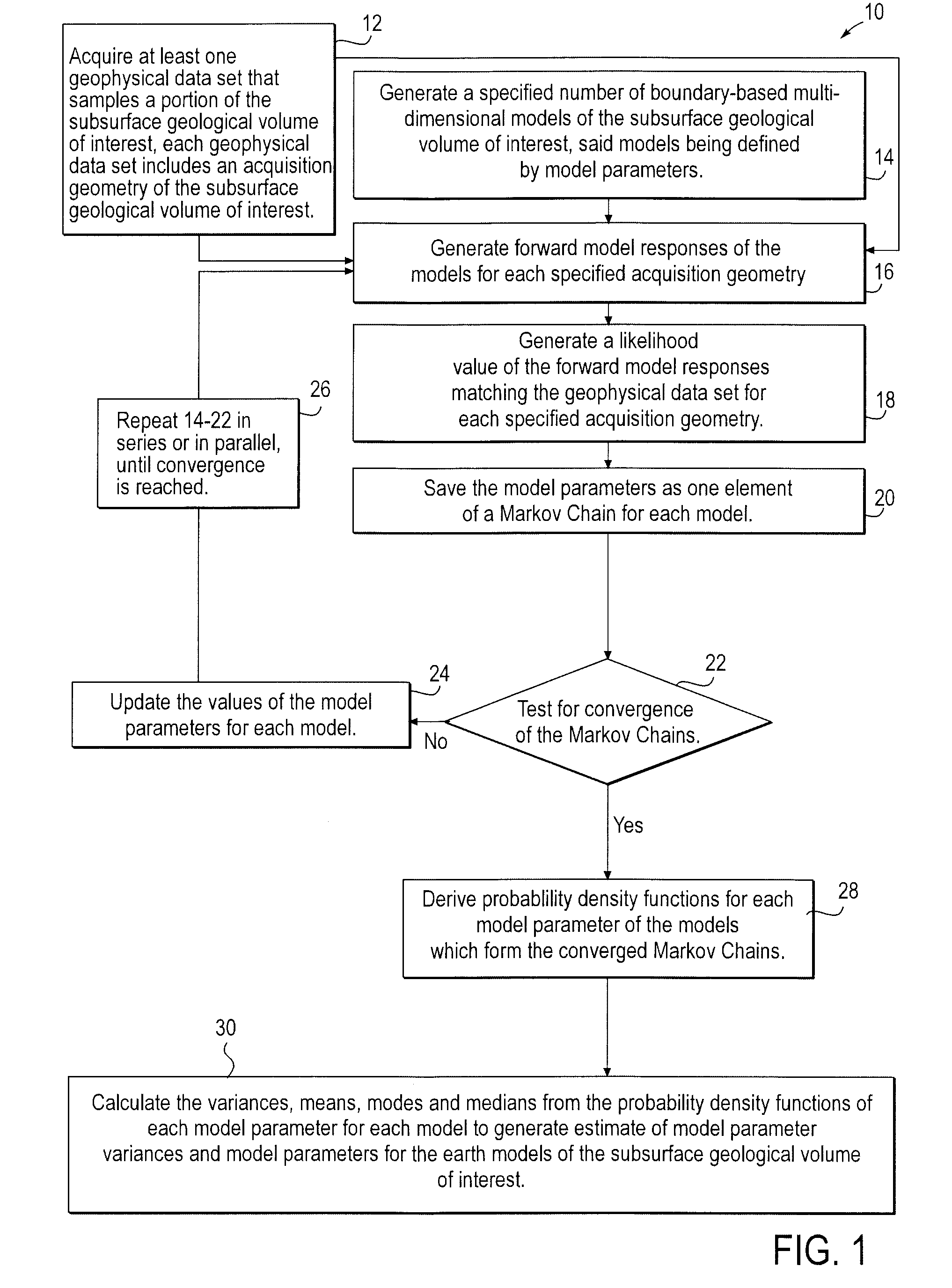
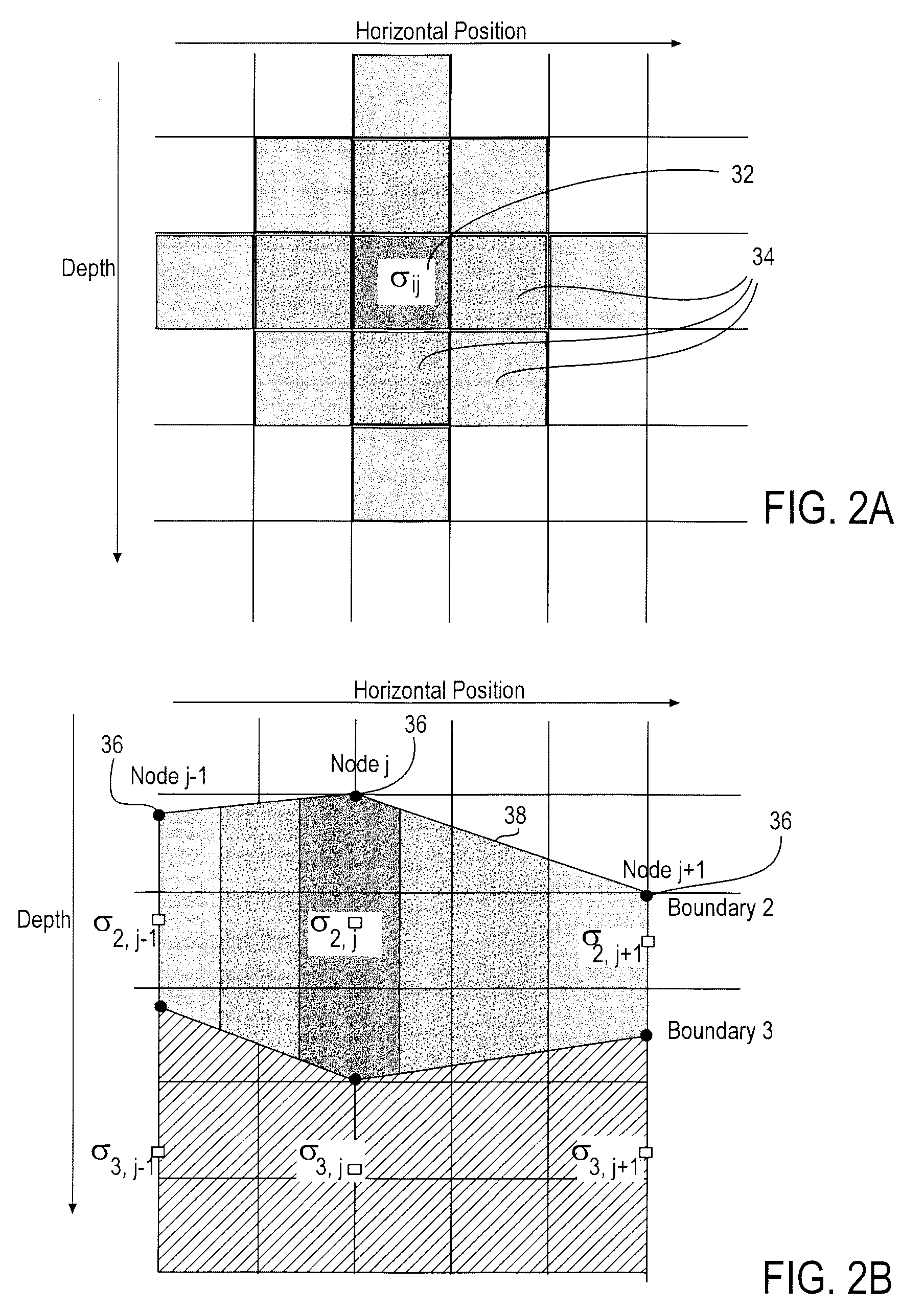
Stochastic inversion of geophysical data for estimating earth model parameters
A computer implemented stochastic inversion method for estimating model parameters of an earth model. In an embodiment, the method utilizes a sampling-based stochastic technique to determine the probability density functions (PDF) of the model parameters that define a boundary-based multi-dimensional model of the subsurface. In some embodiments a sampling technique known as Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is utilized. MCMC techniques fall into the class of “importance sampling” techniques, in which the posterior probability distribution is sampled in proportion to the model's ability to fit or match the specified acquisition geometry. In another embodiment, the inversion includes the joint inversion of multiple geophysical data sets. Embodiments of the invention also relate to a computer system configured to perform a method for estimating model parameters for accurate interpretation of the earth's subsurface.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Voiceprint identification method based on Gauss mixing model and system thereof
InactiveCN102324232AGood estimateEasy to trainSpeech recognitionMel-frequency cepstrumNormal density
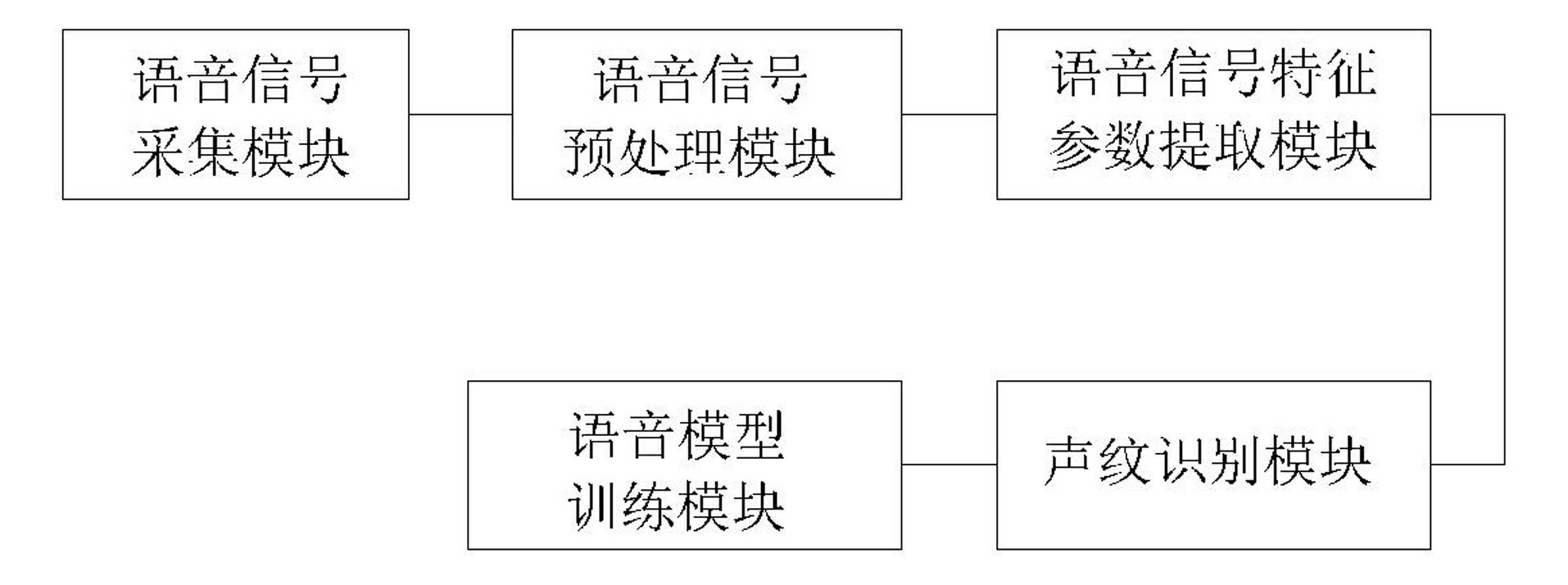
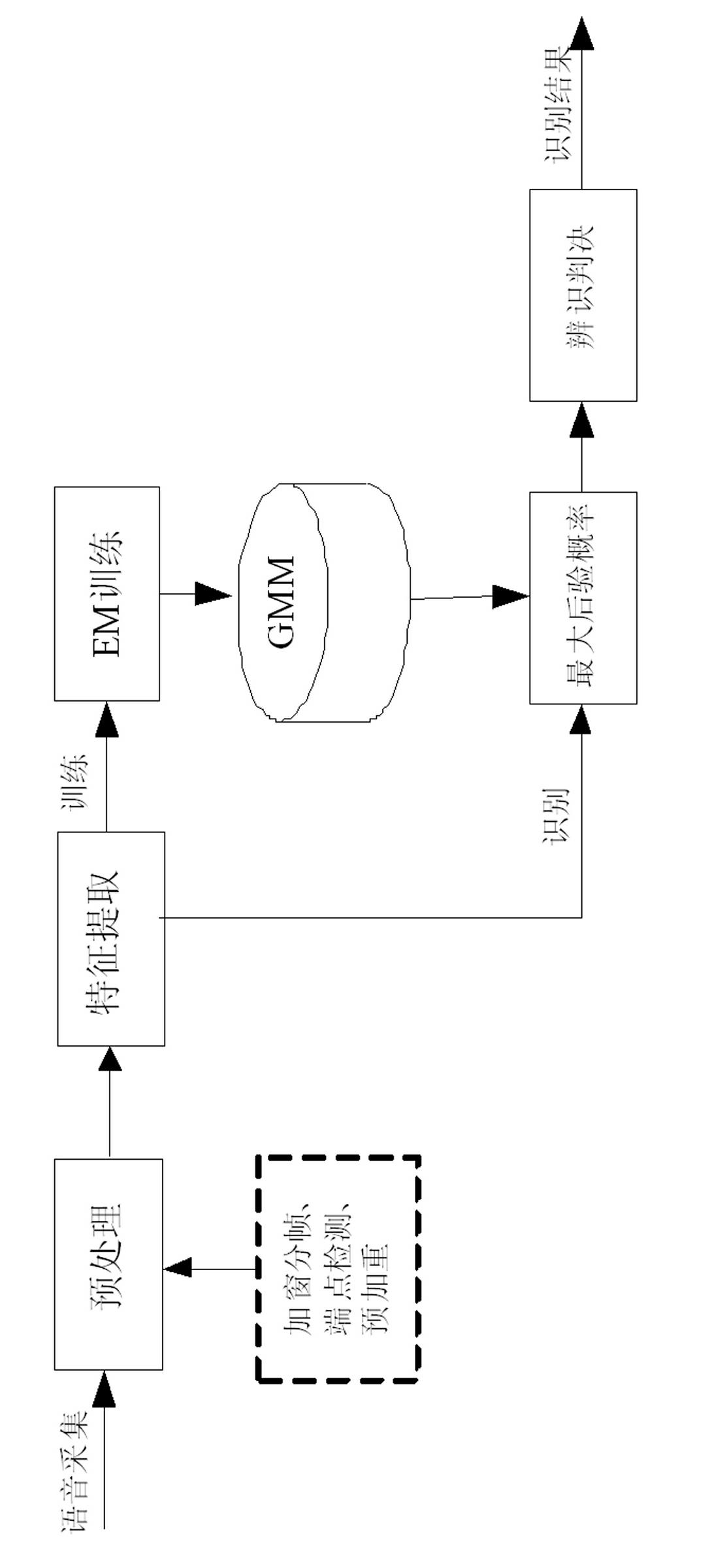
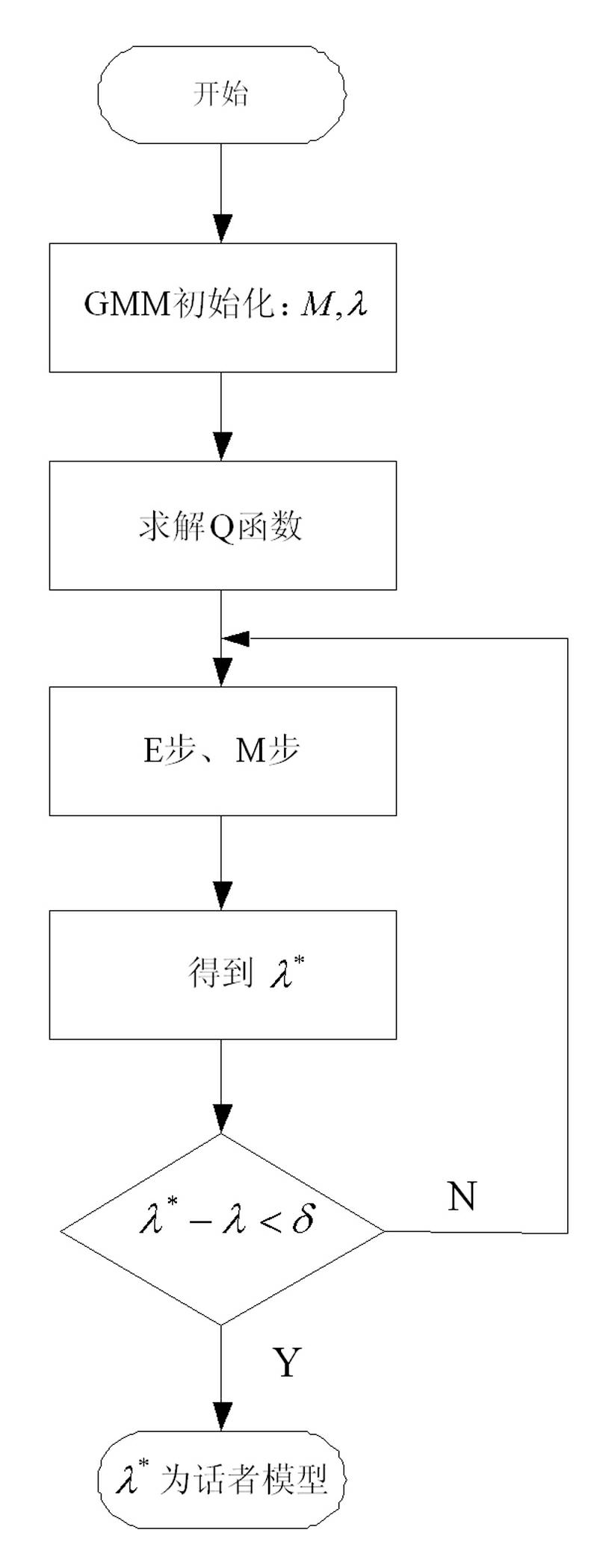
The invention provides a voiceprint identification method based on a Gauss mixing model and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: voice signal acquisition; voice signal pretreatment; voice signal characteristic parameter extraction: employing a Mel Frequency Cepstrum Coefficient (MFCC), wherein an order number of the MFCC usually is 12-16; model training: employing an EM algorithm to train a Gauss mixing model (GMM) for a voice signal characteristic parameter of a speaker, wherein a k-means algorithm is selected as a parameter initialization method of the model; voiceprint identification: comparing a collected voice signal characteristic parameter to be identified with an established speaker voice model, carrying out determination according to a maximum posterior probability method, and if a corresponding speaker model enables a speaker voice characteristic vector X to be identified to has maximum posterior probability, identifying the speaker. According to the method, the Gauss mixing model based on probability statistics is employed, characteristic distribution of the speaker in characteristic space can be reflected well, a probability density function is common, a parameter in the model is easy to estimate and train, and the method has good identification performance and anti-noise capability.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Multi-dimensional method and apparatus for automated language interpretation
InactiveUS7403890B2Sufficient massImprove abilitiesSemantic analysisChaos modelsShort-term memoryMulti dimensional
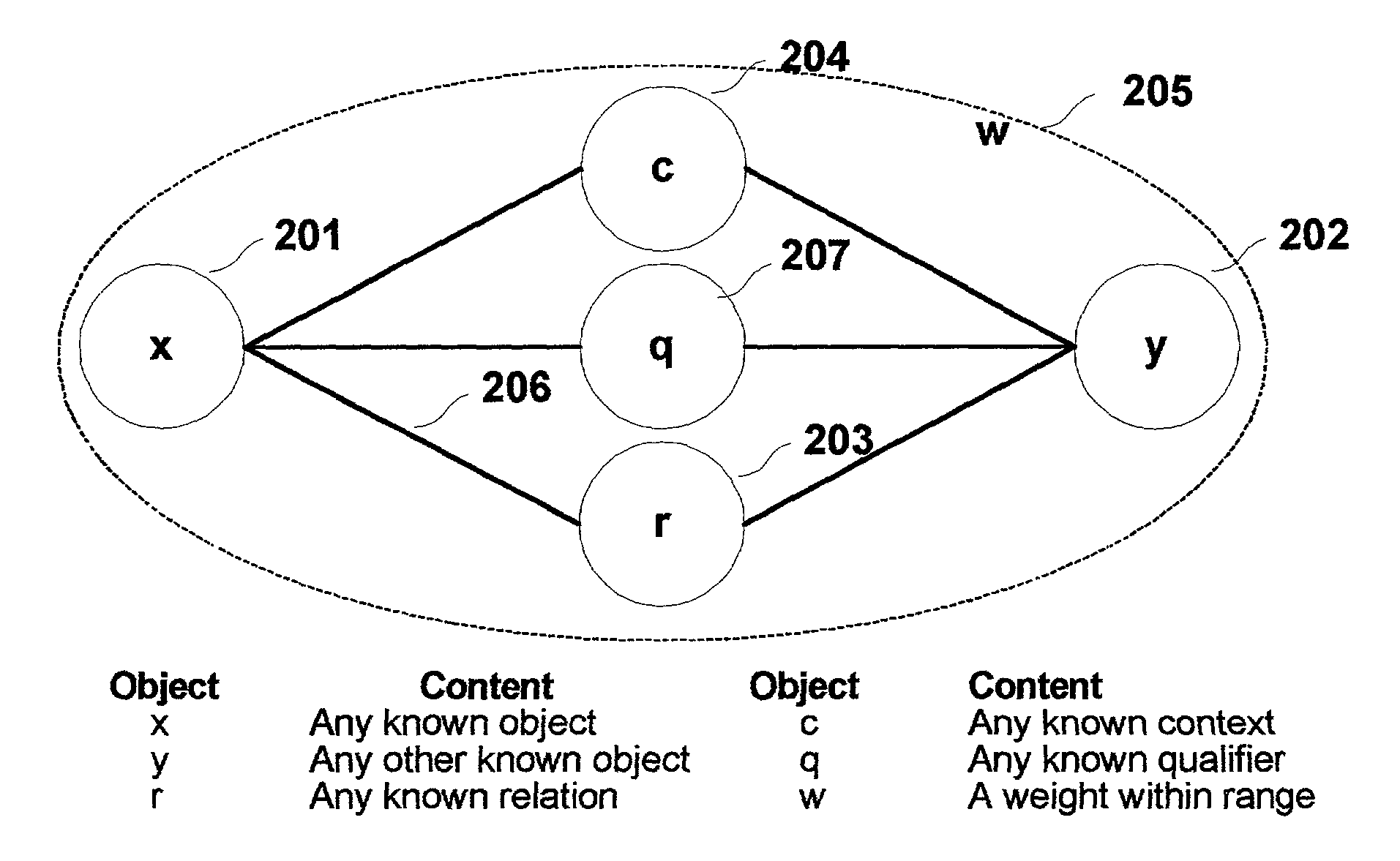
A method and apparatus for natural language interpretation are described. The invention includes a schema and apparatus for storing, in digital, analog, or other machine-readable format, a network of propositions formed of a plurality of text and / or non-text objects, and the steps of retrieving a string of input text, and locating all associated propositions in the network for each word in the input string. Embodiments of the invention also include optimization steps for locating said propositions, and specialized structures for storing them in a ready access storage area simulating human short-term memory. The schema and steps may also include structures and processes for obtaining and adjusting the weights of said propositions to determine posterior probabilities representing the intended meaning. Embodiments of the invention also include an apparatus designed to apply an automated interpretation algorithm to automated voice response systems and portable knowledge appliance devices.
Owner:KNOWLEDGENETICA CORP
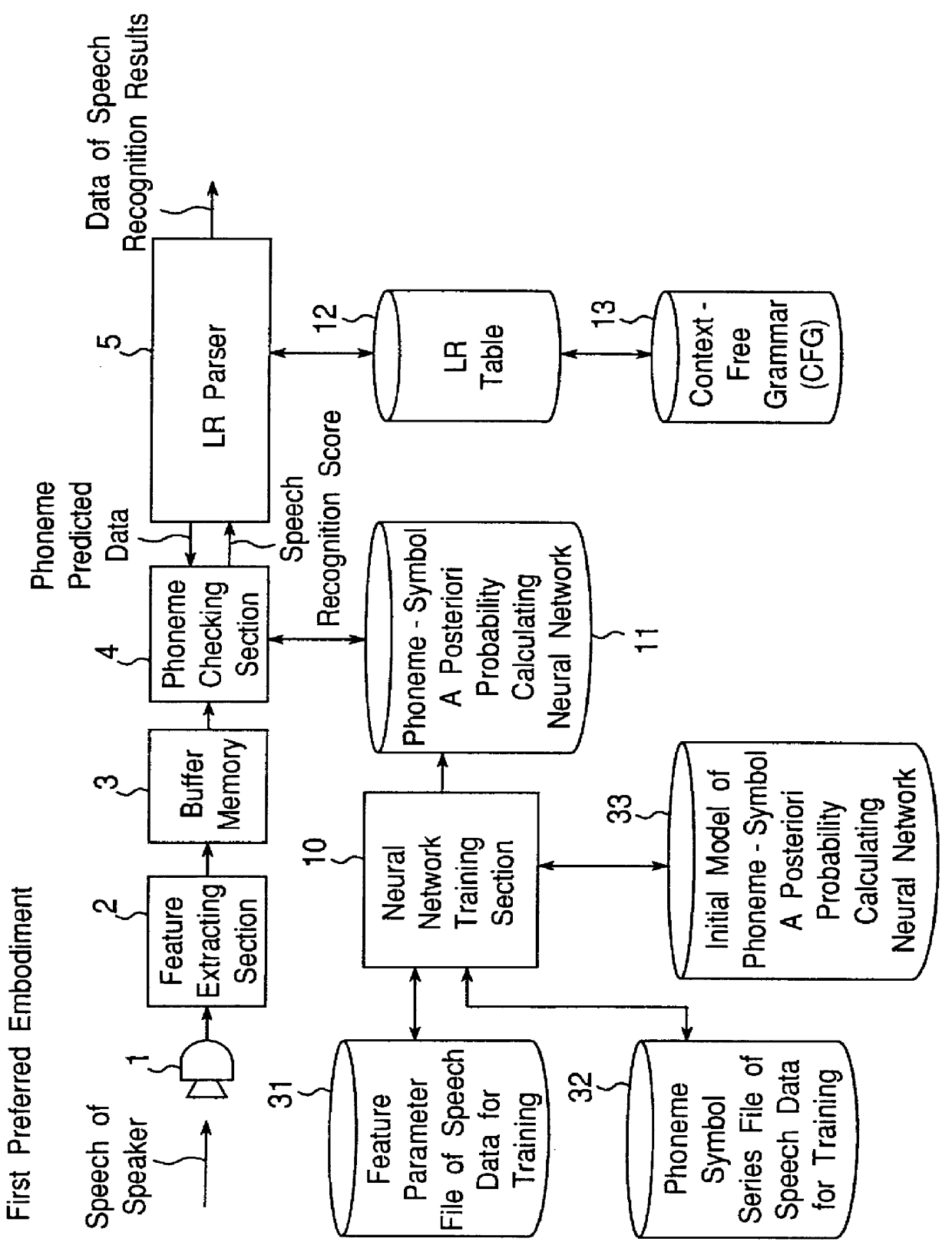
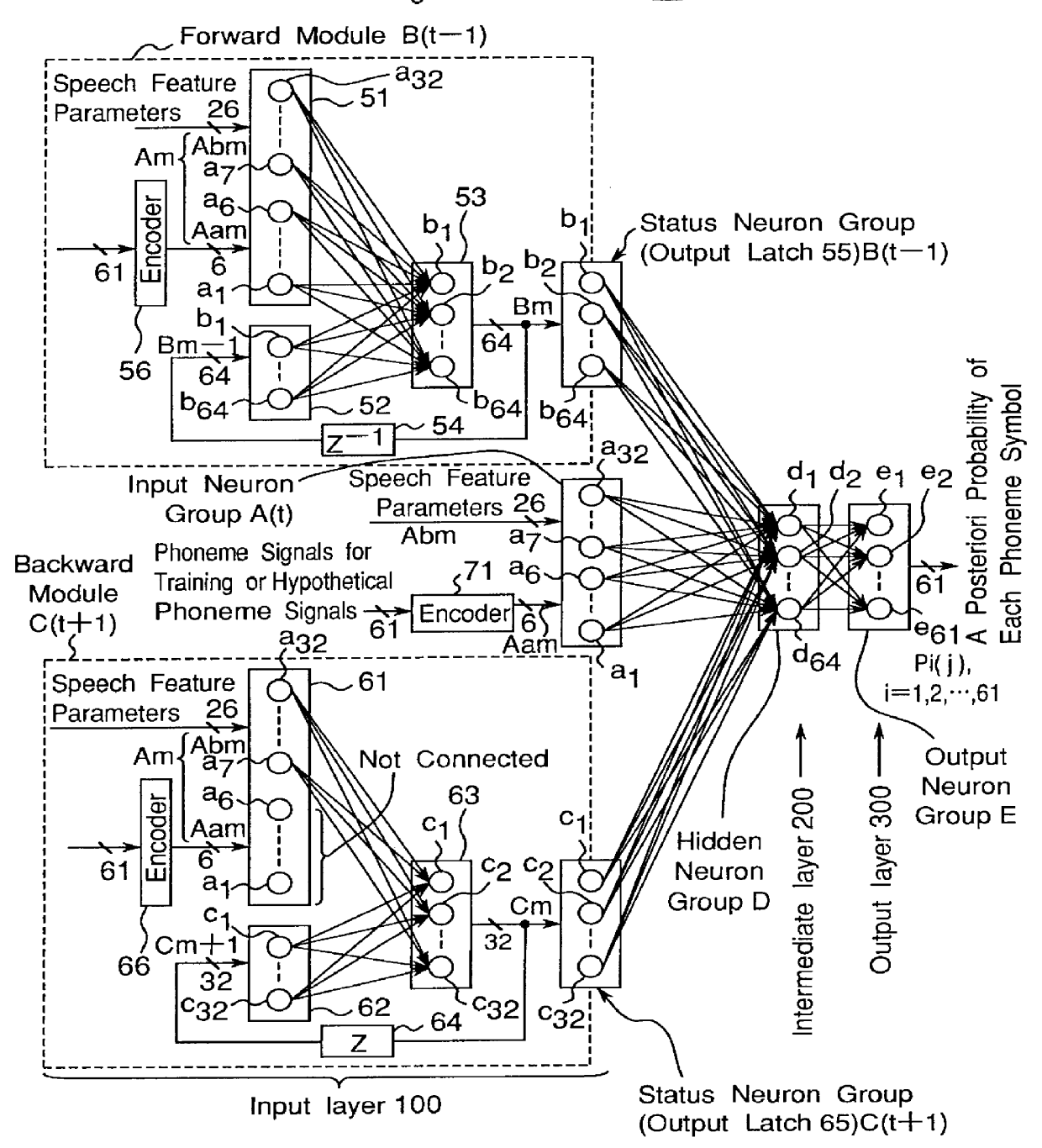
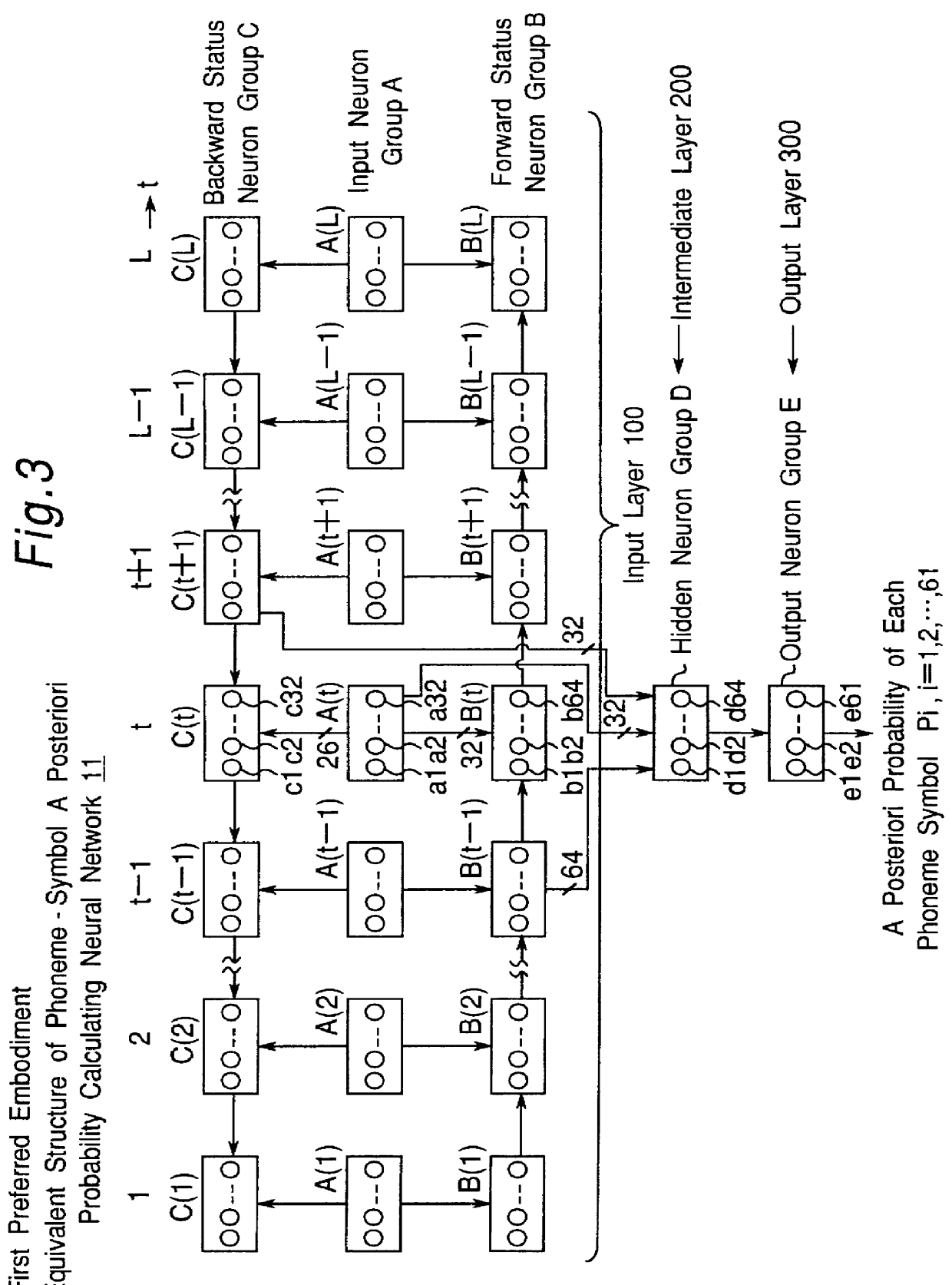
Apparatus for calculating a posterior probability of phoneme symbol, and speech recognition apparatus
There are disclosed an apparatus for calculating a posteriori probabilities of phoneme symbols and a speech recognition apparatus using the apparatus for calculating a posteriori probabilities of phoneme symbols. A feature extracting section extracts speech feature parameters from a speech signal of an uttered speech sentence composed of an inputted character series, and a calculating section calculates a a posteriori probability of a phoneme symbol of the speech signal, by using a bidirectional recurrent neural network. The bidirectional recurrent neural network includes (a) an input layer for receiving the speech feature parameters extracted by the feature extracting means and a plurality of hypothetical phoneme symbol series signals, (b) an intermediate layer of at least one layer having a plurality of units, and (c) an output layer for outputting a a posteriori probability of each phoneme symbol. The input layer includes (a) a first input neuron group having a plurality of units, for receiving a plurality of speech feature parameters and a plurality of phoneme symbol series signals, (b) a forward module, and (c) a backward module.
Owner:A T R ONSEI HONYAKU TSUSHIN KENKYUSHO KK
Highly constrained tomography for automated inspection of area arrays
InactiveUS20050105682A1Radiation/particle handlingUsing wave/particle radiation meansPattern recognitionPrior information
A tomographic reconstruction method and system incorporating Bayesian estimation techniques to inspect and classify regions of imaged objects, especially objects of the type typically found in linear, areal, or 3-dimensional arrays. The method and system requires a highly constrained model M that incorporates prior information about the object or objects to be imaged, a set of prior probabilities P(M) of possible instances of the object; a forward map that calculates the probability density P(D|M), and a set of projections D of the object. Using Bayesian estimation, the posterior probability p(M|D) is calculated and an estimated model MEST of the imaged object is generated. Classification of the imaged object into one of a plurality of classifications may be performed based on the estimated model MEST, the posterior probability p(M|D) or MAP function, or calculated expectation values of features of interest of the object.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
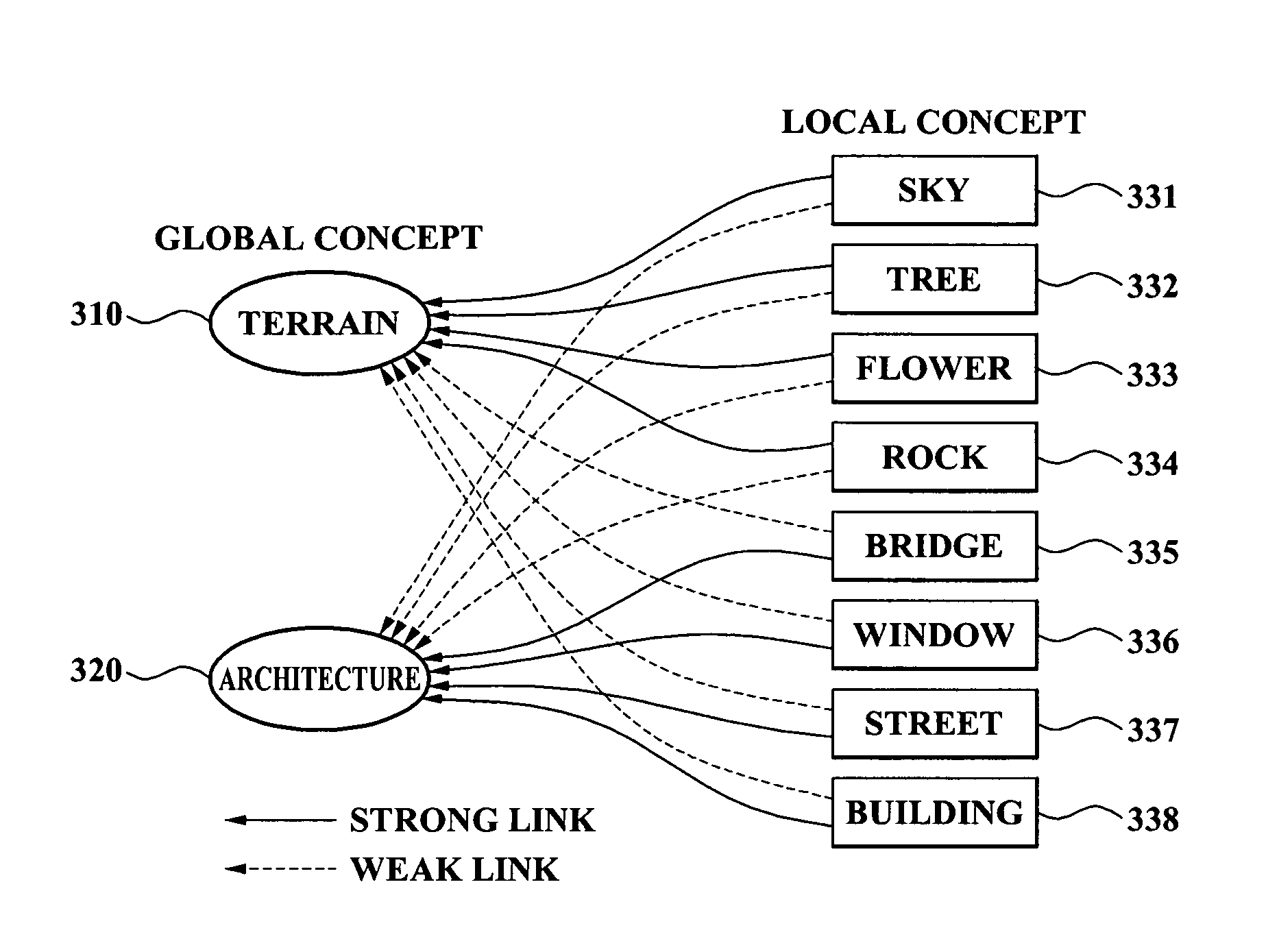
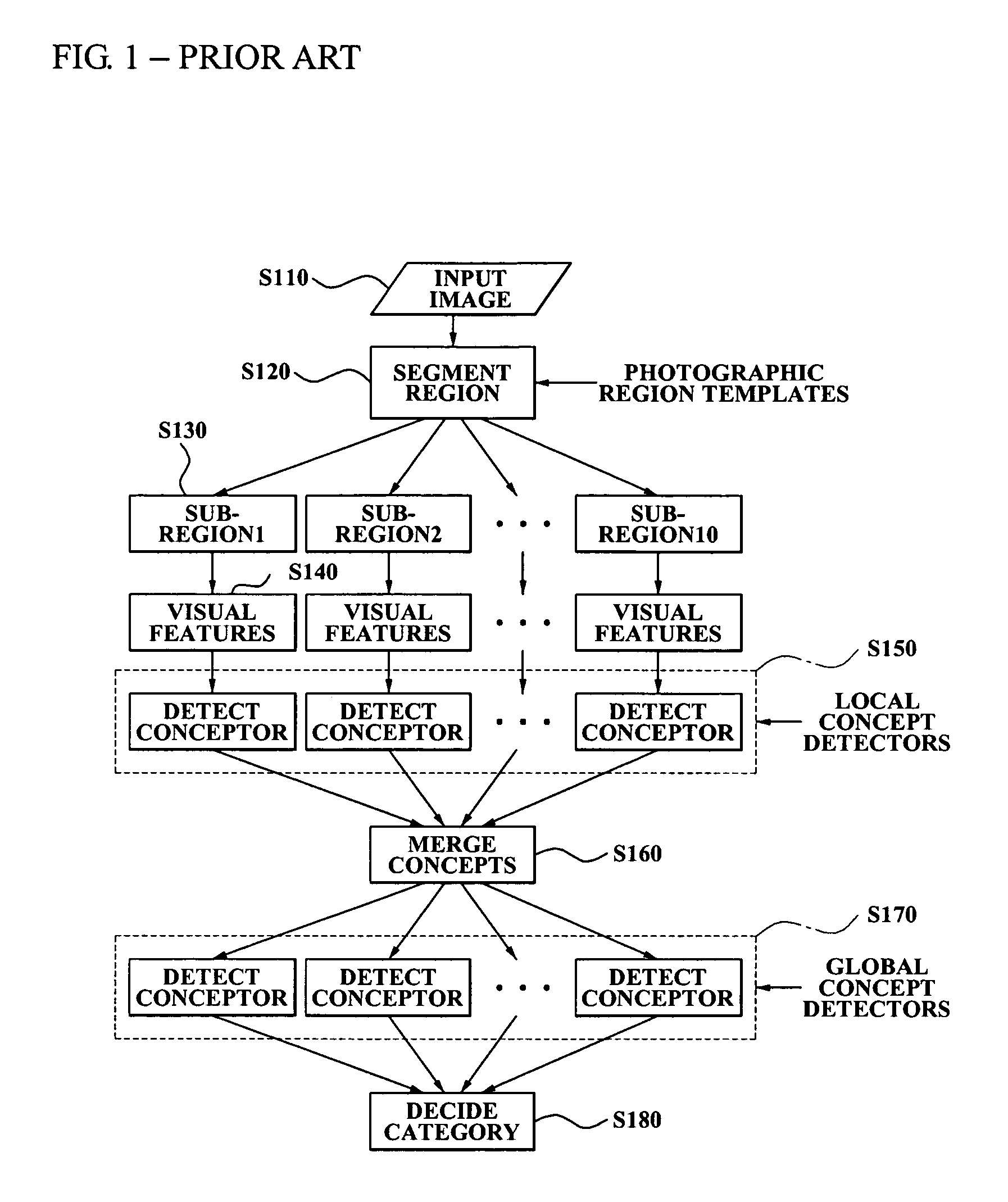
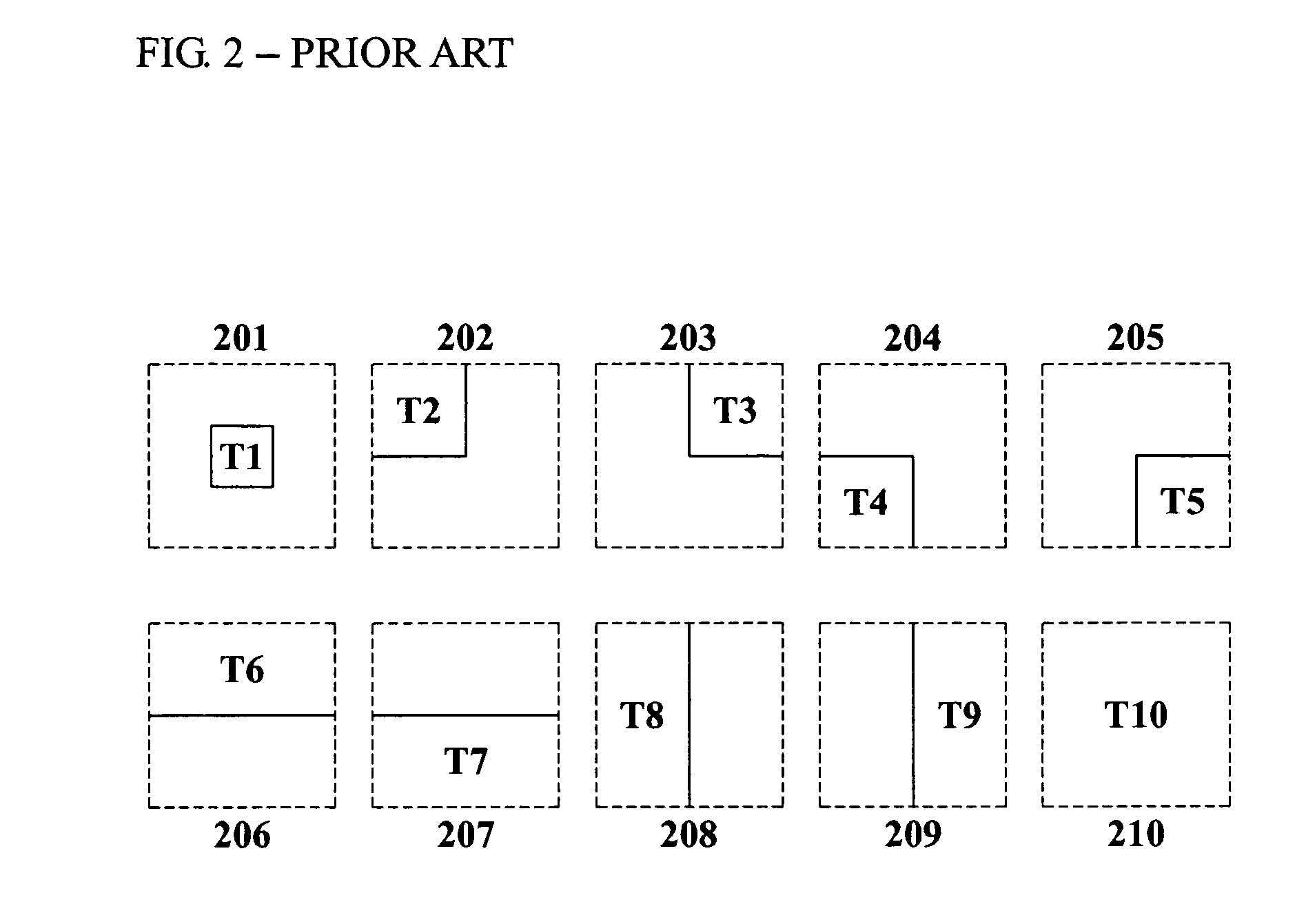
Method, system, and medium for classifying category of photo
InactiveUS20080013940A1Amount of timeMinimally deteriorating category classification performanceImage analysisProcessed material treatmentRegression analysisClassification methods
A photo category classification method including dividing a region of a photo based on content of the photo and extracting a visual feature from the segmented region of the photo, modeling at least one local semantic concept included in the photo according to the extracted visual feature, acquiring a posterior probability value from confidence values acquired from the modeling of the at least one local semantic concept by normalization using regression analysis, modeling a global semantic concept included in the photo by using the posterior probability value of the at least one local semantic concept; and removing classification noise from a confidence value acquired from the modeling the global semantic concept.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Extensible bayesian network editor with inferencing capabilities
A system for the representation, editing, evaluation, and inference of graphical models is disclosed which can be used to construct and evaluate a graphical model or graphical network and to calculate inference values. An efficient method of updating graphical models is demonstrated, and provides the basis for an improved system for manipulation and evaluation of probabilistic models. The graphical network editor is useful in the construction of graphical modes such as Bayesian Networks. The graphical network and network graphical user interface (GUI) are used in conjunction with each other to model a system wherein failure probabilities and the current state of components are taken into account to monitor the health and progress of a system for an engineer or engineering software to evaluate and monitor. The evaluation is useful in the monitoring of assets and other real systems having multiple, dependent, and independently operating components such as a pump, a manufacturing plant, a production line, an assembly line, where asset health and quality control is a concern. The asset components each influencing some overall outcome of a system or situation. Success or failure or probability of success, probability of failure and health of the system can be monitored and manipulated by altering the values of prior probability and posterior probability values. Failure correlation between components can be evaluated wherein failure rates of asset is unknown. Production and quality can be monitored and altered.
Owner:QUANTUM LEAP RES
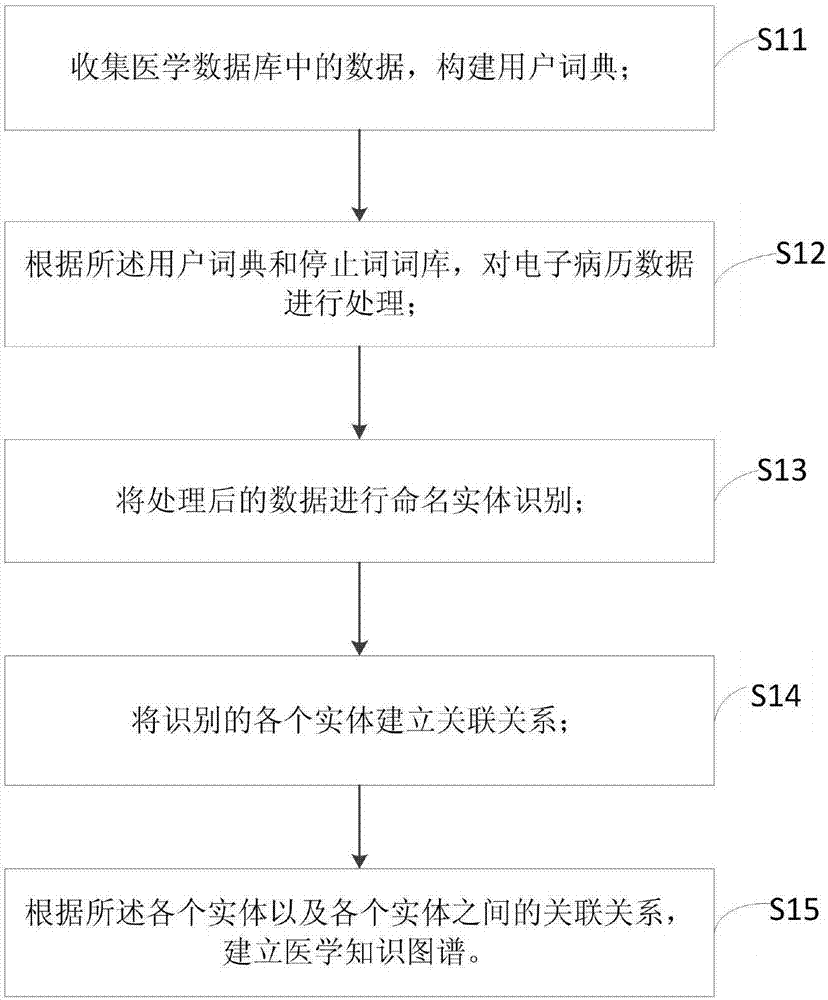
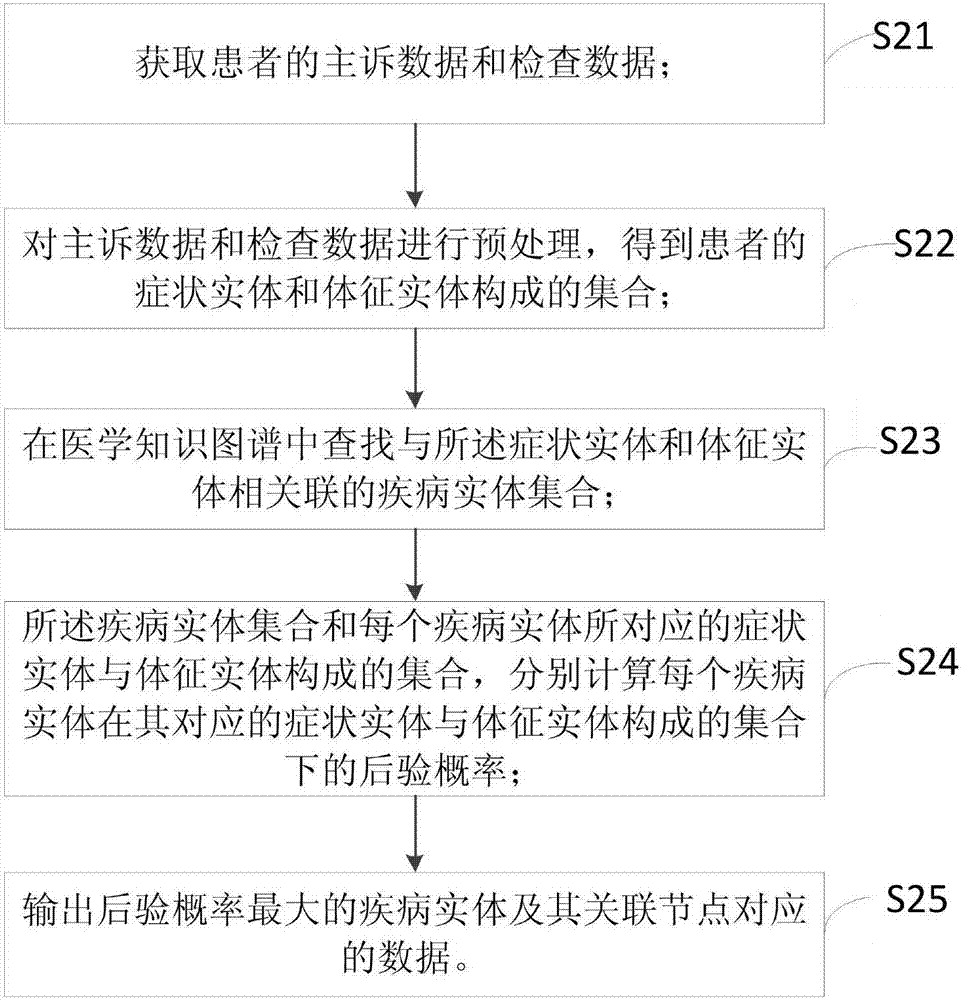
Method and device for establishing medical knowledge graph, and auxiliary diagnosis method
ActiveCN107145744AReduce workloadRelieve medical stressMedical data miningMedical automated diagnosisMedical recordNODAL
The invention discloses a method and device for establishing a medical knowledge graph, and an auxiliary diagnosis method. The method for establishing the medical knowledge graph comprises the steps that a user dictionary is established according to a medical database; electronic medical record data is processed, and named entity recognition is conducted; correlation relations are established for each recognized entity; and the medical knowledge graph is established according to the correlation relations. The auxiliary diagnosis method based on the medical knowledge graph comprises the steps that a patient's chief complaint data and inspection data are acquired and processed, so that a symptom entity and a sign entity of the patient can be obtained; a disease entity correlated with the symptom entity and the sign entity is searched in the medical knowledge graph, and a posterior probability of each disease entity in a set composed of the corresponding symptom entity and the sign entity is computed respectively; and the disease entity with the maximum posterior probability and data corresponding to correlated nodes of the disease entity are output. According to the invention, intelligent auxiliary diagnosis is provided for clinical medical science, so that working burdens of medical workers are relieved; medical stress is relieved; and occurrence rate of medical accidents is reduced.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
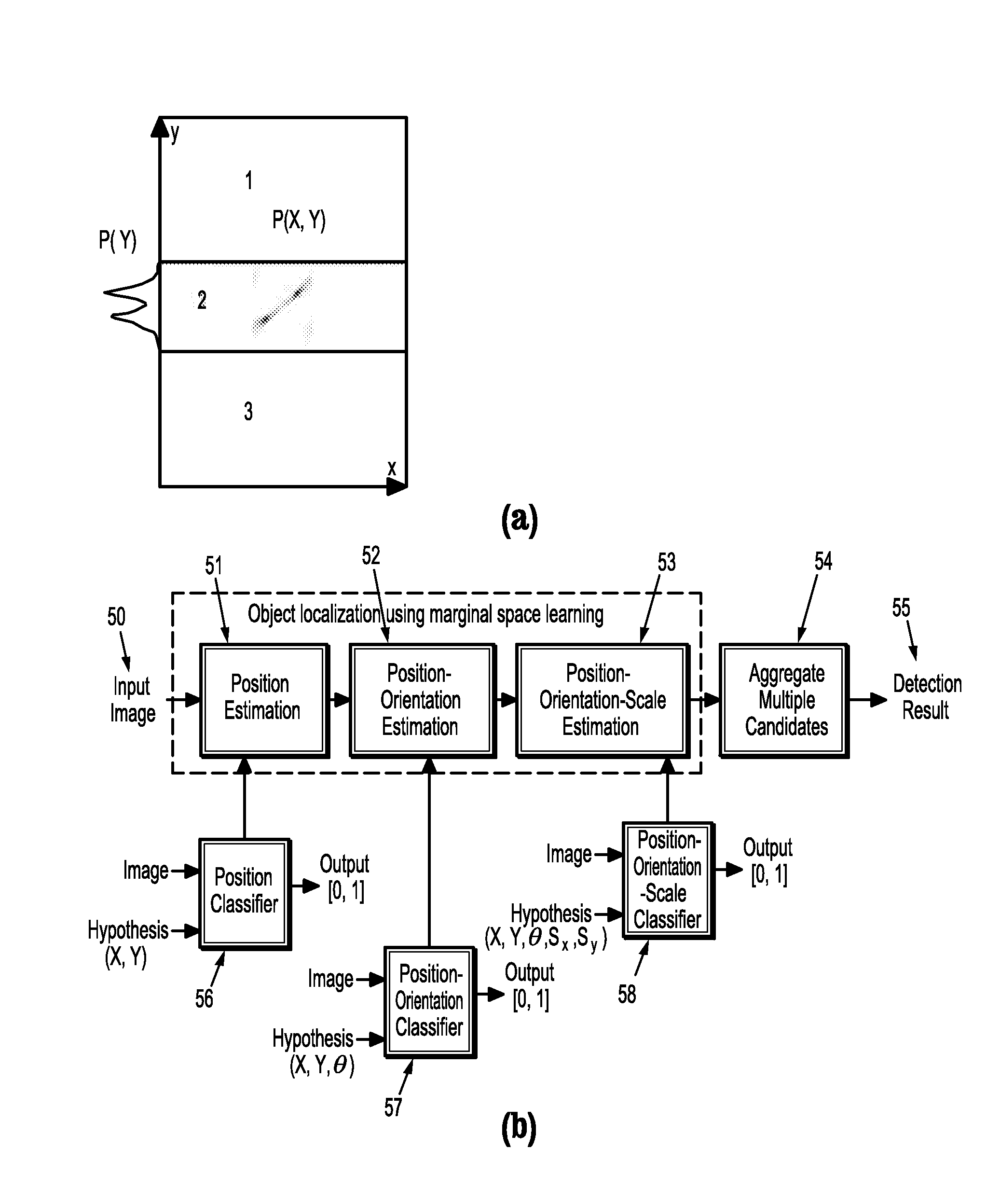
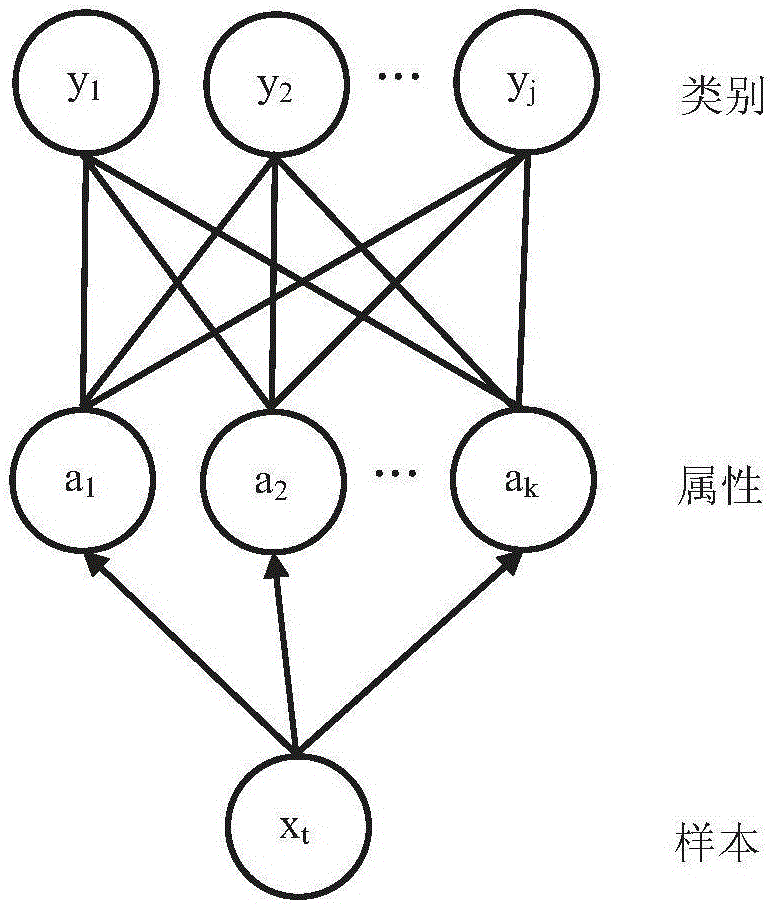
Marginal space learning for multi-person tracking over mega pixel imagery
ActiveUS20120274781A1Facilitate high accuracy target trackingFacilitate re-acquisitionTelevision system detailsImage enhancementHypothesisMarginal space learning
A method for tracking pedestrians in a video sequence, where each image frame of the video sequence corresponds to a time step, includes using marginal space learning to sample a prior probability distribution p(xt|Zt−1) of multi-person identity assignments given a set of feature measurements from all previous image frames, using marginal space learning to estimate an observation likelihood distribution p(zt|xt) of the set of features given a set of multi-person identity assignments sampled from the prior probability distribution, calculating a posterior probability distribution p(xt|Zt) from the observation likelihood distribution p(zt|xt) and the prior probability distribution p(xt|Zt−1), and using marginal space learning to estimate the prior probability distribution p(xt+1|Zt) for a next image frame given the posterior probability distribution p(xt|Zt) and a probability p(xt+1|xt), where the posterior probability distribution of multi-person identity assignments corresponds to a set of pedestrian detection hypotheses for the video sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Pedestrian recognition method based on combination of depth learning and property learning
ActiveCN104992142ALow costImprove recognition rateBiometric pattern recognitionPedestrian recognitionDeconvolution
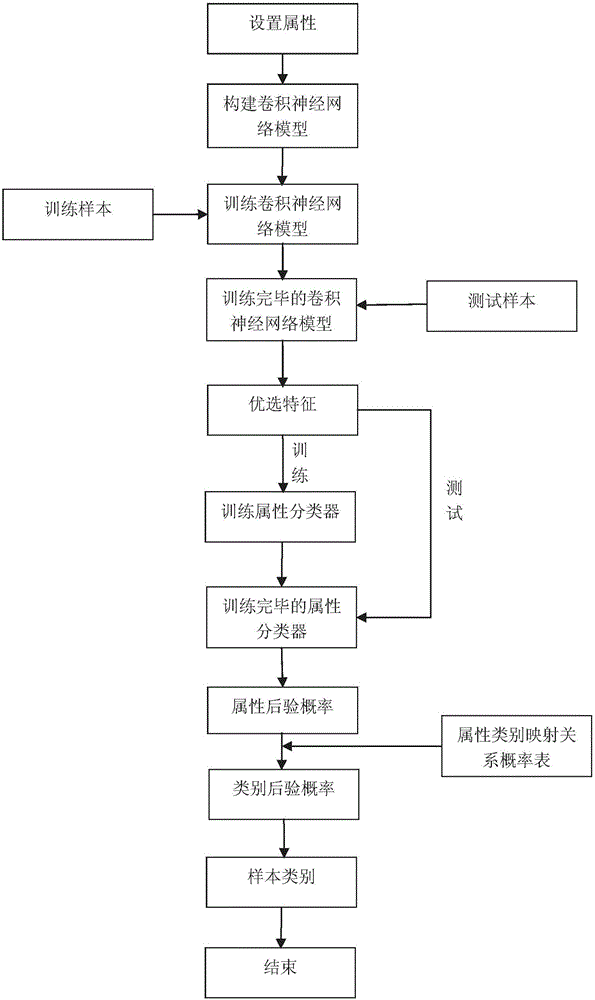
The invention discloses a pedestrian recognition method based on combination of depth learning and property learning. According to the invention, a convolution neural network containing five implicit strata is constructed. Network training is performed by an anti-convolution method and a concept of property learning is combined. Preferred features obtained from the convolution neural network are input to property classifiers, so that the posterior probability of the property of a sample is obtained. Then by combining with a property class mapping relation, the posterior probability of the class is obtained, so that the class of the sample can be judged. The method is good in detection recognition performance and intrinsic features of an image can be extracted. Besides, since the property has better semantic expression performance than low-stratum features and due to the insensitivity to light and view angles, the algorithm has a good recognition effect.
Owner:南京昭视智能科技有限公司
Method and device for detecting road traffic abnormal events in real time
InactiveCN103971521AImprove work efficiencyReduce work intensityDetection of traffic movementClosed circuit television systemsMultiple frameMerge algorithm
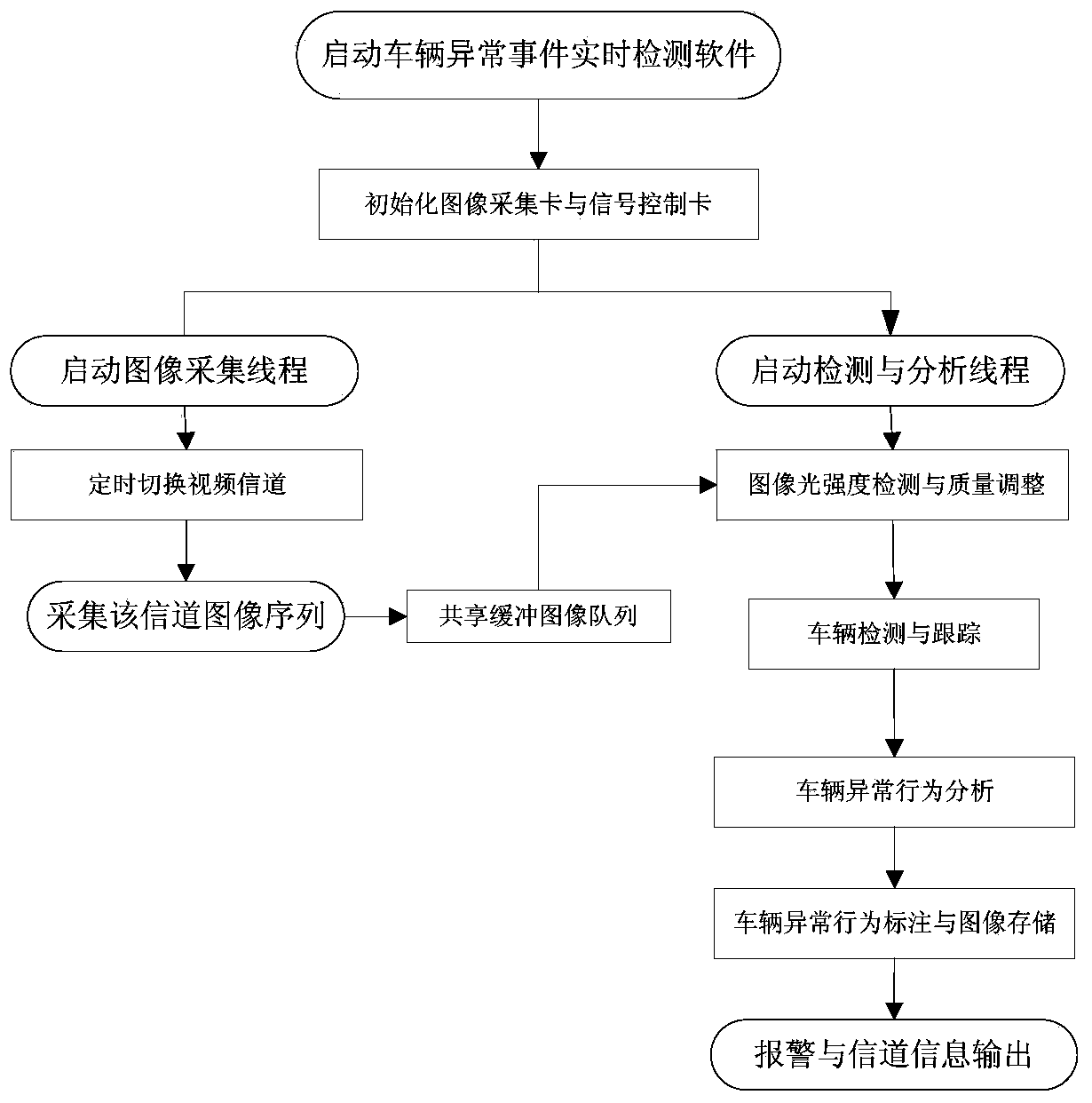
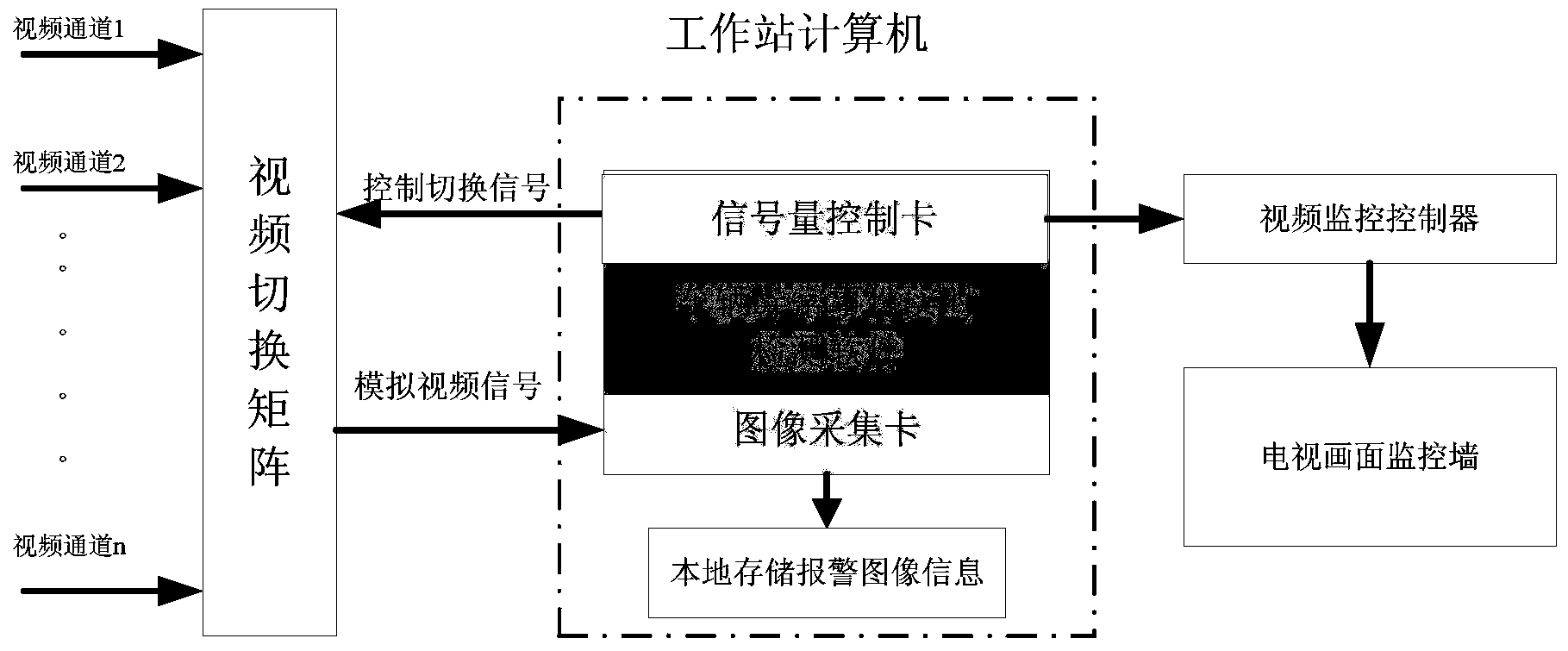
The invention provides a method and device for detecting road traffic abnormal events in real time. The method includes the steps of monitoring a road, obtaining a plurality of frames of continuous monitor images, extracting bright white segments from the monitor images, obtaining lane lines and lane end points through processing, building a lane model, determining a bidirectional detection area of a lane according to the lane model, detecting a moving object in the bidirectional detection area according to a Gaussian mixture model background subtraction method, determining the position of the moving object, building the mapping relation between the moving target and an actual vehicle according to the position of the moving target in the multiple frames of continuous monitor images by the adoption of a posterior probability splitting and merging algorithm and a feature point matching and tracking method, obtaining the running track and running speed of the actual vehicle, detecting the lane model and the running track and running speed of the actual vehicle according to a prestored road traffic abnormal behavior semantic model, and judging whether the road traffic abnormal events exist or not. The method has the advantages of being intelligent, high in accuracy and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method and device for calculating bit error rate of received signal
InactiveUS20070162788A1Low circuit complexityReduce loadData representation error detection/correctionError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorDigital radioData field
System and method of estimating radio channel bit error rate (BER) in a digital radio telecommunications system wherein the soft output of the turbo decoder is used as pointer or index to look-up-tables containing the bit-wise BER of a certain bit in the data field of the received frame. A quantizer quantizes the received data frame and the quantized bit operates on a switch which selects the appropriate look-up-table. By means of accumulation and scaling the average BER of a certain amount of bits are calculated. Decoding bit-errors may occur but as they are submitted to posterior probability estimation, systematic errors which normally happen at low SNR are avoided.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
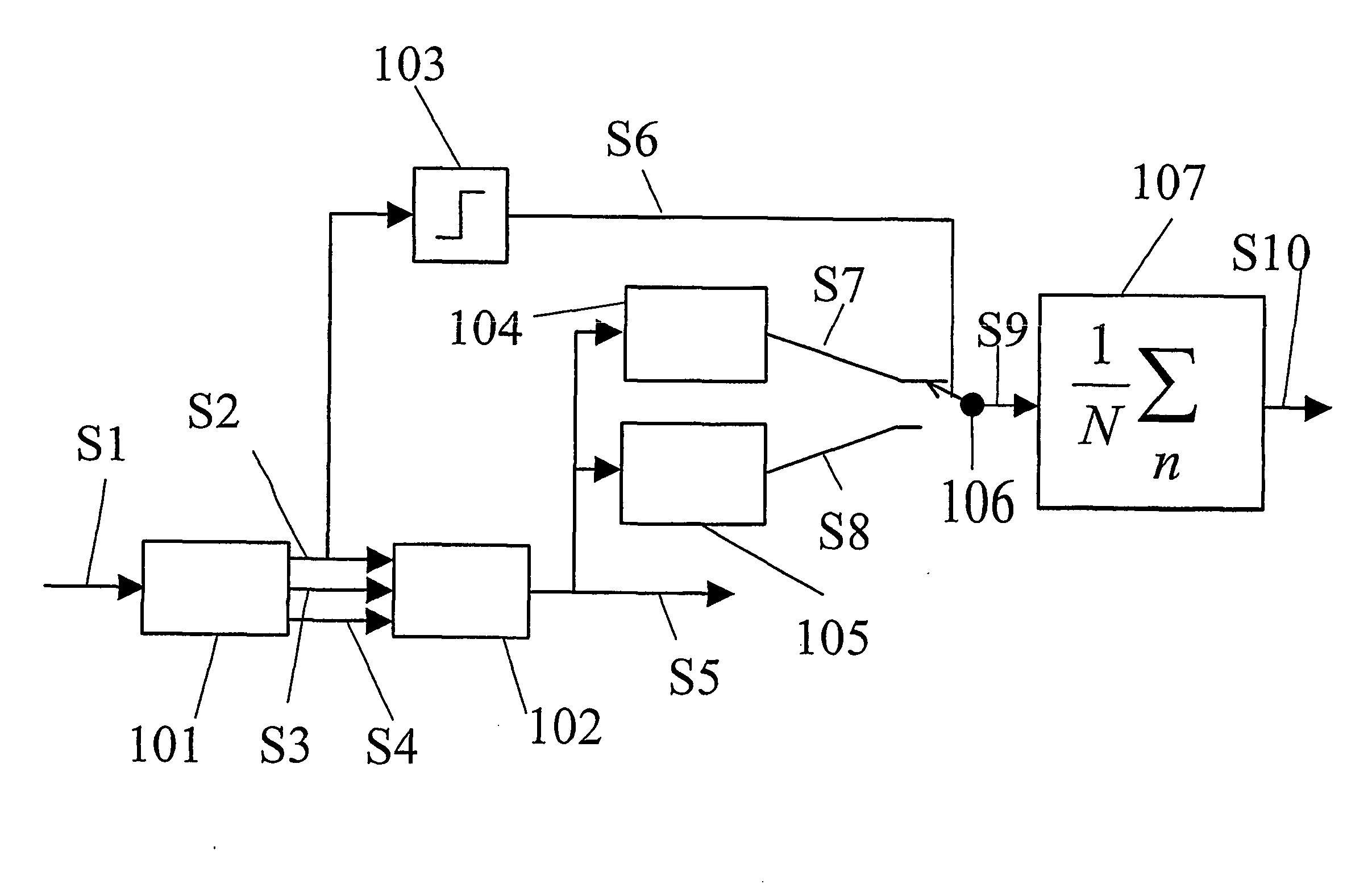
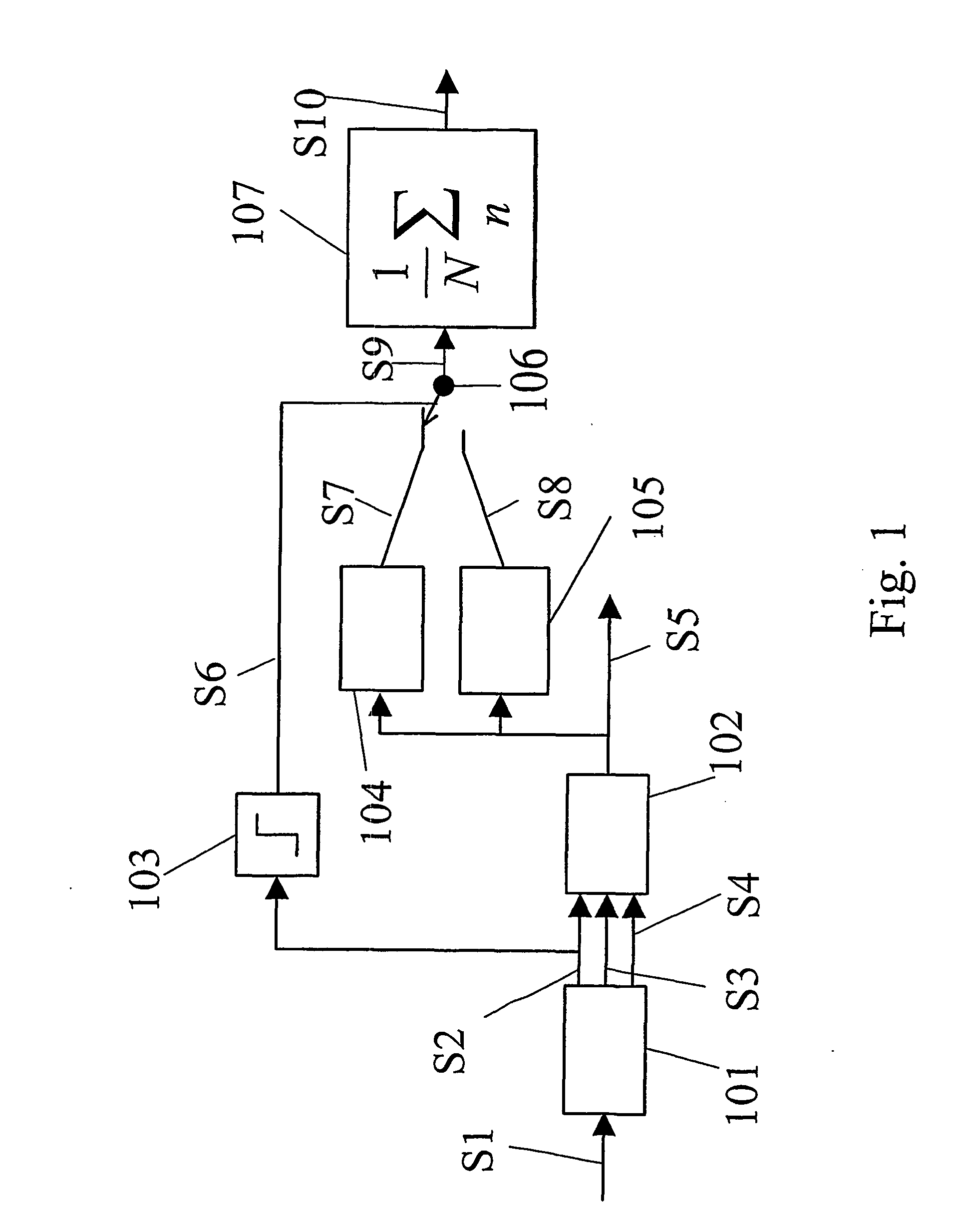
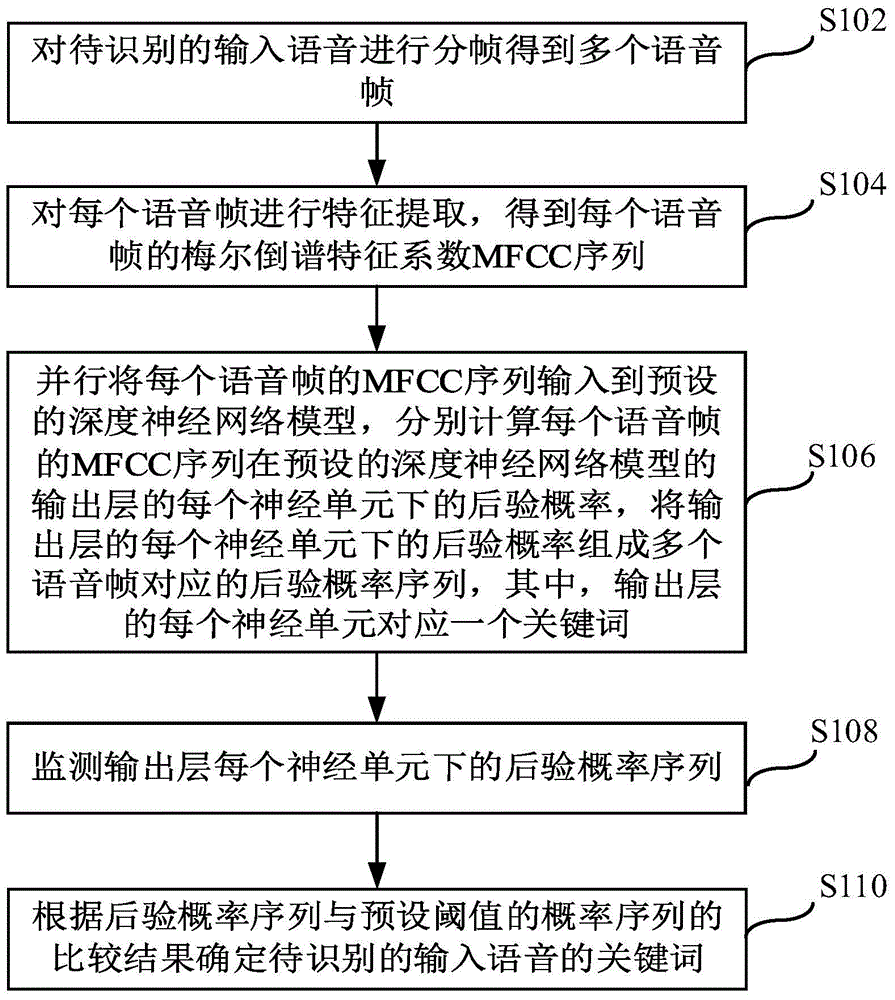
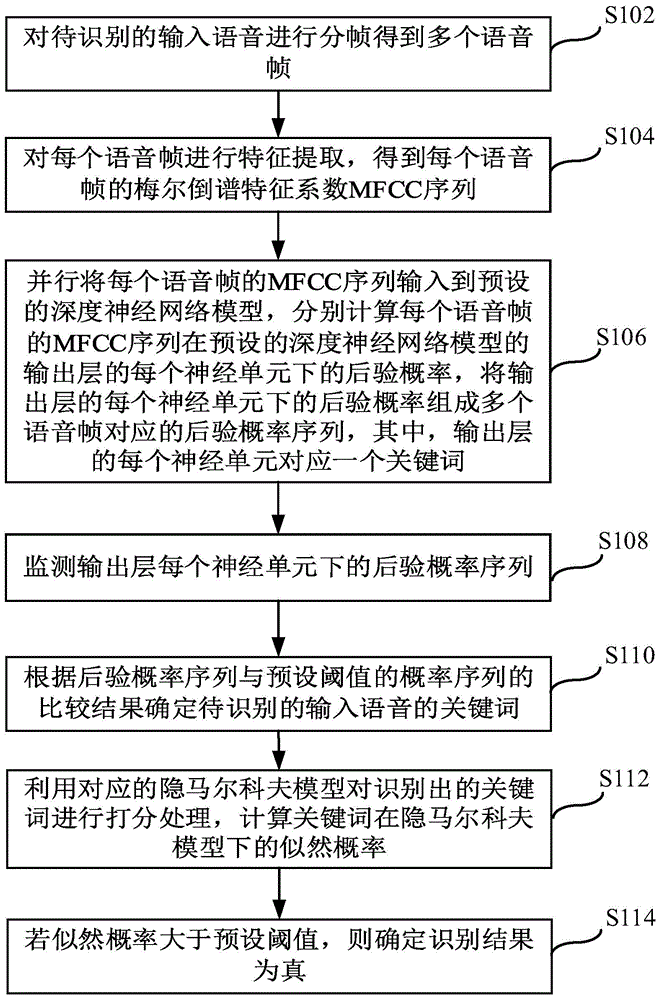
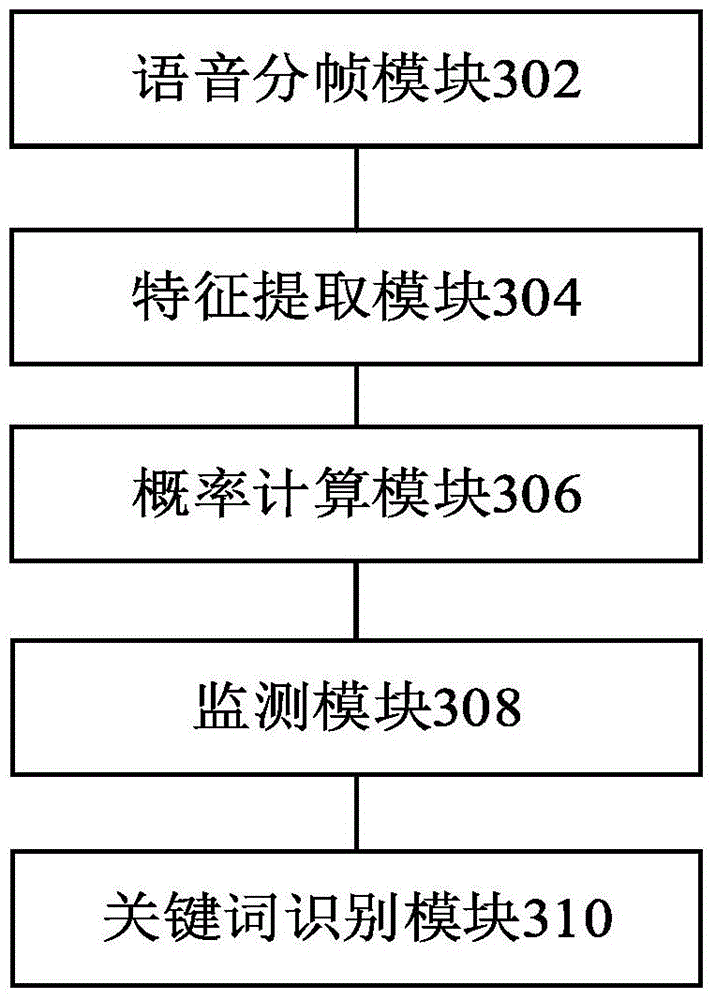
Voice keyword identification method and apparatus based on deep neural network
InactiveCN105679316AFast recognitionAlleviate the recognition delay problemSpeech recognitionFeature extractionNetwork model
Owner:SHENZHEN WEIFU ROBOT TECH CO LTD
Bayesian belief network query tool
InactiveUS20090106734A1Easy to judgeDigital data processing detailsProbabilistic networksData setData mining
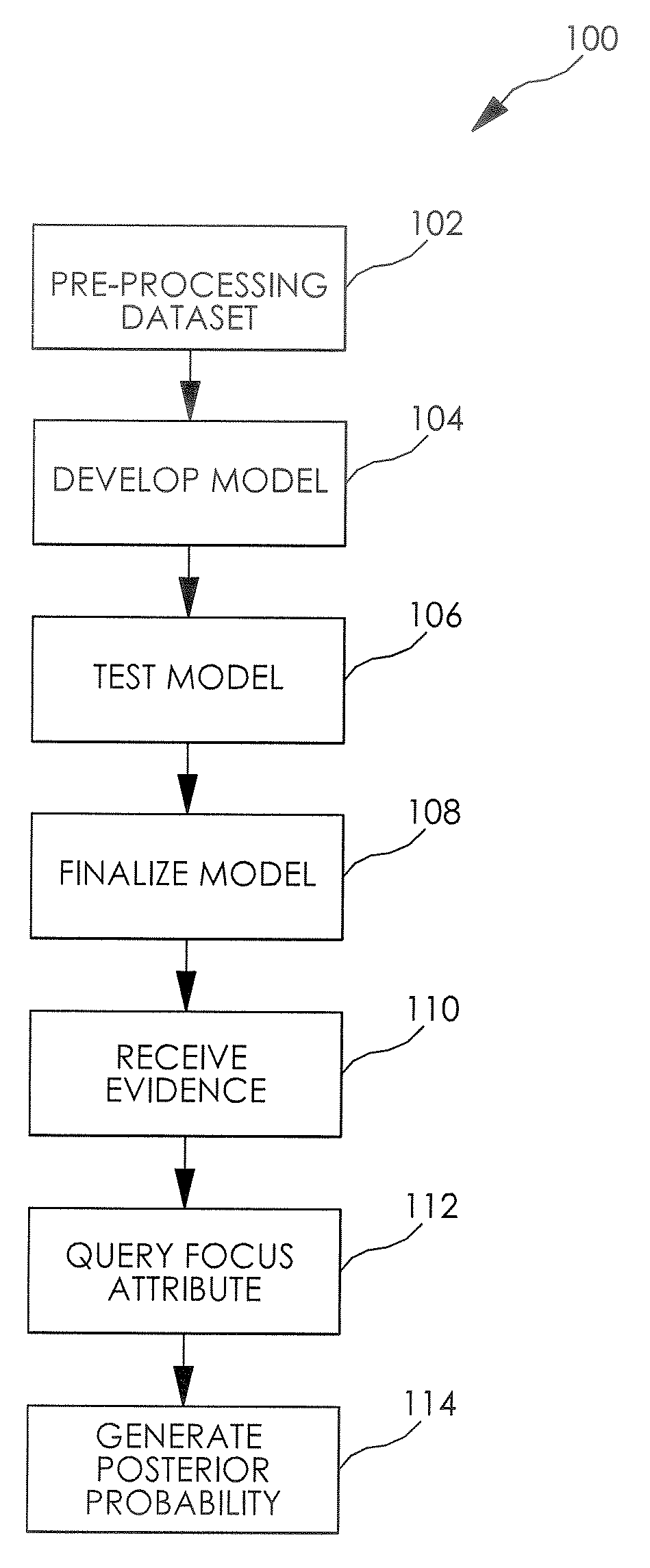
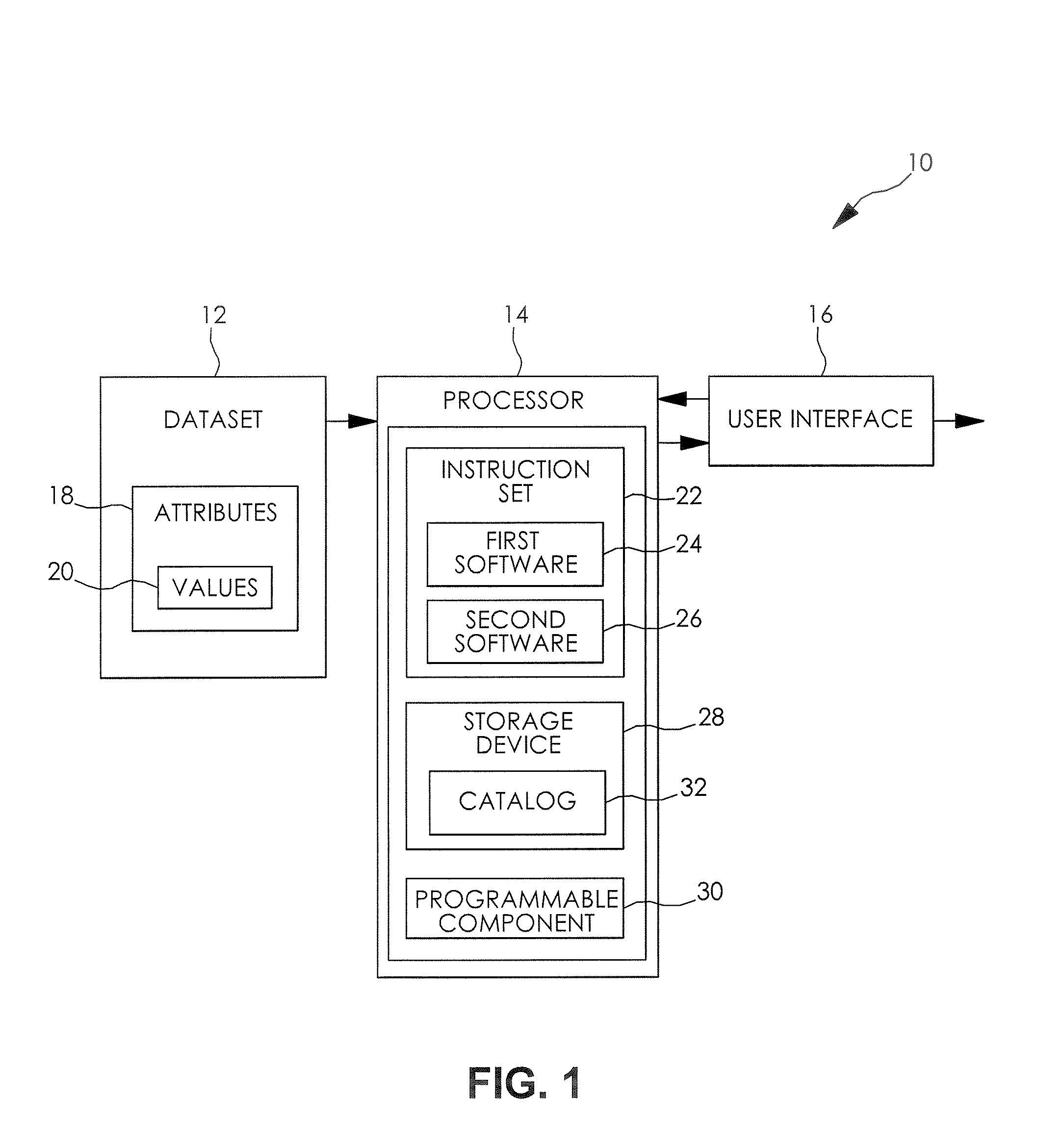
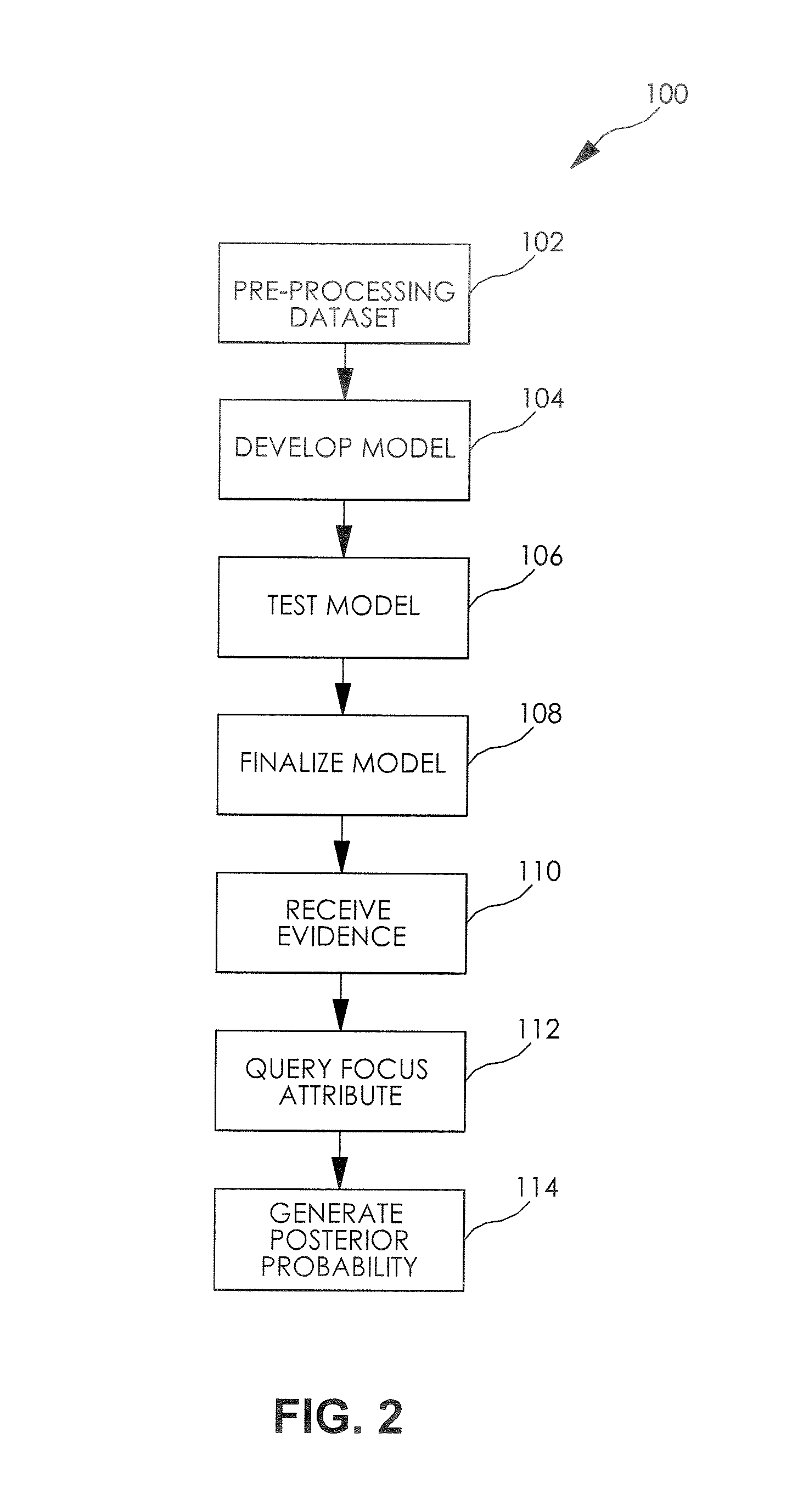
A dataset query tool is disclosed, the query tool including a dataset having a plurality of attributes, wherein each of the attributes has one of a plurality of potential values, a processor adapted to develop a model of the dataset and calculate a posterior probability of at least one of the attributes of the dataset, wherein the model represents an approximation of the joint probability distribution of the dataset, a user interface in communication with the processor, wherein the user interface provides a means for a user to selectively identify values for at least one of the attributes of the dataset and selectively query at least one of the other attributes for a posterior probability calculation based on the identified values.
Owner:RIESEN MICHAEL J +1
Image appearance based loop closure detecting method in monocular vision SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping)
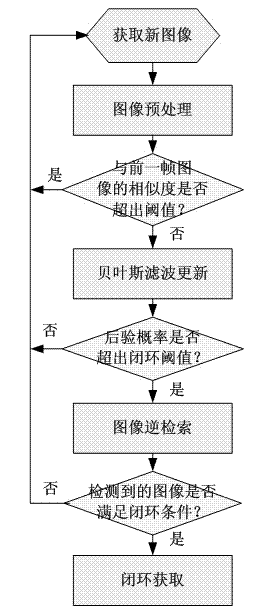
InactiveCN102831446AReduce the amount of calculationLower requirementCharacter and pattern recognitionPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimultaneous localization and mappingVisual perception
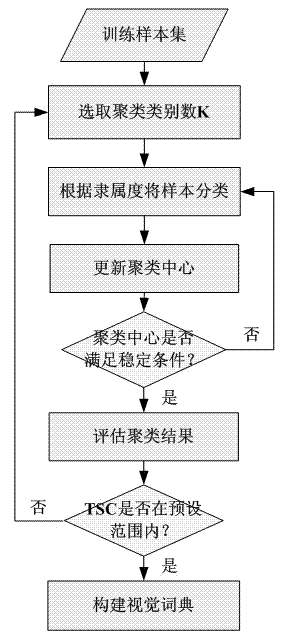
The invention discloses an image appearance based loop closure detecting method in monocular vision SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping). The image appearance based loop closure detecting method includes acquiring images of the current scene by a monocular camera carried by a mobile robot during advancing, and extracting characteristics of bag of visual words of the images of the current scene; preprocessing the images by details of measuring similarities of the images according to inner products of image weight vectors and rejecting the current image highly similar to a previous history image; updating posterior probability in a loop closure hypothetical state by a Bayesian filter process to carry out loop closure detection so as to judge whether the current image is subjected to loop closure or not; and verifying loop closure detection results obtained in the previous step by an image reverse retrieval process. Further, in a process of establishing a visual dictionary, the quantity of clustering categories is regulated dynamically according to TSC (tightness and separation criterion) values which serve as an evaluation criterion for clustering results. Compared with the prior art, the loop closure detecting method has the advantages of high instantaneity and detection precision.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
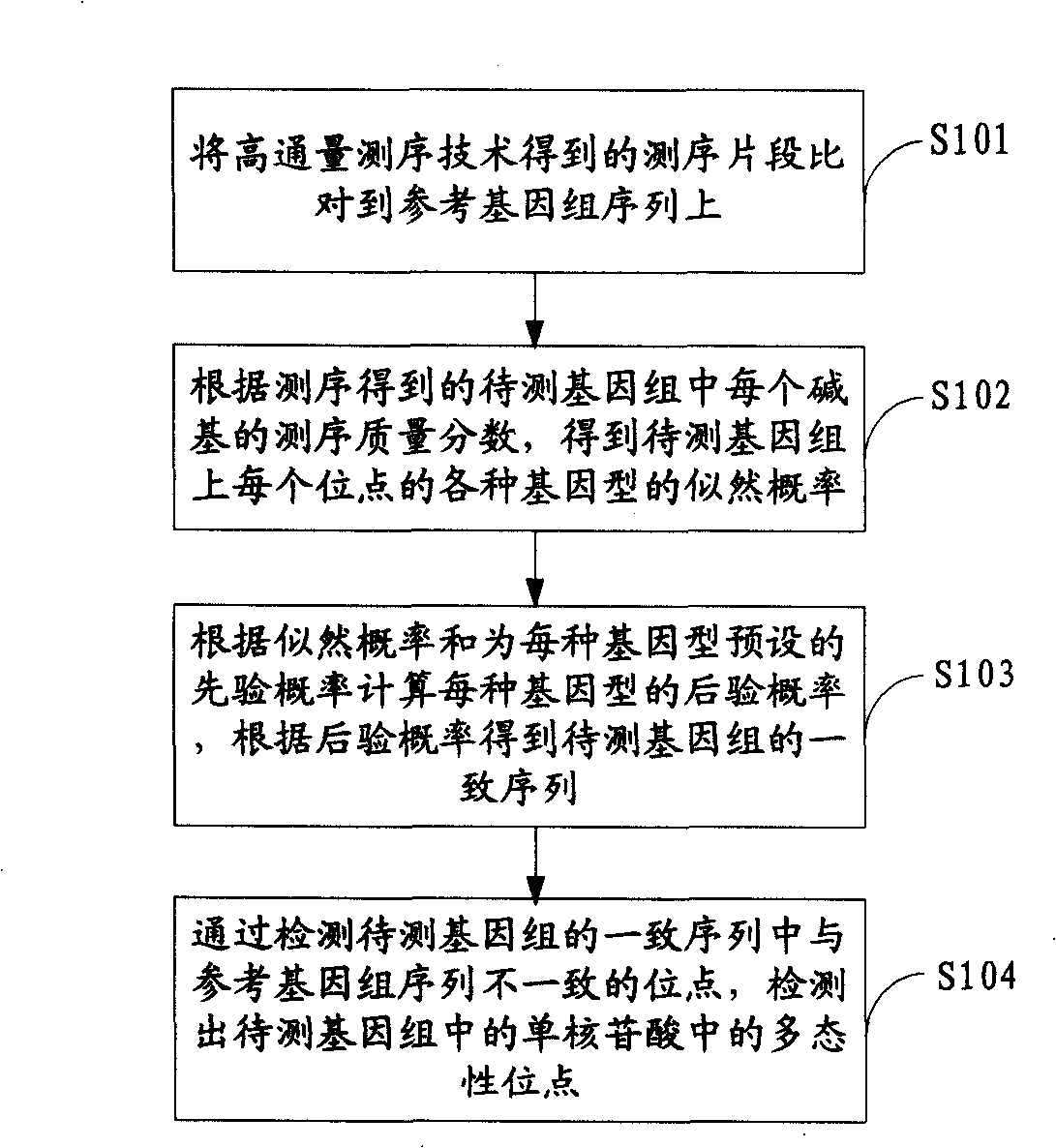
Method for detecting mononucleotide polymorphism
ActiveCN101539967AMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceGenotype determination
The invention is applicable to the field of biological engineering and provides a method for detecting mononucleotide polymorphism. The method comprises the following steps: sequencing fragments obtained by high throughput sequencing technology are compared on a referenced genome sequence; the likelihood ratio of various genotypes of the corresponding sites on the genome to be tested is obtained according to the sequencing mass fraction of each basic group in the genome to be tested and obtained by sequencing; the posterior probability of each genotype of each site on the referenced genome is calculated according to the likelihood ratio and the prior probability preset for each genotype, and the genotype which has the highest posterior probability is determined as the most likely right genotype of the corresponding sites on the genome to be tested to obtain the consistent sequence of the genome to be tested; and the sites of the genome to be tested, which are inconsistent with the sequence of the referenced genome in the consistent sequence are detected to obtain the polymorphism sites of the genome to be tested. The embodiment of the invention can achieve a more accurate test result as the influence of the prior probability on mononucleotide polymorphism test result is considered in advance.
Owner:WUHAN BGI CLINICAL LAB CO LTD
Classification using probability estimate re-sampling
ActiveUS7194380B2Improve fitEffective calculationMathematical modelsFinanceAlgorithmClass membership
Embodiments of a computer-implemented method of calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership given combinations of attribute values of a pair of attributes are disclosed. The calculating is performed on the basis of data representing a training set of a plurality of instances defined by attribute values for a plurality of attributes together with a class membership outcome. Embodiments of the method comprise calculating first and second estimates of a posterior probability of class membership given attribute values of a first and second attribute of the pair, respectively, and binning the first and second estimates into a respective plurality of first and second probability range bins. Instances of the training set are mapped to combinations of one of each of the first and second pluralities of probability range bins, and on the basis of the mapping, calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership.
Owner:CHORDIANT SOFTWARE INT
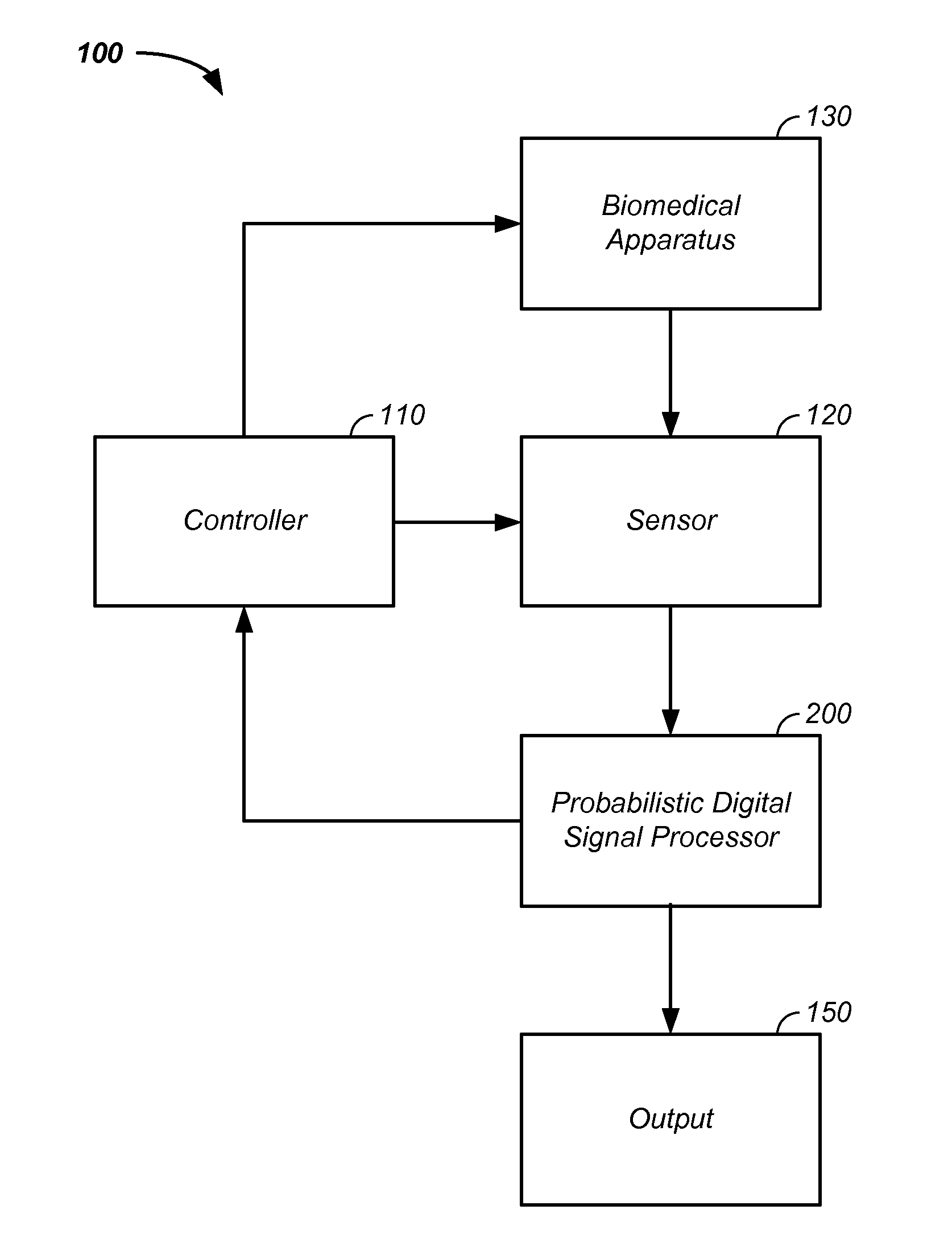
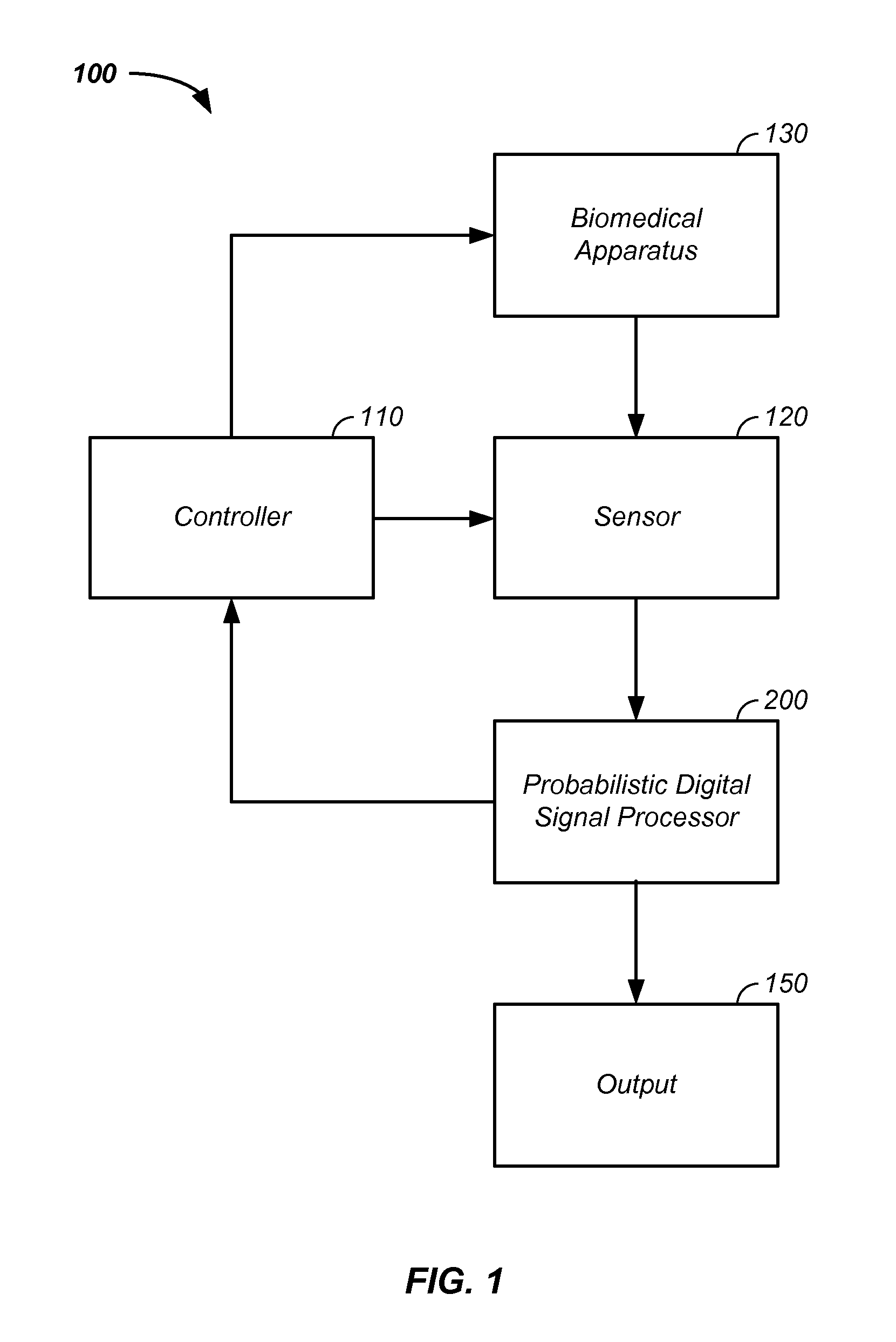
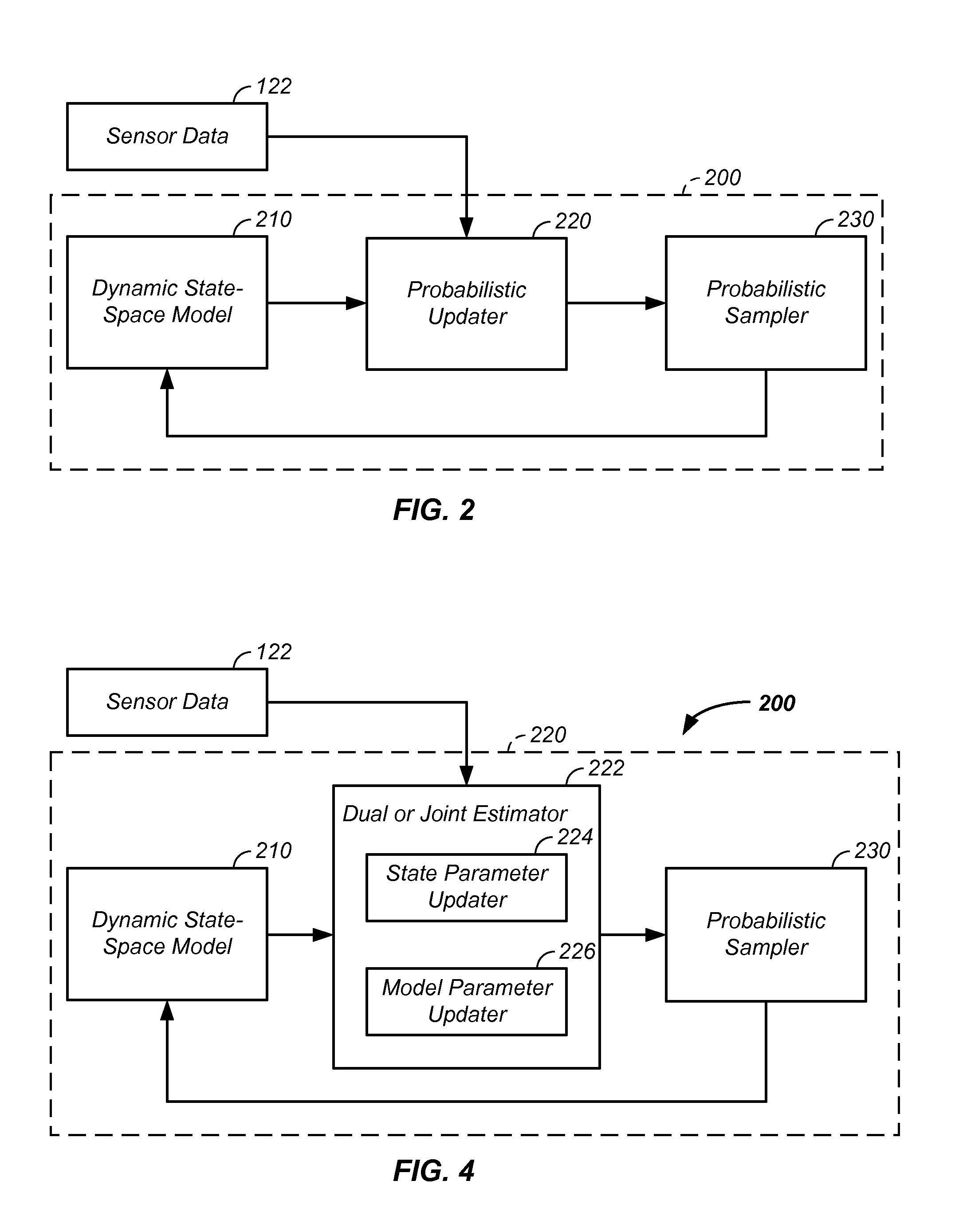
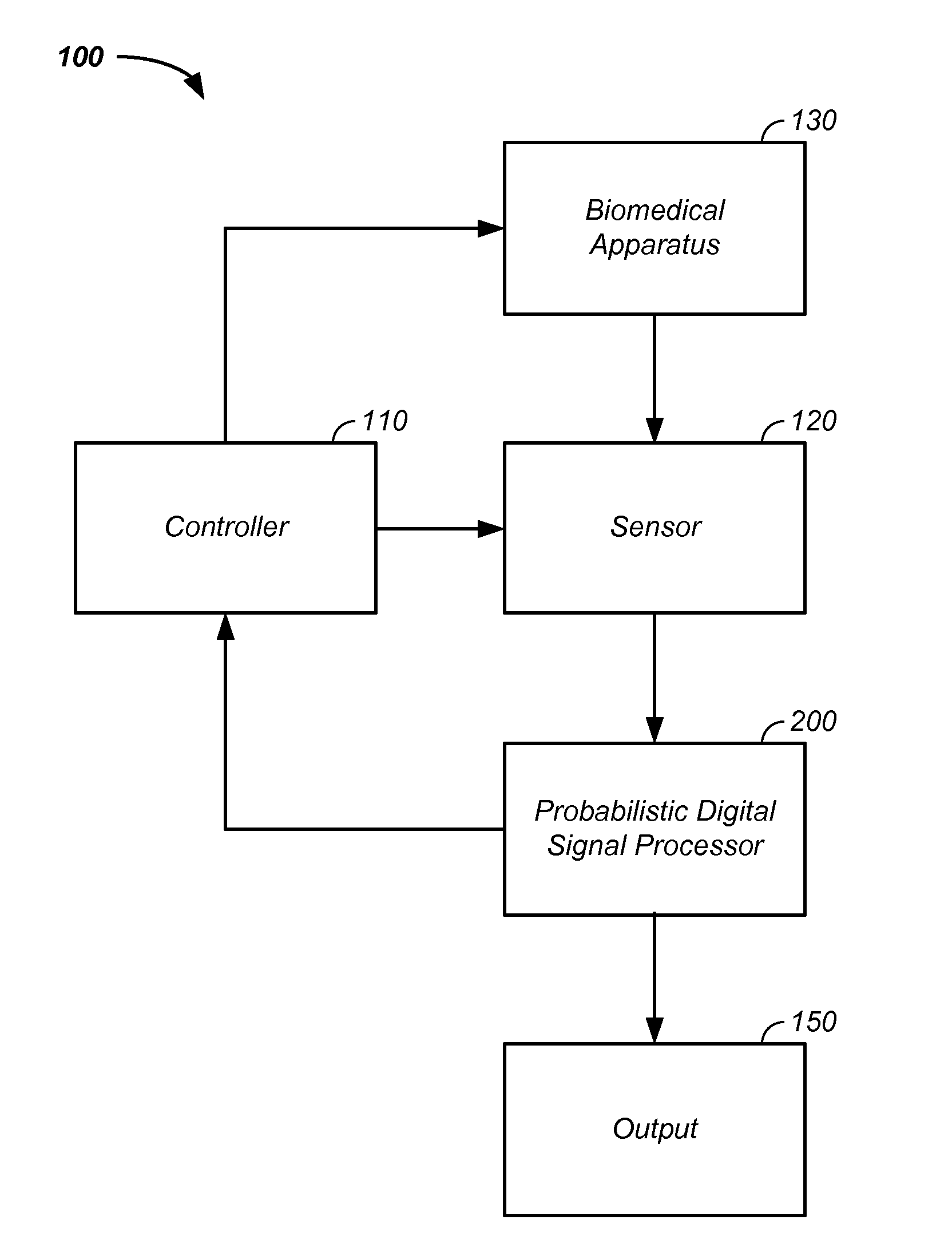
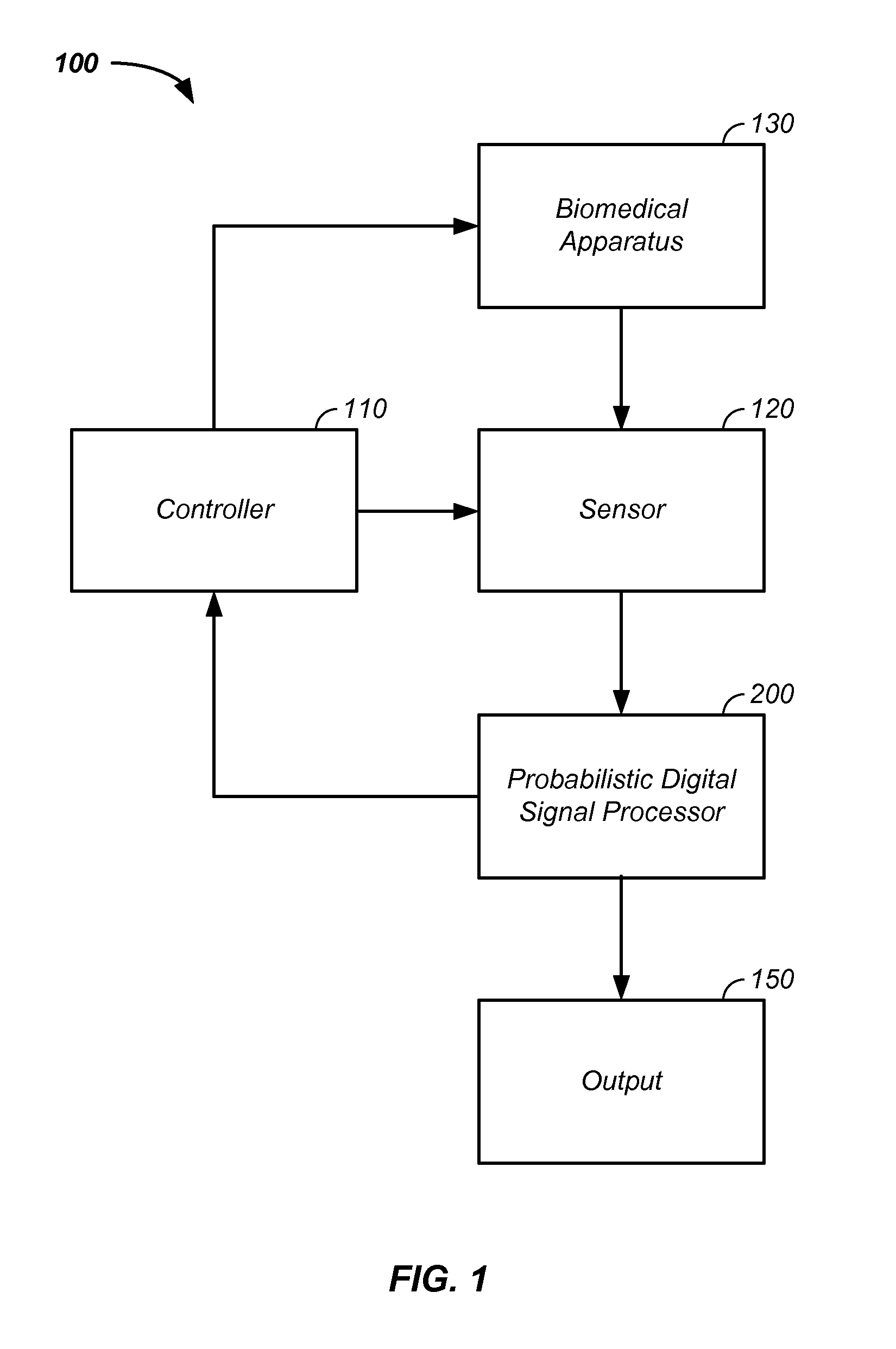
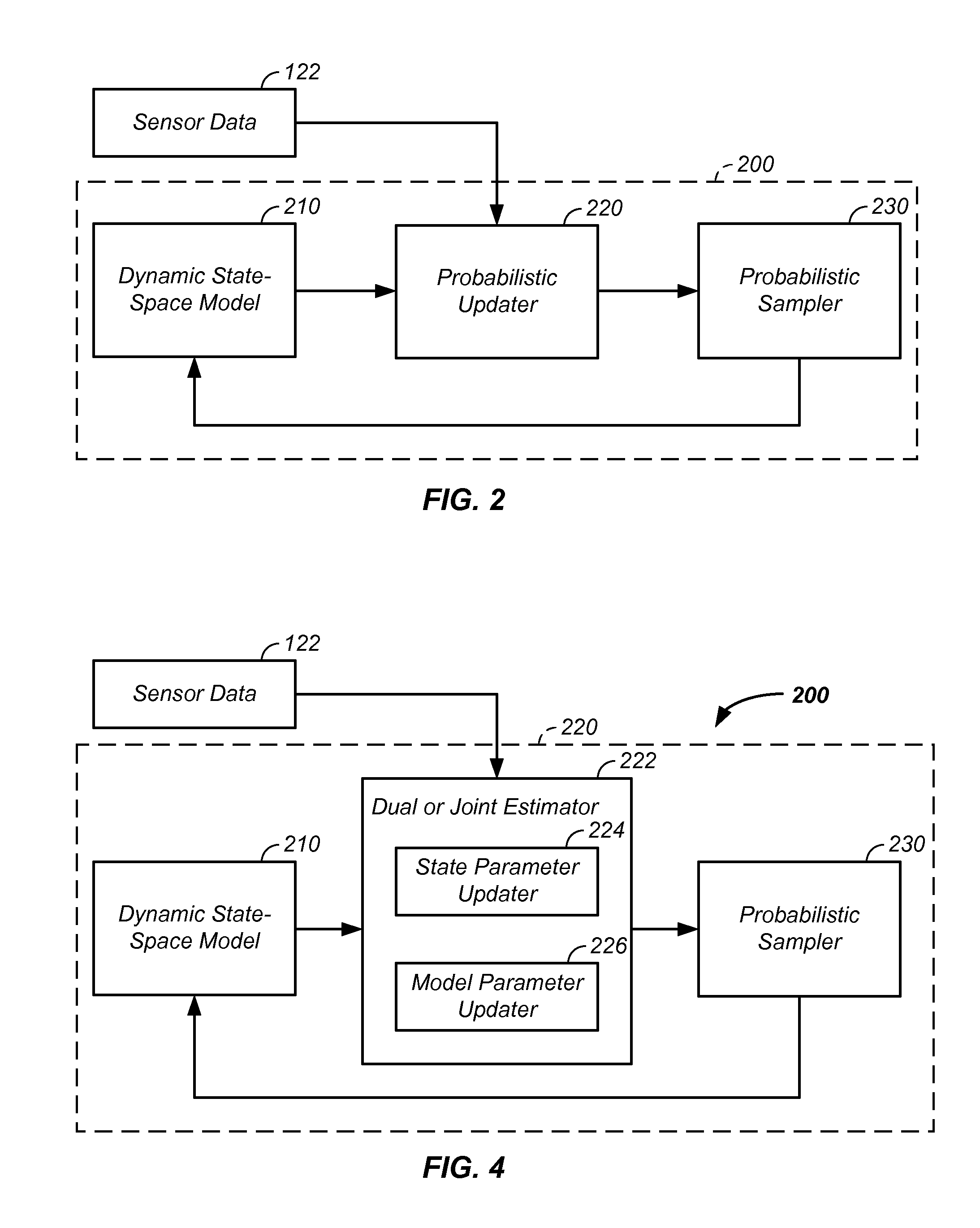
Sensor fusion and probabilistic parameter estimation method and apparatus
A probabilistic digital signal processor using data from multiple instruments is described. Initial probability distribution functions are input to a dynamic state-space model, which operates on state and / or model probability distribution functions to generate a prior probability distribution function, which is input to a probabilistic updater. The probabilistic updater integrates sensor data from multiple instruments with the prior to generate a posterior probability distribution function passed (1) to a probabilistic sampler, which estimates one or more parameters using the posterior, which is output or re-sampled in an iterative algorithm or (2) iteratively to the dynamic state-space model. For example, the probabilistic processor operates on fused data using a physical model, where the data originates from a mechanical system or a medical meter or instrument, such as an electrocardiogram or pulse oximeter to generate new parameter information and / or enhanced parameter information.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
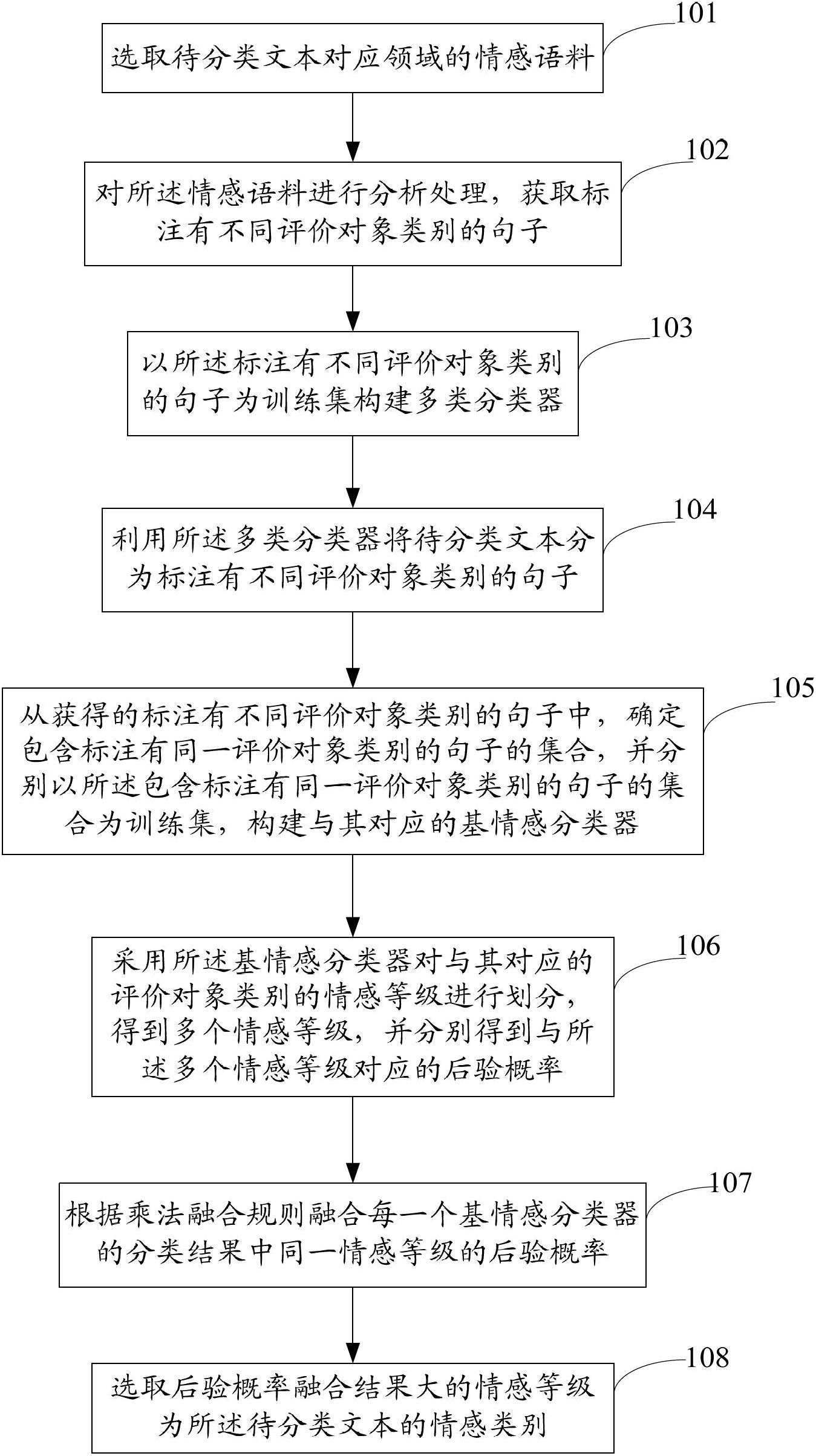
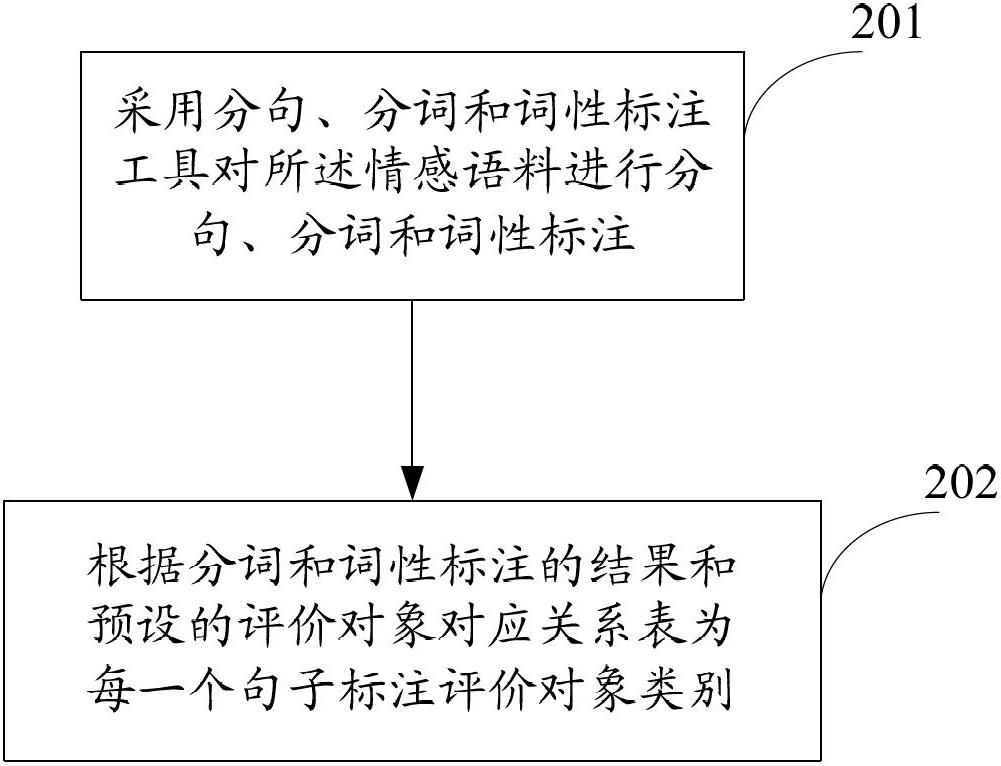
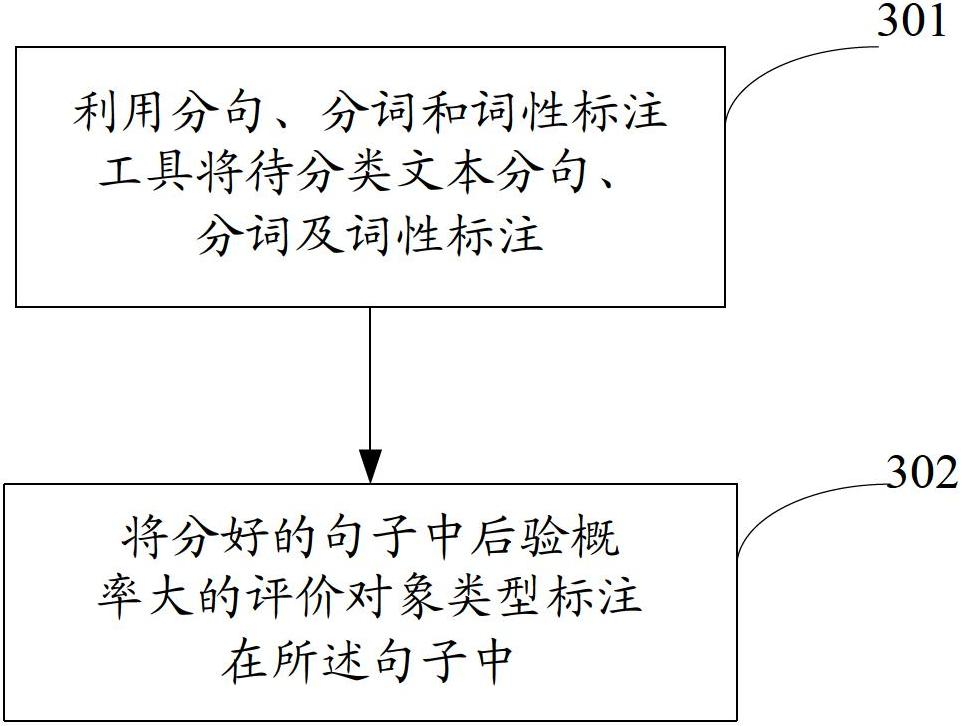
Emotion classifying method and device for text
ActiveCN102682124AImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsObject ClassPosterior probability
The invention discloses an emotion classifying method and an emotion classifying device for a text. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing one multi-class classifier through the analysis processing towards an emotional corpus in a relevant field, dividing the text to be classified into sentences of a plurality of evaluation object classes by utilizing the multi-class classifier, respectively constructing one basic emotion classifier by utilizing sentence aggregates of different evaluation objects, so as to judge the emission trends of the sentences of the evaluation object classes, finally, fusing posterior probabilities denoting a same emotion level in the different evaluation object classes, and selecting the emotion level with the large fusion result of the posterior probabilities as the emotion class of the text to be classified. Through the emotion classifying method and the device for the text, which is disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, the evaluation objects are classified into several fixed classes; the emotion trend of the sentence of each evaluation object class is respectively analyzed; the emotion trends of the different evaluation object classes are fused; the emotion class of the text to be classified is judged according to the fusion result; and by using such a method, the accurate rate of the emotion classification of the text is improved greatly.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
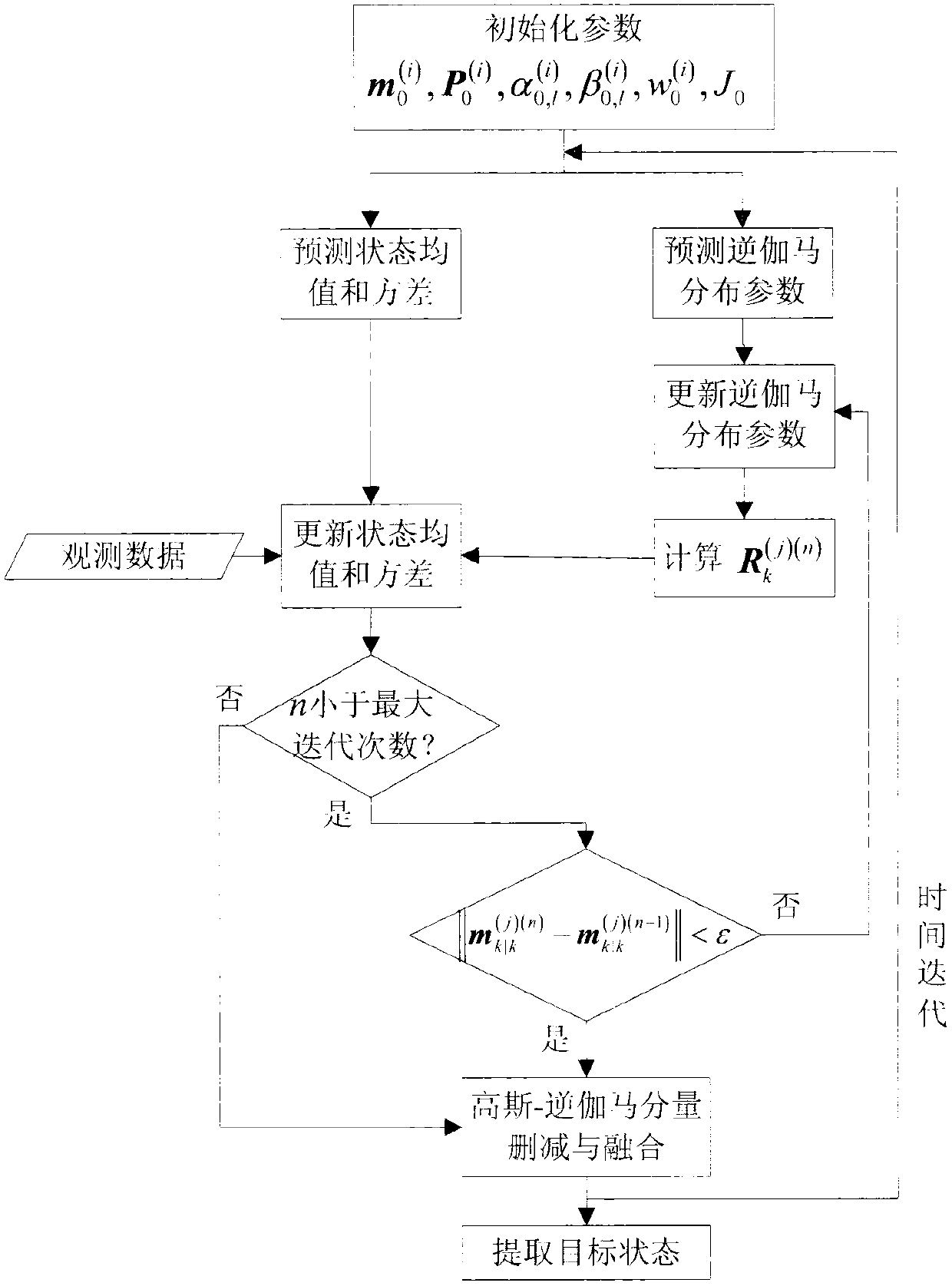
Probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on variational Bayesian approximation technology
ActiveCN103345577AEfficient estimation of true measurement noiseAchieve goal trackingSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingHypothesis
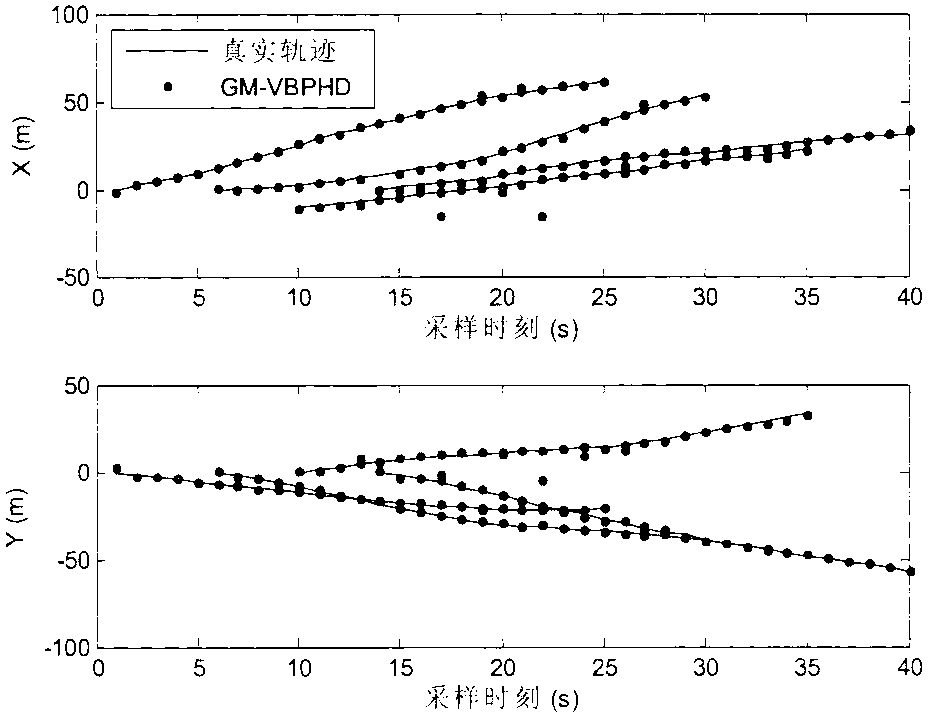
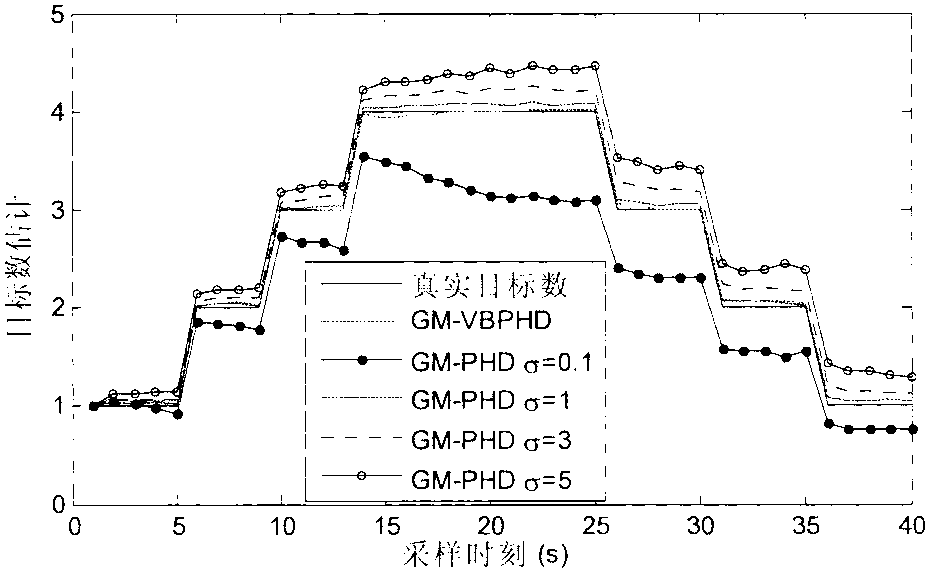
The invention discloses a probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on a variational Bayesian approximation technology, and belongs to the technical field of guidance and intelligent information processing. The probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on the variational Bayesian approximation technology mainly solves the problem that an existing random set filtering method can not achieved varied number multi-target tracking under an unknown quantity measurement noise environment. According to the method, the variational Bayesian approximation technology is introduced, posterior probability hypothesis density of target states and measurement noise covariance is estimated in a combination mode, a Gaussian mixture inverse gamma distribution recurrence closed solution is adopted, and thus the varied number multi-target tracking under the unknown quantity measurement noise environment is achieved. The probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on the variational Bayesian has a good tracking effect and robustness, is capable of meeting the design demands on practical engineering systems and has good engineering application value.
Owner:江苏华文医疗器械有限公司
Customizable voice wake-up method and system
ActiveCN106098059AReduce consumptionImprove wake-up effectSpeech recognitionCategorical modelsSpeech sound
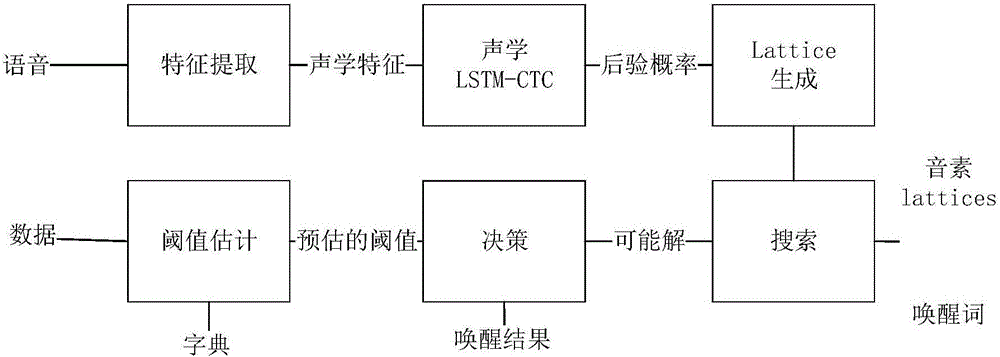
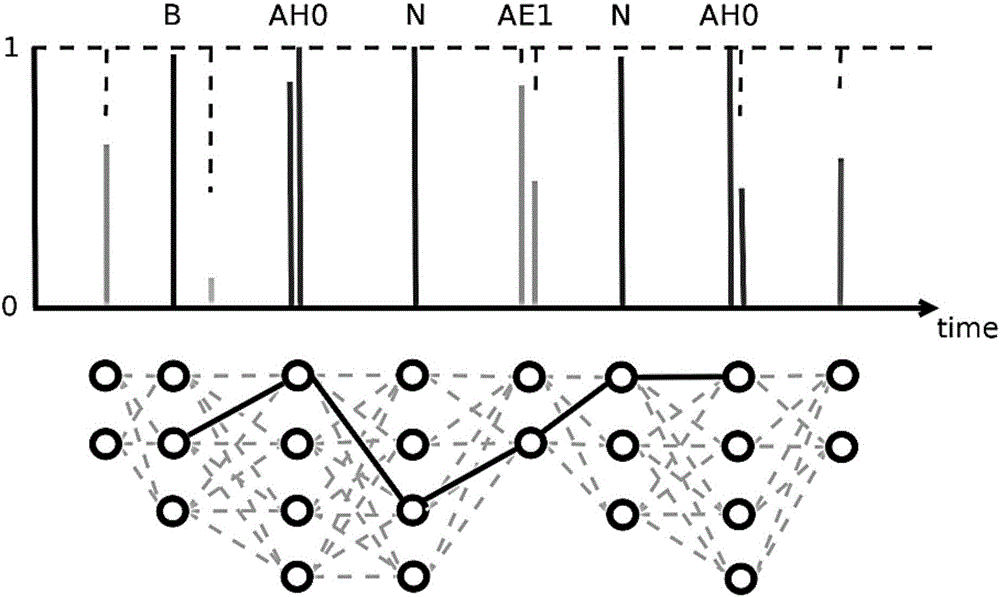
The invention discloses a customizable voice wake-up method and a system. Through using a long and short memory network and a connection time sequence classification model, phoneme information of the voice information is modeled, the model is trained, the model after training is adopted for testing, and a possible phoneme sequence most similar to a customized wake-up word is searched in a generated Lattice network structure and serves as a judgment basis. The feature of CTC model output posteriori probability sparsity is used for high-efficiency searching, and the technique of calculating the confidence of the wake-up word is completed. On one hand, high wake-up performance can be obtained, that is, high accuracy and low error wake-up can be obtained; and on the other hand, the calculation resources of the application system are relatively little consumed.
Owner:AISPEECH CO LTD
System and method for vascular segmentation by Monte-Carlo sampling
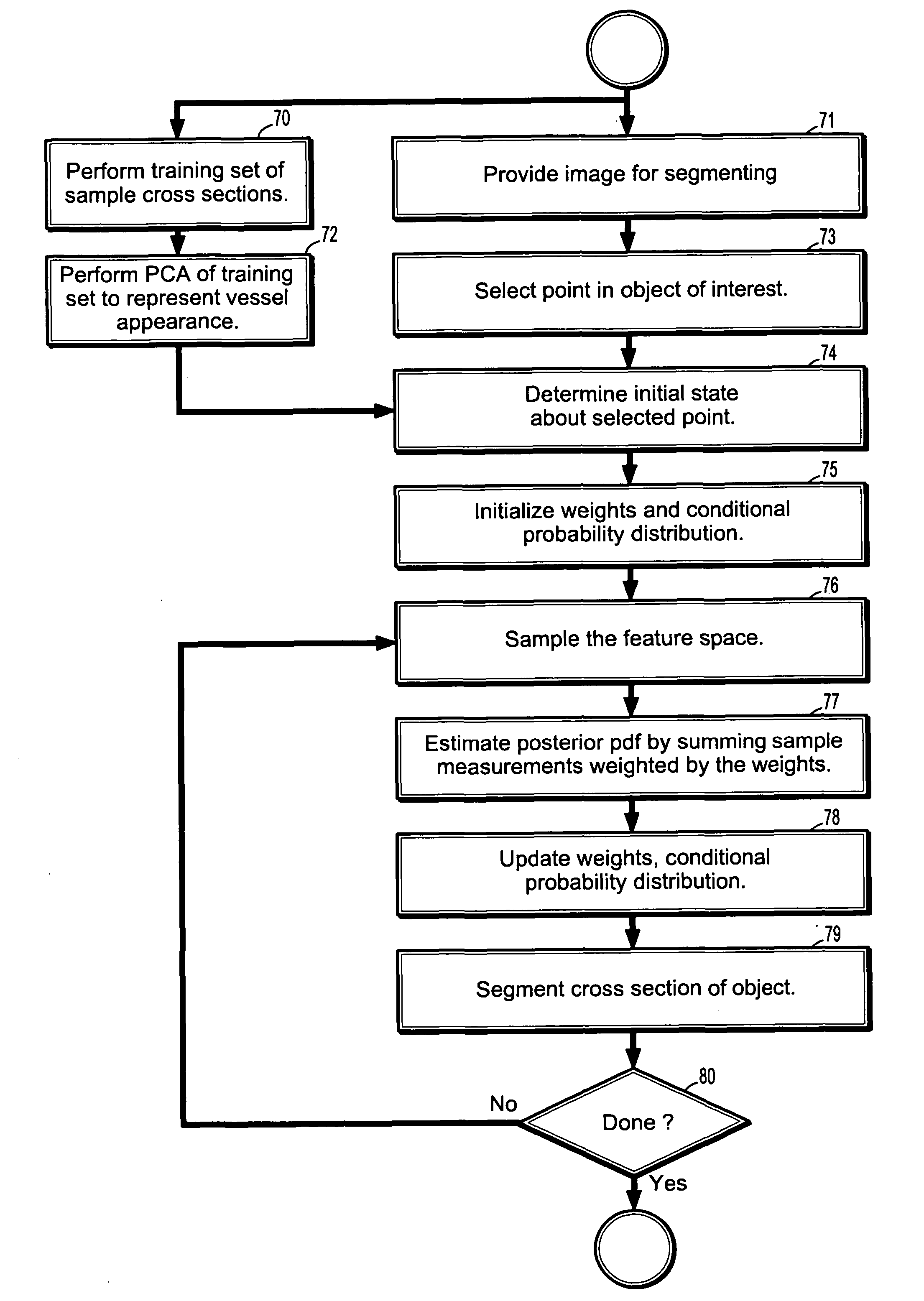
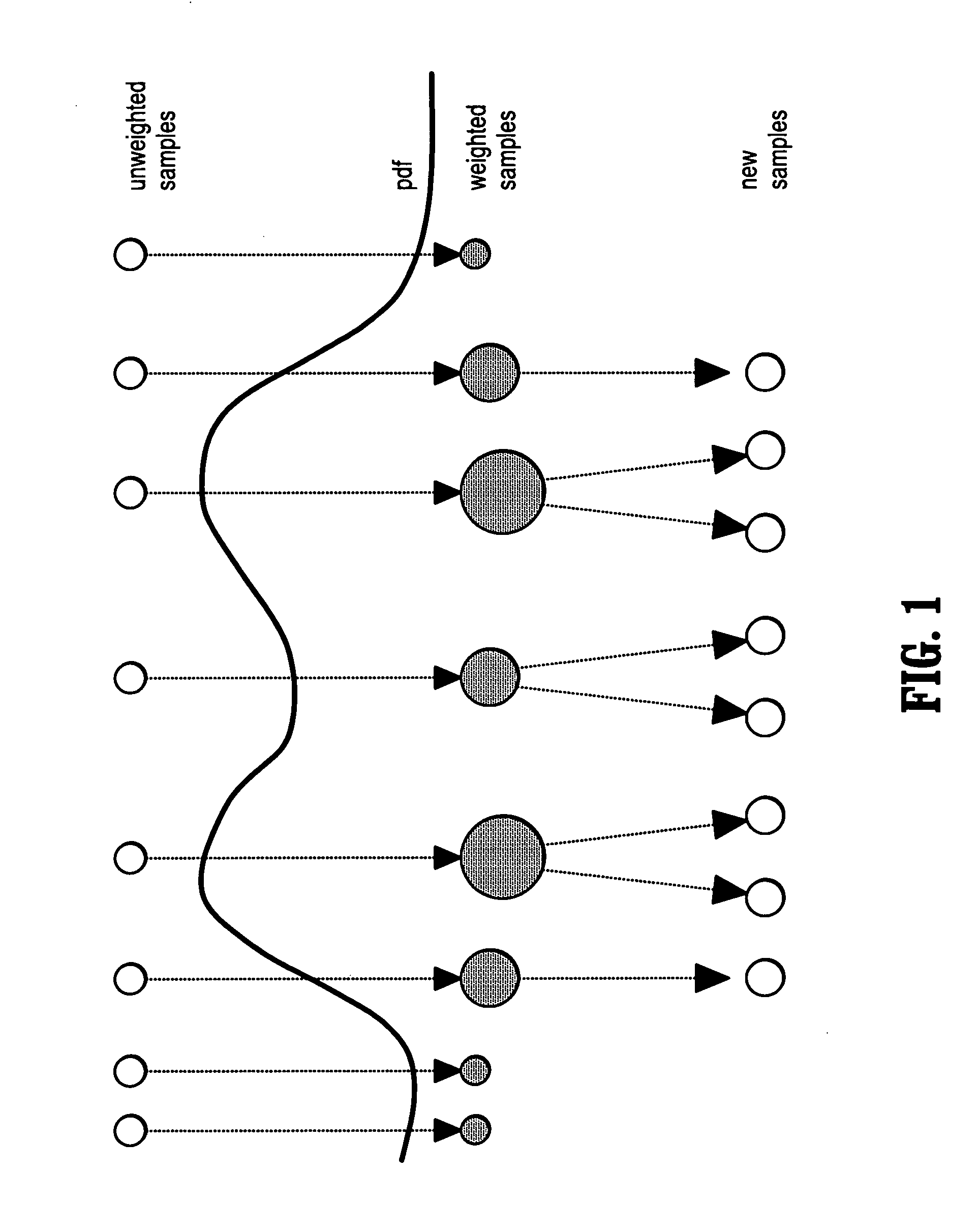
InactiveUS7715626B2Reduce in quantityIssue to overcomeImage enhancementImage analysisCharacteristic spaceDigital image
A method of segmenting tubular structures in digital images includes selecting a point in an image of a tubular object to be segmented, defining an initial state of the selected point, initializing measurement weights, a conditional probability distribution and a prior probability distribution of a feature space of the initial state, sampling the feature space from the prior probability distribution, estimating a posterior probability distribution by summing sample measurements weighted by the measurement weights, and segmenting a cross section of the tubular object from the posterior probability distribution.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
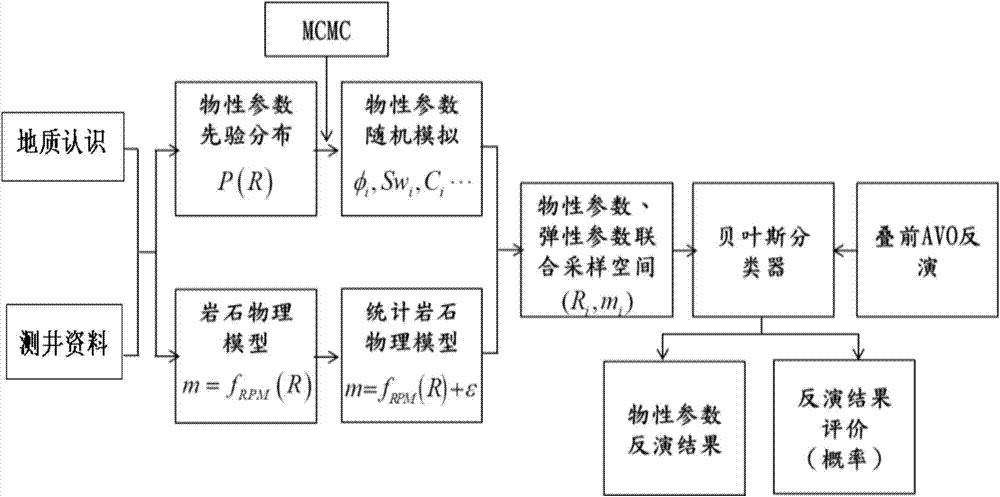
Carbonate rock physical parameter seismic inversion method
ActiveCN104516017AAchieve simultaneous inversionReduce credibilitySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingS-waveMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention provides a carbonate rock physical parameter seismic inversion method, which belongs to the field of petroleum geophysical exploration. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out pre-stack AVO three-parameter inversion based on a pre-stack angle gather to obtain formation elasticity parameters M, wherein M includes P-wave velocity, S-wave velocity and density; (2) establishing a statistical rock physical model based on logging data; (3) randomly simulating physical conditions of a reservoir based on the rock physical model obtained from step (2) to obtain a random simulation result; and (4) carrying out Bayes classified simulation on the random simulation result obtained from step (3) to obtain a posterior probability distribution, and taking the M obtained from step (1) as the input of inversion to find a R with the maximum posteriori probability distribution, wherein R is the final inversion result.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Iterative probabilistic parameter estimation apparatus and method of use therefor
A probabilistic digital signal processor using data from multiple instruments is described. In one example, a digital signal processor is integrated into a biomedical device. The processor is configured to: use a dynamic state-space model configured with a physiological model of a body system to provide a prior probability distribution function; receive sensor data input from at least two data sources; and iteratively use a probabilistic updater to integrate the sensor data as a fused data set and generate a posterior probability distribution function using all of: (1) the fused data set; (2) an application of Bayesian probability; and (3) the prior probability distribution function. The processor further generates an output of a biomedical state using the posterior probability function.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
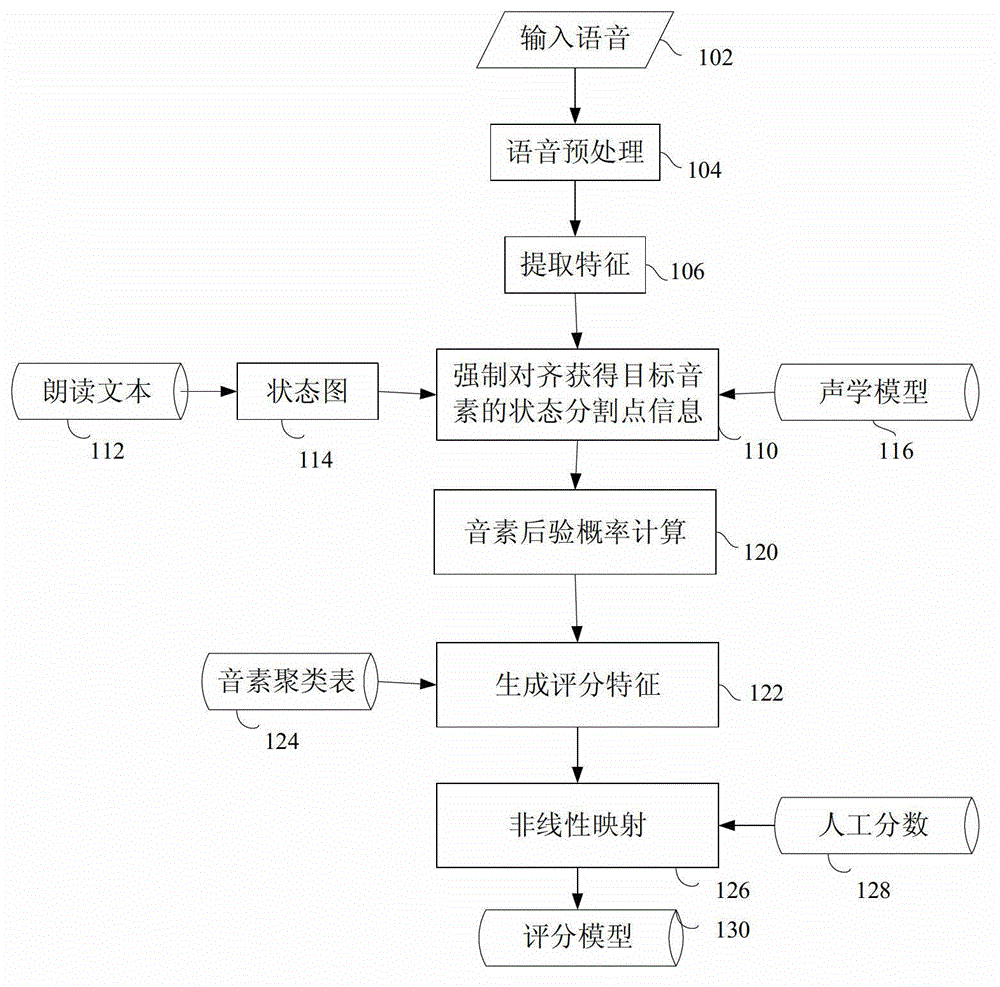
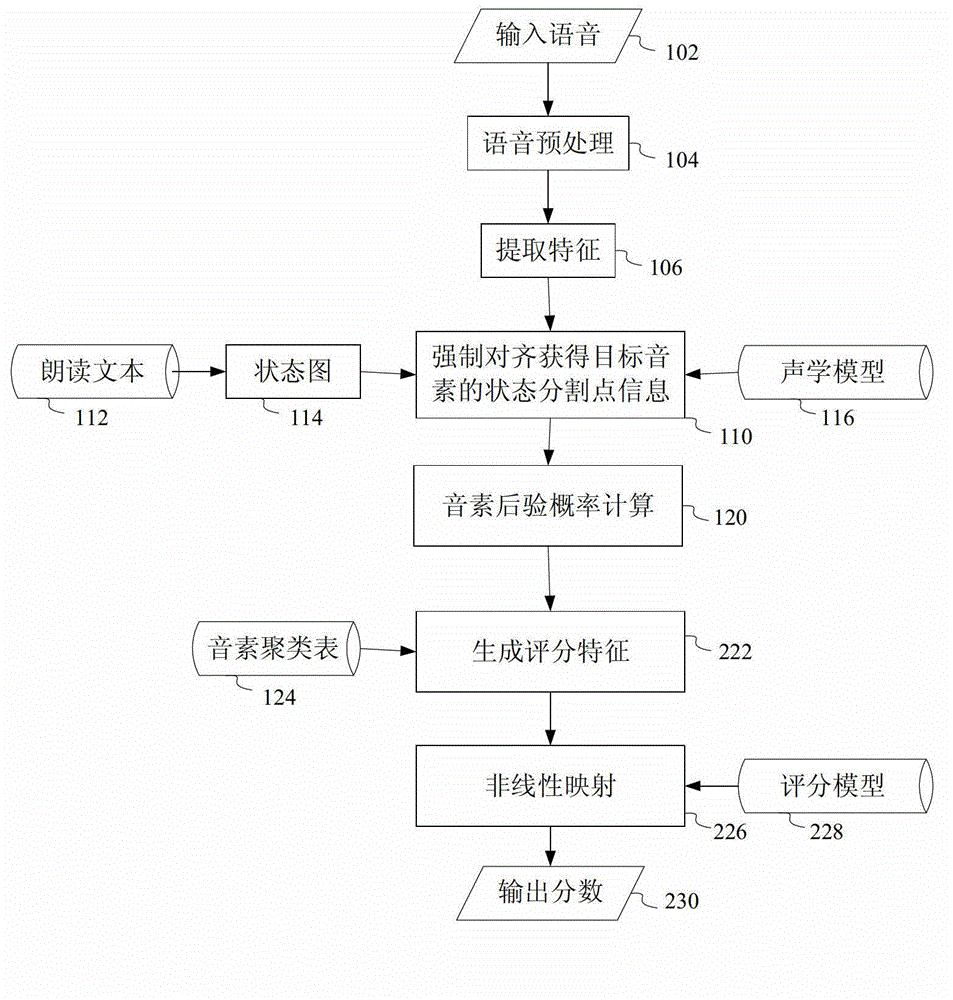
Automatic grading method and automatic grading equipment for read questions in test of spoken English
ActiveCN103065626ADoes not deviate from human scoringSpeech recognitionTeaching apparatusSpoken languageAlgorithm
The invention provides an automatic grading method and automatic grading equipment for read questions in a test of spoken English. According to the automatic grading method, preprocessing is carried out on input voice; the preprocessing comprises framing processing; phonetic feature is extracted from the preprocessed voice; by means of a linear grammar network and an acoustic model set up by reading texts, phonetic feature vector order is forcedly aligned to acquire information of the each break point of each phoneme; according to the information of the each break point of each phoneme, the posterior probability of each phoneme is calculated; based on the posterior probability of each phoneme, multi-dimensional grading characteristics are extracted; and based on the grading characteristics and manual grading information, a nonlinear regression model is trained by means of a support vector regression method, so that the nonlinear regression model is utilized to grade on reading of spoken English. The grading model is trained by means of expert scoring data, and therefore a result of machining grading is guaranteed not to deviate from a manual grading result in statistics, and the high simulation of a computer on the expert grading is achieved.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method and system for autocompletion of multiple fields in electronic forms
InactiveUS20080154824A1Good choiceAccurate valueProbabilistic networksKnowledge representationElectronic formData mining
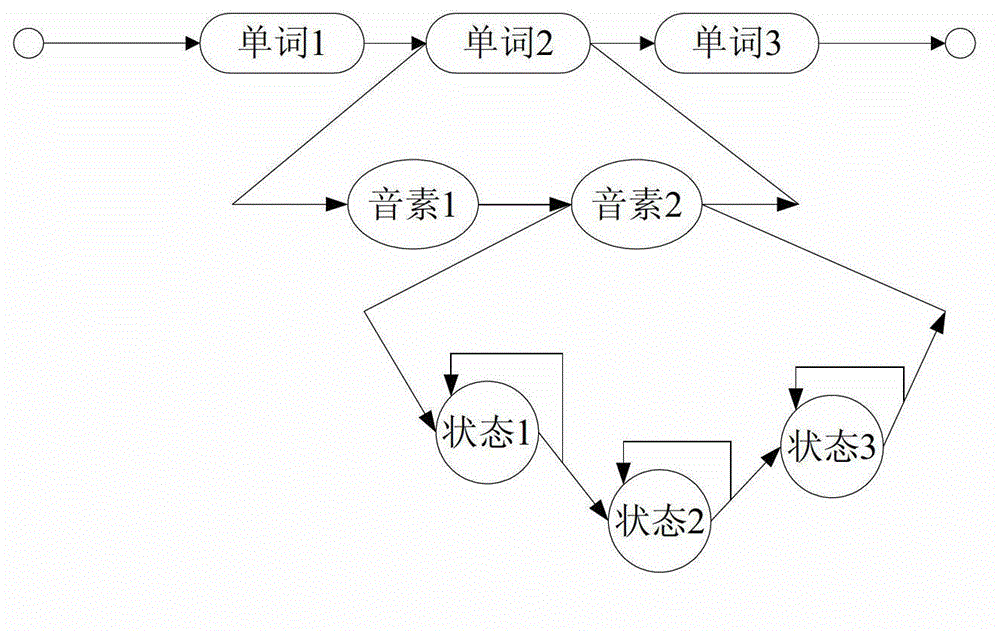
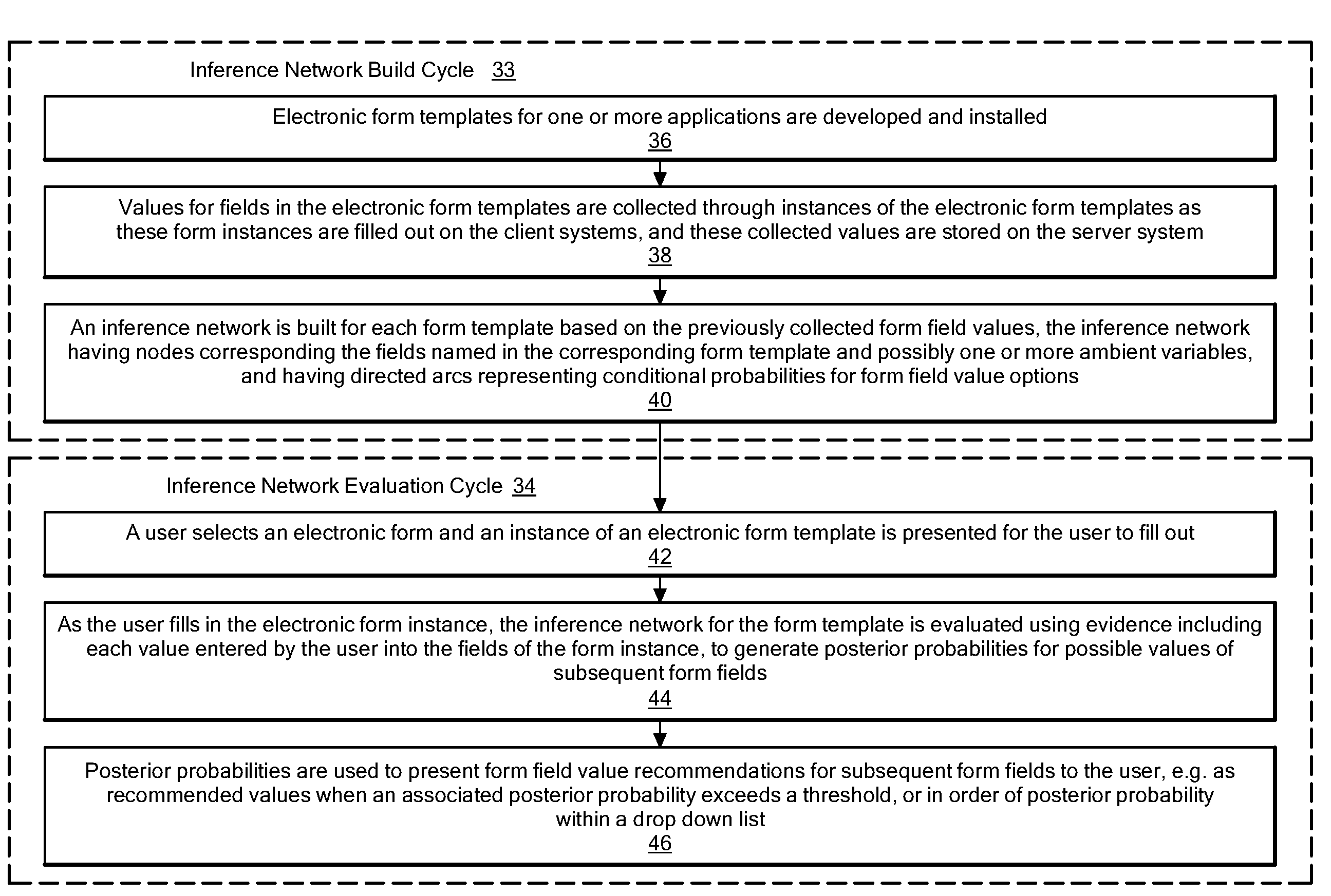
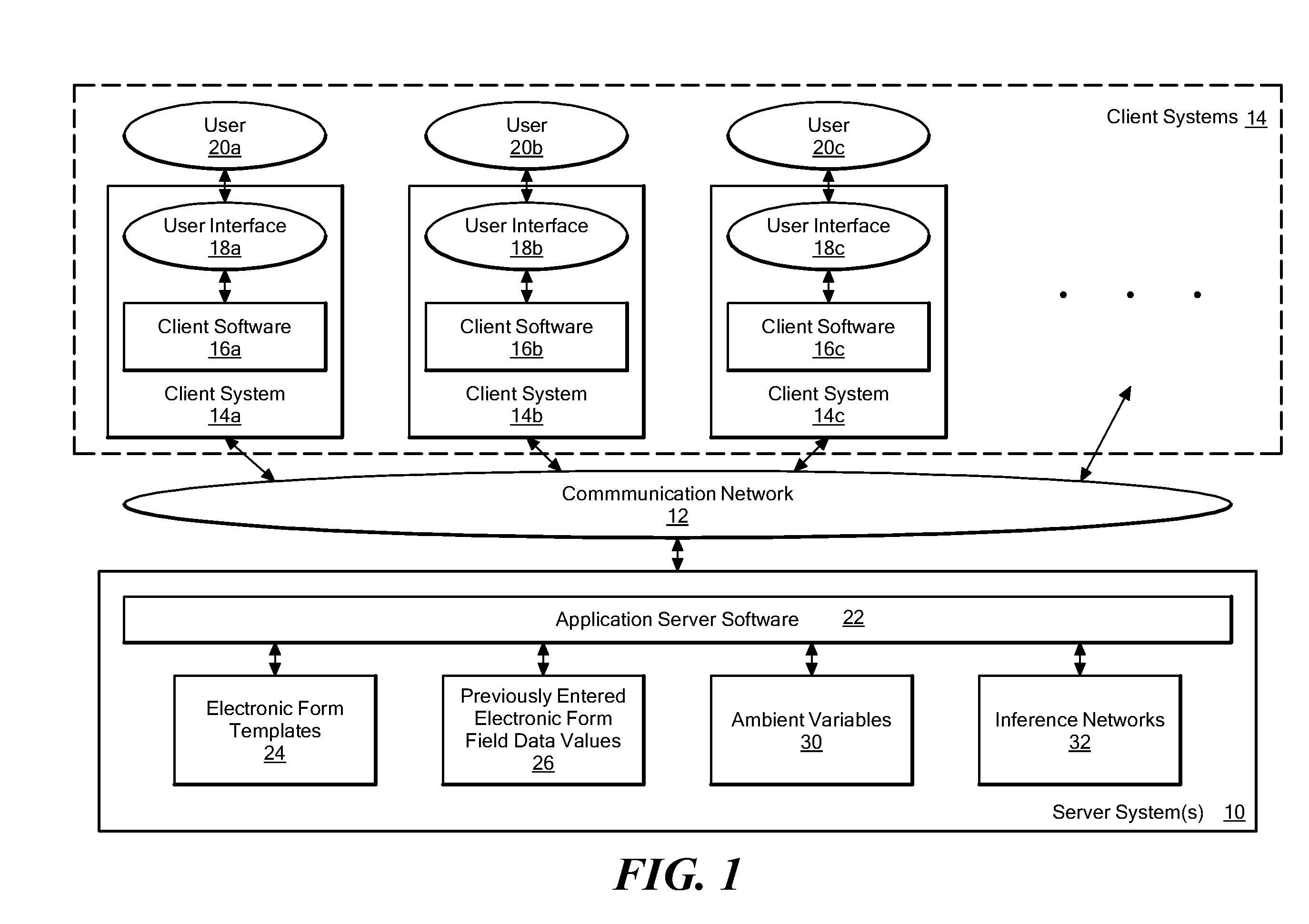
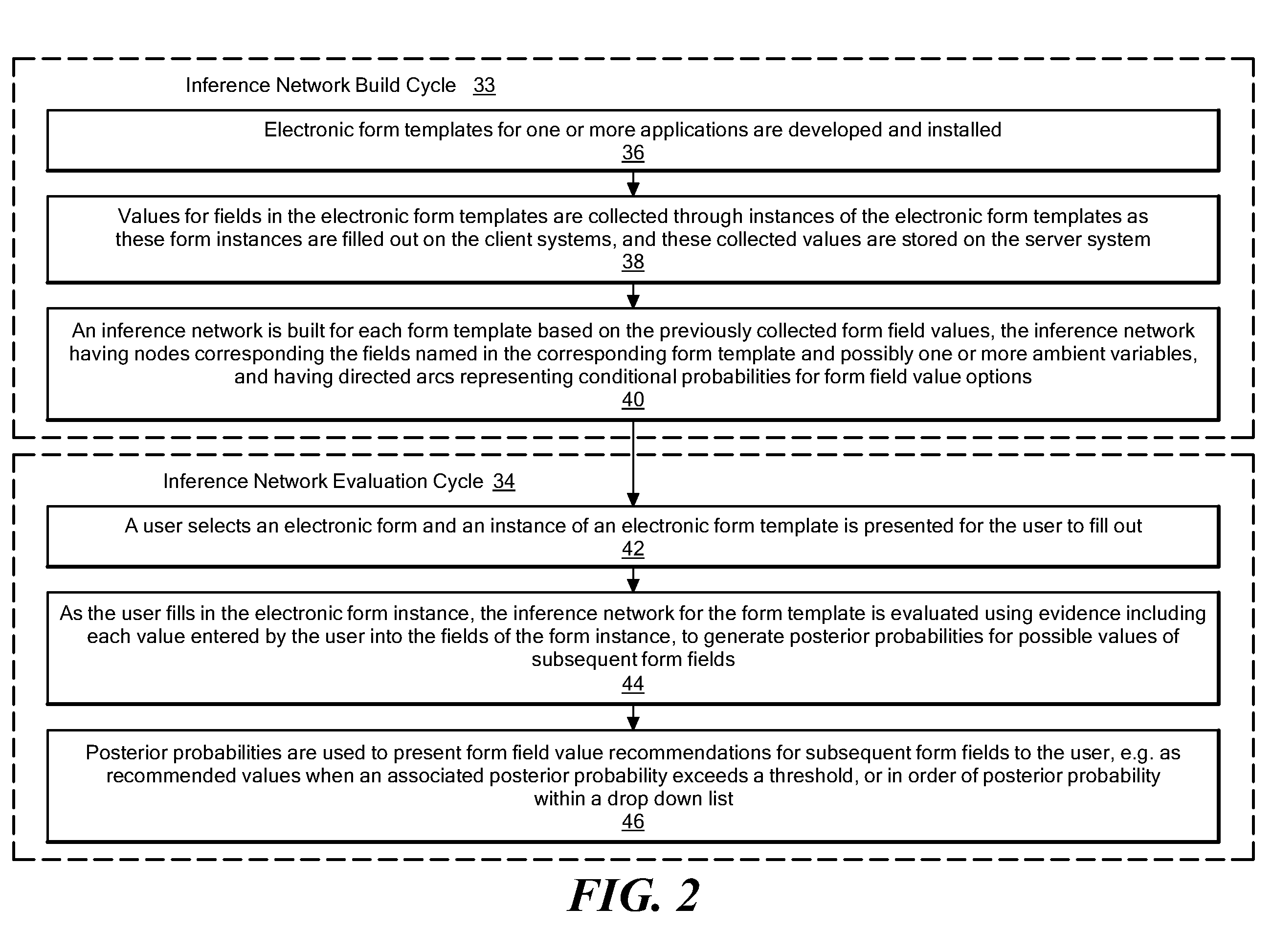
A method and system for autocompletion of multiple fields in electronic forms that generates “inference networks” (Bayesian networks), and evaluates them to suggest likely options for user selection while filling out fields in corresponding electronic forms. The disclosed Bayesian networks are generated and evaluated based on a broad set of information. The information used by the disclosed system for generating an inference network includes form previously selected field values. The information used in the disclosed system to evaluate an inference networks while a current instance of a given form is being filled out includes values previously entered by a current user into preceding form fields, and values of ambient variables that are external to the forms, such as current day of the week, current time of day, etc. When the inference network is evaluated in this way, posterior probabilities are determined for values of fields not yet filled out in the current form instance. These posterior probabilities are used to present value options for the unfilled fields in a way that makes selection of the most-probable options convenient to the user.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and a system for assessing neurological conditions
InactiveUS20090220429A1Minimize changesIncreased intraocular pressureElectroencephalographyMedical simulationMedicineNeurophysiology
This invention relates to a method and a system for generating a discriminatory signal for a neurological condition, where at least one probe compound that has a neurophysiologic effect is provided. Biosignal data are obtained from a subject based on biosignal measurements obtained from biosignal measuring device adapted for placement on a subject, wherein said biosignal data are obtained posterior to the administering of said probe compound to the subject. Analogous biosignal reference data are provided for reference subjects in at least one reference group posterior to the administering of the probe compound, wherein the reference data are utilized for defining reference features having common characteristics between the reference subjects in the at least one reference group, wherein the reference data are processed for defining reference posterior probability vectors for each respective reference subject, wherein each respective posterior probability vector comprises particular feature or a feature combination elements with probability values associated to said elements, the posterior probability vectors resulting in a distribution of said features or feature combinations for said reference subjects. Subsequently, the biosignal data obtained from the subject are used for calculating analogues posterior probability vector for said subject. The discriminatory signal is then generated based on comparison between said posterior probability vector for said subject and the distribution of said features or feature combinations.
Owner:MENTIS CURA EHF
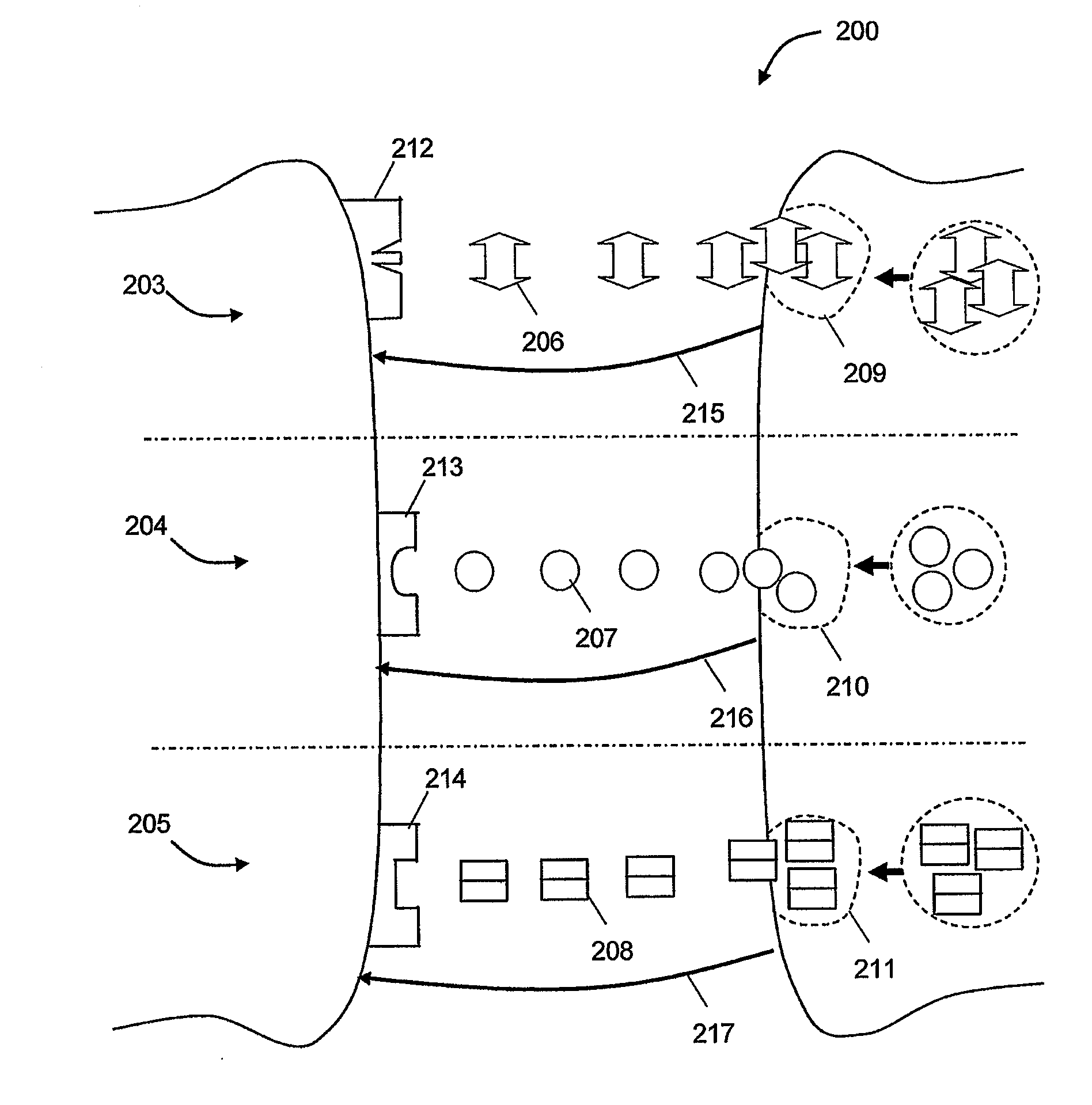
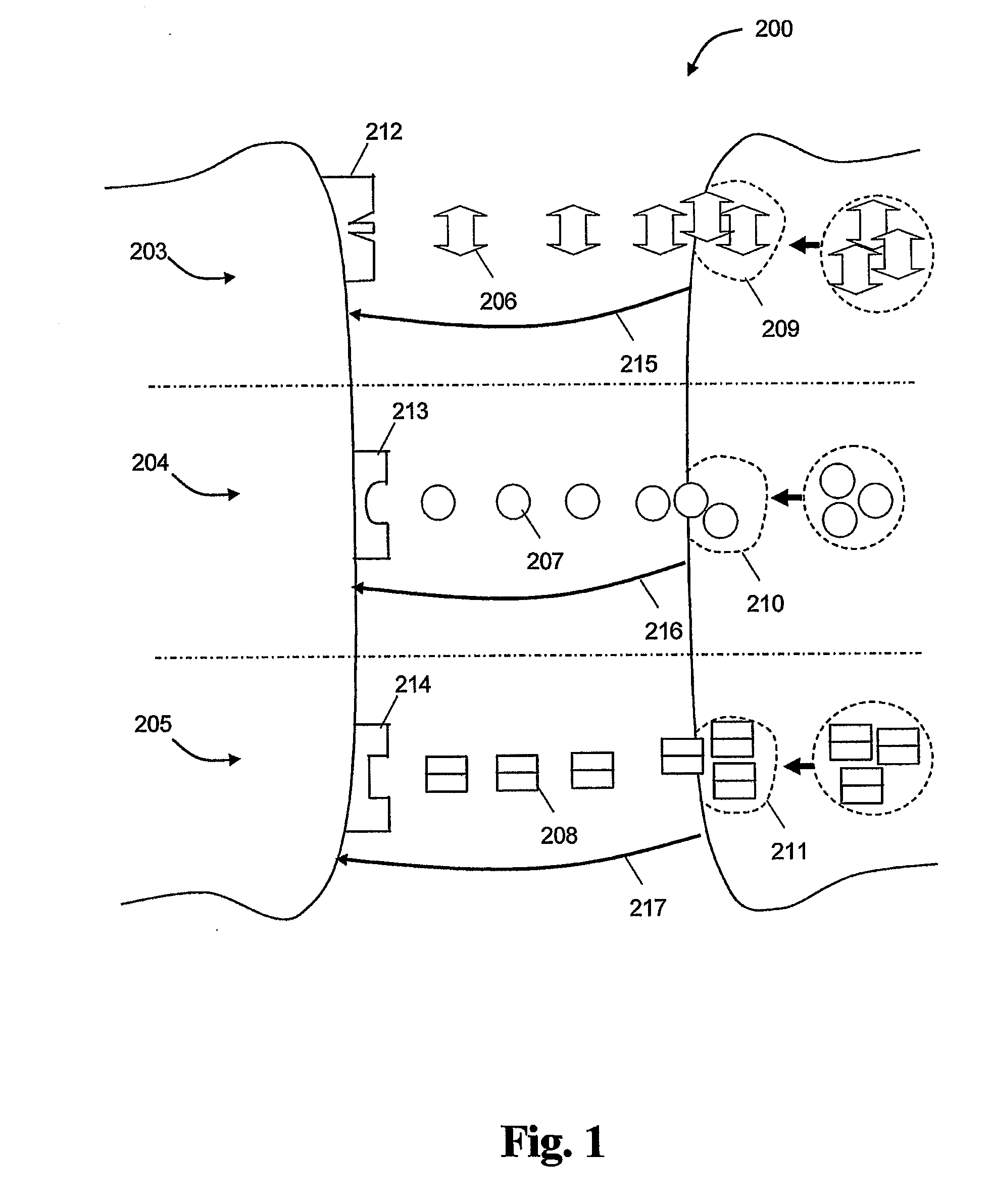
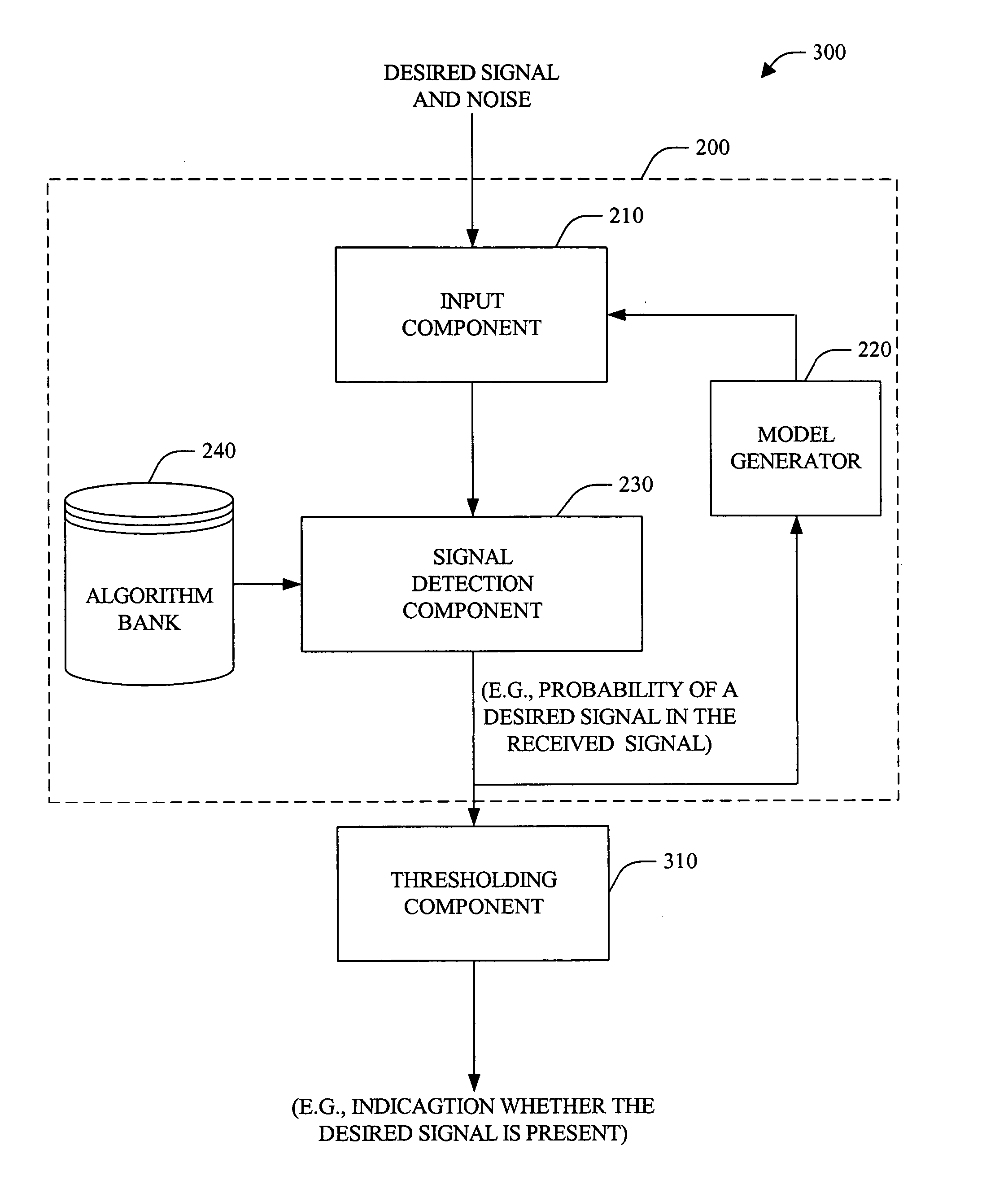
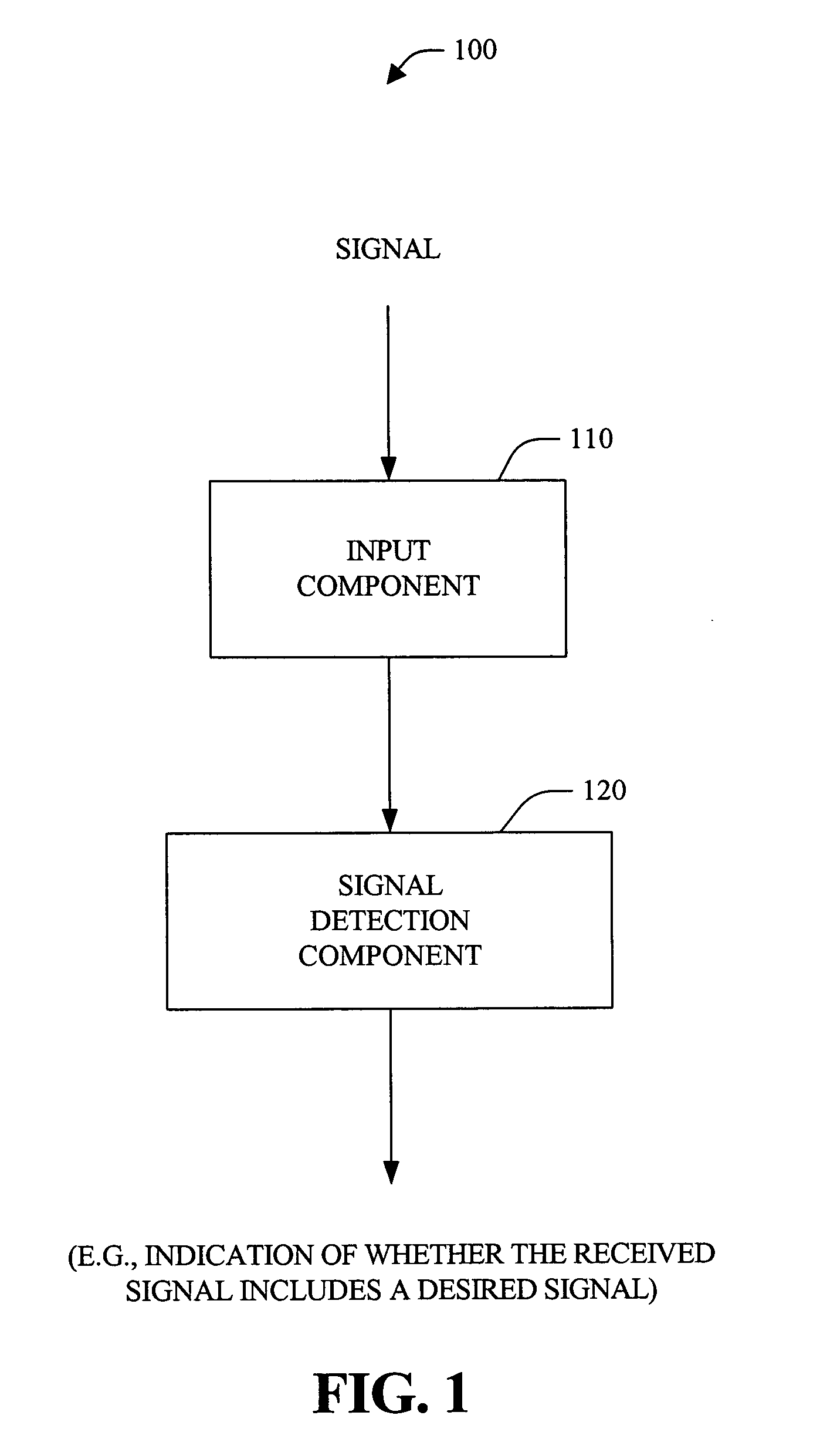
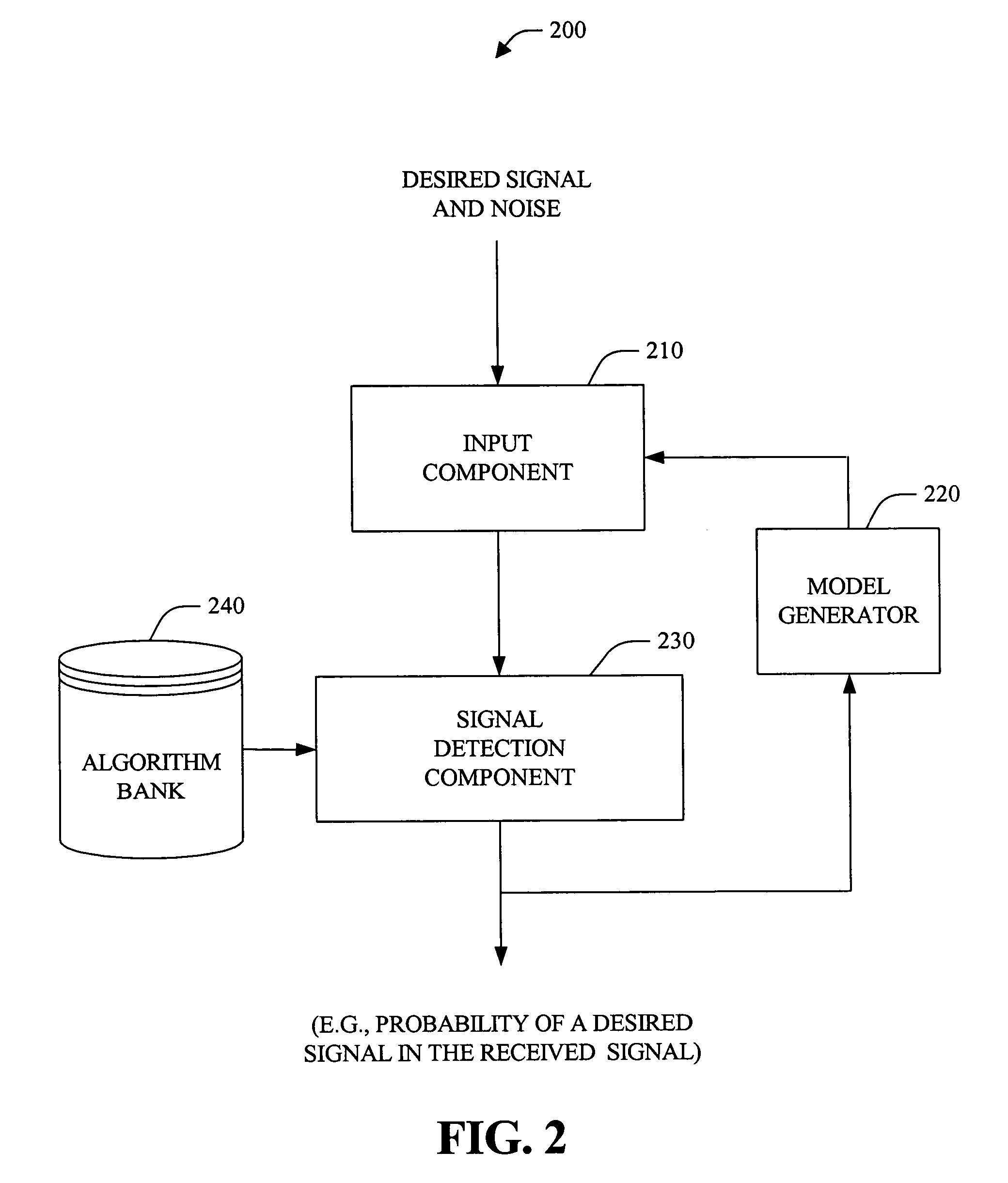
Systems and methods that detect a desired signal via a linear discriminative classifier that utilizes an estimated posterior signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)
The present invention provides systems and methods for signal detection and enhancement. The systems and methods utilize one or more discriminative classifiers (e.g., a logistic regression model and a convolutional neural network) to estimate a posterior probability that indicates whether a desired signal is present in a received signal. The discriminative estimators generate the estimated probability based on one or more signal-to-noise ratio (SNRs) (e.g., a normalized logarithmic posterior SNR (nlpSNR) and a mel-transformed nlpSNR (mel-nlpSNR)) and an estimated noise model. Depending on the resolution desired, the estimated SNR can be generated at a frame level or at an atom level, wherein the atom level estimates are utilized to generate the frame level estimate. The novel systems and methods can be utilized to facilitate speech detection, speech recognition, speech coding, noise adaptation, speech enhancement, microphone arrays and echo-cancellation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com