Automatically and adaptively determining execution plans for queries with parameter markers
a technology of parameter markers and execution plans, applied in the direction of instruments, computing, electric digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of complex task of the optimizer, the cost of optimization itself may represent a significant fraction of the elapsed time between query submission and the time of query submission, and achieve the effect of accurate model and high prediction accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
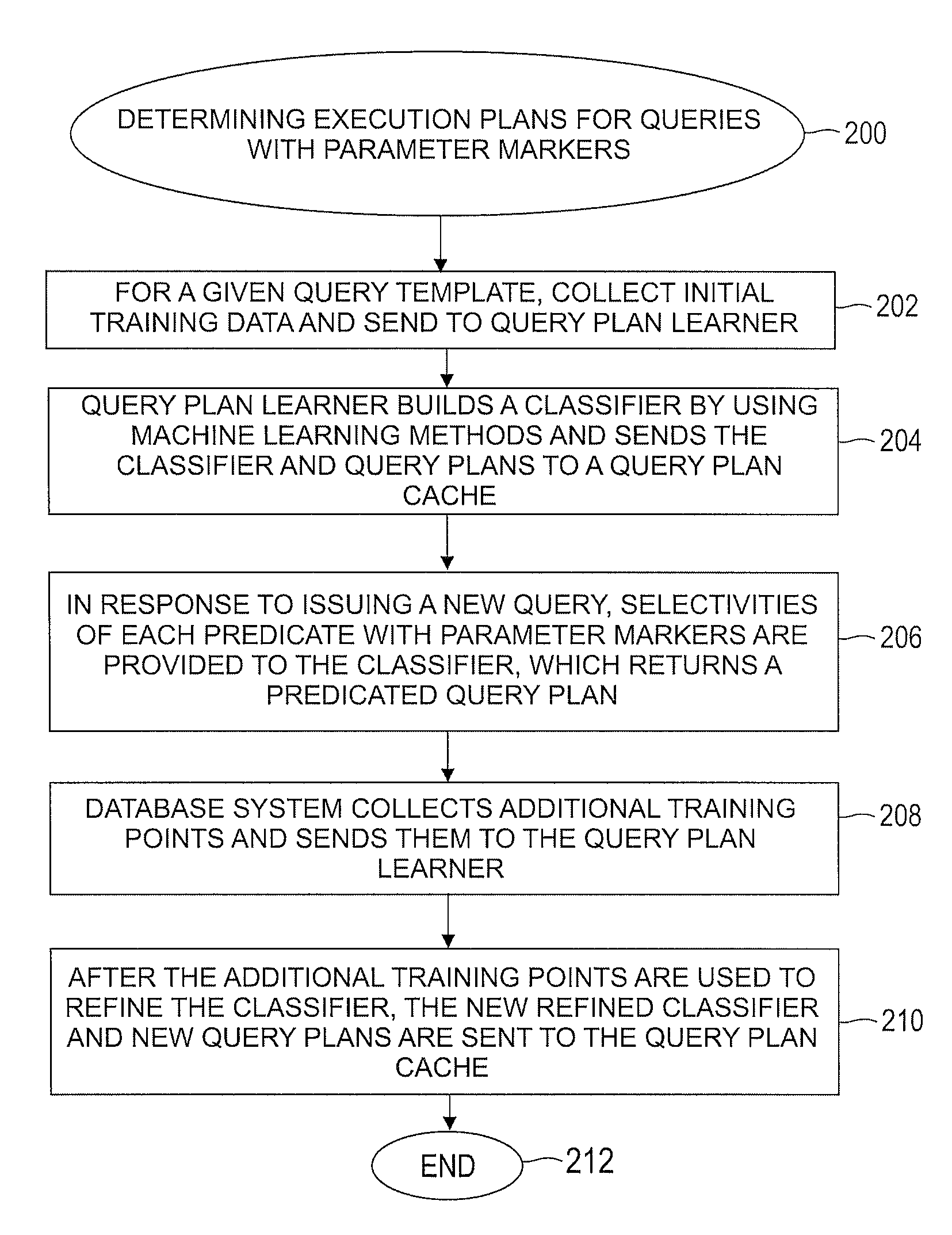
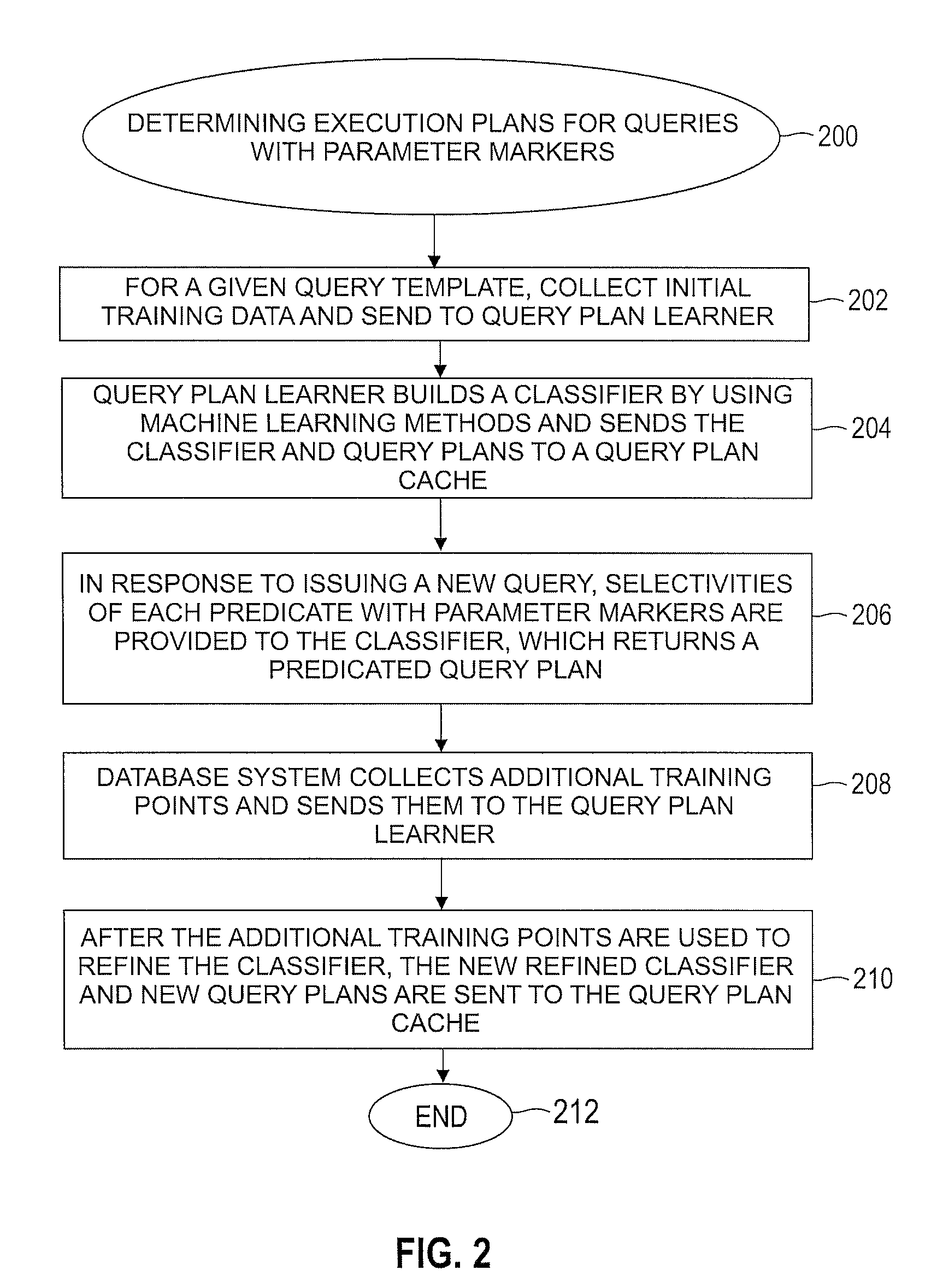
1 Overview
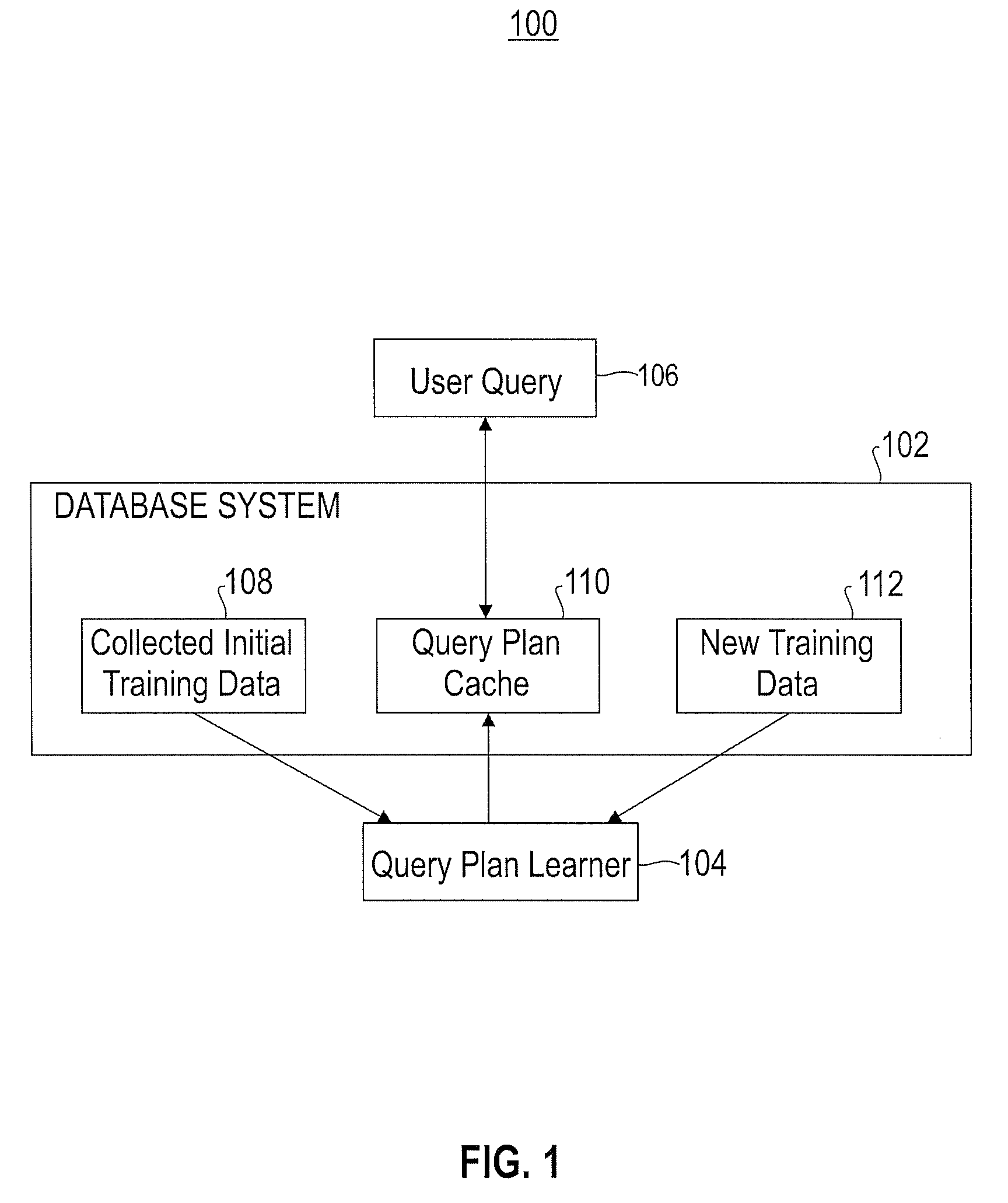
[0038]The task of query optimization in modern relational database systems is important but can be computationally expensive. Parametric query optimization (PQO) has as its goal the prediction of optimal query execution plans based on historical results, without consulting the query optimizer. The machine learning techniques disclosed herein accurately model the output of a query optimizer for queries having parameter markers (a.k.a. parametric queries). The algorithms of the present invention scale gracefully with the number of query parameters, handle non-linear boundaries in plan space, and achieve high prediction accuracy even when a limited amount of data is available for training. Both predicted and actual query execution times are used for learning, and the experimental results disclosed herein demonstrate a total net win of a PQO-based method over a state-of-the-art query optimizer for some workloads. The present invention realizes savings not only in optimization ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com