Patents
Literature
5035 results about "Execution time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer science, run time, runtime or execution time is the time during which a program is running , in contrast to other program lifecycle phases such as compile time, link time and load time. A run ...
Method and apparatus for product lifecycle management in a distributed environment enabled by dynamic business process composition and execution by rule inference
InactiveUS20040162741A1Detect and resolve conflictOffice automationResourcesDistributed servicesNetwork topology
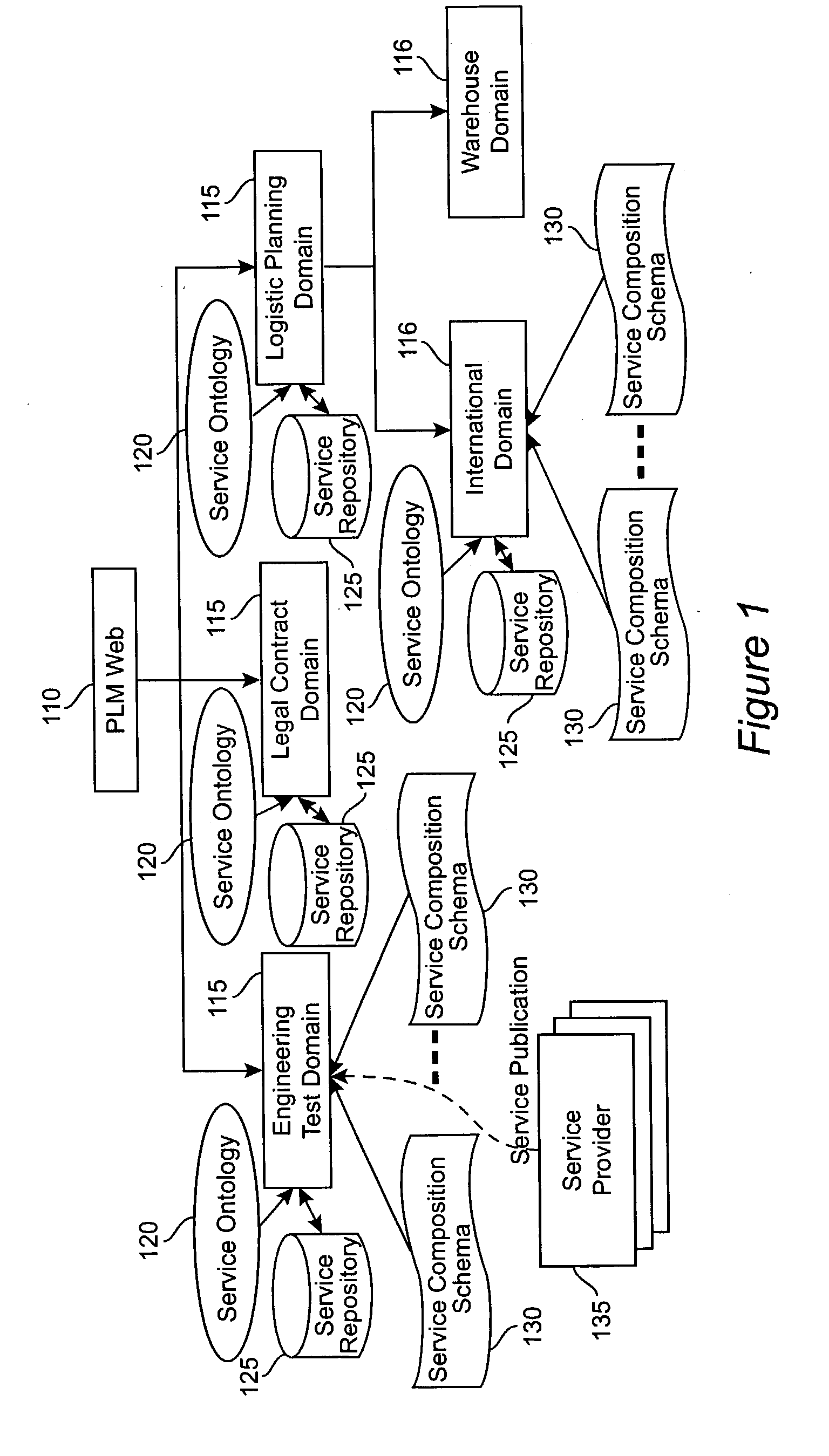
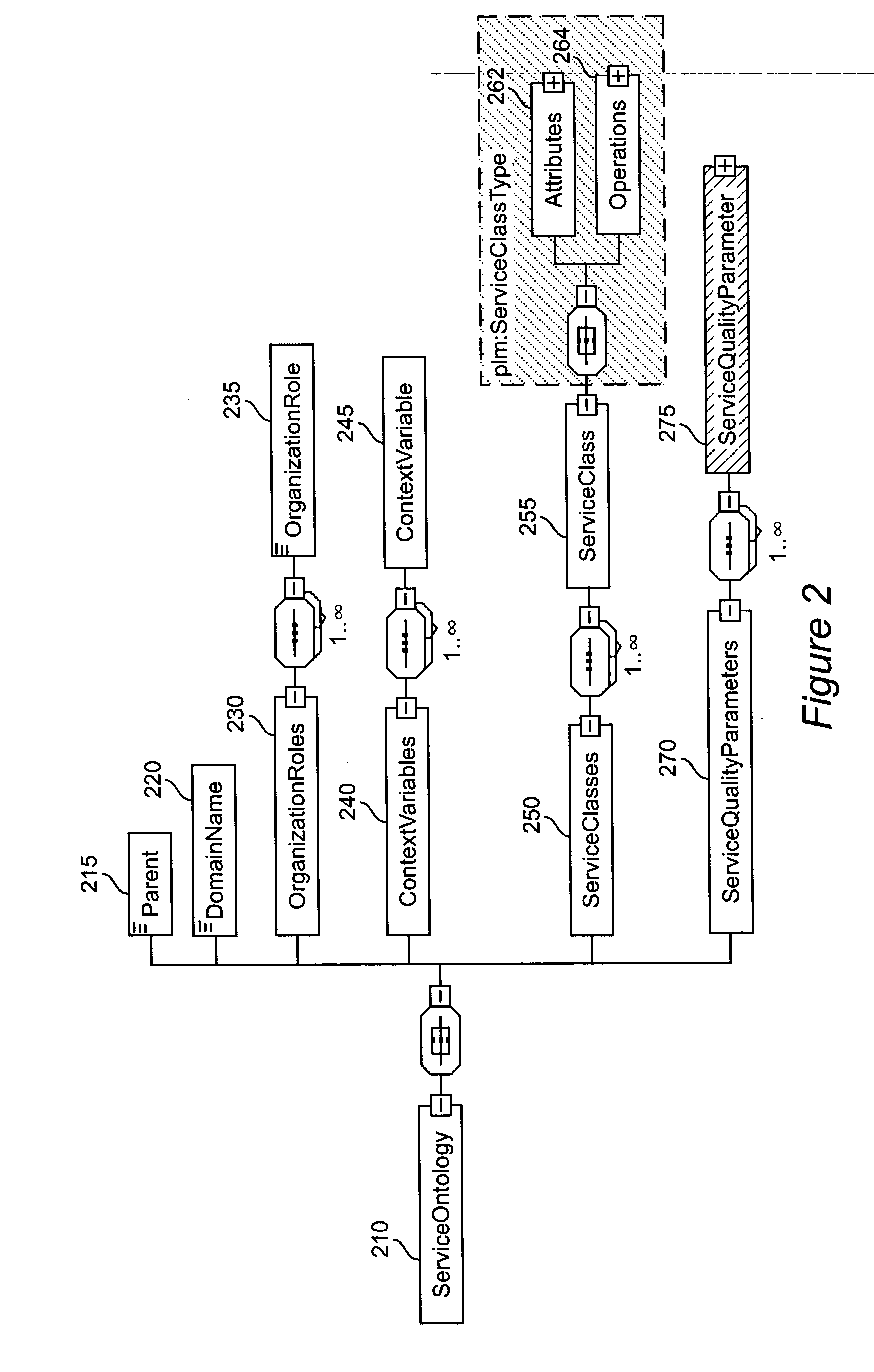
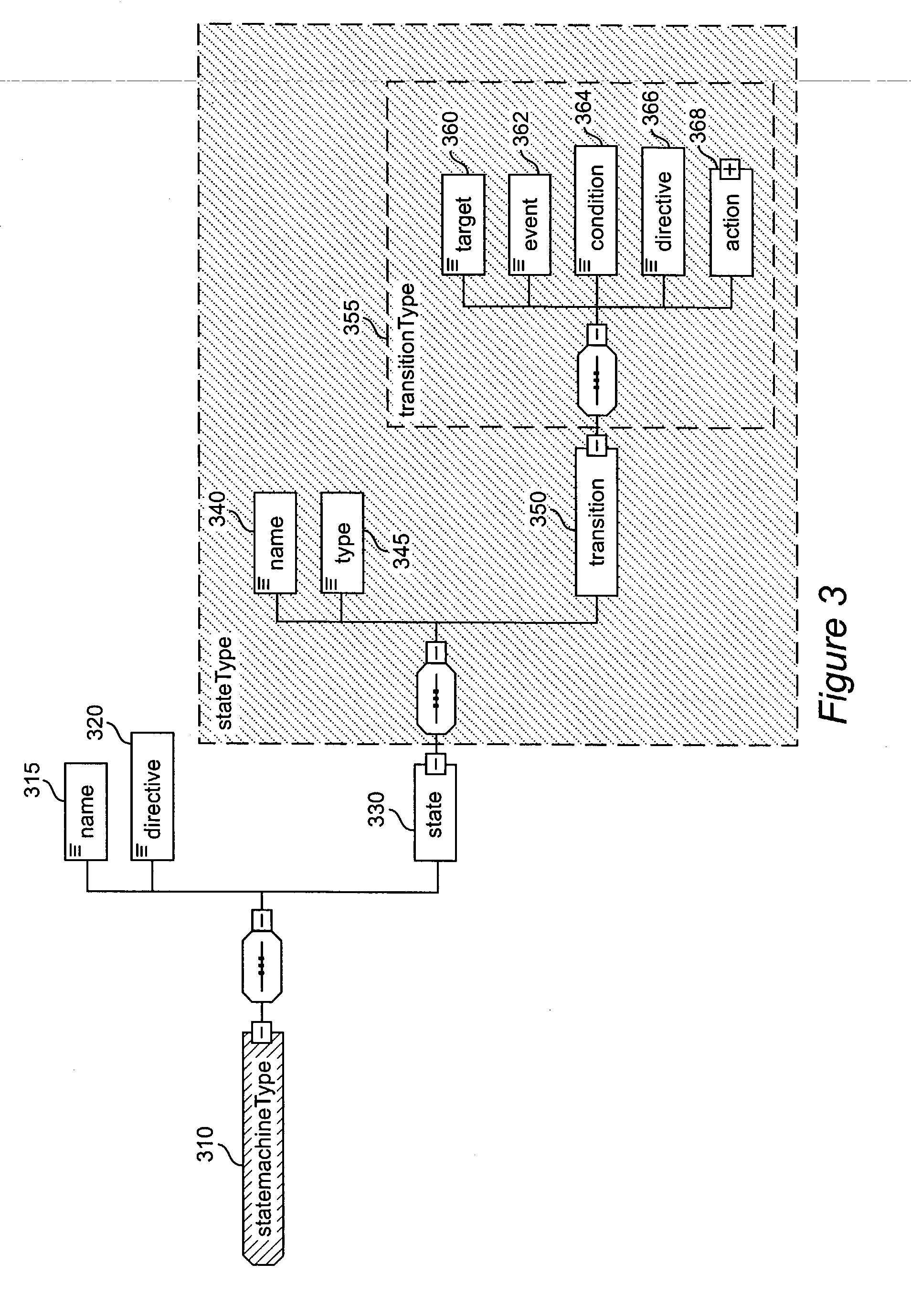
A system and method for supporting Product Lifecycle Management over a distributed service network topology that connects a hierarchy of functional domains, each domain having a service ontology and one or more service composition schemas defined by the service ontology. Each service composition schema models a business process in its domain. Descriptions of services provided to each domain are published to a service repository by providers of the services, in conformity with one of the service composition schemas. There is a business process proxy provided by the service provider for each service description, which encapsulates for public access the internal processes of the service provider. The invention makes use of an event messaging protocol that enables service collaboration and ad-hoc workflow composition. Each business process is implemented by an ad-hoc workflow comprised of one or more tasks connected by one or more business rules. For each business process there is a business flow manager that dynamically composes ad-hoc workflow prior to execution and dynamically modifies the ad-hoc workflow as the business process executes. The business flow manager uses backward-chain inferencing and then forward-chain inferencing to generate the ad-hoc workflows, based on user identification of a target task. The business flow manager is able to stop execution of the workflow and regenerate a workflow for remaining tasks in response to events received over the network from service providers, and is also able to detect conflicts in the workflows at composition time and at execution time.
Owner:IBM CORP
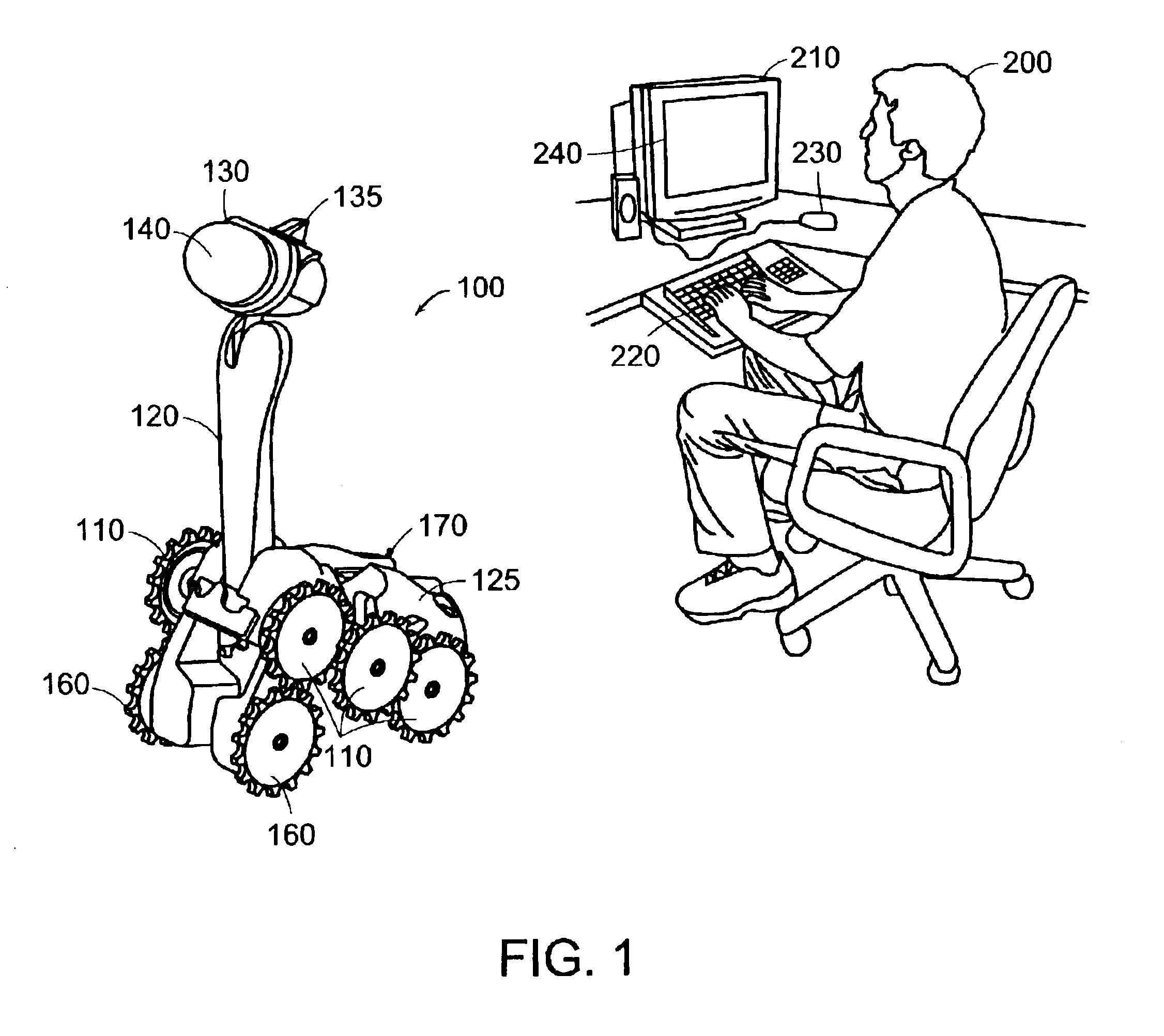
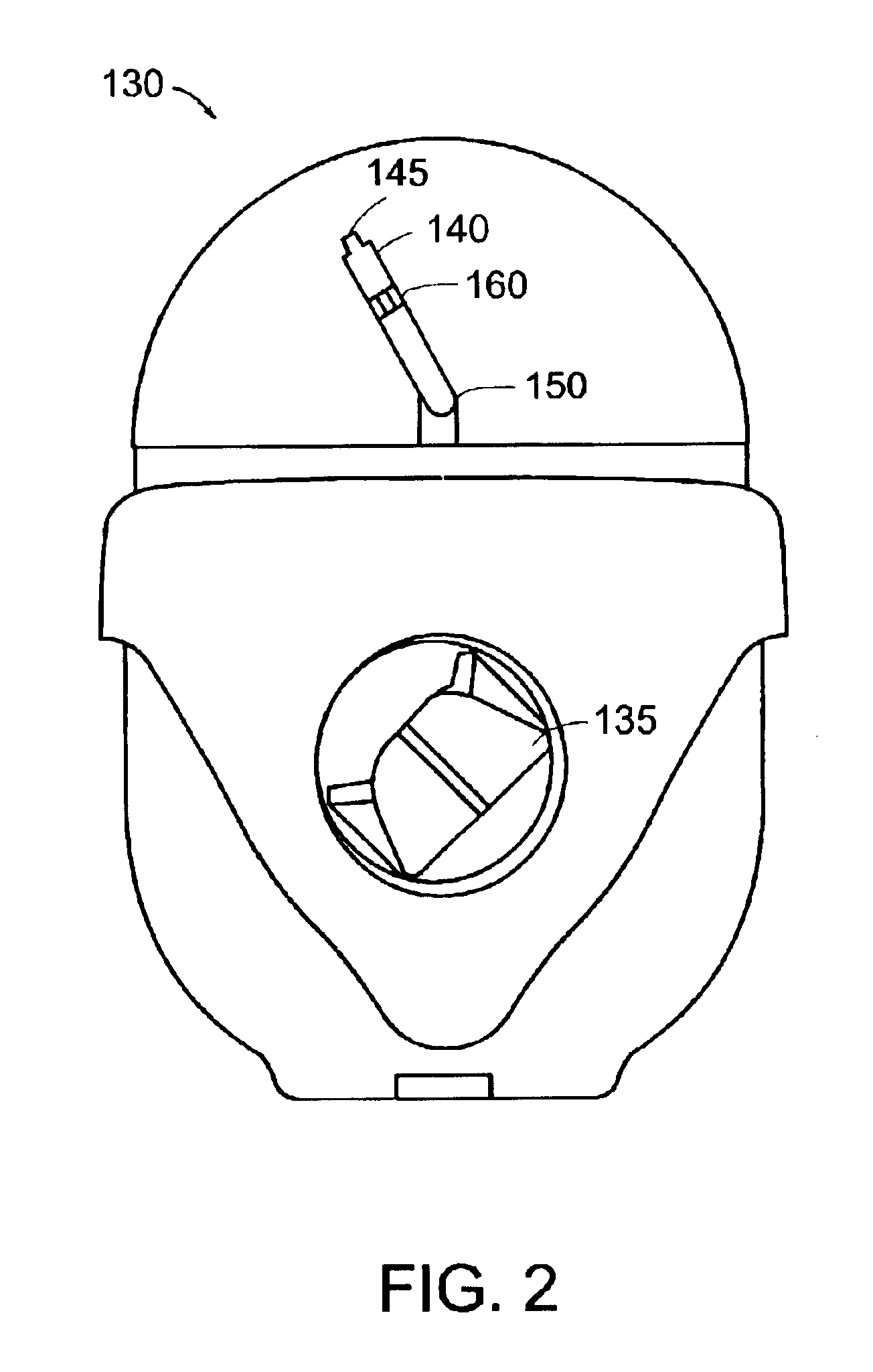
Method and system for remote control of mobile robot
InactiveUS6845297B2Easy to navigateSimplified user interfaceProgramme-controlled manipulatorBronchoscopesRobot environmentTele operation
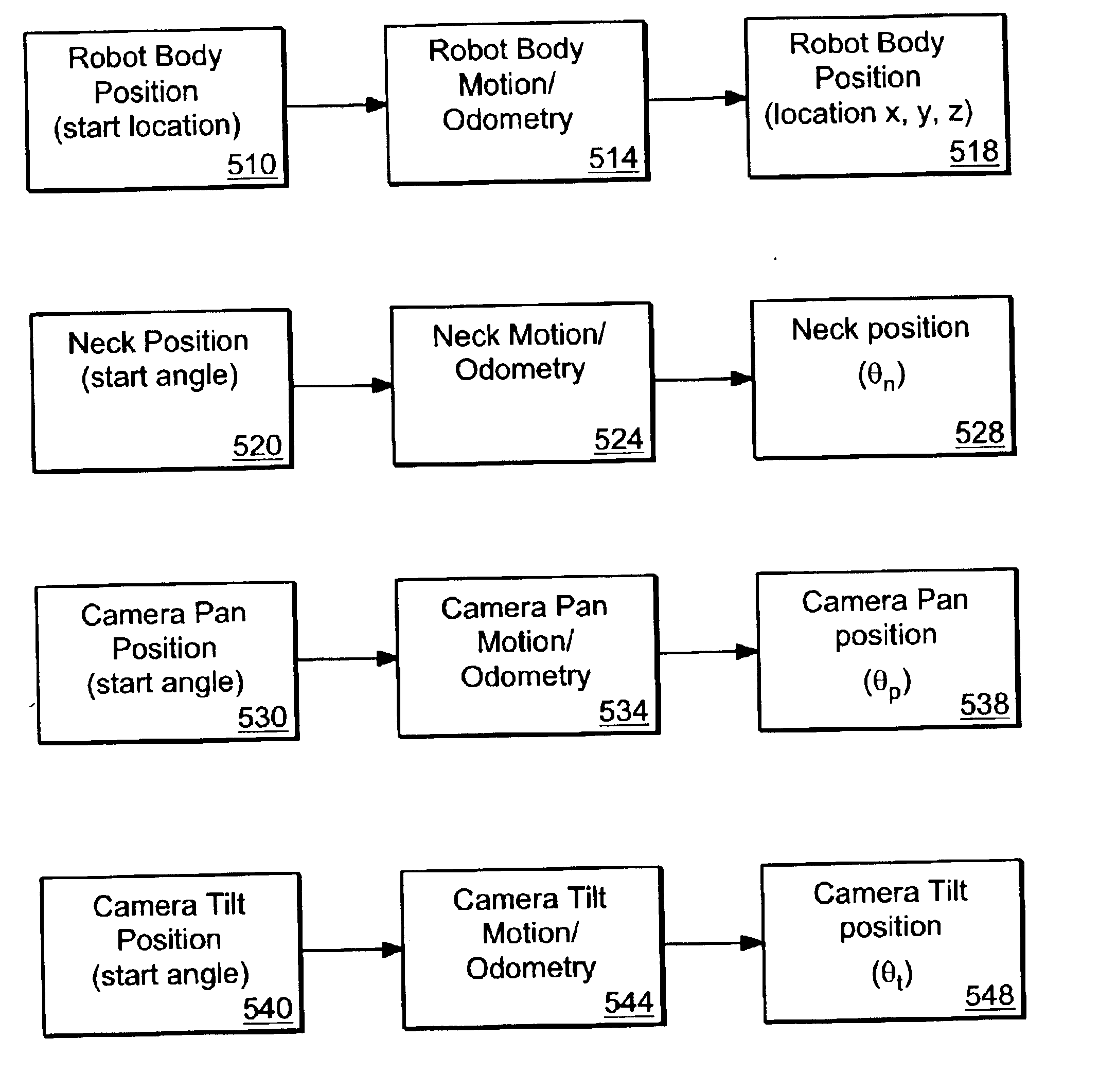
A system for tele-operating a robot in an environment includes a user interface for controlling the tele-operation of the robot, an imaging device associated with the robot for providing image information representative of the environment around the robot, means for transmitting the image information to the user interface, means for converting the image information to a user-perceptible image at the user interface, means for designating one or more waypoints located anywhere in the user-perceptible image towards which the robot will move, the waypoint in the user-perceptible image towards which the robot will first move being designated as the active waypoint using an icon, means for automatically converting the location of the active waypoint in the user-perceptible image into a target location having x, y, and z coordinates in the environment of the robot, means for providing real-time instructions to the robot from the user interface to move the robot from the robot's current location in the environment to the x, y, and z coordinates of the target location in the environment, and means for moving the icon representing the active waypoint in the user-perceptible image to a new location in the user-perceptible image while the robot is executing the real-time instruction, wherein the location-converting means automatically converts the new location of the icon representing the active waypoint into a new target location having x, y, and z coordinates in the environment of the robot towards which the robot will move.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
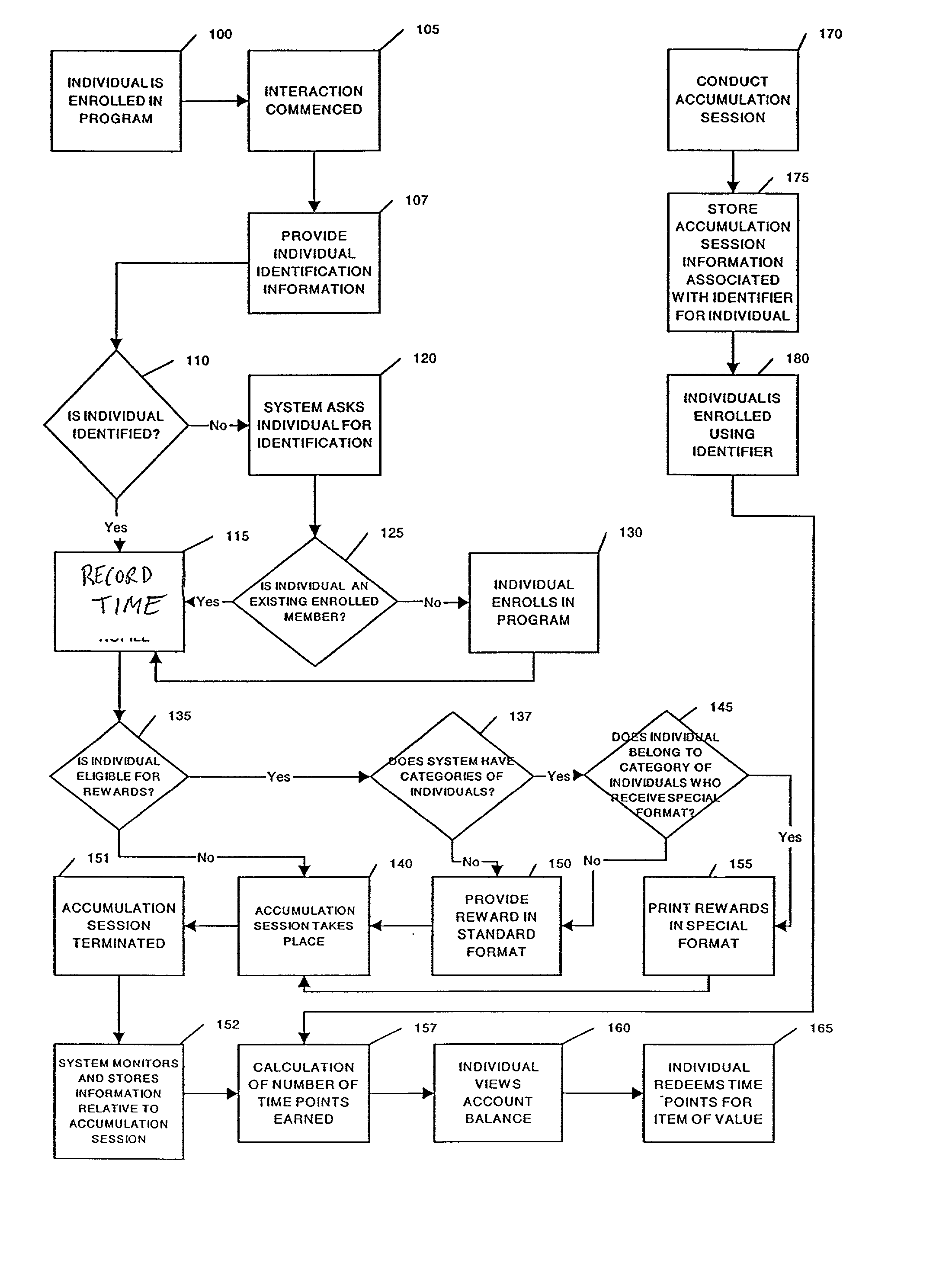
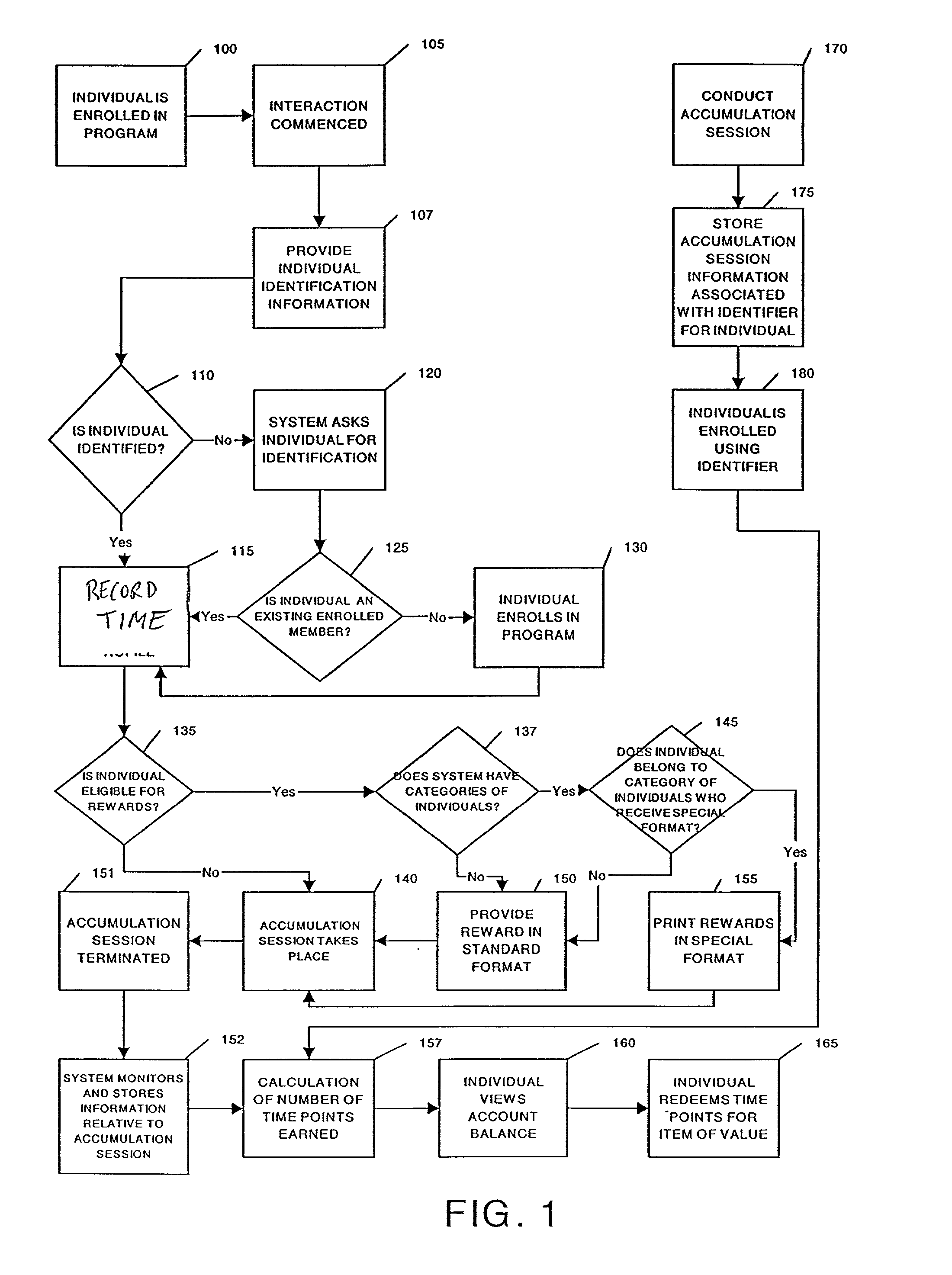
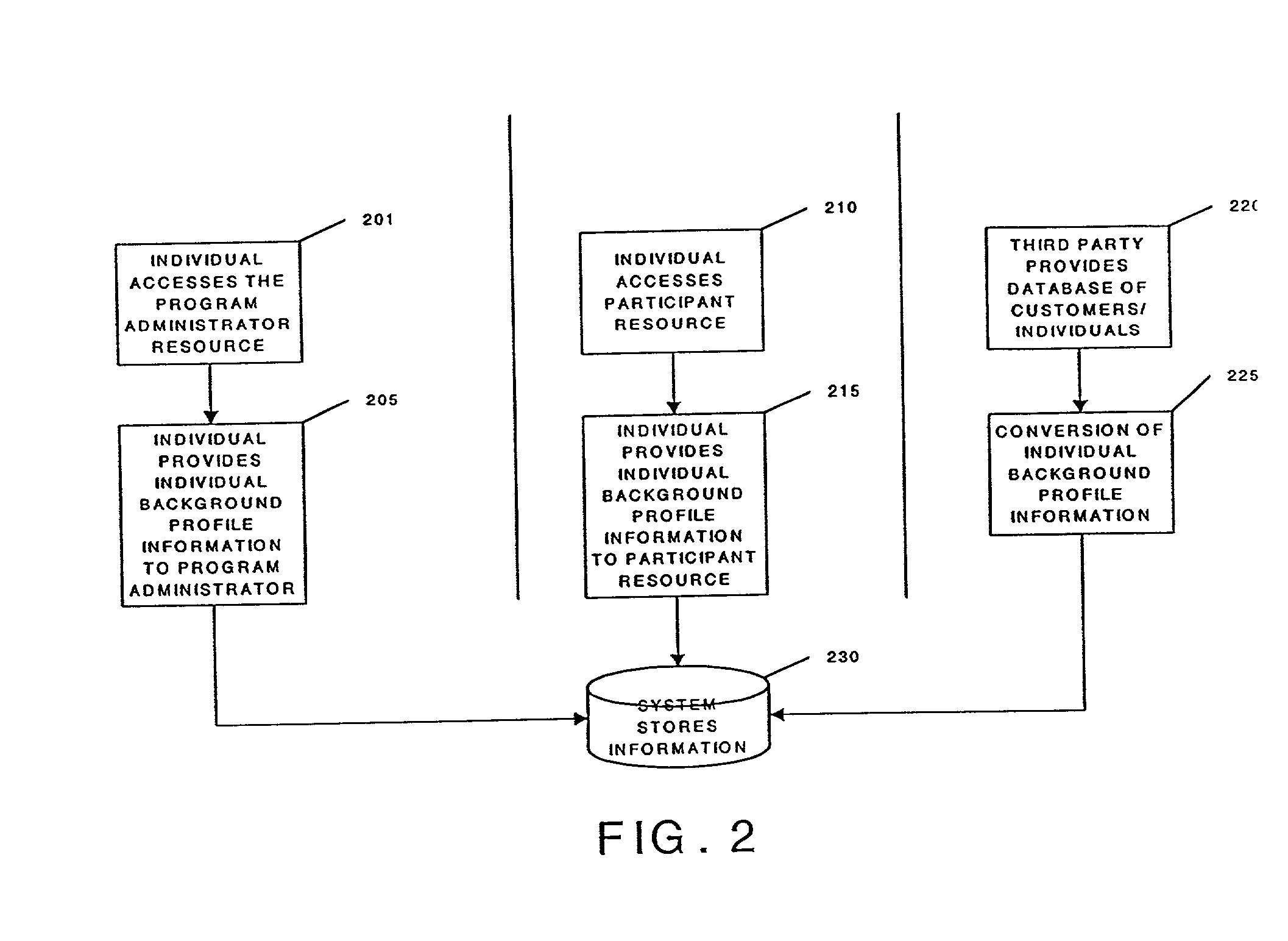
Method and system for tracking and providing incentives for time and attention of persons and for timing of performance of tasks
InactiveUS20020116266A1Payment architectureApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingPaymentProgram planning
A method for tracking and rewarding the desirable activities, including providing time and attention of individuals, and performing of tasks at desired times, includes providing an incentive rewards program. Individuals, groups, companies, or families are enrolled in a program. Interactions, including in-person sales presentations, viewing of pre-recorded videos, visits to stores and other facilities, and connections to internet websites are recorded. The level of attention provided by individuals during interactions may be measured directly or by proxies, and rewards are provided in greater amounts for greater lengths of interactions and for higher levels of attention. The timing of performance of tasks, including for example early payment of bills, particularly utility bills may be tracked, and rewarded. Points may be redeemed for goods and services, including include entry in a drawing, enhanced likelihood of winning in a drawing, and enhanced prizes in a drawing. Various factors may be included in determining the number of time points awarded, including the time of day and day of week of accumulation sessions, the length of the accumulation sessions, the activities and tasks accomplished, and purchases completed. The formula may also award a varying number of time points depending on the individual's background profile characteristics, including, but not limited to previous purchase history and previous responses to offers of time points. A central program administrator may maintain records relating to the backgrounds of each enrolled individual, and record awards and administer redemption of awards for earned time points.
Owner:MARSHALL THADDEUS
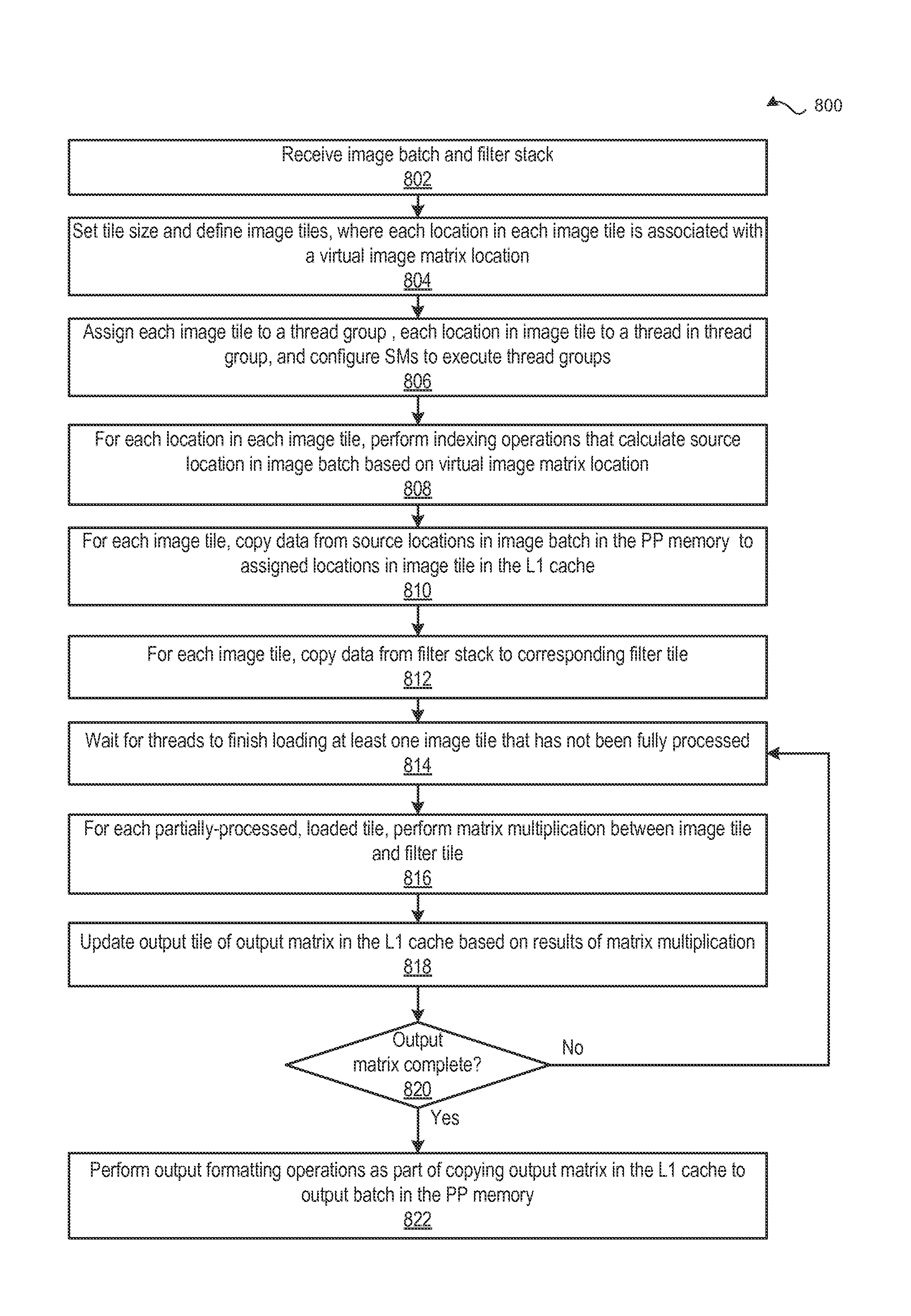
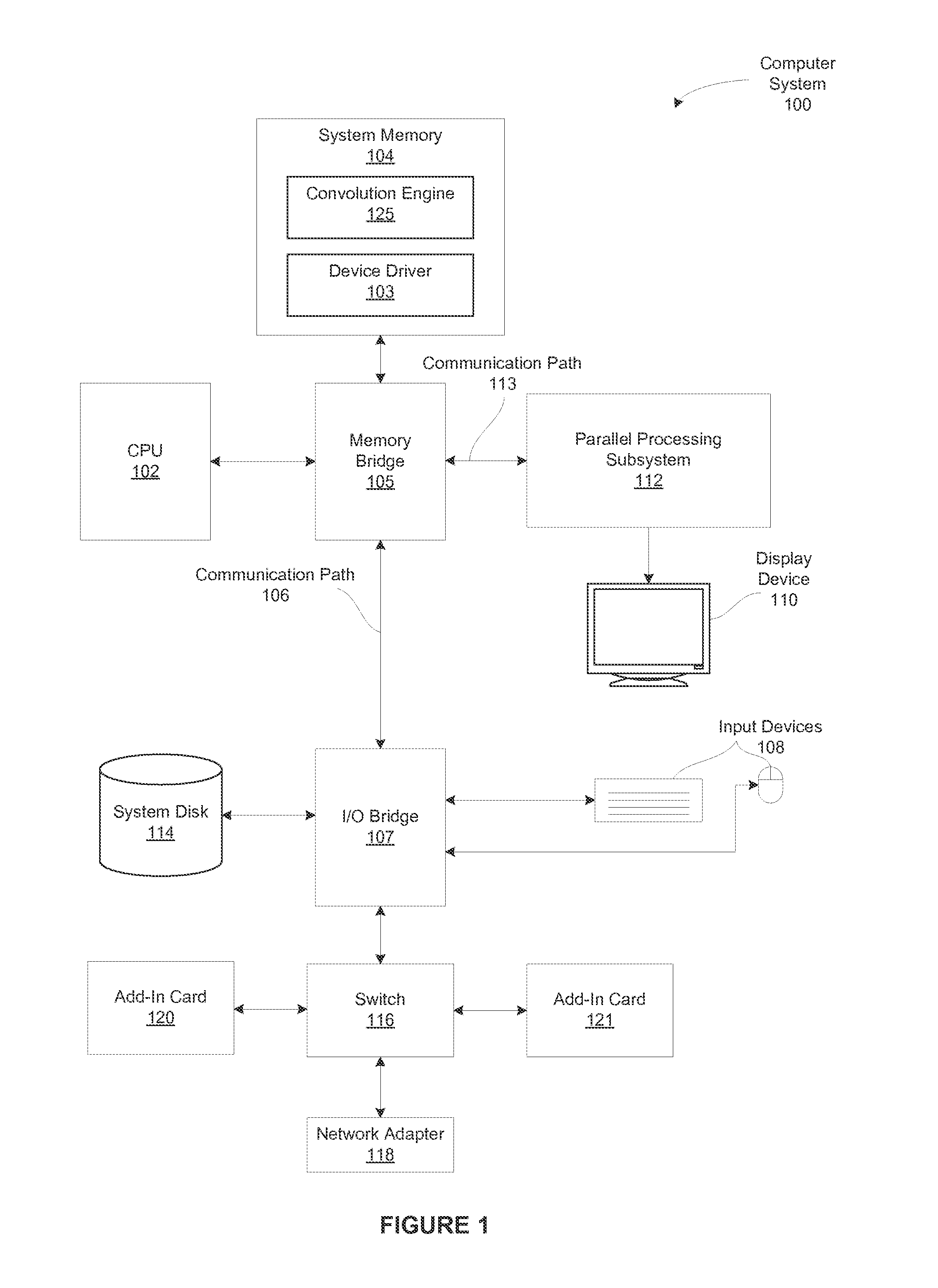
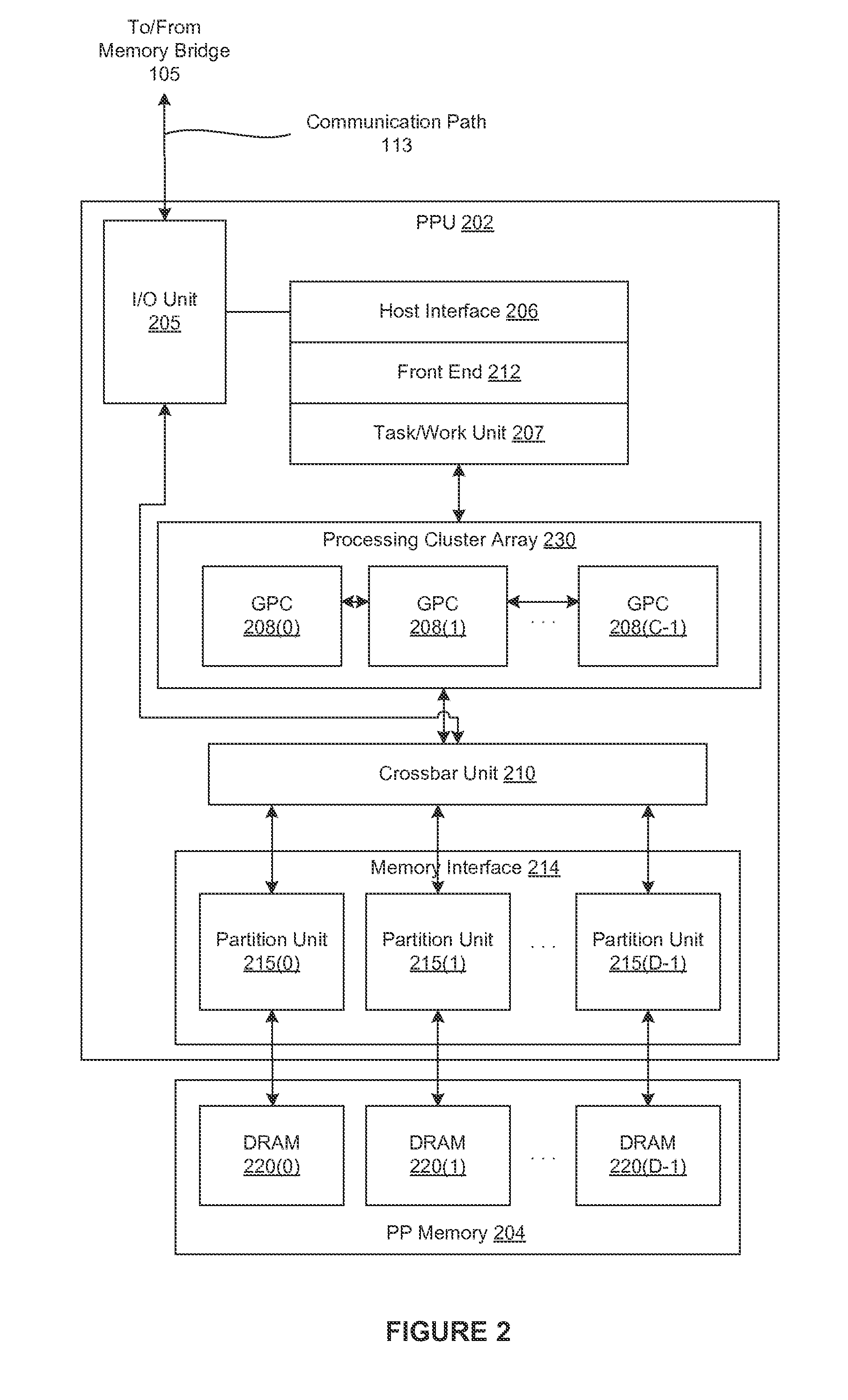
Performing multi-convolution operations in a parallel processing system
ActiveUS20160062947A1Easy to operateOptimizing on-chip memory usageBiological modelsComplex mathematical operationsLine tubingParallel processing
In one embodiment of the present invention a convolution engine configures a parallel processing pipeline to perform multi-convolution operations. More specifically, the convolution engine configures the parallel processing pipeline to independently generate and process individual image tiles. In operation, for each image tile, the pipeline calculates source locations included in an input image batch. Notably, the source locations reflect the contribution of the image tile to an output tile of an output matrix—the result of the multi-convolution operation. Subsequently, the pipeline copies data from the source locations to the image tile. Similarly, the pipeline copies data from a filter stack to a filter tile. The pipeline then performs matrix multiplication operations between the image tile and the filter tile to generate data included in the corresponding output tile. To optimize both on-chip memory usage and execution time, the pipeline creates each image tile in on-chip memory as-needed.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
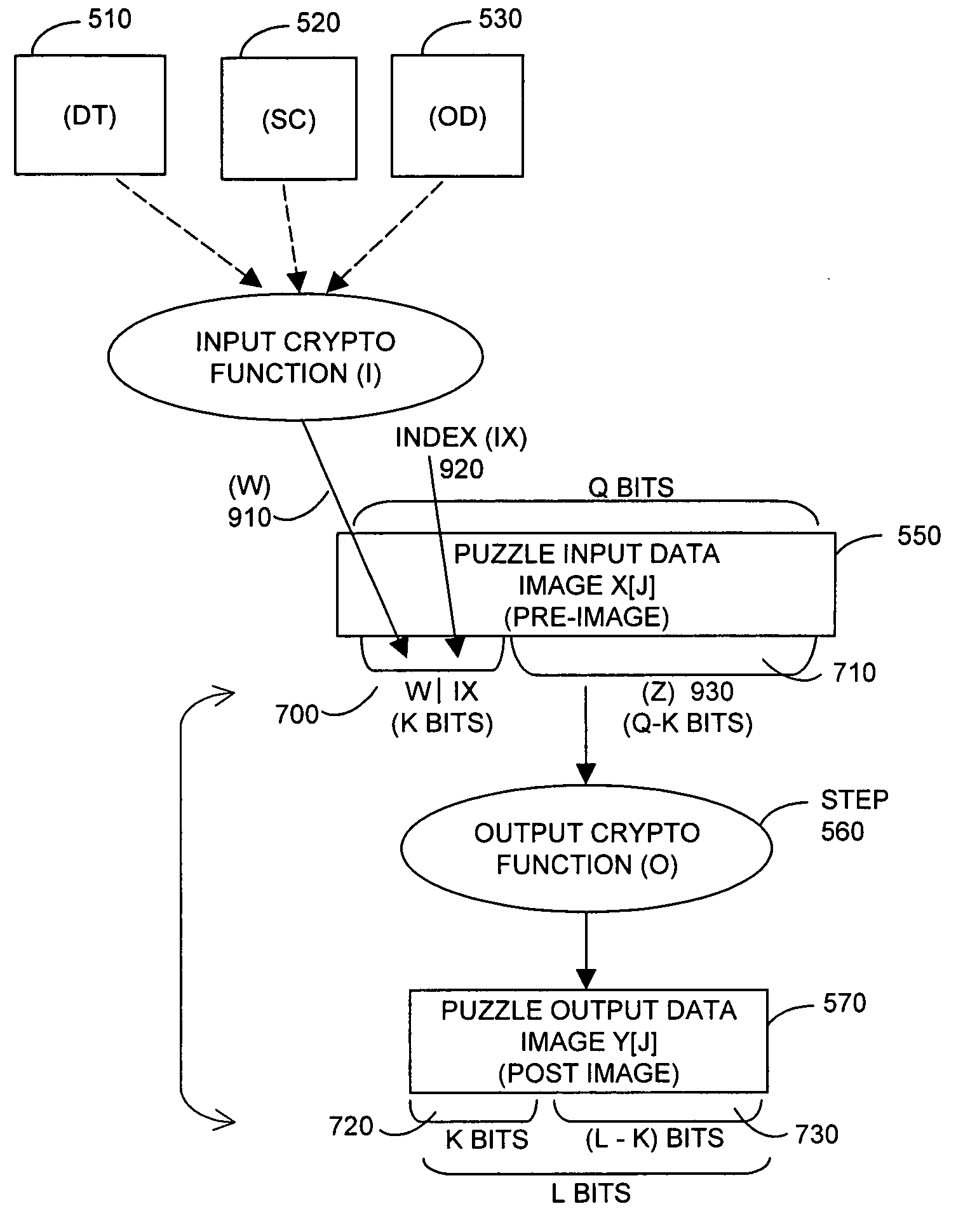
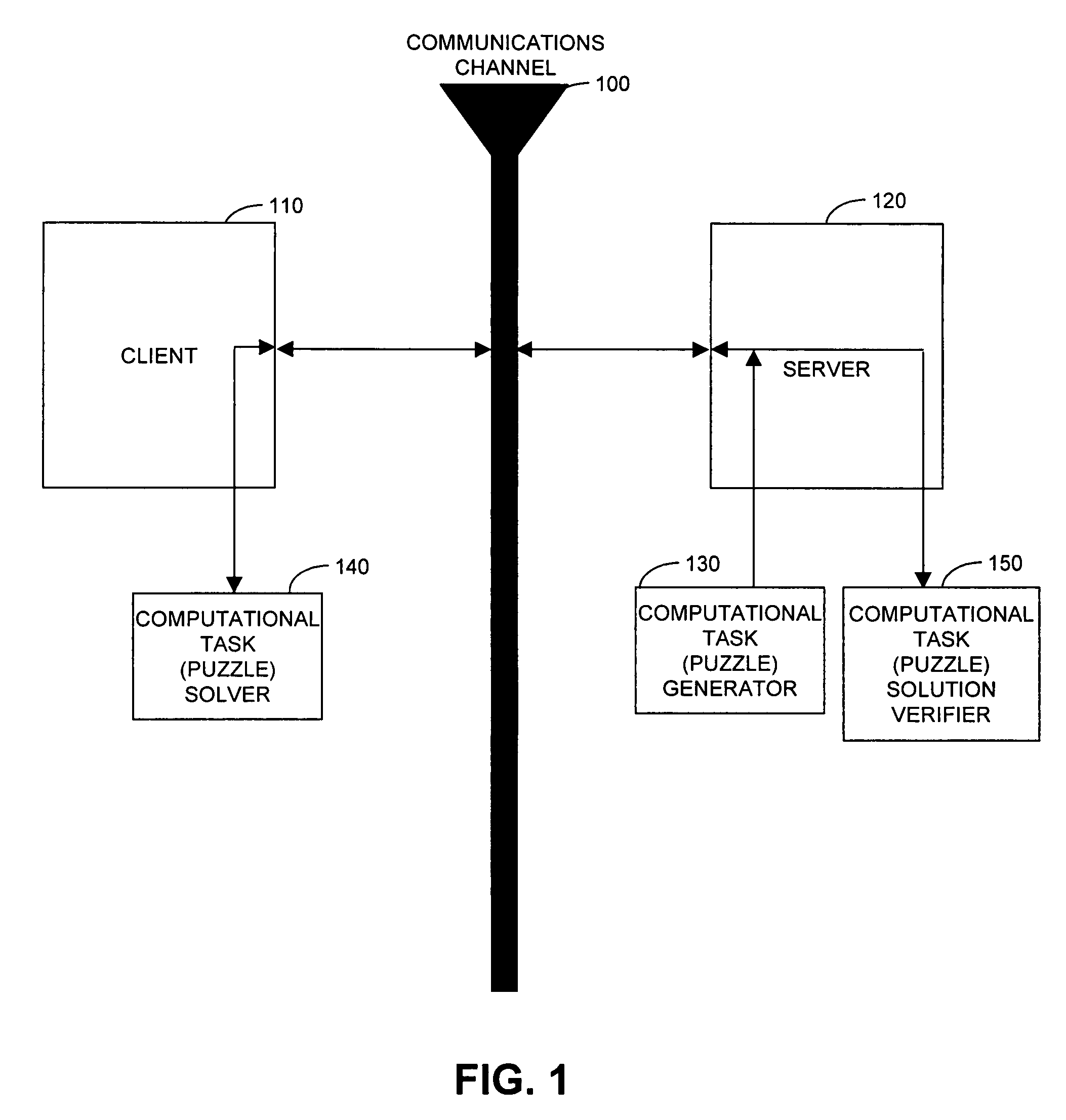
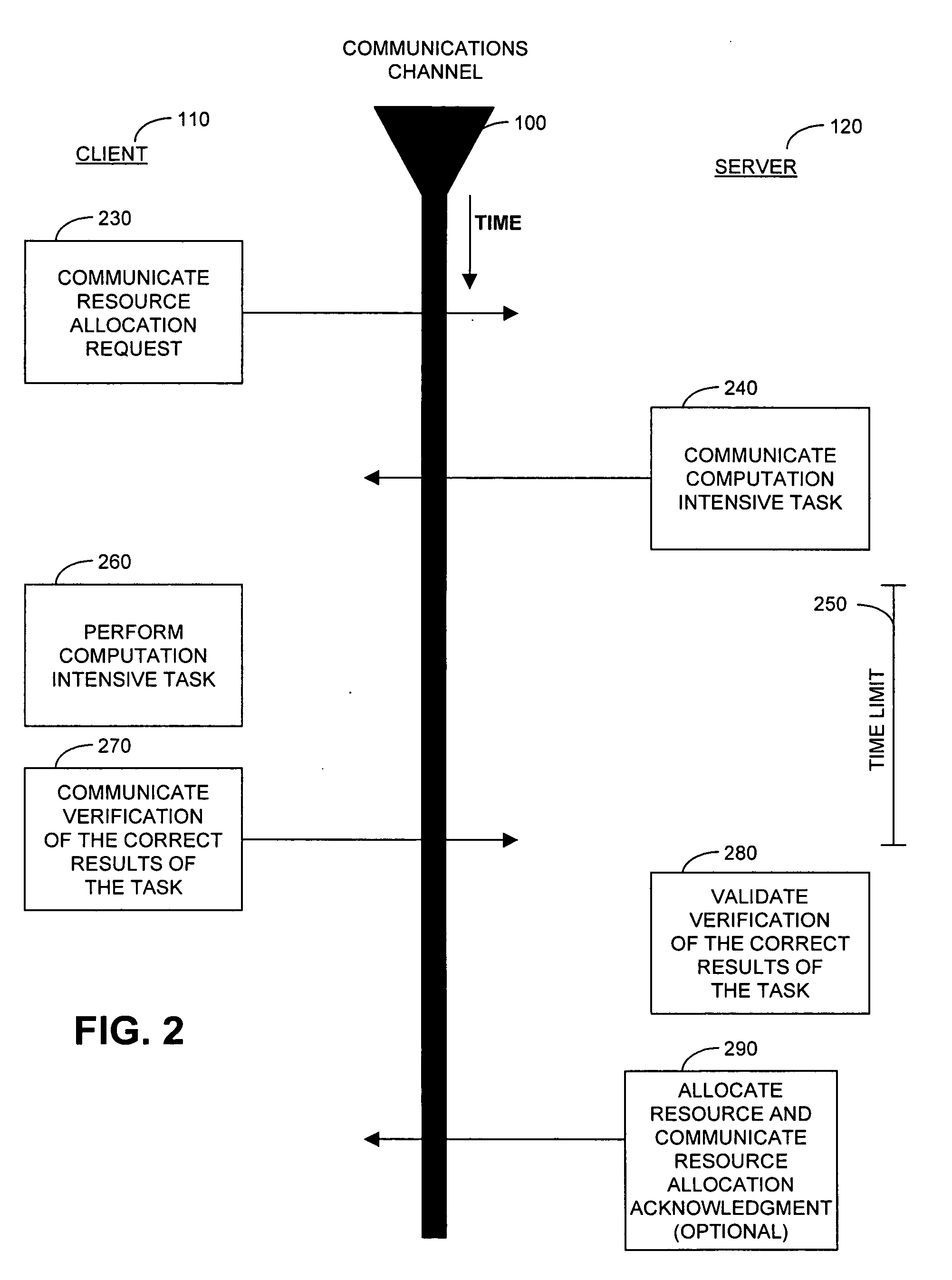
Cryptographic countermeasures against connection depletion attacks
InactiveUS7197639B1Ensure correct executionDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationCountermeasureTime limit
This invention relates to cryptographic communications methods and systems that protect a server from a connection depletion attack. Specifically, the invention presents a method for allocating a resource comprising the steps of receiving a resource allocation request from a client, imposing a computational task and a time limit for correct completion of the task upon the client, verifying that the task was performed correctly within the time limit, and allocating the resource if the task was correctly performed within the time limit.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
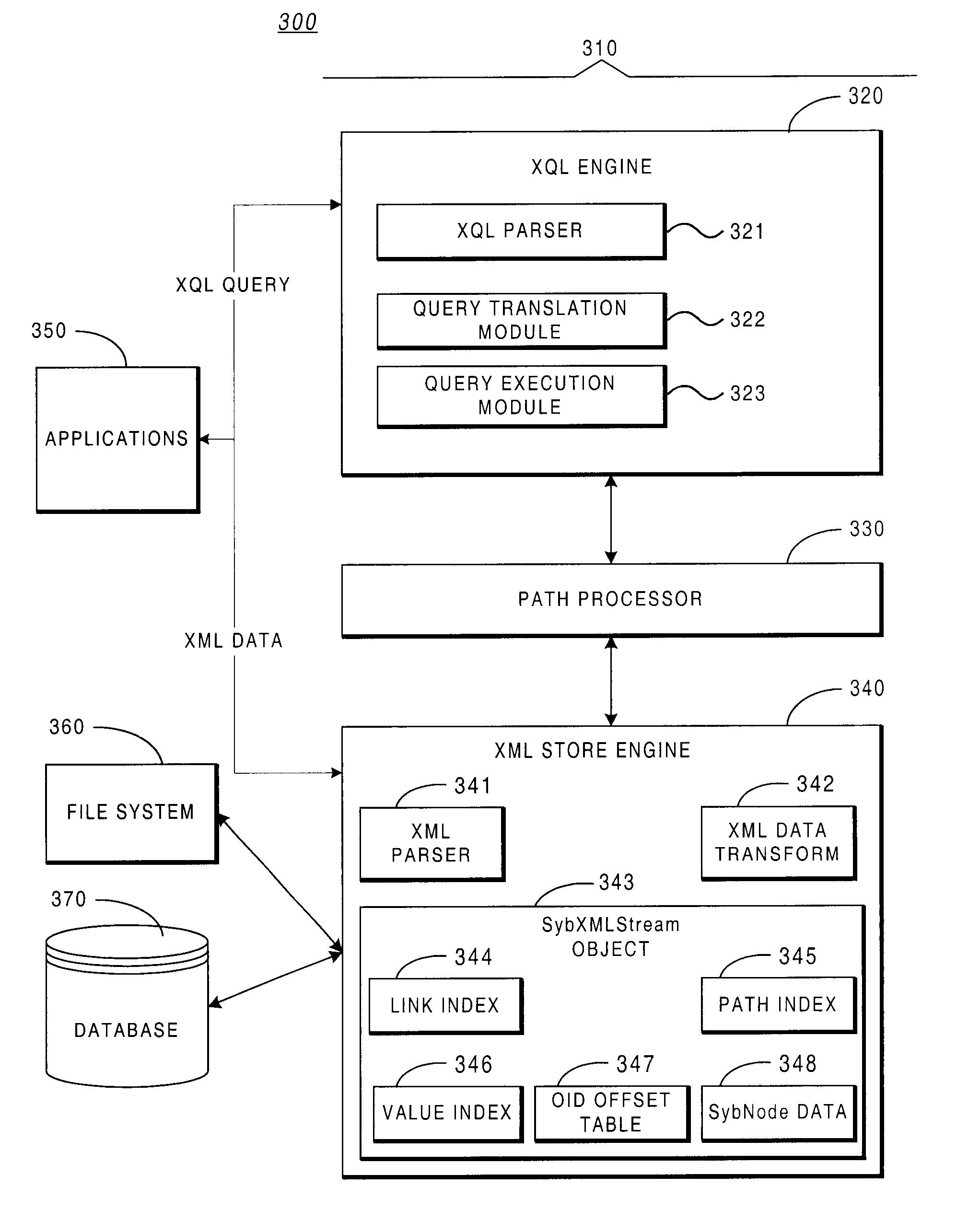
Relational database system providing XML query support
InactiveUS6799184B2Efficient accessImprove efficiencyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRelational databaseFile system
A system providing methods enabling data in Extensible Markup Language ("XML") format to be extracted, transformed and stored in a database, file system or main memory is described. The extraction and transformation process is generalized and can be used on various types of XML data, enabling XML data to be stored and queried using standard database query methodologies. The system includes parse-time functionality to transform XML documents into a structure having an interface that enables efficient access to the underlying data. The system also includes query execution-time functionality providing greater efficiency by bringing only the relevant portions of transformed XML data into memory in response to a query. The system parses and translates queries into a structure that can be executed without the need to write custom application-specific navigation code to search XML data. The system also enables original XML documents (or portions thereof) to be recomposed when required.
Owner:SYBASE INC
Storage system snapshot assisted by SSD technology
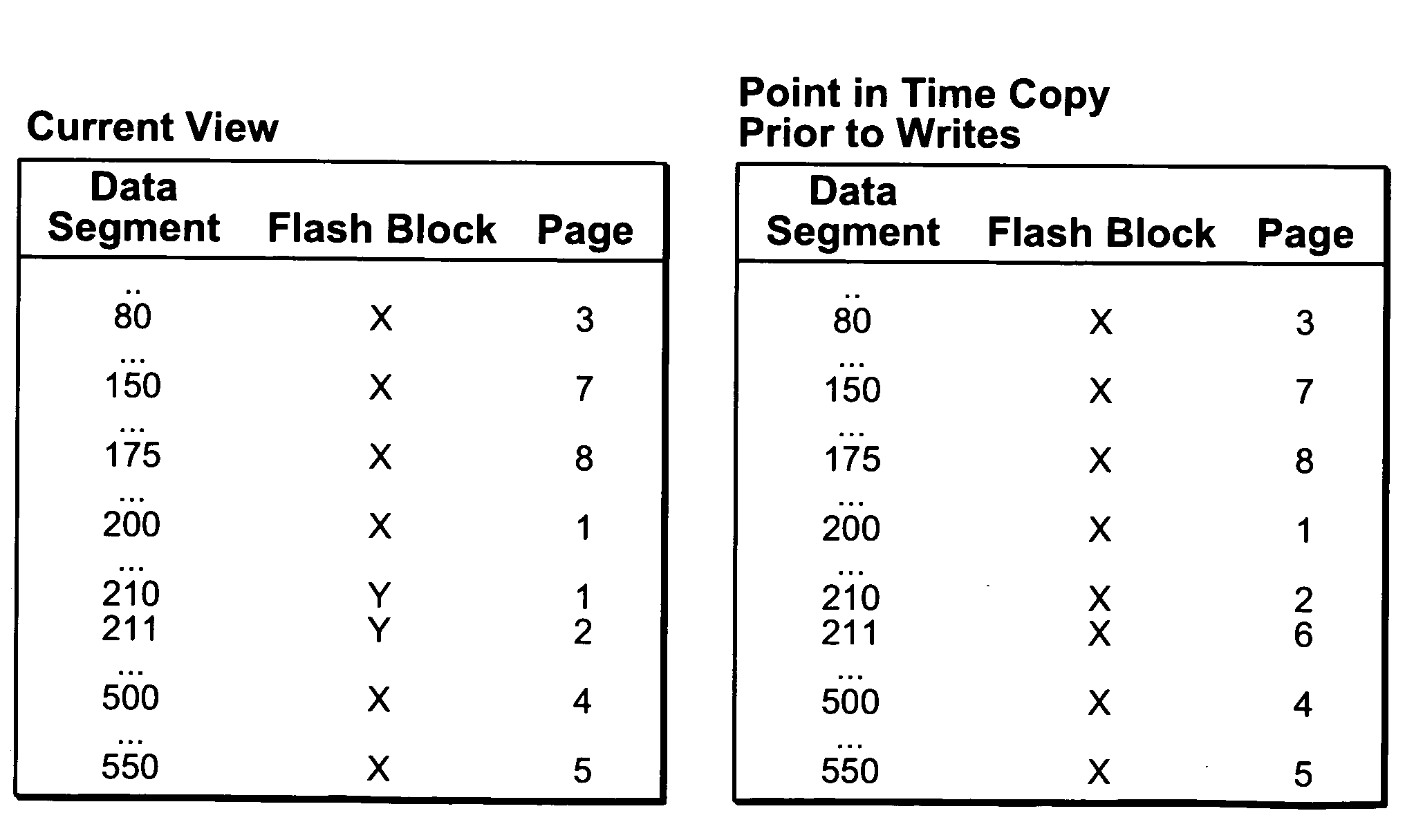
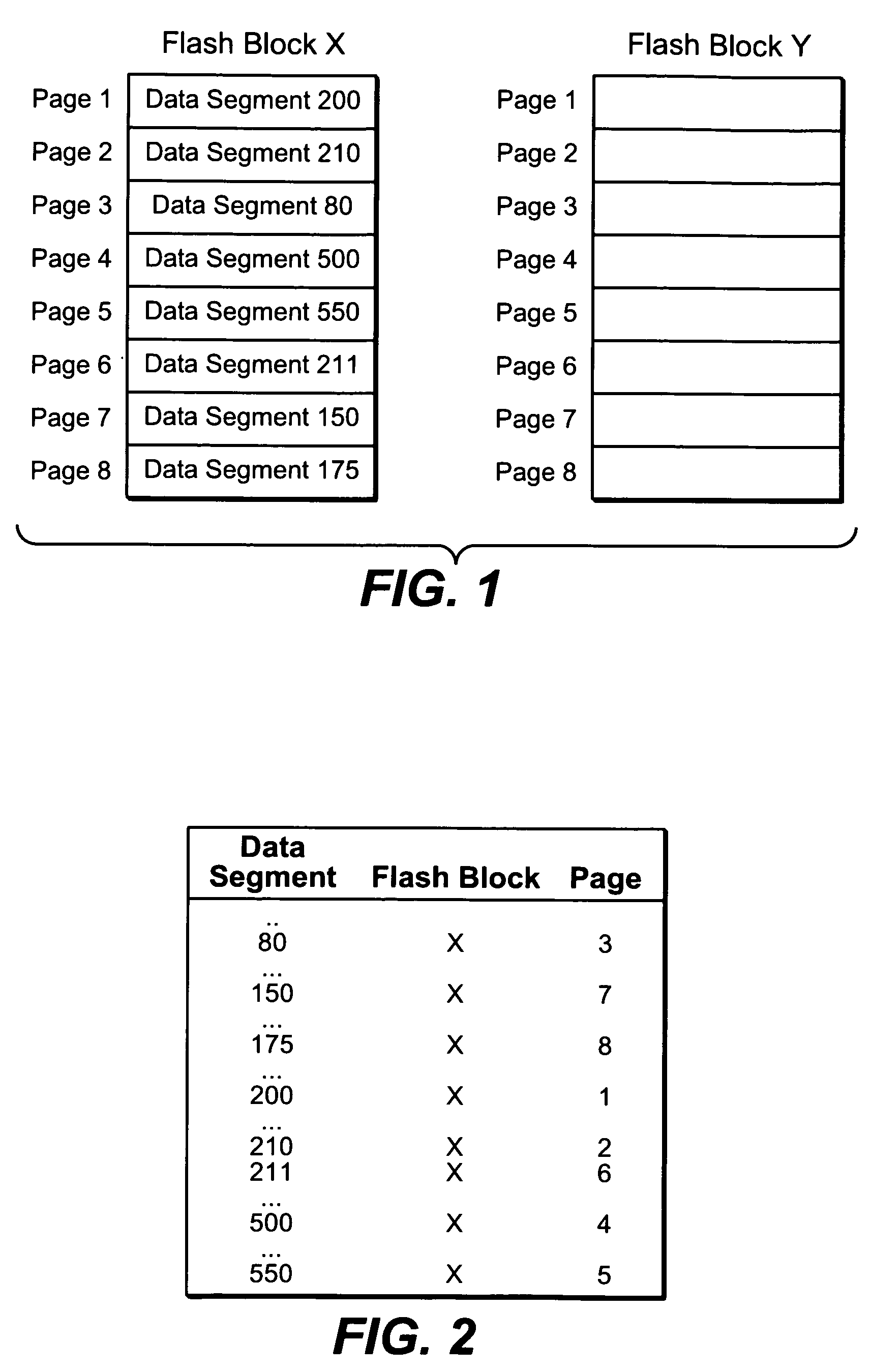
ActiveUS20100153620A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionOriginal dataData needs
A method and apparatus for taking a snapshot of a storage system employing a solid state disk (SSD). A plurality of mapping tables in the SSD store data needed to create a one or more point in time snapshots and a current view of the SSD. In response to a write command, the SSD executes its normal write process and updates its mapping tables to indicate the current view of the SSD and additionally retains the original data in a table of pointers to the original data, as the snapshot of an earlier state of the SSD. In the preferred embodiment, the innate ability of SSDs to write data to a new location is used to perform a point-in-time copy with little or no loss in performance in performing the snapshot.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Method and system for monitoring performance of a client-server architecture
InactiveUS7933988B2Monitor performanceError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsServer logClient-side
An arrangement which jointly exploits an agent component installed in a server-side portion of client-server architecture for emulating requests of actual clients of the client-server architecture and measuring a server execution time indicative of a time elapsed between reception of an emulated end-user request at a server component and generation of a result of said emulated end-user request at said server component; information stored in a server log file about a hit end to end response time, i.e., the time elapsed between the instant in which the end-user sends a request to the server component and the instant in which result of the request reaches the end-user. From the server execution time and the hit response time, the delay due to the network connecting the server-side portion of the client-server architecture to a client-side portion may be determined. The network delay and the server execution time are then used for monitoring performance of the client-server architecture by distinguishing network related problems from server-related problems or even from client-related problems.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
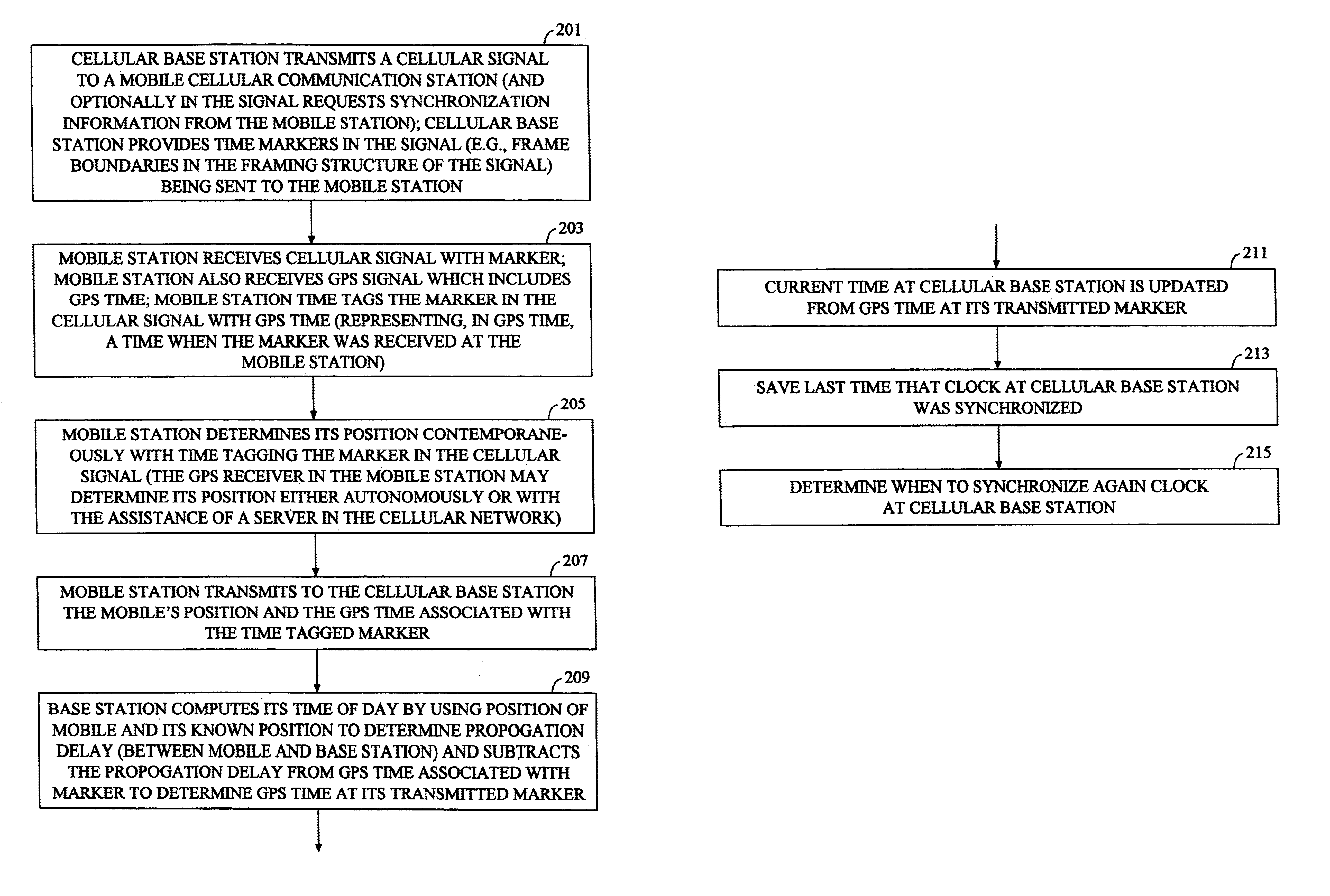
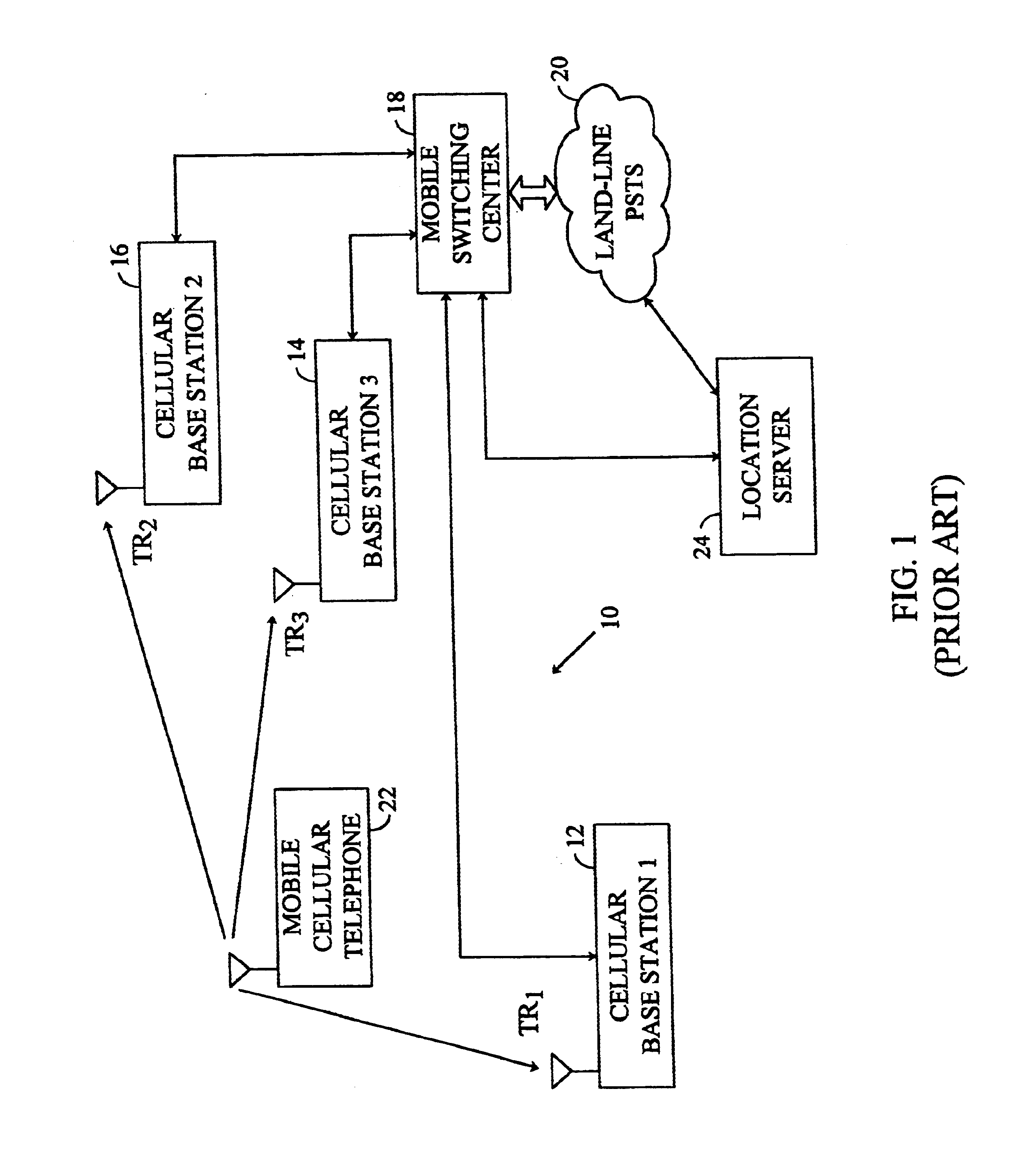
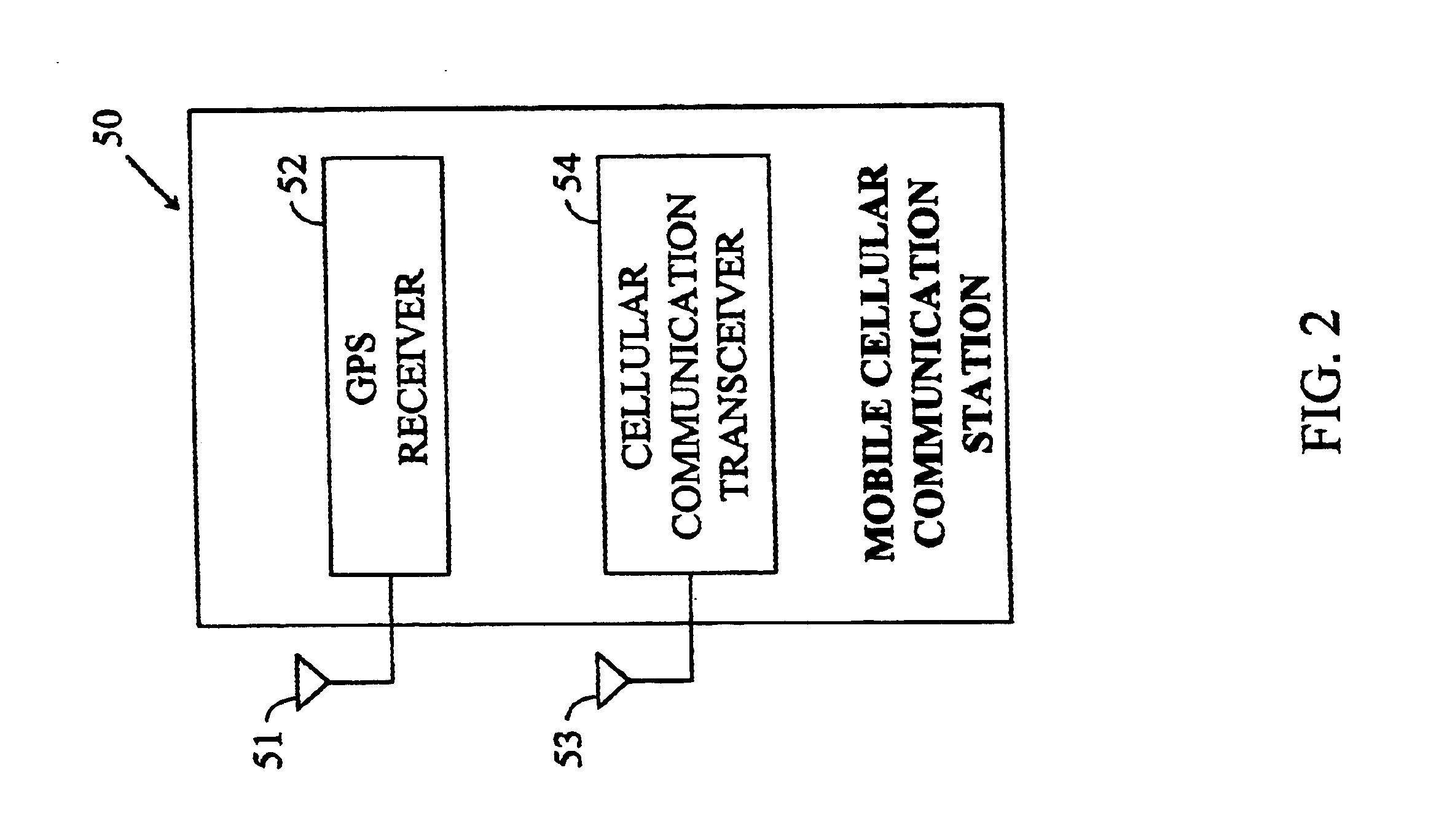
Methods and apparatuses for using mobile GPS receivers to synchronize basestations in cellular networks
InactiveUS6665541B1Low costSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexGeolocationGps receiver
Methods and apparatuses for synchronizing basestations in a cellular network. One exemplary method performs time synchronization between at least two basestations, a first basestation and a second basestation, of a cellular communication system. In this exemplary method, a first time-of-day and a first geographical location of a first mobile cellular receiver station (MS) are determined from a first satellite positioning system (SPS) receiver which is co-located with the first MS, and the first time-of-day and first location are transmitted by the first MS to a first basestation which determines a time-of-day of the first basestation from the first time-of-day and first location and from a known location of the first basestation. Also in this exemplary method, a second time-of-day and a second geographical location of a second MS are determined from a second SPS receiver which is co-located with the second MS, and the second time-of-day and the second location are transmitted to a second basestation which determines a time-of-day of the second basestation from the second time-of-day and the second location and a known location of the second basestation. Other methods and apparatuses are also described for synchronizing basestations in a cellular network.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
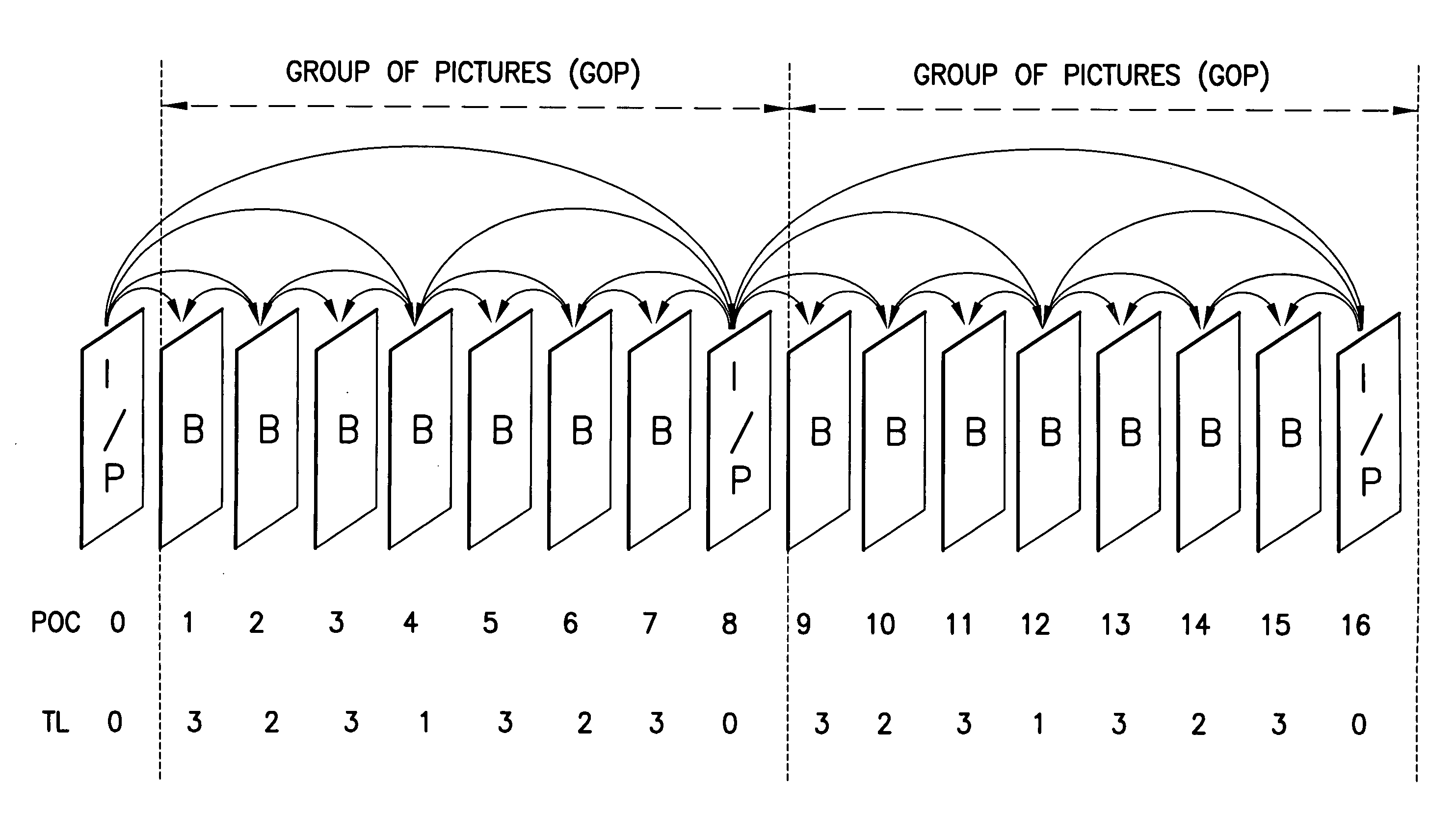
System and method for indicating temporal layer switching points
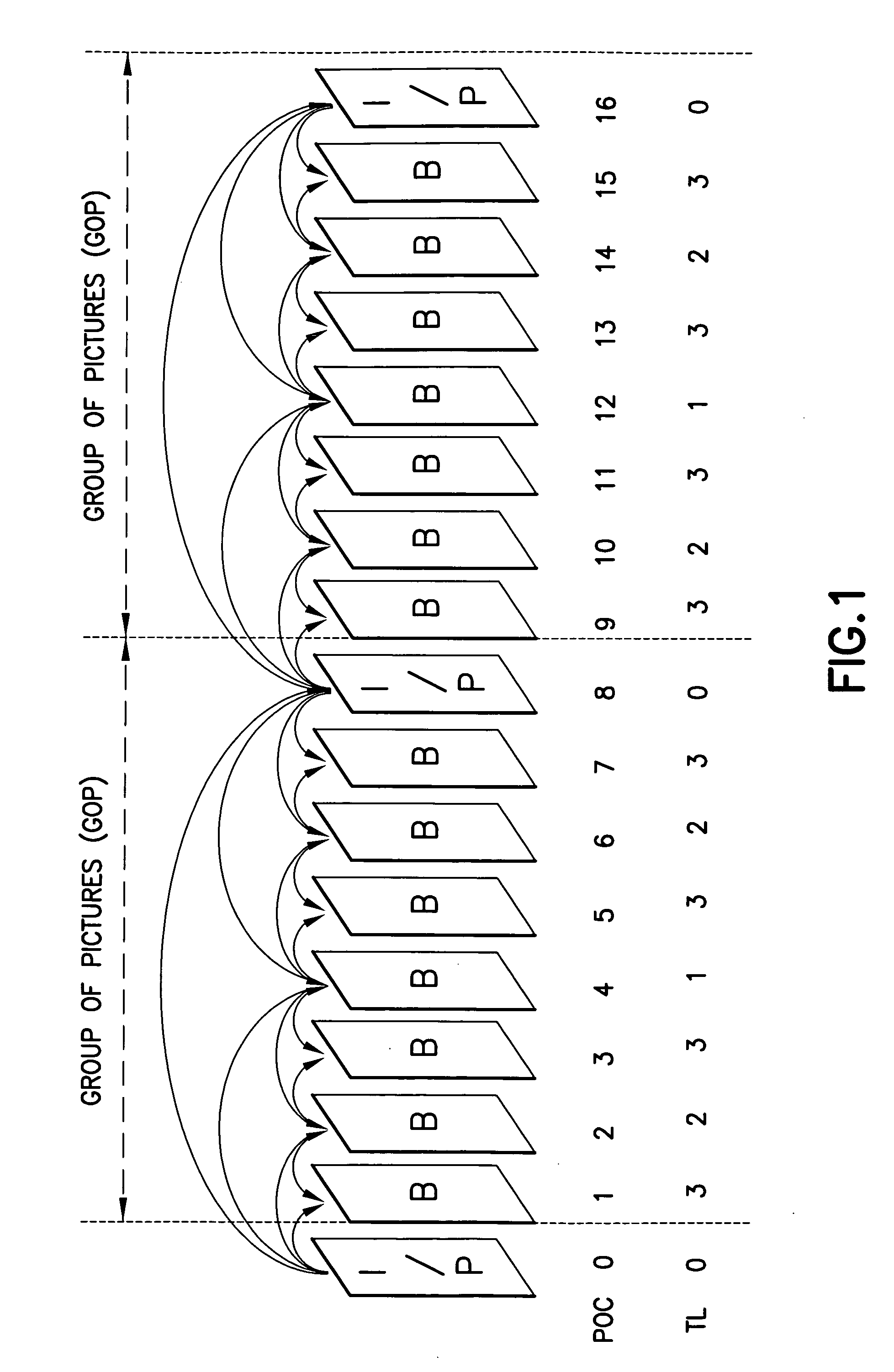
ActiveUS20090003439A1Accurately indicatedAccurate decodingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo bitstreamComputer architecture
Disclosed are a system, apparatus, computer programs and methods for indicating proper temporal layer switching points for temporal scalable coding. Various embodiments provide an apparatus and method for properly indicating temporal layer switching points in a scalable video bit stream or in a scalable video file container. Using these indications, a decoder can determine where to perform temporal layer switching, after which all of the pictures at and below the desired temporal layer can be correctly decoded.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Storage system snapshot assisted by SSD technology
ActiveUS8200922B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionOriginal dataData needs
A method and apparatus for taking a snapshot of a storage system employing a solid state disk (SSD). A plurality of mapping tables in the SSD store data needed to create a one or more point in time snapshots and a current view of the SSD. In response to a write command, the SSD executes its normal write process and updates its mapping tables to indicate the current view of the SSD and additionally retains the original data in a table of pointers to the original data, as the snapshot of an earlier state of the SSD. In the preferred embodiment, the innate ability of SSDs to write data to a new location is used to perform a point-in-time copy with little or no loss in performance in performing the snapshot.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Processing data in data migration
ActiveUS9460171B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsBusiness processProcess information
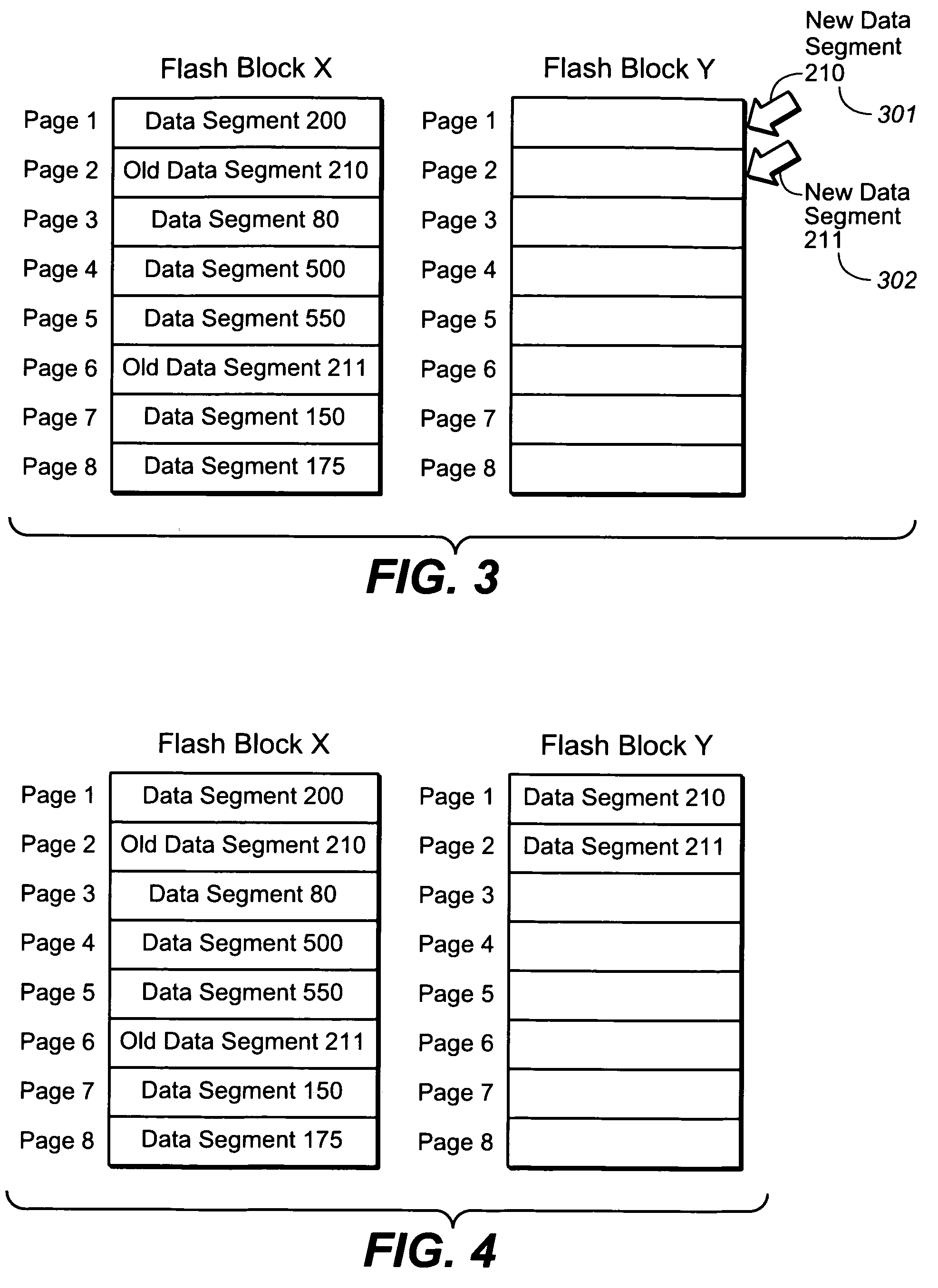
A computer-implemented method for processing information related to an extract-transform-load (ETL) data migration, including aggregating operational metadata and determining: a plurality of metrics, organized by business object, corresponding to the migration; a number of business object instances not successfully loaded; a first end-to-end execution time for at least one business object; relevant input metadata; load readiness status per business object; impact of a business object that is not load ready by analyzing business process hierarchies; business object load readiness by reference to incomplete development status or data defects; scope per test cycle based, at least in part, upon business object load readiness; and high-priority defects of business objects that stop testing based, at least in part, upon analysis of business process hierarchies.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
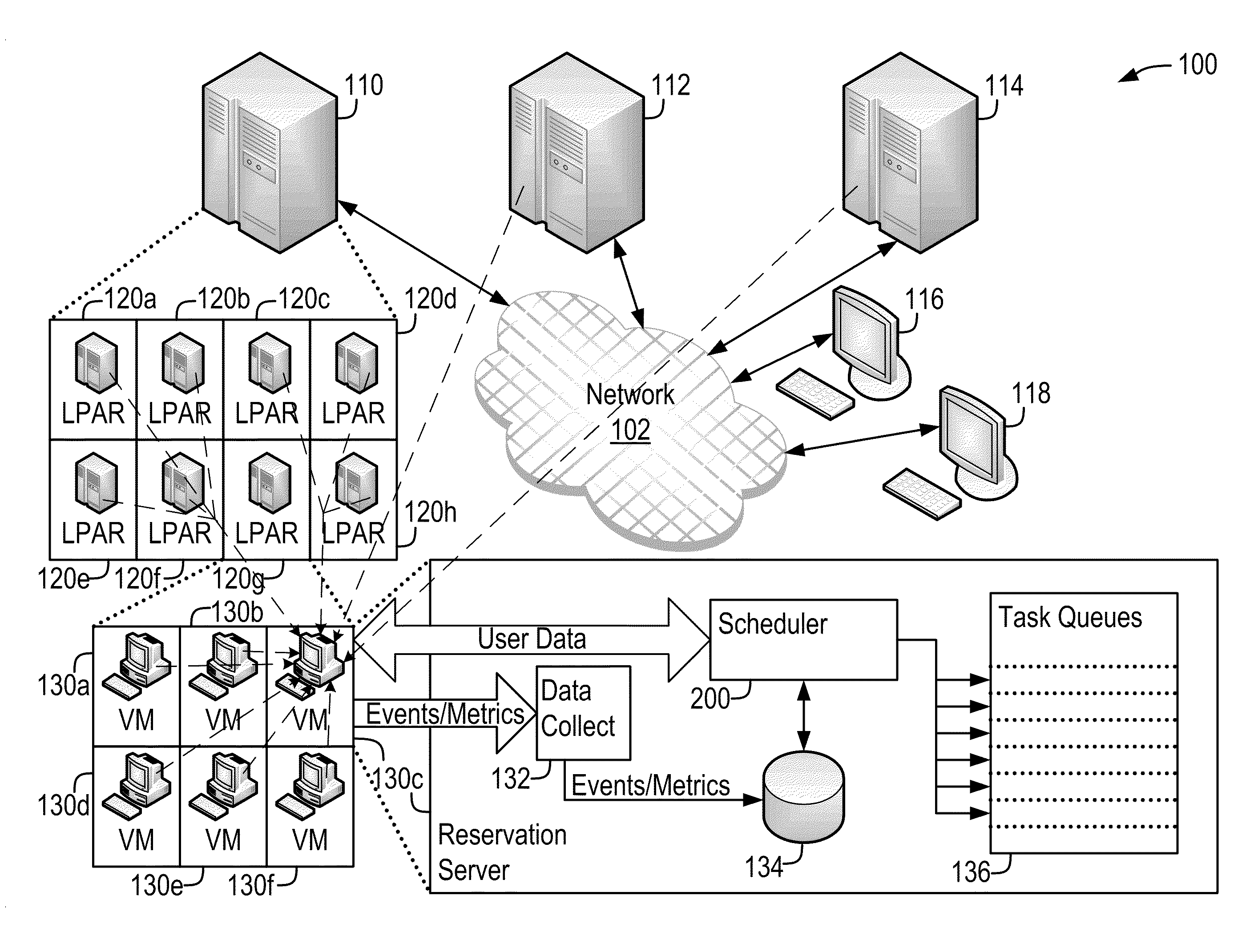
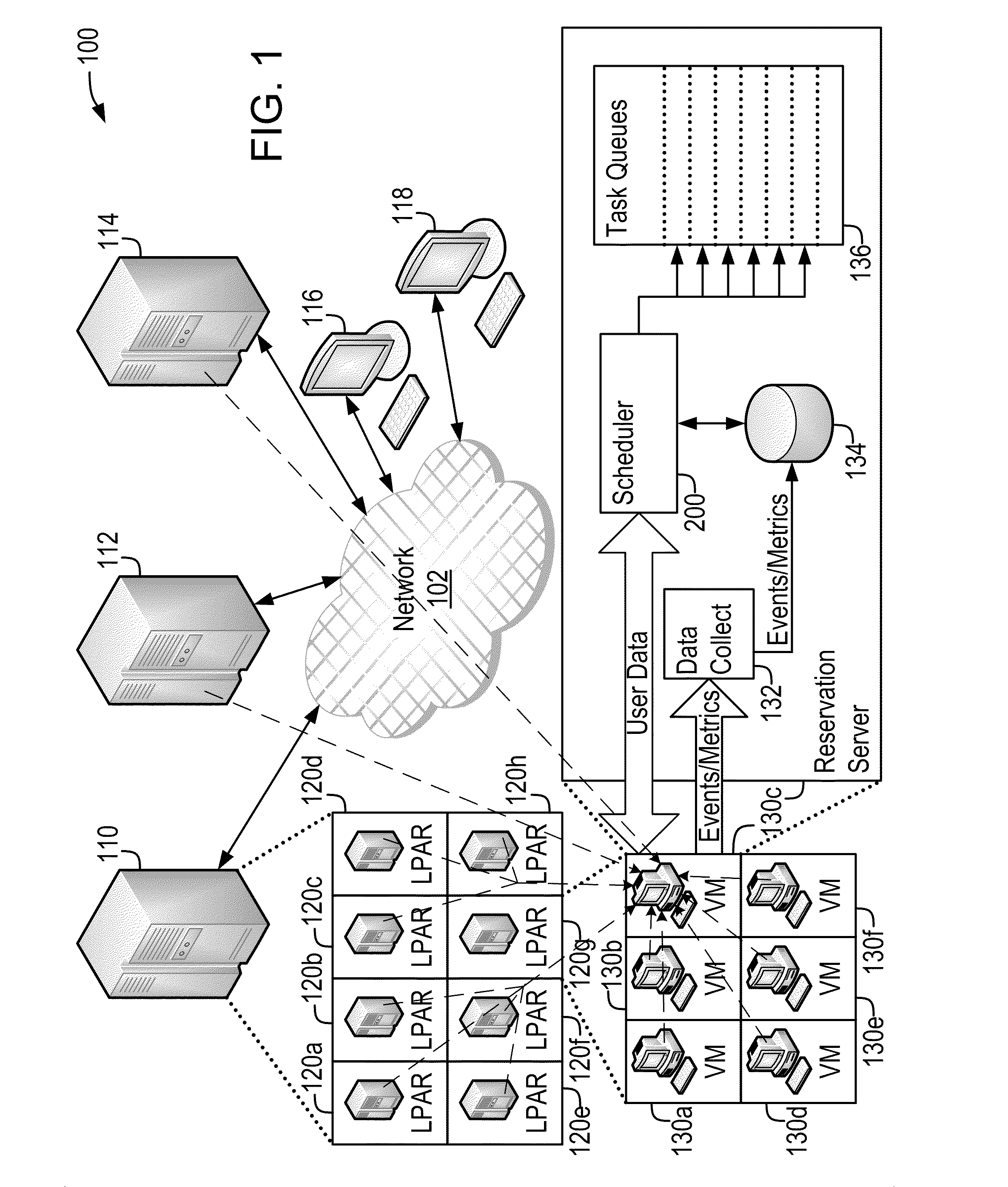
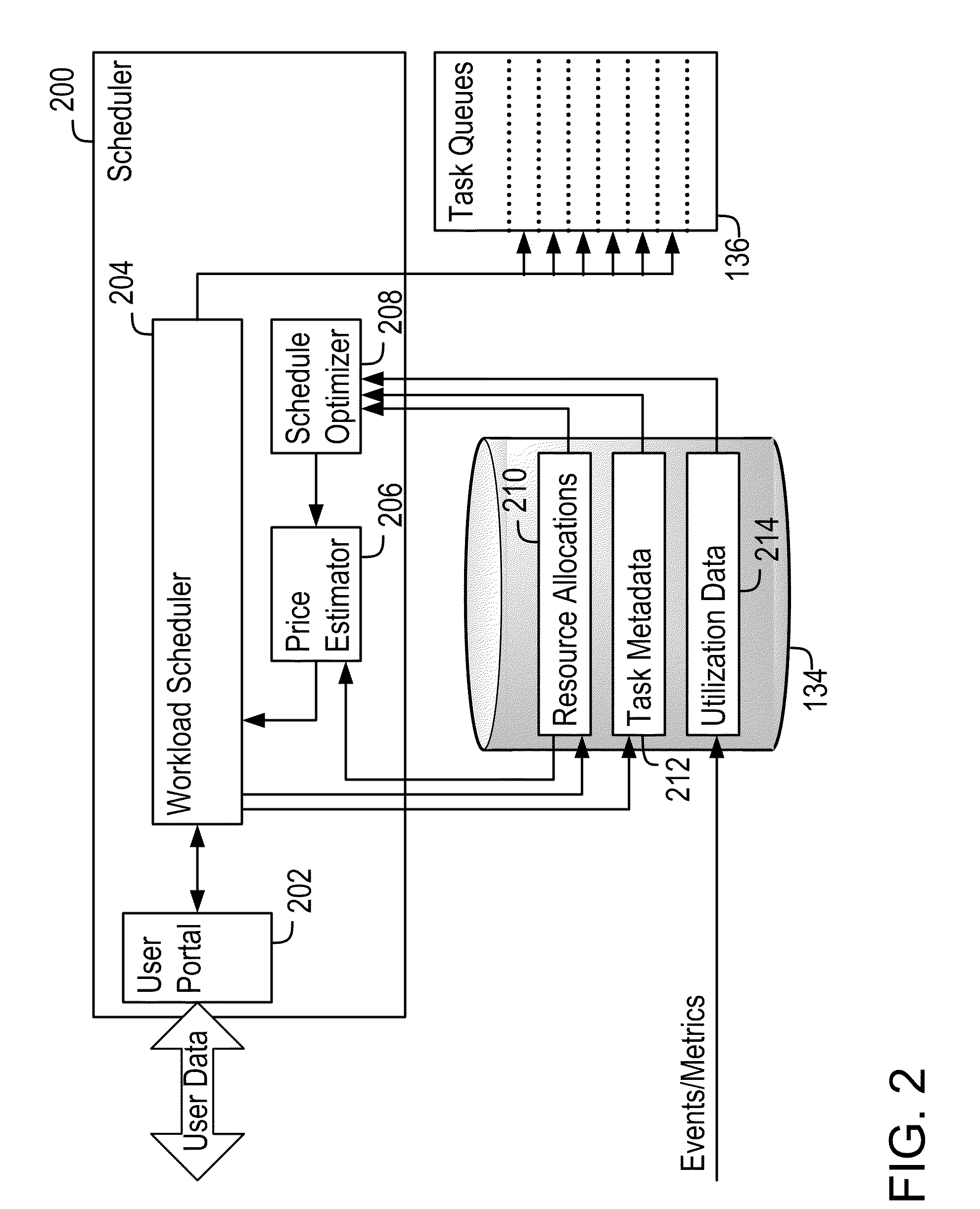
Demand-Driven Workload Scheduling Optimization on Shared Computing Resources
InactiveUS20110154353A1Low costHinder taskResource allocationMemory systemsTime scheduleProgram planning
Systems and methods implementing a demand-driven workload scheduling optimization of shared resources used to execute tasks submitted to a computer system are disclosed. Some embodiments include a method for demand-driven computer system resource optimization that includes receiving a request to execute a task (said request including the task's required execution time and resource requirements), selecting a prospective execution schedule meeting the required execution time and a computer system resource meeting the resource requirement, determining (in response to the request) a task execution price for using the computer system resource according to the prospective execution schedule, and scheduling the task to execute using the computer system resource according to the prospective execution schedule if the price is accepted. The price varies as a function of availability of the computer system resource at times corresponding to the prospective execution schedule, said availability being measured at the time the price is determined.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
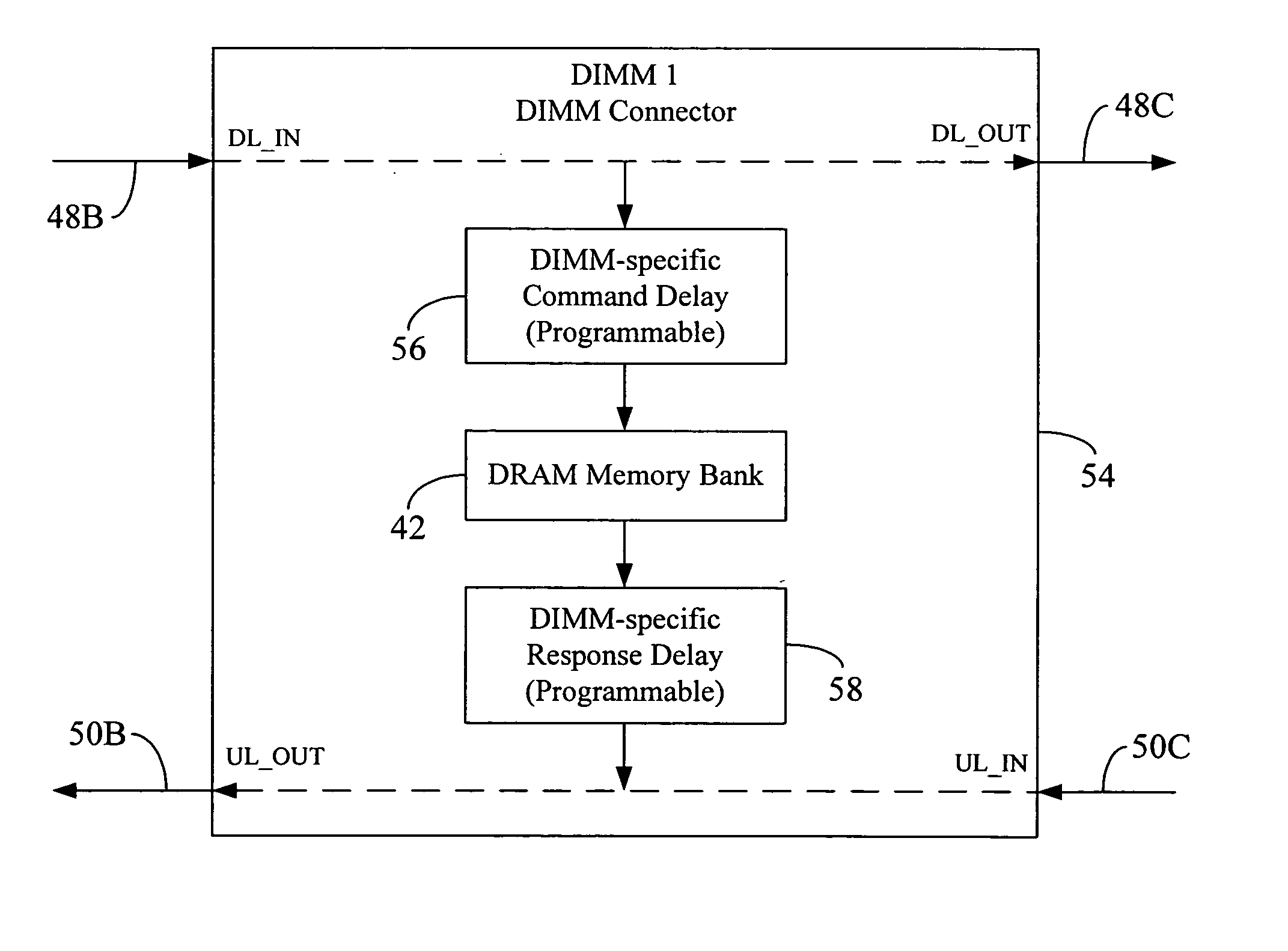
Memory command delay balancing in a daisy-chained memory topology
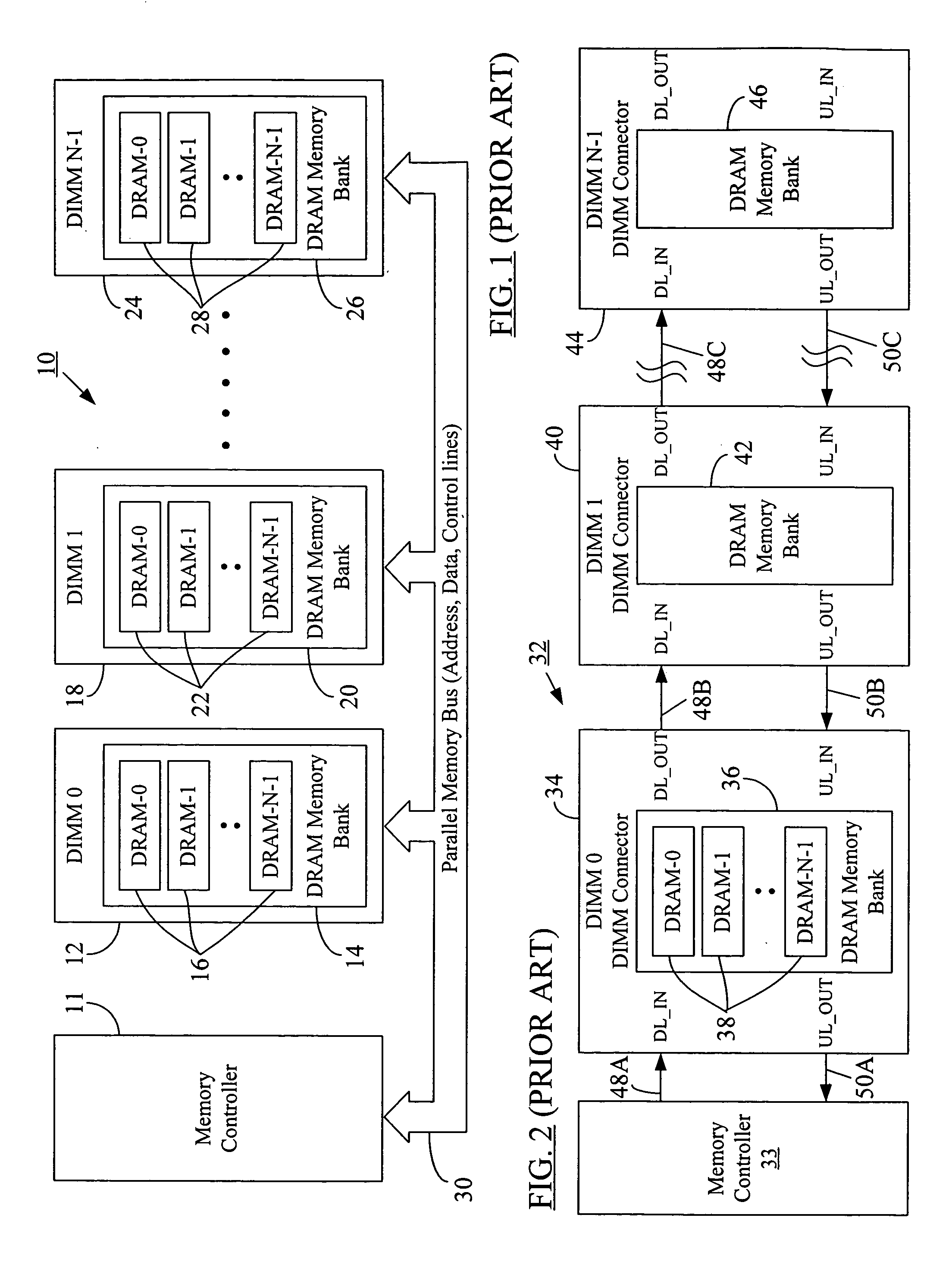
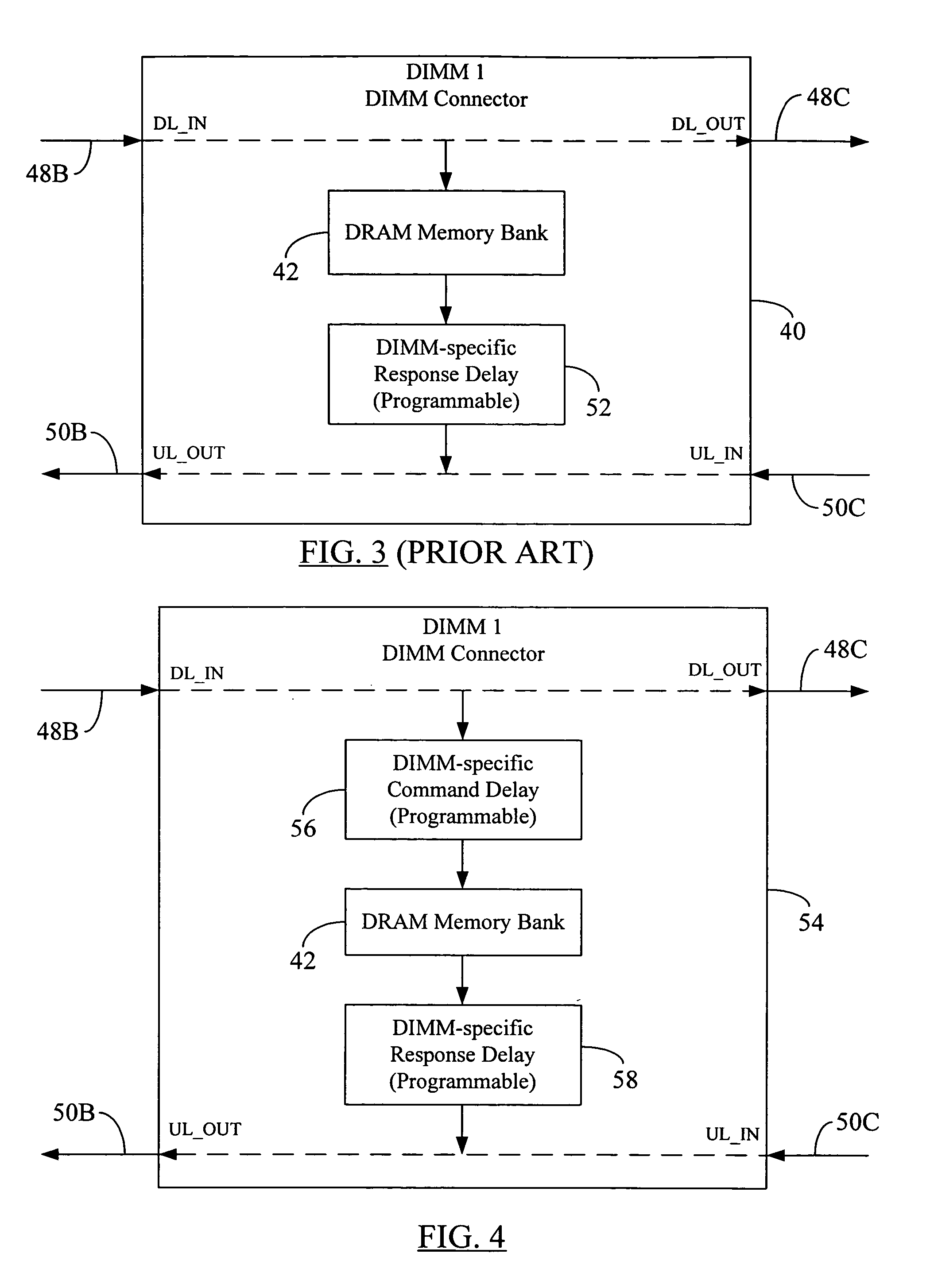
InactiveUS20060041730A1Effective predictionAccurately ascertainedEnergy efficient ICTDigital storageDIMMControl power
A methodology for a daisy-chained memory topology wherein, in addition to the prediction of the timing of receipt of a response from a memory module (DIMM), the memory controller can effectively predict when a command sent by it will be executed by the addressee DIMM. By programming DIMM-specific command delay in the DIMM's command delay unit, the command delay balancing methodology according to the present disclosure “normalizes” or “synchronizes” the execution of the command signal across all DIMMs in the memory channel. With such ability to predict command execution timing, the memory controller can efficiently control power profile of all the DRAM devices (or memory modules) on a daisy-chained memory channel. A separate DIMM-specific response delay unit in the DIMM may also be programmed to provide DIMM-specific delay compensation in the response path, further allowing the memory controller to accurately ascertain the timing of receipt of a response thereat, and, hence, to better manage further processing of the response.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
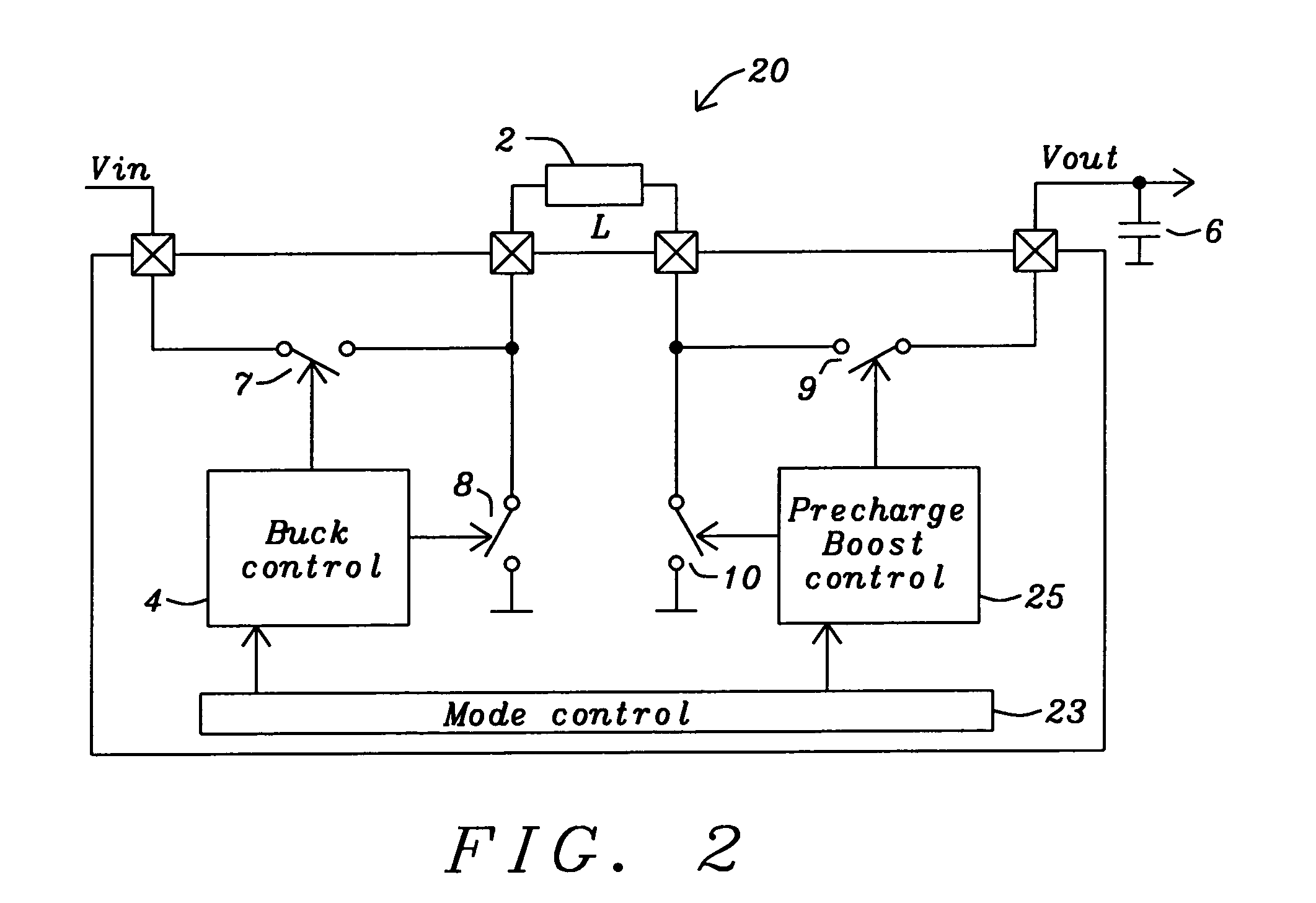
Buck converter with inductor pre-energizing
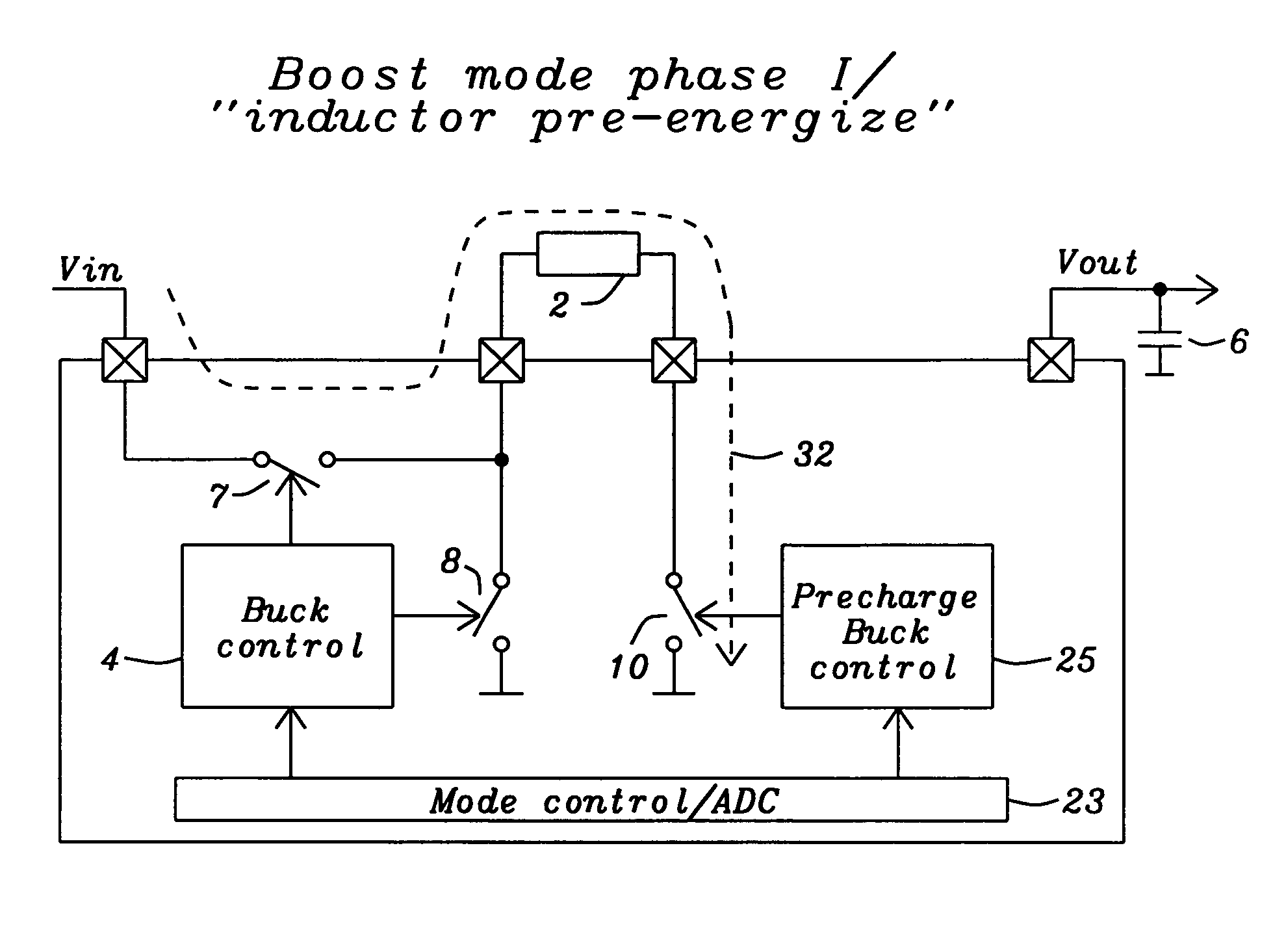
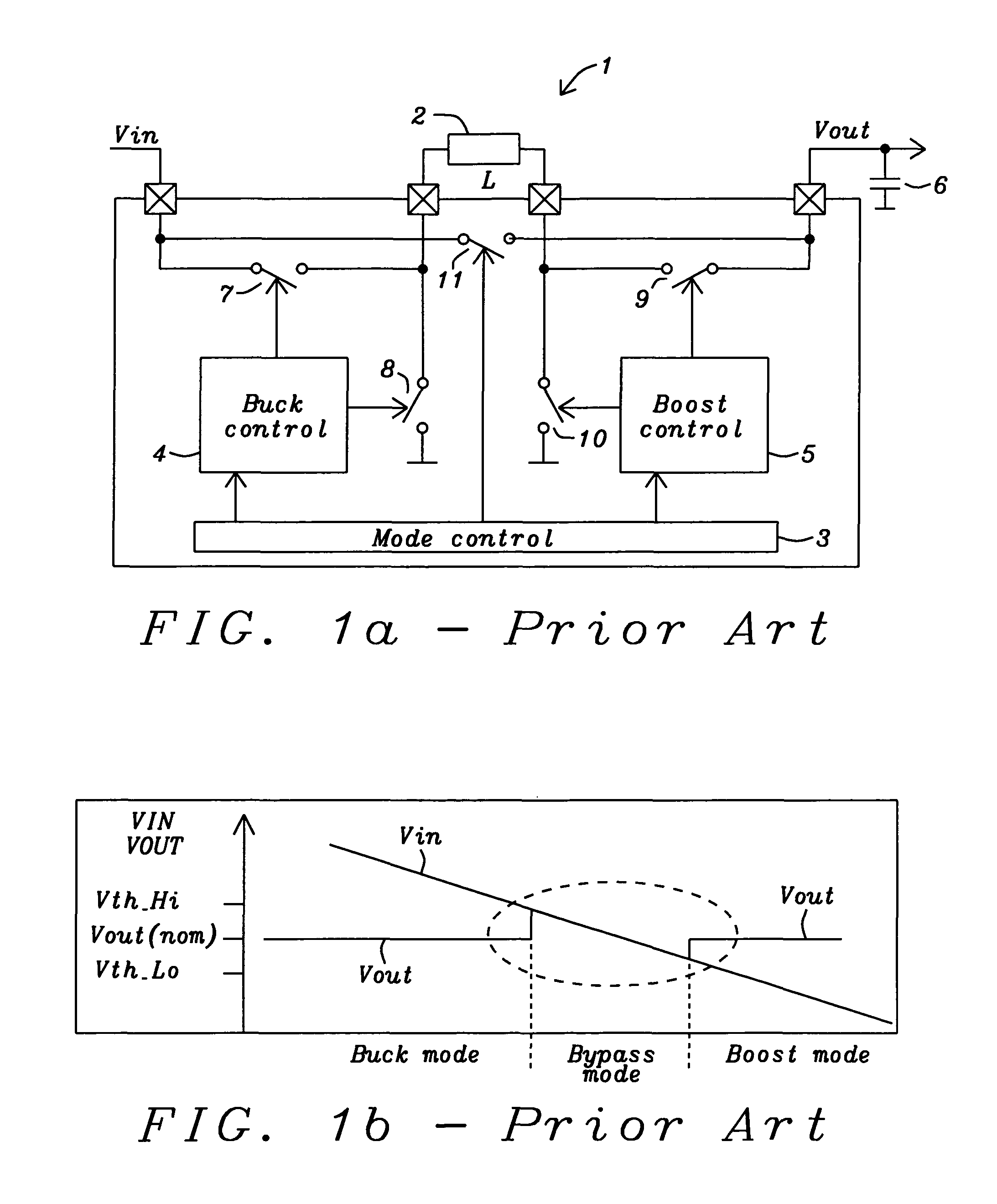
ActiveUS7804282B2Simple control circuitDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationBuck converterĆuk converter
Circuits and methods to achieve a buck-boost converter, capable to achieve a constant output voltage by pre-charging of an inductor if the input voltage is close to the output voltage has been achieved. The prior art problem of output voltage variations occurring while the input voltage is close to the output voltage is avoided. In case the input voltage is lower than a defined threshold voltage or the duty cycle exceeds a defined maximum allowable level, the inductor of the converter is pre-charged followed by boosting of the energy of the inductor to the output of the converter. In both modes the control loops of the buck converter can be used for buck duty cycle control. The duration of the pre-charge depends upon the level of the input voltage, the lower the input level is the longer is the pre-charge performed.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Preprocessor to improve the performance of message-passing-based parallel programs on virtualized multi-core processors
InactiveUS20070038987A1Reduced execution timeEasy to implementMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsCluster basedParallel processing
Provided is a complier which optimizes parallel processing. The complier records the number of execution cores, which is the number of processor cores that execute a target program. First, the compiler detects a dominant path, which is a candidate of an execution path to be consecutively executed by a single processor core, from a target program. Subsequently, the compiler selects dominant paths with the number not larger than the number of execution cores, and generates clusters of tasks to be executed by a multi-core processor in parallel or consecutively. After that, the compiler computes an execution time for which each of the generated clusters is executed by the processor cores with the number equal to one or each of a plurality natural numbers selected from the natural numbers not larger than the number of execution cores. Then, the compiler selects the number of processor cores to be assigned for execution of each of the clusters based on the computed execution time.
Owner:IBM CORP
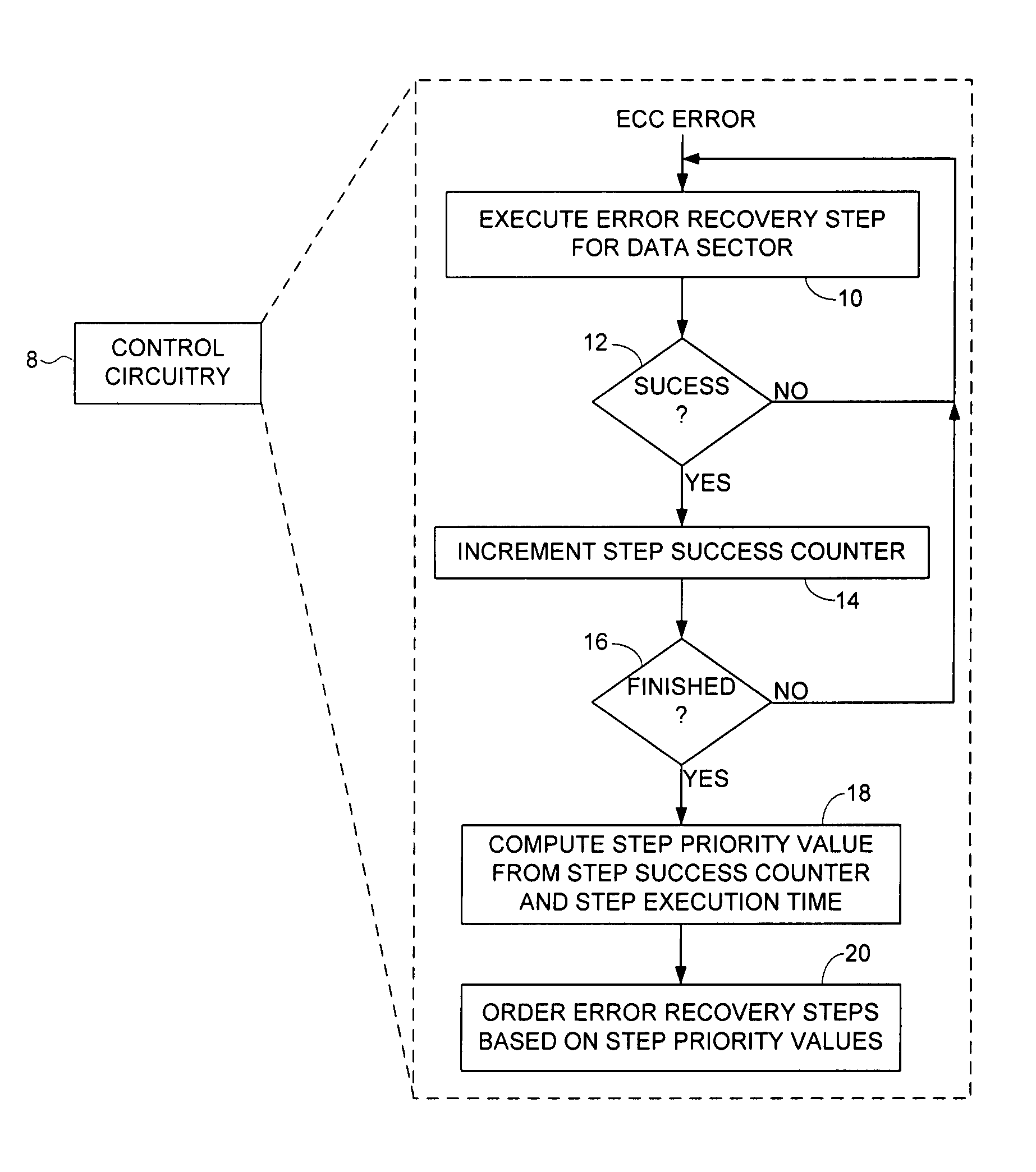
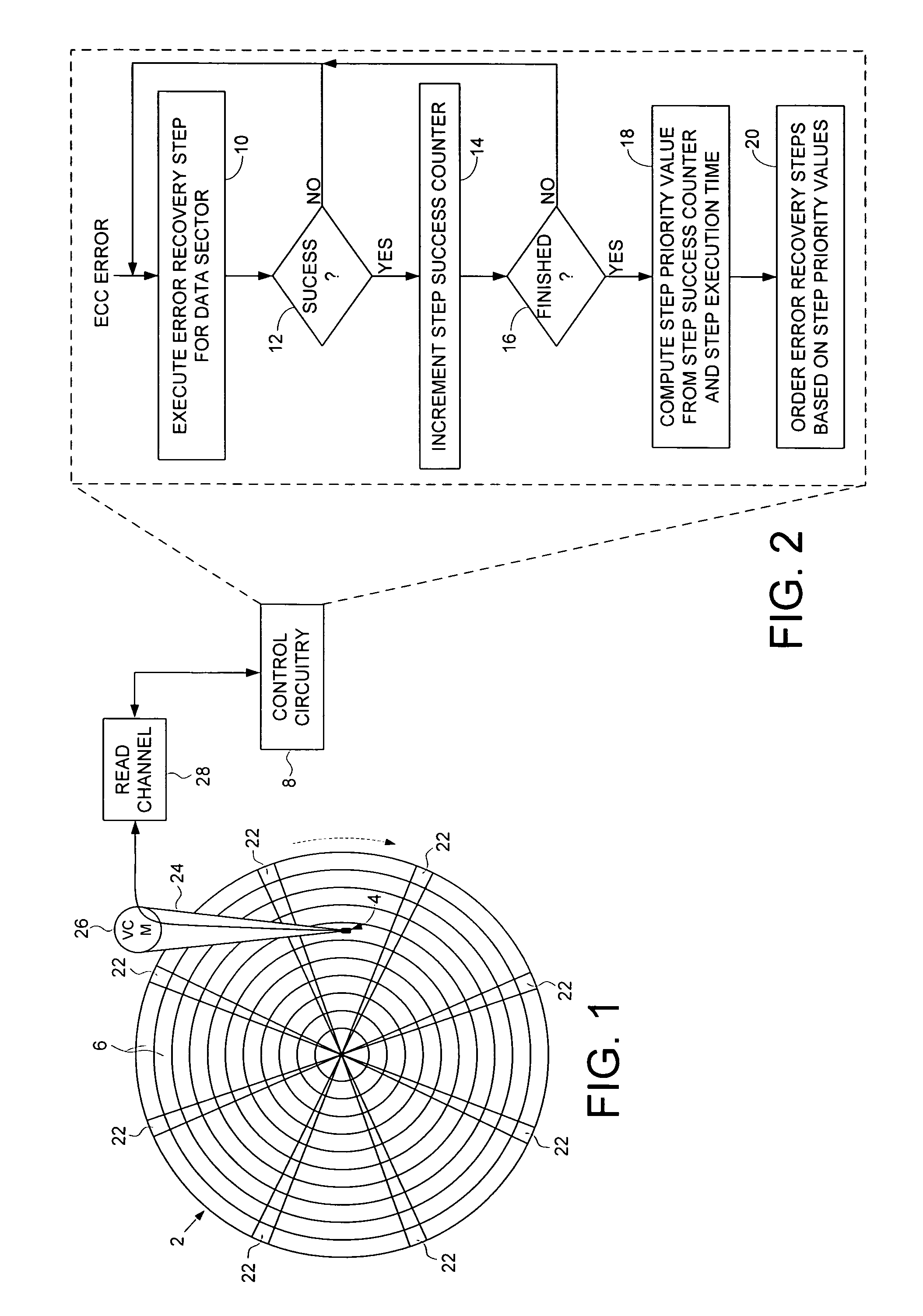
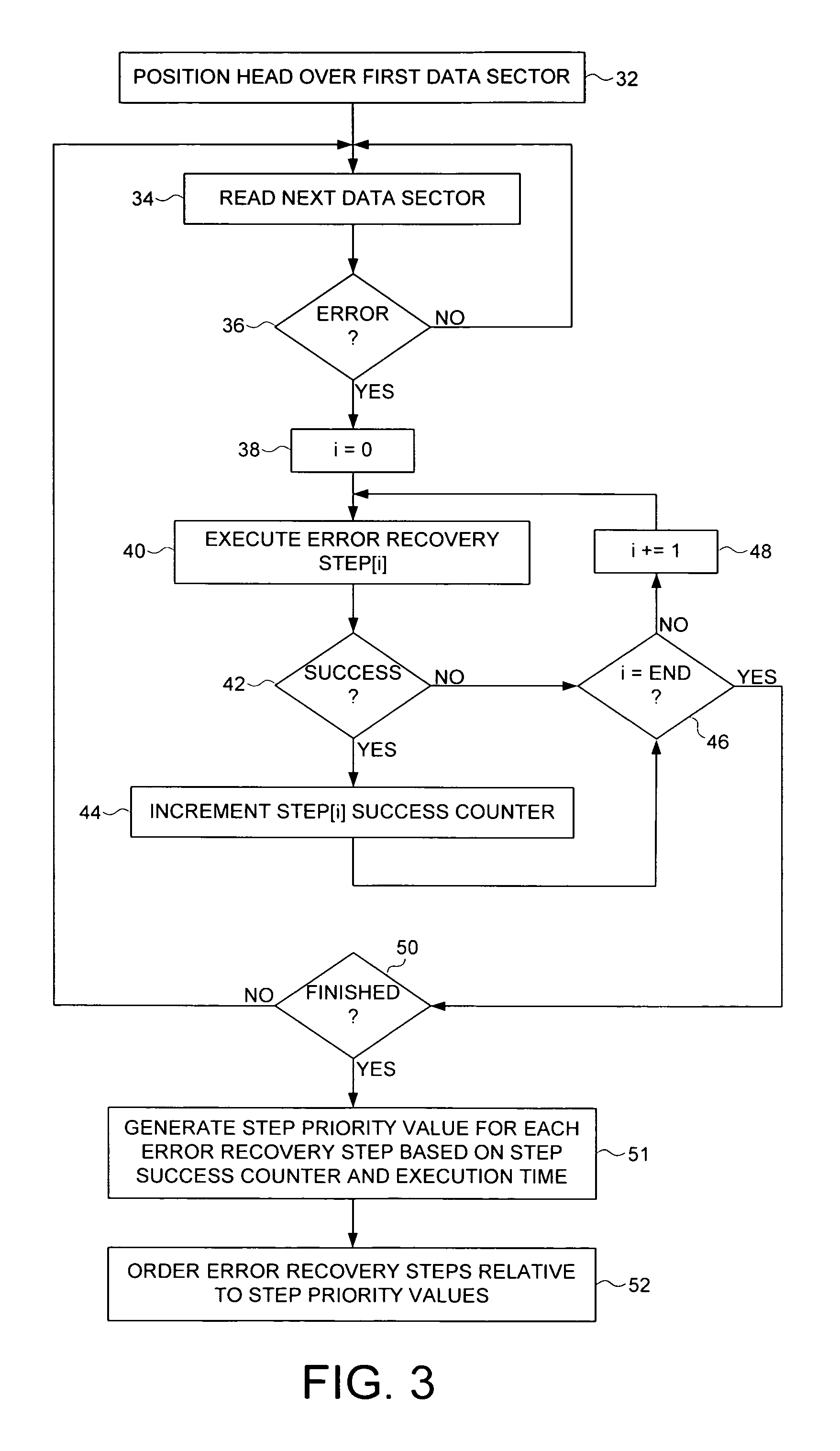
Optimizing order of error recovery steps in a disk drive
ActiveUS7451344B1Successful recoveryDisc-shaped record carriersError detection/correctionRecovery procedureComputer science
A method is disclosed for ordering error recovery steps of an error recovery procedure executed by a disk drive, wherein each error recovery step having an execution time. The disk drive comprises a disk having a plurality of tracks, wherein each track comprises a plurality of data sectors. A plurality of step success counters are initialized, wherein each counter corresponds to one of the error recovery steps. A plurality of the error recovery steps are executed, wherein if an error recovery step successfully recovers one of the data sectors the corresponding step success counter is incremented. A step priority value is computed for each error recovery step in response to the step success counter and execution time for each step. The error recovery steps are then ordered in response to the step priority values.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
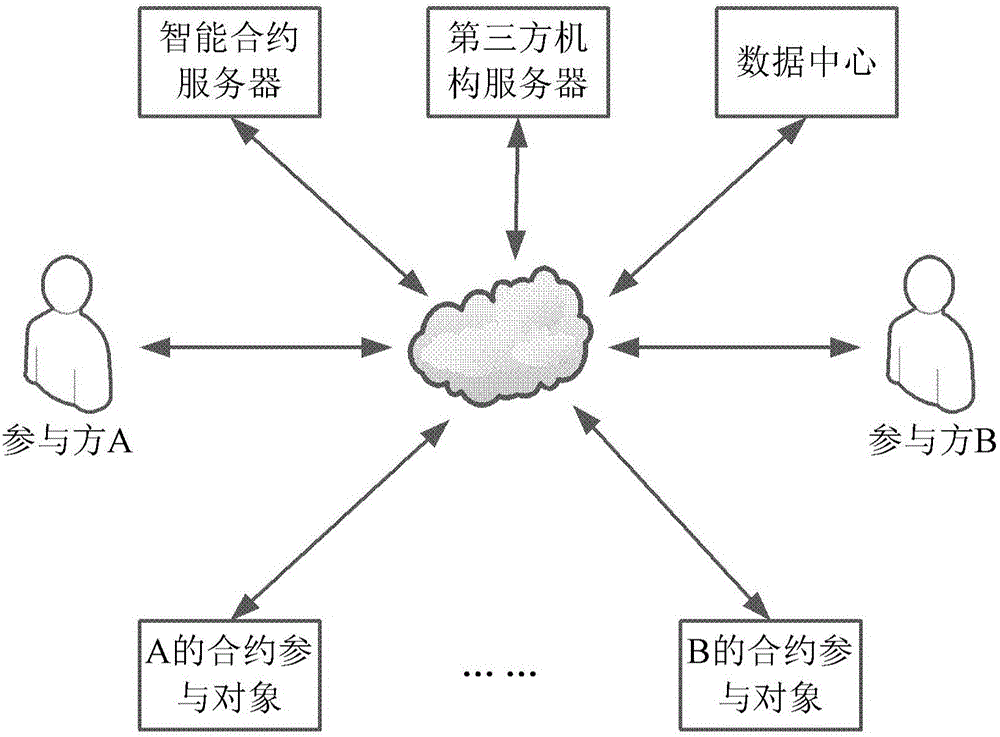
Contract construction and execution methods and apparatuses
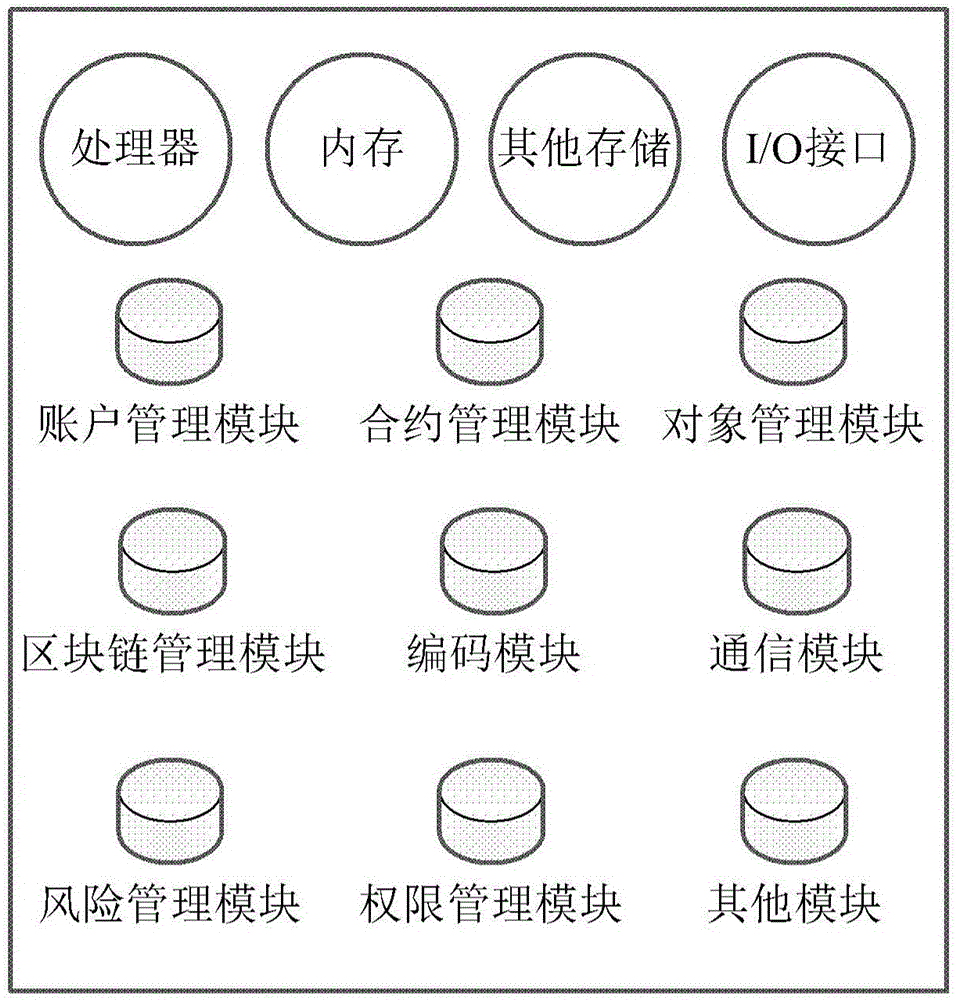
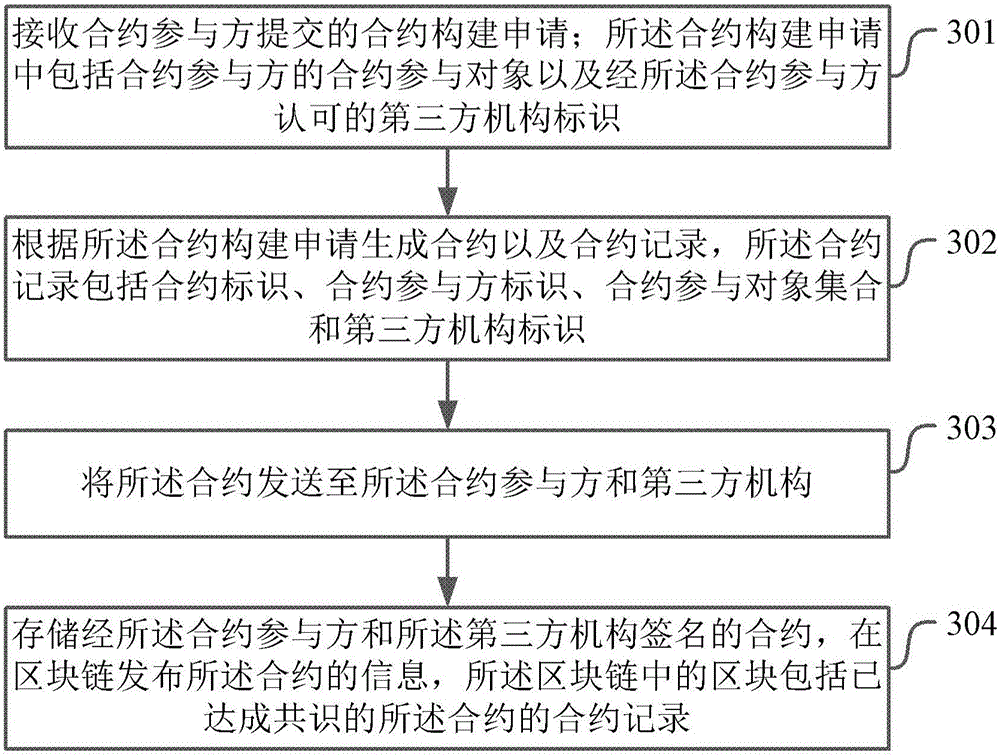
ActiveCN105809062AAvoid interferenceCustomer relationshipDigital data protectionThird partyComputer science
The present invention provides a contract construction and execution methods and apparatuses. The contract construction method comprises: receiving a contract construction application submitted by a contract participant; generating a contract and a contract record according to the contract construction application, and sending the contract to a third-party mechanism of the contract participant; storing the contract signed by the contract participant and the third-party mechanism, and issuing information of the contract at a block chain; acquiring a pre-created state of the contract participant of the contract; when the state of the contract participant meets a trigger condition, creating a contract transaction record; and issuing the contract transaction record signed by a contract server and the third-party mechanism to the block chain and executing a contract transaction. By adopting the scheme provided by the present invention, the contract in the digital form is written into the block chain, and storage, reading and execution are guaranteed by the characteristic of the block chain technology, and the whole process is transparent and can not be tampered, so that interference of malicious behaviors towards normal execution of the contract can be avoided.
Owner:BUBI BEIJING NETWORK TECH CO LTD
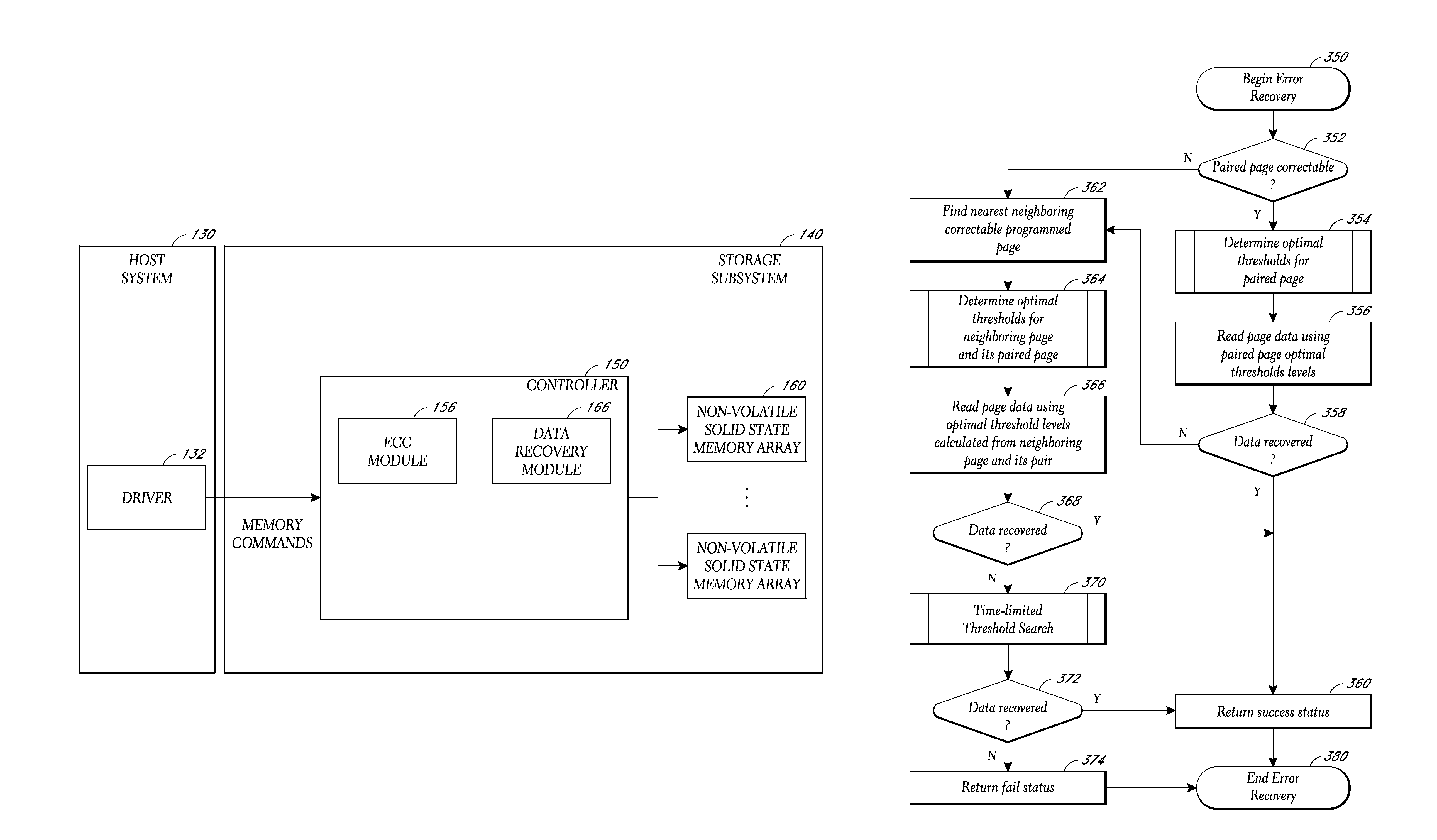
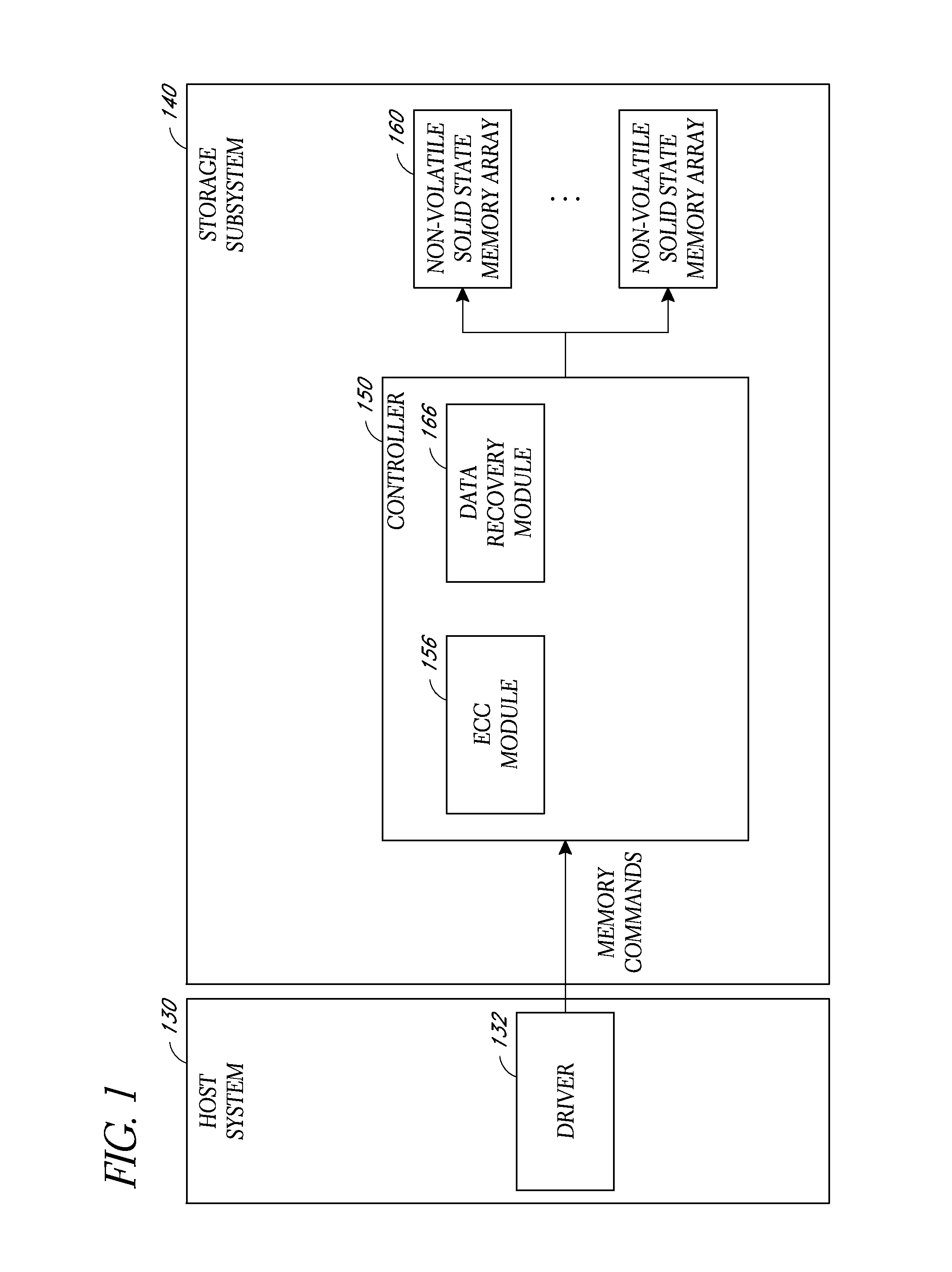
System and method for data recovery in a solid state storage device
Embodiments of solid-state storage system are provided herein include data recovery mechanism to recover data upon detection of a read error (e.g., an uncorrectable ECC error) in a storage element such as a page. In various embodiments, the system is configured to determine optimal reference voltage value(s) by evaluating the reference voltage value(s) of page(s) that are related to the page where the failure occurred. The related page(a) may include a page that is paired with the initial page where the failure occurred (e.g., the paired pages reside in a common memory cell), or a neighboring page that is physically near the page where the initial page, and / or a paired page of the neighboring page. In another embodiment, the system is configured to perform a time-limited search function to attempt to determine optimal reference voltage values through an iterative process that adjusts voltage values in a progression to determine a set of values that can retrieve the data.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Moving object detection apparatus and method
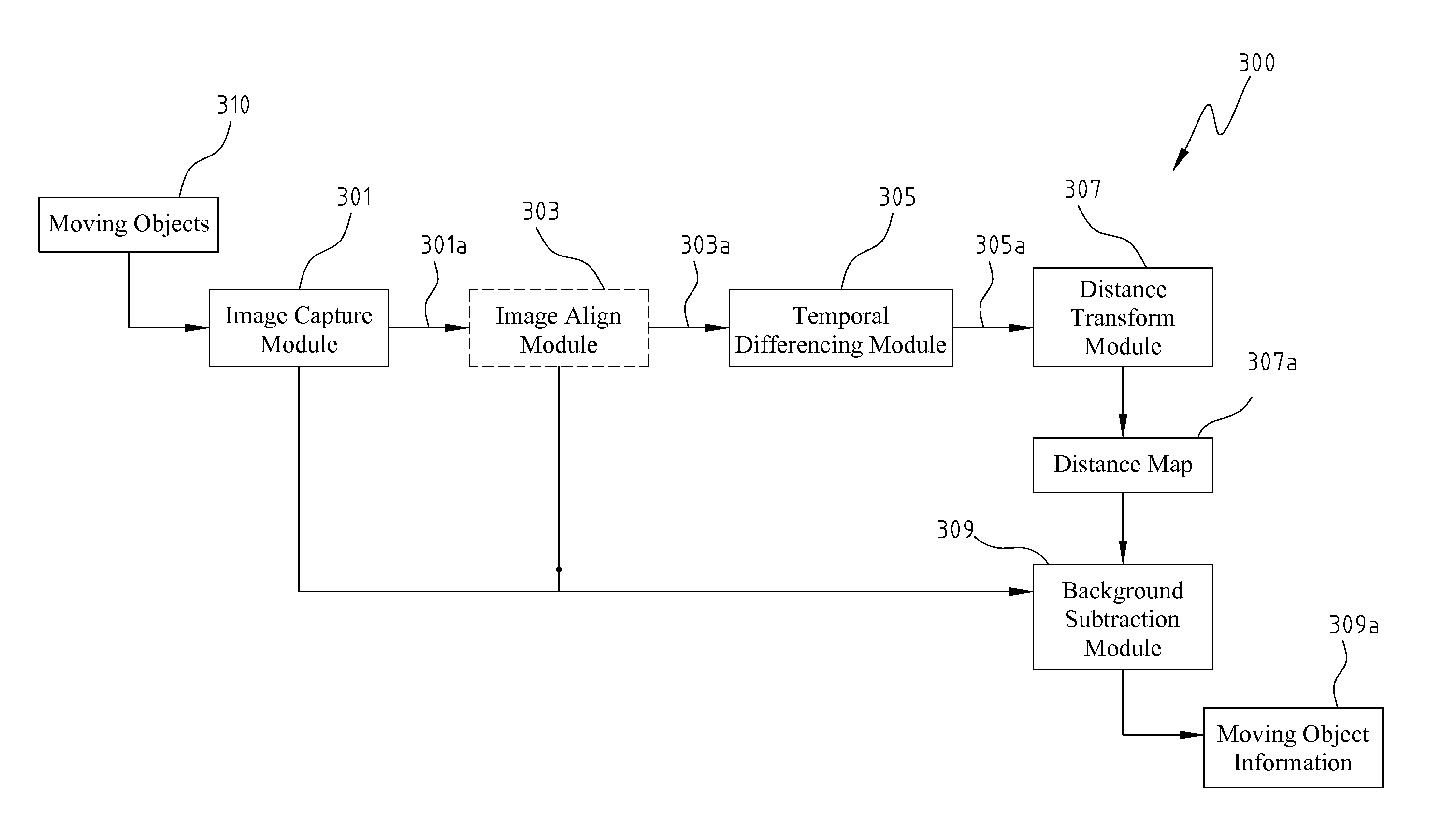
InactiveUS8000498B2Improve reliabilityEnhancing subtractionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage alignmentImage capture
Disclosed is directed to a moving object detection apparatus and method. The apparatus comprises an image capture module, an image alignment module, a temporal differencing module, a distance transform module, and a background subtraction module. The image capture module derives a plurality of images in a time series. The image alignment module aligns the images if the image capture module is situated on a movable platform. The temporal differencing module performs temporal differencing on the captured images or the aligned images, and generates a difference image. The distance transform module transforms the difference image into a distance map. The background subtraction module applies the distance map to background subtraction technology and compares the results with the current captured image, so as to obtain the information for moving objects.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Relational database system providing XML query support
InactiveUS20030101169A1Efficient accessImprove efficiencyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRelational databaseFile system
A system providing methods enabling data in Extensible Markup Language ("XML") format to be extracted, transformed and stored in a database, file system or main memory is described. The extraction and transformation process is generalized and can be used on various types of XML data, enabling XML data to be stored and queried using standard database query methodologies. The system includes parse-time functionality to transform XML documents into a structure having an interface that enables efficient access to the underlying data. The system also includes query execution-time functionality providing greater efficiency by bringing only the relevant portions of transformed XML data into memory in response to a query. The system parses and translates queries into a structure that can be executed without the need to write custom application-specific navigation code to search XML data. The system also enables original XML documents (or portions thereof) to be recomposed when required.
Owner:SYBASE INC
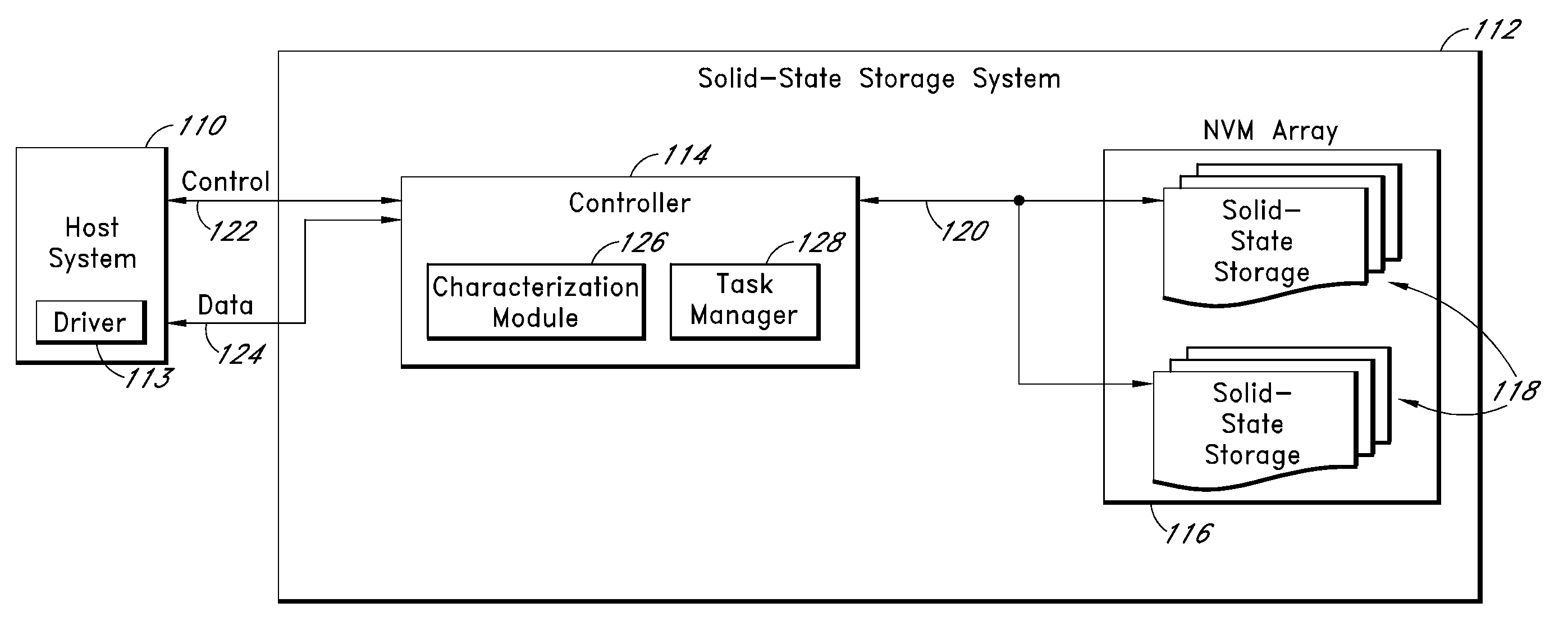
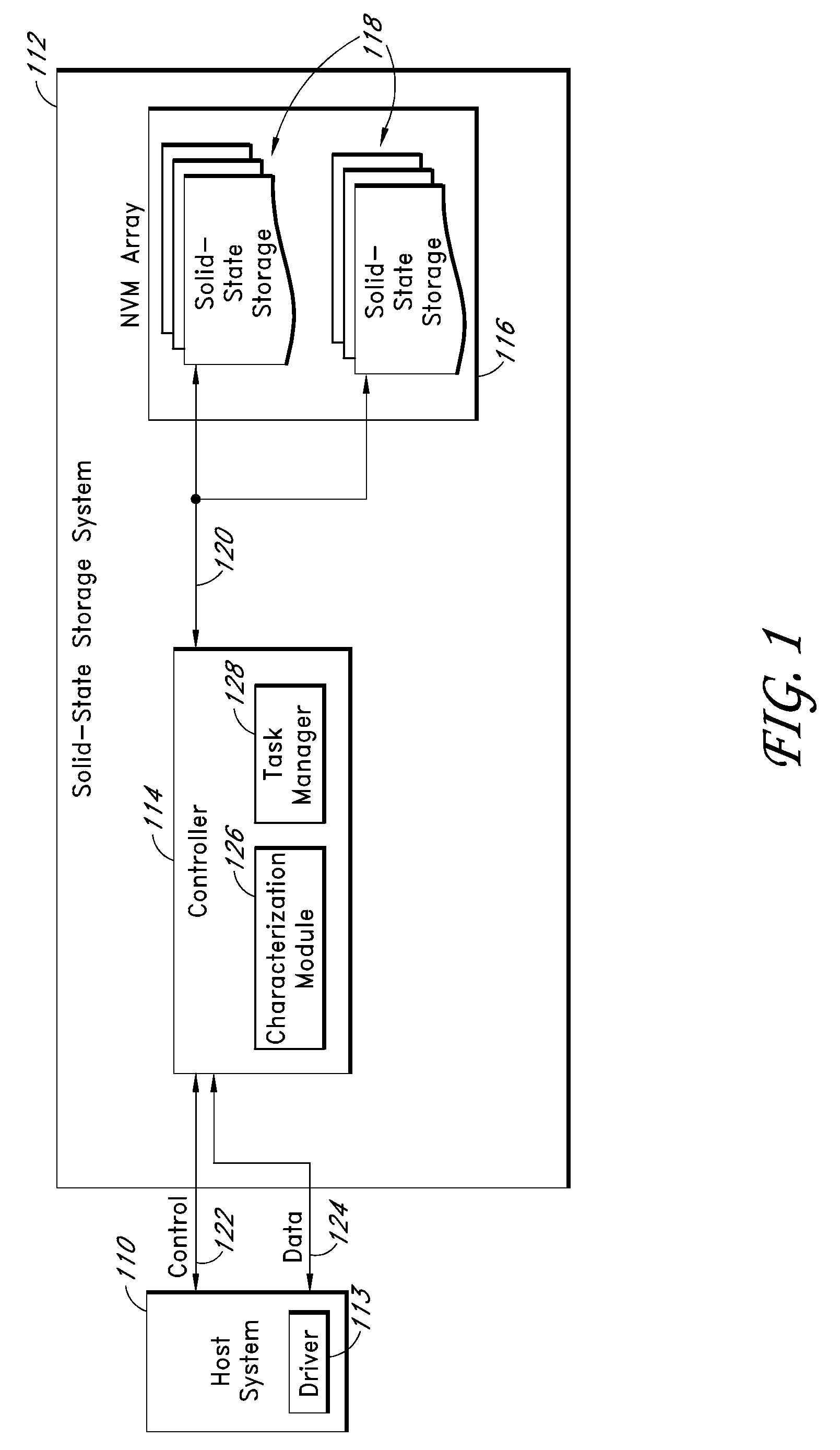
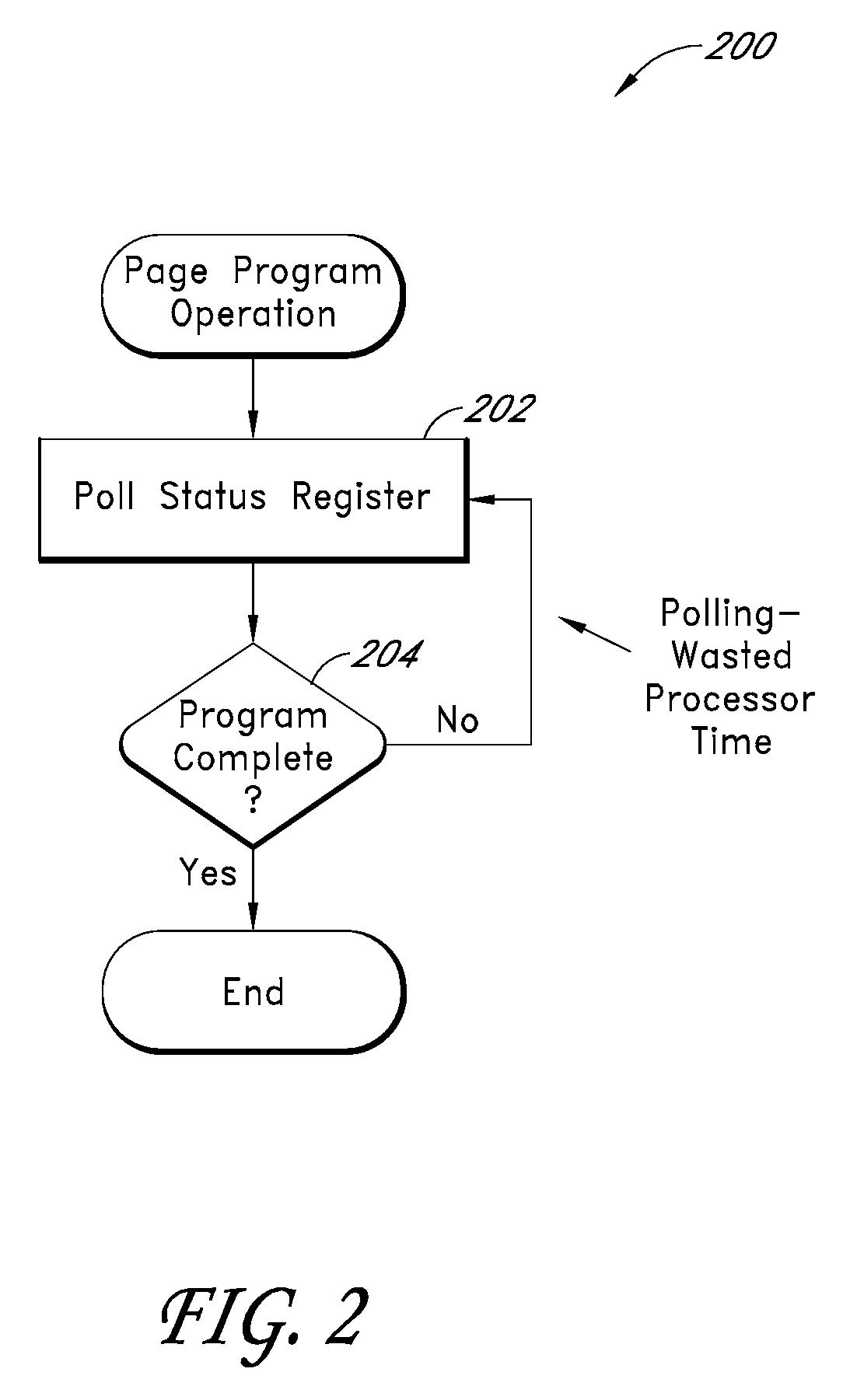
Systems and methods for improving the performance of non-volatile memory operations
ActiveUS20100174849A1Efficient use ofMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingStart up
Disclosed herein are systems and methods that recognize and recapture potentially unused processing time in typical page program and block erase operations in non-volatile memory (NVM) devices. In one embodiment, a characterization module within a controller executes a characterization procedure by performing page program and block erase operations on one or more NVM devices in an array and storing execution time data of the operations in a calibration table. The procedure may be executed at start-up and / or periodically so that the time values are reflective of the actual physical condition of the individual NVM devices. A task manager uses the stored time values to estimate the time needed for completing certain memory operations in its task table. Based on the estimated time for completion, the task manager assigns tasks to be executed during page program and / or block erase cycles, so that otherwise unused processing time can be utilized.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Scheduling of tasks based upon historical execution times
Methods, systems, and implementations are disclosed to schedule a plurality of tasks on one or more processors. The tasks may be part of a larger job based on a user initiated query for information retrieval. One example method of operation may include estimating, based upon historical actual execution times of tasks of a respective corresponding type, an expected execution time for each task of the plurality of tasks. The method may further include scheduling the plurality of tasks for execution on the one or more processors based upon the estimated expected execution time of each task. The scheduling procedure utilized ultimately produces an optimized task execution schedule, and in turn, minimizes the expected job completion time.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
System, method, and program for measuring performance in a network system
InactiveUS6587878B1Unacceptable delayAvoid delayDigital computer detailsHardware monitoringApplication softwareReal-time computing
Disclosed is a method, system, and program for generating network performance data. Performance information including a performance time to download a page and execute the page within an application program is received. The received performance information is processed and then performance information output indicating network performance is generated in response to processing the performance information.
Owner:IBM CORP
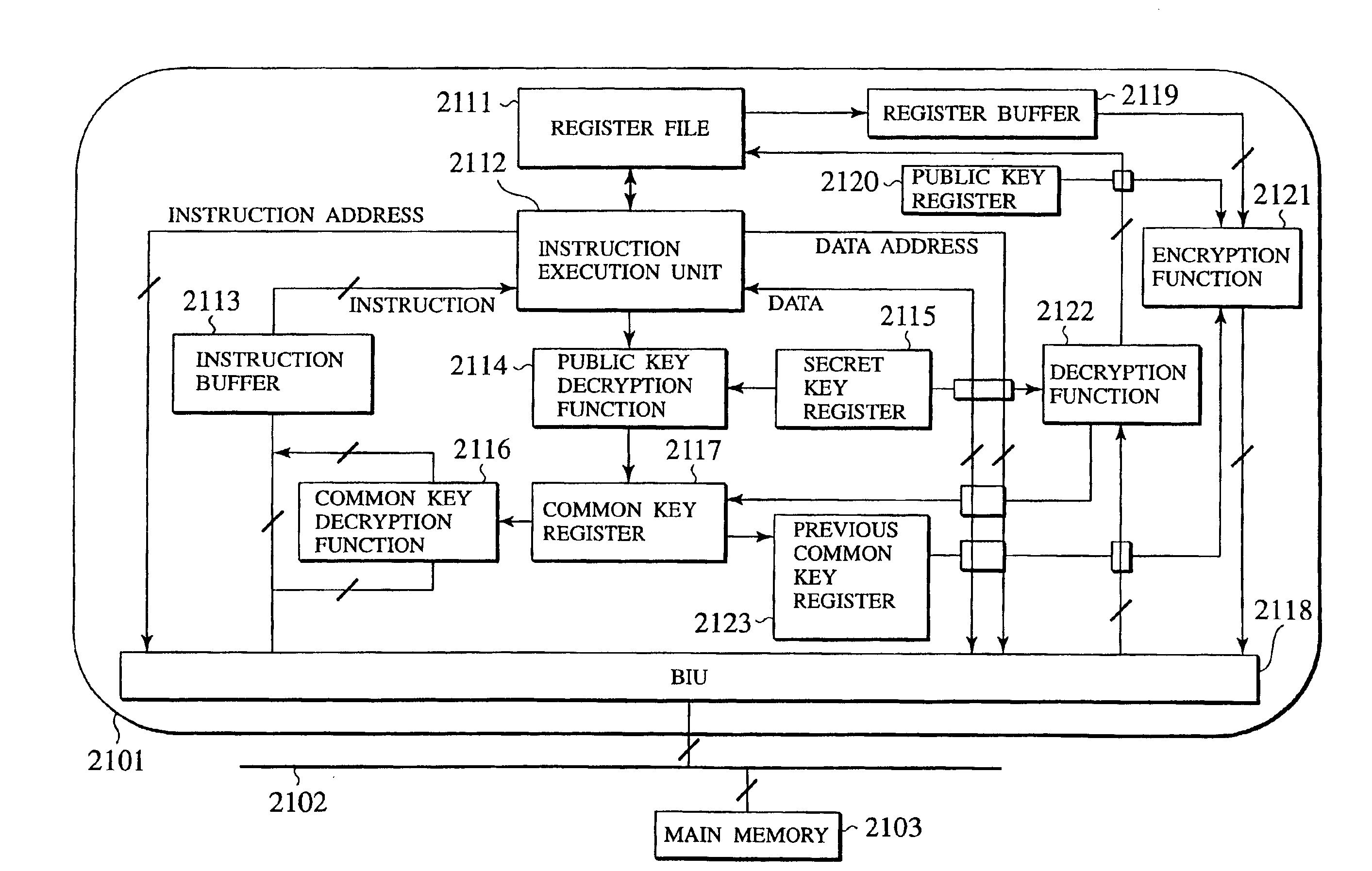
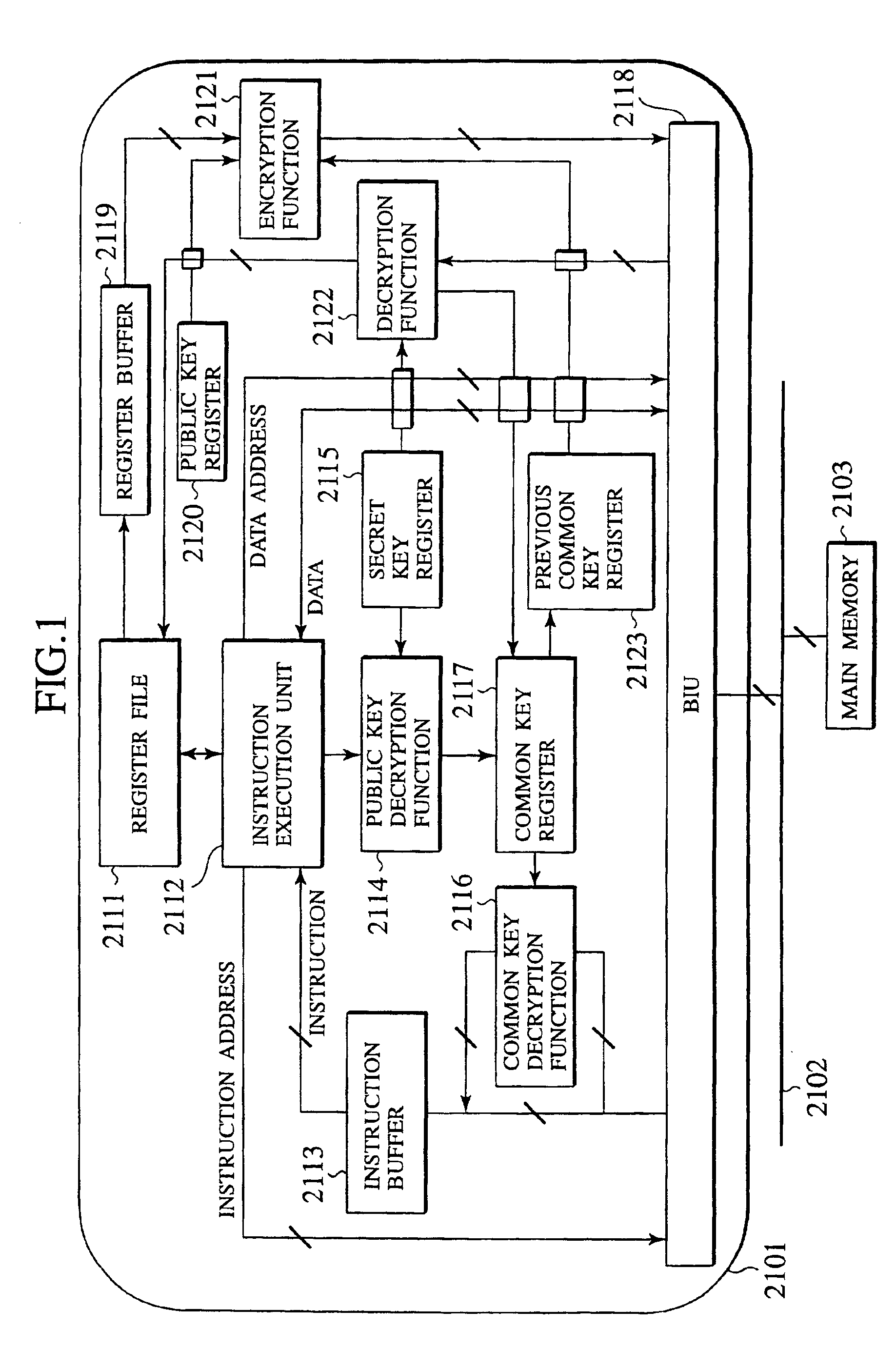
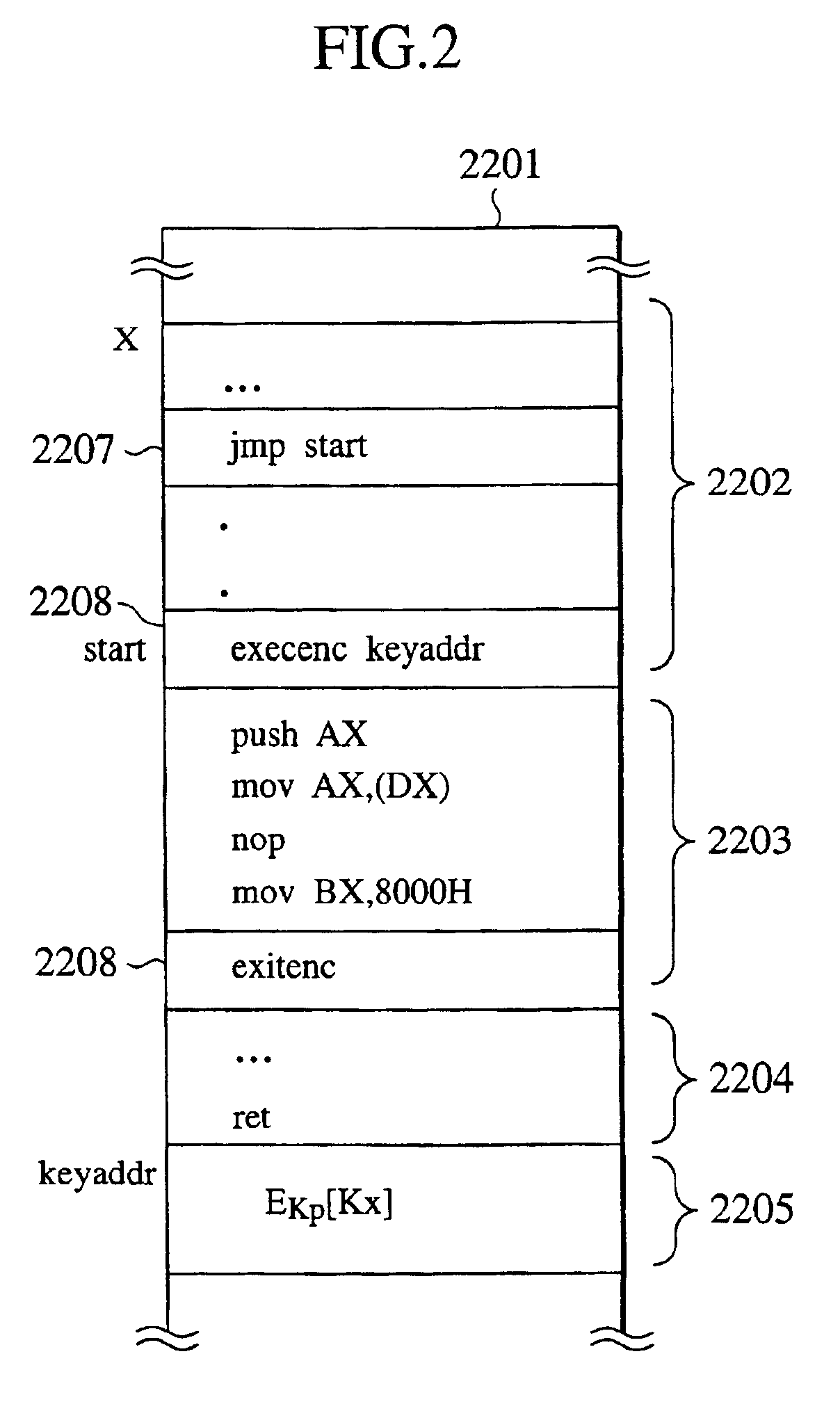
Tamper resistant microprocessor
InactiveUS6983374B2Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionTheoretical computer scienceEncryption
Under a multi-task environment, a tamper resistant microprocessor saves a context information for one program whose execution is to be interrupted, where the context information contains information indicating an execution state of that one program and the execution code encryption key of that one program. An execution of that one program can be restarted by recovering the execution state of that one program from the saved context information. The context information can be encrypted by using the public key of the microprocessor, and then decrypted by using the secret key of the microprocessor.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
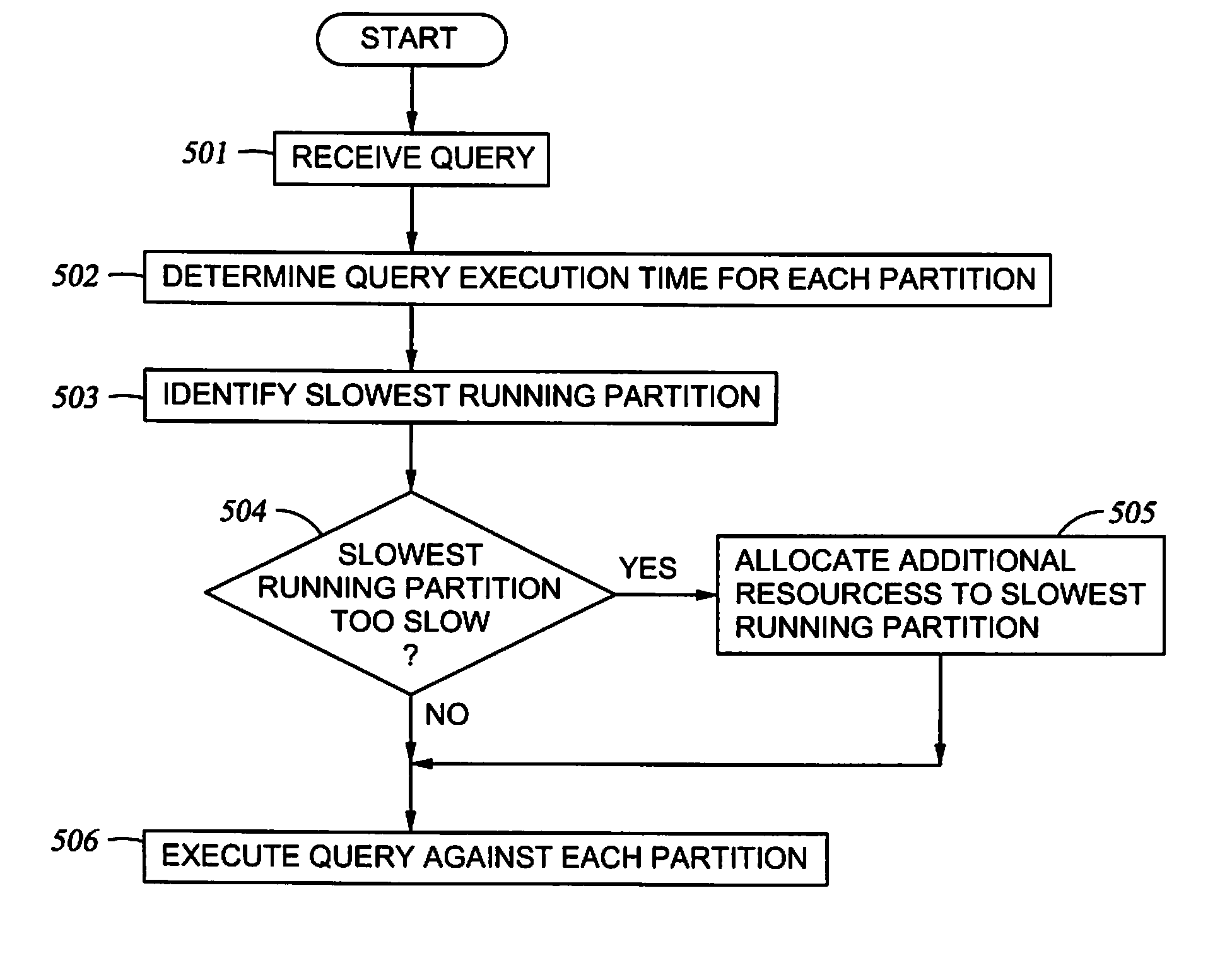
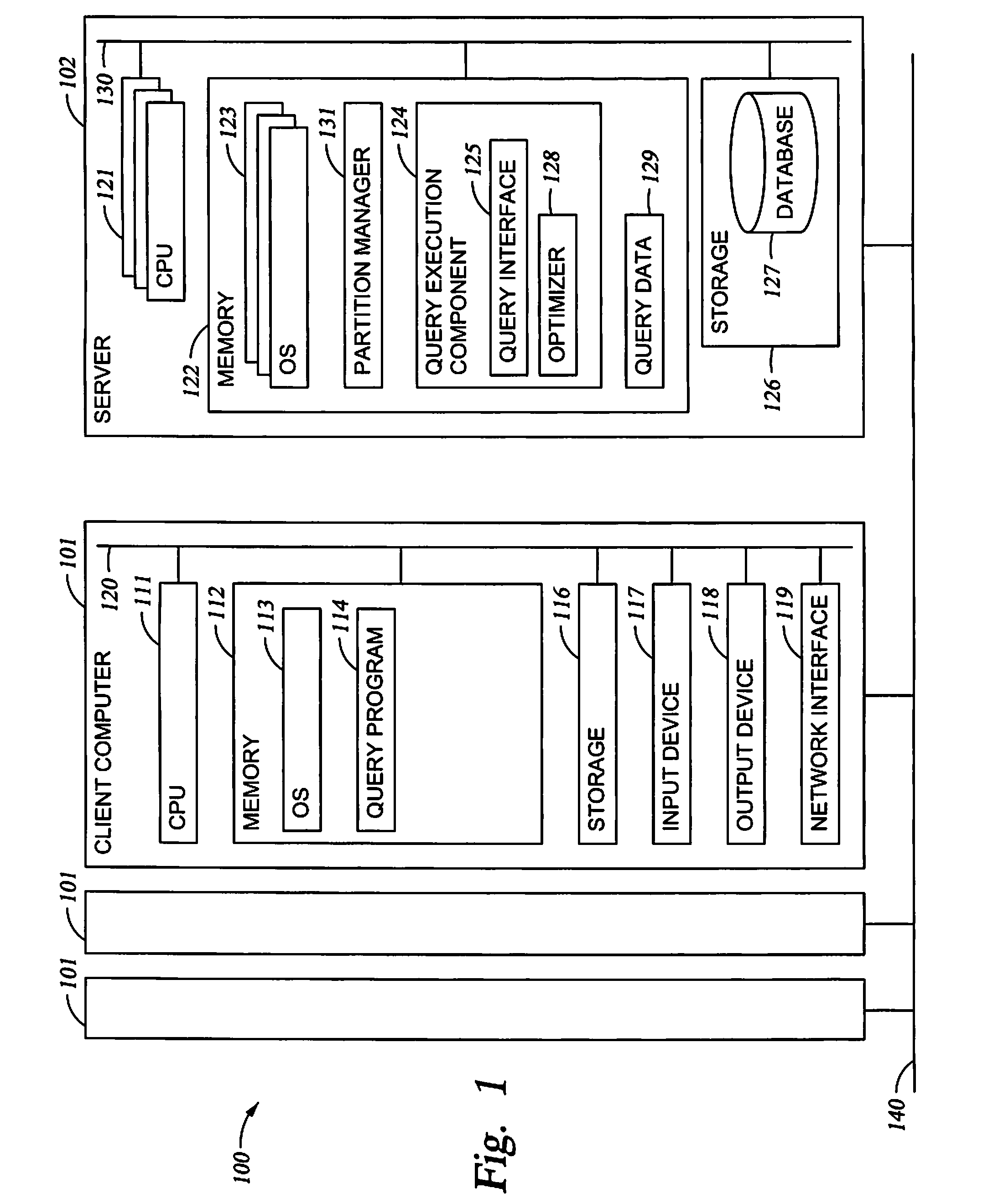
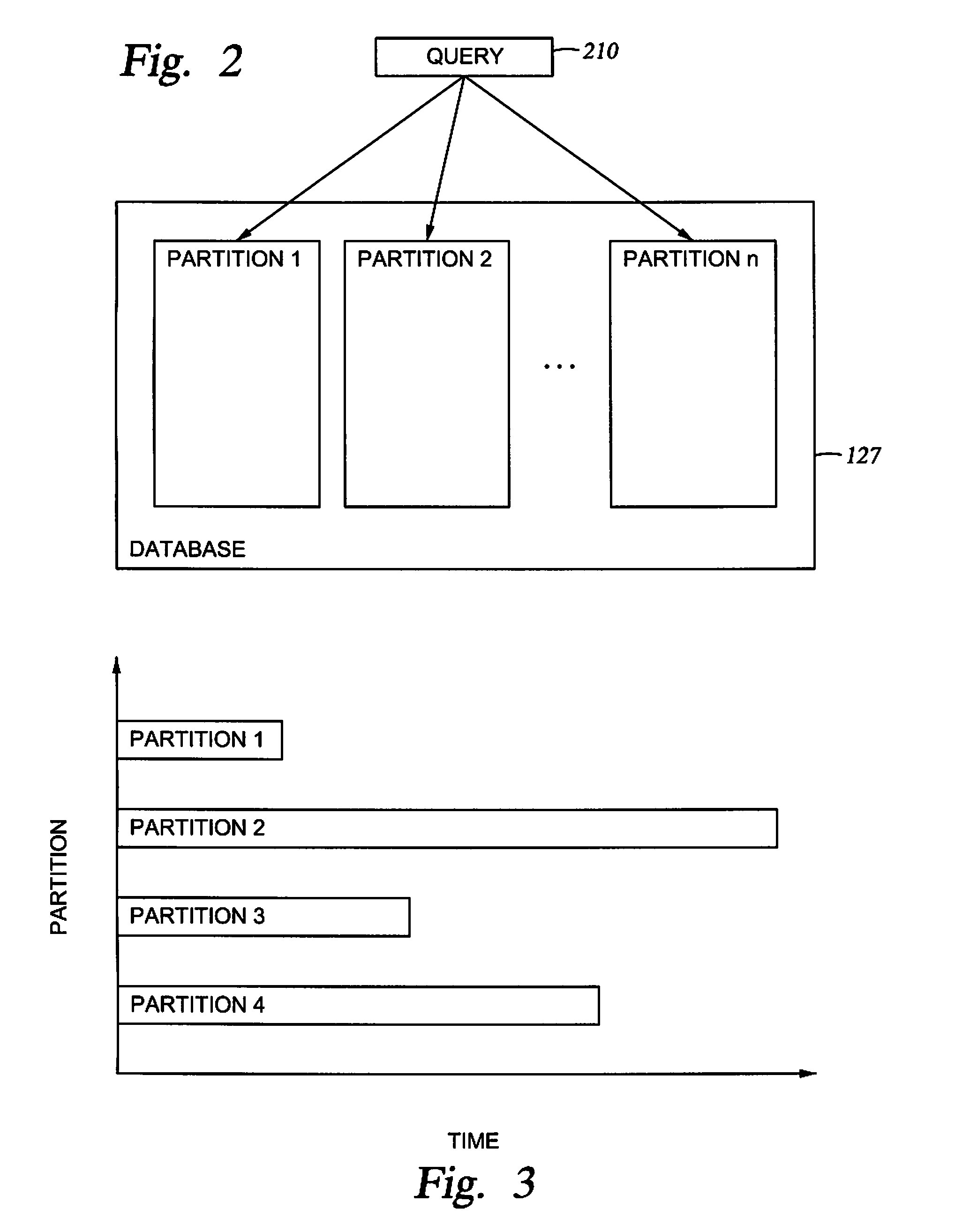
Re-allocation of resources for query execution in partitions
InactiveUS20080071755A1Relational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsResource reallocationRetrieval result
Embodiments of the invention provide methods, systems, and articles of manufacture for executing a query against a partitioned database. The query may be executed against each partition of the database to retrieve results from each partition. The results from the partitions may be integrated to provide the results of the query. Each partition may take different amounts of time to retrieve results for the query. Embodiments of the invention allow reallocation of resources to logical partitions of a system executing the query based on the relative execution times of the query for the various database partitions.
Owner:IBM CORP
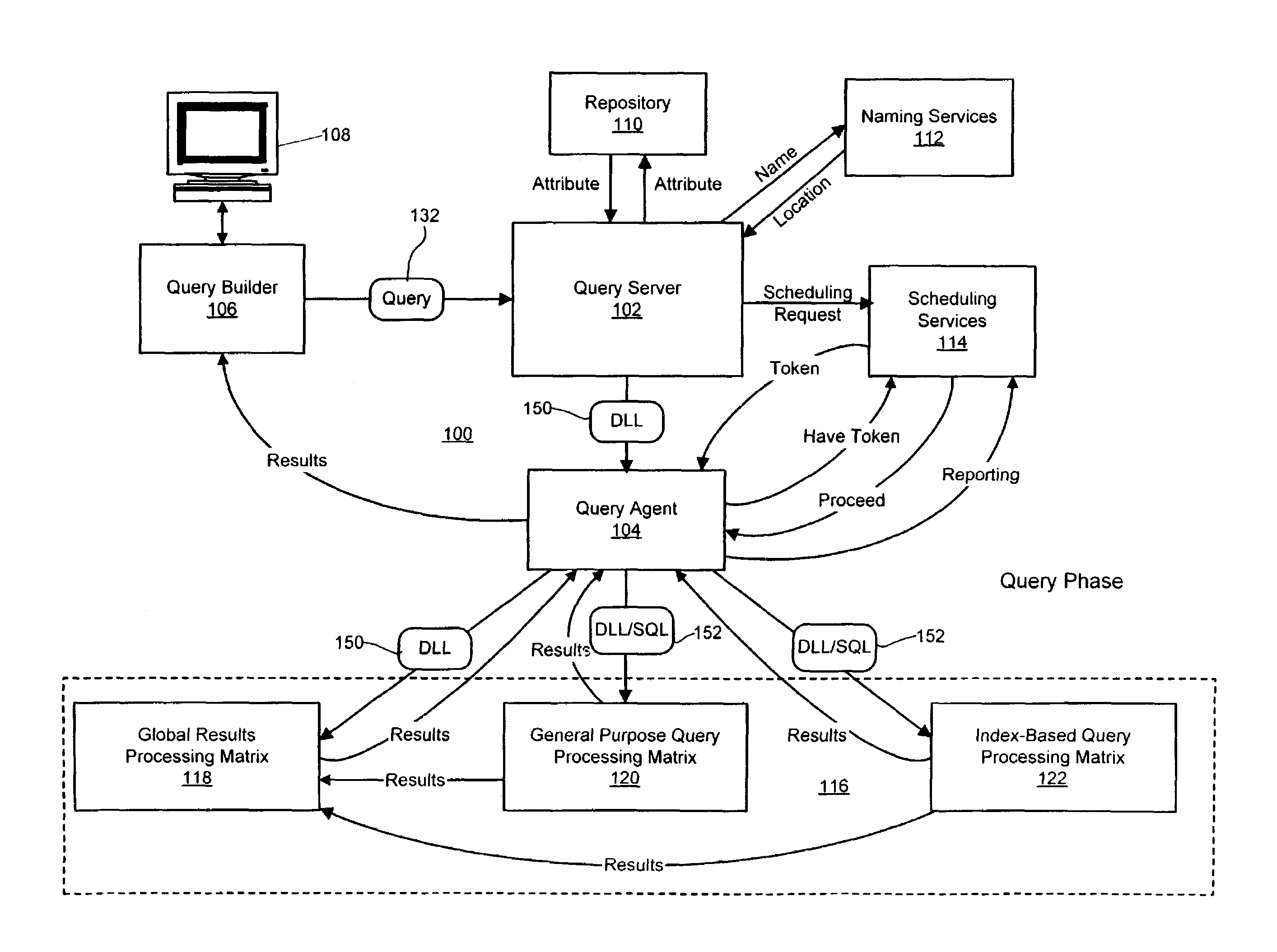
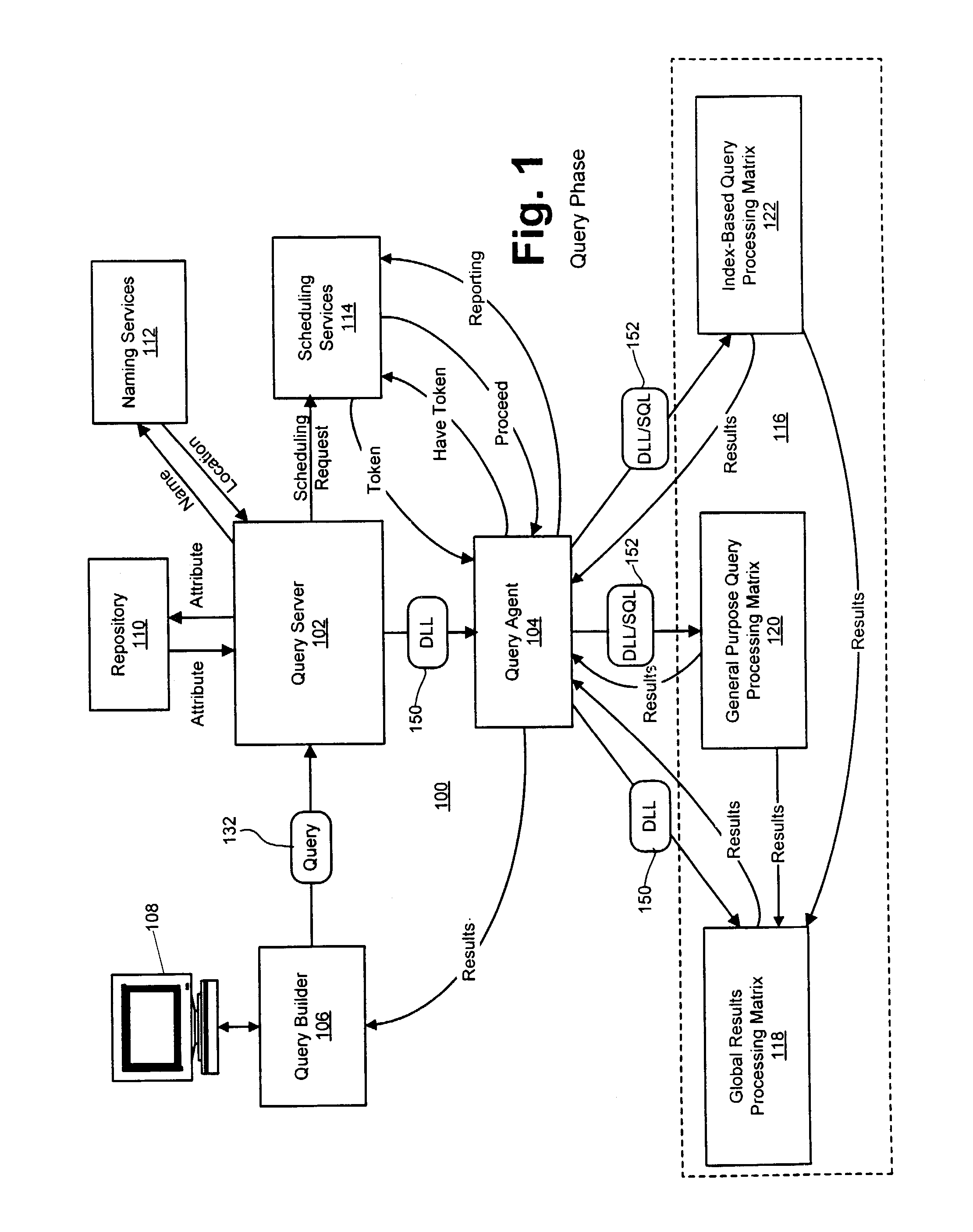
Query scheduling in a parallel-processing database system
ActiveUS7185003B2Transparent operationLow costData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalParallel processingService module
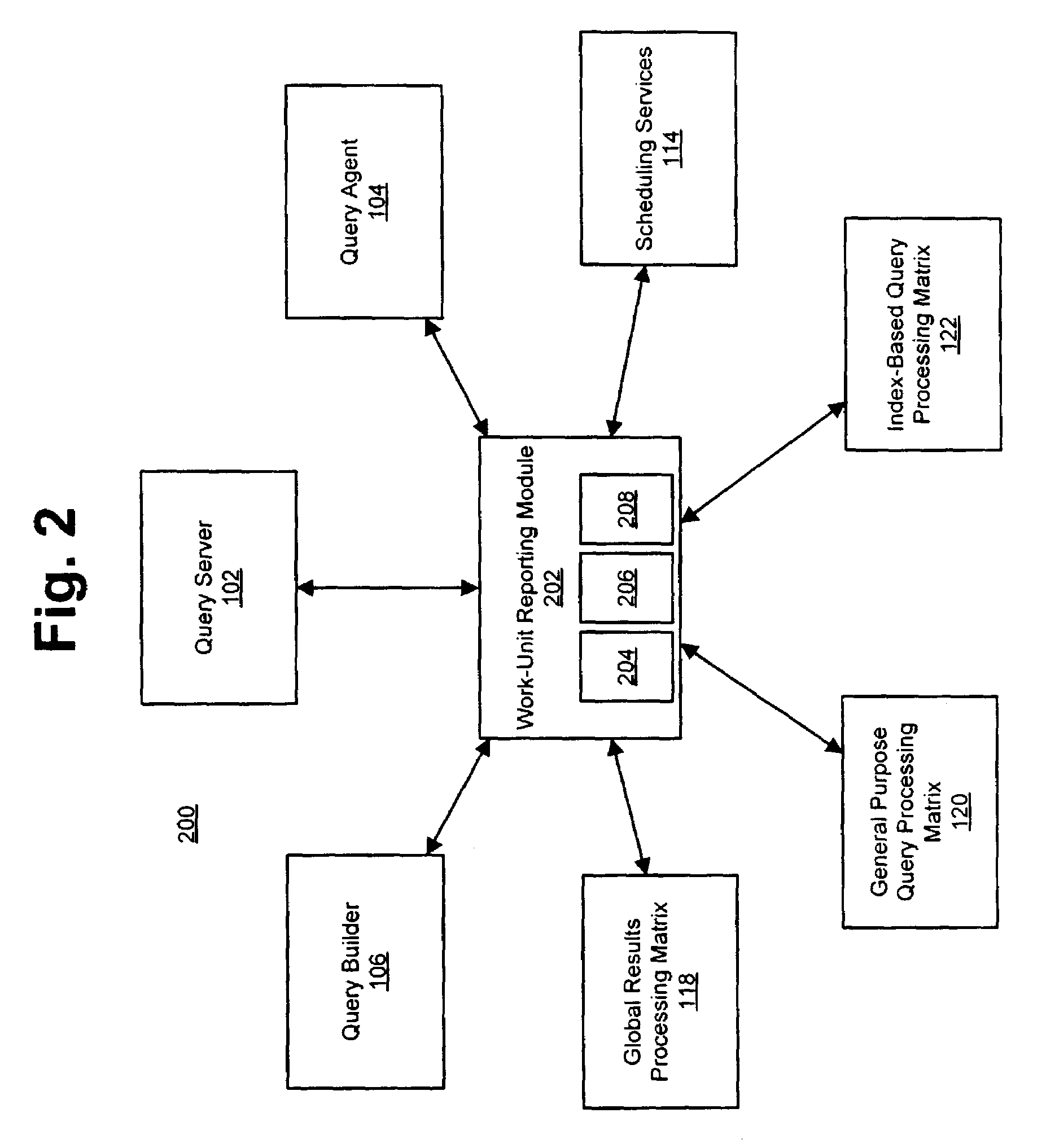
A system and method for scheduling database operations to one or more databases in a parallel-processing database system are described herein. After a query server generates a dynamic-link library (DLL) or other executable representative of one or more database operations to a database, the query server notifies a scheduling services module of the generation of the DLL and submits the DLL to a query agent. The query agent notifies the scheduling services module of its receipt of the DLL. Based on any of a variety of considerations, the scheduling services module schedules a time of execution for the DLL by one or more processing matrices that store the database. At the scheduled time, the scheduling services module directs the query agent to submit the DLL to the indicated processing matrices. The scheduling services module also can be adapted to monitor the execution of previously submitted DLLs by one or more processing matrices and adjust the scheduled times of execution for subsequent DLLs accordingly.
Owner:LEXISNEXIS RISK DATA MANAGEMENT
System and method for selective insertion of content into streaming media
ActiveUS7203758B2Targeted optimizationMinimize effortPulse modulation television signal transmissionAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSystem usageOn demand
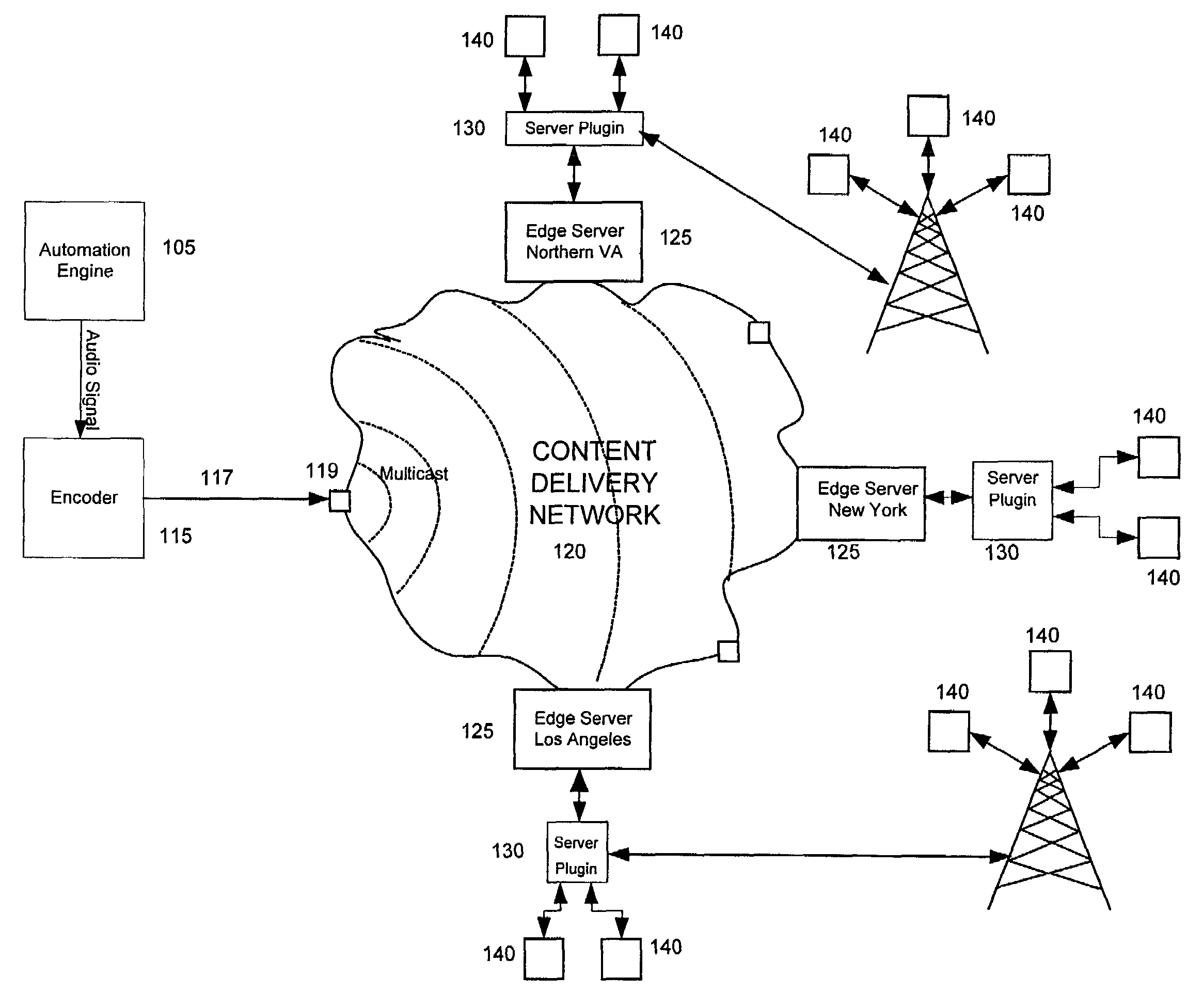
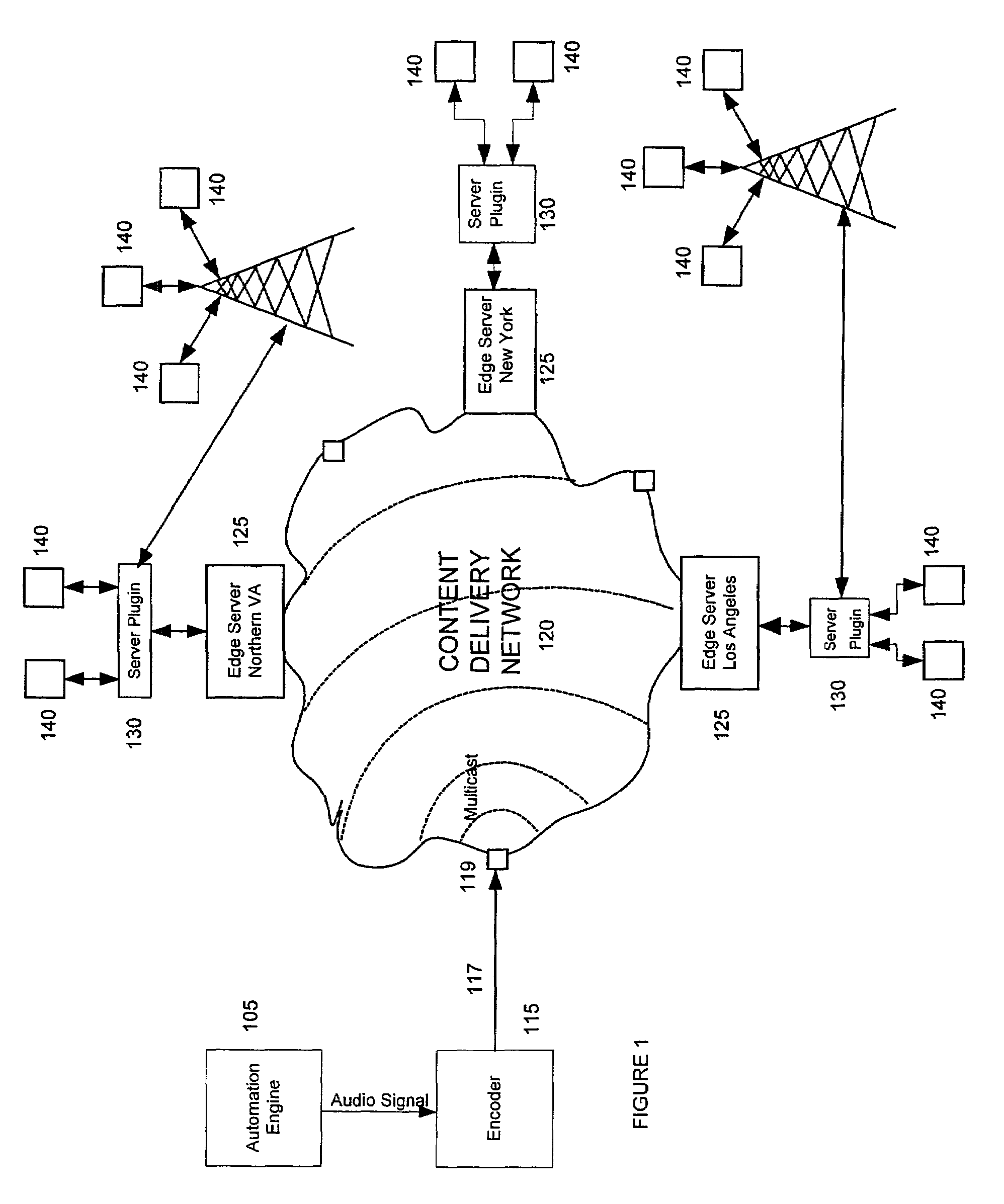
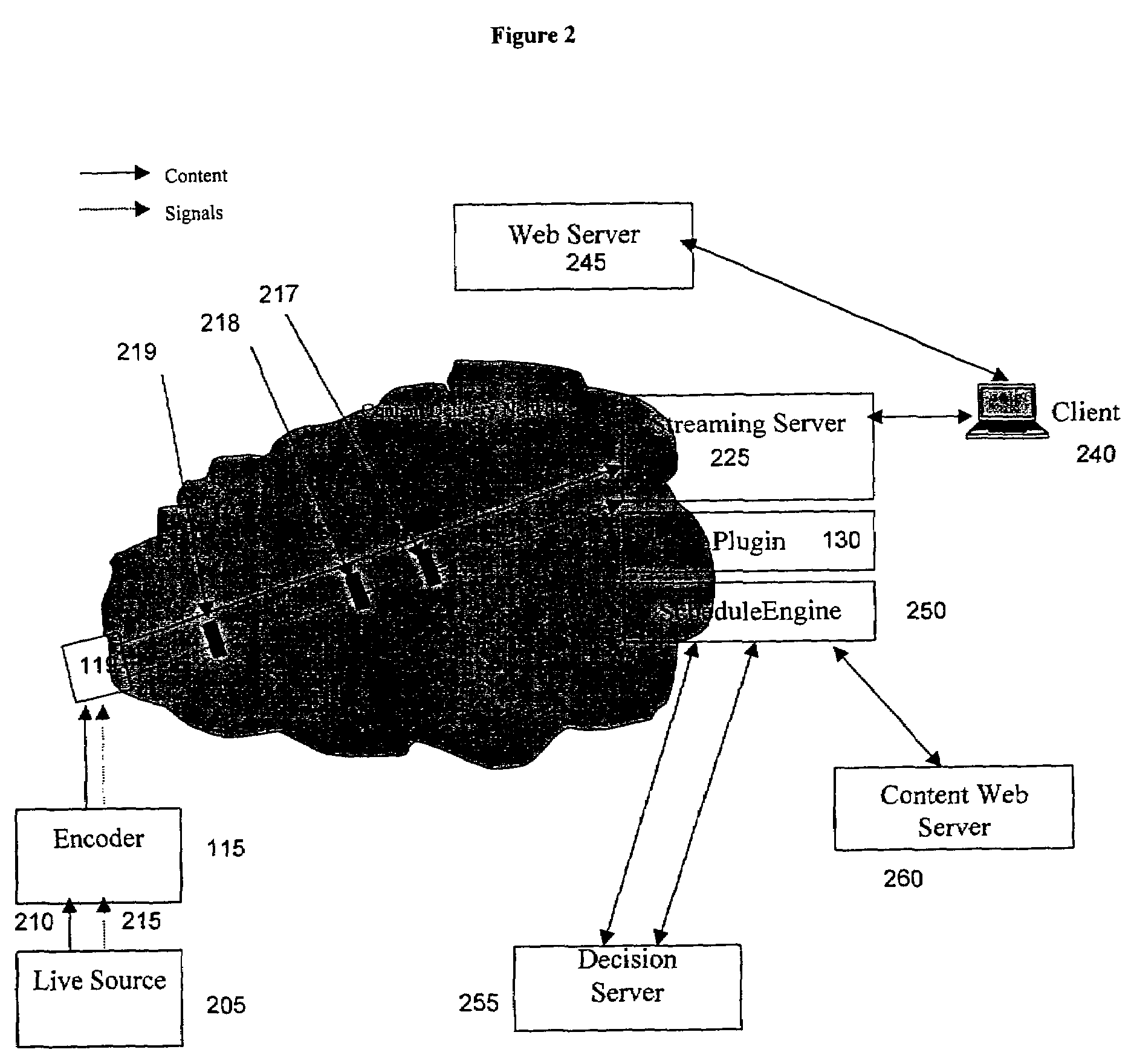
Method and system for server side insertion of rich content into a media stream uses an insertion plugin to redirect users' requests for streaming media through a server, and operates on either live broadcasts or on demand playlists. The live broadcast identifies impending local interrupt breaks and seamlessly inserts content chosen to match user attributes. The on demand implementation broadcasts a playlist of encoded content including predetermined file content and additional rich content inserted based on user attributes as selected by a decision engine. The insertion of content can be performed on already encoded media. In one embodiment, time matching is performed to avoid rebuffering.
Owner:RPX CORP
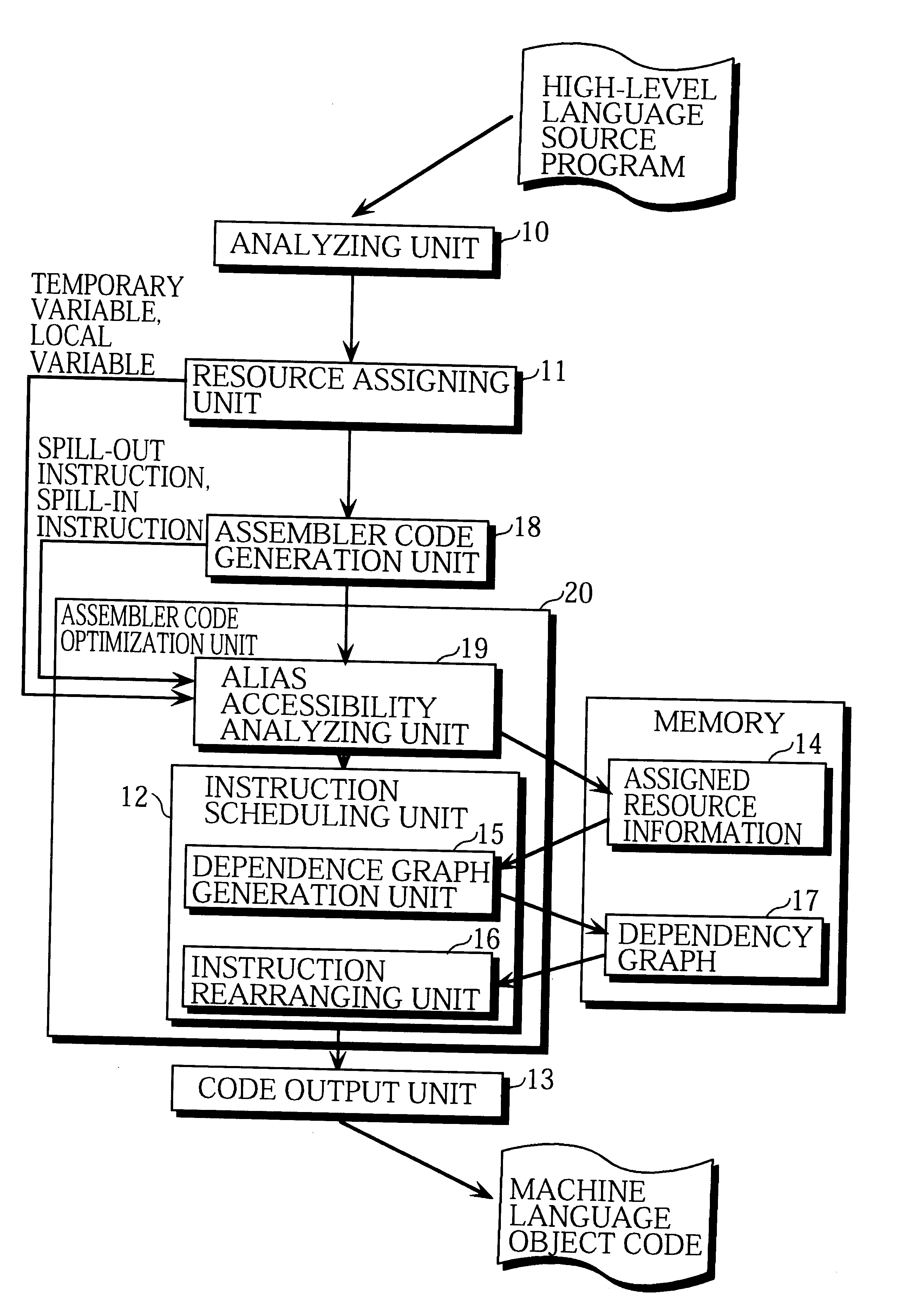
Compiler for optimizing memory instruction sequences by marking instructions not having multiple memory address paths
Internal variables generated by a compiler are assigned to machine resources such as registers and memory by the resource assigning unit 11, and when the assembler code generation unit 18 has outputted an instruction sequence, the alias accessibility analyzing unit 19 registers memory access instructions in the instruction sequence in the assigned resource information 14 according to whether the instructions have a possibility of access by alias. The assembler code optimization unit 20 refers to the assigned resource information 14 and performs optimization at assembler level, thereby reducing the program size and execution time of the instruction sequence.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
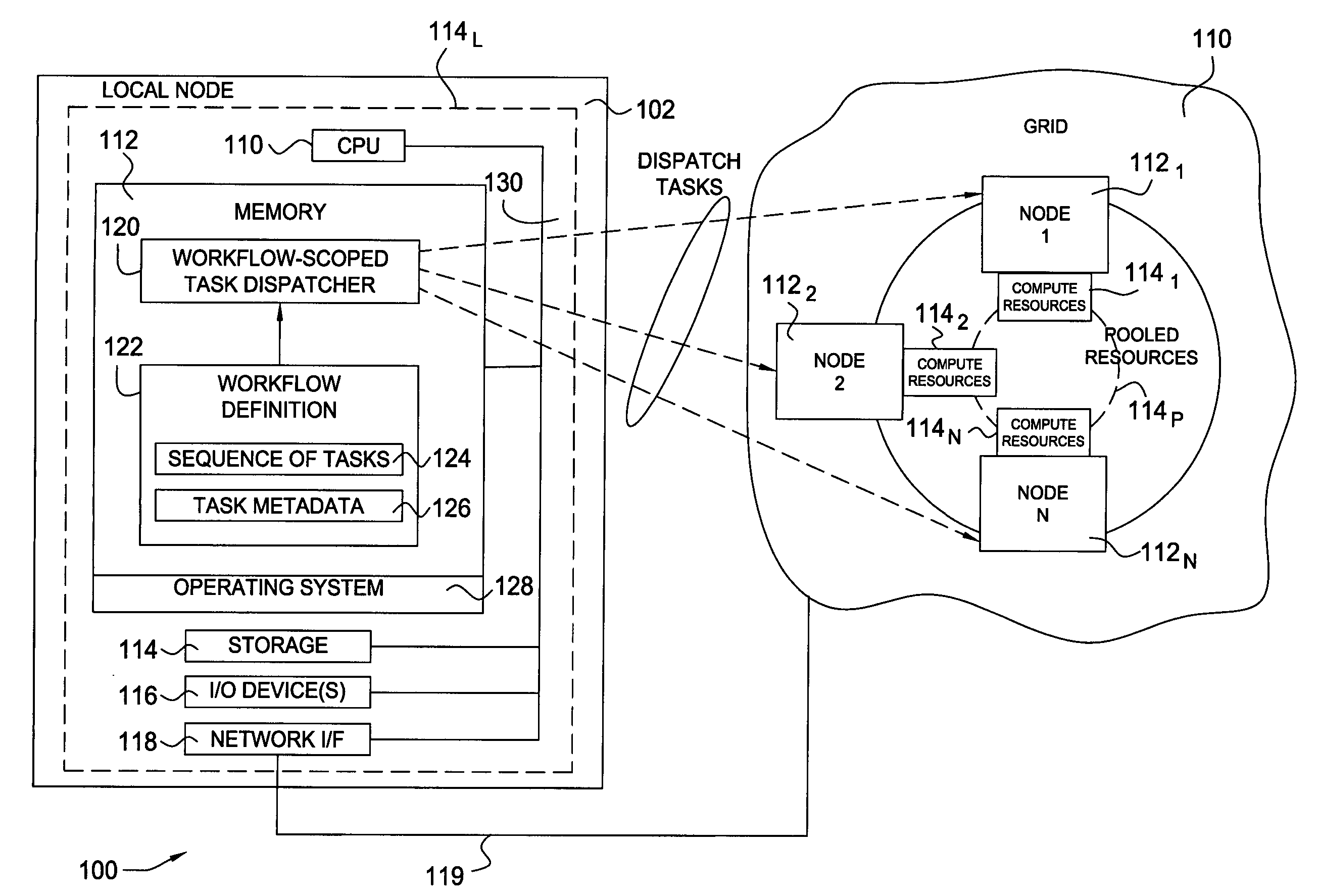
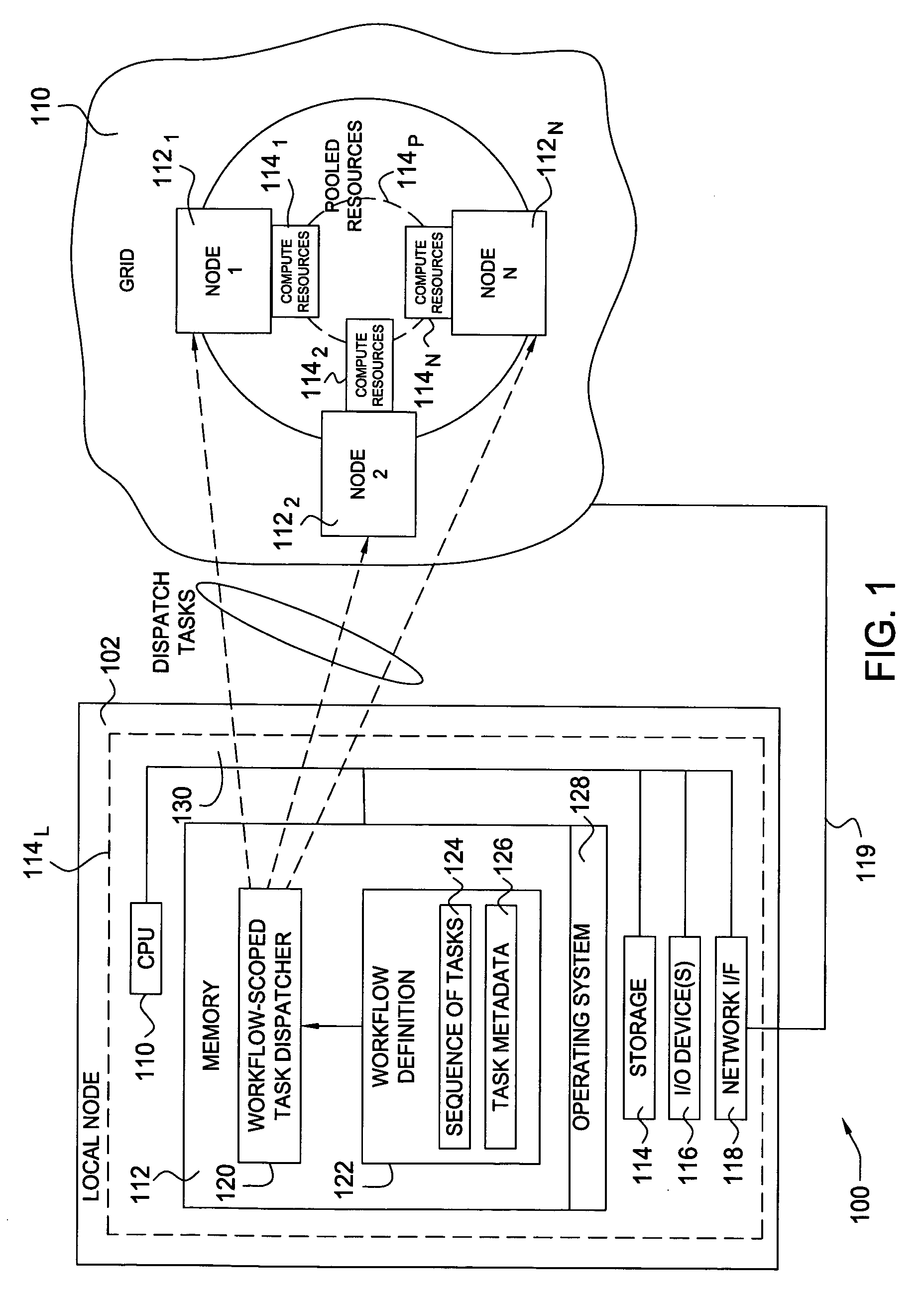
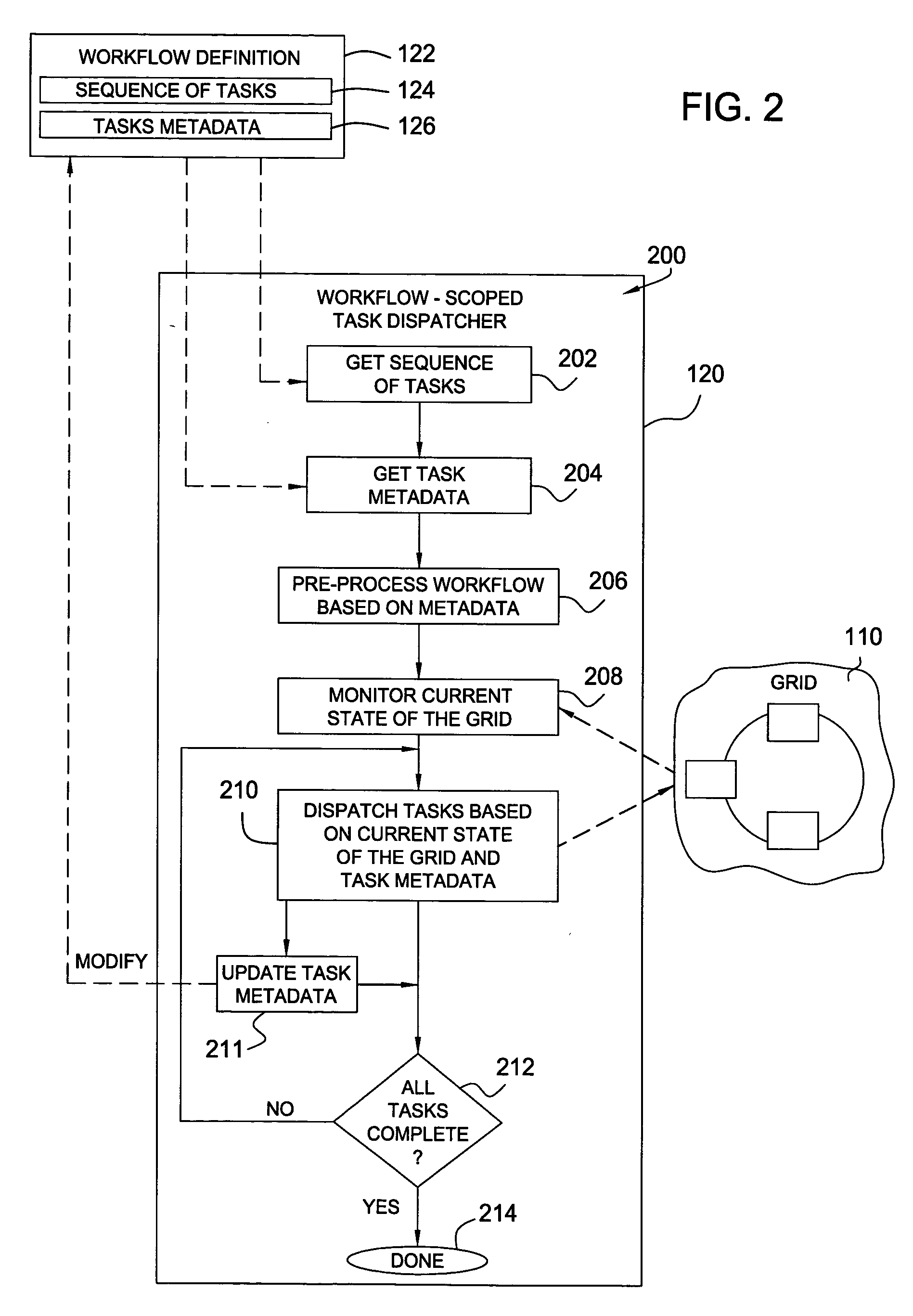
Optimizing workflow execution against a heterogeneous grid computing topology
InactiveUS20050283786A1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsComputational topologyMetadata
Methods and apparatus to optimize workflow execution by the intelligent dispatching of workflow tasks against a grid computing system or infrastructure are provided. For some embodiments, a grid task dispatcher may be configured to dispatch tasks in a manner that takes into account information about an entire workflow, rather than just an individual task. Utilizing information about the tasks (task metadata), such a workflow-scoped task dispatcher may more optimally assign work to compute resources available on the grid, leading to a decrease in workflow execution time and more efficient use of grid computing resources.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com