Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Hinder task" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
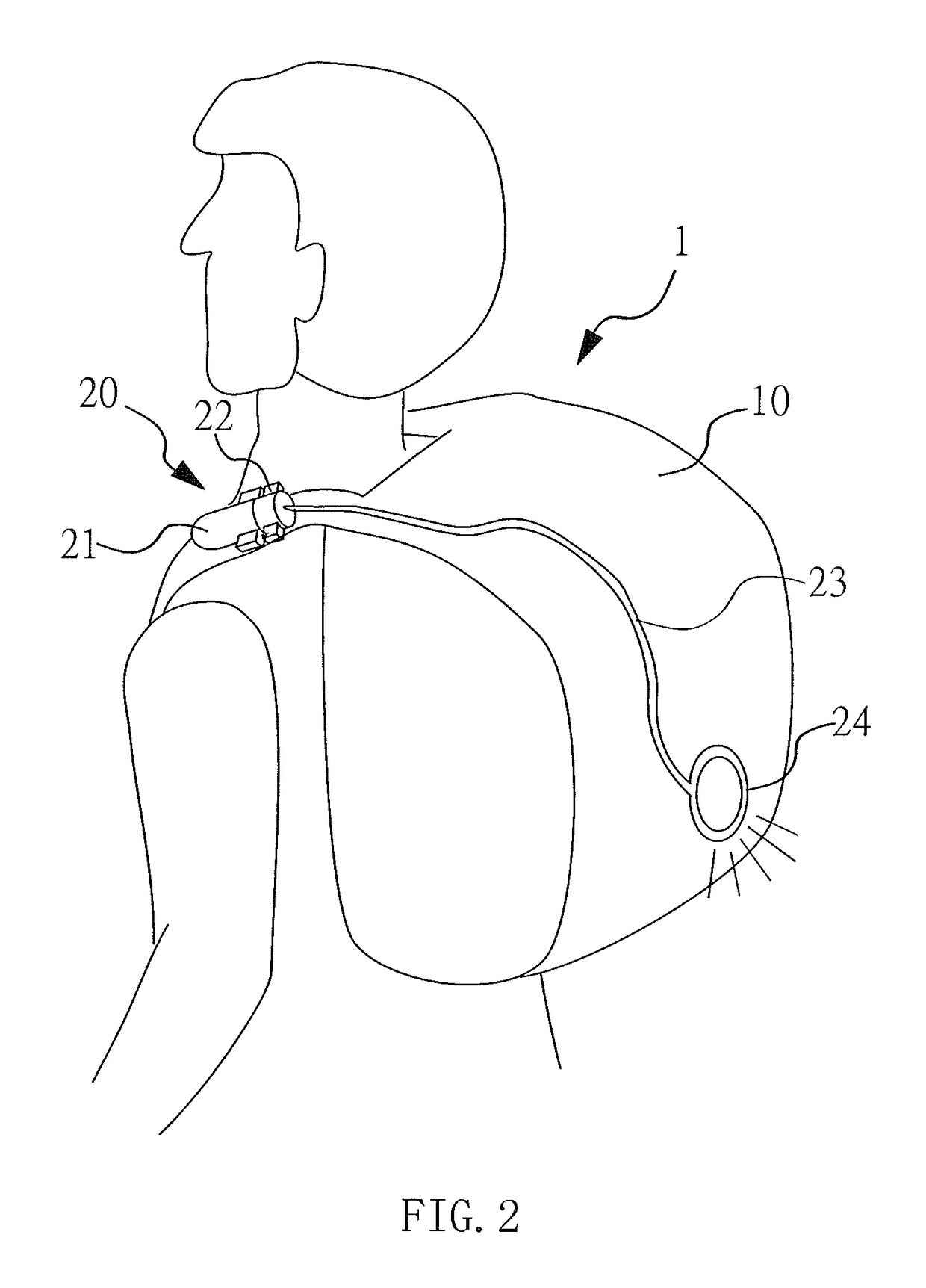
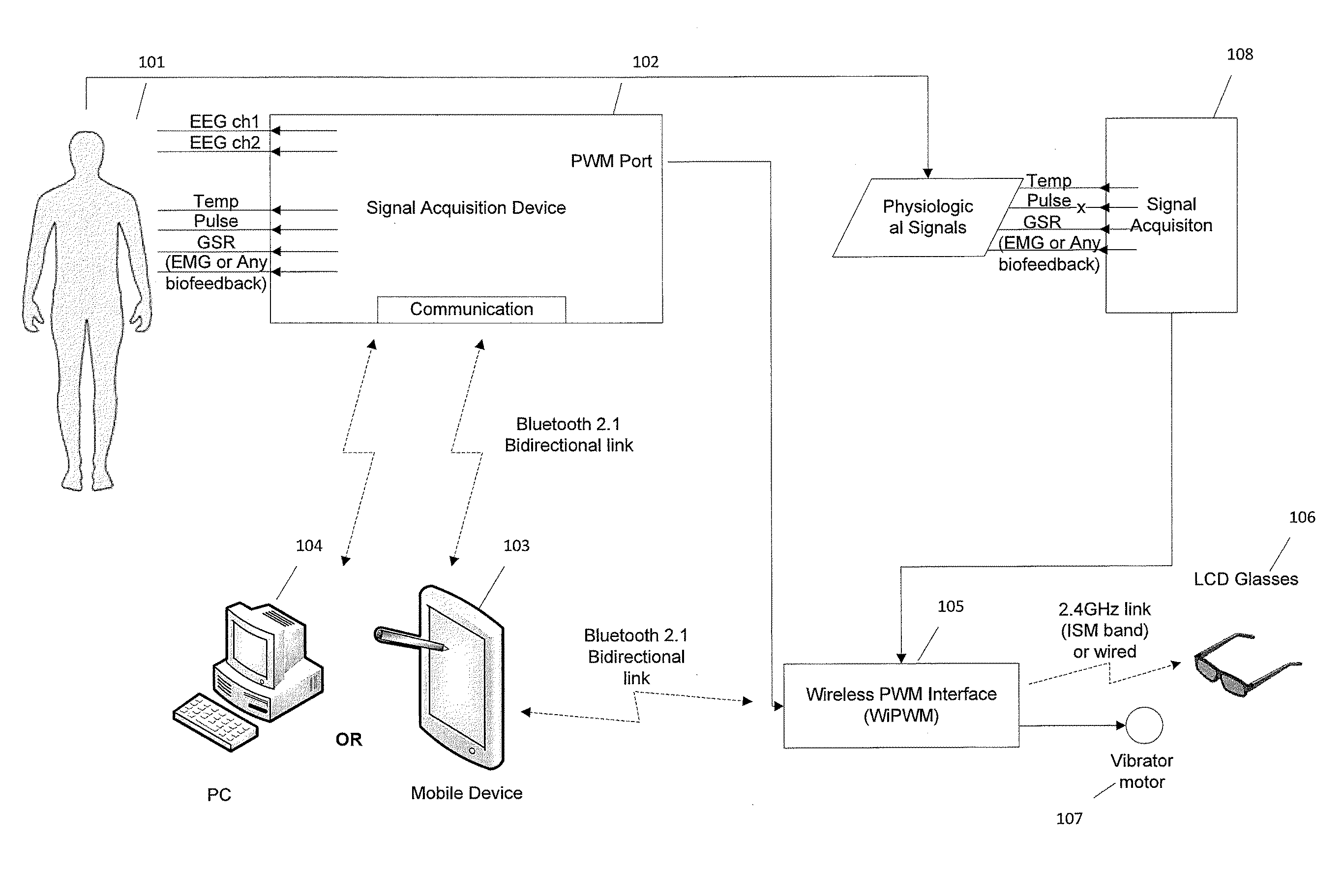
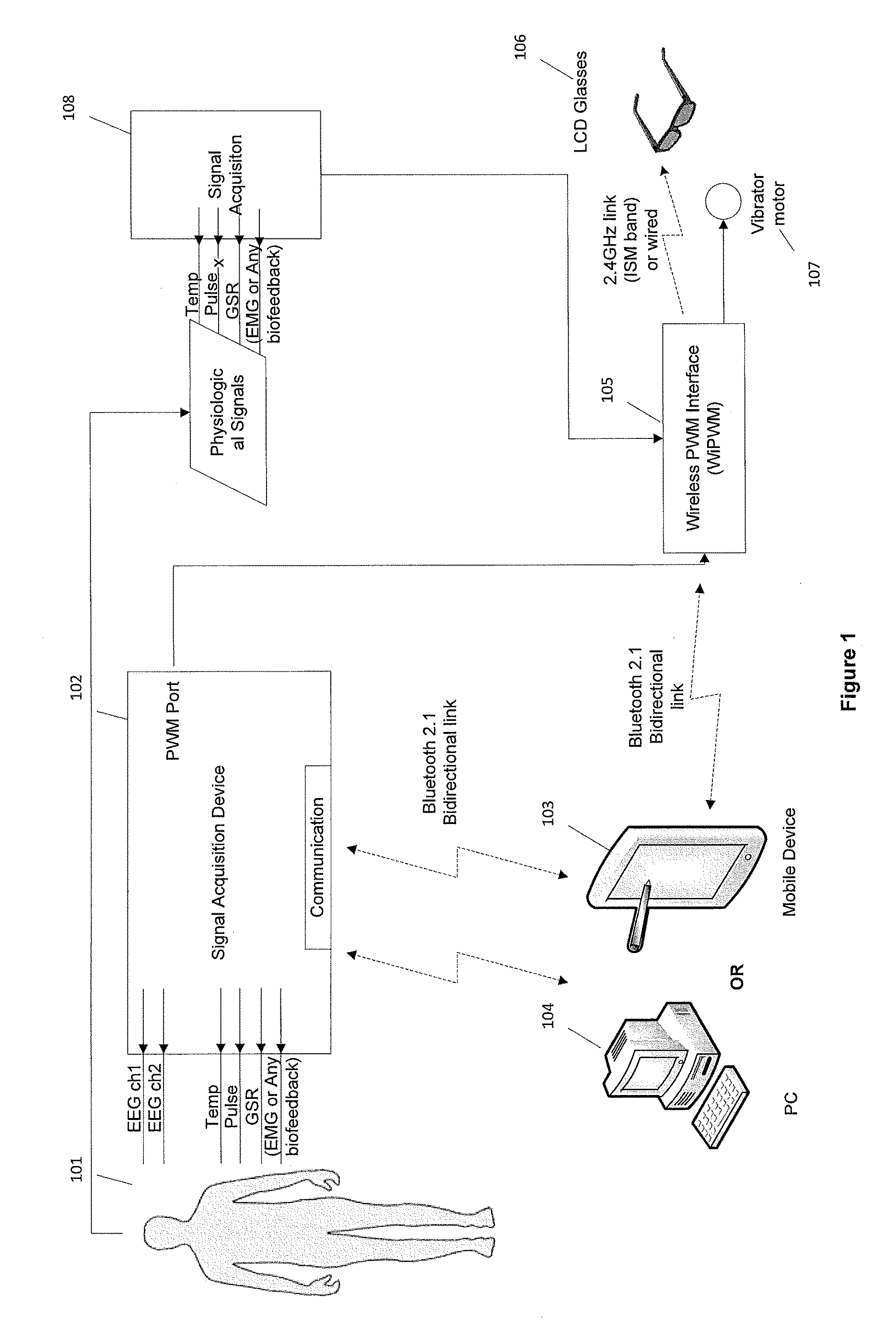
Method and Apparatus for Encouraging Physiological Change Through Physiological Control of Wearable Auditory and Visual Interruption Device
ActiveUS20140336473A1Efficiency to taskHinder taskElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyTouch PerceptionData processing
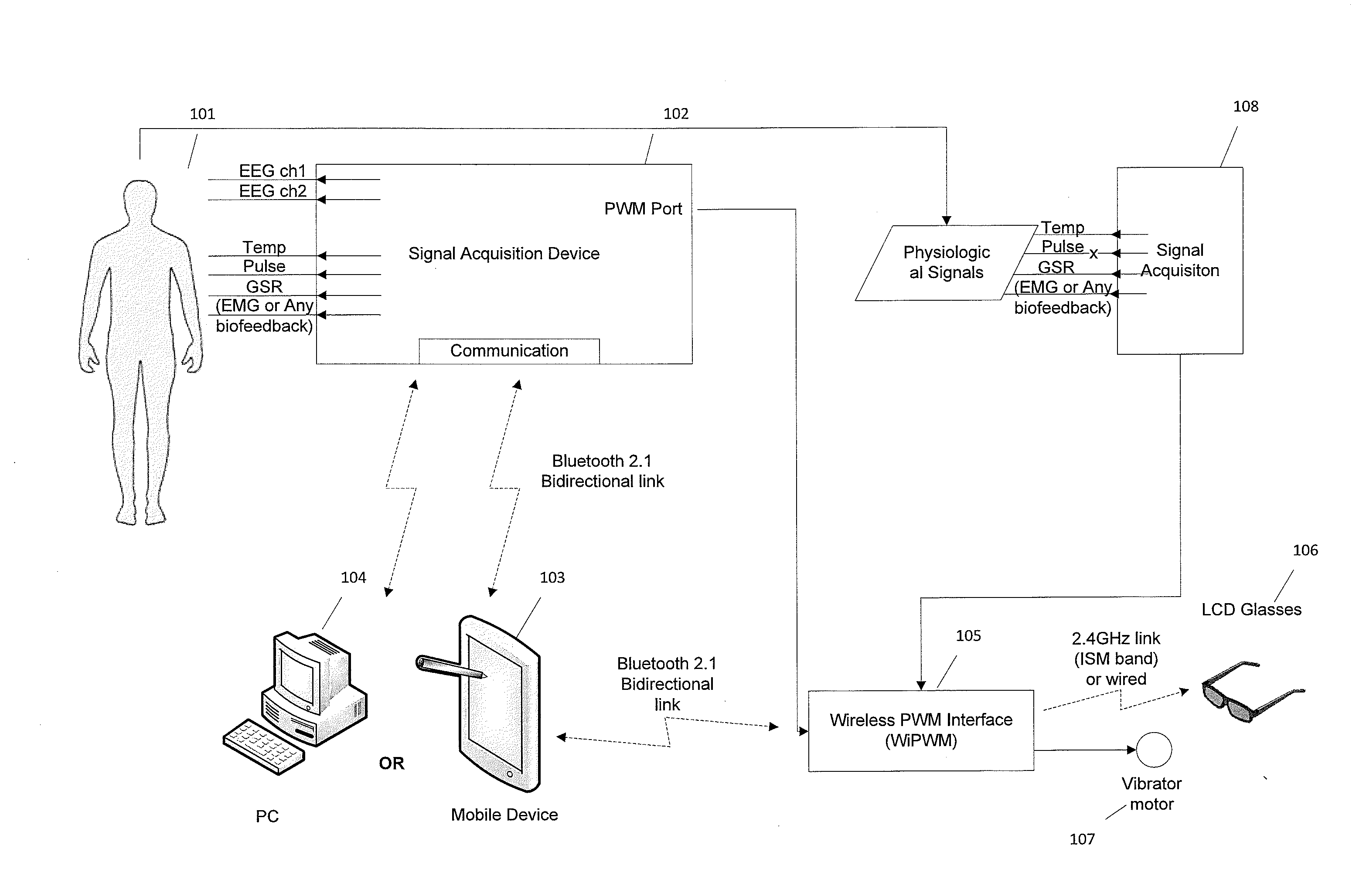
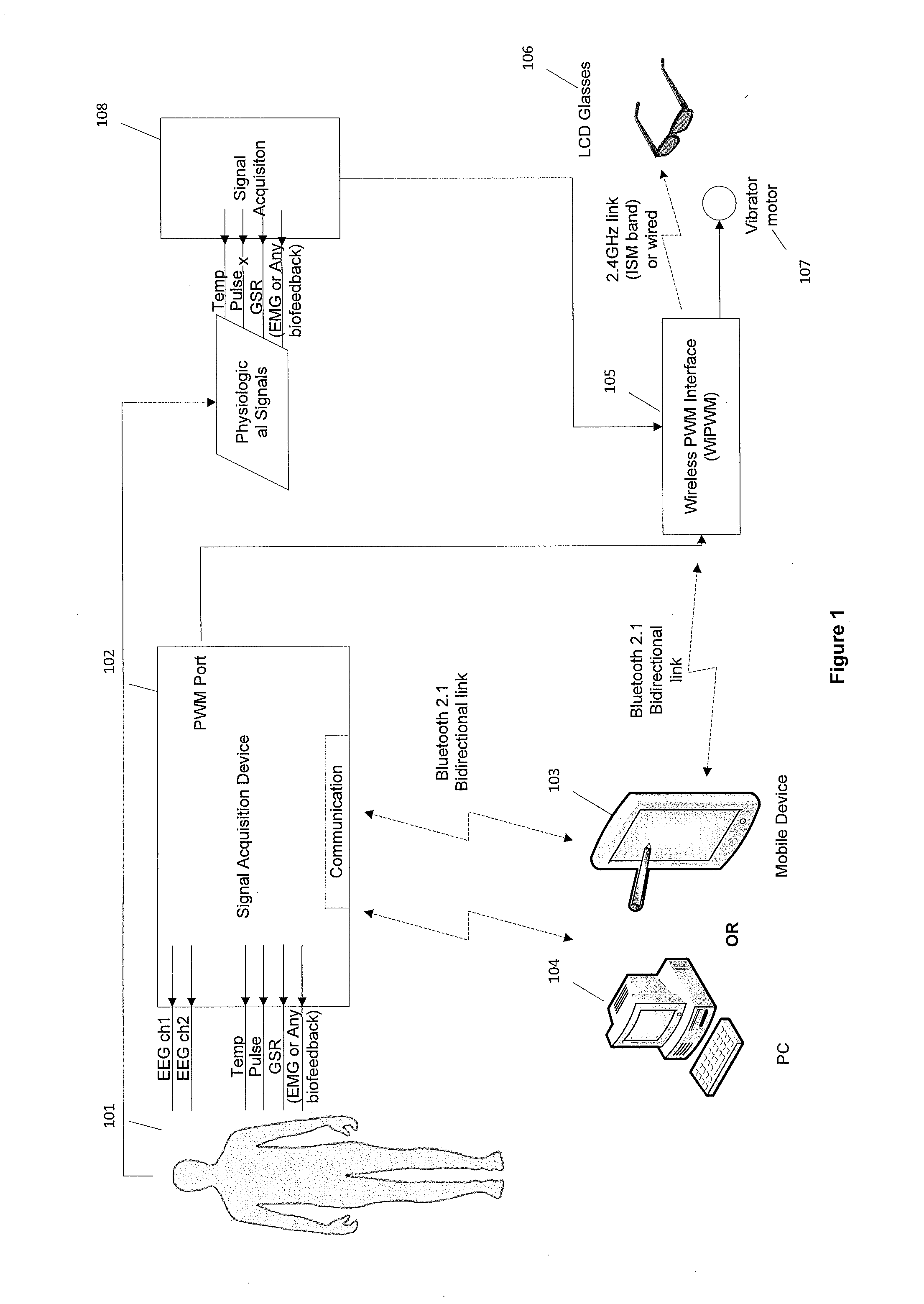
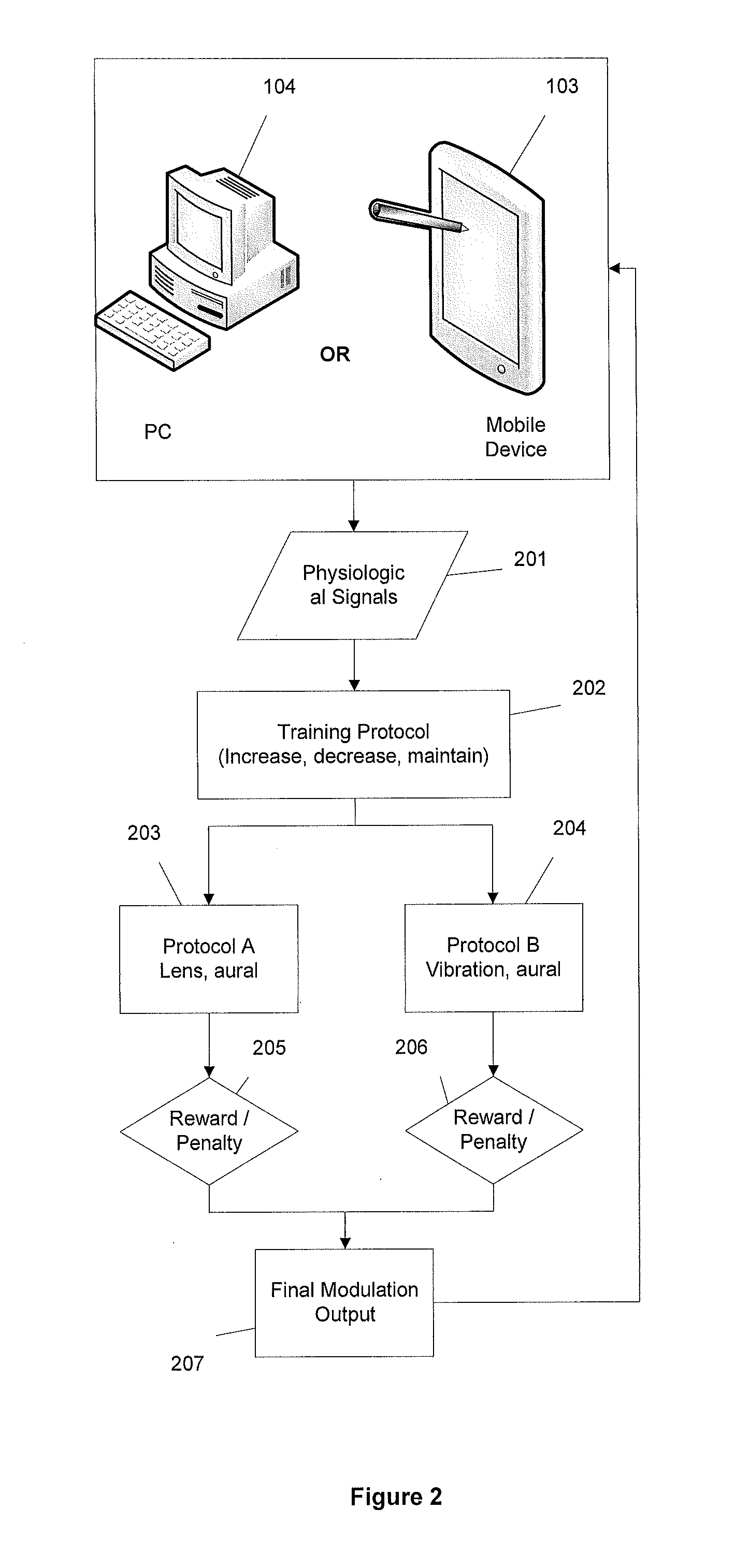
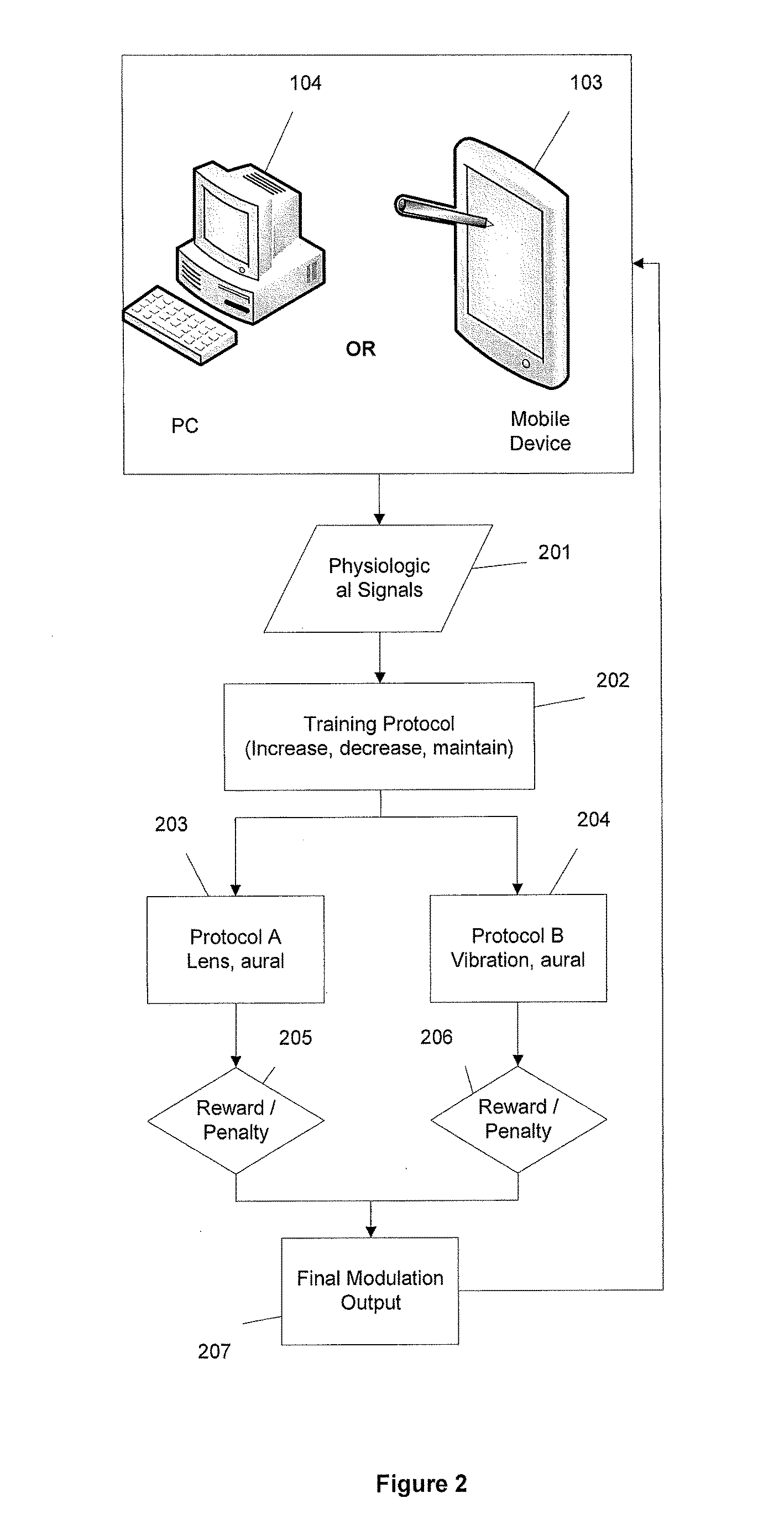
A biofeedback system and method enables biofeedback training to be accomplished during normal interaction by an individual with the individual's environment, for example while reading, playing video games, watching TV, participating in sports activities, or at work. Physiologic data is processed and used to generate one or more control signals based on the physiologic data. The control signals may be proportional to a result of the data processing, or based on comparison of the processing results with at least one fixed or adaptive threshold. The control signal is supplied to a wearable device through which the individual receives sensory information from the individual's environment, and serves to interrupt or modify the sensory information. The wearable device may be an eyeglass device including a dynamic lens display, with the control signal being supplied to the dynamic lens display to modulate visual information received through the eyeglass device by obscuring, distorting, or otherwise affecting the clarity of the visual information. Feedback may also be provided in the form of auditory or tactile feedback.
Owner:GRECO DEVON
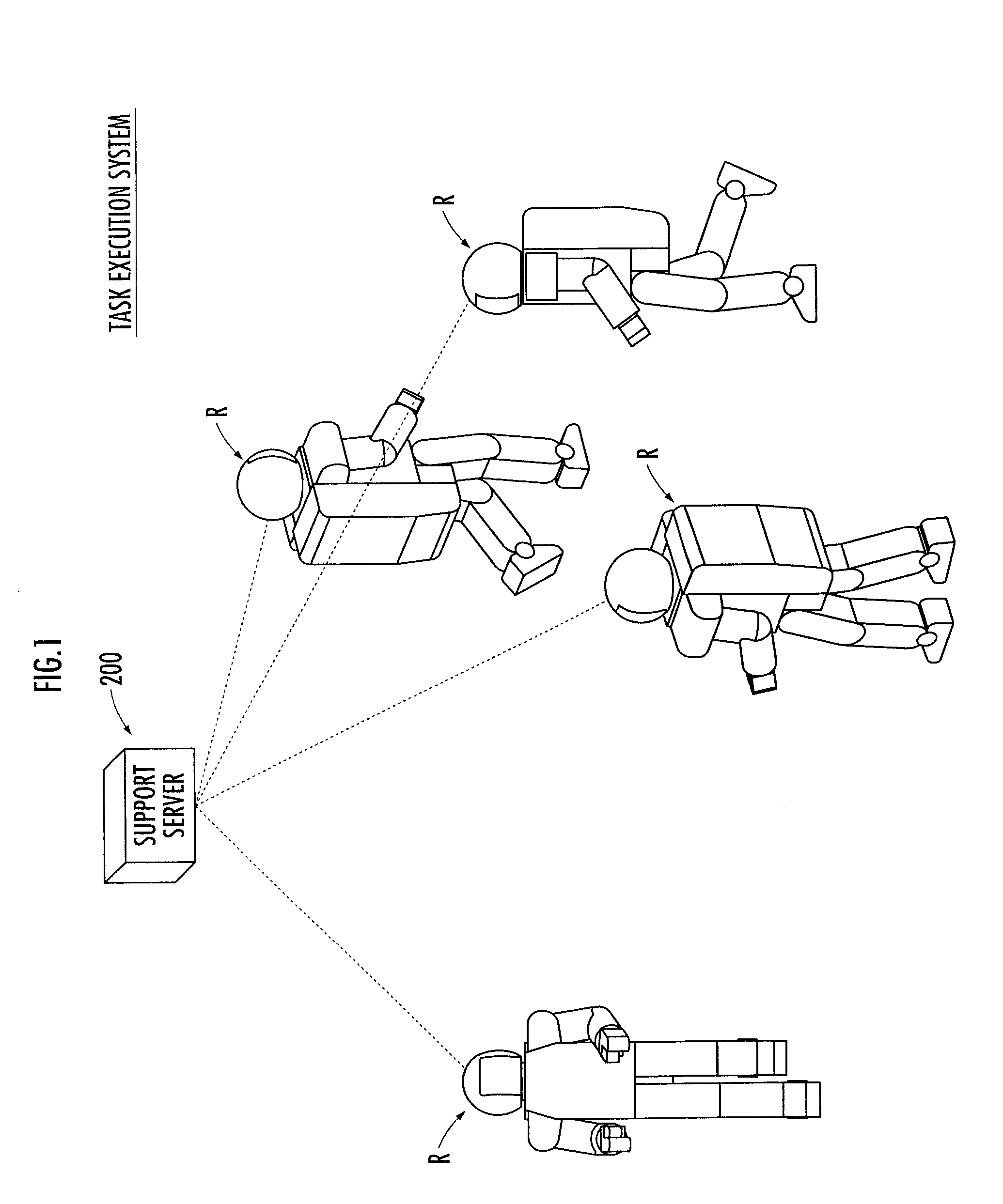
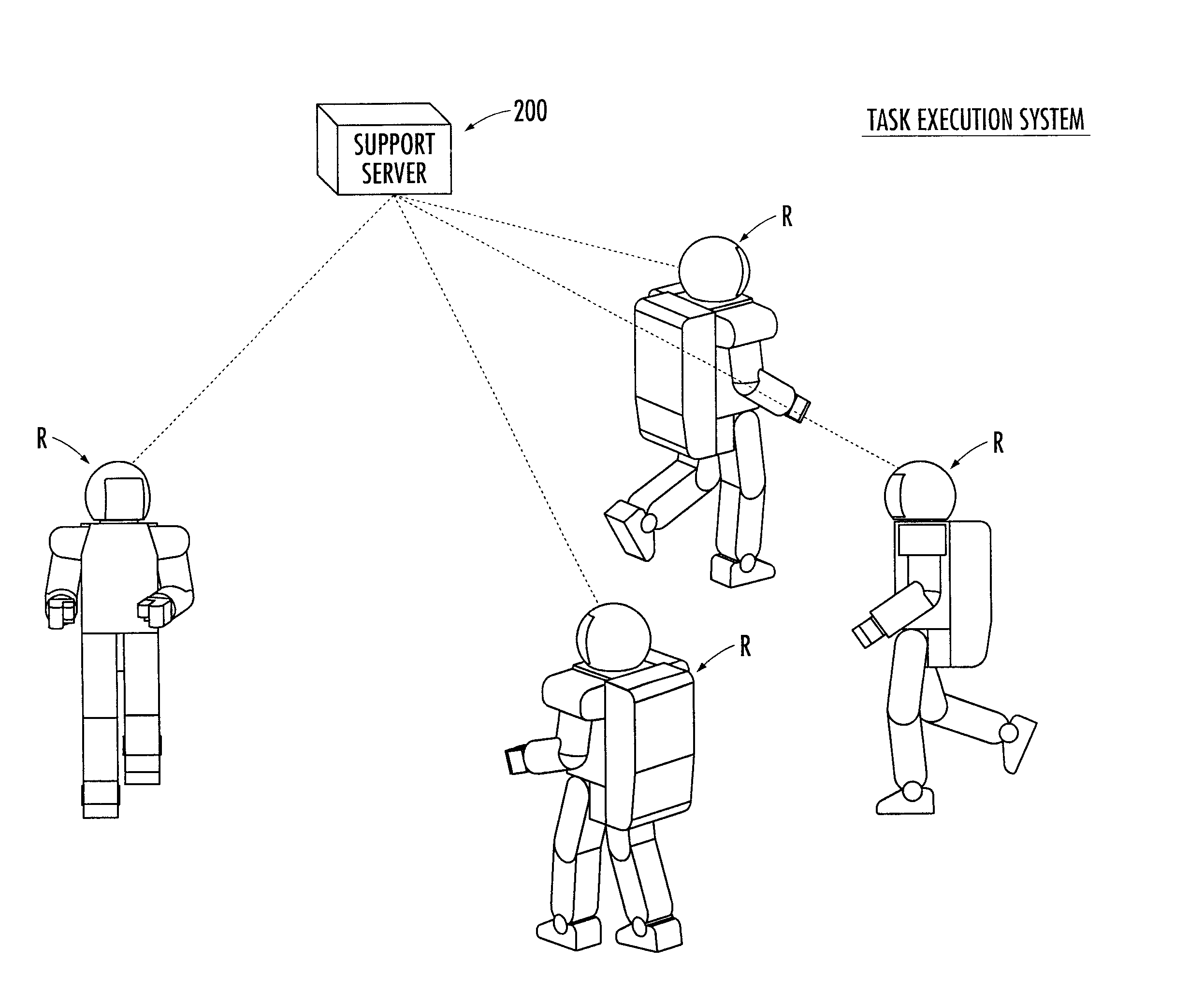
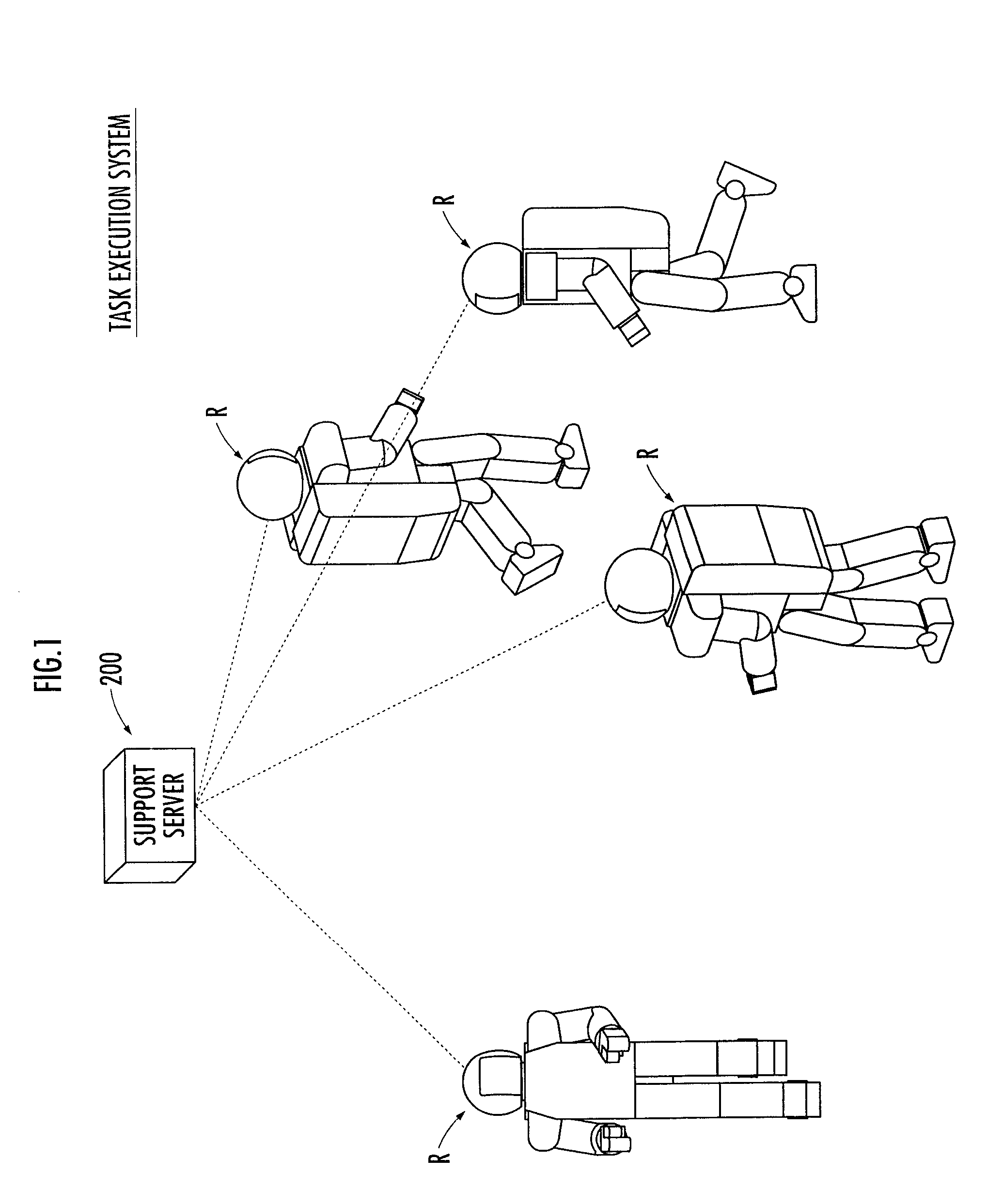
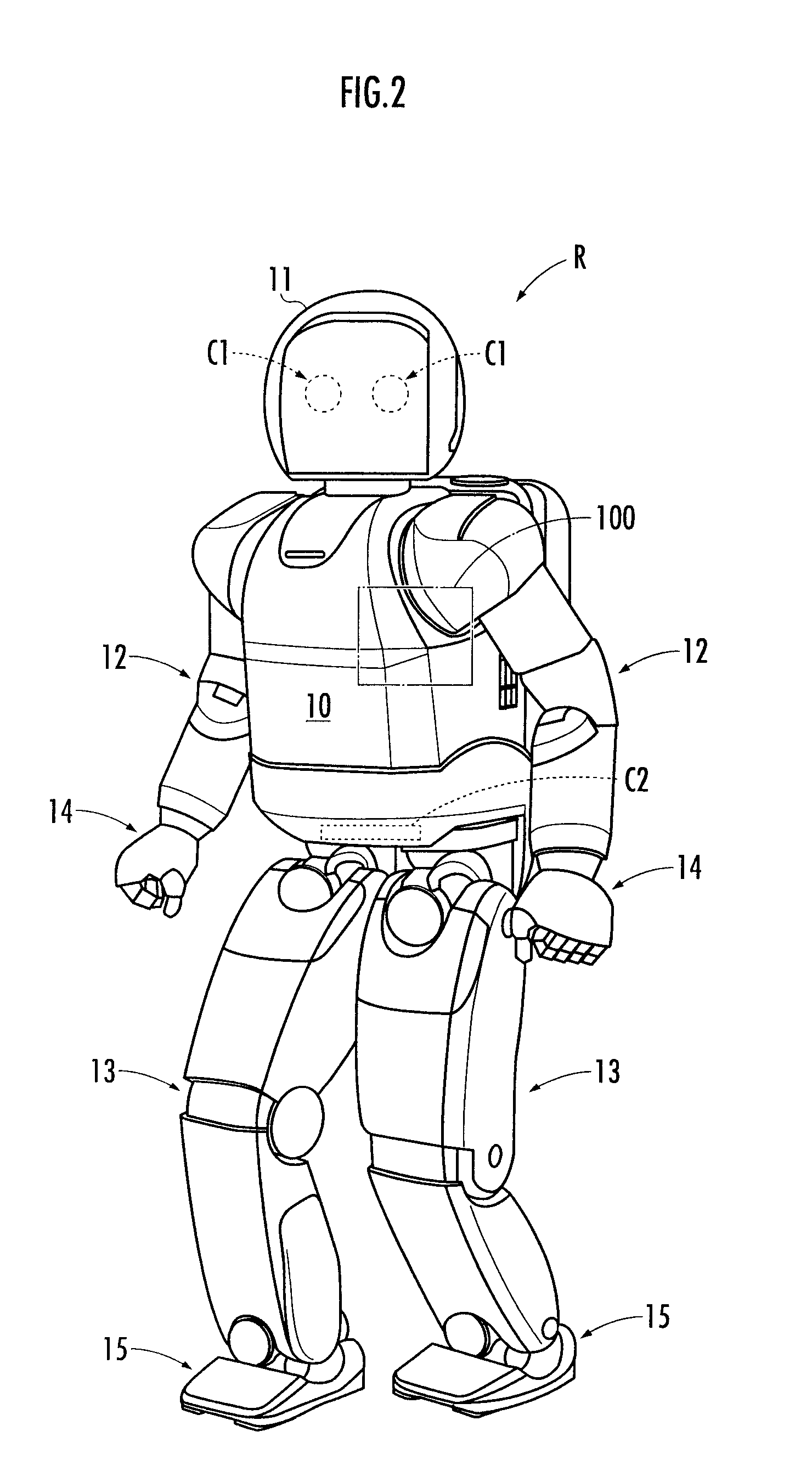
Robot and task execution system
ActiveUS20100217438A1Sufficient energyPreventing executionProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlViewpointsEmbedded system
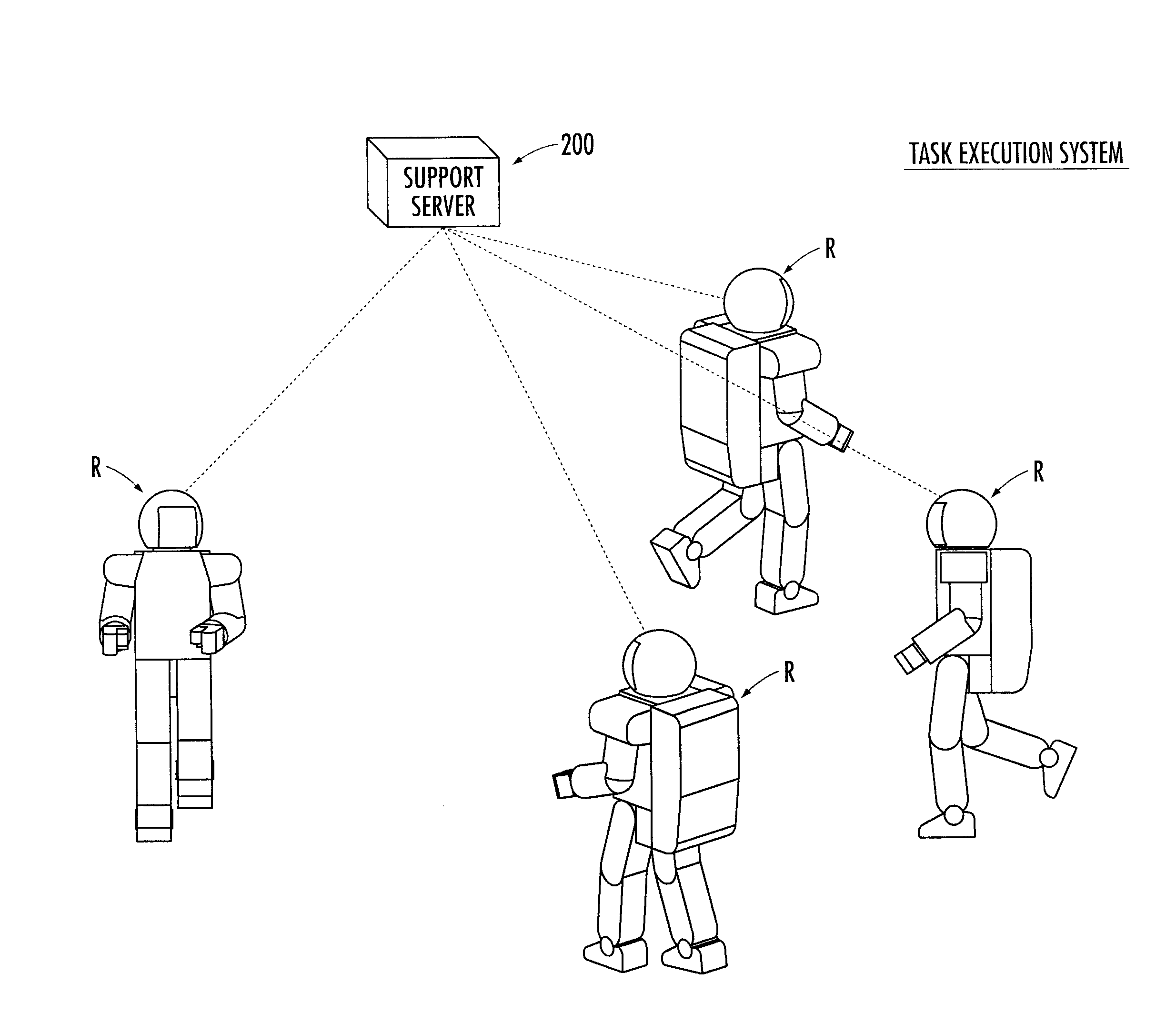
A robot and the like capable of executing a task in an appropriate condition from the viewpoint of execution economy even when a state of the task is altered. A cost is evaluated that represents a load or labor required for a robot (1) to execute a new task, and the cost information indicating the cost is transmitted to a support server (200) (bid procedure). The support server (200) designates the robot (1) having the lowest cost as a designated robot (1) and transmits an execution instruction for executing the new task to the designated robot (1). The robot (1) executes the task according to the execution instruction (contract procedure). By employing the task bid and contract system, a designated task is executed by an adequate robot (R) among a plurality of robots (R) in consideration of the execution economy of the designated task.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
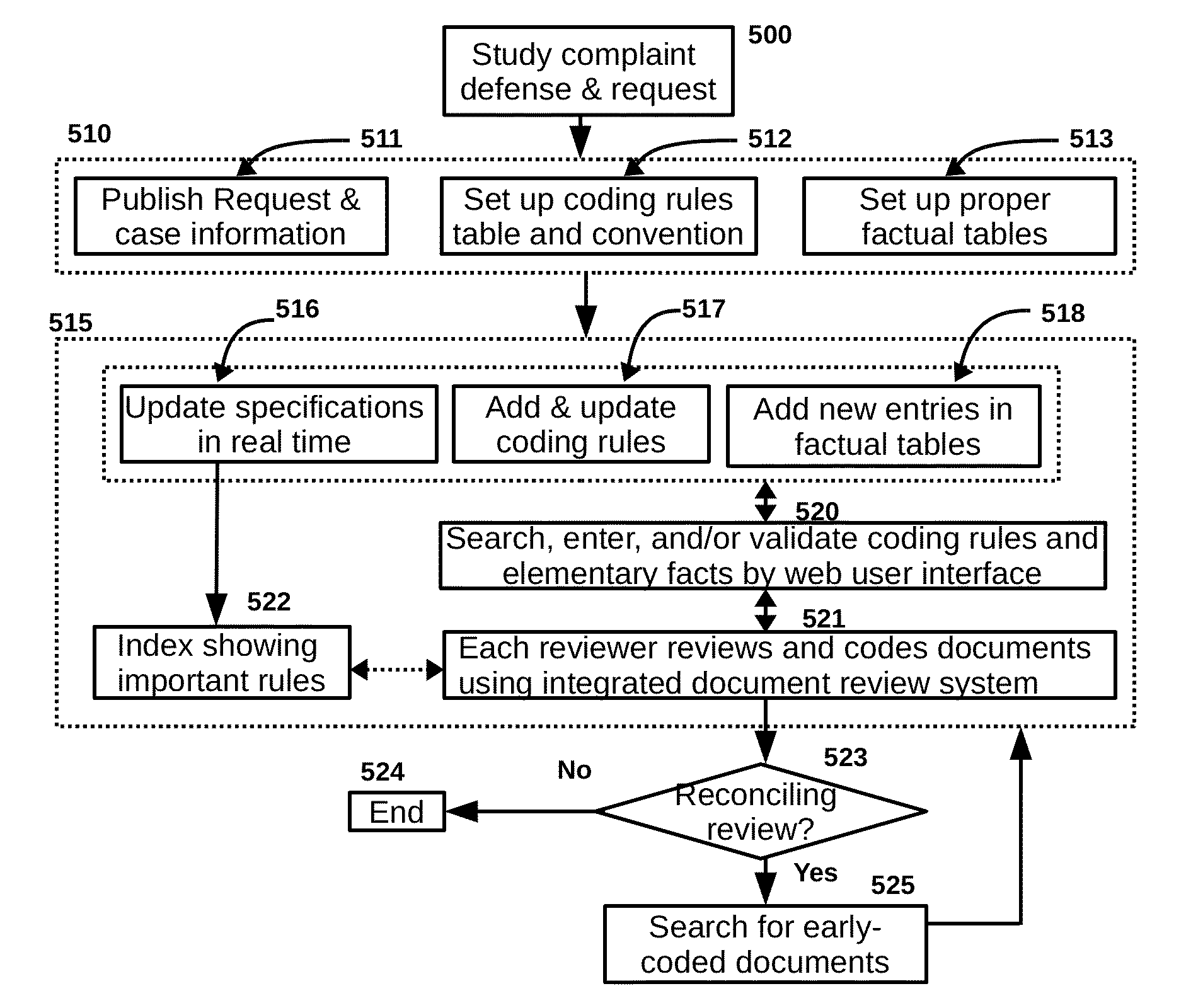
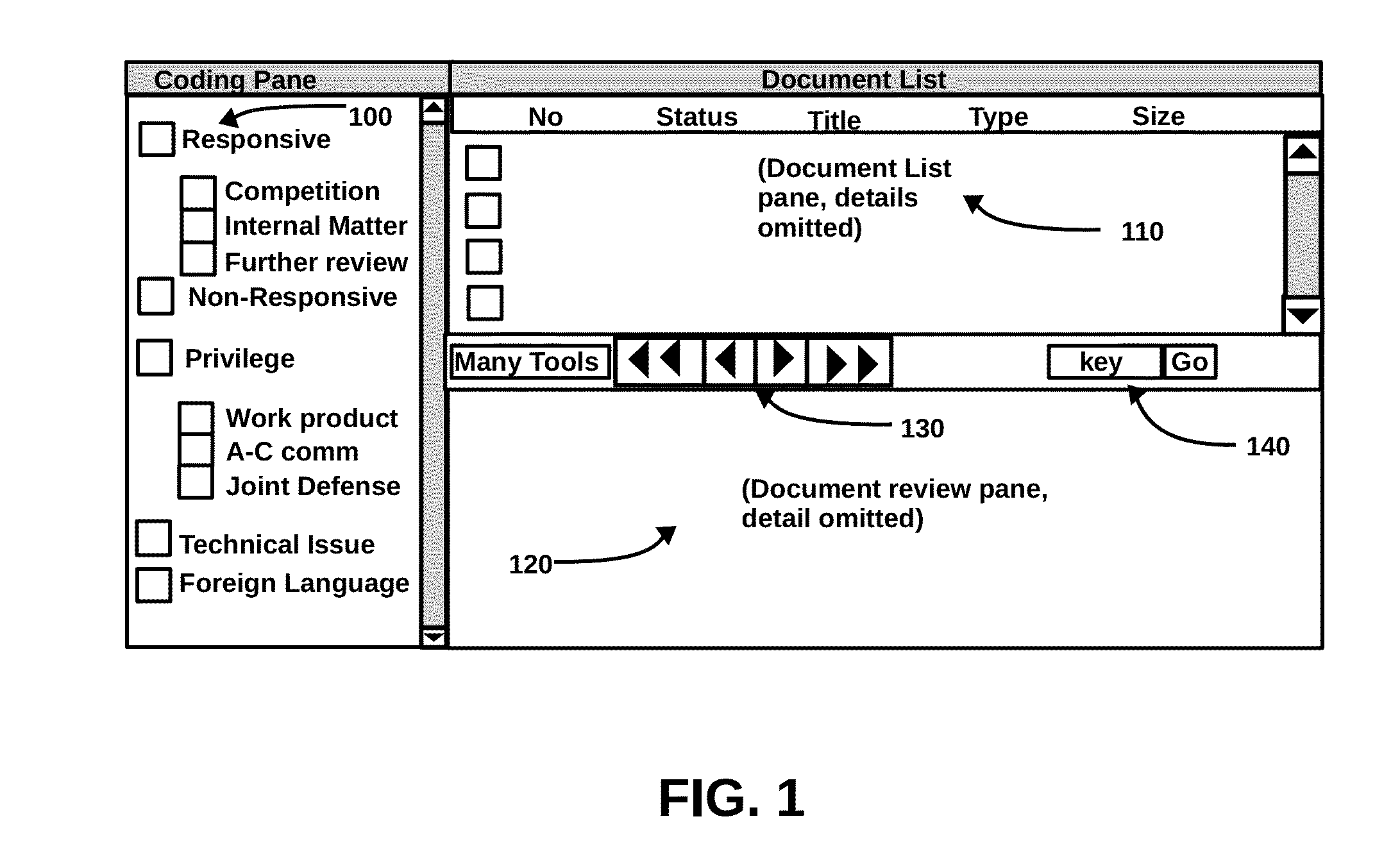
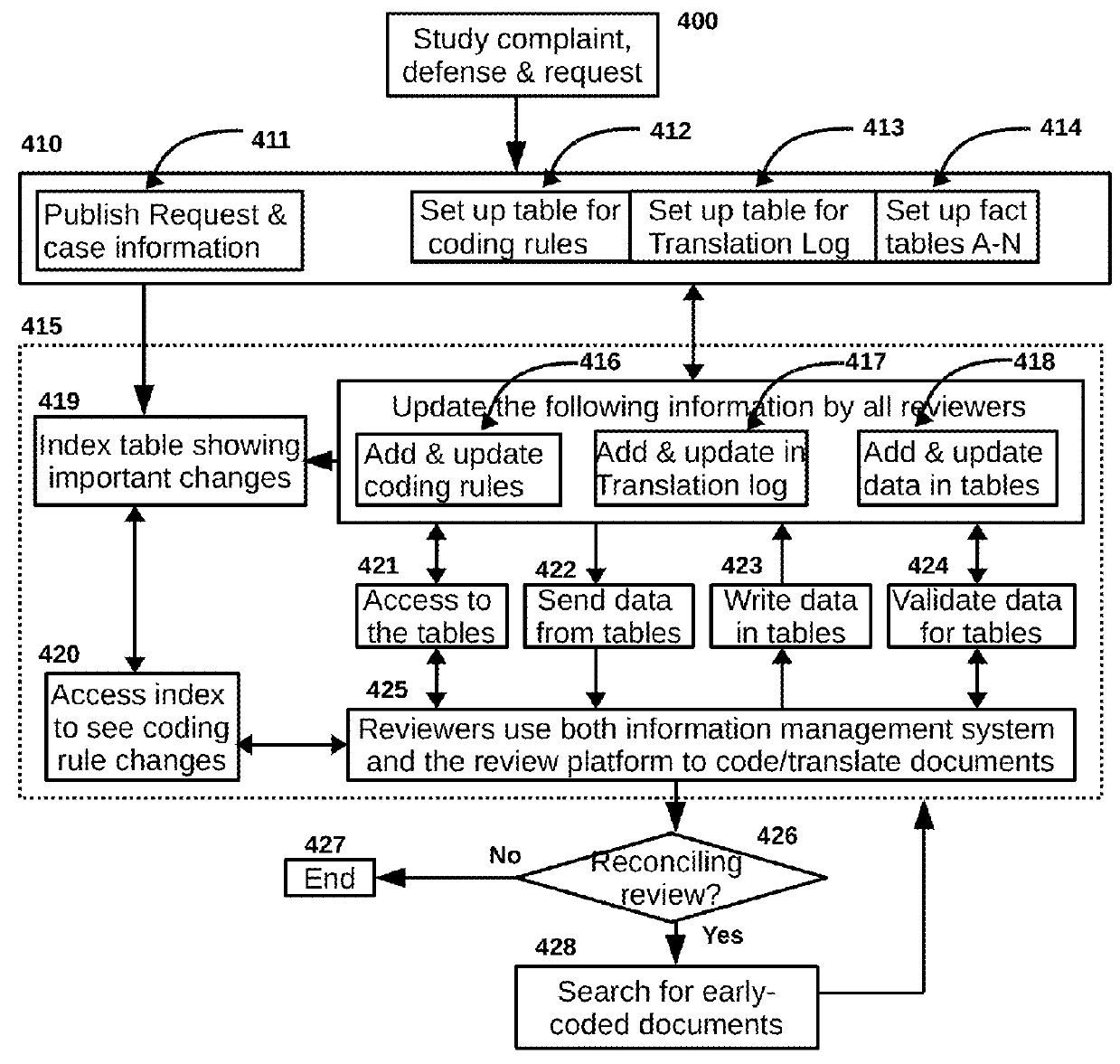
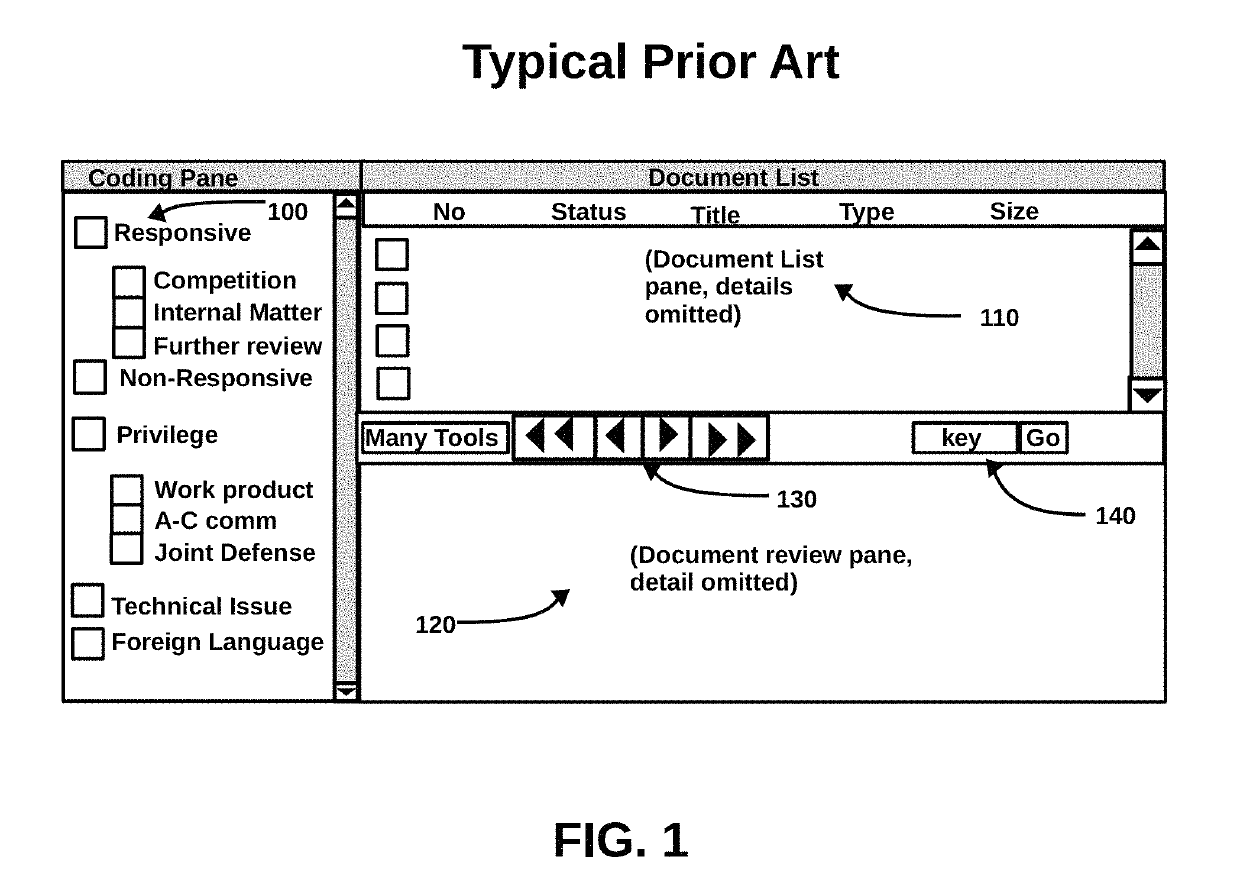
Method for Improving Document Review Performance
ActiveUS20140317147A1Work well togetherAvoid misunderstandingDigital data processing detailsResourcesElectronic discoveryDocument preparation
The present invention is a method and process for accurately and efficiently coding documents in electronic discovery. The method, if used by highly experienced and motivated document reviewers in a collegial and harmonic environment, has the potential to increase adjusted review consistency, reduce coding errors, eliminate duplicate efforts, increase review speed, decrease the risks of exposure, and dramatically improve review performance. The method will also result in useful case history files, which are useful in every phrase of litigation, including motion argument, merit trial, appeal, and future litigation.
Owner:WU JIANQING
Parallel remembered-set processing respecting popular-object detection
ActiveUS7617264B1Hinder taskCompromise performanceDigital data processing detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWaste collectionParallel computing
A garbage collector that operates in multiple threads divides a generation of a garbage-collected heap into heap sections, with which it associates respective remembered sets of locations where references to objects in those heap sections have been found. When such a heap section comes up for collection, each of a plurality of parallel garbage-collector threads that is processing its remembered set maintains a separate “popularity”—indicating count map, which includes an entry for each of a set of segments into which the collector has divided that heap section. The thread increments an entry in its count map each time it finds a reference to an object in the associated segment. If an object is located in a segment for which the associated count-map entry has exceeded a threshold, the thread evacuates the object in a manner different from that in which it evacuates objects not thus been found to be popular.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
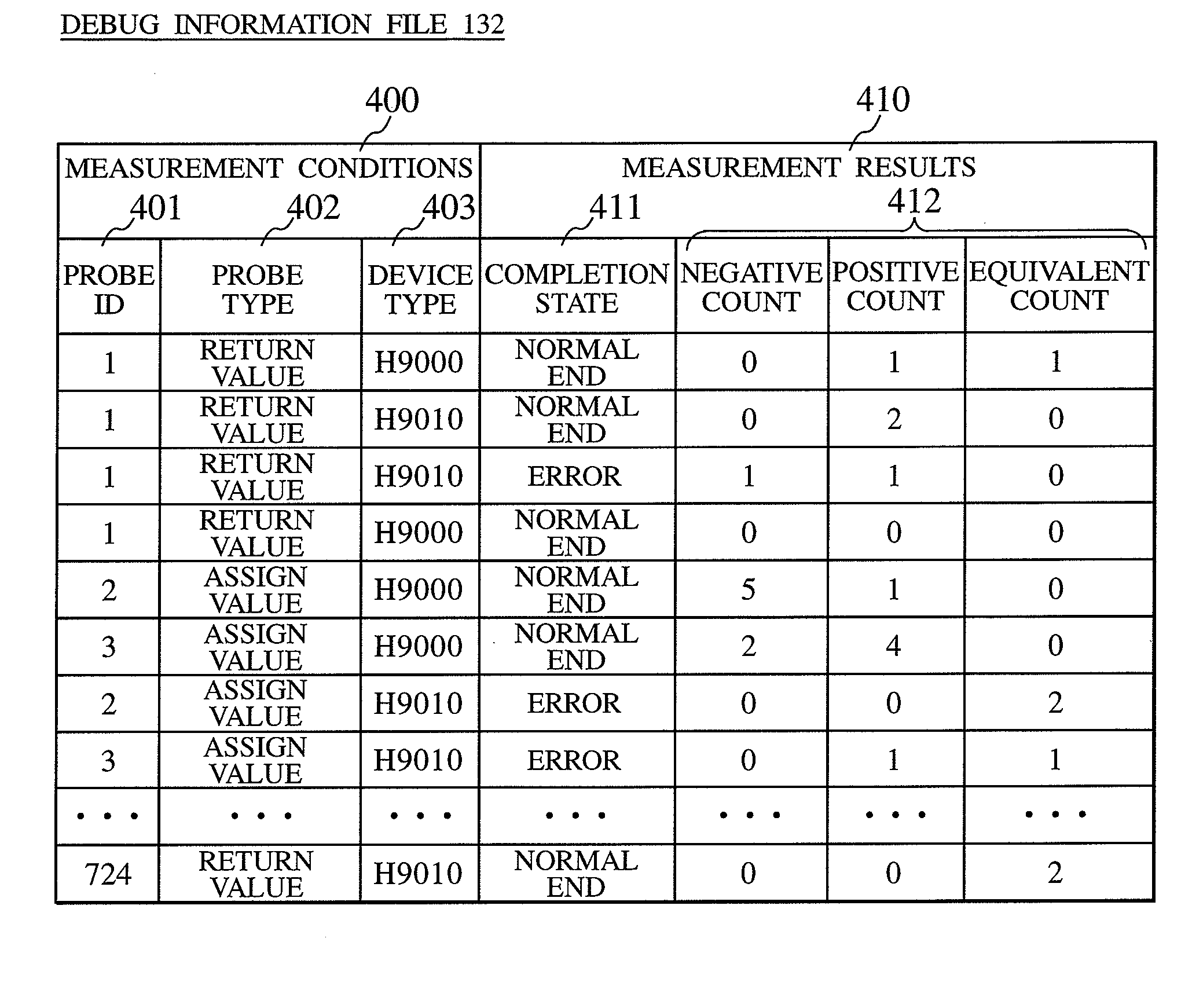
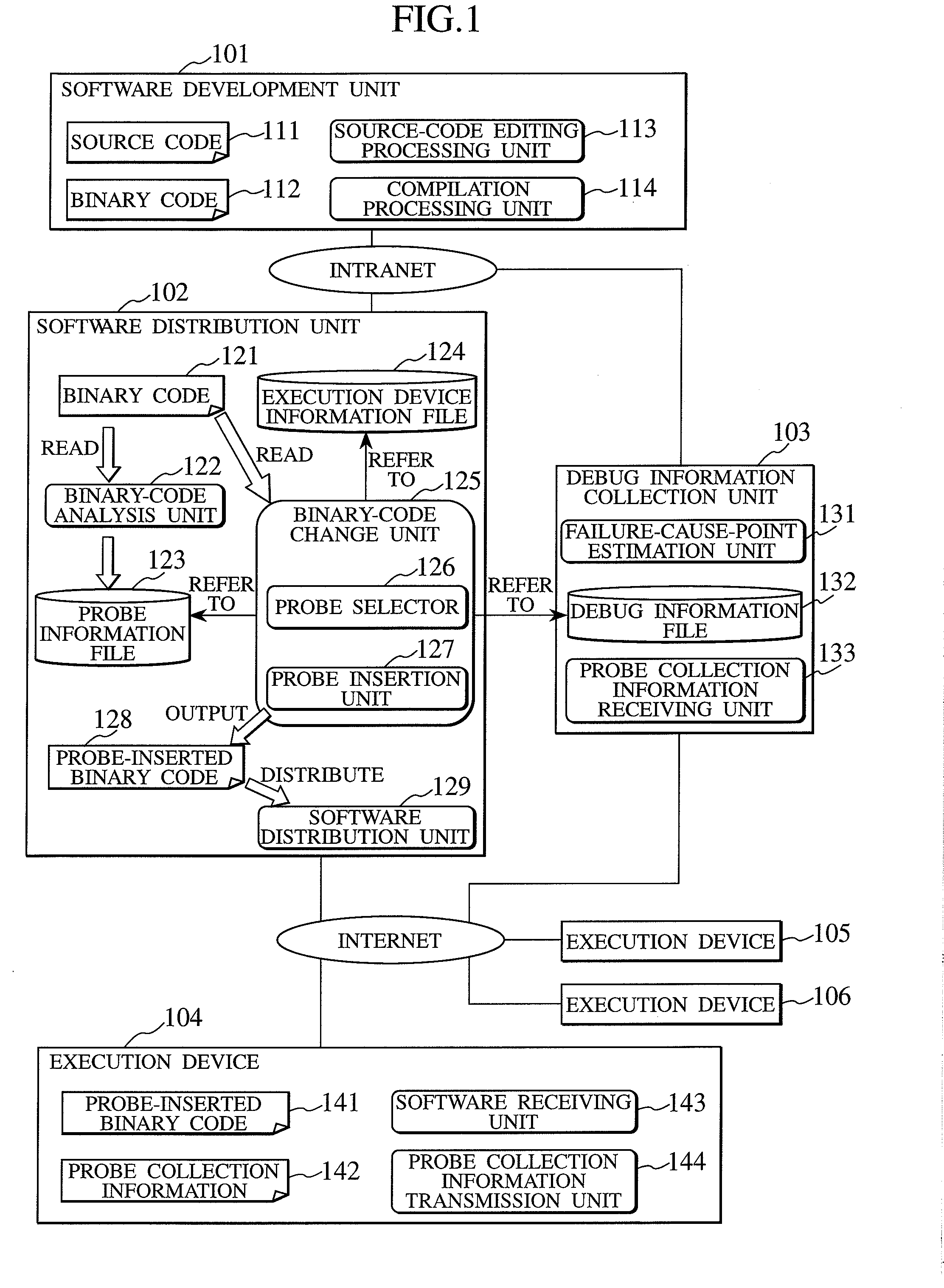
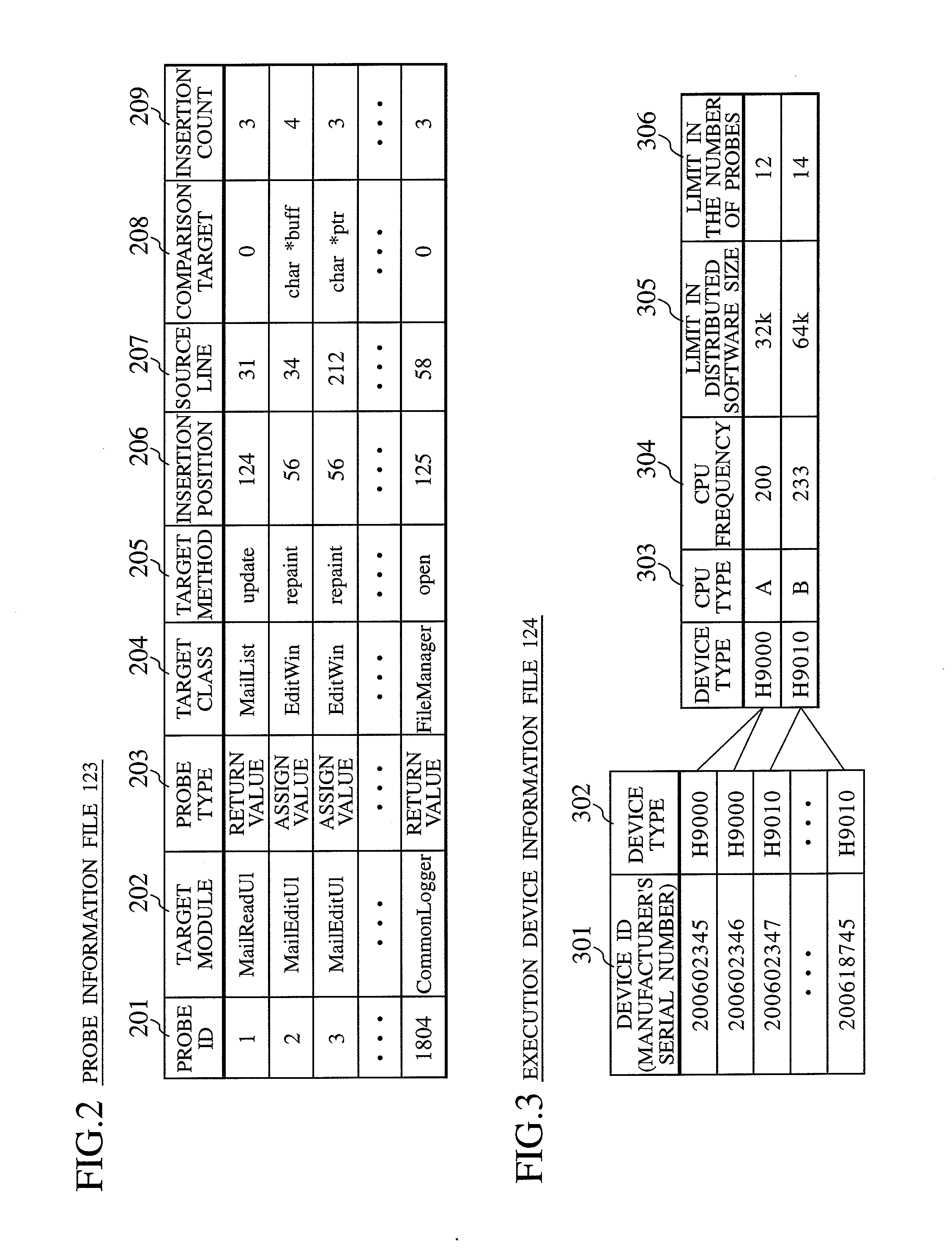
Debug information collection method and debug information collection system
InactiveUS20080141224A1Reduce loadSpeed up failure-cause analysisHardware monitoringSoftware testing/debuggingSoftware distributionCollection system
In a software distribution unit, a binary-code analysis unit determines a total set of insertion positions at which probes can be inserted into software. A binary-code change unit determines the population of insertion positions of probes to be inserted into the software and the number of insertion positions of probes to be inserted on a device basis. Then, the binary-code change unit selects, from the population, insertion positions of probes as many as the determined number of insertion positions and inserts the probes into the software at the selected insertion positions. A software distribution unit distributes, to the device, the software into which the probes are inserted. As a result, it is possible to reduce both a load on the device side and a load on the software developer side at the same time and to acquire uniform debug information without deviations.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
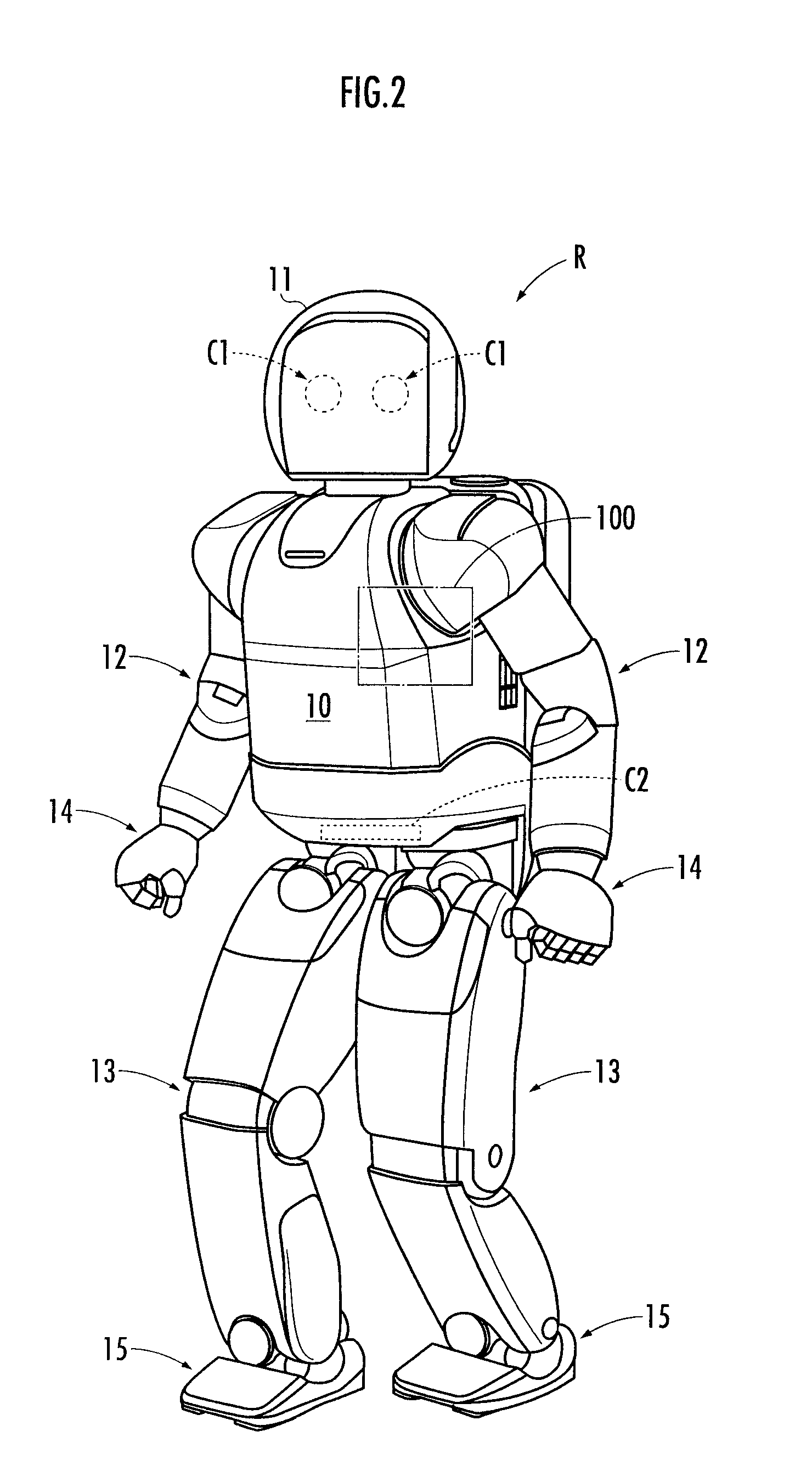
Robot and task execution system
ActiveUS8285417B2Hinder taskProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlViewpointsEmbedded system
A robot and the like capable of executing a task in an appropriate condition from the viewpoint of execution economy even when a state of the task is altered. A cost is evaluated that represents a load or labor required for a robot (1) to execute a new task, and the cost information indicating the cost is transmitted to a support server (200) (bid procedure). The support server (200) designates the robot (1) having the lowest cost as a designated robot (1) and transmits an execution instruction for executing the new task to the designated robot (1). The robot (1) executes the task according to the execution instruction (contract procedure). By employing the task bid and contract system, a designated task is executed by an adequate robot (R) among a plurality of robots (R) in consideration of the execution economy of the designated task.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
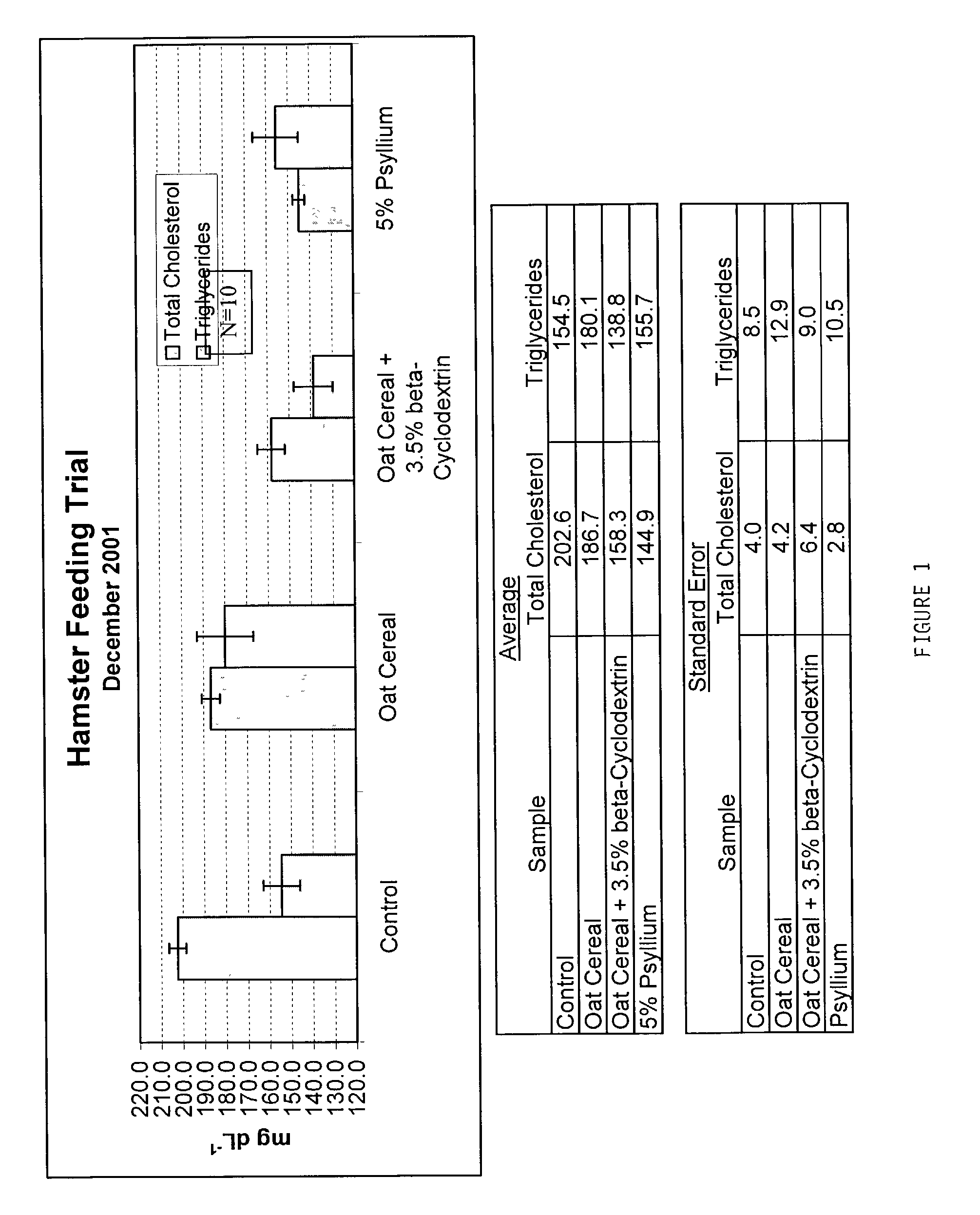
Food product having increased bile acid binding capacity
InactiveUS20030232068A1Enhanced hypocholesterolemic propertyHigh affinityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSide effectBile-acid Binding Activity
The present invention is related to a novel component for use in a consumer food product. More specifically, the ingredient or component, provided either alone or acting synergistically with other select ingredients, is part of an ingestible food product intended for human or animal consumption that provides a health benefit. The food product provides beneficial hypocholesterolemic activity through increased bile acid binding activity through the use of cyclodextrins alone or in combination with dietary fibers and / or sterols while simultaneously delivering a food product which is not adversely affected by its inclusion, either in taste or texture or in any undesirable side effects.
Owner:GENERAL MILLS INC
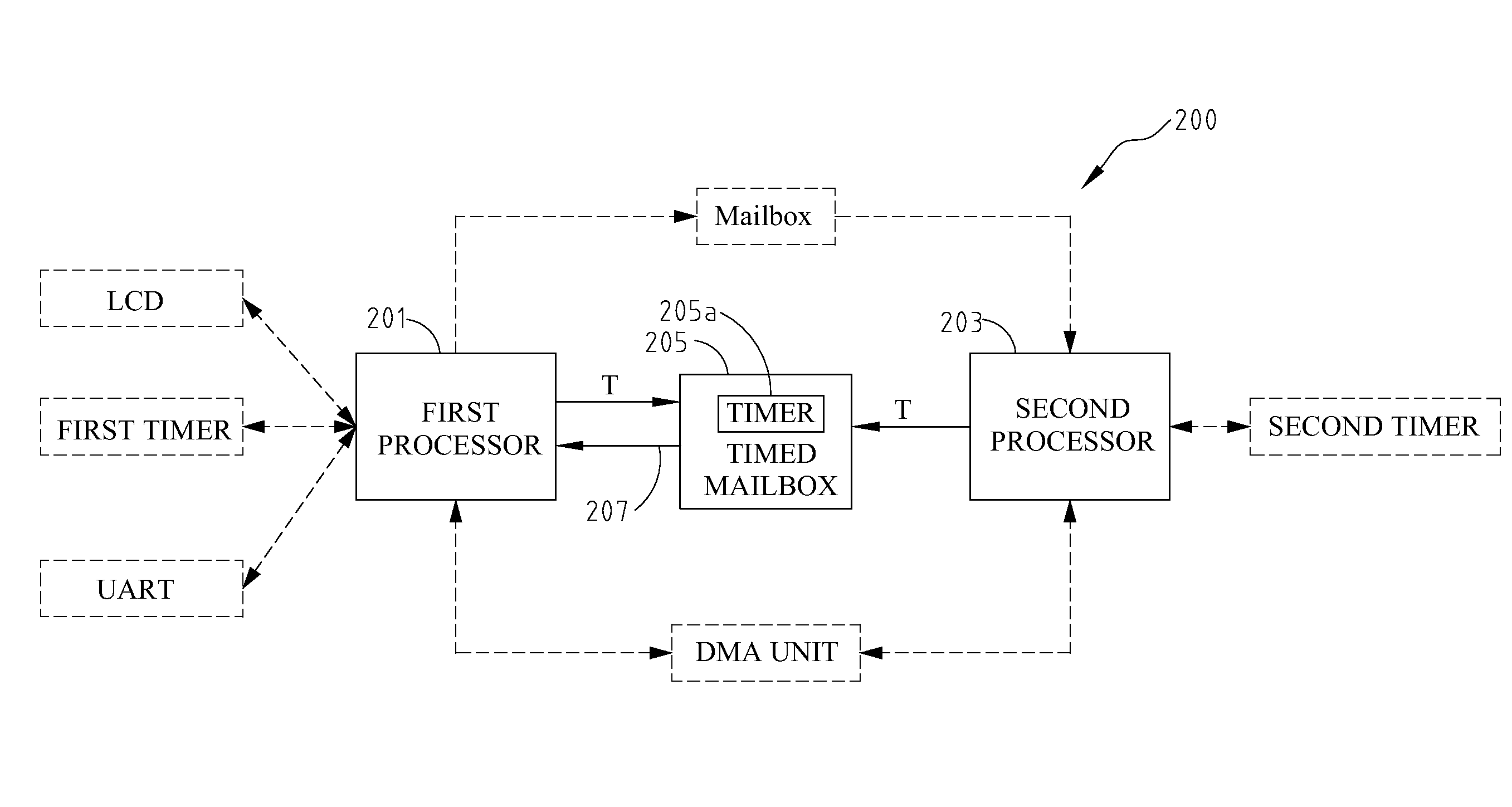
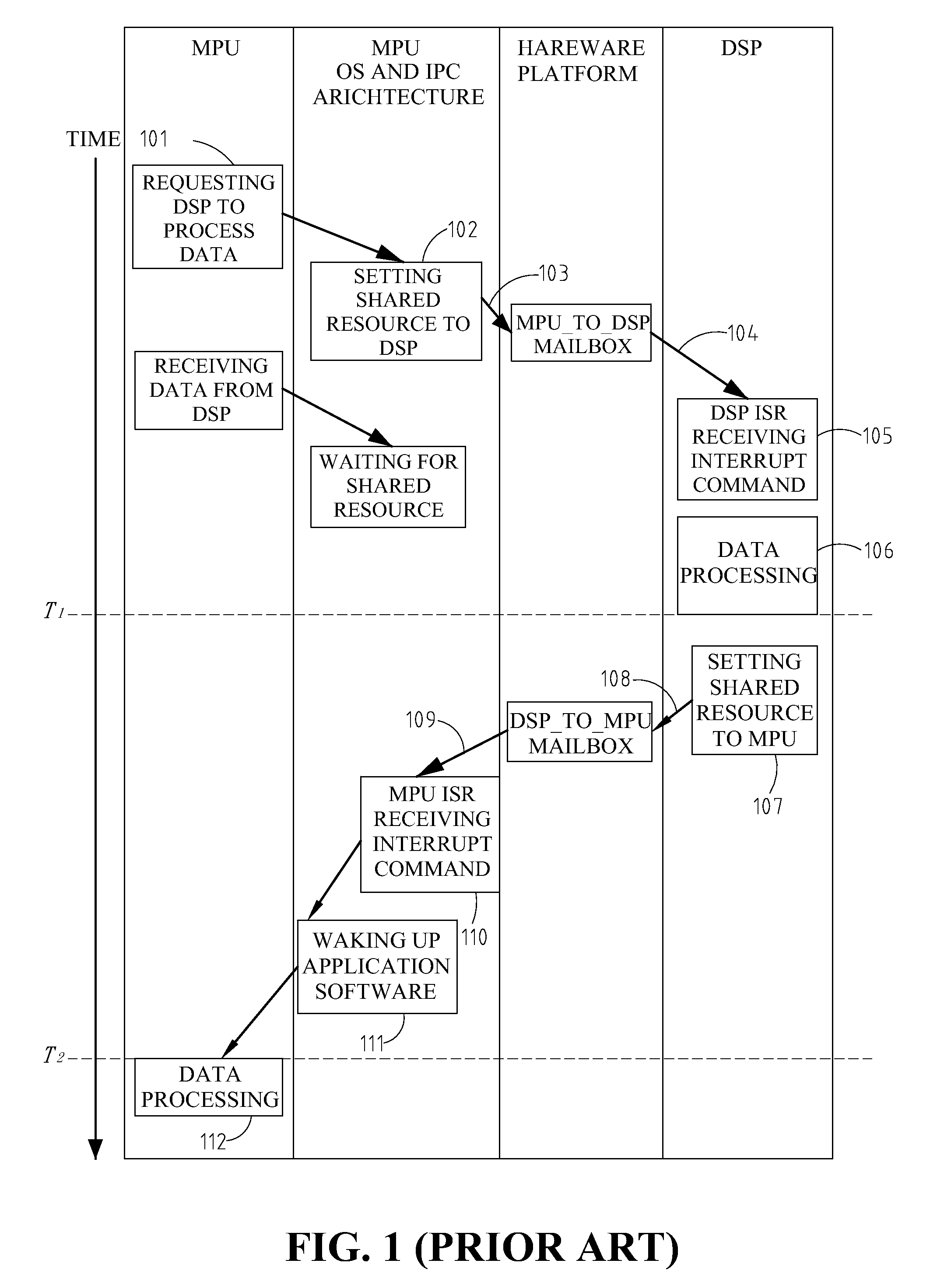
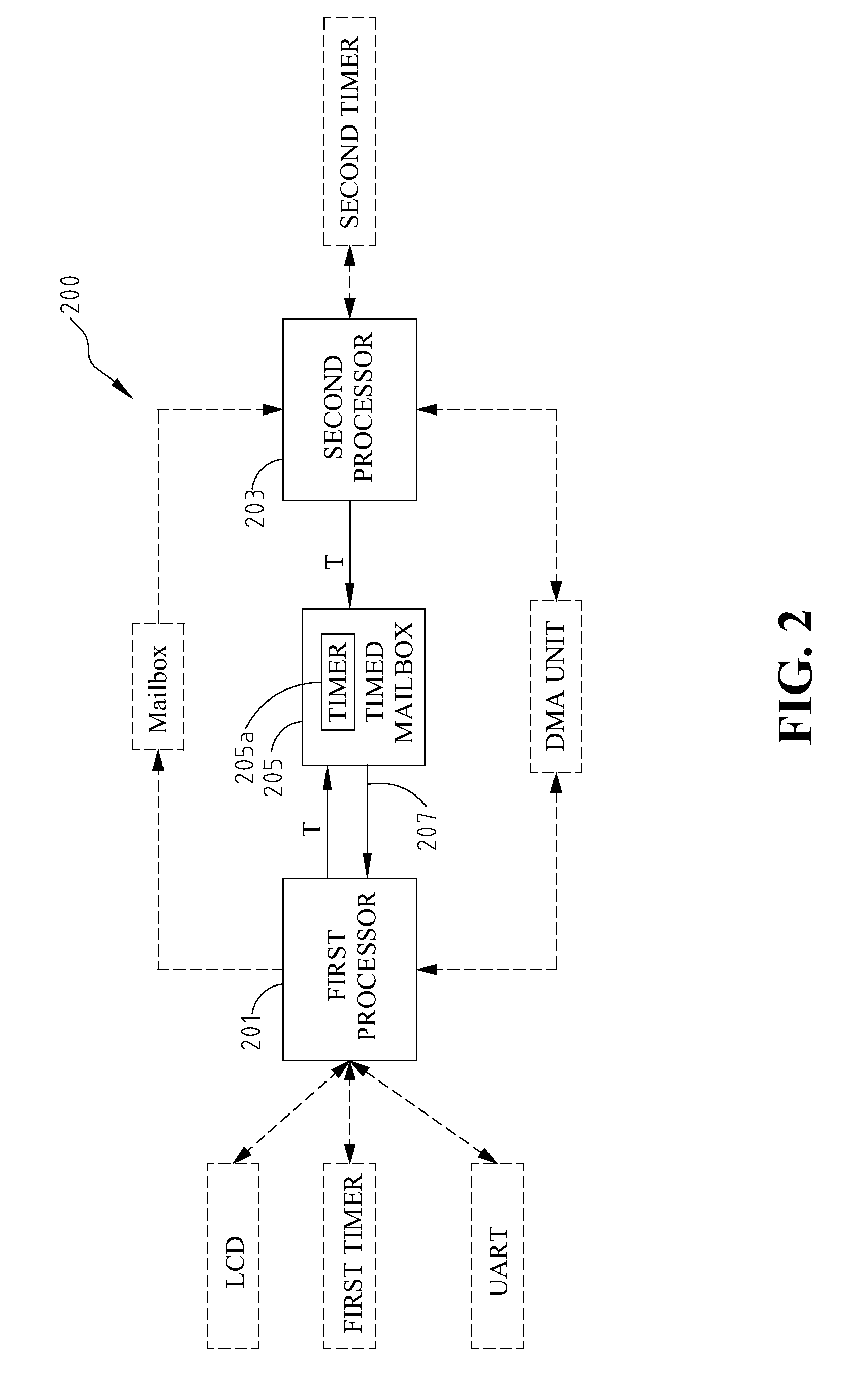
System having minimum latency using timed mailbox to issue signal in advance to notify processor of the availability of the shared resources
ActiveUS8099731B2Increase profitOvercomes drawbackMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsMulti processorTimer
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
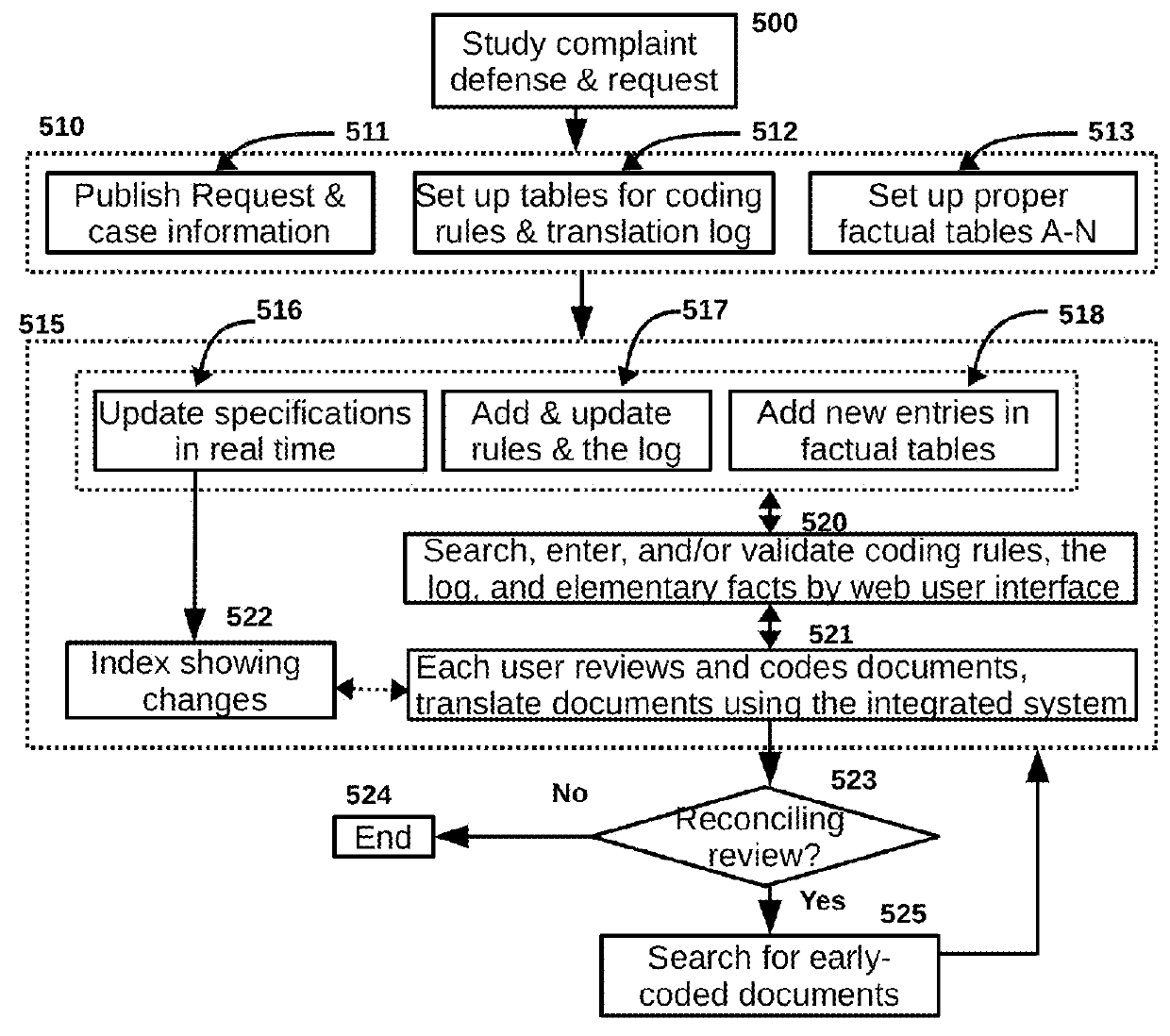
Translation protocol for large discovery projects
ActiveUS9342505B2Improving review performance and translation qualityWork well togetherNatural language translationOffice automationDocument preparationDocumentation
The present invention is a server-based translation protocol for improving translation performance for cases where a large number of documents are generated in a source language context but the controversies are adjudicated in a different language context. The protocol is intended to improve terminology consistency, offset the effects of contextual shift on perceived facts in translations, and improve task-tracking order. If the protocol is used by well trained and motivated document reviewers in a collaborative and harmonic environment, it can reduce unnecessary translations, improve translation accuracy, minimize the needs for amendments, control translation costs, and help the client significantly improve its litigation position.
Owner:WU JIANQING +1
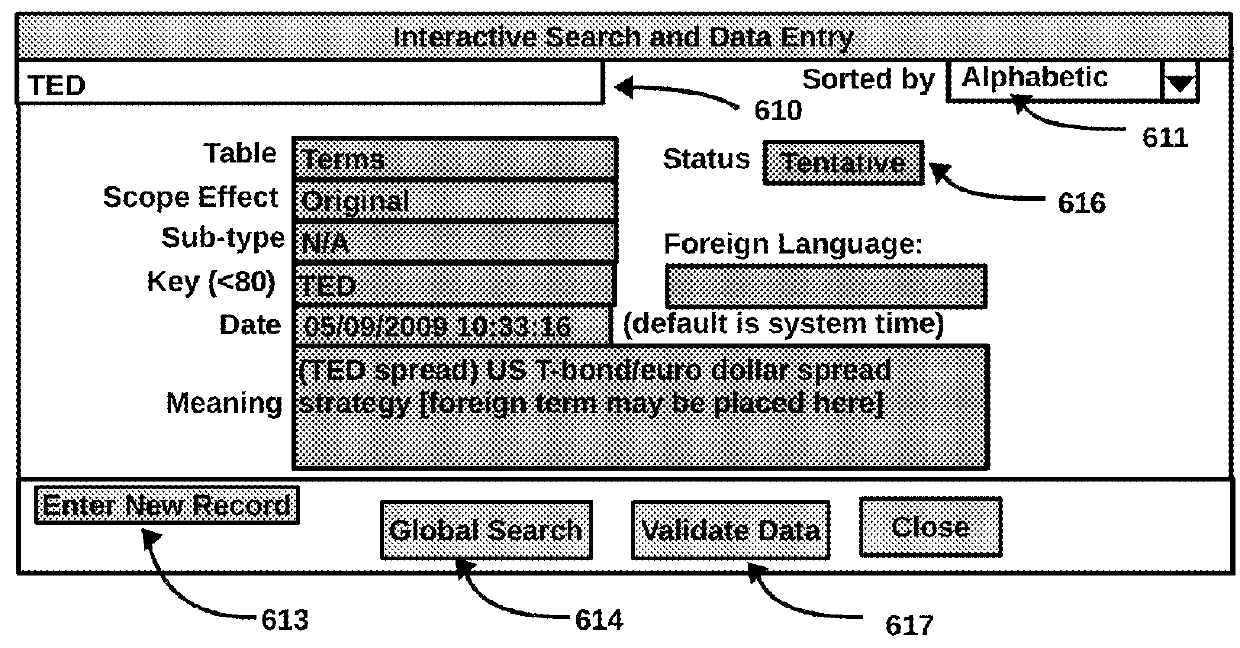
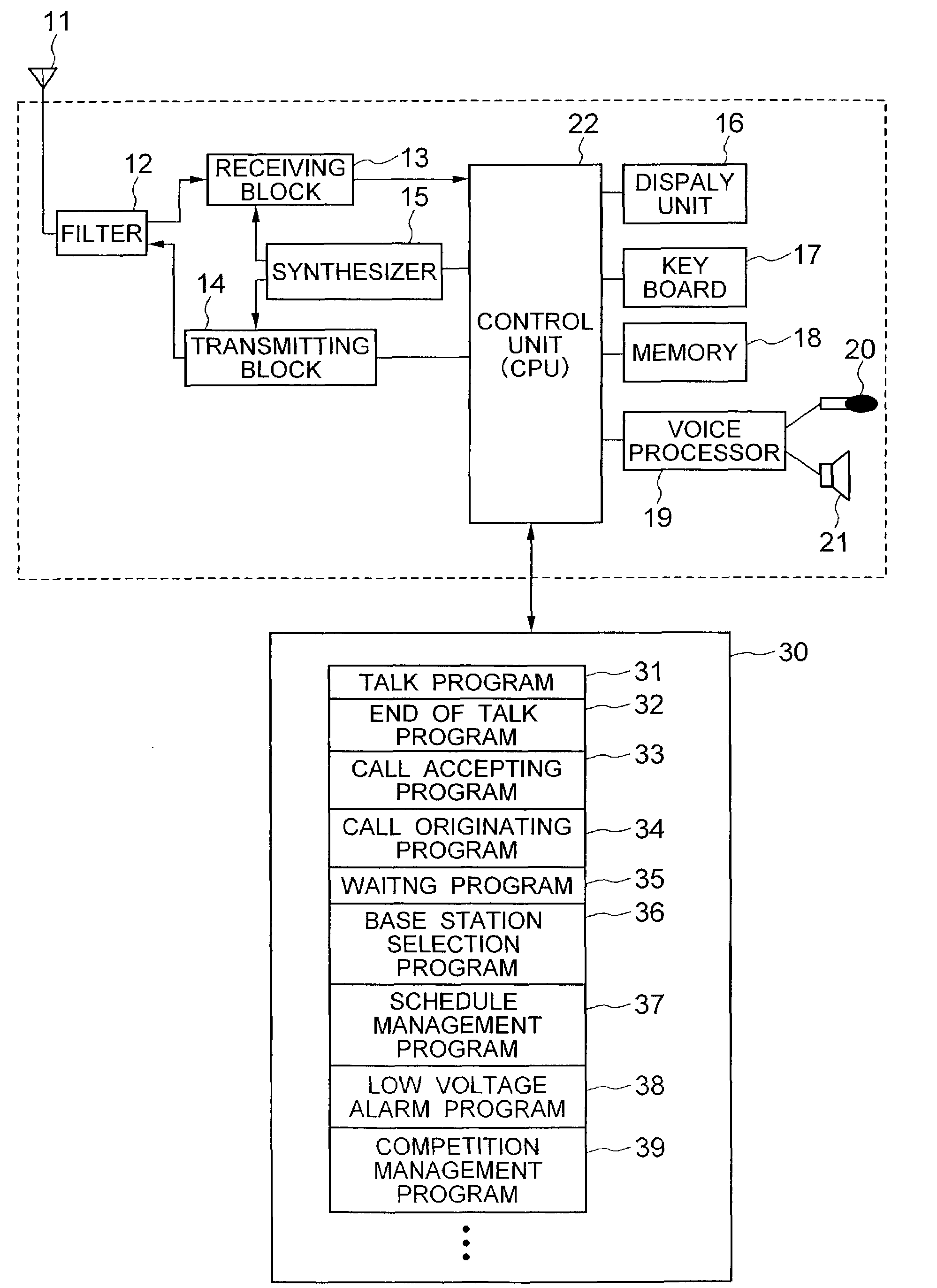
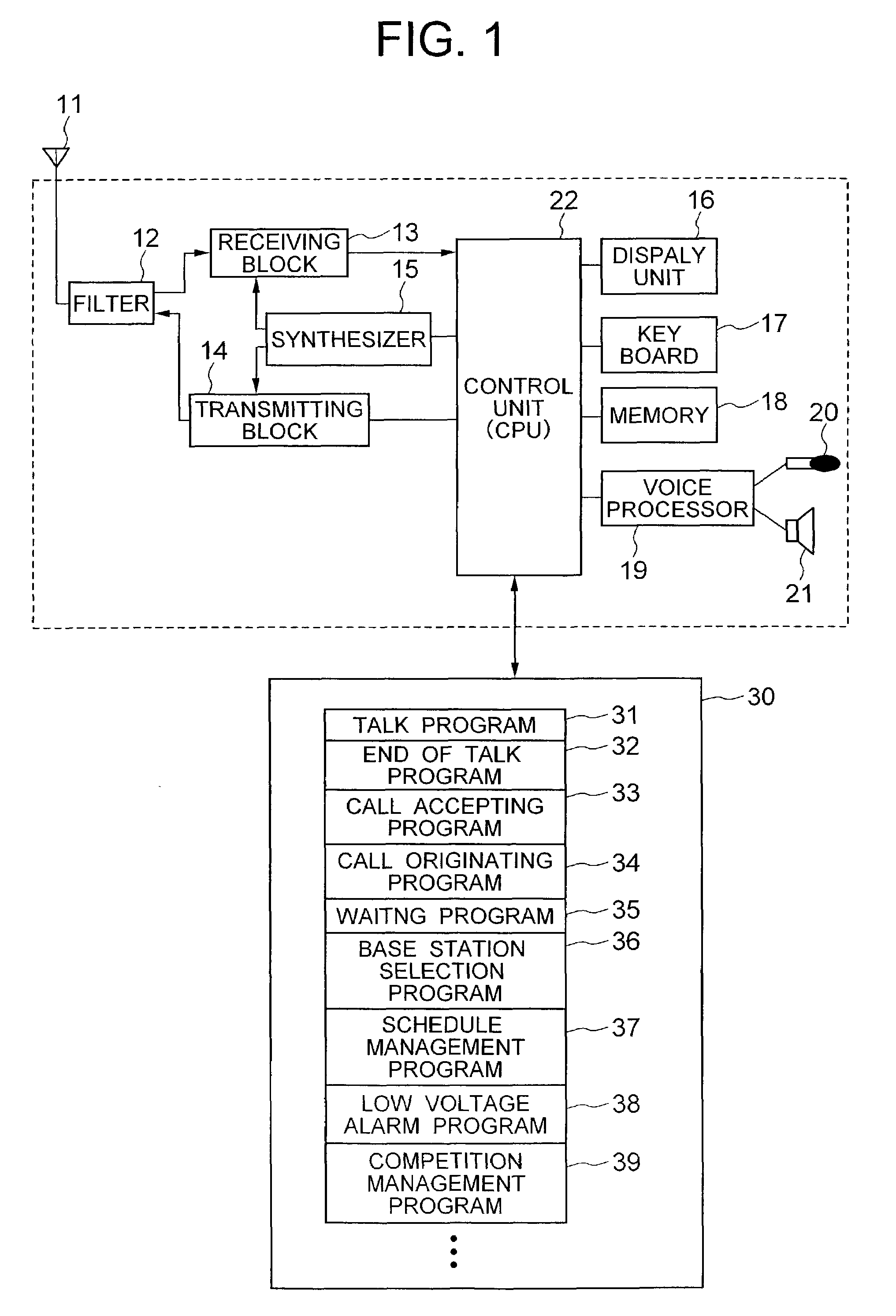
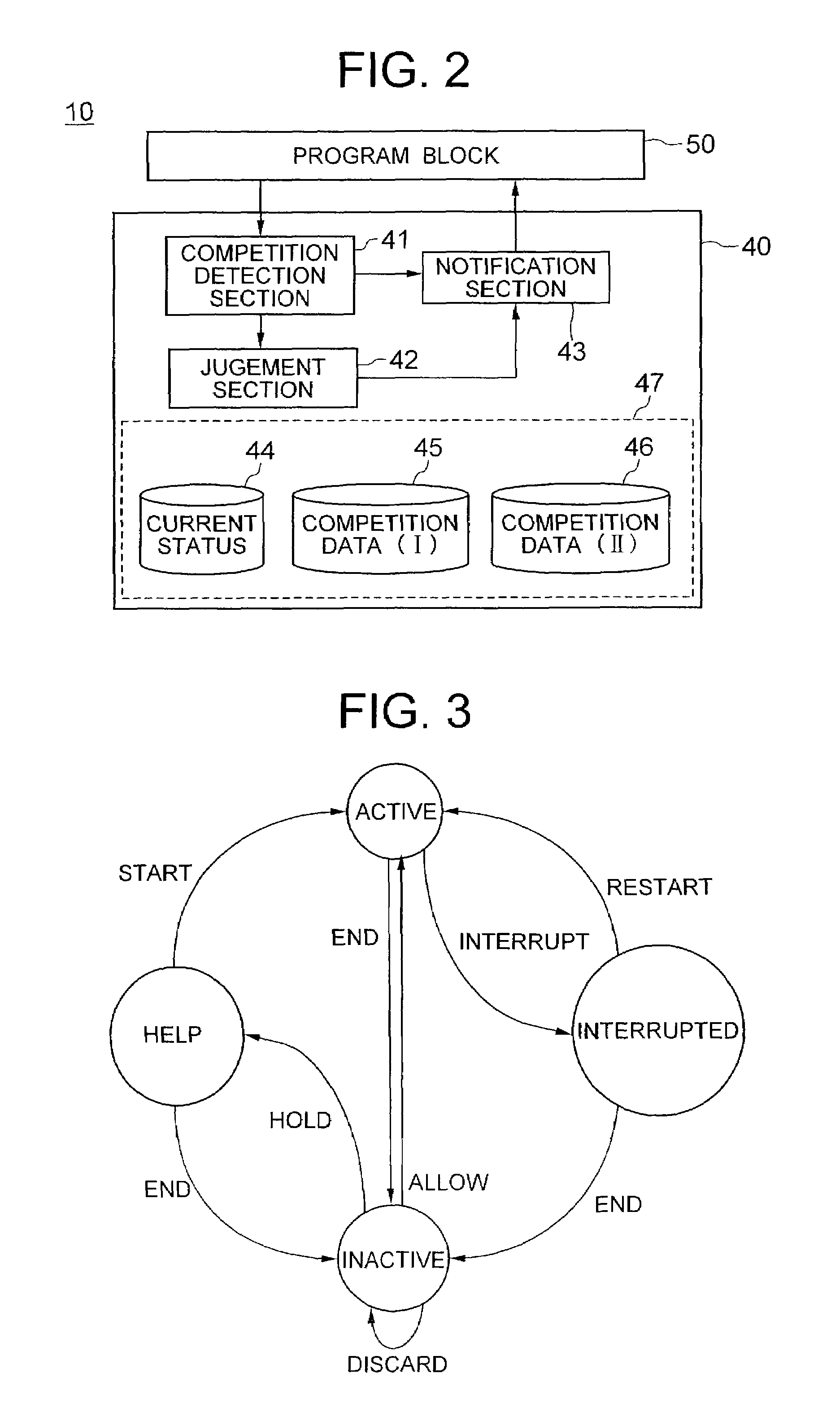
Portable data-processing terminal including a program competition manager
InactiveUS7302688B2Hinder taskLow costNetwork traffic/resource managementProgram synchronisationComputer terminalApplication software
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
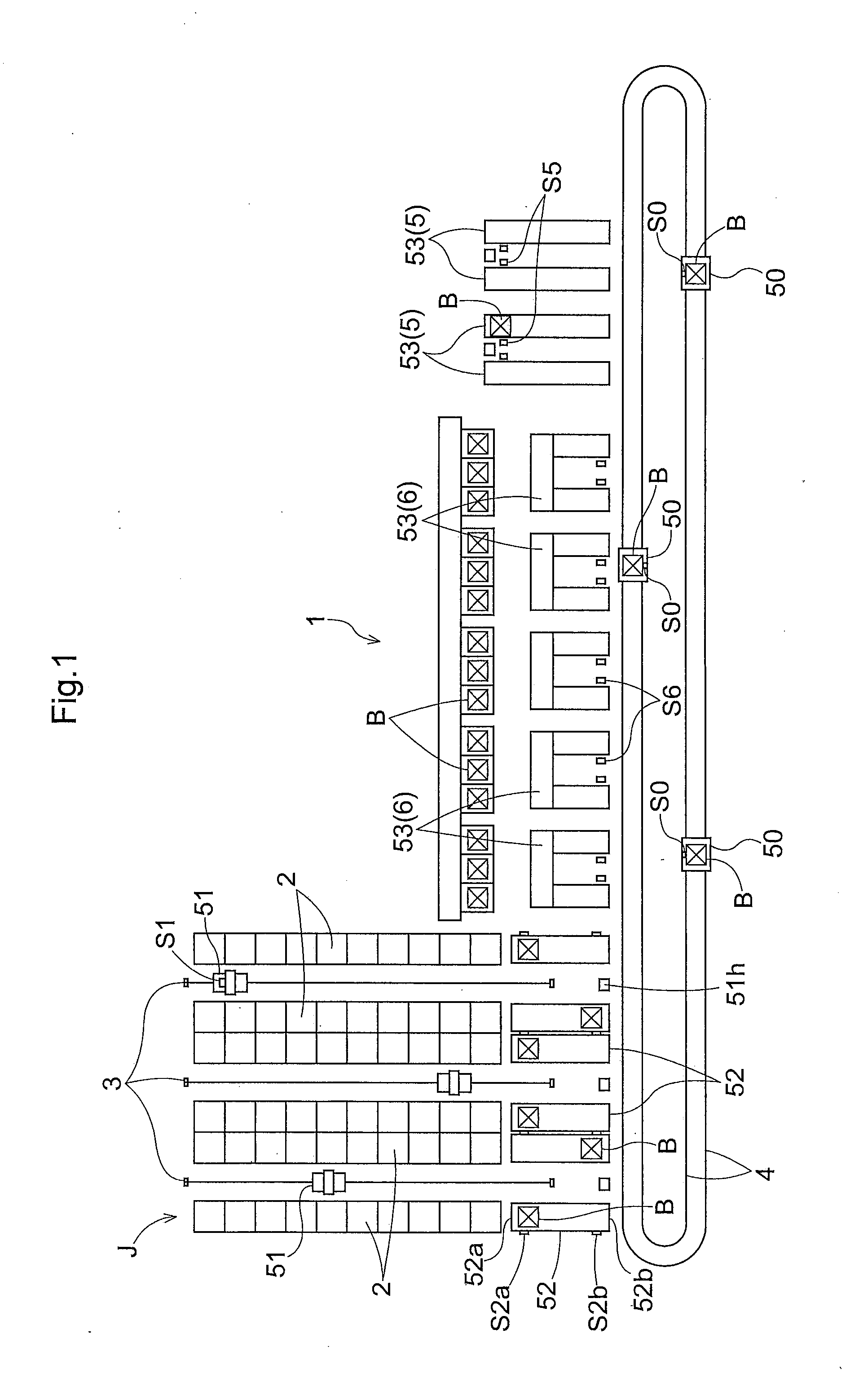
Device for unloading trays using a pivot member
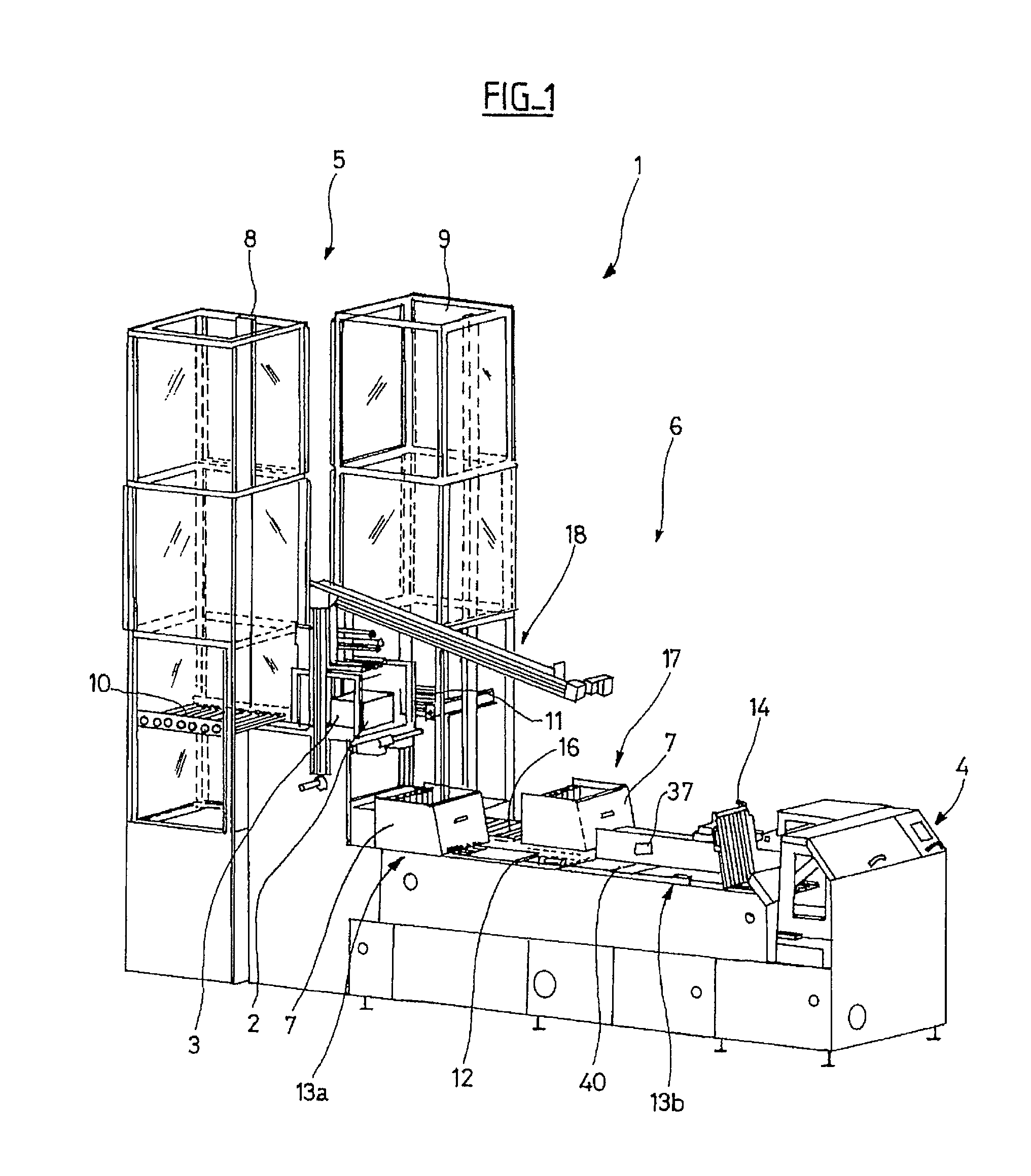
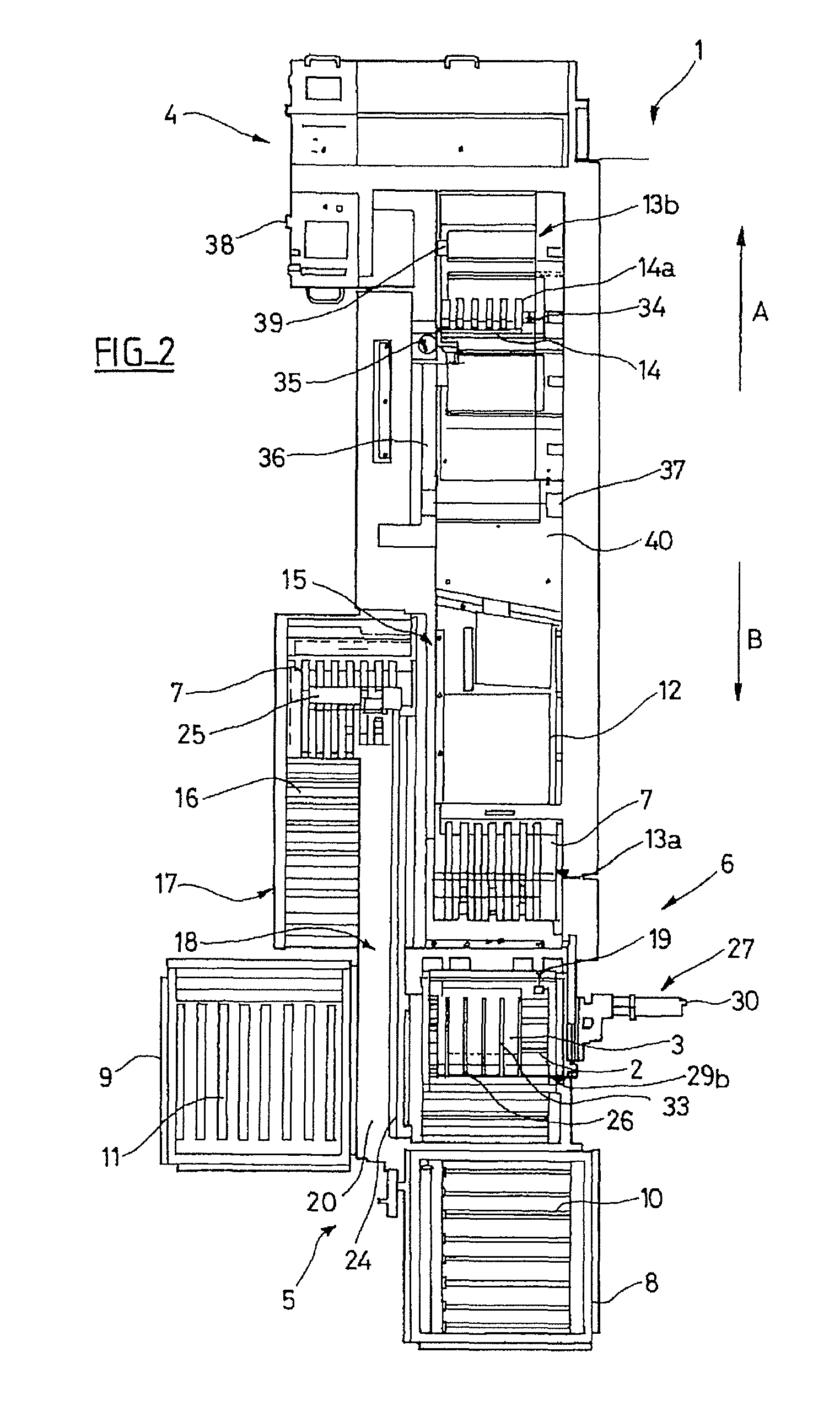
InactiveUS20100316473A1Reduce workloadAvoid manual unloading taskArticle unpackingSortingVertical alignmentEngineering
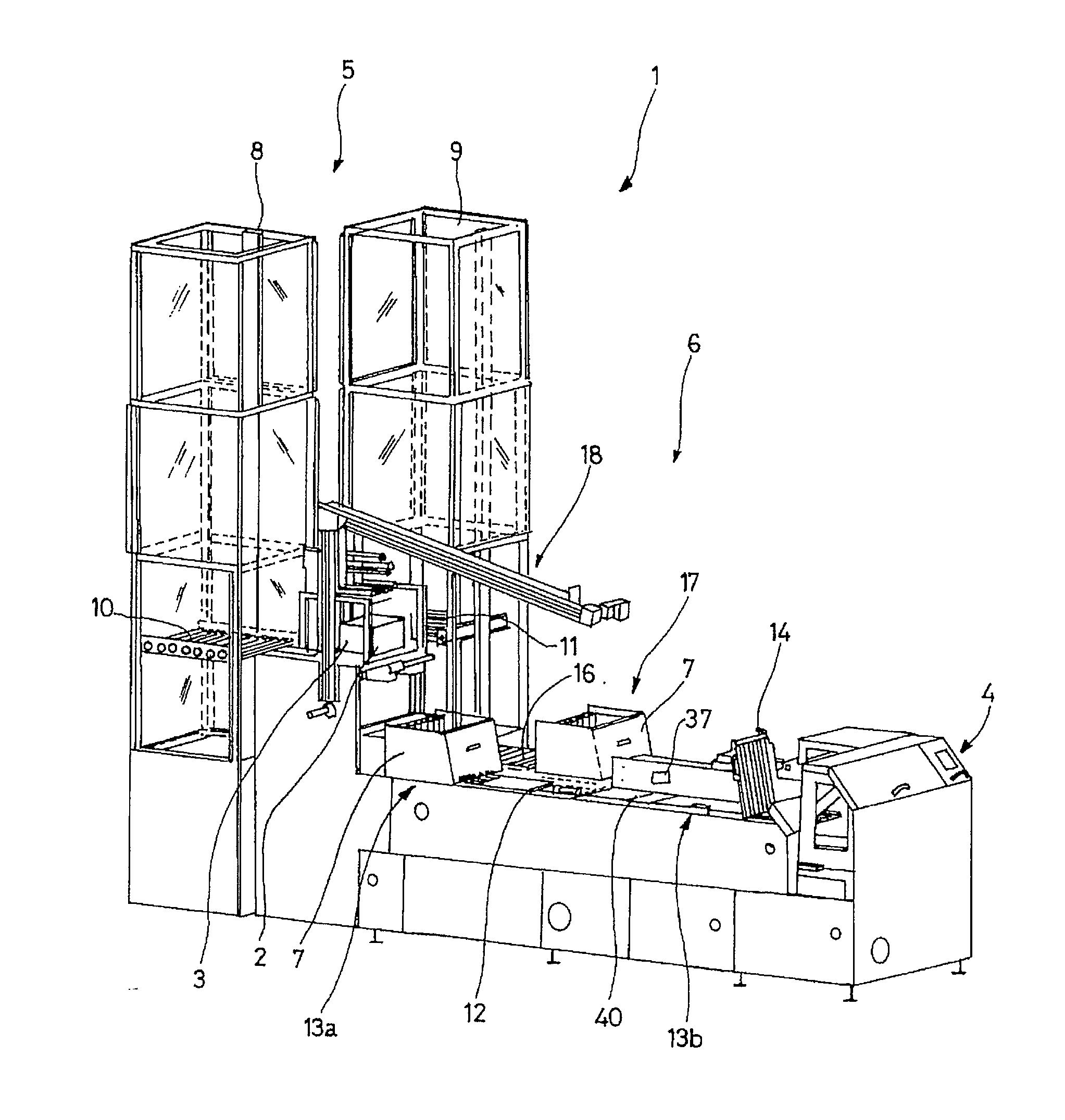
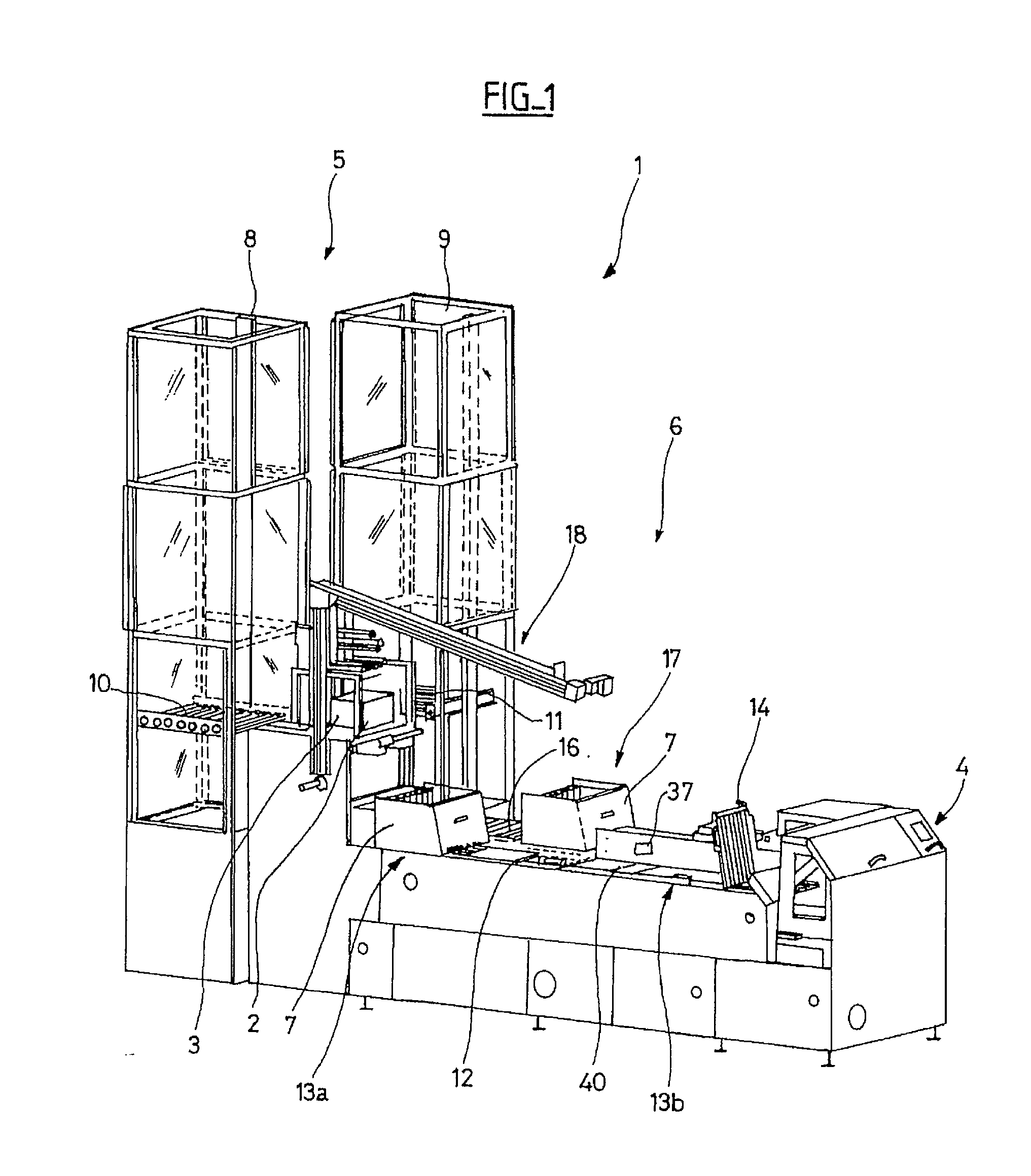
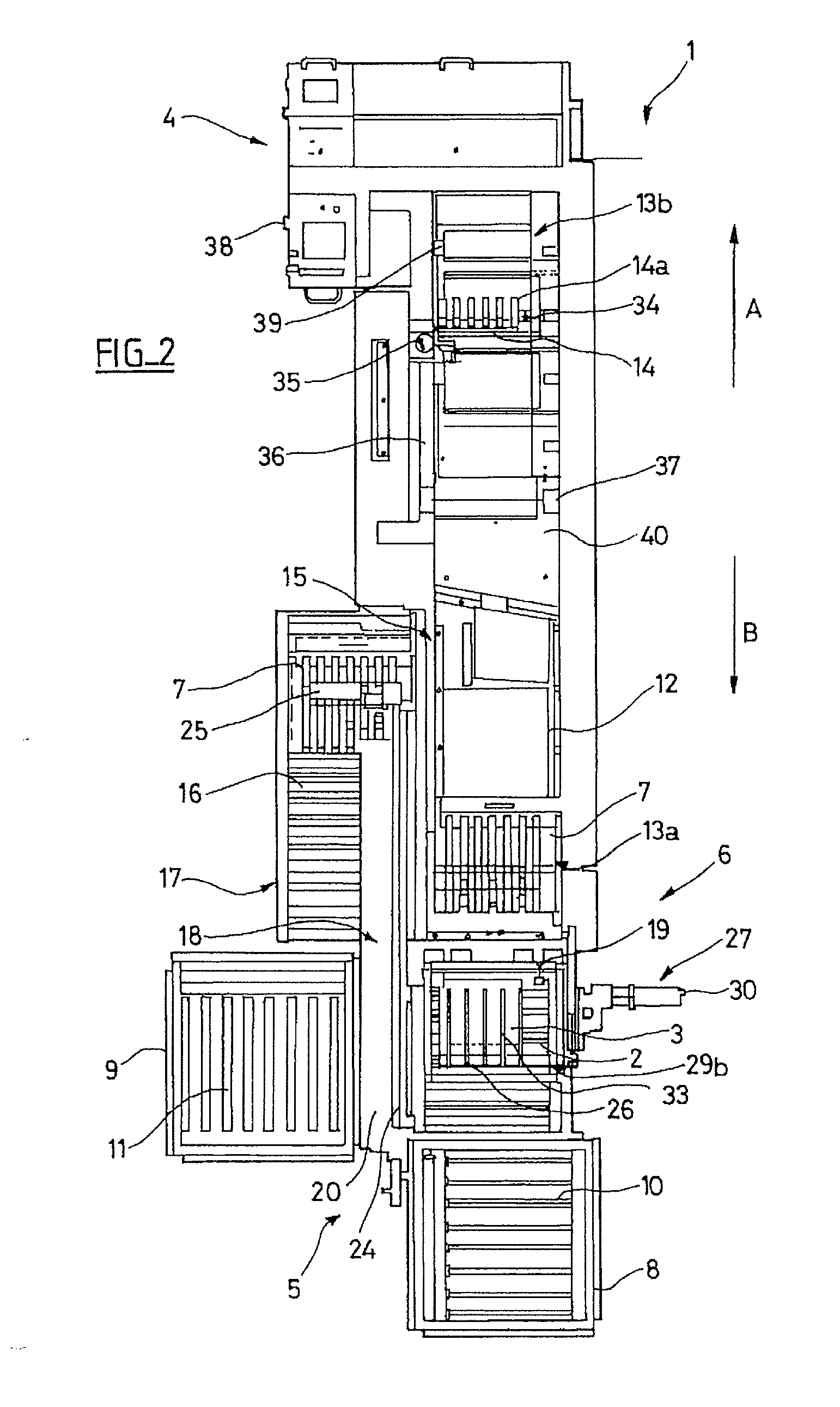
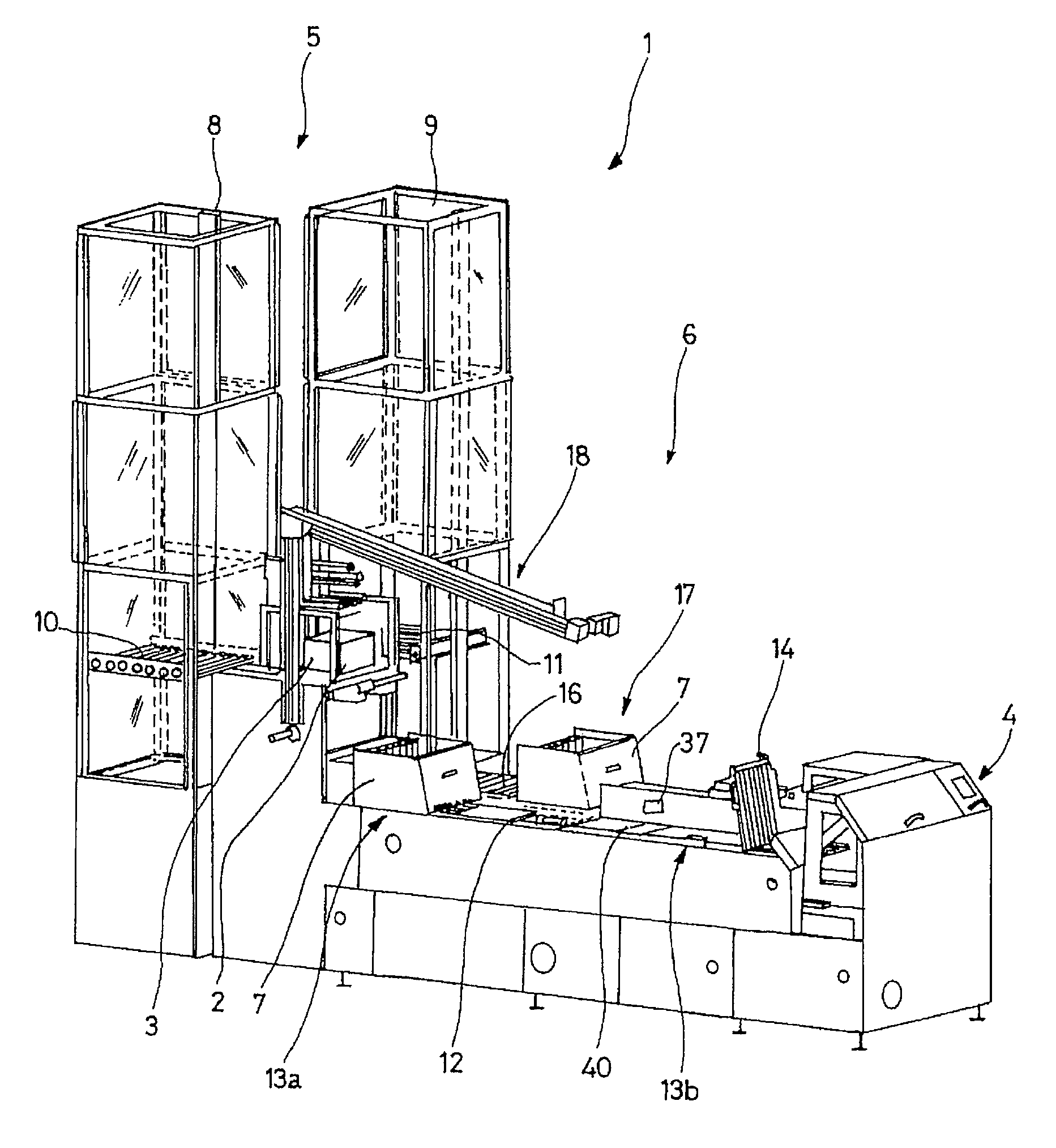
The device (6) for unloading an open-top receptacle (2) filled with flat objects (3) arranged in a stack in the bottom of the receptacle comprises a pivoting member (18) capable of taking hold of the receptacle (2) and of downwardly inclining its opening (2a). The device (6) additionally comprises a pusher (26) for holding the flat objects (3) in place in the bottom of the receptacle (2) when the receptacle (2) is inclined, a shuttle compartment (7) moved by a conveyor (12) between the pivoting member (18) and a compartment unloading zone (13b) remote from the pivoting member (18), the compartment (7) having a bottom (7b) with rear (7d) and front (7c) walls which are removable with respect to the bottom (7b), a compartment inclination device (31) for inclining the compartment (7) into an inclined position in vertical alignment with the receptacle (2), and a moving pallet (14) which can be moved vertically and horizontally and which is designed so as to retract the front wall (7c) of the compartment (7) and to insert itself between the rear wall (7d) of the compartment (7) and the stack of flat objects (3).
Owner:SOLYSTIC
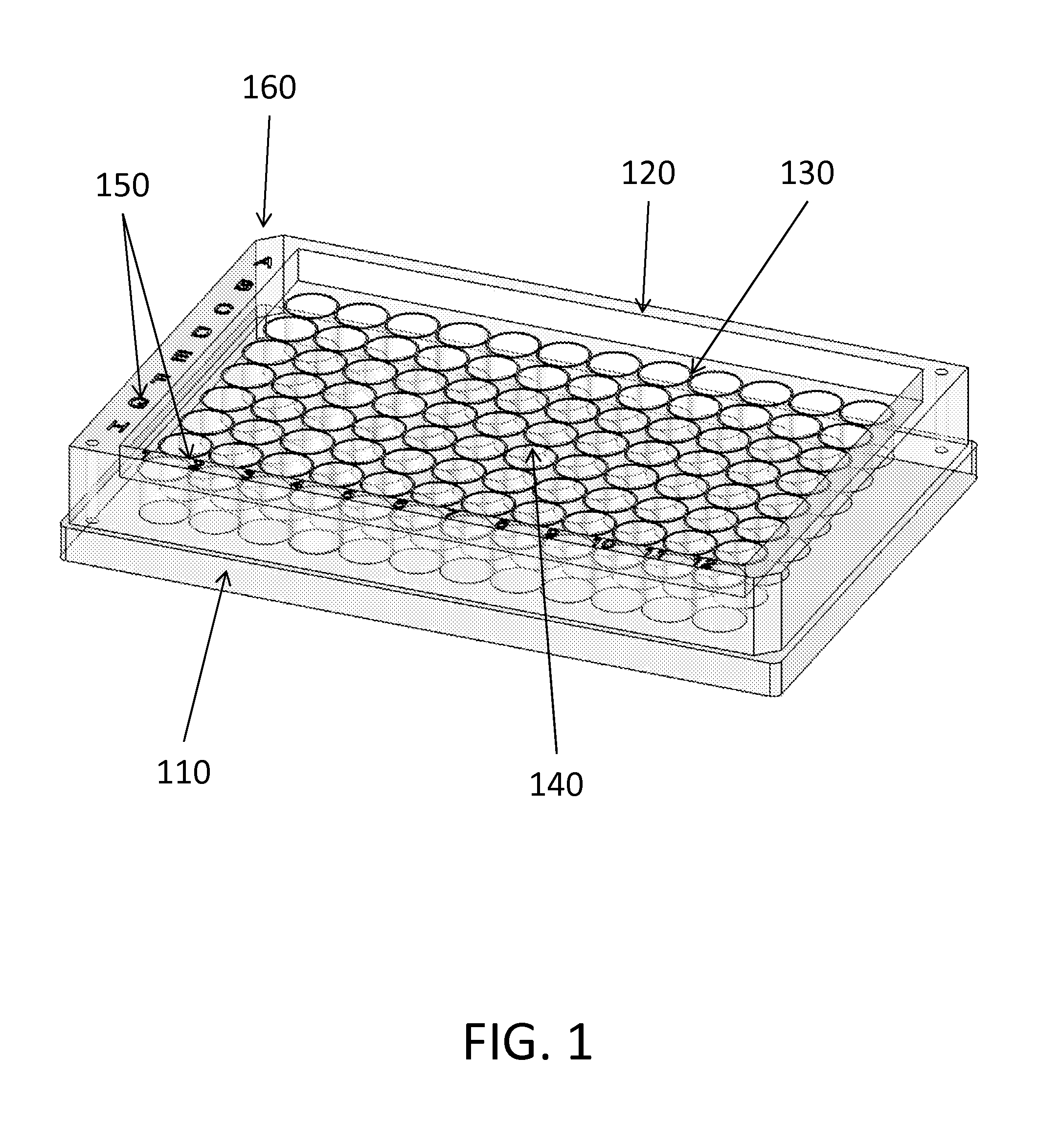
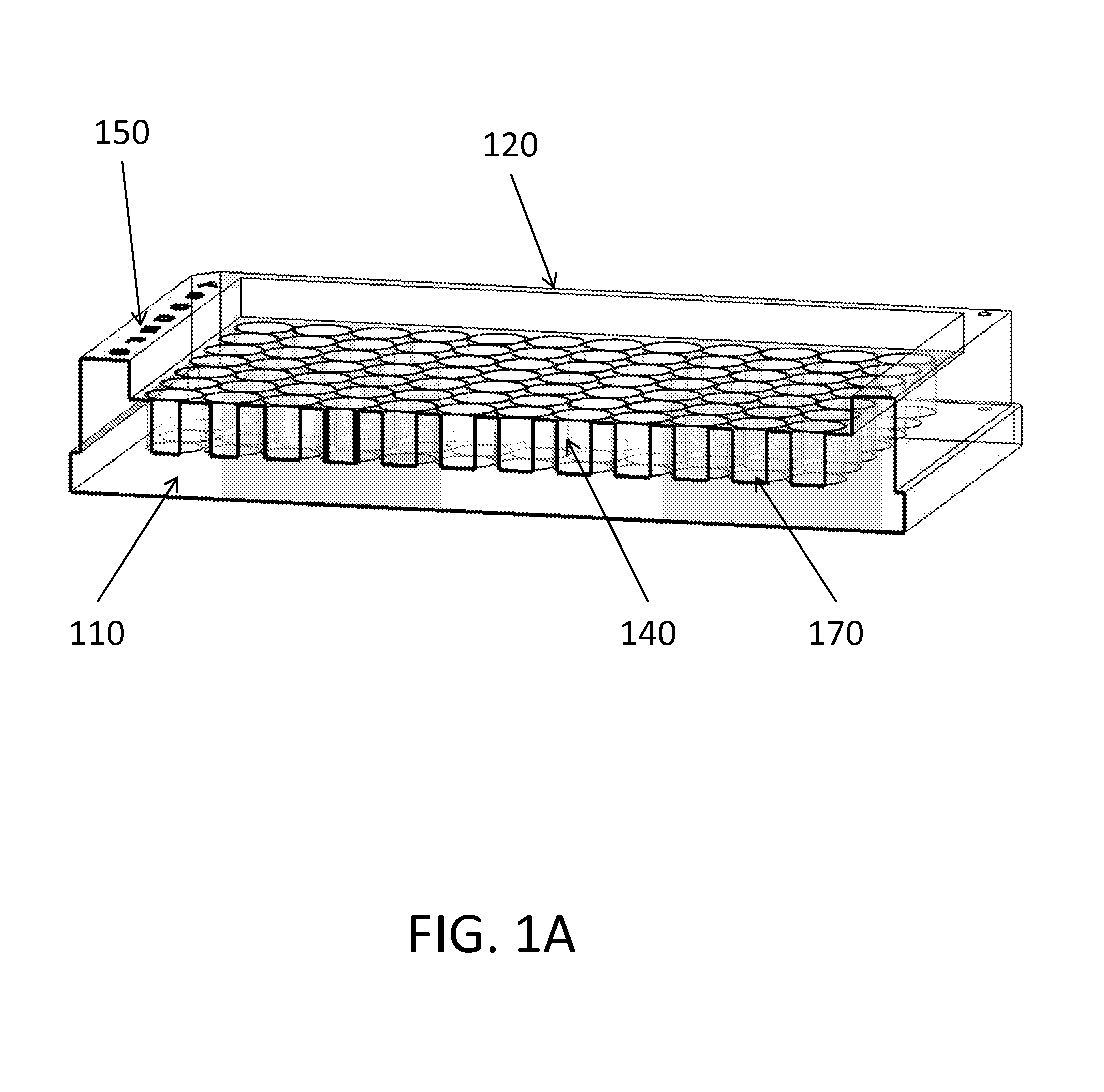
Multi-compartment device for cell cloning and method of performing the same
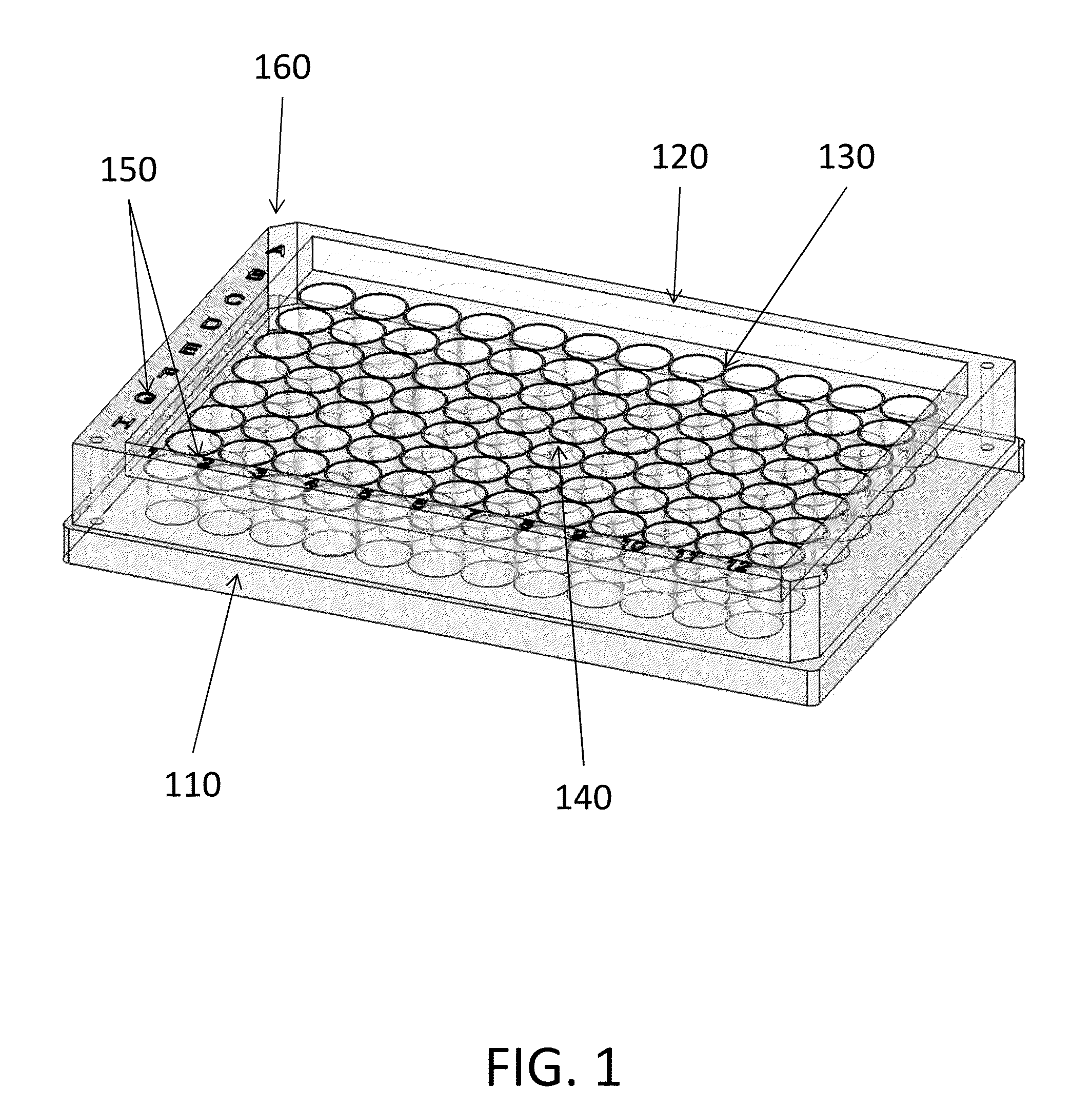
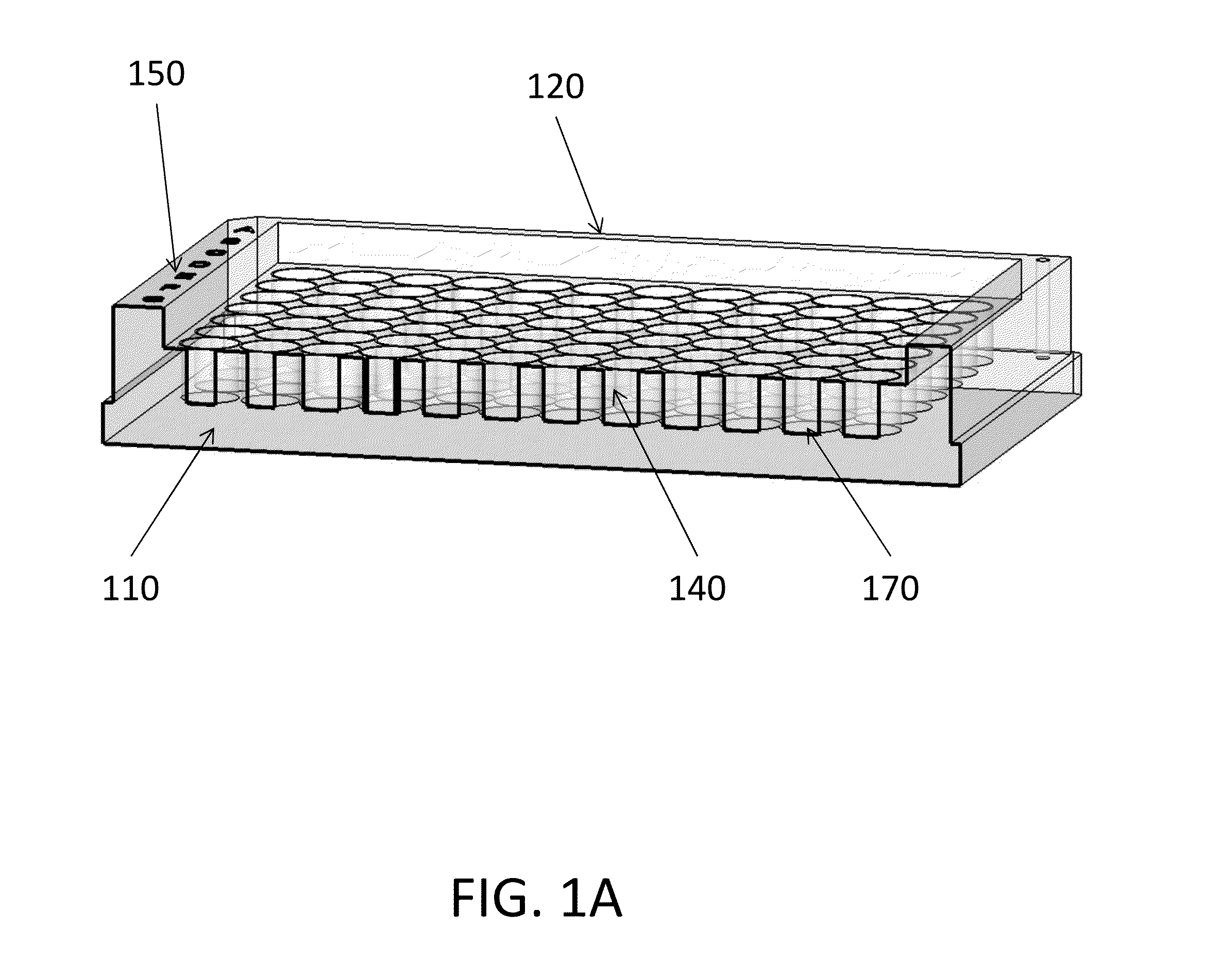
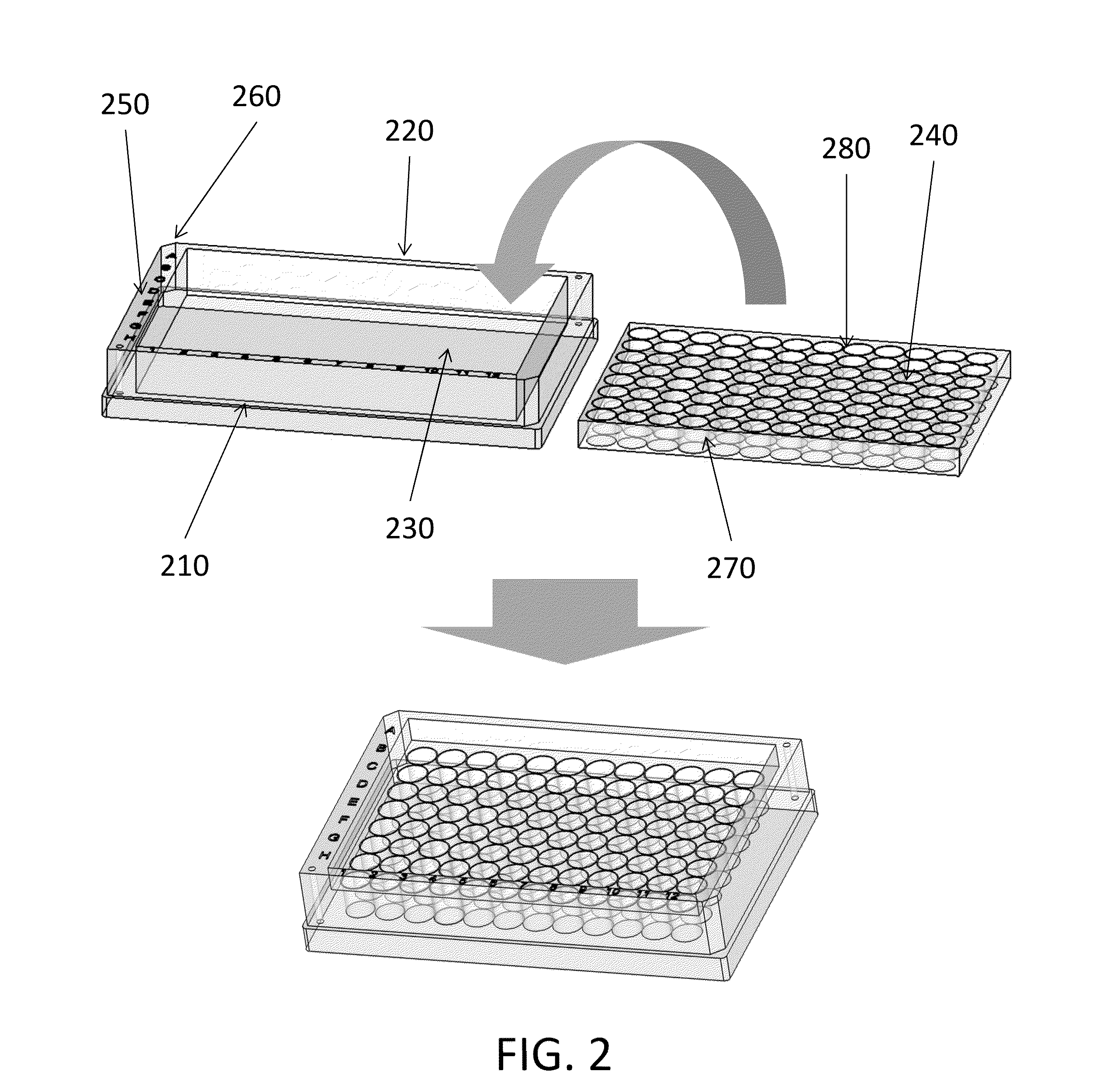
InactiveUS20140045253A1Avoid cross contaminationNegligible riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrowell PlateEngineering
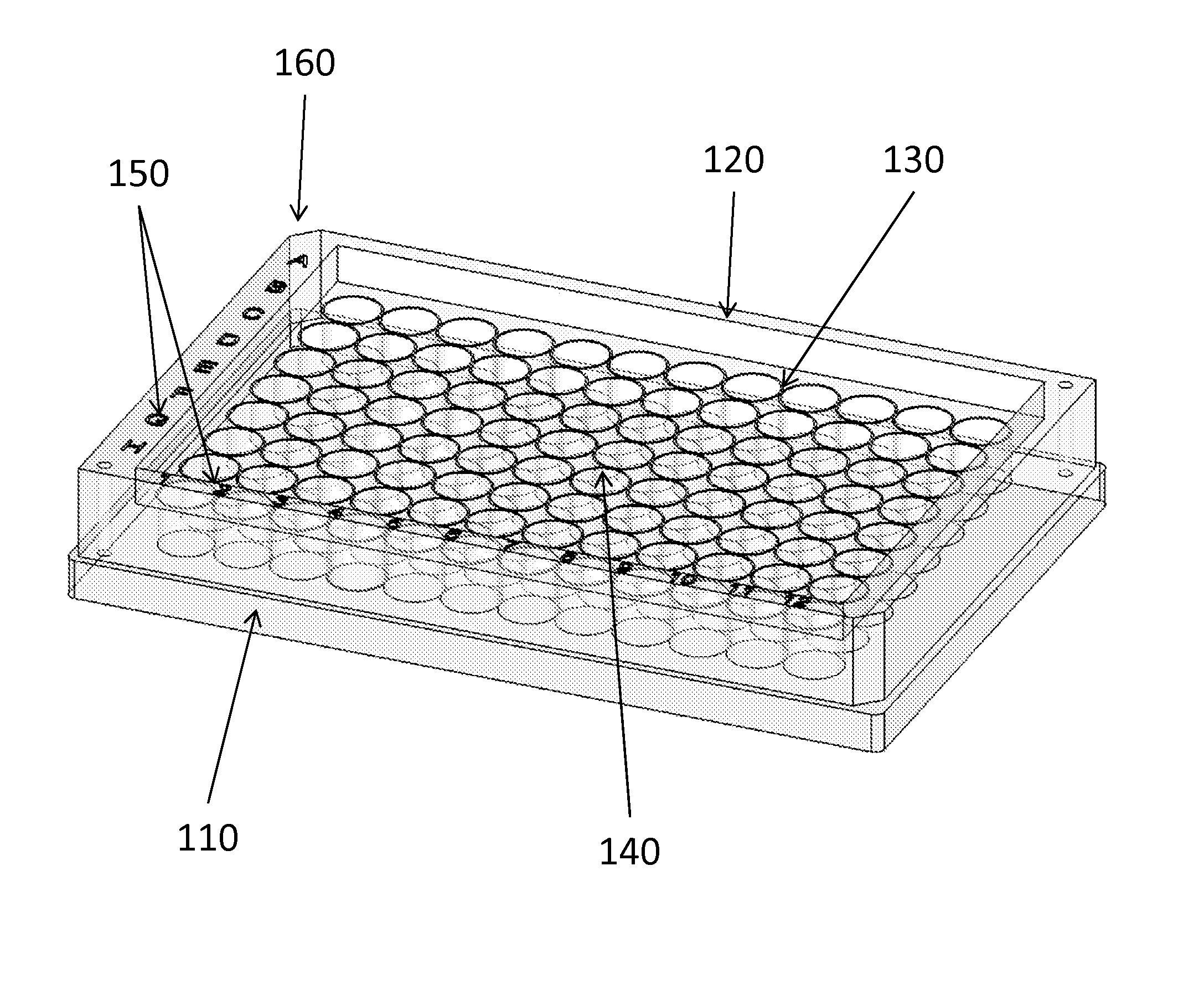
The problems associated with the traditional methods and devices in the field of cell cloning have been solved by the multi-compartment device and method in the present invention. The device combines the advantages of a traditional petri-dish and a traditional microplate. The multi-compartment device in the present invention comprises sidewalls, which are taller than openings of the multi-compartments. The cells in the suspension flow across the multi-compartments and seed inside the compartments during a plating process. The multi-compartment device in the present invention allows easier plating process, changing conditioned medium, and cell colony detachment and transfer. The multi-compartment device also minimizes the risk of cross-contamination during cloning process and during cell colony transfer. The invention also provides an exemplary method of using the multi-compartment device for cell cloning. In one aspect of the method, the multi-compartment device may be tilted before or after adding the cell suspension during plating process.
Owner:ZOU QIAN
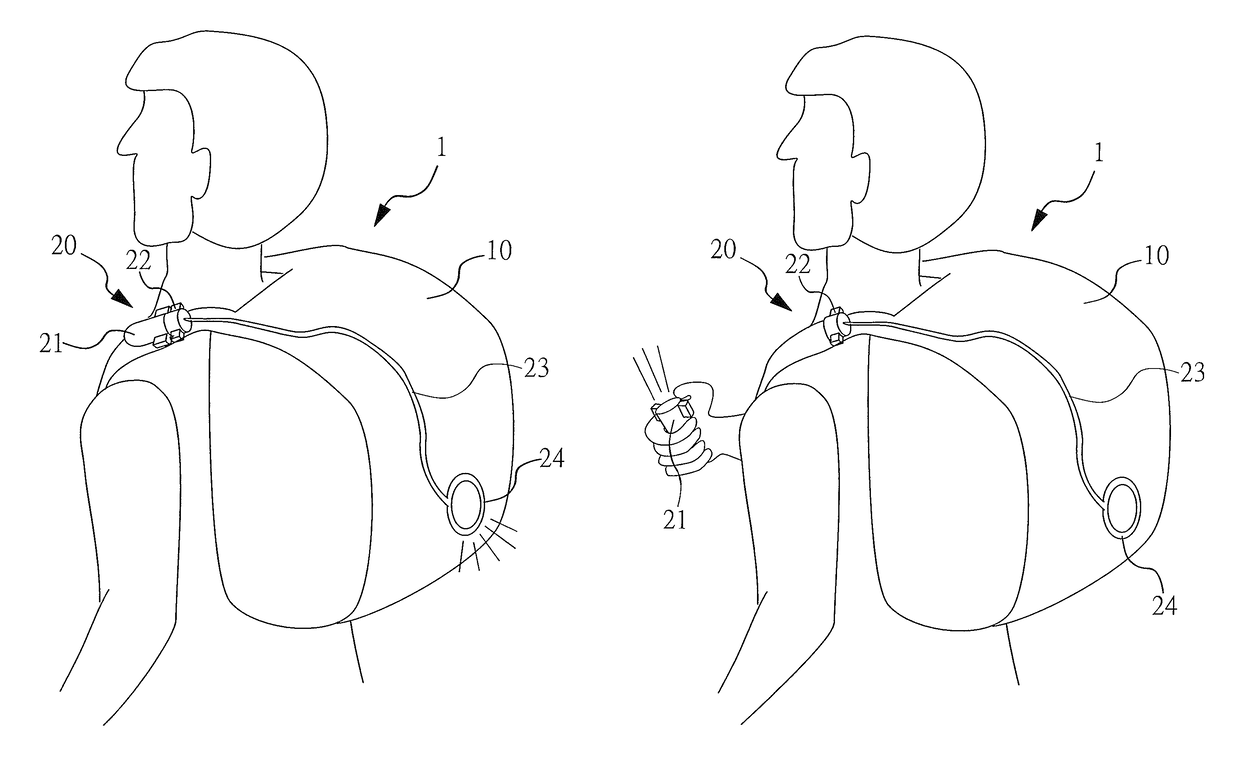
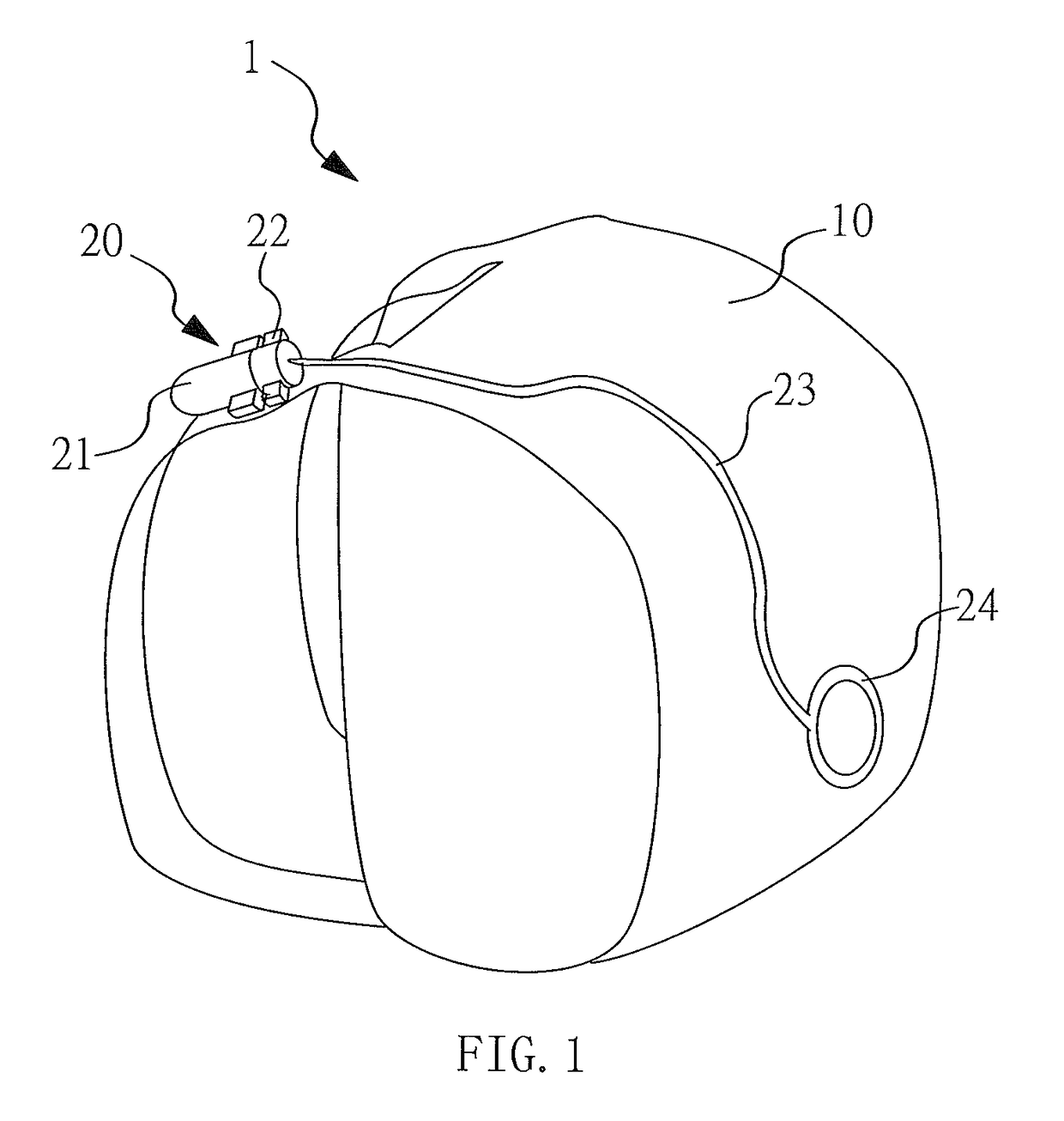
Detachable lighting source device having a light guiding wire set equipped with a detachable lighting source
InactiveUS9684107B2Power supply flexibilityReduce weightTravelling sacksMechanical apparatusLight guideElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:WANG PO FENG
Piece of fabric for hand-sewn works and method for making said works with said fabrics
ActiveUS20180177256A1Method of creating the project is notably reducedPrecise and accurate mannerHand sewingLayered productsEngineeringHand sewn
A piece of fabric for manual sewing projects and method of creating said projects with said fabric, consisting of a piece (1) of cloth that incorporates, with identical or different colors, prints and / or textures, the figures (2) for creating a certain patchwork design (3), each figure (2) being marked with a seam line (4) that defines the outline thereof and a cutting line (5) that defines a perimeter border that is optionally pre-perforated. The method only comprises obtaining said piece (1), cutting the figures (2) along the cutting line (5) and sewing them together. Optionally, the patchwork design (3) is selected and the piece (1) is ordered with the desired figures (2) and colors, prints and / or textures.
Owner:DAMA INT 1991 SA
Bulk CAS bit change detection
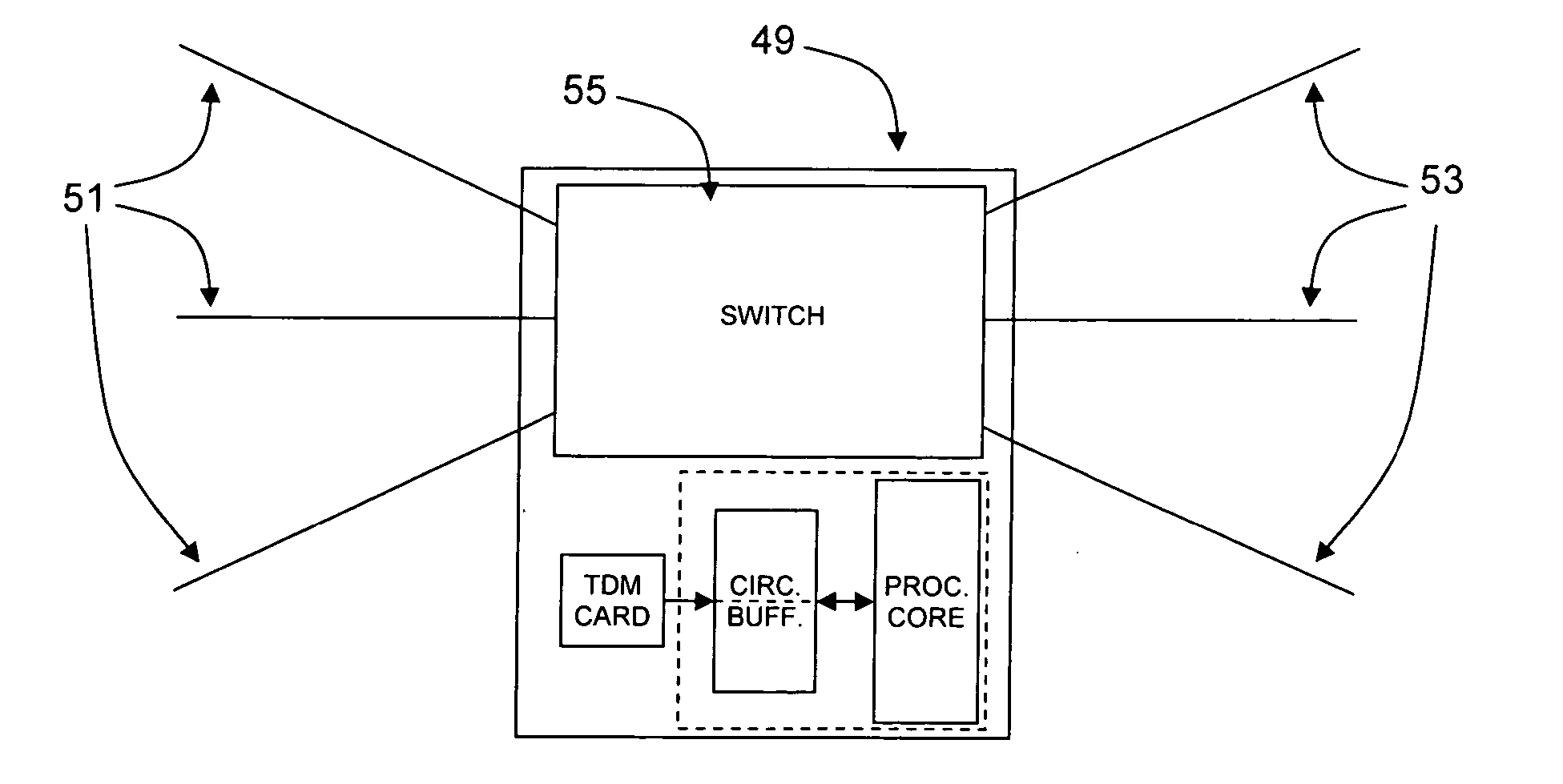
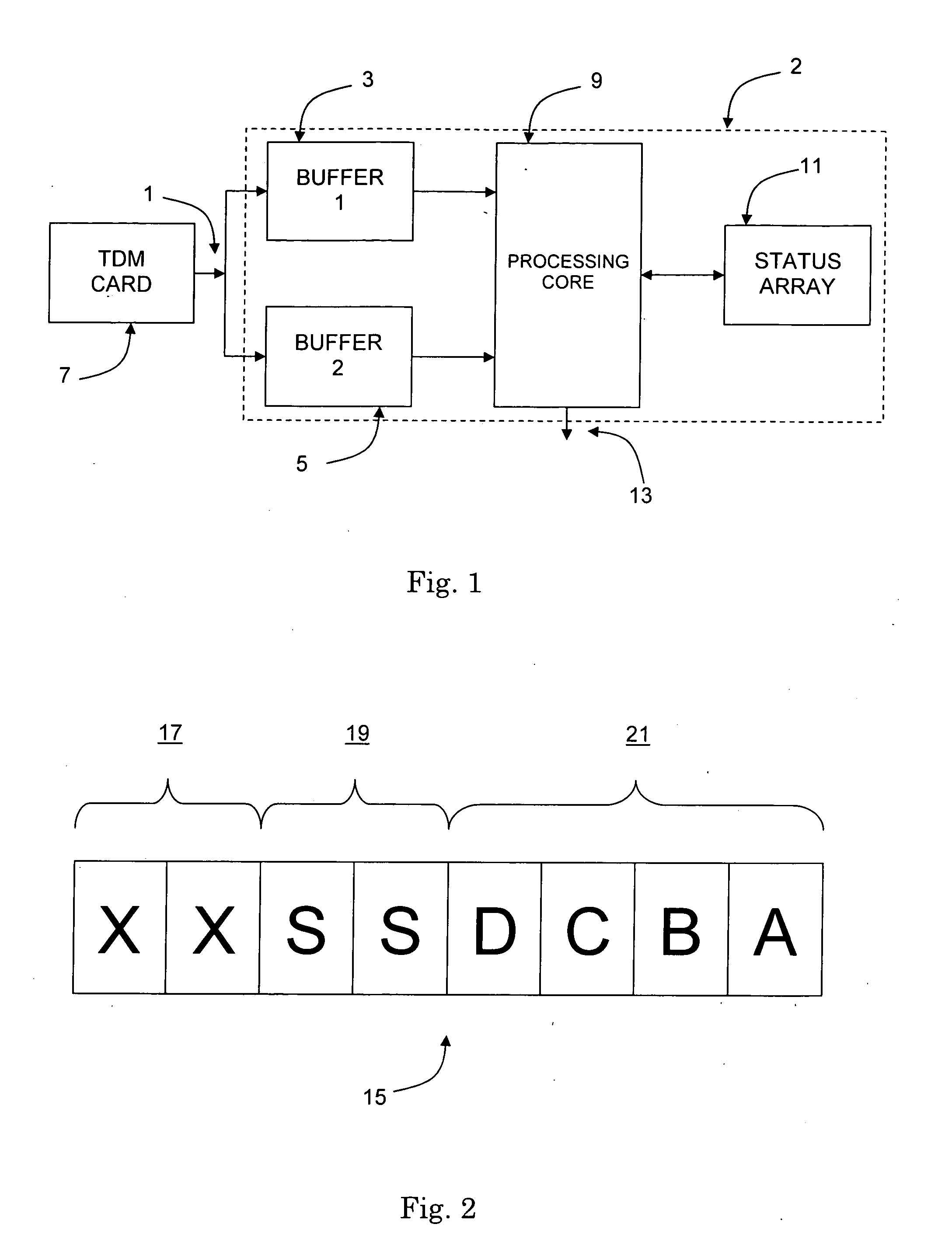
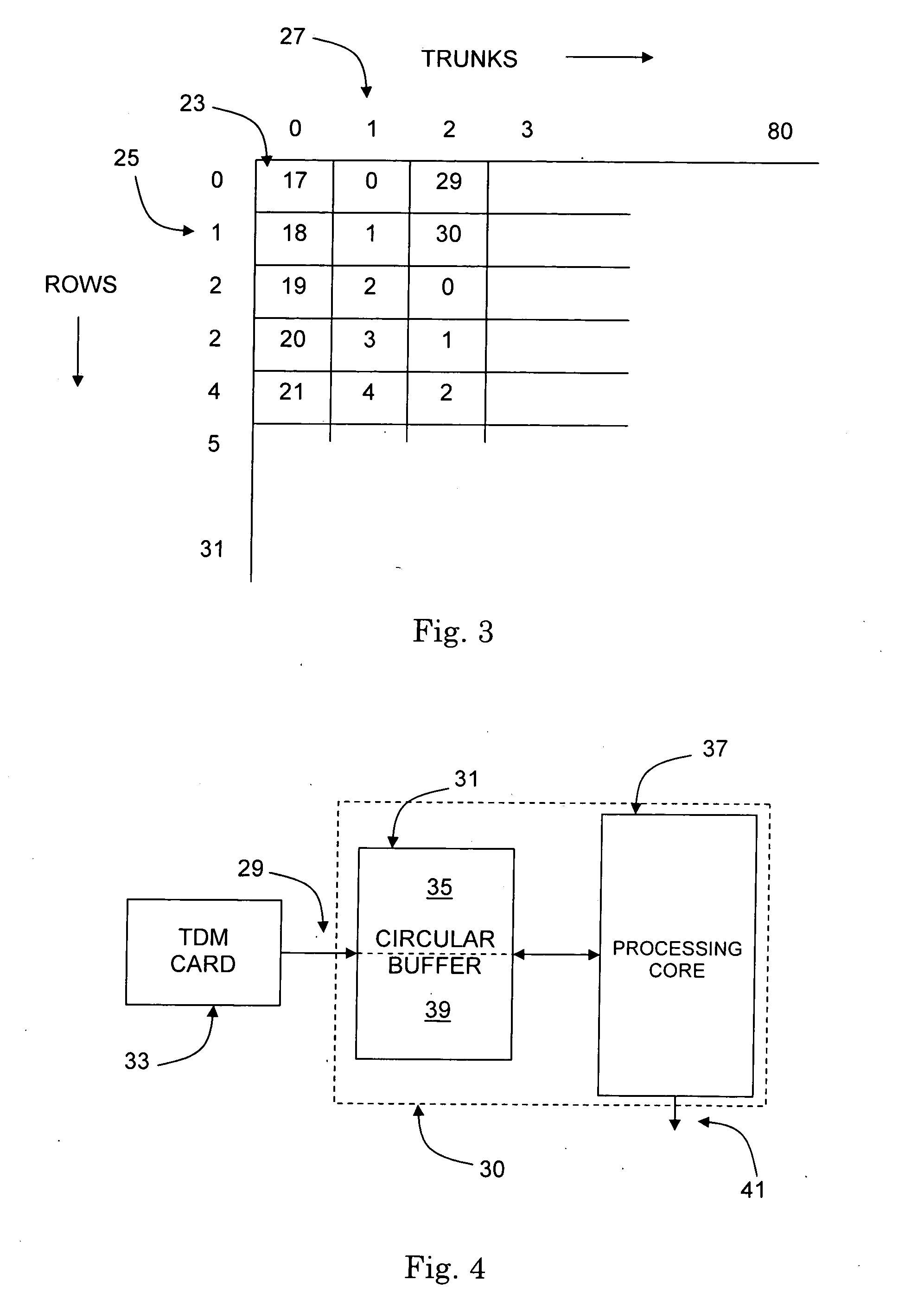
InactiveUS20050105562A1Hinder taskLow processing overheadTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionComputer hardwareChange detection
A method of detecting changes in a continuous stream of channel associated signalling (CAS) data for a plurality of communication channels is described. The method comprises the steps of: writing a block of data to an area of a circular memory buffer as a plurality of rows; writing a next block of data to an area of the circular memory buffer located sequentially after the area occupied by the previous block of data as a plurality of rows, wherein after writing each row of said next block of data, changes in the data contained in the row are determined by comparing the row with the corresponding row in the previous block of data; and repeating step (ii) a plurality of times.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Device for unloading trays using a pivot member
InactiveUS8182191B2Reduce workloadReduce actionArticle unpackingSortingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SOLYSTIC
Method for improving document review performance
ActiveUS10430903B2Work well togetherAvoid misunderstandingDigital data processing detailsResourcesElectronic discoveryDocumentation
The present invention is a method and process for accurately and efficiently coding documents in electronic discovery. The method, if used by highly experienced and motivated document reviewers in a collegial and harmonic environment, has the potential to increase adjusted review consistency, reduce coding errors, eliminate duplicate efforts, increase review speed, decrease the risks of exposure, and dramatically improve review performance. The method will also result in useful case history files, which are useful in every phrase of litigation, including motion argument, merit trial, appeal, and future litigation.
Owner:WU JIANQING
Anti-mycoplasma spp. subunit vaccine
ActiveUS20150366959A1Easy to useLow costAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmune effectsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Provided in the present invention are anti-Mycoplasma spp. subunit vaccines, especially proteins suitable for being used as the active ingredient of the Mycoplasma spp. subunit vaccines, and a vaccine prepared therefrom. Upon experimenting, it is confirmed that the proteins can elicit an immune response having sufficient strength to avoid the infection of Mycoplasma spp. in pigs. The vaccine can comprise one of the aforementioned proteins as an active ingredient, or can comprise two or more of the proteins to form a form of cocktail vaccine. The vaccine of the present invention is not only more safe than conventional vaccines, but also has equivalent or even better immune effects.
Owner:AGRI TECH RES INST
Method for predicting call quality and call quality prediction service apparatus for performing the same
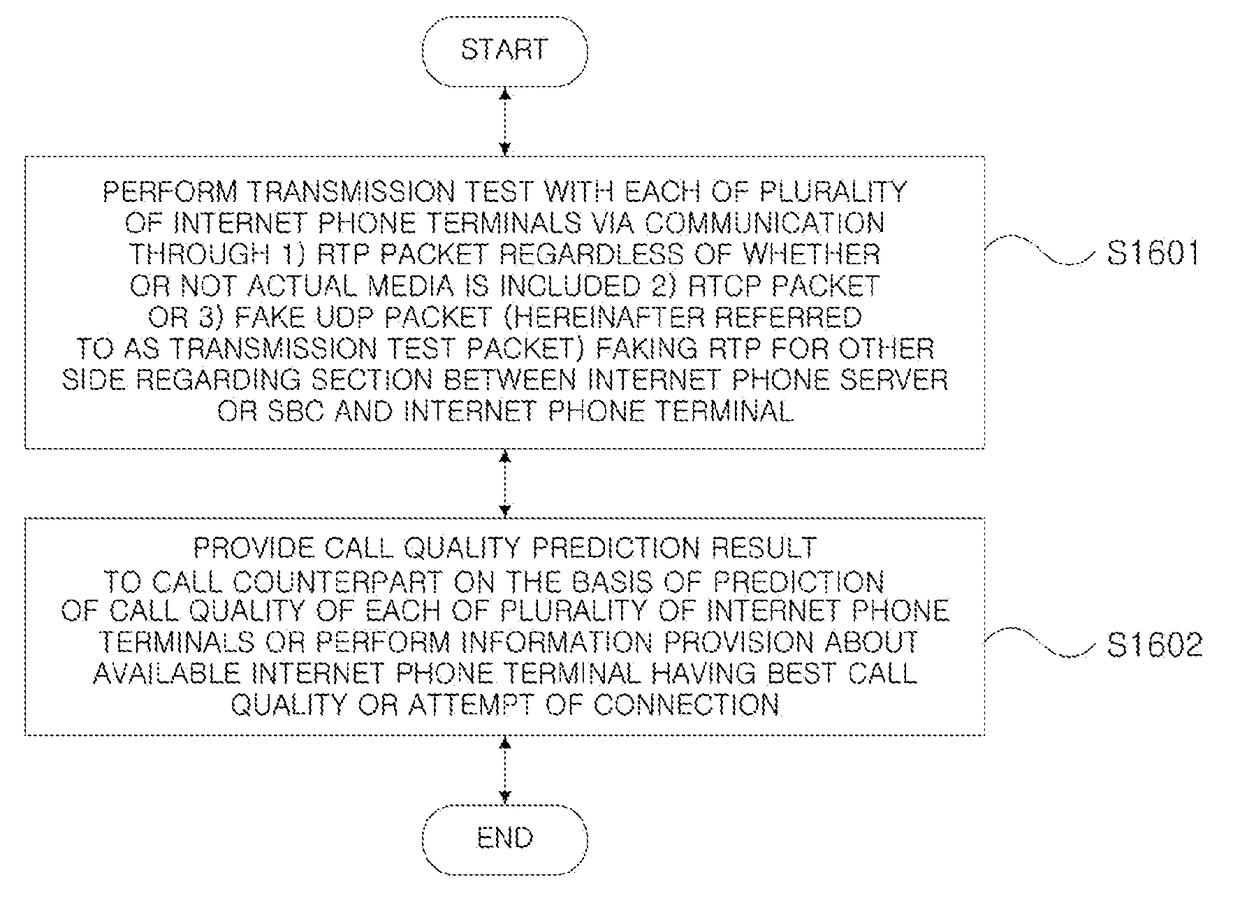
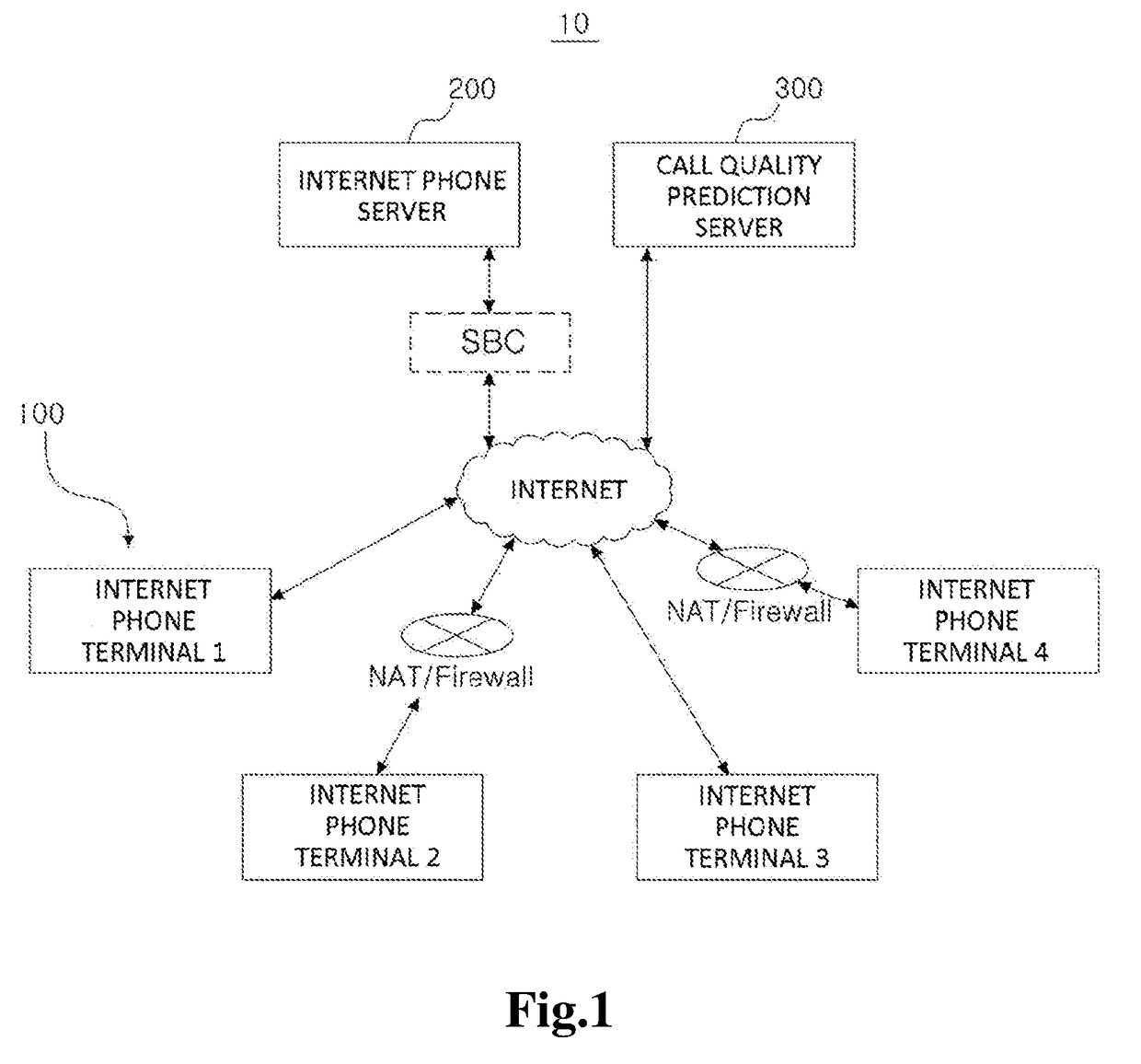
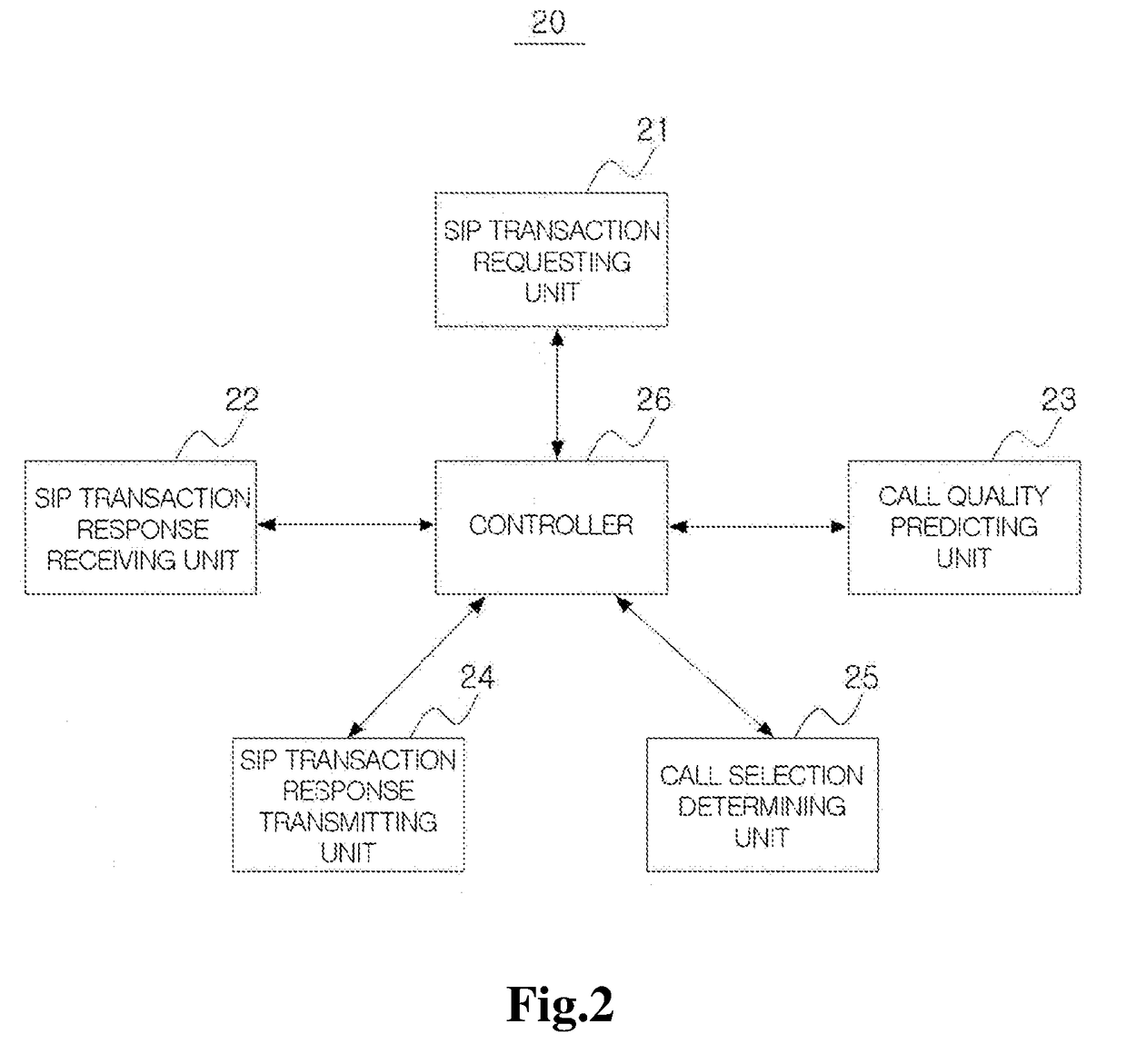
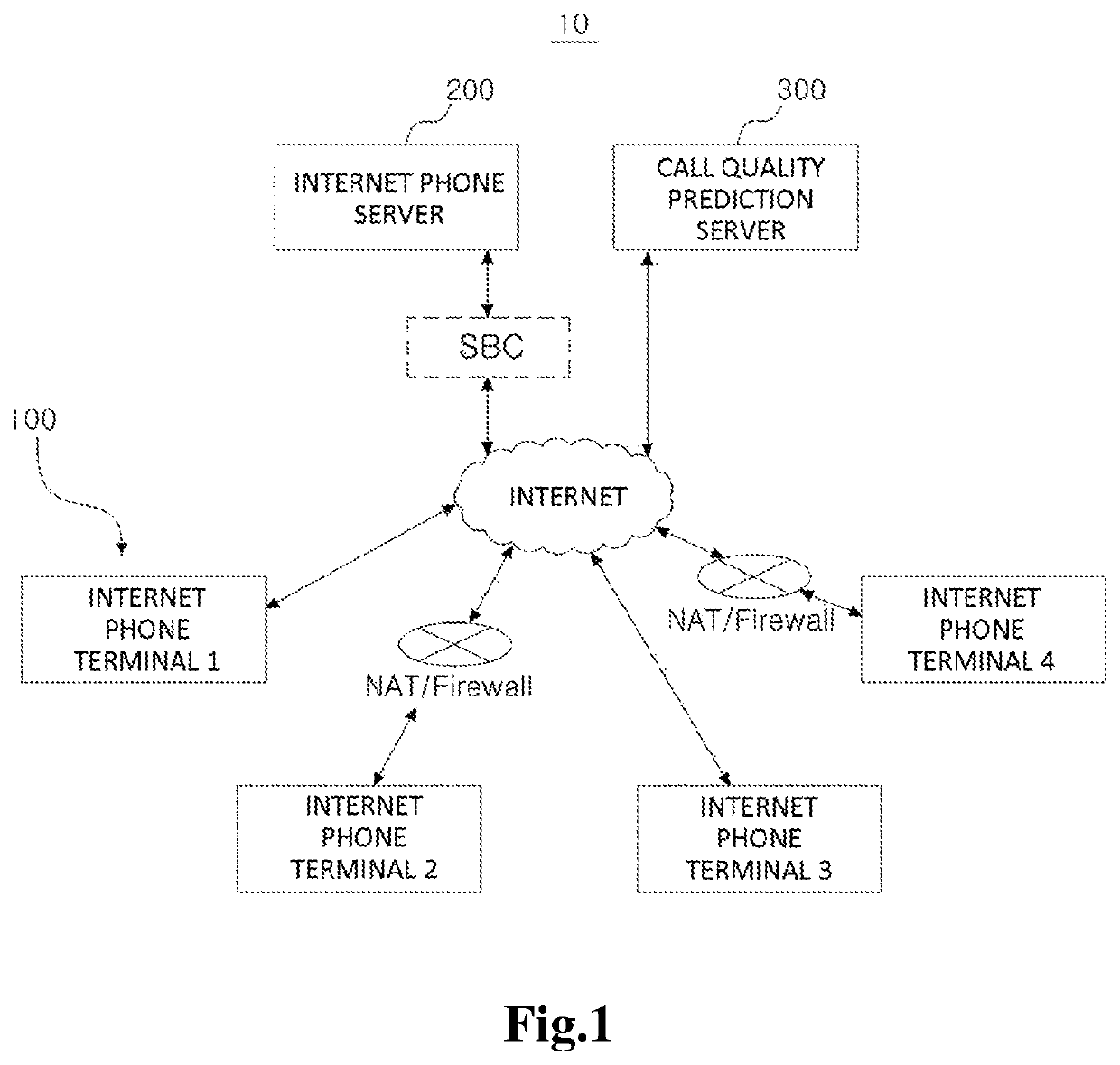
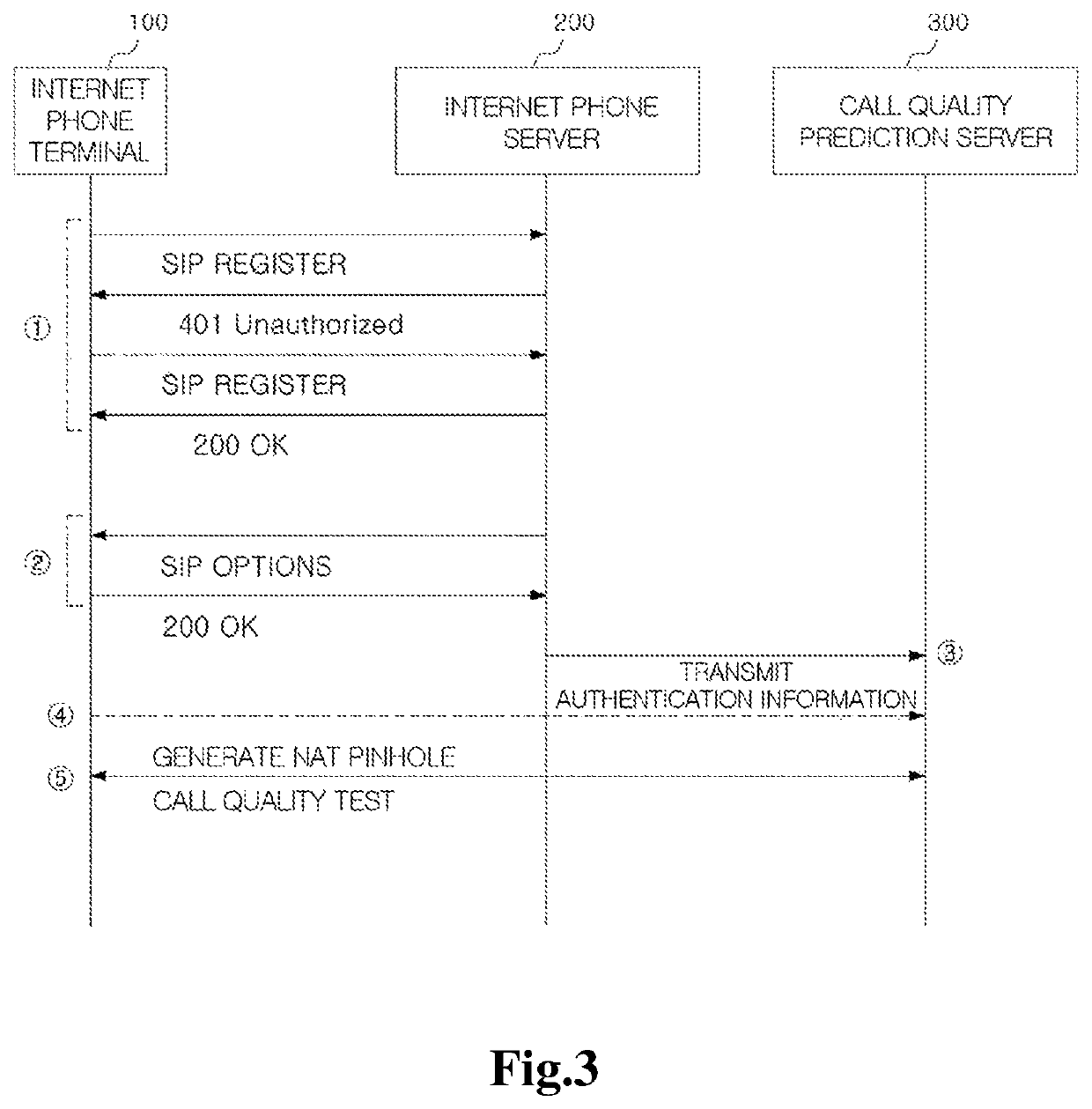
ActiveUS20180332097A1Call quality will deteriorateAvoid unnecessary prediction taskAutomatic exchangesCommerceInternet communicationComputer science
Disclosed herein is a method for predicting a call quality with respect to the other side by one side of the first and second Internet communication apparatuses, the method comprising: performing a transmission test for predicting call quality between one side and other side through address information of the one side or address information of the other side; and sequentially completing a call quality prediction regarding a relay section formed between the first and second Internet communication apparatuses and mutually adjacent call quality prediction apparatuses in at least one media relay apparatus when there is at least one media relay apparatus that performs media relay among the relay apparatuses between the first and second internet communication apparatuses.
Owner:MOON BYUNG JIN
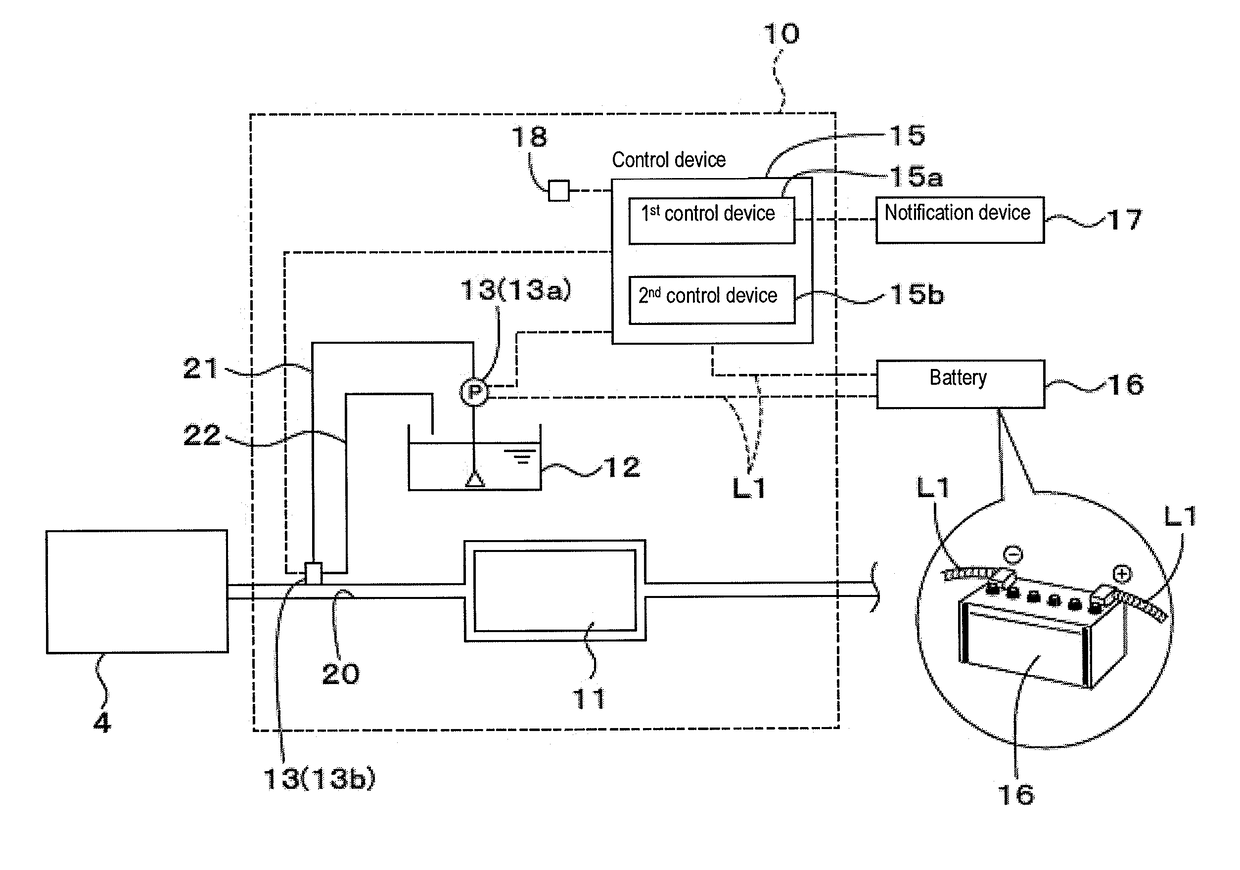
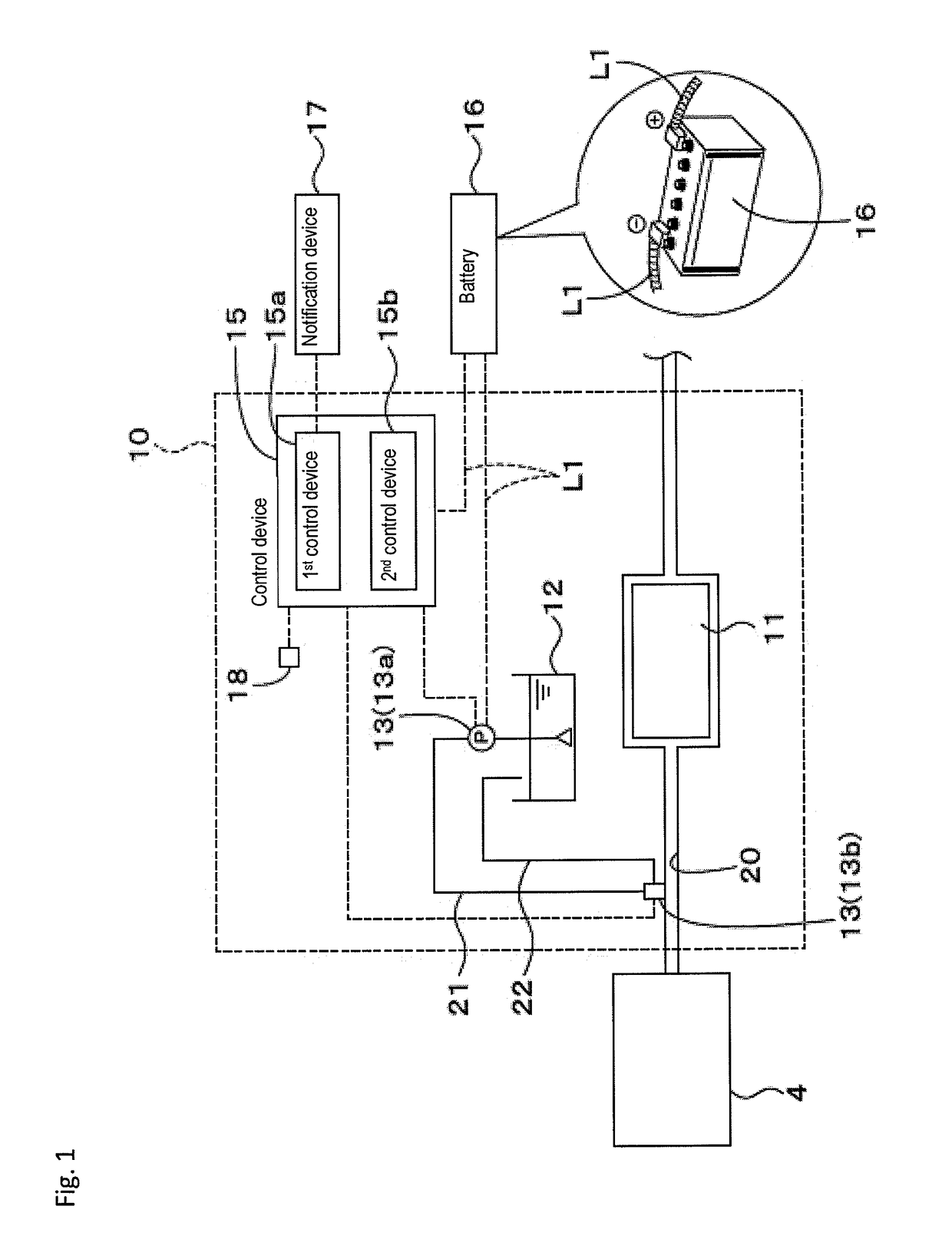
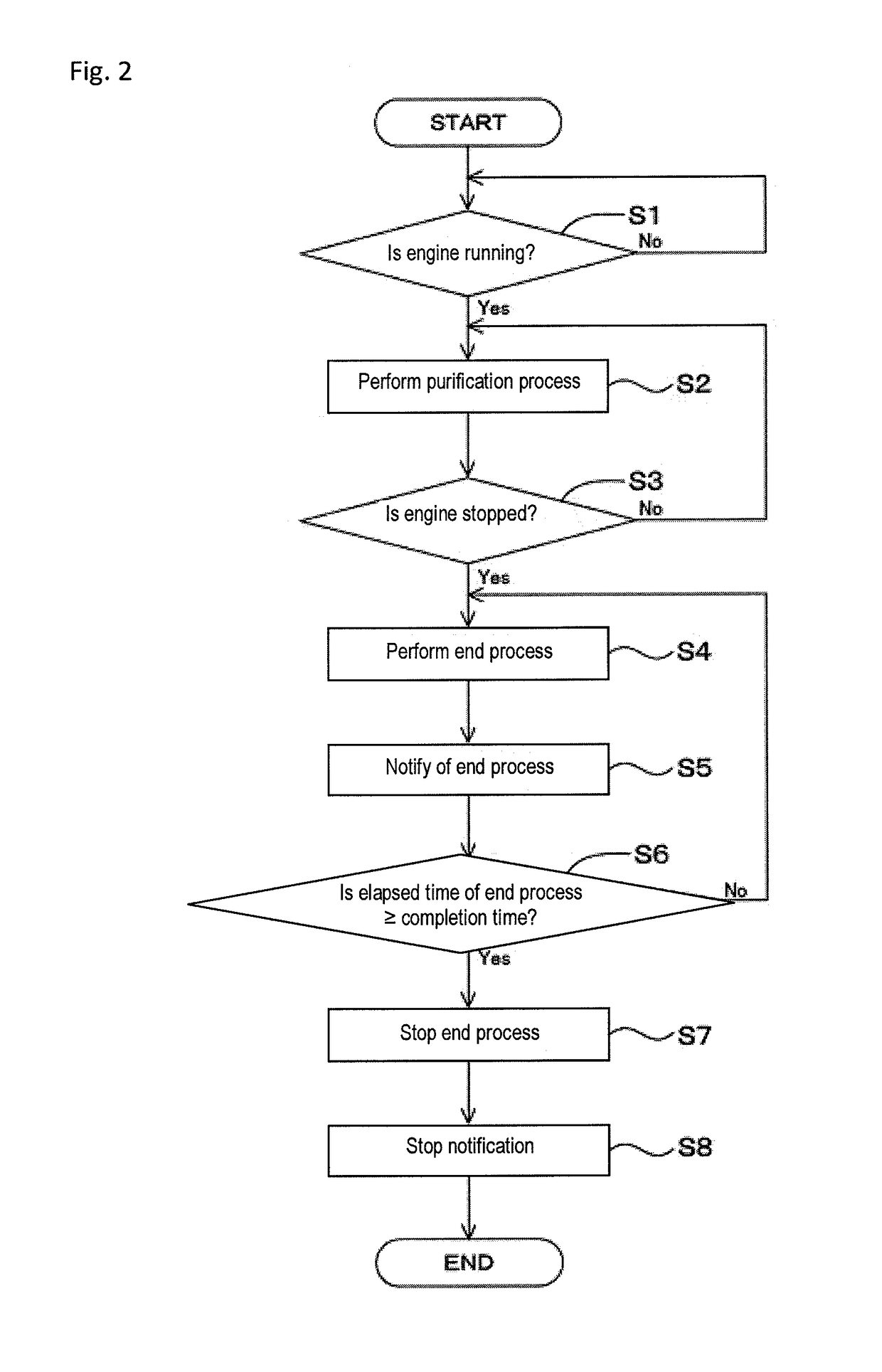
Exhaust gas purification system and method for a work vehicle
ActiveUS20170342885A1Hinder taskInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusExhaust gas recirculationElectric power
A work vehicle includes an engine, a battery, an exhaust gas purification system or device, and a notification device. The exhaust gas purification system or device is capable of performing a purification process purifying exhaust gas of the engine, and operates with electric power from the battery and performs an end process. The notification device provides notification that the exhaust gas purification system or device is performing the end process or that the end process is completed.
Owner:KUBOTA LTD
Method and apparatus for encouraging physiological change through physiological control of wearable auditory and visual interruption device
ActiveUS9521976B2Efficiency to taskHinder taskElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographySports activityTouch Perception
A biofeedback system and method enables biofeedback training to be accomplished during normal interaction by an individual with the individual's environment, for example while reading, playing video games, watching TV, participating in sports activities, or at work. Physiologic data is processed and used to generate one or more control signals based on the physiologic data. The control signals may be proportional to a result of the data processing, or based on comparison of the processing results with at least one fixed or adaptive threshold. The control signal is supplied to a wearable device through which the individual receives sensory information from the individual's environment, and serves to interrupt or modify the sensory information. The wearable device may be an eyeglass device including a dynamic lens display, with the control signal being supplied to the dynamic lens display to modulate visual information received through the eyeglass device by obscuring, distorting, or otherwise affecting the clarity of the visual information. Feedback may also be provided in the form of auditory or tactile feedback.
Owner:GRECO DEVON
Method for predicting call quality and call quality prediction service apparatus for performing the same
Disclosed herein is a method for predicting a call quality with respect to the other side by one side of the first and second Internet communication apparatuses, the method comprising: performing a transmission test for predicting call quality between one side and other side through address information of the one side or address information of the other side; and sequentially completing a call quality prediction regarding a relay section formed between the first and second Internet communication apparatuses and mutually adjacent call quality prediction apparatuses in at least one media relay apparatus when there is at least one media relay apparatus that performs media relay among the relay apparatuses between the first and second internet communication apparatuses.
Owner:MOON BYUNG JIN
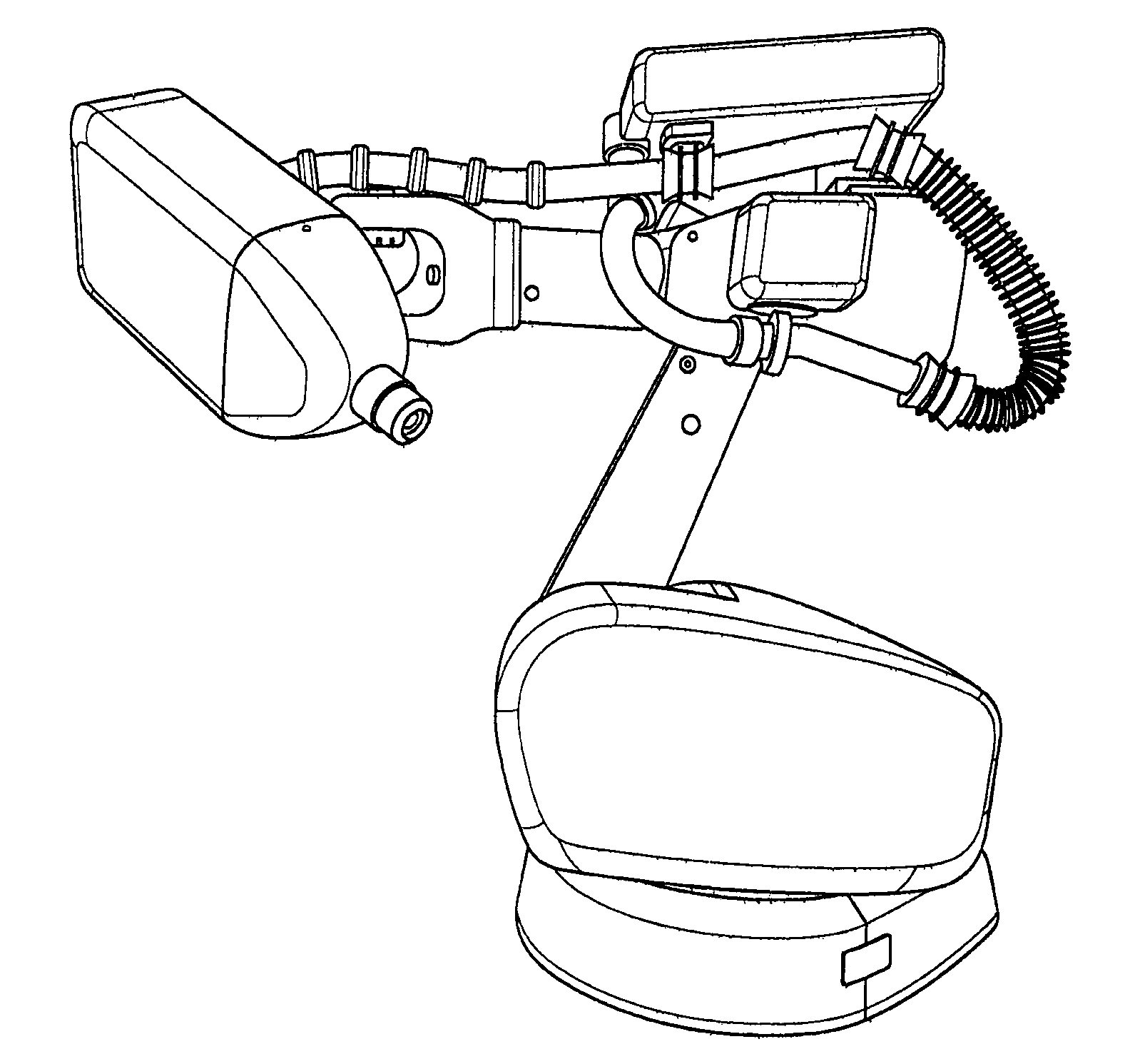
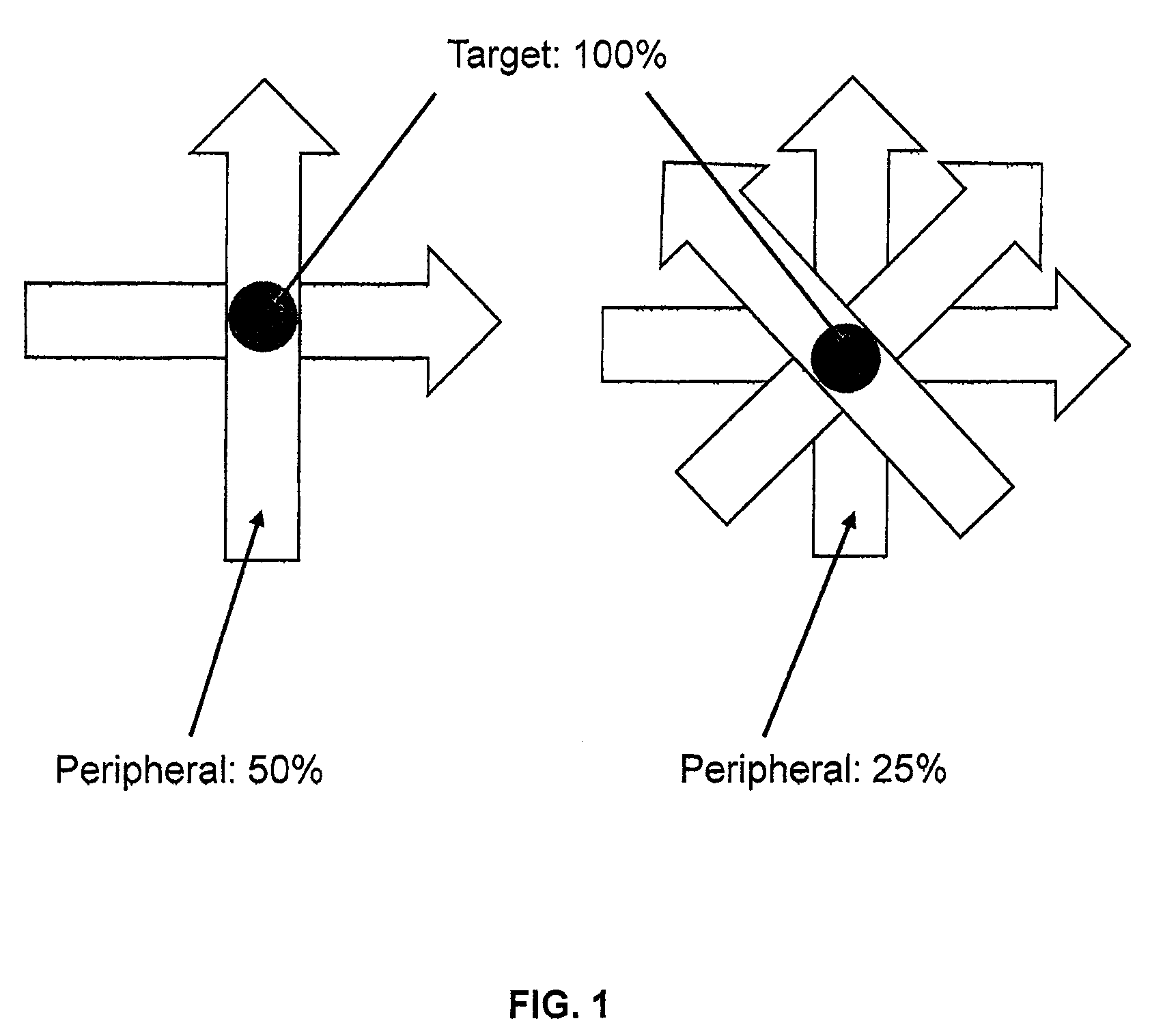
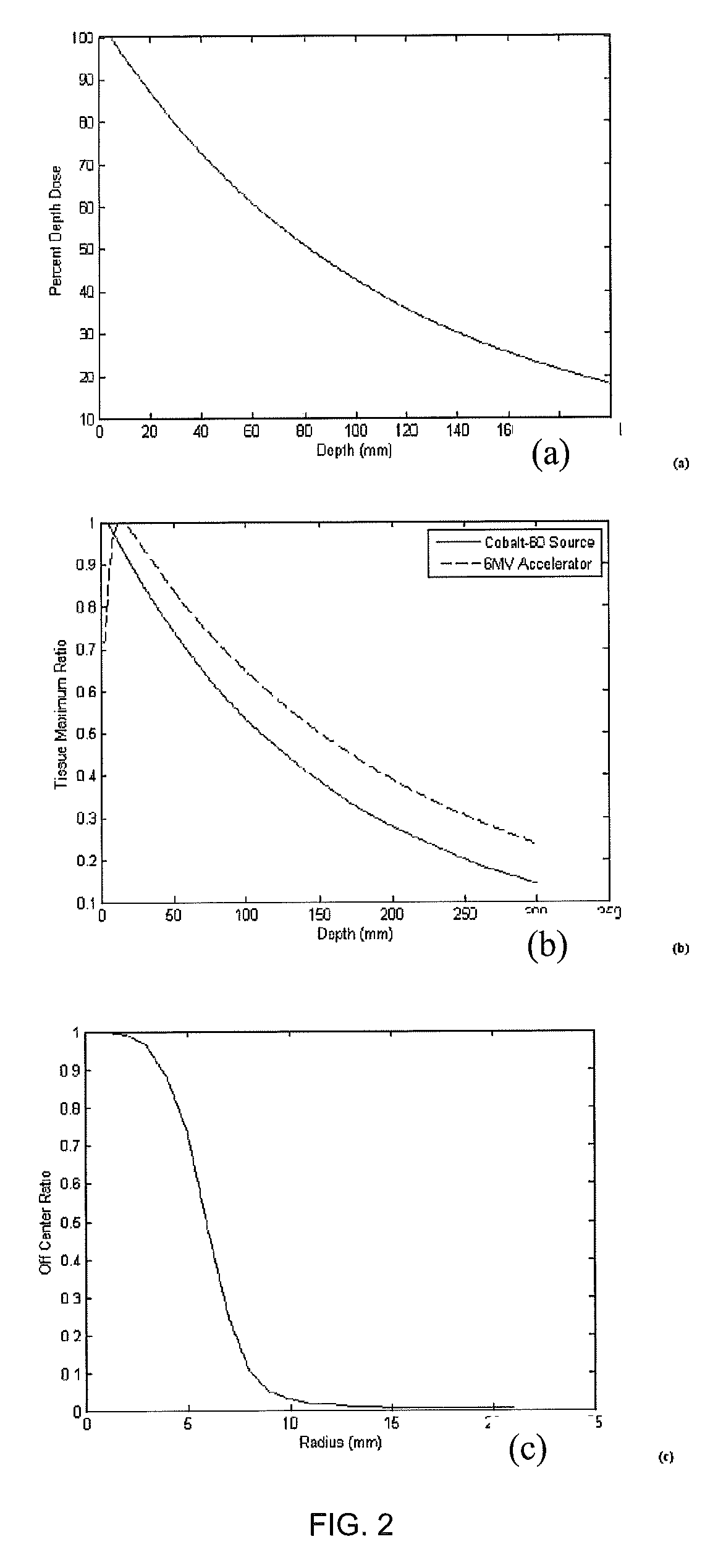
System and methods of photon-based radiotherapy and radiosurgery delivery
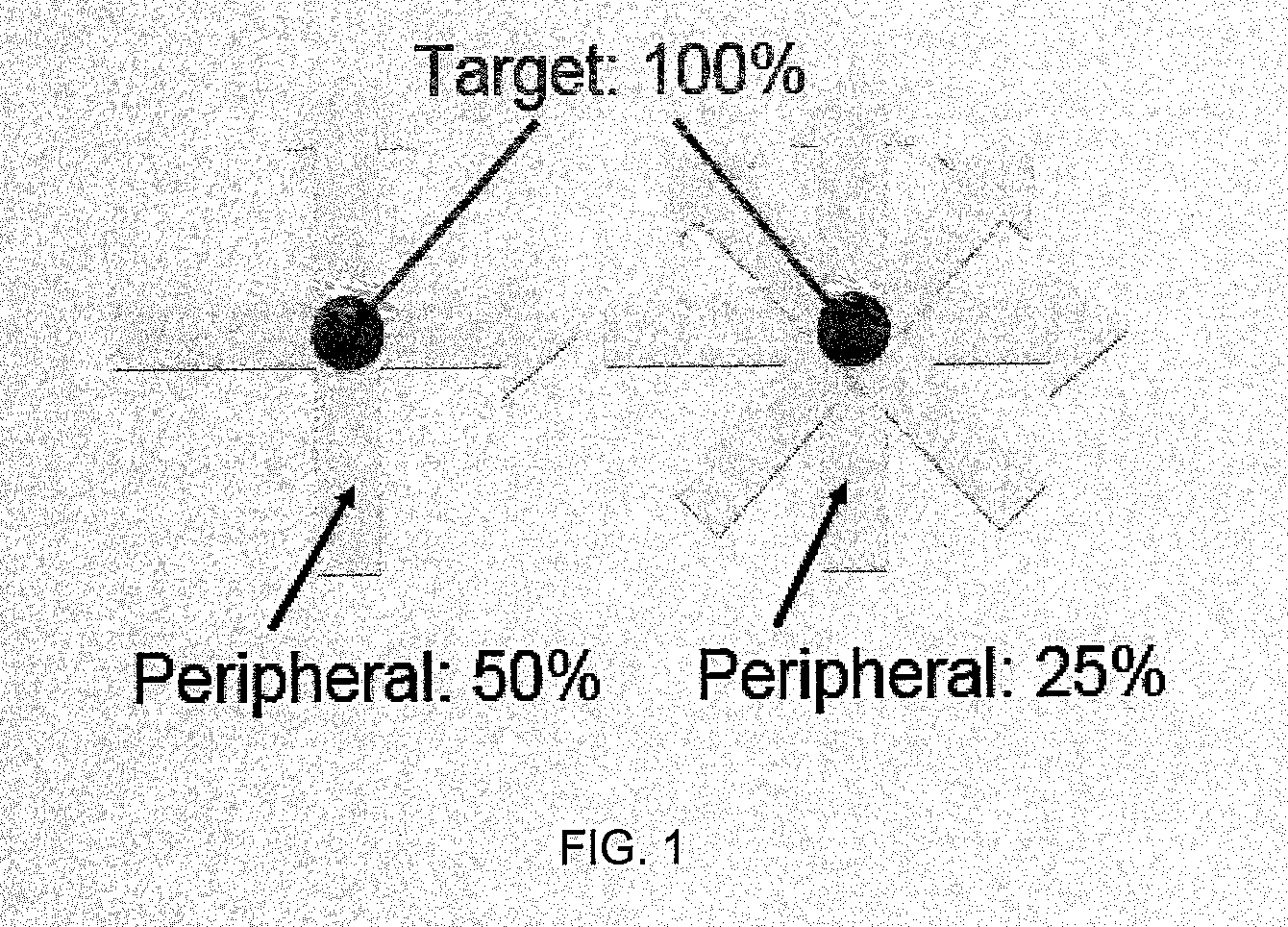
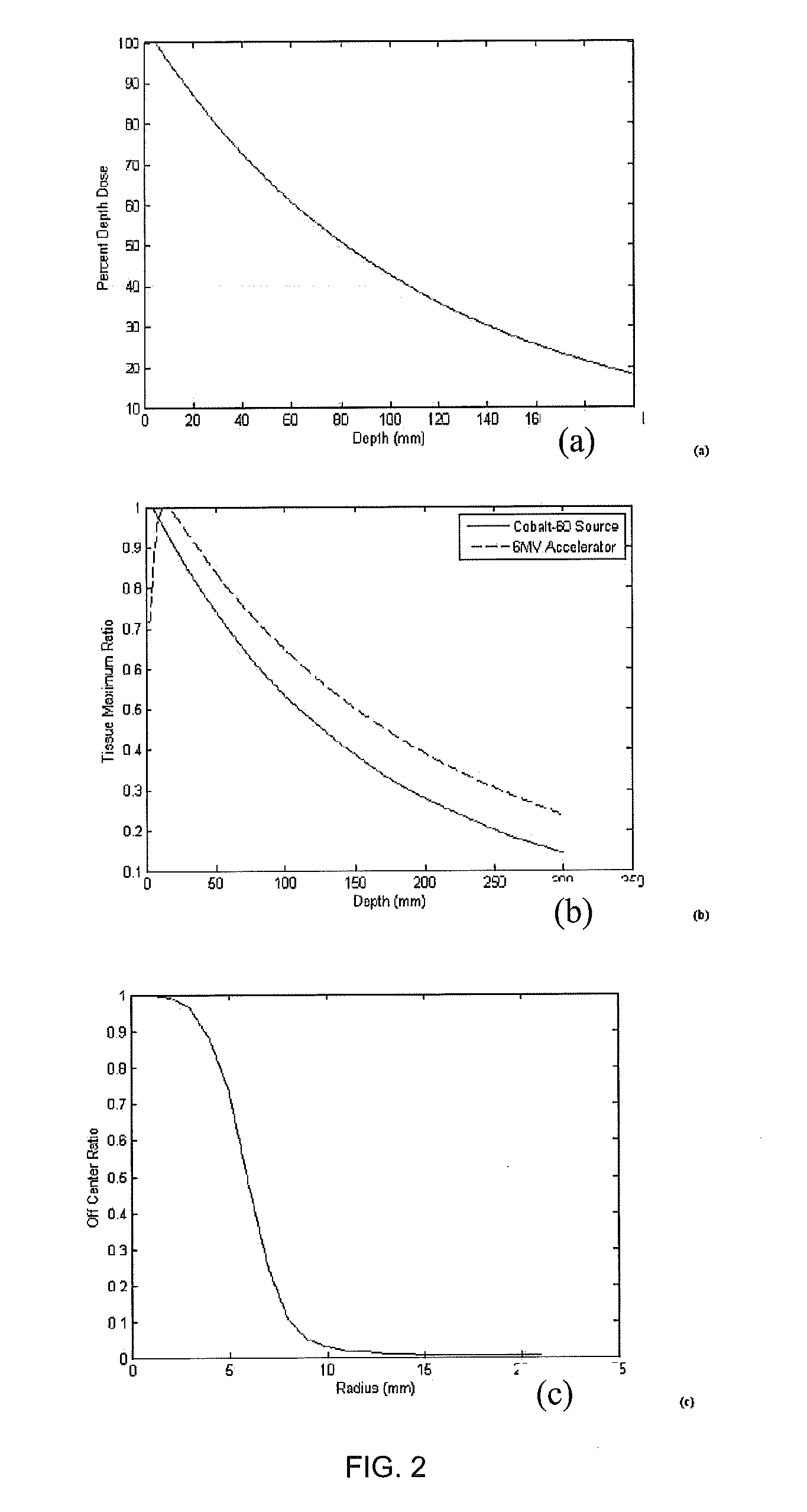
ActiveUS8835877B2Quality improvementIncrease ratingsEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesChemical conversion by chemical reactionDose gradientBragg peak
Photon-based radiosurgery is widely used for treating local and regional tumors. The key to improving the quality of radiosurgery is to increase the dose falloff rate from high dose regions inside the tumor to low dose regions of nearby healthy tissues and structures. Dynamic photon painting (DPP) further increases dose falloff rate by treating a target by moving a beam source along a dynamic trajectory, where the speed, direction and even dose rate of the beam source change constantly during irradiation. DPP creates dose gradient that rivals proton Bragg Peak and outperforms Gamma Knife® radiosurgery.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
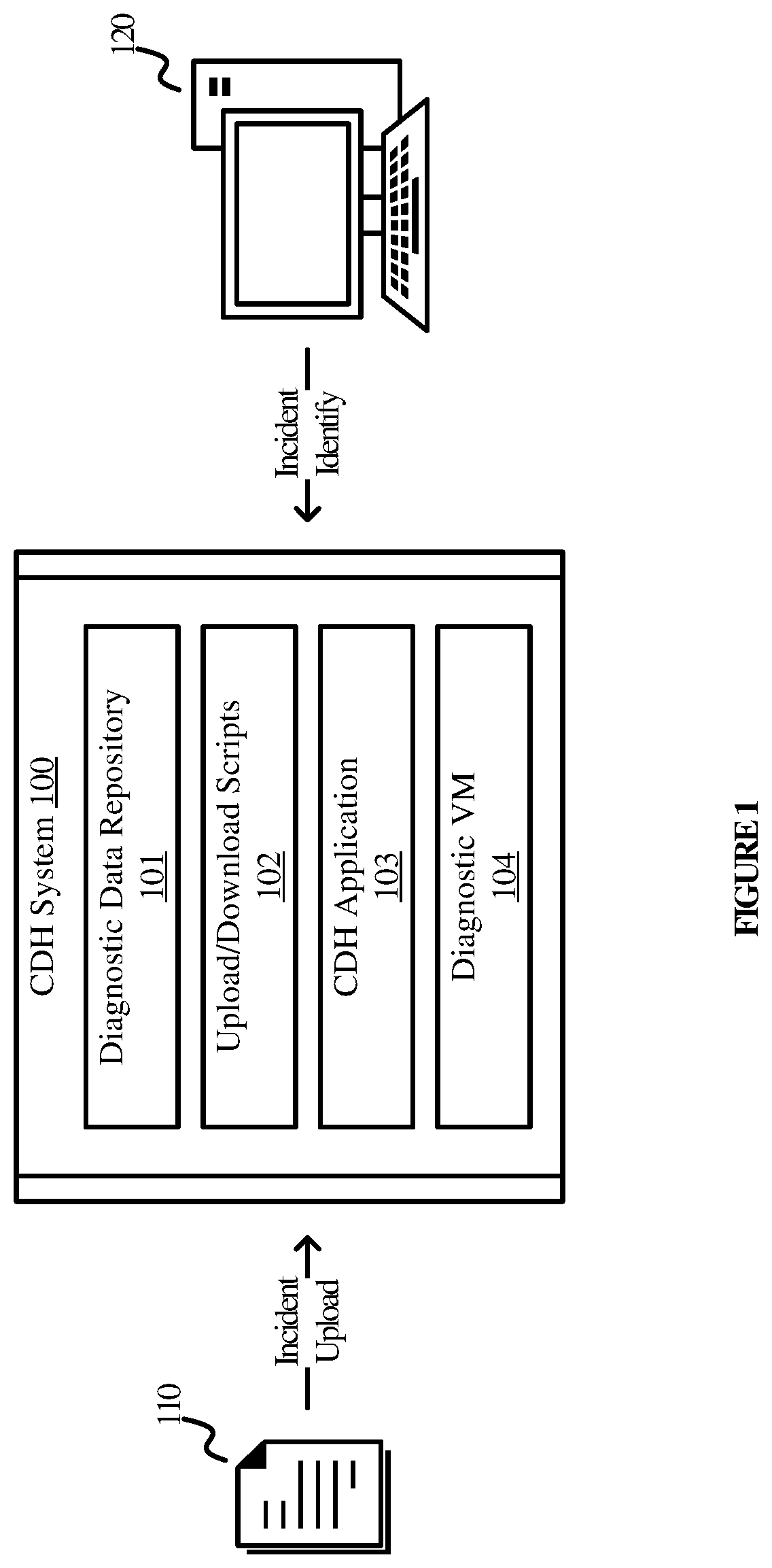
Systems and methods for customer data handling
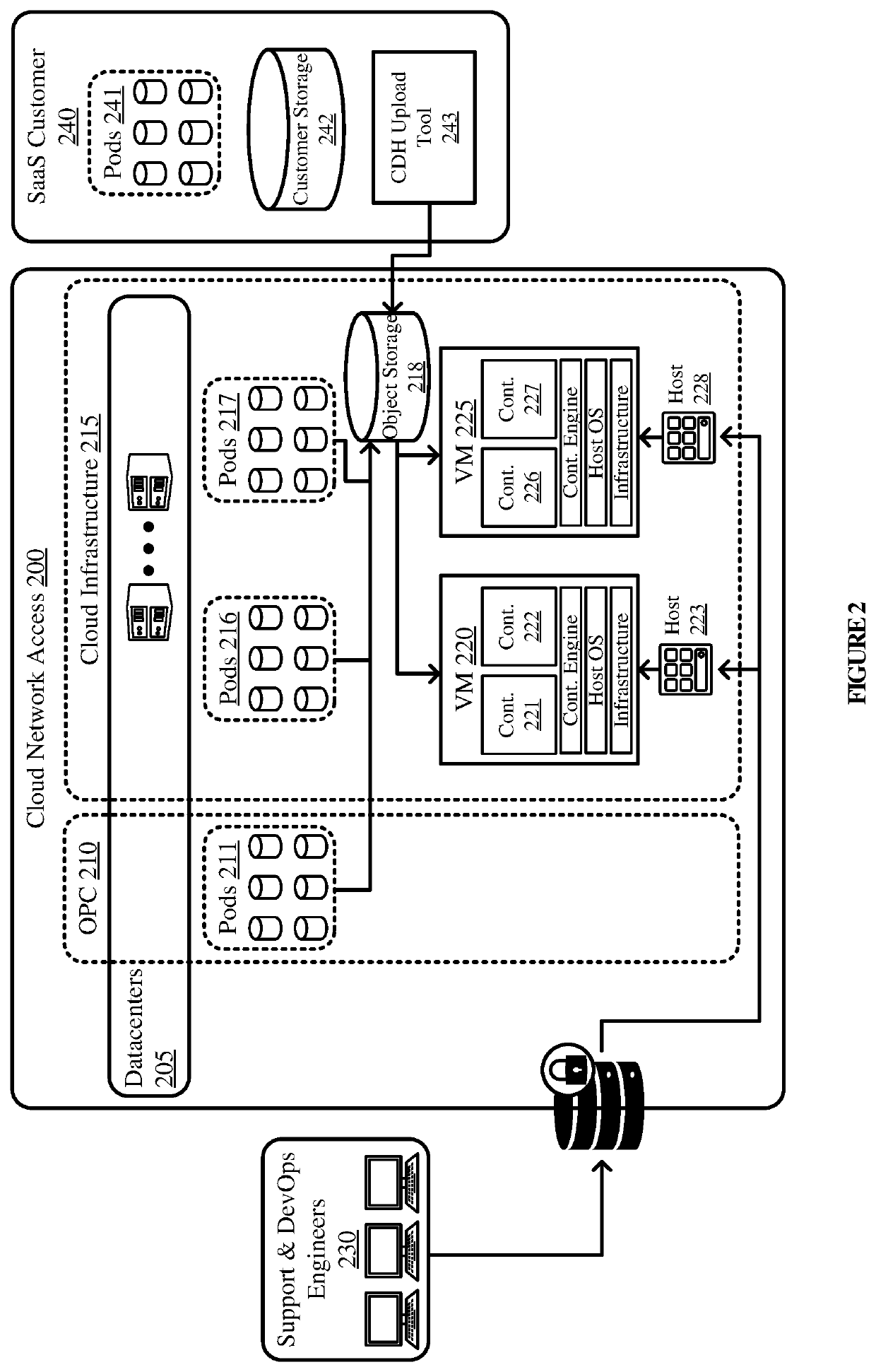
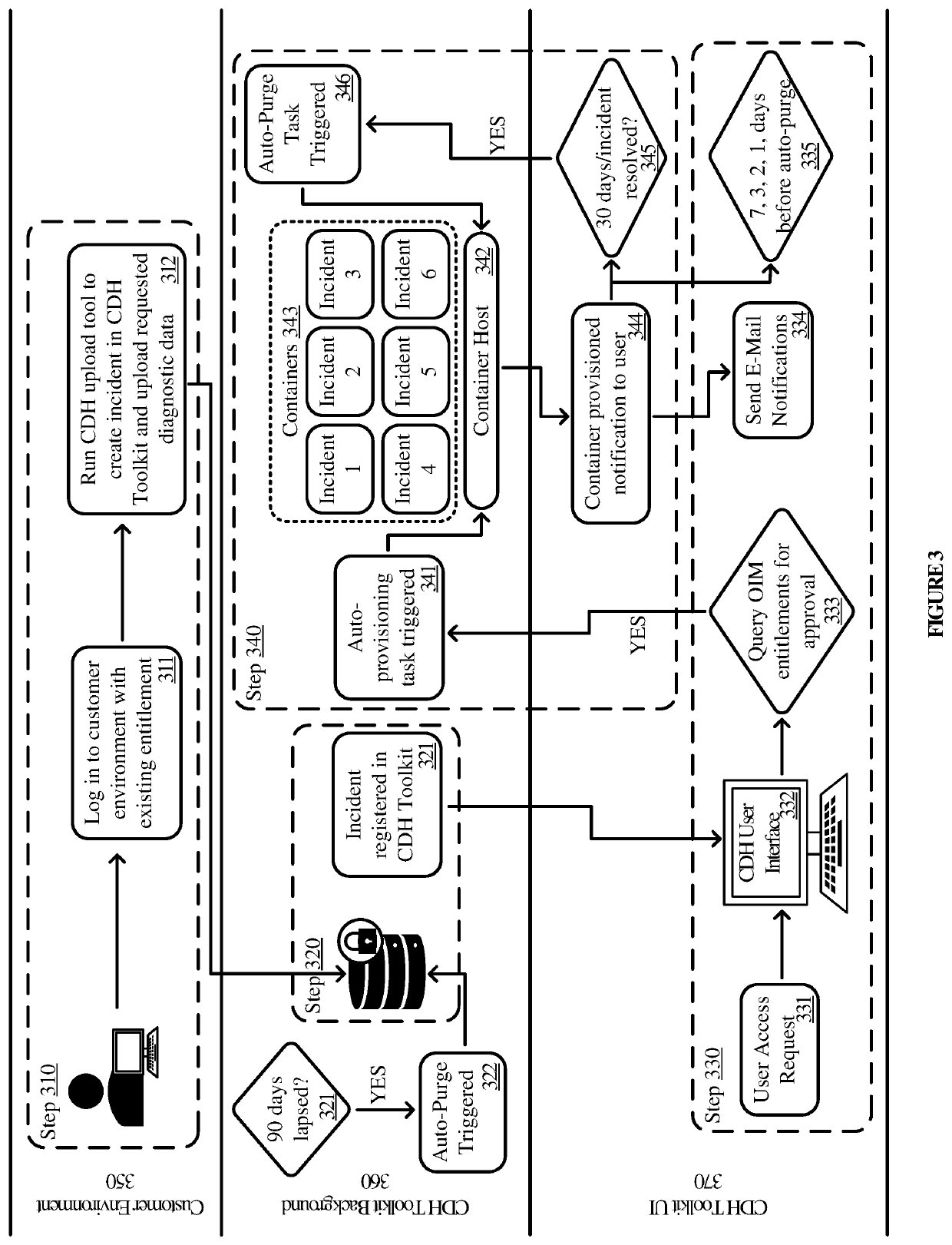
PendingUS20220100892A1Hinder taskImprove protectionCustomer relationshipDigital data protectionData processing systemDiagnostic data
Various embodiments of the present technology generally relate to systems and methods for secure customer data handling. More specifically, some embodiments relate to handling of derivative data as a provider in a manner that supports security and provides a stronger level of control over the data. The solution supports four core principles of customer data handling: no export of customer data, unless authorized; remote operations only via shell access or equivalent; temporary and task-based privileges; and diagnostic data to be ephemeral. The customer data handling system herein includes a central repository for the storage of diagnostic data, an upload tool for uploading to the central repository and automated staging on containers, a diagnostic virtual machine that enables task-based access to diagnostic data and analysis tools hosted on a dedicated container, and an application for handling requests, provisioning and staging containers, and purging.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and methods of photon-based radiotherapy and radiosurgery delivery
ActiveUS20120175531A1Improve qualityIncrease rateEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesChemical conversion by chemical reactionHigh dosesBragg peak
Photon-based radiosurgery is widely used for treating local and regional tumors. The key to improving the quality of radiosurgery is to increase the dose falloff rate from high dose regions inside the tumor to low dose regions of nearby healthy tissues and structures. Dynamic photon painting (DPP) further increases dose falloff rate by treating a target by moving a beam source along a dynamic trajectory, where the speed, direction and even dose rate of the beam source change constantly during irradiation. DPP creates dose gradient that rivals proton Bragg Peak and outperforms Gamma Knife® radiosurgery.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Anti-Mycoplasma spp. subunit vaccine
ActiveUS9561267B2Low costImprove performanceAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmune effectsMycoplasma
Provided in the present invention are anti-Mycoplasma spp. subunit vaccines, especially proteins suitable for being used as the active ingredient of the Mycoplasma spp. subunit vaccines, and a vaccine prepared therefrom. Upon experimenting, it is confirmed that the proteins can elicit an immune response having sufficient strength to avoid the infection of Mycoplasma spp. in pigs. The vaccine can comprise one of the aforementioned proteins as an active ingredient, or can comprise two or more of the proteins to form a form of cocktail vaccine. The vaccine of the present invention is not only more safe than conventional vaccines, but also has equivalent or even better immune effects.
Owner:AGRI TECH RES INST
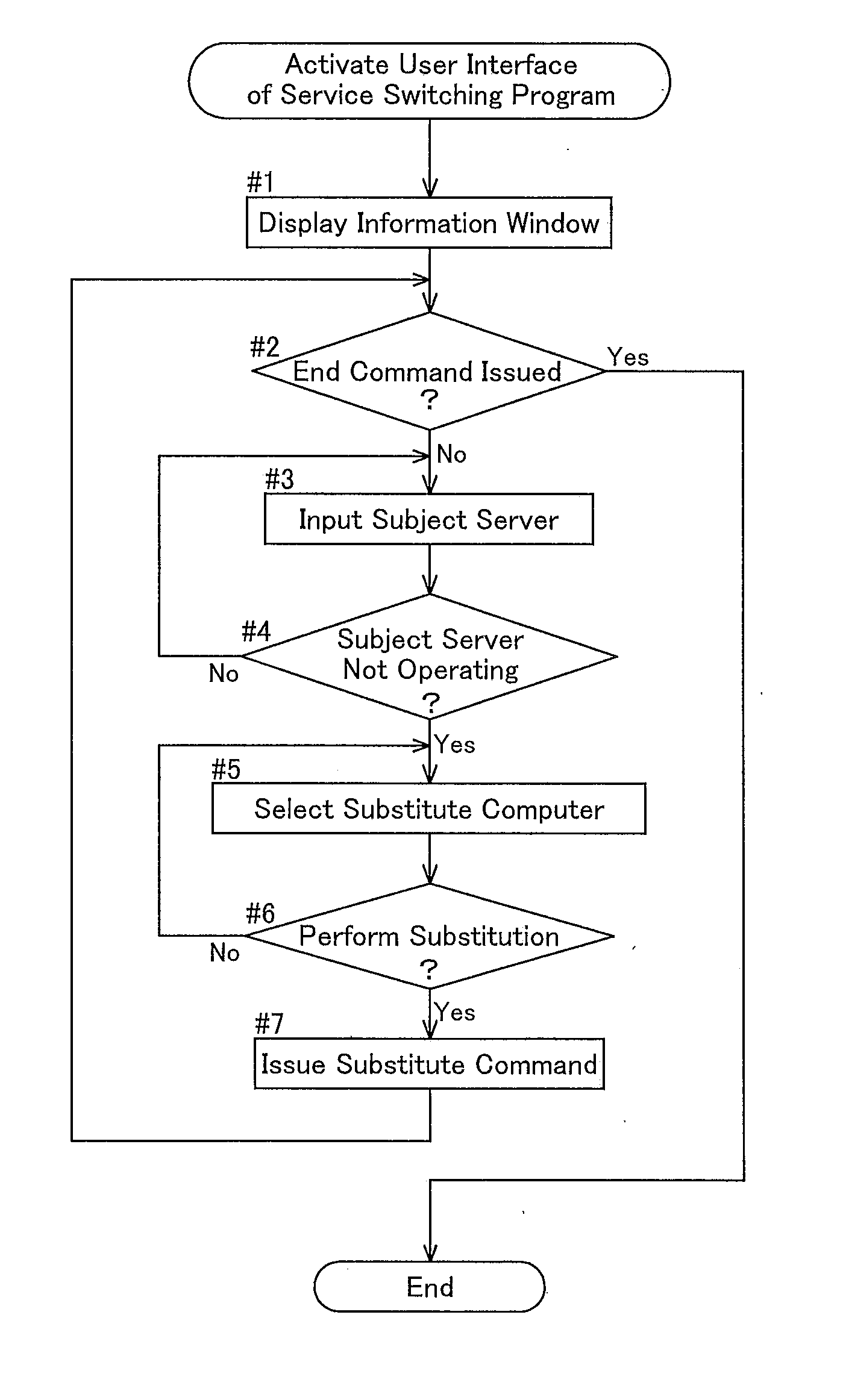
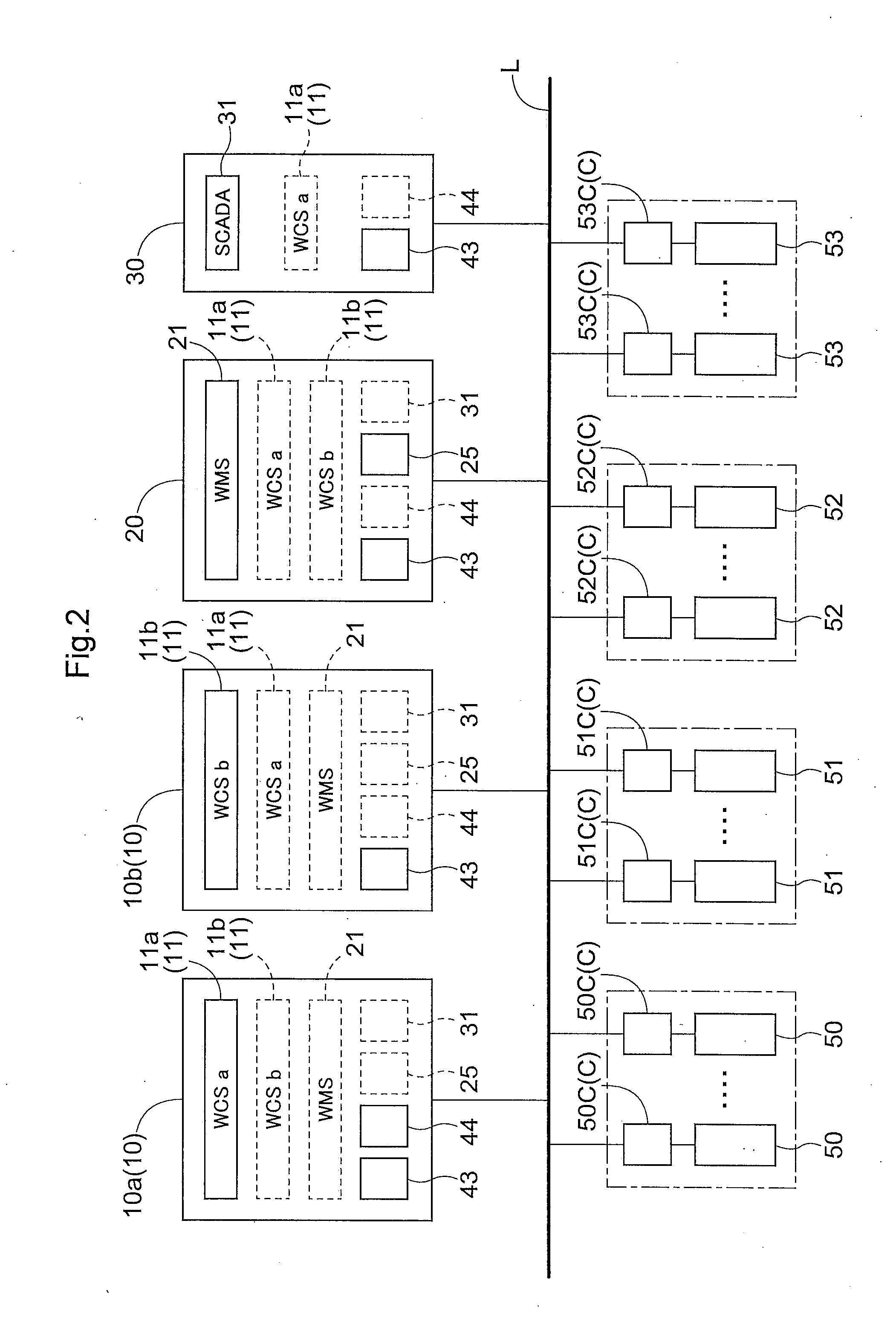
Facility Control System and Facility Control Method
ActiveUS20130253669A1Increasing facility costLow efficiencySafety arrangmentsError detection/correctionControl systemEmbedded system
A facility control system comprises a selection processing portion that selects, based on a manual operation and when an abnormal condition occurs in a second-layer computer that issues a task command to a first-layer program which issues an apparatus operating command to an apparatus controller, whether to cause a first-layer computer to execute a second-layer program that had been executed by the second-layer computer, and a substitute command output processing portion which outputs a substitute command in accordance with selection information selected by the selection processing portion. The first-layer computer executes the second-layer program that had been executed by the second-layer computer in which the abnormal condition occurred based on a substitute command outputted by the substitute command output processing portion.
Owner:DAIFUKU CO LTD
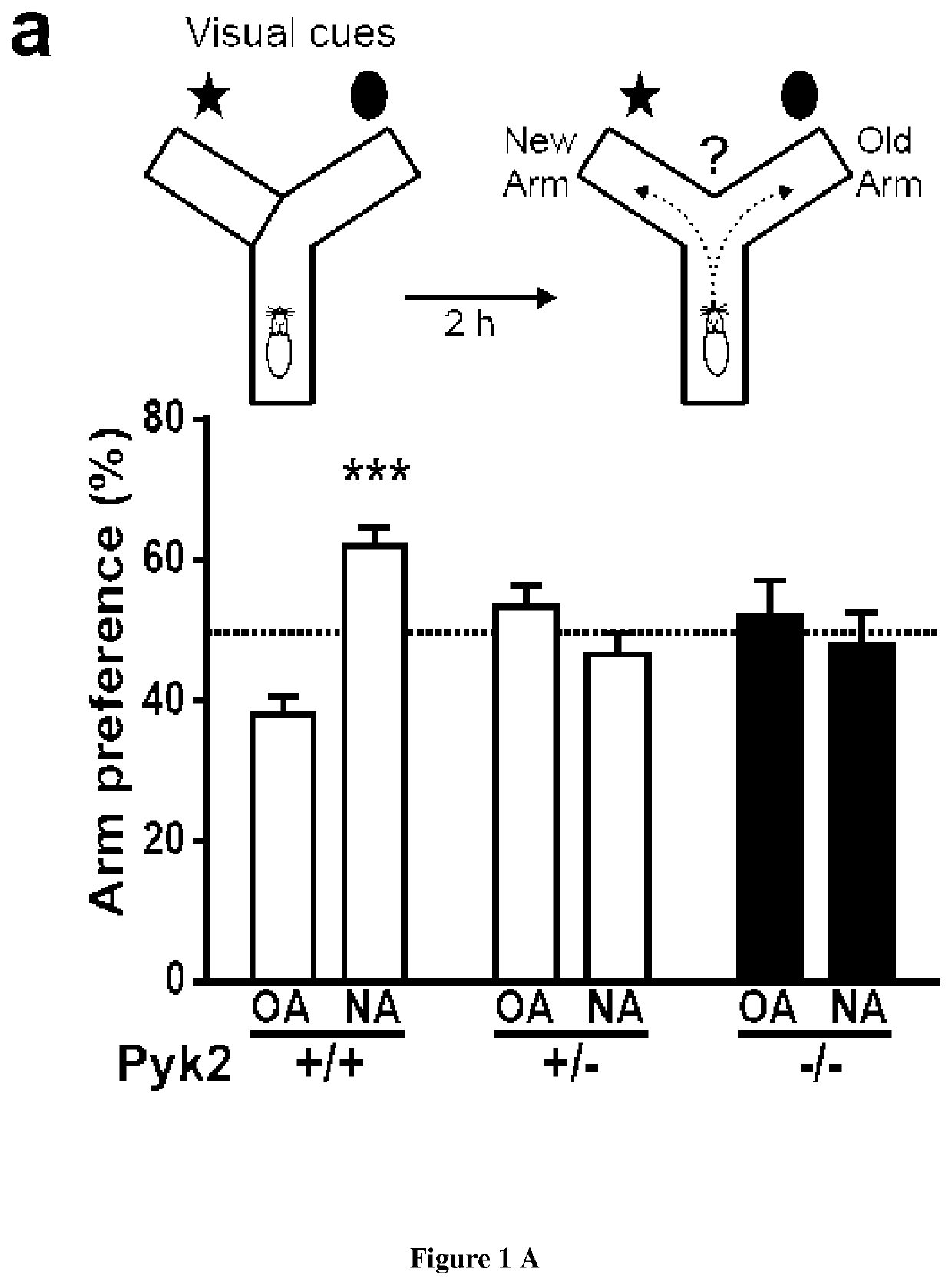
Methods and pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of neurodegenerative disease
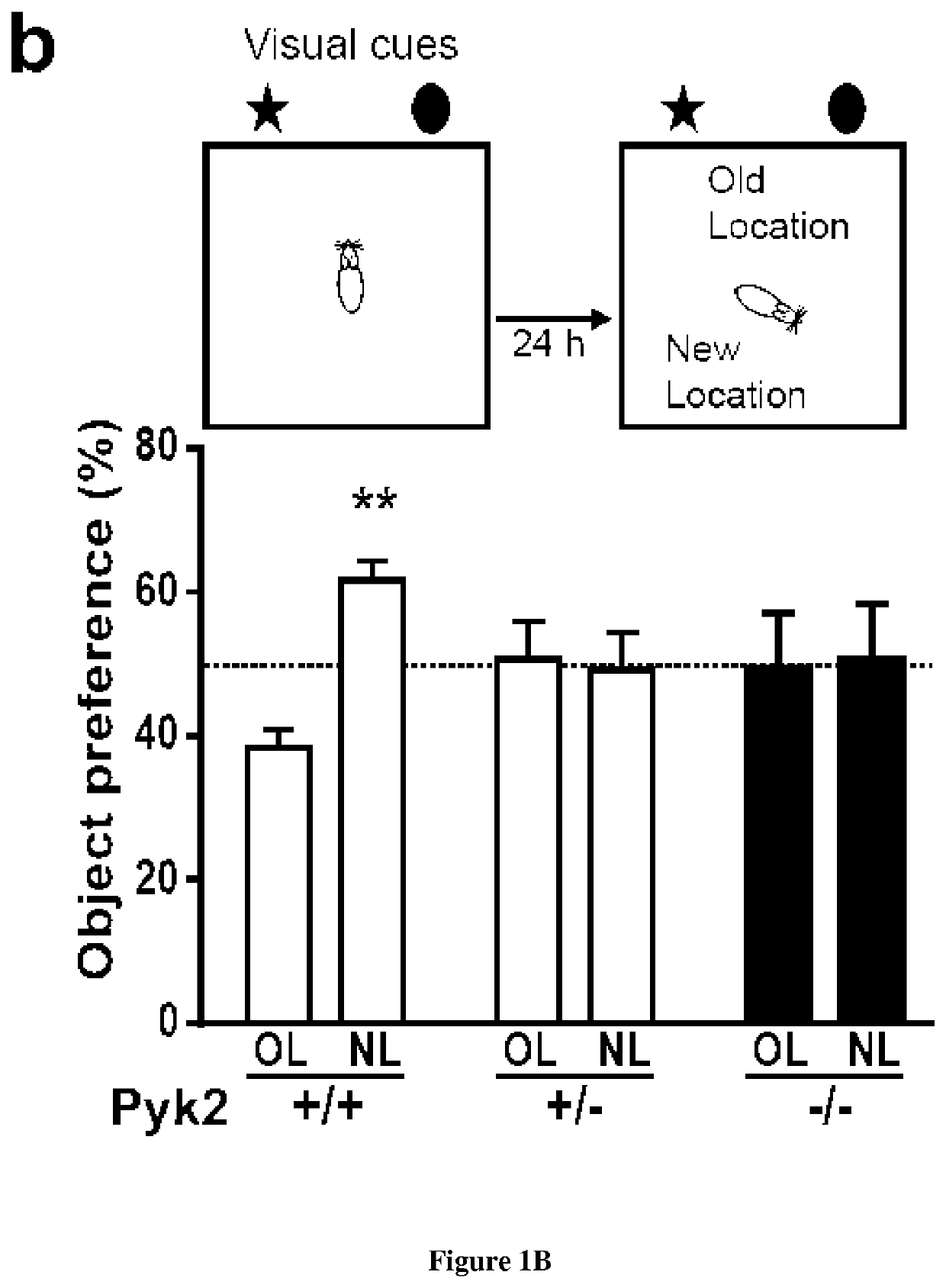
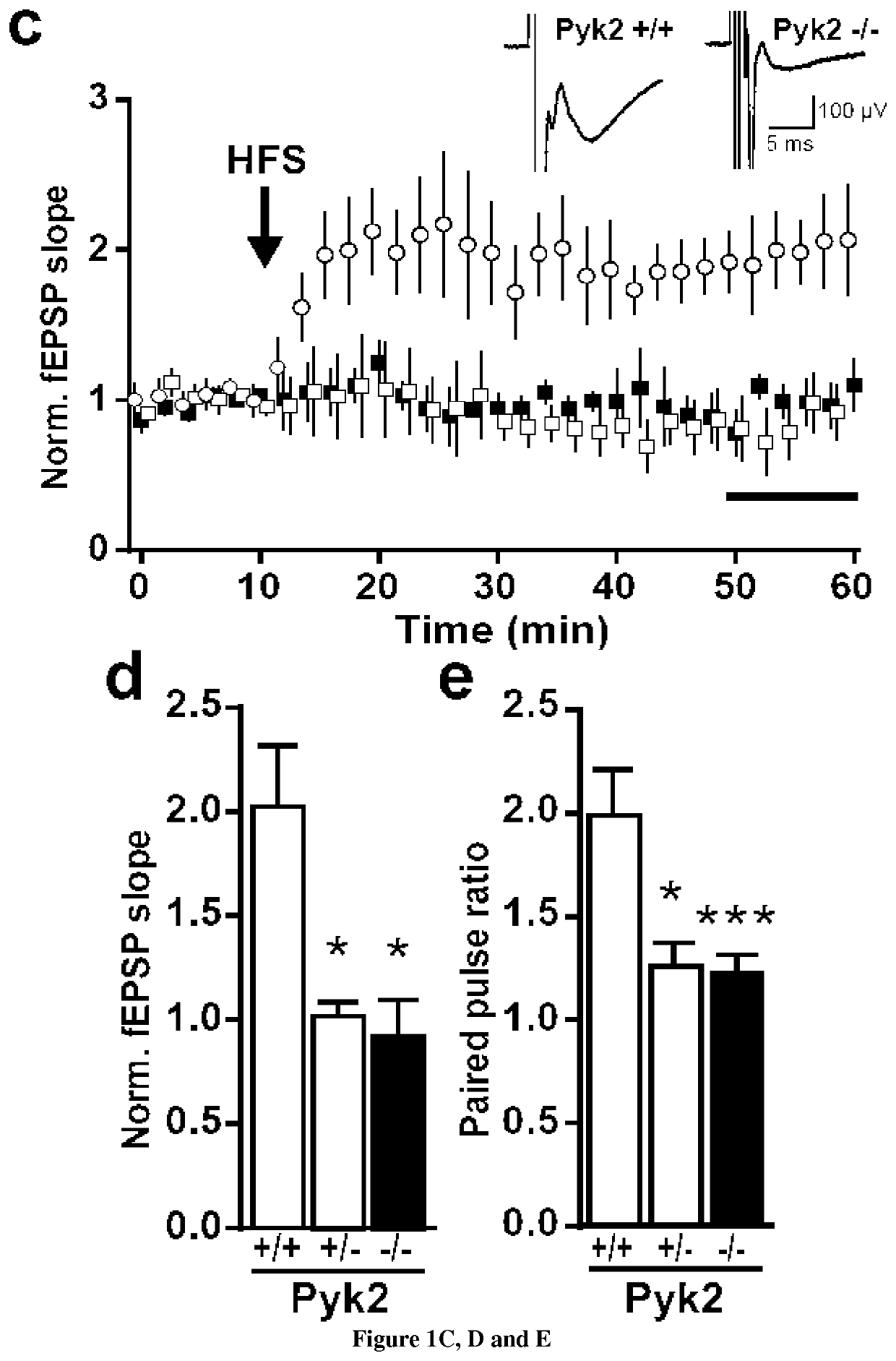
ActiveUS20200316102A1Hinder taskPyk2 is decreasedOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPharmacologyAlzheimer Syndrome
In the present invention it is shown that the inactivation of the Pyk2 gene does not alter hippocampal development but prevents hippocampal-dependent memory tasks and LTP. Inventors clearly provide evidence for multiple roles of Pyk2 in spine morphology and postsynaptic structure. Thus, the inventors used direct overexpression of PYK2 by AAV-mediated gene transfer into the brain of Huntington's and Alzheimer's mouse models and found that overexpression of PYK2 in these 2 models improves synaptic properties and spine density deficits which is also accompanied by a rescue of spatial memory. Accordingly it was demonstrated that PYK2 may restore cognitive functions in neurodegenerative diseases. Thus the present invention relates to methods and pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of neurodegenerative disease. In particular the present invention relates to a method of treating neurodegenerative disease in a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a vector which comprises a nucleic acid molecule encoding for PYK2 polypeptide.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Piece of fabric for hand-sewn works and method for making said works with said fabrics
ActiveUS10561186B2Method of creating the project is notably reducedPrecise and accurate mannerHand sewingLayered productsTextile printerEngineering
A piece of fabric for manual sewing projects and method of creating said projects with said fabric, consisting of a piece (1) of cloth that incorporates, with identical or different colors, prints and / or textures, the figures (2) for creating a certain patchwork design (3), each figure (2) being marked with a seam line (4) that defines the outline thereof and a cutting line (5) that defines a perimeter border that is optionally pre-perforated. The method only comprises obtaining said piece (1), cutting the figures (2) along the cutting line (5) and sewing them together. Optionally, the patchwork design (3) is selected and the piece (1) is ordered with the desired figures (2) and colors, prints and / or textures.
Owner:DAMA INT 1991 SA
Multi-compartment device for cell cloning and method of performing the same
InactiveUS20150240196A1Avoid cross contaminationNegligible riskMicroorganismsBiological material testing proceduresMicrowell PlateEngineering
The problems associated with the traditional methods and devices in the field of cell cloning have been solved by the multi-compartment device and method in the present invention. The device combines the advantages of a traditional petri-dish and a traditional microplate. The multi-compartment device in the present invention comprises sidewalls, which are taller than openings of the multi-compartments. The cells in the suspension flow across the multi-compartments and seed inside the compartments during a plating process. The multi-compartment device in the present invention allows easier plating process, changing conditioned medium, and cell colony detachment and transfer. The multi-compartment device also minimizes the risk of cross-contamination during cloning process and during cell colony transfer. The invention also provides an exemplary method of using the multi-compartment device for cell cloning. In one aspect of the method, the multi-compartment device may be tilted before or after adding the cell suspension during plating process.
Owner:ZOU QIAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com