Patents
Literature
59results about How to "Compromise performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dual feel multi-band planar antenna
InactiveUS6670923B1Reduce Design ComplexityCompromise performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandPlanar inverted f antenna
A three-band, two-antenna, assembly includes a planar inverted-F antenna (PIFA) having a radiating / receiving element that is spaced from and extends generally parallel to a ground plane element. The planar radiating / receiving element of an inverted-F antenna (IFA) is located in an open space that exists between the radiating / receiving element of the PIFA and the ground plane element. The radiating / receiving element of the IFA extends either perpendicular to, or parallel to, the radiating / receiving element of the PIFA. The radiating / receiving element of the PIFA includes one or more open slot configurations that operate to provide dual resonant frequencies for the IPFA (AMPS / PCS or GSM / DCS). The radiating / receiving element of the IFA operates in a non-cellular frequency band (ISM or GPS).
Owner:LAIRD CONNECTIVITY LLC
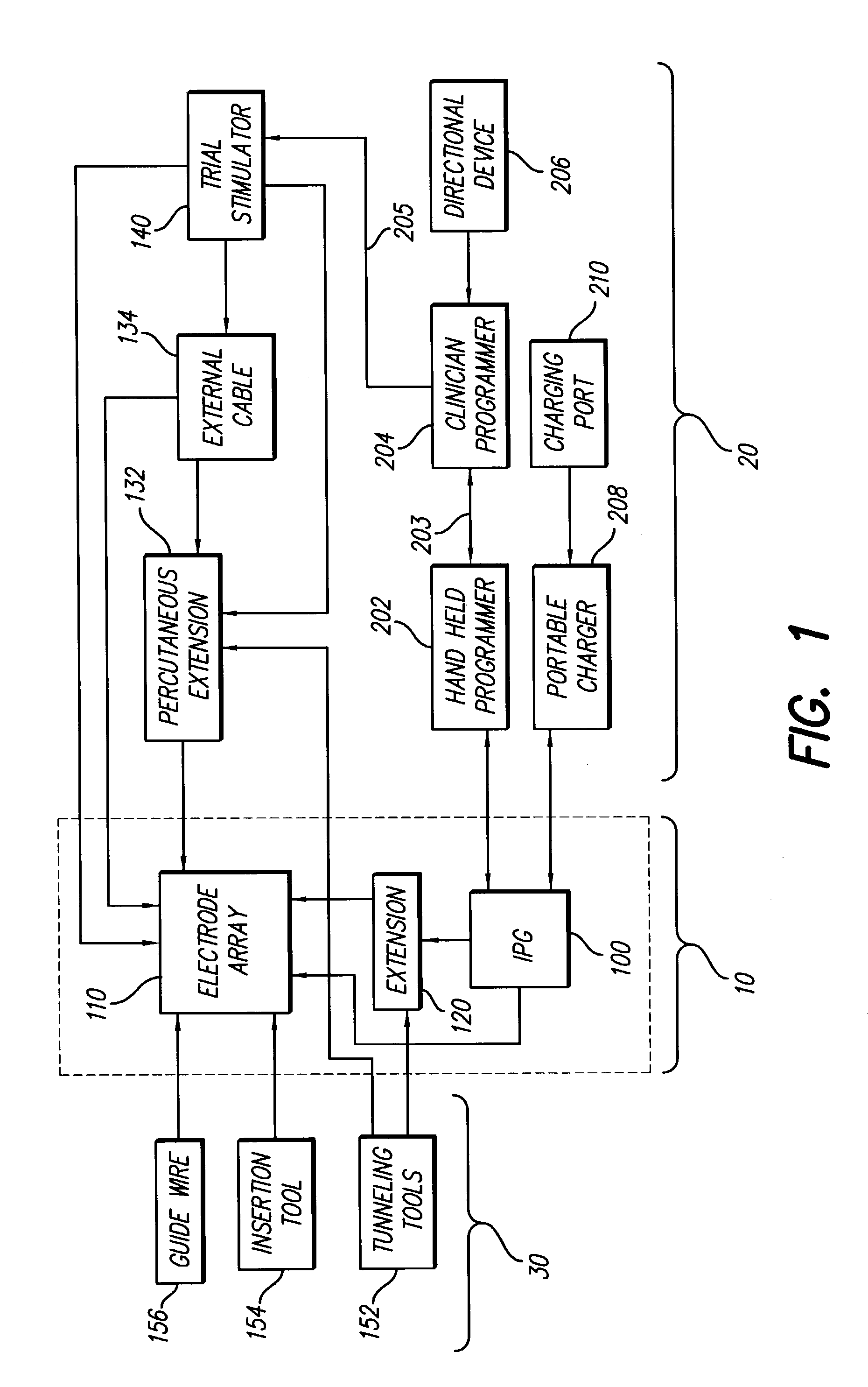
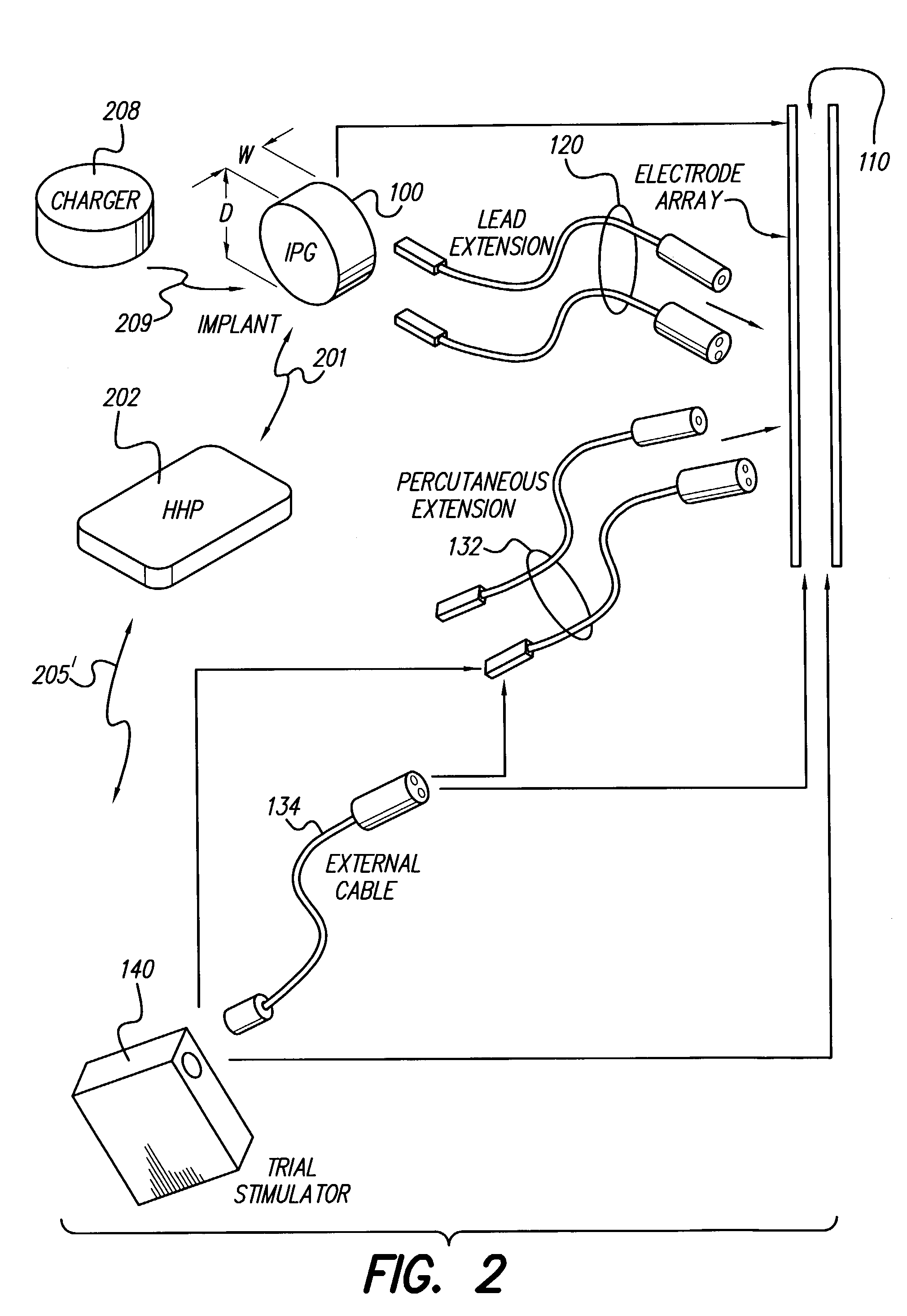
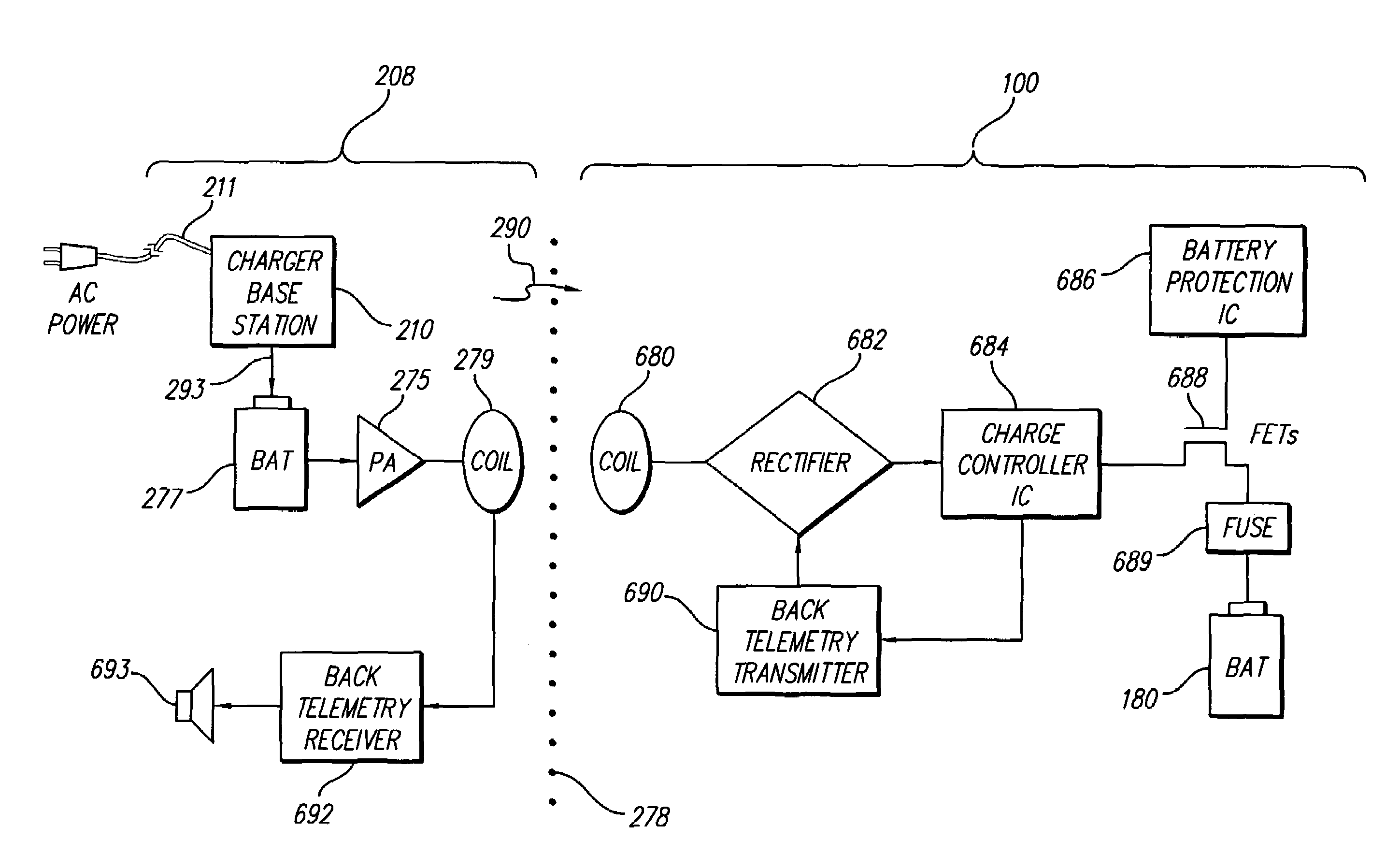
Implantable devices using rechargeable zero-volt technology lithium-ion batteries
InactiveUS7184836B1Assures safe and reliable operation of systemFirmly connectedElectrotherapyLoad circuitLow voltage
An implantable medical device, such as an implantable pulse generator (IPG) used with a spinal cord stimulation (SCS) system, includes a rechargeable lithium-ion battery having an anode electrode with a substrate made substantially from titanium. Such battery construction allows the rechargeable battery to be discharged down to zero volts without damage to the battery. The implantable medical device includes battery charging and protection circuitry that controls the charging of the battery so as to assure its reliable and safe operation. A multi-rate charge algorithm is employed that minimizes charging time while ensuring the battery cell is safely charged. Fast charging occurs at safer lower battery voltages (e.g., battery voltage above about 2.5 V), and slower charging occurs when the battery nears full charge higher battery voltages (e.g., above about 4.0 V). When potentially less-than-safe very low voltages are encountered (e.g., less than 2.5 V), then very slow (trickle) charging occurs to bring the battery voltage back up to the safer voltage levels where more rapid charging can safely occur. The battery charging and protection circuitry also continuously monitors the battery voltage and current. If the battery operates outside of a predetermined range of voltage or current, the battery protection circuitry disconnects the battery from the particular fault, i.e. charging circuitry or load circuits.
Owner:QUALLION +1
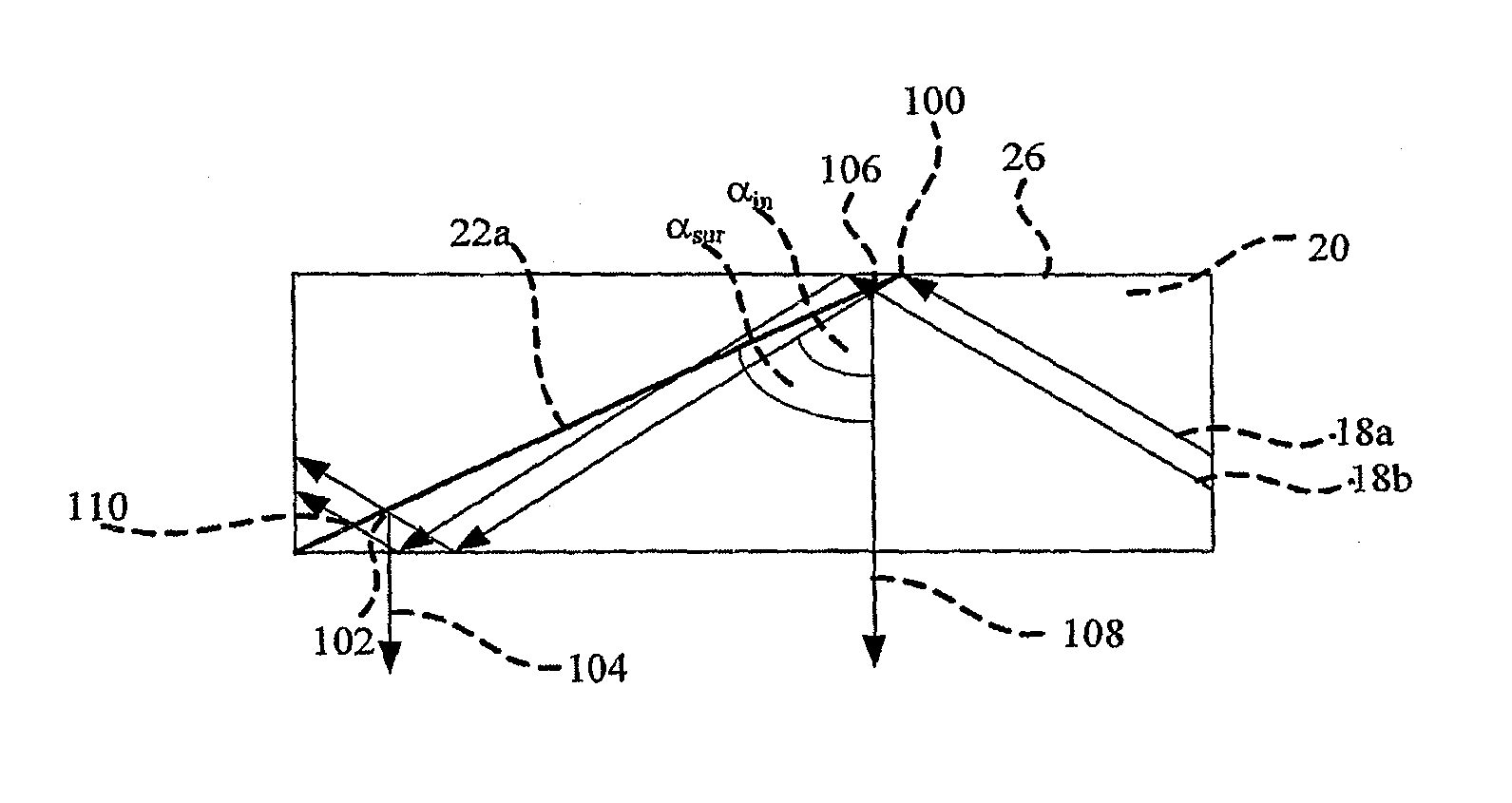
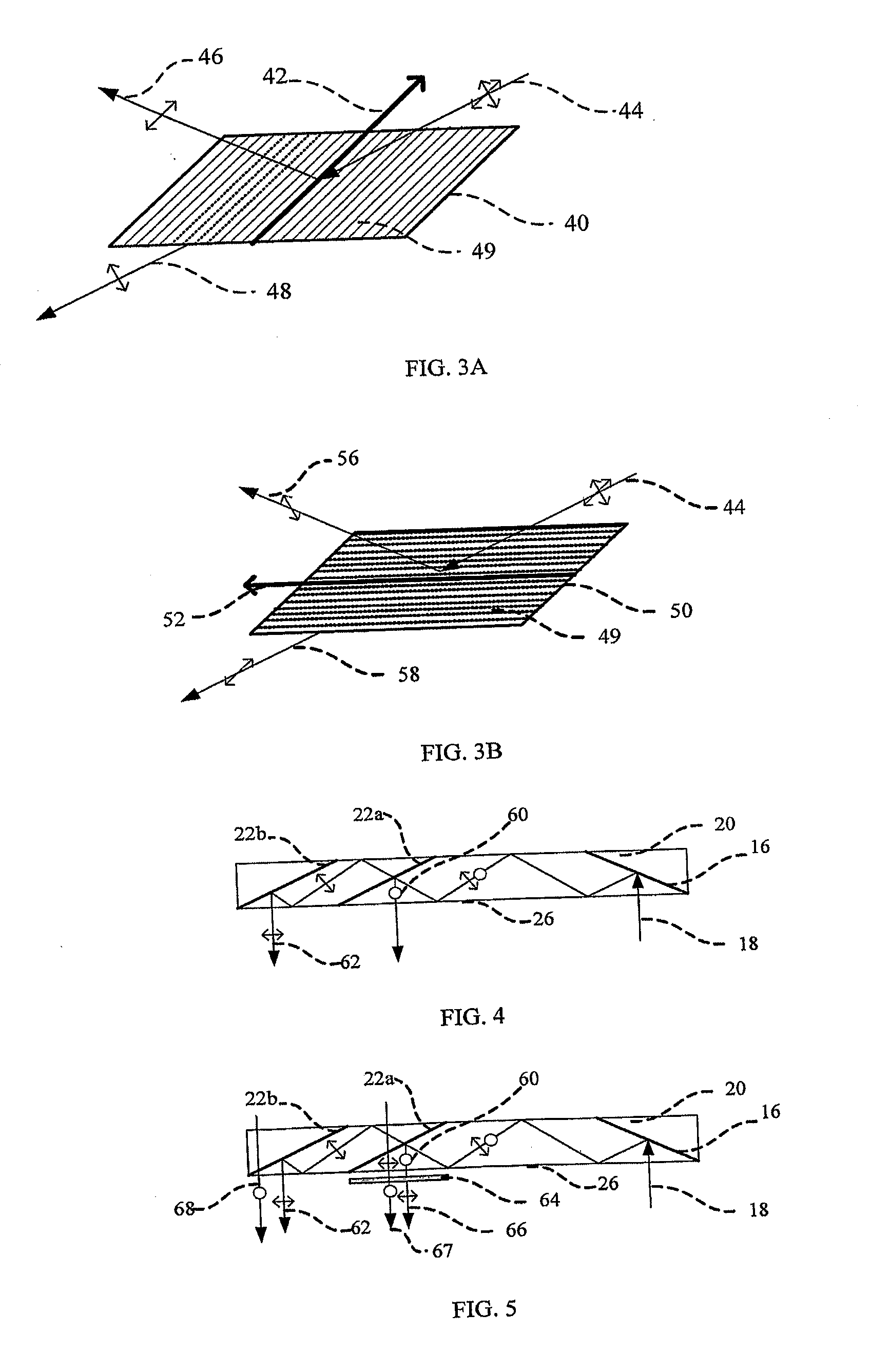
Substrate-Guide Optical Device
ActiveUS20130229717A1Design and fabrication is facilitatedEasy to mergeNon-optical adjunctsPolarising elementsTotal internal reflectionLight wave
There is provided an optical device, including a light waves-transmitting substrate having two major surfaces and edges, optical means for coupling light into the substrate by total internal reflection, and a plurality of partially reflecting surfaces (22a, 22b) carried by the substrate wherein the partially reflecting surfaces (22a, 22b) are parallel to each other and are not parallel to any of the edges of the substrate, and wherein one or more of the partially reflecting surfaces (22a, 22b) is an anisotropic surface.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Implantable devices using rechargeable zero-volt technology lithium-ion batteries
InactiveUS7295878B1Assures safe and reliable operation of systemFirmly connectedImplantable neurostimulatorsLoad circuitLow voltage
An implantable medical device, such as an implantable pulse generator (IPG) used with a spinal cord stimulation (SCS) system, includes a rechargeable lithium-ion battery having an anode electrode with a substrate made substantially from titanium. Such battery construction allows the rechargeable battery to be discharged down to zero volts without damage to the battery. The implantable medical device includes battery charging and protection circuitry that controls the charging of the battery so as to assure its reliable and safe operation. A multi-rate charge algorithm is employed that minimizes charging time while ensuring the battery cell is safely charged. Slow charging occurs at lower battery voltages (e.g., battery voltage below about 2.5 V), and fast charging occurs when the battery voltage has reached a safe level (e.g., above about 2.5 V). When potentially less-than-safe very low voltages are encountered (e.g., less than 2.5 V), then very slow (trickle) charging occurs to bring the battery voltage back up to the safer voltage levels where more rapid charging can safely occur. The battery charging and protection circuitry also continuously monitors the battery voltage and current. If the battery operates outside of a predetermined range of voltage or current, the battery protection circuitry disconnects the battery from the particular fault, i.e. charging circuitry or load circuits.
Owner:QUALLION +1
Electromagnetic interference shield
InactiveUS20120037803A1Improve blockageSubstantial transparencyRadiation pyrometryWave amplification devicesMicrowaveElectromagnetic interference
An improved EMI shielded detection system. The disclosed system may include features configured to increase radio wave and microwave absorbance while retaining significant transparency at visible and / or infrared wavelengths, thus increasing EMI shielding efficiency. This may be accomplished through the use of a conductive mesh having appropriately chosen dimensions and spacing, and embedded in a transparent medium. To minimize the impact of the mesh on the effective aperture of the medium, the strands of the mesh may be made relatively narrow, and to provide sufficient shielding despite the narrow strand width, the mesh may be embedded relatively deeply in the medium.
Owner:FLIR SYST INC
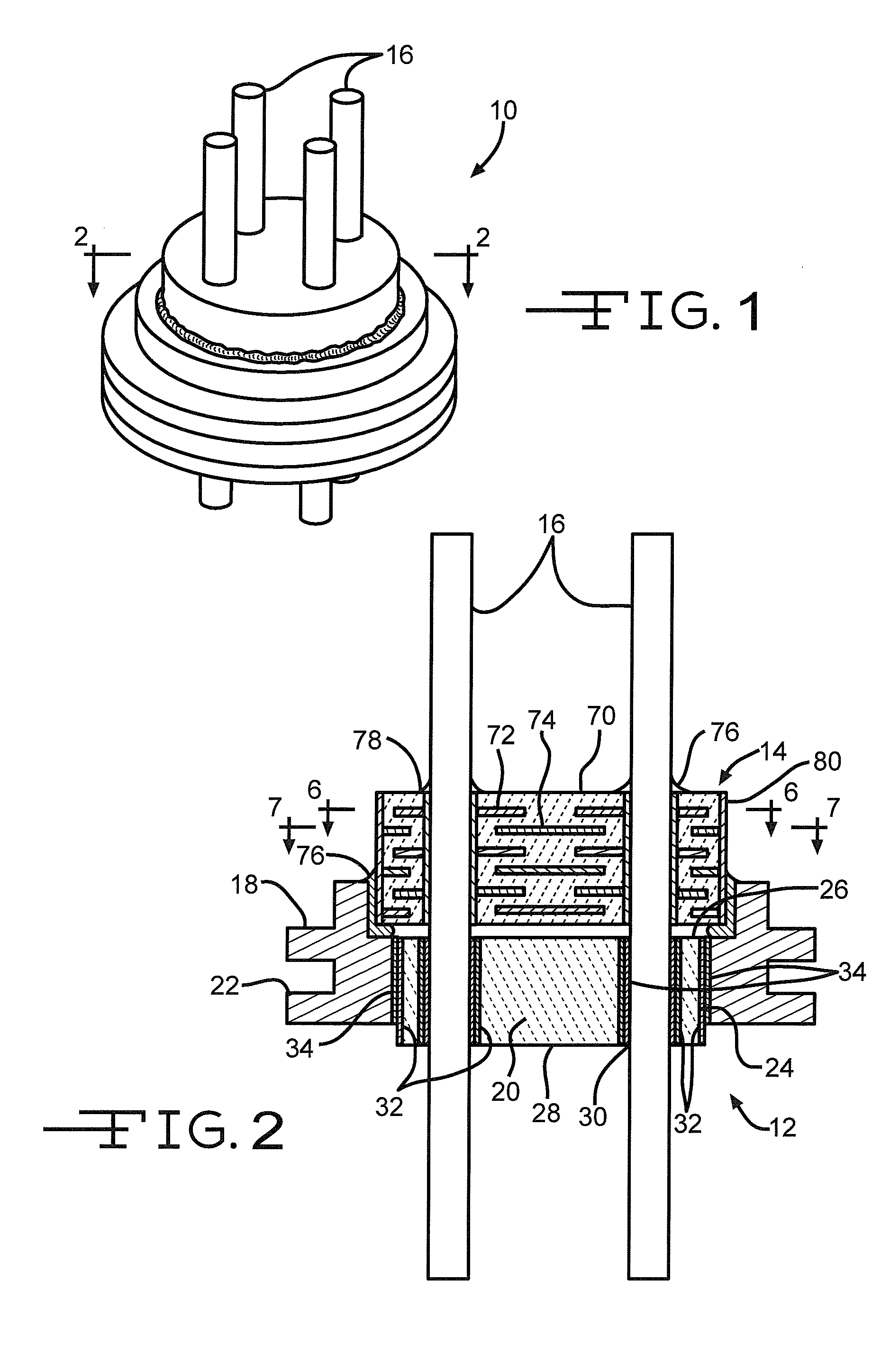
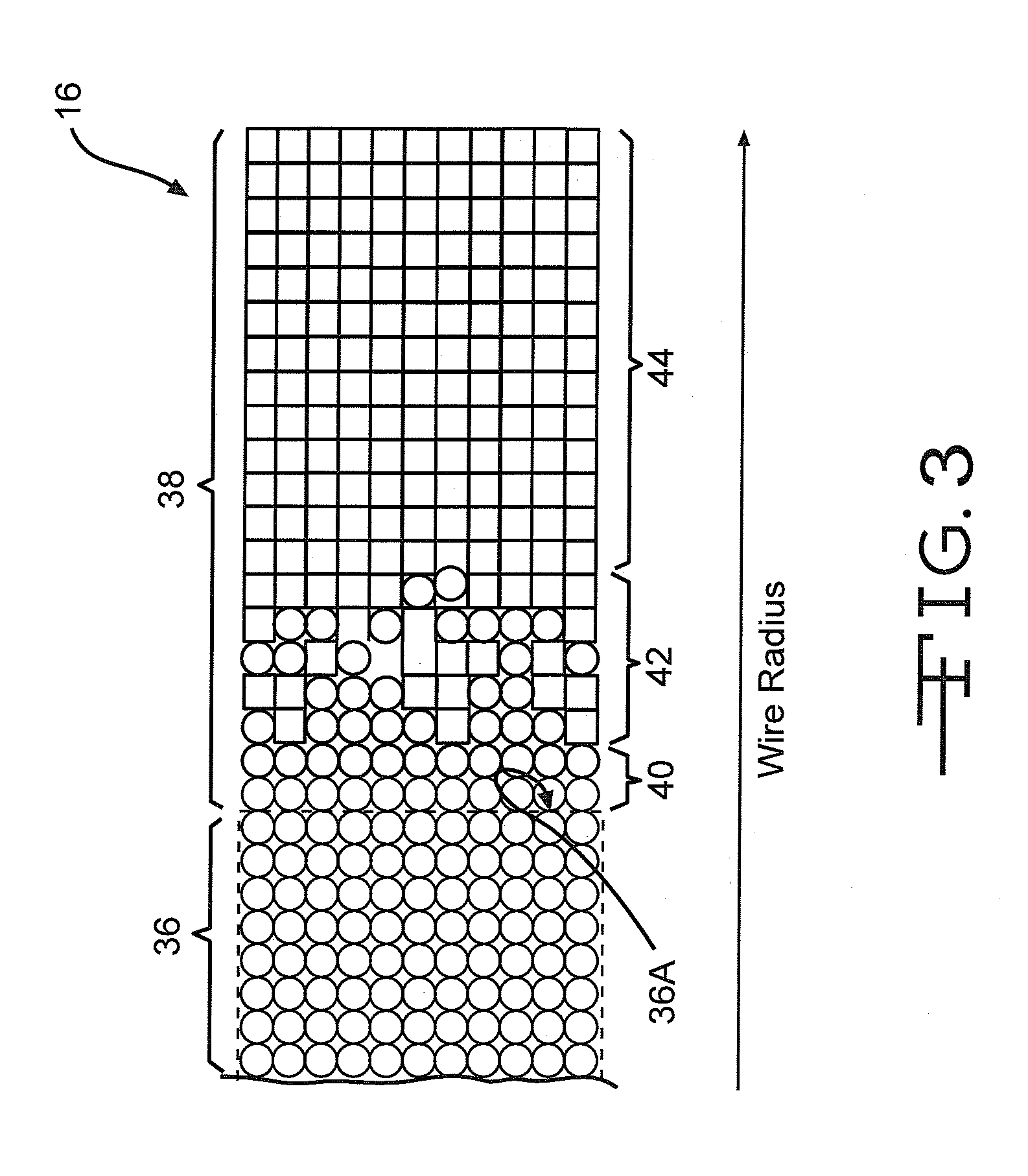
Functionally graded coatings for lead wires in medical implantable hermetic feedthrough assemblies
A feedthrough filter capacitor assembly is described. The feedthrough filter capacitor assembly comprises an outer ferrule hermetically sealed to an insulator of a dielectric material seated within the ferrule. The insulative material is also hermetically sealed to at least one lead wire. Instead of being made of platinum or platinum / iridium, the lead wire comprises a core of a non-noble metal supporting a functionally graded coating. The metal core has an inner layer of the same the non-noble metal of the core and an outer layer of a noble metal. A gradient transition zone exists between the non-noble metal and the outer noble metal. Consequently, lead wires having all the beneficial attributes of platinum and platinum / iridium wire can be built into hermetic feedthroughs, but at a significantly reduced cost. In a preferred form, a filter capacitor is mounted on the insulator and electrically connected to the lead wires and to the ferrule to prevent unwanted EMI signals from traveling along the wires and entering the interior of the medical device.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
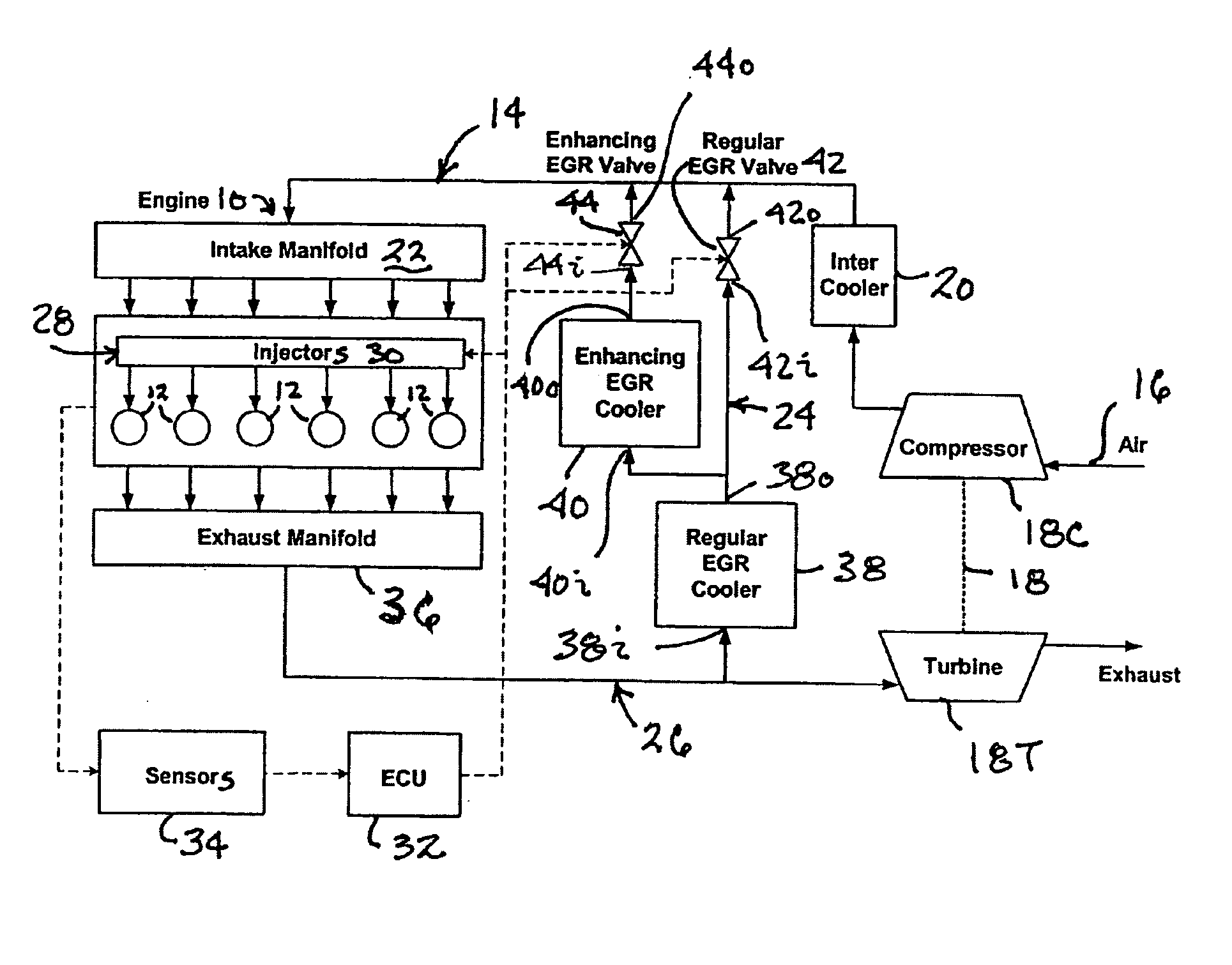
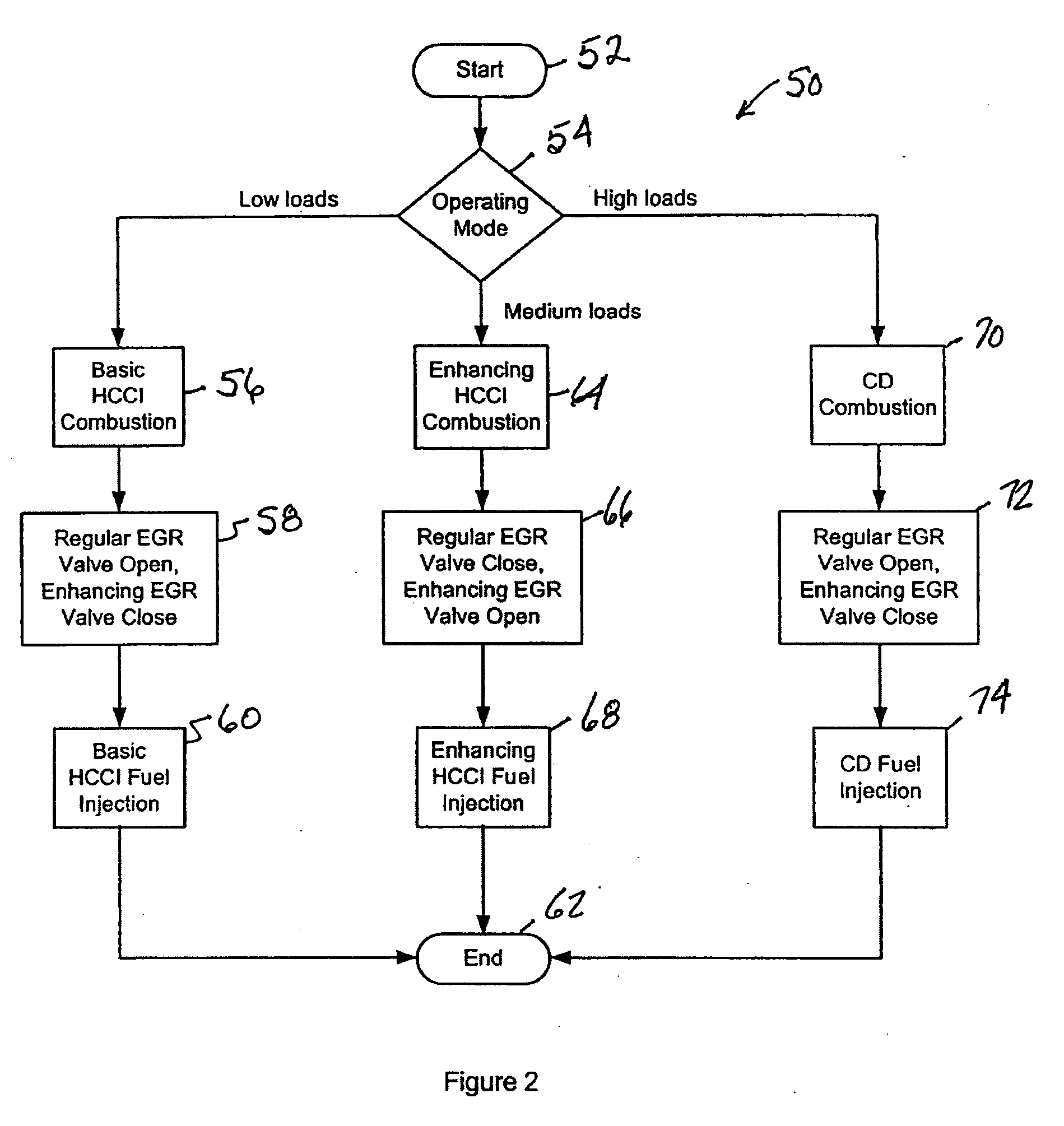
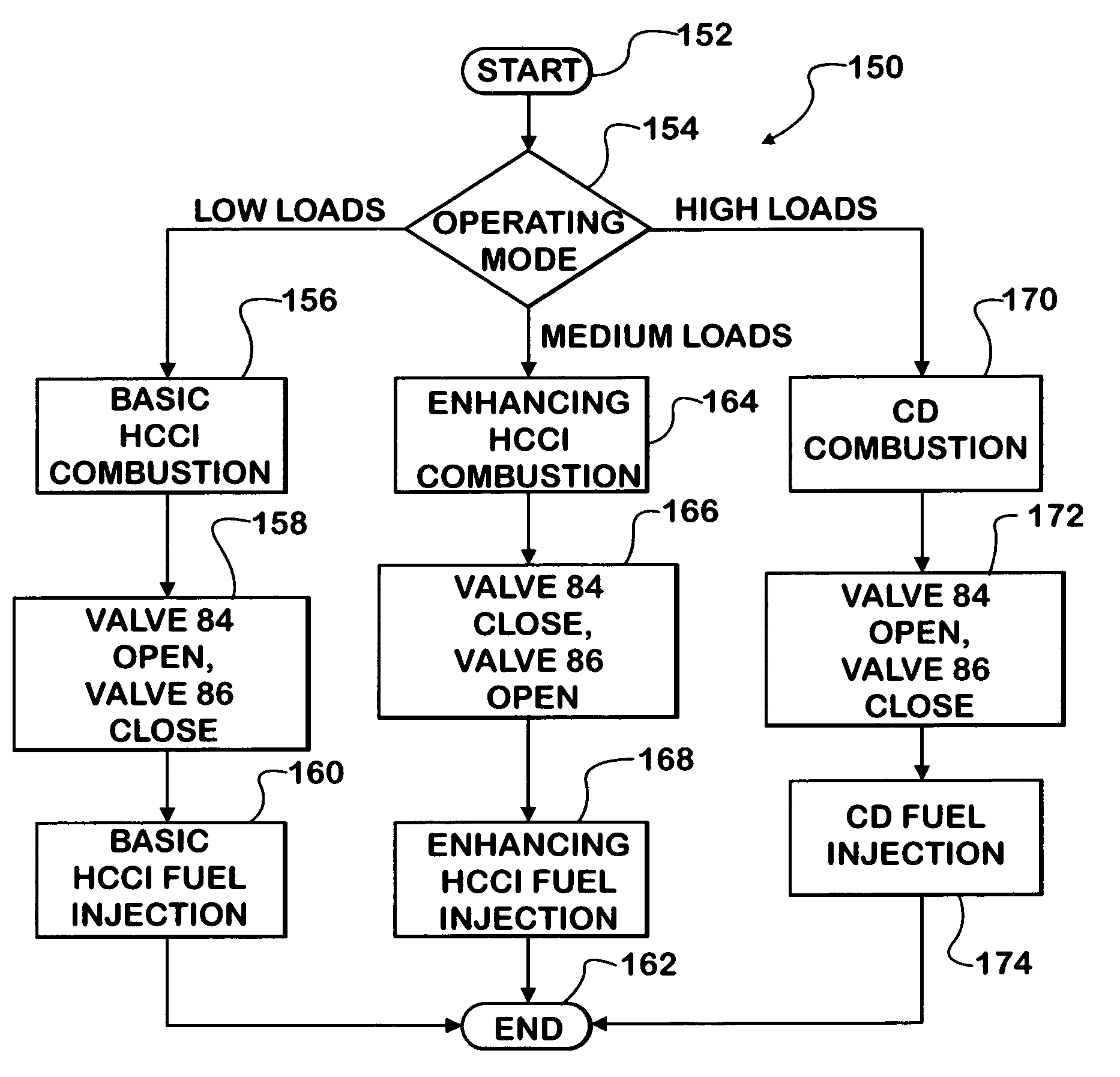
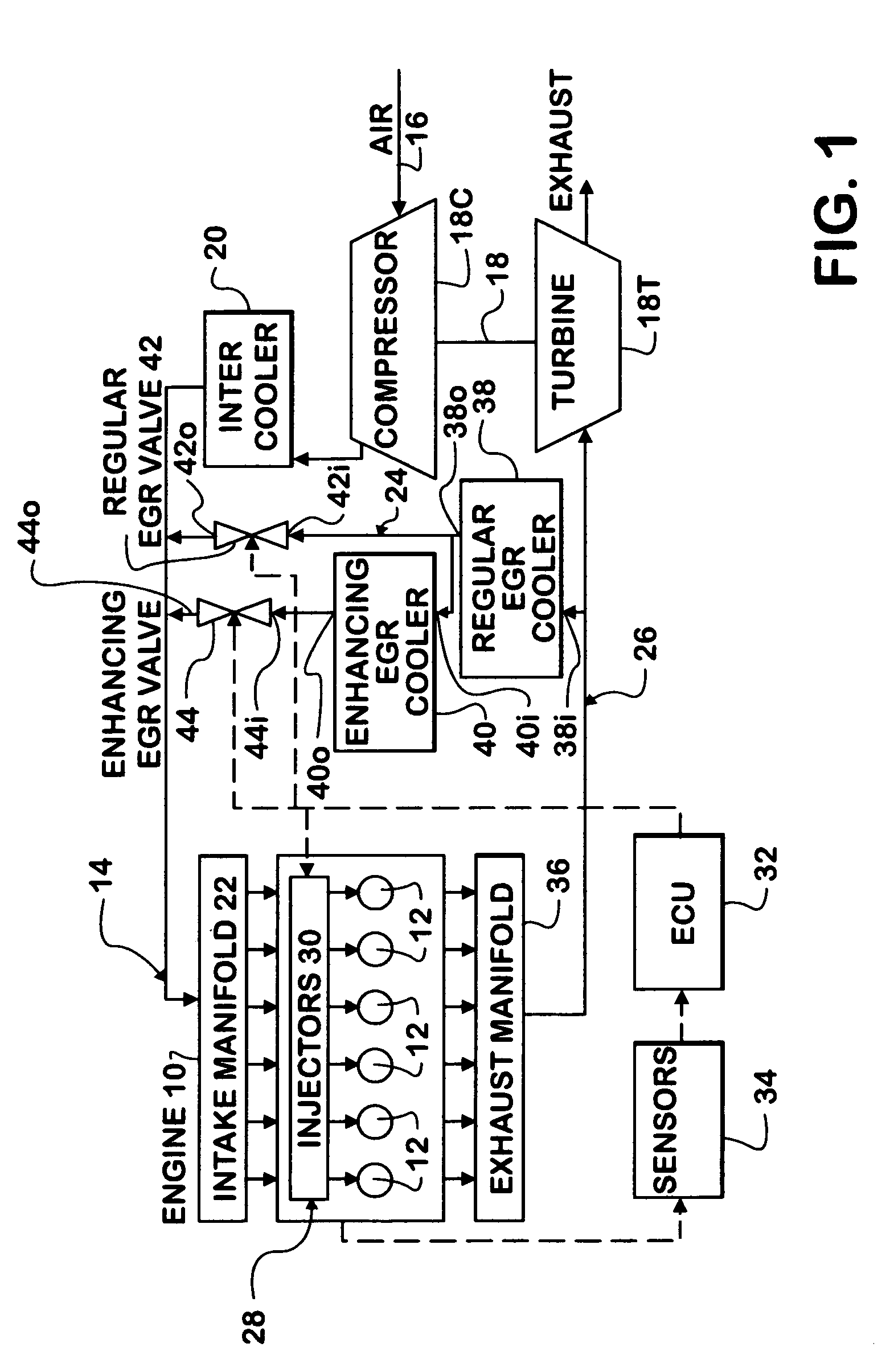
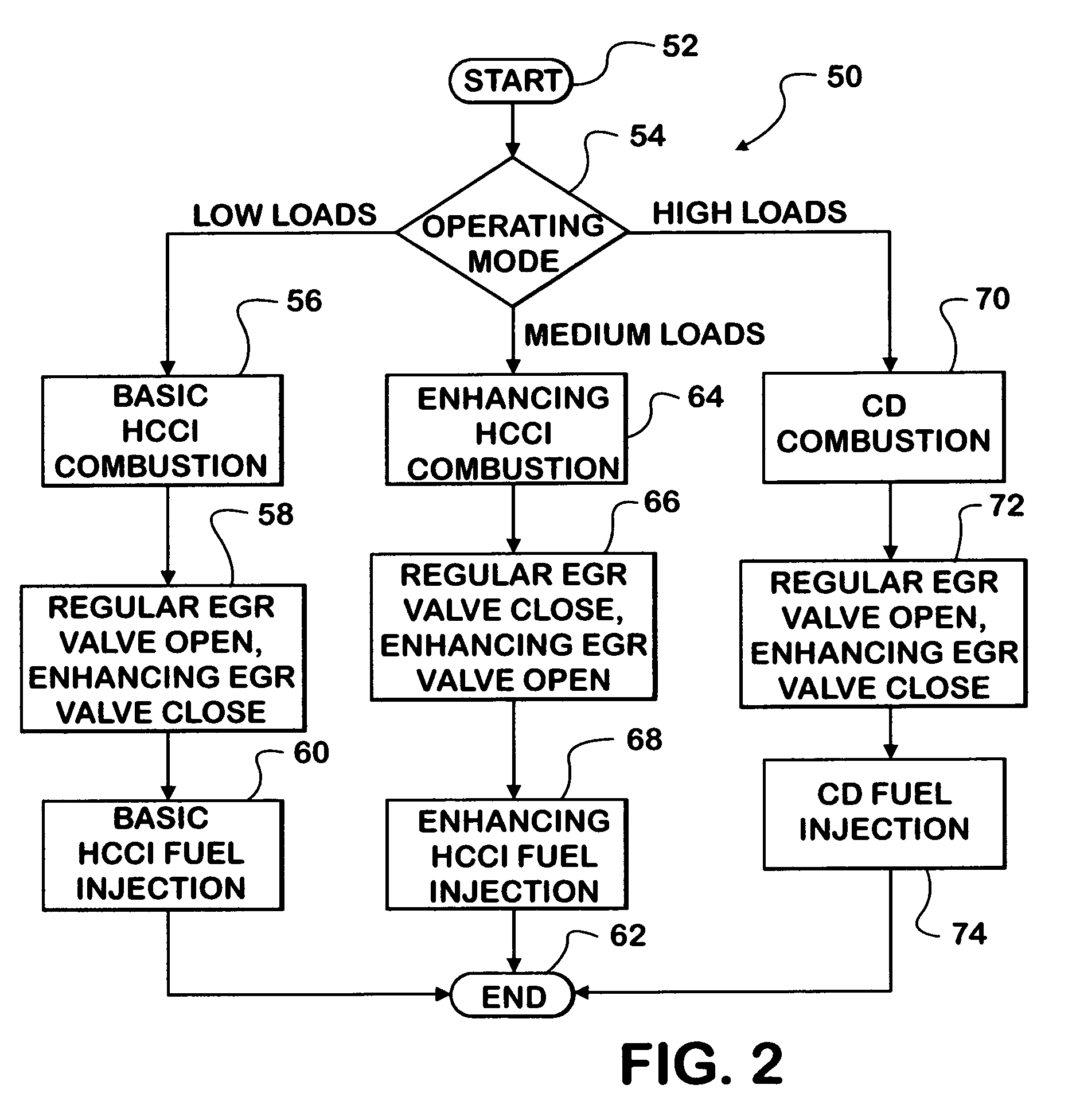
Control strategy for expanding diesel HCCI combustion range by lowering intake manifold temperature
ActiveUS20060200297A1Large loading rangeWide speed rangeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionLow load
An engine (10, 100) utilizes “regular EGR cooling” when operating in HCCI mode within a low load range and “enhanced EGR cooling” that allows the engine to continue to operate in HCCI mode when engine load increases beyond the low load range. When engine load increases to a high load range, the combustion mode changes over to conventional diesel combustion, and exhaust gas recirculation reverts to “regular EGR cooling”. In a first embodiment, cooling is provided by two heat exchangers, one being a regular EGR cooler always used when cooling is needed and the other, an enhancing EGR cooler that is selectively used. In a second embodiment, cooling is also provided by two heat exchangers, one being an EGR cooler through which liquid coolant always flows when cooling is needed, and the other being a radiator used selectively to cool the liquid coolant before it enters the EGR cooler.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC +1
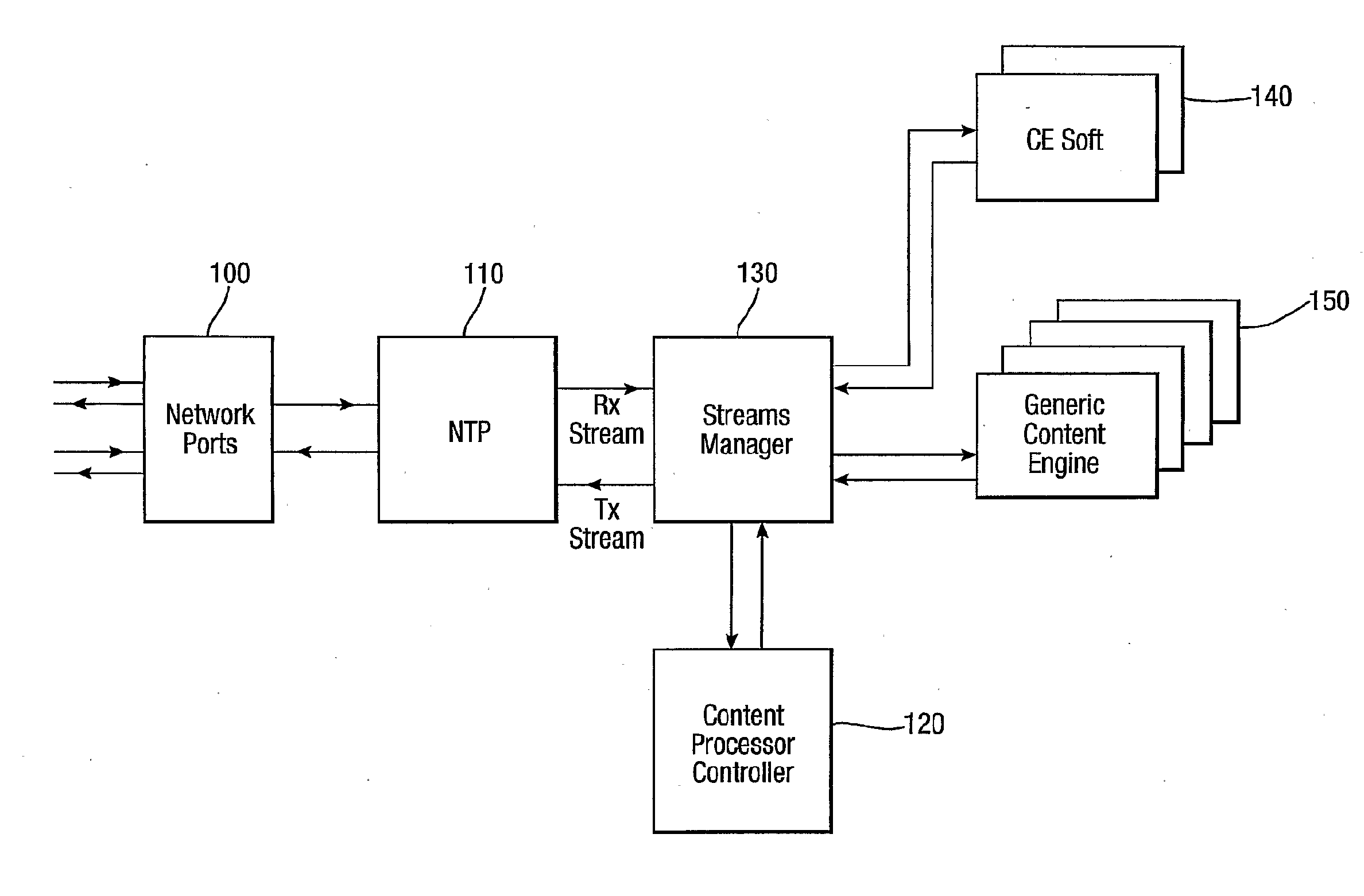
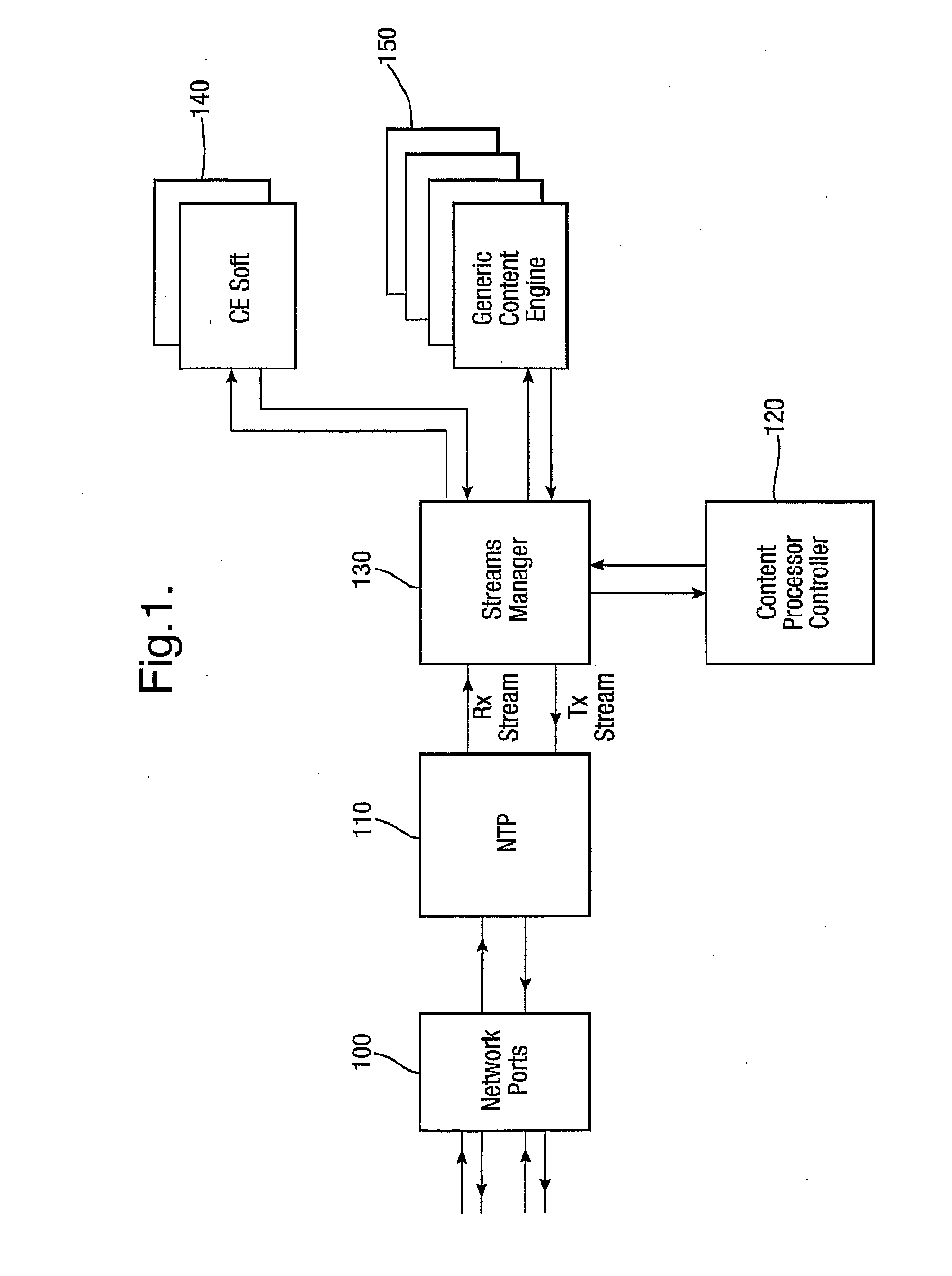
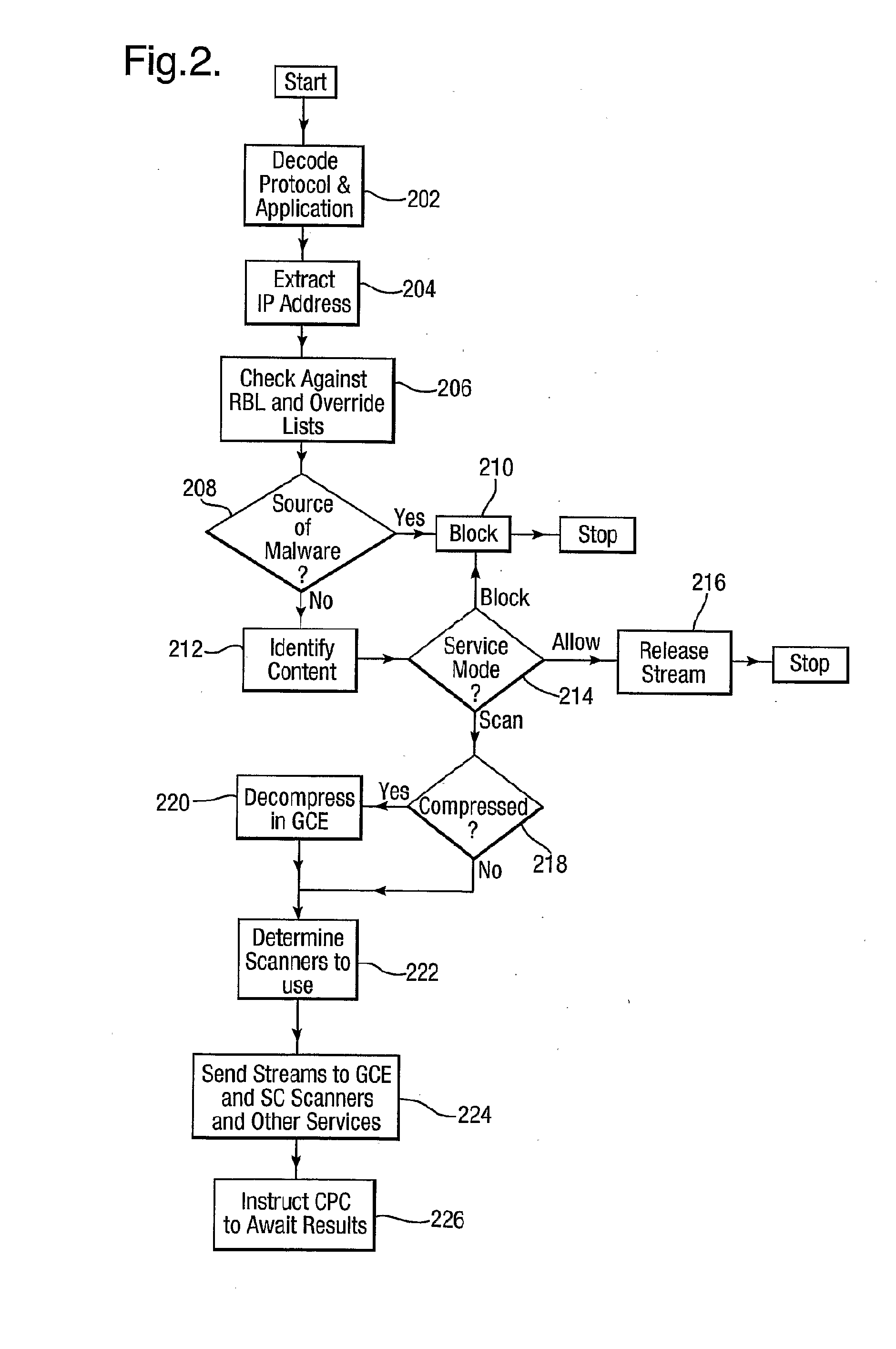
Method and apparatus for providing network security by scanning for viruses
InactiveUS20090307776A1Need can be performedReduce workloadMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionVirusComputer science
The invention relates to the provision of virus scanning capabilities in a network environment. A plurality of preliminary content processing functions are carried out on content passed over the network before the content is passed to one or more virus scanners. The virus scanners then scan the content for viruses using one or more results of the content processing functions.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
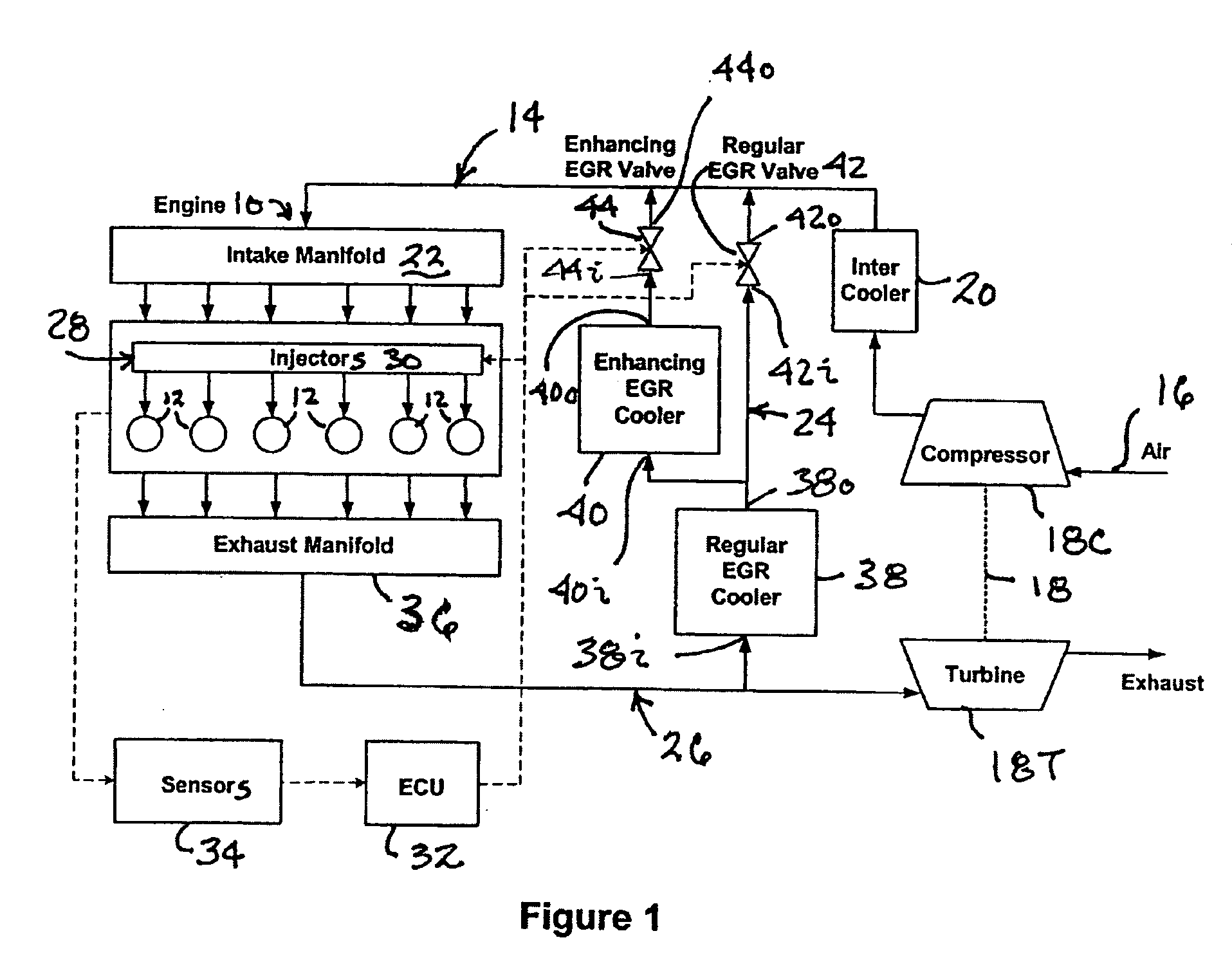
Control strategy for expanding diesel HCCI combustion range by lowering intake manifold temperature
ActiveUS7171957B2Less undesirableCompromise performanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHcci combustionLow load
An engine (10, 100) utilizes “regular EGR cooling” when operating in HCCI mode within a low load range and “enhanced EGR cooling” that allows the engine to continue to operate in HCCI mode when engine load increases beyond the low load range. When engine load increases to a high load range, the combustion mode changes over to conventional diesel combustion, and exhaust gas recirculation reverts to “regular EGR cooling”. In a first embodiment, cooling is provided by two heat exchangers, one being a regular EGR cooler always used when cooling is needed and the other, an enhancing EGR cooler that is selectively used. In a second embodiment, cooling is also provided by two heat exchangers, one being an EGR cooler through which liquid coolant always flows when cooling is needed, and the other being a radiator used selectively to cool the liquid coolant before it enters the EGR cooler.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC +1
Collection of secondary electrons through the objective lens of a scanning electron microscope
InactiveUS6946654B2Enhanced signalReduce acquisition timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesImage resolutionLight beam
A high resolution scanning electron microscope collects secondary Auger electrons through its objective lens to sensitively determine the chemical make-up with extremely fine positional resolution. The system uses a magnetic high resolution objective lens, such as a snorkel lens or a dual pole magnetic lens which provides an outstanding primary electron beam performance. The Auger electrons are deflected from the path of the primary beam by a transfer spherical capacitor. The primary beam is shielded, by a tube or plates, as it traverses the spherical capacitor to prevent aberration of the primary beam and the external wall of the shield maintains a potential gradient related to that of the spherical capacitor to reduce aberration of the primary electron beam. The coaxial configuration of the primary electron beam and the collected secondary electron beam allows the Auger image to coincide with the SEM view.
Owner:FEI CO
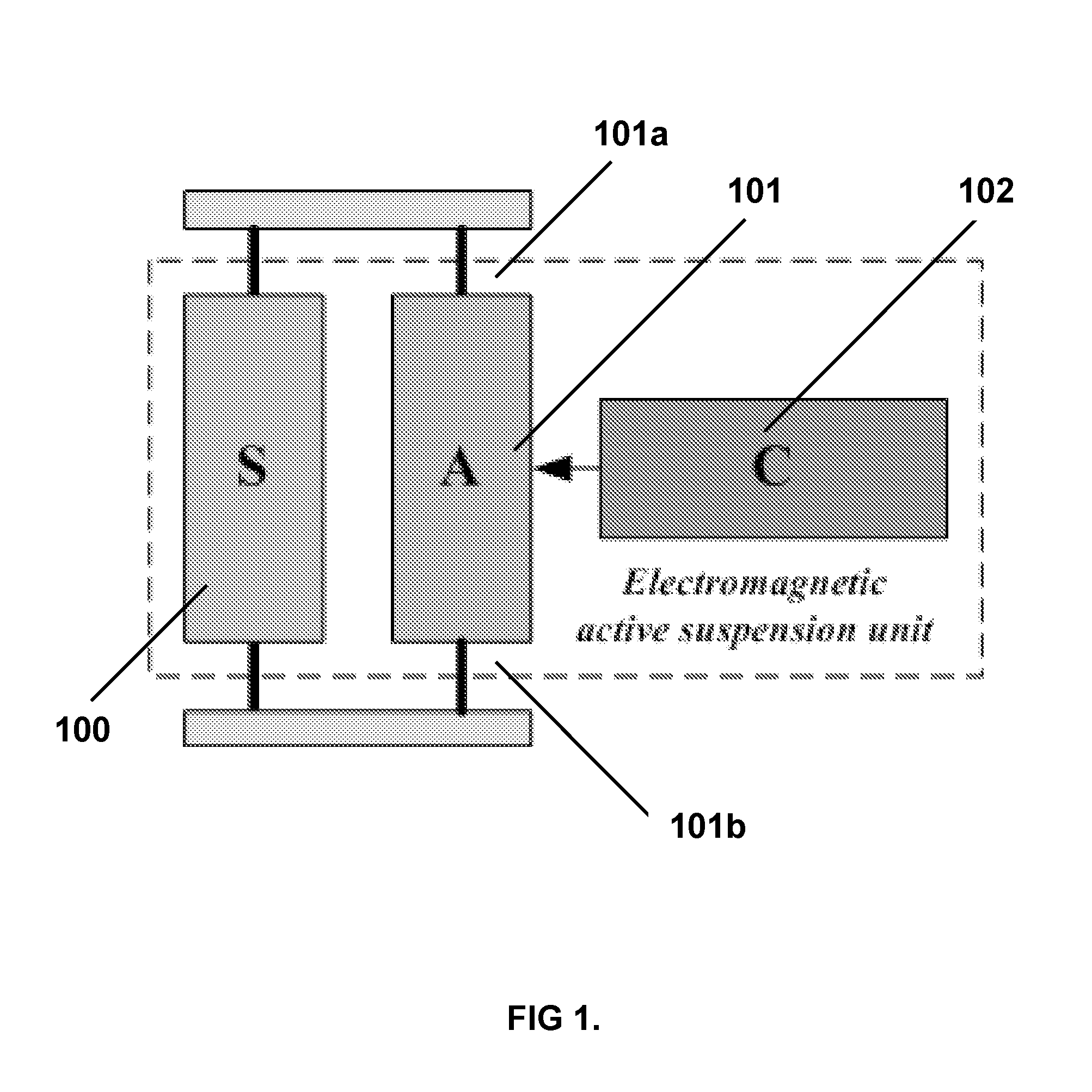
Active suspension system and method
ActiveUS20130161921A1Improve dynamic performanceDecrease pitchNon-rotating vibration suppressionResilient suspensionsSprung massControl theory
An active suspension system suitable for use with a vehicle, includes a passive suspension element with a first end adapted for rigid engagement to a sprung mass of the vehicle and a second end adapted for rigid engagement to an unsprung mass of the vehicle. Also included is an active suspension element with a linear switched reluctance actuator which has a first end adapted for rigid engagement to the sprung mass of the vehicle and a second end adapted for rigid engagement to the unsprung mass of the vehicle.
Owner:HONG KONG PRODUCTIVITY COUNCIL
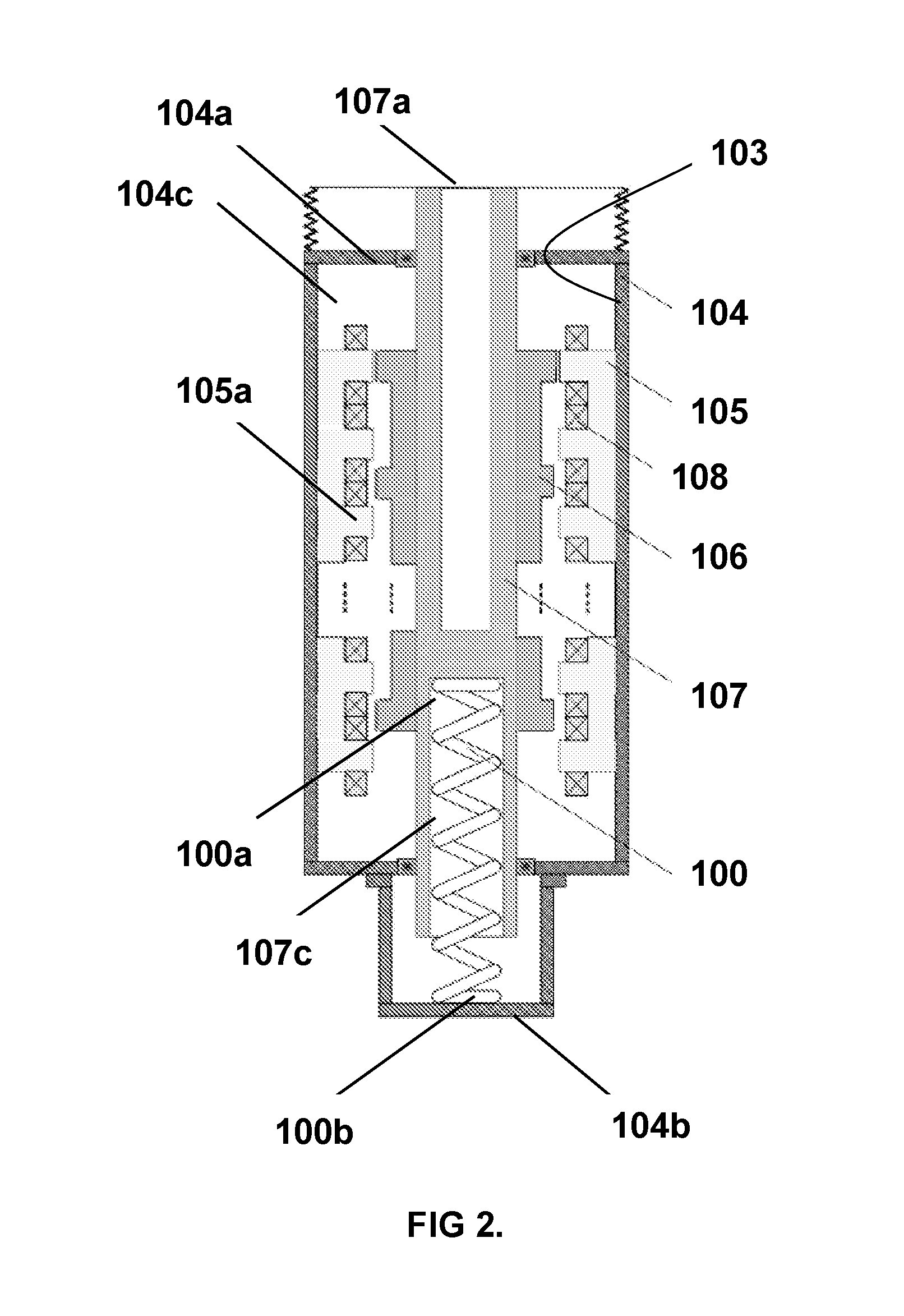
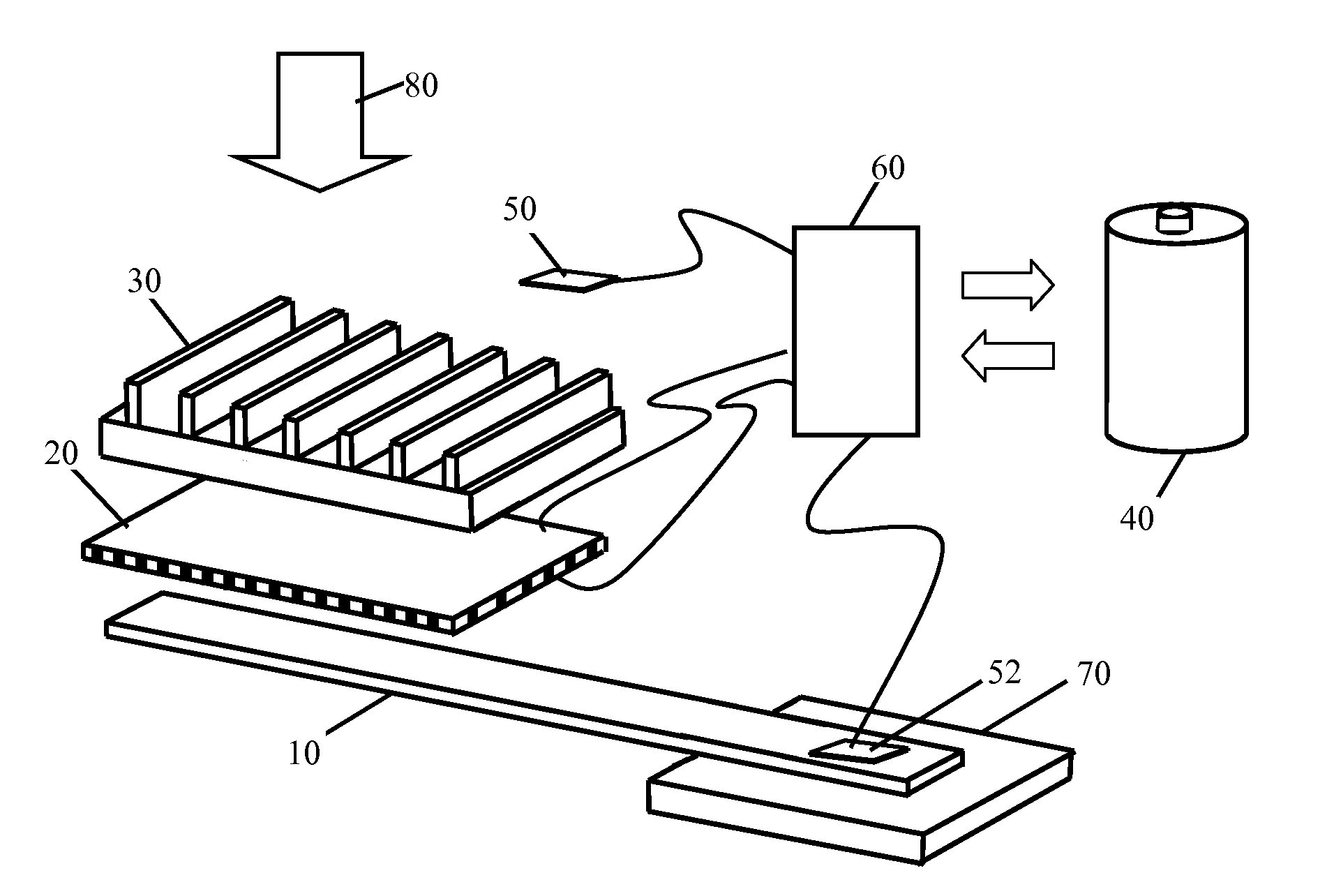
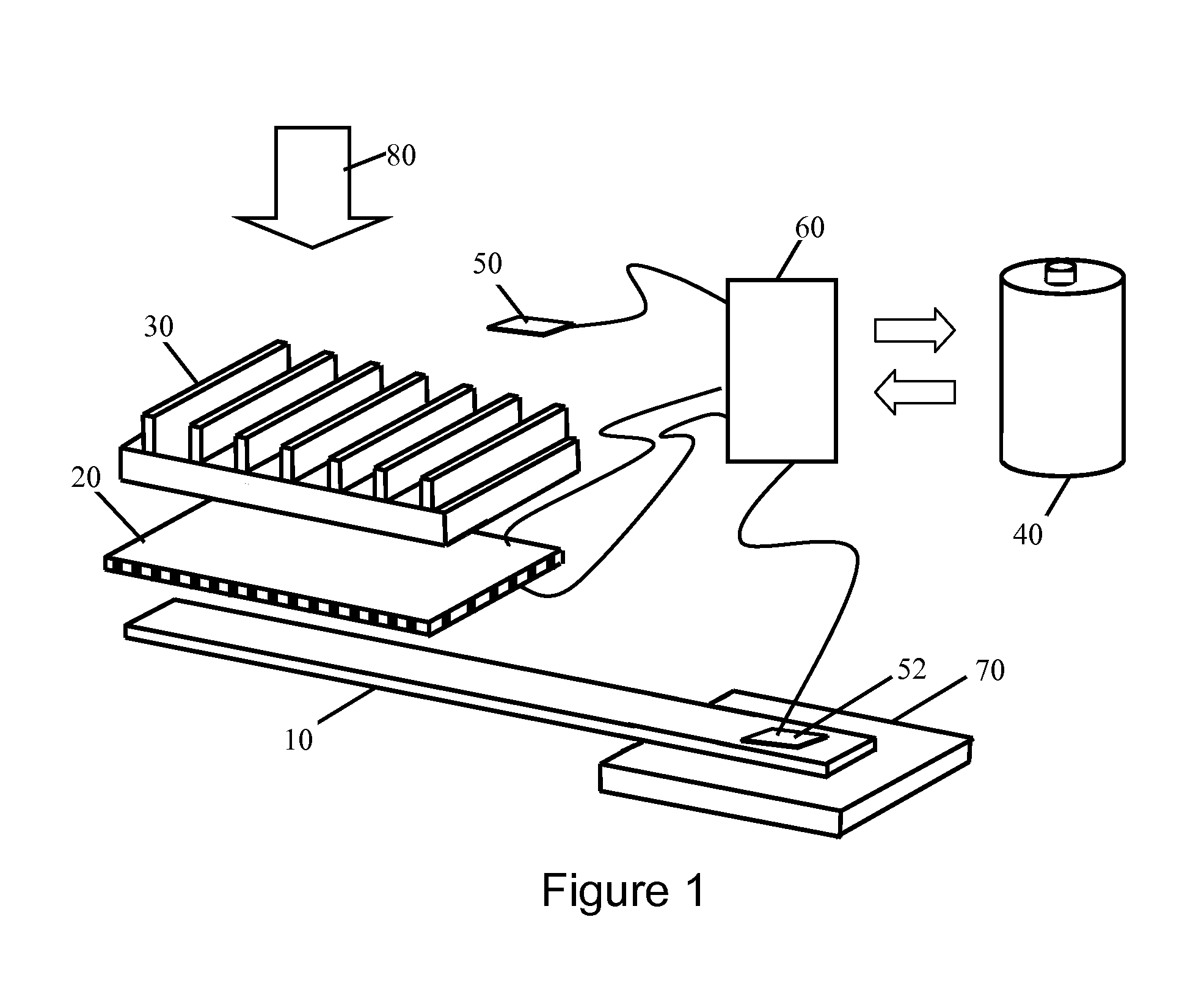
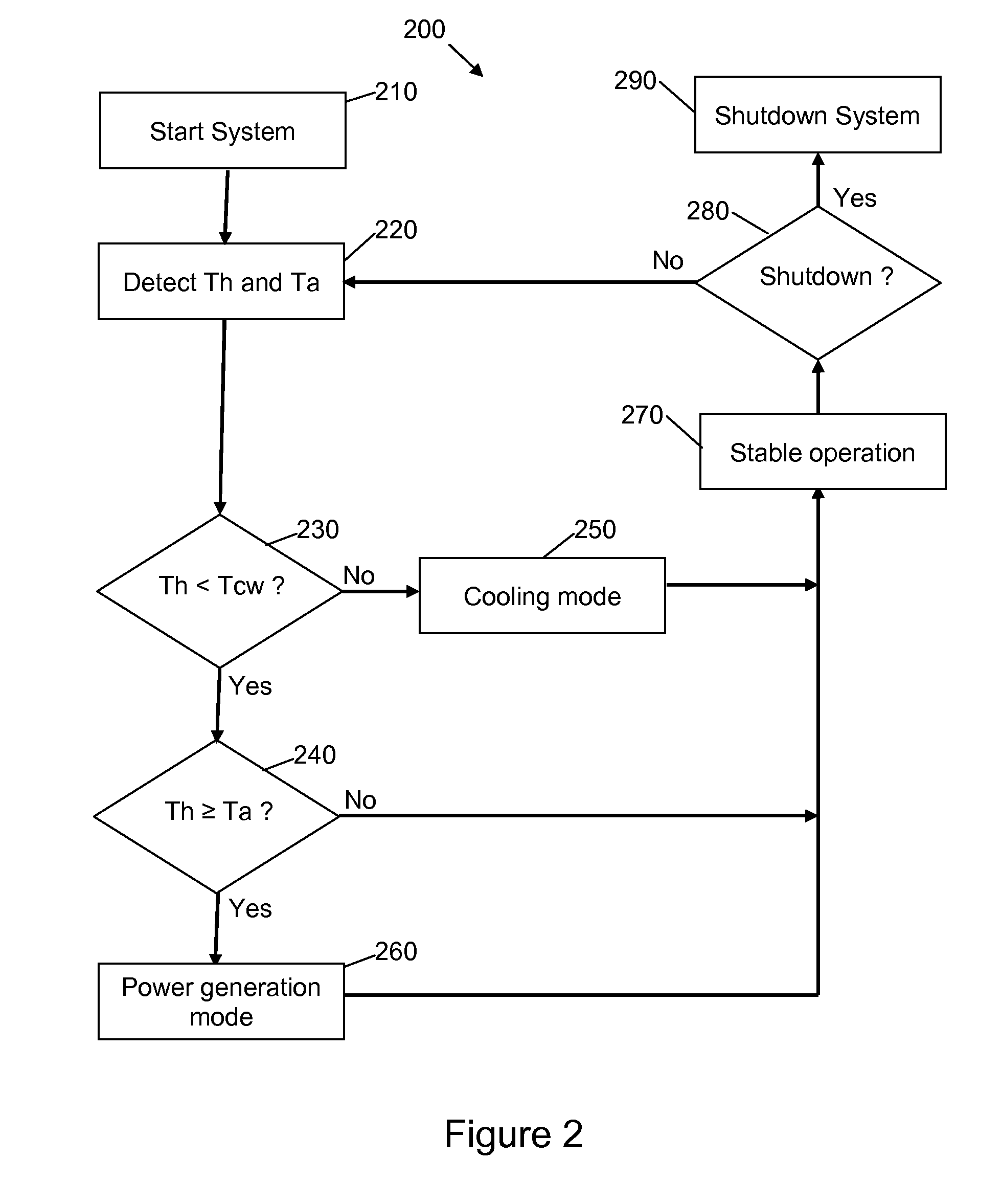
Dynamic switching thermoelectric thermal management systems and methods
InactiveUS20120096871A1Improve conductivityLow thermal conductivityMachines using electric/magnetic effectsRefrigeration safety arrangementTemperature differenceEngineering
A dynamic switching thermoelectric thermal management system and method is disclosed. The thermal management system includes a heat dissipation device, a thermoelectric module, an ambient temperature sensor, a heat source temperature sensor, an energy storage device and a controller. One side of the thermoelectric module is thermally coupled to the heat source and another side is thermally coupled to the heat dissipation device. The controller periodically samples the temperature sensors and dynamically switches the thermoelectric module between a power generation mode in which the thermoelectric module uses the temperature difference between the heat source and ambient to charge the energy storage device, a cooling mode in which the thermoelectric module is powered to create a voltage difference across the thermoelectric module to cool the heat source, and an idle mode. The thermal management system can be integrated into a portable electronic device, for example a portable computing device.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Parallel remembered-set processing respecting popular-object detection
ActiveUS7617264B1Hinder taskCompromise performanceDigital data processing detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWaste collectionParallel computing
A garbage collector that operates in multiple threads divides a generation of a garbage-collected heap into heap sections, with which it associates respective remembered sets of locations where references to objects in those heap sections have been found. When such a heap section comes up for collection, each of a plurality of parallel garbage-collector threads that is processing its remembered set maintains a separate “popularity”—indicating count map, which includes an entry for each of a set of segments into which the collector has divided that heap section. The thread increments an entry in its count map each time it finds a reference to an object in the associated segment. If an object is located in a segment for which the associated count-map entry has exceeded a threshold, the thread evacuates the object in a manner different from that in which it evacuates objects not thus been found to be popular.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
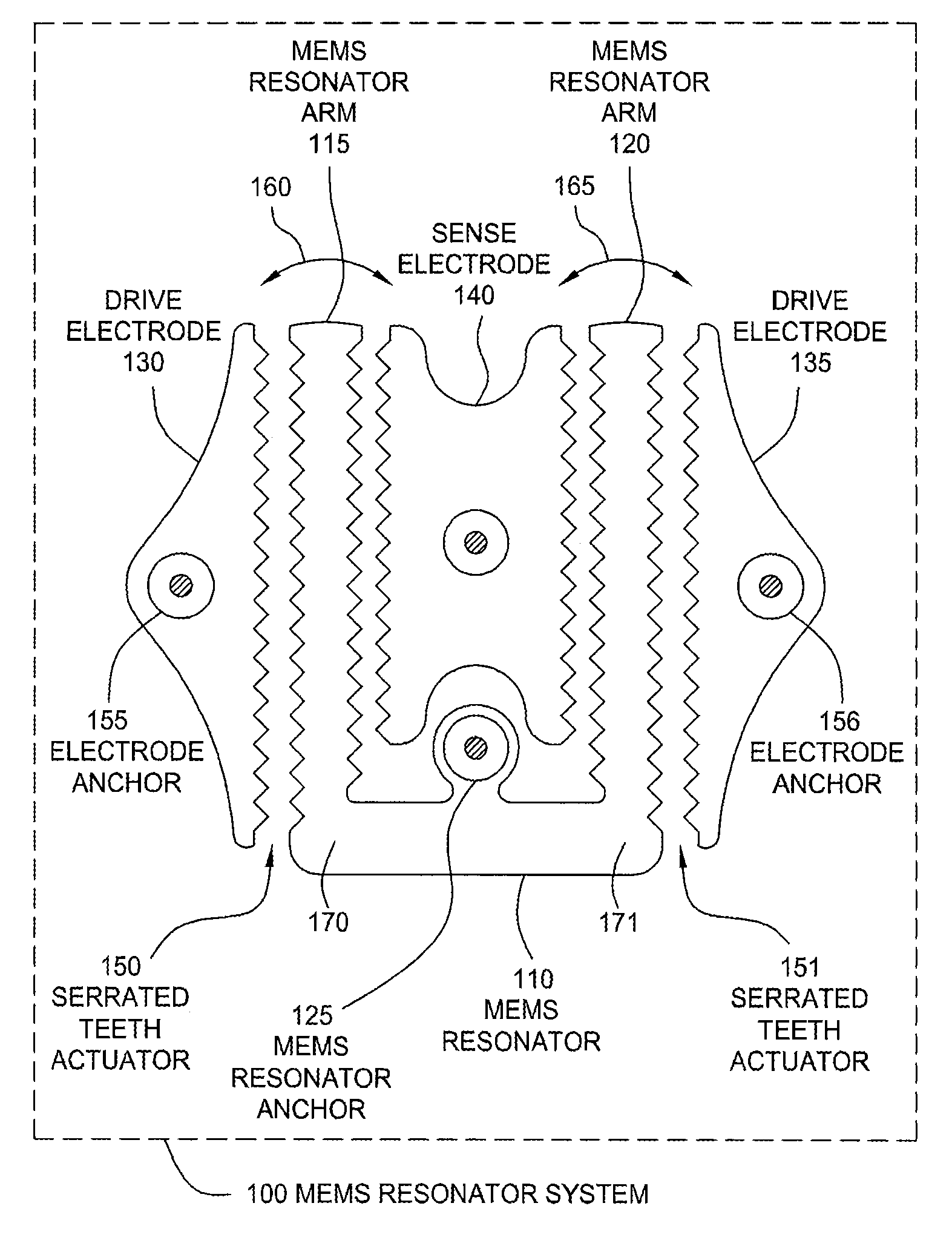
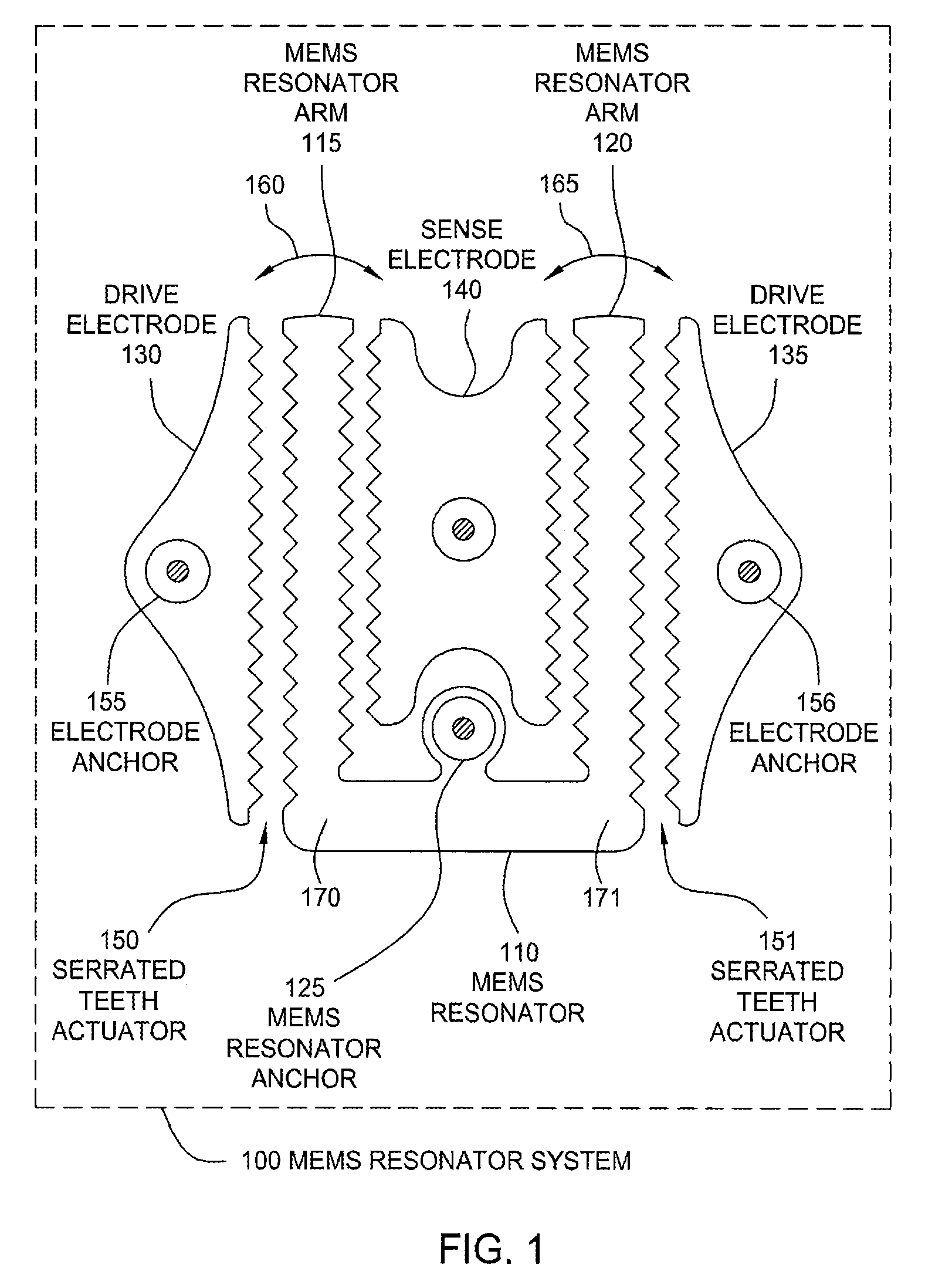
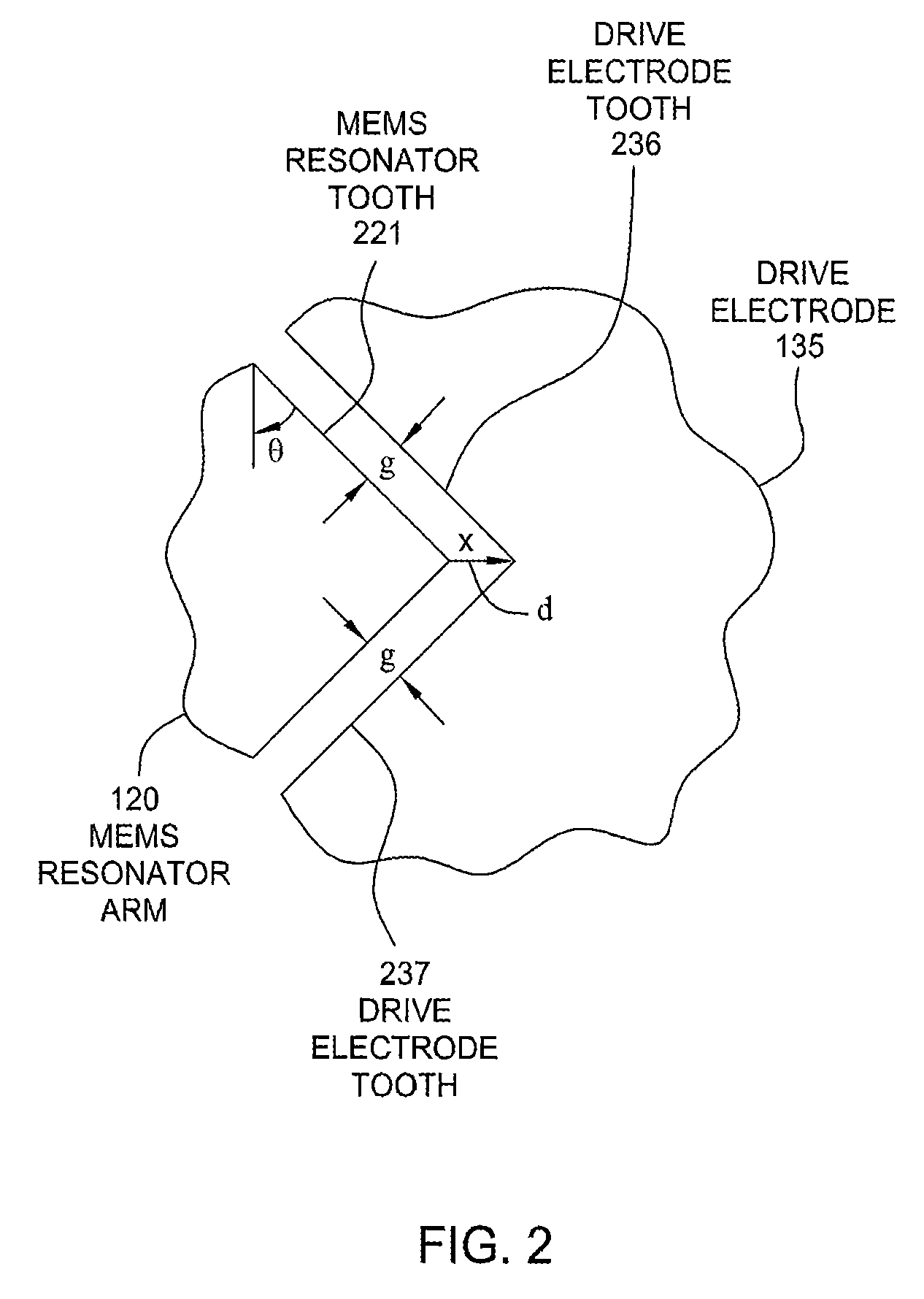
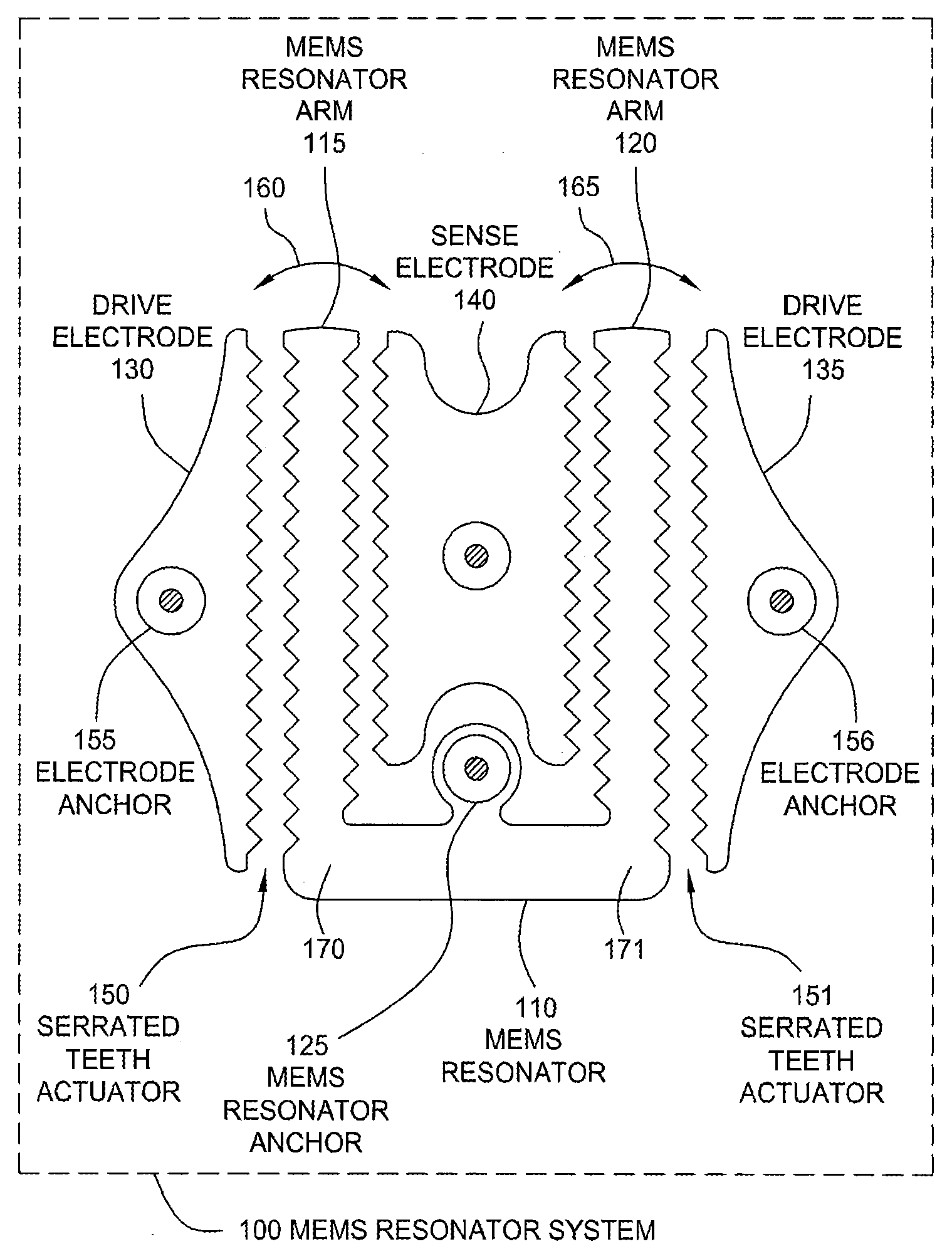
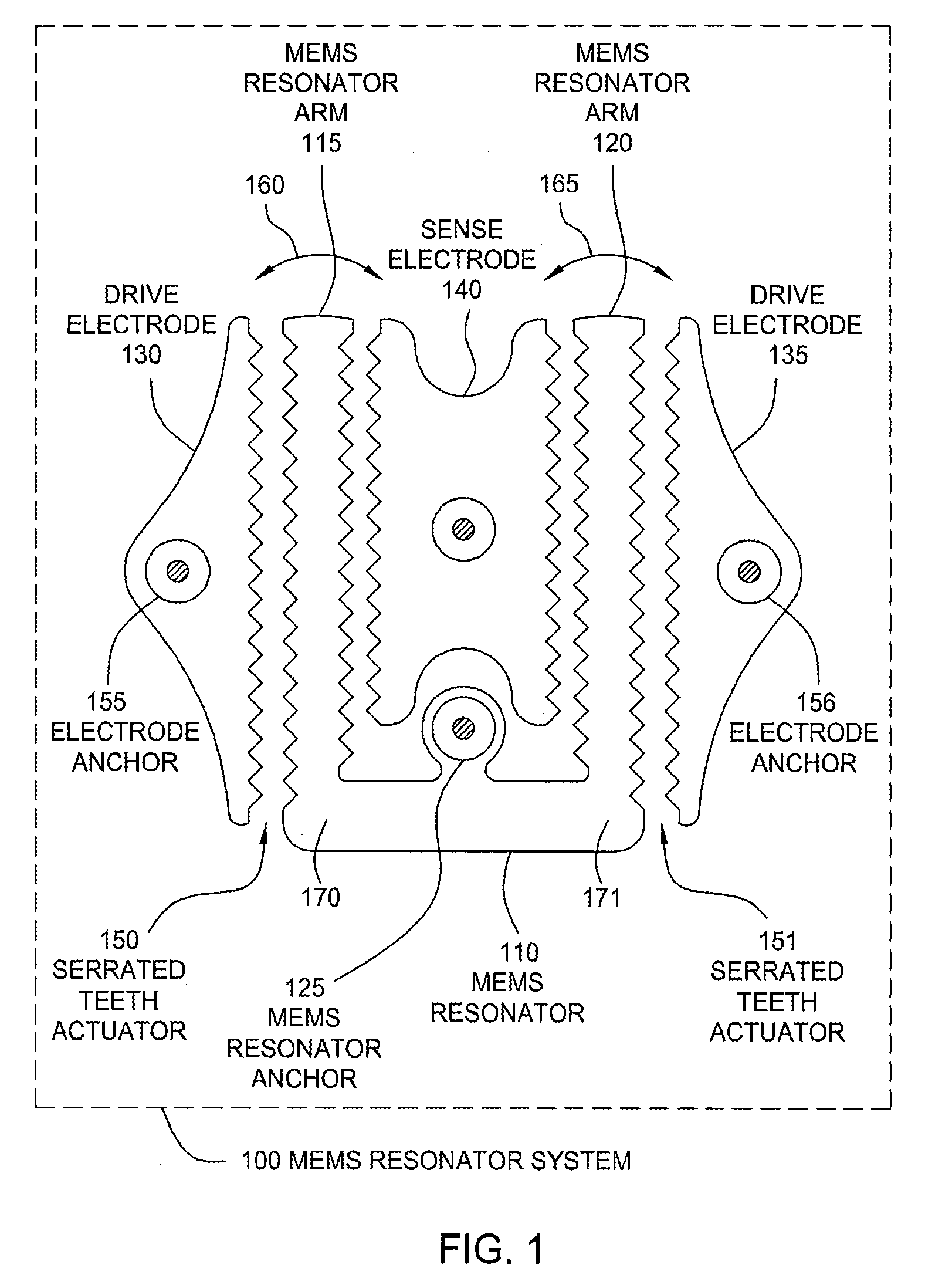
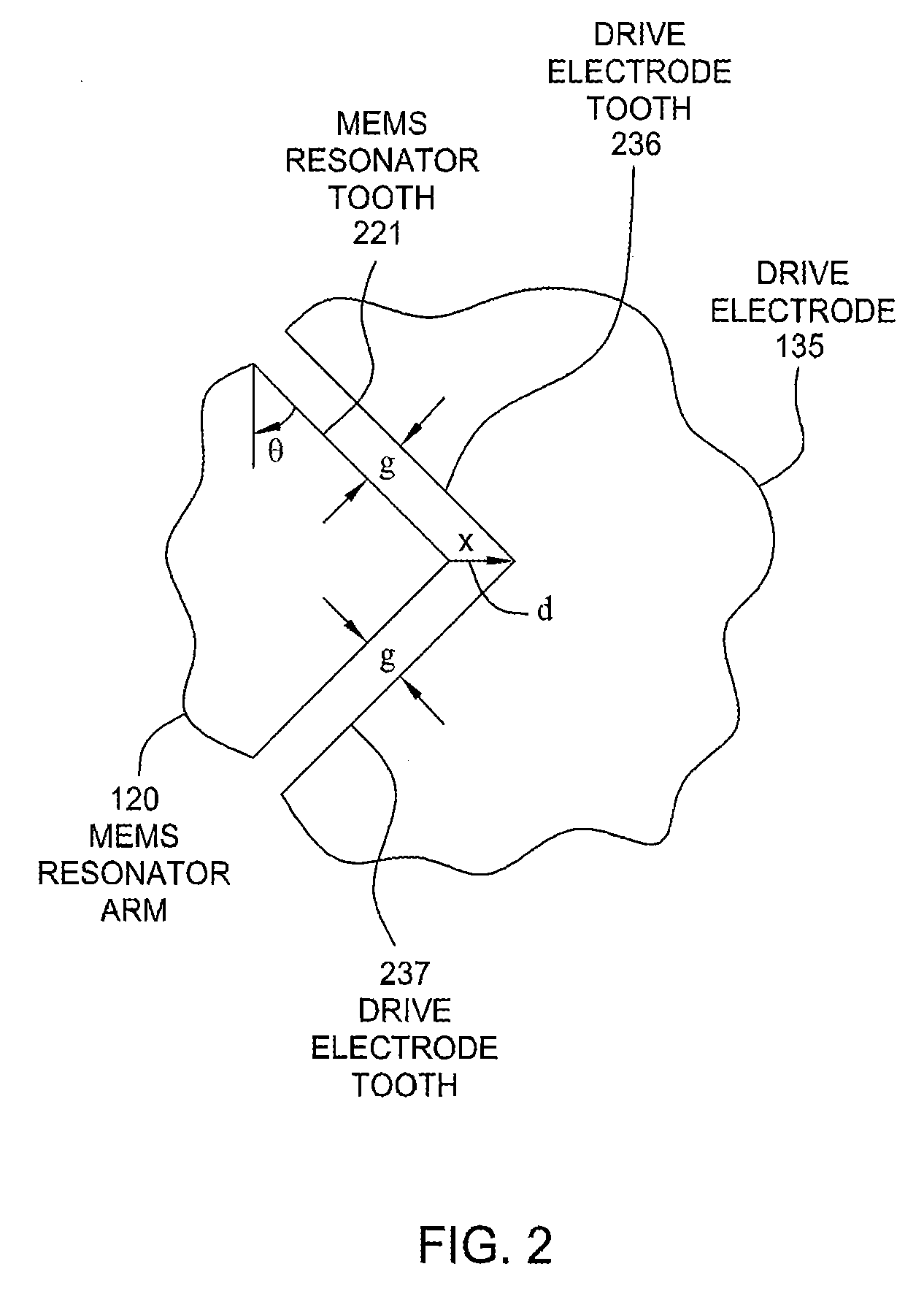
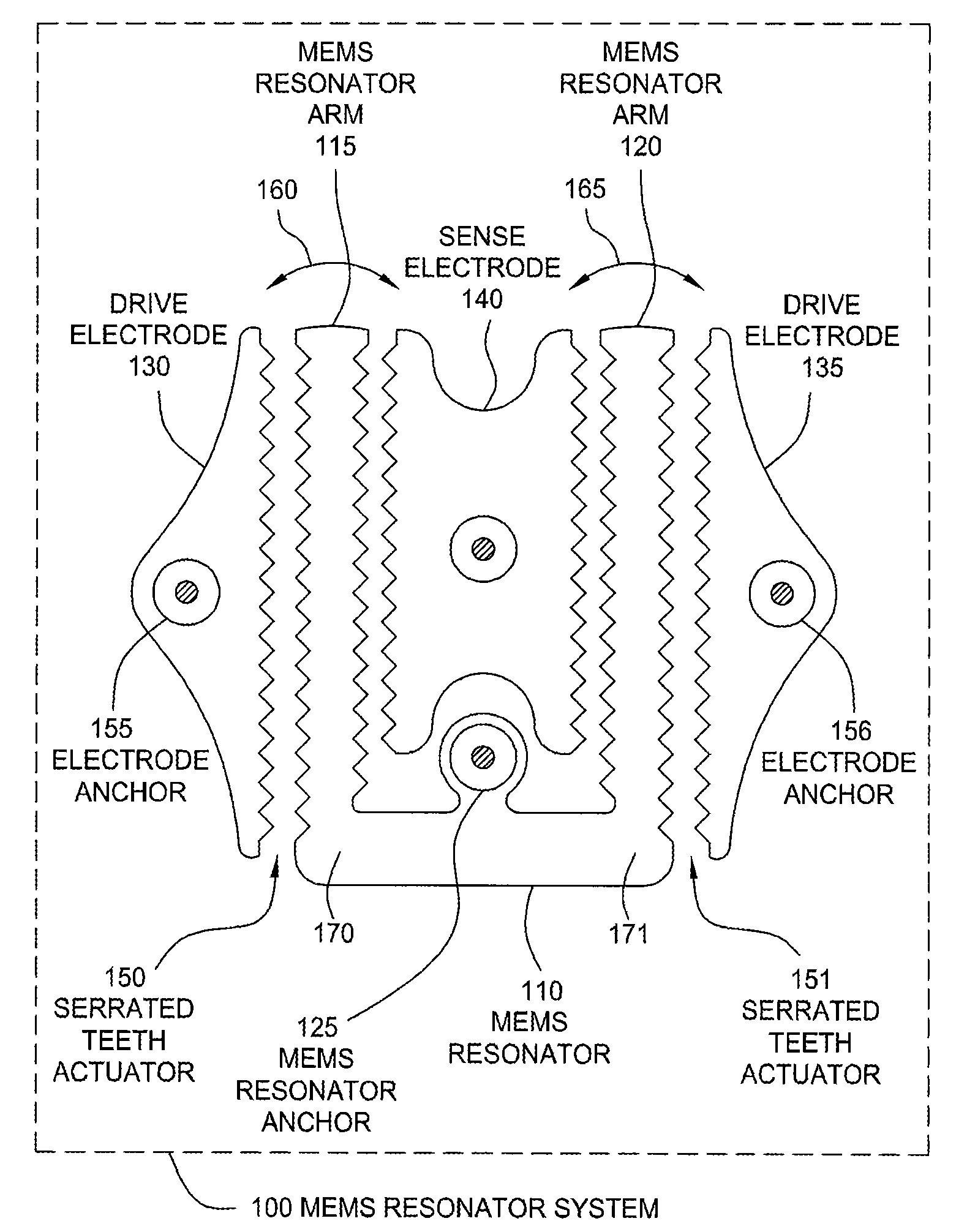
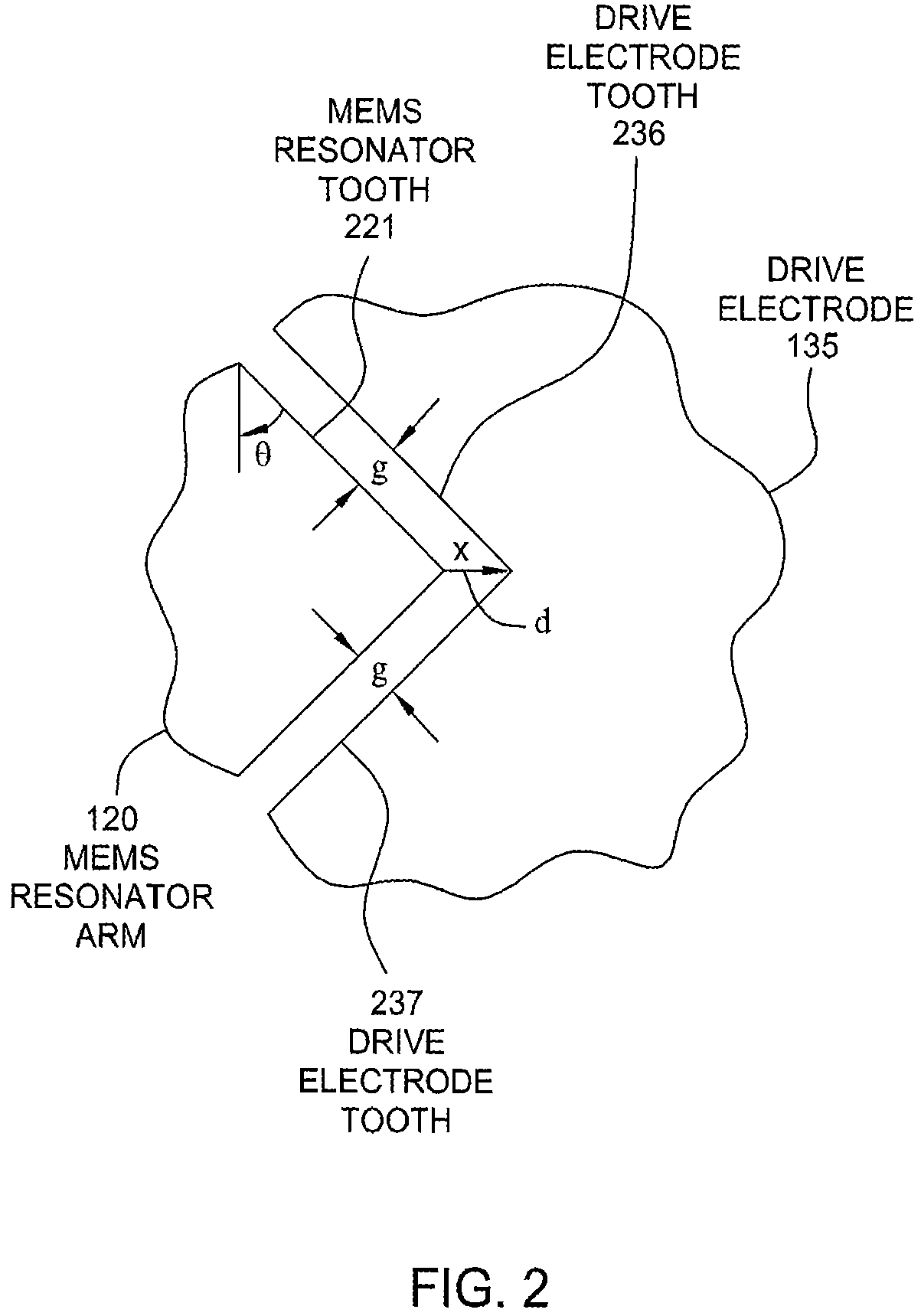
Serrated MEMS resonators
ActiveUS7545239B2Enhanced signalCompromise performanceImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesActuatorControl theory
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a serrated tooth actuator for driving MEMS resonator structures. The actuator includes a fixed drive electrode having a serrated tooth surface opposing a MEMS resonator arm also having a serrated tooth surface, where the MEMS resonator arm is configured to rotate towards the drive electrode when an AC signal is applied to the drive electrode. Such a configuration permits higher amplitude signals to be applied to the drive electrode without the performance of the actuator being compromised by nonlinear effects. In addition, the serrated tooth configuration enables a sufficiently high actuating force to be maintained even though the distance traversed by the MEMS resonator arm during operation is quite small. Further, the serrated configuration allows a MEMS resonator system to withstand larger fluctuations in voltage and larger substrate stresses without experiencing a substantial shift in resonant frequency.
Owner:SITIME
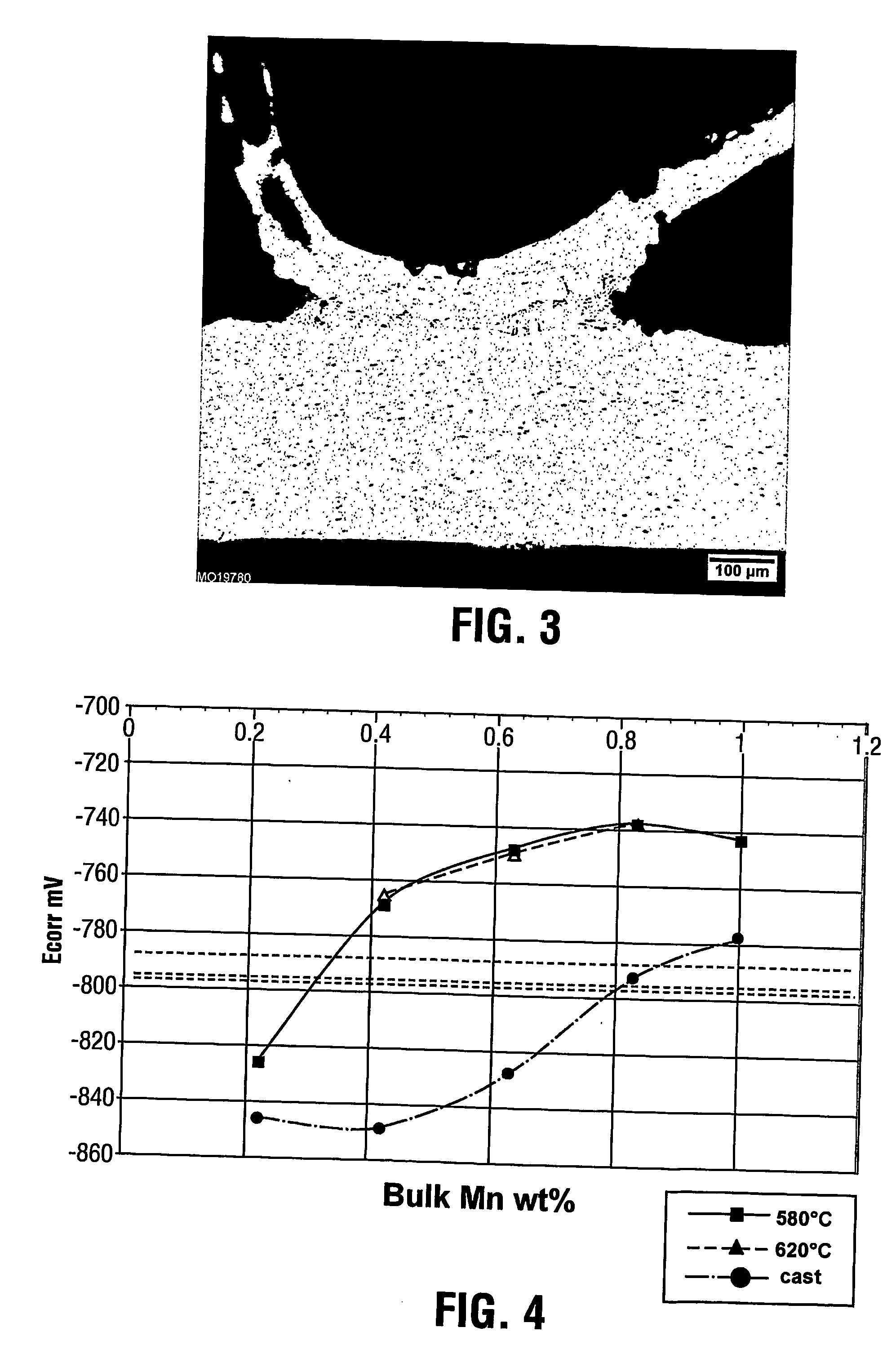
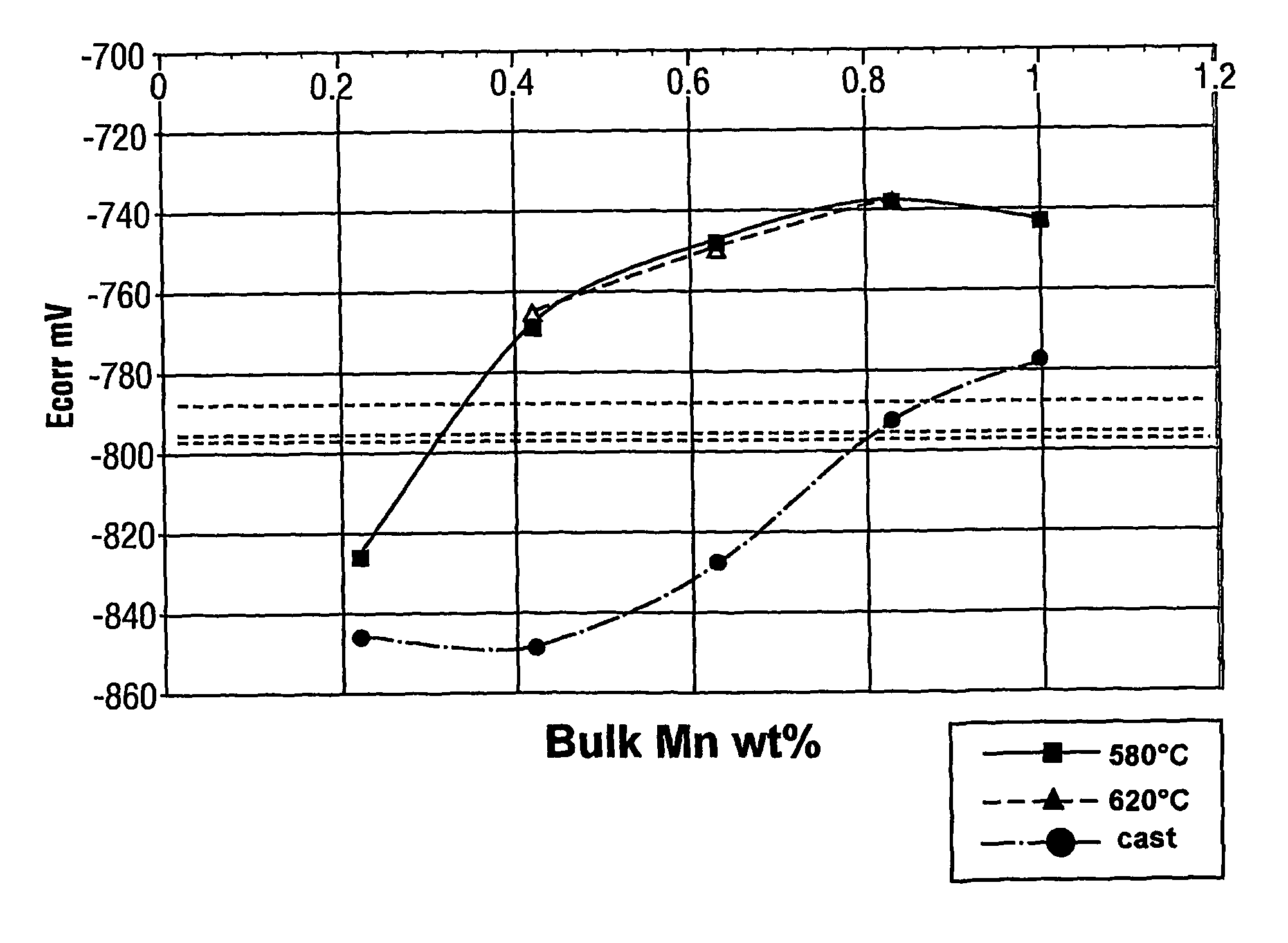
Aluminum alloy tube and fin assembly for heat exchangers having improved corrosion resistance after brazing
ActiveUS20060231170A1Good self anti-corrosion resultCompromise performanceHeat exchange apparatusThin material handlingManganeseTitanium
The present invention provides extruded tubes for heat exchangers having improved corrosion resistance when used alone and when part of a brazed heat exchanger assembly with compatible finstock. The tubes are formed from a first aluminum alloy containing 0.4 to 1.1% by weight manganese, up to 0.01% by weight copper, up to 0.05% by weight zinc, up to 0.2% by weight iron, up to 0.2% by weight silicon, up to 0.01% by weight nickel, up to 0.05% by weight titanium and the balance aluminum and incidental impurities. The fins are formed from a second aluminum alloy containing 0.9 to 1.5% by weight manganese or an alloy of the AA3003 type, this second aluminum alloy further containing at least 0.5% by weight zinc.
Owner:ALCAN INT LTD
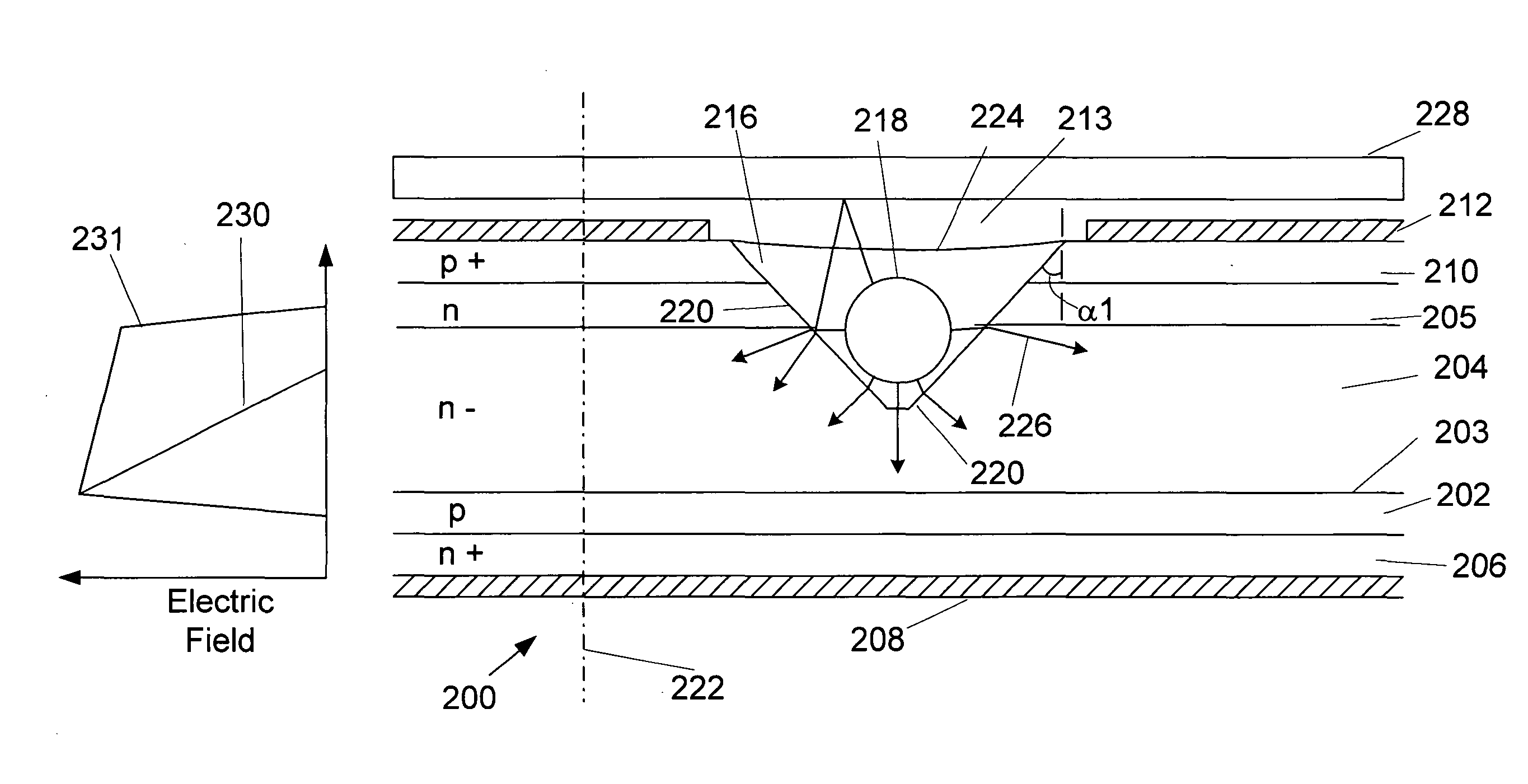
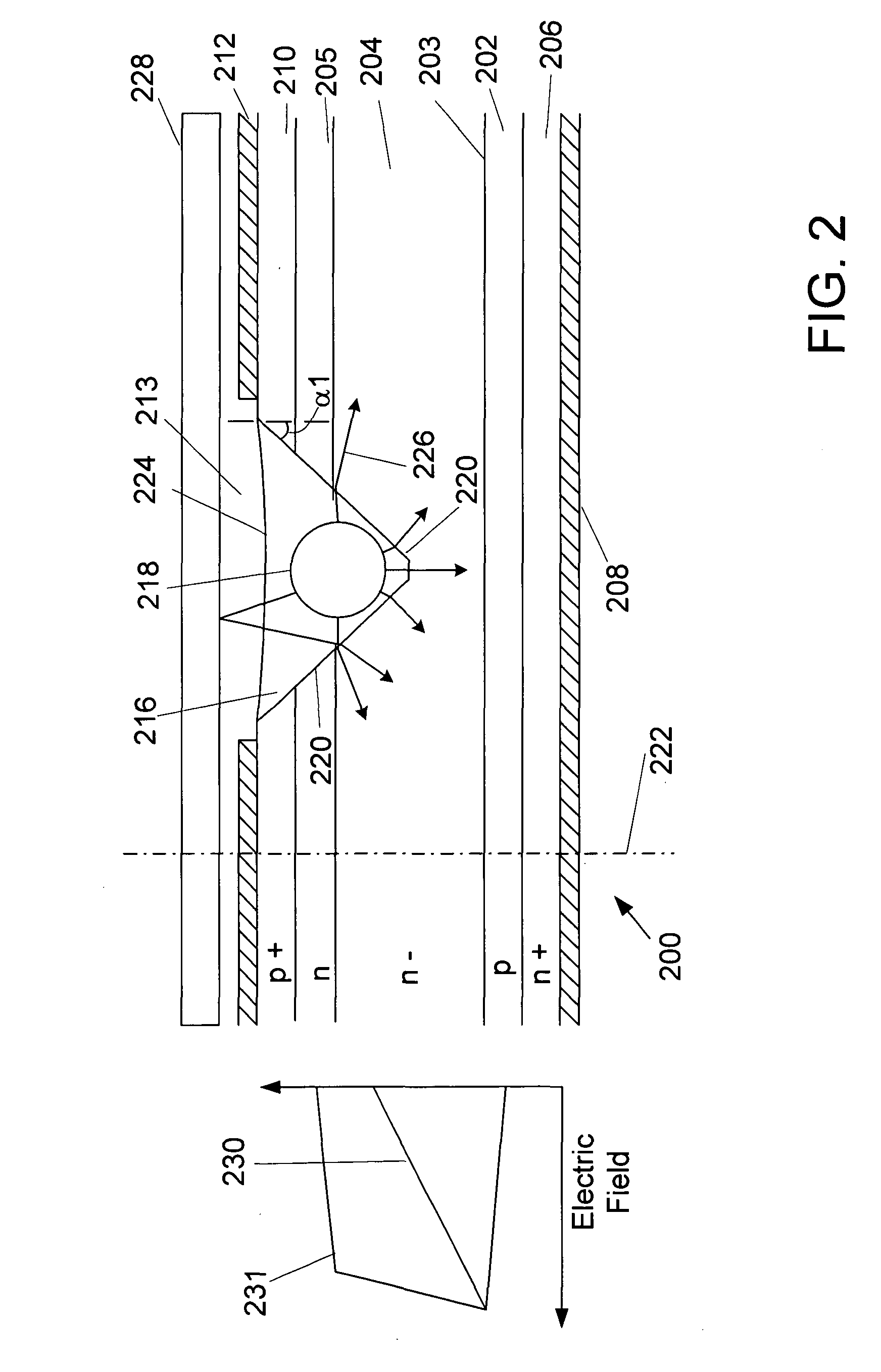
Light-activated semiconductor switches
ActiveUS20050001332A1Reduction of voltage holdingCompromise performanceSolid-state devicesCoupling light guidesElectricityEngineering
Semiconductor switches, such as thyristors, may be light activated by introducing the light into the switch via a groove having a sloped surface to receive the triggering light. The use of a sloped surface increases the surface path length between points of different electrical potential in the groove and, therefore, reduces the likelihood of electrical breakdown on the groove wall. In one particular embodiment, a light-activated thyristor comprises a semiconductor anode layer, an n-base layer, a p-base layer and a semiconductor cathode layer disposed parallel to a thyristor plane. A thyristor axis lies perpendicular to the thyristor plane. A groove having a light refracting side wall extends into the thyristor from the anode layer. A portion of the light refracting side wall is disposed non-parallel to the thyristor plane and to the thyristor axis, and extends in the n-drift layer.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Beam stop apparatus for an ion implanter
InactiveUS6093456ACompromise performanceReduce cross contaminationThermometer detailsVacuum evaporation coatingLight beamAtomic physics
PCT No. PCT / GB95 / 01309 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 5, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 5, 1997 PCT Filed Jun. 7, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 41364 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 19, 1996An ion beam absorbing apparatus for an ion implanter comprises an ion absorber for absorbing ions in an ion beam generated by the ion implanter, and support means for supporting the ion absorber and adapted for connection with the ion implanter, so that when so connected, the ion absorber can intercept the ion beam and absorb ions not intercepted by a target to be implanted with beam ions. The support means is further adapted for supporting the ion absorber in a plurality of different positions which can be selected so that respective different parts of the ion absorber intercept the ion beam.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
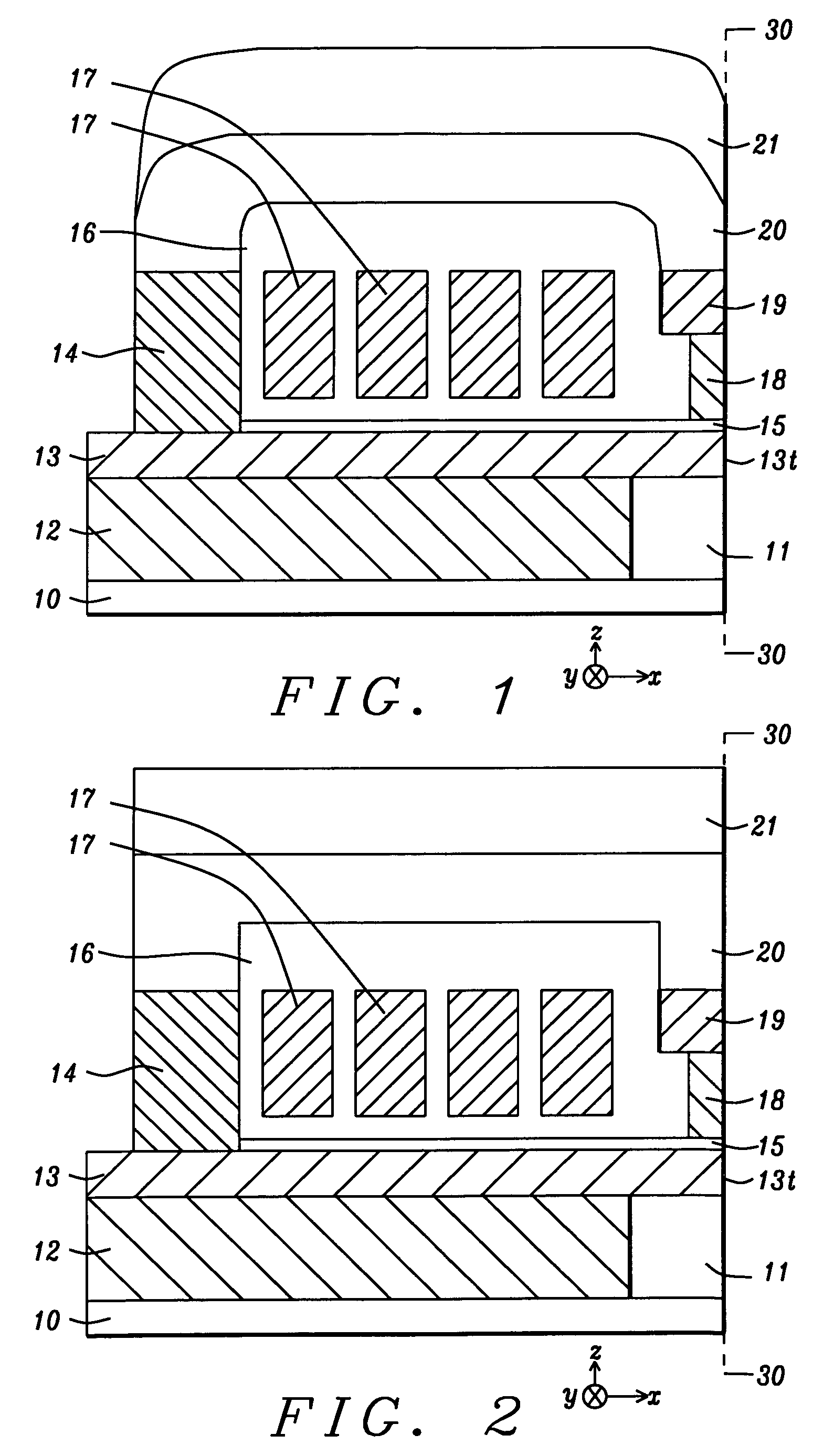
Composite writer shield for improving writer performance
ActiveUS8274758B2Improve performanceImprove mechanical propertiesRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsEngineeringRecording density
A PMR writer in a read / write head is disclosed wherein an upper shield covering the coil layer is comprised of a magnetic layer optimized for magnetic performance and a second layer used for tuning mechanical protrusion. The composite layer simultaneously provides high saturation magnetization and high permeability from the magnetic layer and low CTE from the second layer which tunes the relative spacing between the writer, reader, and the rest of the slider. In one embodiment, first and second write shields are formed on a write gap layer and have front portions at the ABS and back portions in a back gap region. The upper write shield connects on one side with the second write shield at the ABS and on a second side with the back gap region. This design can yield better reader and writer spacing for the same physical clearance which enables products with higher recording density.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Aluminum alloy tube and fin assembly for heat exchangers having improved corrosion resistance after brazing
ActiveUS7781071B2Promote resultsCompromise performanceCoatingsHeat exchange apparatusManganeseTitanium
The present invention provides extruded tubes for heat exchangers having improved corrosion resistance when used alone and when part of a brazed heat exchanger assembly with compatible finstock. The tubes are formed from a first aluminum alloy containing 0.4 to 1.1% by weight manganese, up to 0.01% by weight copper, up to 0.05% by weight zinc, up to 0.2% by weight iron, up to 0.2% by weight silicon, up to 0.01% by weight nickel, up to 0.05% by weight titanium and the balance aluminum and incidental impurities. The fins are formed from a second aluminum alloy containing 0.9 to 1.5% by weight manganese or an alloy of the AA3003 type, this second aluminum alloy further containing at least 0.5% by weight zinc.
Owner:ALCAN INT LTD
Uniform illumination without specular reflection in imaging reader
InactiveUS20080035732A1Avoid specular reflectionsImprove performanceVisual representatino by photographic printingSensing by electromagnetic radiationSpecular reflectionField of view
A target is uniformly illuminated with illumination light without specular reflections from a window and / or from the target in a field of view of a solid-state imager of an imaging reader to improve reader performance.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
Use of hydrocarbon diluents to enhance conversion in a dehydrogenation process at low steam/oil ratios
InactiveUS20140114107A1Eliminating cost benefitLessens dehydrogenation efficiencyHydrocarbonsChemical recyclingDiluentDehydrogenation
A process for preparing styrene via the catalytic dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene, comprising recirculation of reaction byproducts to the initial reaction stream as an oil based diluent, providing an effective means for reducing the steam to oil ratio required to operate the catalytic dehydrogenation reactor.
Owner:LUMMUS TECH INC
Method of preventing silver tarnishing
ActiveUS20130224515A1Avoid tarnishingReduce contact resistanceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingJewelleryIndiumElectroplating
A thin indium metal layer is electroplated onto silver to prevent silver tarnishing. The indium and silver composite has high electrical conductivity.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
Serrated MEMS resonators
ActiveUS20080150656A1Increase amplitudeCompromise performanceImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesActuatorControl theory
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a serrated tooth actuator for driving MEMS resonator structures. The actuator includes a fixed drive electrode having a serrated tooth surface opposing a MEMS resonator arm also having a serrated tooth surface, where the MEMS resonator arm is configured to rotate towards the drive electrode when an AC signal is applied to the drive electrode. Such a configuration permits higher amplitude signals to be applied to the drive electrode without the performance of the actuator being compromised by nonlinear effects. In addition, the serrated tooth configuration enables a sufficiently high actuating force to be maintained even though the distance traversed by the MEMS resonator arm during operation is quite small. Further, the serrated configuration allows a MEMS resonator system to withstand larger fluctuations in voltage and larger substrate stresses without experiencing a substantial shift in resonant frequency.
Owner:SITIME
Direct digital sampling method for radios
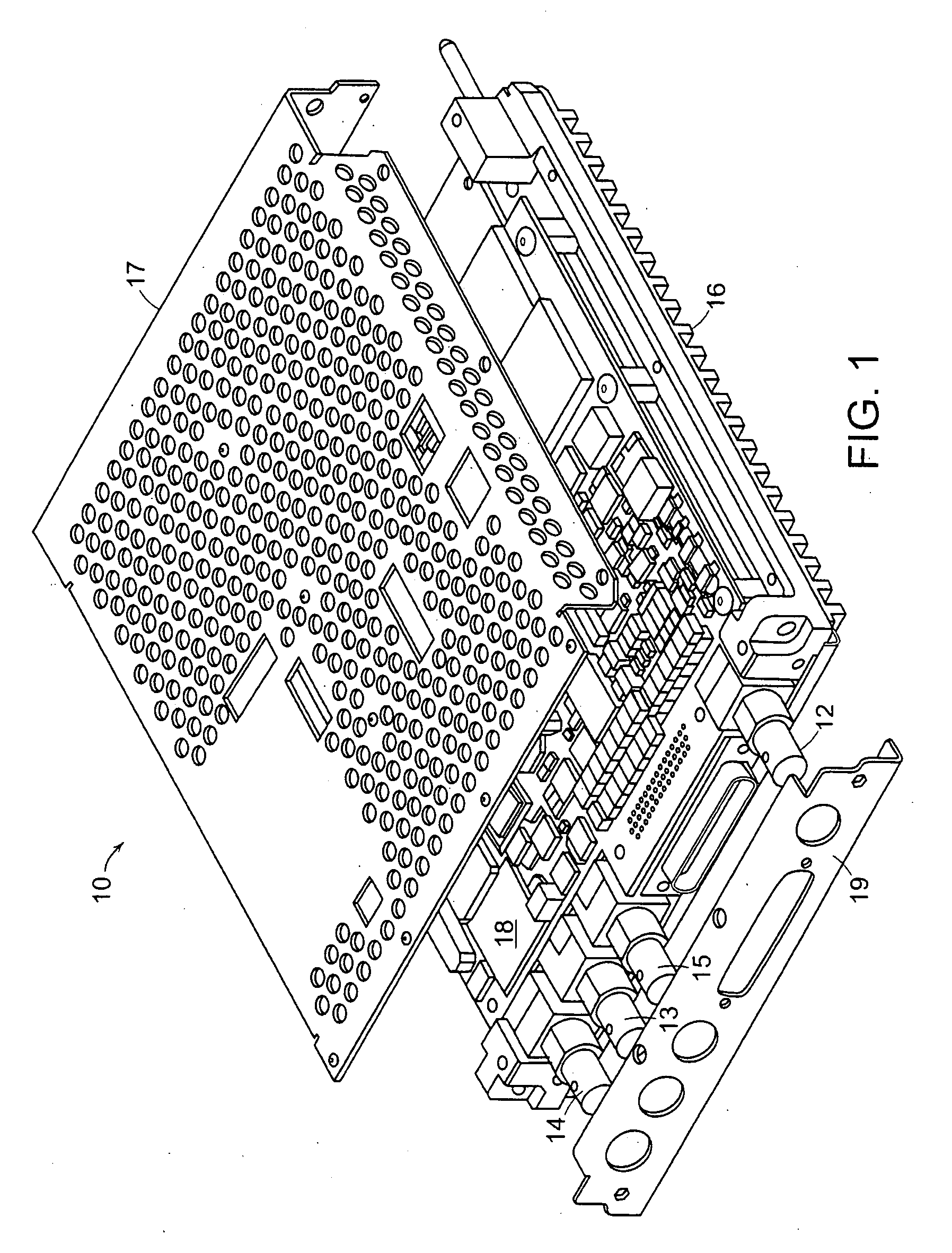
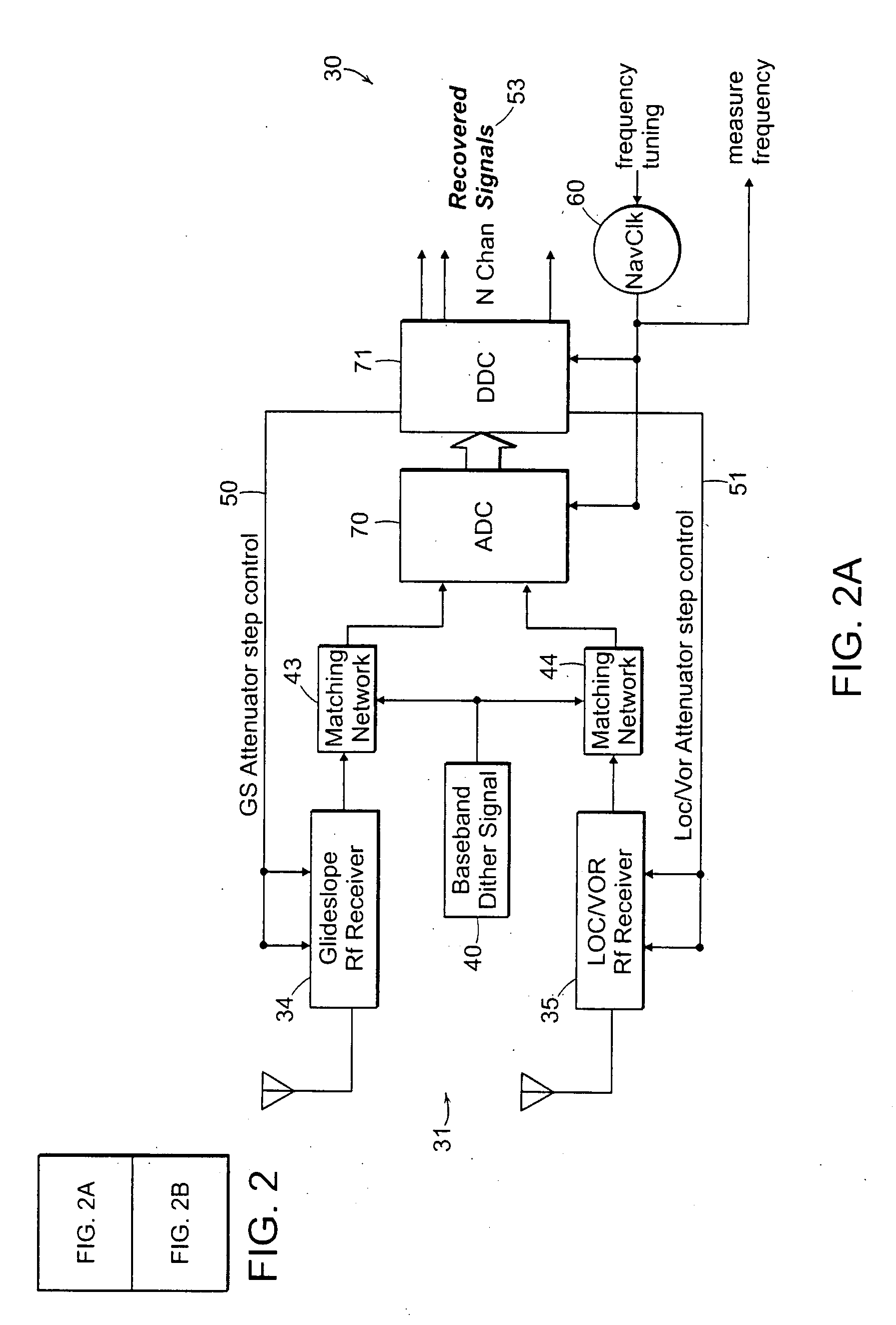
InactiveUS20080261638A1Reduce impactEasy and less-expensive to implementRadio transmissionAnalogue-digital convertersMarker beaconUp conversion
A direct digital sampling and synthesis general purpose radio system is disclosed which employs single or multiple receiver and / or transmitter sub-systems that require no analog frequency conversion or translation circuitry. Receiver signal processing is disclosed that describes methods of conditioning and digitizing an entire received RF signal band in which the down conversion, channelization and demodulation are performed digitally. In addition, a method for direct synthesis of transmitter signals is also disclosed where up conversion and carrier modulation is performed digitally. Several mitigation techniques are described which aid in overcoming device limitations as well as overcoming problems created by combining multiple digital transmitters and receivers into a single integrated system. One embodiment of the invention describes an integrated VHF / UHF aircraft NAV / COMM radio system which combines a VHF transmitter with four VHF / UHF receivers all of which require no IF circuitry. This embodiment allows for multiple simultaneous airborne radio services on a single platform such as voice and data communication modes (AM, ACARS, VDLM2, LAAS, etc.) as well as navigational modes such as VOR, ILS, and Marker Beacon. By utilizing direct digital methods, the signal processing burden is moved almost entirely to the digital domain where the processing can be optimized for each signal type and where linearity is guaranteed. Fewer RF components are required which result in less unit to unit variability, lower production costs, and improved reliability.
Owner:AVIDYNE CORPORATION
Semipermeable coating for building materials
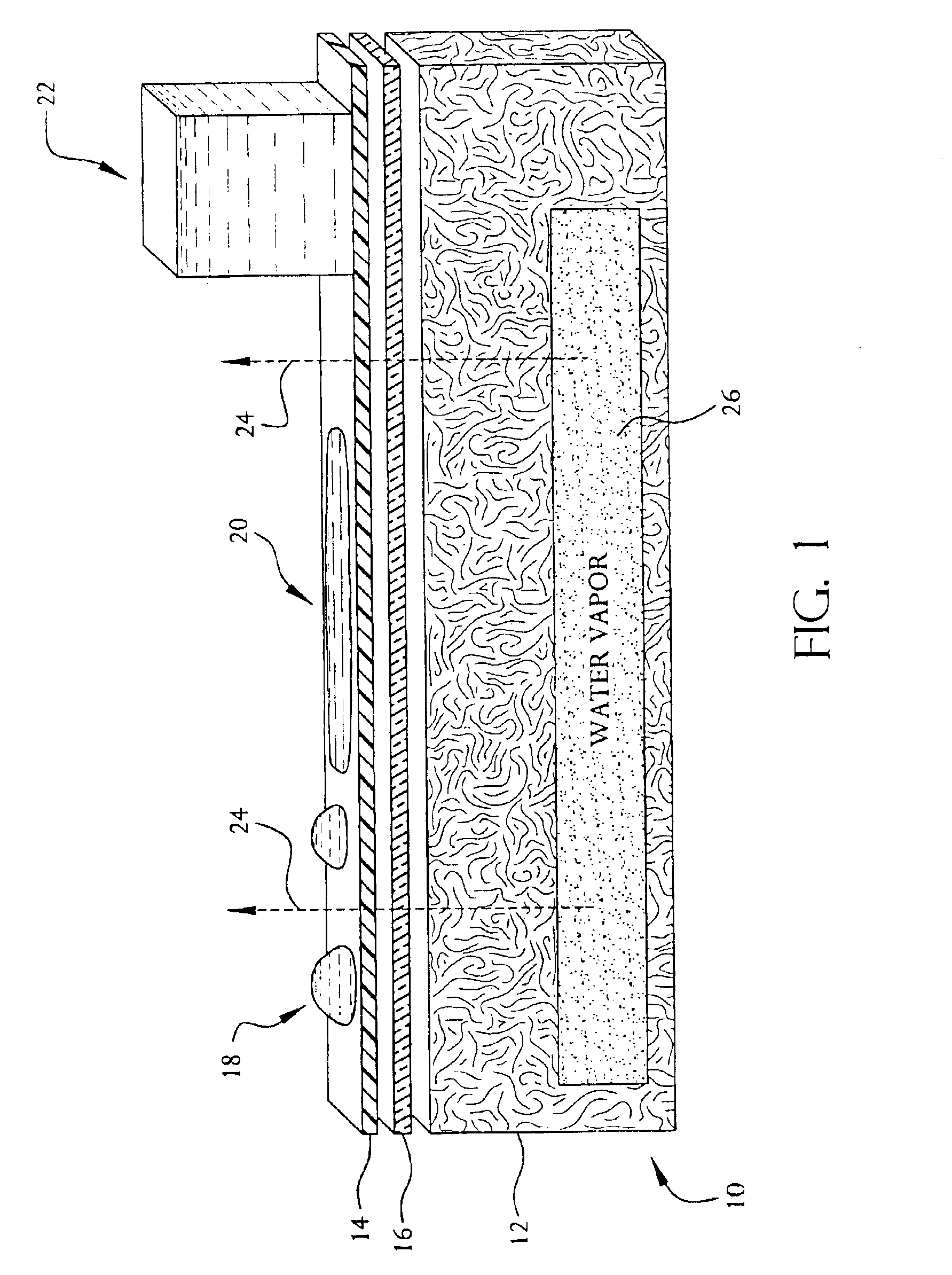
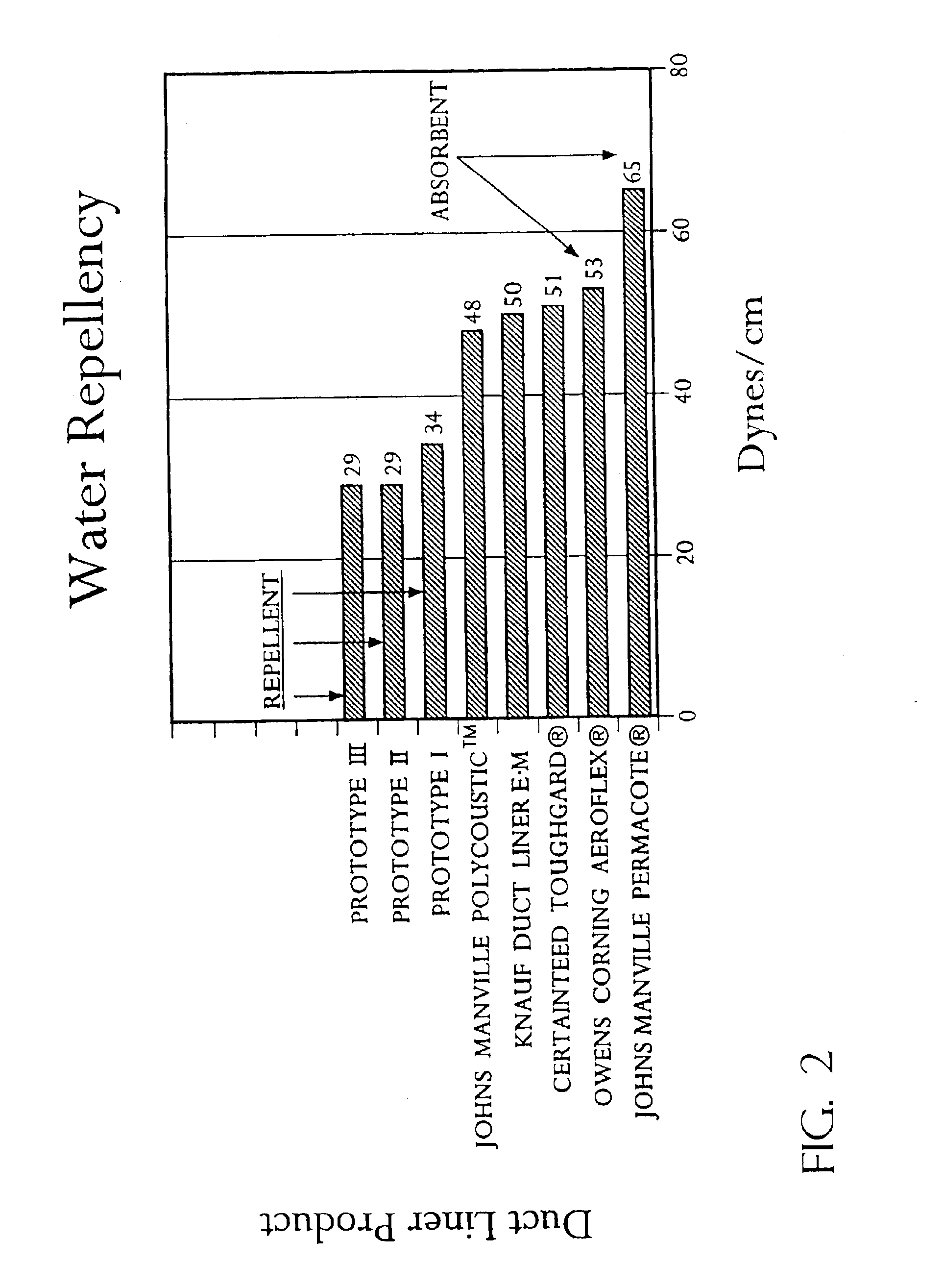
InactiveUS6972145B1Substantial water hold-out propertyKeep drySynthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsWater vaporLiquid water
The present invention provides coating materials (14), insulation-containing building material products bearing the materials and methods for applying the coatings to the building material products. The coating materials (14) possess one-way “breathability” characteristics with respect to water and aqueous solutions. That is, the coatings are essentially impermeable to liquid water and permeable to water vapor. Vapor from water insulation coated by the material may thus pass through the coating, whereas liquid water is effectively prevented from passing through the coating and entering the insulation.
Owner:CERTAINTEED CORP
Composite writer shield for improving writer performance
ActiveUS20090310262A1Improve performanceImprove mechanical propertiesRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsEngineeringRecording density
A PMR writer in a read / write head is disclosed wherein an upper shield covering the coil layer is comprised of a magnetic layer optimized for magnetic performance and a second layer used for tuning mechanical protrusion. The composite layer simultaneously provides high saturation magnetization and high permeability from the magnetic layer and low CTE from the second layer which tunes the relative spacing between the writer, reader, and the rest of the slider. In one embodiment, first and second write shields are formed on a write gap layer and have front portions at the ABS and back portions in a back gap region. The upper write shield connects on one side with the second write shield at the ABS and on a second side with the back gap region. This design can yield better reader and writer spacing for the same physical clearance which enables products with higher recording density.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Light-activated semiconductor switches
ActiveUS7057214B2Reduce voltageReducing voltage holding capabilityThyristorSolid-state devicesPath lengthThyratron
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Analysis of signals from pixellated detectors of ionizing radiation
ActiveUS10168438B2Lower performance requirementsCompromise performanceX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTime domainSemiconductor detector
The invention relates to signals representing energy of photons or particles of ionizing radiation incident on pixels of a semiconductor detector. Cross talk between the signals from different pixels is compensated using cross talk compensation signatures in the form of time domain series or functions which are aligned and applied to the cross talk signal in accordance with timing of the event which gave rise to the cross talk.
Owner:DIAMOND LIGHT SOURCE
Cross-car structural support with integrated HVAC floor duct
ActiveUS20150217624A1Maintain structural integrityCompromise performanceVehicle seatsAir-treating devicesStructural engineeringHVAC
A cross-car structure integrates an HVAC duct with a structural beam. An upper steel beam has opposing ends attached to opposite body sides. A pair of center brackets extend downward from the upper steel beam. An HVAC unit secured to a center bracket has an outlet for an air flow for ventilating a floor region. A plastic cross member has a center plate secured to the center brackets, a first hollow beam extending from the center plate to one steel beam end, and a second hollow beam extending from the center plate to the other steel beam end. Each hollow beam has an in-board opening fluidically coupled to the HVAC outlet and at least one floor outlet directed toward the floor region thereby providing a respective HVAC duct between the outlet of the HVAC unit and each of the floor outlets.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Serrated MEMS resonators
ActiveUS7545237B2Enhanced signalCompromise performancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksActuatorControl theory
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a serrated tooth actuator for driving MEMS resonator structures. The actuator includes a fixed drive electrode having a serrated tooth surface opposing a MEMS resonator arm also having a serrated tooth surface, where the MEMS resonator arm is configured to rotate towards the drive electrode when an AC signal is applied to the drive electrode. Such a configuration permits higher amplitude signals to be applied to the drive electrode without the performance of the actuator being compromised by nonlinear effects. In addition, the serrated tooth configuration enables a sufficiently high actuating force to be maintained even though the distance traversed by the MEMS resonator arm during operation is quite small. Further, the serrated configuration allows a MEMS resonator system to withstand larger fluctuations in voltage and larger substrate stresses without experiencing a substantial shift in resonant frequency.
Owner:SITIME +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com