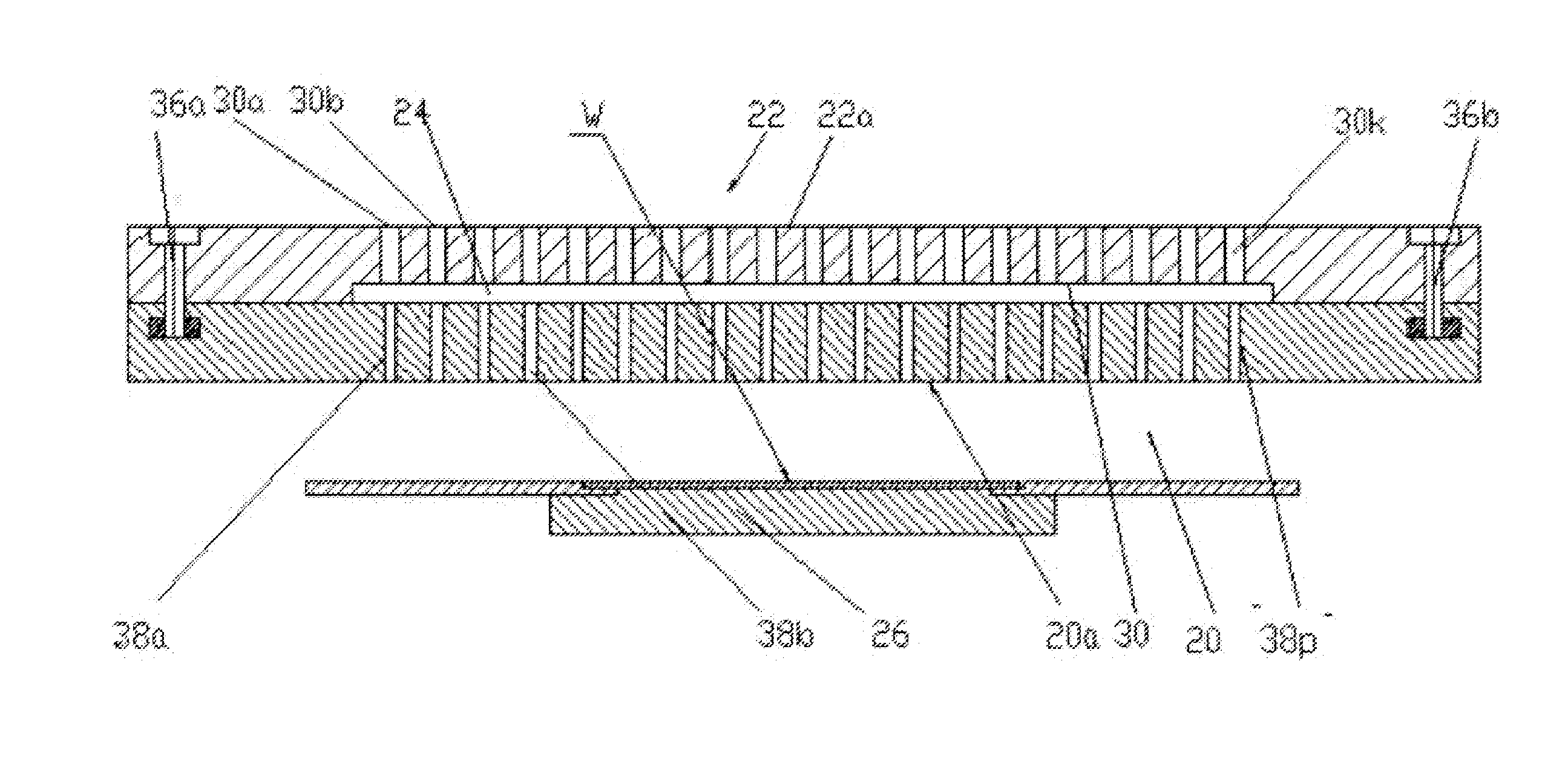
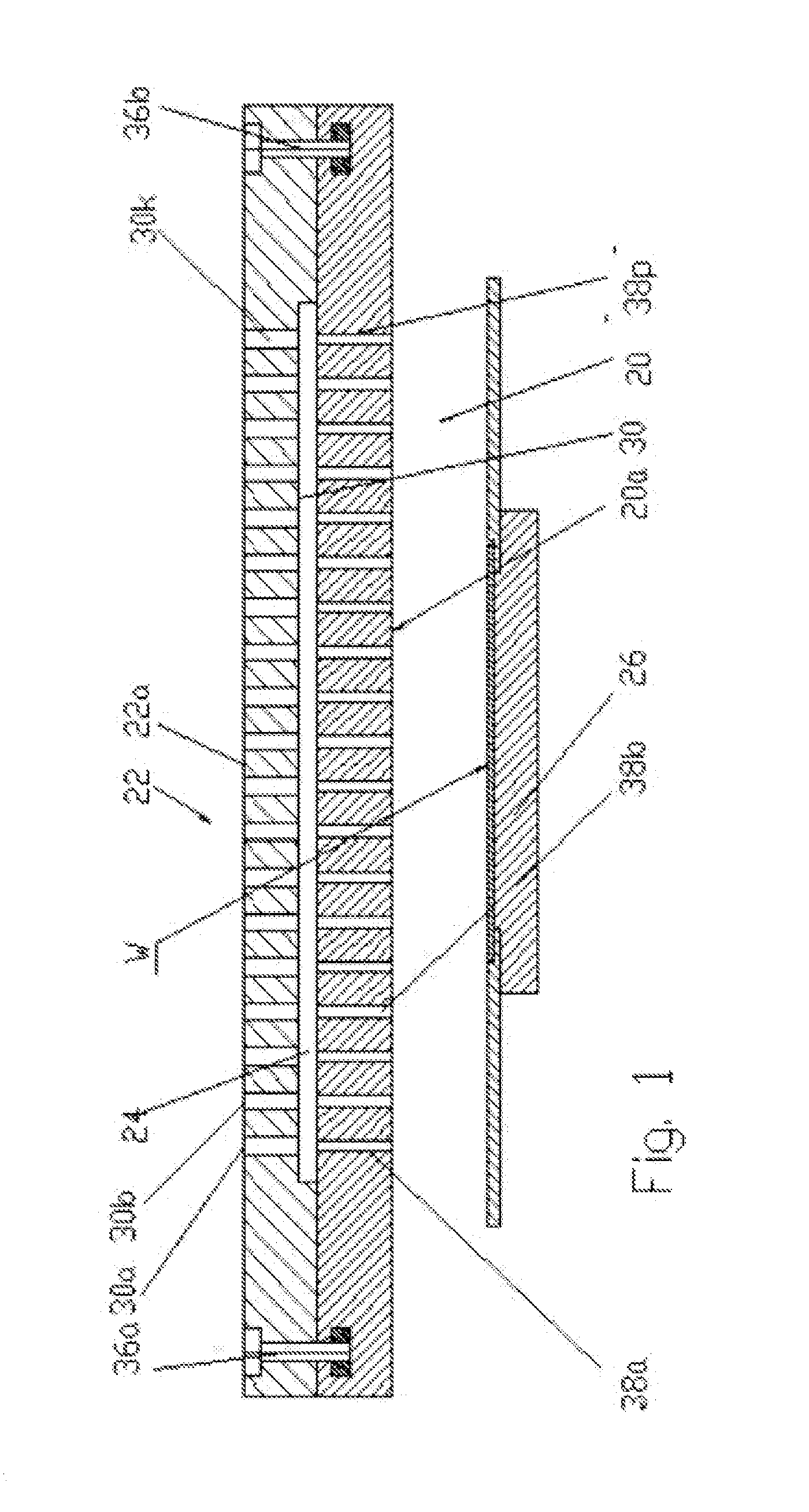
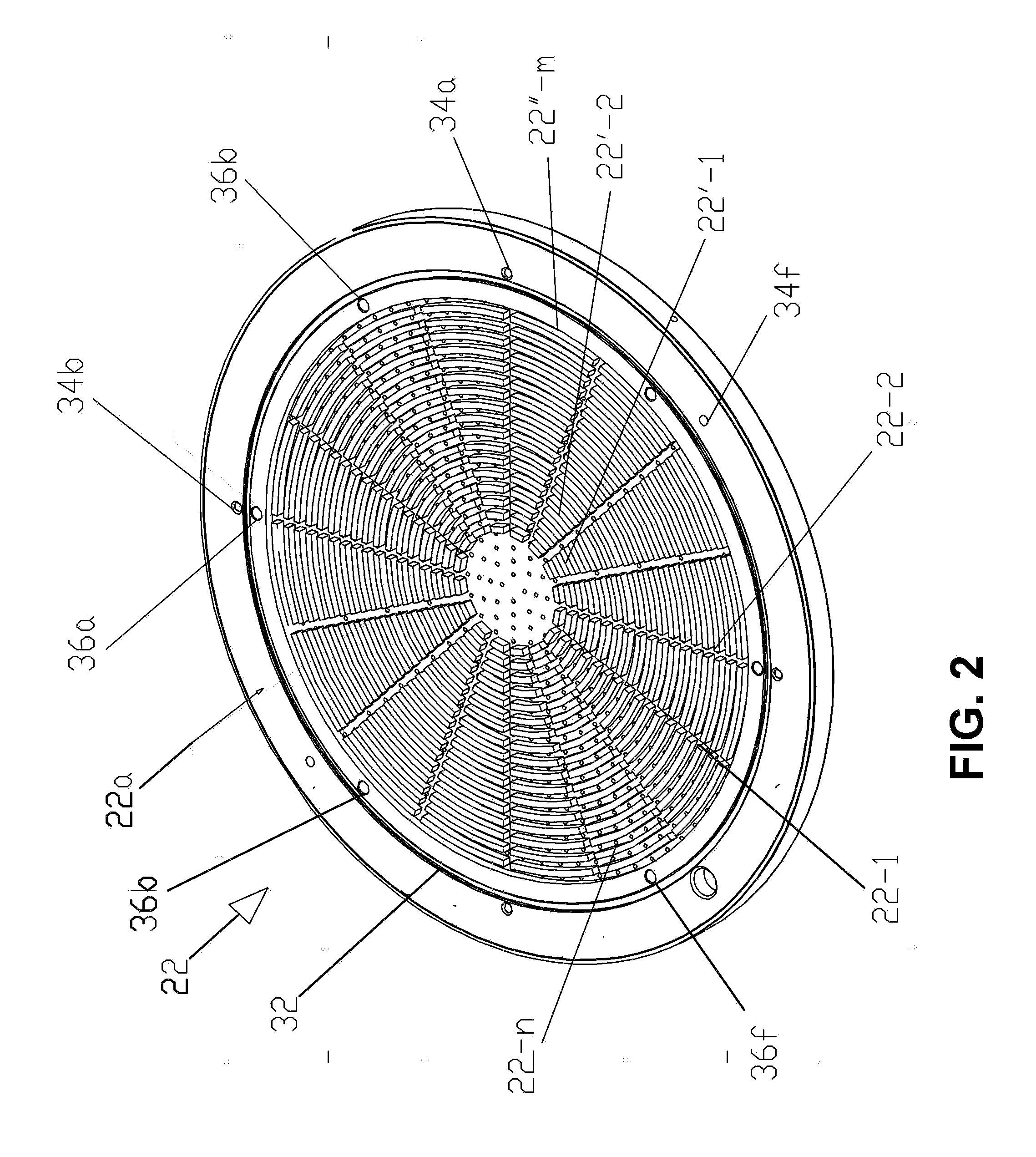
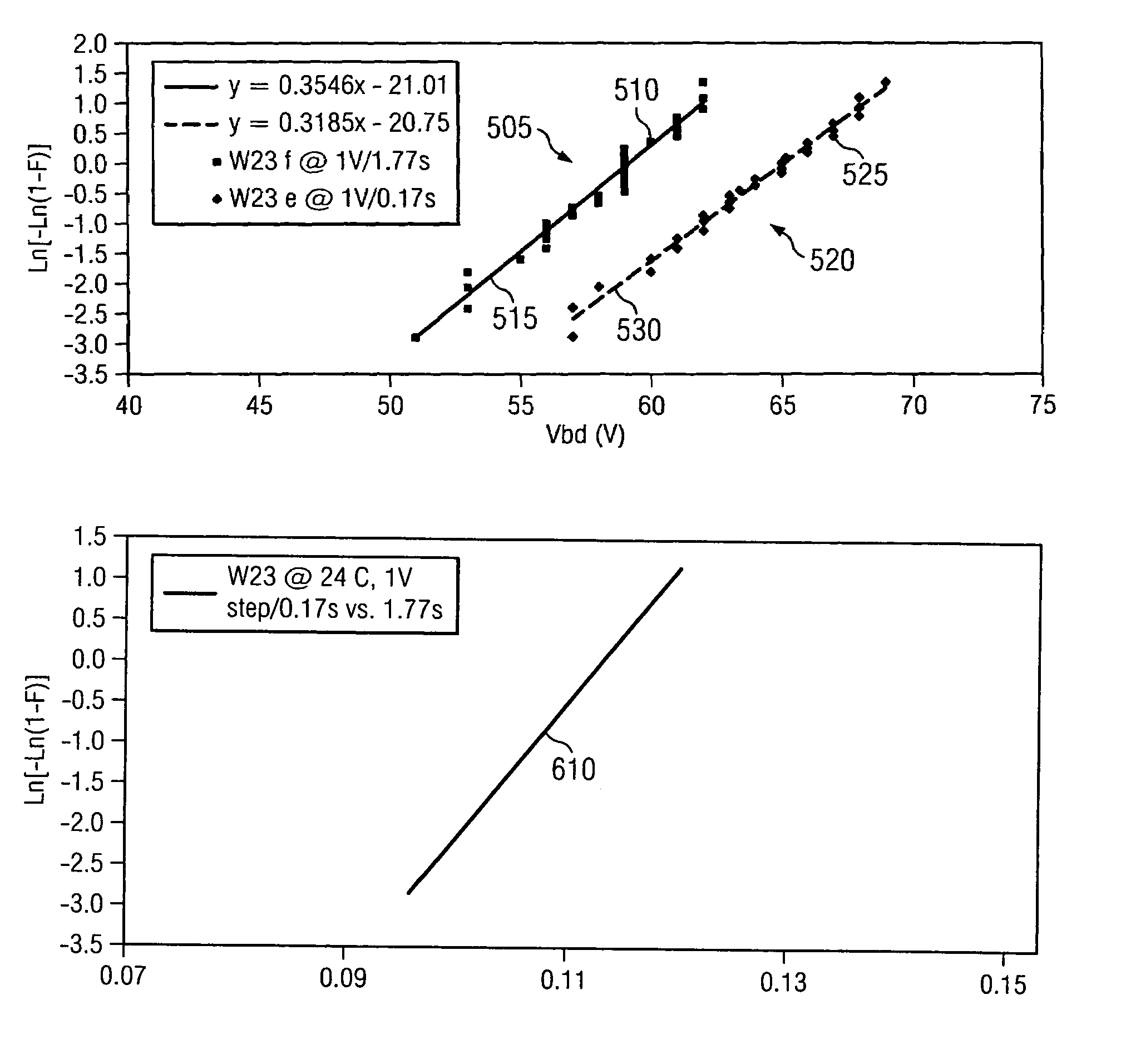
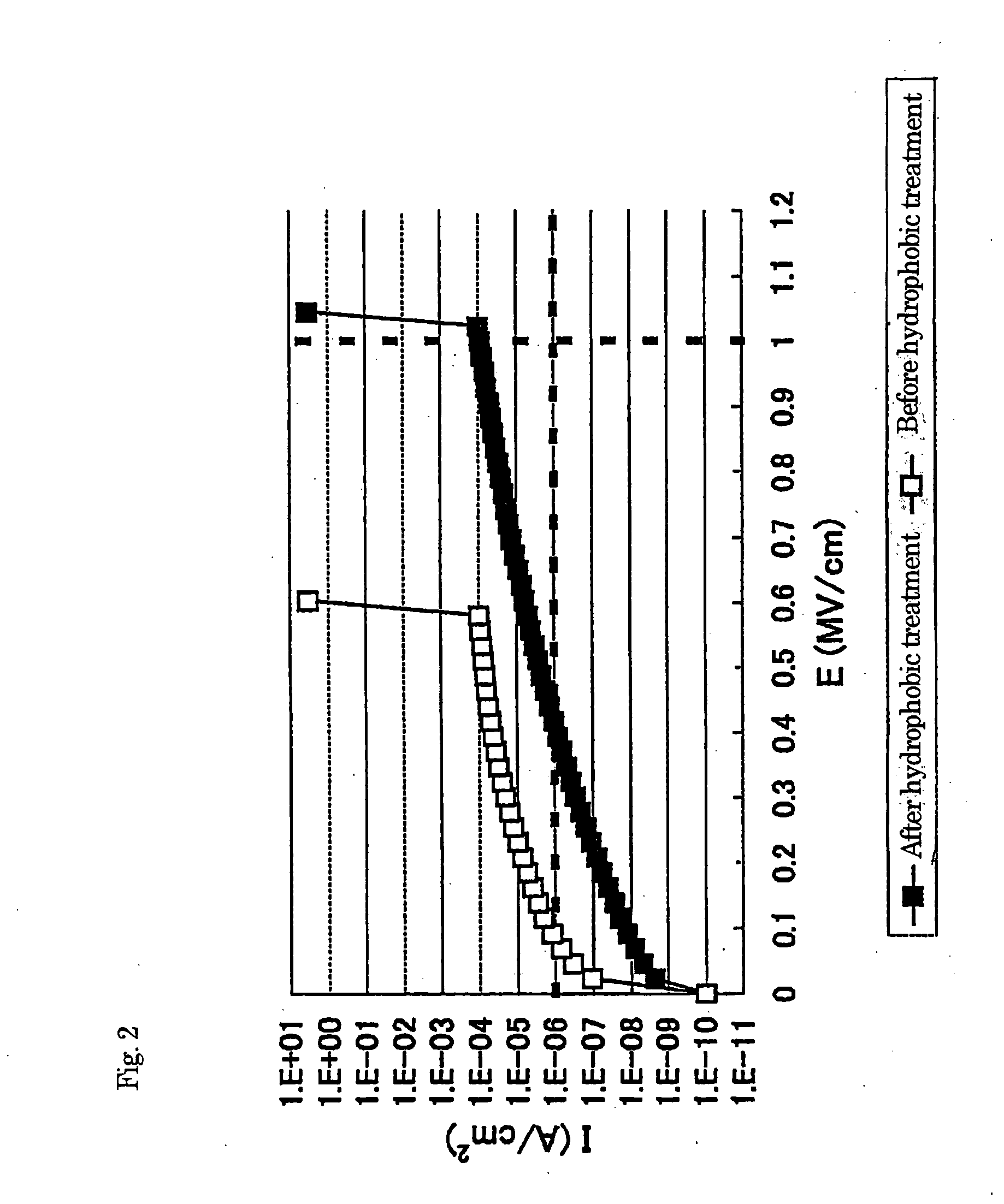
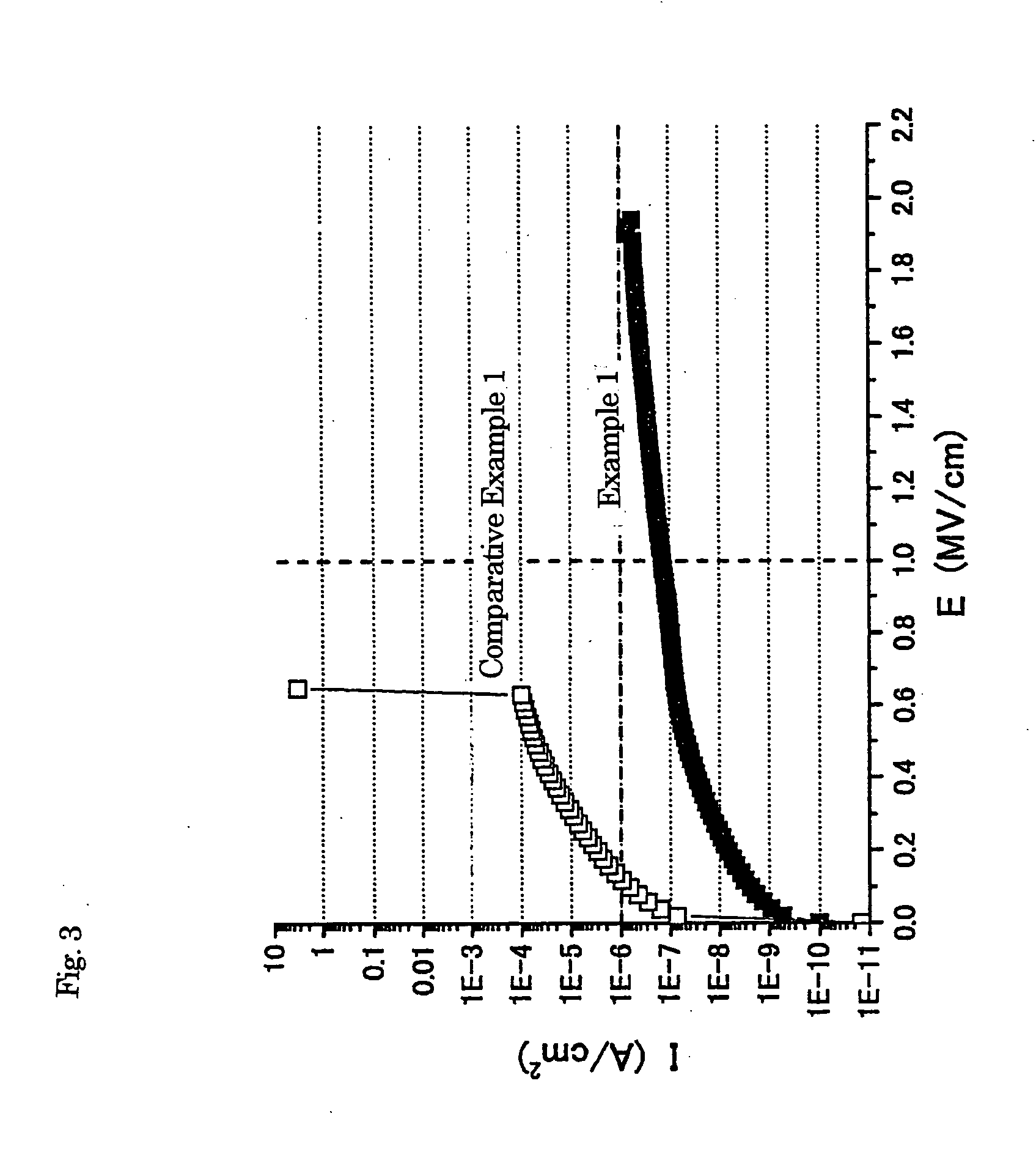
Patents
Literature
247 results about "Electrical breakdown" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrical breakdown or dielectric breakdown is when current flows through an electrical insulator when the voltage applied across it exceeds the breakdown voltage. This results in the insulator becoming electrically conductive. Electrical breakdown may be a momentary event (as in an electrostatic discharge), or may lead to a continuous arc if protective devices fail to interrupt the current in a power circuit.
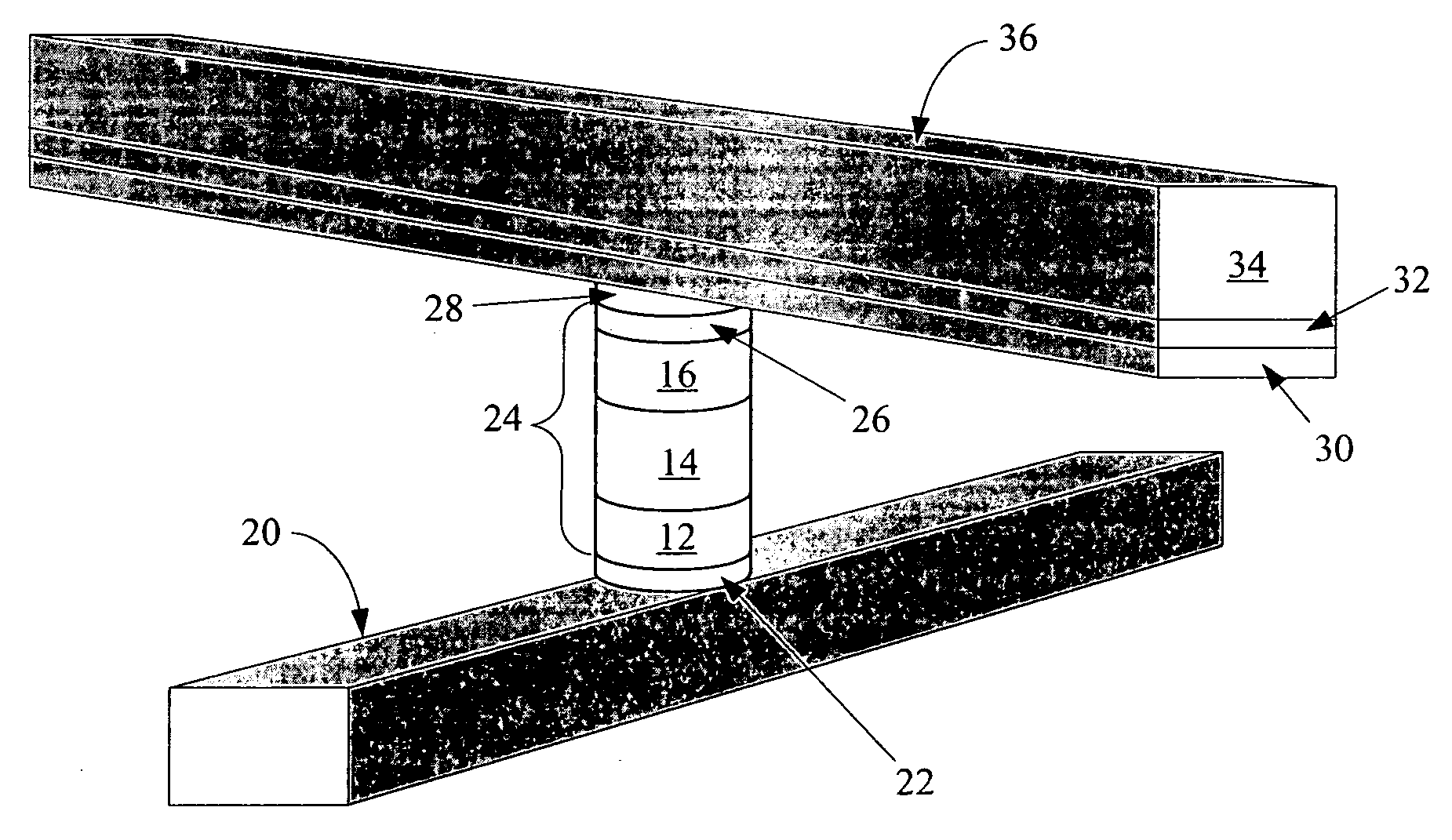
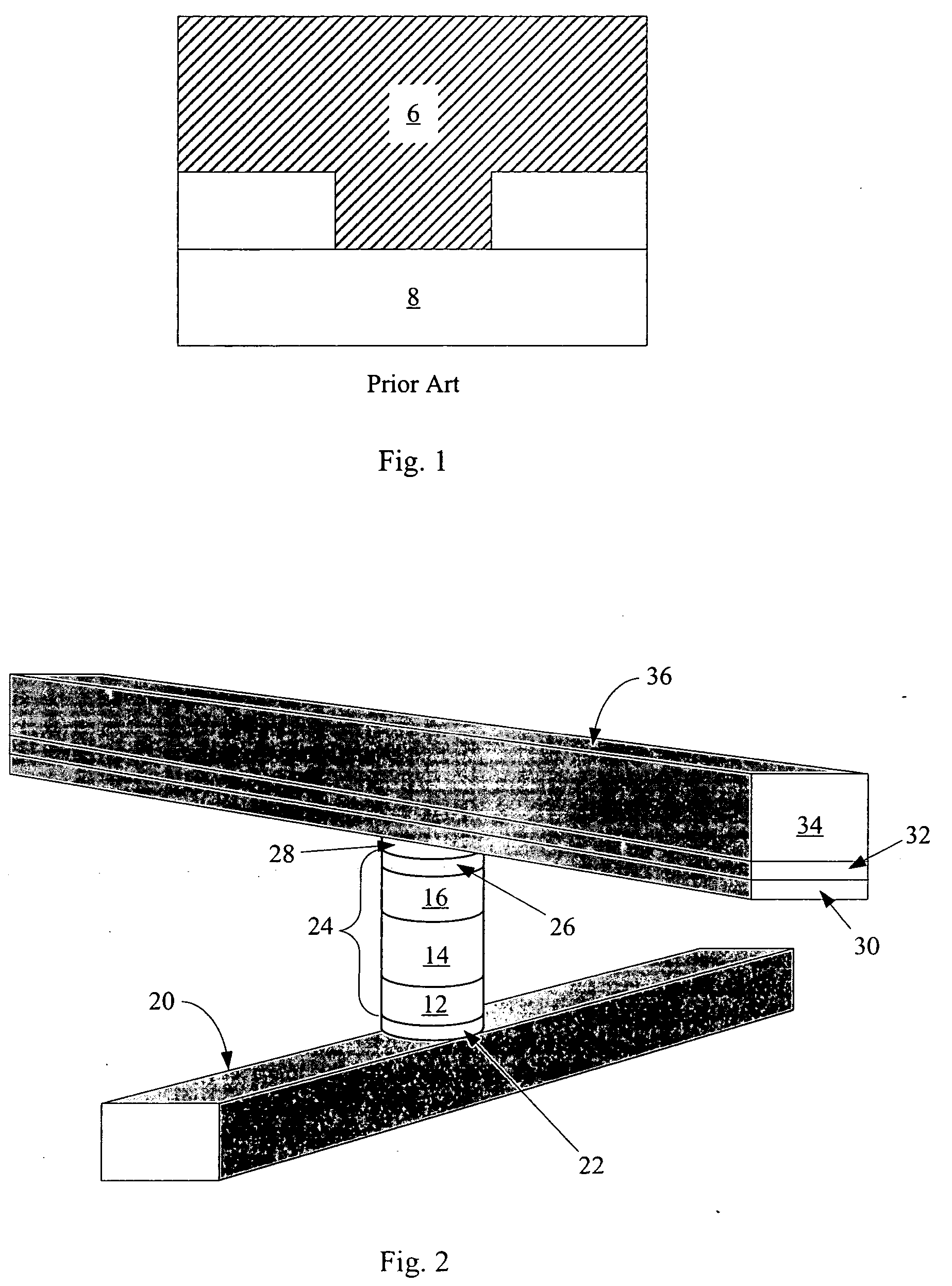
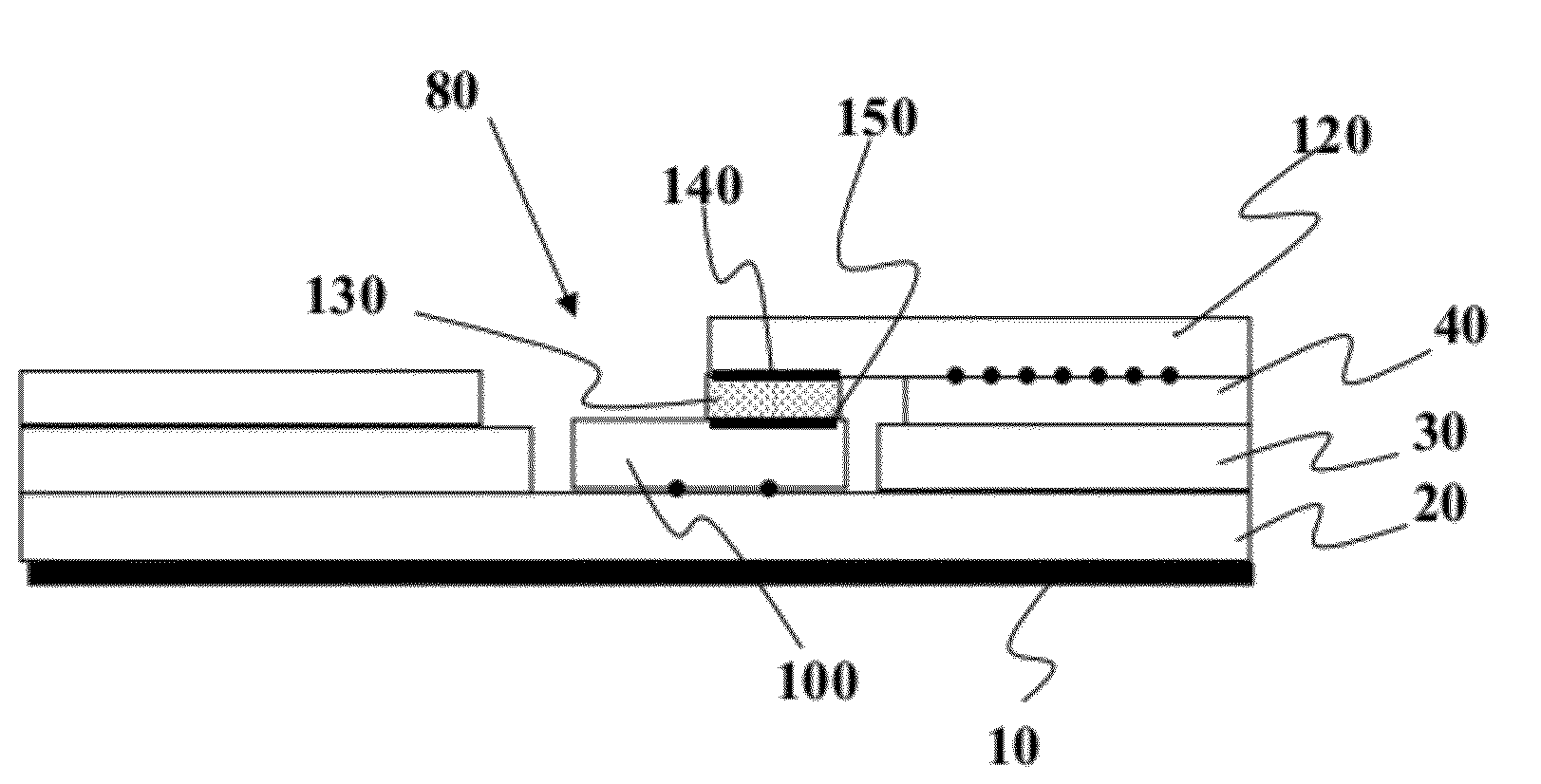
Non-volatile memory cell comprising a dielectric layer and a phase change material in series
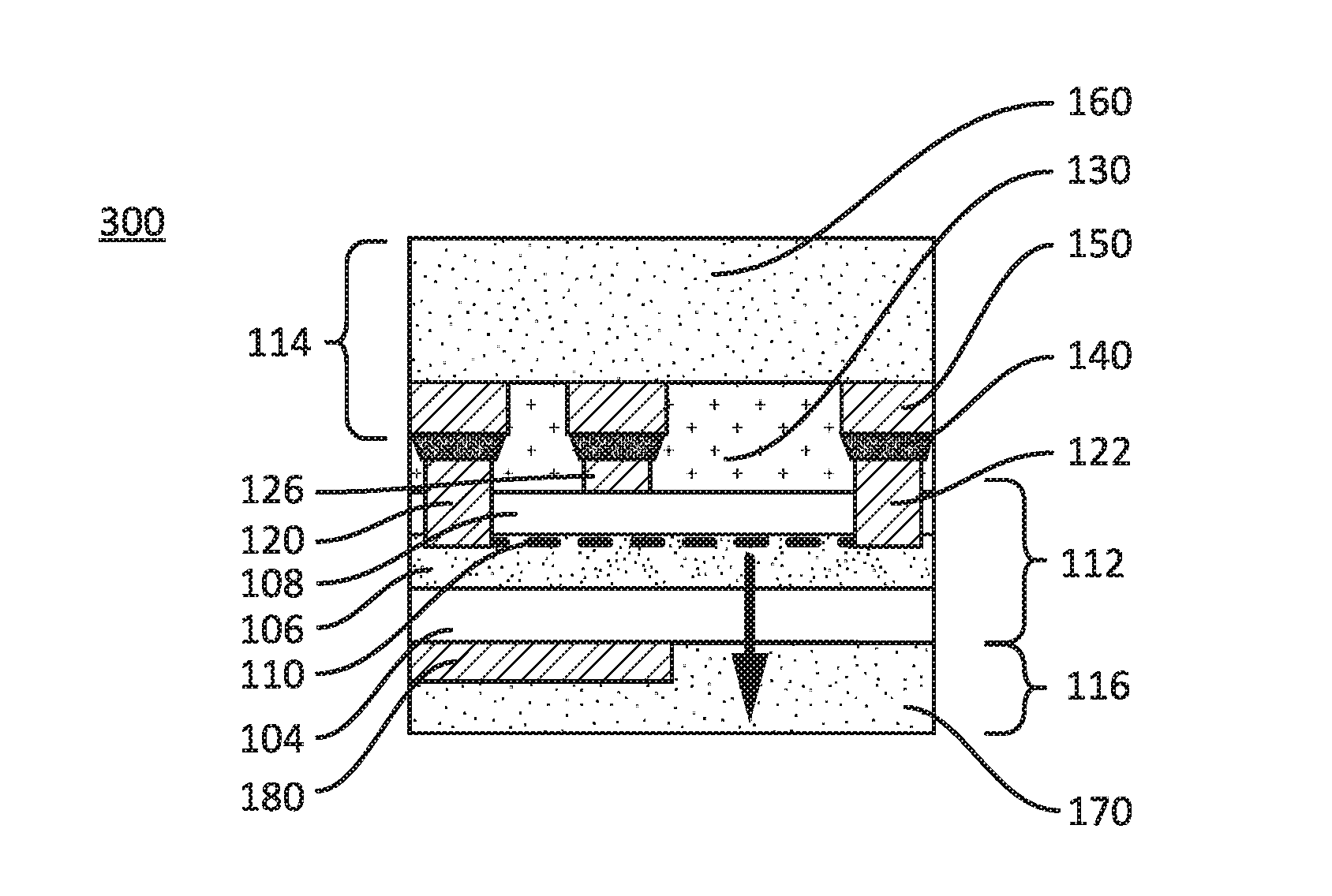
The invention provides for a nonvolatile memory cell comprising a dielectric material in series with a phase change material, such as a chalcogenide. Phase change is achieved in chalcogenide memories by thermal means. Concentrating thermal energy in a relatively small volume assists this phase change. By applying high voltage across a dielectric layer, dielectric breakdown occurs, forming a low-resistance rupture region traversing the dielectric layer. This rupture region can serve to concentrate thermal energy in a phase-change memory cell. In a preferred embodiment, such a cell can be used in a monolithic three dimensional memory array.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
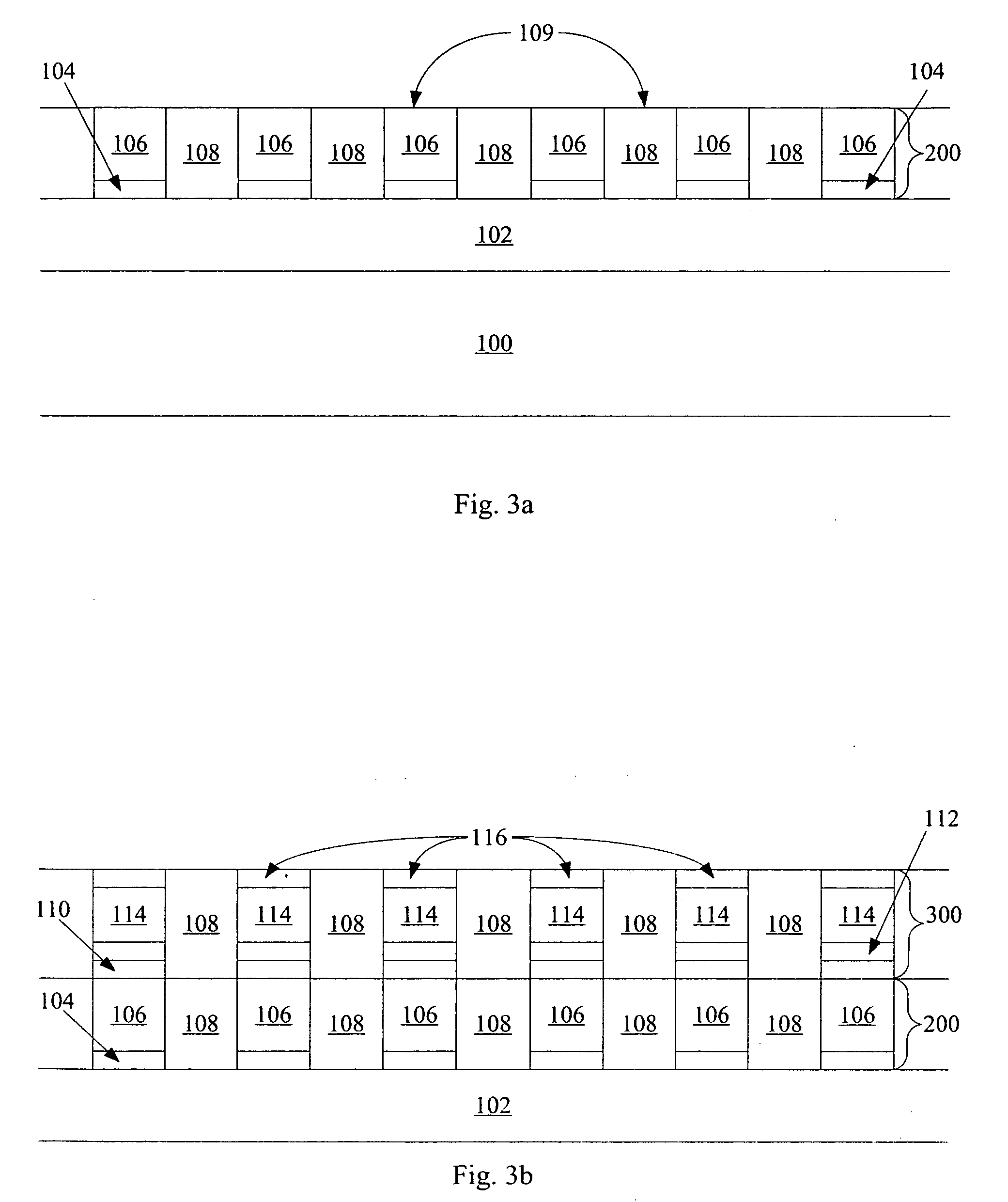
Rectification element and method for resistive switching for non volatile memory device
ActiveUS20110317470A1High densityFast switching speedSolid-state devicesDigital storageComputational physicsResistive switching
A method of suppressing propagation of leakage current in an array of switching devices. The method includes providing a dielectric breakdown element integrally and serially connected to a switching element within each of the switching device. A read voltage (for example) is applied to a selected cell. The propagation of leakage current is suppressed by each of the dielectric breakdown element in unselected cells in the array. The read voltage is sufficient to cause breakdown in the selected cells but insufficient to cause breakdown in the serially connected, unselected cells in a specific embodiment. Methods to fabricate of such devices and to program, to erase and to read the device are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
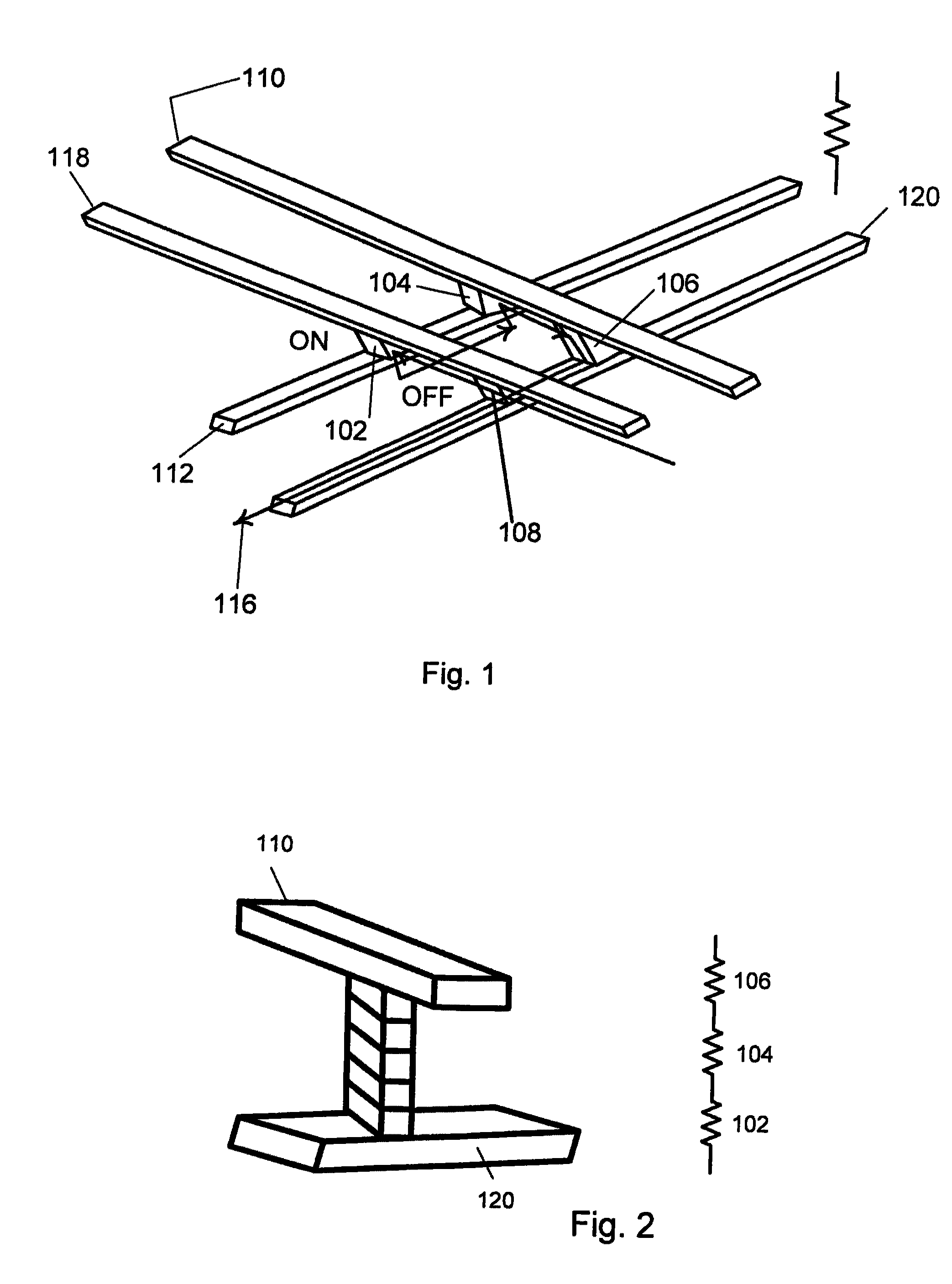
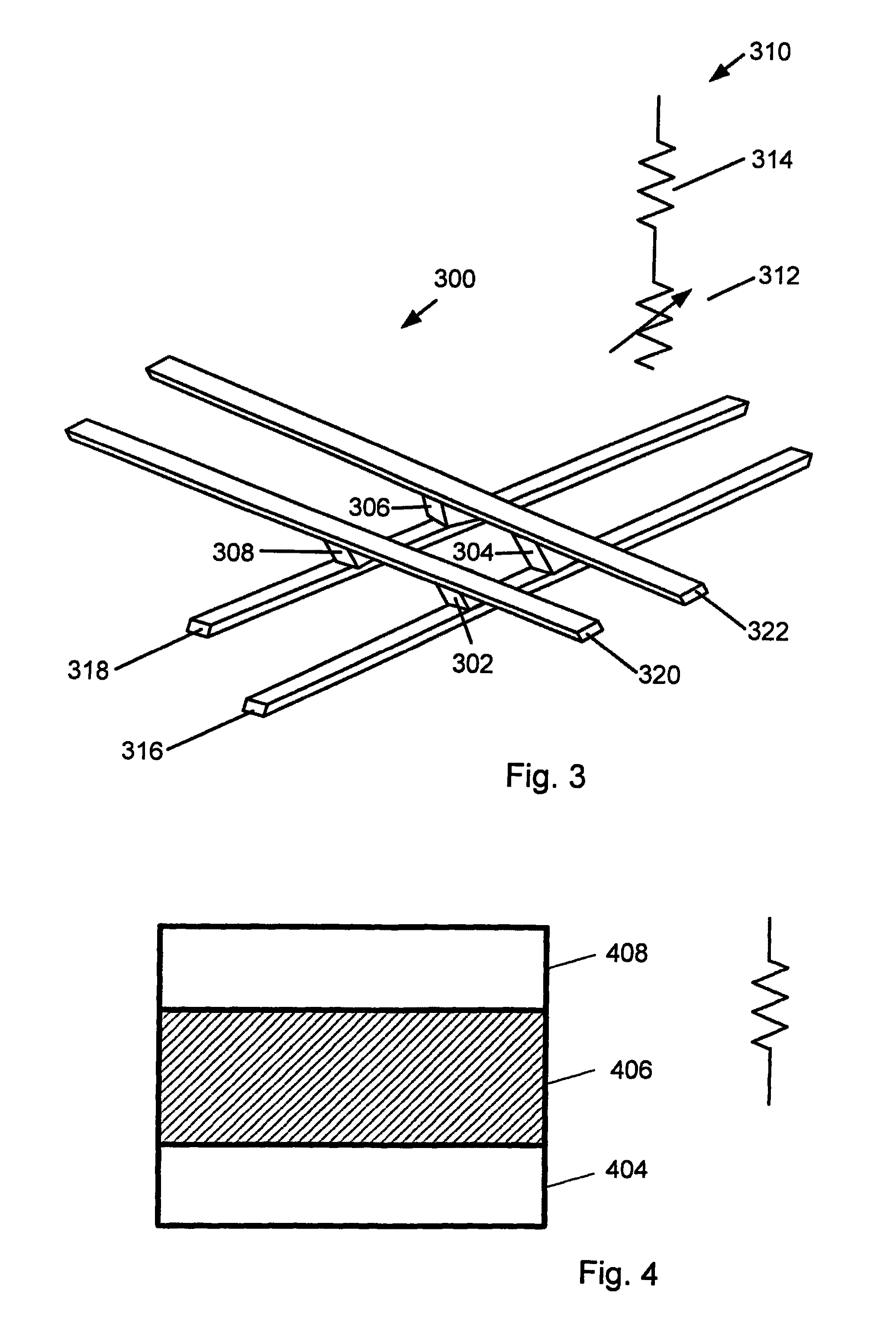
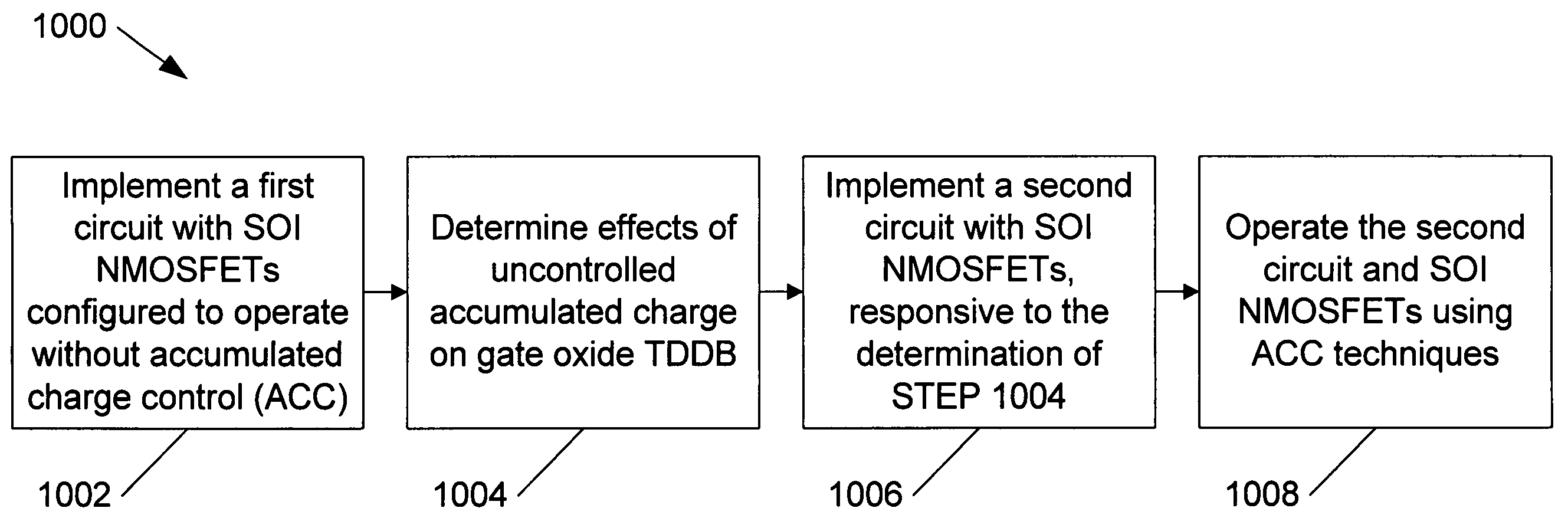
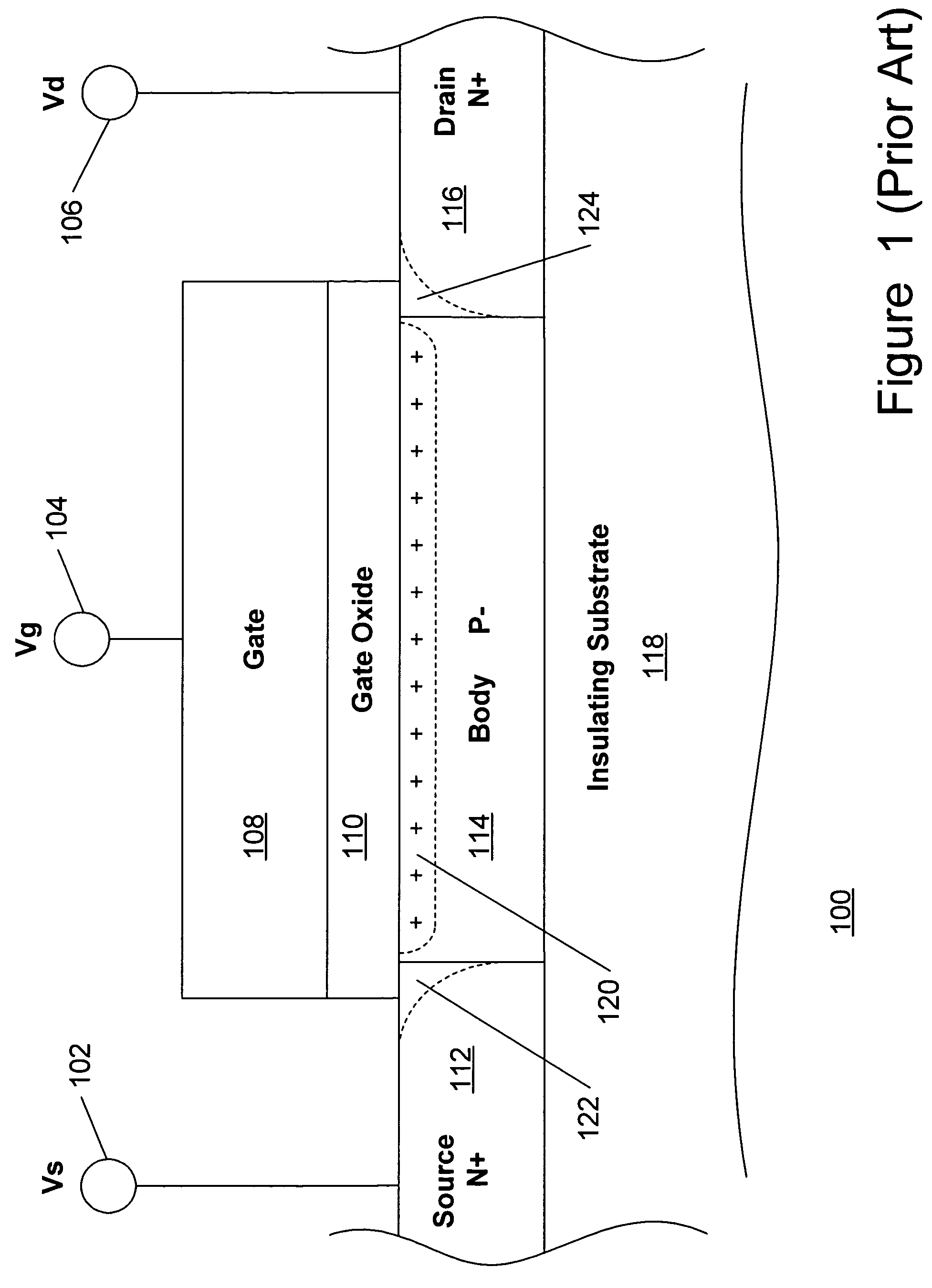
Method and apparatus improving gate oxide reliability by controlling accumulated charge
ActiveUS7890891B2Improving nonlinear responses and harmonic and intermodulaton distortion effectsReduce non-linearitySolid-state devicesElectronic switchingMOSFETDielectric
A method and apparatus are disclosed for use in improving the gate oxide reliability of semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) metal-oxide-silicon field effect transistor (MOSFET) devices using accumulated charge control (ACC) techniques. The method and apparatus are adapted to remove, reduce, or otherwise control accumulated charge in SOI MOSFETs, thereby yielding improvements in FET performance characteristics. In one embodiment, a circuit comprises a MOSFET, operating in an accumulated charge regime, and means for controlling the accumulated charge, operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET. A first determination is made of the effects of an uncontrolled accumulated charge on time dependent dielectric breakdown (TDDB) of the gate oxide of the SOI MOSFET. A second determination is made of the effects of a controlled accumulated charge on TDDB of the gate oxide of the SOI MOSFET. The SOI MOSFET is adapted to have a selected average time-to-breakdown, responsive to the first and second determinations, and the circuit is operated using techniques for accumulated charge control operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET. In one embodiment, the accumulated charge control techniques include using an accumulated charge sink operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET body.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Method and apparatus for nonvolatile memory
Method and apparatus on charges injection using piezo-ballistic-charges injection mechanism are provided for nonvolatile memory device. The device has a strain source, an injection filter, a tunneling gate, a ballistic gate, a charge storage region, a source, and a drain with a channel defined between the source and drain. The strain source permits piezo-effect in ballistic charges transport to enable the piezo-ballistic-charges injection mechanism. The injection filter permits transporting of charge carriers of one polarity type from the tunneling gate through the blocking material and the ballistic gate to the charge storage region while blocking the transport of charge carriers of an opposite polarity from the ballistic gate to the tunneling gate. The present invention further provides an energy band engineering method permitting the memory device be operated without suffering from disturbs, from dielectric breakdown, from impact ionization, and from undesirable RC effects.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Plasma channel drilling process
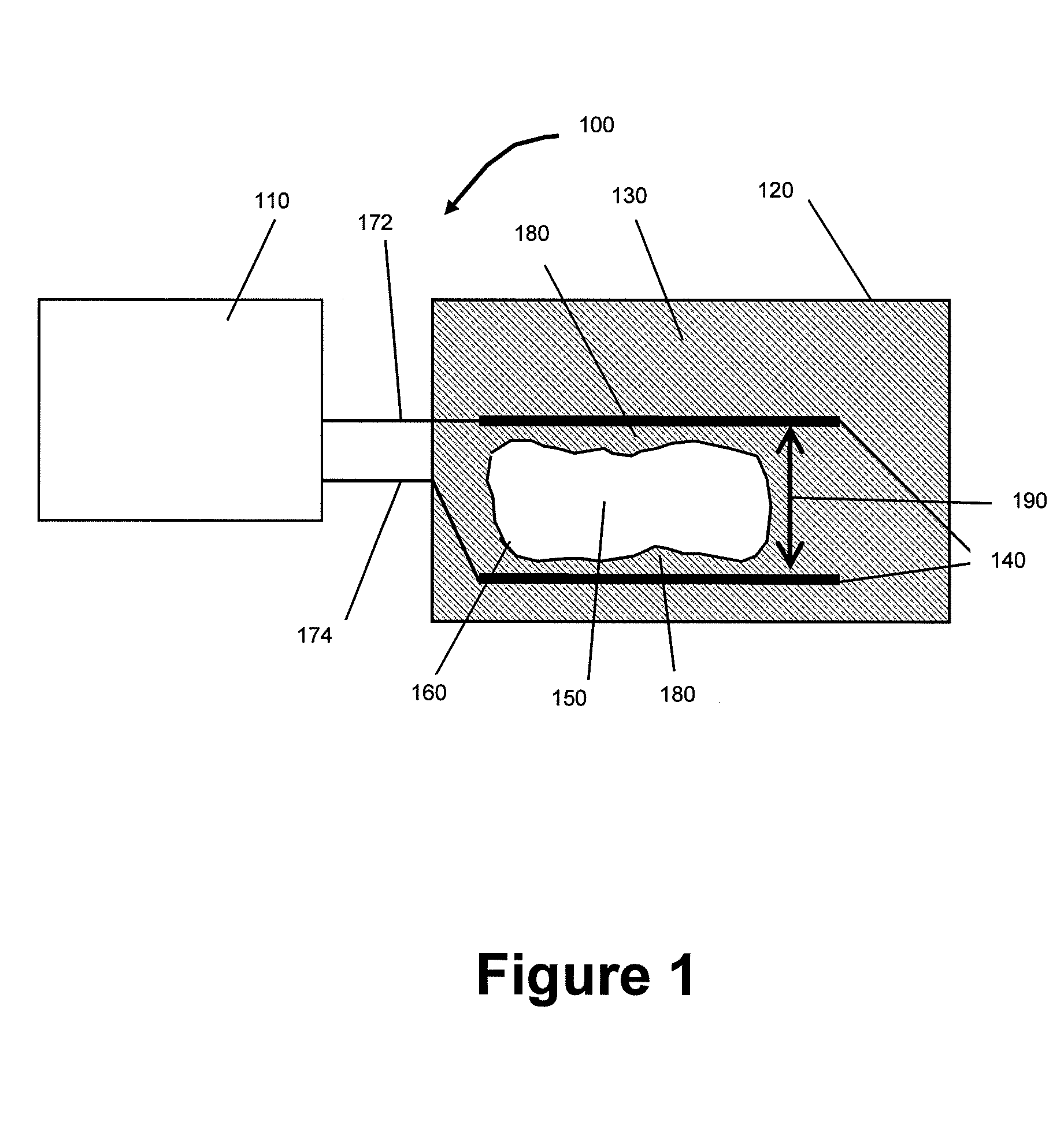
Material is removed from a body of material, e.g. to create a bore hole, by plasma channel drilling. High voltage, high energy, rapid rise time electrical pulses are delivered many times per second to an electrode assembly in contact with the material body to generate therein elongate plasma channels which expand rapidly following electrical breakdown of the material causing the material to fracture and fragment.
Owner:STRATHCLYDE UNIV OF
Conductive path in switching material in a resistive random access memory device and control
ActiveUS20120074374A1Low forming voltageReduce leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBulk negative resistance effect devicesAmorphous siliconResistive switching
A non-volatile memory device structure. The device structure includes a first electrode, a second electrode, a resistive switching material comprising an amorphous silicon material overlying the first electrode, and a thickness of dielectric material having a thickness ranging from 5 nm to 10 nm disposed between the second electrode and the resistive switching layer. The thickness of dielectric material is configured to electrically breakdown in a region upon application of an electroforming voltage to the second electrode. The electrical breakdown allows for a metal region having a dimension of less than about 10 nm by 10 nm to form in a portion of the resistive switching material.
Owner:INNOSTAR SEMICON SHANGHAI CO LTD
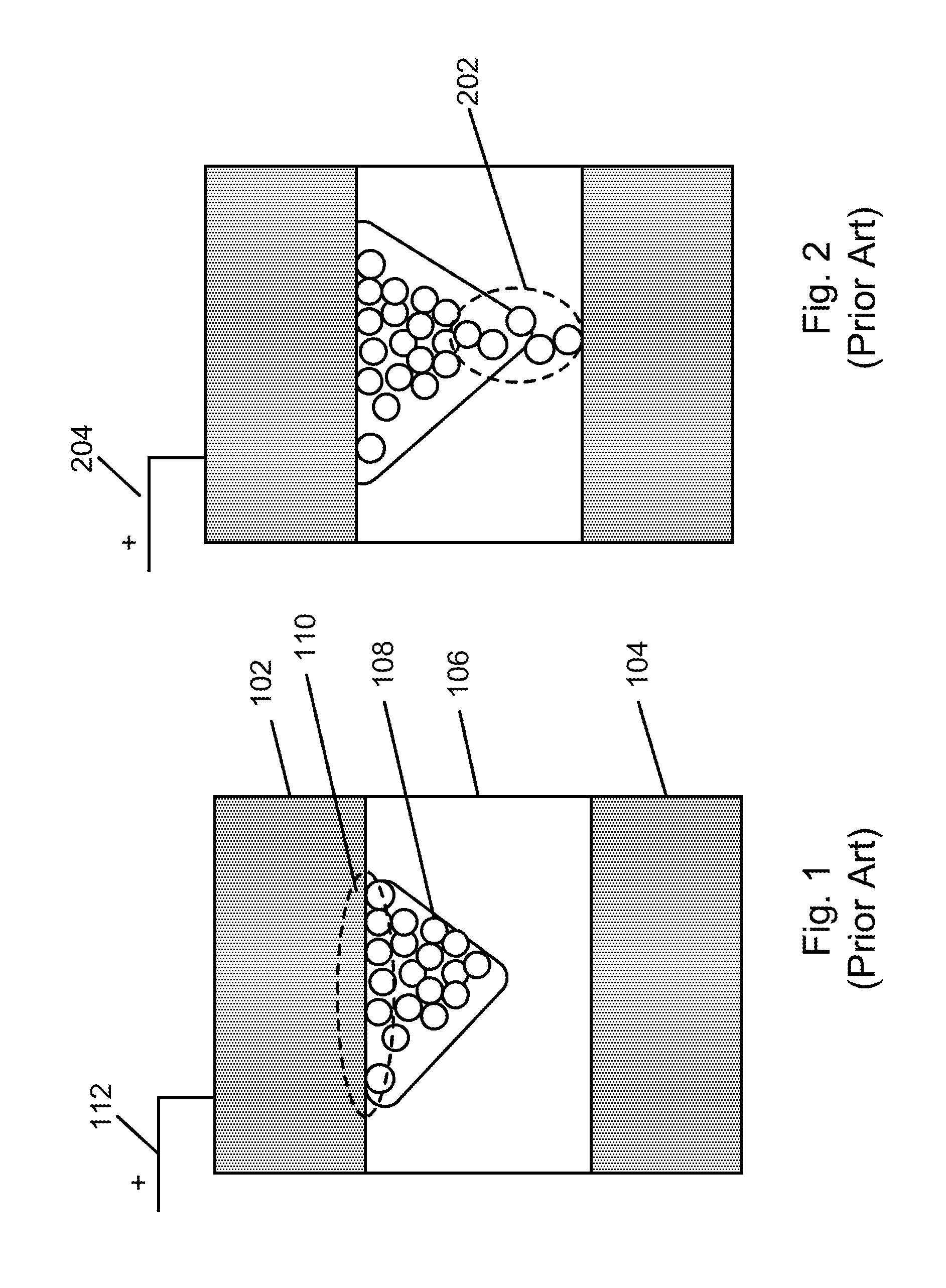
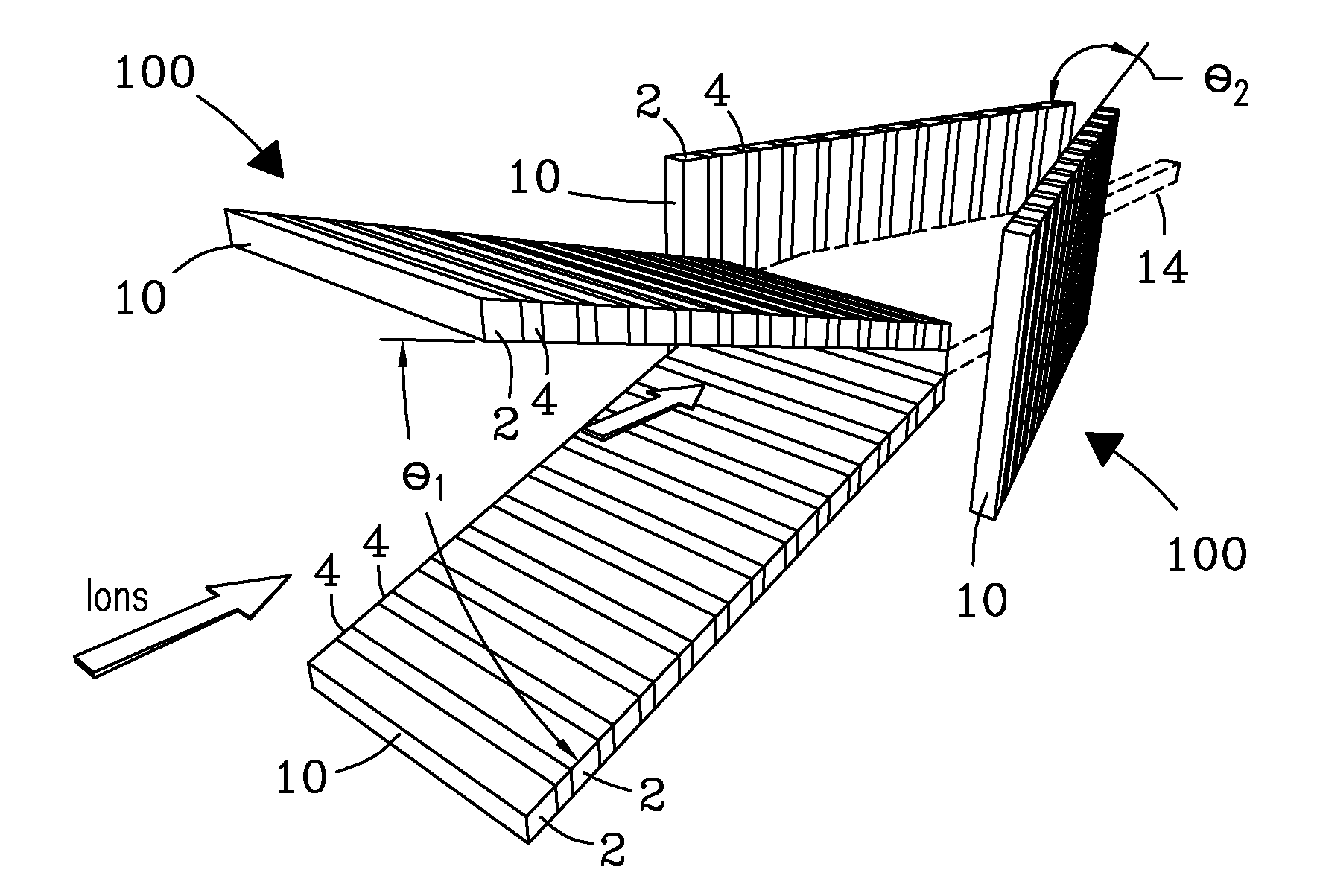
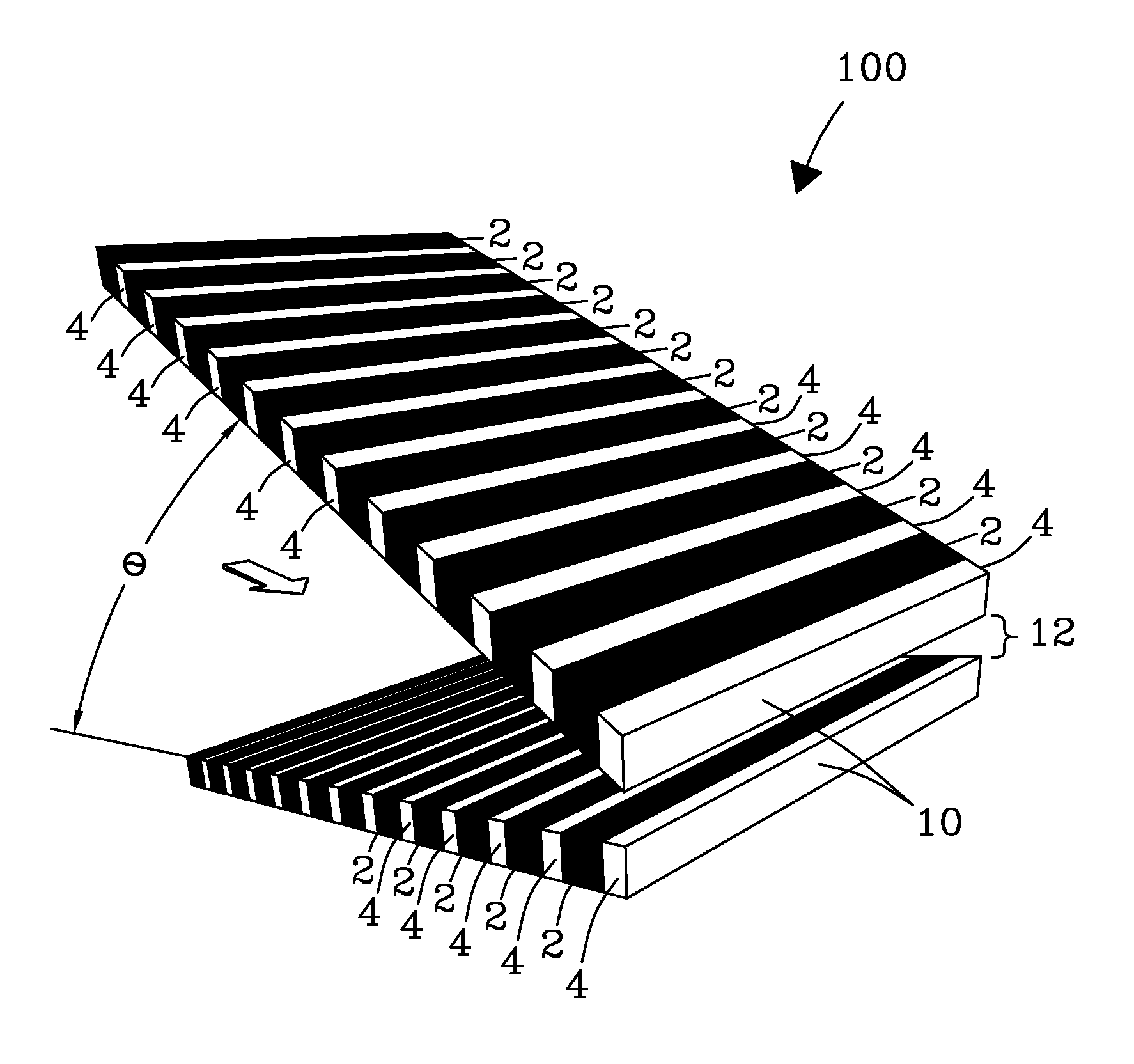
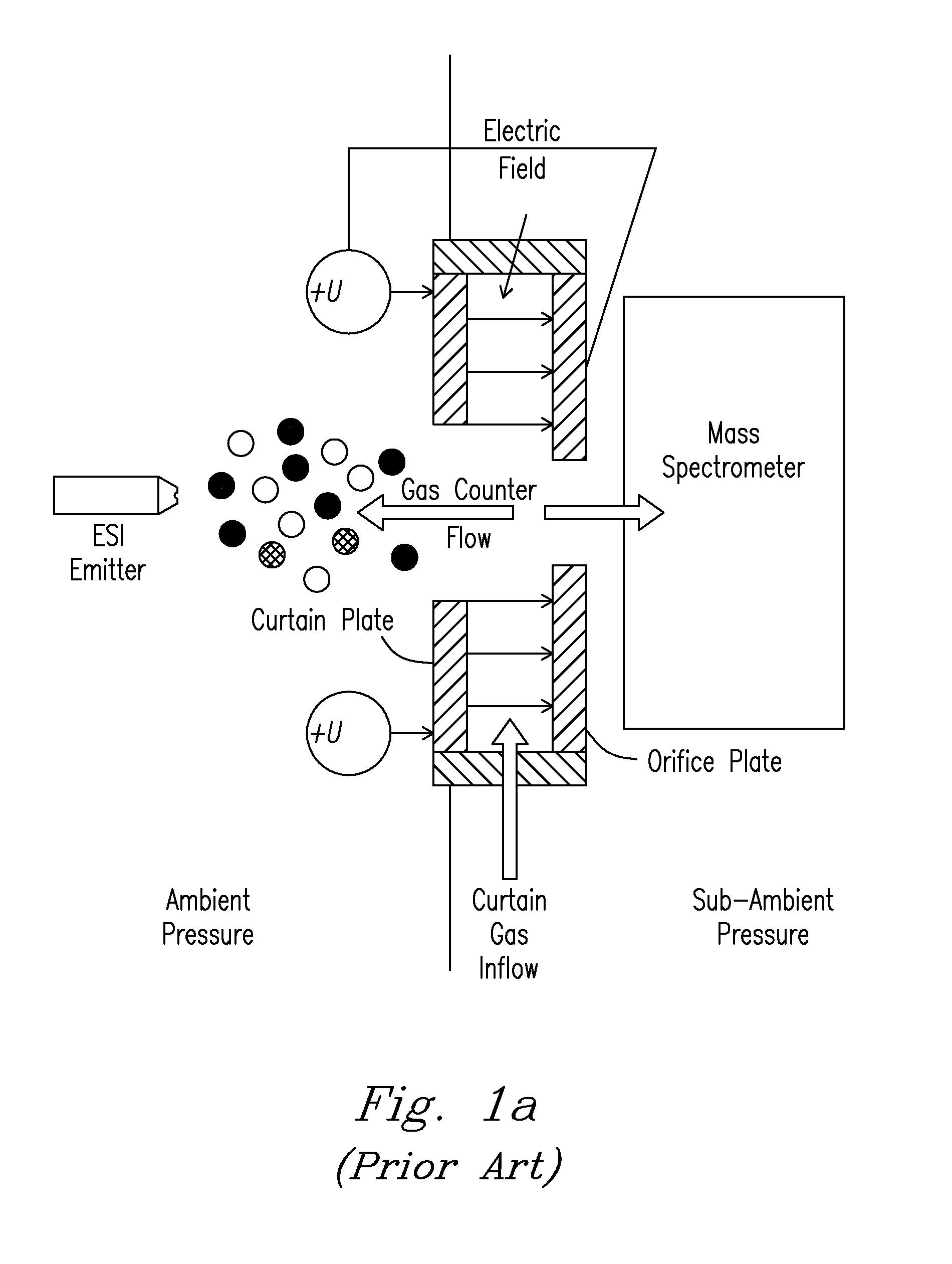
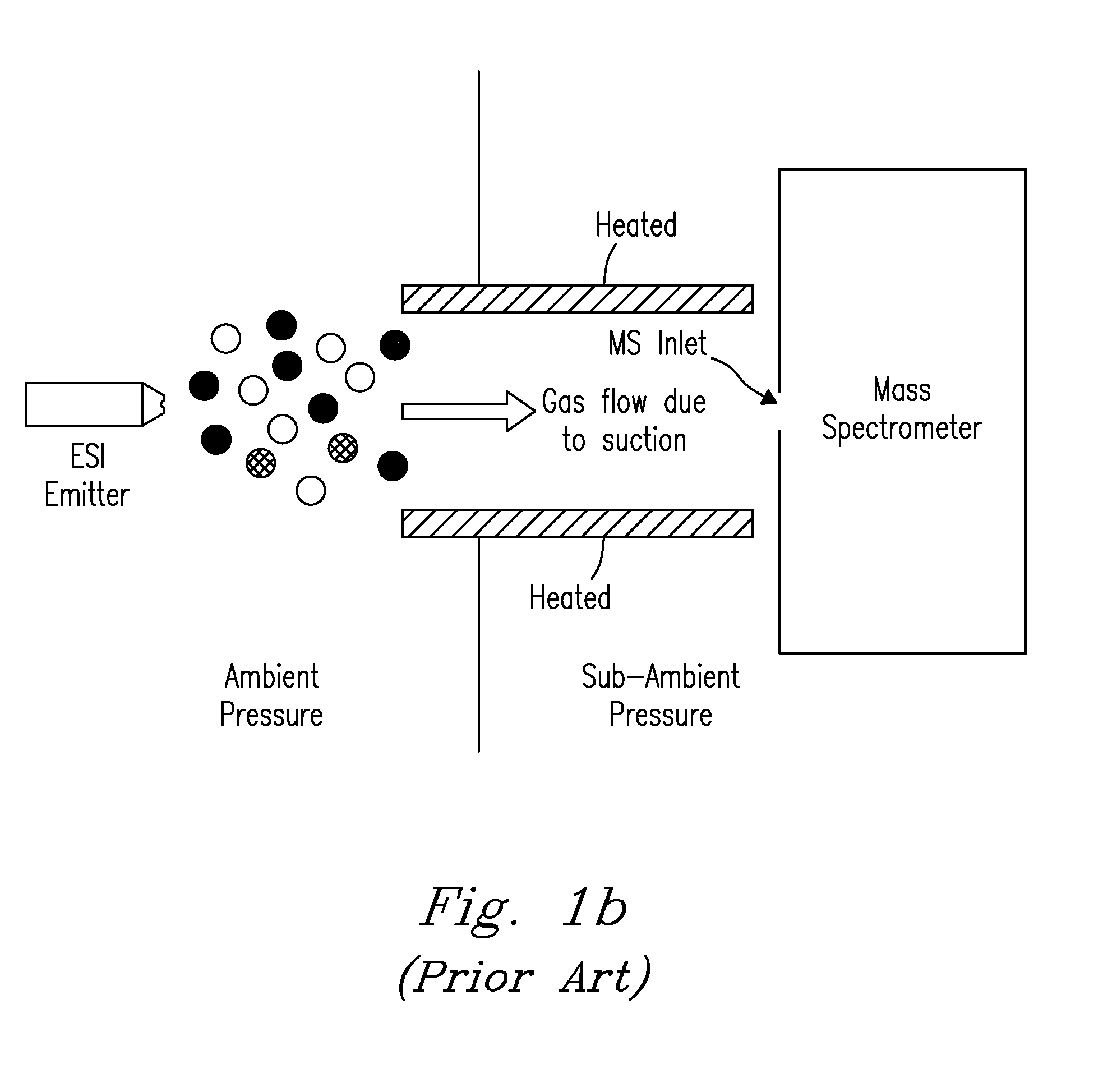
Microchip and wedge ion funnels and planar ion beam analyzers using same
ActiveUS20120261570A1Time-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionMicroscopic scaleMeasurement precision
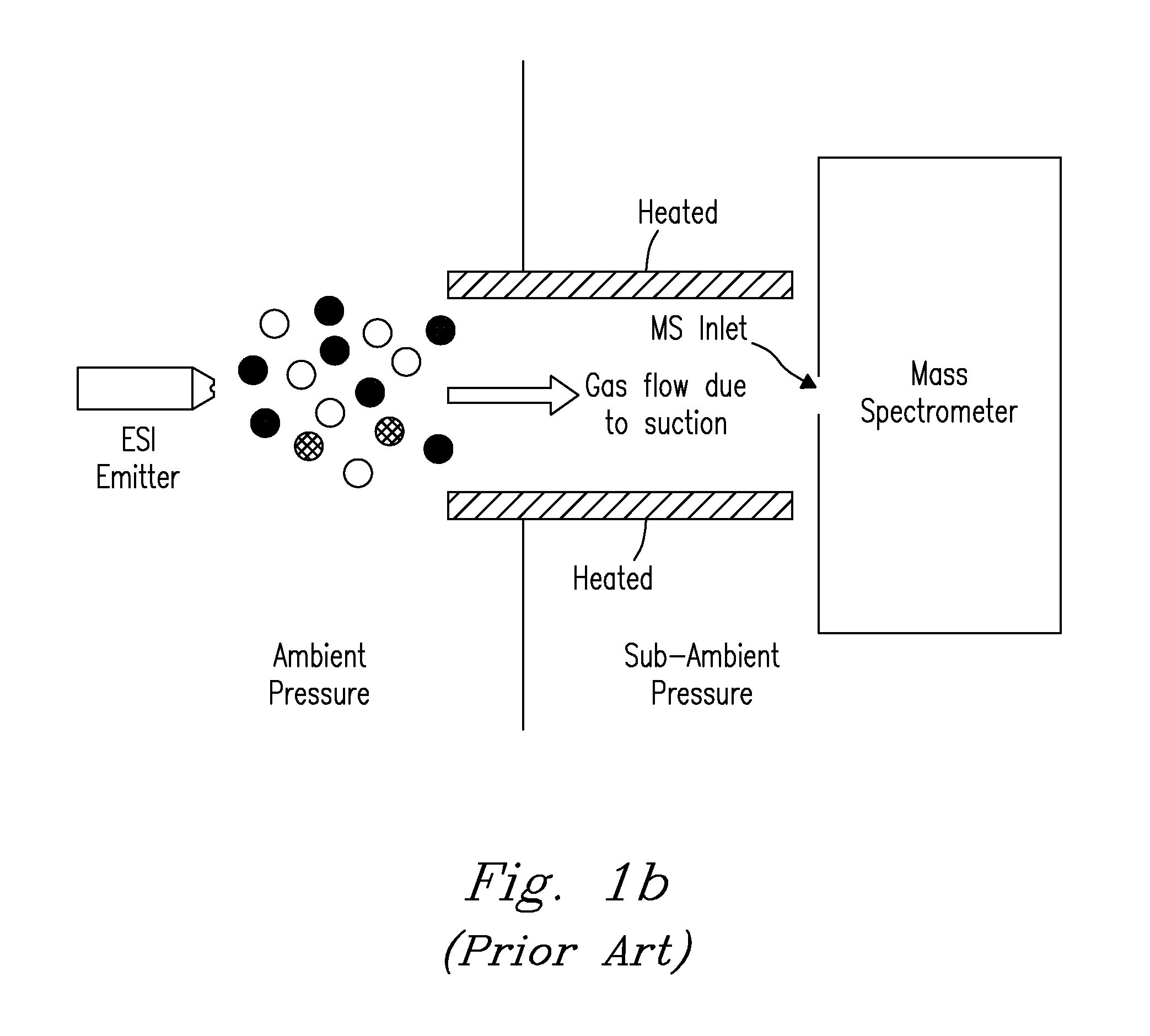
Electrodynamic on funnels confine, guide, or focus ions in gases using the Dehmelt potential of oscillatory electric field. New funnel designs operating at or close to atmospheric gas pressure are described. Effective on focusing at such pressures is enabled by fields of extreme amplitude and frequency, allowed in microscopic gaps that have much higher electrical breakdown thresholds in any gas than the macroscopic gaps of present funnels. The new microscopic-gap funnels are useful for interfacing atmospheric-pressure ionization sources to mass spectrometry (MS) and on mobility separation (IMS) stages including differential IMS or FAIMS, as well as IMS and MS stages in various configurations. In particular, “wedge” funnels comprising two planar surfaces positioned at an angle and wedge funnel traps derived therefrom can compress on beams in one dimension, producing narrow belt-shaped beams and laterally elongated cuboid packets. This beam profile reduces the ion density and thus space-charge effects, mitigating the adverse impact thereof on the resolving power, measurement accuracy, and dynamic range of MS and IMS analyzers, while a greater overlap with coplanar light or particle beams can benefit spectroscopic methods.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
GaN SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE STRUCTURE AND METHOD OF FABRICATION BY SUBSTRATE REPLACEMENT
ActiveUS20160380090A1Increased vertical breakdown resistanceImprove cooling effectTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementContact padDevice material
Devices and systems comprising high current / high voltage GaN semiconductor devices are disclosed. A GaN die, comprising a lateral GaN transistor, is sandwiched between an overlying header and an underlying composite thermal dielectric layer. Fabrication comprises providing a conventional GaN device structure fabricated on a low cost silicon substrate (GaN-on-Si die), mechanically and electrically attaching source, drain and gate contact pads of the GaN-on-Si die to corresponding contact areas of conductive tracks of the header, then entirely removing the silicon substrate. The exposed substrate-surface of the epi-layer stack is coated with the composite dielectric thermal layer. Preferably, the header comprises a ceramic dielectric support layer having a CTE matched to the GaN epi-layer stack. The thermal dielectric layer comprises a high dielectric strength thermoplastic polymer and a dielectric filler having a high thermal conductivity. This structure offers improved electrical breakdown resistance and effective thermal dissipation compared to conventional GaN-on-Si device structures.
Owner:GAN SYST
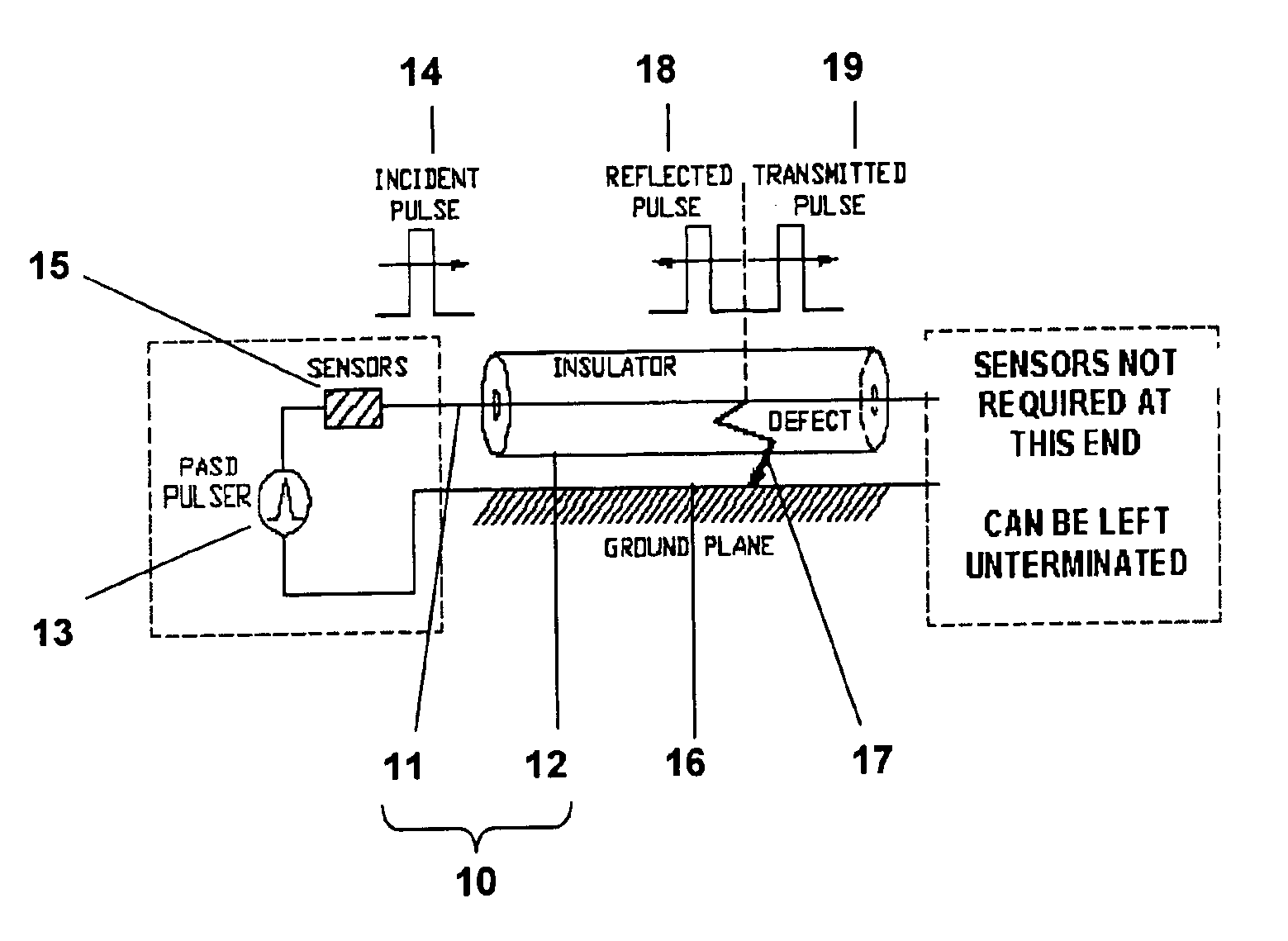
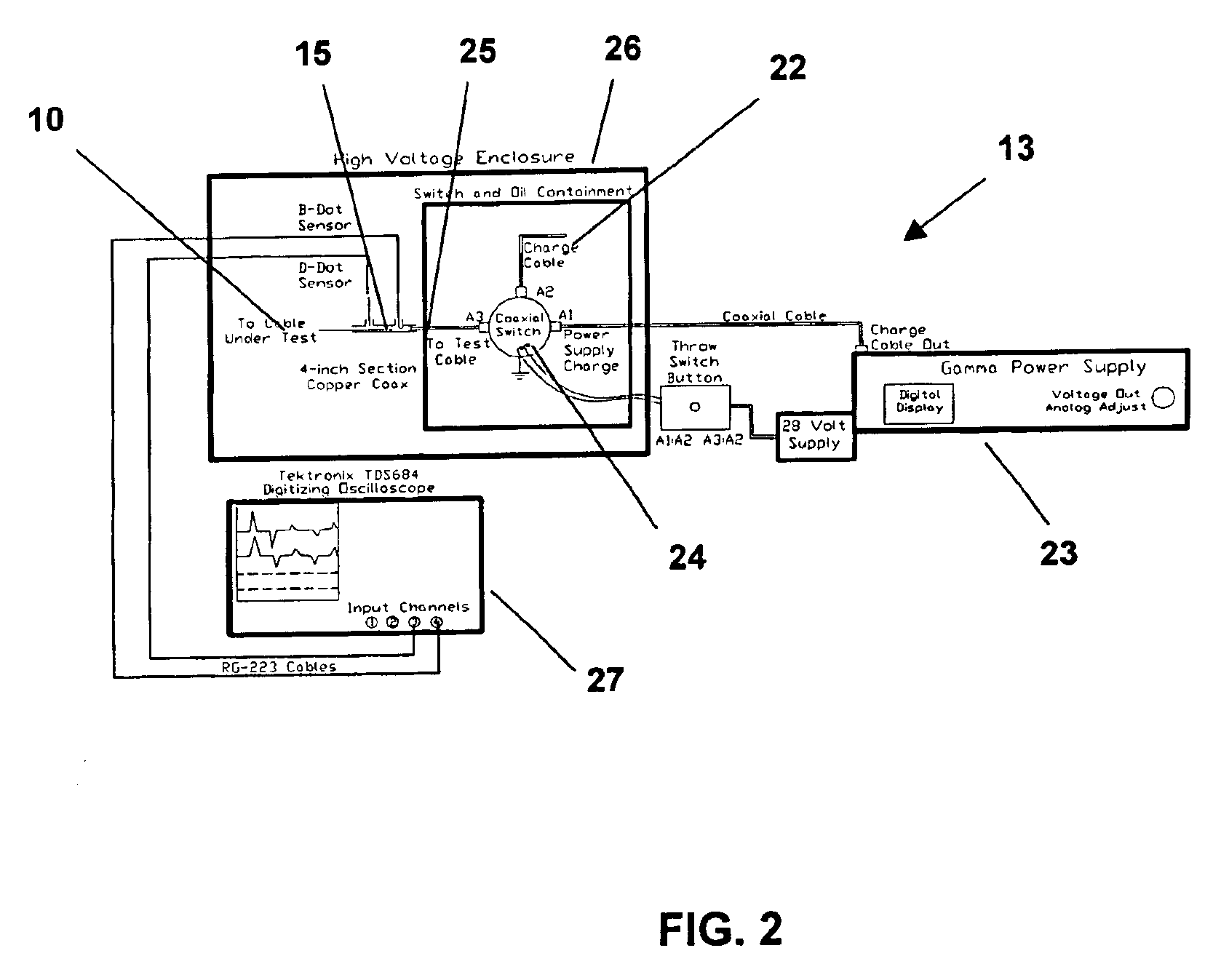
Method and apparatus for electrical cable testing by pulse-arrested spark discharge
InactiveUS6853196B1Enhance and inhibit onsetLower breakdown voltageResistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by pulse reflection methodsElectricityNuclear power
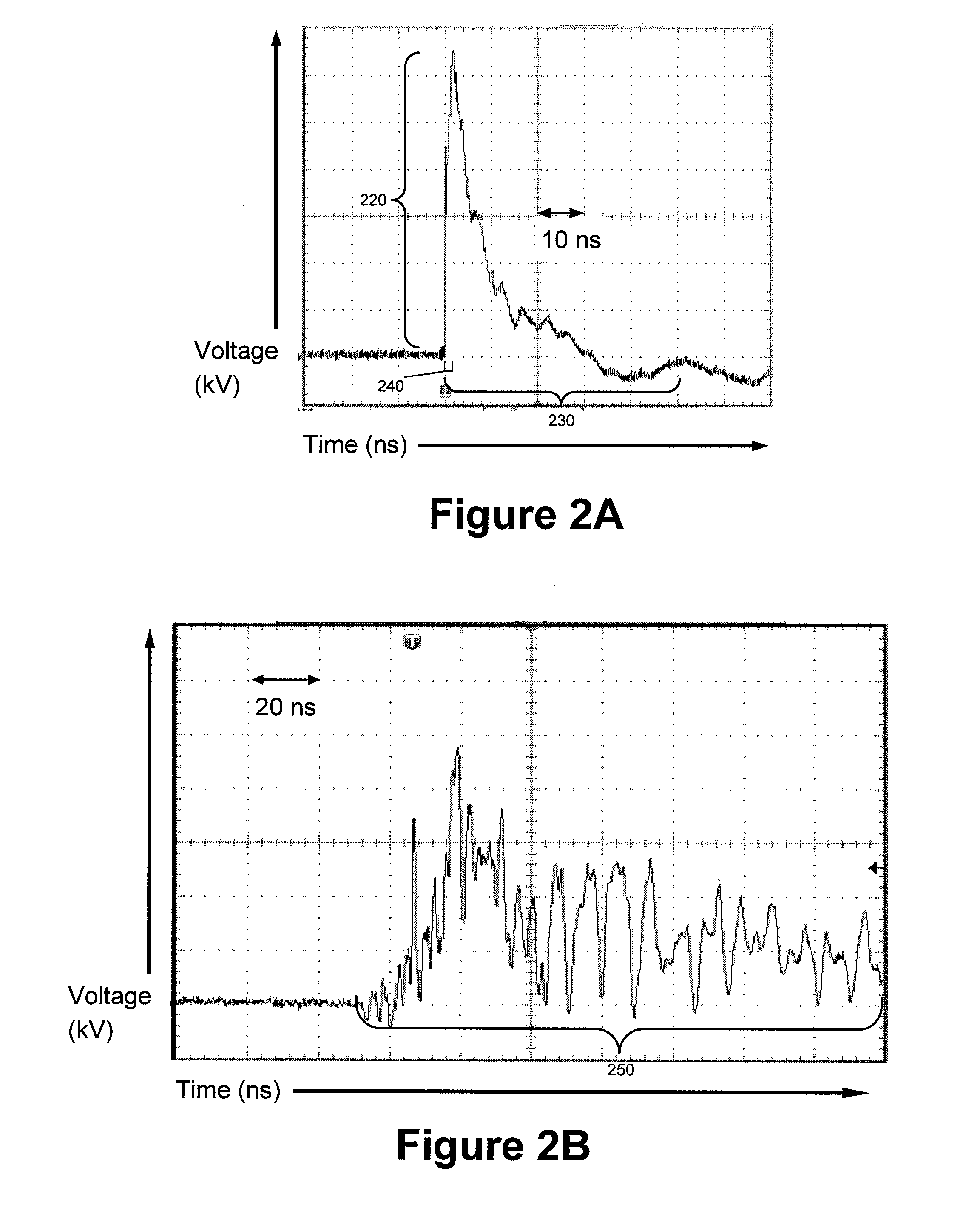
A method for electrical cable testing by Pulse-Arrested Spark Discharge (PASD) uses the cable response to a short-duration high-voltage incident pulse to determine the location of an electrical breakdown that occurs at a defect site in the cable. The apparatus for cable testing by PASD includes a pulser for generating the short-duration high-voltage incident pulse, at least one diagnostic sensor to detect the incident pulse and the breakdown-induced reflected and / or transmitted pulses propagating from the electrical breakdown at the defect site, and a transient recorder to record the cable response. The method and apparatus are particularly useful to determine the location of defect sites in critical but inaccessible electrical cabling systems in aging aircraft, ships, nuclear power plants, and industrial complexes.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
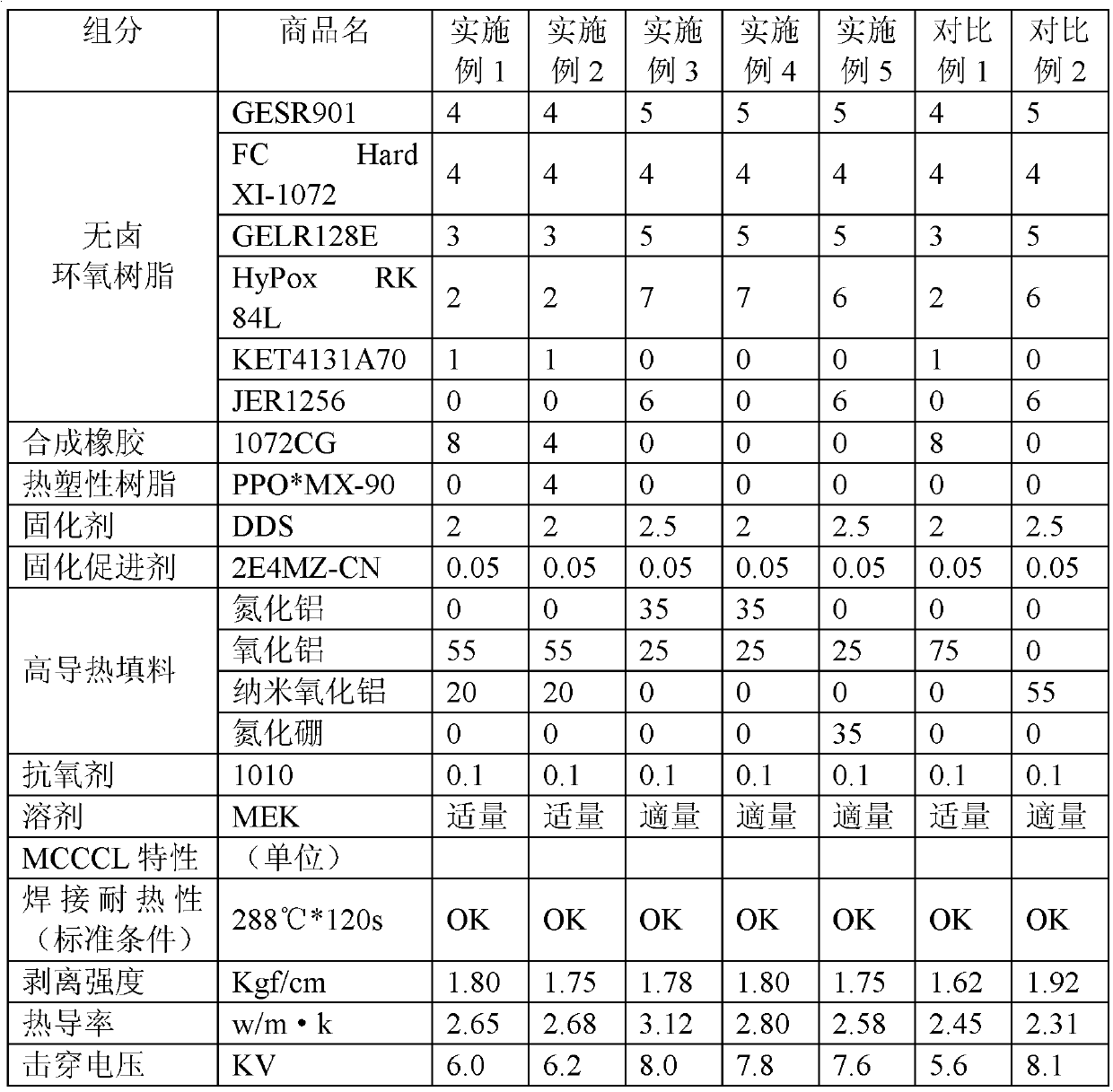
Halogen-free fire-retardant high heat conducting insulating resin composition and heat dissipation metal-base copper clad plate
ActiveCN102558765AImprove heat resistanceHigh peel strengthSynthetic resin layered productsEpoxy resin adhesivesEpoxyHeat conducting
The invention discloses a halogen-free fire-retardant high heat conducting insulating resin composition and a heat dissipation metal-base copper clad plate (CCL). The composition comprises the following components in parts by weight: 10-45 parts of halogen-free epoxy resin, 0-15 parts of thermoplastic resin and / or synthetic rubber, 0.1-5 parts of curing agent, 0.02-1 parts of accelerator, 0.5-1 parts of antioxidant and 25-80 parts of heat conducting filler. The halogen-free fire-retardant high heat conducting insulating resin composition of the invention adopts high heat conducting filler, and the cured composition shows good thermal conductivity, electric insulativity and welding heat resistance as well as high adhesive force. The invention also discloses a heat dissipation metal-base CCL prepared by using the above halogen-free fire-retardant high heat conducting insulating resin composition, which has high thermal conductivity and high peel strength, does not have the problems of peel-off and deterioration even being subjected to thermal cycle of quick heating and quick cooling, and also has high electrical breakdown resistance, good heat resistance and soldering resistance and the like, and the flame retardant rating of the heat dissipation metal-base CCL reaches UL-94V0.
Owner:ALLSTAE TECH ZHONGSHAN
Microchip and wedge ion funnels and planar ion beam analyzers using same
ActiveUS8299443B1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMicroscopic scaleMeasurement precision
Electrodynamic ion funnels confine, guide, or focus ions in gases using the Dehmelt potential of oscillatory electric field. New funnel designs operating at or close to atmospheric gas pressure are described. Effective ion focusing at such pressures is enabled by fields of extreme amplitude and frequency, allowed in microscopic gaps that have much higher electrical breakdown thresholds in any gas than the macroscopic gaps of present funnels. The new microscopic-gap funnels are useful for interfacing atmospheric-pressure ionization sources to mass spectrometry (MS) and ion mobility separation (IMS) stages including differential IMS or FAIMS, as well as IMS and MS stages in various configurations. In particular, “wedge” funnels comprising two planar surfaces positioned at an angle and wedge funnel traps derived therefrom can compress ion beams in one dimension, producing narrow belt-shaped beams and laterally elongated cuboid packets. This beam profile reduces the ion density and thus space-charge effects, mitigating the adverse impact thereof on the resolving power, measurement accuracy, and dynamic range of MS and IMS analyzers, while a greater overlap with coplanar light or particle beams can benefit spectroscopic methods.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Assembly for electrical breakdown protection for high current, non-elongate solar cells with electrically conductive substrates
InactiveUS20120234388A1Improve cooling effectImprove long-term reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationElectrical batteryEngineering
Methods and devices are provided for avalanche breakdown in a thin-film solar cell. In one embodiment, a method of breakdown protection assembly comprises providing a single reel of material which is pre-cut in a pattern so that a first portion of the material can be overlapped to a second portion of material to sandwich a breakdown protection device therebetween
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Method for providing uniform distribution of plasma density in a plasma treatment apparatus
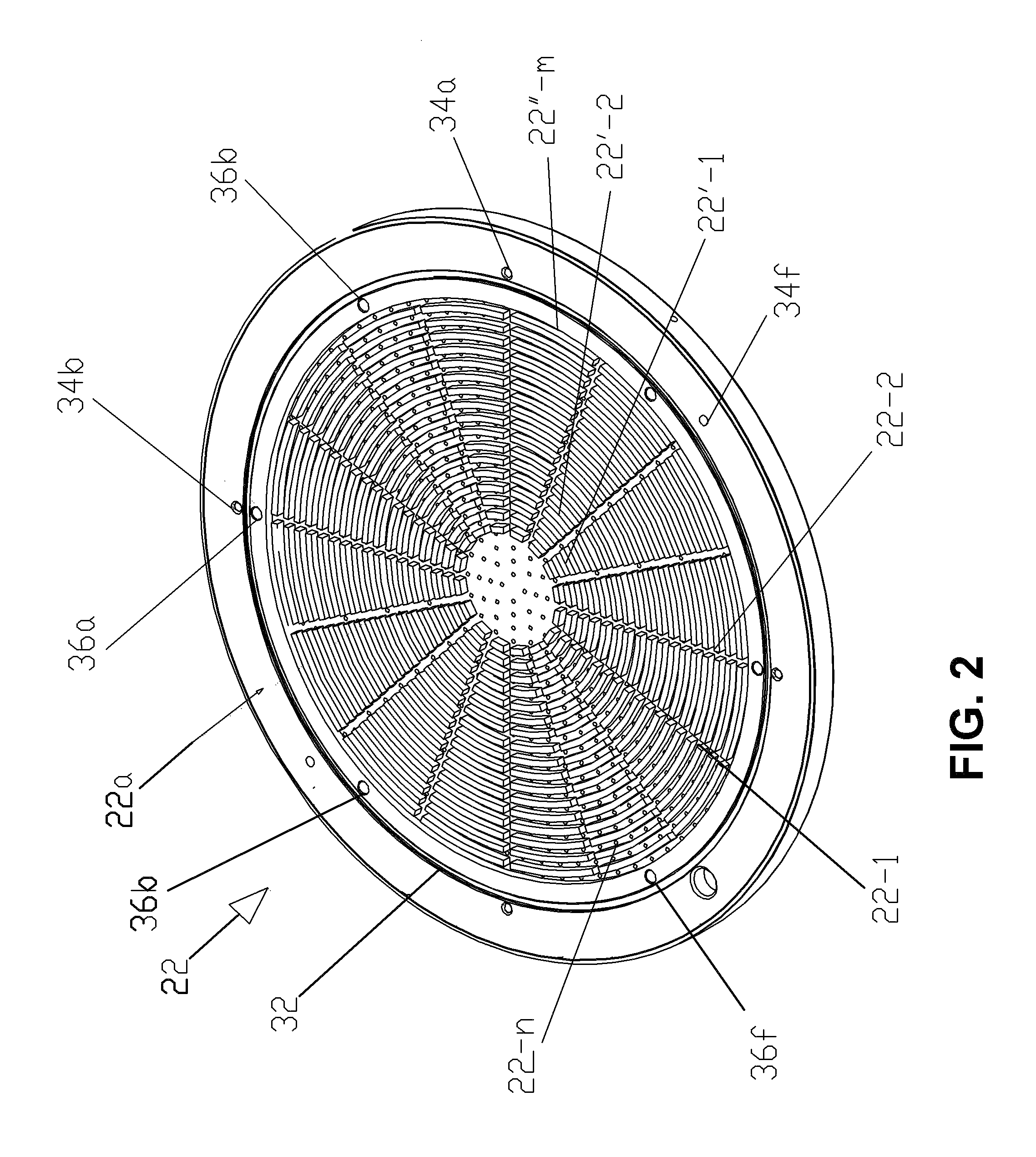
ActiveUS20150214013A1High plasma uniformityEvenly distributedLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesElectricityPlasma density
Proposed is a method for providing uniform distribution of plasma density in a CCP plasma processing apparatus. According to the method the through gas holes of the showerhead of used in the plasma processing chamber of the apparatus are provided with conical nozzles formed on the side of the gas holes that face the gas reservoir of the cooler plate. The cone angle θ of the nozzles decreases in the direction from the peripheral portion to the central area of the showerhead in the range from 120° to 0°. Since the conical nozzles increase the gas gap between the showerhead and the cooler plate, more favorable conditions are created for electric breakdown. In order to protect the surfaces of the conical nozzles and gas holes from deterioration by hollow cathode discharge, these surface are coated by a protective coating resistant to electrical breakdown and chemical corrosion.
Owner:GLUKHOY YURI
Insulating sheet and multilayer structure
InactiveUS20100297453A1Improve thermal conductivitySuitable for usePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhenolGlass transition
The present invention provides an insulating sheet which is used for bonding a heat conductor having a thermal conductivity of 10 W / m·K or higher to an electrically conductive layer. The handleability of the insulating sheet is excellent when it is uncured, and a cured product of the insulating sheet has higher adhesion, heat resistance, dielectric breakdown characteristics, and thermal conductivity. The insulating sheet used for bonding a heat conductor having a thermal conductivity of 10 W / m·K or higher to an electrically conductive layer comprises: (A) a polymer having an aromatic skeleton and a weight average molecular weight of 10,000 or more; (B) at least one of an epoxy monomer (B1) having an aromatic skeleton and a weight average molecular weight of 600 or less and an oxetane monomer (B2) having an aromatic skeleton and a weight average molecular weight of 600 or less; (C) a curing agent composed of a phenol resin, an acid anhydride having an aromatic skeleton or an alicyclic skeleton, a hydrogenated product of the acid anhydride, or a modified product of the acid anhydride; and (D) a filler. When the insulating sheet is uncured, the insulating sheet has a glass transition temperature Tg of 25° C. or lower.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Showerhead-cooler system of a semiconductor-processing chamber for semiconductor wafers of large area
InactiveUS20150214009A1Uniform plasma densityAvoid turbulenceElectric discharge tubesSpraying apparatusPlasma densityEngineering
Proposed is a showerhead-cooler system of a semiconductor-processing chamber with uniform distribution of plasma density. The showerhead has a plurality of through gas holes that are coaxial with respective channels of the gas-feeding cooler plate. On the gas inlet side, the though passages of the showerhead are provided with unequal conical nozzles characterized by a central angle that decreases from the peripheral part of the showerhead to the showerhead center. Such design provides uniformity of plasma density. Furthermore, in order to protect the walls of the nozzle and the walls of the gas holes from erosion that may be caused by the hollow-cathode phenomenon, these areas are coated with a thin protective coating that is resistant to electrical breakdown and chemical corrosion.
Owner:GLUKHOY YURI +2
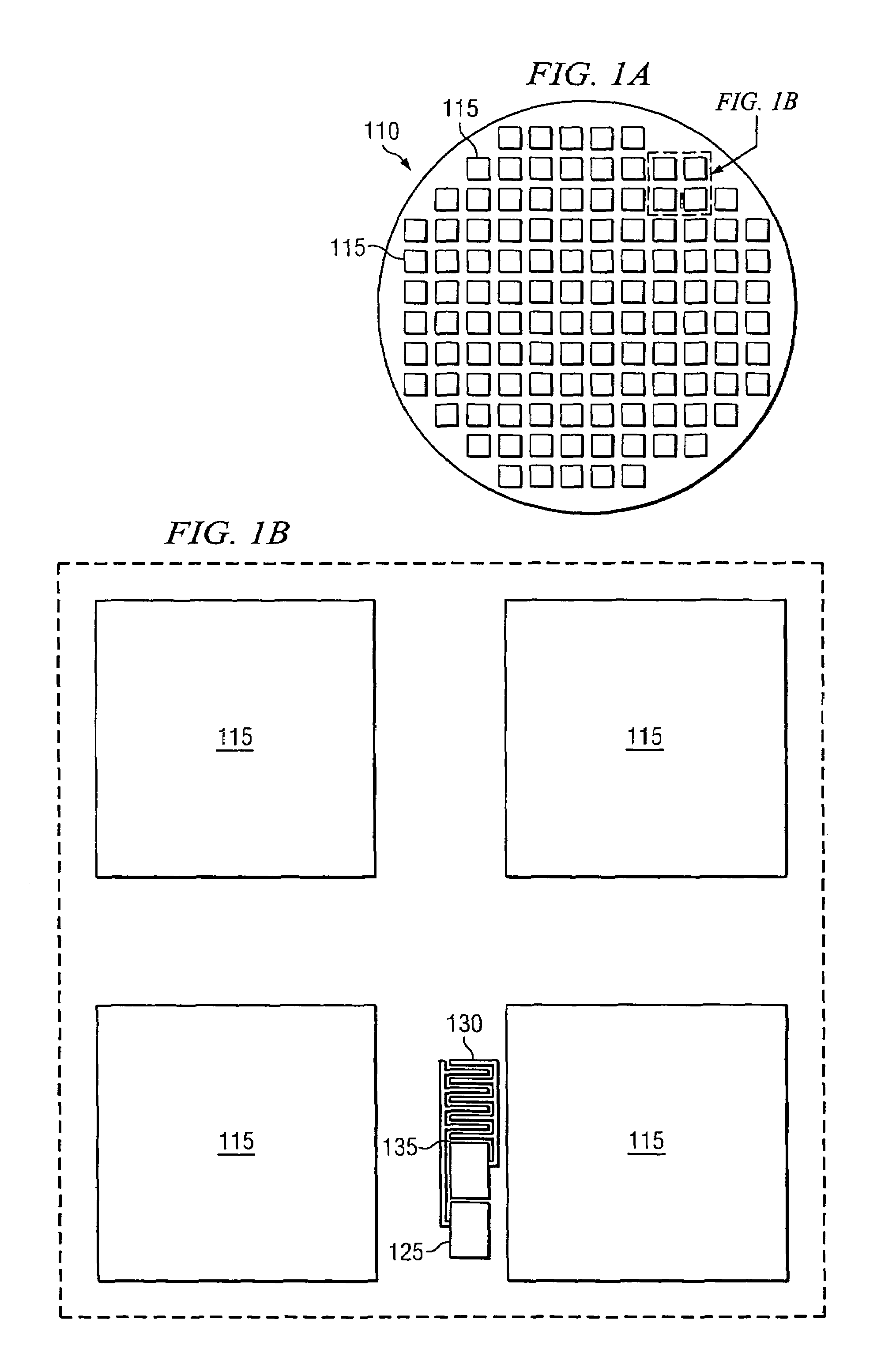
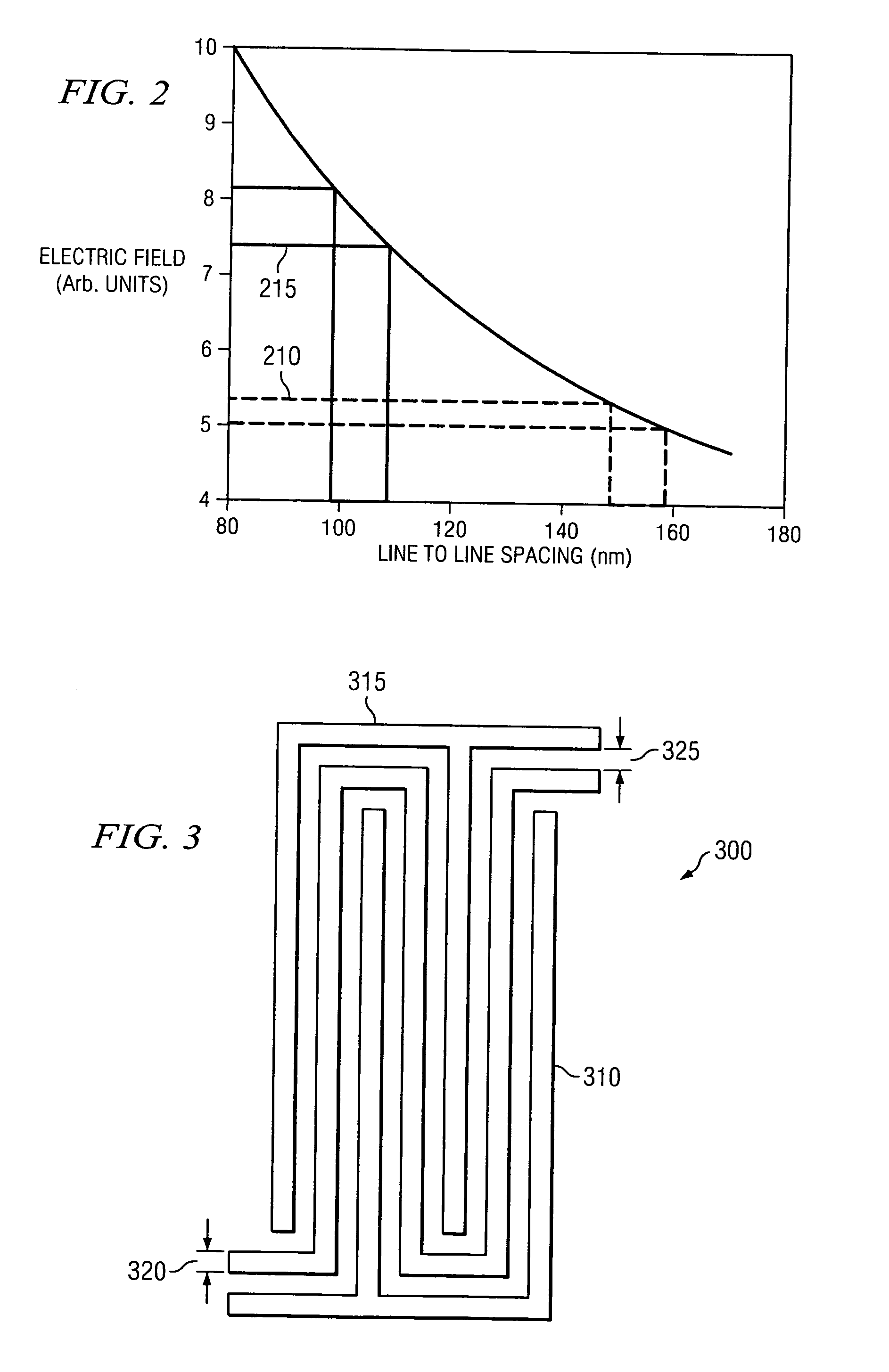
Dual ramp rate dielectric breakdown testing methodology
ActiveUS6967499B1Testing dielectric strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectricityAcceleration factor
The present invention provides, in one aspect, a method of testing an electrical breakdown characteristic of a dielectric in a microelectronic device. This method includes determining a first dielectric breakdown voltage distribution of a first test sample by using a first voltage ramp rate, determining a second dielectric breakdown voltage distribution of a second test sample by using a second voltage ramp rate and determining a spacing distribution between conductive lines in the first and second test samples based on a field acceleration factor associated with the dielectrics of the first and second test samples, the first and second voltage ramp rates, and a difference between the first and second breakdown voltage distributions. This spacing distribution is used to determine corrected electric breakdown fields based on a measured breakdown voltage of a test sample, to improve microelectronic-device screening for interconnect dielectric reliability.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
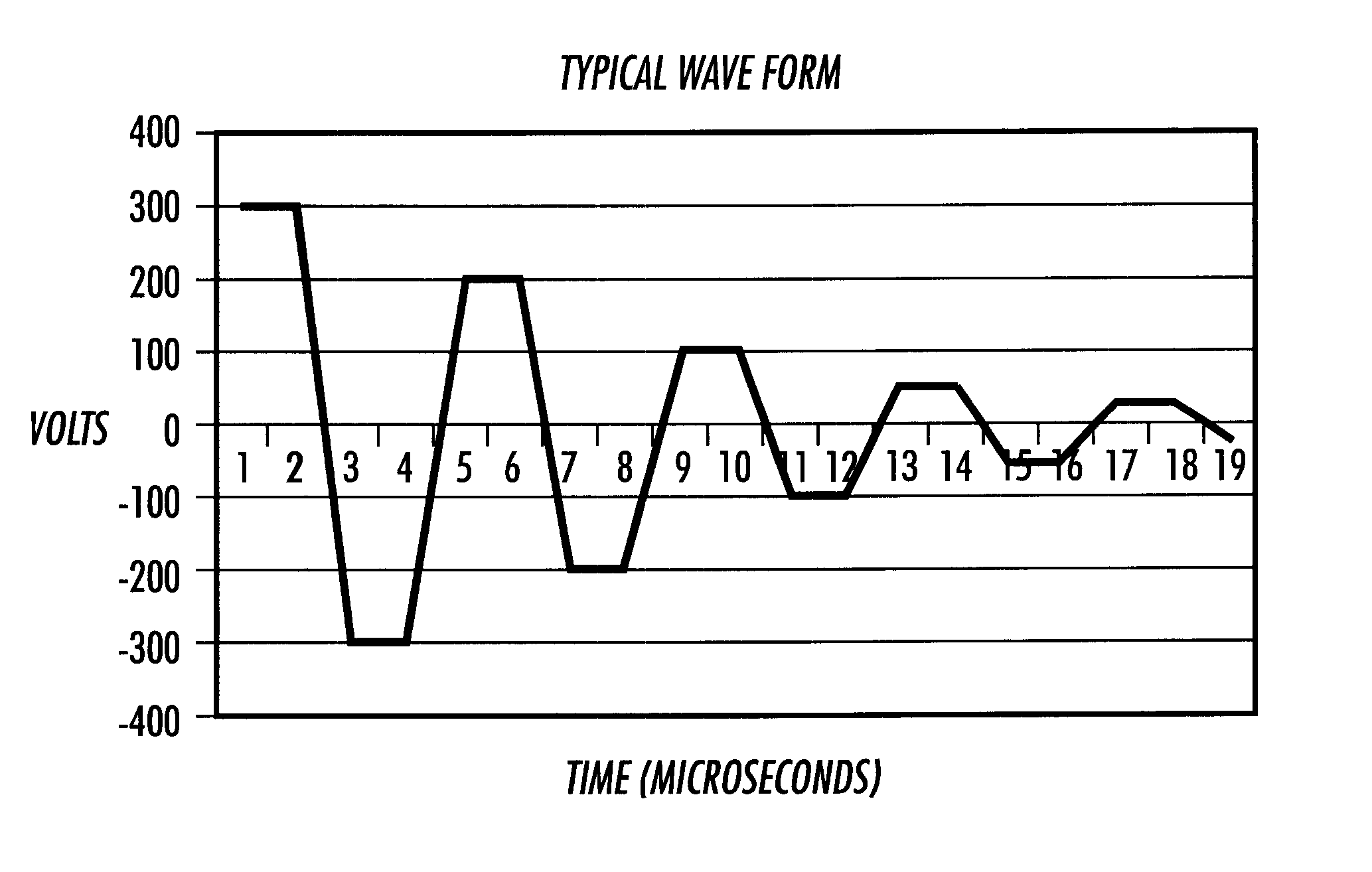
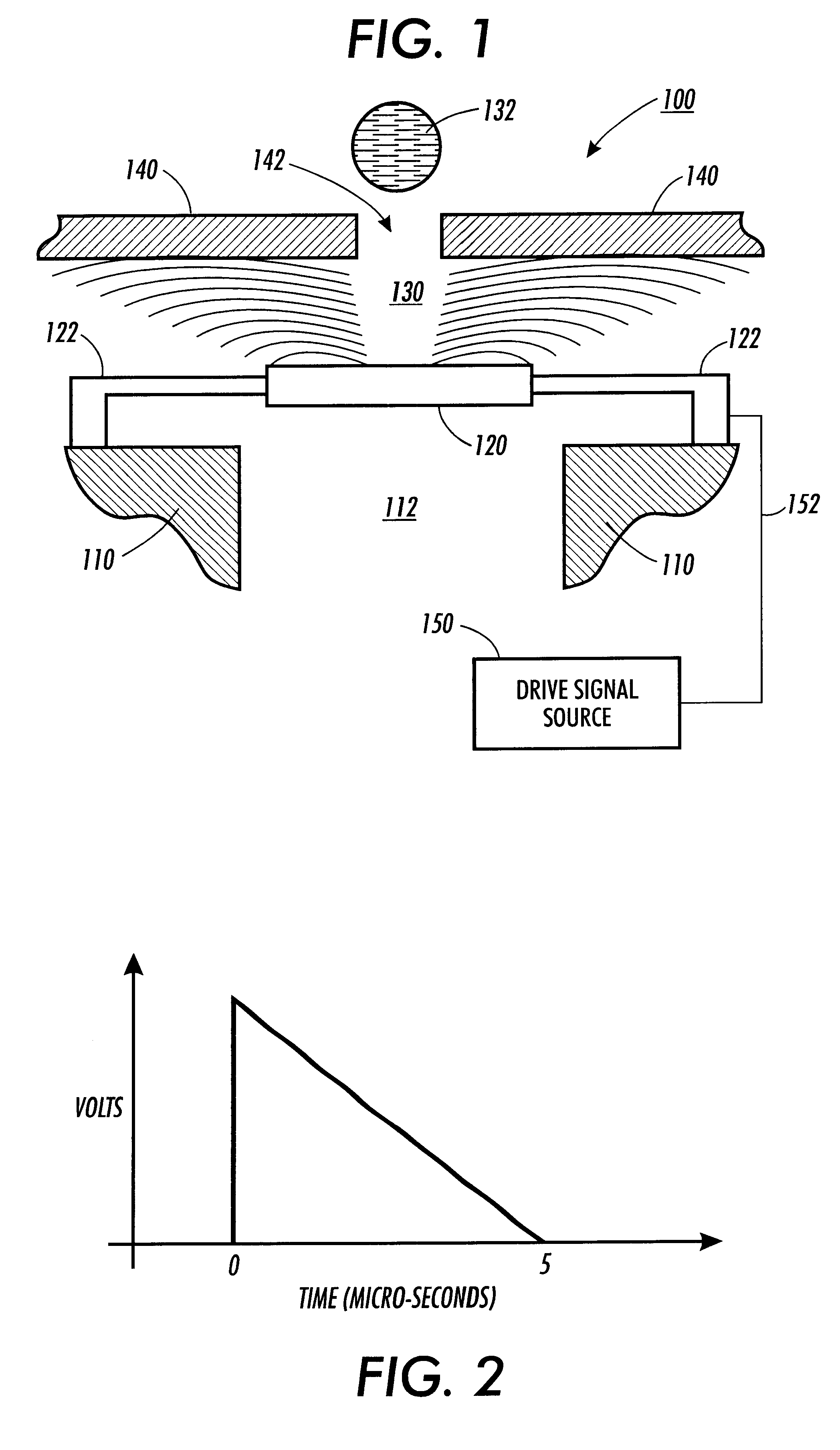
Electronic drive systems and methods
InactiveUS6419335B1Reduce potential impactPotent effectOther printing apparatusElectrochemical responseEngineering
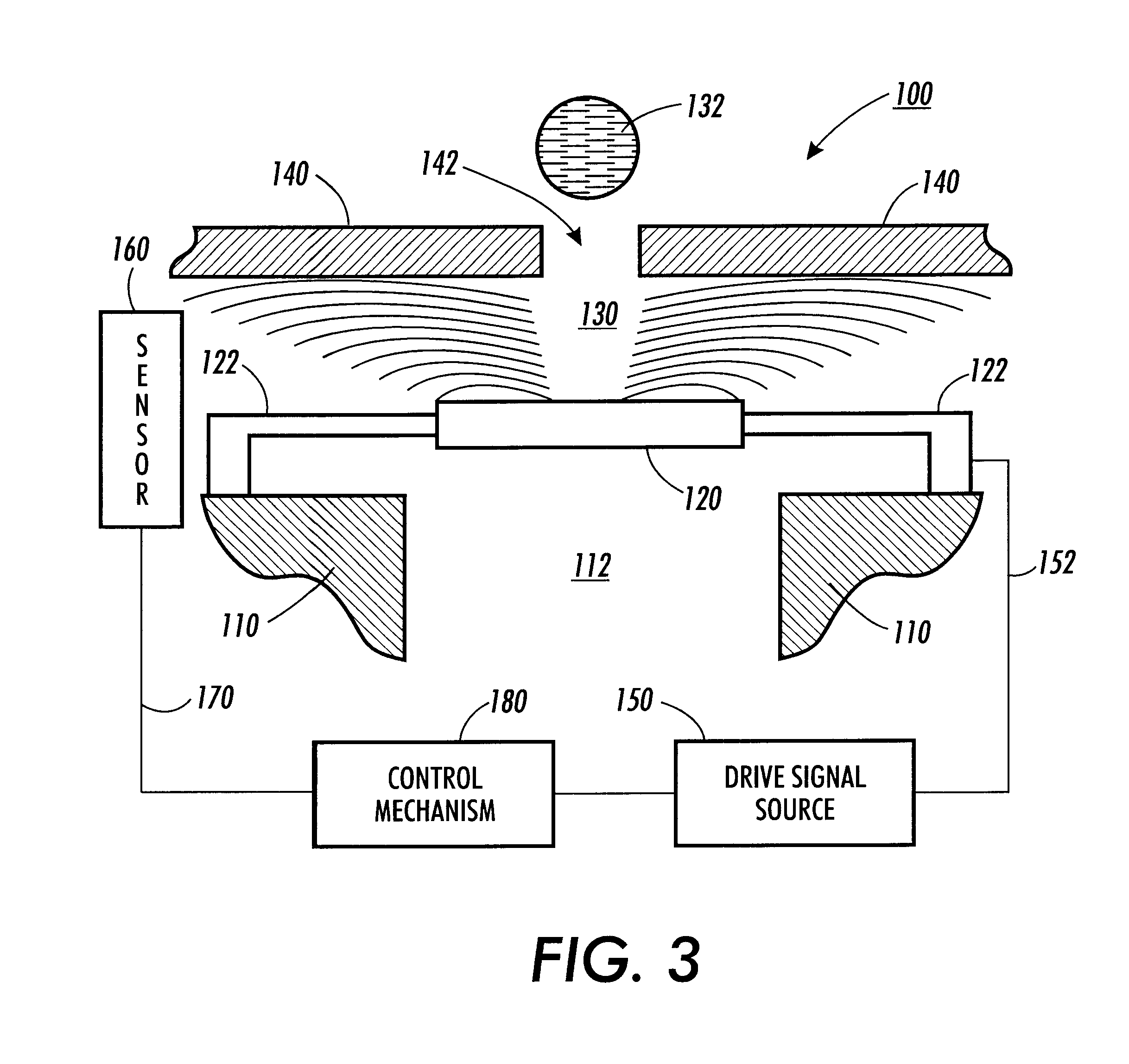
An electronic drive system applies a drive signal to an electrostatically actuated device such that a resulting electric field has a constant force. In various exemplary embodiments, the electronic drive system applies a drive signal to an electrostatically actuated fluid ejector that has a piston and a faceplate including a nozzle hole. A dielectric fluid to be ejected is supplied between the piston and the faceplate. The drive signal is applied to one of the piston and the faceplate. The drive signal generates an electric field across the fluid between the piston and the faceplate. The electric field causes the piston to be electrostatically attracted towards the faceplate so that a jet or drop of fluid is ejected through the nozzle hole of the faceplate. According to exemplary embodiments, the drive signal is from a constant current source or is reduced over the course of its lifetime. Further, according to various exemplary embodiments, the drive signal is of a suitable high frequency to reduce the potential of electrochemical reactions or electrical breakdown, or both. The drive signal may also be a bi-polar drive signal to reduce the possibility of electrochemical reactions.
Owner:XEROX CORP +1
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20070252168A1Increase junction areaIncrease the resistance valueThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZener diodeField-effect transistor
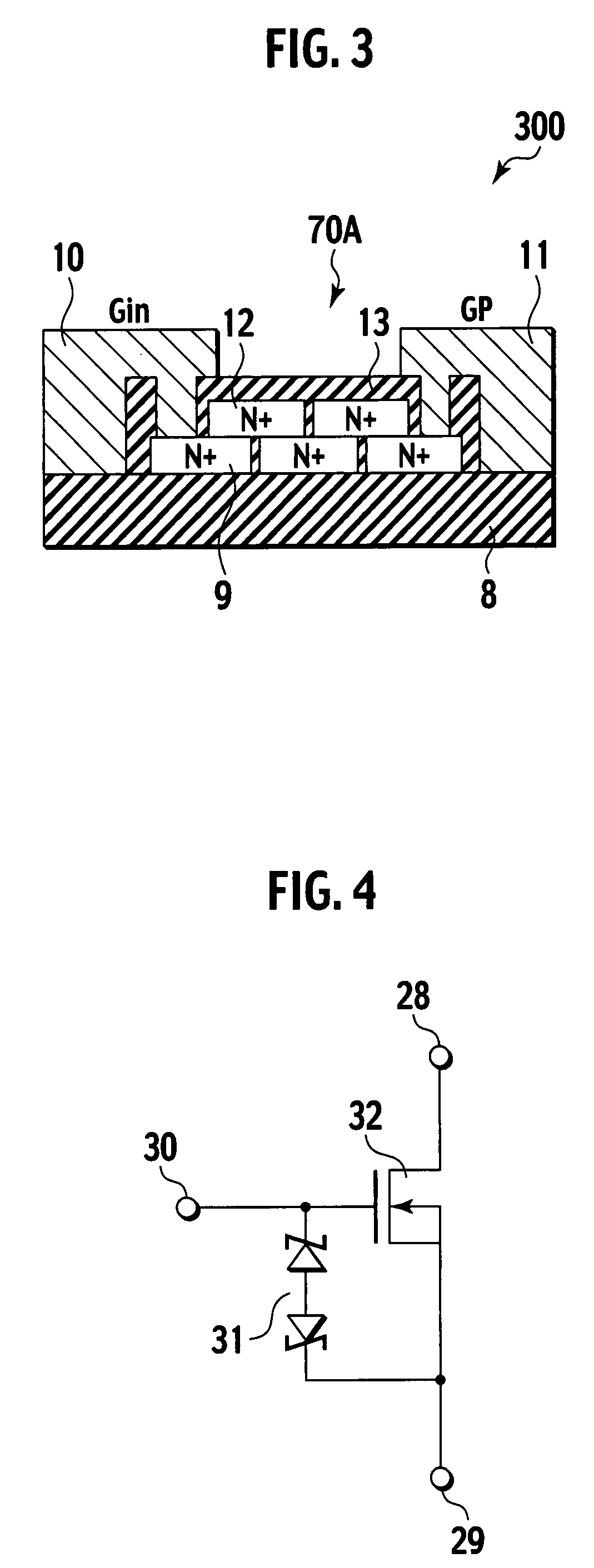
An electrostatic discharge protection element and a protection resistor, which are formed on an N-drain region with a field oxide film interposed therebetween for the purpose of preventing electrical breakdown of a field effect transistor, are composed as a stacked bidirectional Zener diode of one or a plurality of N+ polycrystalline silicon regions of a first layer and a P+ polycrystalline silicon region of a second layer, and a stacked resistor of one or a plurality of N+ resistor layers of the first layer and an N+ resistor layer of the second layer, respectively. One end of the plurality of N+ polycrystalline silicon regions of the first layer is connected to an external gate electrode terminal, and the other end is connected to a source electrode. One end of the plurality of N+ resistor layers of the first layer is connected to a gate electrode, and the other end is connected to the external gate electrode terminal. Semiconductor regions of the first layer and the second layer are formed by using semiconductor films, which form a hetero semiconductor region and the gate electrode, respectively.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
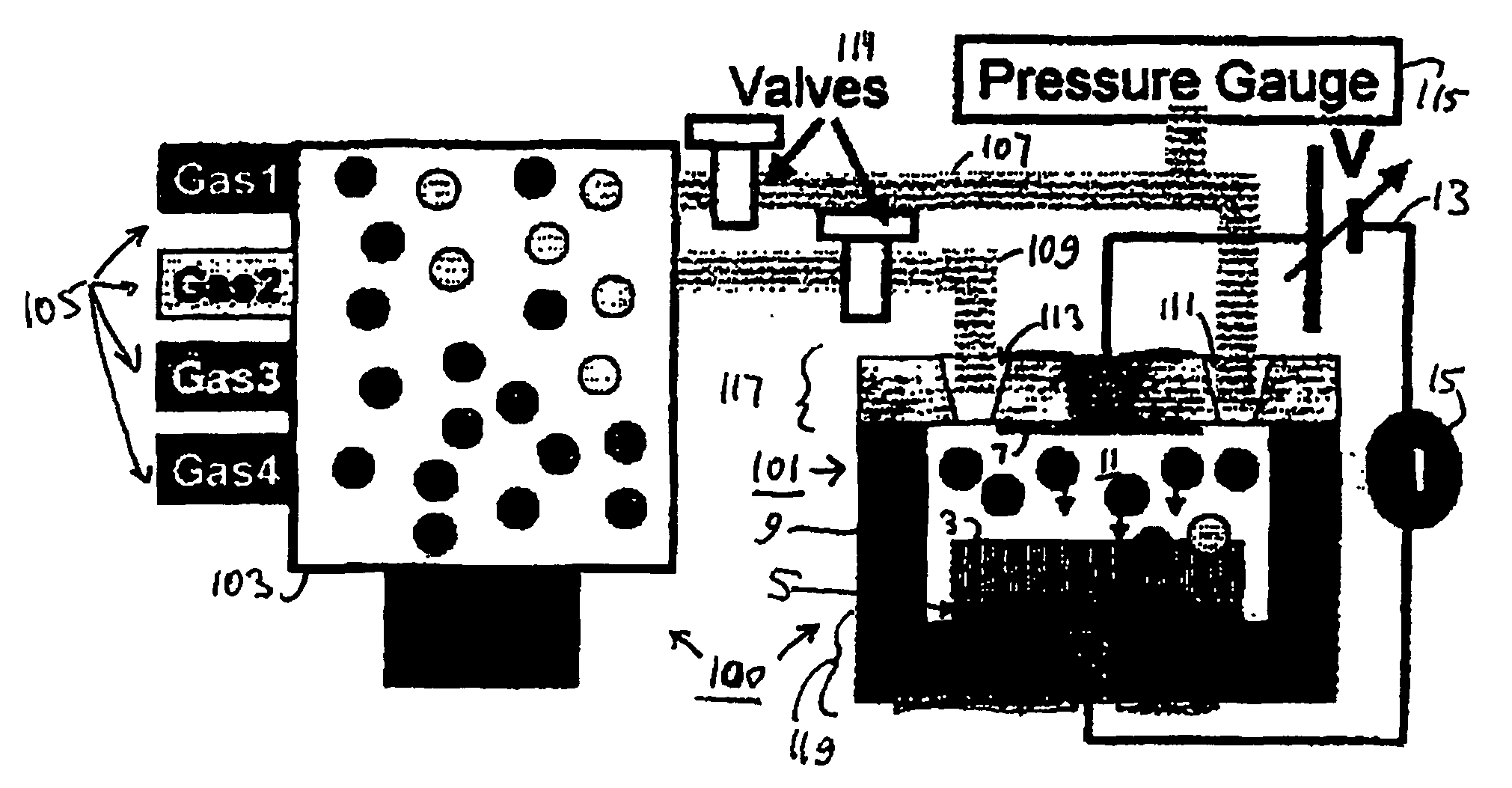
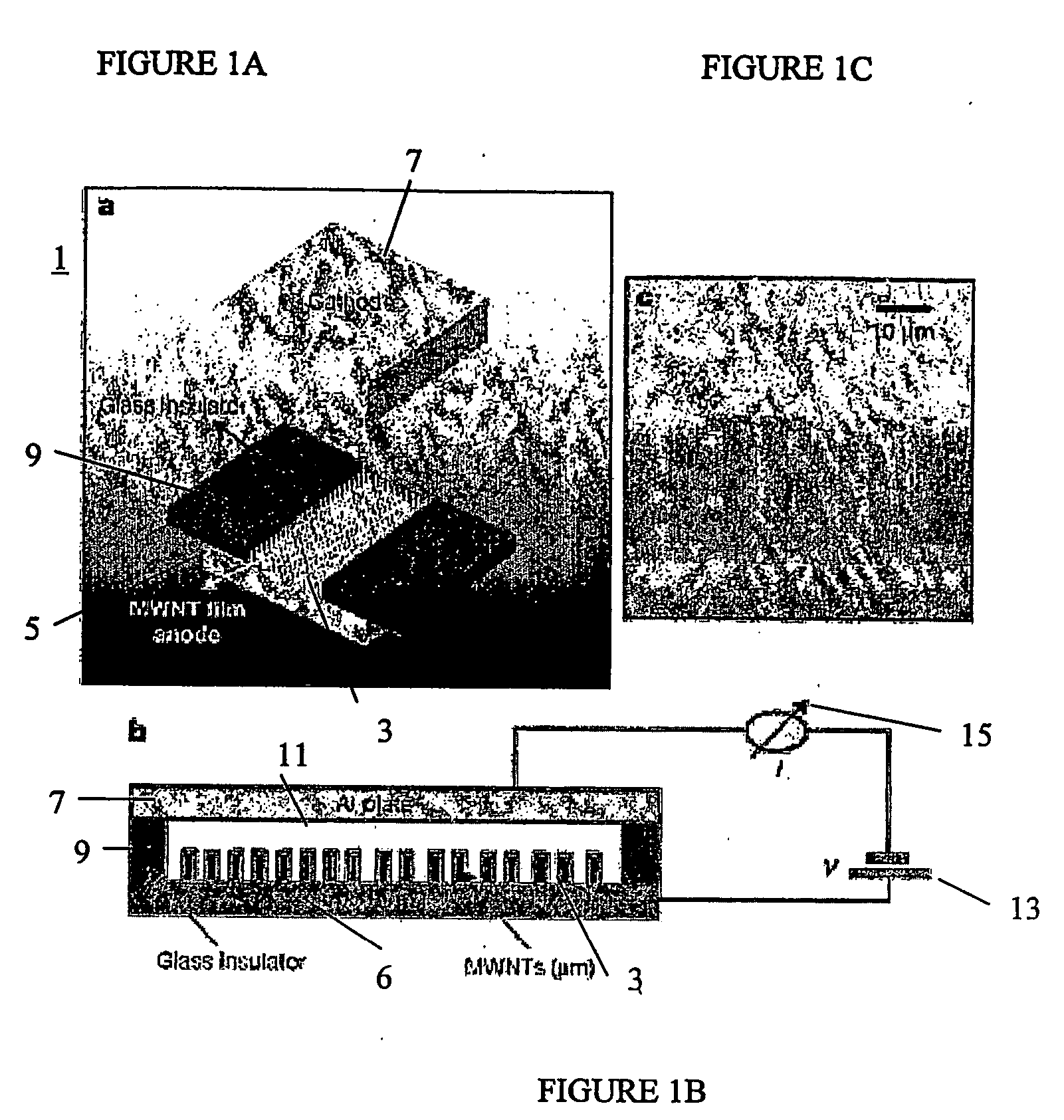
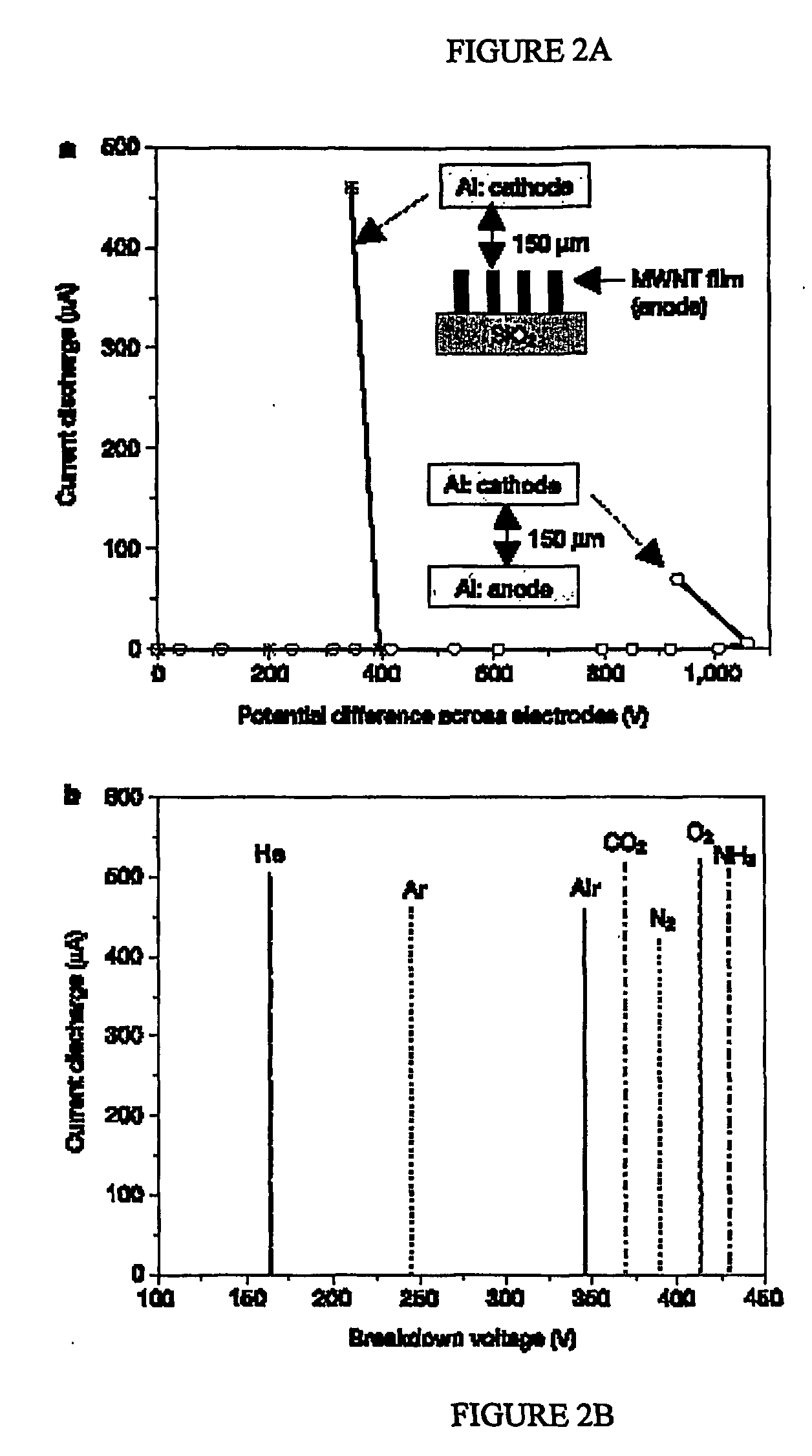
Miniaturized gas sensors featuring electrical breakdown in the vicinity of carbon nanotube tips
An ionization gas sensor includes a first electrode and a second electrode, such as cathode and anode electrodes. The second electrode is a carbon nanotube film having a carbon nanotube density such that the film behaves as a conducting sheet electrode. The sensor also includes a voltage source electrically connected to the first and to the second electrodes. The voltage source is adapted to generate an electric field near tips of carbon nanotubes in the carbon nanotube film which induces electrical breakdown of an analyte gas, which leads to a self-sustaining inter-electrode arc discharge
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Low-dielectric films, and manufacturion method thereof, and electronic component using it
InactiveUS20060244034A1High insulation breakdown voltageGuaranteed functionTransistorSemi-permeable membranesDisiloxaneIntegrated circuit
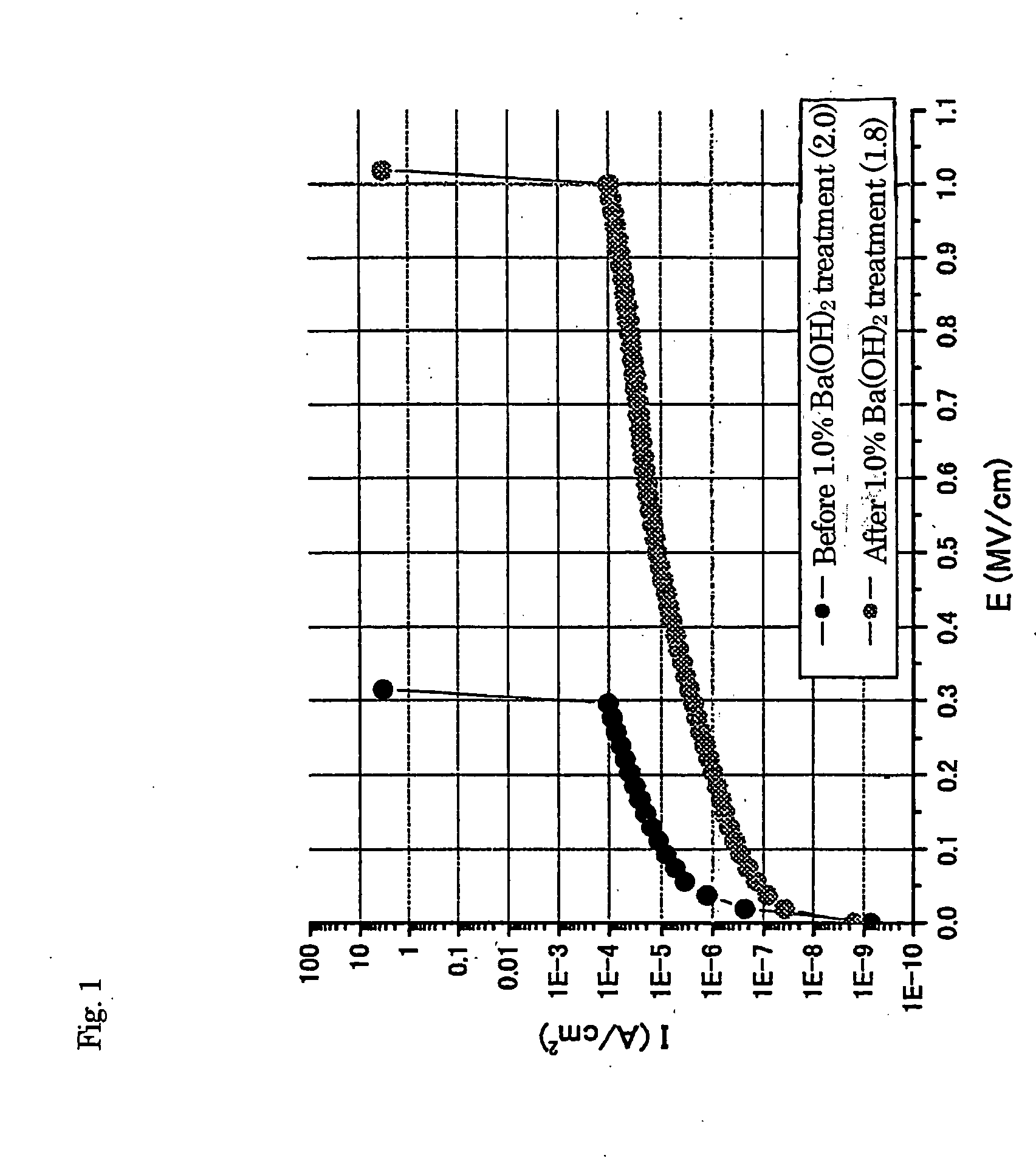
While a fine porous diamond particle film has been known as a high heat resistant and low dielectric constant film and also has high mechanical strength and heat conductivity, and is expected as an insulating film for multi-layered wirings in semiconductor integrated circuit devices, it is insufficient in current-voltage characteristic and has not yet been put into practical use. According to the invention, by treating the fine porous diamond particle film with an aqueous solution of a salt of a metal such as barium and calcium, the carbonate or sulfate of which is insoluble or less soluble, and a hydrophobic agent such as hexamethyl disilazane or triethyl monochlolo silane, as well as a reinforcing agent containing one of dichlorotetramethyl disiloxane or dimethoxytetramethyl disiloxane, thereby capable of putting the dielectric breakdown voltage and the leak current within a specified range of a practical standard.
Owner:RORZE CORP
Fast start RF induction lamp with ferromagnetic core
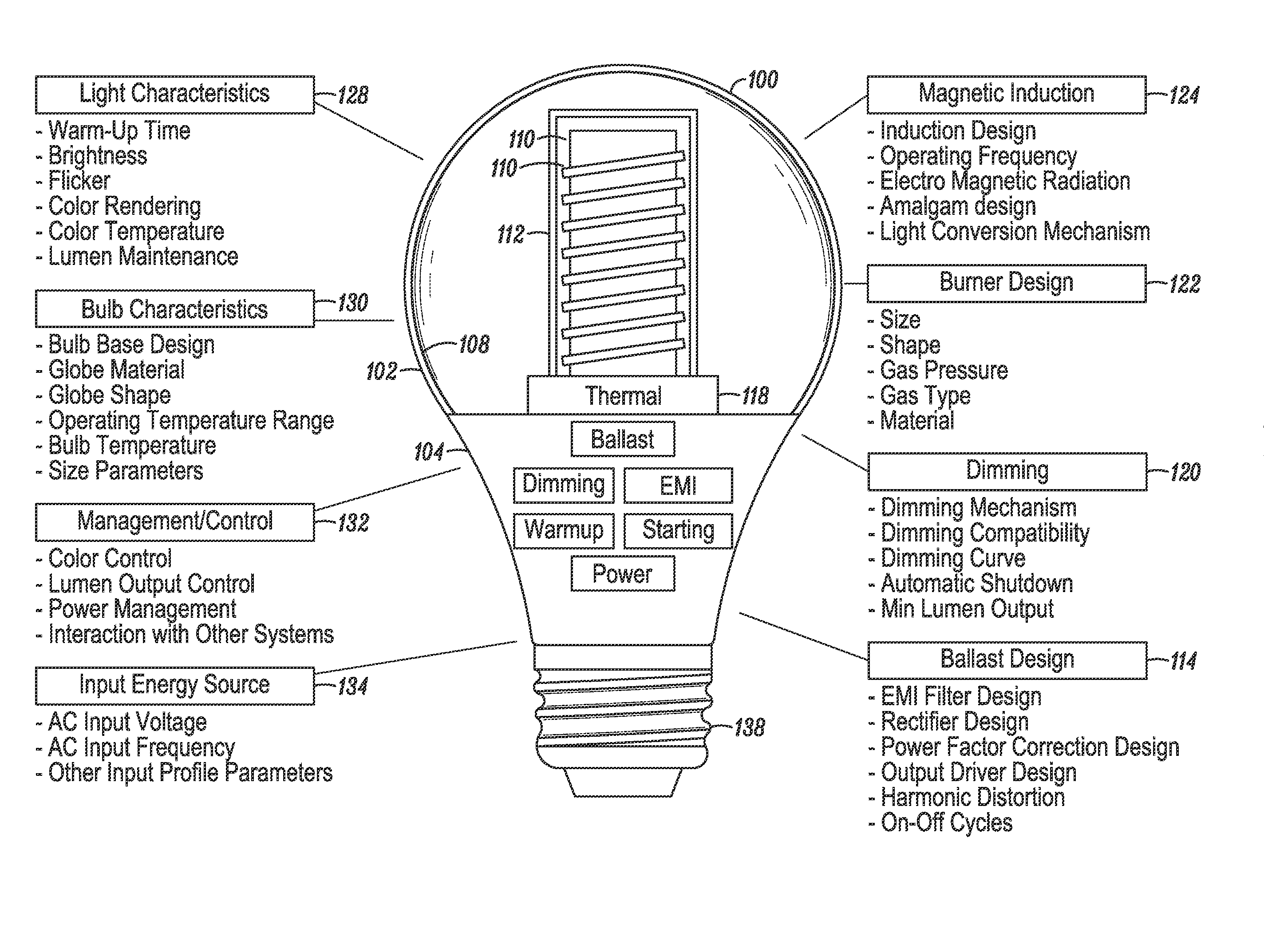
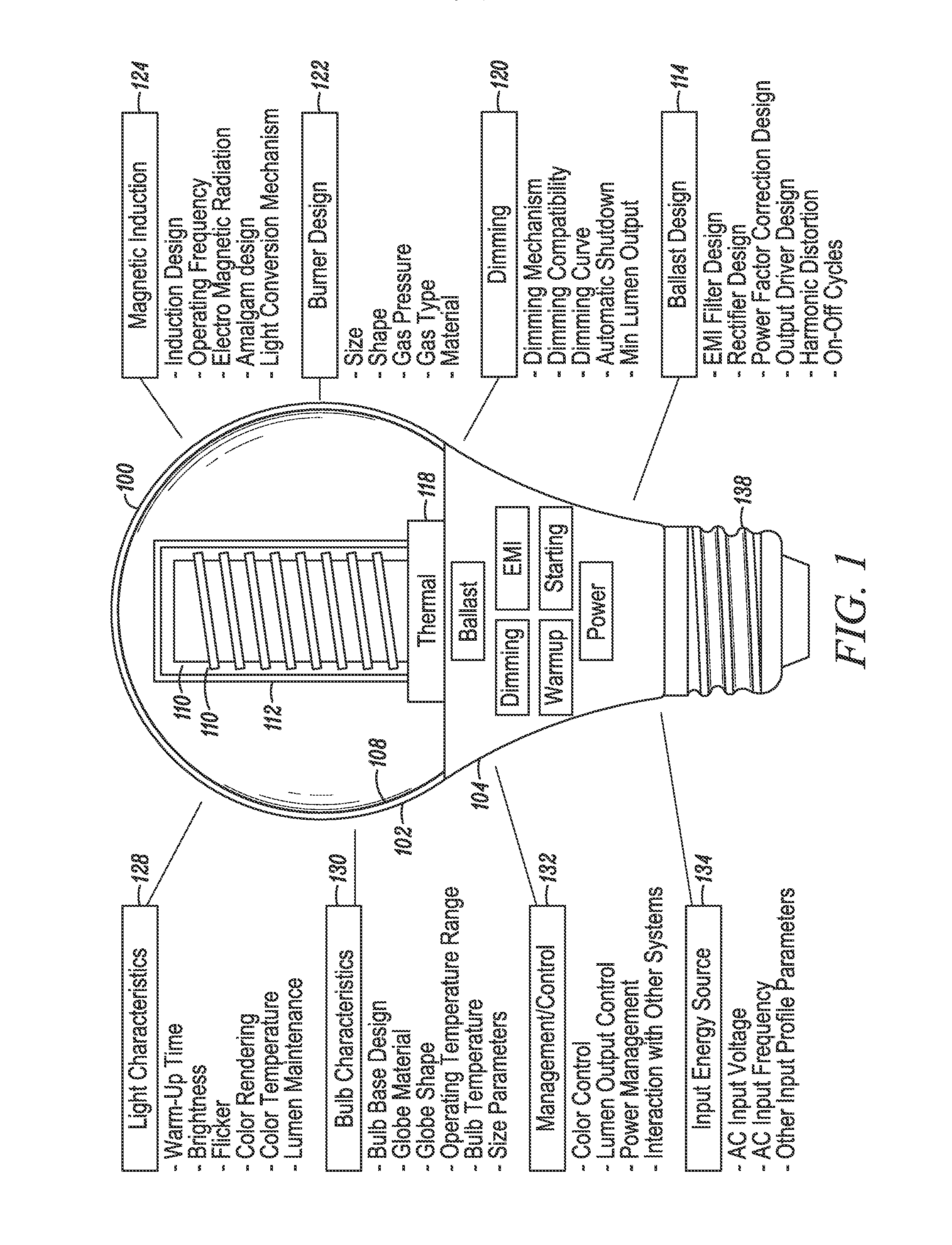
InactiveUS20140145593A1Maximize absorption of powerFast heatingAntenna supports/mountingsElectric lighting sourcesFluorescenceRe entrant
An induction RF fluorescent lamp, comprising a lamp envelope and re-entrant cavity filled with a fluorescing gas mixture, a power coupler receiving an alternating voltage and current to generate an alternating magnetic field and thereby inducing an alternating electric field within the lamp envelope, a first metallic structure mounted within the lamp envelope in such a location and orientation to rapidly heat and vaporize mercury to promote rapid luminous development during the turn-on phase of the induction RF fluorescent lamp and a second metallic structure so as to promote electrical breakdown of the fluorescing gas mixture during the turn-on phase of the induction RF fluorescent lamp.
Owner:LUCIDITY LIGHTS
Device for preventing withdrawing and inserting of a circuit breaker
Disclosed is a device for preventing withdrawing and inserting of a circuit breaker. The device for preventing withdrawing and inserting of a circuit breaker include: a lead screw is coupled between a carriage and a girder assembly and rotated by an external force to allow a breaker body to be closed or released while the carriage is moved with respect to a cradle, and a braking unit preventing the lead screw for operating when the girder assembly is released from the cradle. In an unstable state in which the girder assembly is not coupled to the cradle, a withdrawal handle is prevented from being inserted into the girder assembly. Therefore, an abnormal withdrawing operation can be prevented, and thus, various safety accidents, a contact resistance and temperature rise, damage to a device due to electrical breakdown can be prevented.
Owner:LS IND SYETEMS CO LTD
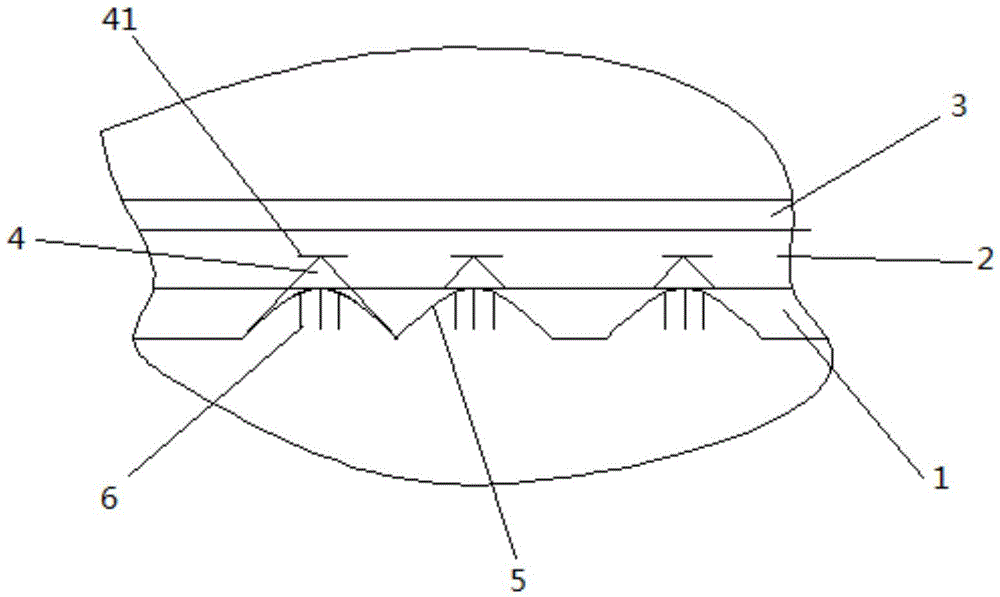
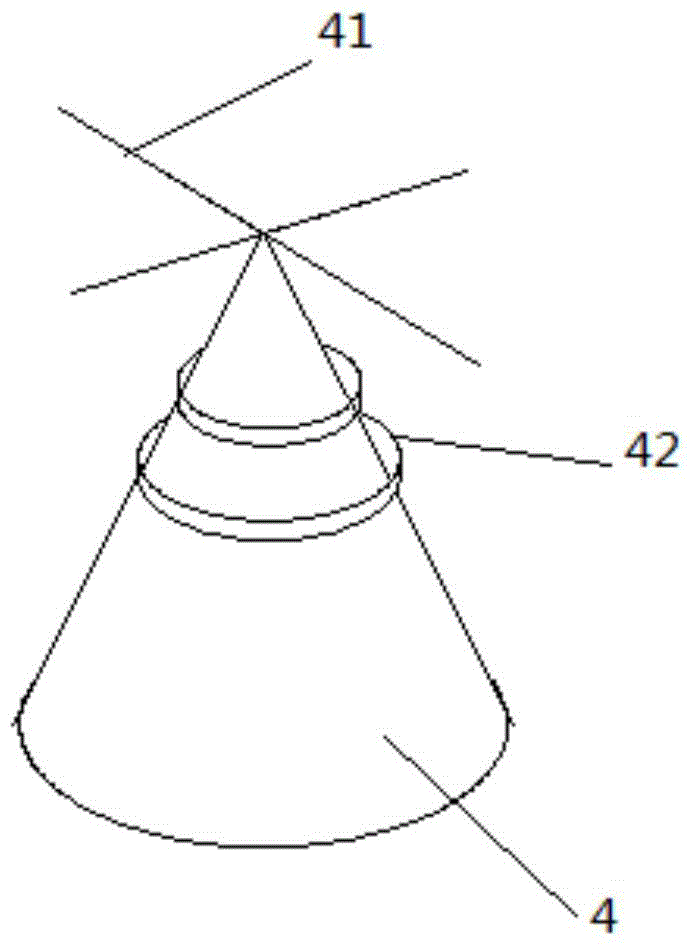
High-radiating LED circuit board
ActiveCN104470200AImprove aging resistanceHigh bonding strengthPrinted circuit detailsPrinted circuit aspectsElectricityEngineering
The invention discloses a high-radiating LED circuit board which is provided with a radiating base layer, an insulation heat conduction layer and a circuit layer from bottom to top in sequence. The radiating base layer is a metal plate, and a plurality of taper lugs are arranged on the upper surface of the metal plate, and two crossed heat conduction bars are arranged on the top of each taper lug. The contact area of the radiating base layer and the insulation heat conduction layer is increased through the taper lugs stretching into the insulation heat conduction layer, and thus the heat conduction efficiency between the radiating base layer and the insulation heat conduction layer is improved. In addition, the area of the tops of the taper lugs is small, and thus the insulation heat conduction layer can be prevented from being broken through by high tension electricity.
Owner:SHENZHEN BOMIN ELECTRONICS
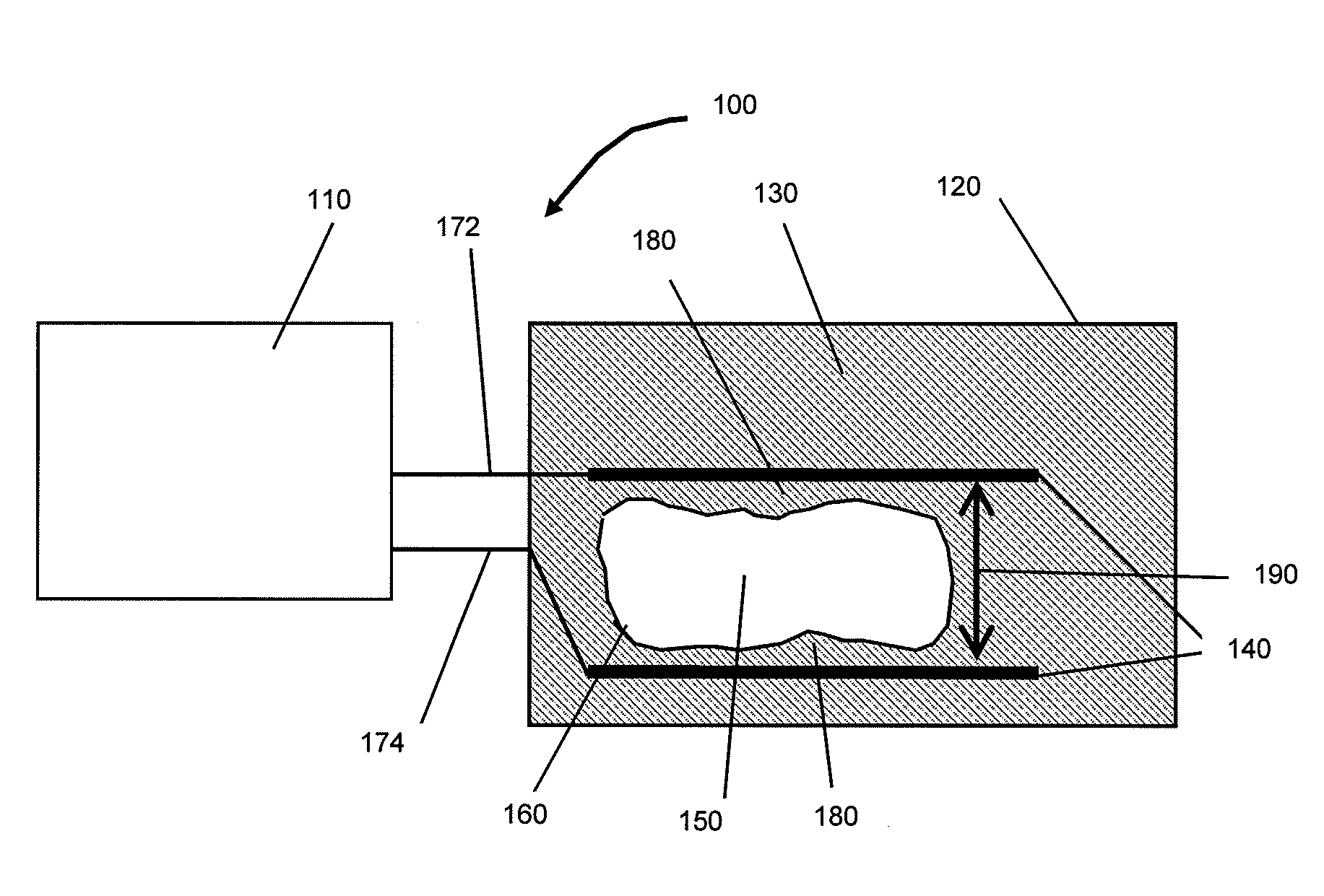
High-voltage pulsed electrical field for antimicrobial treatment
InactiveUS20100112151A1Avoid failureOvercome disadvantagesMilk preparationDough treatmentElectricityNanosecond
Aspects of the invention relate to a device and method for non-contact inactivation of undesirable and / or harmful microorganisms in products using high-voltage nanosecond pulsed electrical field. In certain embodiments, a product may be packaged into a container which is made from a dielectric material and placed between electrodes to be processed by a pulsed electrical field. In certain embodiments, the electrodes, together with the container, may be placed into a treatment assembly filled with a high dielectric permeability media that allows the formation of a quasi-uniform electrical field inside the product and prevents the electrical breakdown of the dielectric material of the container. The electrodes may be connected to a high voltage generator, which forms nanosecond pulses that allow an electrical field of high intensity to penetrate the dielectric material of container walls and gaps between the electrodes and the container's walls to the product without significant energy losses.
Owner:PEPSICO INC
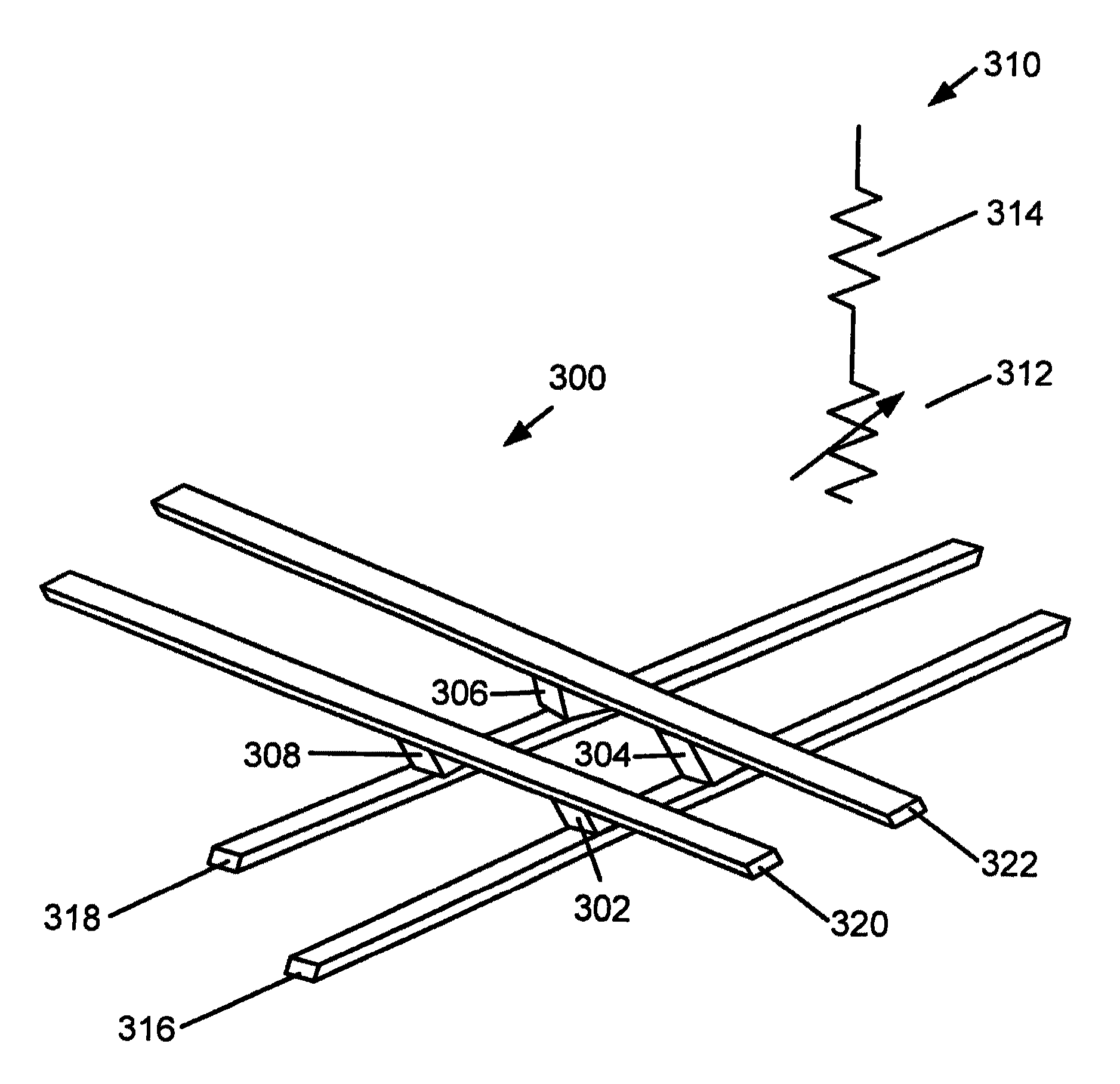
Isolated converter
InactiveUS6373736B2Transformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsPrinted circuit aspectsReduced sizeEngineering
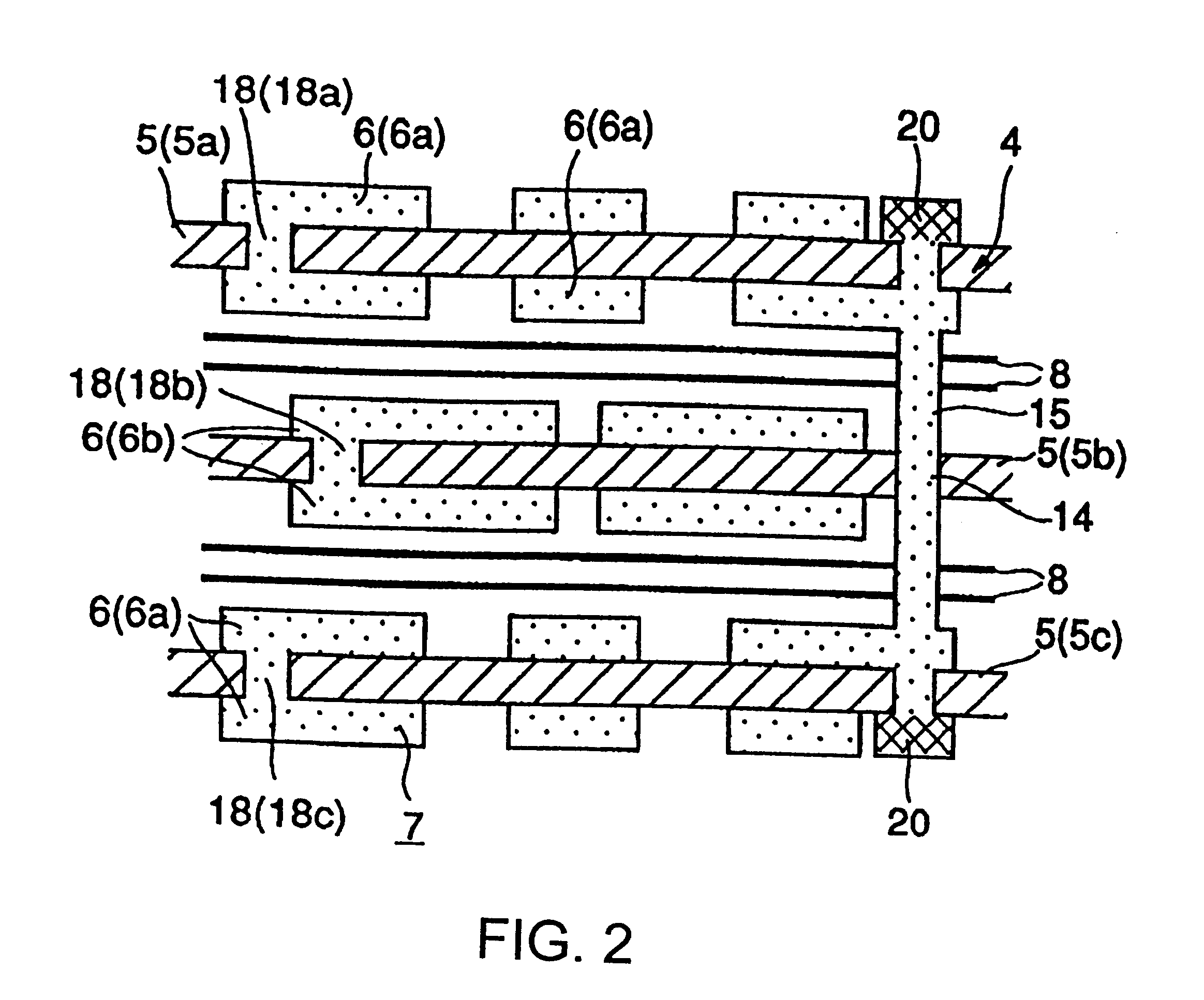
An isolated converter with a reduced size is disclosed. A small-sized multilayer sheet transformer includes a multilayer circuit board composed of a plurality of sheet substrates, coil patterns of primary and secondary coils disposed coaxially on the sheet substrates, and a core member disposed in a coil pattern unit formed of the coil patterns. In this multilayer sheet transformer, a coil pattern formed on the outer surface of the top layer and a coil pattern formed on the outer surface of the bottom layer are for the same coil on either the primary or secondary side. In the case where the coil patterns formed on the outer surfaces of the top and bottom layers of the multilayer sheet transformer are for the primary coil, an isolation gap is formed between the multilayer sheet transformer and a circuit on the secondary side to prevent an electrical breakdown between the primary and secondary sides. In the case where the coil patterns formed on the outer surfaces of the top and bottom layers of the multilayer sheet transformer are for the secondary coil, an isolation gap is formed between the multilayer sheet transformer and a circuit on the primary side to prevent an electrical breakdown between the primary and secondary sides.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Showerhead-cooler system of a semiconductor-processing chamber for semiconductor wafers of large area
InactiveUS9484190B2Avoid turbulenceImprove evenlyElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingElectricityPlasma density
Proposed is a showerhead-cooler system of a semiconductor-processing chamber with uniform distribution of plasma density. The showerhead has a plurality of through gas holes that are coaxial with respective channels of the gas-feeding cooler plate. On the gas inlet side, the though passages of the showerhead are provided with unequal conical nozzles characterized by a central angle that decreases from the peripheral part of the showerhead to the showerhead center. Such design provides uniformity of plasma density. Furthermore, in order to protect the walls of the nozzle and the walls of the gas holes from erosion that may be caused by the hollow-cathode phenomenon, these areas are coated with a thin protective coating that is resistant to electrical breakdown and chemical corrosion.
Owner:GLUKHOY YURI +2
Insulated gate semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080079066A1High emitter ballast resistanceIncrease resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
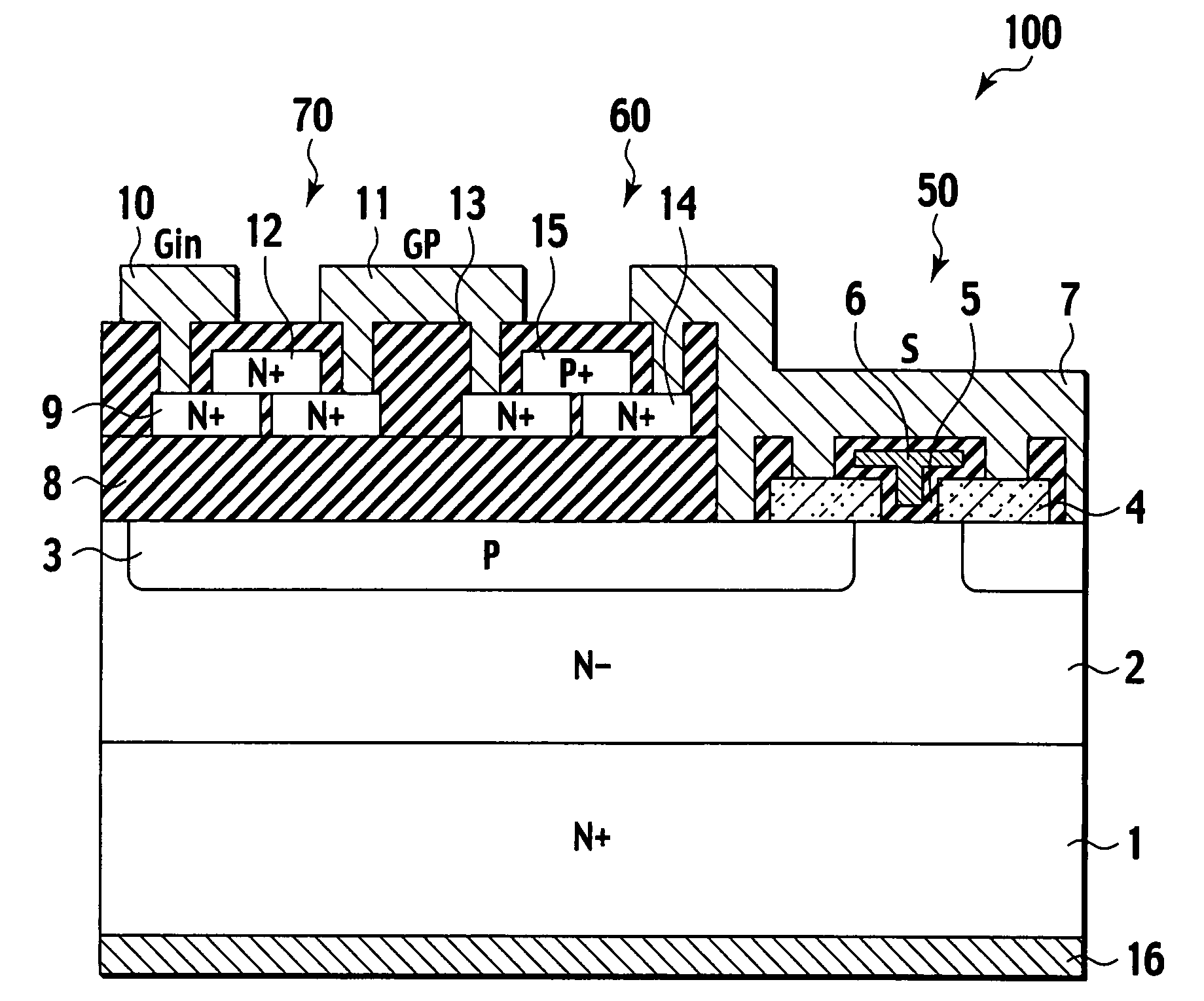
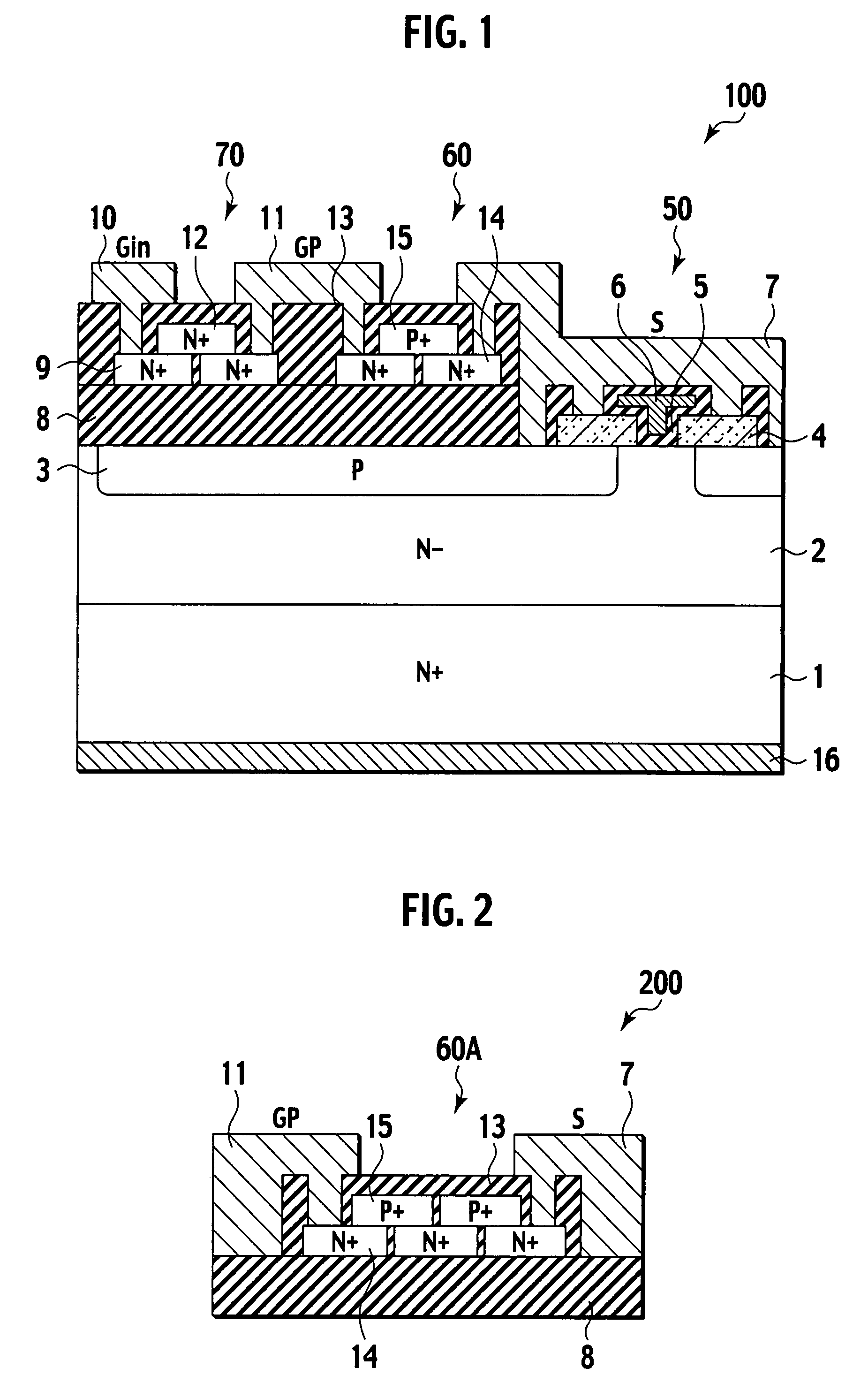
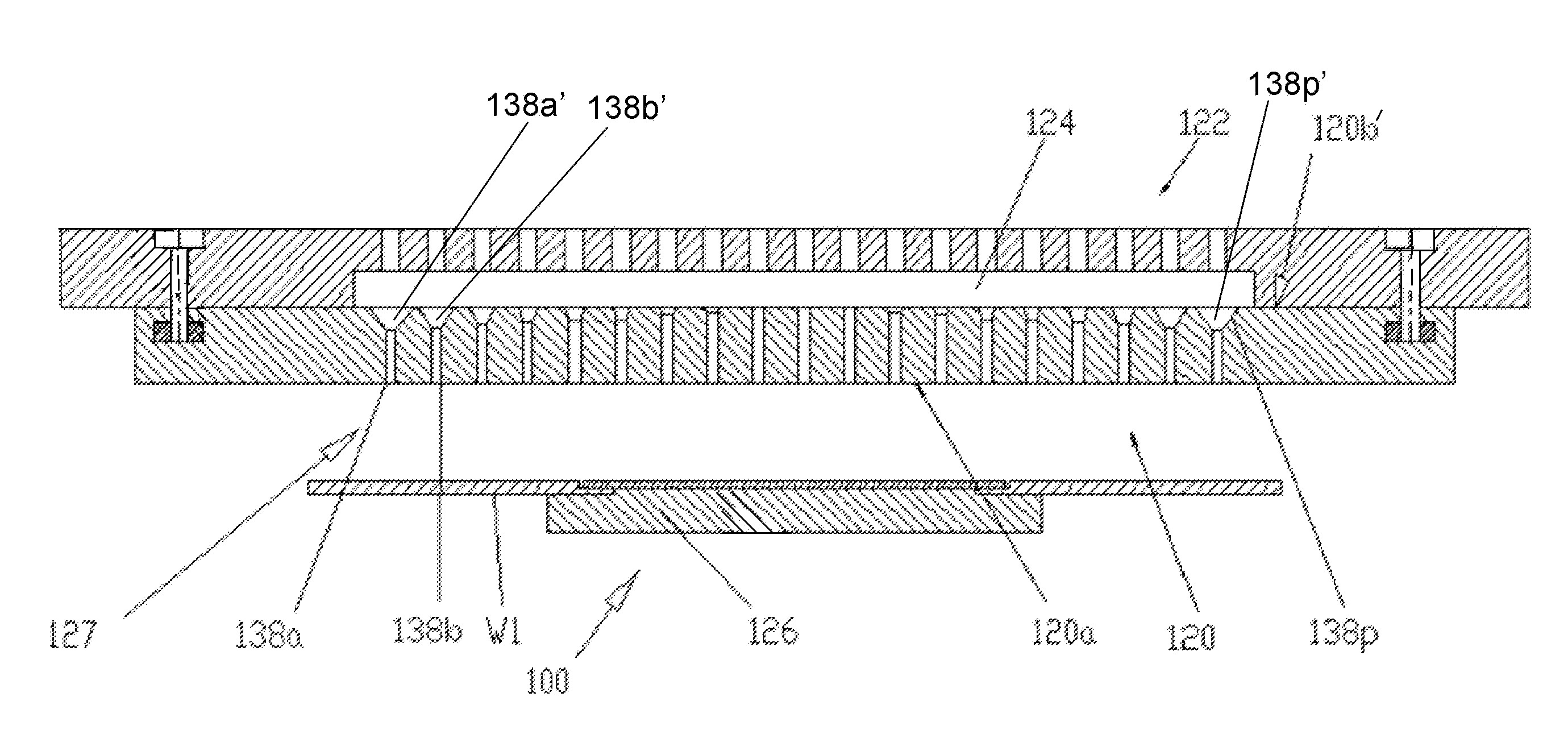
An IGBT comprises trenches arranged in strips, first emitter diffusion layers formed so as to extend in a direction intersecting the trenches, and contact regions formed to have a rectangular shape. The portions of the contact regions on the first emitter diffusion layers have a smaller width than the other portions, the width extending in the direction intersecting the trenches. This configuration allows for an increase in the emitter ballast resistance of the emitter diffusion layers, resulting in enhanced resistance to electrical breakdown due to short circuit.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
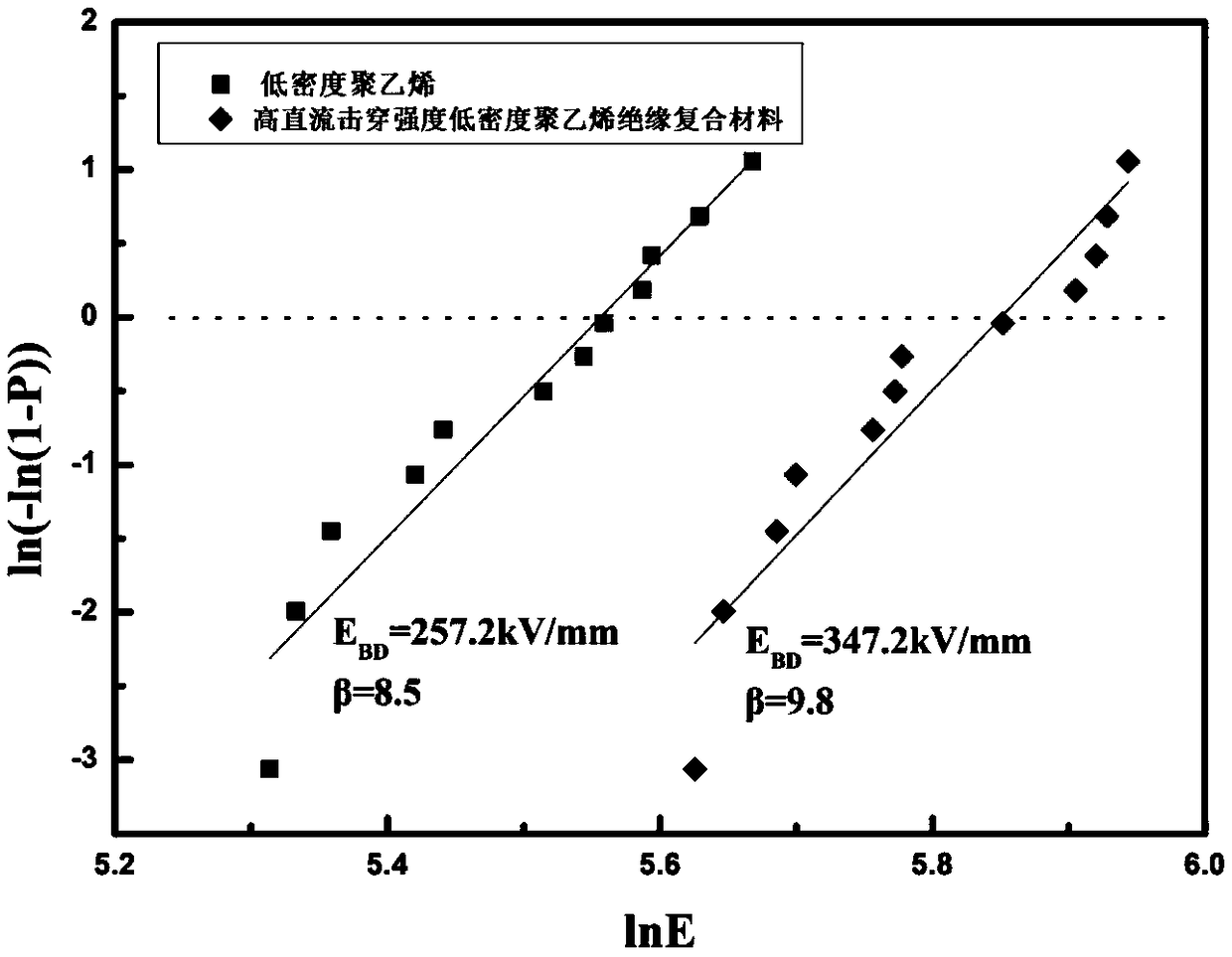
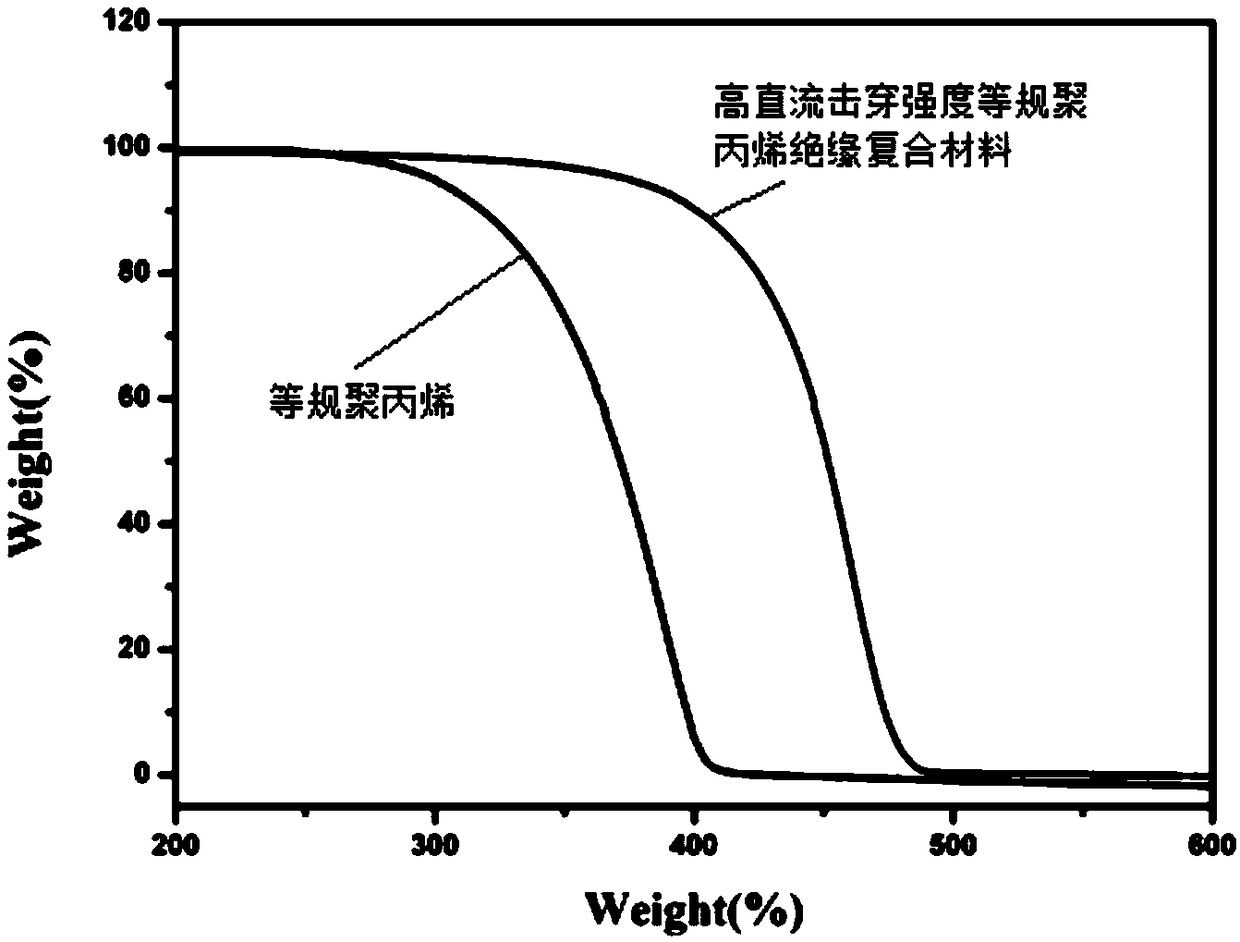
Polyolefin nano composite insulation material with high direct-current breakdown strength and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a polyolefin nano composite insulation material with high direct-current breakdown strength and a preparation method thereof. The material comprises 96-99.75% polyolefin dielectric substrate and 0.25-4% modified nano particle filler; the modified nano particle filler is voltage stabilizer functionalized nano particles. By clicking grafting voltage stabilizer which is formedon the surfaces of the nano particles as the filler, the direct-current breakdown strength of the composite material can be improved, wherein the voltage stabilizer can capture high energy electronsto consume the energy of the electrons to reduce electrical breakdown caused by the collision of the electrons and polymers, and the compatibility of the nano particles and polyolefin can be improved.The nano particles has the advantages of inhibiting the accumulation and injection of the migration of the voltage stabilizer and spatial charges. The obtained composite material has the advantages of high direct-current breakdown strength and high thermal stability, and the composite material is applied to the field of high voltage direct current cable insulation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
High Peak and Average Power-Capable Microwave Window for Rectangular Waveguide
InactiveUS20100214043A1Increased power capacityMaximize operating bandwidthWaveguide type devicesHigh peakPeak value
A high peak and high average power-capable microwave / radio frequency window for use in rectangular or other waveguide transmission line geometries. The waveguide microwave window provides a physical barrier, or interface, between two regions on either side of the window. The window presents a relatively transparent interface for the microwave signal that is propagating in the waveguide. In an electrical sense the window will exhibit low return loss. The microwave window inhibits multipactor phenomena, suppresses electrical breakdown and transmits high peak power radio frequency signals. The microwave window also provides a mechanism for both passive and active cooling to allow operation at high average power. The applications for the claimed invention include use as part of: High Power Microwave (HPM) generators and systems; HPM sources and systems employed in and by particle accelerators; plasma processing systems; and numerous other applications that utilize high power microwave signals.
Owner:VOSS SCI
Electrical apparatuses containing polytrimethylene homo- or copolyether glycol based electrical insulation fluids
Electrical apparatuses and a method for their production, the apparatuses containing electrical insulation fluids comprising polytrimethylene homo- or copolyether glycol having a dielectric breakdown voltage greater than about 30 kV, wherein from about 50 to 100 mole percent of the repeating units of the polytrimethylene homo- or copolyether glycol are trimethylene ether units. An electrical insulation fluid comprising (a) polytrimethylene homo- or copolyether glycol having trimethylene ether units at about 50 to 100 mole percent of the repeating units and (b) a blending component selected from the group consisting of vegetable oils, mineral oil, poly alpha olefins, synthetic esters, and silicone fluids, and mixtures thereof, wherein the electrical insulation fluid has a dielectric breakdown voltage of greater than about 30 kV.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com