Patents
Literature
116 results about "Re entrant" patented technology
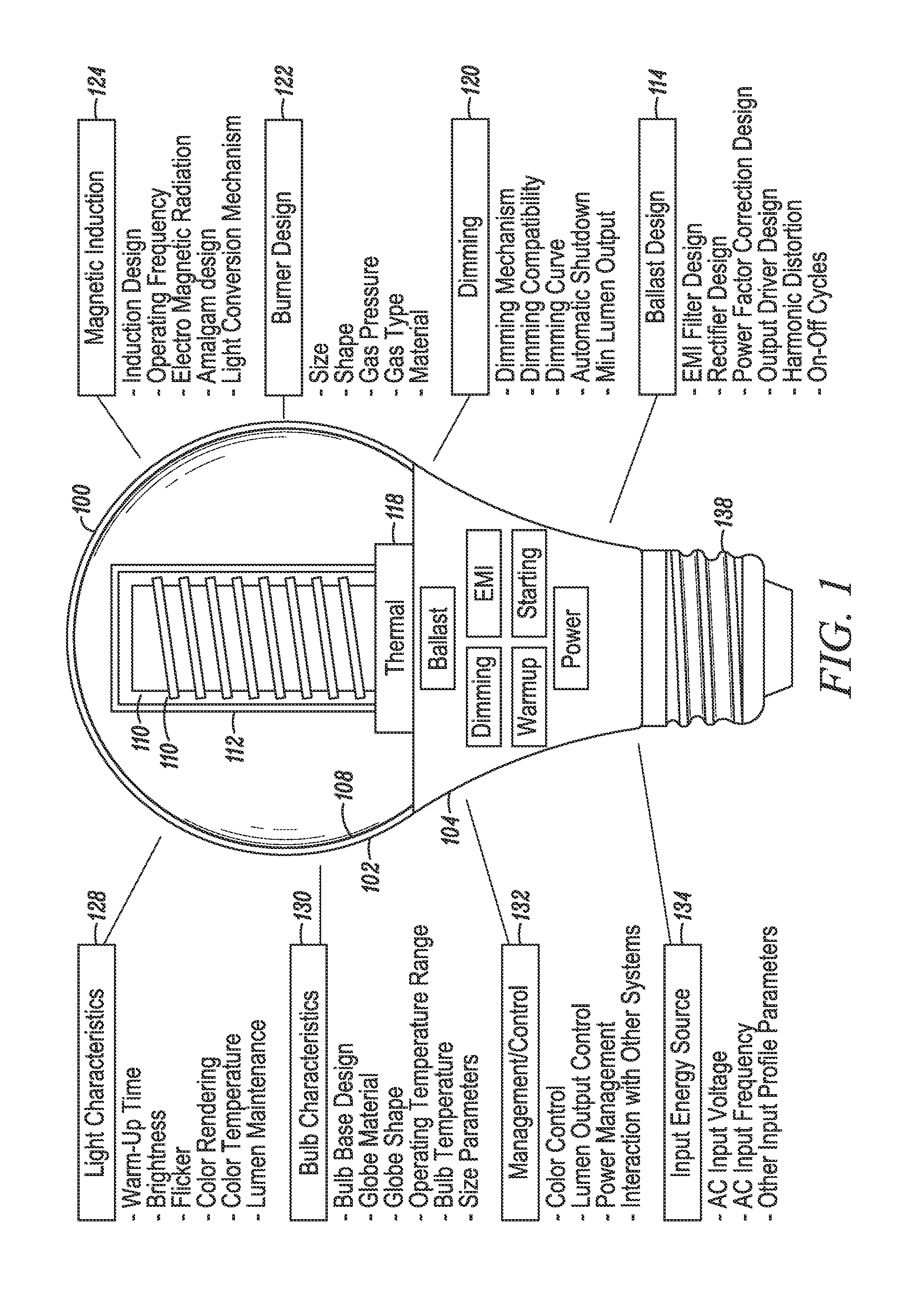
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reentrant or re-entrant can refer to: Re-entrant (landform), the low ground formed between two hill spurs. Reentrancy (computing) in computer programming. Reentrant mutex in computer science.
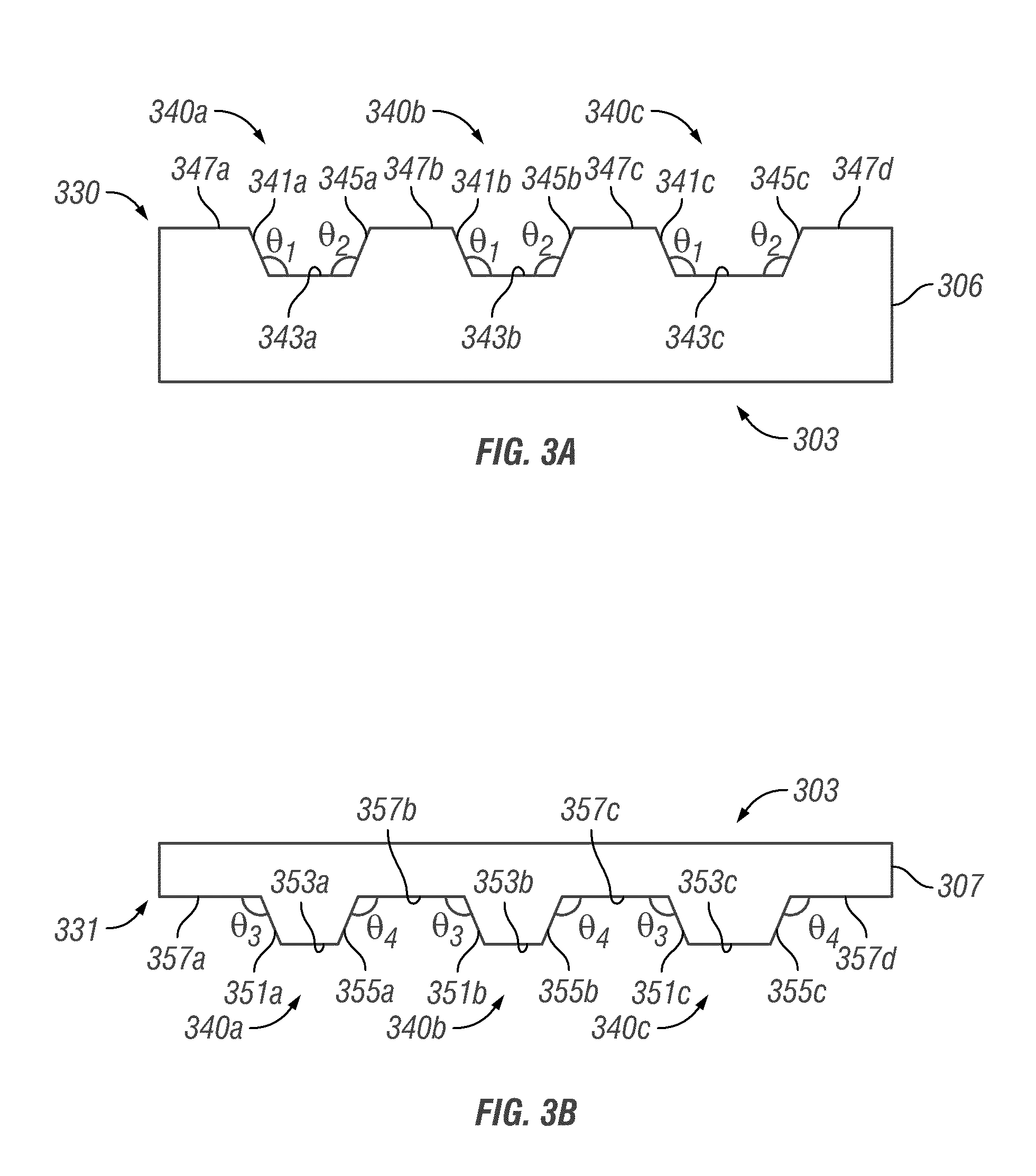
Hermetic MEMS package and method of manufacture
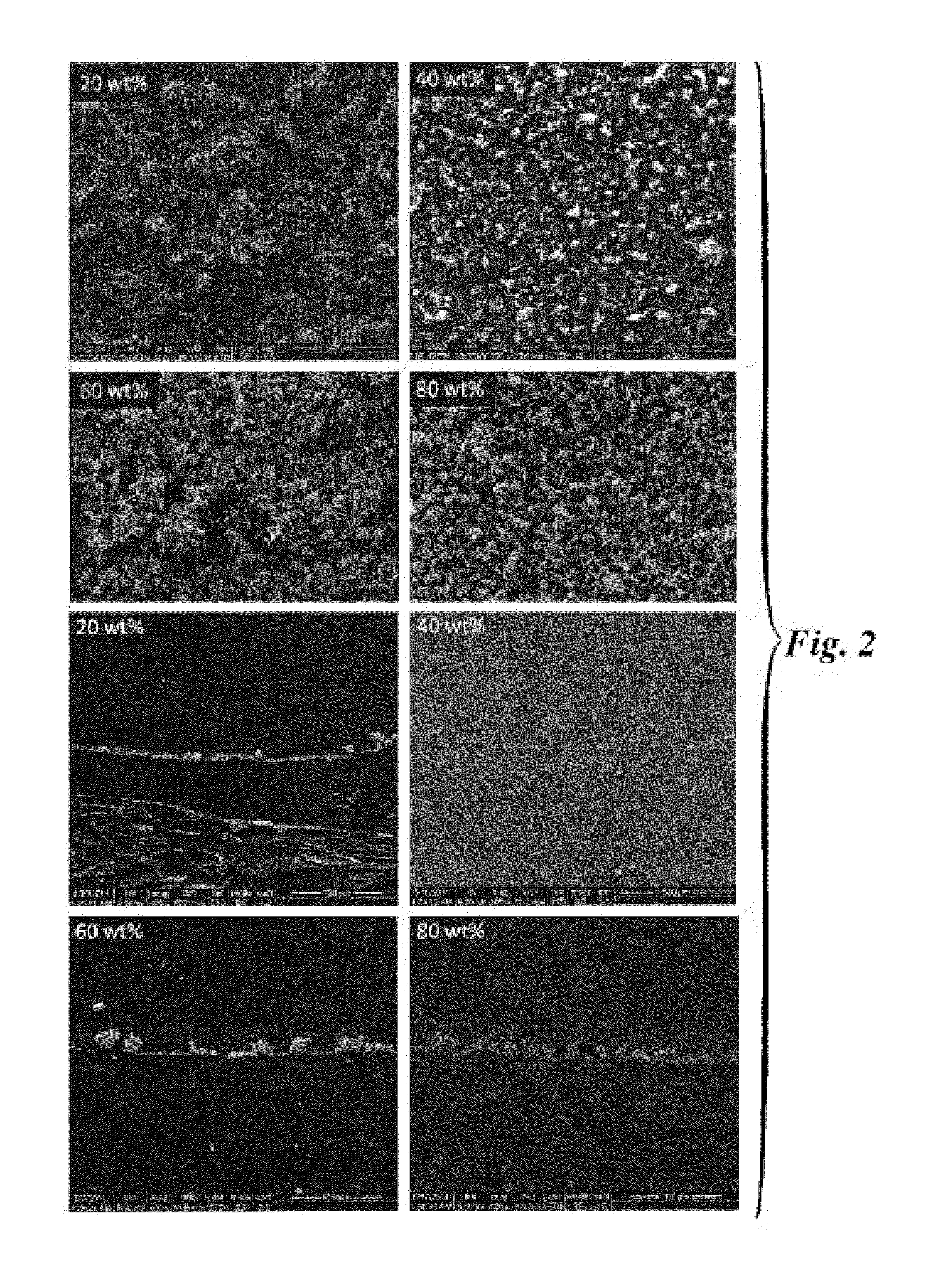
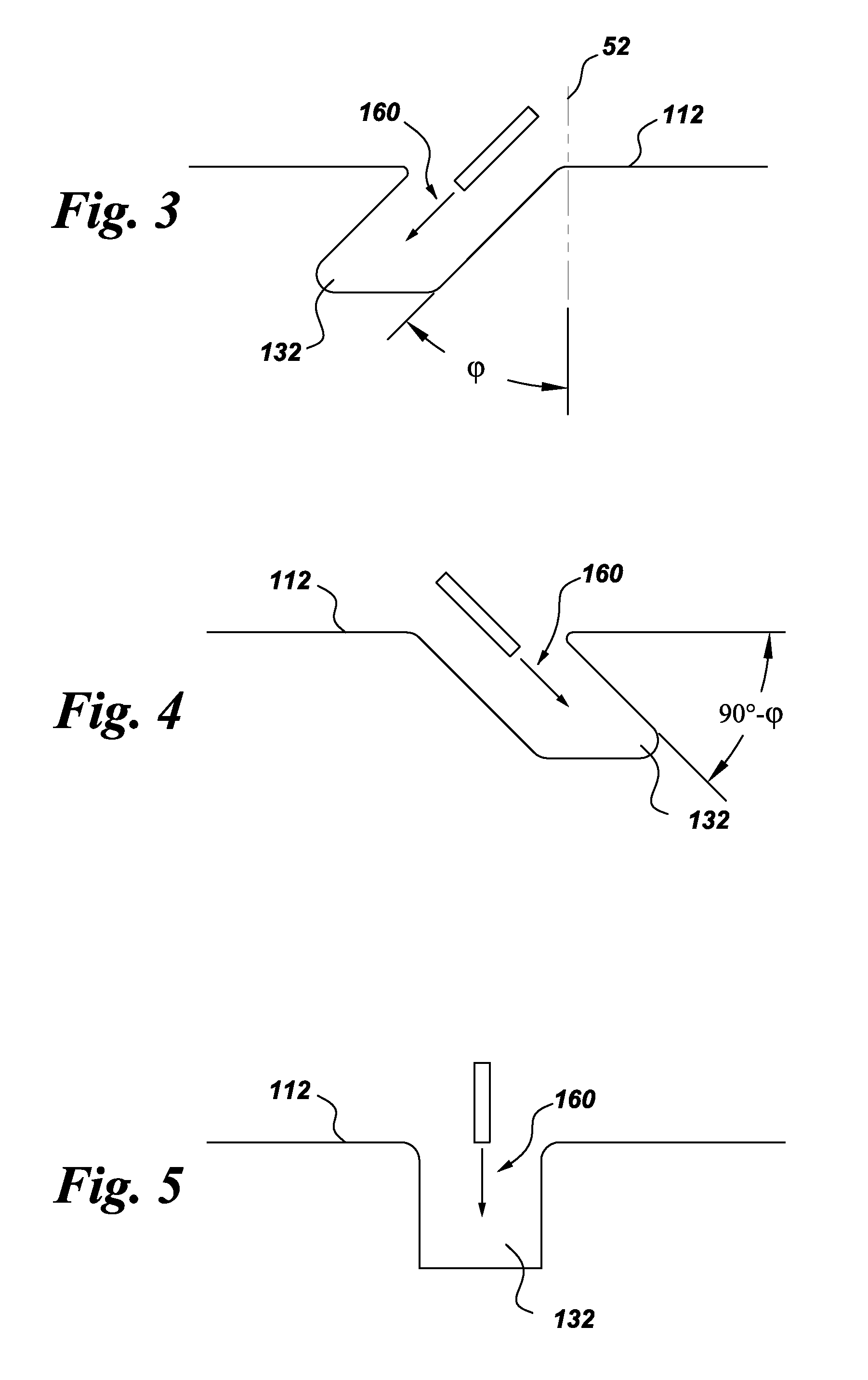
InactiveUS20060197215A1Easy to compressImprove sealingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRe entrantEngineering
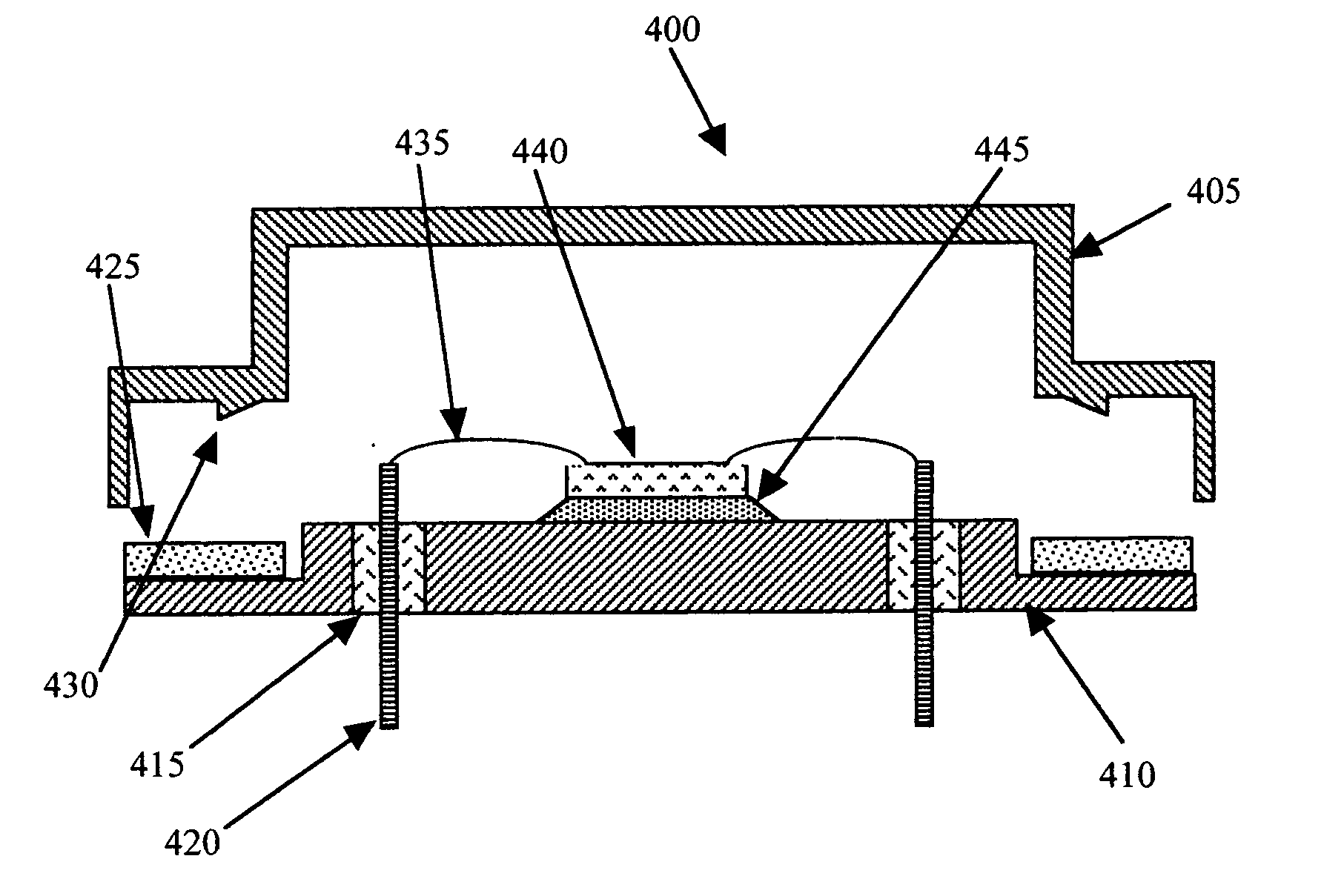
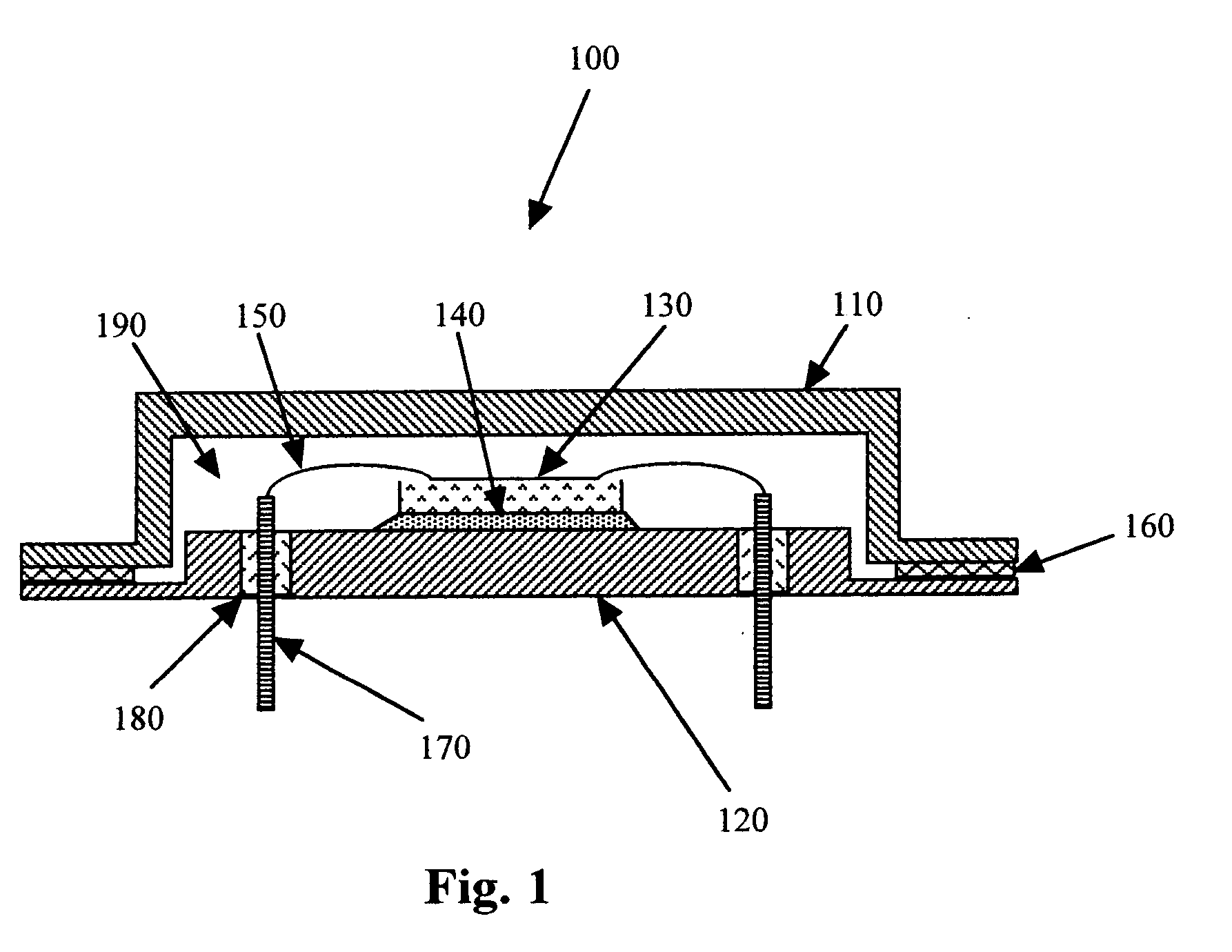
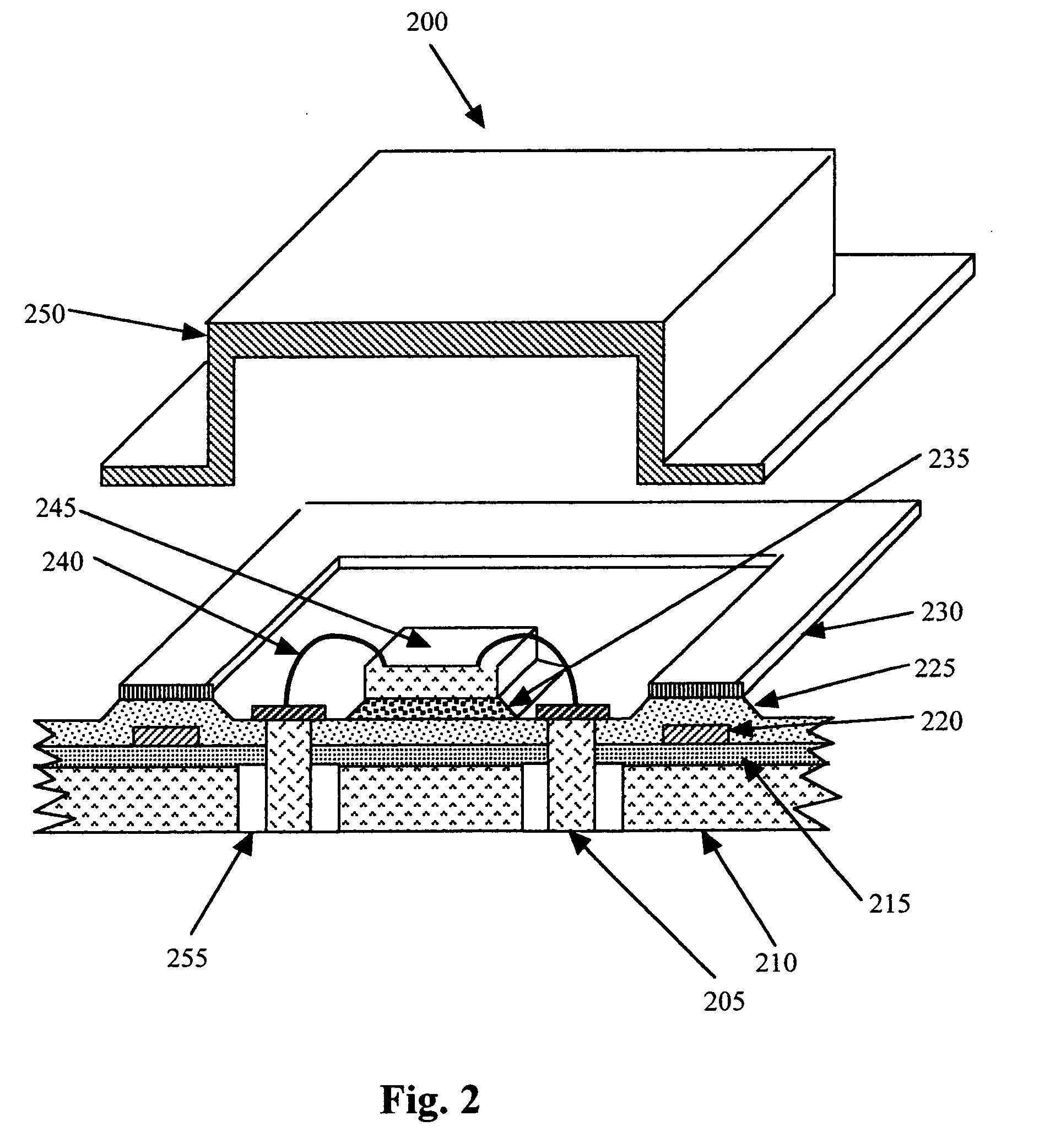
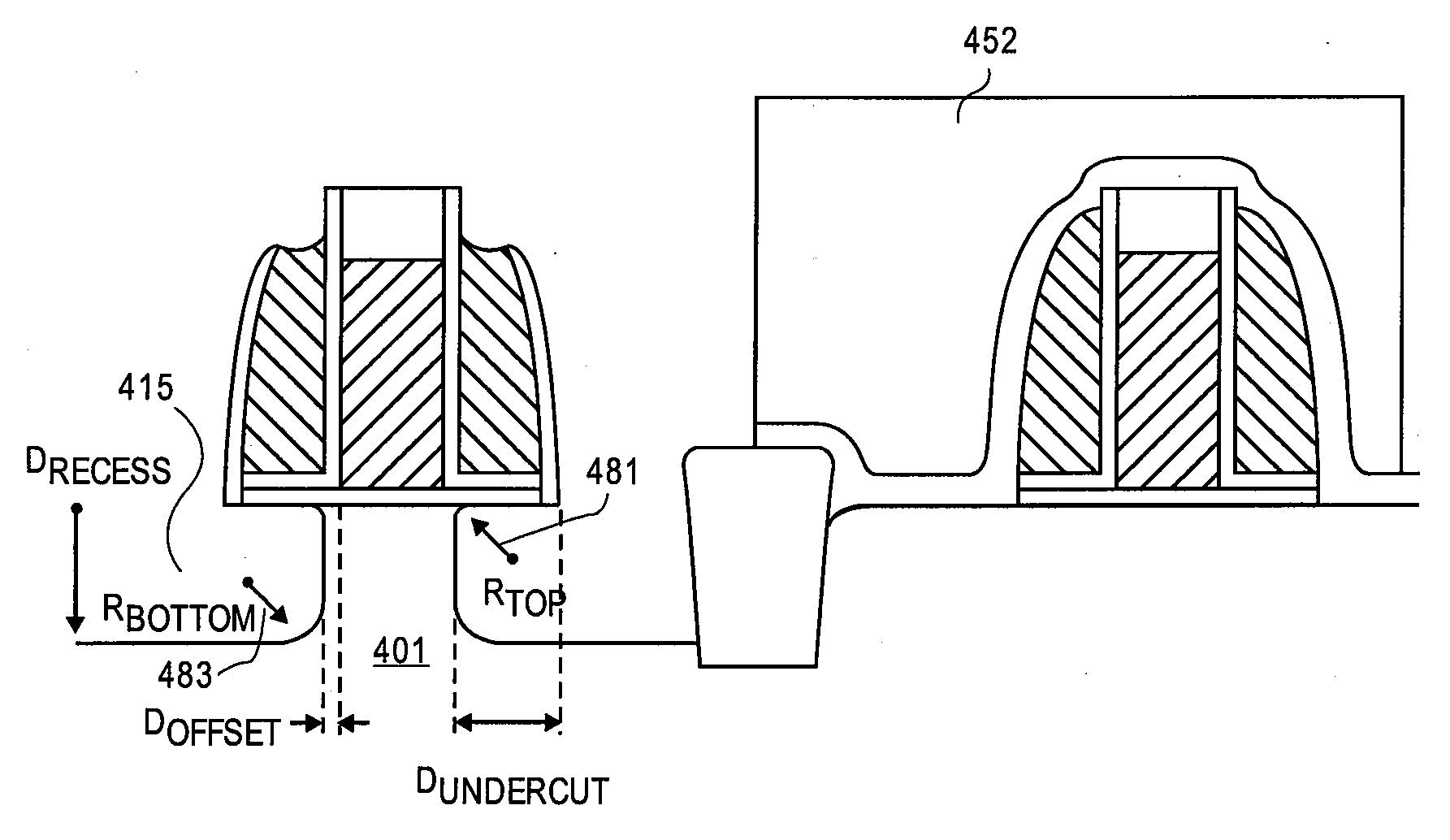
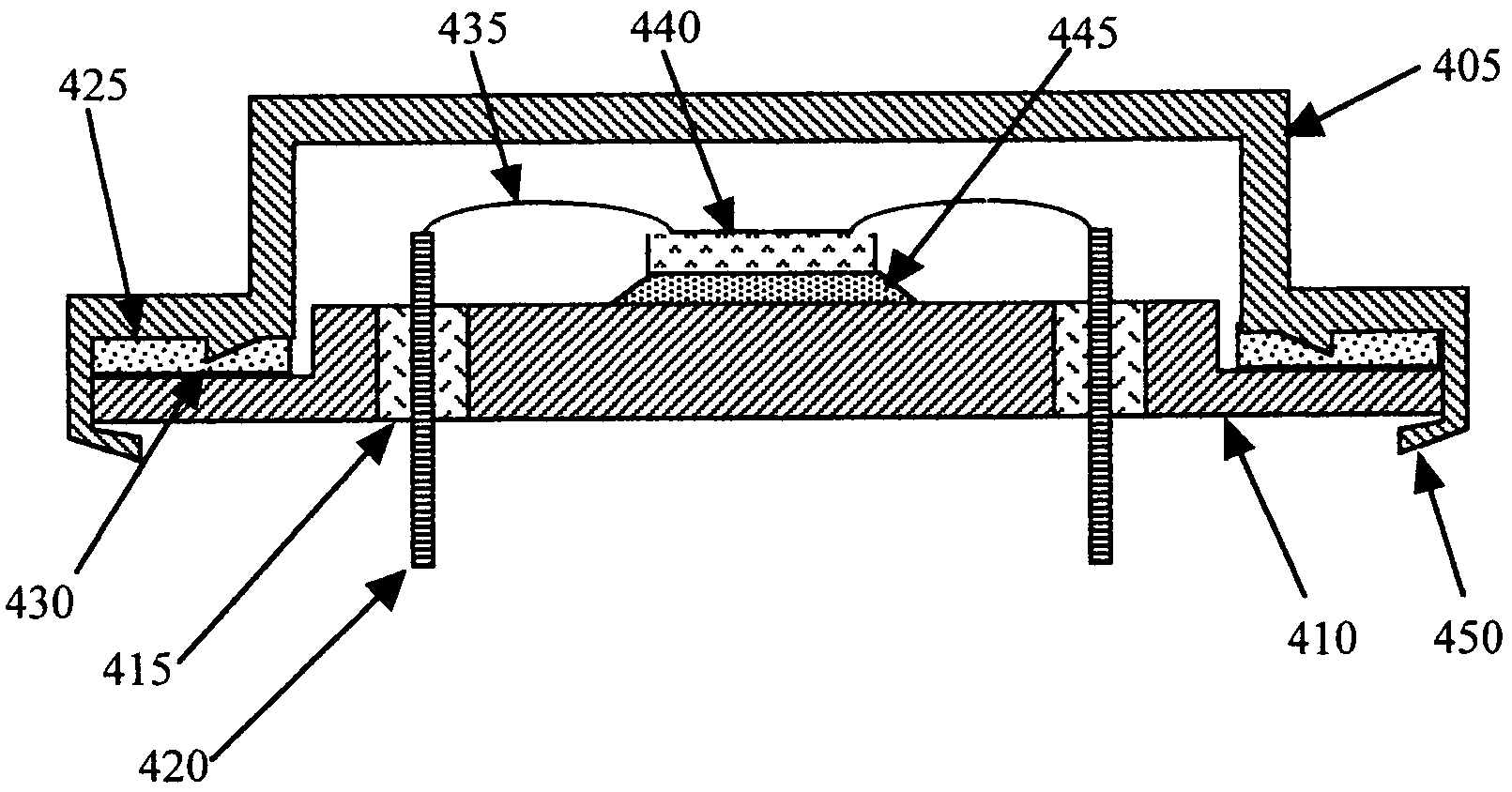
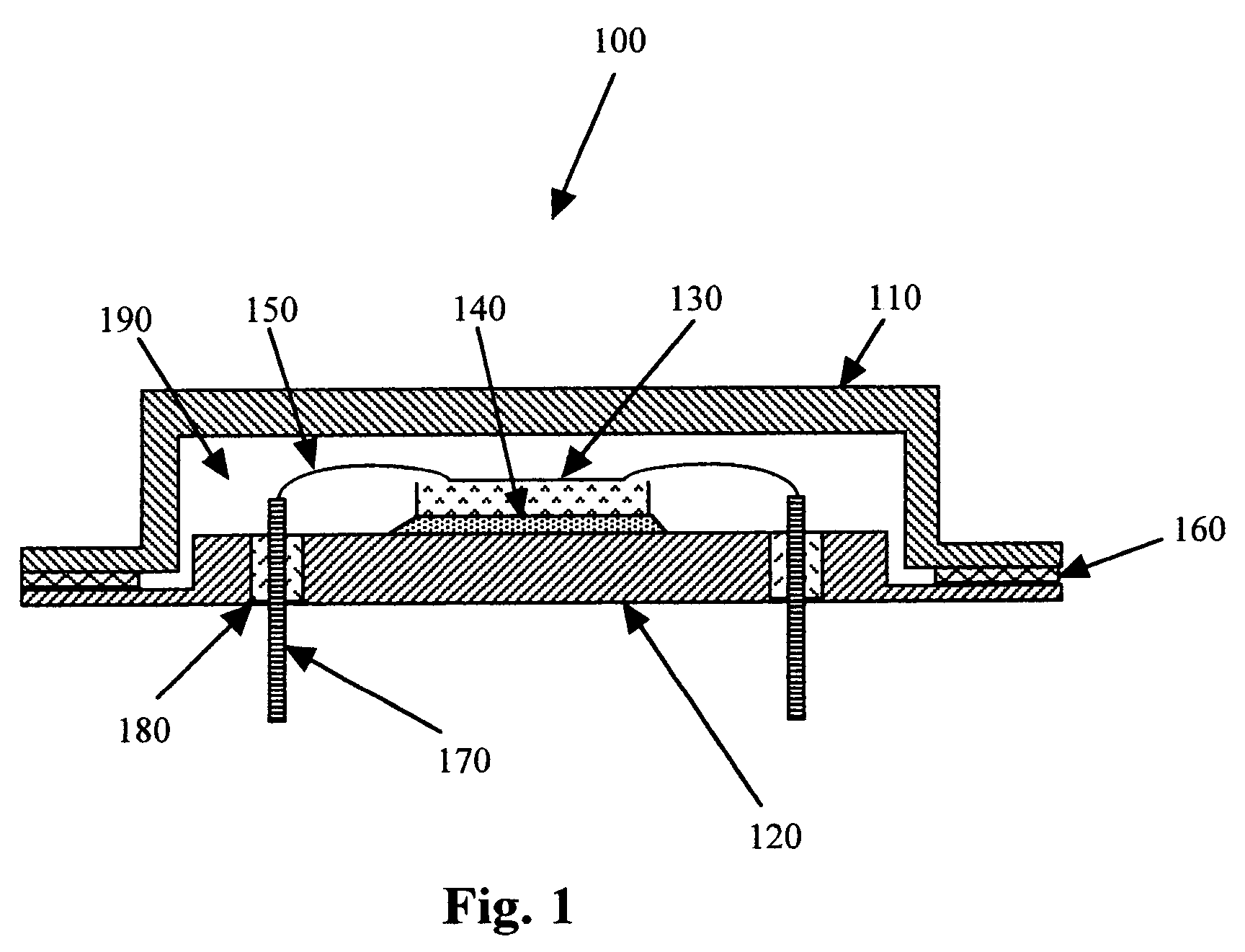
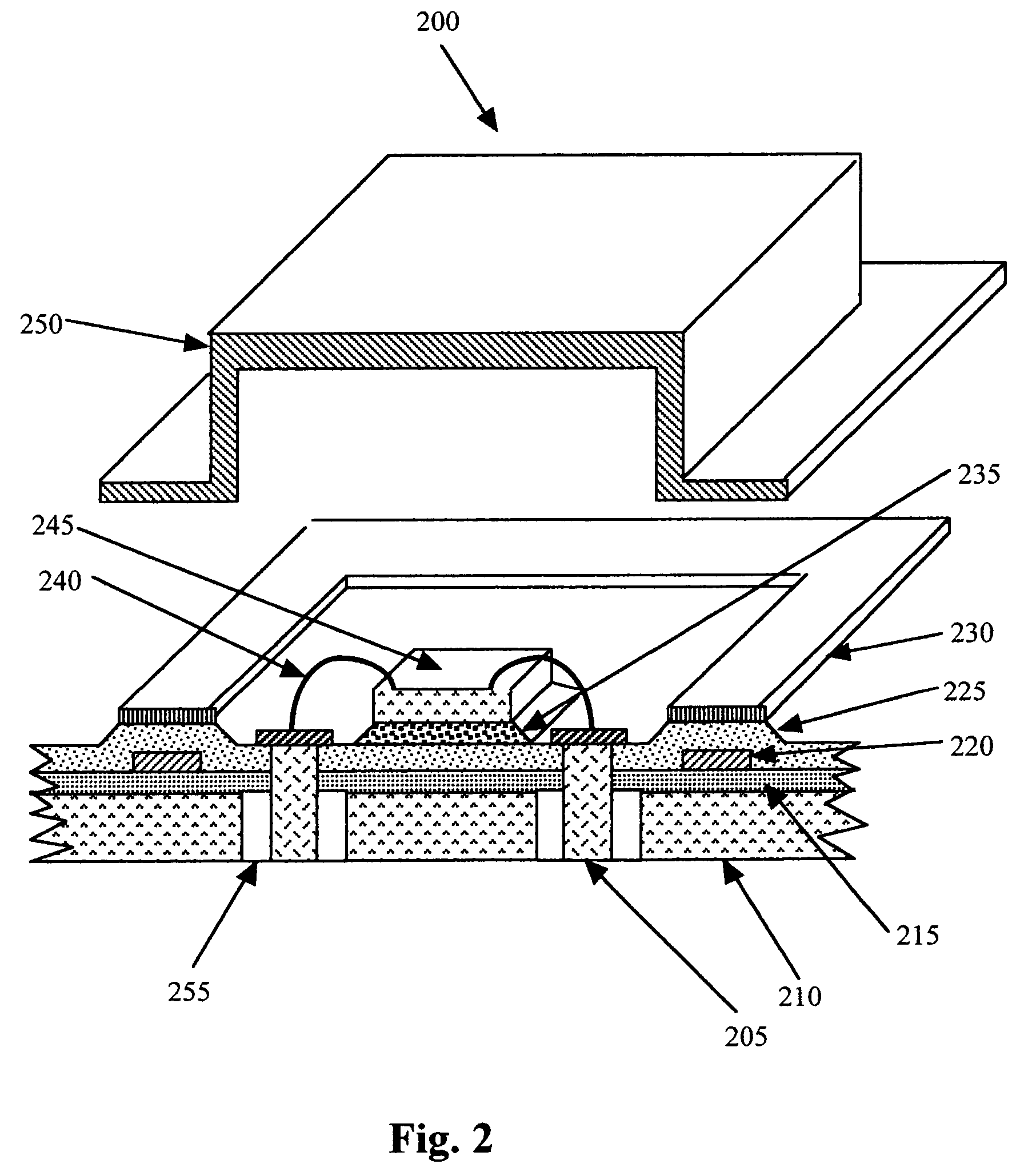
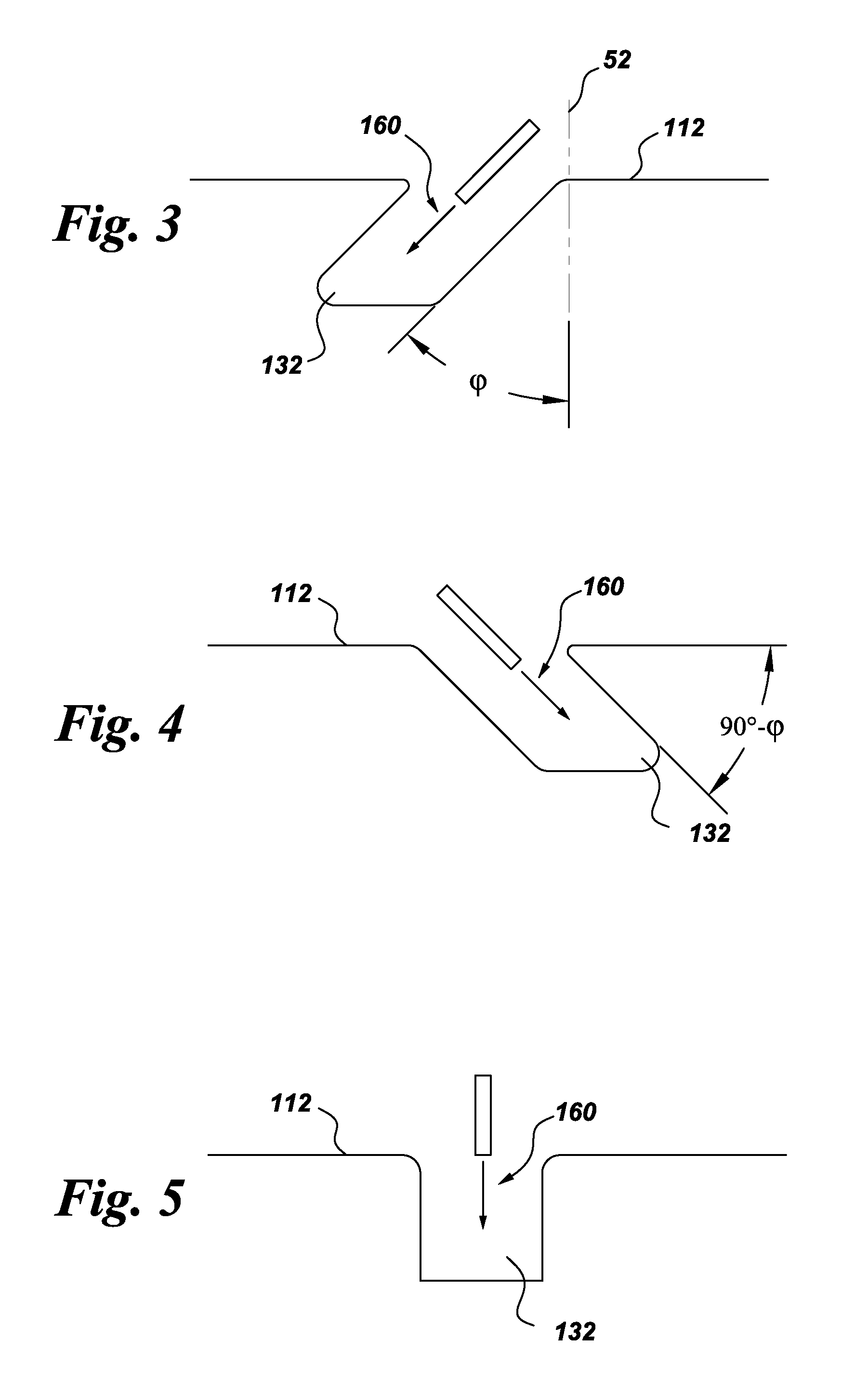
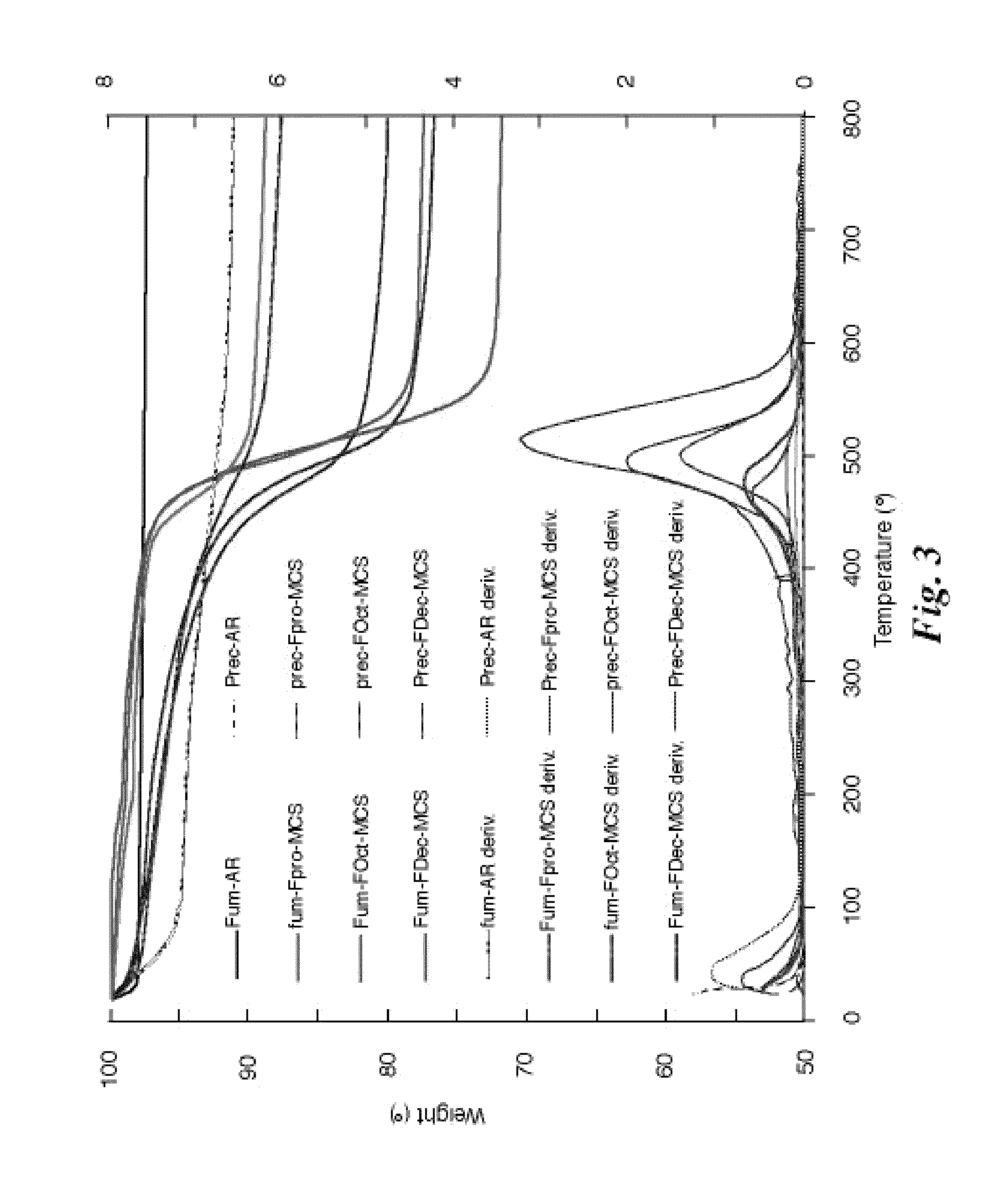
A swage hermetic sealing of a MEMS or microdevice or nanodevice package using high force. A cutting and flowing edge 430 is formed on a package cover which is pressed into a mating , integral gasket 425 on a package base. A material extension of the package cover 450 is simultaneously folded under the package base to supply force maintenance for permanent hermaticity. The swage hermetic sealing of single or an array of covers to an extended wafer or substrate is accomplished by a cutting and flowing edge 560. Permanent force maintenance is achieved through a re-entrant cavity 565 and annular ring 535 on the wafer or substrate.
Owner:STELLAR MICRO DEVICES
Method and apparatus for tunable isotropic recess etching of silicon materials
InactiveUS20090032880A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesRe entrantAnisotropic plasma
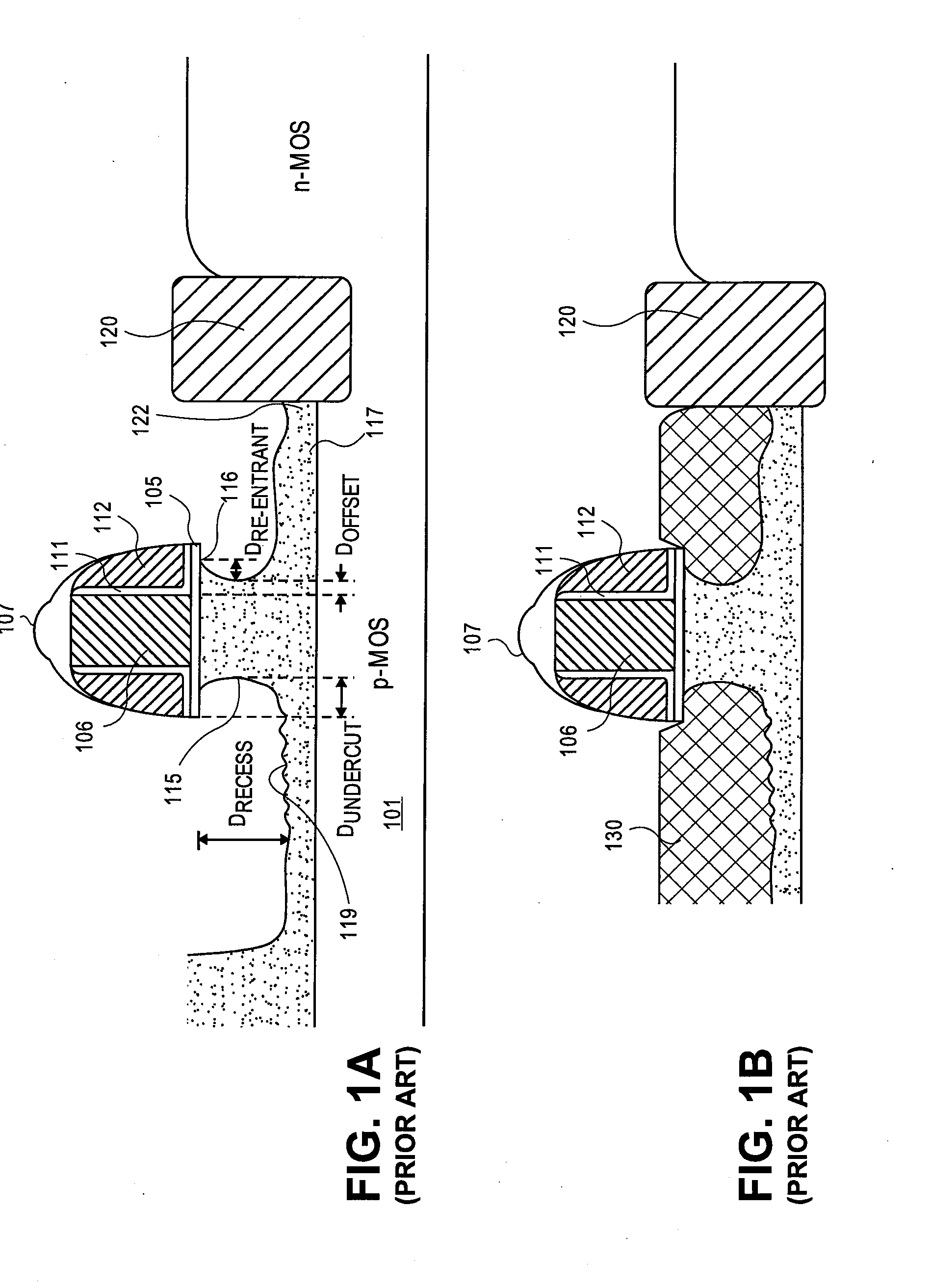
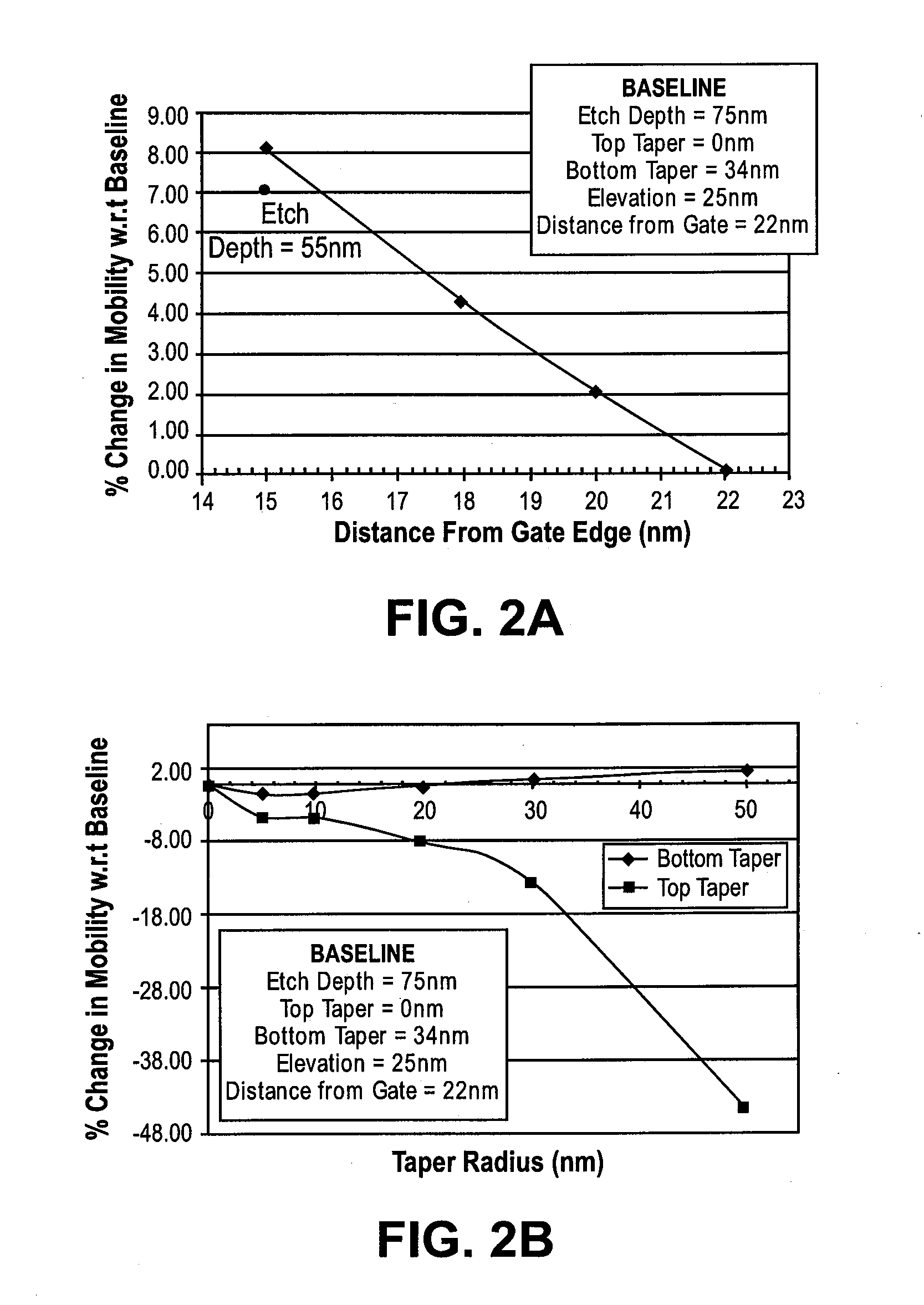
Methods and apparatuses to etch recesses in a silicon substrate having an isotropic character to undercut a transistor in preparation for a source / drain regrowth. In one embodiment, a cap layer of a first thickness is deposited over a transistor gate stack and spacer structure. The cap layer is then selectively etched in a first region of the substrate, such as a p-MOS region, using a first isotropic plasma etch process and a second anisotropic plasma etch process. In another embodiment, an at least partially isotropic plasma recess etch is performed to provide a recess adjacent to the channel region of the transistor. In a particular embodiment, the plasma etch process provides a recess sidewall that is neither positively sloped nor more than 10 nm re-entrant.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Charged particle source and operation thereof
ActiveUS7183716B2Reduce the overall diameterIncrease or decrease lengthElectric arc lampsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRe entrantConductor Coil
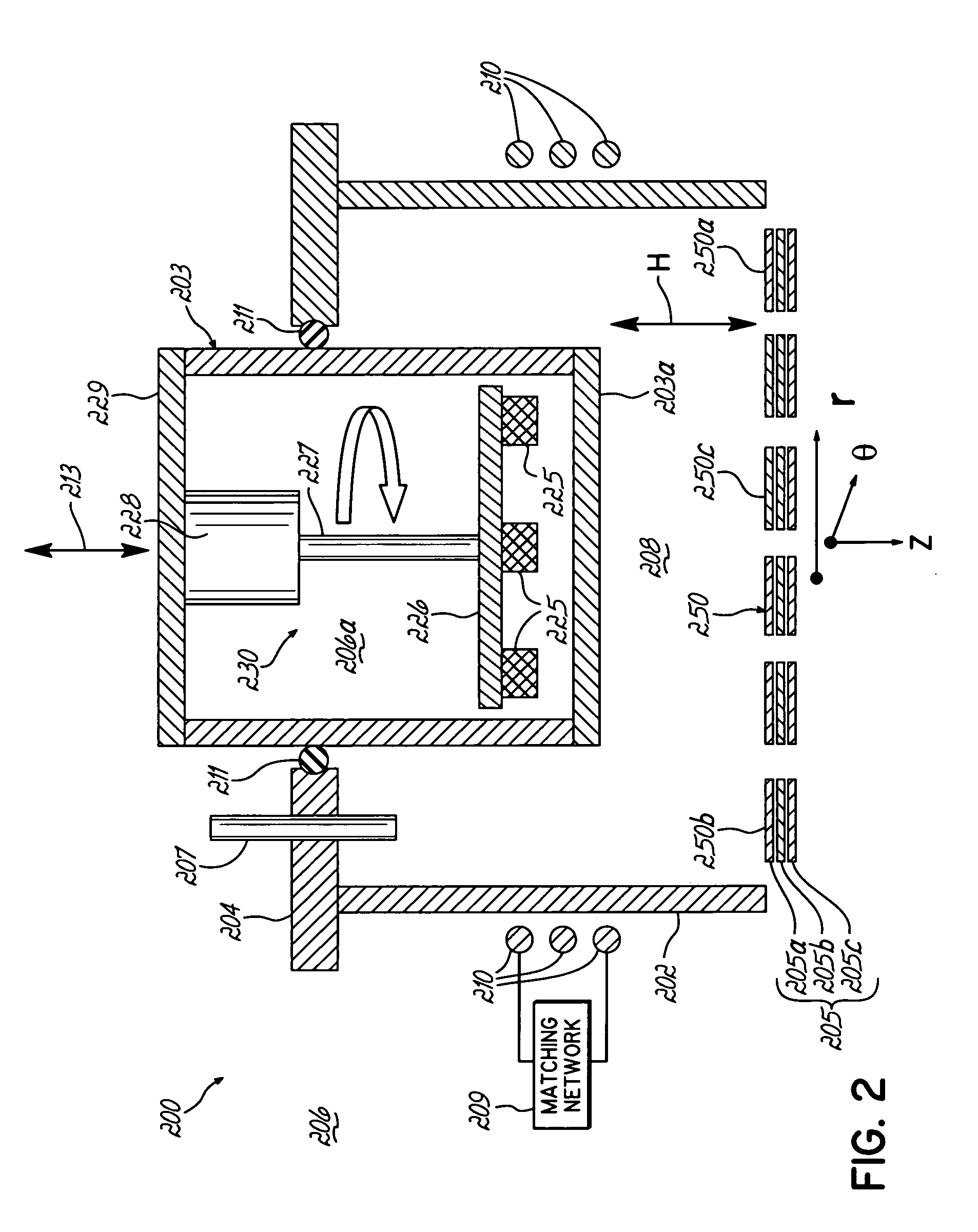
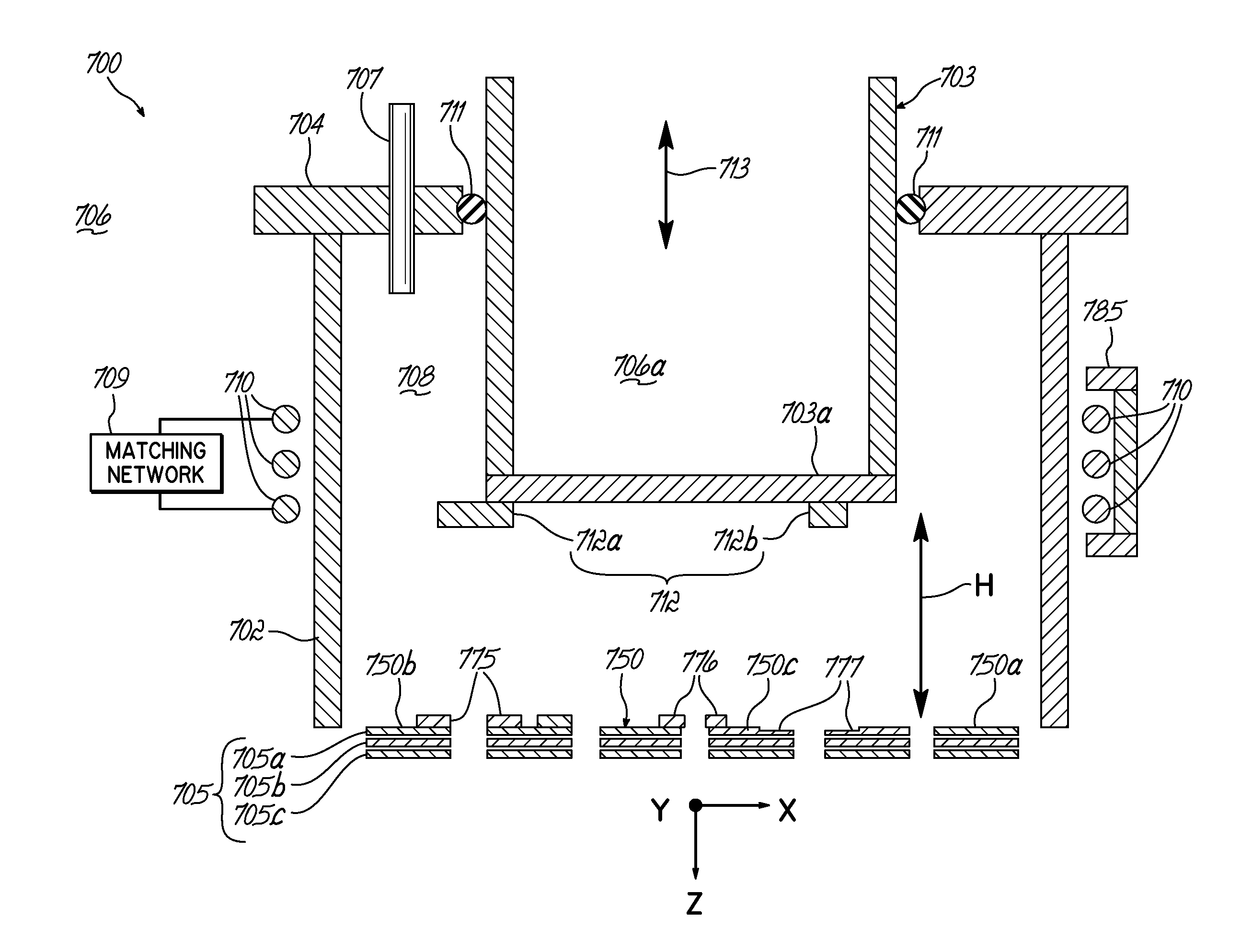
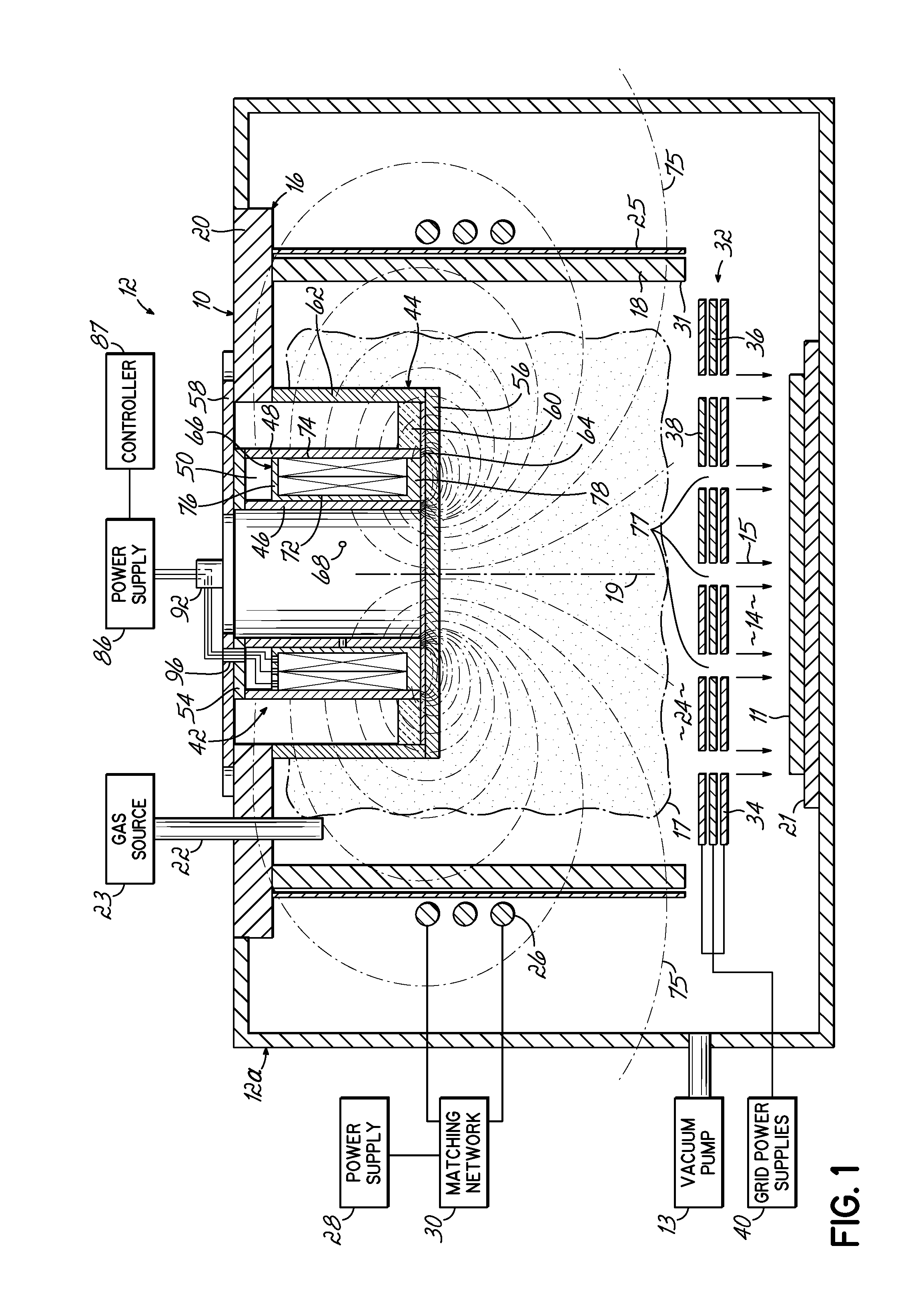
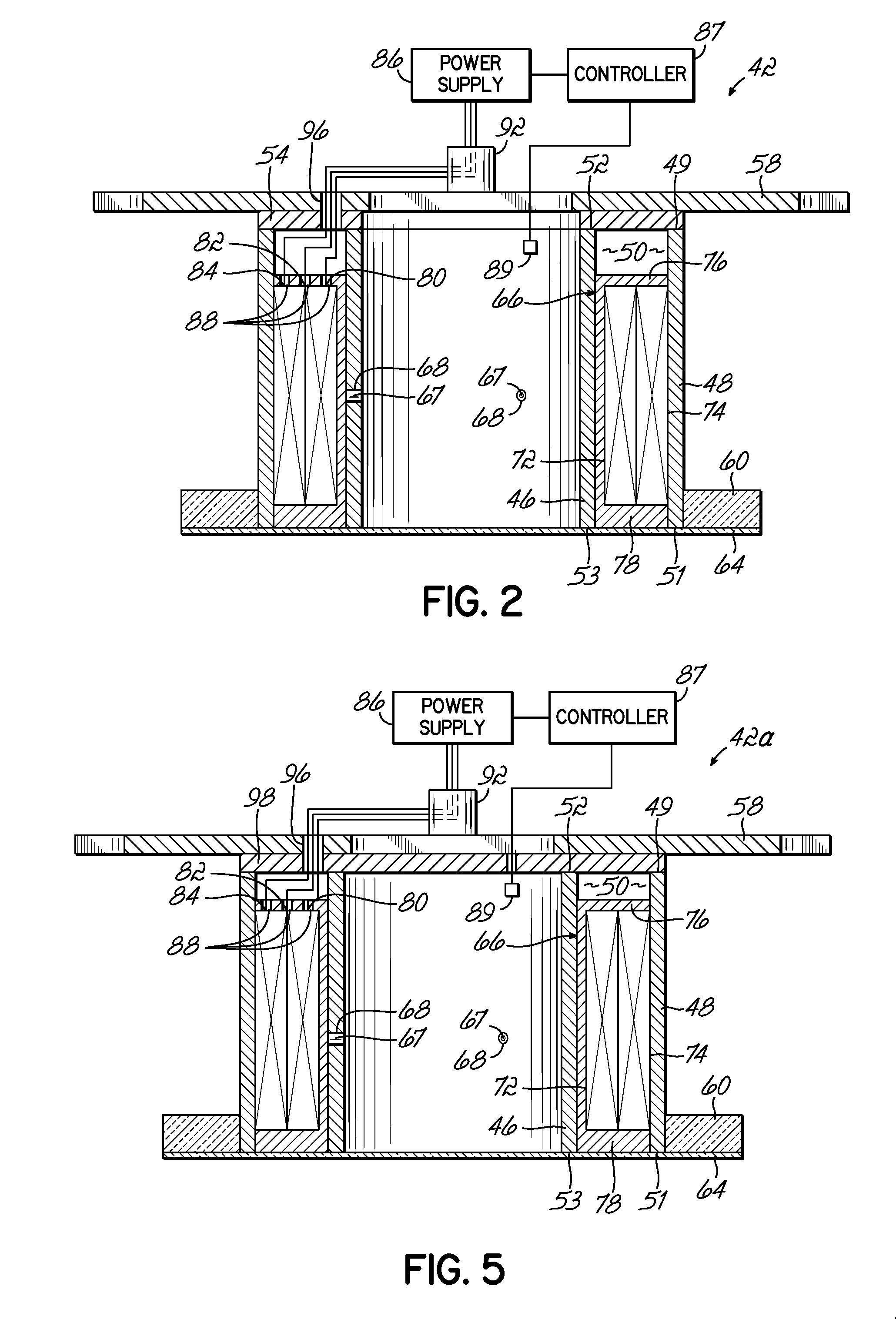
A charged particle source utilizes a novel plasma processing chamber, RF coil and ion optics, to achieve high uniformity. The plasma processing chamber has a re-entrant vessel which is movable, and which includes extensions of adjustable shape or position, to make more uniform the plasma contained within the chamber. One or more magnets, which may be static or moving, may be included within the re-entrant vessel. The ion optics include a grid with a number of apertures, and tuning features each surrounding an aperture. These tuning features either reduce the diameter of the associated aperture, or increase the length of that aperture, to create more uniform beamlets emerging from the grid. The RF coil includes a flux concentrator positioned adjacent to the winding in at least one angular region thereof to tune the magnetic field produced thereby.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Hermetic MEMS package and method of manufacture
InactiveUS7358106B2Improve sealingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRe entrantEngineering
Owner:STELLAR MICRO DEVICES
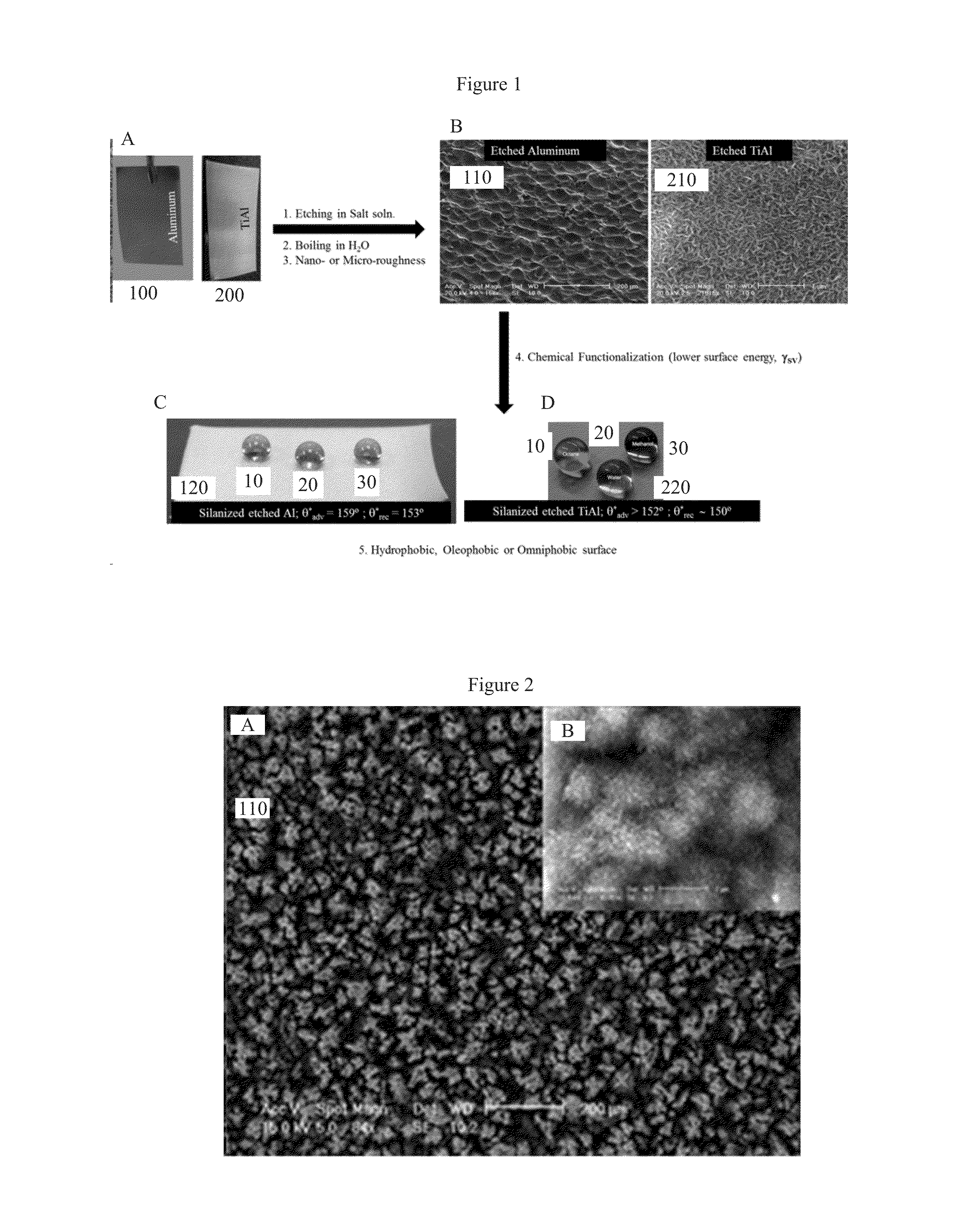
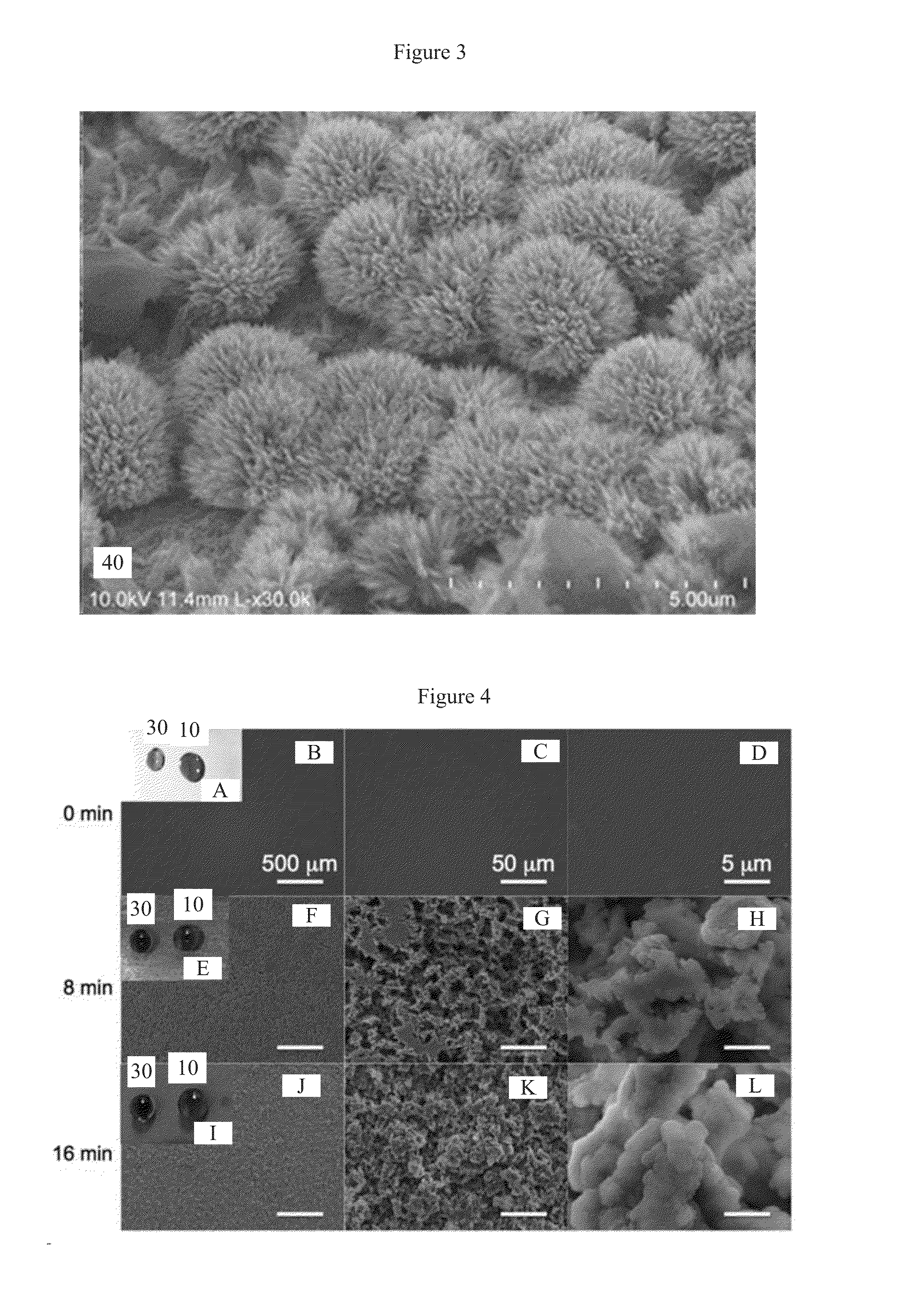
Salt Based Etching of Metals and Alloys for Fabricating Superhydrophobic and Superoleophobic Surfaces
InactiveUS20160153094A1Reduce etchingEasy disposalDecorative surface effectsMetallic material coating processesEtchingRe entrant
A process to etch hierarchical, re-entrant texture into the surface of metals and their alloys using salt-based etching solutions. The process imbues superhydrophobic, oleophobic or superoleophobic, omniphobic or superomniphobic properties by further imparting a low surface energy coating onto the etched surfaces by chemical functionalization by low surface energy hydrophobilizing compounds.
Owner:TUTEJA ANISH +2
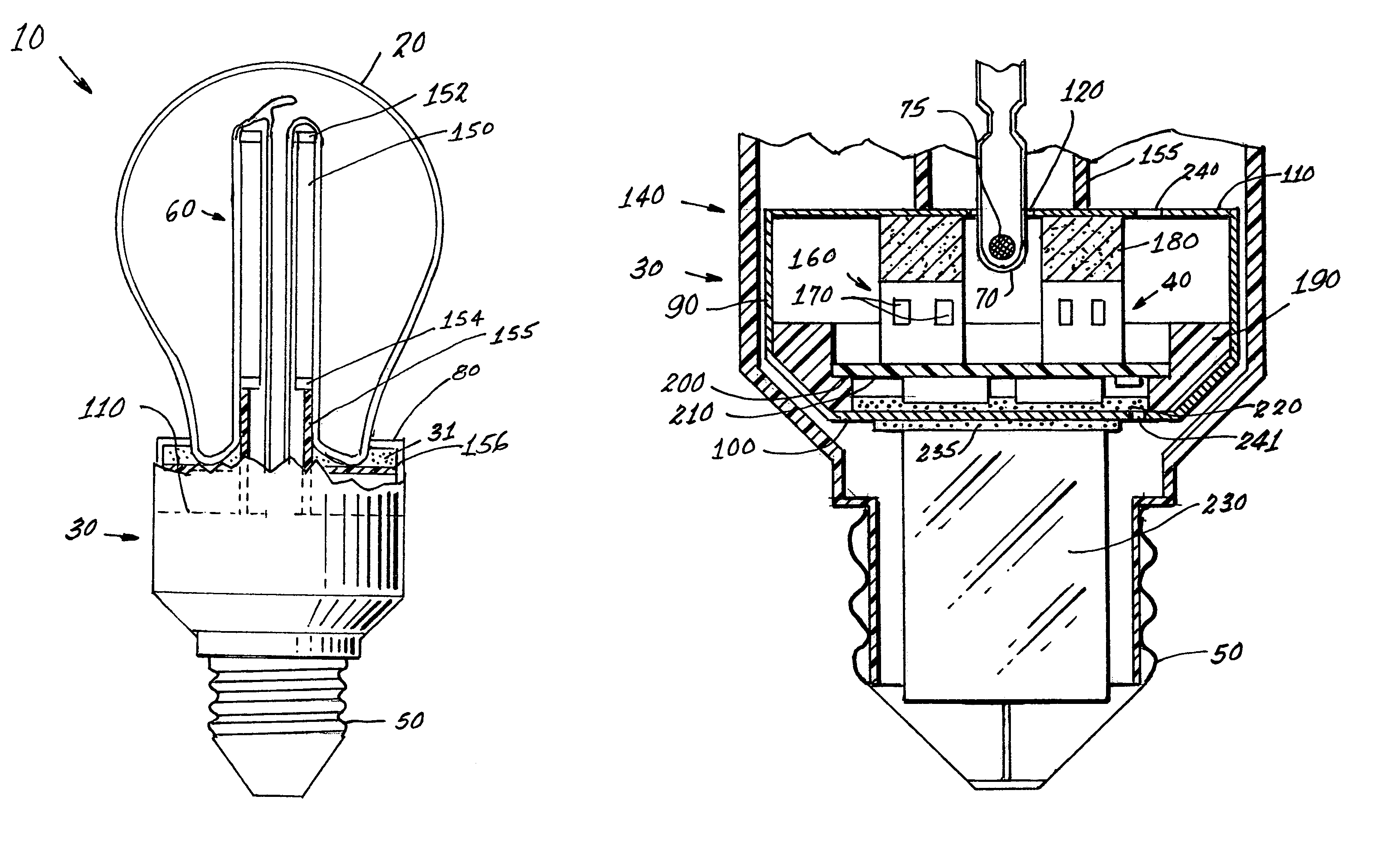
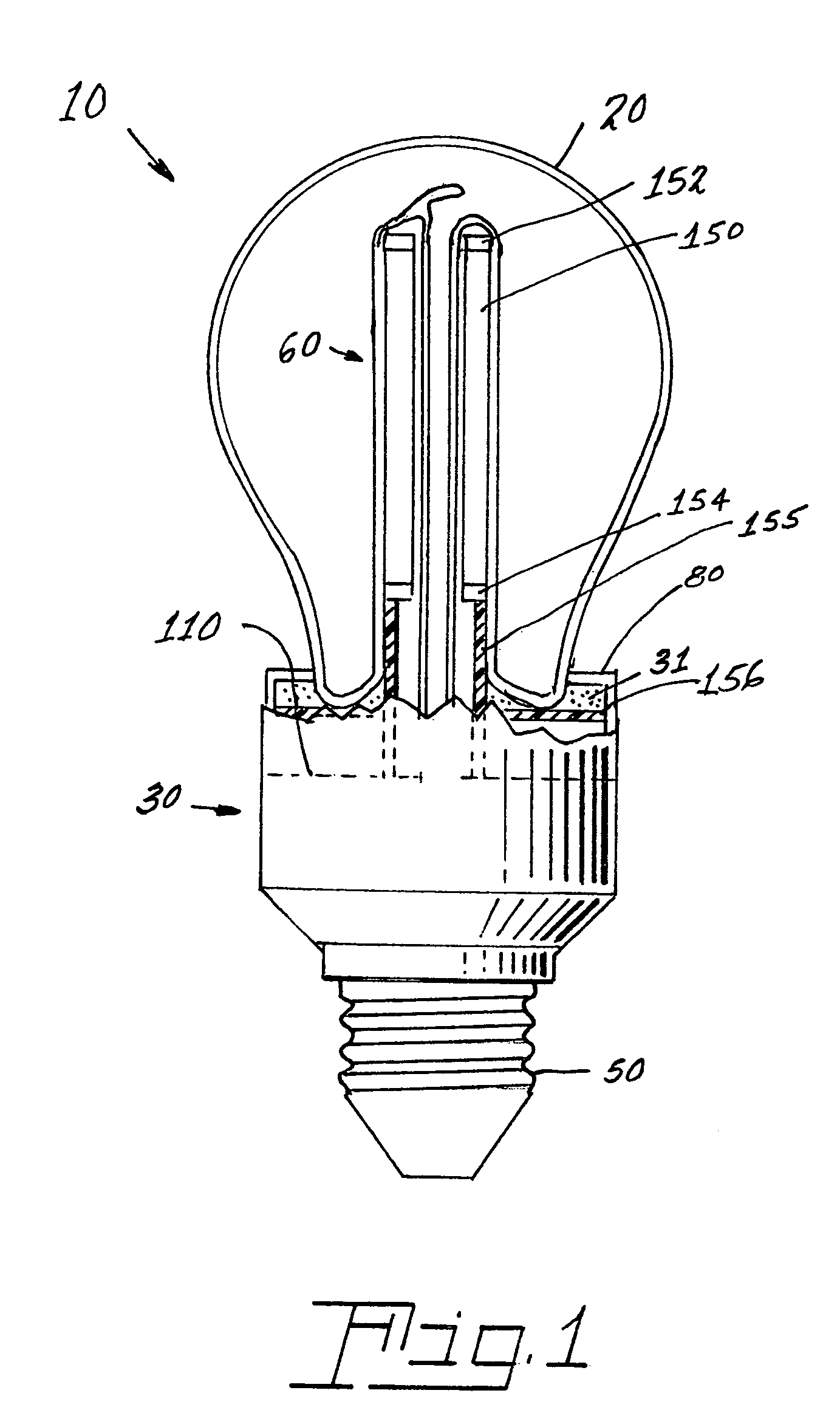
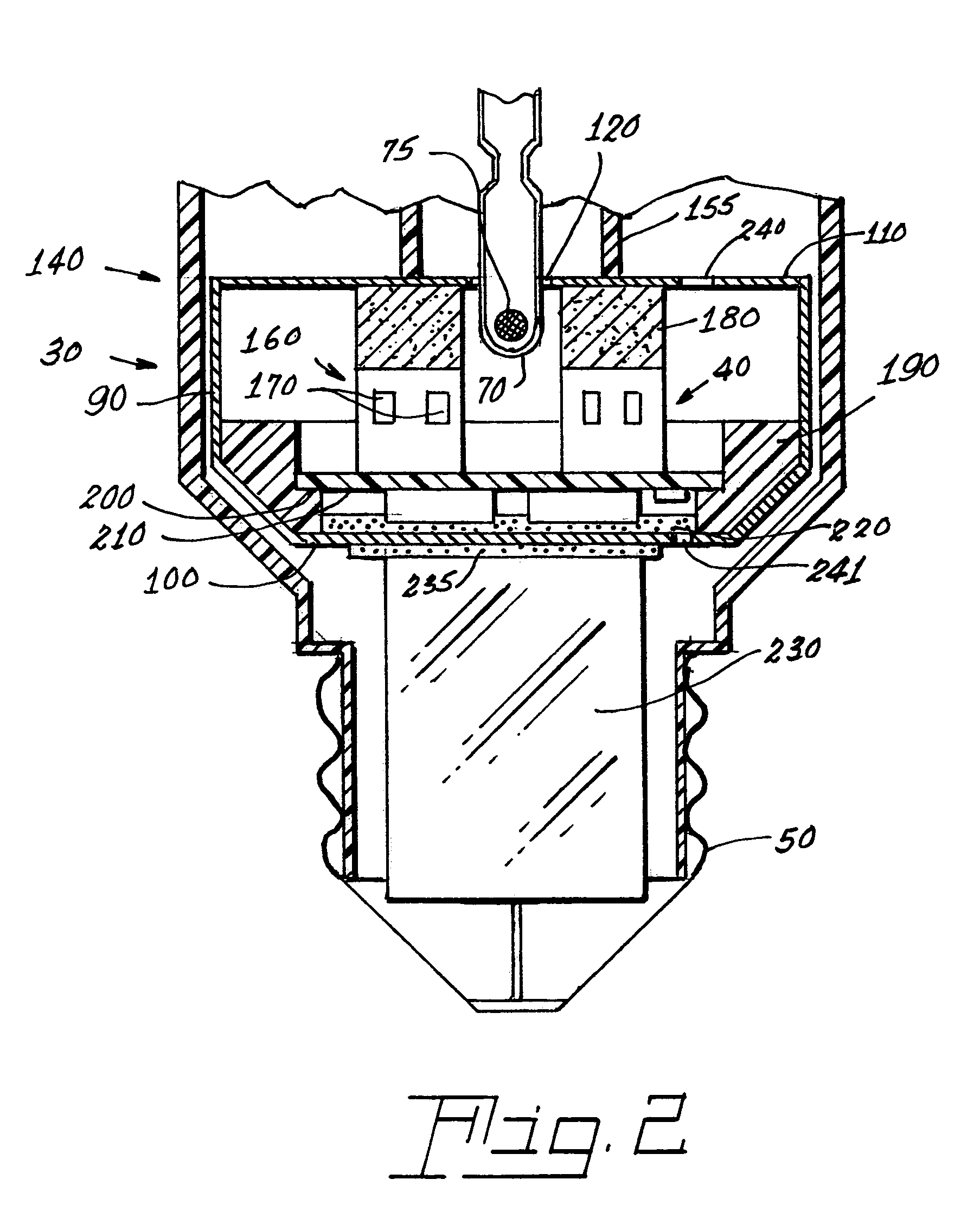
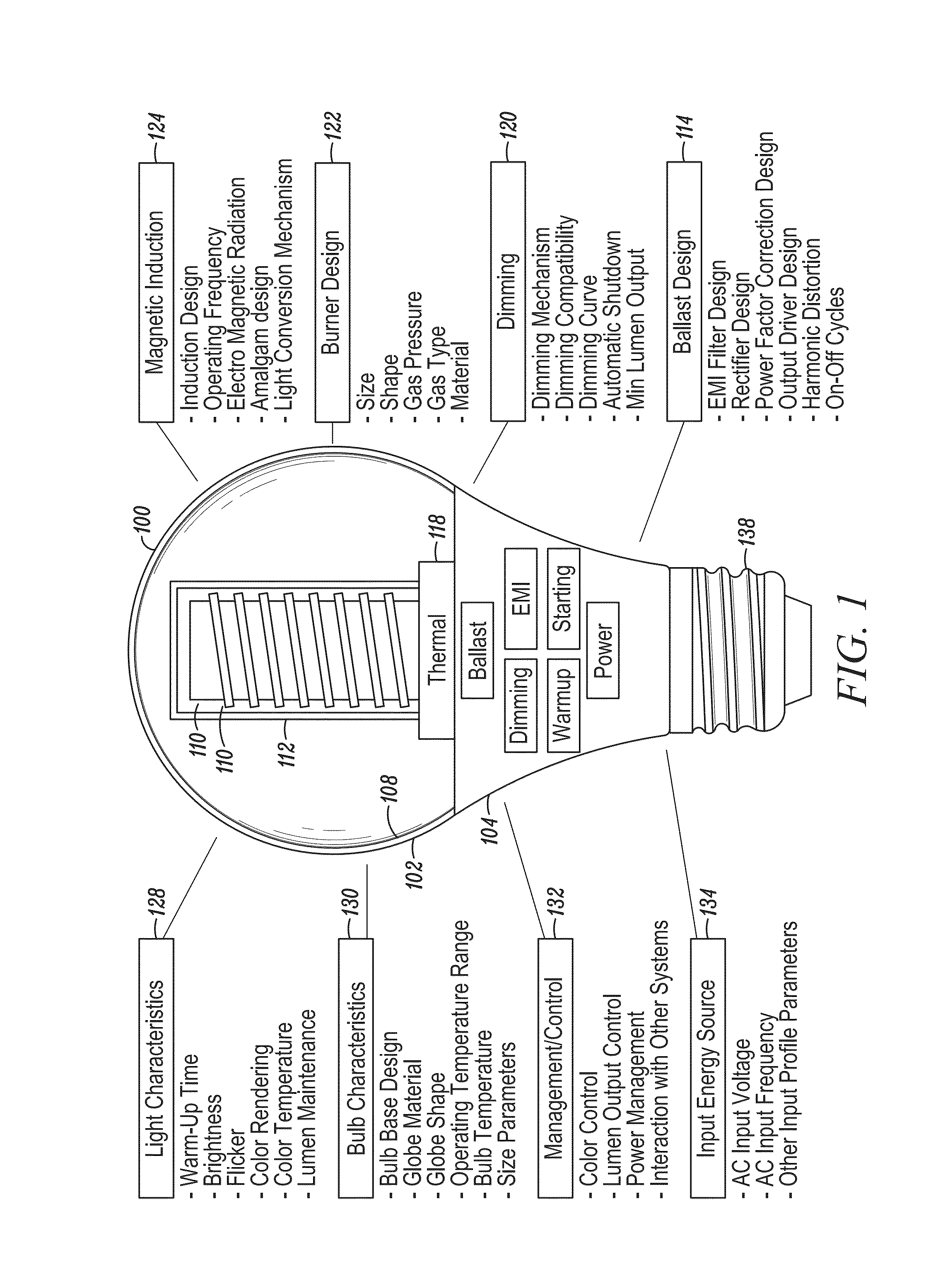
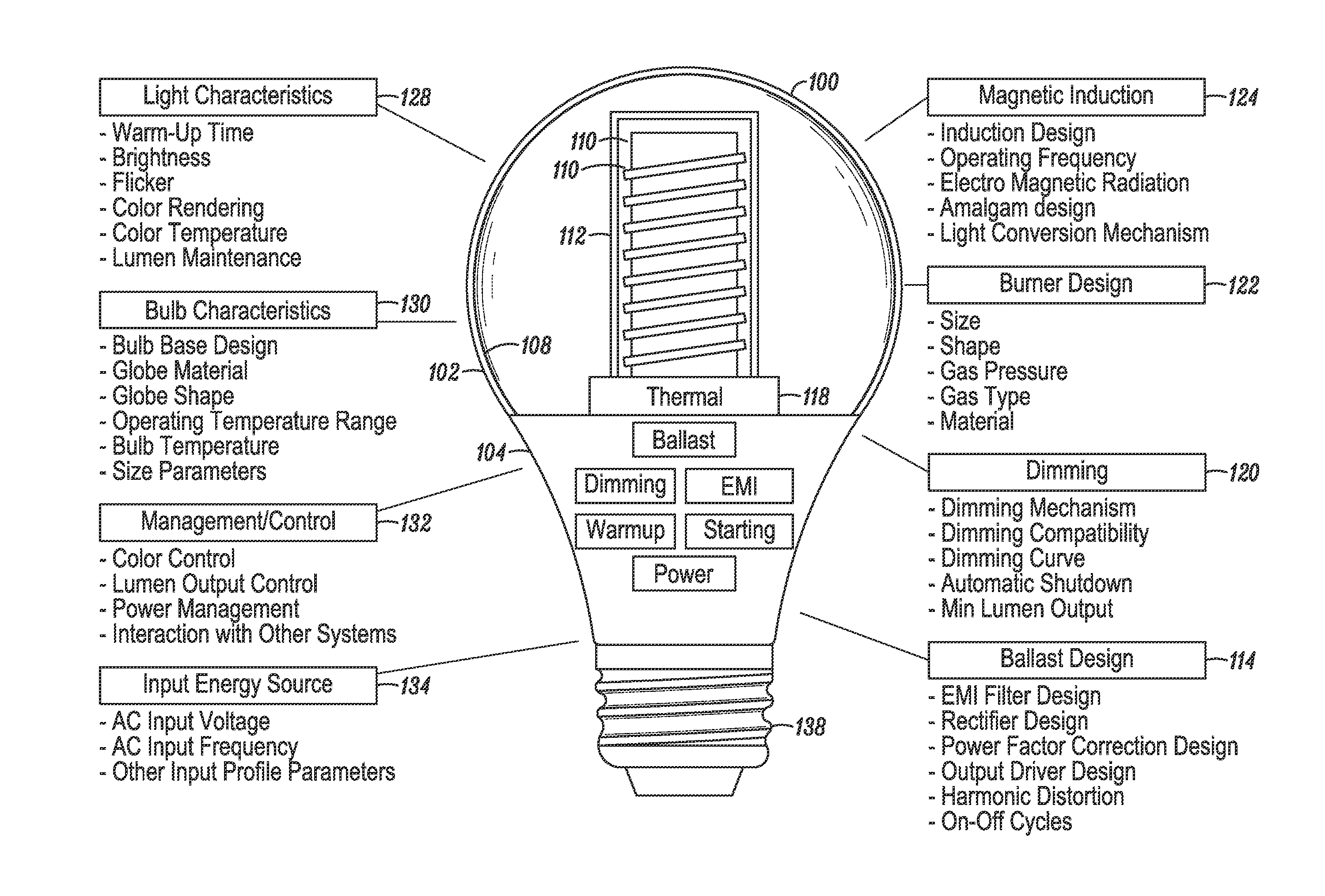
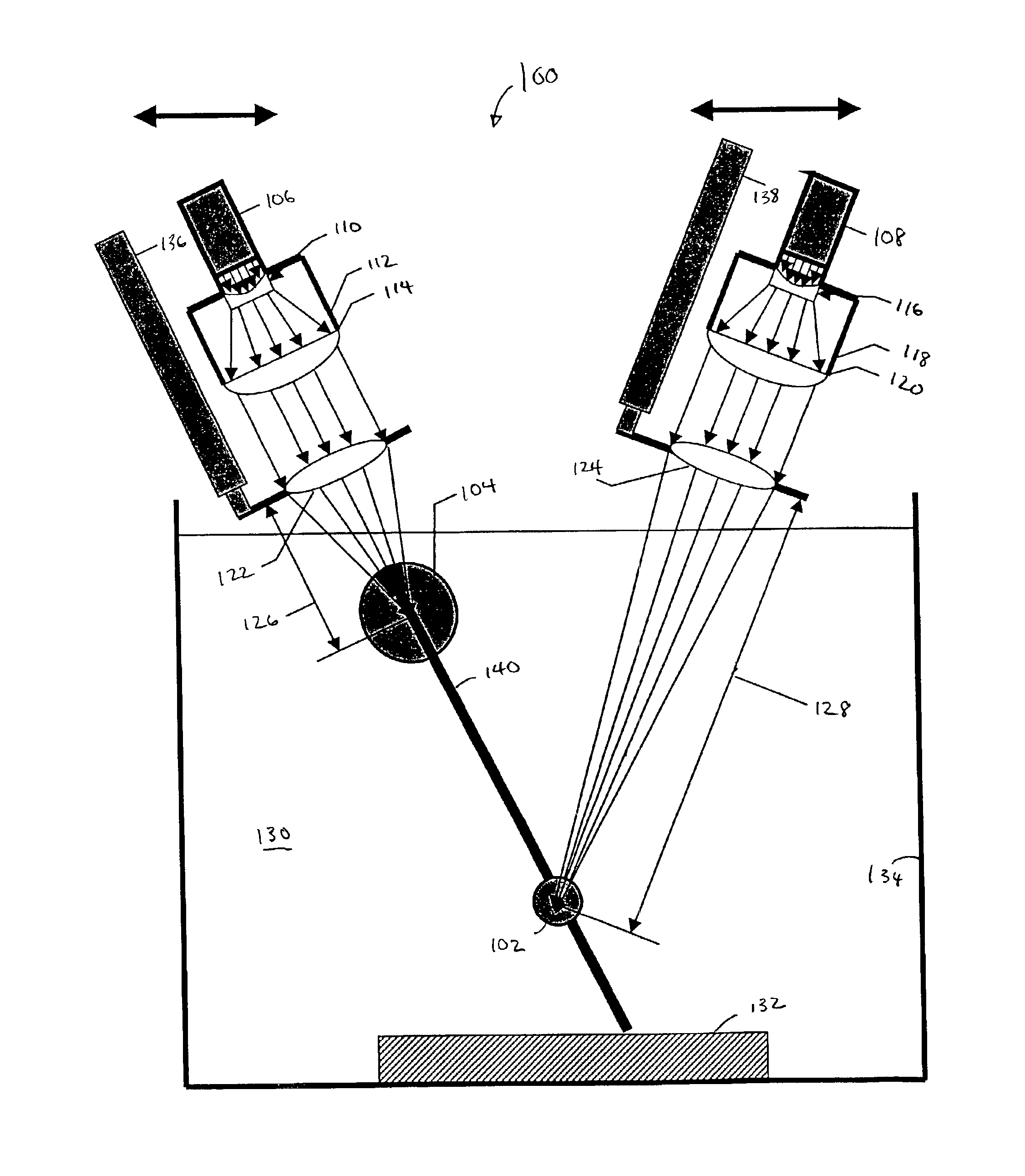
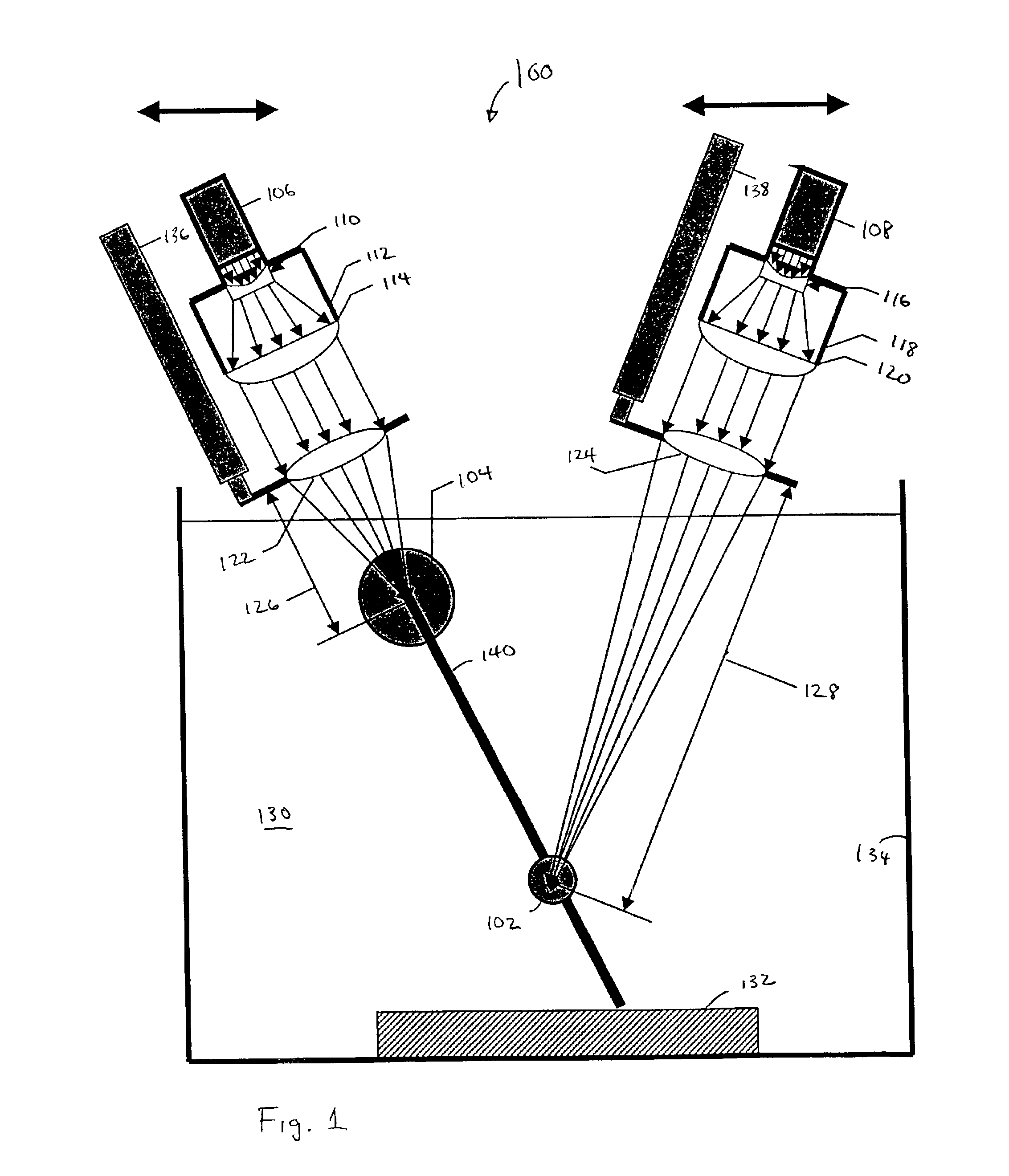
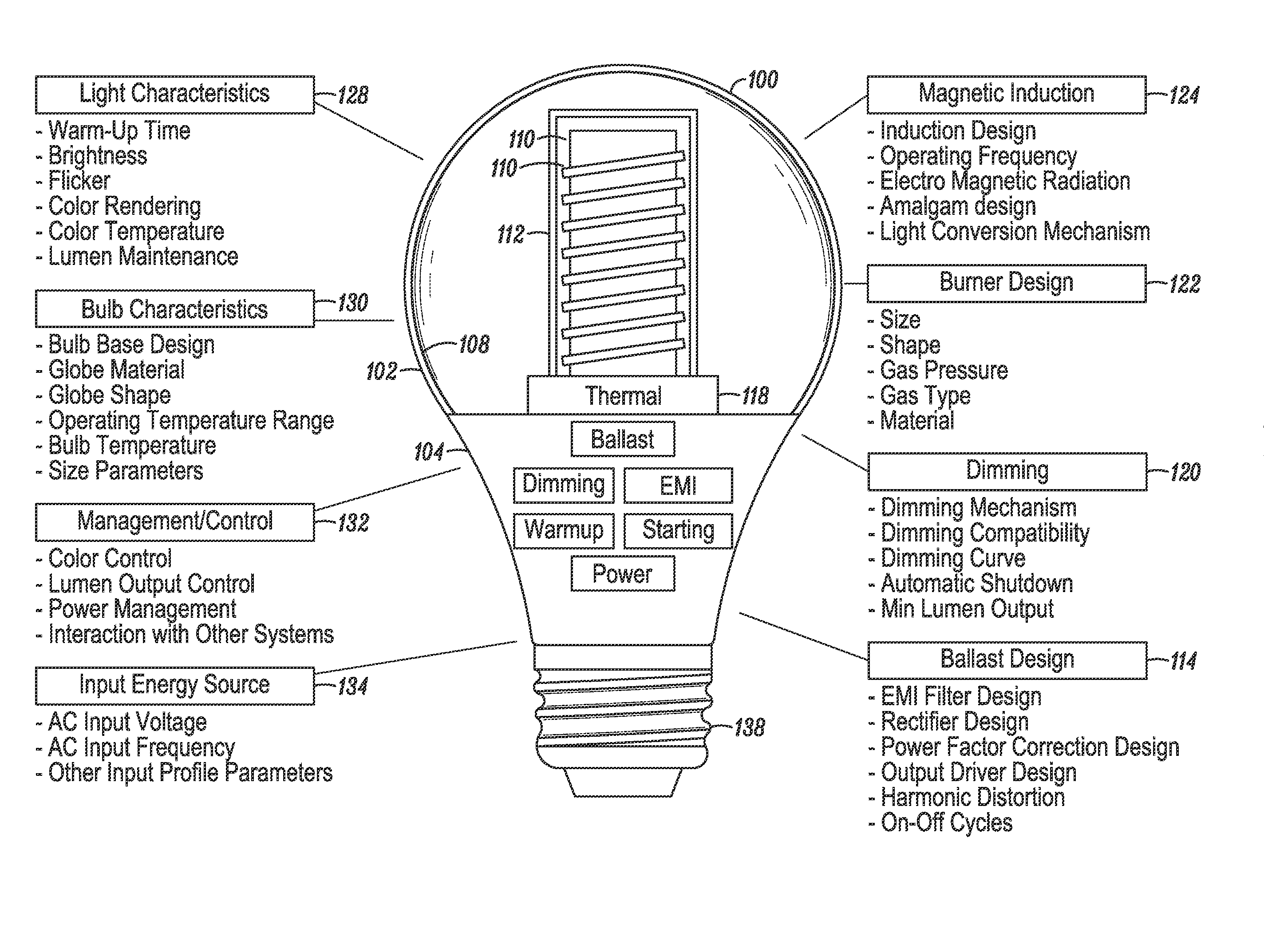
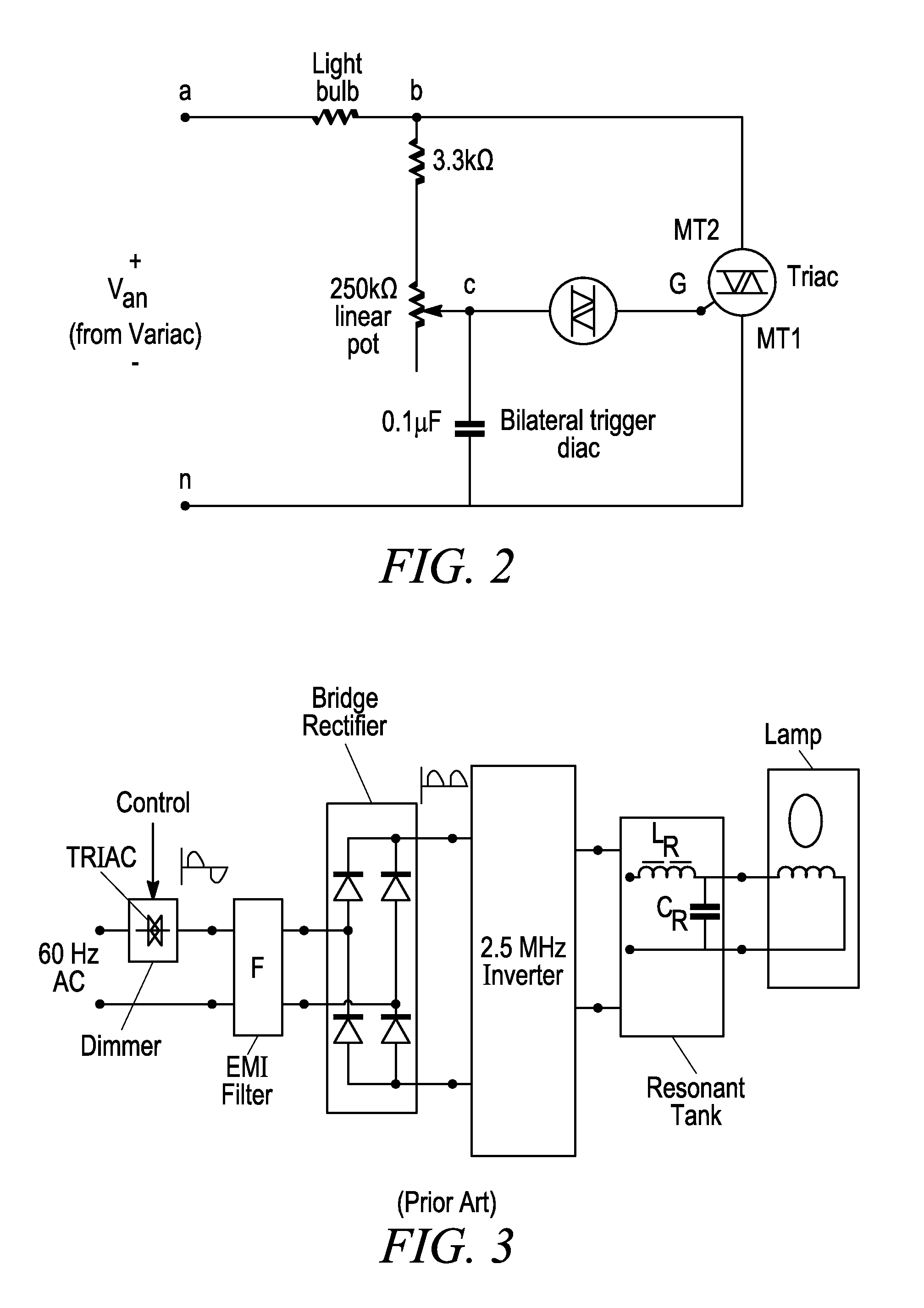
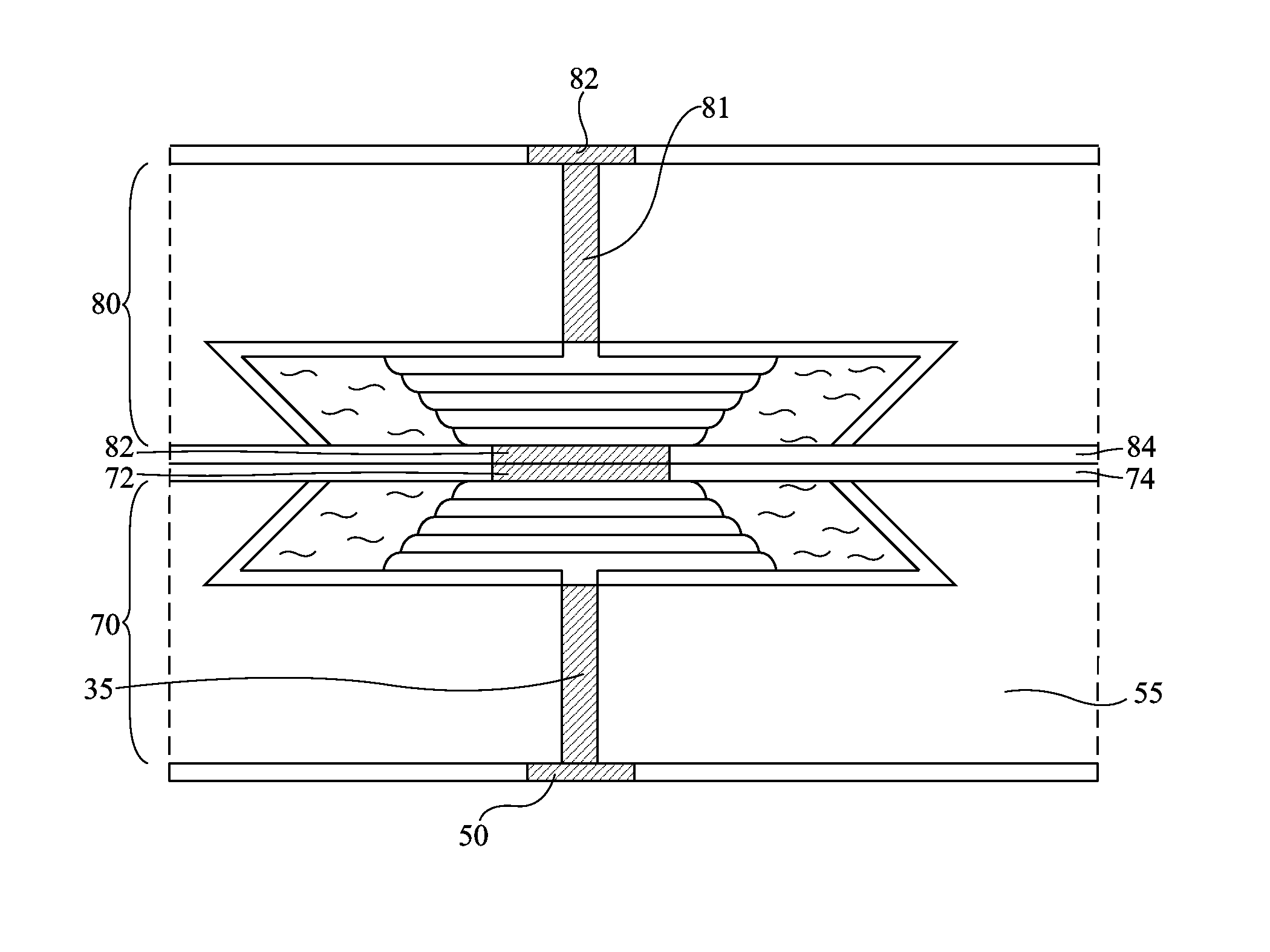
Re-entrant cavity fluorescent lamp system
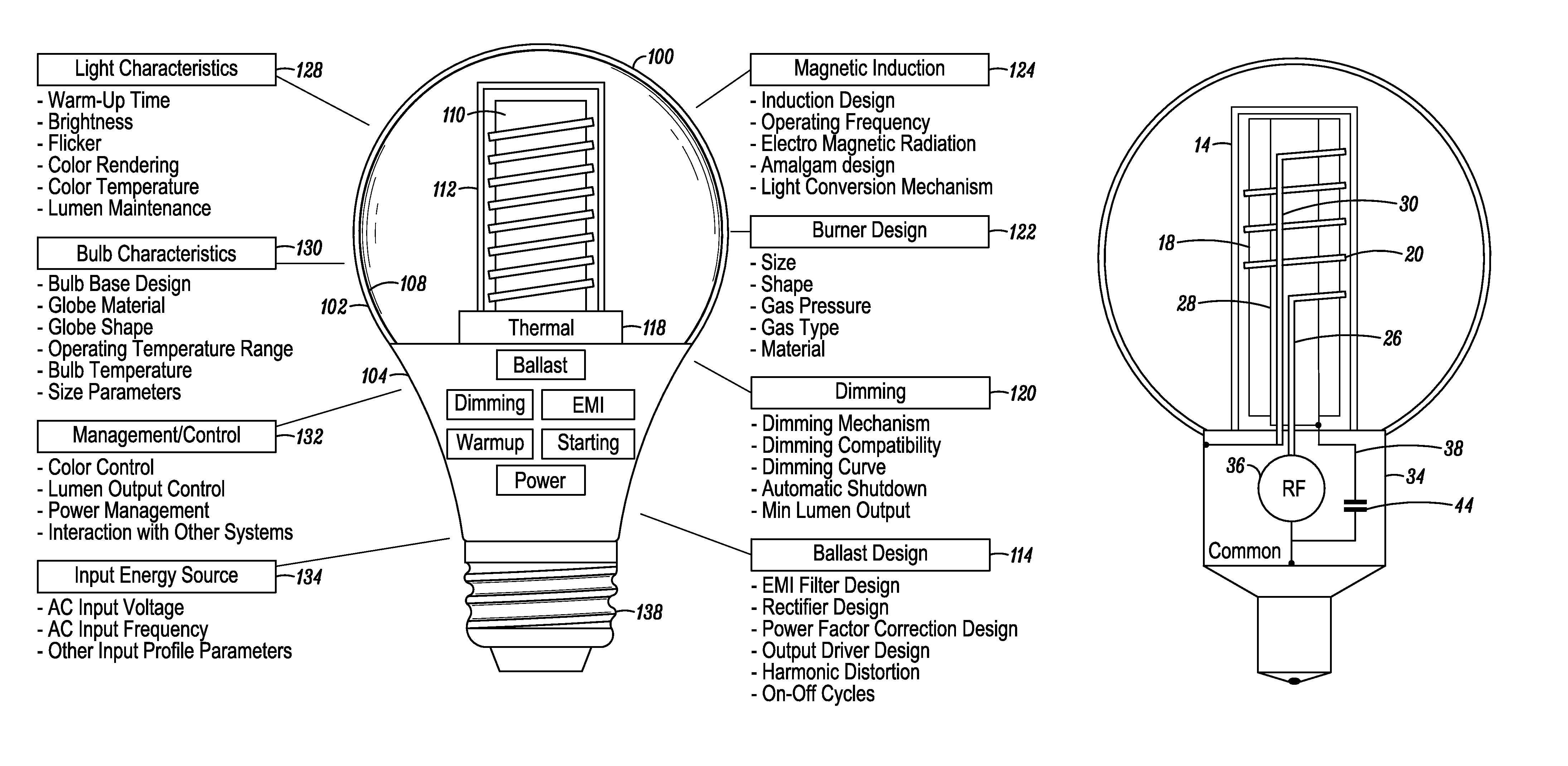
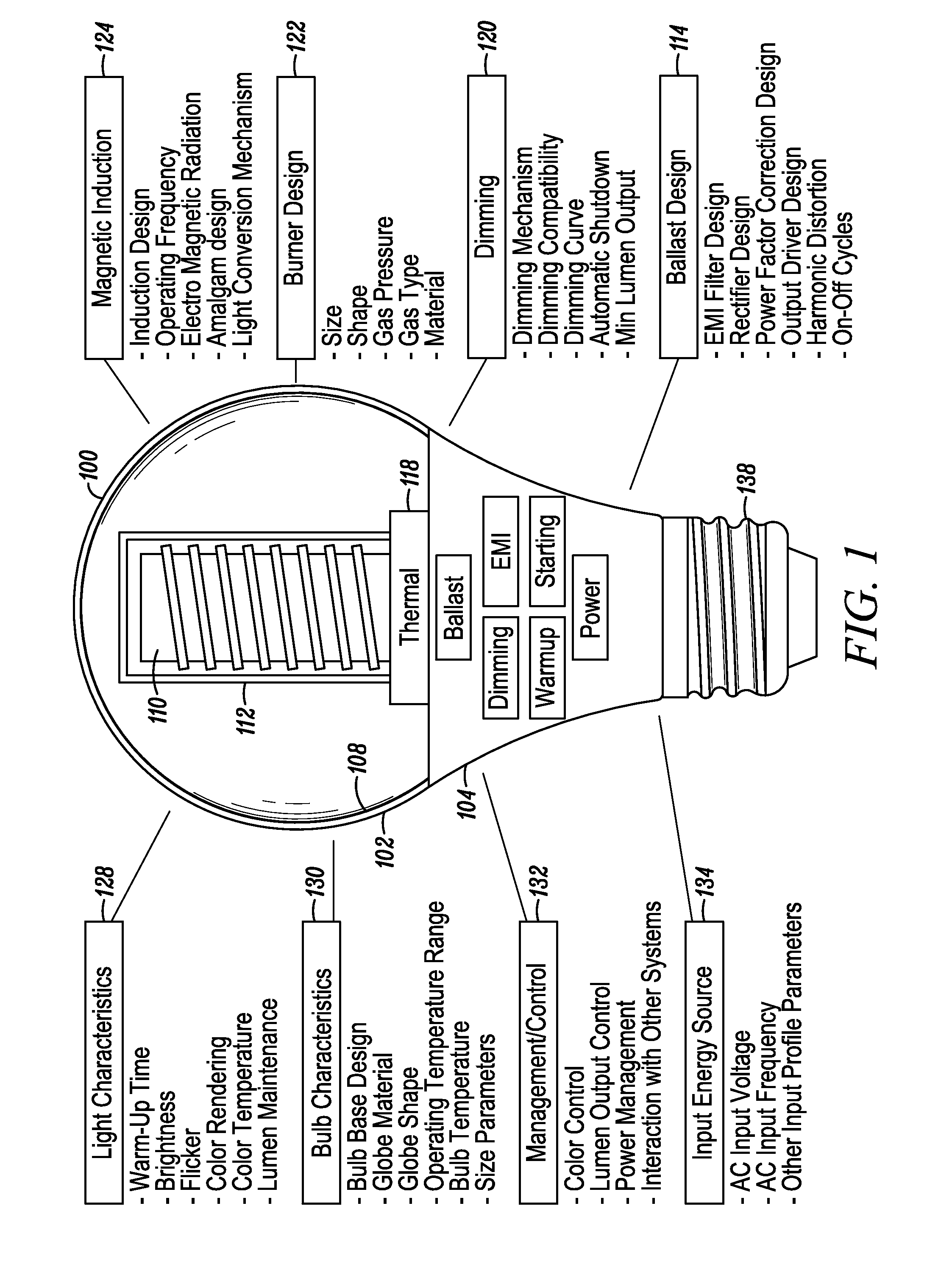
InactiveUS7119486B2Easy to operateAmalgam temperature controlDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectric discharge tubesAdhesiveEngineering
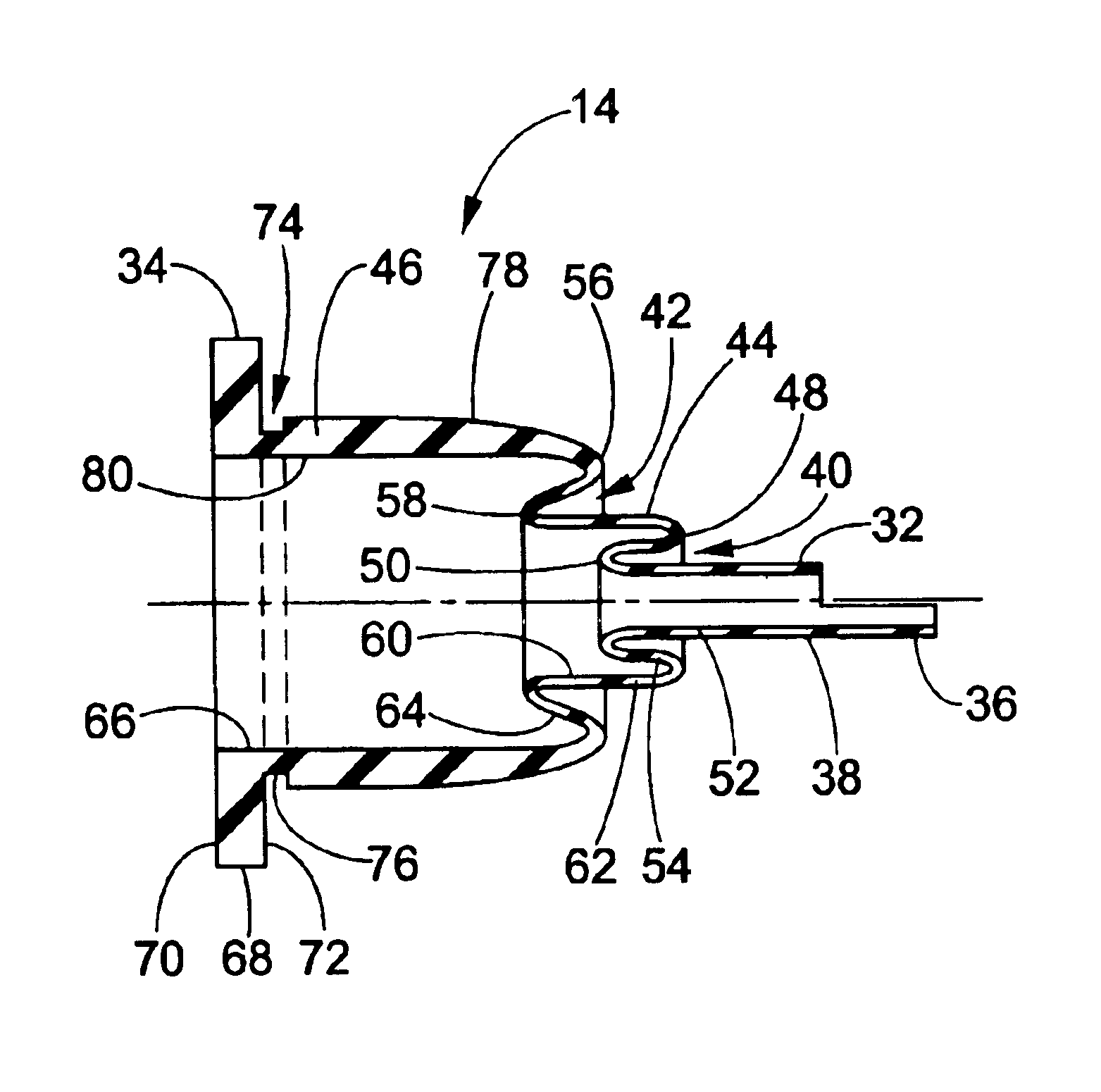
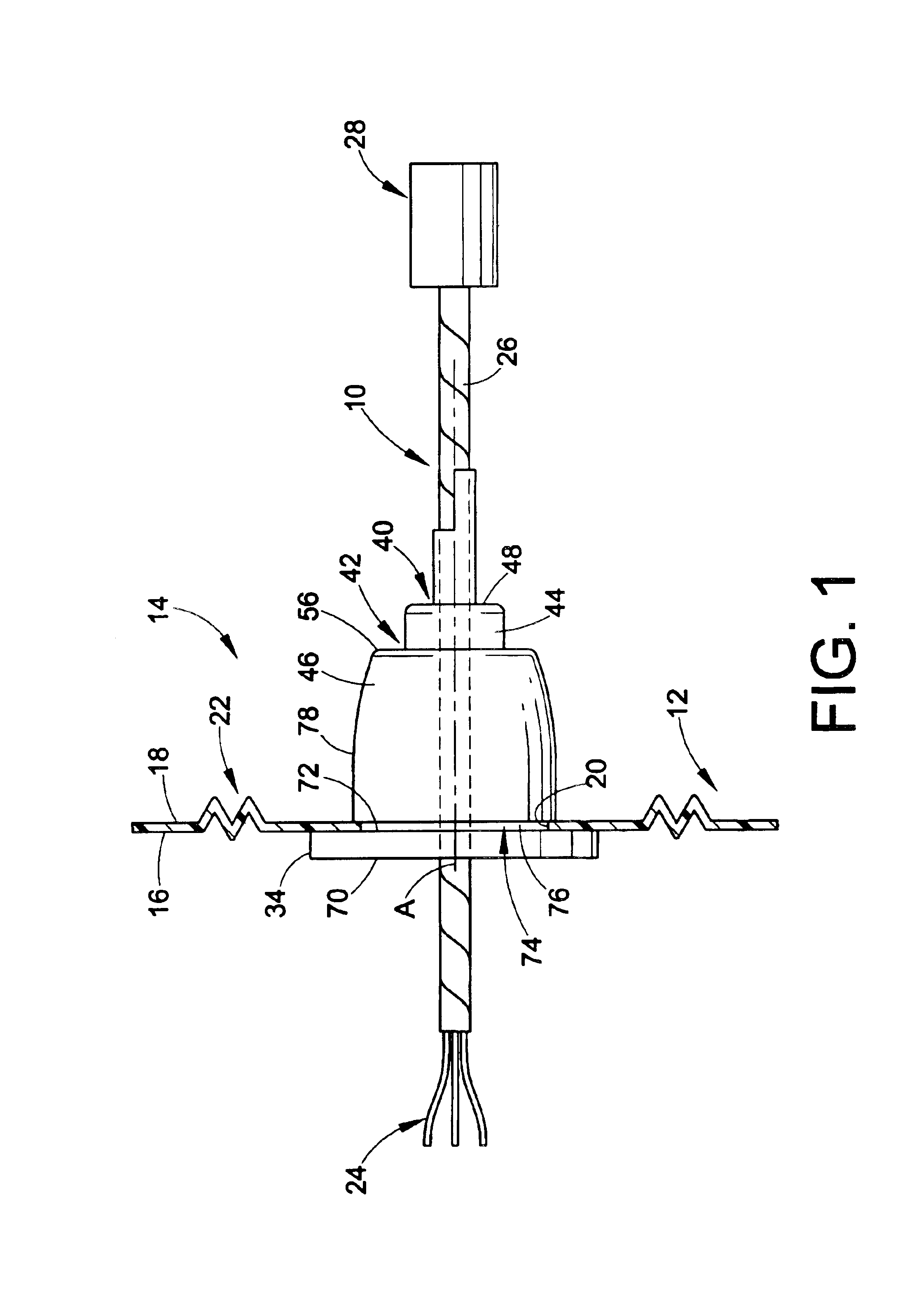
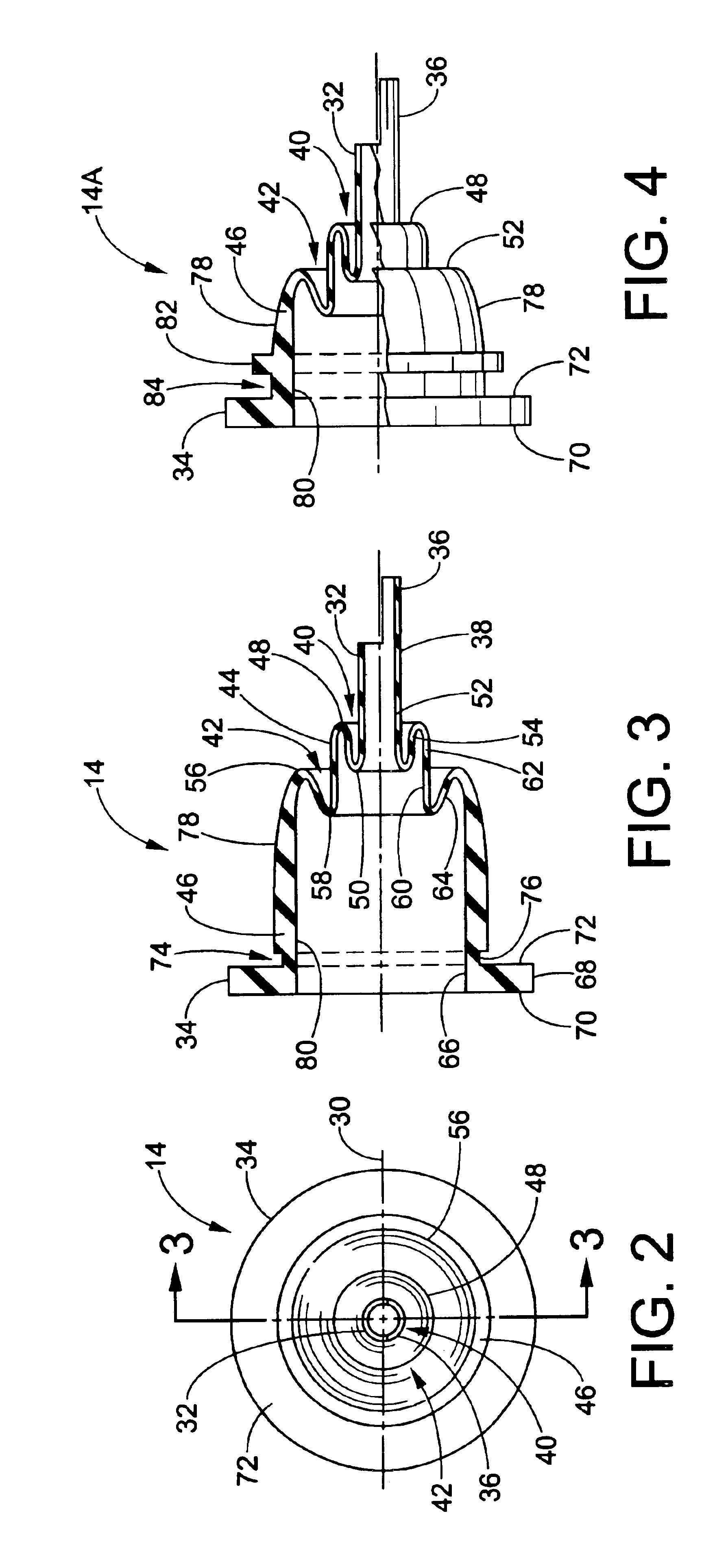
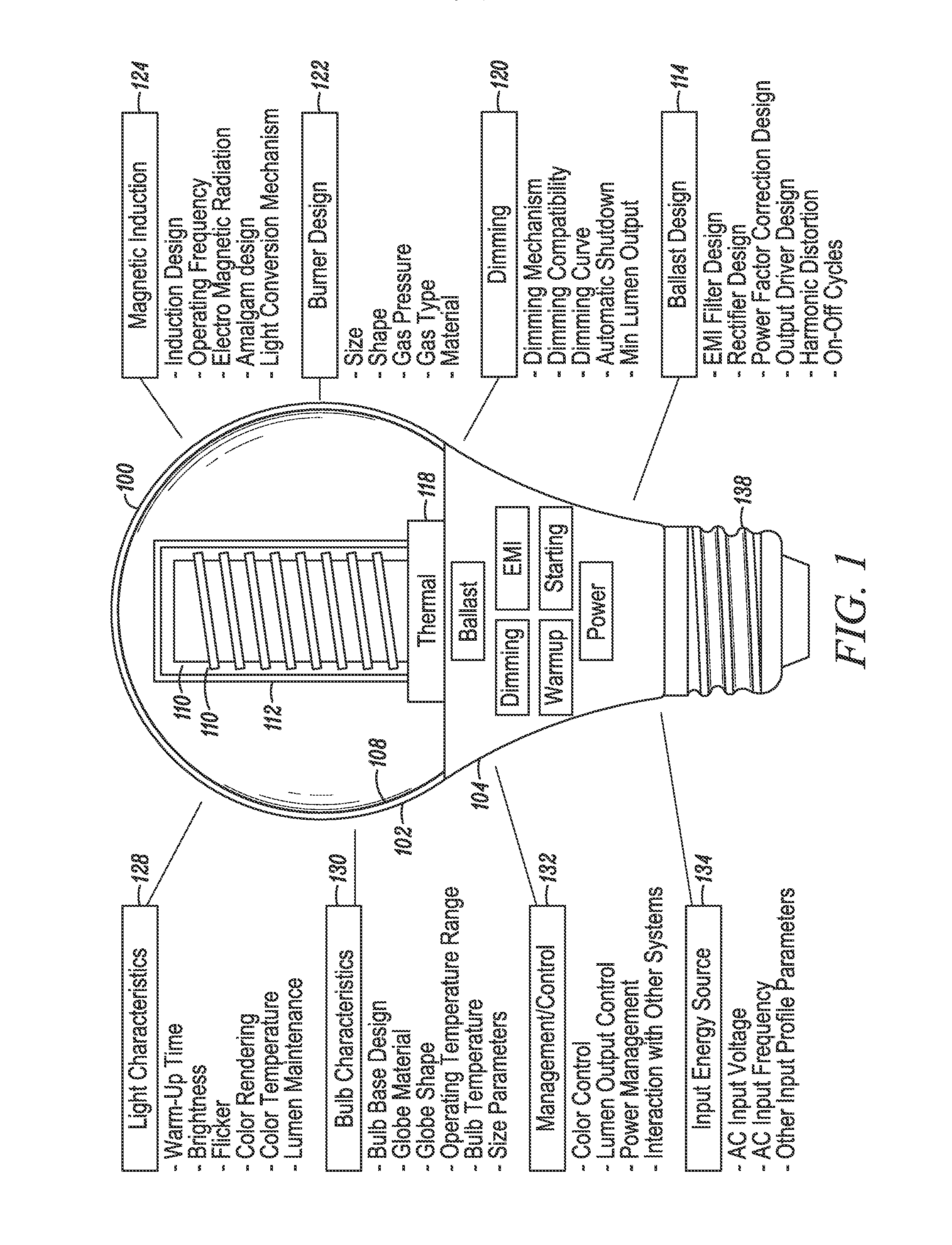
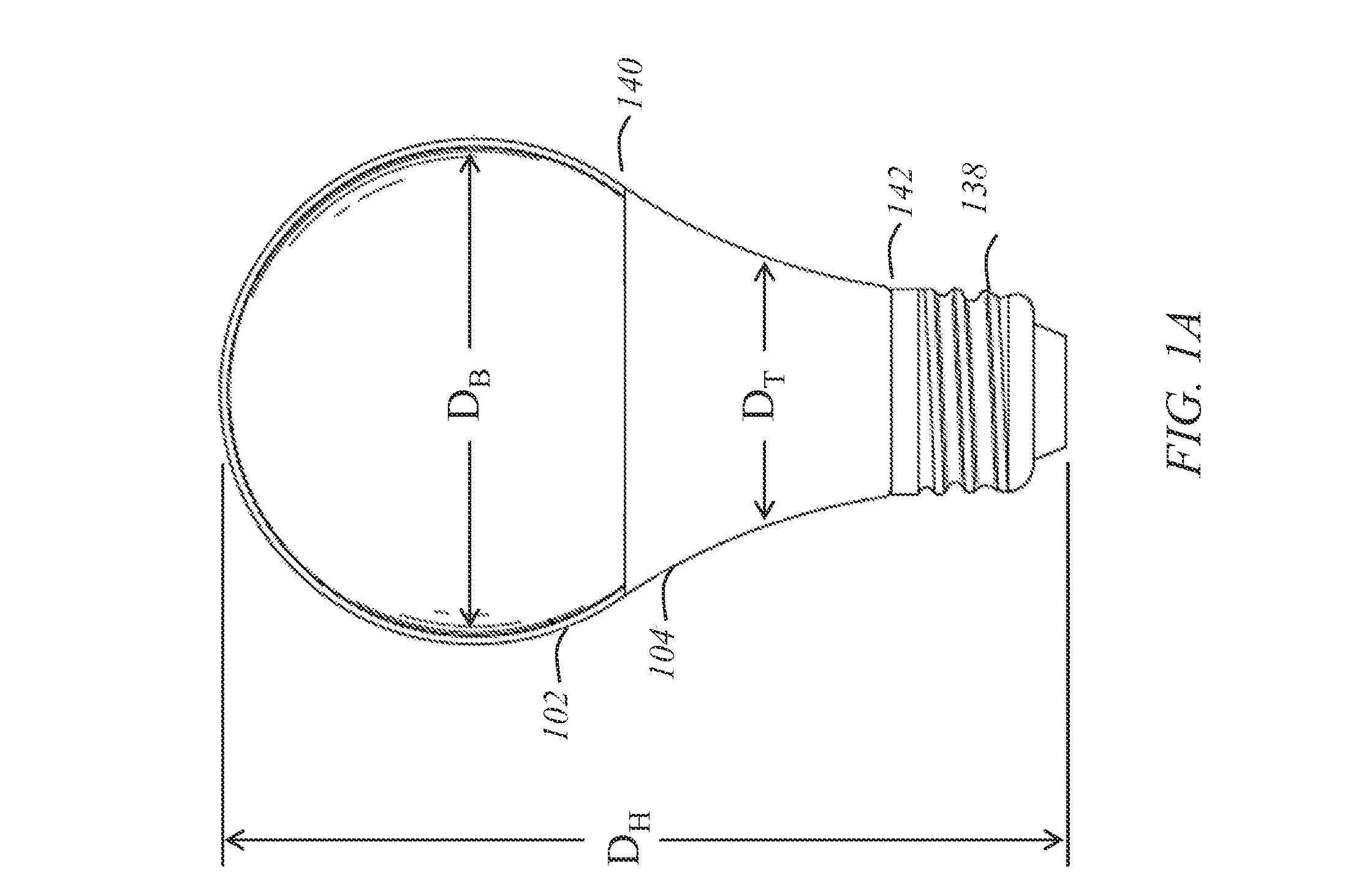
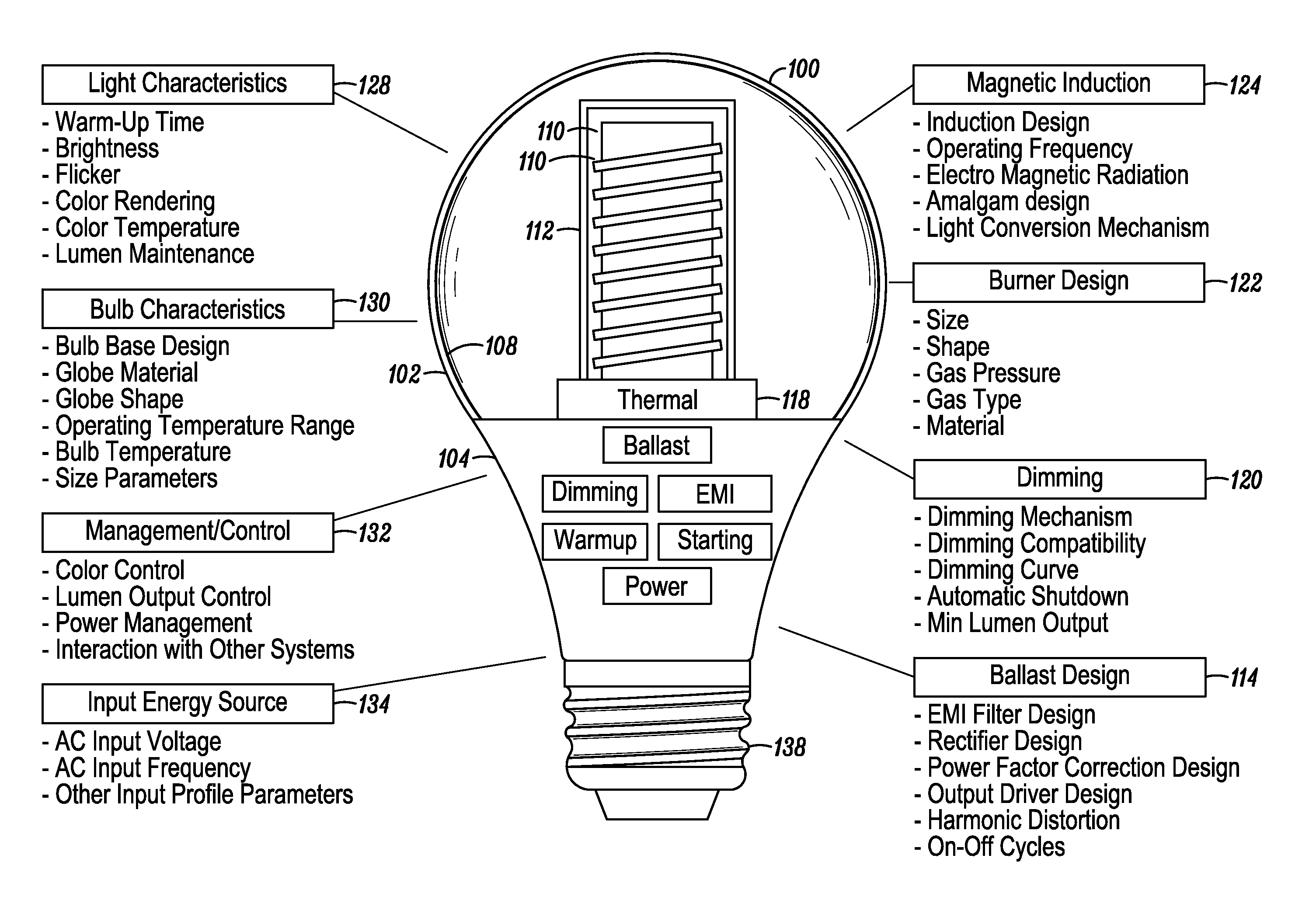
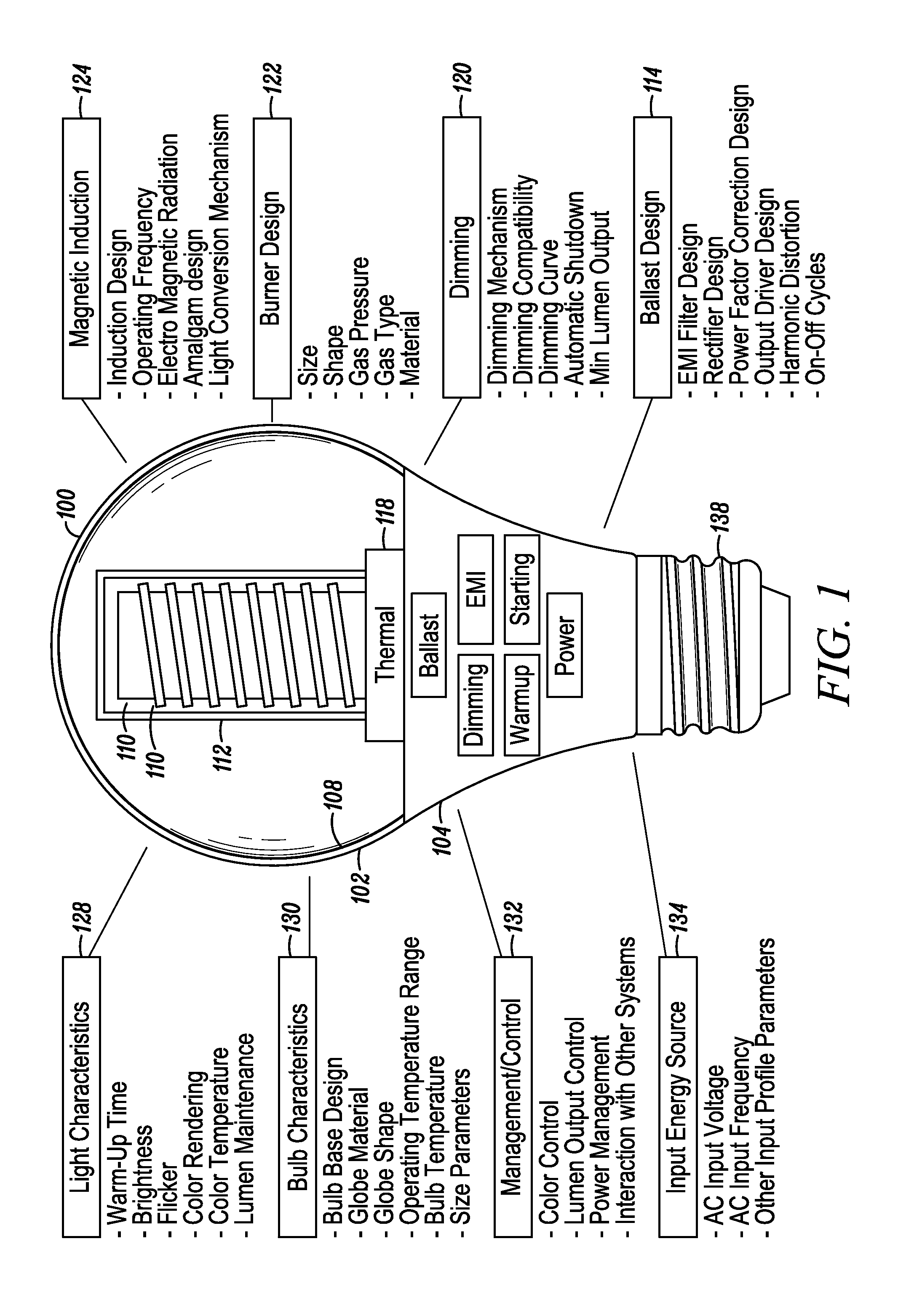
An electrodeless fluorescent lamp (10) having a burner (20), a ballast housing (30) containing a ballast (40) and a screw base (50) for connection to a power supply. A reentrant cavity (60) is formed in the burner (20) and an amalgam receptacle (70) containing amalgam (75) is formed as a part of the reentrant portion and in communication with the burner (20). A housing cap (80), formed of a suitable plastic, connects the burner (20) to the ballast housing (30) and a suitable adhesive (31) fixes the burner to the housing cap (80). An EMI cup (90) is formed as an insert to fit into the ballast housing (30), which also is formed of a suitable plastic, and has a bottom portion (100) and an EMI cap (110) with an aperture (120) therein closing an upper portion (140). The EMI cup (90) and the EMI cap (110) are preferably formed from 0.5 mm brass. The amalgam receptacle (70) extends through the aperture (120) and into the cup (90). For a fixed amalgam position, changing the aperture size allows adjustment of the amalgam tip temperature, and thus, allows control of the system lumen output, efficacy, CCT and CRI, all of which are dependent on the amalgam temperature.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
RF induction lamp with reduced electromagnetic interference
InactiveUS8698413B1Low costEMI suppressionAlternating current plasma display panelsDischarge tube main electrodesPhosphorEnd-group
An induction RF fluorescent lamp configuration provides reduced EMI, including a lamp envelope with a re-entrant cavity both covered on the partial vacuum side with phosphor and filled with a working gas mixture, a tubular ferromagnetic core on the non-vacuum side said re-entrant cavity wound directly on the said core with two windings having different numbers of turns, a first active winding having one end connected to an RF ballast and the other end connected to local ground, and a second passive winding having one end grounded and the other end free.
Owner:LUCIDITY LIGHTS
Induction RF fluorescent lamp with helix mount
InactiveUS20140375203A1Operational flexibilitySmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionElectric discharge tubesRe entrantFluorescent lamp
An induction RF fluorescent lamp, comprising: a lamp envelope with a re-entrant cavity and evacuation tube; a power coupler, wherein the power coupler is located inside the re-entrant cavity; an electronic ballast, wherein the electronic ballast provides appropriate voltage and current to the power coupler; and an amalgam held within a capsule located above the power coupler within the lamp envelope, wherein the capsule is positioned with a mount comprising at least one wire attached to the capsule and having at least two wire ends extending from the capsule into the evacuation tube with contact made between the wire ends and the interior surface of the evacuation tube of the re-entrant cavity.
Owner:LUCIDITY LIGHTS
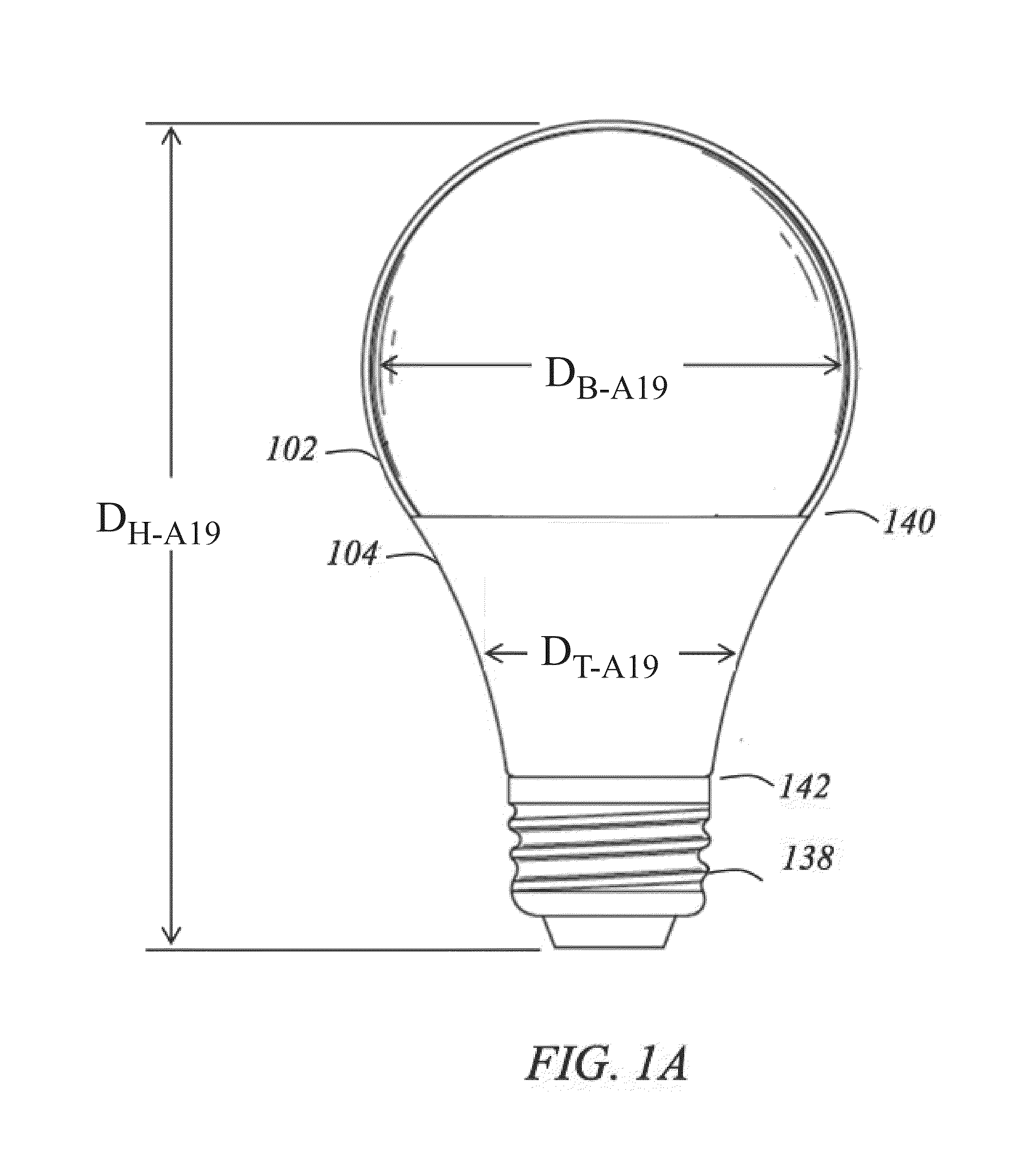
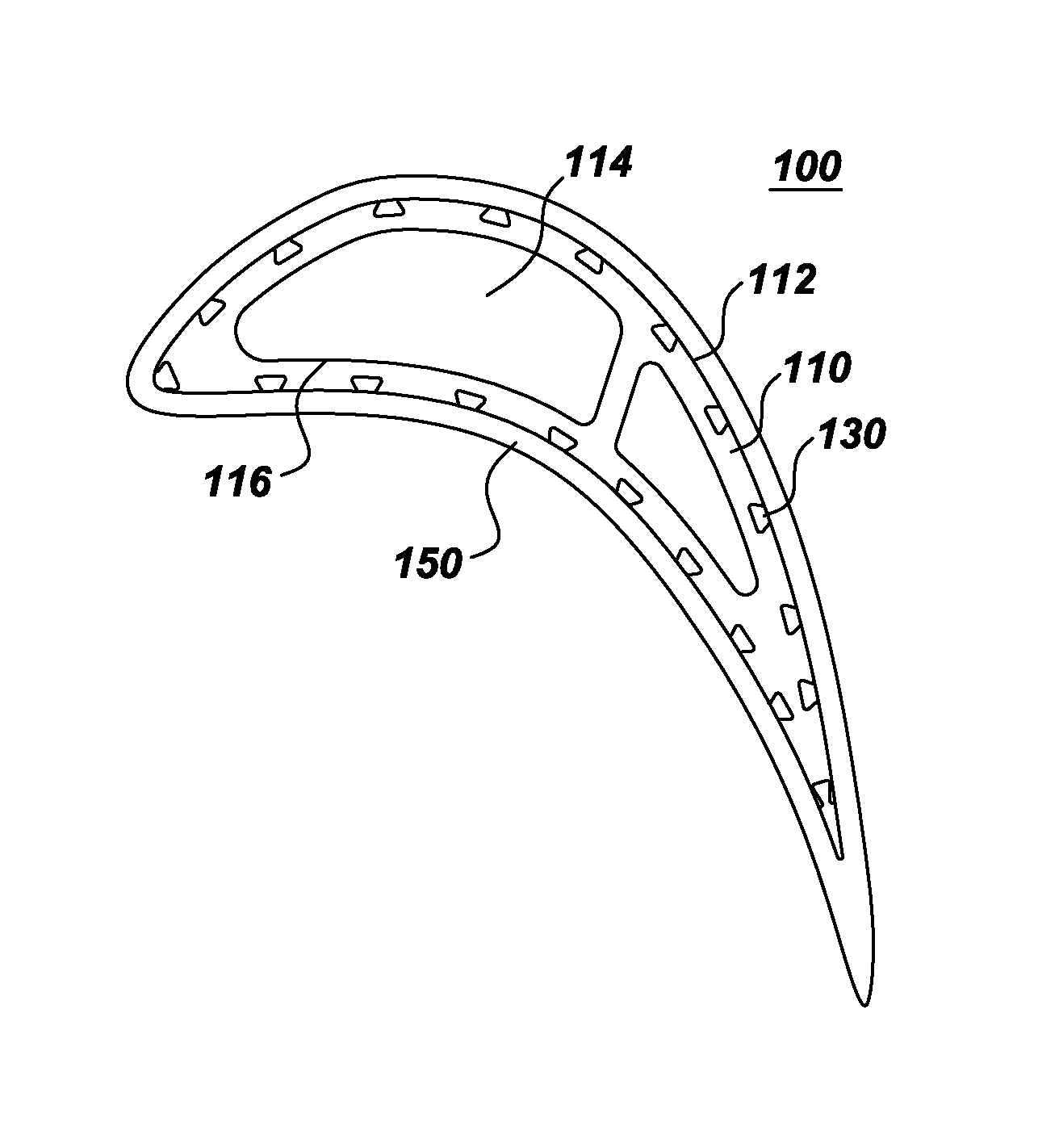
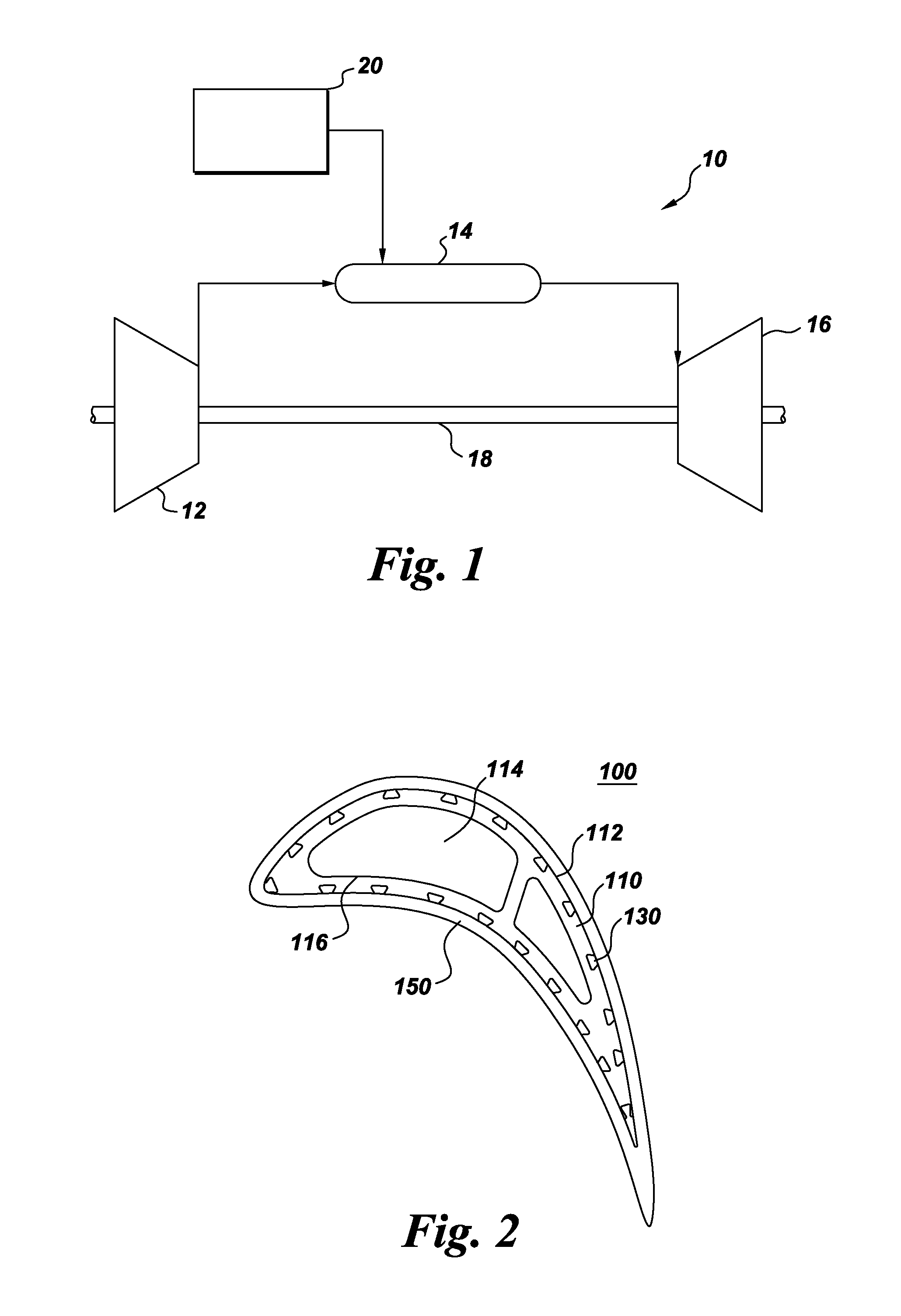
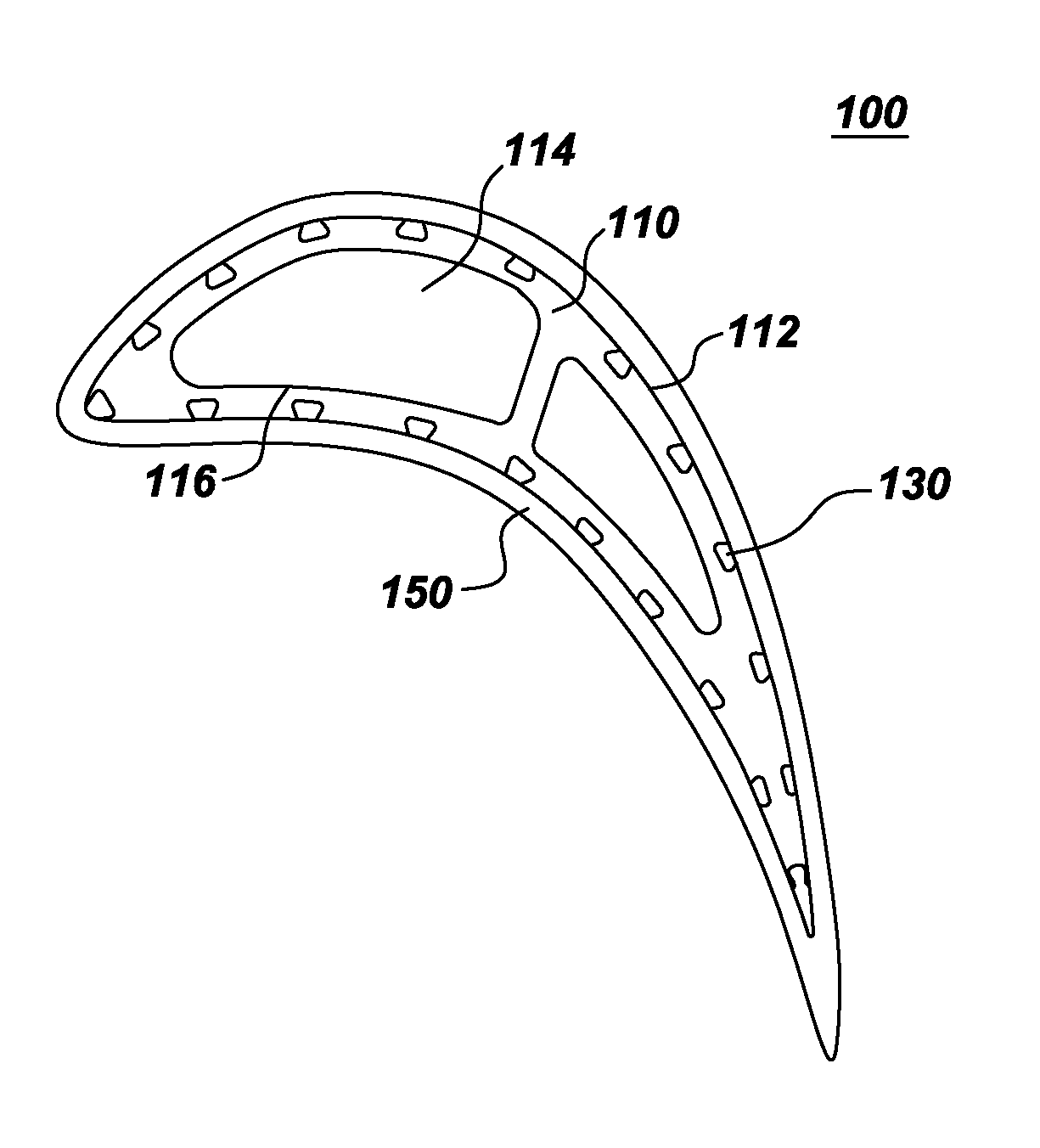
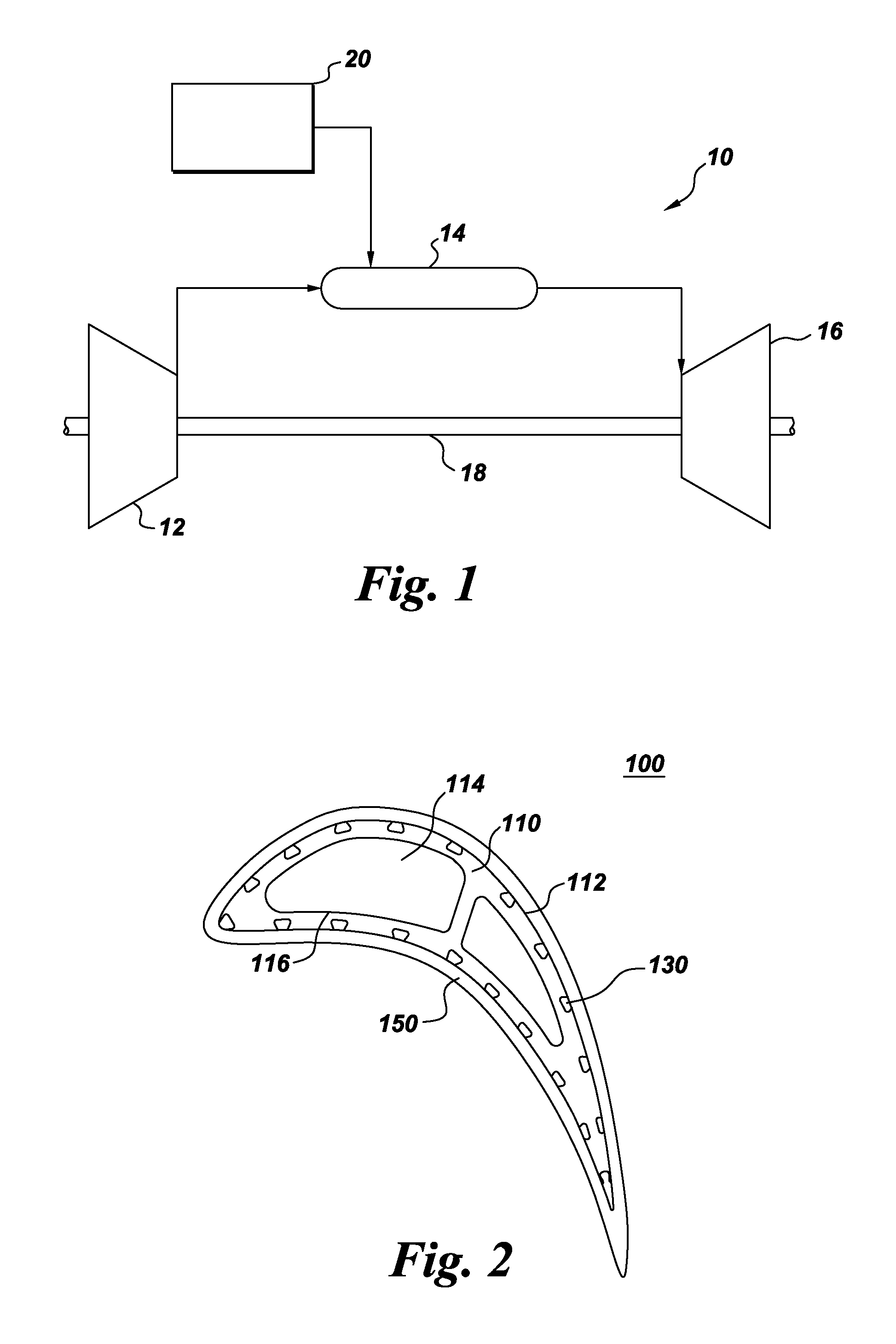
Components with re-entrant shaped cooling channels and methods of manufacture
A method of fabricating a component is provided. The method includes forming one or more grooves in a surface of a substrate, where the substrate has at least one hollow interior space. Each of the one or more grooves extends at least partially along the substrate surface and has a base and a top. The base is wider than the top, such that each of the one or more grooves comprises a re-entrant shaped groove. The method further includes forming one or more access holes through the base of a respective groove, to connect the groove in fluid communication with respective ones of the hollow interior space(s), and disposing a coating over at least a portion of the substrate surface. The one or more grooves and coating define one or more re-entrant shaped channels for cooling the component. A component with one or more re-entrant shaped channels and a method of coating a component are also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Resonator device, filter, composite filter device, duplexer, and communication device
In a cavity body, a conductor rod is provided with least one end thereof being electrically connected to the cavity. A dielectric core is disposed in the cavity and the conductor rod extends through a hole in the dielectric core. With this structure, the cavity and the conductor rod constitute a resonator which operates in the quasi-TEM mode of a re-entrant cylindrical cavity resonator. The cavity and the dielectric core constitute a resonator which operates in the quasi-TM mode.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Use of autonomic nervous system neurotransmitters inhibition and atrial parasympathetic fibers ablation for the treatment of atrial arrhythmias and to preserve drug effects
InactiveUSRE42961E1Increased occurrence of initiation of atrial flutterShorten the construction periodDiagnosticsHeart defibrillatorsNervous systemRight atrium
Atrial arrhythmias, a major contributor to cardiovascular morbidity, are believed to be influenced by autonomic nervous system tone. The main purpose of this invention was to highlight new findings that have emerged in the study of effects of autonomic nervous system tone on atrial arrhythmias, and its interaction with class III antiarrhythmic drug effects. This invention evaluates the significance of sympathetic and parasympathetic activation by determining the effects of autonomic nervous system using a vagal and stellar ganglions stimulation, and by using autonomic nervous system neurotransmitters infusion (norepinephrine, acetylcholine). This invention evaluates the autonomic nervous system effects on the atrial effective refractory period duration and dispersion, atrial conduction velocity, atrial wavelength duration, excitable gap duration during a stable circuit (such atrial flutter circuit around an anatomical obstacle), and on the susceptibility of occurrence (initiation, maintenance and termination) of atrial re-entrant arrhythmias in canine. This invention also evaluates whether autonomic nervous system activation effects via a local neurotransimitters infusion into the right atria can alter those of class III antiarrhythmic drug, sotalol, during a sustained right atrial flutter. This invention represents an emergent need to set-up and develop a new class of anti-cholinergic drug therapy for the treatment of atrial arrhythmias and to combine this new anti-cholinergic class to antiarrhythmic drugs. Furthermore, this invention also highlights the importance of a local application of parasympathetic neurotransmitters / blockers and a catheter ablation of the area of right atrium with the highest density of parasympathetic fibers innervation. This may significantly reduce the occurrence of atrial arrhythmias and may preserve the antiarrhythmic effects of any drugs used for the treatment of atrial re-entrant arrhythmias.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Ion sources and methods for generating an ion beam with controllable ion current density distribution
Ion sources and methods for generating an ion bean with a controllable ion current density distribution. The ion source includes a discharge chamber having an optical grid position proximate at a first end and a re-entrant vessel positioned proximate a second end that opposes the first end. A plasma shaper extends from the re-entrant vessel and into the plasma discharge chamber. A position of the plasma shaper is adjustable relative to the grid-based ion optic such that the plasma shaper may operably change a plasma density distribution within the discharge chamber.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Sprayed on superoleophobic surface formulations
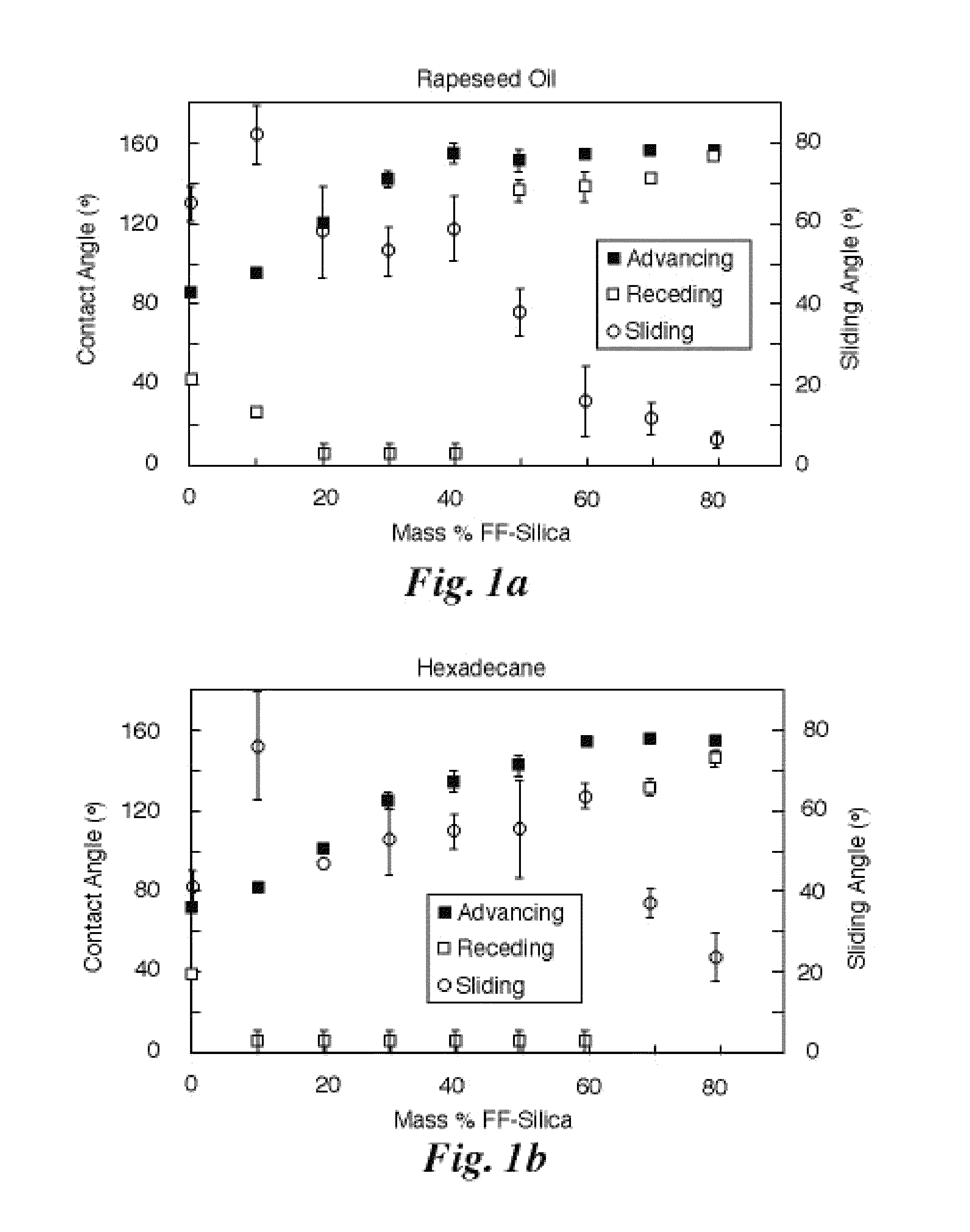
InactiveUS8580027B1Surface energy is lowLower surface energyGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsDispersed particle filtrationCelsius DegreeRe entrant
Fluoroalkylsilane-treated metal oxide particles and a fluoroelastomeric binder are dispersed in a fluorinated solvent with a low boiling point and applied to a substrate via spray deposition. The spray deposition process rapidly produces a conformal coating that features low surface energy and surface topography with a large range of characteristic length scales and re-entrant curvature, thereby imparting superoleophobicity. The degree of superoleophobicity is readily adjusted by means of altering the ratio of particles to binder. The choice of particle and binder result in coatings with thermal stability for thousands of hours at temperatures up to 200 degrees Celsius as well as desirable mechanical characteristics.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Wire pass through seal with grommets
InactiveUS6927338B2Sealing interengagementPrecise positioningPipesStands/trestlesElectrical conductorRe entrant
A tubular grommet for sealing a conductor relative to a substrate having opposite sides and an opening therethrough for the conductor has axially opposite ends, one of which sealing engages with the conductor and the other of which is radially spaced from the conductor, diametrically larger than the opening through the substrate, and includes a radially outwardly extending peripheral flange for engaging against the substrate when the grommet is mounted thereon. A wall between the ends includes first and second re-entrant wall portions facing the one end, and the grommet can be provided with a recess in the wall adjacent the flange for receiving the peripheral edge of the opening through the substrate and / or can be adhesively bonded to the substrate by an adhesive interposed between the flange and substrate.
Owner:KEY CAPITAL +2
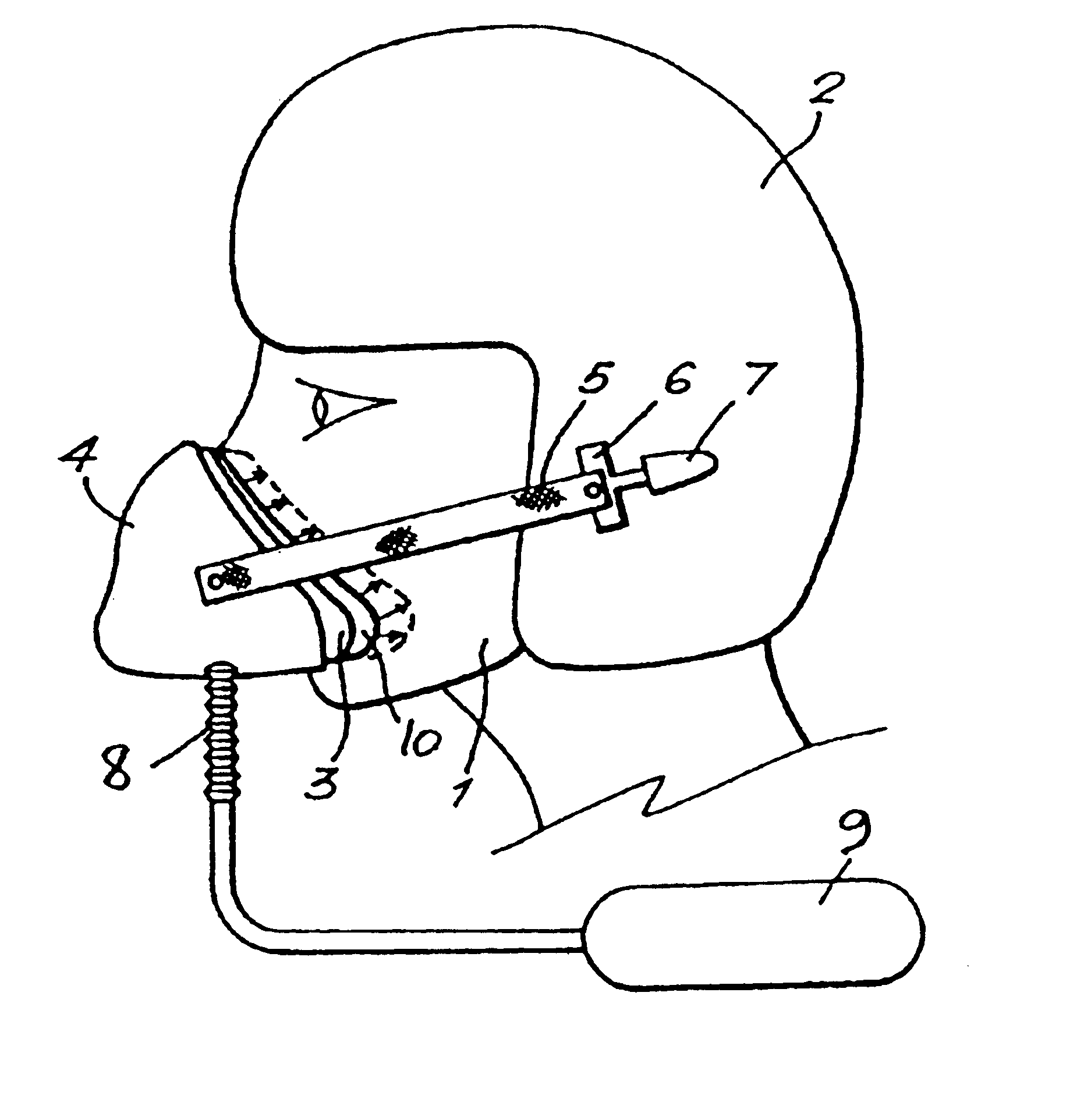
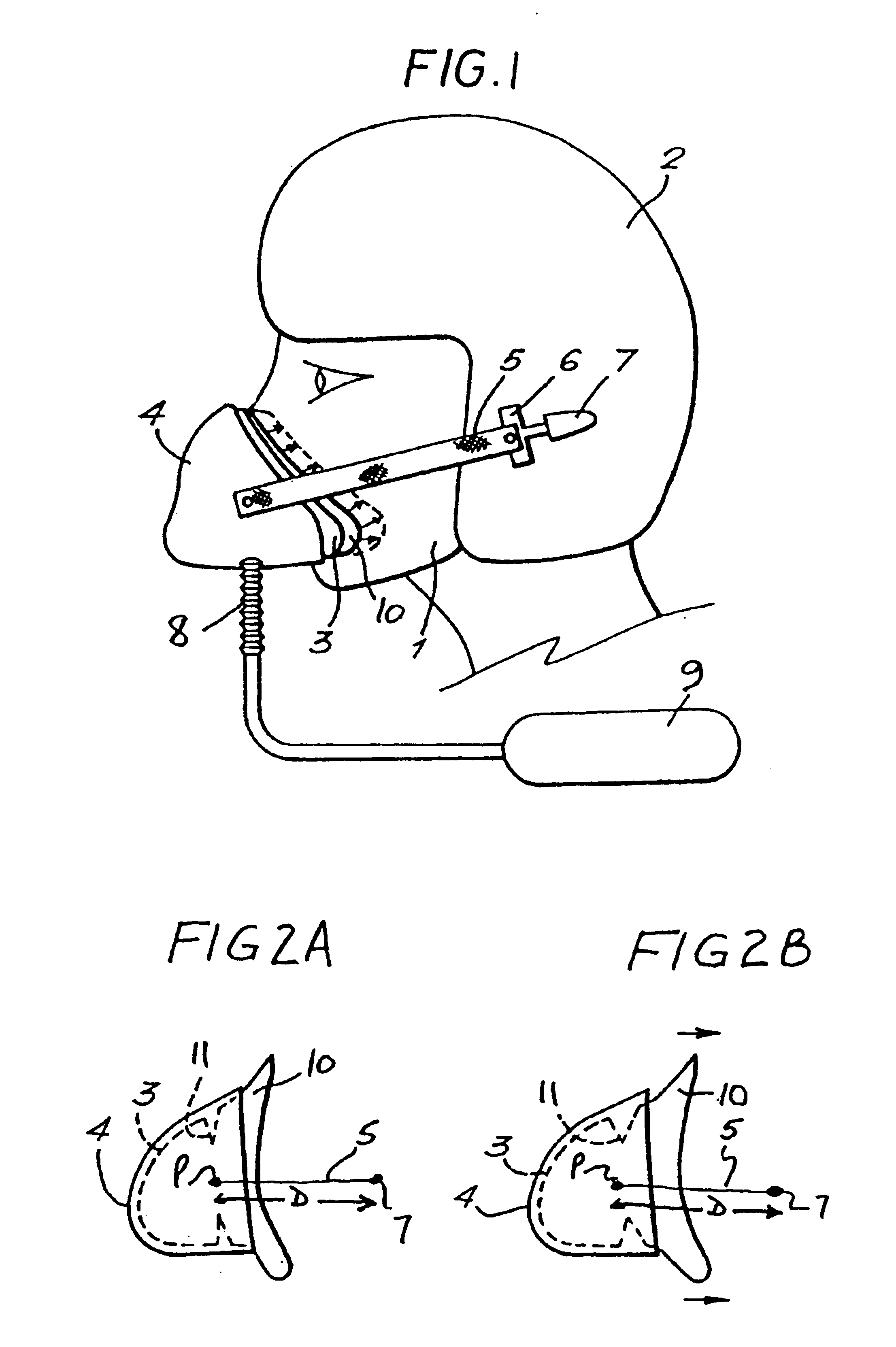
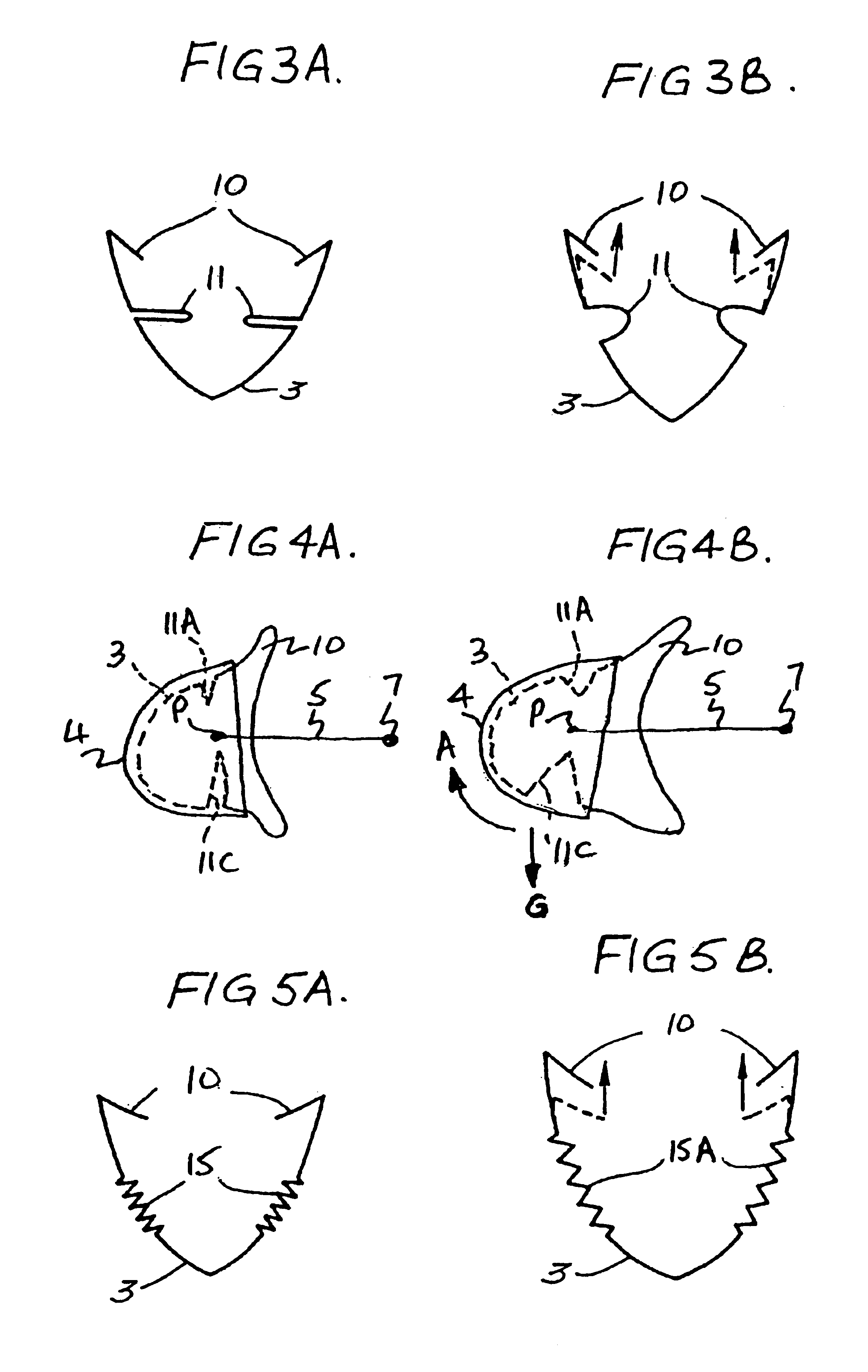
High G oxygen mask for aircrew
A flexible oro-nasal mask for mounting in a rigid shell attached to the helmet of aircrew at a fixed distance therefrom. The flexible oro-nasal mask incorporates an inspiratory and expiratory valve and the periphery of the mask is adapted to make a seal with the pilot's face. The oro-nasal mask includes an extendable structure which presses the periphery of the mask automatically towards the pilot's face to improve the seal therewith when gas at a pressure above that required for normal breathing is supplied to the mask. The extendable structure is configured so that when gas at a high pressure is supplied to the interior of the mask, the portion in the bottom region of the mask extends more than the portion in the upper region of the mask and the bottom of the mask is moved away from the wearer's face by a greater amount in the chin region than the nose region and the mask pivots upwardly automatically to compensate for the effects of G thereon. One embodiment of an extendable structure comprises an annular inwardly directed re-entrant recess formed in the wall of the mask adjacent the peripheral seal, the depth of said recess in the bottom half of the mask being greater than the depth in the top half thereof.
Owner:GRIFFITHS JOSEPH ANTHONY
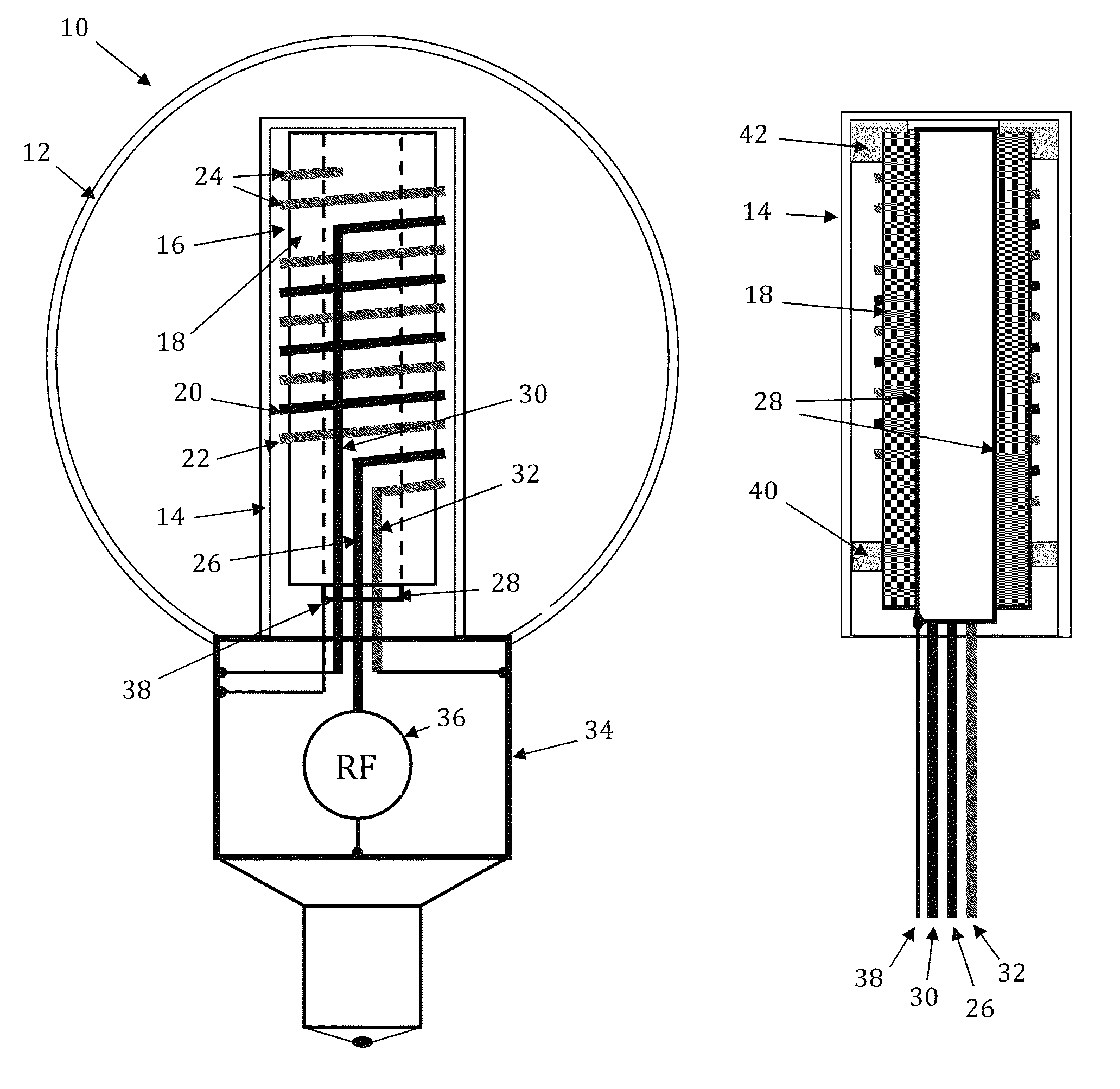
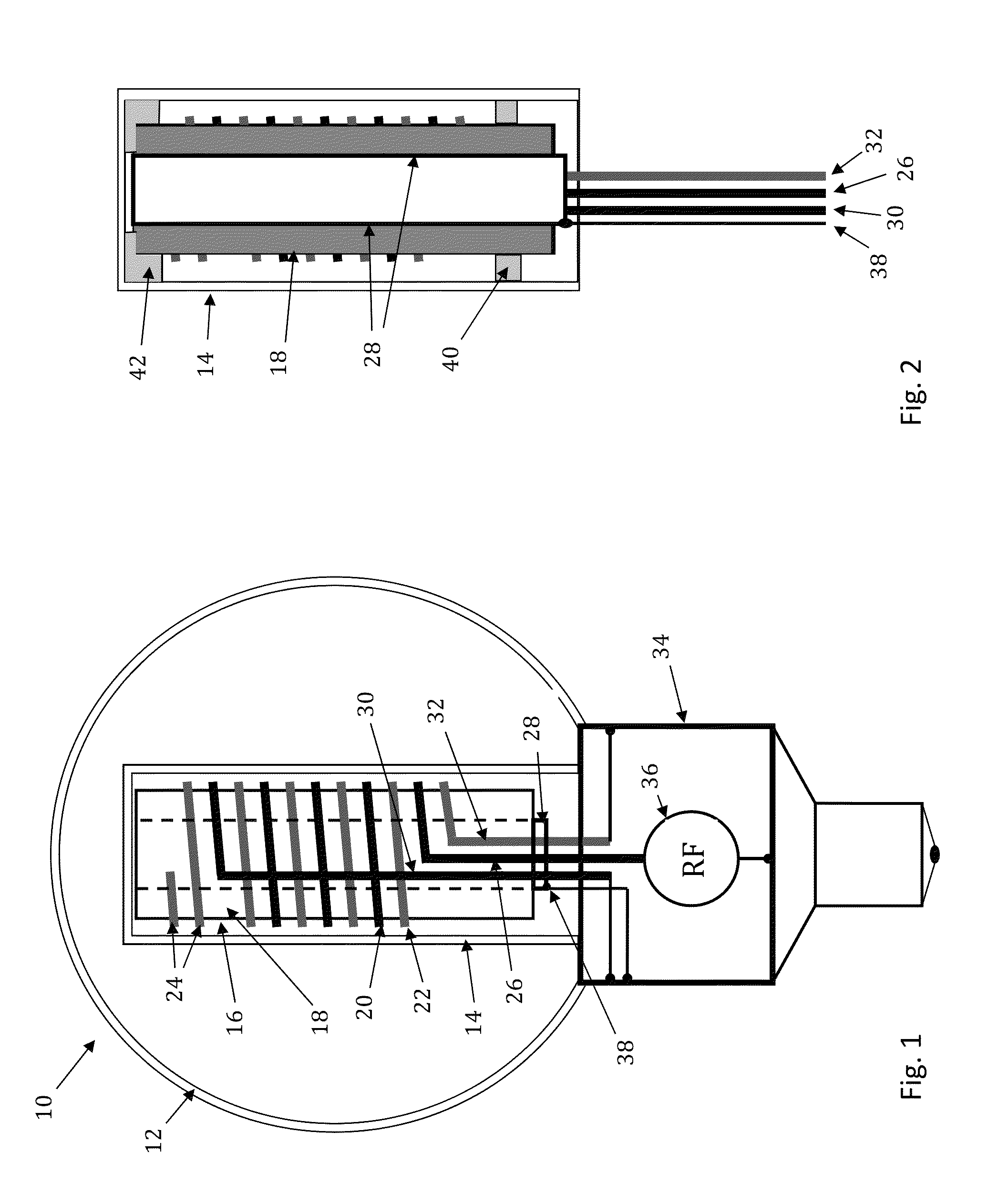
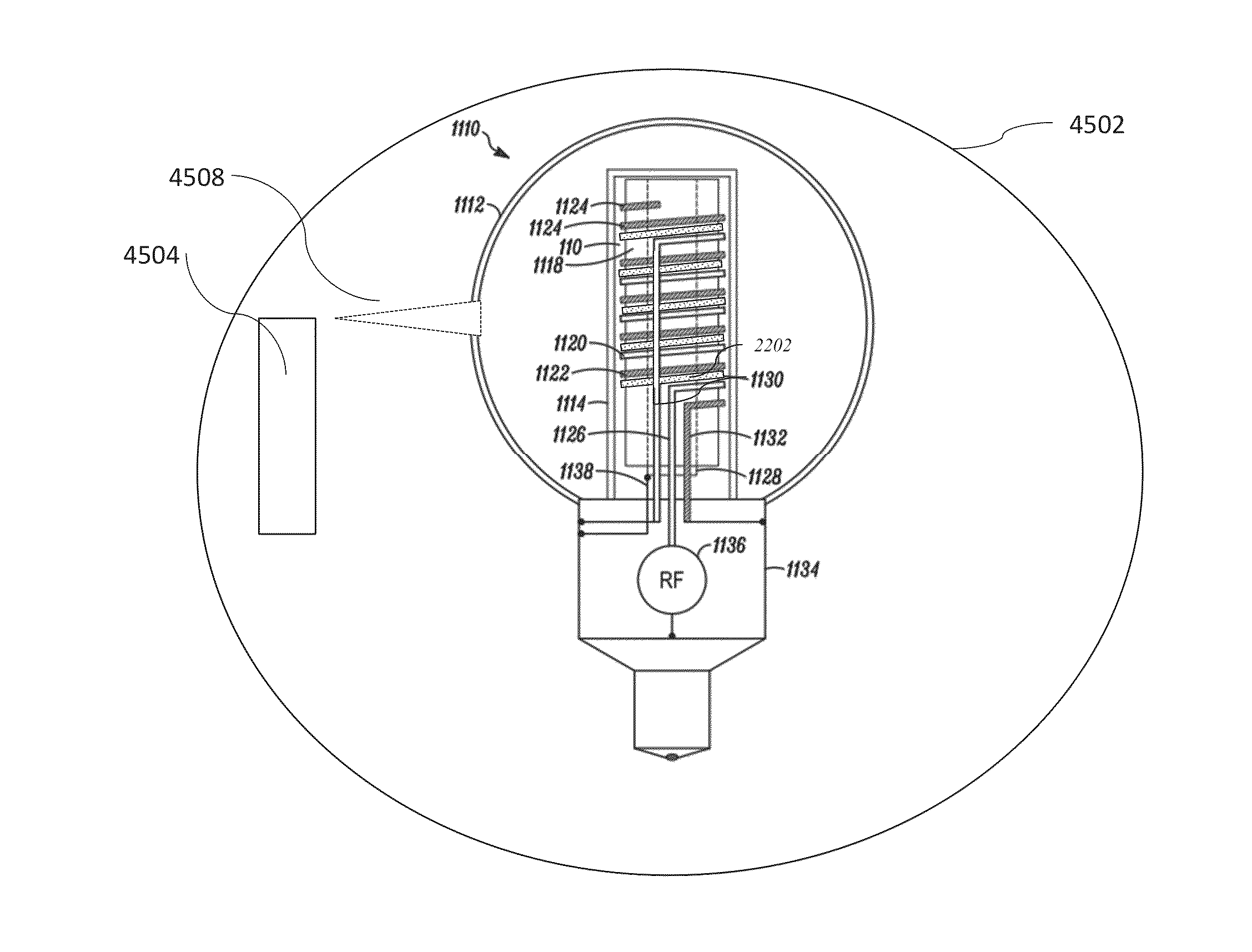
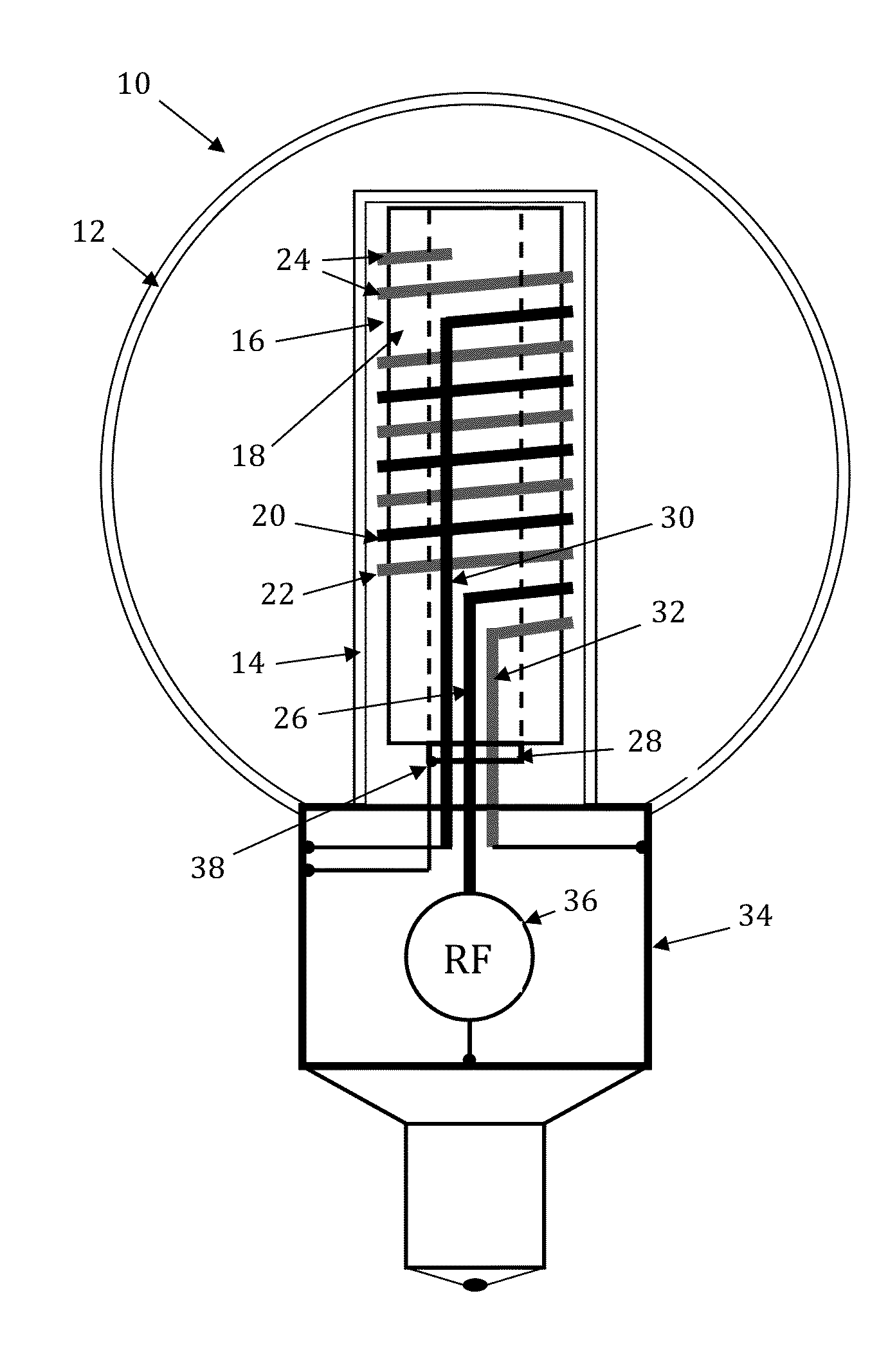
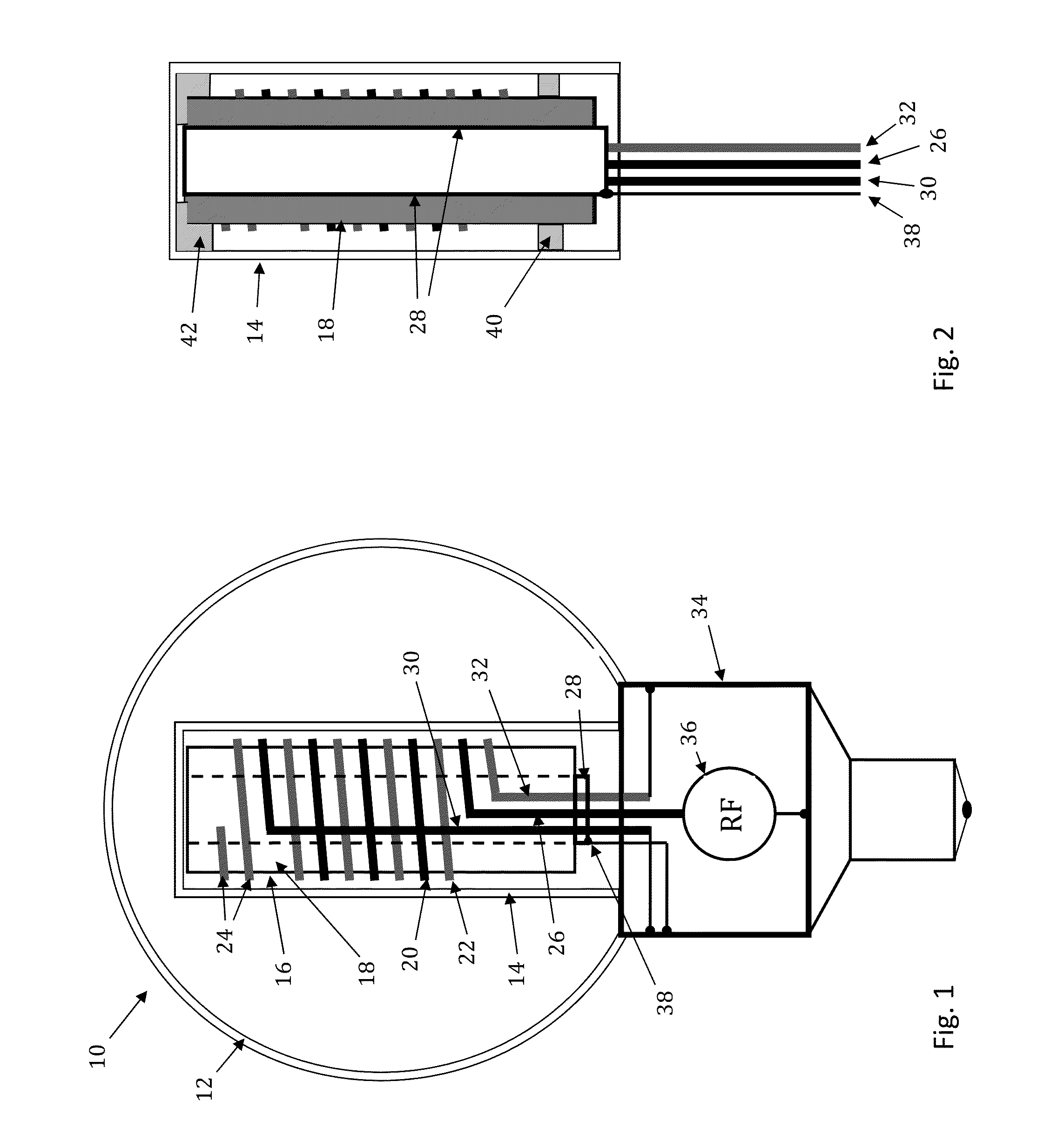
RF coupler stabilization in an induction RF fluorescent light bulb
ActiveUS20140145591A1Increase RF coupler positional stabilizationImprove structural supportAntenna supports/mountingsElectric lighting sourcesPhosphorRe entrant
An induction RF fluorescent light lamp capable of providing increased structural support and axial alignment for a power coupler located in a re-entrant cavity of a lamp envelope of the induction RF fluorescent light lamp, the lamp envelope with re-entrant cavity both covered on a partial vacuum side with phosphor and filled with a working gas mixture, the re-entrant cavity having an open entrance end and a closed innermost end, and a pliable spacer positioned between and in contact with both the innermost end of the power coupler and the innermost end of the re-entrant cavity, the pliable spacer having a shape that both provides structural support to prevent movement of the power coupler with respect to the re-entrant cavity and to provide axial alignment of the power coupler to the re-entrant cavity.
Owner:LUCIDITY LIGHTS
RF induction lamp with reduced electromagnetic interference
InactiveUS20140145609A1Low costReduce conductive electromagnetic interference (EMI) levelSolid cathode detailsStructural circuit elementsPhosphorElectromagnetic interference
An induction RF fluorescent lamp configuration providing reduced EMI includes a lamp envelope with a re-entrant cavity both covered on a partial vacuum side with phosphor and filled with a working gas mixture, a tubular ferromagnetic core on the non-vacuum side said re-entrant cavity wound directly on the said core with two windings having different numbers of turns, a first active winding having one end connected to an RF ballast and the other end connected to local ground, and a second passive winding having one end grounded and the other end free.
Owner:LUCIDITY LIGHTS
Method and apparatus for the controlled formation of cavitation bubbles using target bubbles
The present invention discloses a method and apparatus for the directed formation of a re-entrant micro-jet formed upon the collapse of a working cavitation bubble formed proximate to a work surface. A target bubble, formed between the work surface and the working cavitation bubble, is utilized to direct the re-entrant micro-jet to the work surface.
Owner:LECLAIR MARK L
Fast start RF induction lamp with ferromagnetic core
InactiveUS20140145593A1Maximize absorption of powerFast heatingAntenna supports/mountingsElectric lighting sourcesFluorescenceRe entrant
An induction RF fluorescent lamp, comprising a lamp envelope and re-entrant cavity filled with a fluorescing gas mixture, a power coupler receiving an alternating voltage and current to generate an alternating magnetic field and thereby inducing an alternating electric field within the lamp envelope, a first metallic structure mounted within the lamp envelope in such a location and orientation to rapidly heat and vaporize mercury to promote rapid luminous development during the turn-on phase of the induction RF fluorescent lamp and a second metallic structure so as to promote electrical breakdown of the fluorescing gas mixture during the turn-on phase of the induction RF fluorescent lamp.
Owner:LUCIDITY LIGHTS
RF induction lamp with isolation system for air-core power coupler
InactiveUS20140320005A1Lower impedanceHigh impedanceAntenna supports/mountingsElectric lighting sourcesElectricityElectrical conductor
An induction RF fluorescent lamp includes a lamp envelope with a re-entrant cavity both covered on a partial vacuum side with phosphor and filled with a working gas mixture; an air-core power coupler on the non-vacuum side of said re-entrant cavity comprising a coil composed of at least one turn of an electrical conductor; an electronic ballast, wherein the ballast converts mains frequency voltage and current to a power coupler frequency voltage and current, the electronic ballast providing the voltage and current to the power coupler through at least two of a plurality of electrical terminals of the electronic ballast; and a capacitor electrically connected between the air-core power coupler and at least one of the plurality of electrical terminals of the electronic ballast, wherein the magnitude of the impedance of the capacitor is high at the mains frequency and the magnitude of the impedance of that same capacitor is low at the operating frequency of the RF fluorescent lamp.
Owner:LUCIDITY LIGHTS
Ion sources and methods for generating an ion beam with controllable ion current density distribution
ActiveUS8835869B2Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsGratingIon beam
Ion sources and methods for generating an ion bean with a controllable ion current density distribution. The ion source includes a discharge chamber having an optical grid position proximate at a first end and a re-entrant vessel positioned proximate a second end that opposes the first end. A plasma shaper extends from the re-entrant vessel and into the plasma discharge chamber. A position of the plasma shaper is adjustable relative to the grid-based ion optic such that the plasma shaper may operably change a plasma density distribution within the discharge chamber.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
RF induction lamp with ferrite isolation system
InactiveUS8901842B2Lower impedanceHigh impedanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
An induction RF fluorescent lamp includes a lamp envelope with a re-entrant cavity both covered on a partial vacuum side with phosphor and filled with a working gas mixture; a power coupler on the non-vacuum side of said re-entrant cavity comprising a ferromagnetic core overwound with at least one turn of an electrical conductor; an electronic ballast, wherein the ballast converts mains frequency voltage and current to a power coupler frequency voltage and current, the electronic ballast providing the voltage and current to the power coupler through at least two of a plurality of electrical terminals of the electronic ballast; a capacitor electrically connected between the ferromagnetic core and at least one of the plurality of electrical terminals of the electronic ballast, wherein the magnitude of the impedance of the capacitor is high at the mains frequency and the magnitude of the impedance of that same capacitor is low at the operating frequency of the RF fluorescent lamp.
Owner:LUCIDITY LIGHTS
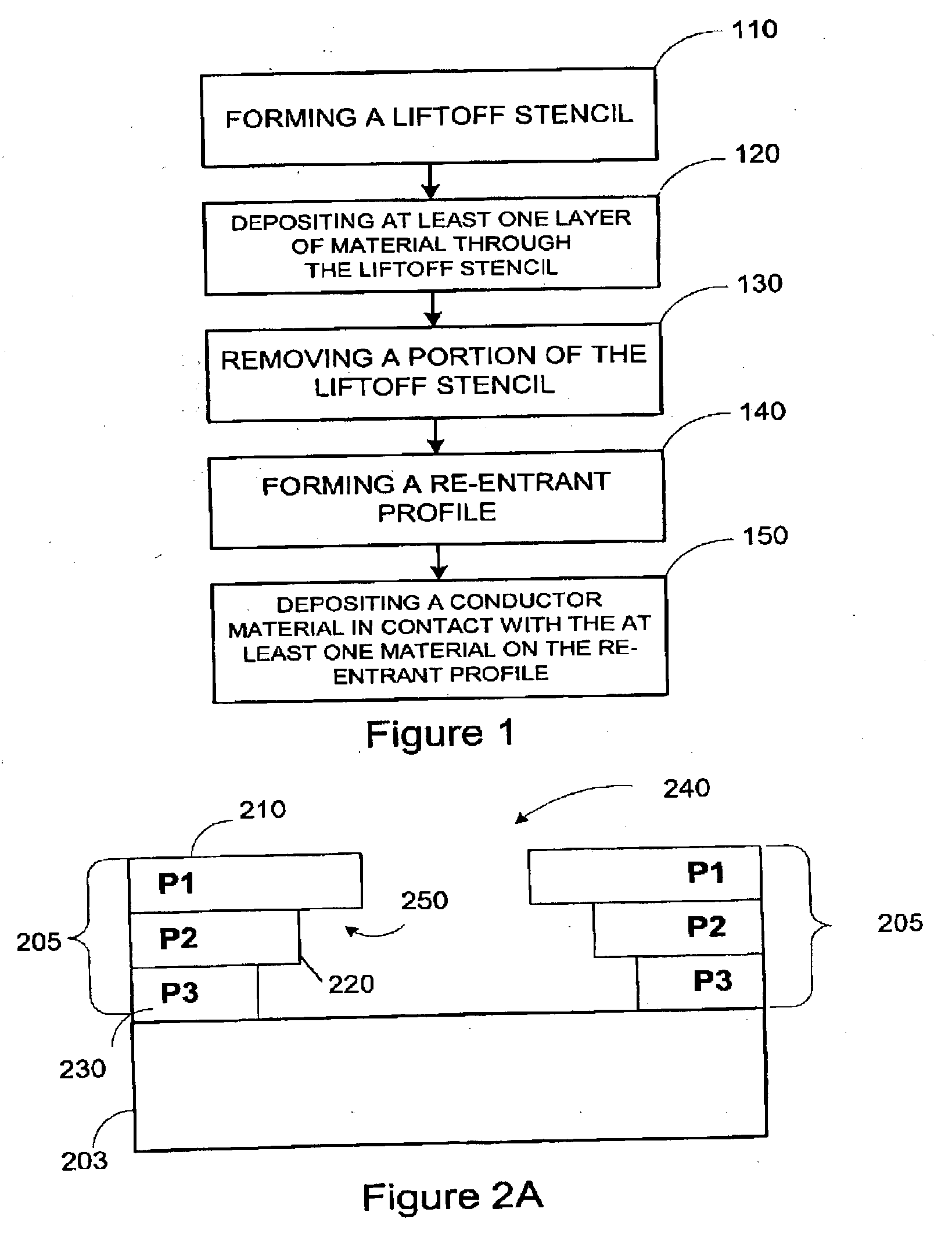
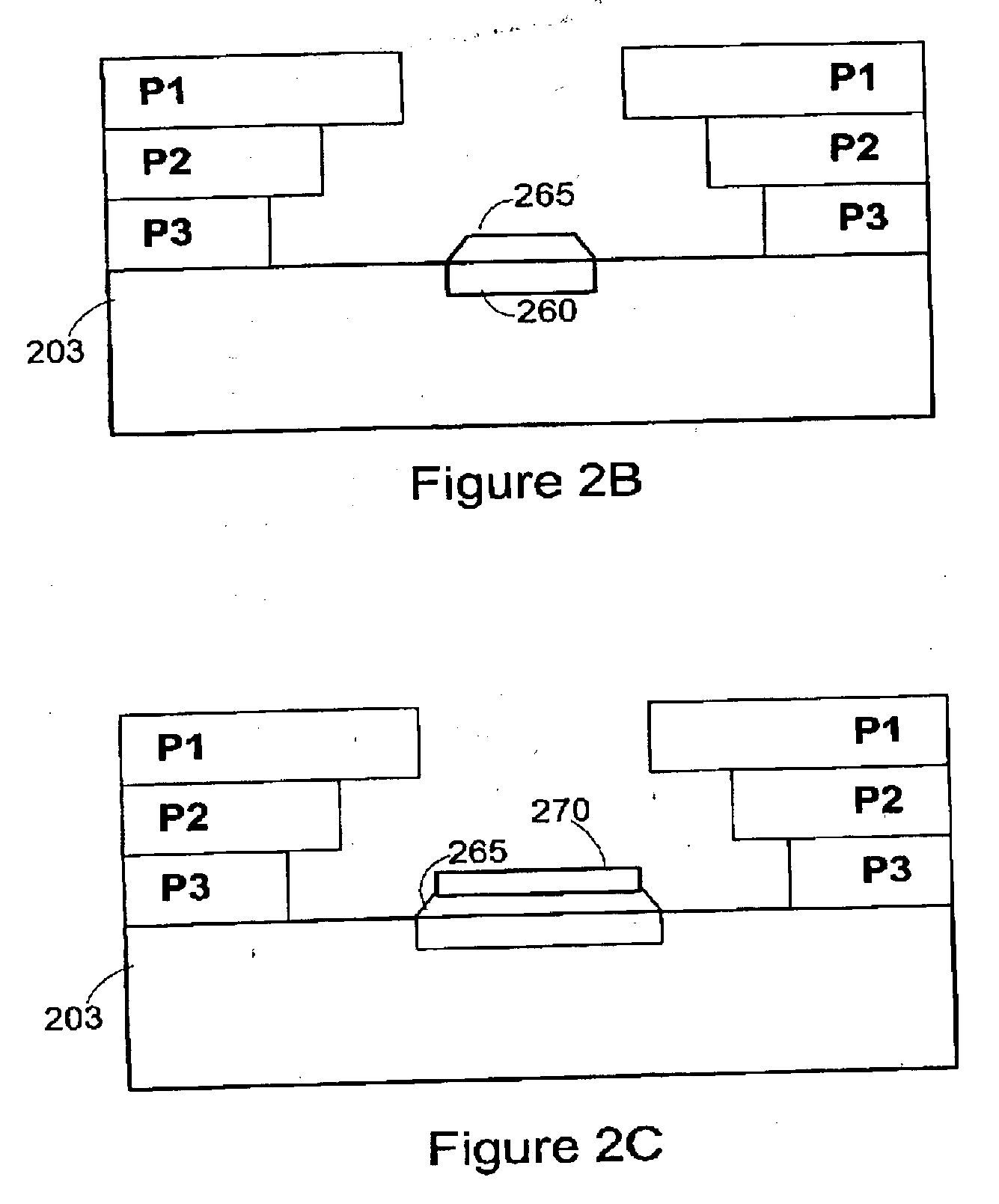
Forming a contact in a thin-film device
InactiveUS20050170628A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device manufacture/treatmentElectrical conductorEngineering
Owner:DATA QUILL
Components with re-entrant shaped cooling channels and methods of manufacture
A method of fabricating a component is provided. The component includes a substrate that has at least one interior space. The method includes forming one or more grooves in the component. Each groove extends at least partially along an outer surface of the substrate and narrows at an opening thereof, such that each groove is re-entrant shaped. A cross-sectional area A of each groove is in a range of about 2 to about 3 times an area R=W*D, where W is the width of the opening and D is the depth of the re-entrant-shaped groove. Components with grooves formed in the substrate and components with grooves formed at least partially in a structural coating are also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for forming a lithium-ion type battery
ActiveUS20140038028A1Small thicknessFinal product manufactureSmall-sized flat cells/batteriesEngineeringRe entrant
A method for manufacturing a lithium-ion type battery including the steps of forming in a substrate a recess having lateral walls having a re-entrant profile; depositing, by successive non-conformal physical vapor depositions, a stack of the different layers forming a lithium-ion battery, this stack having a thickness smaller than the depth of the recess; depositing on the structure a filling layer filling the space remaining in the recess; and planarizing the structure to expose the upper surface of the stack.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Calendar interface
ActiveUS20170124517A1Office automationInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceRe entrant
Described herein is a computer implemented method for generating a calendar interface. The method includes determining a total time period value indicating a total time period to be displayed, determining a segment duration, determining an interval duration, calculating timeline coordinates defining a timeline extending from a foreground of the display to a background of the display and having a perspective appearance, and displaying a timeline in accordance with the timeline coordinates. The timeline coordinates define the timeline to have a plurality of segments, each segment representing a period of time within the total time period equal to the segment duration. Each segment is composed of a plurality of timeline intervals, each timeline interval representing a period of time within the total time period equal to the interval duration. Each segment has a display length, and wherein the display length of a segment representing an earlier period of time is longer than a display length of a segment representing a later period of time. A given segment travels in a direction that is re-entrant relative to a direction travelled by an adjacent segment.
Owner:MRP SYST
Re-entrant structure for thin disk resonators
ActiveUS20090059991A1Low saturated gain levelReduce wavefront error buildupOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionComputational physicsRe entrant
The present embodiment provides a system and method for lowering the saturated gain level of a thin-disk laser oscillator by multipassing each gain generator in such a way to cancel some of the wavefront error contributions from the disk surfaces. Wavefront aberrations introduced on one pass of the gain disk are canceled through symmetry on successive passes. The reduced wavefront error significantly improves design space for single-mode resonators. Maximum effectiveness is achieved by rotating the gain disk so that the fold plane-of-symmetry reverses the largest wavefront error or specifically chosen functional forms.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Methods of manufacturing illumination systems
InactiveUS20120047715A1Printed circuit assemblingContact member assembly/disassemblyEngineeringRe entrant
Methods of manufacturing light panels having at least one re-entrant turning feature. In one embodiment, a method of manufacturing a light panel includes providing a base layer, providing a cover layer, and coupling the cover layer to the base layer to form at least one re-entrant turning feature between the base layer and the cover layer. In another embodiment, a method of manufacturing a light panel includes providing a base layer, forming at least one receiving space in the base layer, providing at least one prismatic block, and coupling at least a portion of the prismatic block into the receiving space such that re-entrant turning features are formed between the prismatic block and the base layer.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
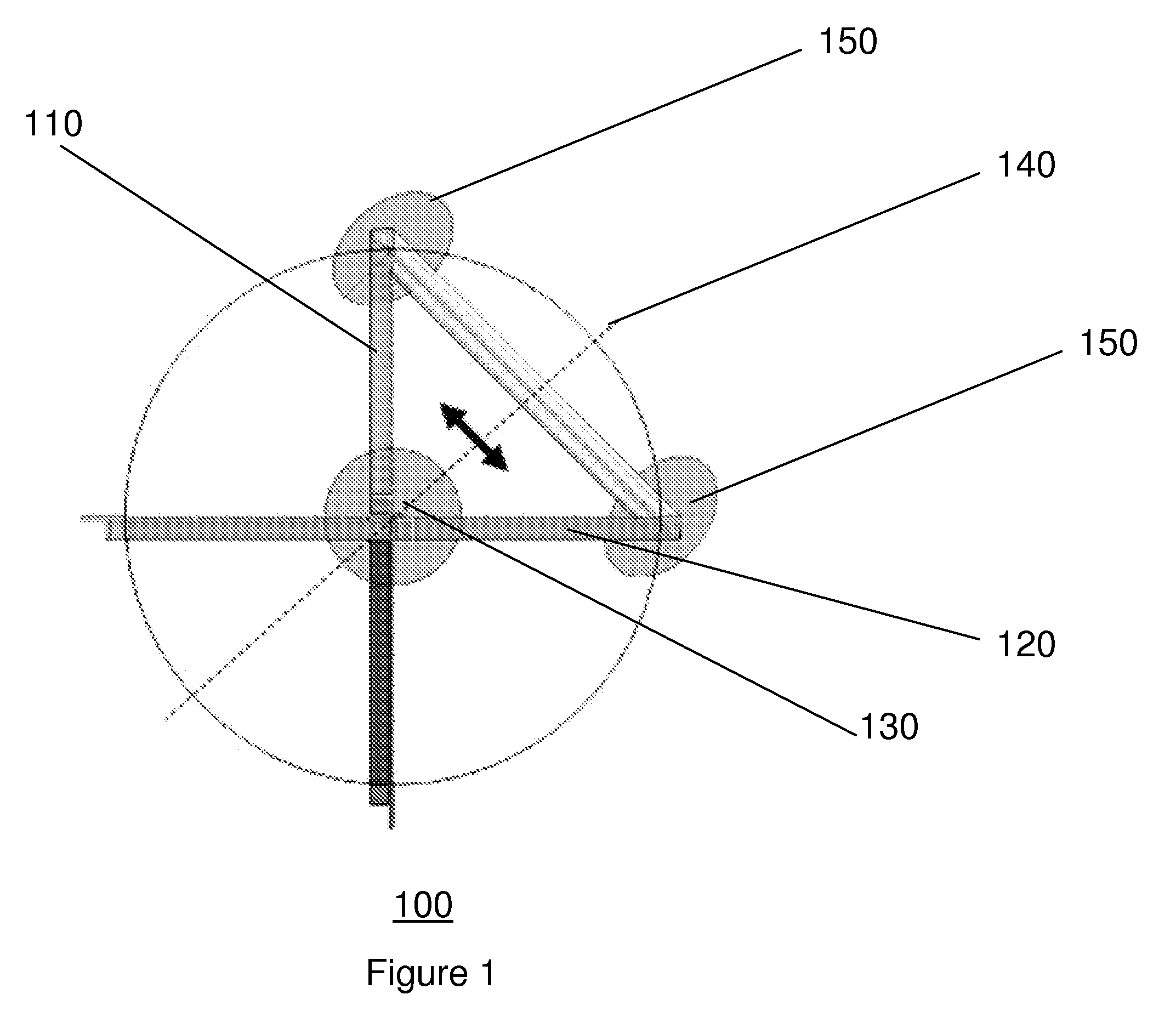
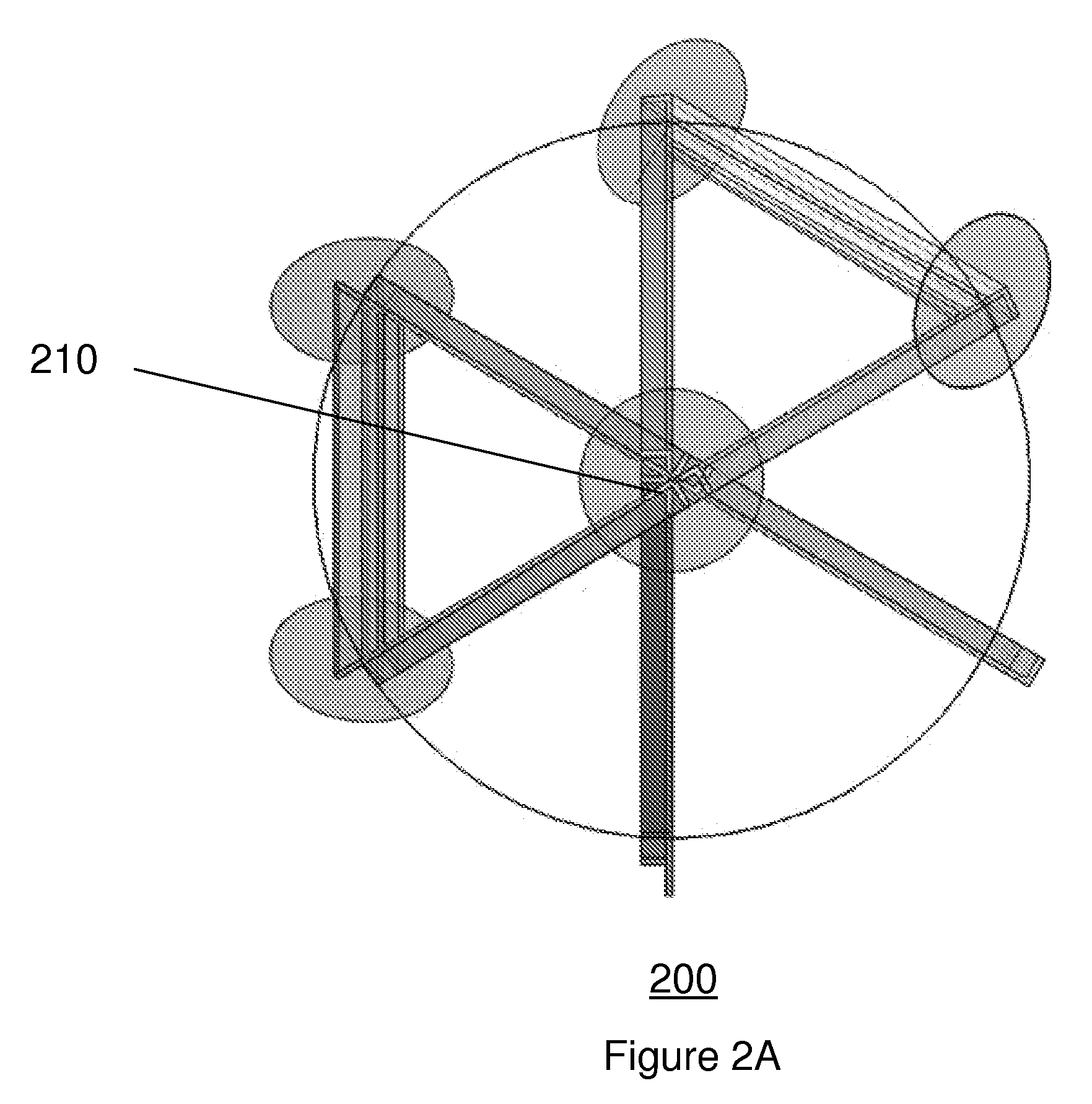
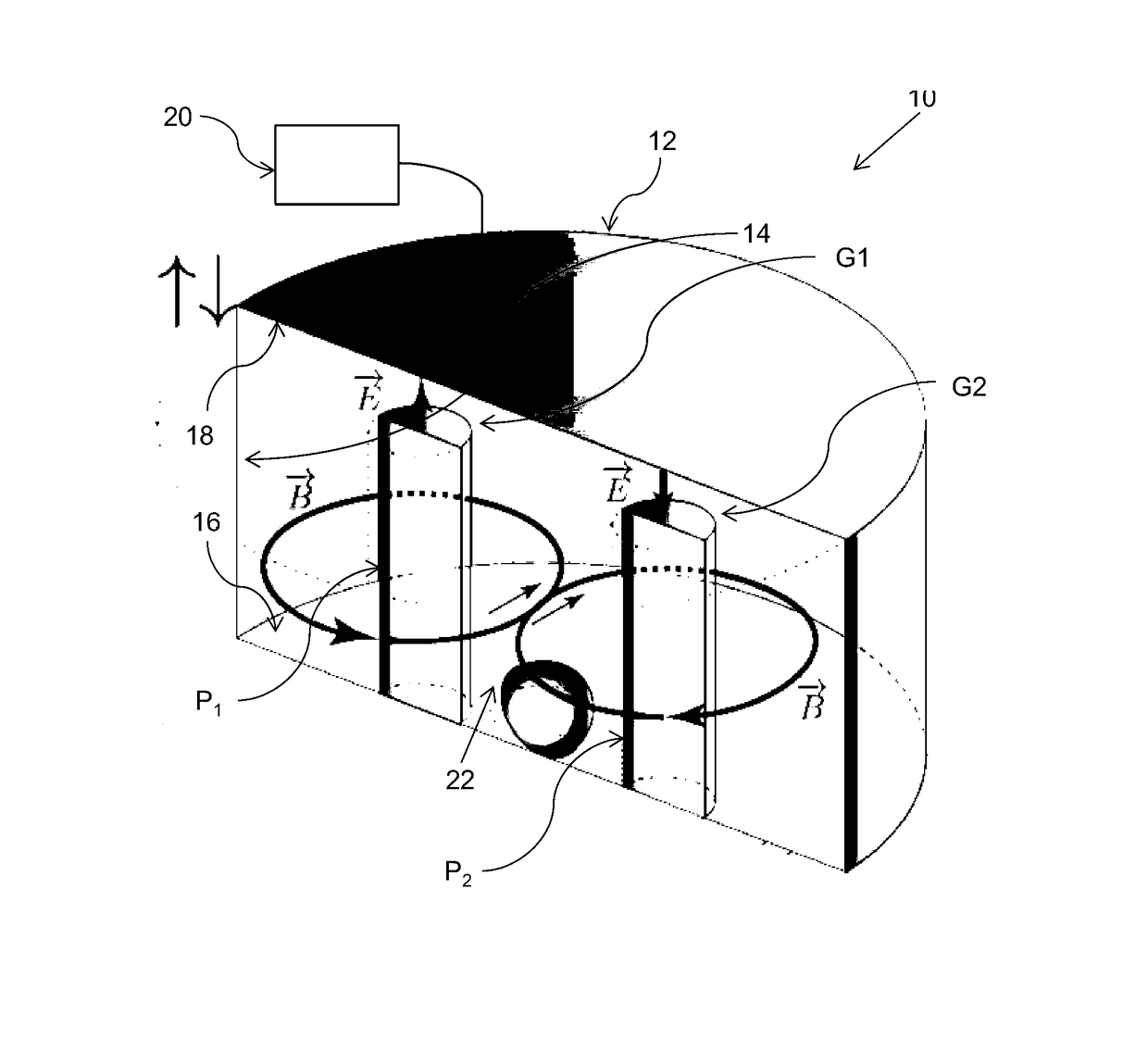
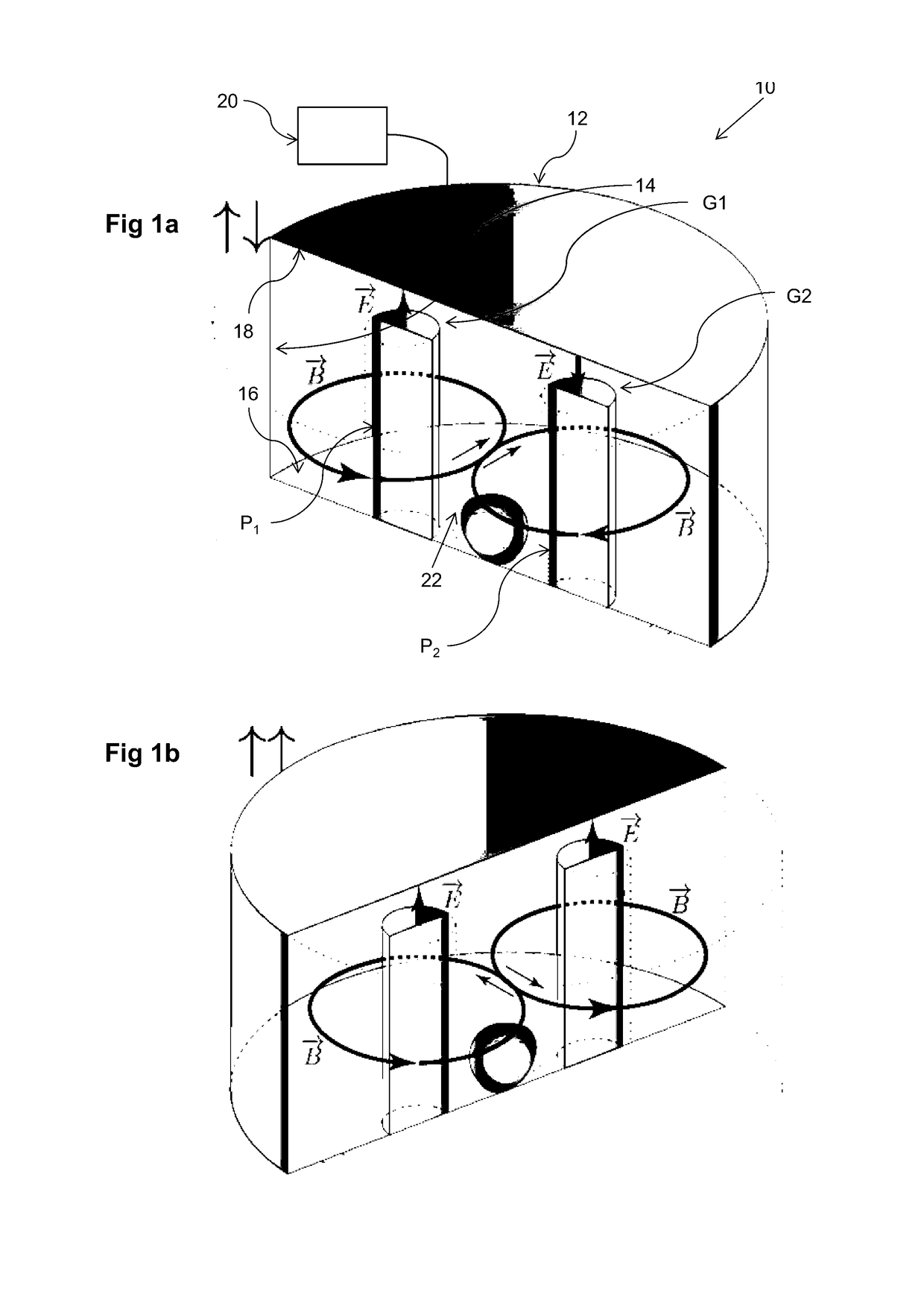
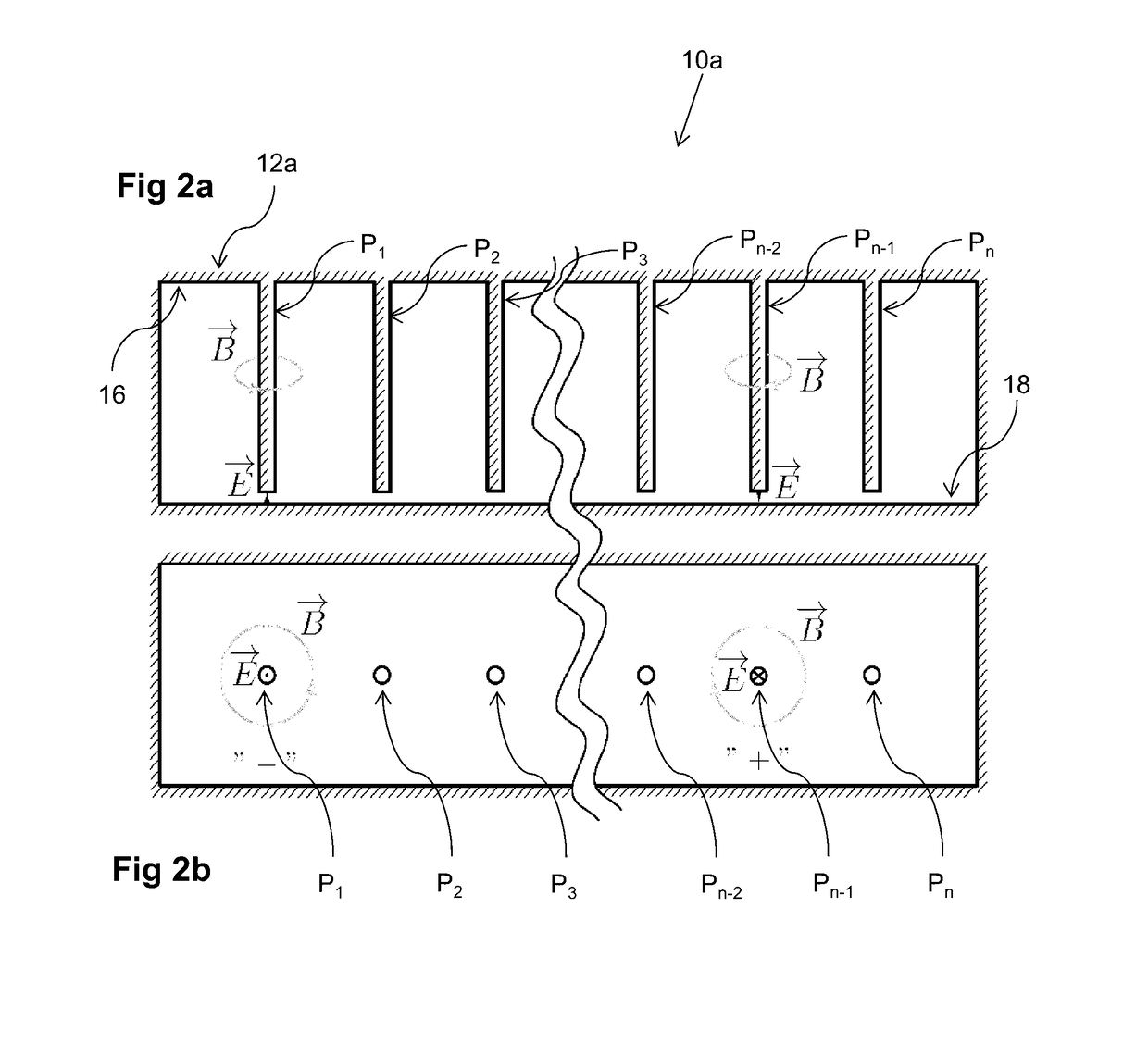
Microwave frequency magnetic field manipulation systems and methods and associated application instruments, apparatus and system
A microwave frequency magnetic field manipulation system (10) comprises a re-entrant microwave cavity (12) having a substantially continuous and closed internal surface (14) with at least two opposite sides (16 and 18). Two or more posts, P1, P2, . . . Pn (hereinafter referred to in general as “posts P”) are provided in the cavity (12). The posts P are in physical and more particularly electrical contact with one of the sides 16. Respective gaps G atre or can be formed between free ends of the posts P and the side (18). The system (10) also has a signal source (20) coupled to the cavity (12) for supplying microwaves. The source (20) supplies microwave signals at frequencies that facilitate the generation of magnetic fields in opposite directions about at least two mutually adjacent posts P. Accordingly the magnetic field is reinforced in a common region (22) between the mutually adjacent posts P.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
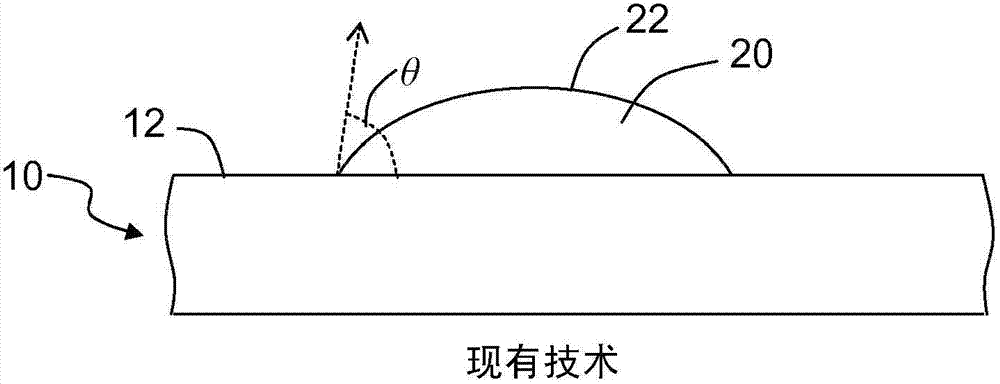
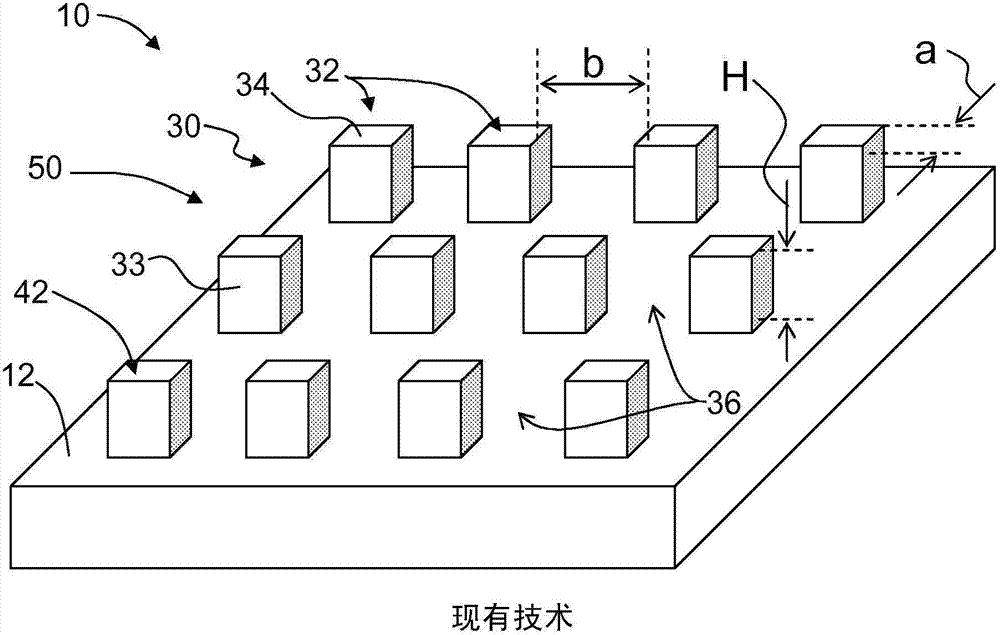
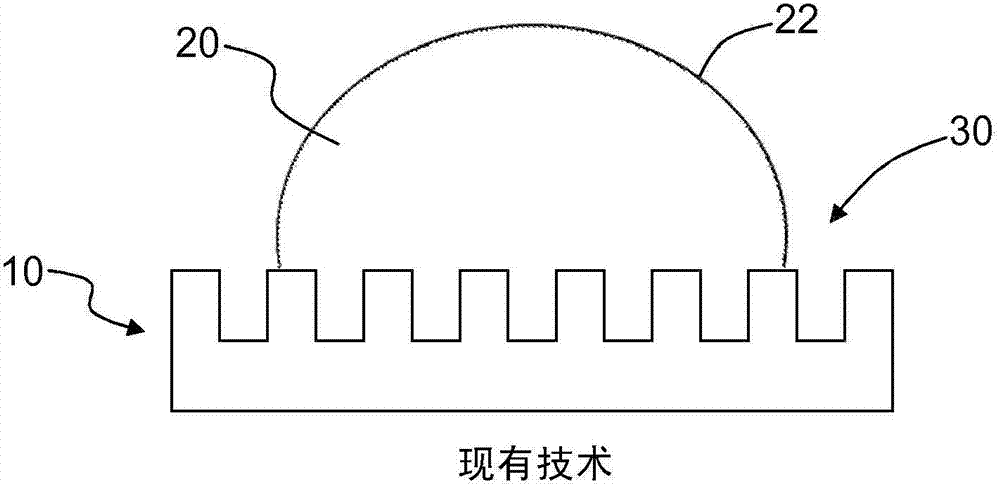
Superoleophobic substrates and methods of forming same
Superoleophobic substrates (110) and methods of forming same are disclosed. The methods include providing a laser-ablatable substrate (10) comprising glass and directing a laser beam (122) to the substrate surface (12) and laser-ablating at least a portion thereof to form an array of spaced-apart micropillars (232) having sidewalls (233). The laser beam is provided with sufficient energy to form on the sidewalls an irregular rough surface with re-entrant microscale and nanoscale features that render the substrate surface superoleophobic when coated with a low-surface-energy coating (246).
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com