Superoleophobic substrates and methods of forming same
An oleophobic, substrate technology that can be used in the manufacture of tools, transportation and packaging, welding/welding/cutting items, etc., which can solve the problems of long time and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
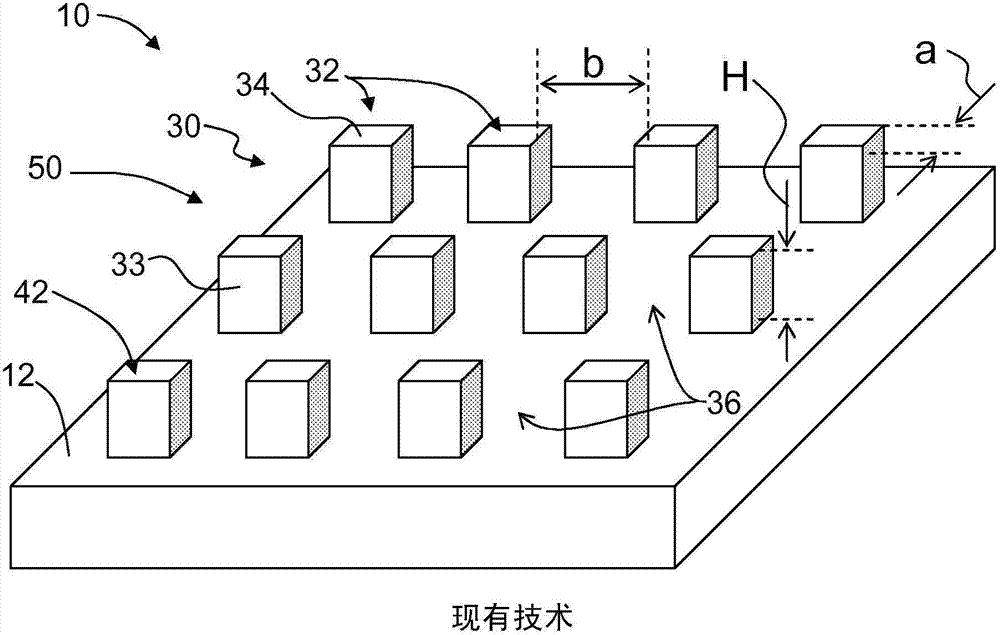
[0048] Various embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below, and examples of these embodiments are shown in the accompanying drawings. Whenever possible, the same or similar reference numerals are used in all the drawings to denote the same or similar parts. In the following discussion, the symbol "~" means "about". In addition, the term "micropillars" does not necessarily mean micrometers, but indicates that micropillars are very small relative to liquid droplets, and they can be nanometers, micrometers, millimeters, and combinations thereof.
[0049] Contact angle
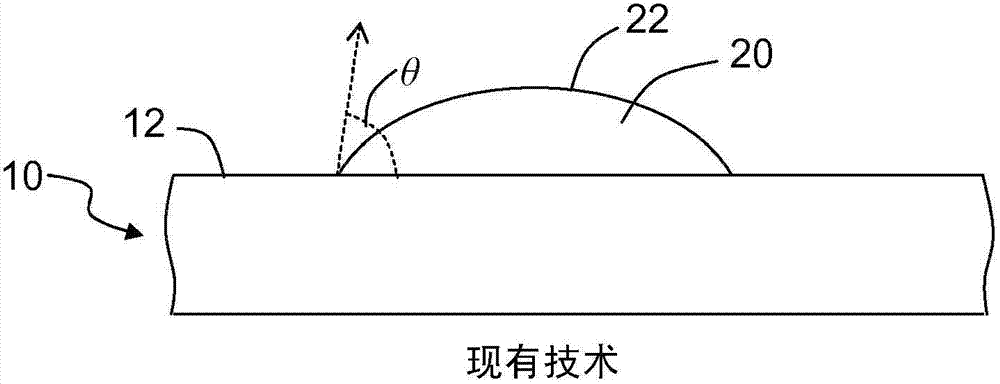
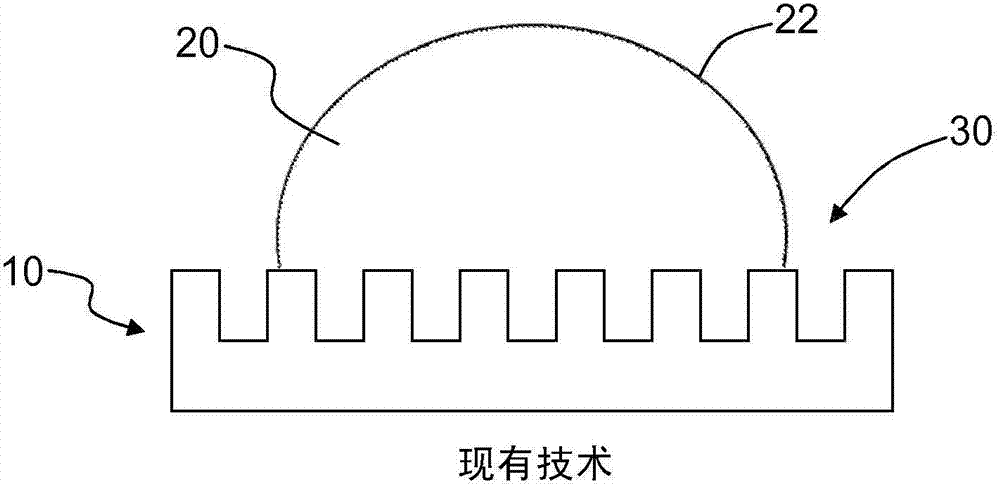
[0050] figure 1 It is a close-up view of a cross-section of an exemplary substrate 10 having a smooth surface 12 with droplets 20 formed thereon. The liquid 20 has a liquid surface 22. The liquid 20 may be water or an organic substance such as oil. The liquid 20 forms a contact angle θ with the surface 12, which depends on the surface energy and surface roughness of the substrate. If the su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com