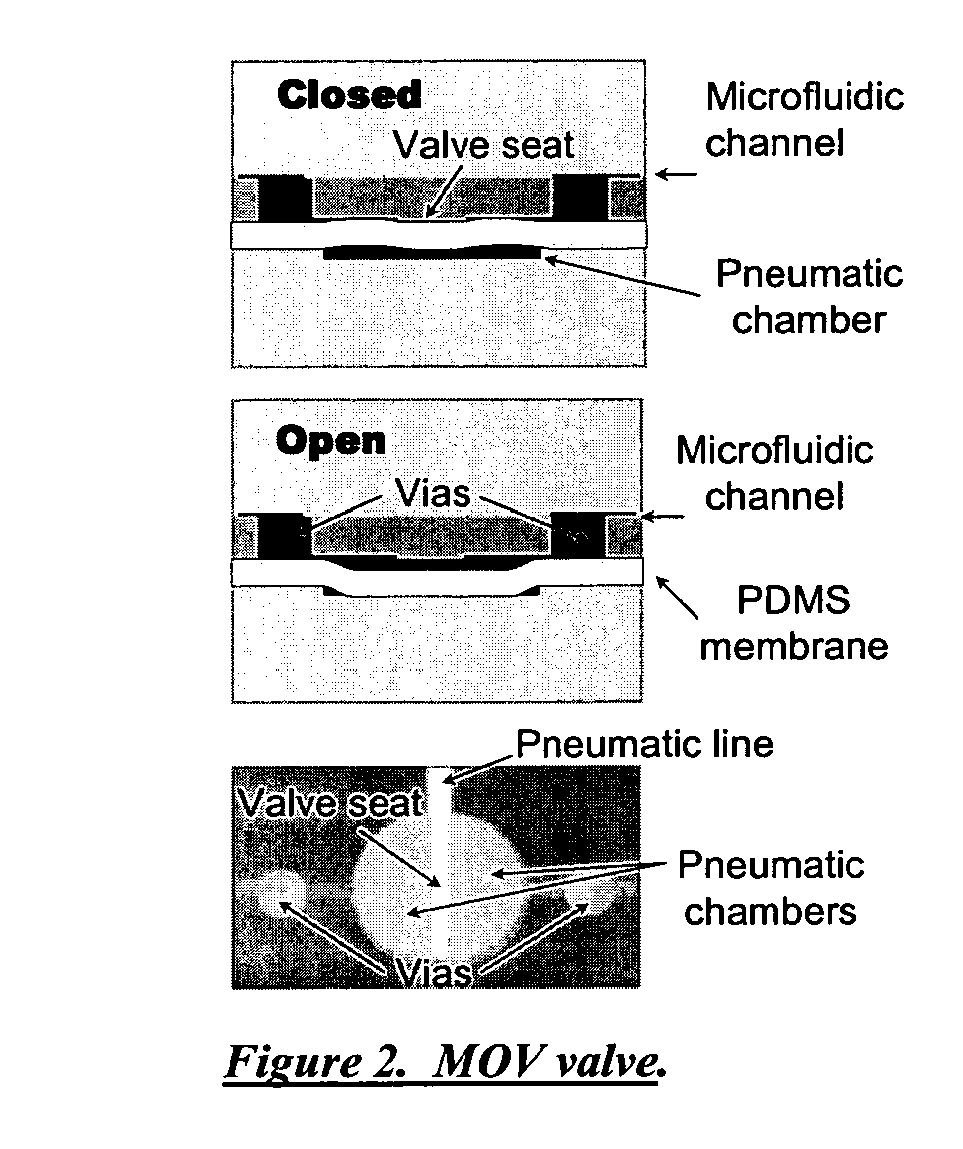
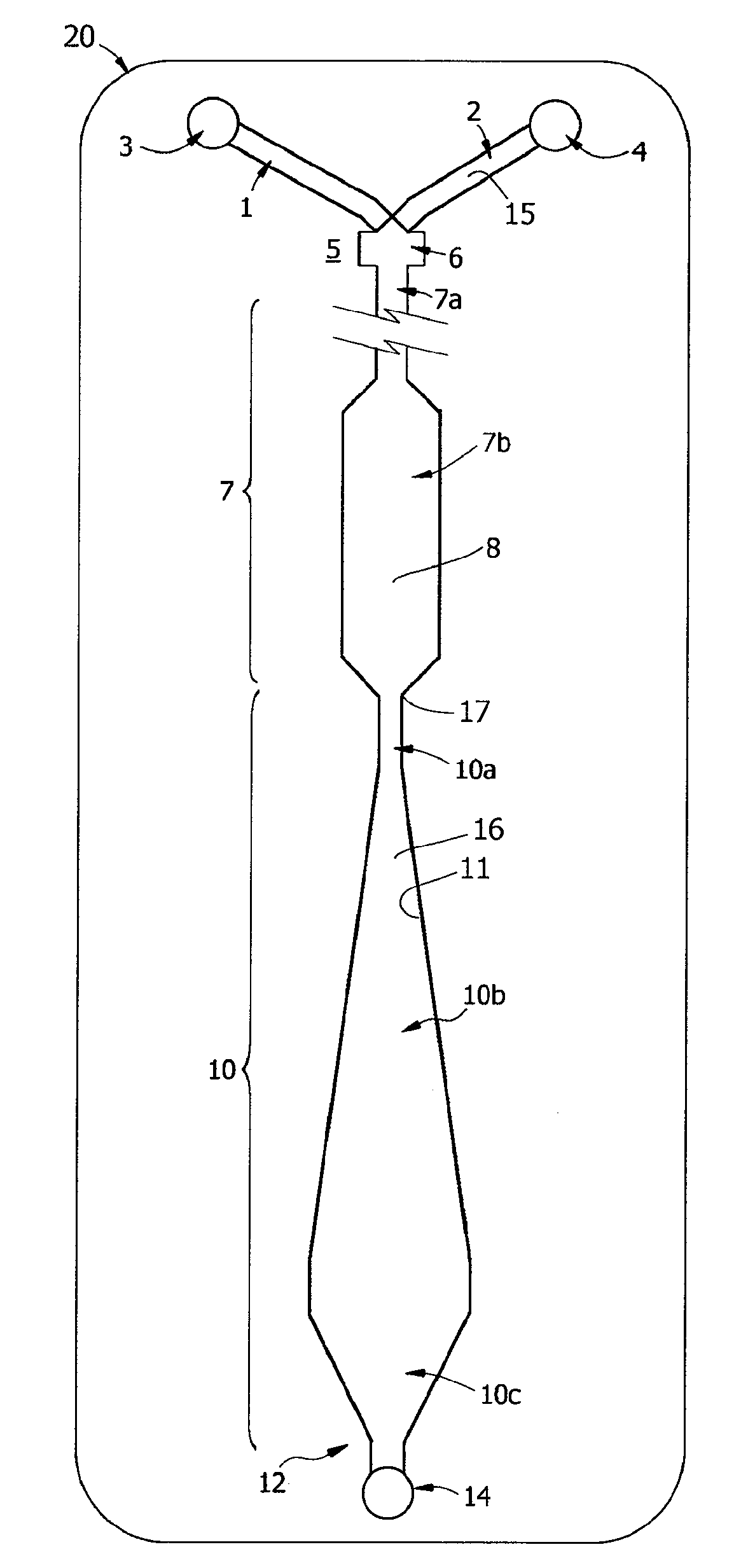
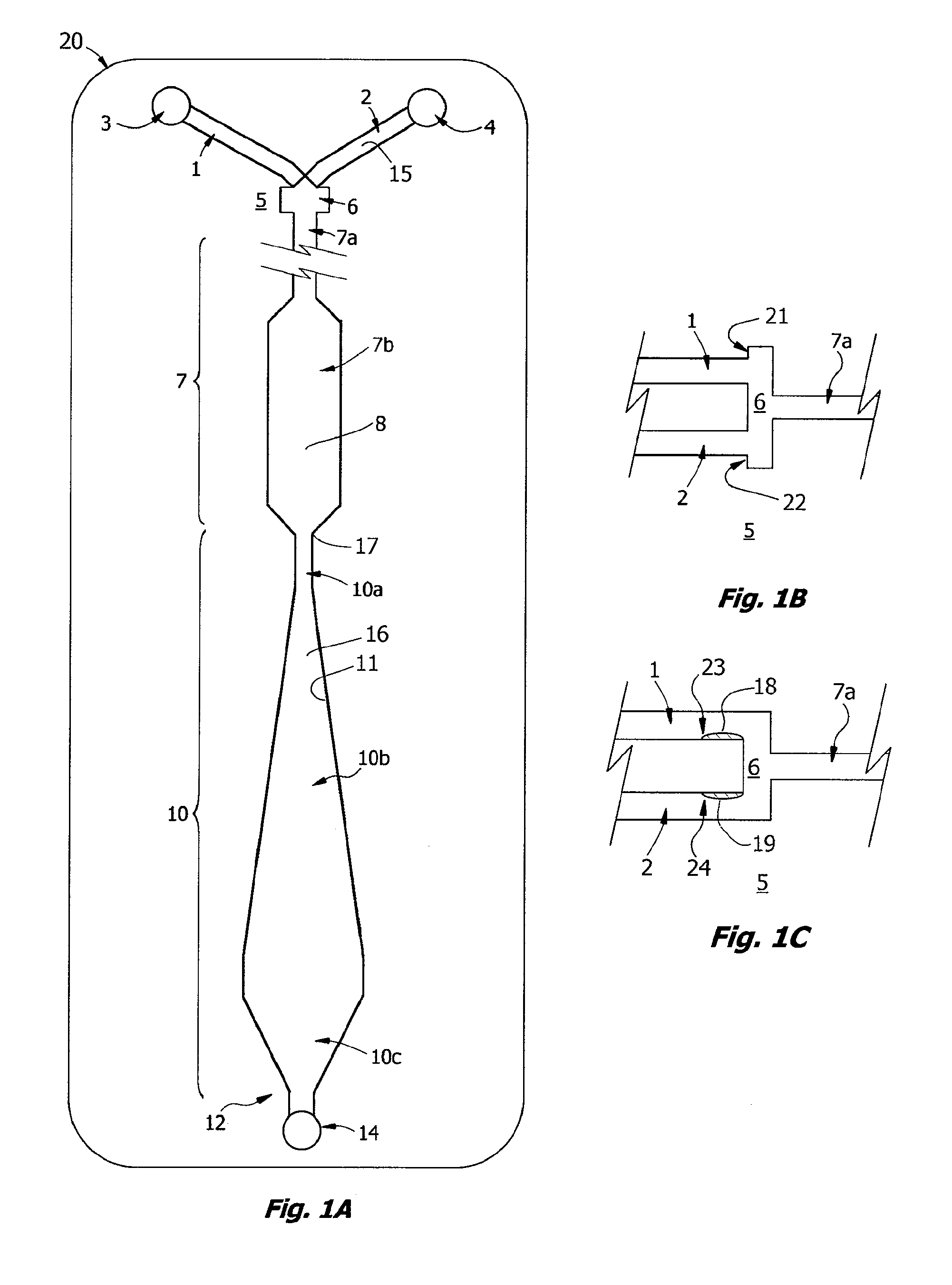
Patents
Literature
1814 results about "Microfluidics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
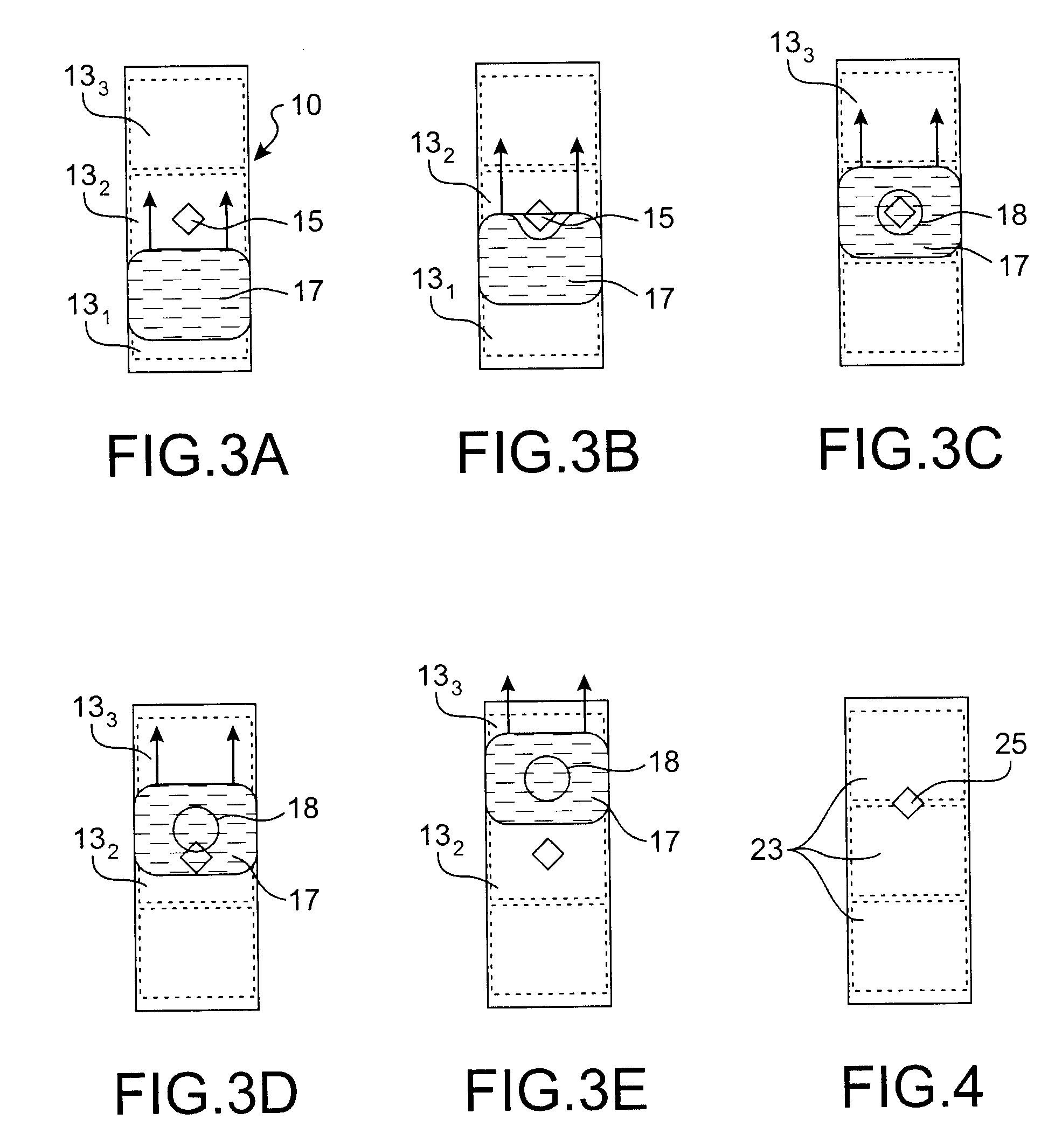
Microfluidics deals with the behaviour, precise control and manipulation of fluids that are geometrically constrained to a small, typically sub-millimeter, scale at which capillary penetration governs mass transport. It is a multidisciplinary field at the intersection of engineering, physics, chemistry, biochemistry, nanotechnology, and biotechnology, with practical applications in the design of systems in which low volumes of fluids are processed to achieve multiplexing, automation, and high-throughput screening. Microfluidics emerged in the beginning of the 1980s and is used in the development of inkjet printheads, DNA chips, lab-on-a-chip technology, micro-propulsion, and micro-thermal technologies.
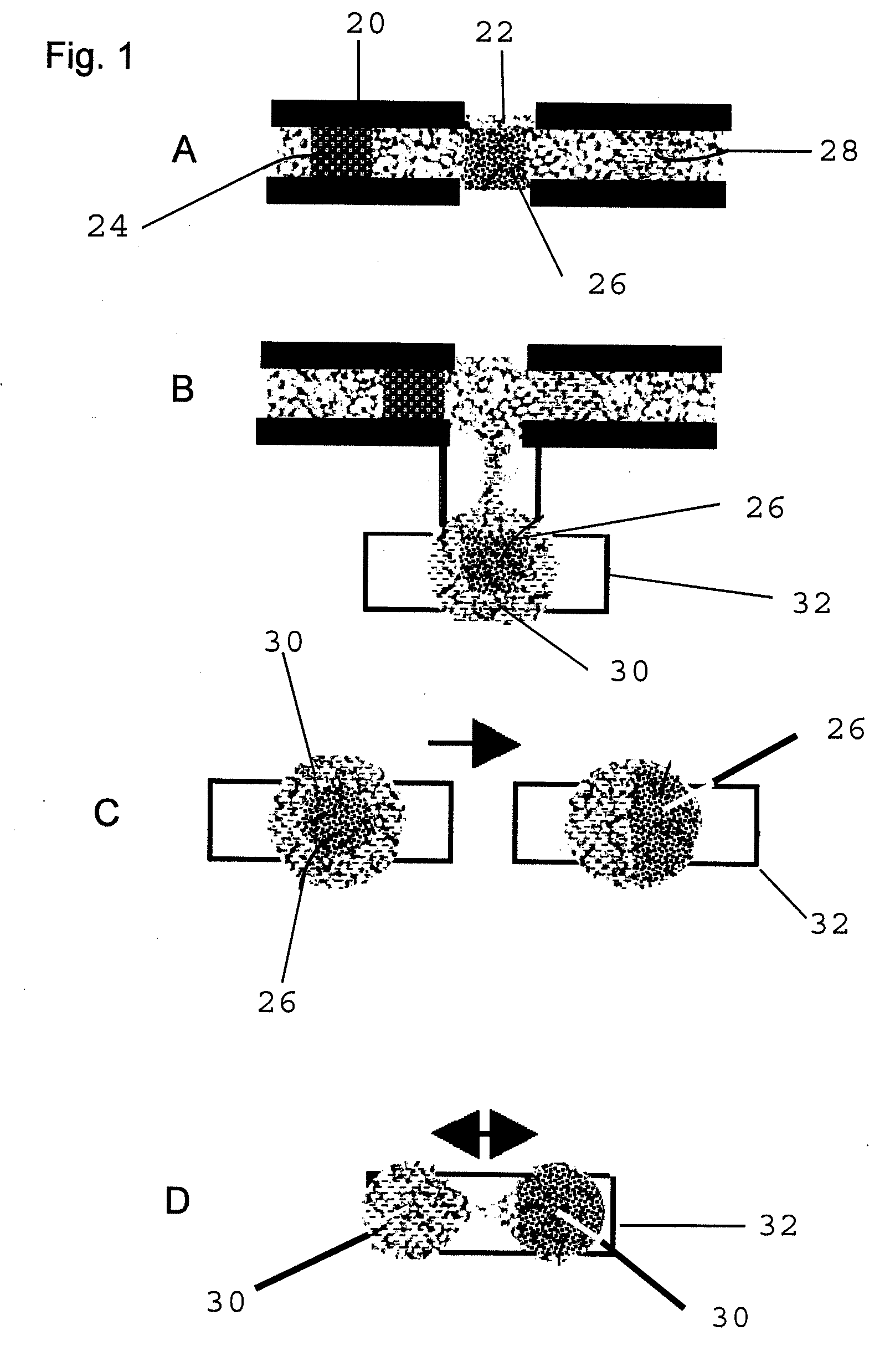
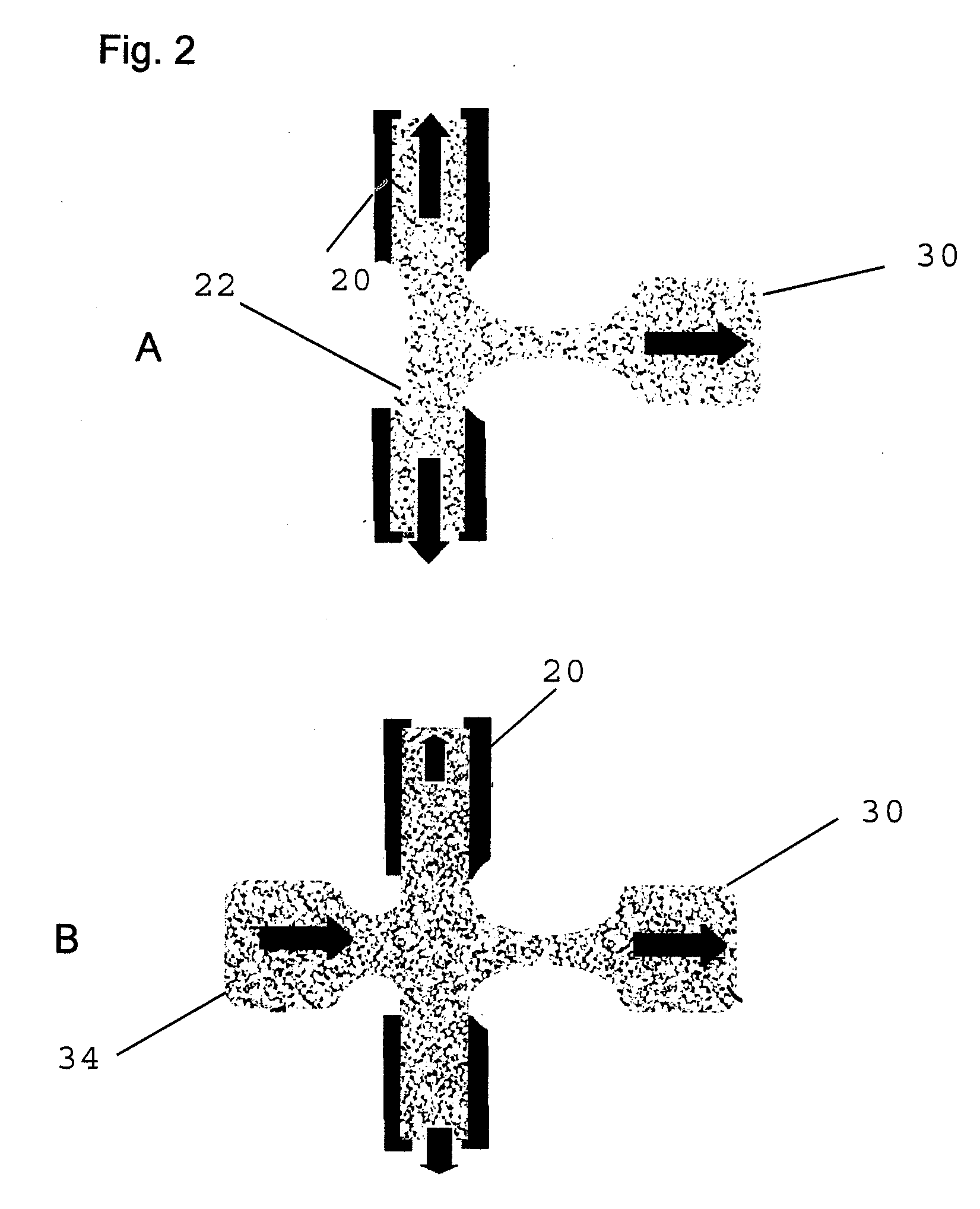
Systems and methods for optical actuation of microfluidics based on opto-electrowetting
InactiveUS6958132B2Improve performanceSludge treatmentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityMicrofluidics
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
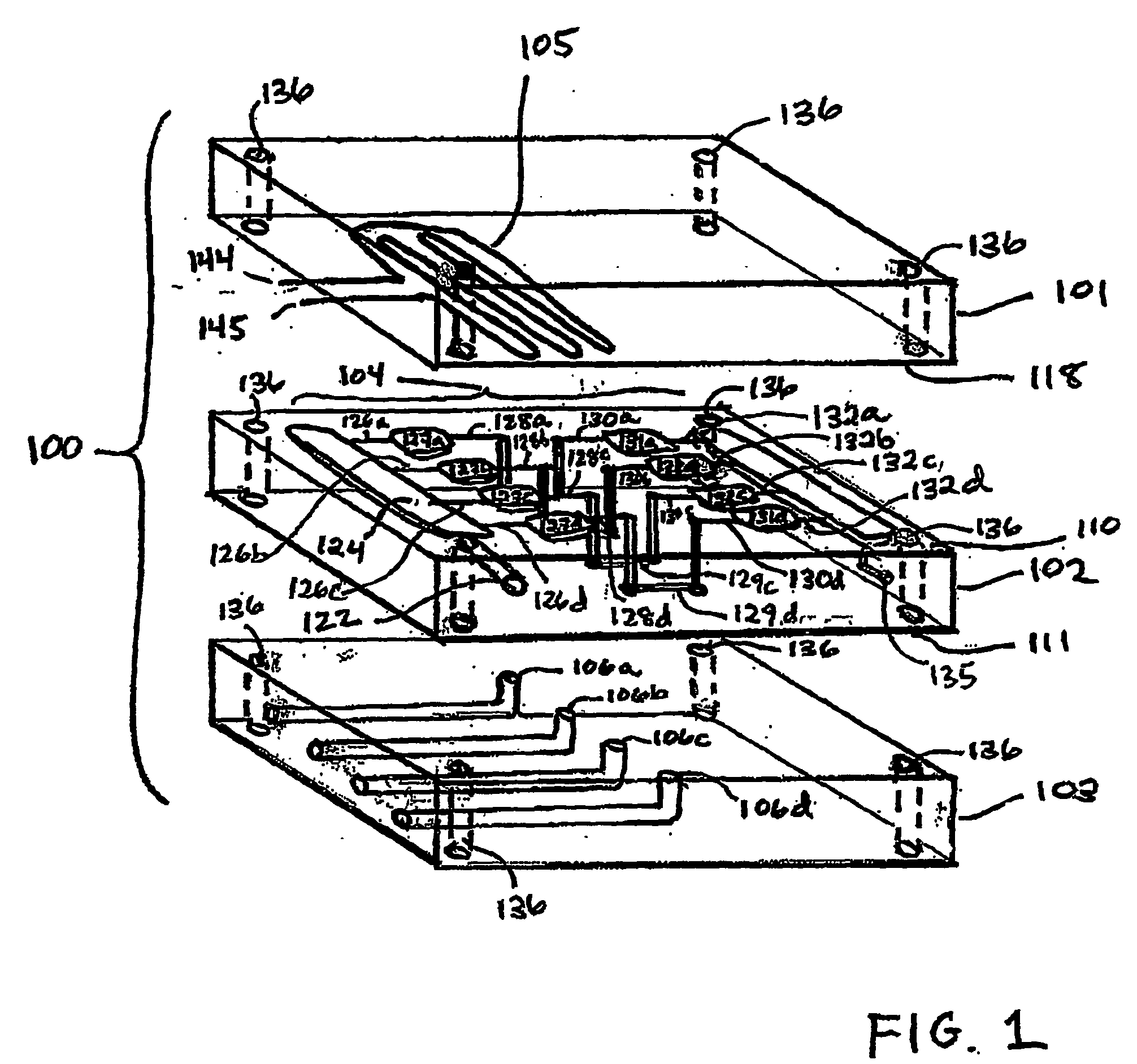
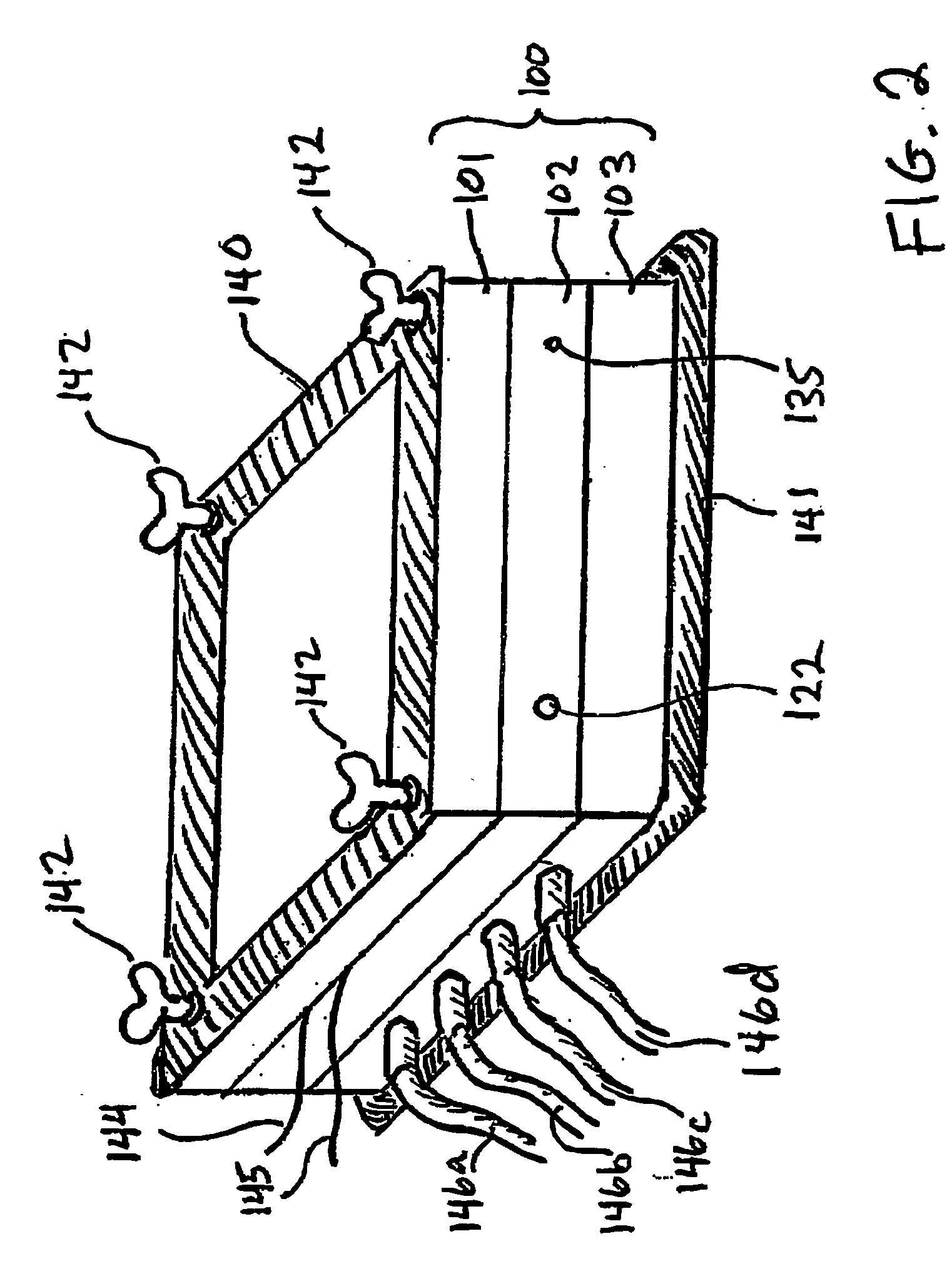
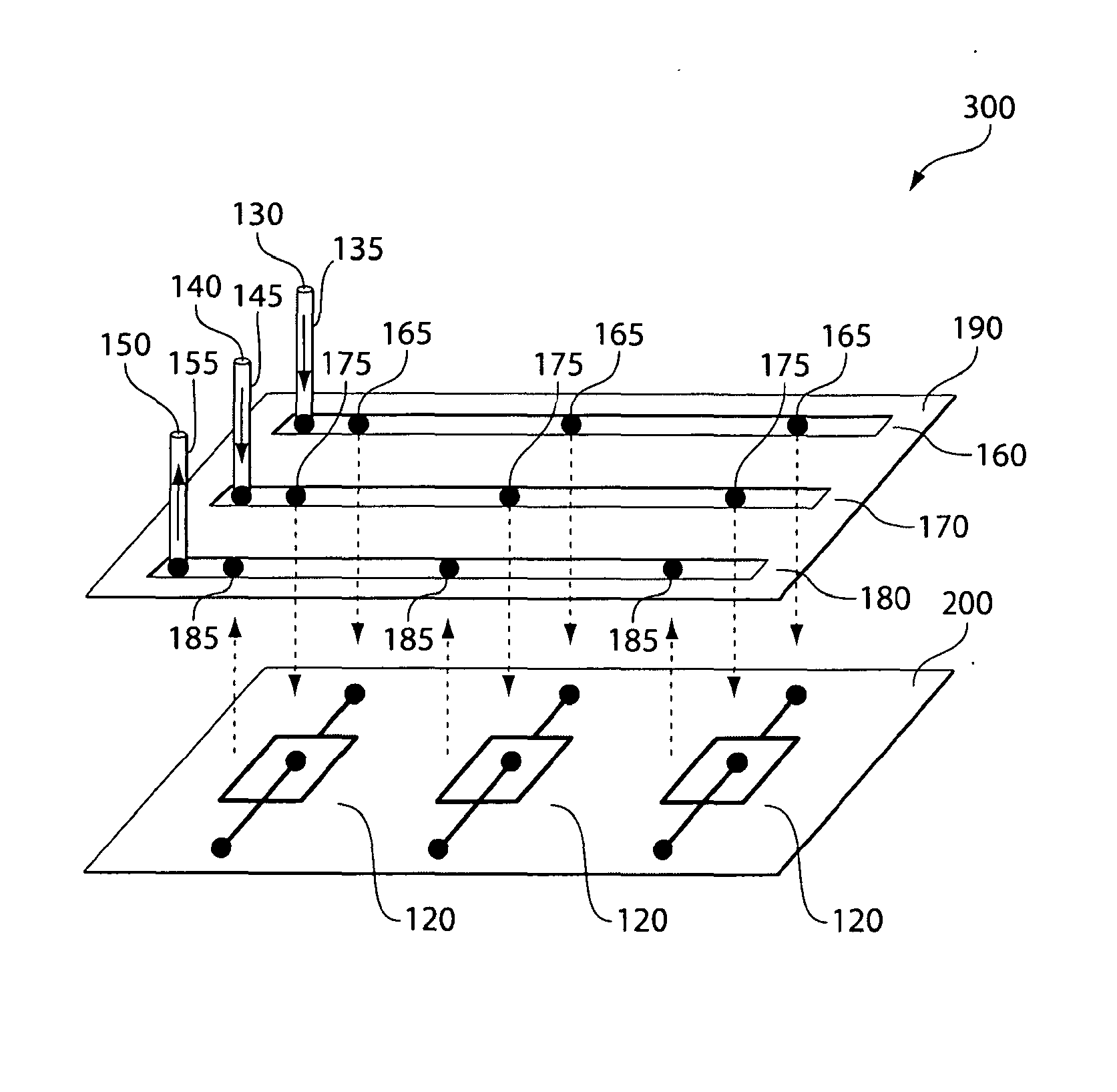
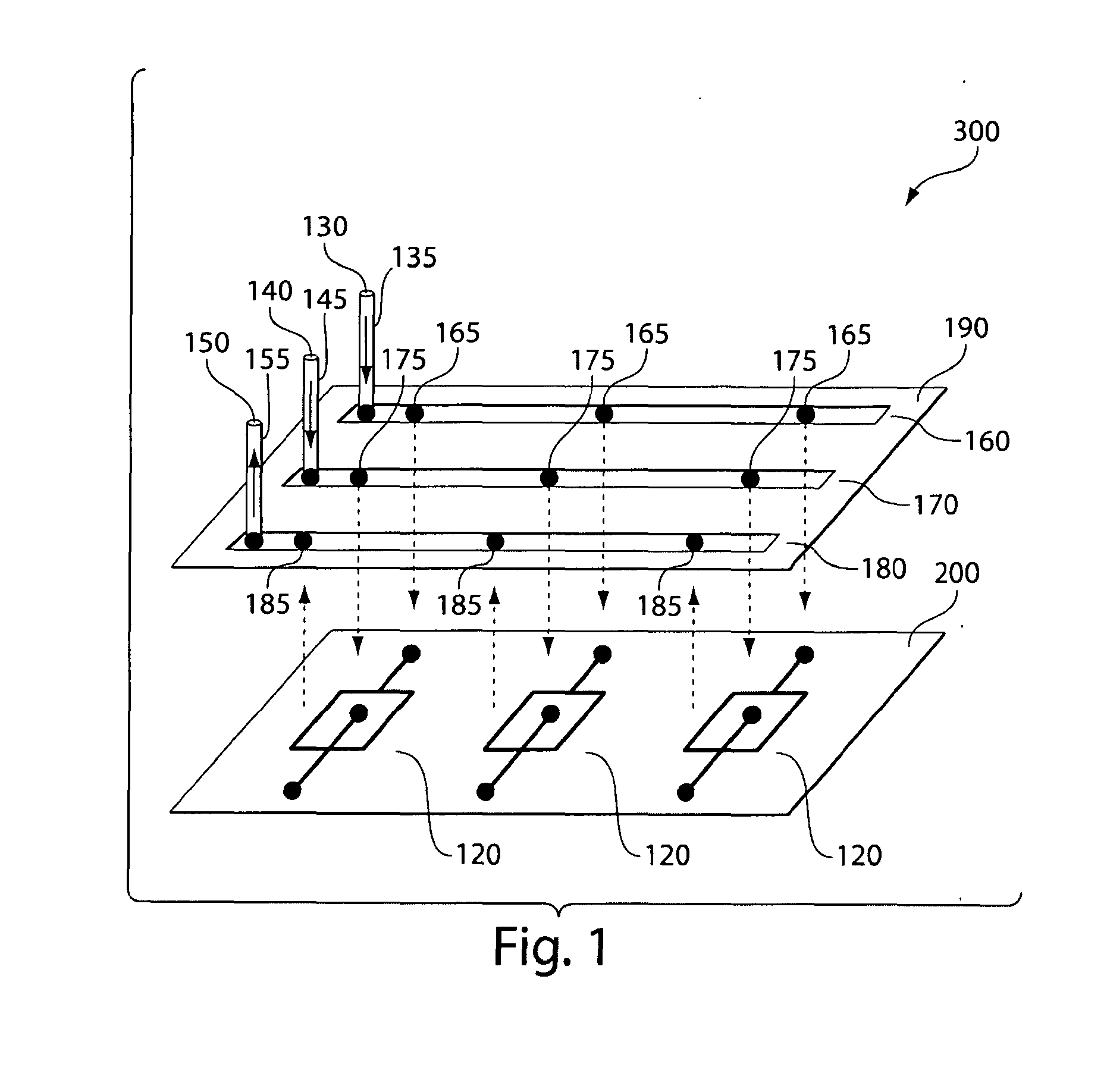
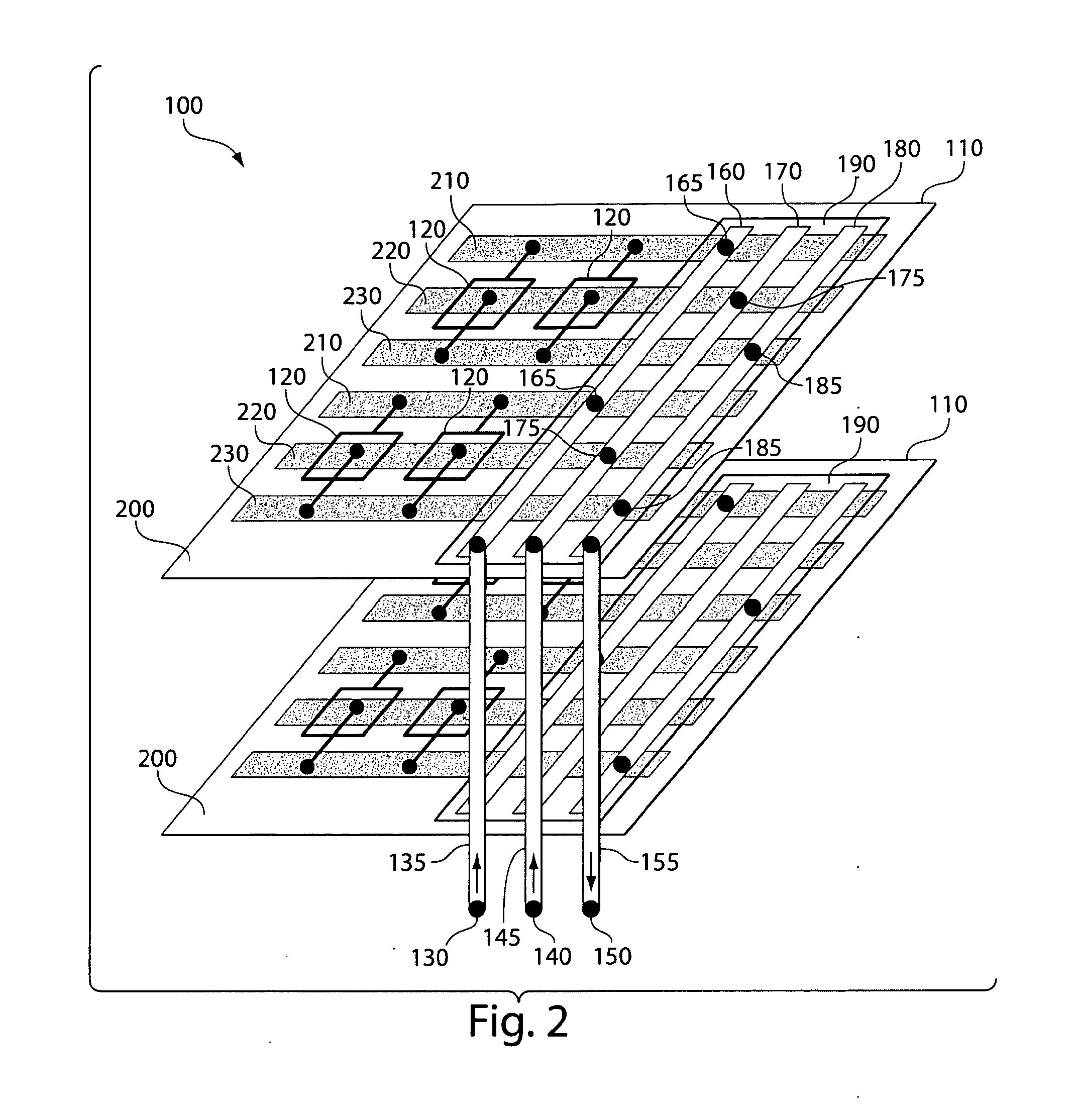
Three-dimensional microfluidics incorporating passive fluid control structures
InactiveUS20040109793A1Simple and effective and versatile controlShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersHeating or cooling apparatusFluid controlMicrofluidics
A three-dimensional microfluidic device (100) formed from a plurality of substantially planar layers (101, 102, 103) sealed together is disclosed
Owner:BIOMICRO SYST
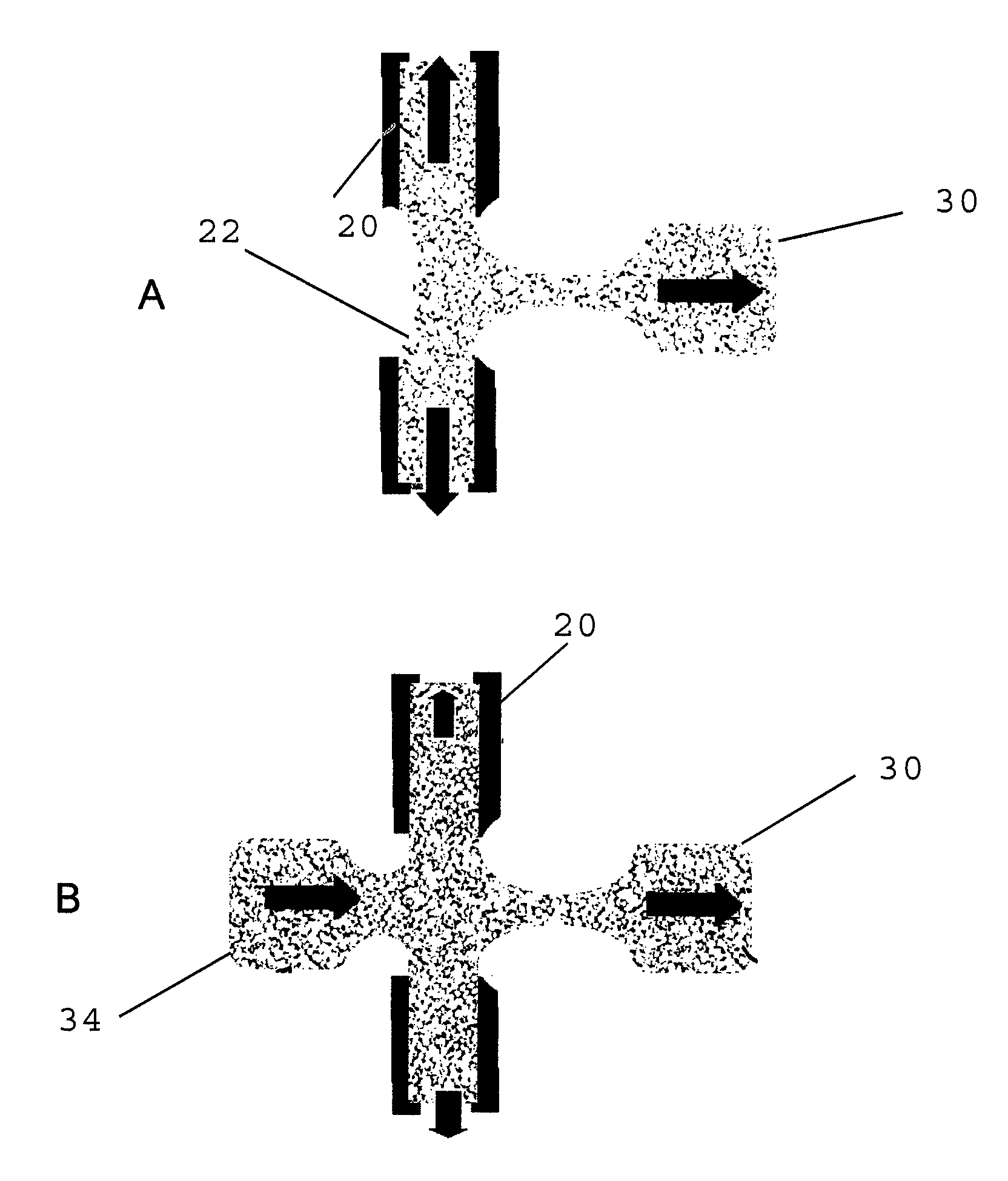
Method of using actuators for microfluidics without moving parts
InactiveUS7255780B2Maximize area overlapEffectively converting the surface into more hydrophilicSludge treatmentFlow mixersElectricityMicrofluidics
A series of microactuators for manipulating small quantities of liquids, and methods of using these for manipulating liquids, are disclosed. The microactuators are based on the phenomenon of electrowetting and contain no moving parts. The force acting on the liquid is a potential-dependent gradient of adhesion energy between the liquid and a solid insulating surface.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Microfluidic Chemical Reaction Circuits
InactiveUS20080281090A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingChemical reactionCompound (substance)
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +3
Microfluidic devices and methods for cell sorting, cell culture and cells based diagnostics and therapeutics
ActiveUS20140248621A1Uniform pressure distributionReduce widthHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurement3D cell cultureTumor cells
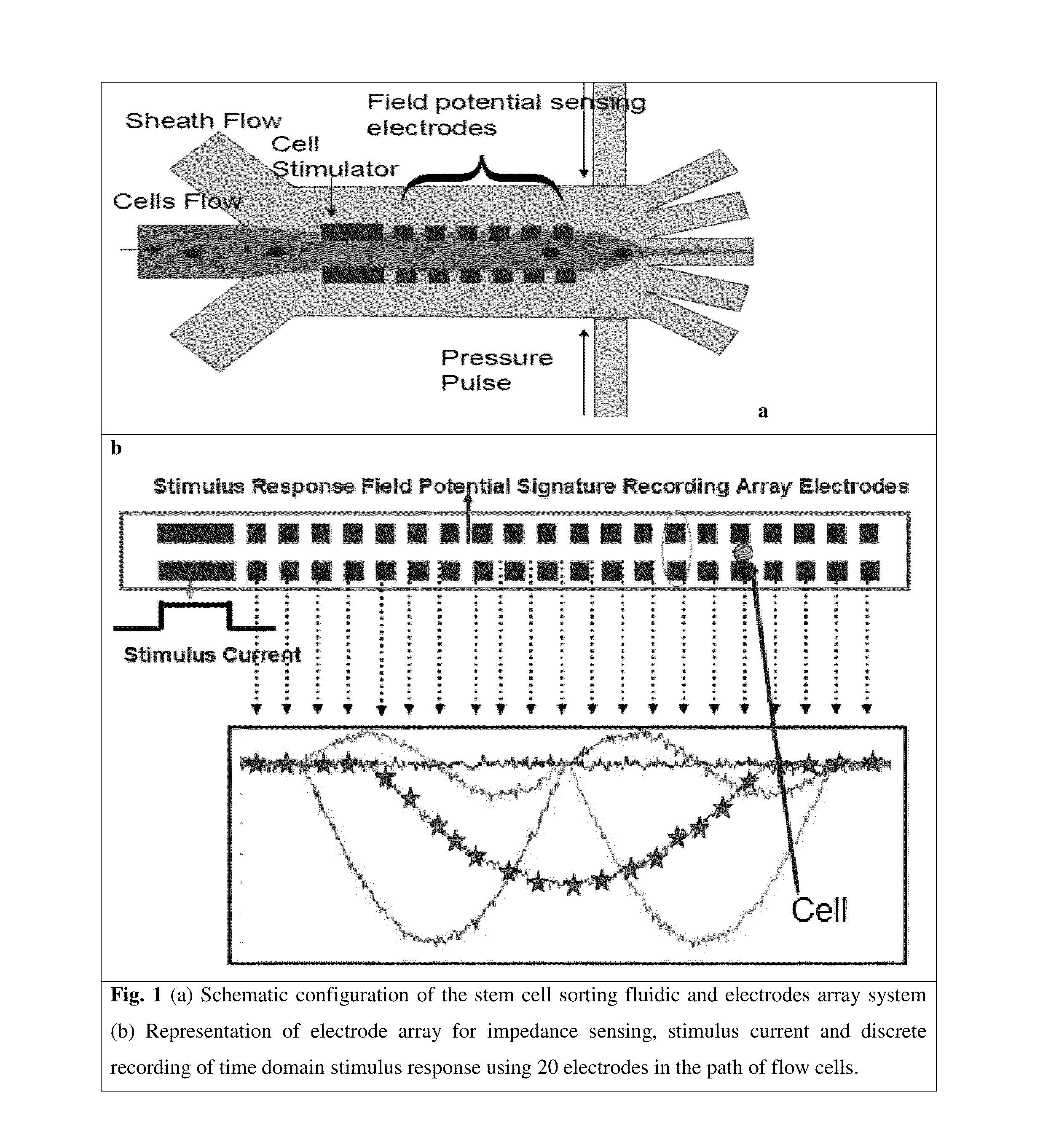
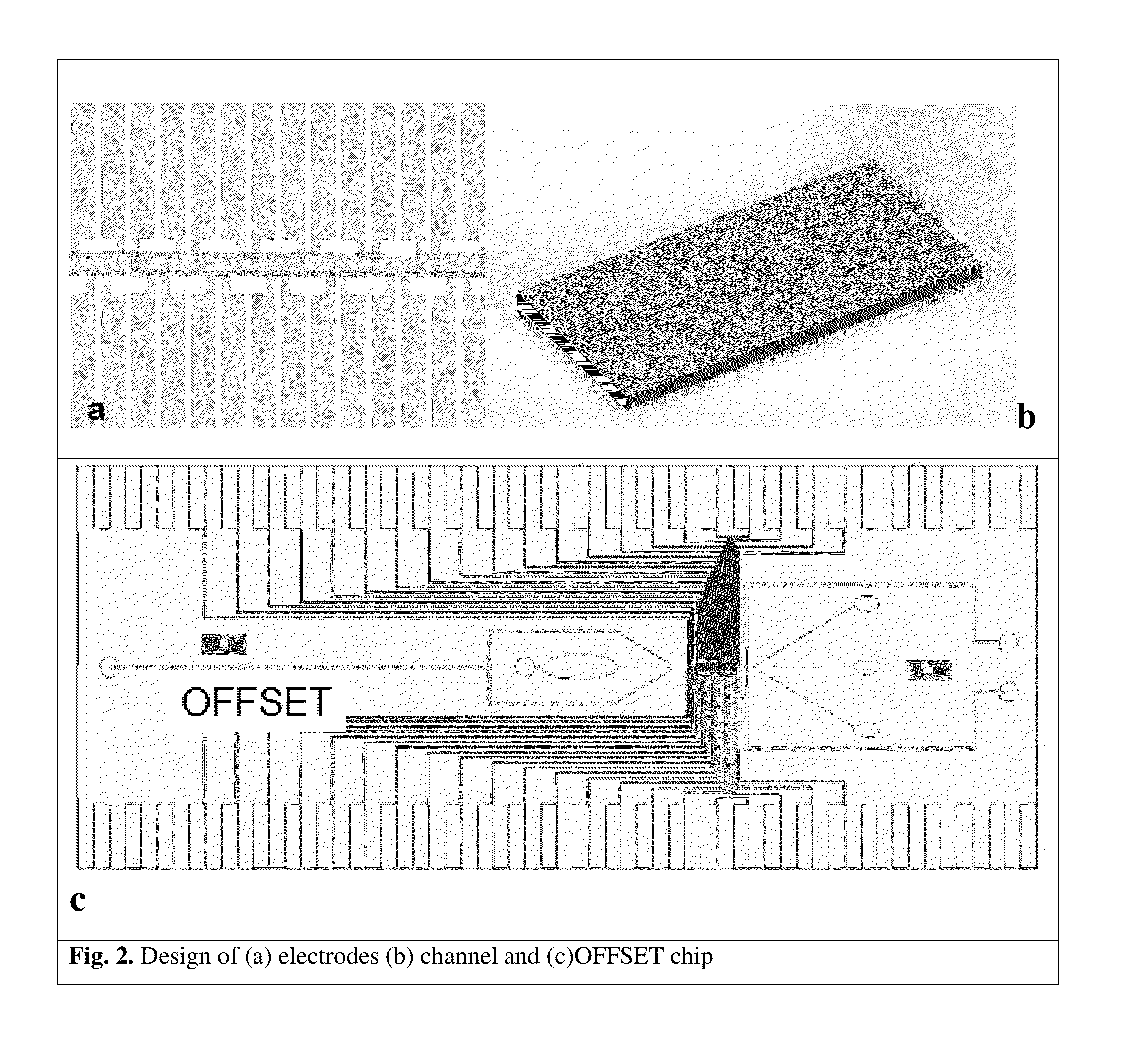
Microfluidic devices and methods that use cells such as cancer cells, stem cells, blood cells for preprocessing, sorting for various biodiagnostics or therapeutical applications are described. Microfluidics electrical sensing such as measurement of field potential or current and phenomena such as immiscible fluidics, inertial fluidics are used as the basis for cell and molecular processing (e.g., characterizing, sorting, isolation, processing, amplification) of different particles, chemical compositions or biospecies (e.g., different cells, cells containing different substances, different particles, different biochemical compositions, proteins, enzymes etc.). Specifically this invention discloses a few sorting schemes for stem cells, whole blood and circulating tumor cells and also extracting serum from whole blood. Further medical diagnostics technology utilizing high throughput single cell PCR is described using immiscible fluidics couple with single or multi cells trapping technology.
Owner:BIOPICO SYST
Microfluidic reactor system
ActiveUS20120177543A1Endpoint detectionReduce incubation timeShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingDiaphragm pumpReactor system
A compact device for operatively coupling a solid planar substrate, for example a glass slide, to a microfluidic circuit and performing a reaction or reactions on organic matter bound to the face of the planar substrate. Typical reactions include binding, staining and / or labeling reactions. In use, a sealed reaction chamber is formed, the chamber enclosing the organic matter and at least a part of the solid substrate. Headspace in the sealed chamber between the solid substrate is generally of microfluidic dimensions, and diaphragm pump members are used to inject, exchange and / or mix the fluids in the chamber.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
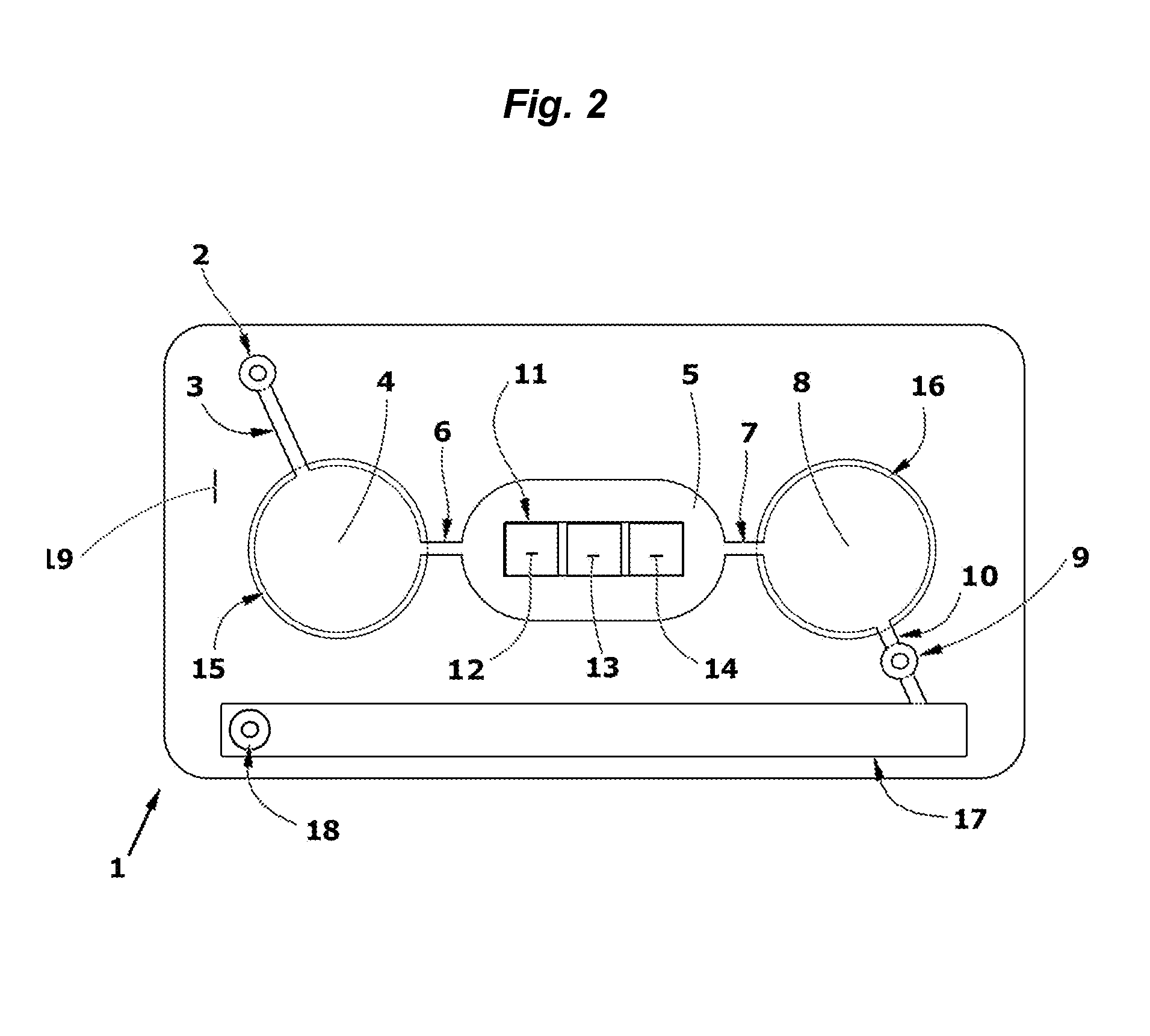
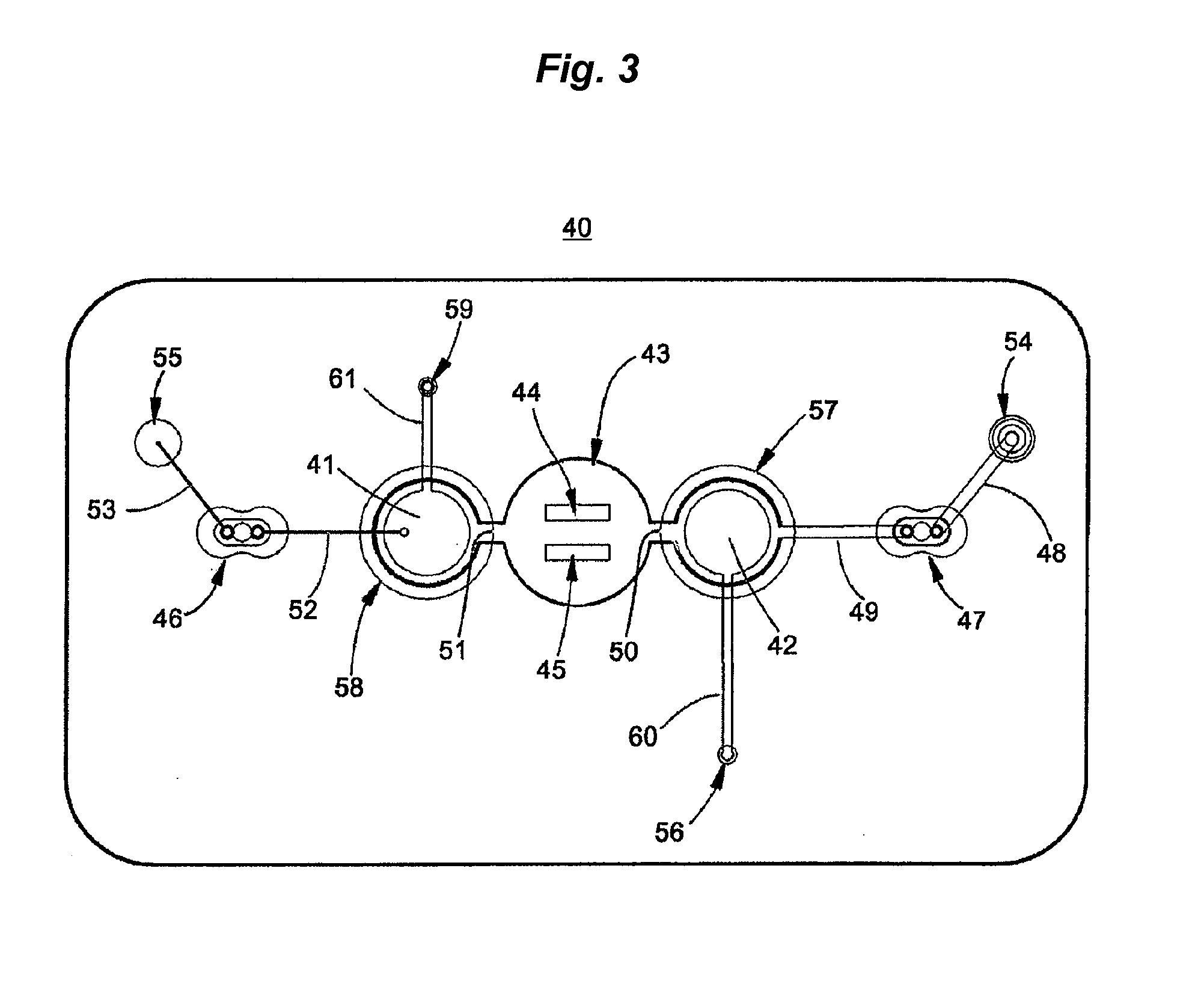
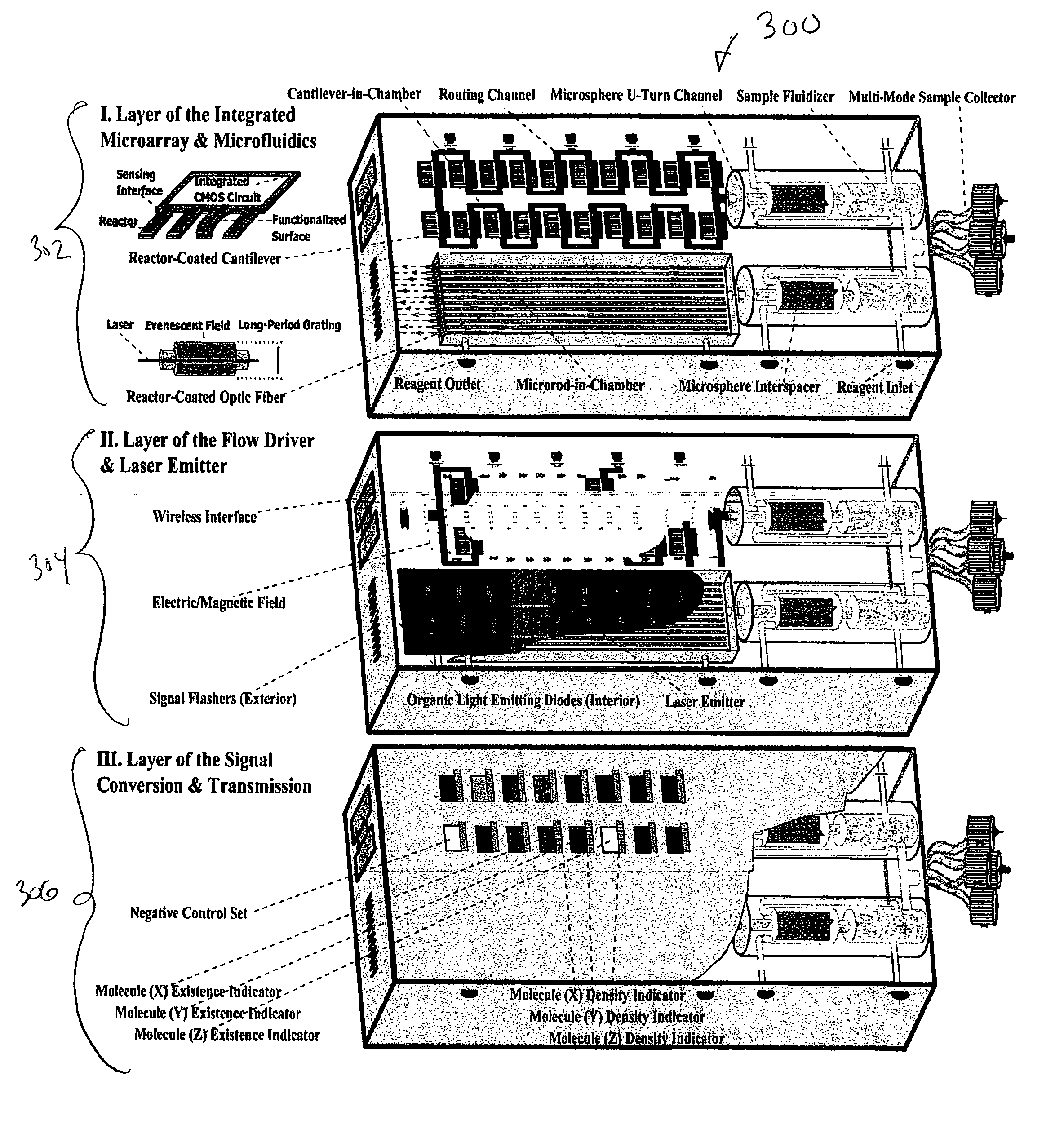
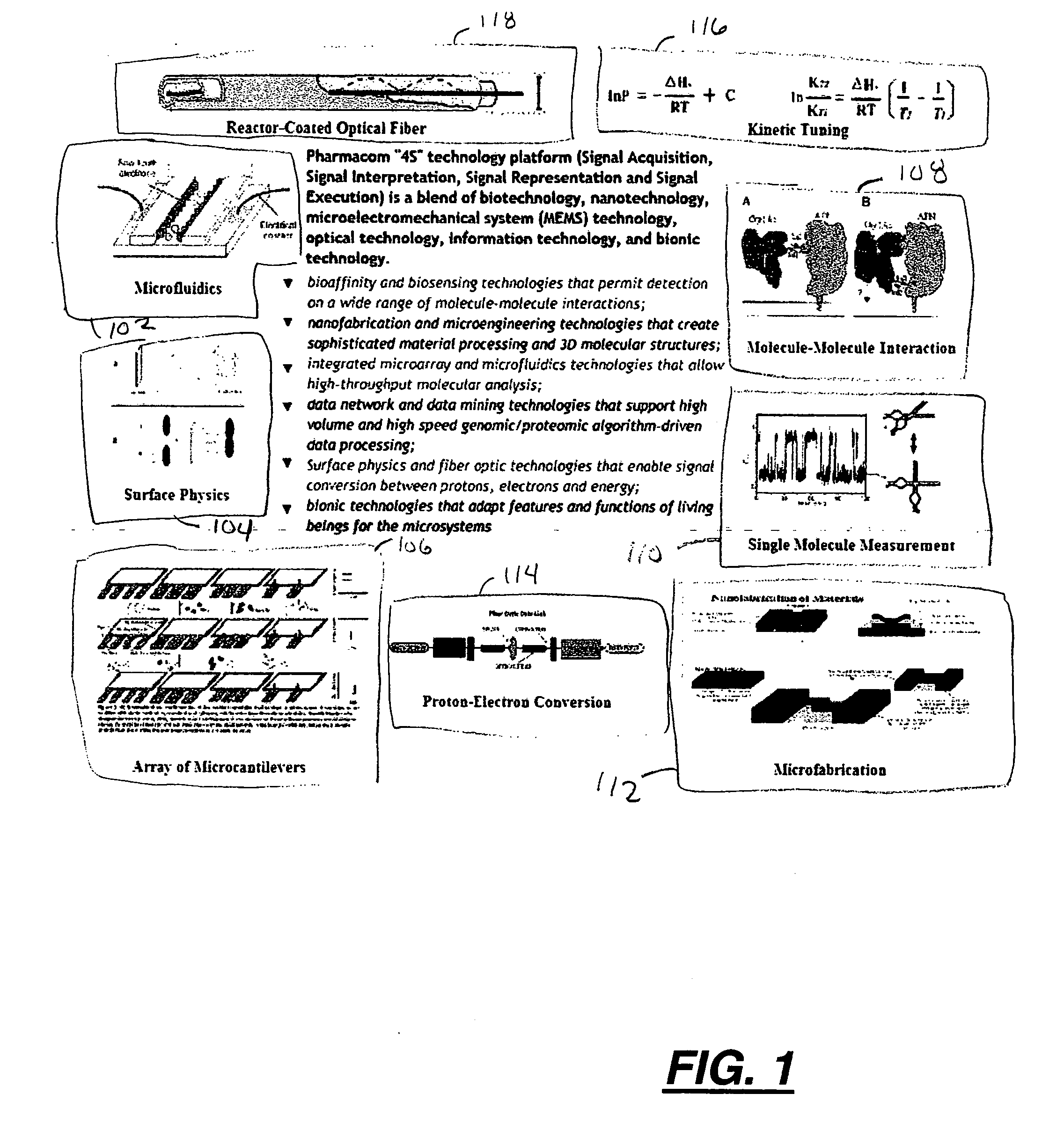
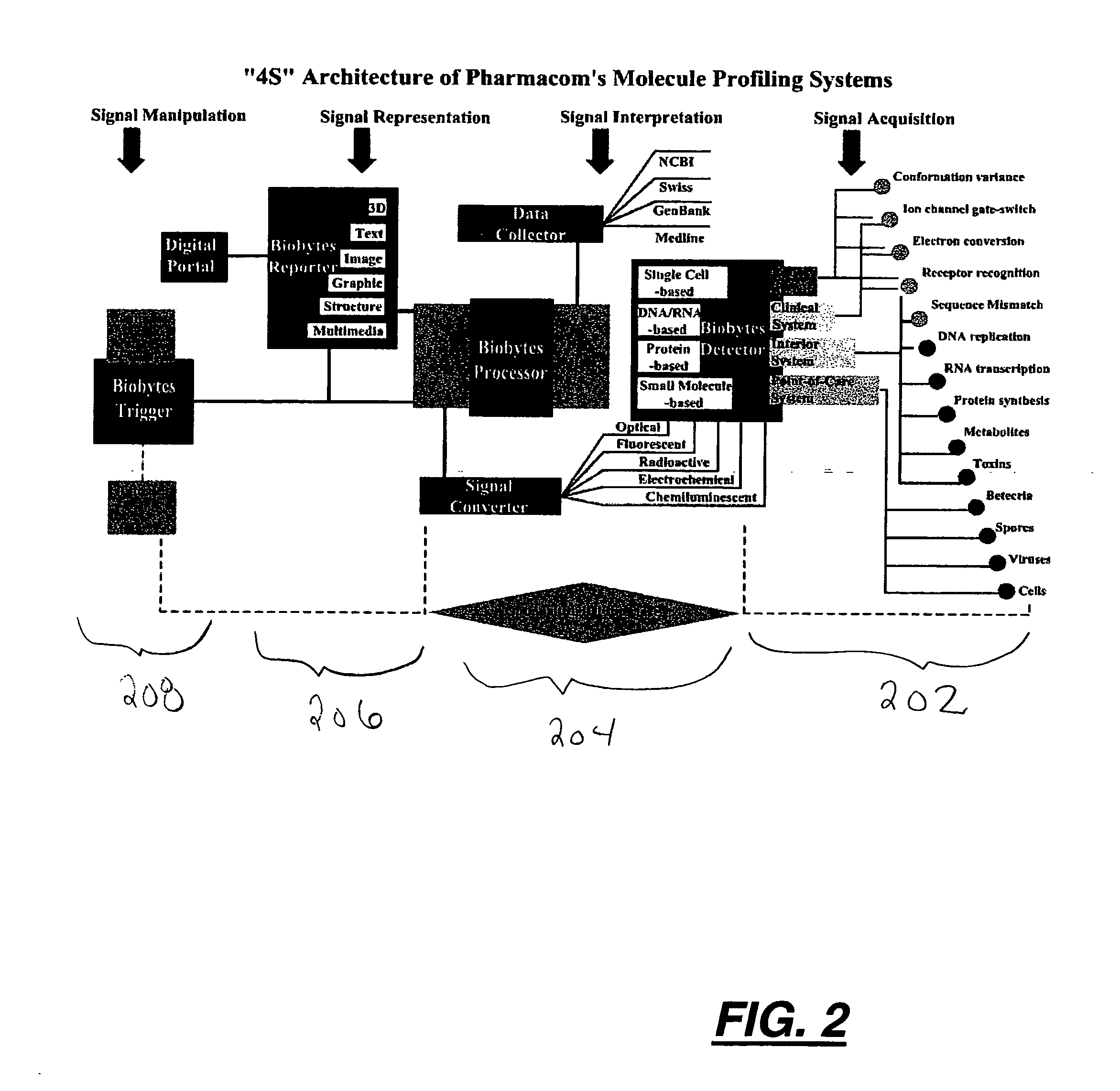
Microsystems that integrate three-dimensional microarray and multi-layer microfluidics for combinatorial detection of bioagent at single molecule level
InactiveUS20070116607A1Reduce resultHigh detection sensitivityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWithdrawing sample devicesBiological bodyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Stand-alone microsystems adapted for performing combinatorial detection of bioagents at single molecule level wherein the microsystems are featured with three-dimensional microarray and multi-layer microfluidics to thereby provide high throughput screening and high content screening sufficient to allow for substantially real-time performance of the microsystem. Methods for detection of bioagents at a single molecule level or single organism level include providing a reconfigurable microsystem adapted for performing combinatorial detection of bioagents at a single molecule level and reconfiguring the reconfigurable microsystem for various environments.
Owner:PHARMACOM MICROELECTRONICS
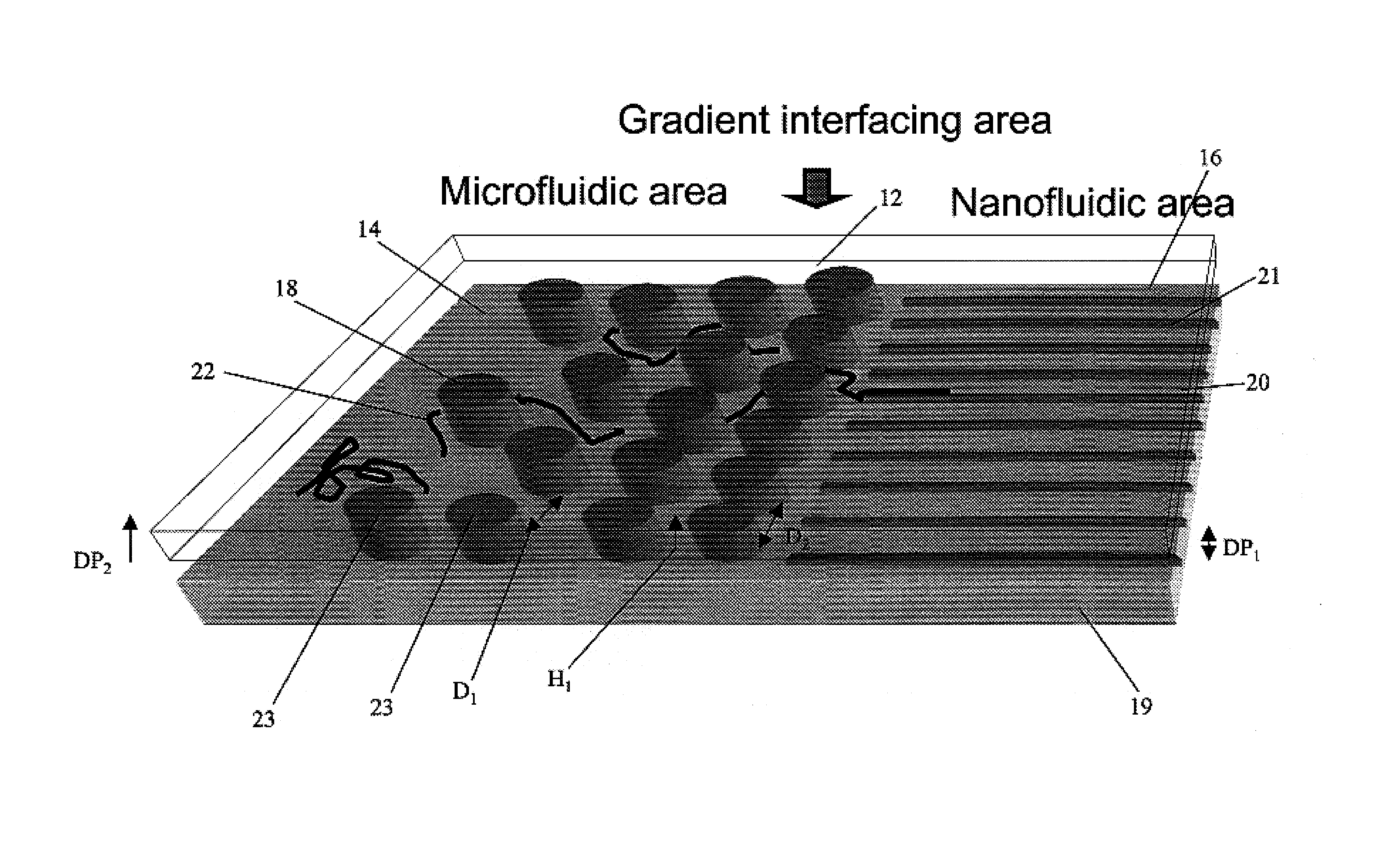
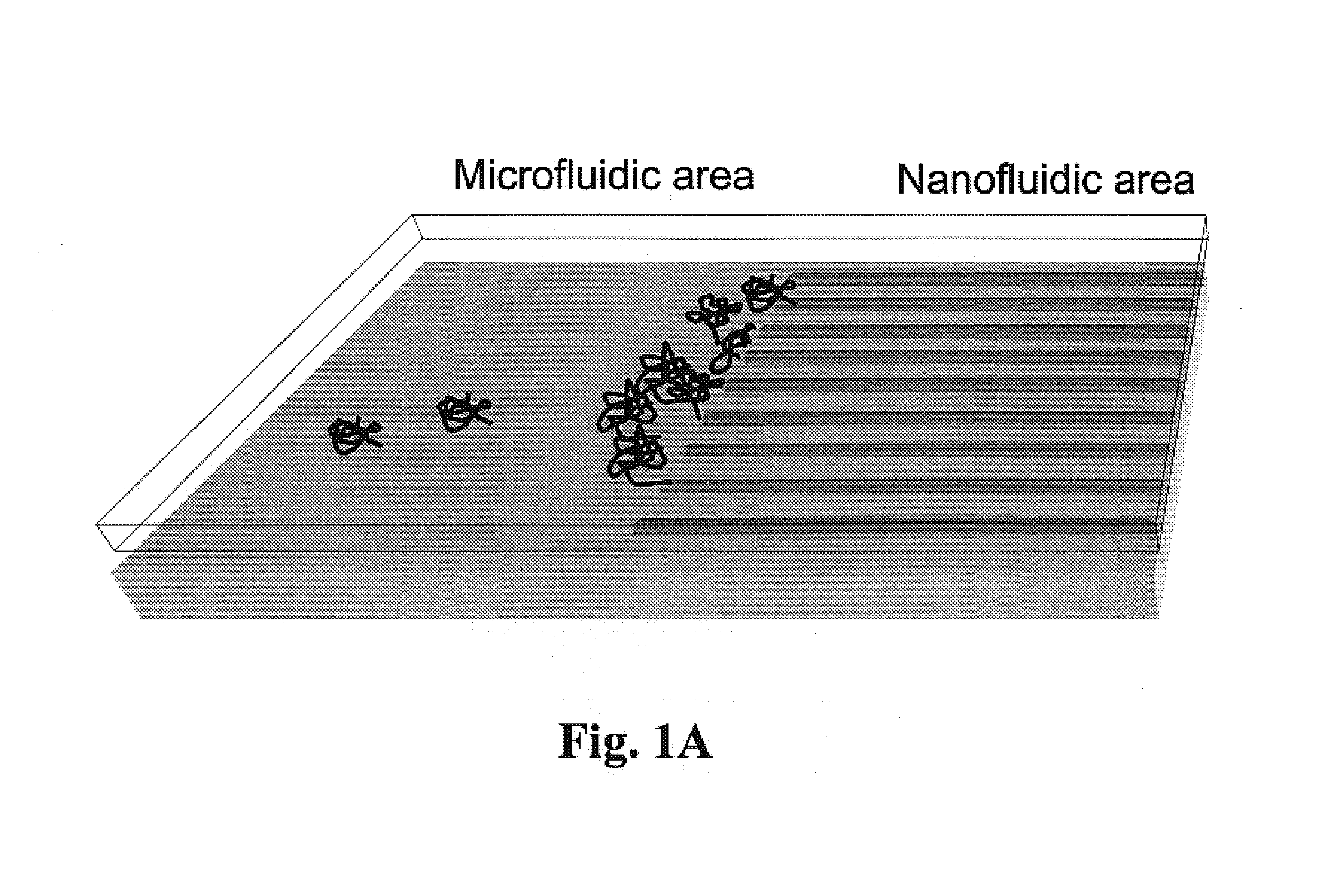
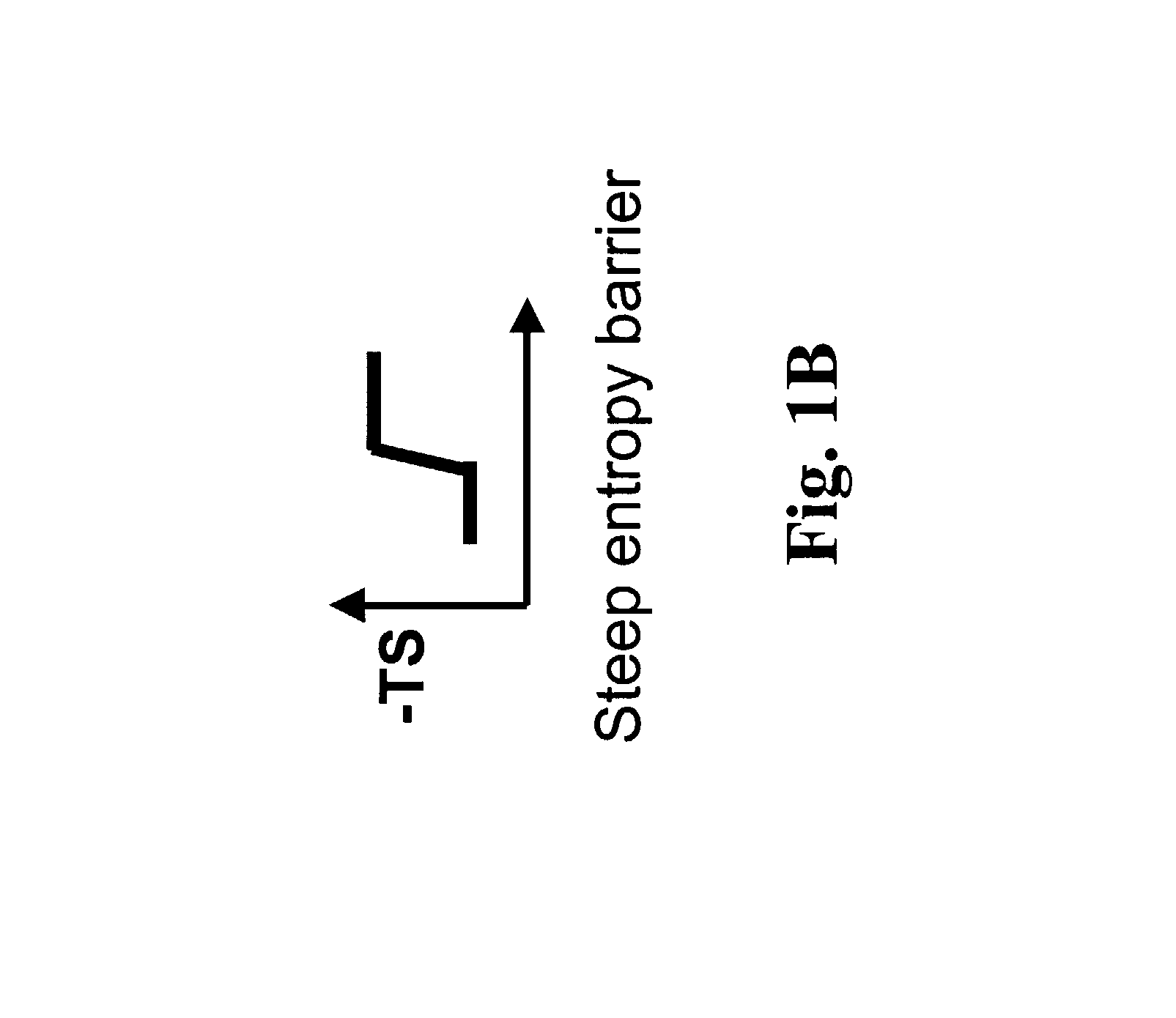
Gradient structures interfacing microfluidics and nanofluidics, methods for fabrication and uses thereof
ActiveUS7217562B2Improve throughputReduces the local entropic barrierMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureVertical gradientMicrofluidics
The present invention relates to a device for interfacing nanofluidic and microfluidic components suitable for use in performing high throughput macromolecular analysis. Diffraction gradient lithography (DGL) is used to form a gradient interface between a microfluidic area and a nanofluidic area. The gradient interface area reduces the local entropic barrier to nanochannels formed in the nanofluidic area. In one embodiment, the gradient interface area is formed of lateral spatial gradient structures for narrowing the cross section of a value from the micron to the nanometer length scale. In another embodiment, the gradient interface area is formed of a vertical sloped gradient structure. Additionally, the gradient structure can provide both a lateral and vertical gradient.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
Micro-array evanescent wave fluorescence detection device
InactiveUS7175811B2Quench emissionAvoid disadvantagesOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsWaveguidePolymer
Novel nanowell microarrays are disclosed in optical contact with polymer waveguides wherein evanescent field associated with lightwaves propagated in the waveguide excite target substances in the nanowells either by a common waveguide or by individual waveguides. Fluid samples are conveyed to the nanowells by means of microfluidics. The presence of the target substances in fluid samples is detected by sensing fluorescent radiation generated by fluorescent tag bound to the target substances. The fluorescent tags generate fluorescent radiation as a result of their excitation by the evanescent field. One or more PMT detectors or a CCD detector are located at the side of the waveguide opposite to the nanowells. Fluorescent radiation is detected due to its coupling with the waveguide or its emission through the waveguide.
Owner:EDGELIGHT BIOSCI
Method and apparatus for energy harvesting using microfluidics
ActiveUS7898096B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesMicrofluidicsEngineering
An apparatus comprising a mechanical-to-electrical energy converting device having a plurality of electrodes and a fluidic body which comprises spatially separated conductive and dielectric liquid regions. Said fluidic body is configured to reversibly move as a whole with respect to said plurality of electrodes under the influence of a mechanical force. Each cycle of said reversible motion of said fluidic body causes multiple alternations of the amount of electrical charge accumulated by the electrodes, whereby generating electrical current flow between said electrodes.
Owner:KRUPENKIN THOMAS NIKITA
Microfluidic chromatography
InactiveUS20050000900A1Ion-exchange process apparatusComponent separationChromatography columnDelivery system
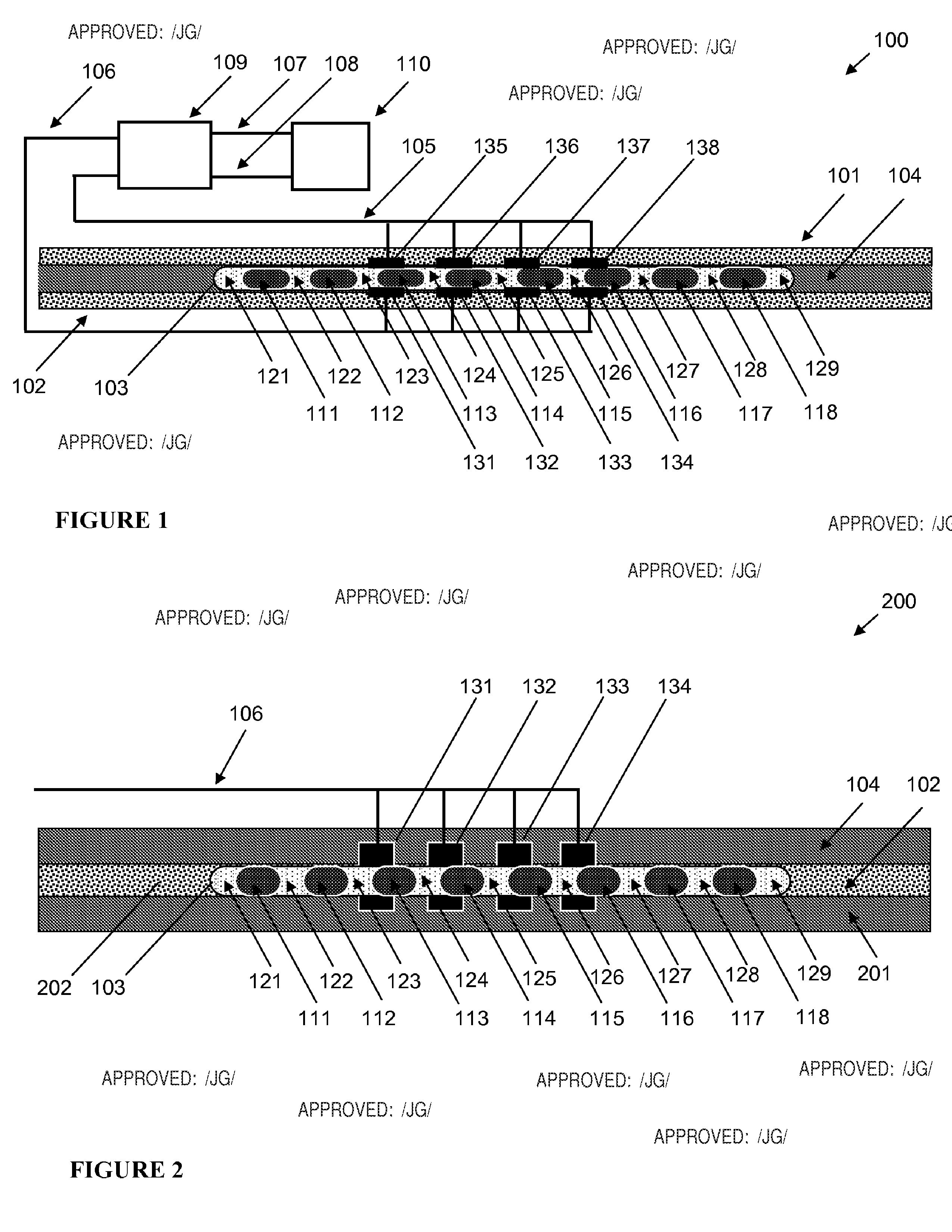
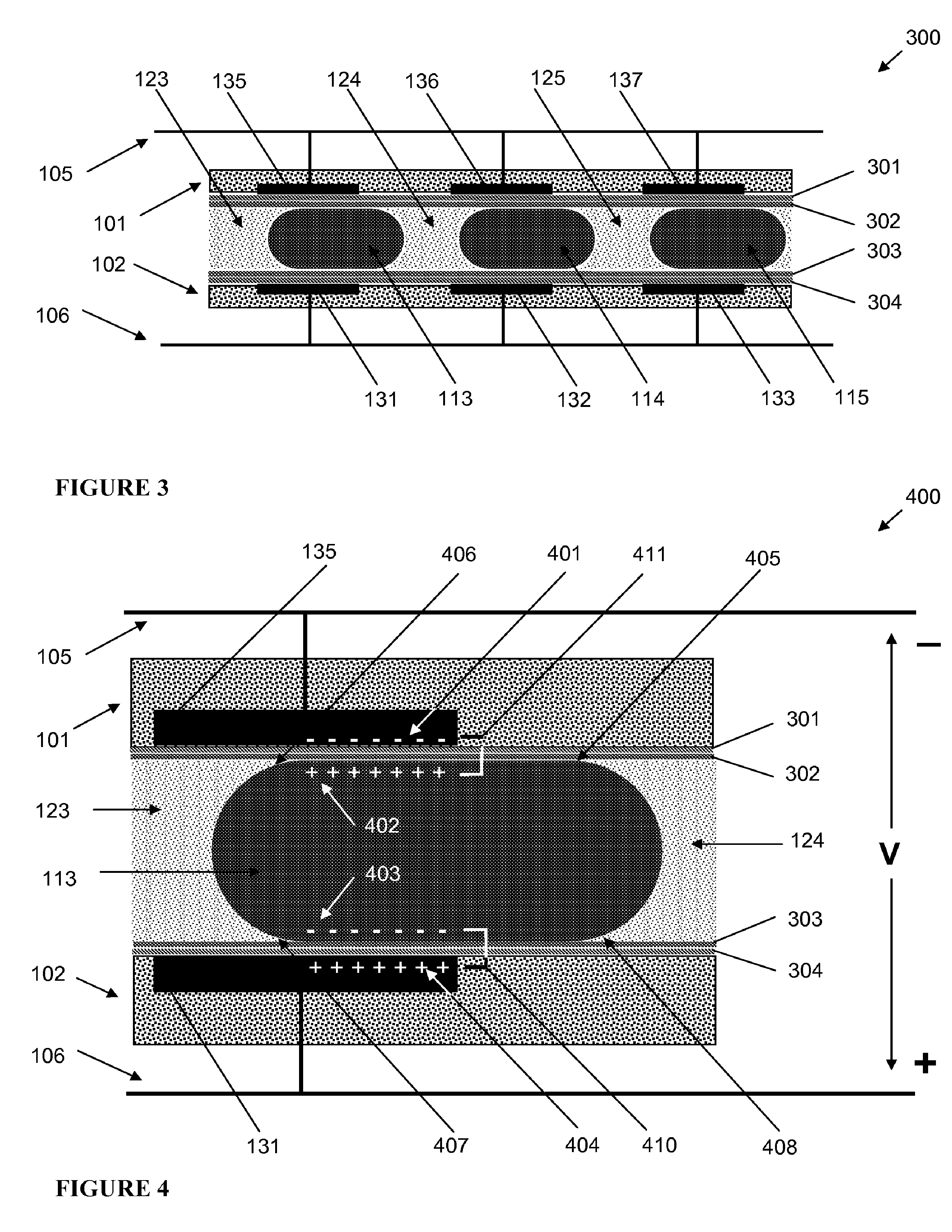
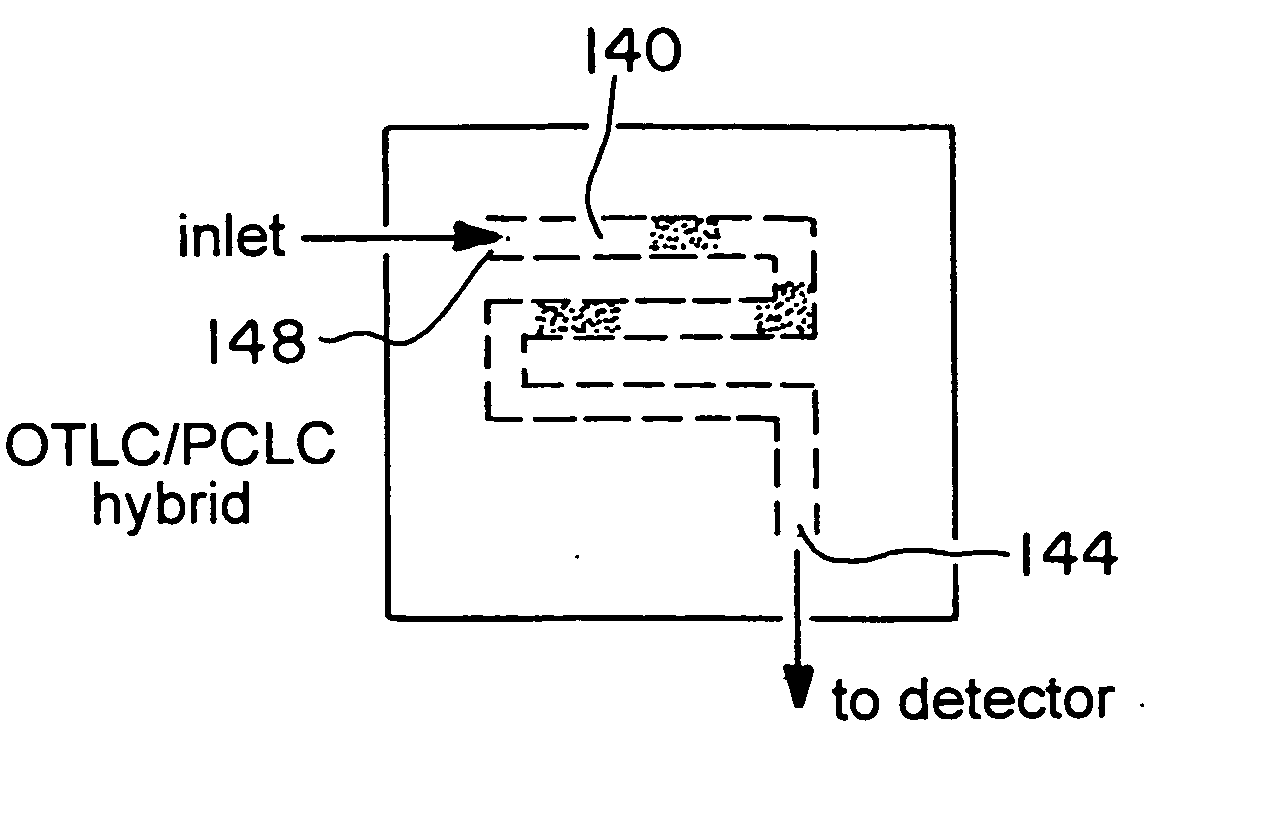
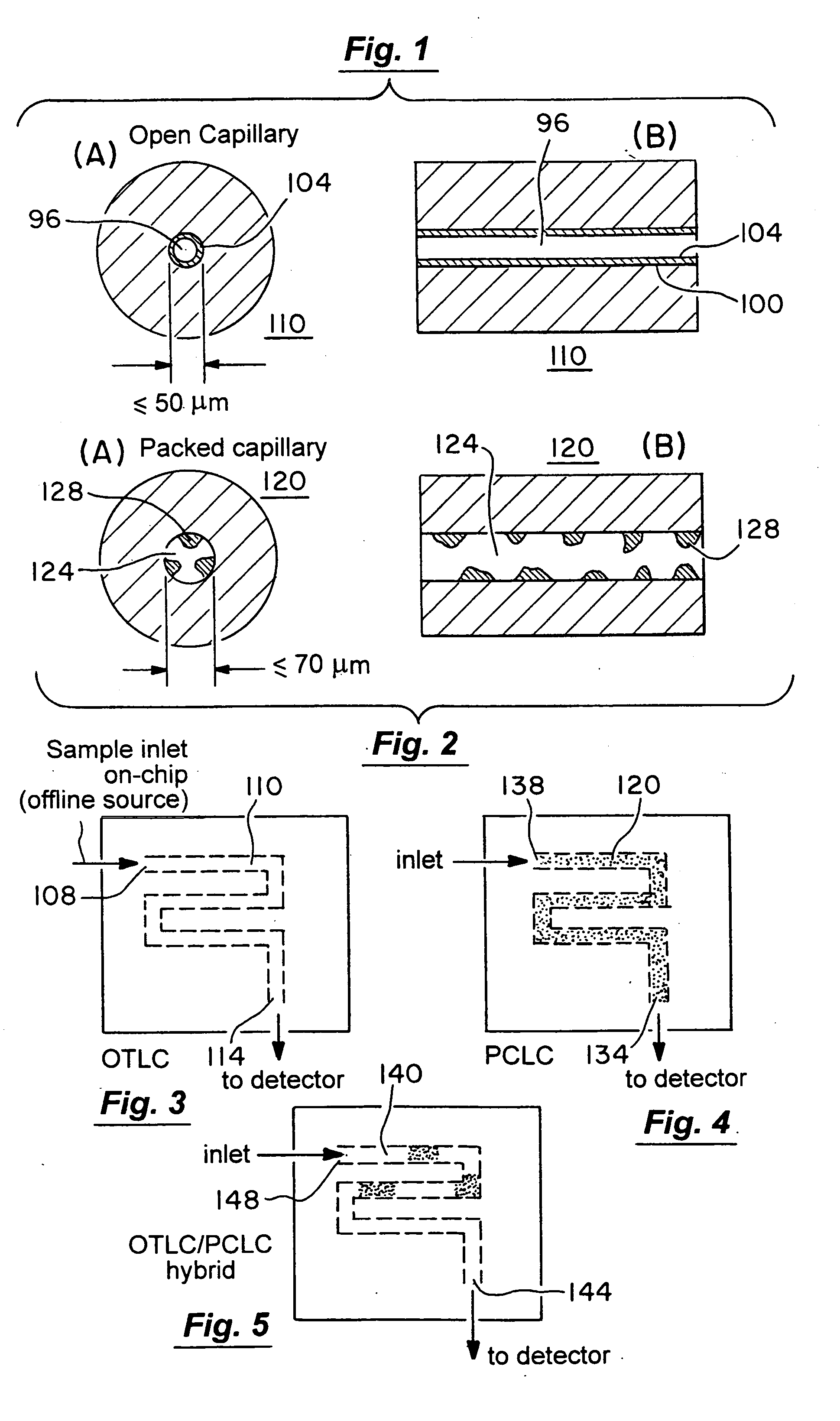
The present invention is directed to a microfluidic chromatography apparatus comprising a microfabricated fluid delivery system and a chromatography column which is in fluid communication with the fluid delivery system, and a method for producing and using the same. Preferably, the chromatography column comprises an OTLC, PCLC, or combinations thereof.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Protein Crystallization Screening and Optimization Droplet Actuators, Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20080044914A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsFrom normal temperature solutionsProtein solutionMicrofluidics
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Scale-up of flow-focusing microfluidic devices
ActiveUS20120121481A1Avoid pressure fluctuationsIntroducing fluctuationPipe supportsFlow mixersMicrofluidicsMulti phase
Parallel uses of microfluidic methods and devices for focusing and / or forming discontinuous sections of similar or dissimilar size in a fluid are described. In some aspects, the present invention relates generally to flow-focusing-type technology, and also to microfluidics, and more particularly parallel use of microfluidic systems arranged to control a dispersed phase within a dispersant, and the size, and size distribution, of a dispersed phase in a multi-phase fluid system, and systems for delivery of fluid components to multiple such devices.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Droplet extraction from a liquid column for on-chip microfluidics
InactiveUS8304253B2Effective drainageAvoid distortionSemi-permeable membranesWithdrawing sample devicesMicrofluidicsDistortion
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Making a two-phase liquid/liquid or gas system in microfluidics
The invention relates to a microfluidic device for making a liquid / liquid or gas biphasic system using a first liquid or a gas and a second liquid, non-miscible with each other, the device having a first hydrophobic surface for the second liquid, the first liquid forming a layer (6) on said first hydrophobic surface. The device comprises means for introducing a drop (7) of the second liquid into the layer of first liquid or gas and in contact with said first hydrophobic surface, and means for displacing the drop on said first hydrophobic surface along a determined path, the device having on the path of the drop, at least one wetting defect causing, upon passing of the drop over this defect, failure of the triple line of contact of the drop on the first hydrophobic surface and inclusion of first liquid (8) or gas into the drop.The invention also relates to the associated method.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
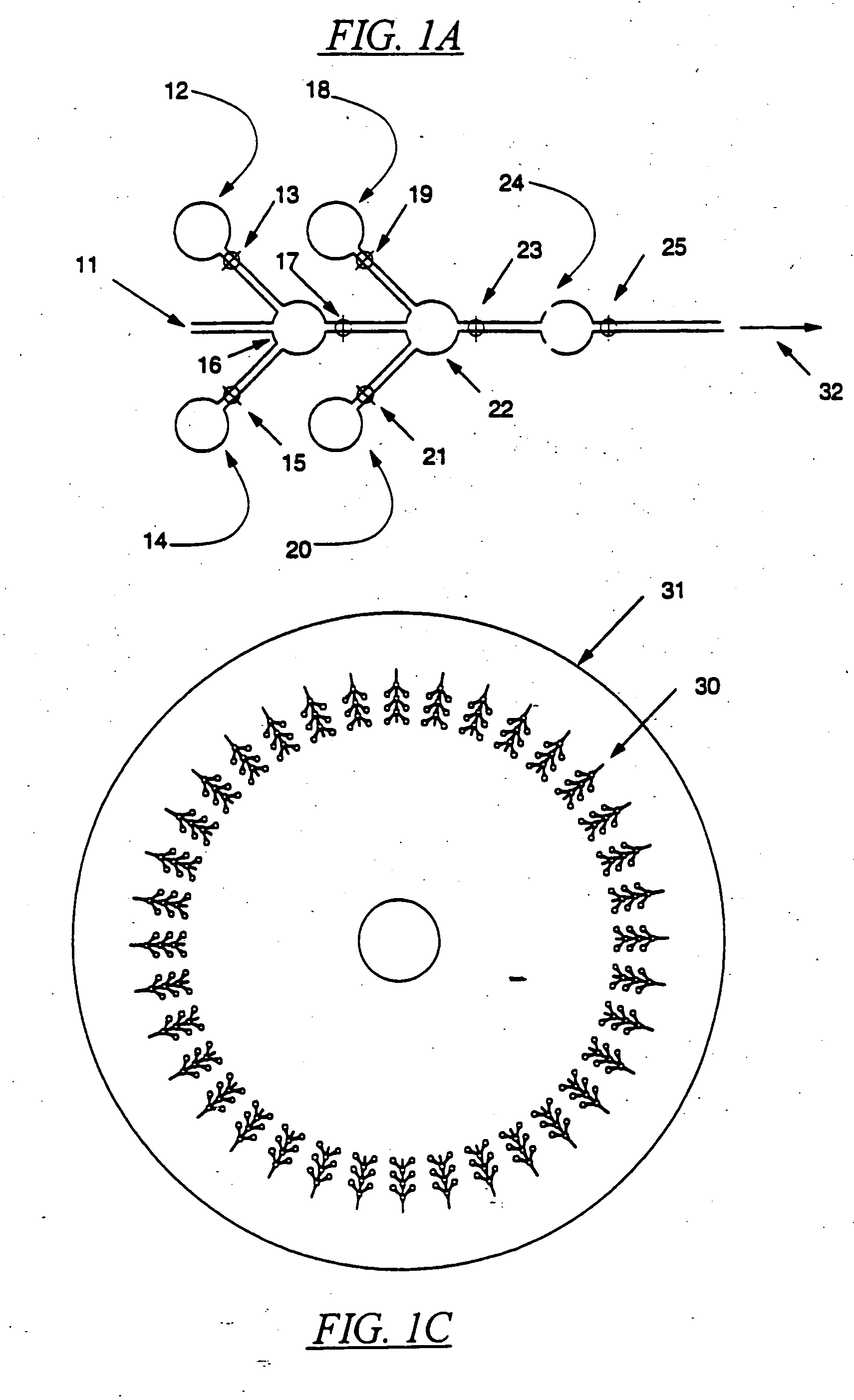
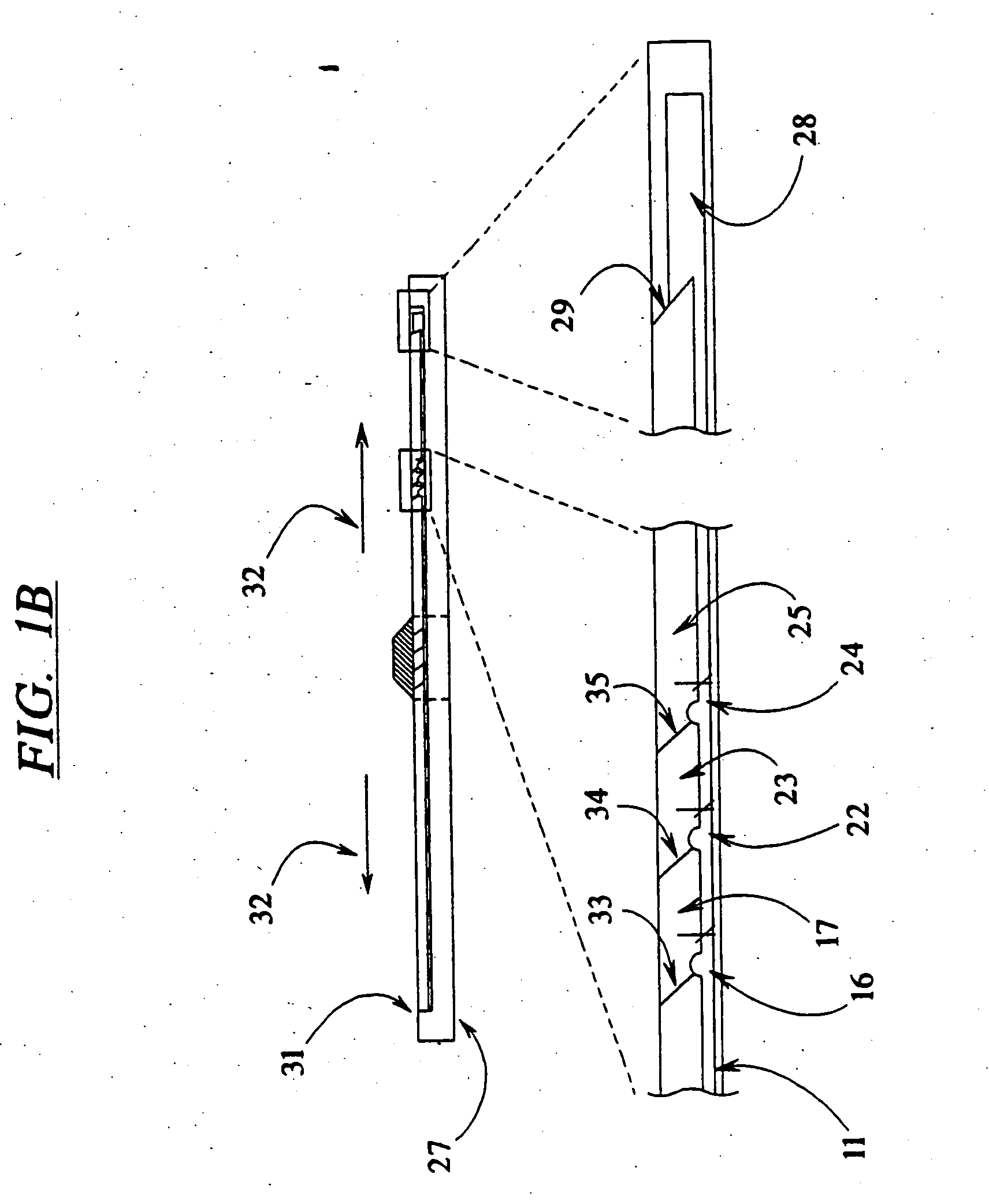
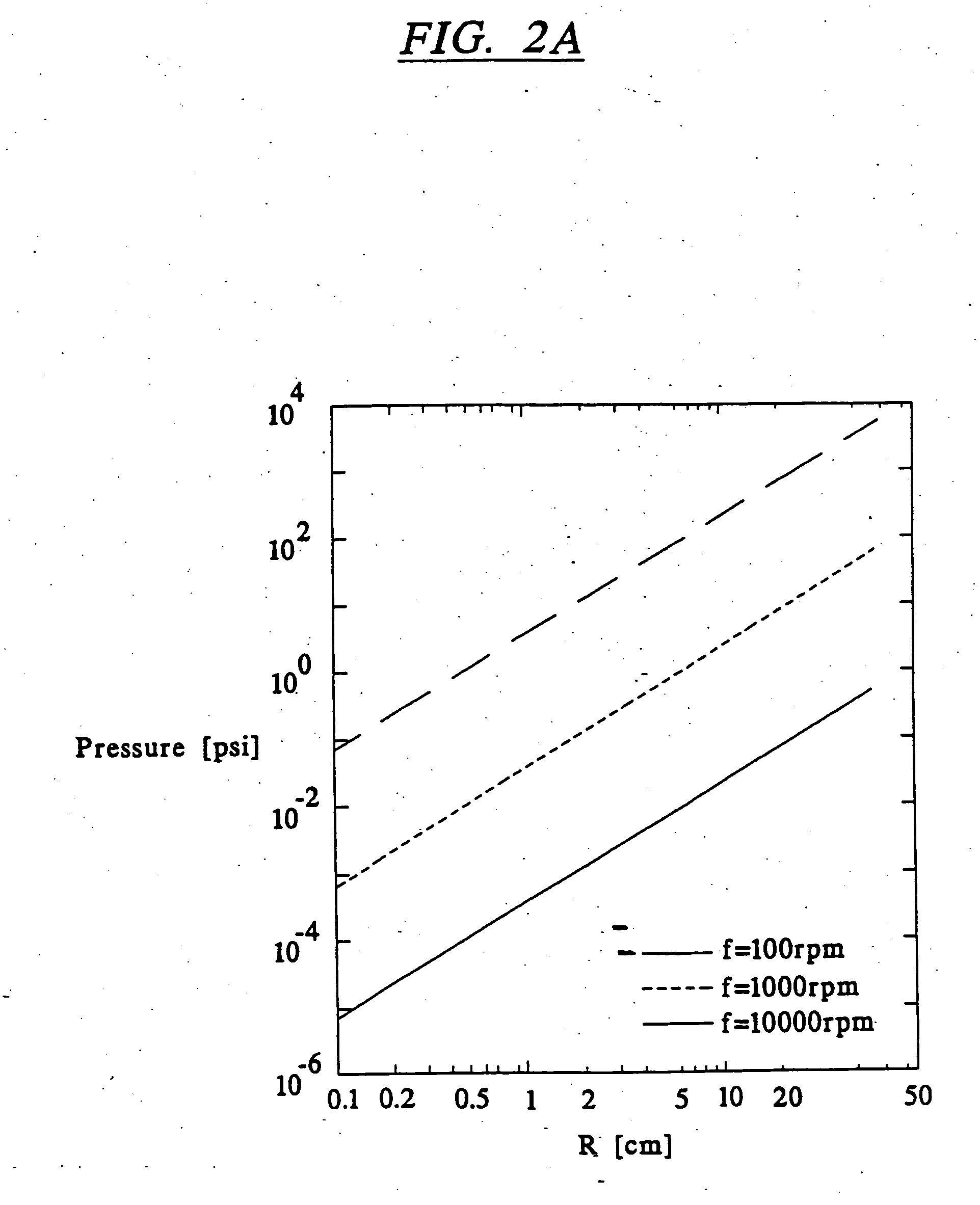
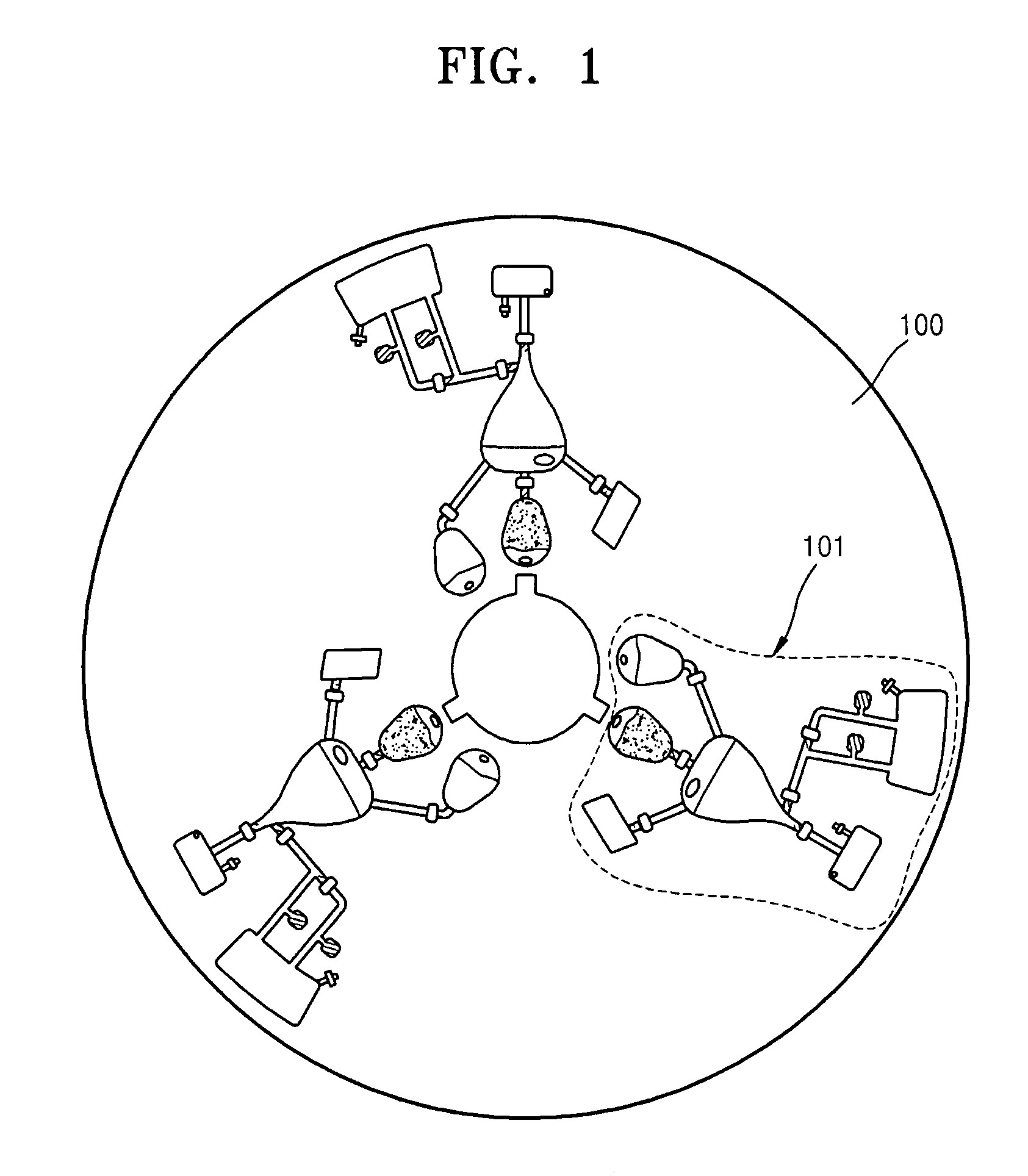
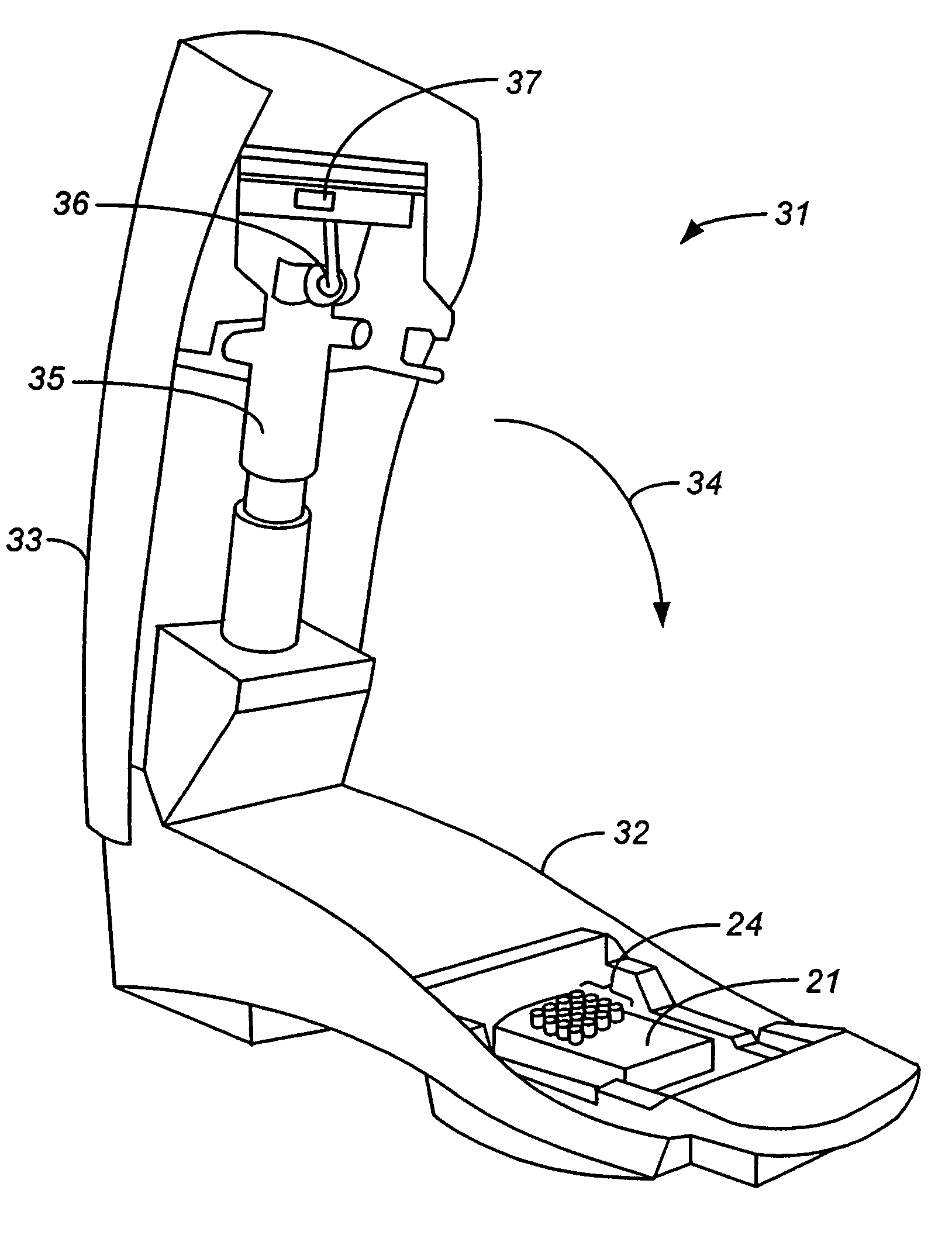
Devices and methods for using centripetal acceleration to drive fluid movement in a microfluidics system
InactiveUS20050069913A1Promote sportsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsValve arrangementsMicrofluidicsData acquisition
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for performing microanalytic and microsynthetic analyses and procedures. The invention provides a microsystem platform and a micromanipulation device for manipulating the platform that utilizes the centripetal force resulting from rotation of the platform to motivate fluid movement through microchannels. The microsystem, platforms of the invention are also optionally provided having system informatics and data acquisition, analysis and storage and retrieval informatics encoded on the surface of the disk opposite to the surface containing the fluidic components. Methods specific for the apparatus of the invention for performing any of a wide variety of microanalytical or microsynthetic processes are provided.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG TECAN GRP LTD
Microfluidic Chaotic Mixing Systems And Methods
Microfluidic nucleic acid hybridization systems are described that include a first reaction chamber to hold an analyte solution comprising nucleic acids, and a first mixing channel in fluid communication with the chamber. The mixing channel includes a textured surface to mix the analyte solution. The systems may also include pump coupled to the mixing channel to circulate the analyte solution through the reaction chamber and the mixing channel, and an input port in fluid communication with the mixing channel and the reaction chamber to supply the analyte solution to the microfluidic system. The input port can be closed to create a closed circulation path for the analyte solution through the reaction chamber and the mixing channel.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Droplet extraction from a liquid column for on-chip microfluidics
InactiveUS20090014394A1Effective drainageAvoid distortionSemi-permeable membranesWithdrawing sample devicesMicrofluidicsDistortion
A refill droplet facilitates the extraction of a droplet laterally from a channel in a microfluidic apparatus. Such extraction allows a discrete band of separated particles or solute molecules to be excised from a fluid stream and processed and analyzed separately. An extraction point is located along the length of the channel and includes an EWOD surface or similar microfluidic technology to extract a droplet. An opening in the channel opposite the extraction means is equipped with microfluidic technology to transport a refill droplet to the opening. The refill droplet is moved into the channel or column to occupy the area previously occupied by the extracted droplet. This prevents distortion or mixing of the bands of particles or molecules within the channel and prevents the draining of any portion of the fluidic system.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
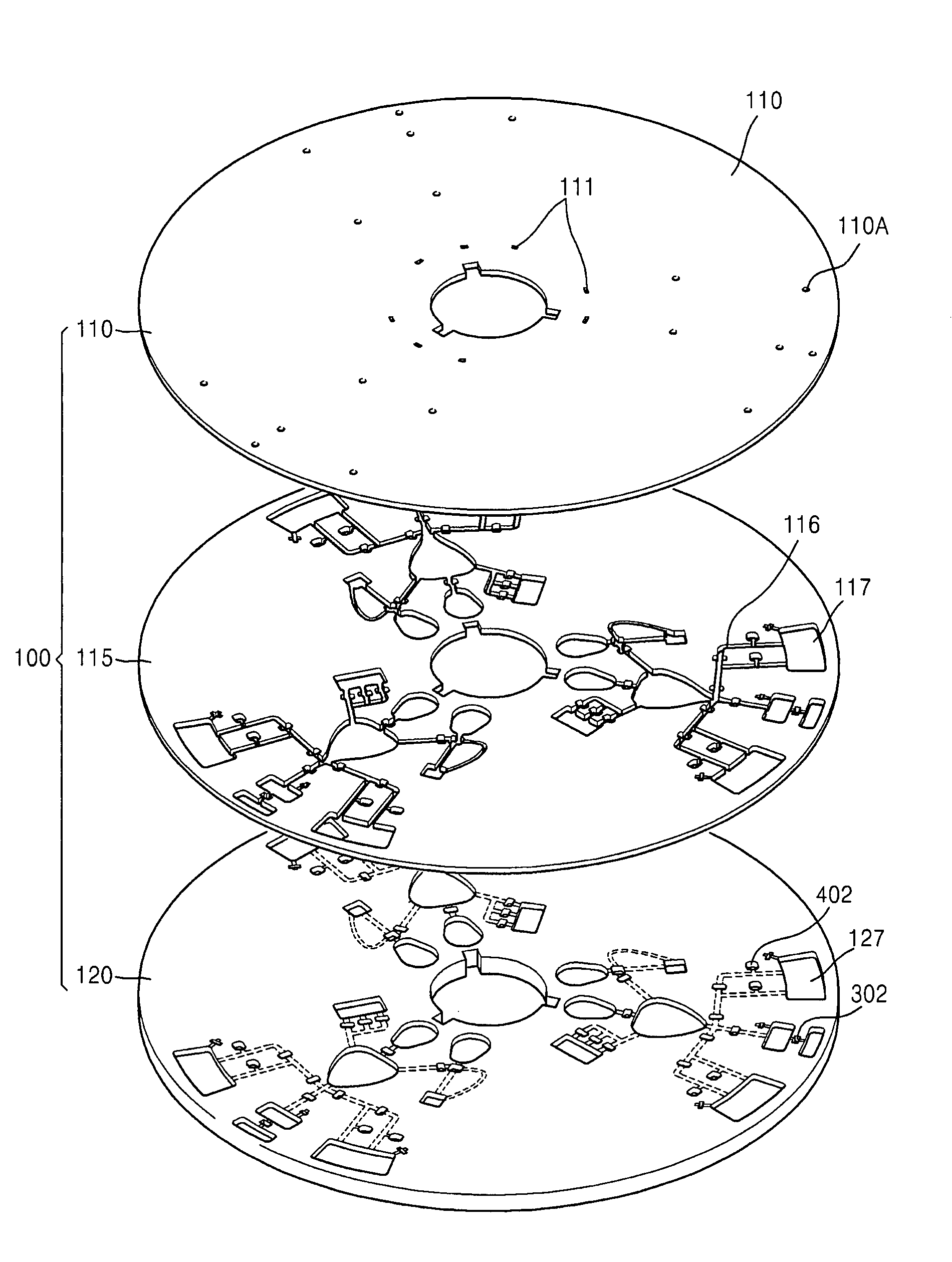
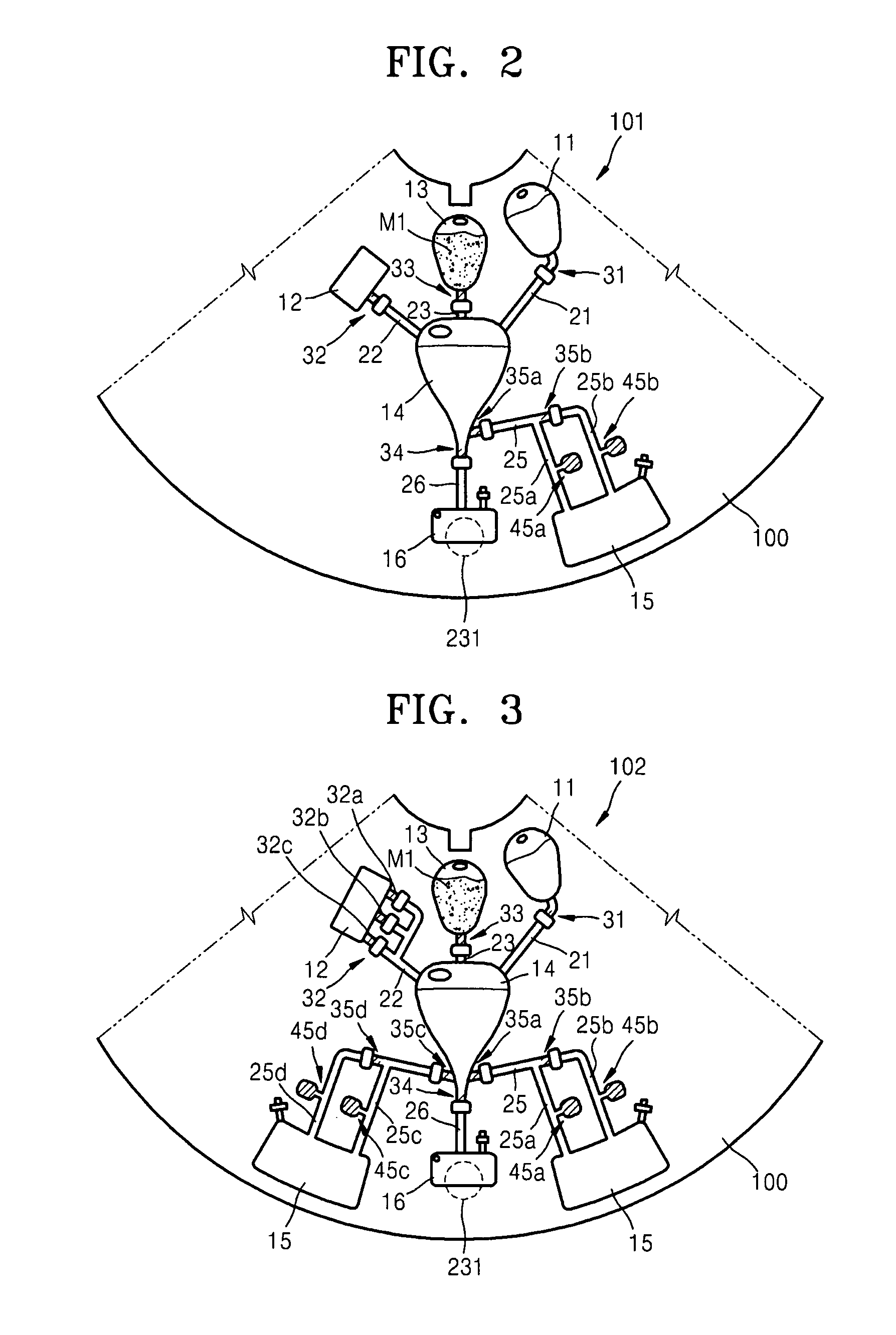
Centrifugal force-based microfluidic device for protein detection and microfluidic system including the same
ActiveUS20080056949A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein detectionProtein target
A centrifugal force-based microfluidic device for the detection of a target biomolecule and a microfluidic system including the same are provided. The device includes a body of revolution; a microfluidic structure disposed in the body of revolution including chambers, channels connecting the chambers, and valves disposed in the channels to control fluid flow, the microfluidic structures transmitting fluid using centrifugal force due to rotation of the body of revolution; and beads disposed in the microfluidic structures, the beads having capture probes on the surfaces thereof which are selectively bonded with target protein; and a detection probe disposed in the microfluidic structures and selectively bonded to the target protein, and which includes a material required to express an optical signal, wherein the microfluidic structure mixes the beads, biological samples, and the detection probe to react and washes and separates the beads after the reaction.
Owner:PRECISIONBIOSENSOR INC
Microfluidic device and method for improved sample handling
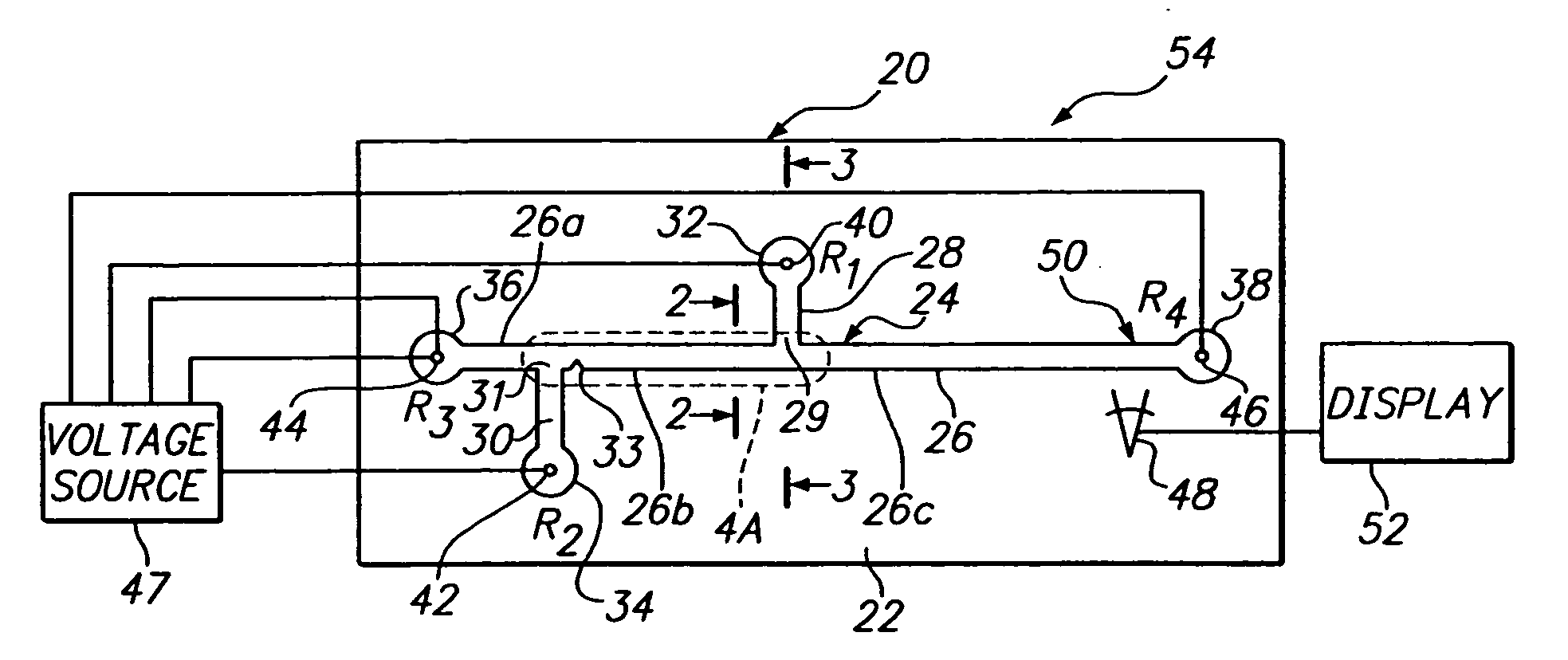
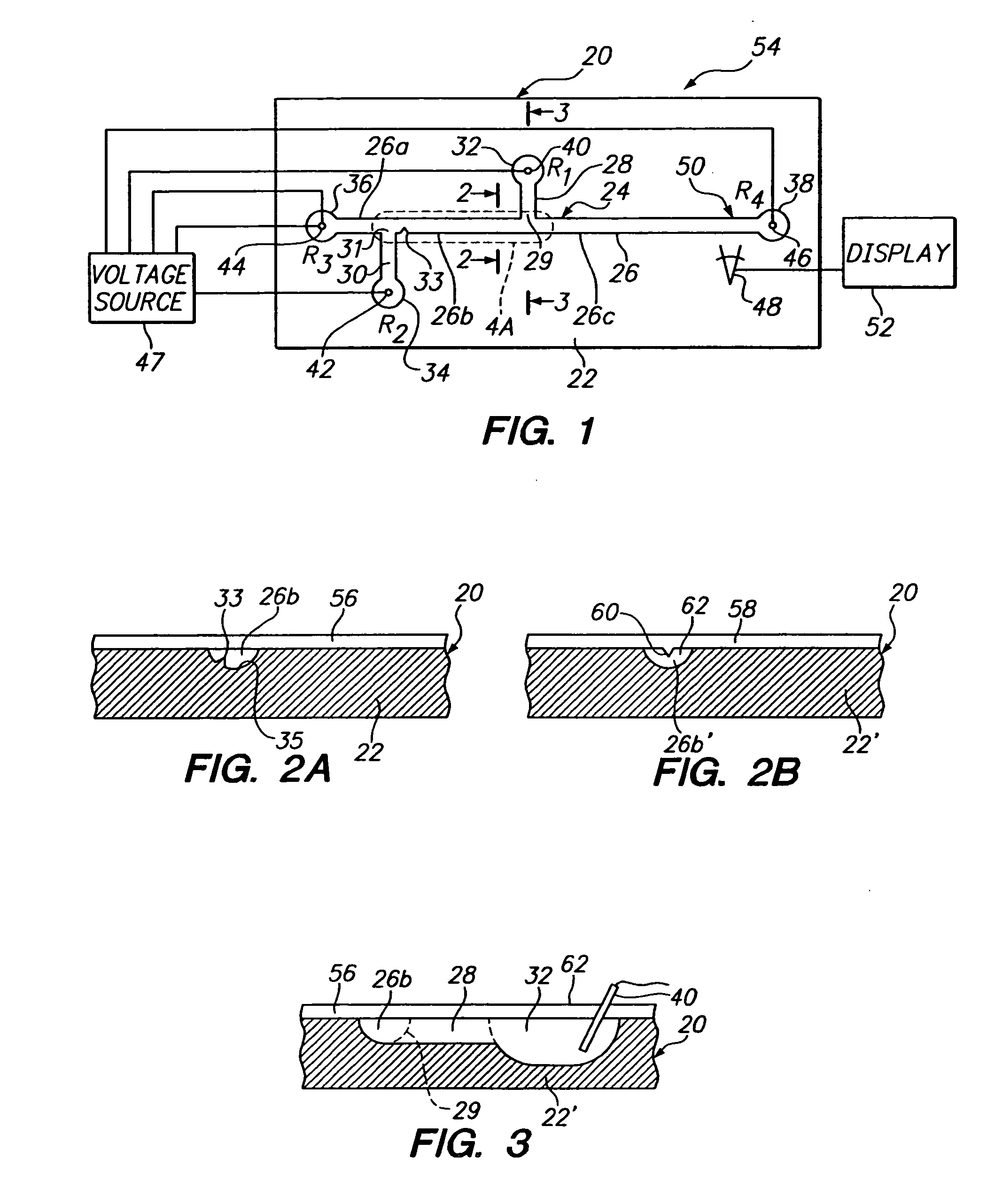
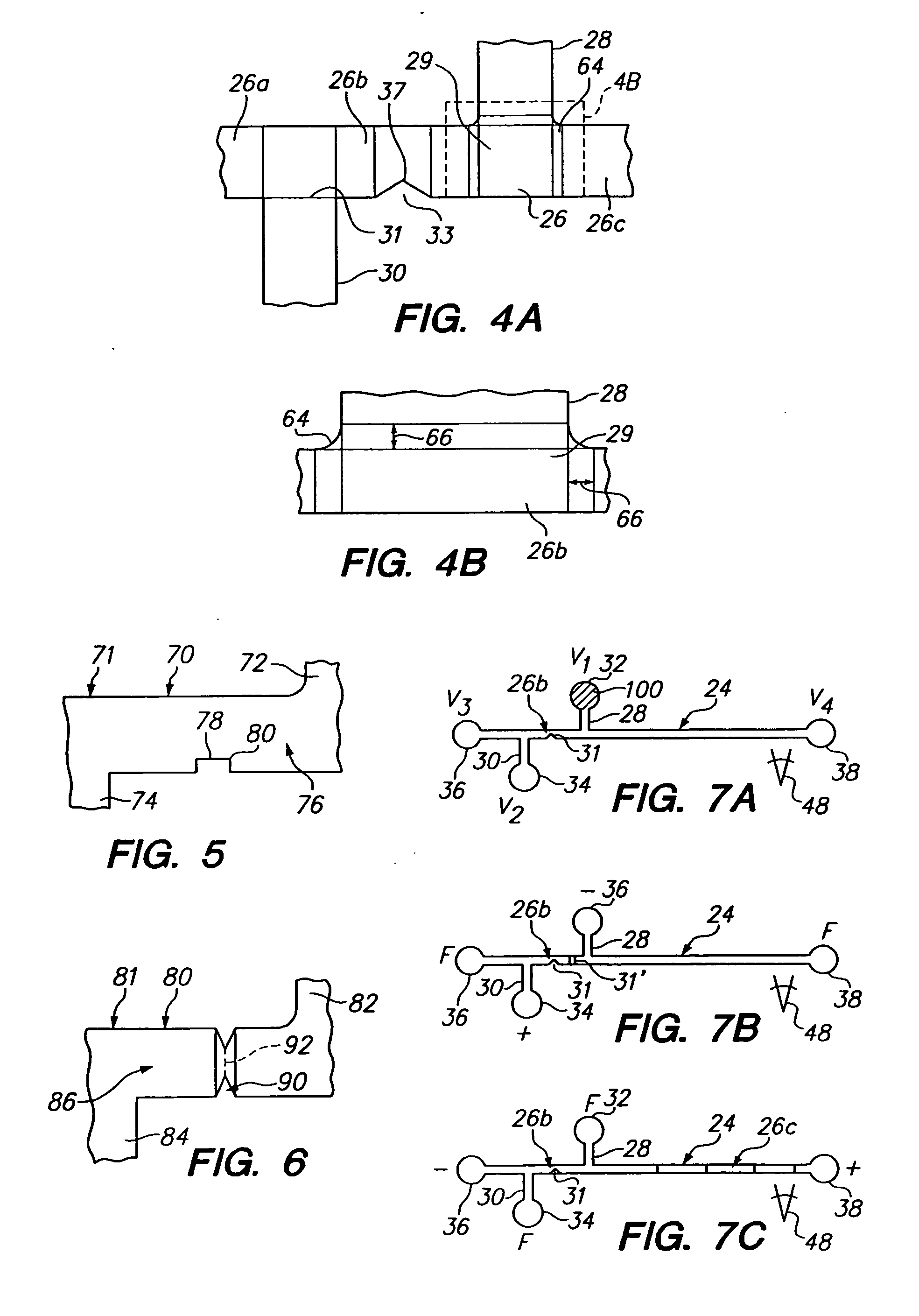
InactiveUS20060113190A1Effective movementSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementMicrofluidicsElectrophoresis
A microfluidics device and method for sample loading, concentrating, mixing, and / or reacting is disclosed. The device has a microchannel network that includes a channel segment communicating with first and second reservoirs. A projection formed on a wall portion of the channel segment terminates therein at a point or edge. When a voltage potential is applied across the two reservoirs, the projection functions to create an electric field gradient within the channel segment that causes charged components in the channel segment to concentrate in the region of the projection. The device is useful, for example, in loading a sample of dilute charged components for electrophoretic separation in the device.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
DNA and RNA sequencing by nanoscale reading through programmable electrophoresis and nanoelectrode-gated tunneling and dielectric detection
An apparatus and method for performing nucleic acid (DNA and / or RNA) sequencing on a single molecule. The genetic sequence information is obtained by probing through a DNA or RNA molecule base by base at nanometer scale as though looking through a strip of movie film. This DNA sequencing nanotechnology has the theoretical capability of performing DNA sequencing at a maximal rate of about 1,000,000 bases per second. This enhanced performance is made possible by a series of innovations including: novel applications of a fine-tuned nanometer gap for passage of a single DNA or RNA molecule; thin layer microfluidics for sample loading and delivery; and programmable electric fields for precise control of DNA or RNA movement. Detection methods include nanoelectrode-gated tunneling current measurements, dielectric molecular characterization, and atomic force microscopy / electrostatic force microscopy (AFM / EFM) probing for nanoscale reading of the nucleic acid sequences.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Microfluidic and nanofluidic devices, systems, and applications
InactiveUS20110039303A1Block fluid flowMaterial nanotechnologyValve arrangementsChemical reactionMicrofluidics
The present invention discloses the integration of programmable microfluidic circuits to achieve practical applications to process biochemical and chemical reactions and to integrate these reactions. In some embodiments workflows for biochemical reactions or chemical workflows are combined. Microvalves such as programmable microfluidic circuit with Y valves and flow through valves are disclosed. In some embodiments microvalves of the present invention are used for mixing fluids, which may be part of an integrated process. These processes include mixing samples and moving reactions to an edge or reservoir for modular microfluidics, use of capture regions, and injection into analytical devices on separate devices. In some embodiments star and nested star designs, or bead capture by change of cross sectional area of a channel in a microvalve are used. Movement of samples between temperature zones are further disclosed using fixed temperature and movement of the samples by micropumps.
Owner:INTEGENX
Microfluidic apparatus and methods for performing blood typing and crossmatching
ActiveUS20100112723A1Small dimensionIncrease ratingsBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAntigenGroup A - blood
Microfluidic cartridges for agglutination reactions are provided. The cartridges include a microfluidic reaction channel with at least two intake channels, one for an antigen-containing fluid and the other for an antibody-containing fluid, conjoined to a reaction channel modified by incorporation of a downstream flow control channel. At low Reynolds Number, the two input streams layer one on top of the other in the reaction channel and form a flowing, unmixed horizontally-stratified laminar fluid diffusion (HLFD) interface for an extended duration of reaction. Surprisingly, the design, surface properties, and flow regime of microfluidic circuits of the present invention potentiate detection of antibody mediated agglutination at the stratified interface. Antigen:antibody reactions involving agglutination potentiated by these devices are useful in blood typing, in crossmatching for blood transfusion, and in immunodiagnostic agglutination assays, for example.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Centrifugal force-based microfluidic device for nucleic acid extraction and microfluidic system including the microfluidic device
ActiveUS20080108120A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsValve arrangementsExternal energyMicrofluidics
A centrifugal force-based microfluidic device for nucleic acid extraction and a microfluidic system are provided. The microfluidic device includes a body of revolution; a microfluidic structure disposed in the body of revolution, the microfluidic structure including a plurality of chambers, channels connecting the chambers, and valves disposed in the channels to control fluid flow, the microfluidic structure transmitting the fluid using centrifugal force due to rotation of the body of revolution; and magnetic beads contained in one of the chambers which collect a target material from a biomaterial sample flowing into the chamber, wherein the microfluidic structure washes the magnetic beads which collect the target material, and separates nucleic acid by electromagnetic wave irradiation from an external energy source to the magnetic beads. The microfluidic system includes the microfluidic device; a rotation operating unit which rotates the body of revolution; and an external energy source which irradiates electromagnetic waves.
Owner:PRECISIONBIOSENSOR INC
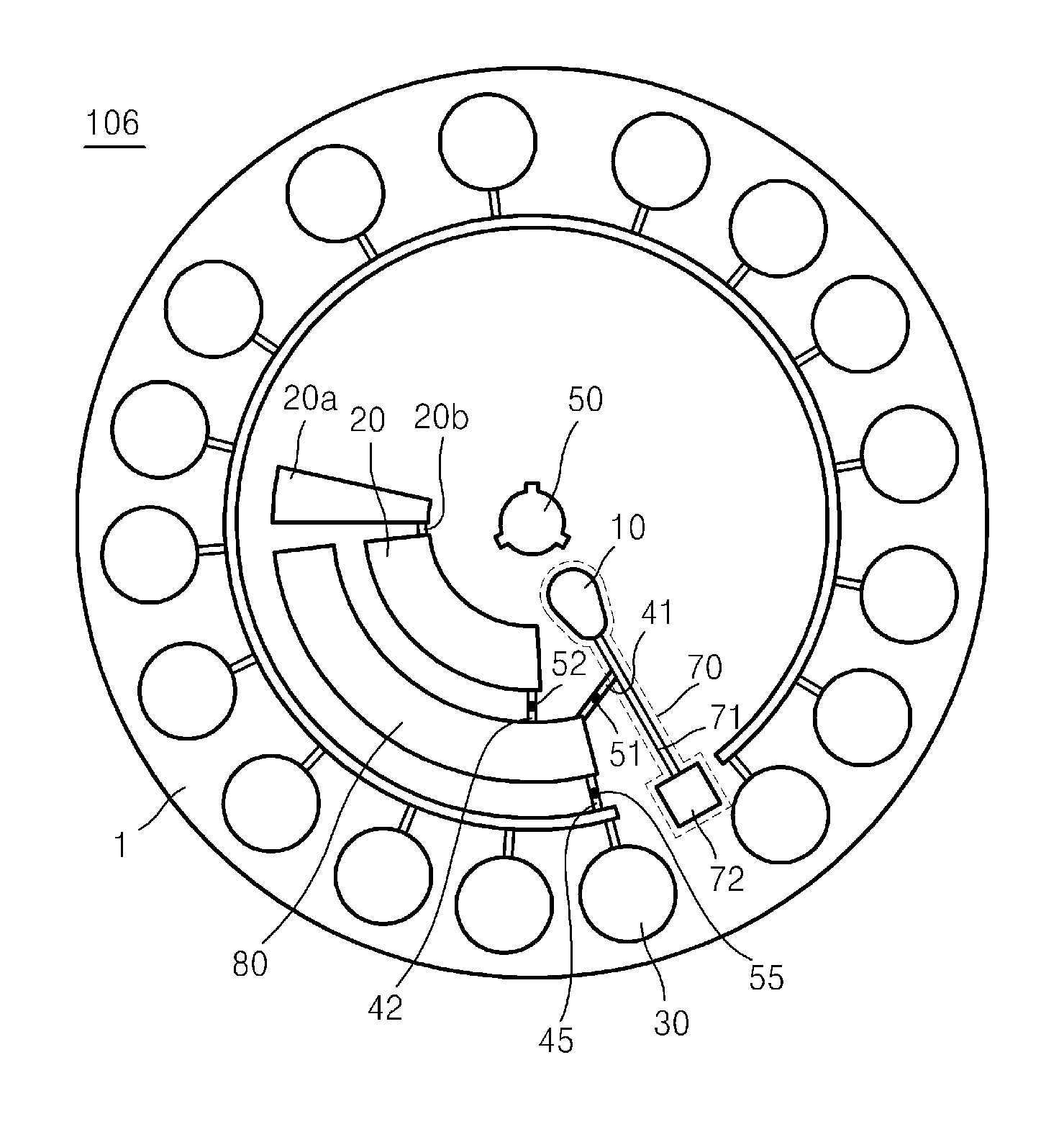
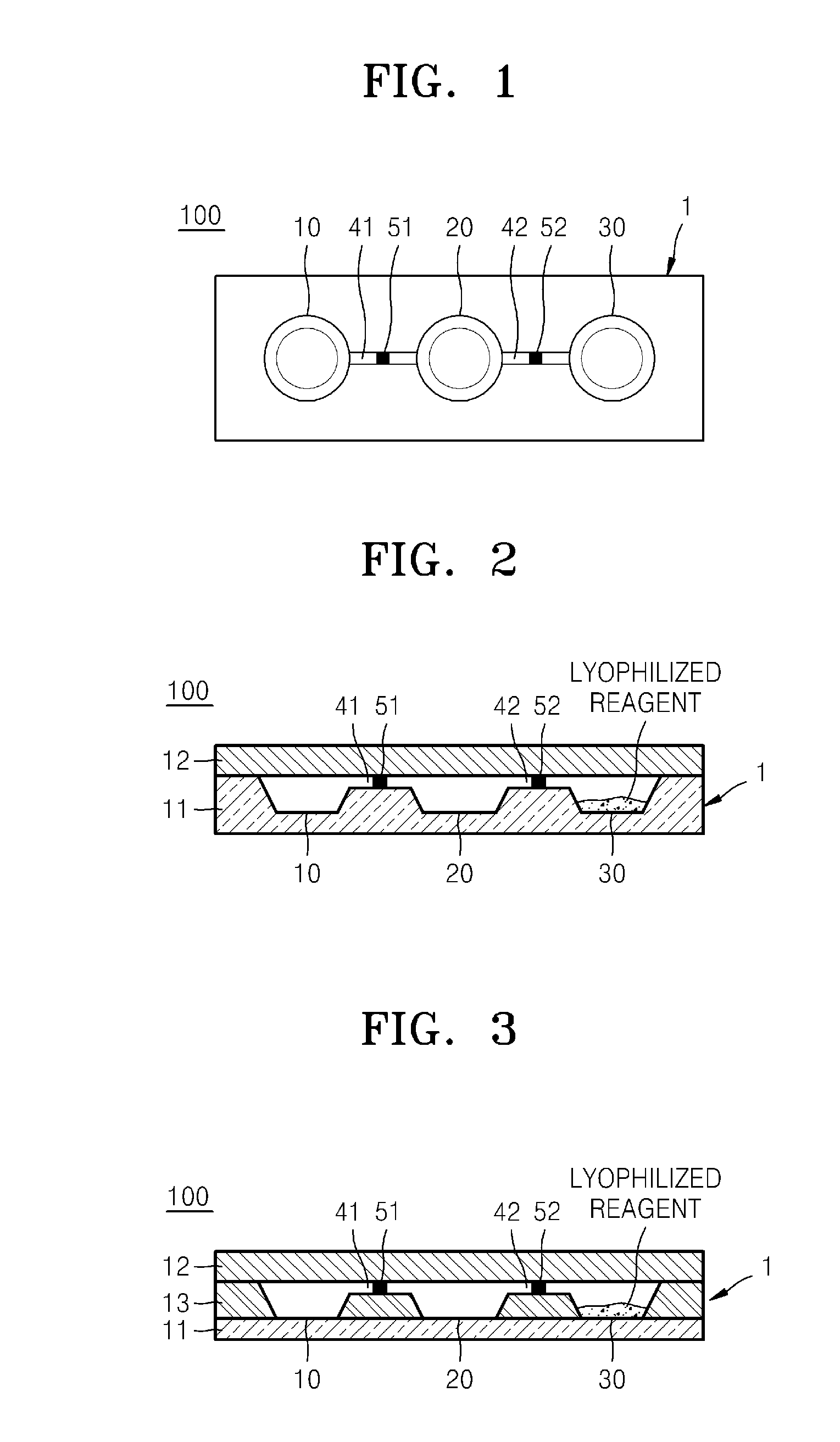
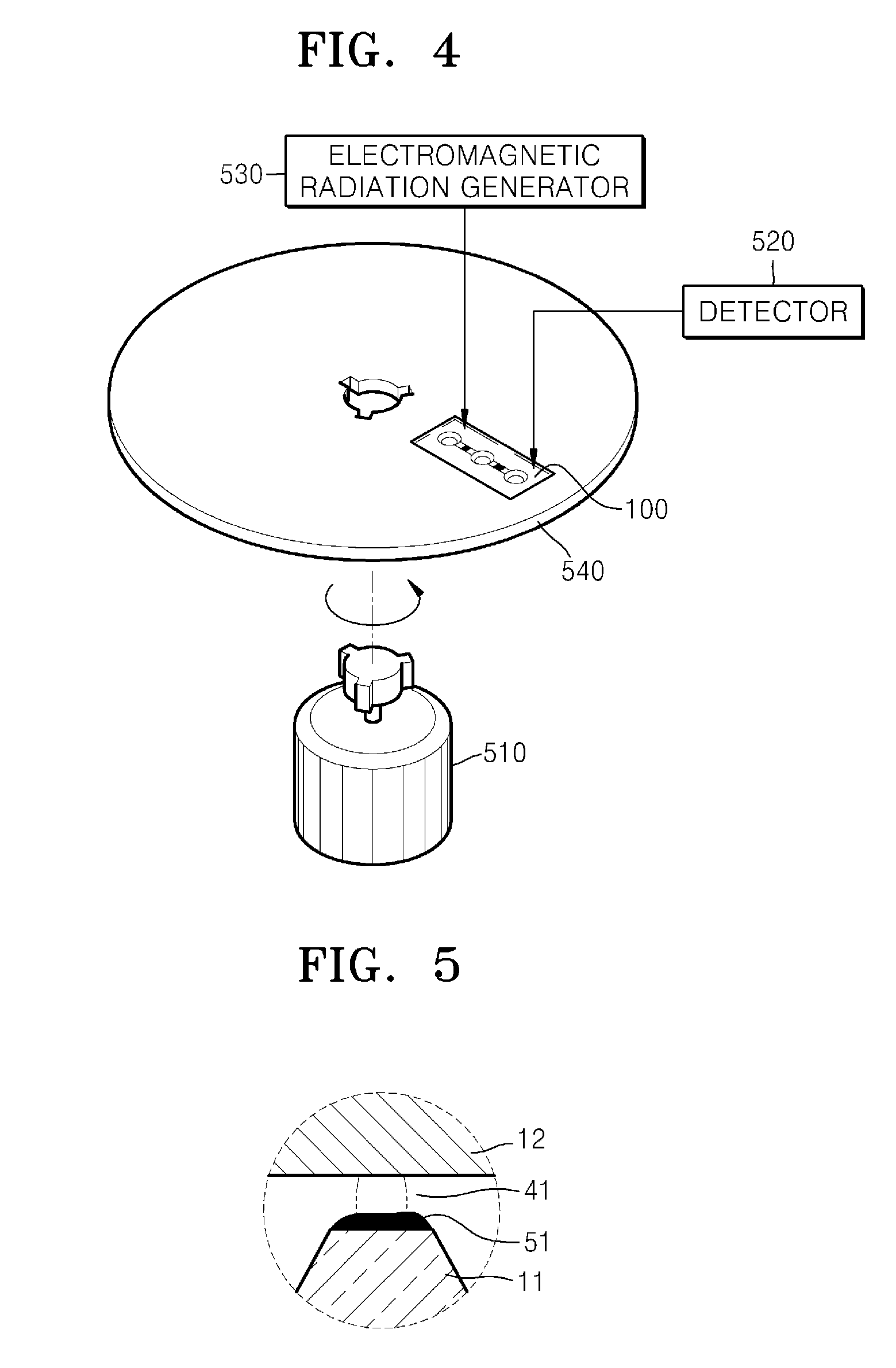
Microfluidic device containing lyophilized reagent therein and analyzing method using the same
InactiveUS20090286327A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrofluidicsAnalysis method
Provided is a microfluidic device suitable for analyzing a liquid sample. The device includes a first chamber to contain a sample; a second chamber to contain a liquid first reagent; a third chamber containing a lyophilized second reagent; a plurality of channels connecting the first, second, and third chambers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus for priming microfluidics devices with feedback control
ActiveUS7727477B2Easy to remove and replaceGuaranteed economic efficiencySludge treatmentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMicrofluidicsFeedback control
A priming unit for a microfluidics device contains a pressurization unit and pressure and temperature detectors as part of a feedback loop that controls the pressure applied by the pressurization unit and the time during which the pressure is applied. This control feature is particularly useful in controlling the exposure time of the microchannels to dyes in the priming liquids since certain dyes tend to adhere to the walls of the channels and produce non-uniform results.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC +1
Actuators for microfluidics without moving parts
InactiveUS20070267294A1Effectively converting the surface into more hydrophilicArea maximizationSludge treatmentFlow mixersElectricityMicrofluidics
A series of microactuators for manipulating small quantities of liquids, and methods of using these for manipulating liquids, are disclosed. The microactuators are based on the phenomenon of electrowetting and contain no moving parts. The force acting on the liquid is a potential-dependent gradient of adhesion energy between the liquid and a solid insulating surface.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
System and method for serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS20120052560A1Rapid serial processingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHandling systemData store
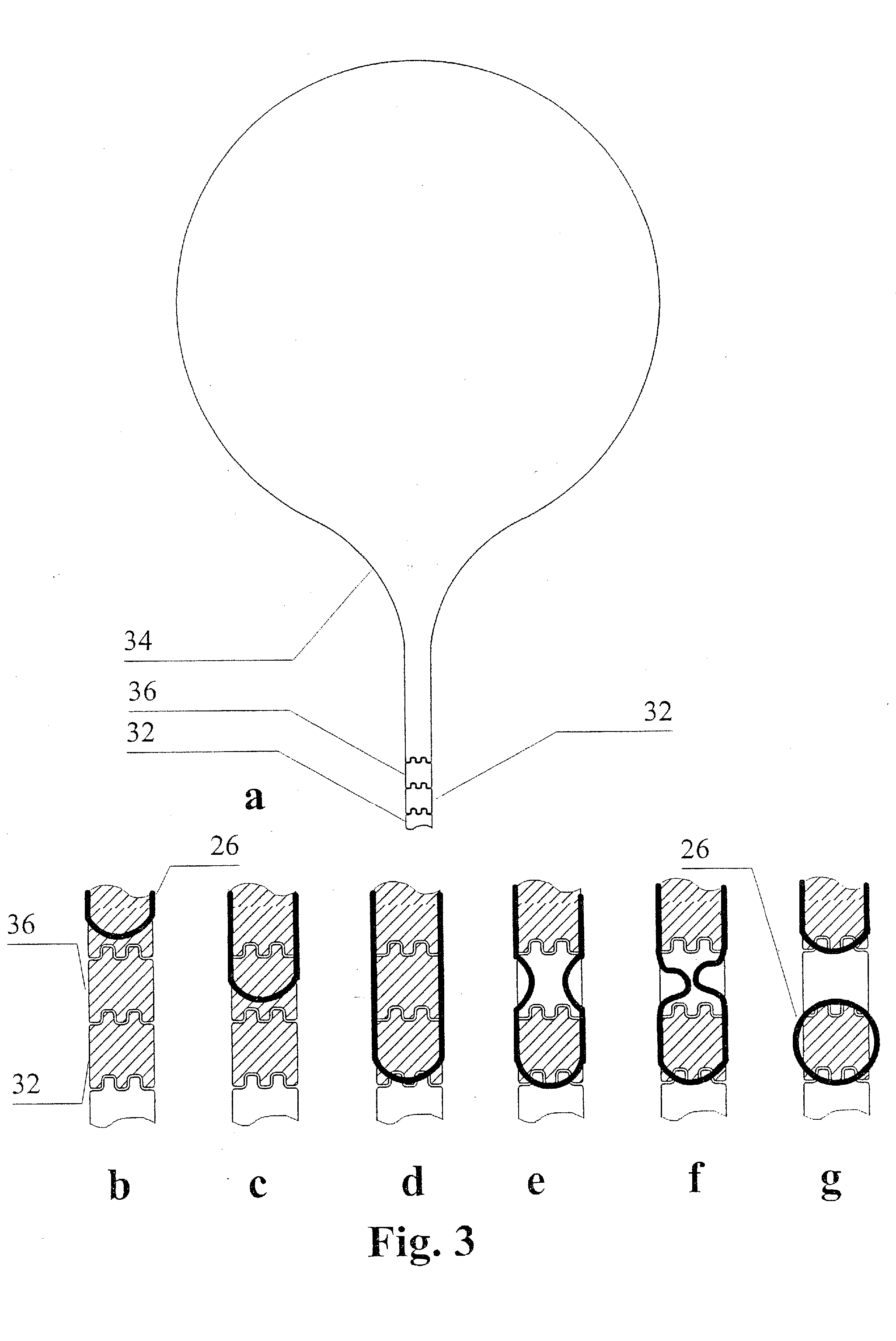
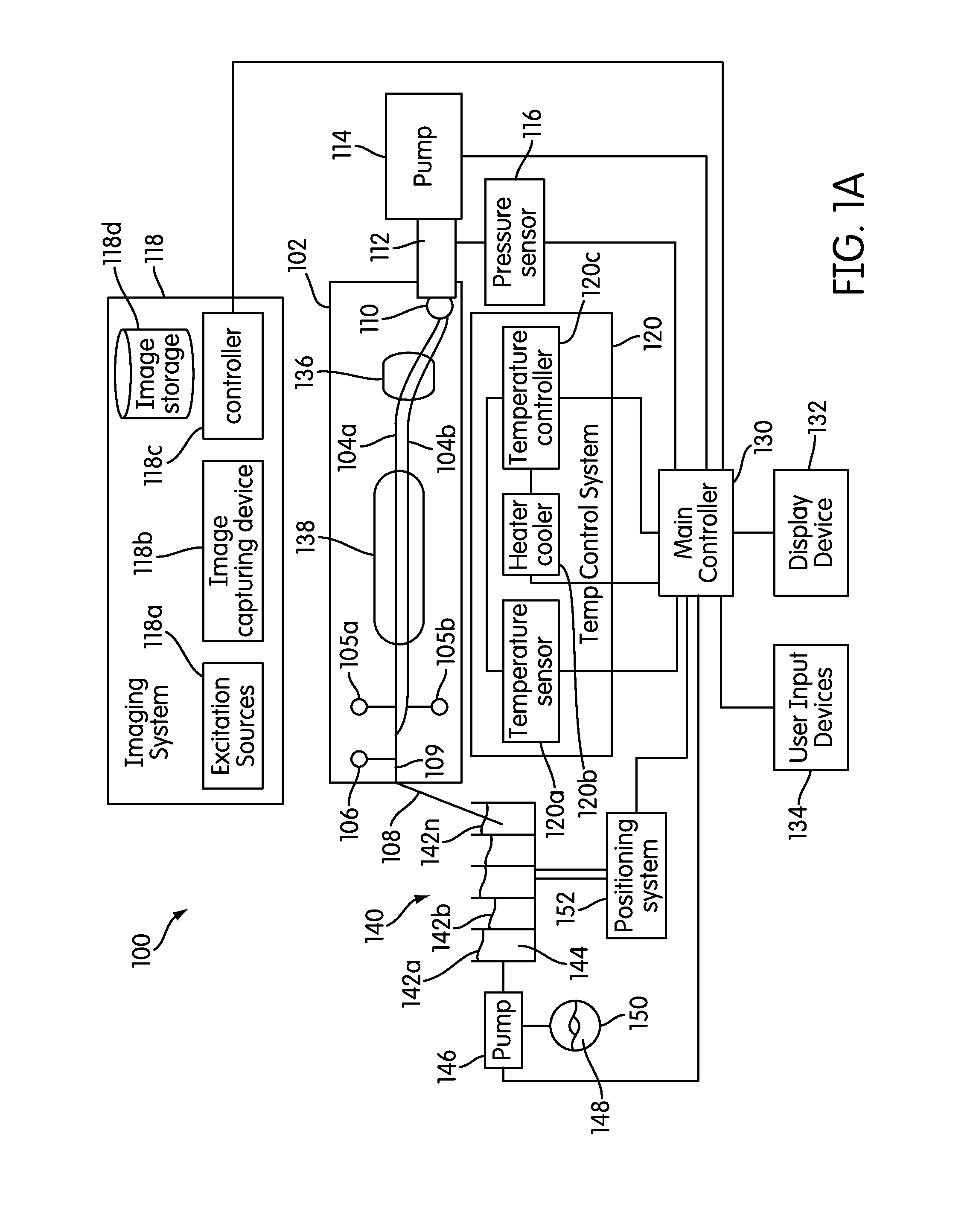
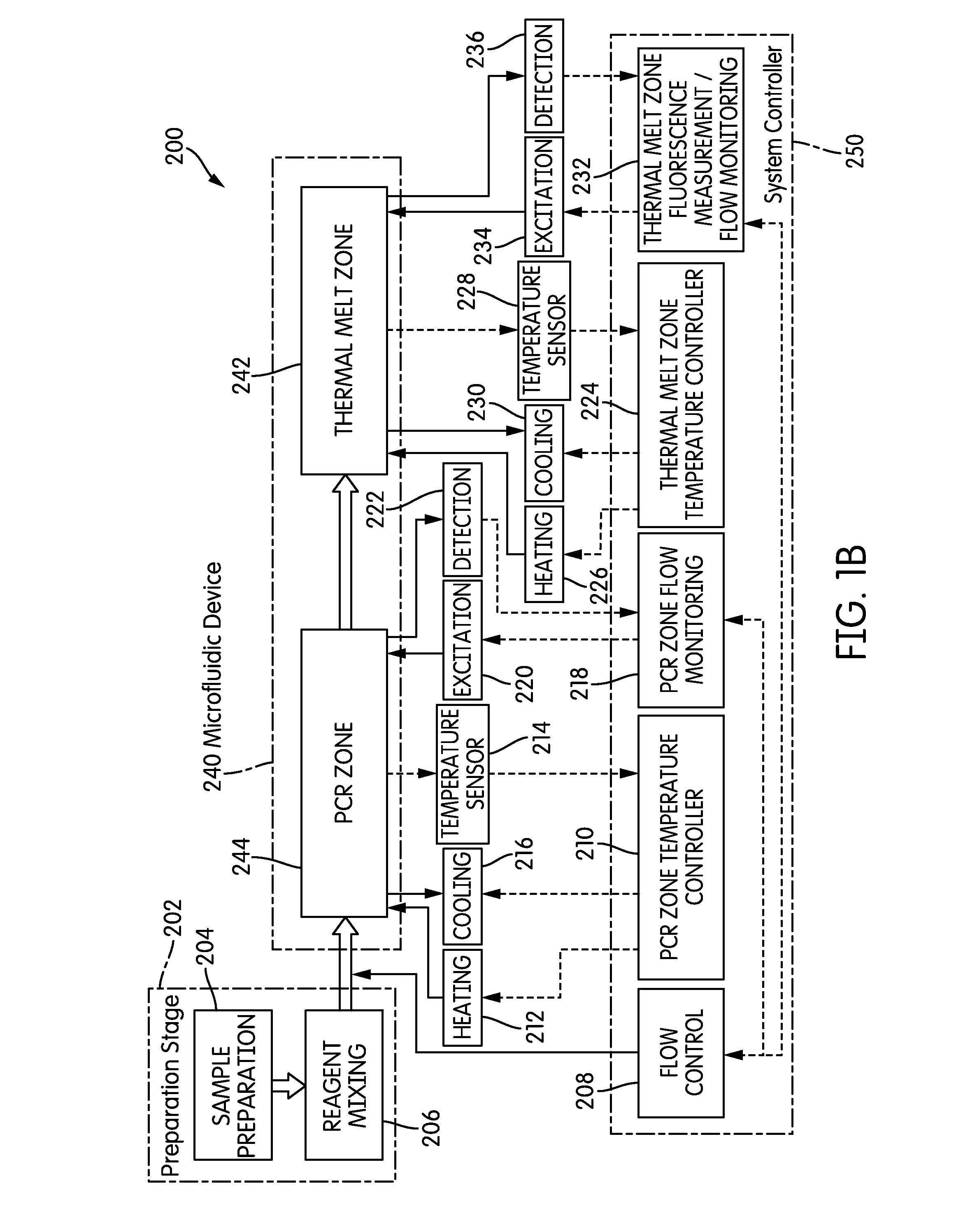
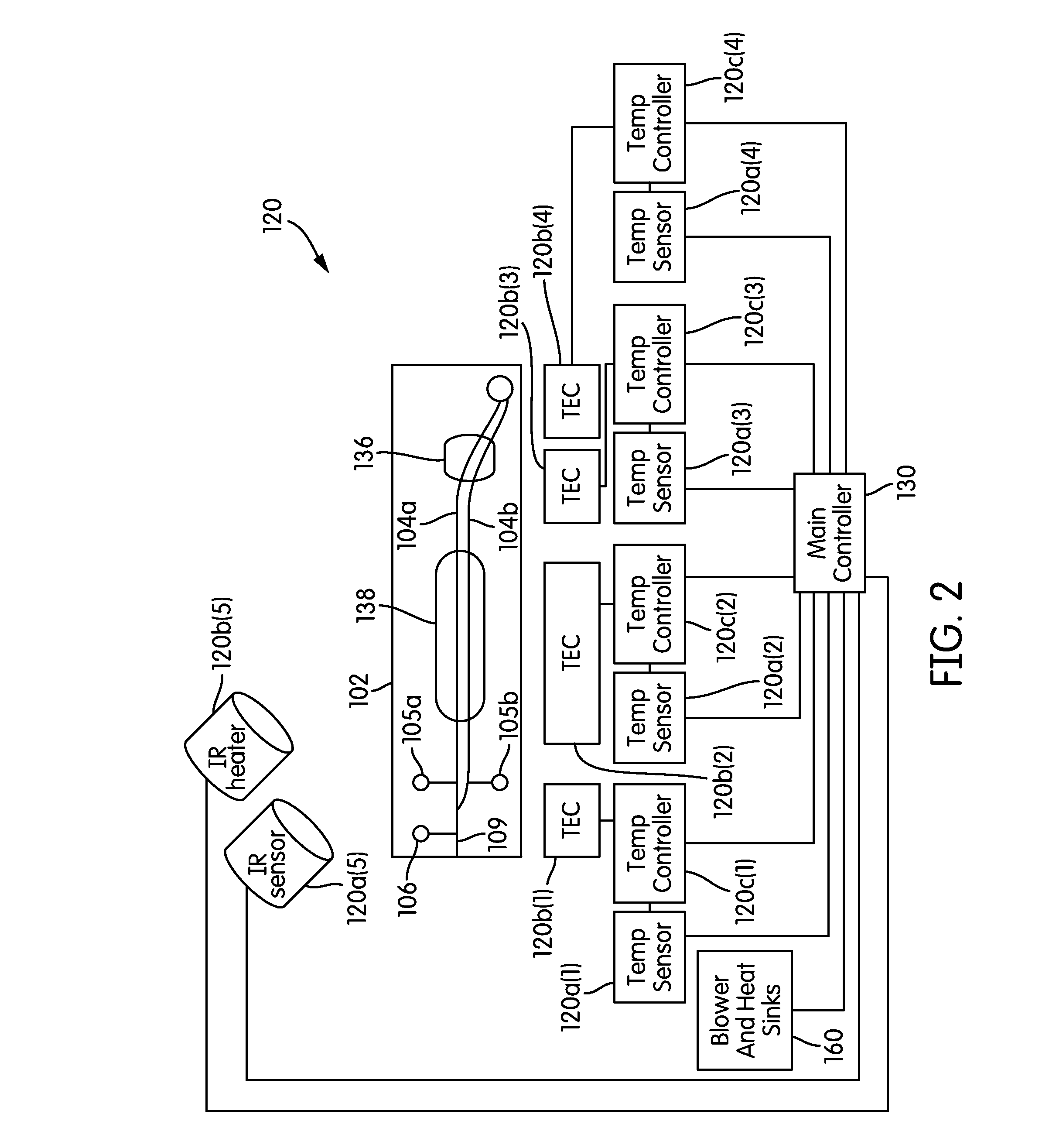
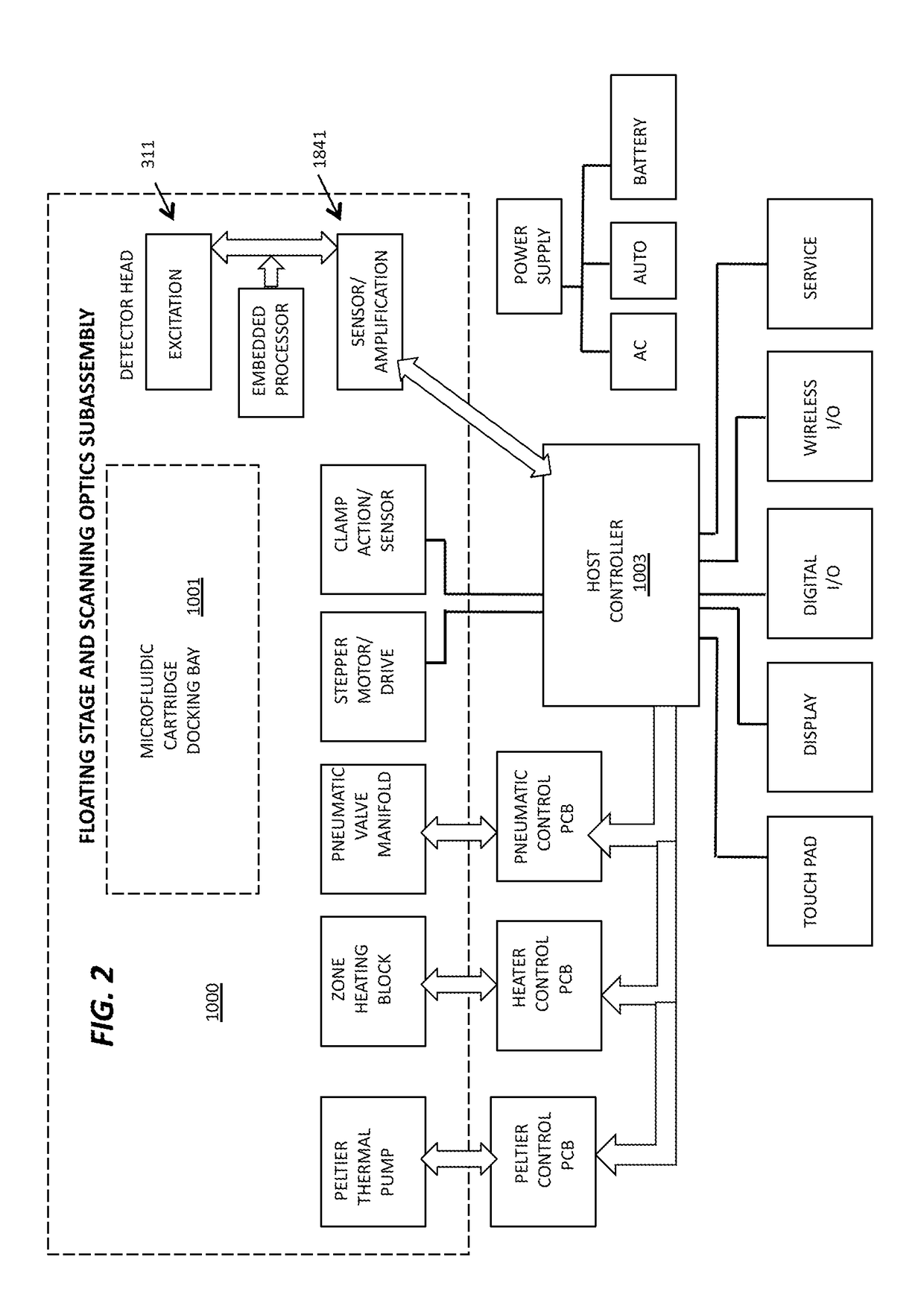
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for the rapid serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays. More particularly, the present invention provides for the real time processing of nucleic acid during polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and thermal melt applications. According to an aspect of the invention, a system for the rapid serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays is provided. In one embodiment, the system includes, but is not limited to: a microfluidic cartridge having microfluidic (flow-through) channels, a fluorescence imaging system, a temperature measurement and control system; a pressure measurement and control system for applying variable pneumatic pressures to the microfluidic cartridge; a storage device for holding multiple reagents (e.g., a well-plate); a liquid handling system comprising at least one robotic pipettor for aspirating, mixing, and dispensing reagent mixtures to the microfluidic cartridge; systems for data storage, processing, and output; and a system controller to coordinate the various devices and functions.
Owner:CANON USA
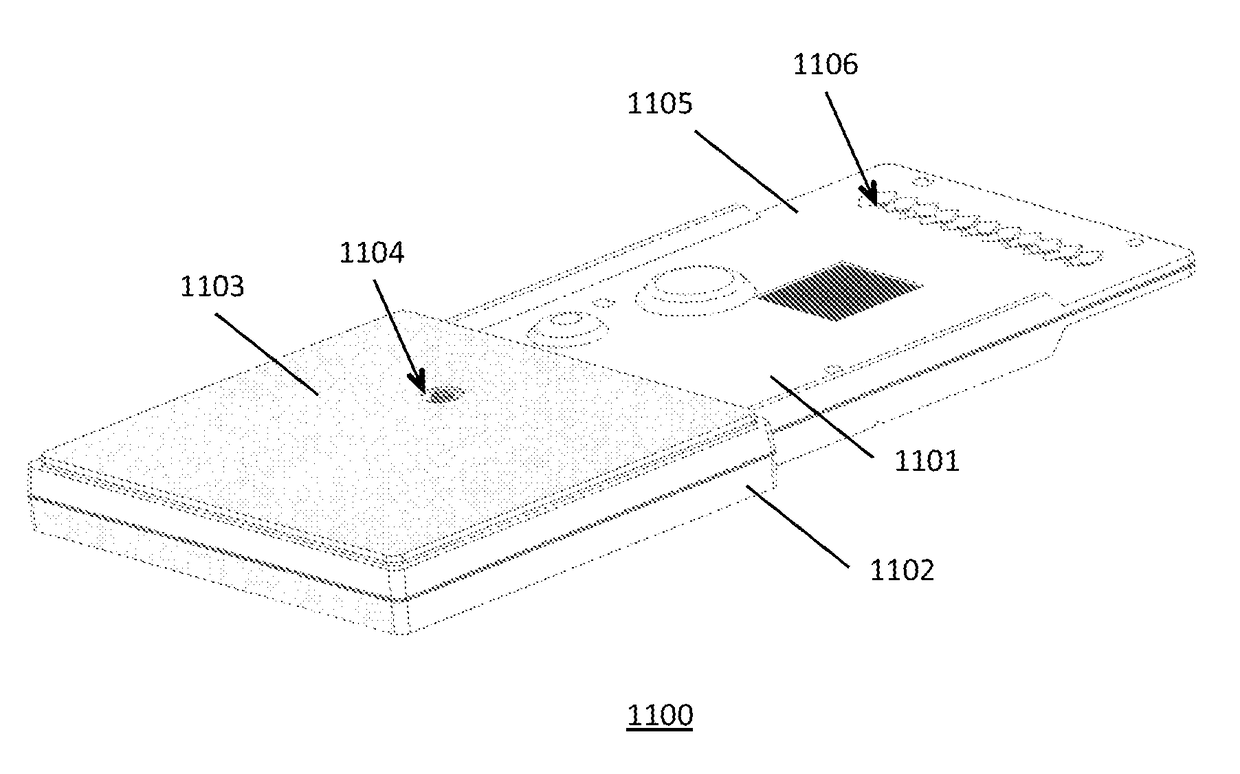
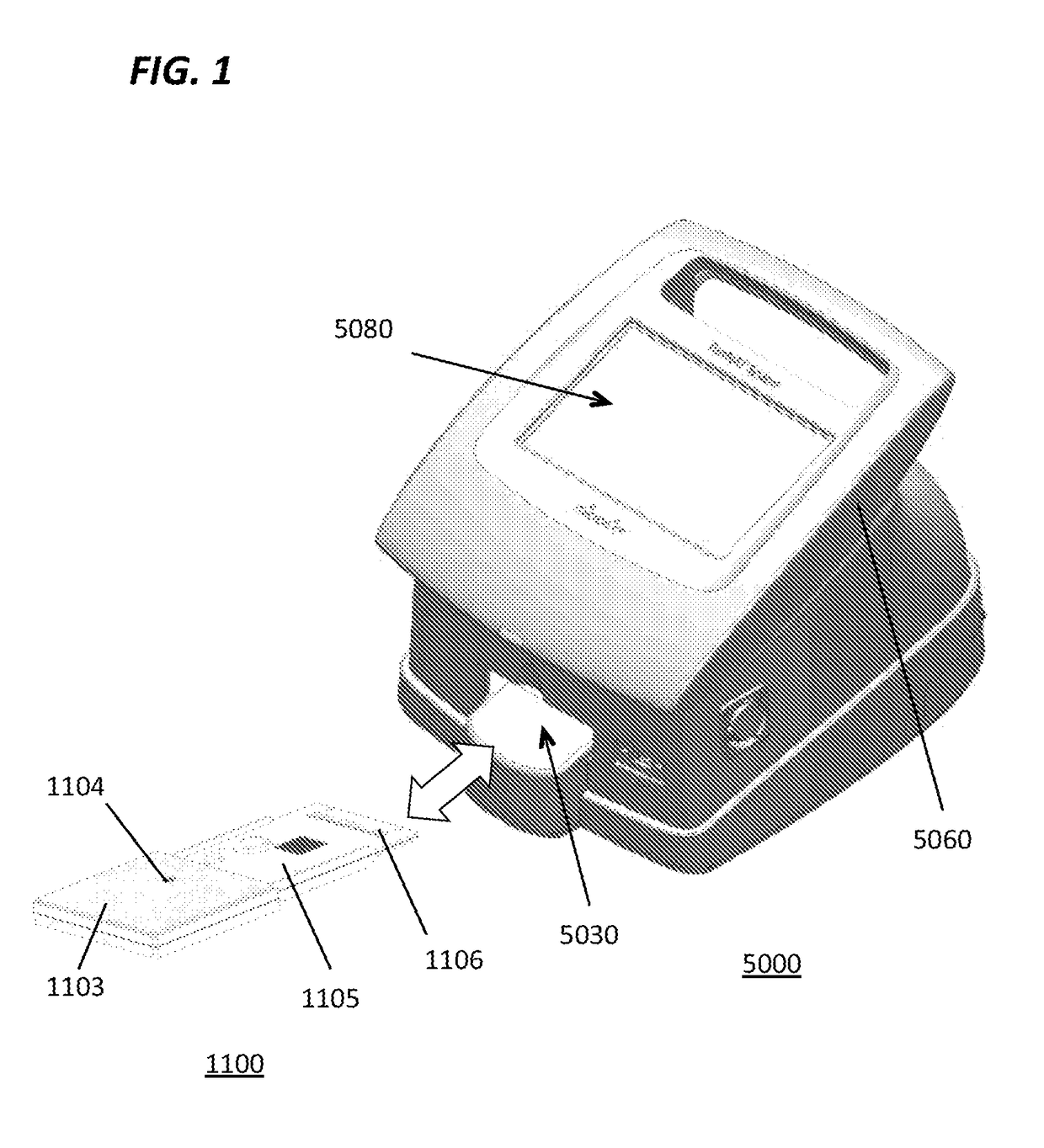
Microfluidic cartridges and apparatus with integrated assay controls for analysis of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20170113221A1Eliminate needAccurate methodReagent containersHeating or cooling apparatusAnalyteMicro assay
Disclosed is a microassay testing system, including a microfluidic cartridge and a compact microprocessor-controlled instrument for fluorometric assays in liquid samples, the cartridge having integrated process controls and positive and negative assay controls. The instrument has a scanning detector head incorporating multiple optical channels. In a preferred configuration, the assay is validated using dual channel optics for monitoring a first fluorophore associated with a target analyte and a second fluorophore associated with a process control. Integrated positive and negative assay controls provide enhanced assay validation capabilities and facilitate analysis of test results. Applications include molecular biological assays based on PCR amplification of target nucleic acids and fluorometric assays in general.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
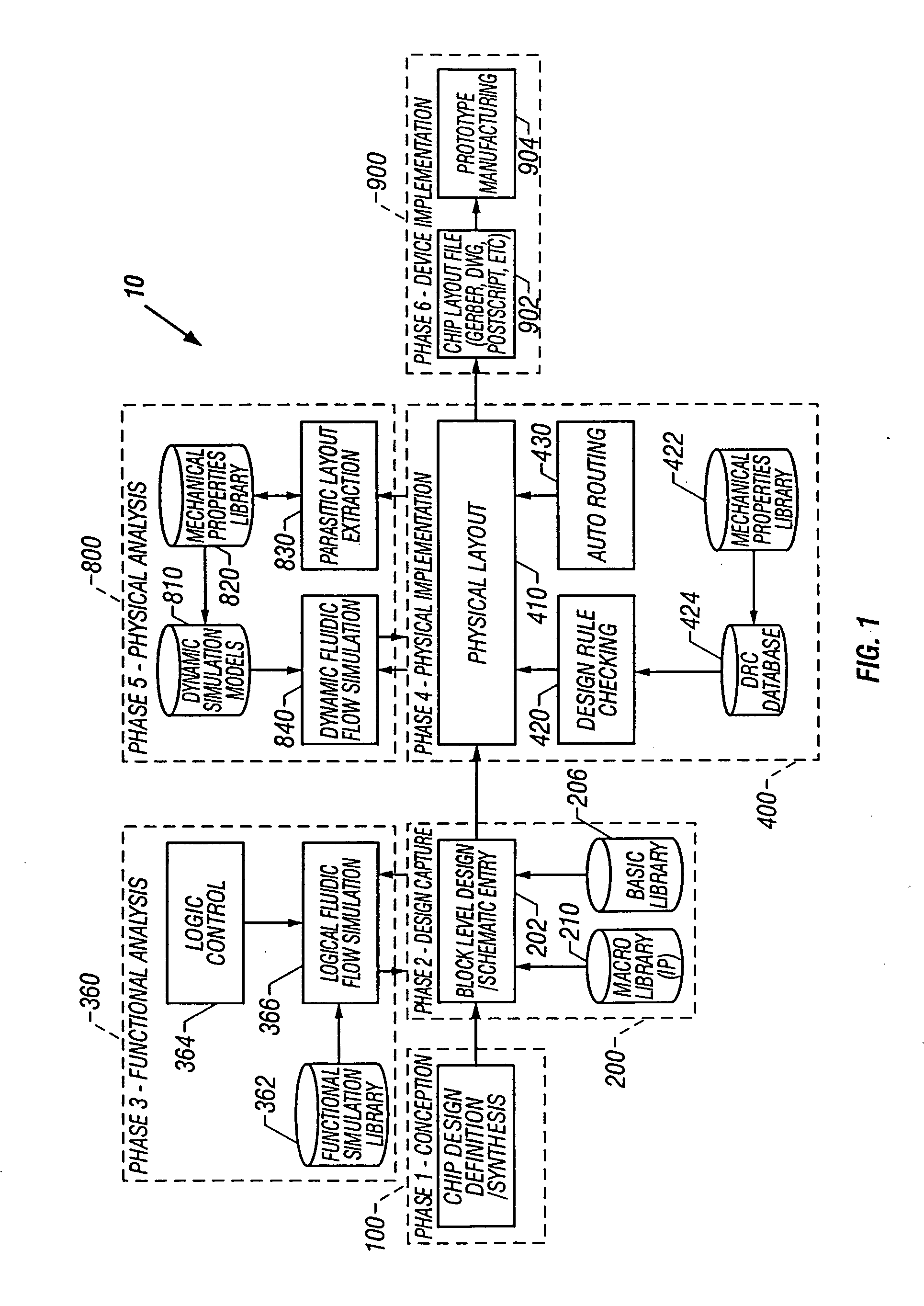
Microfluidic design automation method and system
InactiveUS20050065735A1Shorten the timeEasy placement and routingFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementComputer Aided DesignSystems design
The present invention generally relates to microfluidics and more particularly to the design of customized microfluidic systems using a microfluidic computer aided design system. In one embodiment of the present invention a microfluidic circuit design method is provided. The method includes developing synthesizable computer code for a design. Next, a microfluidic circuit schematic, including a plurality of symbols for microfluidic components, is generated either interactively or using the synthesizable computer code. The microfluidic circuit schematic is then functionally simulated. The microfluidic components are placed and routed on a template to form a physical layout. Then the physical layout is physically simulated using dynamic simulation models of the microfluidic components; and the physical layout is written to a layout file.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com