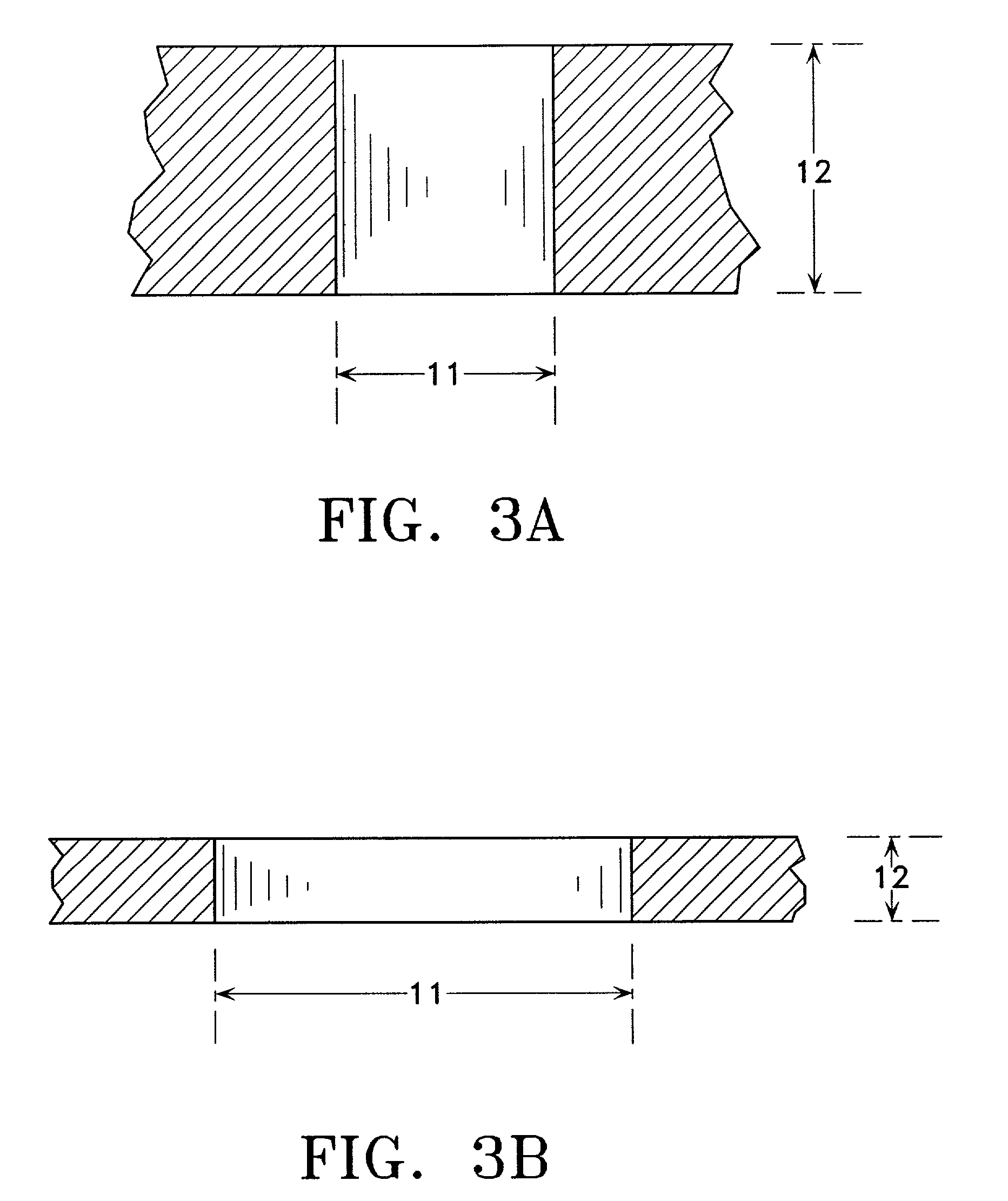
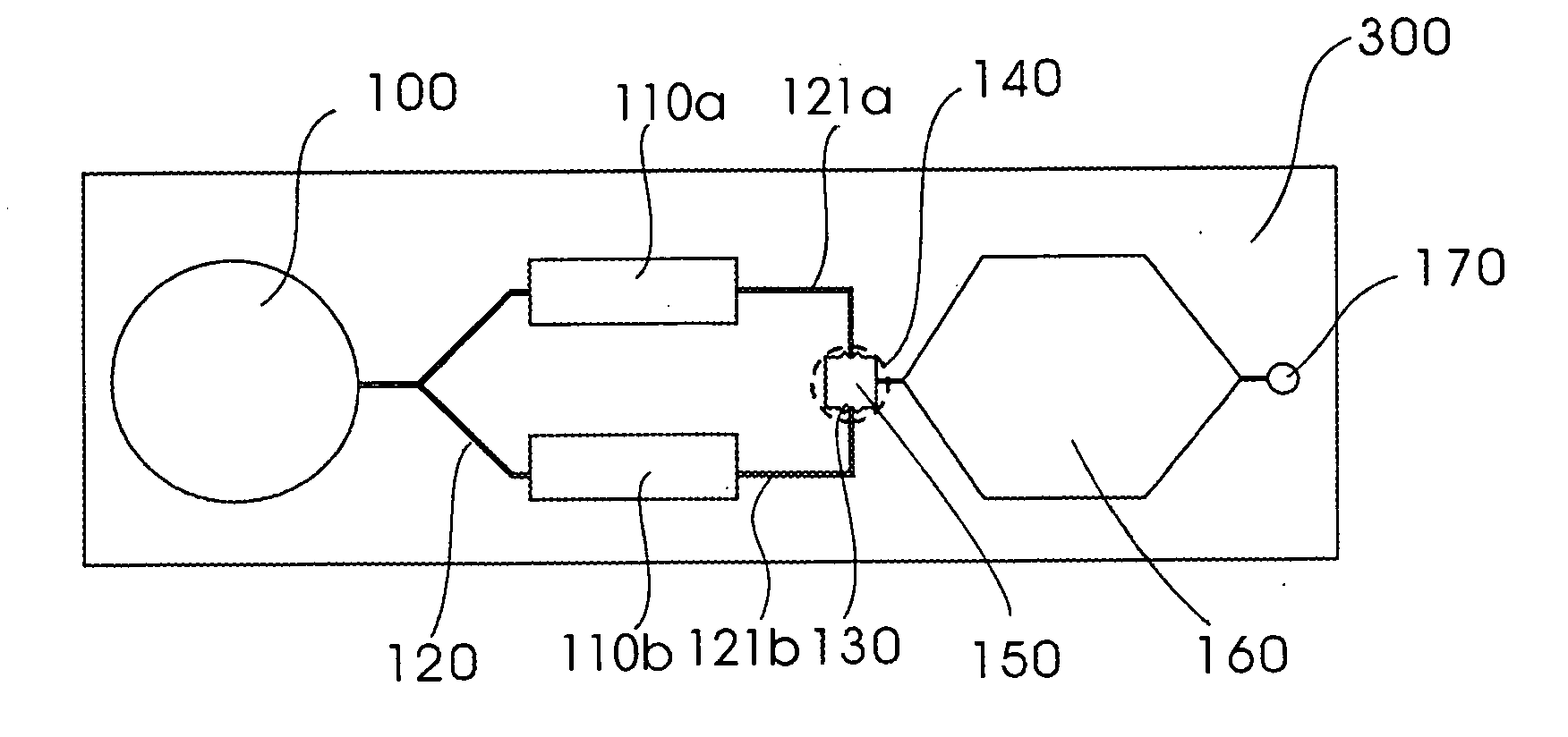
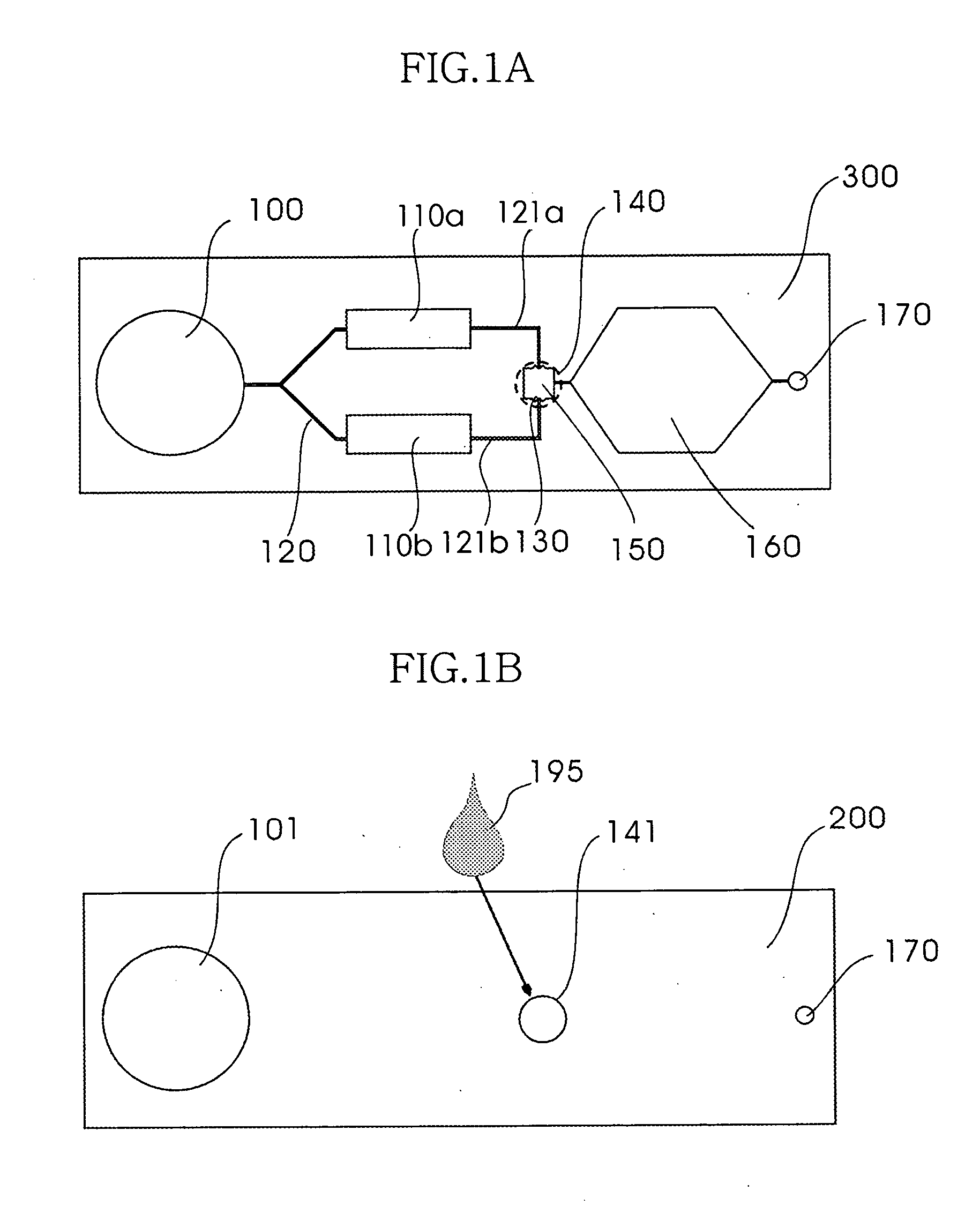
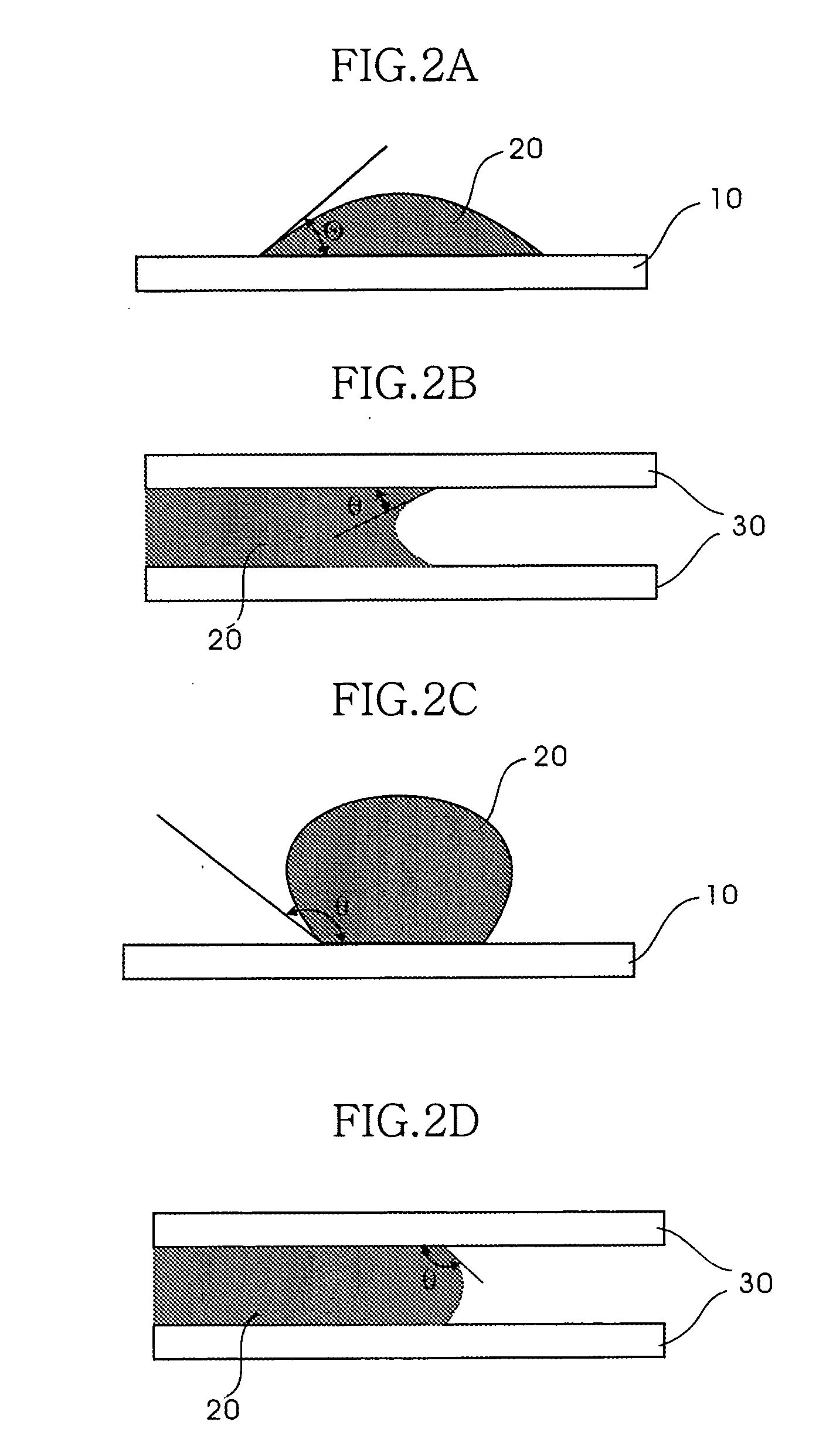
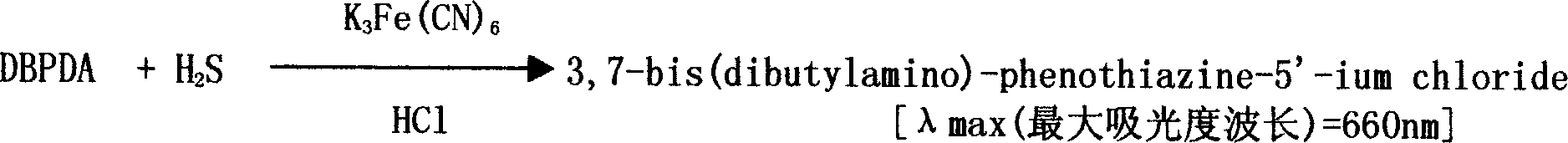Patents
Literature
2130 results about "Biochemical reactions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
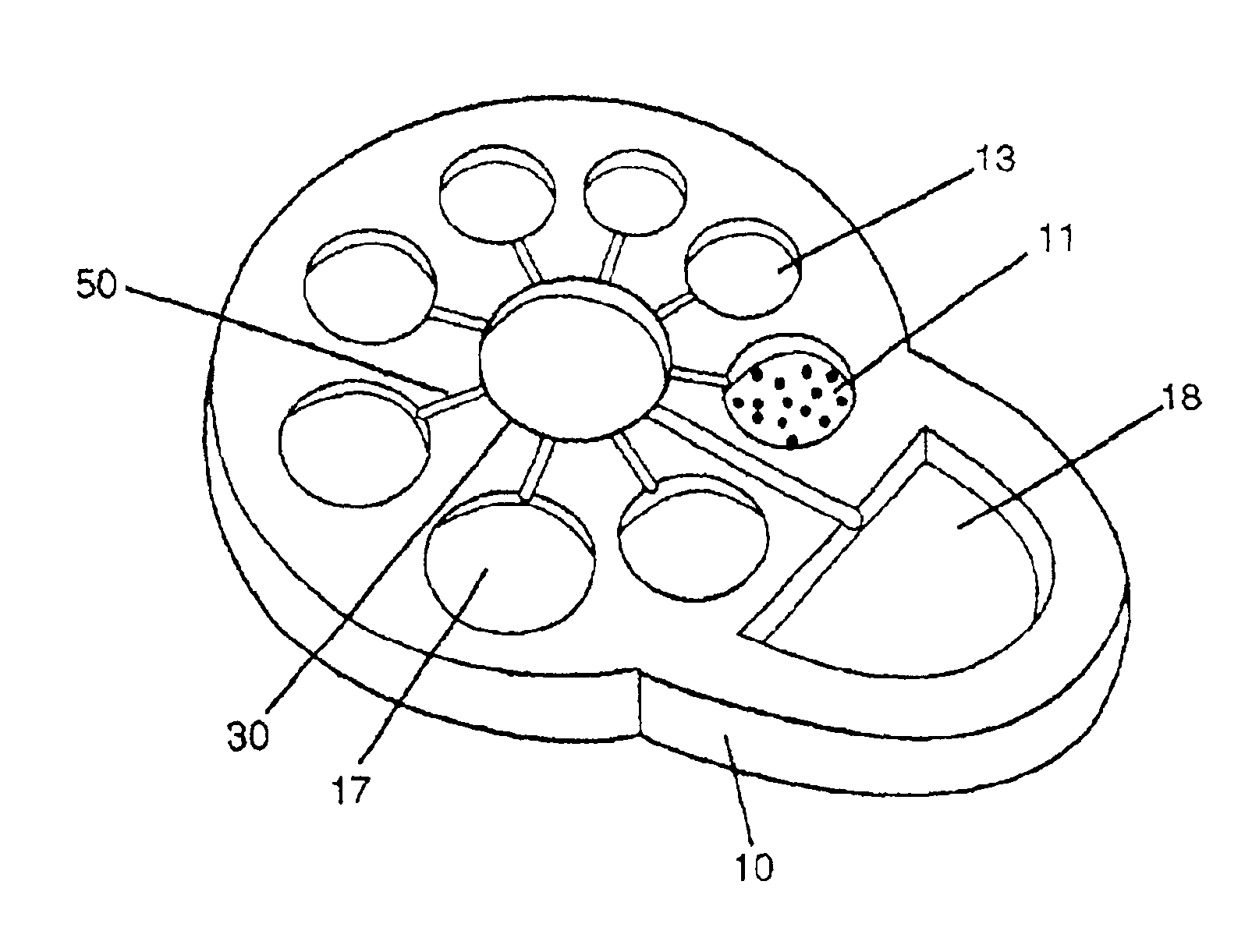
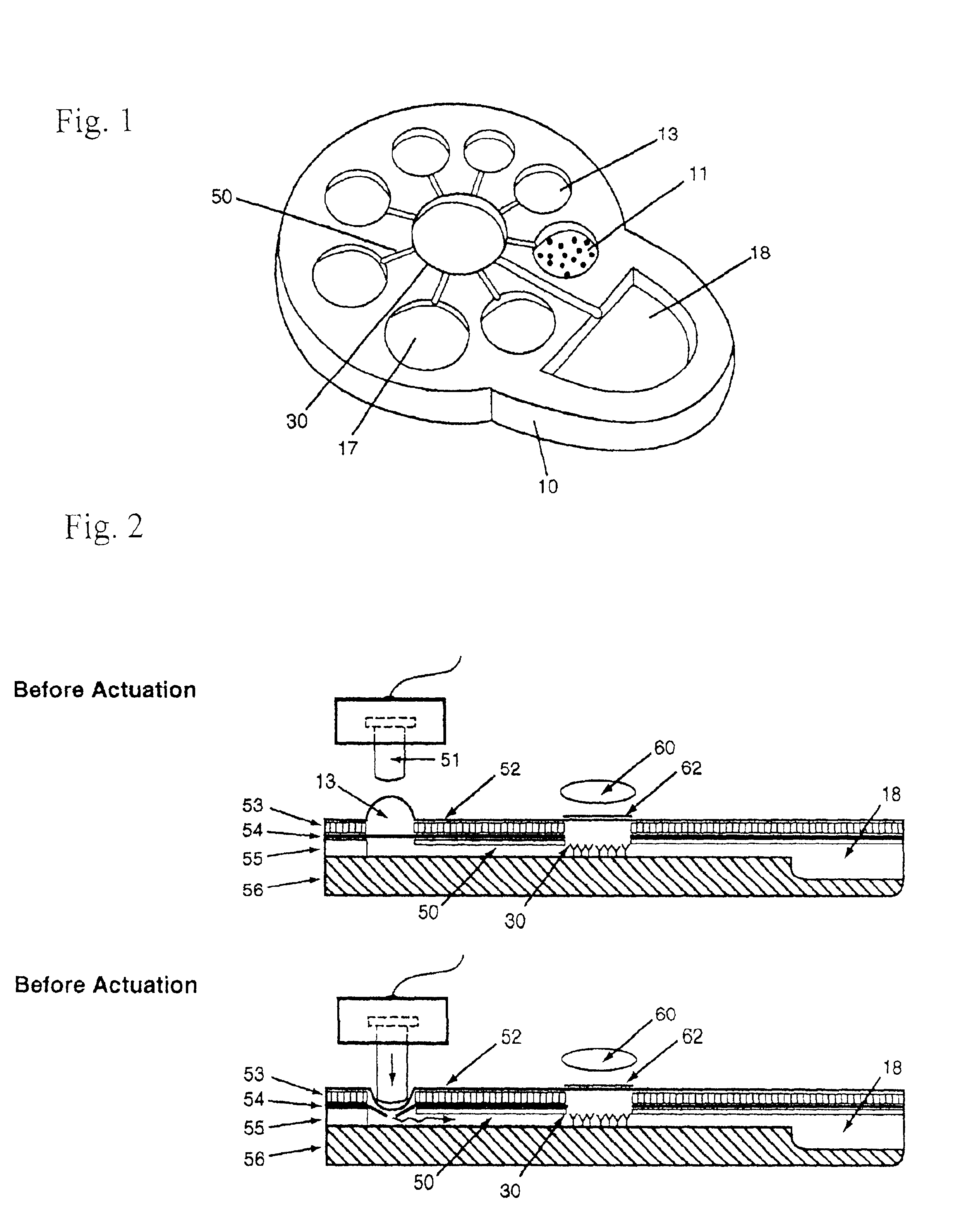
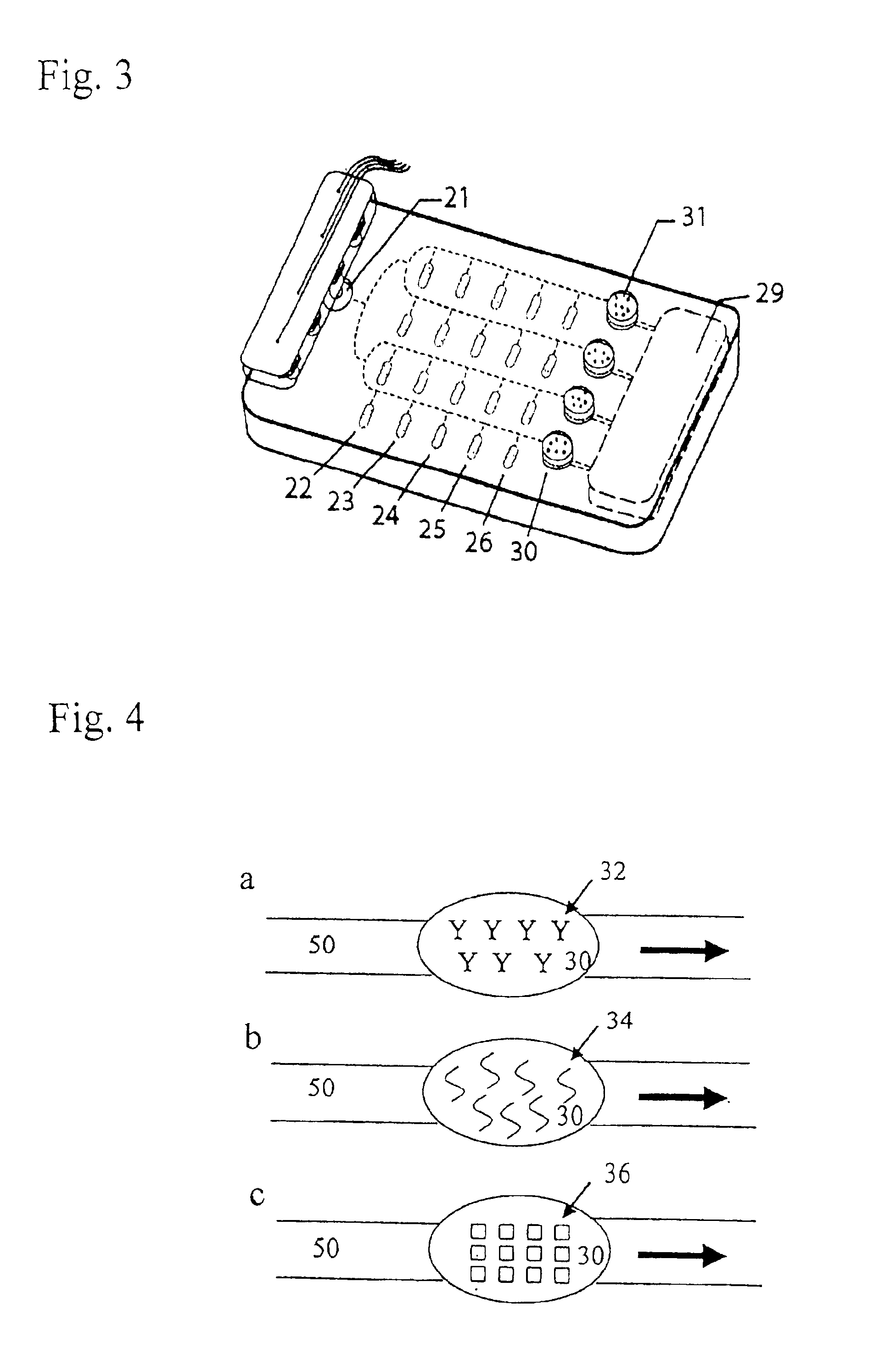
Biochemical reactions are chemical reactions that take place inside the cells of living things. The field of biochemistry demonstrates that knowledge of chemistry as well as biology is needed to understand fully the life processes of organisms at the level of the cell. The sum of all the biochemical reactions in an organism is called metabolism.
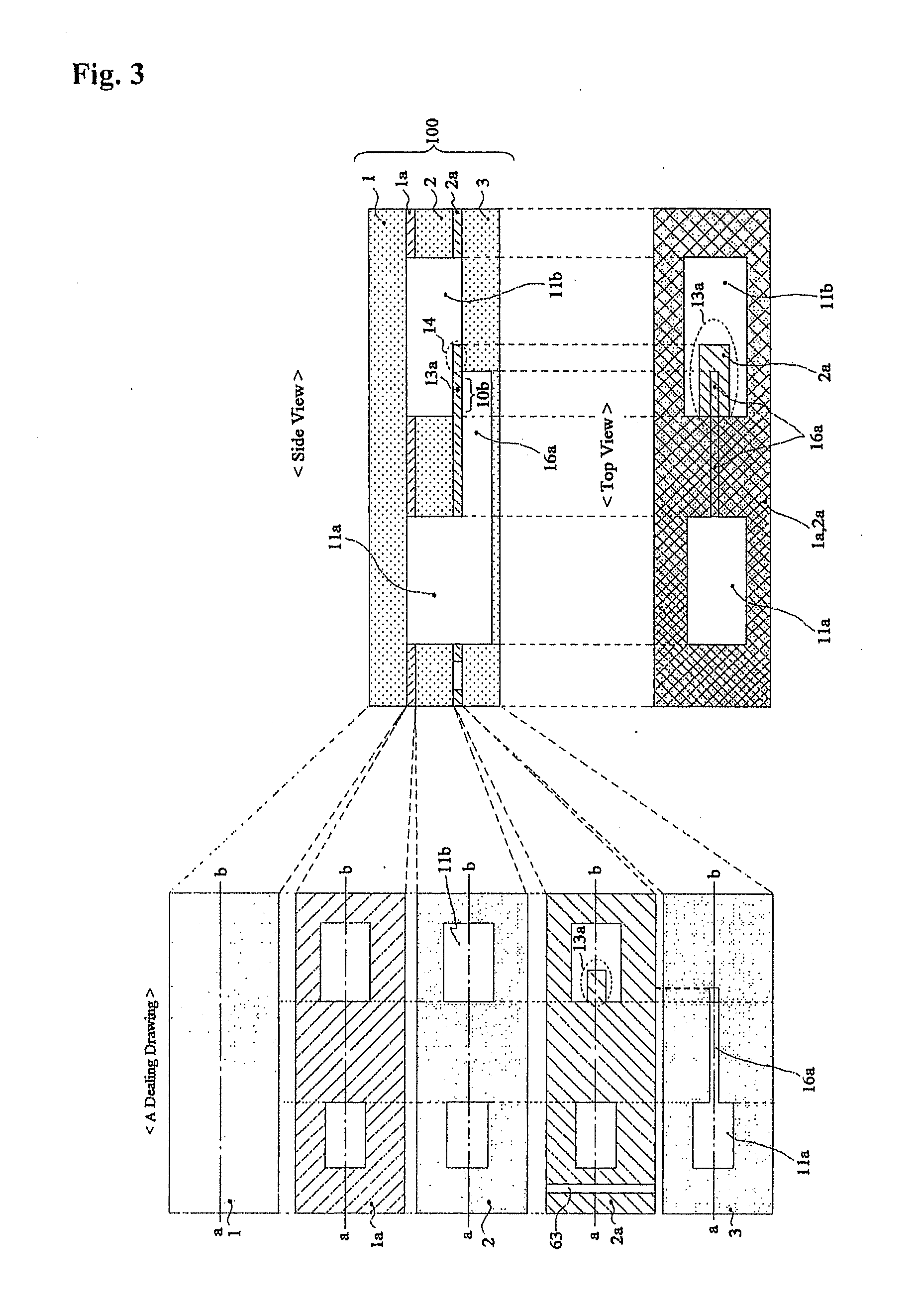
Method for the evolutionary design of biochemical reaction networks
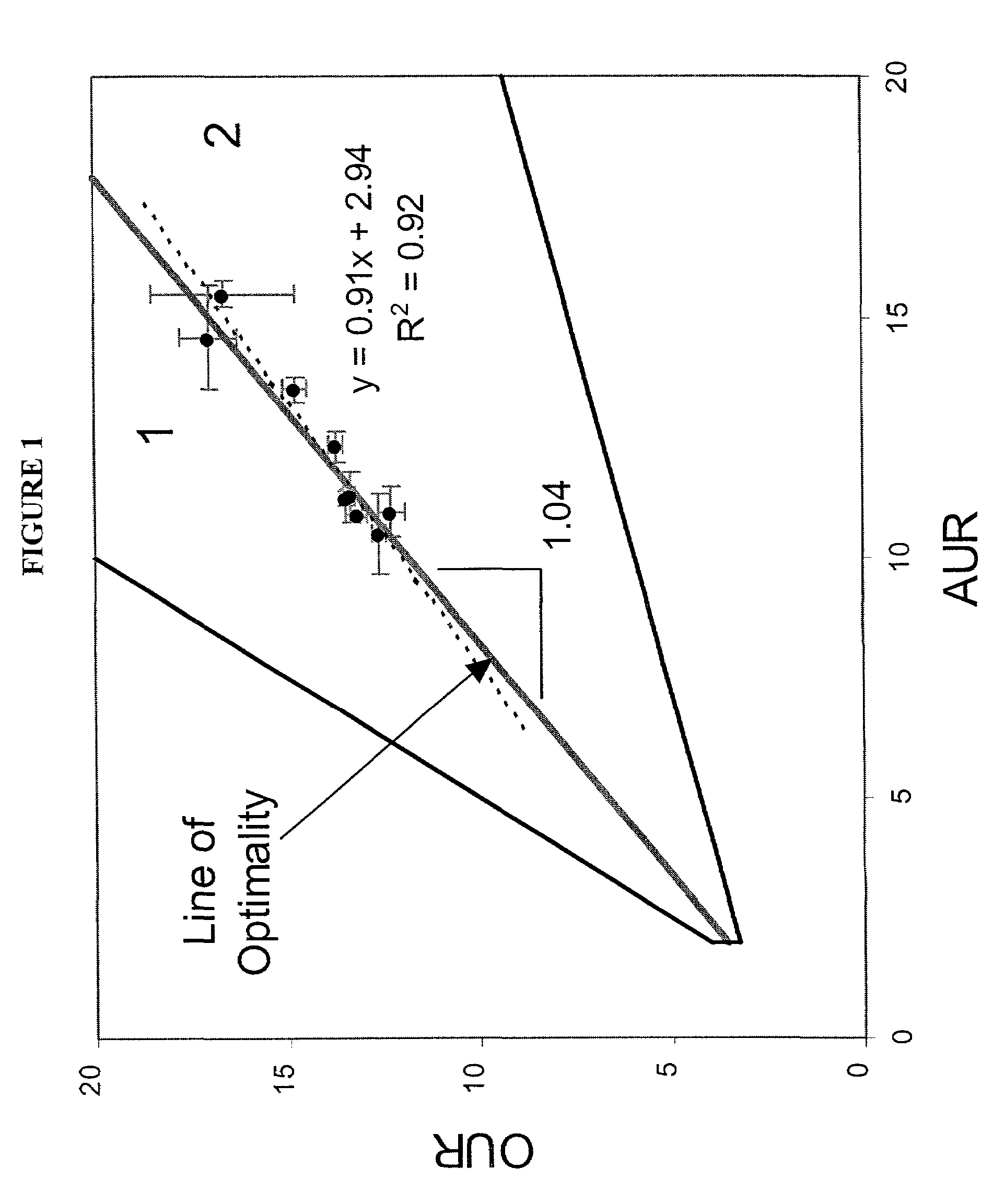
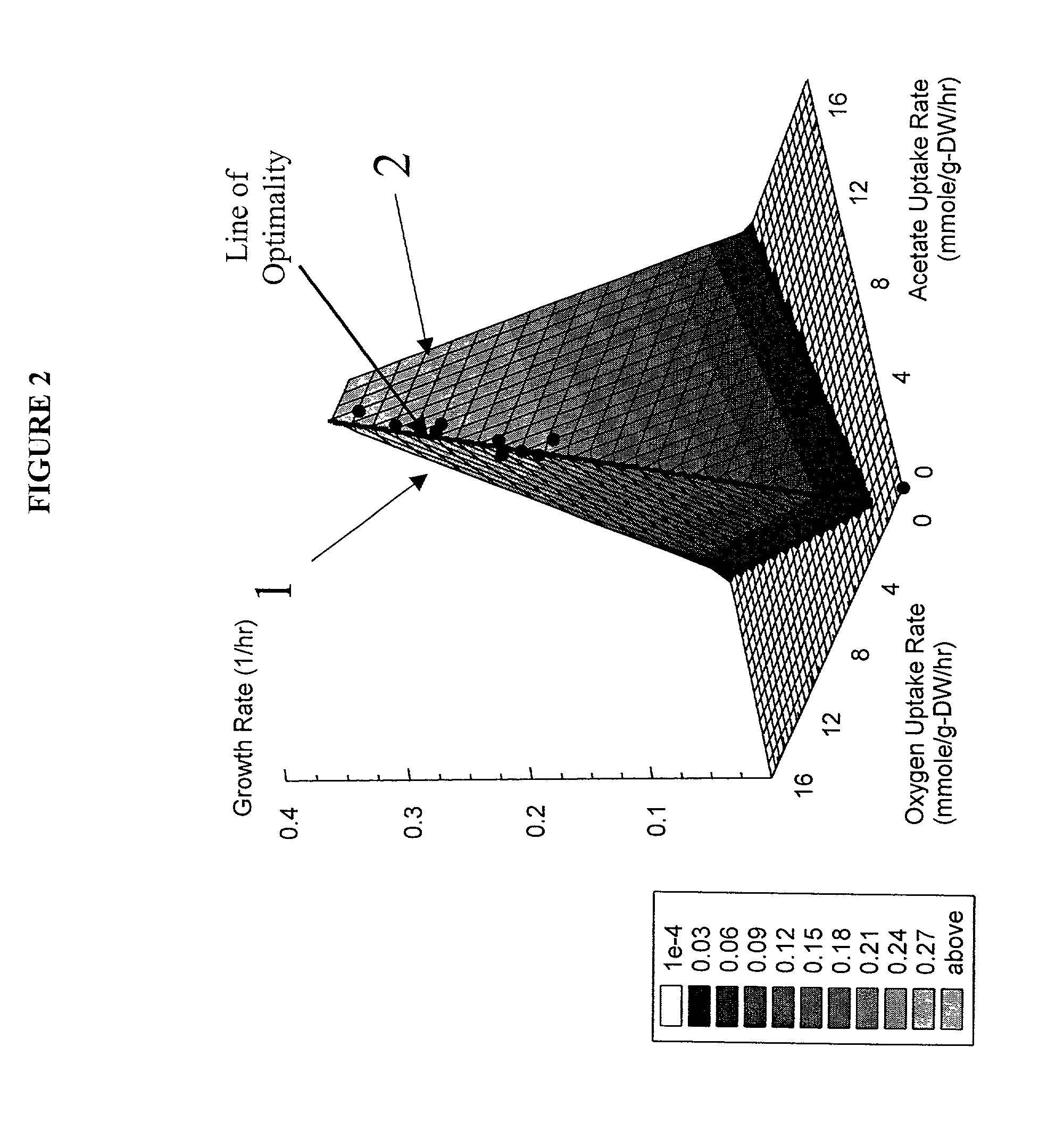
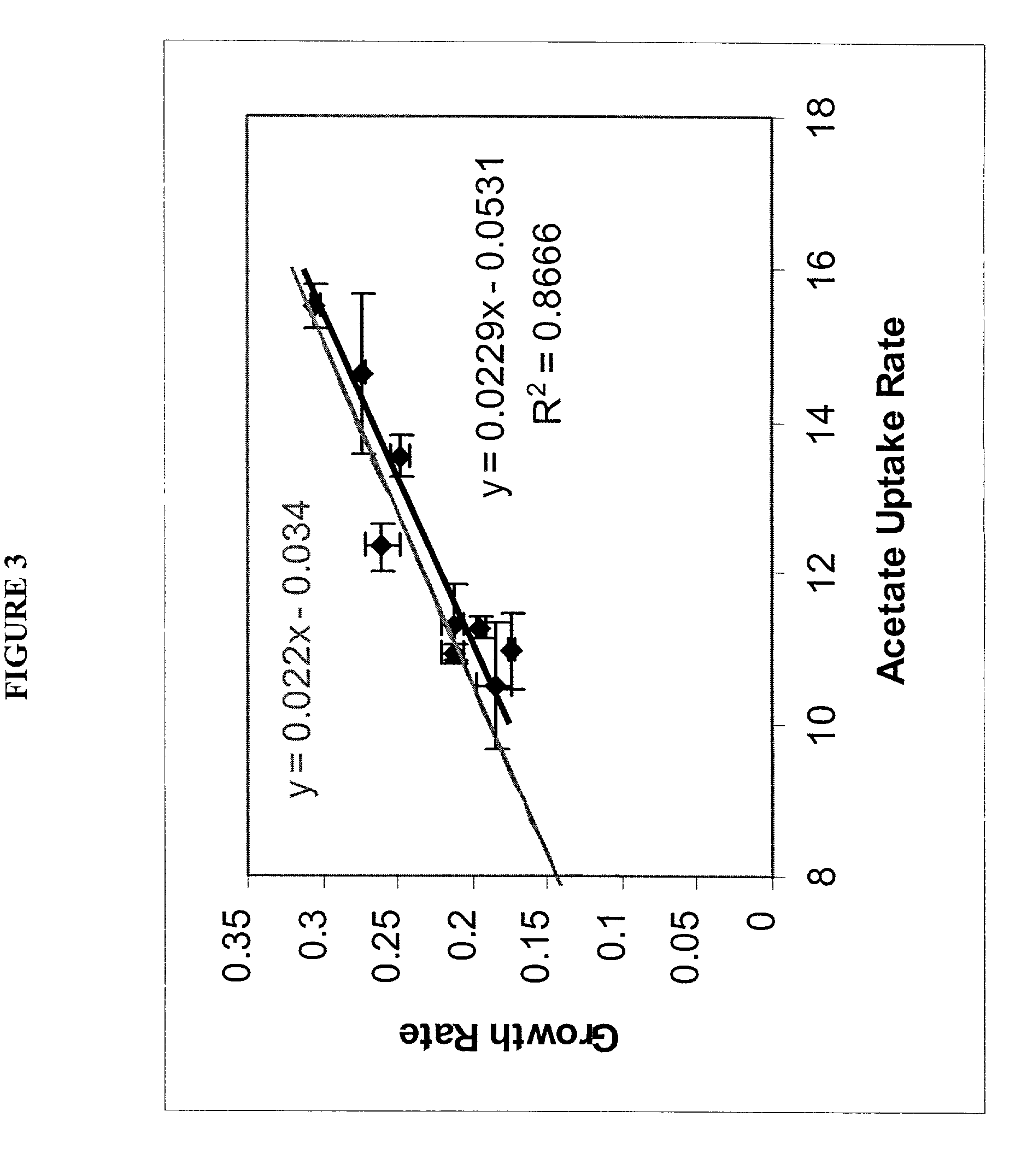
The present invention relates to methods for achieving an optimal function of a biochemical reaction network. The methods can be performed in silico using a reconstruction of a biochemical reaction network of a cell and iterative optimization procedures. The methods can further include laboratory culturing steps to confirm and possibly expand the determinations made using the in silico methods, and to produce a cultured cell, or population of cells, with optimal functions. The current invention includes computer systems and computer products including computer-readable program code for performing the in silico steps of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Droplet Microreactor
InactiveUS20080124252A1Improve purification effectInexpensive to fabricateChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMicroreactorLab-on-a-chip
The present invention relates to a droplet microreactor, i.e. a microreactor consisting of a droplet of a specific liquid, the microreactor being wall-less, wherein the interface of the specific liquid with the ambient environment and with the support on which the droplet is deposited defines the limits of the microreactor. The microreactor is characterized in that it consists of a droplet comprising at least one ionic liquid. The present invention also relates to methods for carrying out chemical or biochemical reactions and / or mixes using said droplet microreactor, and also to a lab-on-chip comprising a microreactor according to the invention.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Universal sample preparation system and use in an integrated analysis system
ActiveUS20110005932A1Optical radiation measurementSludge treatmentSample purificationCapillary Tubing
The invention provides a system that can process a raw biological sample, perform a biochemical reaction and provide an analysis readout. For example, the system can extract DNA from a swab, amplify STR loci from the DNA, and analyze the amplified loci and STR markers in the sample. The system integrates these functions by using microfluidic components to connect what can be macrofluidic functions. In one embodiment the system includes a sample purification module, a reaction module, a post-reaction clean-up module, a capillary electrophoresis module and a computer. In certain embodiments, the system includes a disposable cartridge for performing analyte capture. The cartridge can comprise a fluidic manifold having macrofluidic chambers mated with microfluidic chips that route the liquids between chambers. The system fits within an enclosure of no more than 10 ft3. and can be a closed, portable, and / or a battery operated system. The system can be used to go from raw sample to analysis in less than 4 hours.
Owner:INTEGENX
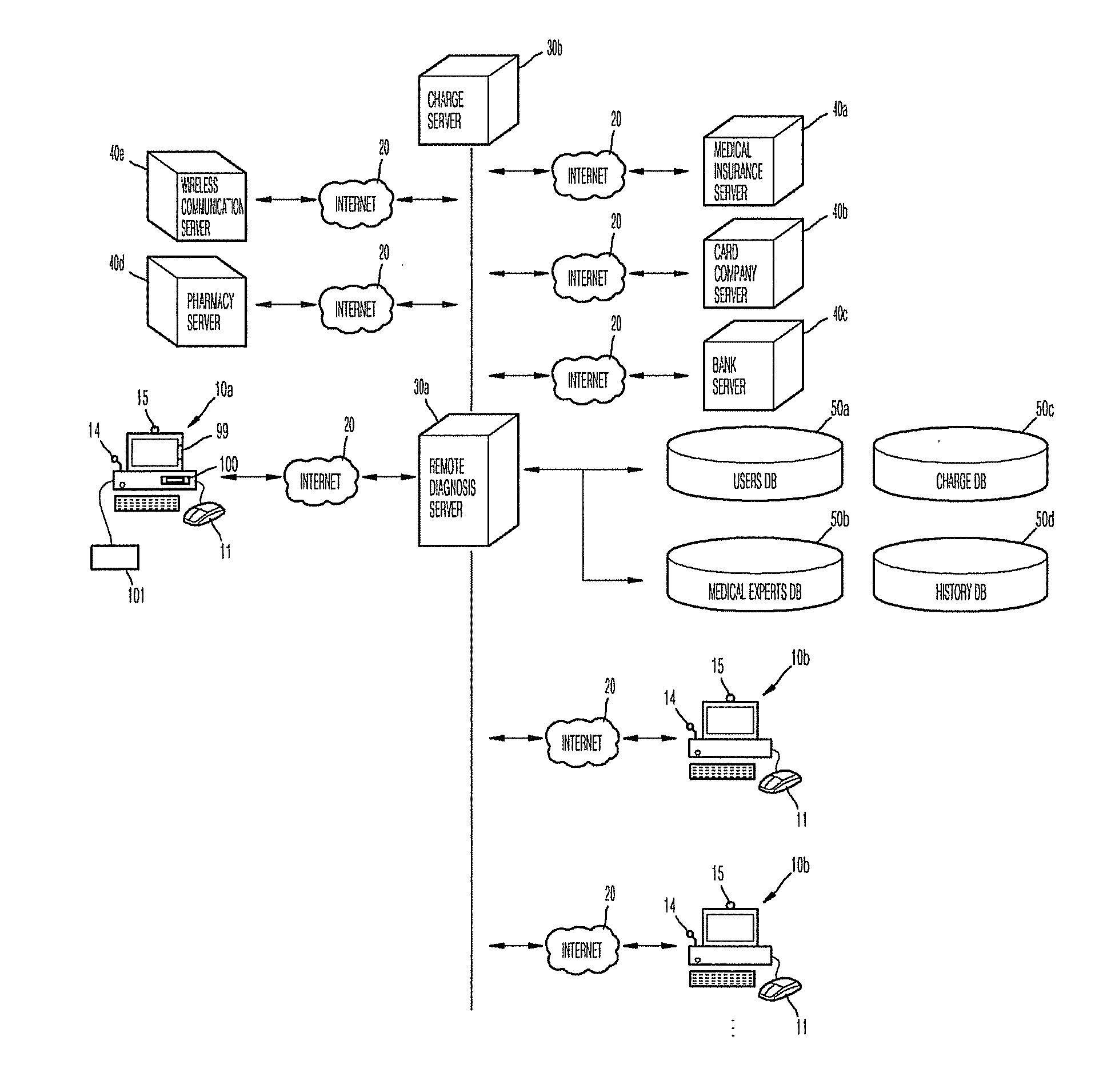
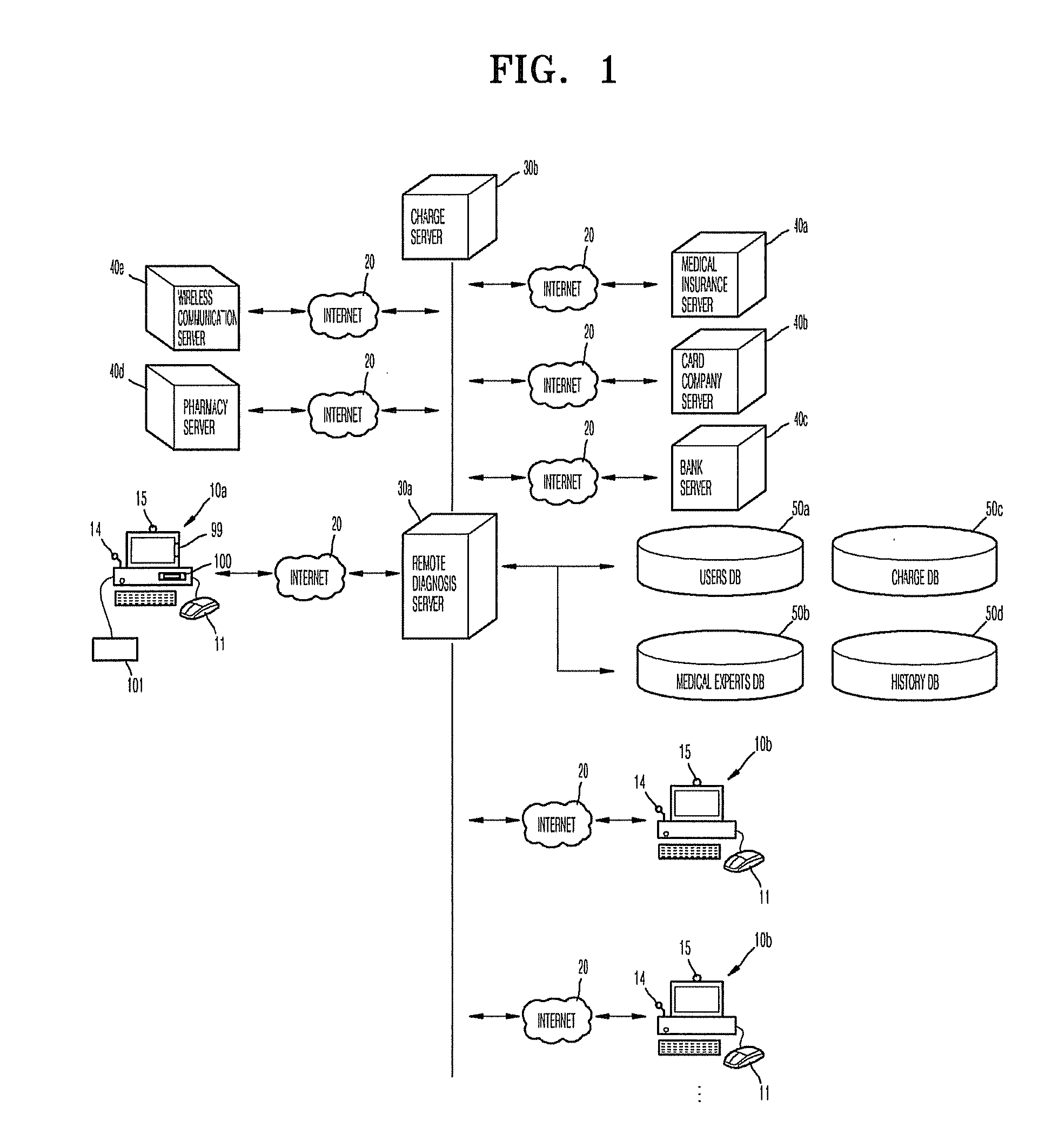
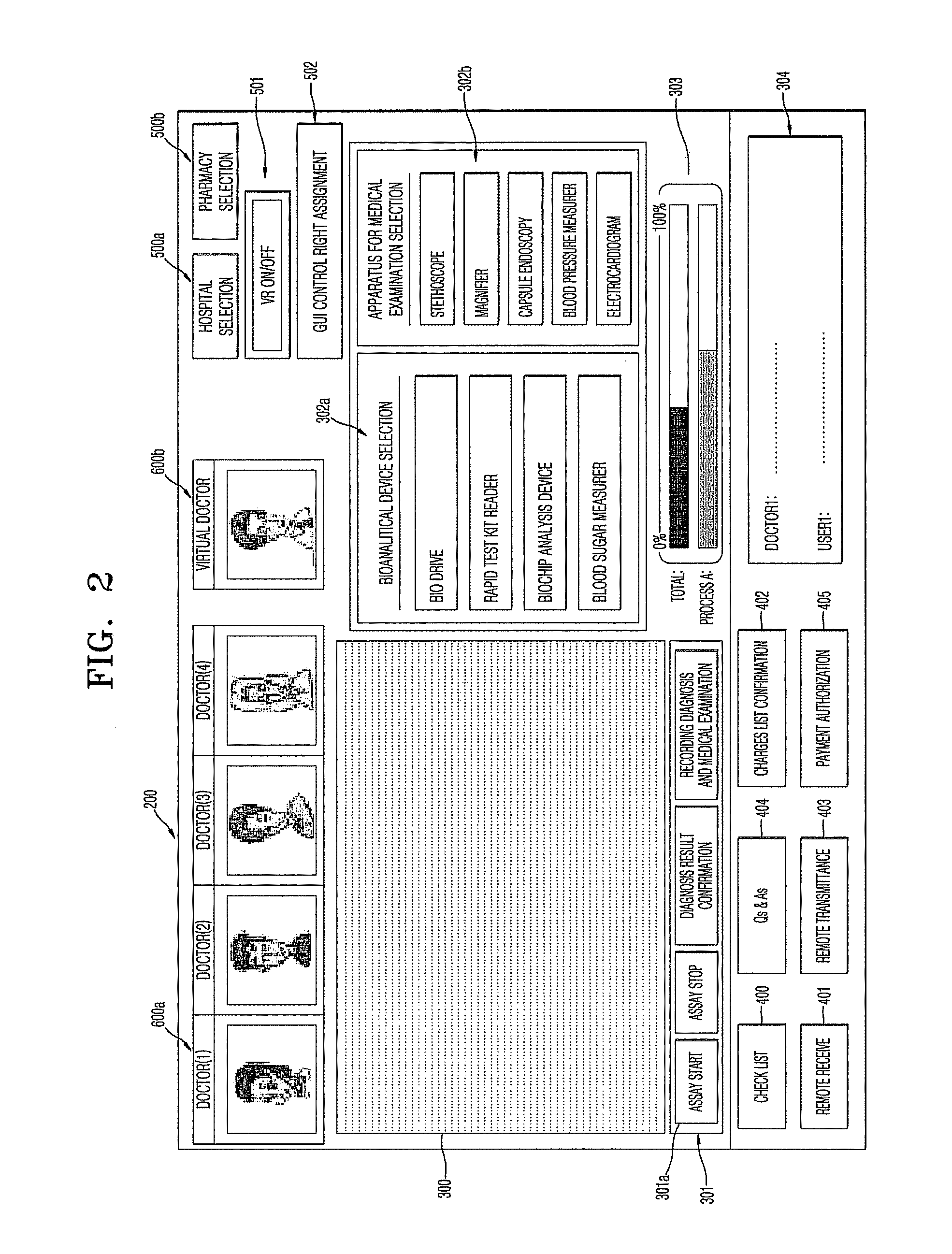
Remote-medical-diagnosis system method
ActiveUS20100121156A1Drug and medicationsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionGuidelineBlocked Connection
Provided are a remote medical-diagnosis system including: a bio-disc or a biochip performing biological, chemical or biochemical reactions with a sample, and having a barcode or a RF IC; a bioanalytical device analyzing results of reactions performed by the bio-disc or the biochip and including a reader reading the barcode or the RF IC to authenticate the bio-disc or the biochip or recording the measured data to the RF IC regardless of a connection with a remote diagnosis server; a virtual doctor as a software in a user's terminal, the virtual doctor providing a user with guidelines and instructions as how to use the bioanalytical device, and providing the user with a consulting service, a diagnosis unit self-analyzing the measured data using mathematical calculations and outputing results of a diagnosis; a user's terminal providing the user with a consulting service from a medical expert or a virtual doctor; a medical expert's terminal providing the user with a consulting service; and a remote diagnosis server connecting the user with the medical expert during periodic medical consultations, connecting the user with the virtual doctor during non-periodic medical consultations, blocking connection between the user and the virtual doctor if a periodic medical consultations term has elapsed; and a method of performing the remote medical-diagnosis.
Owner:PRECISIONBIOSENSOR INC
Chemiluminescence-based microfluidic biochip
InactiveUS6949377B2Accurate and reproducible resultSimple and rapid and POCT applicationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPositive pressureBiochip
The disclosure describes how to use luminescence detection mechanism, move microfluid, and control multiple-step biochemical reactions in closed confined microfluidic biochip platform. More particularly, a self-contained disposable biochip with patterned microchannels and compartments having storage means for storing a plurality of samples, reagents, and luminescent substrates. At least one external microactuator in the biochip system produces positive pressure and automates multiple-step reactions in microfluidic platforms for clinical chemistry, cell biology, immunoassay and nucleic acid analysis. The method comprises the steps of transferring sequentially at least one of samples, reagents, and then luminescent substrate from compartments through microchannels to reaction sites. The luminescent substrates react with probes to form a probe complex resulting into luminescence, which is detected by an optical detector.
Owner:HO WINSTON Z
Preparation method of biological detergent
InactiveCN103224840AExtended service lifeNo residueCosmetic preparationsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsChitin formationFermentation
The invention relates to a preparation method of a biological detergent. The biological detergent is prepared by mixing APG (C8-16), maltose, ethanol, composite amino acid, aloe, chitin, salt, probiotics, lactic acid, spice and water. According to the method, the maltose serving as a main raw material, the APG biosurfactant and the probiotics are subjected to biochemical reaction to form various biological resolvase under the auxiliary edge action of the chitin. The process comprises the following steps of: preparing the maltose, the APG and the water according to the percentage; adding the probiotics and the chitin and mixing; stirring uniformly; performing sealed fermentation for 48 to 72 hours; adding the ethanol, the composite amino acid, the aloe, the lactic acid and the spice, and mixing and stirring uniformly; adding the salt and mixing; and standing for 24 hours. The biological detergent has a good pollutant-removing effect and a wide using range, does not damage a human body, protects objects, prolongs the service life of the objects, and is safe and environment-friendly.
Owner:湖南天孚生物科技有限责任公司
Method and kit for investigating humotype semi-cystinol by enzyme biochemical reaction
InactiveCN1693879AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsChemical reactionFluorescence
The invention is an enzyme biologic and chemical reaction measure method to mensurate homotype cysteine in a biologic sample. Cysteine can lose its ammonia and be changed into alpha-4-ketone acid, ammonia and sulfureted hydrogen by L-ovi-ammonia acid and Y-dispeling enzyme. Sulfureted hydrogen and fluorescence cpd.DMPD2HCL can create blue product-sub-armour blue whose degree of absorbing light is 670nm, in the situation of Fe3+ and acid. Thus, people can mensurate the chroma of homotype cysteine in a biologic sample by knowing this degree. This method can measure the chroma of homotype cysteine(3-1000 uMs). The invention also involves a reagent box used for implementing the method mentioned above. The box uses liquid double reagents, and needs less quantity of samples(25 microlitre or serum or plasm);In addition, the respond time is short, and the operation is easy. Thus, this method is suitable for a great deal of examinations. The reagent box costs less than other types.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YAKE SCI & TECH +1
Fluidic devices and methods for multiplex chemical and biochemical reactions
InactiveUS20110143964A1Easy pathLarge sectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMultiplexingCompound (substance)
The present invention describes microfluidic devices that provide novel fluidic structures to facilitate the separation of fluids into isolated, pico-liter sized compartments for performing multiplexing chemical and biological reactions. Applications of the novel devices including biomolecule synthesis, polynucleotide amplification, and binding assays are also disclosed.
Owner:LC SCI LC
Fluidic devices and methods for multiplex chemical and biochemical reactions
InactiveUS8765454B2Easy pathLarge sectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusMultiplexingCompound (substance)
Owner:LC SCI LC
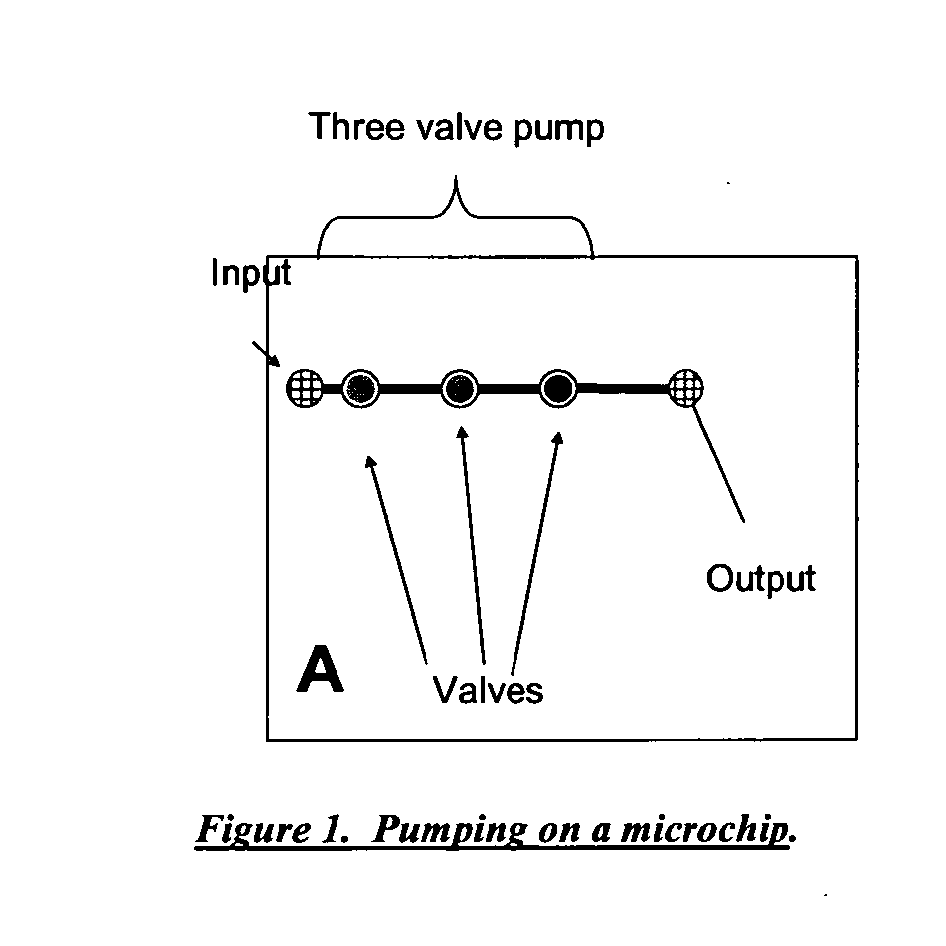
Microfluidic and nanofluidic devices, systems, and applications
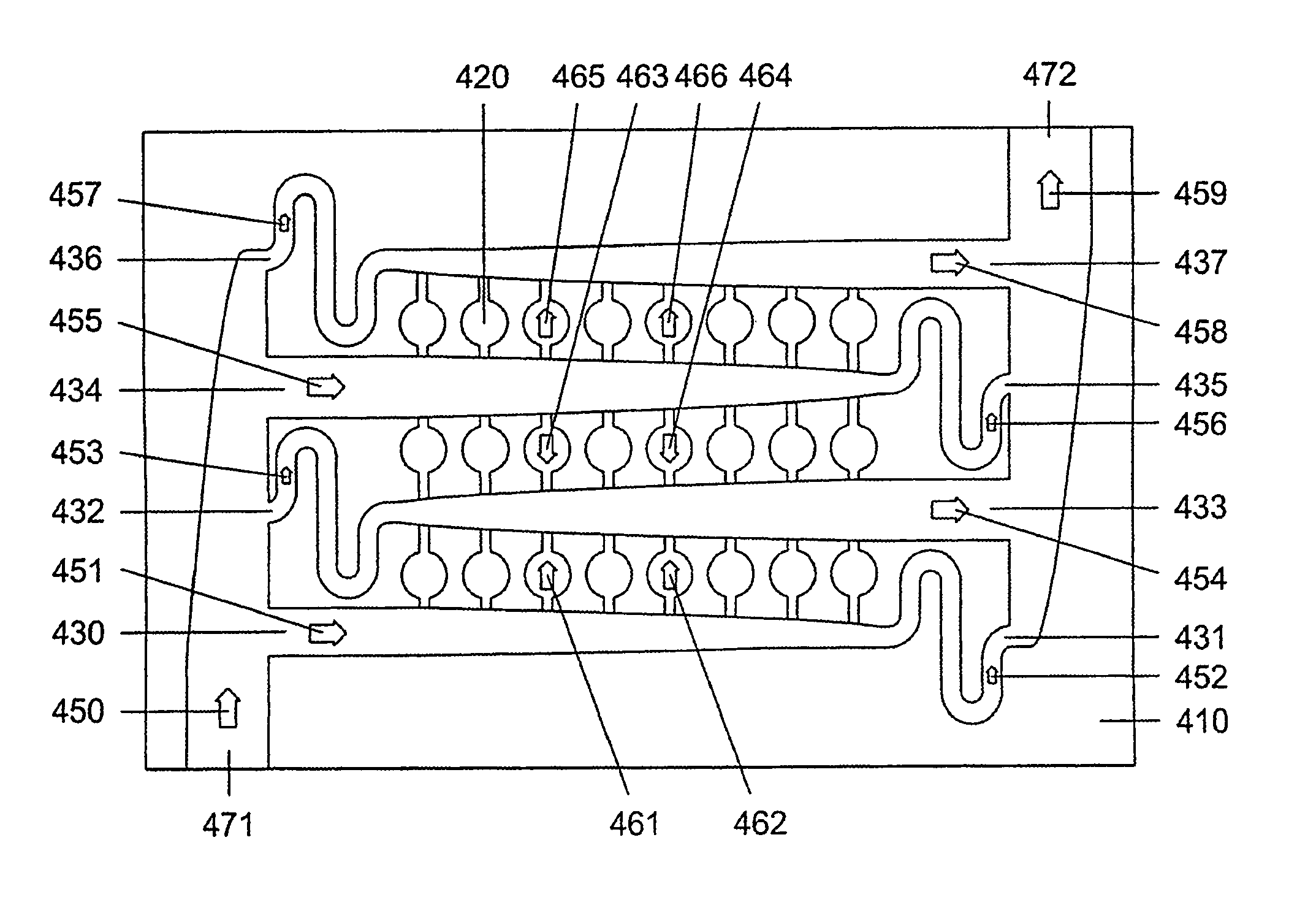
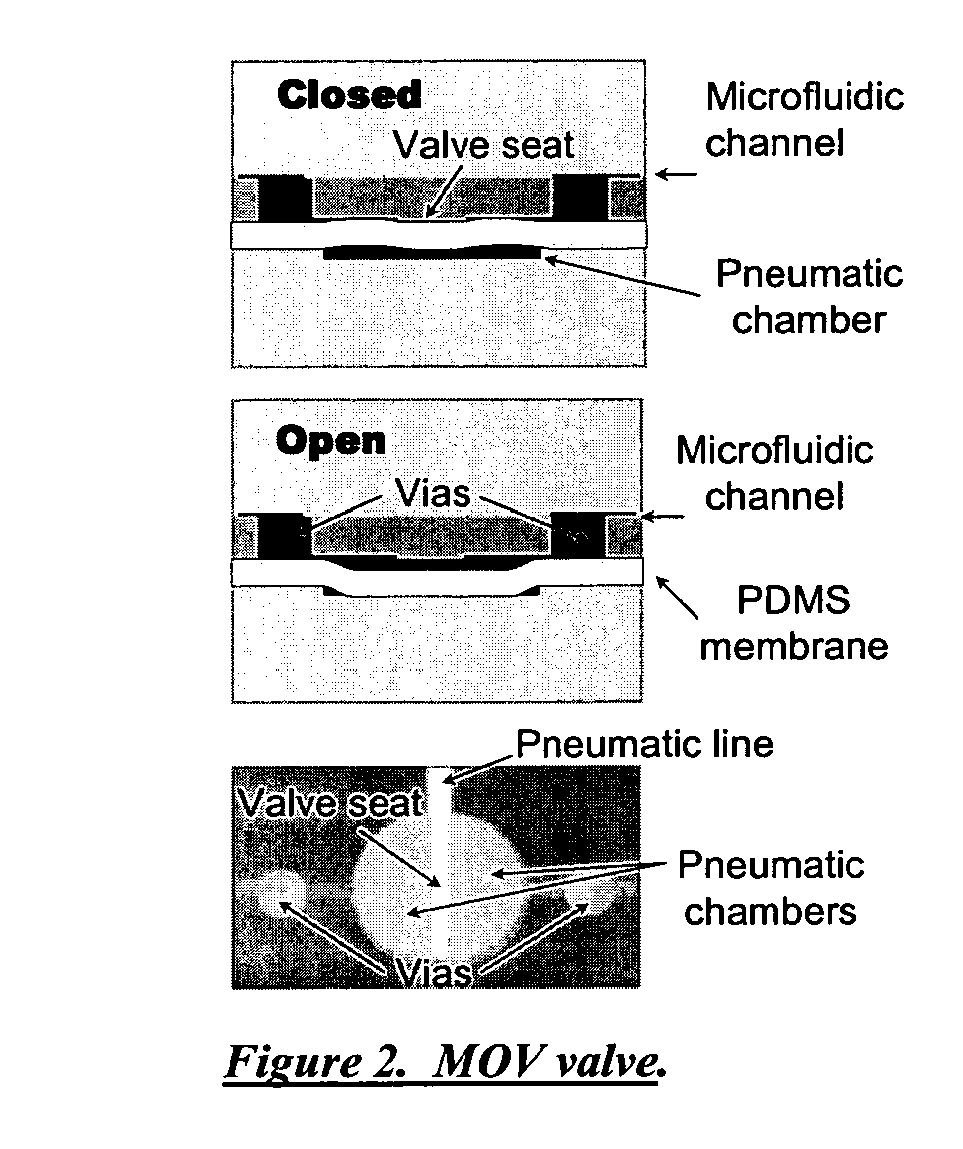
InactiveUS20110039303A1Block fluid flowMaterial nanotechnologyValve arrangementsChemical reactionMicrofluidics
The present invention discloses the integration of programmable microfluidic circuits to achieve practical applications to process biochemical and chemical reactions and to integrate these reactions. In some embodiments workflows for biochemical reactions or chemical workflows are combined. Microvalves such as programmable microfluidic circuit with Y valves and flow through valves are disclosed. In some embodiments microvalves of the present invention are used for mixing fluids, which may be part of an integrated process. These processes include mixing samples and moving reactions to an edge or reservoir for modular microfluidics, use of capture regions, and injection into analytical devices on separate devices. In some embodiments star and nested star designs, or bead capture by change of cross sectional area of a channel in a microvalve are used. Movement of samples between temperature zones are further disclosed using fixed temperature and movement of the samples by micropumps.
Owner:INTEGENX
Apparatus and methods for parallel processing of micro-volume liquid reactions
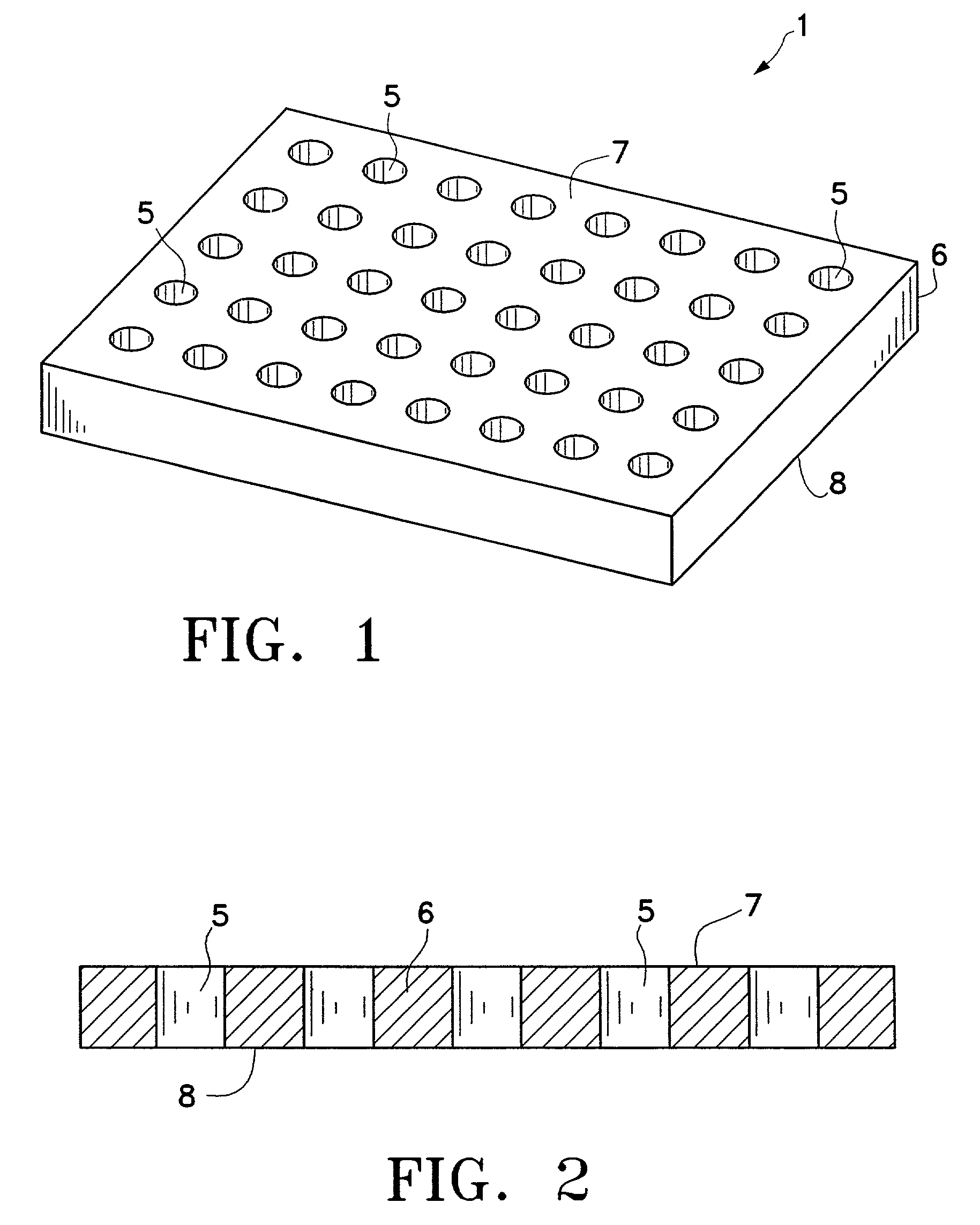
InactiveUS7332271B2Easy to displayBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParallel processingMicrochemistry
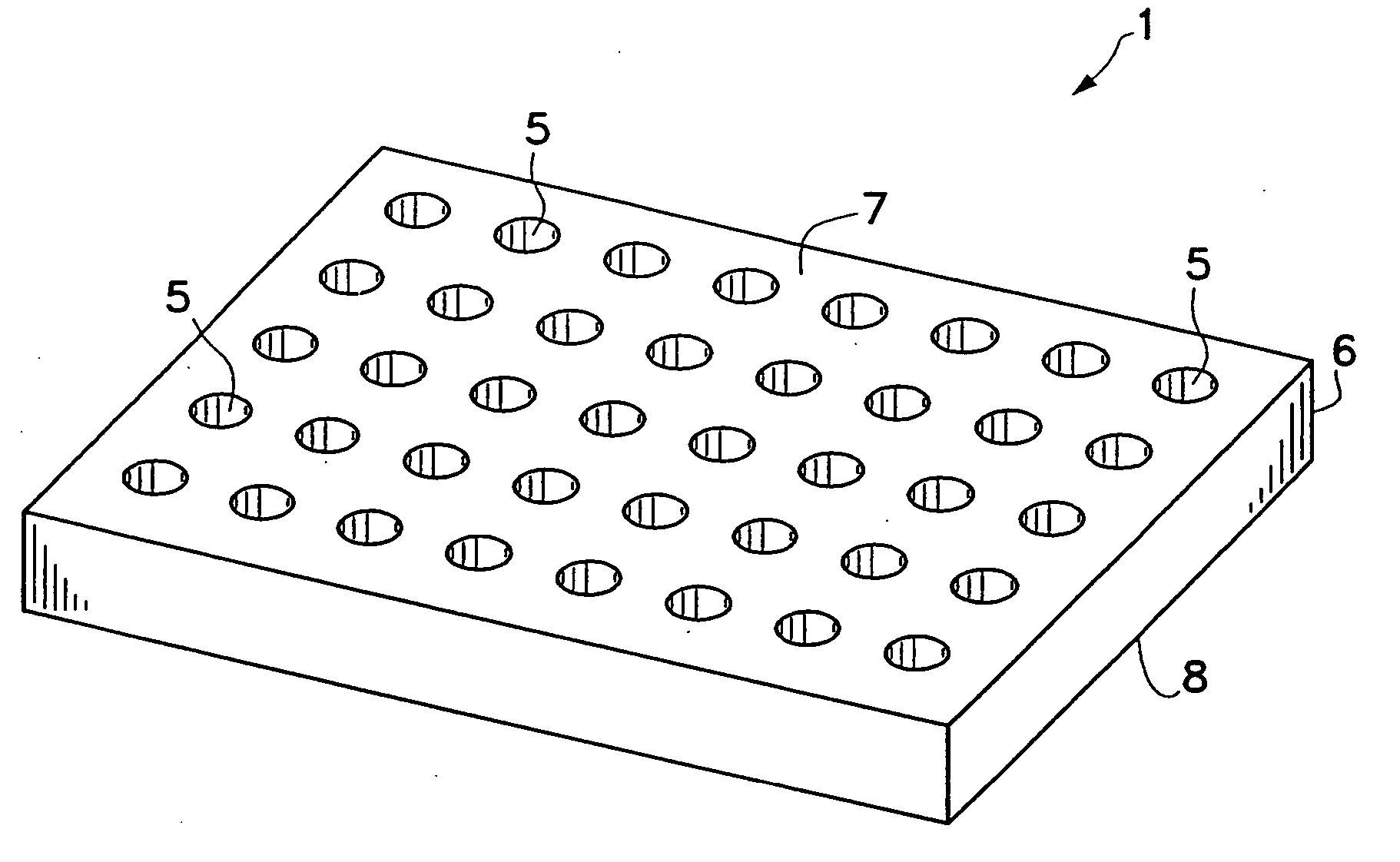
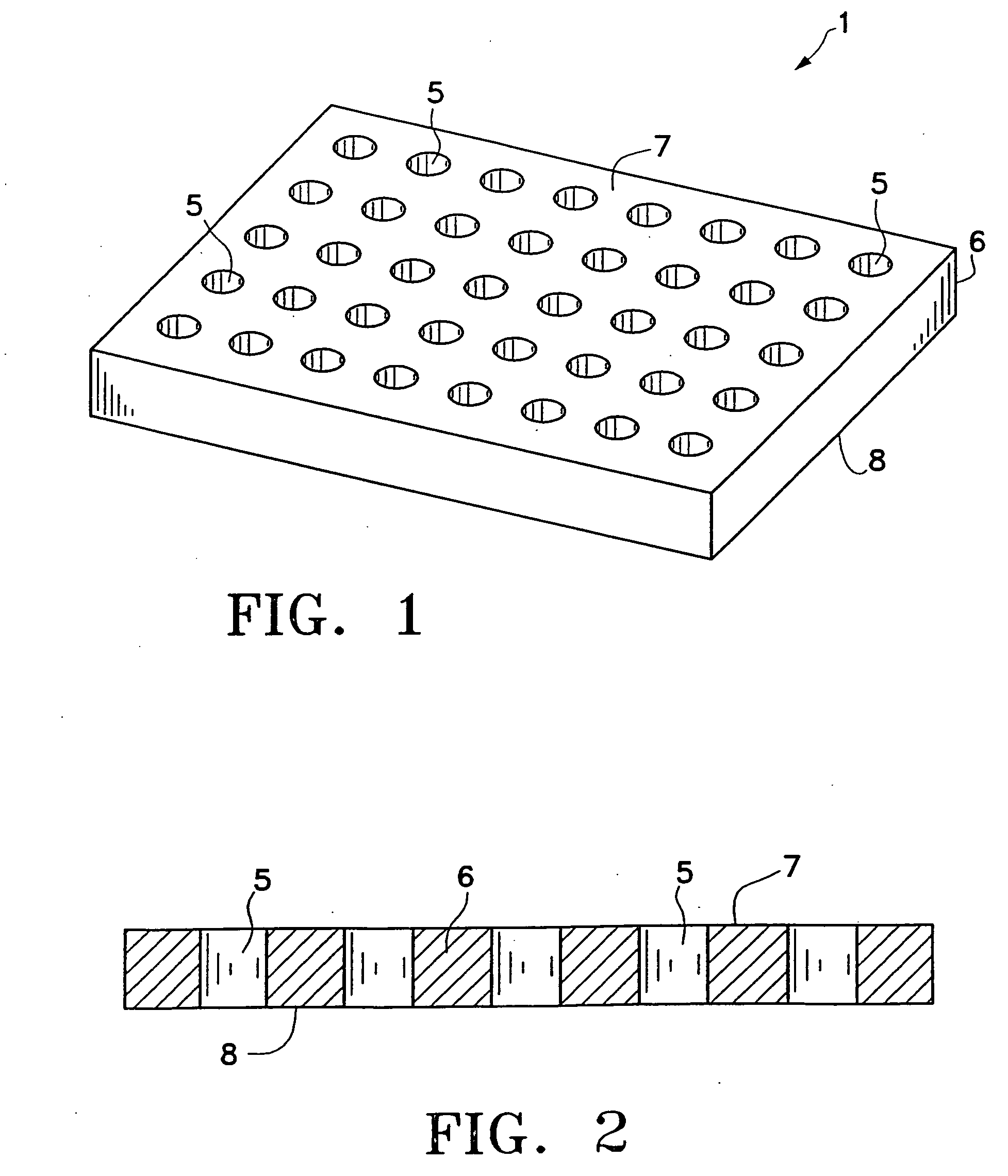
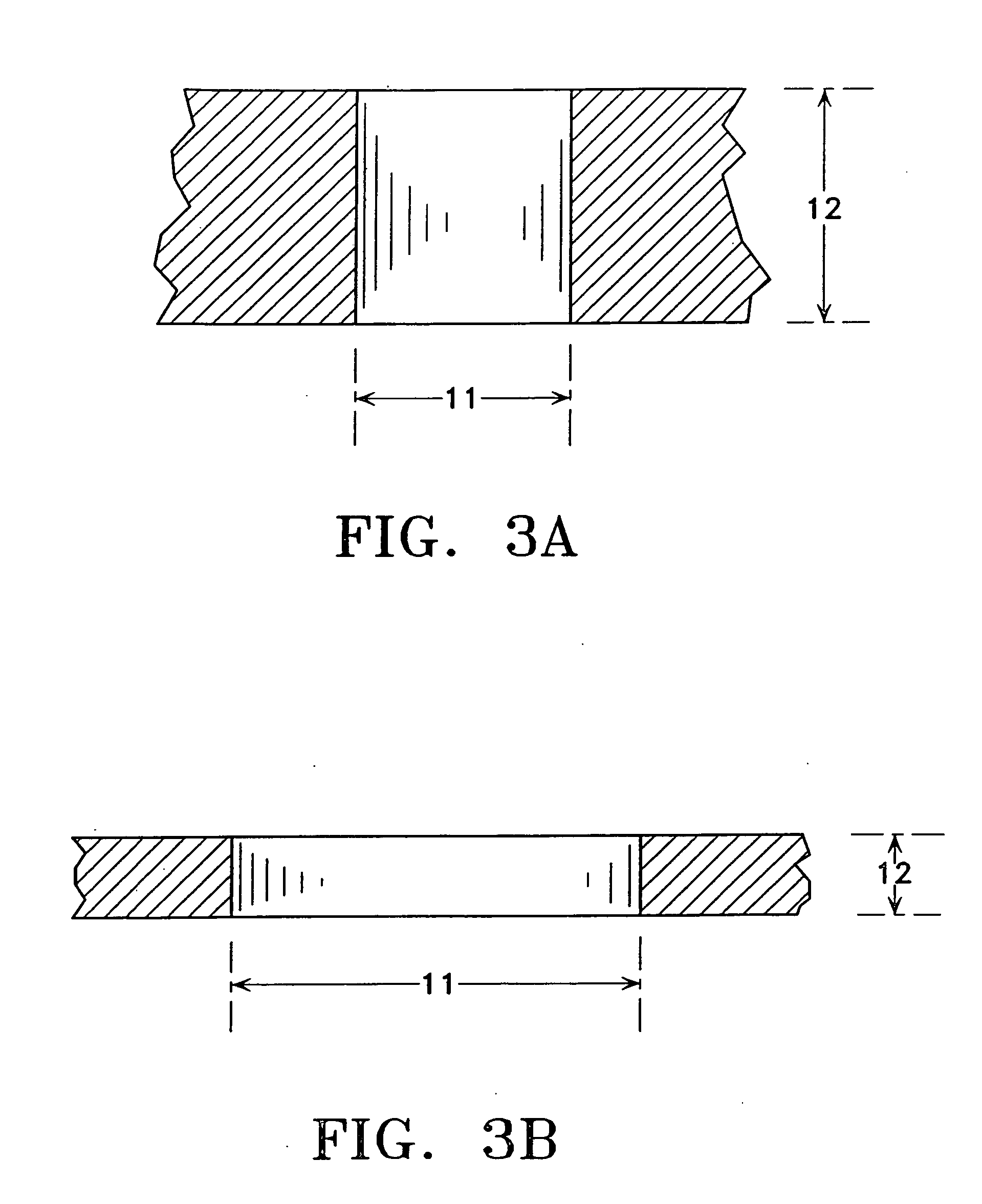
Disclosed herein are apparatuses and methods for conducting multiple simultaneous micro-volume chemical and biochemical reactions in an array format. In one embodiment, the format comprises an array of microholes in a substrate. Besides serving as an ordered array of sample chambers allowing the performance of multiple parallel reactions, the arrays can be used for reagent storage and transfer, library display, reagent synthesis, assembly of multiple identical reactions, dilution and desalting. Use of the arrays facilitates optical analysis of reactions, and allows optical analysis to be conducted in real time. Included within the invention are kits comprising a microhole apparatus and a reaction component of the method(s) to be carried out in the apparatus.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Microfluidic control device and method for controlling microfluid
InactiveUS20050133101A1Loss of functionAdditive manufacturing apparatusCircuit elementsFluid controlTime delays
Provided is a microfluidic control device and method for controlling the microfluid, and a fine amount of fluid is controlled even with natural fluid flow and solution injection, wherein a pressure barrier of a capillary is removed by a surface tension change resulted from the solution injection to thereby obtain transport, interflow, mixing, and time delay of the microfluid, and to detail this, solution is injected to meet the boundary surface of the stopped fluid when the fluid is stopped by the stop valve, so that a function of the stop valve is removed to obtain the transport, interflow, and mixing of the fluid, and the method for controlling the microfluid may be applied to the microfluidic control device for biochemical reaction, and it uses only the capillary force change resulted from solution injection to thereby have its structure simplified.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Arrays of integrated analytical devices and methods for production
Arrays of integrated analytical devices and their methods for production are provided. The arrays are useful in the analysis of highly multiplexed optical reactions in large numbers at high densities, including biochemical reactions, such as nucleic acid sequencing reactions. The integrated devices allow the highly sensitive discrimination of optical signals using features such as spectra, amplitude, and time resolution, or combinations thereof. The arrays and methods of the invention make use of silicon chip fabrication and manufacturing techniques developed for the electronics industry and highly suited for miniaturization and high throughput.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Magnetic bead manipulation and transport device
InactiveUS20050284817A1Increase speedLow magnetic fieldsElectrostatic separationTransportation and packagingClinical chemistryMagnetic bead
A device for transporting magnetic or magnetisable microbeads (25) in a capillary chamber (14) comprises a permanent magnet (10) or an electromagnet (11) for subjecting the capillary chamber to a substantially uniform magnetic field, to apply a permanent magnetic moment to the microbeads (25). At least one planar coil (22) and preferably an array of overlapping coils are located adjacent to the capillary chamber (14) for applying a complementary magnetic field on the microbeads parallel or antiparallel to said substantially uniform magnetic field, to drive the microbeads. An arrangement is provided for switching the current applied to the coil(s) (22) to invert the field produced thereby, to selectively apply an attractive or repulsive driving force on the microbeads (25). The device is usable to transport microbeads for performing chemical and biochemical reactions or assay, as is done for instance in clinical chemistry assays for medical diagnostic purposes.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Microfabricated reactor, process for manufacturing the reactor, and method of amplification
ActiveUS7297313B1Faster cycle timeHeating or cooling apparatusFlow propertiesUltrasonic lamb wavesEngineering
An integrated microfabricated instrument for manipulation, reaction and detection of microliter to picoliter samples. The instrument is suited for biochemical reactions, particularly DNA-based reactions such as the polymerase chain reaction, that require thermal cycling since the inherently small size of the instrument facilitates rapid cycle times. The integrated nature of the instrument provides accurate, contamination-free processing. The instrument may include reagent reservoirs, agitators and mixers, heaters, pumps, and optical or electromechanical sensors. Ultrasonic Lamb-wave devices may be used as sensors, pumps and agitators.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Micromirror arrays having self aligned features
ActiveUS20110222179A1Easy alignmentEliminate needMirrorsDecorative surface effectsOptical limitingNanostructure
Methods, arrays, and systems for the optical analysis of multiple chemical, biological, or biochemical reactions are provided. The invention includes methods for producing arrays of micromirrors on transparent substrates, each micromirror comprising a nanostructure or optical confinement on its top. The arrays are produced by a process in which lateral dimensions of both the nanostructures and micromirrors are defined in a single step, allowing for control of the relative placement of the features on the substrate, minimizing the process-related defects, allowing for improved optical performance and consistency. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of selectively etching large features on a substrate while not concurrently etching small features. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of etching large features on a substrate using hard mask materials.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
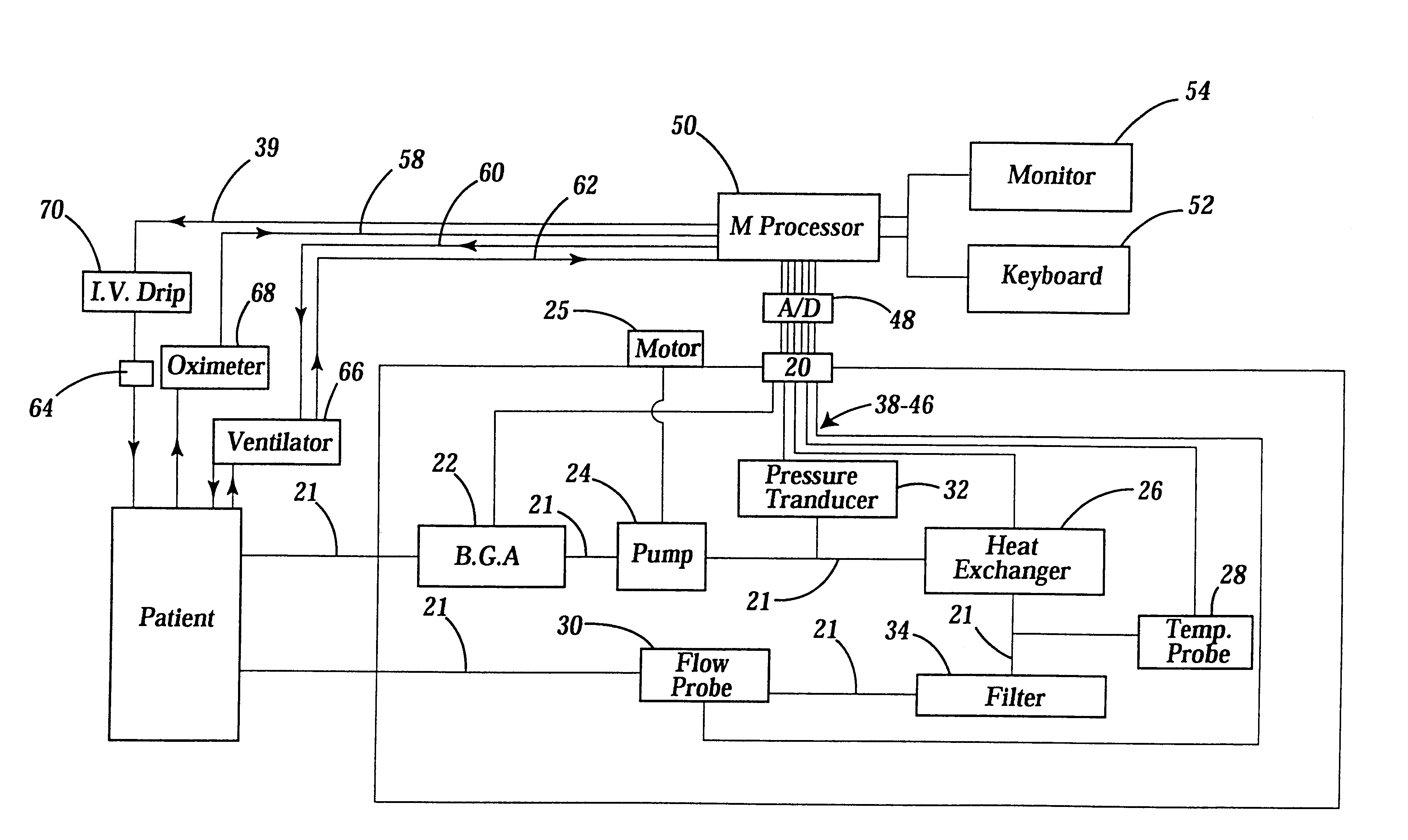
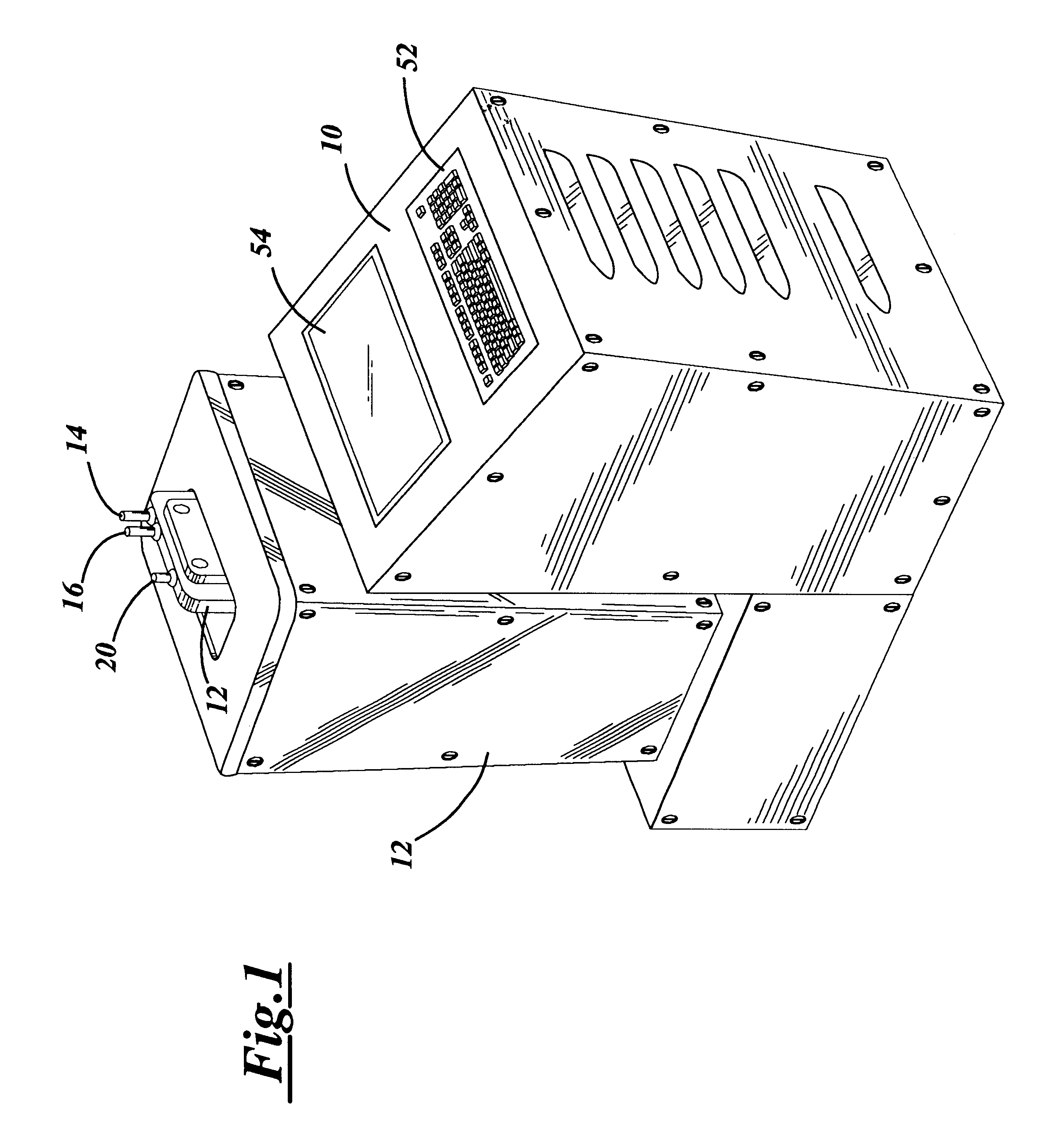
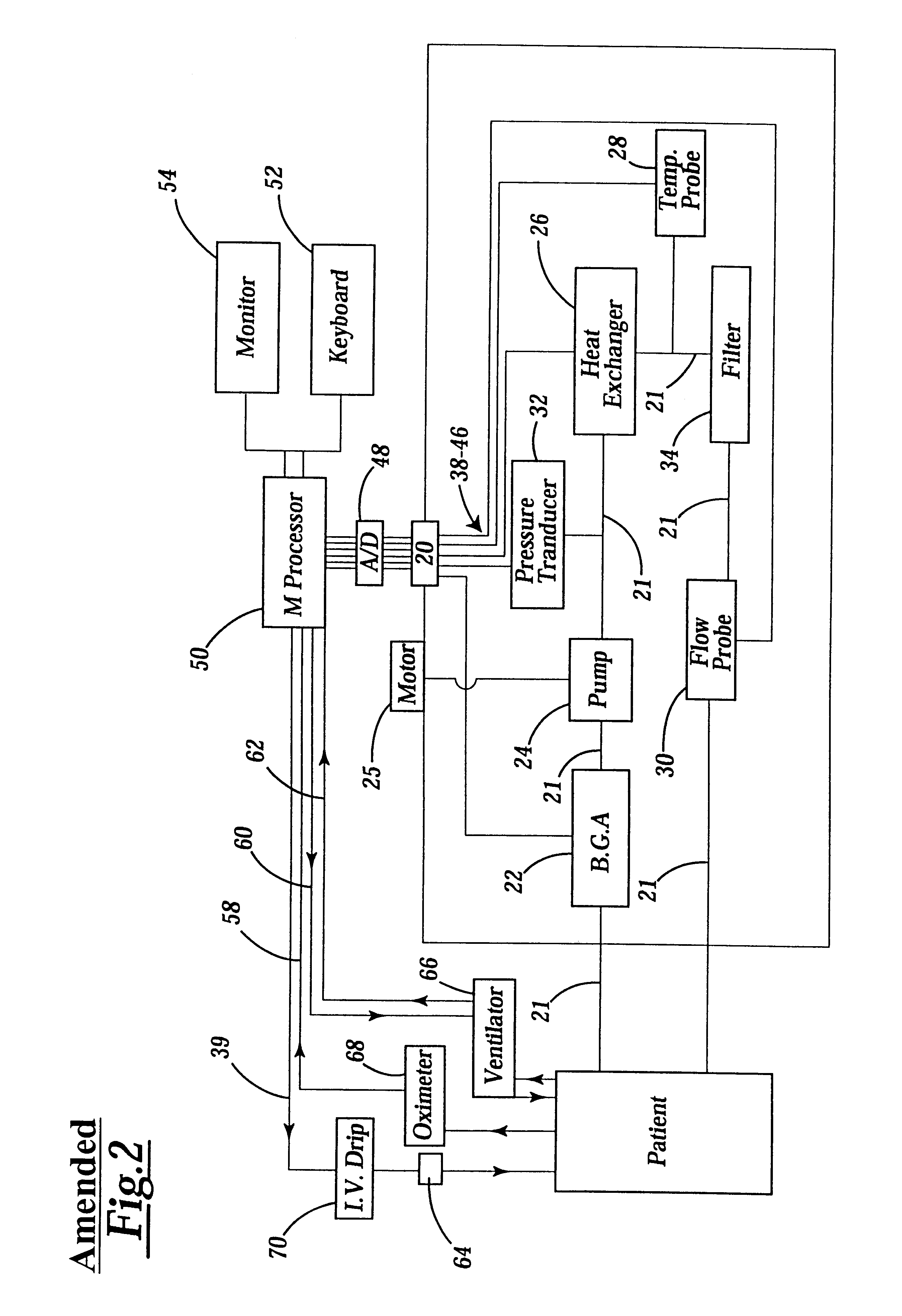
Extracorporeal whole body hyperthermia using alpha-stat regulation of blood pH and pCO2
InactiveUSRE38203E1Stabilizing biochemical reactionRespiratorsOther blood circulation devicesBiological bodyWhole body
A device and method for extracorporeal whole body hyperthermia treatment of a patient's blood using alpha-stat regulation of blood pH and pCO2 is described. The respiratory rate of a patient is either increased or decreased in accordance with the changes in pH, pCO2, and base excess. The regulation of blood during the hyperthermic treatment of the patient's blood stabilizes the biochemical reactions fundamental to the metabolic welfare of the organisms within the patient's blood while the viruses within the patient's blood are eliminated.
Owner:FIRST CIRCLE MEDICAL
Integrated target waveguide devices and systems for optical coupling
ActiveUS20160363728A1Reduce the numberMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCoupling light guidesMultiplexingHigh density
Integrated target waveguide devices and optical analytical systems comprising such devices are provided. The target devices include an optical coupler that is optically coupled to an integrated waveguide and that is configured to receive optical input from an optical source through free space, particularly through a low numerical aperture interface. The devices and systems are useful in the analysis of highly multiplexed optical reactions in large numbers at high densities, including biochemical reactions, such as nucleic acid sequencing reactions. The devices provide for the efficient and reliable coupling of optical excitation energy from an optical source to the optical reactions. Optical signals emitted from the reactions can thus be measured with high sensitivity and discrimination. The devices and systems are well suited for miniaturization and high throughput.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Multiple barrier biological treatment systems
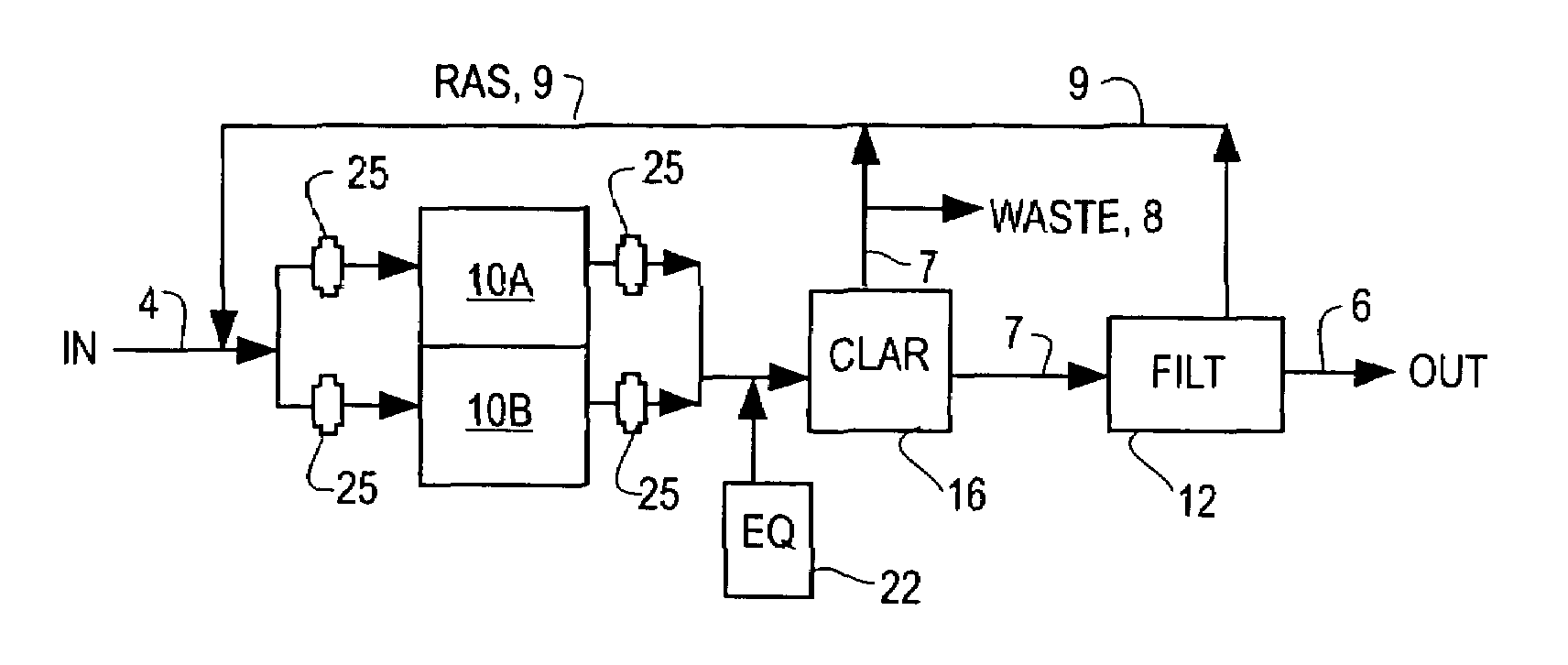
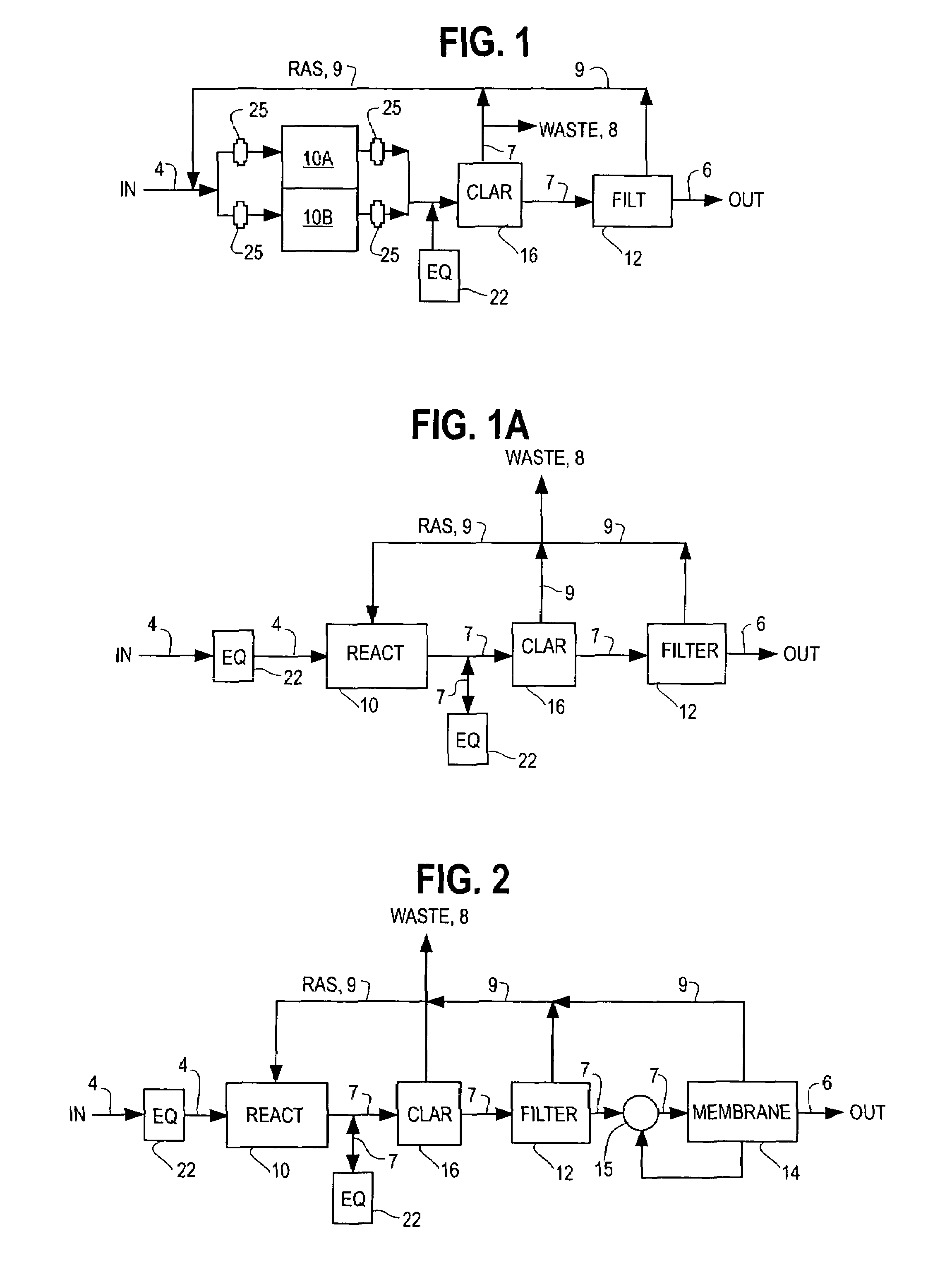
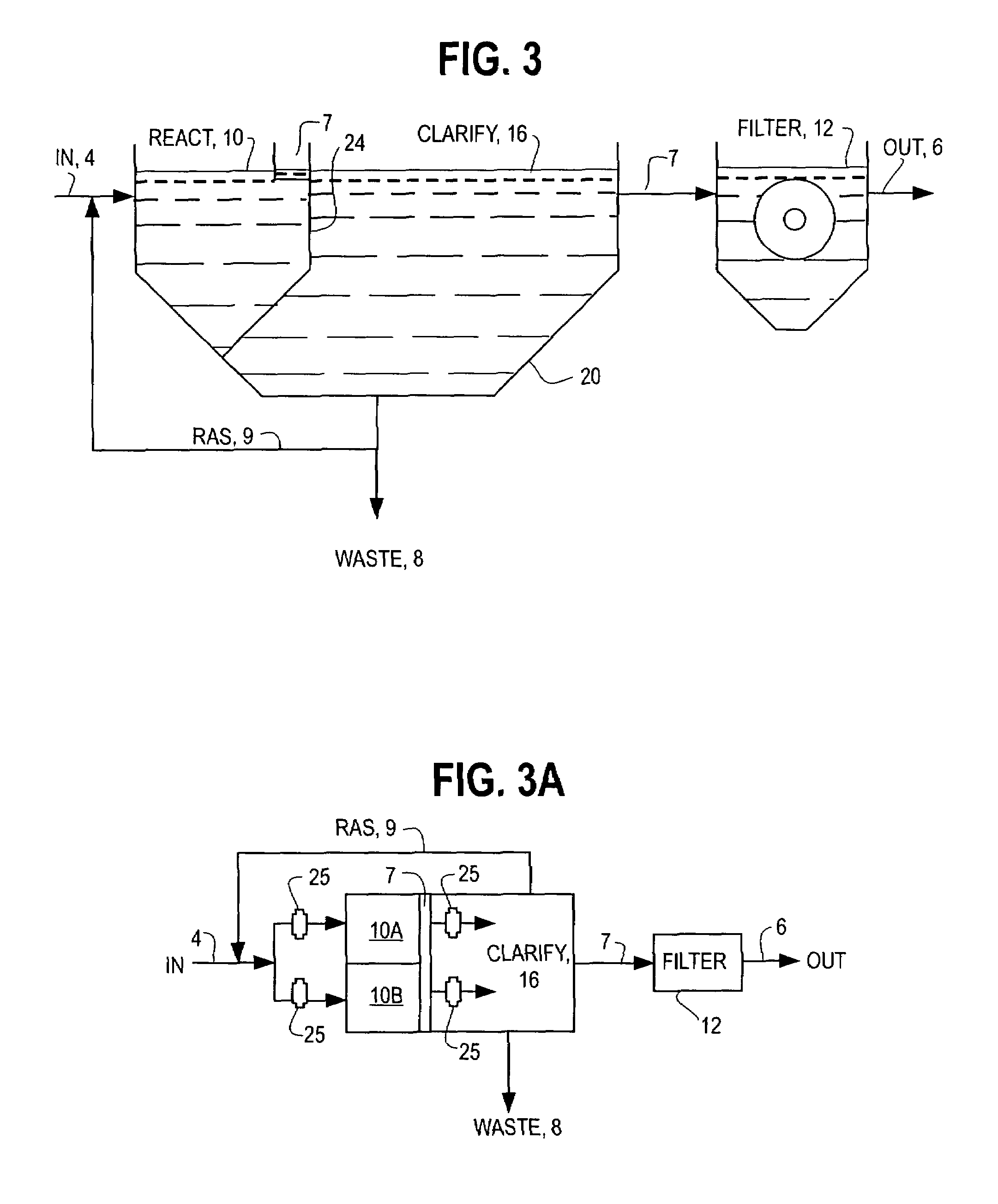
InactiveUS7014763B2Small footprintReduce construction costsTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorSingle vessel
The inventions separate the activated sludge, biochemical reaction stages of the batch treatment process of a sequencing batch reactor from the clarification and sedimentation stages by separating the locations where each process takes place. The separation may be accomplished in a variety of ways including constructing separate basins for each process, installing baffles or other partitions in a single vessel to isolate the areas where each process takes place, or other methods of process separation as are known in the art. In each process, treatment occurs through the performance of a series of operations. The operations are repeated for each batch of wastewater processed by the SBR. In a conventional SBR process, the cycle of operations for clarification and sedimentation are dependent on a preceding biochemical reaction step. However, in the present invention the clarification and sedimentation operations are independent of the biochemical reaction operations. It remains possible to coordinate operations so that the process cycles are coincident, however the benefits of the invention are more readily realized by the practice of independent operation.
Owner:AQUA AEROBIC SYST
Illumination of optical analytical devices
ActiveUS9223084B2Reduce areaReduce the cross-sectional areaOptical fibre with polarisationMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh densityImage resolution
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Fluidic devices and methods for multiplex chemical and biochemical reactions
ActiveCN1942590ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMultiplexingCompound (substance)
The present invention describes microfluidic devices that provide novel fluidic structures to facilitate the separation of fluids into isolated, pico-liter sized compartments for performing multiplexing chemical and biological reactions. Applications of the novel devices including biomolecule synthesis, polynucleotide amplification, and binding assays are also disclosed.
Owner:HANGZHOU LC BIOTECH
Micro flow control chip used for multi-index biochemical detection
ActiveCN102671729AReduce consumptionEasy to operateLaboratory glasswaresBiochemical engineeringControl channel
The invention discloses a micro flow control chip used for multi-index biochemical detection. The micro flow control chip comprises a micro-fluid channel, a plurality of reaction tanks and a pneumatic micro-valve, wherein one opening end of the micro-fluid channel is a sample inlet while the other opening end is communicated with a chamber arranged in the micro flow control chip; the top wall of the chamber is an elastic film and is exposed in air; reaction tanks are connected in series or in parallel through the micro-fluid channel; the pneumatic micro-valve comprises a control channel; one sidewall of the control channel is an elastic film; and the control channel and the micro-fluid channel are arranged crossly. The micro flow control chip used for multi-index biochemical detection integrates sample introduction with multi-index biochemical reaction based on a micro flow control chip technical platform, so that the micro flow control chip used for multi-index biochemical detection, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of greatly simplifying operating process, reducing consumption of samples and reagents, having no need to allocate expensive instruments, greatly reducing use cost, making on-site instant detection possible and having great foreseeable economic value and social value.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +1
Thin film chemical analysis apparatus and analysis method using the same
ActiveUS20090317896A1Long circulationLong maintenance periodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsValve arrangementsAnalyteCompound (substance)
Disclosed is a thin film chemical analysis apparatus and an analysis method using the same, which can solve the sealing problem caused by environmental factors (e.g. impact, temperature) for long circulation and storage periods, as well as can detect an analyte quickly and easily. The thin film chemical analysis apparatus includes at least one chamber adapted to store a fluid necessary for biological or biochemical analysis or to conduct a biological or biochemical reaction; channels for fluid-connection of the chambers; holes arranged between or inside the channels and connected to the channels; a rotatable body having the chambers, the channels, and the holes integrated into the body; and a burst valve having a sealing means for closing the hole and sealing a fluid in the chamber, the sealing means being torn away from the hole by centrifugal force resulting from rotation of the body and opening the hole.
Owner:PRECISIONBIOSENSOR INC
Integrated devices and systems for free-space optical coupling
ActiveUS20160273034A1Reduce the numberMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsHigh densityMiniaturization
Optical delivery devices and integrated analytical systems comprising the optical delivery devices are provided. The optical delivery devices include optical inputs, optical outputs, and integrated optical waveguides that are configured for coupling of optical energy to a target waveguide device through free space. The integrated analytical systems include the optical delivery devices in combination with the target waveguide device. The devices and systems are useful in the analysis of highly multiplexed optical reactions in large numbers at high densities, including biochemical reactions, such as nucleic acid sequencing reactions. The devices provide for the efficient coupling of optical excitation energy from an optical source to the optical reactions. Optical signals emitted from the reactions can thus be measured with high sensitivity and discrimination. The devices and systems are well suited for miniaturization and high throughput.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Apparatus and methods for parallel processing of micro-volume liquid reactions
InactiveUS20080108112A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCompound (substance)Parallel processing
Disclosed herein are apparatuses and methods for conducting multiple simultaneous micro-volume chemical and biochemical reactions in an array format. In one embodiment, the format comprises an array of microholes in a substrate. Besides serving as an ordered array of sample chambers allowing the performance of multiple parallel reactions, the arrays can be used for reagent storage and transfer, library display, reagent synthesis, assembly of multiple identical reactions, dilution and desalting. Use of the arrays facilitates optical analysis of reactions, and allows optical analysis to be conducted in real time. Included within the invention are kits comprising a microhole apparatus and a reaction component of the method(s) to be carried out in the apparatus.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
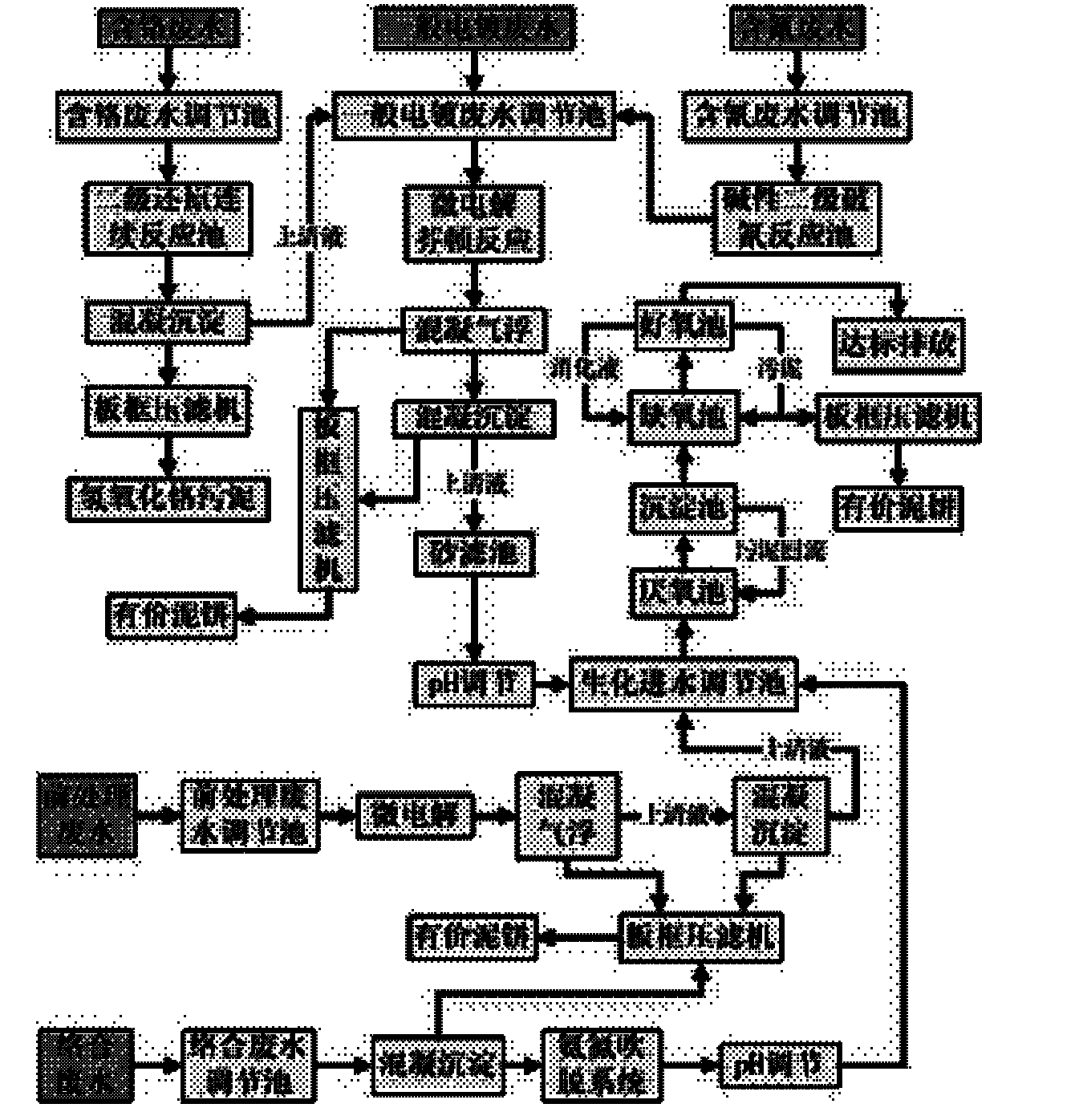
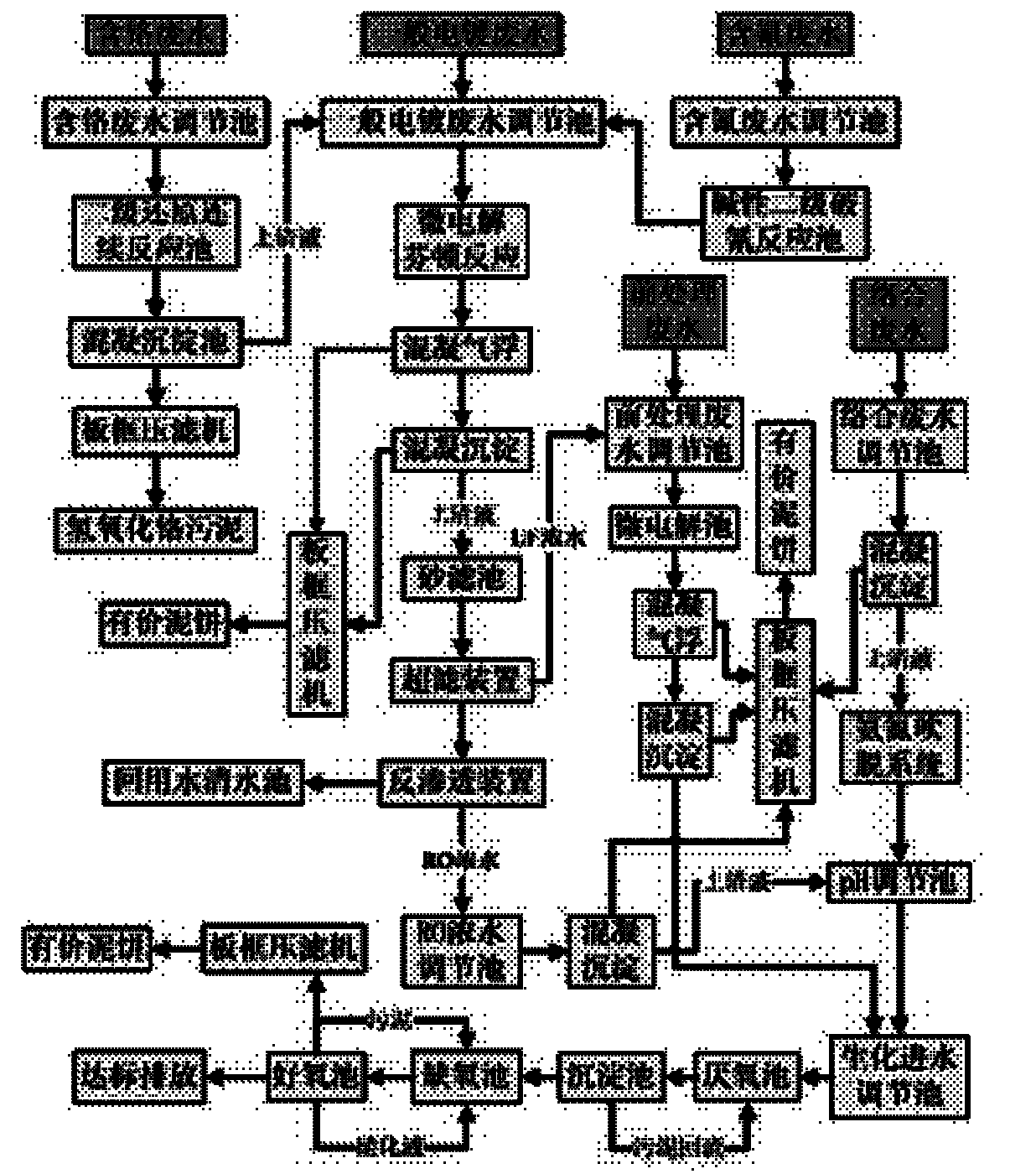
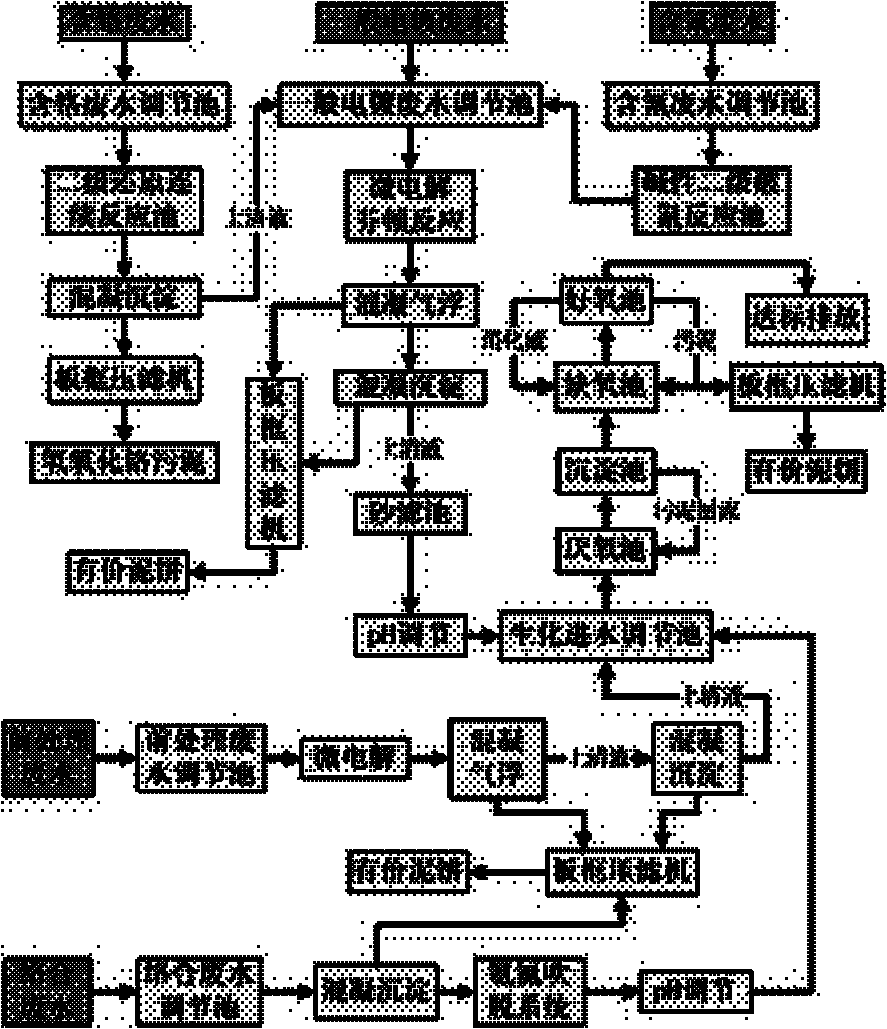
Method for treating comprehensive electroplating wastewater
InactiveCN101830600AAchieve environmental goalsAchieve emissionsWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from metallurgical processChemical oxygen demandElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for treating comprehensive electroplating wastewater. The electroplating wastewater is separated and the recycling utilization rate of heavy metals resources can be improved by carrying out targeted treatment on each strand of separated water while improving the treatment efficiency. By using the micro-electrolysis function of iron and carbon, complex can be removed while removing COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) and the biochemical property can be improved, which provides the guarantee for a subsequent biochemical reaction. By using the displacement action of the ion and the carbon, heavy metal ions in the water can be displaced and heavy metal resources can be recycled. Meanwhile, residual heavy metal ions in the water can be recycled by using the combining action of precipitating hydroxides and sulfides. On the basis, the water quality can meet the standard by using the ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis actions. The total hardness and the electric conductivity of the wastewater are superior to the water quality of tap water. Usable metal resources can be recycled, the economic benefit is obtained while achieving the aim of environmental protection and the production cost can be reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
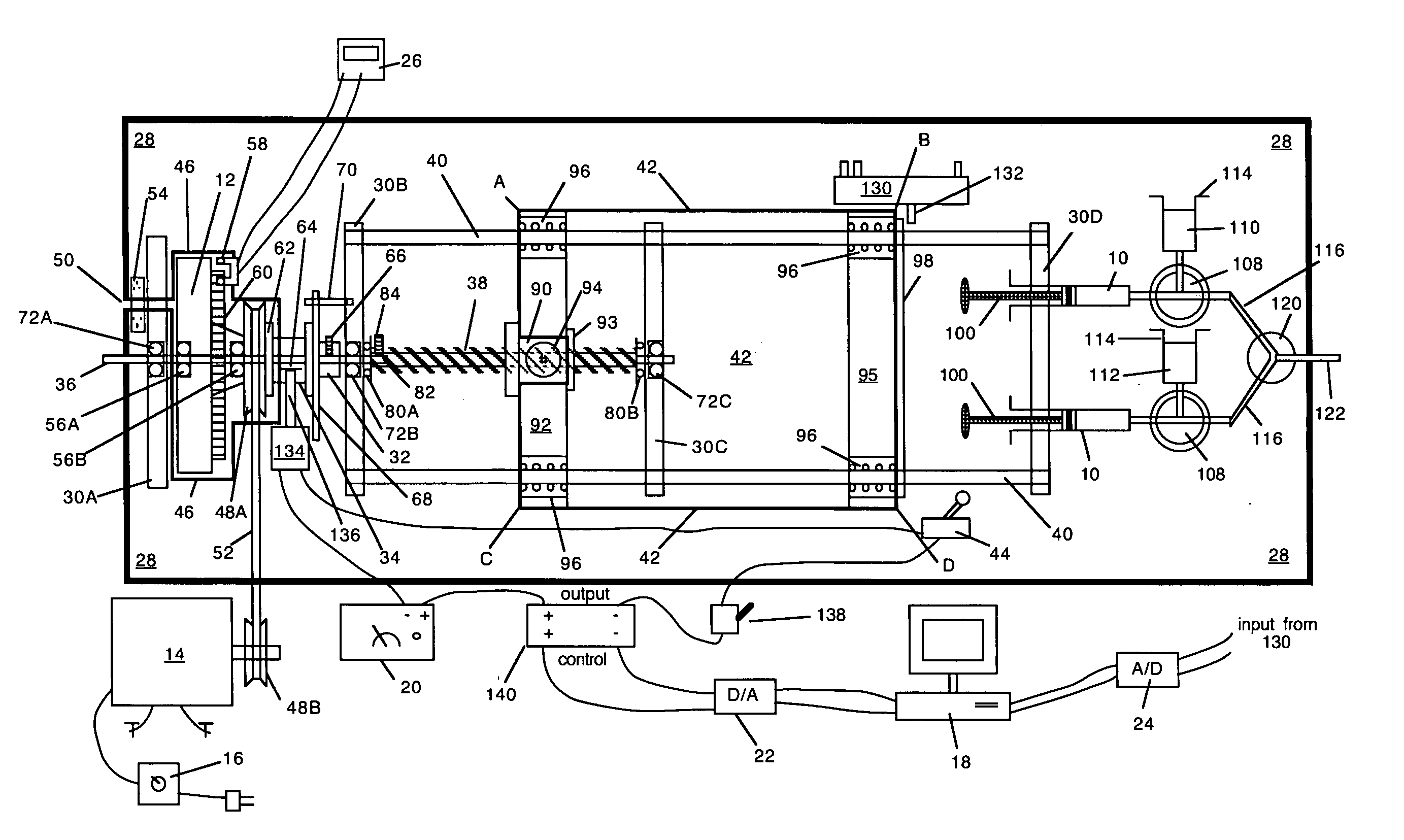
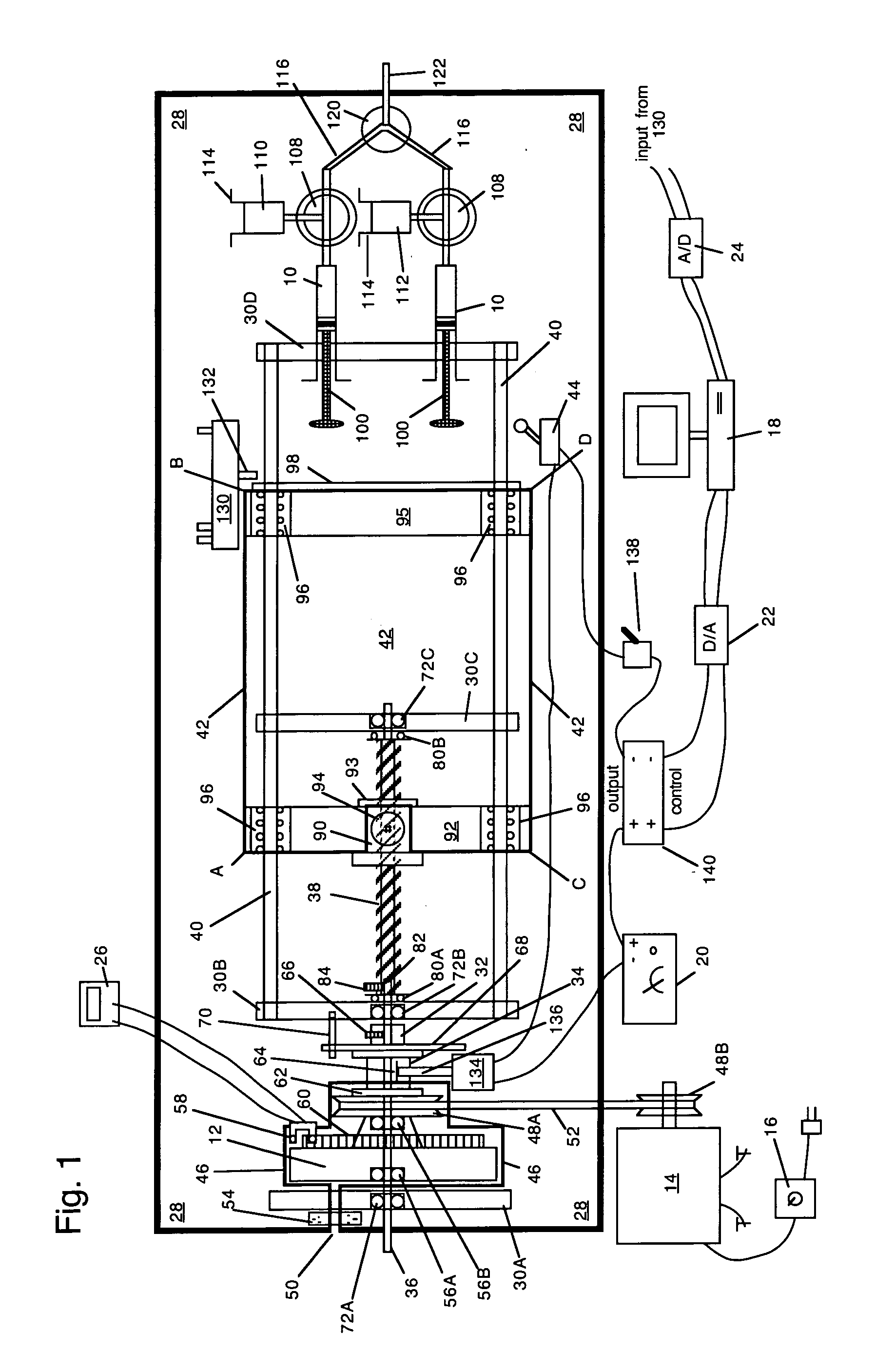
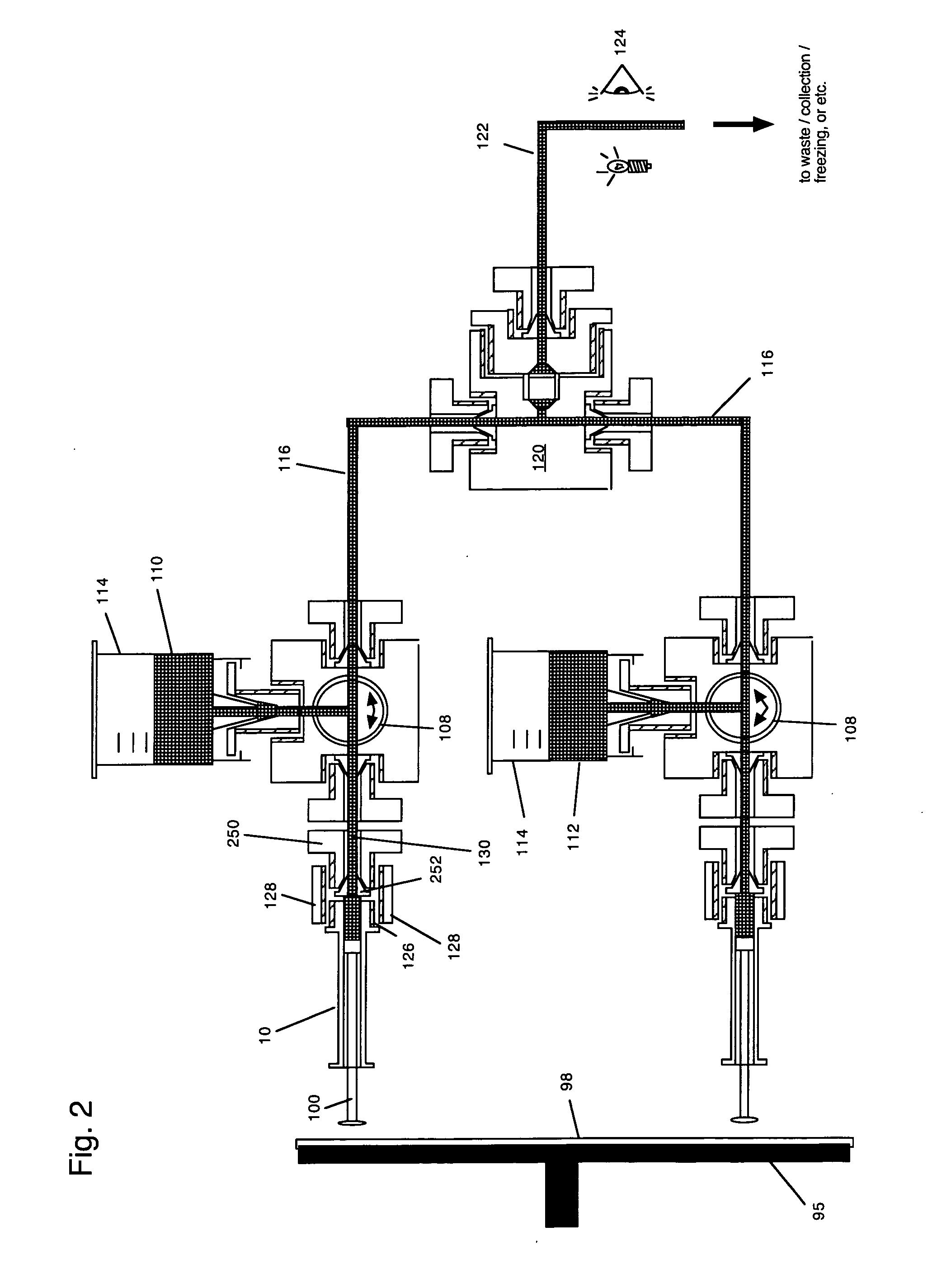
Wrap spring clutch syringe ram and frit mixer
A wrap spring clutch syringe ram pushes at least one syringe with virtually instantaneous starting and stopping, and with constant motion at a defined velocity during the intervening push. The wrap spring clutch syringe ram includes an electric motor, a computer, a flywheel, a wrap spring clutch, a precision lead screw, a slide platform, and syringe reservoirs, a mixing chamber, and a reaction incubation tube. The electric motor drives a flywheel and the wrap spring clutch couples the precision lead screw to the flywheel when a computer enables a solenoid of the wrap spring clutch. The precision lead screw drives a precision slide which causes syringes to supply a portion of solution into the mixing chamber and the incubation tube. The wrap spring clutch syringe ram is designed to enable the quantitative study of solution phase chemical and biochemical reactions, particularly those reactions that occur on the subsecond time scale.
Owner:SIMPSON FR B
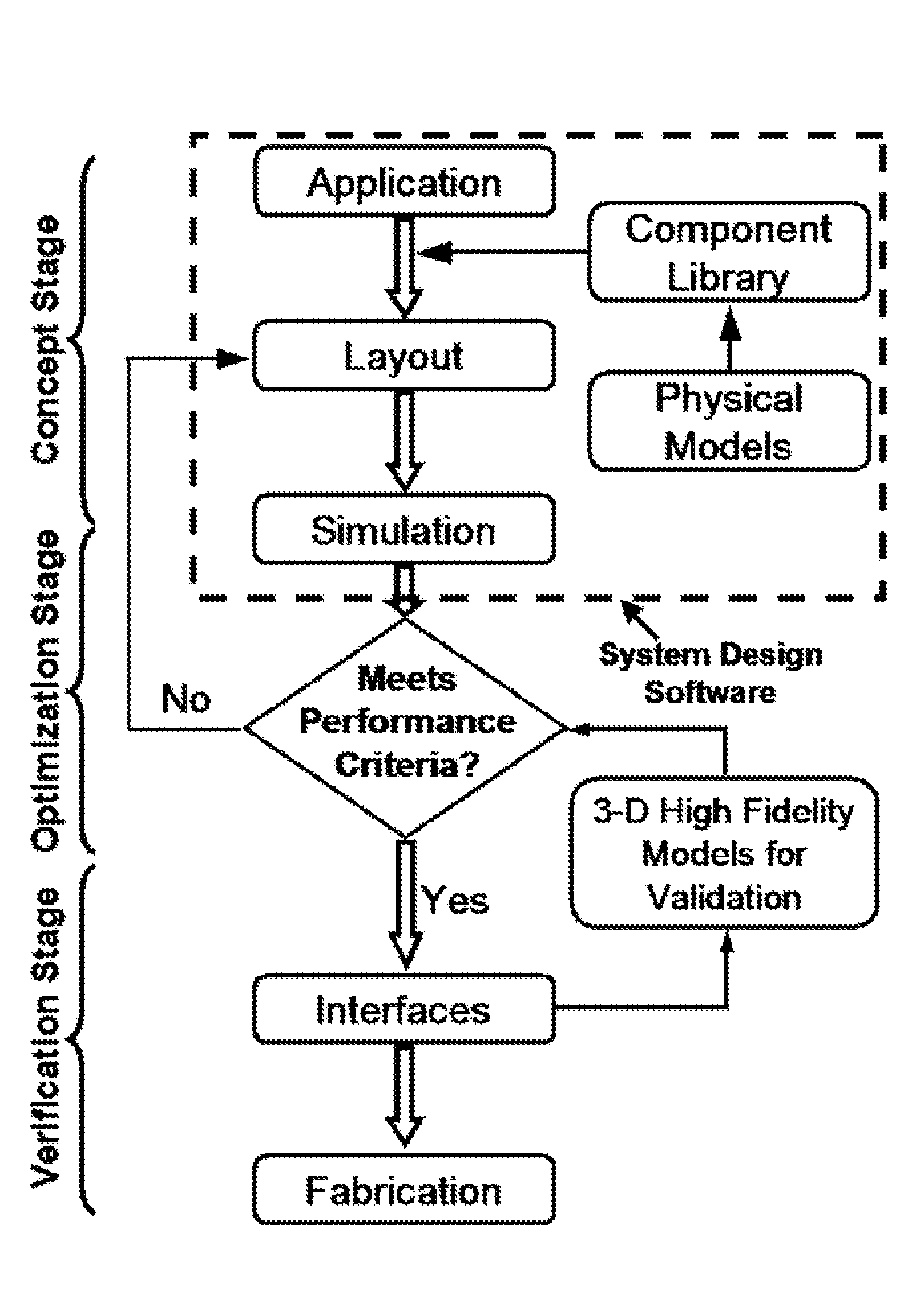
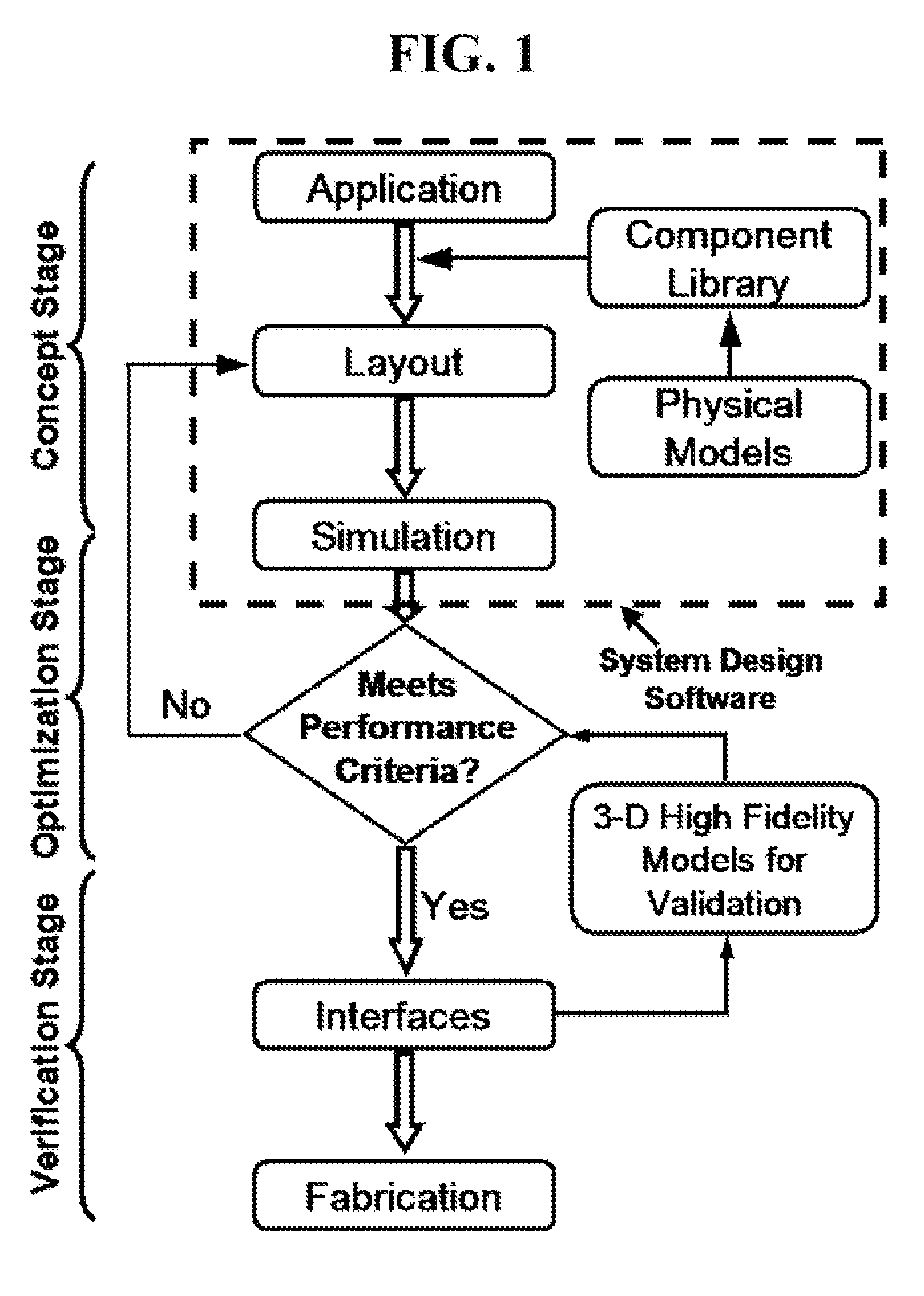
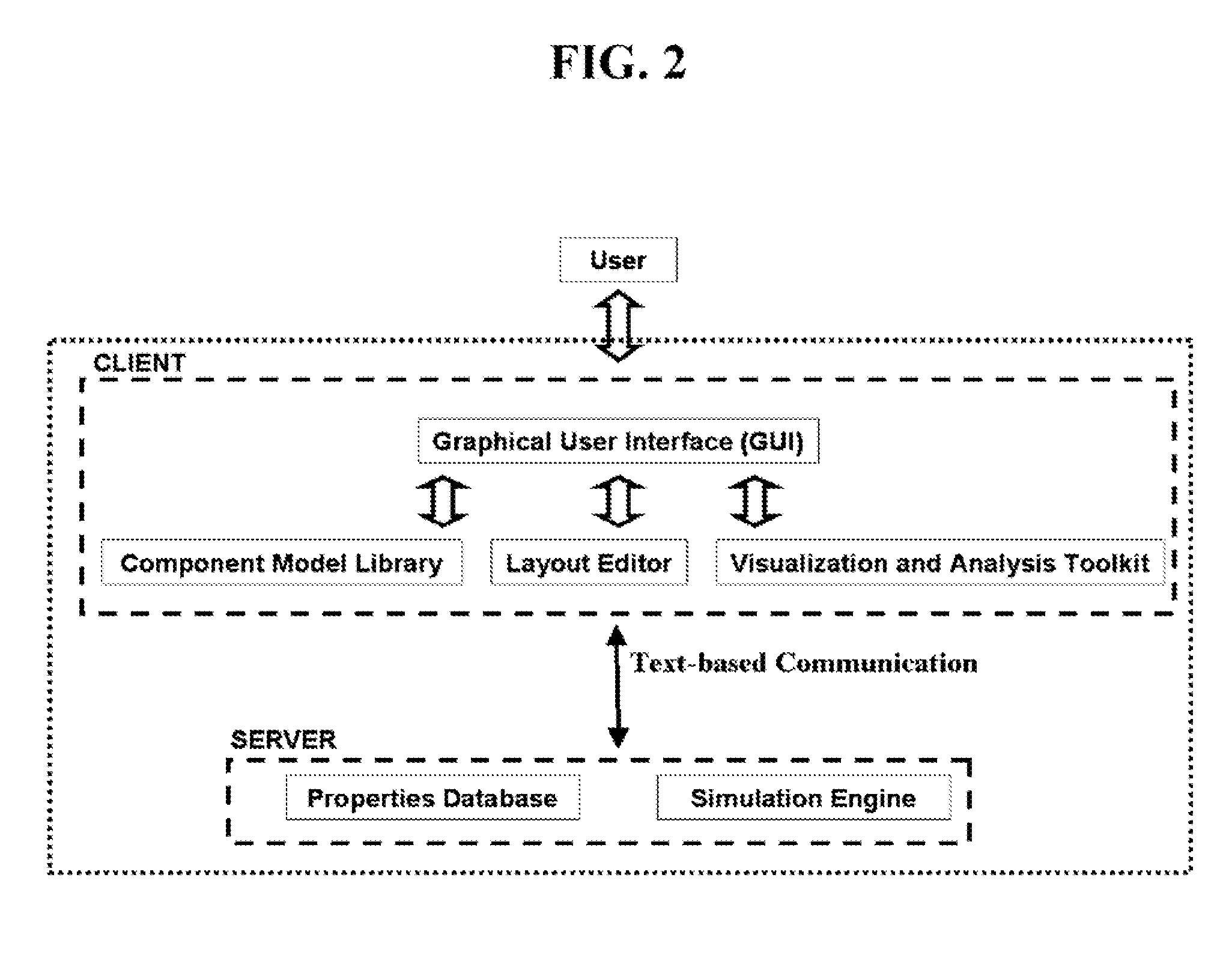
Integrated Microfluidic System Design Using Mixed Methodology Simulations
InactiveUS20080177518A1Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSystems designAnalyte
Owner:CFD RES CORP
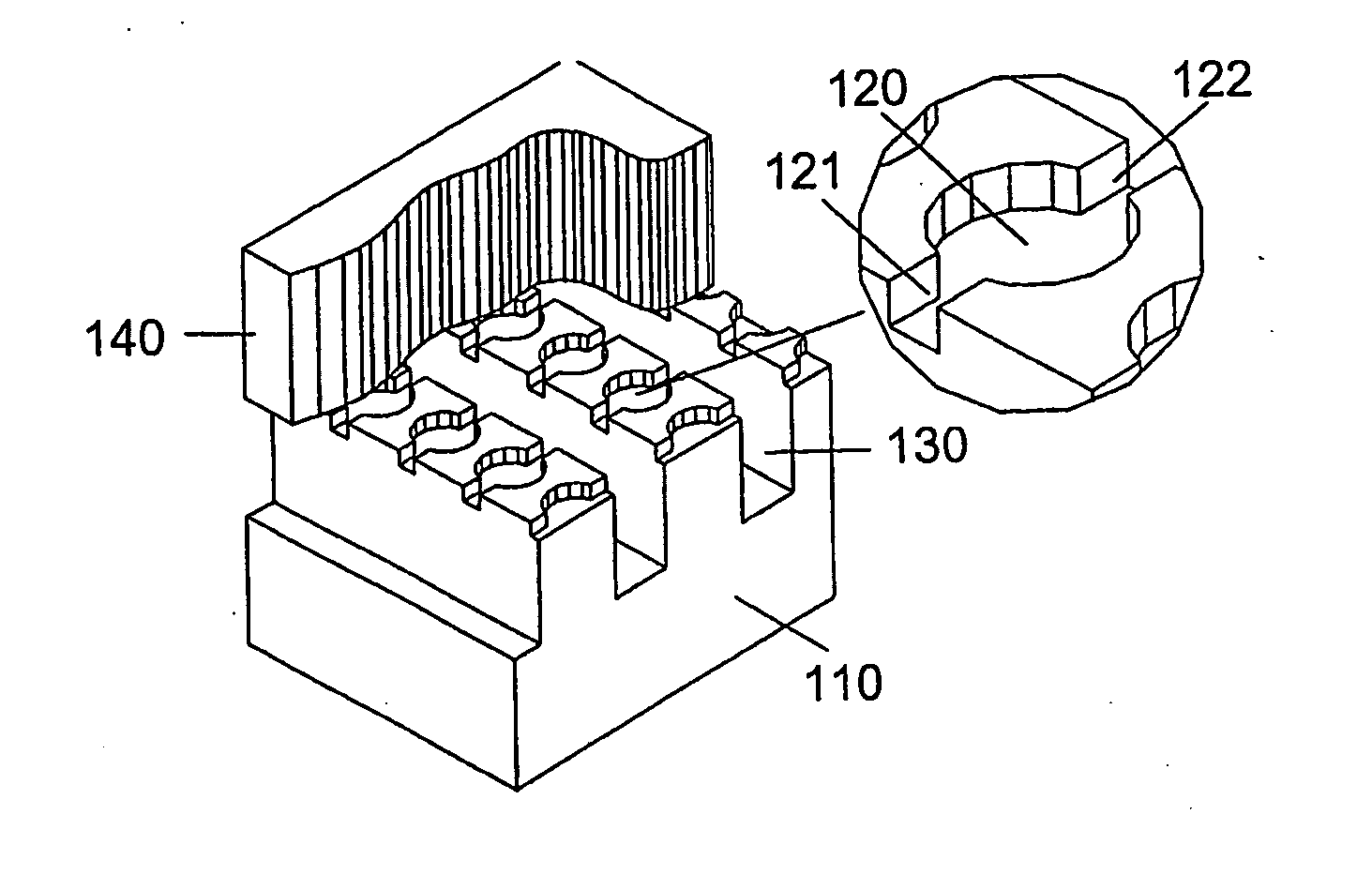
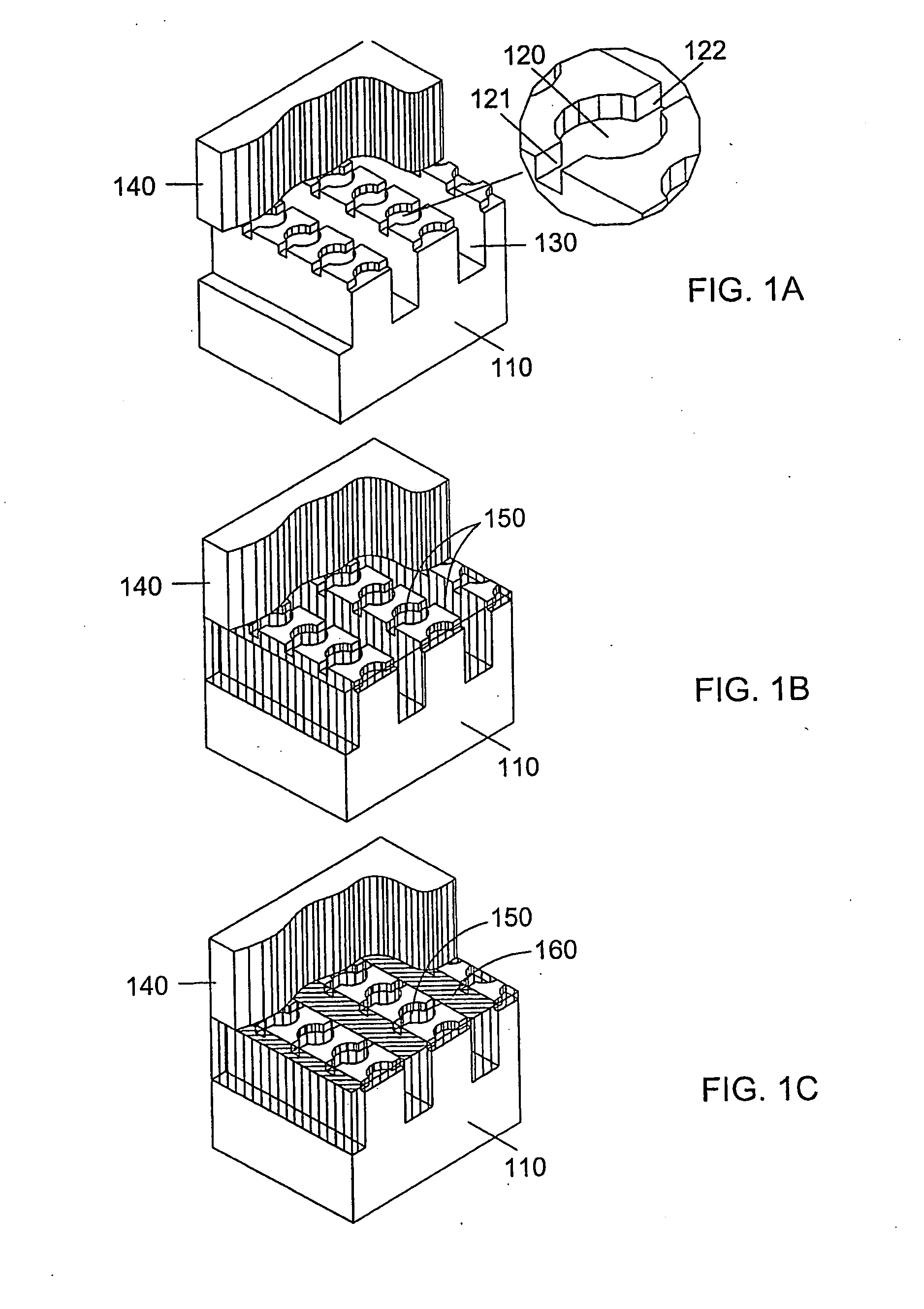
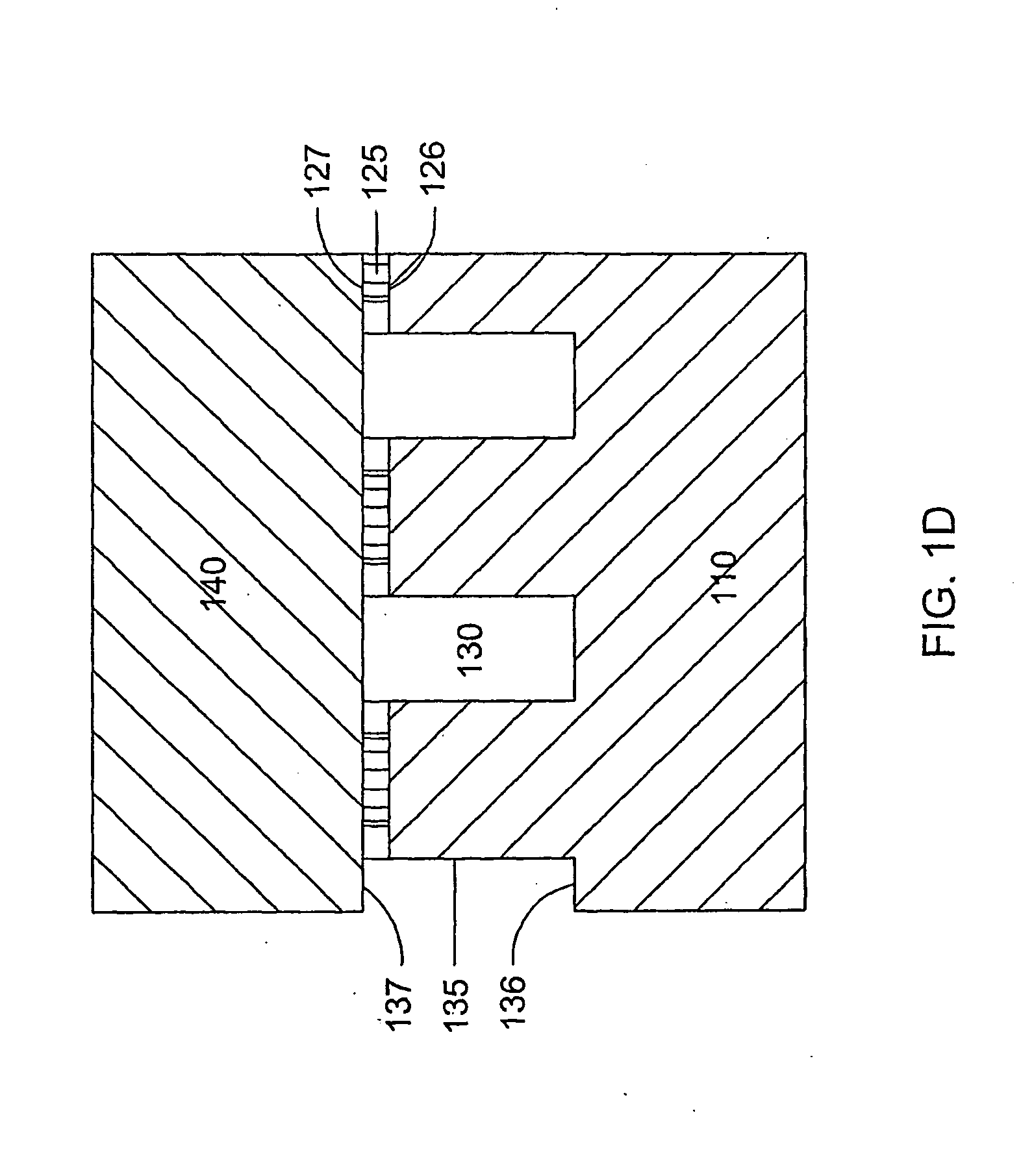
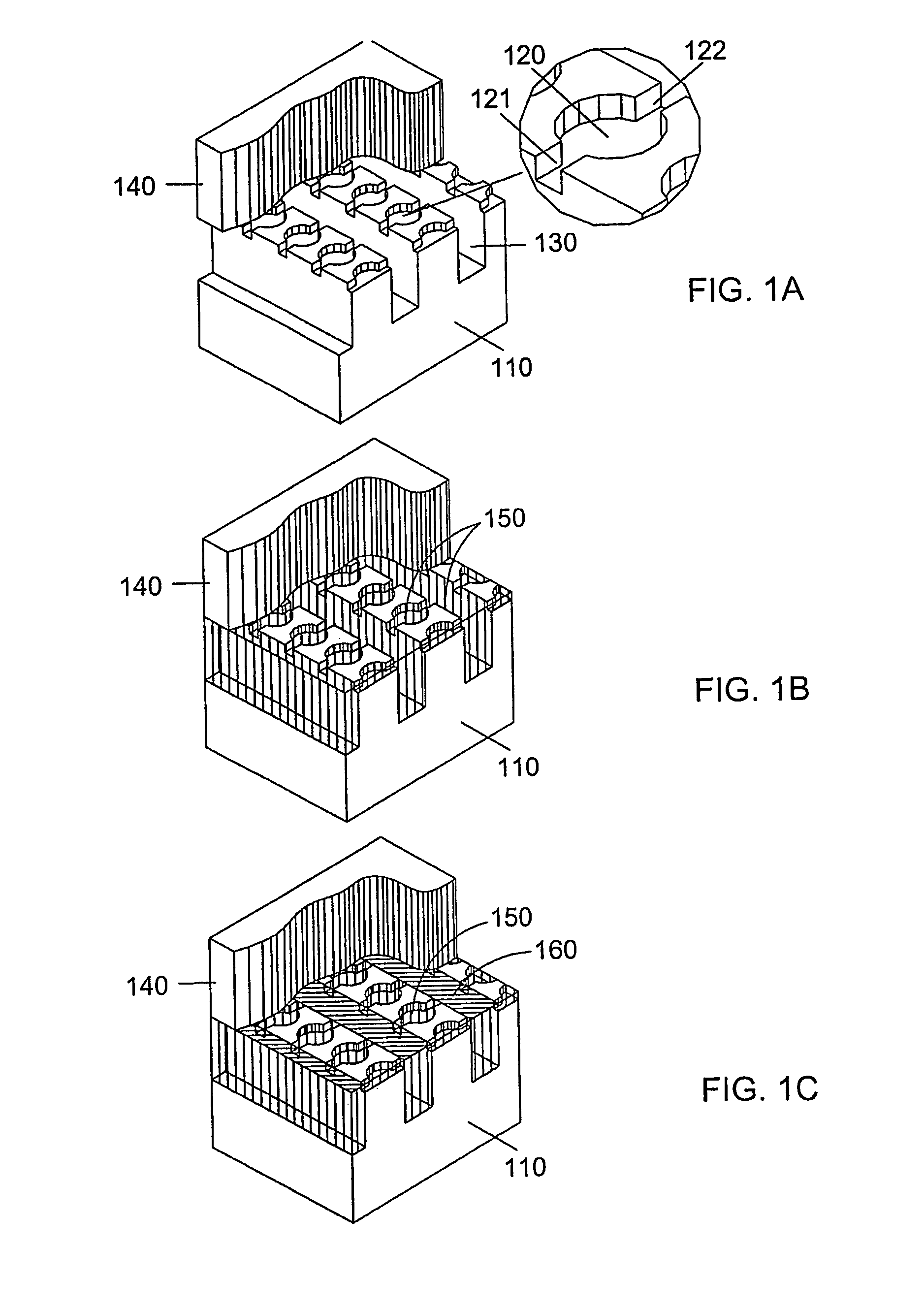
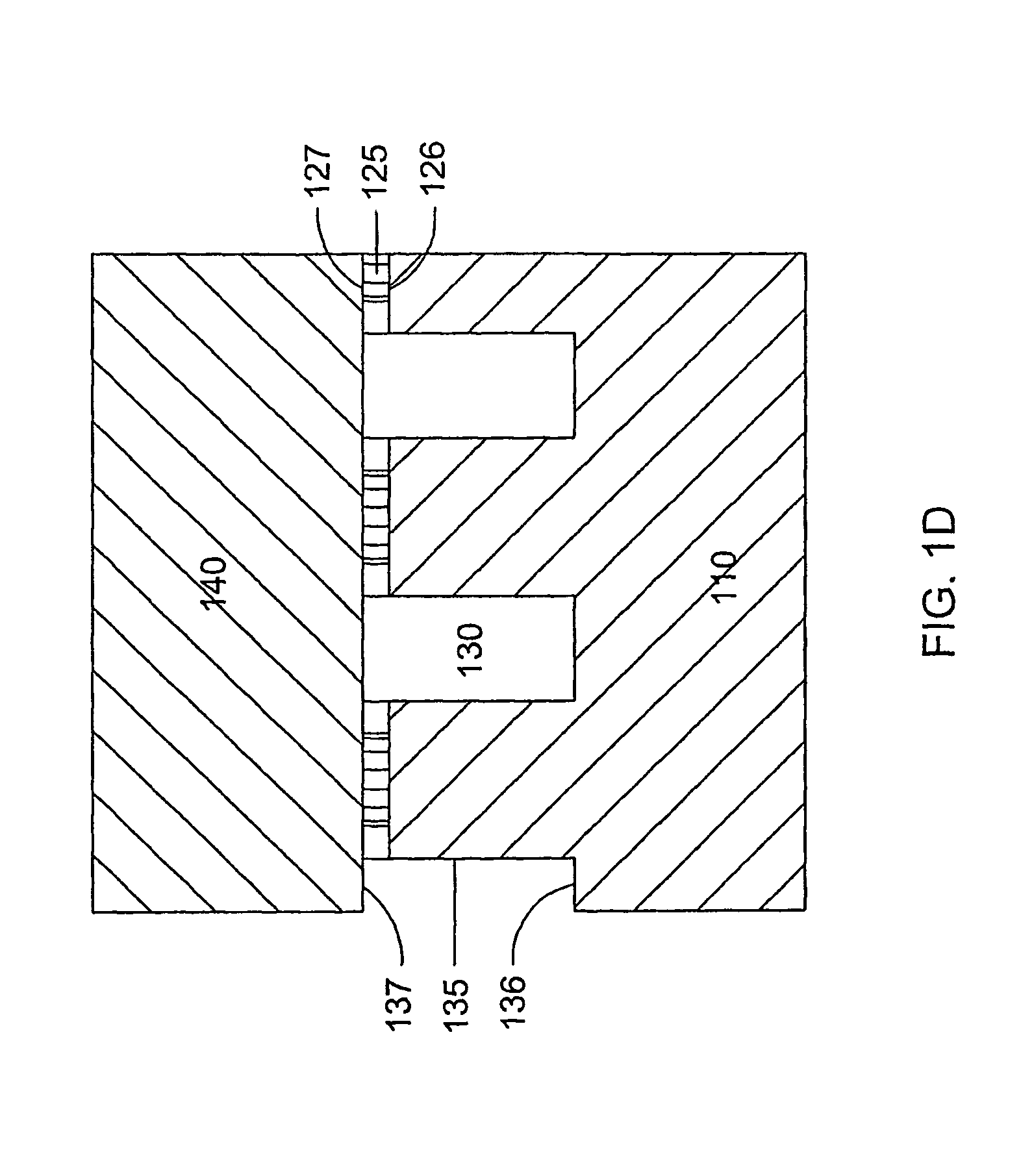
Reaction vessel, cassette and system for performing biochemical reactions
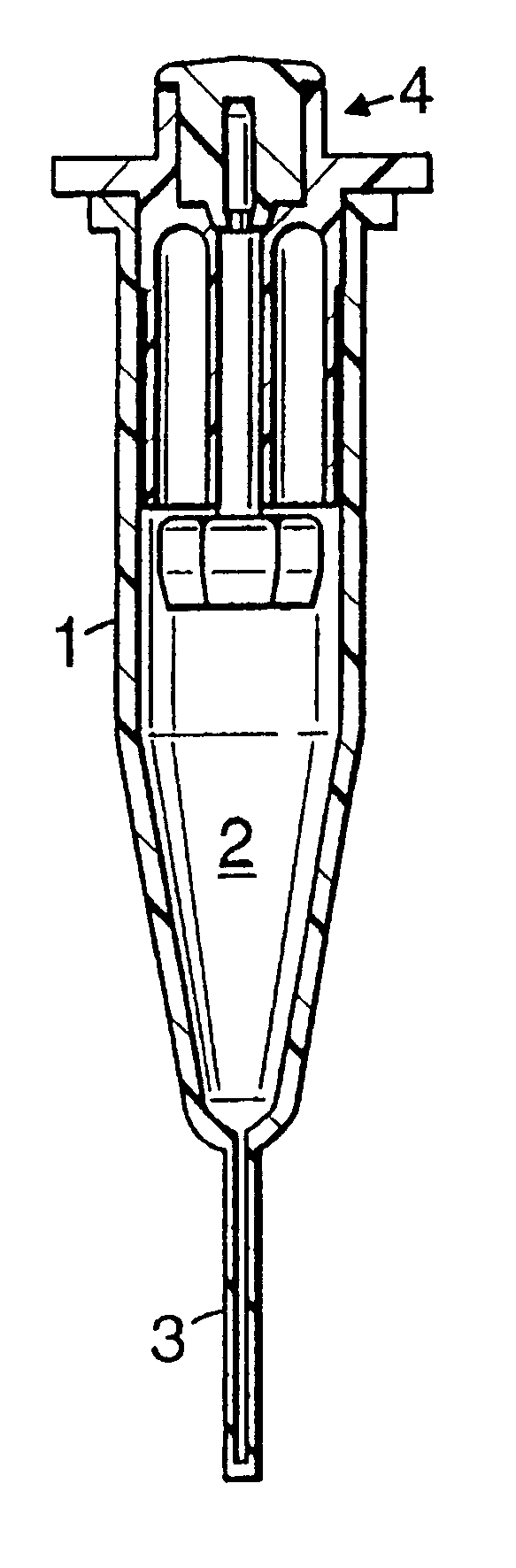
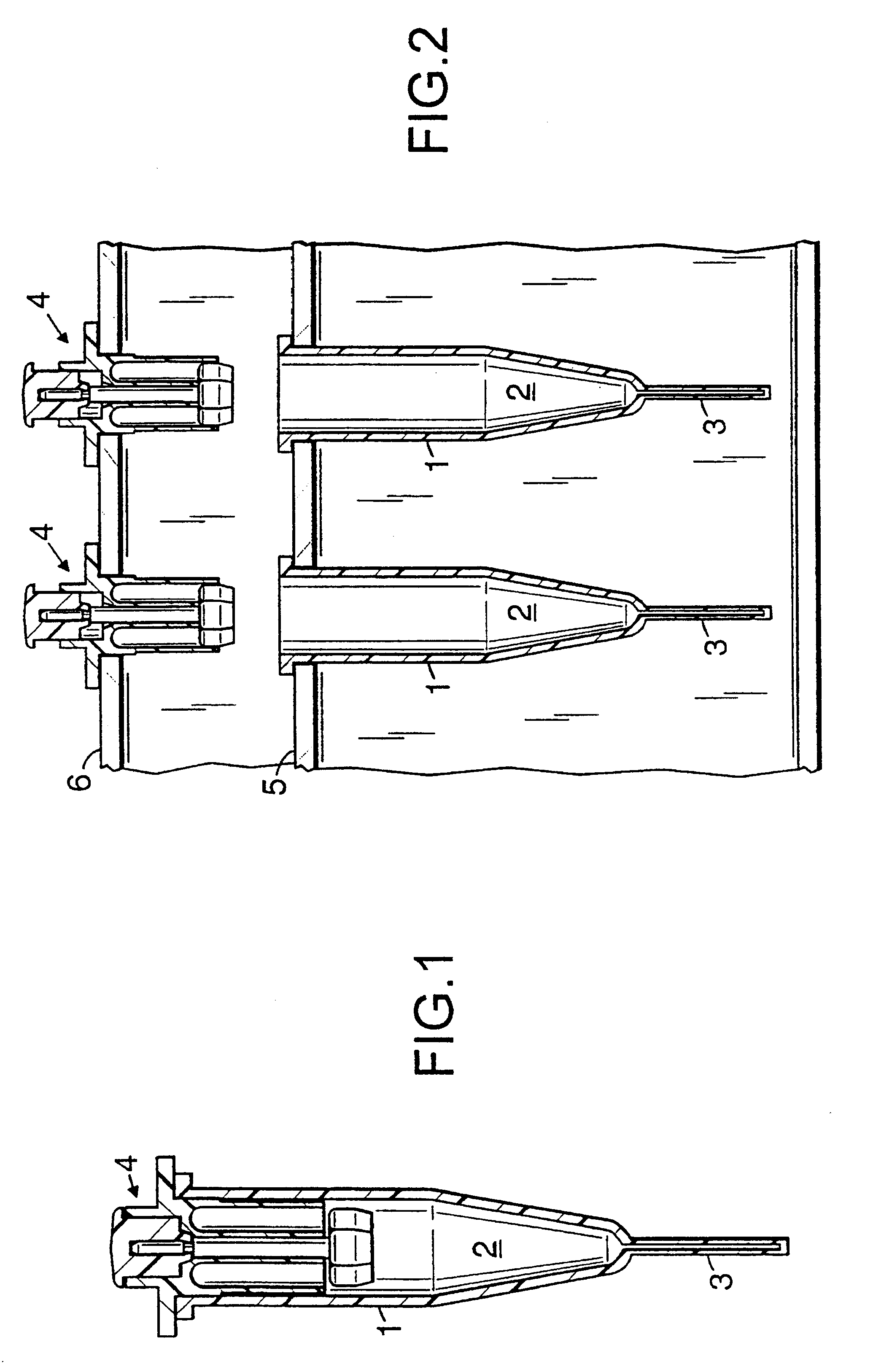
InactiveUS6451258B1Minimize risk of contaminationMitigate such drawbackAnalysis using chemical indicatorsHeating or cooling apparatusChemical reactionAnalytical chemistry
A reaction vessel includes a receiving portion and a capillary portion. The capillary portion has a first end having an opening in fluid connection with the receiving portion, and a second end closed by a plug portion formed as an integral one-piece member with the capillary portion. The capillary portion is optionally detachable from the receiving portion of the reaction vessel. The reaction vessel simplifies many processes involving small volume chemical reactions, such as Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) determinations.
Owner:ALPHAHELIX
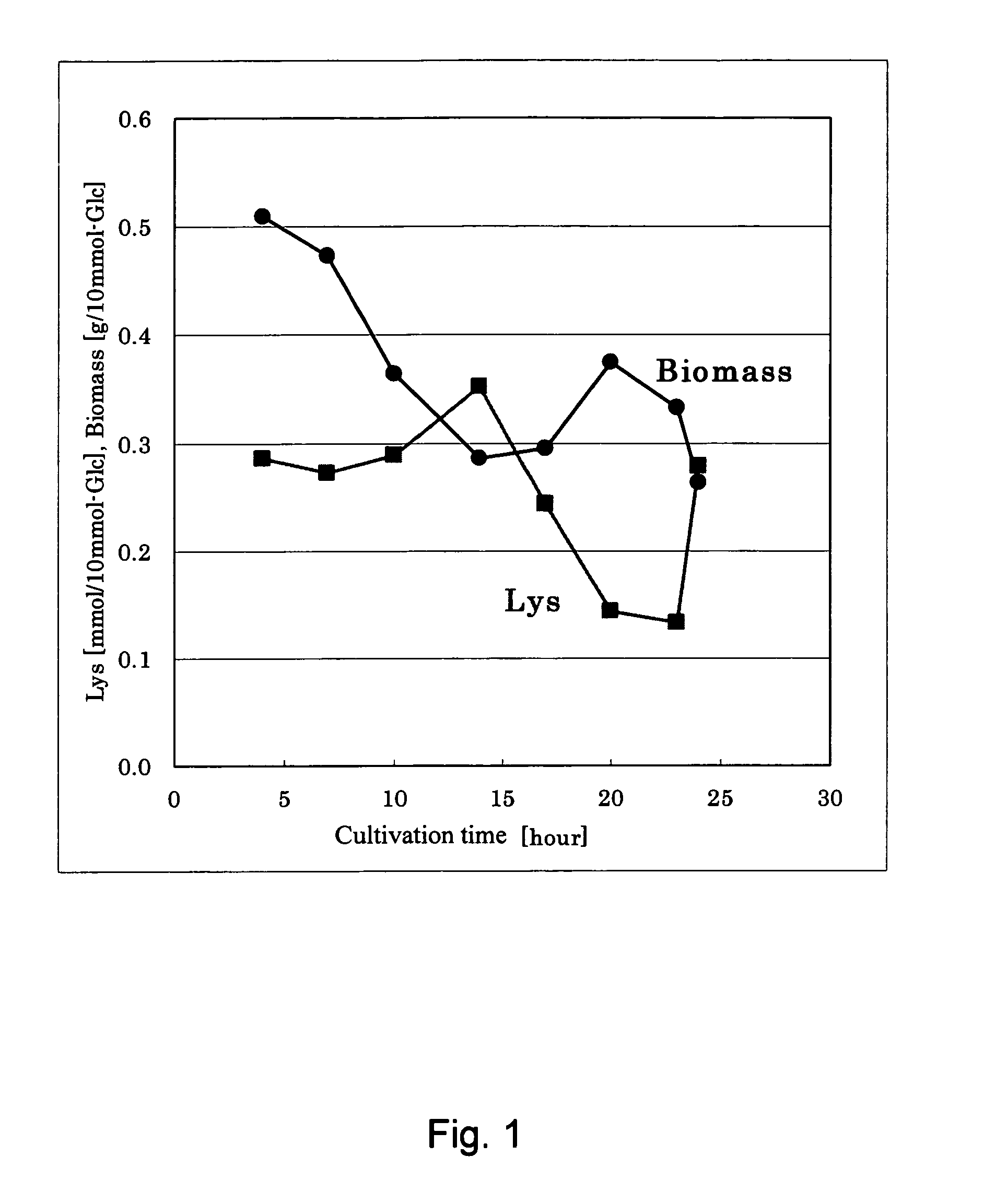
Method for determining metabolic flux
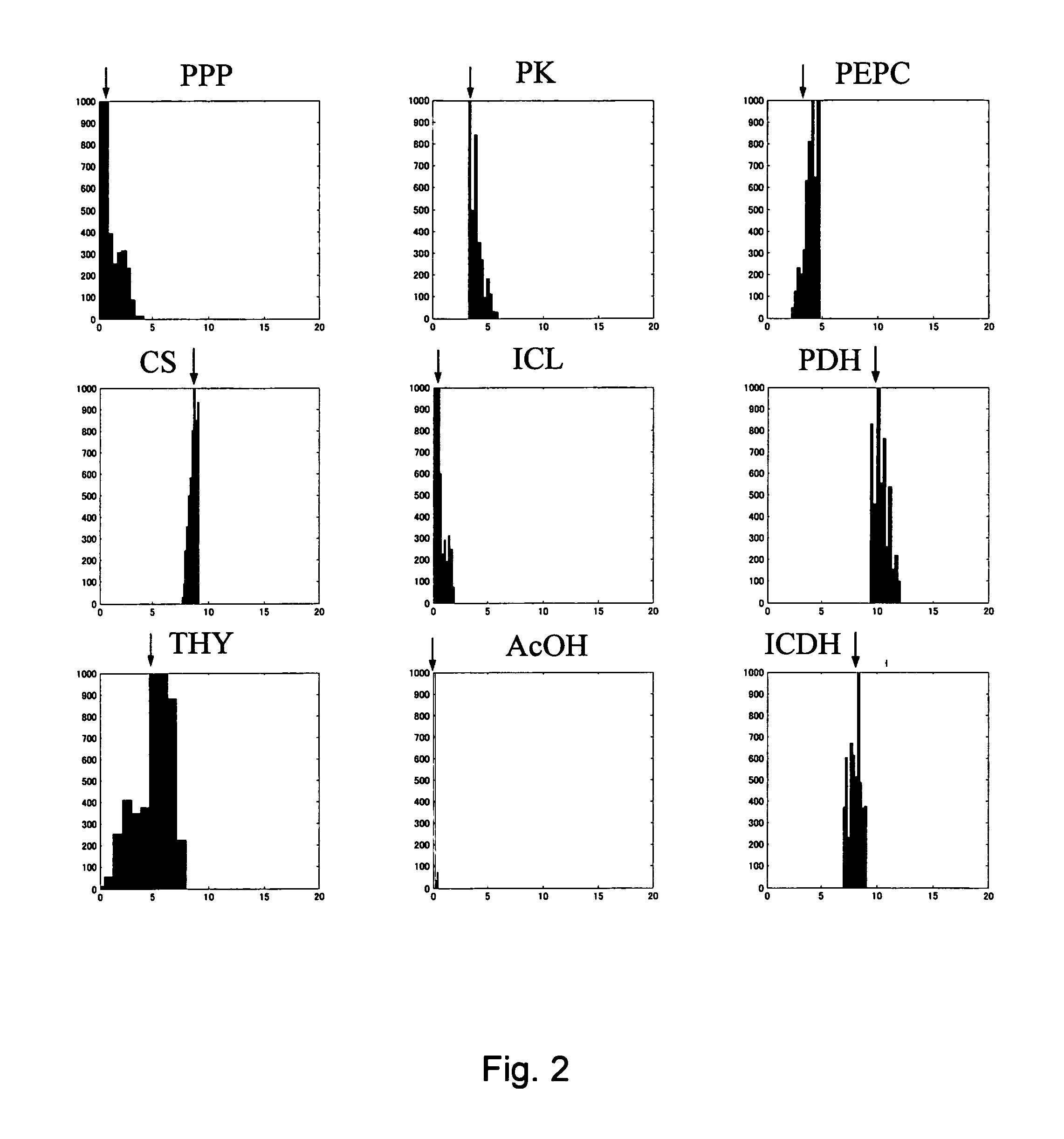
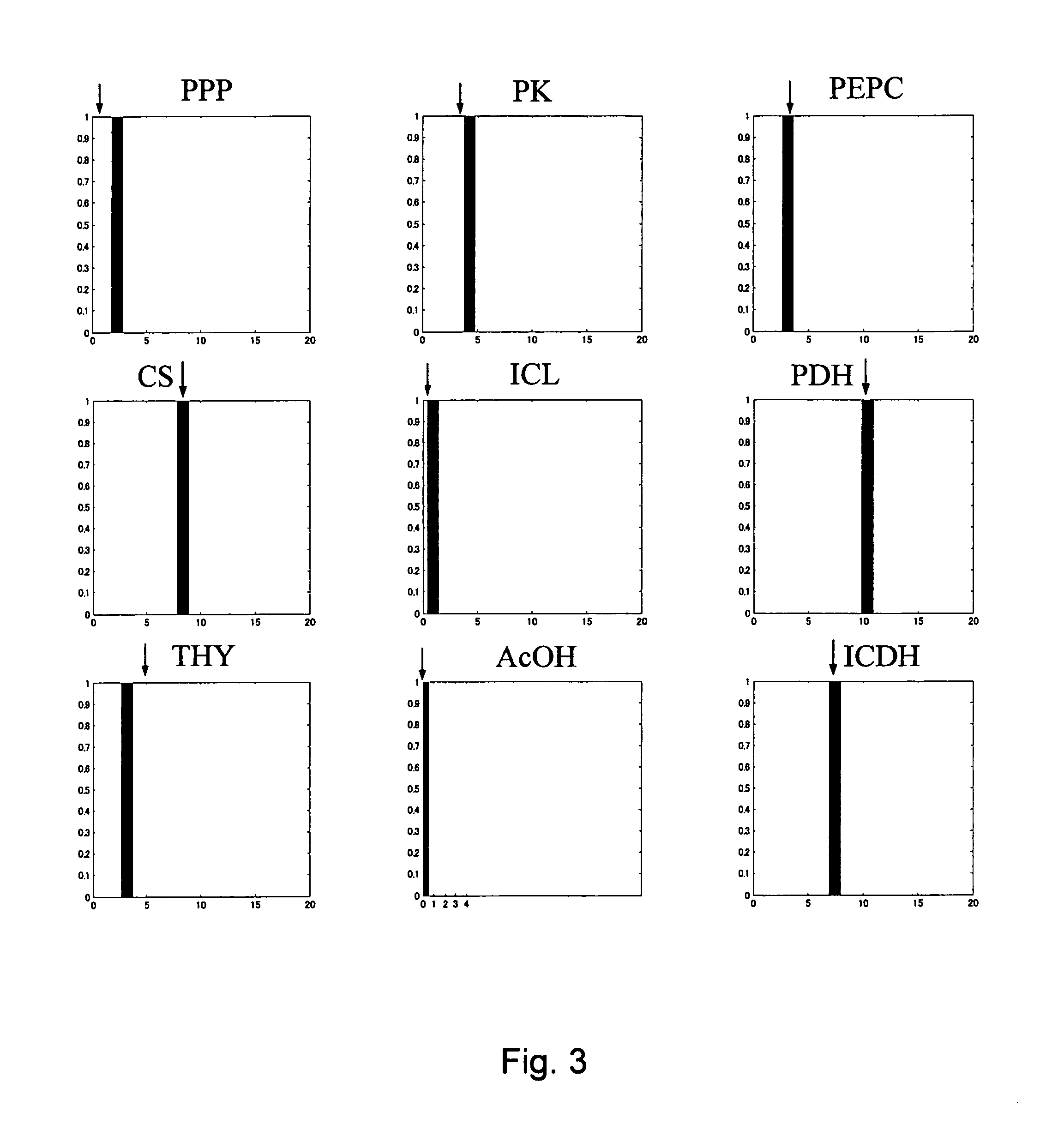
InactiveUS20050221278A1High yieldIncrease productivityData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementAlgorithmVector element
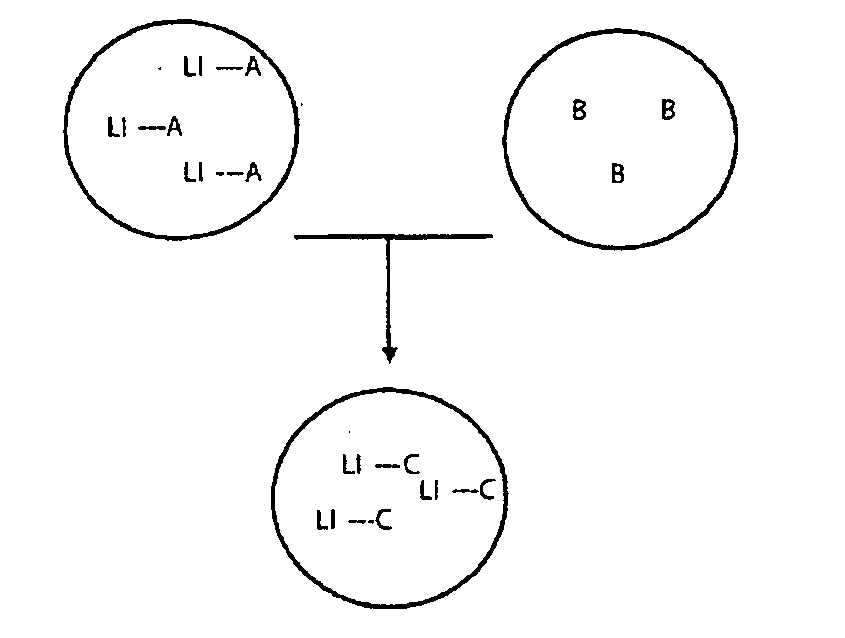
A method for determining metabolic flux distribution of a cell, which comprises the steps of: 1) creating a stoichiometric matrix based on formulas of biochemical reactions from a substrate to a product, 2) computing a set of vectors of solutions existing in a solution space which the stoichiometric matrix may have, 3) selecting, from the computed set of vectors of solutions, maximum vectors whose vector elements corresponding to respective substances for which input values can be obtained are maximum, and 4) performing linear combination for the selected vectors in accordance with the following equations to obtain a vector representing metabolic flux distribution: Sflux=∑i=1nai·pi·S(i)+∑i=1nbi·qi·A(i)(I)∑i=1nai+∑i=1nbi=1(II)Sflux: Vector representing metabolic flux distribution to be determined, S(i): Vector selected for substance for which inputted value can be obtained, A(i): Adjustment vector, a, b: Coefficients for linear combination (b may be 0), p: Coefficient for obtaining consistency with input value as numerical value, q: Coefficient of adjustment vector.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com