Patents
Literature
56 results about "Clinical chemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clinical chemistry or Chemical pathology (also known as clinical biochemistry or medical biochemistry) is the area of chemistry that is generally concerned with analysis of bodily fluids for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It is an applied form of biochemistry (not to be confused with medicinal chemistry, which involves basic research for drug development).
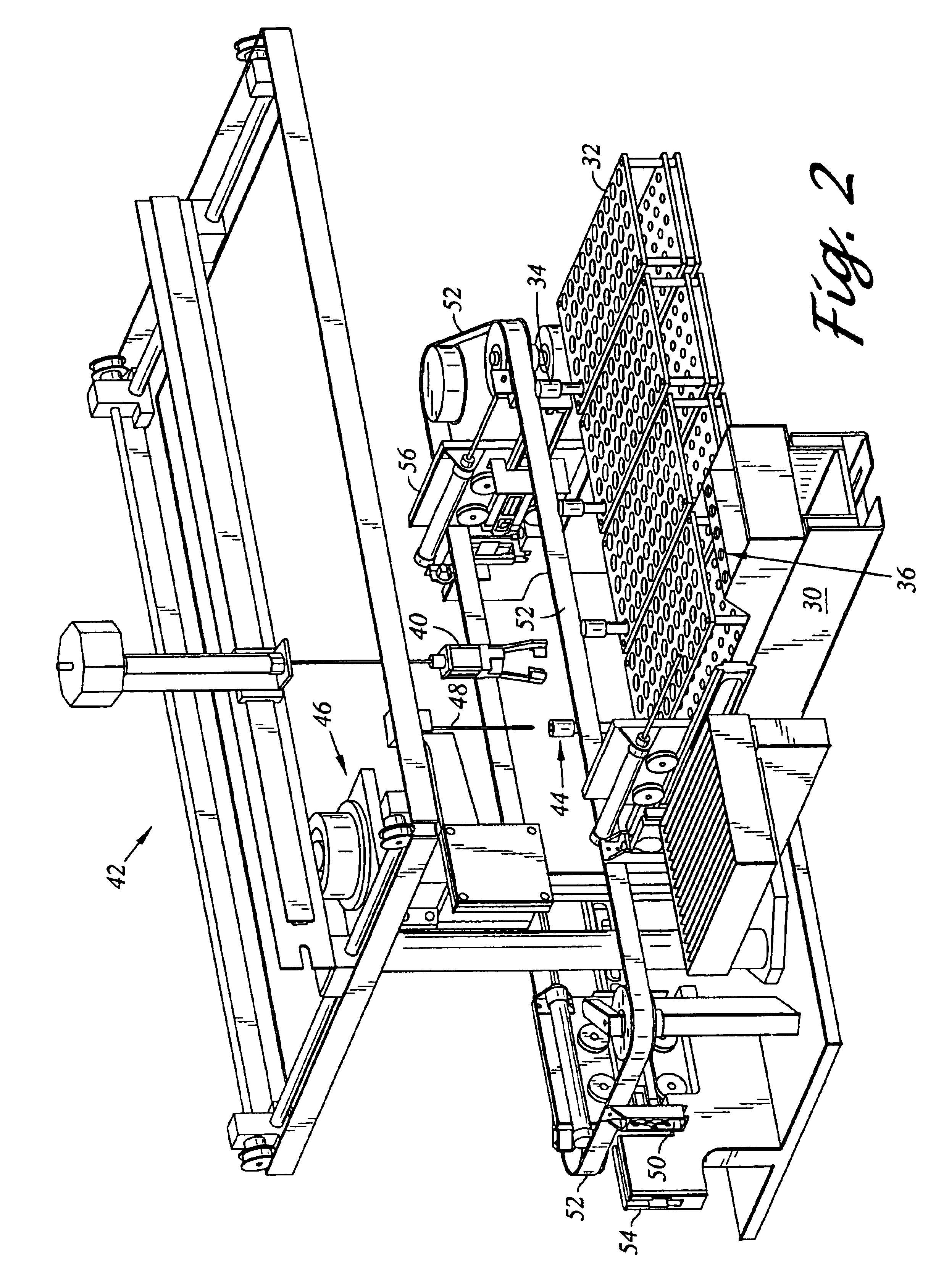
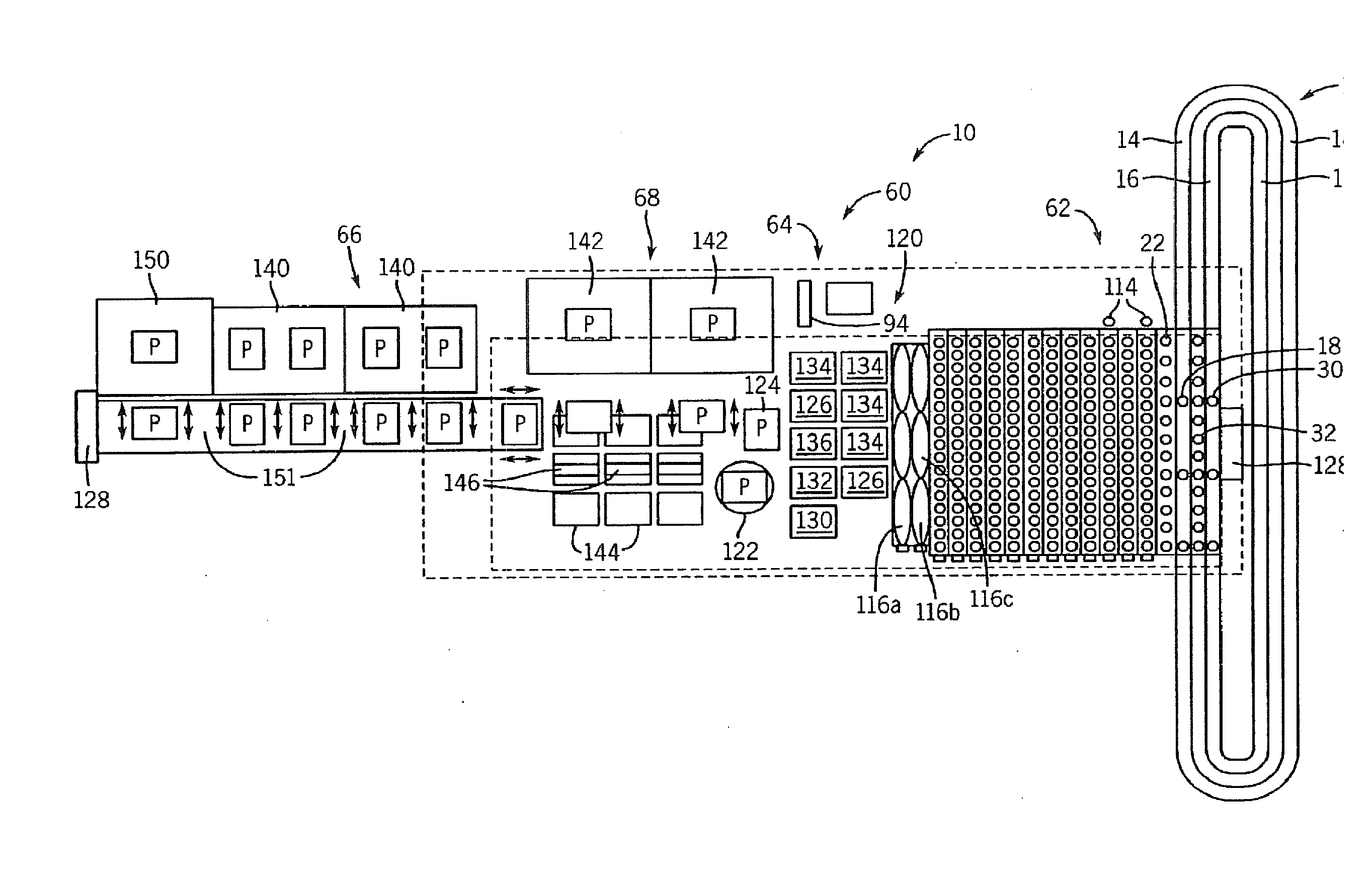
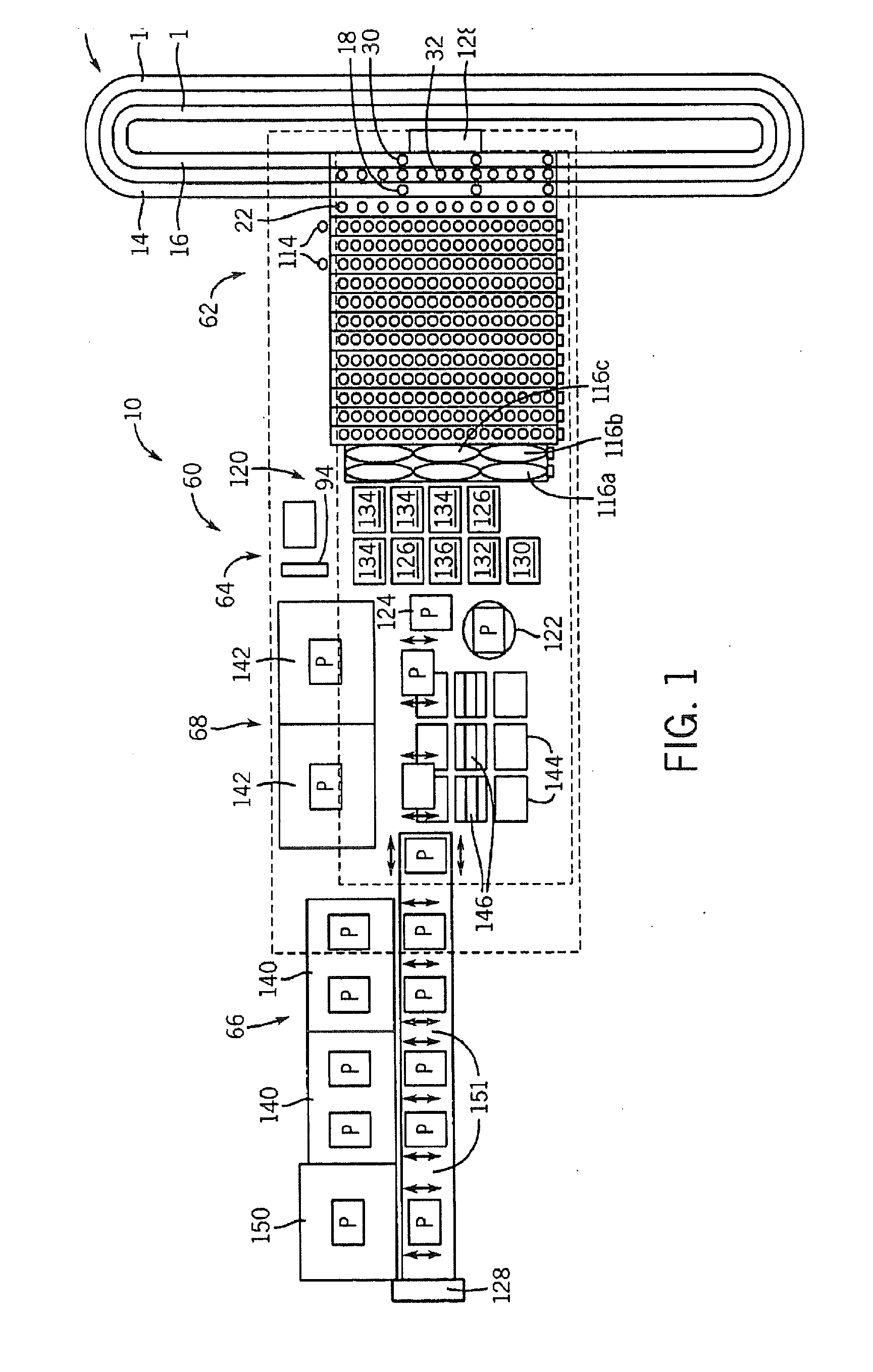
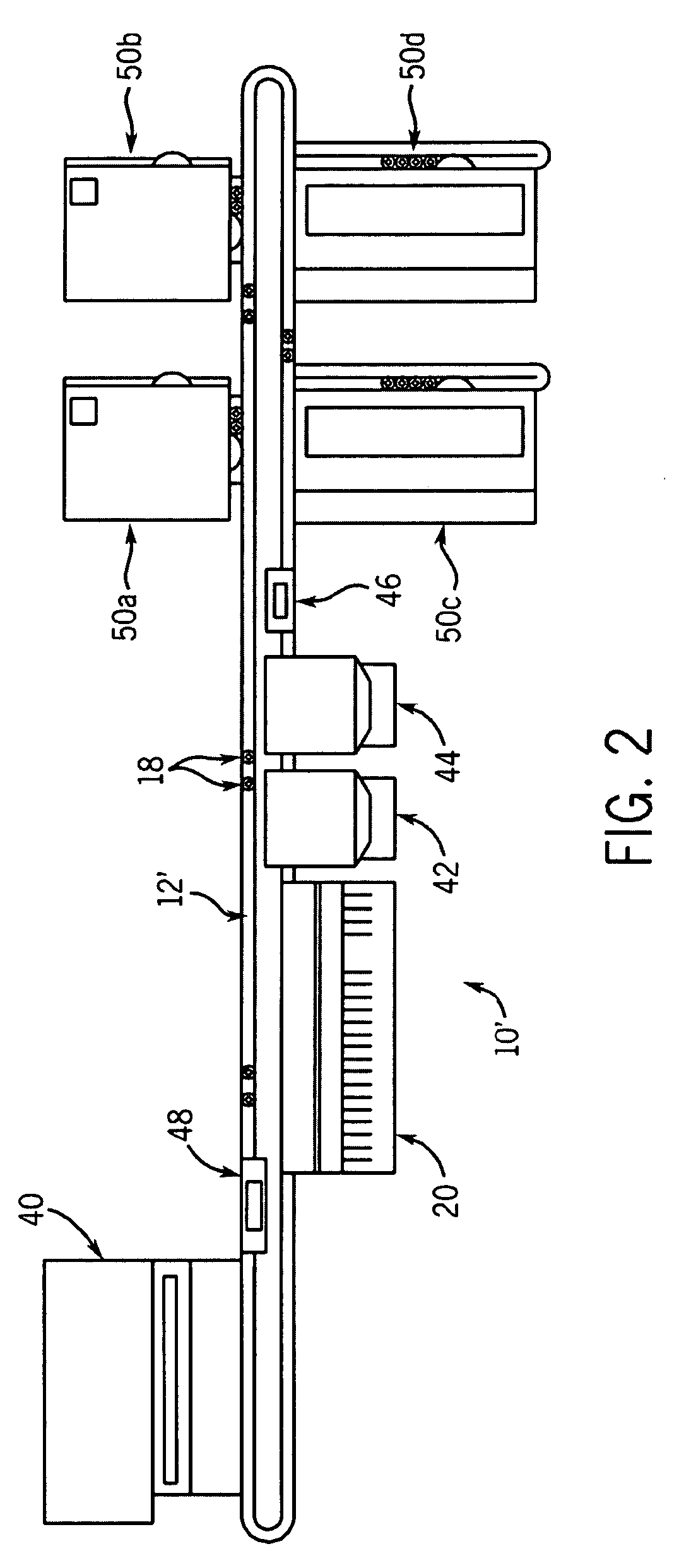
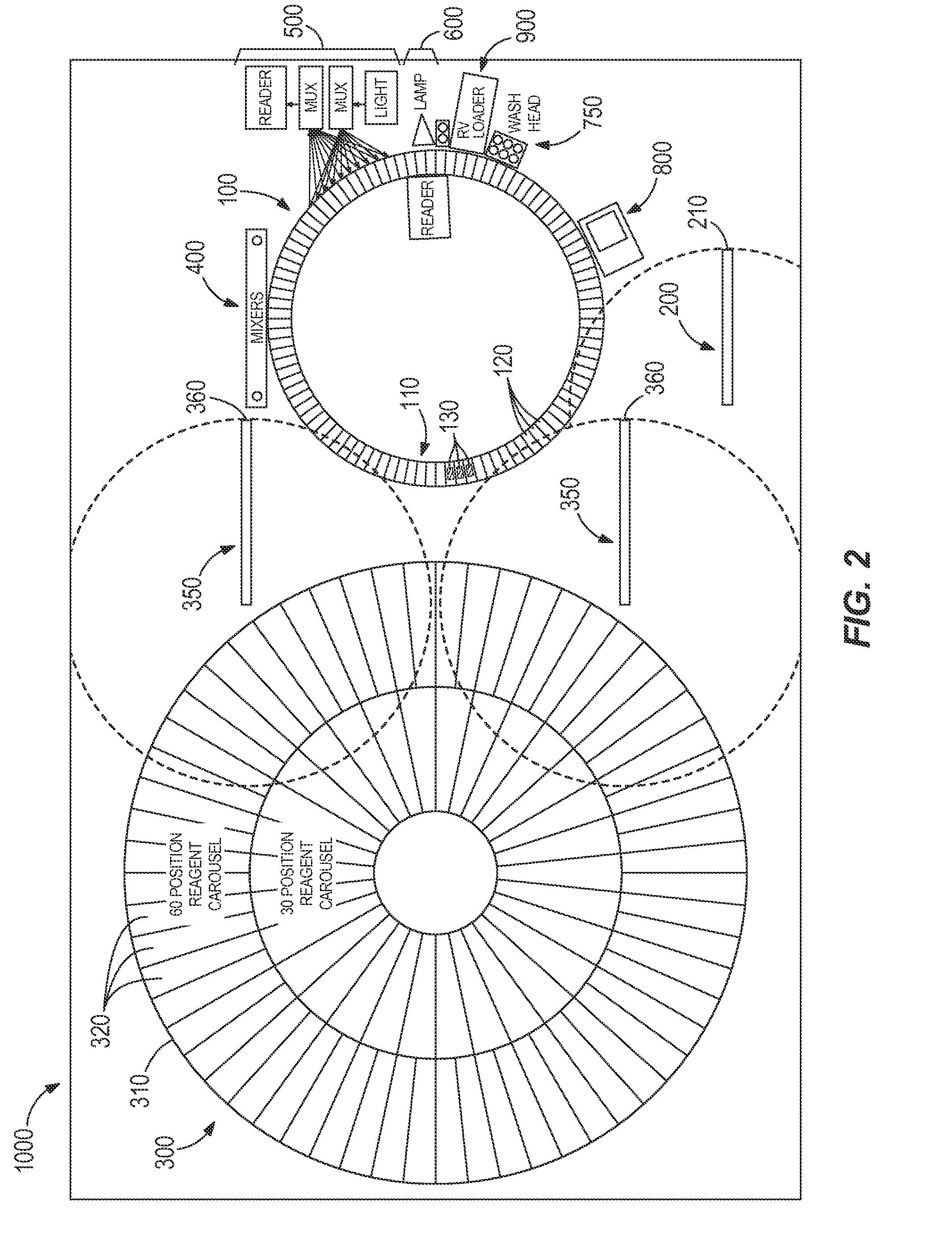
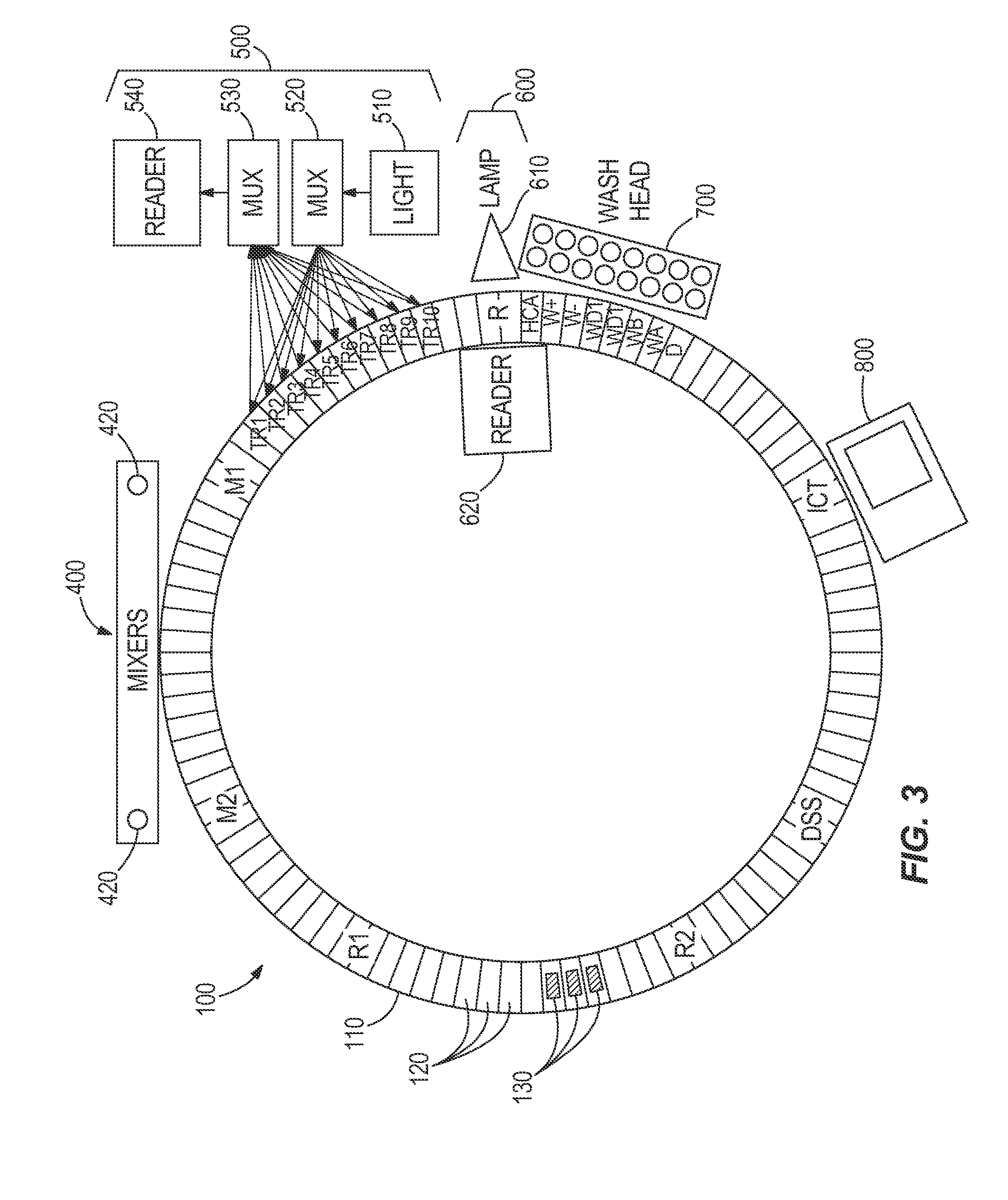
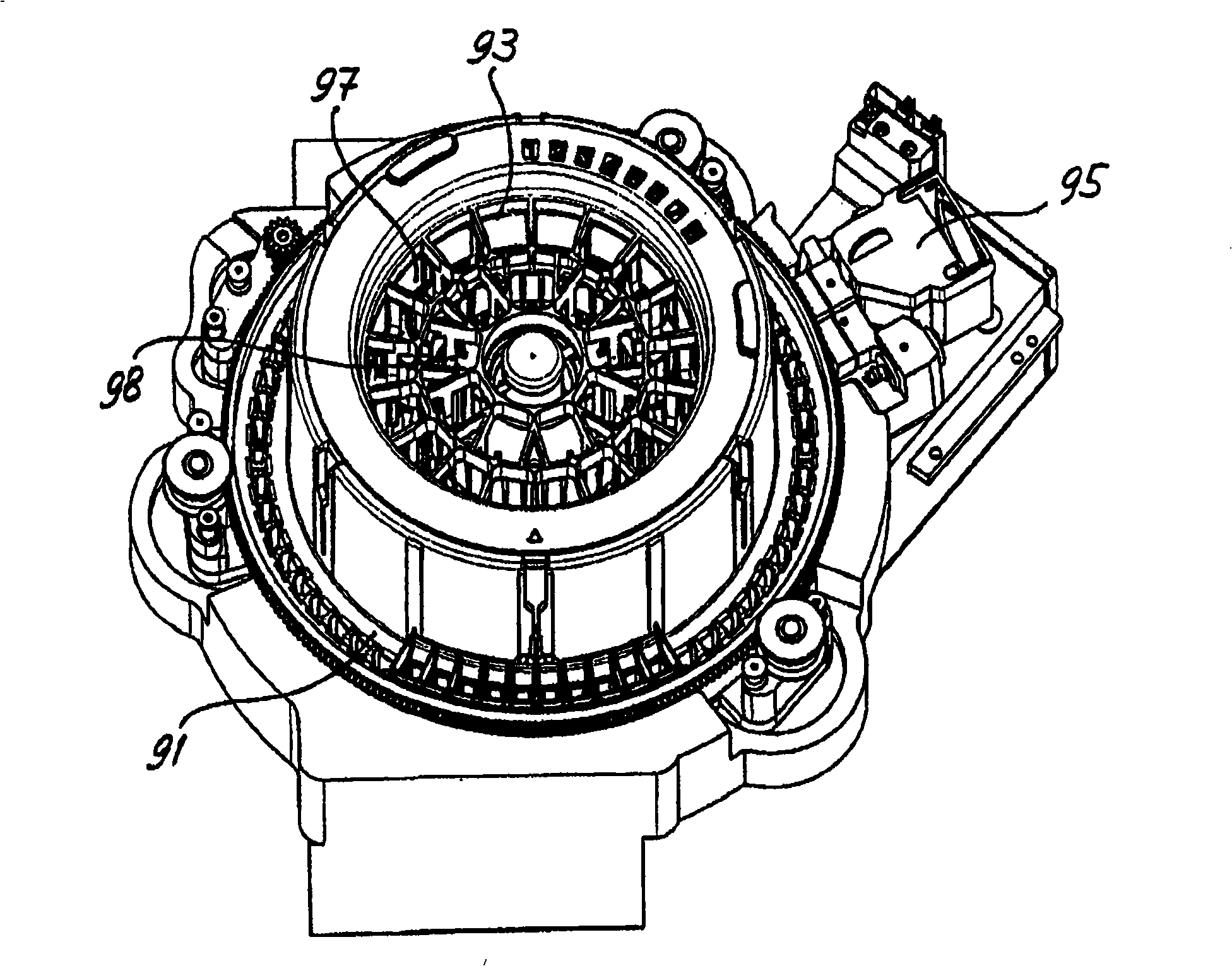
Automated analyzer for clinical laboratory
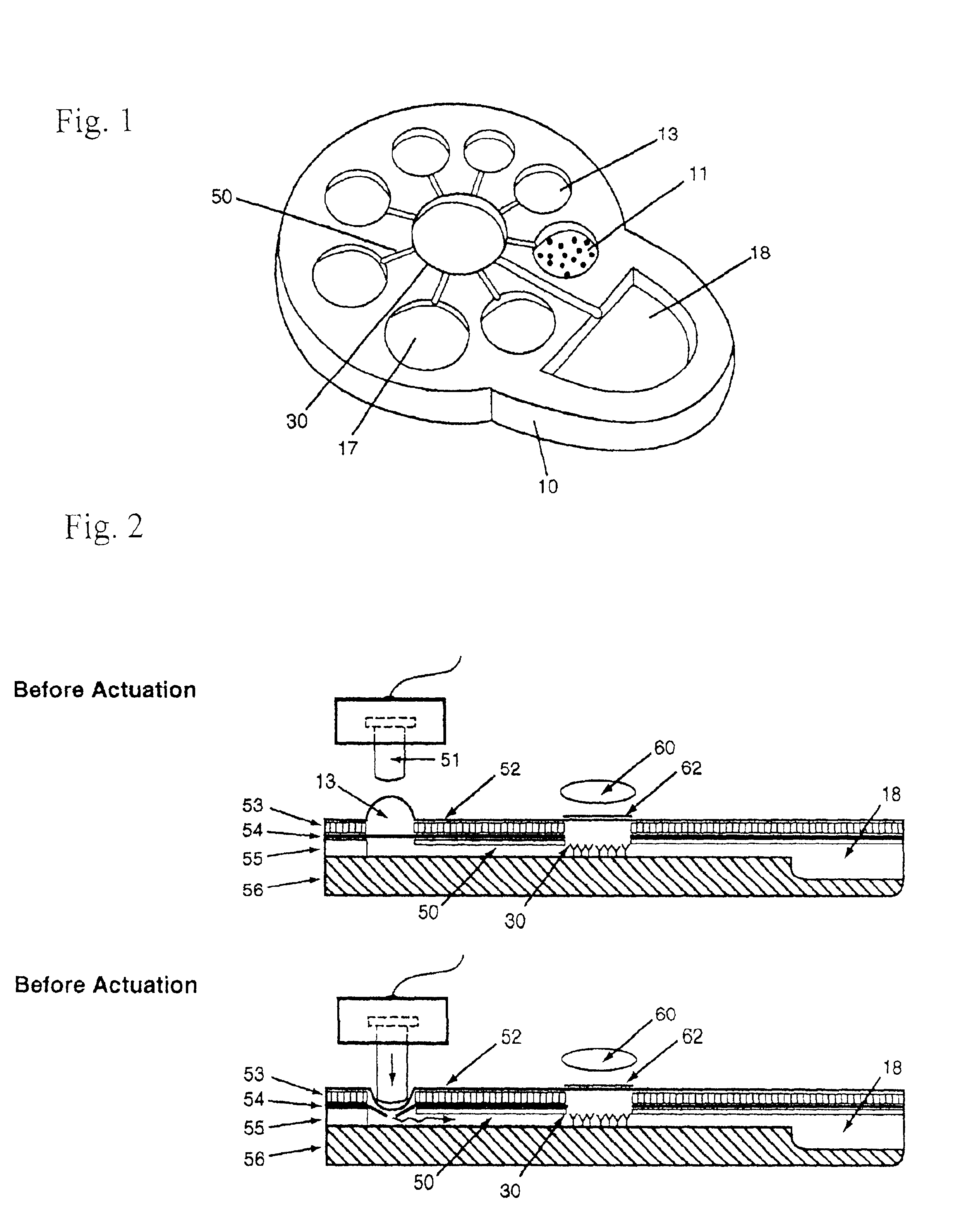
InactiveUS20090117620A1Manual loadingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClinical chemistryMicro perforated plate
A laboratory automation system that is capable of carrying out clinical chemistry assays, immunoassays, amplification of nucleic acid assays, and any combination of the foregoing, said laboratory automation system employing at least one of micro-well plates and deep multi-well plates as reaction vessels. The use of micro-well plates as reaction vessels enables the laboratory automation system to assume a variety of arrangements, i.e., the laboratory automation system can comprise a variety of functional modules that can be arranged in various ways. In order to effectively carry out immunoassays by means of micro-well plates, a technique known as inverse magnetic particle processing can be used to transfer the product(s) of immunoassays from one micro-well of a micro-well plate to another.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Chemiluminescence-based microfluidic biochip
InactiveUS6949377B2Accurate and reproducible resultSimple and rapid and POCT applicationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPositive pressureBiochip
The disclosure describes how to use luminescence detection mechanism, move microfluid, and control multiple-step biochemical reactions in closed confined microfluidic biochip platform. More particularly, a self-contained disposable biochip with patterned microchannels and compartments having storage means for storing a plurality of samples, reagents, and luminescent substrates. At least one external microactuator in the biochip system produces positive pressure and automates multiple-step reactions in microfluidic platforms for clinical chemistry, cell biology, immunoassay and nucleic acid analysis. The method comprises the steps of transferring sequentially at least one of samples, reagents, and then luminescent substrate from compartments through microchannels to reaction sites. The luminescent substrates react with probes to form a probe complex resulting into luminescence, which is detected by an optical detector.
Owner:HO WINSTON Z
Sample loading and handling interface to multiple chemistry analyzers
InactiveUS6919044B1Easy to useLayered productsMaterial analysis by optical meansClinical chemistryEngineering
A front-end system accepts samples and selectively provides aliquots of those samples to selected clinical chemistry analyzers coupled to the front-end system. The front-end system is coupled to an assembly of one or more clinical chemistry analyzers that might, for example, provide complementary analytical tools so that the overall system of front-end system and clinical chemistry analyzers provides a predetermined broad range of clinical analytical testing. The testing protocols for samples input to the overall system can be independently determined. Any sample may undergo a test within one or more of the clinical chemistry analyzers or a series of tests within a single or more typically within plural ones of the analyzers, depending upon the testing sequence defined in for that sample. The front-end system automatically identifies samples, draws aliquots, and transports the aliquots to the one or more clinical chemistry analyzers coupled to the front-end system. Sample identification, handling and testing are preferably automated A within the overall system to provide complex testing with reduced operator involvement. Consequently, the overall system may facilitate reduced operator costs and a reduced likelihood of errors in the routing and processing of samples.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
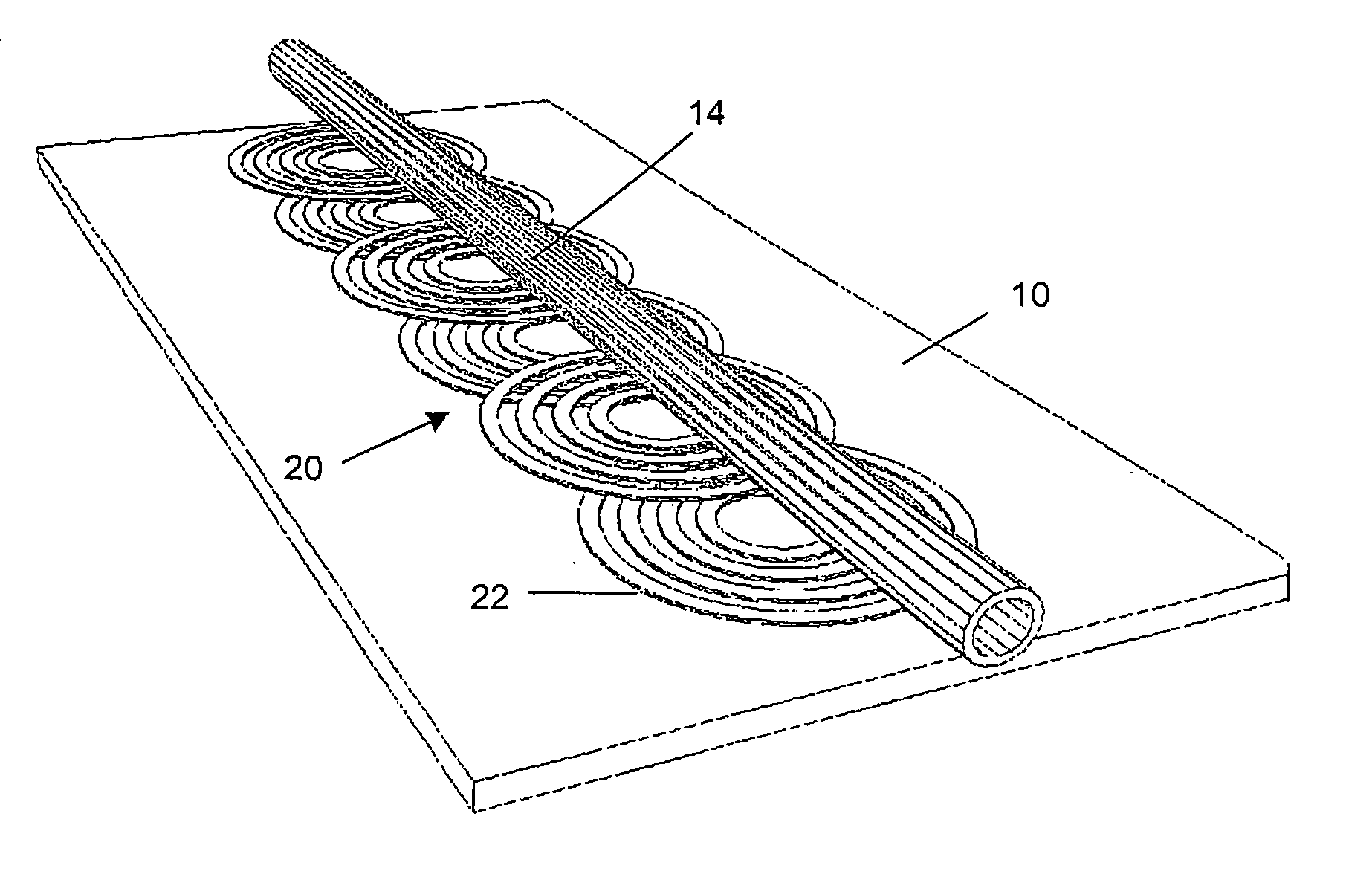
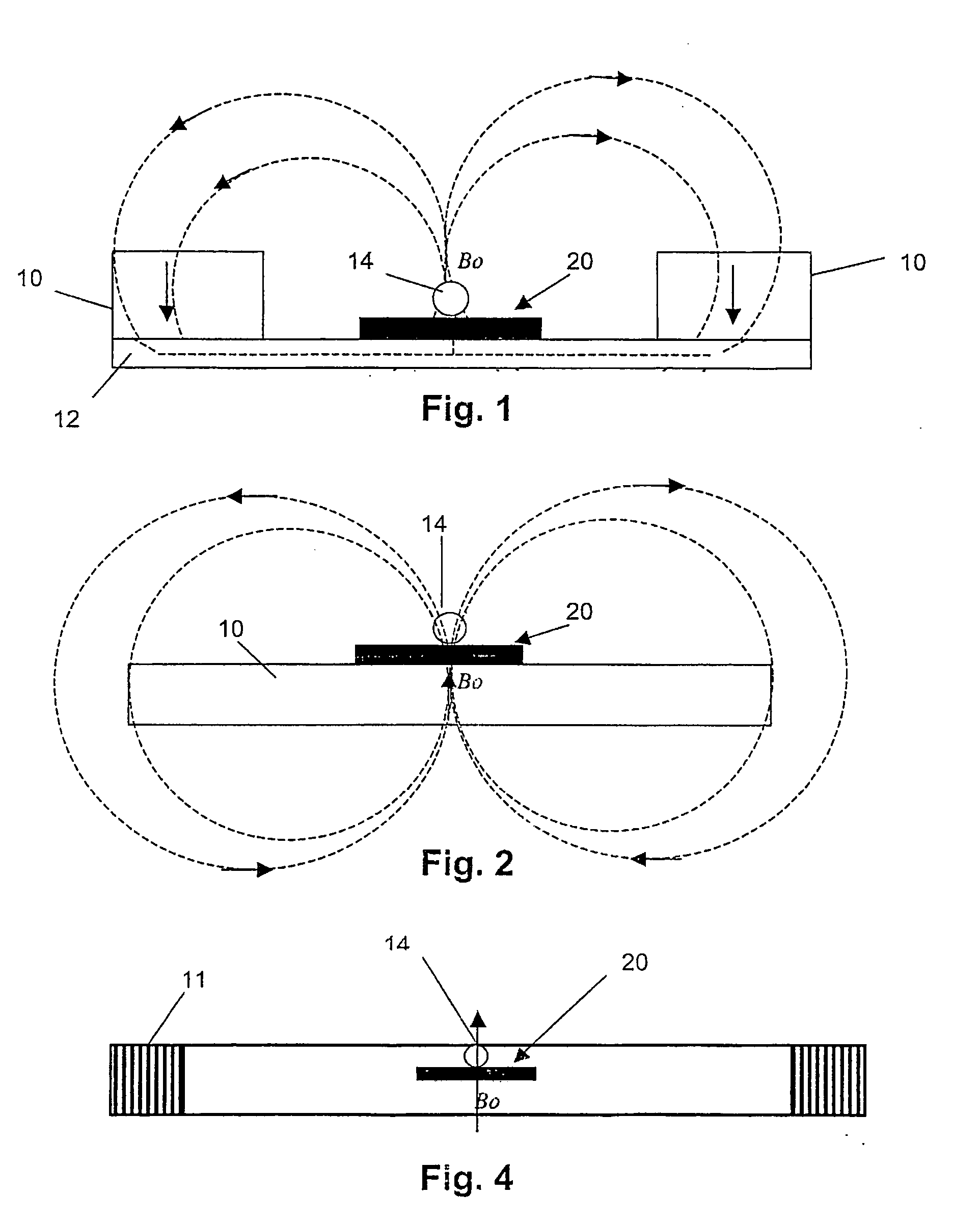
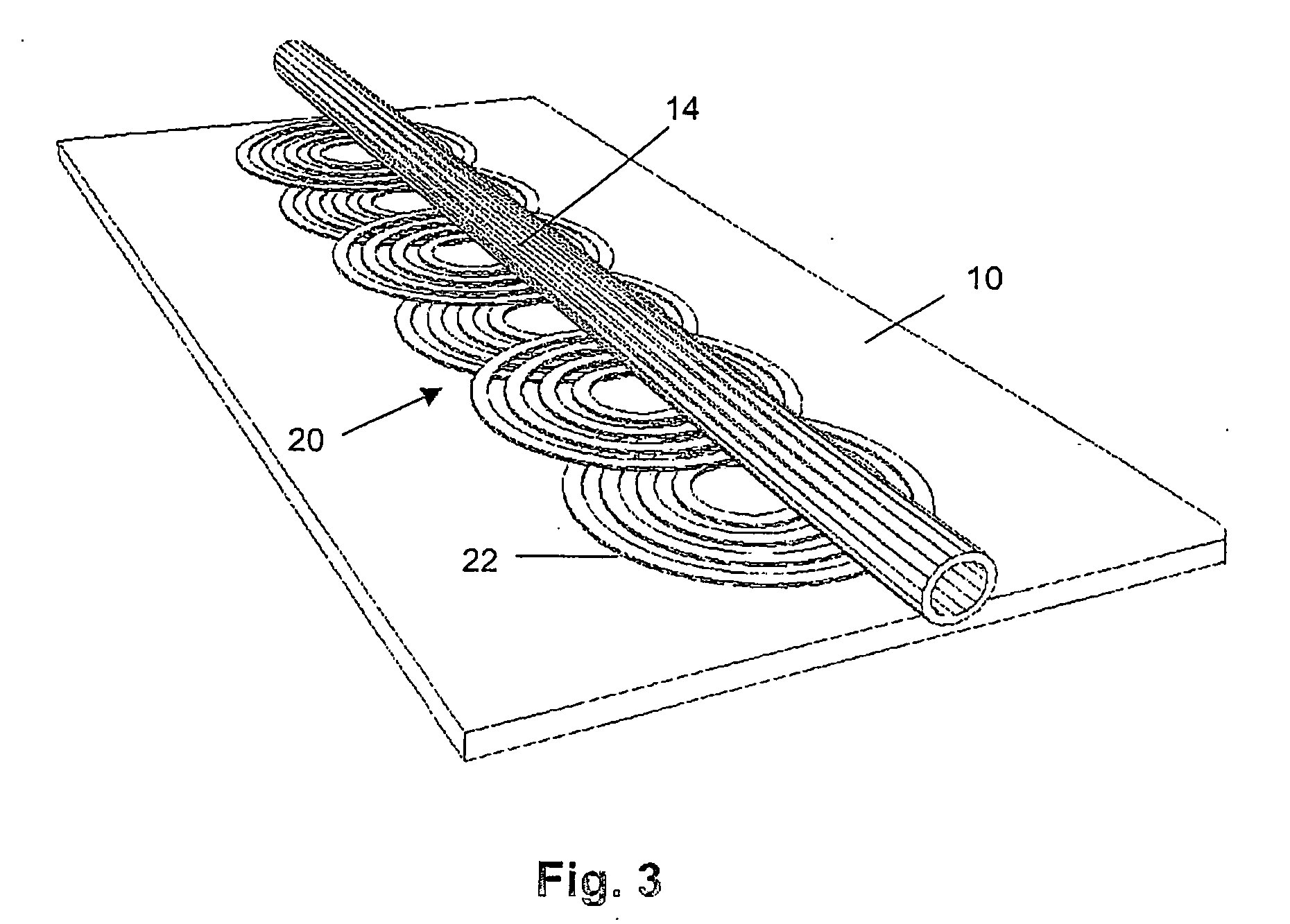
Magnetic bead manipulation and transport device
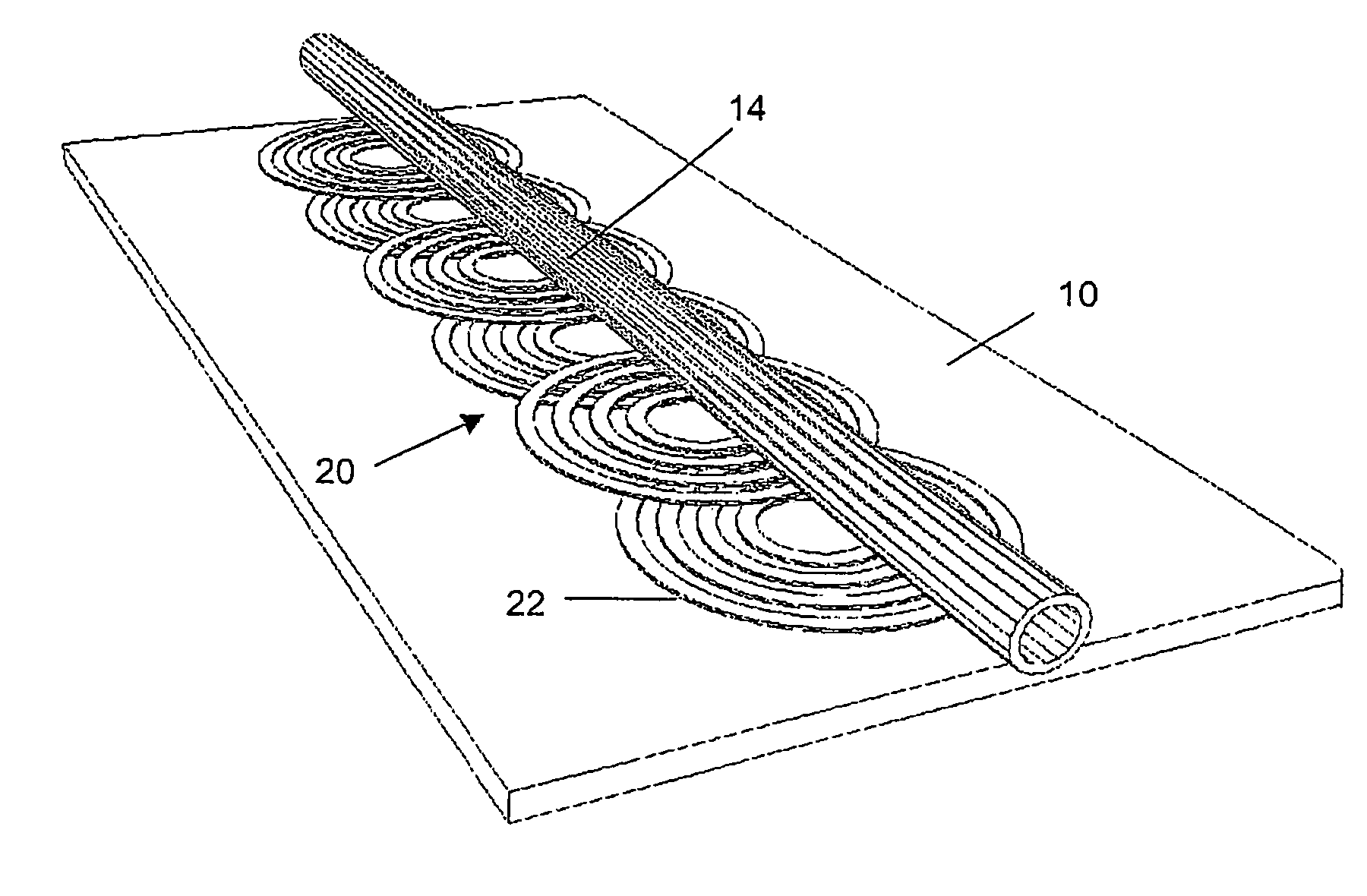
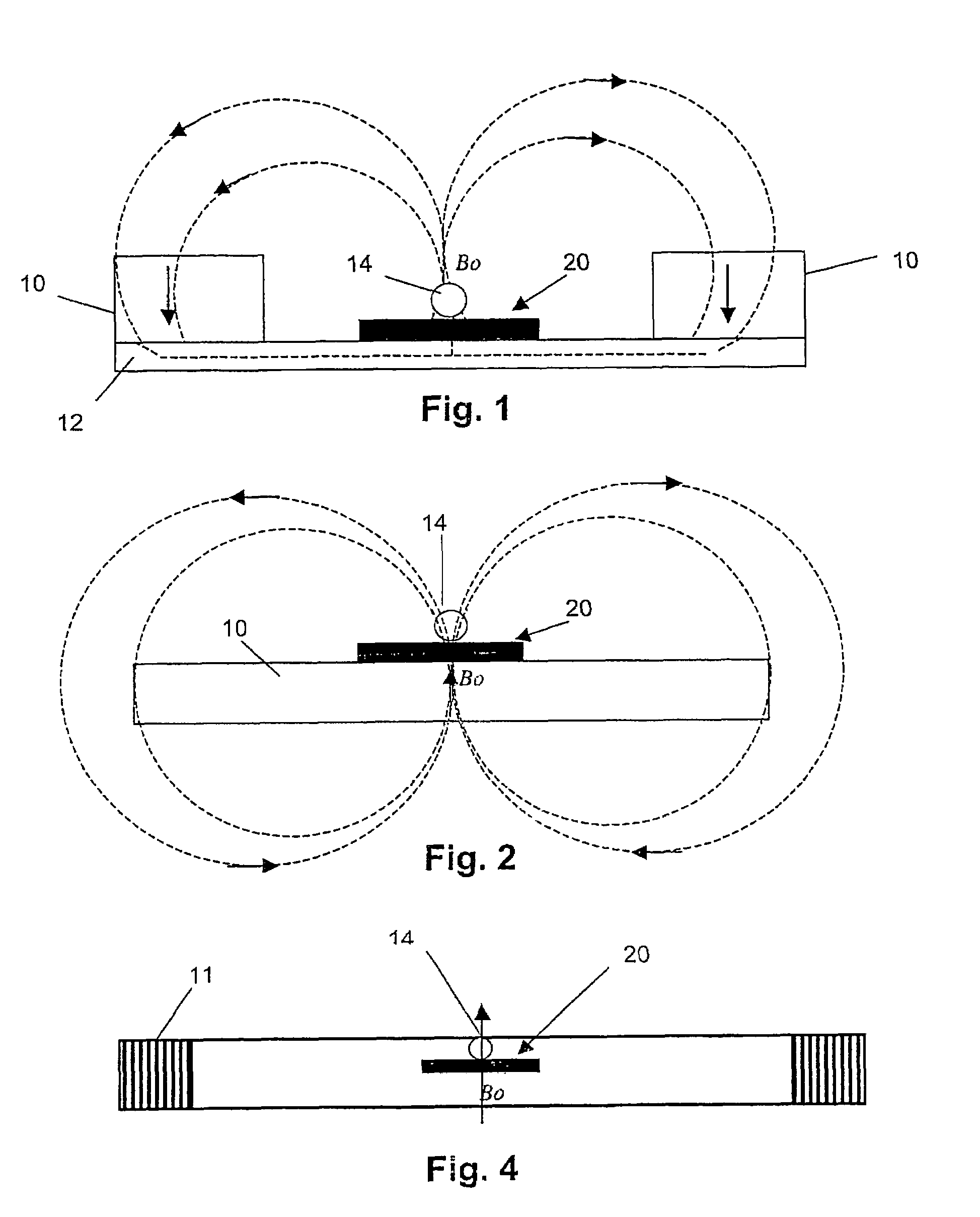
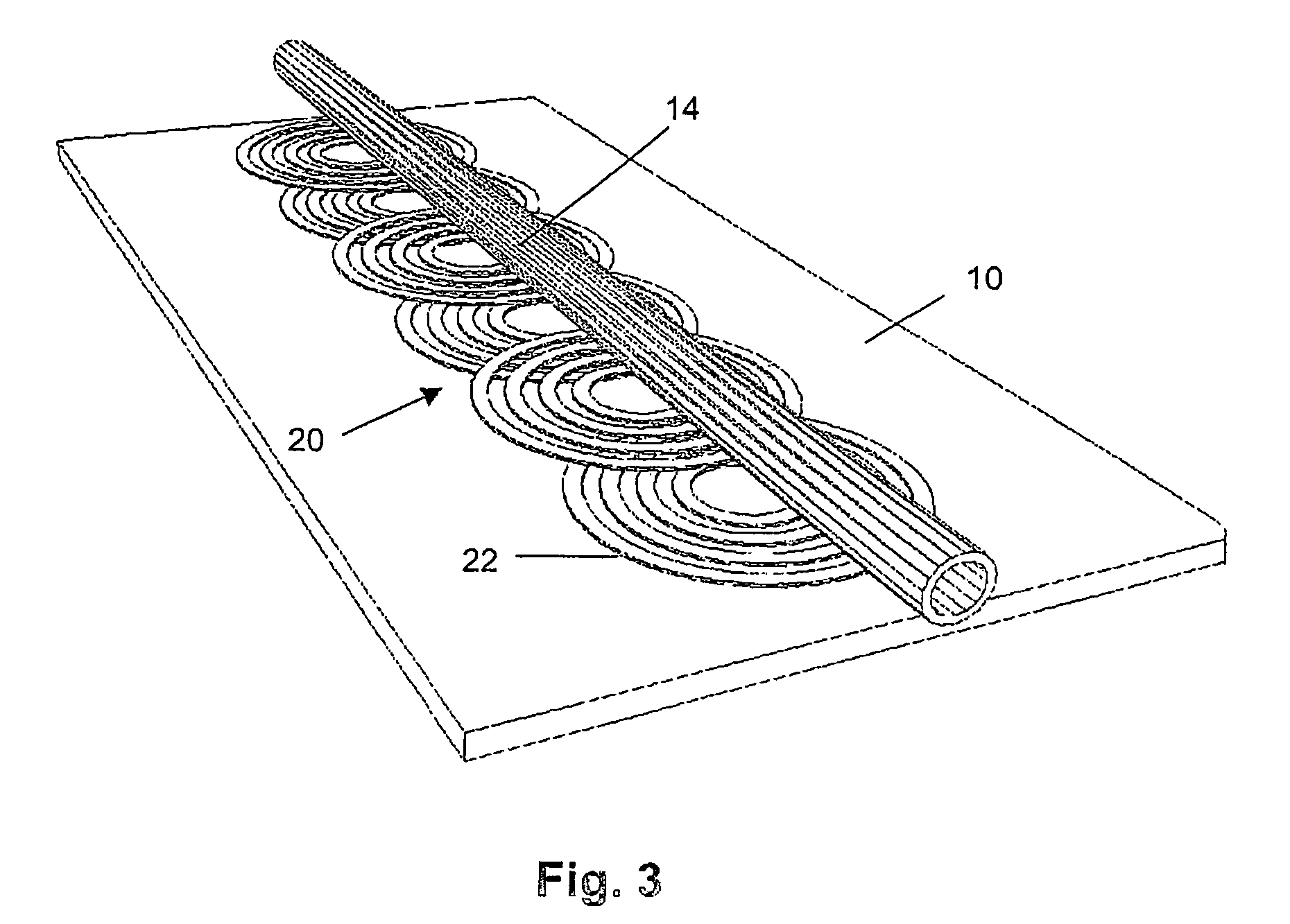
InactiveUS20050284817A1Increase speedLow magnetic fieldsElectrostatic separationTransportation and packagingClinical chemistryMagnetic bead
A device for transporting magnetic or magnetisable microbeads (25) in a capillary chamber (14) comprises a permanent magnet (10) or an electromagnet (11) for subjecting the capillary chamber to a substantially uniform magnetic field, to apply a permanent magnetic moment to the microbeads (25). At least one planar coil (22) and preferably an array of overlapping coils are located adjacent to the capillary chamber (14) for applying a complementary magnetic field on the microbeads parallel or antiparallel to said substantially uniform magnetic field, to drive the microbeads. An arrangement is provided for switching the current applied to the coil(s) (22) to invert the field produced thereby, to selectively apply an attractive or repulsive driving force on the microbeads (25). The device is usable to transport microbeads for performing chemical and biochemical reactions or assay, as is done for instance in clinical chemistry assays for medical diagnostic purposes.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Automated analyzer for clinical laboratory
ActiveUS20120282684A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicro perforated plateClinical chemistry
A laboratory automation system that is capable of carrying out clinical chemistry assays, immunoassays, amplification of nucleic acid assays, and any combination of the foregoing, said laboratory automation system employing at least one of micro-well plates and deep multi-well plates as reaction vessels. The use of micro-well plates as reaction vessels enables the laboratory automation system to assume a variety of arrangements, i.e., the laboratory automation system can comprise a variety of functional modules that can be arranged in various ways. In order to effectively carry out immunoassays by means of micro-well plates, a technique known as inverse magnetic particle processing can be used to transfer the product(s) of immunoassays from one micro-well of a micro-well plate to another.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
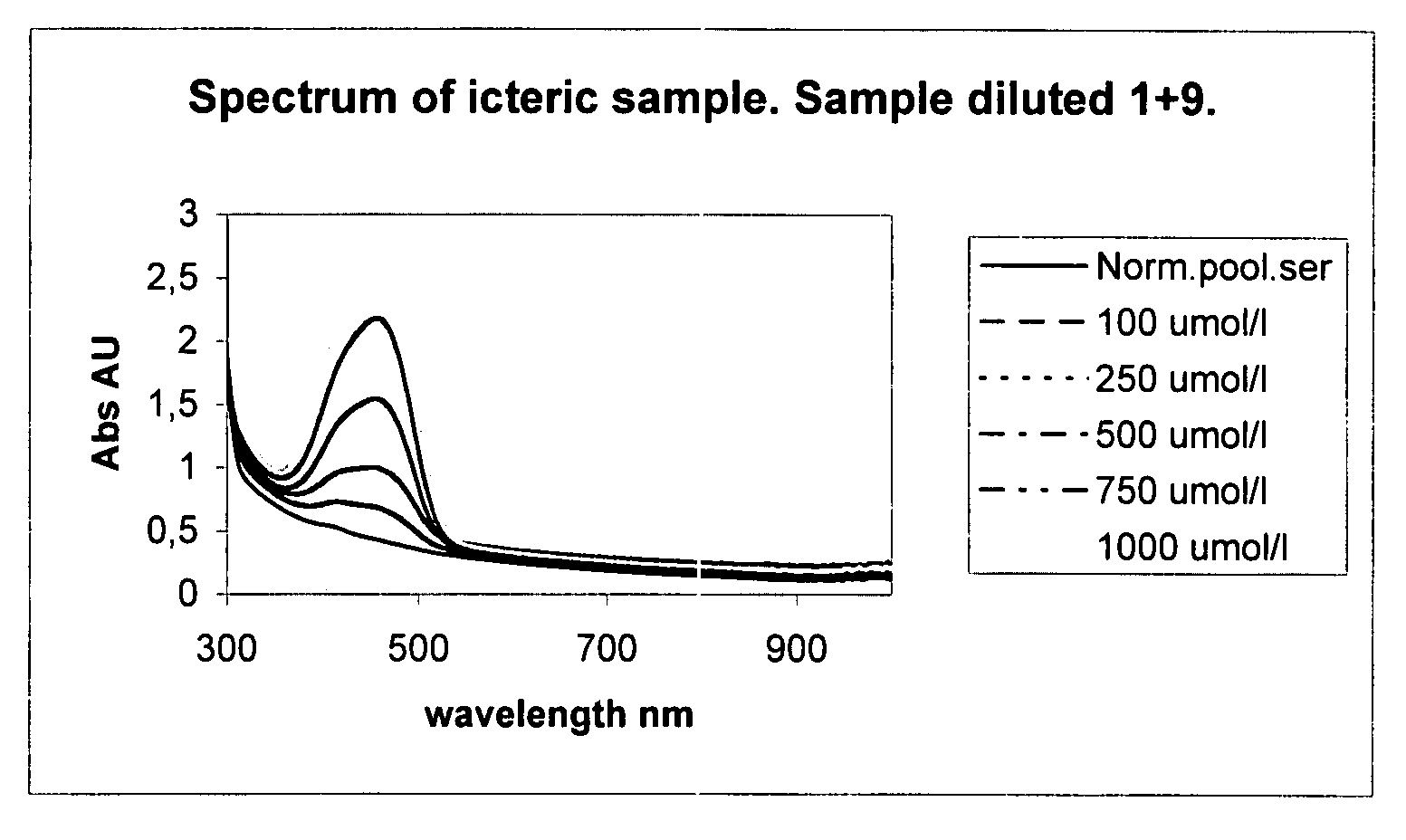
Method for automatically detecting factors that disturb analysis by a photometer
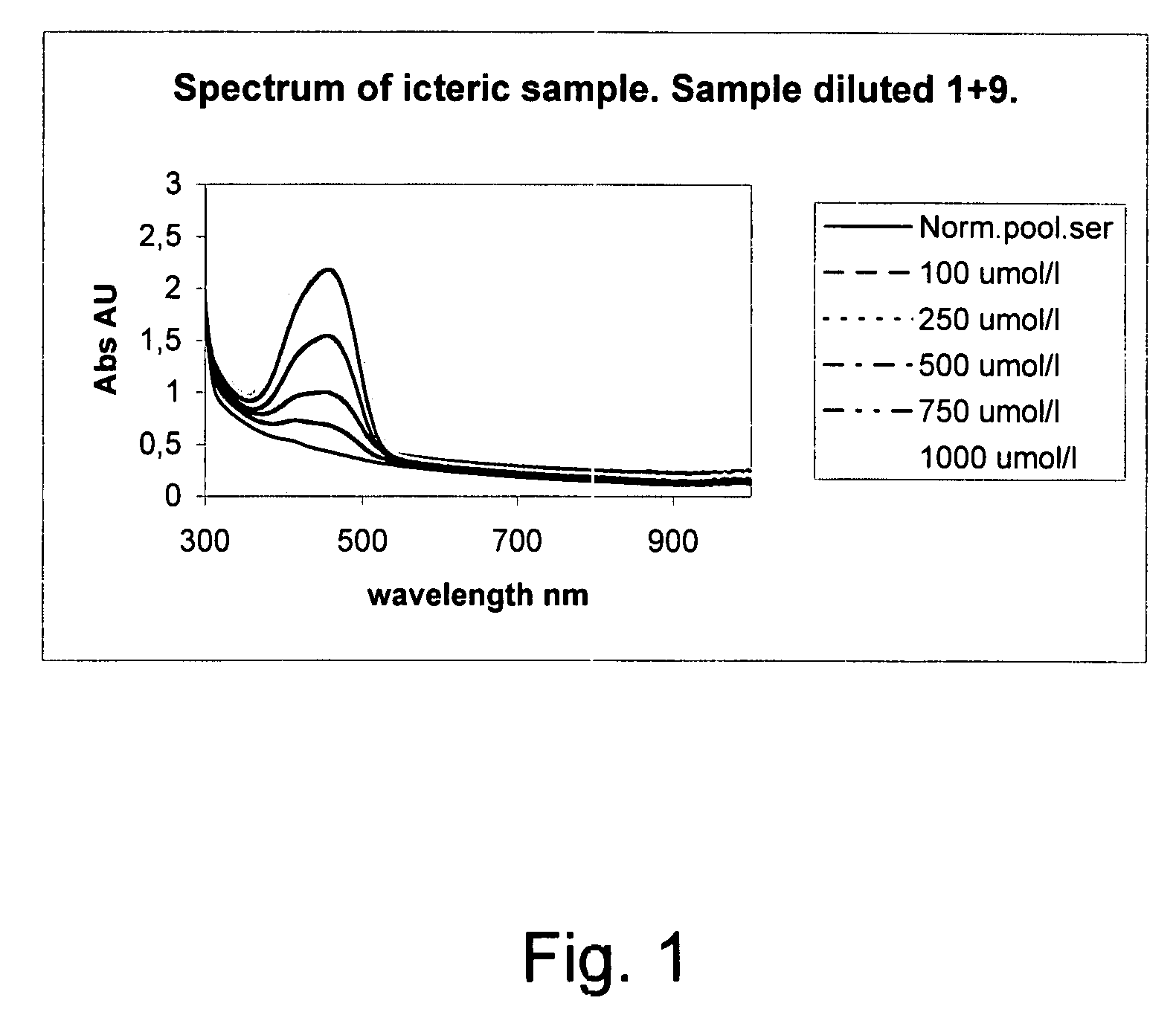
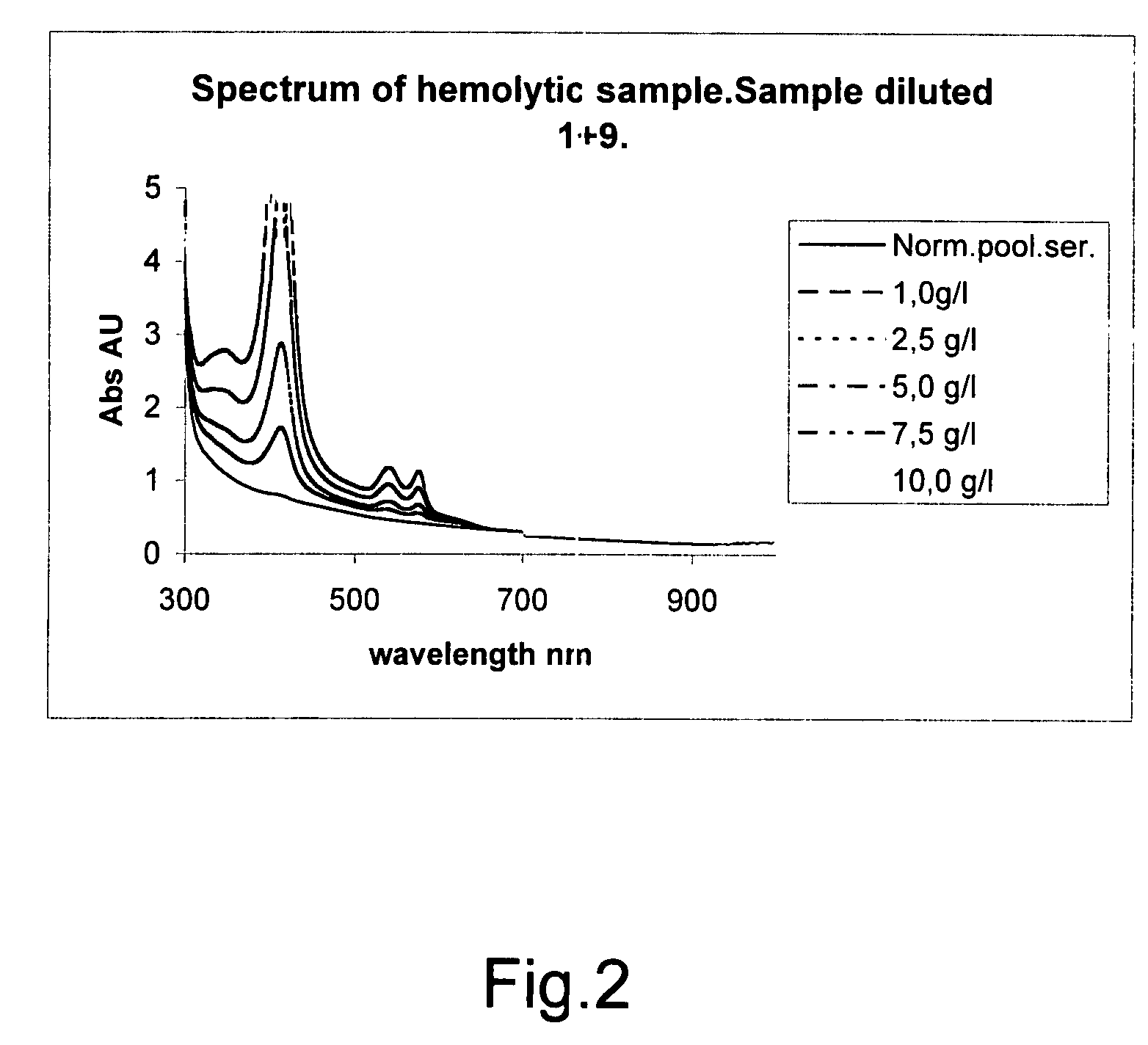
ActiveUS7663738B2Easy to detectCost effectiveBiological material analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansClinical chemistryMedicine
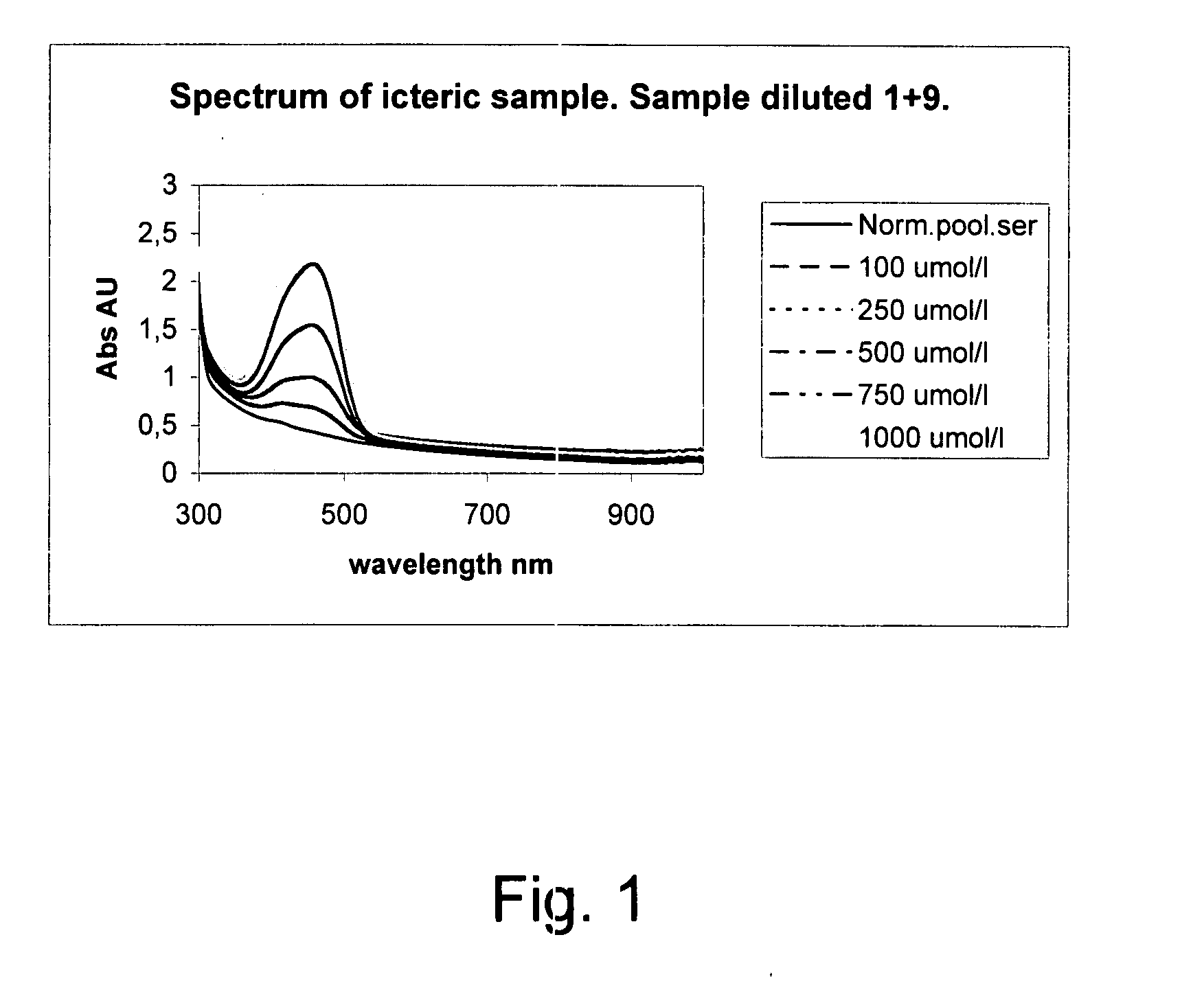
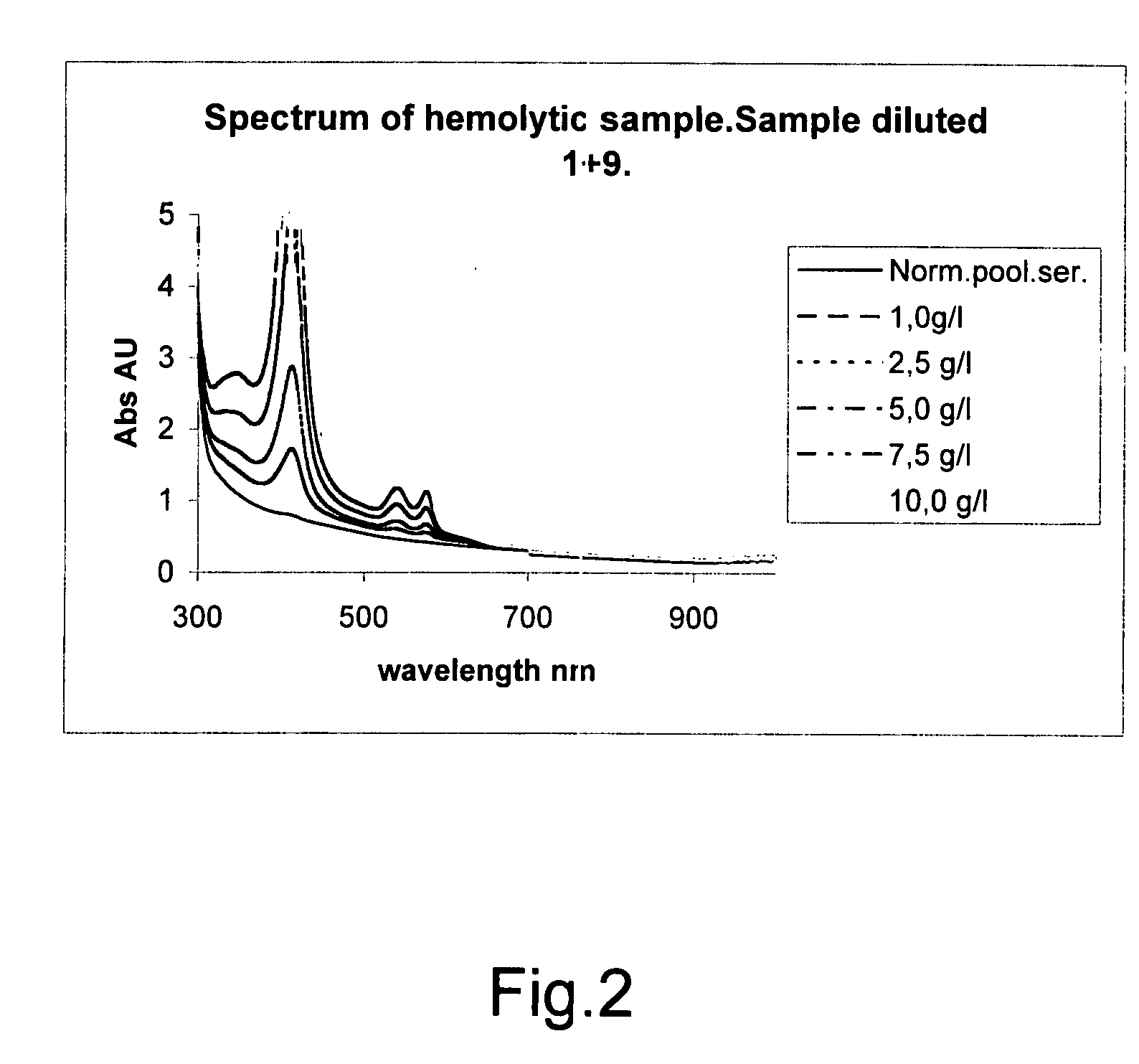
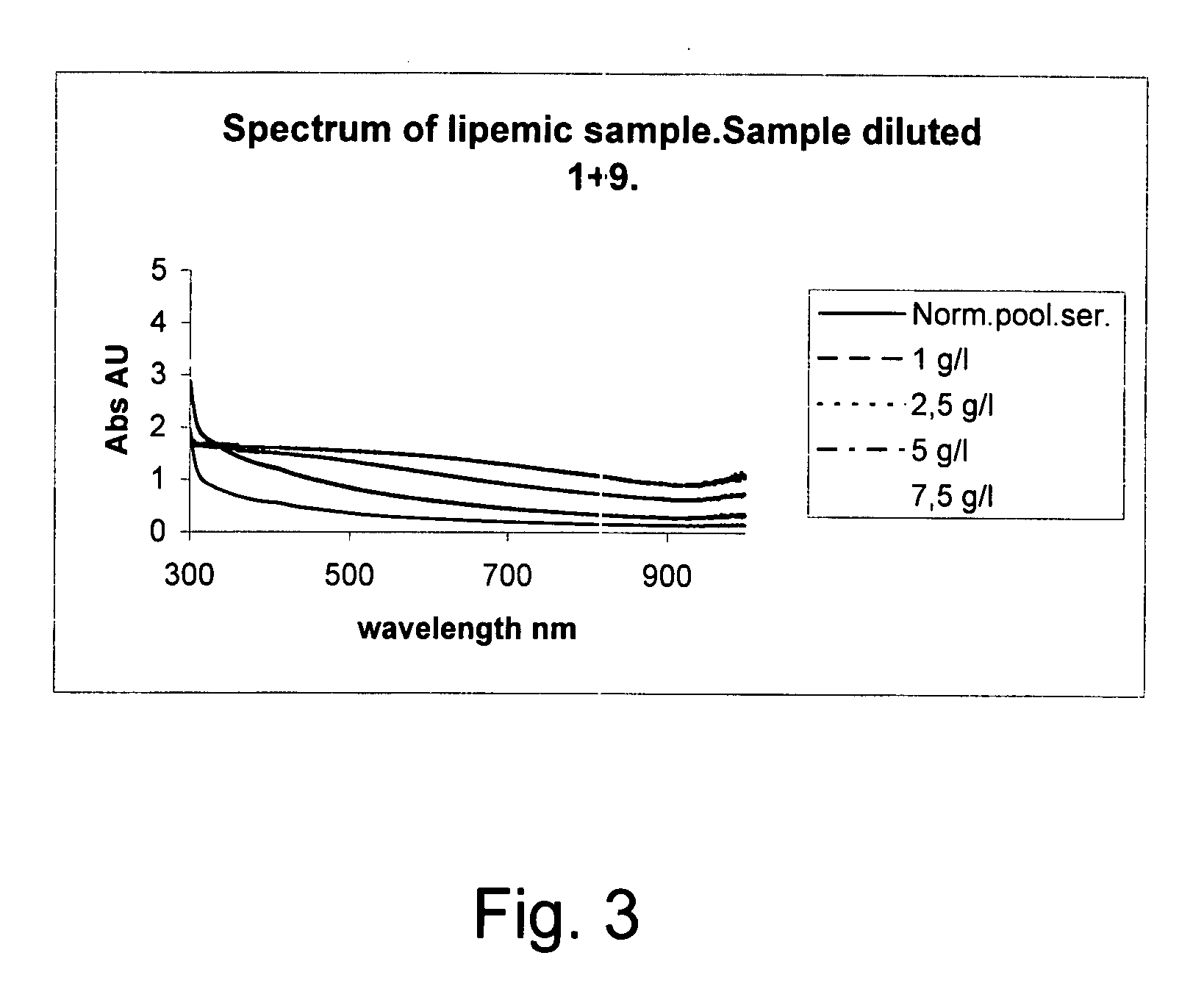
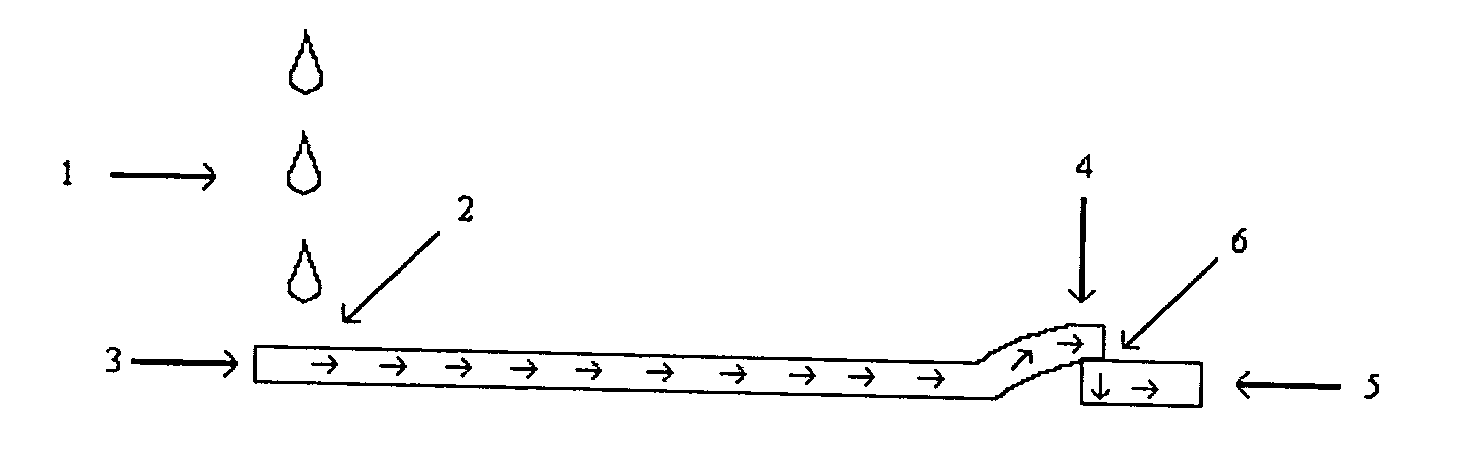
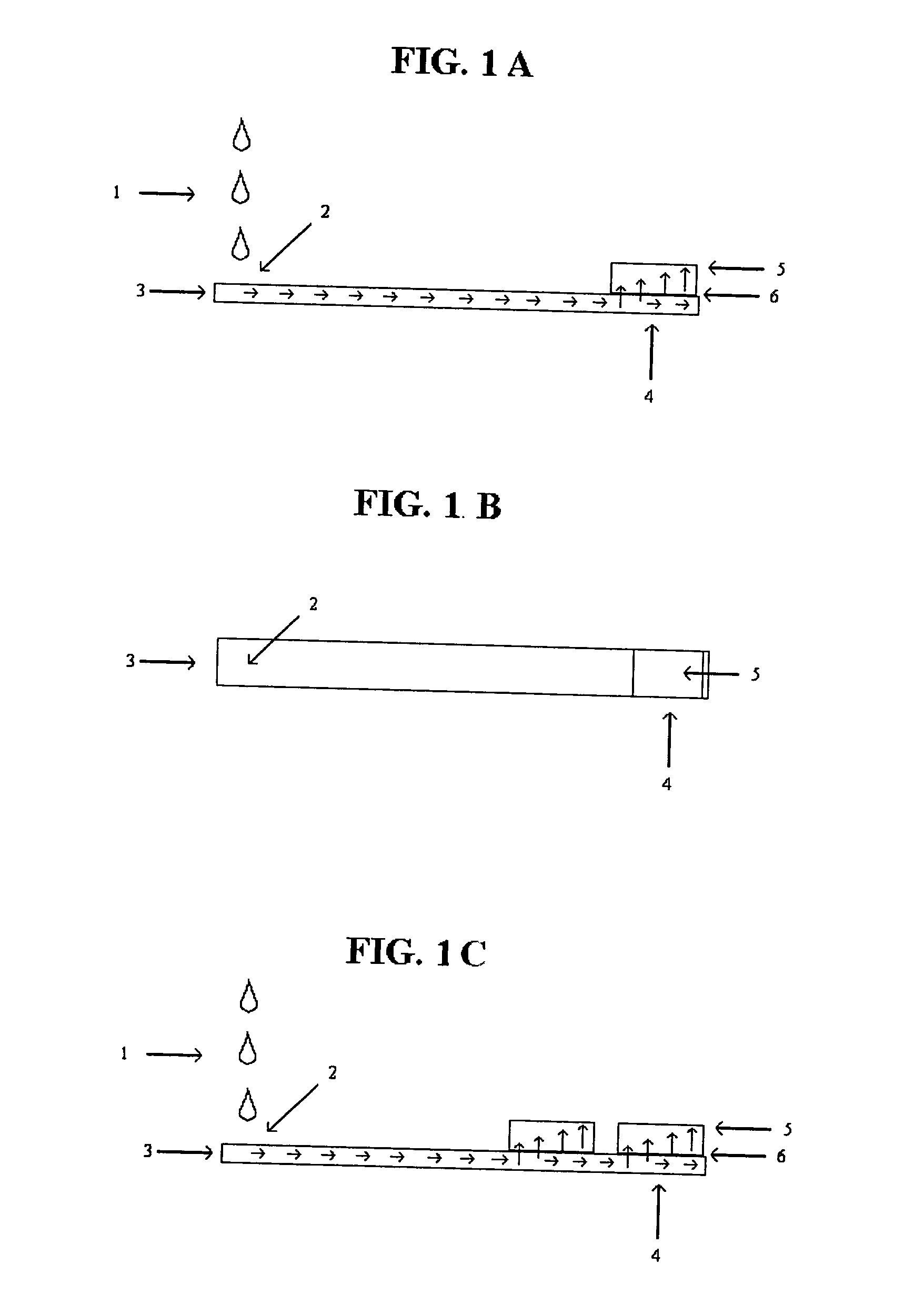
The invention concerns a method for detecting the amounts of substances that may disturb chemical analysis performed by an analyzer for clinical chemistry. The presence and concentration of hemoglobin, bilirubin and lipemia are detected by measuring the absorbance or reflectance on at least two, preferably six, different wavelengths over the measured spectrum. The measurements are performed at two wavelengths for each substance, preferably on the absorbance peaks of the specific substance and on the root of the specific peaks. Since the three substances mentioned above each have at least one peak in the spectrum, the measurement is done on three peaks and three root positions respectively when three substances have to be measured.
Owner:THERMO FISCHER SCI OY
Automated analyzer for clinical laboratory
InactiveUS8222048B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClinical chemistryMicrowell Plate
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
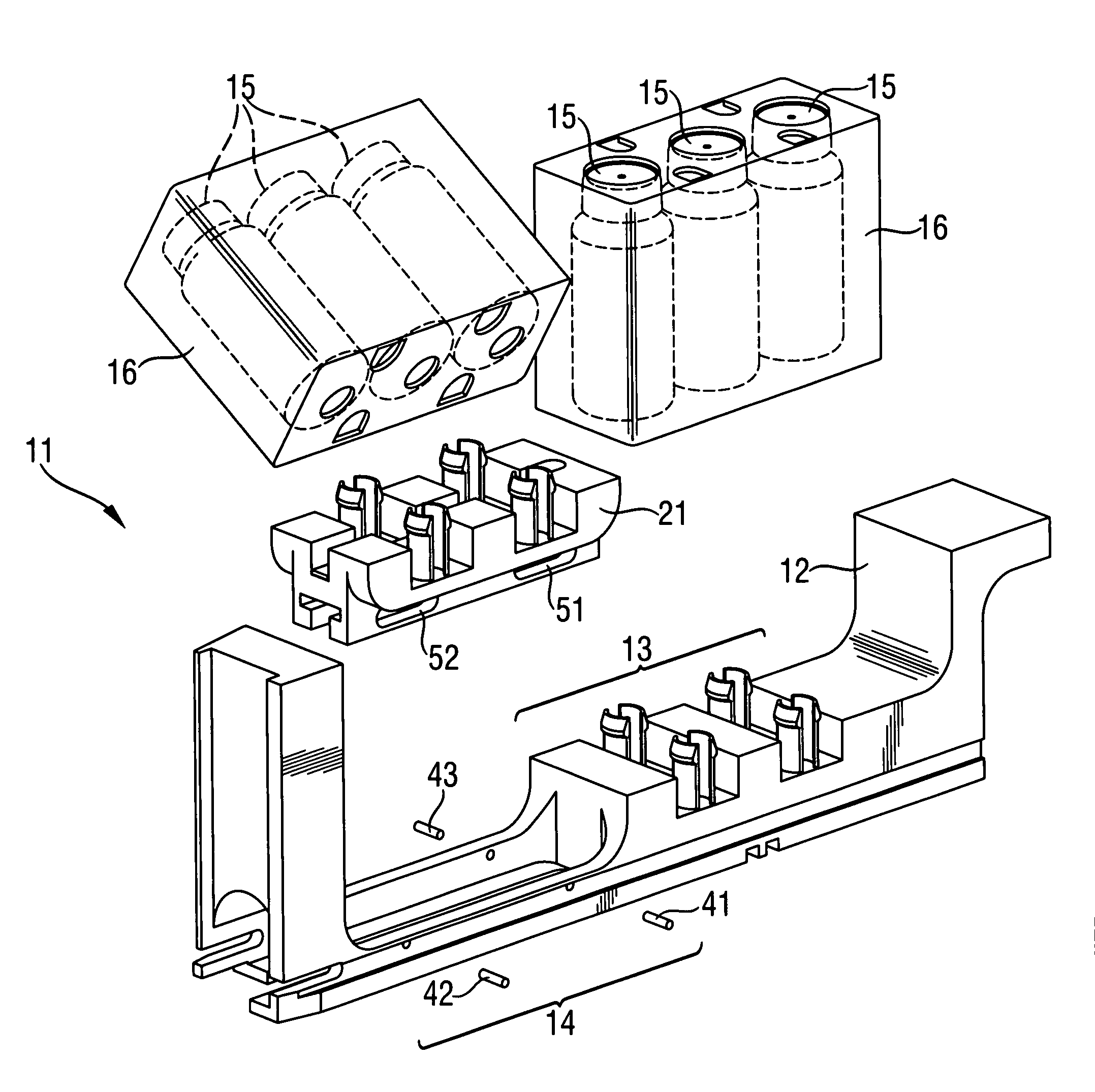
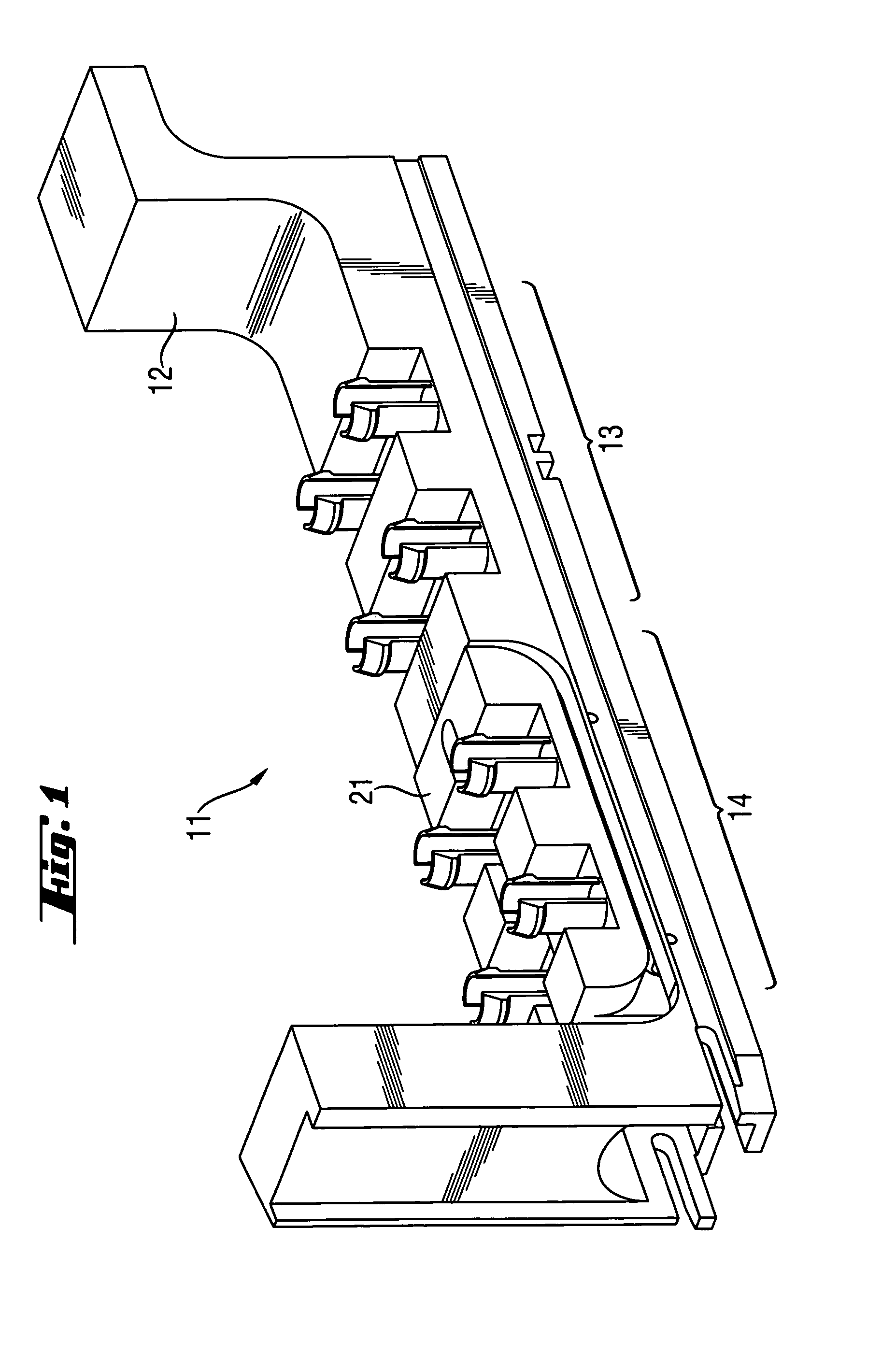
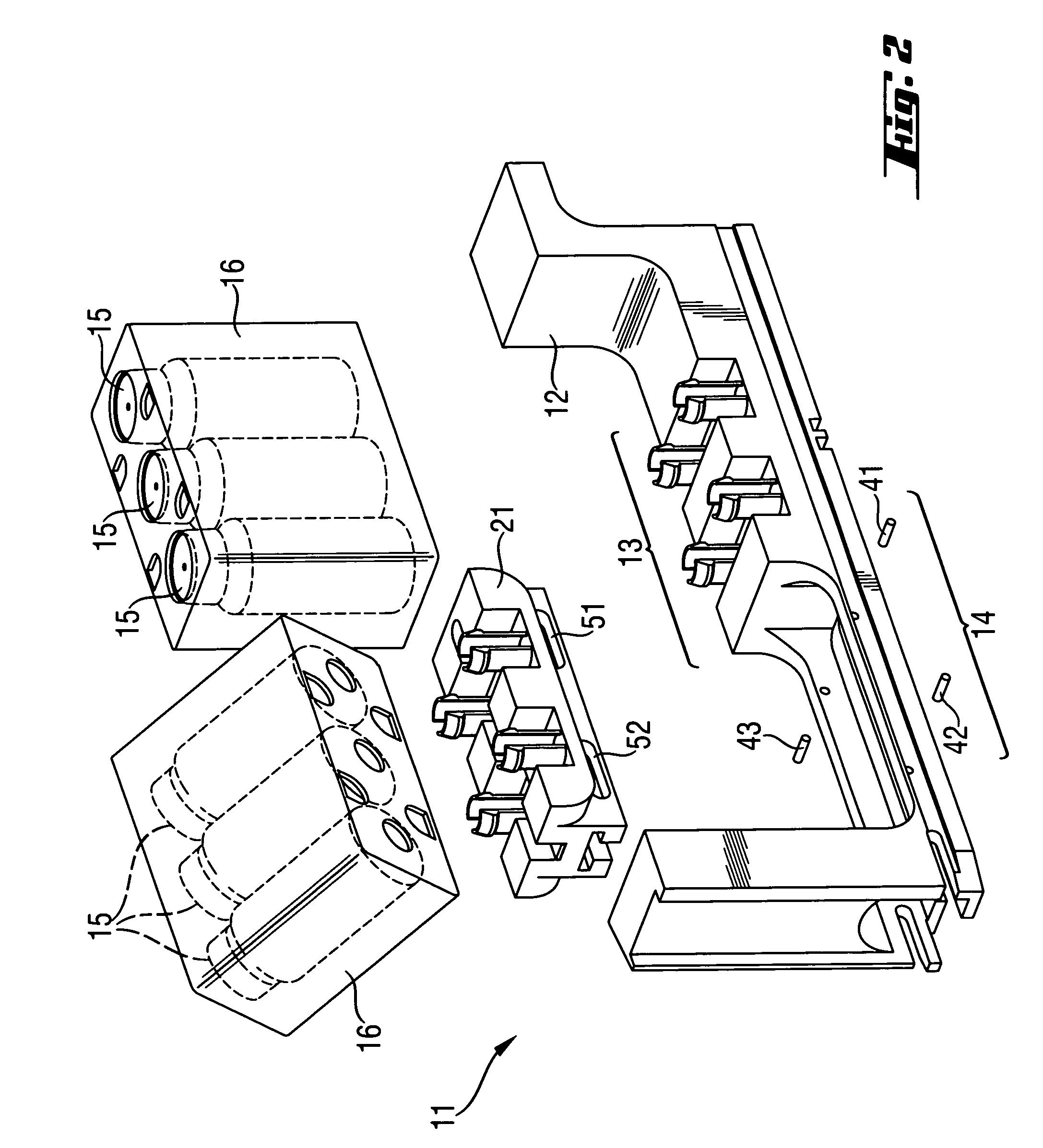
Rack for analyzer and analyzer comprising such a rack
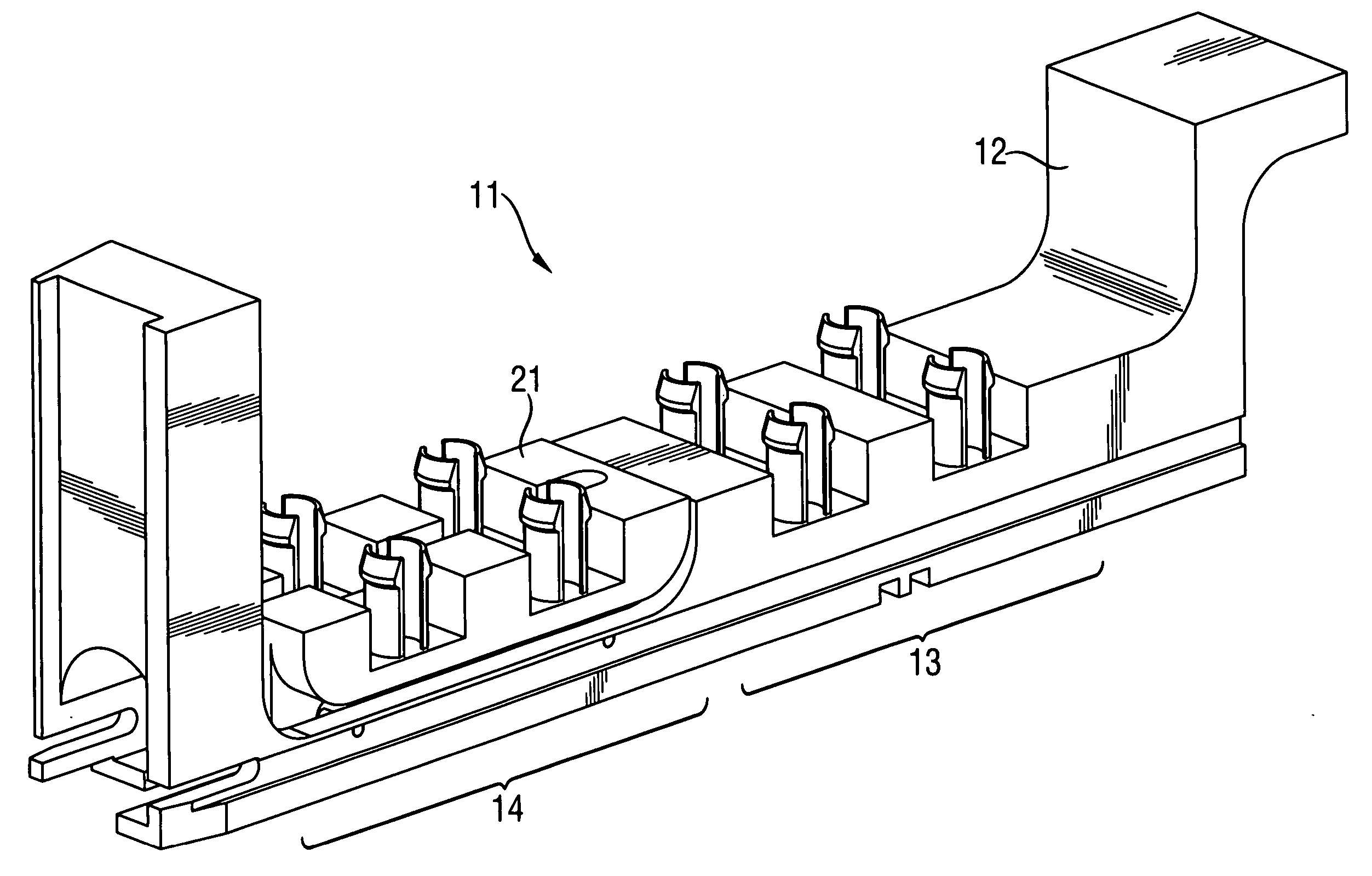
InactiveUS8017094B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersClinical chemistryEngineering
A rack for holding containers containing liquids used in clinical chemistry analyzers. The rack comprises(a) a frame having two or more sections, each section being adapted for receiving a liquid containing component,at least one of the sections of the frame being adapted for receiving a first liquid containing component which is adapted for being removably but tightly mechanically connected to said frame,(b) at least one movable part adapted to be removably coupled to a shaker device, the movable part being adapted for receiving and holding a second liquid containing component,at least one of the sections of the frame being adapted for receiving the movable part and allowing motion of the movable part within predetermined limits.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Magnetic bead manipulation and transport device
InactiveUS7309439B2Low magnetic fieldsIncrease speedElectrostatic separationTransportation and packagingClinical chemistryMagnetic bead
A device for transporting magnetic or magnetizable microbeads (25) in a capillary chamber (14) comprises a permanent magnet (10) or an electromagnet (11) for subjecting the capillary chamber to a substantially uniform magnetic field, to apply a permanent magnetic moment to the microbeads (25). At least one planar coil (22) and preferably an array of overlapping coils are located adjacent to the capillary chamber (14) for applying a complementary magnetic field on the microbeads parallel or antiparallel to said substantially uniform magnetic field, to drive the microbeads. An arrangement is provided for switching the current applied to the coil(s) (22) to invert the field produced thereby, to selectively apply an attractive or repulsive driving force on the microbeads (25). The device is usable to transport microbeads for performing chemical and biochemical reactions or assay, as is done for instance in clinical chemistry assays for medical diagnostic purposes.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Rack for analyzer and analyzer comprising such a rack
InactiveUS20060093529A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersClinical chemistryEngineering
A rack for holding containers containing liquids used in clinical chemistry analyzers. The rack comprises (a) a frame having two or more sections, each section being adapted for receiving a liquid containing component, at least one of the sections of the frame being adapted for receiving a first liquid containing component which is adapted for being removably but tightly mechanically connected to said frame, (b) at least one movable part adapted to be removably coupled to a shaker device, the movable part being adapted for receiving and holding a second liquid containing component, at least one of the sections of the frame being adapted for receiving the movable part and allowing motion of the movable part within predetermined limits.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Method for automatically detecting factors that disturb analysis by a photometer
ActiveUS20090009750A1Easily and reliably detectedReliable analysisBiological material analysisTransmissivity measurementsClinical chemistryMedicine
The invention concerns a method for detecting the amounts of substances that may disturb chemical analysis performed by an analyzer for clinical chemistry. The presence and concentration of hemoglobin, bilirubin and lipemia are detected by measuring the absorbance or reflectance on at least two, preferably six, different wavelengths over the measured spectrum. The measurements are performed at two wavelengths for each substance, preferably on the absorbance peaks of the specific substance and on the root of the specific peaks. Since the three substances mentioned above each have at least one peak in the spectrum, the measurement is done on three peaks and three root positions respectively when three substances have to be measured.
Owner:THERMO FISCHER SCI OY
Delta cup
InactiveUS20050053519A1Easy to useMinimal instructionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSurgeryClinical chemistryPregnancy
The present invention is a device for assaying and collection of biological and other specimens and is especially designed for the collection and determination of the presence of chemical constituents in clinical chemistry, pregnancy, drugs of abuse testing, infectious disease testing, and other fields of analysis of fluids.
Owner:SMITH JACK V
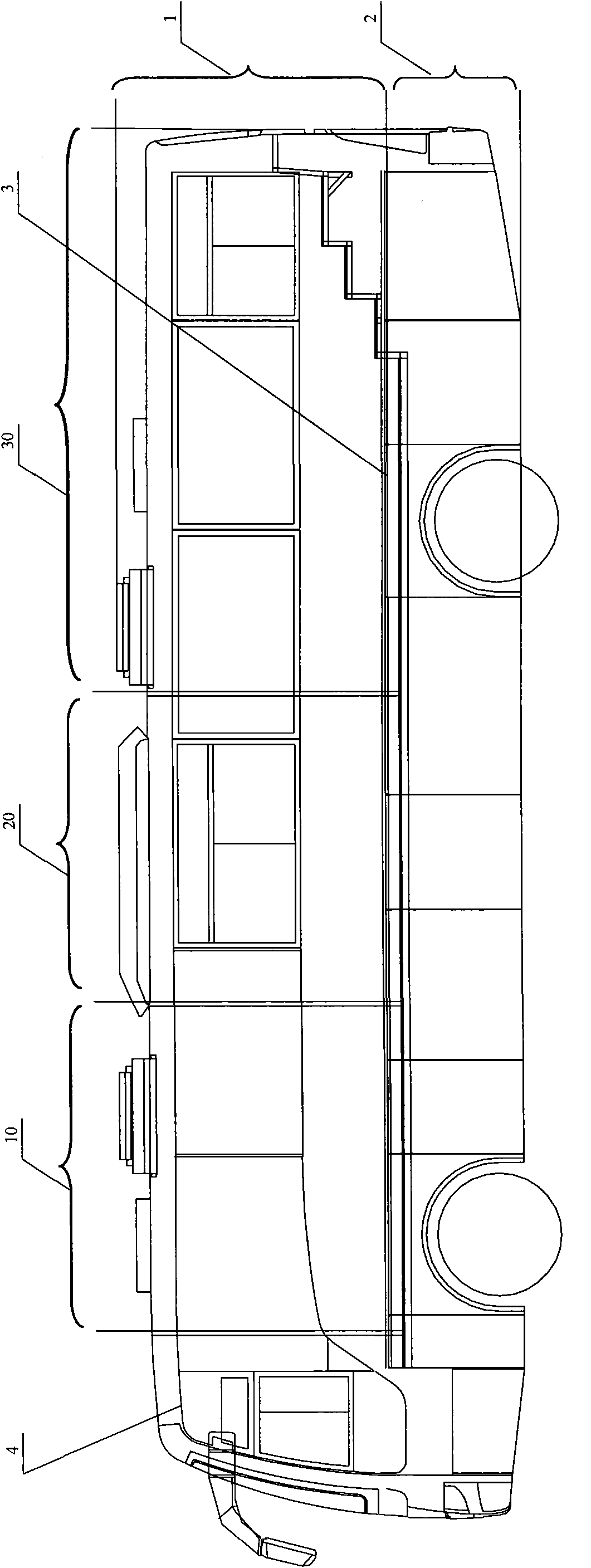
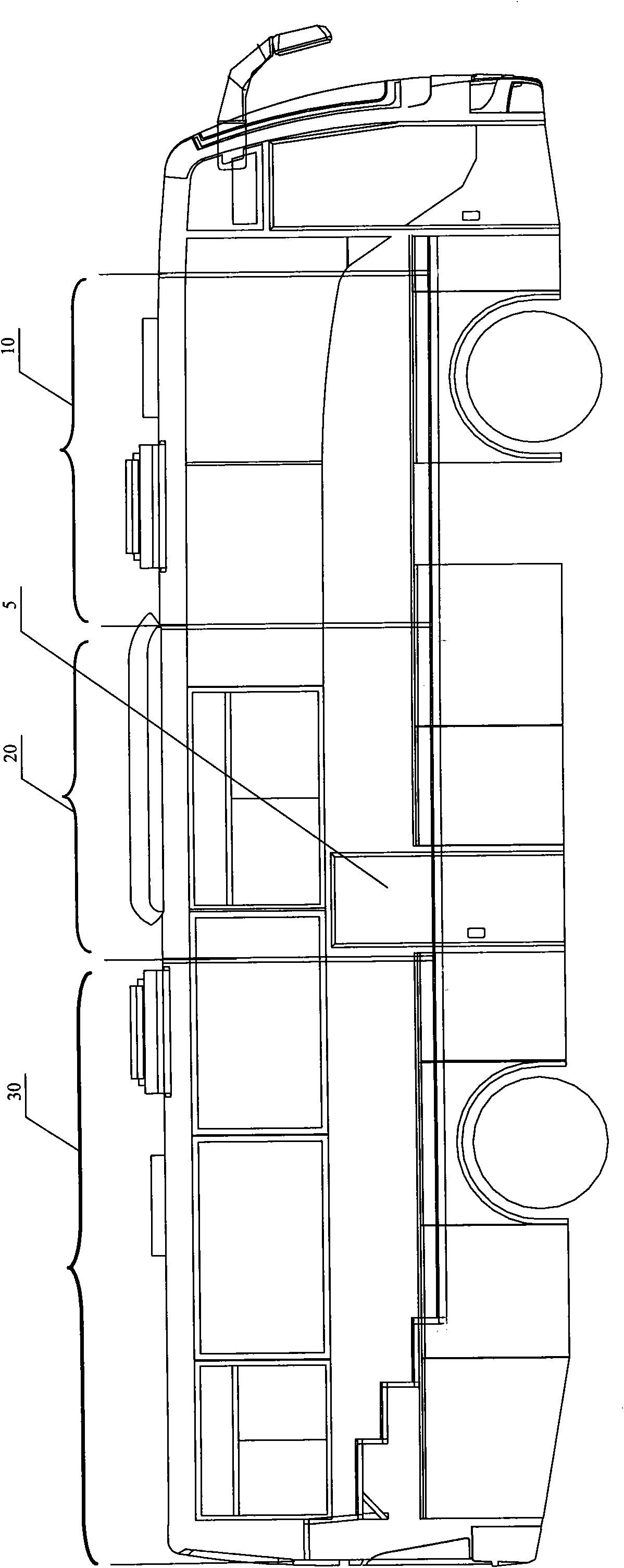
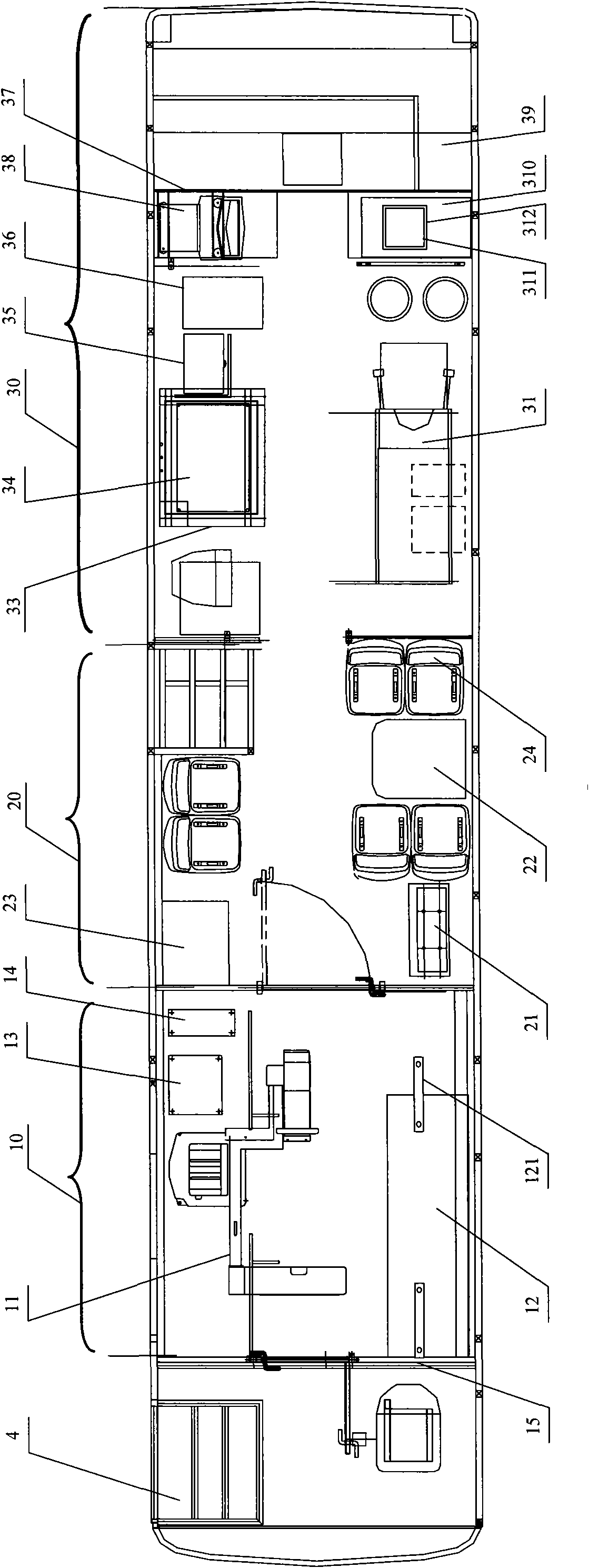
Medical vehicle-mounted system
ActiveCN101953714AReasonable layoutReduce manufacturing costDiagnosticsSurgeryClinical chemistryX-ray
The invention relates to a medical vehicle-mounted system. The medical vehicle-mounted system comprises a vehicle body; the vehicle body comprises a vehicle body upper part and a vehicle body lower part; the vehicle body upper part is provided with an X-ray inspection region, an inquiry region and a routine examination region sequentially from a vehicle head to a vehicle tail, wherein X-ray inspection equipment is arranged in the X-ray inspection region; a medicament refrigerator, an inquiry table and an operation table of the X-ray inspection equipment are arranged in the inquiry region; anda multi-function examination table, an electrocardiogram cabinet, a defibrillator monitor cabinet, an automatic clinical chemistry analyzer, a urine analyzer, an oxygenerator, B ultrasonic inspectionequipment, a blood cell analyzer and a blood sample centrifugal machine are arranged in the routine examination region. The medical vehicle-mounted system has the advantages of meeting the requirements of diagnosis and treatment on a plurality of common diseases, conducting the function of a general hospital, and meeting the requirement of medical services of marginal areas or the areas which need immediate support, along with reasonable layout.
Owner:BEIQI FOTON MOTOR CO LTD +1
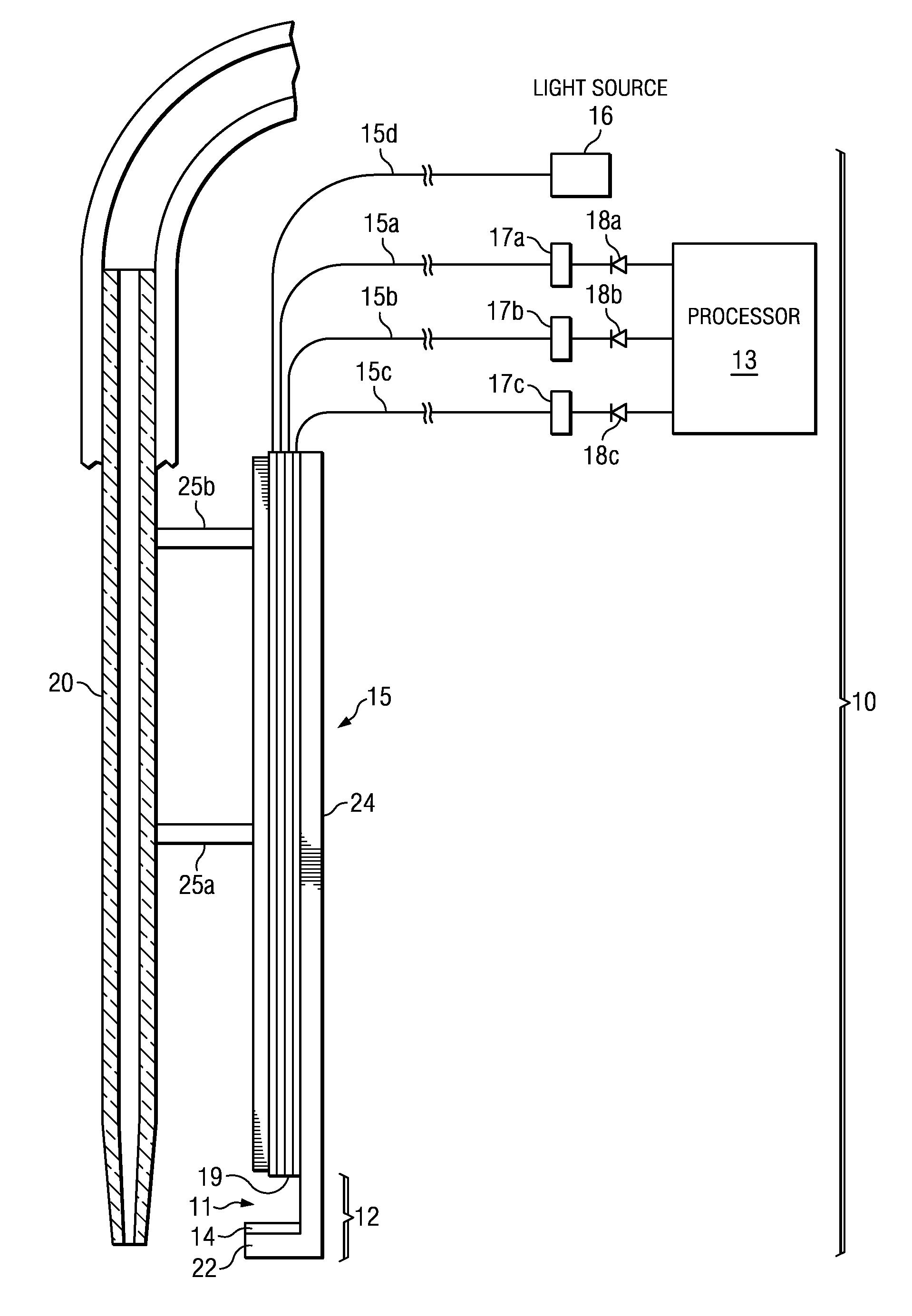
Serum sample quality determination
ActiveUS20150168371A1Easy to mergeImprove the level ofScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsLight intensityLight source
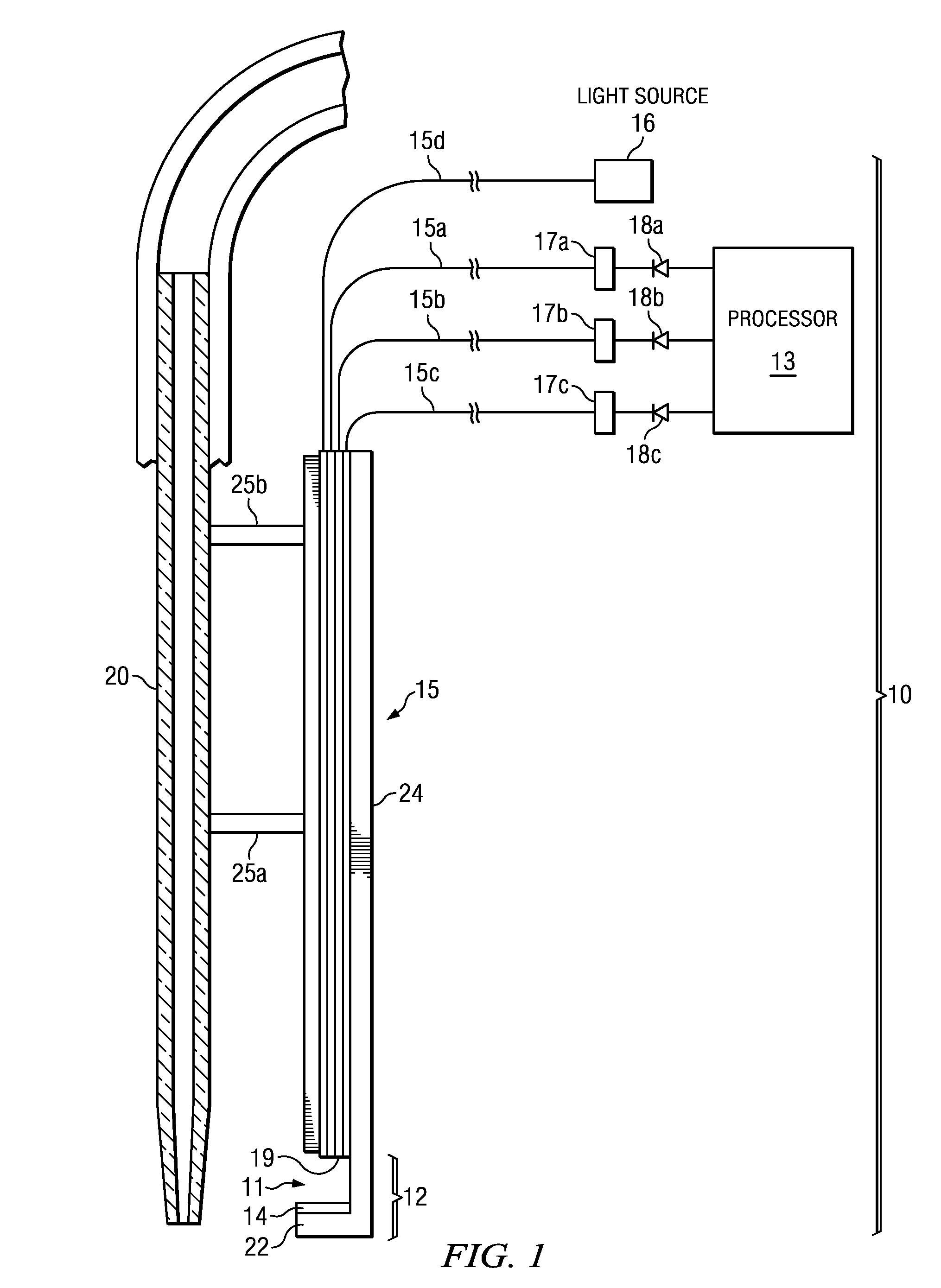
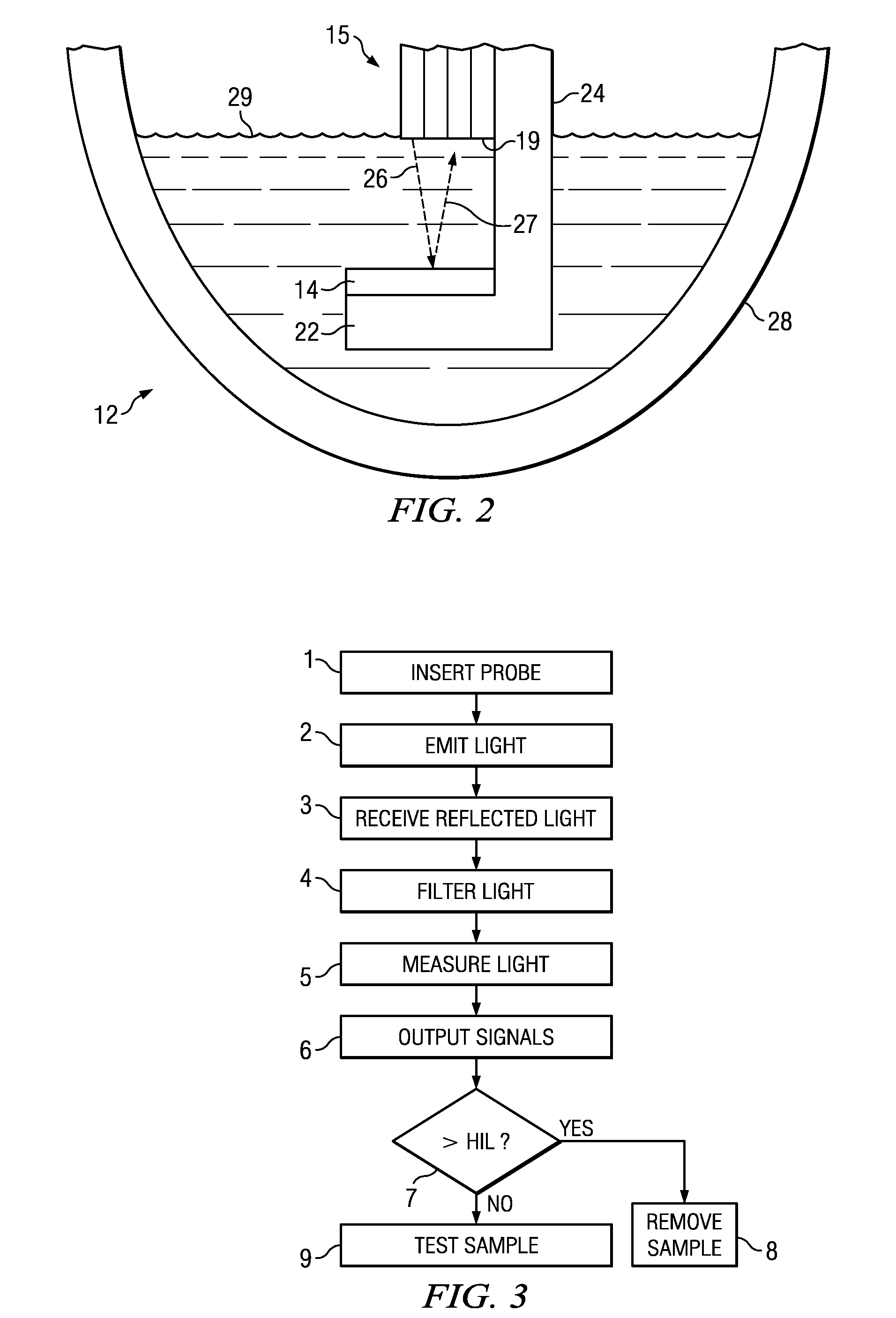
A method and device for measuring HIL levels in blood serum samples that are disposed in an automated, clinical chemistry analyzer. The device probe can be attached adjacent to a pipette or sample probe of the analyzer and includes fiber optic bundles and a light-reflecting surface. A cutaway portion is provided between the ends of each of the fiber optic bundles and the light-reflecting surface. One of the four fiber optic bundles is optically coupled to a light-emitting source. Each of the other three fiber optic bundles collects and filters reflected light from the reflecting surface. The light filters correspond to the optimal absorption wavelengths for one of hemoglobin, bilirubin, and triglycerides. A light intensity-measuring device is optically coupled to each of the three fiber optic bundles, to measure the intensity of the filtered, reflected light. A processing device receives output data signal from the light intensity-measuring devices; stores the data; and calculates whether a serum sample has elevated levels of one or more of HIL.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Liquid quality control serum for clinical chemical detection
The invention relates to liquid quality control serum for clinical chemical detection, in particular to application of combination of glycol and propylene glycol in preparing liquid quality control serum, a method for stabilizing the liquid quality control serum by using the combination of glycol and propylene glycol, liquid quality control serum containing glycol and propylene glycol serving as protective agents, and a method for preparing the liquid quality control serum. The liquid quality control serum prepared by the method keeps the stability for at least one year when stored at -20 DEGC, keeps the stability for at least two weeks when stored and used at 2 to 8 DEG C, can stabilize for 4 hours at room temperature, and has some quality control indexes superior to those of the liquidquality control serum prepared by the prior art or the liquid quality control serum on sale.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
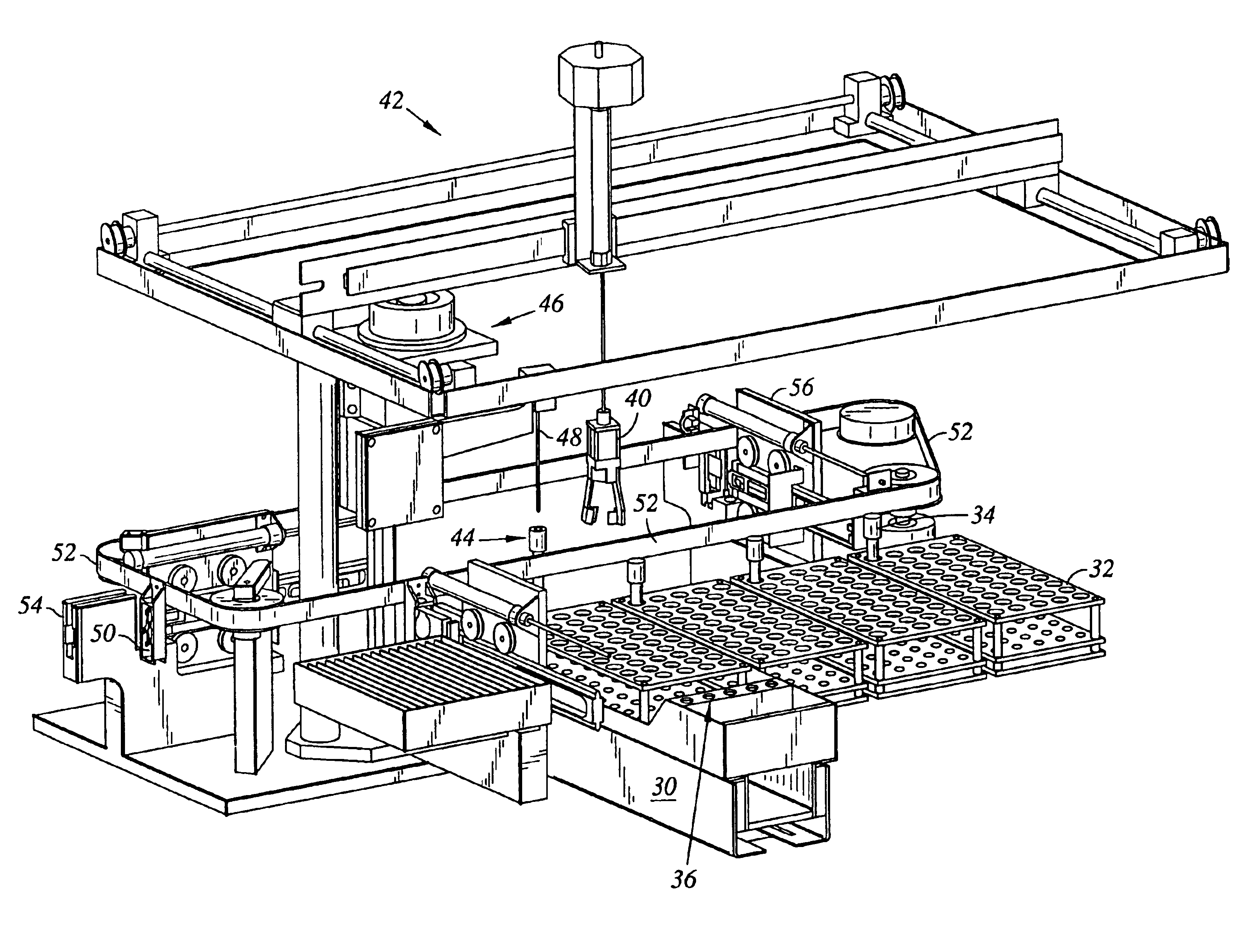
Shaker device for analyzer apparatus and analyzer comprising same
InactiveUS20070253284A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersMaterial analysisCircular discClinical chemistry
A shaker device for shaking liquids in a clinical chemistry analyzer comprises an eccentric pin on a rotatable disk, a motor for rotating the disk and a movable piece having a joint for receiving the eccentric pin. The movable piece is mounted on a first movable part of a first linear motion guide having a first rail on which the first movable part can slide in a first direction (Y-direction). The first rail of the first linear motion guide is mounted on an intermediate plate which is mounted on a second movable part of a second linear motion guide having a second rail on which the second movable part can slide in a second direction (X-direction) which is normal to the first direction.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Use of pulse-activating injection in preparing synergetic medicine for treating tumor
InactiveCN1473615AExpanded indicationsSynergistic effect is obviousUnknown materialsAntineoplastic agentsClinical chemistryCancer cell
The present invention relates to Chinese medicine, and is the use of pulse-activating injection in preparing synergistic medicine for treating tumor. Based on the features of clinical chemotherapy, the present invention combines the use of pulse-activating injection and chemotherapeutic medicine in treating tumor and shows the obvious synergistic effect of pulse-activating injection to chemotherapeutic medicine, especially 5-Fu, MTX, DDP, etc. in cancer cell. The present invention expands the indications of pulse-activating injection, and uses it as the synergistic medicine in the clinical treatment of colon cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer and cancer of pancreas.
Owner:HEHUANG PHARMA SHANGHAI +1
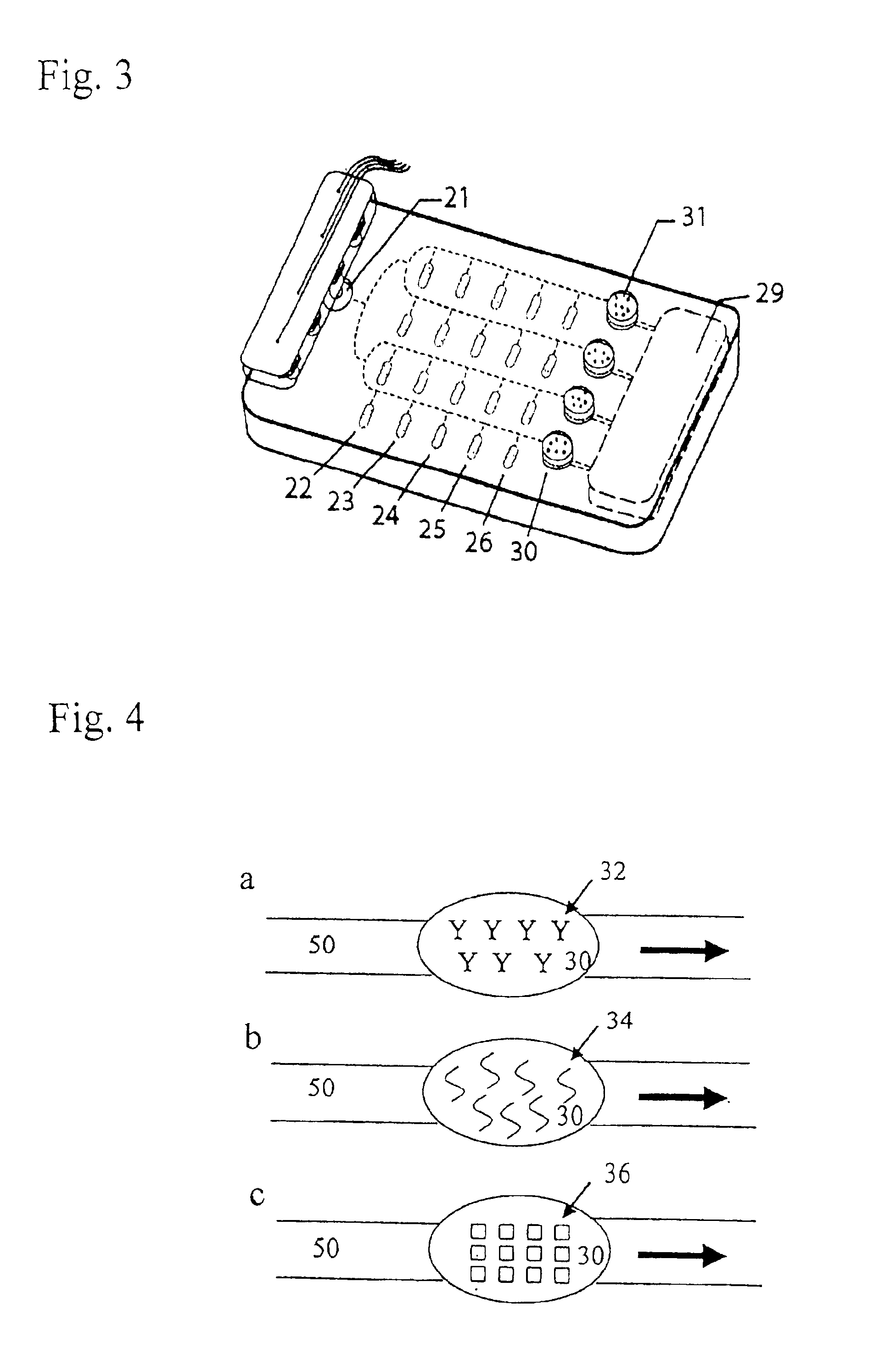
Clinical chemistry integrated and combined multi-reagent-strip detection device and method
InactiveCN105203781ARealize instant measurementMeet the measurementBiological testingReagent stripClinical chemistry
The invention discloses a clinical chemistry integrated and combined multi-reagent-strip detection device and method. The detection device comprises reagent strips, sampling needles, an optical detection system and a displacement device, the sampling needles are installed on the displacement device, each reagent strip is provided with multiple reagent cavities which are connected in parallel into a whole body, and the reagent cavities are located on the movement track of the displacement device. The method comprises the steps of sample suction, R1 reaction, R2 adding, colorimetric analysis, needle cleaning and the like. According to the clinical chemistry integrated and combined multi-reagent-strip detection device and method, the reagent strip structure that the multiple reagent cavities are connected in parallel, the detection procedure can be simplified, an automatic analyser can be compact in structure and high in reliability, and the detection for a small batch of samples is accelerated.
Owner:JIANGSU AUDICOM MEDICAL TECH
System for management of racks and tubes position for clinical chemistry laboratories
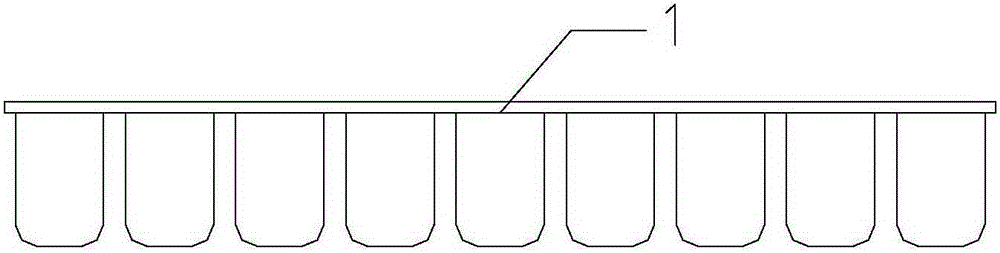
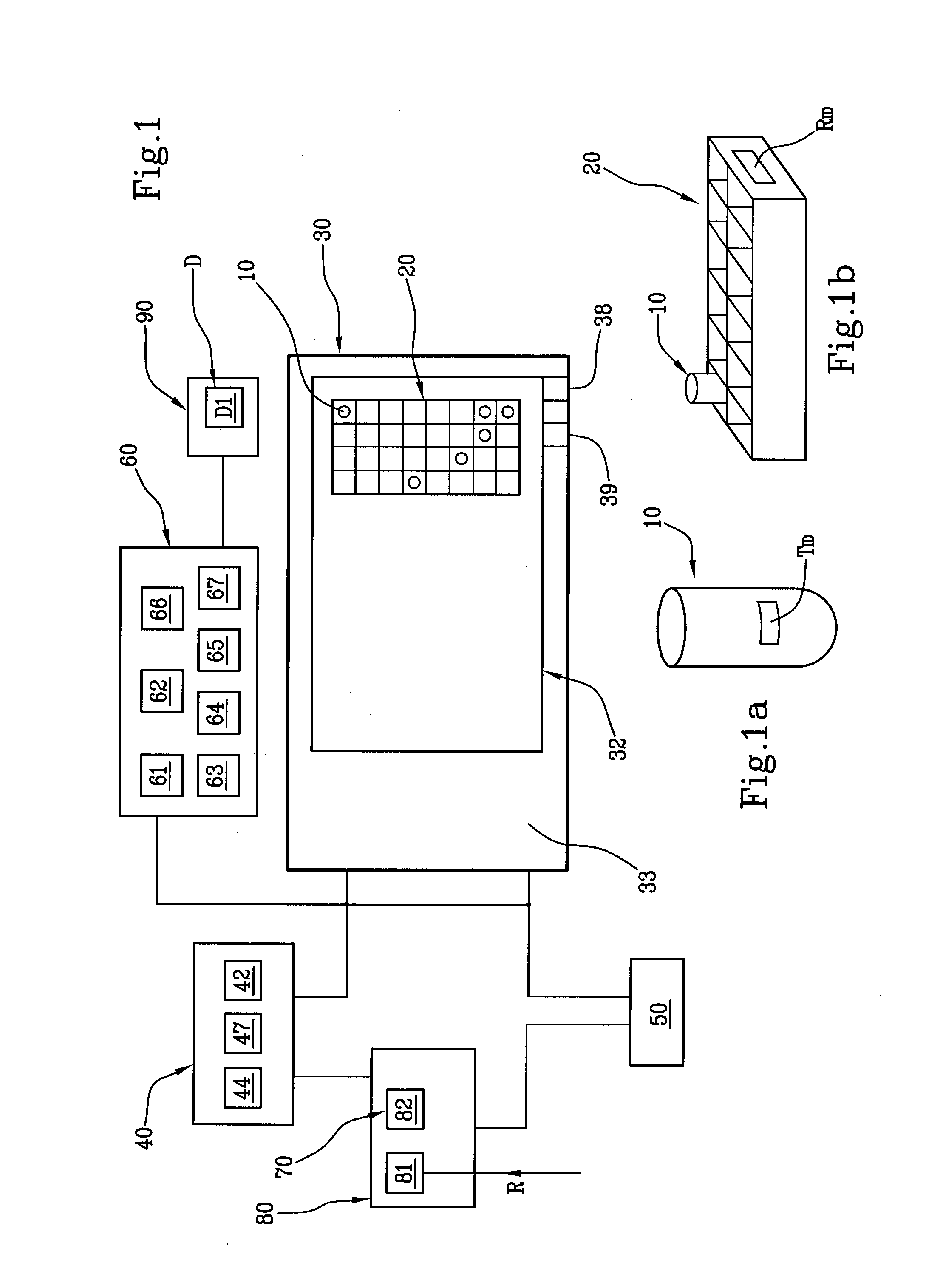
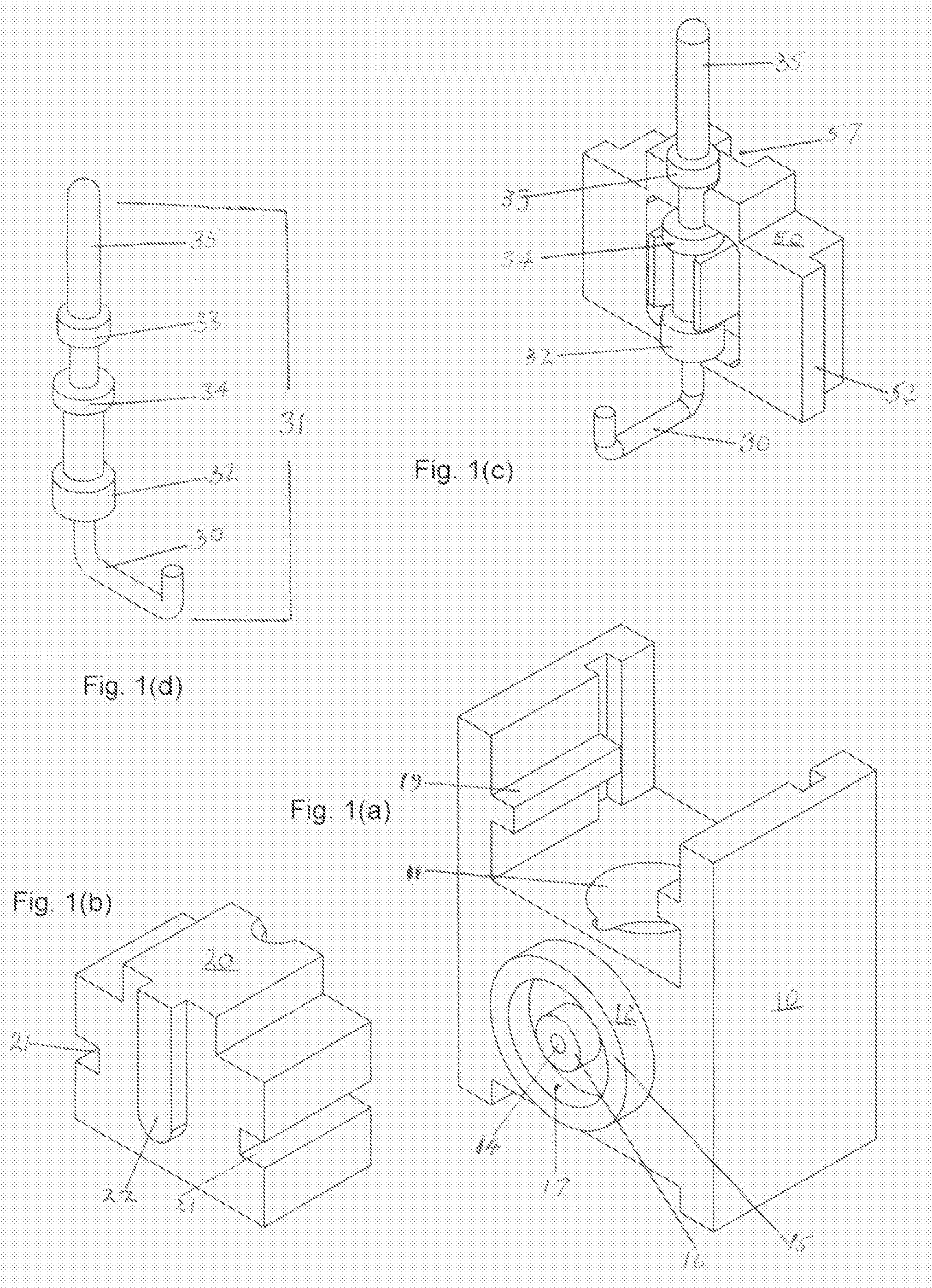
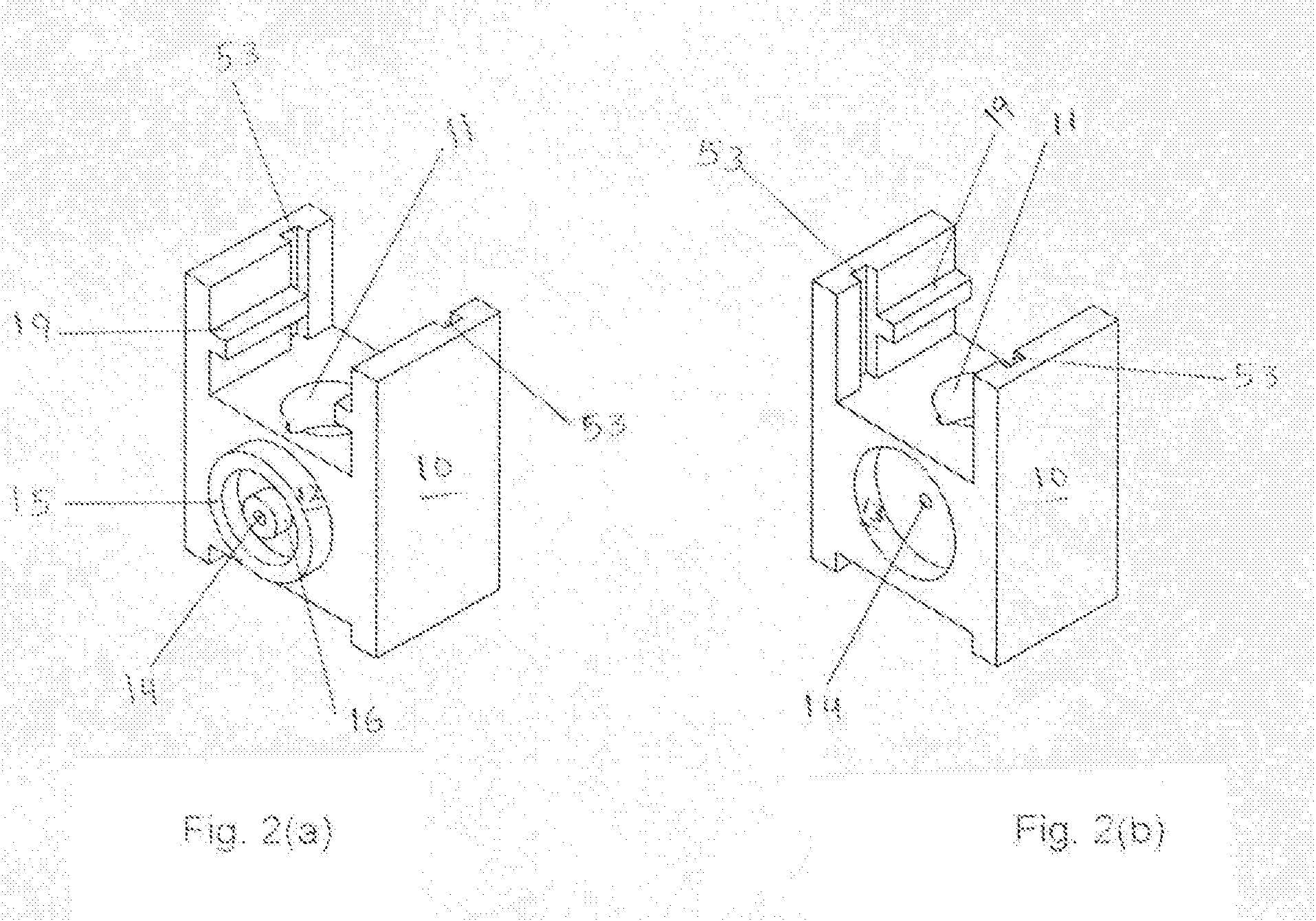
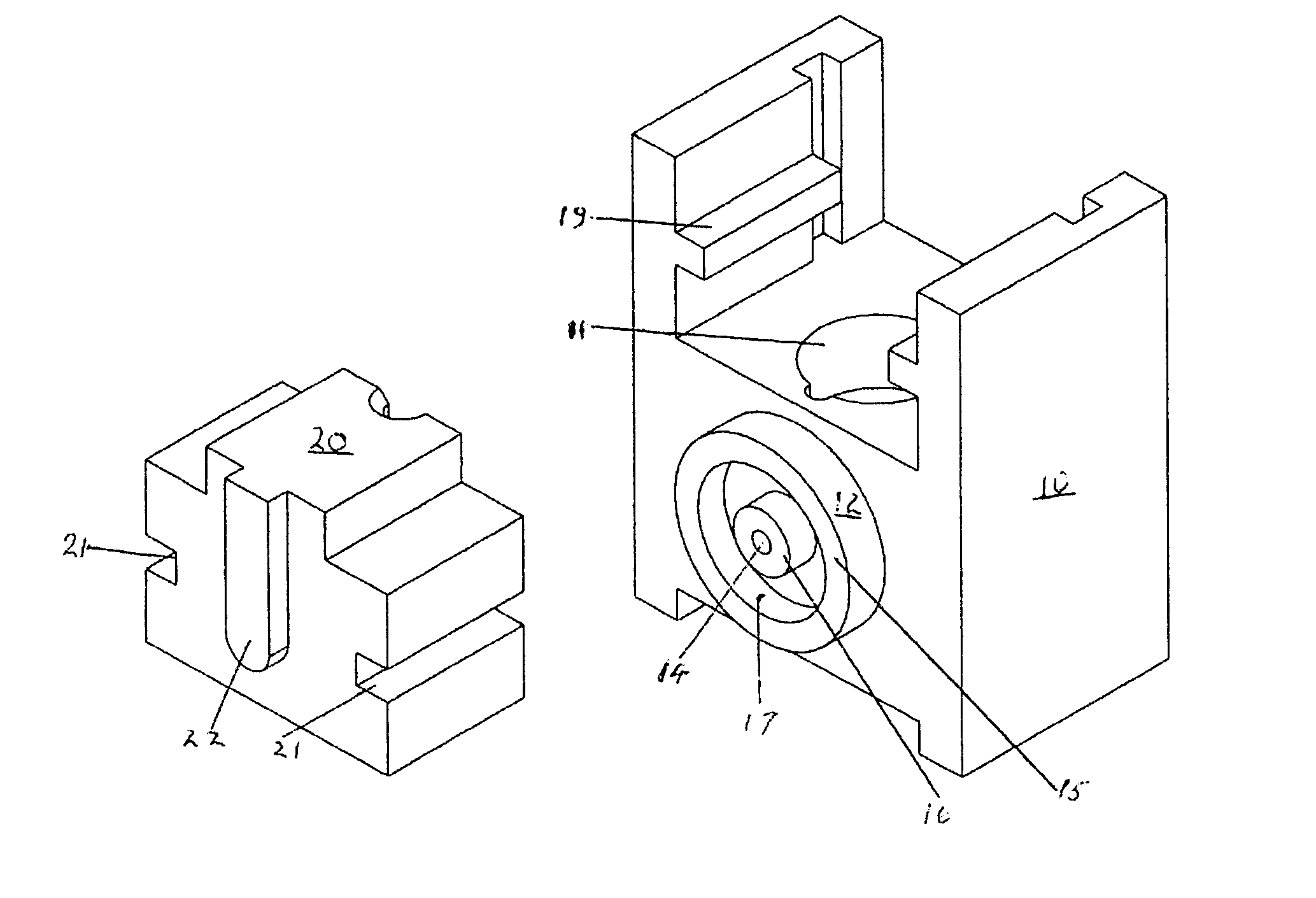
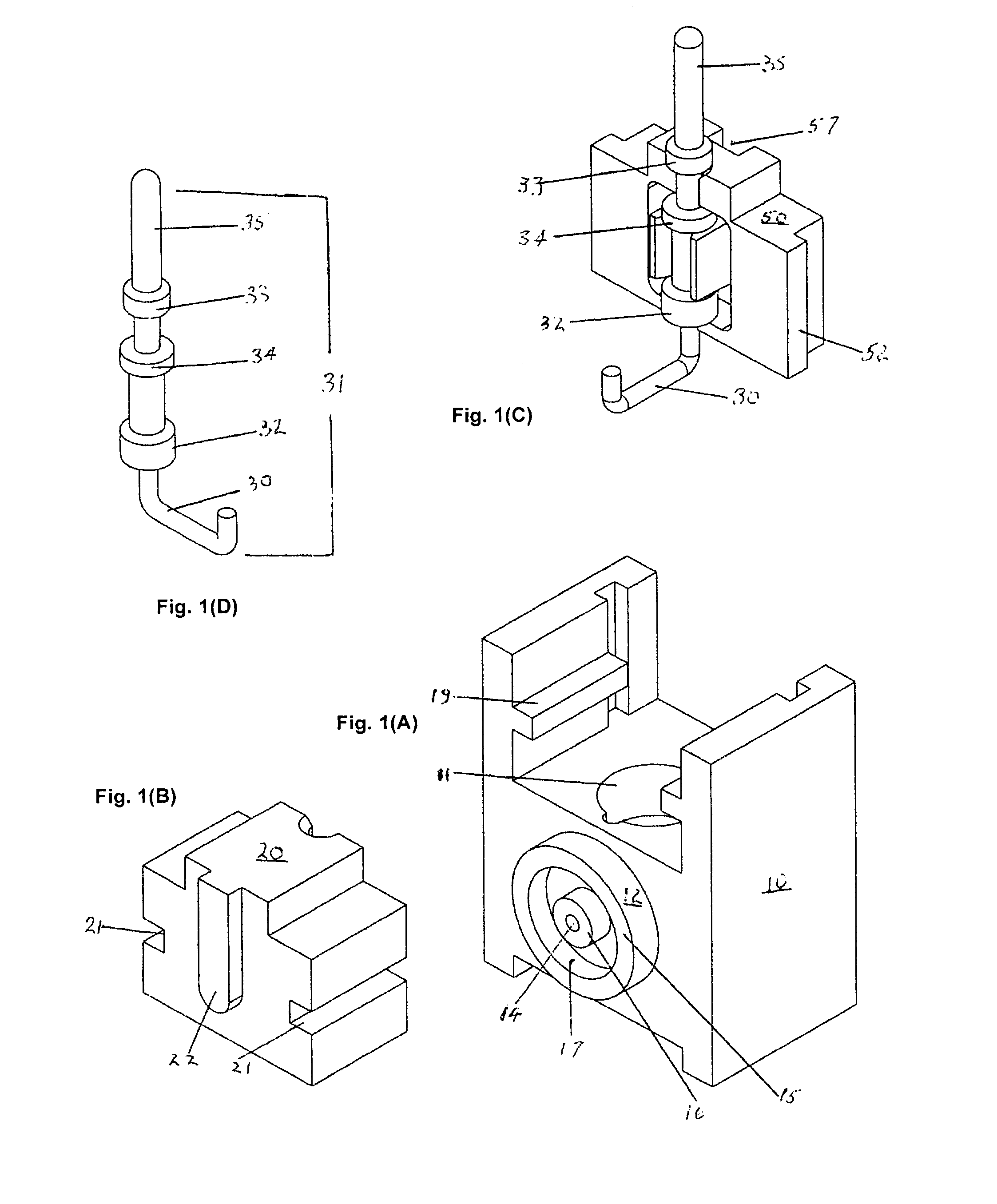
The system for management of racks and tubes position for clinical chemistry laboratories of the invention comprises tubes (10) capable of containing human biological material, a rack (20) configured for receiving and / or holding the tubes (10) to be stocked, a supporting base (30) configured for supporting the rack (20) thereon, reading means (50) configured for reading an identificator (RID) of the rack (20) to be put onto the supporting base (30) and an identificator (TID) of the tube to be put into the rack (20), a camera (40) for detecting the rack (20) on the supporting base (30), and at least one of the tubes (10) into the rack (20), a processing unit (60) for mapping the detected rack (20) into a plurality of allowed positions (Pi) and the detected tube (10) into a tube position (P) comprised in said plurality of allowed positions (Pi).
Owner:OMNILAB TECH SRL
Ion-selective electrode
InactiveUS20100252429A1Use minimizedLess-expensiveImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsClinical chemistryIon selective electrode
A five-part electrode device, including a membrane formed in situ, which is useful in automated clinical chemistry analyzers, and the method of forming a direct solid state connection to the membrane eliminating the need for the use of an internal reference electrode requiring internal filling solutions.
Owner:RAO K JAGAN
Ion selective electrode
InactiveUS20160195491A1Less active reagentUse minimizedMaterial electrochemical variablesClinical chemistryExternal reference
A five-part internal reference electrode, including a membrane formed in situ, which is useful in automated clinical chemistry analyzers, the method of forming a direct solid state connection to the membrane eliminating the need for the use of an internal reference electrode internal filling solution, and a ganged assembly of said internal reference electrodes with a grounding unit and an external reference electrode.
Owner:RAO K JAGAN M
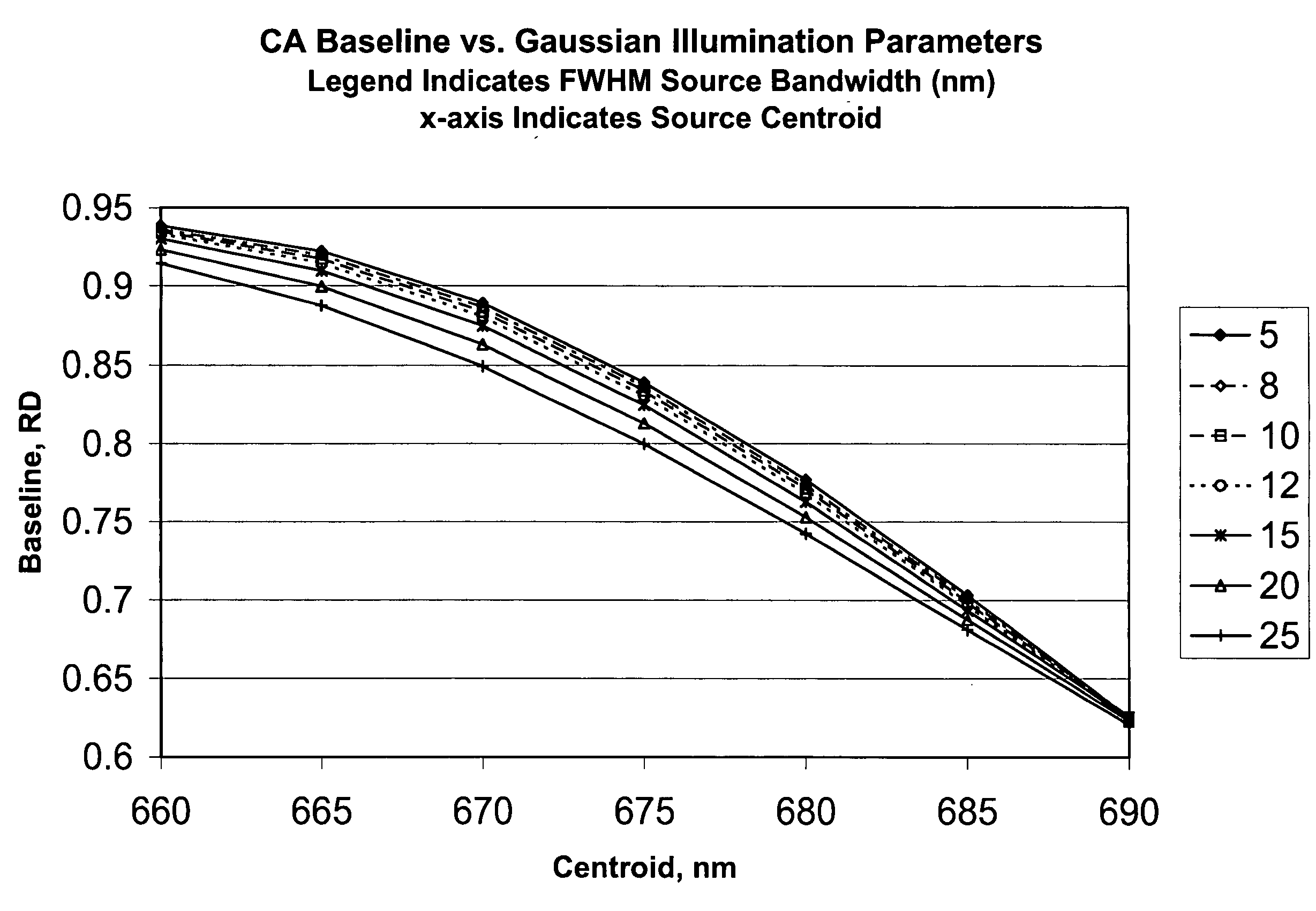
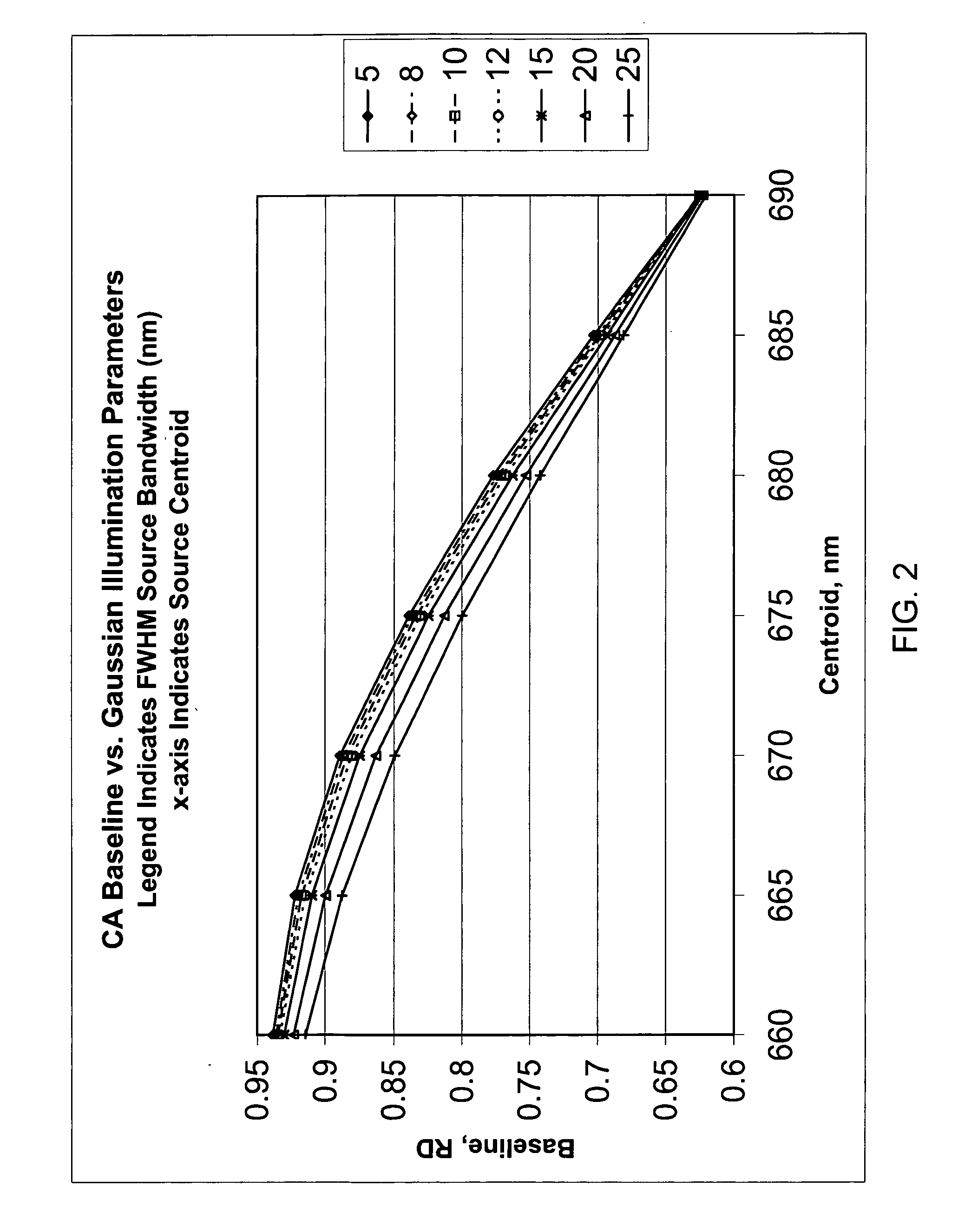
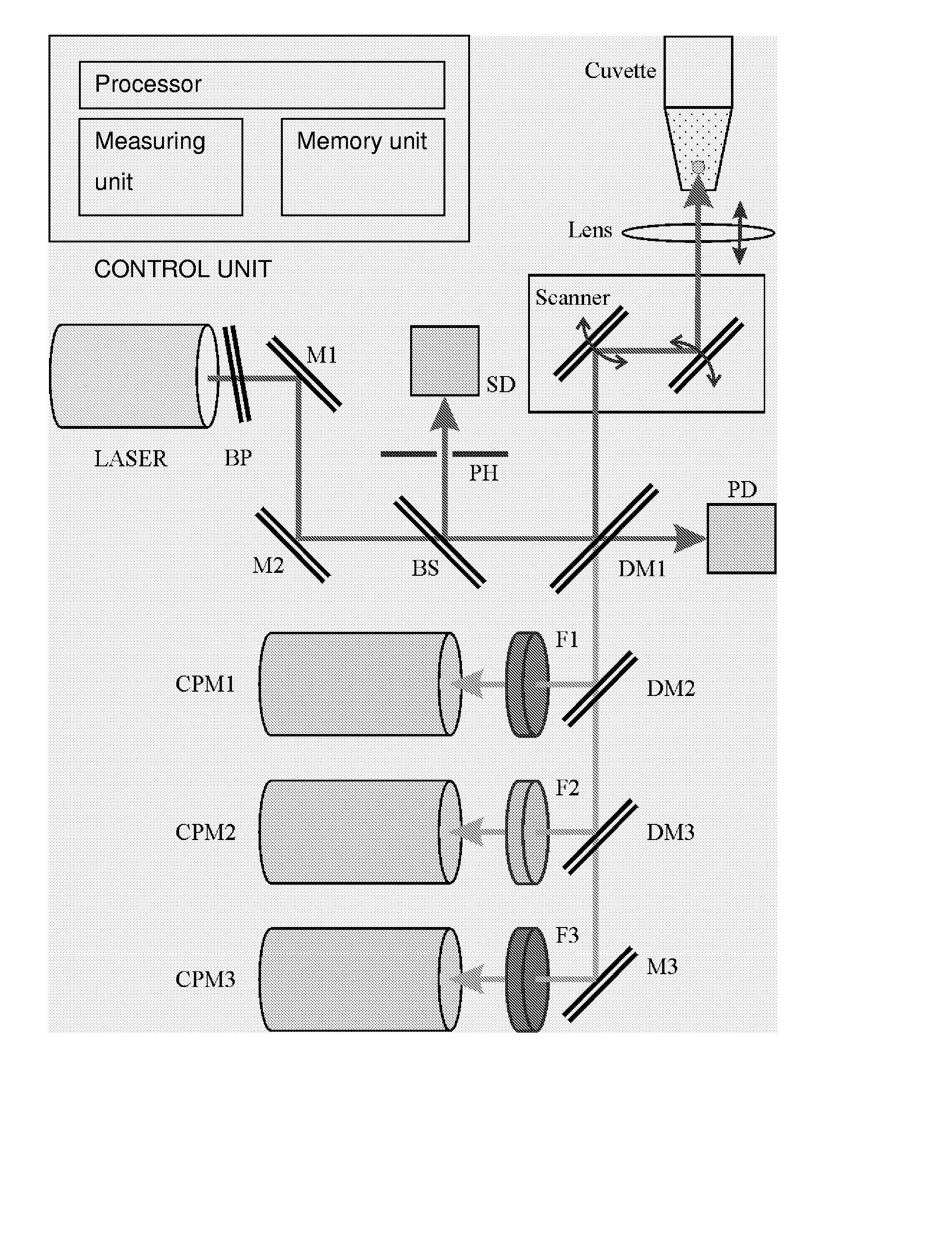
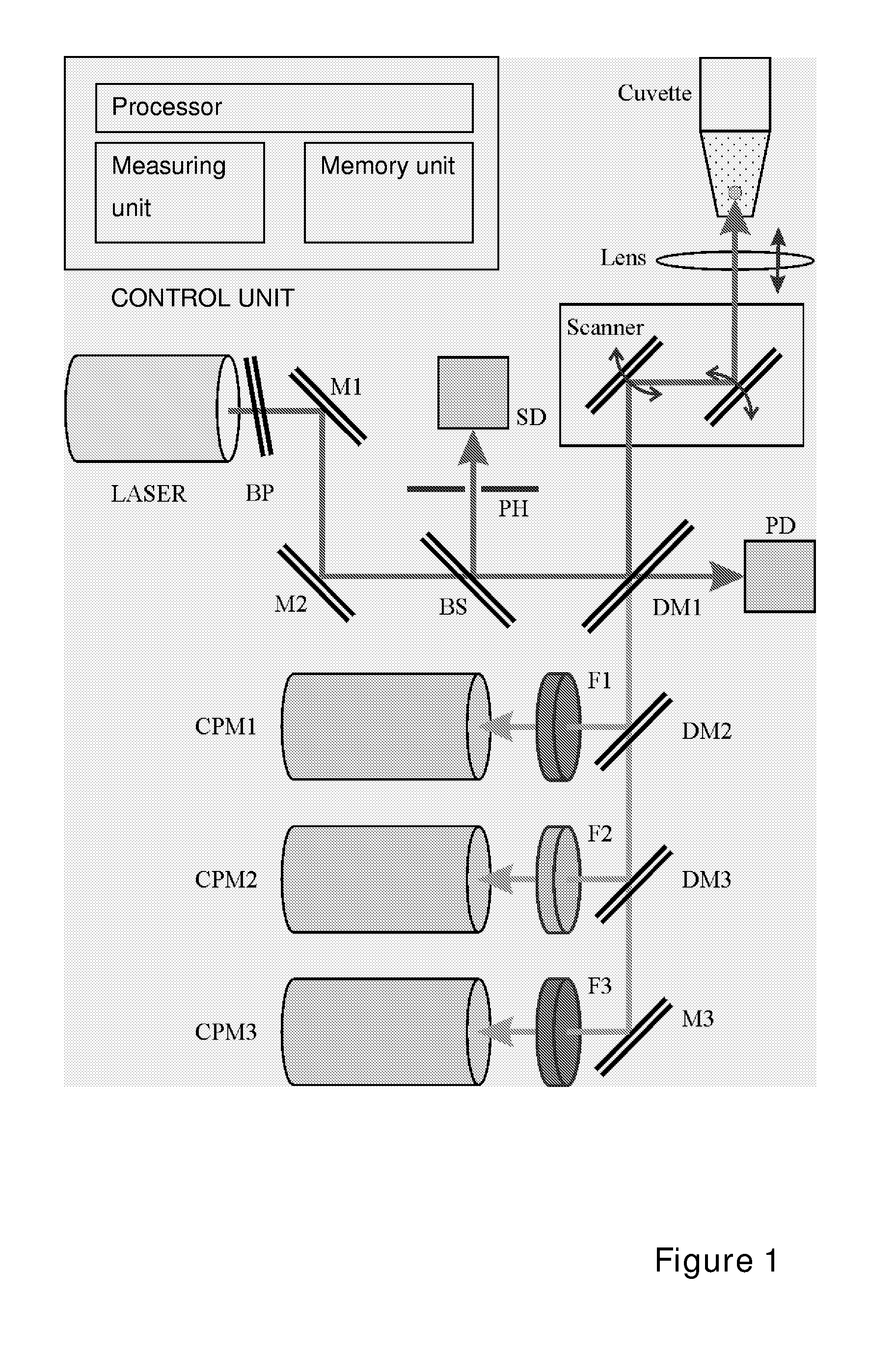
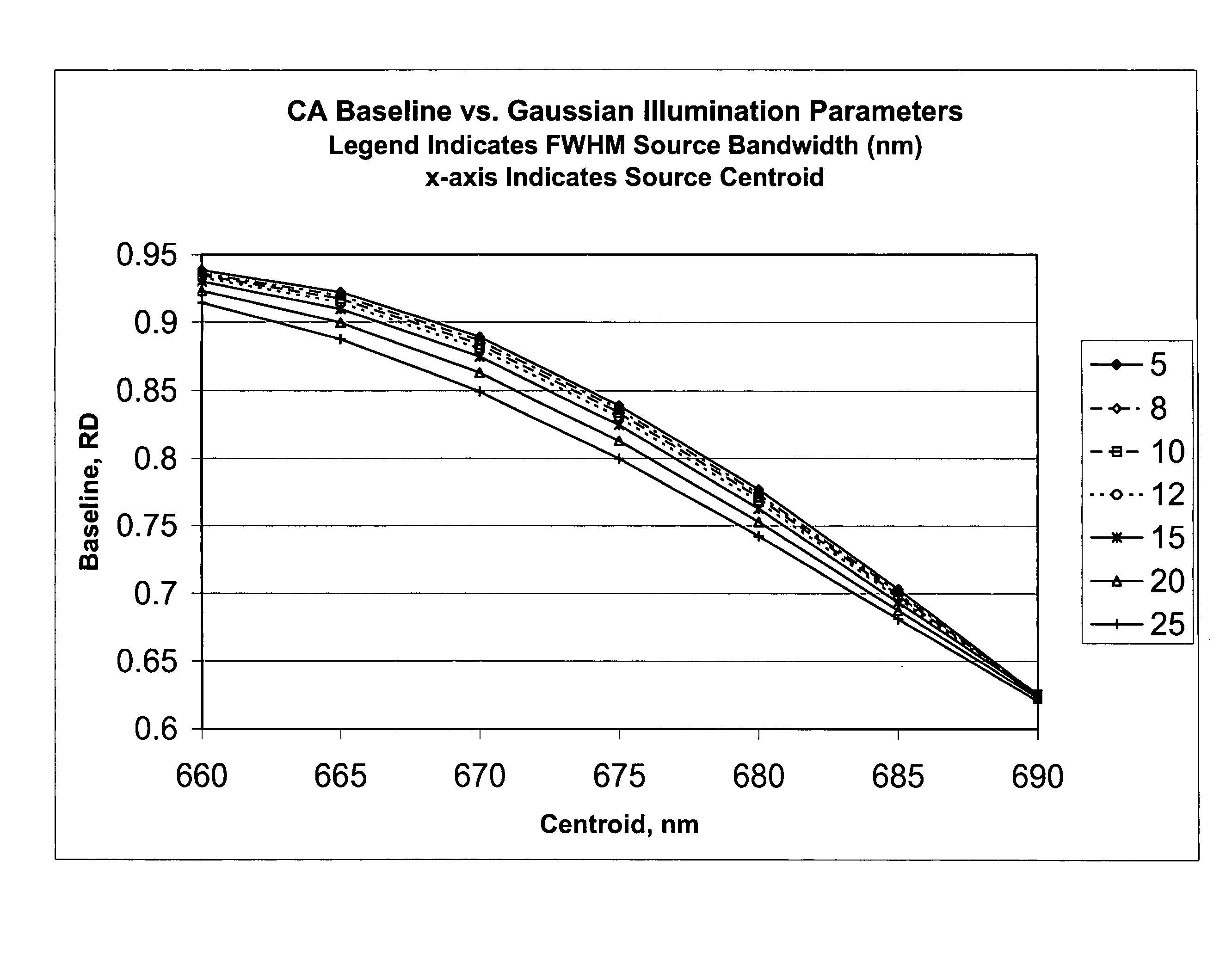
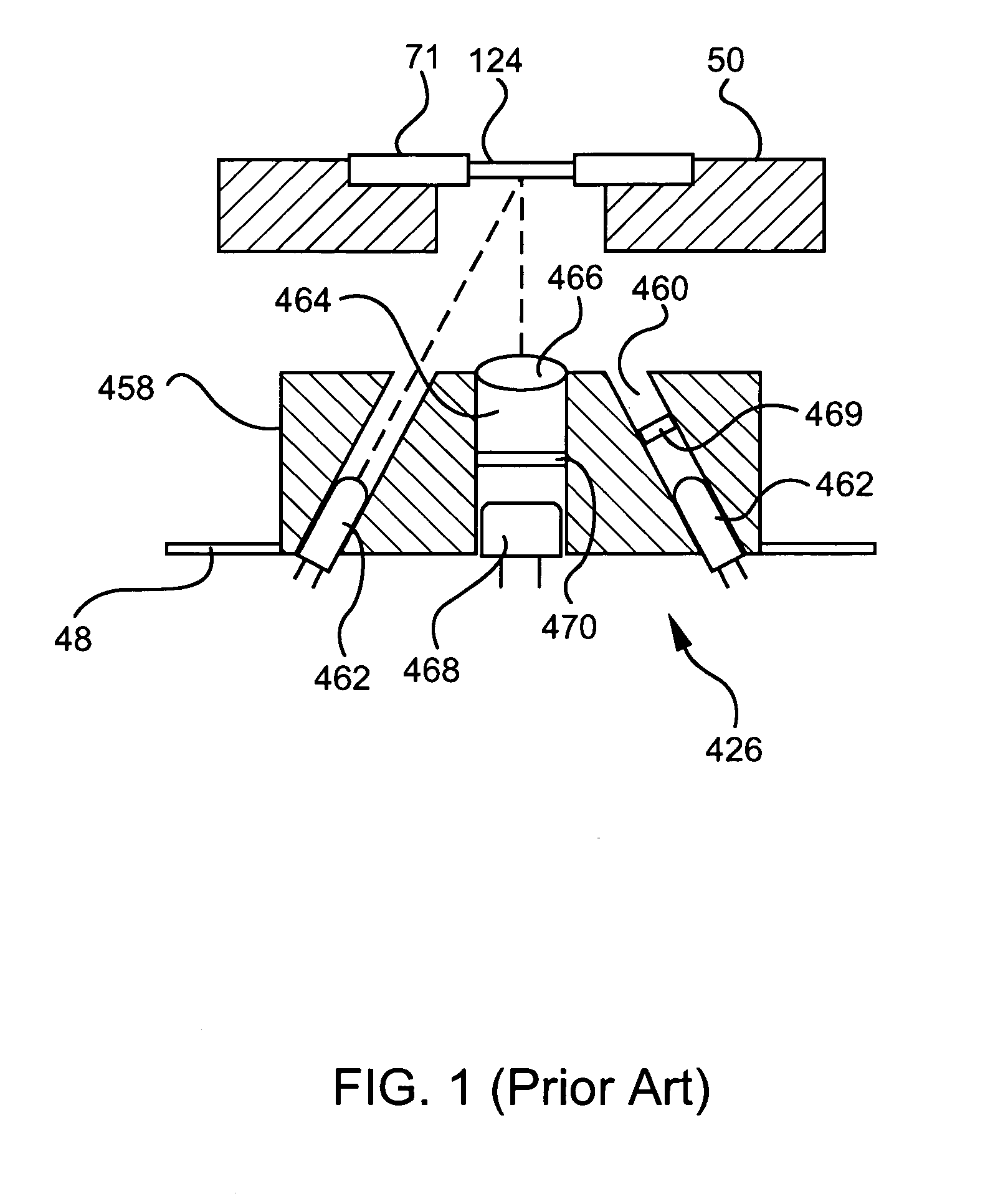
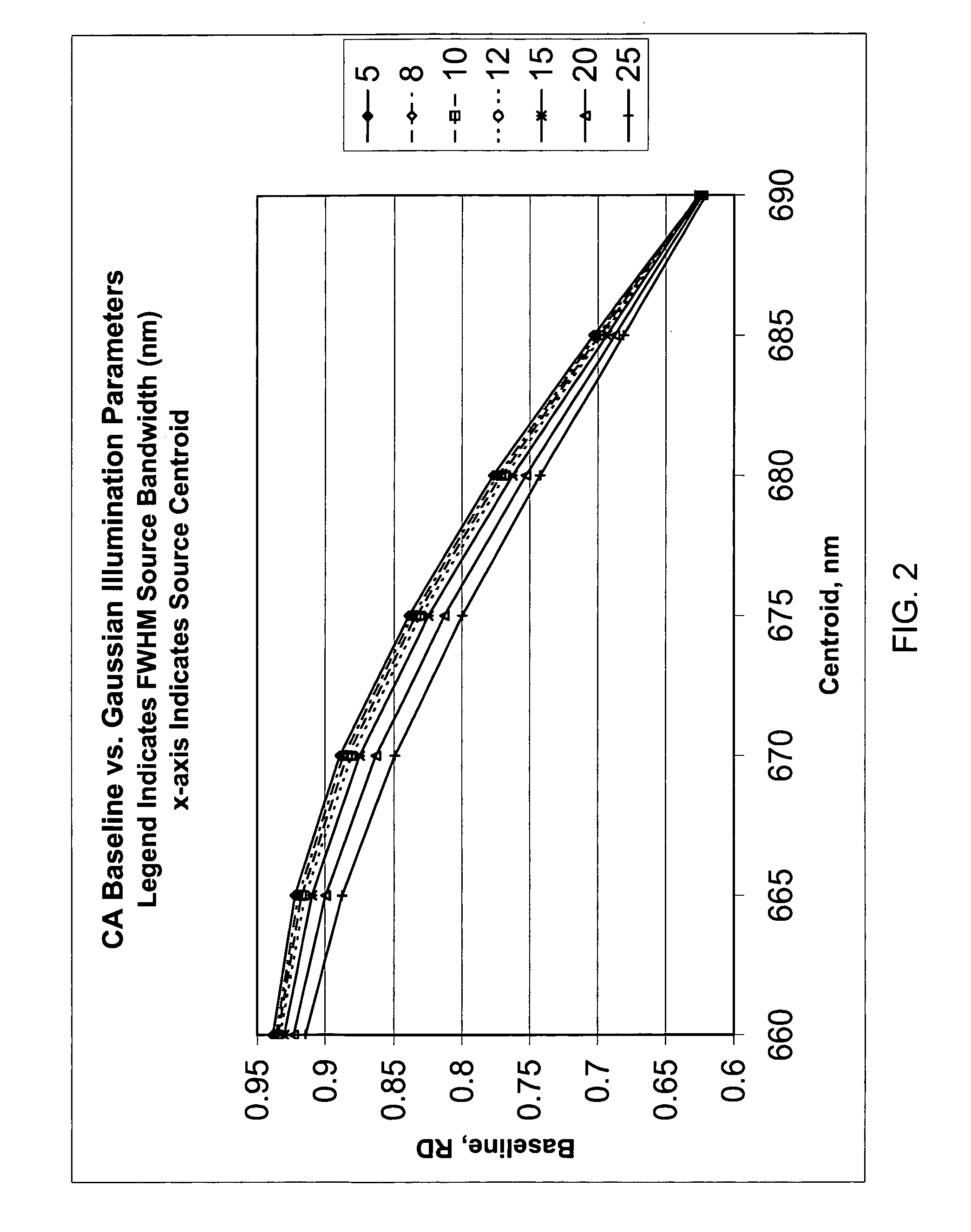
Method for calibrating clinical chemistry instruments
ActiveUS20100268504A1Avoid disadvantagesTesting/calibration apparatusScattering properties measurementsClinical chemistryLength wave
A method of deriving correction for instrument-to-instrument variations in the illumination band centroid wavelengths and wavelength band shapes of the optical systems of clinical chemistry instruments includes the steps of determining the centroid wavelength and wavelength band shape of a light source used in the optical system of a clinical chemistry instrument to provide a determined wavelength band shape and centroid wavelength, comparing the determined wavelength band shape and centroid wavelength with a known reflection density or absorbance wavelength spectrum of a specific type of chemical reagent test to provide a correction value, and calculating the correction value, which is to be used to modify a reflection density or absorbance measurement taken by the instrument of a reagent test of the a specific type of chemical reagent test.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Detection kit based on Trinder reaction and application of detection kit
InactiveCN111808921AAvoid interferenceAvoid introducingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisClinical chemistryPeroxidase
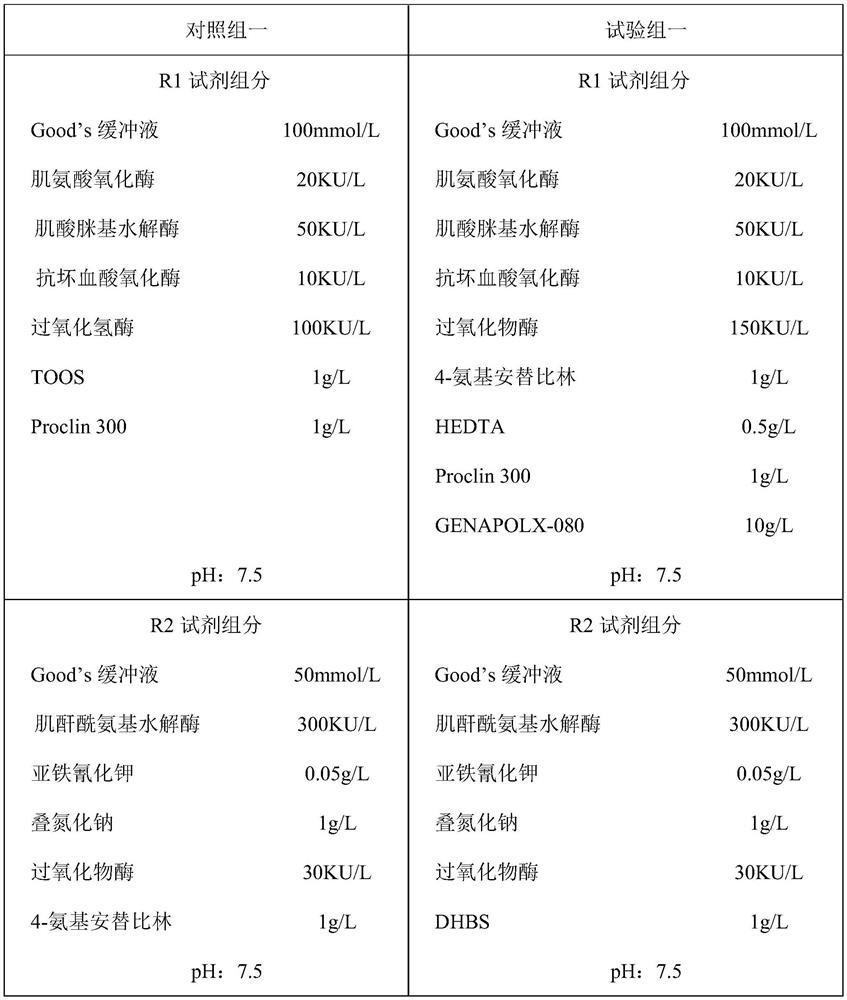
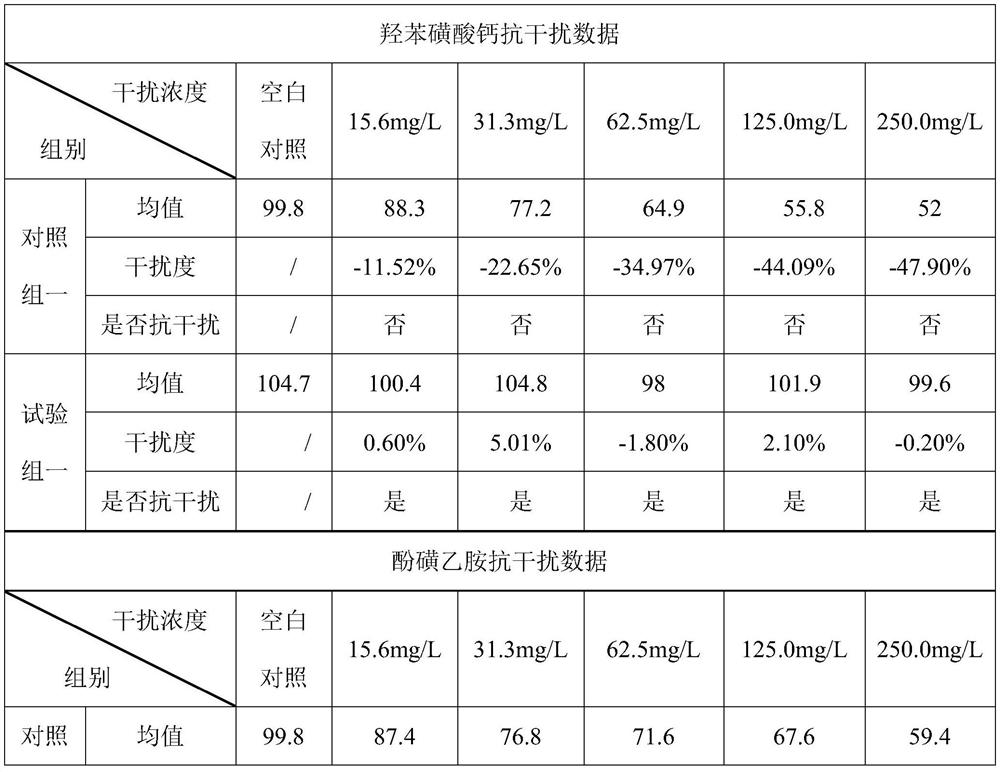
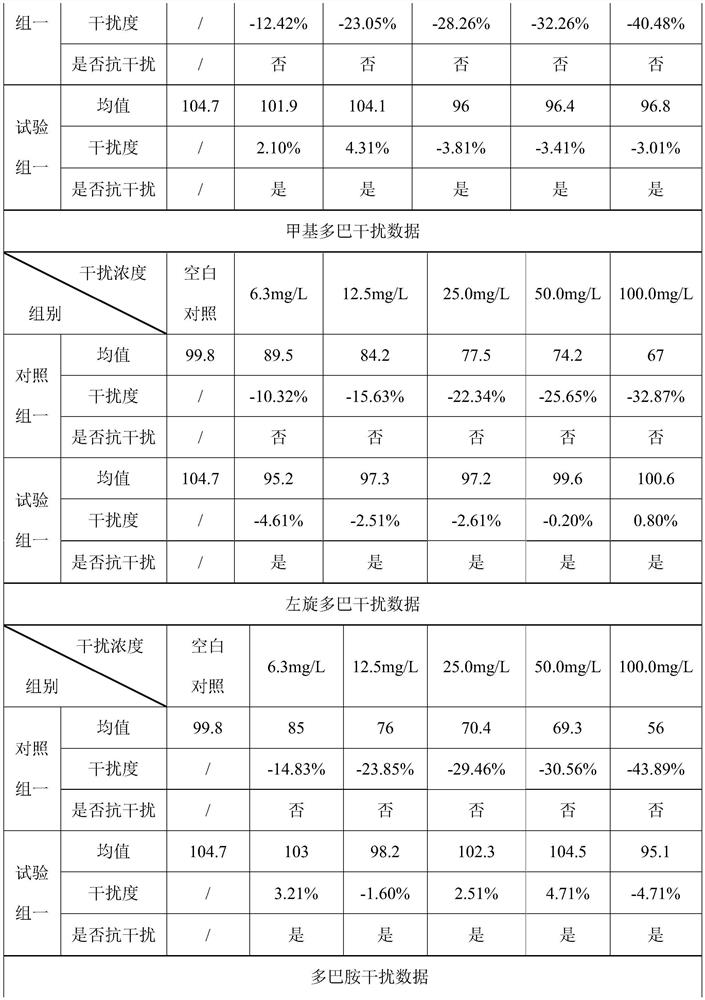
The invention discloses a detection kit based on Trinder reaction and application of the detection kit. The invention belongs to the technical field of clinical chemical detection. The kit consists ofa reagent R1 and a reagent R2, wherein the R1 reagent and the R2 reagent contain enzymes for catalyzing a to-be-detected object to generate hydrogen peroxide, the reagent R1 further contains a buffersolution, a preservative and peroxidase, the reagent R2 contains a buffer solution, a preservative, peroxide and a chromogen substrate, the concentration of peroxidase in the reagent R1 is 100-150 KU / L, and the reagent R1 further contains 4-aminoantipyrine with the concentration of 0.5-1 g / L. the peroxidase and the 4-aminoantipyrine in the reagent R1 can be used for removing clinical drugs capable of participating in the Trinder reaction in a to-be-detected object before the Trinder reaction, so that a detection result is more accurate. According to the invention, other substances do not needto be additionally added into a reaction system, and other impurities cannot be introduced; the method is simple and efficient, can be widely applied to various clinical chemical detections, avoids the interference of clinical drugs, enhances the accuracy of detection results, and also improves the functional sensitivity of the kit.
Owner:WUHAN LIFE ORIGIN BIOTECH LTD
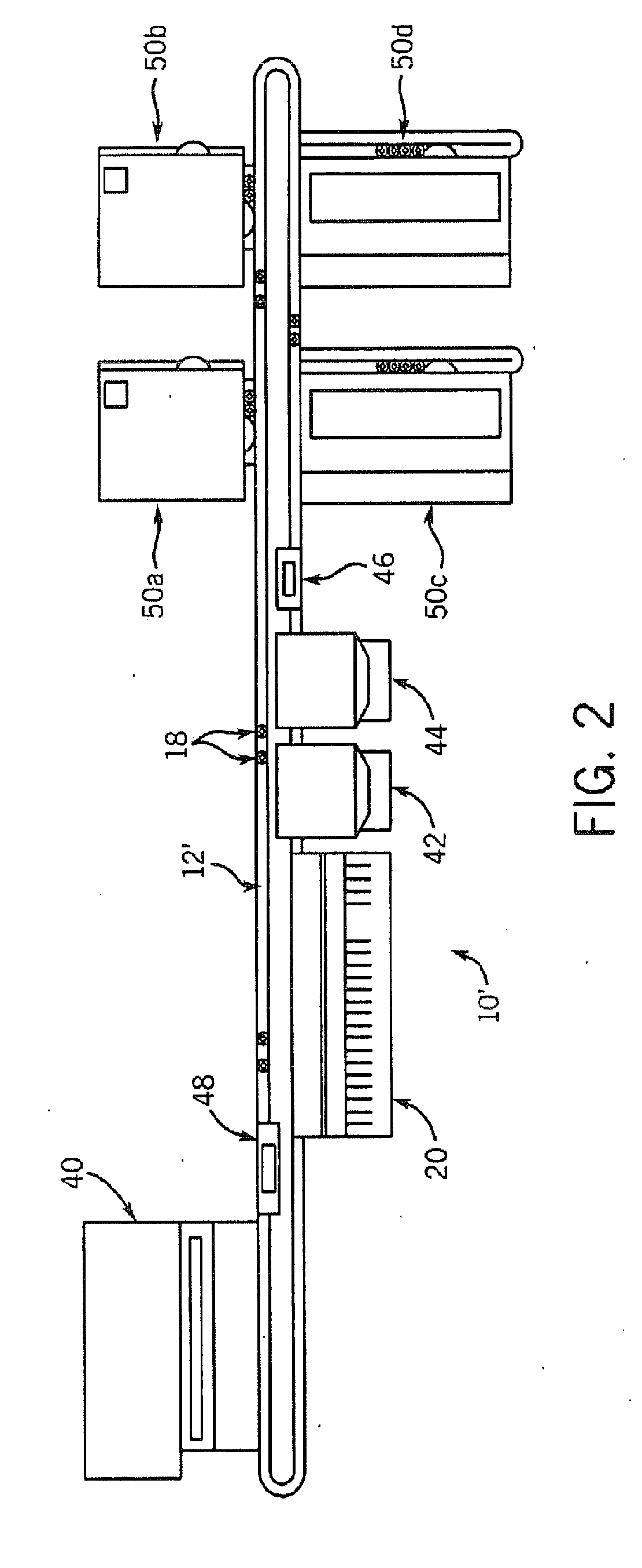
System and Method for Processing Both Clinical Chemistry and Immunoassay Tests
InactiveUS20140271369A1Analysis by electrical excitationBiological testingClinical chemistryImmunochemistry assay
Disclosed herein are instruments, systems and methods for performing automated integrated analysis of both clinical chemistry assay and immunoassay tests on a sample. The system includes a common process subsystem module; a clinical chemistry analyzer module; an immunoassay analyzer module; and a plurality of additional modules. The common process subsystem module is configured to position one or more reaction vessels containing aliquots of the sample for analysis by the clinical chemistry analyzer module, the immunochemistry analyzer module or both analyzer modules. The included immunochemistry analyzer module of the instrument and system is configured to perform multiplex FRET analysis on homogeneous solutions, thereby increasing the flexibility, throughput and robustness of the resultant instrument and systems.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Analyzer with automatically actuated movable closure of pipetting openings
InactiveCN101256192AIncrease manufacturing costEliminate or at least substantially reduce the amount of water vaporLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisClinical chemistryEngineering
A clinical chemistry analytical apparatus for automatically analyzing a plurality of biological fluids samples is disclosed. The apparatus provides a movable cover having a pipetting opening which allows insertion of a pipetting needle therethrough, a closure mechanism which in a first state closes the pipetting opening and in a second state leaves it open, a conveyor automatically transporting a reagent container to a pipetting position, at which an opening of the reagent container is aligned with the pipetting opening, and an actuation mechanism which automatically brings the closure mechanism into the second state before introducing the pipetting needle through the pipetting opening and which brings the closure mechanism into the first state after withdrawal of the pipetting needle from the pipetting opening. The actuation mechanism is adapted to actuate the closure mechanism by a displacement of a transport device that moves the pipetting needle to and from at least one pipetting position.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Use of Two-Photon Excited Fluorescence in Assays of Clinical Chemistry Analytes
ActiveUS20070287186A1Chemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingChemical reactionData treatment
The invention relates to an in vitro diagnostic method for quantification of a clinical chemistry analyte from a clinical sample wherein the clinical chemistry analyte undergoes a chemical reaction or reactions with a reagent or reagents in one or several steps, or in a reaction sequence, or catalyses a chemical reaction, or reactions, or a reaction in a reaction sequence of a reagent or reagents, in one or several steps, in a reaction system. The reaction or reactions or reaction sequence result in a change of a measurable property of a compound or compounds of said reaction or reactions or reaction sequence. Characteristic for the method is that said chemical reaction or reactions or reaction sequence results in formation of a two-photon fluorescent compound, or a change in two-photon fluorescence properties of the reaction system comprising at least one two-photon fluorescent compound, and the analyte is quantified by exciting said two-photon fluorescent compound or compounds and measuring two-photon exited fluorescence, and relating said measured fluorescence to method standardization data based on measurements obtained from reference material of said analyte. The present invention also relates to use of a fluorometric device employing two-photon fluorescence excitation for quantification of a clinical chemistry analytes. The present invention further relates to a system for quantification of clinical chemistry analytes from samples containing the analyte. Characteristic for the system is that it comprises a fluorometric device employing two-photon excited fluorescence for quantifying one or several clinical chemistry analytes, and a data processing unit with software for dedicated data reduction for quantification of the analyte or analytes using said fluorometric device. The present invention further relates to a software product for the system.
Owner:ARCTIC DIAGNOSTICS
Method for calibrating clinical chemistry instruments
ActiveUS8949059B2Avoid disadvantagesTesting/calibration apparatusScattering properties measurementsClinical chemistryAbsorbance
A method of deriving correction for instrument-to-instrument variations in the illumination band centroid wavelengths and wavelength band shapes of the optical systems of clinical chemistry instruments includes the steps of determining the centroid wavelength and wavelength band shape of a light source used in the optical system of a clinical chemistry instrument to provide a determined wavelength band shape and centroid wavelength, comparing the determined wavelength band shape and centroid wavelength with a known reflection density or absorbance wavelength spectrum of a specific type of chemical reagent test to provide a correction value, and calculating the correction value, which is to be used to modify a reflection density or absorbance measurement taken by the instrument of a reagent test of the a specific type of chemical reagent test.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
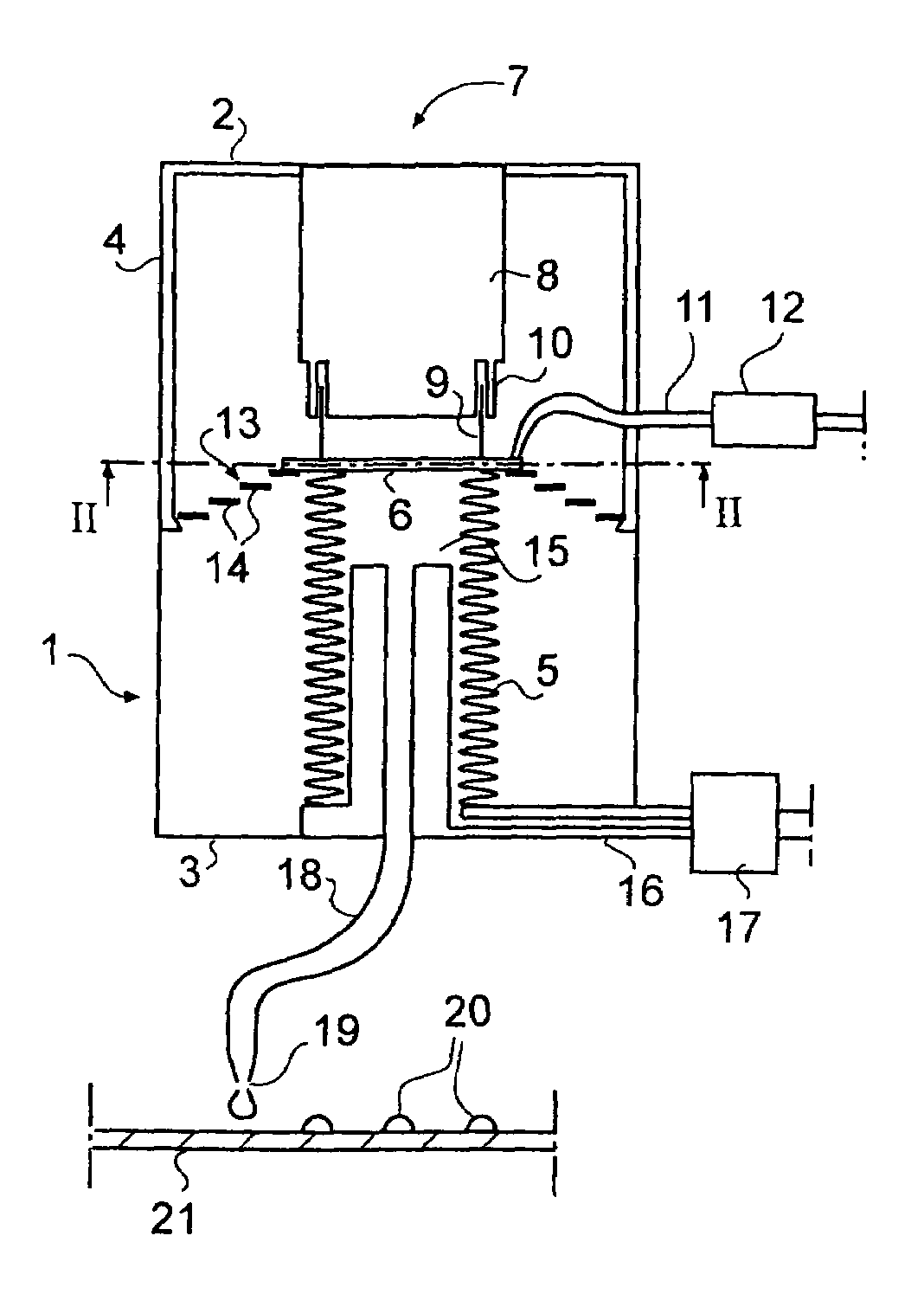
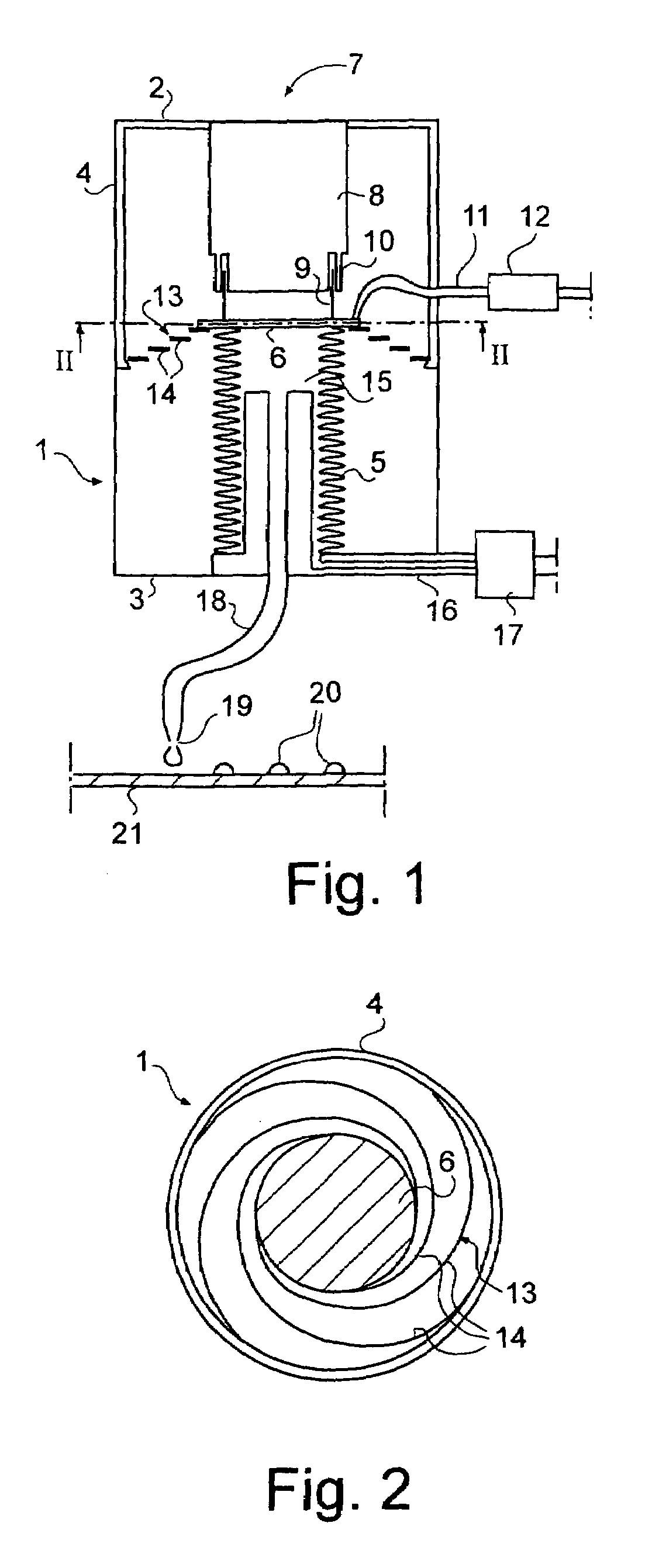
Quantitative dosing of small amounts of liquids
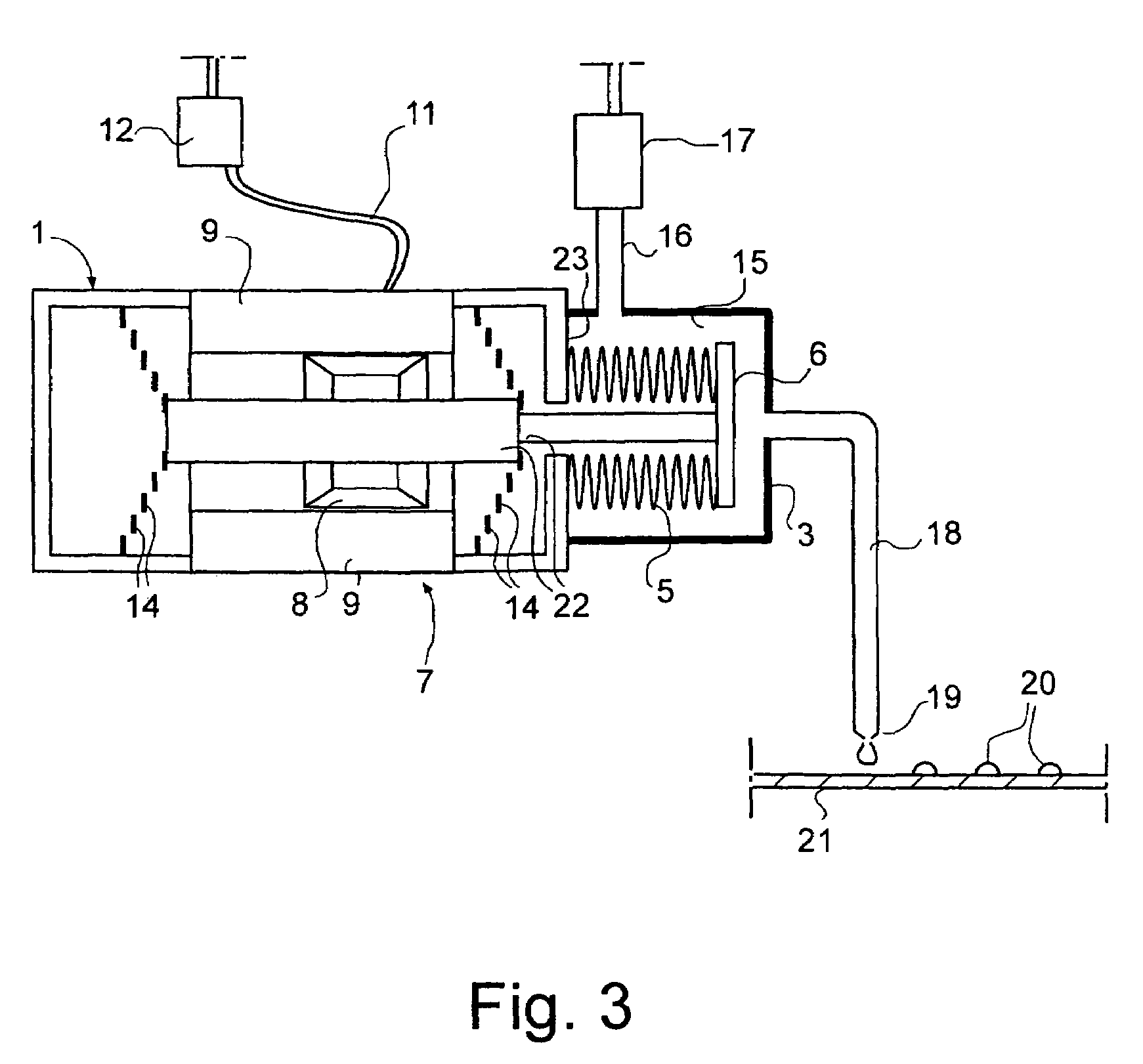
InactiveUS7316336B2Increase heightEasy to separateSamplingContracting/expanding measuring chambersClinical chemistrySmall droplet
The invention relates to quantitative dosing of small amounts of liquids having a volume of microliter or nanoliter order. Such a dosing technique is useful for instance for productive serial dosing in applications of clinical chemistry. In dosing device of the invention, flexible bellows (5) attached to a body (1) define a liquid space (15) filled with a liquid to be dosed and communicate with a dosing tip (19). The bellows (5) are provided with an actuator (7) for operation thereof, constricting the liquid space to cause a liquid dose to be discharged from the dosing tip. The invention is further directed to a dosing method based on movements of bellows moved by a magnetic actuator, and to a method wherein liquid is dosed as individual small droplets from the dosing tip by first accelerating and then by slowing down the motion of the bellows by means of the actuator.
Owner:FLUILOGIC OYU
Detection method and kit for quantitatively detecting anti-cyclic guanidine polypeptide antibody
PendingCN111208303AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityDisease diagnosisBiological testingClinical chemistryAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to a detection method and a kit for quantitatively detecting an anti-cyclic guanidine polypeptide antibody. The method for enhancing competitive turbidimetry by latex is adopted,An anti-cyclic citrulline polypeptide antibody in a to-be-detected sample and latex microspheres coated with antibodies in a reagent compete to be combined with cyclic guanidine acid polypeptide in the reagent, an absorbance value of the reagent is measured through a 500-700 nm wavelength spectrophotometric method, and a concentration value of the anti-cyclic guanidine acid antibody in the to-be-detected sample is calculated according to the attenuation amount of the absorbance value. The method is advantaged in that a linear range of the anti-cyclic guanidine acid antibody measured by the method can reach 7-500U / L, moreover, the kit is not interfered by rheumatoid arthritis and the like, and detection performance of the reagent can reach consistency of ELISA and electrochemical luminescence immunoassay. The detection kit of the method is high in sensitivity, good in specificity and suitable for a clinical chemical analyzer, moreover, detection cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:叶卫玲
Messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) level in-situ hybridization detection kit for neoplasia early stage of intracranial glioma, and detection method and application
InactiveCN102559881AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeImmune complex deposition
The invention discloses an in-situ hybridization detection kit which comprises a hybridization probe and a marker, and a method for performing n-situ hybridization detection on messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) of a circulating immune complex (CIC), which is closely related with the pathologic evolution of the early stage of intracranial glioma by using the kit. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) contacting RNA to be detected in substrate and a hybridization probe under the condition that the hybridization probe and a target sequence can form a stable hybridization complex to form the hybridization complex; and (2) detecting the hybridization complex. By the kit and the detection method, the gen expression level can be detected at the mRNA level; the obtained detection index is earlier than the detection indexes of medical imaging and the conventional clinical chemistry; real mRNA-level screening of the earlier stage of canceration can be realized; and meanwhile, the detection method is simple and convenient, and low in cost, and can be conveniently popularized and applied in county hospitals.
Owner:NATUREGEN BIOTECH SHANGHAI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com