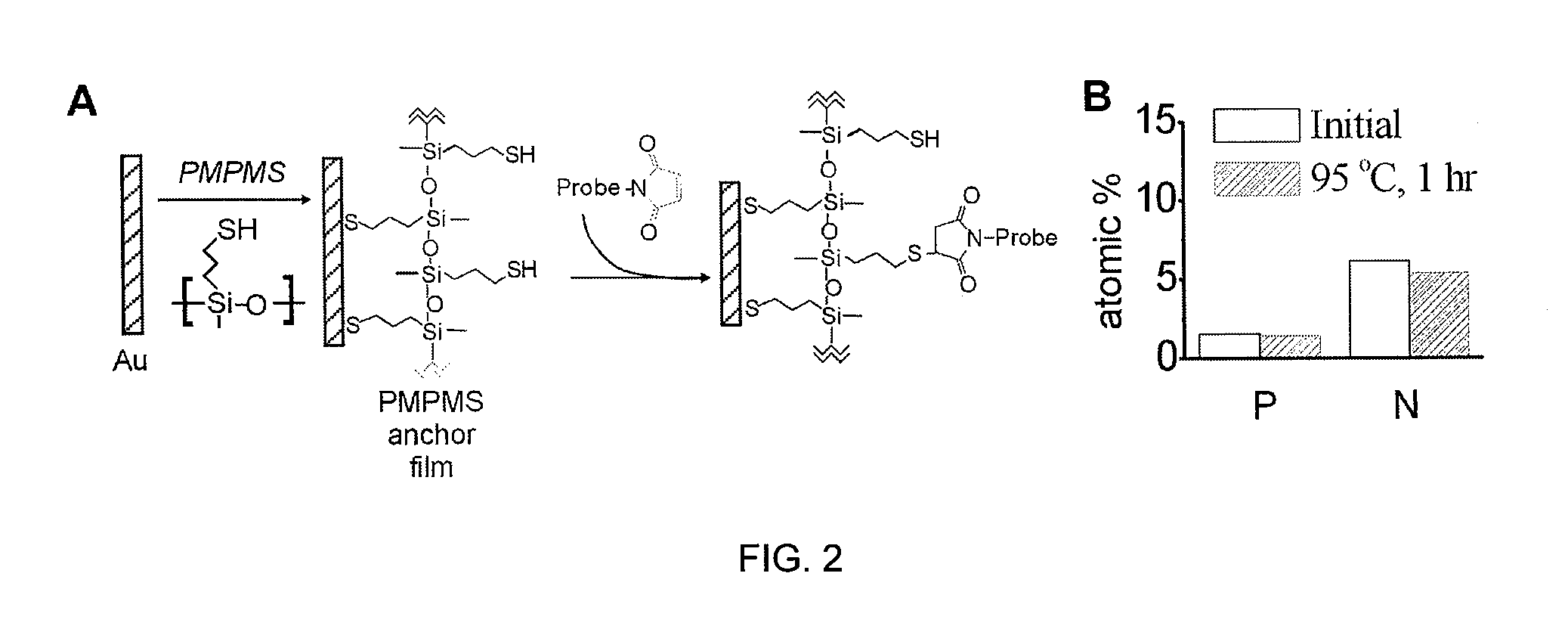
Patents
Literature
91 results about "Nucleic acid assay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
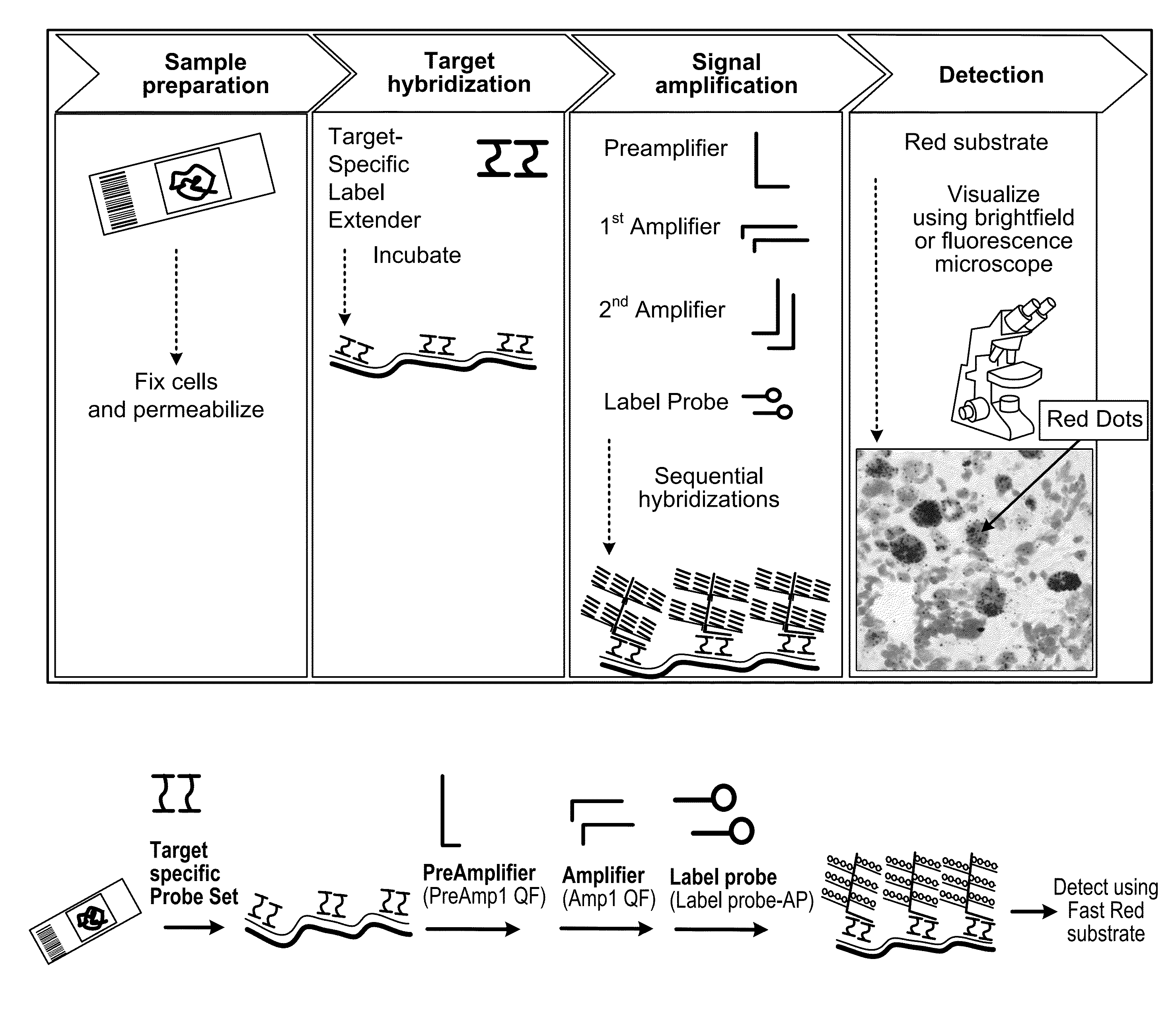
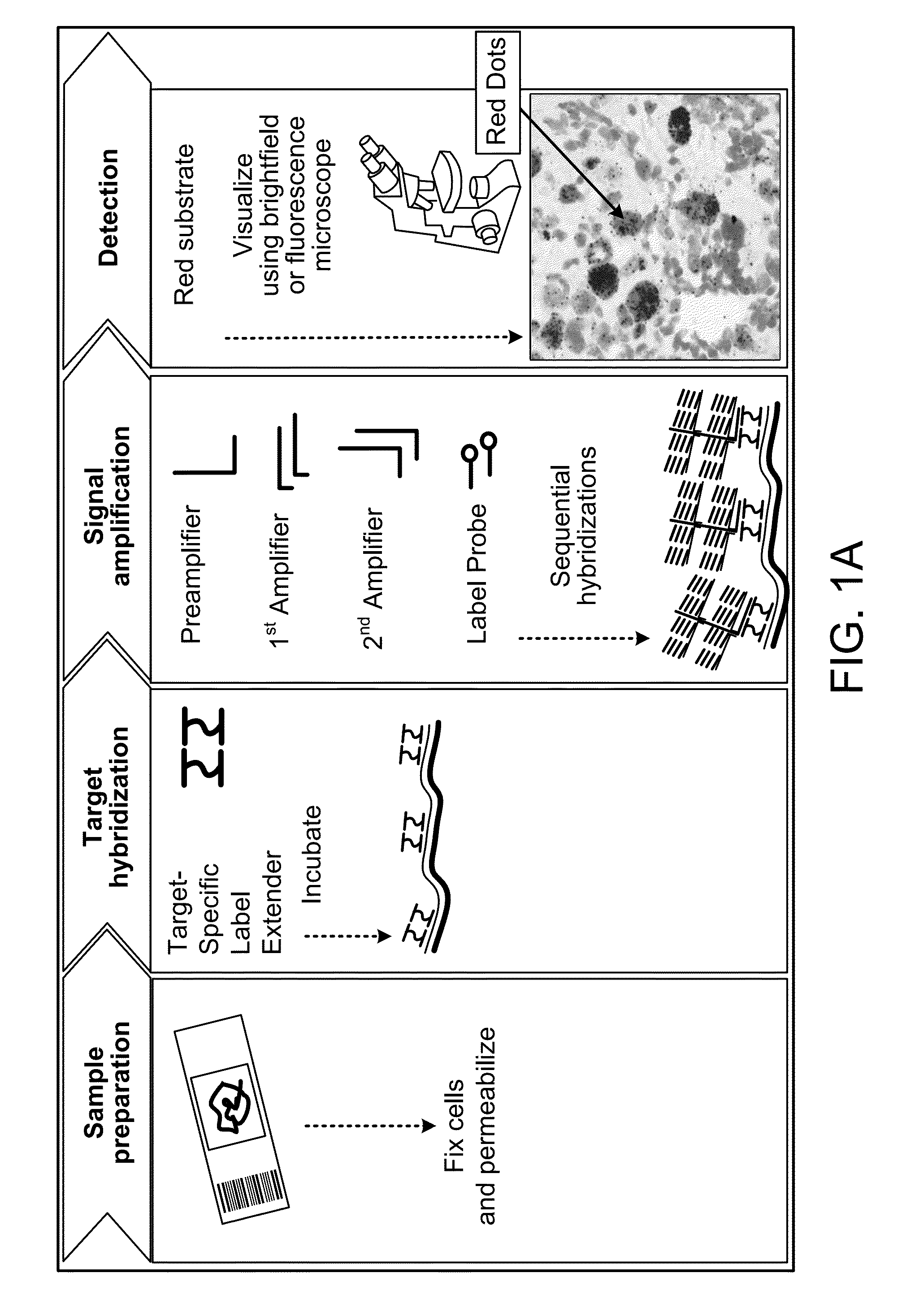
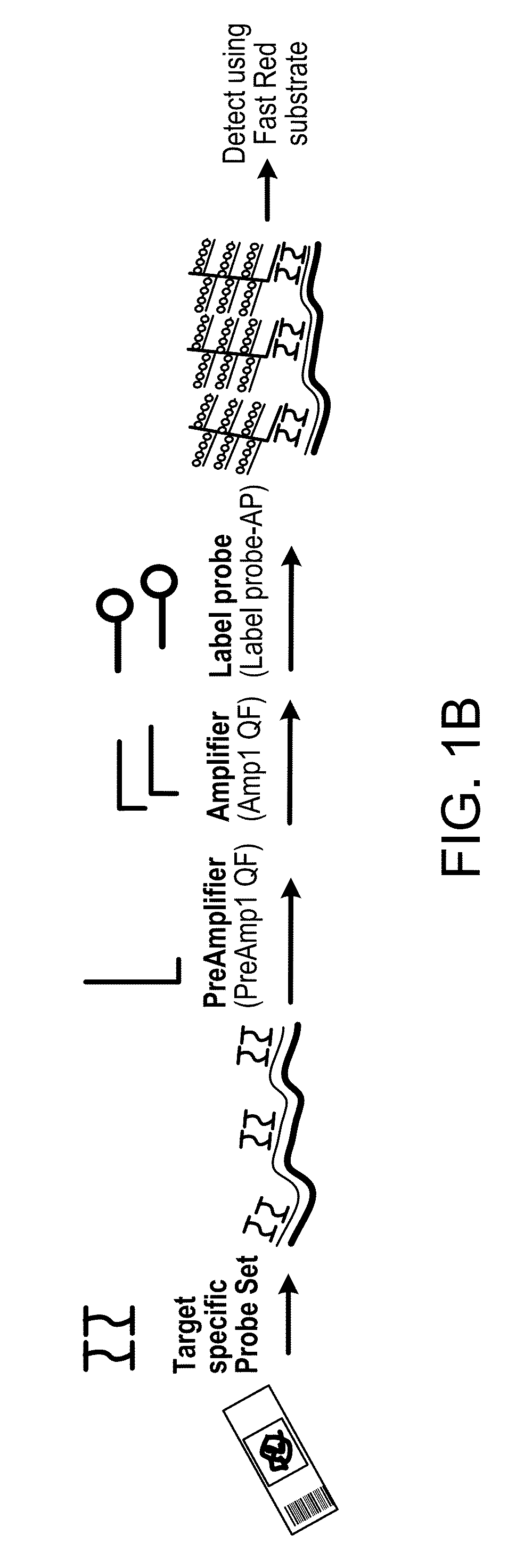
In biology, a branched DNA assay is a signal amplification assay (as opposed to a target amplification assay) that is used to detect nucleic acid molecules.
Integrated nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS20090148933A1Reduce pervasive dangerEasy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusCancer cellAssay
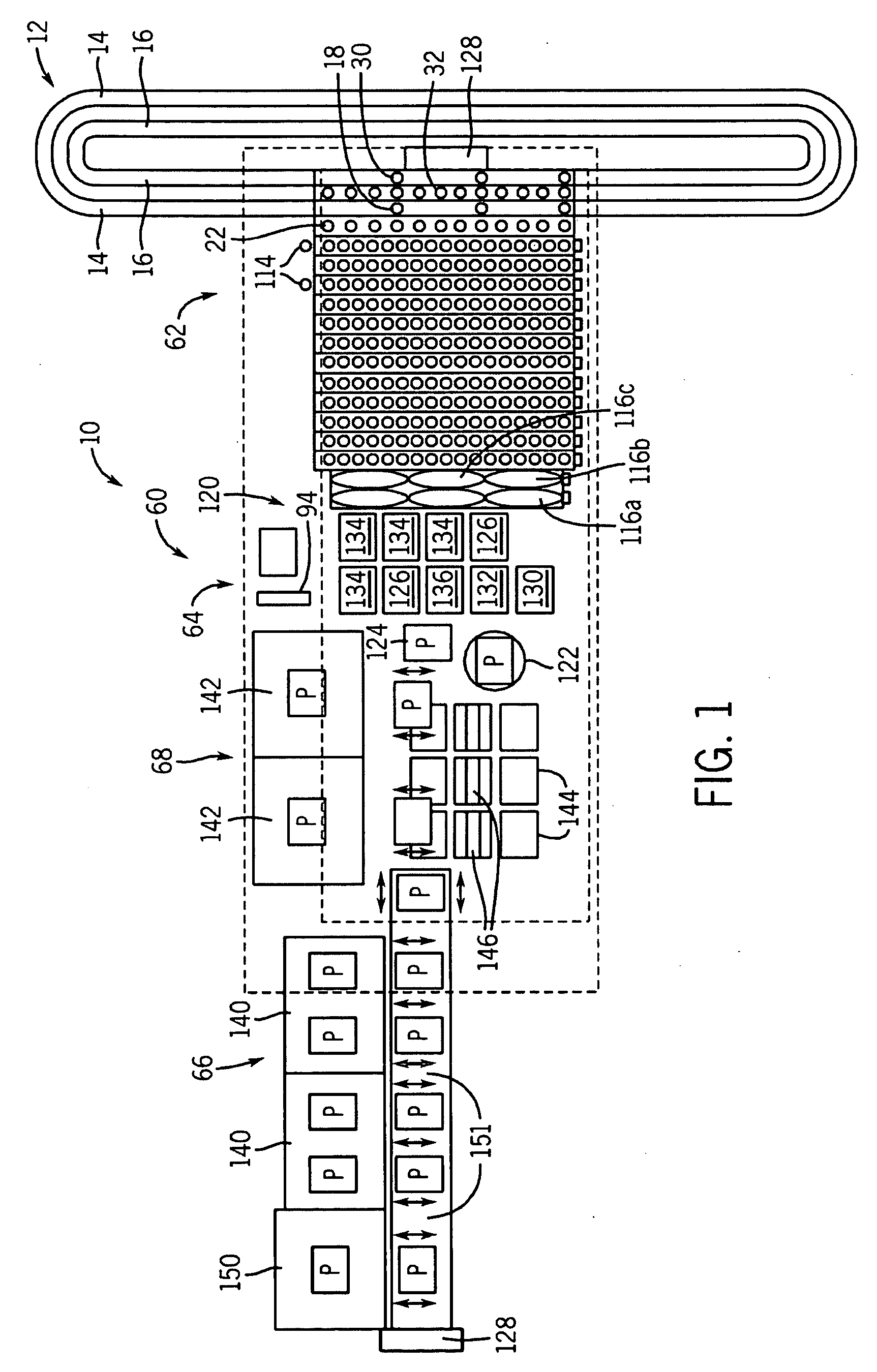
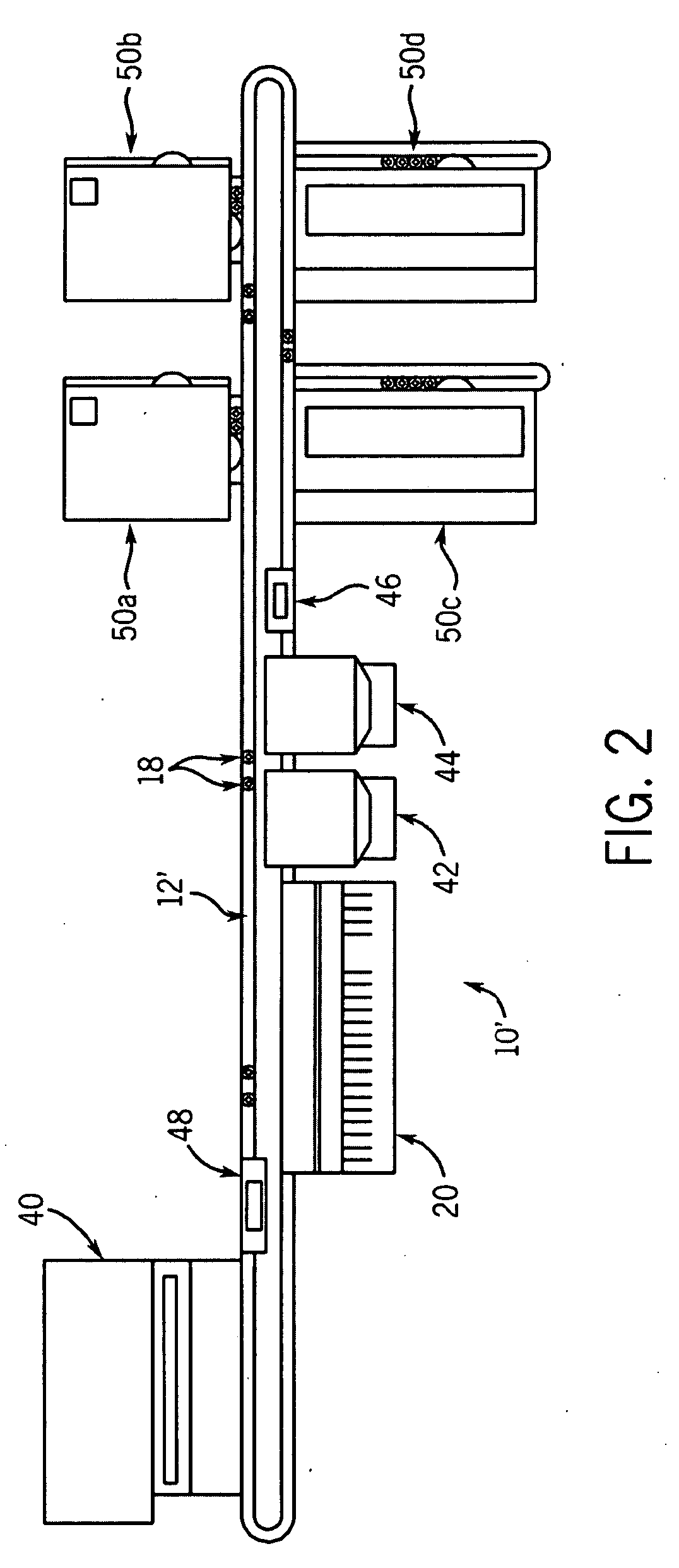
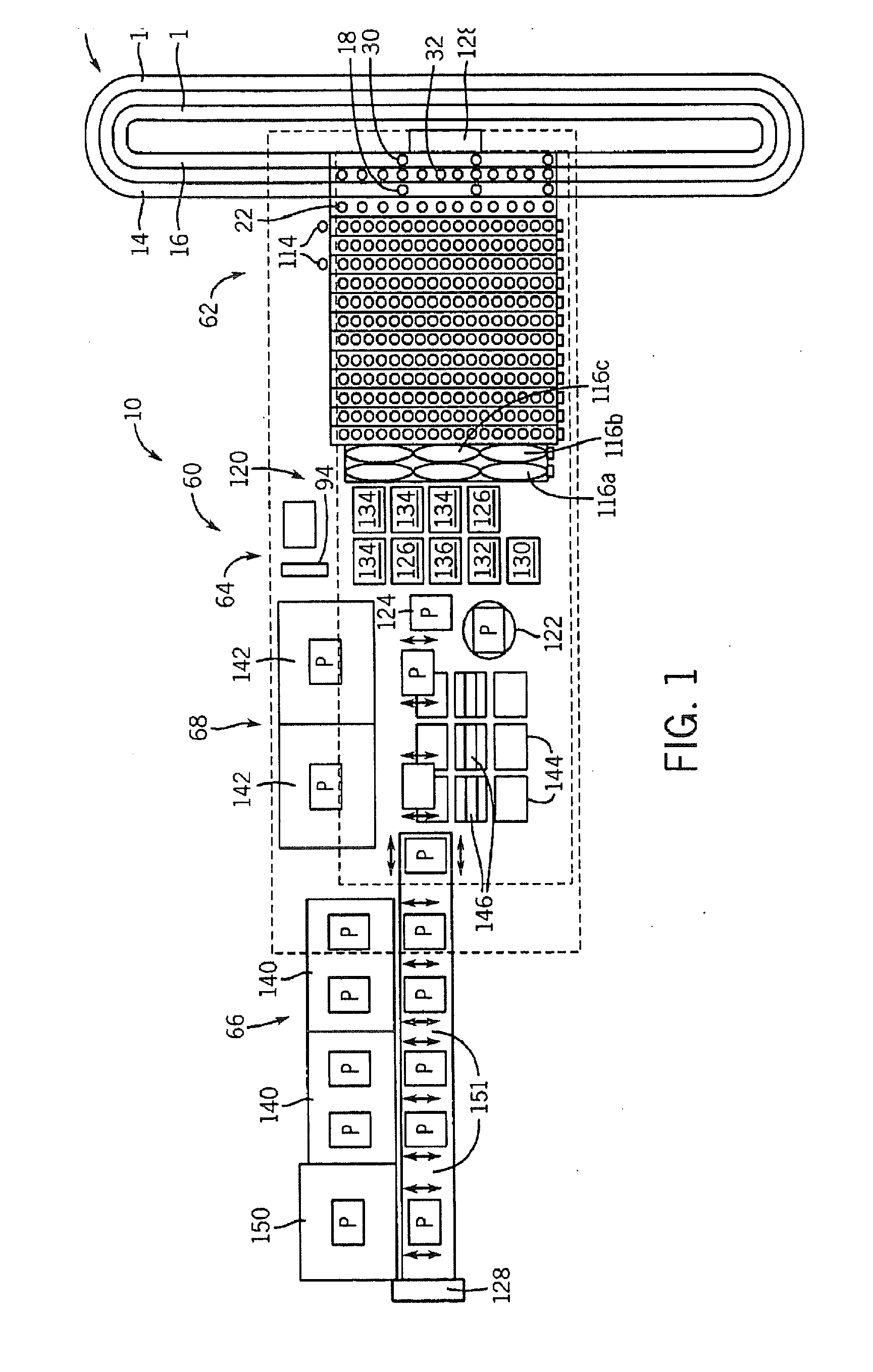
Integrated microfluidic cartridges for nucleic acid extraction, amplification, and detection from clinical samples are disclosed. The devices are single-entry, sanitary, and disposable. The devices enable simplex or multiplex nucleic acid target detection, as for example: assay panels for multiple infectious agents, or assay panels for cancerous cell types. Methods for use of microfluidic cartridges in a fully automated, pneumatically controlled apparatus are also disclosed.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Automated analyzer for clinical laboratory
InactiveUS20090117620A1Manual loadingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClinical chemistryMicro perforated plate
A laboratory automation system that is capable of carrying out clinical chemistry assays, immunoassays, amplification of nucleic acid assays, and any combination of the foregoing, said laboratory automation system employing at least one of micro-well plates and deep multi-well plates as reaction vessels. The use of micro-well plates as reaction vessels enables the laboratory automation system to assume a variety of arrangements, i.e., the laboratory automation system can comprise a variety of functional modules that can be arranged in various ways. In order to effectively carry out immunoassays by means of micro-well plates, a technique known as inverse magnetic particle processing can be used to transfer the product(s) of immunoassays from one micro-well of a micro-well plate to another.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Integrated nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS8222023B2Reduce pervasive dangerEasy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusCancer cellInfectious agent
Integrated microfluidic cartridges for nucleic acid extraction, amplification, and detection from clinical samples are disclosed. The devices are single-entry, sanitary, and disposable. The devices enable simplex or multiplex nucleic acid target detection, as for example: assay panels for multiple infectious agents, or assay panels for cancerous cell types. Methods for use of microfluidic cartridges in a fully automated, pneumatically controlled apparatus are also disclosed.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Materials and methods for detection of nucleic acids
InactiveUS7422850B2Avoid and reduce problem and concernMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LSingle strand
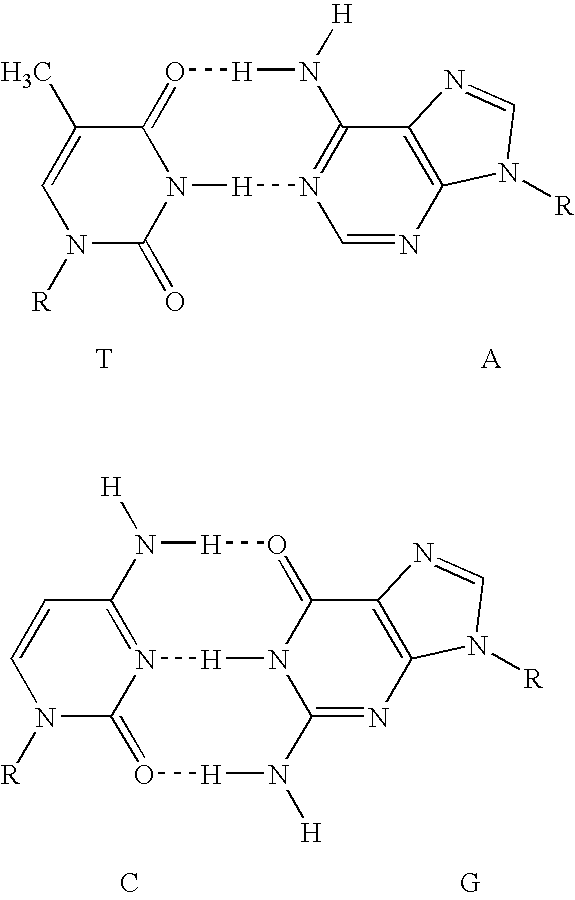
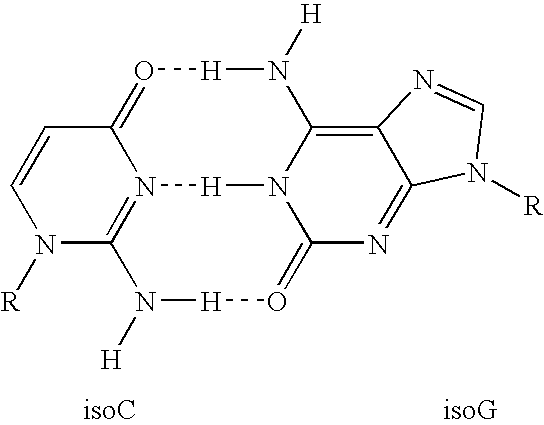
Assays using non-natural bases are described. In one embodiment, the method involves contacting a sample suspected of containing the target nucleic acid with a polymerase and first and second primers; amplifying the target nucleic acid, if present in the sample, by PCR using the first and second primers to generate an amplification product having a double-stranded region and a single-stranded region that comprises the non-natural base; contacting the sample with a reporter comprising a label and a non-natural base that is complementary to the non-natural base of the single-stranded region; annealing at least a portion of the reporter to the single-stranded region of the amplification product; cleaving, after annealing, at least a portion of the reporter to release at least one reporter fragment; and correlating the release of the at least one reporter fragment with the presence of the target nucleic acid in the sample. The invention also provides corresponding kits for use in detecting target nucleic acids in a sample. Alternatively, the reporter can be incorporated into the amplification product rather than annealing and then cleaving.
Owner:LUMINEX
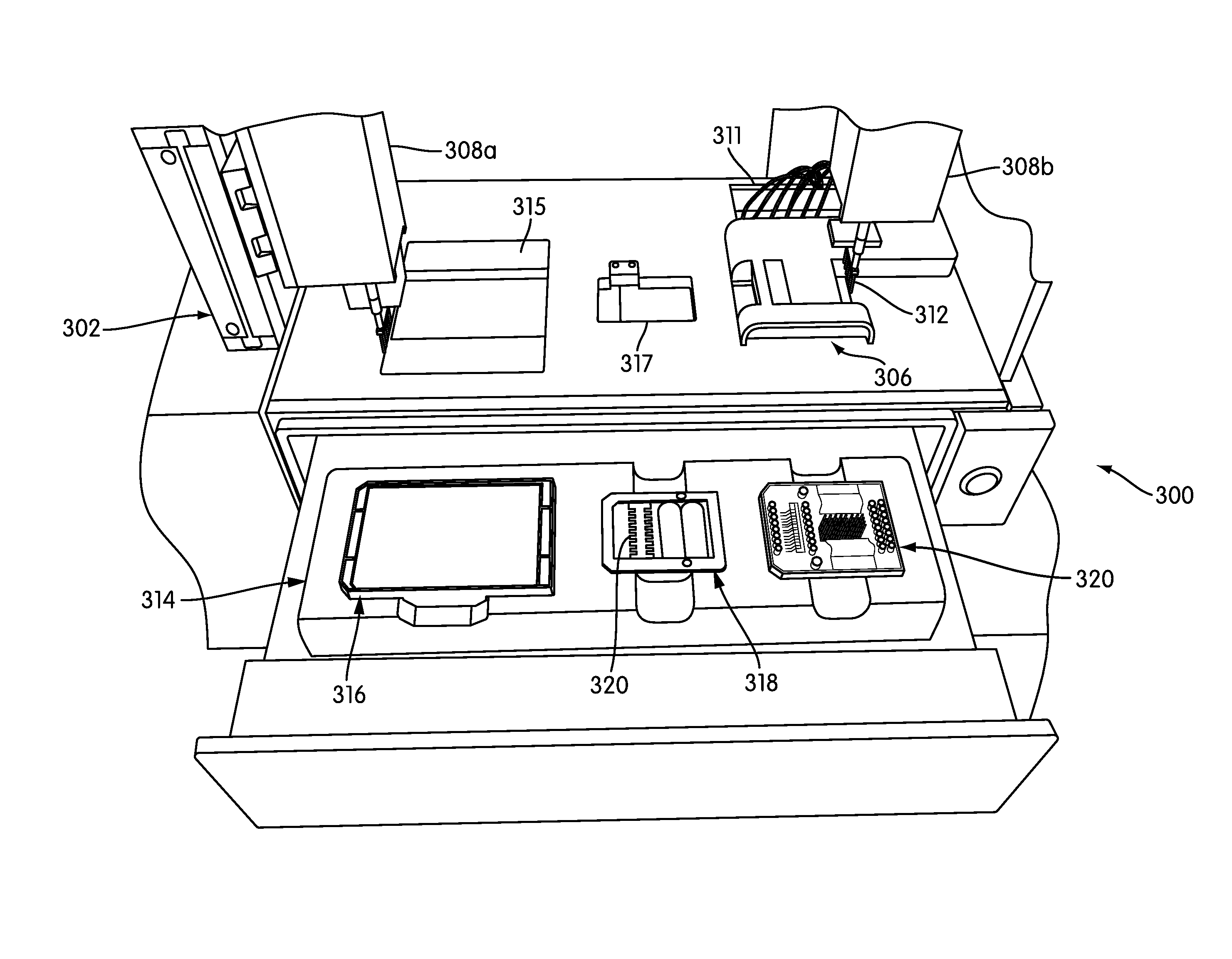
System and method for serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS20120052560A1Rapid serial processingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHandling systemData store
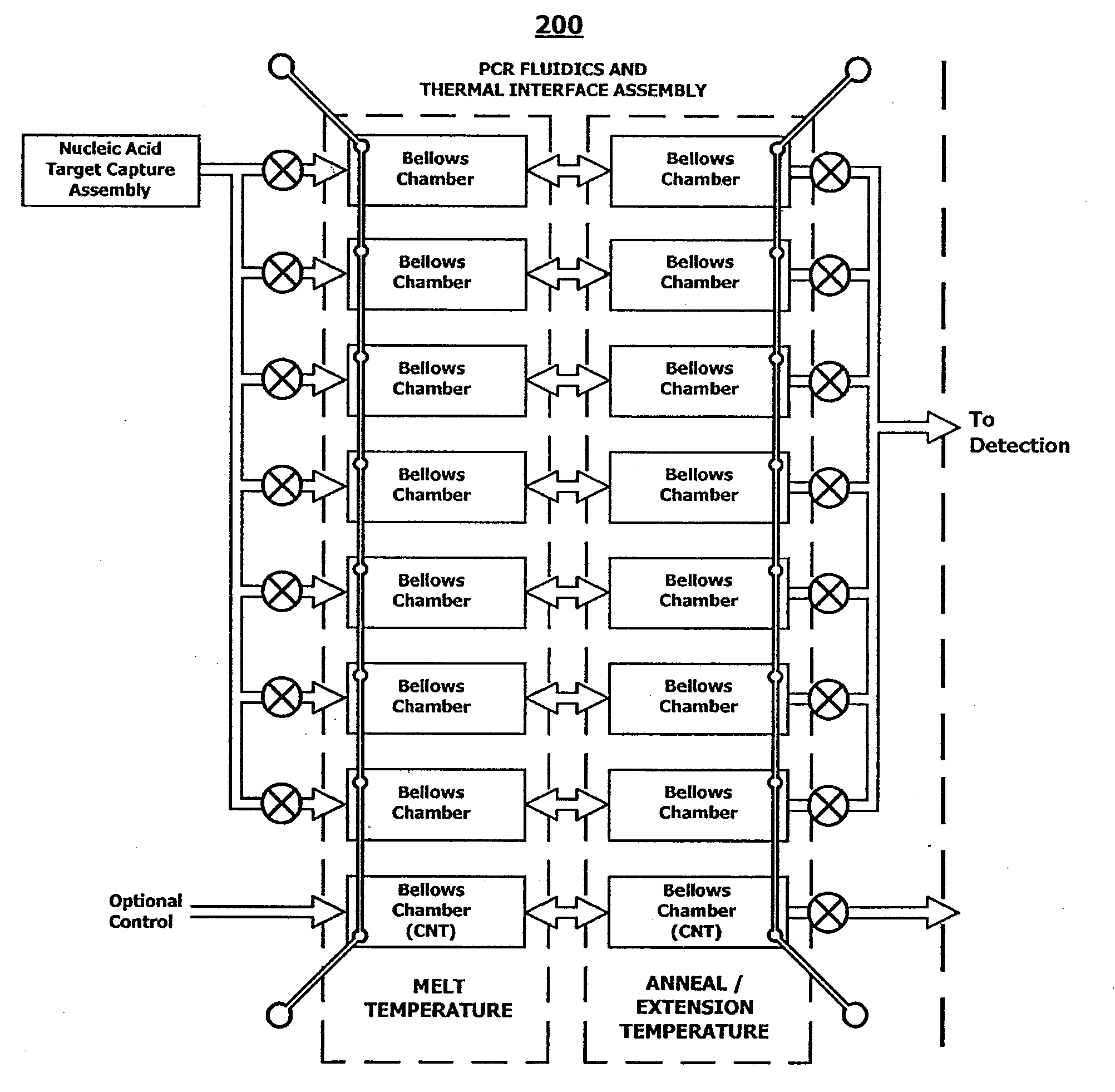
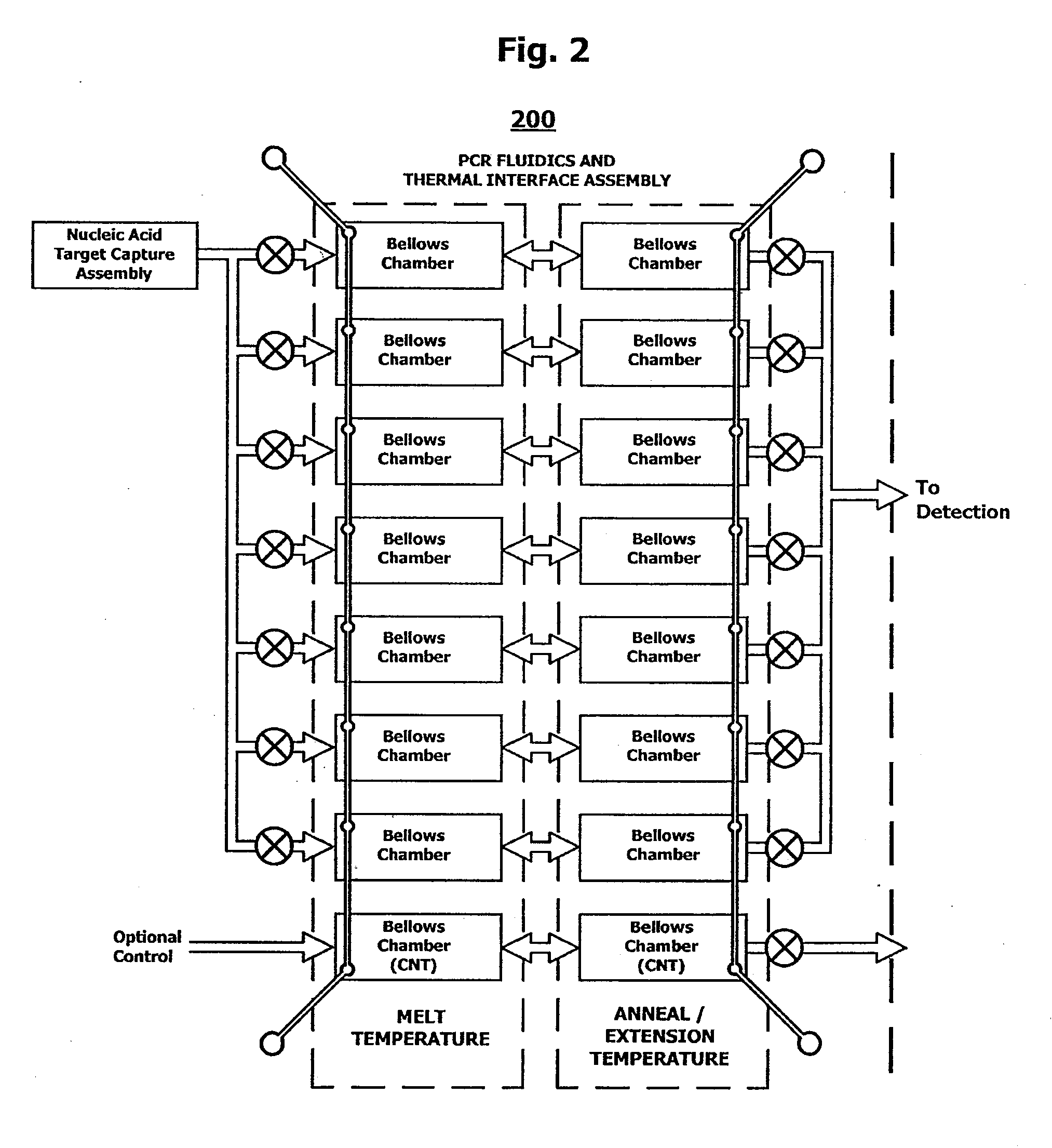
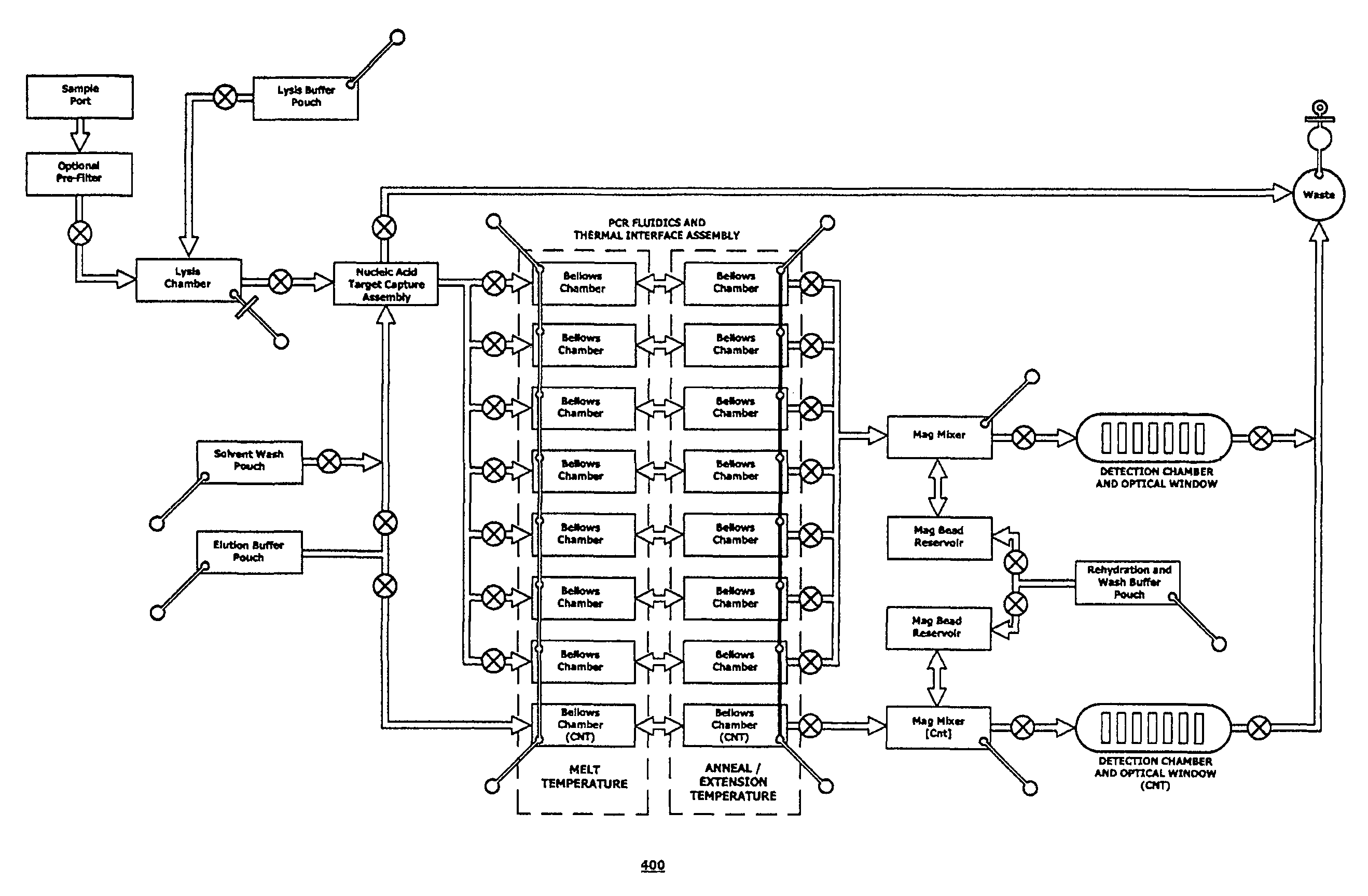
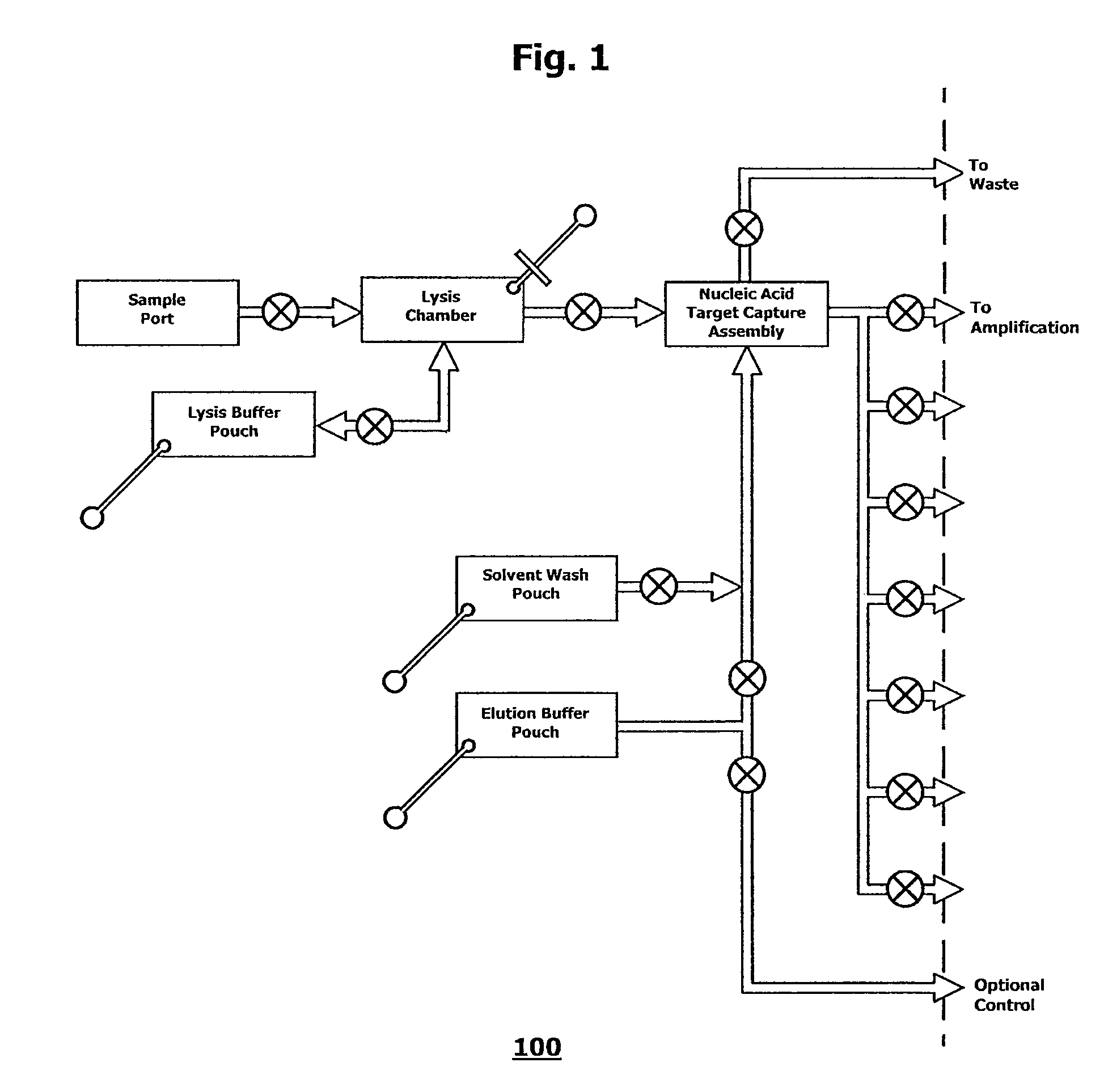
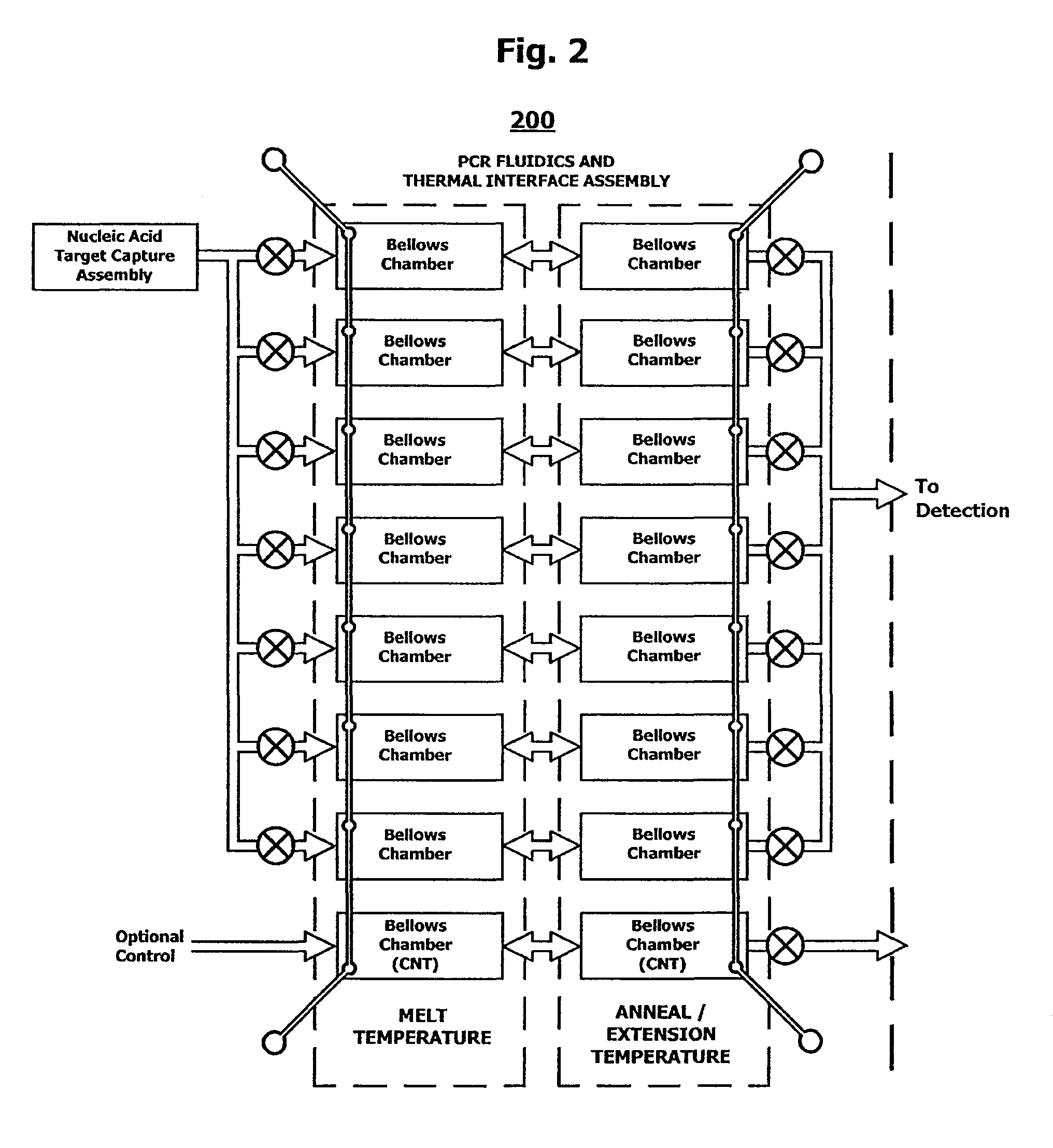
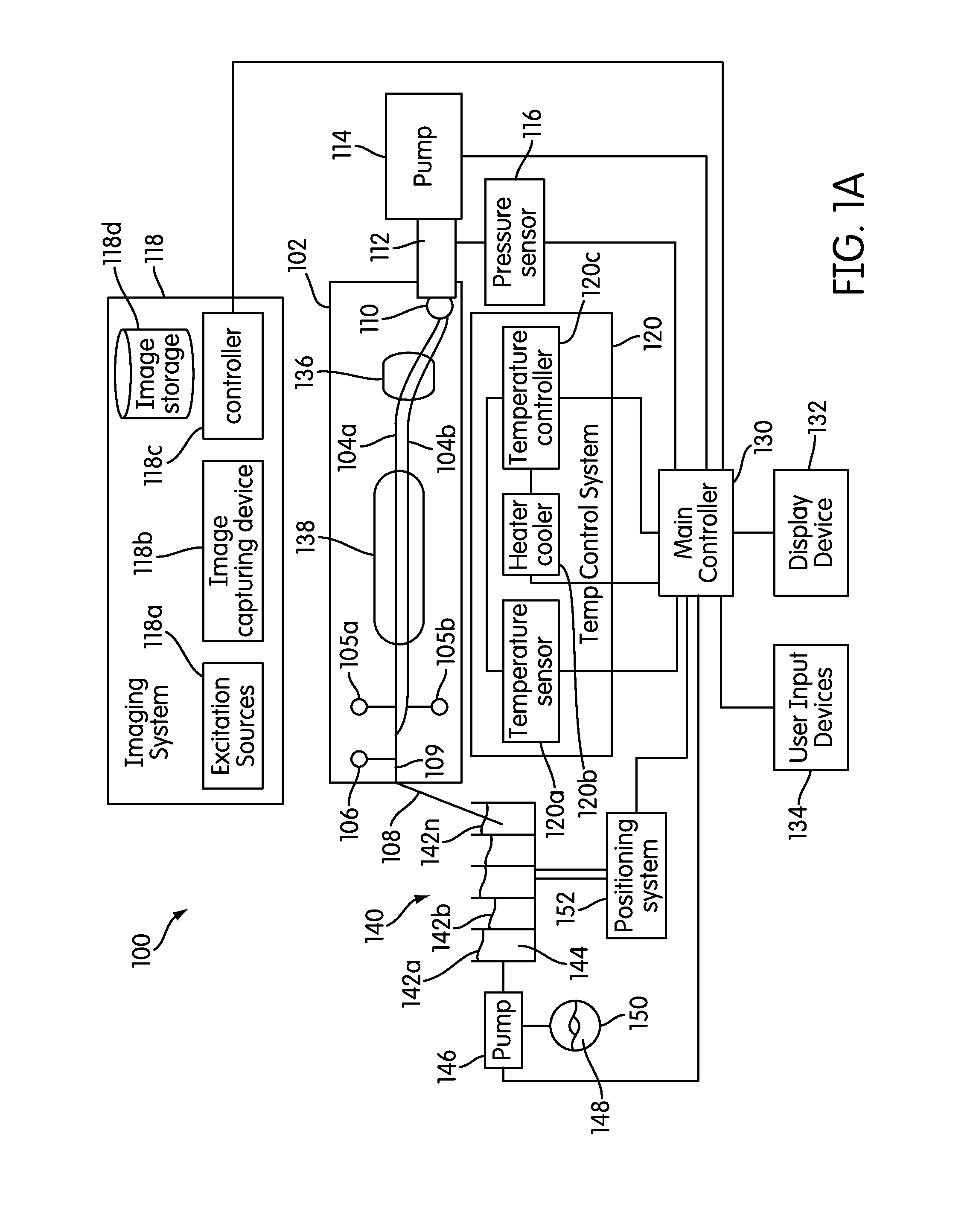
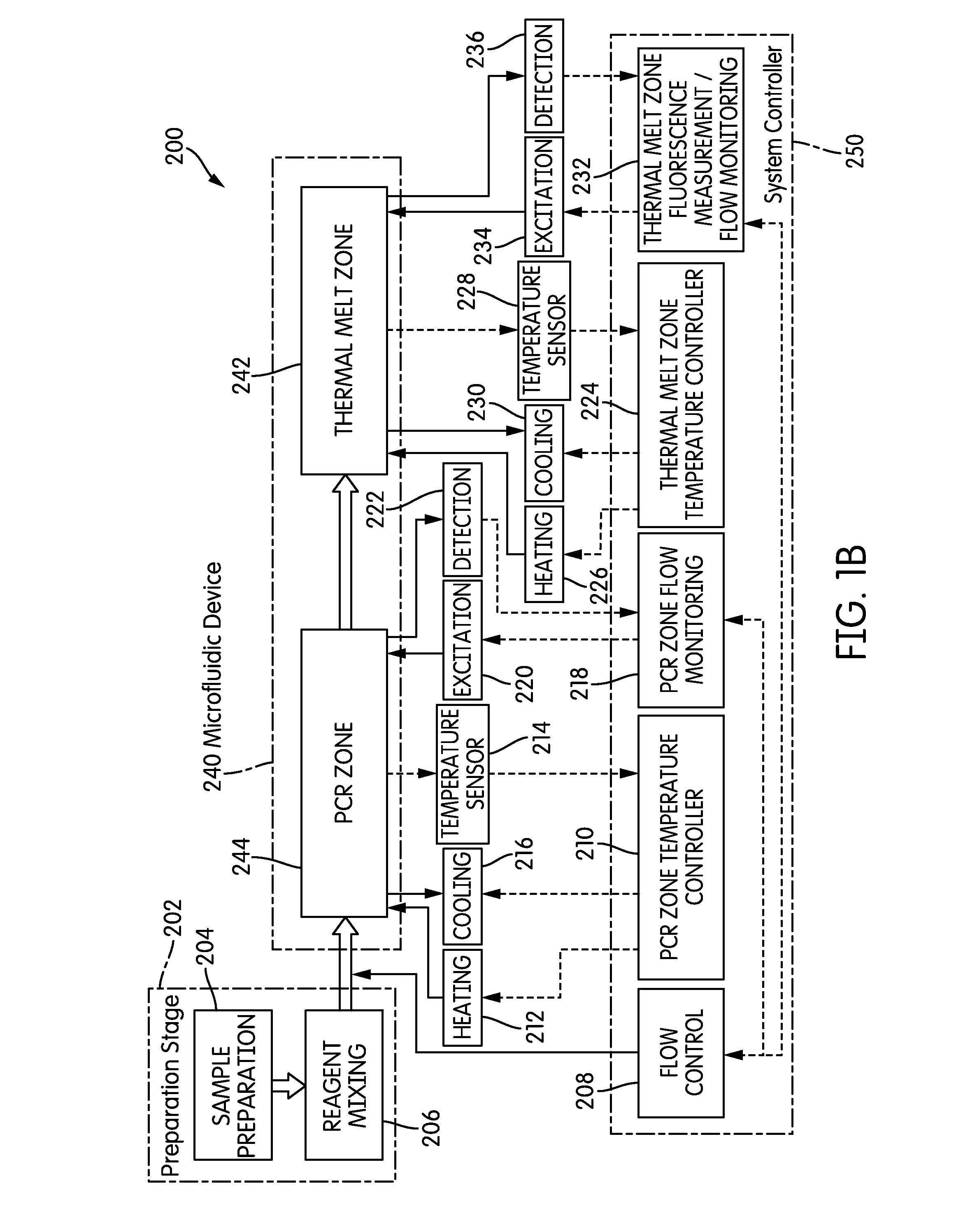
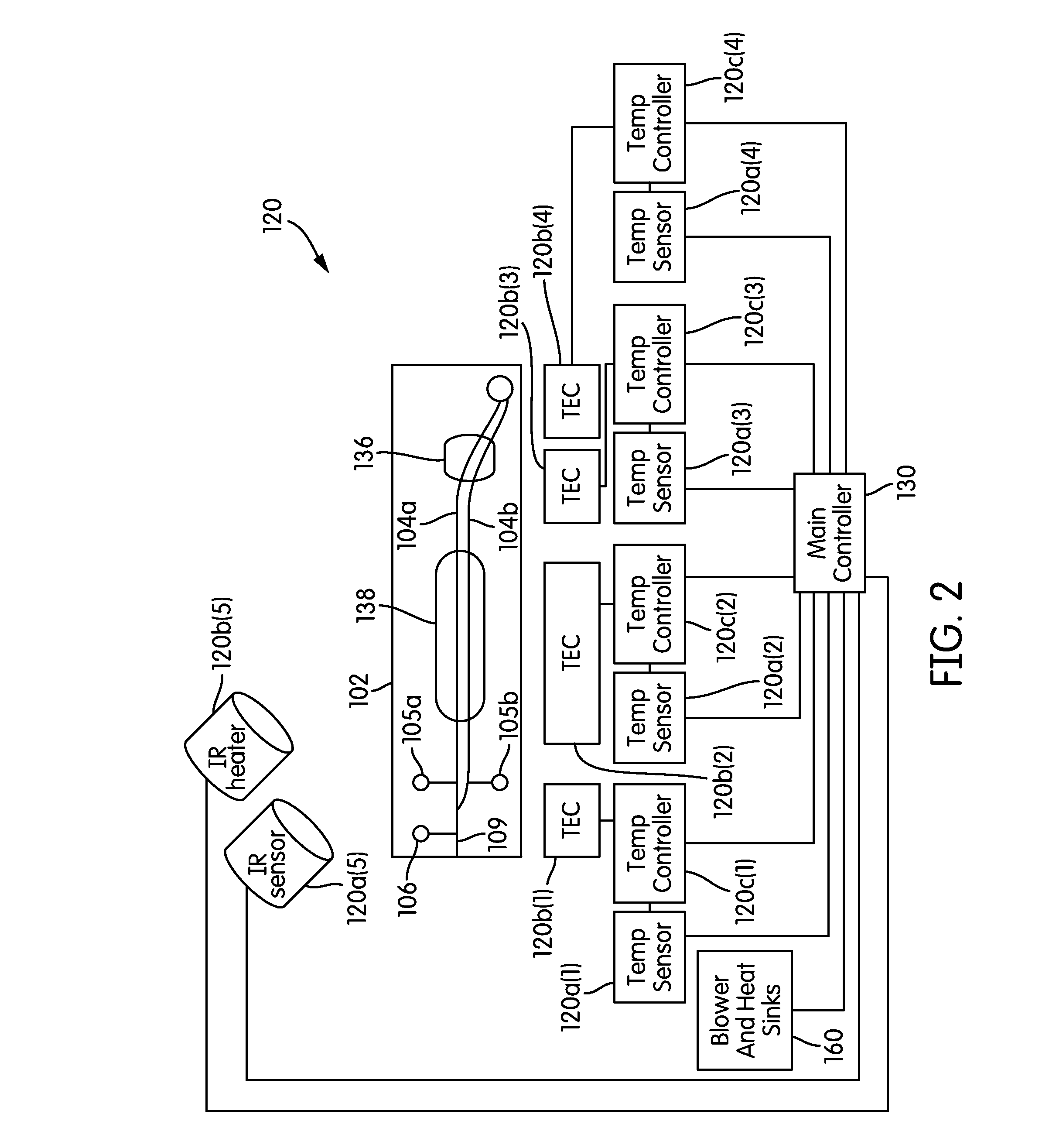
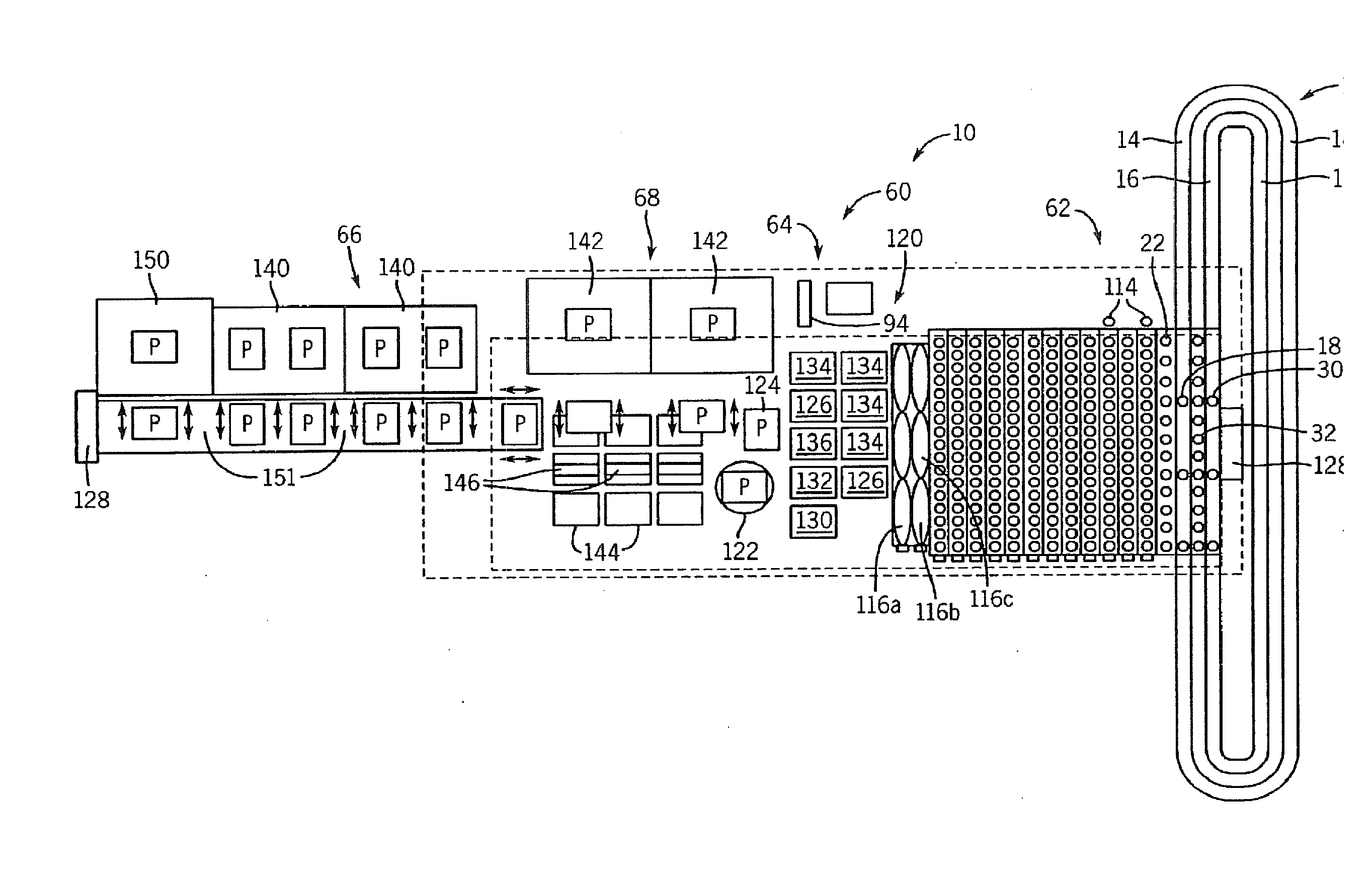
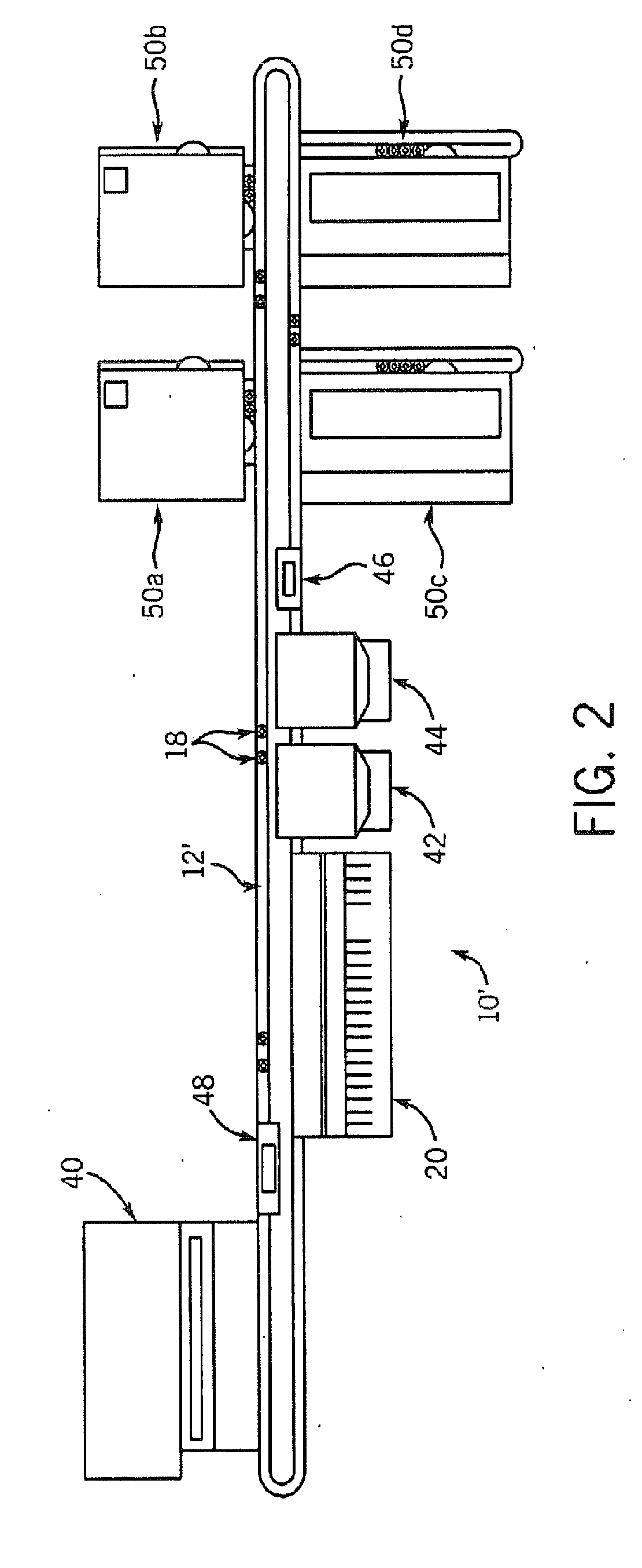
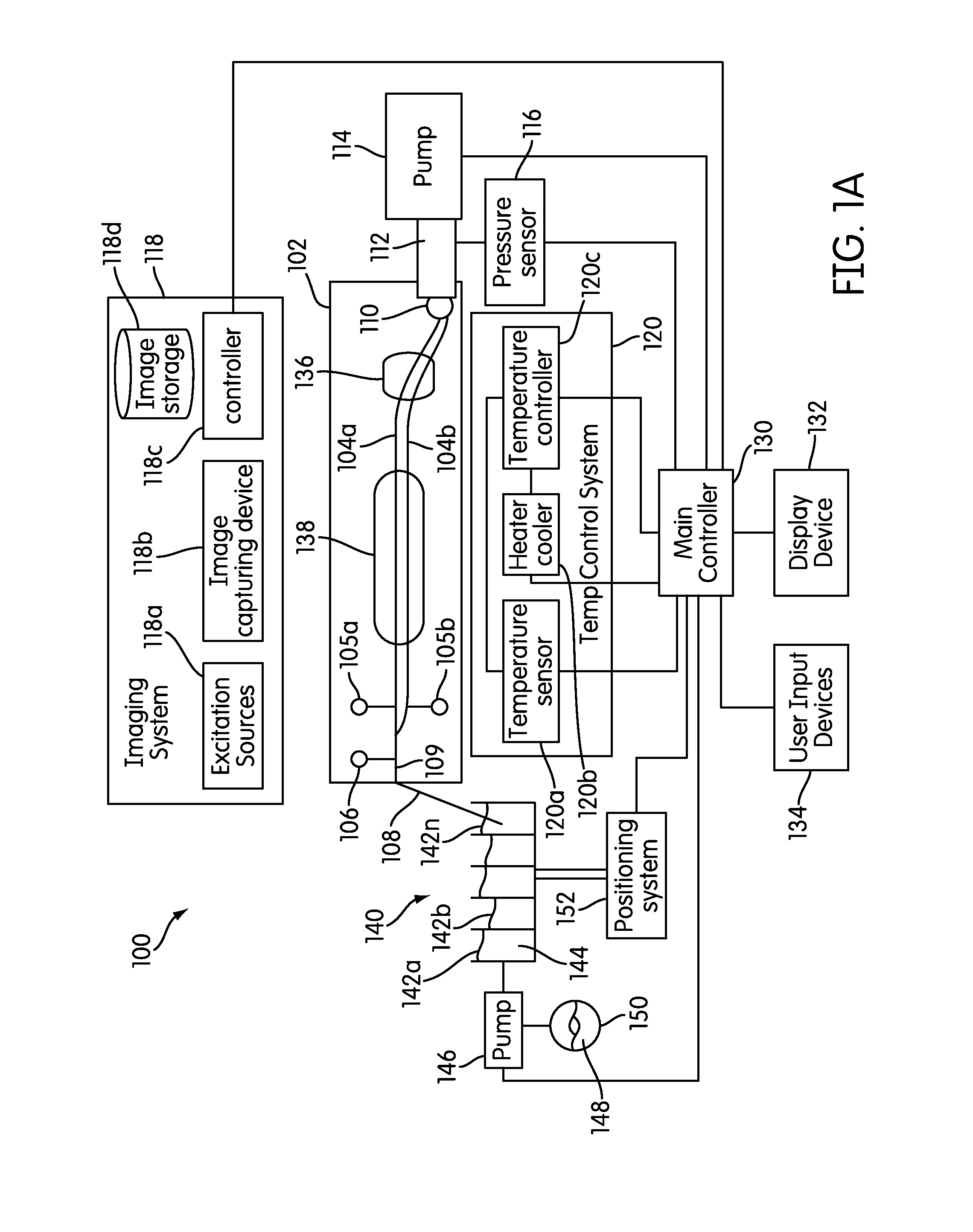
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for the rapid serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays. More particularly, the present invention provides for the real time processing of nucleic acid during polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and thermal melt applications. According to an aspect of the invention, a system for the rapid serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays is provided. In one embodiment, the system includes, but is not limited to: a microfluidic cartridge having microfluidic (flow-through) channels, a fluorescence imaging system, a temperature measurement and control system; a pressure measurement and control system for applying variable pneumatic pressures to the microfluidic cartridge; a storage device for holding multiple reagents (e.g., a well-plate); a liquid handling system comprising at least one robotic pipettor for aspirating, mixing, and dispensing reagent mixtures to the microfluidic cartridge; systems for data storage, processing, and output; and a system controller to coordinate the various devices and functions.
Owner:CANON USA
Automated analyzer for clinical laboratory
ActiveUS20120282684A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicro perforated plateClinical chemistry
A laboratory automation system that is capable of carrying out clinical chemistry assays, immunoassays, amplification of nucleic acid assays, and any combination of the foregoing, said laboratory automation system employing at least one of micro-well plates and deep multi-well plates as reaction vessels. The use of micro-well plates as reaction vessels enables the laboratory automation system to assume a variety of arrangements, i.e., the laboratory automation system can comprise a variety of functional modules that can be arranged in various ways. In order to effectively carry out immunoassays by means of micro-well plates, a technique known as inverse magnetic particle processing can be used to transfer the product(s) of immunoassays from one micro-well of a micro-well plate to another.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
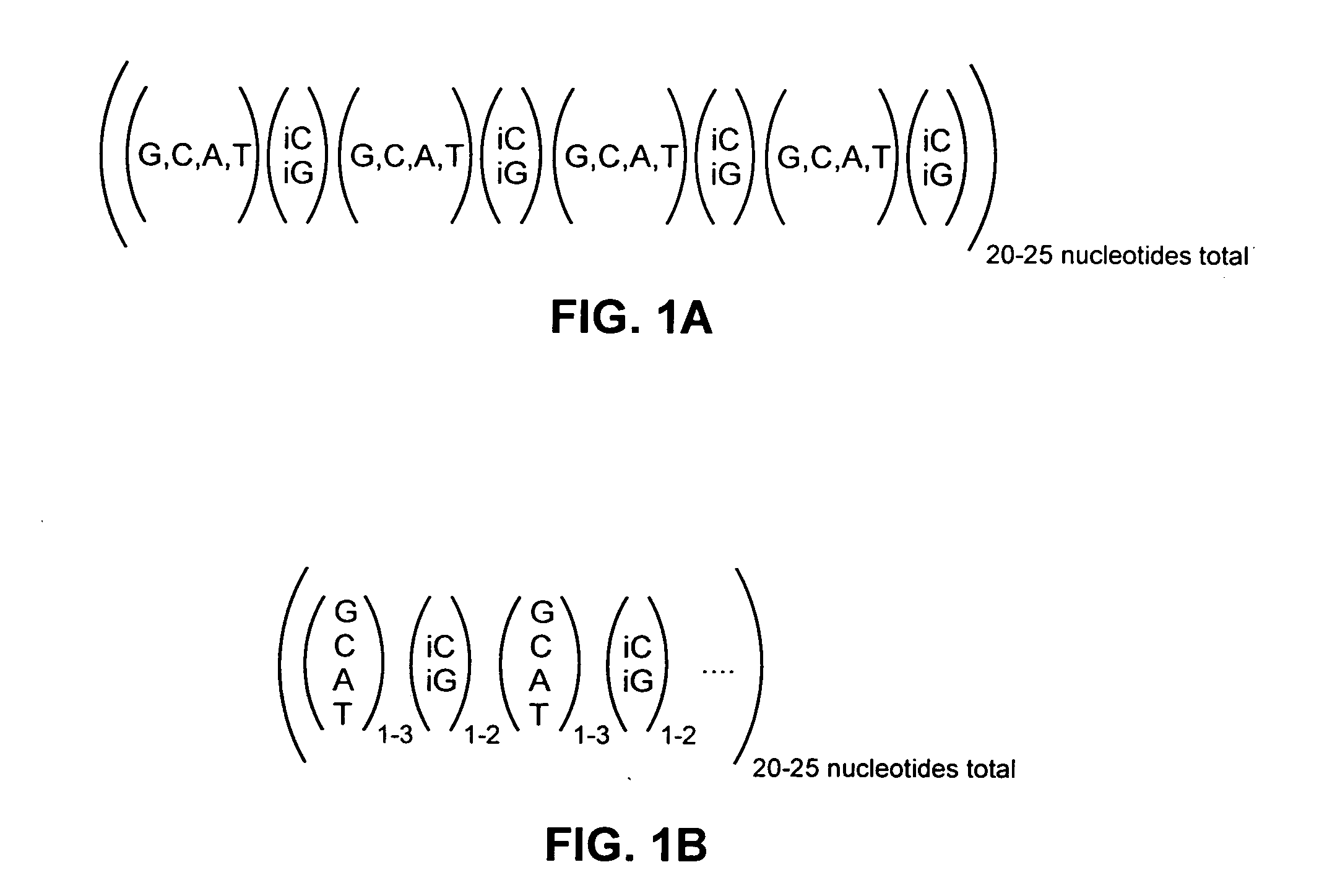
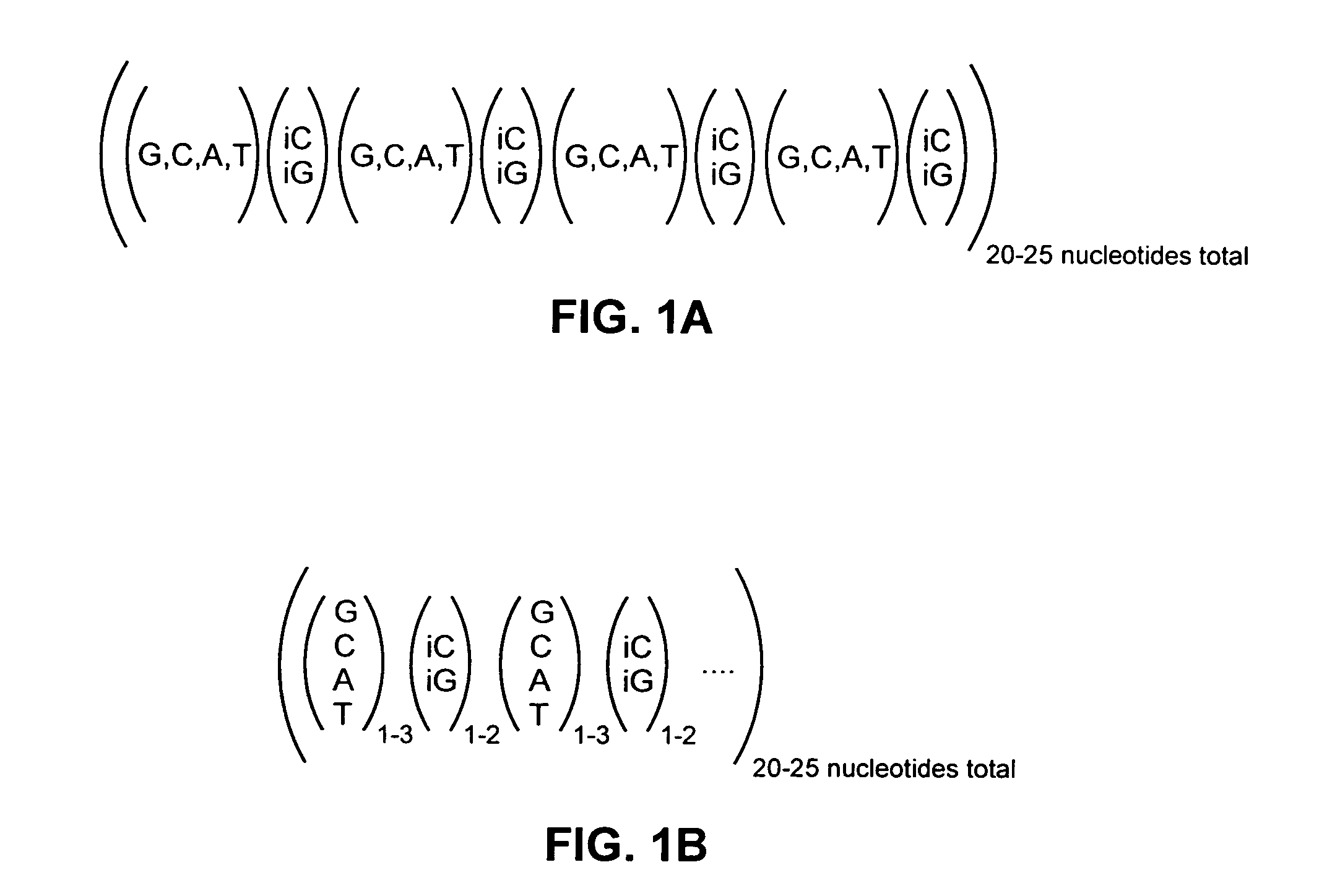
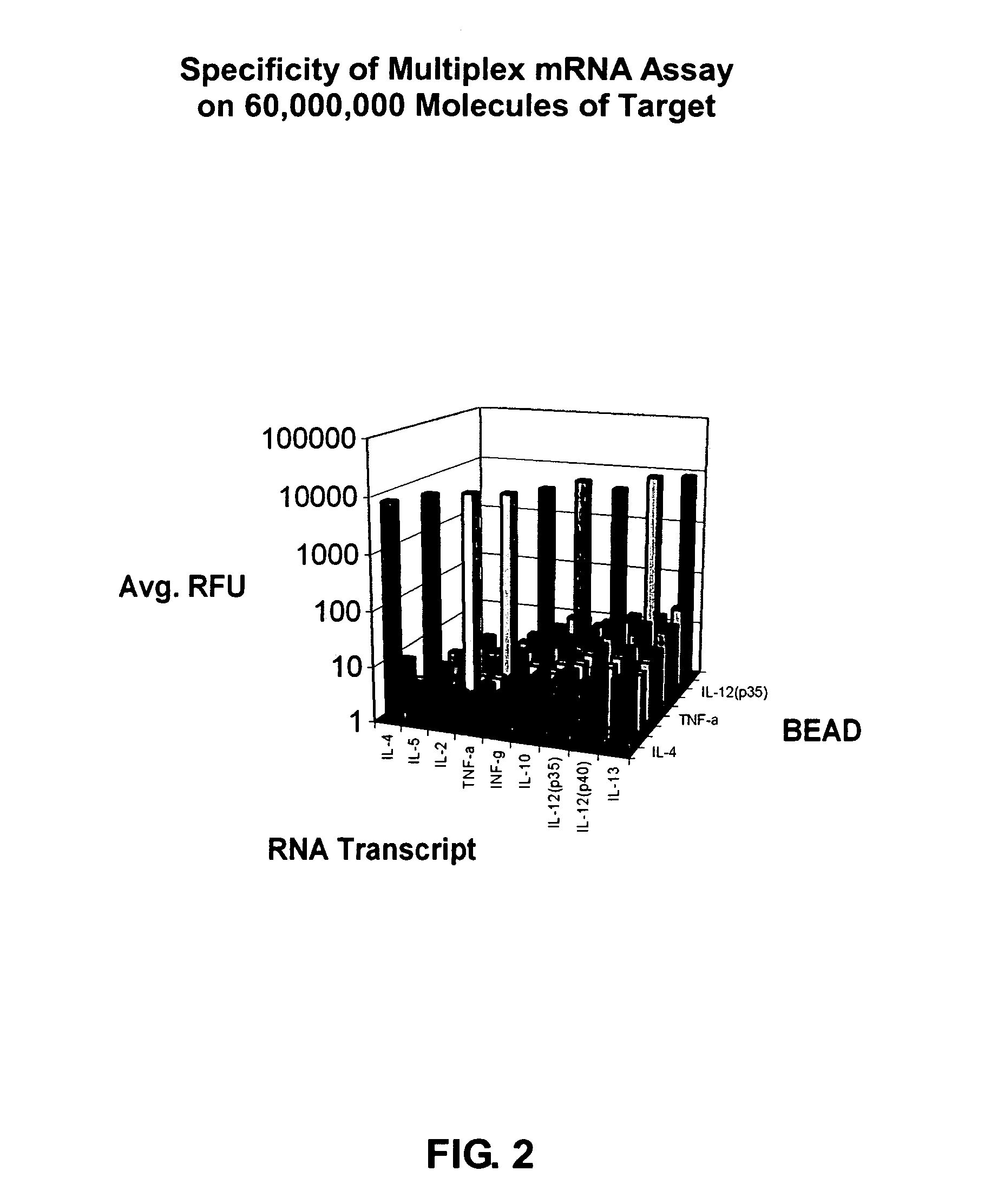
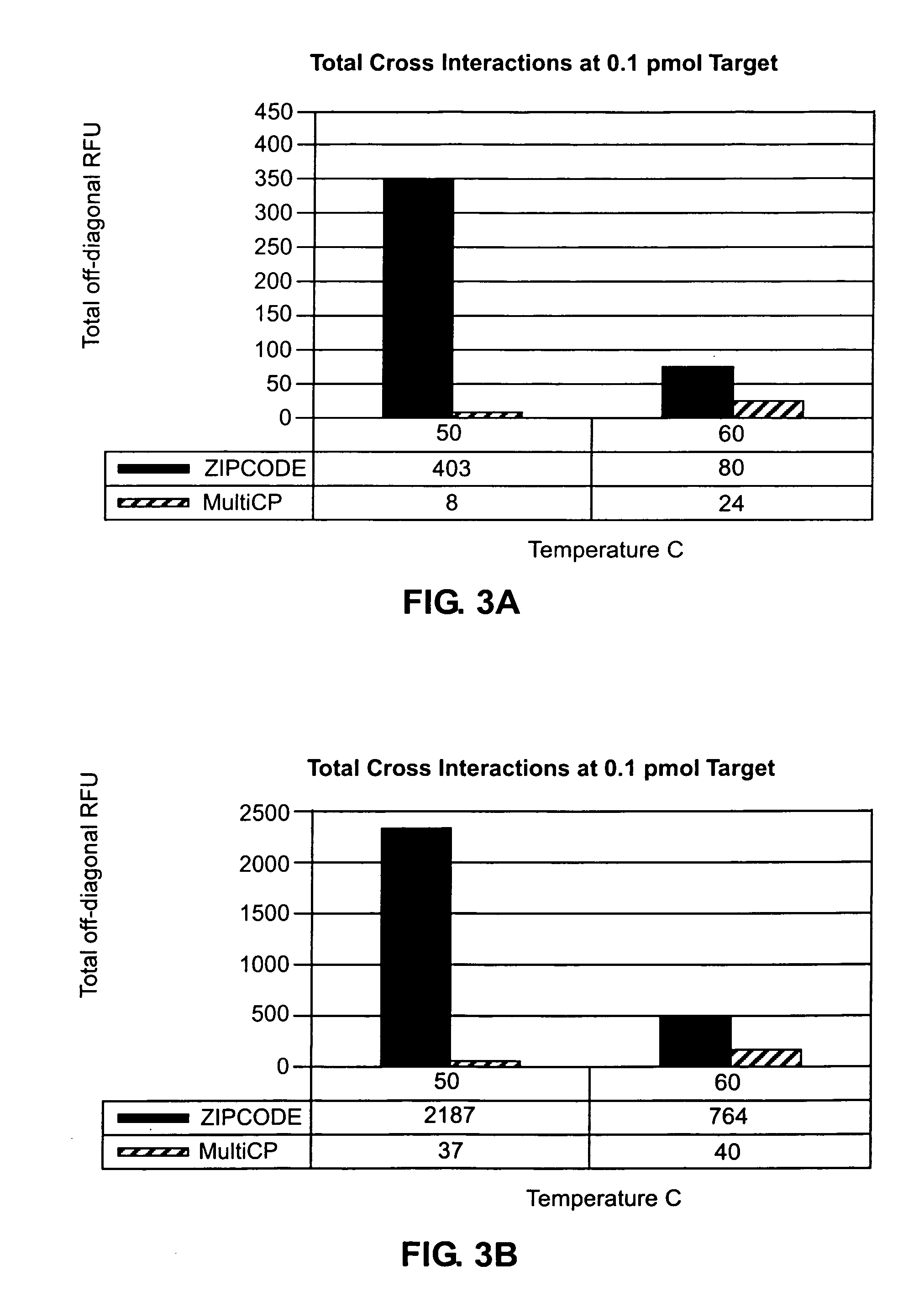
Highly orthogonal universal sequences for use in nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS20060172284A1Easy to analyzeDeletion increaseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementThird generationOrthogonal sequence
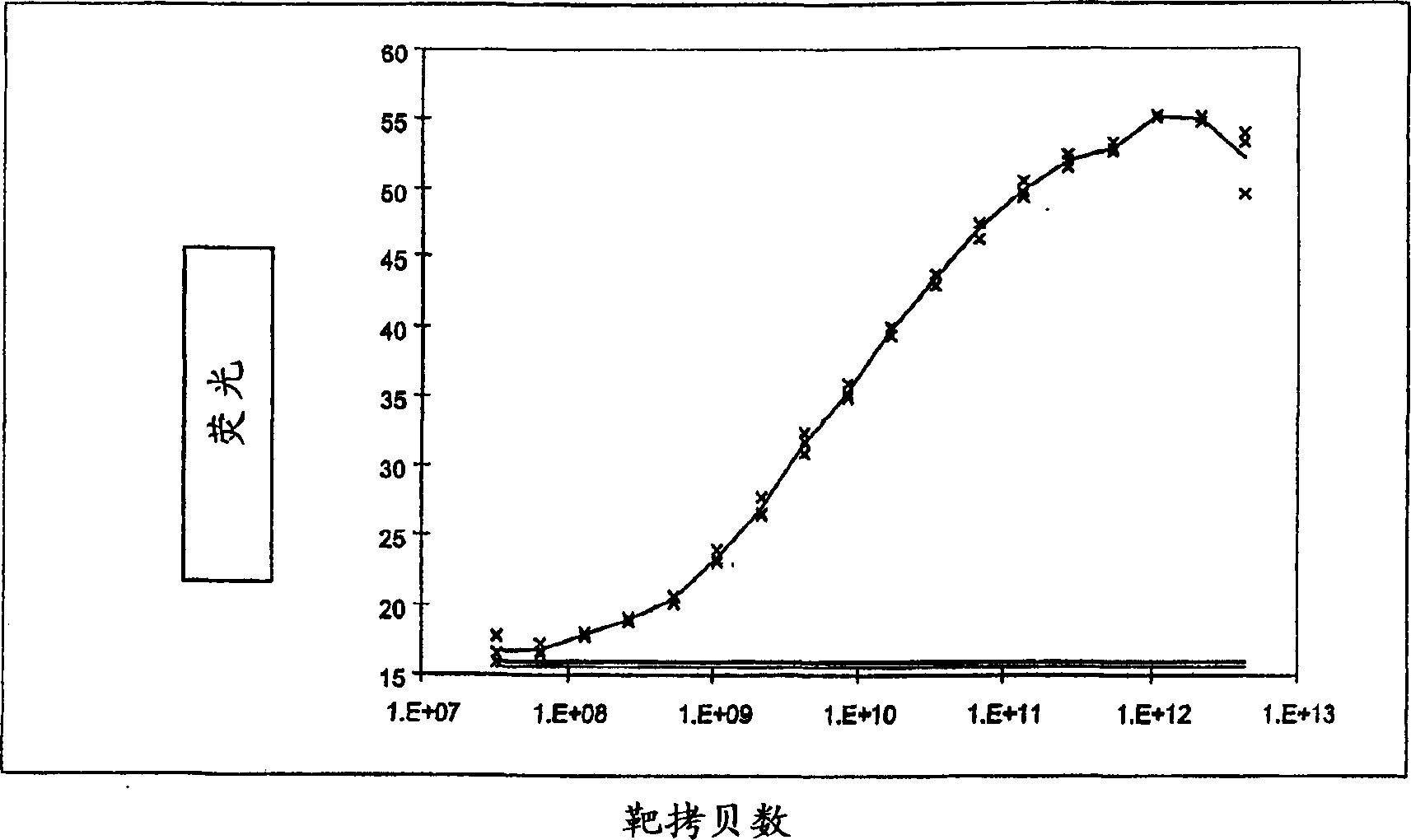
The invention provides a set of highly orthogonal six-code universal sequences for use in bDNA singleplex and multiplex nucleic acid hybridization assays. The six-code orthogonal sequences do not cross-hybridize and thus, minimize or eliminate the 3-mer cross-hybridization inherent in the second and third generation bDNA assays. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may be used in singleplex or multiplex bDNA assays quantitatively and qualitatively to determine mRNA levels in a sample; to screen for and genotype targets, such as viruses, that are present in low volumes in a sample; to screen for and genotype SNPs; and to measure changes in the amount of a gene in a sample such as when gene amplifications or deletions occur. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may also be used as universal capture probes to selectively bind assay components in a way that facilitates their further analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Automated analyzer for clinical laboratory
InactiveUS8222048B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClinical chemistryMicrowell Plate
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Enzymatic modification of a nucleic acid-synthetic binding unit conjugate
InactiveUS6893822B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsEnzyme catalysisImproved method
The present invention relates to conjugates of synthetic binding units and nucleic acids. The present invention also relates to methods for sorting and immobilizing nucleic acids on support materials using such conjugates by specific molecular addressing of the nucleic acids mediated by the synthetic binding systems. Particularly, the present invention also relates to novel methods of utilizing conjugates of synthetic binding units and nucleic acids to in active electronic array systems to produce novel array constructs from the conjugates, and the use of such constructs in various nucleic acid assay formats. In addition, the present invention relates to various novel forms of such conjugates, improved methods of making solid phase synthesized conjugates, and improved methods of conjugating pre-synthesized synthetic binding units and nucleic acids. The present invention also relates to the use of conjugates of synthetic binding units and nucleic acids as substrates for various enzymatic reactions, including nucleic acid amplification reactions.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS SA
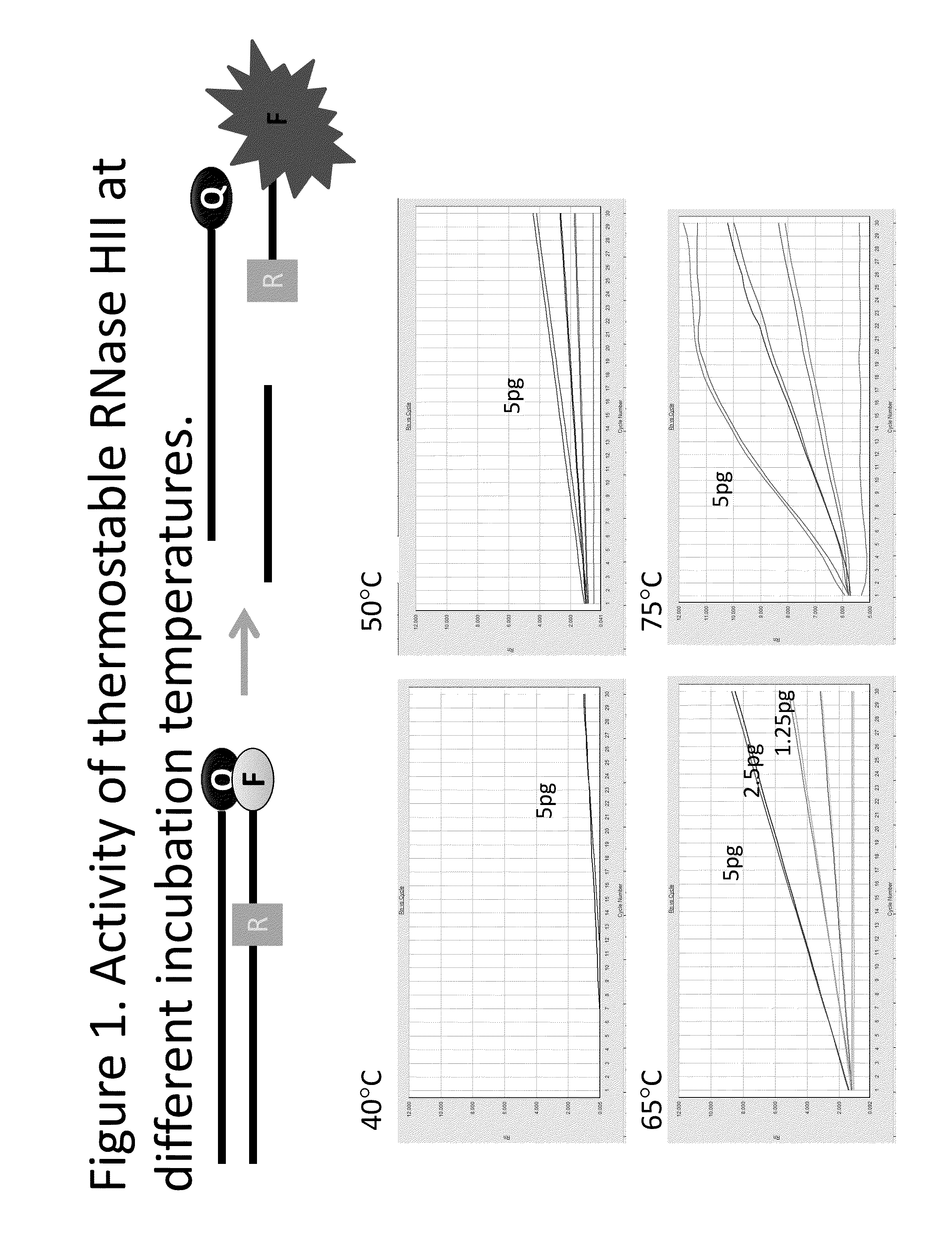
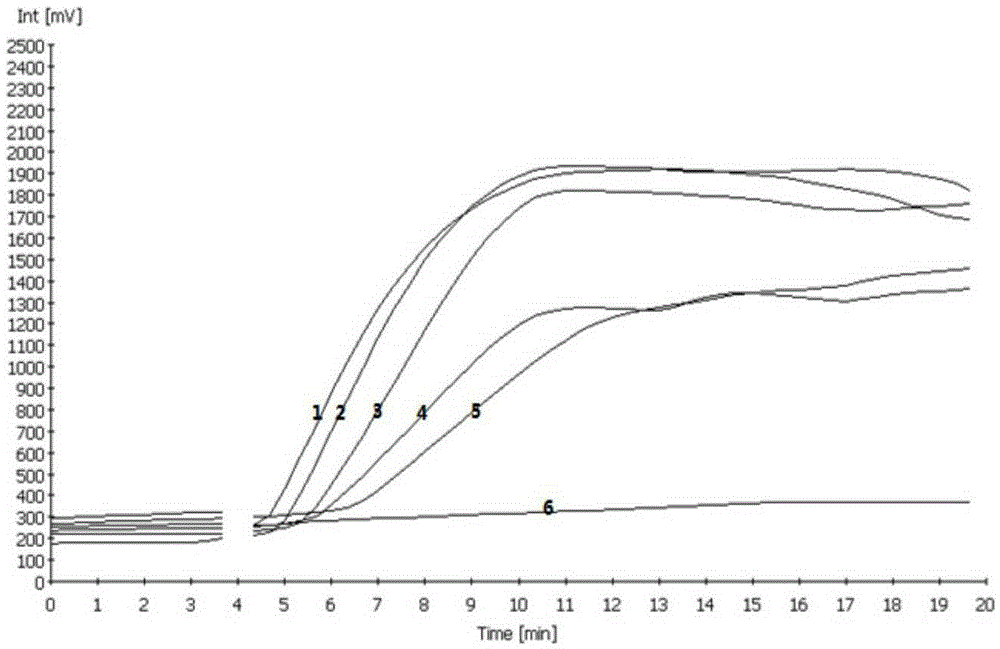
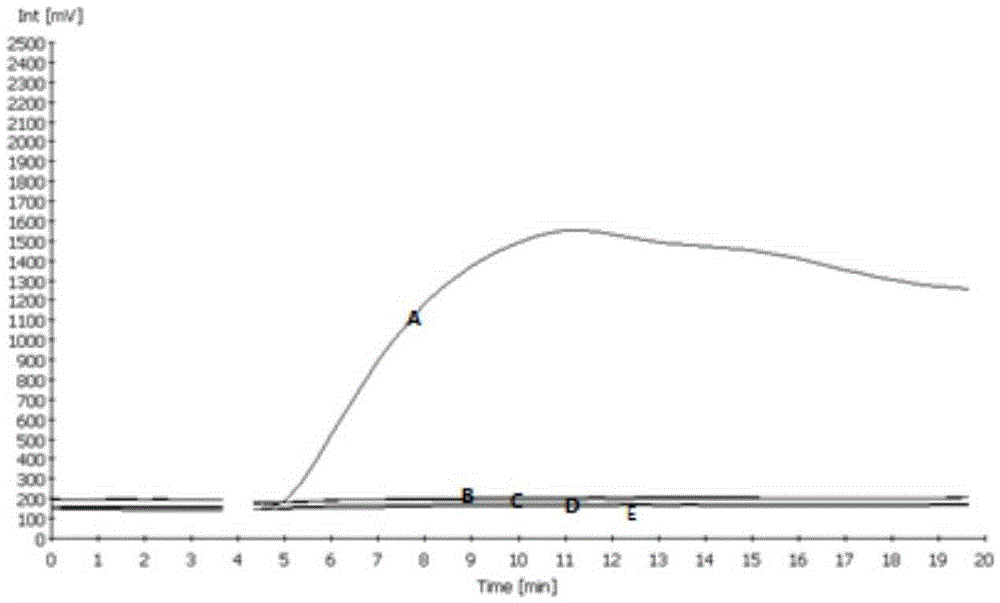
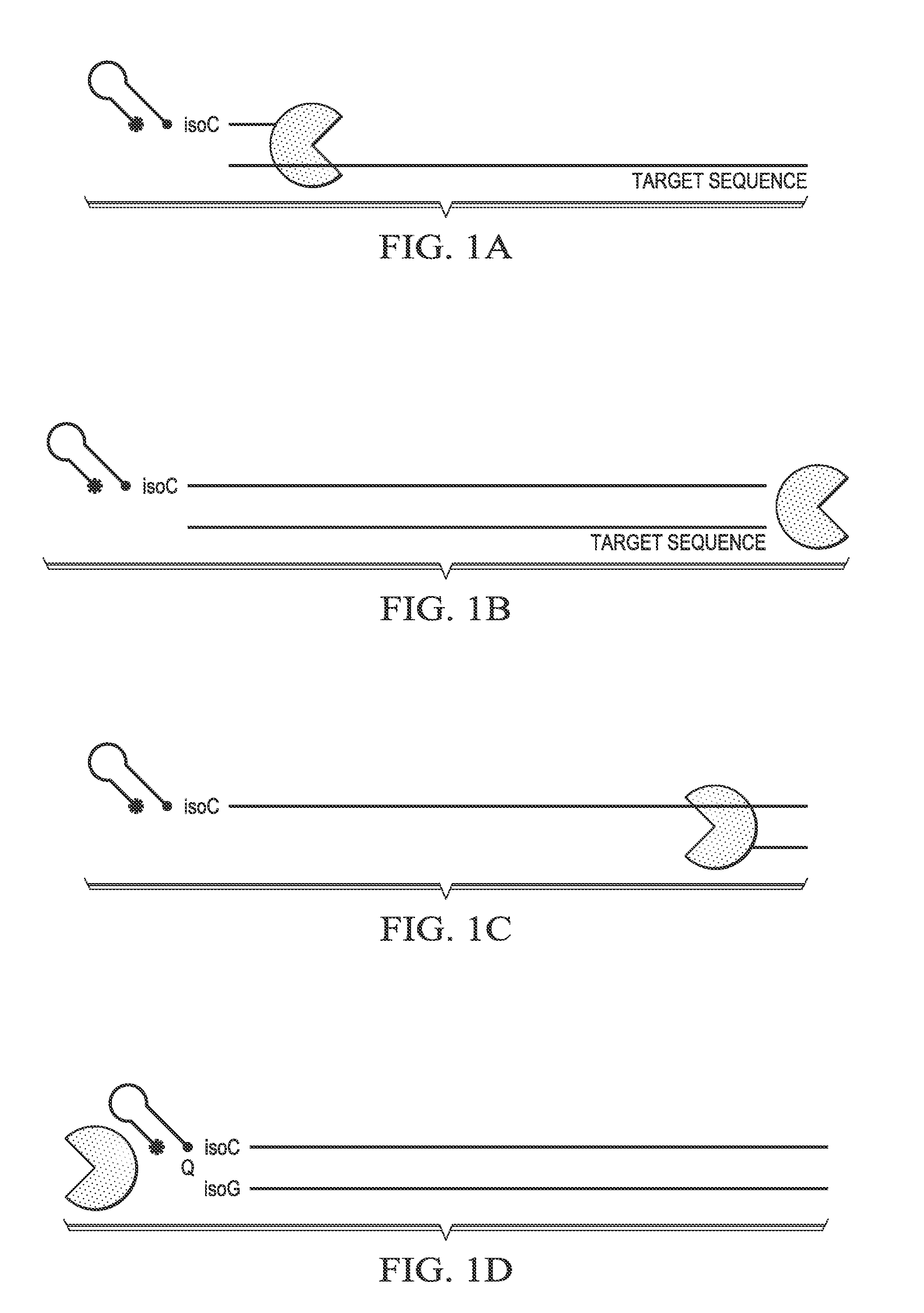
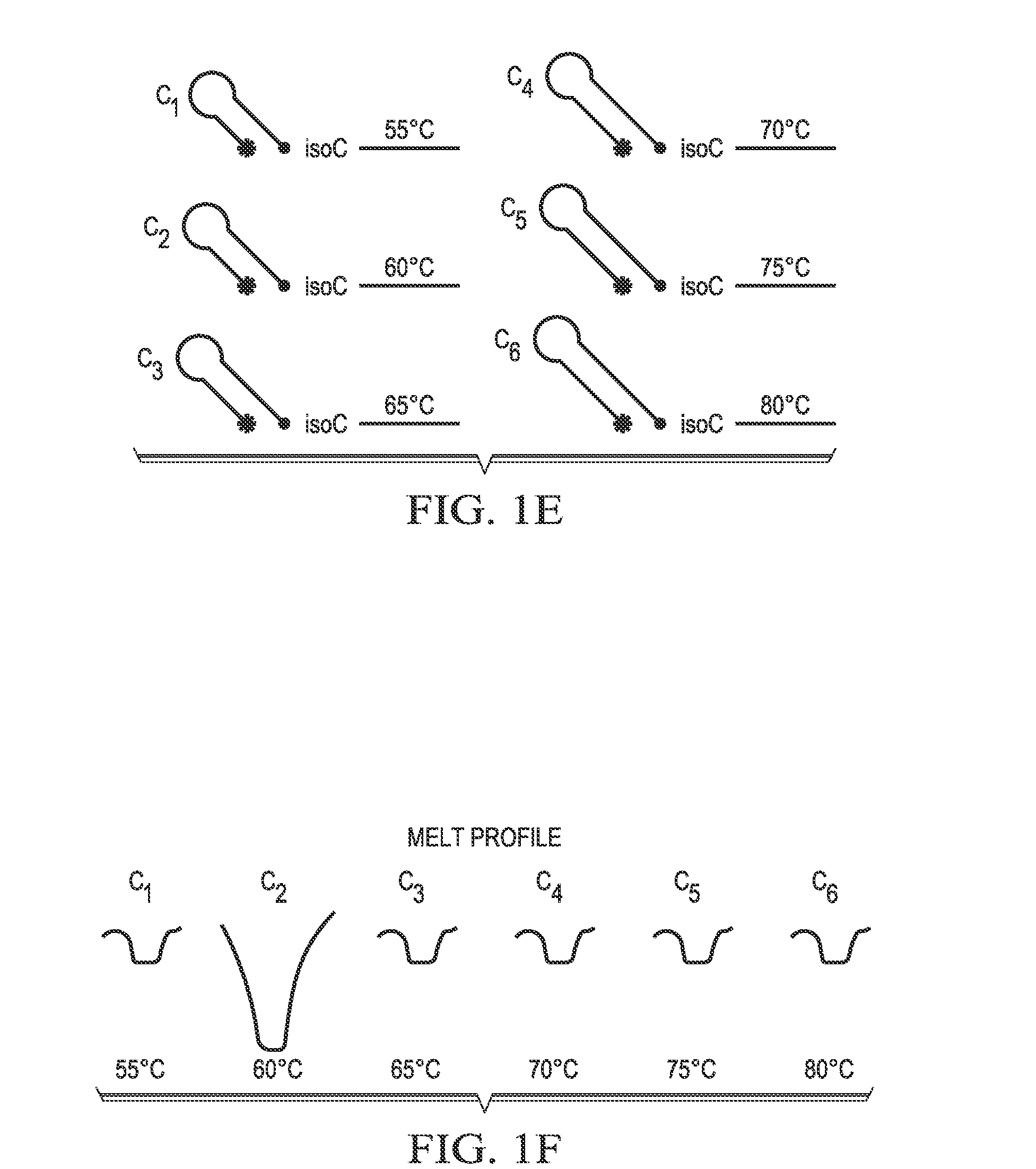
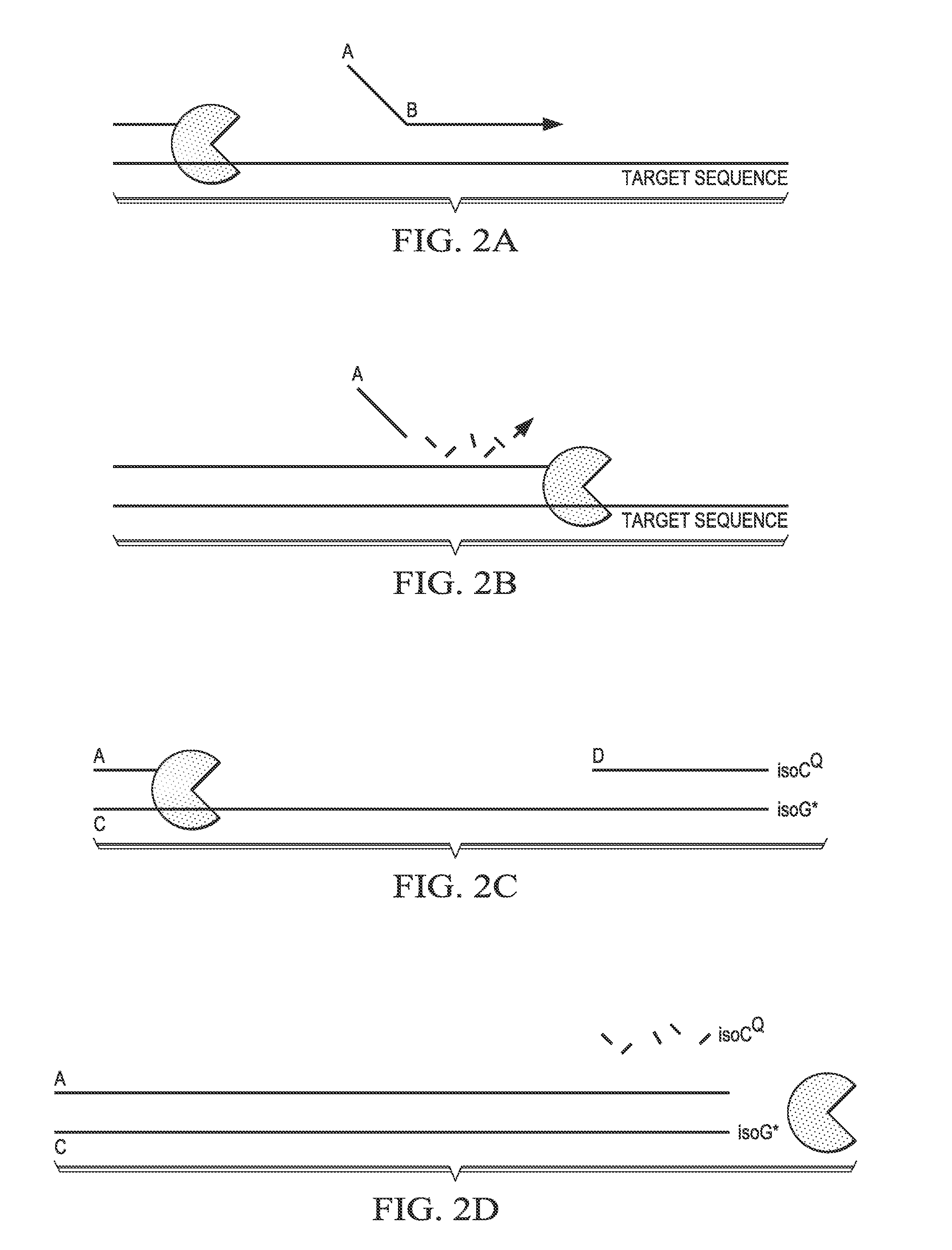
Step-wise detection of multiple target sequences in isothermal nucleic acid amplification reactions
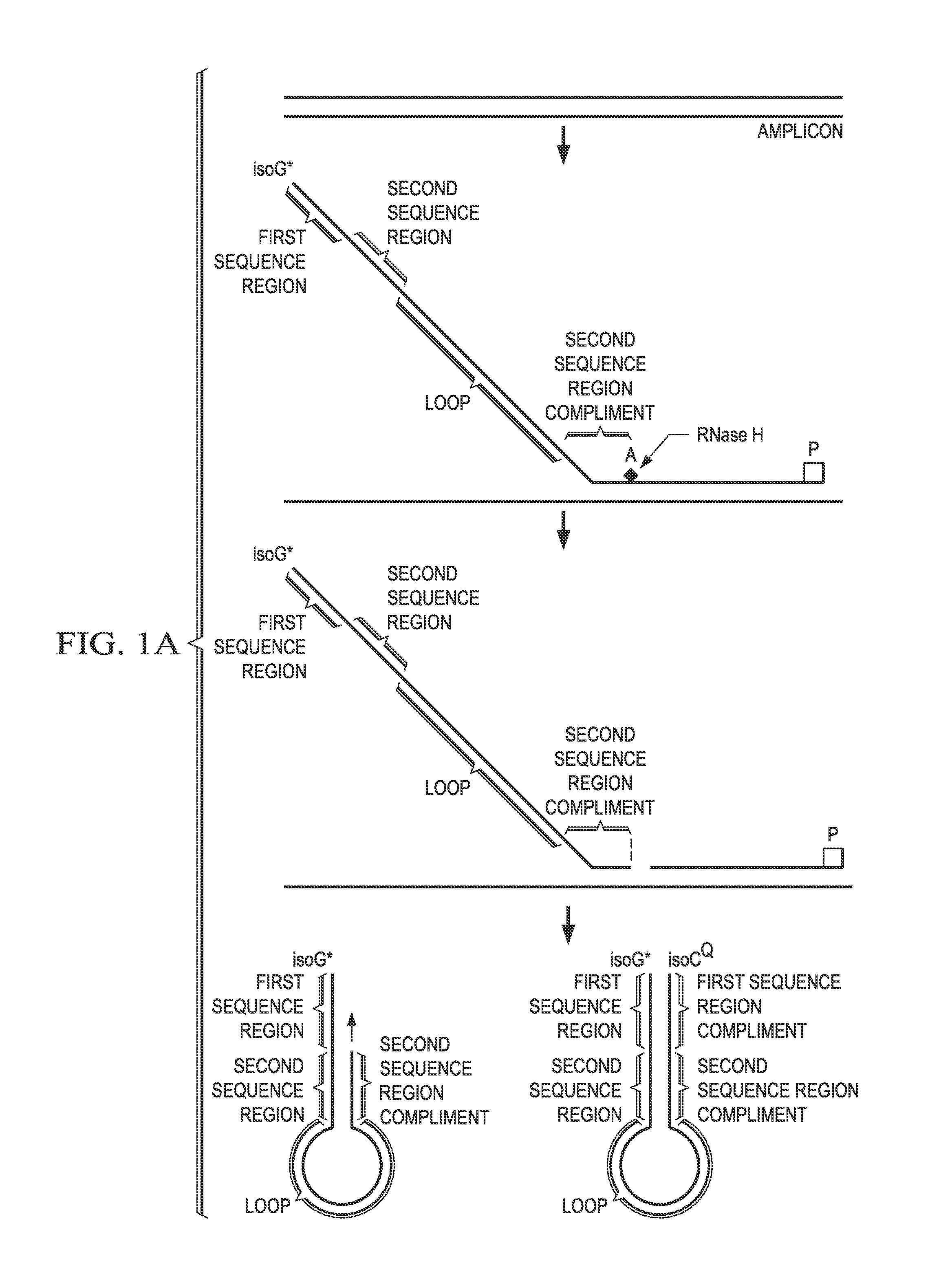
Compositions and methods useful in nucleic acid assays are provided. The invention permits detection of multiple target sequences and control nucleic acids using isothermal nucleic acid amplification methods and subsequent detection of amplification products at different temperature steps by at least two probes with different annealing temperatures. This method can be used in isothermal nucleic acid amplification reactions to detect multiple targets of interest. In a particular example, cycling hybridization probes with different spectral and hybridization temperatures are used to detect different target sequences. Probes become fluorescent when they are cleaved by a thermostable ribonuclease, which only acts when the probes are hybridized to their respective templates.
Owner:BIOHELIX CORP
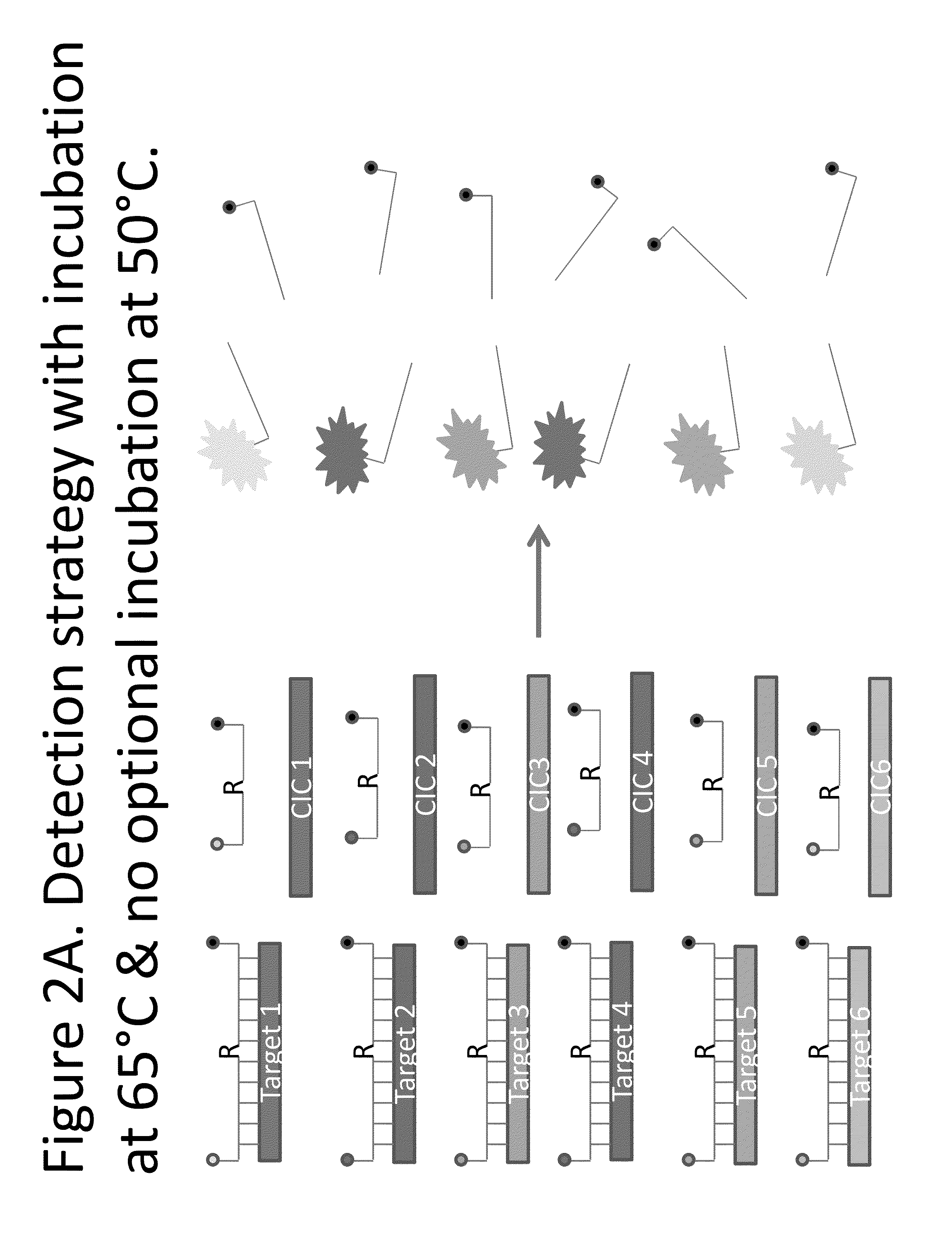
Replication Stable and RNase Resistant Chimeras of Pestivirus with Insertion in 3' Nontranslated Region (3'NTR)
The invention relates to the field of nucleic acid amplification, particularly to quality control materials for use in viral RNA assays. It specifically relates to the construction of a recombinant Pestivirus by the identification of a region in the 3′NTR of the viral RNA genome where additional sequence elements can be stably inserted. Chimeric Pestivirus with sequence insertions in the 3′ nontranslated region (3′NTR) of the viral RNA genome were stable in replication and capable of forming infectious, RNase resistant virus particles. This chimeric Pestivirus with a 3′NTR insertion can be utilized as a quality control material in analytical assays for RNA targets, including external, internal controls, quantitative standards in PCR and NAT nucleic acid assays.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Magnetic field enhanced hybridization of target molecules to immobilized probes
InactiveUS6852493B2Increase hybridization rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsComplementary pairNucleic acid hybridisation
The invention provides a method for increasing the hybridization rate of nucleic acids in a nucleic acid assay by labeling nucleic acid molecules with paramagnetic labels and activating a magnetic field inducing rapid migration of the labeled molecules to a solid support, where the labeled molecule hybridizes with its complementary pair. The paramagnetic label may be present on the target nucleic acid or the probe nucleic acid, depending upon whether the target or probe are the immobile phase.
Owner:IRIS BIOTECH
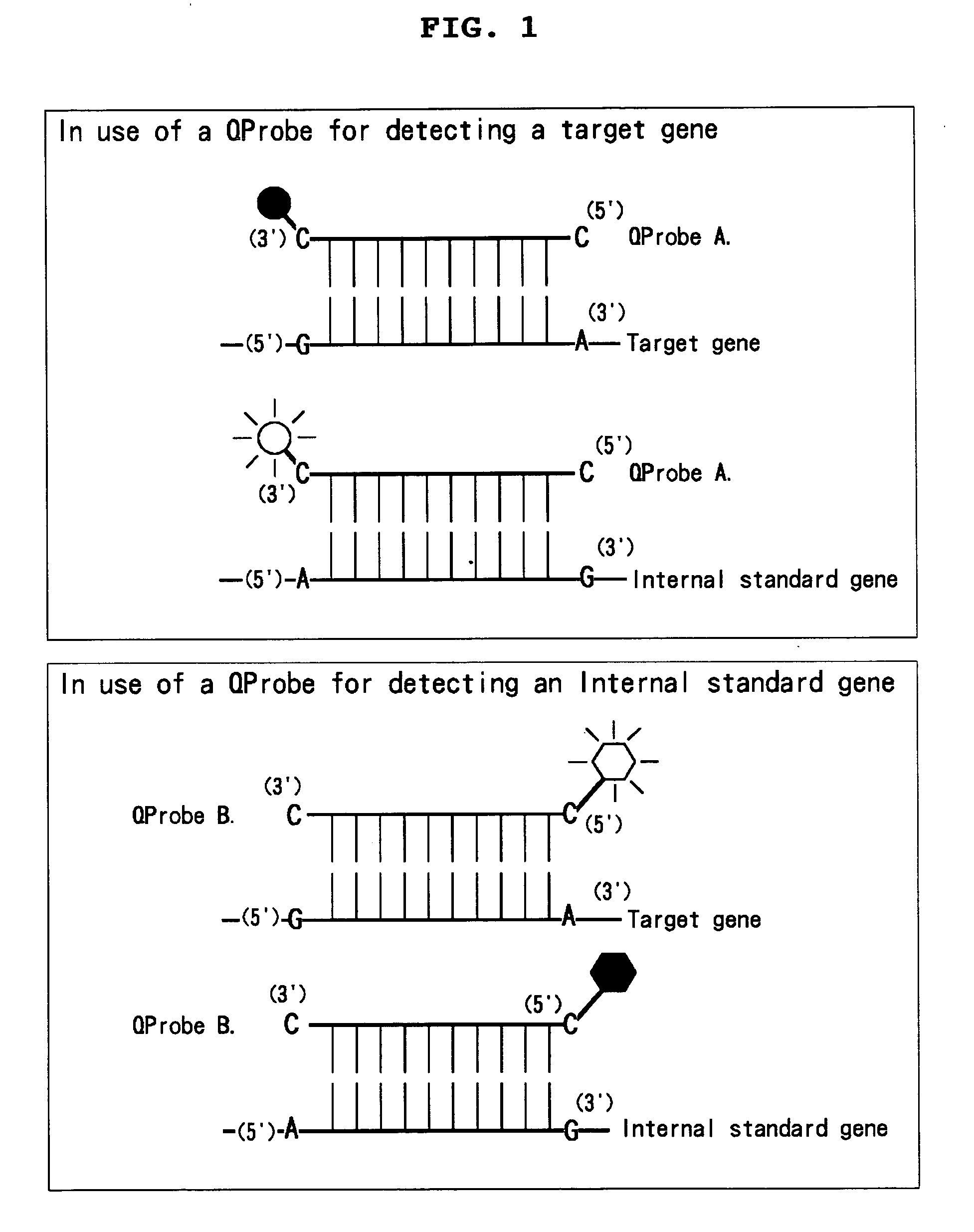
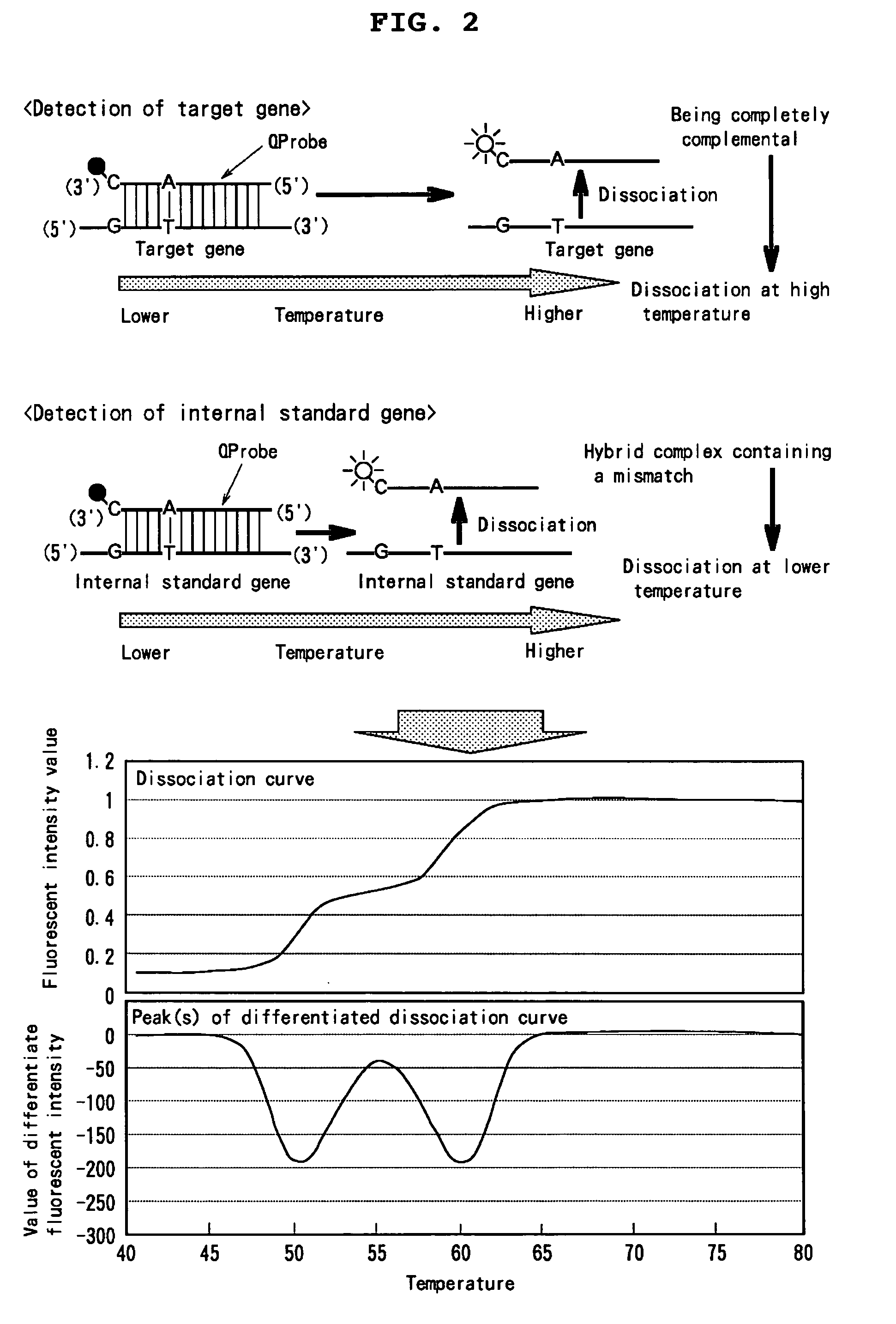
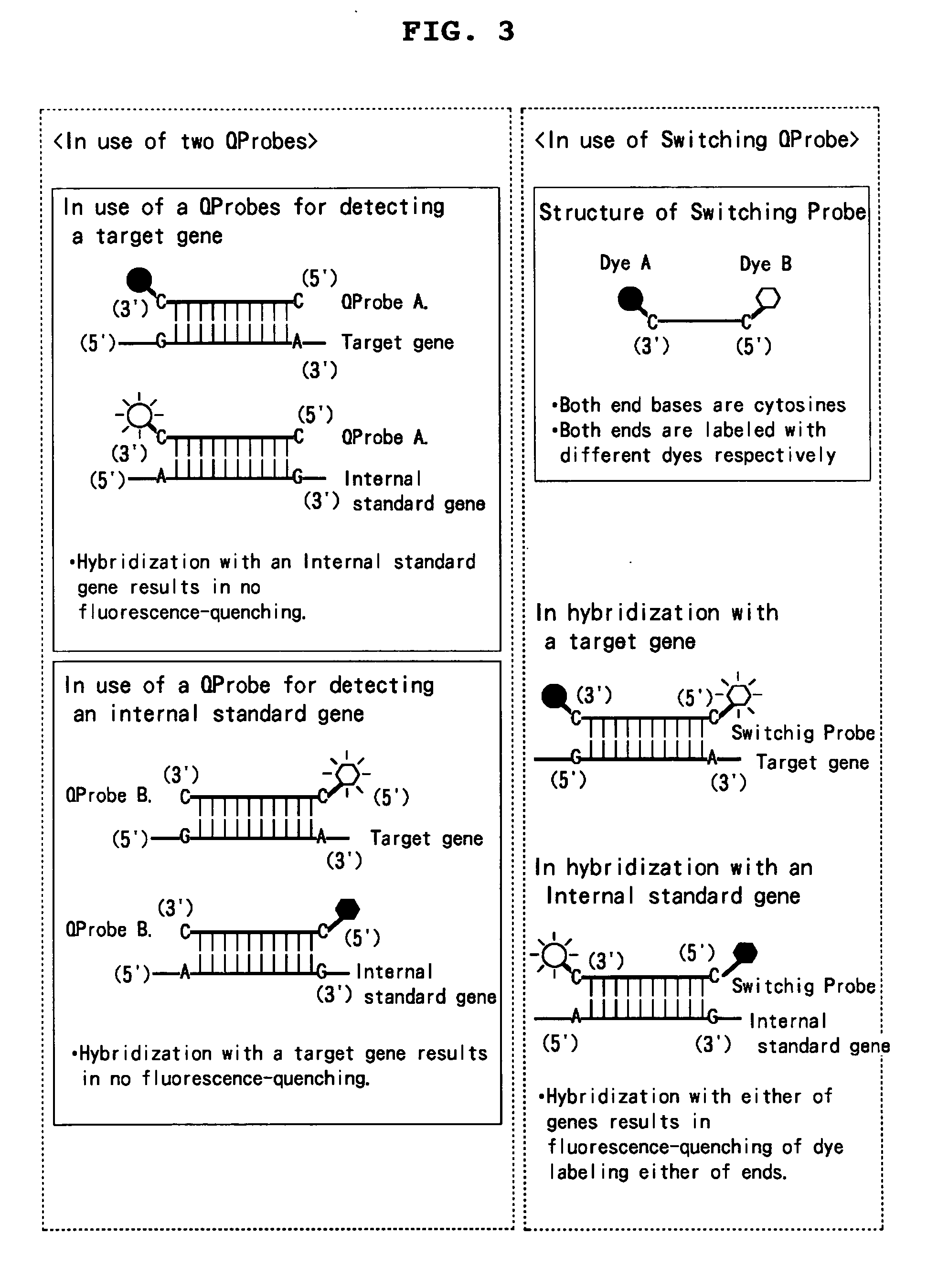
Novel mixtures for assaying nucleic acid, novel method of assaying nucleic acid with the use of the same and nucleic acid probe to be used therefor
InactiveUS20070128608A1High detection sensitivityEasily and rapidlySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceNucleic acid assay
[Problems] To provide a novel mixture for assaying a target nucleic acid, characterized by enabling a nucleic acid assay while: 1) requiring no step of diluting the target nucleic acid; 2) requiring no procedure of changing a probe concentration depending on a concentration of the target nucleic acid. [Means for Solving Problems] 1) A mixture which comprises one internal standard nucleic acid and two nucleic acid probes labeled with a fluorescent dye; 2) a mixture for measuring Km value which comprises one internal standard nucleic acid having a partial mutation and one nucleic acid probe labeled with a fluorescent dye; 3) a mixture which comprises one internal standard nucleic acid and one double nucleic acid probe labeled with two fluorescent dyes; and a method for assaying a nucleic acid by making use thereof.
Owner:KANKYO ENJINIARINGU +1
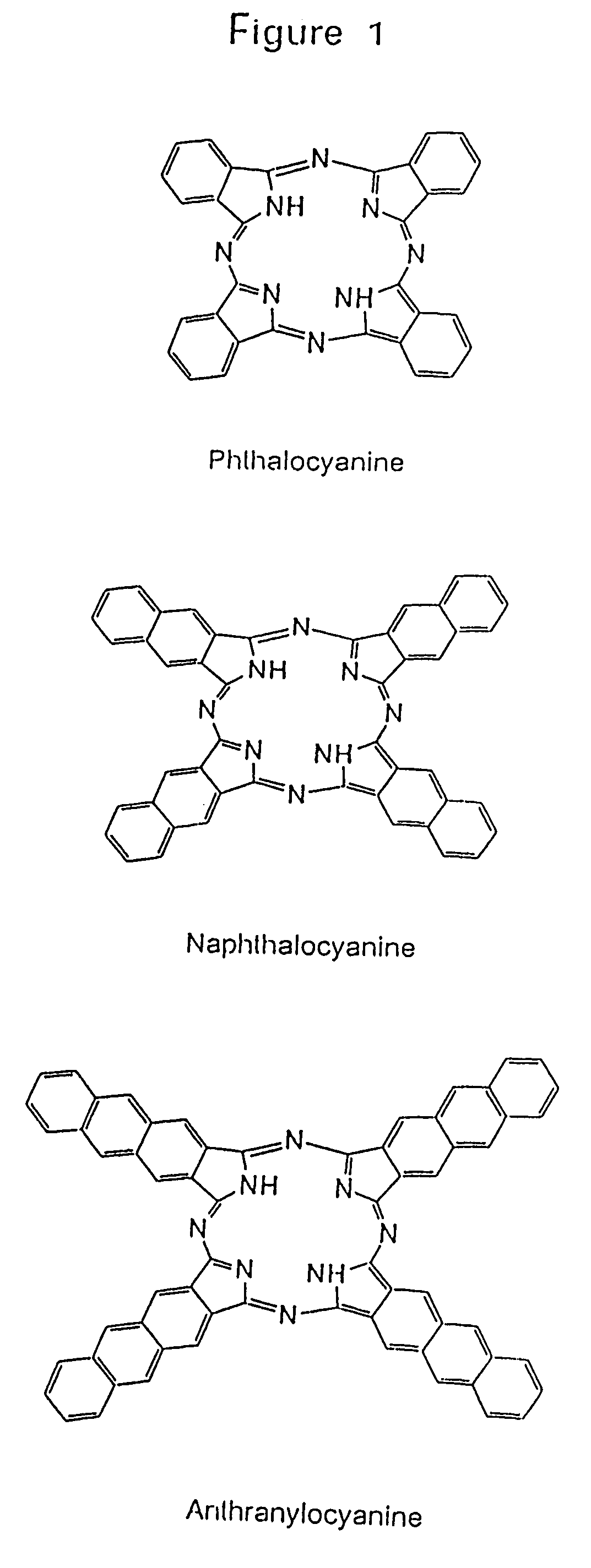
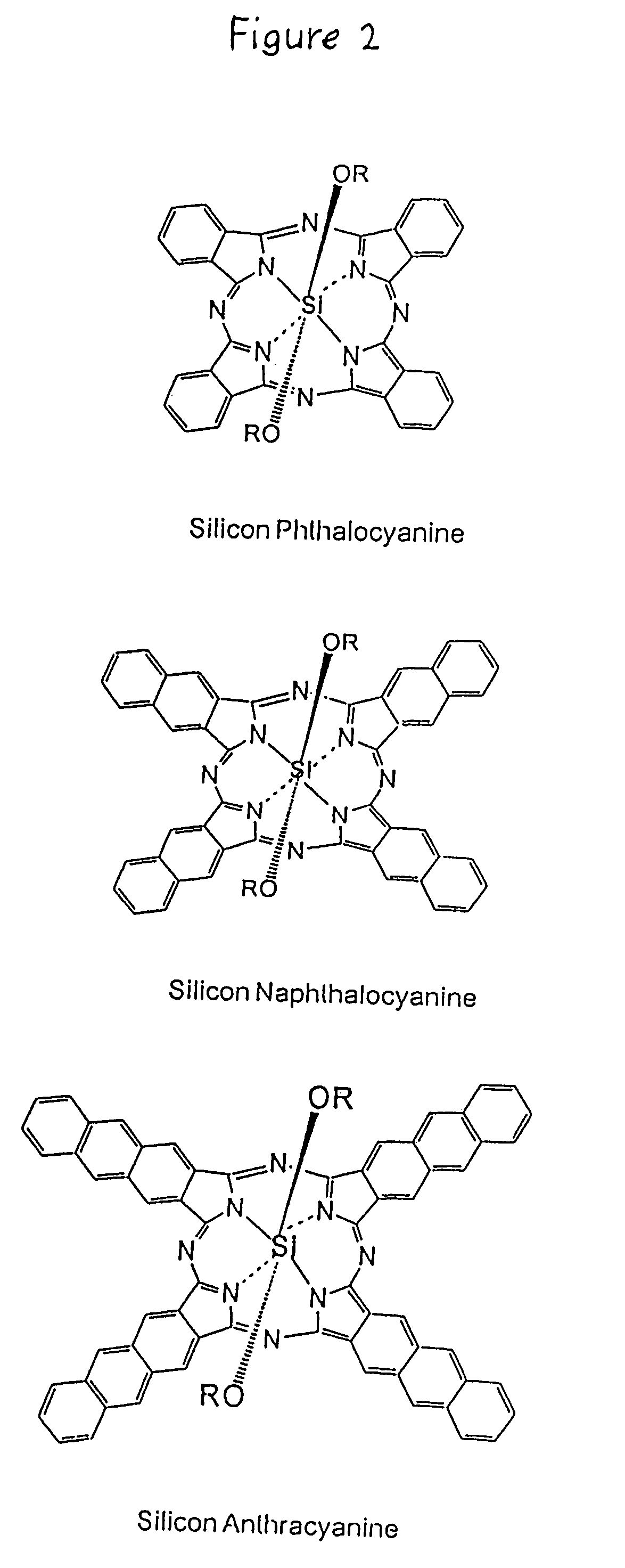
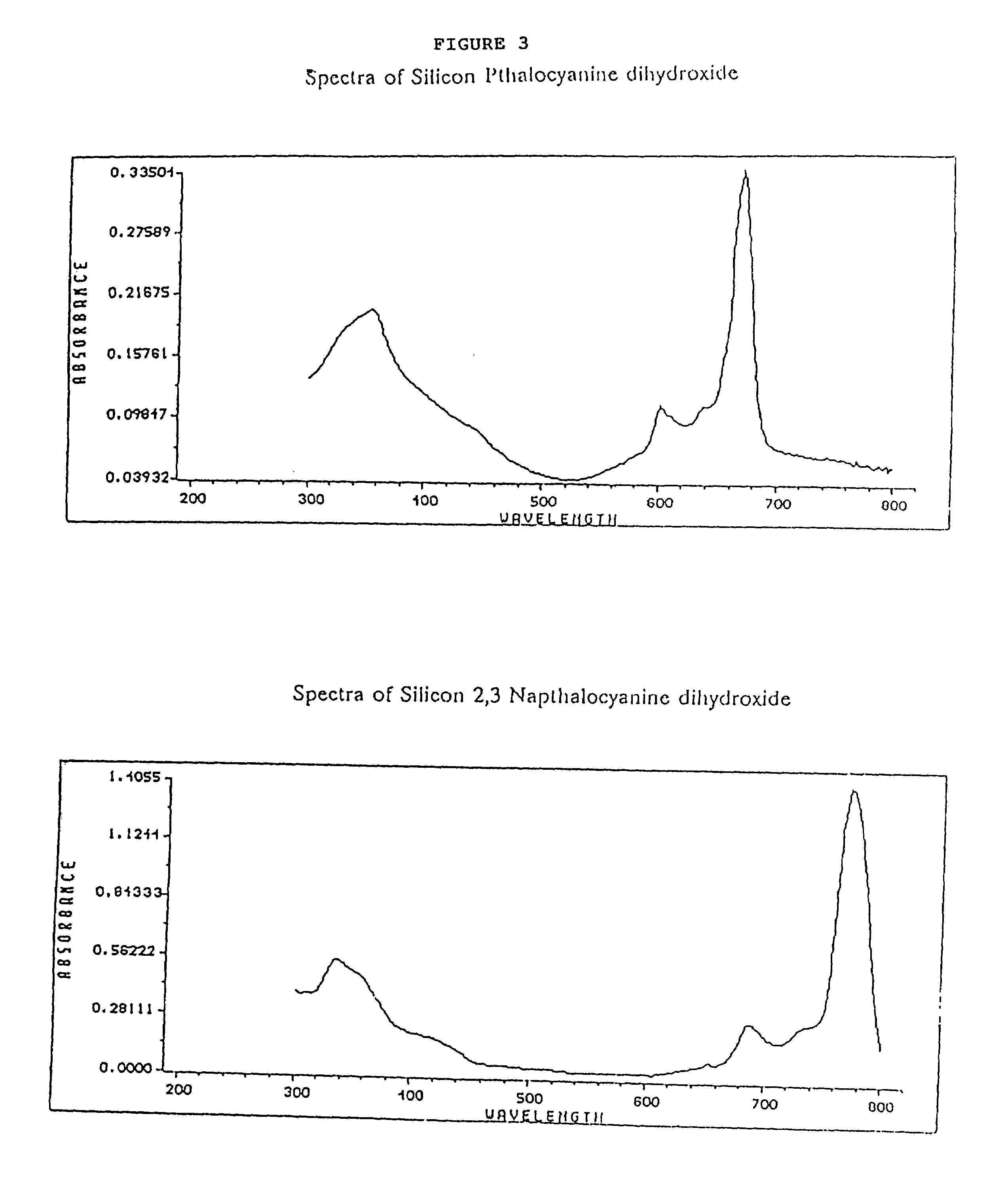
Hybrid phthalocyanine derivatives and their uses
InactiveUS6964844B1Minimize fluorescence quenchingMaximize fluorescence intensityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy transferPhthalocyanine derivatives
Water soluble hybrid phthalocyanine derivatives useful in competitive and noncompetitive assays immunoassays, nucleic acid and assays are disclosed and claimed having (1) at least one donor subunit with a desired excitation peak; and (2) at least one acceptor subunit with a desired emission peak, wherein said derivative(s) is / are capable of intramolecular energy transfer from said donor subunit to said acceptor subunit. Such derivatives also may contain an electron transfer subunit. Axial ligands may be covalently bound to the metals contained in the water soluble hybrid phthalocyanine derivatives. Ligands, ligand analogues, polypeptides, proteins and nucleic acids can be linked to the axial ligands of the dyes to form dye conjugates useful in immunoassays and nucleic acid assays.
Owner:BIOSITE INC
Detection of nucleic acids
InactiveCN1434874ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsFluorescenceLight scattering by particles
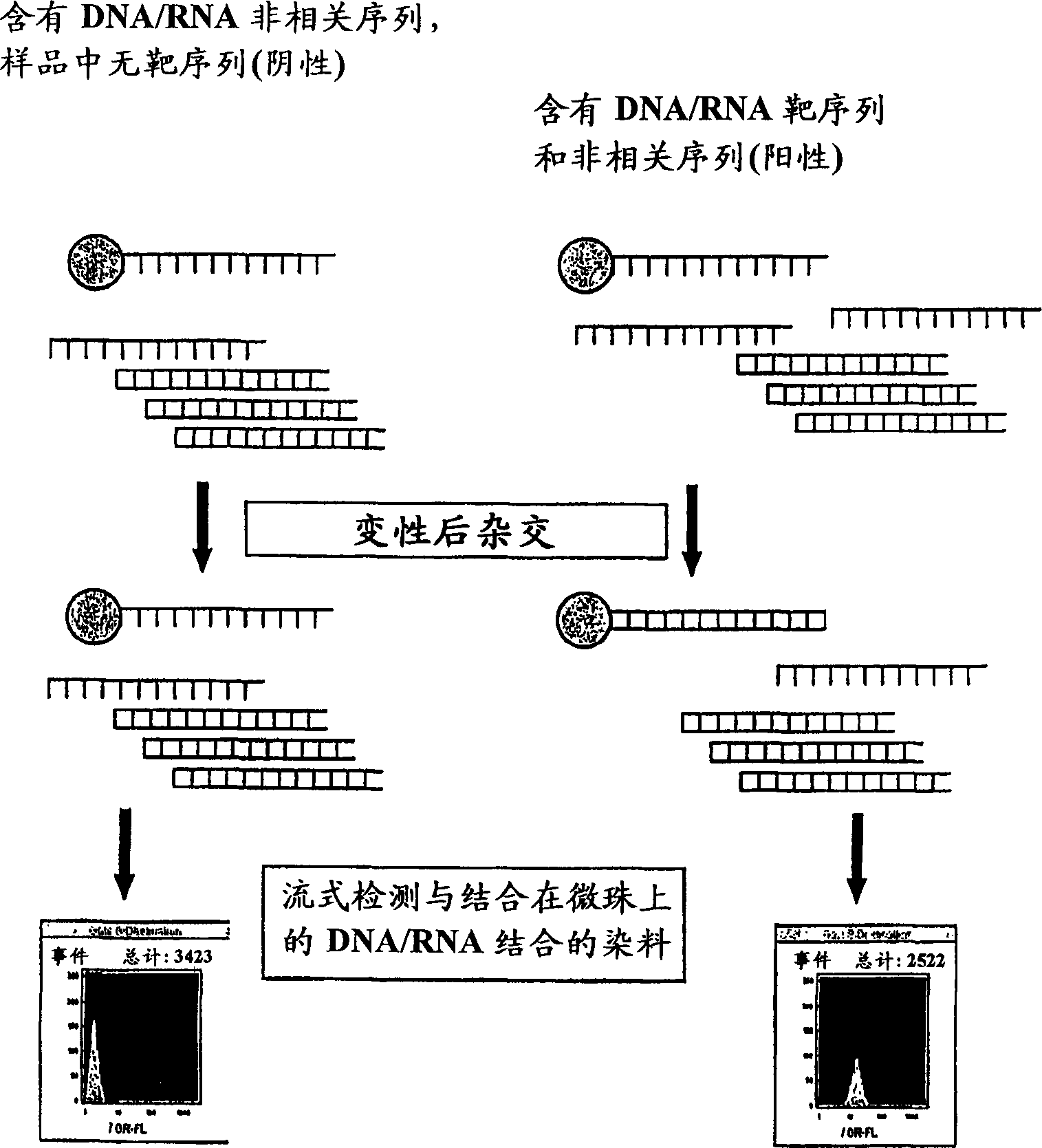
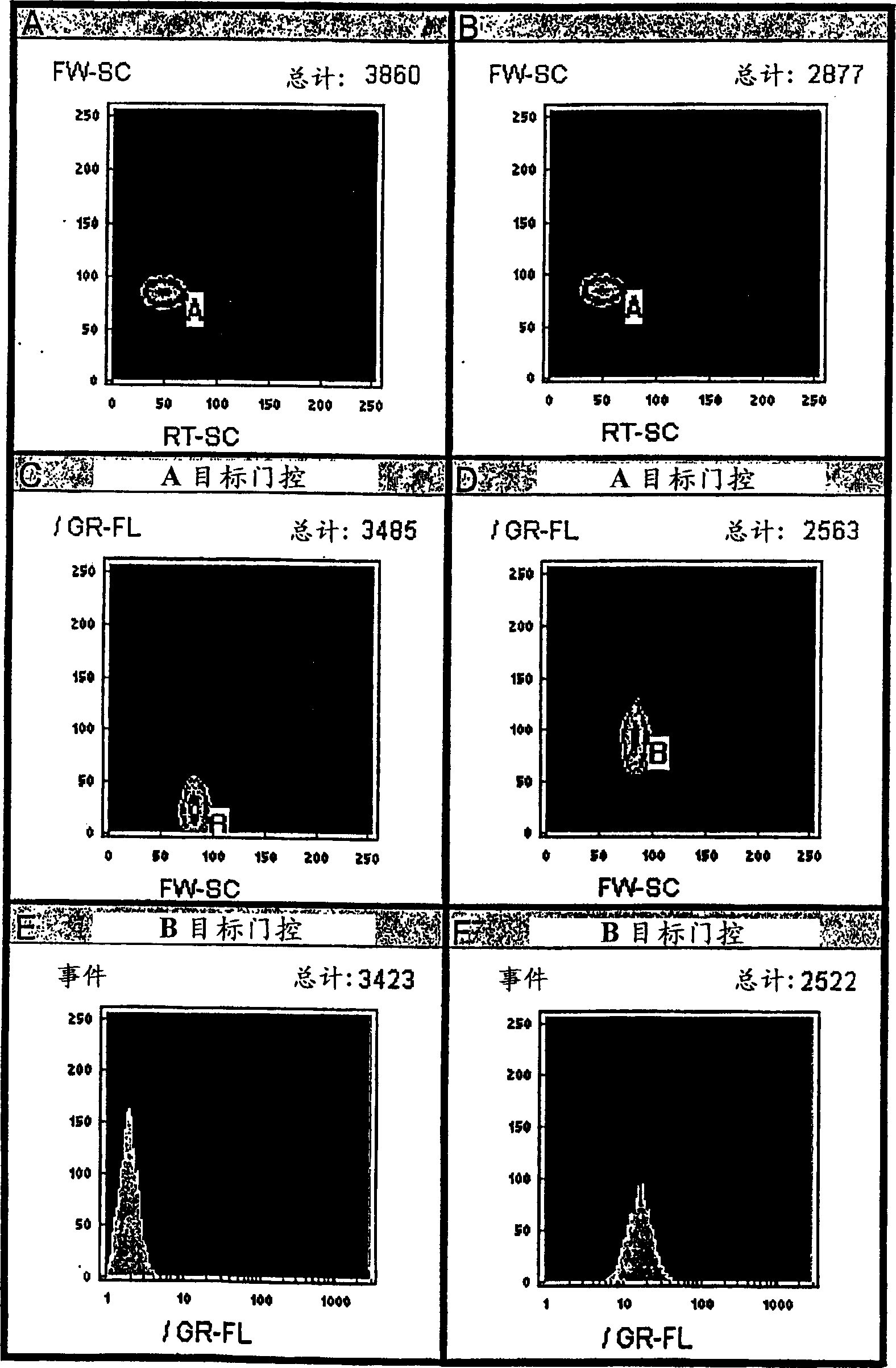
Homogeneous and multiplex assays for target nucleic acids hybridized to oligonucleotide probes immobilized on particulate and non-particulate substrates are described. Target nucleic acids are determined using detection methods, such as flow cytometric methods, capable of particle discrimination based on the light scattering or fluorescence properties of the particle, or by spatial resolution of oligonucleotides immobilized at specific loci on a substrate. Target-correlated fluorescence signal, originating from a target nucleic acid hybridized to the substrate-immobilized oligonucleotide is determined as a measure of the presence or amount of the target nucleic acid.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
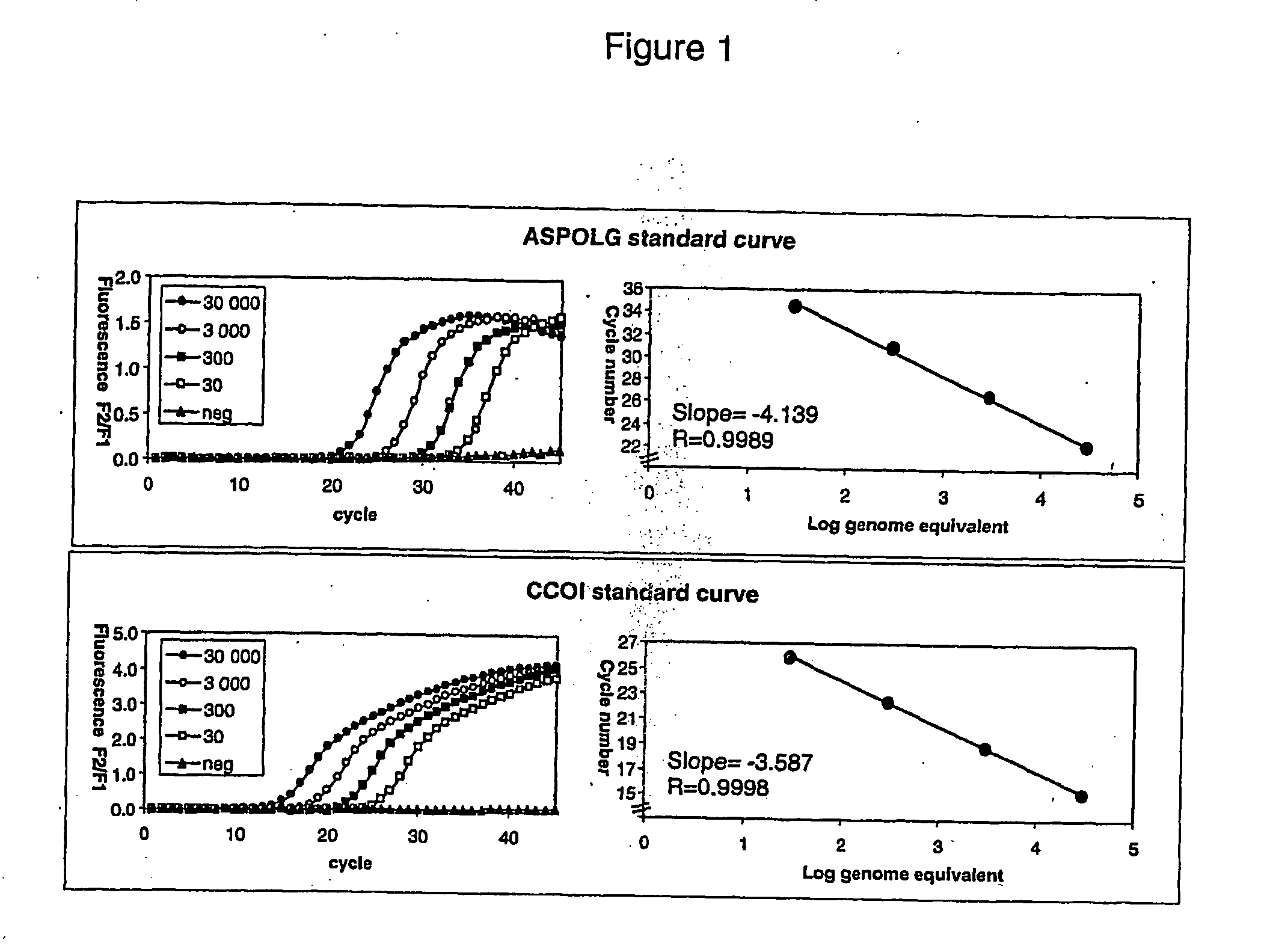
Diagnosis of sepsis using mitochondrial nucleic acid assays
InactiveUS20090181367A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyPcr assayMitophagy
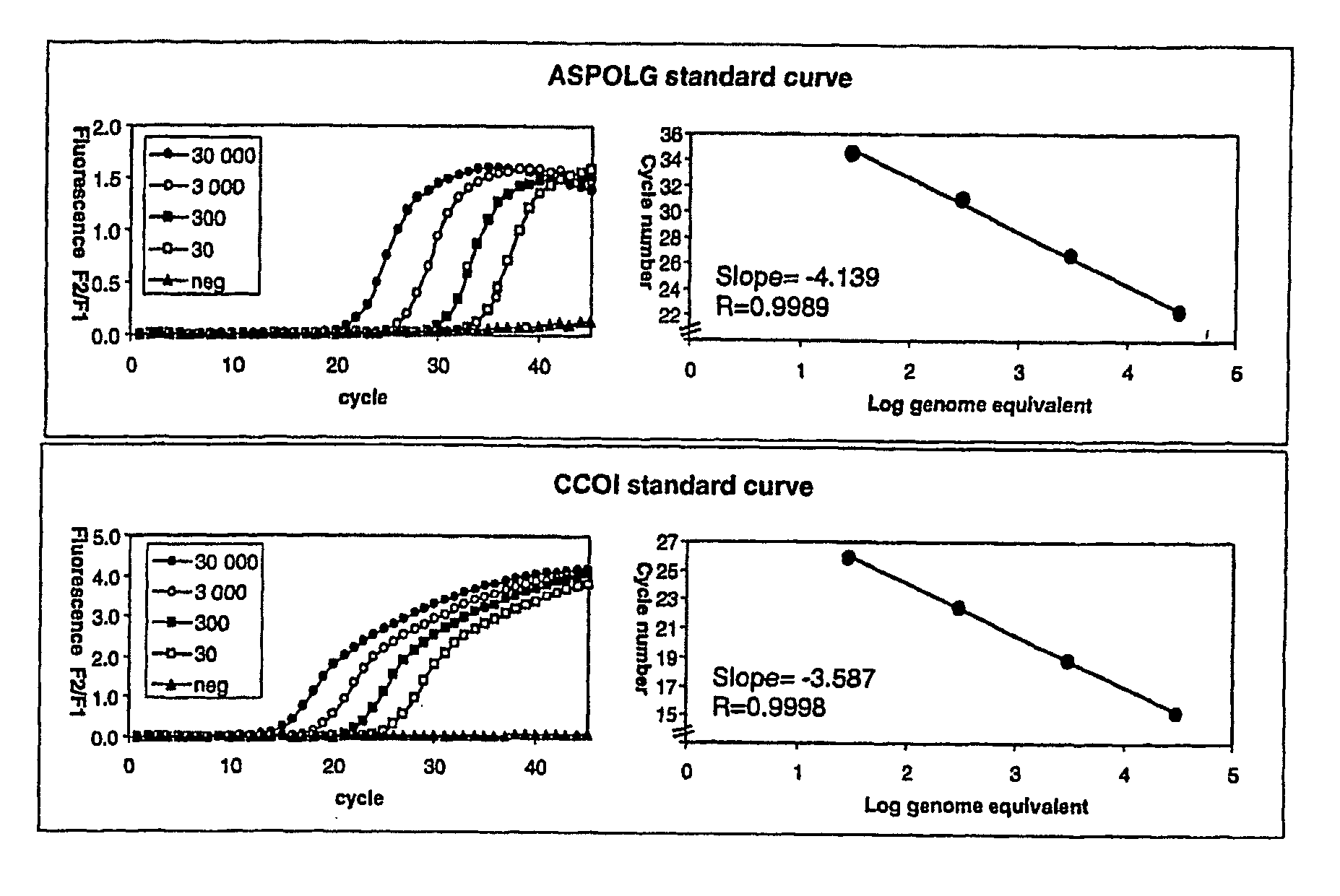
The invention provides assays to detect sepsis disease states in a subject by determining the relative amount of mitochondrial nucleic acid in the subject. The assays of the invention may include PCR assays, such semi-quantitative or quantitative PCR involving the co-amplification of a mitochondrial sequence and a reference sequence, such as a genomic sequence. Information from such assays may be evaluated to provide a ratio of mitochondrial nucleic acid to nuclear nucleic add in the cells of the subject.
Owner:COTE HELENE +2
Methods for diagnosing igg4-related disease
InactiveUS20150232935A1Accurate diagnosisAccurately optionally treatingBiocideOrganic active ingredientsIgG4-related diseaseDNA
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Diagnosis of sepsis using mitochondrial nucleic acid assays
InactiveUS20050214820A1Useful in detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyPcr assayMitophagy
The invention provides assays to detect sepsis disease states in a subject by determining the relative amount of mitochondrial nucleic acid in the subject. The assays of the invention may include PCR assays, such semi-quantitative or quantitative PCR involving the co-amplification of a mitochondrial sequence and a reference sequence, such as a genomic sequence. Information from such assays may be evaluated to provide a ratio of mitochondrial nucleic acid to nuclear nucleic acid in the cells of the subject.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
System and method for serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays
InactiveUS9114399B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceHandling system
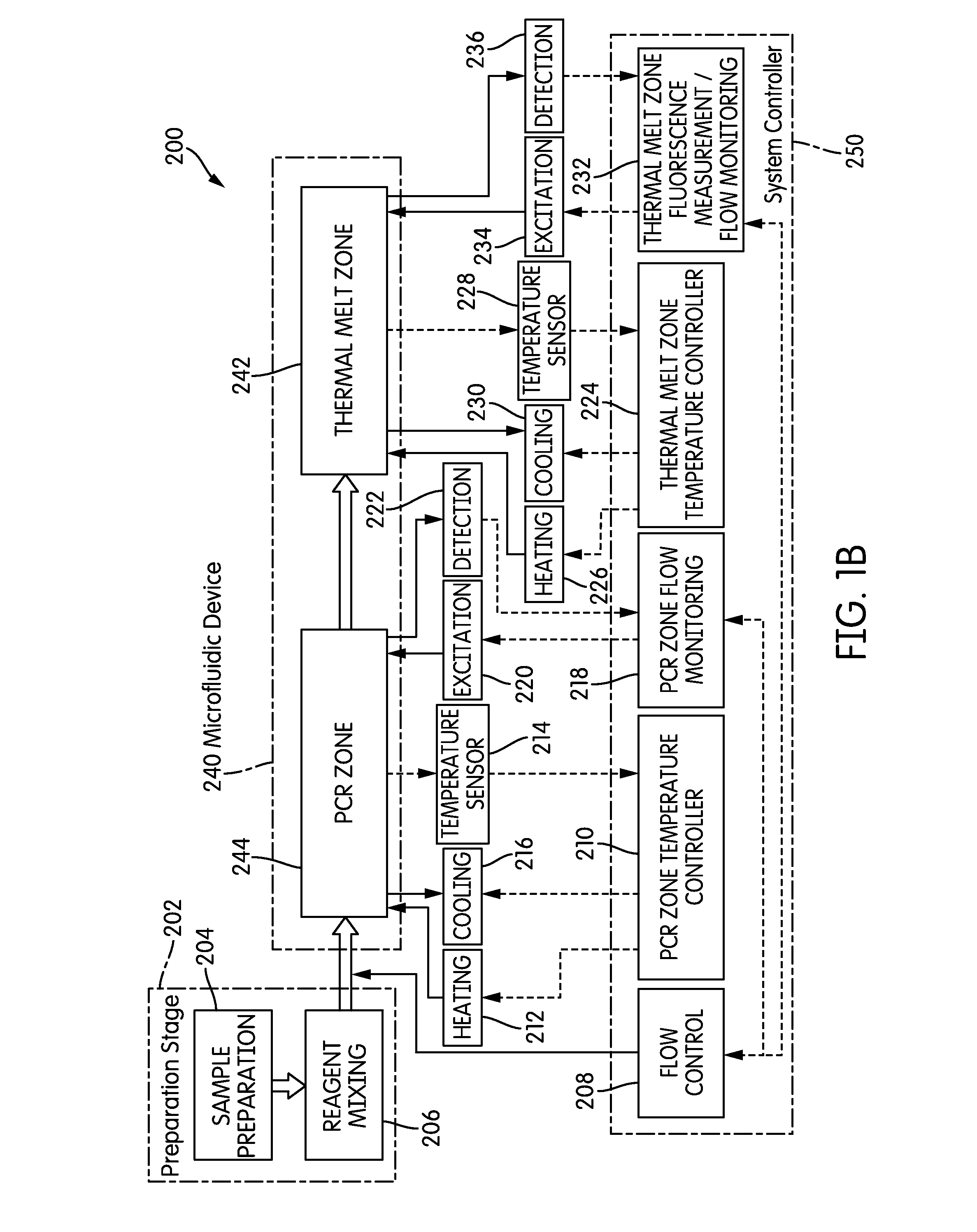
The present invention relates to systems and methods for the real time processing of nucleic acid during polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and thermal melt applications. According to an aspect of the invention, a system for the rapid serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays is provided. In one embodiment, the system includes, but is not limited to: a microfluidic cartridge having microfluidic (flow-through) channels, a fluorescence imaging system, a temperature measurement and control system; a pressure measurement and control system for applying variable pneumatic pressures to the microfluidic cartridge; a storage device for holding multiple reagents (e.g., a well-plate); a liquid handling system comprising at least one robotic pipettor for aspirating, mixing, and dispensing reagent mixtures to the microfluidic cartridge; systems for data storage, processing, and output; and a system controller to coordinate the various devices and functions.
Owner:CANON USA
Methods and computer program products for the quality control of nucleic acid assay
InactiveUS20050255467A1High dimensionalReduce dimensionalityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsData setQuality control
The disclosed invention provides methods and computer program products for the improved verification and controlling of assays for the analysis of nucleic acid variations by means of statistical process control. The invention is characterised in that variables of each experiment are monitored by measuring deviations of said variables from a reference data set and wherein said experiments or batches thereof are indicated as unsuitable for further interpretation if they exceed predetermined limits.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Probes for improved melt discrimination and multiplexing in nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS20160040219A1Increase multiplexing capacityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEndoribonucleaseMoiety
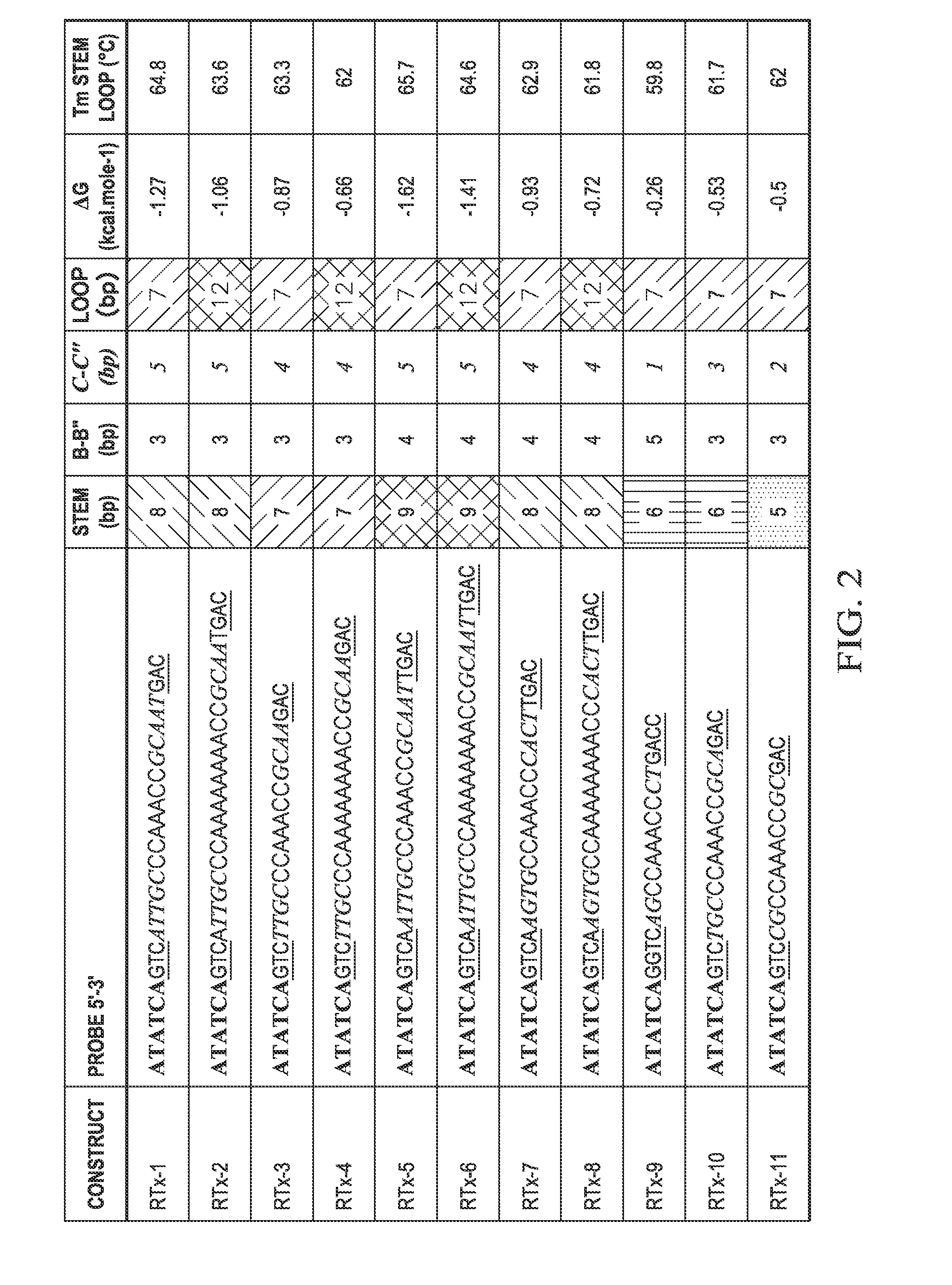
Methods and compositions for the detection and quantification of nucleic acids are provided. In certain embodiments, methods involve the use of cleavable probes that comprise a ribonucleotide position that is susceptible to endoribonuclease (e.g., RNase H) cleavage in the presence of target nucleic acid molecules. Probes of the embodiments may also comprise non-natural nucleotide linked to a reporter and / or quenching moiety.
Owner:LUMINEX
Highly orthogonal universal sequences for use in nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS8063196B2Easy to analyzeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeOrthogonal sequence
The invention provides a set of highly orthogonal six-code universal sequences for use in bDNA singleplex and multiplex nucleic acid hybridization assays. The six-code orthogonal sequences do not cross-hybridize and thus, minimize or eliminate the 3-mer cross-hybridization inherent in the second and third generation bDNA assays. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may be used in singleplex or multiplex bDNA assays quantitatively and qualitatively to determine mRNA levels in a sample; to screen for and genotype targets, such as viruses, that are present in low volumes in a sample; to screen for and genotype SNPs; and to measure changes in the amount of a gene in a sample such as when gene amplifications or deletions occur. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may also be used as universal capture probes to selectively bind assay components in a way that facilitates their further analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
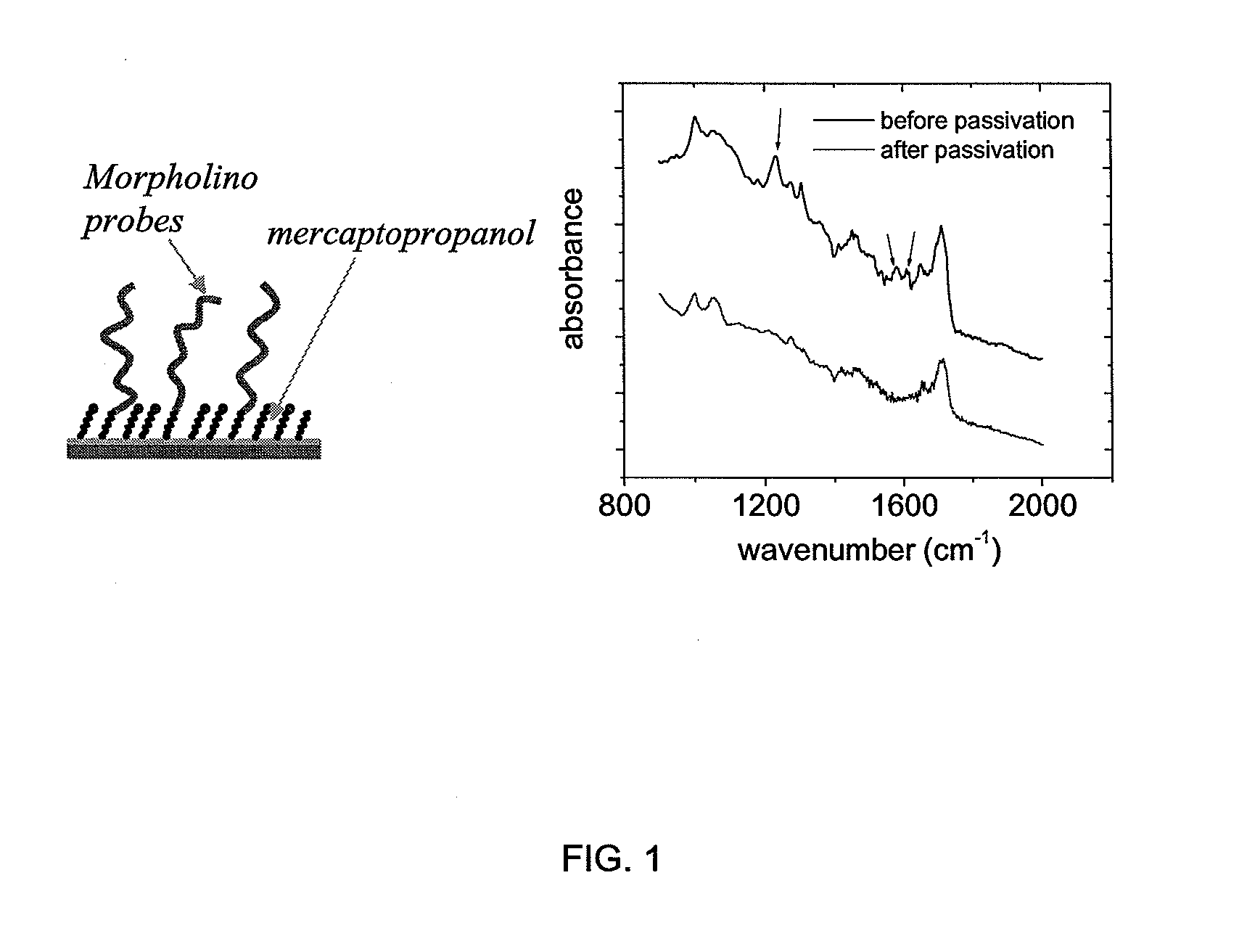
Surface-based nucleic acid assays employing morpholinos
InactiveUS20100035248A1Low backgroundEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSequence determinationNucleic acid molecule
The sequence determination, detection, and quantification of nucleic acid molecules through sequence-specific binding (hybridization) on a solid support, specifically when Morpholinos are used as the surface-immobilized probe species in surface-based nucleic acid assays, and the assays as disclosed herein.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
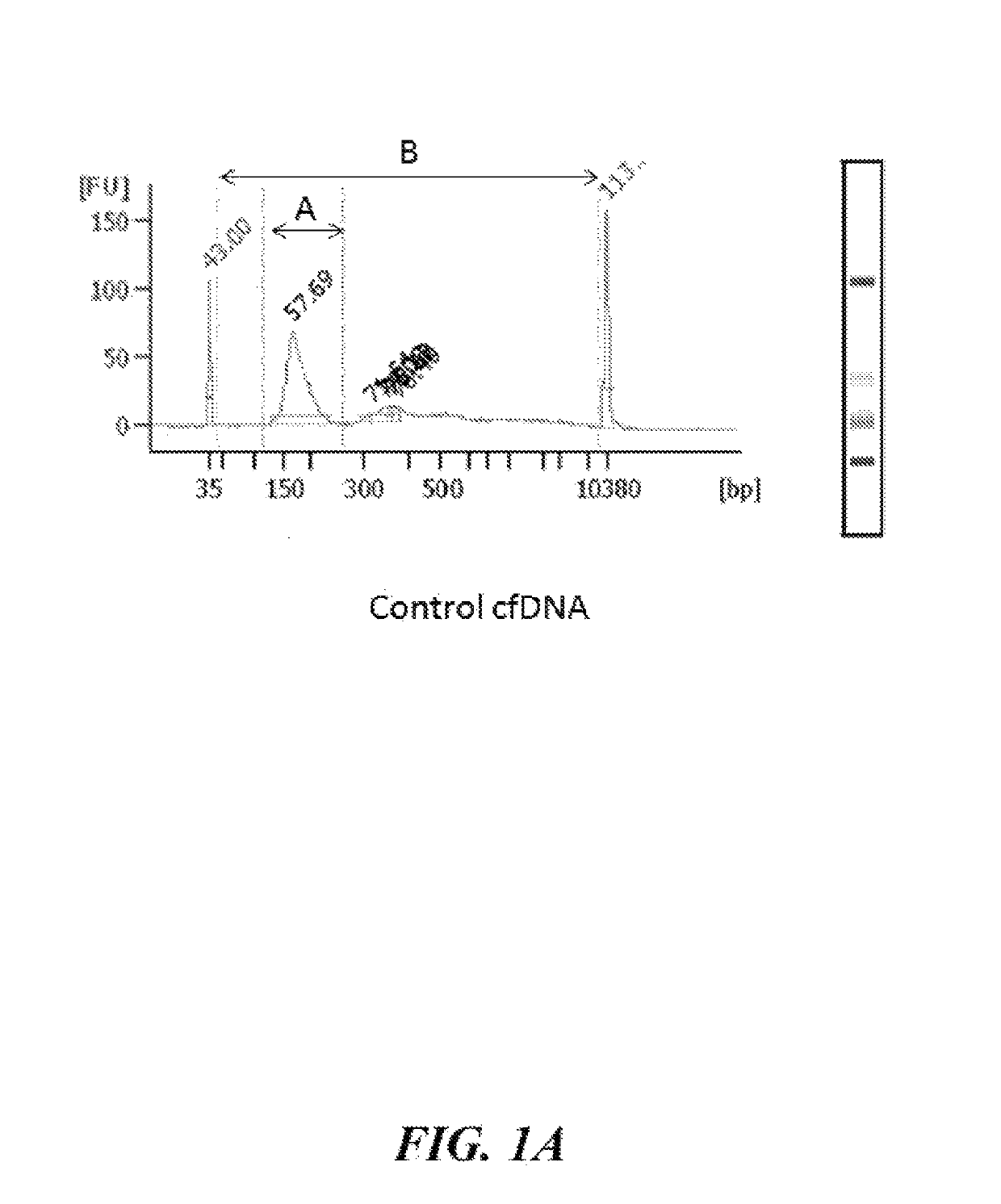
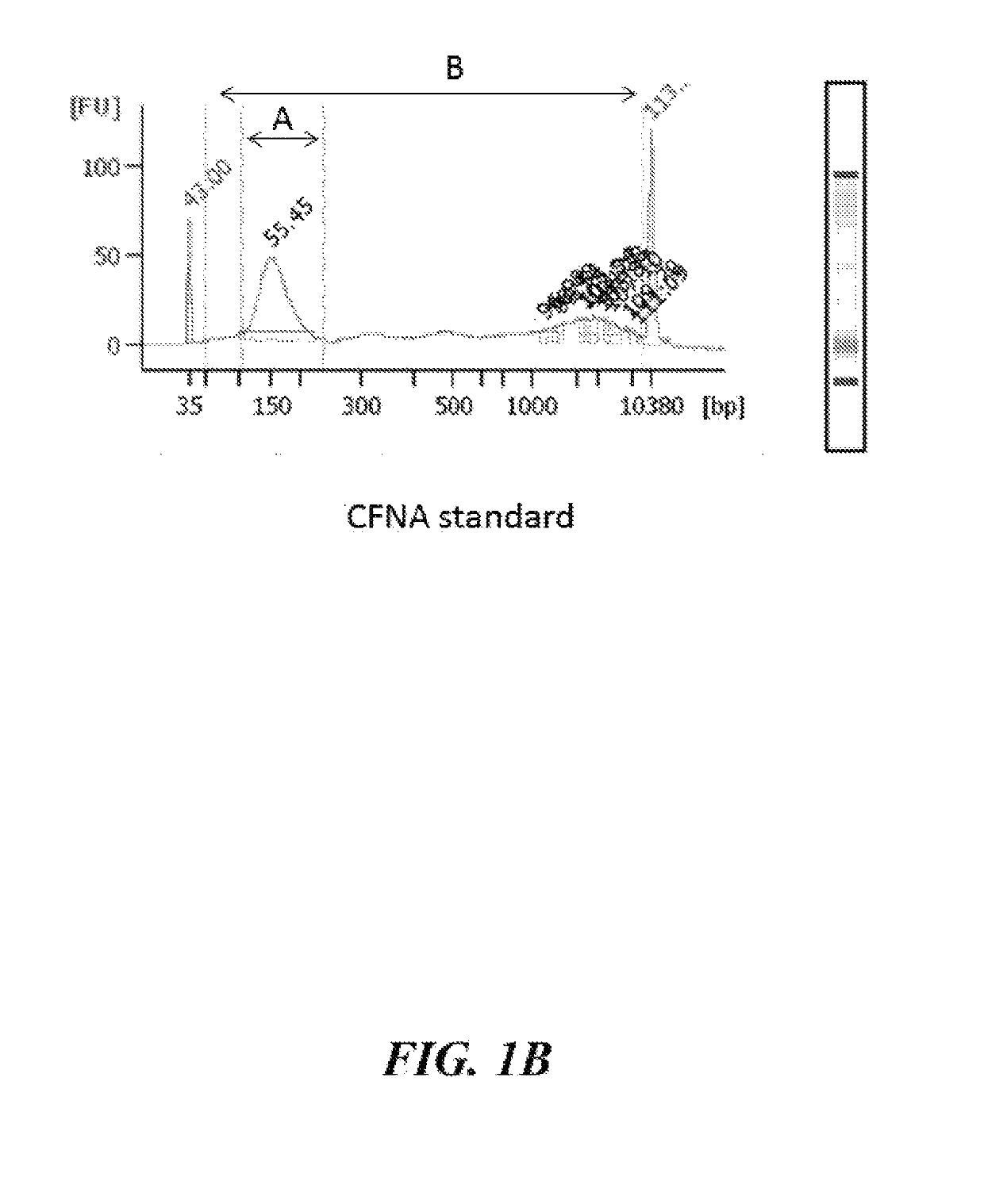
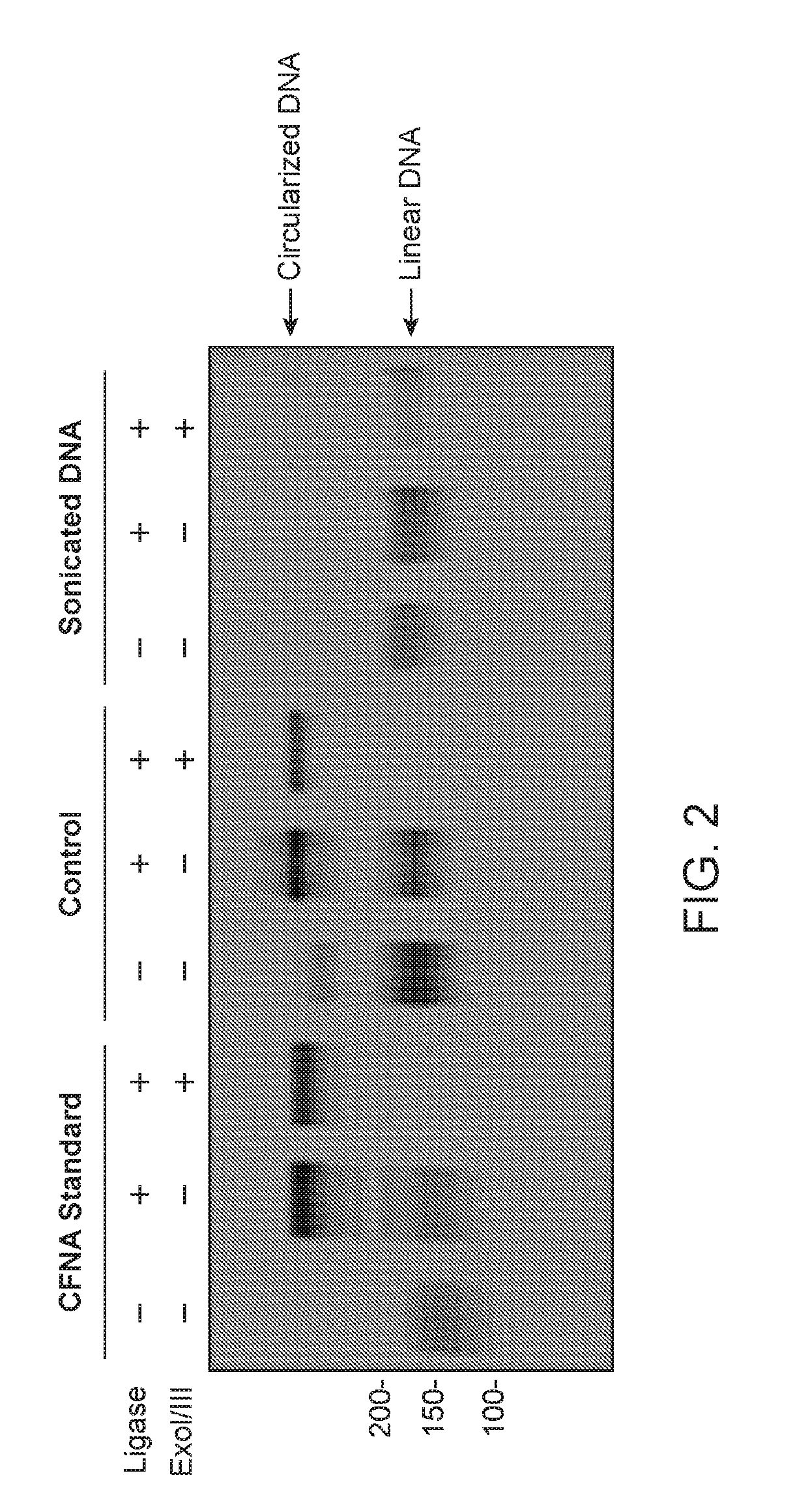
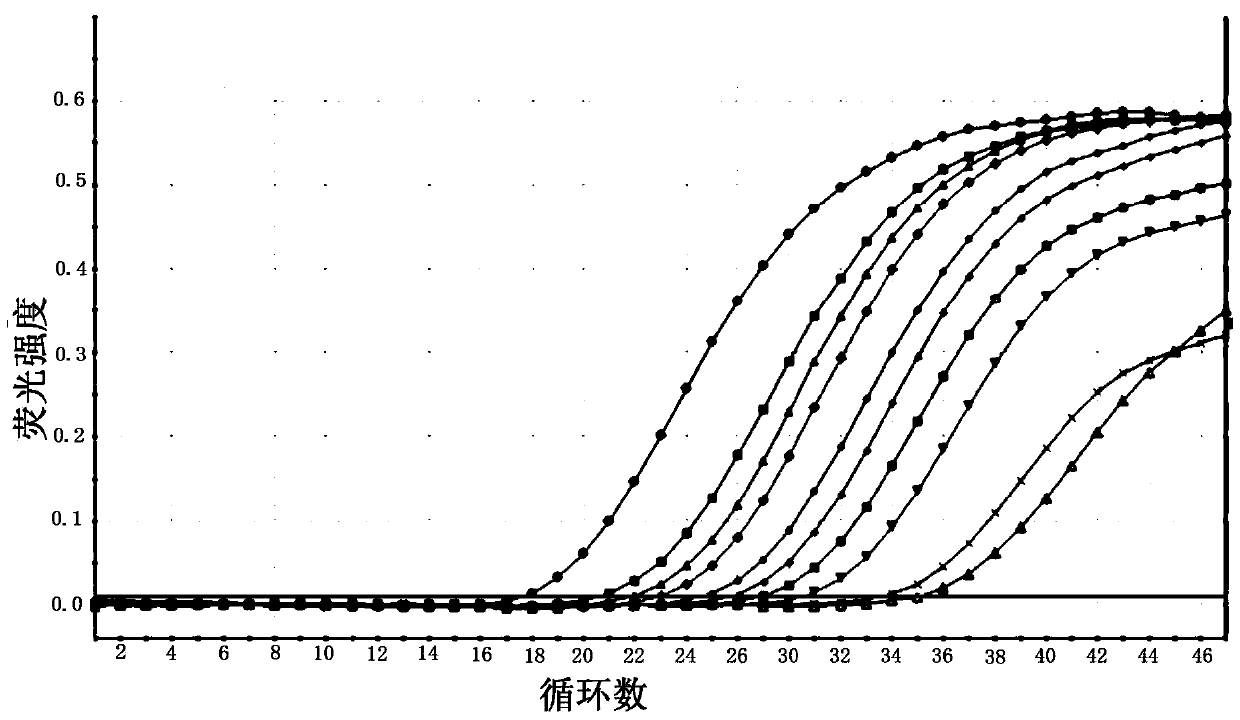
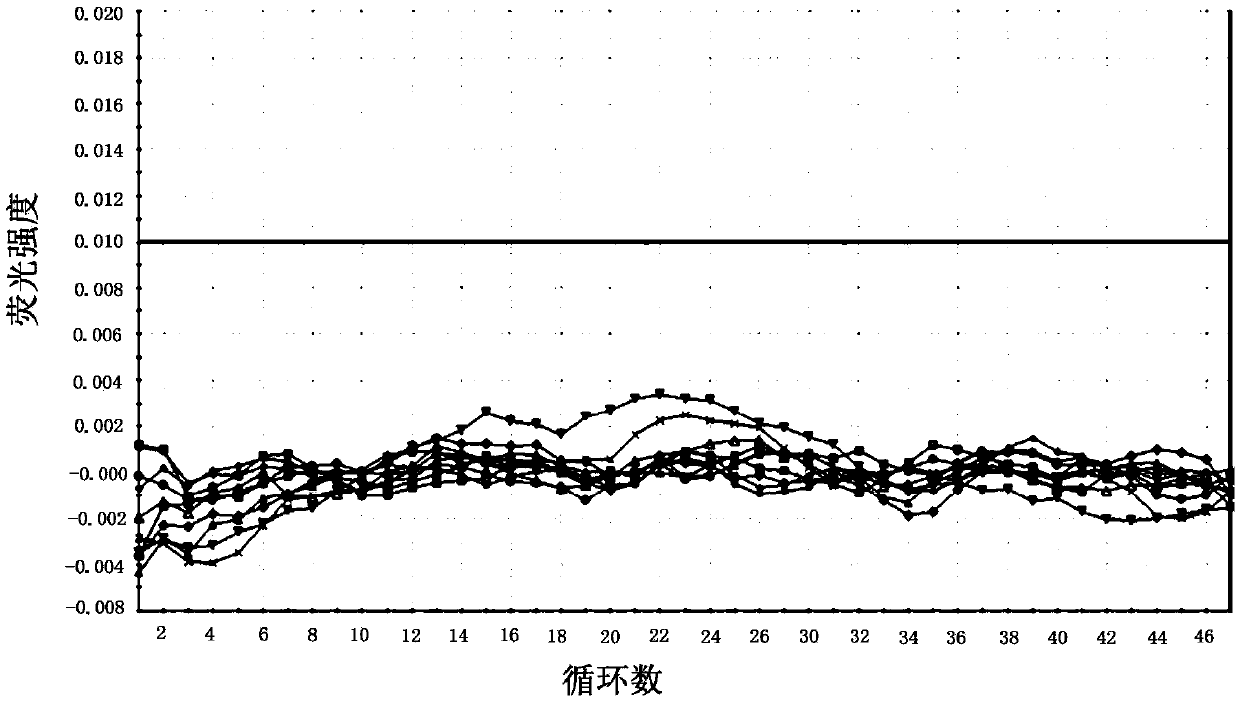
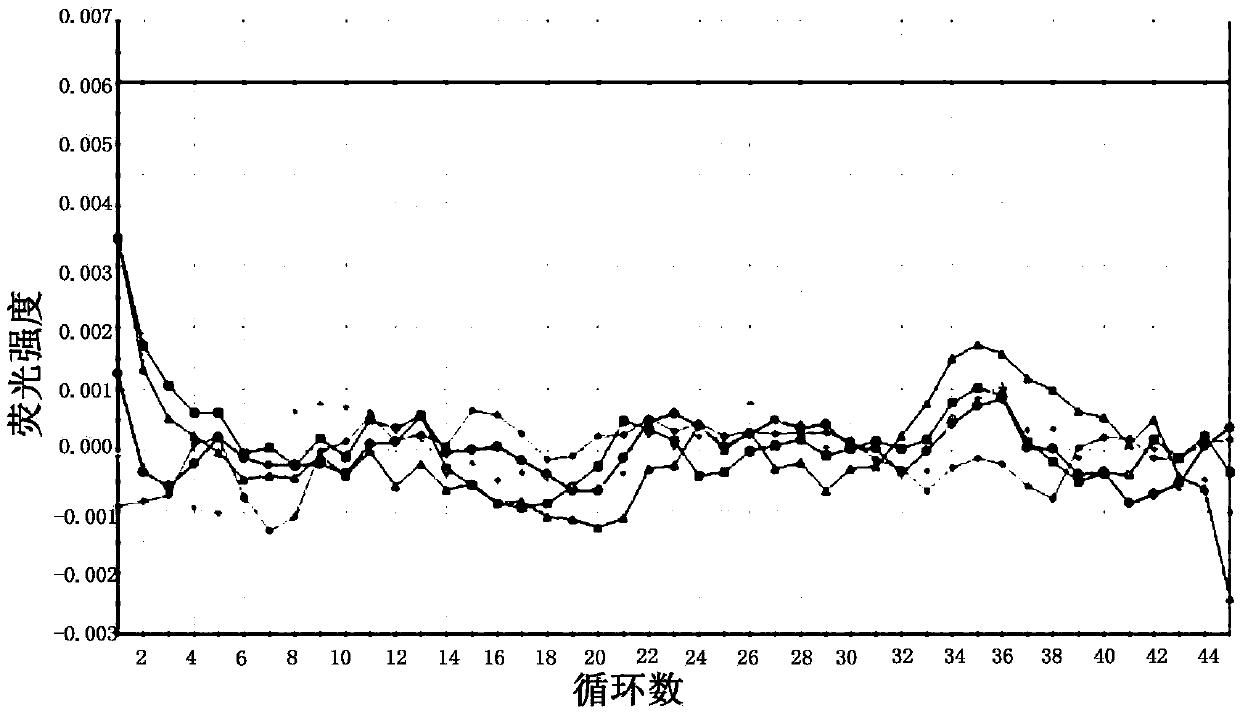
Cell-free nucleic acid standards and uses thereof
The present disclosure provides cell-free nucleic acid standards comprising genomic polynucleotides and methods of using cell-free nucleic acid standards comprising genomic polynucleotides for developing, optimizing, and validating cell-free nucleic acid assays.
Owner:ACCURAGEN HLDG LTD
Group B streptococcus nucleic acid assay kit based on PCR (polymerase chain reaction) fluorescent probe method
InactiveCN105368946AEasy to operateSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerFluorescence
The invention provides a group B streptococcus nucleic acid assay kit based on a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) fluorescent probe method. The group B streptococcus nucleic acid assay kit comprises nucleic acid releasing agents and PCR reaction fluid, wherein the nucleic acid releasing agents include 0.05-0.5mM / L surfactin, 100-300mM / L potassium chloride, 0.05-3% sodium dodecyl sulfate and 0.01-1% ethyl alcohol, the PCR reaction fluid comprises a forward primer, a reverse primer and a probe, the forward primer and the reverse primer are used for target polynucleotide amplification, and the probe is used for target polynucleotide assay. The group B streptococcus nucleic acid assay kit has the advantages that a nucleic acid release method is adopted, a pathogen coat protein structure is rapidly destroyed by strong protein denaturants, group B streptococcus-DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in unknown samples such as genital secretions and rectum secretions of perinatal pregnant women can be assayed rapidly, and assay sensitivity can be up to 500 copies / ml, so that reliable experimental bases are provided for group B streptococcus infection diagnosis, and the problems of poor assay specificity and low sensitivity of the prior art can be solved.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
JEV (Japanese type B encephalitis virus) nucleic acid assay kit and application thereof
ActiveCN105349696AReduce sensitivityLow specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFreeze-dryingMagnesium salt
The invention discloses a JEV (Japanese type B encephalitis virus) nucleic acid assay kit and application thereof. The kit comprises RPA (recombinase polymerase amplification) freeze-dried reagents, PRA reaction primers, an RPA reaction probe, buffer solution, magnesium salt solution and double-distilled water. The RPA reaction probe is used for real-time quantitative detection of RPA nucleic acid amplification products. Low contamination is achieved due to the fact that users do not need to open caps during the whole detection. The whole reaction is performed in a constant temperature of 38 DEG C, and users can determine and read results within 5-20 minutes by observing fluorescent curves. The JEV nucleic acid assay kit has the advantages of high sensitivity and specificity, operational convenience, quick reaction, portability, low contamination and the like.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Probes for improved melt discrimination and multiplexing in nucleic acid assays
Methods and compositions for the detection and quantification of nucleic acids are provided. In certain embodiments, methods involve the use of primers or probes that comprise a non-natural nucleotide linked to a reporter. Target nucleic acids are detected by the polymerization of a complementary probe or primer that incorporated a cognate non-natural nucleotide linked to a quencher.
Owner:LUMINEX
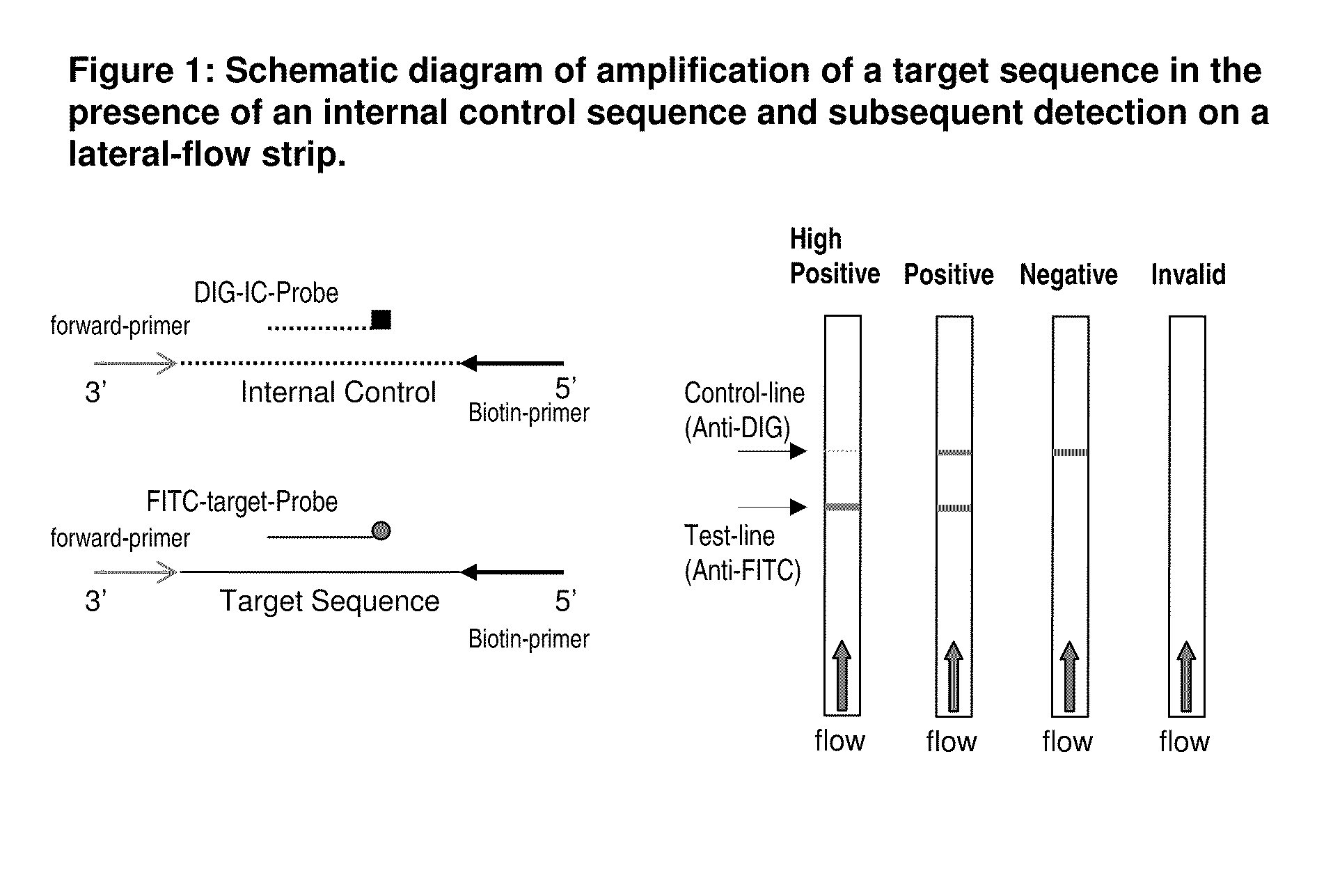
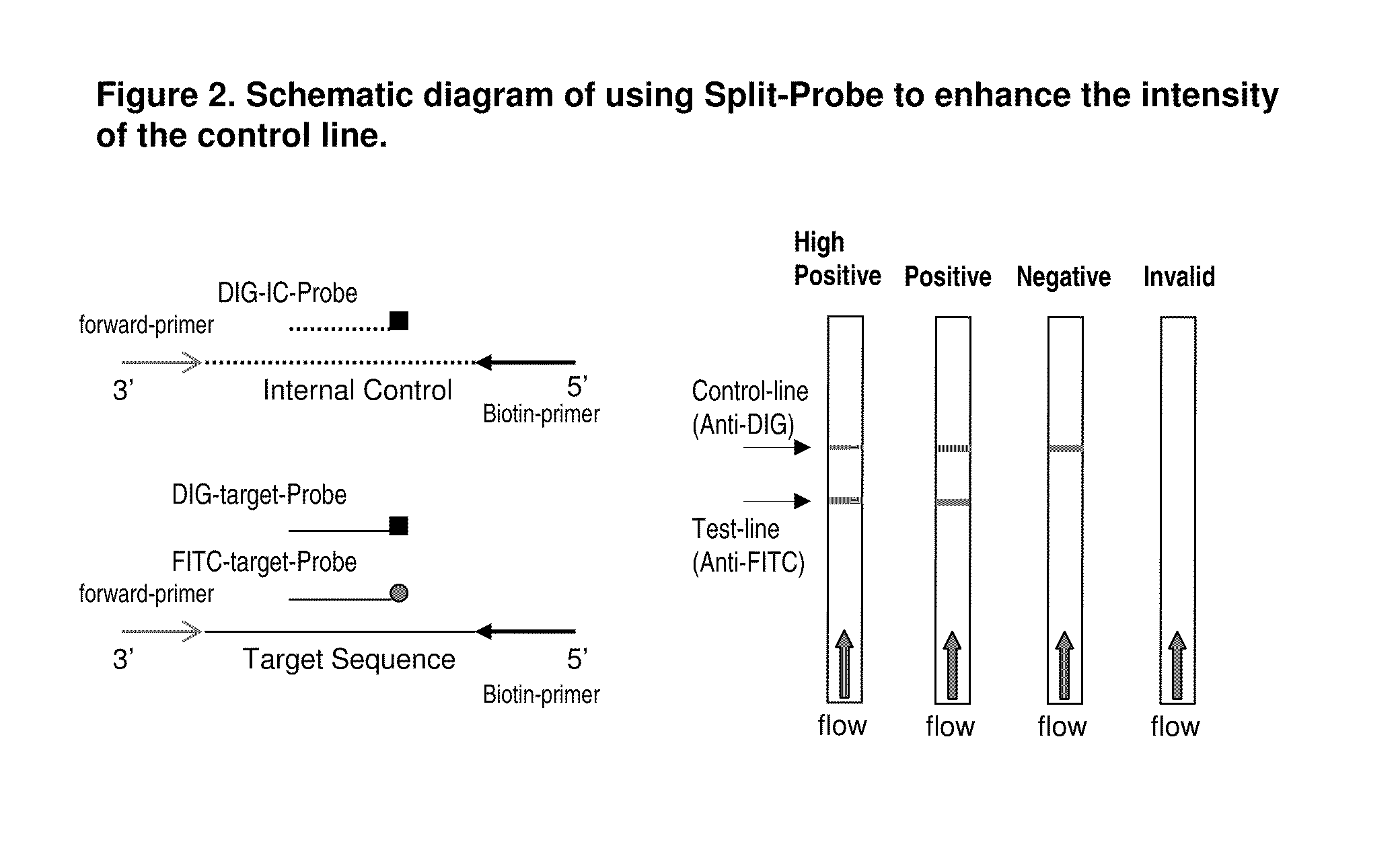
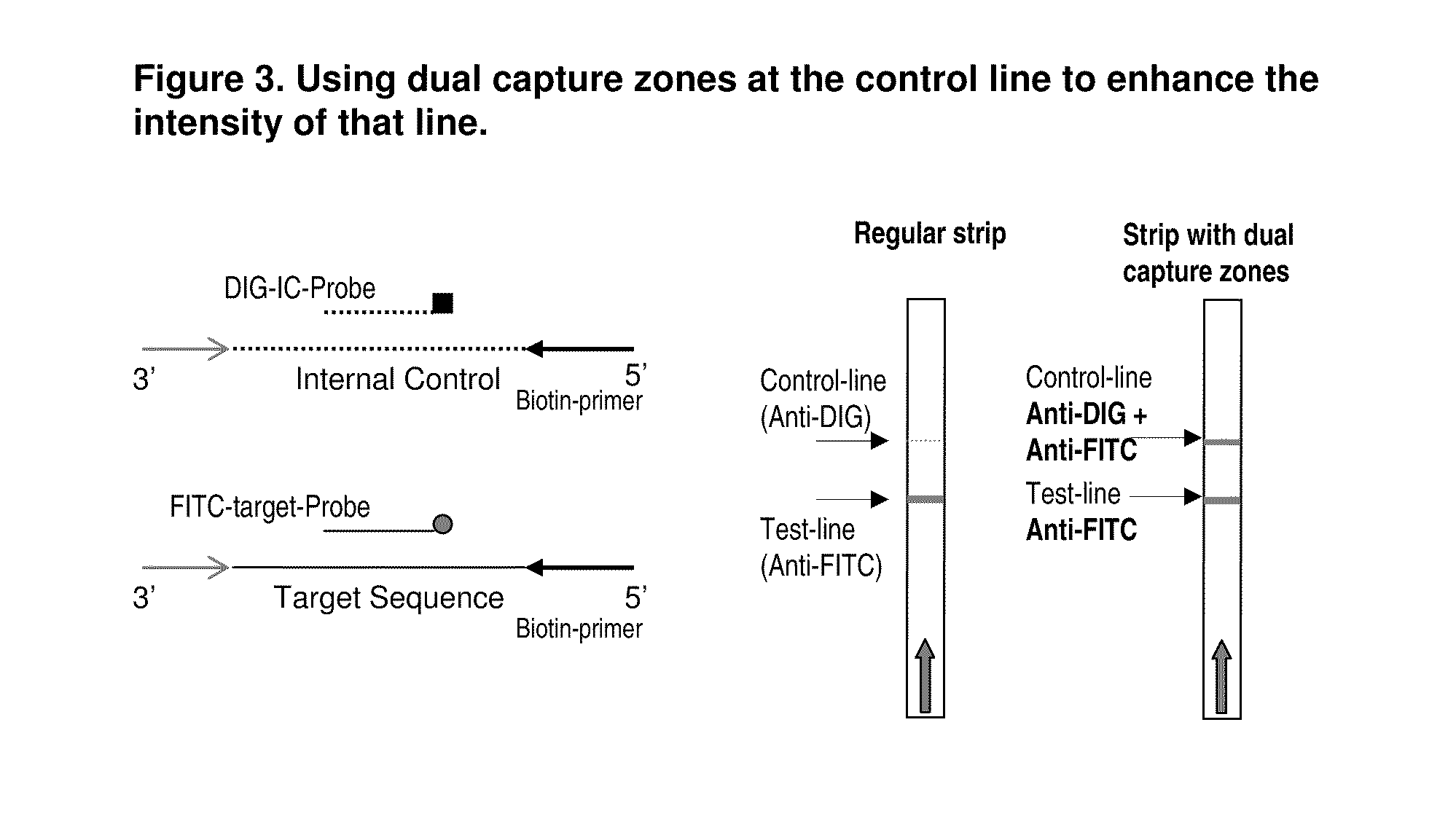
Detection of nucleic acid amplification products in the presence of an internal control sequence on an immunochromatographic strip
ActiveUS20110229887A1Easy to confirm successAccurate explanationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisMolecular biologyNucleic acid assay
Compositions and methods useful in nucleic acid assays are provided. The invention permits detection of test and control nucleic acids. Test nucleic acids can be immobilized at multiple locations, such that amplification of either a test nucleic acid or a control nucleic acid provides a captured nucleic acid in a control capture zone.
Owner:BIOHELIX CORP
Coxsackie virus A16 type RT-LAMP (reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification) nucleic acid assay kit
InactiveCN102373293ALow costStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHand-foot-and-mouth diseaseCoxsackievirus a16
The invention relates to the field of biological assay technical application, and in particular relates to a coxsackie virus A16 type RT-LAMP (reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification) nucleic acid assay kit. The kit comprises RT-LAMP reaction solutions containing four RT-LAMP primers, as well as 10000X SYBR Green I dye. The kit has the characteristics of good specificity, high sensitivity, simple operation method, quick assay, easily judged result, low cost and the like, can well fulfill the current urging requirement for field assay of hand-foot-and-mouth disease, can beused for field quick assay of disease prevention and control institutions, hospitals and kindergartens, is easy for large-scale popularization and application in grass-roots places, and has wide market prospect and great economical and social benefit.
Owner:何雅青 +2
Compositions and methods relating to nucleic acid reference standards
The invention relates to novel nucleic acid reference standards comprising a nucleic acid comprising a known target sequence bound with a microparticulate binding agent where the binding agent includes liposomes, polyamines (e.g., nylon), siliceous compounds (e.g., silica gel, fumed silica, diatomaceous earth, glass particles, amine-modified silica, and the like), zeolites (e.g., low alumina zeolyte), polystyrene (e.g., amine-modified polystyrene, carboxy-polystyrene particles, and the like), chitin, chitosan, and combinations of these compounds. The reference standard is useful for use as a standard in any nucleic acid assay where the presence or absence of a nucleic acid of interest is being assessed. The reference standard is stable and provides a control for assessing whether the nucleic acid assay was performed properly. The invention further relates to methods of producing such reference standards and kits for using and producing the same pursuant to the teachings of the invention.
Owner:MAINE MOLECULAR QUALITY CONTROLS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com