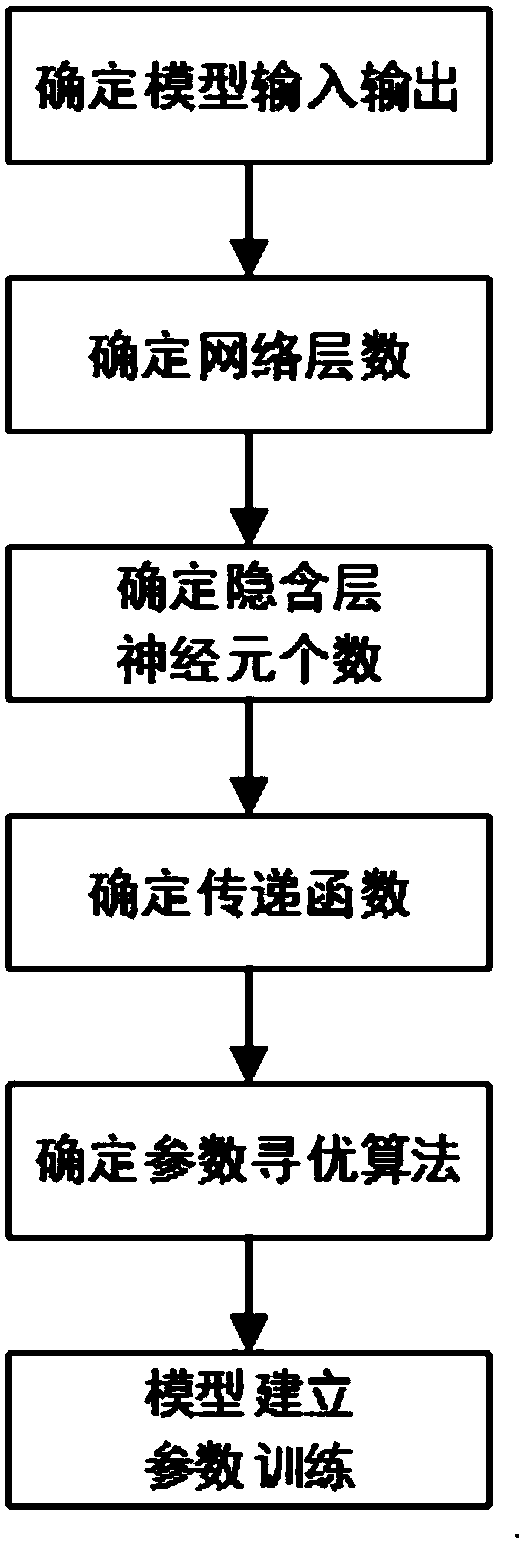
Patents
Literature
252 results about "Statistical process control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Statistical process control (SPC) is a method of quality control which employs statistical methods to monitor and control a process. This helps to ensure that the process operates efficiently, producing more specification-conforming products with less waste (rework or scrap). SPC can be applied to any process where the "conforming product" (product meeting specifications) output can be measured. Key tools used in SPC include run charts, control charts, a focus on continuous improvement, and the design of experiments. An example of a process where SPC is applied is manufacturing lines.
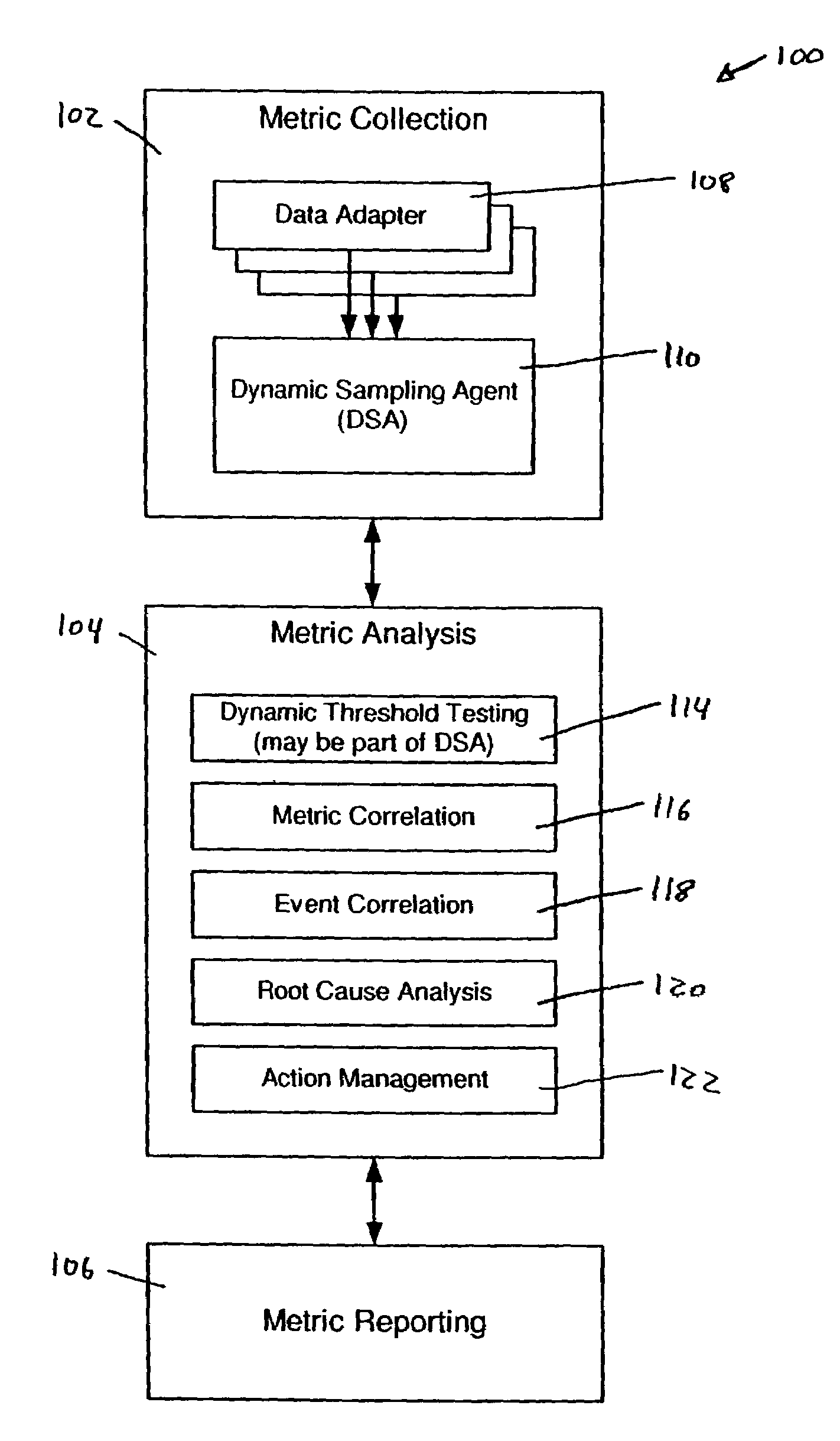
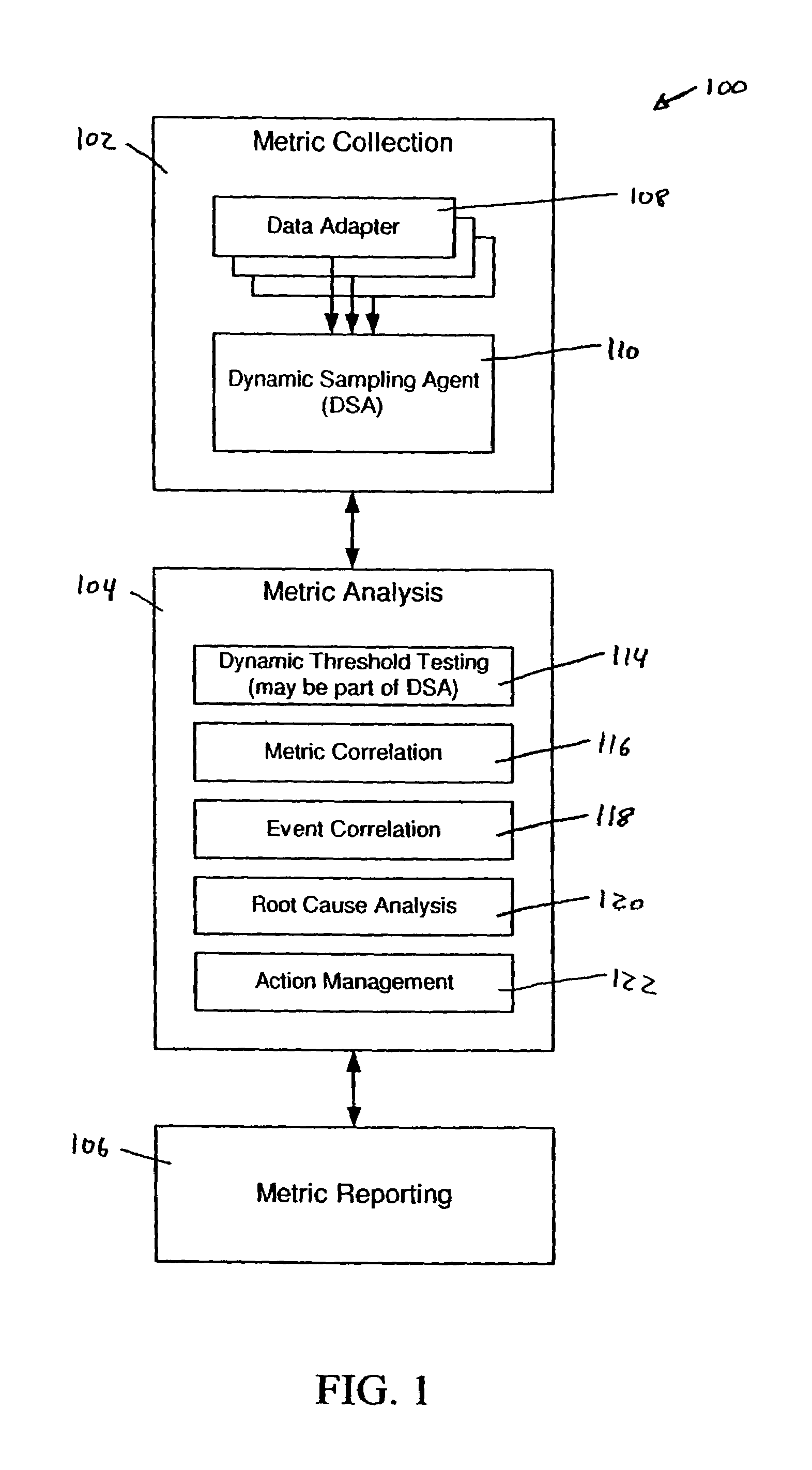
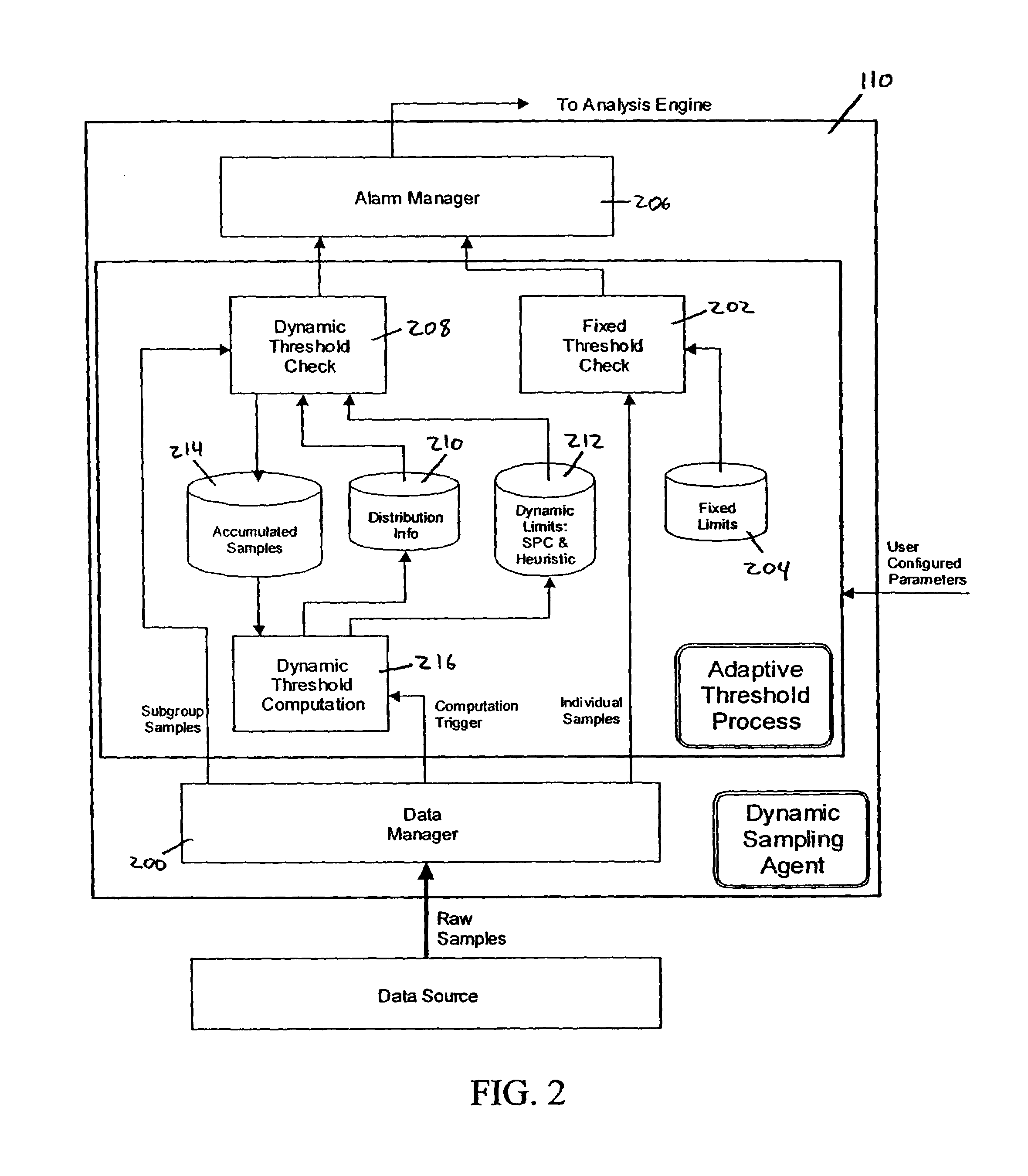
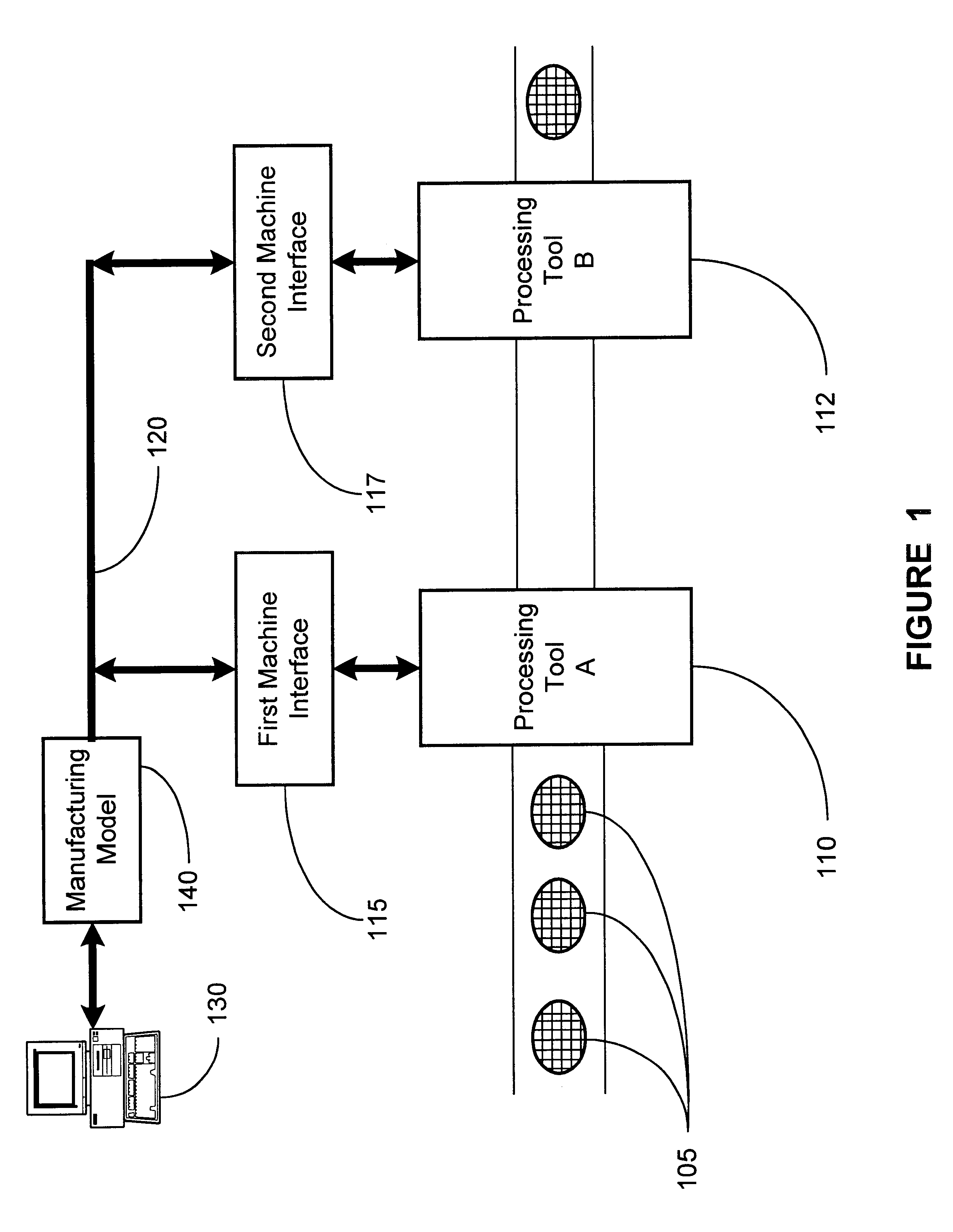
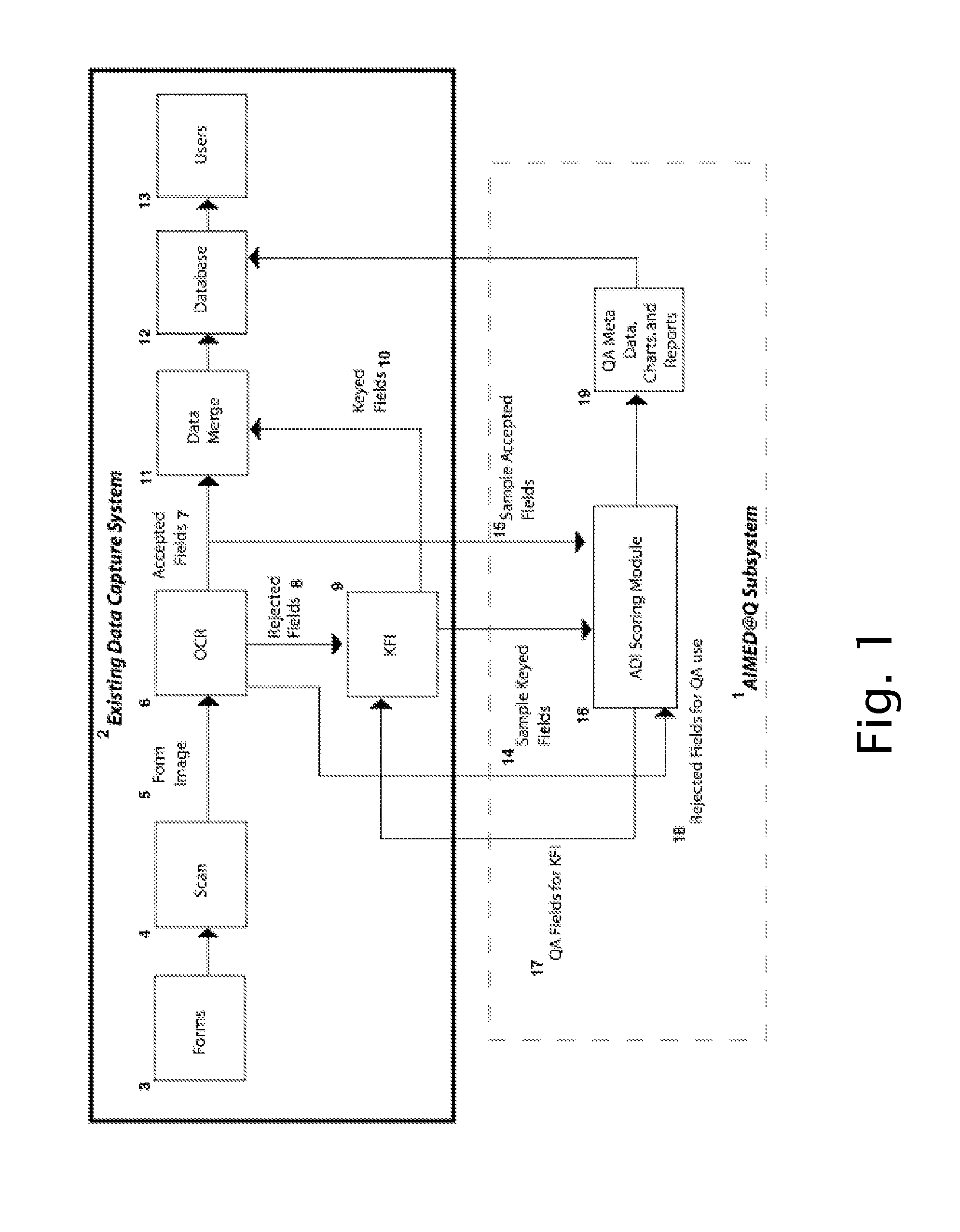
System and methods for adaptive threshold determination for performance metrics
A system and method for dynamically generating alarm thresholds for performance metrics, and for applying those thresholds to generate alarms is described. Statistical methods are used to generate one or more thresholds for metrics that may not fit a Gaussian or normal distribution, or that may exhibit cyclic behavior or persistent shifts in the values of the metrics. The statistical methods used to generate the thresholds may include statistical process control (SPC) methods, normalization methods, and heuristics.
Owner:ATERNITY LLC
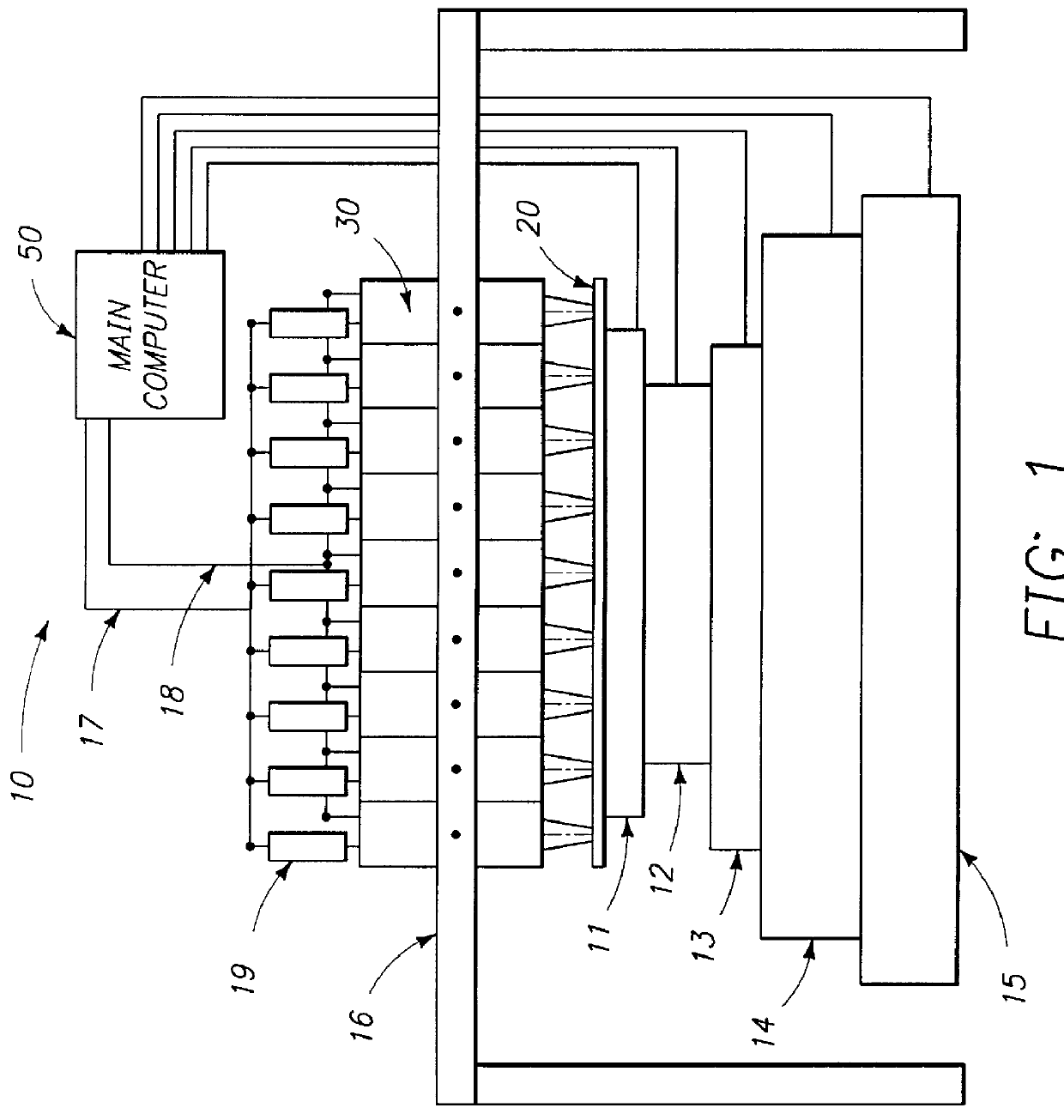
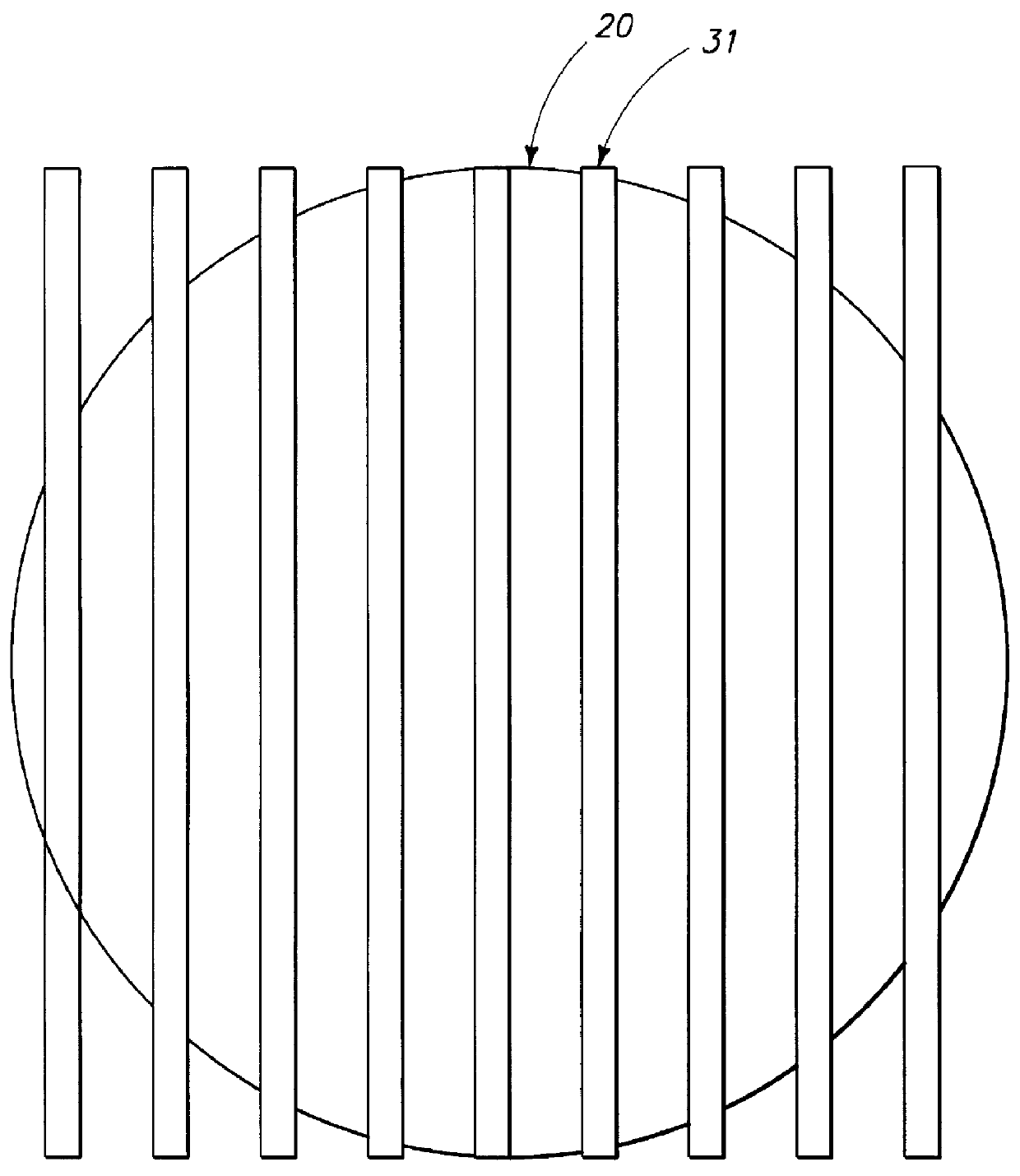
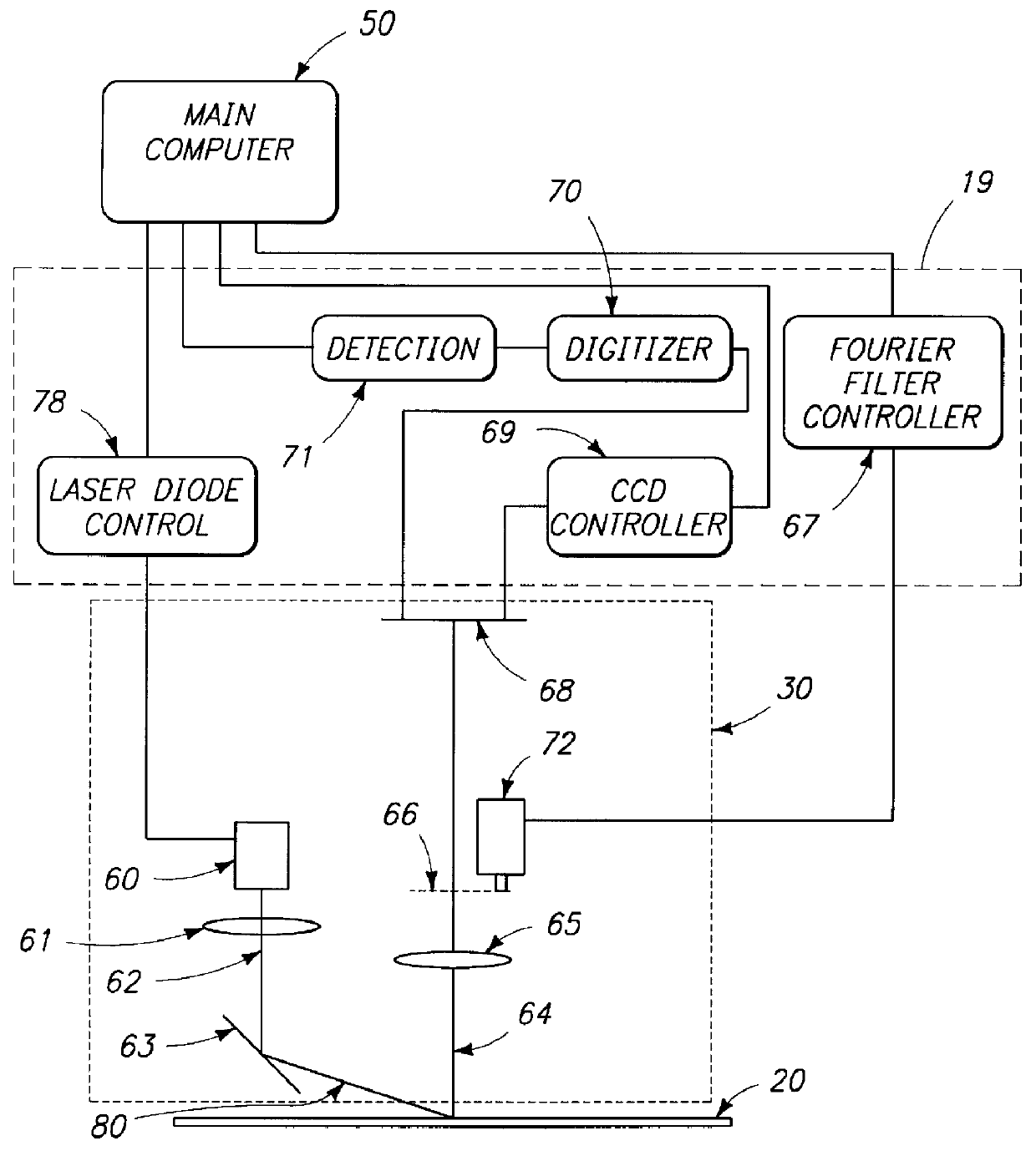
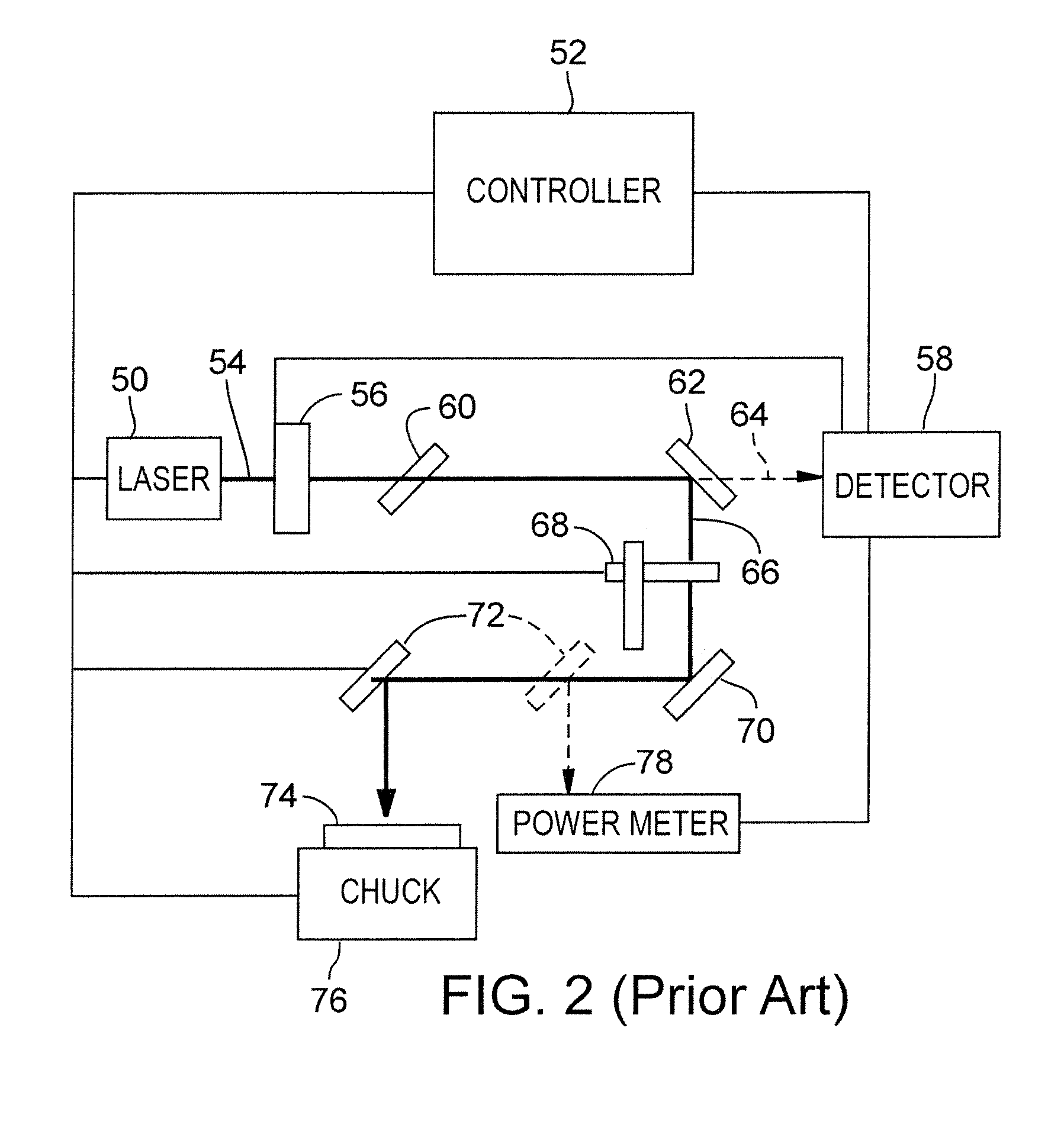
System and method for inspecting semiconductor wafers
InactiveUS6020957ALow costFaster throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingImage subtraction
A method for inspecting semiconductor wafers is provided in which a plurality of independent, low-cost, optical-inspection subsystems are packaged and integrated to simultaneously perform parallel inspections of portions of the wafer, the wafer location relative to the inspection being controlled so that the entire wafer is imaged by the system of optical subsystems in a raster-scan mode. A monochromatic coherent-light source illuminates the wafer surface. A darkfield-optical system collects scattered light and filters patterns produced by valid periodic wafer structures using Fourier filtering. The filtered light is processed by general purpose digital-signal processors. Image subtraction methods are used to detect wafer defects, which are reported to a main computer to aid in statistical process control, particularly for manufacturing equipment.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
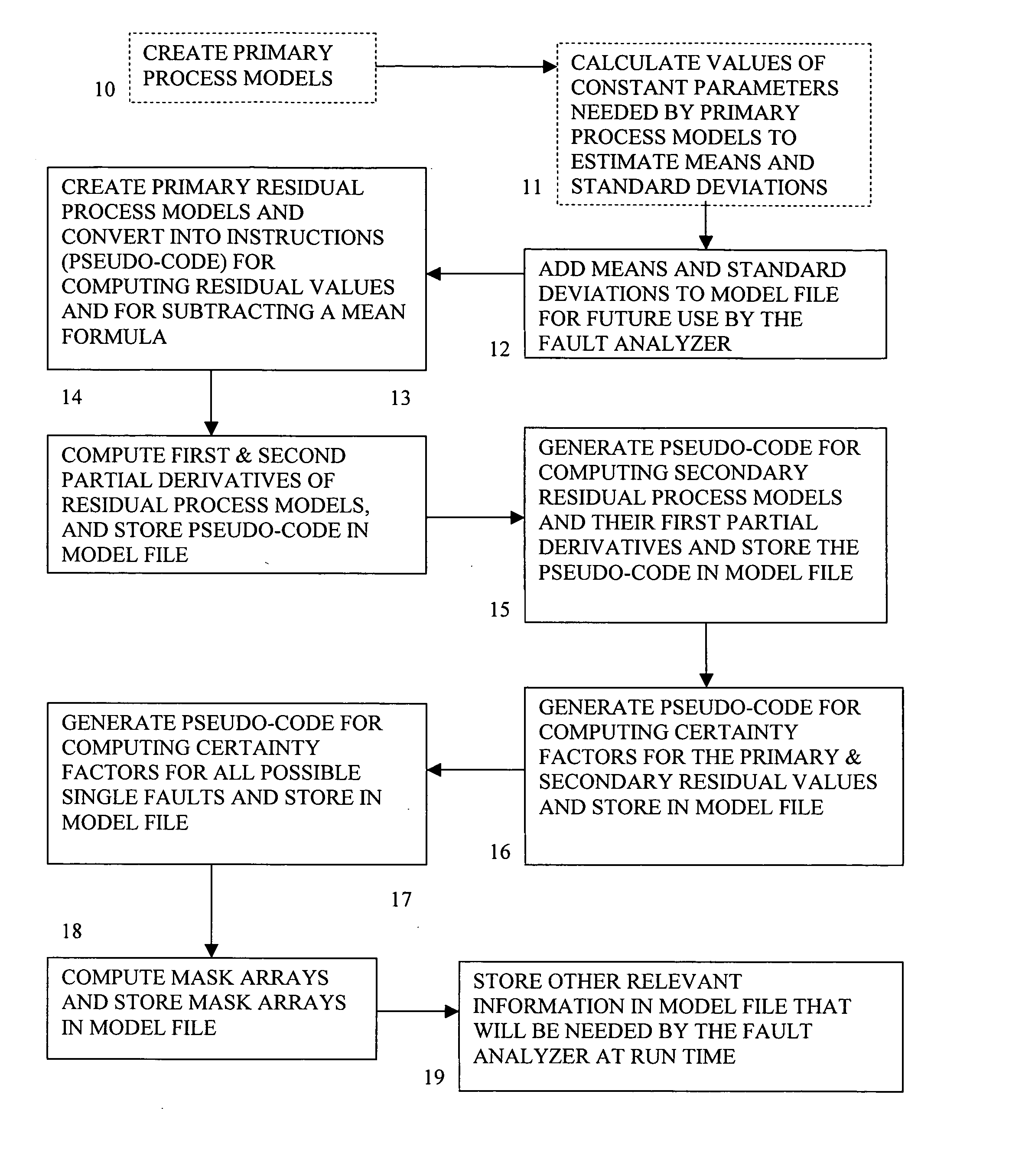
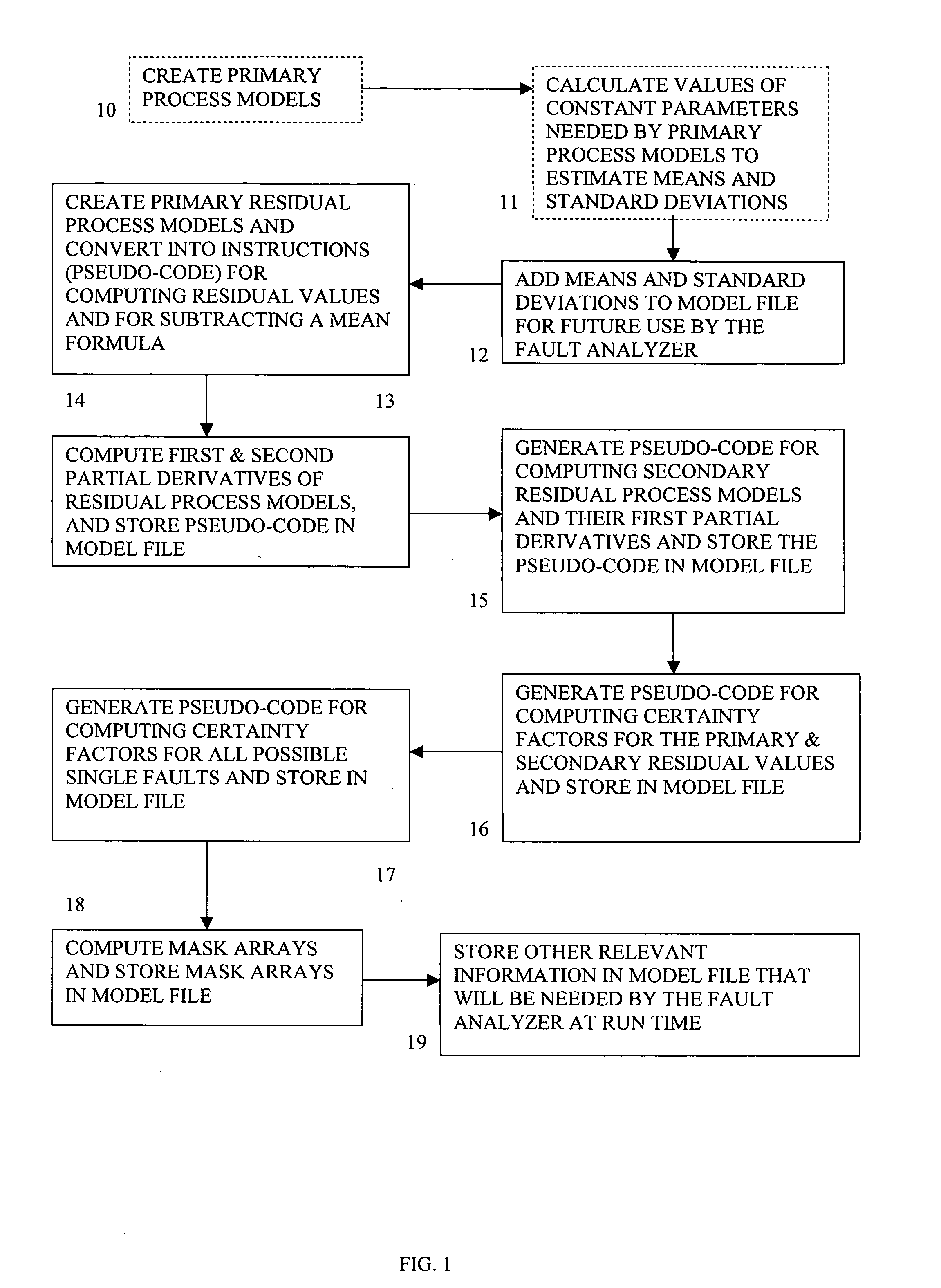
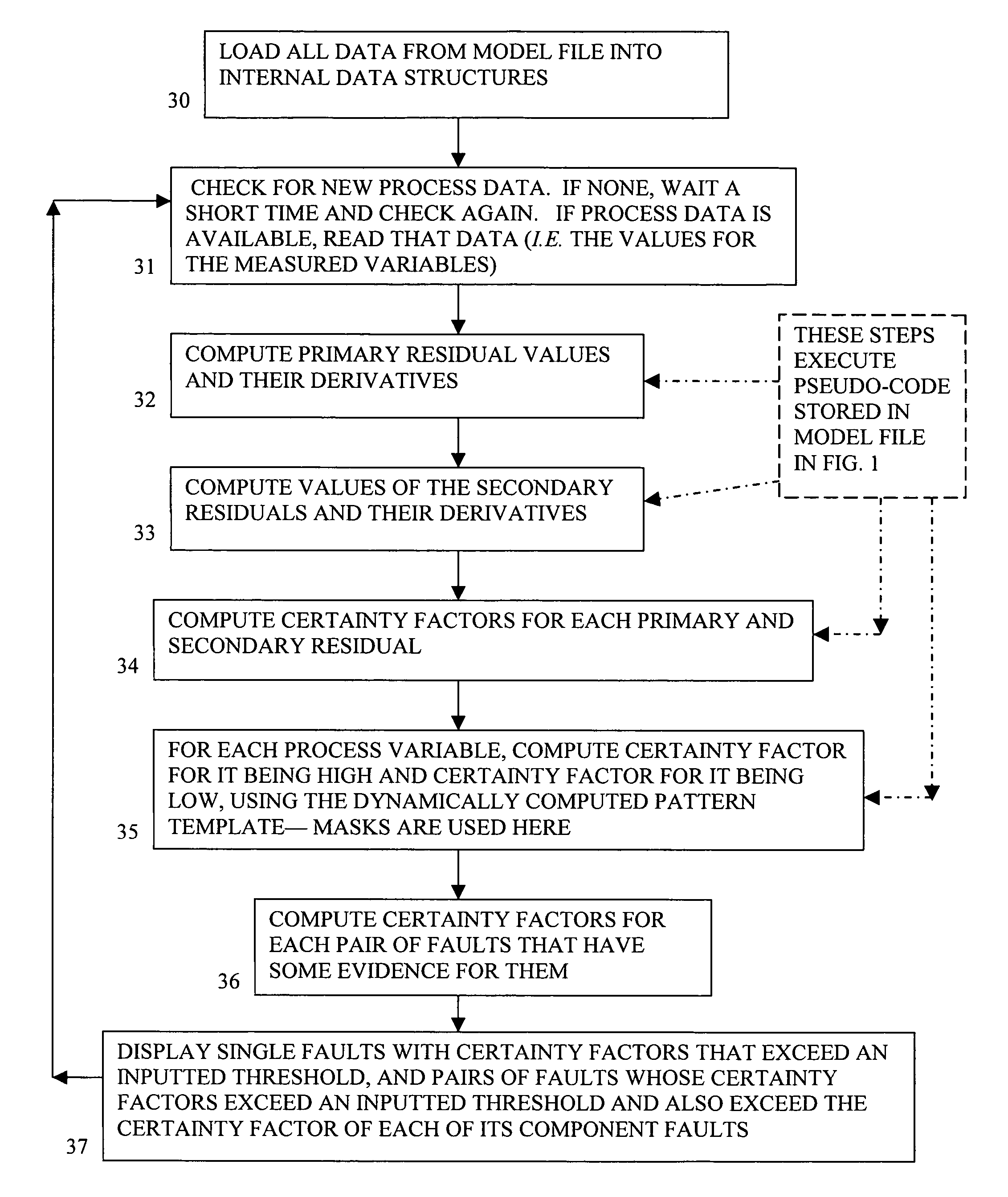
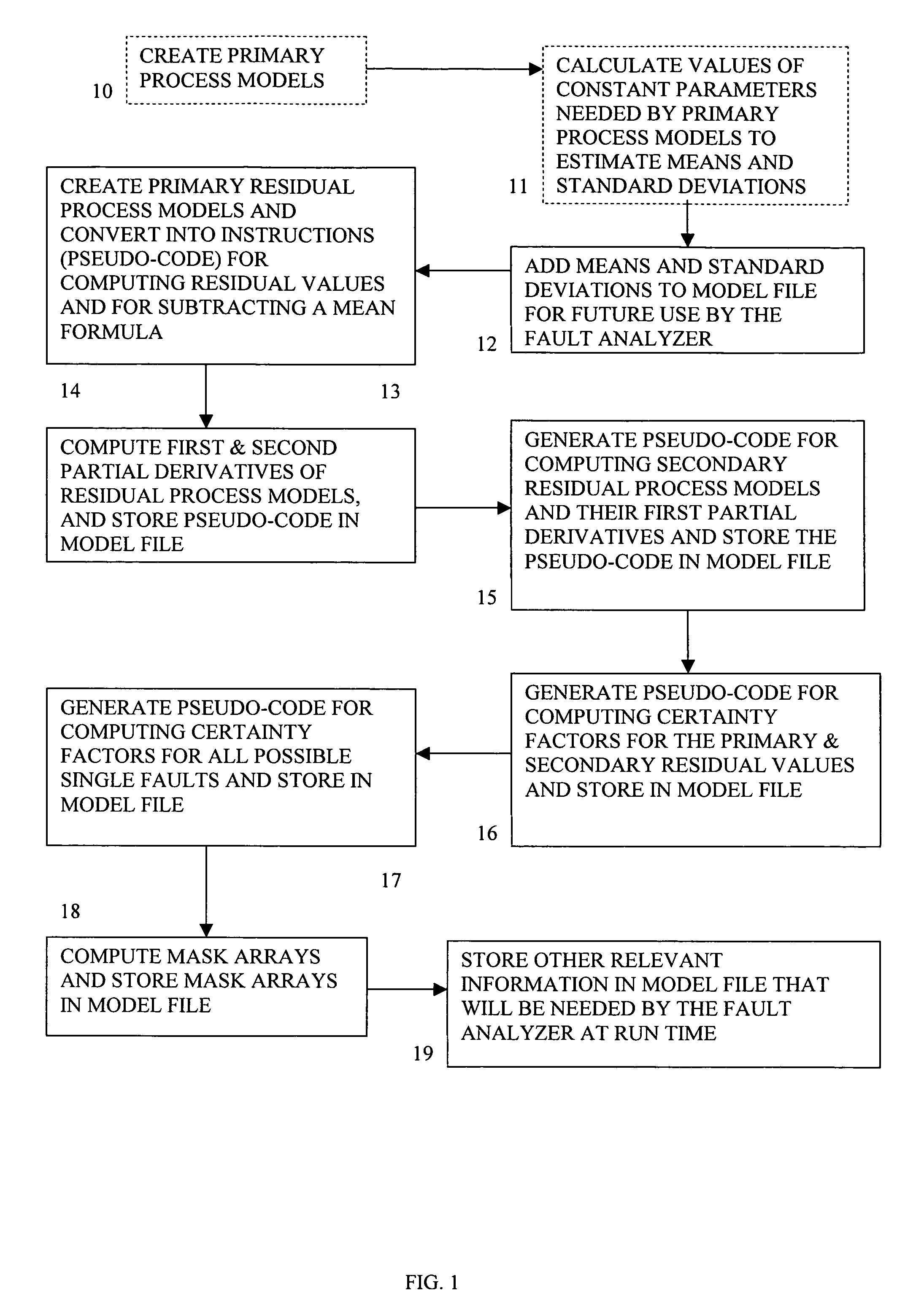
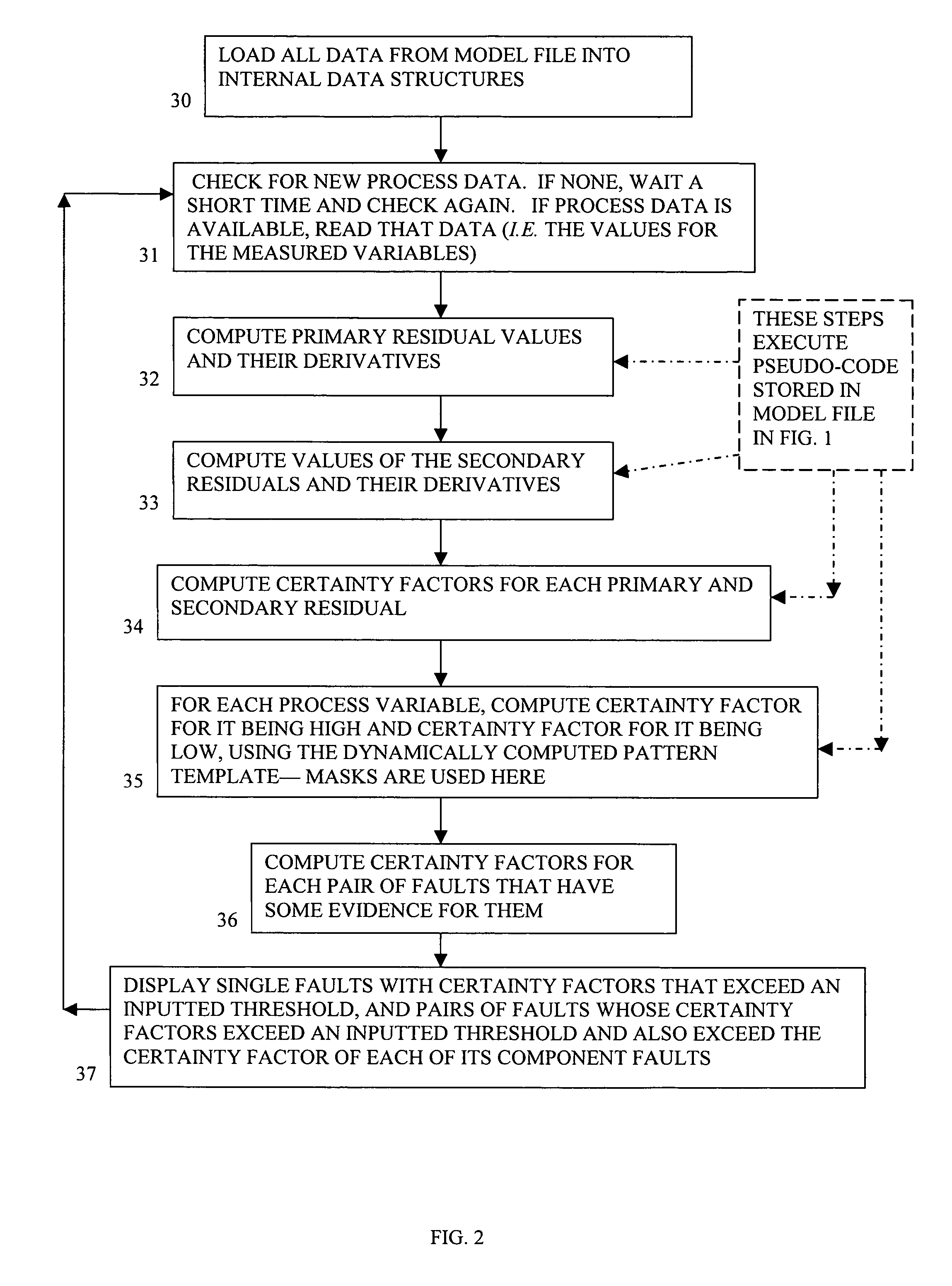
Method and system of monitoring, sensor validation and predictive fault analysis
InactiveUS20050210337A1Simplicity of implementationEasy maintenanceError detection/correctionElectric testing/monitoringLinear correlationPredictive failure analysis
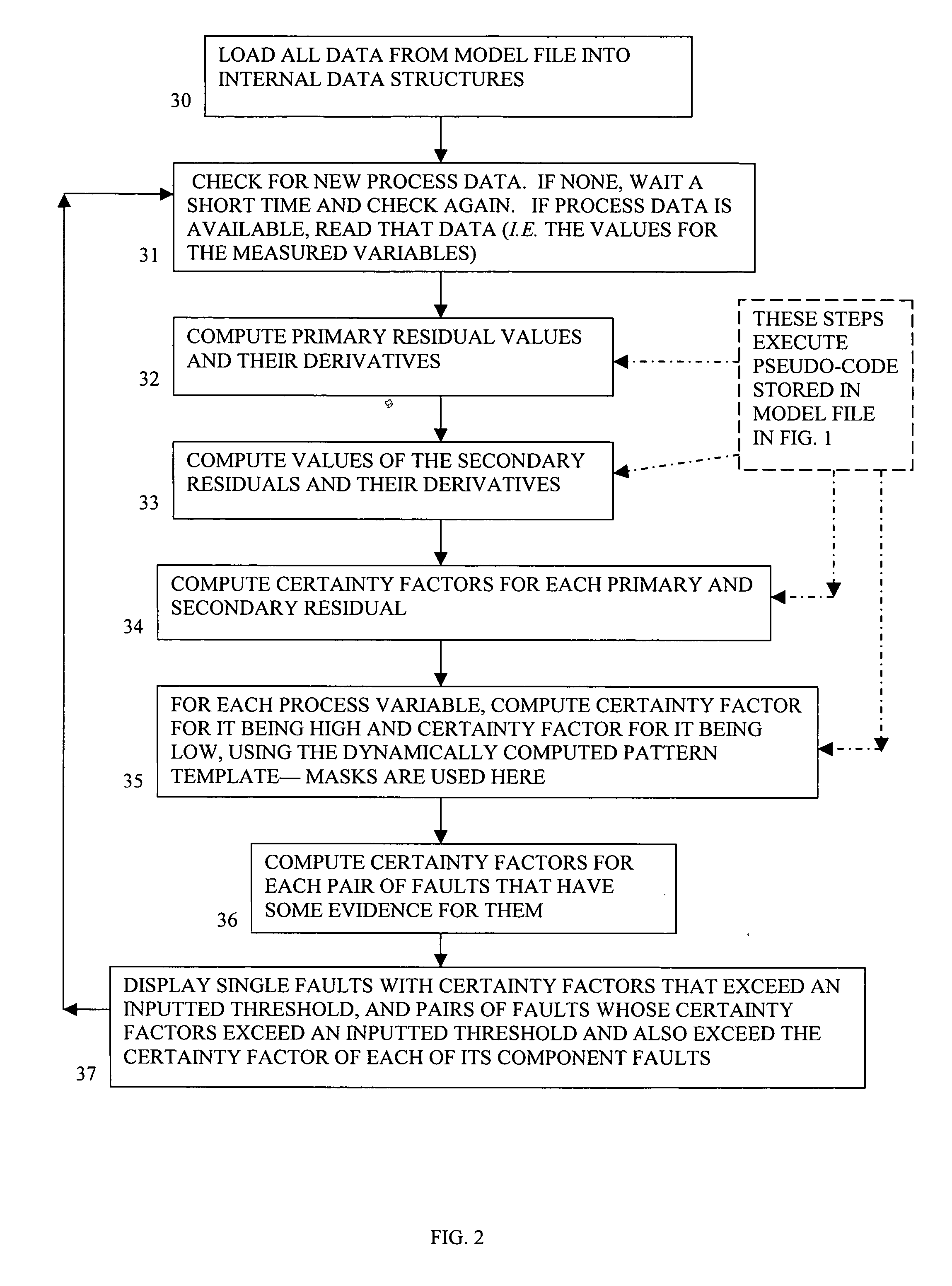
The present invention provides an improved method and system for real-time monitoring, validation, optimization and predictive fault analysis in a process control system. The invention monitors process operations by continuously analyzing sensor measurements and providing predictive alarms using models of normal process operation and statistical parameters corresponding to normal process data, and generating secondary residual process models. The invention allows for the creation of a fault analyzer directly from linearly independent models of normal process operation, and provides for automatic generation from such process models of linearly dependent process models. Fuzzy logic is used in various fault situations to compute certainty factors to identify faults and / or validate underlying assumptions. In one aspect, the invention includes a real-time sensor data communications bridge module; a state transition logic module; a sensor validation and predictive fault analysis module; and a statistical process control module; wherein each of the modules operates simultaneously.
Owner:FALCONEER TECH
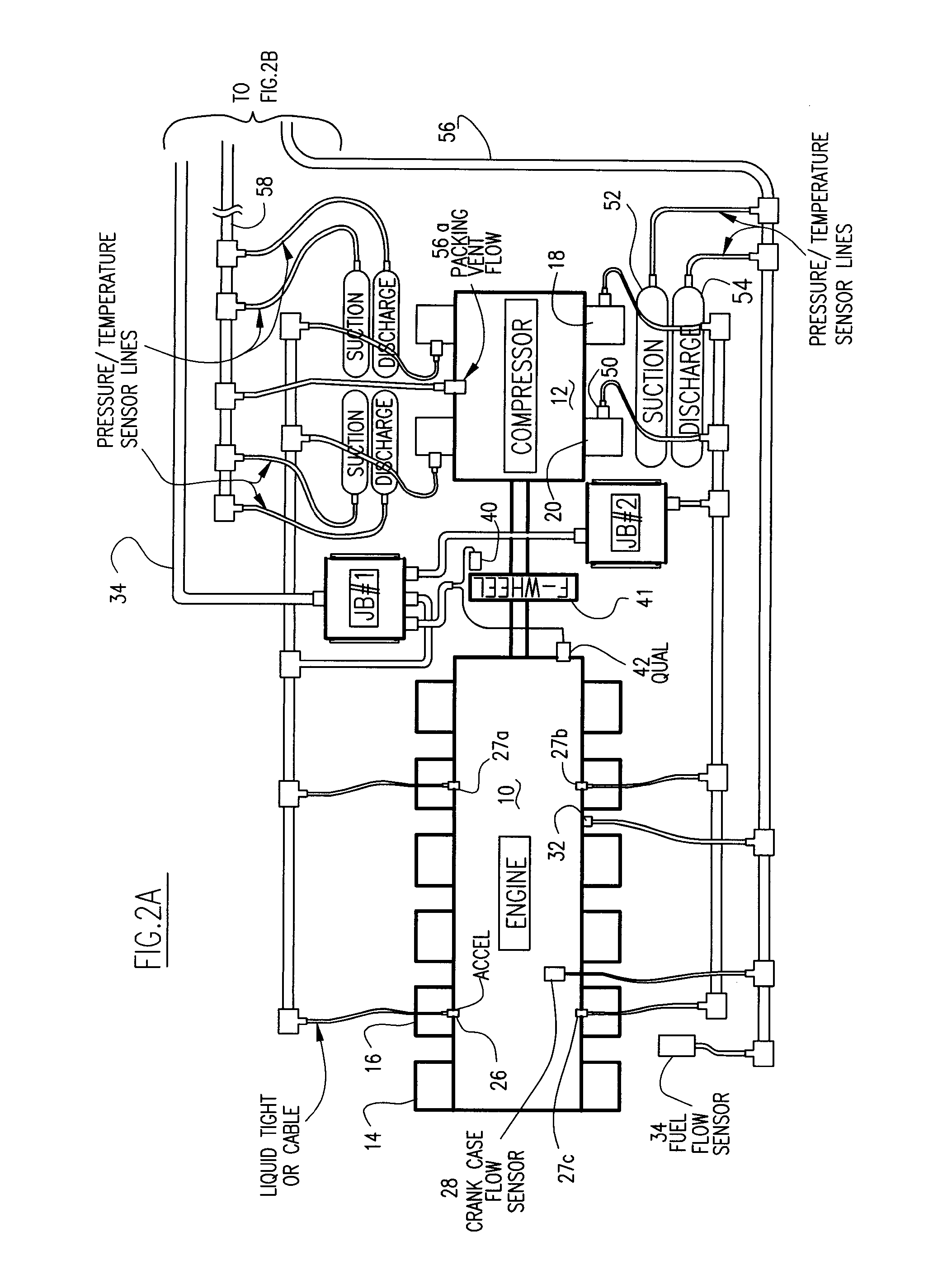
Automated fault diagnosis method and system for engine-compressor sets
InactiveUS7403850B1Improve economic performanceIncrease fuel consumptionInternal-combustion engine testingAutomatic initiationsBaseline dataData acquisition
The automated fault diagnostic system operates on engine-compressor sets with one vibration sensor per sub-group of engine cylinders and one sensor per compressor cylinder. Vibration signals linked to crankshaft phase angle windows (“VT”) mark various engine events and compressor events. In data-acquisition-learning mode, VT is stored for each engine and compressor event per operating load condition, statistical process control (SPC) theory identifies alarm threshold bands. Operator input-overrides are permitted. If no baseline data is stored, the system automatically enters the learn mode. To monitor, current VT are obtained and current load condition is matched to the earlier load set and alarms issue linking predetermined engine or compressor event to the over-under VT. Baseline data, SPC analysis, alarms and monitoring are set for crankcase flow, engine cylinder exhaust temperatures, ignition system diagnostic messages. Compressor performance alarms use suction and discharge temperatures and pressures.
Owner:WINDROCK
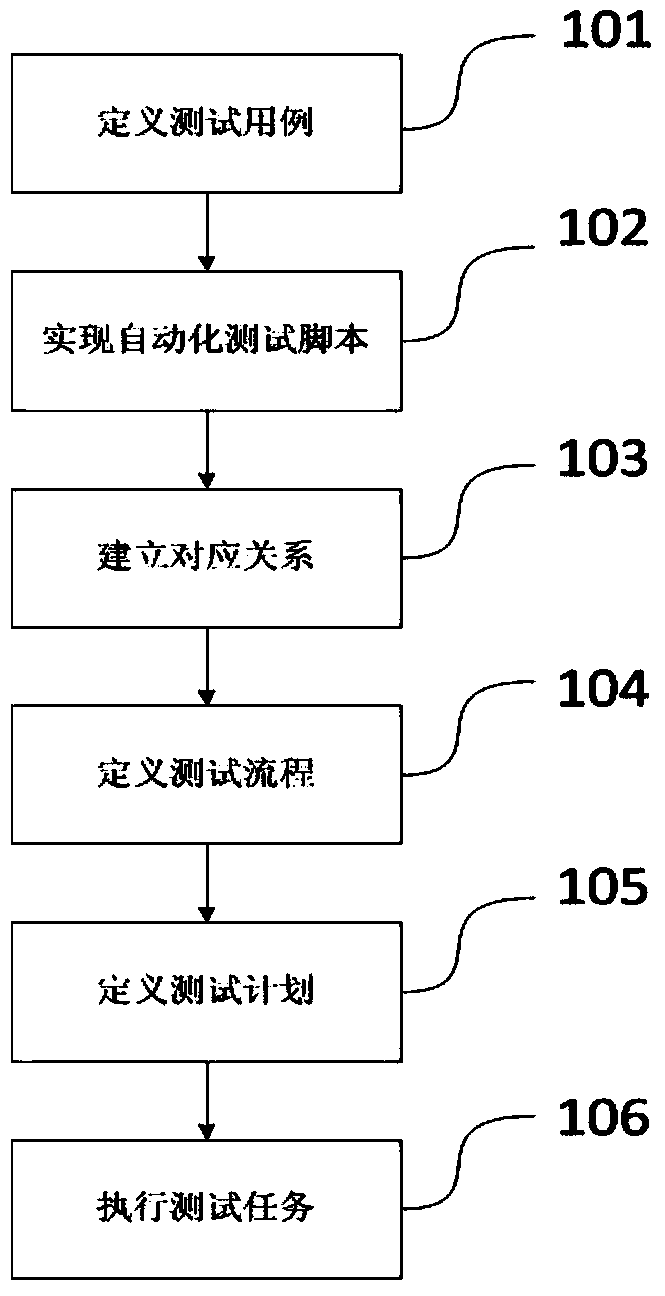
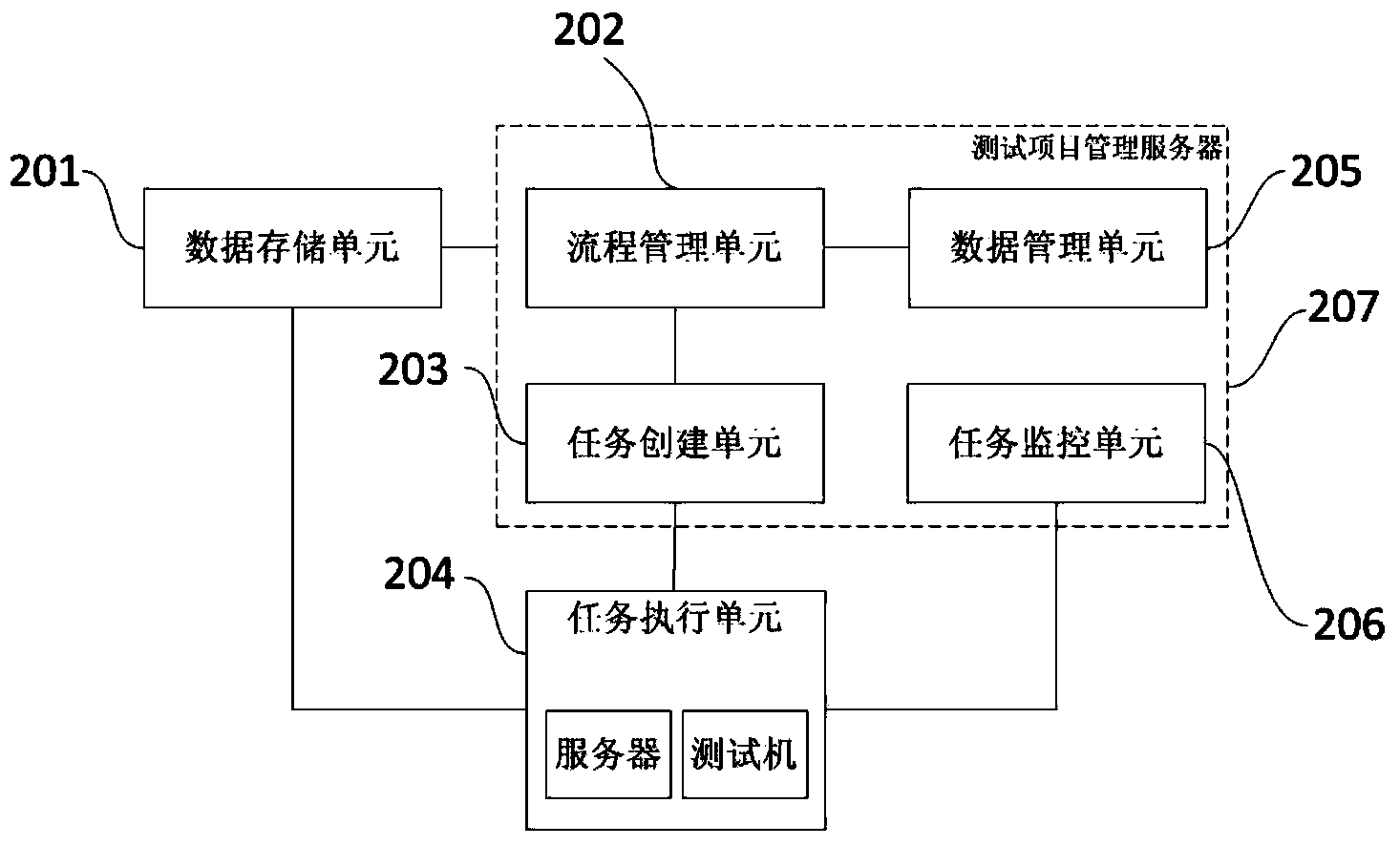
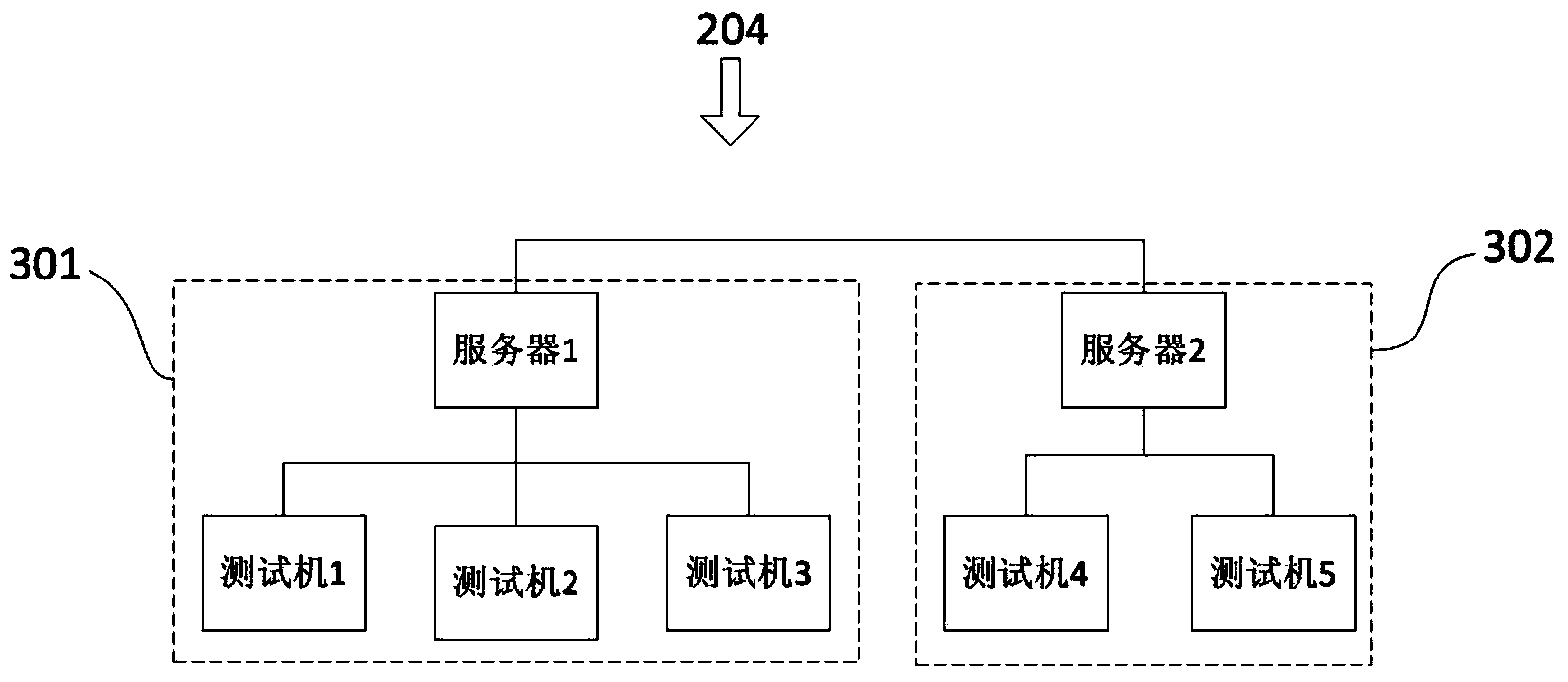
Application program testing method and system based on service process control
ActiveCN103530231AImprove test coverageImprove test qualitySoftware testing/debuggingTest scriptProgram planning
The invention provides an application program testing method and system based on service process control. According to the method, distribution type automated testing is conducted on application programs through the steps of defining a test case, obtaining automatic testing script, setting up a corresponding relation, defining the testing process, defining the test plan and executing the test task. Correspondingly, the invention provides a system. The system comprises a data storage unit, a process management unit, a task establishing unit, a task executing unit and the like. The method and system are designed for the highly-procedural application programs and are the method and system based on the testing process control. According to the application program testing method and system based on service process control, the testing coverage rate can be effectively improved, the testing quality is improved, the testing cost is reduced, the staff efficiency is improved, the environment maintaining cost is reduced, and the time spent on traditional automated testing is shortened.
Owner:重庆天极云服科技有限公司
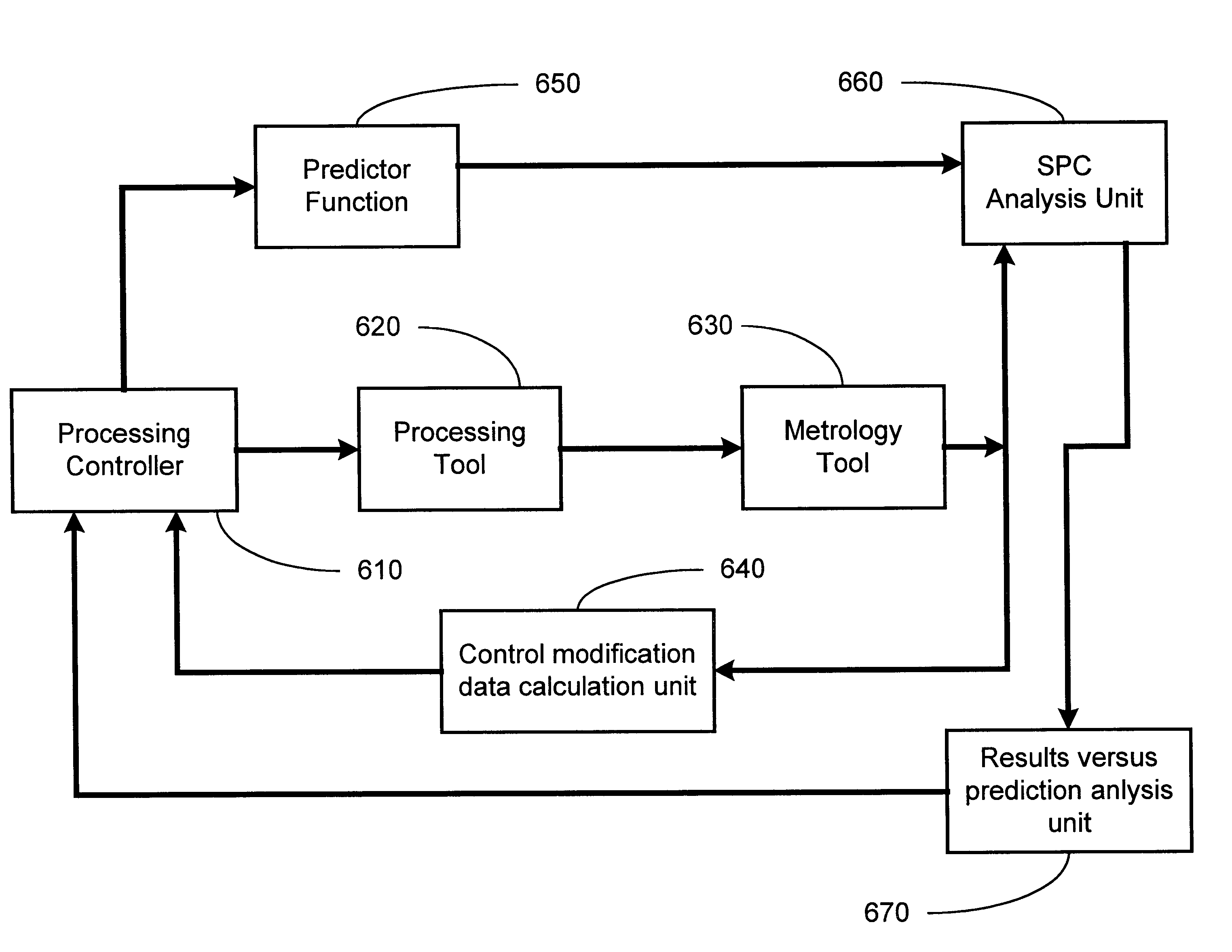
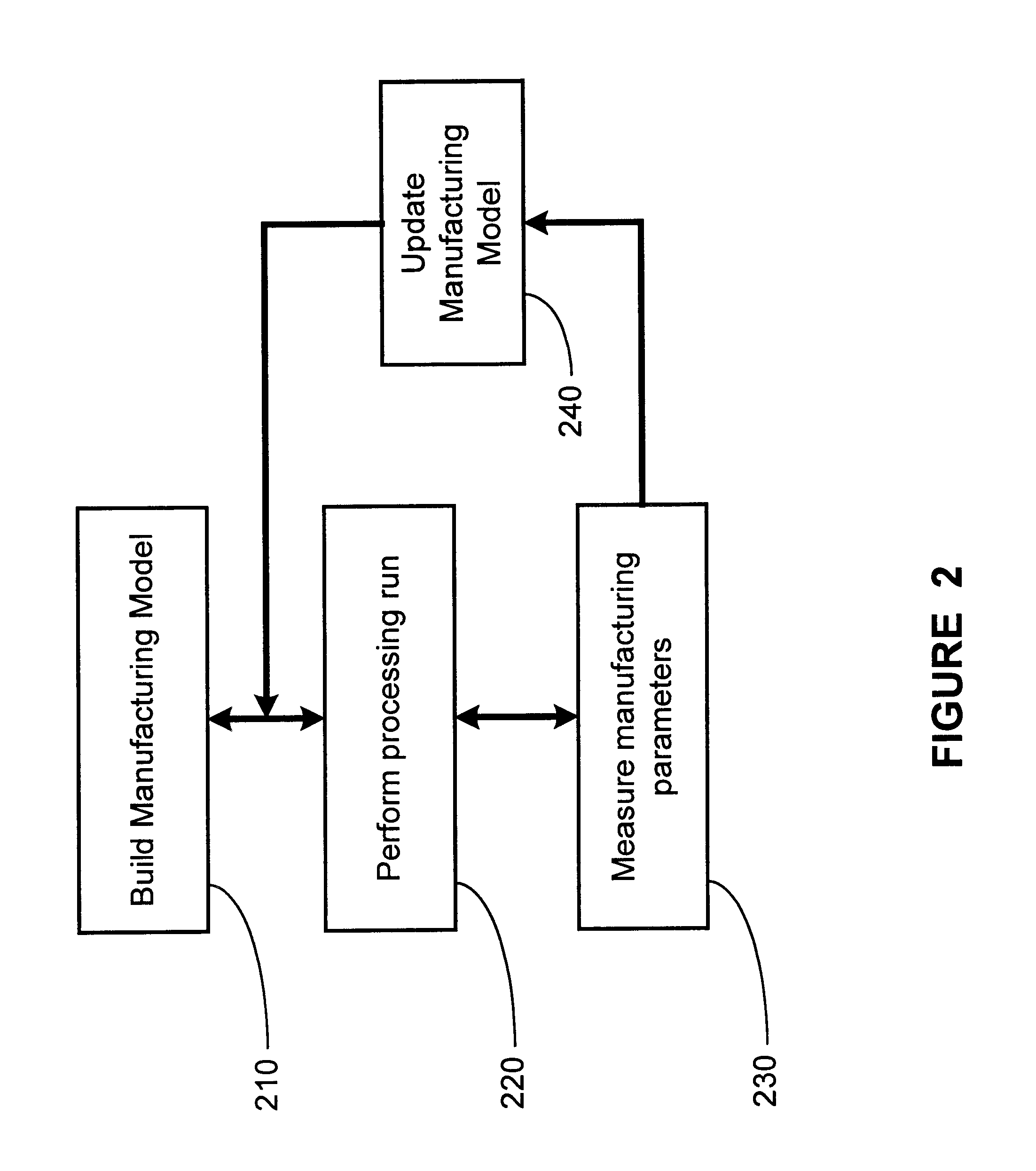
Method and apparatus for monitoring controller performance using statistical process control
InactiveUS6560503B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetrologyStatistical process control
The present invention provides for a method and an apparatus for monitoring controller performance using statistical process control analysis. A manufacturing model is defined. A processing run of semiconductor devices is performed as defined by the manufacturing model and implemented by a process controller. A fault detection analysis is performed on the process controller. At least one control input signal generated by the process controller is updated. The apparatus of the present invention comprises: a processing controller; a processing tool coupled with the processing controller; a metrology tool interfaced with the processing tool; a control modification data calculation unit interfaced with the metrology and connected to the processing controller in a feedback manner; a predictor function interfaced with the processing controller; an statistical process control analysis unit interfaced with the predictor function and the processing tool; and a results versus prediction analysis unit interfaced with the statistical process control analysis unit and connected to the processing controller in a feedback manner.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
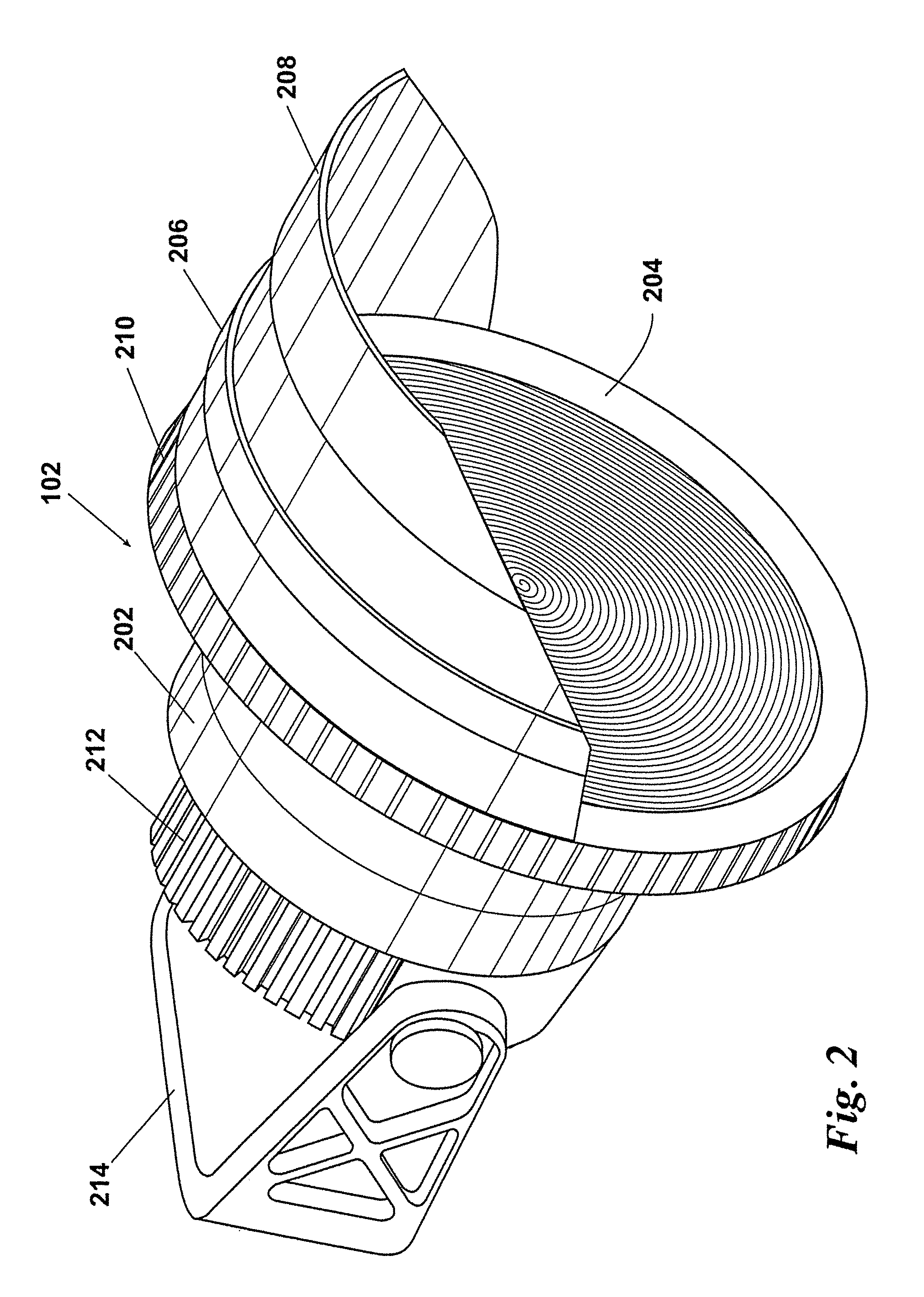
LED venue lighting system and method
ActiveUS20150308655A1Increase heatMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceOutdoor areaEngineering
An outdoor area LED lighting system including: a housing containing a large array of LEDs mounted to an aluminum direct thermal path printed circuit board and a single lens. The large array of LEDs are capable of producing light rays directed through the single lens to produce a beam of light to illuminate the outdoor area. The single lens is preferably a Fresnel lens. The housing is preferably capable of being sealed in a weather-tight manner. A second housing may at least partially surround the first housing such that at least one air passage is provided between the first housing and the second housing. A heat sink including a heat block in thermal communication with a plurality of heat tubes and fin assemblies may be in partial thermal contact with the LED module and in fluid communication with the at least one air passage. At least one fan may be provided in or in fluid communication with said at least one air passage to cool the heat sink. A digital interface may connect the LED module to a host computer to monitor and track information and trending for statistical process control.
Owner:SPORTSBEAMS LIGHTING INC
Method and system of monitoring, sensor validation and predictive fault analysis
InactiveUS7451003B2Simplicity of implementationEasy maintenanceError detection/correctionVolume/mass flow measurementLinear correlationControl system
The present invention provides an improved method and system for real-time monitoring, validation, optimization and predictive fault analysis in a process control system. The invention monitors process operations by continuously analyzing sensor measurements and providing predictive alarms using models of normal process operation and statistical parameters corresponding to normal process data, and generating secondary residual process models. The invention allows for the creation of a fault analyzer directly from linearly independent models of normal process operation, and provides for automatic generation from such process models of linearly dependent process models. Fuzzy logic is used in various fault situations to compute certainty factors to identify faults and / or validate underlying assumptions. In one aspect, the invention includes a real-time sensor data communications bridge module; a state transition logic module; a sensor validation and predictive fault analysis module; and a statistical process control module; wherein each of the modules operates simultaneously.
Owner:FALCONEER TECH
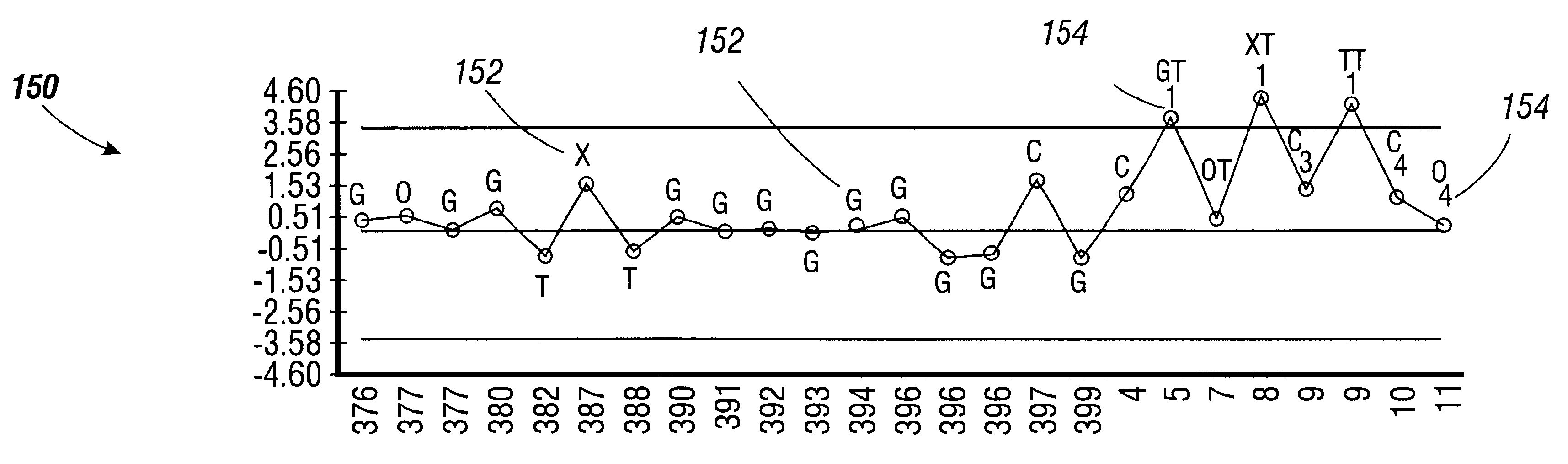
Statistical process control system with normalized control charting
A method for monitoring the performance of a manufacturing entity is provided. Metrology data indicating an output parameter of the manufacturing entity is retrieved. The output parameter has an associated target value. The metrology data is normalized based on the target value to generate normalized performance data points. A performance rule violation is determined based on the normalized performance data. A manufacturing system includes a metrology tool, a first database, and a processor. The metrology tool is adapted to measure an output parameter of a manufacturing entity to generate metrology data. The output parameter has an associated target value. The first database is adapted to receive the metrology data. The processor is adapted to retrieve the metrology data from the database, normalize the metrology data based on the target value to generate normalized performance data points, and determine a performance rule violation based on the normalized performance data.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
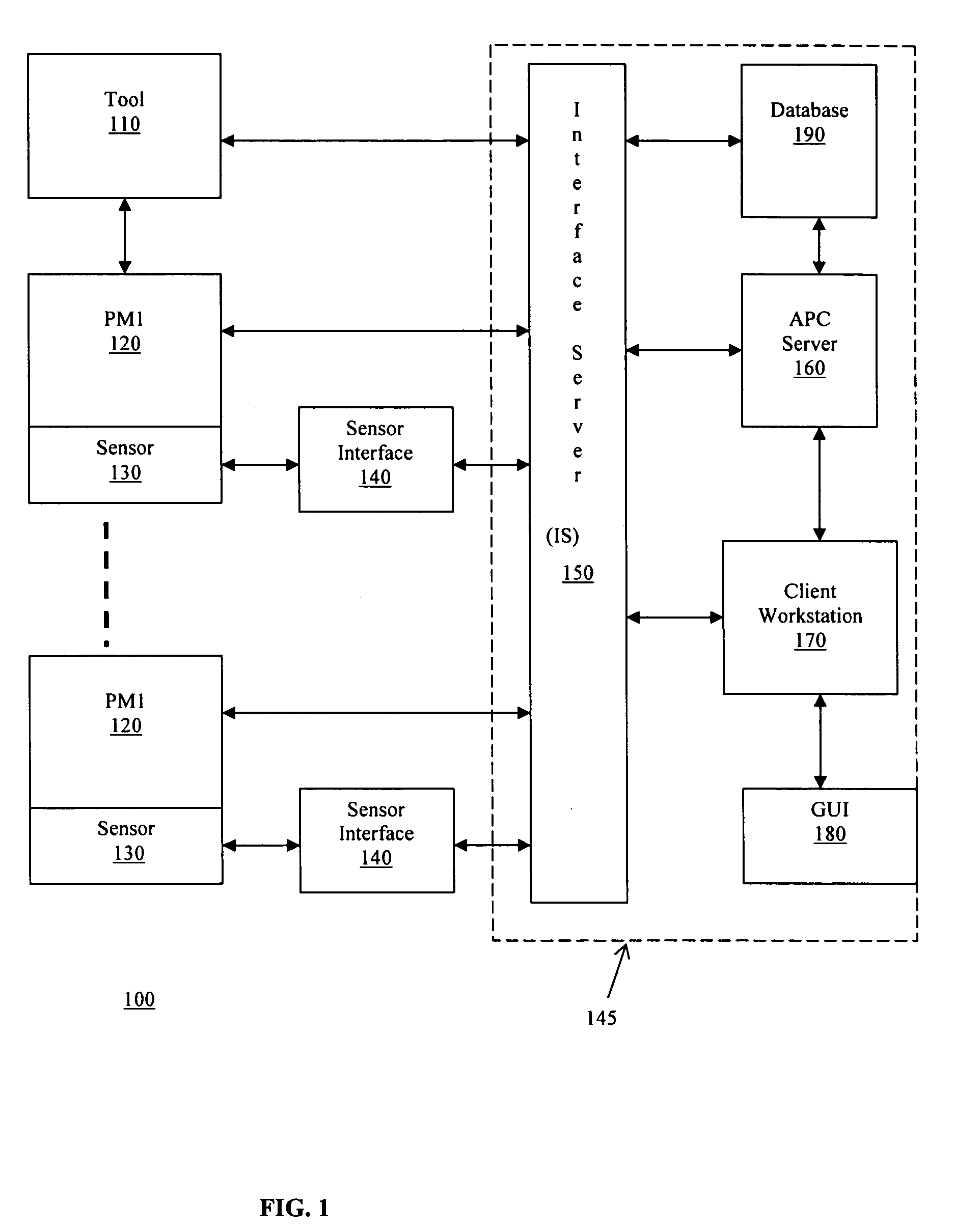
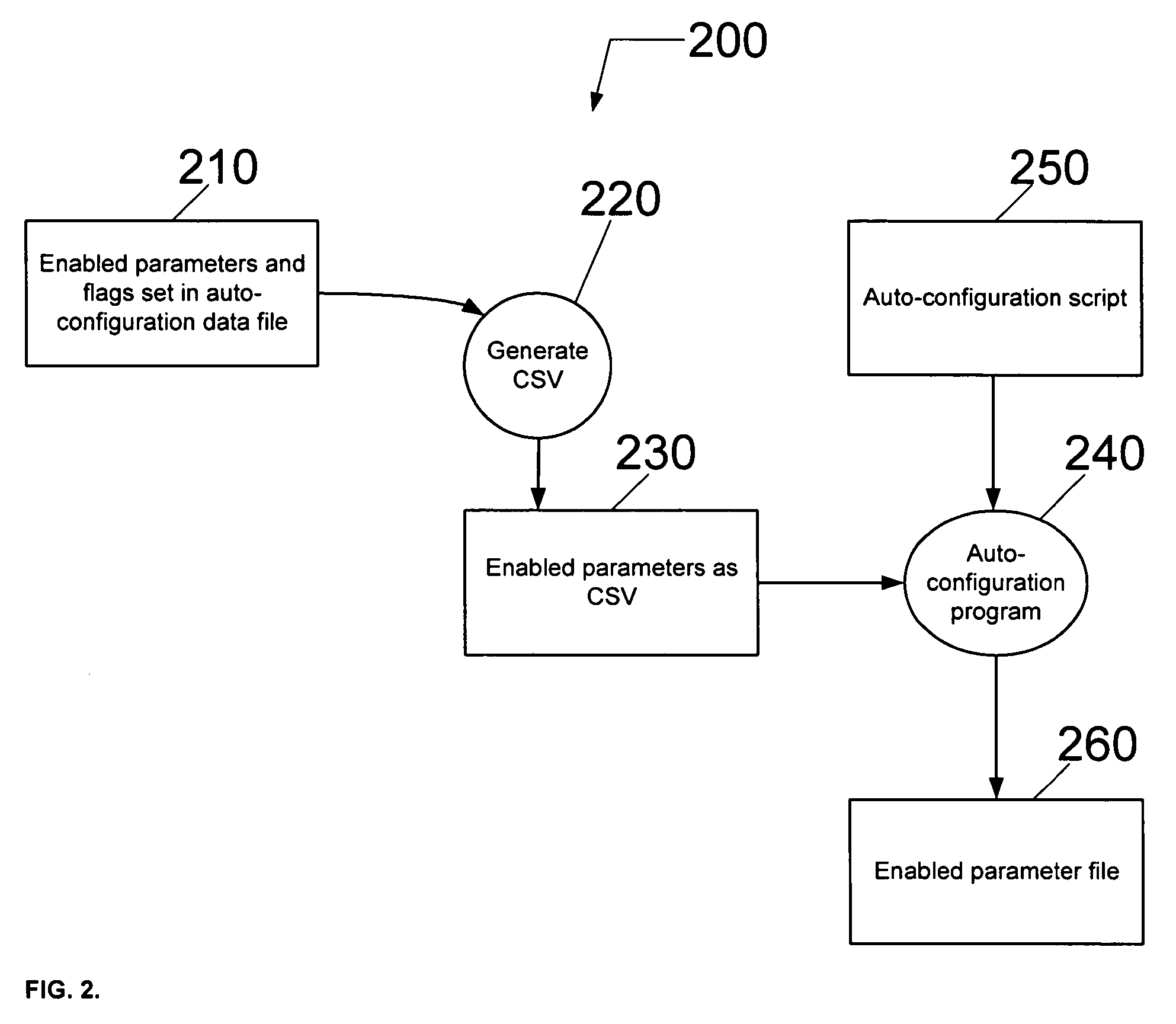
Method for automatic configuration of processing system
ActiveUS7213478B2Wave based measurement systemsCalibration apparatusAuto-configurationHandling system
A method of automatically configuring an Advanced Process Control (APC) system for a semiconductor manufacturing environment in which an auto-configuration script is generated for executing an auto-configuration program. The auto-configuration script activates default values for input to the auto-configuration program. The auto-configuration script is executed to generate an enabled parameter file output from the auto-configuration program. The enabled parameter file identifies parameters for statistical process control (SPC) chart generation.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
System and method for detecting optical defects
InactiveUS20090154789A1Character and pattern recognitionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationVisibilityComputer science
A system and method for detecting optical defects on a surface of a transparent or semi-transparent structure, tube or article is provided. Defects are identified and analyzed by using a digital camera to capture an image of a target having a pattern of light and dark areas through a portion of the article. The images are processed to enhance the visibility of the defects, and the distribution of the defects as function of their location on the surface of the article is determined. This determination is used as part of a statistical process control method for controlling the level of defects present on the surface of the article.
Owner:TENSOR ID
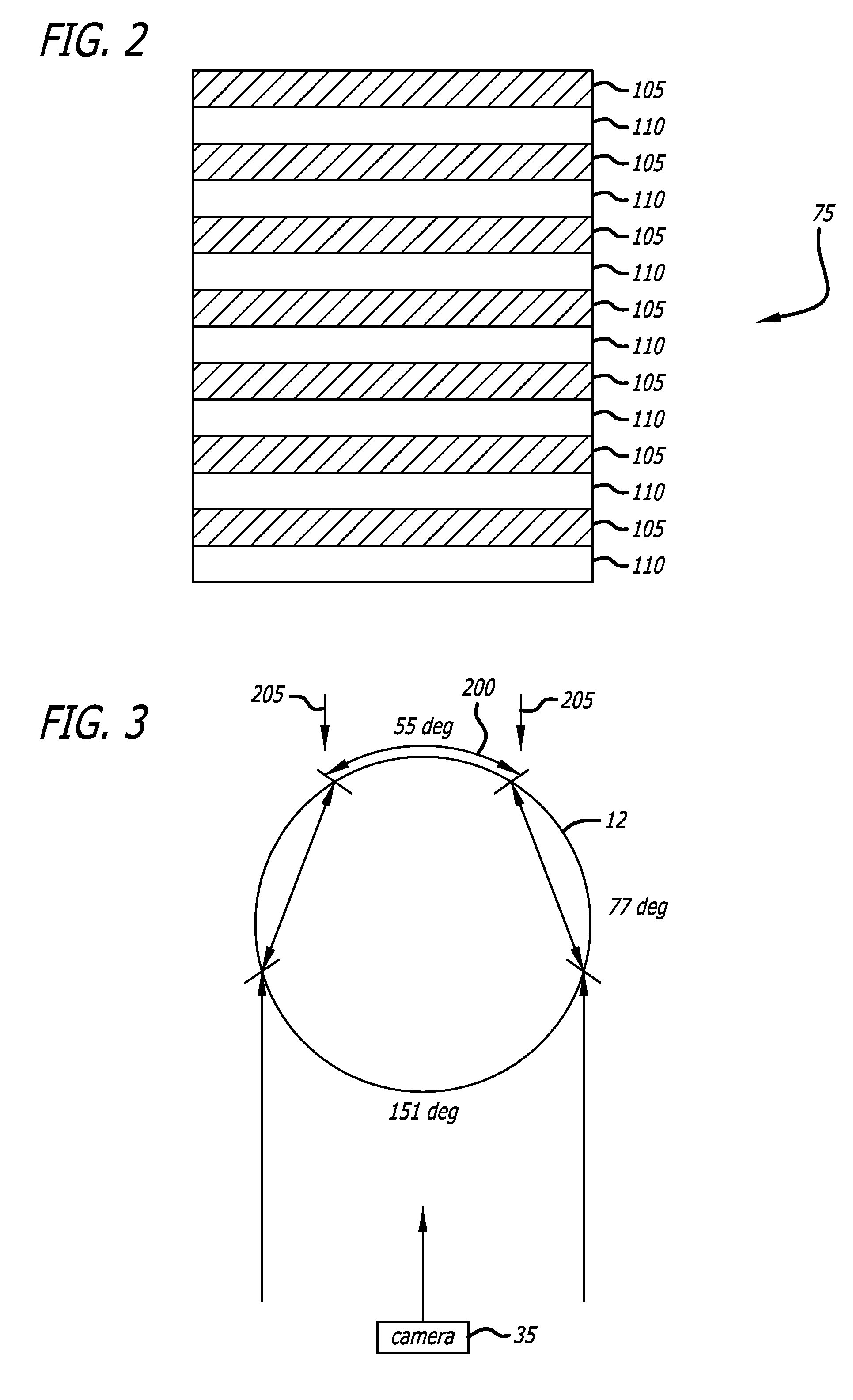
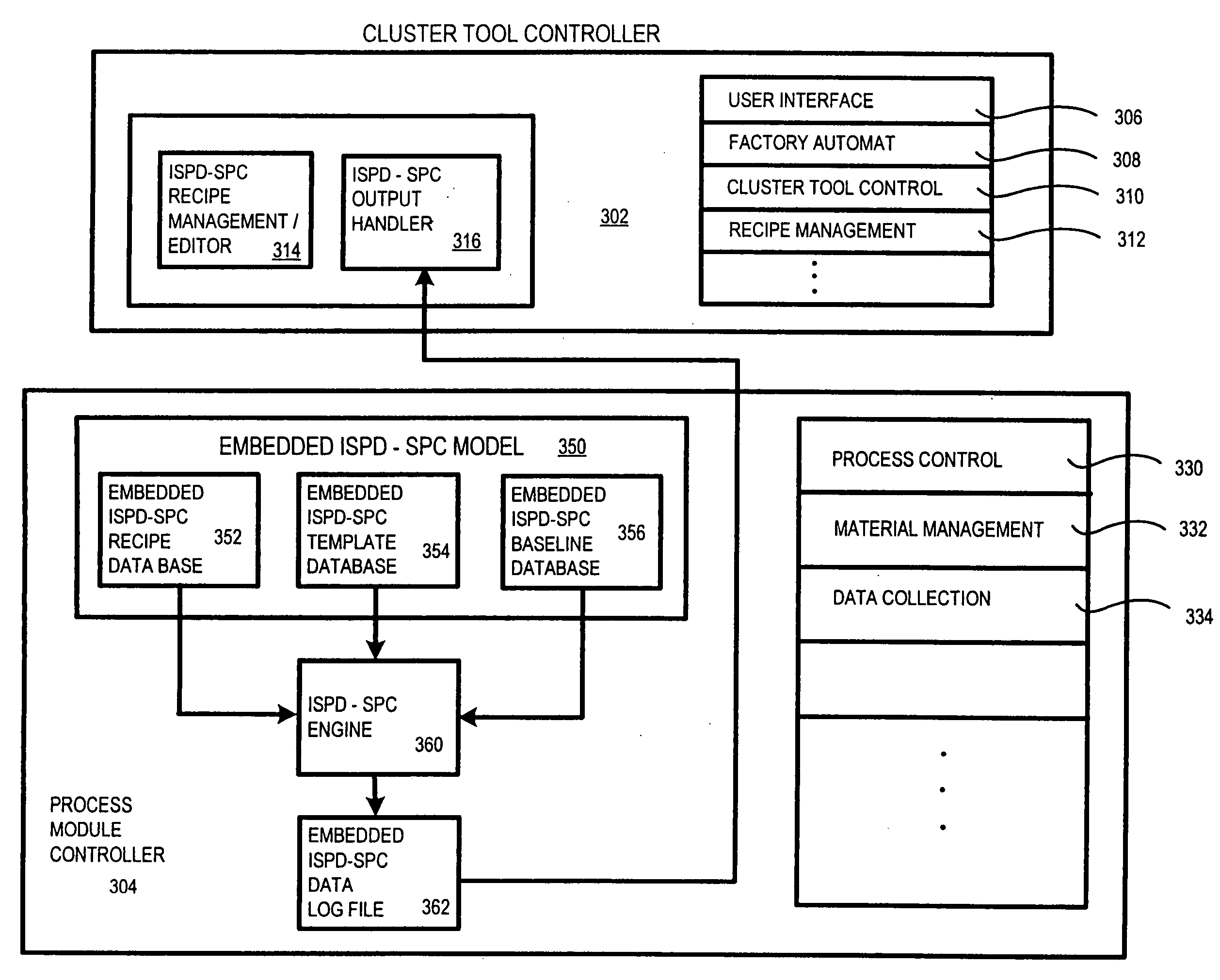
Integrated stepwise statistical process control in a plasma processing system
InactiveUS20050084988A1Process be stopImprove efficiencySafety arrangmentsElectric discharge tubesControl systemAutomatic process control
An automated process control system configured for controlling a plasma processing system having a chamber, the chamber being configured for processing a substrate. The automatic process control system includes a first sensor disposed within the chamber, the first sensor being configured for making a first plurality of measurements pertaining to a first parameter associated with a structure disposed at least partially within the chamber. The performing the first plurality of measurements is performed during the processing of the substrate. The automatic process control system further includes first logic coupled to receive the first plurality of measurements from the first sensor. The first logic is configured for analyzing using SPC methodologies the first plurality of measurements during the processing. There is also included second logic coupled to receive a first signal from the first logic, the second logic being configured to stop the processing prior to completing the processing if the first signal indicates a fault with the processing.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
LED venue lighting system with first and second housing having an air passage therebetween
An outdoor area LED lighting system including: a housing containing a large array of LEDs mounted to an aluminum direct thermal path printed circuit board and a single lens. The large array of LEDs are capable of producing light rays directed through the single lens to produce a beam of light to illuminate the outdoor area. The single lens is preferably a Fresnel lens. The housing is preferably capable of being sealed in a weather-tight manner. A second housing may at least partially surround the first housing such that at least one air passage is provided between the first housing and the second housing. A heat sink including a heat block in thermal communication with a plurality of heat tubes and fin assemblies may be in partial thermal contact with the LED module and in fluid communication with the at least one air passage. At least one fan may be provided in or in fluid communication with said at least one air passage to cool the heat sink. A digital interface may connect the LED module to a host computer to monitor and track information and trending for statistical process control.
Owner:SPORTSBEAMS LIGHTING INC
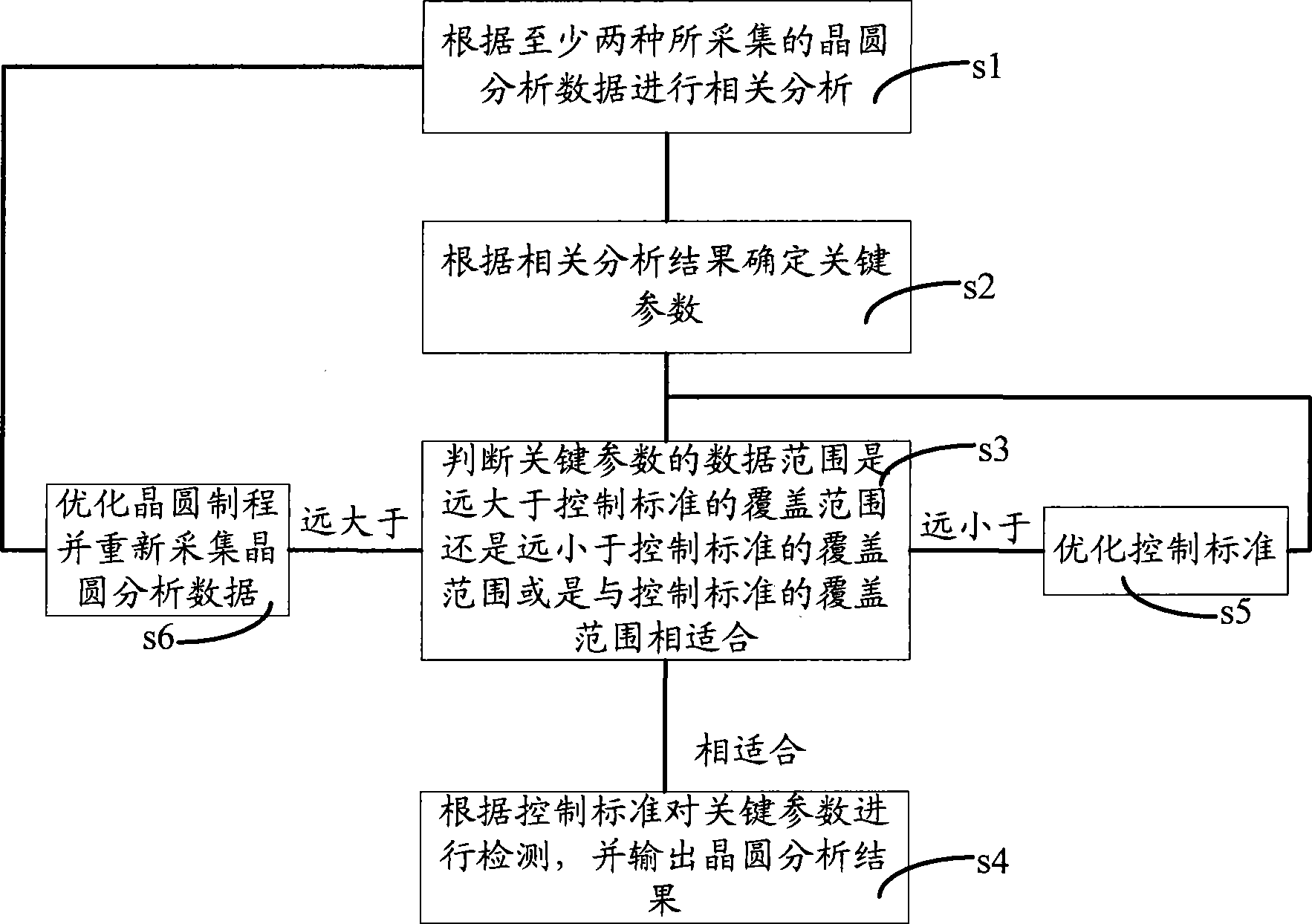
Wafer quality analysis apparatus and method
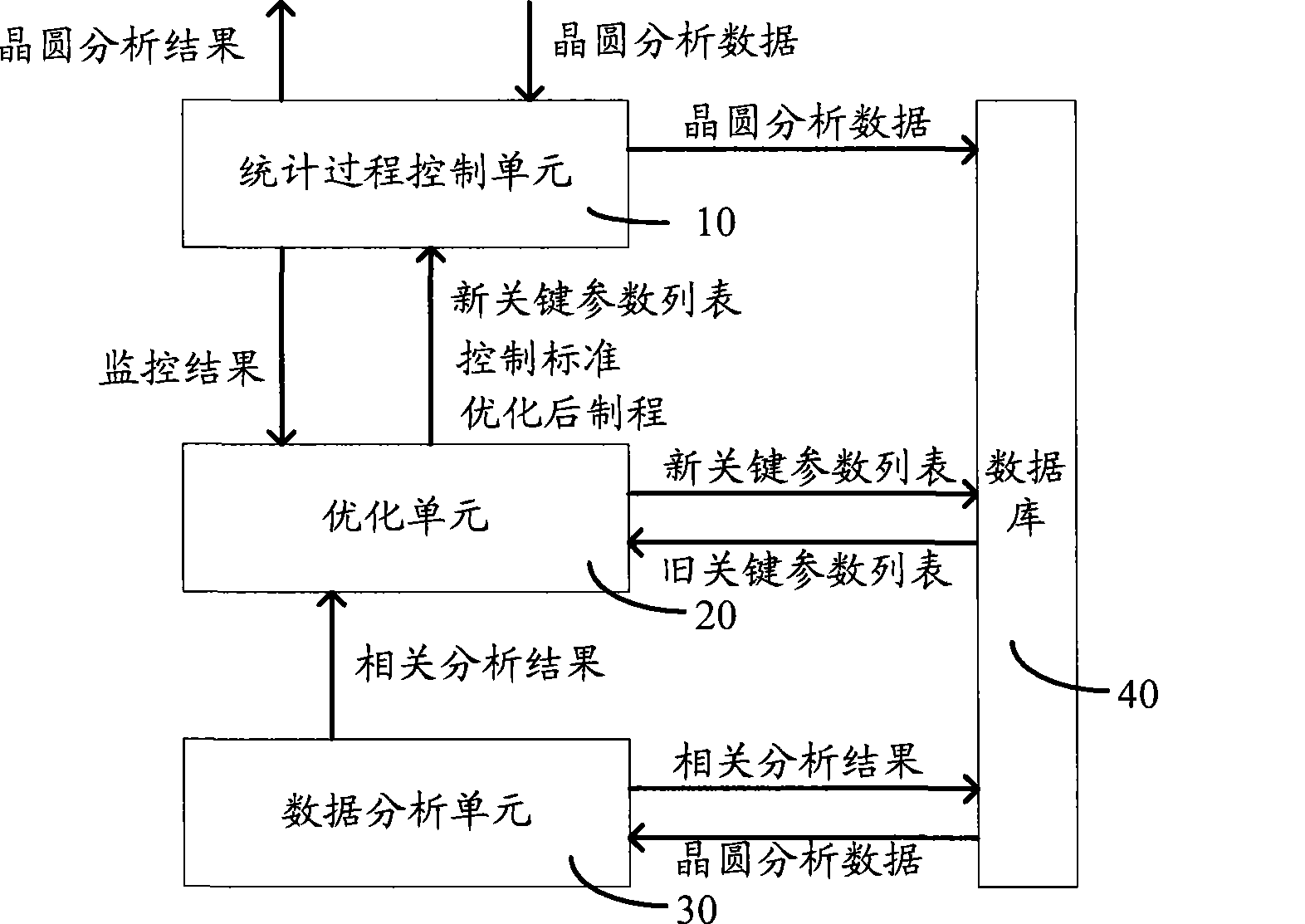
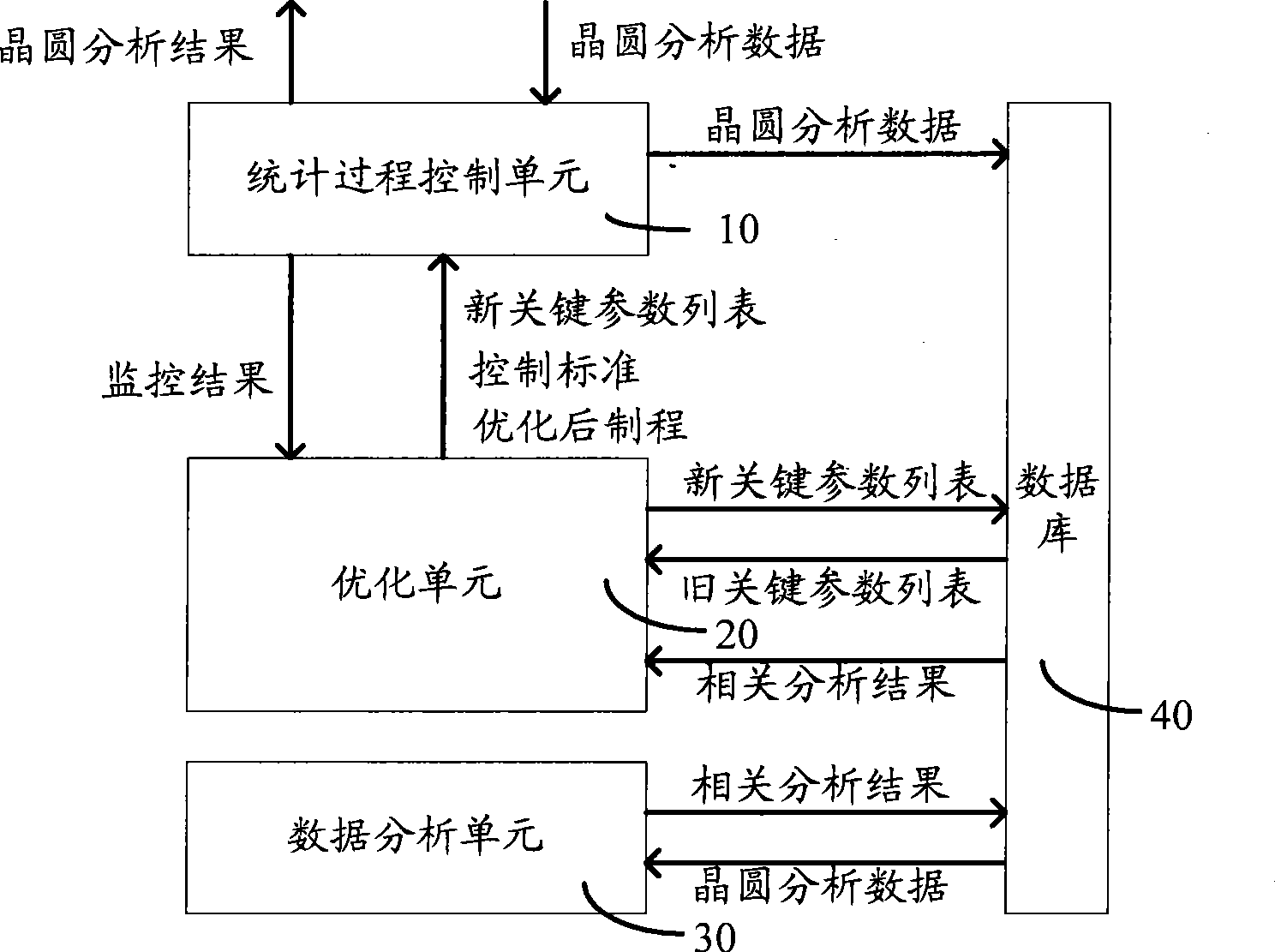
InactiveCN101458515AImprove accuracyTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlAnalysis dataCorrelation analysis
The invention provides a wafer quality analysis device which includes: a data base for temporary storing wafer analysis data, reference data and middle result; a data analysis unit for calling at least two wafer analysis data in the data base to process correlated analysis and output correlated analysis result; an optimizing unit for determining and outputting key parameter list according with correlated analysis result output by the data analysis unit, and optimizing and outputting control standard or wafer production according with monitor result feedback by a statistic process control unit; a statistic processes control unit for collecting wafer analysis data, monitoring key parameter according with the key parameter list output by the optimizing unit, and feedback monitored result to the optimizing unit, and monitoring the key parameter again according with optimizing control standard or wafer production output by the optimizing unit, and outputting wafer analysis result finally. The invention also discloses a wafer quality analysis method. The wafer quality analysis device and method increase accuracy of quality analysis.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Energy monitoring or control of individual vias formed during laser micromachining
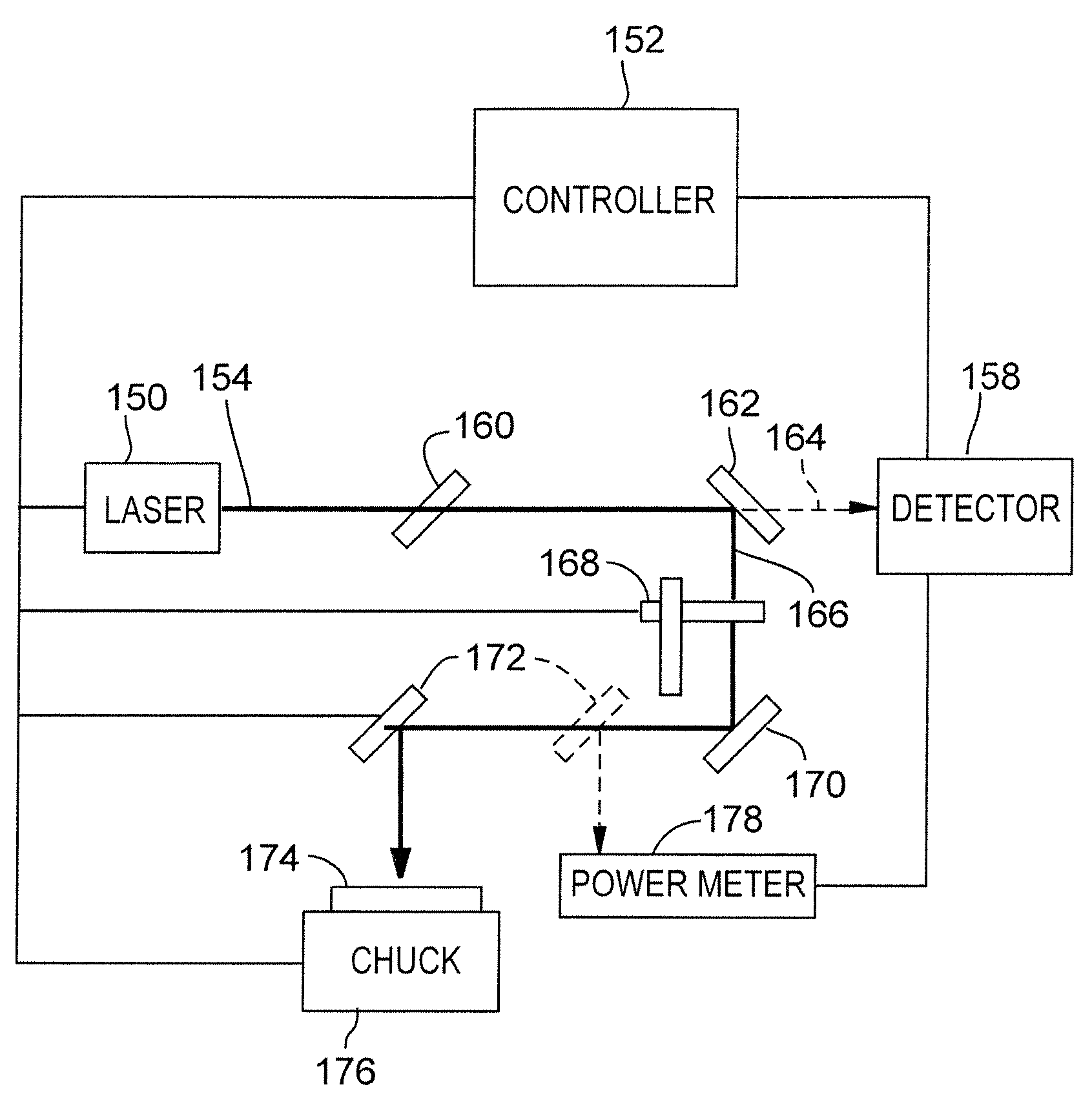
InactiveUS20070045253A1Improving quality of laserQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesEngineeringTime control
A method and system increase the quality of results achieved by laser micromachining systems. Data relating to parameters controlling laser micromachining process are recorded during the micromachining process, identified by the feature associated with the parameters used to micromachine, and stored on the system. The stored data can be either retrieved during the micromachining process to enable real time control or retrieved after workpiece processing to conduct statistical process control.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
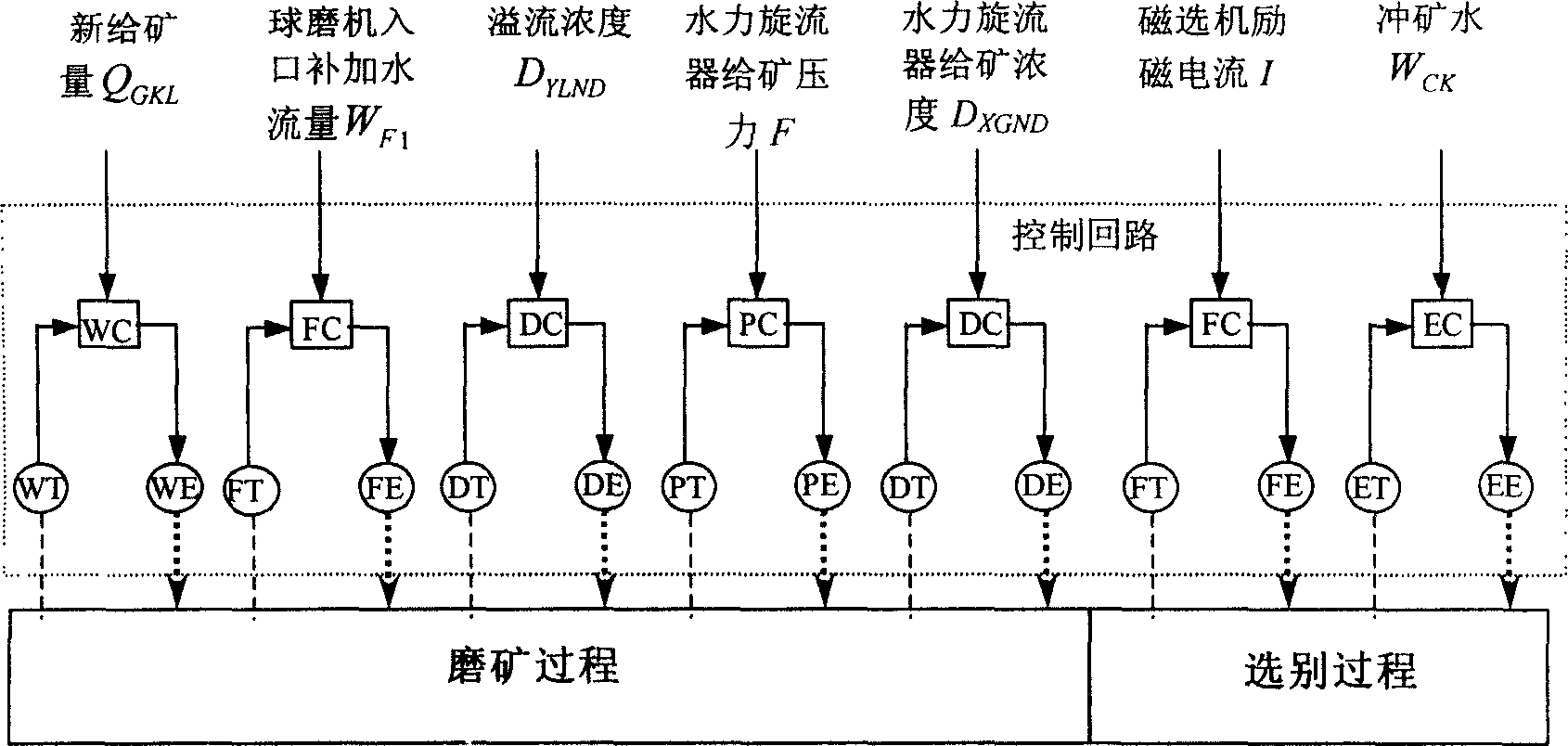
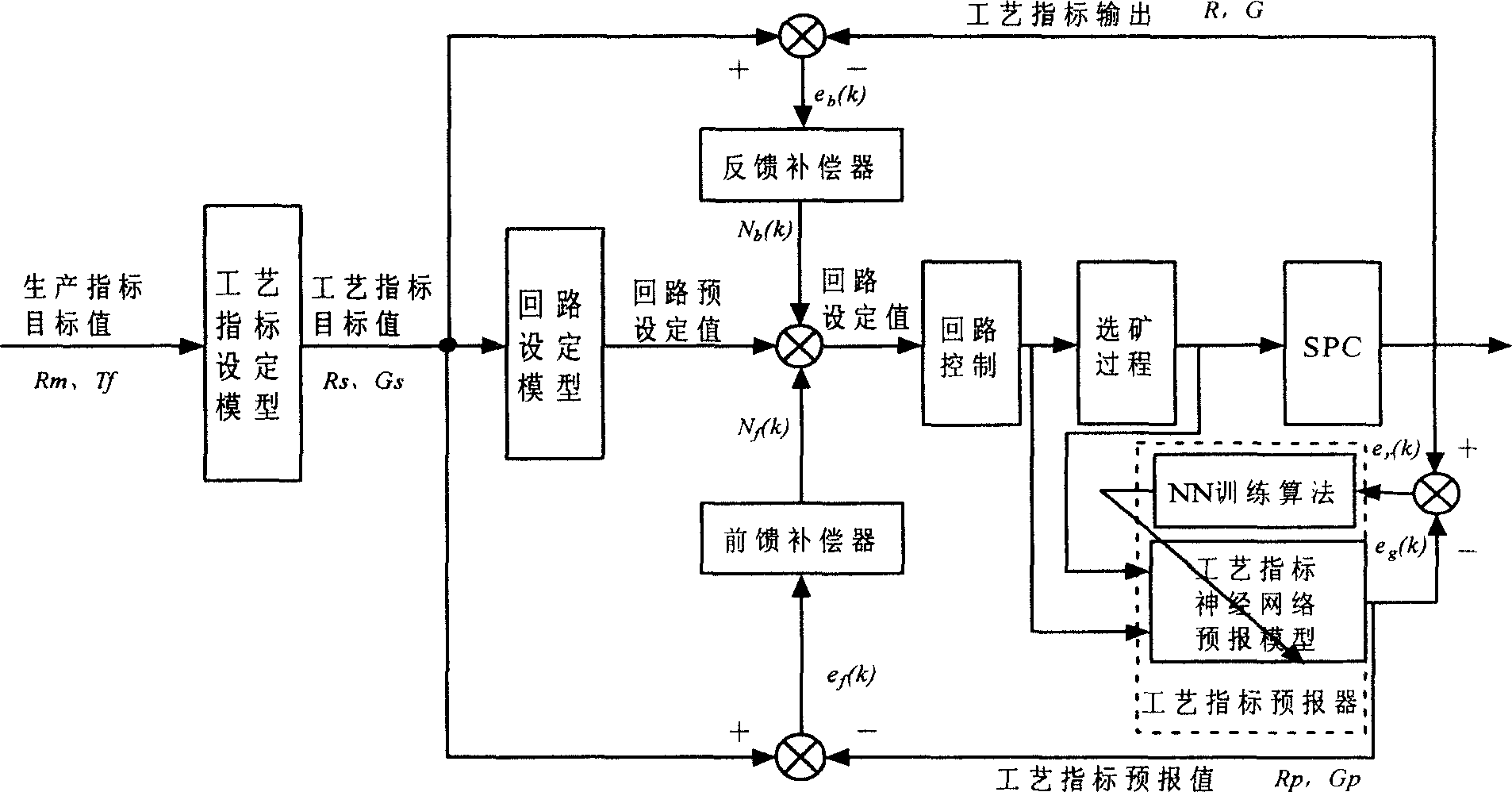
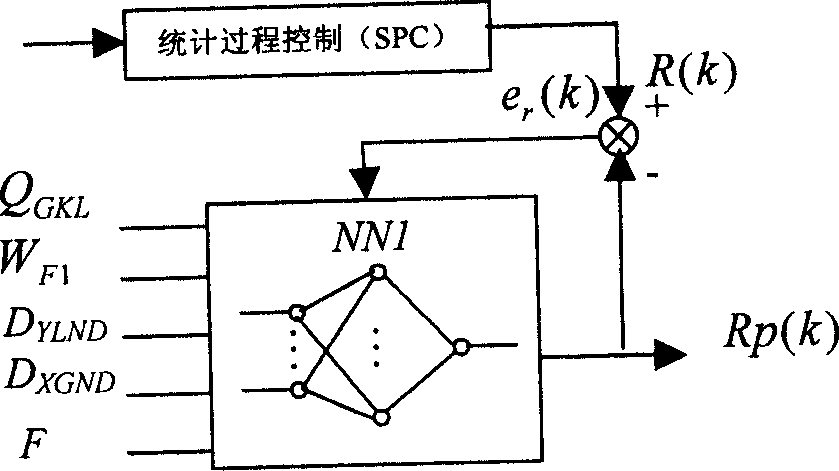
Intelligent optimized control method for comprehensive production index in ore dressing process
InactiveCN1749891AHigh recovery rateComputer controlSpecial data processing applicationsAutomatic controlNerve network
The present invention belongs to the field of automatic control technology. The intelligent optimized control process for comprehensive production indexes in ore dressing process includes the steps of: setting technological indexes, setting control loop, controlling statistical process, predicting technological indexes with the nerve network, feedback compensation, feedforward compensation, etc. The present invention is superior in that based on the requirement of the ore dressing process in concentrate grade and metal recovering rate and through the said control process, the optimized set values for ore grinding work section and selecting work section are given and the loop setting values are then given to realize comprehensive production index optimization in the ore dressing process.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
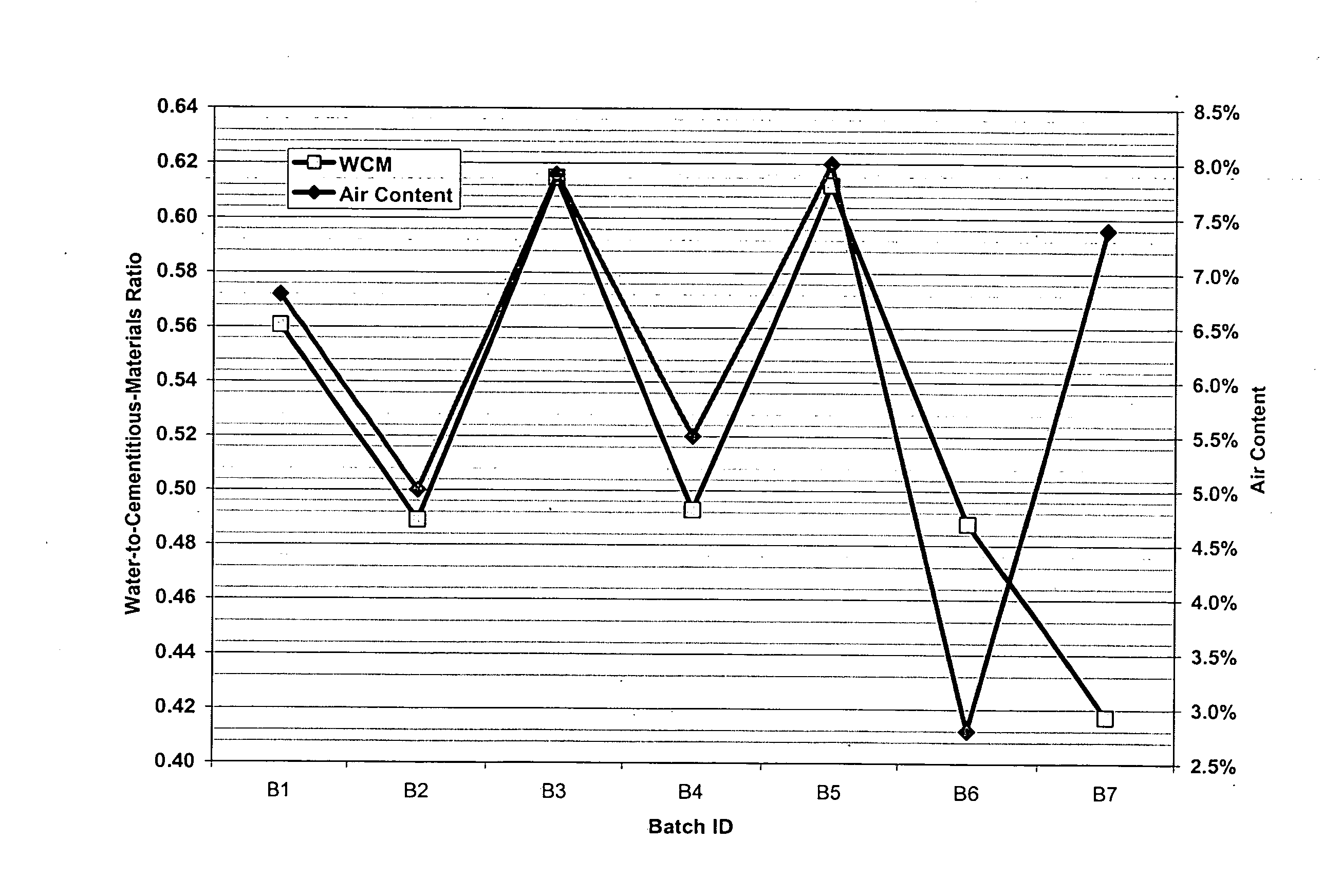
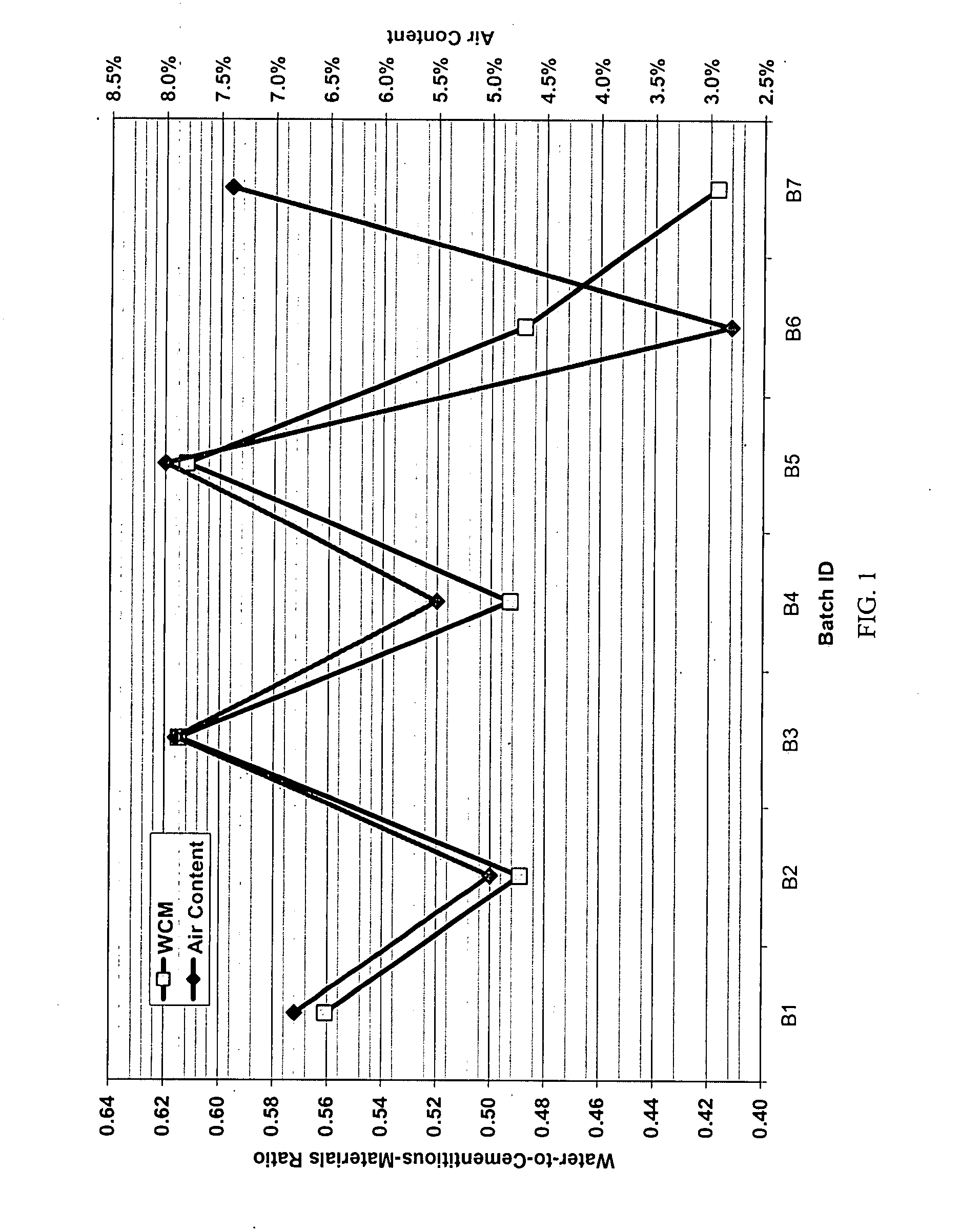
Method and system for concrete quality control based on the concrete's maturity
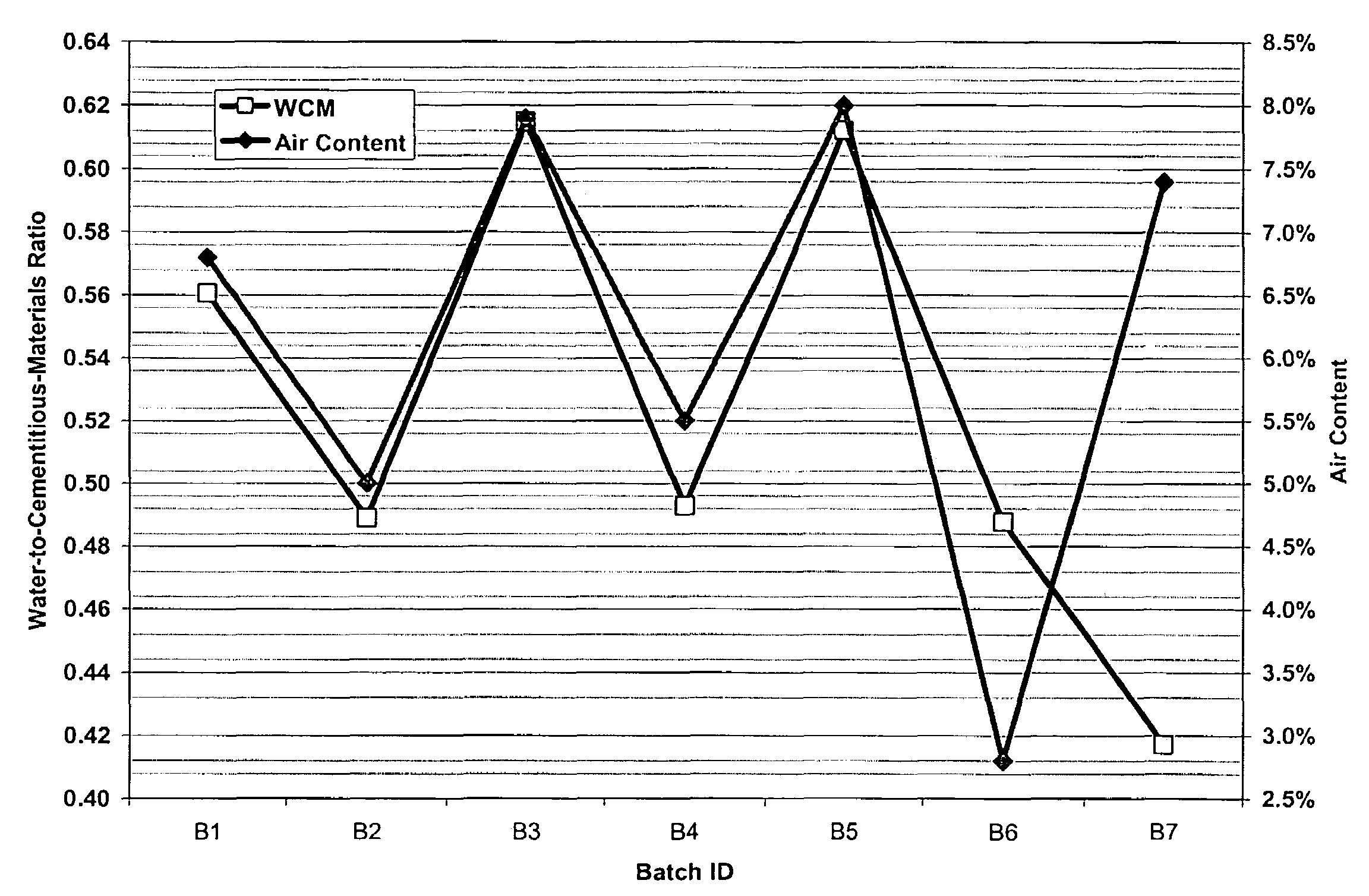
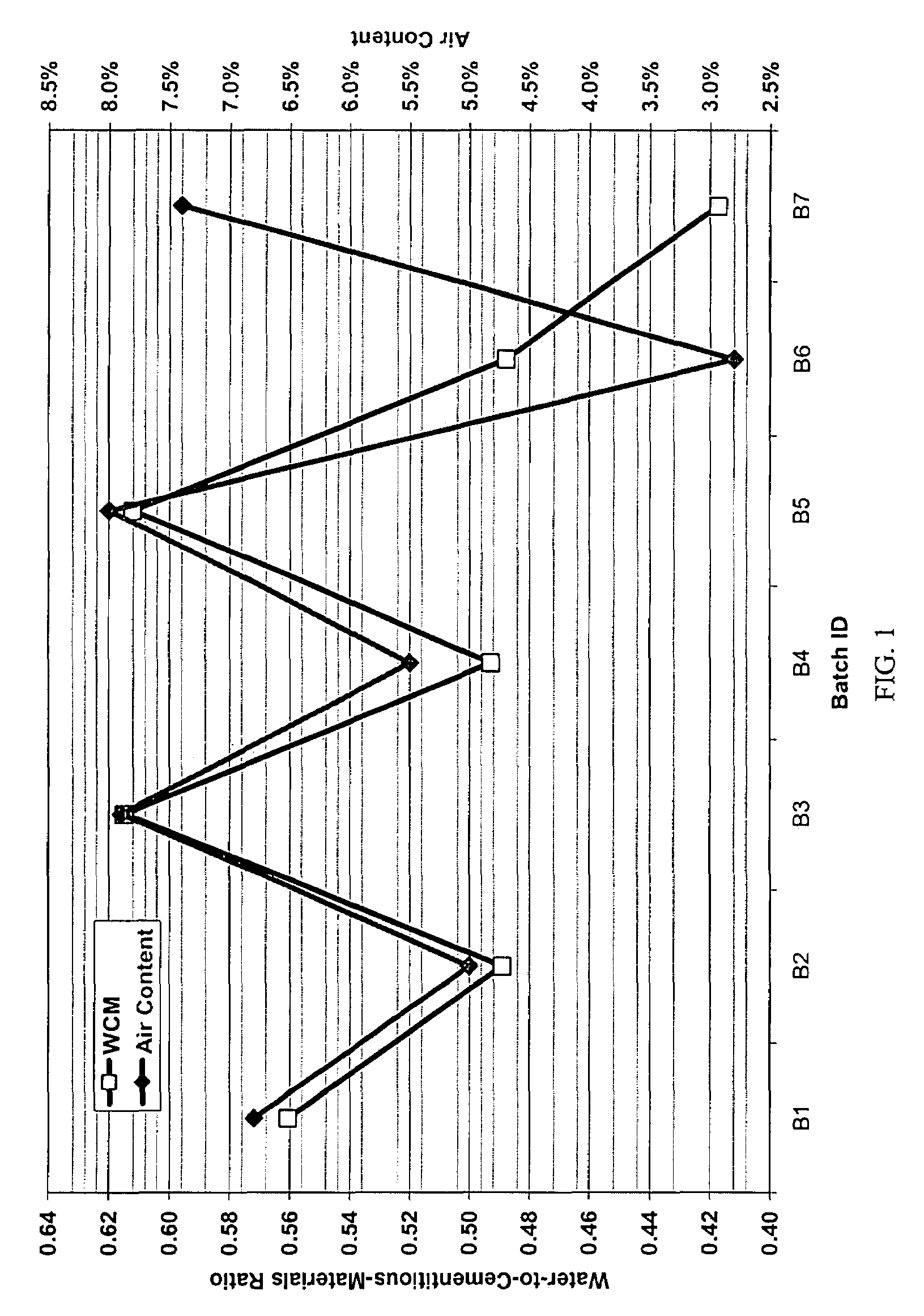
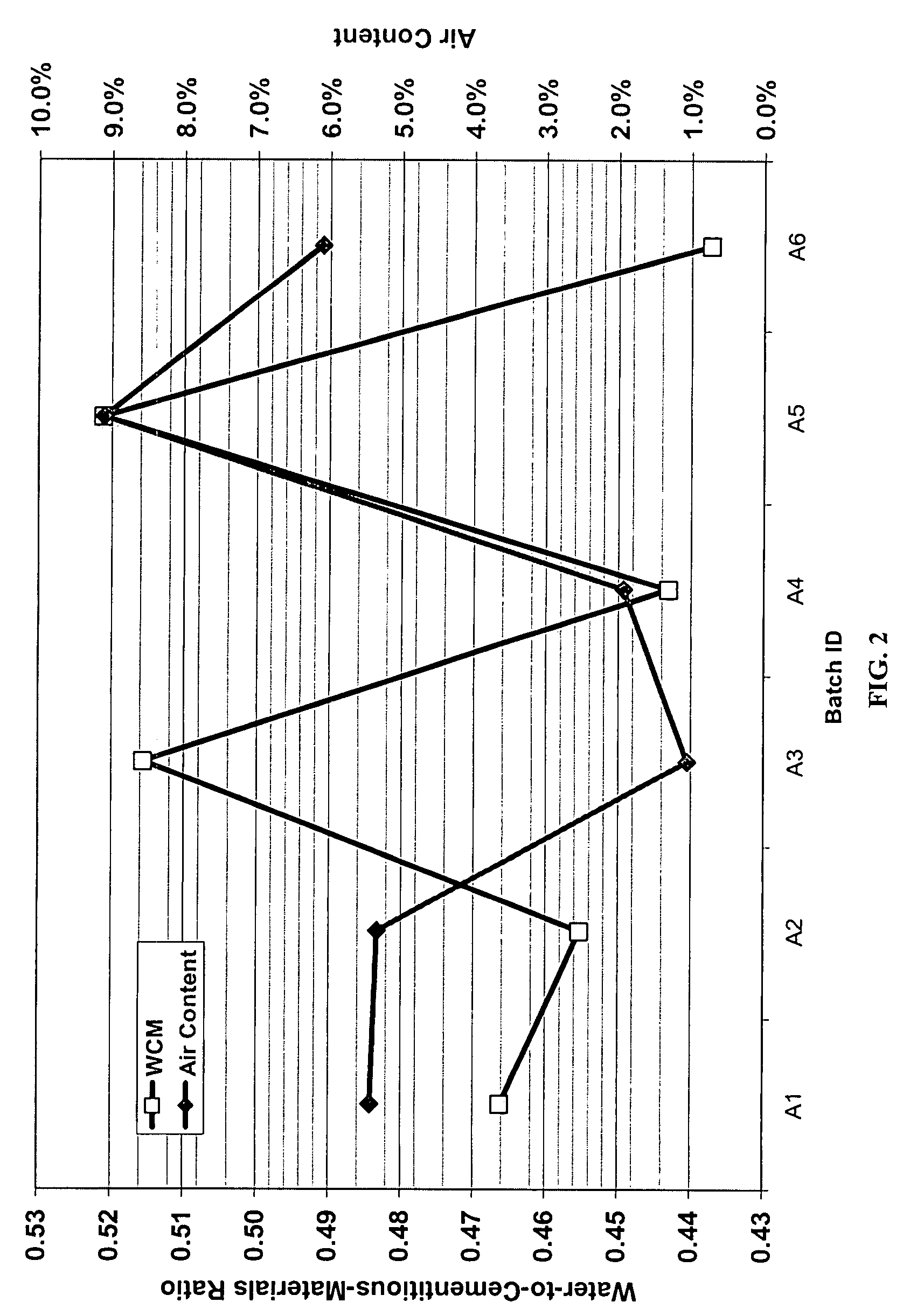
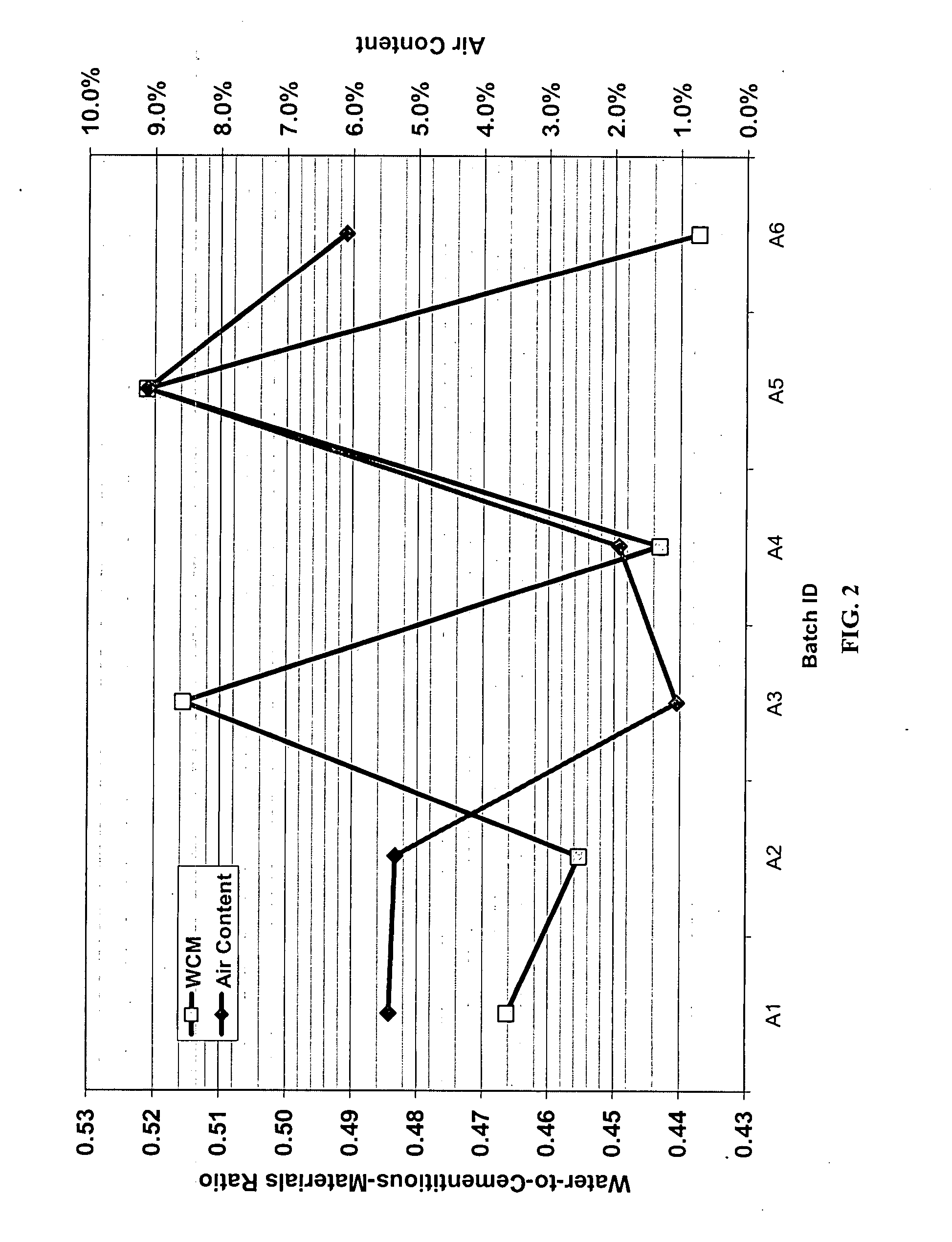
Method and system for controlling and monitoring the quality of concrete based on the concrete's maturity. Various embodiments of the present invention are discussed. First, Enhanced Maturity involves a maturity calibration method to account for the water-to-cementitious-materials ratio, air content, and gross unit weight of the concrete. Second, Moisture-Loss Maturity is a method for determining the appropriate time to terminate moisture-loss protection of concrete and concrete structures. Third, Improved Maturity is a method and system for determining the strength of curing concrete using improved maturity calculations. Fourth, SPC Maturity is a method that beneficially couples maturity measurements and calculations with Statistical Process Control (SPC) methods to enable rapid recognition of changes to the concrete mix and / or incompatibilities between the various components of the concrete mix. Fifth, Loggers, Readers, and Software represent the preferred embodiment for automating and simplifying the implementations of the aforementioned methods.
Owner:FLIR COMML SYST
Energy monitoring or control of individual vias formed during laser micromachining
InactiveUS7244906B2Quality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesEngineeringTime control
A method and system increase the quality of results achieved by laser micromachining systems. Data relating to parameters controlling laser micromachining process are recorded during the micromachining process, identified by the feature associated with the parameters used to micromachine, and stored on the system. The stored data can be either retrieved during the micromachining process to enable real time control or retrieved after workpiece processing to conduct statistical process control.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
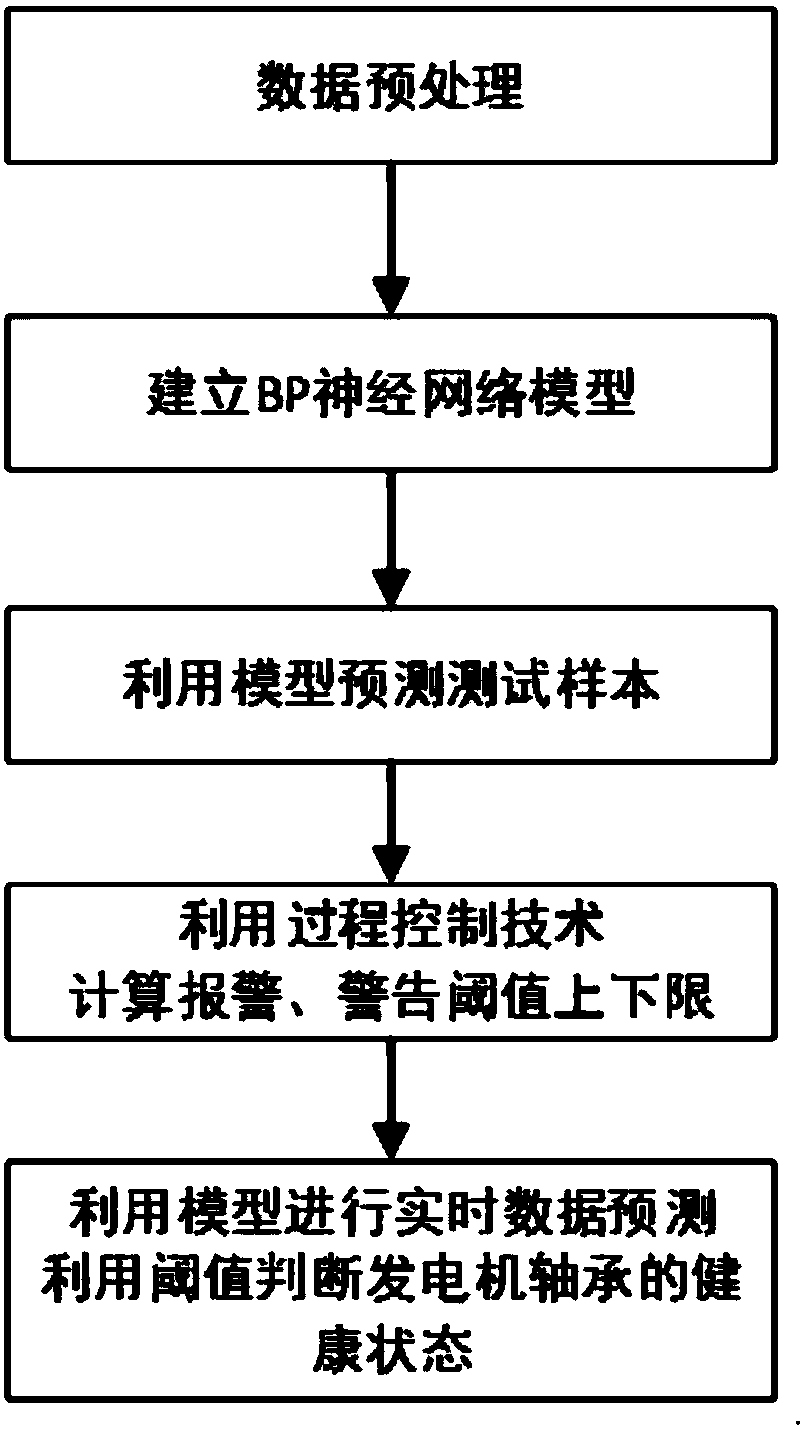
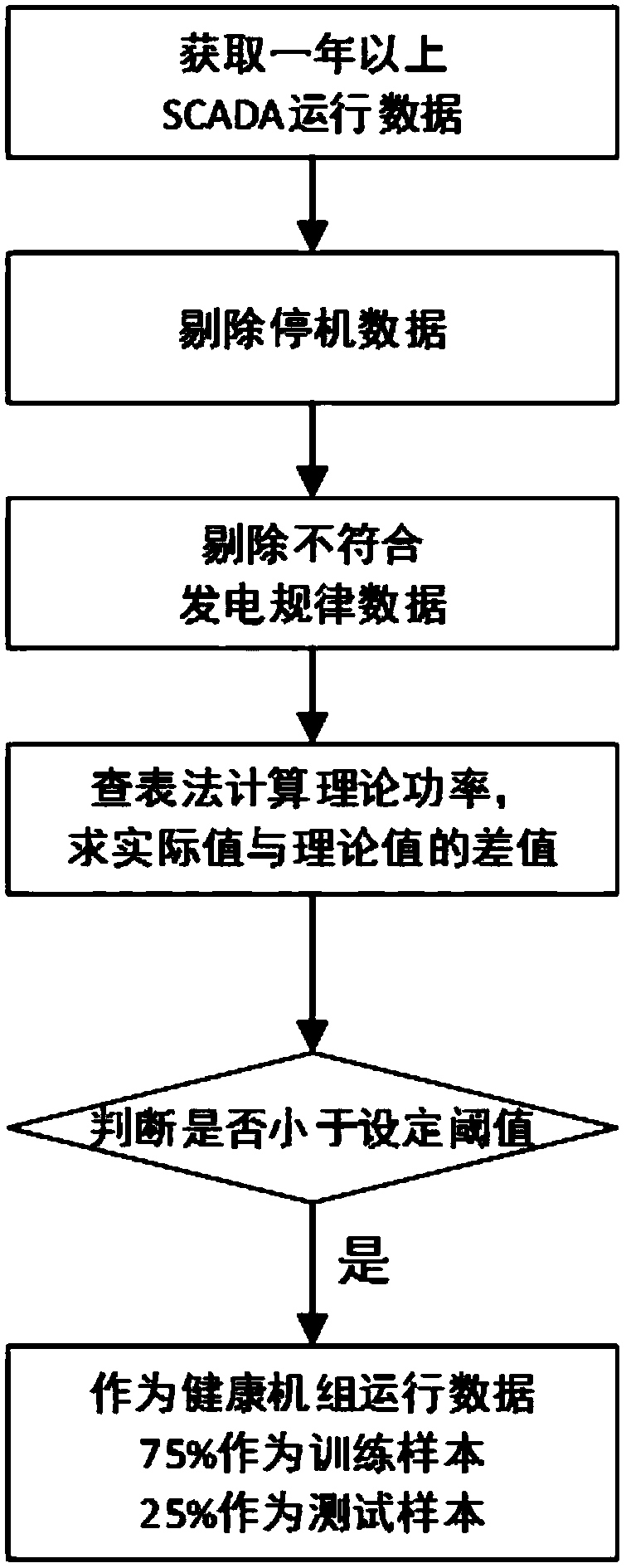
Generator bearing fault prediction method
InactiveCN107977508AEarly warning failureImprove usage management capabilitiesGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationLower limitElectricity
The invention discloses a generator bearing fault prediction method. According to the method, first, SCADA data of a healthy wind turbine generator set is selected based on a power curve method to serve as training samples and test samples; second, a generator bearing fault prediction model of target parameters is established; third, the prediction model is utilized to predict target parameters ofthe test samples, and the target parameters are compared with actual values to obtain residual errors; fourth, a process control technology is utilized to calculate an upper limit and a lower limit of an alarm threshold and an upper limit and a lower limit of a warning; and last, the prediction model is utilized to predict an actual operation target parameter of the wind turbine generator set, the actual operation target parameter is compared with an actual value to obtain a first residual error, and the health state of a generator bearing is judged. The method has the advantages that the SCADA data of the wind turbine generator set is utilized to perform modeling prediction, the statistical process control ideology is utilized to divide the state of the generator bearing into a health state, a sub-health state and a fault state, an early warning to generator bearing failure is given in advance, and the use management capability of the bearing is improved.
Owner:北京优利康达科技股份有限公司
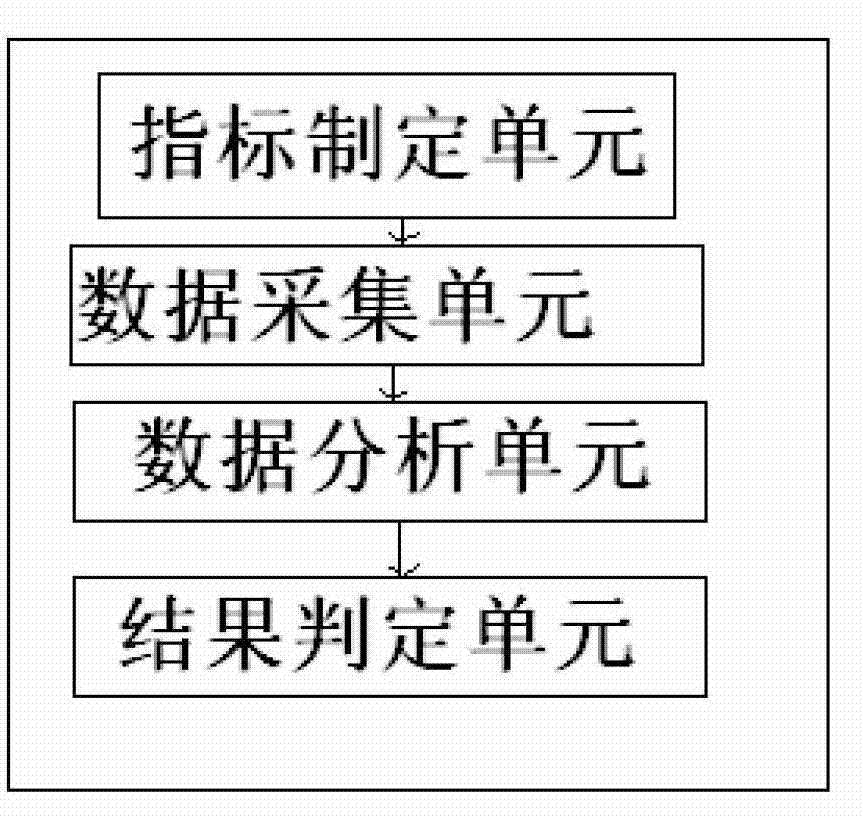
Quality monitoring system and method of tobacco primary process
ActiveCN102885392AGuaranteed processing effectEasy to operateTobacco preparationAutoanalysisControl data
The invention relates to a quality monitoring system and a method of a tobacco primary process. The quality monitoring system of the tobacco primary process comprises an index formulating unit, a data collection unit, a data analysis unit and a result determination unit; the collected data is modeled and analyzed on the basis of a tobacco primary process center control data system, so that the indexes according with current tobacco requirements, device processing capacity and processing direction are obtained, and the indexes are subjected to SPC (statistical process control) tracking determination. According to the technical scheme, the technical problem that a tobacco primary process parameter in the prior art cannot objectively reflect an actual production condition is effectively avoided. The quality monitoring method and the system are capable of monitoring and automatically analyzing the tobacco primary process.
Owner:ZHANGJIAKOU CIGARETTE FACTORY
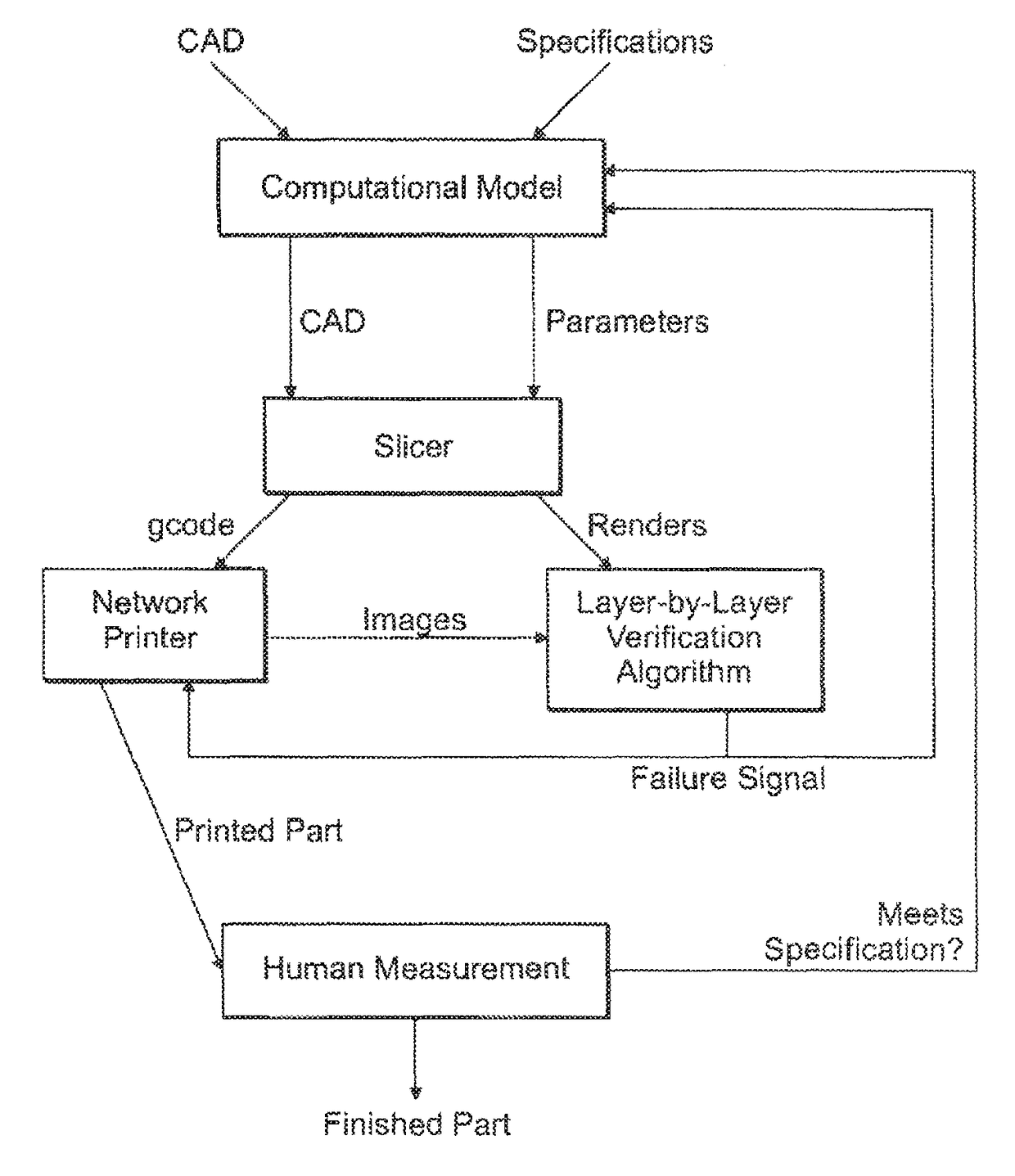
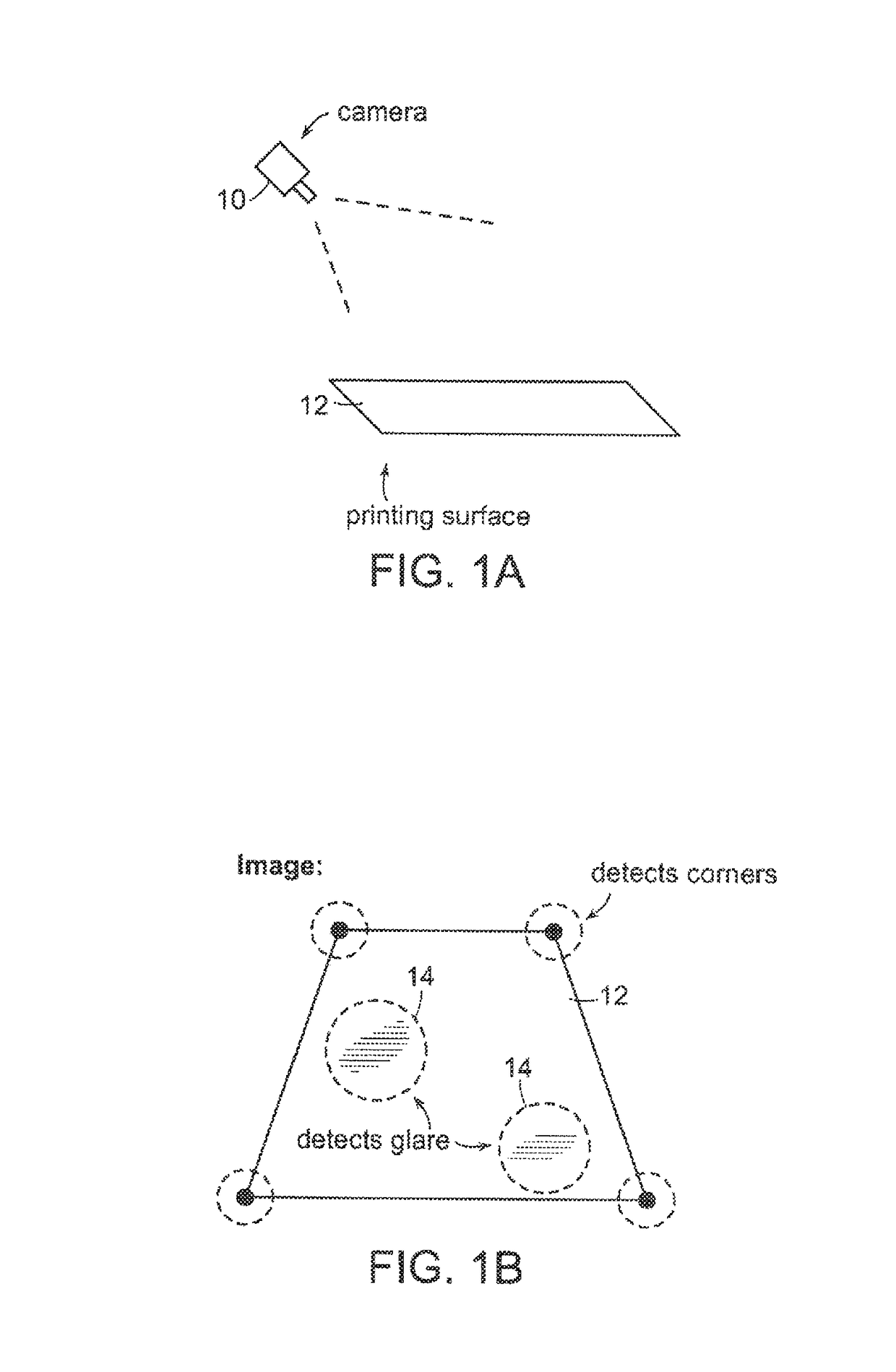
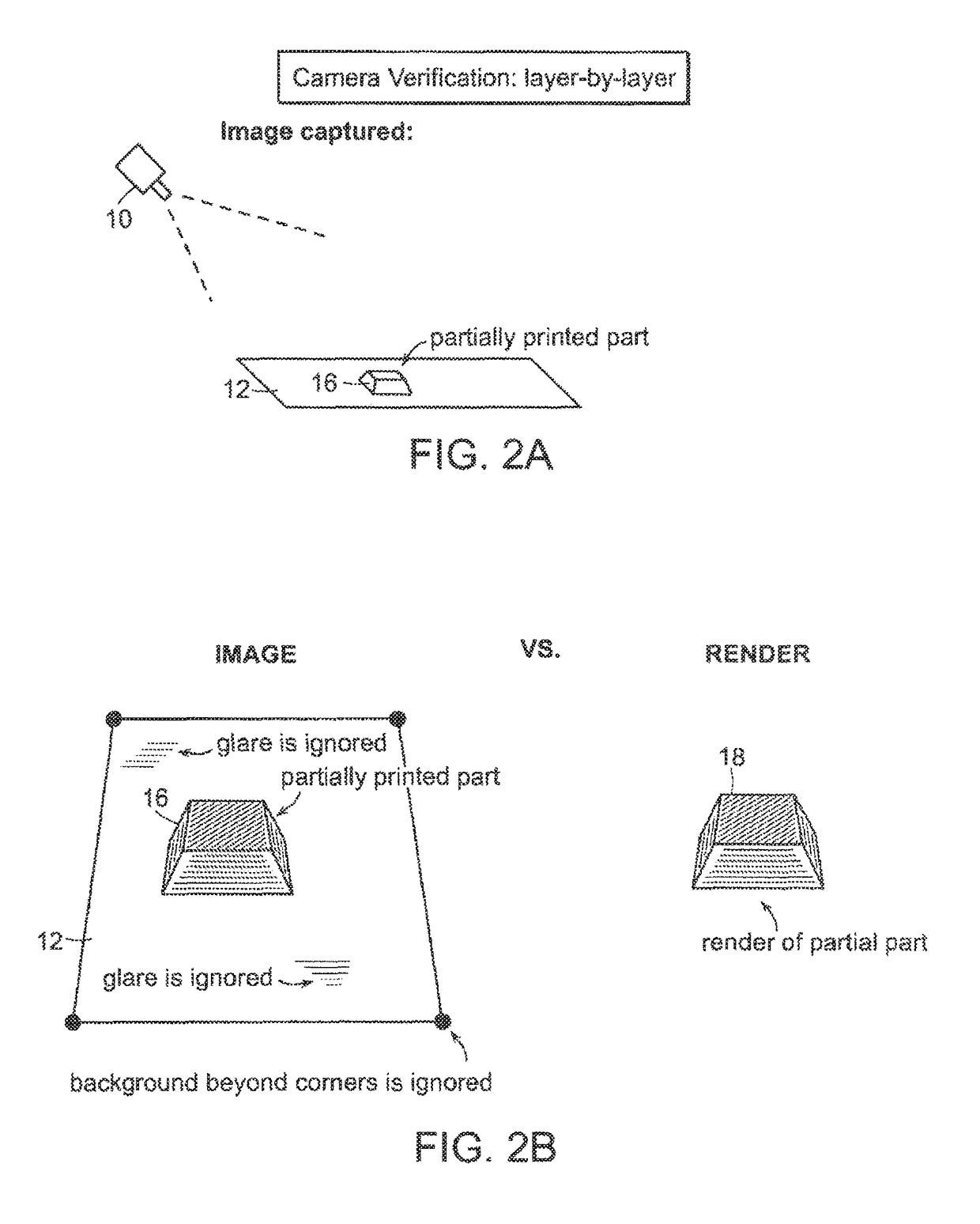
Automatic process control of additive manufacturing device
ActiveUS9855698B2Minimize the numberImprove efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsAutomatic controlAutomatic process control
Automatic process control of additive manufacturing. The system includes an additive manufacturing device for making an object and a local network computer controlling the device. At least one camera is provided with a view of a manufacturing volume of the device to generate network accessible images of the object. The computer is programmed to stop the manufacturing process when the object is defective based en the images of the object.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and system for concrete quality control based on the concrete's maturity
A method and system for controlling and monitoring the quality of concrete based on the concrete's maturity (which is a function of its time-temperature profile, or temperature history). Five different applications or embodiments of the present invention are discussed, namely, Enhanced Maturity, Moisture-Loss Maturity, Improved Maturity, SPC Maturity, Loggers, Readers, and Software. Enhanced Maturity involves a maturity calibration method to account for the water-to-cementitious-materials ratio, air content, and gross unit weight of the concrete. Moisture-Loss Maturity is a method for determining the appropriate time to terminate moisture-loss protection of concrete and concrete structures. Improved Maturity is a method and system for determining the strength of curing concrete using improved maturity calculations. SPC Maturity is a method that beneficially couples maturity measurements and calculations with Statistical Process Control (SPC) methods to enable rapid recognition of changes to the concrete mix and / or incompatibilities between the various components of the concrete mix. Loggers, Readers, and Software represent the preferred embodiment for automating and simplifying the implementations of Enhanced Maturity, Moisture-Loss Maturity, Improved Maturity, and SPC Maturity.
Owner:FLIR COMML SYST
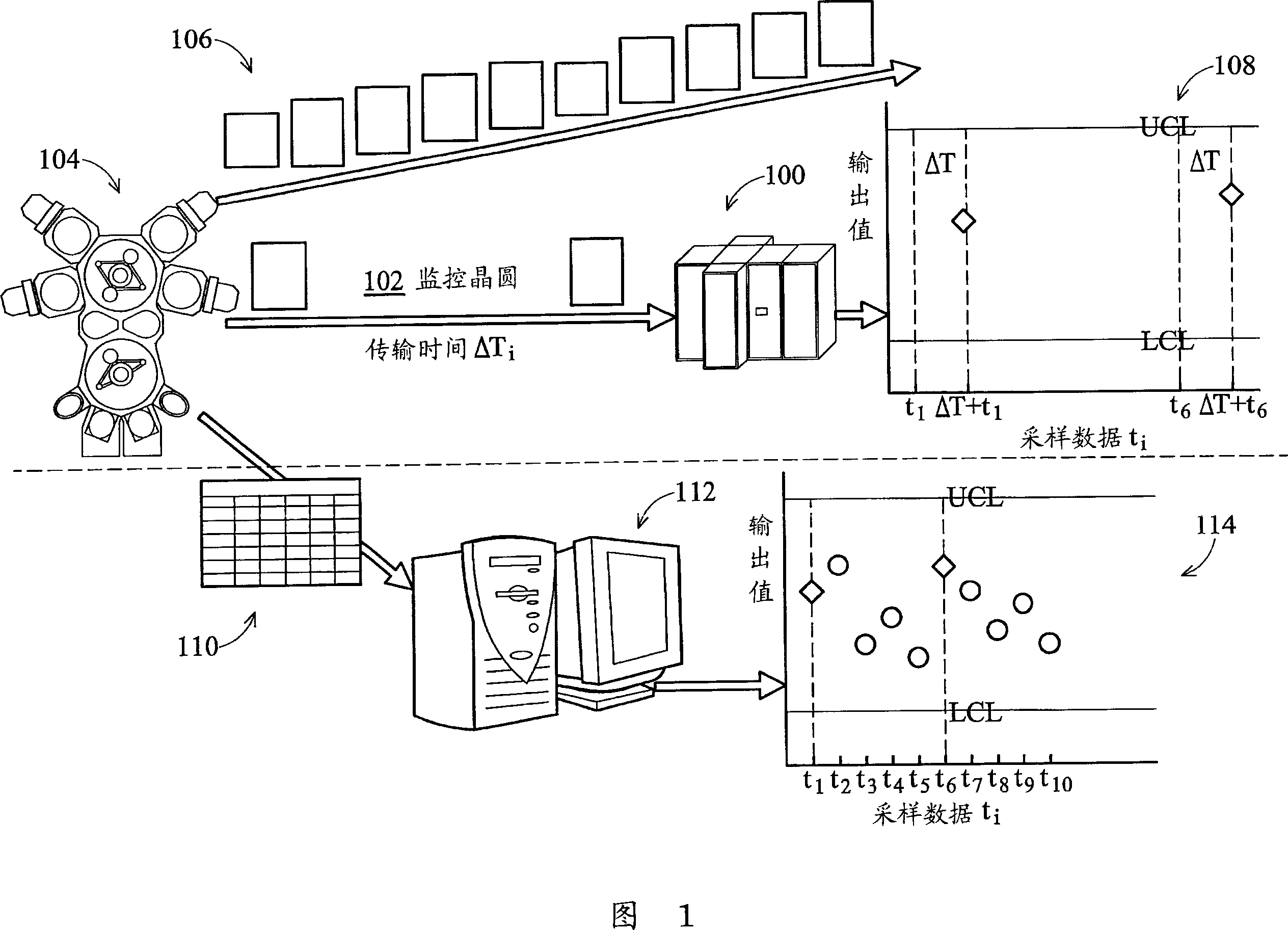
Automatic monitoring and statistical analysis of dynamic process metrics to expose meaningful changes
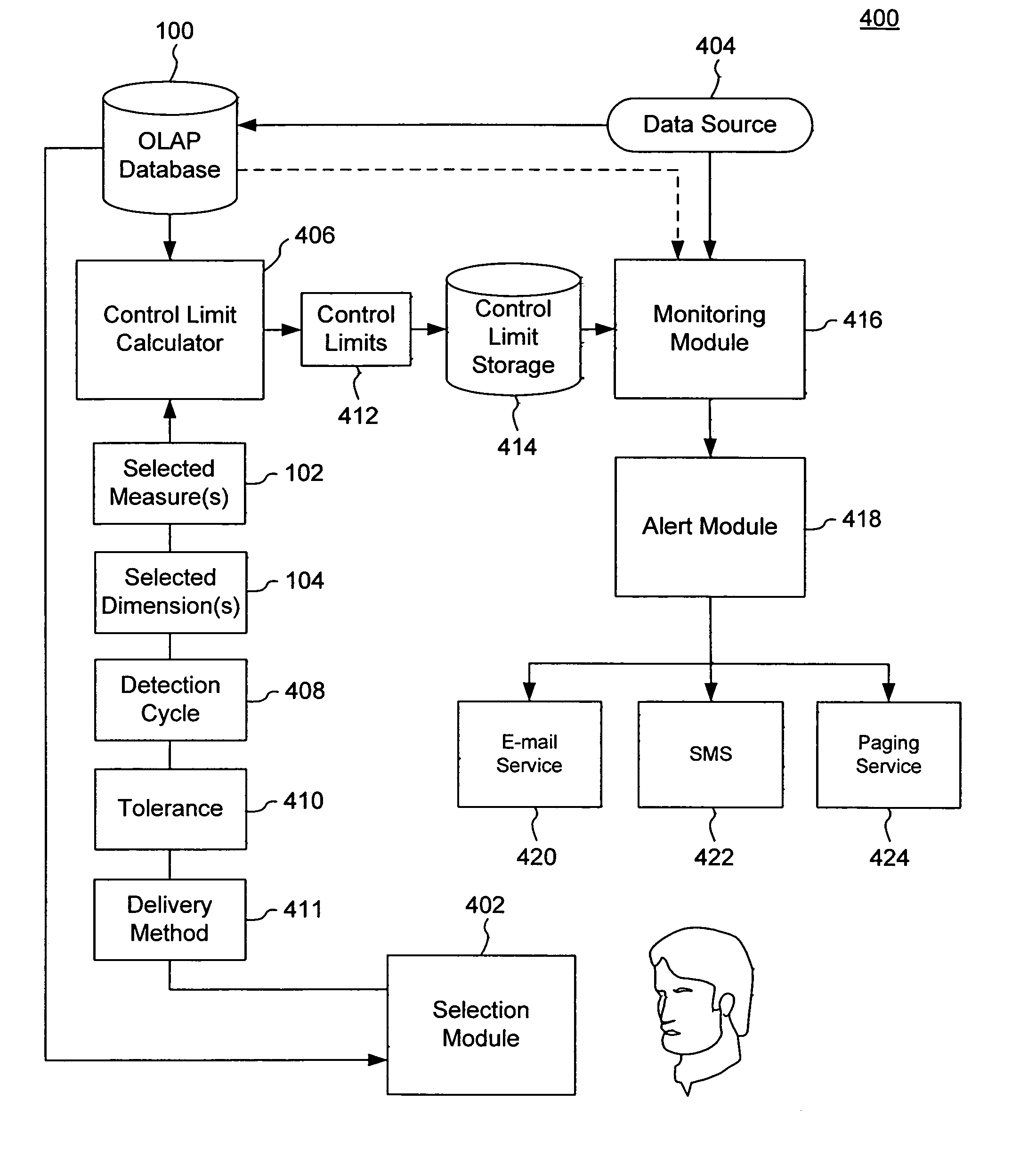
InactiveUS7072899B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsStatistical analysisMultidimensional data
A selection module allows a user to specify at least one measure to be monitored in at least one dimension of a dimensional hierarchy. A control limit calculator extracts, for each specified measure and for each specified dimension, a time series from a multidimensional database for the specified measure in the specified dimension and automatically calculates one or more control limits for the specified measure in the specified dimension based on the extracted time series using a Statistical Process Control (SPC) technique. Thereafter, a monitoring module monitors newly acquired data including each specified measure in each specified dimension for an out-of-limits condition based on one or more automatically-calculated control limits. An alert module triggers an alert in response to an out-of-limits condition being detected.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
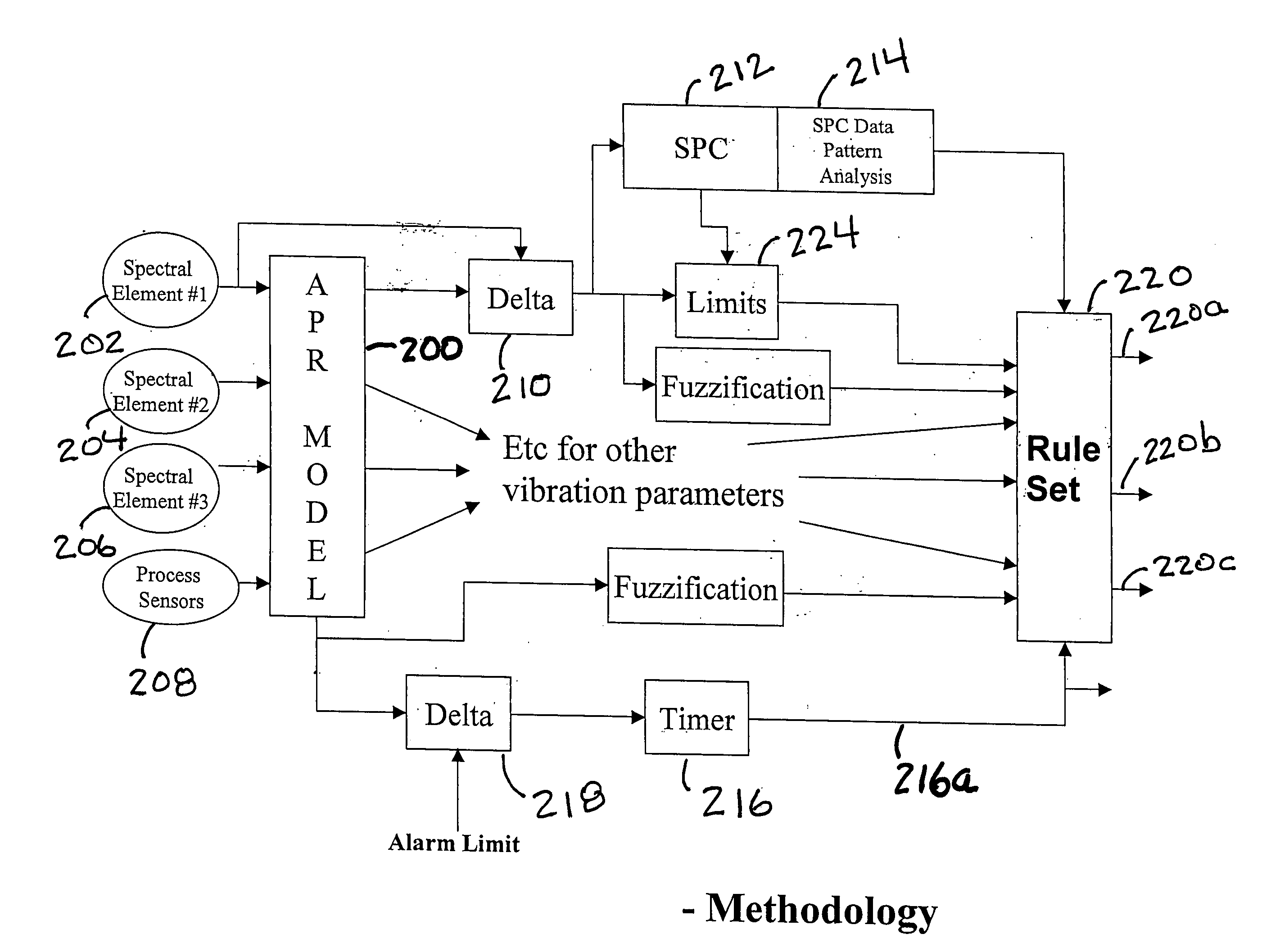
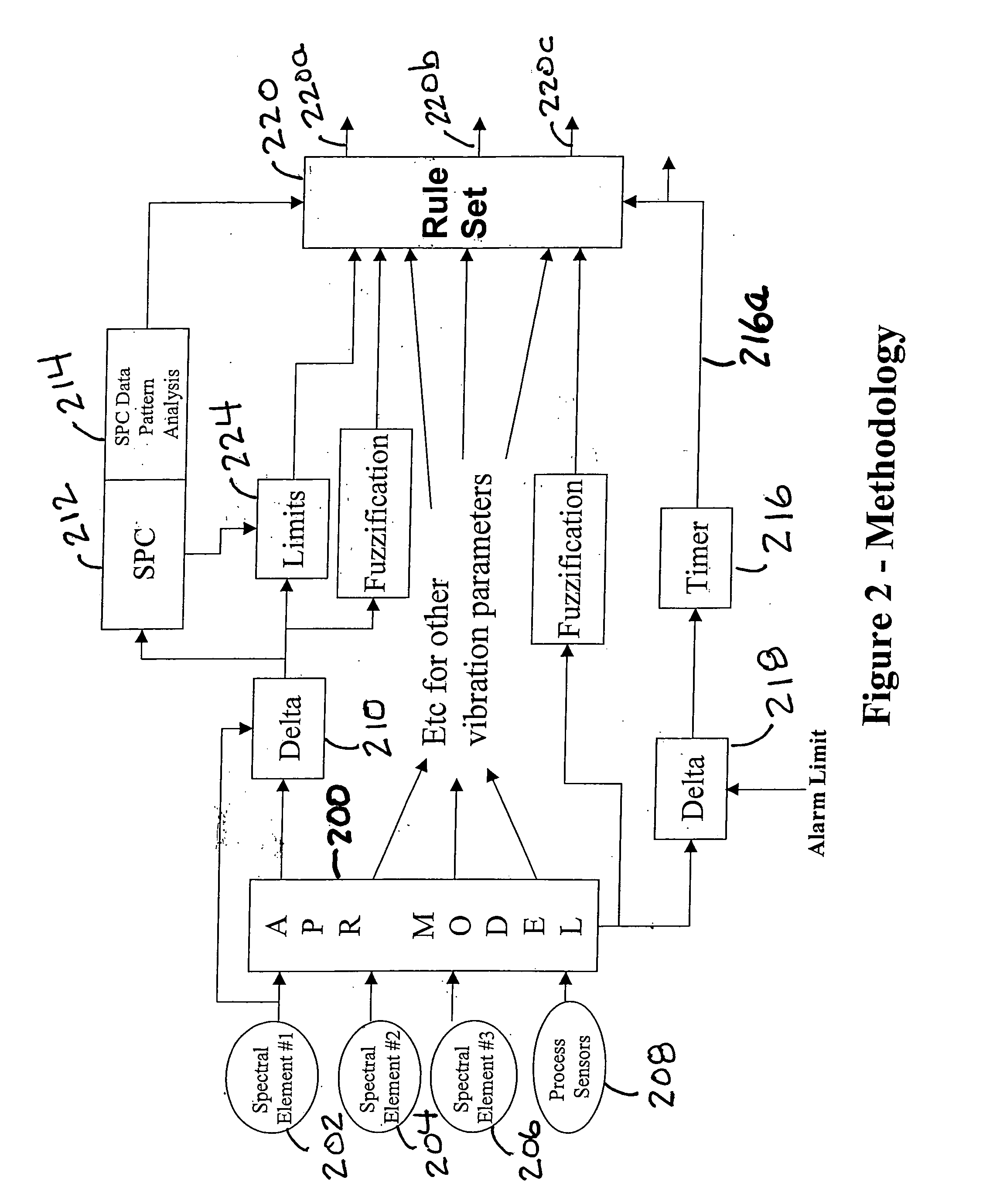
Method and apparatus to diagnose mechanical problems in machinery
A method and apparatus for detecting mechanical problems in machinery used in a process. A model of the process is developed using a modeling technique such as advanced pattern recognition and the model is used to generate predicted values for a predetermined number of the operating parameters of the process and vibration parameters of the machinery. Statistical process control methods are used to determine if the difference between the predicted and actual measured values for one or more of the parameters exceeds a configured statistical limit. A rule set is used to indicate an actual or probable fault in the machinery.
Owner:ABB INC
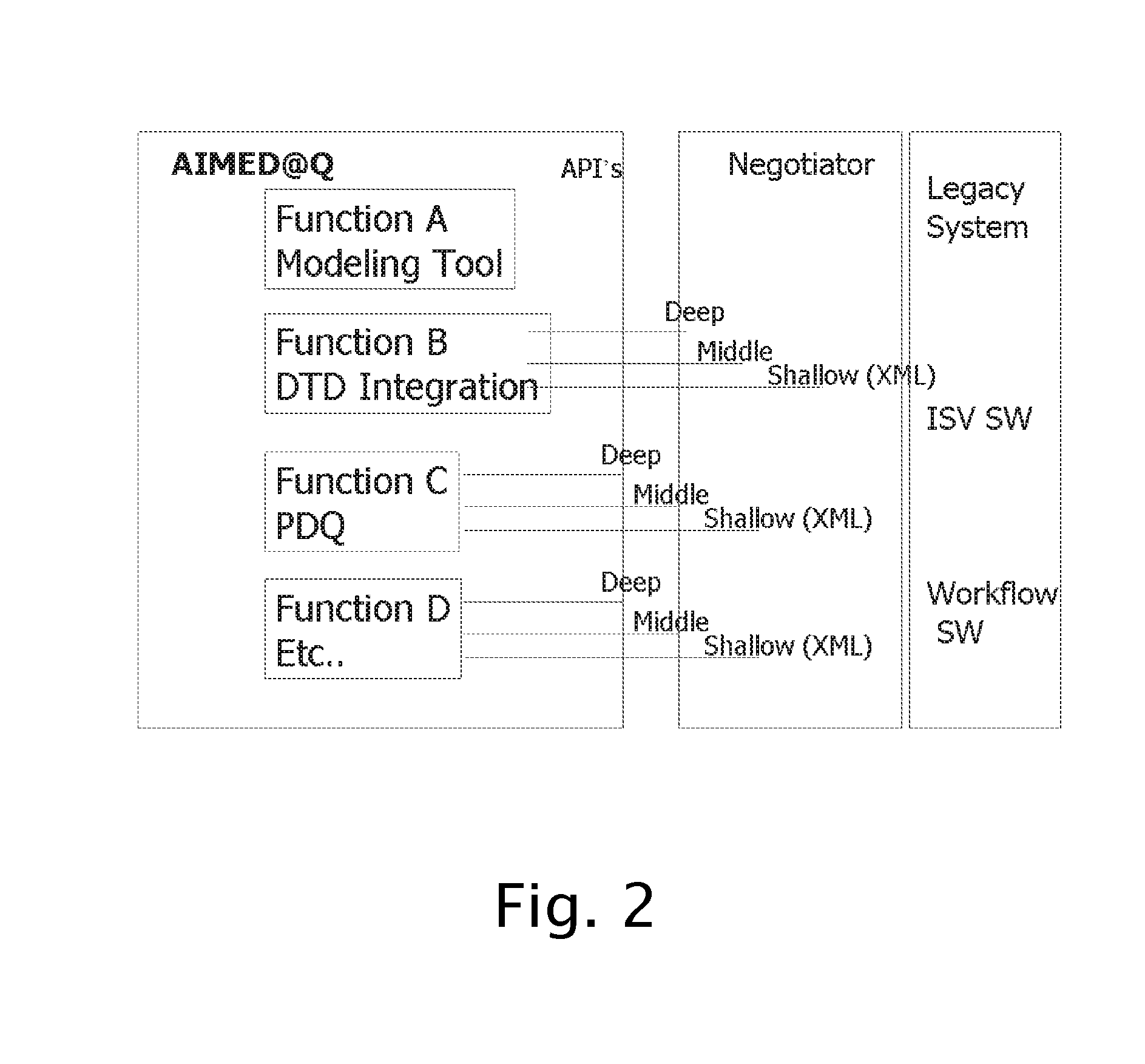
Process Performance Evaluation for Enterprise Data Systems
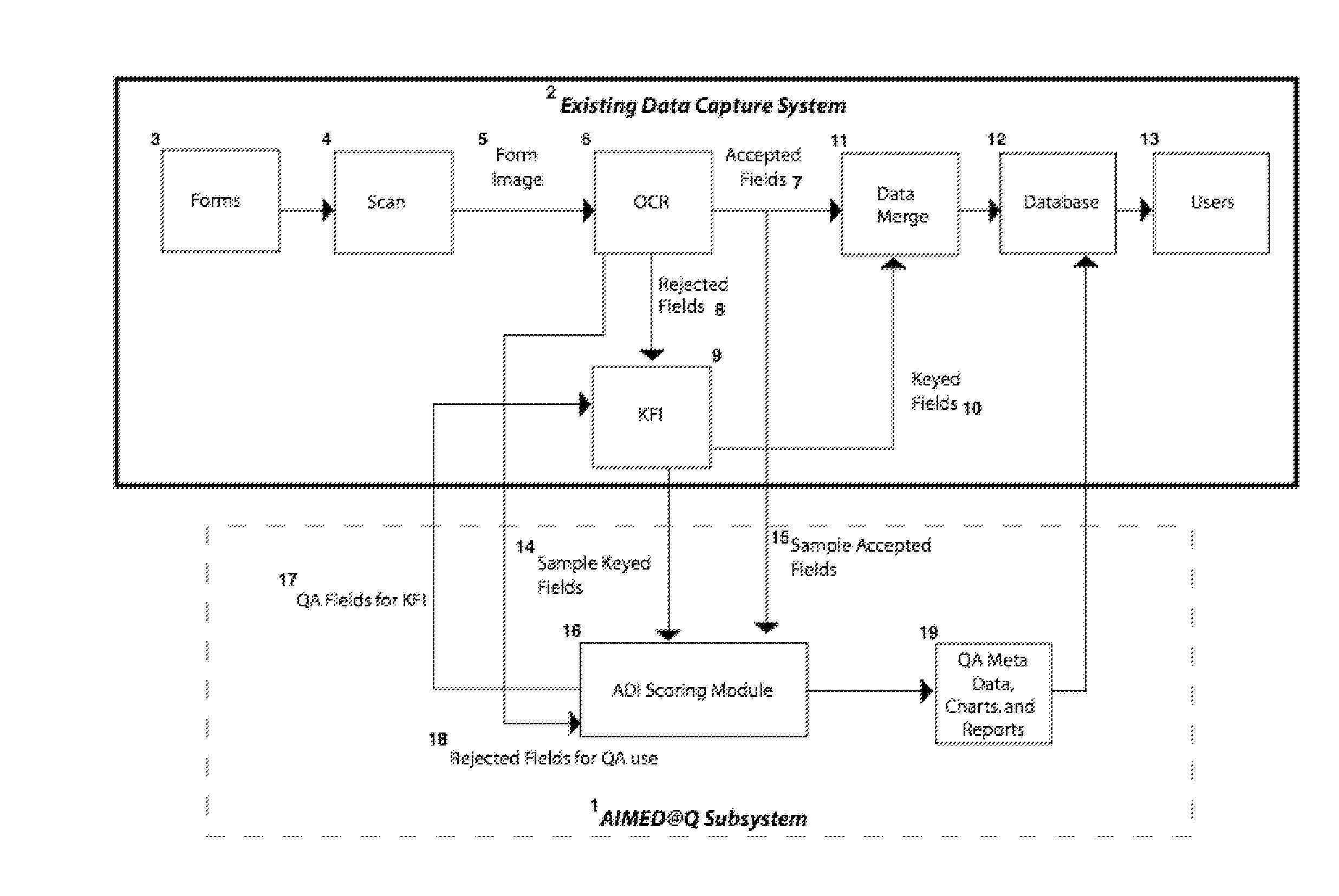
ActiveUS20080219557A1Easy to measureLow costCharacter and pattern recognitionScoring algorithmEnterprise content management
A method using integrated software and algorithms for measuring, modeling, benchmarking and validating any Enterprise Content management system, forms processing data capture system or data entry system, including, at the user's option, ingest of special engineered test materials such as a Digital Test Deck®, applying data quality scoring algorithms, use of cost models, validation of downstream business processes, and implementing statistical process control.
Owner:ADI +1
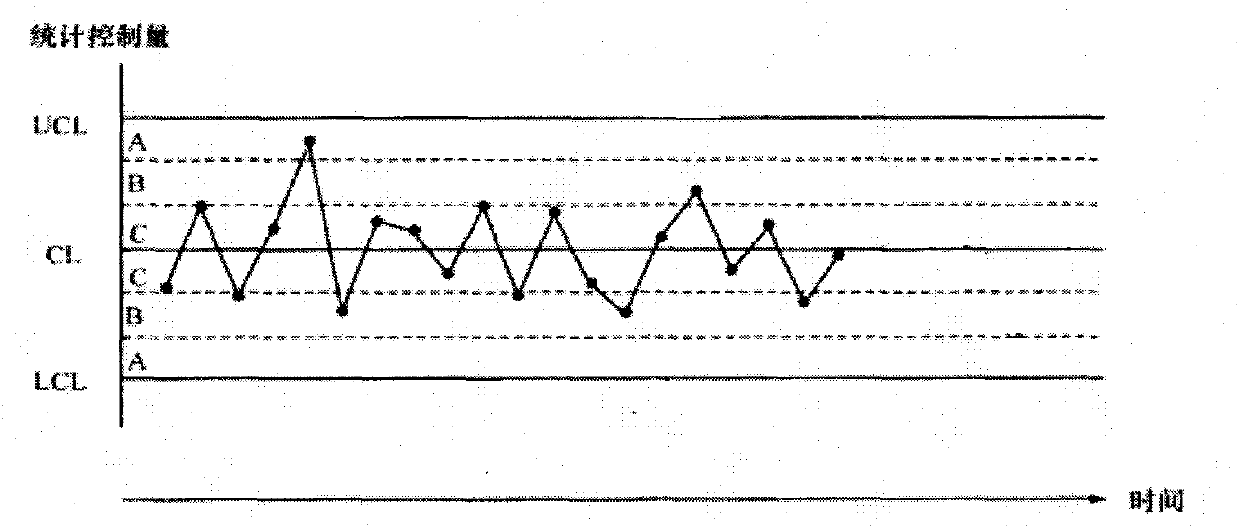
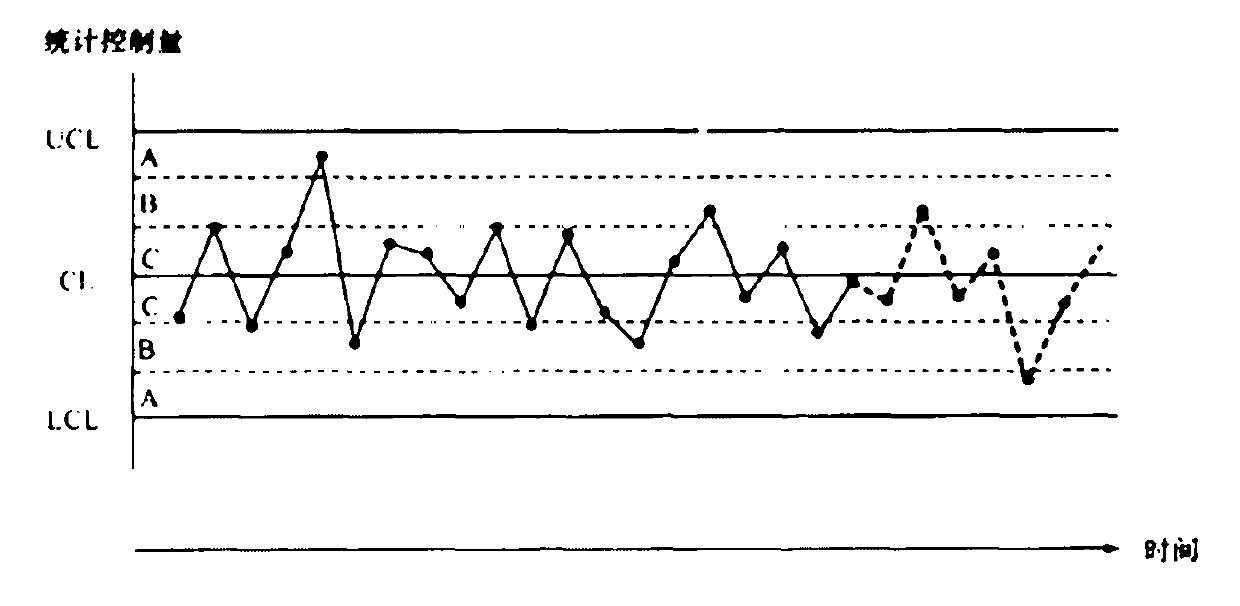
Statistical control method based on measurement assurance plan
InactiveCN101770233ANo processing involvedTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlLower limitComputer science
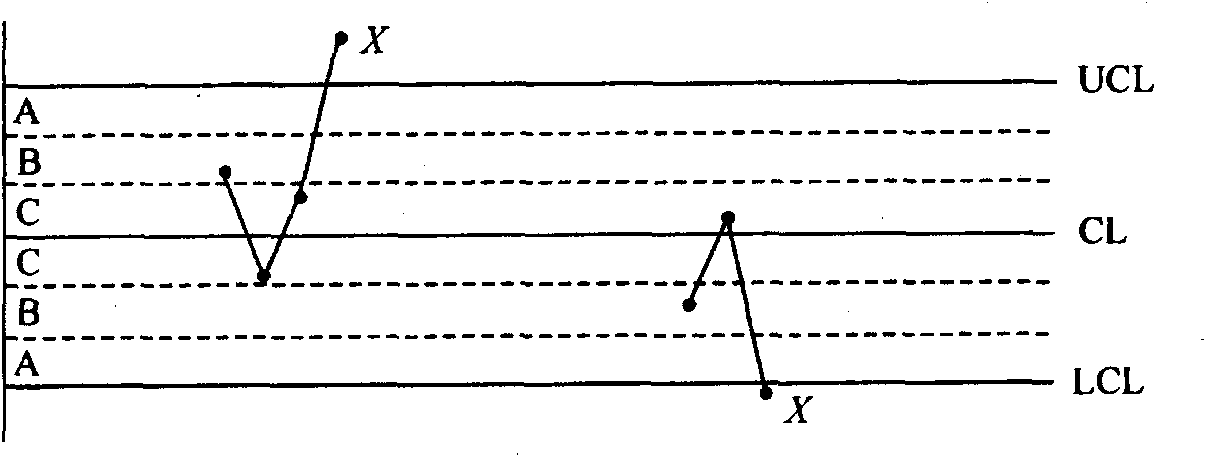
The invention discloses a statistical control method based on a measurement assurance plan, which comprises the following steps: firstly, calculating the average value x of each sub group and the average value of the average values of m sub groups, which is the same as a Shewhart control chart; and then, calculating the intergroup standard difference sb according to the average values of m sub groups, and setting a control boundary according to sb, which is different from the Shewhart control chart. The corresponding center line CL, the upper control limitation UCL and the lower control imitation LCL are respectively shown as the accompanying drawing. Thereby, the control boundary does not represent the short-period mobility of the measurement, but also can reflect the long-term mobility of the measurement, so the plan can carry out the statistical control on the influence of the measurement process by the effect of an uncontrolled system and the influence of the measurement process by the uncontrolled random effect.
Owner:SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
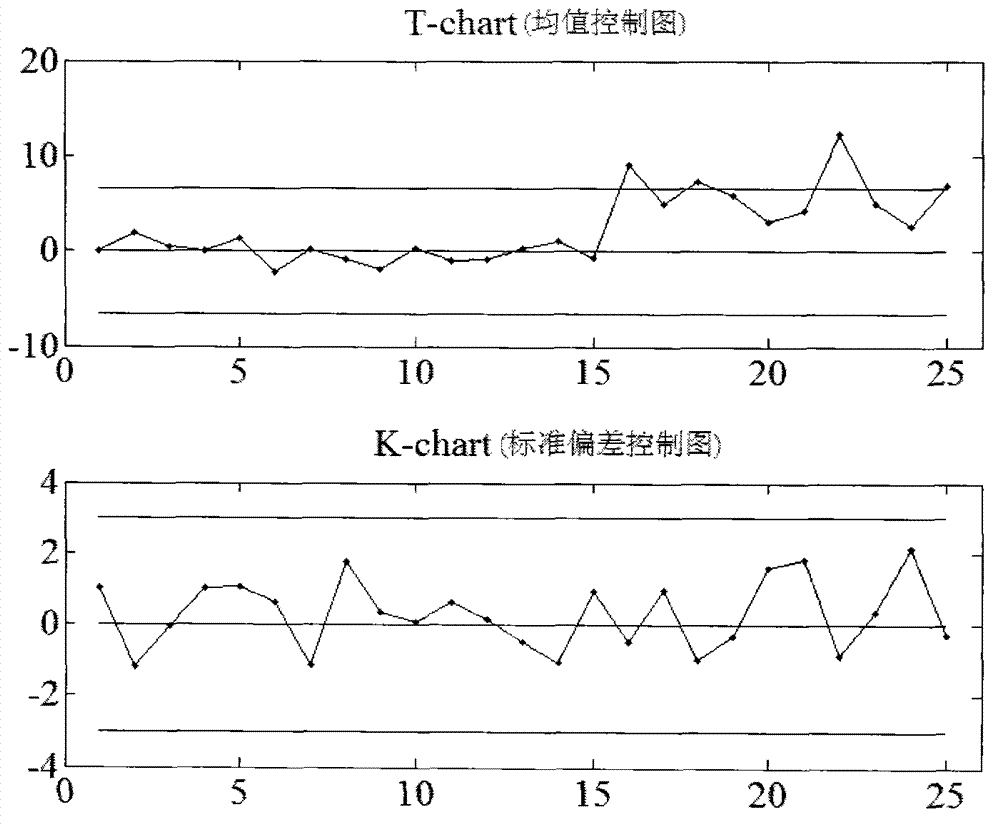
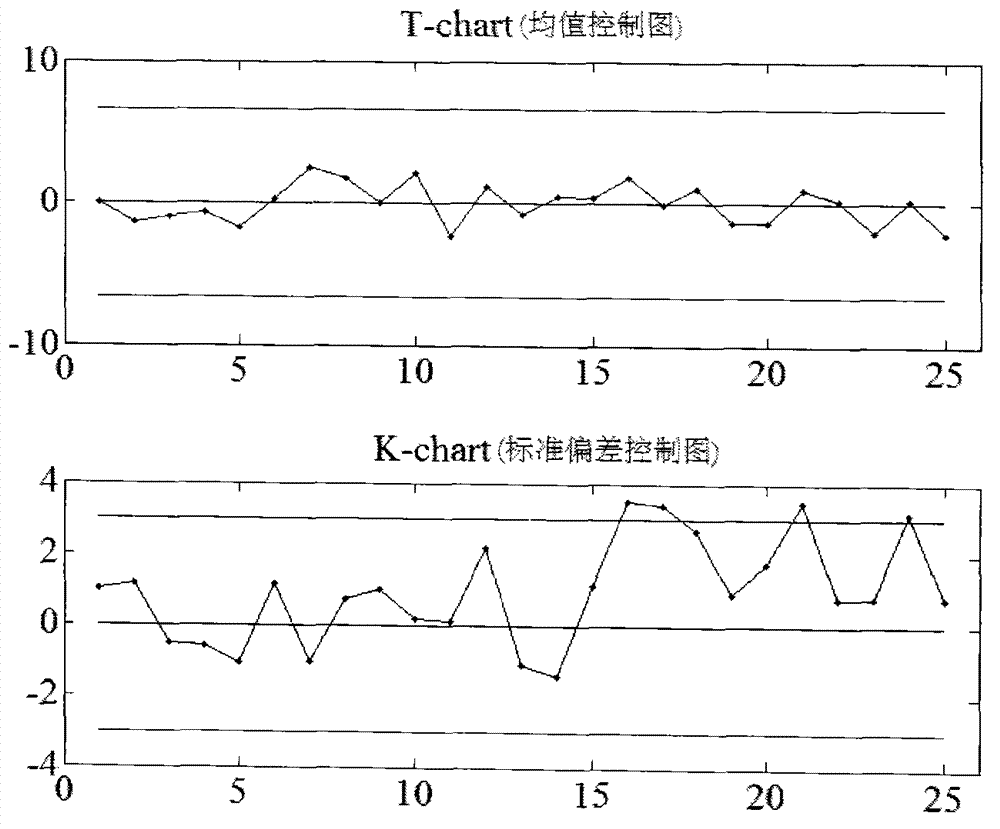
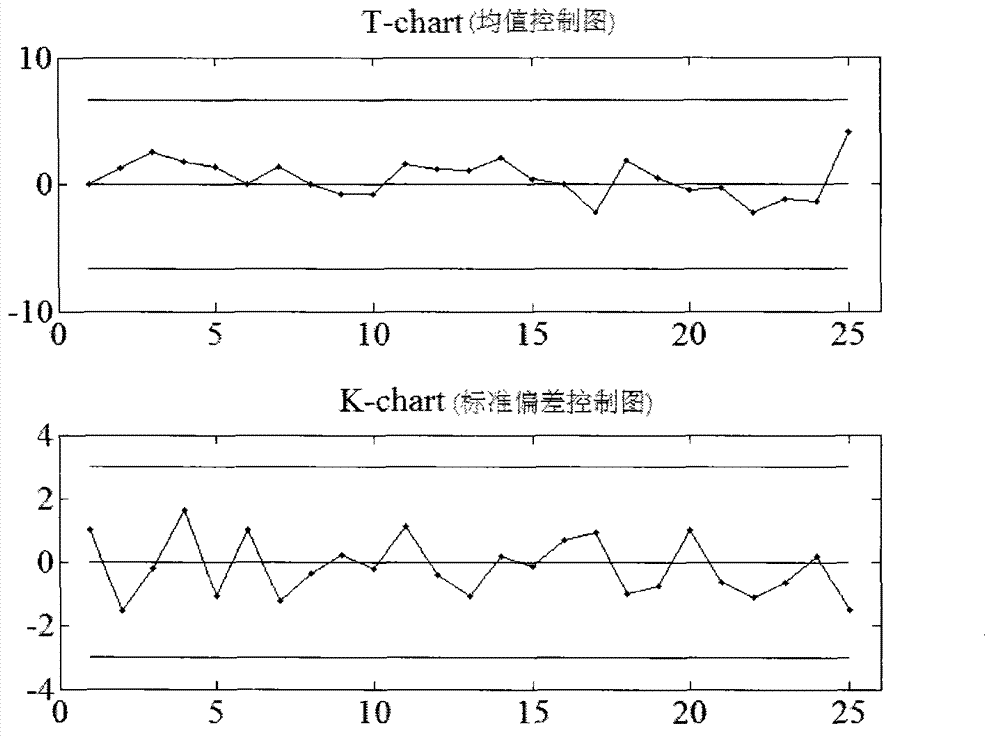
Multiple product production mode statistical process control method based on T-K control chart
The invention discloses a multiple product production mode statistical process control method based on a T-K control chart. The multiple product production mode statistical process control method includes the following steps: (1) building a T control chart for monitoring process parameter mean value; (2) building a K control chart for monitoring process parameter standard deviation; and (3) under a multiple product production mode, the T-K control chart is used for monitoring a device operation state, as long as each type of product sample data reaches more than 2 batches, if distribution parameters are known, one batch of data is enough, and sample capacity of each batch of products is guaranteed to be identical and larger than 1. Control limits are determined according to whether the mean value of the process parameter matrix or standard deviation is known, and the T-K control chart is built. Instance analysis and simulation verification prove that the process control method can detect abnormal factors causing an incontrollable phenomenon in a production process under the multiple product production mode timely and effectively, prompts operation staff to make response timely, and enables the production process to remain in a statistical controlled state so as to guarantee product quality.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
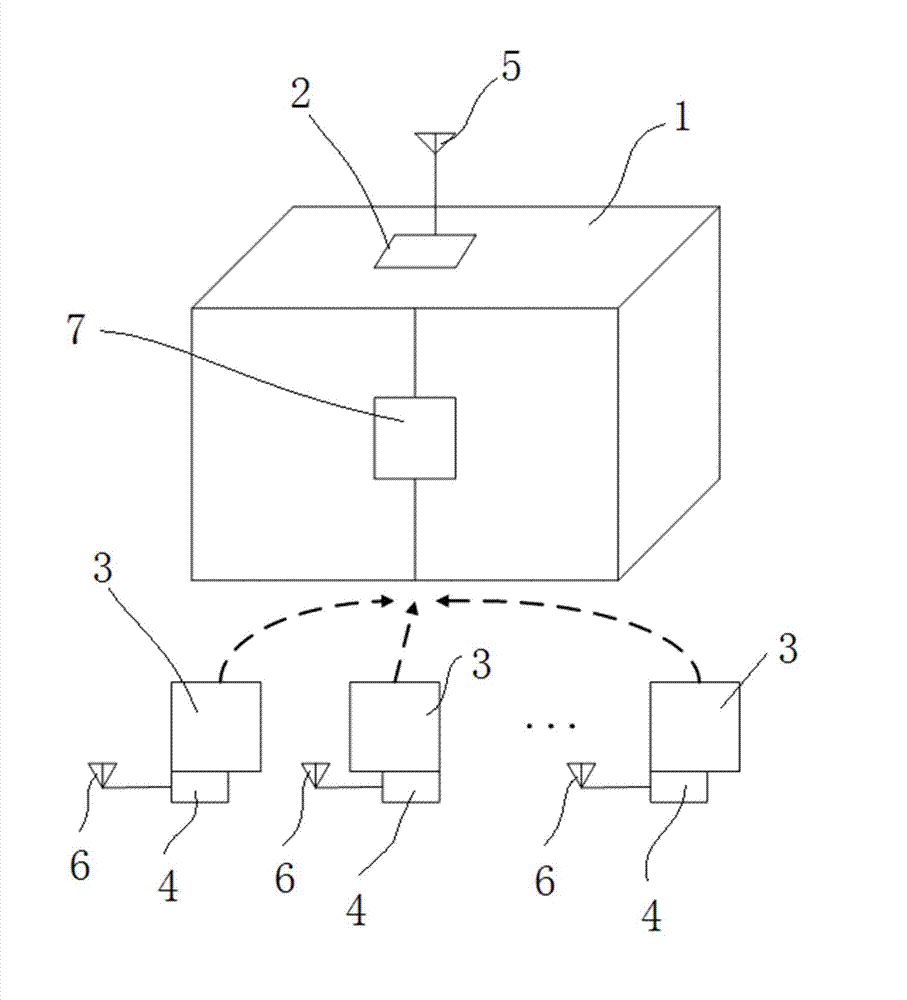
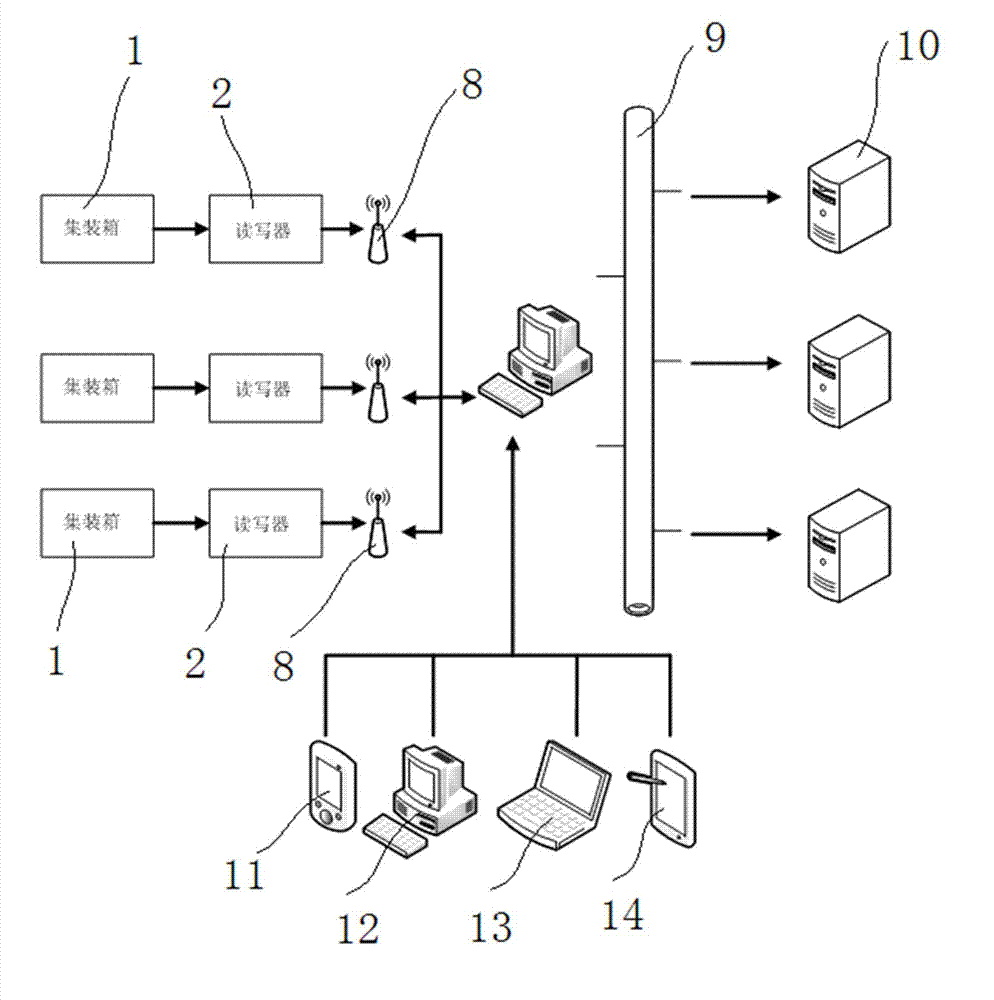
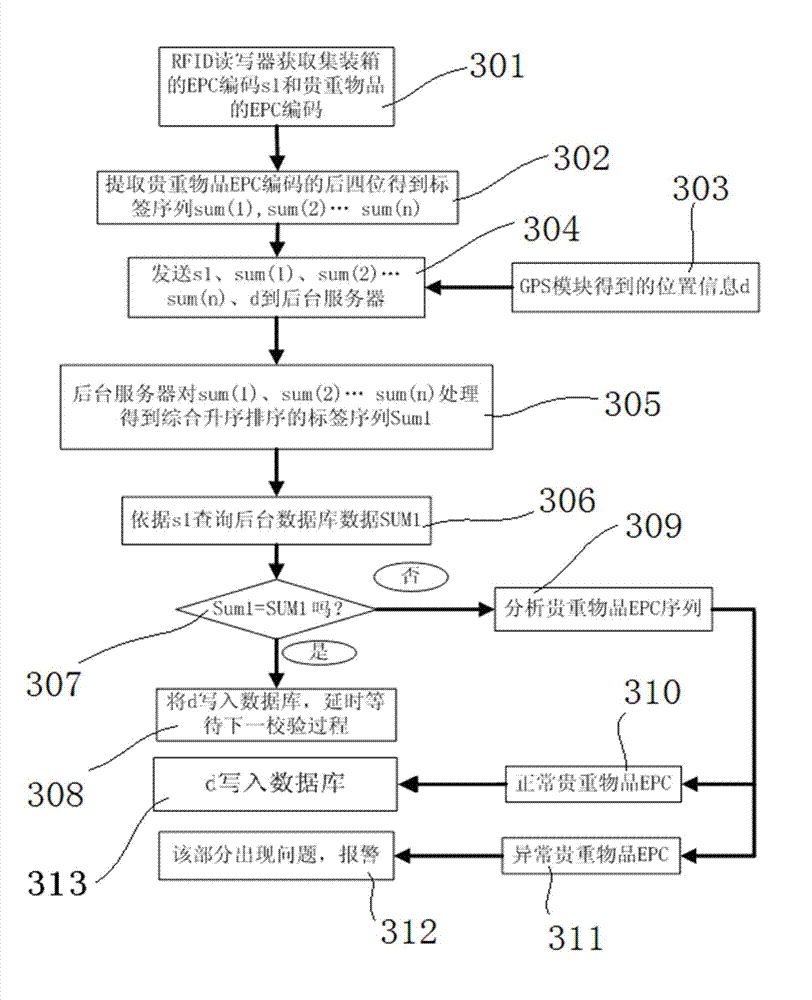
Monitoring system for transport of valuables based on radio frequency identification (RFID) and monitoring method of monitoring system
InactiveCN102902992AEnsure safetyLong reading distanceCo-operative working arrangementsLogisticsLogistics managementMonitoring system
The invention relates to the application field of the radio frequency identification technology and provides a monitoring system for transport of valuables based on radio frequency identification (RFID). An RFID reader is installed on a container, RFID tags are attached to all valuables, the RFID reader sends read codes and container location information to a background server and checks the read codes and the container location information with the data inside a database, when the exam of the information of valuables is passed, the container location information is read to the database, and when the exam of the information of valuables fails, the system alarms. The invention also provides a monitoring method of the system. The data exam is conducted through statistical process control (SPC) data sequences, and valuables are monitored. By the aid of the system and the method, for logistics corporations, the cost is saved, the efficiency is improved and the hazard is reduced.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method and system for virtual metrology
The present invention provides a method and a metrology system which are especially suitable for semiconductor manufacturing are provided in this patent. Process data and metrology data are received. Prediction data is generated from the process data and metrology data using a learning control model. The virtual measuring system which is suitable for manufacturers is composed of a fault detection and classification system which receives process data, a statistical process control system which performs statistical process control on a history of physical metrology data to form metrology data, a virtual metrology application system which generates prediction data based on the process data and the metrology data using a learning control model. The method and the metrology system presented in this patent can shorten production period through lowering application procedures or tool measuring parameters.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method for measuring the control performance provided by an industrial process control system
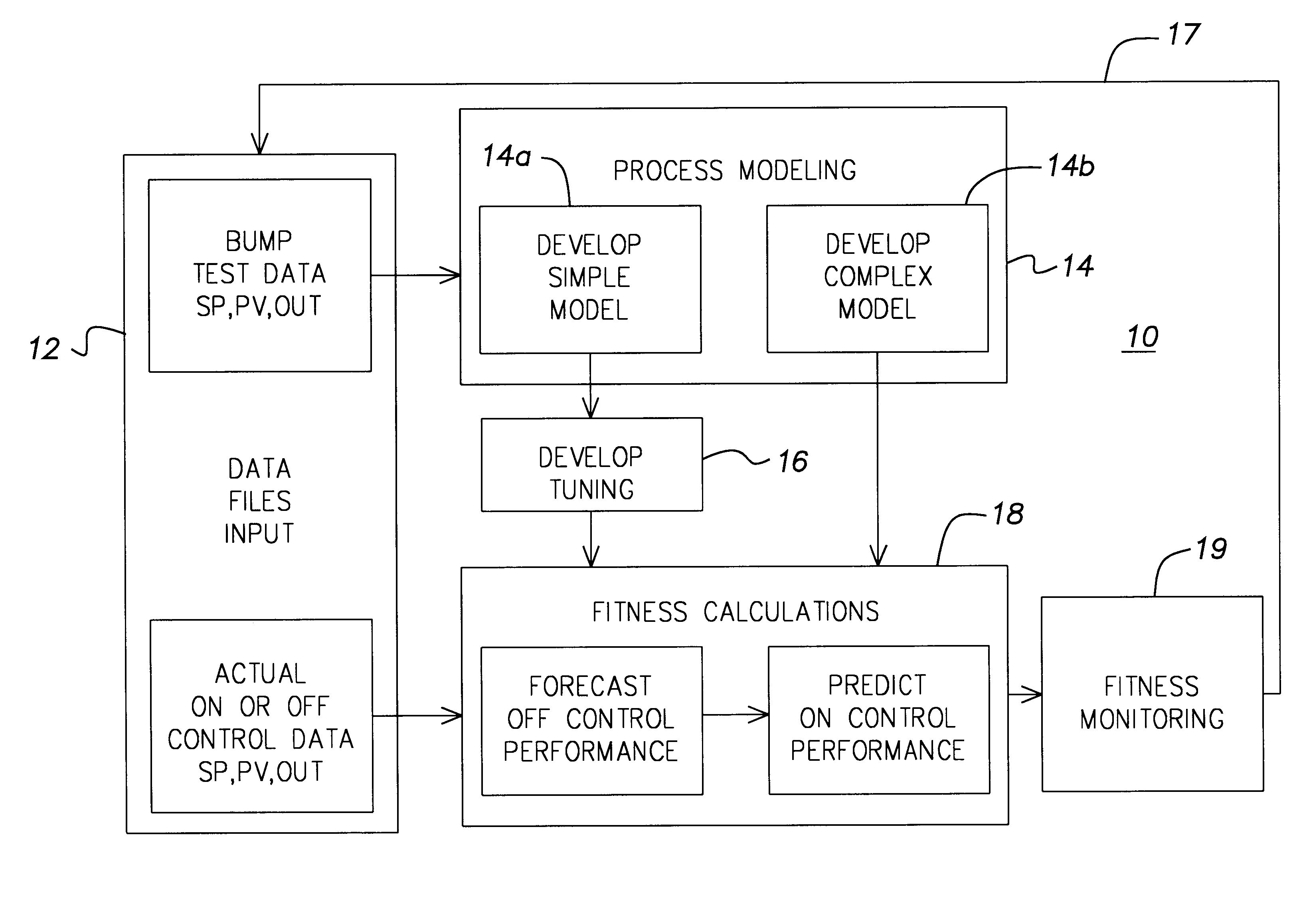
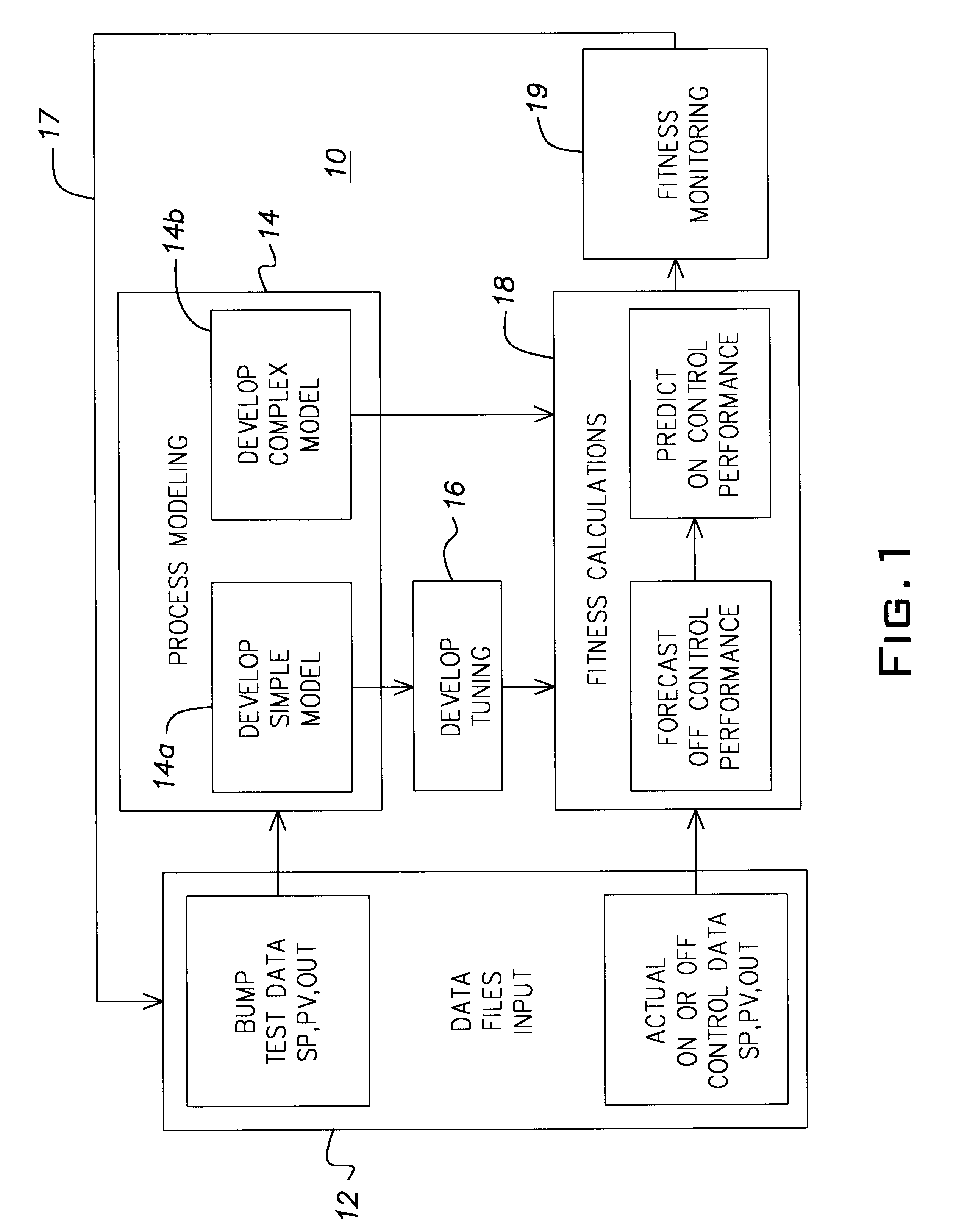
InactiveUS6597958B1Electric testing/monitoringComputation using non-denominational number representationOptimal tuningControl system
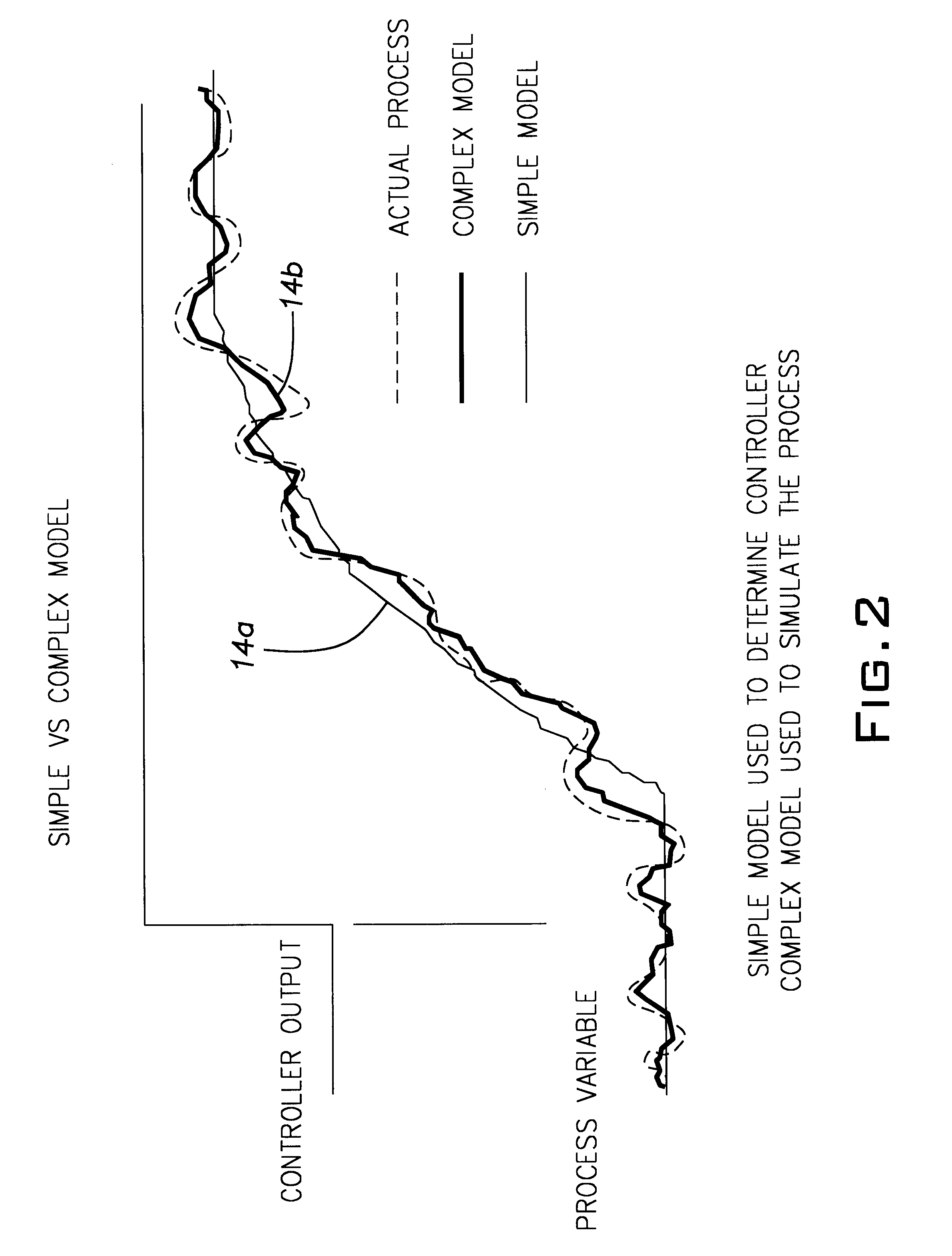
A method for determining the measure of control provided to a process by a control system. The determines process model parameters for a simple and complex model of the process and uses those parameters along with the value of the process variable and the final control element position to predict the off control data. The method also uses the process model parameters to determine the optimal tuning and then forecasts the optimal process performance from the predicted off control data and the determined optimal tuning.
Owner:ABB AUTOMATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com