Patents
Literature
117 results about "Automatic process control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
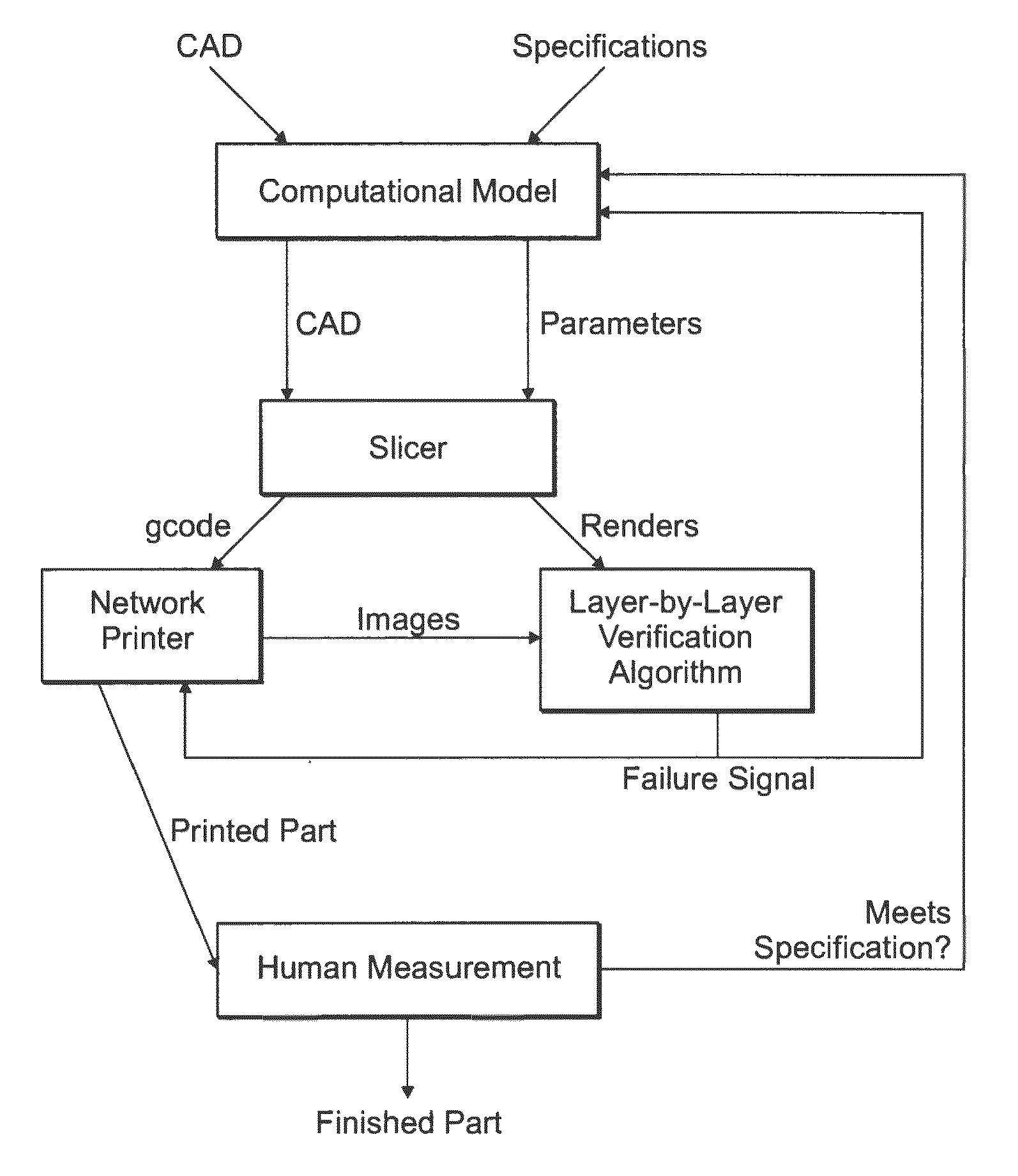
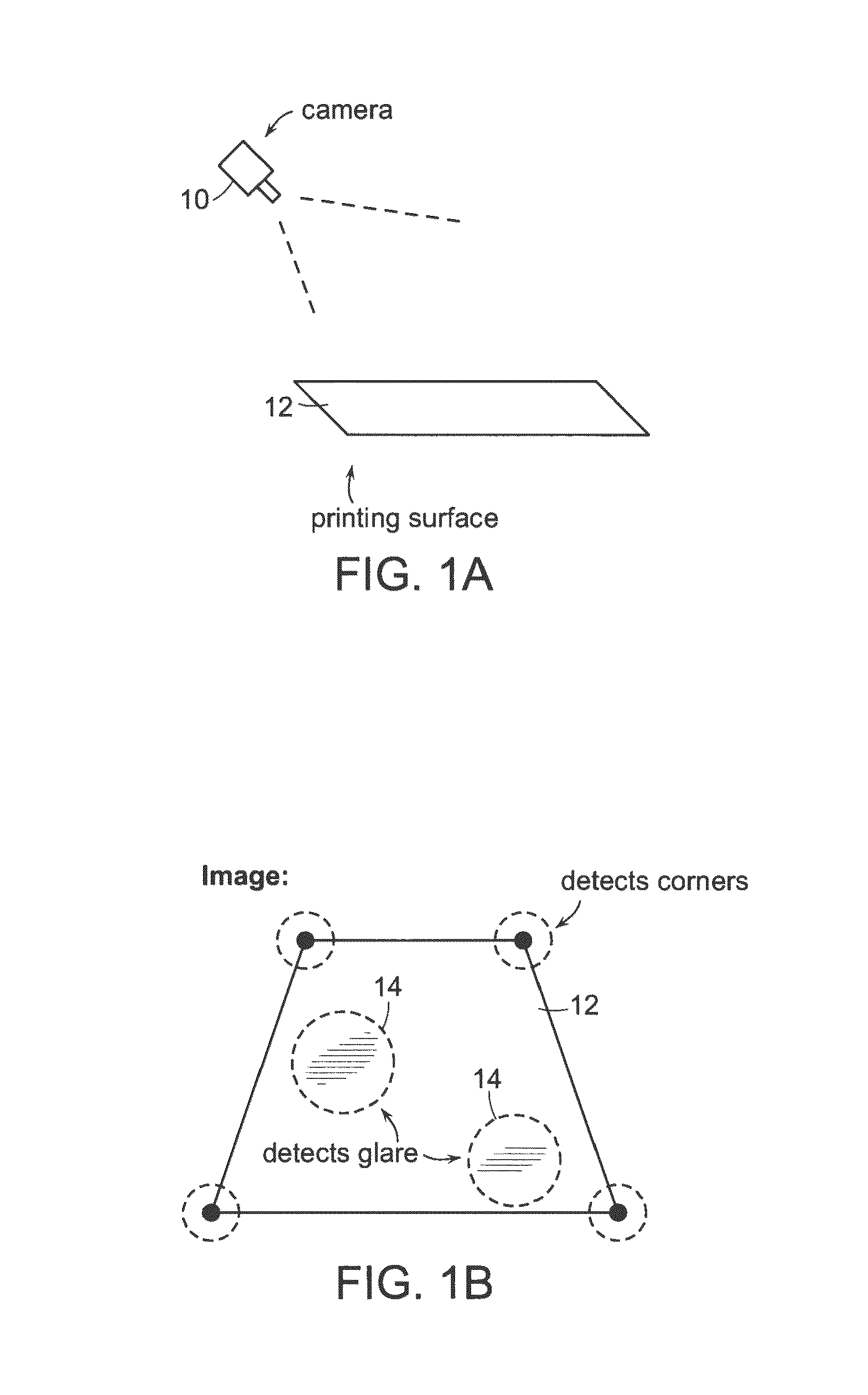
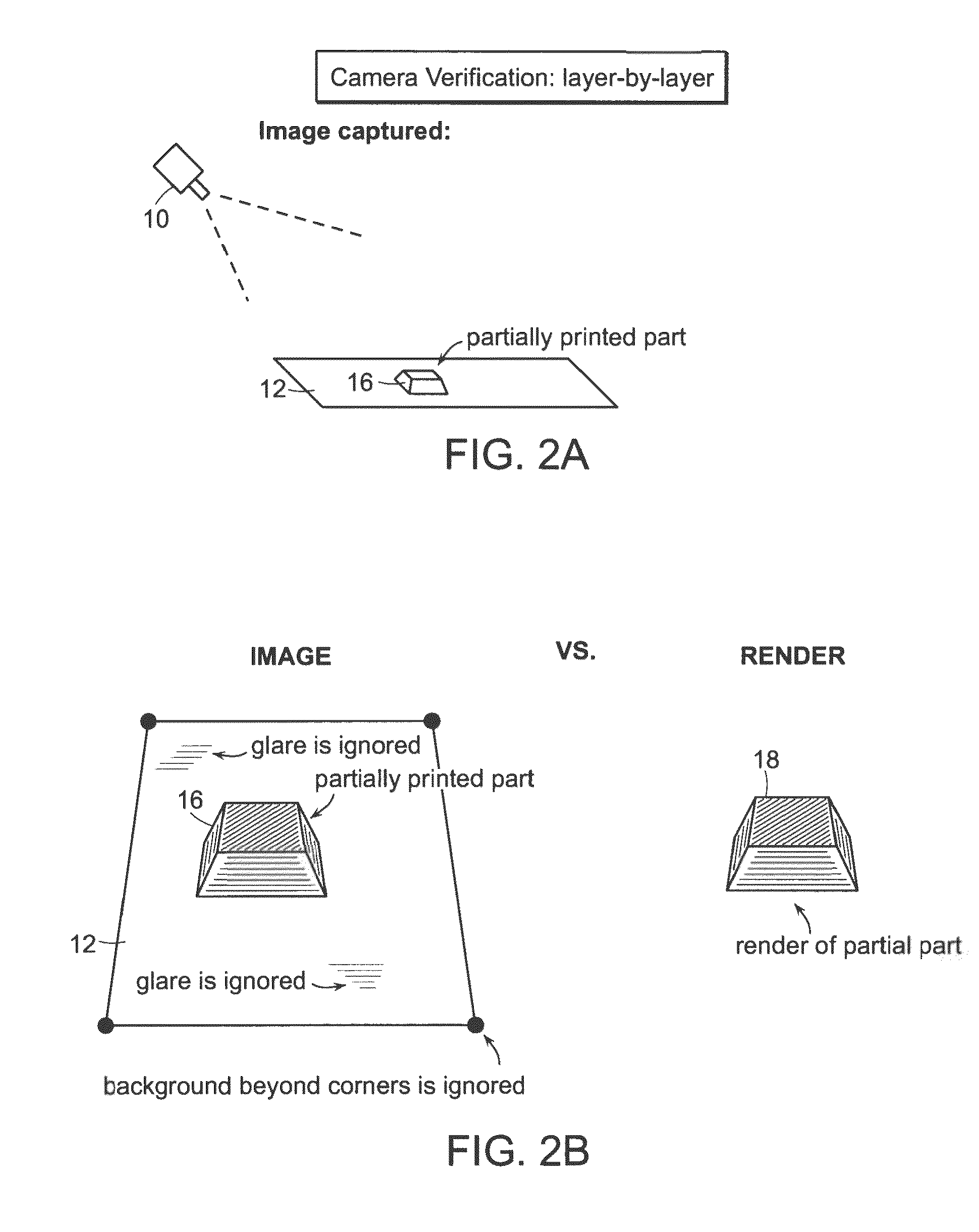
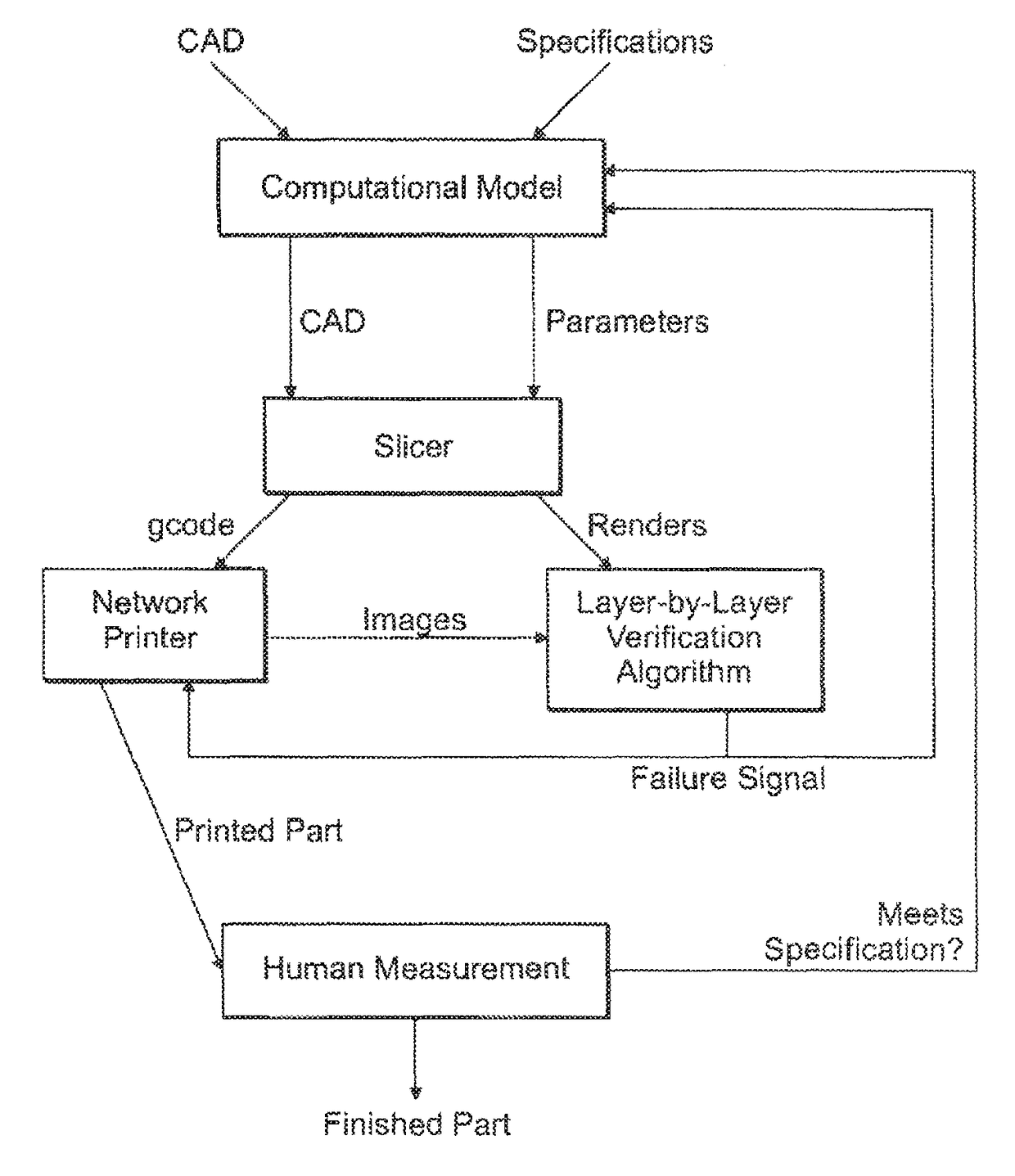
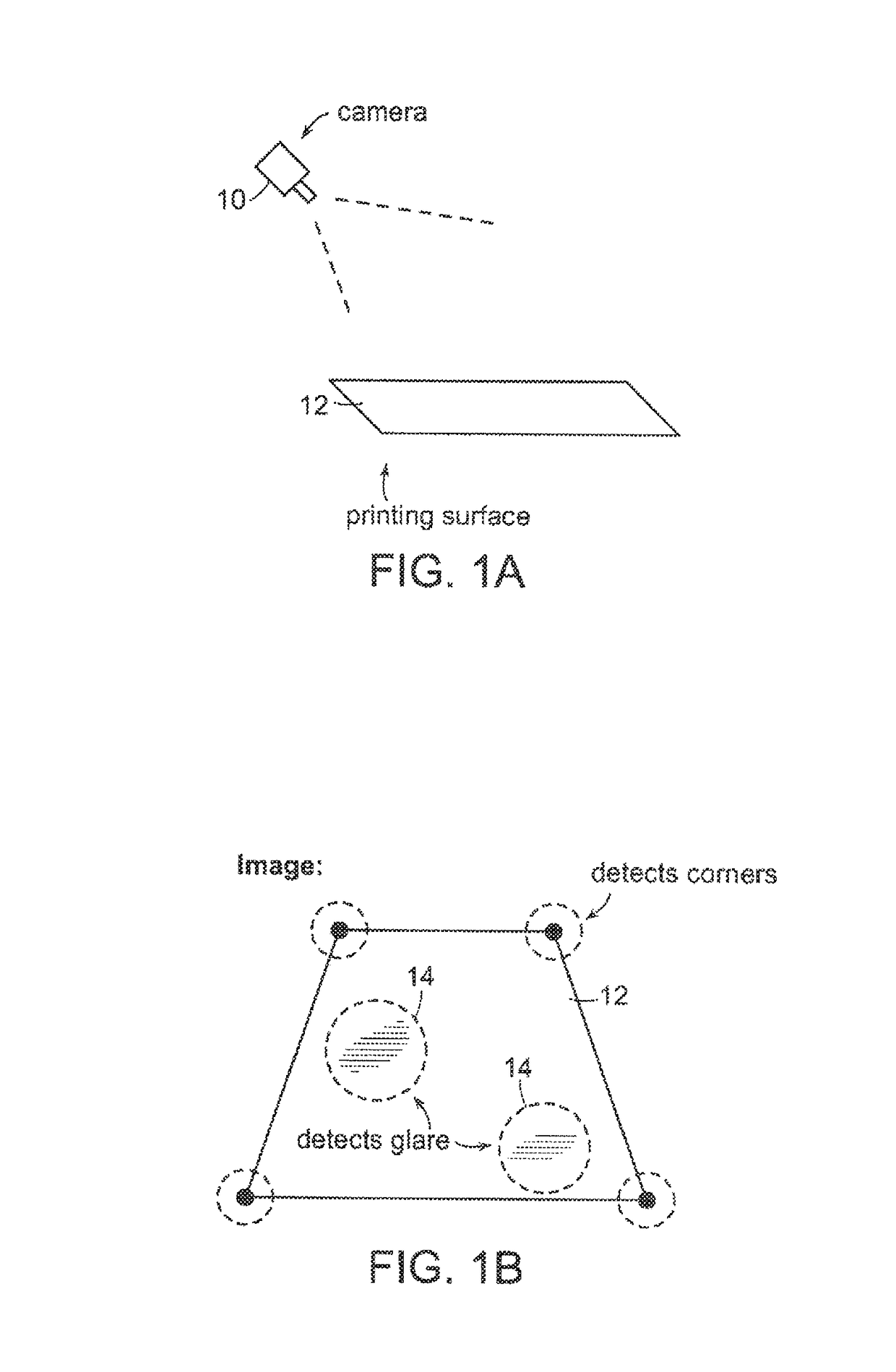
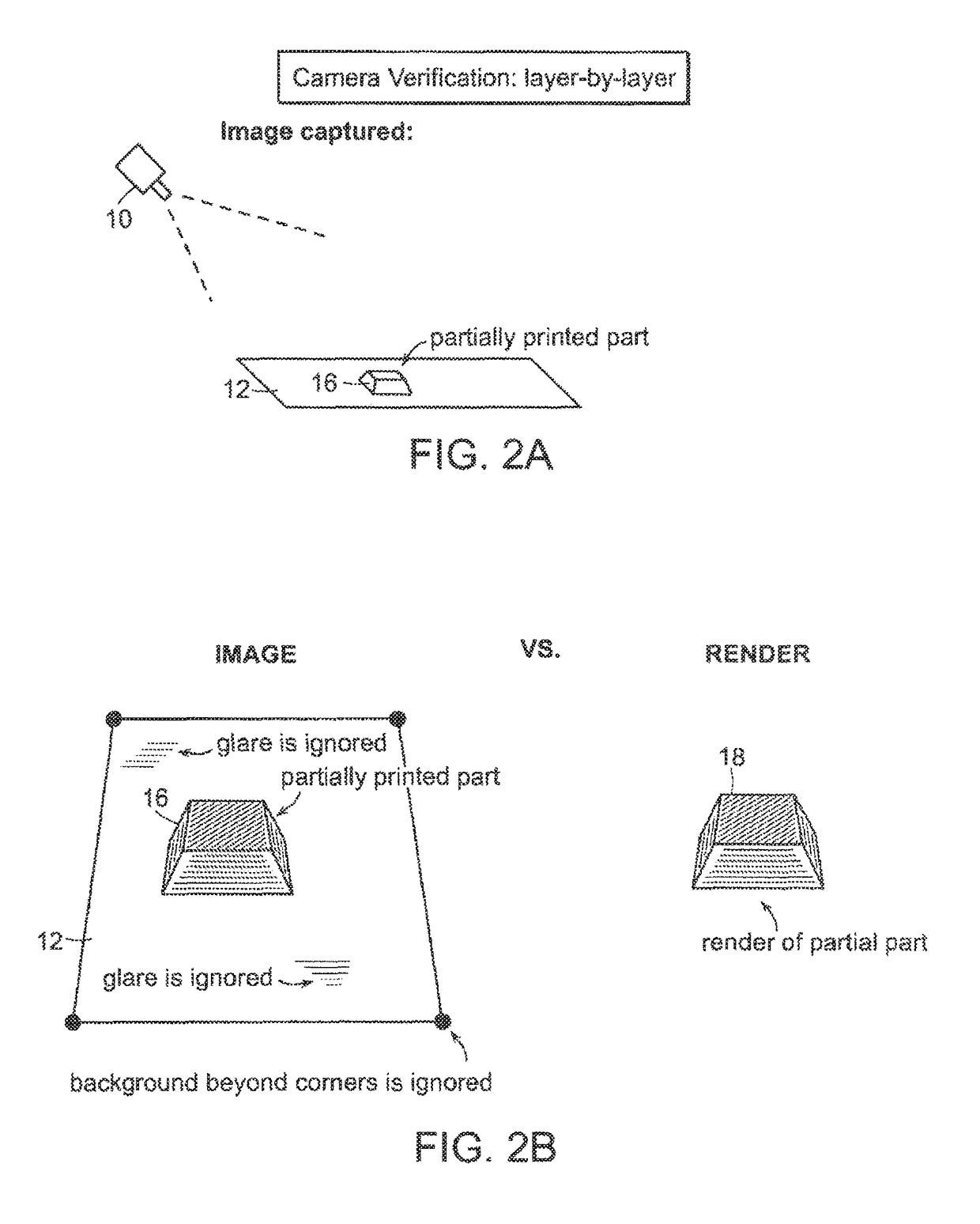
Automatic Process Control of Additive Manufacturing Device
ActiveUS20150045928A1Minimize the numberImprove efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputing modelsAutomatic process controlAccessible image
Automatic process control of additive manufacturing. The system includes an additive manufacturing device for making an object and a local network computer controlling the device. At least one camera is provided with a view of a manufacturing volume of the device to generate network accessible images of the object. The computer is programmed to stop the manufacturing process when the object is defective based en the images of the object.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
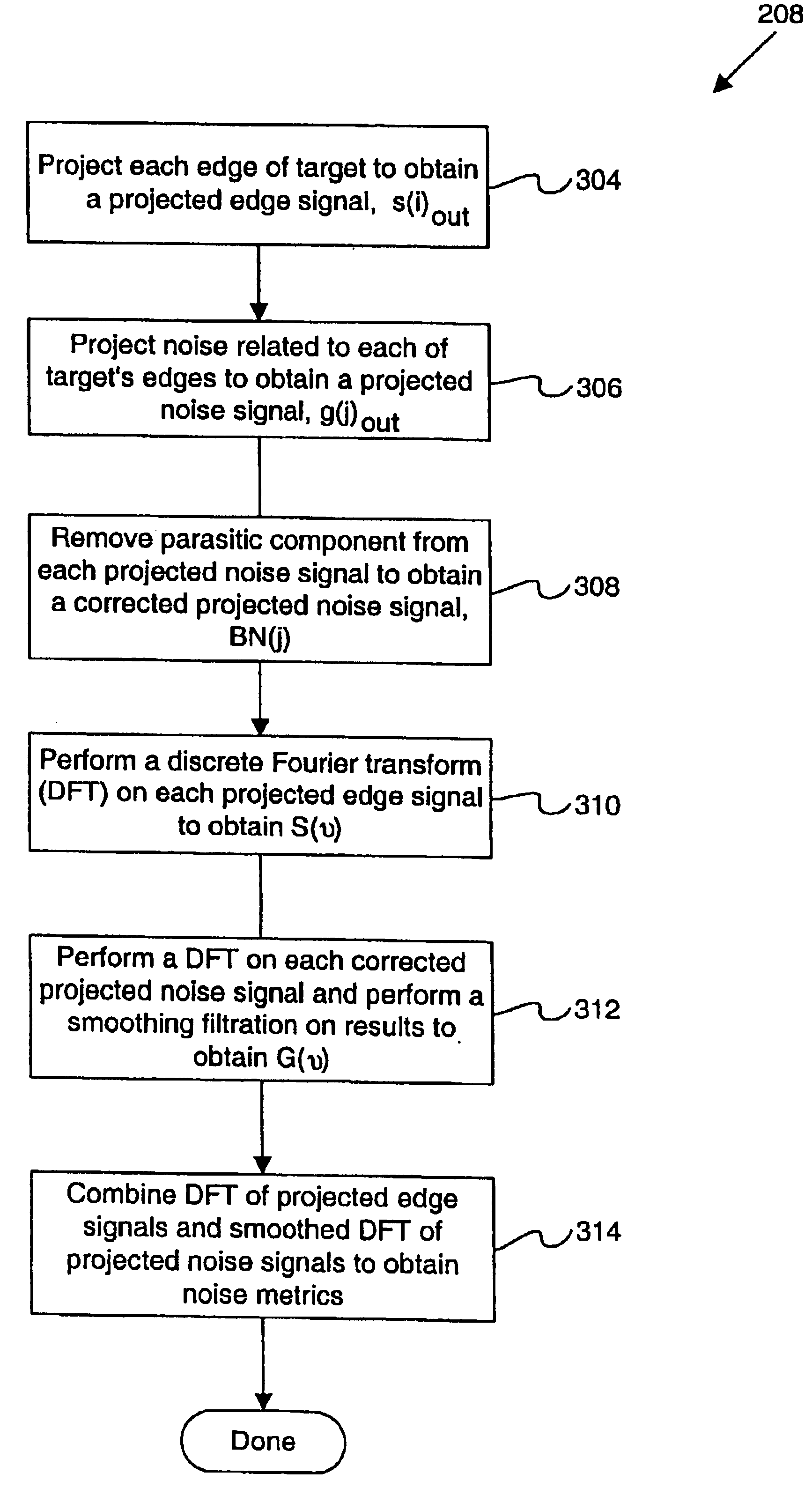
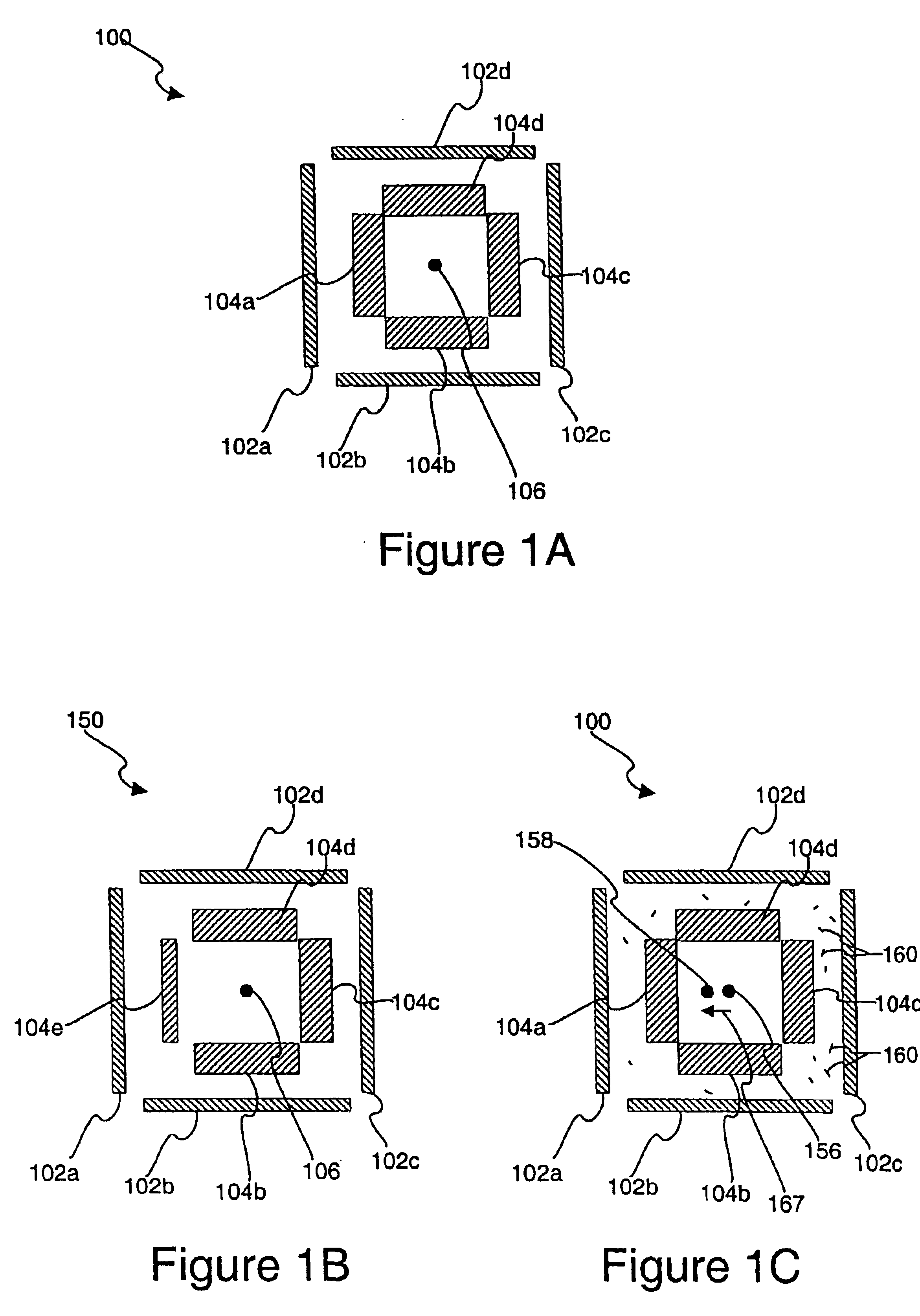
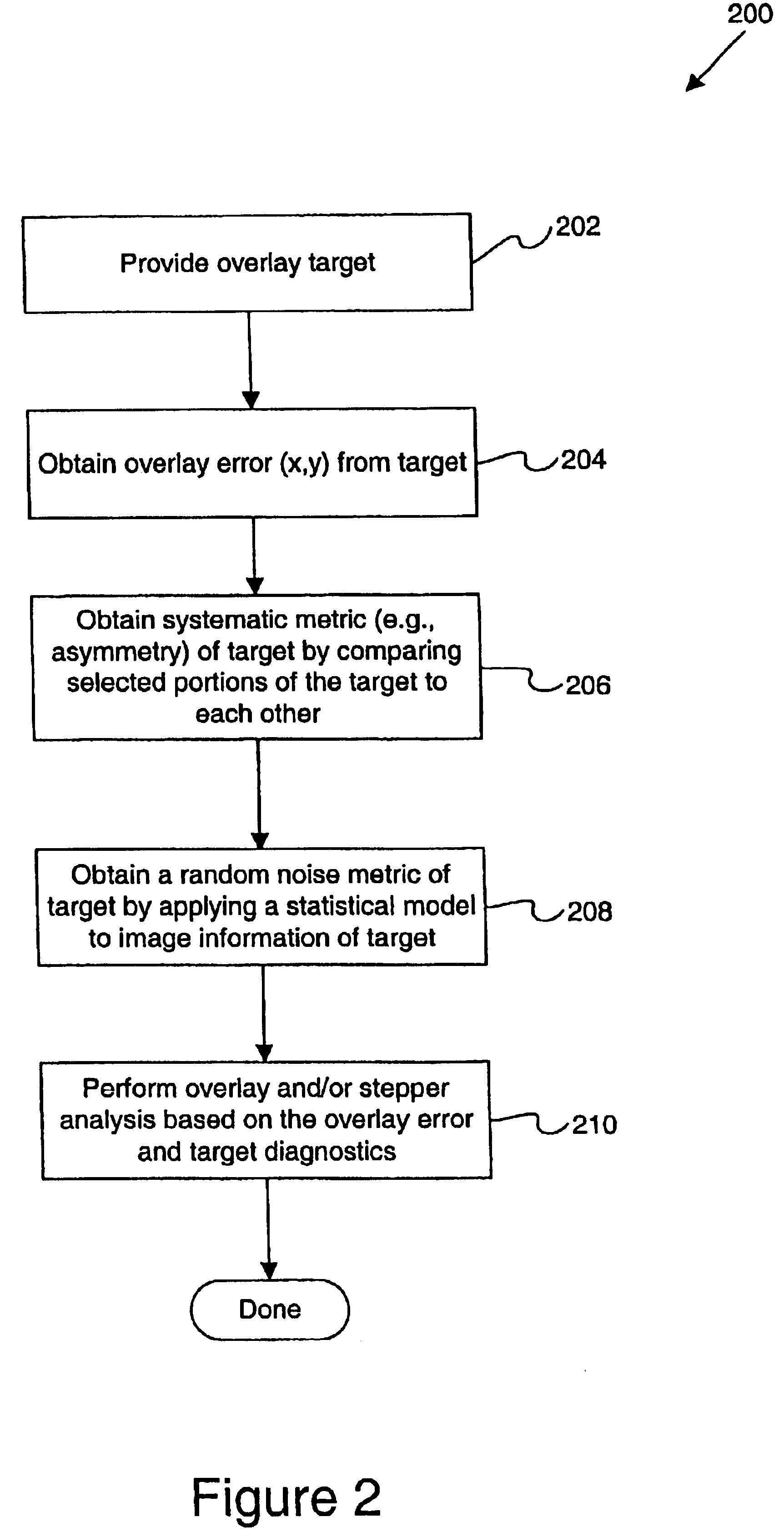
Use of overlay diagnostics for enhanced automatic process control
ActiveUS6928628B2Easy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutomatic controlInternet privacy
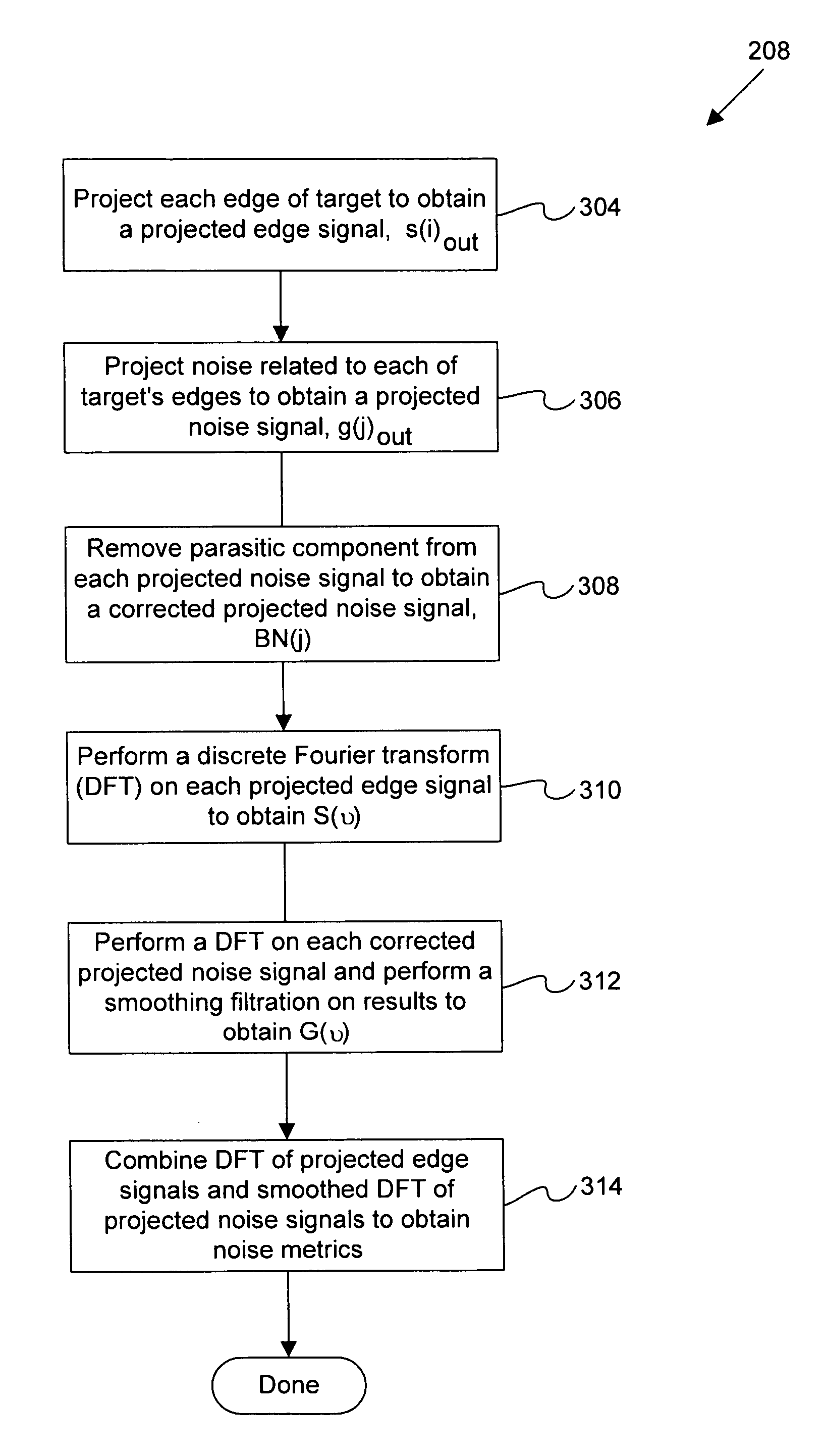
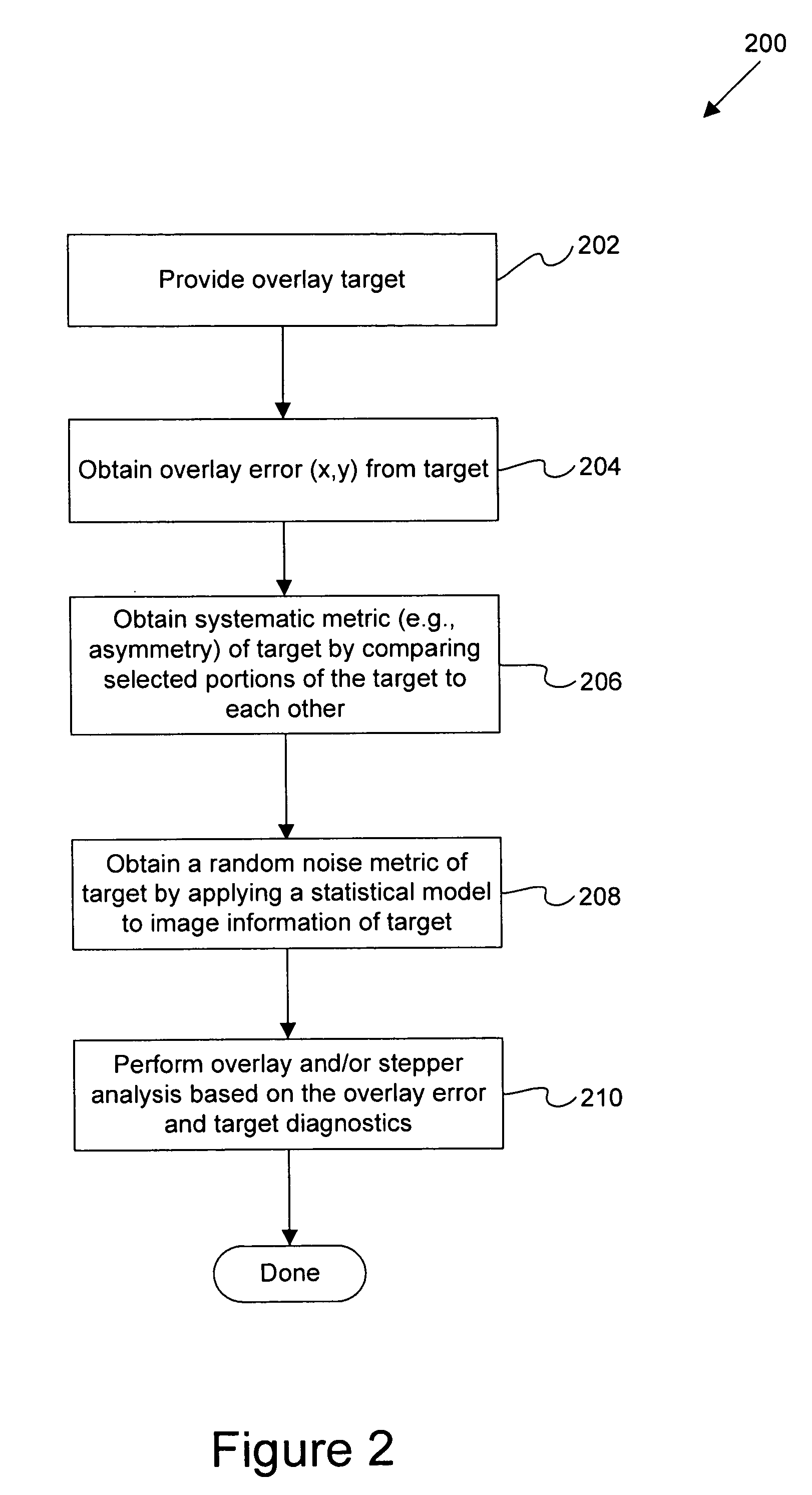
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for analyzing the quality of overlay targets. In one embodiment, a method of extracting data from an overlay target is disclosed. Initially, image information or one or more intensity signals of the overlay target are provided. An overlay error is obtained from the overlay target by analyzing the image information or the intensity signal(s) of the overlay target. A systematic error metric is also obtained from the overlay target by analyzing the image information or the intensity signal(s) of the overlay target. For example, the systematic error may indicate an asymmetry metric for one or more portions of the overlay target. A noise metric is further obtained from the overlay target by applying a statistical model to the image information or the intensity signal(s) of the overlay target. Noise metric characterizes noise, such as a grainy background, associated with the overlay target. In other embodiments, an overlay and / or stepper analysis procedure is then performed based on the systematic error metric and / or the noise metric, as well as the overlay data.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
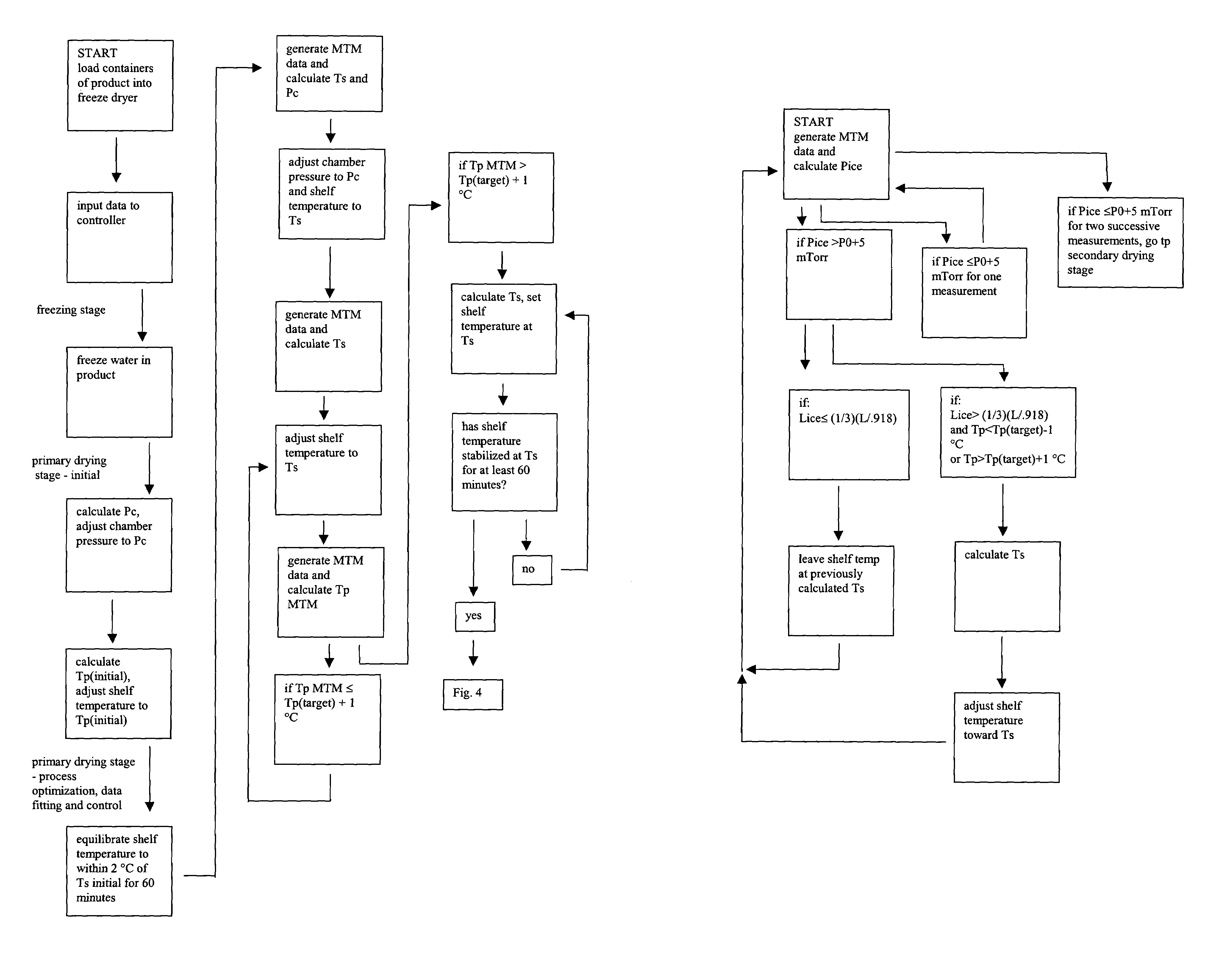
Automated process control using manometric temperature measurement
ActiveUS6971187B1Simple processDrying solid materials without heatDrying machines with progressive movementsFreeze-dryingControl system
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
Method and apparatus for monitoring consumable performance
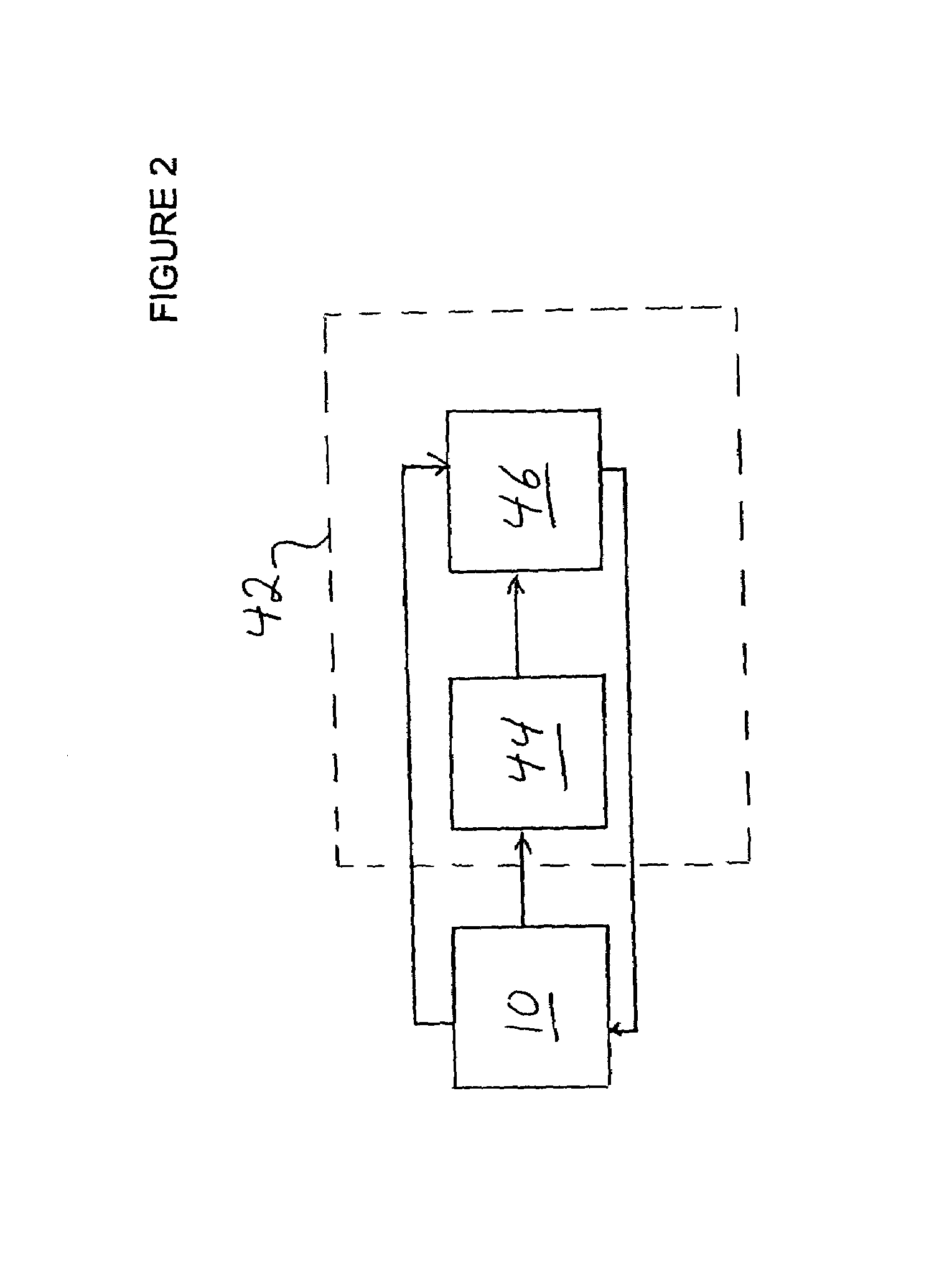
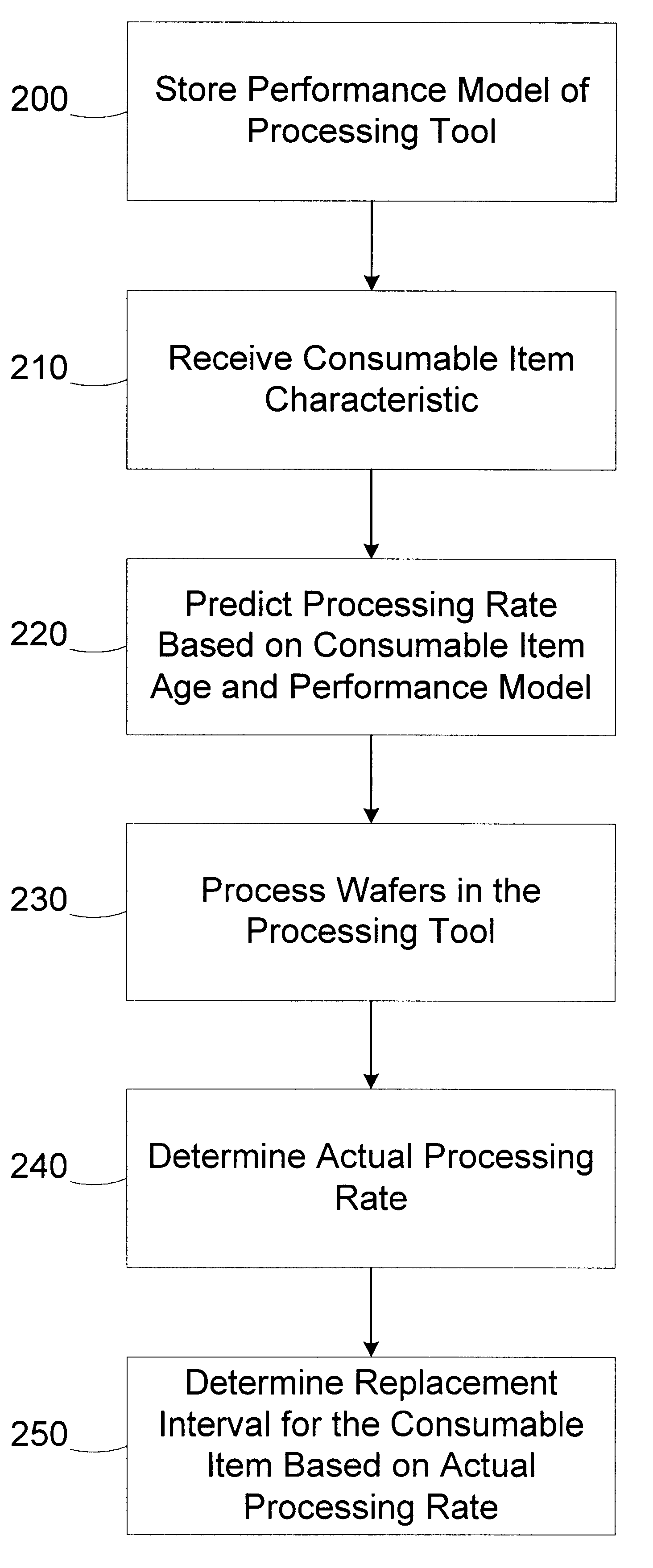
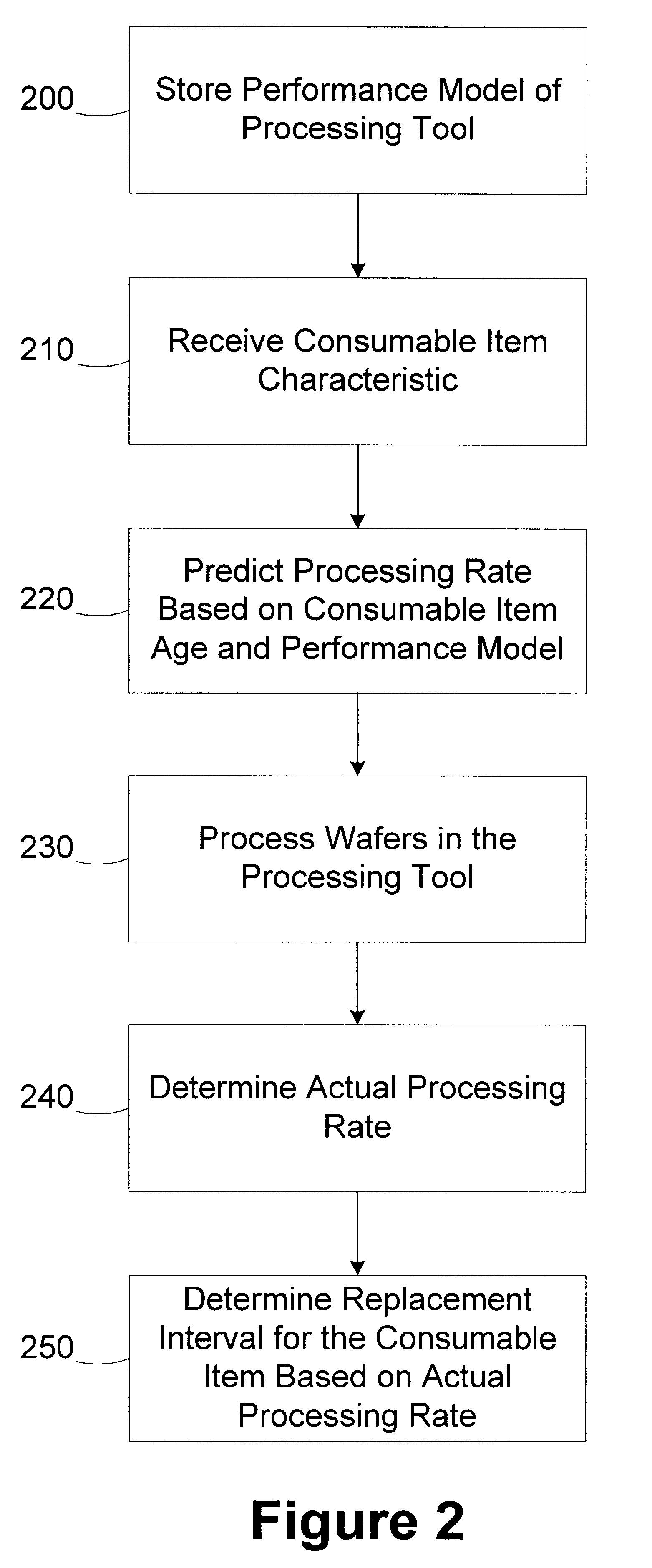
InactiveUS6567718B1Polishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesParallel computingAutomatic process control
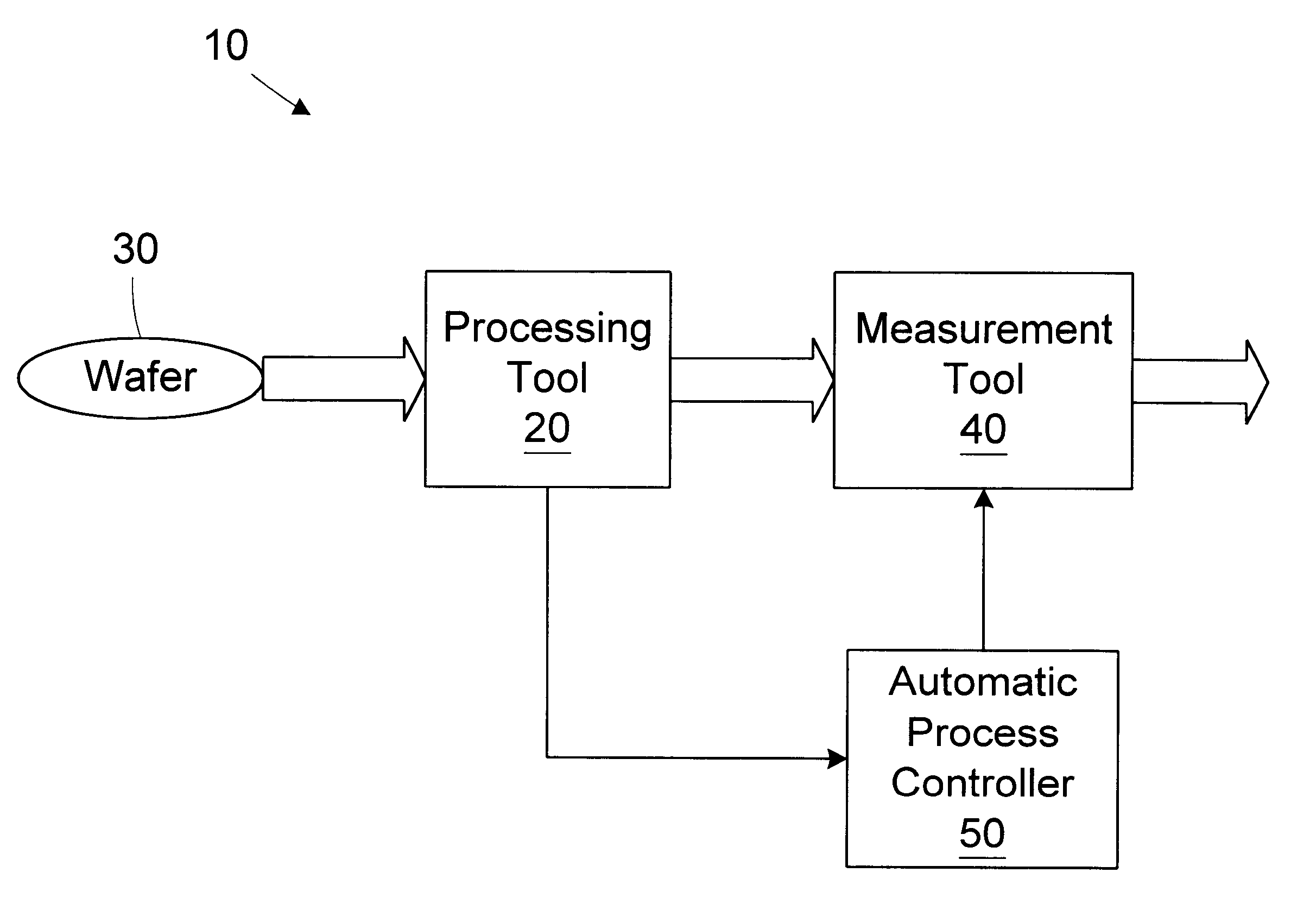
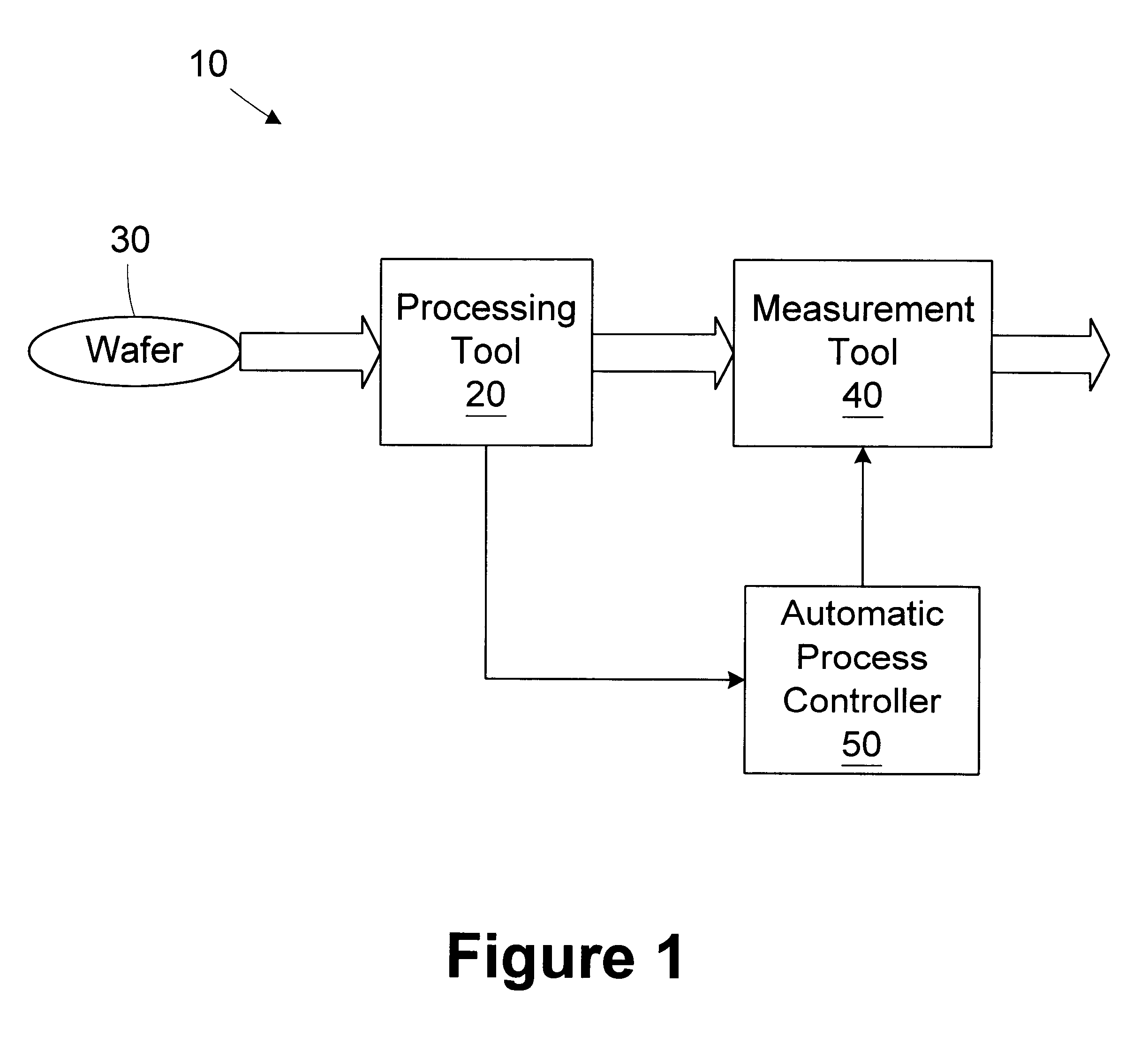
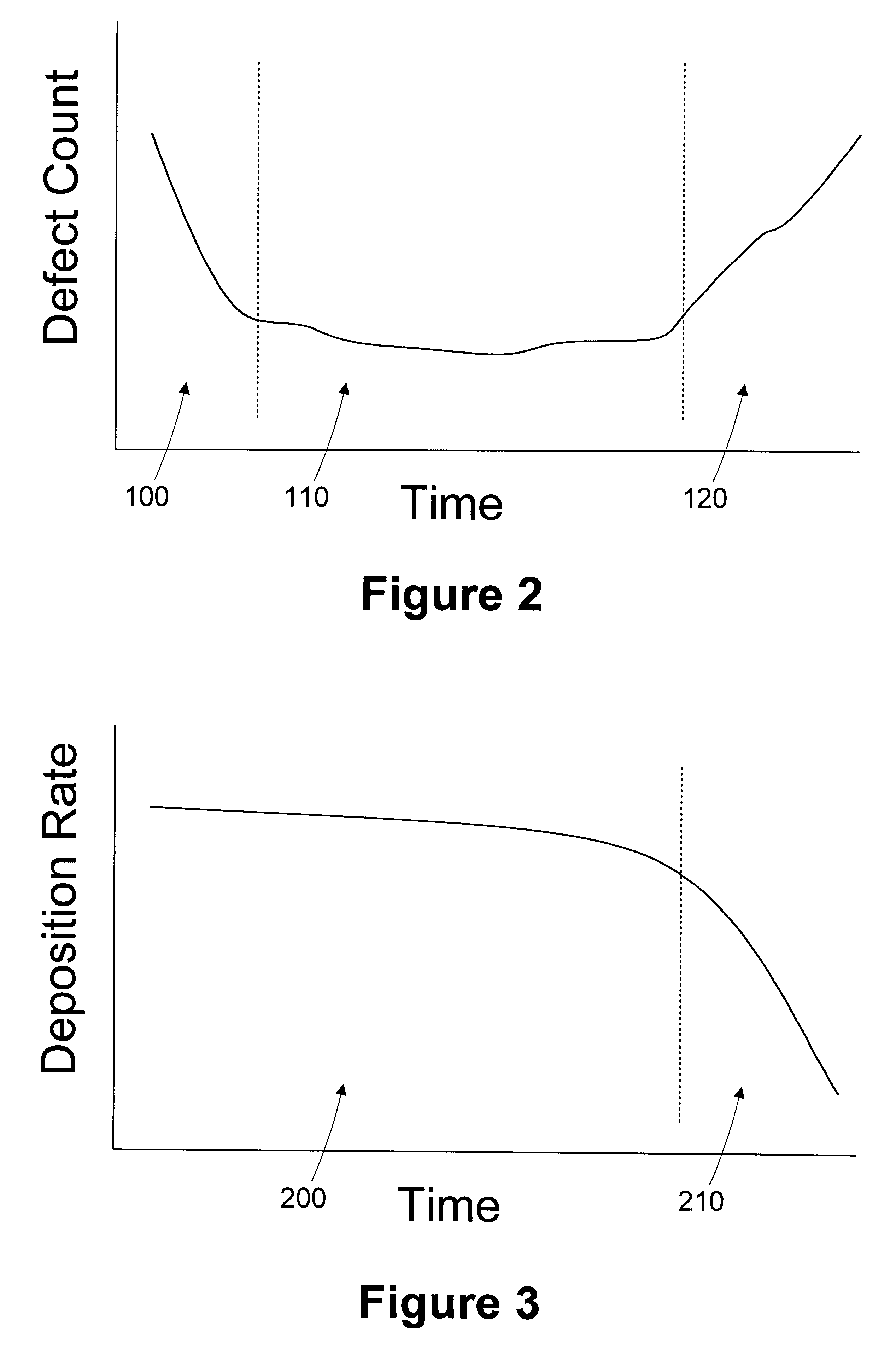
A method for monitoring consumable performance in a processing tool comprises storing a performance model of the processing tool; receiving a consumable item characteristic of a consumable item in the processing tool; determining a predicted processing rate for the processing tool based on the consumable item characteristic and the performance model; determining an actual processing rate of the processing tool; and determining a replacement interval for the consumable item based on at least the actual processing rate. A processing system includes a processing tool and an automatic process controller. The processing tool is adapted to process wafers and includes a consumable item.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
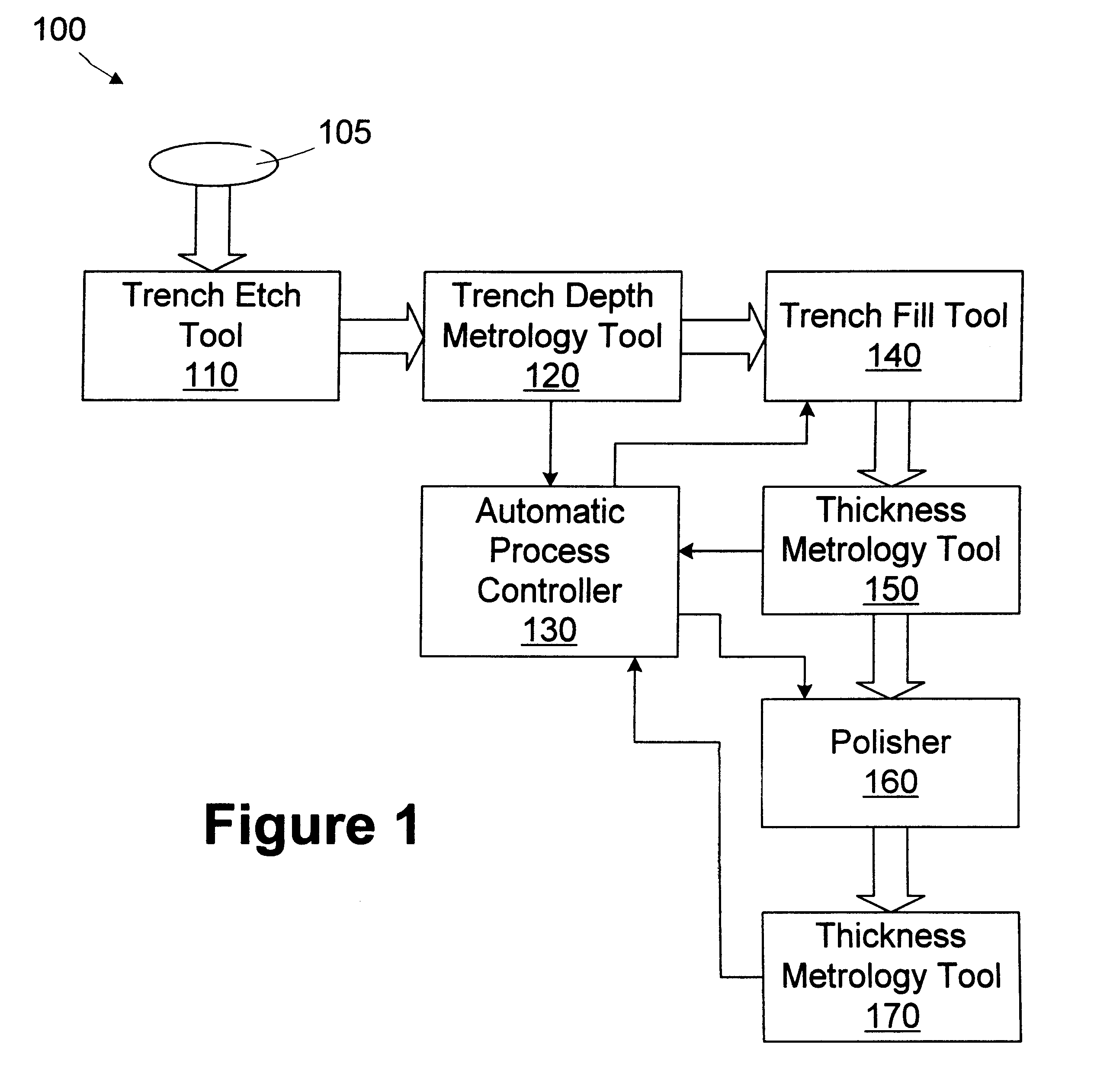
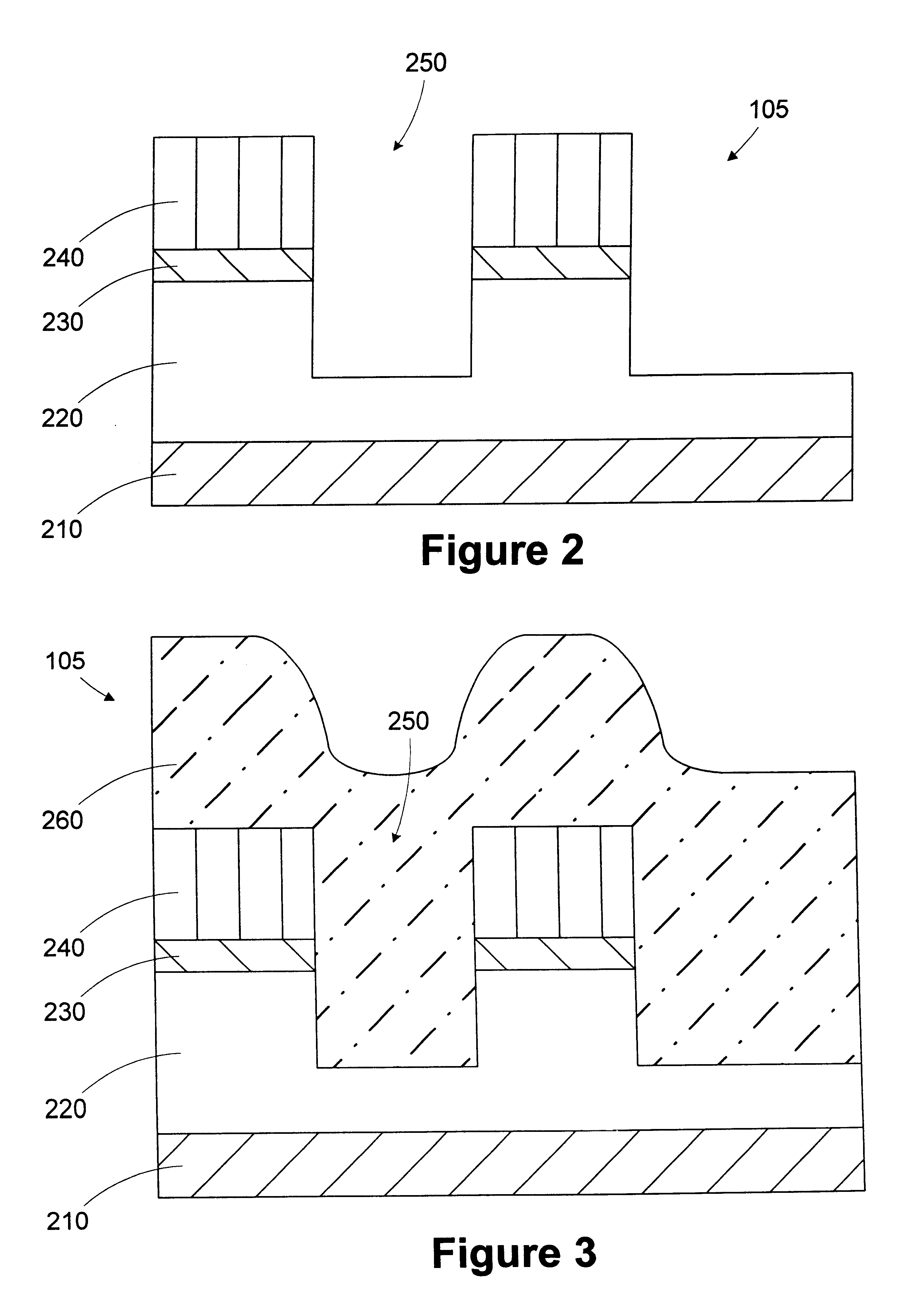
Method for filling trenches
InactiveUS6284622B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetrologyEngineering
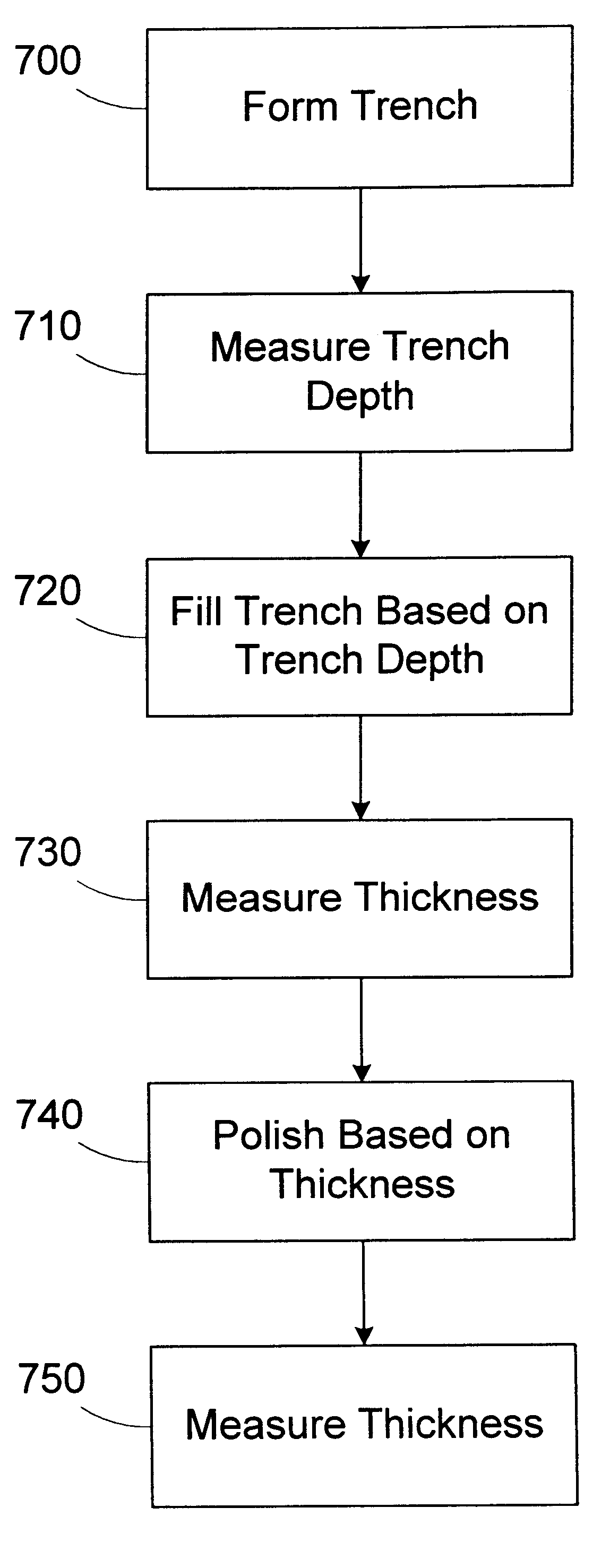
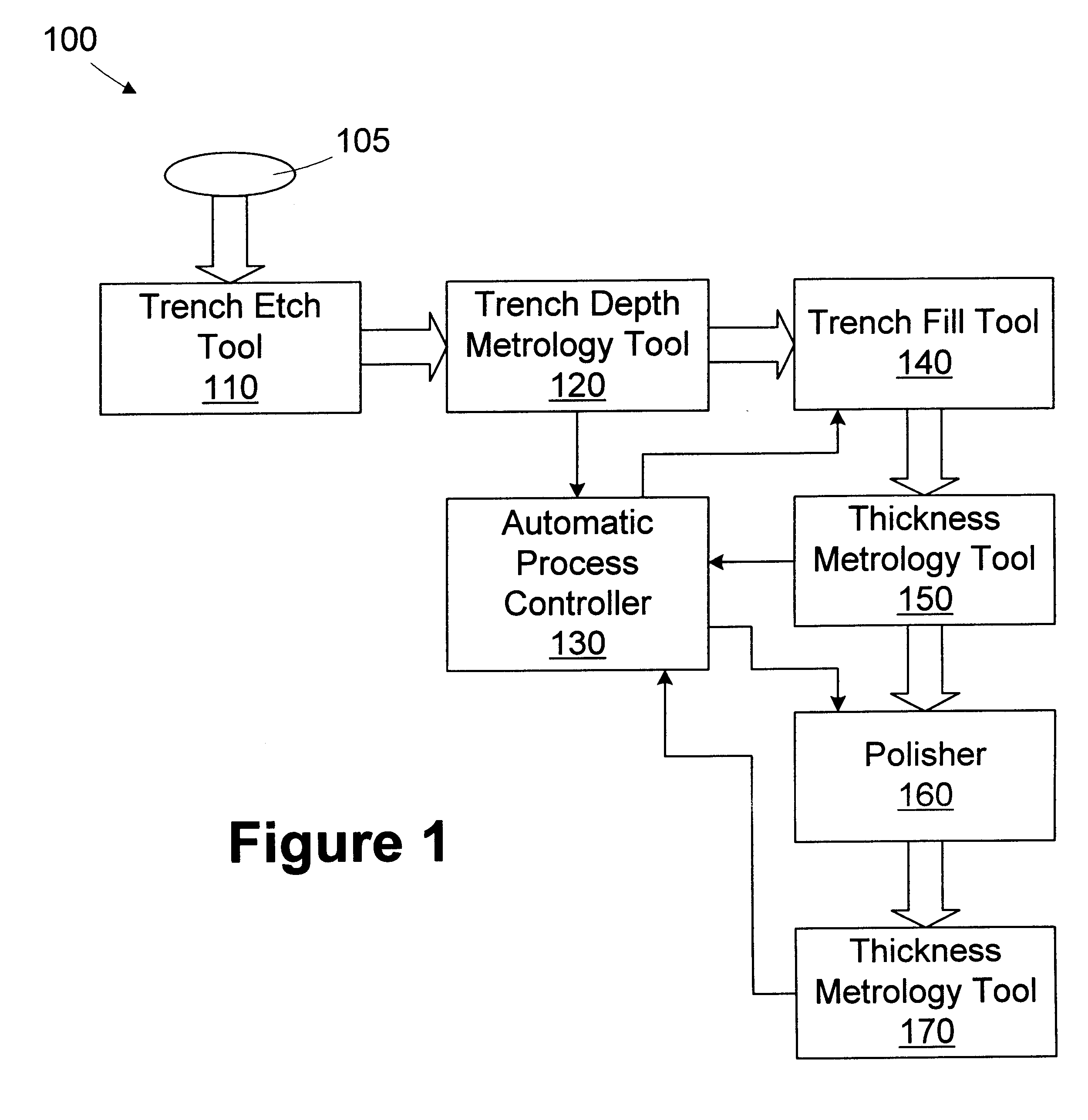
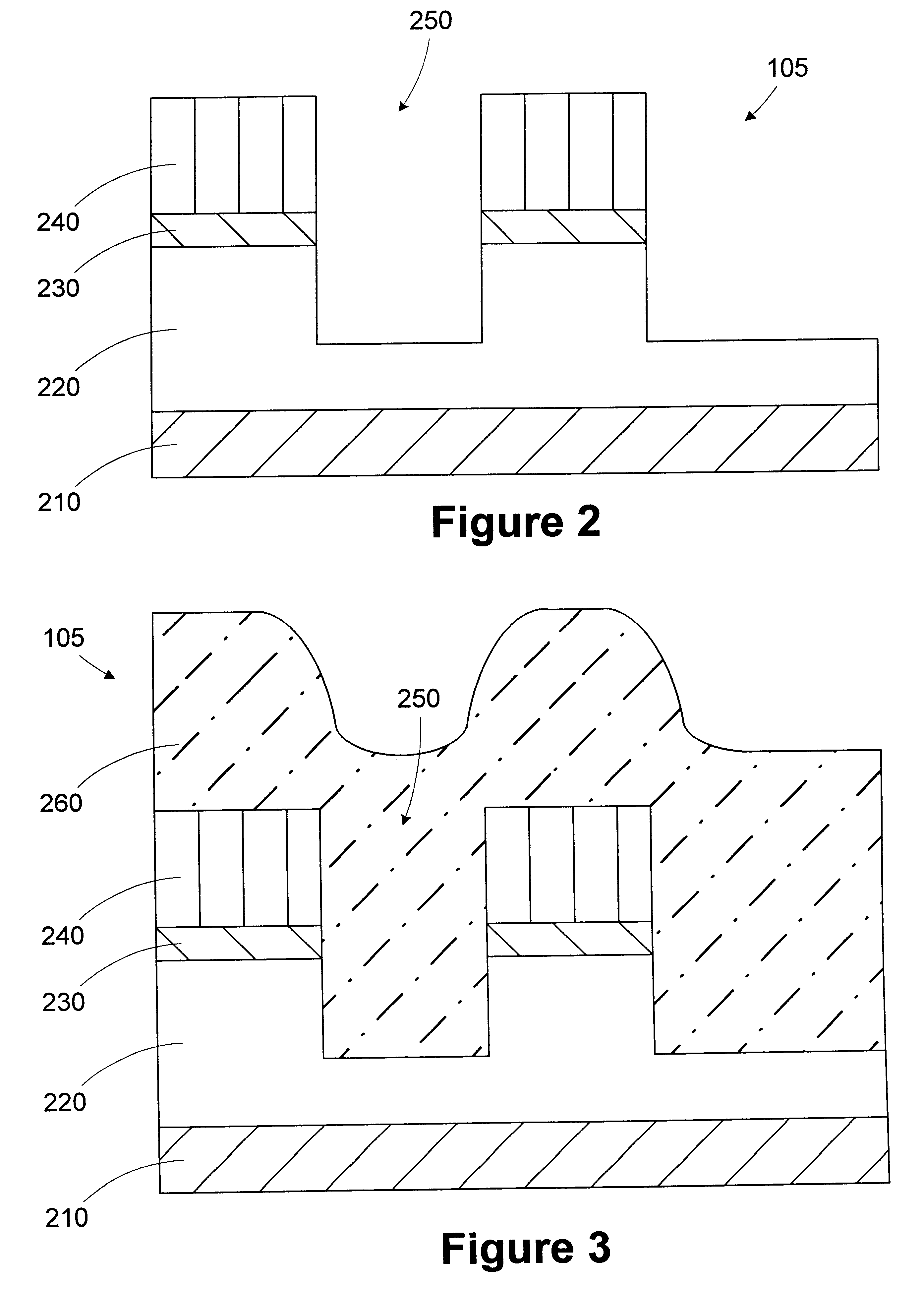
A method for filling a trench is provided. A wafer having at least a first layer formed thereon is provided. A trench is formed in the first layer. The depth of the trench is measured. A target thickness is determined based on the depth of the trench. A second layer of the target thickness is formed over the trench. A processing line includes a trench etch tool, a first metrology tool, a trench fill tool, and an automatic process controller. The trench etch tool is adapted to form a trench in a first layer on a wafer. The first metrology tool is adapted to measure the depth of the trench. The trench fill tool is adapted to form a second layer over the first layer based on an operating recipe. An automatic process controller is adapted to determine a target thickness based on the depth of the trench and modify the operating recipe of the trench fill tool based on the target thickness.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Graphical user interface for automated process control
InactiveUS7266764B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalGraphicsGraphical user interface
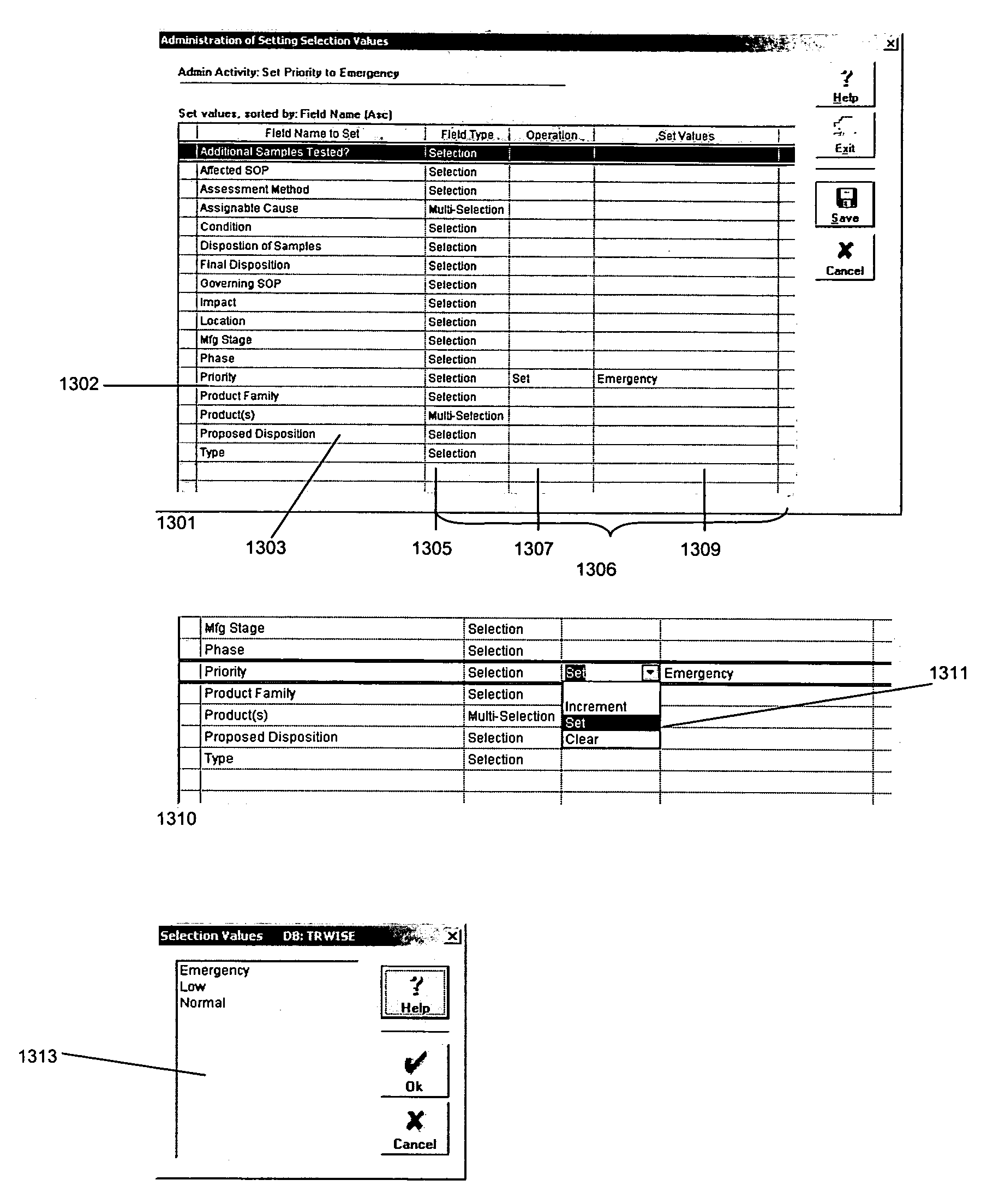
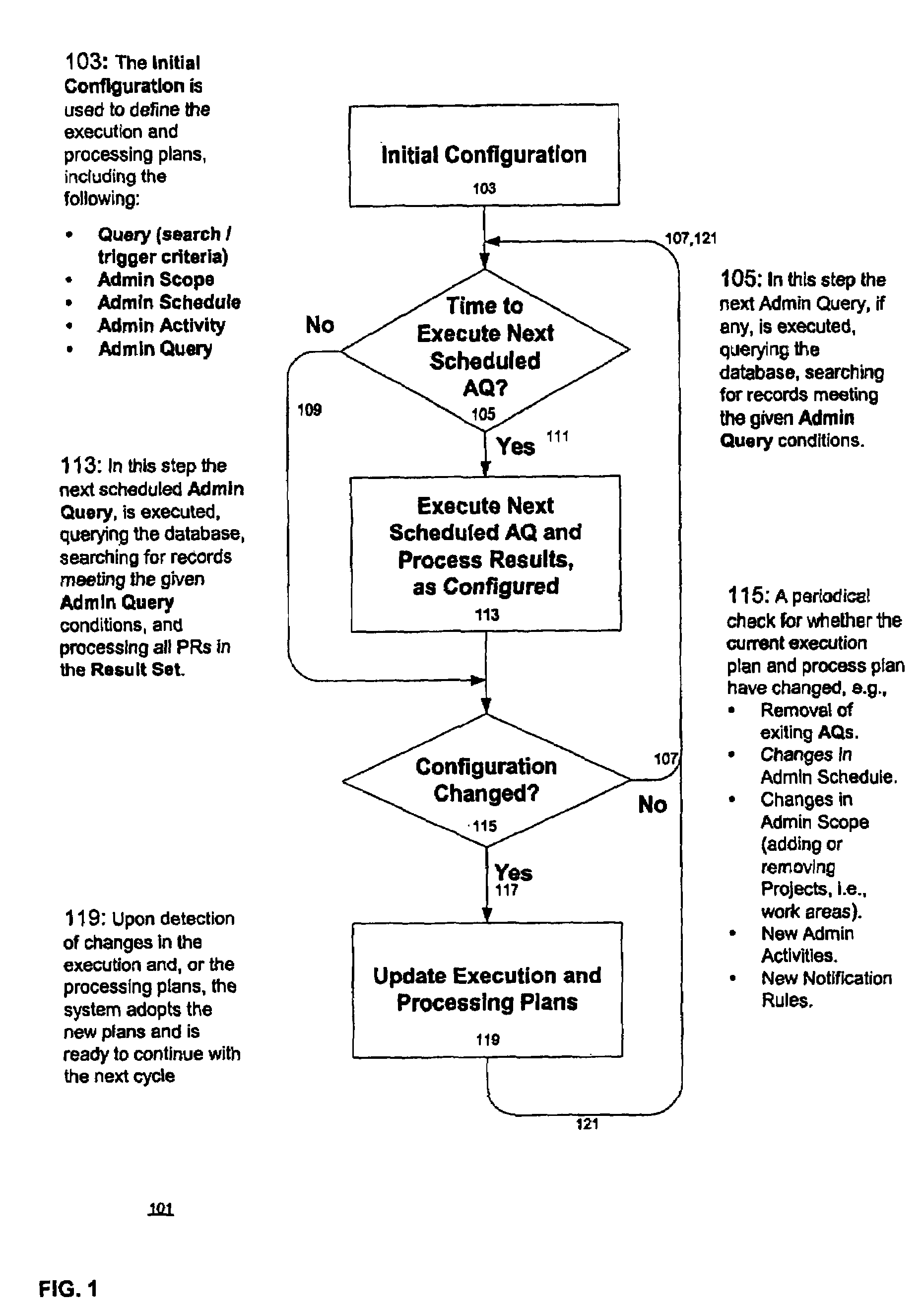
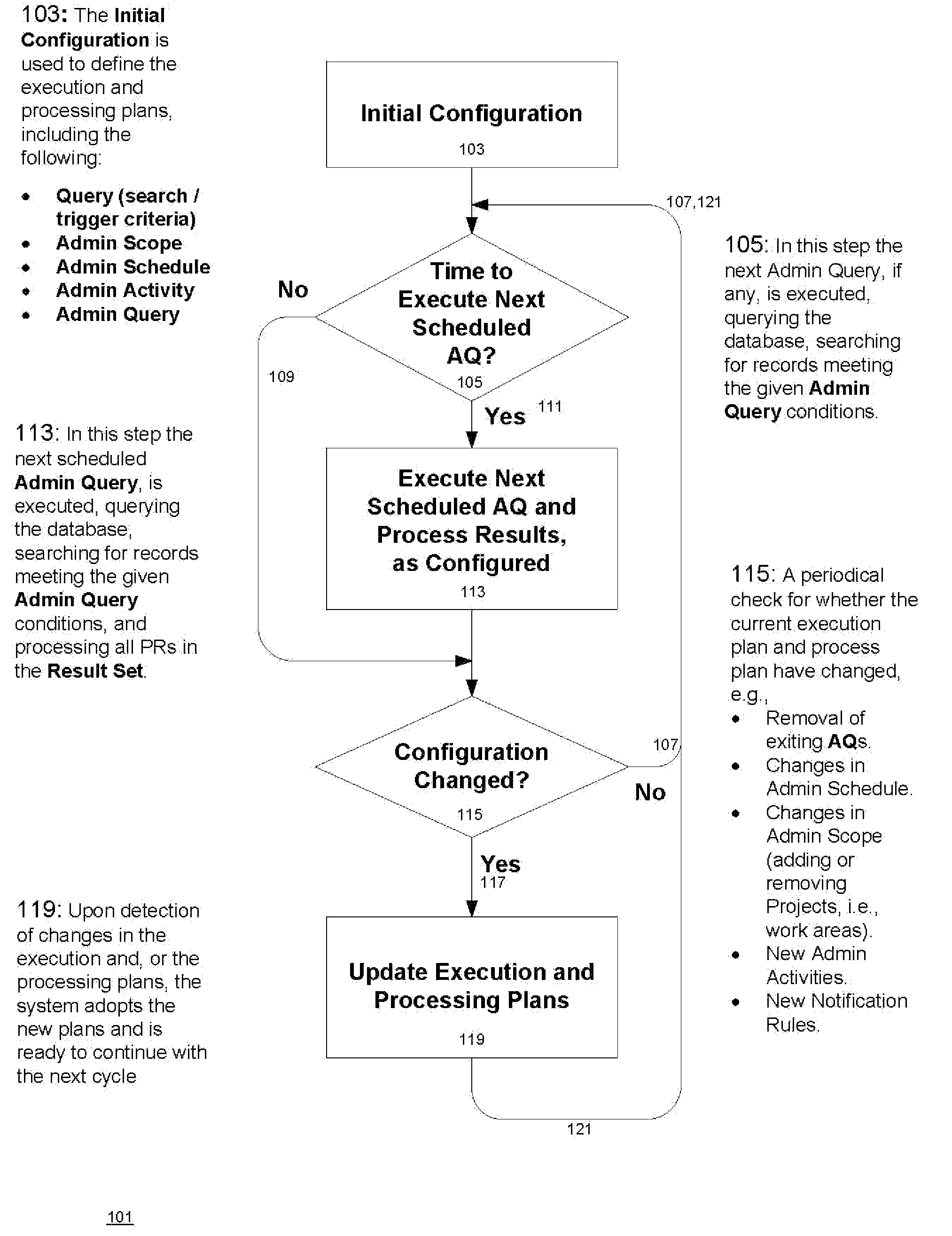
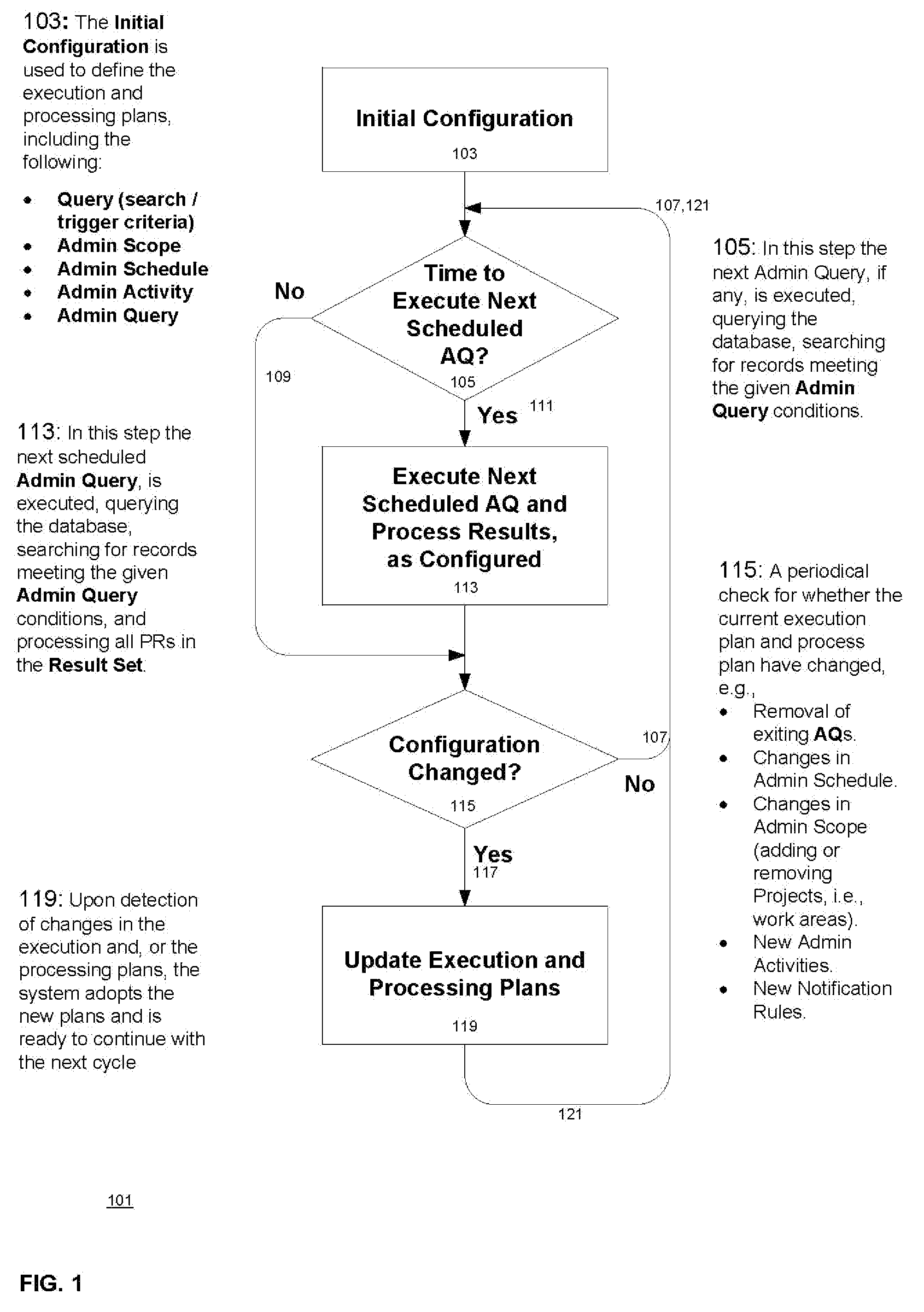
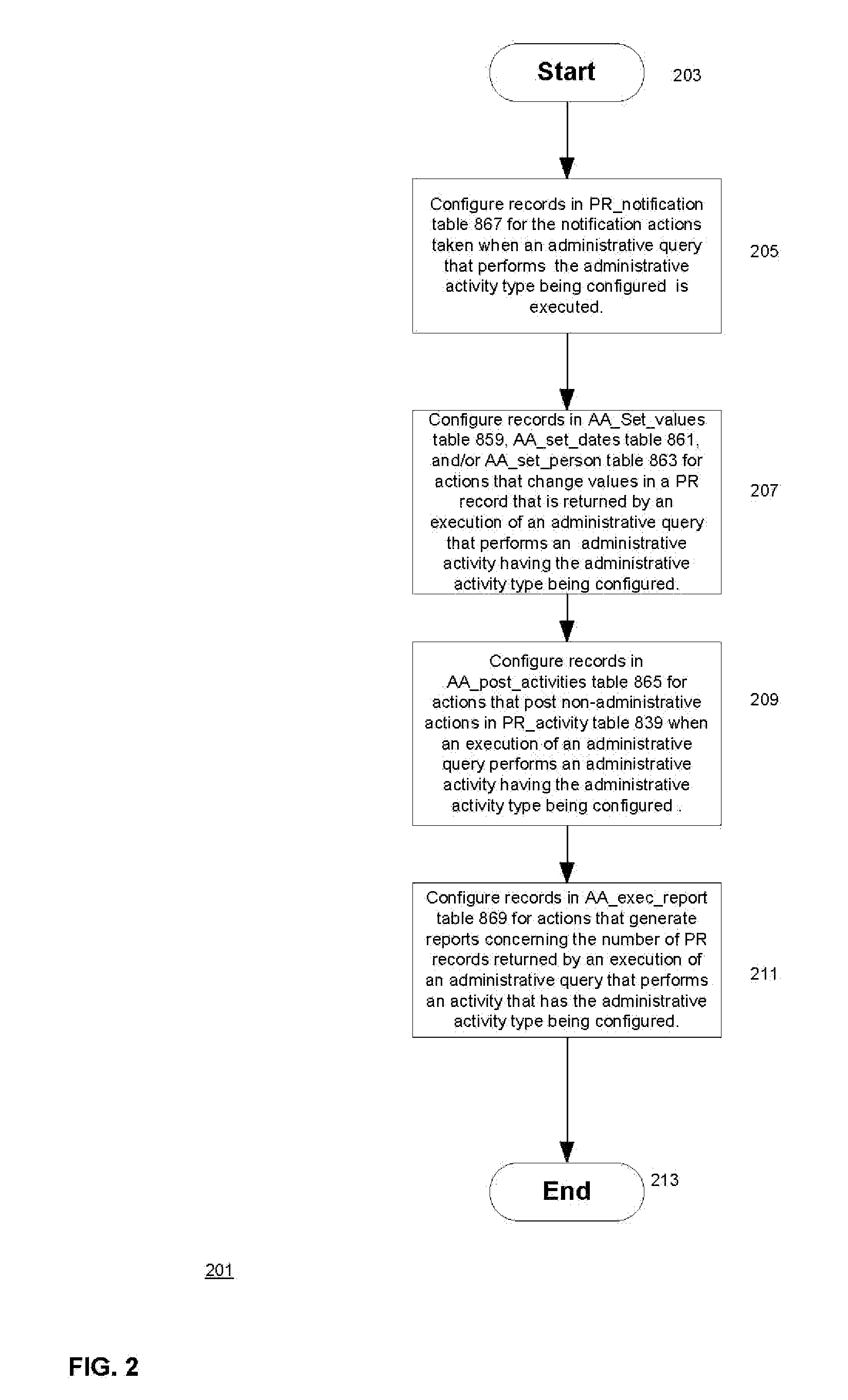
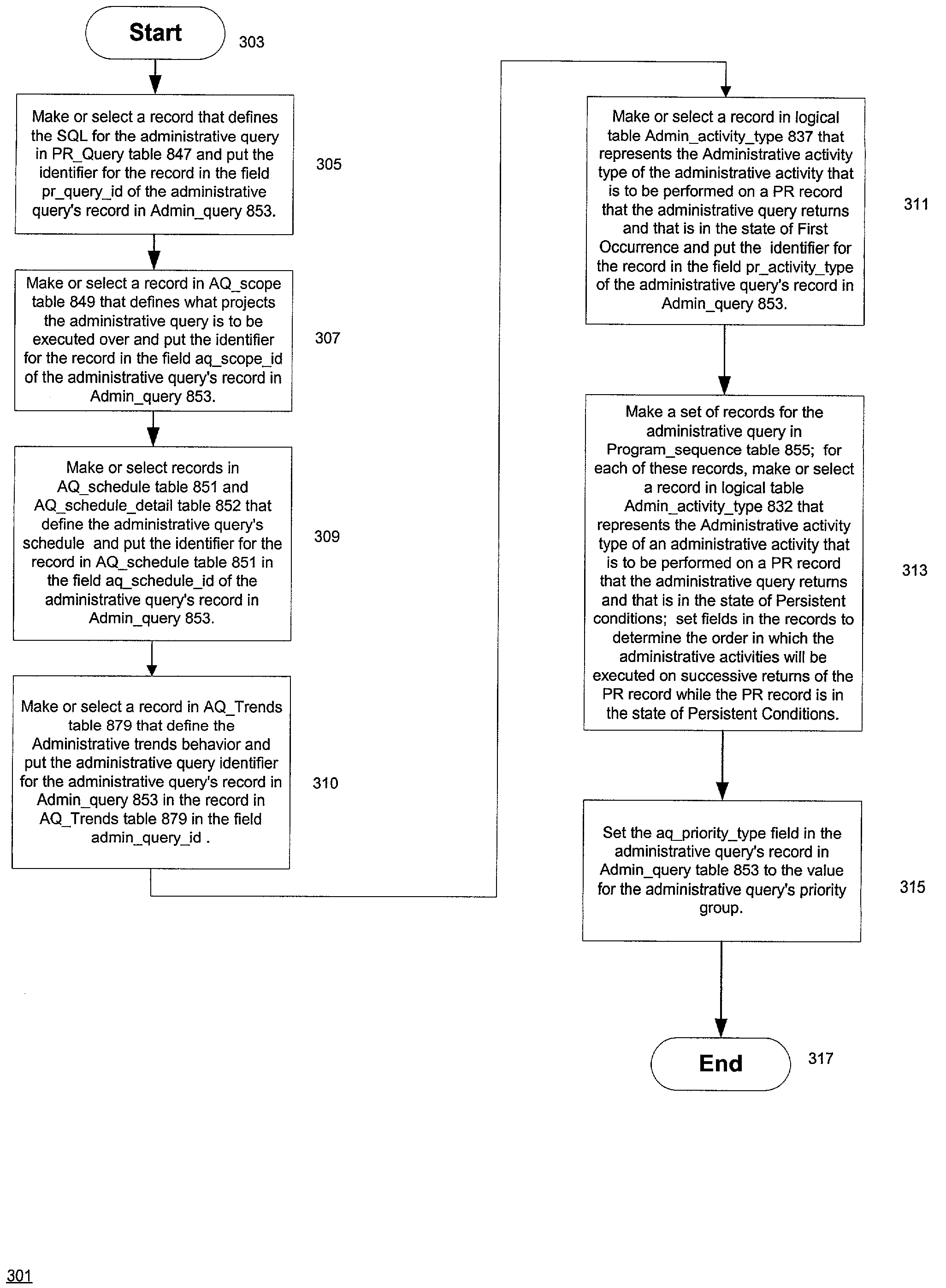
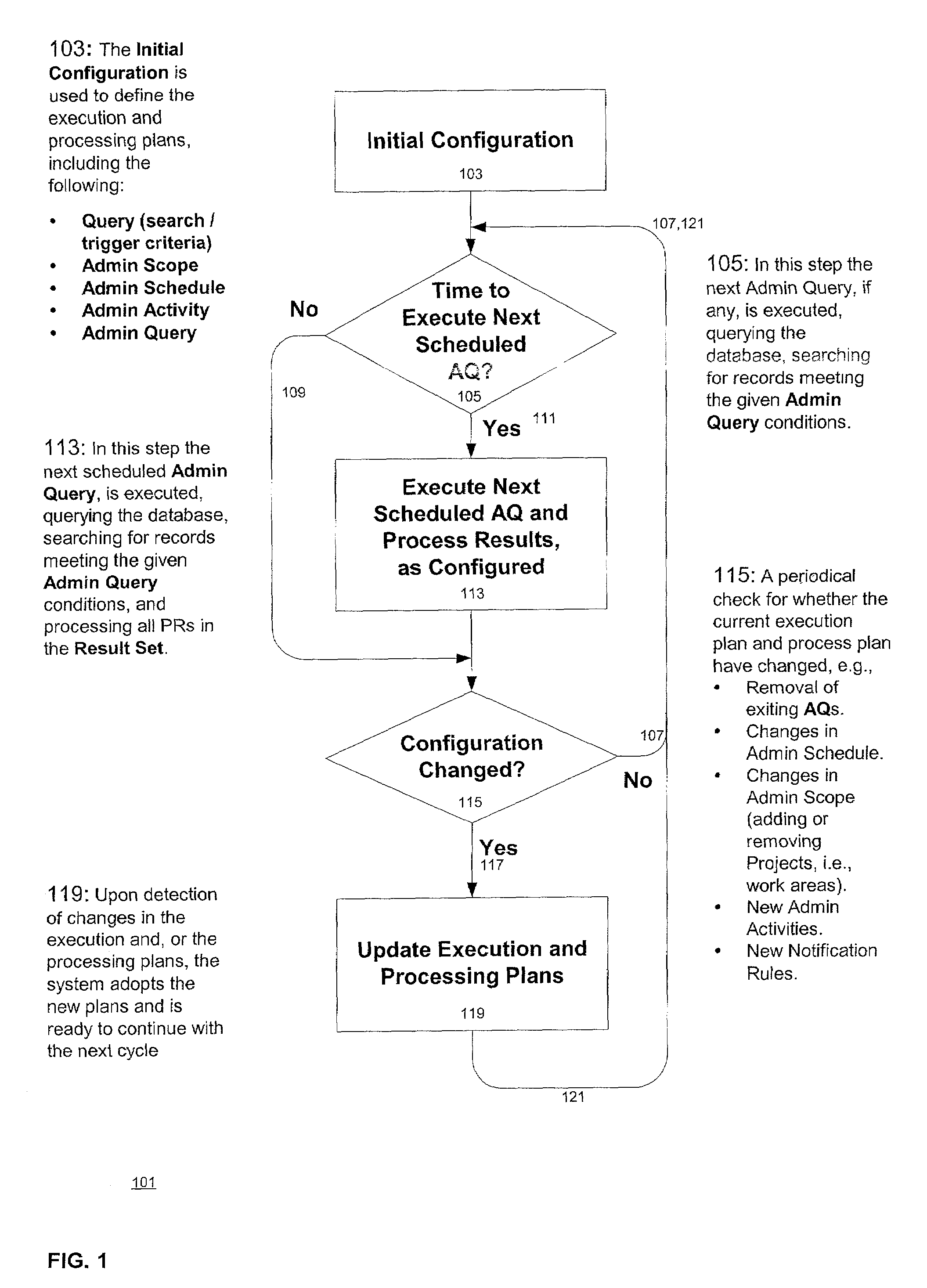
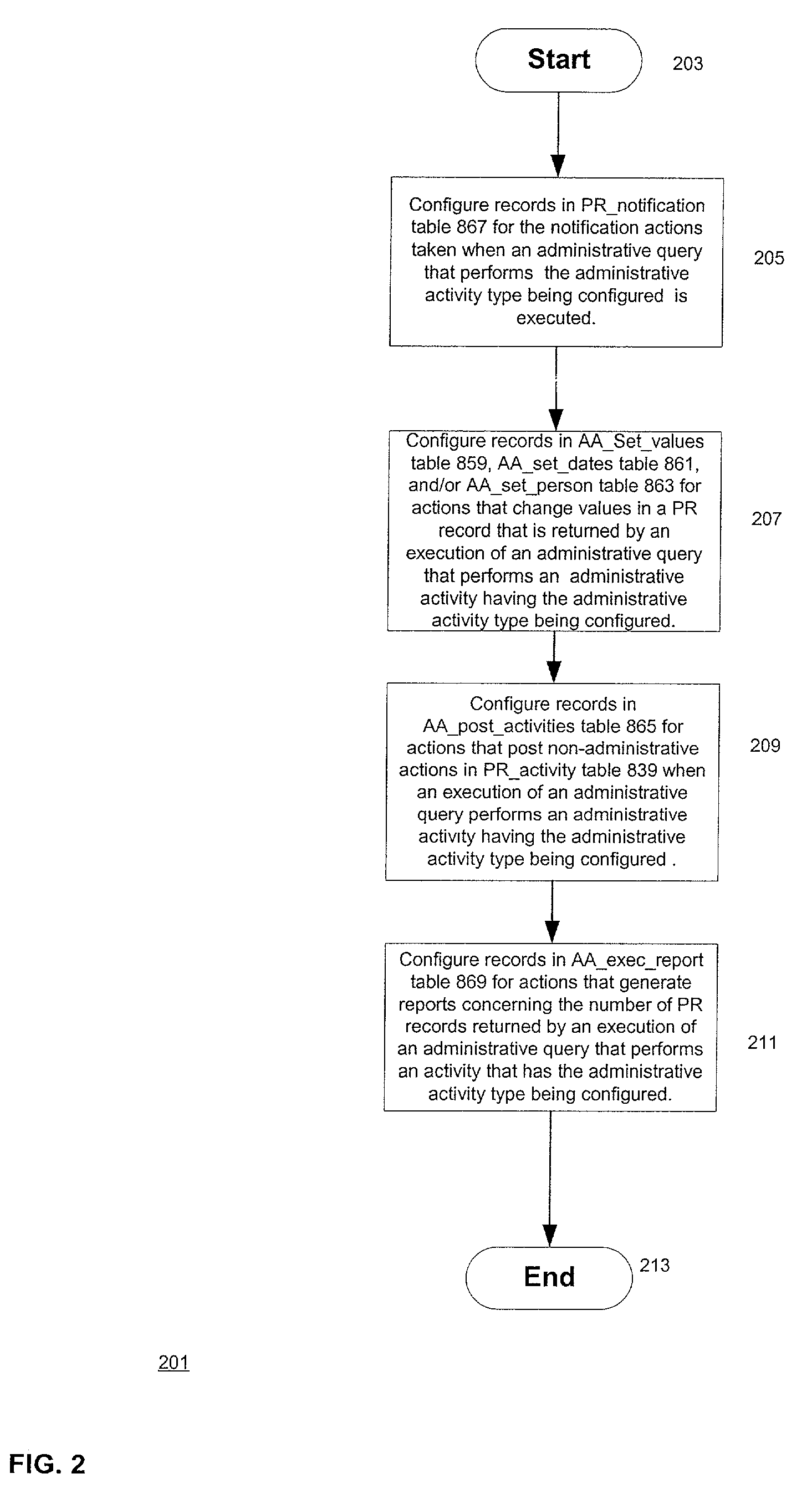
A process control system that automatically monitors processes and performs activities based on conditions detected during monitoring. The information needed to do the monitoring and perform activities is contained in tables in a database system. The process control system may be configured by configuring entries in the tables. An administrative query table has records that define administrative queries. Each administrative query has associated with it a query to be executed on a table of process records that indicate statuses of the processes being monitored, a scope that defines a subset of the process records upon which the query is to be executed, a schedule from which a time of next execution of the administrative query can be computed, and an activity. The activity is a set of one or more actions. When an administrative query is executed and the query associated with the administrative query is run on the table of process records and the result set is not empty, the activity is performed with regard to the process records of the result set. A plurality of administrative activities may be associated with the administrative query, with the activity to be performed being selected on the basis of a state of a given process record with regard to the query. An administrative activity is made up of one or more actions; also disclosed is a graphical user interface for defining administrative queries, administrative activities, and administrative actions.
Owner:SPARTA SYST INC
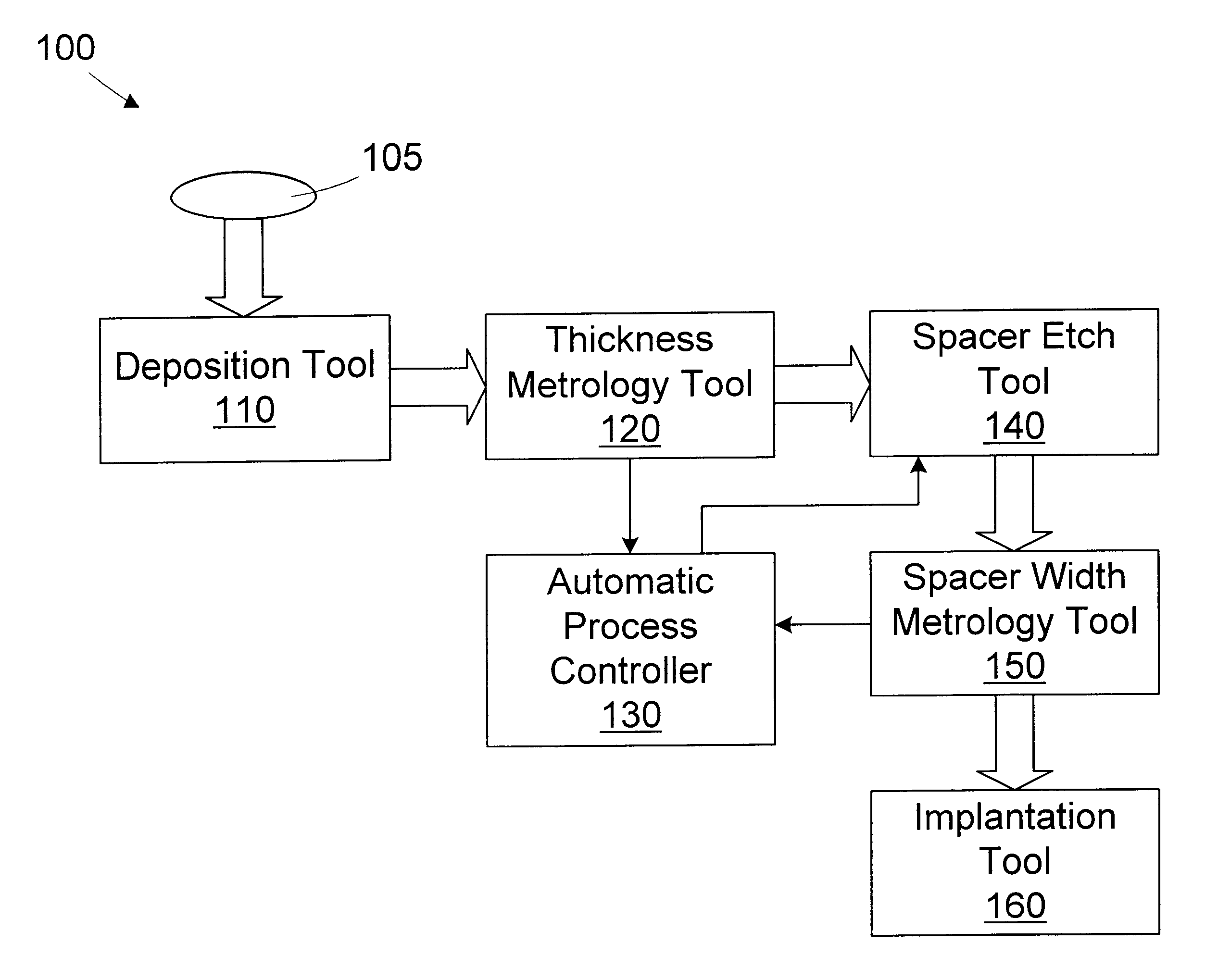
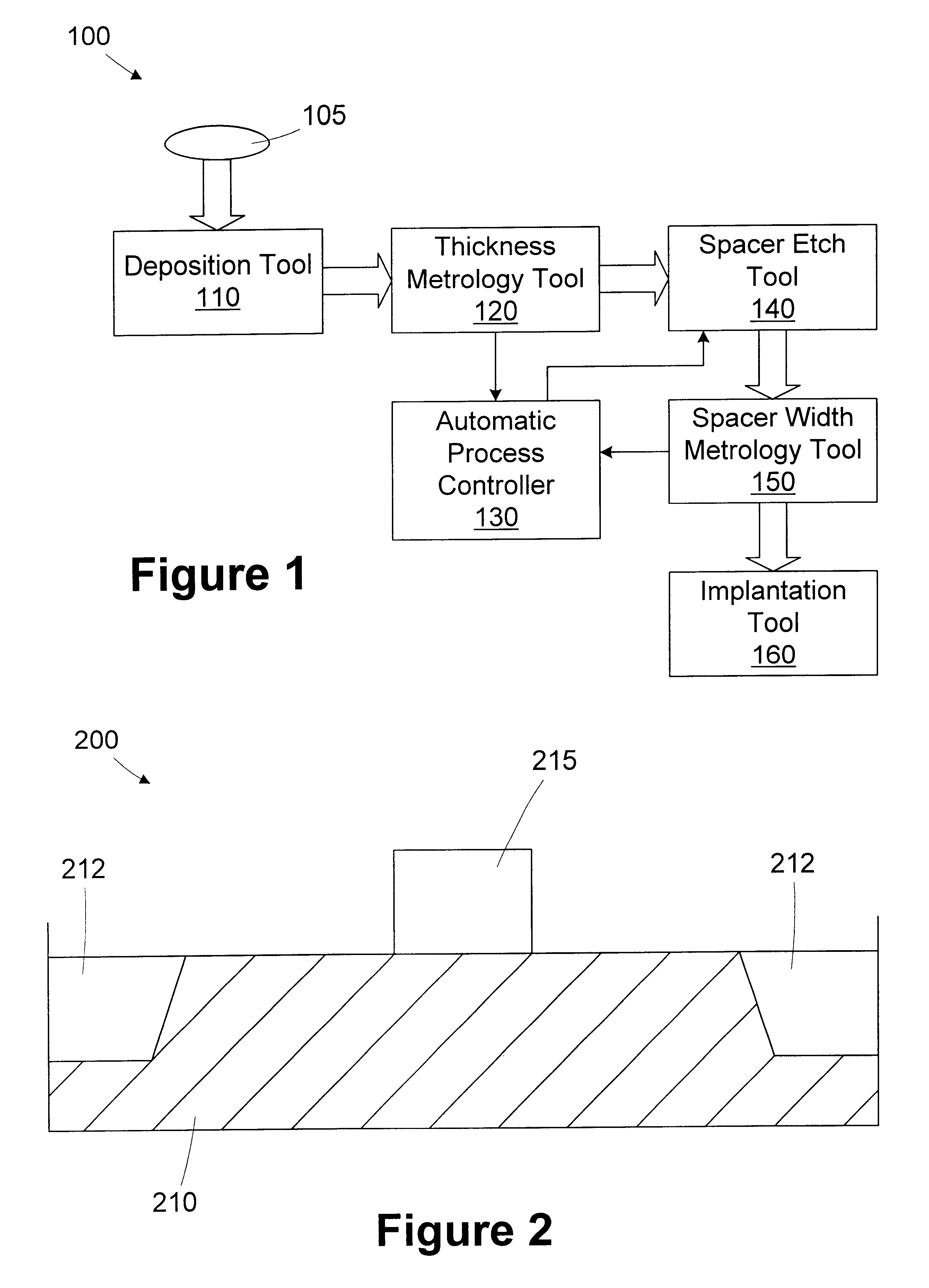
Method for controlling transistor spacer width
InactiveUS6133132ATransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyEngineering
A method for controlling spacer width in a semiconductor device is provided. A substrate having a gate formed thereon is provided. An insulative layer is formed over at least a portion of the substrate. The insulative layer covers the gate. The thickness of the insulative layer is measured. A portion of the insulative layer to be removed is determined based on the measured thickness of the insulative layer. The portion of the insulative layer is removed to define a spacer on the gate. A processing line for forming a spacer on a gate disposed on a substrate includes a deposition tool, a thickness metrology tool, and automatic process controller, and a spacer etch tool. The deposition tool is adapted to form an insulative layer over at least a portion of the substrate. The insulative layer covers the gate. The thickness metrology tool is adapted to measure the thickness of the insulative layer. The automatic process controller is adapted to determine a portion of the insulative layer to be removed based on the measured thickness of the insulative layer. The spacer etch tool is adapted to remove the portion of the insulative layer to define a spacer on the gate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method and apparatus for reducing wafer to wafer deposition variation
InactiveUS6417014B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutomatic process controlSemiconductor
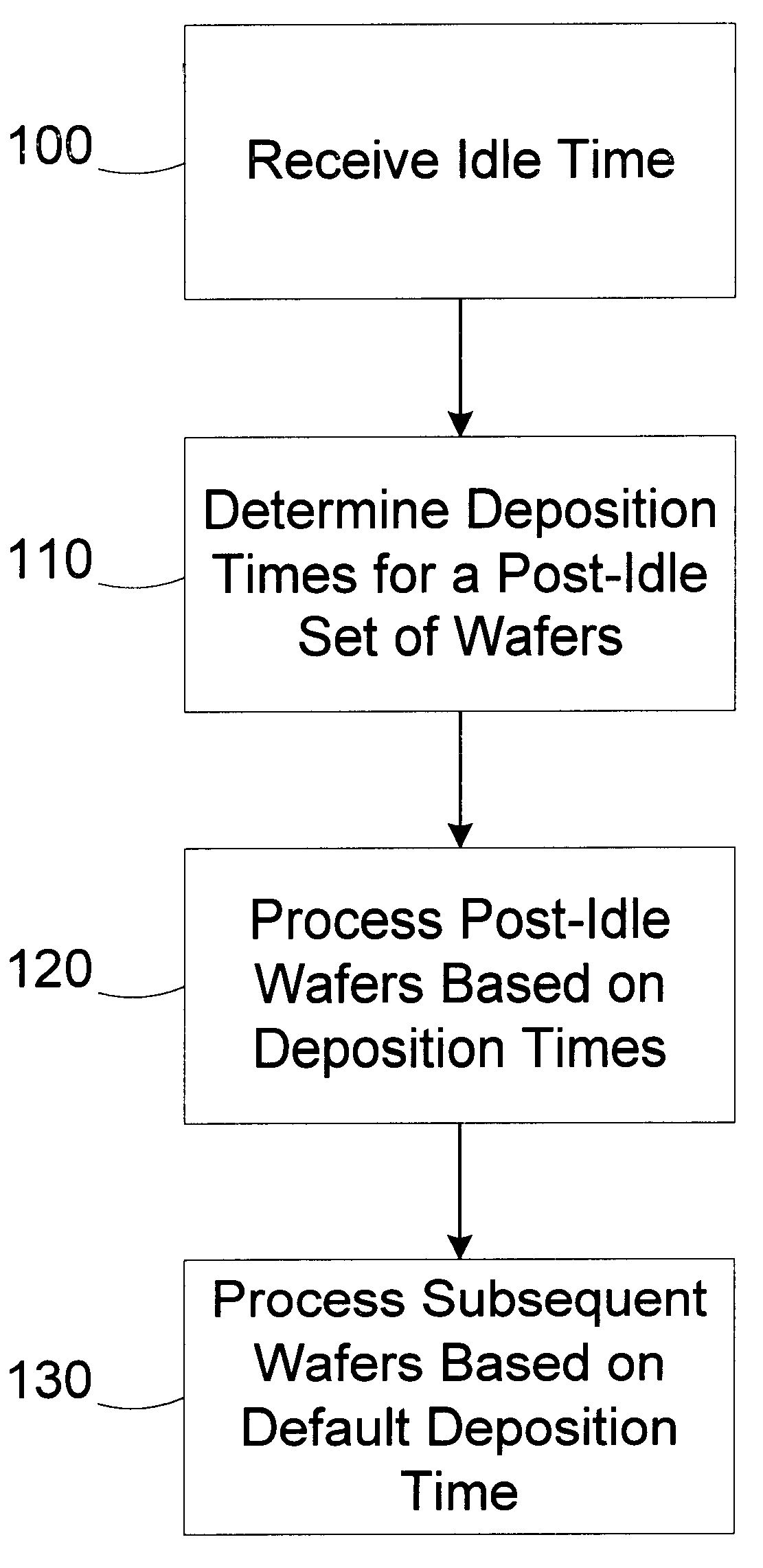
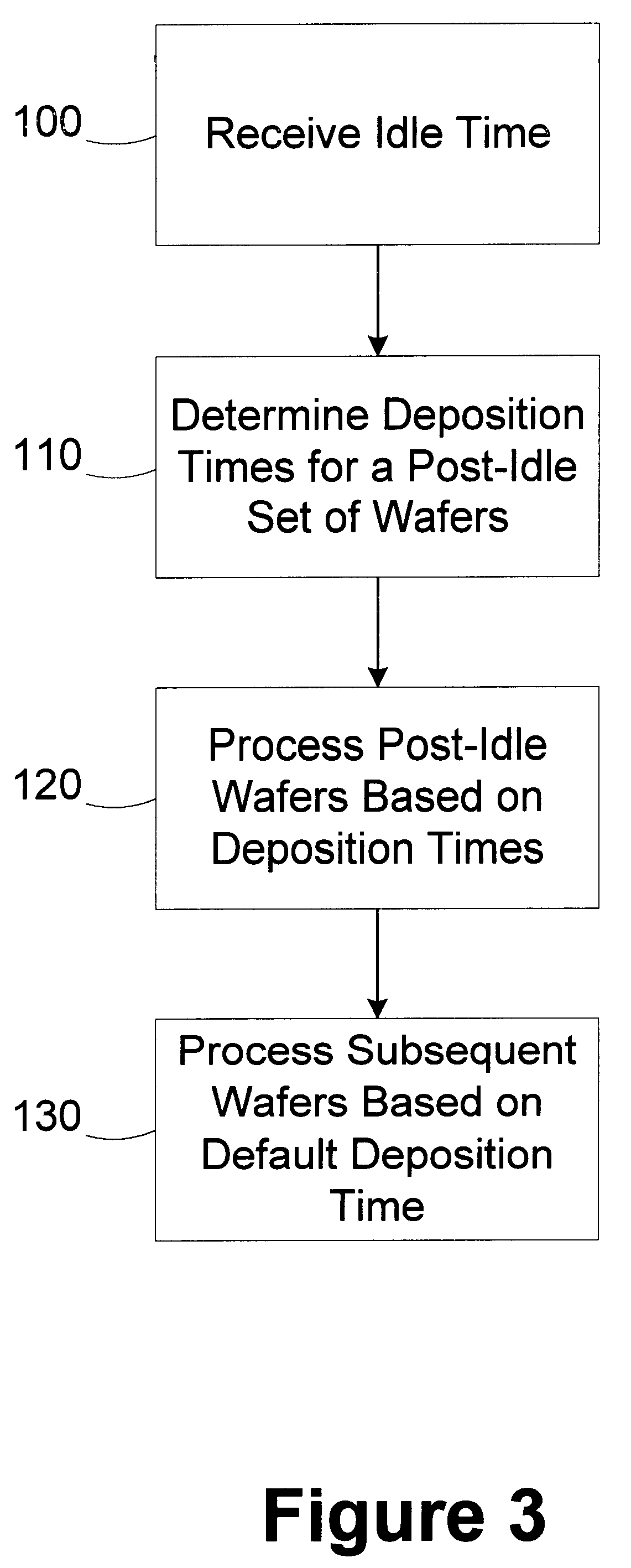
A processing line includes a processing tool and an automatic process controller. The processing tool is adapted to deposit a layer of material on a semiconductor wafer based on an operating recipe. The automatic process controller is adapted to identify a post-idle set of wafers to be processed in the processing tool after an idle period, determine deposition times for wafers in the set of post-idle wafers, and modify the operating recipe of the processing tool for each of the wafers in the post-idle set based on the deposition times. A method for reducing wafer to wafer deposition variation includes designating a set of post-idle wafers; determining a deposition time for each of the wafers in the post-idle set, at least two of the deposition times being different; and depositing a layer on the wafers in the post-idle set based on the deposition times determined.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Protection against unauthorized access to automated system for control of technological processes
InactiveUS8667589B1Programme controlMemory loss protectionAutomatic process controlData transmission
A protection system for an automate process control system (APCS) includes a plurality of programmable anti-intrusion (PAI) modules. The PAI modules are places throughout the APCS used for: analyzing a system for presence of un-authorized devices or un-authorized connections; detection of undocumented (i.e., not declared) devices and suspicious commands from connected devices; filtering various types of activities (i.e., wrong packets, unidentified activities, certain types of commands etc.); analyzing different network layers for un-authorized data transmissions; and maintaining device behavior (heuristic) logs.
Owner:SAPRYGIN KONSTANTIN
System and method for automated process control
A process control system that automatically monitors processes and performs activities based on conditions detected during monitoring. The information needed to do the monitoring and perform activities is contained in tables in a database system. The process control system may be configured by configuring entries in the tables. An administrative query table has records that define administrative queries. Each administrative query has associated with it a query to be executed on a table of process records that indicate statuses of the processes being monitored, a scope that defines a subset of the process records upon which the query is to be executed, a schedule from which a time of next execution of the administrative query can be computed, and an activity. The activity is a set of one or more actions. When an administrative query is executed and the query associated with the administrative query is run on the table of process records and the result set is not empty, the activity is performed with regard to the process records of the result set. A plurality of activities may be associated with the administrative query, with the activity to be performed being selected on the basis of a state of a given process record with regard to the query.
Owner:SPARTA SYST INC
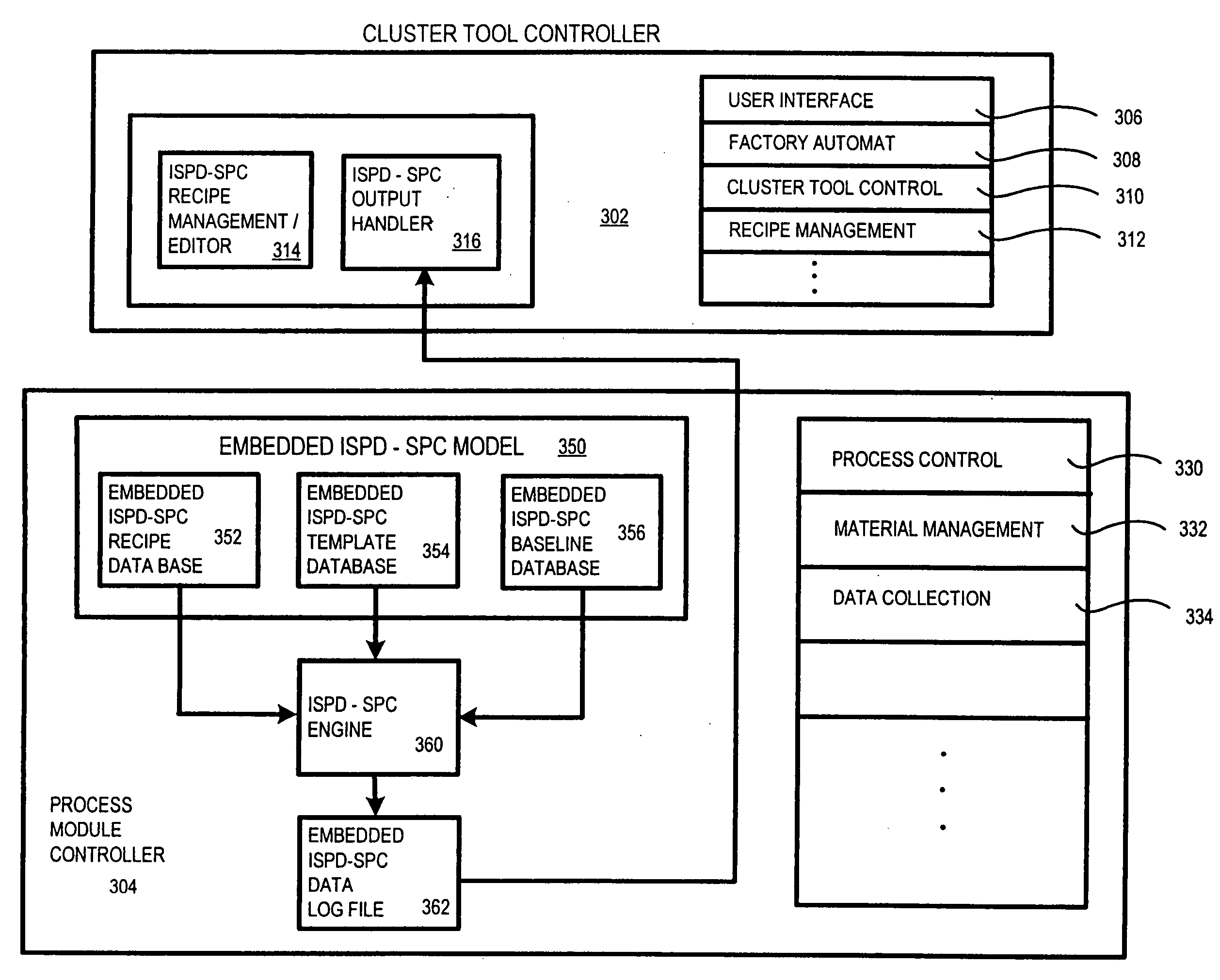
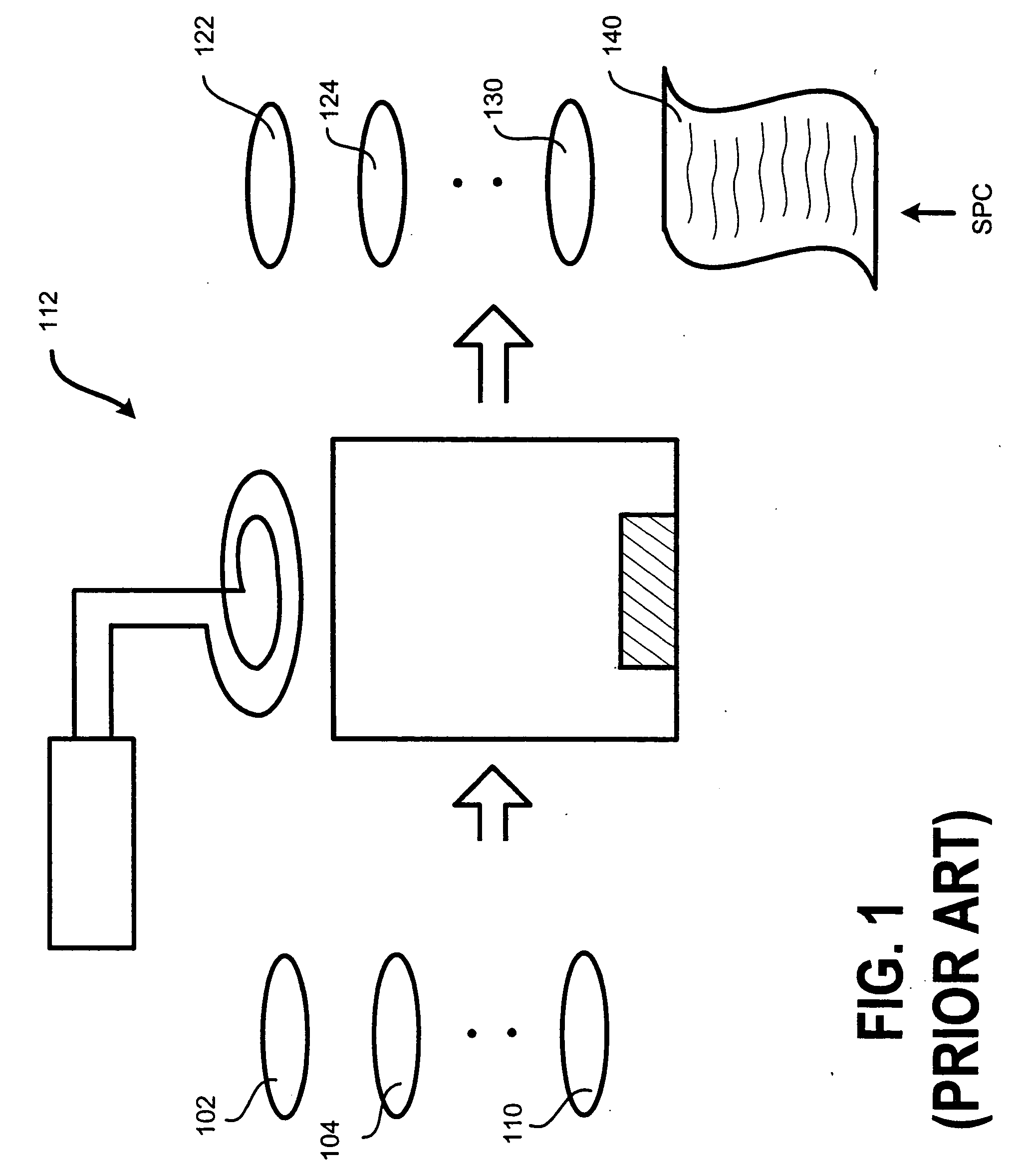
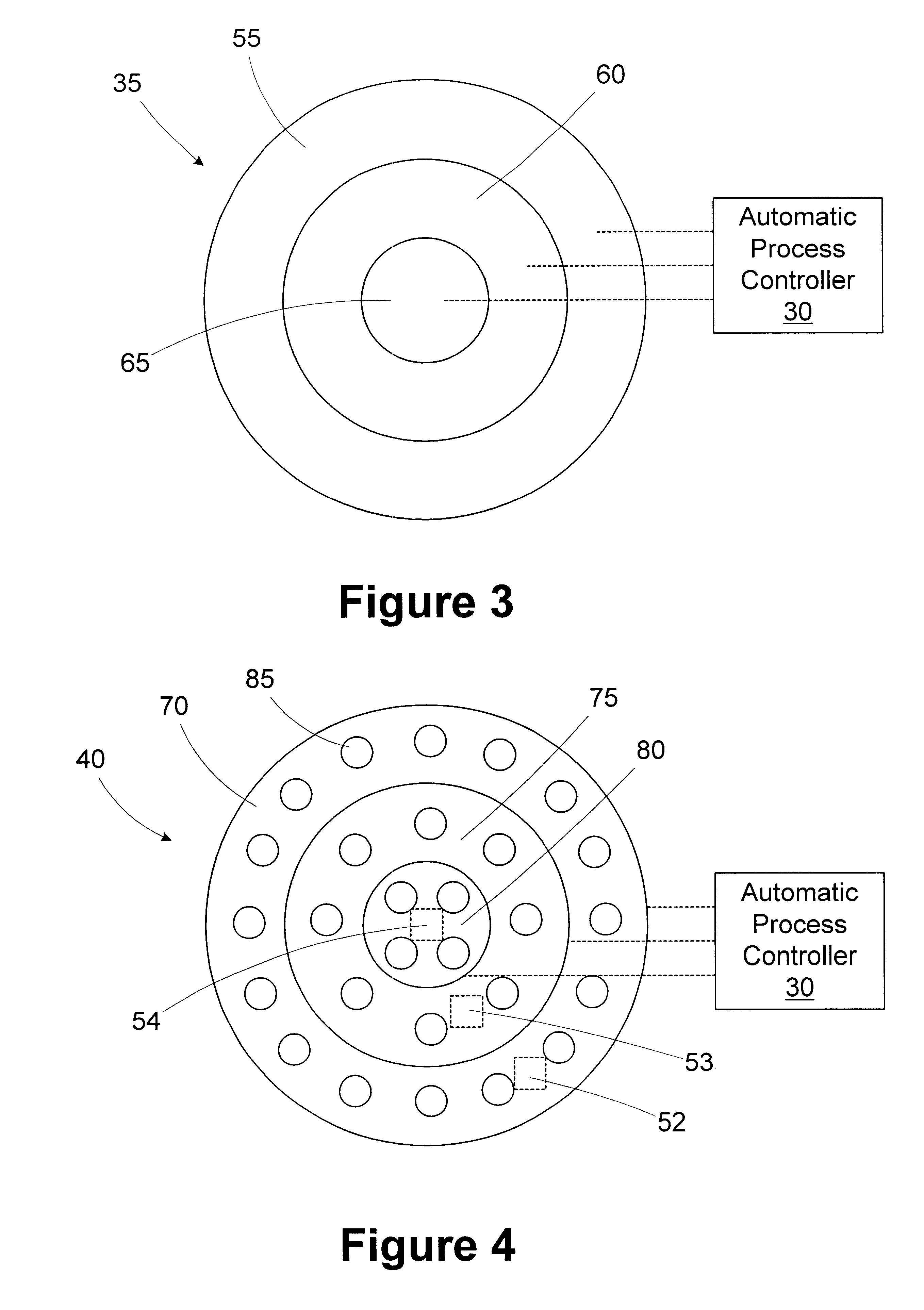
Integrated stepwise statistical process control in a plasma processing system
InactiveUS20050084988A1Process be stopImprove efficiencySafety arrangmentsElectric discharge tubesControl systemAutomatic process control
An automated process control system configured for controlling a plasma processing system having a chamber, the chamber being configured for processing a substrate. The automatic process control system includes a first sensor disposed within the chamber, the first sensor being configured for making a first plurality of measurements pertaining to a first parameter associated with a structure disposed at least partially within the chamber. The performing the first plurality of measurements is performed during the processing of the substrate. The automatic process control system further includes first logic coupled to receive the first plurality of measurements from the first sensor. The first logic is configured for analyzing using SPC methodologies the first plurality of measurements during the processing. There is also included second logic coupled to receive a first signal from the first logic, the second logic being configured to stop the processing prior to completing the processing if the first signal indicates a fault with the processing.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
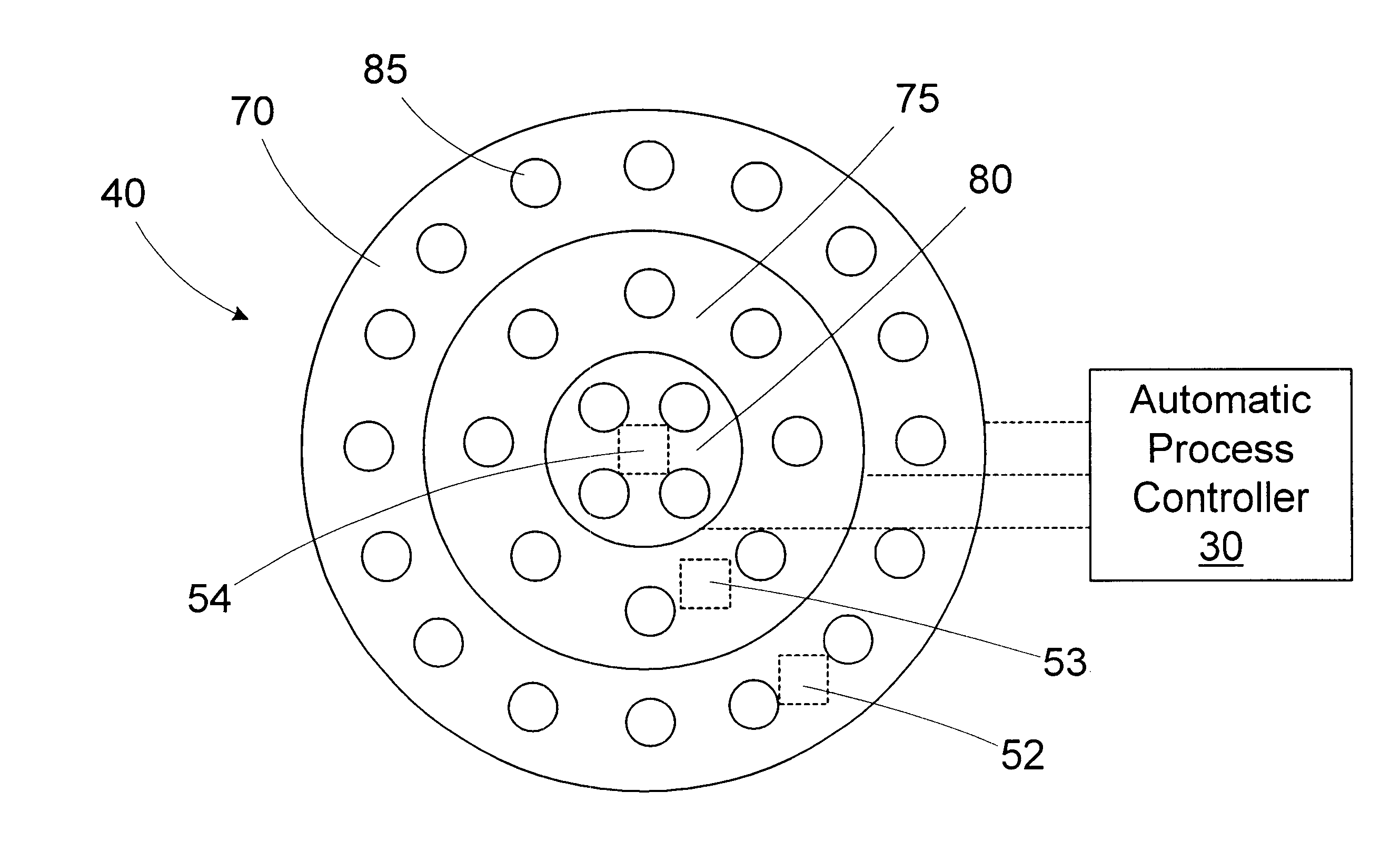
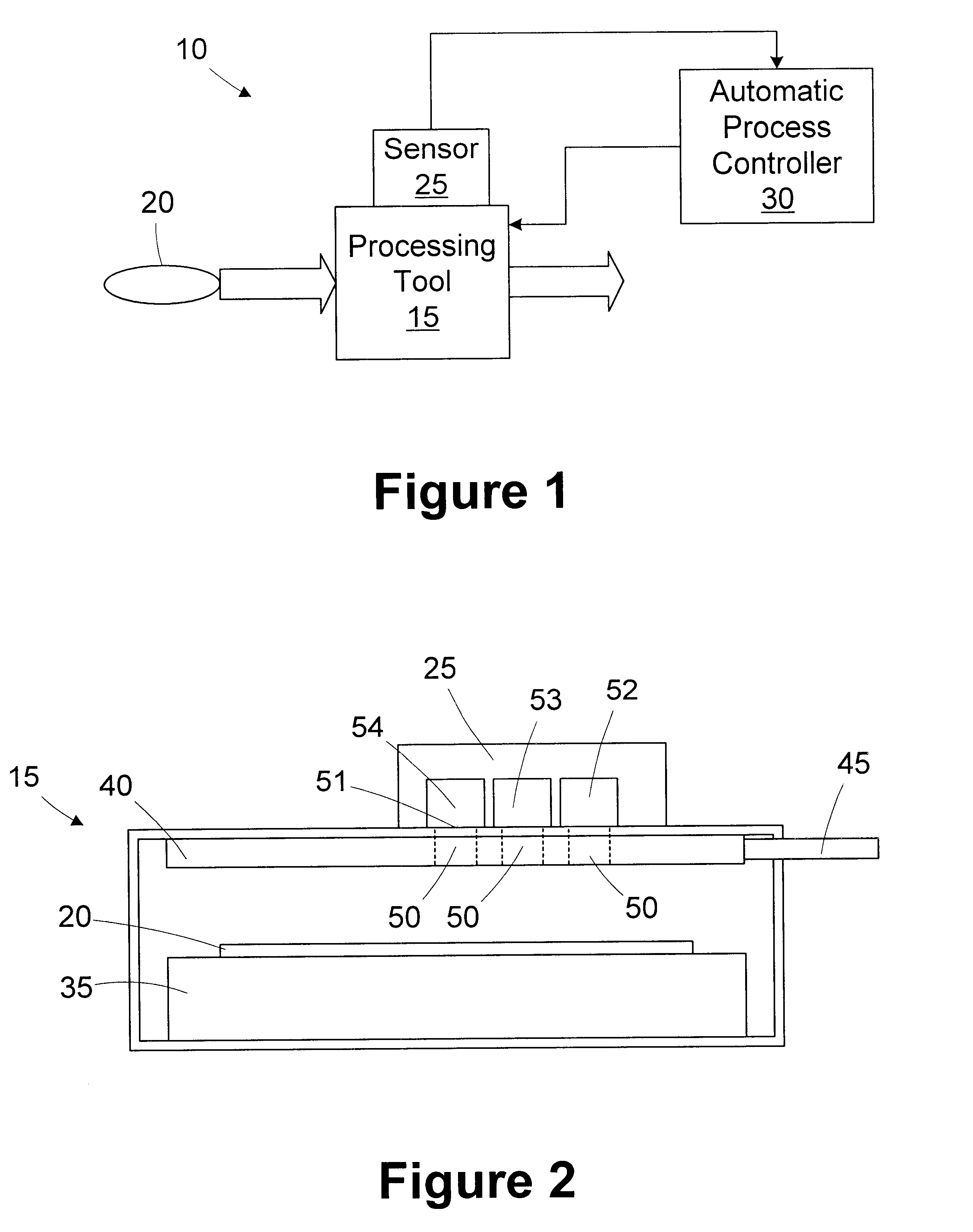
Method and apparatus for controlling wafer uniformity using spatially resolved sensors
InactiveUS6706541B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesSpatially resolvedProcess engineering
A processing system includes a sensor, a processing tool, and an automatic process controller. The sensor has a plurality of sensing regions. The processing tool is adapted to process at least one process layer on a wafer. The process tool includes a process control device controllable by a process control variable. The sensor is adapted to measure a process layer characteristic of the process layer in a selected one of the sensing regions. The automatic process controller is adapted to receive the process layer characteristics measured by the sensor and adjust the process control variable in response to the process layer characteristic measured in one sensing region differing from the process layer characteristic measured in another sensing region. A method for controlling wafer uniformity includes processing a process layer on a wafer; measuring a characteristic of the layer in a plurality of sensing locations; and changing a process control variable of a process control device in response to the process layer characteristic measured in one sensing location differing from the process layer characteristic measured in another sensing location to affect the rate of processing the process layer in at least one of the sensing locations.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Apparatus for filling trenches
InactiveUS6454899B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetrologyEngineering
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
System and method for automated process control
A process control system that automatically monitors processes and performs activities based on conditions detected during monitoring. The information needed to do the monitoring and perform activities is contained in tables in a database system. The process control system may be configured by configuring entries in the tables. An administrative query table has records that define administrative queries. Each administrative query has associated with it a query to be executed on a table of process records that indicate statuses of the processes being monitored, a scope that defines a subset of the process records upon which the query is to be executed, a schedule from which a time of next execution of the administrative query can be computed, and an activity. The activity is a set of one or more actions. When an administrative query is executed and the query associated with the administrative query is run on the table of process records and the result set is not empty, the activity is performed with regard to the process records of the result set. A plurality of activities may be associated with the administrative query, with the activity to be performed being selected on the basis of a state of a given process record with regard to the query.
Owner:SPARTA SYST INC
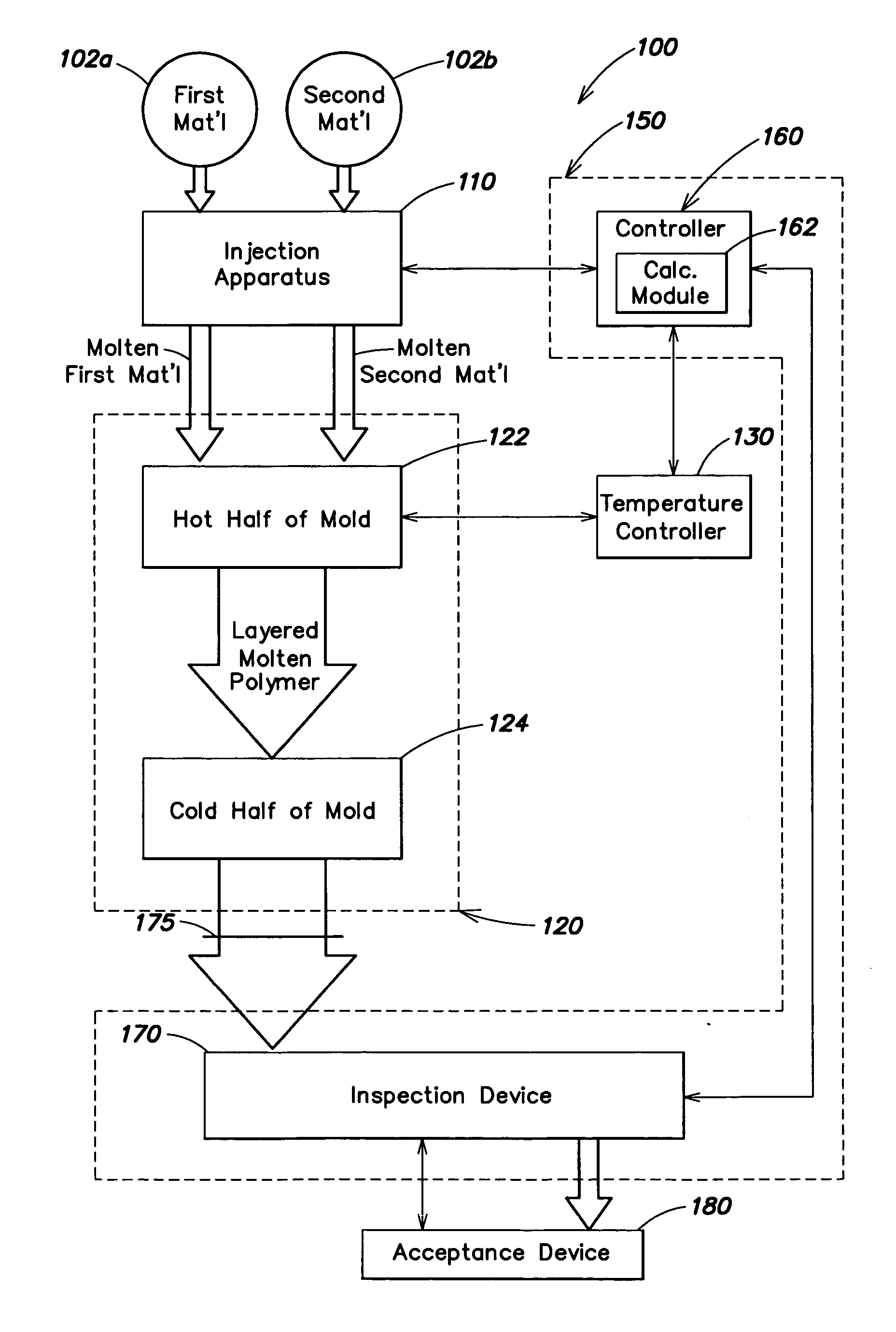
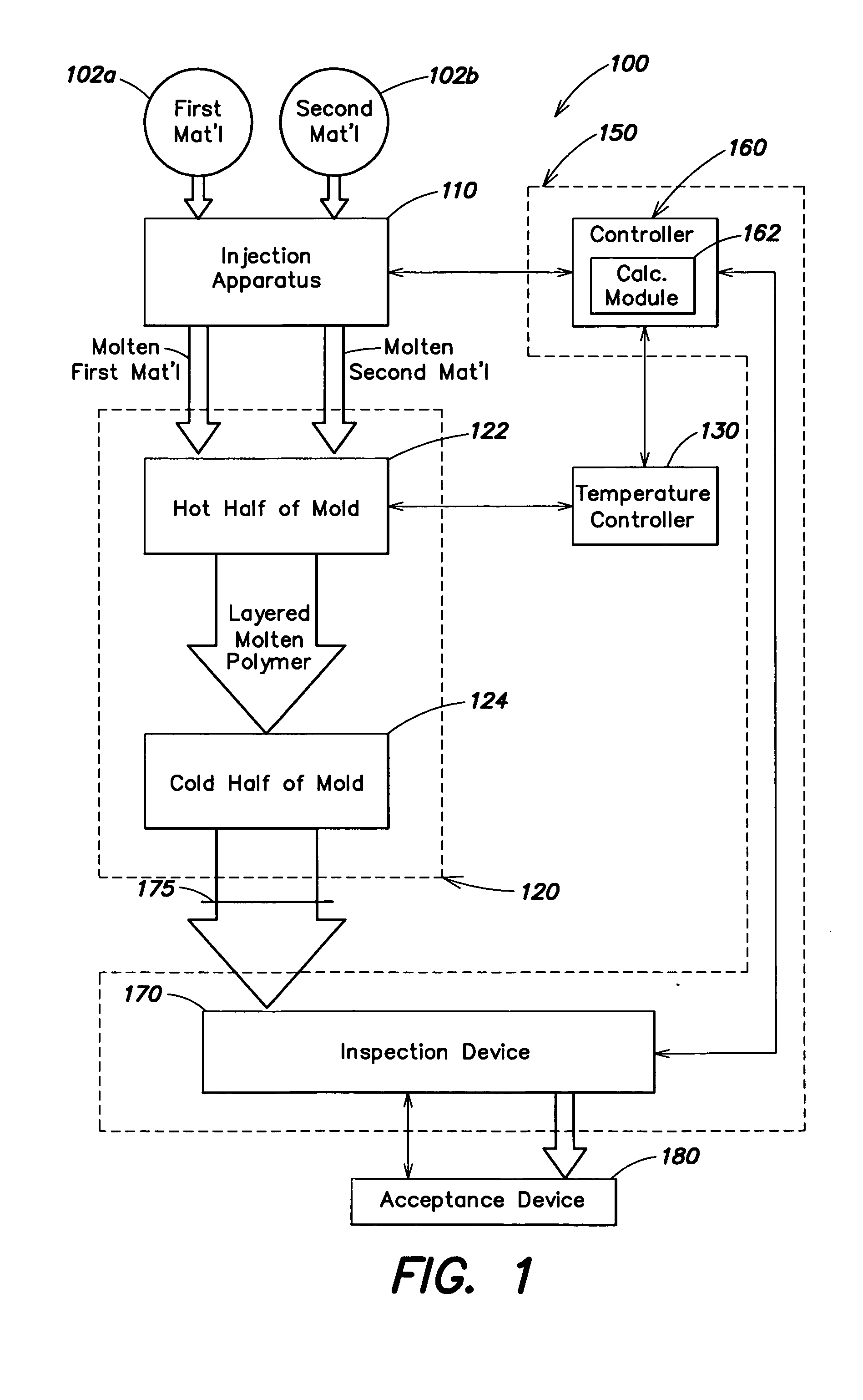
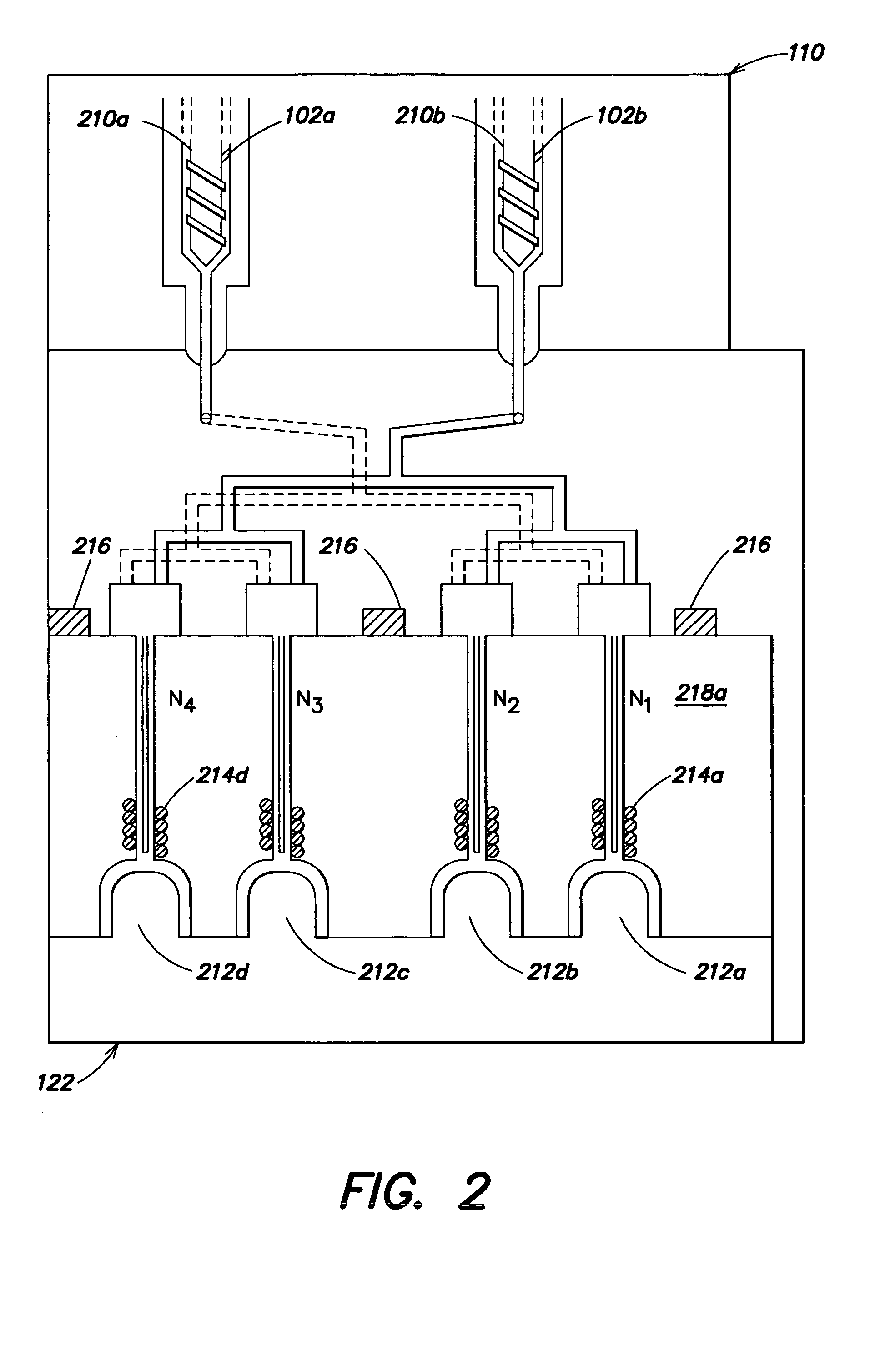
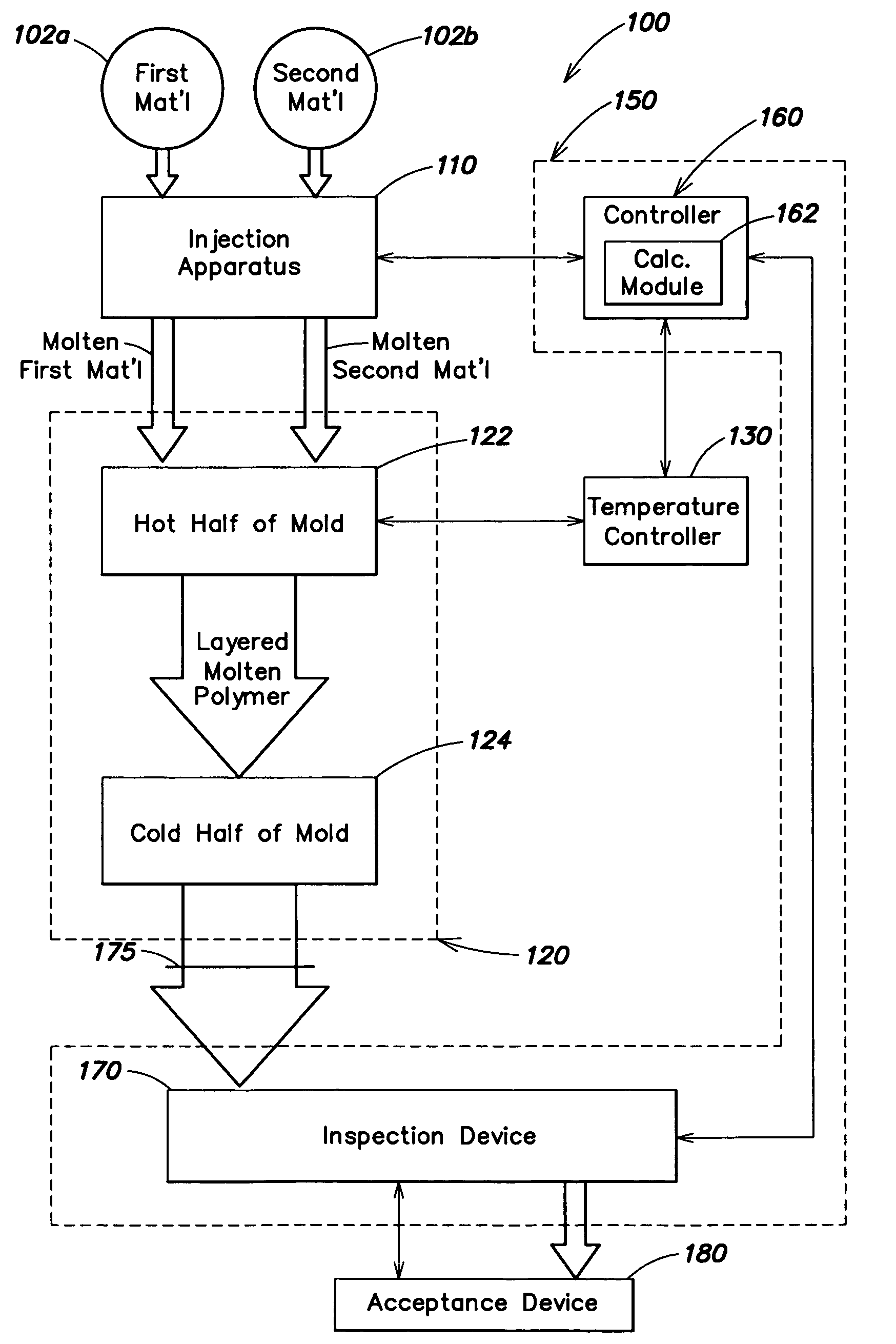
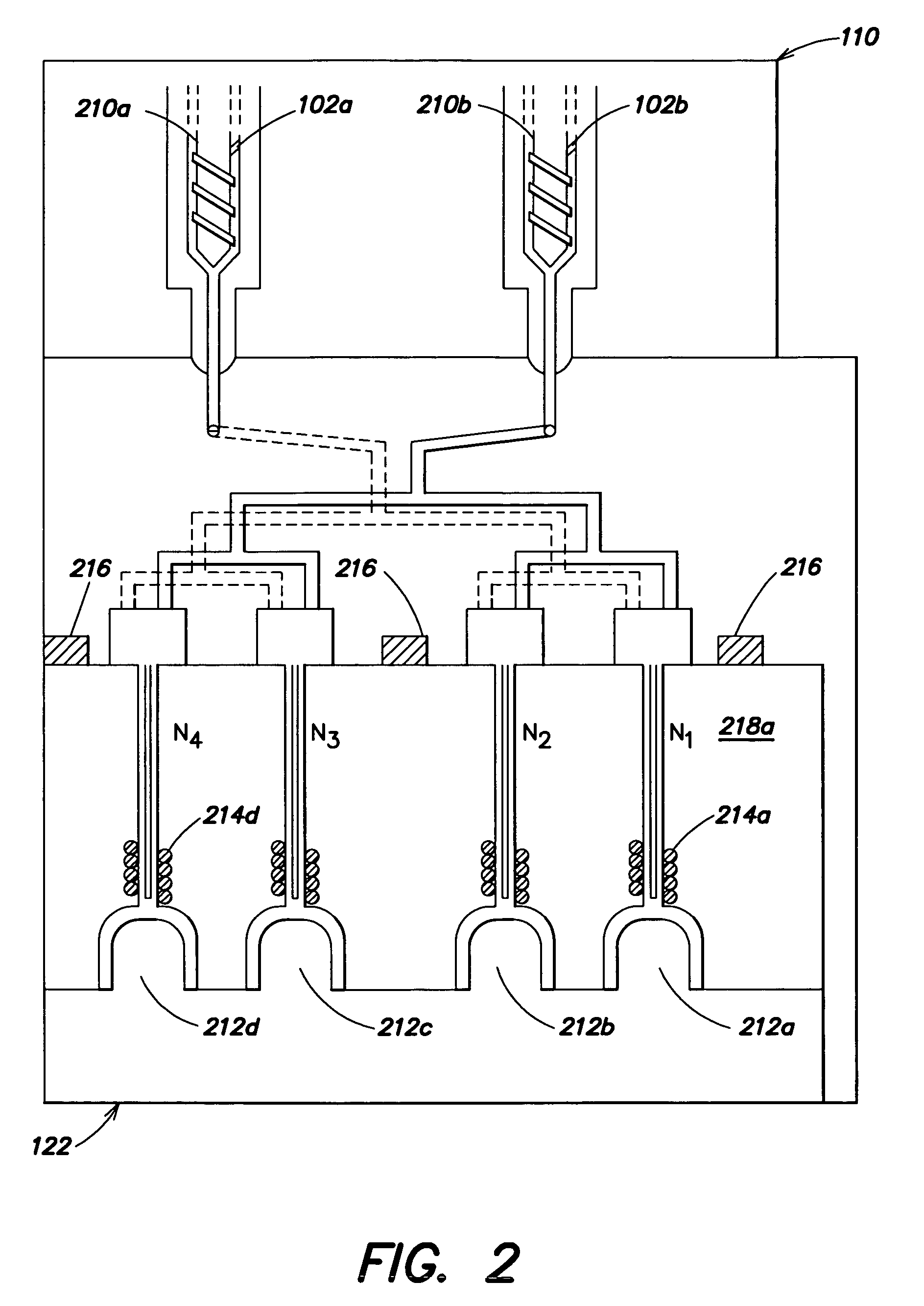
Automatic process control for a multilayer injection molding apparatus
A control system for use with a multi-layer molding device having an inspection device for measuring a characteristic of a product of a cavity of the molding device and a controller adapted to receive information corresponding to the at least one characteristic from the inspection device and to alter the molding device based on the information.
Owner:CINCINNATI MILACRON INC
Automatic process control of additive manufacturing device
ActiveUS9855698B2Minimize the numberImprove efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsAutomatic controlAutomatic process control
Automatic process control of additive manufacturing. The system includes an additive manufacturing device for making an object and a local network computer controlling the device. At least one camera is provided with a view of a manufacturing volume of the device to generate network accessible images of the object. The computer is programmed to stop the manufacturing process when the object is defective based en the images of the object.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Blood Processing Apparatus with Robust Automated Process Control
ActiveUS20080045394A1Accurate collectionReduce detectionImage enhancementWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationImaging processingAutomatic process control
A centrifuge for separating blood having a camera observing fluid flow, and a controller controlling the flow. The location of an interface is detected by image processing steps, which may comprise the steps of “spoiling” the image, “diffusing” the image, “edge detection”, “edge linking”, “region-based confirmation”, and “interface calculation”. “Spoiling” reduces the number of pixels to be examined preferentially on orthogonal axis oriented with respect to the expected location of the interface or phase boundary. “Diffusing” smoothes out small oscillations in the interface boundary, making the location of the interface more distinct. “Edge detection” computes the rate of change in pixel intensity, or. “Edge linking” connects adjacent maxima. “Region-based confirmation” creates a pseudo image of the regions that qualify as distinct. “Final edge calculation” uses the points where the shade changes in the pseudo image, averages the radial displacement of these points for the interface position.
Owner:CARIDIANBCT
Automatic process control for a multilayer injection molding apparatus
A control system for use with a multi-layer molding device having an inspection device for measuring a characteristic of a product of a cavity of the molding device and a controller adapted to receive information corresponding to the at least one characteristic from the inspection device and to alter the molding device based on the information.
Owner:MILACRON LLC
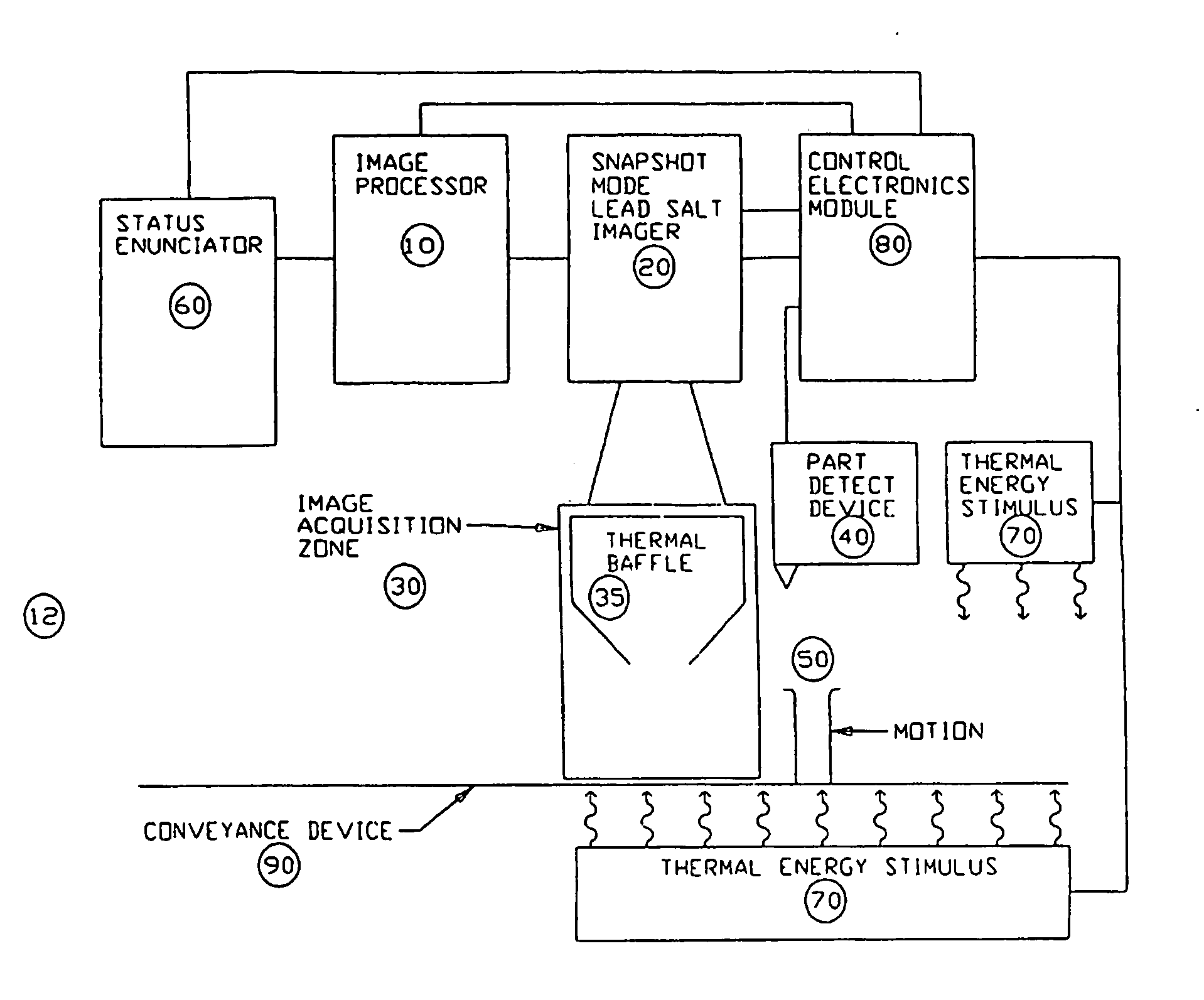
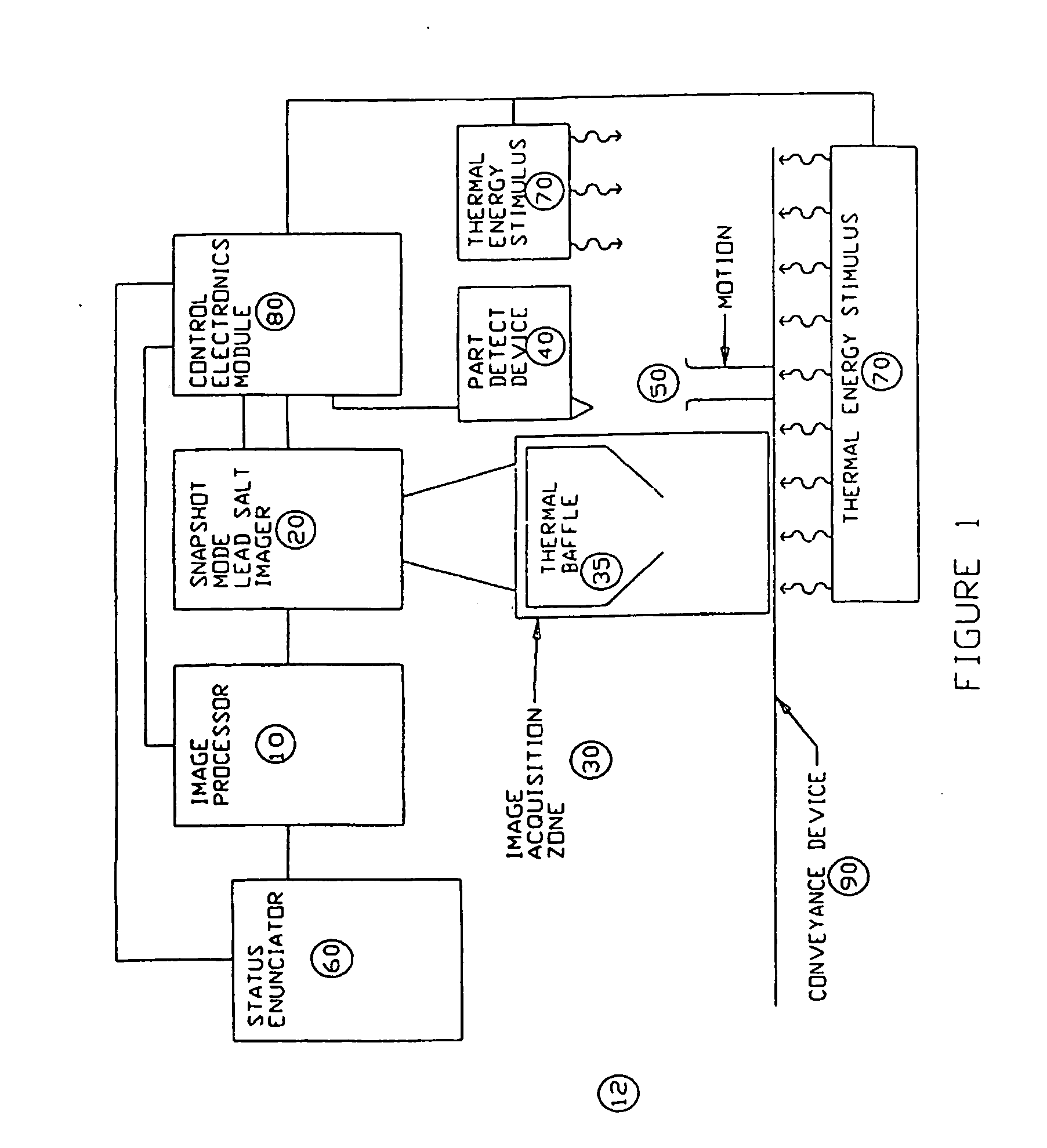
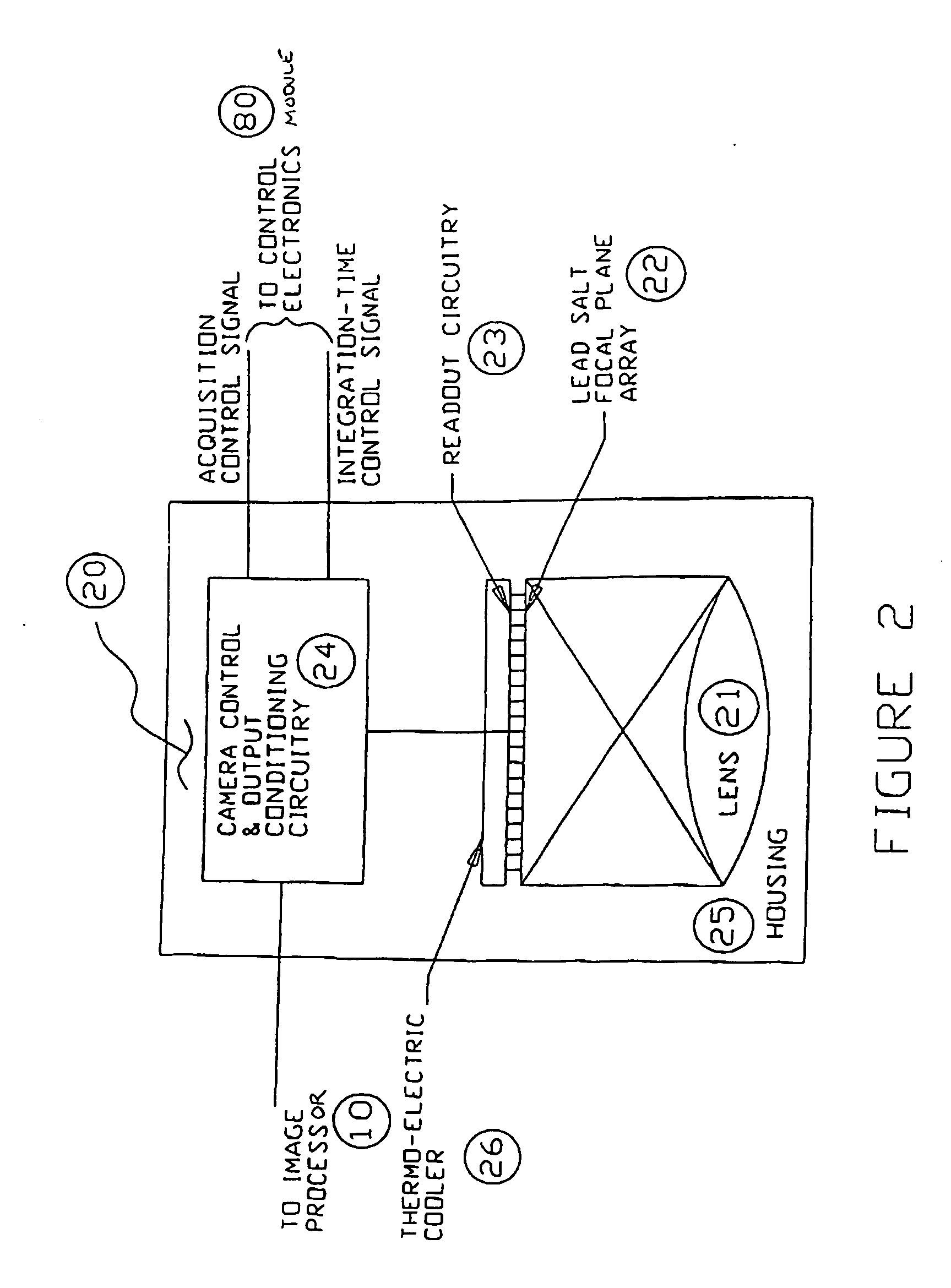
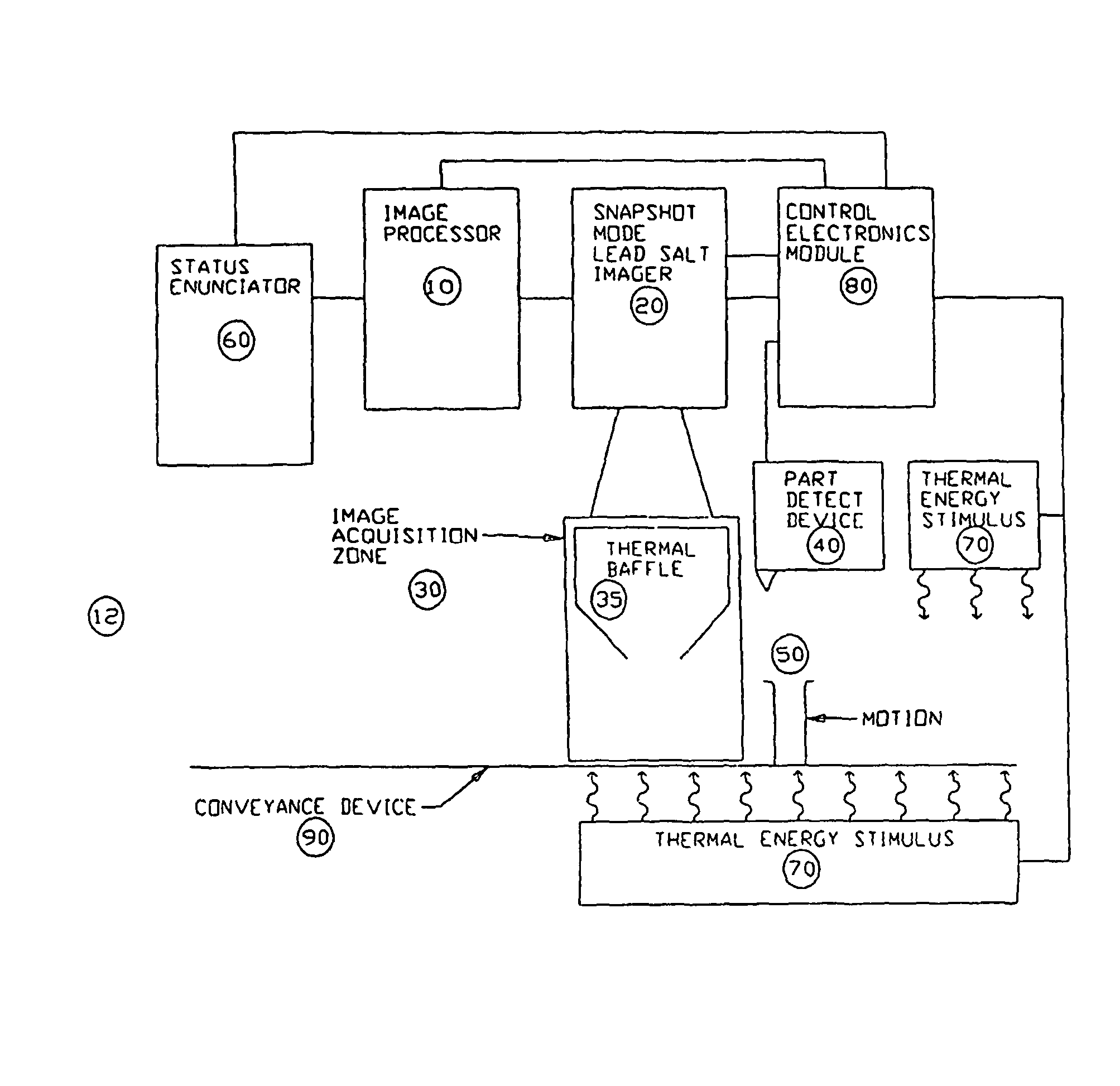
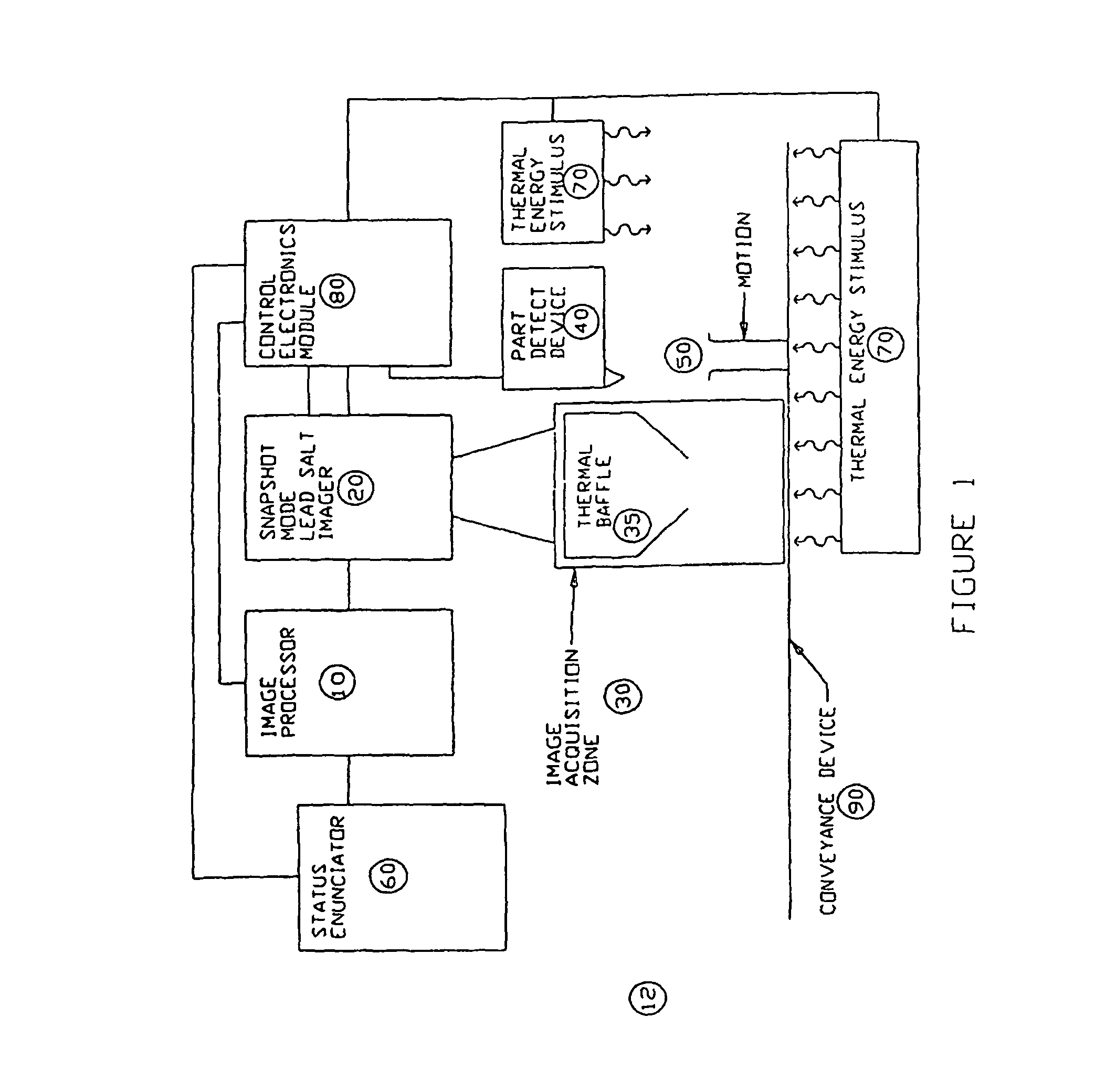
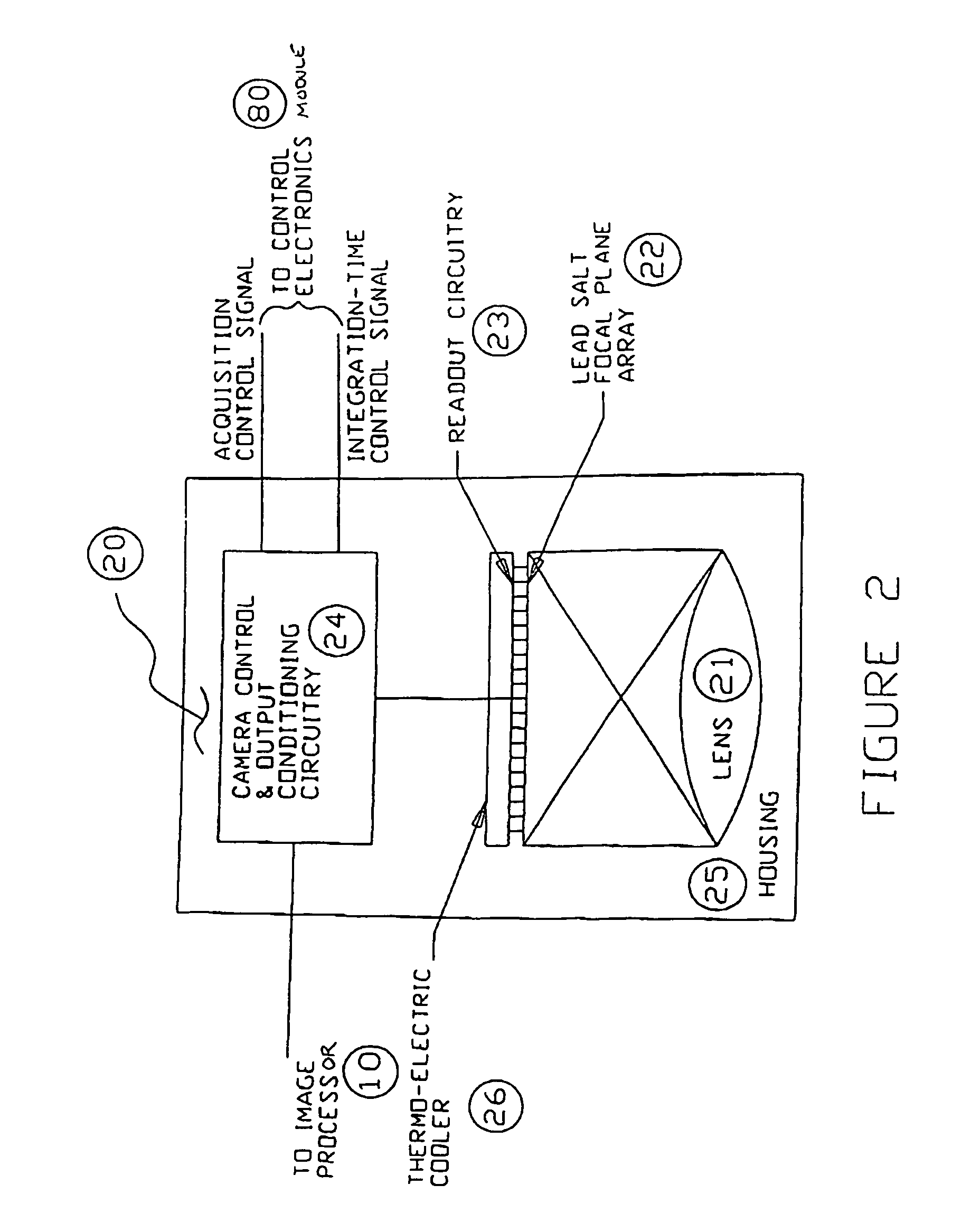
Apparatus and method for providing snapshot action thermal infrared imaging within automated process control article inspection applications
ActiveUS20060232674A1Robust structural integrity inspection capabilityHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryMachine visionLead salt
This application relates to an apparatus and method for providing snapshot action thermal infrared imaging within automated process control article inspection applications. More specifically, it pertains to the use of snapshot mode lead salt area-array imaging sensors (20) as the imaging front-end in high-speed machine vision inspection systems (12). the relatively low-cost, good measurement sensitivity at temperatures consistent with thermo-electric cooling means, and the ability to be operated in snapshot mode enables lead salt-based image acquisition sensors (20) to be used in a variety of automated process control and article inspection applications.
Owner:PRESSCO TECH INC
System for controlling transistor spacer width
A method for controlling spacer width in a semiconductor device is provided. A substrate having a gate formed thereon is provided. An insulative layer is formed over at least a portion of the substrate. The insulative layer covers the gate. The thickness of the insulative layer is measured. A portion of the insulative layer to be removed is determined based on the measured thickness of the insulative layer. The portion of the insulative layer is removed to define a spacer on the gate. A processing line for forming a spacer on a gate disposed on a substrate includes a deposition tool, a thickness metrology tool, and automatic process controller, and a spacer etch tool. The deposition tool is adapted to form an insulative layer over at least a portion of the substrate. The insulative layer covers the gate. The thickness metrology tool is adapted to measure the thickness of the insulative layer. The automatic process controller is adapted to determine a portion of the insulative layer to be removed based on the measured thickness of the insulative layer. The spacer etch tool is adapted to remove the portion of the insulative layer to define a spacer on the gate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
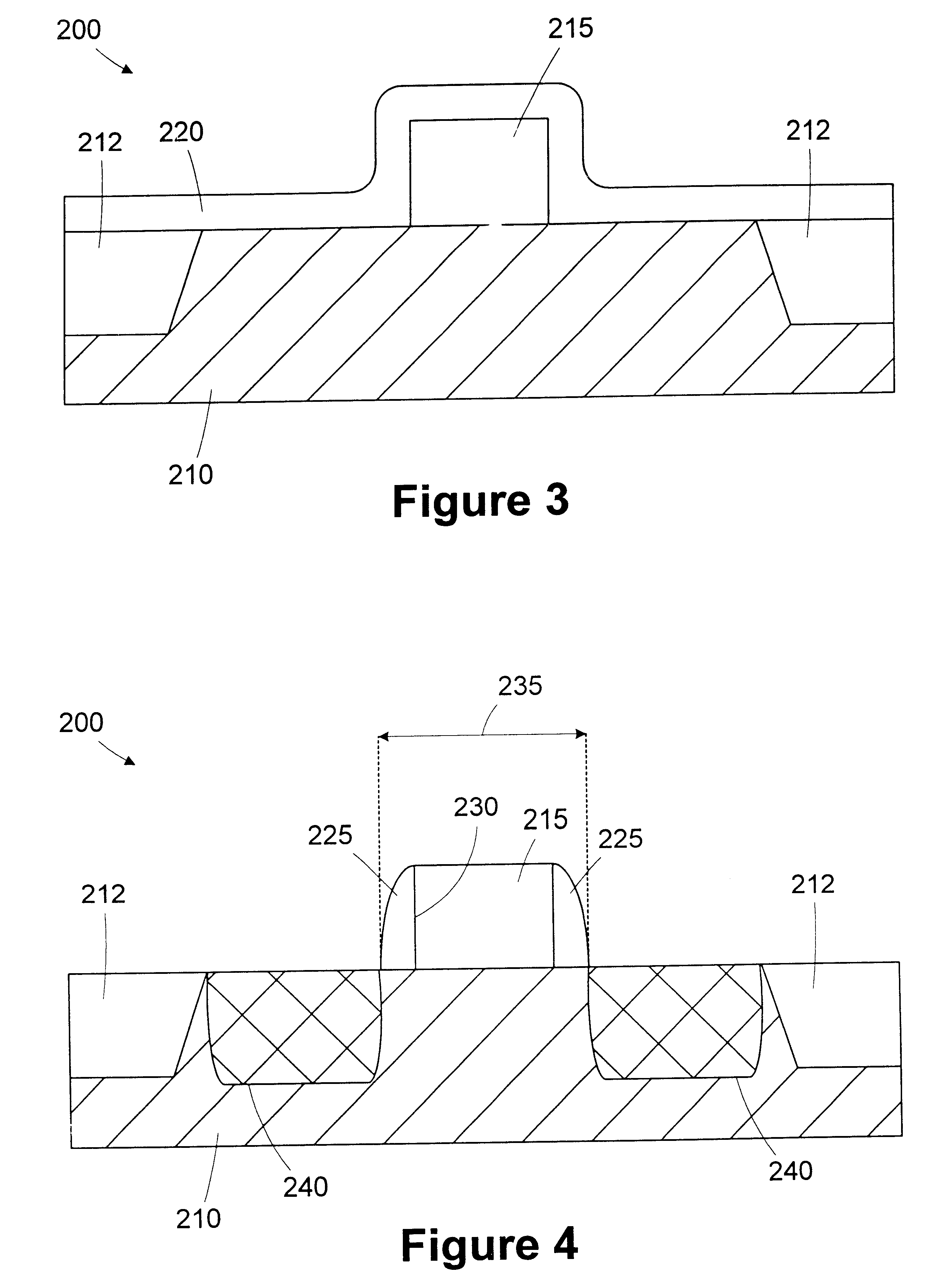
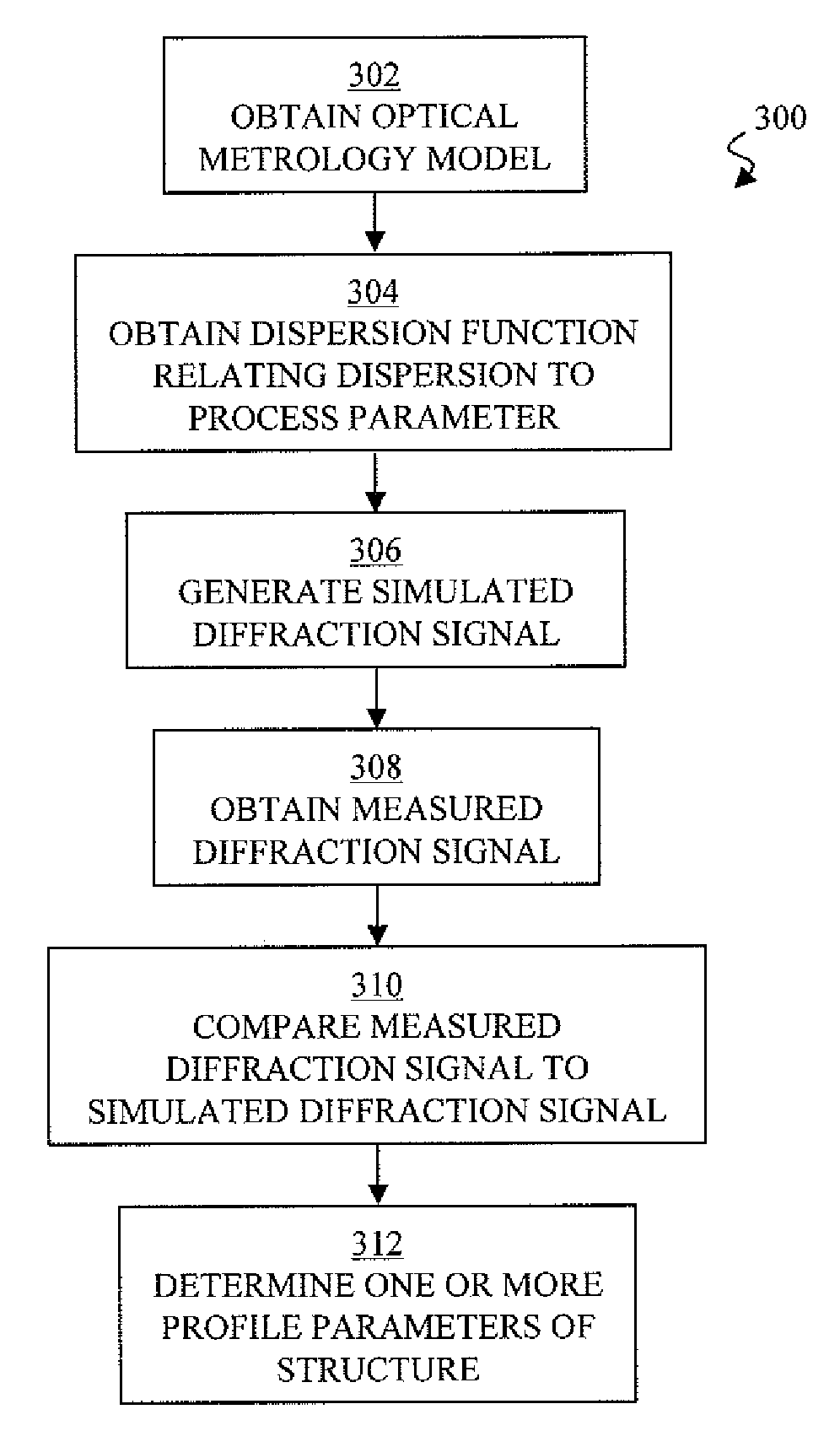
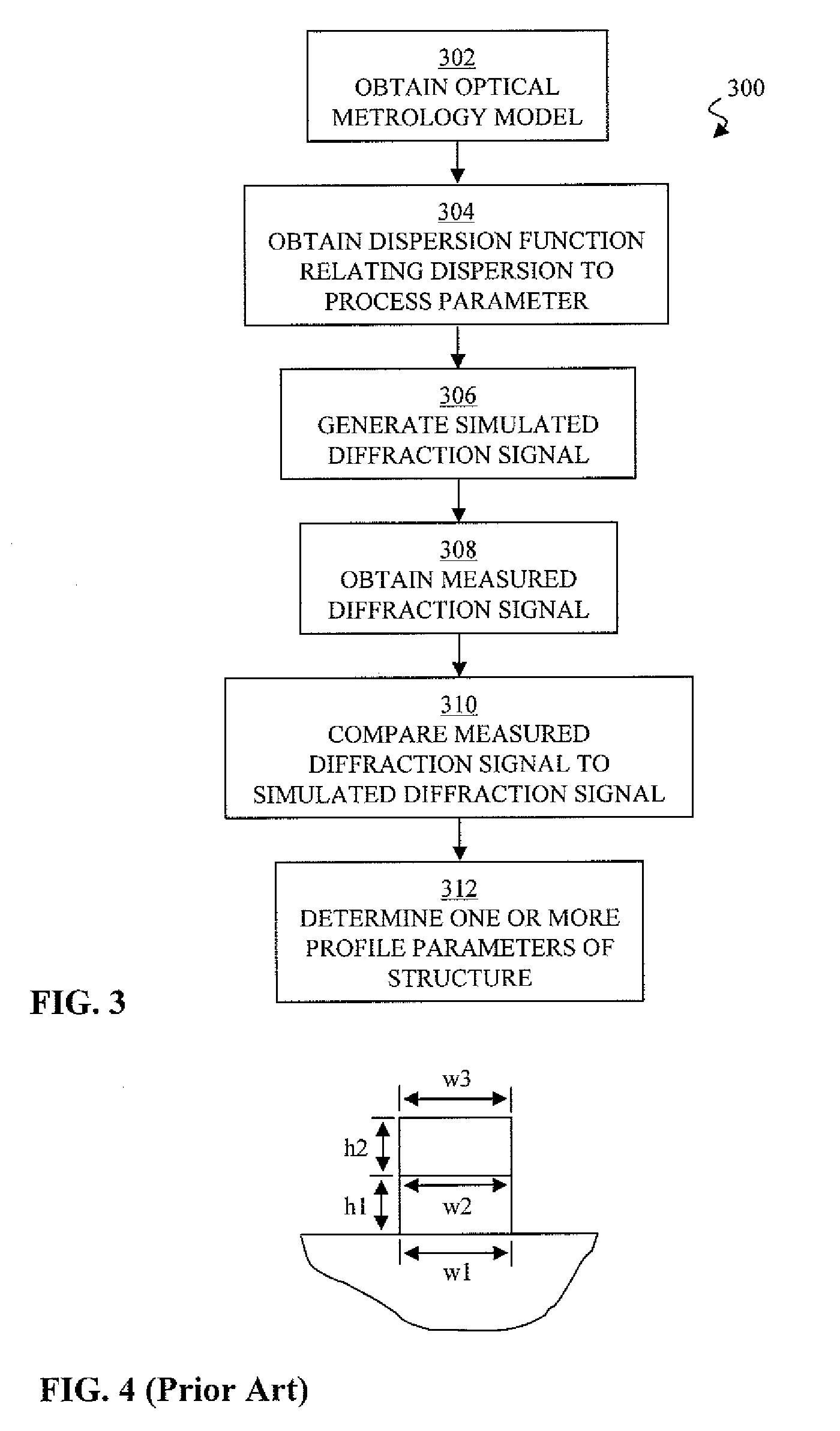
Automated process control of a fabrication tool using a dispersion function relating process parameter to dispersion
InactiveUS20090082993A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementRadiation measurementEngineeringOptical metrology
An optical metrology model for the structure is obtained. The optical metrology model comprising one or more profile parameters, one or more process parameters, and a dispersion. A dispersion function that relates the dispersion to at least one of the one or more process parameters is obtained. A simulated diffraction signal is generated using the optical metrology model and a value for the at least one of the process parameters and a value for the dispersion. The value for the dispersion is calculated using the value for the at least one of the process parameter and the dispersion function. A measured diffraction signal of the structure is obtained using an optical metrology tool. The measured diffraction signal is compared to the simulated diffraction signal to determine one or more profile parameters of the structure. The fabrication tool is controlled based on the determined one or more profile parameters of the structure.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method and apparatus for determining measurement frequency based on hardware age and usage
InactiveUS6469518B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceProcess engineeringEngineering
A processing line includes a processing tool, a measurement tool, and an automatic process controller. The processing tool is adapted to process articles. The measurement tool is adapted to measure a characteristic of selected articles at a measurement frequency. The automatic process controller is adapted to change the measurement frequency based on a usage characteristic of the processing tool. A method for monitoring a processing tool includes processing a plurality of articles in the processing tool; measuring a characteristic of selected articles at a measurement frequency; and changing the measurement frequency based on a usage characteristic of the processing tool.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
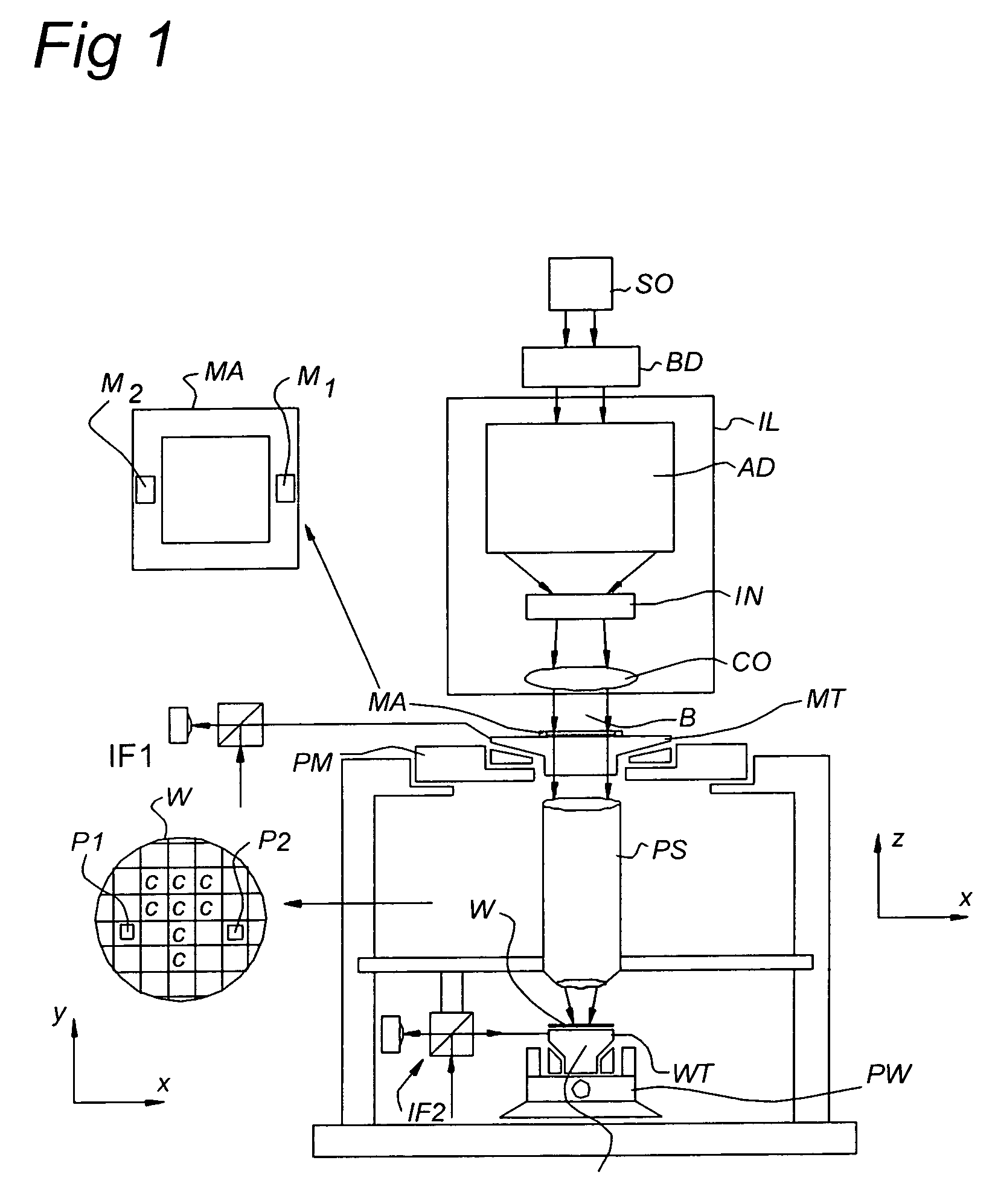
Method and system for automated process correction using model parameters, and lithographic apparatus using such method and system
InactiveUS7126669B2Shorten the timePhotomechanical treatmentPhotographic printingEngineeringModel parameters
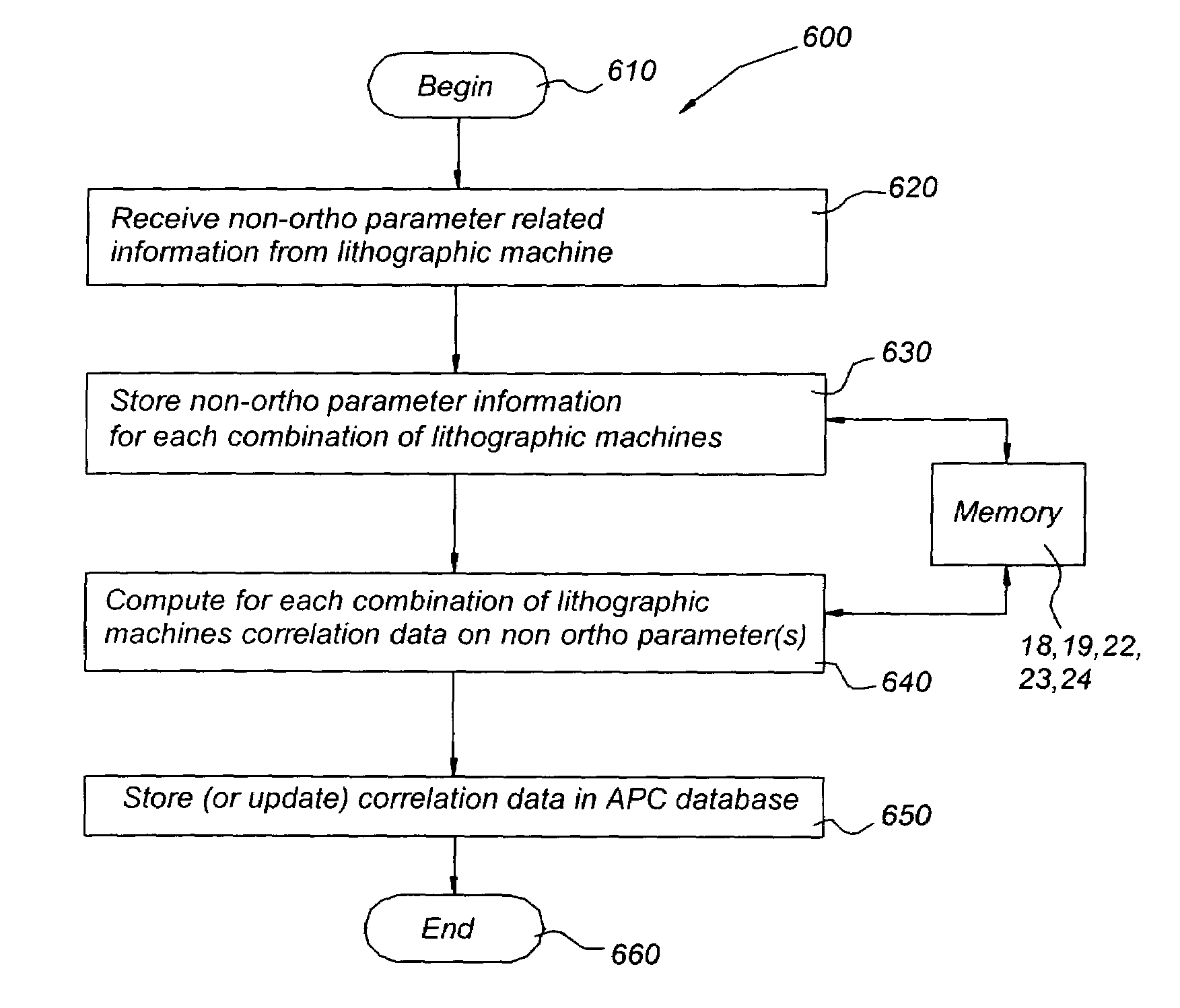
A method for aligning a substrate in a lithographic apparatus is presented. The substrate includes a plurality of alignment marks. The alignment marks have been defined by a second lithographic apparatus and are arranged to provide a substrate grid as a coordinate system that includes a first and a second direction, substantially perpendicular to the first direction. The method includes measuring a location and an orientation of the alignment marks to obtain alignment mark data; determining the substrate grid of the substrate from the alignment mark data by using a first substrate grid model with a first set of parameters; determining the substrate grid of the substrate from the alignment mark data by using a second substrate grid model with a second set of parameters, the second set of parameters including an ortho-scaling parameter in addition to the first set of parameters, and correcting machine-to-machine differences between the lithographic apparatus and the second lithographic apparatus with automated process control data based on the ortho-scaling parameter.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Automatic control bioreactor for breeding maggots and earthworms and culture method
InactiveCN101622972AReasonable handlingRealize automatic controlAnimal husbandryMaggotAutomatic control
The invention relates to an automatic control bioreactor for breeding maggots and earthworms and a solid culture method. By controlling the temperature and humidity of the reactor, the growth of the maggots and the earthworms can be effectively promoted, and the growth period is shortened. Meanwhile, at the maturation period of the maggots and the earthworms, animals are promoted to move to a collector through illumination control and temperature adjustment so as to realize effective separation and reduce separation cost. The bioreactor comprises a reactor bottom, a reactor light transmission window, a reactor top, a charging part, a maggot and earthworm collector, a forced ventilation device, an automatic process controlling device and a heat exchanger. The method of the invention can realize automatic breeding of the maggots and the earthworms, and is applied to scale zooming; and the reactor has the characteristics of simple structure, convenient operation, low operating cost and environmental protection.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Use of overlay diagnostics for enhanced automatic process control
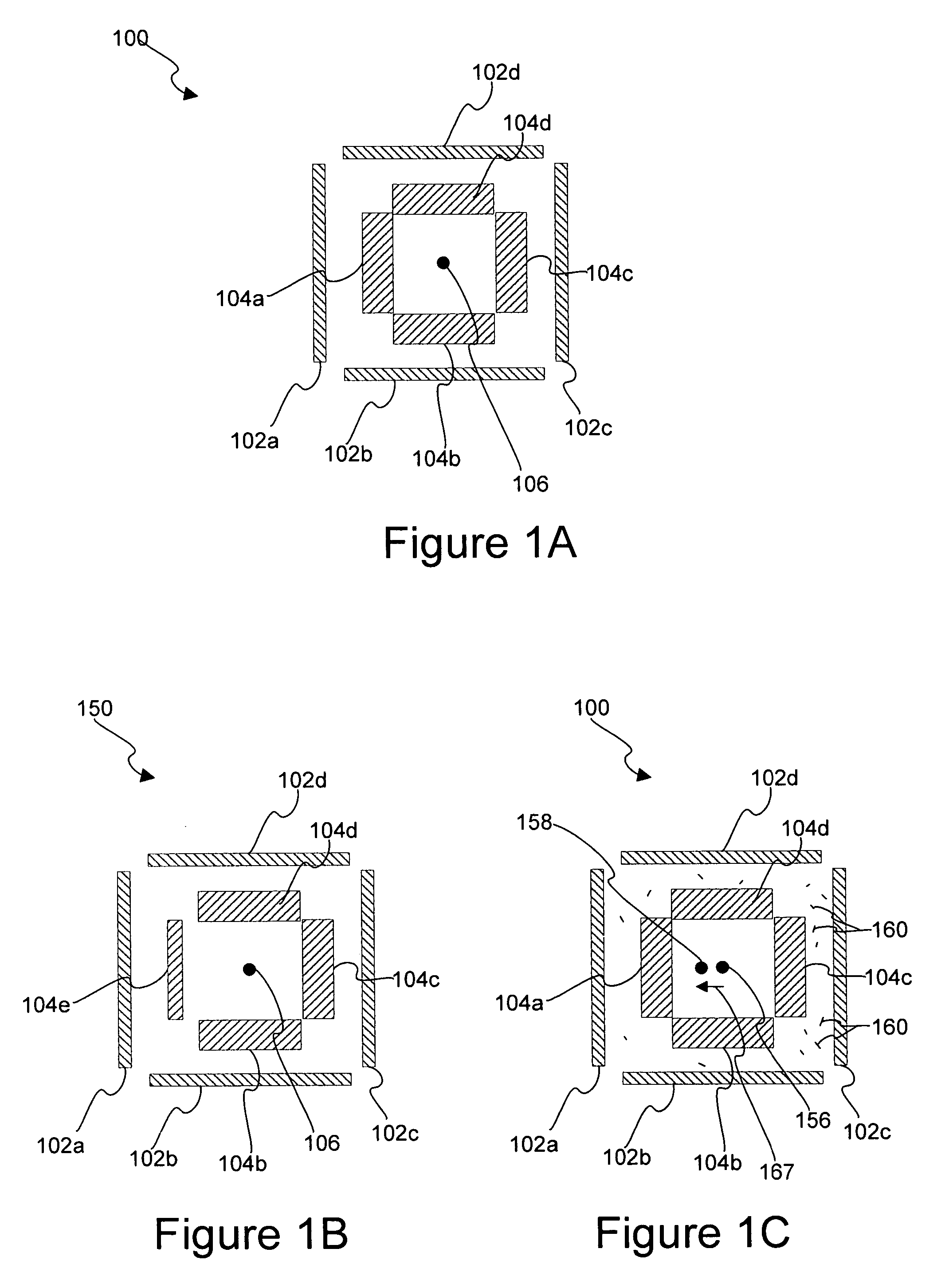
InactiveUS20060280357A1Character and pattern recognitionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOverlaySpatial noise
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for obtaining and analyzing various unique metrics or “target diagnostics” from one or more semiconductor overlay targets. In one embodiment, an overlay target is measured to obtain one or both of two specific types of target diagnostic information, systematic error metrics and / or random noise metrics. The systematic error metrics generally quantify asymmetries of the overlay target, while the random noise metrics quantify and / or qualify the spatial noise that is proximate to or associated with the overlay target.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
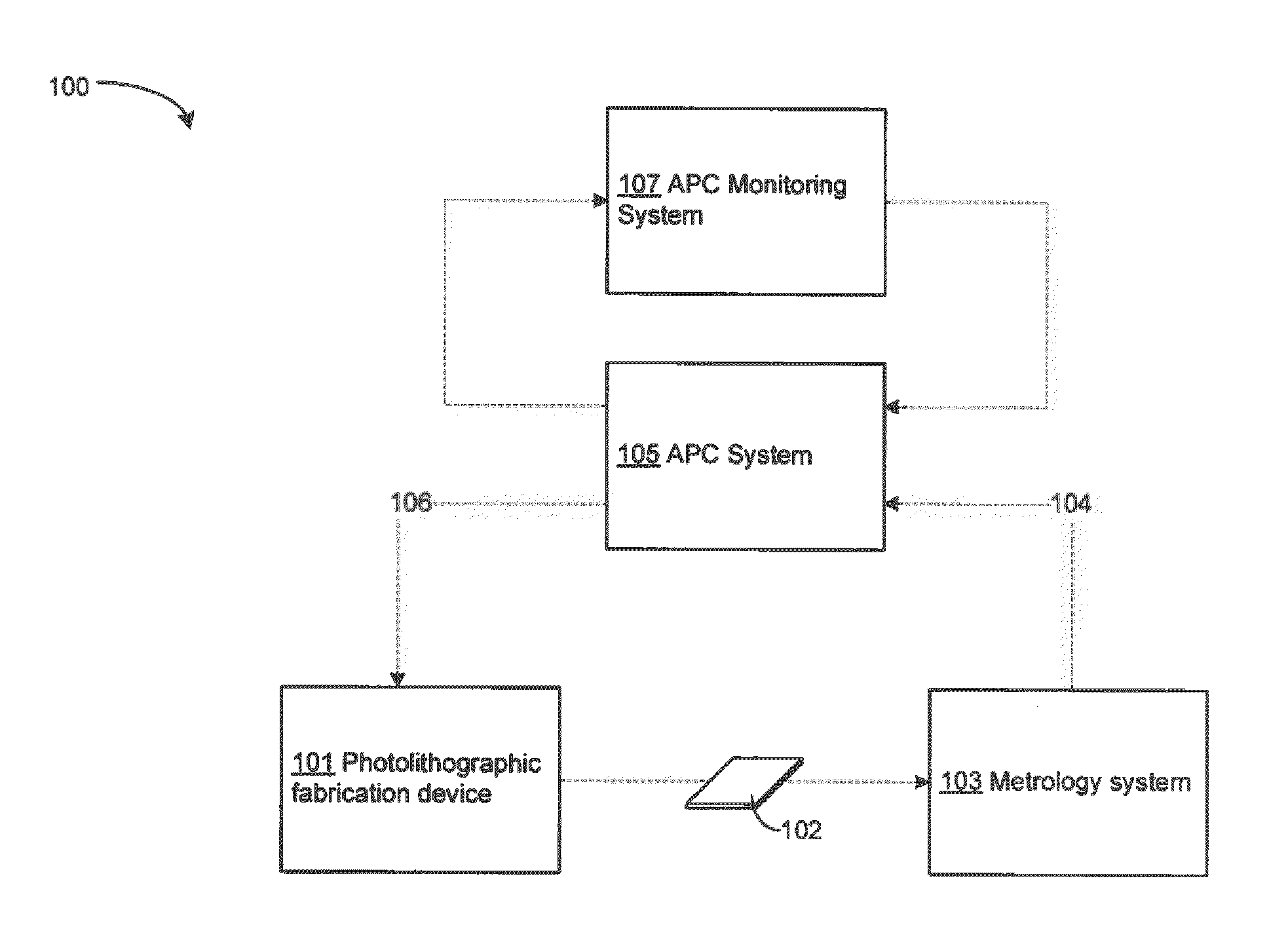
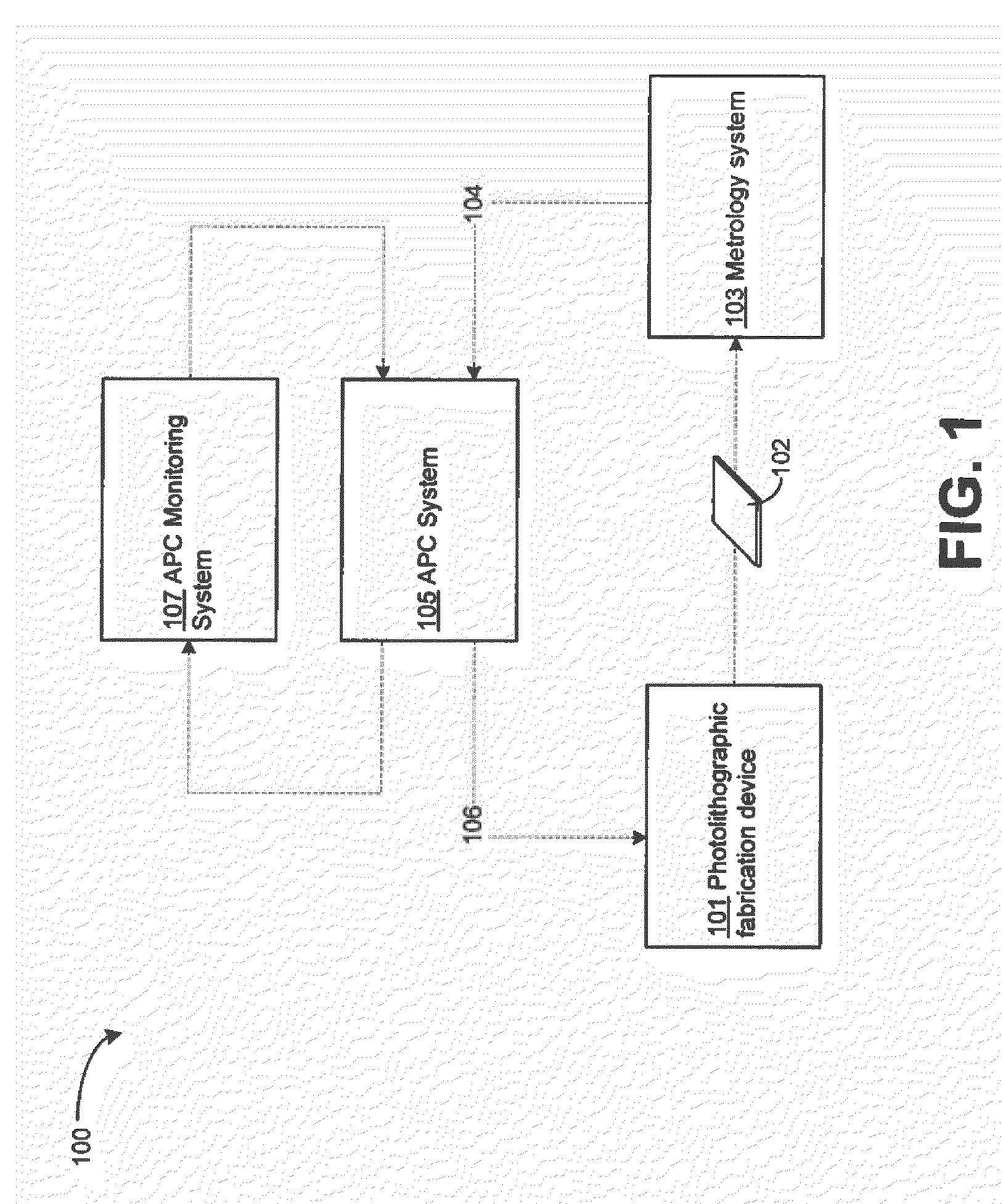
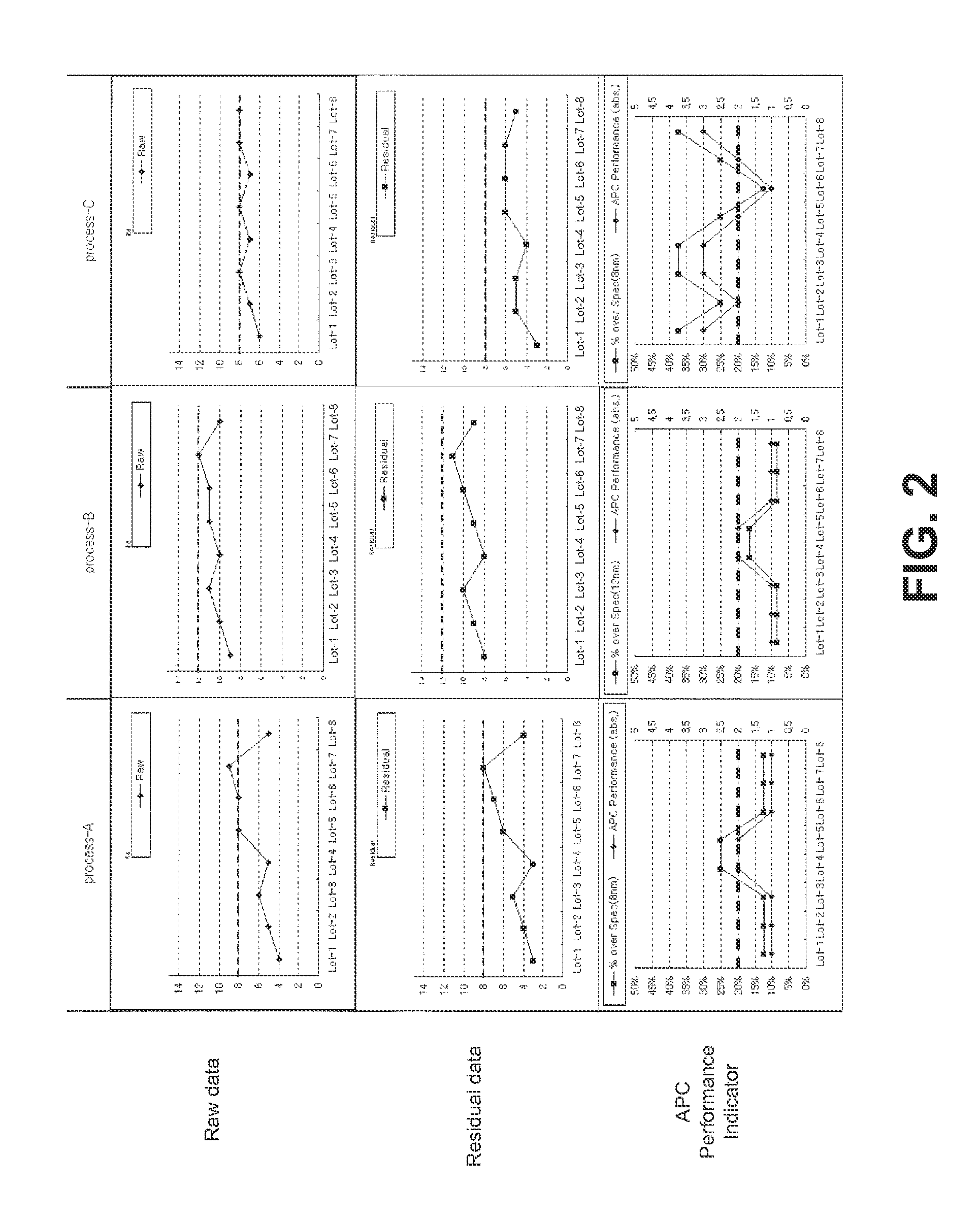
Advanced process control optimization
ActiveUS20120022679A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotomechanical apparatusDevice materialProcess engineering
A method for automatic process control (APC) performance monitoring may include, but is not limited to: computing one or more APC performance indicators for one or more production lots of semiconductor devices; and displaying a mapping of the one or more APC performance indicators to the one or more production lots of semiconductor devices.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
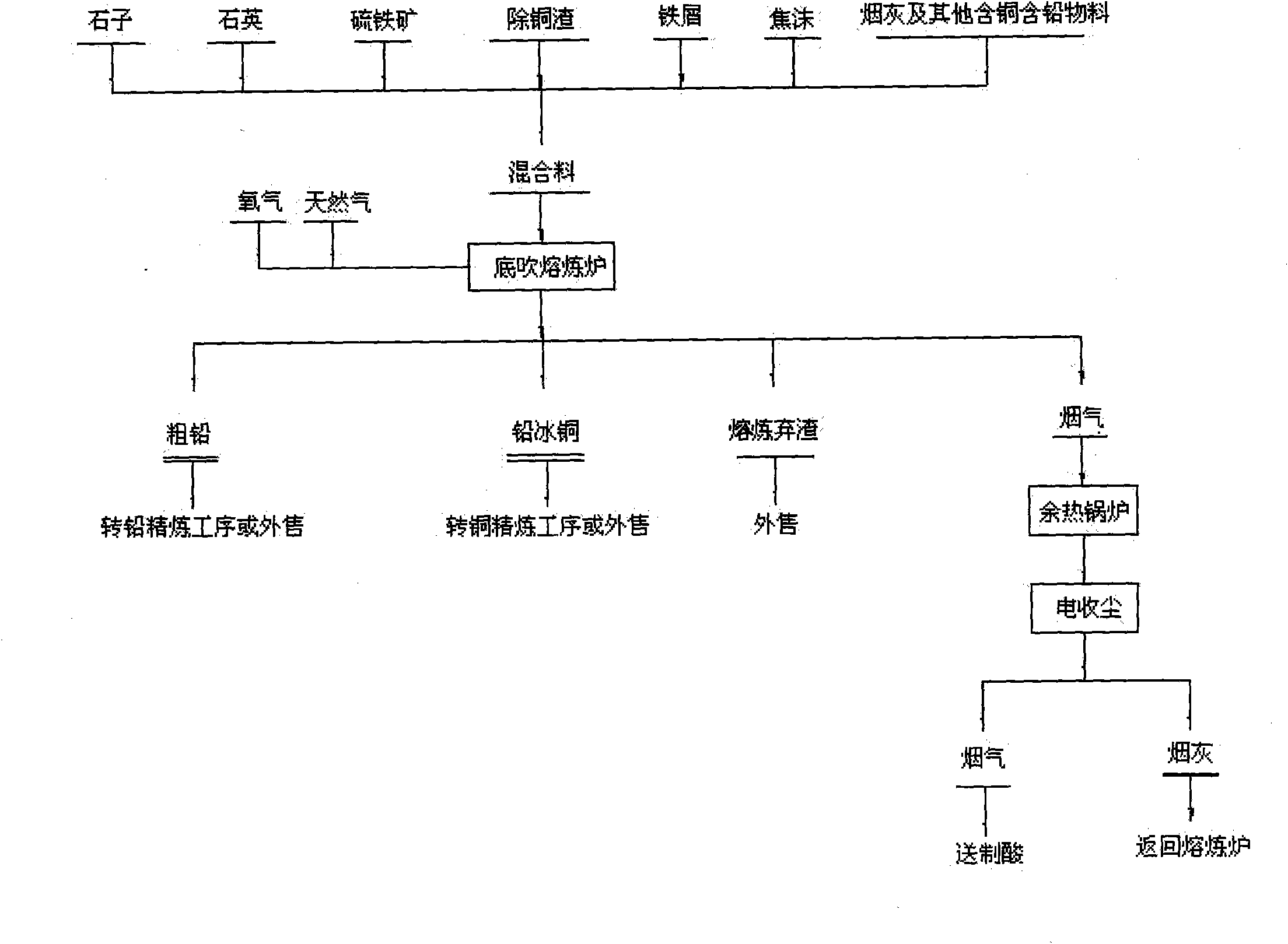
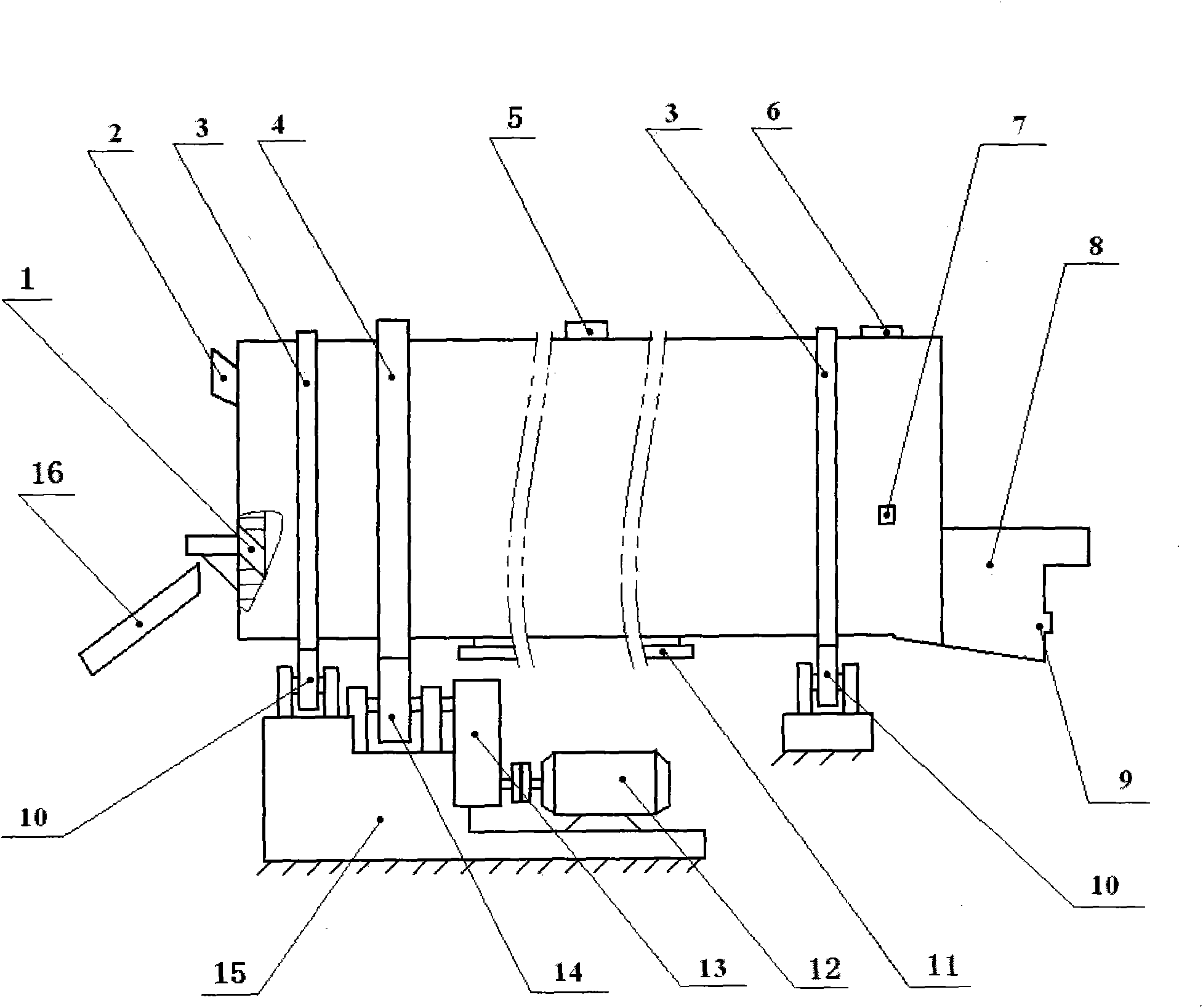
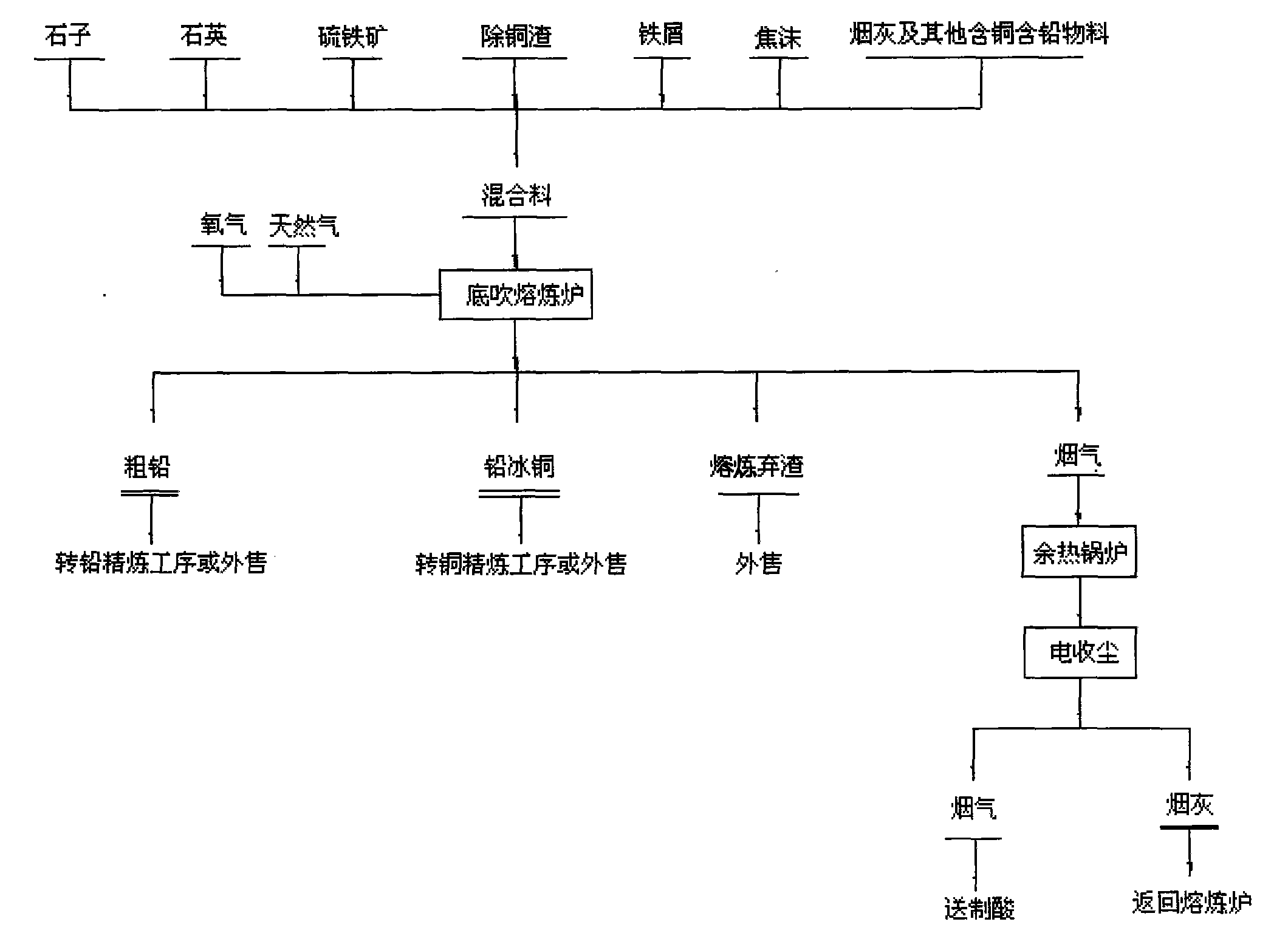
Process for removing copper slag and producing crude lead and lead copper matte by adopting melting treatment in bottom-blowing melting bath and device thereof
ActiveCN101880774AImprove handling productivityAvoid bad luckProcess efficiency improvementCalcium silicateMelting tank
The invention relates to a process for removing copper slag and producing crude lead and lead copper matte by adopting melting treatment in a bottom-blowing melting bath and a device thereof. The process is characterized in that a bottom-blowing melting furnace for melting is utilized to remove copper slag, produce products, such as crude lead, lead copper matte, and the like, produce reasonable waste slag and manufacture iron calcium silicate slag in the melting process so that the furnace slag reaching the waste slag requirement is used as a raw material of a building material plant, and the lead copper matte can be used for producing products of crude copper, and the like. The process has high heat utilization rate, low energy consumption, high production efficiency, long service life, low product cost, good melting environmental protection and easy automatic process control.
Owner:济源豫光有色冶金设计研究院有限公司
Apparatus and method for providing snapshot action thermal infrared imaging within automated process control article inspection applications
ActiveUS8097857B2Low-cost and on-line surfaceRobust structural integrity inspection capabilityTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryElectricityMachine vision
This application relates to an apparatus and method for providing snapshot action thermal infrared imaging within automated process control article inspection applications. More specifically, it pertains to the use of snapshot mode lead salt area-array imaging sensors (20) as the imaging front-end in high-speed machine vision inspection systems (12). the relatively low-cost, good measurement sensitivity at temperatures consistent with thereto-electric cooling means, and the ability to be operated in snap-shot mode enables lead salt-based image acquisition sensors (20) to be used in a variety of automated process control and article inspection applications.
Owner:PRESSCO TECH INC
Method of automatic debris separation
InactiveUS6883668B1Easy to handleEasy to process directlyGas current separationPlastic recyclingFiberAutomatic process control
The invention is an automatic debris separation process for effecting air separation of fragmented materials, such as size-reduced fiber feedstocks derived from textile wastes. The process uses high-velocity air within an elutriation assembly to efficiently remove ferrous and non-ferrous metal debris from recyclable polymer fibers. In particular, the process may employ automatic process control strategies to vary airflow within the elutriation assembly in process-controlled response to measured metal contamination, thereby ensuring that post-separation metal contamination is maintained at or below an upper contamination limit.
Owner:WELLMAN PLASTICS RECYCLING
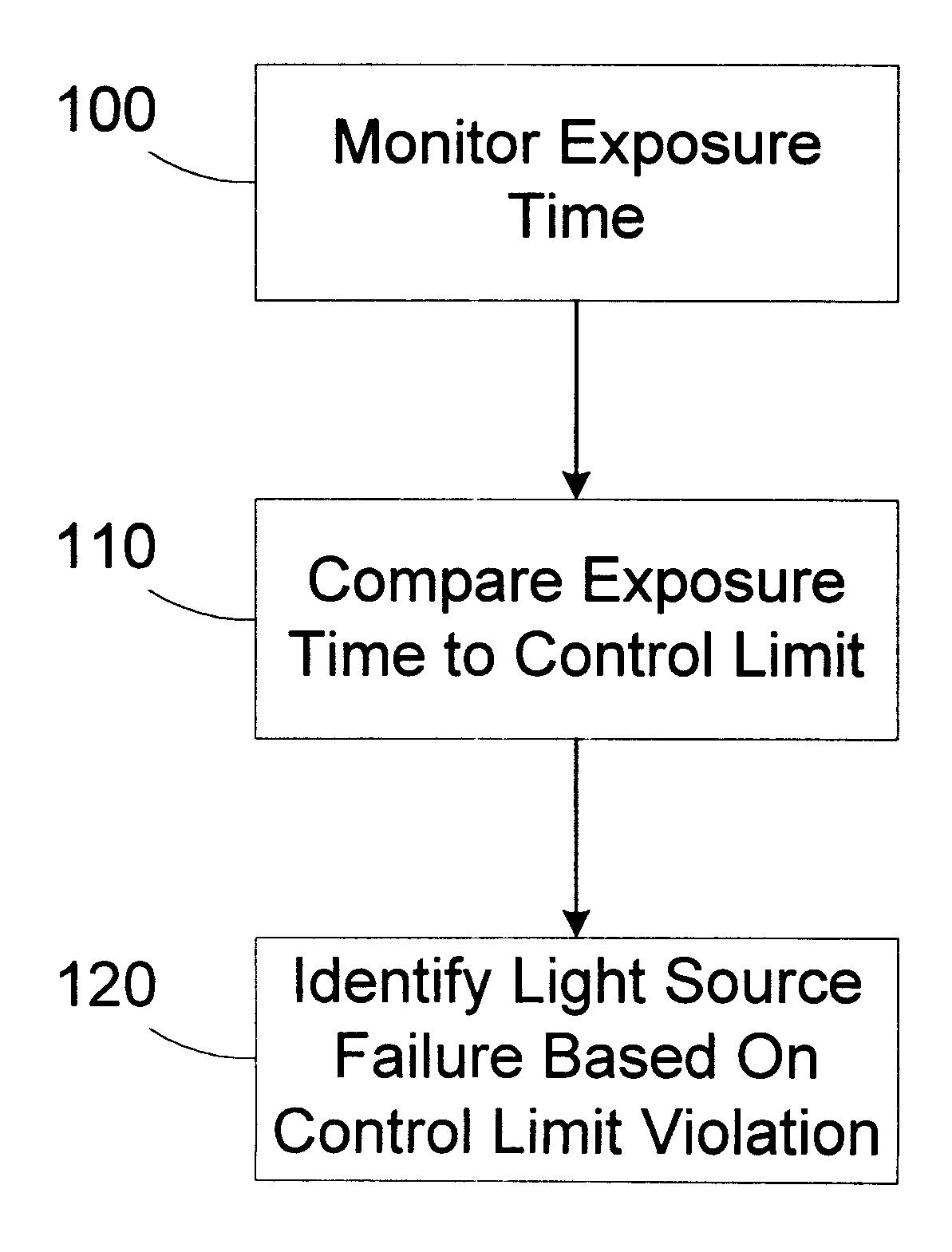
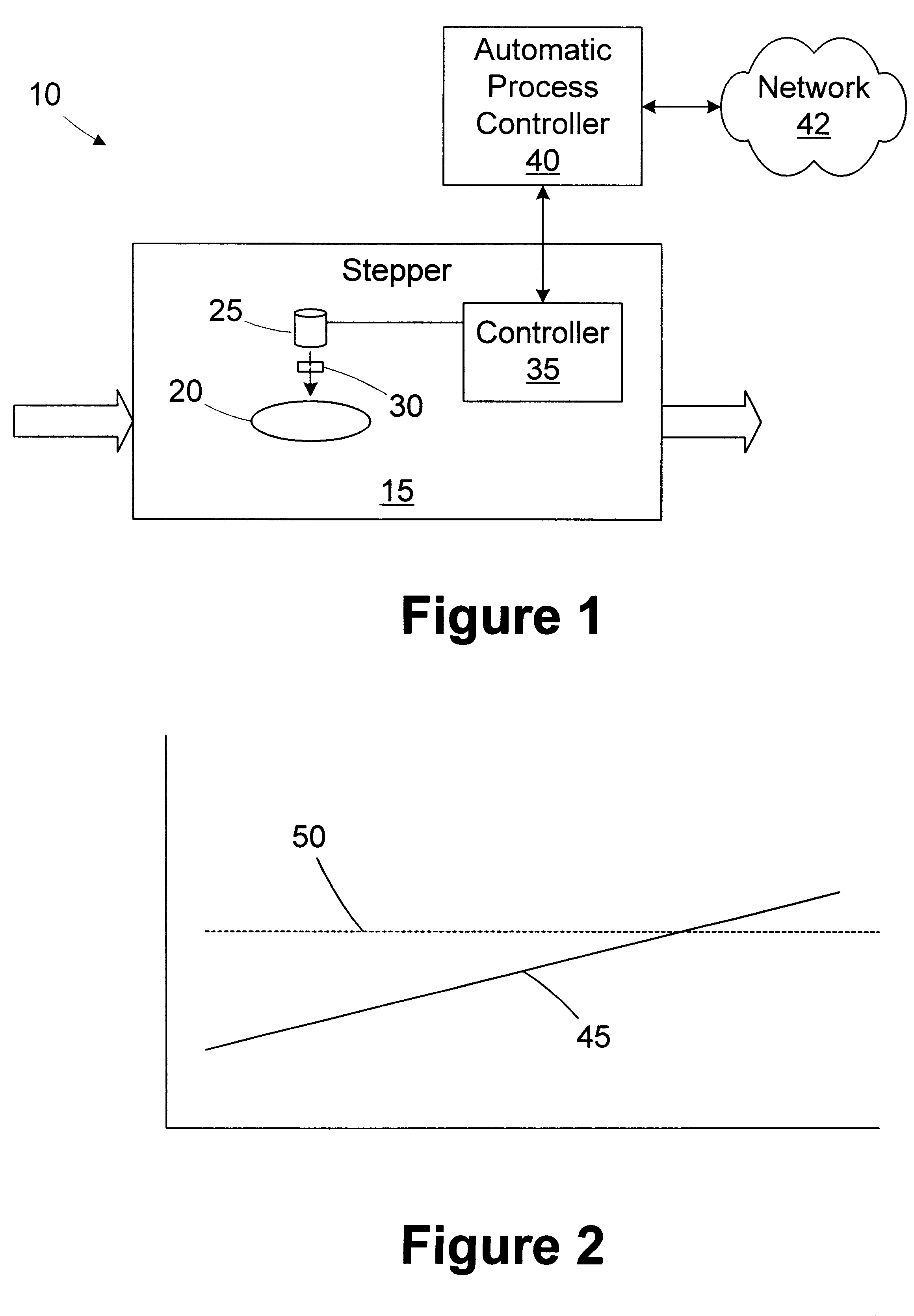
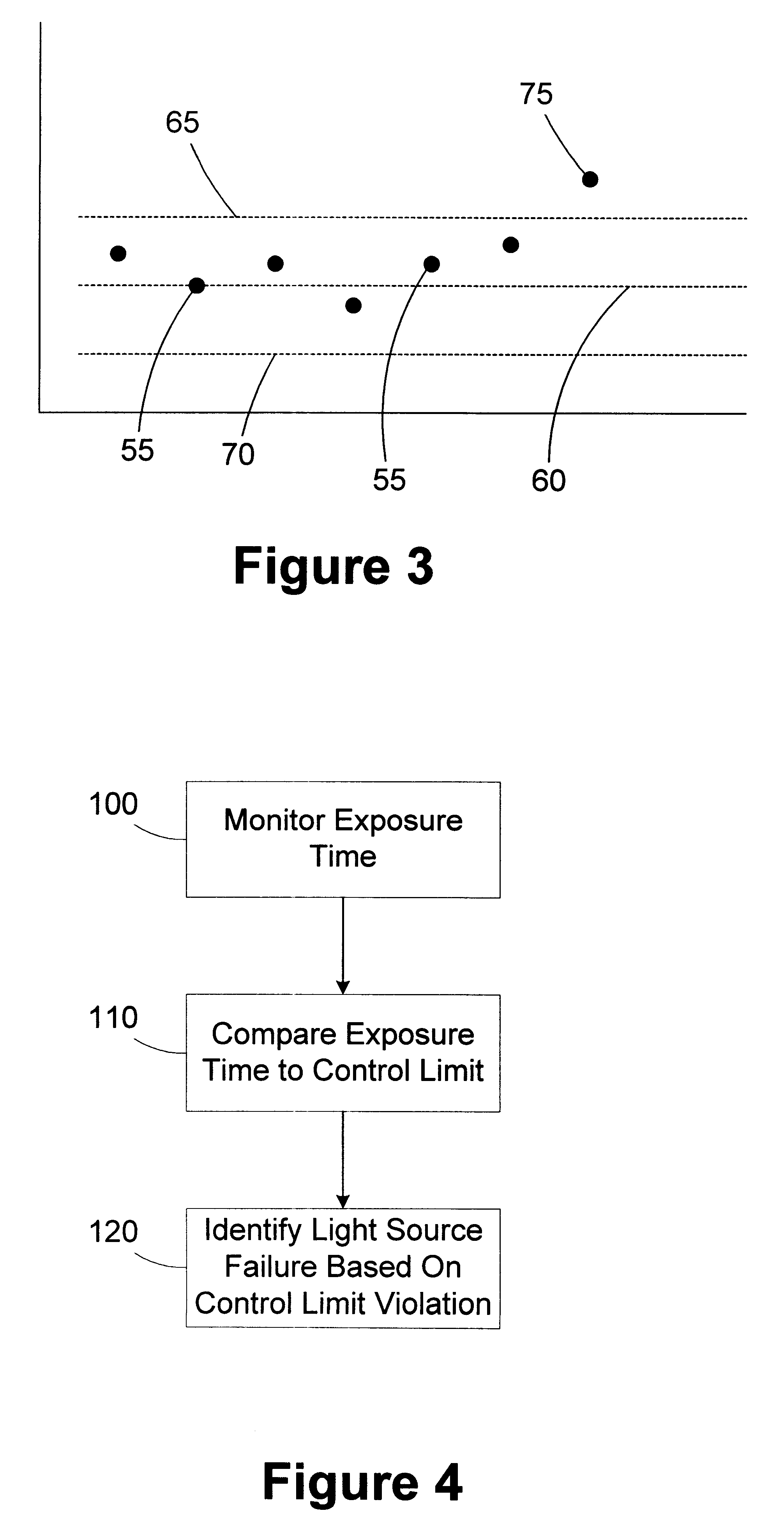
Stepper with exposure time monitor
InactiveUS6266132B1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringControl limits
A method for detecting a degraded light source is provided. An exposure time associated with the light source is monitored. The exposure time is compared to at least one control limit. A degraded condition is identified based on the exposure time violating the control limit. A processing tool includes a stepper and an automatic process controller. The stepper has a light source and is adapted to illuminate a wafer for an exposure time. The automatic process controller is adapted to monitor the exposure time, compare the exposure time to at least one control limit, and identify a degraded condition based on the exposure time violating the control limit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com