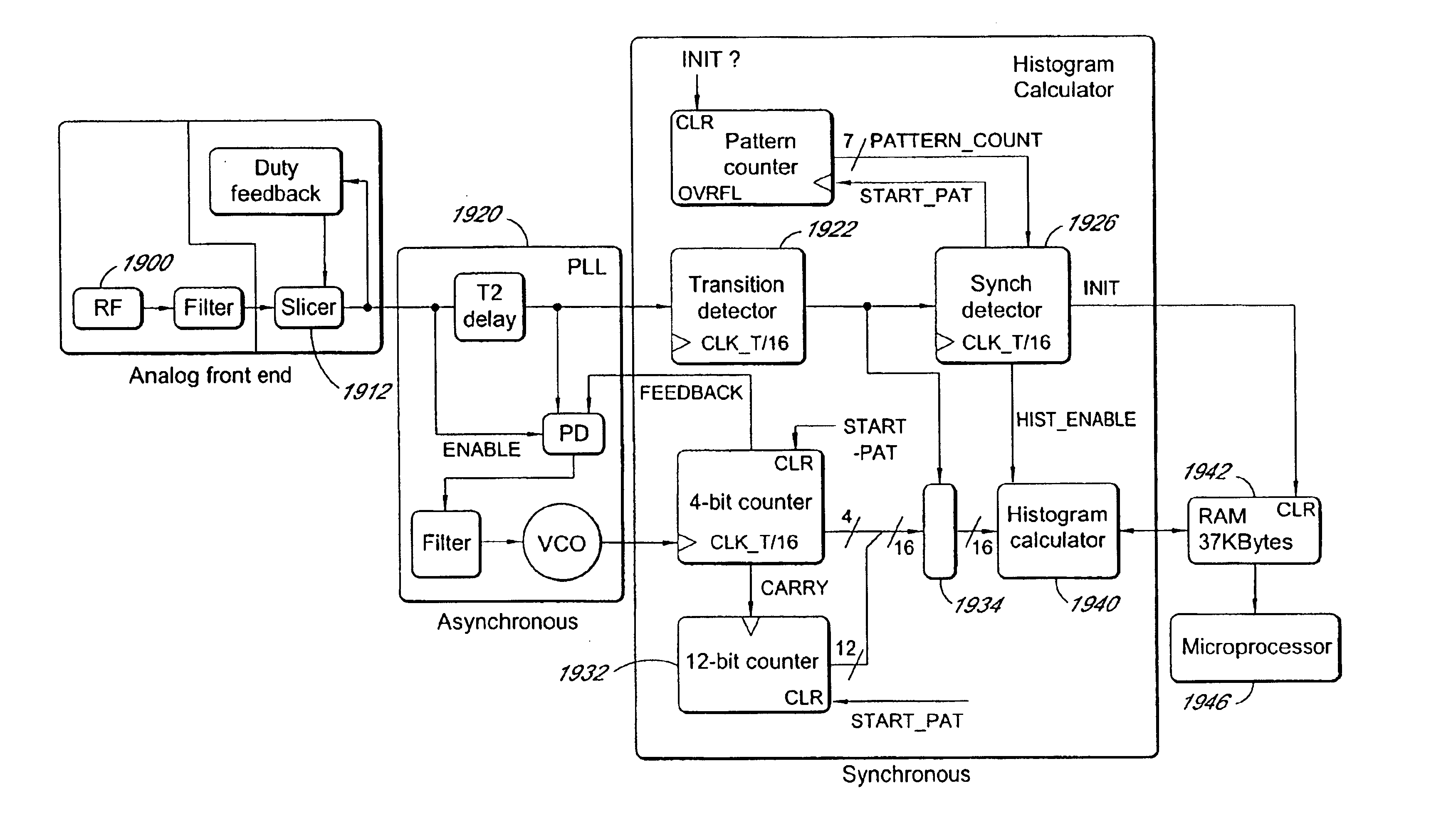
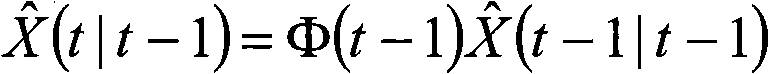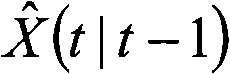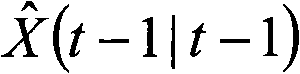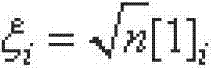Patents
Literature
580 results about "Systematic error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Systematic errors are biases in measurement which lead to the situation where the mean of many separate measurements differs significantly from the actual value of the measured attribute. All measurements are prone to systematic errors, often of several different types. Sources of systematic error may be imperfect calibration of measurement instruments, changes in the environment which interfere with the measurement process and sometimes imperfect methods of observation can be either zero error or percentage error. For example, consider an experimenter taking a reading of the time period of a pendulum swinging past a fiducial mark: If their stop-watch or timer starts with 1 second on the clock then all of their results will be off by 1 second. If the experimenter repeats this experiment twenty times, then there will be a percentage error in the calculated average of their results; the final result will be slightly larger than the true period. Distance measured by radar will be systematically overestimated if the slight slowing down of the waves in air is not accounted for.
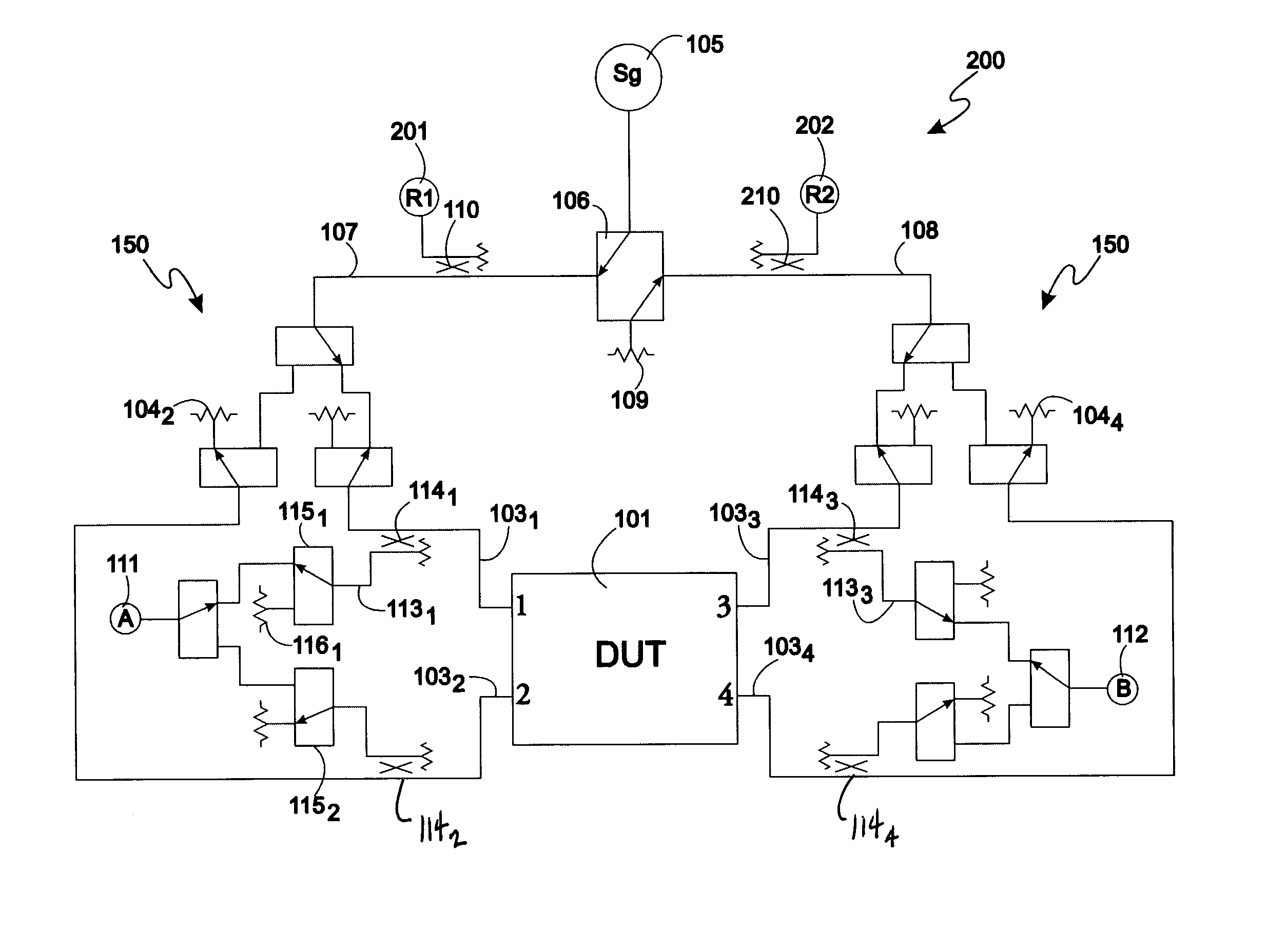
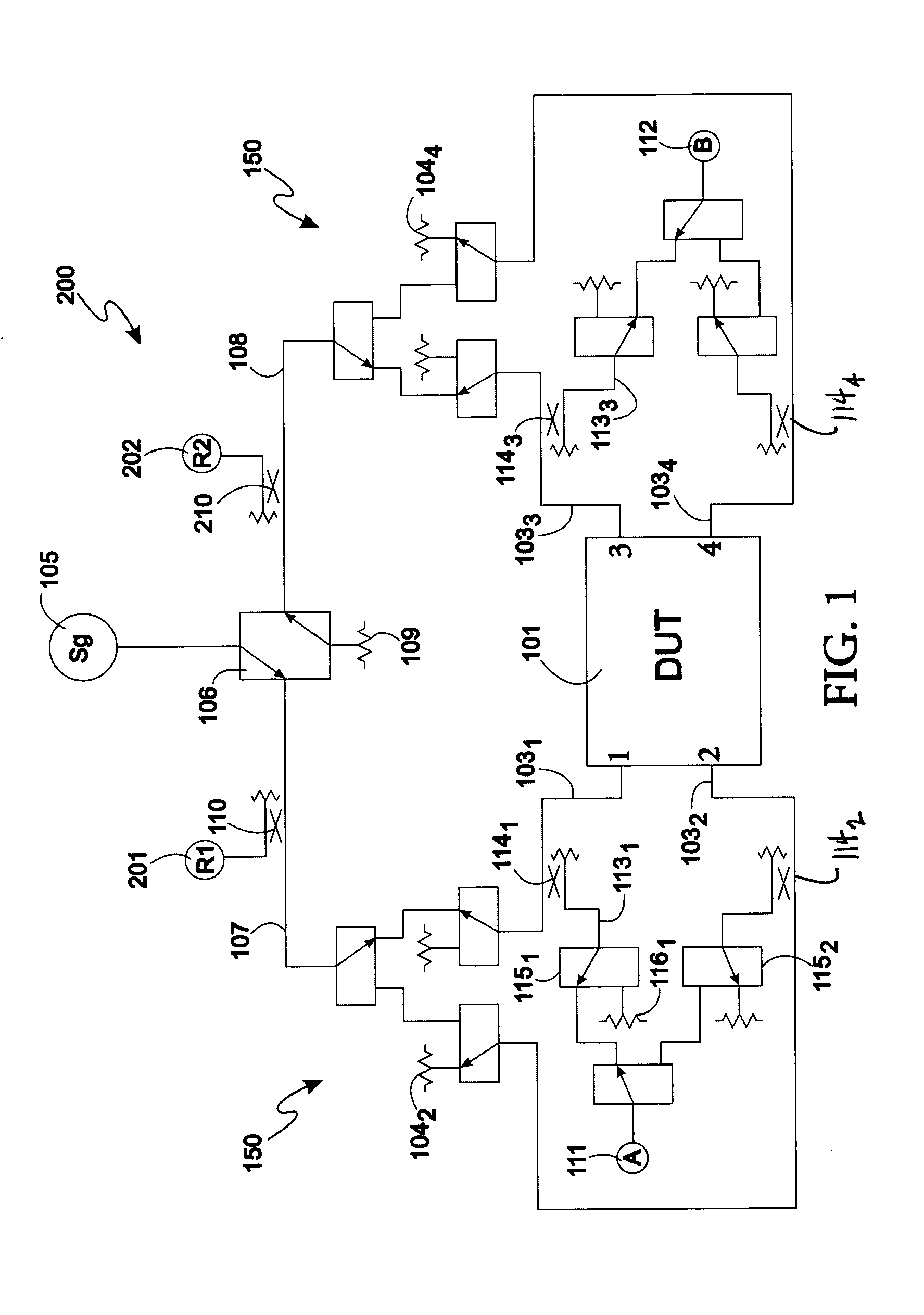
Method and apparatus for calibrating a test system for measuring a device under test
InactiveUS20120109566A1High precisionResistance/reactance/impedenceSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainImpulse response
A calibration method for a two-port VNA includes presenting a high reflection calibration standard and measuring reflection data for each of the two ports, calculating a location of the high reflection calibration standard at each of the two ports, presenting a load calibration standard and measuring the reflection characteristic for each of the two ports to provide load data, converting the load data to the time domain to provide time domain impulse response load data, and gating the time domain impulse response load data based on the locations of the high reflection calibration standard at each of two ports. The method further includes reconstructing frequency domain load data from the gated time domain data, connecting the two ports together and determining forward and reverse transmission characteristics, and calculating systematic error coefficients for the VNA based on the reconstructed frequency domain data and the forward and reverse transmission characteristics.
Owner:ATE SYST
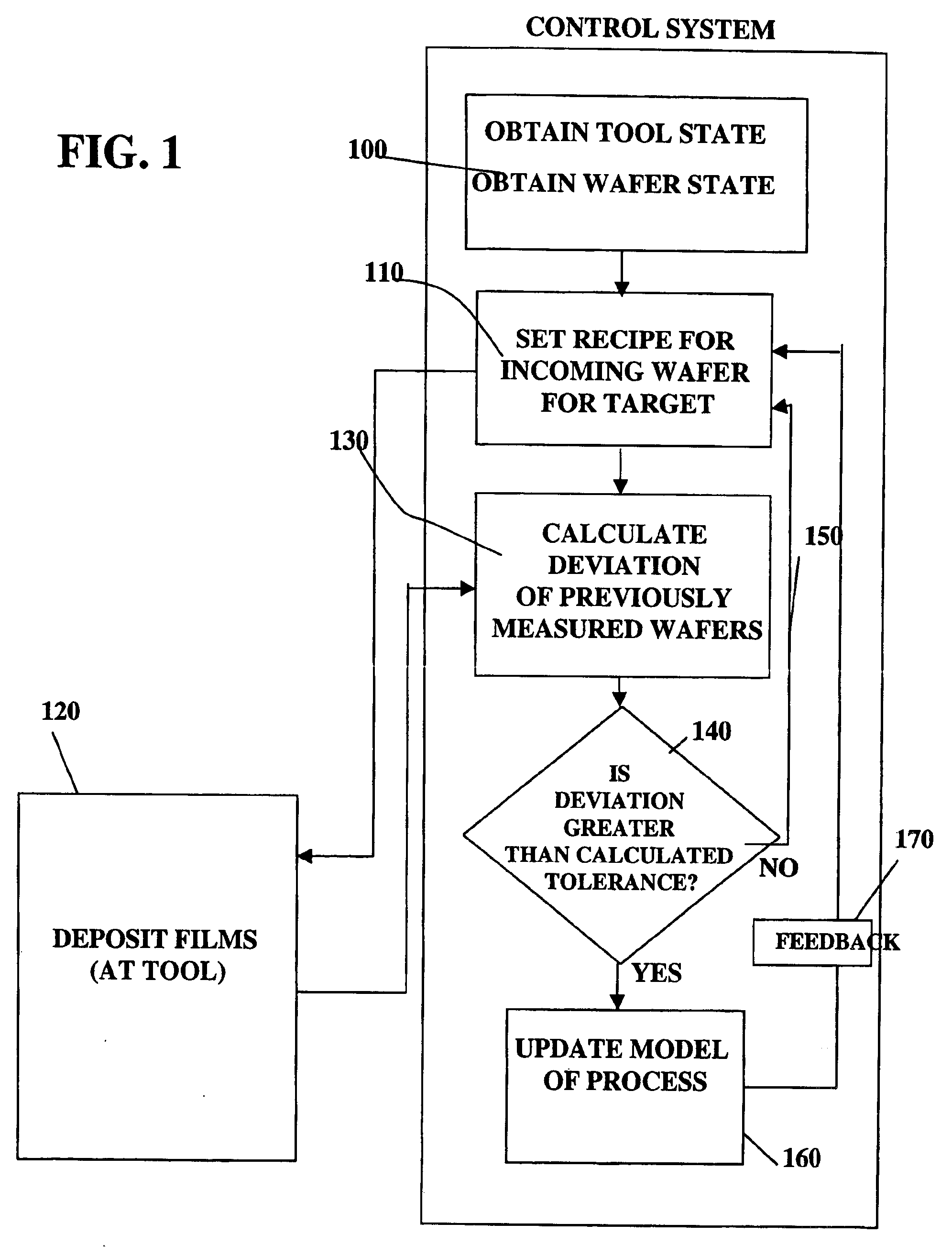
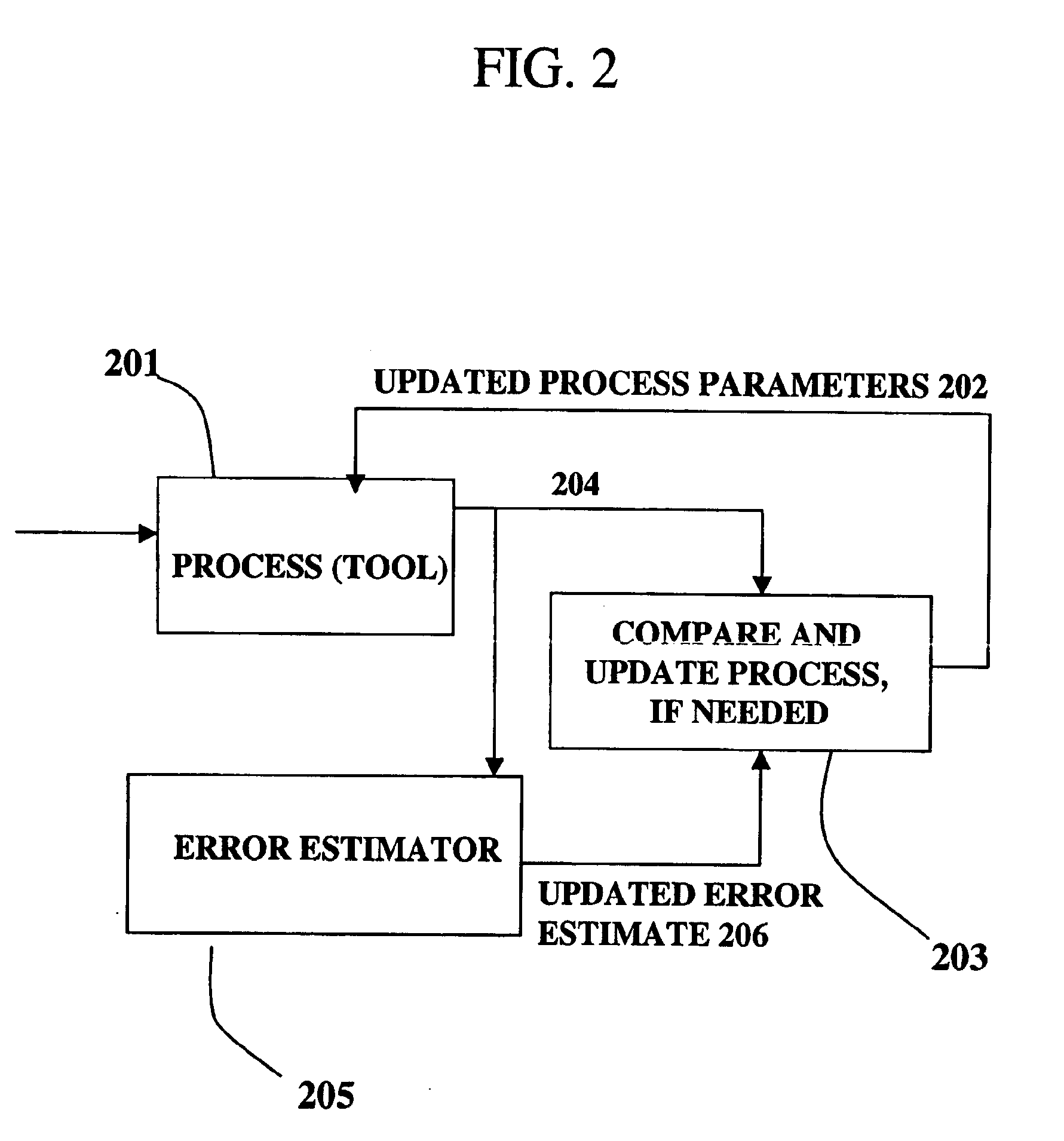
Use of overlay diagnostics for enhanced automatic process control
ActiveUS6928628B2Easy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutomatic controlInternet privacy
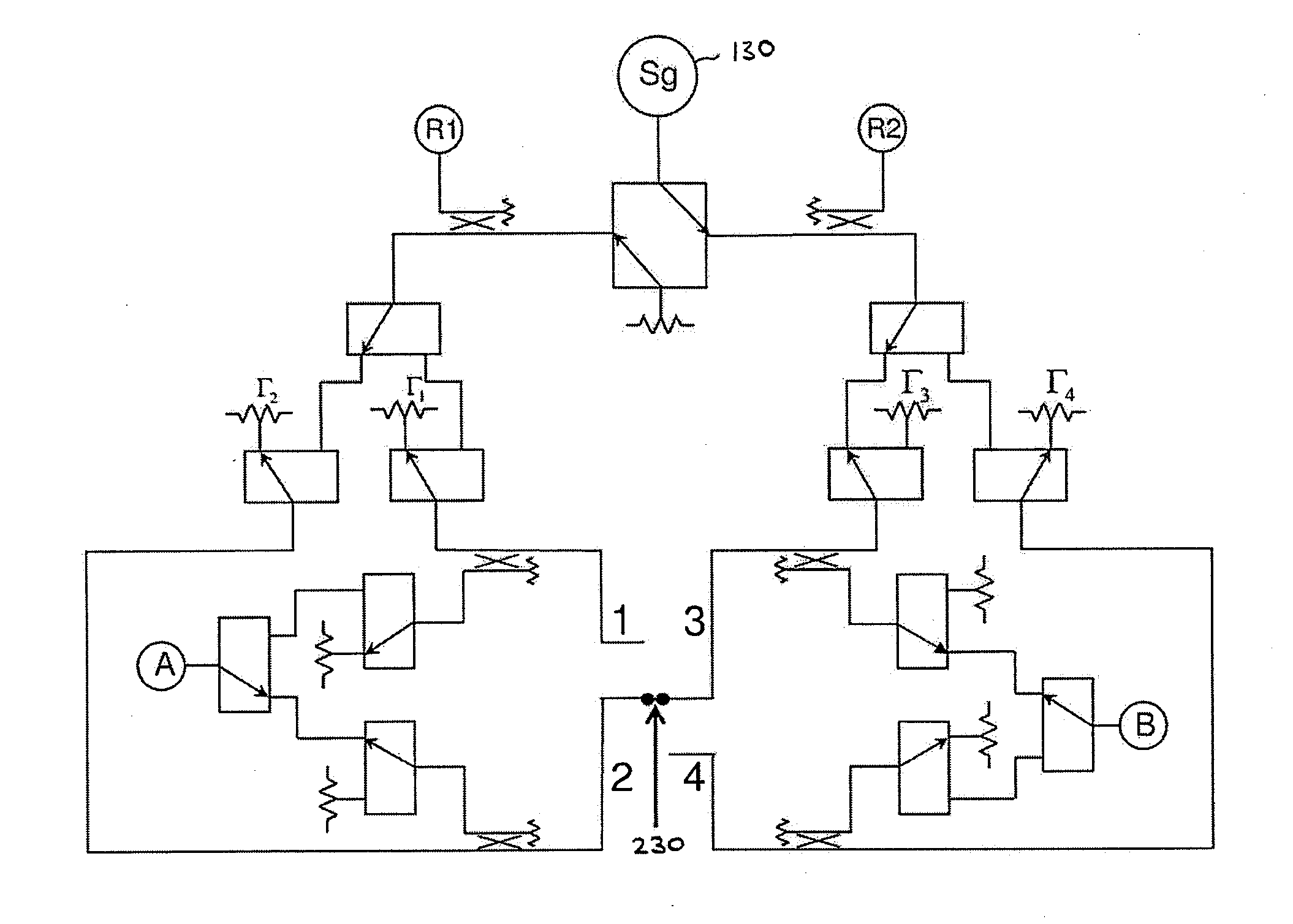
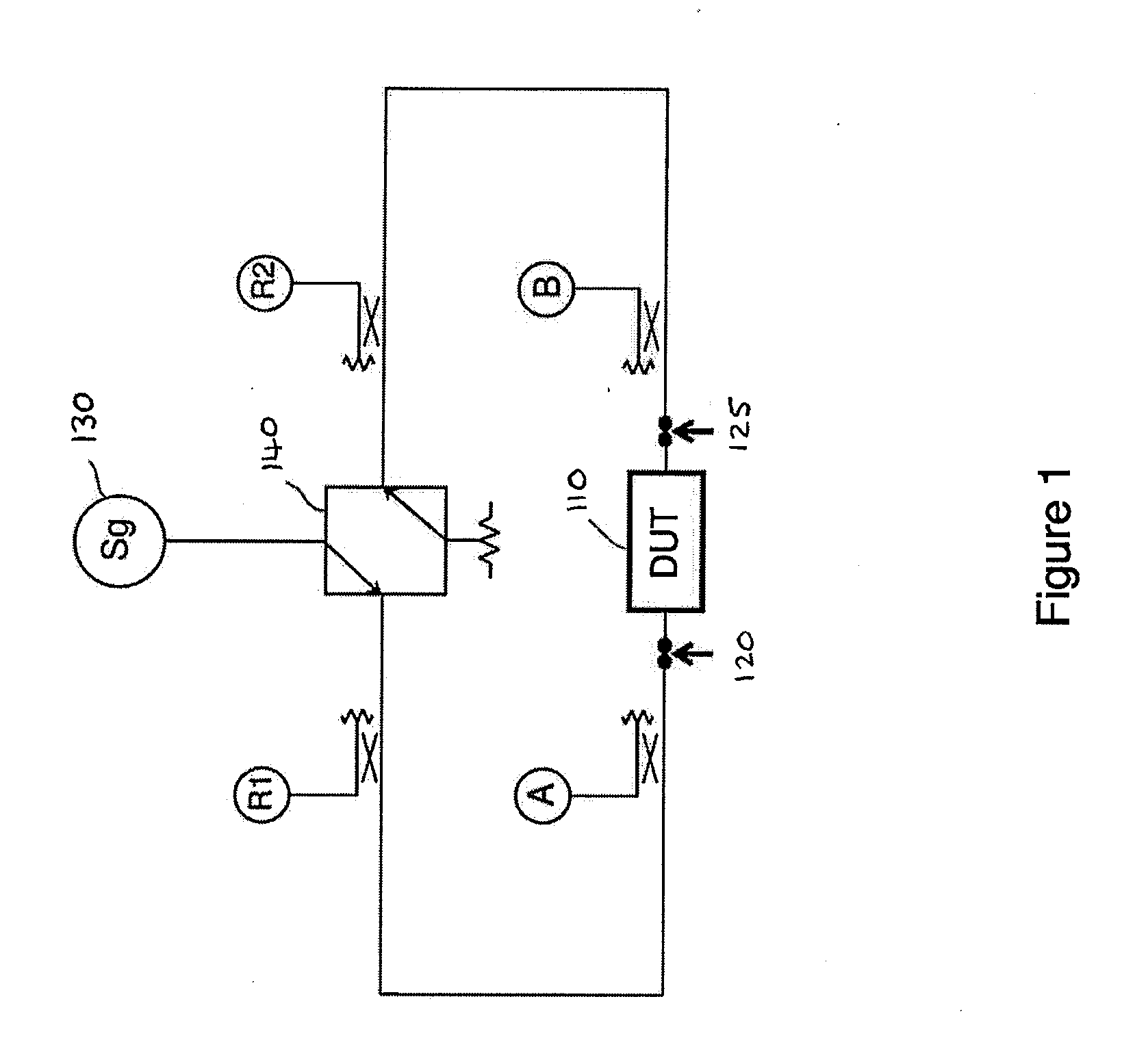
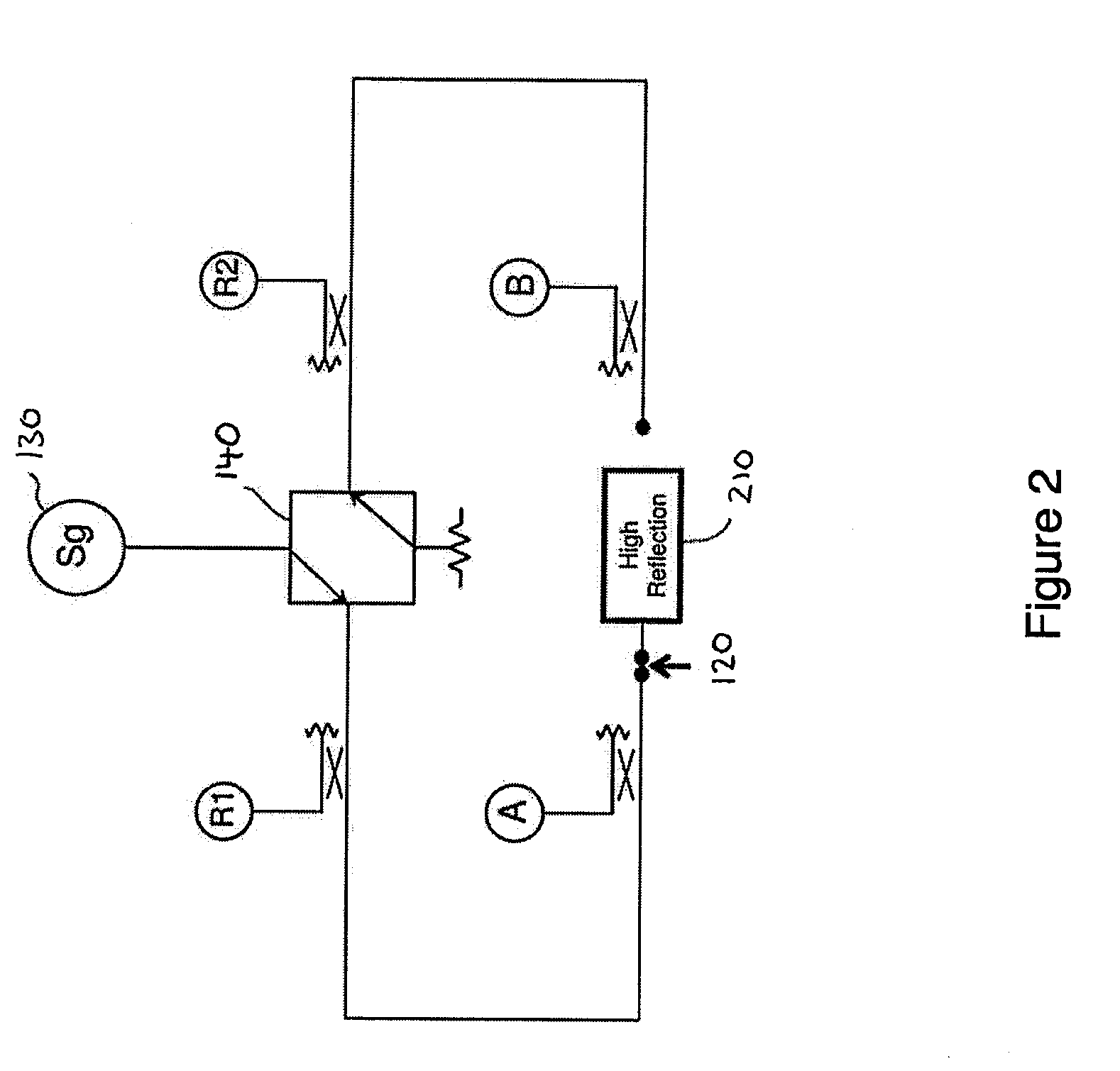
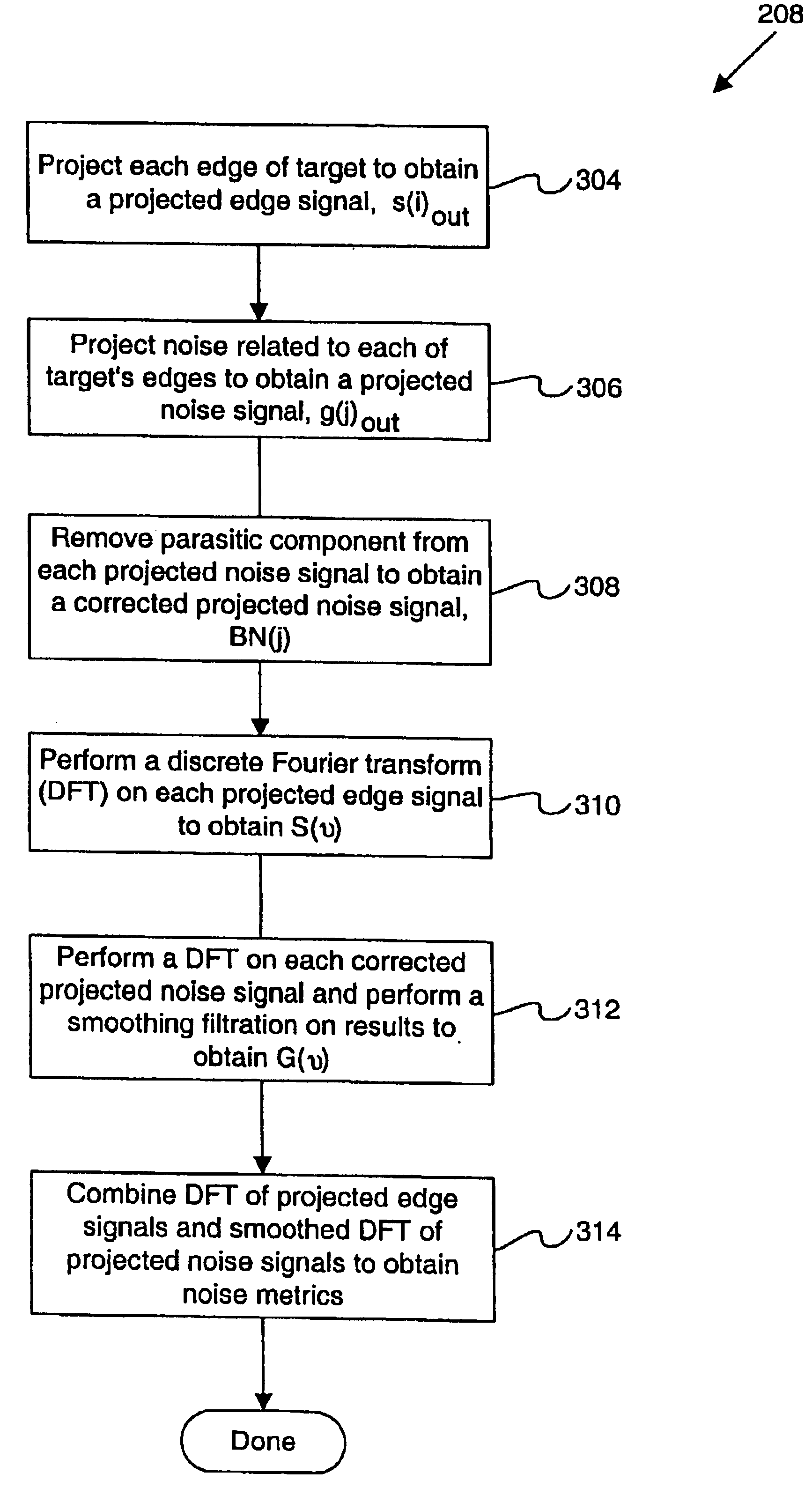
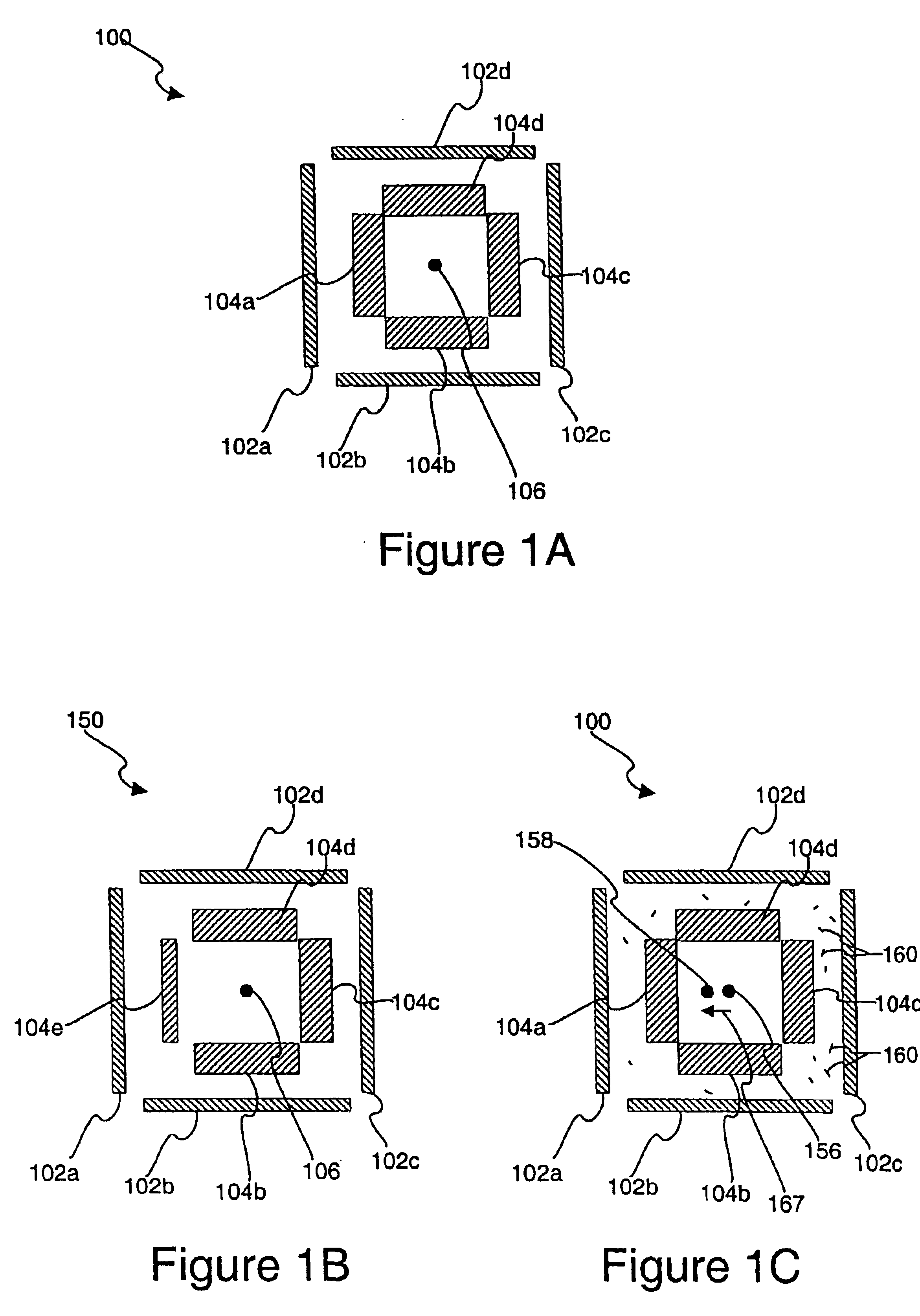
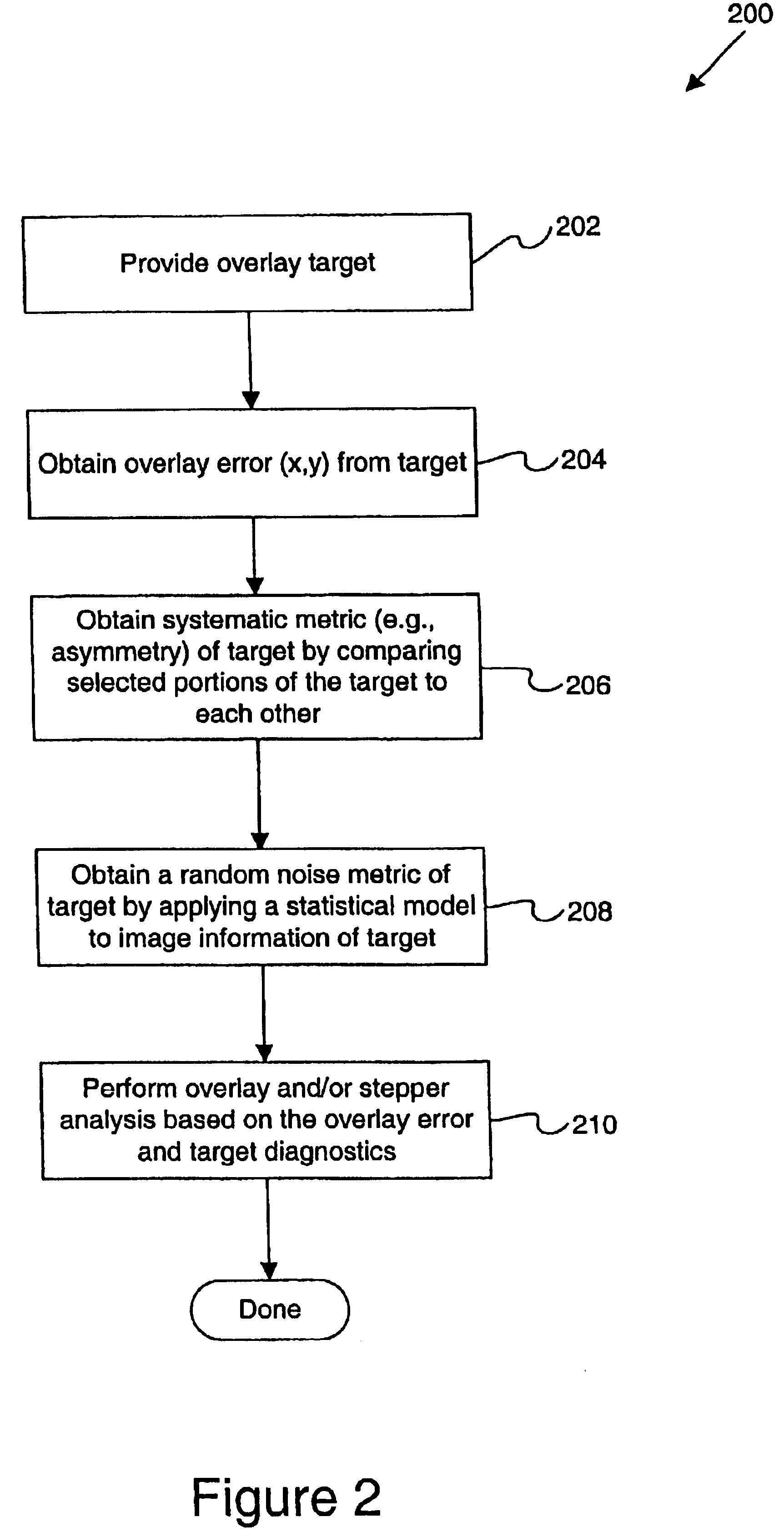
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for analyzing the quality of overlay targets. In one embodiment, a method of extracting data from an overlay target is disclosed. Initially, image information or one or more intensity signals of the overlay target are provided. An overlay error is obtained from the overlay target by analyzing the image information or the intensity signal(s) of the overlay target. A systematic error metric is also obtained from the overlay target by analyzing the image information or the intensity signal(s) of the overlay target. For example, the systematic error may indicate an asymmetry metric for one or more portions of the overlay target. A noise metric is further obtained from the overlay target by applying a statistical model to the image information or the intensity signal(s) of the overlay target. Noise metric characterizes noise, such as a grainy background, associated with the overlay target. In other embodiments, an overlay and / or stepper analysis procedure is then performed based on the systematic error metric and / or the noise metric, as well as the overlay data.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
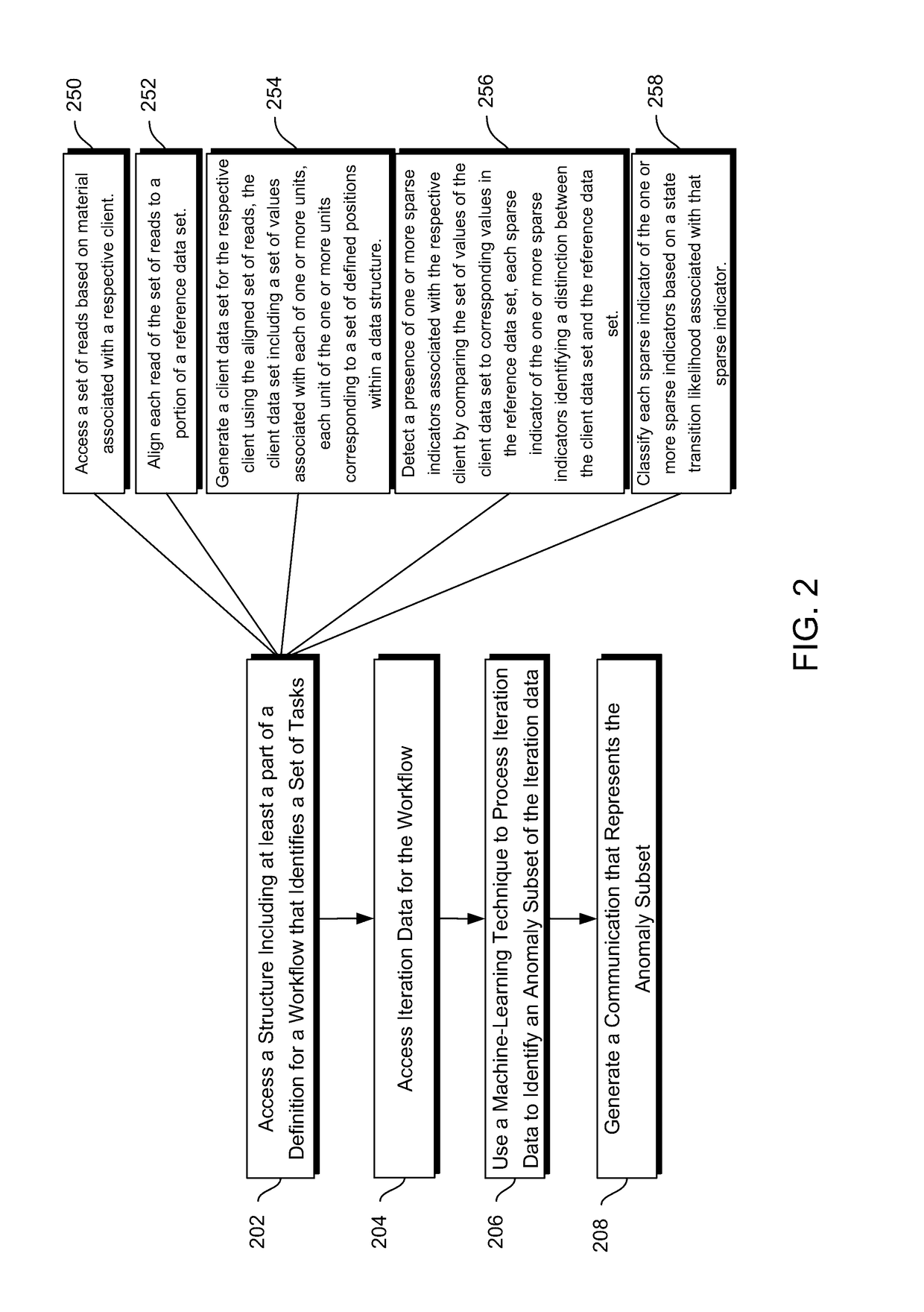
Techniques for processing queries relating to task-completion times or cross-data-structure interactions
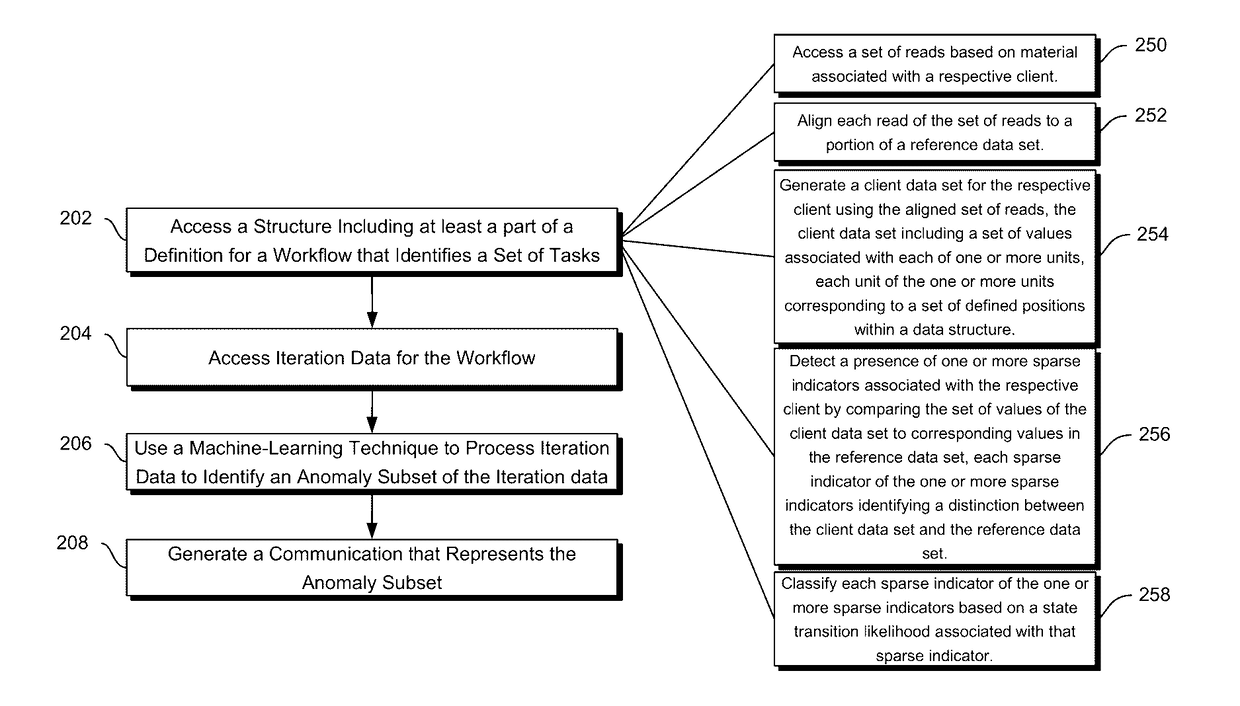
Methods and systems disclosed herein relate generally to data processing by applying machine learning techniques to iteration data to identify anomaly subsets of iteration data. More specifically, iteration data for individual iterations of a workflow involving a set of tasks may contain a client data set, client-associated sparse indicators and their classifications, and a set of processing times for the set of tasks performed in that iteration of the workflow. These individual iterations of the workflow may also be associated with particular data sources. Using the iteration data, anomaly subsets within the iteration data can be identified, such as data items resulting from systematic error associated with particular data sources, sets of sparse indicators to be validated or double-checked, or tasks that are associated with long processing times. The anomaly subsets can be provided in a generated communication or report in order to optimize future iterations of the workflow.
Owner:COLOR HEALTH INC
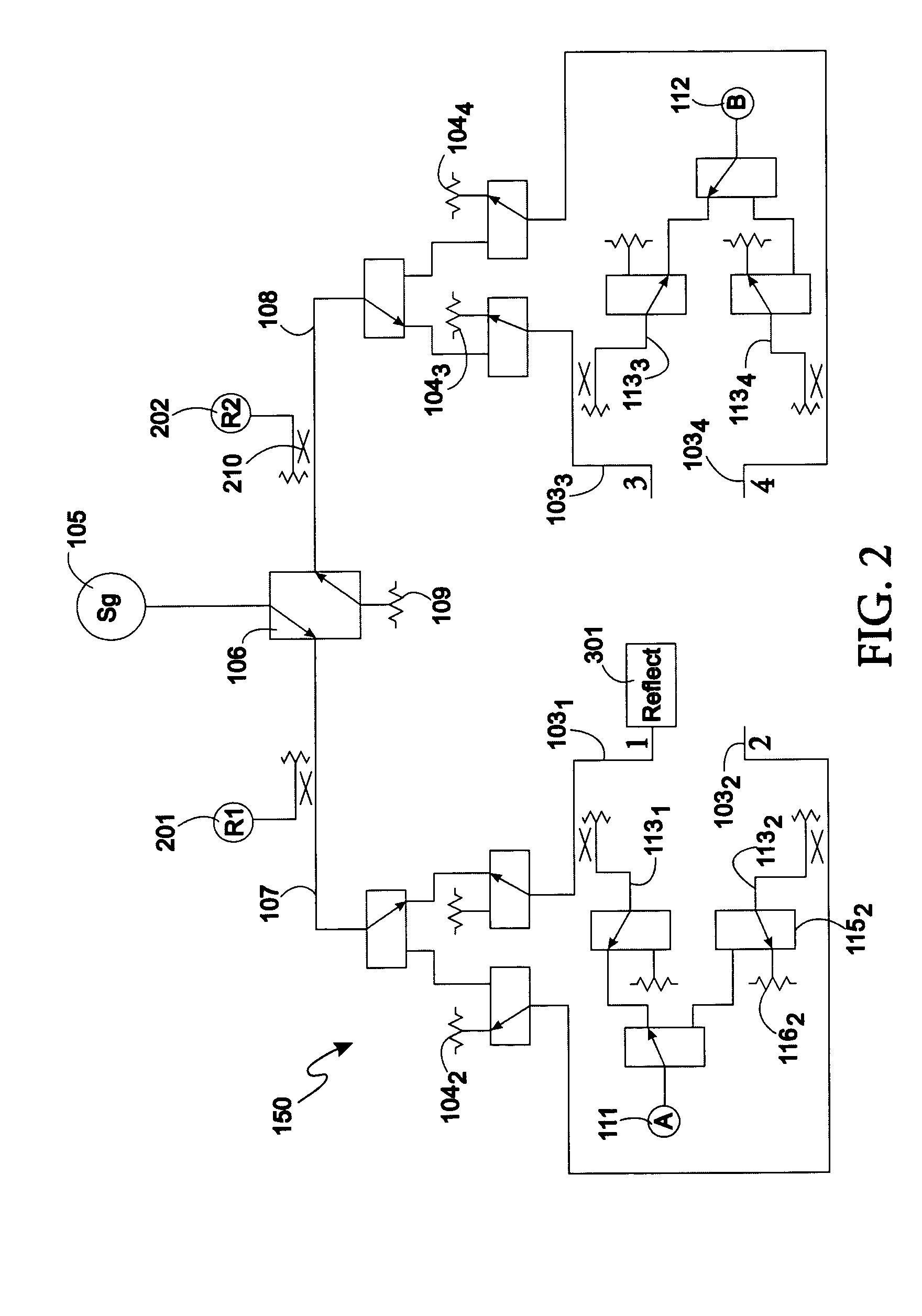
Method and apparatus for measuring a device under test using an improved through-reflect-line measurement calibration
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Inertial GPS navigation system with modified kalman filter
ActiveUS7193559B2Eliminate the effects ofShorten the timeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPhase differenceDirect observation
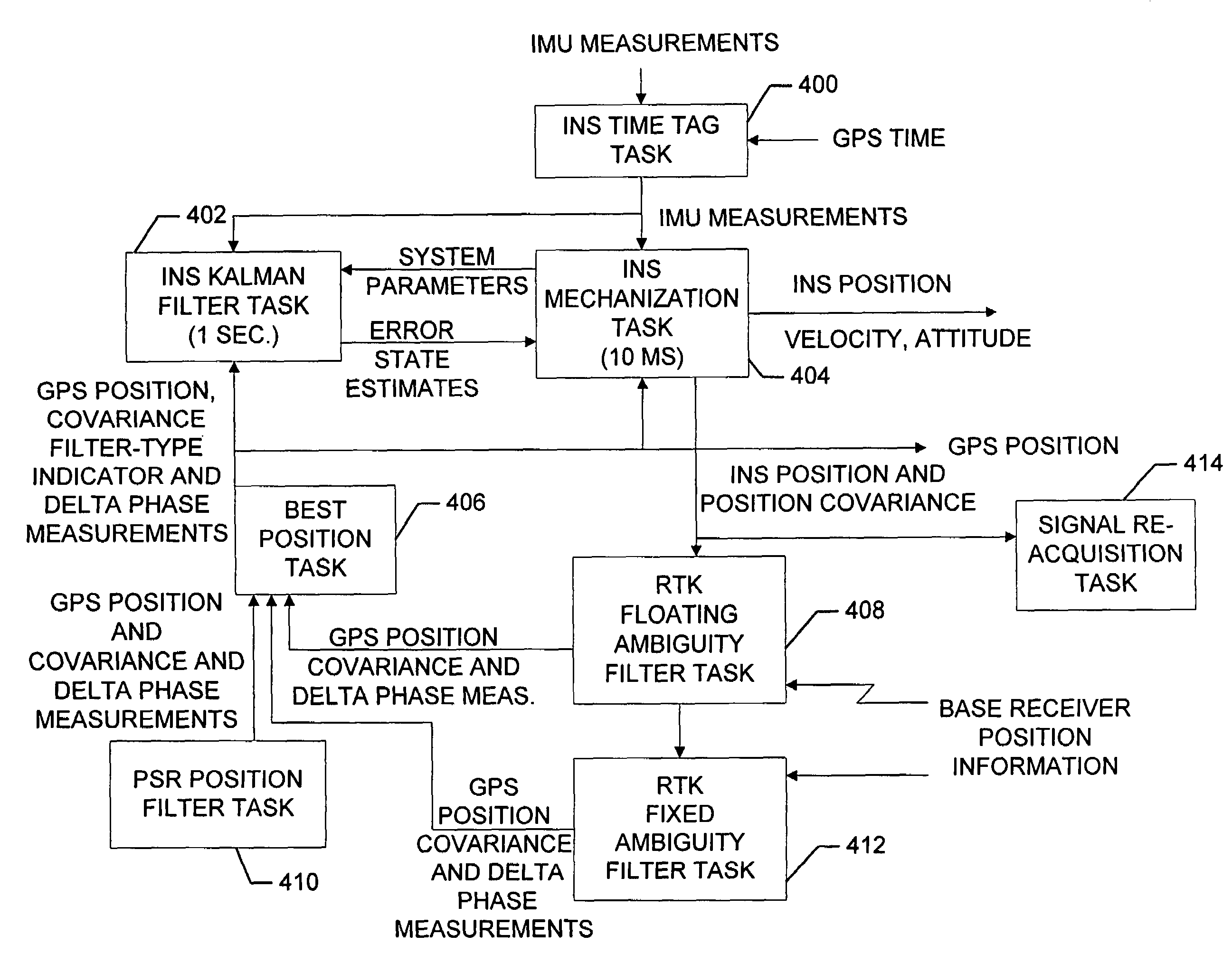
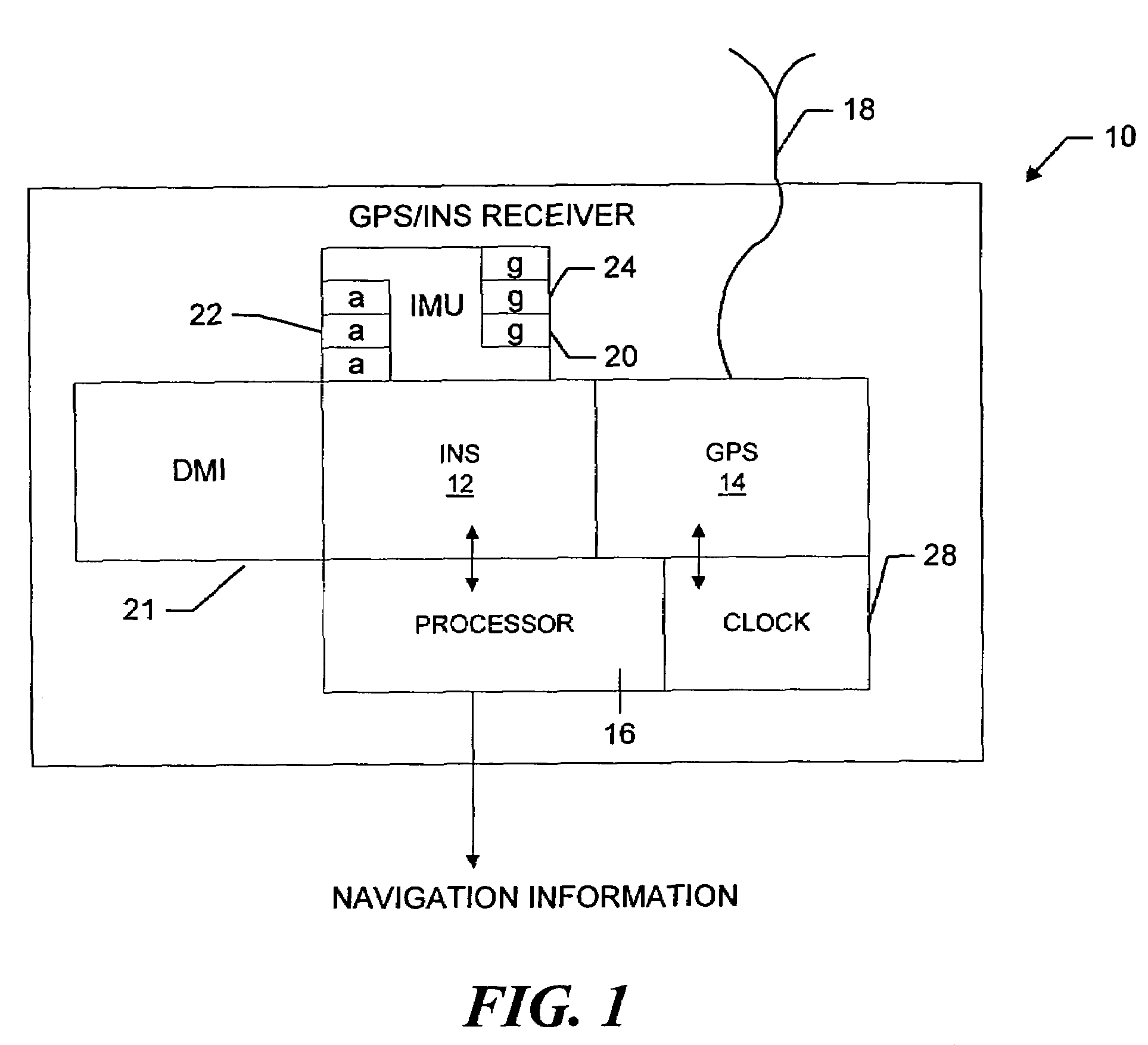
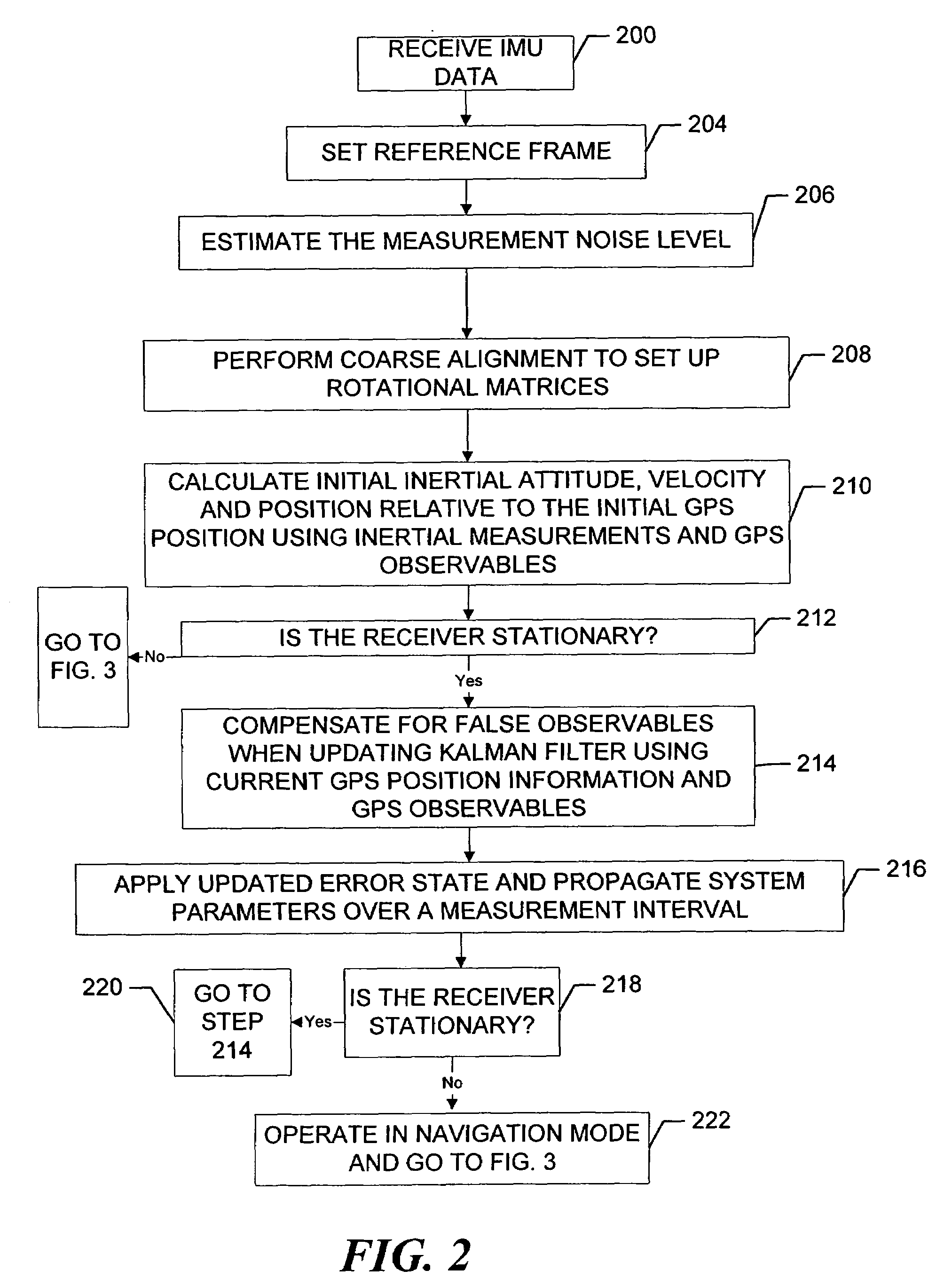
An inertial (“INS”) / GPS receiver includes an INS sub-system which incorporates, into a modified Kalman filter, GPS observables and / or other observables that span previous and current times. The INS filter utilizes the observables to update position information relating to both the current and the previous times, and to propagate the current position, velocity and attitude related information. The GPS observable may be delta phase measurements, and the other observables may be, for example, wheel pick-offs (or counts of wheel revolutions) that are used to calculate along track differences, and so forth. The inclusion of the measurements in the filter together with the current and the previous position related information essentially eliminates the effect of system dynamics from the system model. A position difference can thus be formed that is directly observable by the phase difference or along track difference measured between the previous and current time epochs. Further, the delta phase measurements can be incorporated in the INS filter without having to maintain GPS carrier ambiguity states. The INS sub-system and the GPS sub-system share GPS and INS position and covariance information. The receiver time tags the INS and any other non-GPS measurement data with GPS time, and then uses the INS and GPS filters to produce INS and GPS position information that is synchronized in time. The GPS / INS receiver utilizes GPS position and associated covariance information and the GPS and / or other observables in the updating of the INS filter. The INS filter, in turn, provides updated system error information that is used to propagate inertial current position, velocity and attitude information. Further, the receiver utilizes the inertial position, velocity and covariance information in the GPS filters to speed up GPS satellite signal re-acquisition and associated ambiguity resolution operations
Owner:NOVATEL INC
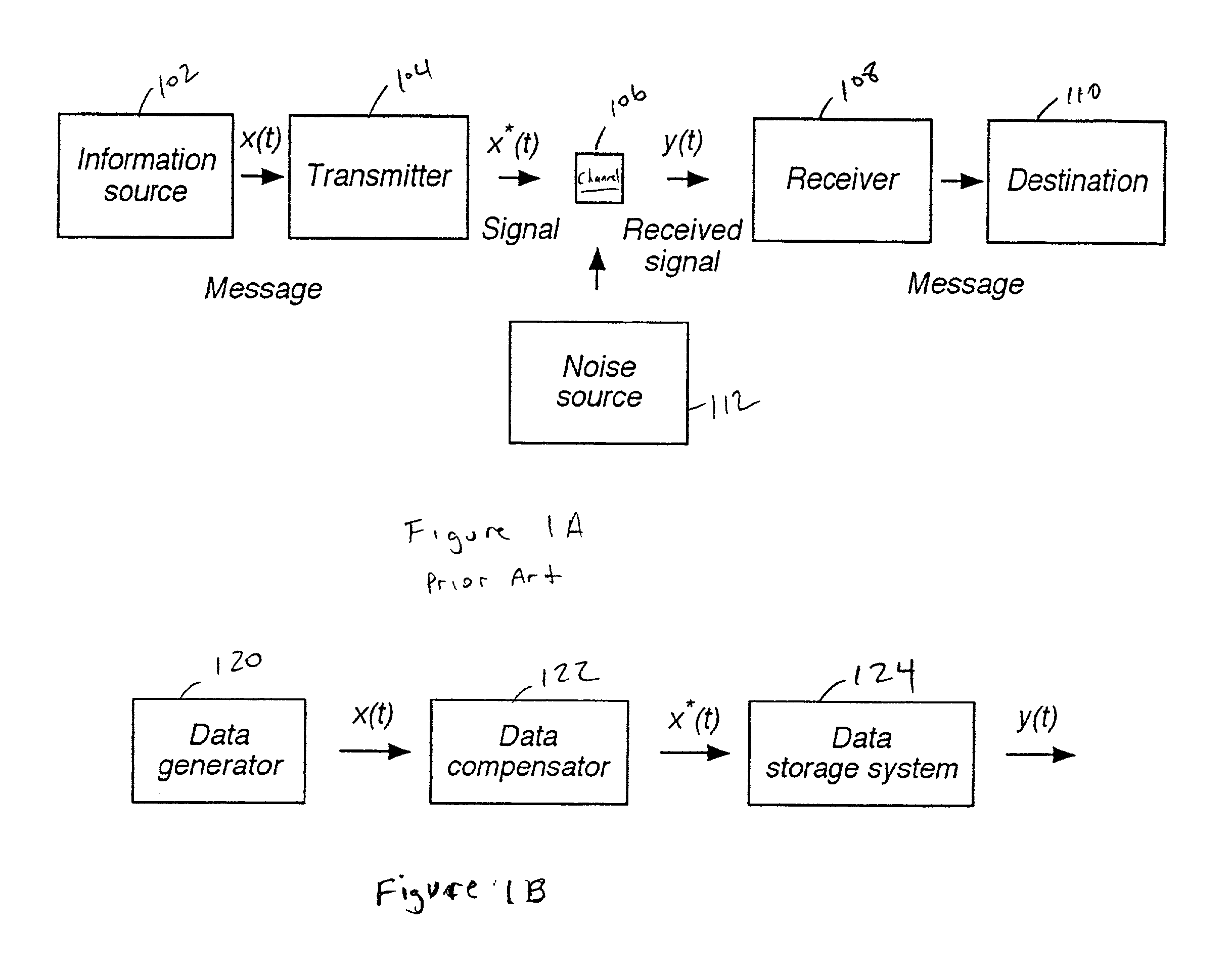
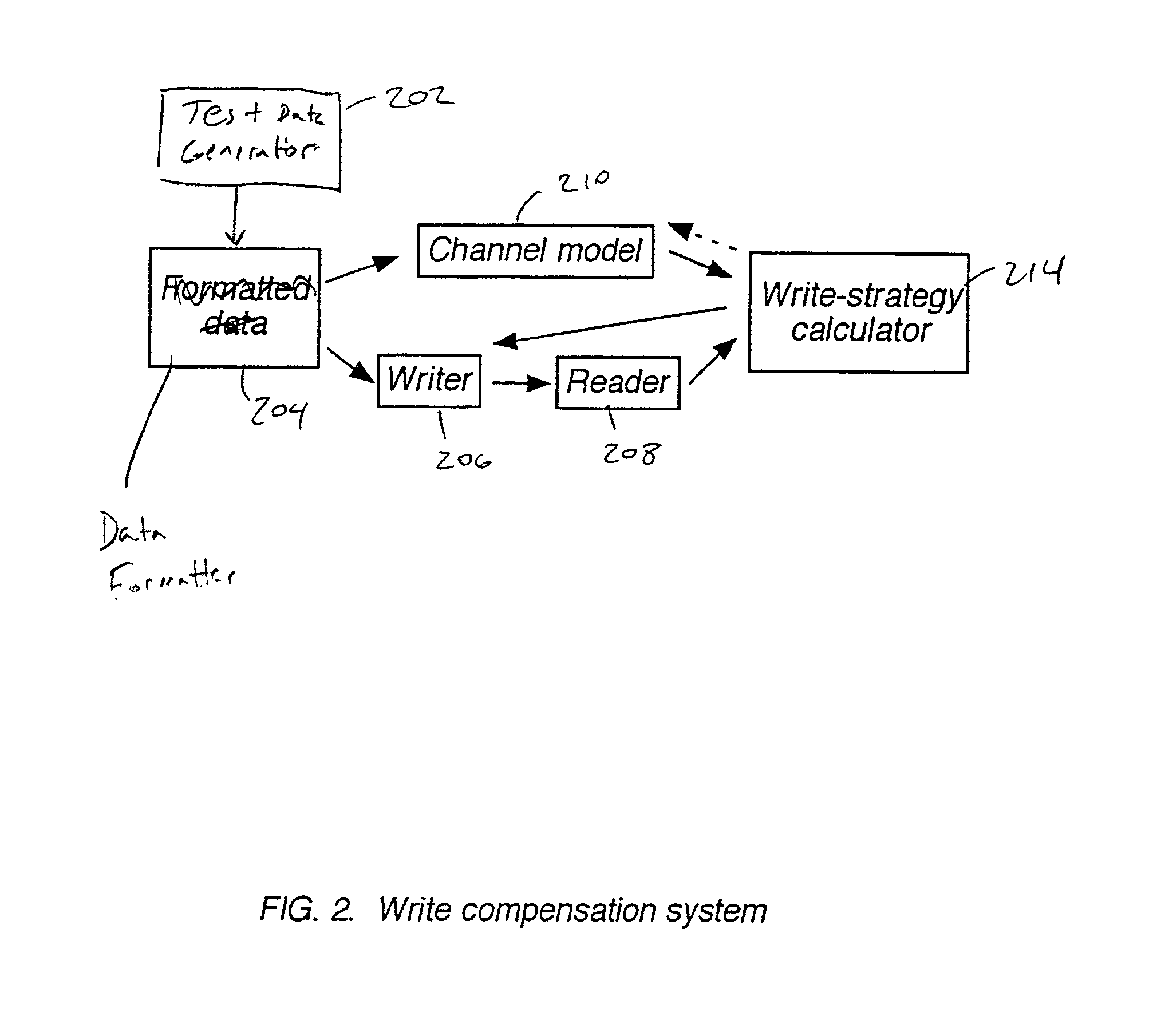
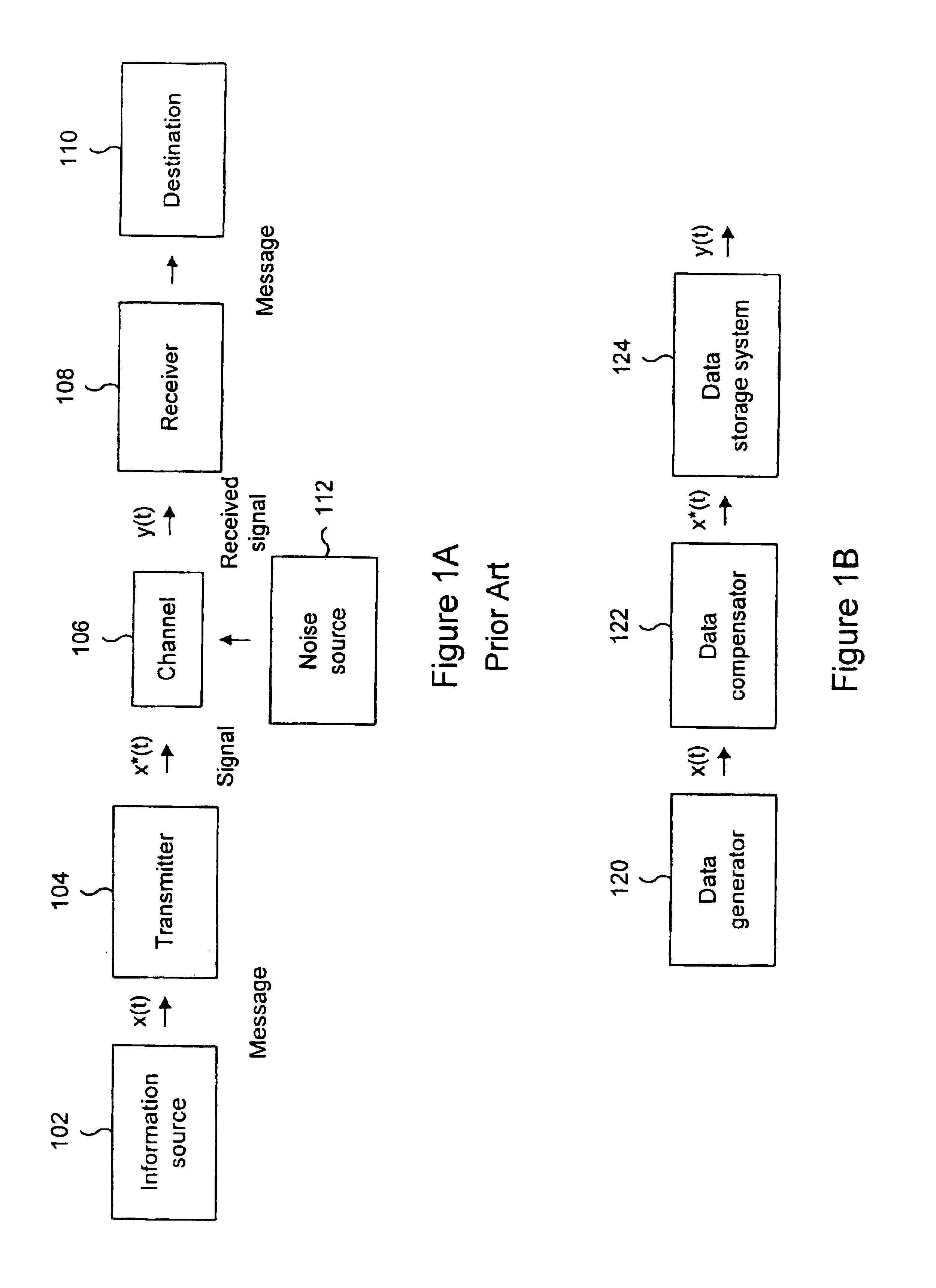
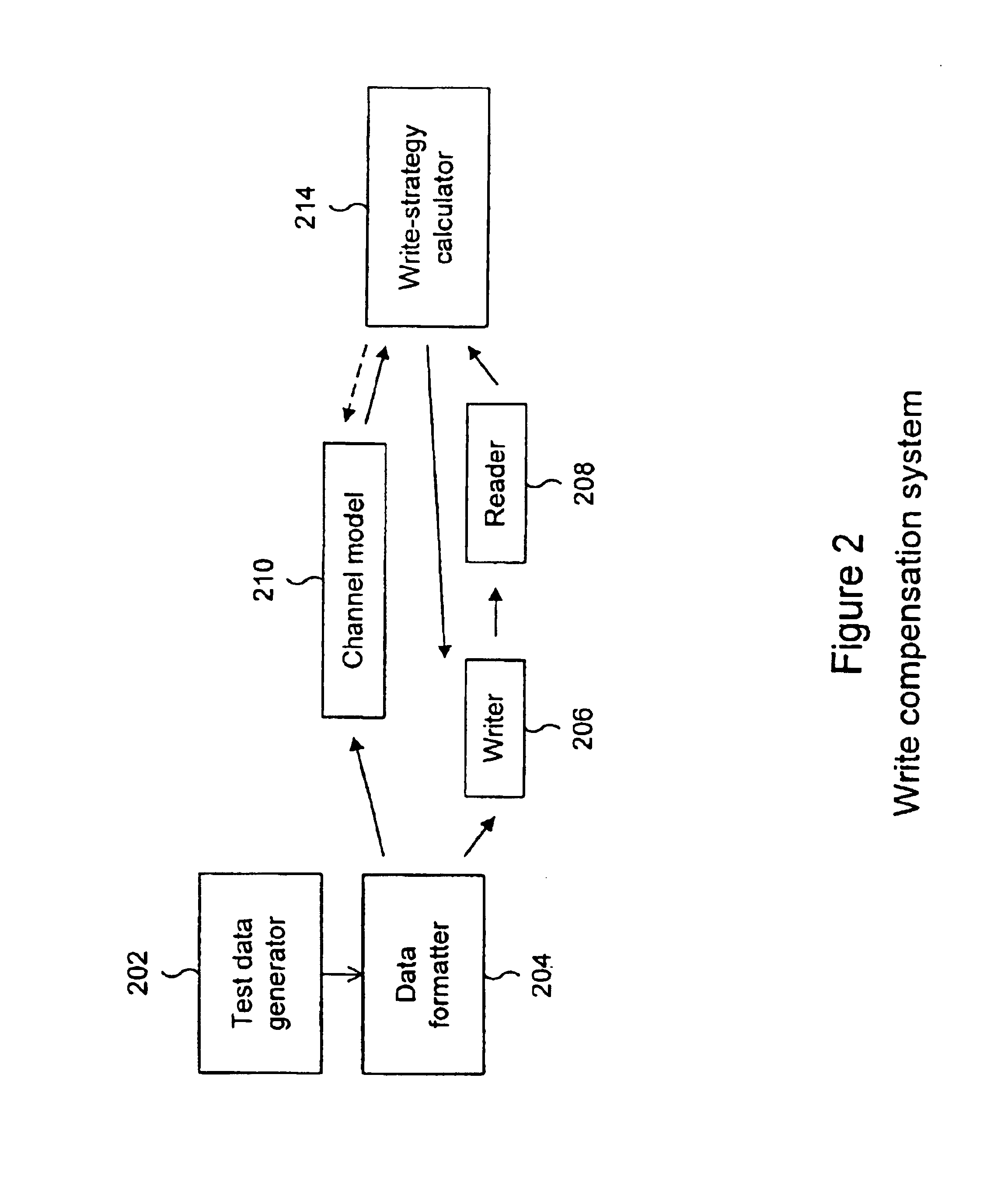
Write compensation for data storage and communication systems
InactiveUS20020126604A1Television system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersCommunications systemChannel sensitivity
Methods and systems for write compensation for optimizing the performance of a data storage or communication channel are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method comprises determining channel sensitivity to modifications in write signal parameters, detecting systematic errors in a read signal recovered from data written with a first set of write parameters, and adjusting the write signal parameters by an amount determined from the channel sensitivity such that the systematic errors are reduced when data are written with the adjusted write parameters.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Defect location identification for microdevice manufacturing and test
InactiveUS20060069958A1Error detection/correctionElectrical testingManufacturing technologyEngineering
A defect identification tool is disclosed that predicts locations at which defects in a microdevice are most likely to occur. The tool may identify both a type of defect and the particular netlists in which that defect is likely to occur. A test circuit generation tool can then subsequently use this defect information to generate a test circuit that tests for the defect in the identified portions of the microcircuit. Similarly, an automatic test pattern generation tool may use the defect location information to generate test data custom-tailored to check for faults corresponding to the identified defect in the specified portions of the microcircuit. Various implementations of the tool may be used both to identify the locations at which defects caused by systematic errors, such as manufacturing process deficiencies or flaws, are most likely to occur and the locations at which randomly-created defects are most likely to occur.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
Dynamic offset and feedback threshold
InactiveUS6961626B1Strict controlNon-controllableTotal factory controlSpecial data processing applicationsProcess varianceSemiconductor chip
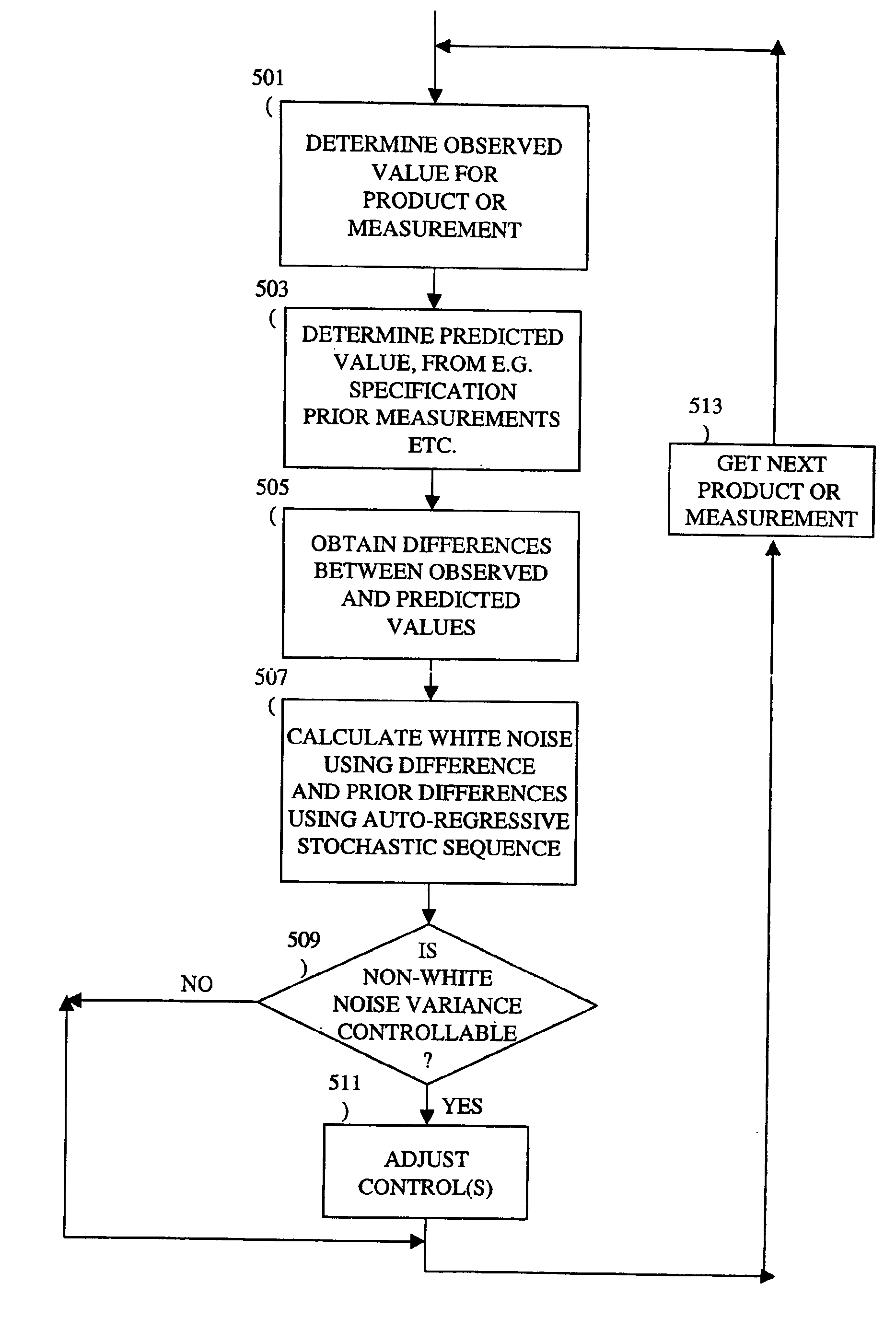
A method, system and medium are provided for enabling improved feedback and feedforward control. An error, or deviation from target result, is observed during manufacture of semi conductor chips. The error within standard deviation is caused by two components: a white noise component and a signal component (such as systematic errors). The white noise component is random noise and therefore is relatively non-controllable. The systematic error, in contrast, may be controlled by changing the control parameters. A ratio between the two components is calculated autoregressively. Based on the ratio and using the observed or measured error, the actual value of the error caused by the signal component is calculated utilizing an autoregressive stochastic sequence. The actual value of the error is then used in determining when and how to change the control parameters. The autoregressive stochastic sequence addresses the issue of real-time control of the effects of run-to-run deviations, and provides a mechanism that can extract white noise from the statistical process variance in real time. This results in an ability to provide tighter control of feedback and feedforward variations.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and device for calculating bit error rate of received signal
InactiveUS20070162788A1Low circuit complexityReduce loadData representation error detection/correctionError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorDigital radioData field
System and method of estimating radio channel bit error rate (BER) in a digital radio telecommunications system wherein the soft output of the turbo decoder is used as pointer or index to look-up-tables containing the bit-wise BER of a certain bit in the data field of the received frame. A quantizer quantizes the received data frame and the quantized bit operates on a switch which selects the appropriate look-up-table. By means of accumulation and scaling the average BER of a certain amount of bits are calculated. Decoding bit-errors may occur but as they are submitted to posterior probability estimation, systematic errors which normally happen at low SNR are avoided.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
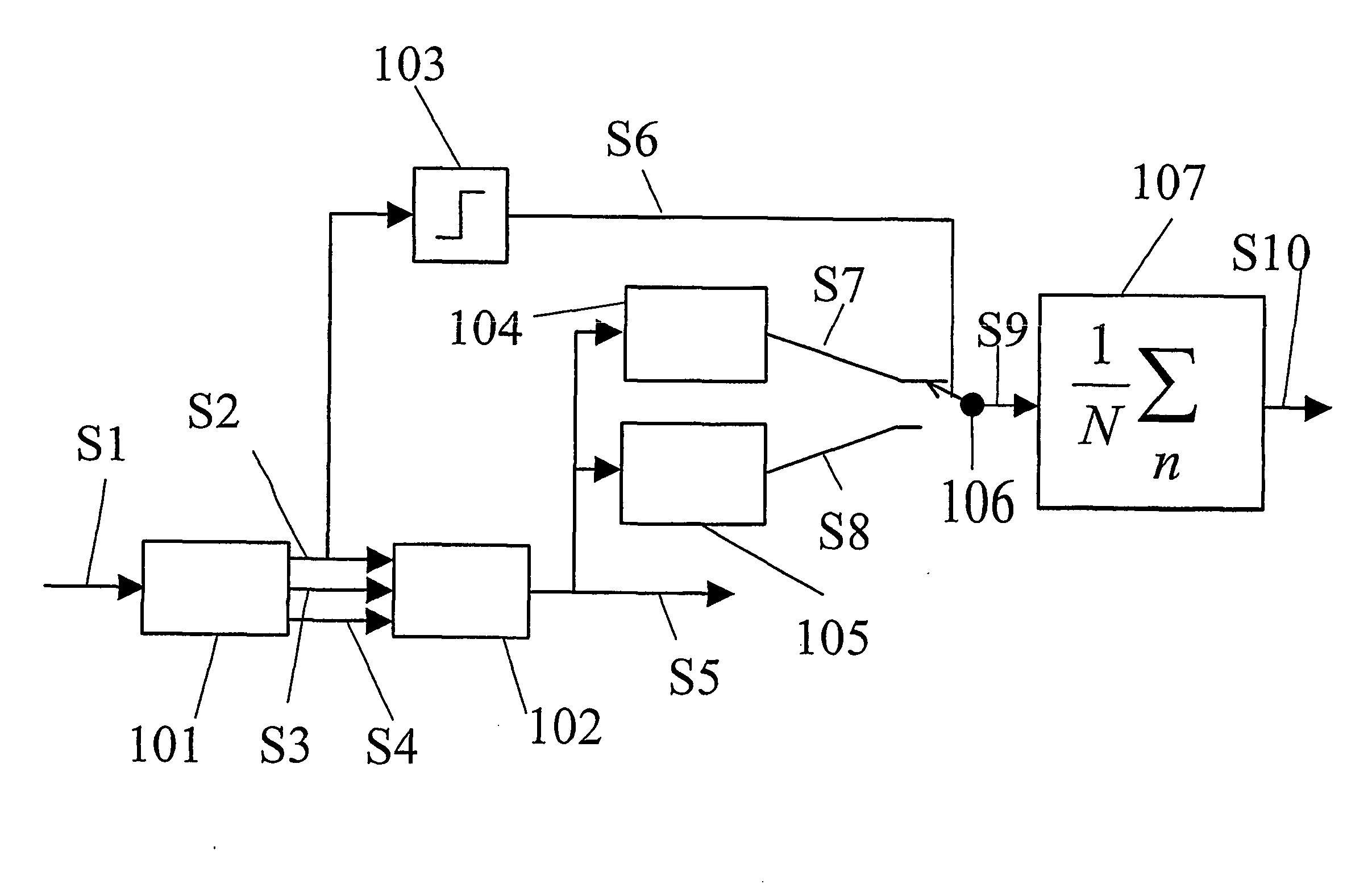
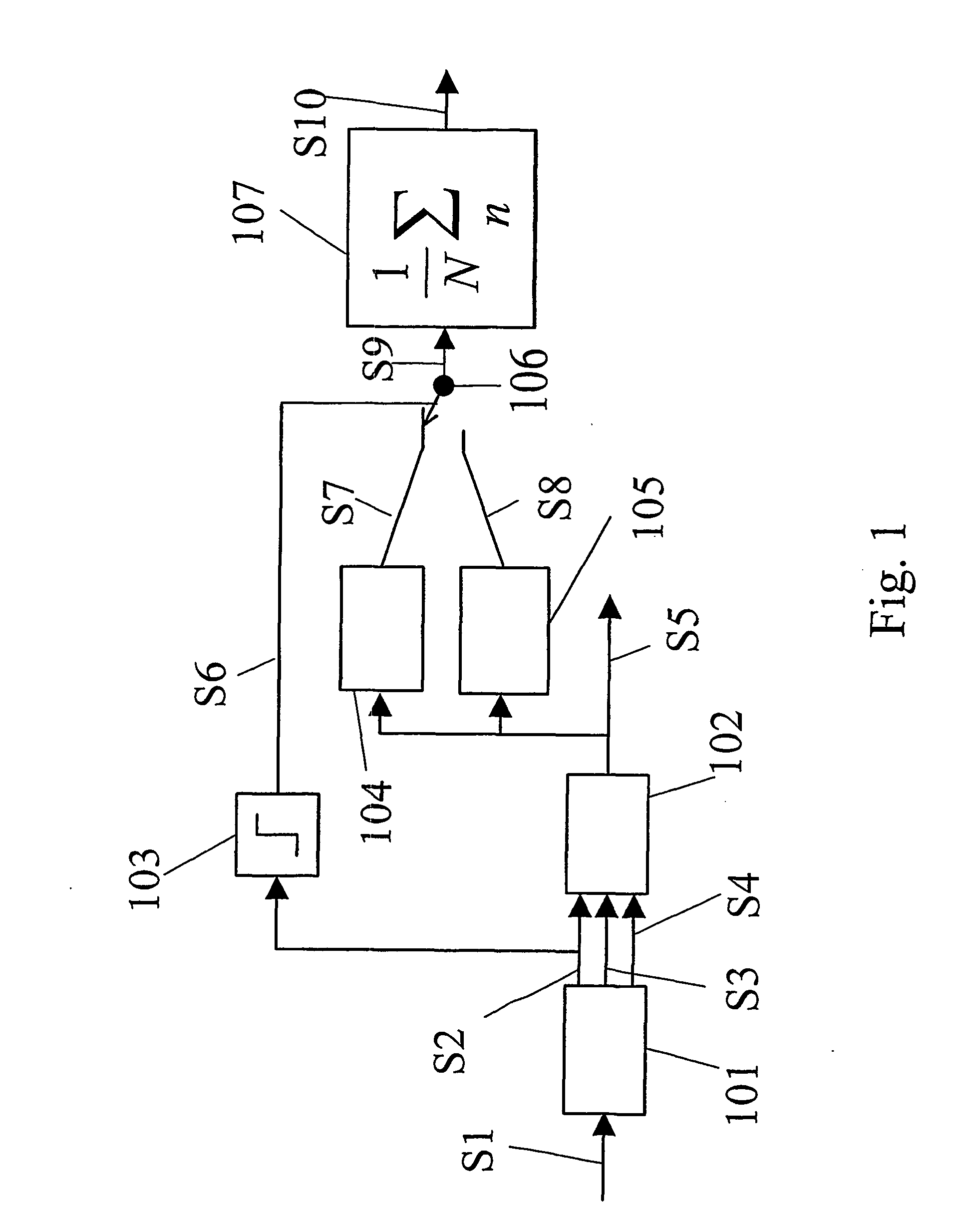
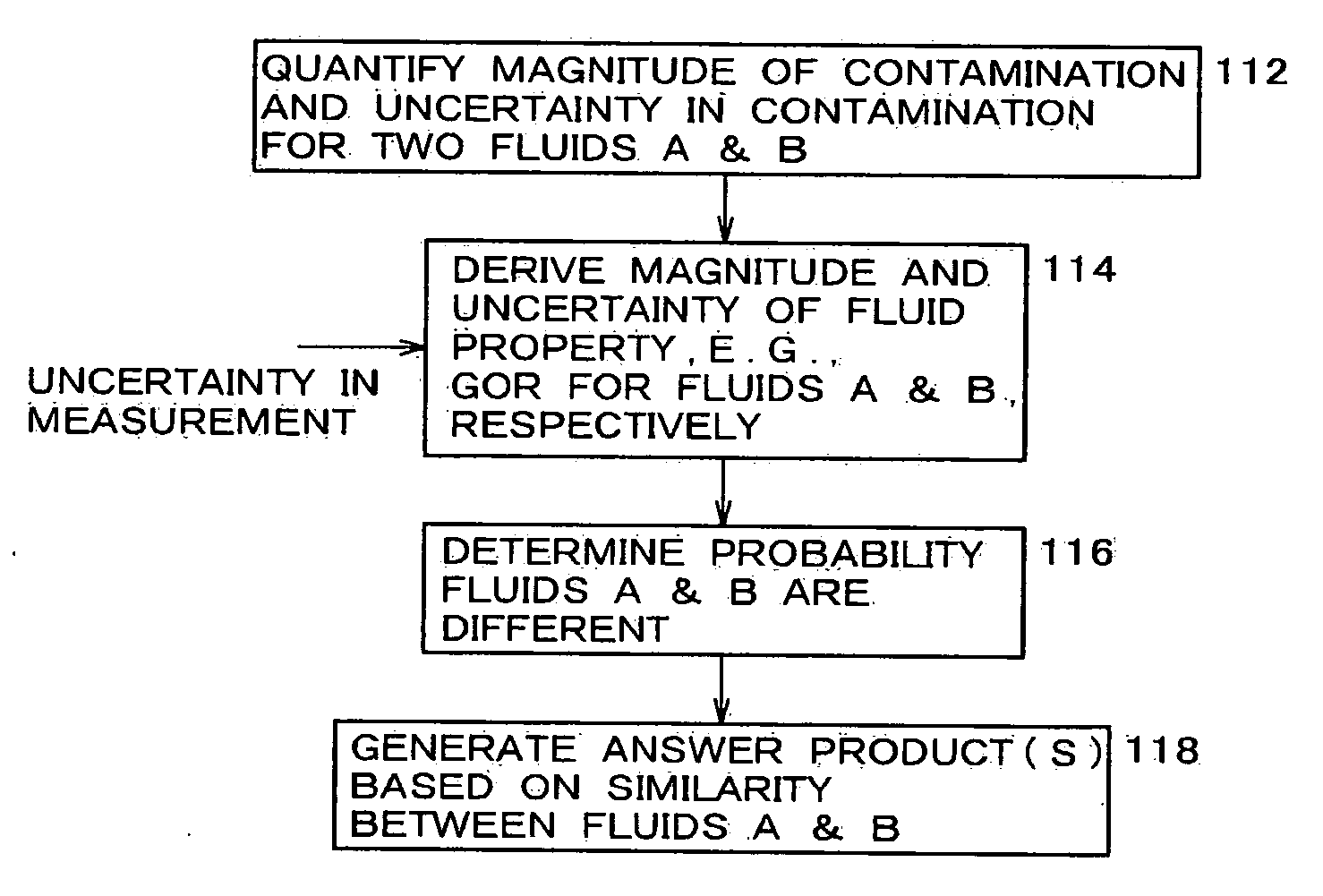
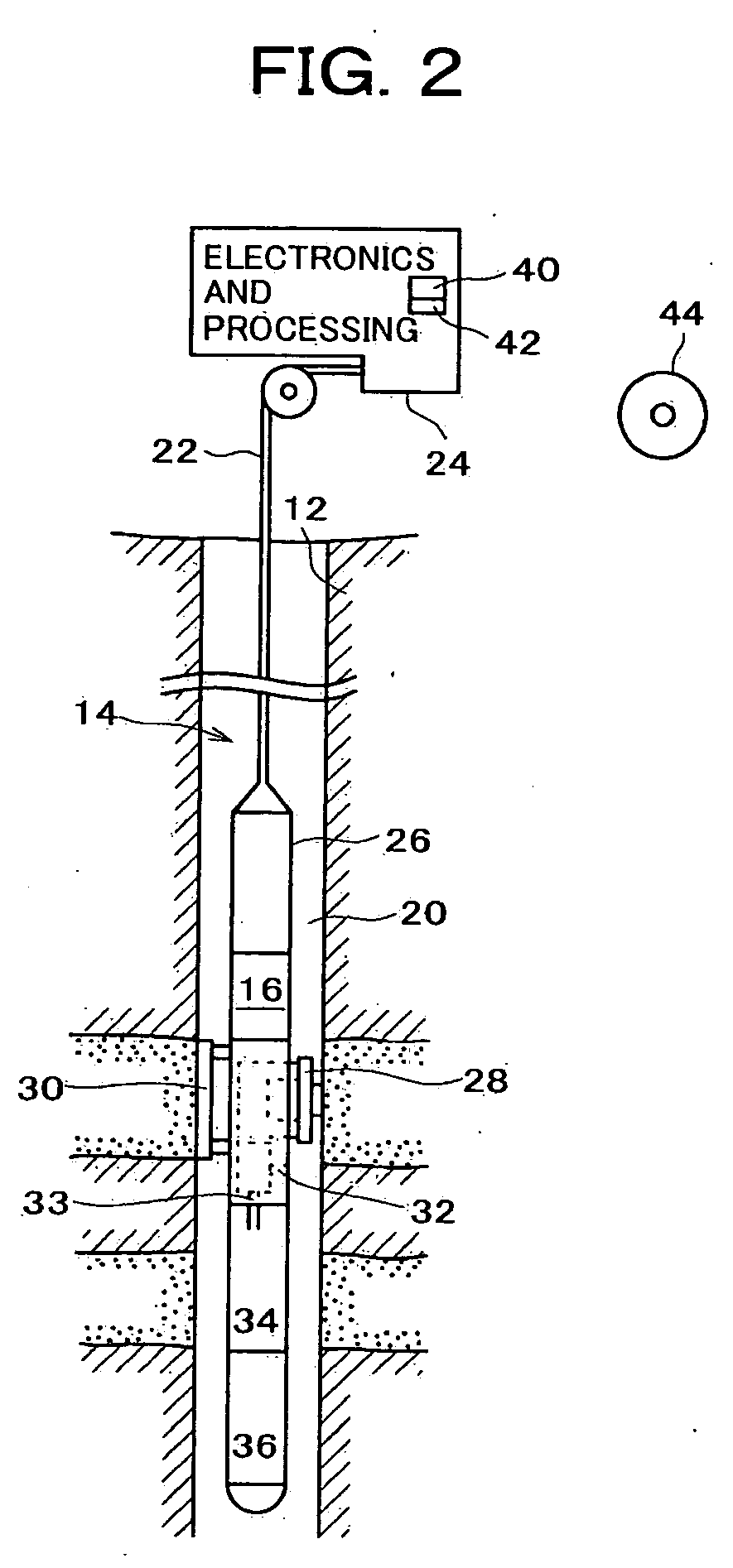
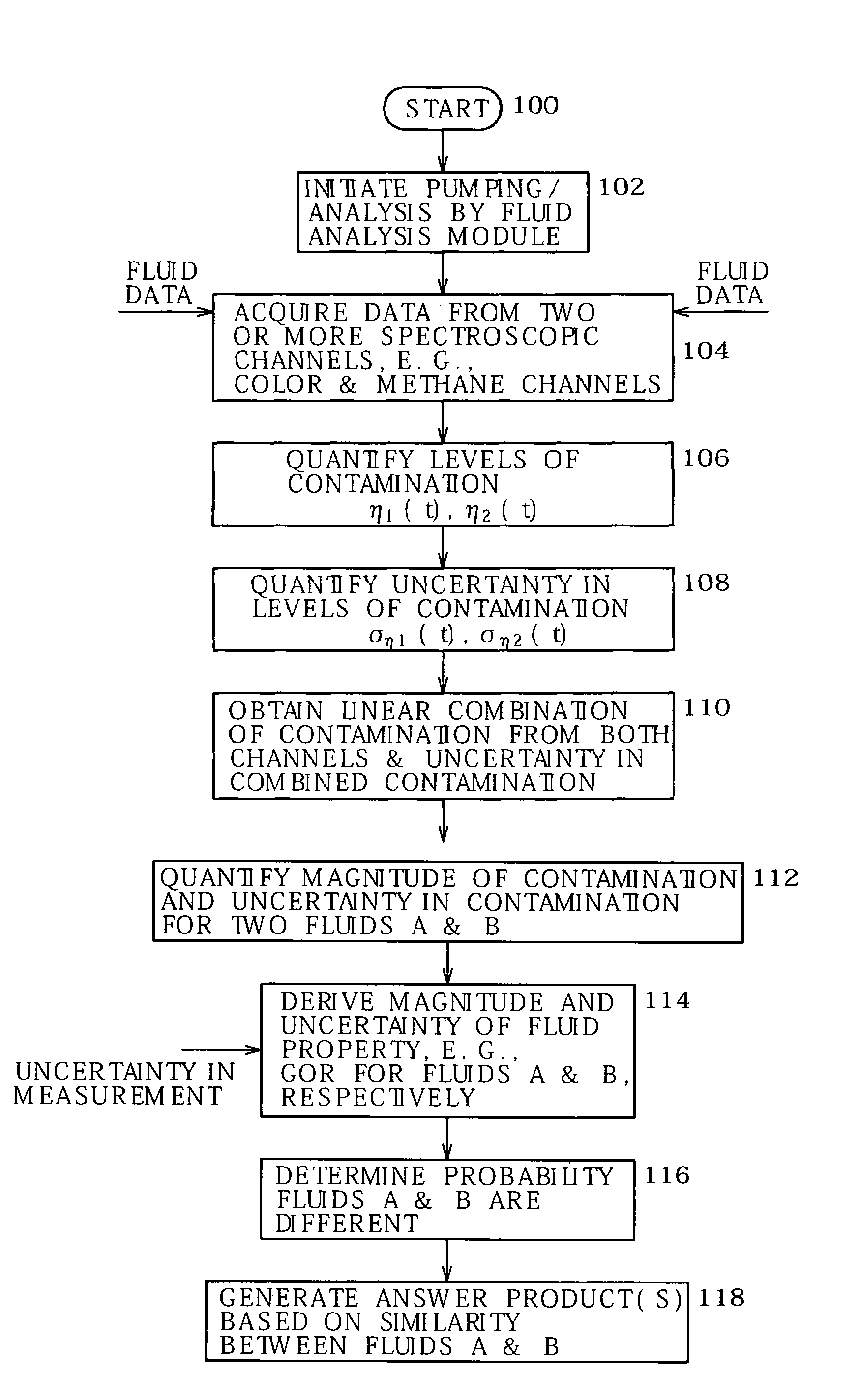
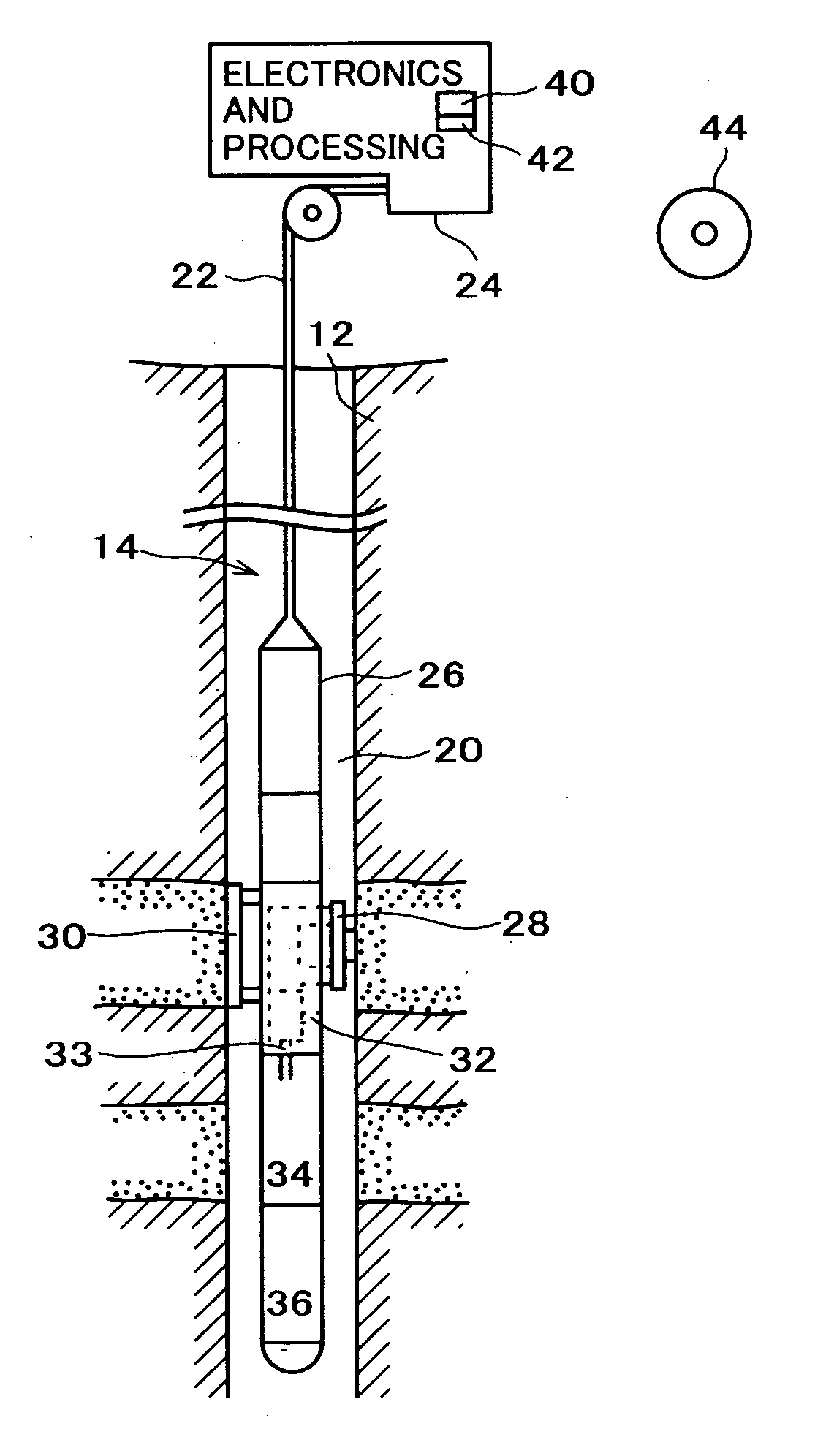
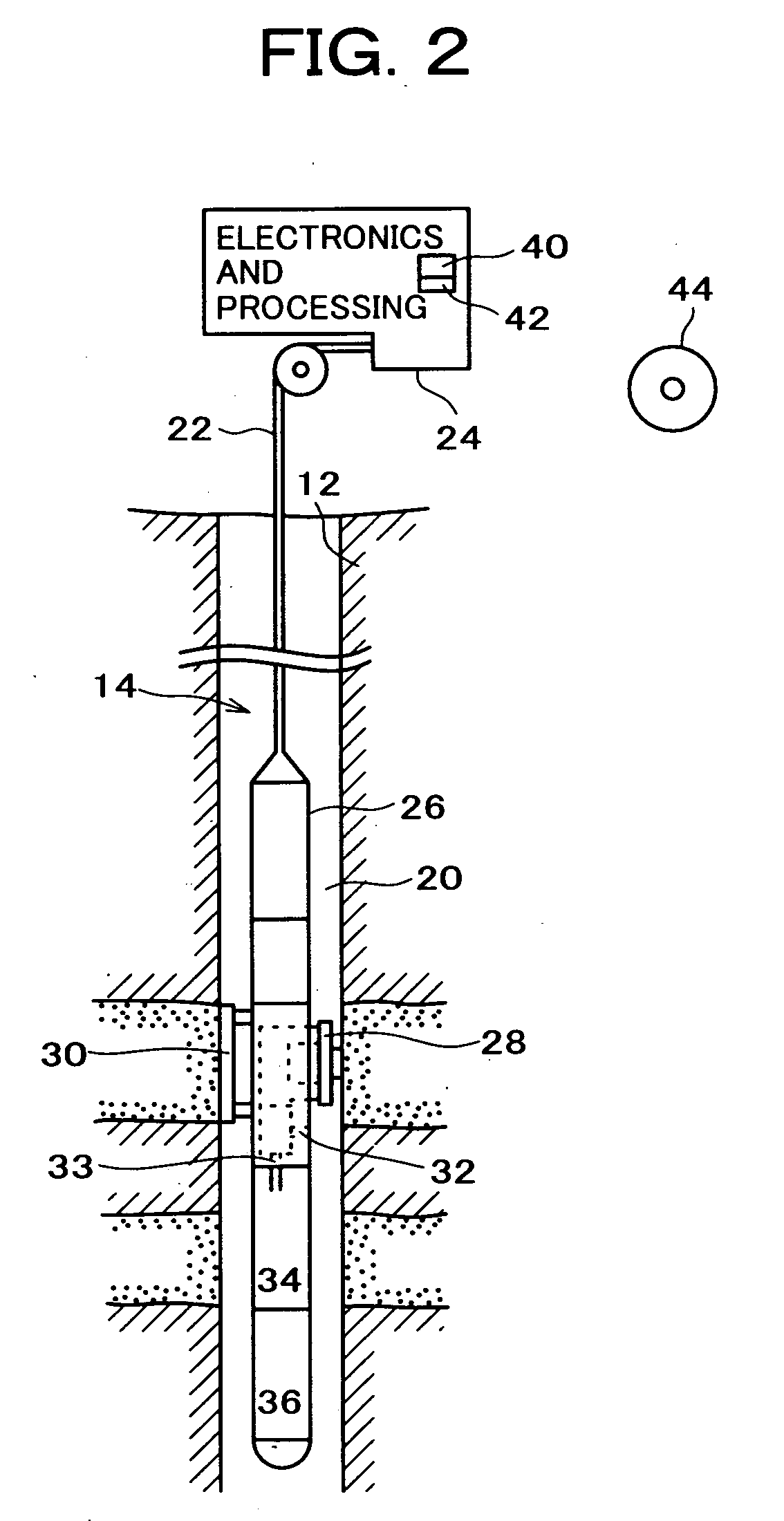
System and methods of deriving fluid properties of downhole fluids and uncertainty thereof
ActiveUS20060155474A1Less sensitive to systematic error in dataGood basisElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyFormation fluidContamination
Methods and systems are provided for downhole analysis of formation fluids by deriving fluid properties and associated uncertainty in the predicted fluid properties based on downhole data, and generating answer products of interest based on differences in the fluid properties. Measured data are used to compute levels of contamination in downhole fluids using an oil-base mud contamination monitoring (OCM) algorithm. Fluid properties are predicted for the fluids and uncertainties in predicted fluid properties are derived. A statistical framework is provided for comparing the fluids to generate, in real-time, robust answer products relating to the formation fluids and reservoirs thereof. Systematic errors in measured data are reduced or eliminated by preferred sampling procedures.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
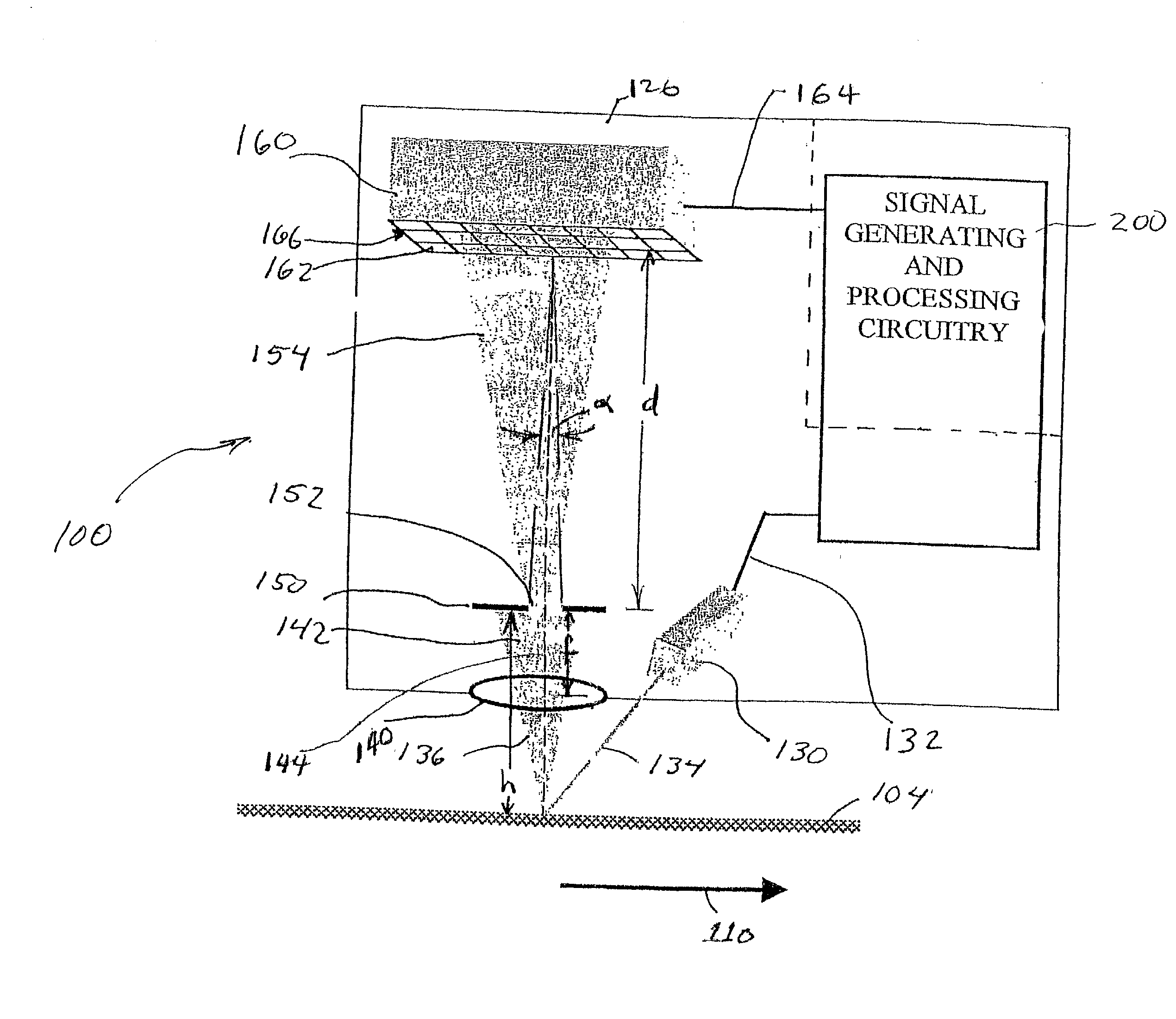
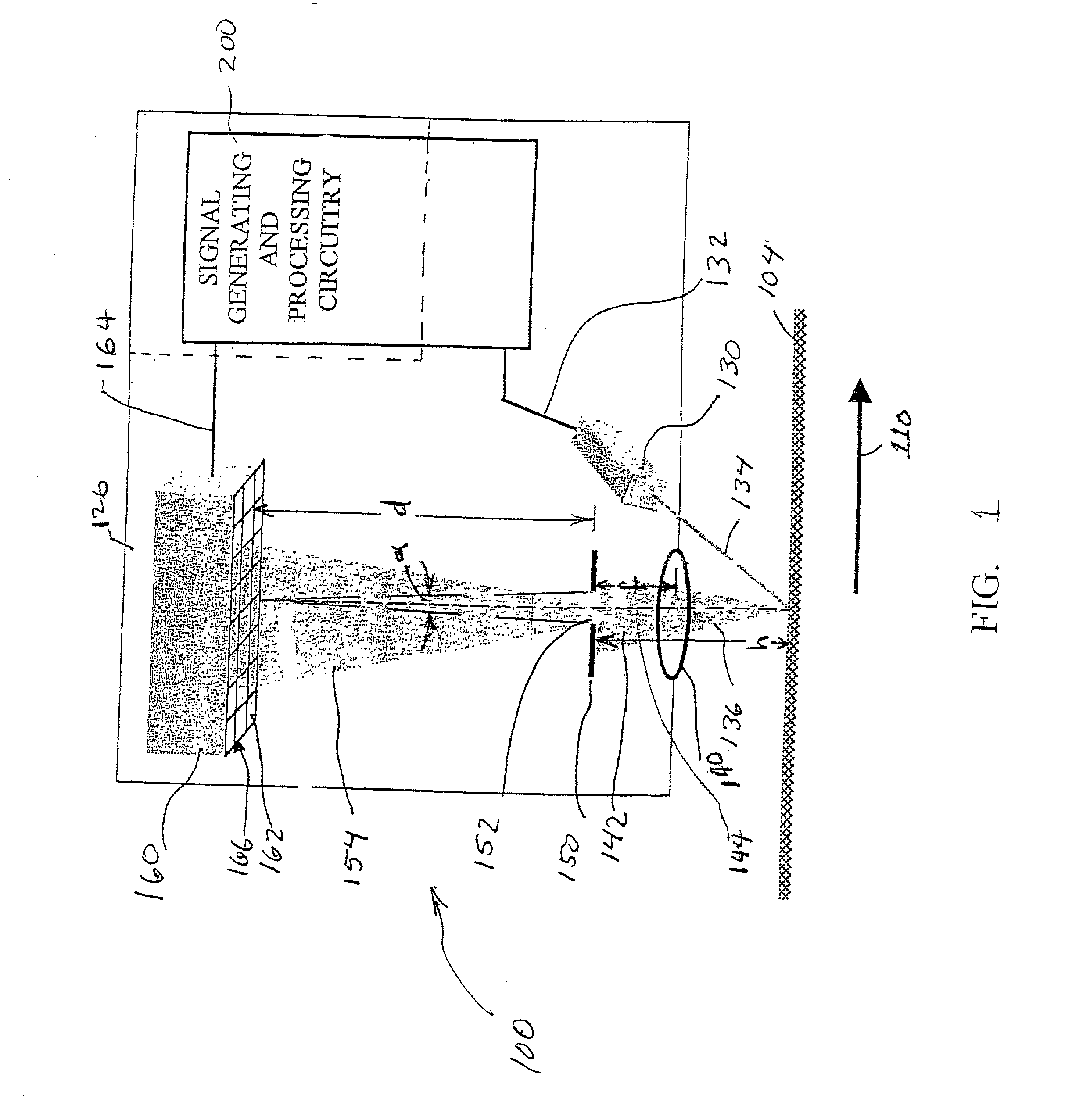
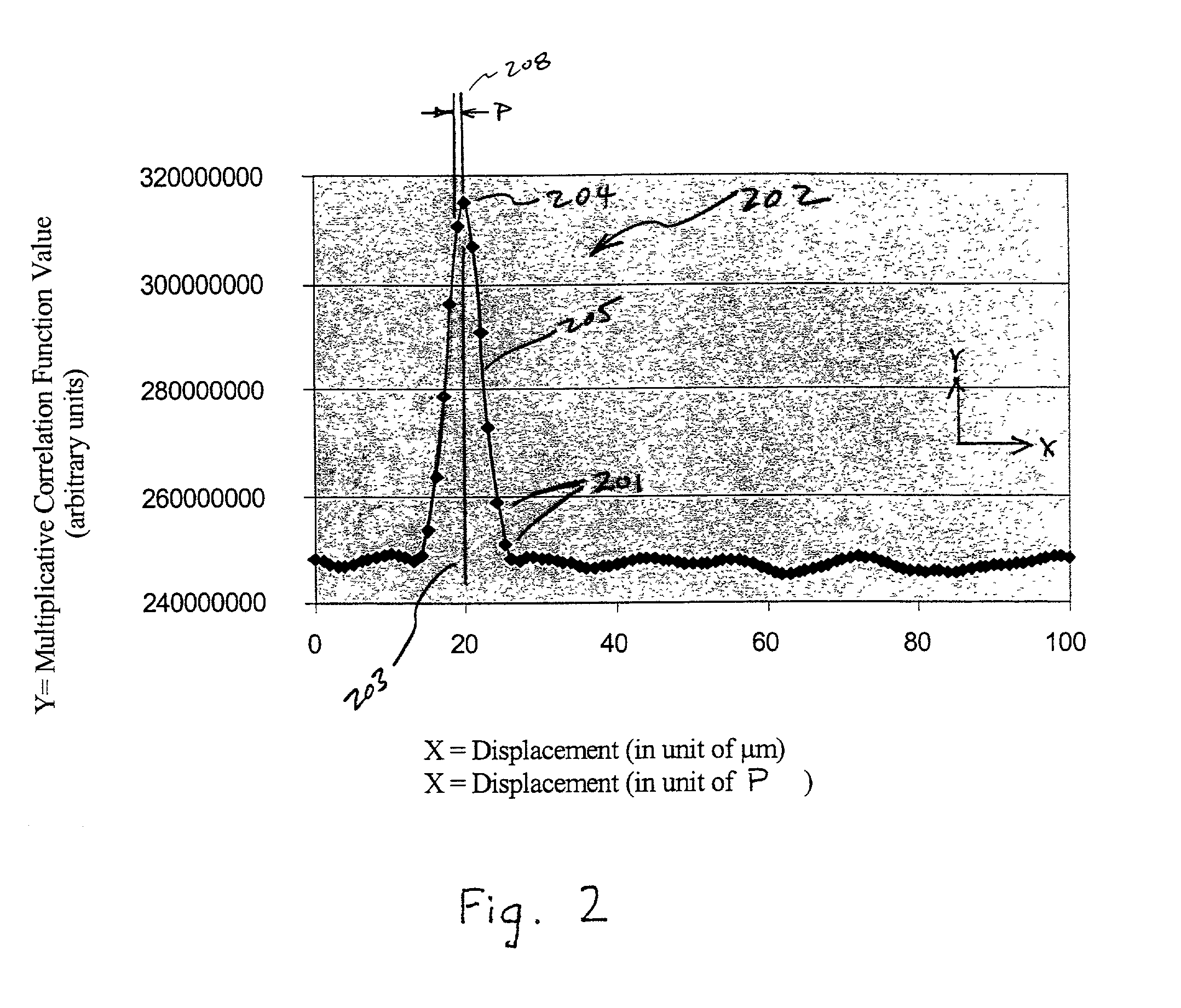
Systems and methods for high-accuracy displacement determination in a correlation based position transducer
InactiveUS20020105656A1Reduce complexityReduce processing timeImage analysisOptical rangefindersCorrelation functionTransducer
An image which is determined by surface is captured and stored by sensing device. Subsequently, at a second image corresponding to a displacement of the surface is captured and stored. The two images are repeatedly compared at different offsets in a displacement direction. Theoretically, the most extreme value of the comparison will occur at the image offset that corresponds exactly with the actual displacement. However, typically none of the comparison offsets correspond exactly with the actual displacement, therefore interpolation between the comparison offsets is required. The method of comparing the images, as well as the method of interpolating to determining the image offset corresponding to the extreme value of the comparison can both contribute to systematic errors in estimating the displacement of the surface from the images. Herein, the systematic errors are rejected by correlation-based comparison systems and methods which reduce the curvature of the correlation function for offsets which bound the extreme value, and by interpolation systems and methods which are relatively insensitive to the asymmetry of the correlation function value points selected as the basis for the interpolation. These systems and methods allow fast, highly accurate, displacement determinations using relatively simplified calculations and relatively few correlation function value points. Thus, such a displacement measuring system can track high speed displacements with high accuracy. The systems and methods are especially suitable for measuring displacement of a surface using speckle images.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
System and methods of deriving fluid properties of downhole fluids and uncertainty thereof
ActiveUS7305306B2Less sensitive to systematic error in dataGood basisElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyFormation fluidContamination
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
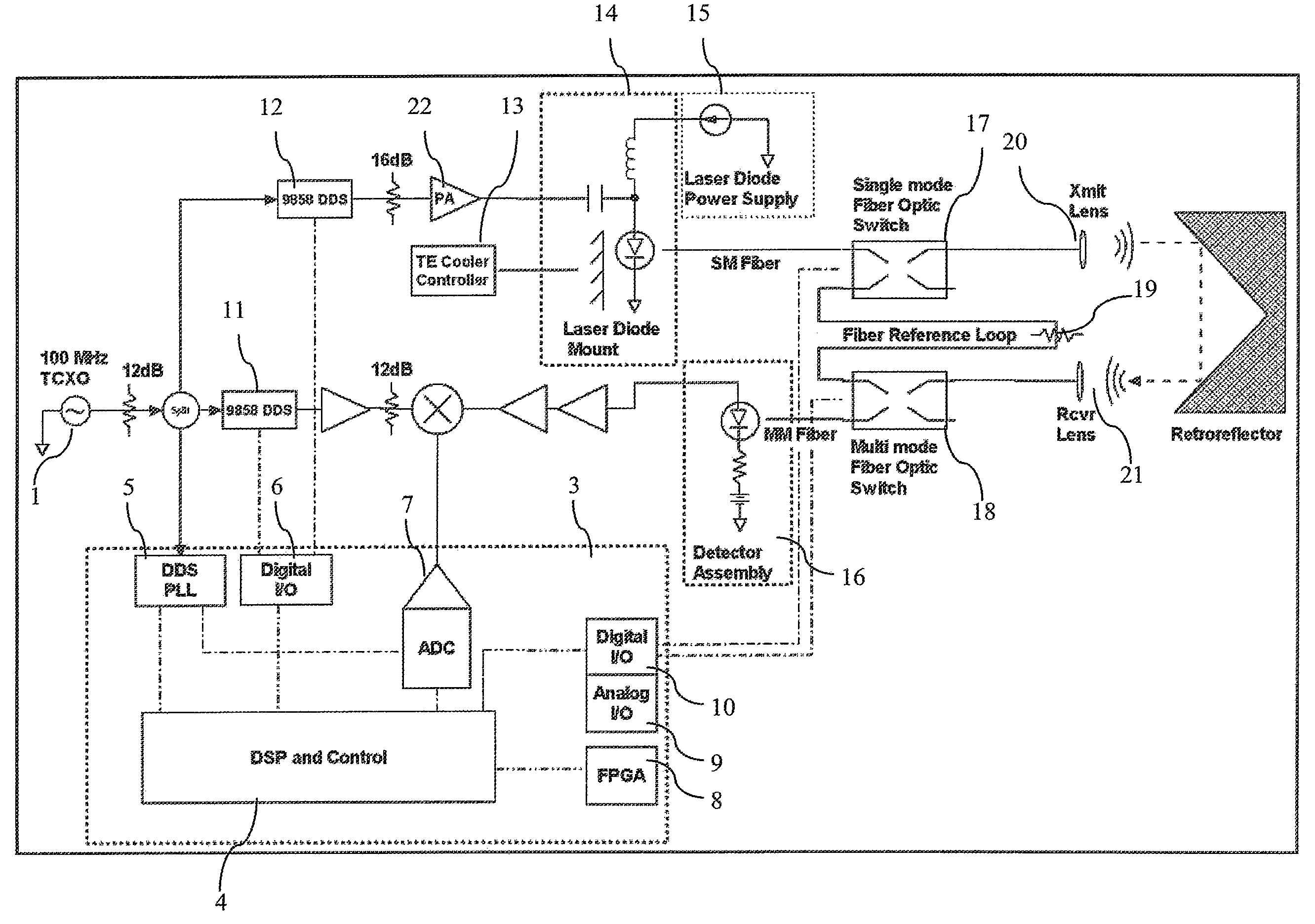
Fiber optically coupled, multiplexed, and chopped laser rangefinder
InactiveUS7586586B2Eliminates phase uncertaintyReduce changesOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationMultiplexingFiber
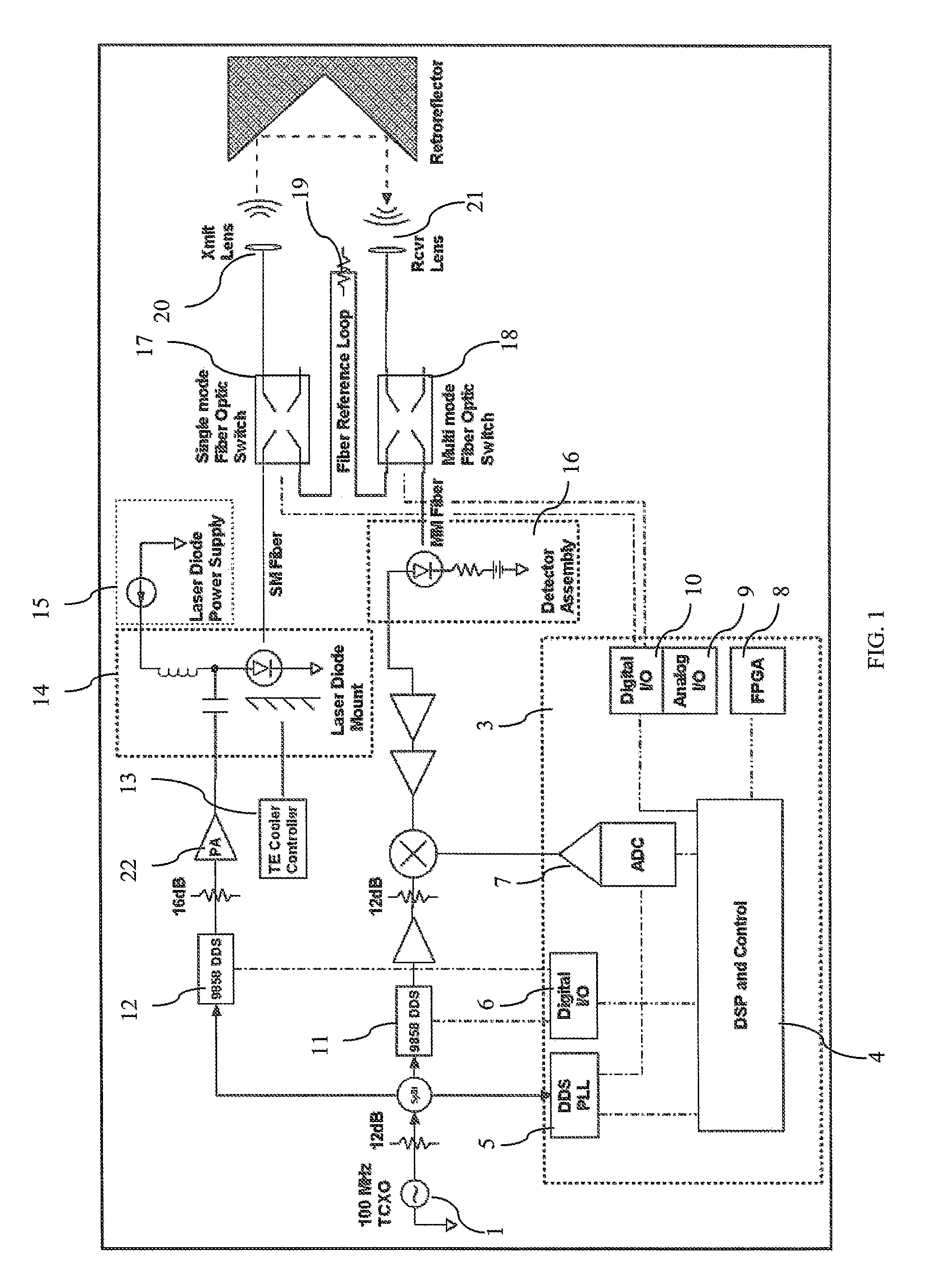
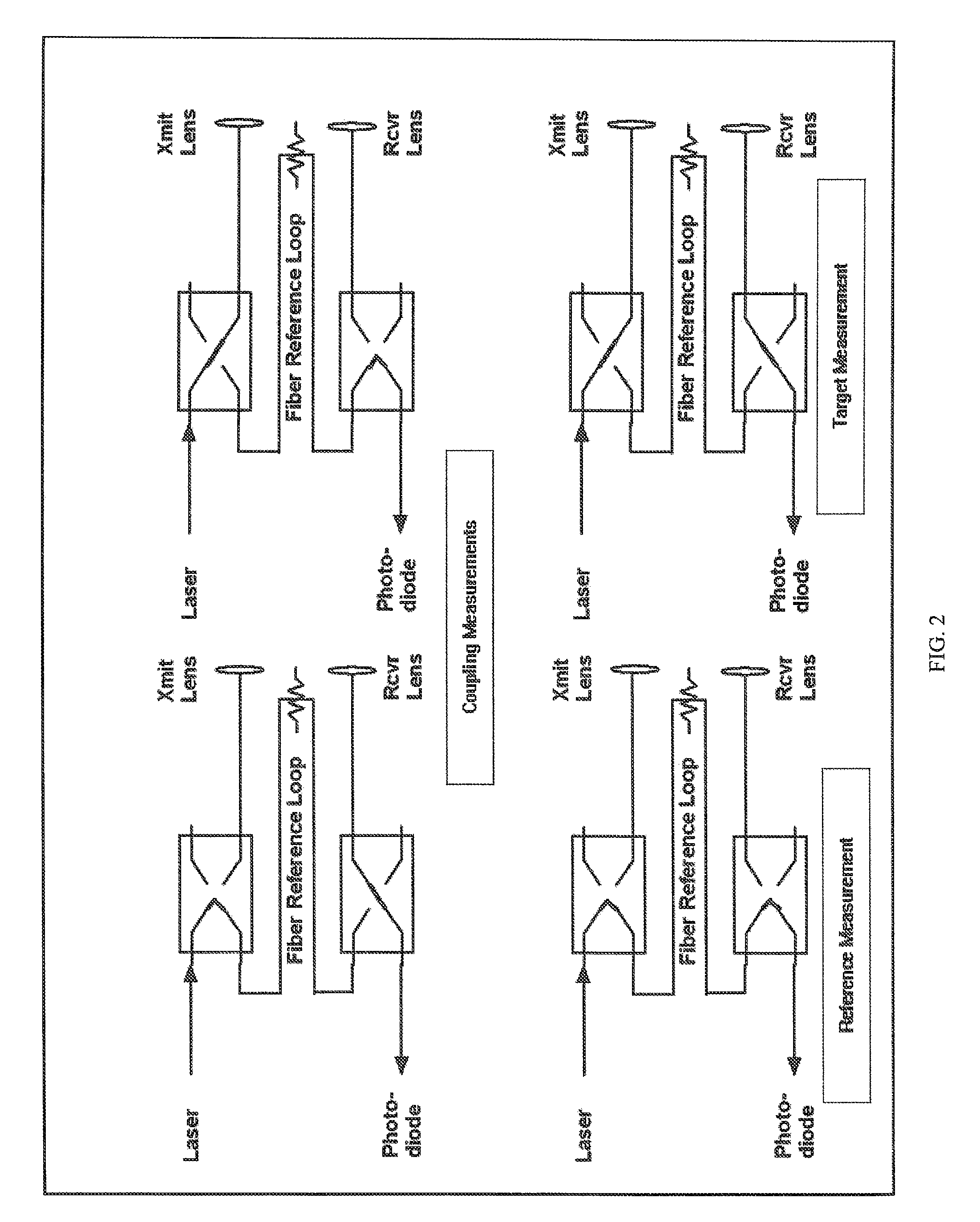
A CW phase-delay distance measuring device is described. The device fiber-optically couples an amplitude modulated laser and a detector though MEMS fiber optic switches to provide chopping and multiplexing capability, and to allow measurement of transmit and receive coupling. Phase continuous direct digital synthesizers are used to generate transmit and local oscillator frequencies in an agile frequency diverse way to disambiguate range. Fiber-optic coupling mitigates systematic errors such as variable detector group delay and provides for multiplexing multiple transmit and receive optics onto a single electro-optical system.
Owner:NATIONAL UNITED UNIVERSITY
Sequential approximation analog to digital converter with digital correction and processing method thereof
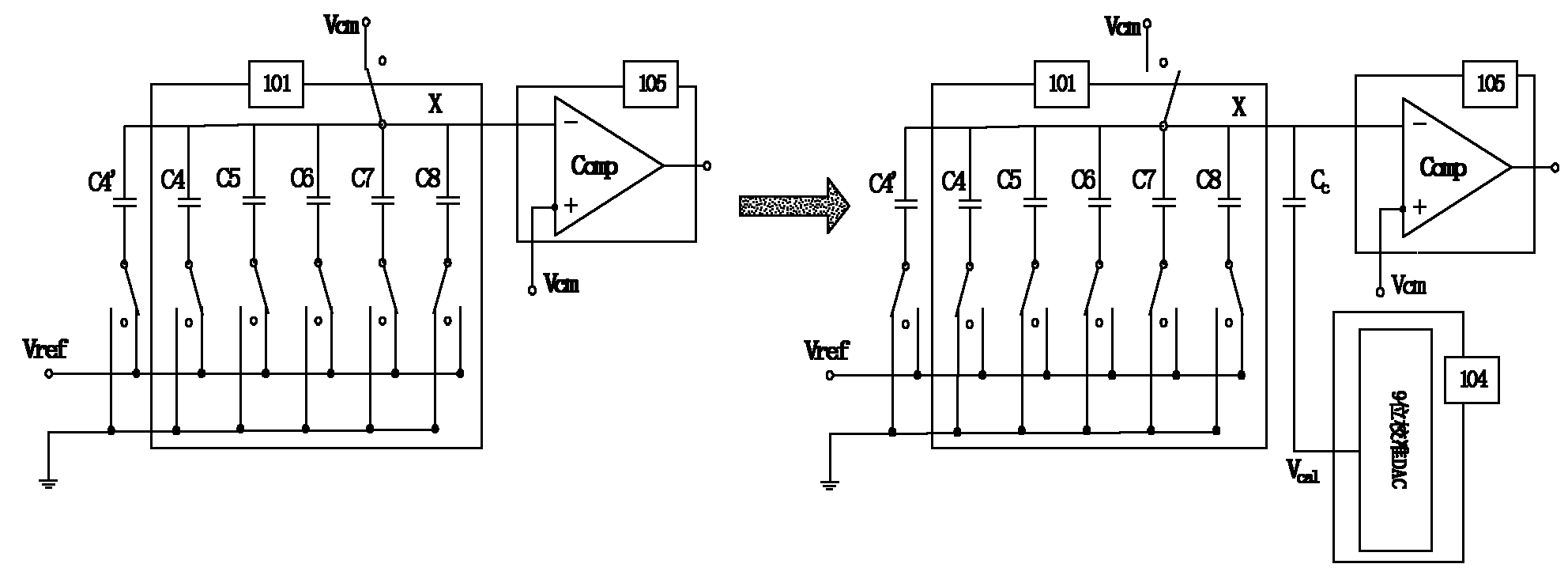
InactiveCN101977058AAvoid makingImprove matchElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingCapacitanceDigital down converter
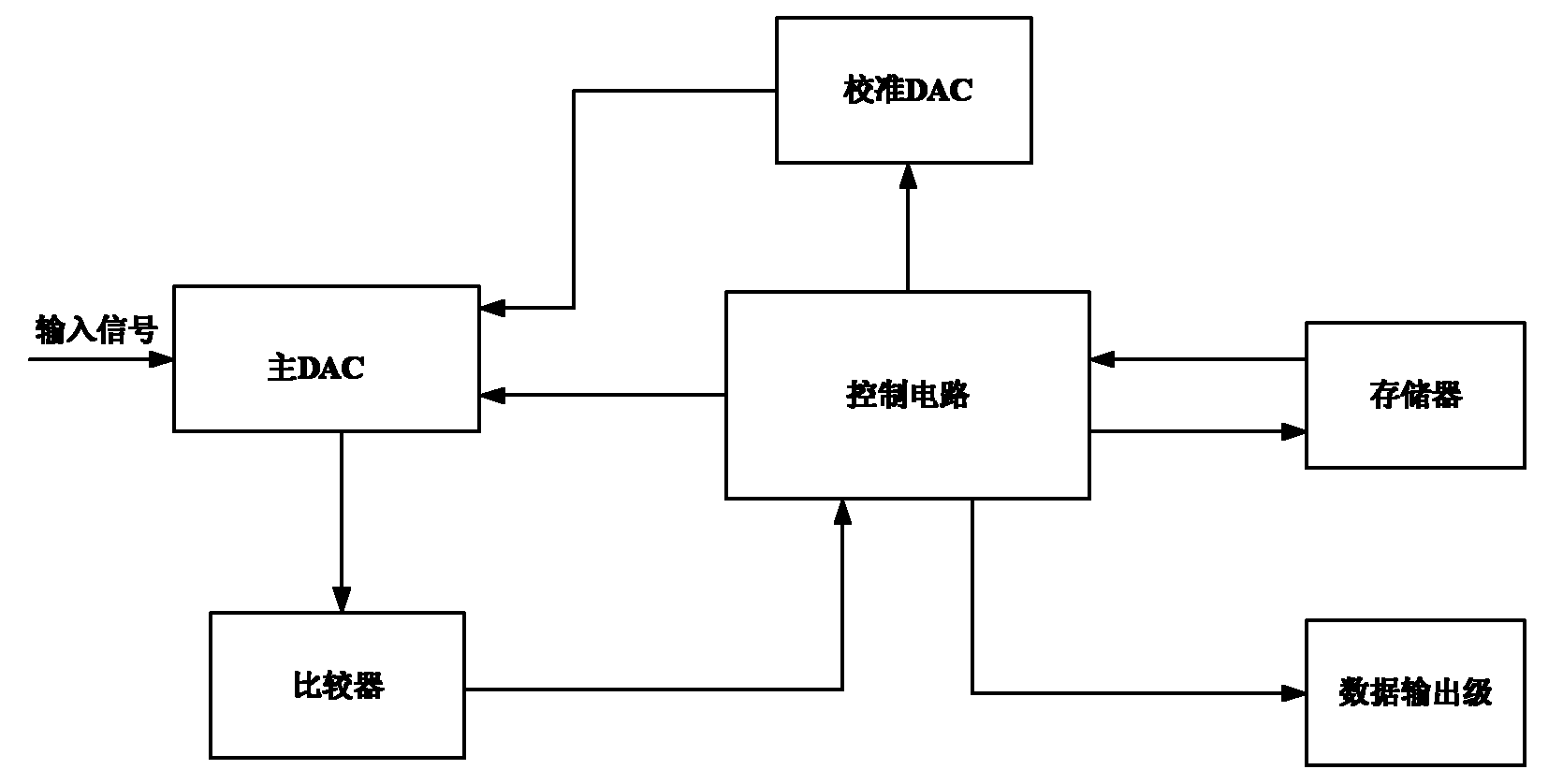
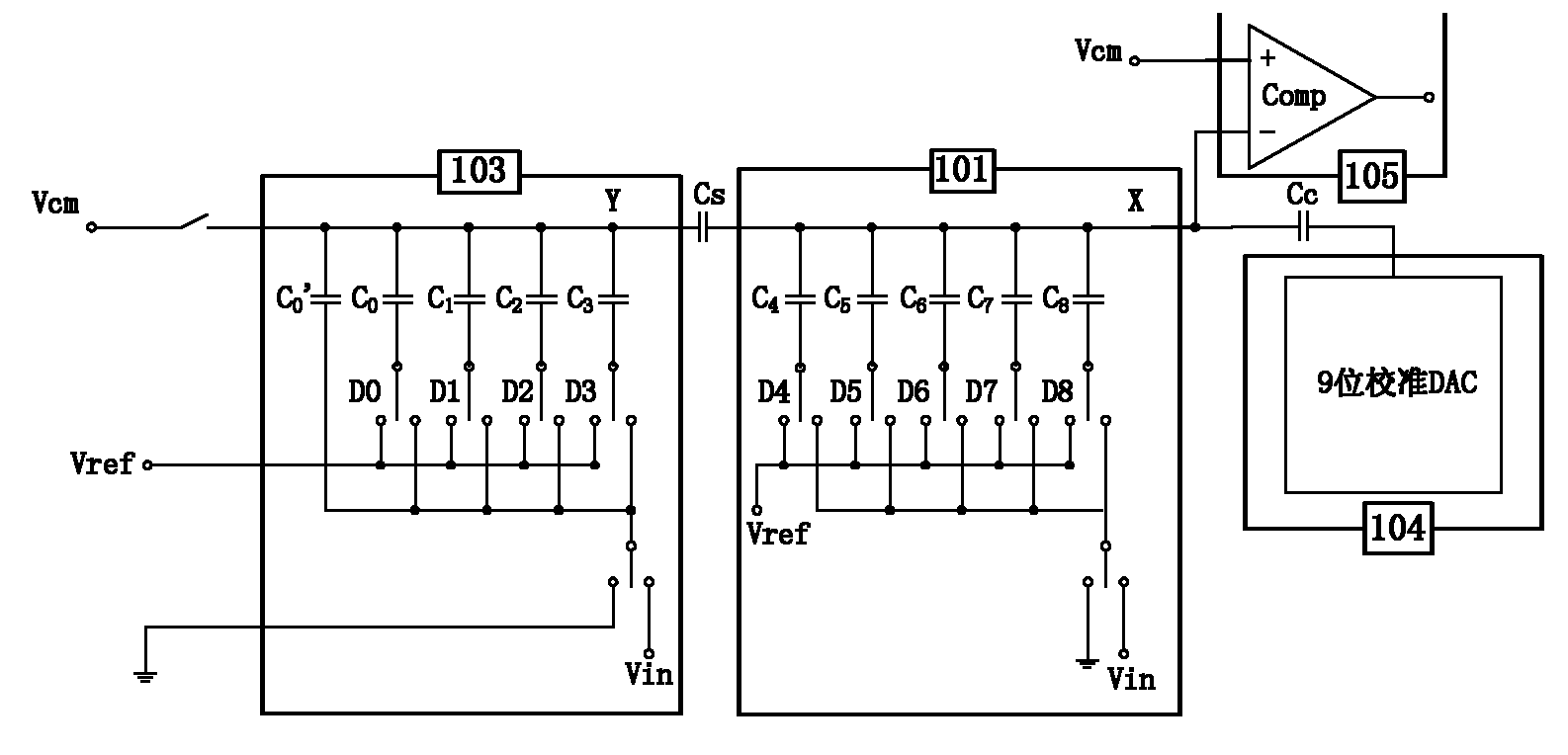
The invention discloses a sequential approximation analog to digital converter with digital correction and a processing method thereof aiming at the defect of difficult composition manufacture of a coupling capacitor in the traditional sequential approximation analog to digital converter. The sequential approximation analog to digital converter comprises a main DAC (Digital Analogue Converter), acalibration DAC, a comparer, a control circuit and a storage. The sequential approximation analog to digital converter is characterized in that the main DAC comprises a high-K-bit CDAC (Capacitance Digital Analogue Converter) and a low-N-bit CDAC. Introduced system errors and capacitance matching errors are digitally corrected and eliminated, error voltages corresponding to capacitors in the high-K-bit CDAC are quantized and stored in the storage, and two-digit 0 are added behind the tail of the quantized residual error voltage digital code and participate in the calculation of the error voltages. When normal conversion is carried out, the error voltage digital codes are accumulated and then last two digits are discarded, the remain digital codes are used as the input of the calibration DAC, thus the accuracy of the analog to digital converter is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and methods of deriving differential fluid properties of downhole fluids
ActiveUS20060155472A1Reducing and eliminating systematic errorRobust and accurate comparisonElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingFormation fluidContamination
Methods and systems are provided for downhole analysis of formation fluids by deriving differential fluid properties and associated uncertainty in the predicted fluid properties based on downhole data less sensitive to systematic errors in measurements, and generating answer products of interest based on the differences in the fluid properties. Measured data are used to compute levels of contamination in downhole fluids using, for example, an oil-base mud contamination monitoring (OCM) algorithm. Fluid properties are predicted for the fluids and uncertainties in predicted fluid properties are derived. A statistical framework is provided for comparing the fluids to generate robust, real-time answer products relating to the formation fluids and reservoirs thereof. Systematic errors in measured data are reduced or eliminated by preferred sampling procedures.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
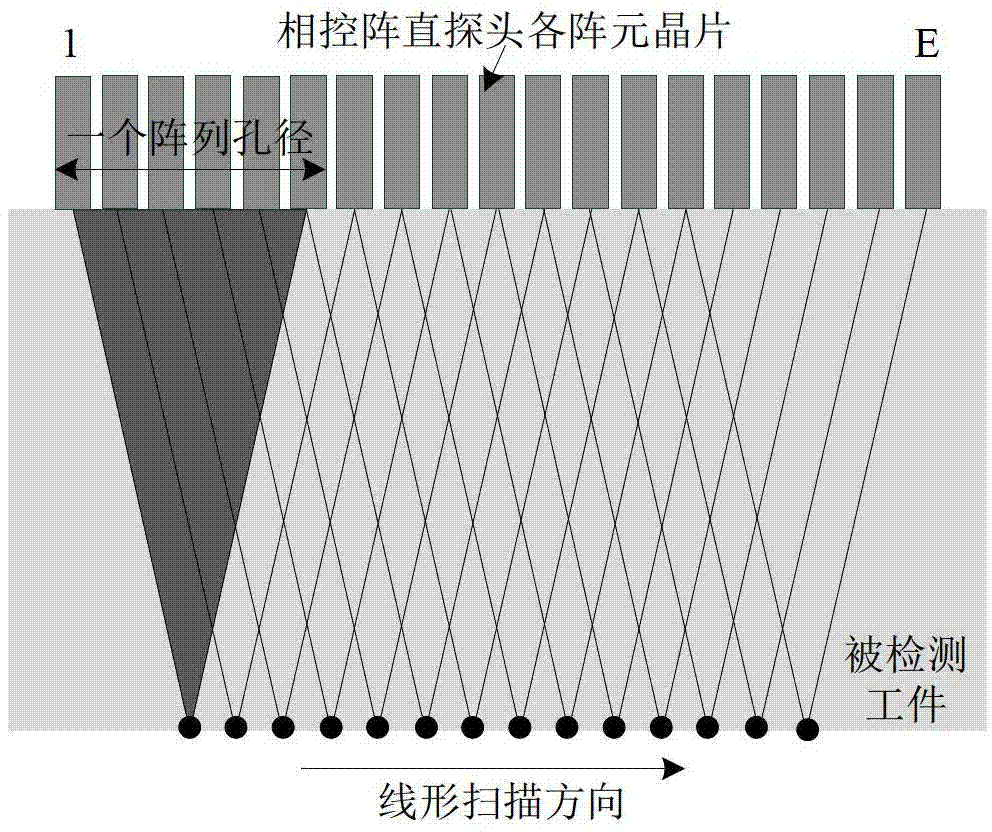
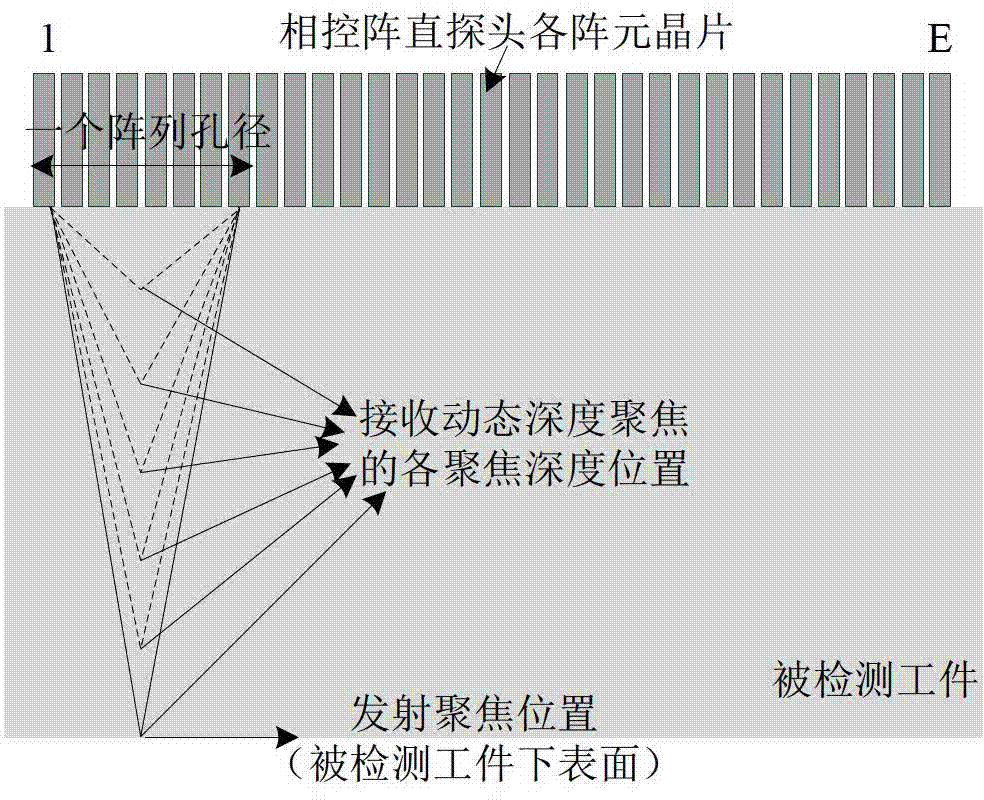
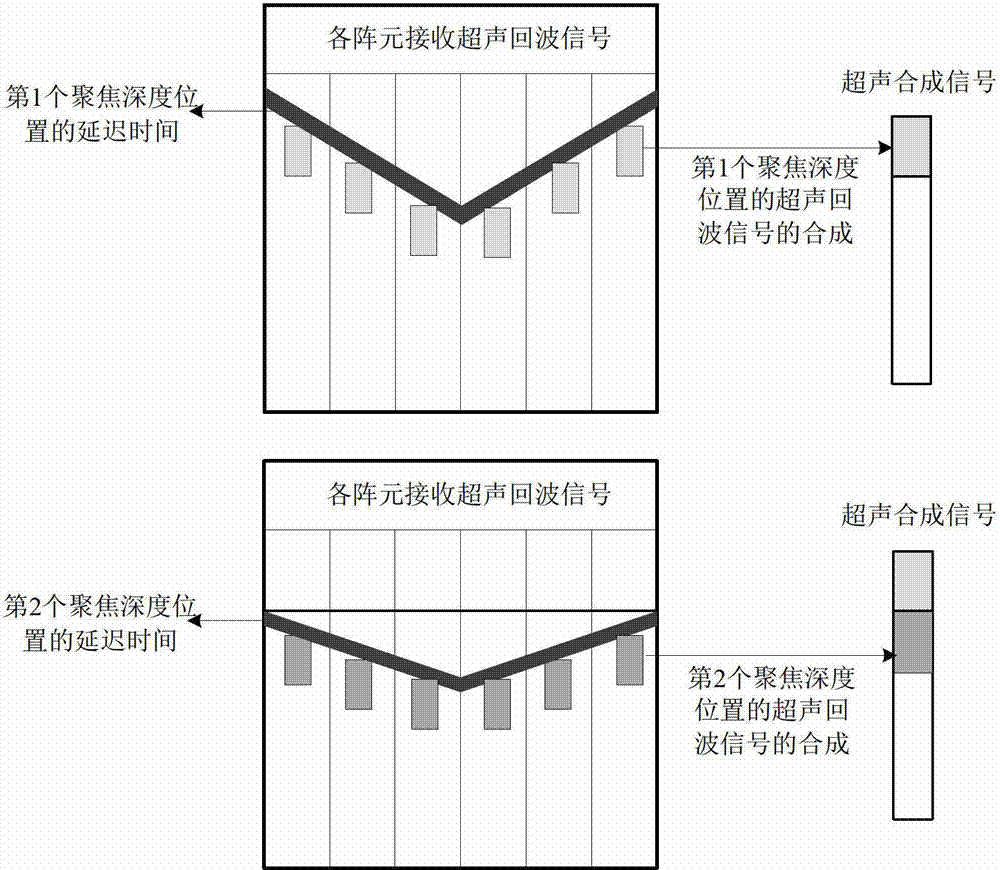
Phased array ultrasonic testing method based on improved dynamic depth focusing
InactiveCN102809610AAccurate focusSolve the problem of difficult defect identificationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalSonificationUltrasonic transmission
The invention belongs to the technical field of non-destructive testing and particularly discloses a phased array ultrasonic testing method based on improved dynamic depth focusing. The method comprises the following five steps of: performing phased array ultrasonic transmission and reception, discriminating a defect, calculating delay time, post-processing echo signals and reconstructing a B type drawing. The ultrasonic echo signals are accurately focused to the position of the defect, so that the problem that the defect is difficult to identify when the signal-to-noise ratio of a reflection echo signal of the defect is too low can be solved; by the method, the problem that the deviation exists between an ideal focus and an actual focus because a material of a tested workpiece is nonuniform can be effectively solved, and the testing resolution of phased array ultrasonic testing of layered media and anisotropic media can be effectively improved; and by the method, the problems that ultrasonic imaging results are fuzzy and distorted due to errors of hardware systems such as phased array flaw detectors can also be solved, and the quality of phased array ultrasonic imaging can also be improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
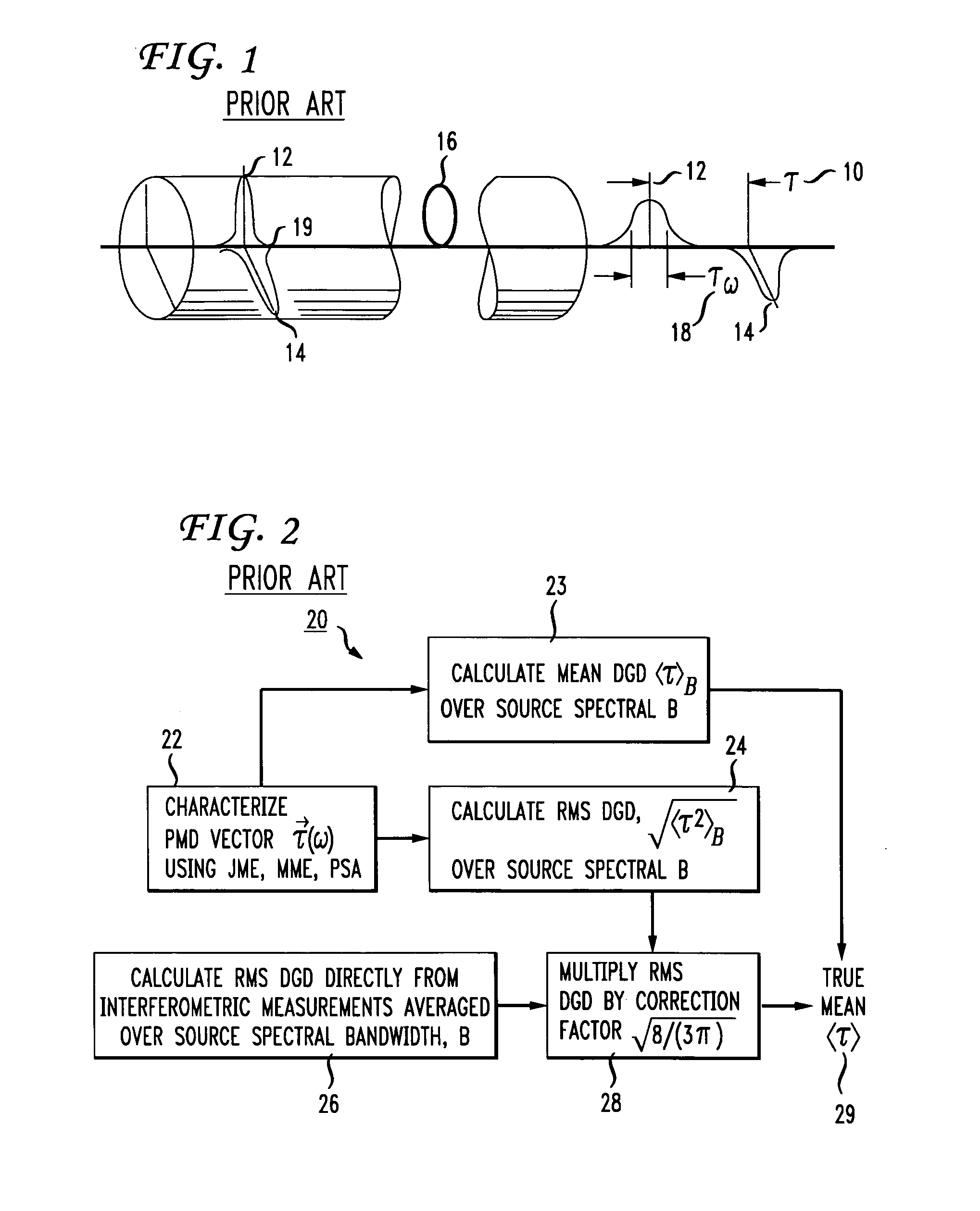
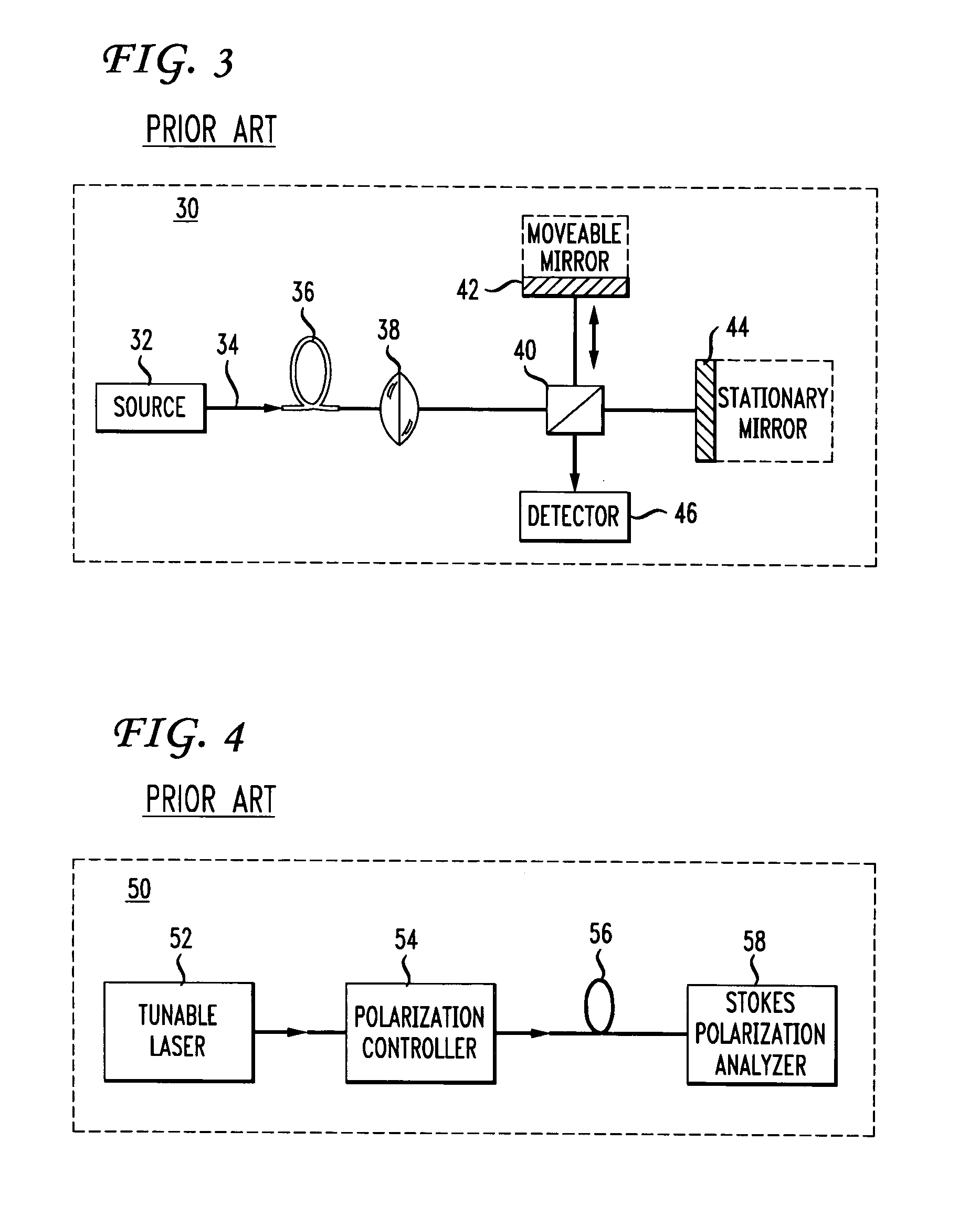
Method for increasing accuracy of measurement of mean polarization mode dispersion
InactiveUS7292322B2High measurement accuracyError minimizationMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic transmissionMean squarePolarization mode dispersion
The present invention provides a method for increasing the accuracy of measurement of mean differential group delay (DGD) from the polarization mode dispersion (PMD) in optical fiber. The method includes a systematic correction to mean-square DGD measured with any conventional mean to minimize systematic error caused by finite source bandwidth. The method further includes a systematic correction to the measurement of mean DGD and mean square DGD from statistics of the second-order PMD (SOPMD) obtained with frequency domain PMD-measuring apparatus. The probability density function (PDF) of either the vector or scalar SOPMD is applied, depending on which quantity is measured. The systematic correction is made to minimize the systematic error in estimating mean DGD, caused by finite source bandwidth, to achieve a two-fold reduction of the measurement variance equivalent to doubling the source bandwidth.
Owner:FICO MIRRORS SA +1
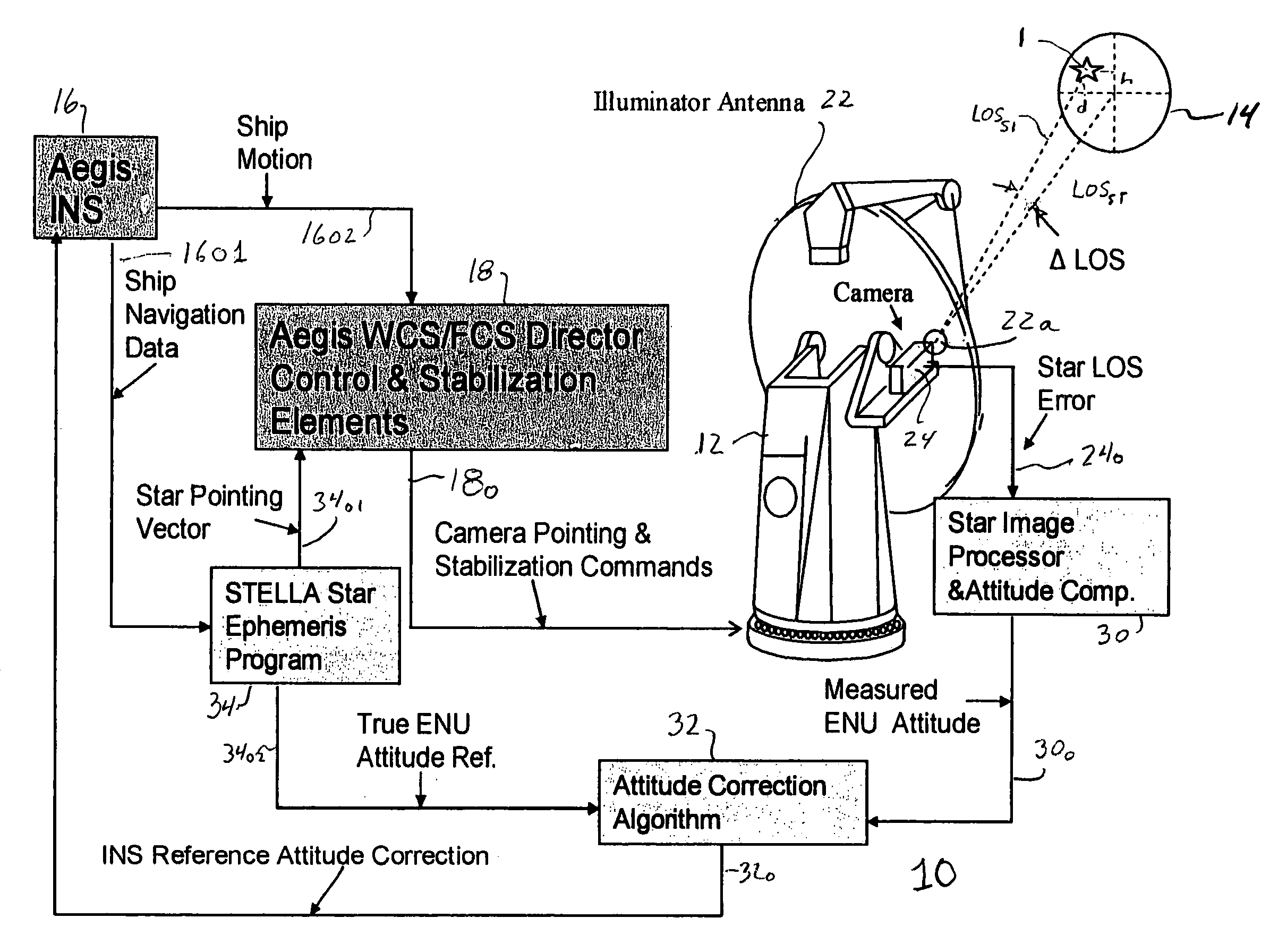
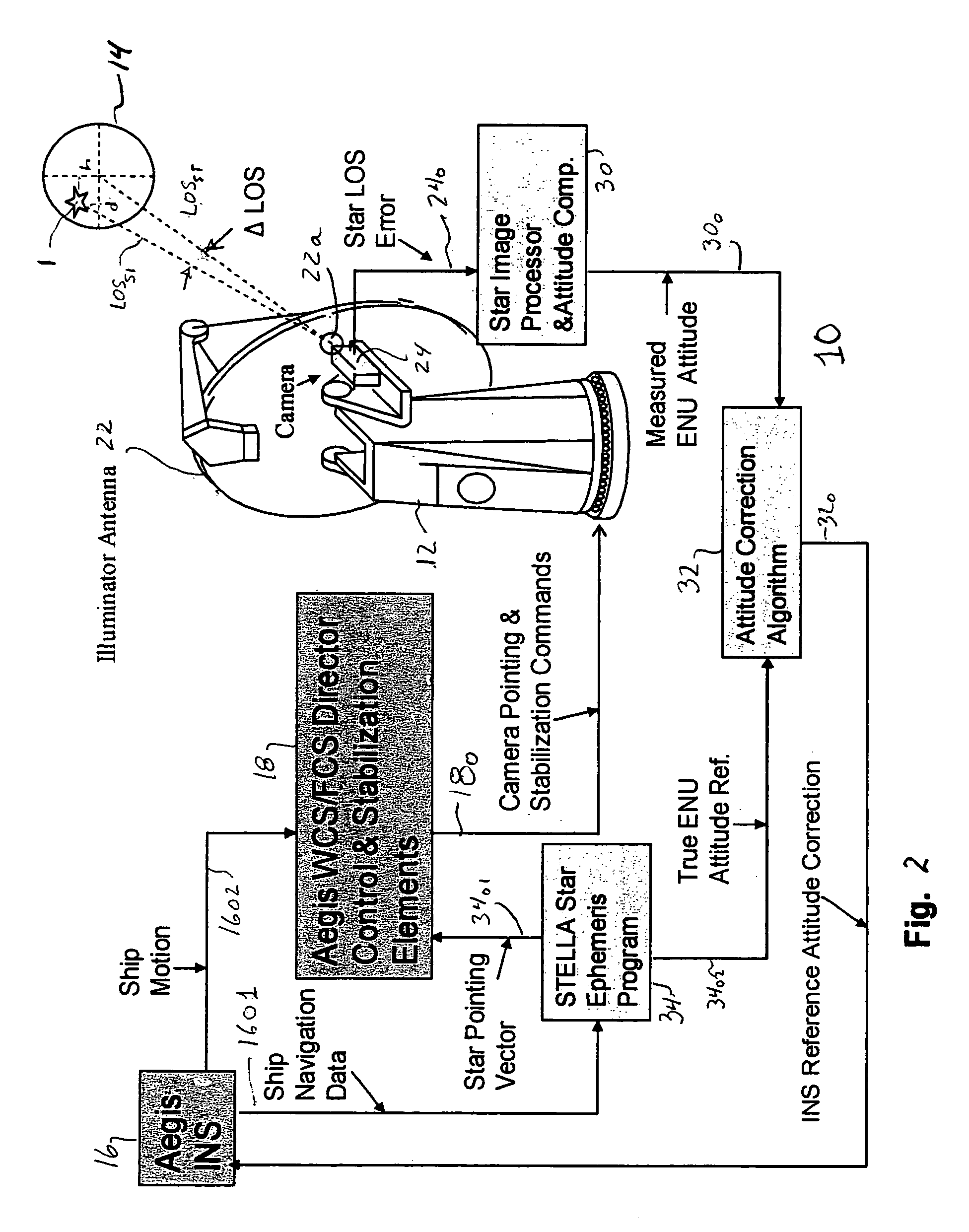
Calibration of ship attitude reference
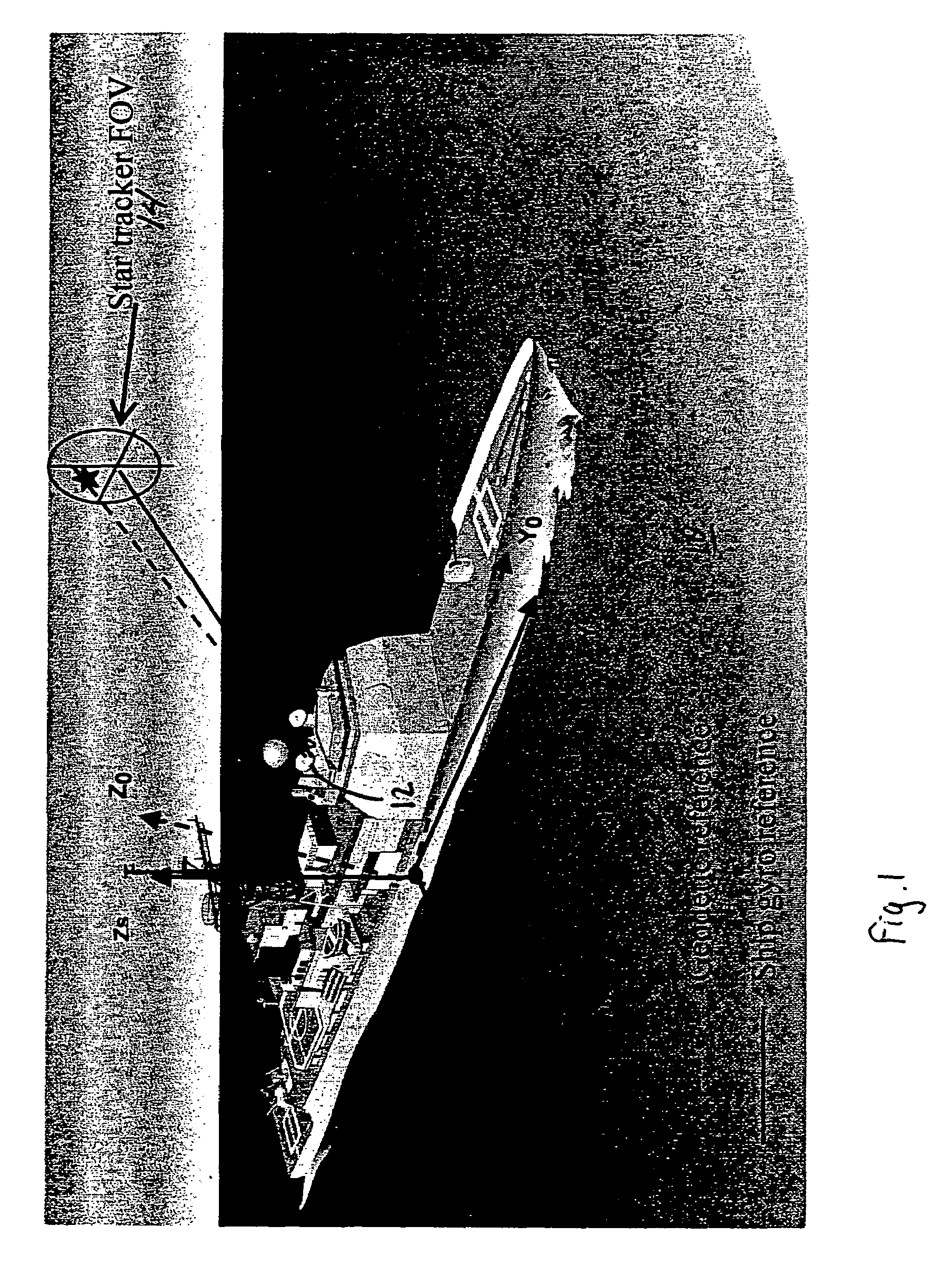
A ship includes a star tracker mounted on a platform stabilized in ENU by the inertial navigation system (INS). The line-of-sight (LOS) of the star tracker is directed toward two separated stars, and the LOS difference angles are noted. The angles are processed to generate vector triads representing geodetic (ephemeris) and navigation system attitude. The triads are processed to generate a coordinate transformation matrix. The transformation matrix is separated into systematic error and reference attitude error. The reference attitude error is summed with the inertial navigation system attitude to generate corrected ENU attitude. The corrected attitude is used as a reference for shipboard sensors, to reduce errors when the sensor data is linked to other platforms.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Agricultural machines navigation hierarchical positioning process and system
InactiveCN101285686AAvoid abnormal resultsStable positionNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterDynamic positioning
The invention discloses a graded positioning method for agricultural machinery navigation, comprising the following steps of acquiring a first positioning parameter, utilizing a Kalman filter to fuse the first positioning parameter, acquiring a second positioning parameter, acquiring a third positioning parameter, utilizing multi-sensor self-adaptive weighted fusion algorithm to fuse the second positioning parameter with the third positioning parameter, acquiring a target positioning parameter and positioning agricultural machinery according to the target positioning parameter. The invention also discloses a graded positioning system for agricultural machinery navigation. By fusing the positioning parameters acquired by measurement equipment for a plurality of times, the graded positioning method can smooth DGPS positioning data, effectively avoid the abnormal results of DGPS dynamic positioning, effectively filter test noise, reduce systematic error, form continuous, stable and accurate the information of the positions and course heading angles of agricultural machinery, and improve the positioning accuracy of agricultural machinery navigation.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Write compensation for data storage and communication systems
InactiveUS6982939B2Television system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersCommunications systemChannel sensitivity
Methods and systems for write compensation for optimizing the performance of a data storage or communication channel are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method comprises determining channel sensitivity to modifications in write signal parameters, detecting systematic errors in a read signal recovered from data written with a first set of write parameters, and adjusting the write signal parameters by an amount determined from the channel sensitivity such that the systematic errors are reduced when data are written with the adjusted write parameters.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Photo-etching machine projection objective wave aberration on-line detection method
InactiveCN101236362AHigh measurement accuracyGood repeatabilityPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPoint diffraction interferometerWave aberration
The invention relates to an on-line detection method for detecting the wave aberration of a projection objective of a photoetching machine. The on-line detection, revising, and controlling are done to the wave aberration of the projection objective by integrating an interferometer device on the photoetching machine. The interferometer device is a point-diffraction interferometer or a slit-diffraction interferometer and is provided with two measuring modules: a PSI measuring module and an FTM measuring module. The PSI measuring module adopts phase shifting interferometry with high measuring precision and is mainly used to detect the error calibration in an interferometer device system; the FIM measuring module adopts fourier transform method to treat with interference fringes with high measuring speed, and is mainly used to on-line detect and control the wave aberration of the projection objective. The method improves the measuring precision without reducing the measuring speed, and improves the measuring precision and reproducibility of the interferometer device by adopting a higher quality spherical reference wave to calibrate the systematic error caused by each component of the interferometer device without reducing the contrast ratio of the interference fringes.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Rotatable orientation independent gravity sensor and methods for correcting systematic errors
InactiveUS20100145620A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingTesting/calibration apparatusAccelerometerGravitation
A method to correct for a systematic error of a sensor having a plurality of accelerometers configured to measure gravitational acceleration, the method including: rotating the plurality of accelerometers about a first axis; obtaining a first set of calibration measurements from the plurality of accelerometers from the rotation about the first axis; determining a first systematic error for each accelerometer in the plurality using the first set of calibration measurements; and removing the first systematic error from sensor measurements to correct for the systematic error.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
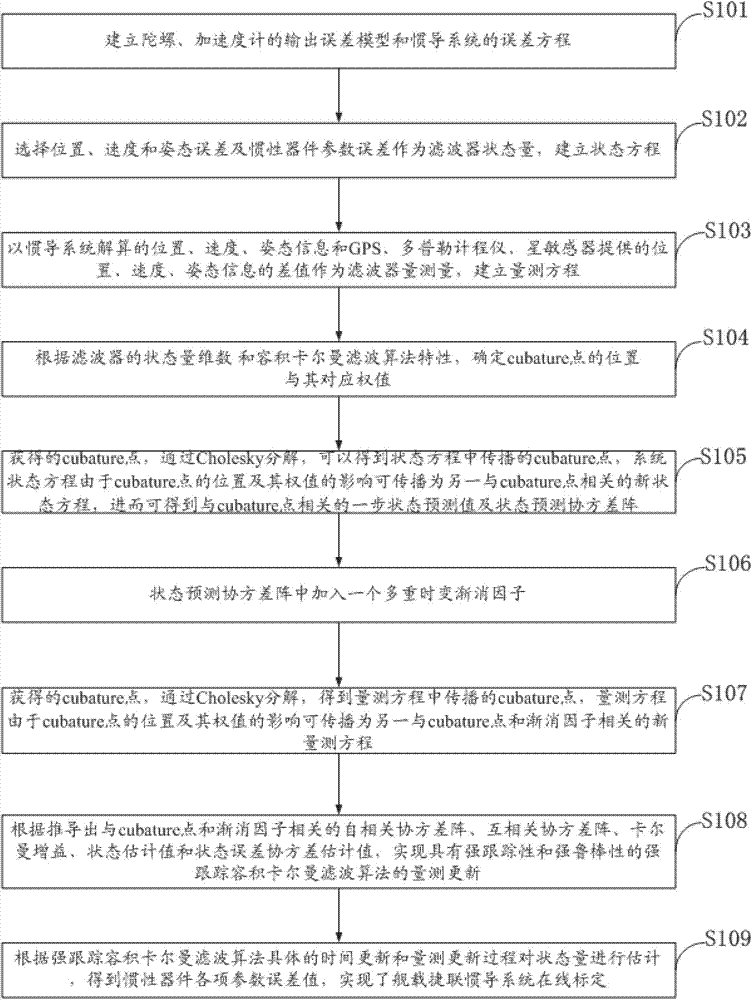
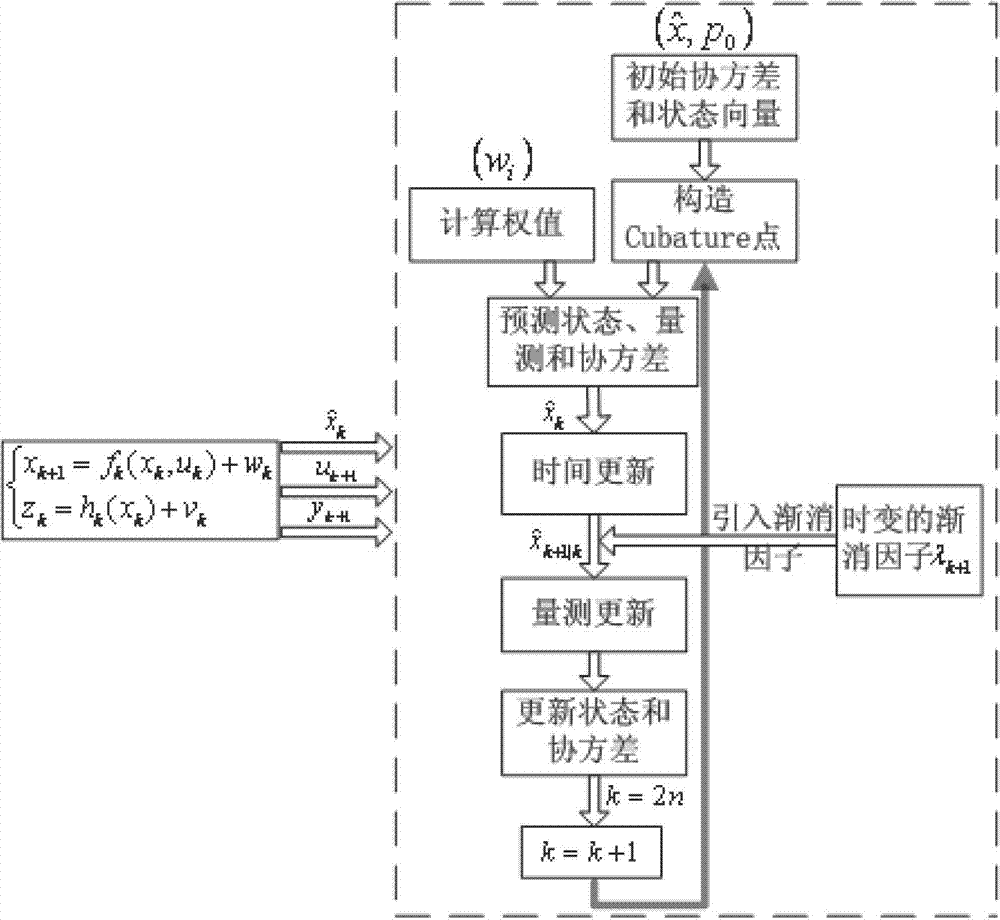
Online calibrating method of ship-based rotary strapdown inertial navigation system
InactiveCN103591965AImprove navigation accuracyEasy to handle calculationsMeasurement devicesState predictionFilter algorithm
The invention discloses an online calibrating method of a ship-based rotary strapdown inertial navigation system. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an inertial component output error model and an inertial navigation system error equation, and researching the calibration of inertial component parameter errors and determining the quantity of state and the quantity of measuration; determining the position and weight of a cubature point according to dimension of the quantity of state, deducing a state equation and a one-step state prediction and state prediction covariance matrix related to the cubature point, and introducing a multiple time-varying fading factor modified state prediction covariance matrix; and deducing a measuring equation related to the cubature point and the fading factors, a self-correlated covariance matrix, a cross-correlated covariance matrix, a gain matrix, a state estimated value and a state error covariance estimated value, and designing a strong tracking volume Kalman filtering method with strong tracking performance and strong robustness. The method disclosed by the invention estimates the inertial component parameter errors by a filtering algorithm and carries out online calibration and compensates the inertial component parameter errors, so that the navigation precision is effectively improved. The method has strong parameter-varying robustness.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
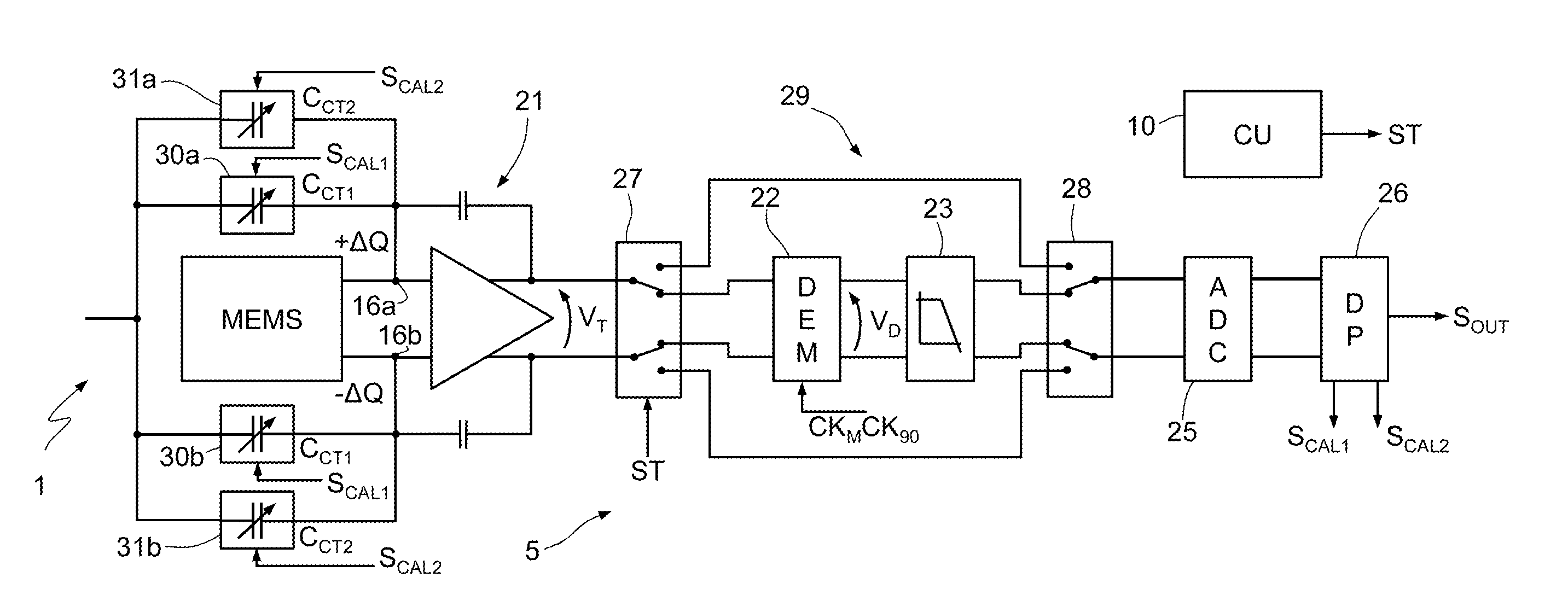
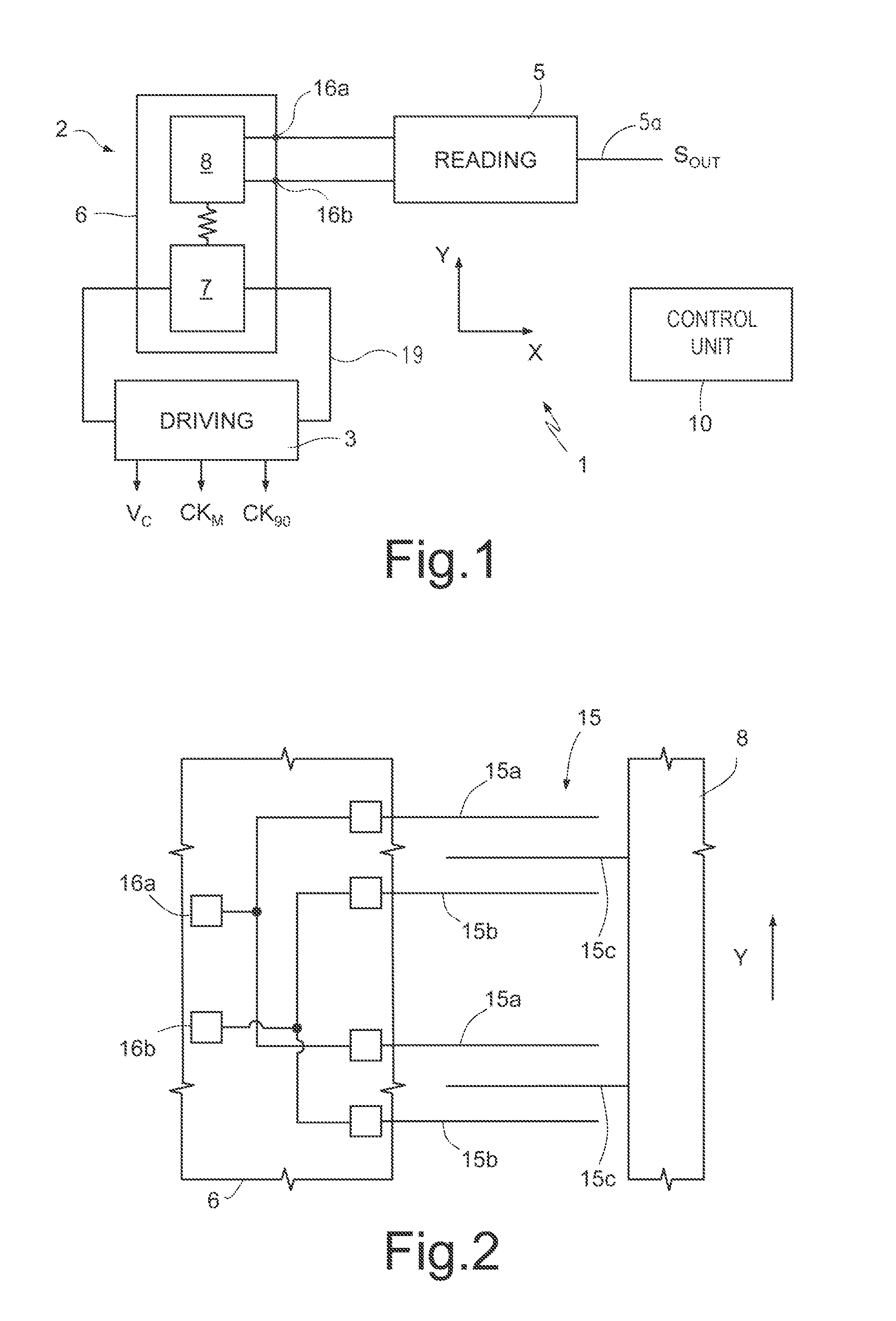
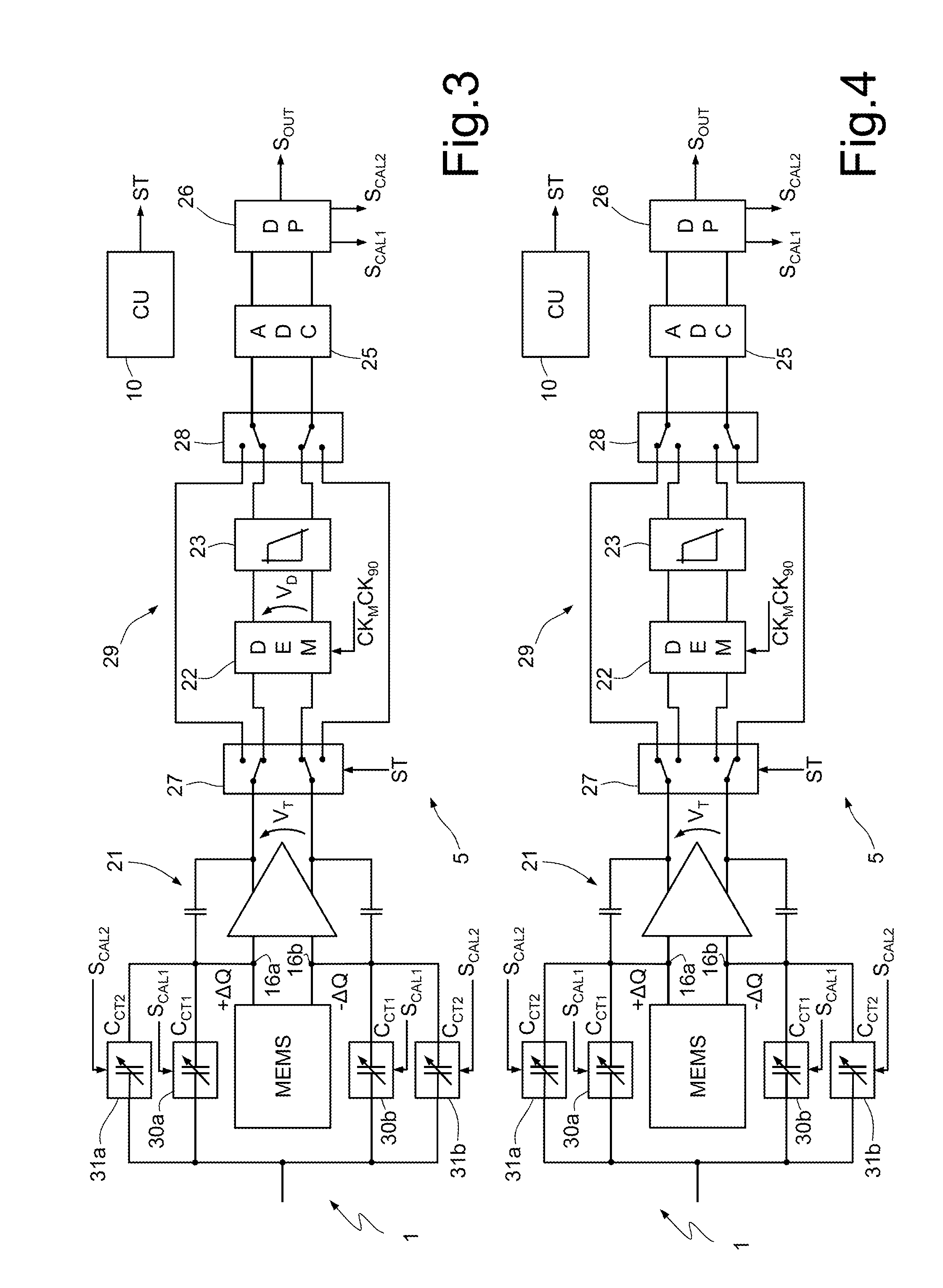
Microelectromechanical gyroscope with self-calibration function and method of calibrating a microelectromechanical gyroscope
A microelectromechanical gyroscope having a supporting structure; a mass capacitively coupled to the supporting structure and movable with a first degree of freedom and a second degree of freedom, in response to rotations of the supporting structure about an axis; driving components, for keeping the mass in oscillation according to the first degree of freedom; a read interface for detecting transduction signals indicating the capacitive coupling between the mass and the supporting structure; and capacitive compensation modules for modifying the capacitive coupling between the mass and the supporting structure. Calibration components detect systematic errors from the transduction signals and modify the capacitive compensation modules as a function of the transduction signals so as to attenuate the systematic errors.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Image navigation and registration accuracy improvement using parametric systematic error correction
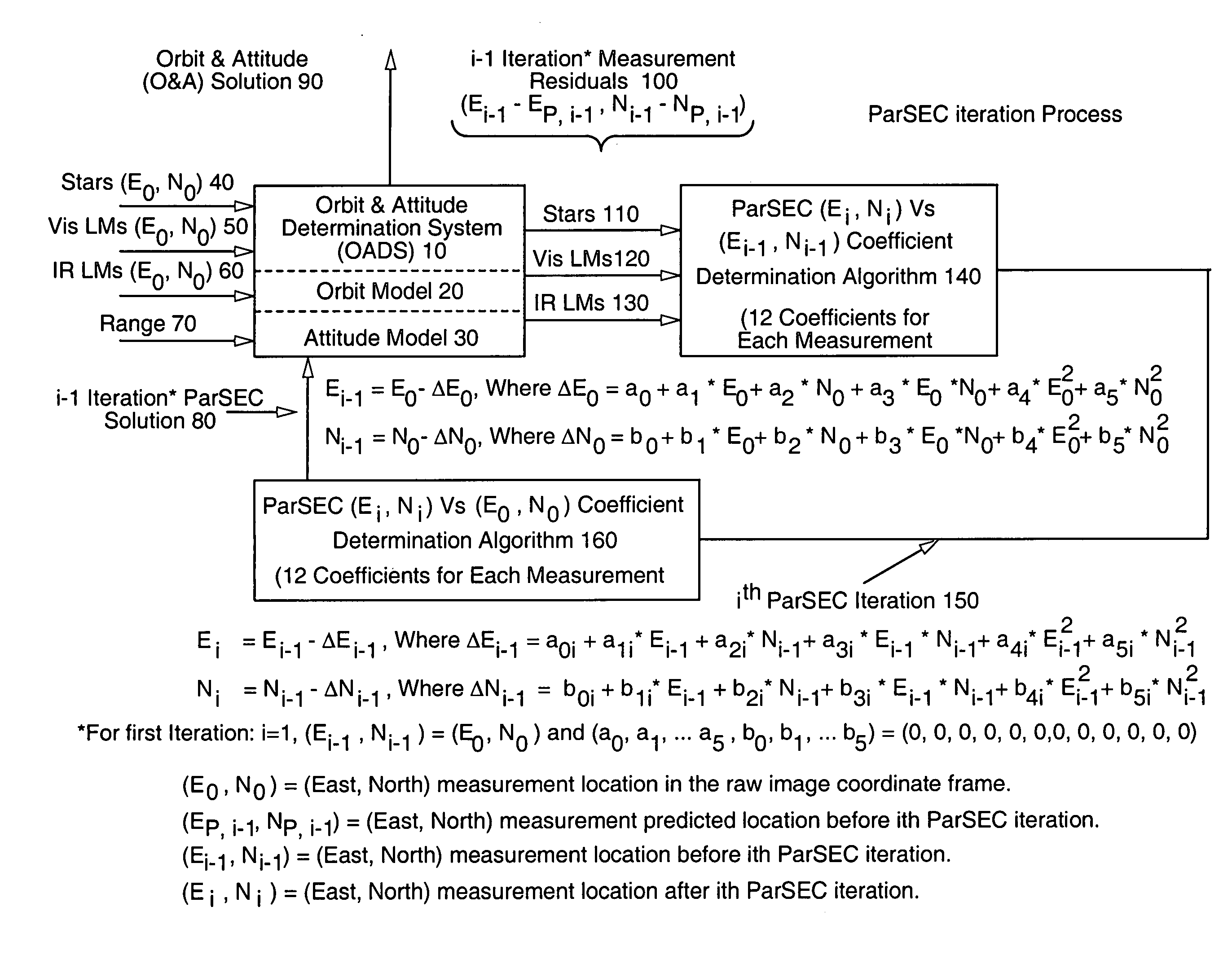
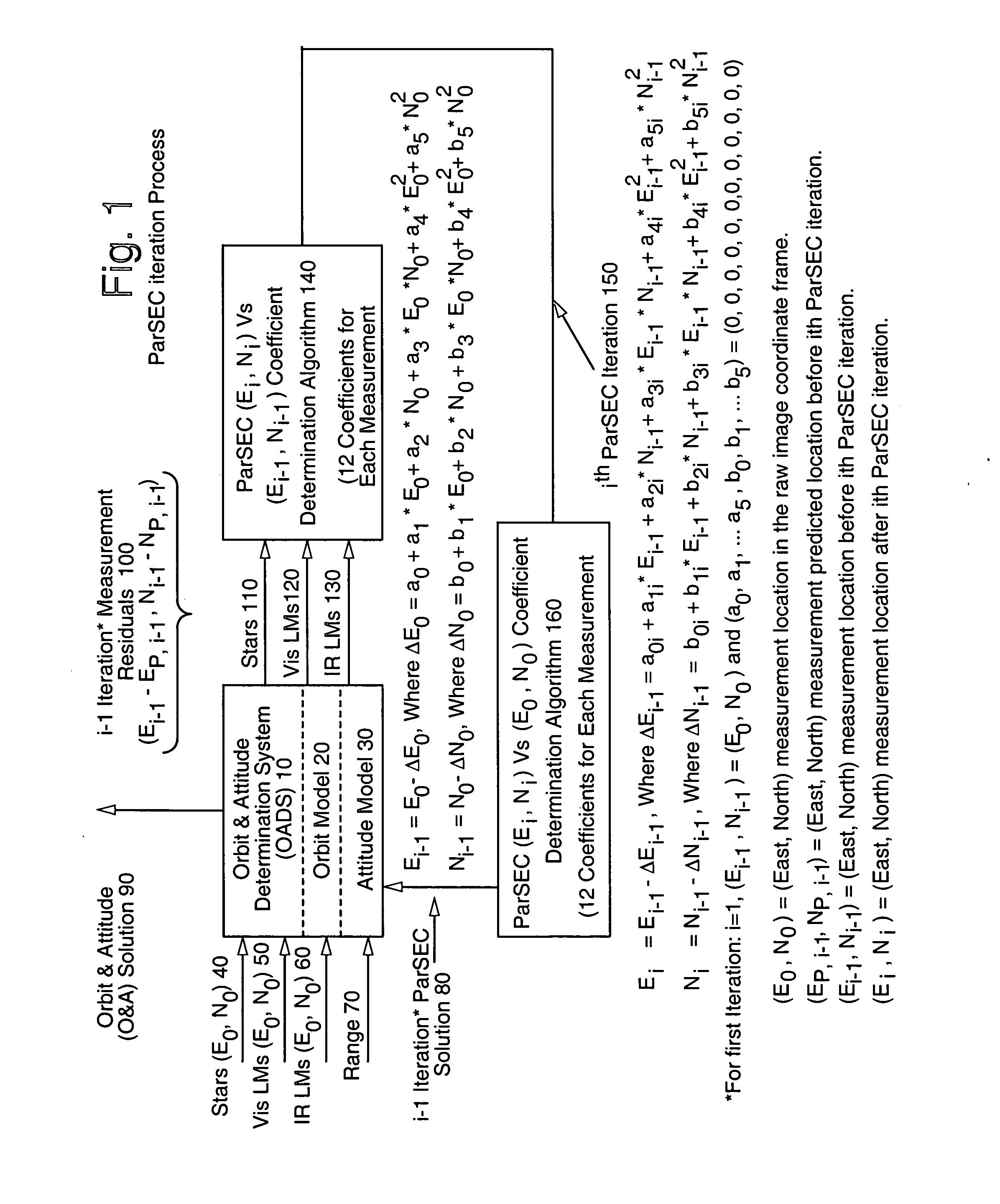
InactiveUS20080114546A1Eliminate the effects ofImprove matchPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsParsecLandmark
A novel Parametric Systematic Error Correction (ParSEC) system is disclosed which provides improved system accuracy for image navigation and registration (INR). This system may be employed in any suitable imaging system and, more specifically, to all imaging systems that exhibit systematic distortion. The ParSEC system may be employed to any such system regardless of sensing type (remote or in situ) or imaging media (photon or charged particle) and is further applicable to corrected imaging of any celestial body currently detectable to remove distortion and systematic error from the imaging system employed. The ParSEC system of the instant invention comprises a software algorithm that generates at least about 12 correction coefficients for each of the INR system measurements such as stars, visible landmarks, infrared (IR) landmarks and earth edges. An iterative estimation algorithm such as, for example, least squares or Kalman filters may be employed to determine the at least about 12 correction coefficients from each set of measurement residuals. The improved image products provide more accurate weather forecasting such as wind velocity and temperature.
Owner:SPACE SYST LORAL INC
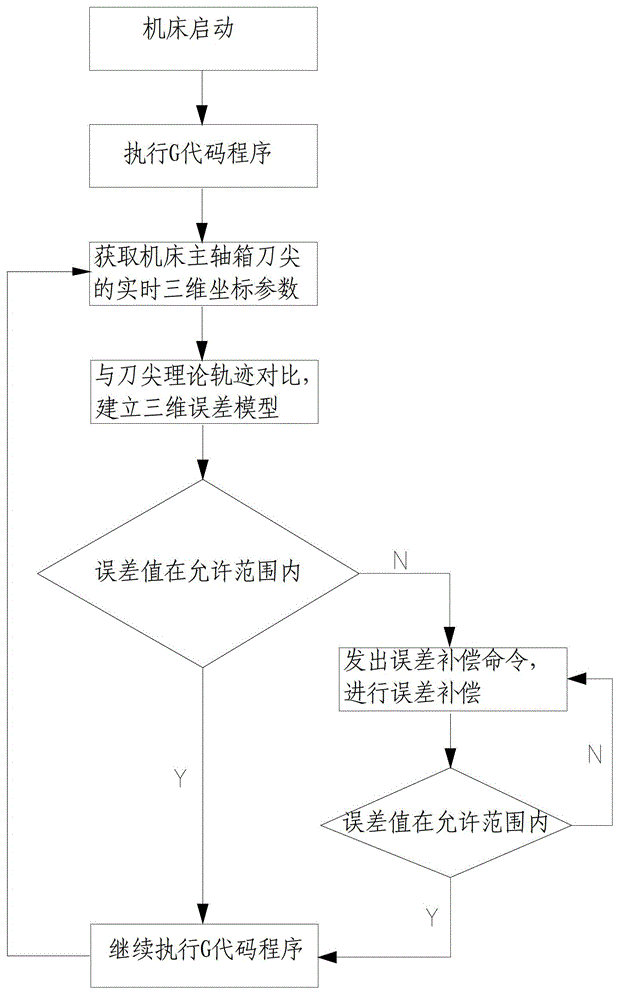
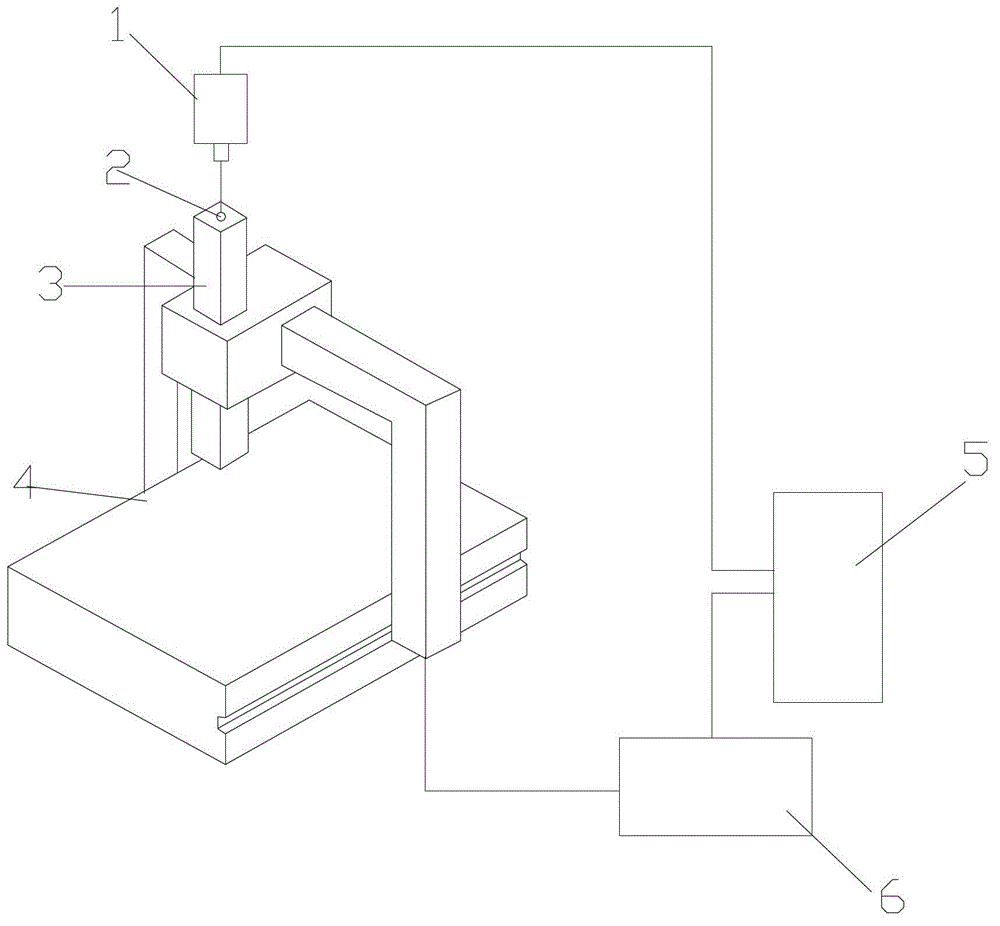
Laser tracker-based machine tool error dynamic compensation method
InactiveCN103143984AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyAutomatic control devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsEngineeringLaser tracker
The invention discloses a laser tracker-based machine tool error dynamic compensation method. A laser tracker is adopted to perform dynamic tracking detection; and the method is suitable for being used in laboratory environments with strictly controlled temperature and humidity and can also be used in workshop site environments with severer conditions. Laser interference ranging, photoelectric detection, precision machinery, a computer and a control and modern numerical value calculation theory are integrated by the laser tracker; a space moving object is tracked and spatial three-dimensional coordinates of an object are measured in real time; and the method has the characteristics of high precision, high efficiency, real-time tracking measurement, quickness and convenience in mounting, easiness in operation and the like. A machine tool is dynamically monitored and compensated in real time based on a laser tracker measurement result; error measured by using the scheme is total error obtained after all system errors and random error are superposed; and thus, all error values can be dynamically compensated in real time by the scheme, the system precision of the machine tool is greatly improved, and a detection device of the machine tool is simplified.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
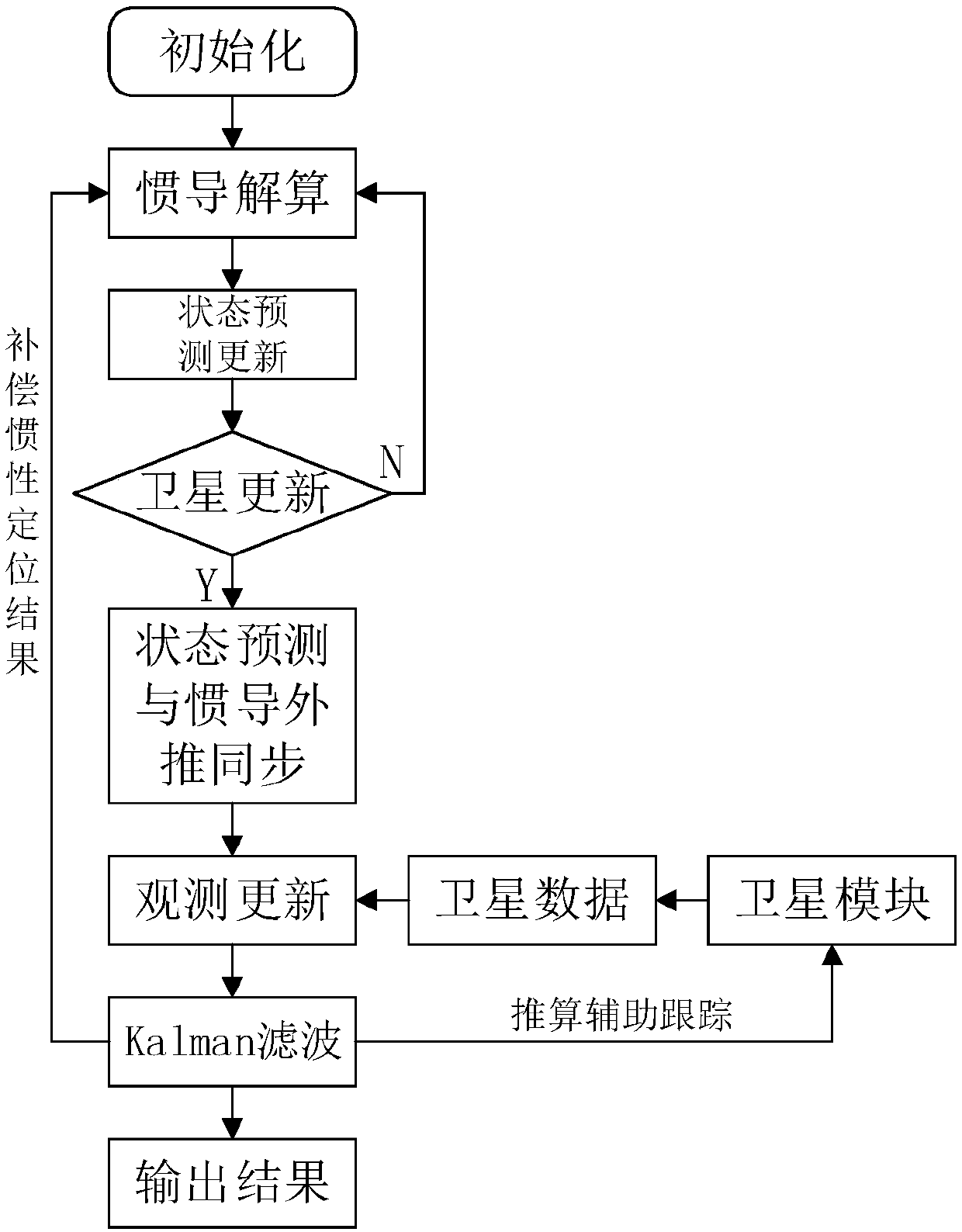
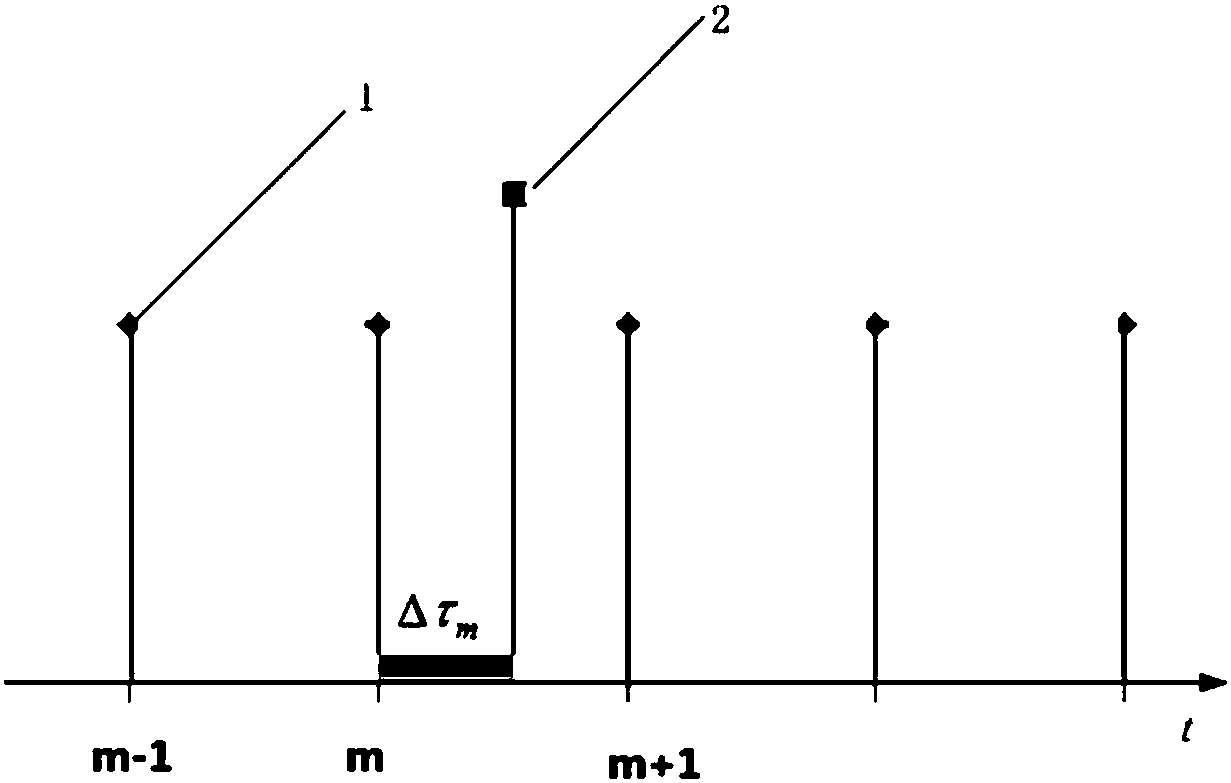
Double-rate Kalman filtering method based on GNSS/INS deep integrated navigation
ActiveCN107643534AHigh positioning accuracyIncrease update frequencyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingSatellite dataState prediction
The invention discloses a double-rate Kalman filtering method based on GNSS / INS deep integrated navigation. The method comprises the following steps of 1, building a state equation according to the initial position, the rate and the attitude information of a carrier, and initializing the parameters of the Kalman filtering; 2, performing state prediction updating on M step lengths and obtaining a predicted value of a prior state quantity which is described in the specification; 3 correcting the prior state quantity which is described in the specification to obtain a predicted value of a posterior state quantity which is described in the specification; 4, adaptively updating the errors of the state quantities and a systematic error covariance matrix, and compensating an inertial navigation result by using the predicted value of the posterior state quantity which is described in the specification to obtain the position, the rate and attitude information of the carrier; and 5, updating thepredicted value of a posterior state quantity which is described in the specification after the compensation. The method can reduce a truncation error caused by the low update frequency of GNSS satellite data or the losing lock of the satellite data during a data fusion algorithm of the GNSS / INS deep integrated navigation, and simultaneously solve a navigation positioning error caused by the non-synchronization of INS data and GNSS data.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for realizing extraction of comprehensive errors and determination of compensation values for jig system
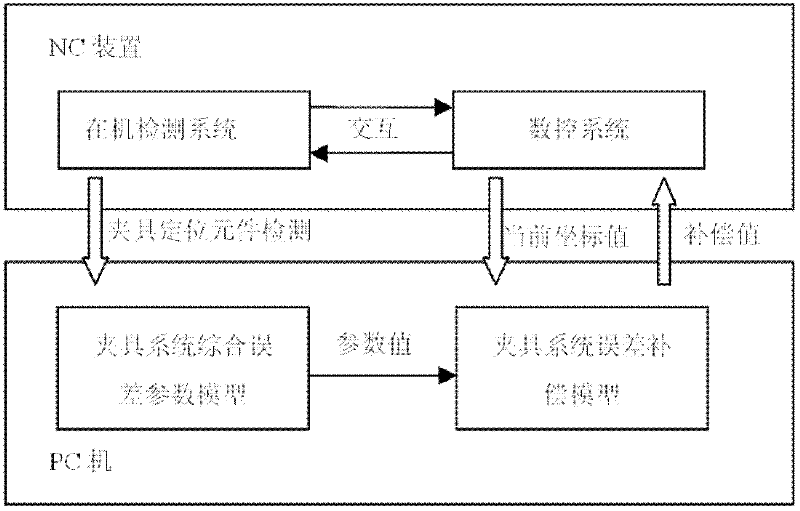
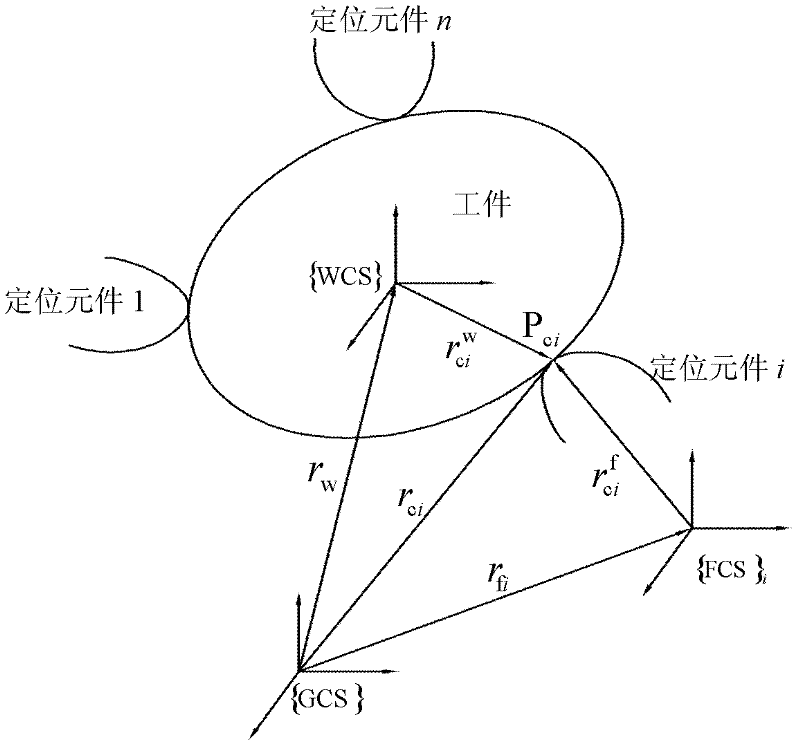
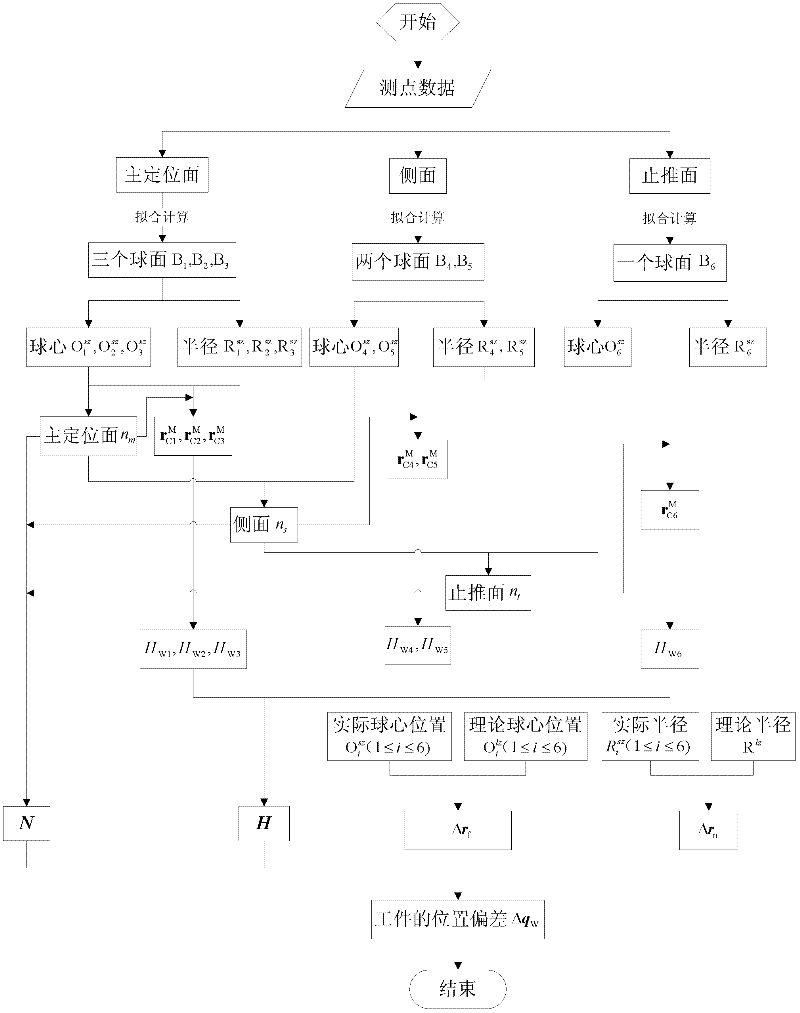
InactiveCN102225516AClarify the mapping relationshipEasy to chooseAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusSimulationErrors and residuals
The invention discloses a method for realizing extraction of comprehensive errors and determination of compensation values for a jig system, and relates to the field of mechanical processing. The method includes the following steps of: acquiring a comprehensive error parameter model of the jig system; establishing an on-machine detection platform, and determining the position and the posture deviation delta qW of a workpiece below a machine tool coordinate system on the basis of an on-machine detection technique and the comprehensive error parameter model of the system; establishing a comprehensive error compensating model of the jig system according to a coordinate transformation theory, and determining compensation values of the machine tool in three directions at each point of the motion track of a cutter by compensating operation. The method clearly and simply clarifies the mapping relation between the jig system error and the workpiece posture offset, and has a sufficient theoretical basis; a concise and precise error extraction method is provided; the precise measurement and calculation of jig errors can be realized. According to the method, the real-time processing compensation can be carried out, and the processing precision is further improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Real-time and online error testing and compensating method of rotary table angle measuring system
InactiveCN102749915AObservable Compensation ProcessObservable effectMeasurement devicesElectric testing/monitoringControl systemHarmonic
The invention discloses a error real-time and online error testing and compensating method of a rotary table angle measuring system, which comprises the steps of: testing a signal output by a controller to ensure that a rotary table system starts a closed loop, monitoring and correcting the signal u(t) output by the controller by using an oscilloscope, giving a rotating speed of the rotary table system, selecting specific rotating speeds 10 DEG / sec, 20 DEG / sec and 30 DEG / sec capable of enabling the system to reproduce, track and amplify a harmonic error signal frequency band within a closed loop bandwidth of the rotary table system, after the speed of the rotary table system is stable and constant, observing and analyzing a harmonic error of the signal output by the controller, and compensating the harmonic error. The real-time and online error testing and compensating method has the characteristics of being clear in error testing and compensating effect of the angle measuring system at a glance, increasing testing and compensating efficiencies, and overcoming the problem that the error testing and compensating method of the angle measuring system comprises complex processes of external precise reference testing and calibrating. Meanwhile, the real-time and online error testing and compensating method has the advantages of high reliability and high timeliness, and has the compensating regulation precision completely meeting the actual requirement of the angle measuring system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for analyzing and estimating measurement error of water quality automatic online monitoring equipment
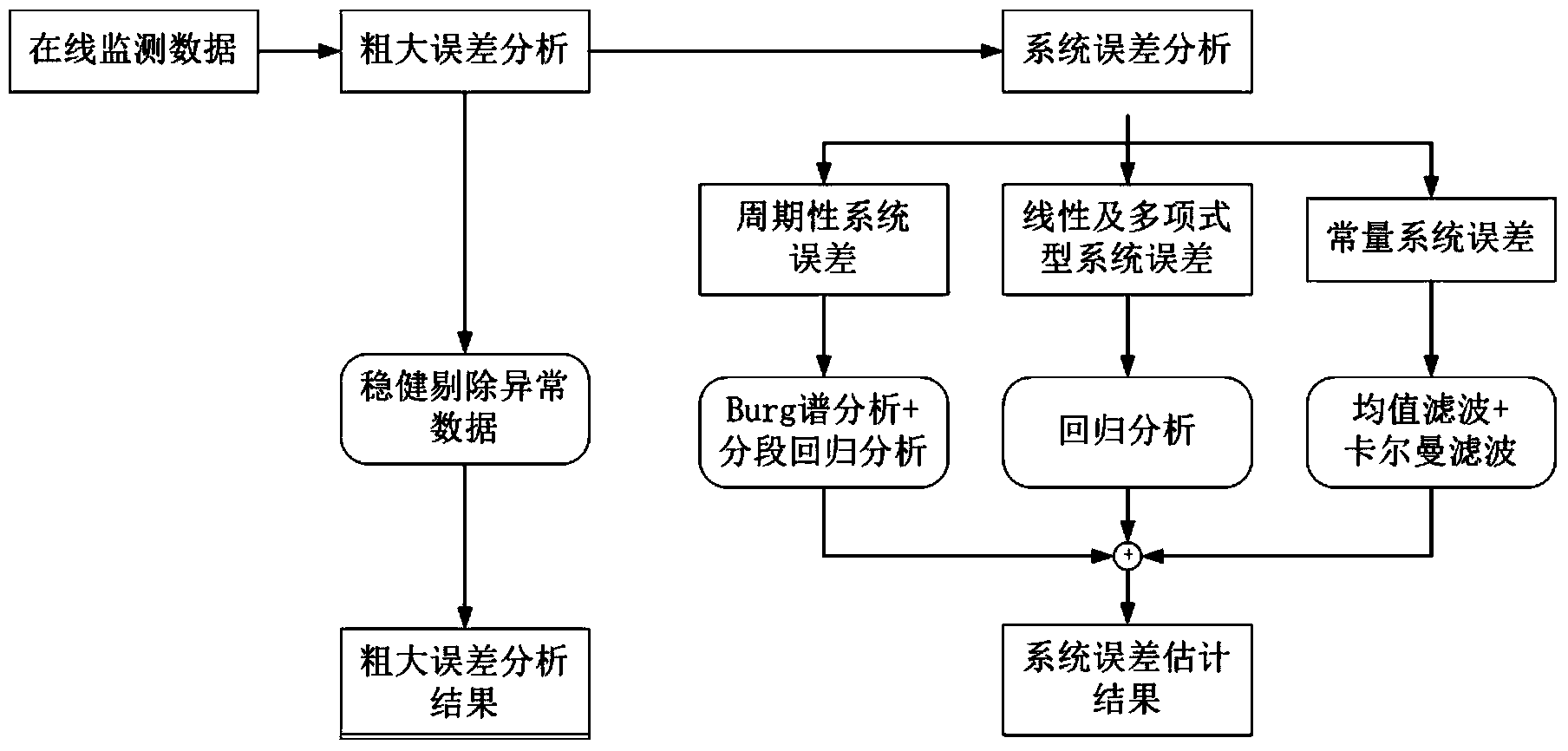
ActiveCN104280526AImprove accuracyImprove estimation accuracyTesting waterObservational errorRegression analysis
The invention discloses a method for analyzing and estimating a measurement error of water quality automatic online monitoring equipment, which is based on data comparative statistics, performs pointed error estimation in a classified manner and can improve accuracy of an estimation result. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, eliminating gross errors in online monitoring data by adopting a robust method for eliminating abnormal data; then extracting a median from the online monitoring data after the gross errors are eliminated and judging whether the median is within a water quality sample mean value confidence interval or not; if not, determining that no system error exists and ending the process; otherwise, determining existing system errors and dividing the system errors into a periodic system error, a linear and multinomial type system error and a constant system error, and estimating by respectively adopting a Burg-method-based spectrum analysis and regression analysis combined method, a regression analysis method, and a mean filtering method and Kalman filtering combined method; finally, adding the estimation results of the three types of the system errors to obtain a final system error estimation result.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com