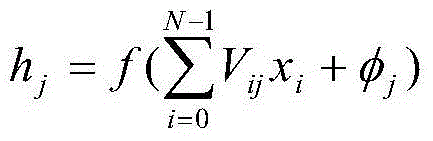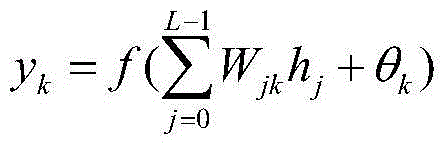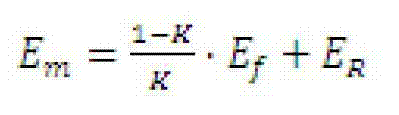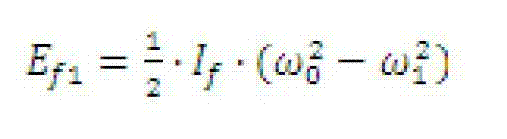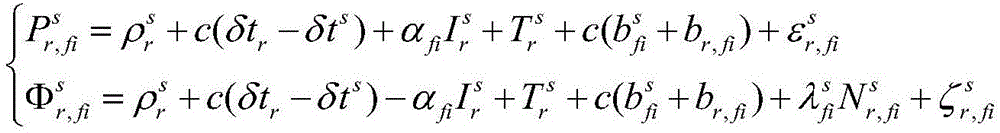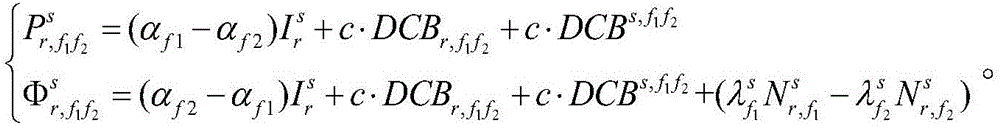Patents
Literature
188 results about "Total error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
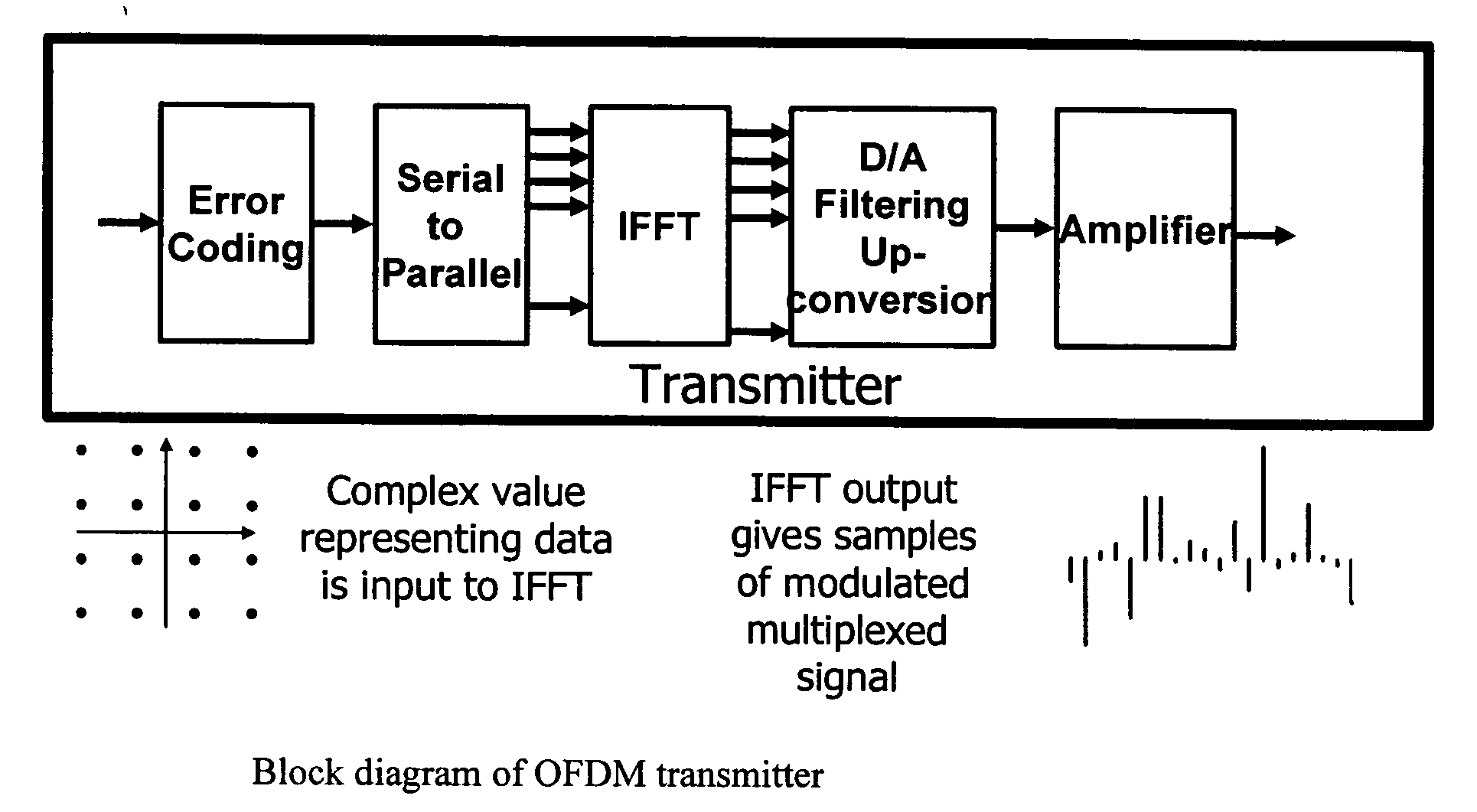
Multicarrier modulation systems
ActiveUS20050243938A1Reduce probabilityMinimize degradationDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationCarrier signalEngineering
The invention provides a new approach which is better suited to FFT design as applied to multicarrier modulation systems such as OFDM. The signals are scaled so that overflow, rather than being completely avoided, occurs with low probability throughout the IFFT and FFT structures. The size of the error that results from an overflow depends on how overflow is handled in the DSP. To minimize the degradation, overflow should result in saturation of the value at the maximum positive or negative value option. This is equivalent to clipping the signal. Using the new technique, signals within the FFT structure are scaled to balance the effect of clipping and round-off. Clipping may result in comparatively large errors in a few signal values but because of the spreading effect of the FFT and because OFDM systems typically include error coding / correction, system performance depends on the total error or, in other words the total noise power, across all of the FFT outputs rather than on any individual value.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
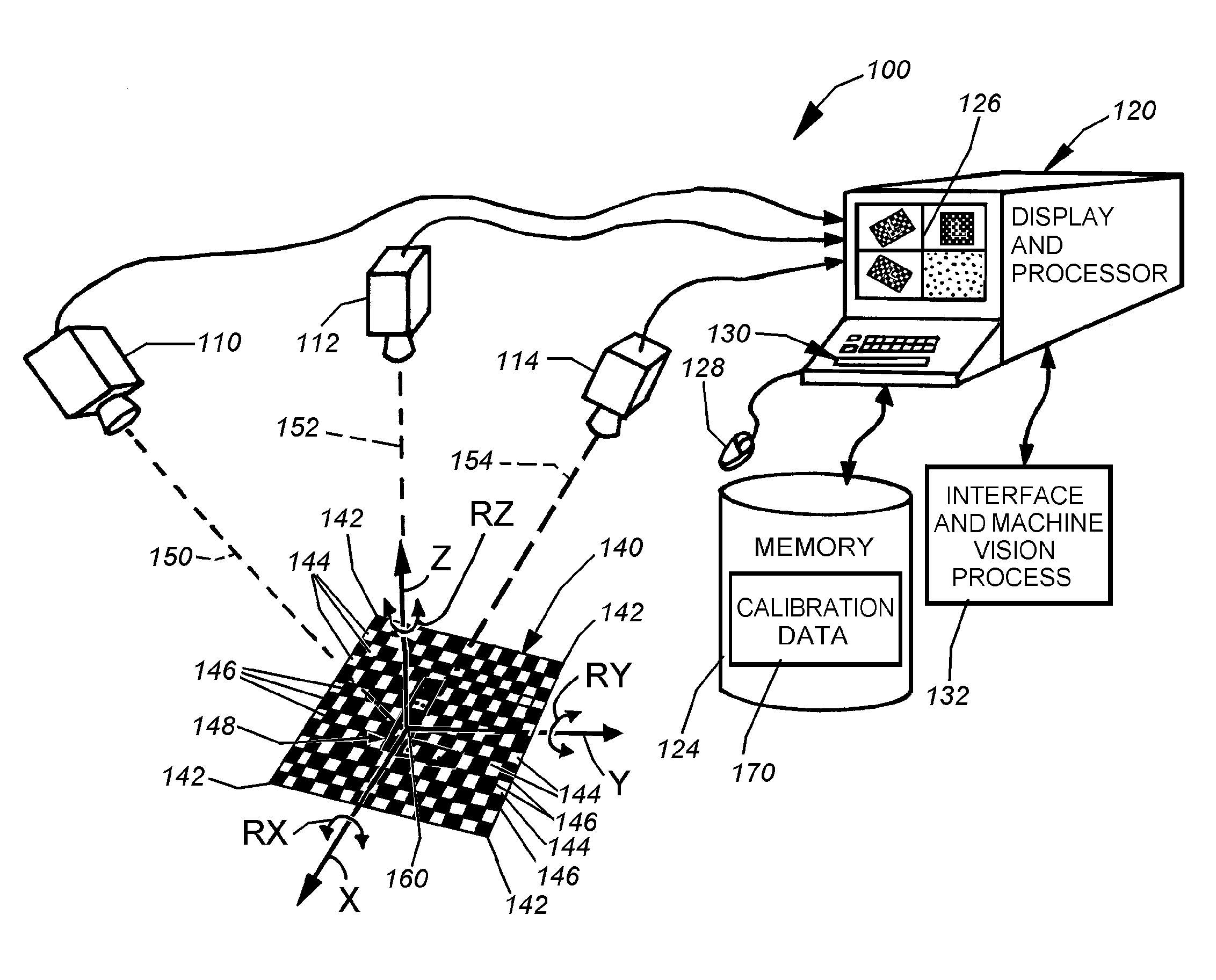
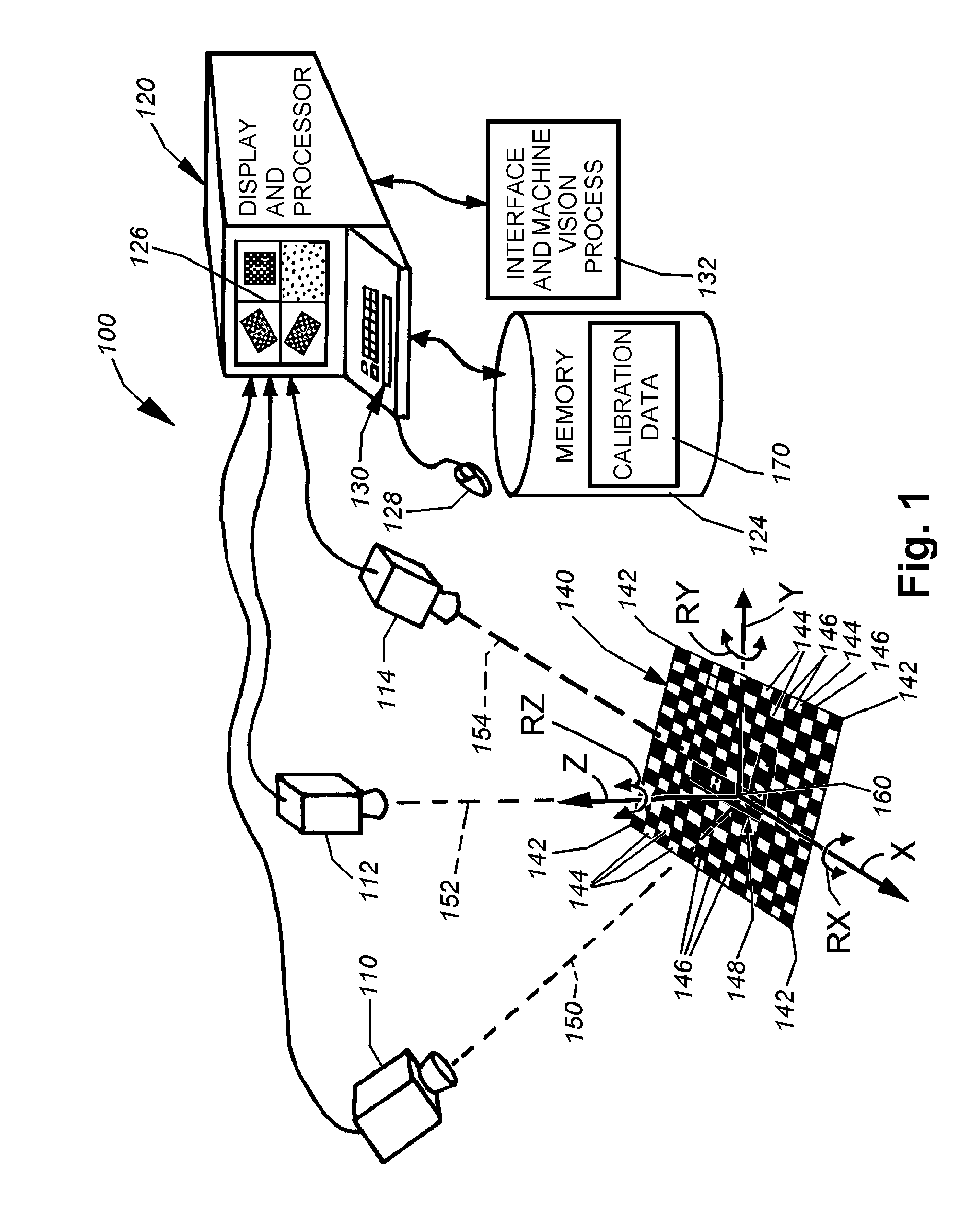
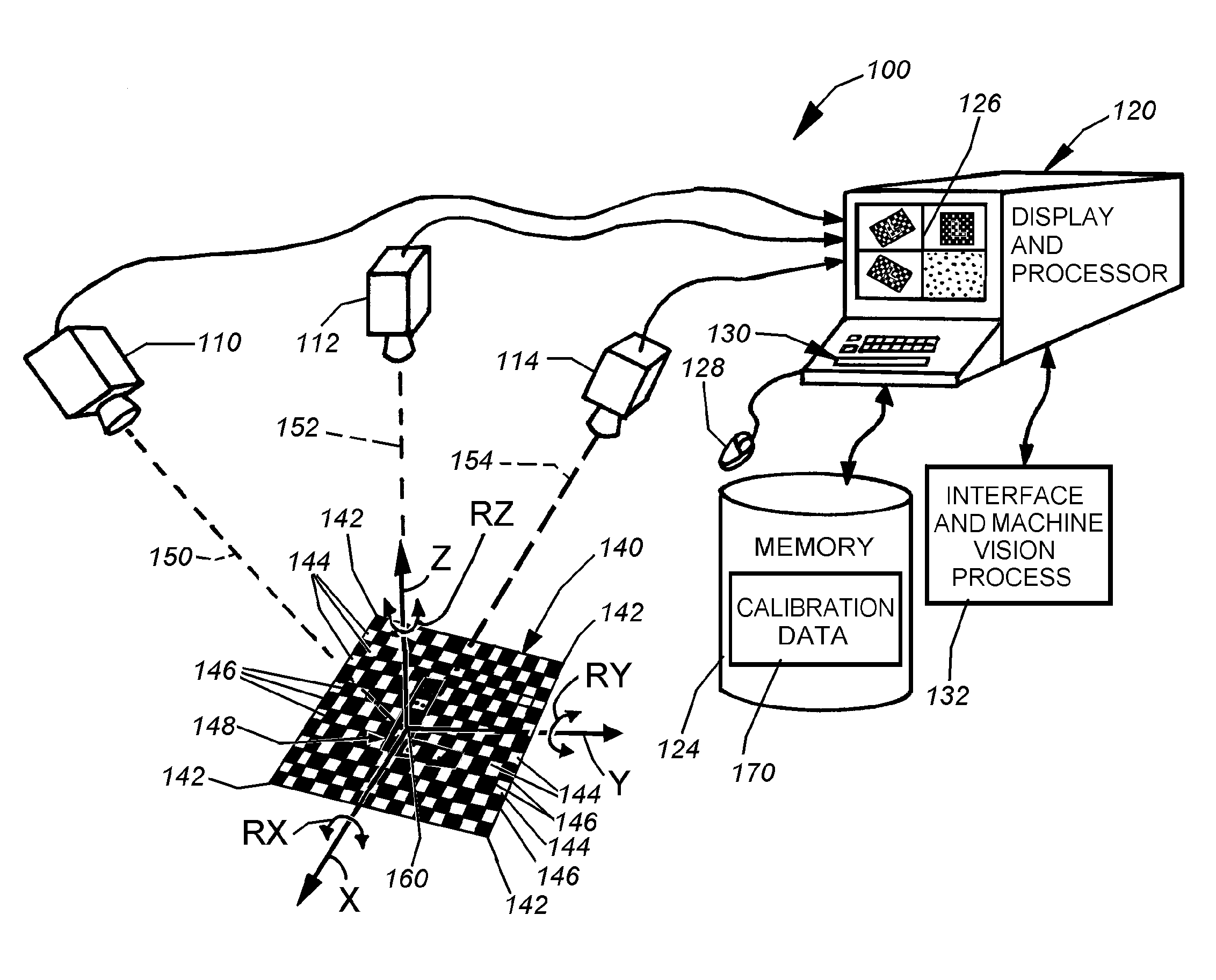
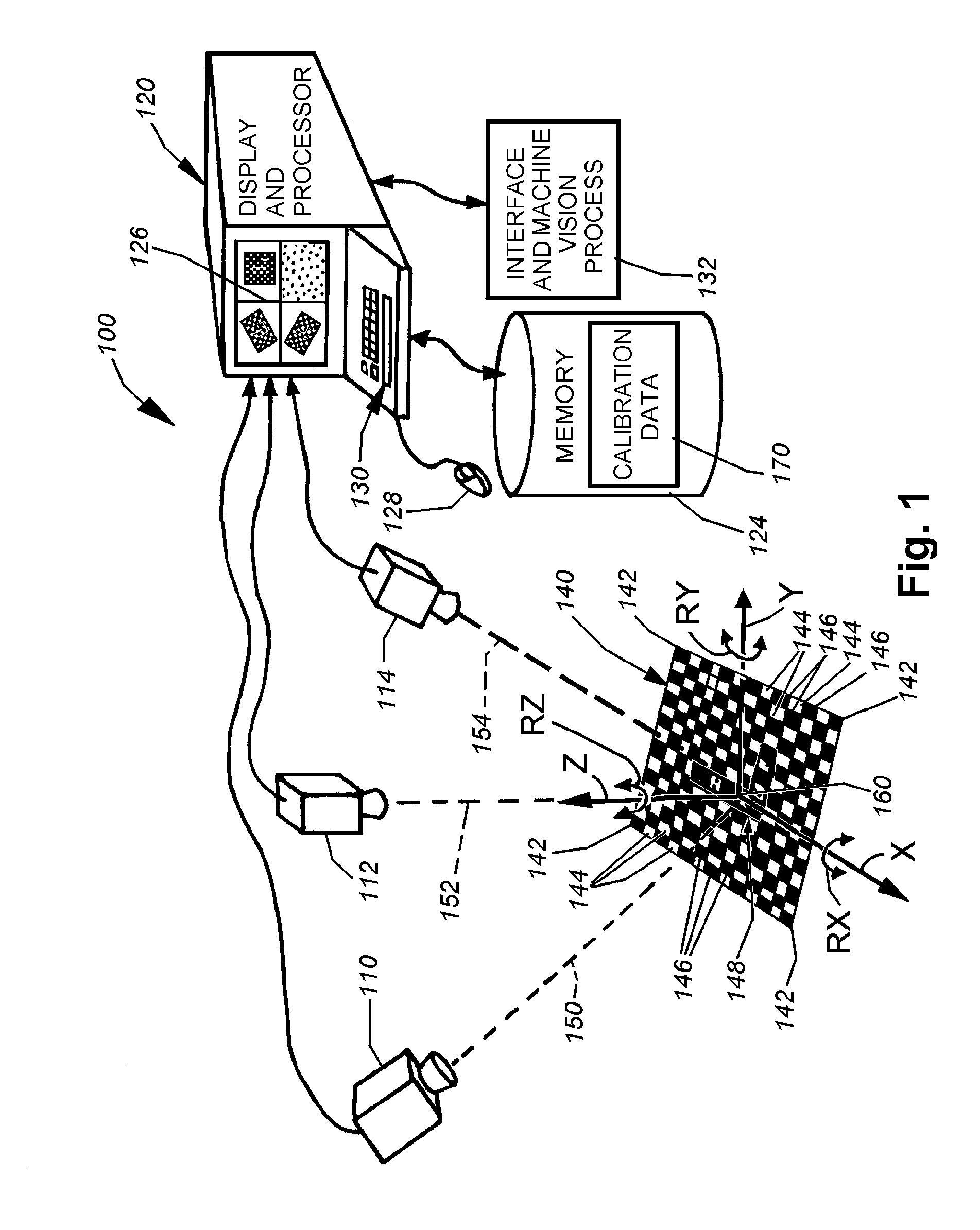
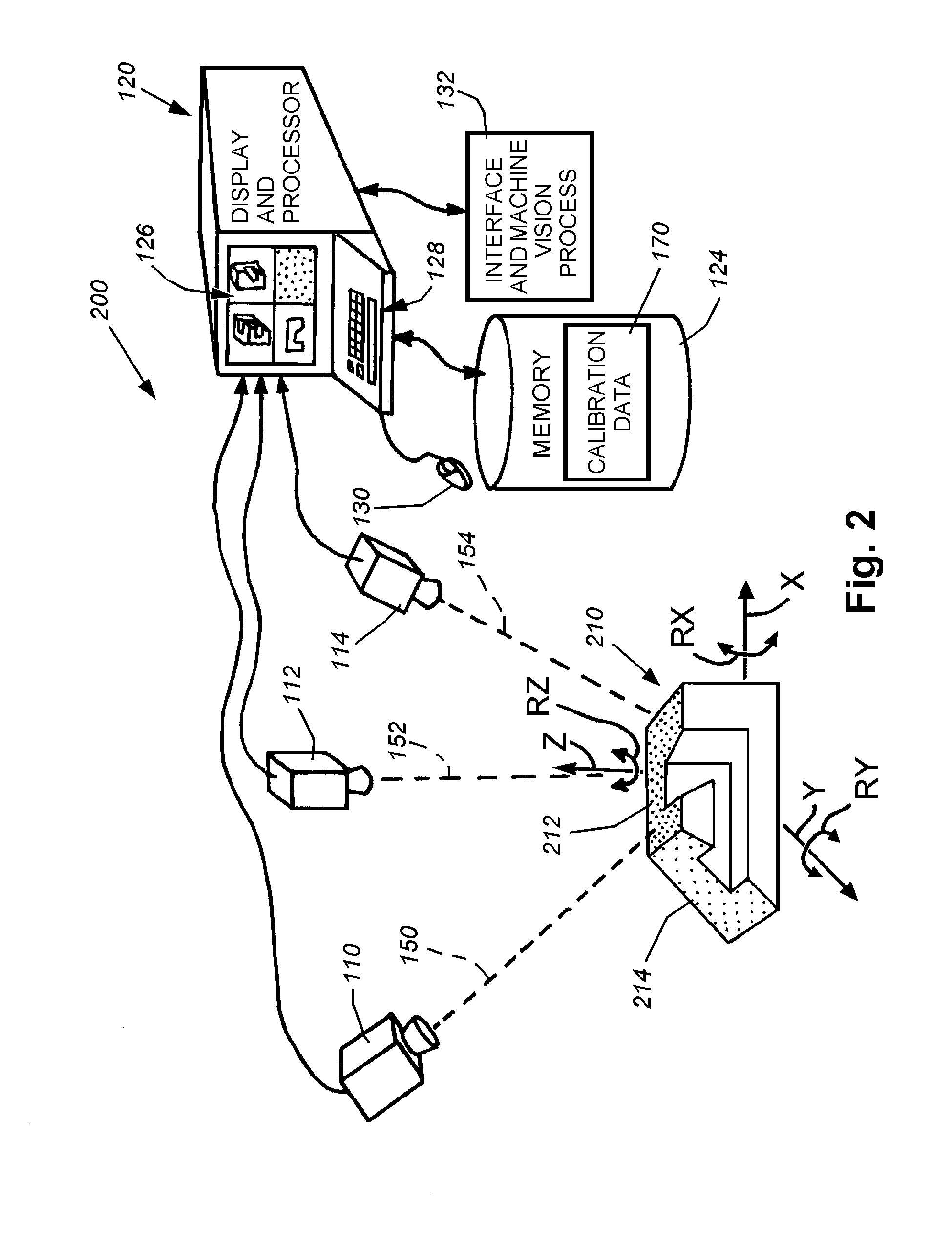
System and method for locating a three-dimensional object using machine vision
ActiveUS20080298672A1Error minimizationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVision processing
This invention provides a system and method for determining position of a viewed object in three dimensions by employing 2D machine vision processes on each of a plurality of planar faces of the object, and thereby refining the location of the object. First a rough pose estimate of the object is derived. This rough pose estimate can be based upon predetermined pose data, or can be derived by acquiring a plurality of planar face poses of the object (using, for example multiple cameras) and correlating the corners of the trained image pattern, which have known coordinates relative to the origin, to the acquired patterns. Once the rough pose is achieved, this is refined by defining the pose as a quaternion (a, b, c and d) for rotation and a three variables (x, y, z) for translation and employing an iterative weighted, least squares error calculation to minimize the error between the edgelets of trained model image and the acquired runtime edgelets. The overall, refined / optimized pose estimate incorporates data from each of the cameras' acquired images. Thereby, the estimate minimizes the total error between the edgelets of each camera's / view's trained model image and the associated camera's / view's acquired runtime edgelets. A final transformation of trained features relative to the runtime features is derived from the iterative error computation.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
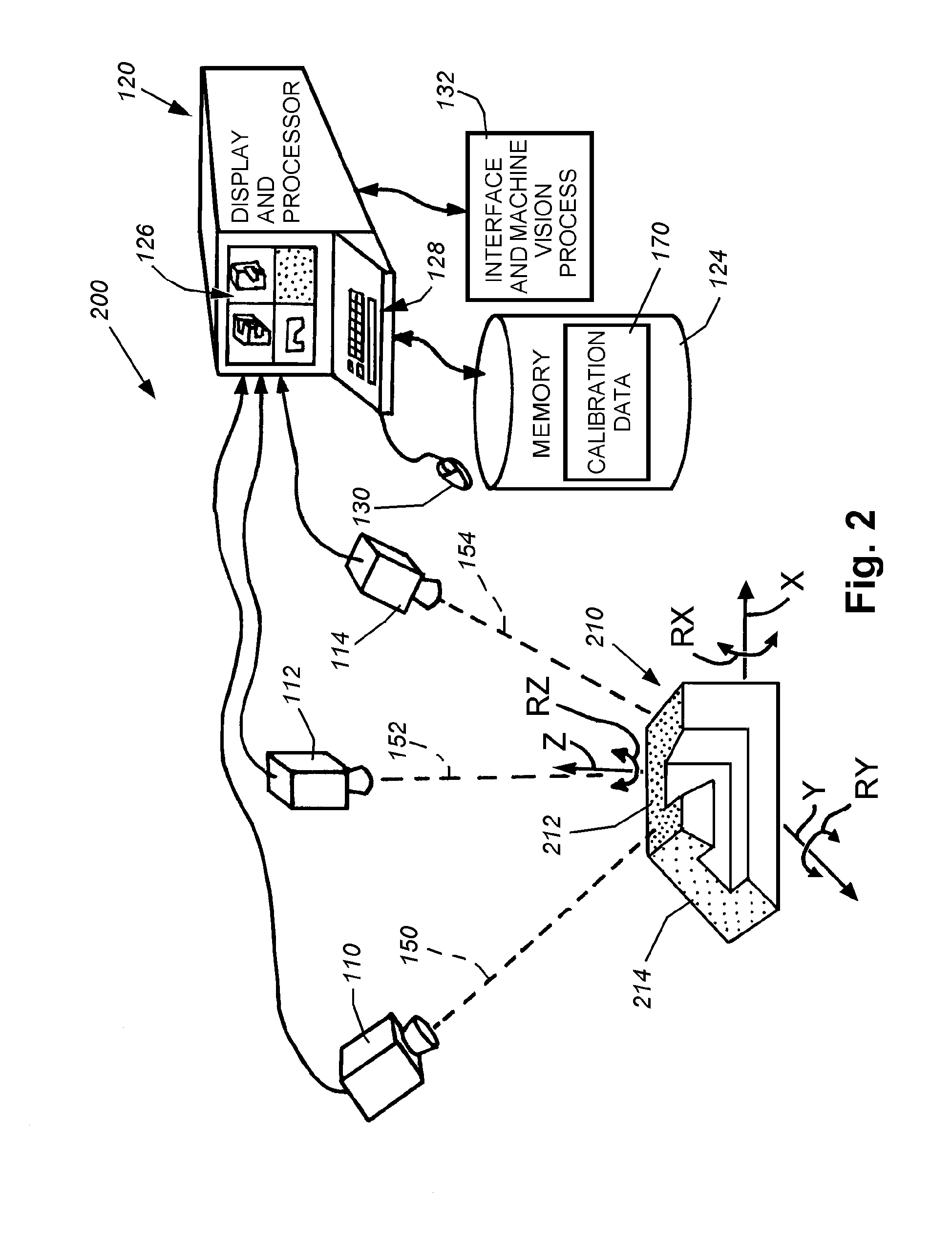
System and method for locating a three-dimensional object using machine vision
ActiveUS8126260B2Error minimizationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMachine vision
This invention provides a system and method for determining position of a viewed object in three dimensions by employing 2D machine vision processes on each of a plurality of planar faces of the object, and thereby refining the location of the object. First a rough pose estimate of the object is derived. This rough pose estimate can be based upon predetermined pose data, or can be derived by acquiring a plurality of planar face poses of the object (using, for example multiple cameras) and correlating the corners of the trained image pattern, which have known coordinates relative to the origin, to the acquired patterns. Once the rough pose is achieved, this is refined by defining the pose as a quaternion (a, b, c and d) for rotation and a three variables (x, y, z) for translation and employing an iterative weighted, least squares error calculation to minimize the error between the edgelets of trained model image and the acquired runtime edgelets. The overall, refined / optimized pose estimate incorporates data from each of the cameras' acquired images. Thereby, the estimate minimizes the total error between the edgelets of each camera's / view's trained model image and the associated camera's / view's acquired runtime edgelets. A final transformation of trained features relative to the runtime features is derived from the iterative error computation.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Method and device for pedestrian detection based on depth convolutional network
ActiveCN104063719AImprove detection accuracySimple calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionHigh rateAlgorithm
The invention discloses a method and a device for pedestrian detection based on a depth convolutional network. The method comprises a convolutional neural network training step and a pedestrian detection step. The convolutional neural network training comprises the following steps: S10, a plurality of groups of sample image data are selected from an image library; S11, one group of sample image data is sent to an input layer of a multilayer neural convolutional network; S12, the output vector of an intermediate layer of the neural convolutional network and the actual output vector of an output layer are calculated to obtain the error of the intermediate layer and the error of the output layer; S13, the weight from an output layer vector element to an intermediate layer output vector element and the weight from the intermediate layer output vector element to the output layer vector element are adjusted; and S14, the total error function value is judged, and pedestrians are detected by use of the trained network. The method and the device of the invention have the advantages of better robustness and high rate of detection accuracy.
Owner:SHENZHEN SUNWIN INTELLIGENT CO LTD
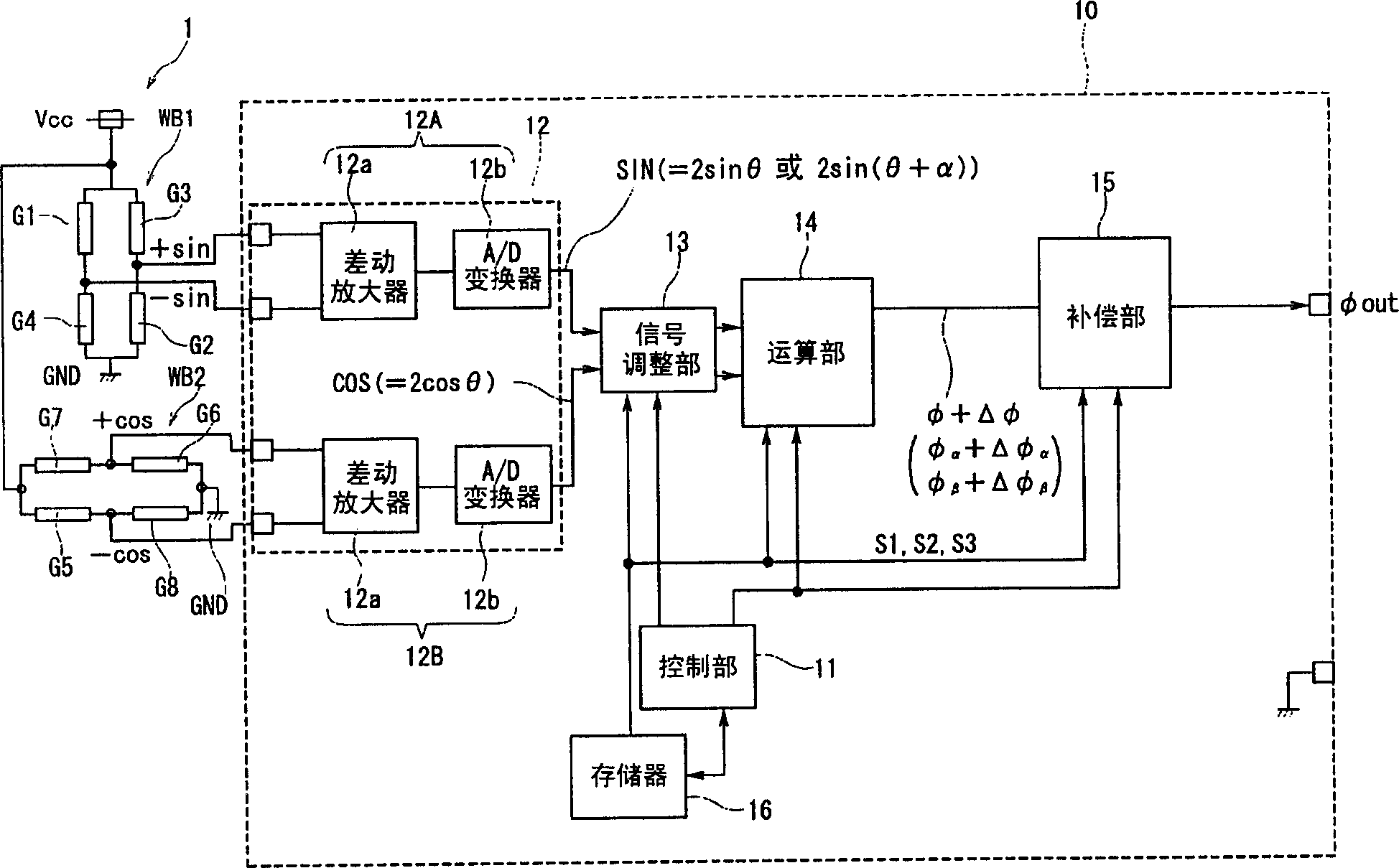
Method of calculating compensation value for angle detecting sensor and angle detecting sensor using the method
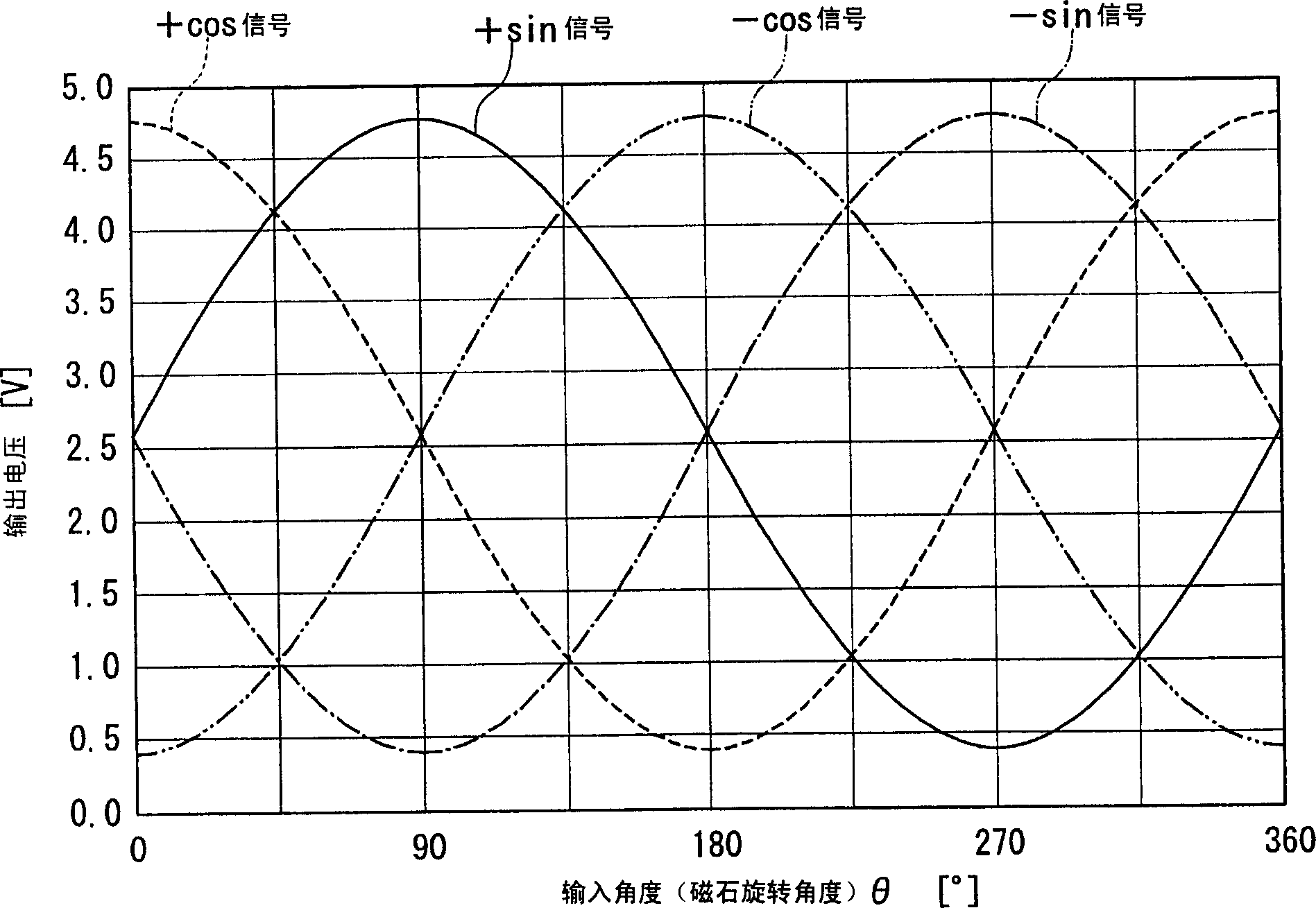
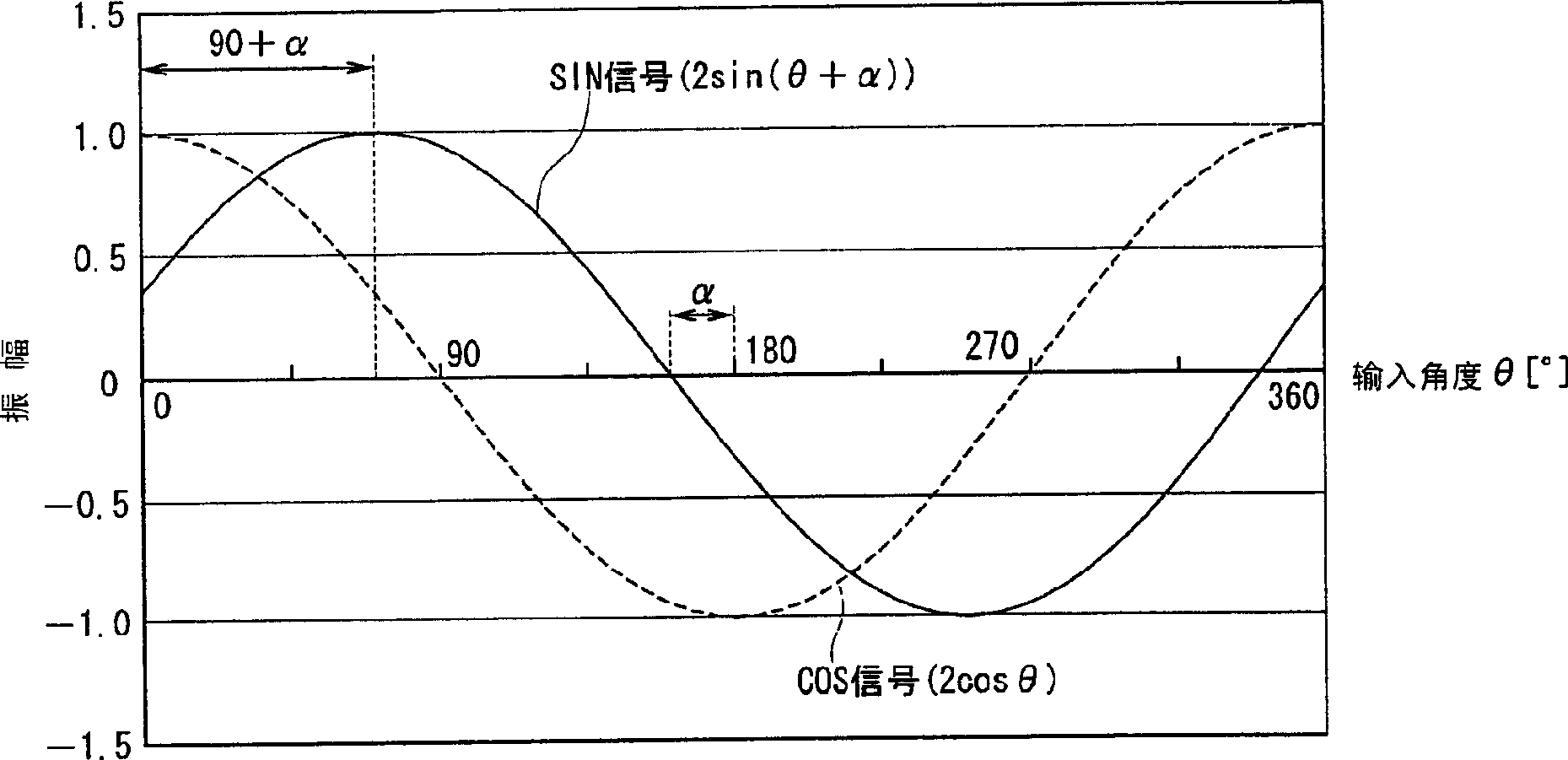
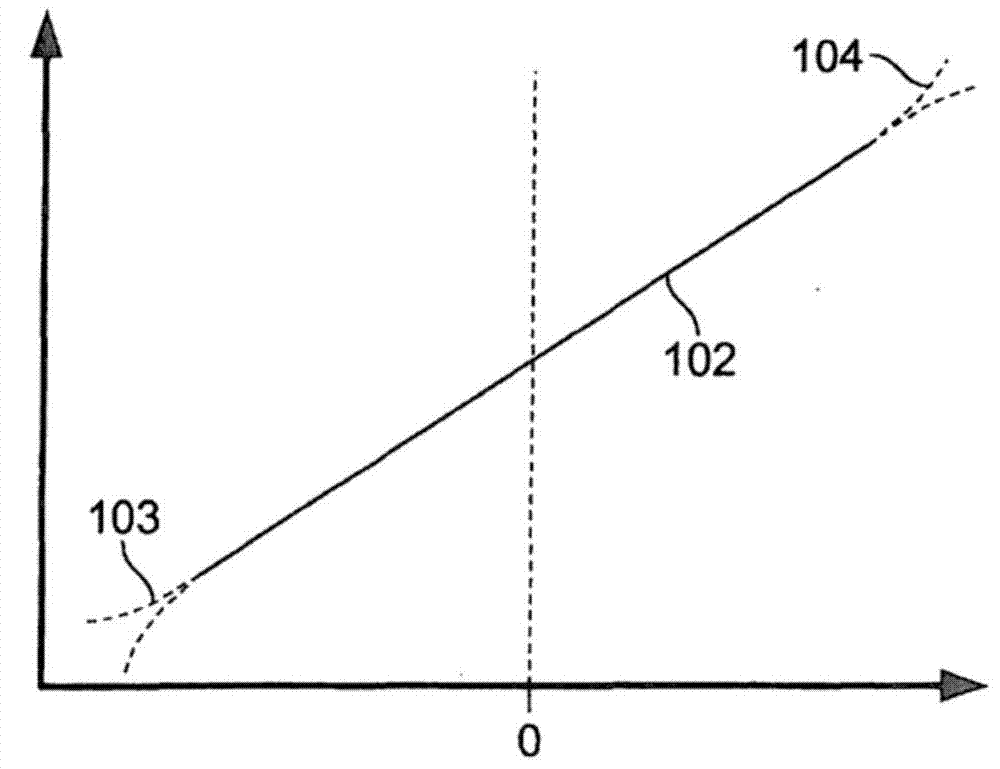
InactiveCN1789920AHigh precisionMagnetic measurementsUsing electrical meansCalculation methodsTotal error
The present invention provides a compensation value calculation method of an angle detection sensor capable of obtaining a high-precision angle output even when an output signal from a sensor includes an error signal, and an angle detection sensor using the same. The computing unit (14) calculates the uncorrected rotation angle (φ) of the object to be measured including the total error signal (Δφ) based on the SIN signal and the COS signal output from the sensor module (1) and the signal conversion unit (12) . A control unit (11) extracts, as a phase compensation value (Sα), a signal having a minimum residual energy (E) from first candidate signals (S1) stored in a memory unit (16). In addition, the strain compensation value (Sβ) and the gain compensation value (Sγ) are extracted in the same manner. And by removing the above-mentioned (Sα), (Sβ), and (Sγ) from the total error signal (Δφ), the angle output can be detected with high accuracy.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
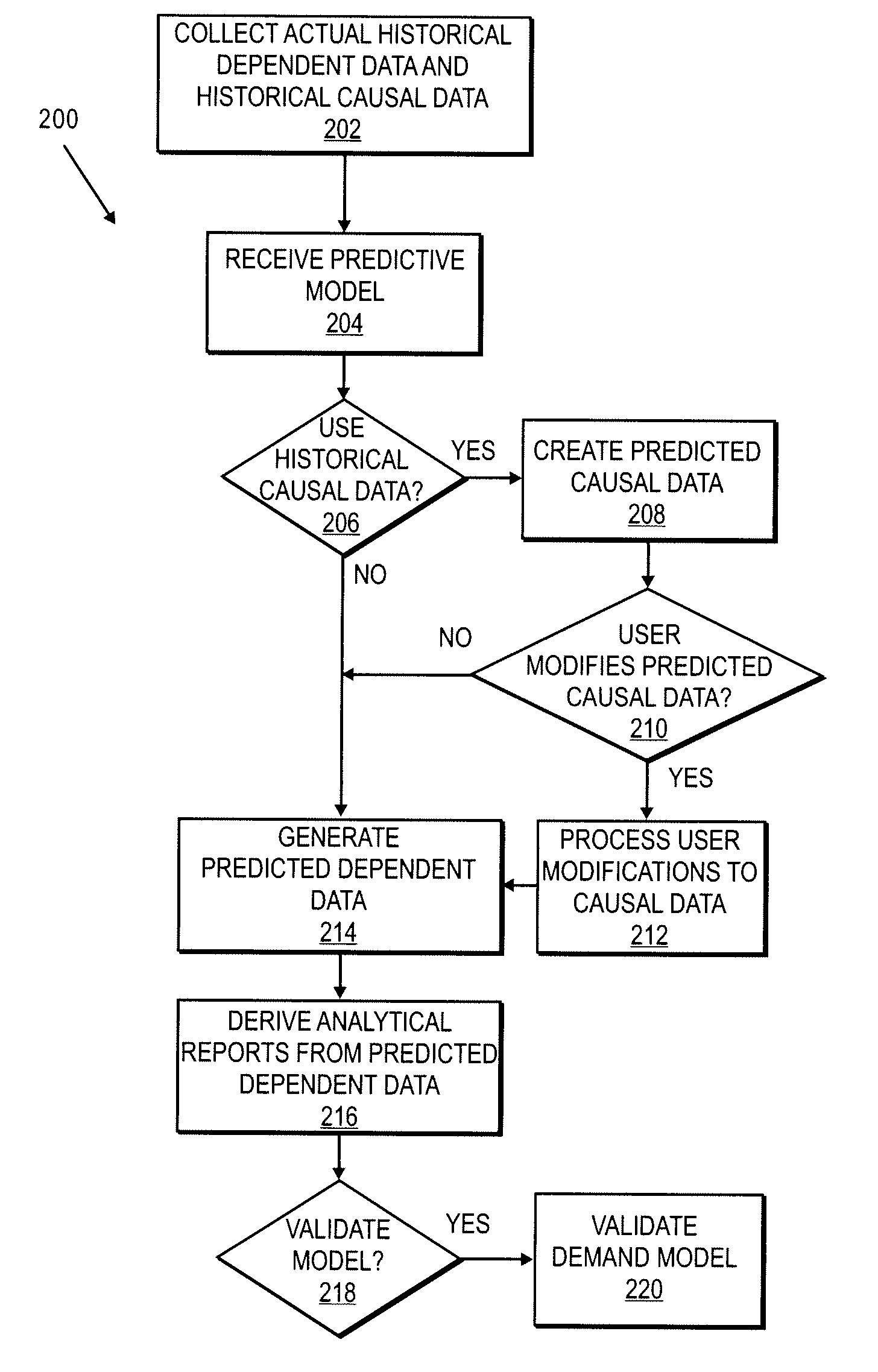
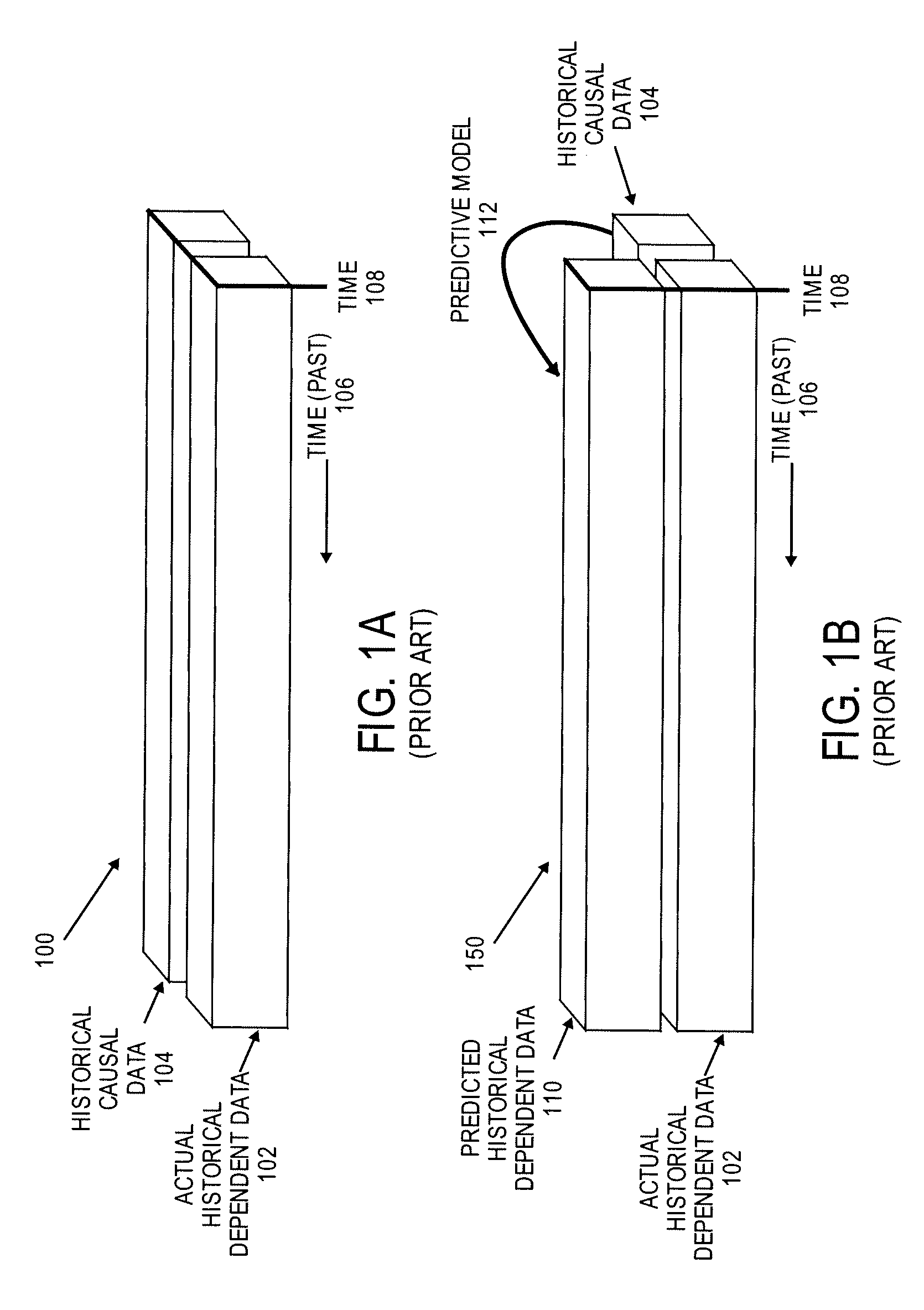
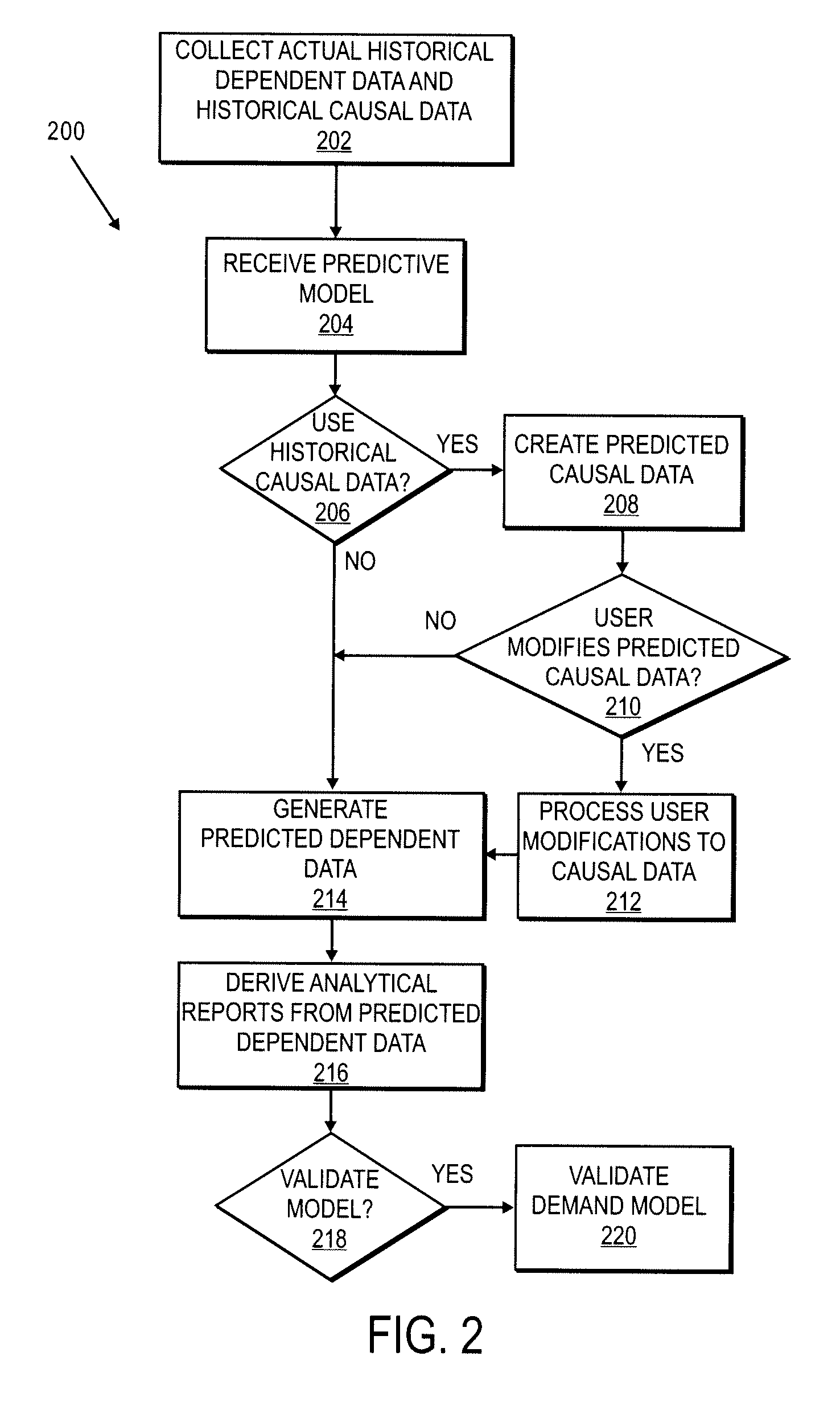
System and Method for Updating Forecast Model
A method for updating a forecast model is disclosed. The forecast model includes parameters that receives collected data representing historical dependent and causal data. The collected data are in different units of measure from one another. Based on the collected data, the forecast model is applied to determine a total error value from a calculation performed on the parameters in the forecast model. To update the forecast model, additional parameters are added, existing parameters are modified, or parameters are removed from the forecast model to determine a modified total error value. The modified total error value is then compared to the original total error value. The parameters are also converted to normalized values to be in a common unit of measure to facilitate the application of the forecast model to determine a total error value.
Owner:IBM CORP
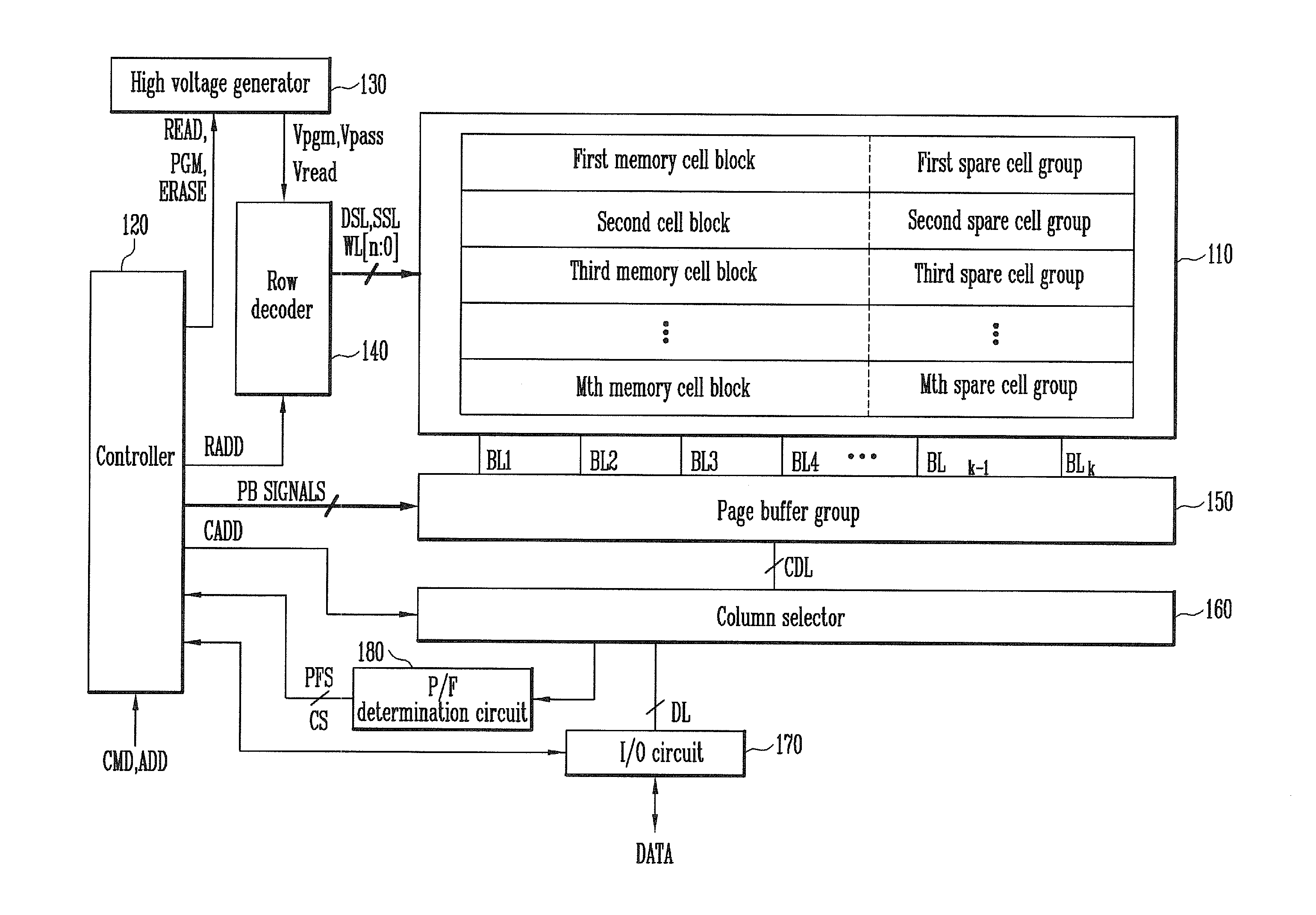
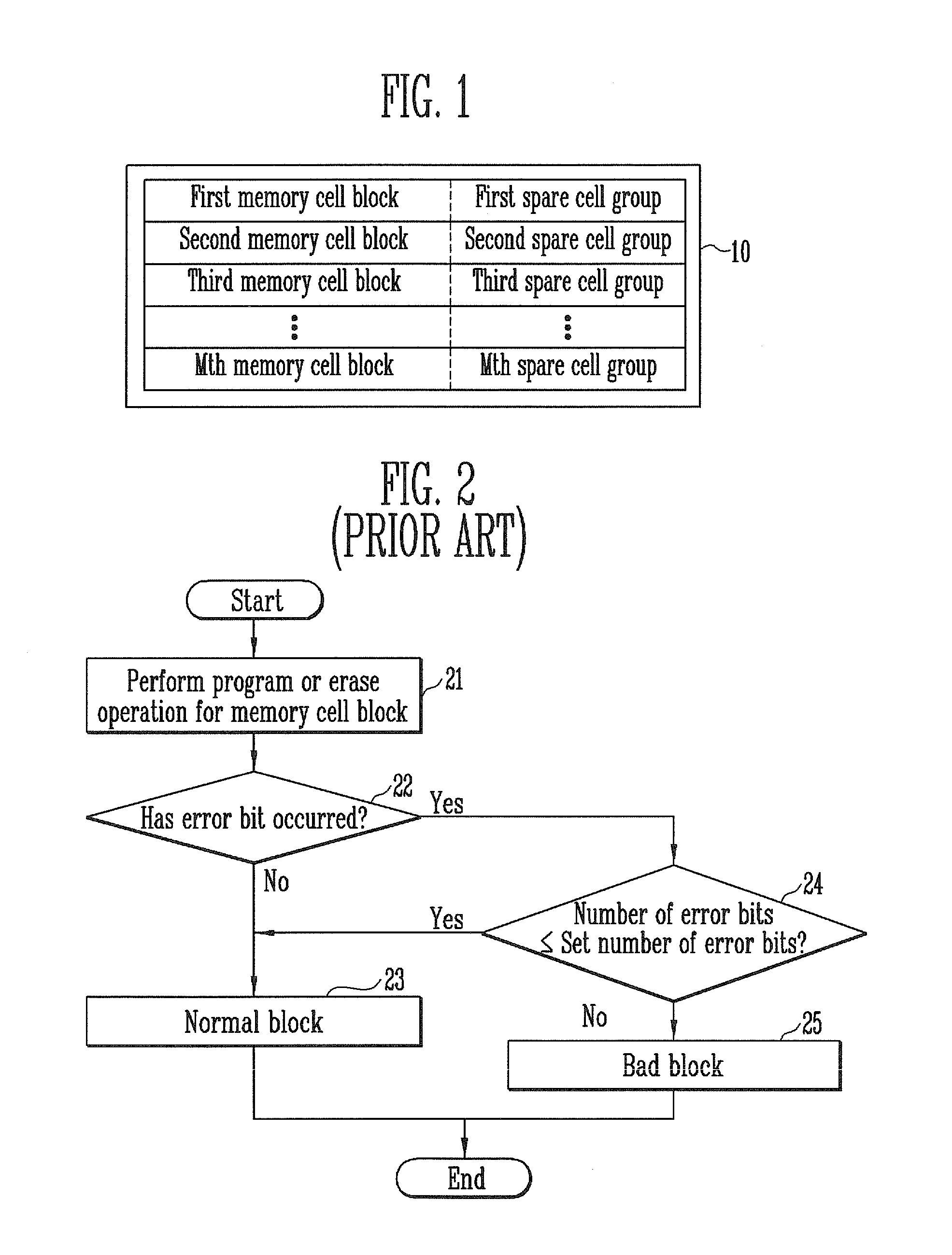
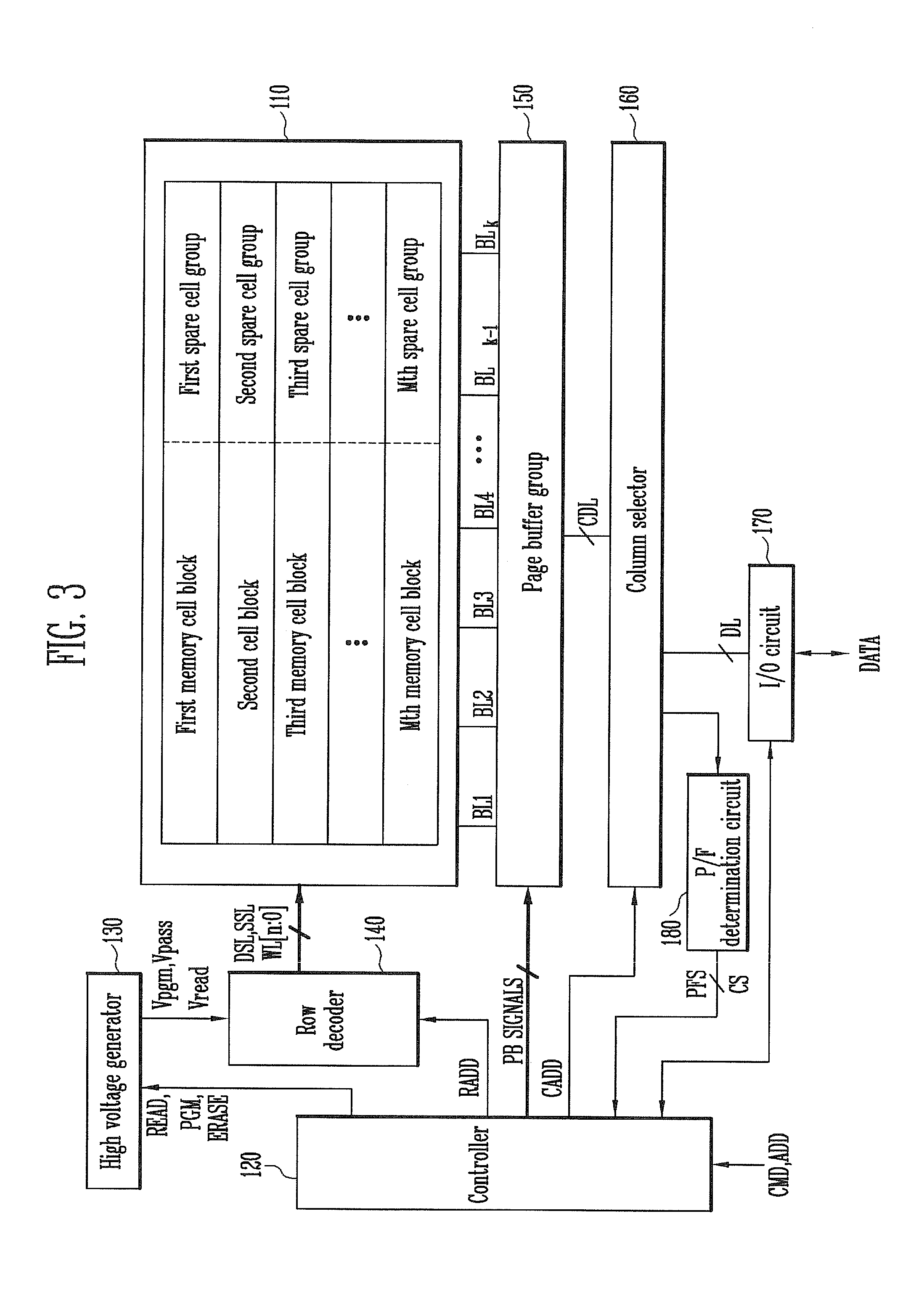
Memory system and method of operating the same
InactiveUS20120173920A1Read-only memoriesRedundant hardware error correctionComputer scienceTotal error
A method of operating a memory system includes classifying numbers of total error bits into a plurality of ranges, assigning a plurality of data to the plurality of ranges, respectively, counting a number of detected error bits for a memory cell block, and storing a selected one of the plurality of data in at least one spare cell when the number of the detected error bits is within one of the ranges that corresponds to the selected data.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method of setting optimum-partitioned classified neural network and method and apparatus for automatic labeling using optimum-partitioned classified neural network
ActiveUS7444282B2Performed accurately and rapidlyDigital computer detailsDigital dataCombination groupComputer science
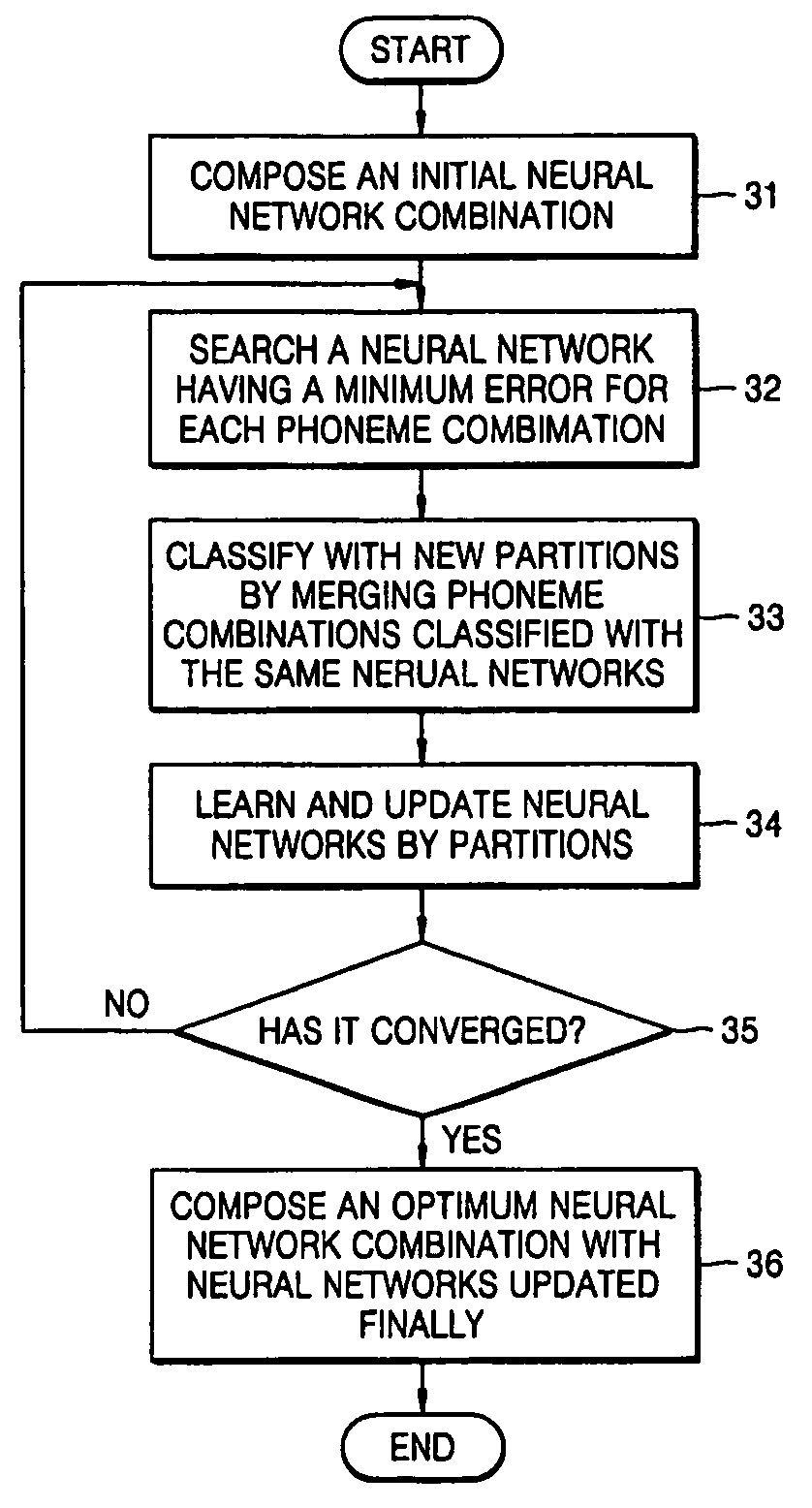
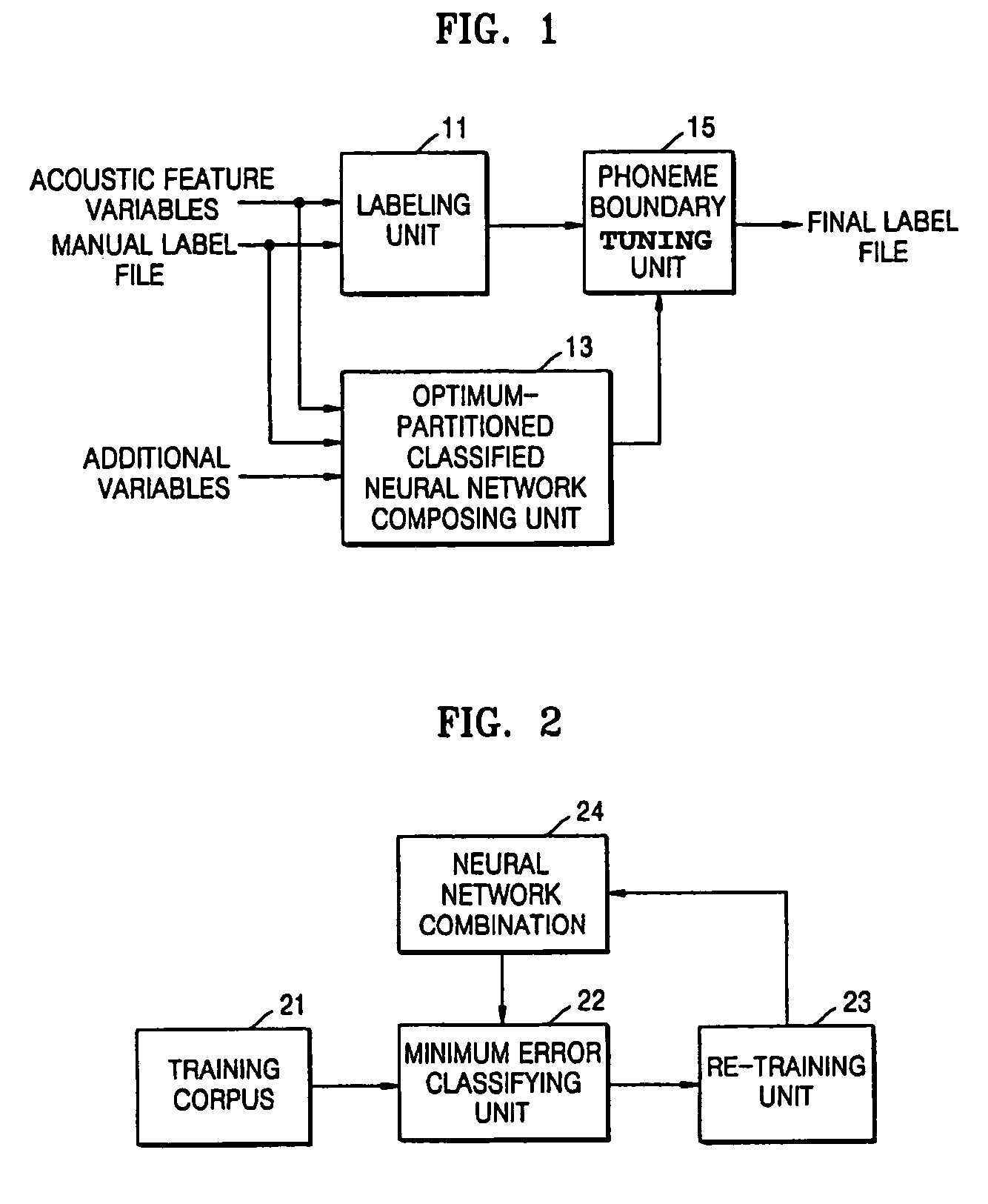
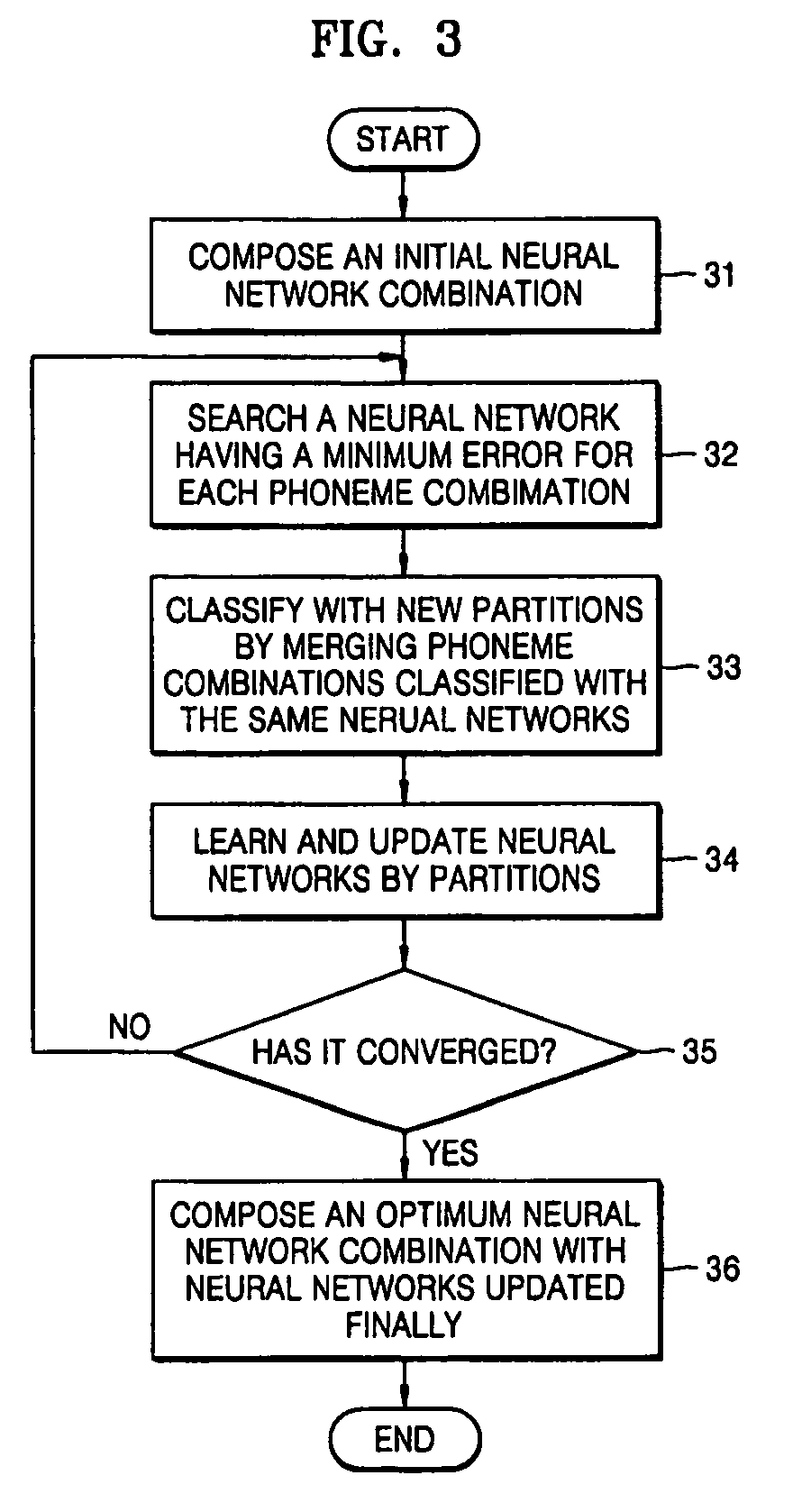
A method of automatic labeling using an optimum-partitioned classified neural network includes searching for neural networks having minimum errors with respect to a number of L phoneme combinations from a number of K neural network combinations generated at an initial stage or updated, updating weights during learning of the K neural networks by K phoneme combination groups searched with the same neural networks, and composing an optimum-partitioned classified neural network combination using the K neural networks of which a total error sum has converged; and tuning a phoneme boundary of a first label file by using the phoneme combination group classification result and the optimum-partitioned classified neural network combination, and generating a final label file reflecting the tuning result.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Universal single event effect detecting method of memory circuit
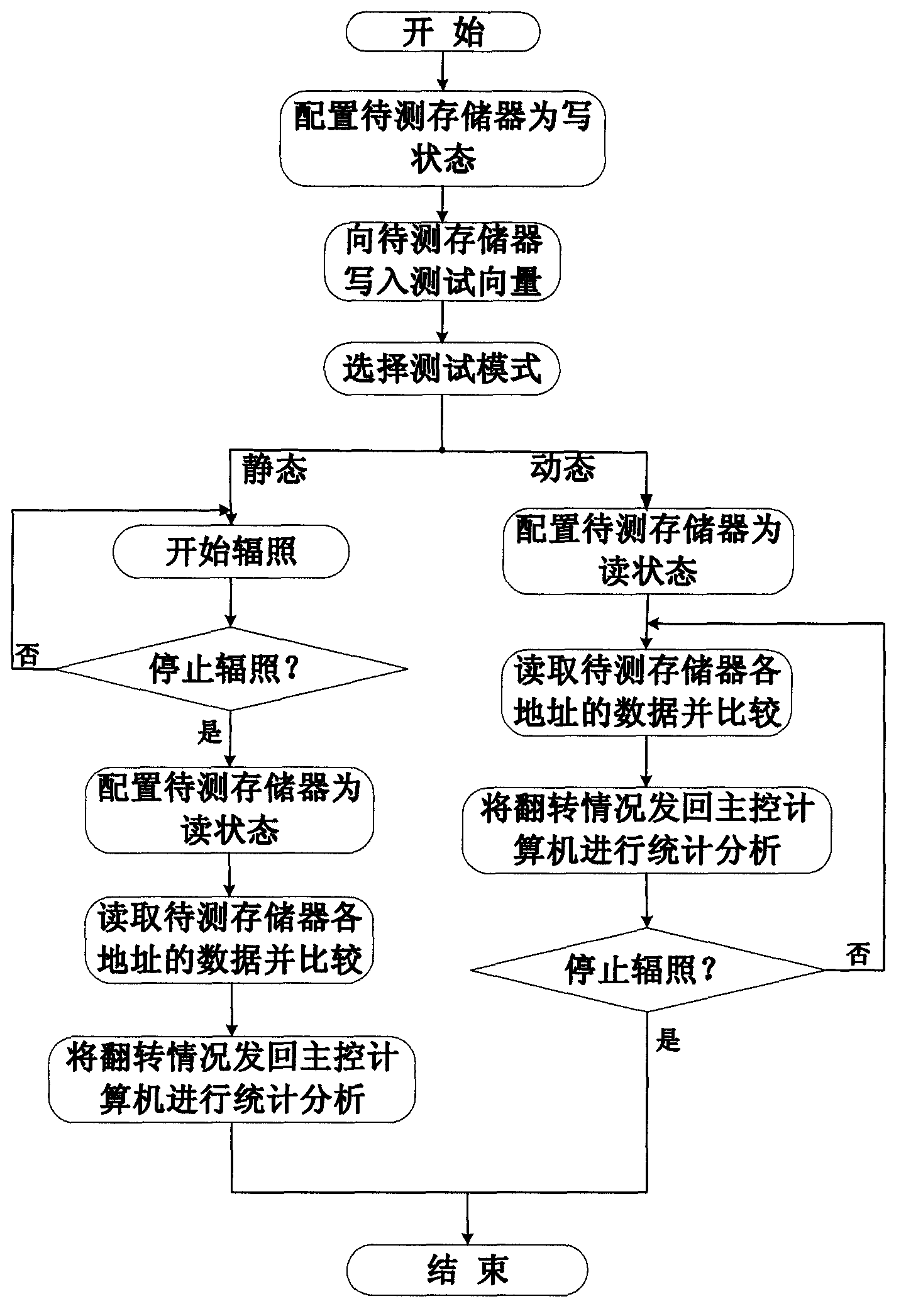
InactiveCN103021469ASuitable for single event effect testingMeet different testing needsStatic storageMemory circuitsFile comparison
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Training method, training device, dialogue method and dialogue system of dialogue model
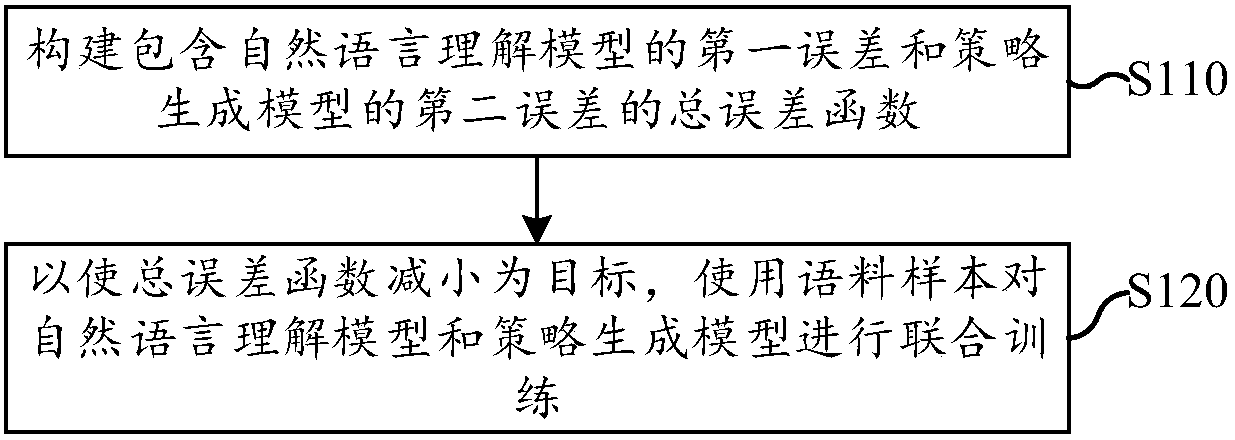
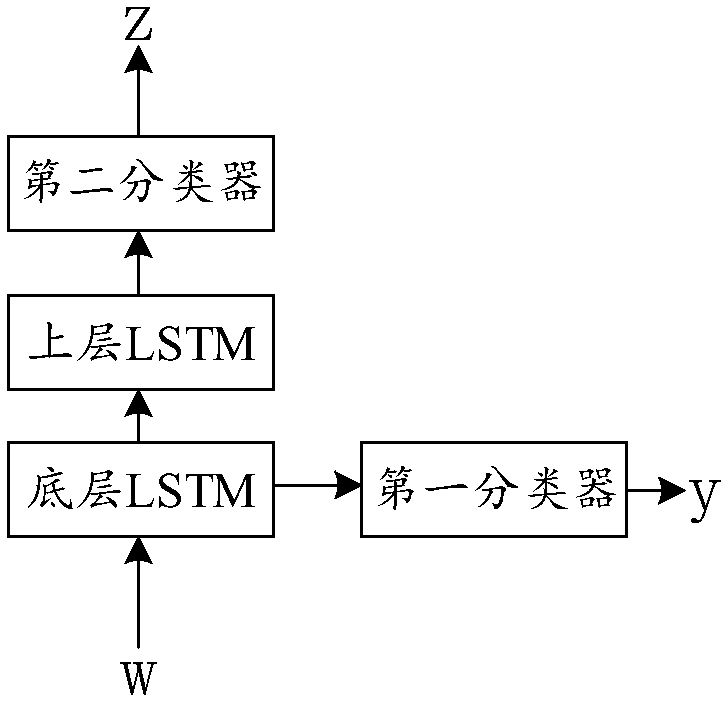
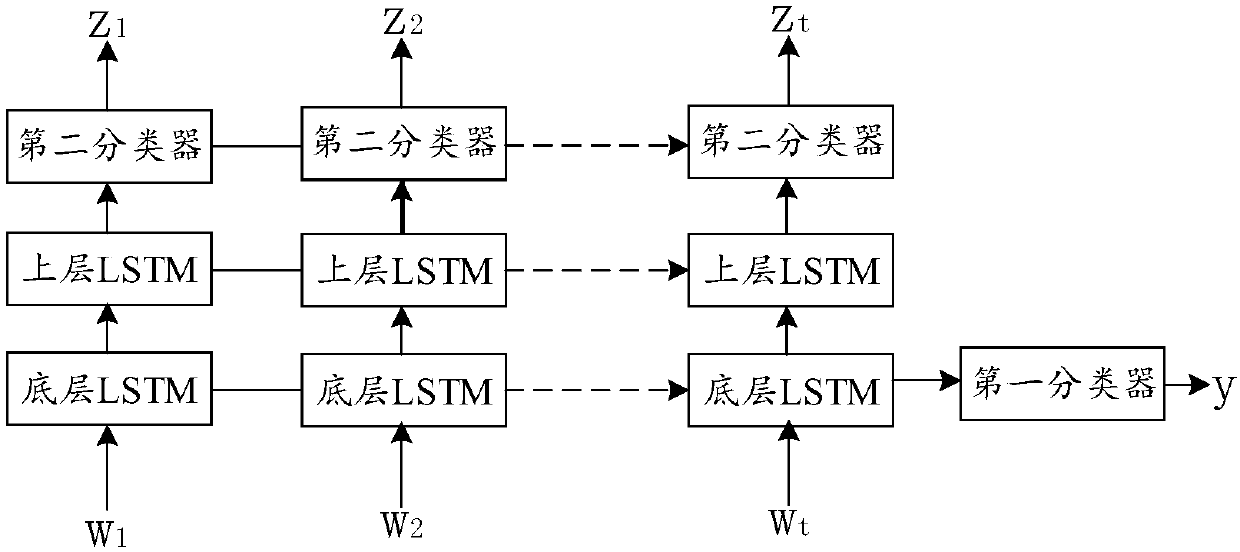
ActiveCN107766559ASolving the Error Propagation ProblemCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsLanguage understandingNatural language understanding
The invention discloses a training method, a training device, a dialogue method and a dialogue system of a dialogue model. The training method comprises the steps of total error constructing, whereina total error function comprising a first error of a natural language understanding model and a second error of a strategy generating model are constructed simultaneously; joint training, wherein withthe target of reducing the total error function, a corpus sample is utilized to jointly train the natural language understanding model and the strategy generating model, input of the natural languageunderstanding model is dialogue sentences, output of the natural language understanding model is internal representation obtained by analyzing the dialogue sentences, input of the strategy generatingmodel at least comprises the output of the natural language understanding model, and output of the strategy generating model is motions aiming at the dialogue sentence. Compared with the prior art, when an error occurs on the natural language understanding model or the strategy generating model, the system can normally conduct dialogues, and the error transferring problem in a traditional methodcaused when the natural language understanding model and a dialogue management model are modeled respectively is solved.
Owner:THE FOURTH PARADIGM BEIJING TECH CO LTD
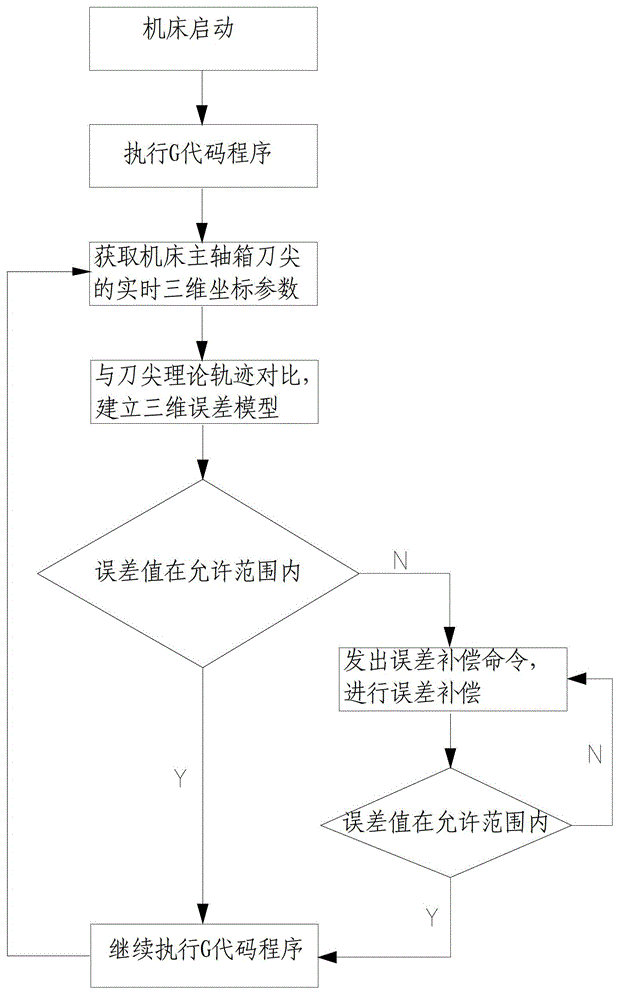
Laser tracker-based machine tool error dynamic compensation method
InactiveCN103143984AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyAutomatic control devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsEngineeringLaser tracker
The invention discloses a laser tracker-based machine tool error dynamic compensation method. A laser tracker is adopted to perform dynamic tracking detection; and the method is suitable for being used in laboratory environments with strictly controlled temperature and humidity and can also be used in workshop site environments with severer conditions. Laser interference ranging, photoelectric detection, precision machinery, a computer and a control and modern numerical value calculation theory are integrated by the laser tracker; a space moving object is tracked and spatial three-dimensional coordinates of an object are measured in real time; and the method has the characteristics of high precision, high efficiency, real-time tracking measurement, quickness and convenience in mounting, easiness in operation and the like. A machine tool is dynamically monitored and compensated in real time based on a laser tracker measurement result; error measured by using the scheme is total error obtained after all system errors and random error are superposed; and thus, all error values can be dynamically compensated in real time by the scheme, the system precision of the machine tool is greatly improved, and a detection device of the machine tool is simplified.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method and system for calculating misalignment of rotational body
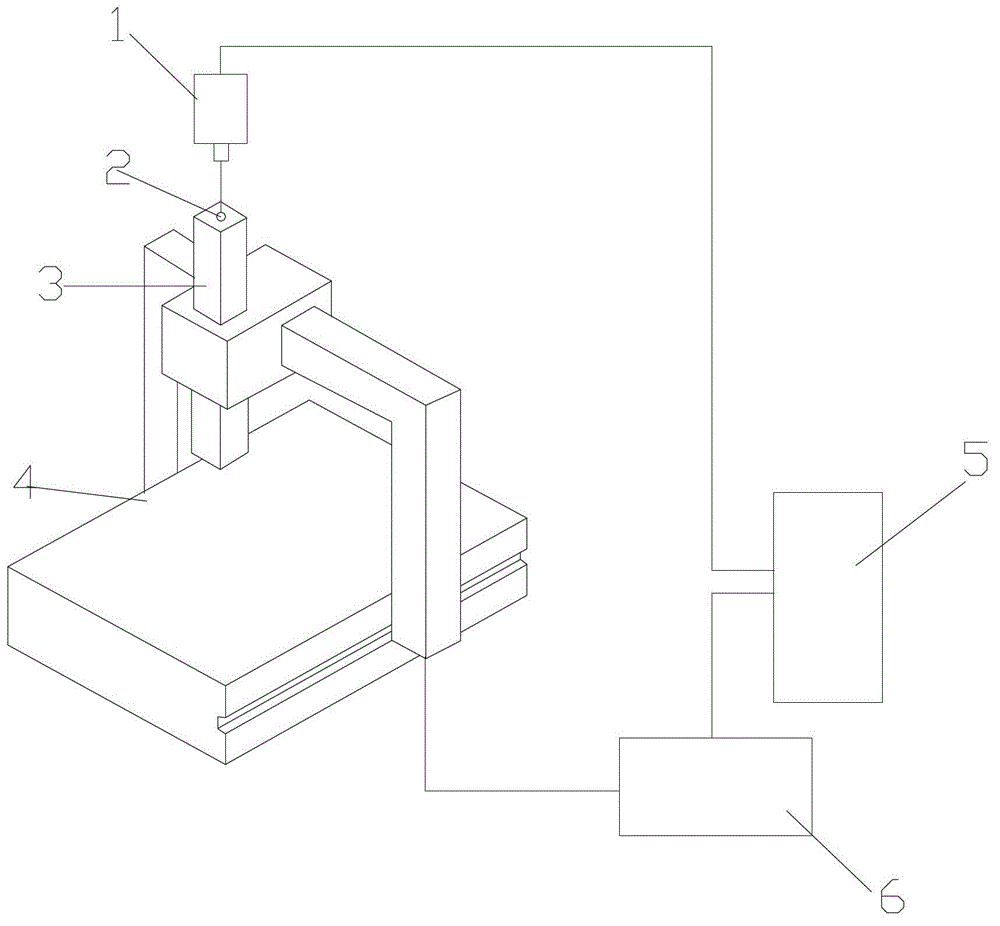
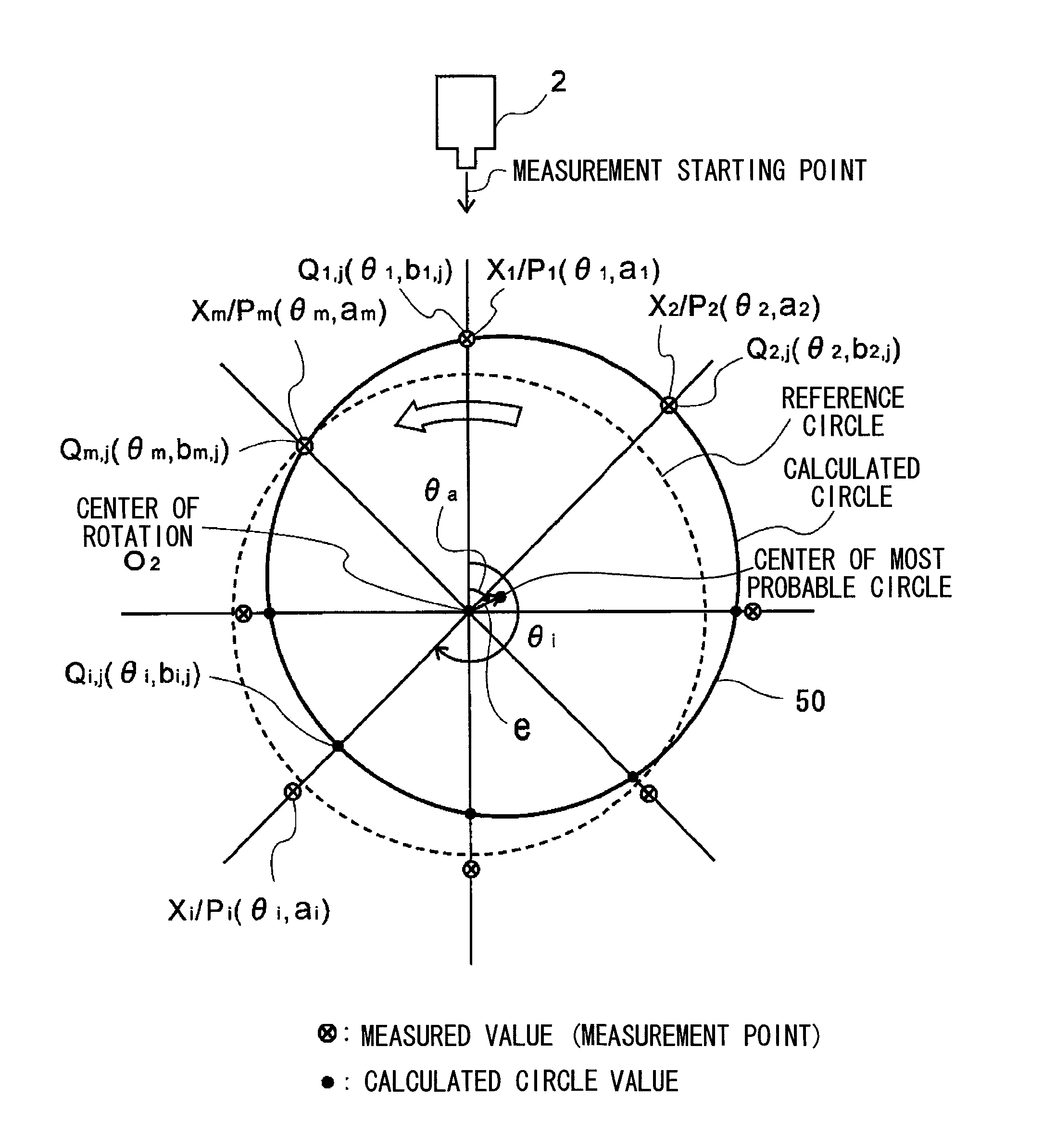
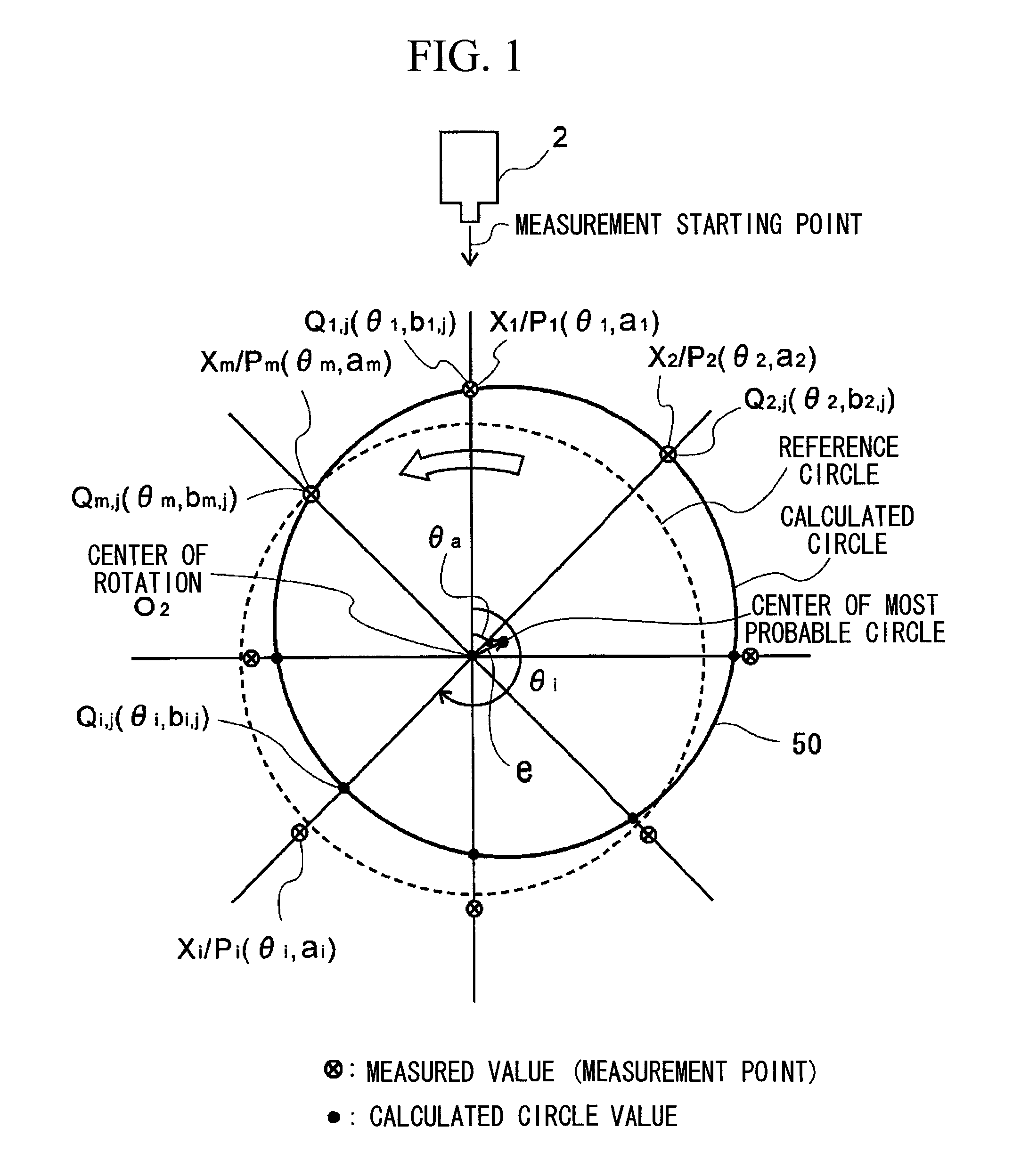
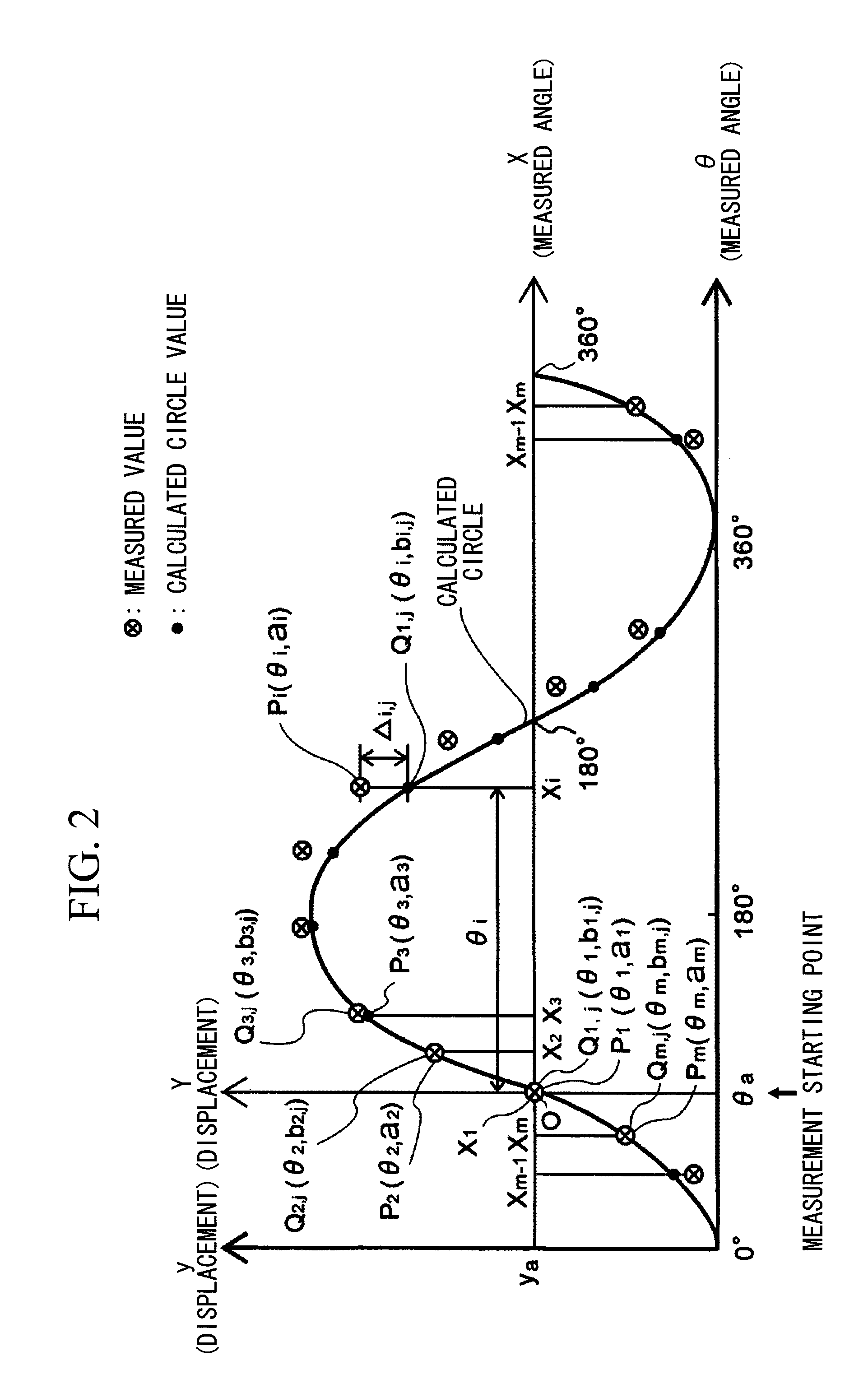
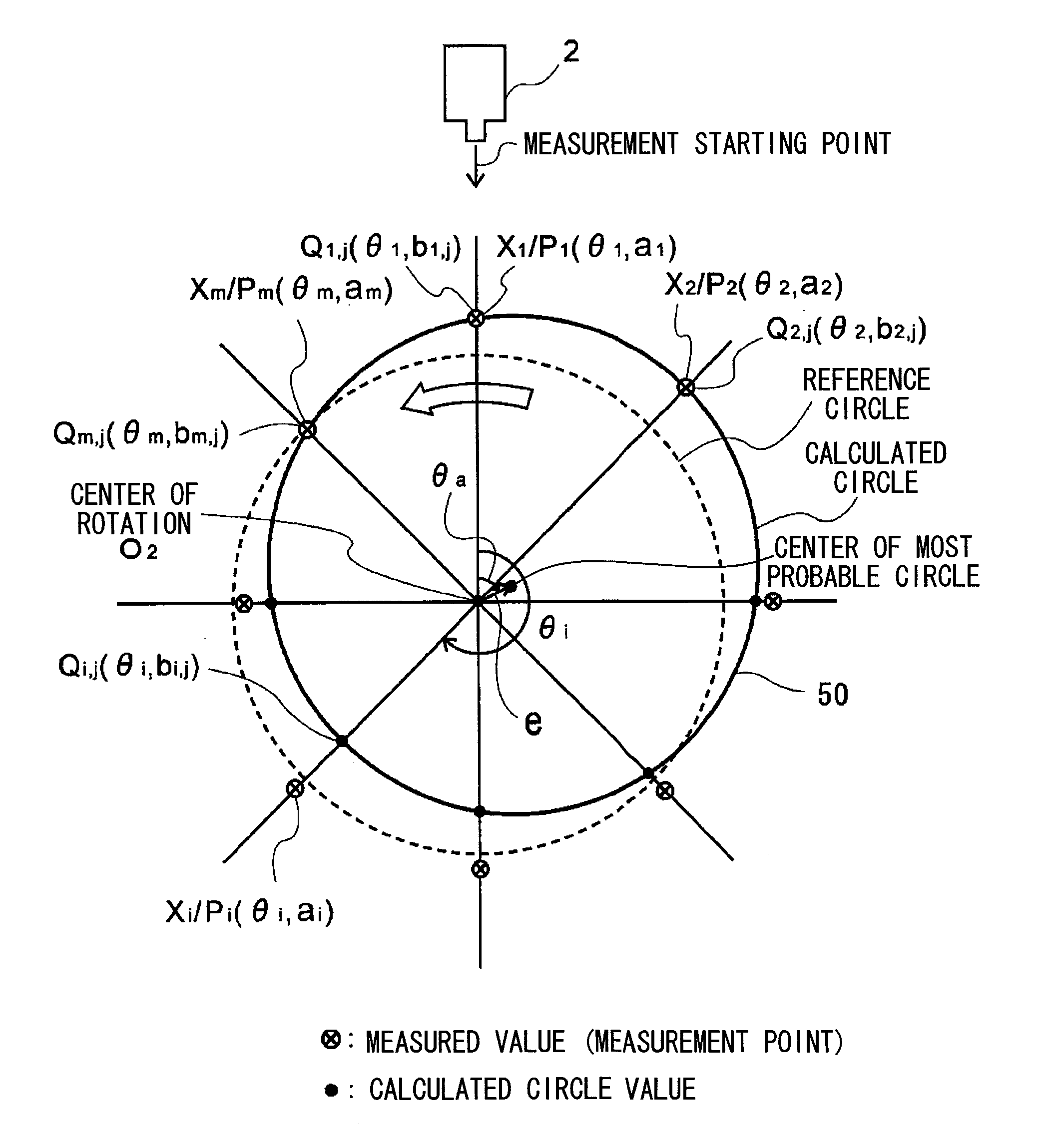
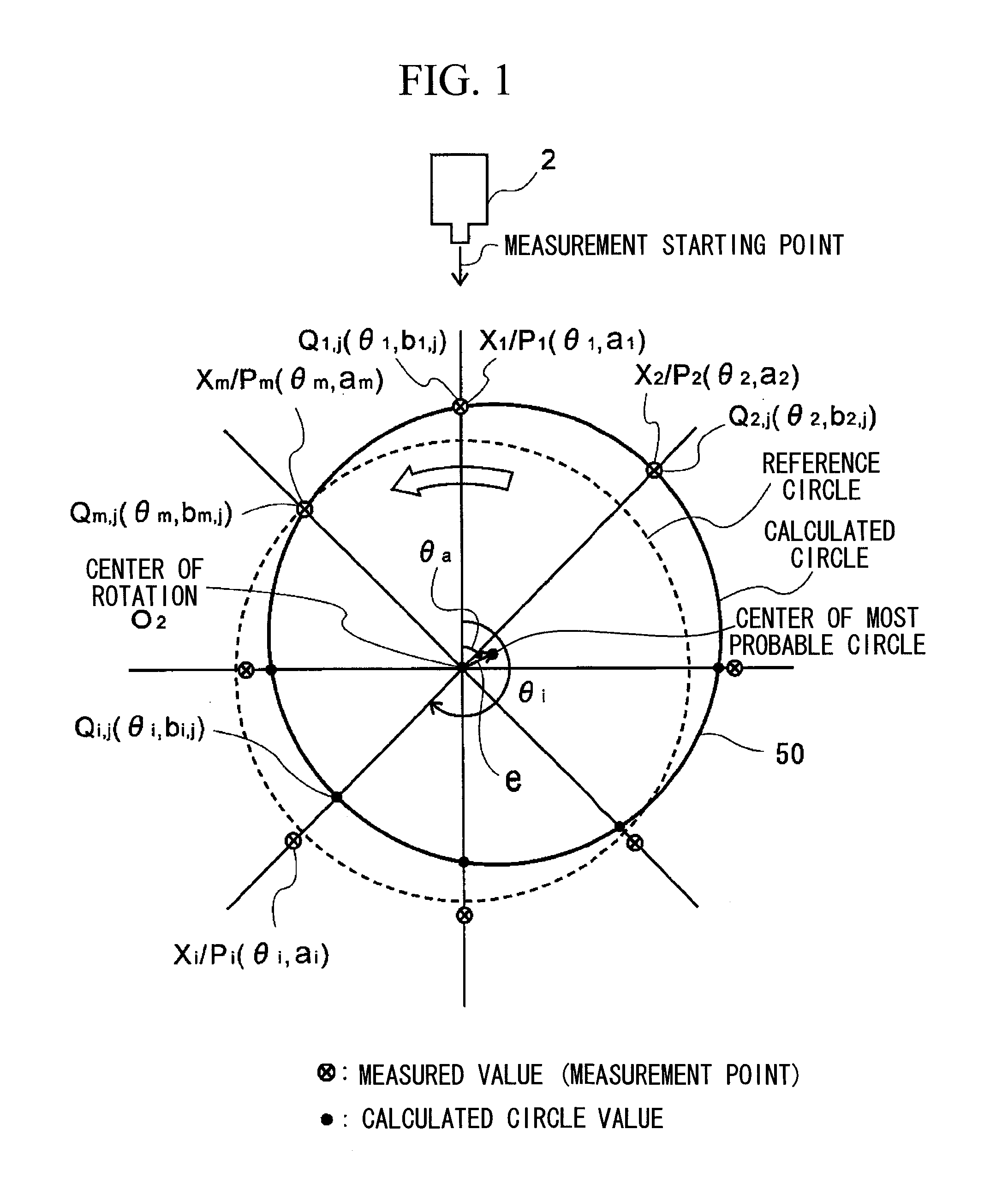
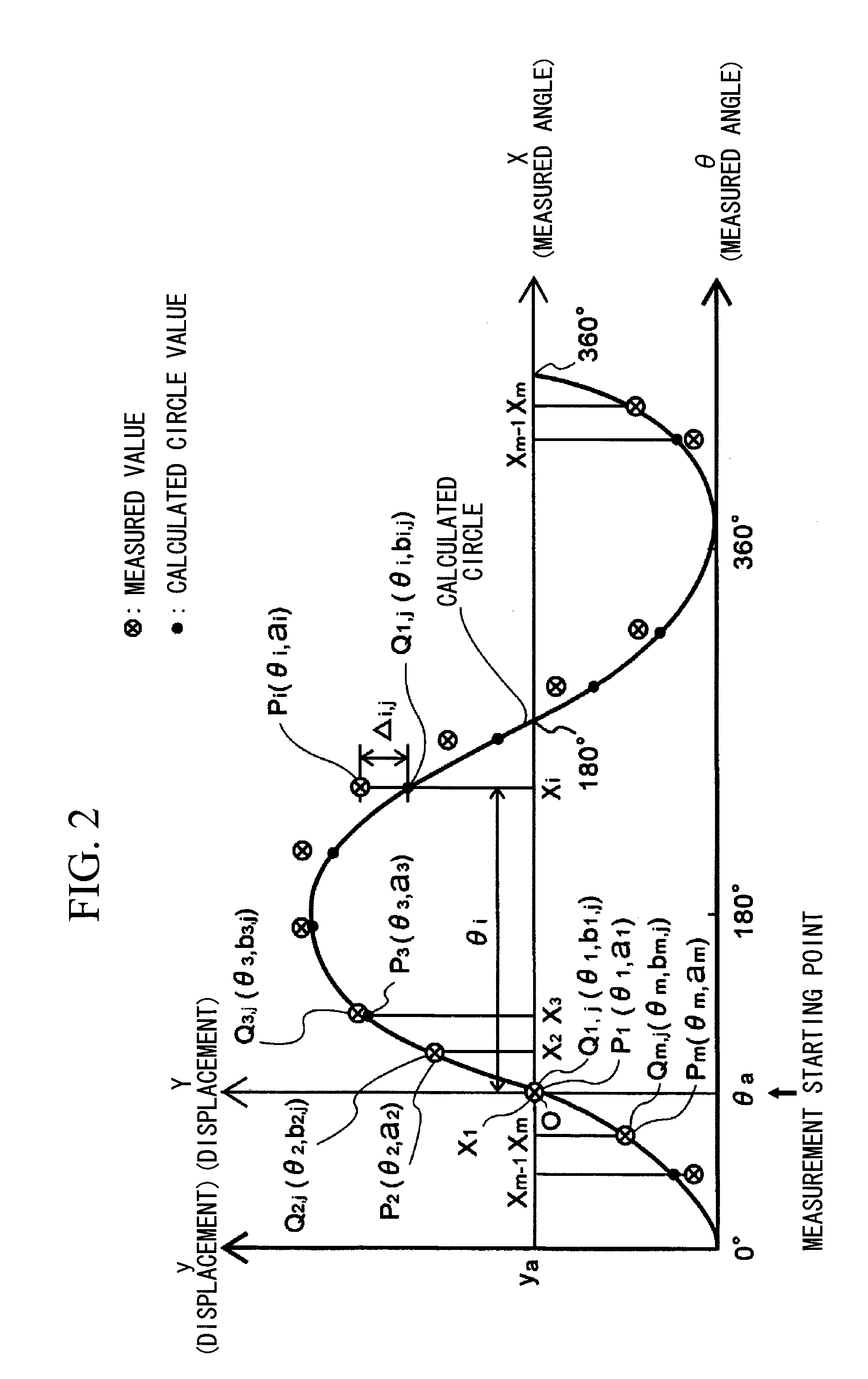
ActiveUS8306776B2Quick and reliable maintenanceElectrical/magnetic diameter measurementsIncline measurementMeasurement pointRepeating circle
In a method of calculating misalignment of a rotational body, radial displacement values are measured using a displacement gauge. A calculation part performs the steps of deriving radial displacement amounts of the rotational body for at least four or more measurement points along an outer surface while rotating the rotational body, selecting three arbitrary points to calculate a circle, calculating circle values for all the measurement points, calculating differences between the calculated circle values and the radial displacement amounts as error amounts, summing the error amounts to derive a total error amount, repeating circle calculation for different combinations and calculating a total error amount for each calculated circle, selecting a circle with a minimum total error amount as a most probable circle, and calculating deviation between the center of the most probable circle and the center of rotation of the rotational body.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
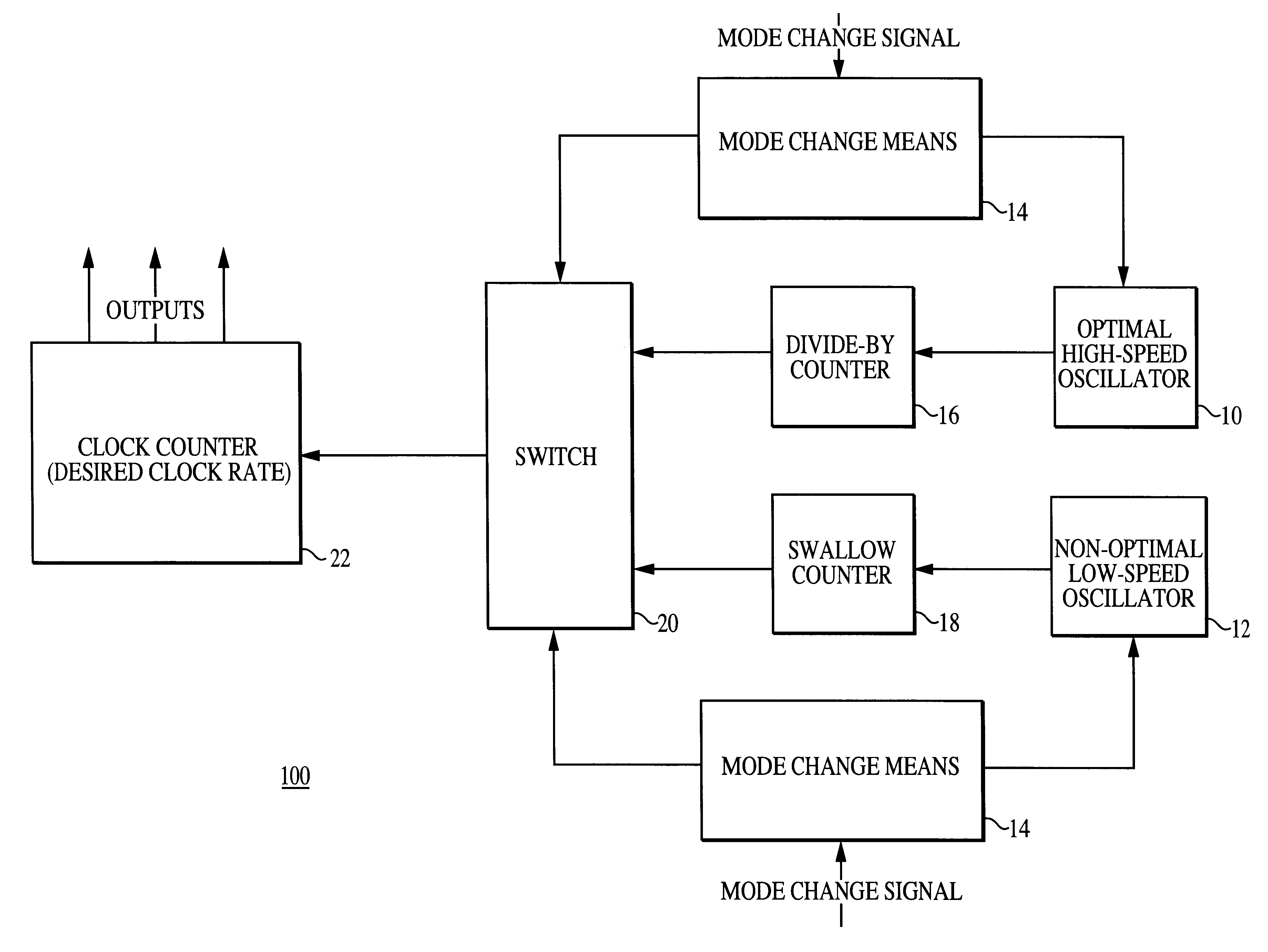
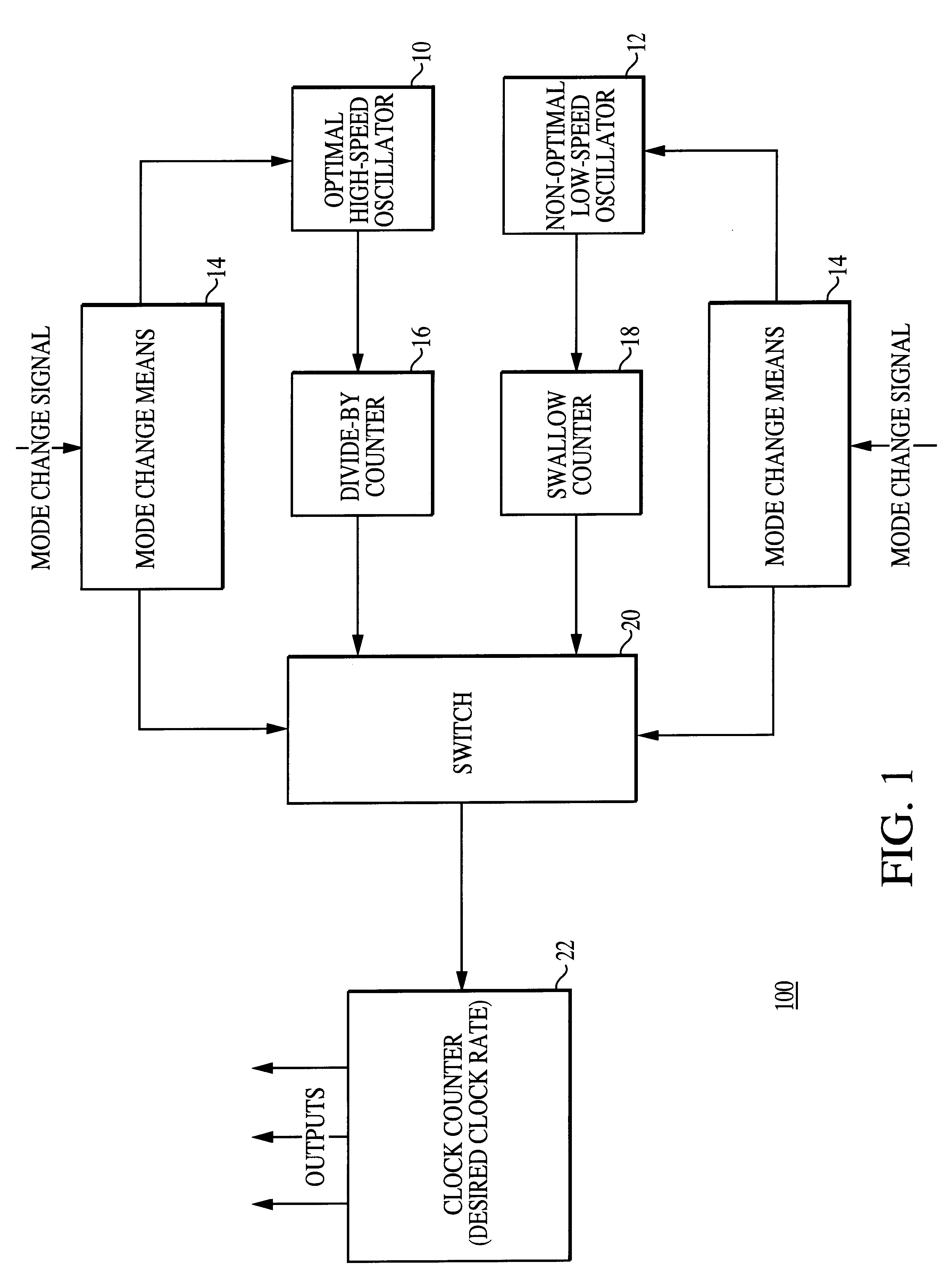
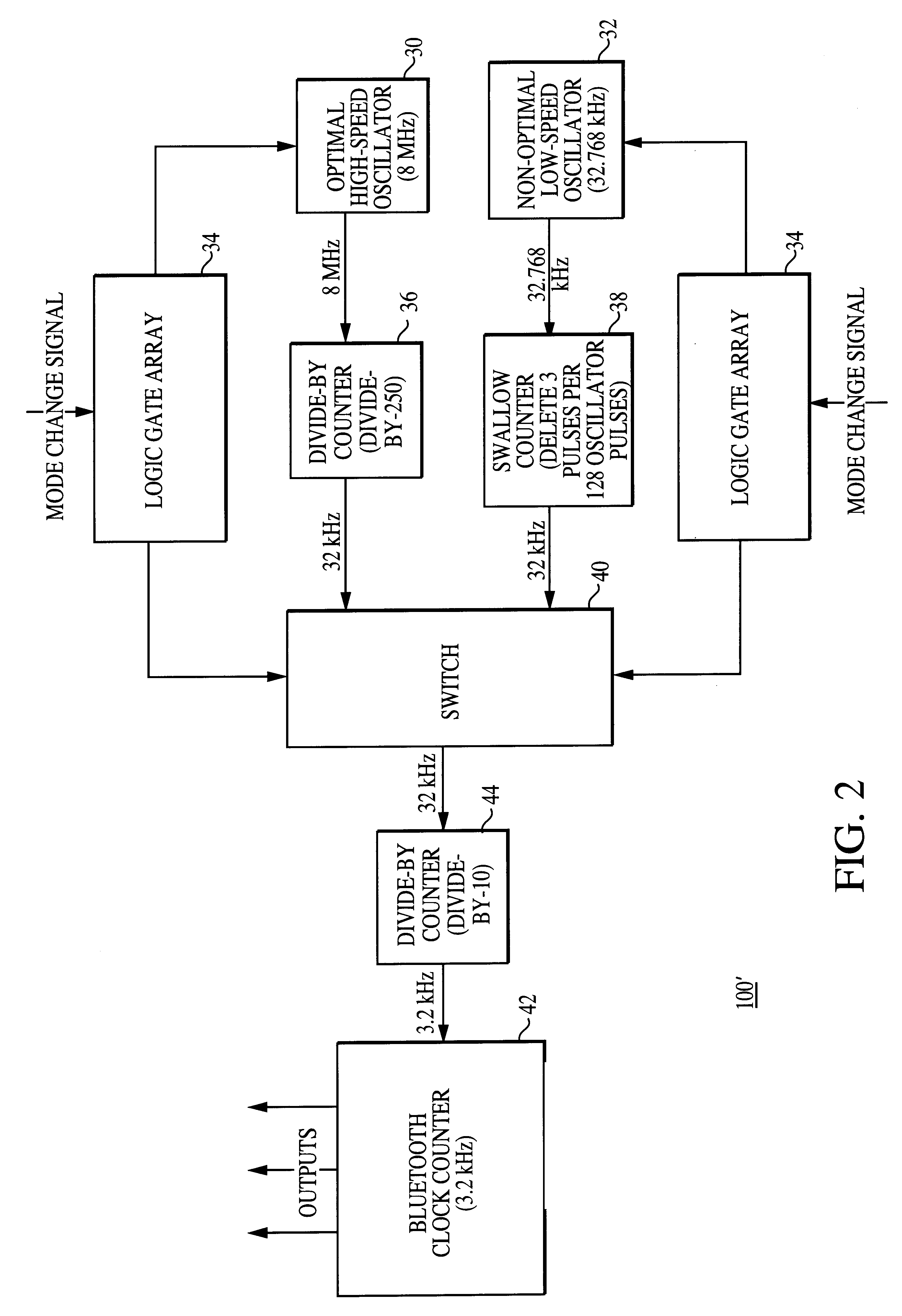
Method and apparatus for implementing a high-precision interval timer utilizing multiple oscillators including a non-optimal oscillator
InactiveUS6292062B1Reduce power consumptionImplement switchPulse automatic controlError detection/correctionLow speedTwo step
The present invention is a novel method and apparatus for implementing a high-precision timer utilizing a non-optimal oscillator and a high-speed oscillator wherein only one oscillator is enabled at a given moment in time. The high-precision timer method and apparatus comprises a timer and an error-correction technique. In one embodiment, the timer of the present invention is constructed from a high-speed oscillator and a low-speed non-optimal oscillator. The timer operates from the high-speed oscillator during on-the-air modes of operation and from the low-speed non-optimal oscillator during sleep modes of operation. The present inventive method corrects errors that are introduced by the non-optimal oscillator and a swallow counter. The errors are corrected using an error-correction technique having two steps: an error-determination step and an error-correction step. In the preferred embodiment of the error-determination step, a total error for a time interval is determined by performing the following steps: (1) calculating an individual error that occurs at each pulse; (2) multiplying the individual error by the number of pulses occurring during the time interval; and (3) adjusting for a non-optimal counter. Once an error has been determined, the error-correction step adjusts a clock counter accordingly. Depending upon the error-correction technique used, the error-correction step can correct the total error at one of several locations within a timer counter chain that is used to practice the present invention. The implementation of the present invention allows a straightforward realization of multiple timers.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
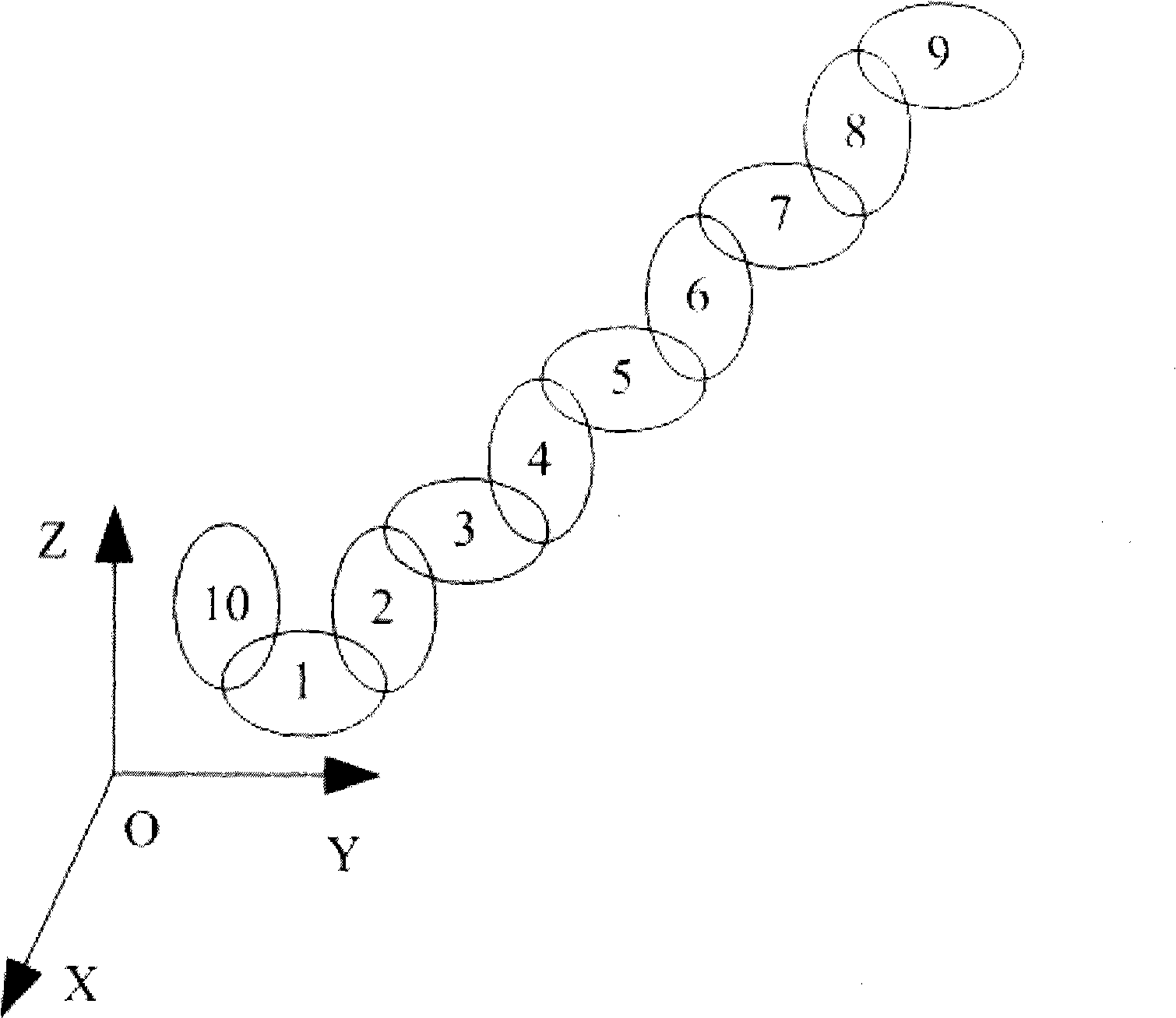
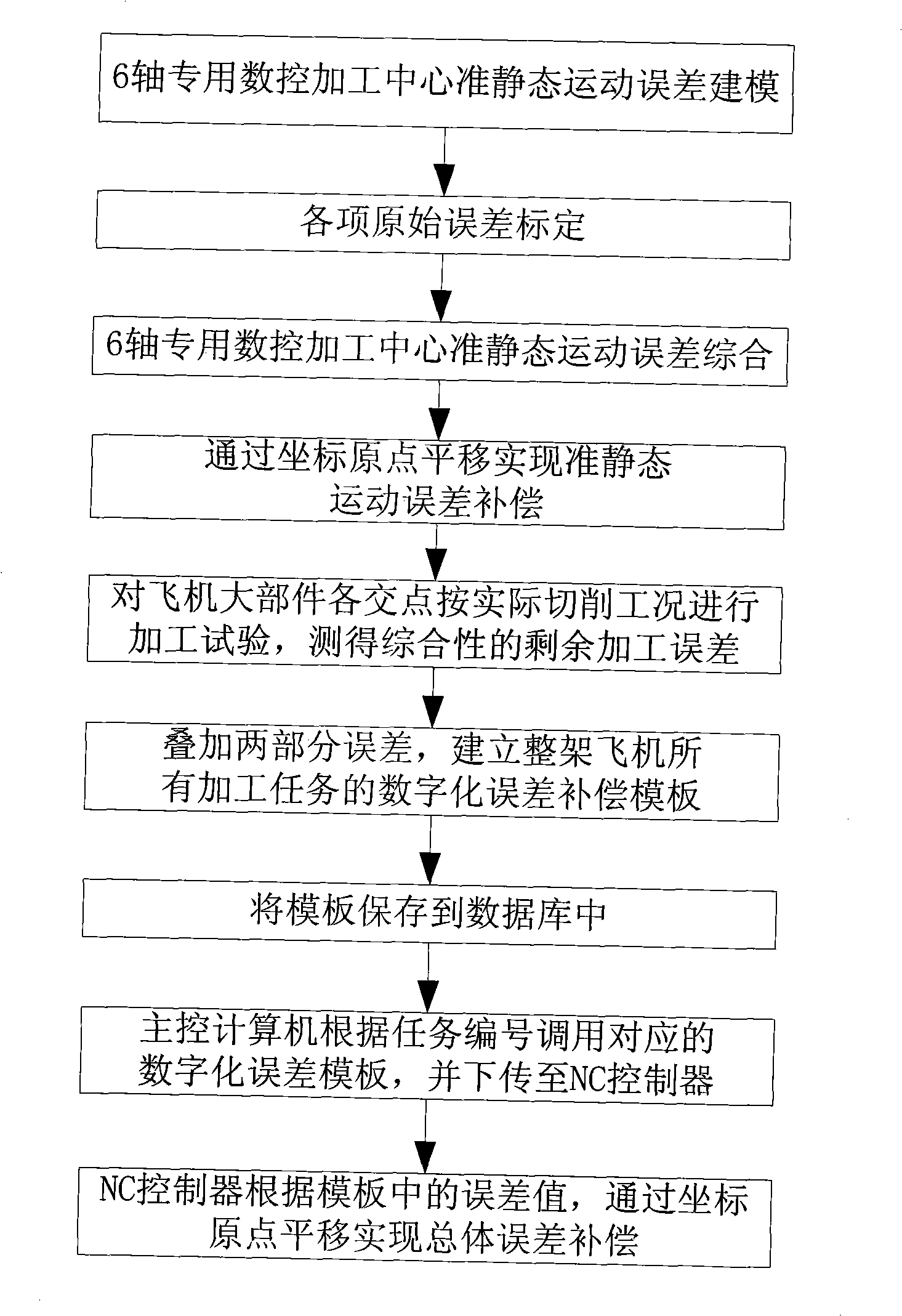
Method for implementing numerical control finish machining for large component of aeroplane based on digitalization error compensation template
InactiveCN101493683AReduced absolute motion precision requirementsReduce control requirementsProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlStatics
The invention discloses a method which realizes numerical control finish machining of intersection of large parts of the airplane on the basis of a digital error compensation template, comprising the steps as follows: firstly, a quasi static movement error model thereof is built, all the original errors are measured and obtained, and then a compensation of the quasi static movement error is realized; all machining tasks are carried out under a practical working condition; the comprehensive machining error residual after the first compensation is measured; and the total error compensation value is obtained comprehensively and a corresponding digital error compensation template is built. The machining precision of the intersection of a plurality of airplane wings of the same type is ensured by the repeated movement precision of a machining center. The method has the advantages that the precise numerical control machining center can be adopted to realize the precise machining of the intersection of the large parts of the airplane, the real-time performance is high, the numerical control program and the software and hardware of the machining center are not required to be changed, the advantages of the high precision of the repeated movement of the numerical control machining center is sufficiently played, and the control requirement on the workshop environmental temperature is reduced.
Owner:CHENGDU AIRCRAFT INDUSTRY GROUP
Brake tester with combination of mechanical analogue and electric inertia analogue and control algorithm
ActiveCN102654431AWith automatic compensation functionMeet high precision test requirementsMachine part testingMathematical modelFlywheel
The invention belongs to a mechanical-electrical integration system, relating to electric transmission analogue of a mechanical rotation inertia system, in particular to a brake tester with combination of mechanical analogue and electric inertia analogue and a control algorithm. The control algorithm comprises the following steps of: calculating a total drop-out value when the kinetic energy of a flywheel is related to a test appointed initial rotation speed by synchronously acquiring a flywheel rotation speed and a motor output torque, calculating total energy compensated by the motor according to a mathematic model, simultaneously calculating total energy compensated by the motor to obtain the difference of the two and calculating a force moment output value of the motor in a next control period so that the tester runs in a state of being equal to an ideal flywheel without system constant resistance. The brake tester has an automatic compensation function of an energy compensation error so as to control the total error within a small range; and exact matching of rotation inertia is realized, the requirement of a high-precision test can be met by the control precision, and the investment and the operation cost are saved.
Owner:CHINA NAT HEAVY MACHINERY RES INSTCO
Zero crossing method of symbol rate and timing estimation
ActiveUS20040131113A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAlgorithmSymbol of a differential operator
System and method for analyzing communication signals. A digital signal comprising multiple samples is received, representing a plurality of binary symbols. Zero crossings of the signal are determined, each comprising a respective first sample immediately preceding the zero crossing and a respective second sample immediately following the zero crossing. Per zero crossing, an error expression is determined interpolating between the first and second samples as a function of estimated period T and estimated offset tau of the signal. Based on the error expressions, values of T and tau are determined using a linear fit that minimizes a total error of values of the error expressions. T and tau are usable in analyzing the signal, e.g., each zero crossing corresponds to a respective symbol represented by a respective segment of the signal. The segments are overlaid based on T and tau, forming an eye diagram usable to analyze the signal.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
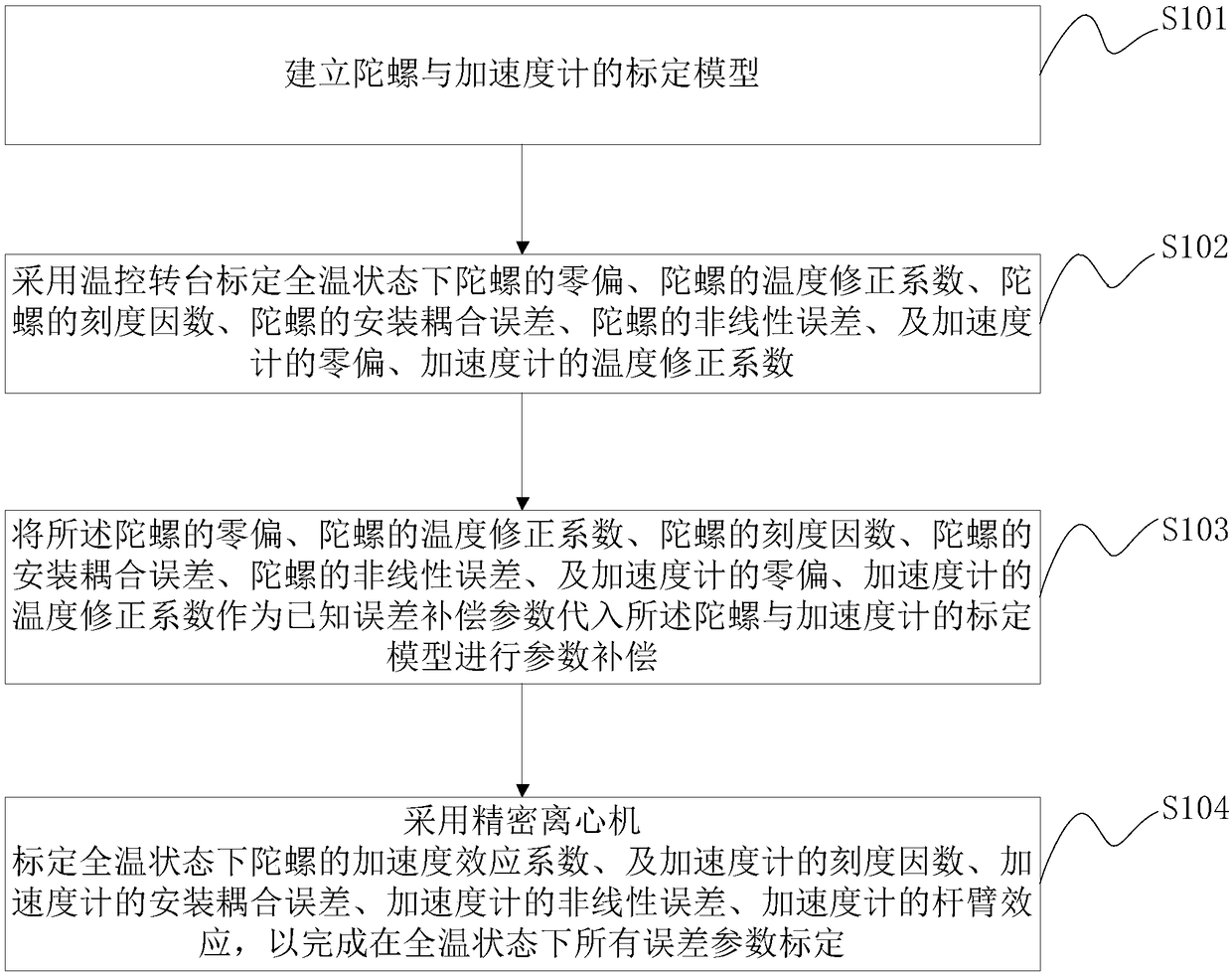
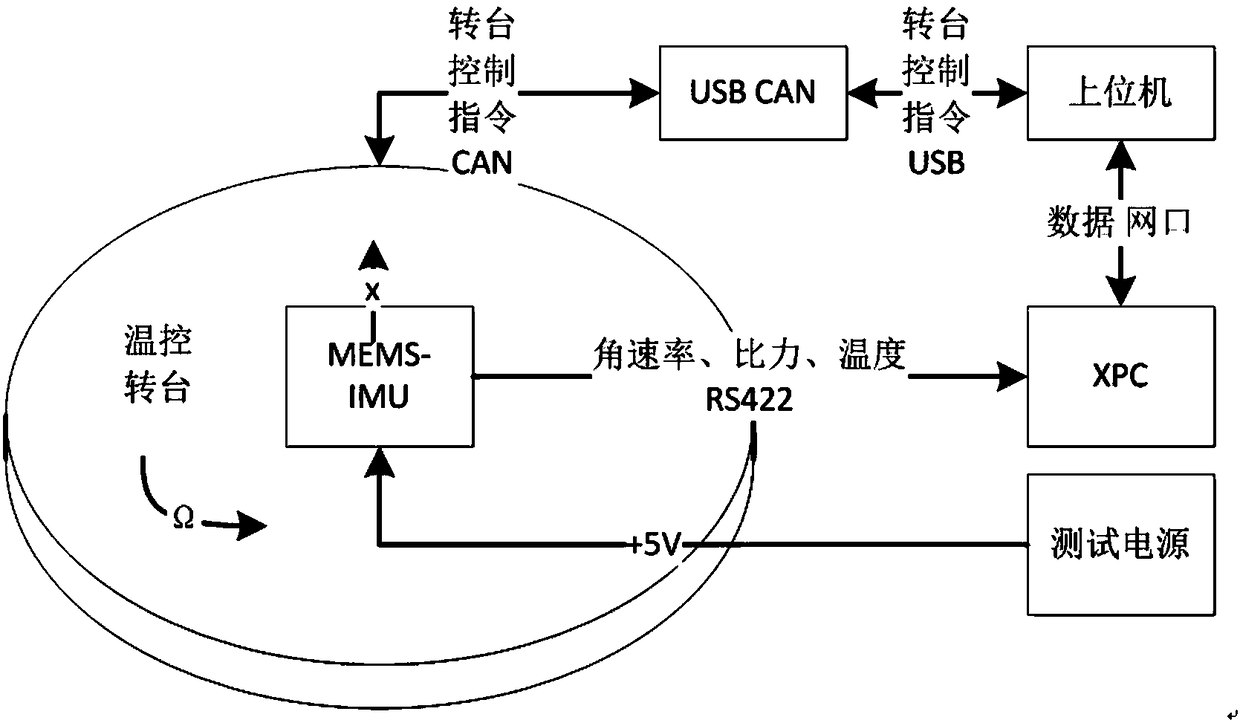
MEMS-IMU (Micro-electromechanical Systems-Inertial Measurement Unit) full-temperature and full-parameter calibration and compensation method
ActiveCN108534800AEliminate the calibration processAvoid the disadvantages of incompletenessMeasurement devicesTemperature controlGyroscope
The invention provides an MEMS-IMU (Micro-electromechanical Systems-Inertial Measurement Unit) total-temperature and total-parameter calibration and compensation method. Temperature-control rotary table calibration and precise centrifugal calibration are tightly combined to complement each other and have a complementary action; the temperature-control rotary table calibration is used for calibrating a zero offset, a temperature coefficient, a scale coefficient, an installation coupling error and a non-linear error of a gyroscope in an MEMS-IMU, and zero offset and a temperature coefficient ofan accelerometer; the precise centrifugal calibration can be used for calibrating an acceleration effect coefficient of the gyroscope, and a scale factor, an installation coupling error, non-linear error, a lever arm effect and the like of the accelerometer; total-error parameters of the MEMS-IMU under a total-temperature state can be accurately calibrated, so that the precision of the MEMS-IMU inan actual application process is improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Displacement detection method for moving device in tunnel
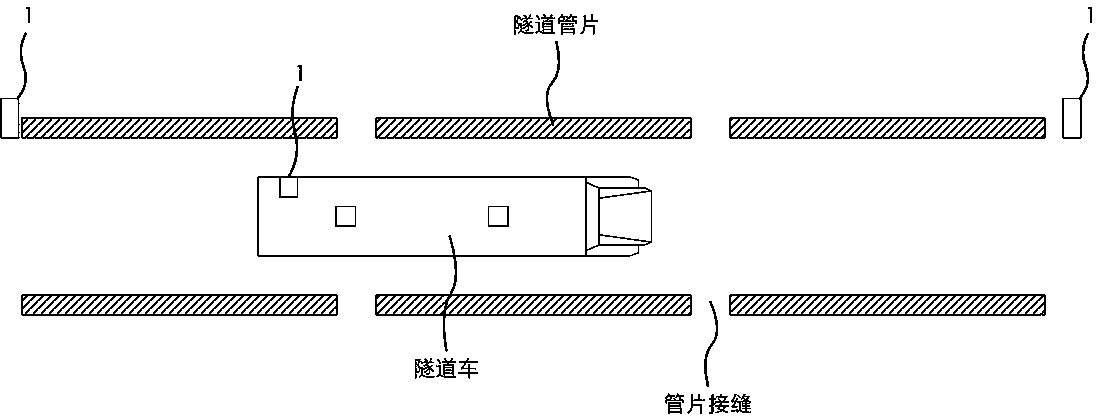
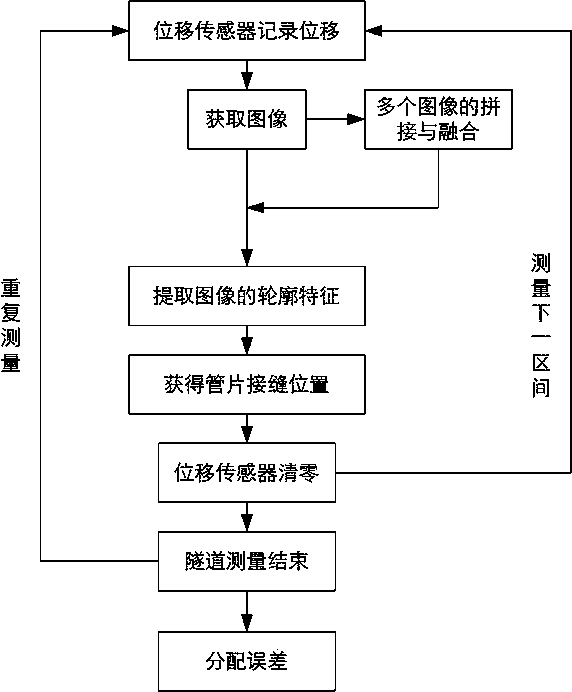
InactiveCN104266591AMonitor settlementSolve the problem of continuous accumulation of errorsUsing optical meansObservational errorImaging algorithm
The invention provides a displacement detection method for a moving device in a tunnel. The displacement detection method effectively corrects displacement of the moving device, and provides more accurate displacement data for obtaining tunnel images through the moving device. The tunnel is divided into a plurality of given sections, infrared geminate transistors are utilized for outputting displacement sensor distance measurement reset signals, and therefore the problem of continuous accumulation of errors caused by long-distance displacement measurement can be effectively solved; an image algorithm is utilized for detecting joint positions of pipe pieces, carrying out measurement many times, and carrying out error analysis, by analyzing a large number of data, a probability distribution model of the displacement measurement errors caused by slipping of a wheel track and S-shaped lines can be obtained, the error expectation is estimated, the total errors are distributed, and the measurement errors of each section are reduced.
Owner:樊晓莉
Method and system for calculating misalignment of rotational body
ActiveUS20100241394A1Sure easyEasy maintenanceElectrical/magnetic diameter measurementsIncline measurementMeasurement pointCentre of rotation
A system and method for calculating misalignment of a rotational body includes: deriving radial displacement amounts of the rotational body for at least four or more measurement points; selecting three arbitrary points among all the measurement points to calculate a circle; calculating circle values for all the measurement points from the calculated circle; calculating differences between the calculated circle values and the radial displacement amounts as error amounts at the measurement points; summing the error amounts to derive a total error amount value; repeating calculation for combinations of three measurement points to calculate each total error amount value; selecting a calculated circle with a minimum total error amount value as a most probable circle; and calculating deviation between the center of the most probable circle and the center of rotation of the rotational body as misalignment data of the most probable circle.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
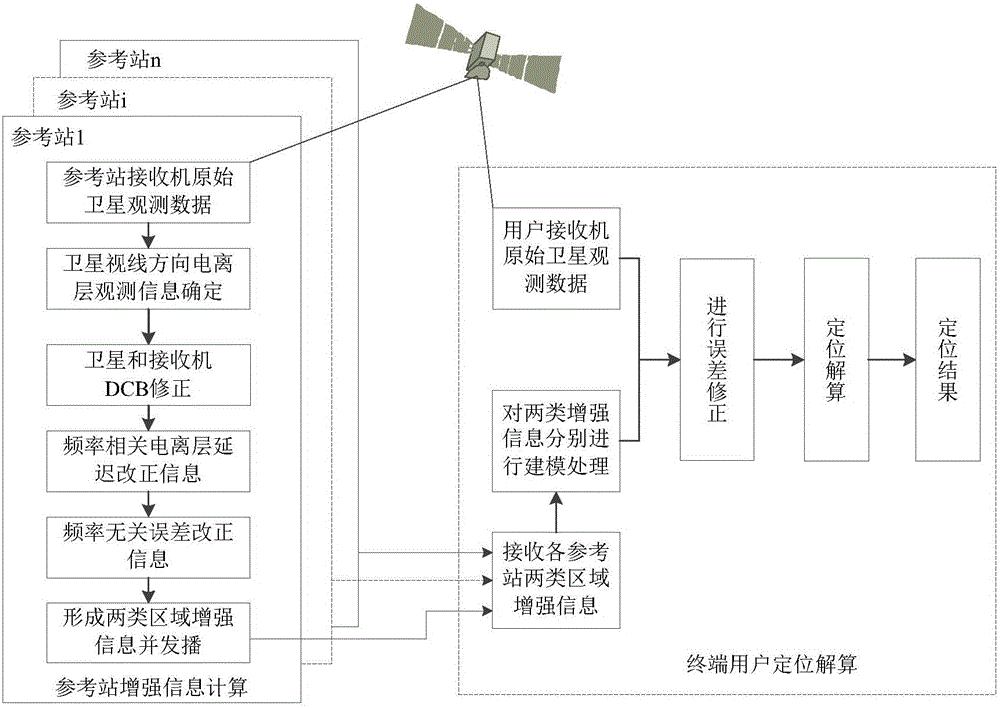
Error-separation-mode-based regional pseudo-range differential enhanced positioning method of GNSS
The invention discloses an error-separation-mode-based regional pseudo-range differential enhanced positioning method of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS). The method comprises: for regional pseudo-range differential enhanced positioning of a GNSS, n reference stations and a terminal user are employed; a receiver of any reference station r receives observation data of a satellite s, and after processing, an error vector correction number of the satellite s on the reference station r is obtained; each reference station sends the obtained error vector correction number of the satellite s to the terminal user, distance weighted mean processing is carried out on a frequency relevant item error correction number of each reference station according to a base line distance between the reference station and the terminal user, and then the processed number adds to a frequency non-relevant item error correction number of one reference number to obtain a total error correction number; and then a pseudo-range measurement value adds to the total error correction number to obtain a corrected user pseudo range and then calculation is carried out according to a standard pseudo-range single-point positioning way so as to obtain a user position after error correction. With the method, the positioning performance of the single-frequency satellite navigation can be improved.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Transmitted wavefront detection apparatus and method for meniscus lens
ActiveCN105157598AAchieve alignmentRealize zero detectionUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesCamera lensWavefront
The invention relates to a transmitted wavefront detection apparatus and method for a meniscus lens. The transmitted wavefront detection apparatus for a meniscus lens comprises an interferometer, a computed hologram, a to-be-detected meniscus lens and a spherical surface reflector, which are all connected in sequence along an optical path. The light emitting end of the interferometer is provided with a standard lens. The transmitted wavefront detection method comprises the following steps: firstly, obtaining a measurement total error W2 of the spherical surface reflector; secondly, obtaining a measurement total error W1 of the meniscus lens; and thirdly, processing data according to a first detection result W1 and a second detection result W2. The invention provides a novel, simple accurate method for measuring a transmitted wavefront of a meniscus lens. By means of the computed hologram, a holographic sheet can be in alignment with the interferometer, spherical aberration caused by the meniscus lens and the spherical surface reflector can be compensated, and then the whole detection system can achieve zero detection. The method provides simple measuring steps and provides an easy data processing means, and has remarkable engineering application values.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Quick splicing device for display screen
ActiveCN102855824AAvoid damageImprove stitching accuracyCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsStands/trestlesLocking mechanismDie casting
The invention discloses a quick splicing device for a display screen. The quick splicing device comprises a left assembly and a right assembly which can be locked to each other, wherein the left assembly comprises a rotating fixing seat, a rotating angle seat and a rotating locking mechanism; the rotating angle seat can be locked to the right assembly and also can be rotatably connected with the rotating fixing seat; once the rotating locking mechanism is released, the rotating angle seat can be rotated relative to the rotating fixing seat; and when the rotating locking mechanism is locked, the rotating angle seat is fixedly connected with the rotating fixing seat. With the adoption of the quick splicing device for the display screen with the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, an arc-shaped display screen can be quickly spliced, and moreover, precise splicing and locking can be achieved; and more importantly, the main parts are all manufactured in combination of die-casting technology and machining technology, and the manufacturing precision can reach a value within 0.02mm; and the total error can be controlled within 0.1mm after splicing; the splicing precision is increased by one order of magnitude, so that precise splicing and locking can be achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN AOTO ELECTRONICS
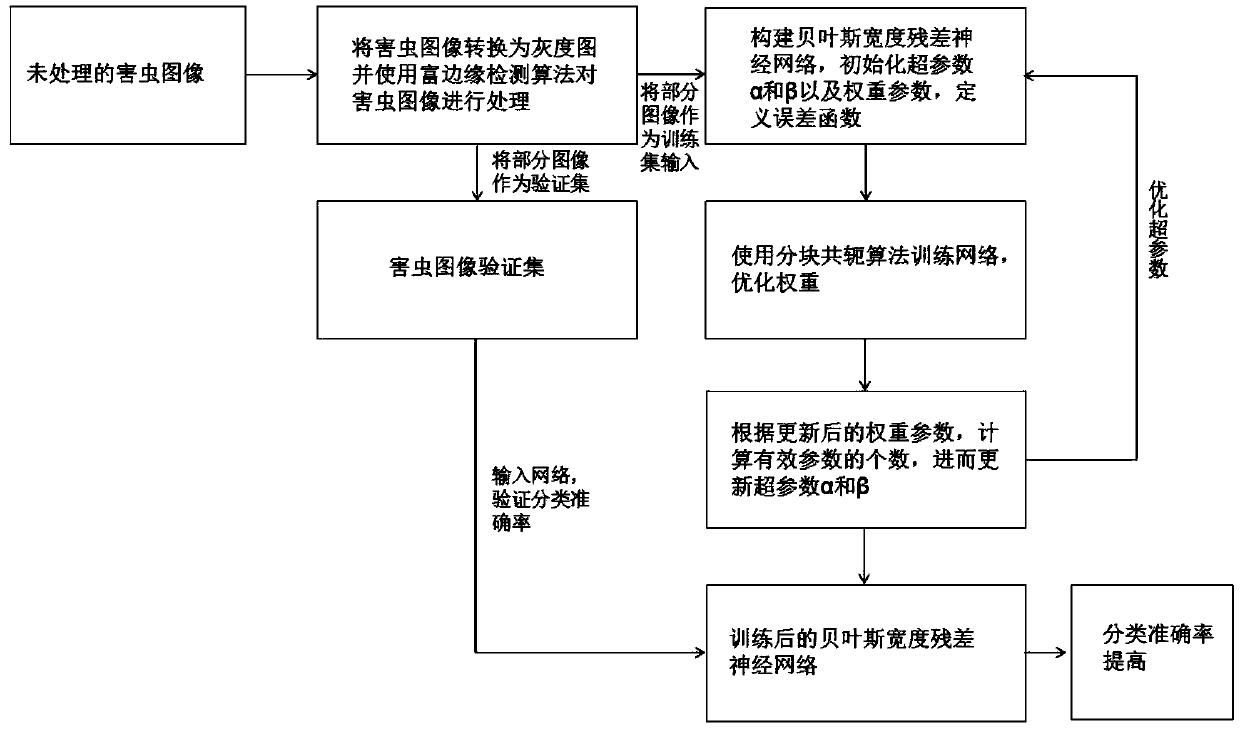
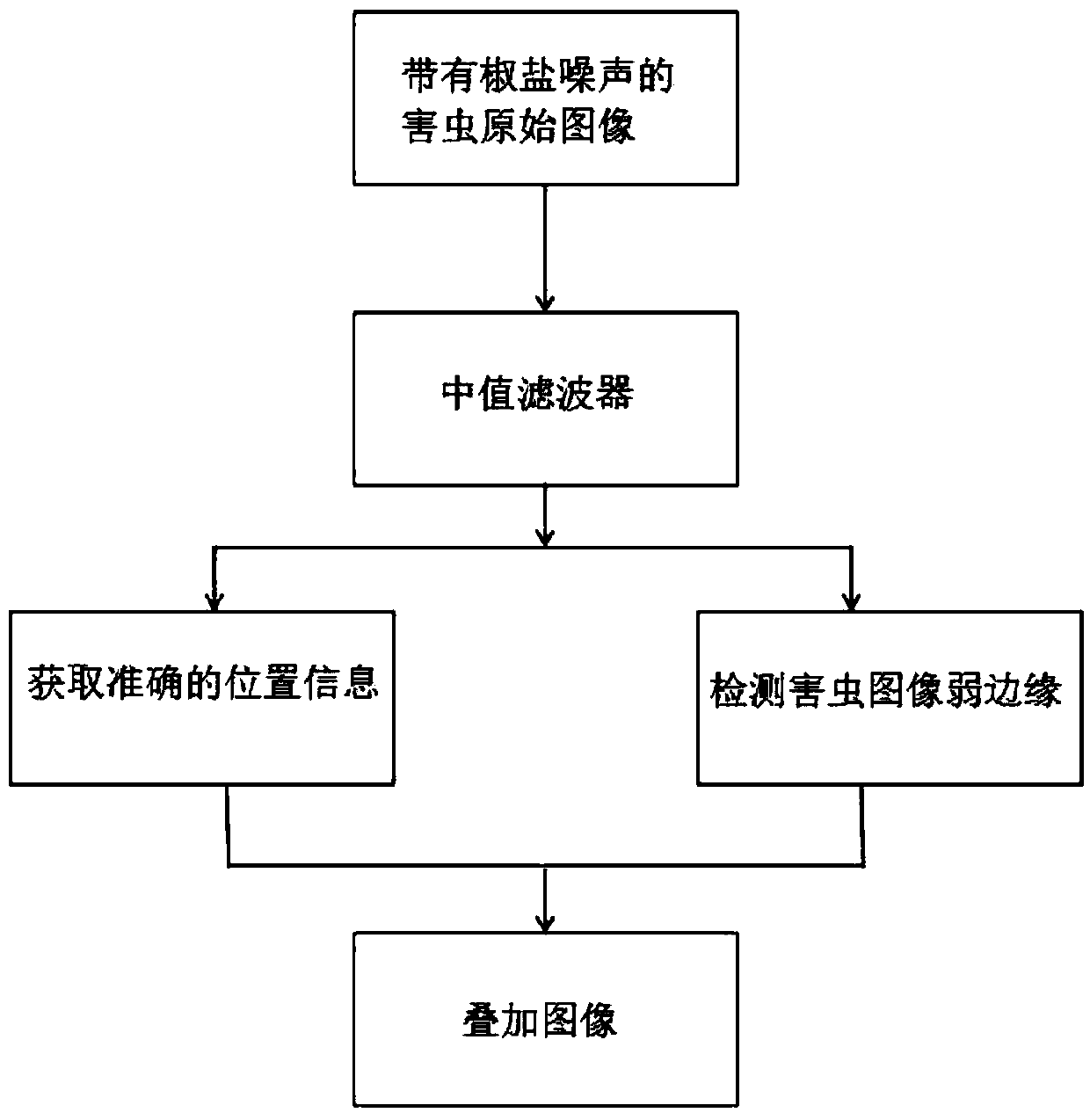
Bayesian wide- residual neural network-based injurious insect image recognition method
ActiveCN108648191APreserve edge detailComplete outlineImage enhancementImage analysisData setResidual neural network
The invention discloses a Bayesian wide-residual neural network-based injurious insect image recognition method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, preprocessing an injurious insect imagerecognition data set and carrying out injurious insect edge detection on a greyscale map by using a Rich-Edge detection algorithm; 2, constructing a Bayesian wide-residual neural network (NWResNet);3, inputting an injurious insect edge image obtained in the step 1 into the NWResNet constructed in the step 2, and obtaining a total error function of the NWResNet by utilizing an injurious insect edge image training set obtained in the step 1; 4, training the network through a Block-cg algorithm by utilizing the error function obtained in the step 3; 5, updating a hyper-parameter according to the network optimized in the step 4; and 6, repeating the steps 4 and 5 to obtain a final network, and inputting an injurious insect image verification set into the network to ensure that the classification correctness is higher.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
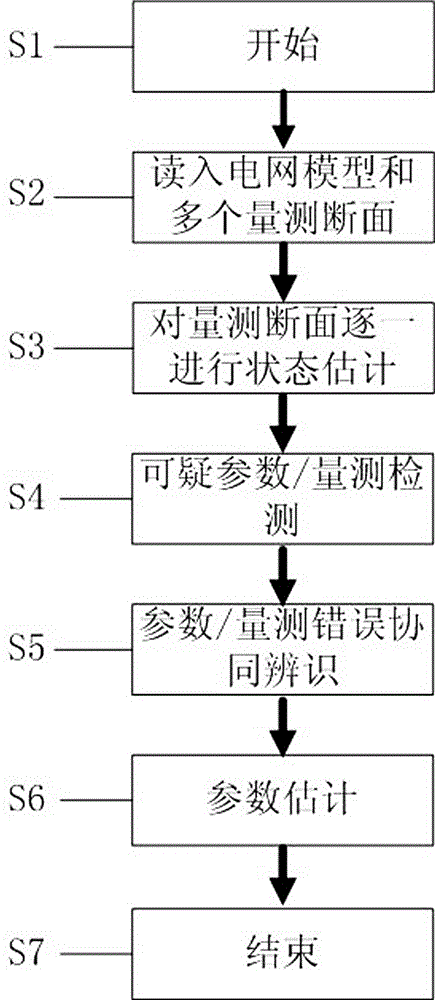
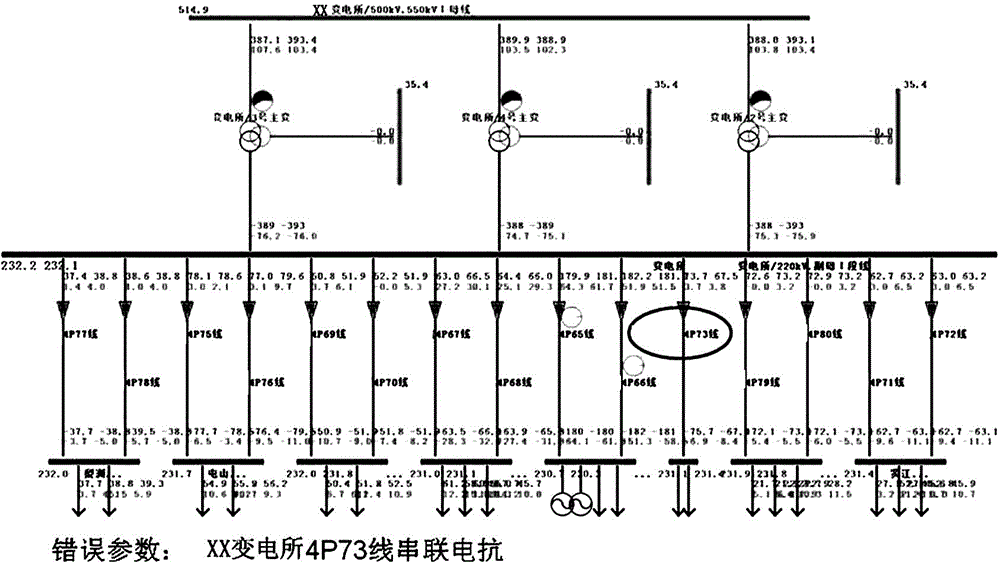
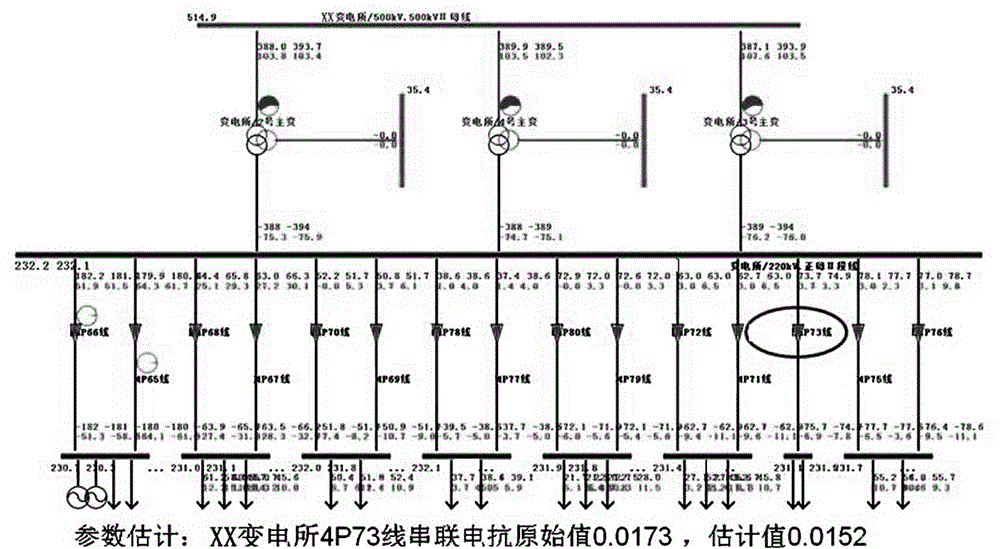
Power grid parameter error and bad data coordinated identification and estimation method
InactiveCN104836223AEfficient collaborative identificationPrecise collaborative identificationAc network circuit arrangementsNumerical stabilityEstimation methods
The invention discloses a power grid parameter error and bad data coordinated identification and estimation method relating to a calculating method of power grid parameter accuracy. The conventional parameter error identification and estimation technology is low in efficiency and accuracy. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: 1) read-in of a power grid model and a plurality of measurement sections; 2) one-by-one state estimation of the measurement sections; 3) suspicious parameter and measurement detection; when the related measurement total error is smaller than the threshold value, the parameters or the measurement can be trusted; when the related measurement total error is greater than the threshold value, the parameters or the measurement can be suspicious, and can be filed in the suspicious parameter / measurement set; 4)parameter / measurement error coordinated identification based on multi-section and total error reduction index; when the suspicious parameter / measurement total error reduction index is greater than 9, the data are the error parameters or the bad data; 5) multi-section combined parameter estimation. The power grid parameter error and bad data coordinated identification and estimation method is advantageous in that the measurement redundancy, the value stability, and the calculating efficiency can be improved, and the parameter error identification and estimation accuracy can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for measuring and compensating surface profile error of large rotary body part in real time
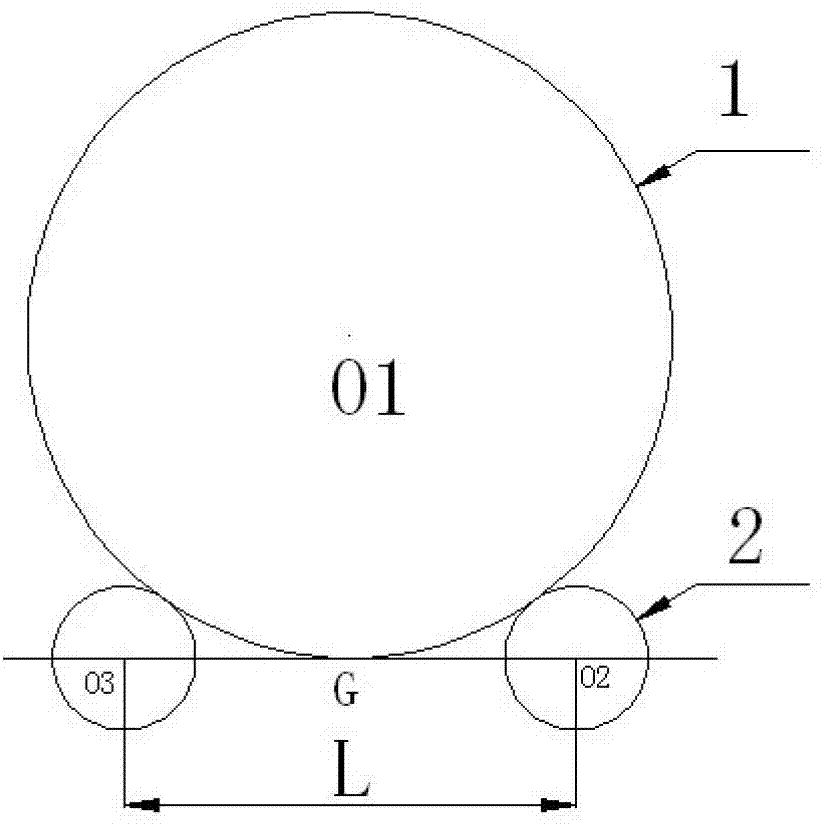
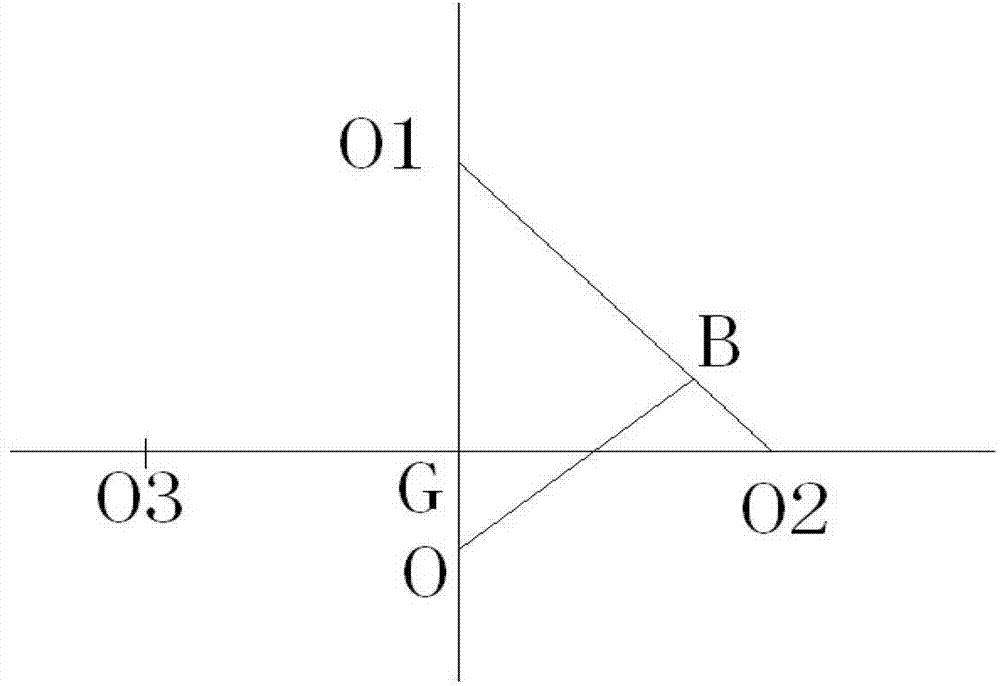
ActiveCN102890475AImprove machining accuracySolve the problem that the jump cannot be compensatedProgramme controlComputer controlEngineeringContour error
The invention discloses a method for measuring and compensating a surface profile error of a rotary body part in real time. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) determining a common tangent of each carrier roller and a profile surface tangency point of the rotary body part, and thus obtaining an included angle which is formed by intersecting two tangents; (2) uniformly sampling the profile surface of the rotary body part to obtain a plurality of sampling points which are uniformly distributed on the circumferential direction, measuring a total error at each sampling point, and thus obtaining a profile error of two carrier rollers, which corresponds to each sampling point; (3) computing the surface profile error of the rotary body part at each sampling point; and (4) measuring a carrier roller radius error in real time, computing an error compensation value of each sampling point according to a real-time measurement value of a carrier roller profile error and a surface profile error value of the rotary body part, and compensating the error in real time. By adoption of the method, the surface profile error of a large rotary body can be measured and compensated in real time. The method has the advantages of convenience for measurement and accuracy in computation. The processing accuracy of a rotary body workpiece can be greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGSU GAOJING MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT CO LTD
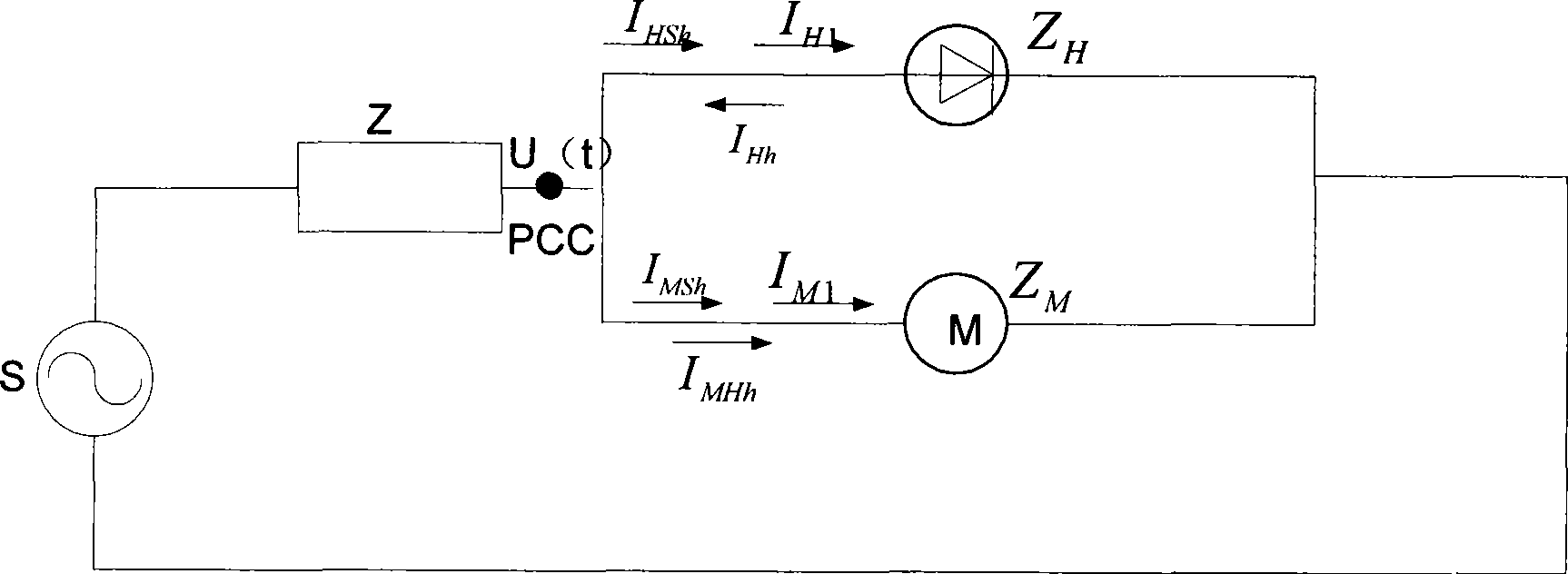
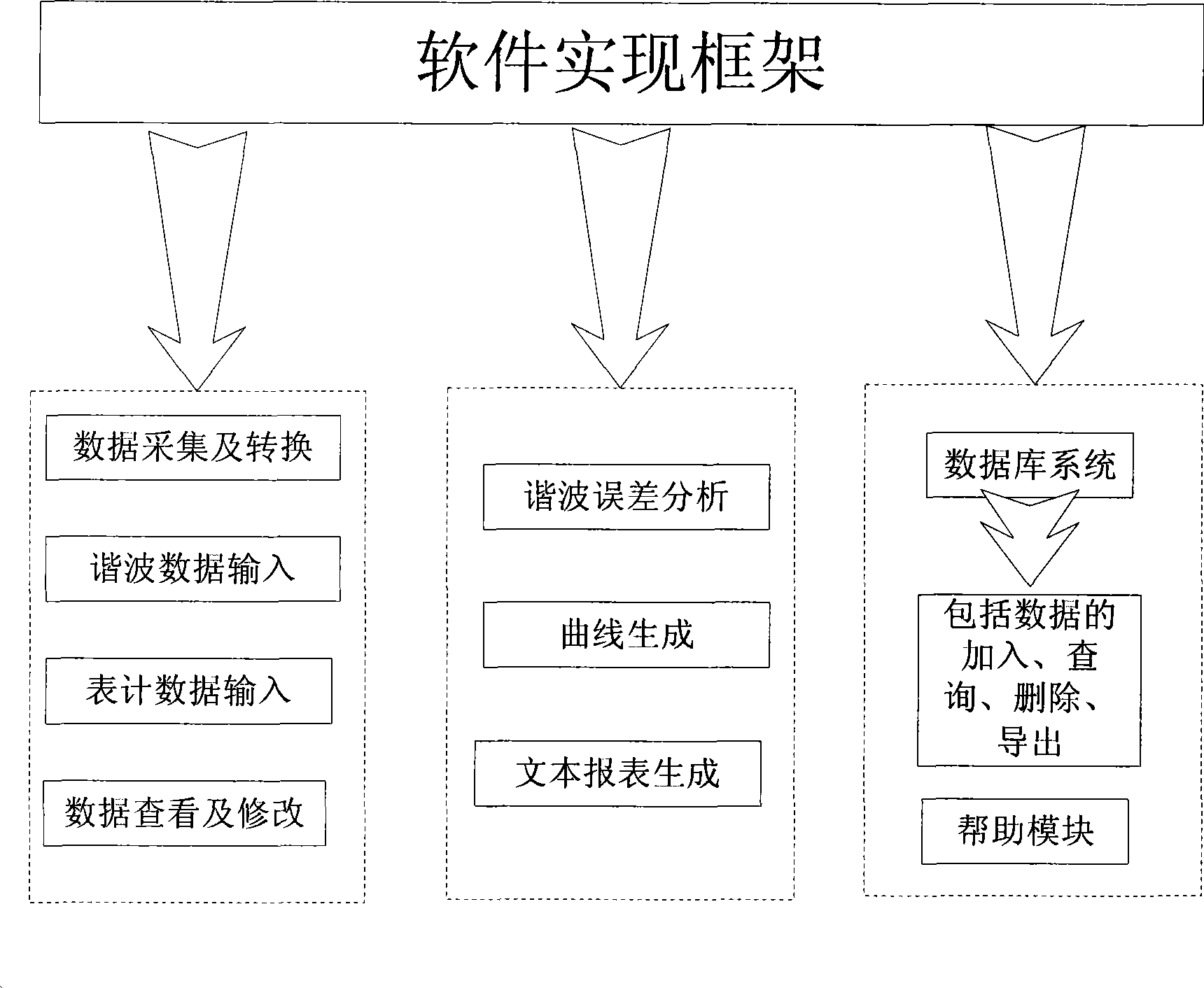
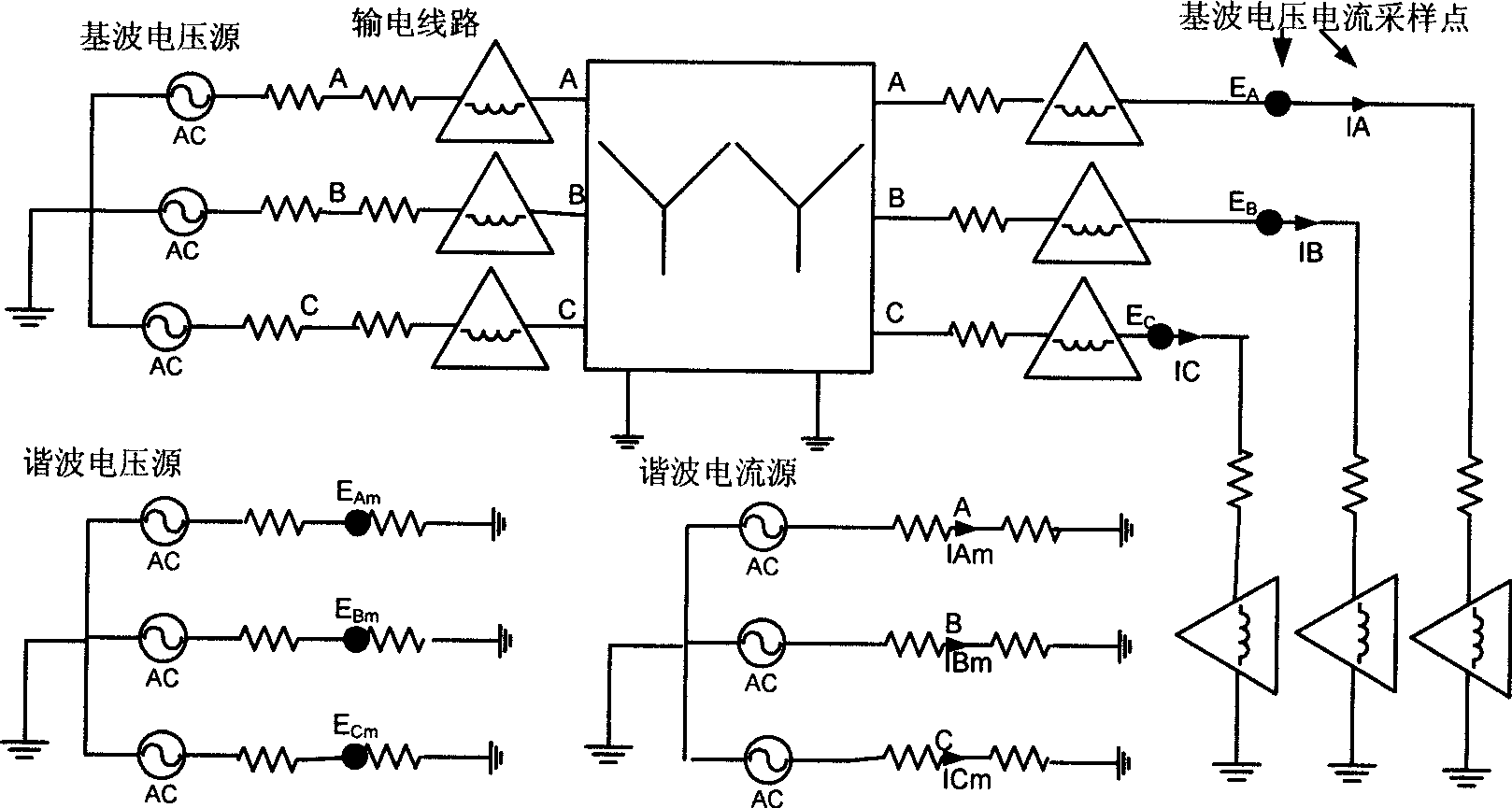
Harmonic electric energy metering error analytical apparatus
InactiveCN101441231AEasy and efficient implementationMeet the needs of real-time monitoring of large-scale industrial power gridsSpectral/fourier analysisPower gridHarmonic pollution
A harmonic energy metering error analytic device comprises a harmonic data collection part used for inputting the harmonic data collected by power network into an electric energy data analytic part, an electric energy metering error data analytic part comprising a model storage module and an error analysis module and an error analytic result output part used for outputting or storing the error data analytic result acquired from the electric energy metering error data analytic part; wherein the model storage module is used for storing metering error models and model functions corresponding to the models of electric energy meters; the error analysis module is used for deriving the theoretical error data to be analyzed of the input harmonic data and deriving the error of each harmonic measurement and the total error. The harmonic energy metering error analytic device can provide quantitative data basis for power supply department to retrieve electric energy metering error loss and control harmonic pollution.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
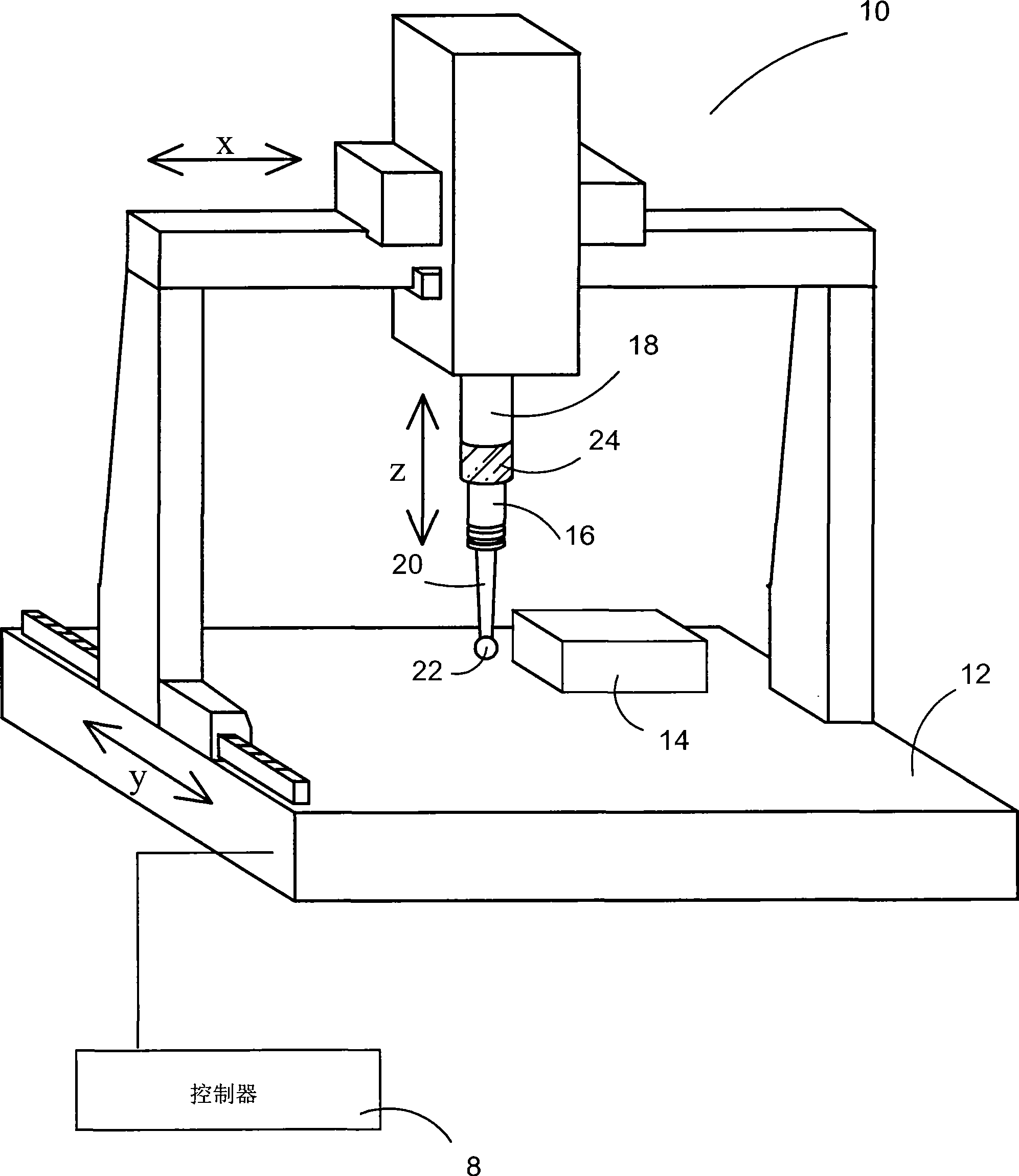
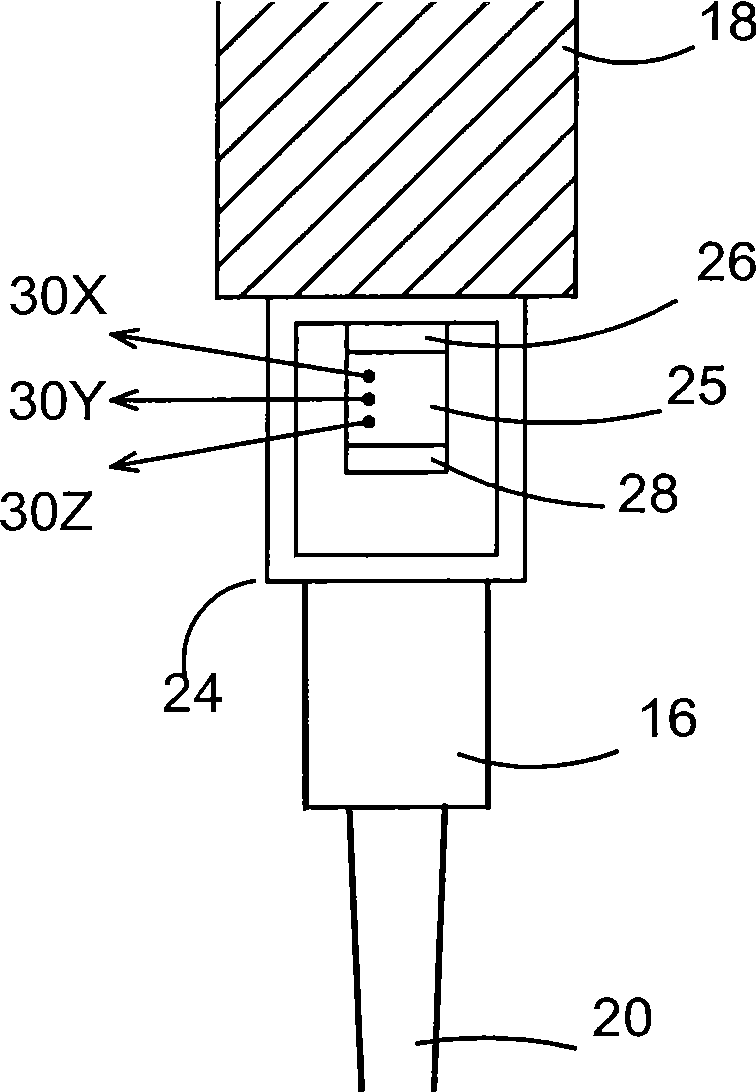
Method of error correction
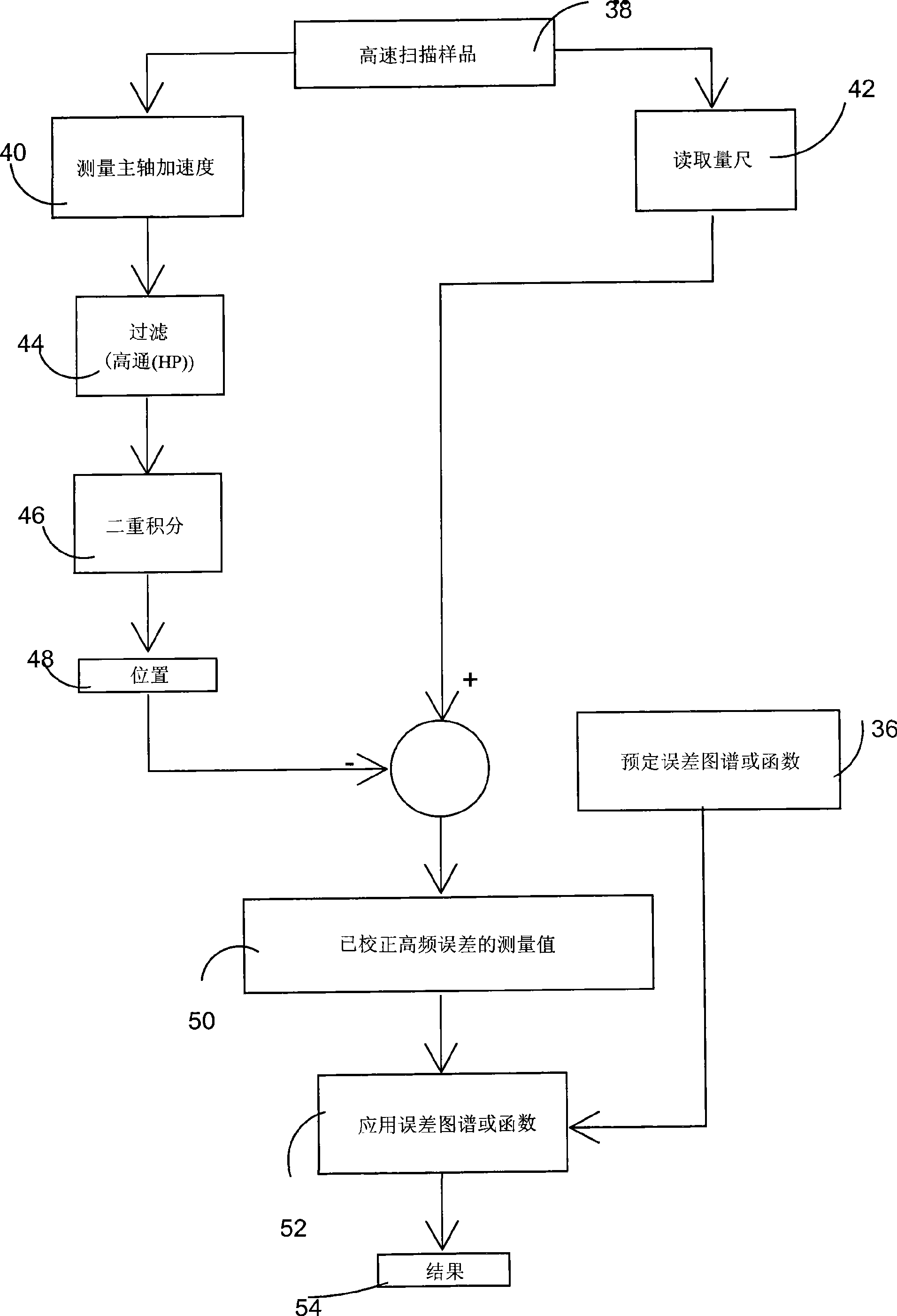
A method of error correction of workpiece measurements using coordinate measuring machines has the steps of measuring the workpiece, determining the repeatable measurement errors from a predetermined error function, look-up table or map, measuring at least a function of the acceleration and calculating the unrepeatable measurement errors as the workpiece is measured, combining the repeatable and non repeatable errors to determine the total errors and using the total errors to correct the measurements of the workpiece.
Owner:RENISHAW PLC
Method and apparatus for diversity control in mutiple description voice communication
InactiveUS20080015856A1Quality improvementReduce errorsSpeech analysisCode conversionVoice communicationLow delay
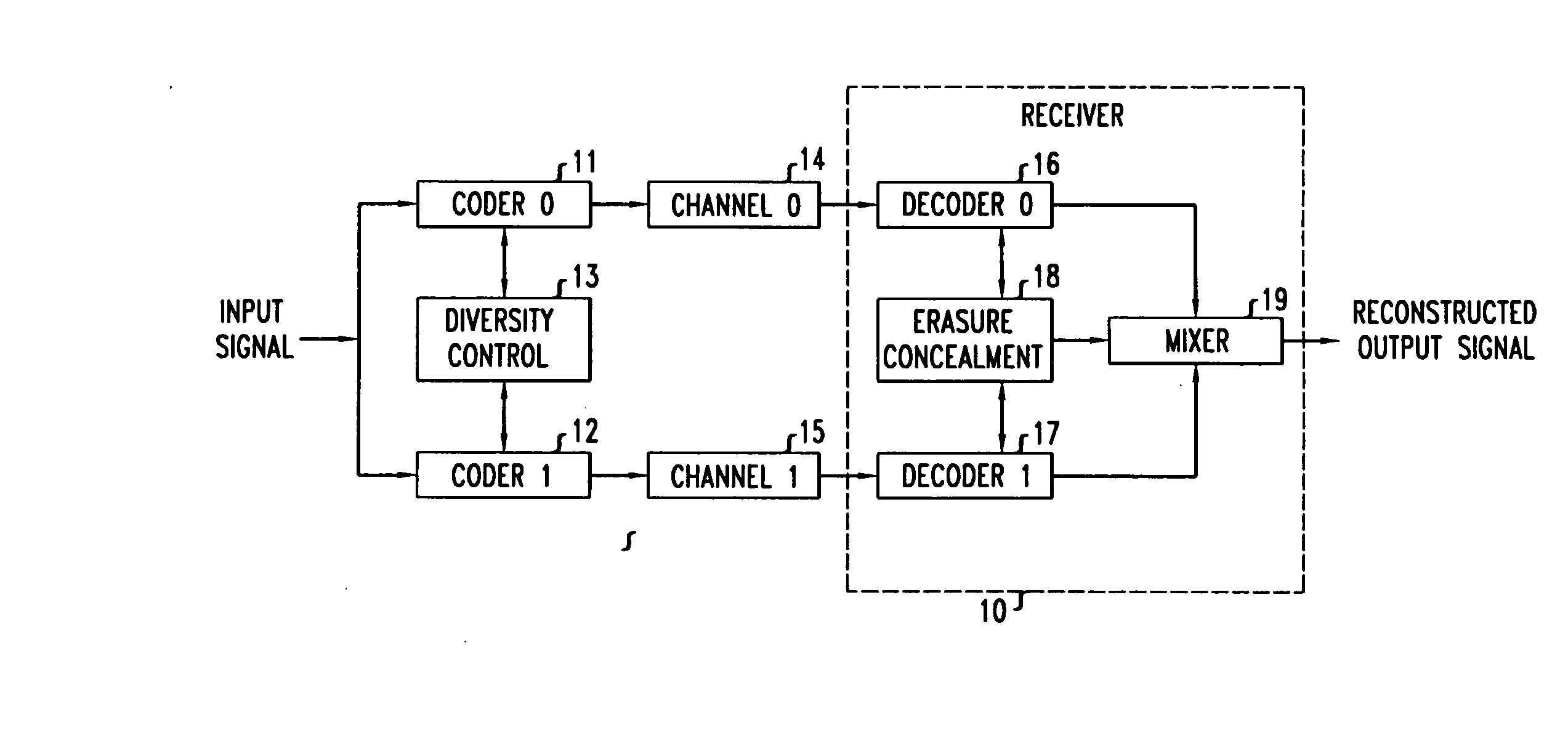
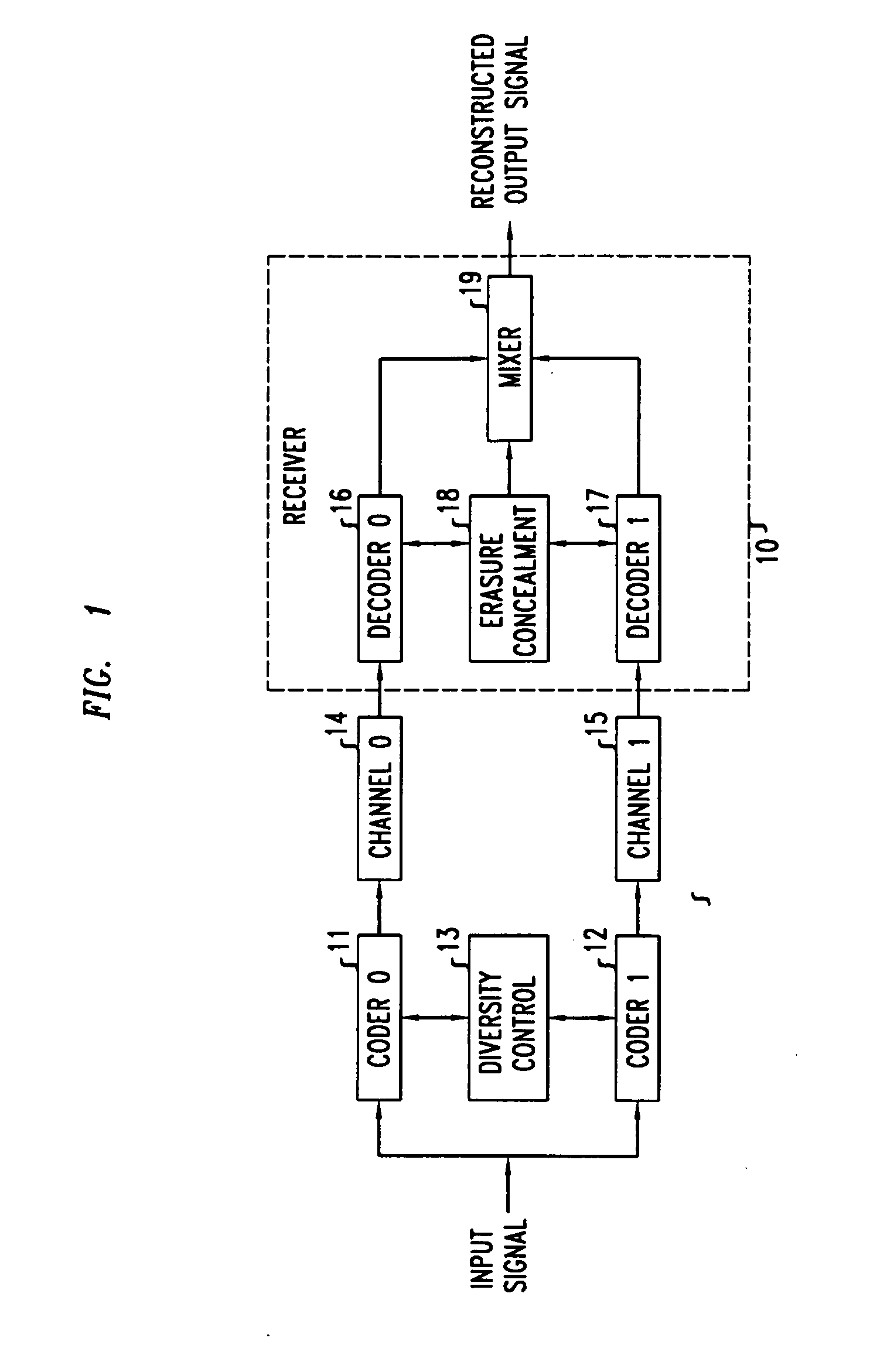
A method and apparatus for performing multiple descriptive source coding in which a plurality of homogeneous encoders are advantageously employed in combination with a corresponding plurality of advantageously substantially identical decoders. In particular, diversity is provided to the multiple encoders by modifying the quantization process in at least one of the encoders such that the modified quantization process is based at least on a quantization error resulting from the quantization process of another one of the encoders. In this manner, diversity among the multiple bit streams is obtained, and in particular, the quality of a reconstructed signal based on a combination of multiple decoded bit streams at the receiver is advantageously superior to that based on any one of the decoded bit streams. In accordance with a first illustrative embodiment of the present invention, two Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) coders are employed. In accordance with a second illustrative embodiment of the present invention, two Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation (ADPCM) coders are employed. And in accordance with a third illustrative embodiment of the present invention, two Low-Delay Code Excited Linear Prediction (LD-CELP) coders are employed. In each case, diversity is ensured by an appropriate modification to the quantization process of at least one of the encoders, and the total error may be advantageously reduced when decoded bit streams from both coders are combined at the receiver.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Displacement sensor for contactlessly measuring a position by means of a plurality of magnetic field sensors arranged in series
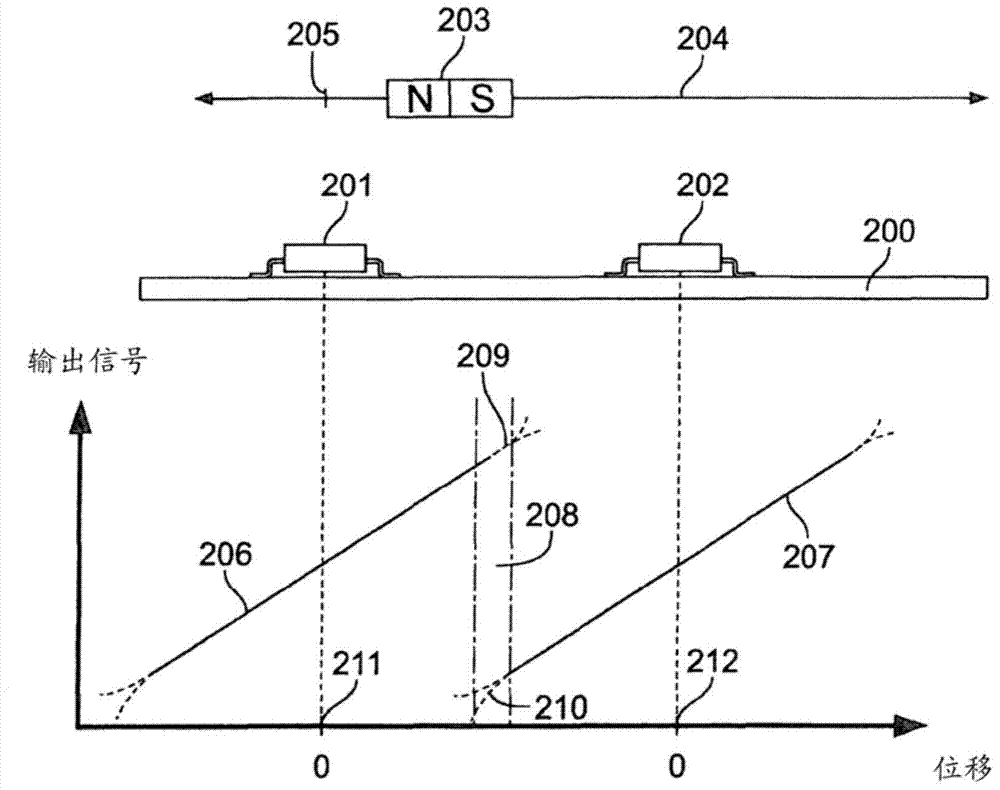
ActiveCN104303018AMeet the maximum allowable total errorLarge displacement measuring rangeConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyPoint coordinate measurementsSignal onTotal error
The present invention relates to a displacement sensor for contactlessly measuring a position of a magnet relative to a reference point. The displacement sensor comprises the magnet which can be displaced along a movement axis, a plurality of magnetic field sensors which are arranged in series and which are arranged parallel with the movement axis of the magnet and a calculation unit for forming a position signal which indicates the position of the magnet relative to the reference point. The plurality of magnetic field sensors which are arranged in series are arranged in such a manner that the displacement measurement ranges of adjacent magnetic field sensors overlap in an overlap range. The calculation unit is constructed in such a manner that, if the position of the magnet is contained in an overlap range, it forms the position signal on the basis of output signals which are output by the magnetic field sensors whose displacement measurement ranges overlap in the overlap range; and, if the position of the magnet is not contained in an overlap range, it forms the position signal on the basis of the output signal which is output by the magnetic field sensor, in the displacement measurement range of which the magnet is located. The overlap range between two displacement measurement ranges of adjacent magnetic field sensors is selected in such a manner that the total error of the position signal formed by the calculation unit in that overlap range is smaller than a maximum tolerable error.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY GERMANY GMBH
Adaptive multi-bit error correction in endurance limited memories
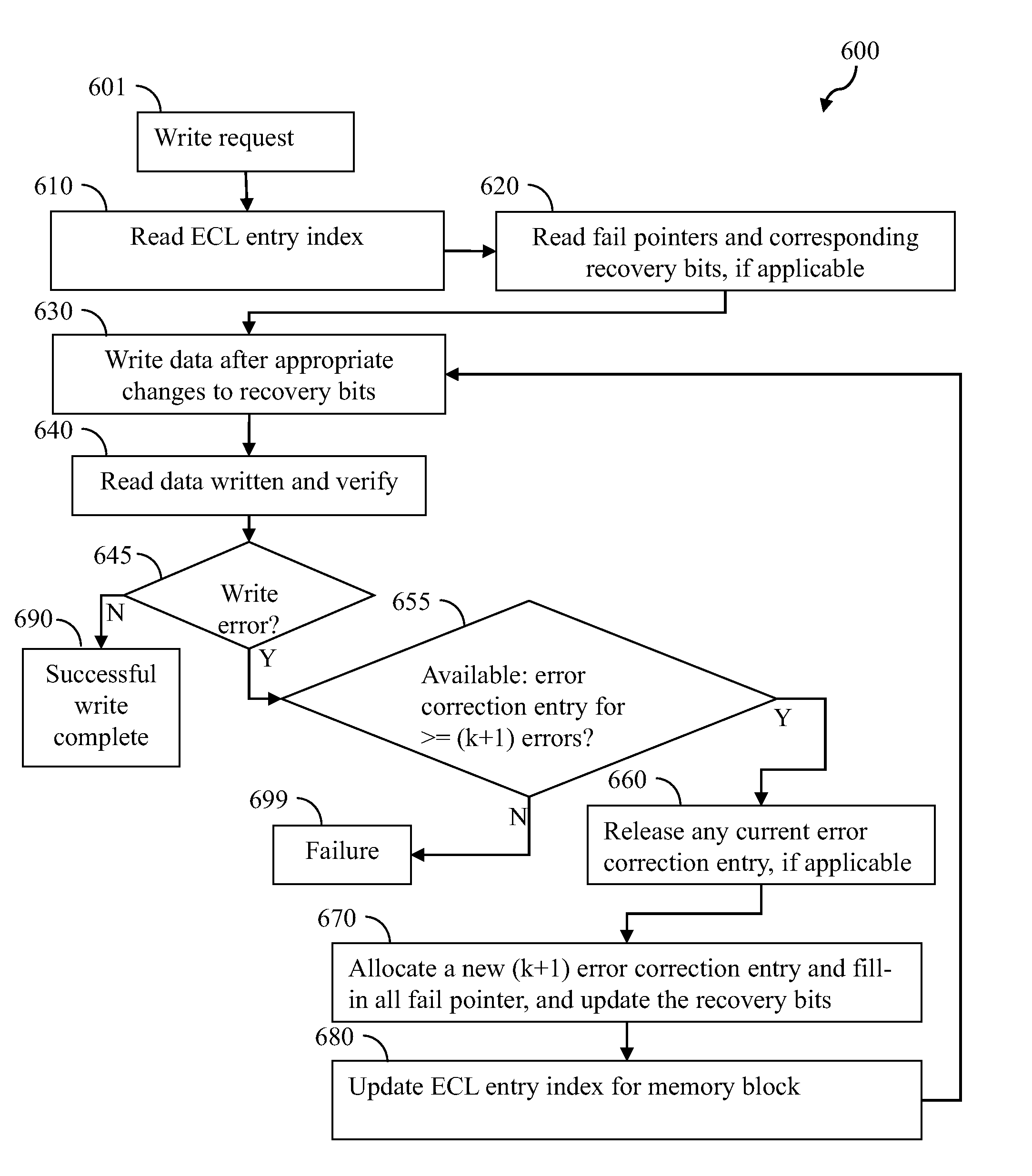
InactiveUS20130013977A1Sufficient error correctionExtended service lifeRead-only memoriesError correction/detection using block codesStuck-at faultSelf adaptive
Multi-bit stuck-at fault error recovery can be enabled by adaptive multi-bit error correction method, in which the overhead of error correction hardware is reduced without affecting the lifetime of the memory device. Error correction logic hardware is decoupled from memory blocks. An error correction logic block is partitioned such that error correction logic entries support different number of error correction capabilities based on the probability of occurrence of the different number of errors in different memory blocks. Faulty memory blocks are mapped to appropriate error correction logic entries. The mapping can be one-to-one or many-to-one depending on embodiments. The adaptive partitioning of the error correction logic entries can be configured to match projected statistical distribution of errors in logic blocks, and can reduce the total error correction logic overhead, provide sufficient error correction, and / or extend the lifetime of the memory device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com