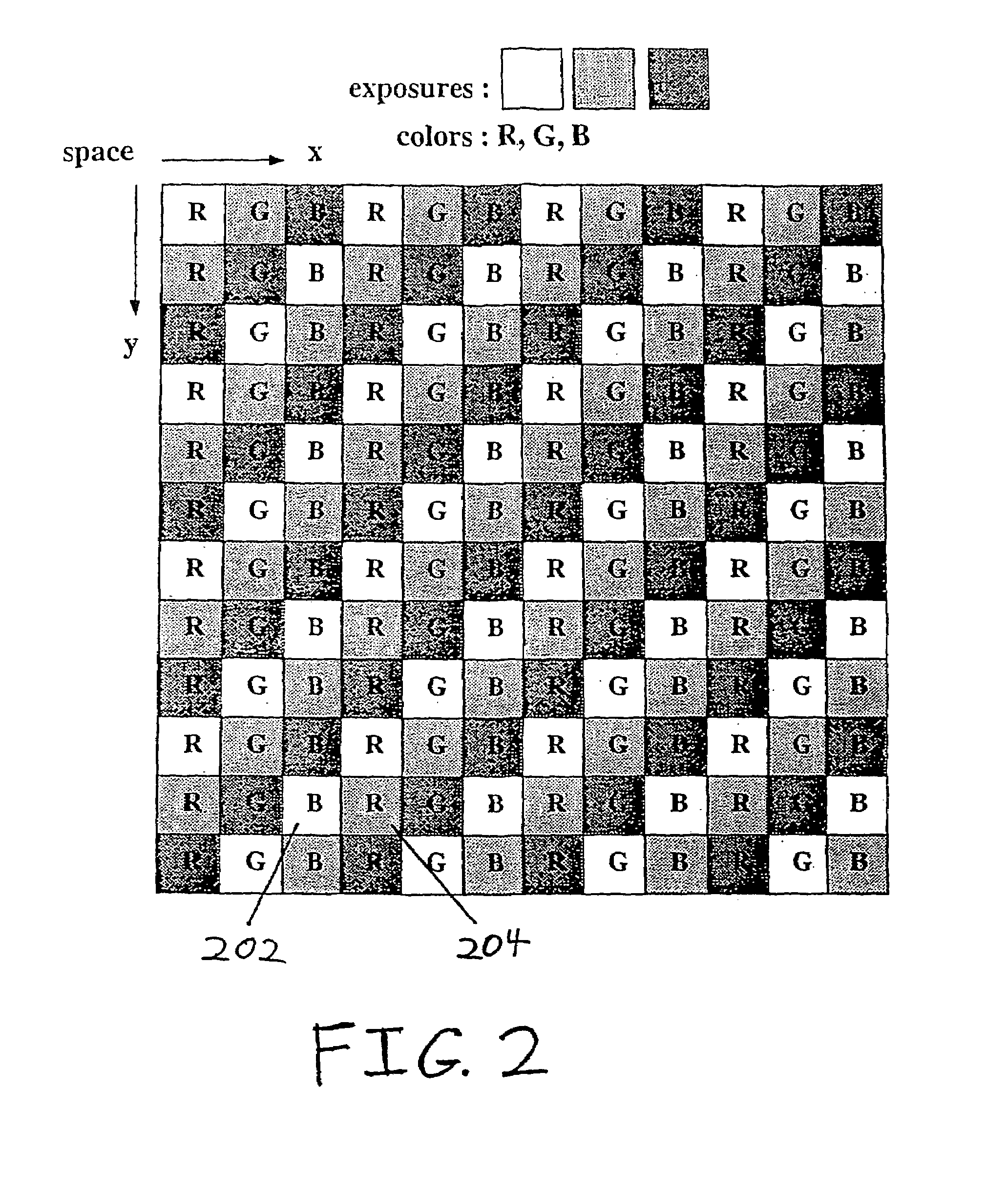
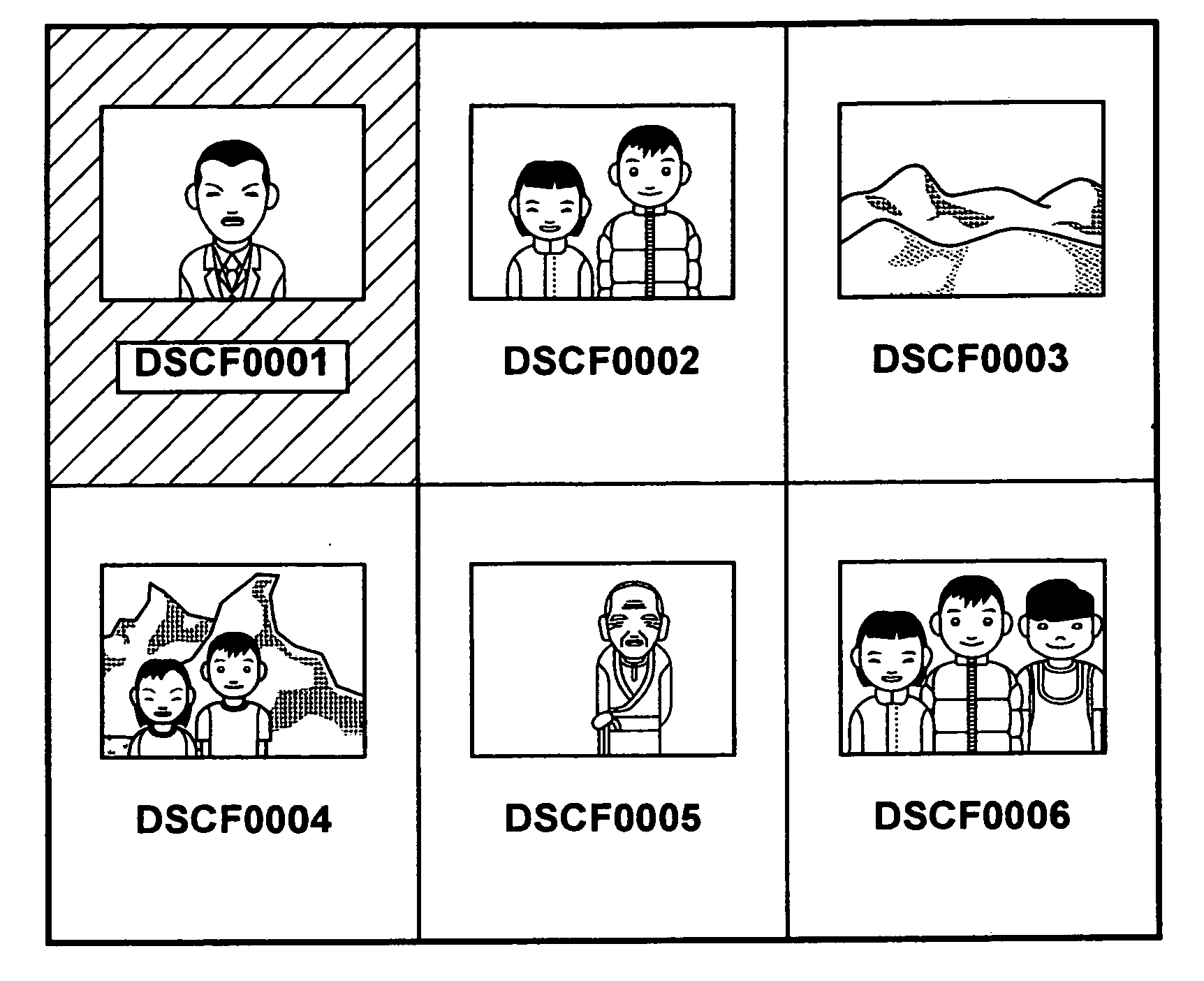
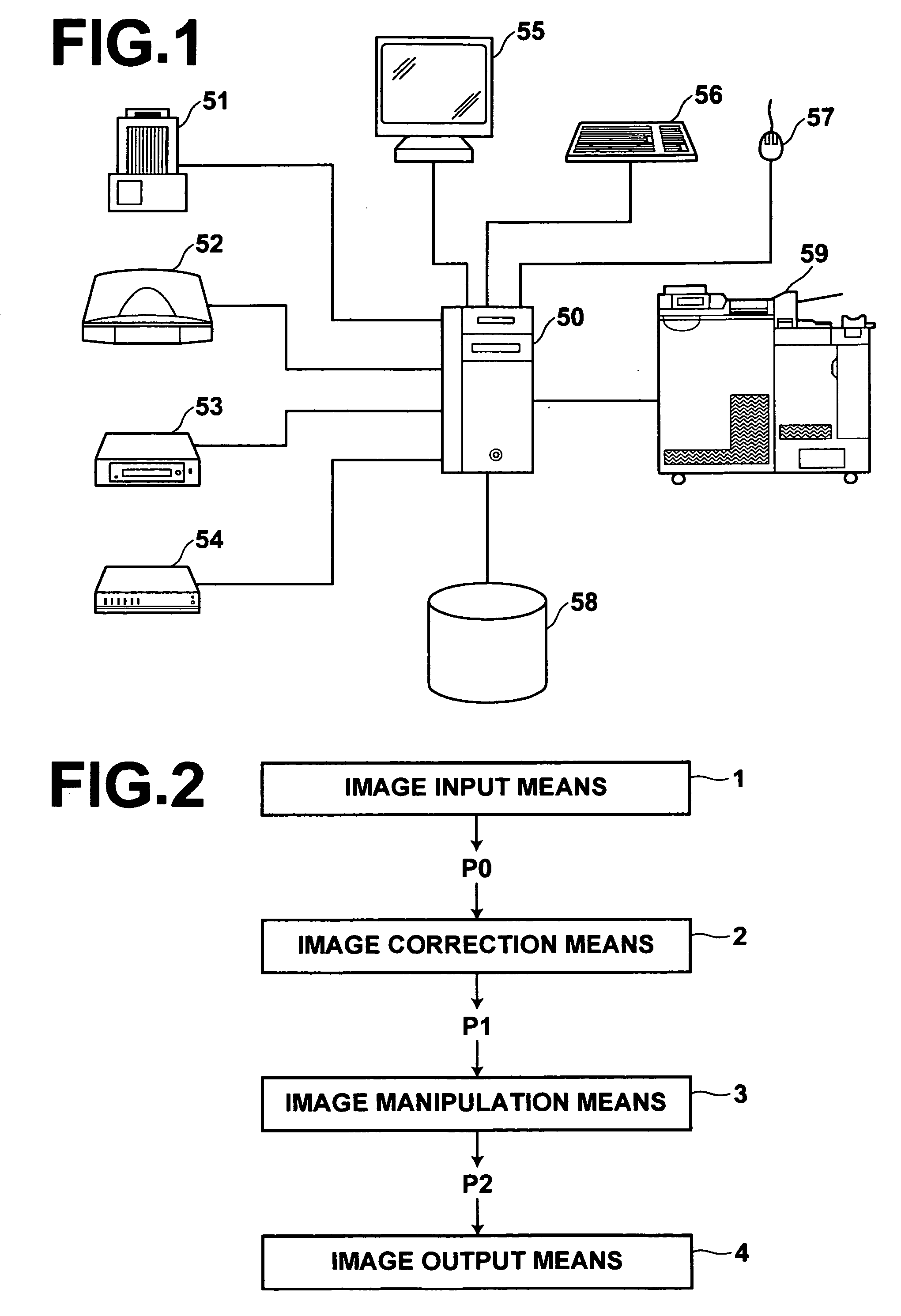
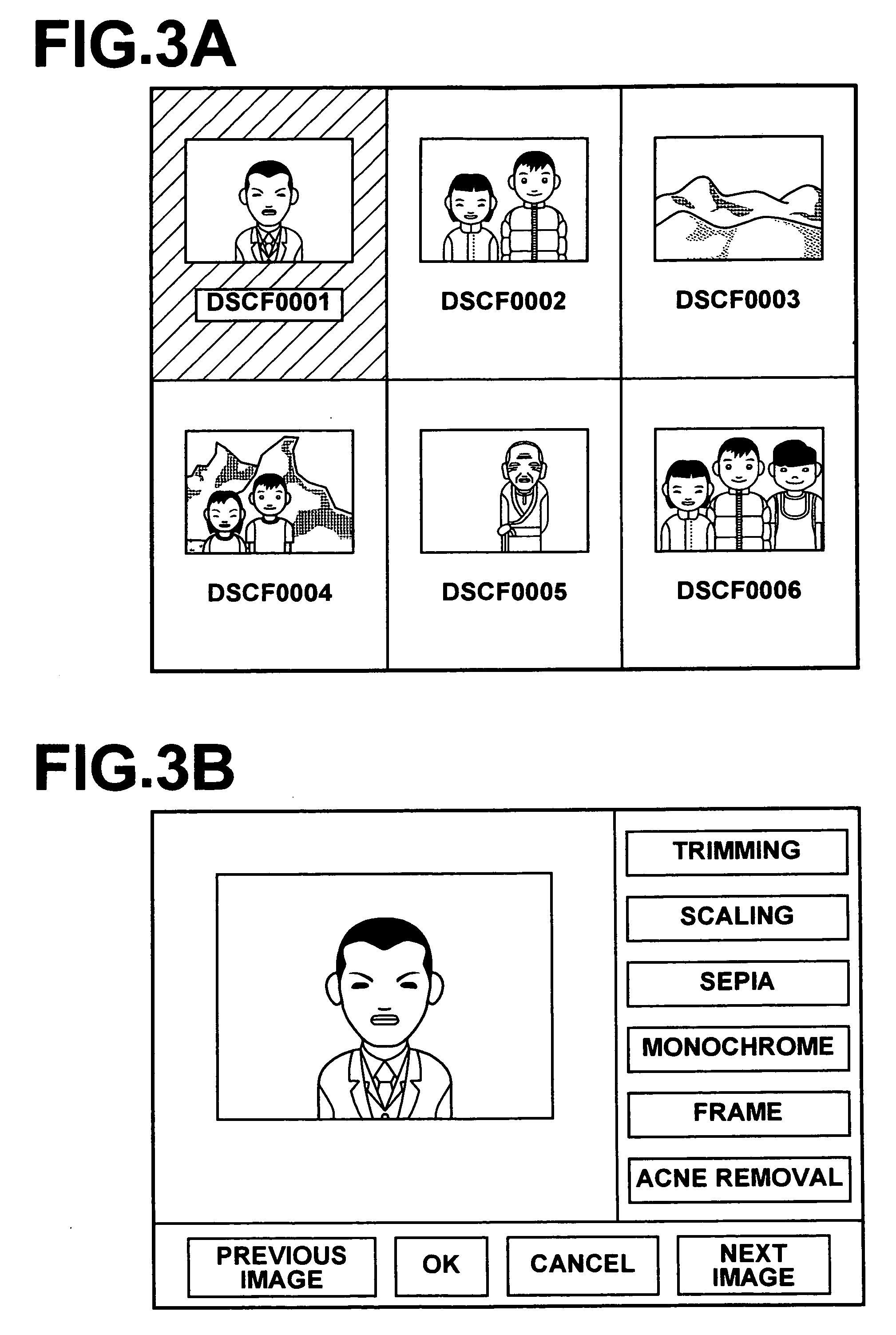
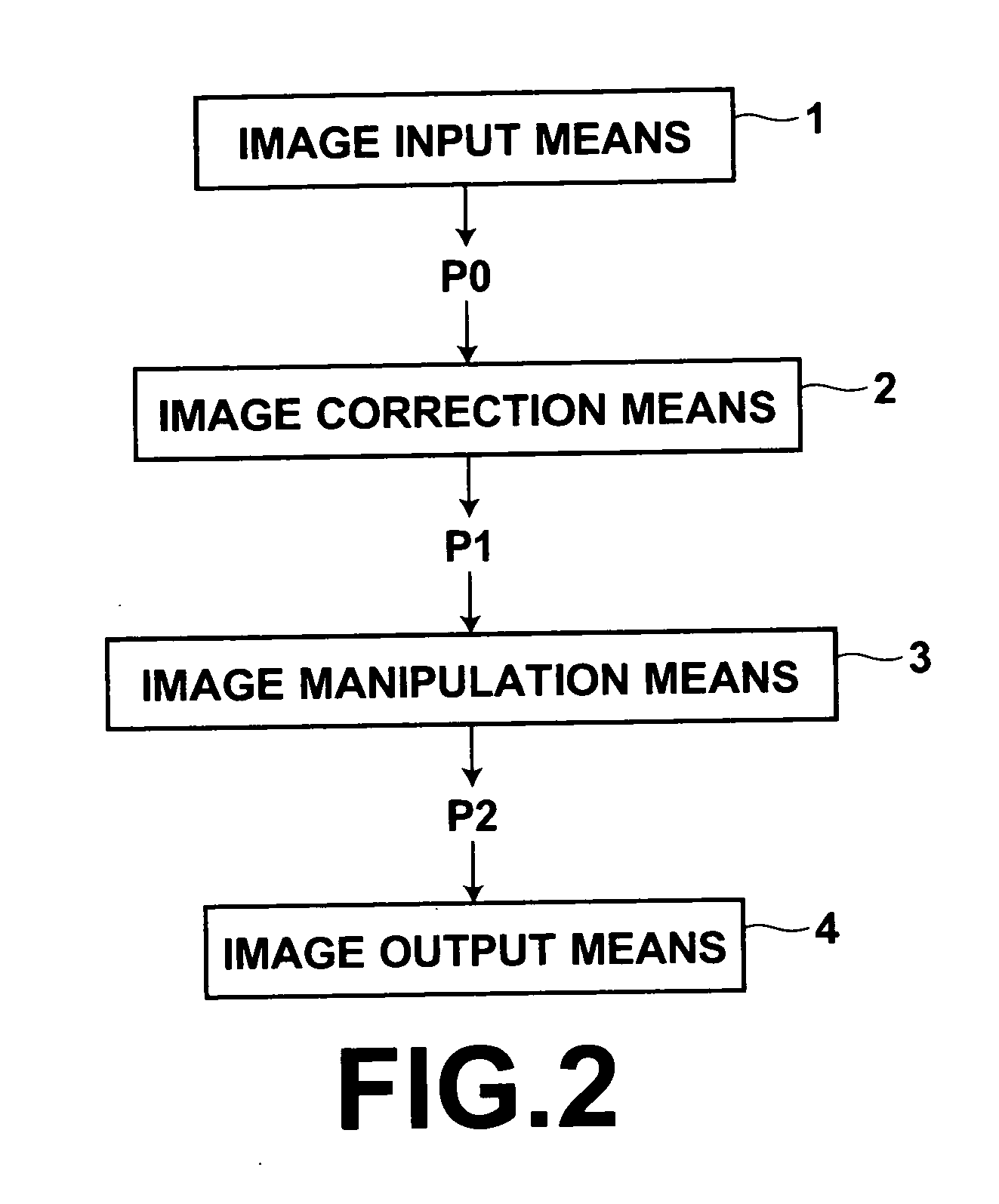
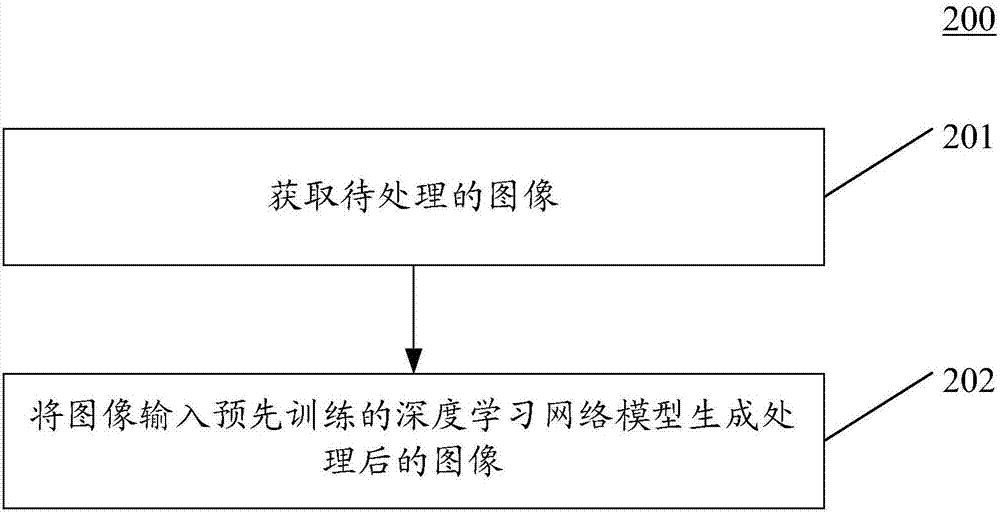
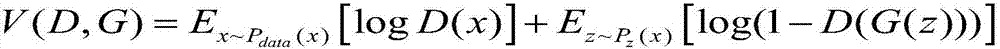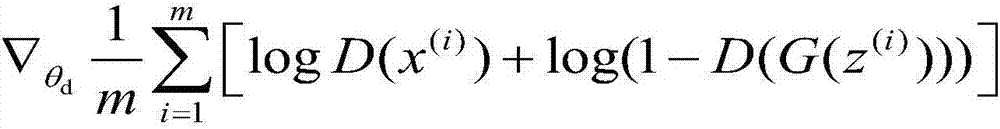Patents
Literature
6767 results about "Sample image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
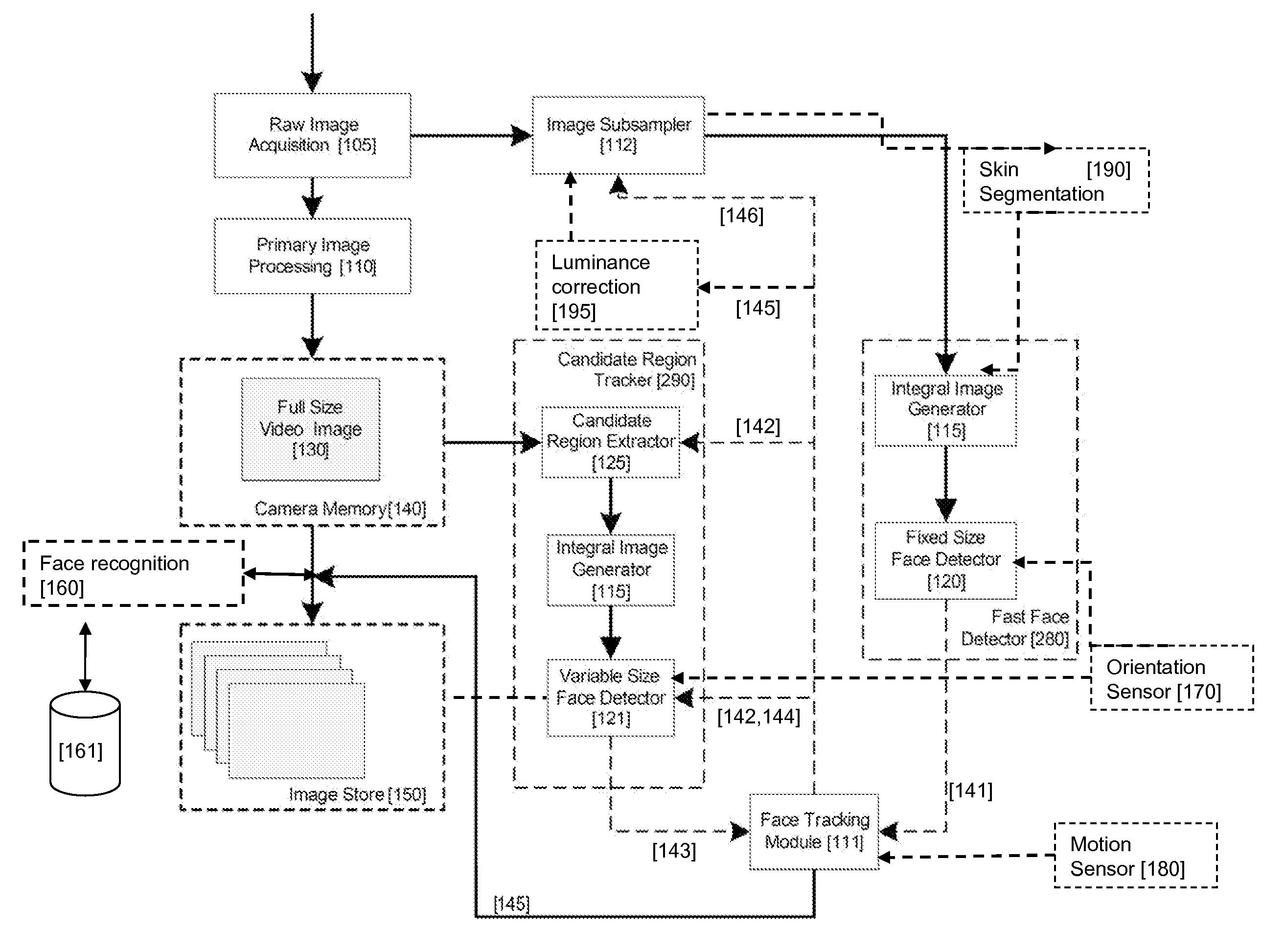
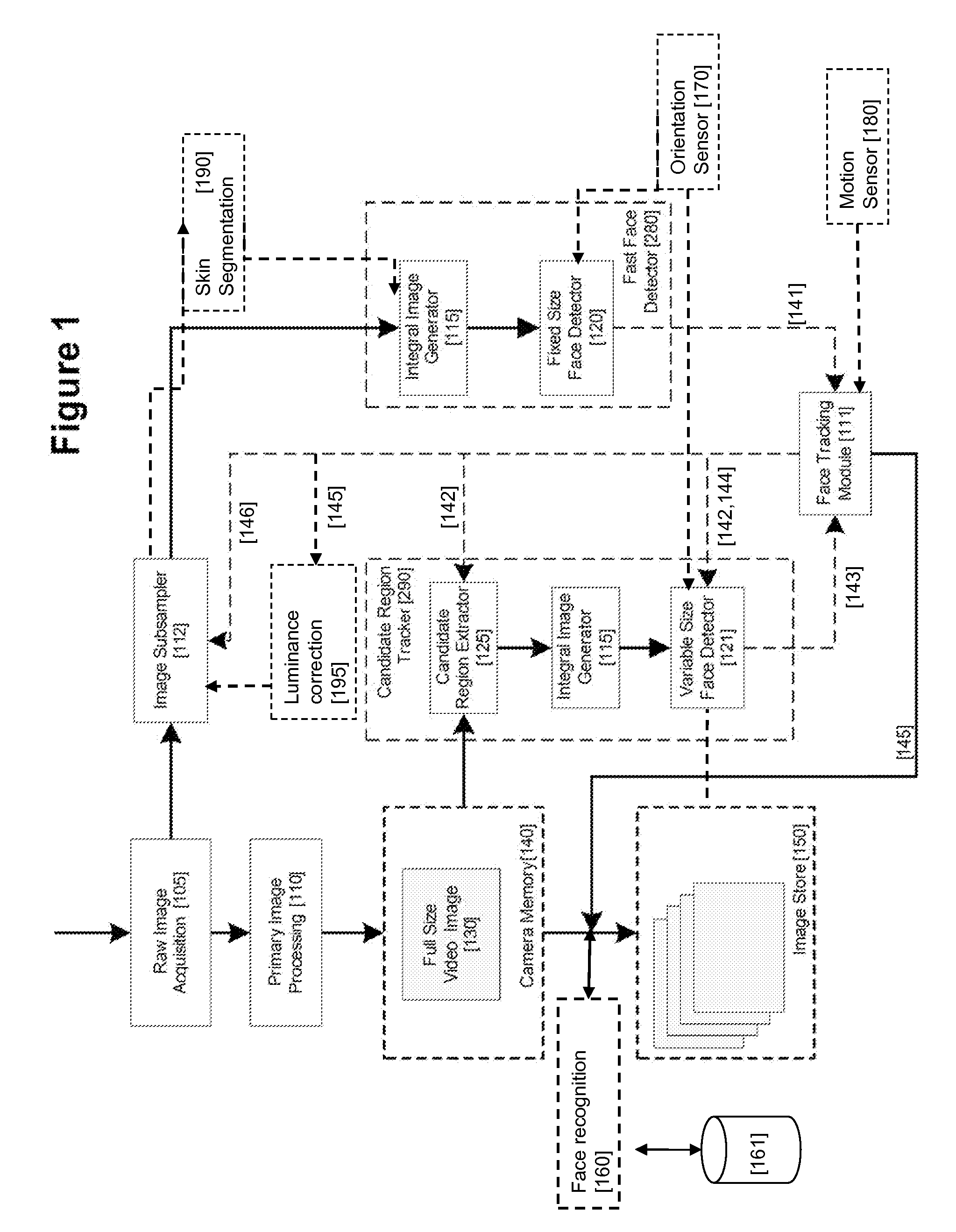
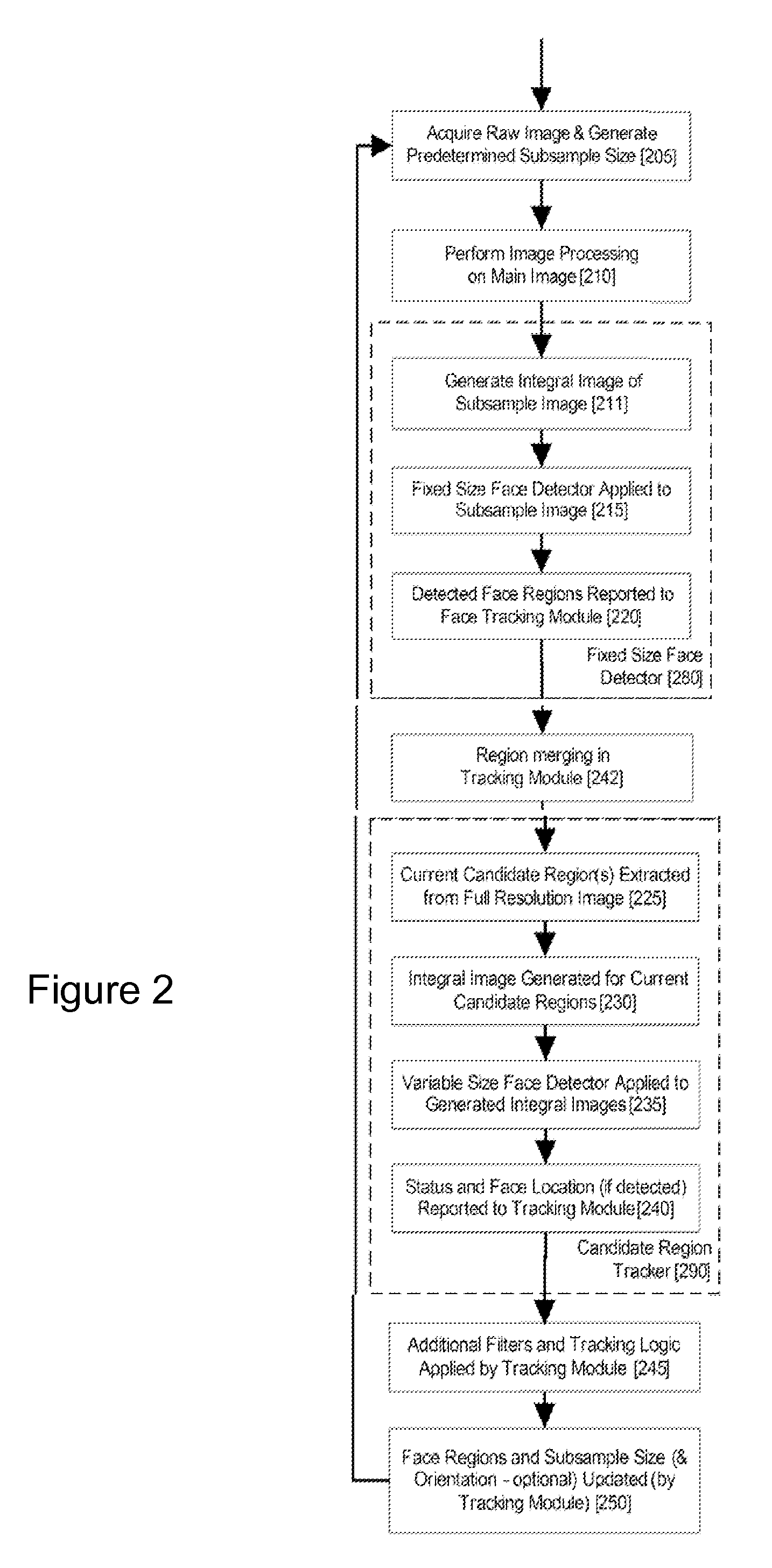
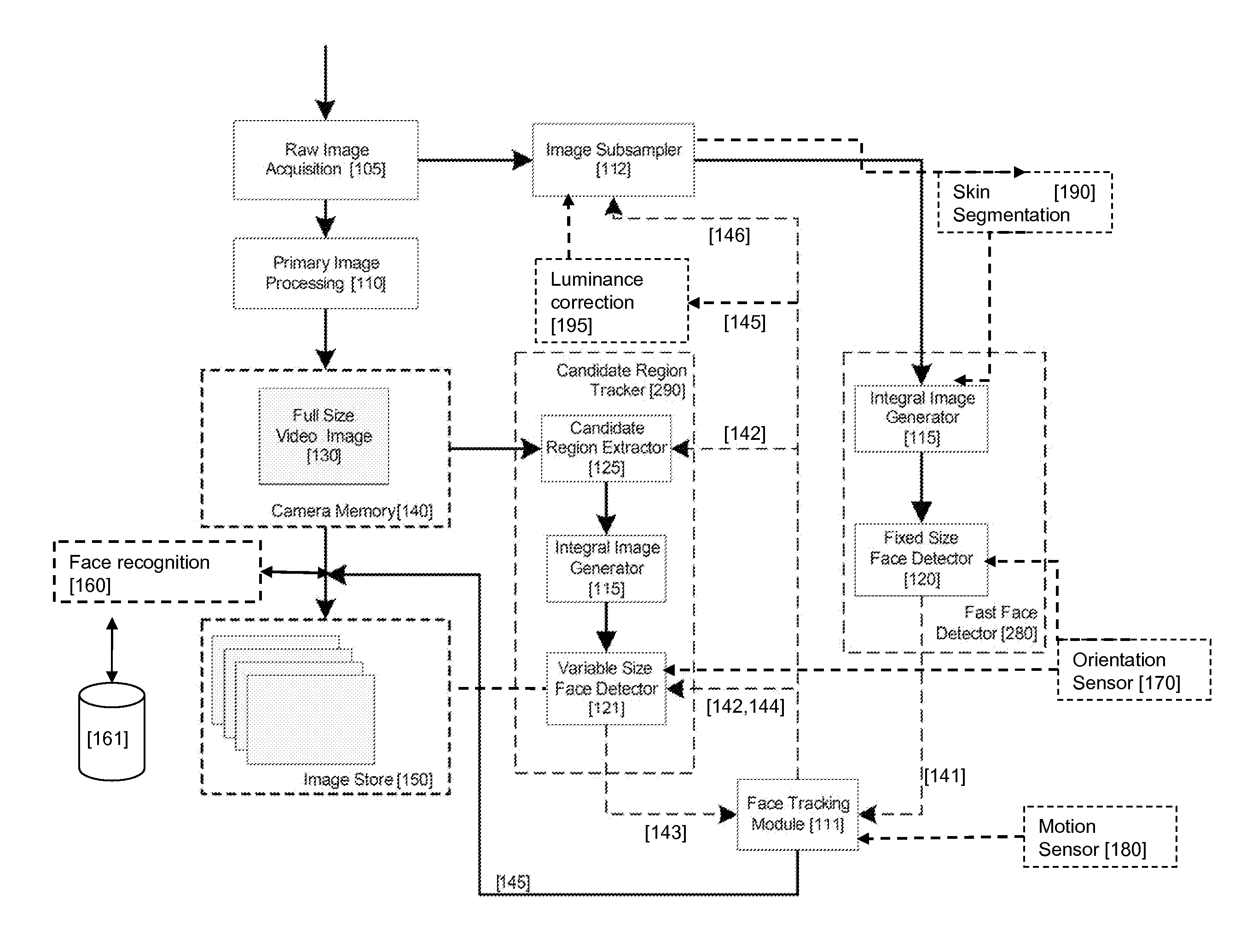
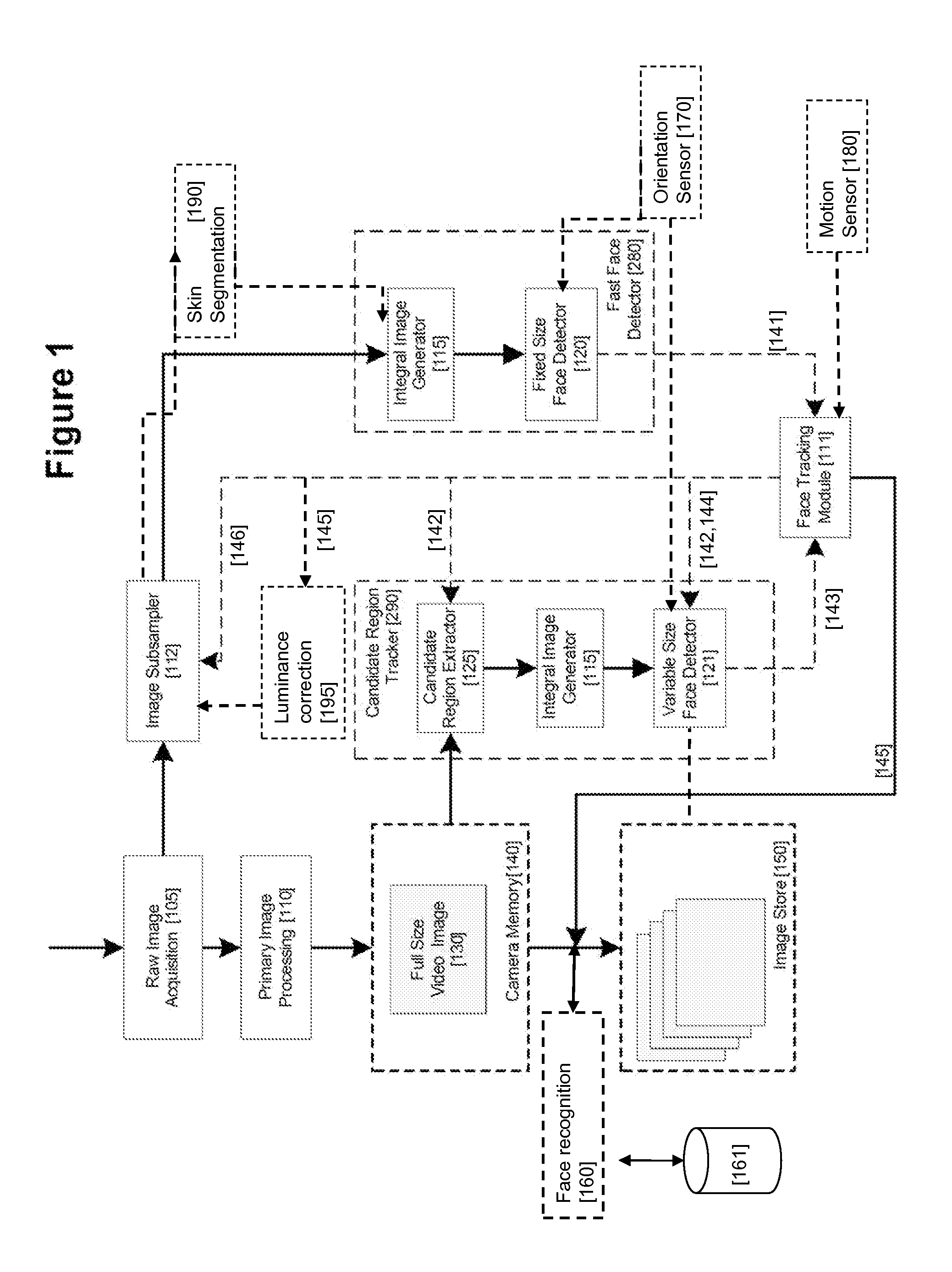
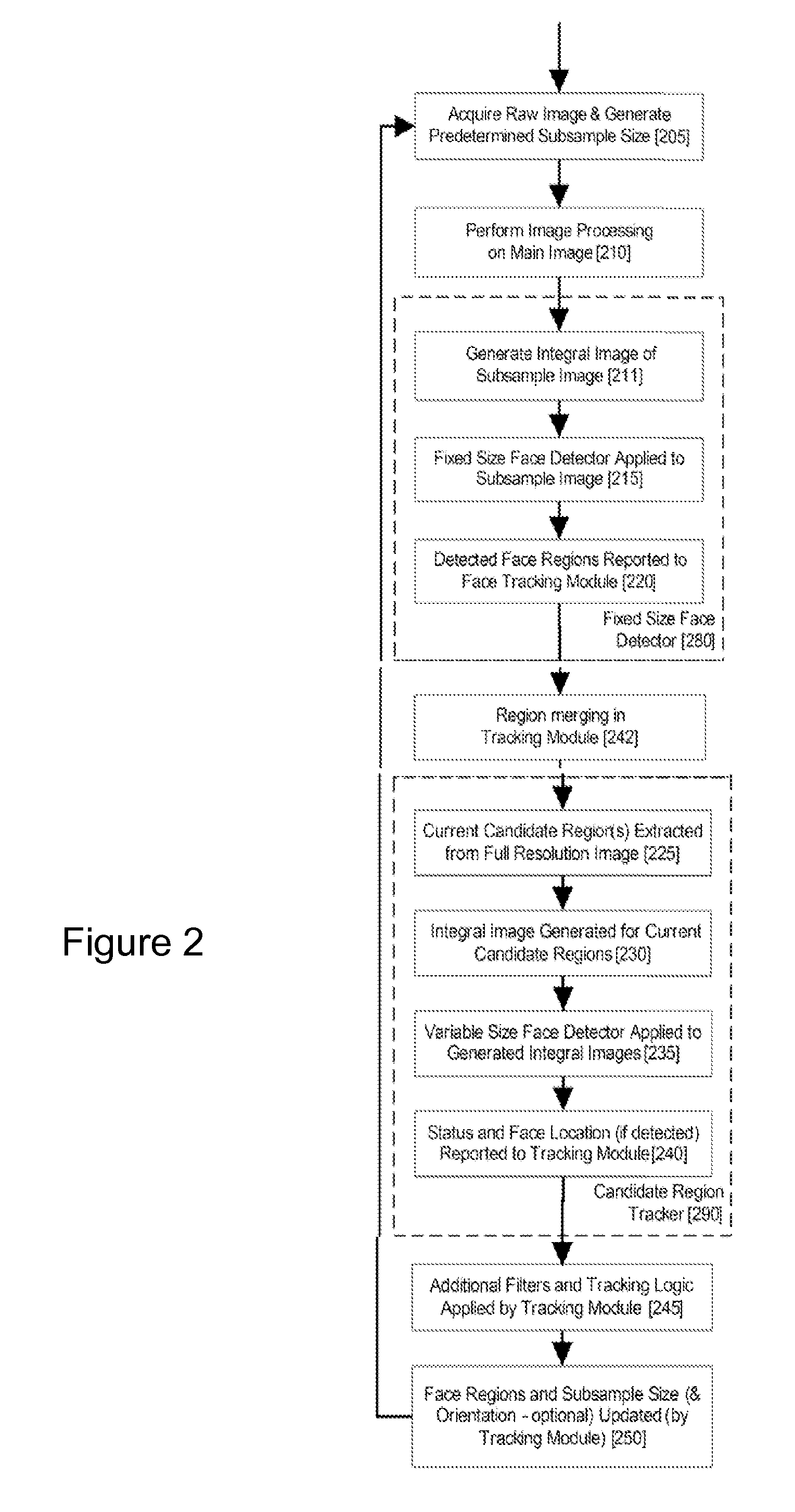
Real-time face tracking in a digital image acquisition device
ActiveUS7315631B1Effectively provide similar quality resultQuick checkTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
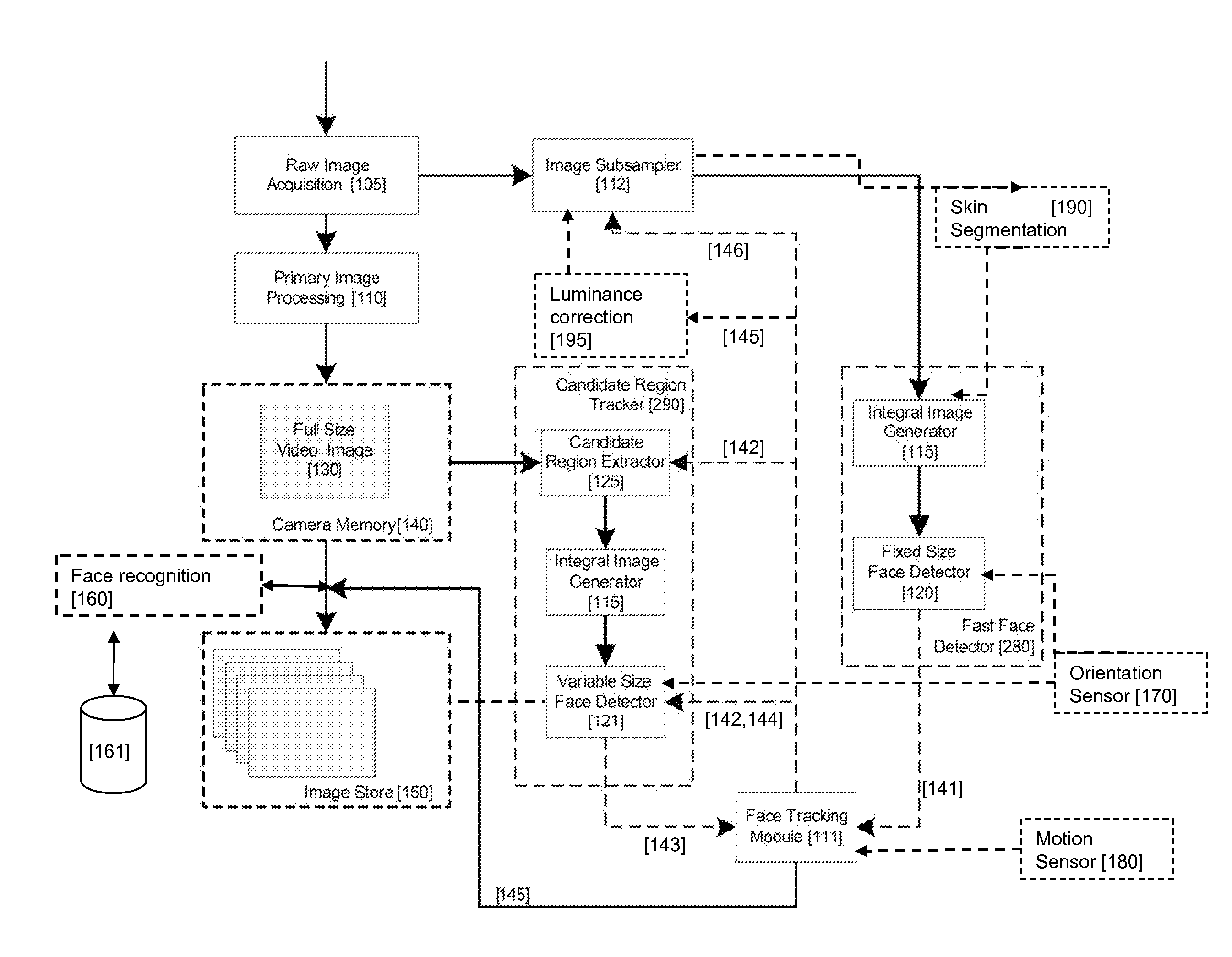
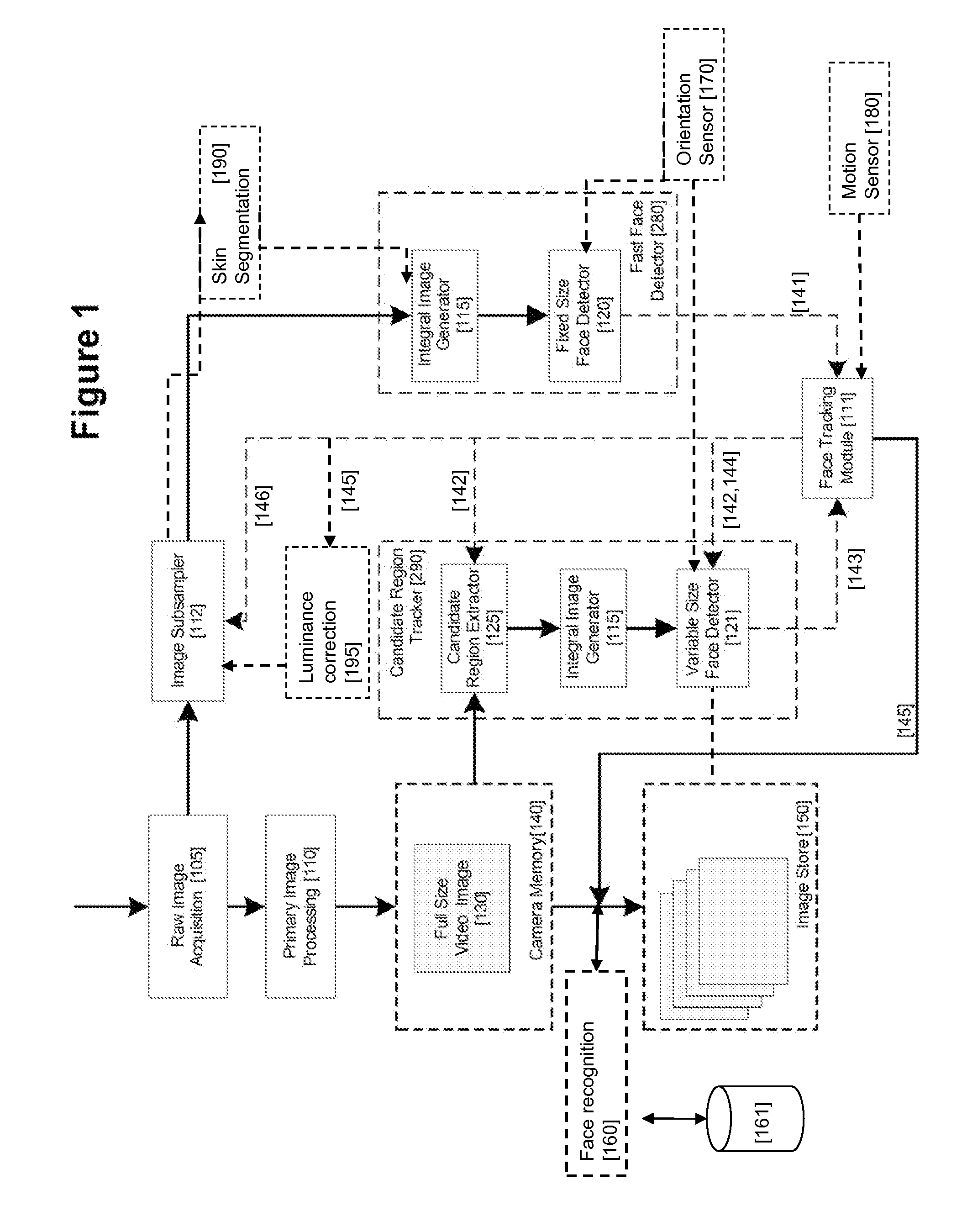
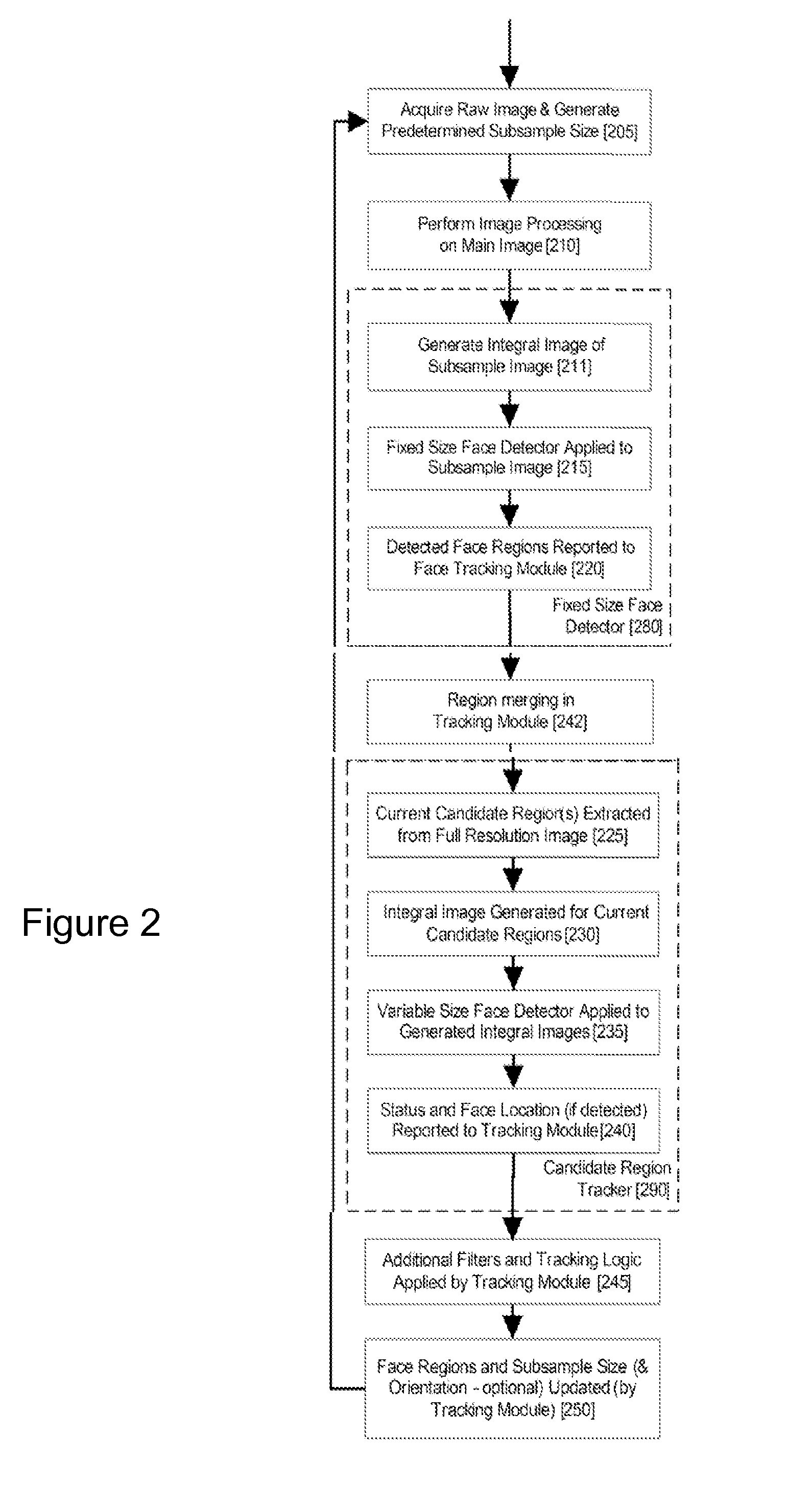
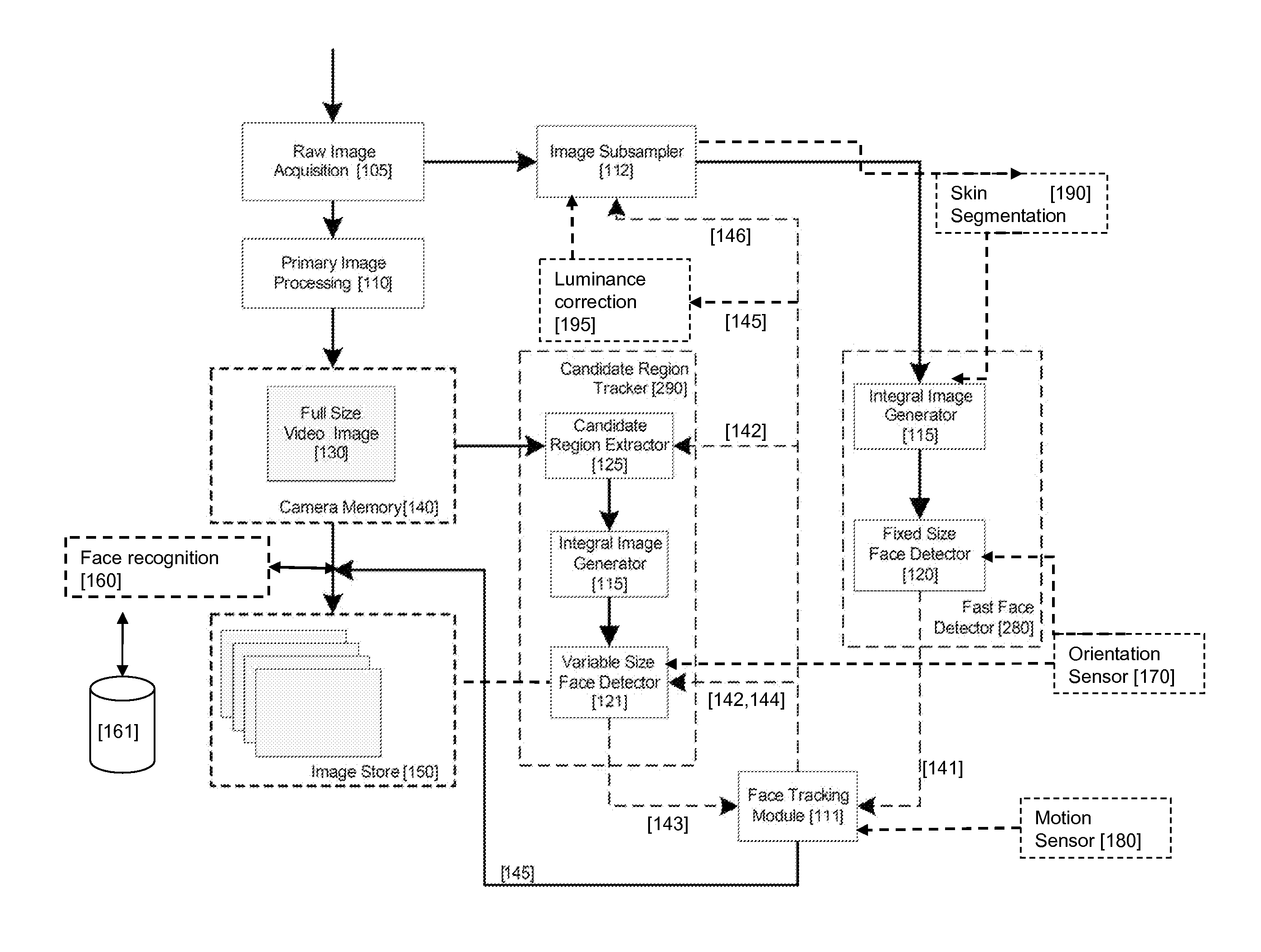
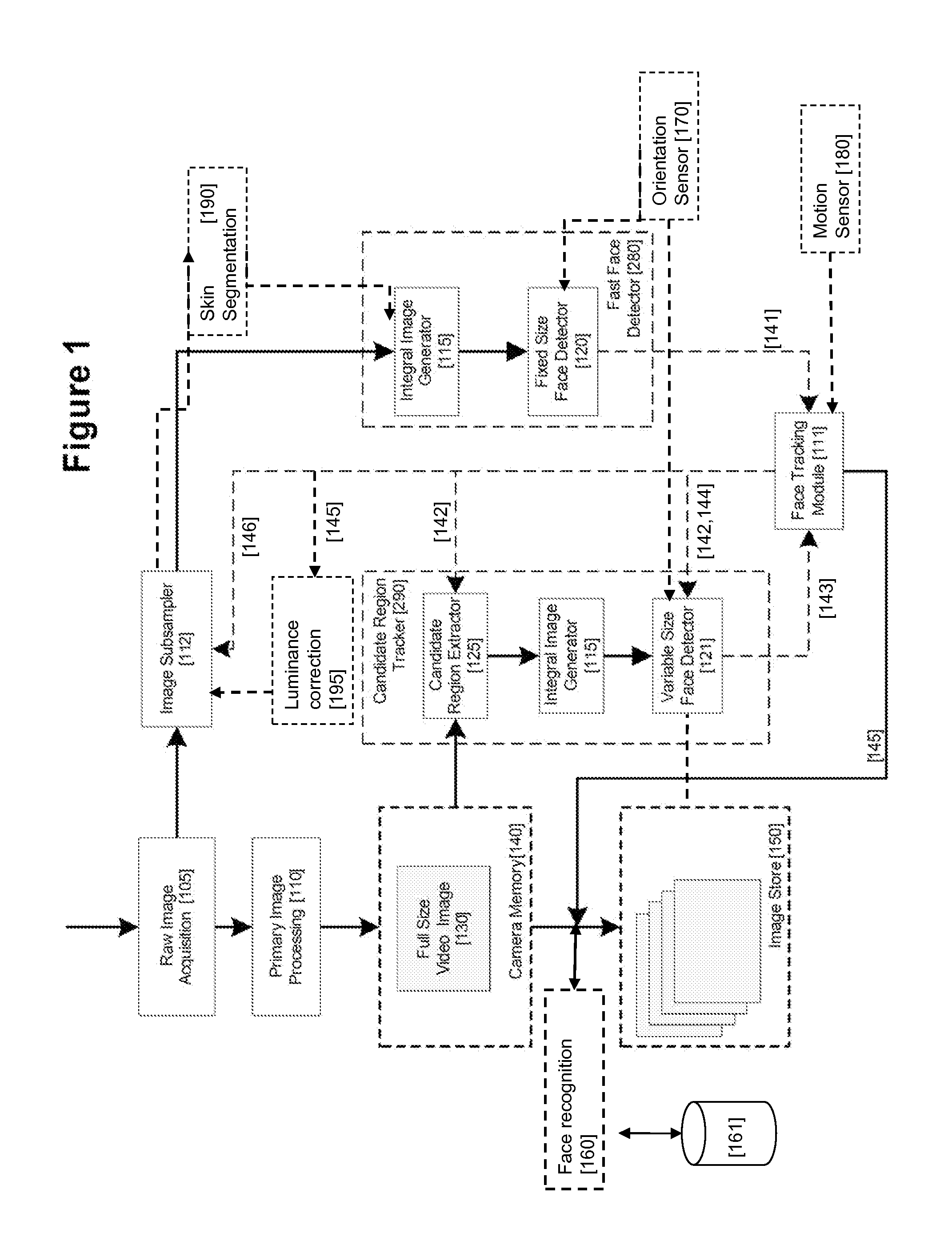
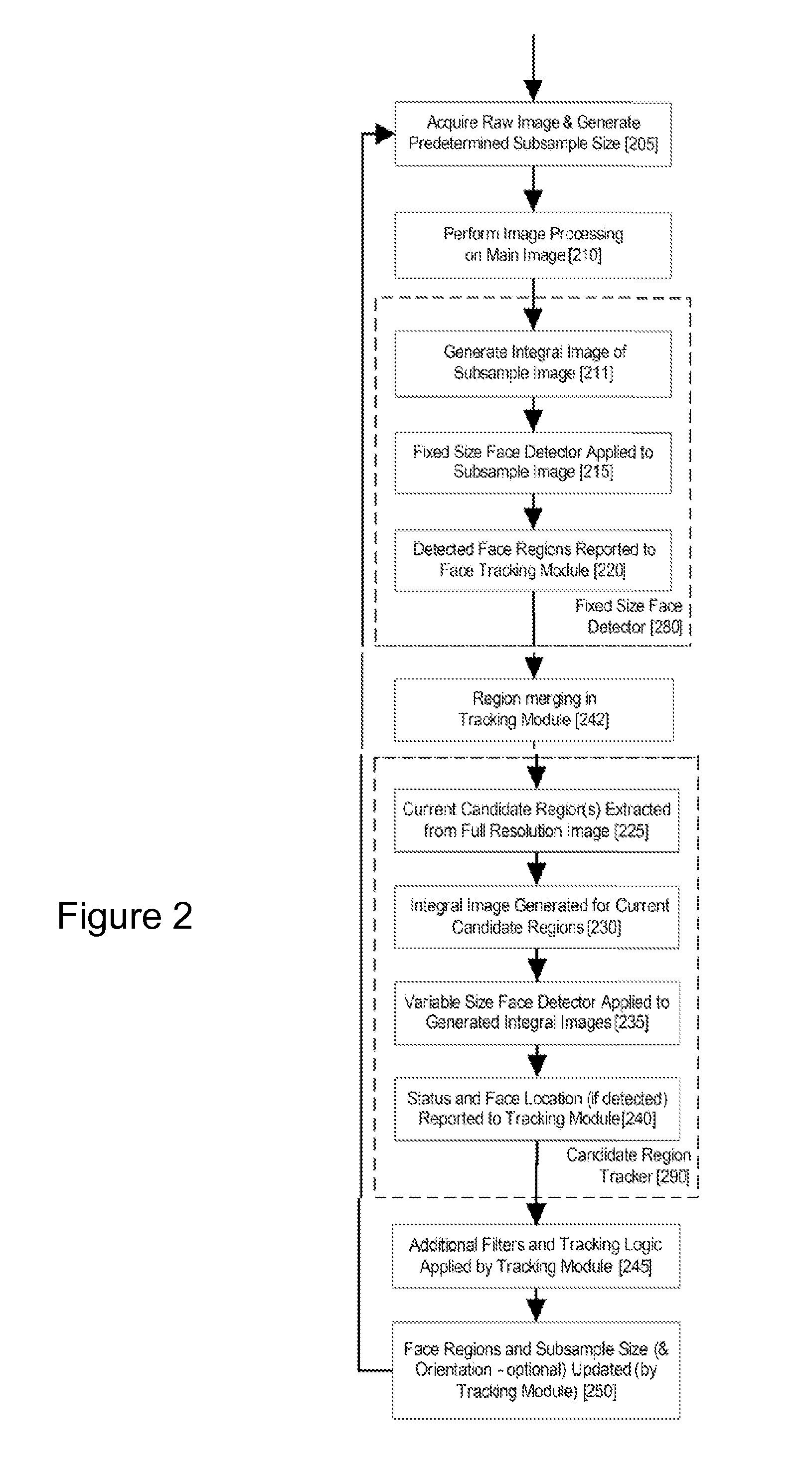
An image processing apparatus for tracking faces in an image stream iteratively receives an acquired image from the image stream potentially including one or more face regions. The acquired image is sub-sampled at a specified resolution to provide a sub-sampled image. An integral image is then calculated for a least a portion of the sub-sampled image. Fixed size face detection is applied to at least a portion of the integral image to provide a set of candidate face regions. Responsive to the set of candidate face regions produced and any previously detected candidate face regions, the resolution is adjusted for sub-sampling a subsequent acquired image.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
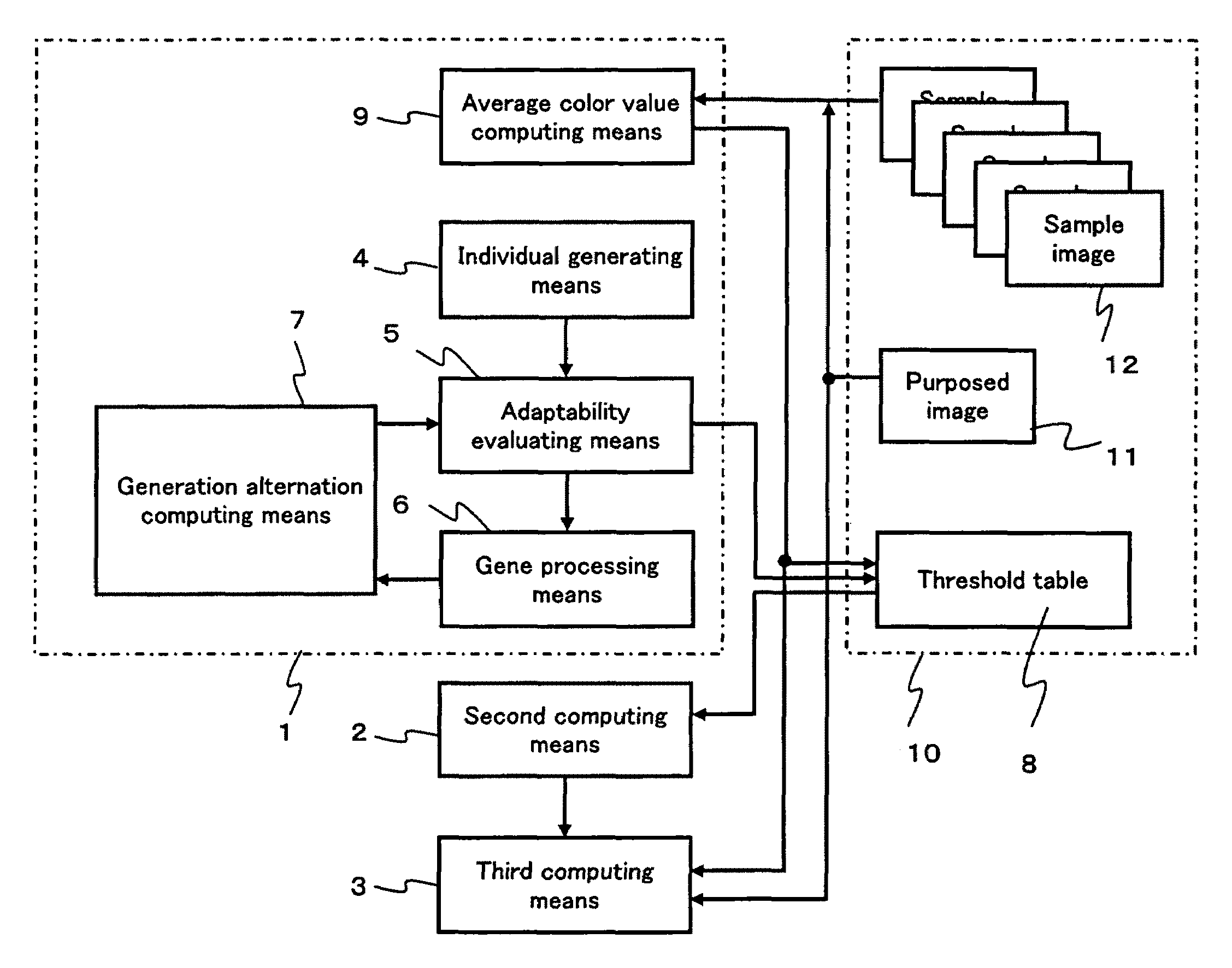
Region detecting method and region detecting apparatus
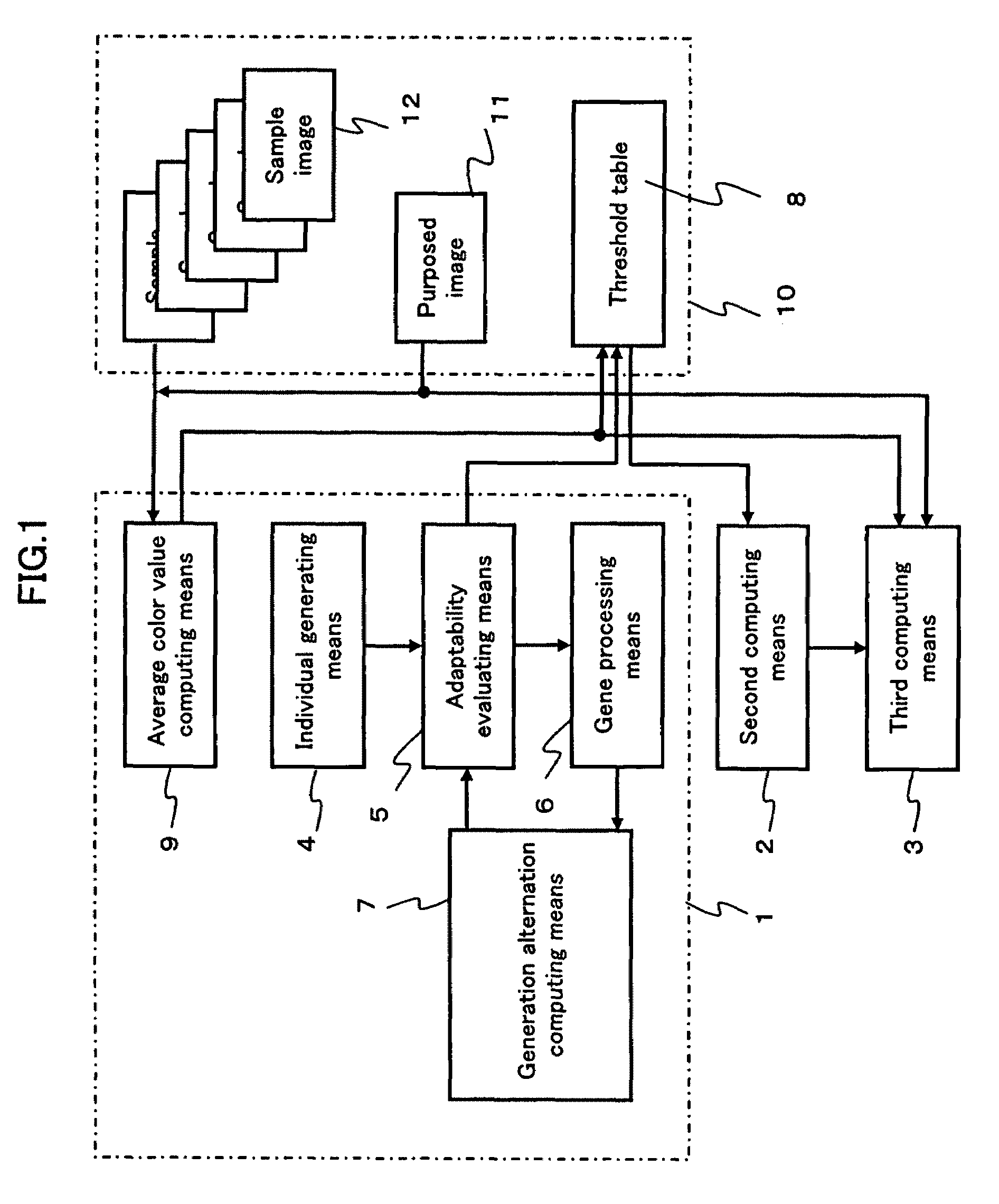
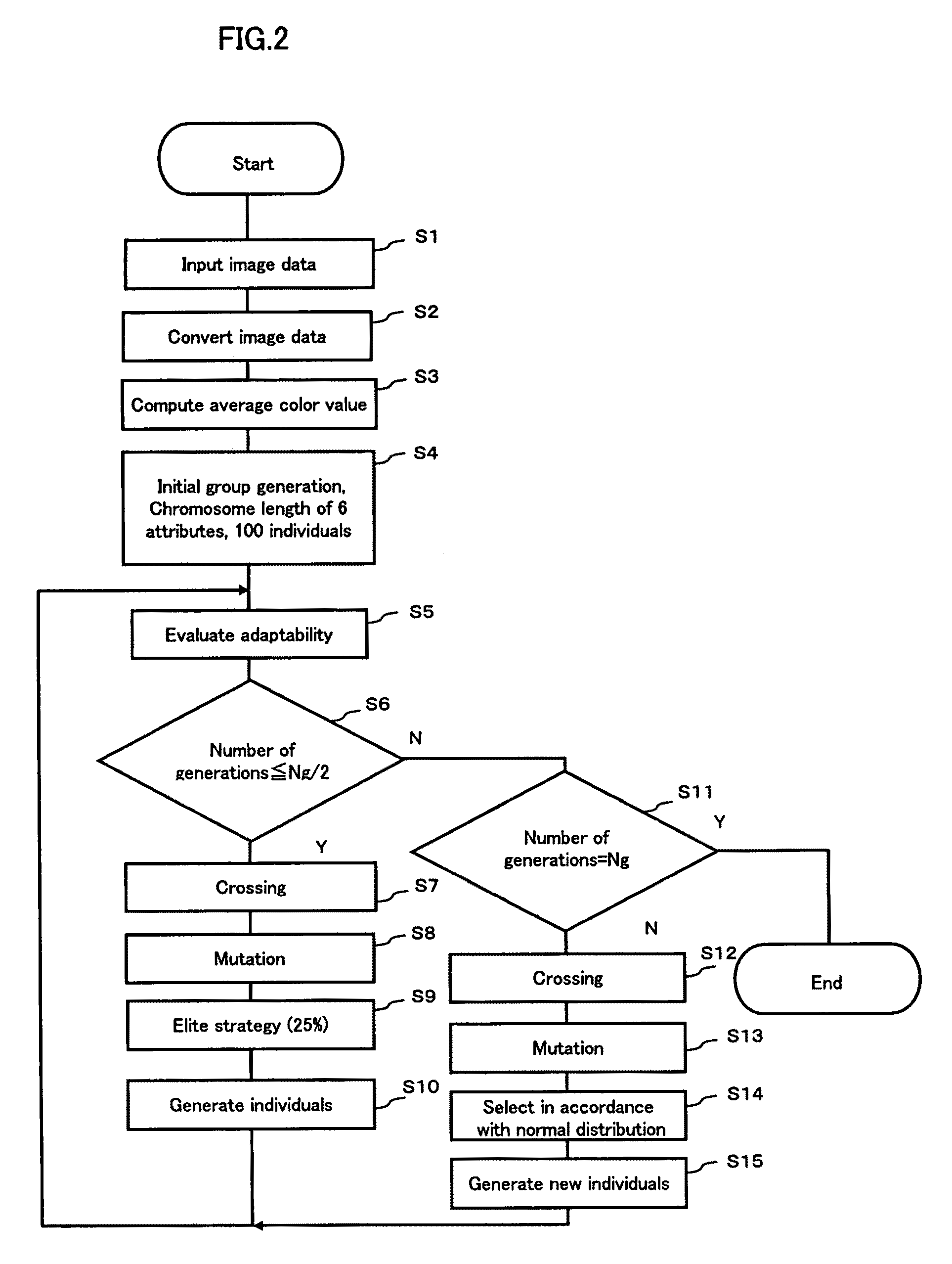
InactiveUS7657090B2Quickly and accurately detectingAccurately and quickly detectedImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Genetic algorithm
To provide a region detecting method capable of setting a proper threshold independently of a photographing condition and moreover, quickly and accurately detecting a specific region, which uses an image data storing section 10 for storing a sample image 12 and a purposed image 11, a first computing means 1 for obtaining the extraction-region-identifying threshold data for a plurality of sample images including a common extraction region but having average color values different from each other in accordance with a genetic algorithm and generating a threshold table 8 for the average color values, a second computing means 2 for adaptively computing the extraction-region-identifying threshold data for the purposed image 11 in accordance with the average color value of the purposed image and the threshold table 8, and a third computing means 3 for detecting an extraction region in accordance with the threshold data computed by the second computing means 12.
Owner:NORITZ CORP
Real-Time Face Tracking in a Digital Image Acquisition Device
ActiveUS20080037839A1Improve performance accuracyReduce calculationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
An image processing apparatus for tracking faces in an image stream iteratively receives a new acquired image from the image stream, the image potentially including one or more face regions. The acquired image is sub-sampled (112) at a specified resolution to provide a sub-sampled image. An integral image is then calculated for a least a portion of the sub-sampled image. Fixed size face detection (20) is applied to at least a portion of the integral image to provide a set of candidate face regions. Responsive to the set of candidate face regions produced and any previously detected candidate face regions, the resolution at which a next acquired image is sub-sampled is adjusted.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Compensator for multiple surface imaging
ActiveUS20090272914A1Reduce aberrationScattering properties measurementsLuminescent dosimetersTotal internal reflectionFluorescence
A system and method for imaging biological samples on multiple surfaces of a support structure are disclosed. The support structure may, for instance, be a flow cell through which a reagent fluid is allowed to flow and interact with the biological samples. Excitation radiation from at least one radiation source may be used to excite the biological samples on multiple surfaces. In this manner, fluorescent emission radiation may be generated from the biological samples and subsequently captured and detected by detection optics and at least one detector. The captured and detected fluorescent emission radiation may then be used to generate image data. This imaging of multiple surfaces may be accomplished either sequentially or simultaneously. In addition, the techniques of the present invention may be used with any type of imaging system. For instance, both epifluorescent and total internal reflection (TIR) methods may benefit from the techniques of the present invention. In addition, the biological samples imaged may be present on the surfaces of the support structure in a random special pattern and need not be at known locations in order for the imaging to be performed.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Real-Time Face Tracking in a Digital Image Acquisition Device
ActiveUS20080037827A1Improve performance accuracyReduce calculationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
An image processing apparatus for tracking faces in an image stream iteratively receives a new acquired image from the image stream, the image potentially including one or more face regions. The acquired image is sub-sampled (112) at a specified resolution to provide a sub-sampled image. An integral image is then calculated for a least a portion of the sub-sampled image. Fixed size face detection (20) is applied to at least a portion of the integral image to provide a set of candidate face regions. Responsive to the set of candidate face regions produced and any previously detected candidate face regions, the resolution at which a next acquired image is sub-sampled is adjusted.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Real-Time Face Tracking in a Digital Image Acquisition Device
InactiveUS20080037840A1Increase probabilityIncrease Brightness ContrastTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
An image processing apparatus for tracking faces in an image stream iteratively receives an acquired image from the image stream potentially including one or more face regions. The acquired image is sub-sampled at a specified resolution to provide a sub-sampled image. An integral image is then calculated for a least a portion of the sub-sampled image. Fixed size face detection is applied to at least a portion of the integral image to provide a set of candidate face regions. Responsive to the set of candidate face regions produced and any previously detected candidate face regions, the resolution is adjusted for sub-sampling a subsequent acquired image.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Method and apparatus for enhancing data resolution
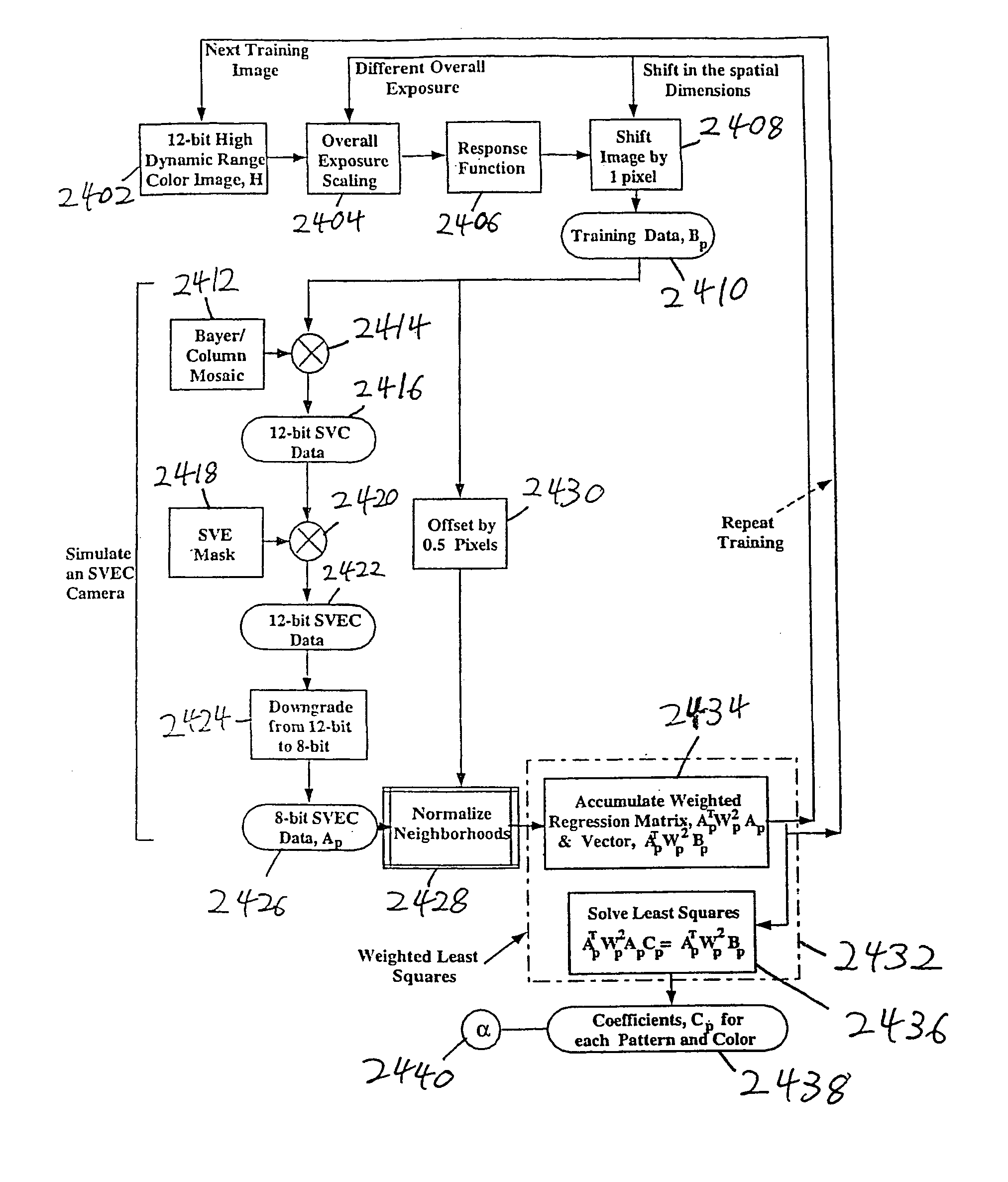
InactiveUS7149262B1High data resolutionGeometric image transformationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsImage resolutionSample image
A resolution enhancement algorithm is trained on sample images to obtain a polynomial model mapping of low resolution image data to high resolution image data. The polynomial model mapping is applied to other low resolution images to obtain corresponding higher resolution images. The mapping provides resolution enhancement which is superior to that of conventional image data interpolation techniques.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
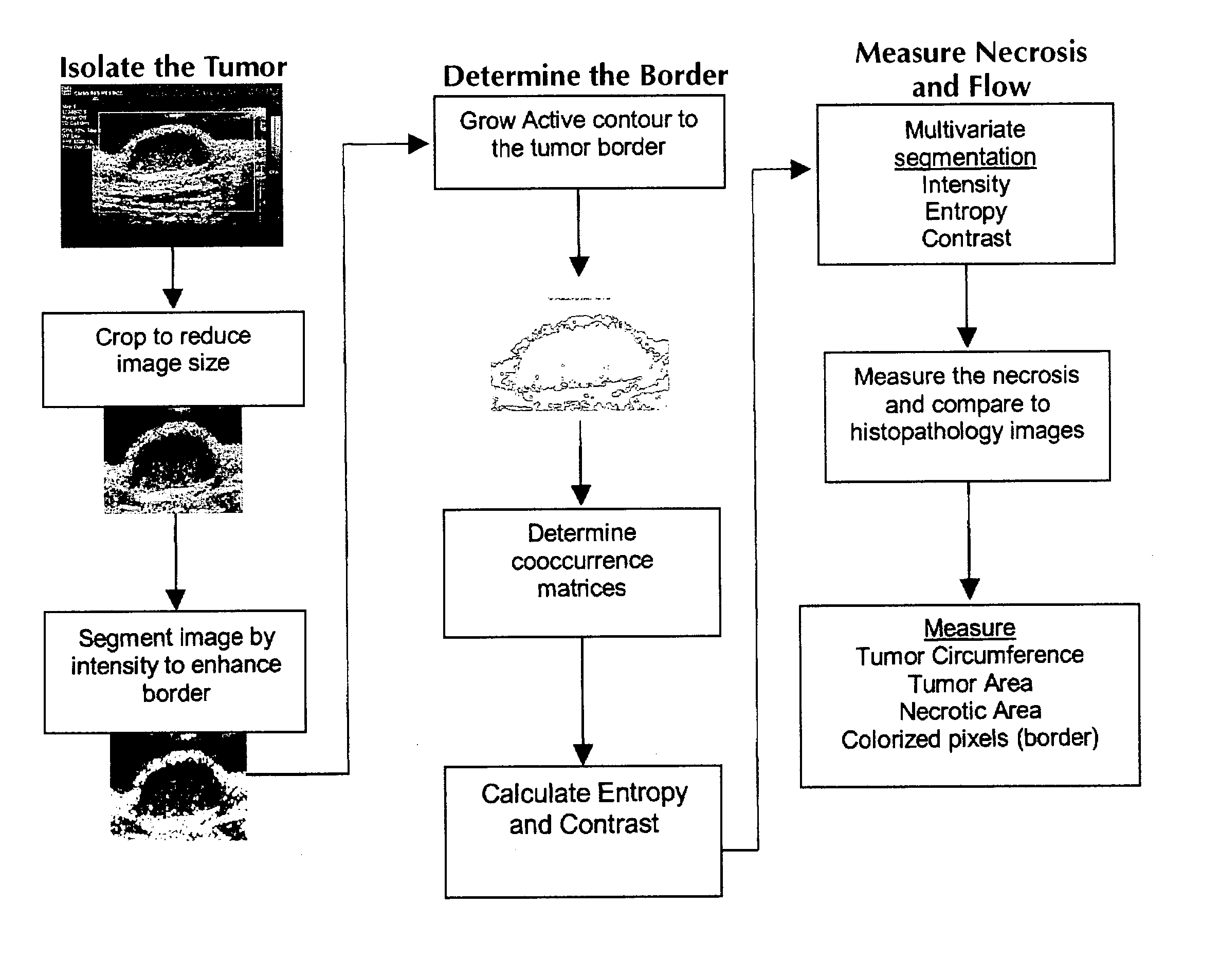
Apparatus and method for statistical image analysis
An apparatus, system, method, and computer readable medium containing computer-executable code for implementing image analysis uses multivariate statistical analysis of sample images, and allows segmentation of the image into different groups or classes, depending on a correlation to one or more sample textures, or sample surface features. In one embodiment, the invention performs multivariate statistical analysis of ultrasound images, wherein a tumor may be characterized by segmenting viable tissue from necrotic tissue, allowing for more detailed in vivo analysis of tumor growth beyond simple dimensional measurements or univariate statistical analysis. Application of the apparatus and method may also be used for characterizing other types of samples having textured features including, for example, tumor angiogenesis biomarkers from Power Doppler.
Owner:PFIZER INC
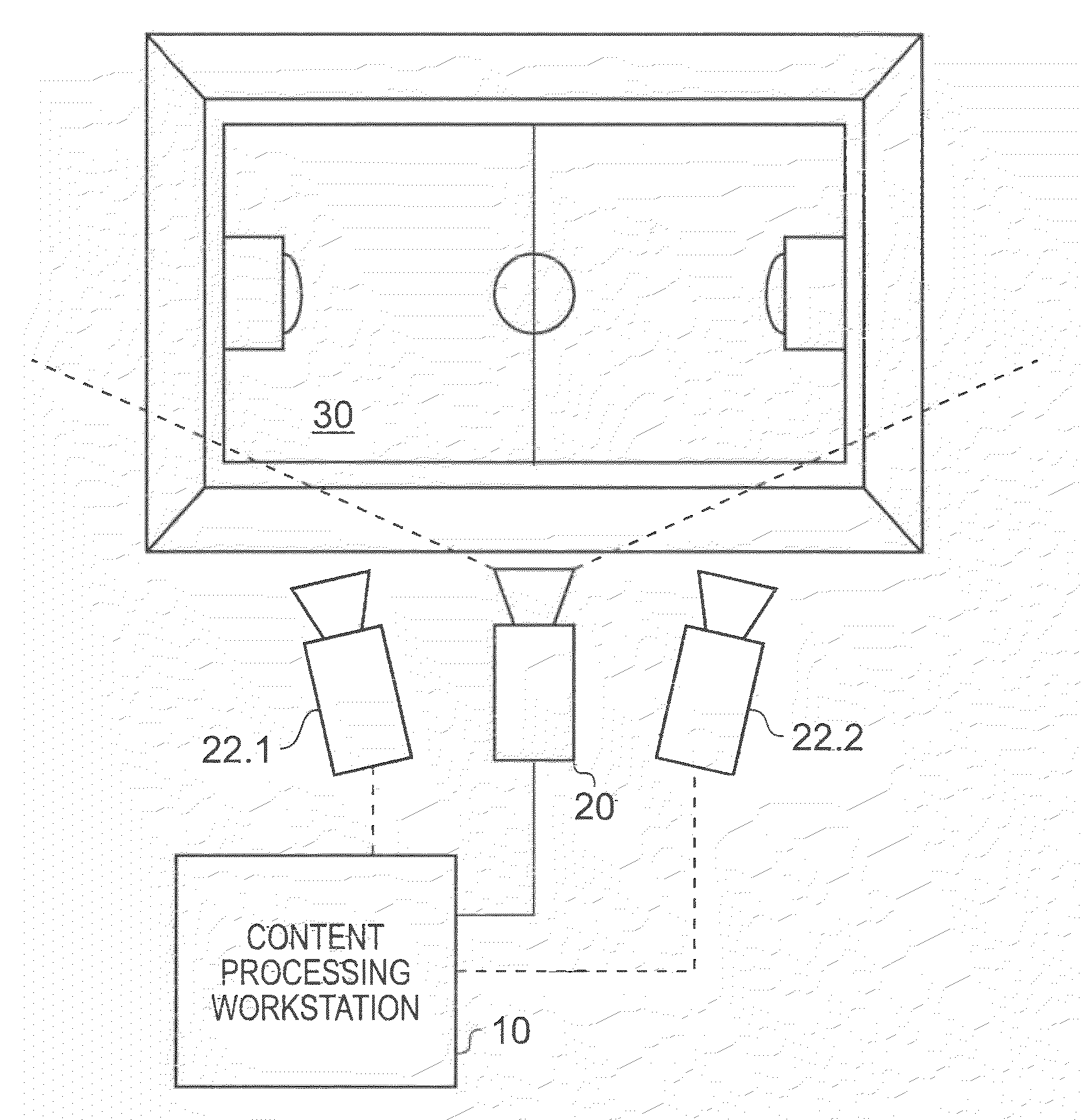
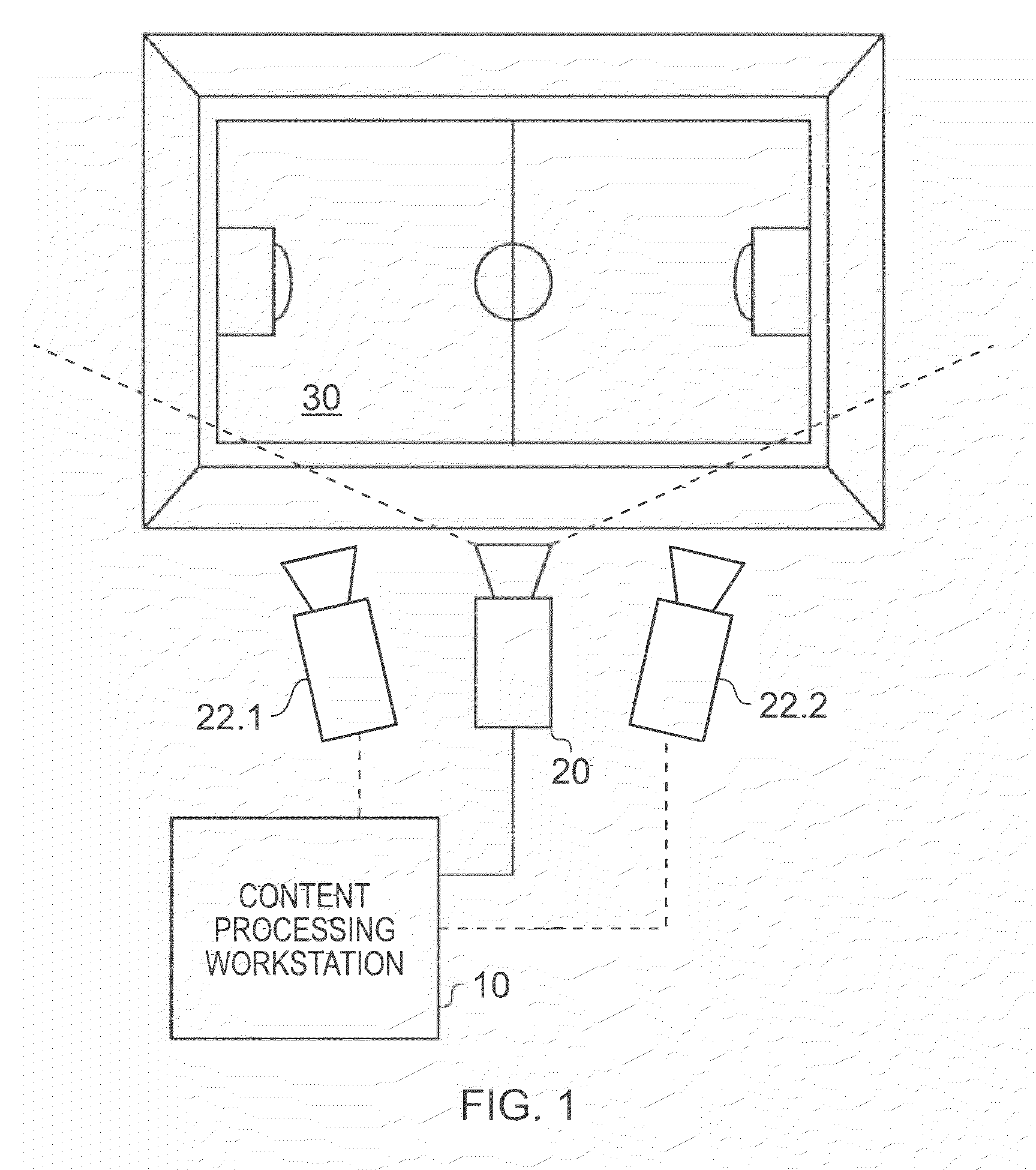
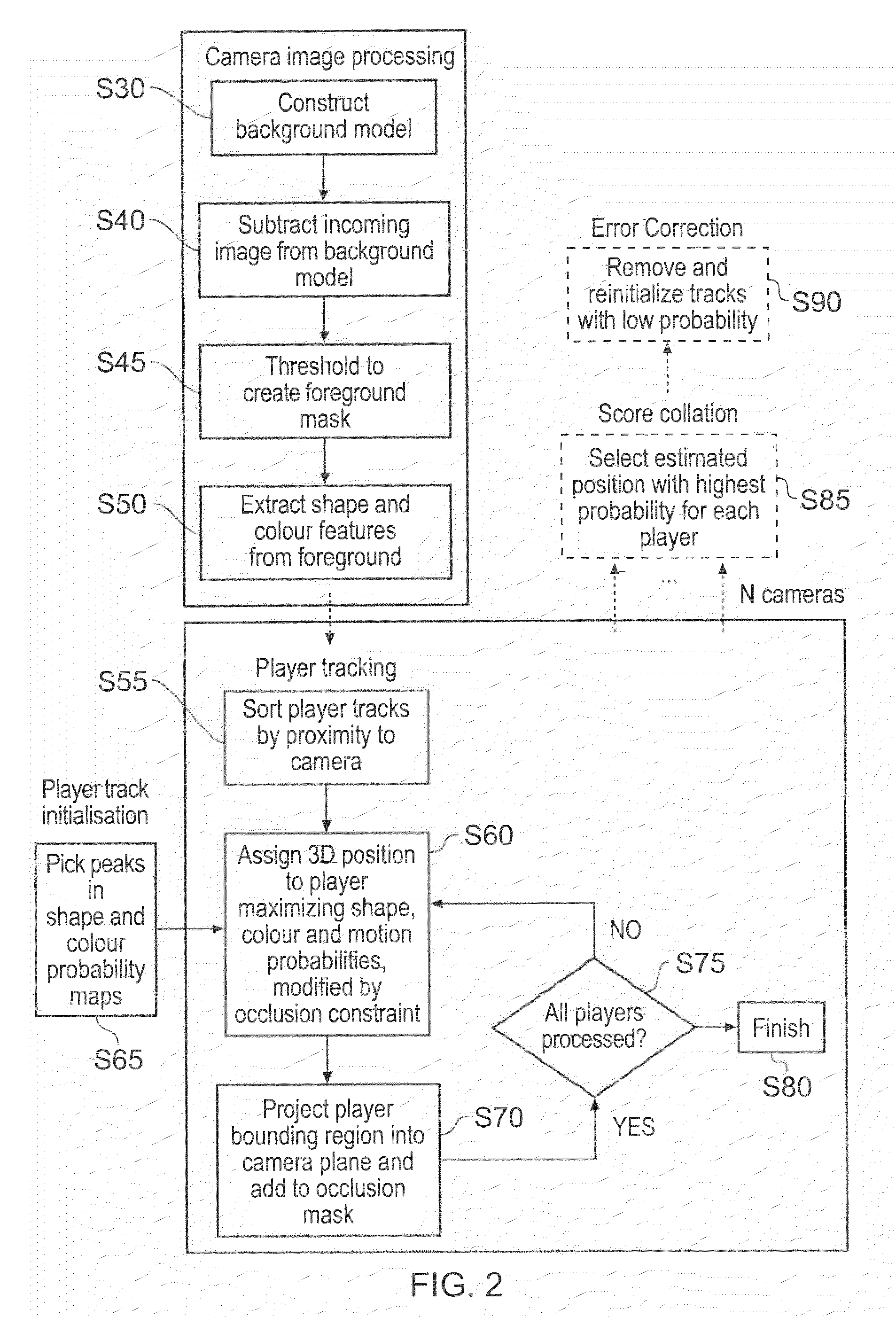
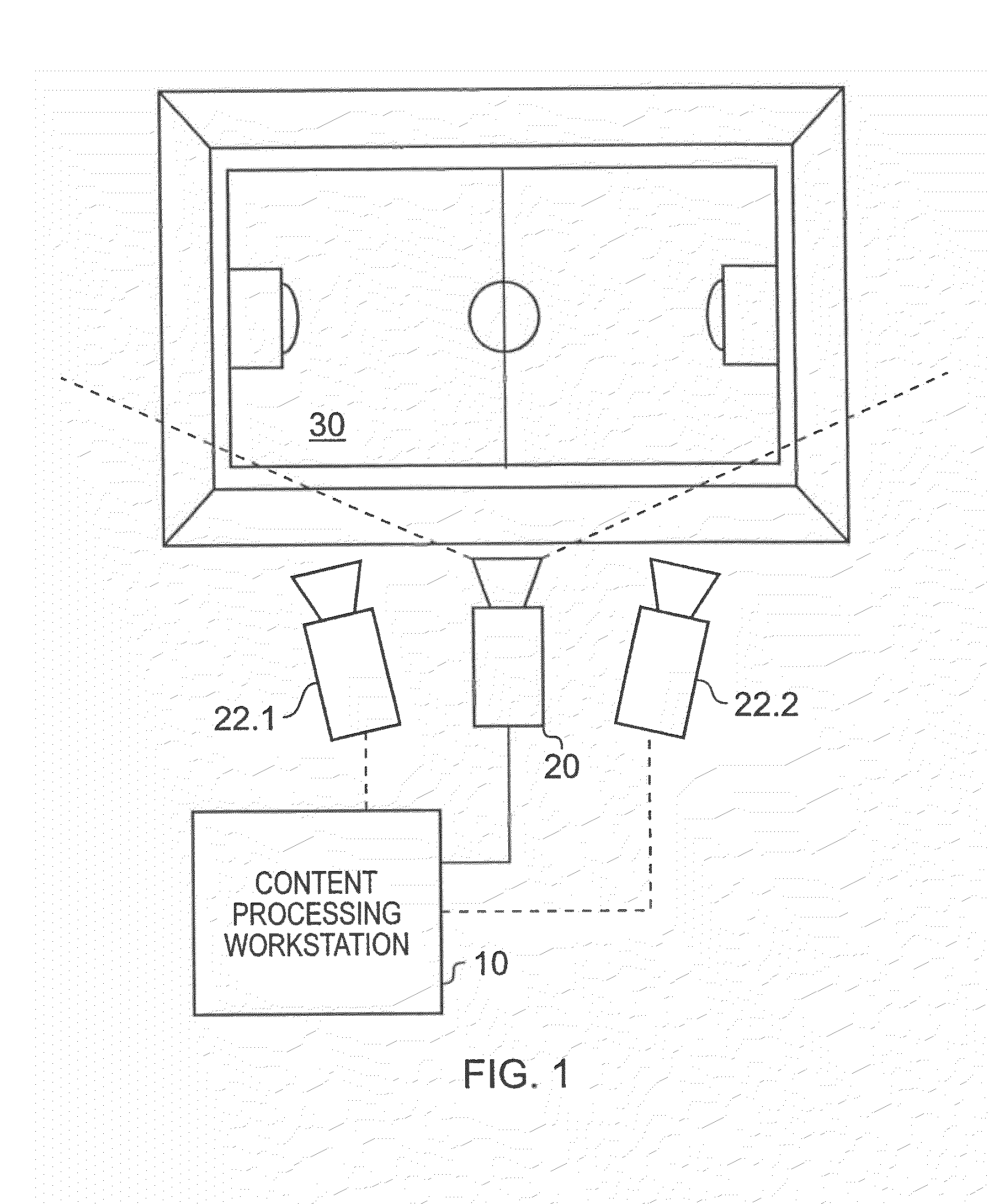
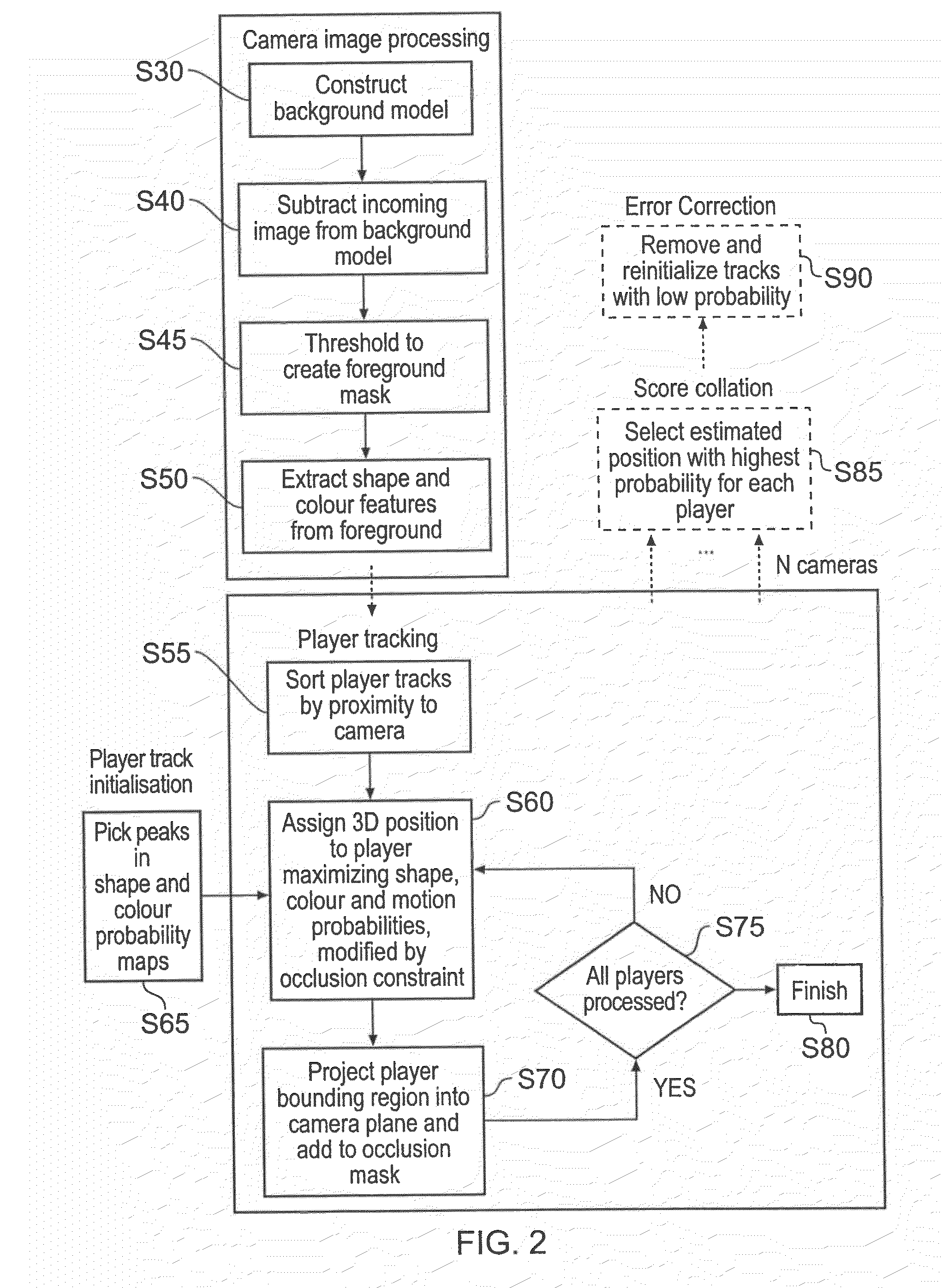
Apparatus and method of object tracking
InactiveUS20090059007A1Low costReduce laborImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSample imageImaging Feature
A method of tracking objects on a plane within video images of the objects captured by a video camera. The method includes processing the captured video images so as to extract one or more image features from each object, detecting each of the objects from a relative position of the objects on the plane as viewed from the captured video images by comparing the one or more extracted image features associated with each object with sample image features from a predetermined set of possible example objects which the captured video images may contain; and generating object identification data for each object, from the comparing, which identifies the respective object on the plane. The method further includes generating a three dimensional model of the plane and logging, for each detected object, the object identification data for each object which identifies the respective object on the plane together with object path data. The object path provides a position of the object on the three dimensional model of the plane from the video images with respect to time and relates to the path that each object has taken within the video images. The logging includes detecting an occlusion event in dependence upon whether a first image feature associated with a first of the objects obscures a whole or part of at least a second image feature associated with at least a second of the objects; and, if an occlusion event is detected, associating the object identification data for the first object and the object identification data for the second object with the object path data for both the first object and the second object respectively and logging the associations. The logging further includes identifying at least one of the objects involved in the occlusion event in dependence upon a comparison between the one or more image features associated with that object and the sample image features from the predetermined set of possible example objects, and updating the logged path data after the identification of at least one of the objects so that the respective path data is associated with the respective identified object.
Owner:SONY CORP
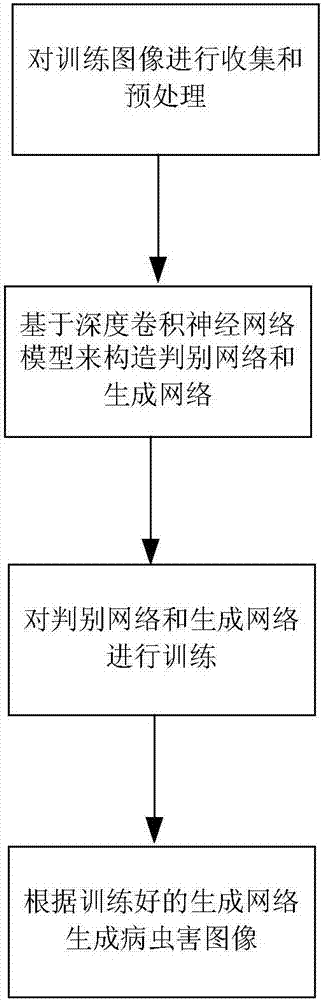
Pest and disease image generation method based on generative adversarial network
InactiveCN107016406AHard to solve problems with few and high acquisition costsCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesDiseaseGenerative adversarial network
The invention relates to a pest and disease image generation method based on a generative adversarial network. In the prior art, sampling images of pest and disease images are less. By using the method of the invention, the above defect is overcome. The method comprises the following steps of collecting and preprocessing trained images; based on a deep-convolution neural network model, constructing a discrimination network and a generation network; training the discrimination network and the generation network; and according to the trained generation network, generating the pest and disease images. In the invention, according to a few of existing pest and disease images, a lot of pest and disease images which are similar to a reality are generated, a sample image is provided for pest and disease image identification, and problems that the pest and disease images in an actual field are less and acquisition cost is high are solved.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus, method, and program for image processing
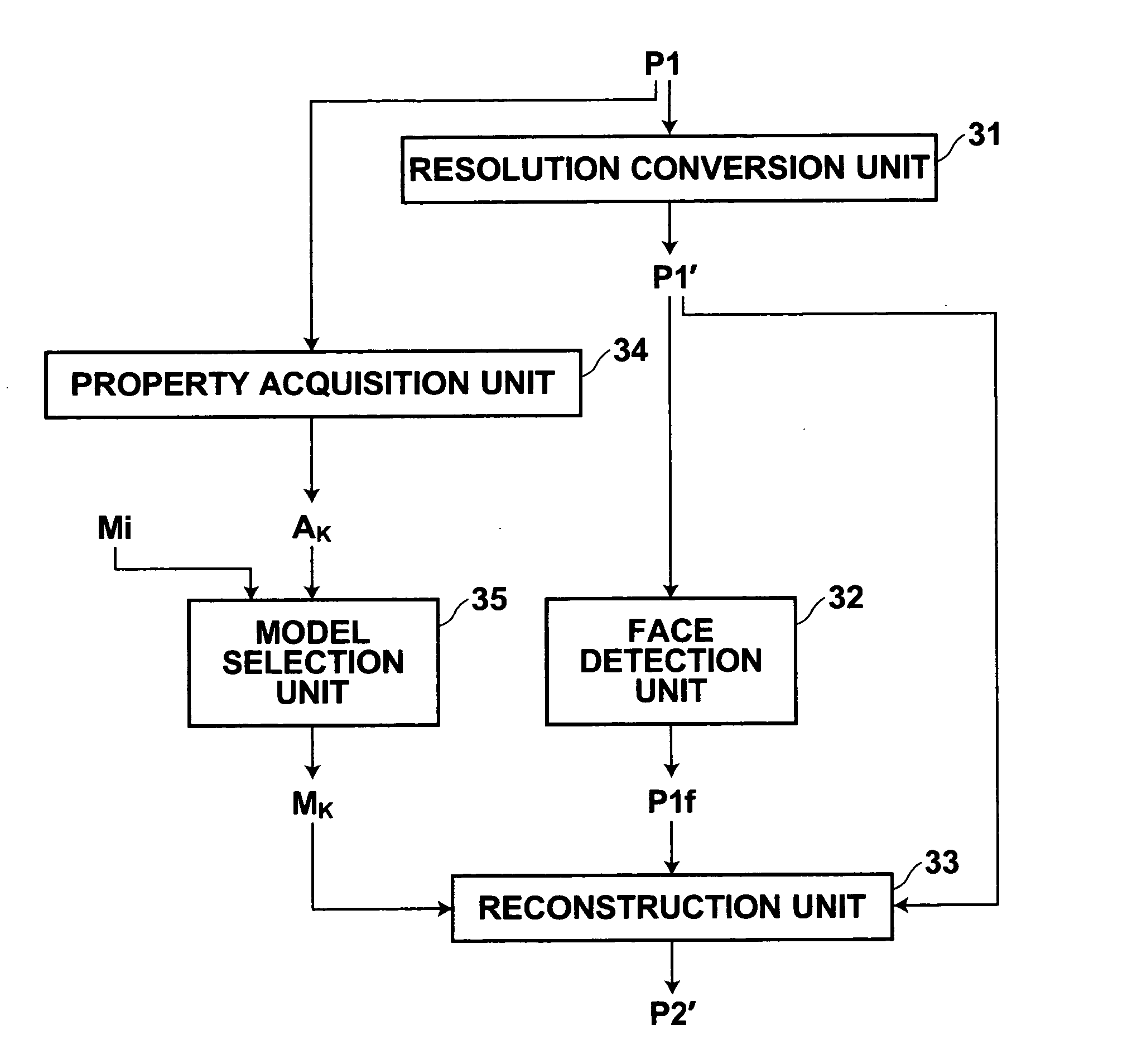
InactiveUS20060280380A1Easy to operateAutomatic detectionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
Resolution of an input image is converted more easily by using a method of AAM. For this purpose, a resolution conversion unit converts resolution of the image having been subjected to correction, and a face detection unit detects a face region in the resolution-converted image. A reconstruction unit fits to the face region detected by the face detection unit a mathematical model generated through the method of AAM using a plurality of sample images representing human faces having the same resolution as the image, and reconstructs an image representing the face region after the fitting. In this manner, an image whose resolution has been converted is obtained.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
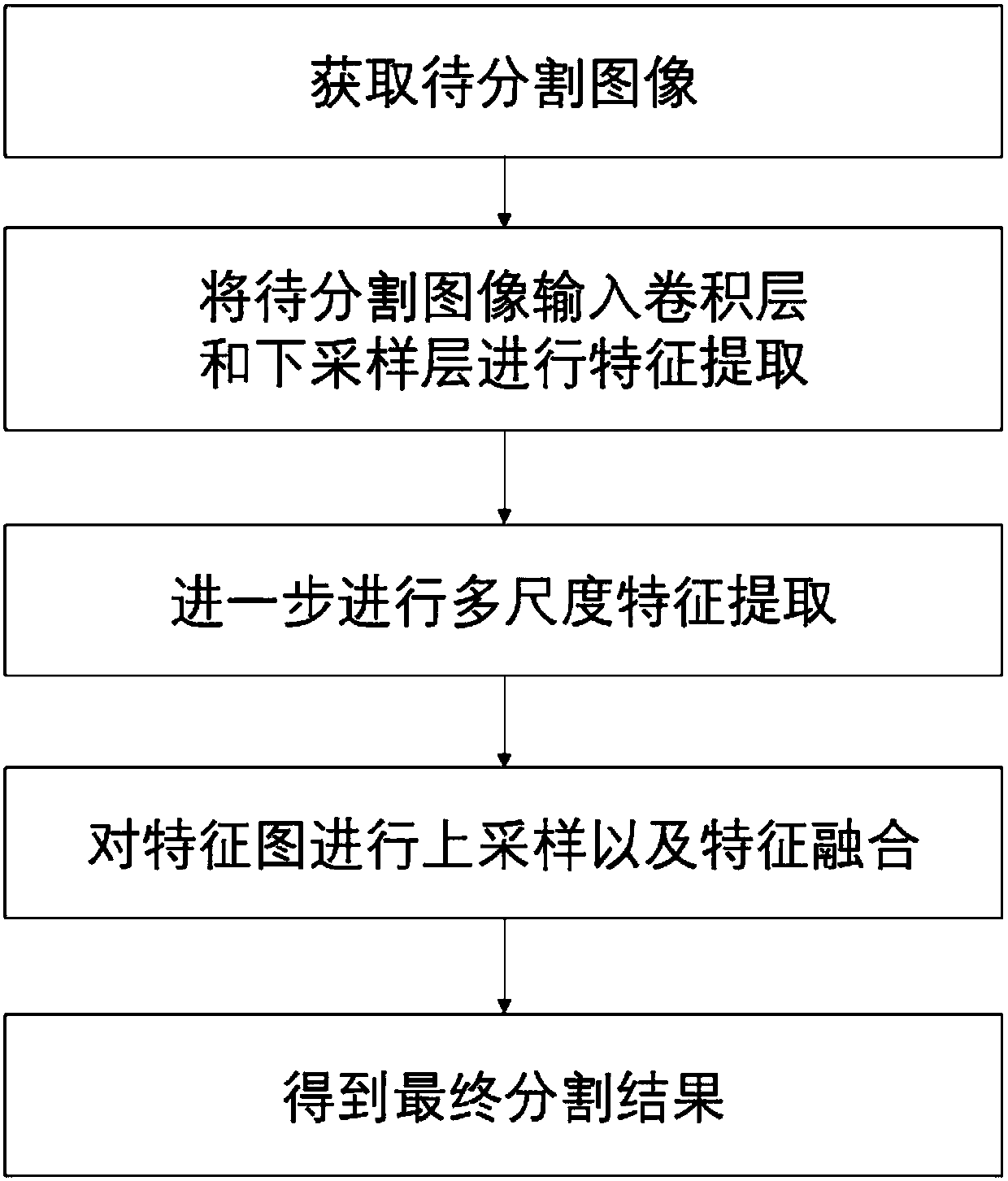
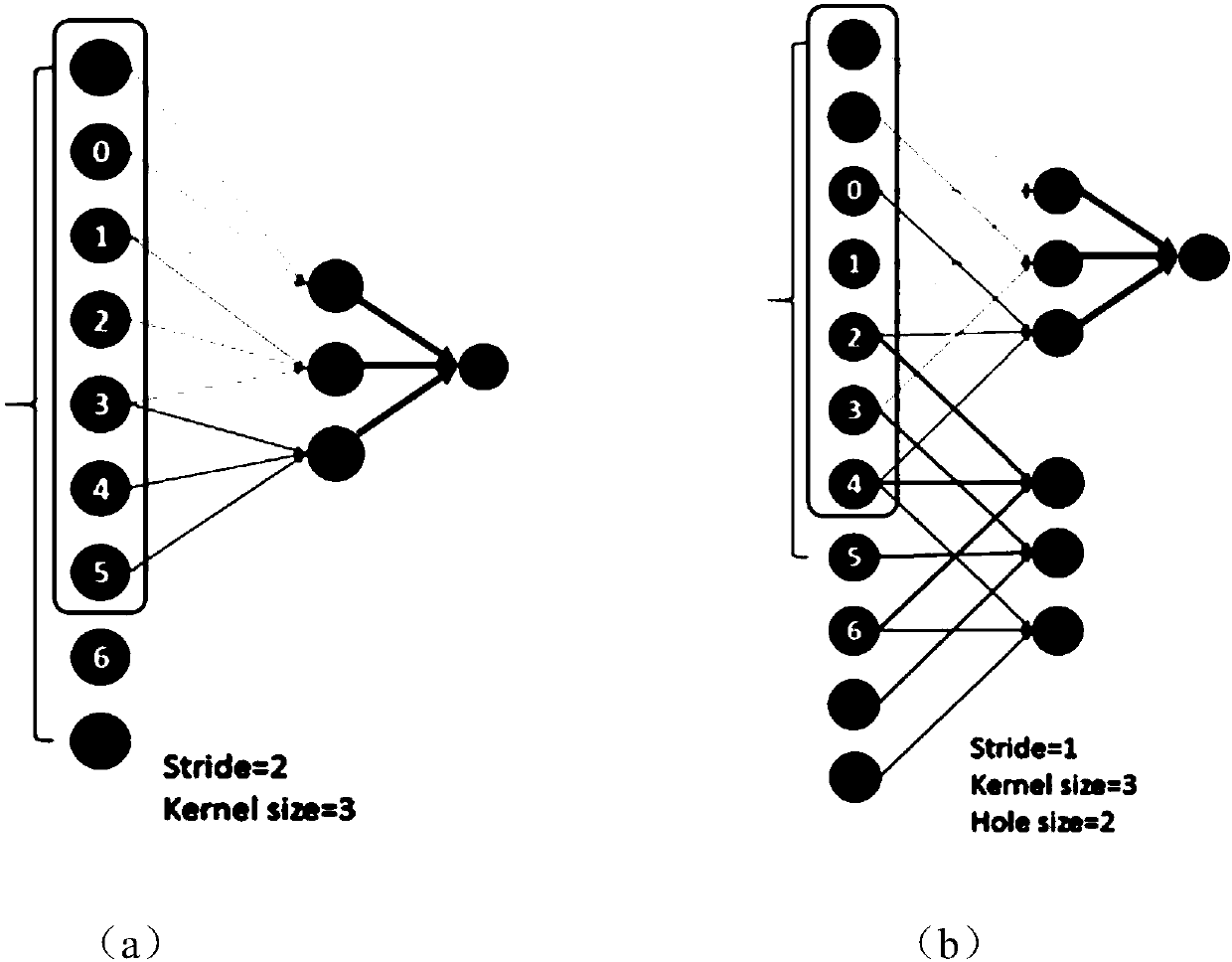
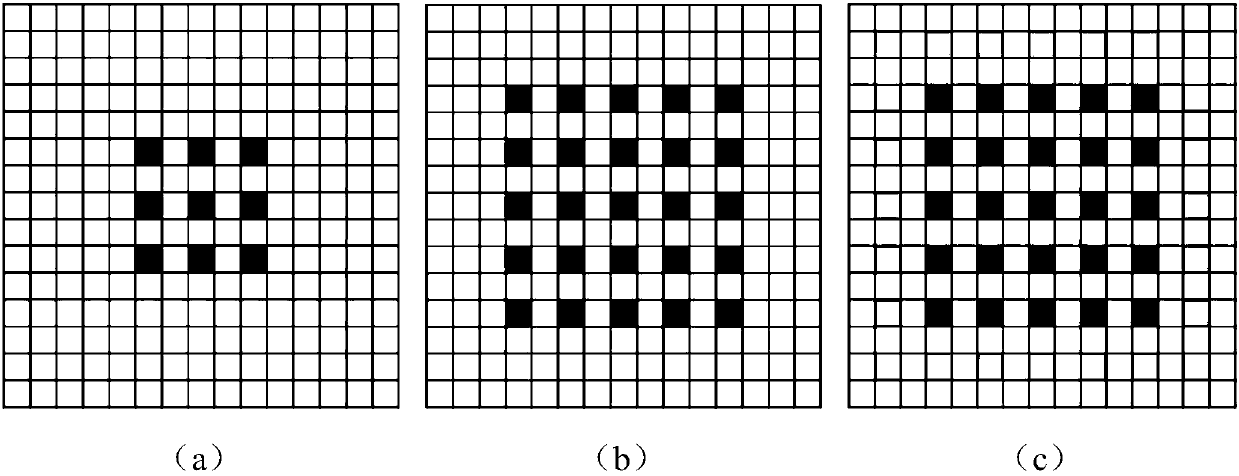
Multi-scale image semantic segmentation method
ActiveCN110232394AIncrease profitEasy to handleCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesSample imageMinutiae
The invention discloses a multi-scale image semantic segmentation method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a to-be-segmented image and a corresponding label; constructing a full convolutional deep neural network, wherein the full convolutional deep neural network comprises a convolution module, a hole convolution module, a pyramid pooling module, a 1 * 1 * depth convolution layer and a deconvolution structure; setting hole convolution as channel-by-channel operation, and utilizing low-scale, medium-scale and high-scale characteristics in a targeted mode; training the full convolutional deep neural network, establishing a loss function, and determining parameters of the full convolutional deep neural network by training the sample image; and inputting the to-be-segmentedimage into the trained full convolutional deep neural network to obtain a semantic segmentation result. By means of the method, the image semantic segmentation problem with complex details, holes andlarge targets can be well solved while the calculated amount and the parameter number are reduced, and the consistency of category labels can be reserved while the target edges can be well segmented.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, and computer-readable recording medium storing image processing program
ActiveUS20070071347A1Quality improvementImprove machining accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingMathematical model
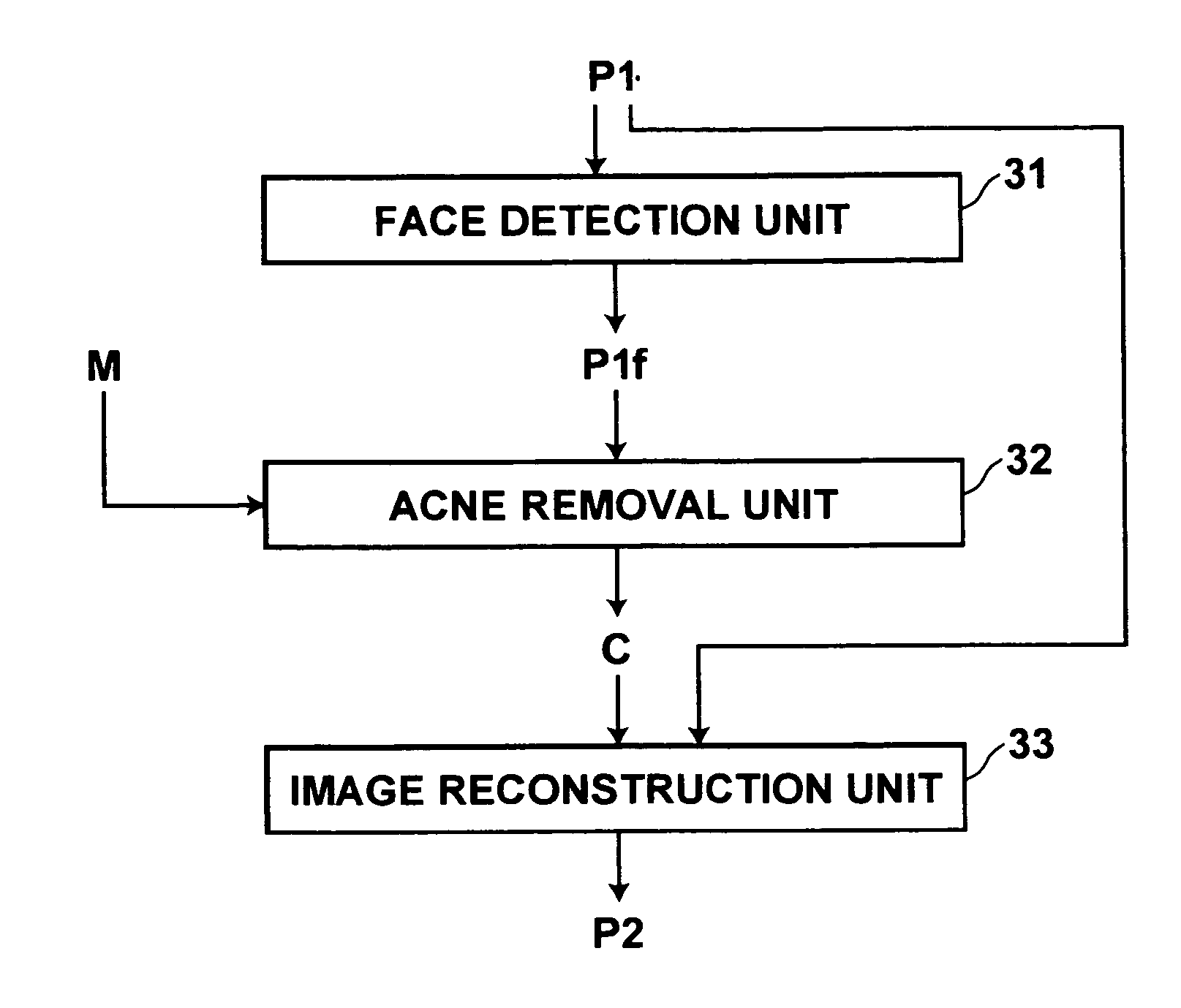
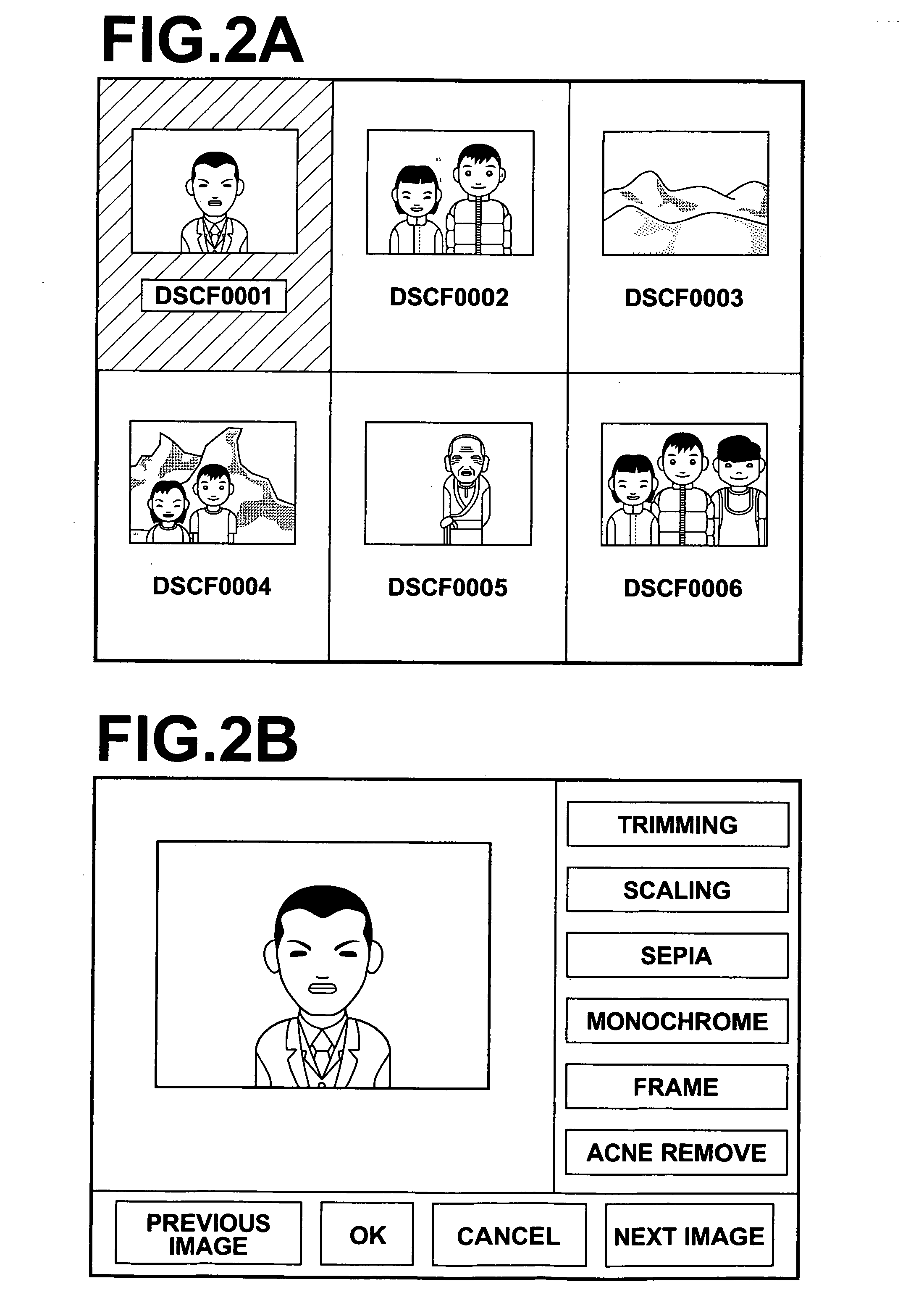
An unnecessary component such as acne is removed completely from a predetermined structure such as a face in a photograph image without manual operation and skills. An acne removal unit fits to a face region as the structure in the image a mathematical model generated according to a statistical method such as AAM using sample images representing the structure without the component to be removed, and an image reconstruction unit reconstructs an image of the face region based on parameters corresponding to the face region obtained by the fitting of the model. An image is then generated by replacing the face region with the reconstructed image. Since the mathematical model has been generated from the sample images of human faces without acne, the model does not include acne. Therefore, the reconstructed face image generated by fitting the model to the face region does not include acne.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
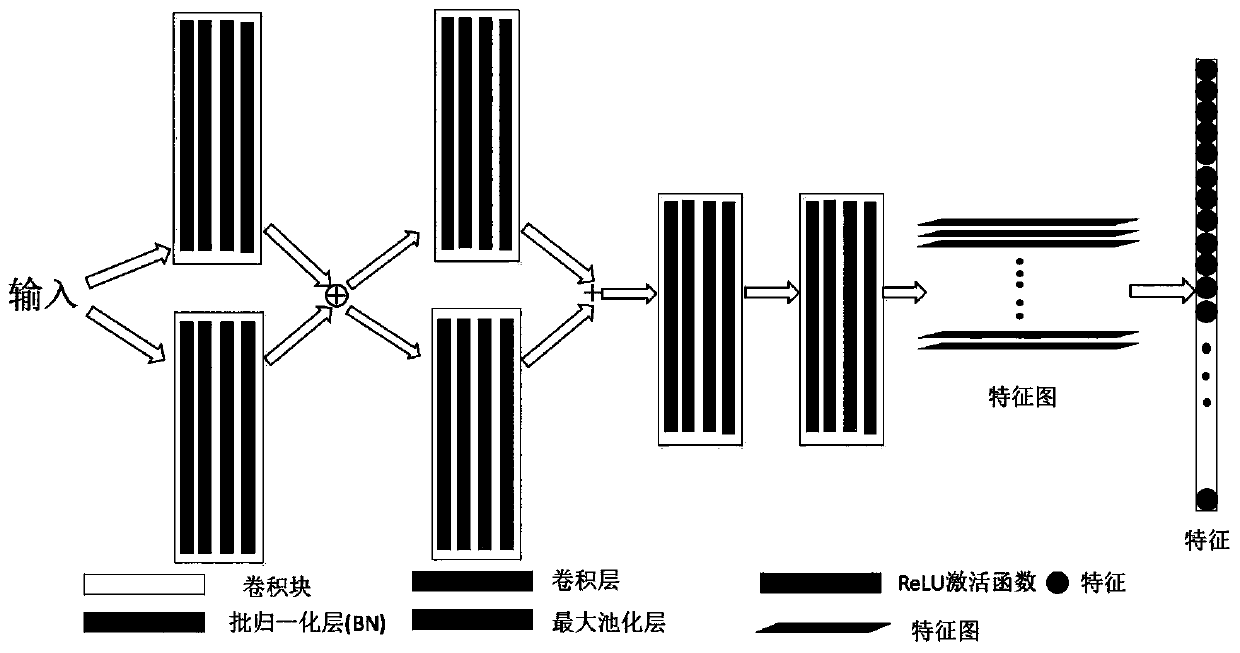
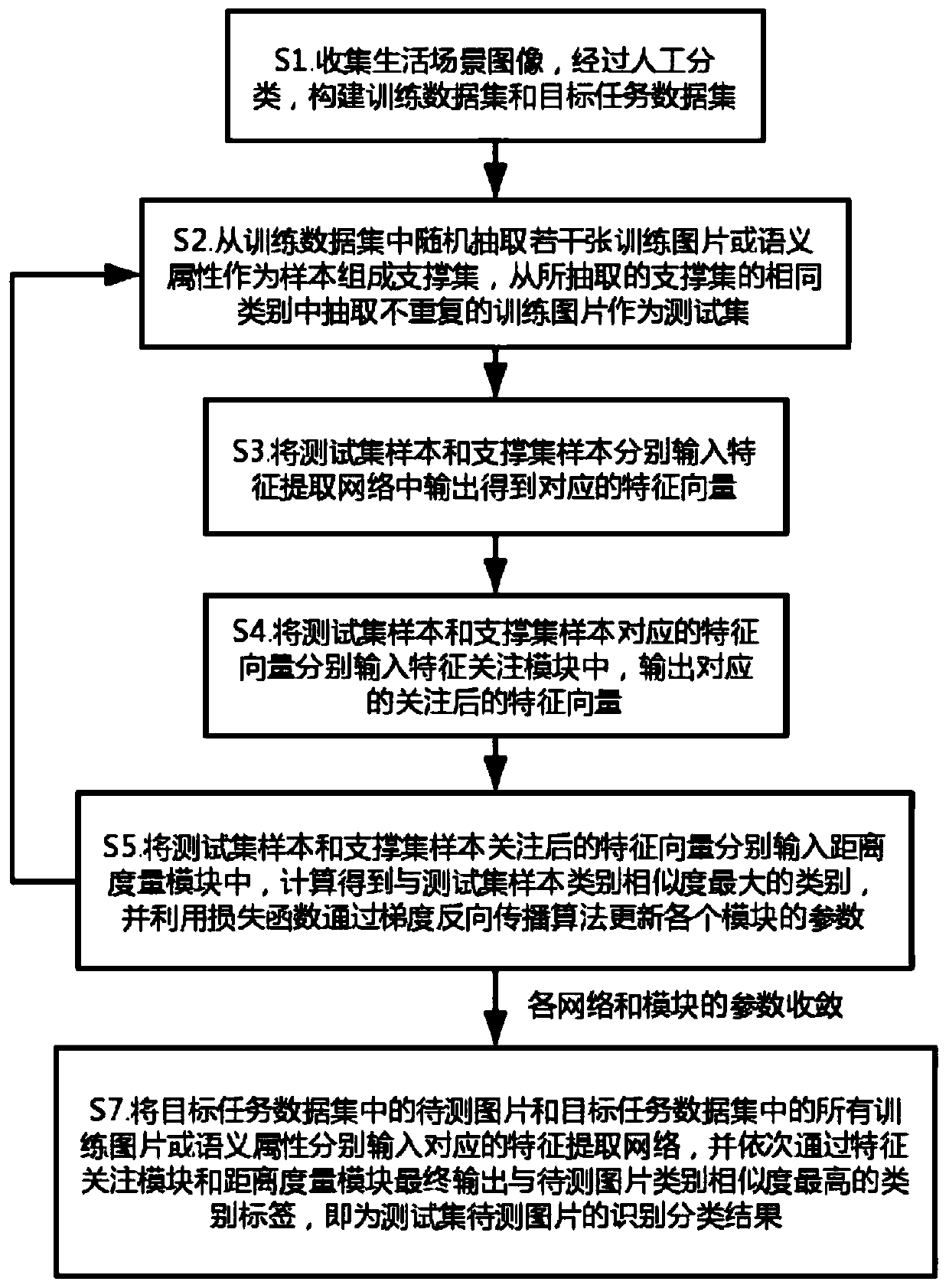
Small sample and zero sample image classification method based on metric learning and meta-learning
ActiveCN109961089ASolve the recognition classification problemAccurate classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionEnergy efficient computingSmall sampleData set
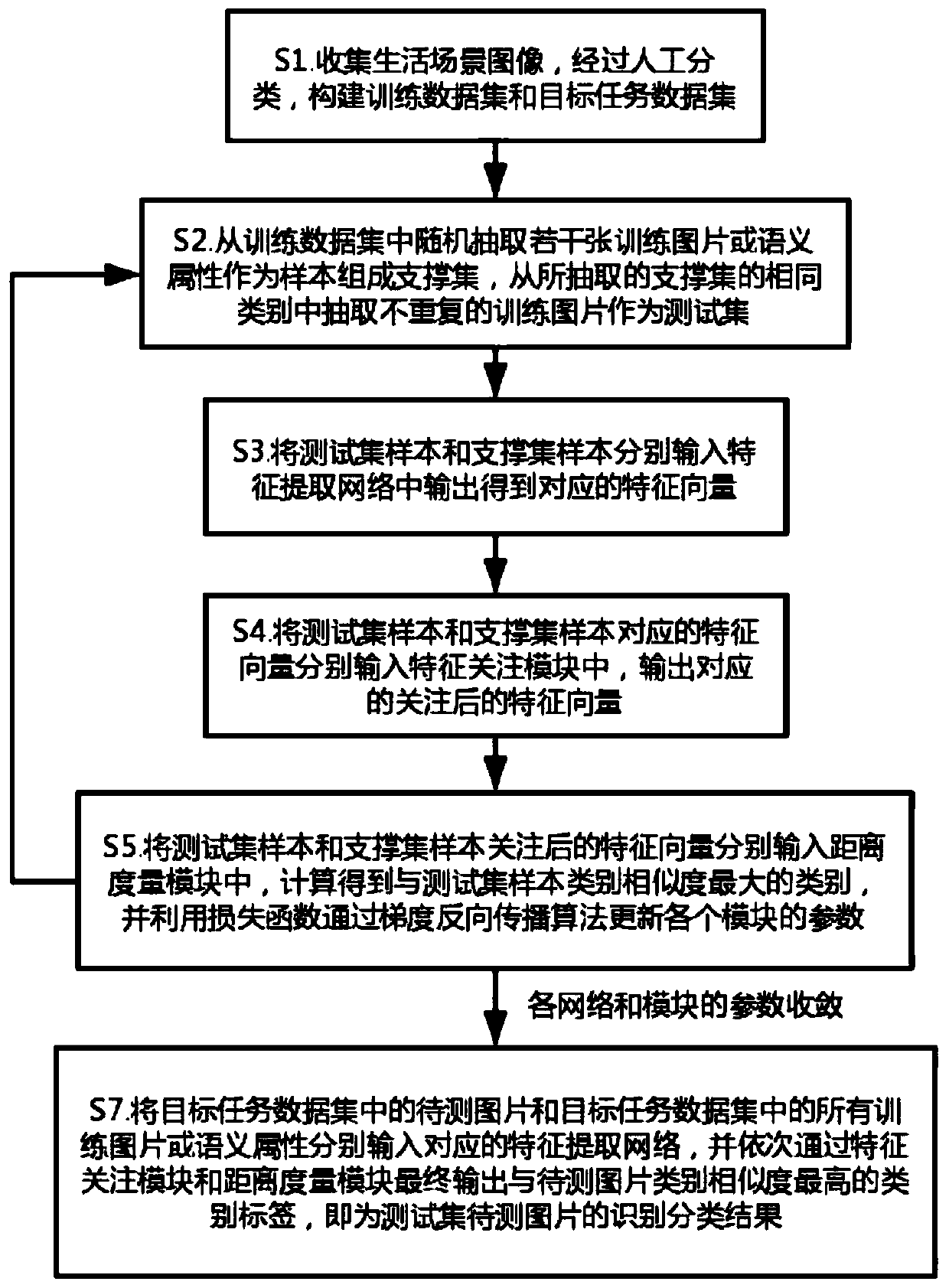
The invention relates to the field of computer vision recognition and transfer learning, and provides a small sample and zero sample image classification method based on metric learning and meta-learning, which comprises the following steps of: constructing a training data set and a target task data set; selecting a support set and a test set from the training data set; respectively inputting samples of the test set and the support set into a feature extraction network to obtain feature vectors; sequentially inputting the feature vectors of the test set and the support set into a feature attention module and a distance measurement module, calculating the category similarity of the test set sample and the support set sample, and updating the parameters of each module by utilizing a loss function; repeating the above steps until the parameters of the networks of the modules converge, and completing the training of the modules; and enabling the to-be-tested picture and the training picture in the target task data set to sequentially pass through a feature extraction network, a feature attention module and a distance measurement module, and outputting a category label with the highestcategory similarity with the test set to obtain a classification result of the to-be-tested picture.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
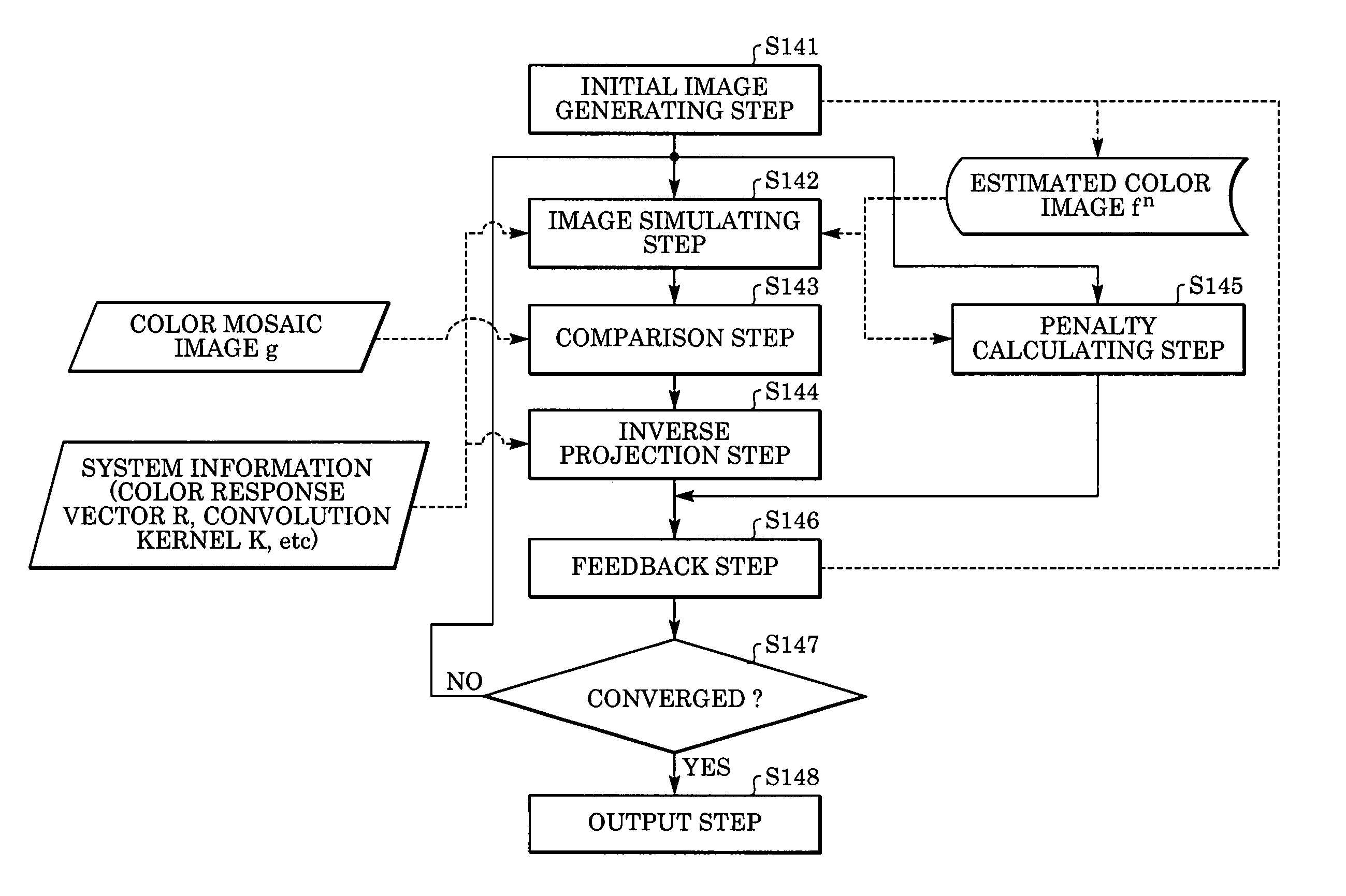
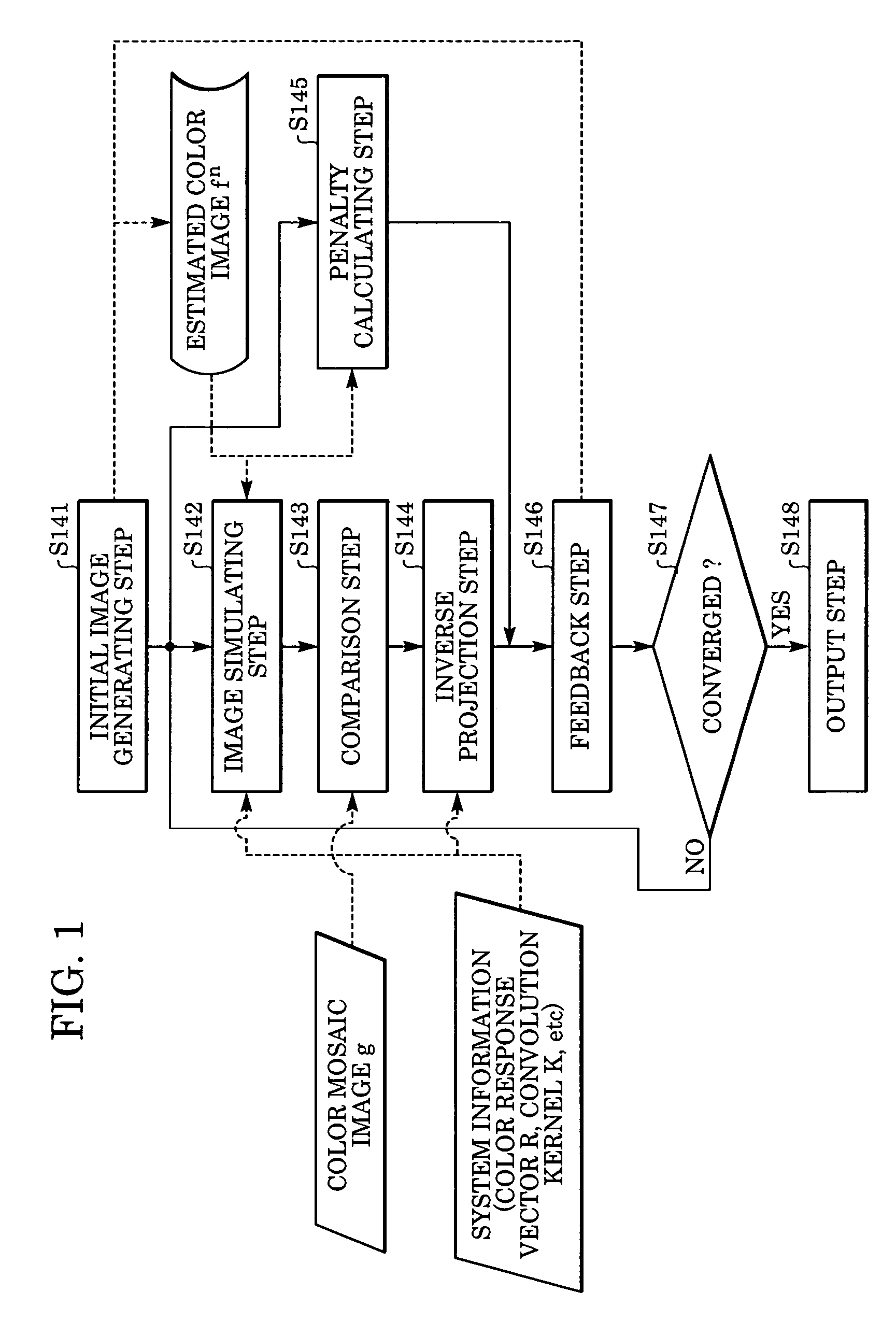
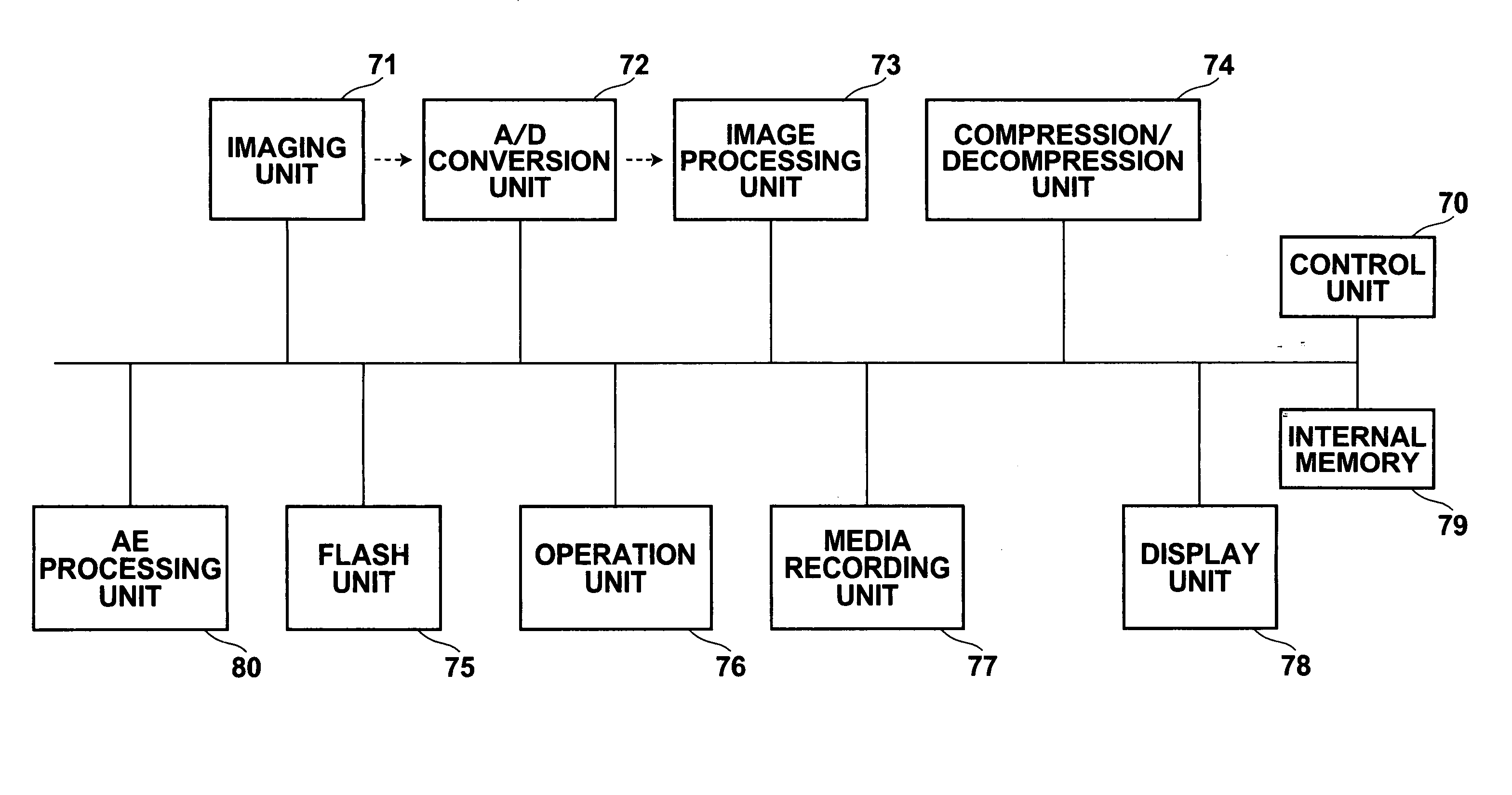
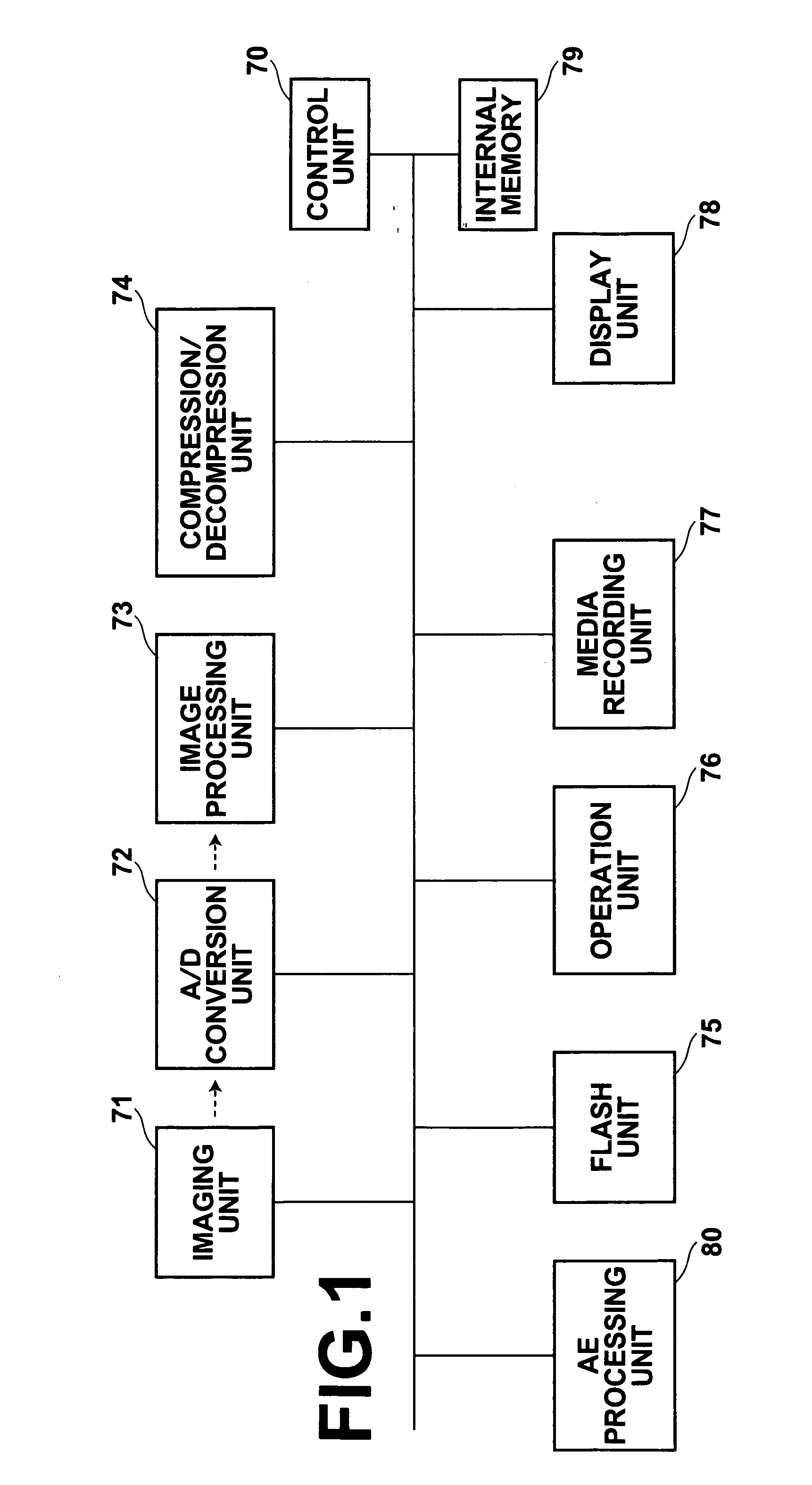
Image processing device, image processing method and image processing program
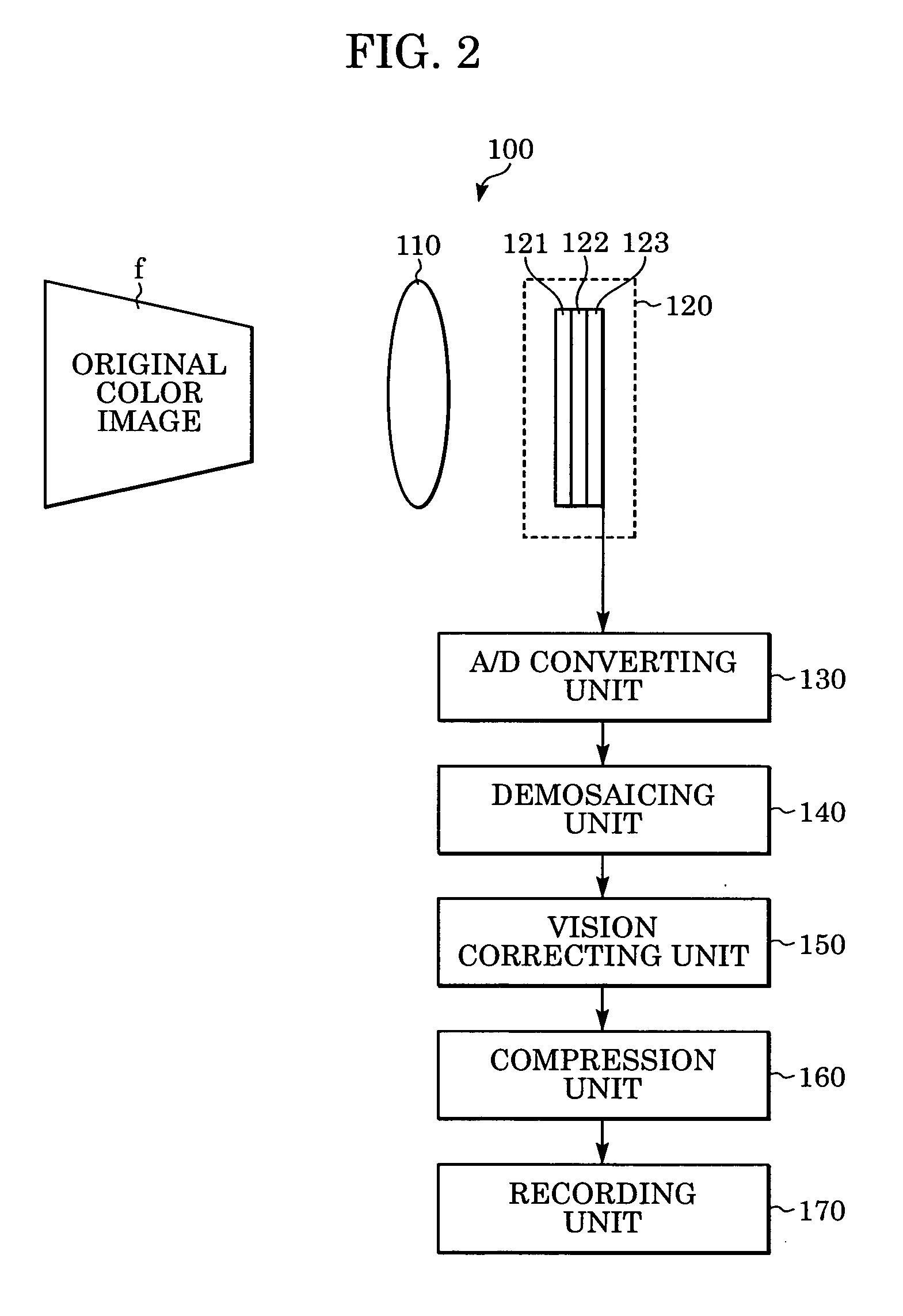
An image processing device generates an output image as a color image wherein each pixel has color information, using a first image as a sparsely color sampled image wherein each pixel has monochromatic information obtained by an image sensor which has multiple pixels each photoelectrically converting light of a plurality of colors. The device includes: a simulation unit for generating a second image as an estimated image of the sparsely color sampled image; a comparison unit for comparing the second image with the first image, and generating first information thereof; a converting unit for converting the first information into second information corresponding to the color image; a penalty computing unit for computing the correction amount of the input image; and a correction unit for generating a third image by correcting the input image based on the second information and the correcting amount; this third image being used as an output image.
Owner:CANON KK
An image segmentation method and system based on a convolutional neural network
InactiveCN109886971AImprove robustnessHigh precisionImage analysisNeural architecturesNerve networkImage segmentation
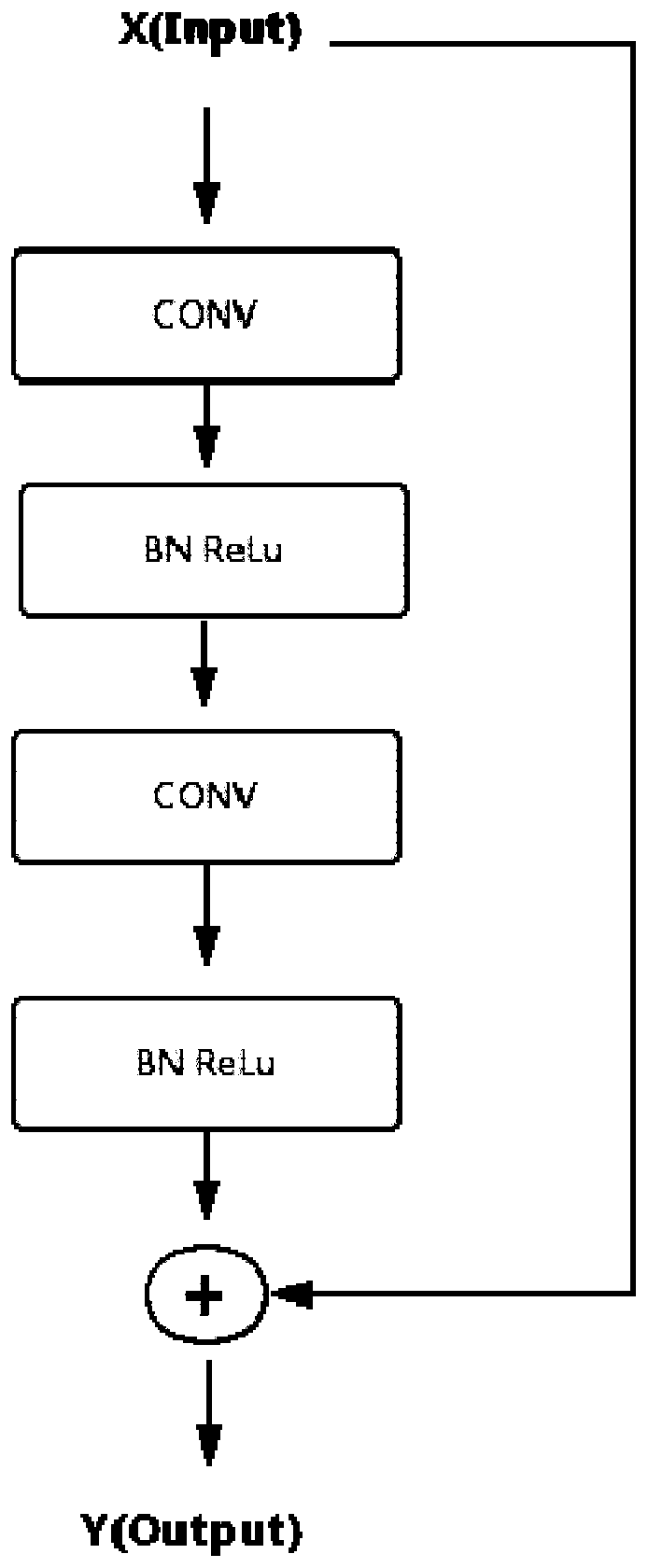
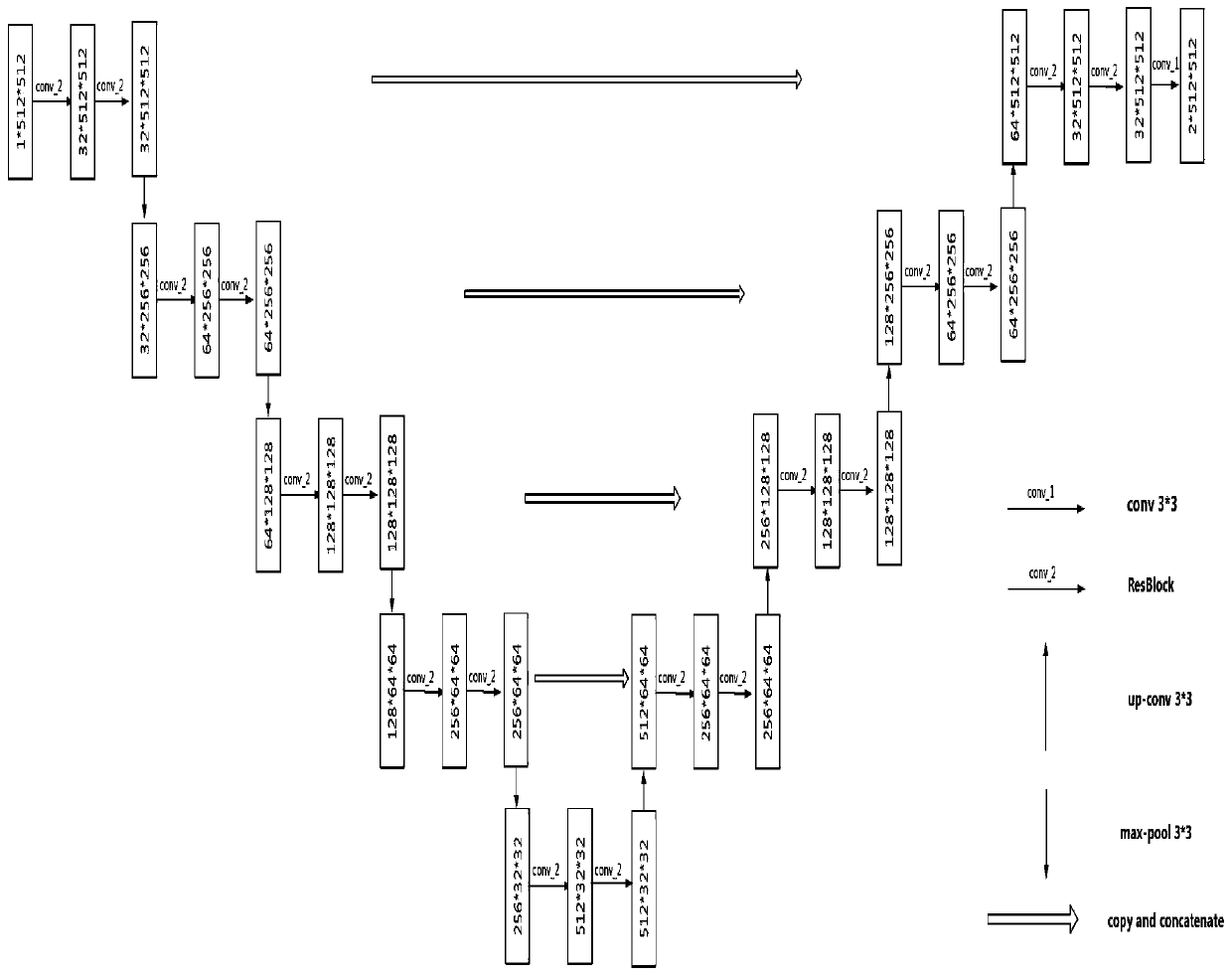
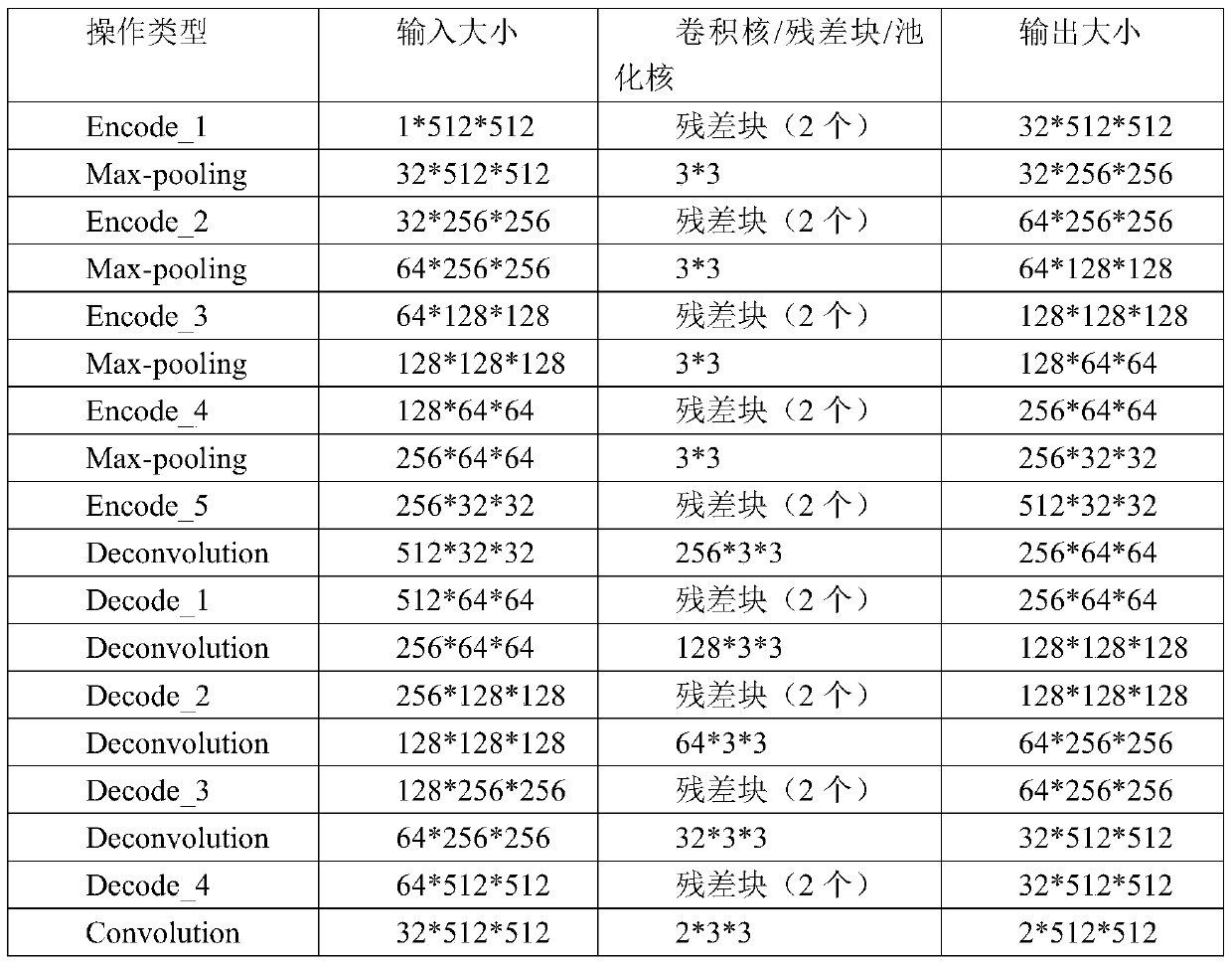
The invention discloses an image segmentation method and system based on a convolutional neural network, and the method comprises the following steps of collecting a preset number of sample images, carrying out the normalization and data enhancement of the sample images, and obtaining the training sample data; training a U-Net convolutional neural network model with a residual block through the training sample data to obtain a trained U-Net convolutional neural network model; carrying out the pixel normalization processing on to-be-segmented images which are the same as the sample images; inputting the image to be segmented after pixel normalization processing into the trained U-Net convolutional neural network model, and finally obtaining a segmented image. The method provided by the invention has the relatively higher segmentation precision, and an end-to-end segmentation mode is adopted, so that the relatively higher segmentation efficiency is achieved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, and computer-readable recording medium storing image processing program
ActiveUS20070070440A1Easy to operateQuality improvementImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
Sharpness is adjusted for more appropriately representing a predetermined structure in an image. A parameter acquisition unit obtains a weighting parameter for a principal component representing a degree of sharpness in a face region detected by a face detection unit as an example of the predetermined structure in the image, by fitting to the face region a mathematical model generated by a statistical method such as AAM based on a plurality of sample images representing human faces in different degrees of sharpness. Based on a value of the parameter, sharpness is adjusted in at least a part of the image. For example, a parameter changing unit changes the value of the parameter to a preset optimal face sharpness value, and an image reconstruction unit reconstructs the image based on the parameter having been changed and outputs the image having been subjected to the sharpness adjustment processing.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Image processing apparatus and method
InactiveUS20090066784A1Realistic representationImage enhancementImage analysisHat matrixImaging processing
An image processing apparatus and method generate a three dimensional representation of a scene which includes a plurality of objects disposed on a plane. The three dimensional representation is generated from one or more video images of the scene, which include the objects on the plane produced from a view of the scene by a video camera. The method comprises processing the captured video images so as to extract one or more image features from each object, comparing the one or more image features with sample image features from a predetermined set of possible example objects which the video images may contain, and identifying the objects from the comparison of the image features with the stored image features of the possible example objects. The method also includes generating object path data, which includes object identification data for each object which identifies the respective object; and provides a position of the object on the plane in the video images with respect to time. The method further includes calculating a projection matrix for projecting the position of each of the objects according to the object path data from the plane into a three dimensional model of the plane. As such a three dimensional representation of the scene which includes a synthesised representation of each of the plurality of objects on the plane can be produced, by projecting the position of the objects according to the object path data into the plane of the three dimensional model of the scene using the projection matrix and a predetermined assumption of the height of each of the objects. Accordingly, a three dimensional representation of a live video image of, for example, a football match can be generated, or tracking information included on the live video images. As such, a change in a relative view of the generated three dimensional representation can be made, so that a view can be provided in the three dimensional representation of the scene from a view point at which no camera is actually present to capture video images of the live scene.
Owner:SONY CORP
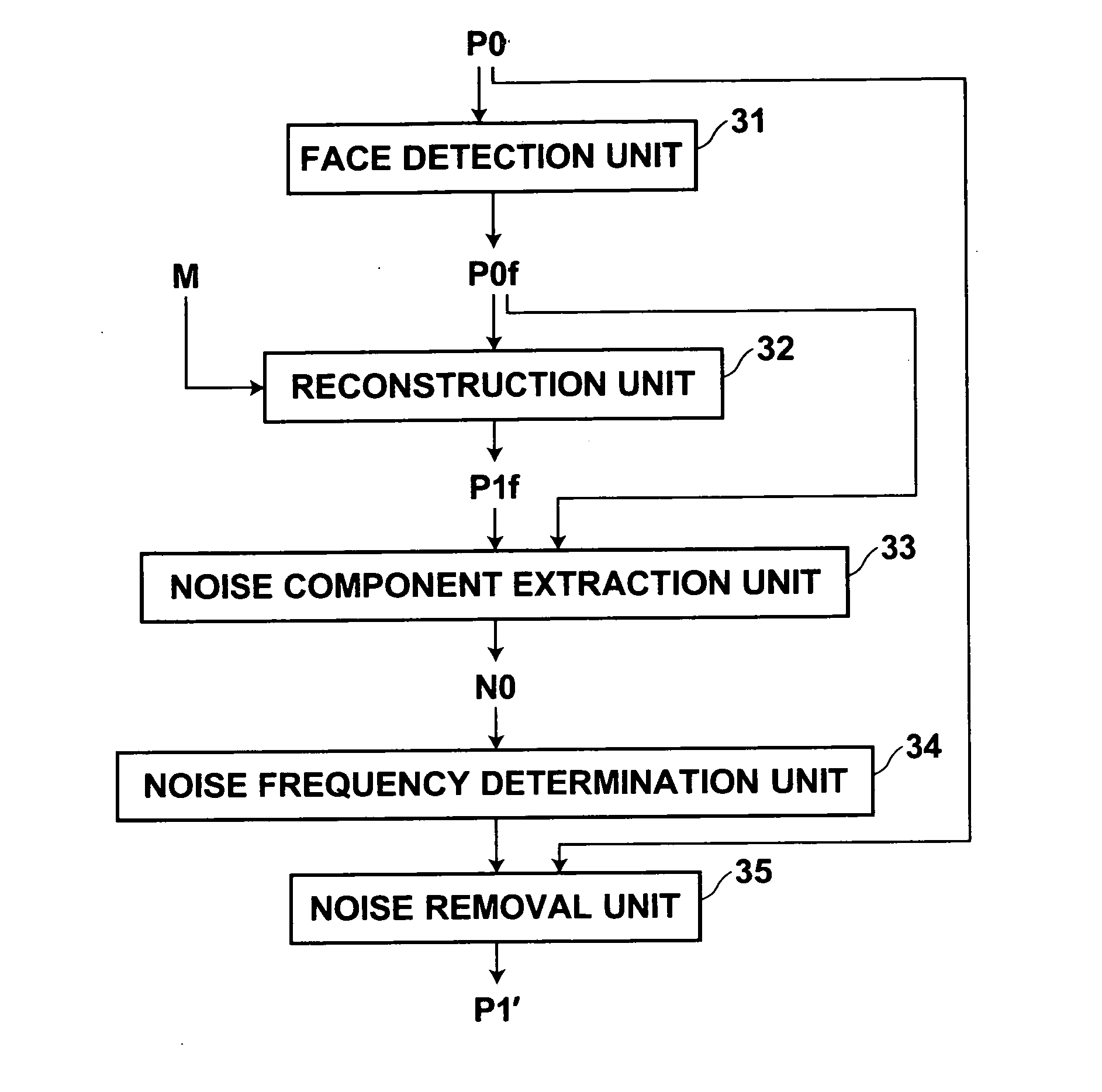
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program
ActiveUS20060257047A1Quality improvementGood removal effectCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
In order to accurately remove an unnecessary periodic noise component from an image, a reconstruction unit generates a reconstructed image without a periodic noise component by fitting to a face region detected in an image by a face detection unit a mathematical model generated according a method of AAM using a plurality of sample images representing human faces without a periodic noise component. The periodic noise component is extracted by a difference between the face region and the reconstructed image, and a frequency of the noise component is determined. The noise component of the determined frequency is then removed from the image.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Image generating method and apparatus
InactiveCN106952239AQuality improvementImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Network model
Owner:厦门黑镜科技有限公司
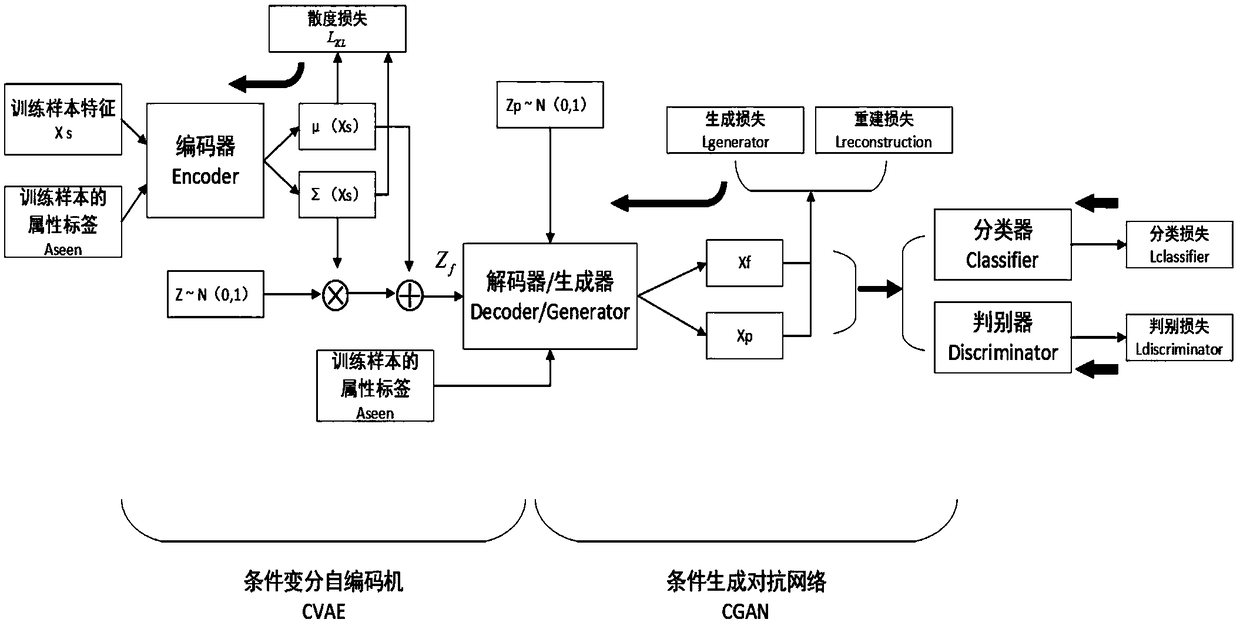
Zero sample image classification method based on combination of variational autocoder and adversarial network
ActiveCN108875818AImplement classificationMake up for the problem of missing training samples of unknown categoriesCharacter and pattern recognitionPhysical realisationClassification methodsSample image
The invention discloses a zero sample image classification method based on combination of a variational autocoder and an adversarial network. Samples of a known category are input during model training; category mapping of samples of a training set serves as a condition for guidance; the network is subjected to back propagation of optimization parameters through five loss functions of reconstruction loss, generation loss, discrimination loss, divergence loss and classification loss; pseudo-samples of a corresponding unknown category are generated through guidance of category mapping of the unknown category; and a pseudo-sample training classifier is used for testing on the samples of the unknown category. The high-quality samples beneficial to image classification are generated through theguidance of the category mapping, so that the problem of lack of the training samples of the unknown category in a zero sample scene is solved; and zero sample learning is converted into supervised learning in traditional machine learning, so that the classification accuracy of traditional zero sample learning is improved, the classification accuracy is obviously improved in generalized zero sample learning, and an idea for efficiently generating the samples to improve the classification accuracy is provided for the zero sample learning.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for automated whole blood sample analyses from microscopy images
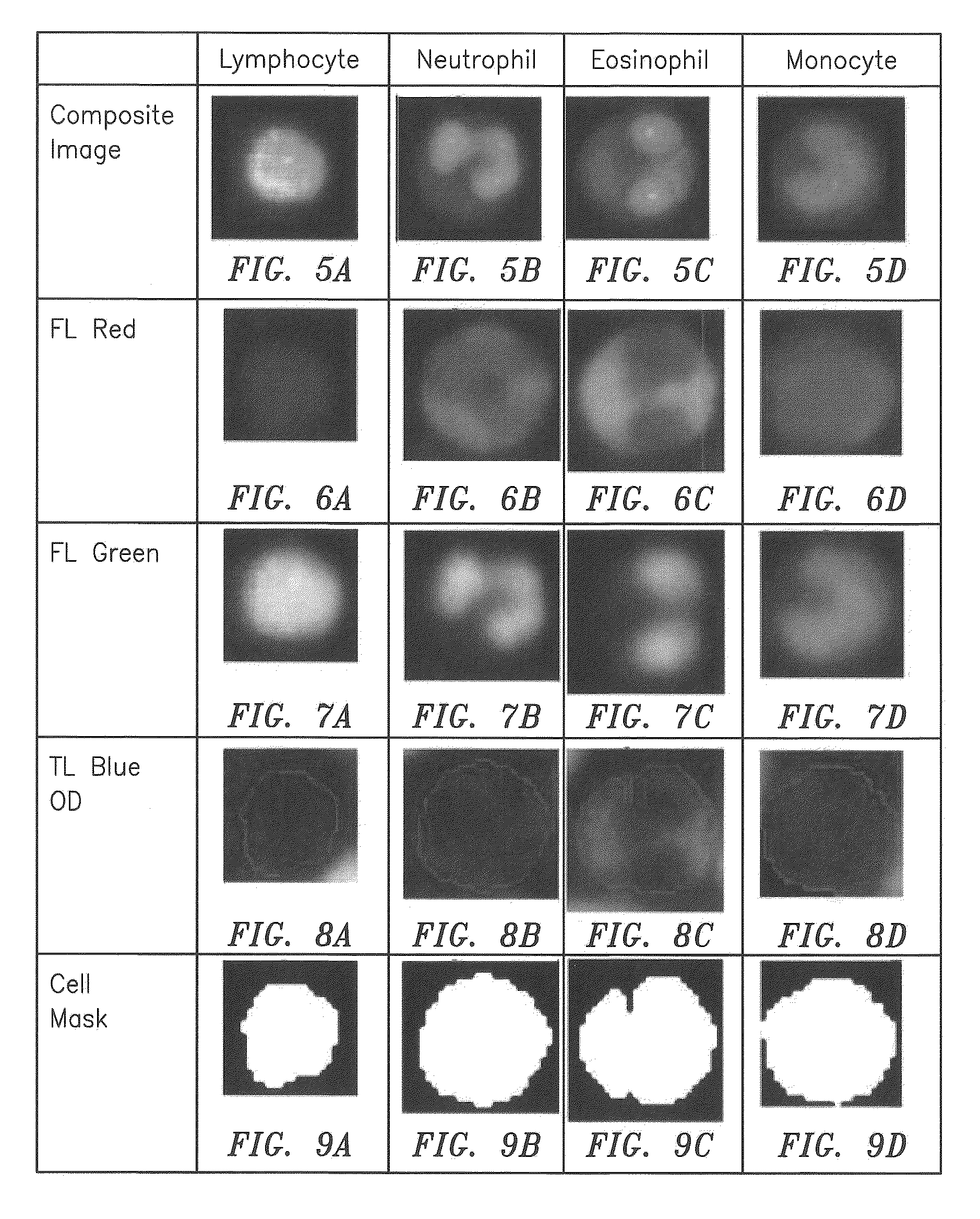
ActiveUS20120034647A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBlood gas analysisWhite blood cell
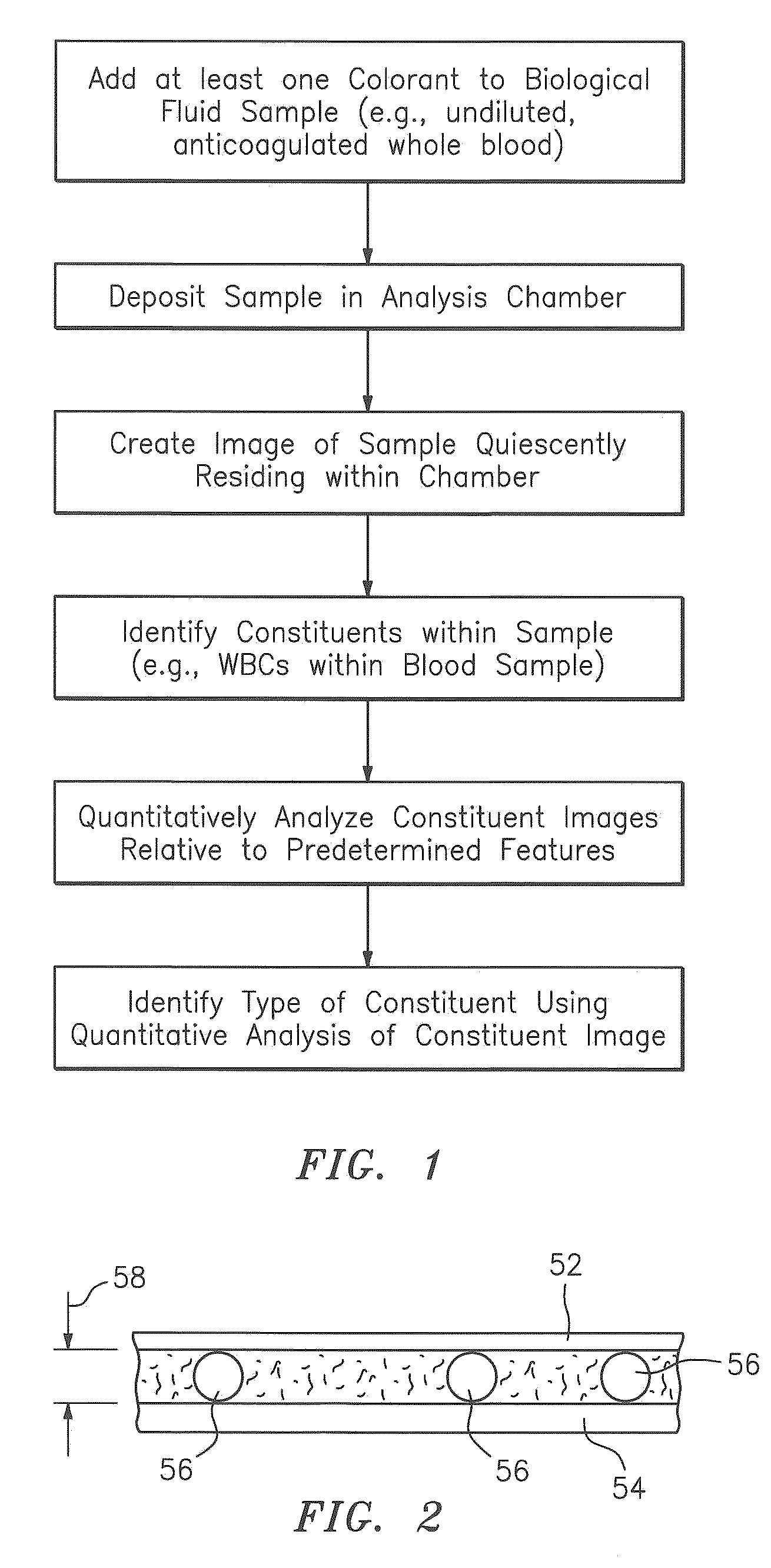
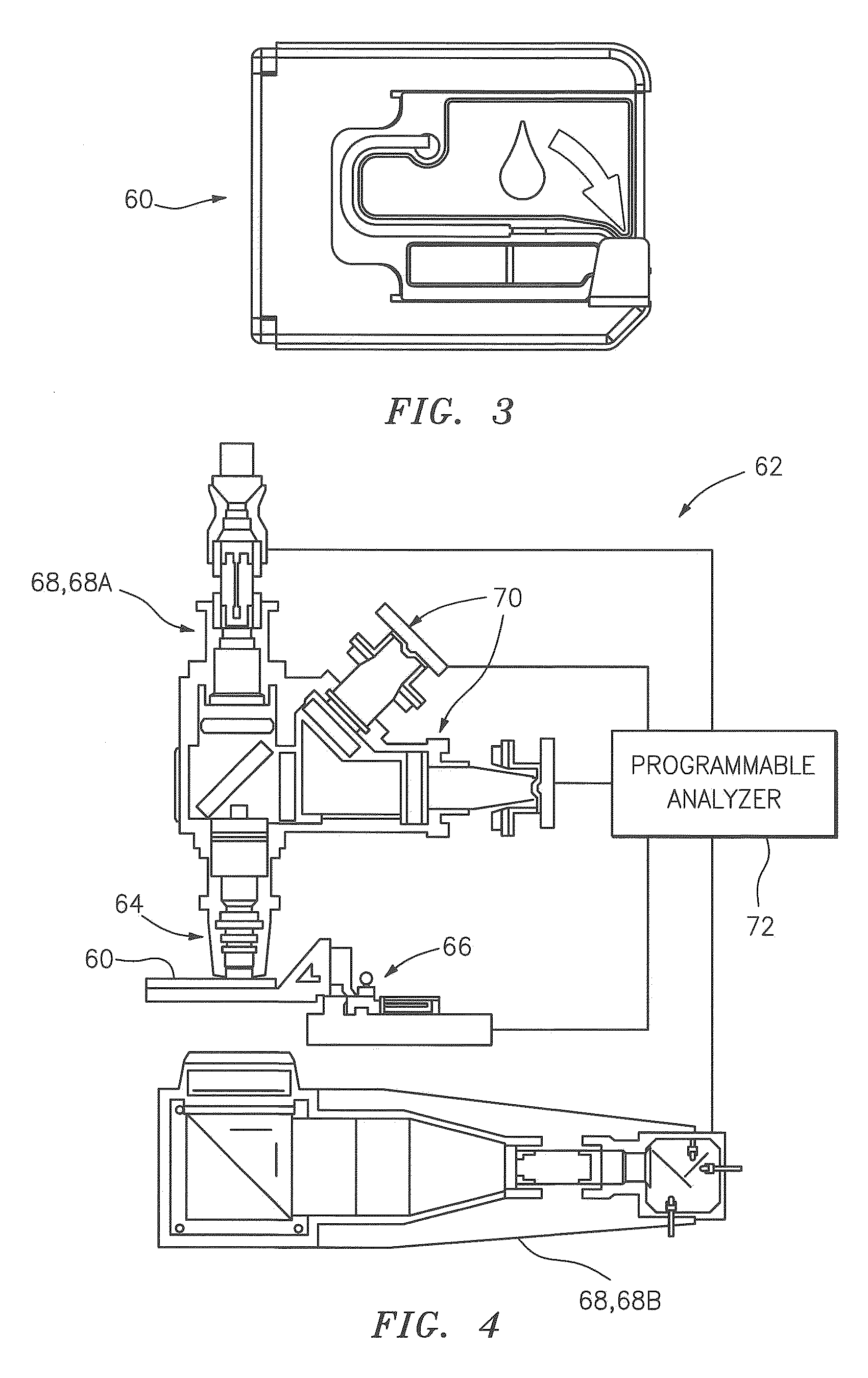
A method and apparatus for identifying one or more target constituents (e.g., white blood cells) within a biological sample is provided. The method includes the steps of: a) adding at least one colorant to the sample; b) disposing the sample into a chamber defined by at least one transparent panel; c) creating at least one image of the sample quiescently residing within the chamber; d) identifying target constituents within the sample image; e) quantitatively analyzing at least some of the identified target constituents within the image relative to one or more predetermined quantitatively determinable features; and f) identifying at least one type of target constituent within the identified target constituents using the quantitatively determinable features.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
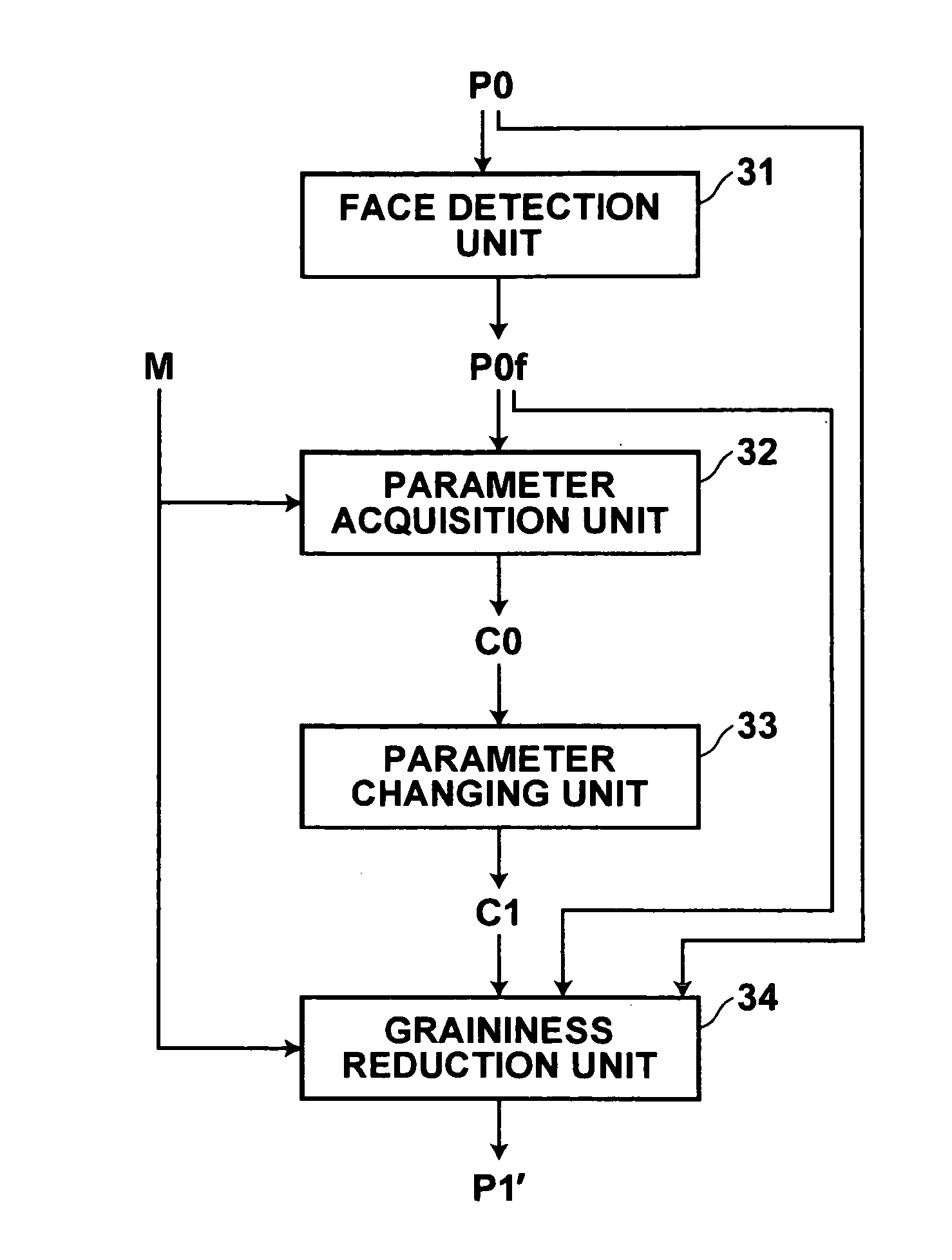
Apparatus, method and program for image processing
InactiveUS20060291739A1Reduce graininessImprove machining accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
Graininess reduction processing is carried out with accuracy by finding a degree of graininess in an image. For this purpose, a parameter acquisition unit obtains a weighting parameter for a principal component representing the degree of graininess in a face region found in the image by a face detection unit, by fitting to the face region a mathematical model generated by a method of AAM using a plurality of sample images representing human faces in different degrees of graininess. A parameter changing unit changes the parameter to have a desired value. A graininess reduction unit reduces graininess of the face region according to the parameter having been changed.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Photography apparatus, photography method, and photography program
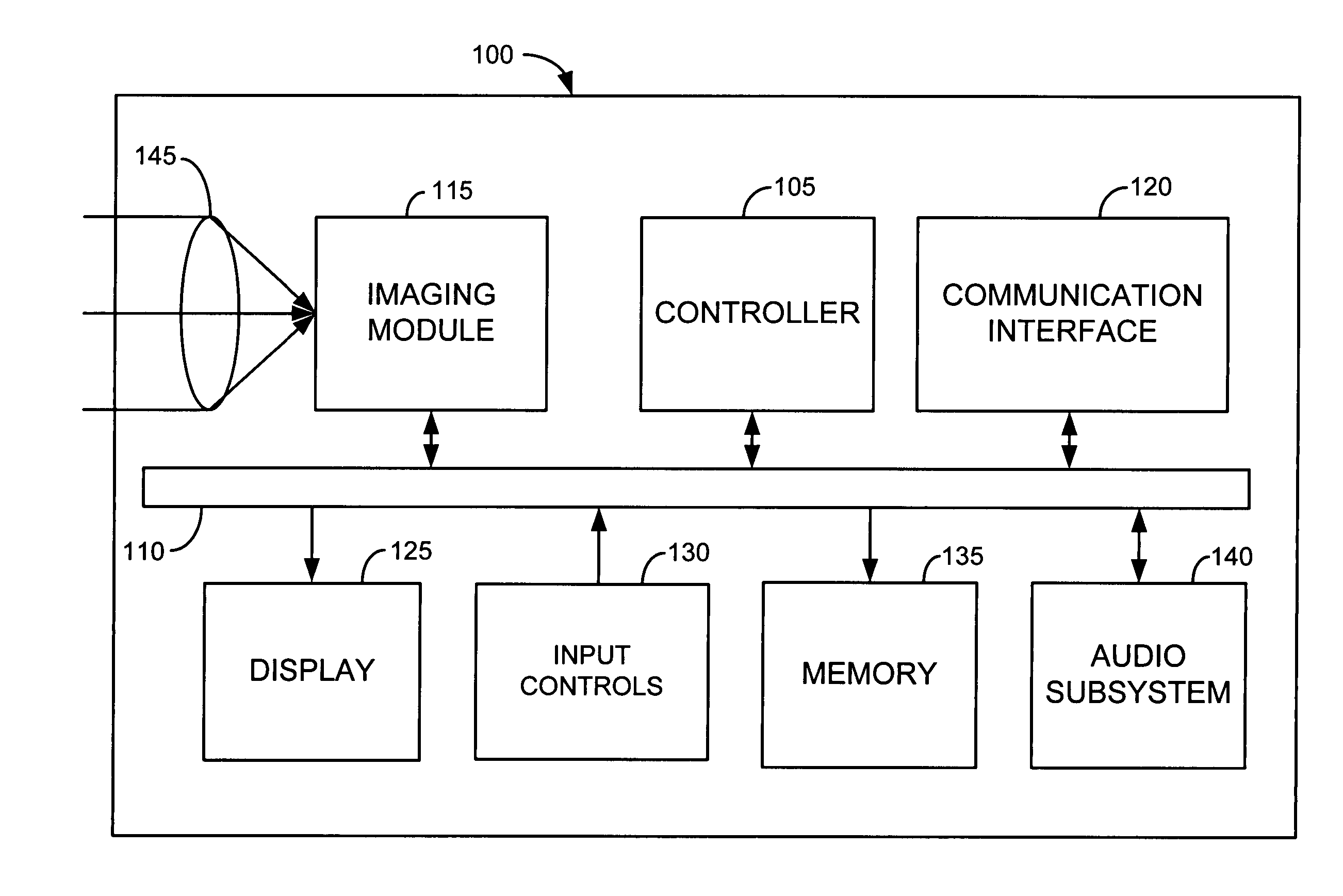
InactiveUS20060268150A1Improve accuracyHigh color reproductionTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionMathematical model
An exposure value is determined based on a face region, with high accuracy and with less effect of a background region or density contrast caused by shadow. For this purpose, a face detection unit detects a face region from a face candidate region in a through image detected by a face candidate detection unit, by fitting to the face candidate region a mathematical model generated by a method of AAM using a plurality of sample images representing human faces. An exposure value determination unit then determines an exposure value for photography, based on the face region.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
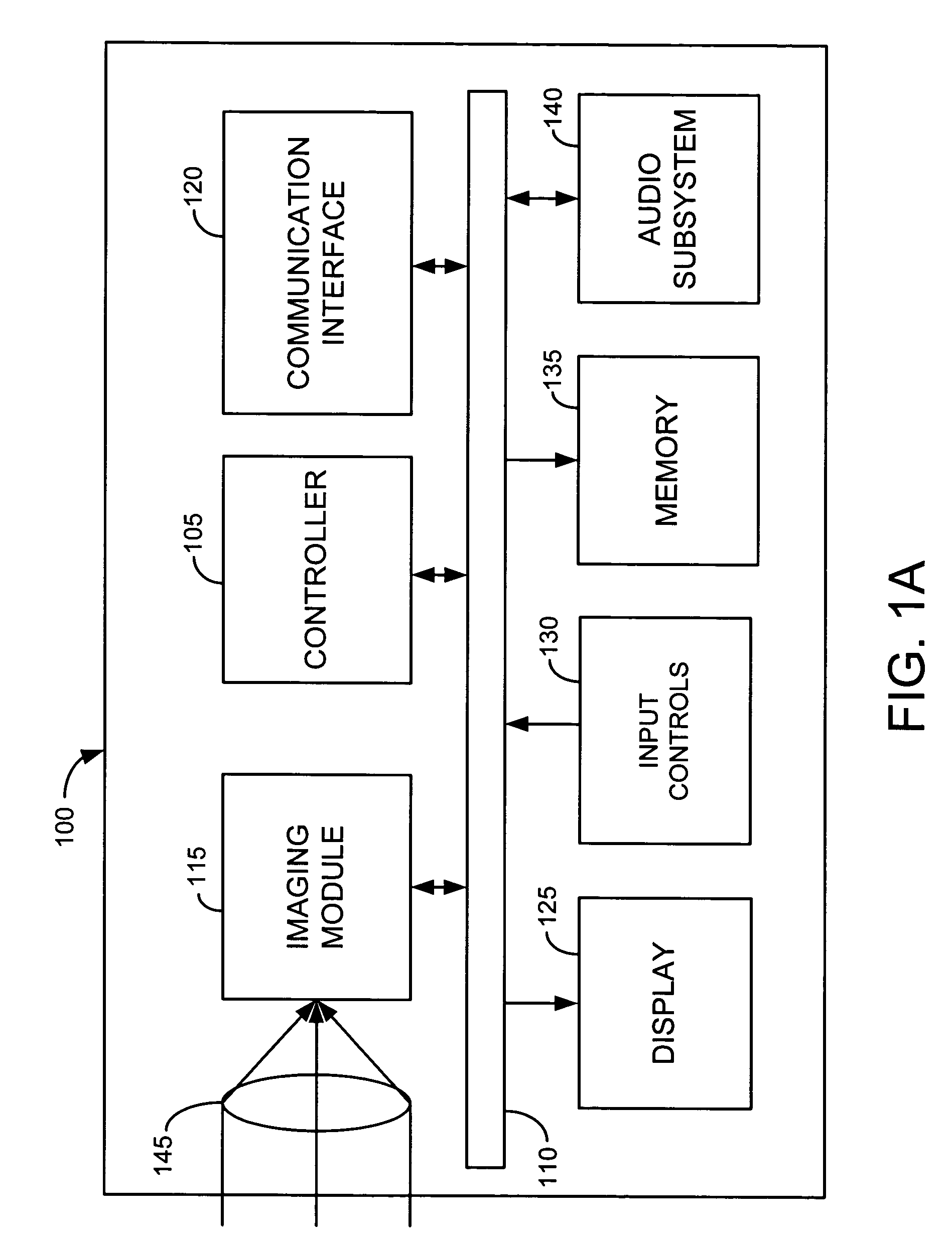
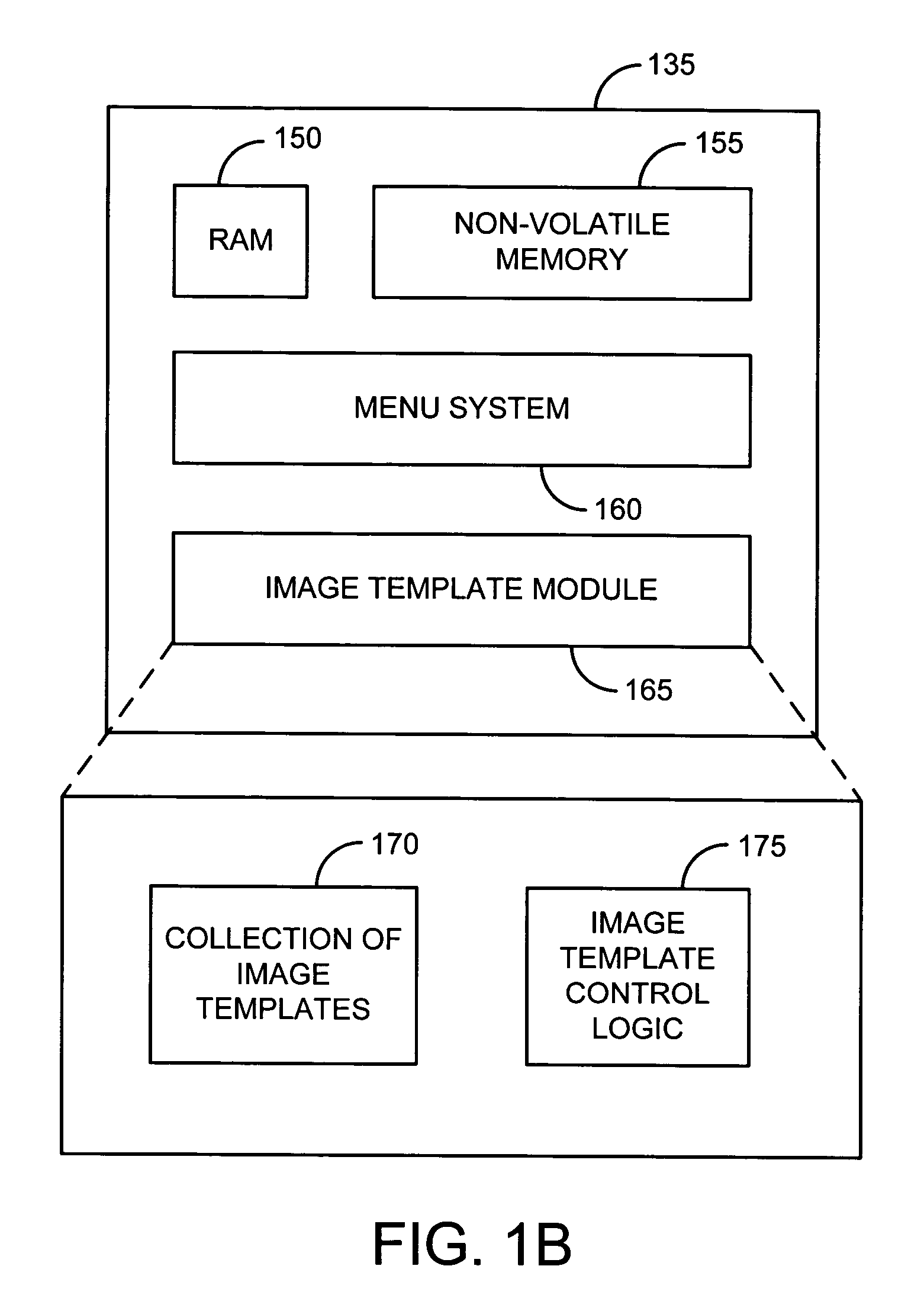
Templates for guiding user in use of digital camera
A collection of image templates in a digital camera guides a user in the taking of pictures. The image templates may have associated sample images that are optionally replaceable, in arbitrary order, by images captured by the user in the digital camera. Textual or audible instructions for capturing user images to replace the sample images may also be provided. A photo album containing images associated with at least one image template in a collection may be generated automatically.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
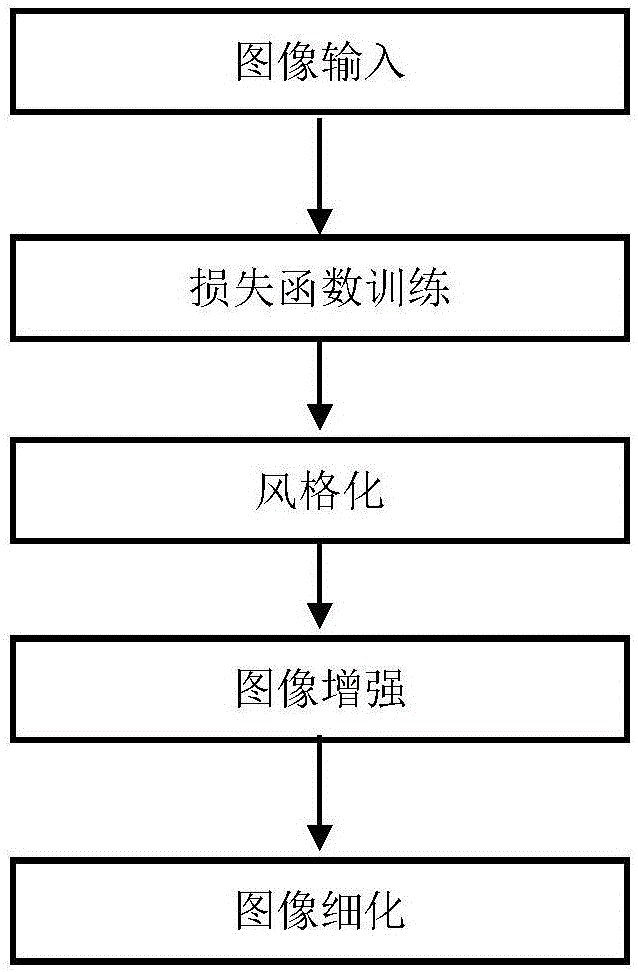
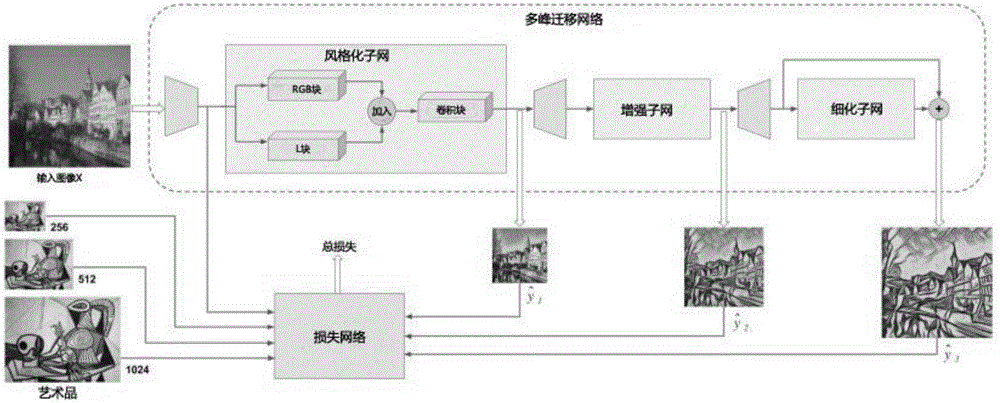
Image style migration method based on deep convolutional neural network
The invention discloses an image text description method based on a visual attention model. The main content comprises the followings: image inputting, loss function training, stylizing, image enhancing and image thinning; and the processes are as follows: an input image is firstly adjusted as a content image (256*256) with a dual-linear down-sampling layer, and then stylized through a style subnet; and then a stylized result as the first output image is up-sampled as an image in the size of 512*512, and then the up-sampled image is enhanced through an enhancement subnet to obtain the second output image; the second output image is adjusted as the image in the size of 1024*1024, and finally, a thinning subnet deletes locally pixelated artifact and further thins the result to obtain a high-resolution result. By use of the image style migration method disclosed by the invention, the brushwork of the artwork can be simulated more closely; multiple models are combined into a network so as to process the image with bigger and bigger size shot by a modern digital camera; and the method can be used for training the combined model to realize the migration of multiple artistic styles.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
Automated Sampling And Analysis Using A Personal Sampler Device
InactiveUS20090093970A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImaging processingMedicine
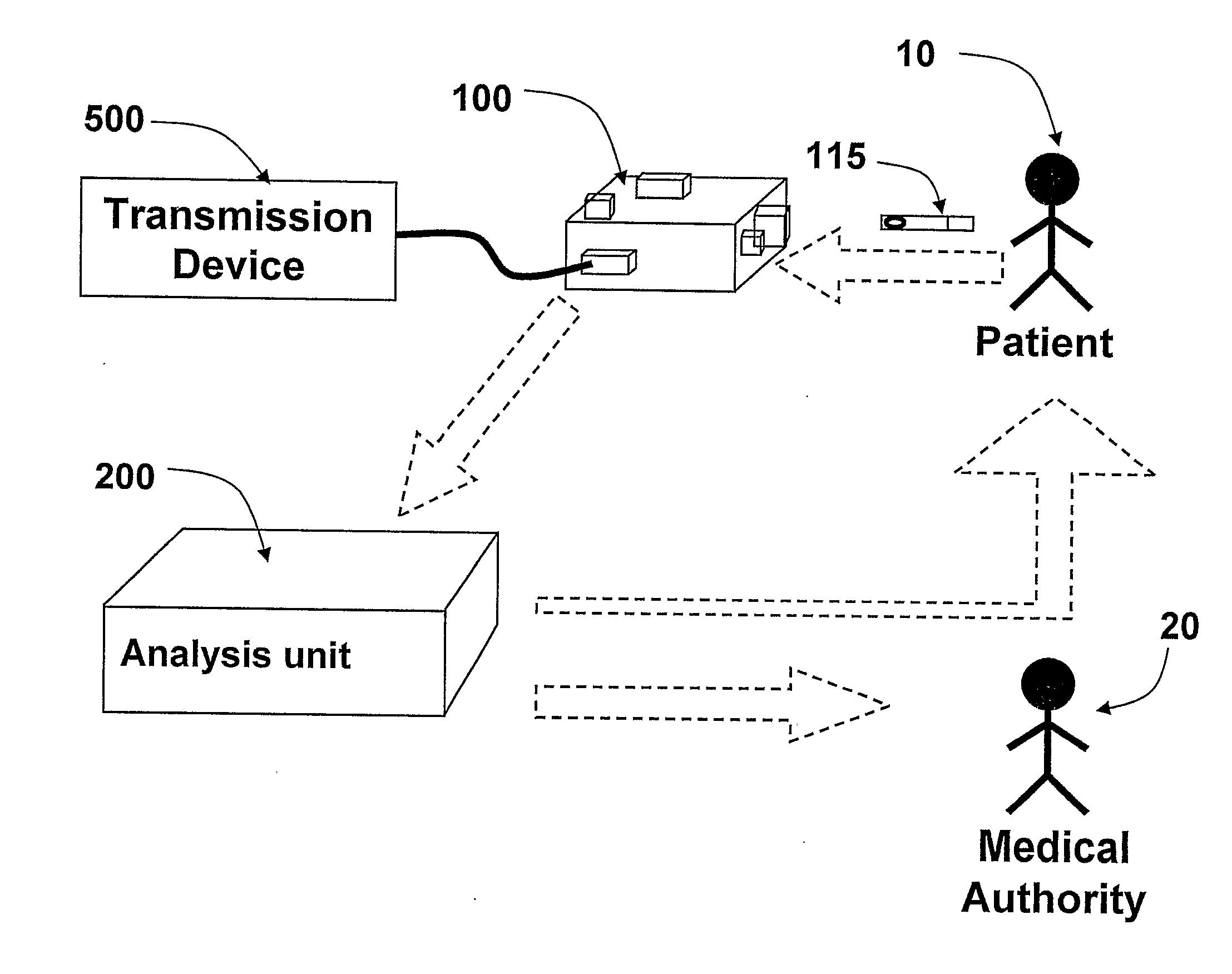
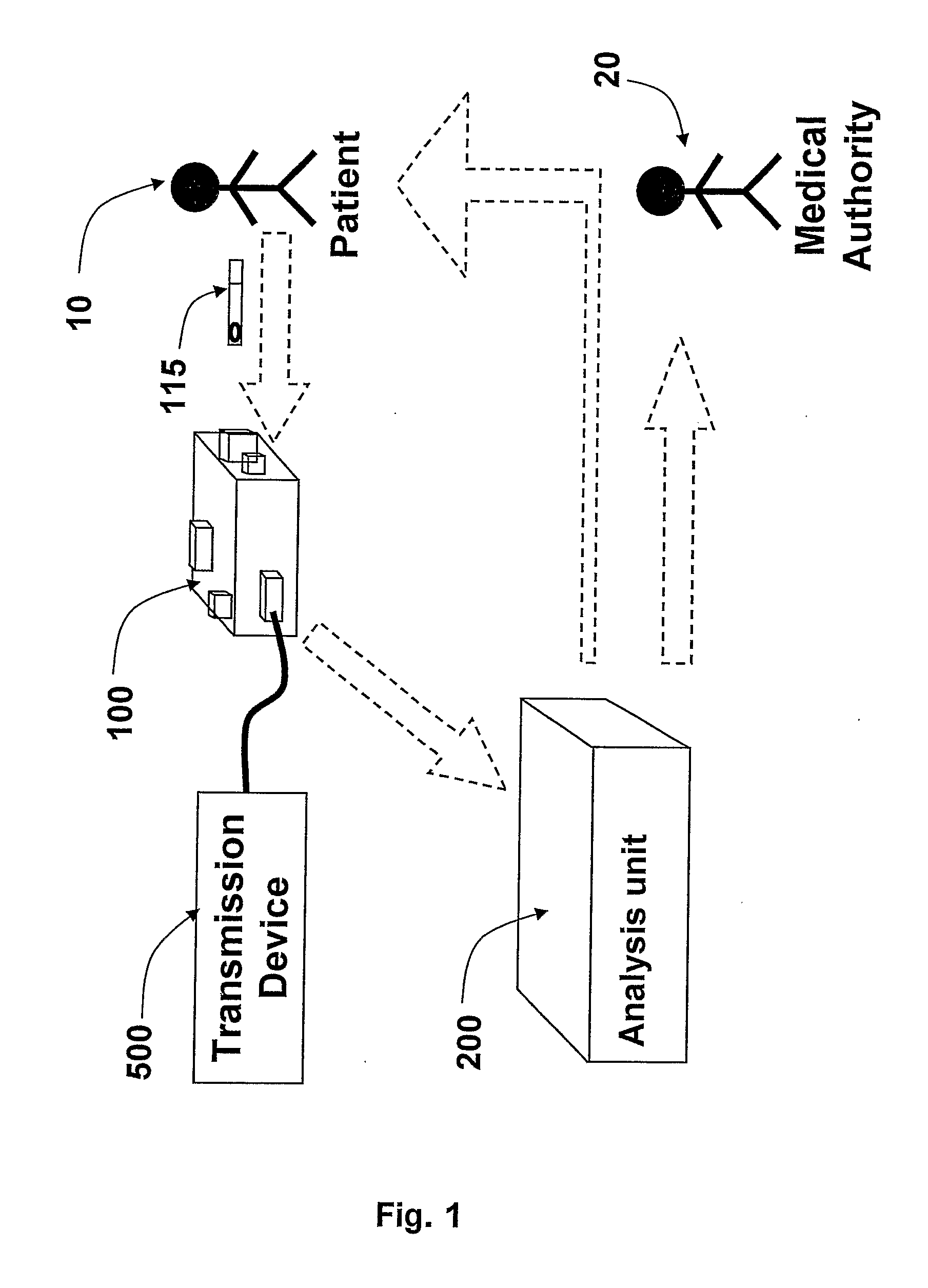
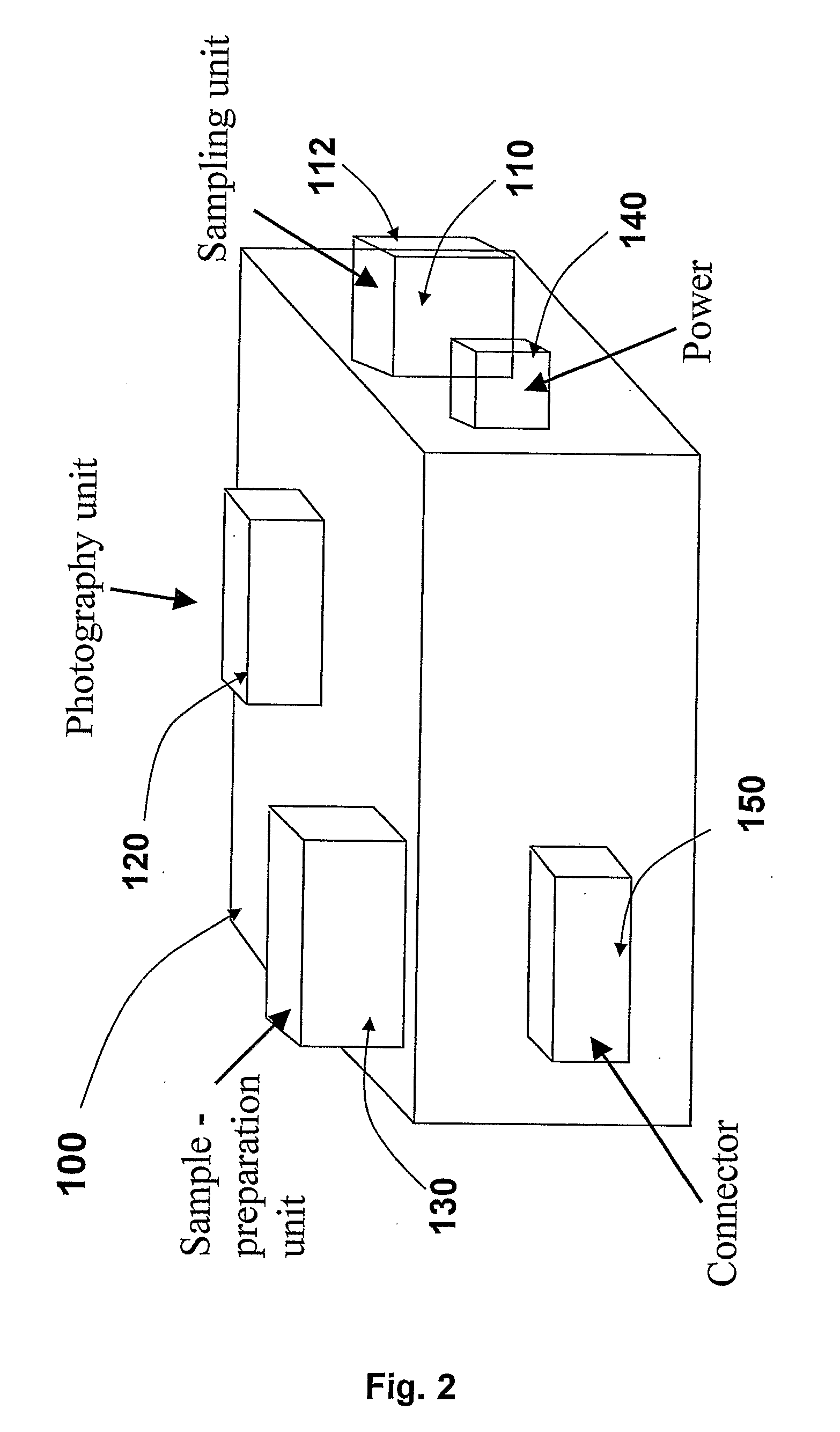
The present invention is a system and a method for blood or urine sampling and sample-analysis, through a sampler that is a self blood-testing device or a urine-testing device. The system comprises a sampler, a transmission unit and an analysis unit. A patient may place a sampled blood drops on a sample strip and insert the strip into the sampler. The sampler may automatically prepare the sample and photograph it using a sample-preparation unit and a photography unit respectively. After the sample has been photographed, the resulting sample image may be transmitted to the analysis unit that may analyze the image through an image-processing algorithm. The analysis results may be automatically transmitted to the patient and to a medical authority, such as the patient's physician, a nurse, a clinic and the like, for further analysis, decision-making and treatment.
Owner:LEWY HADAS +2
Makeup mirror apparatus and makeup method using the same
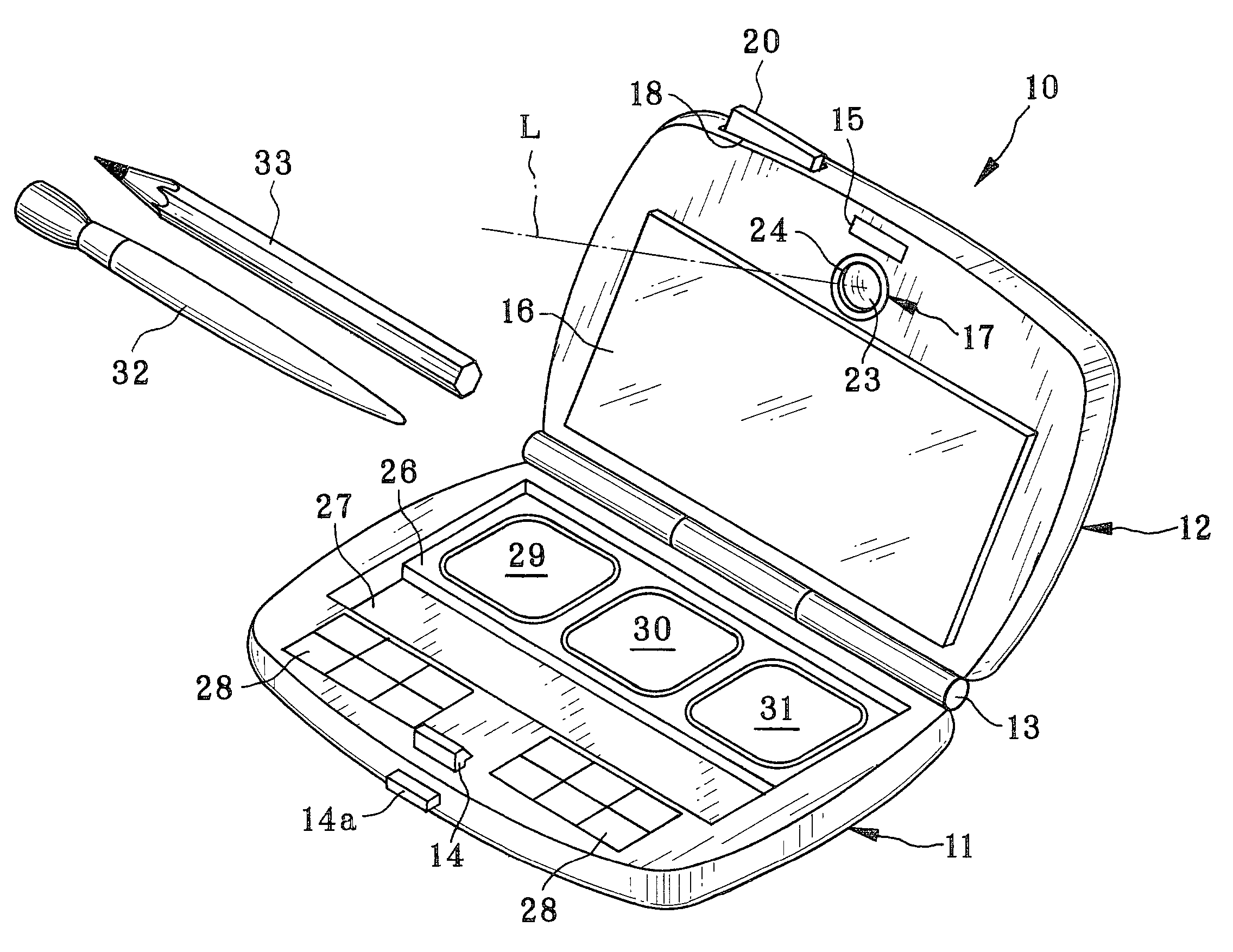
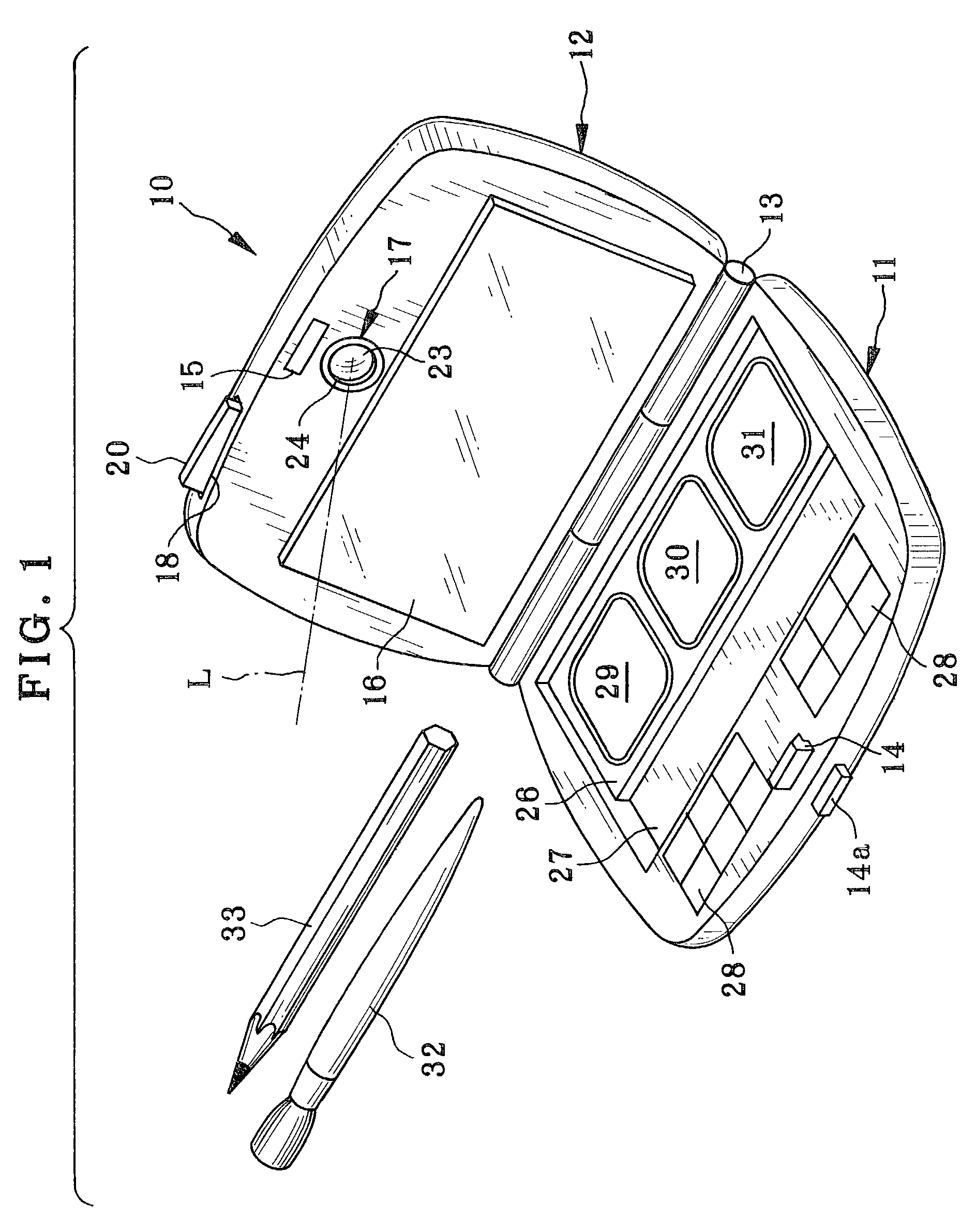
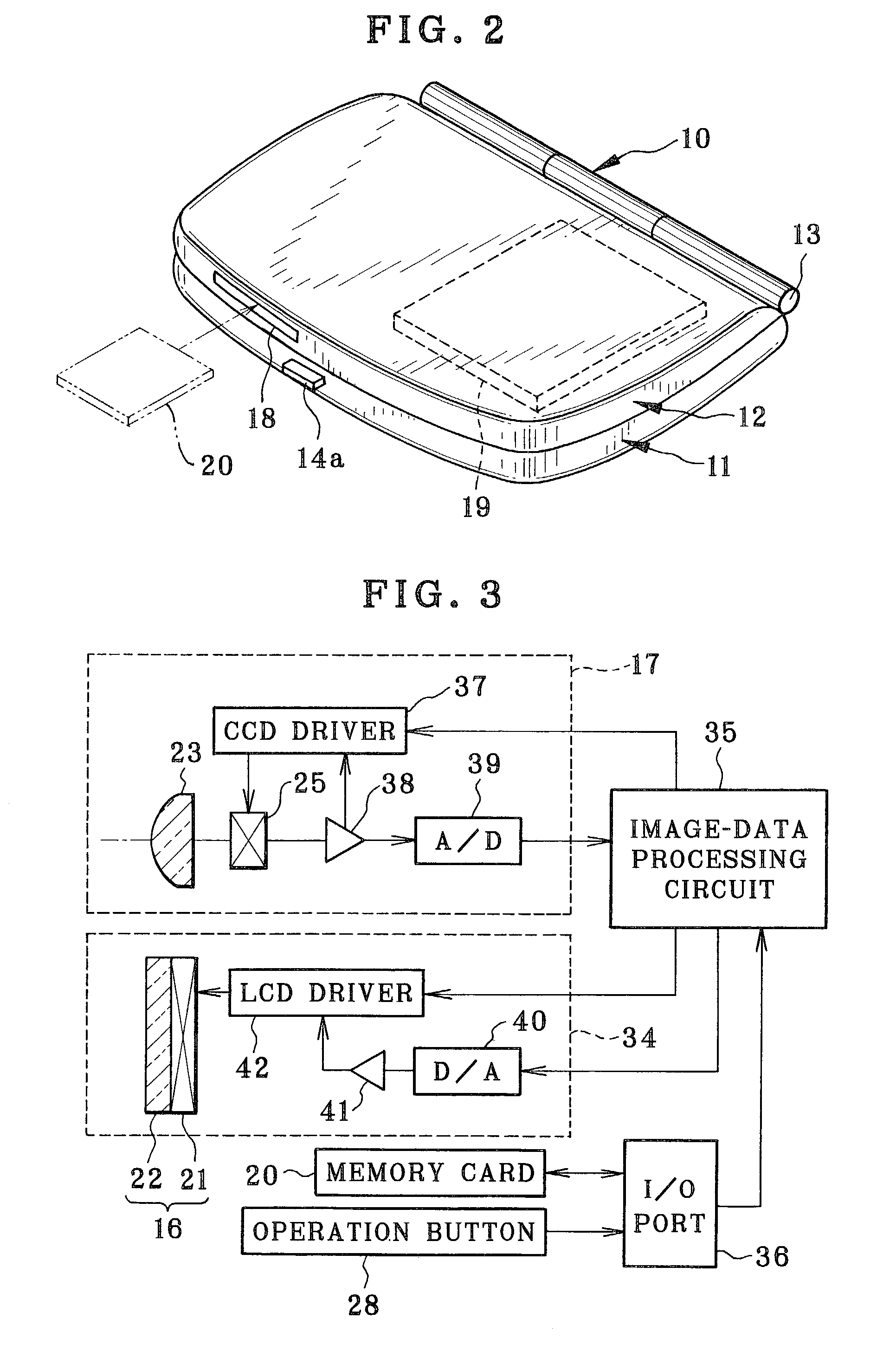
InactiveUS7054668B2Easy to doEasy to operateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSample imageMemory cards
A makeup mirror apparatus comprises a case body, a case lid, and a rotary shaft rotatably connecting the case body and the case lid. The case body is provided with a cosmetic-material containing area, a brush containing area, and operation buttons. The case lid is provided with a mirror unit, a camera portion, and a memory slot. The mirror unit is constituted such that an LCD panel is stacked on a half mirror. By manipulating the operation button, a sample image is read from a memory card loaded in the memory slot. The read sample image is displayed on the LCD panel and is overlapped with a user's face reflected in the half mirror. Makeup is performed by tracing the sample image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Method, system and program for searching area considered to be face image
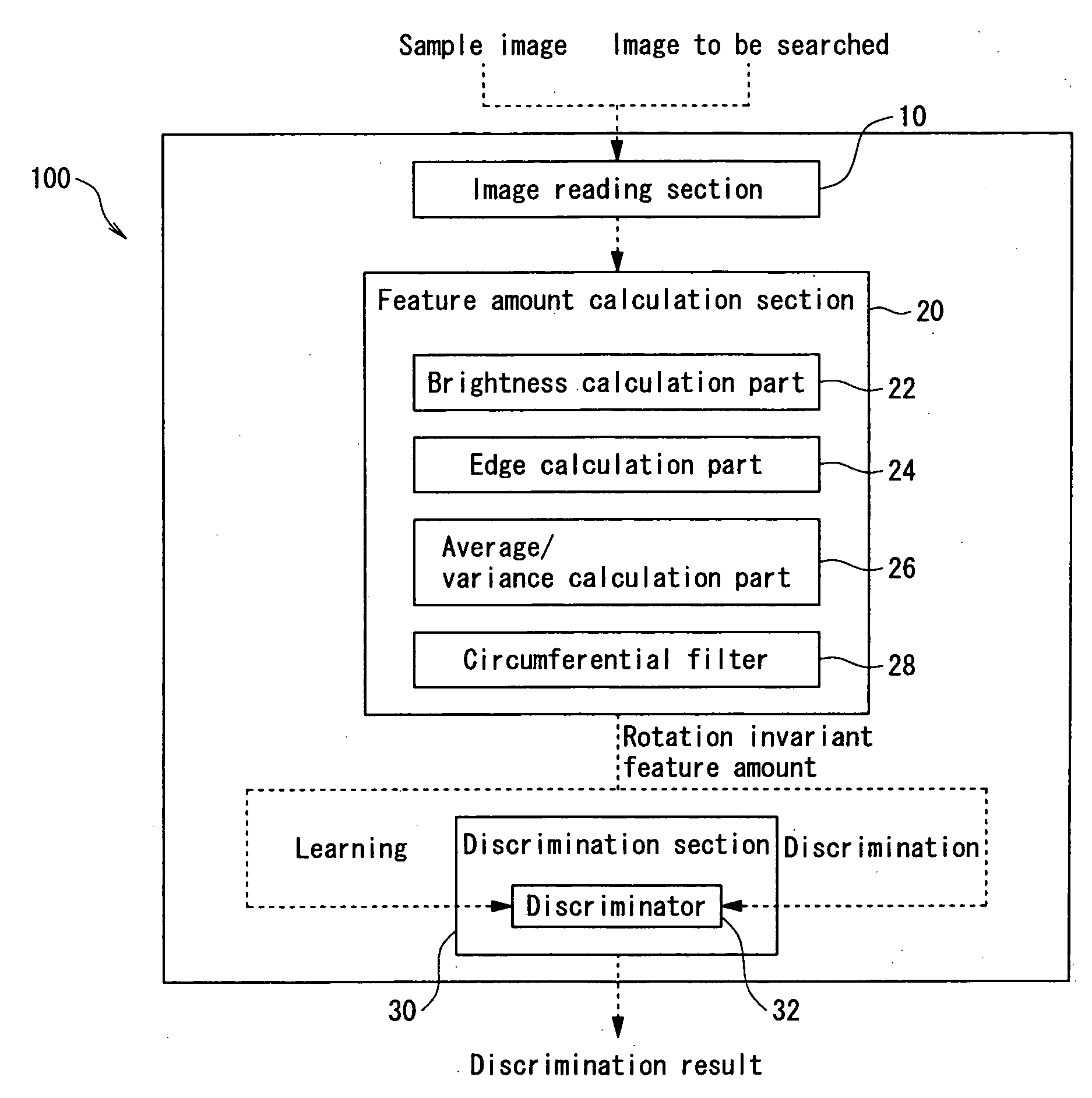
InactiveUS20050141766A1Produced economically and easilyFunction increaseImage enhancementImage analysisSample imageImaging Feature
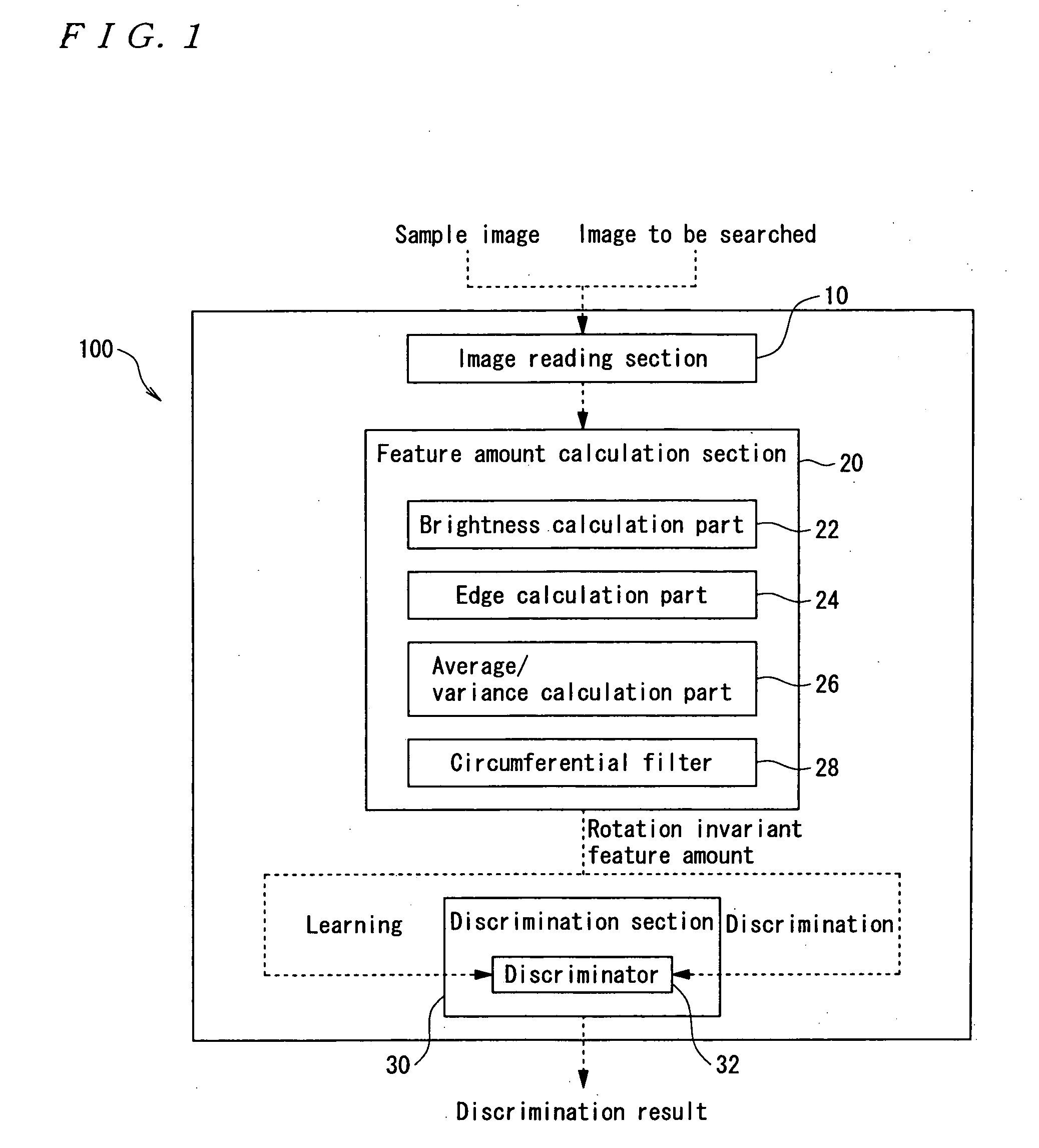
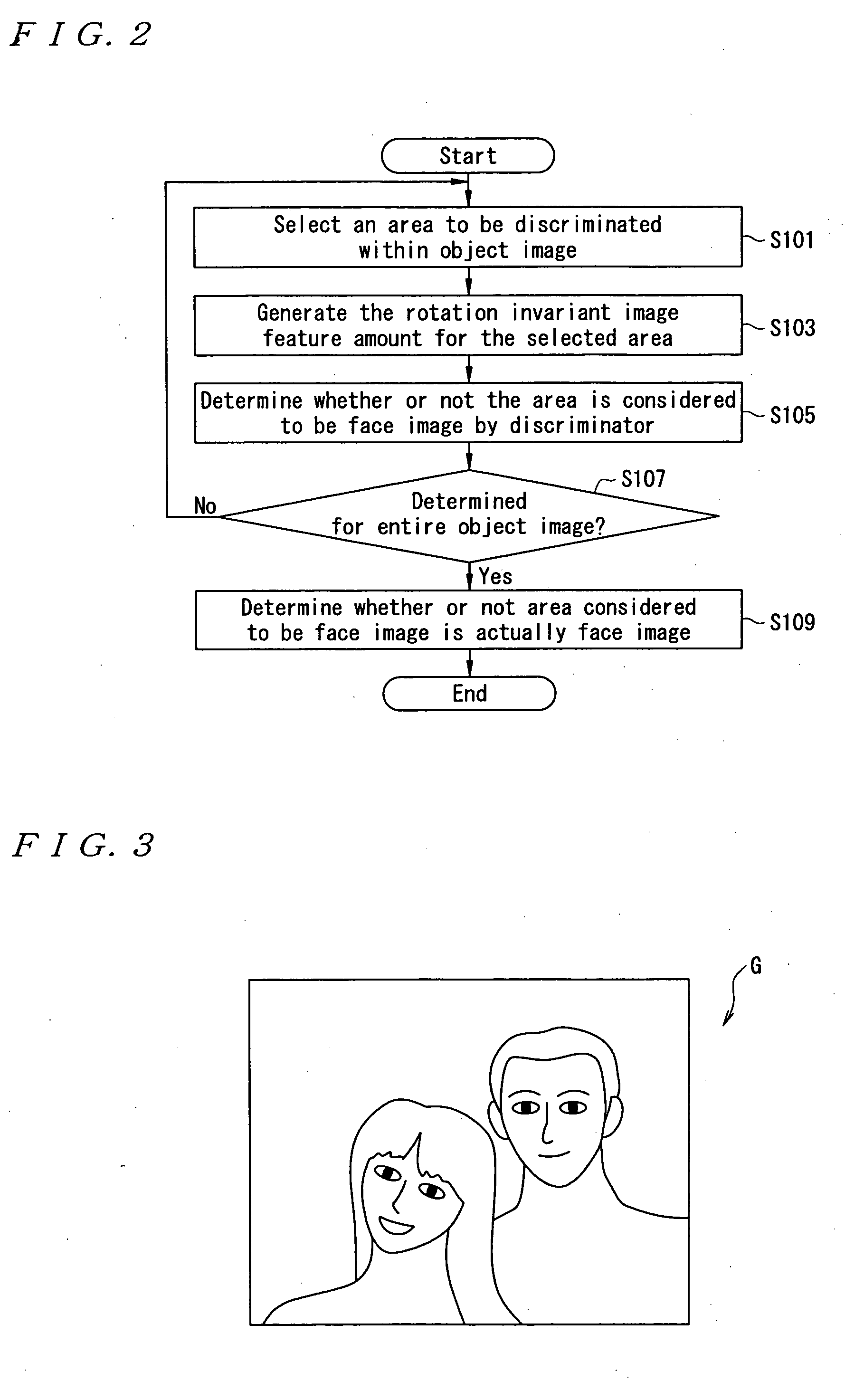
A sample image is filtered through a circumferential filter 28, an image feature amount is learned in a discrimination section 30, an image G to be searched is filtered through the circumferential filter 28 to detect a rotation invariant image feature amount for each filtered area, and each detected image feature amount is inputted into the discrimination section 30. Thereby, it is discriminated whether or not a filtering area is considered to be face image at high speed. And the dimensional number of image feature amounts is greatly reduced, so that not only the discrimination work but also the learning time of the sample image are greatly reduced.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Multi-angle face alignment method based on deep learning and system thereof and photographing terminal
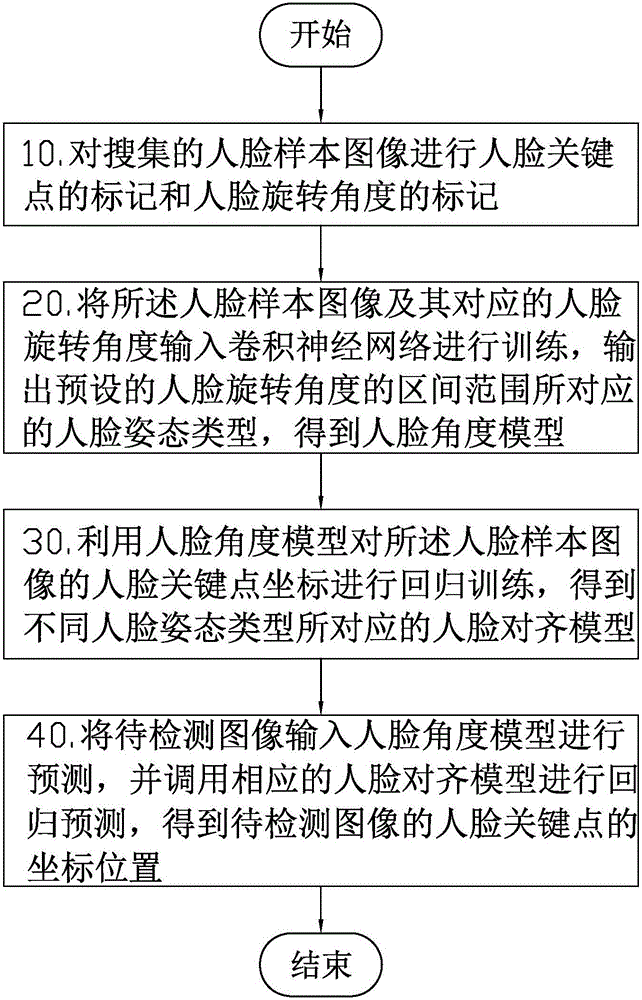
InactiveCN105760836ASmall footprintHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesPhysical spaceSample image
The invention discloses a multi-angle face alignment method based on deep learning and a system thereof and a photographing terminal. Marking of face key points and marking of face rotating angles are performed on a face sample image and the face sample image is inputted to a convolutional neural network to be trained, and different face pose types of the corresponding interval range of the face rotating angles are outputted so that face angle models of different face pose types are obtained; then regression training is performed on the face key point coordinates of the face sample image by utilizing the face angle models so that face alignment models corresponding to different face pose types are obtained; and finally an image to be detected is inputted to the face angle models to perform face angle detection, and the face alignment model of the corresponding angle is called to perform regression prediction. Precision is high, robustness is high and space occupation of the models obtained through training is low, and the method is particularly suitable for the face alignment application of which the situations of the photographed person are complex, the requirement for precision is high and occupation of the algorithm in the physical space is required to be low.
Owner:XIAMEN MEITUZHIJIA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com