Patents
Literature
784results about "Error correction/detection using block codes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
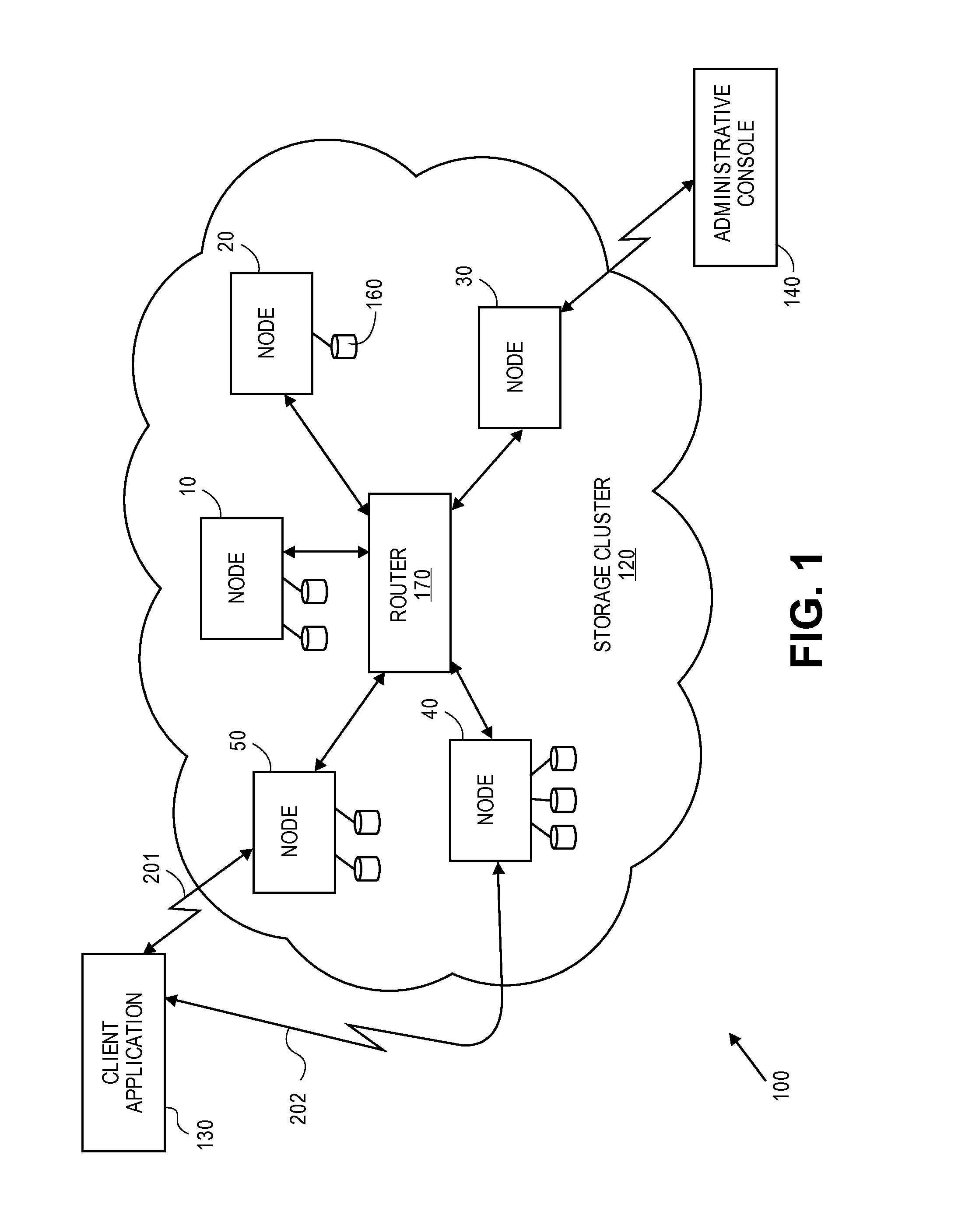
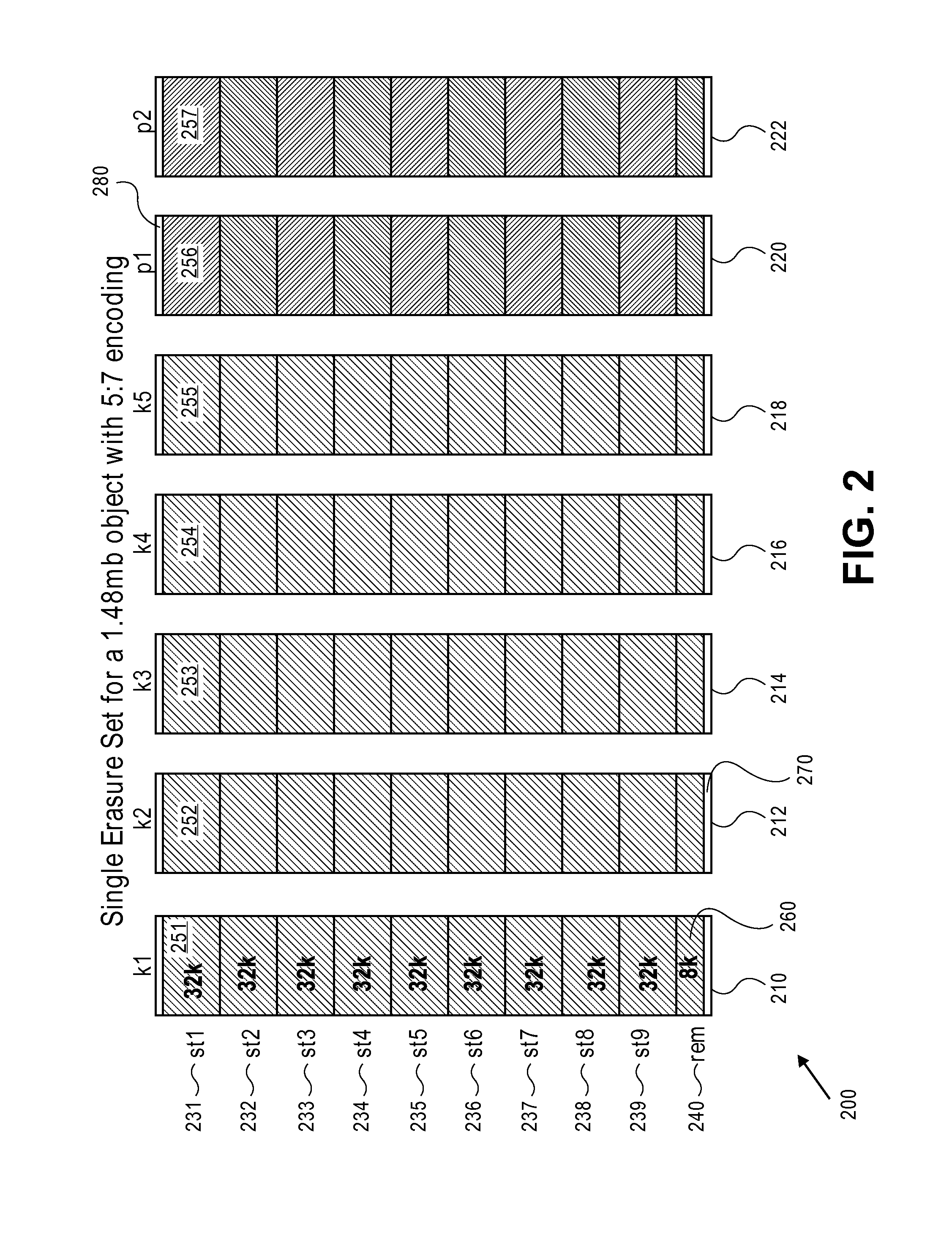
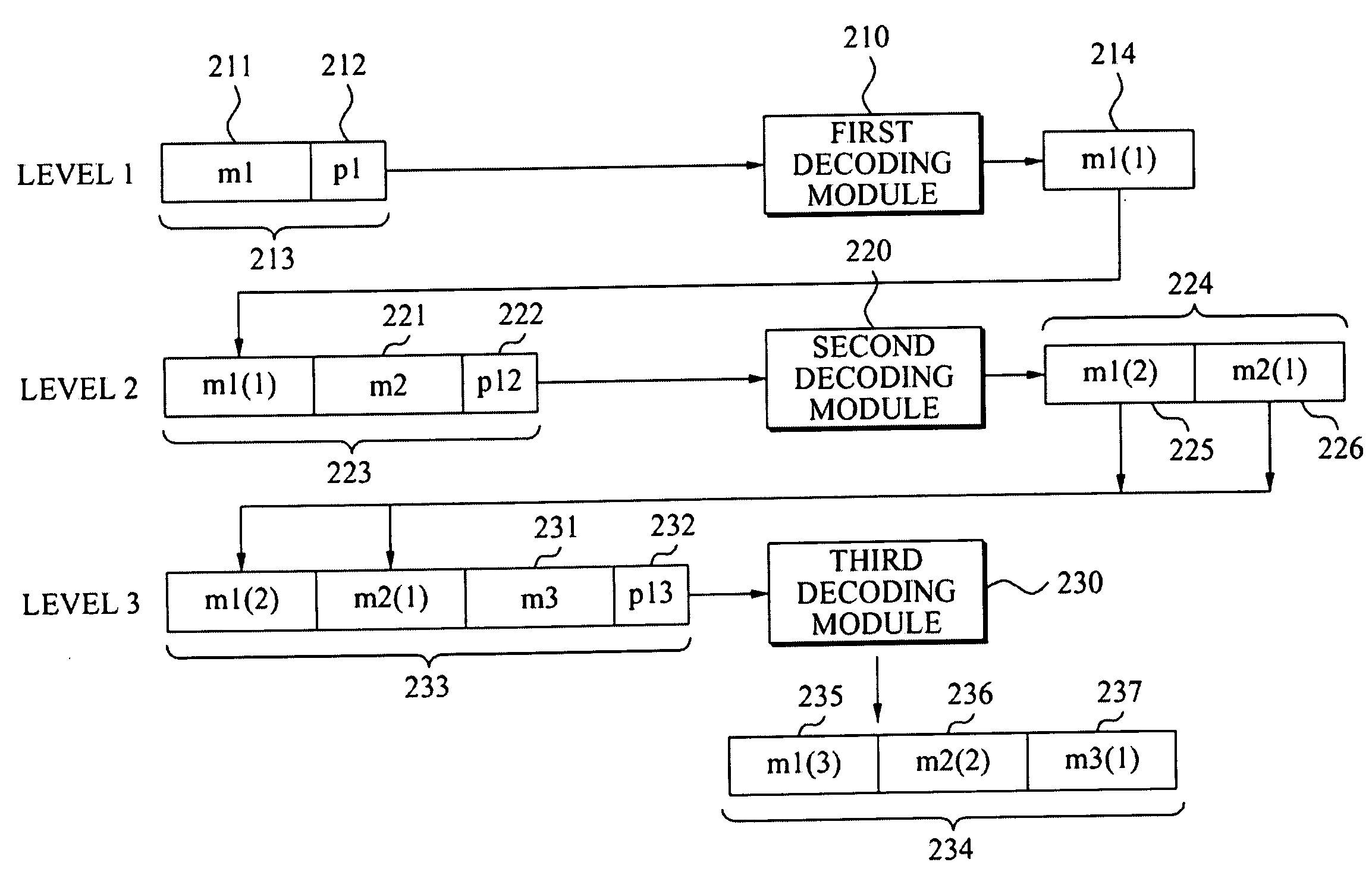
Erasure coding and replication in storage clusters
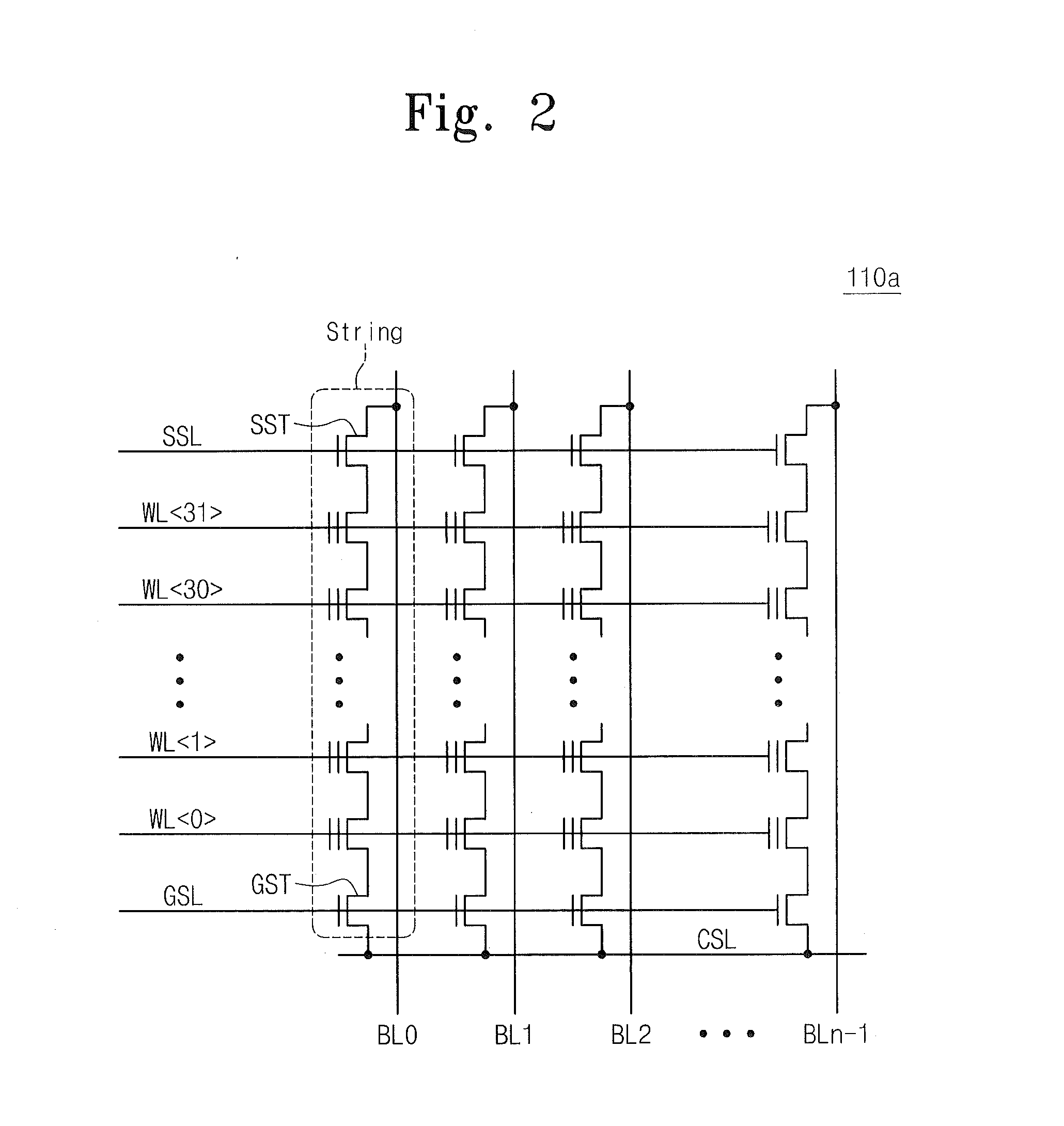
ActiveUS20130339818A1Error correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionUnique identifierOperating system
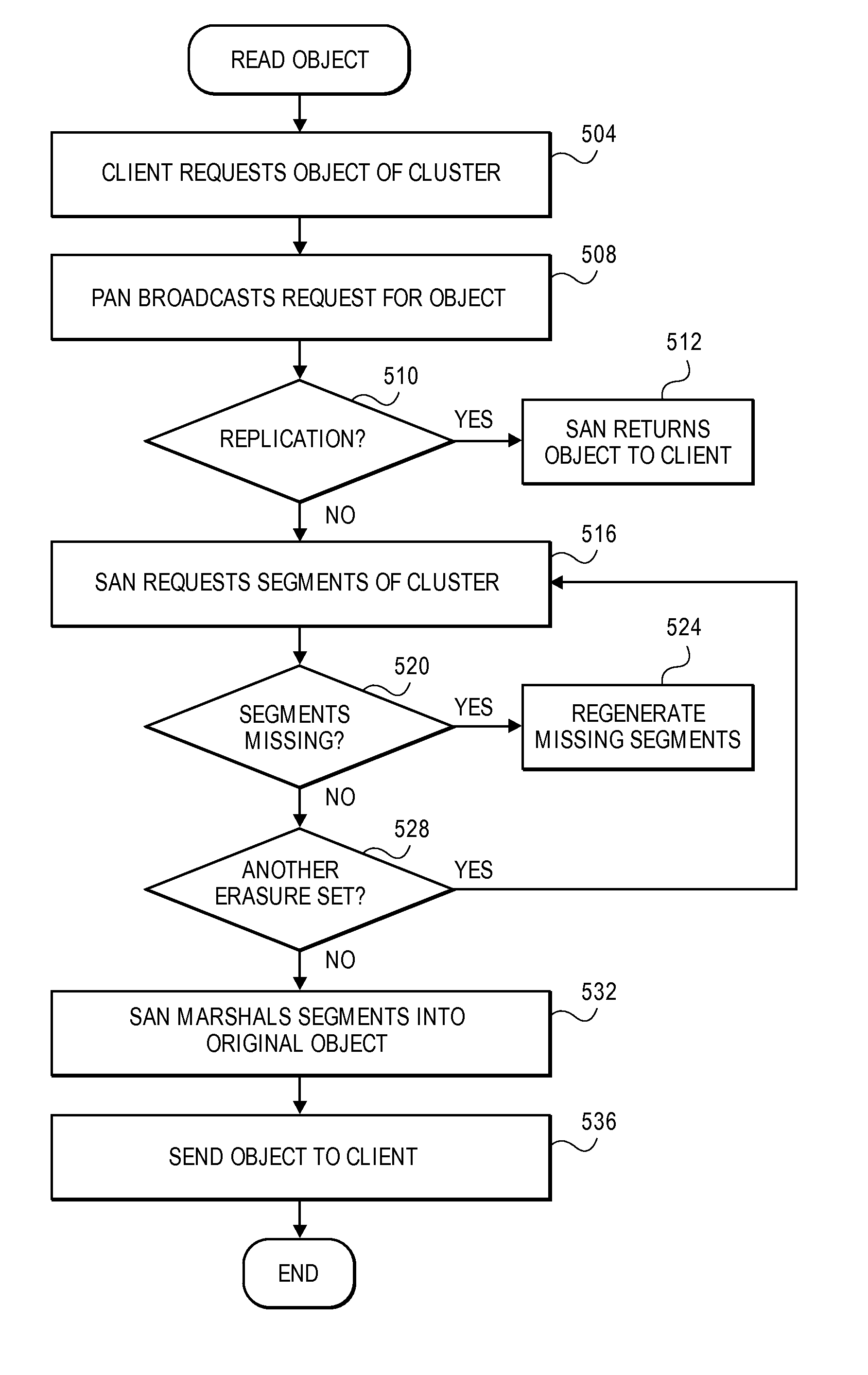
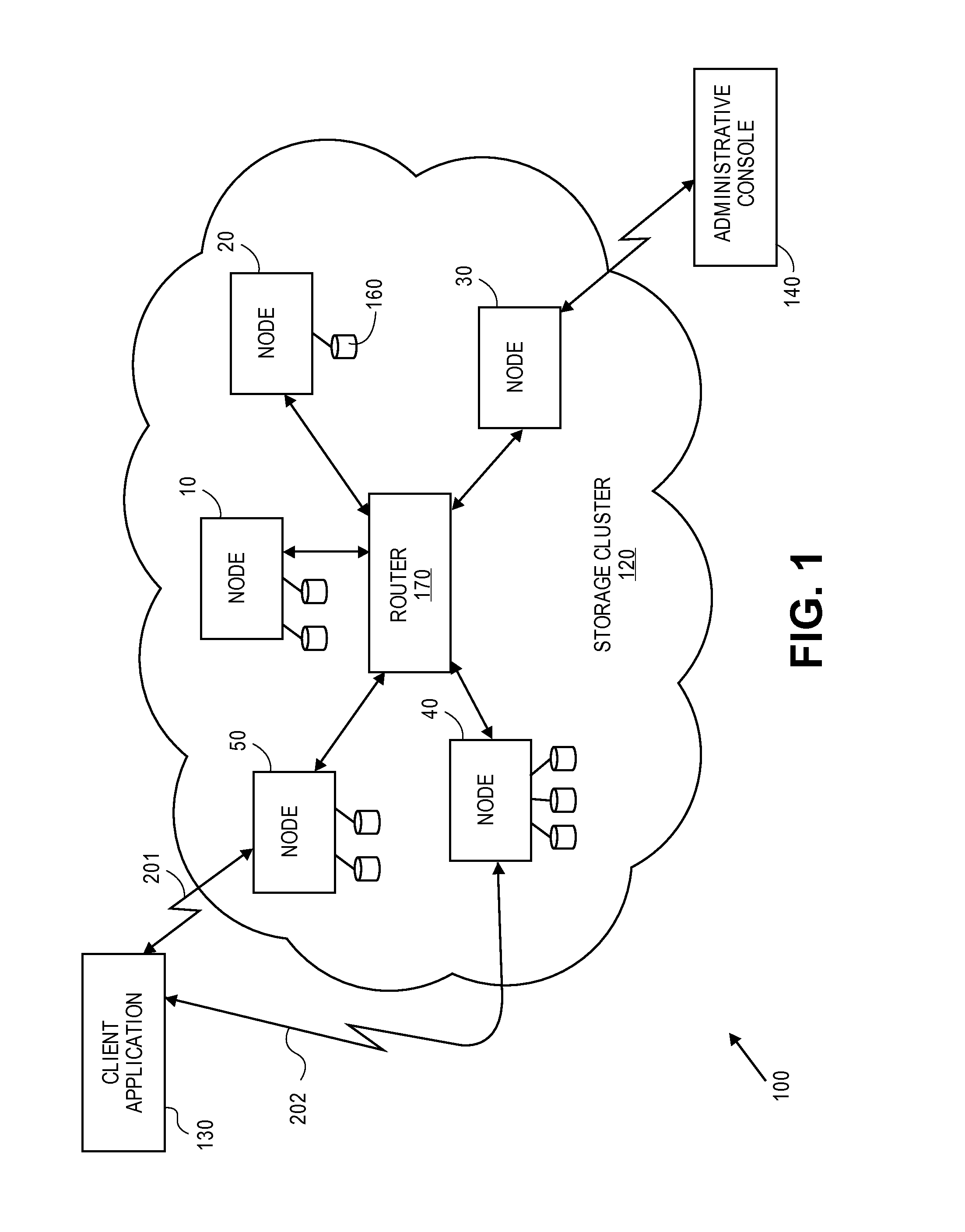
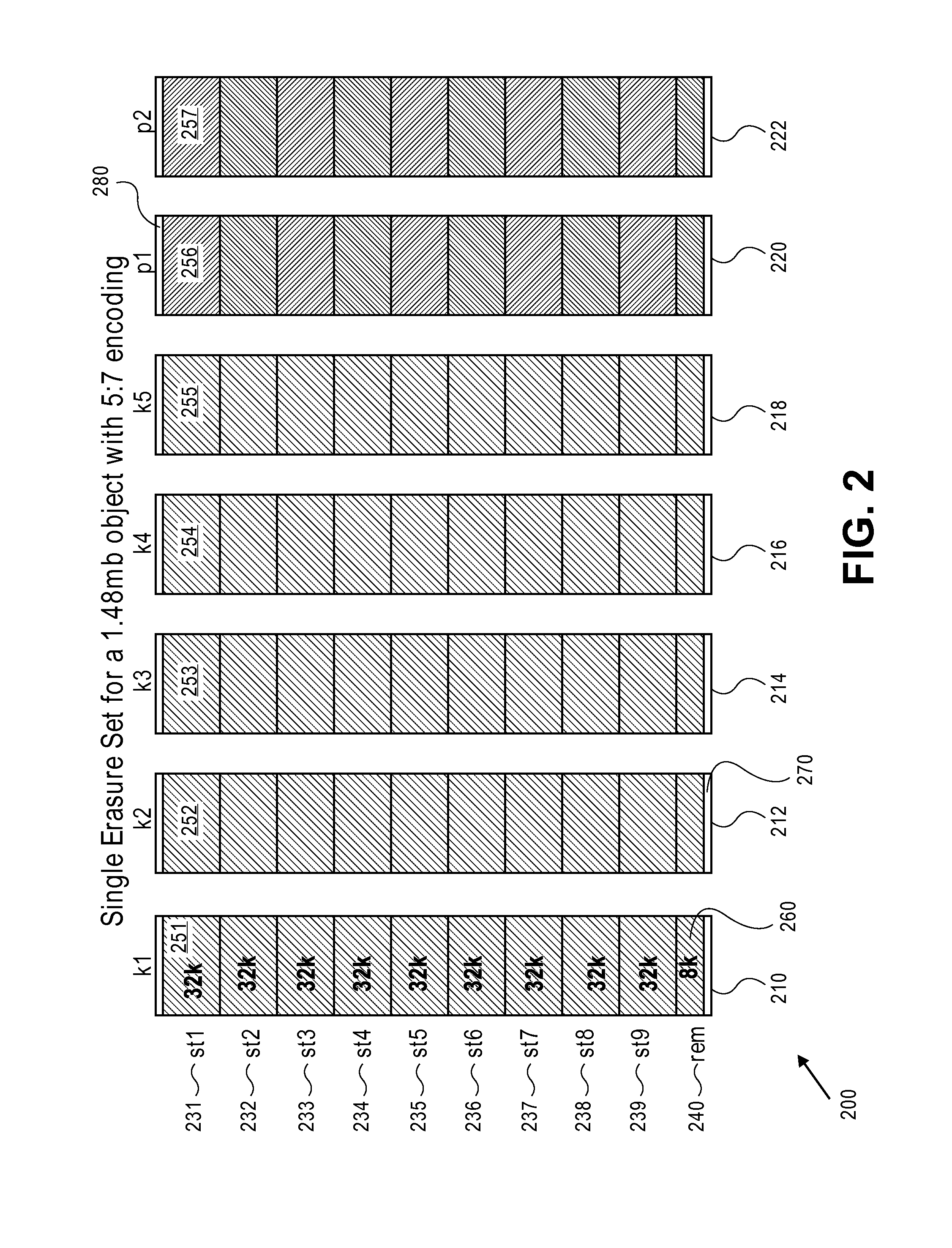
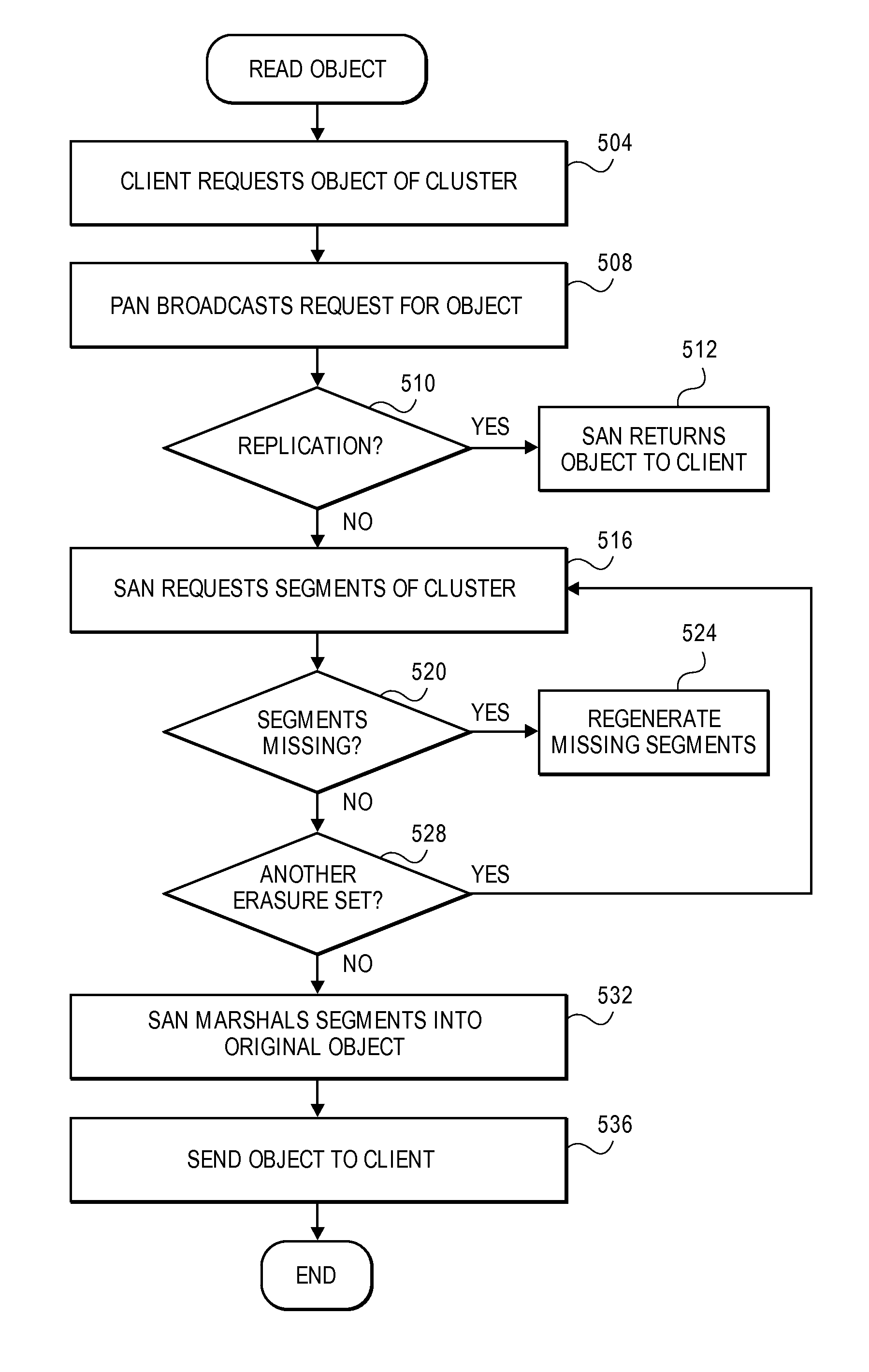
A cluster receives a request to store an object using replication or erasure coding. The cluster writes the object using erasure coding. A manifest is written that includes an indication of erasure coding and a unique identifier for each segment. The cluster returns a unique identifier of the manifest. The cluster receives a request from a client that includes a unique identifier. The cluster determines whether the object has been stored using replication or erasure coding. If using erasure coding, the method reads a manifest. The method identifies segments within the cluster using unique segment identifiers of the manifest. Using these unique segment identifiers, the method reconstructs the object. A persistent storage area of another disk is scanned to find a unique identifier of a failed disk. If using erasure coding, a missing segment previously stored on the disk is identified. The method locates other segments. Missing segments are regenerated.
Owner:DATACORE SOFTWARE
Erasure coding and replication in storage clusters
ActiveUS8799746B2Error correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionUnique identifierOperating system
Owner:DATACORE SOFTWARE
Automatic defect management in memory devices
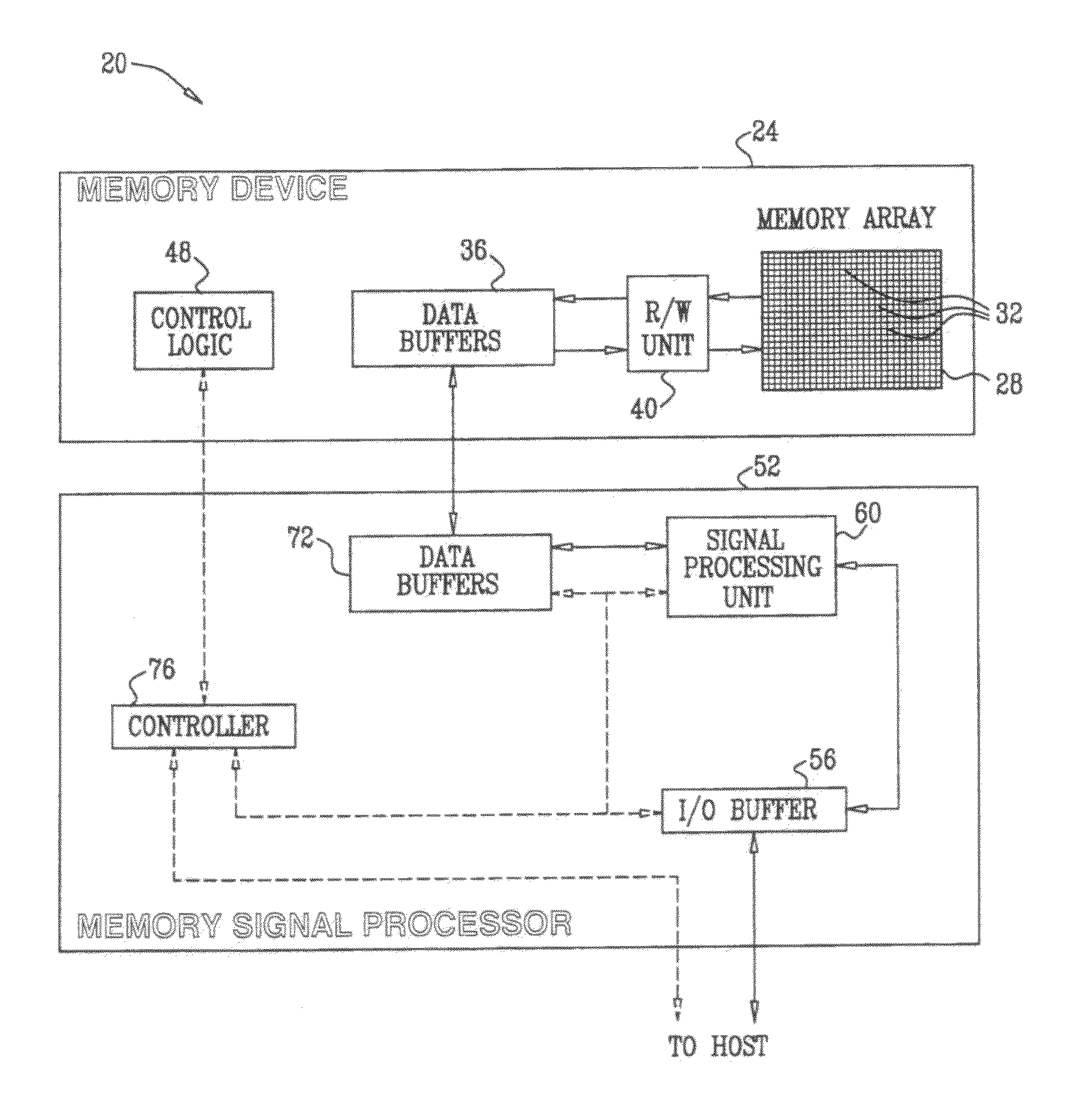
ActiveUS20100115376A1Code conversionError correction/detection using block codesAlternative methodsComputer science
A method for storing data in a memory (28) that includes analog memory cells (32) includes identifying one or more defective memory cells in a group of the analog memory cells. An Error Correction Code (ECC) is selected responsively to a characteristic of the identified defective memory cells. The data is encoded using the selected ECC and the encoded data is stored in the group of the analog memory cells. In an alternative method, an identification of one or more defective memory cells among the analog memory cells is generated. Analog values are read from the analog memory cells in which the encoded data were stored, including at least one of the defective memory cells. The analog values are processed using an ECC decoding process responsively to the identification of the at least one of the defective memory cells, so as to reconstruct the data.
Owner:APPLE INC
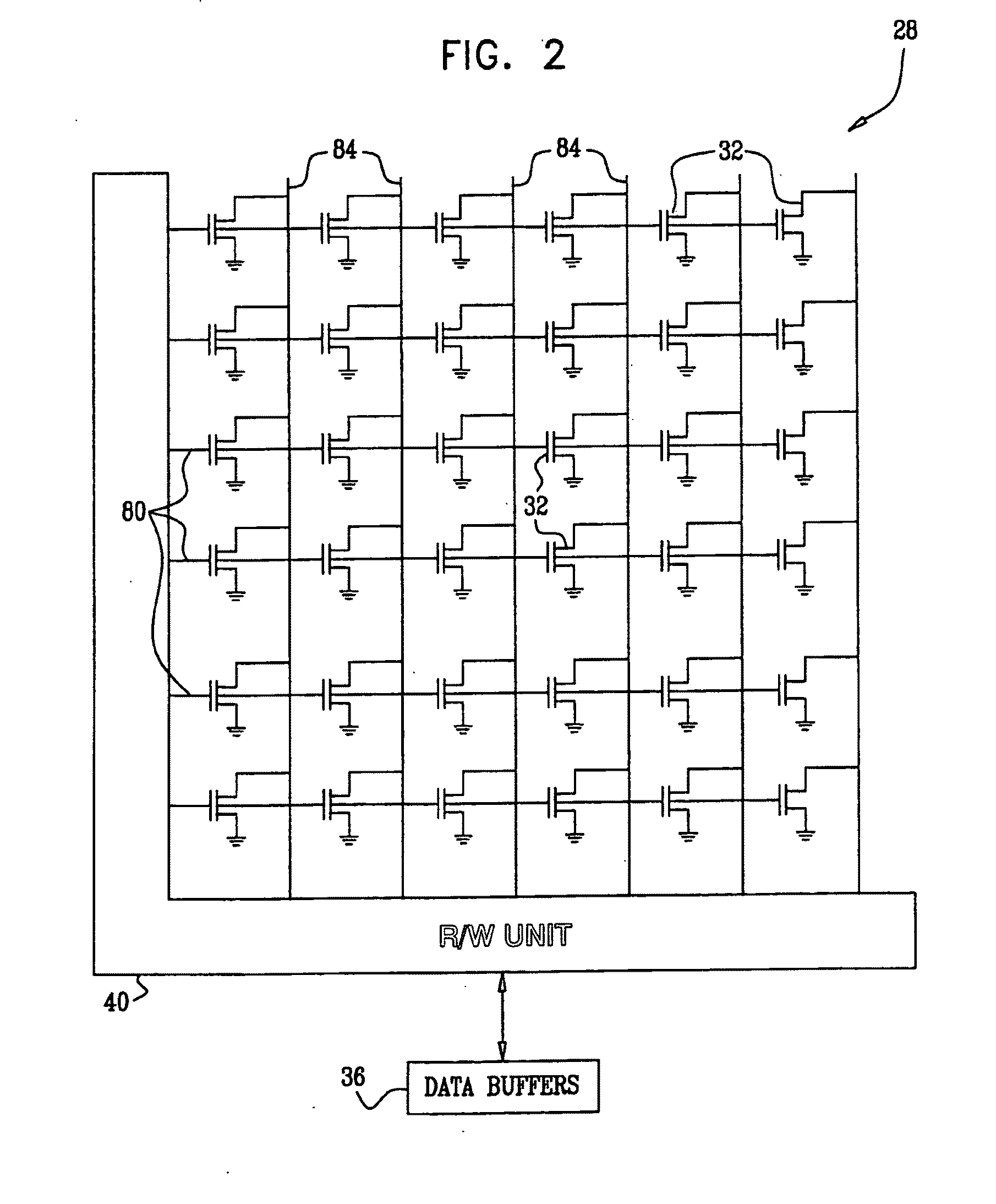
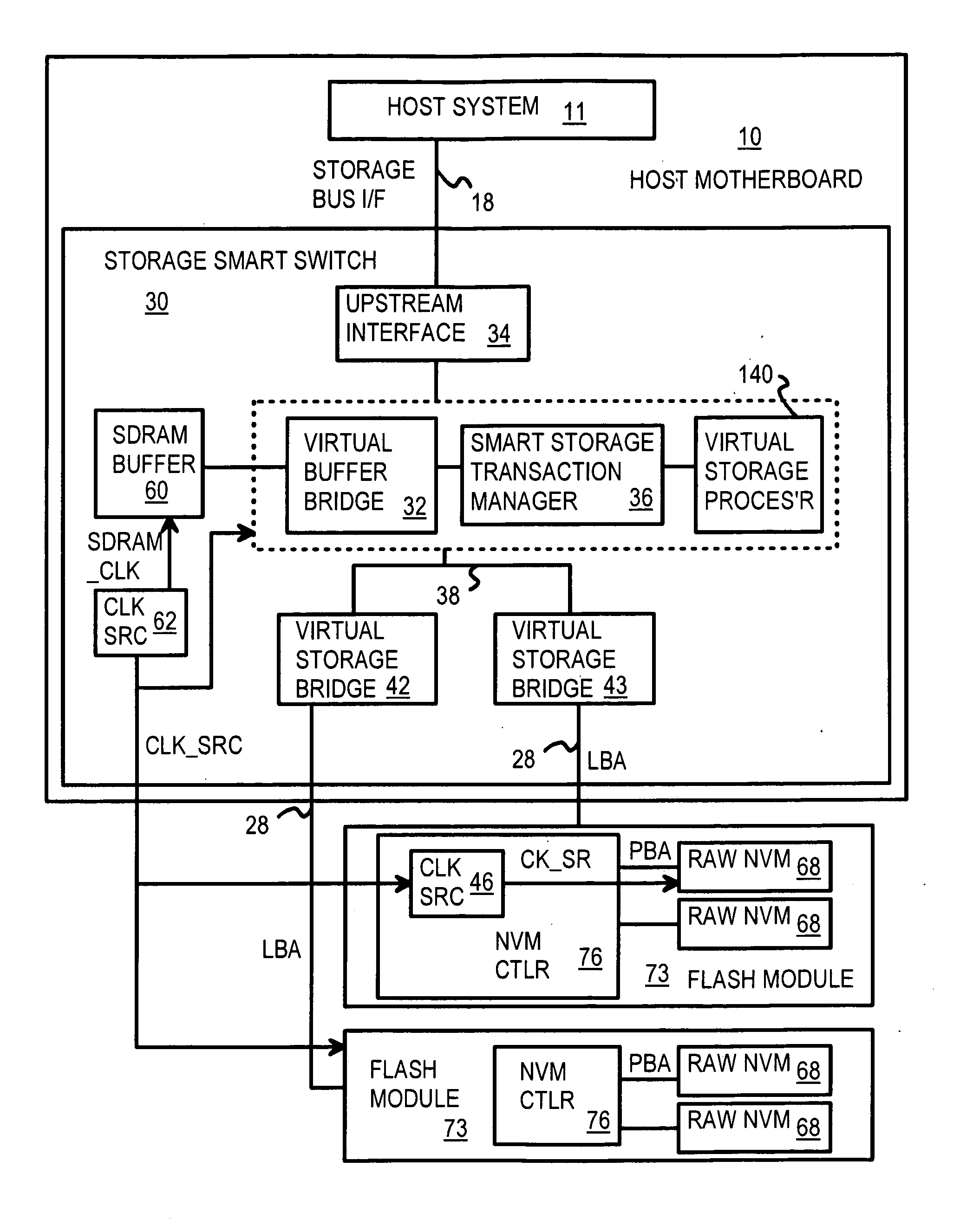
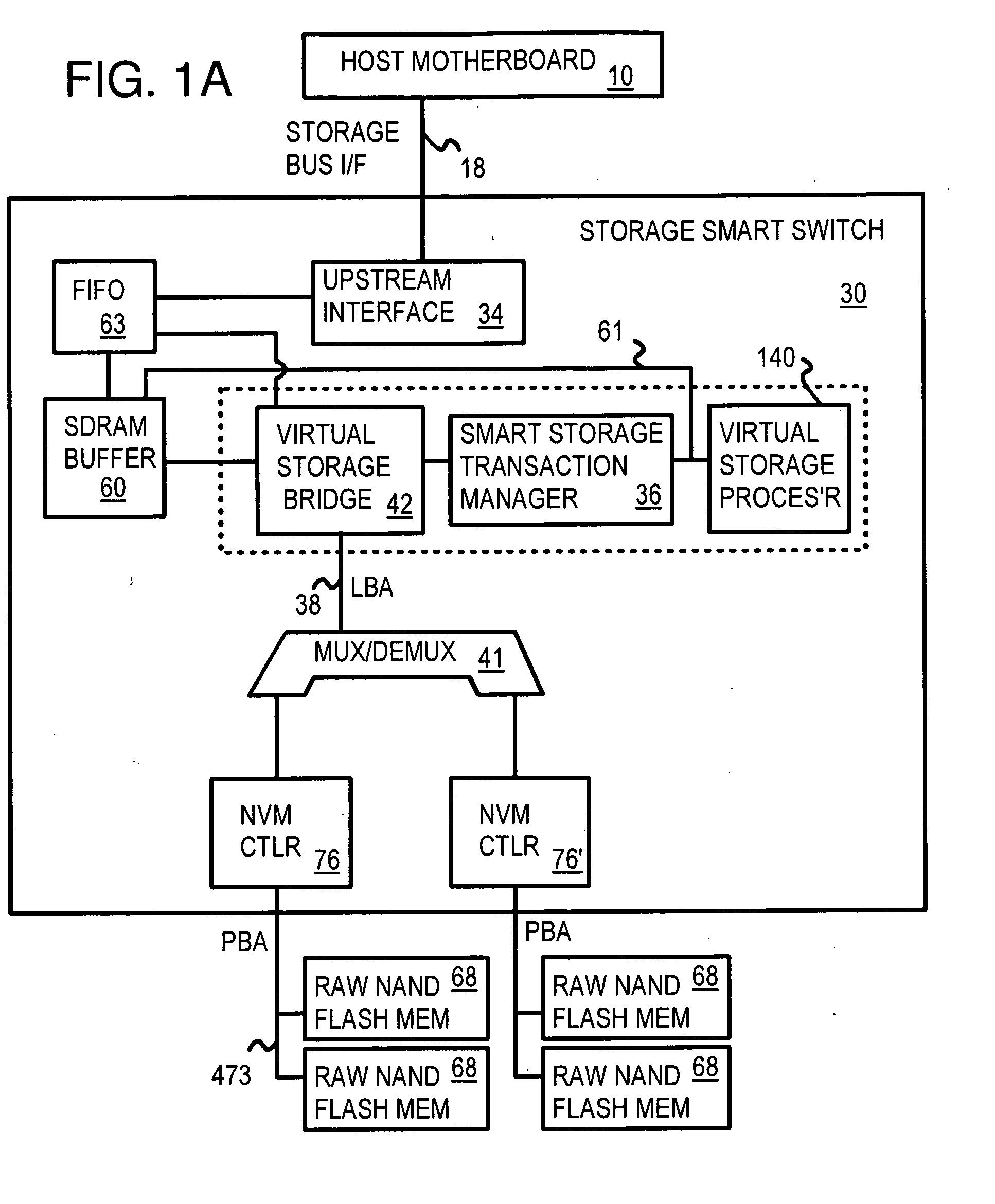
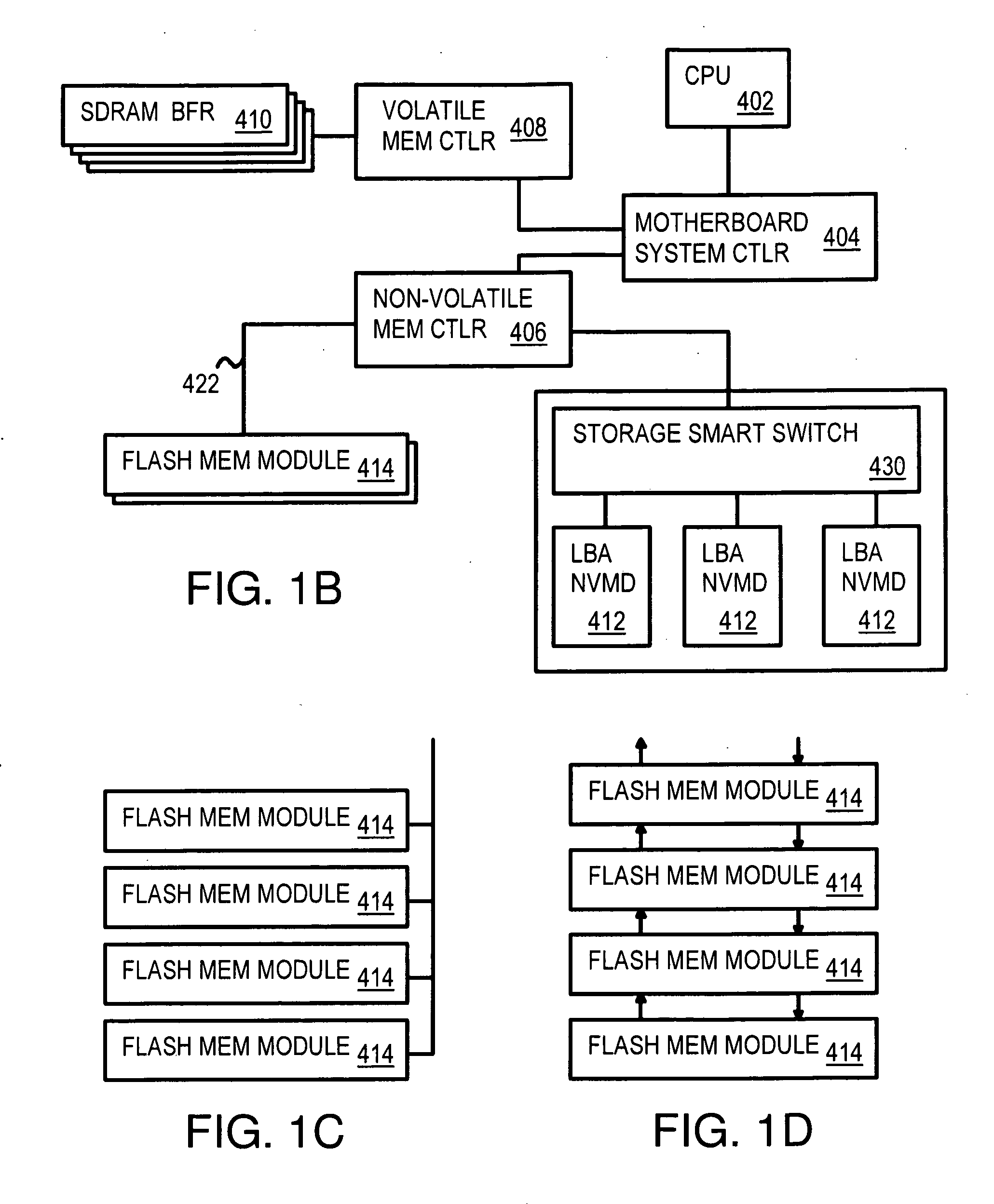
Command Queuing Smart Storage Transfer Manager for Striping Data to Raw-NAND Flash Modules
InactiveUS20090204872A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLogical block addressingComputer module
A flash module has raw-NAND flash memory chips accessed over a physical-block address (PBA) bus by a NVM controller. The NVM controller is on the flash module or on a system board for a solid-state disk (SSD). The NVM controller converts logical block addresses (LBA) to physical block addresses (PBA). Data striping and interleaving among multiple channels of the flash modules is controlled at a high level by a smart storage transaction manager, while further interleaving and remapping within a channel may be performed by the NVM controllers. A SDRAM buffer is used by a smart storage switch to cache host data before writing to flash memory. A Q-R pointer table stores quotients and remainders of division of the host address. The remainder points to a location of the host data in the SDRAM. A command queue stores Q, R for host commands.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device
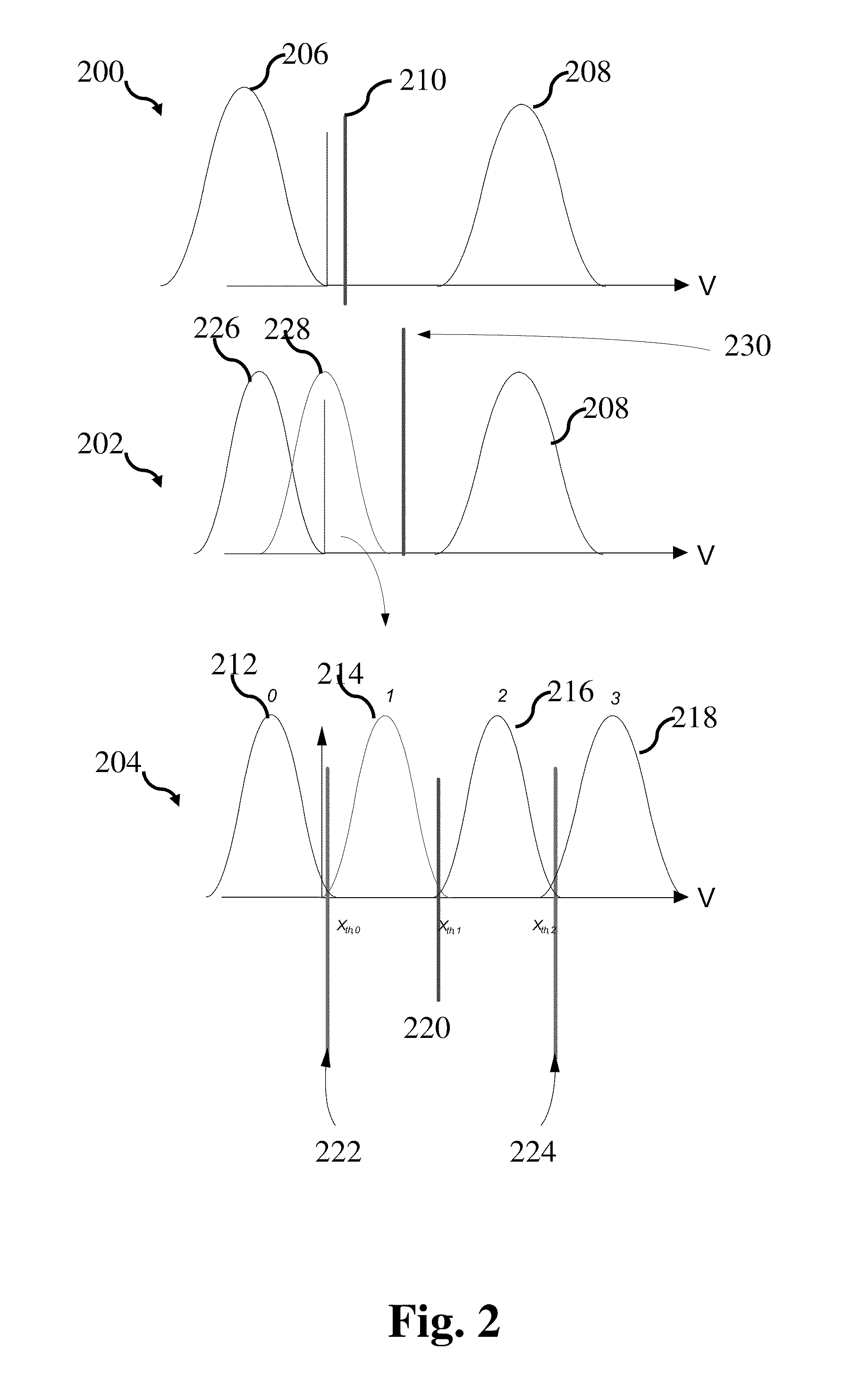
ActiveUS20080301532A1Read-only memoriesError correction/detection using block codesThreshold voltageData bits
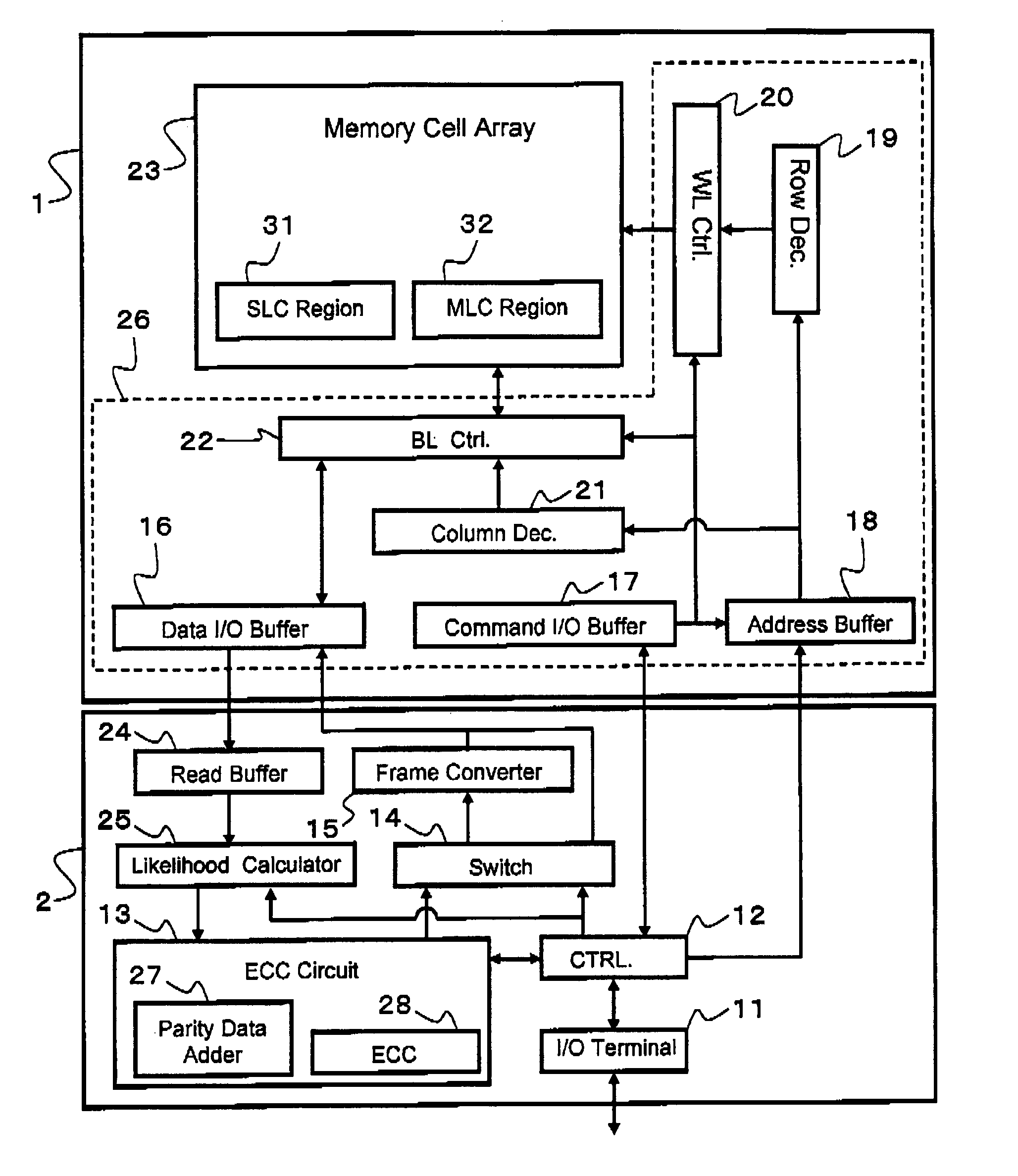
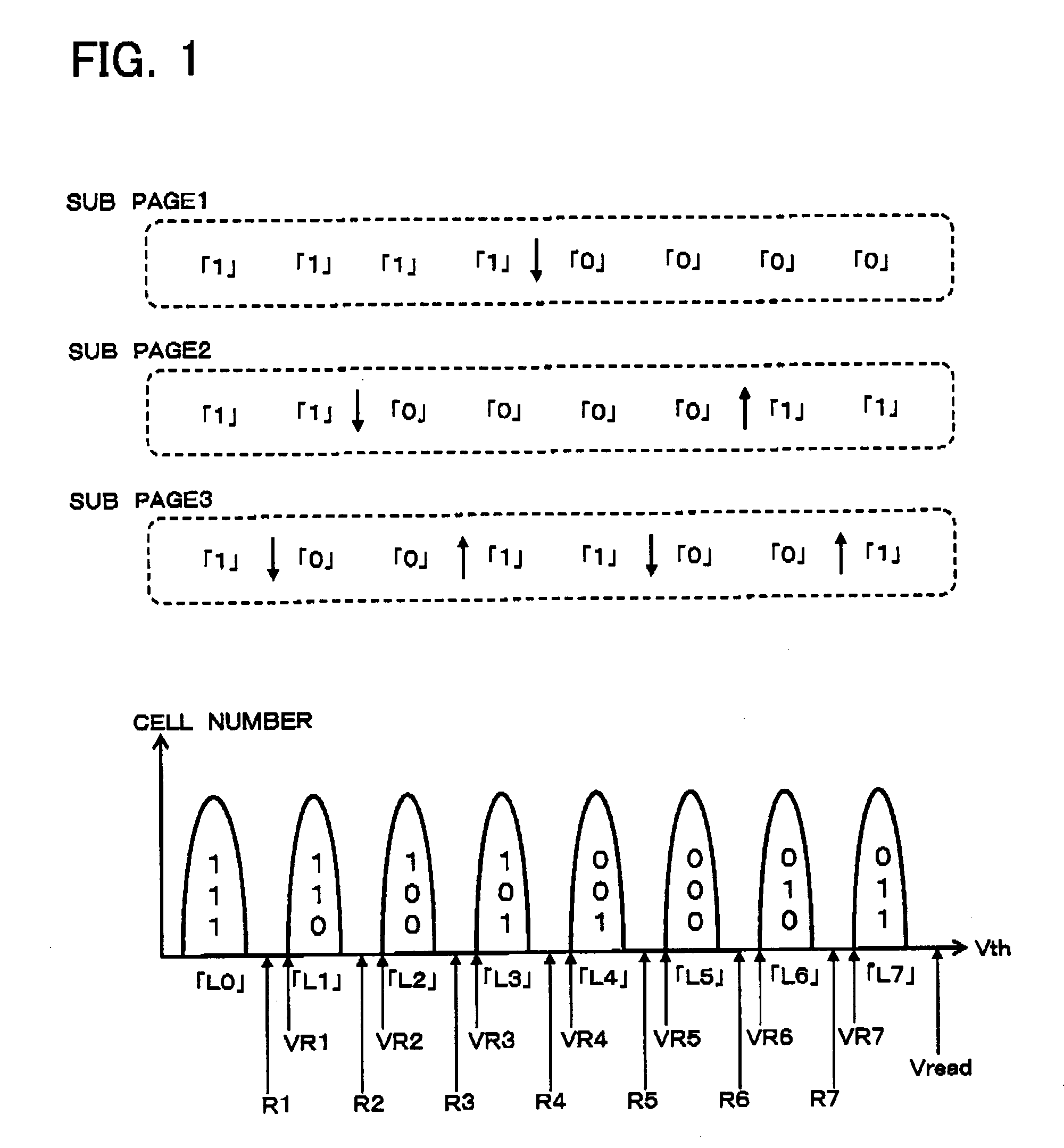
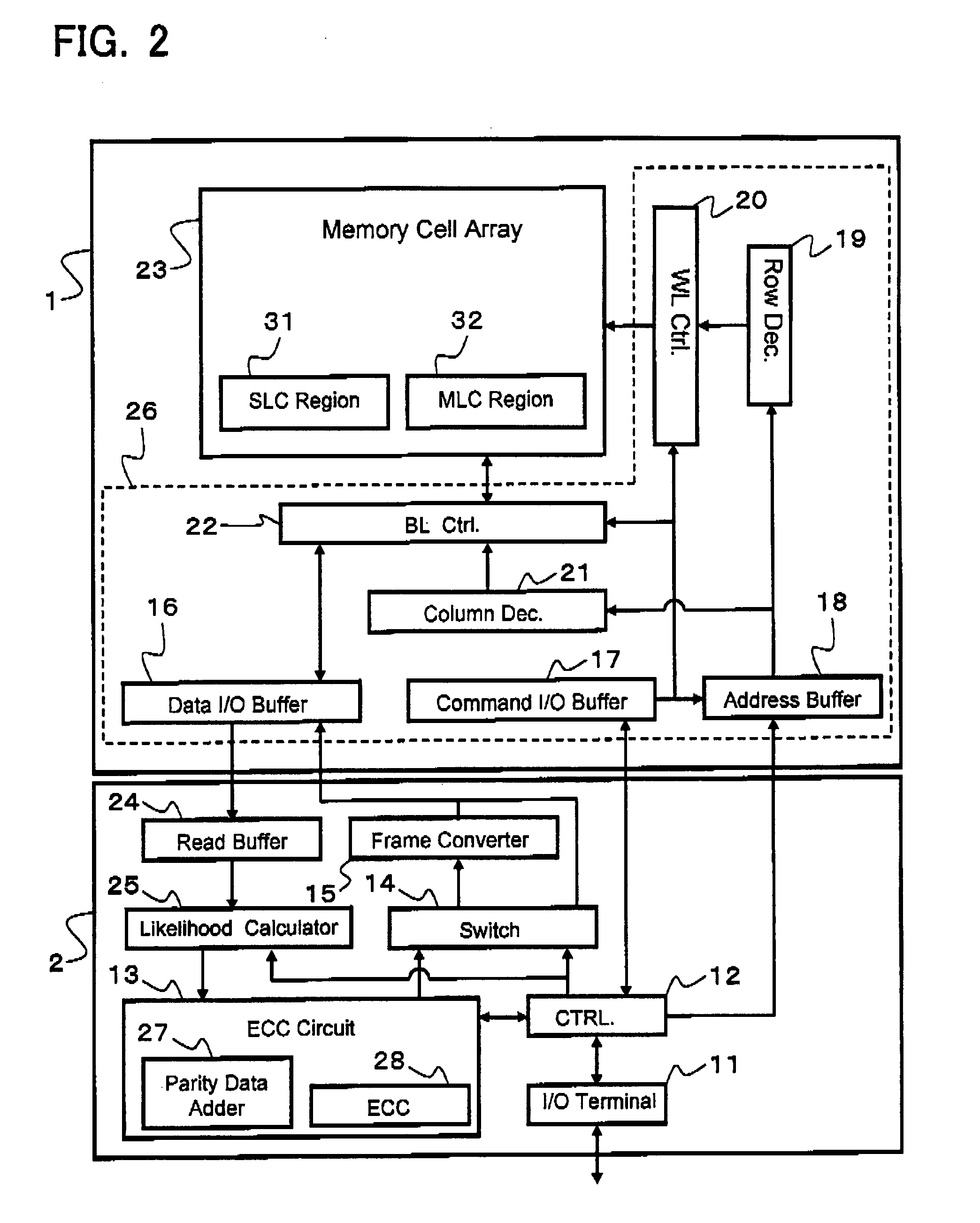
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device comprises a memory cell array including a plurality of memory cells arrayed capable of storing information of N bits (N≧2) in accordance with variations in threshold voltage. A parity data adder circuit adds parity data for error correction to every certain data bits to be stored in the memory cell array. A frame converter circuit uniformly divides frame data containing the data bits and the parity data into N pieces of subframe data. A programming circuit stores the subframe data divided into N pieces in respective N sub-pages formed corresponding to the information of N bits.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Variable sector-count ECC
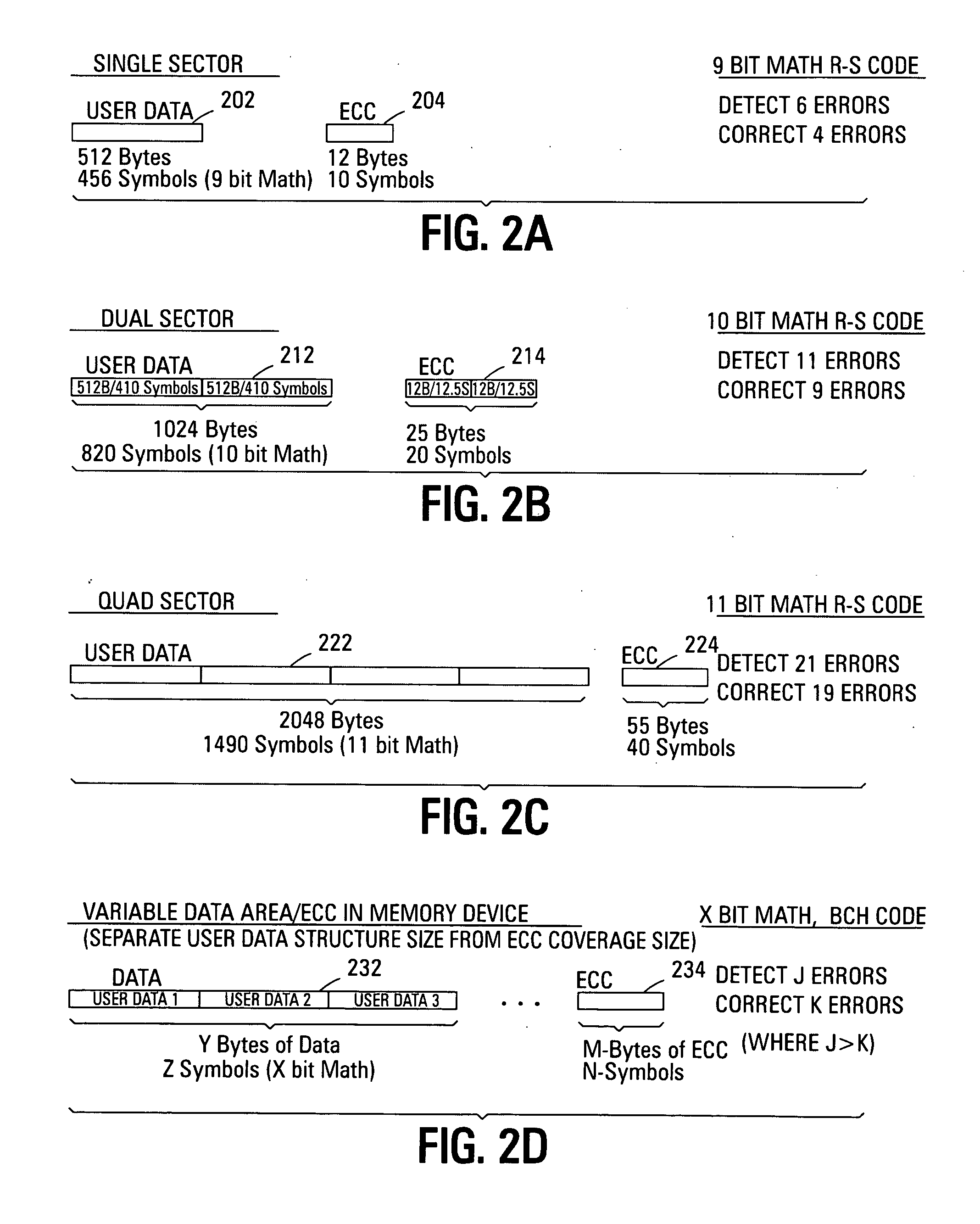
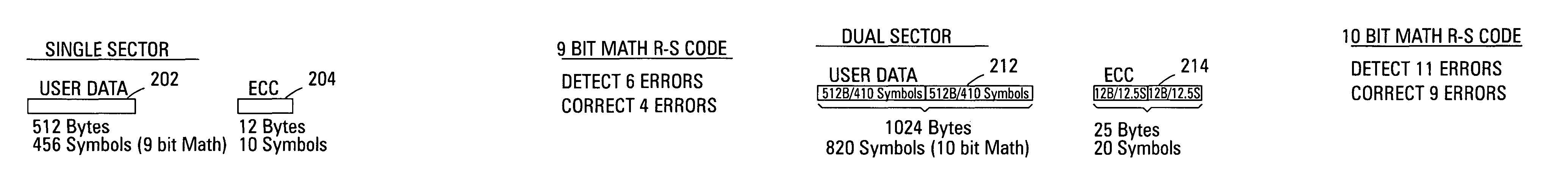
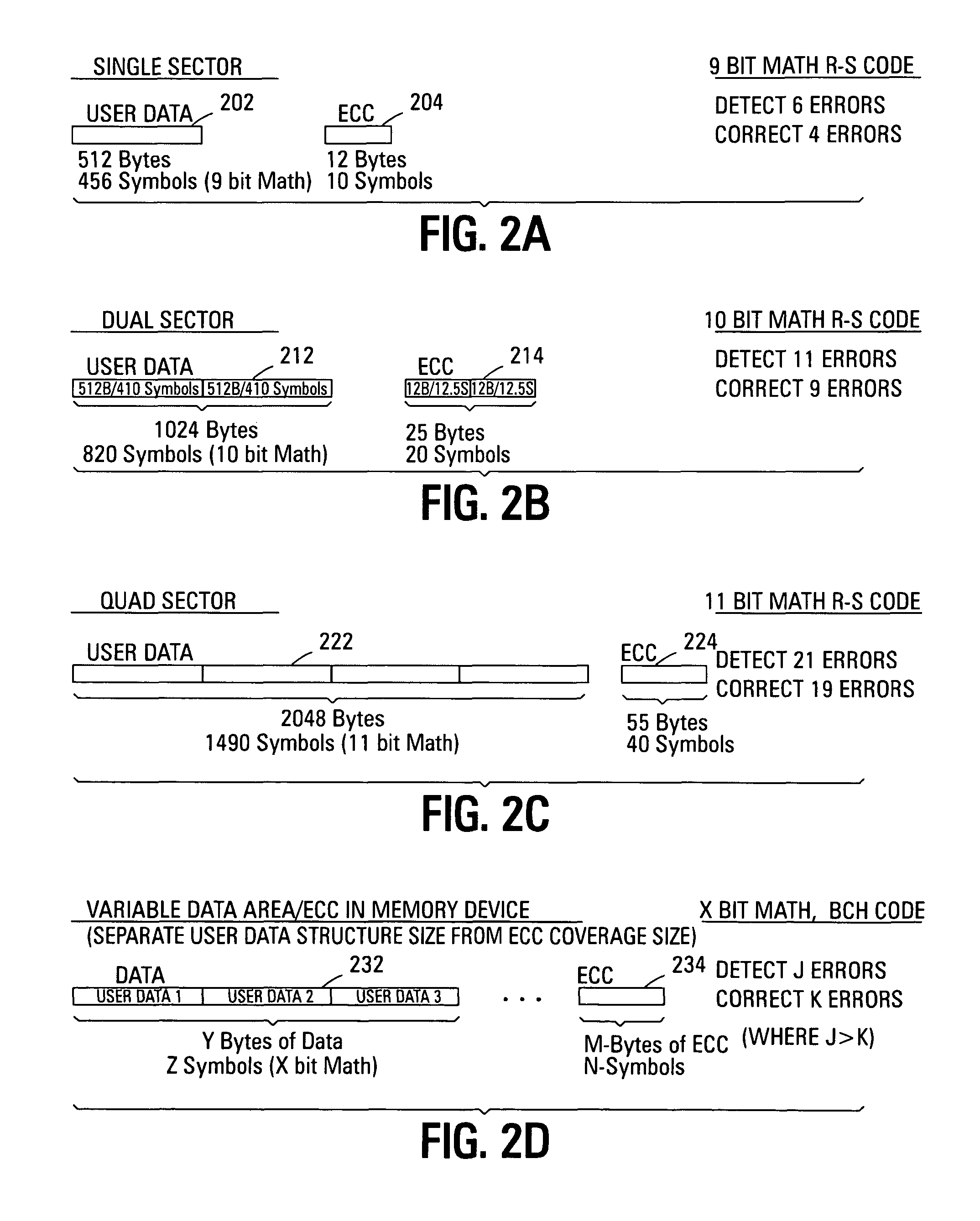
ActiveUS20070226592A1Easy to detectEasy to correctError detection/correctionCode conversionData typeMemory systems
Improved memory devices, circuitry, and data methods are described that facilitate the detection and correction of data in memory systems or devices by increasing the data area of user data being covered by the ECC code. This averages any possible bit errors over a larger data area and allows a greater number of errors to be corrected by a combining the ECC codes in the coverage area without substantially changing the overall size of ECC codes being stored over a single sector approach. In one embodiment of the present invention, the size of the data block utilized for ECC coverage is variable and can be selected such that differing areas of the memory array or data types can have a differing ECC data coverage sizes. It is also noted that the ECC algorithm, math base or encoding scheme can also be varied between these differing areas of the memory array.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
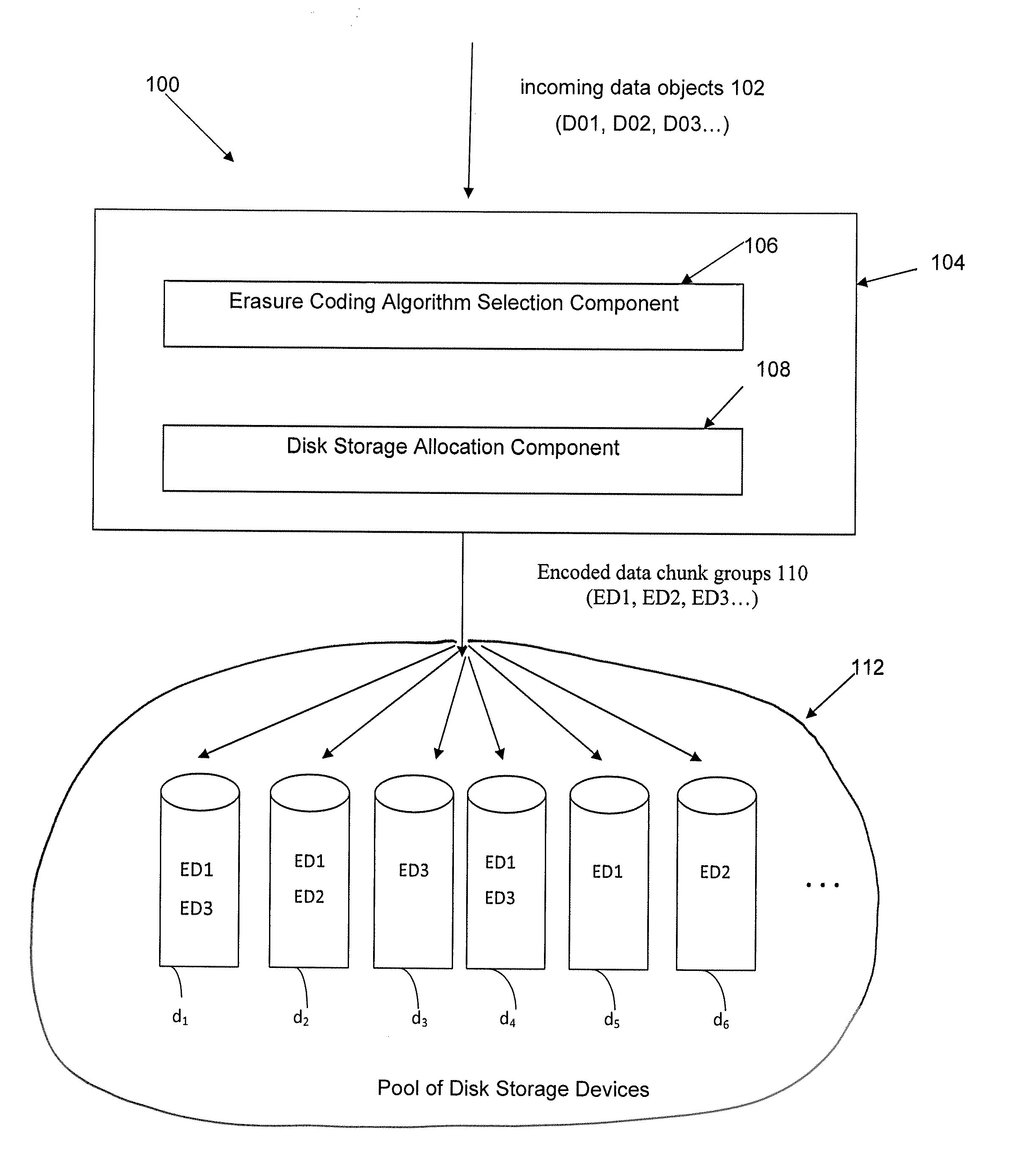
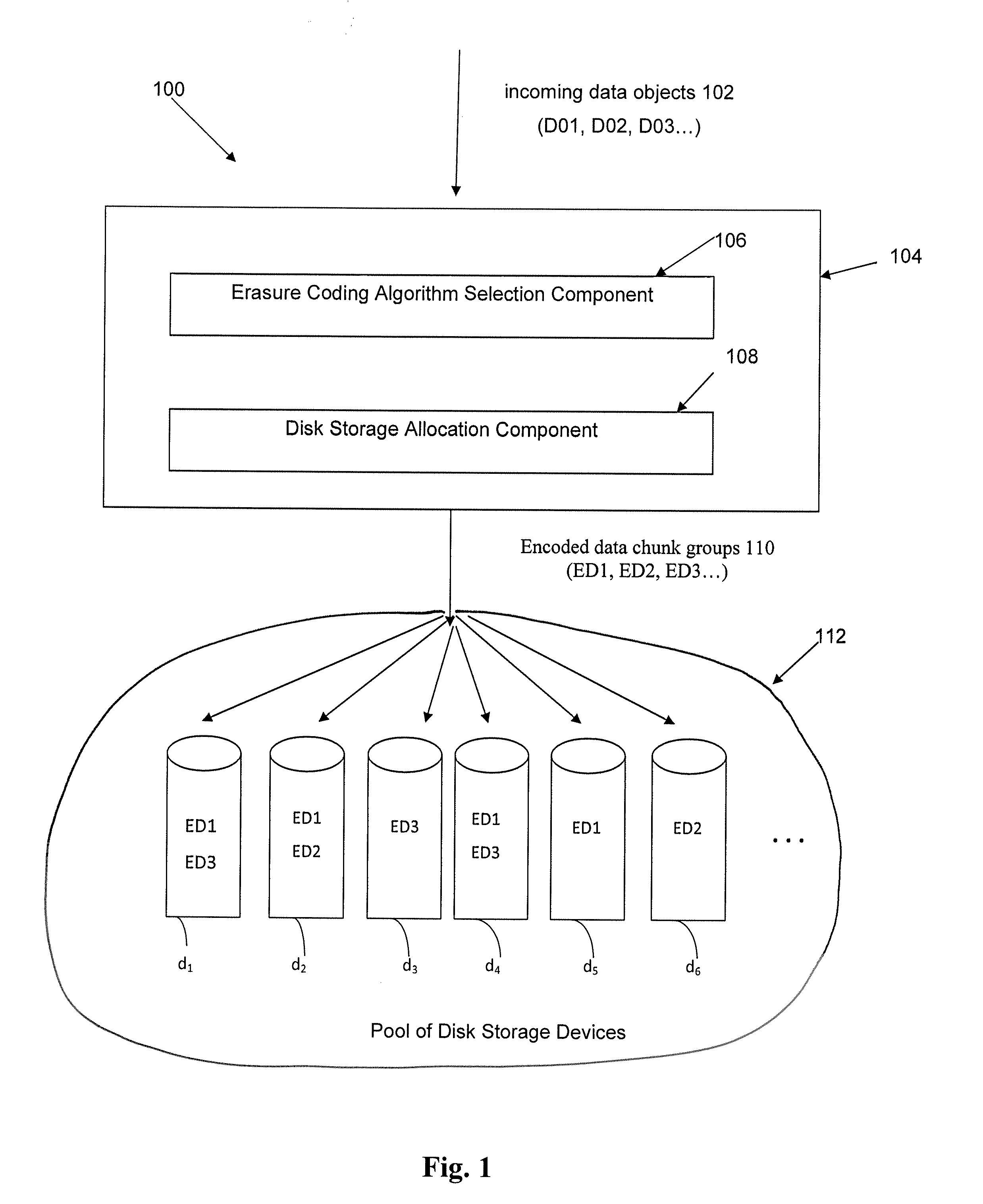
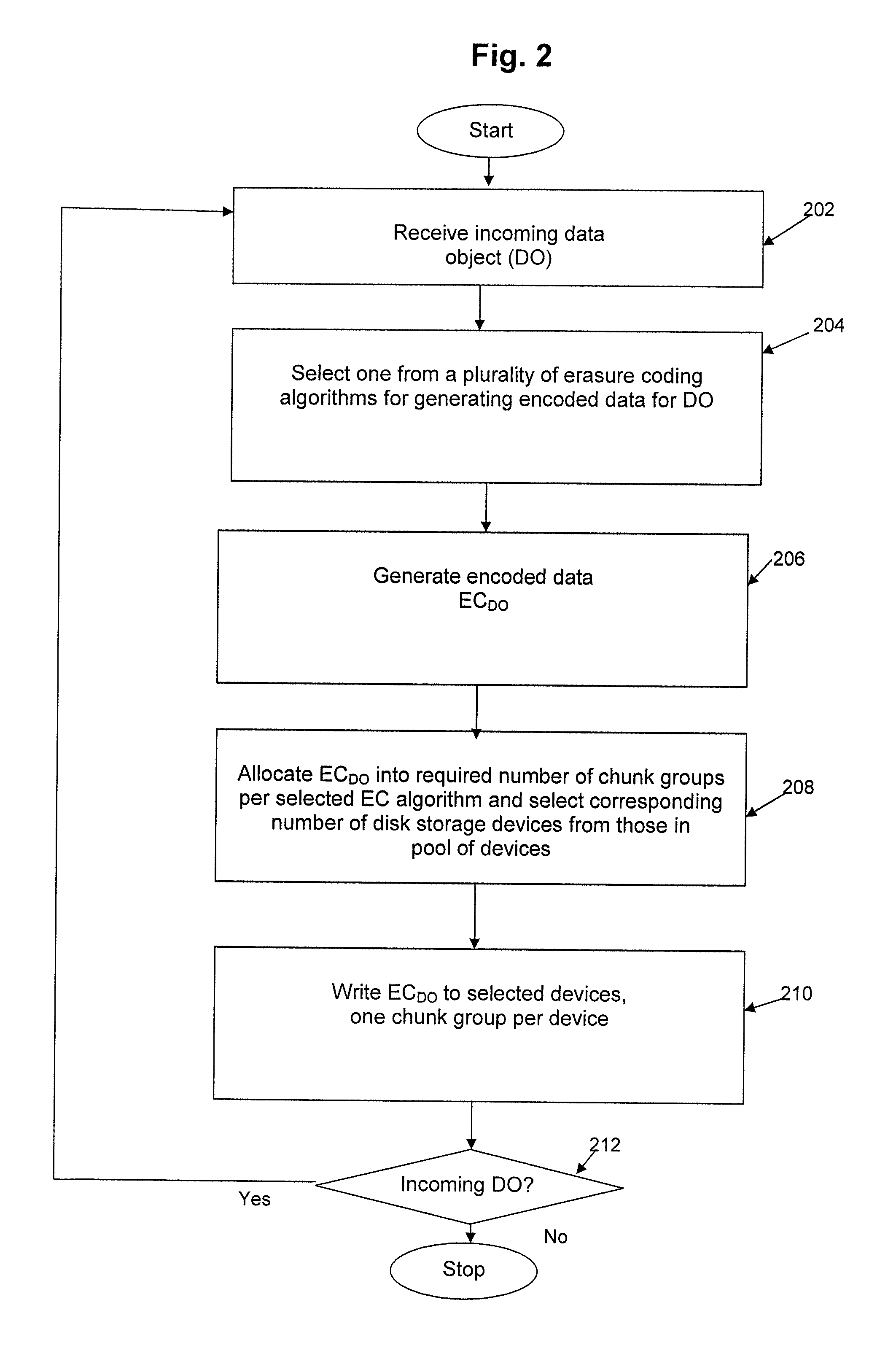
Method and apparatus for allocating erasure coded data to disk storage
ActiveUS20130132800A1Reduce in quantityError correction/detection using block codesStatic storageDisk storageData chunk
Allocation process that allows erasure coded data to be stored on any of a plurality of disk drives, in a pool of drives, so that the allocation is not tied to a fixed group of drives. Still further, the encoded data can be generated by any of multiple different erasure coding algorithms, where again storage of the encoded data is not restricted to a single group of drives based on the erasure algorithm being utilized to encode the data. In another embodiment, the encoded data can be “stacked” (aligned) on select drives to reduce the number of head seeks required to access the data. As a result of these improvements, the system can dynamically determine which one of multiple erasure coding algorithms to utilize for a given incoming data block, without being tied to one particular algorithm and one particular group of storage devices as in the prior art.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
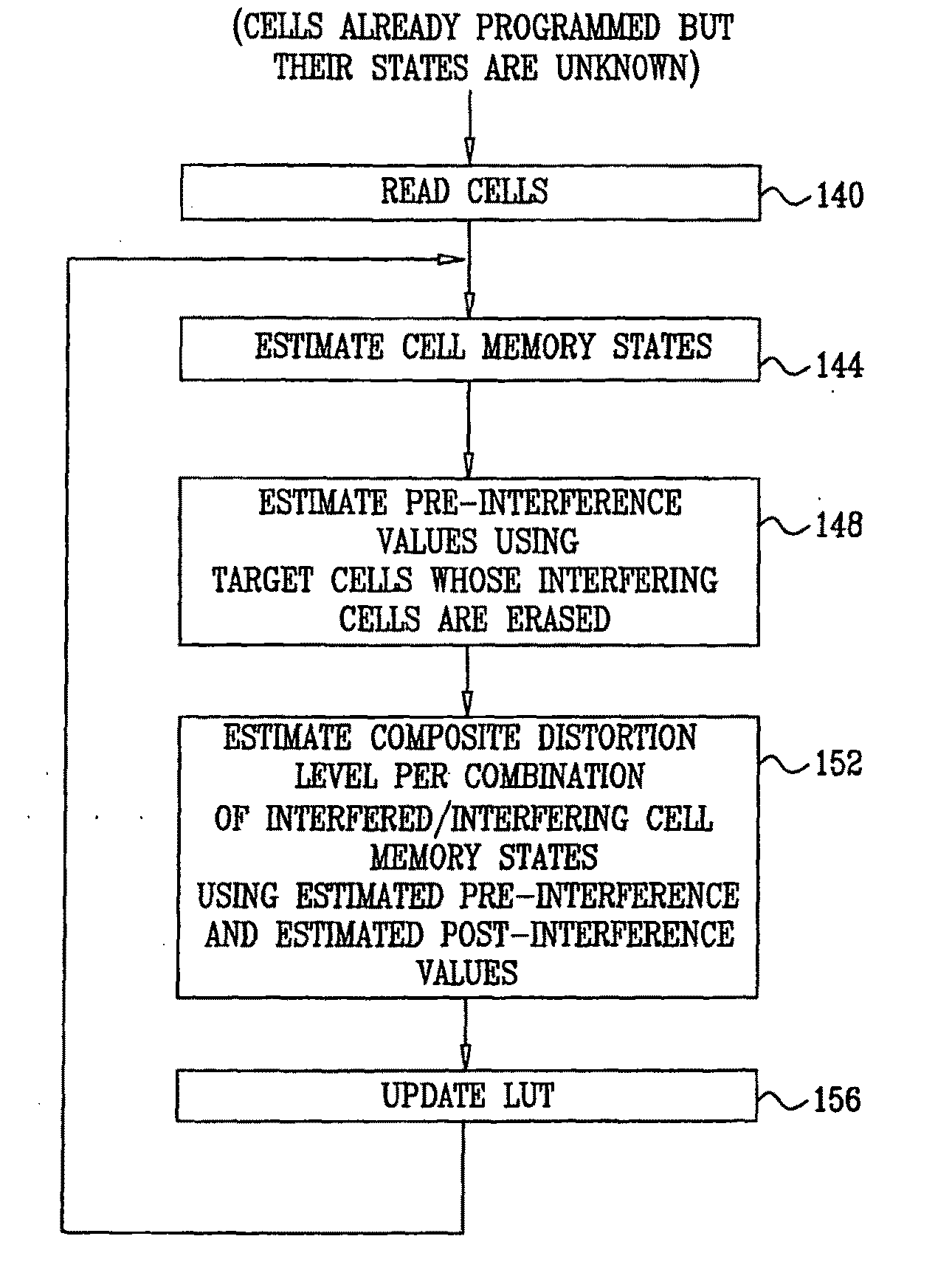
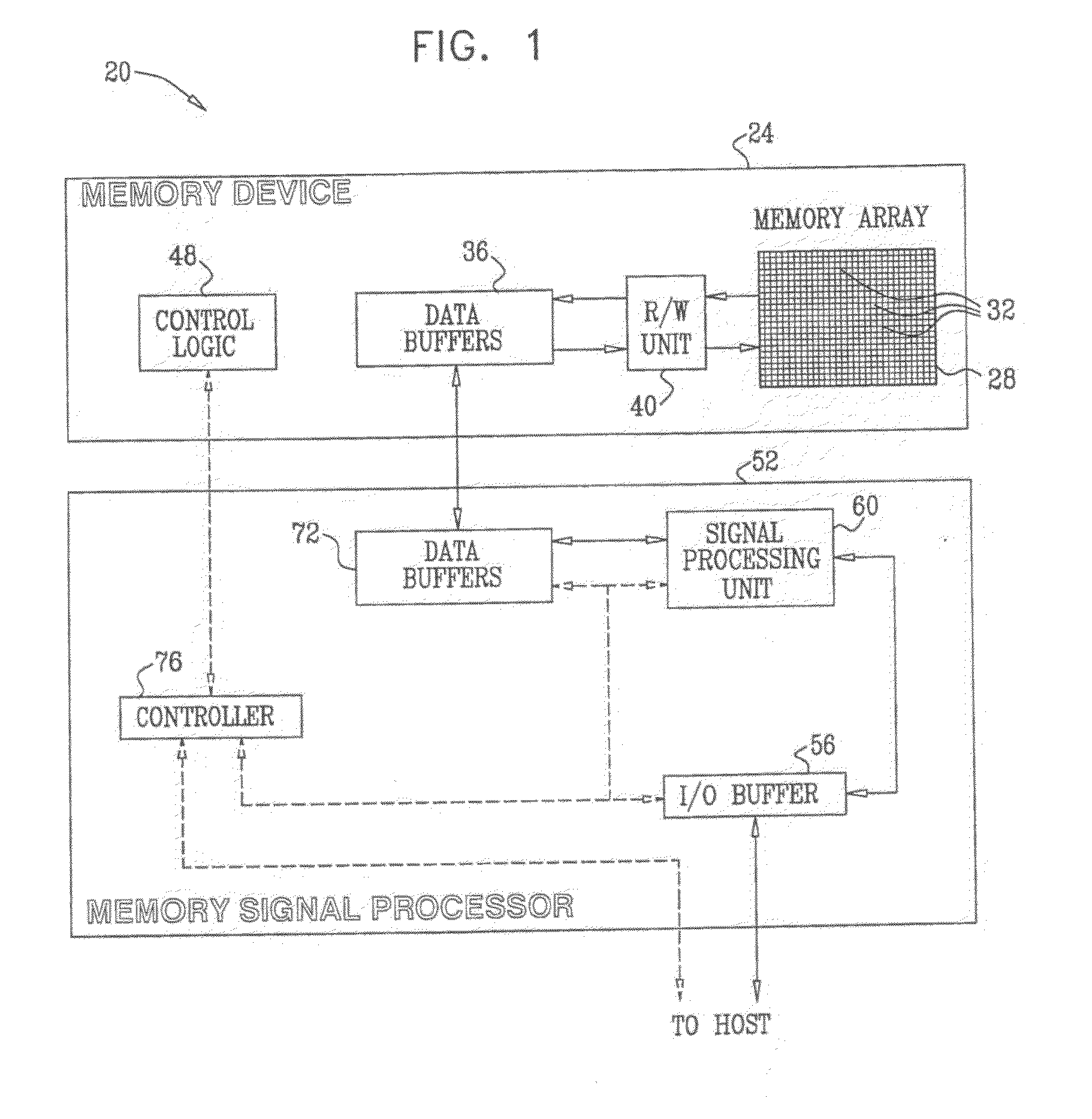
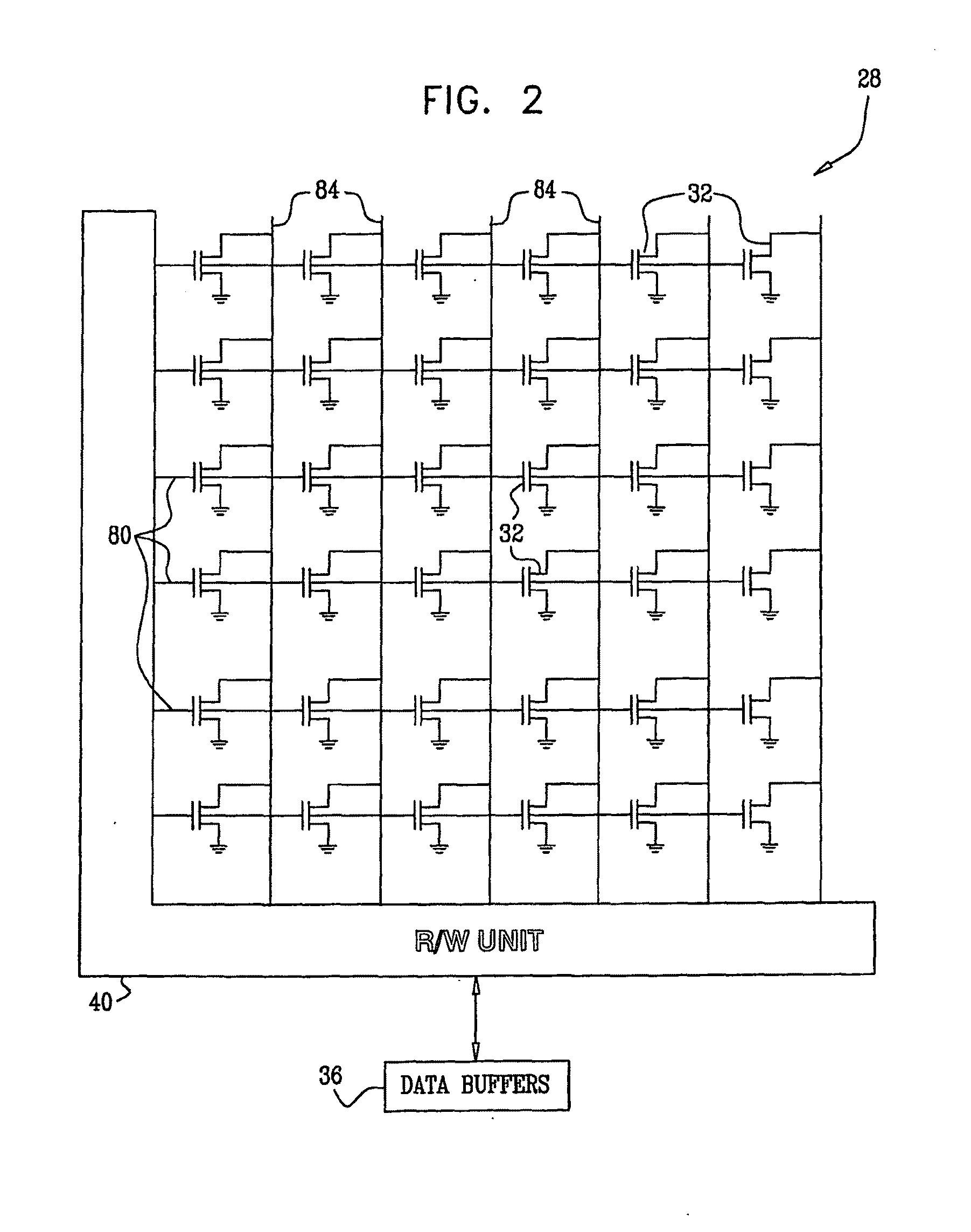
Estimation of non-linear distortion in memory devices
A method for operating a memory (24) includes storing data in analog memory cells (32) of the memory by writing respective analog values to the analog memory cells. A set of the analog memory cells is identified, including an interfered cell having a distortion that is statistically correlated with the respective analog values of the analog memory cells in the set. A mapping is determined between combinations of possible analog values of the analog memory cells in the set and statistical characteristics of composite distortion levels present in the interfered memory cell. The mapping is applied so as to compensate for the distortion in the interfered memory cell.
Owner:APPLE INC
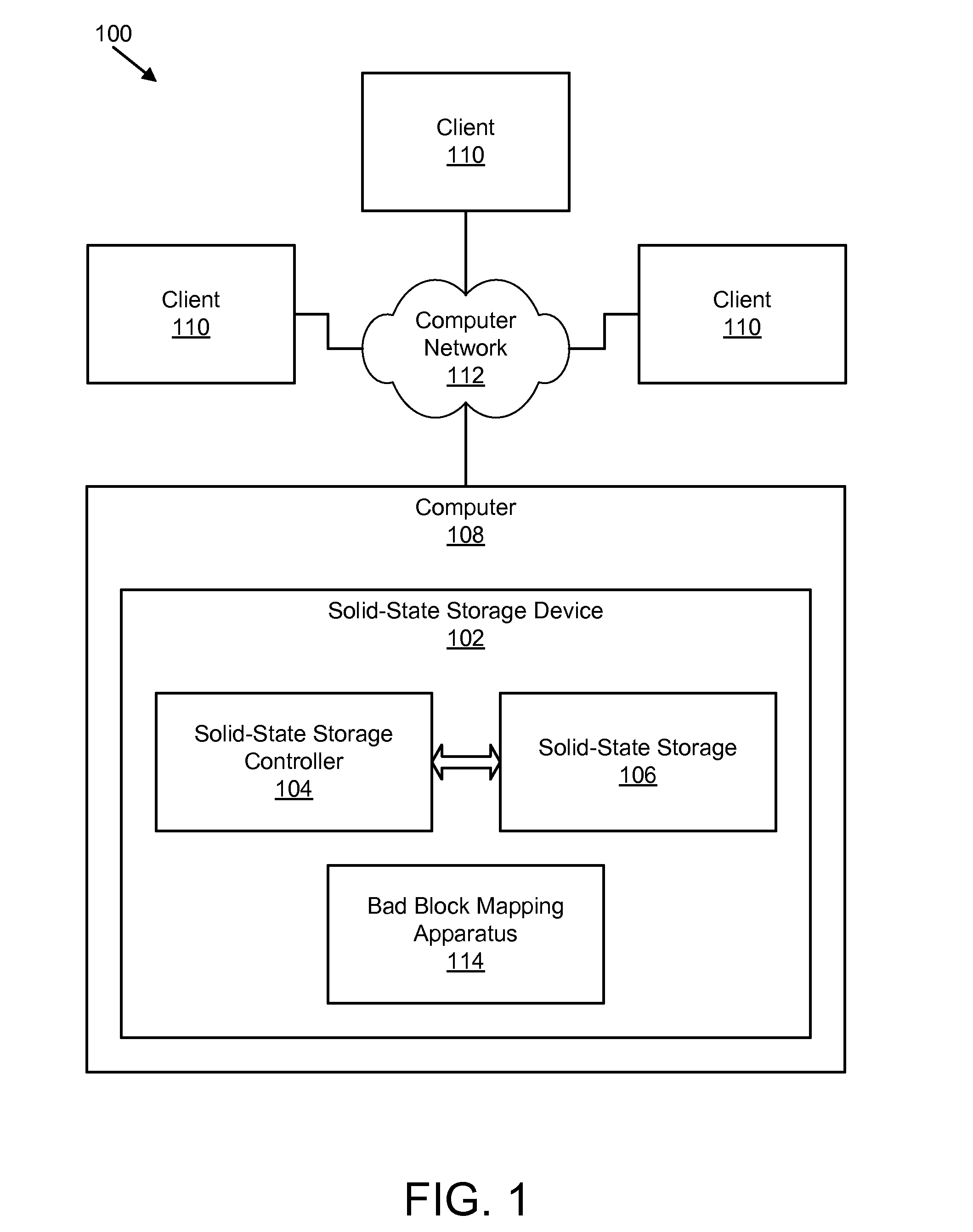
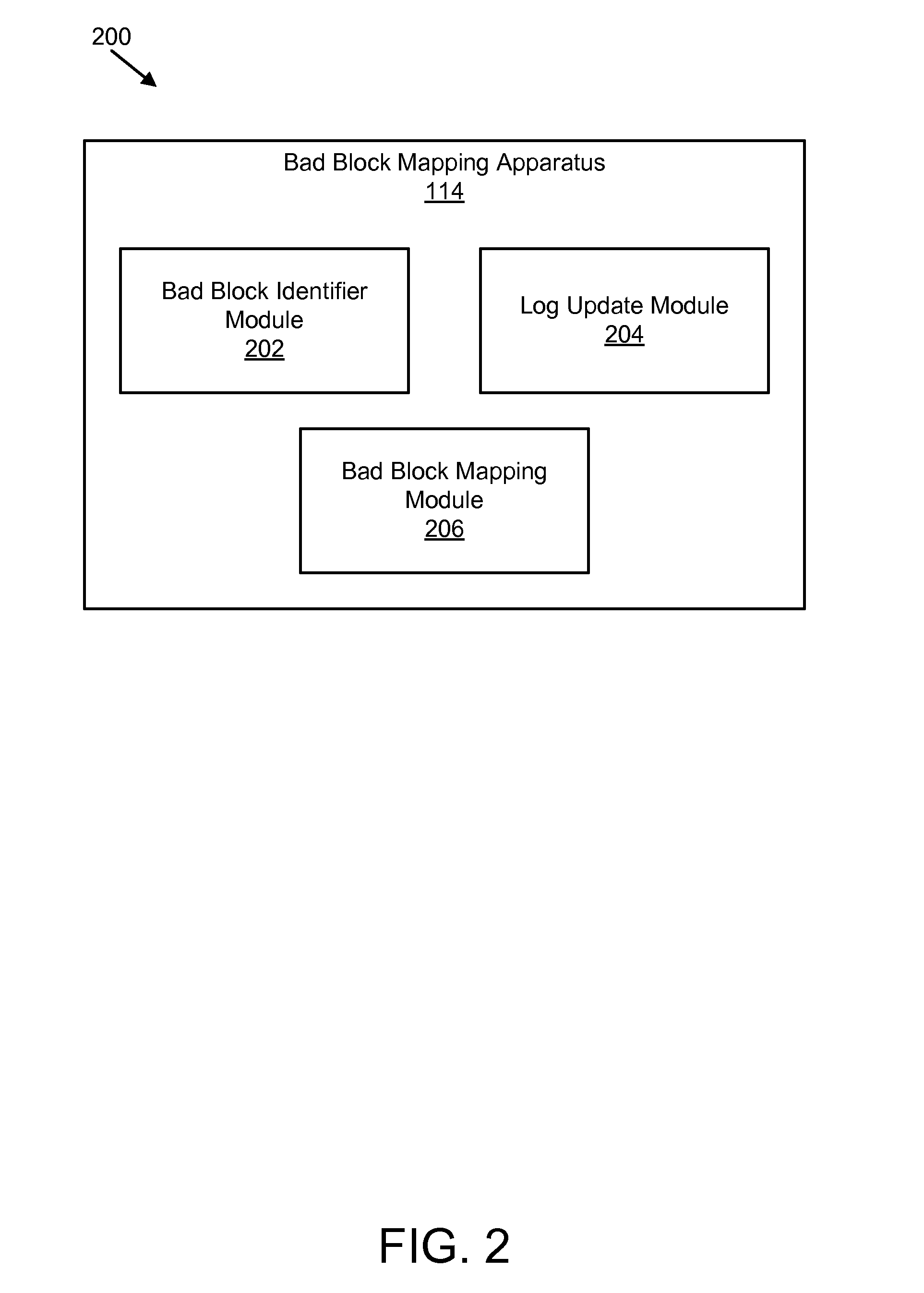
Apparatus, system, and method for bad block remapping
ActiveUS20090282301A1Improve reliabilityAvoid managementMemory architecture accessing/allocationError preventionSolid-state storageParallel computing
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for bad block remapping. A bad block identifier module identifies one or more data blocks on a solid-state storage element as bad blocks. A log update module writes at least a location of each bad block identified by the bad block identifier module into each of two or more redundant bad block logs. A bad block mapping module accesses at least one bad block log during a start-up operation to create in memory a bad block map. The bad block map includes a mapping between the bad block locations in the bad block log and a corresponding location of a replacement block for each bad block location. Data is stored in each replacement block instead of the corresponding bad block. The bad block mapping module creates the bad block map using one of a replacement block location and a bad block mapping algorithm.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
System and method for data recovery in multi-level cell memories
ActiveUS20120005558A1Read-only memoriesError correction/detection using block codesParallel computingMulti-level cell
A system and method are provided for data recovery in a multi-level cell memory device. One or more bits may be programmed sequentially in one or more respective levels of multi-level cells in the memory device. An interruption of programming a subsequent bit in a subsequent second or greater level of the multi-level cells may be detected. Data may be recovered from the multi-level cells defining the one or more bits programmed preceding the programming interruption of the second or greater level.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
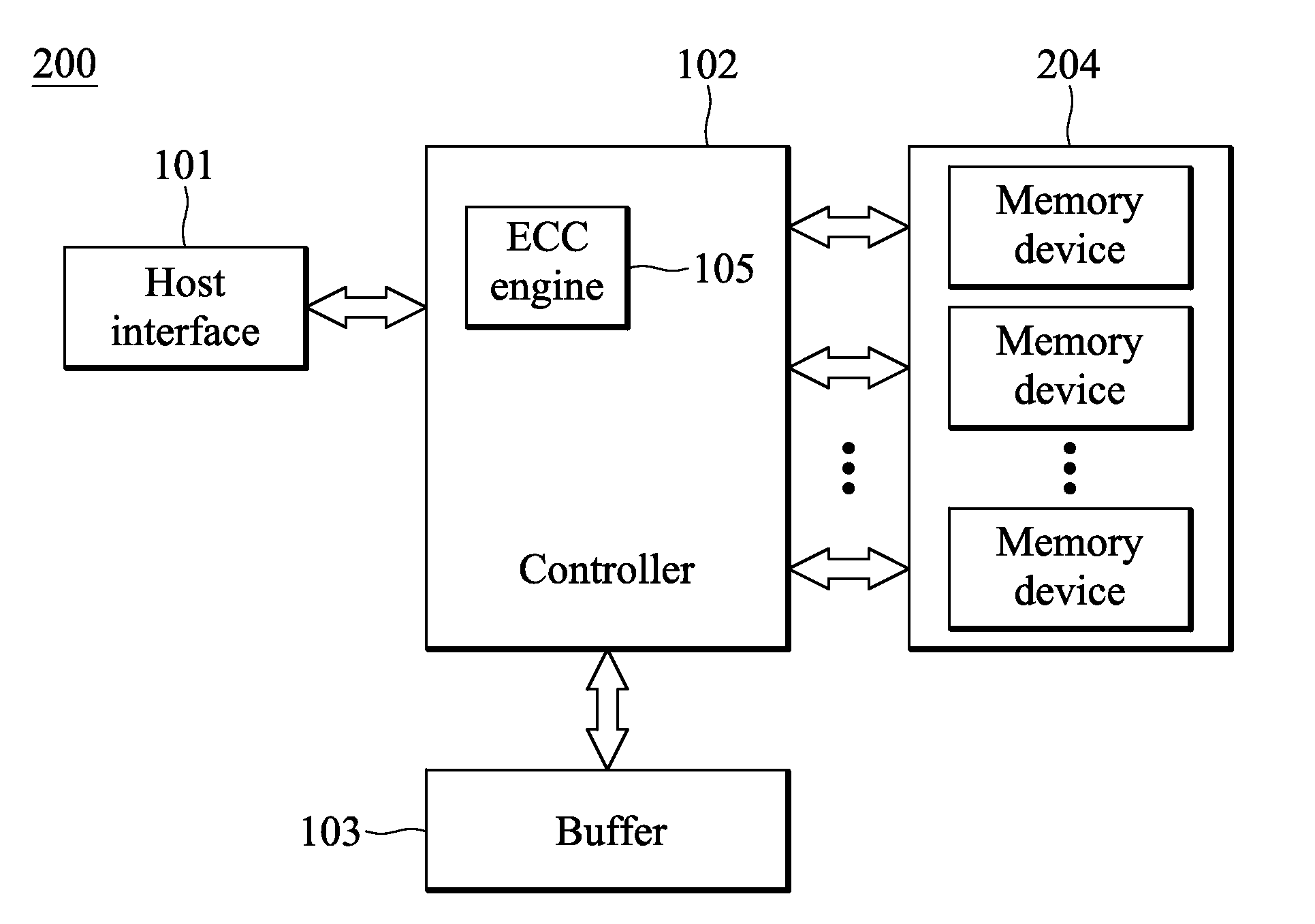
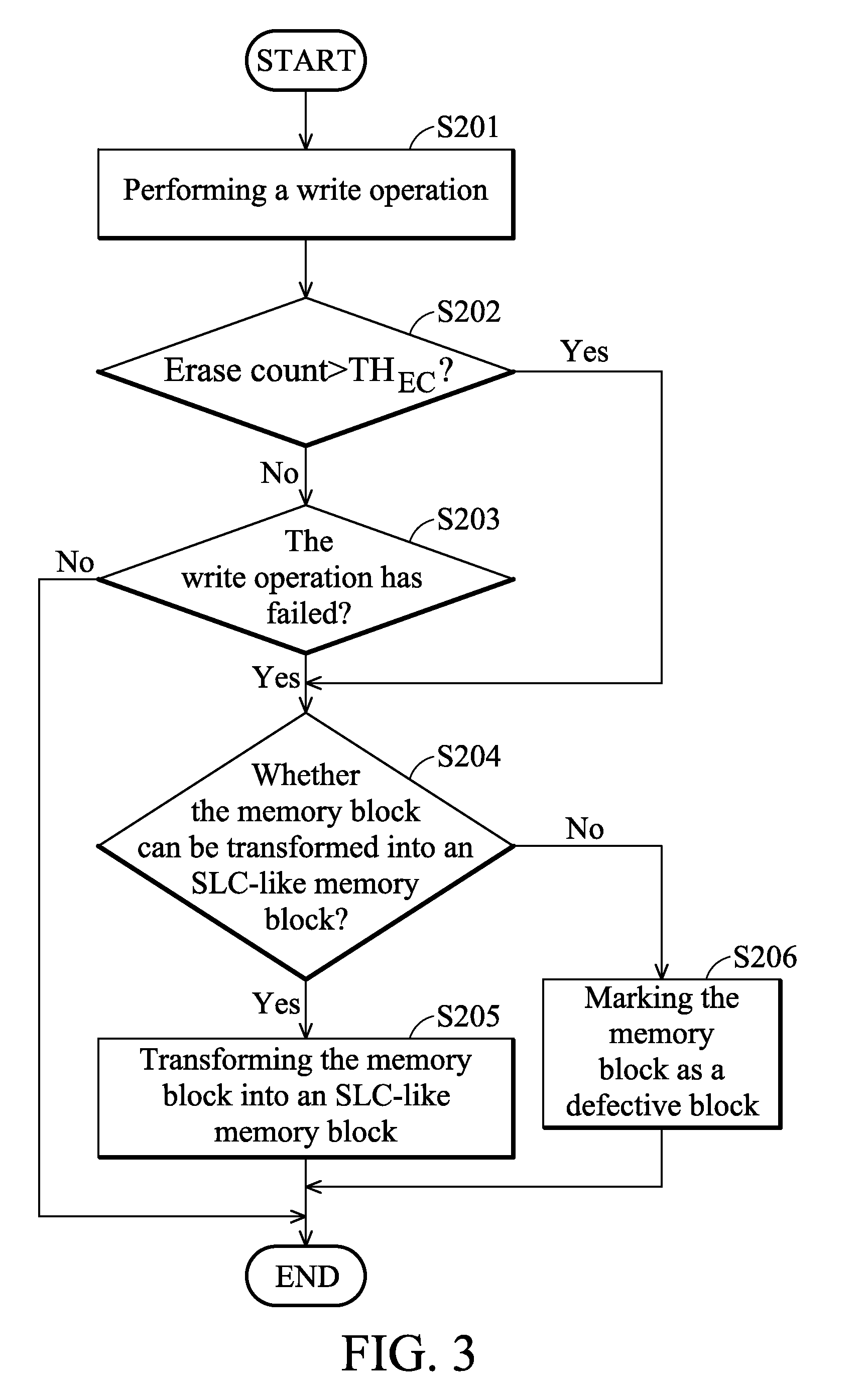
Method for managing device and solid state disk drive utilizing the same
InactiveUS20100332922A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesSingle levelMemory block
A solid state disk drive is provided. The solid state disk drive includes a multiple level cell (MLC) memory device and a controller. The MLC memory device includes memory blocks each comprising memory cells capable of storing more than a single bit of data per cell. The controller transforms at least one memory block into a single level cell (SLC)-like memory block, and accesses the memory block in an SLC manner.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Transmitter and receiver for broadcasting data and providing incremental redundancy
ActiveUS20120272117A1Increase probabilityImprove robustnessError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionData streamBroadcast data
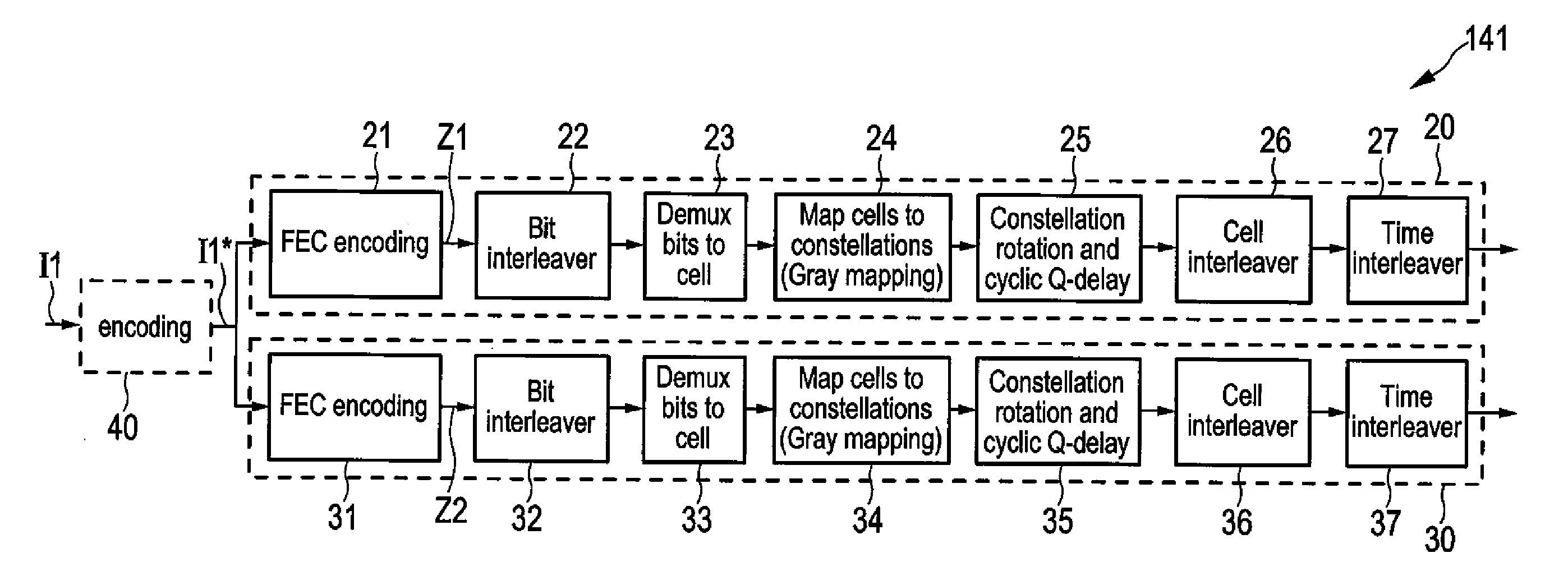
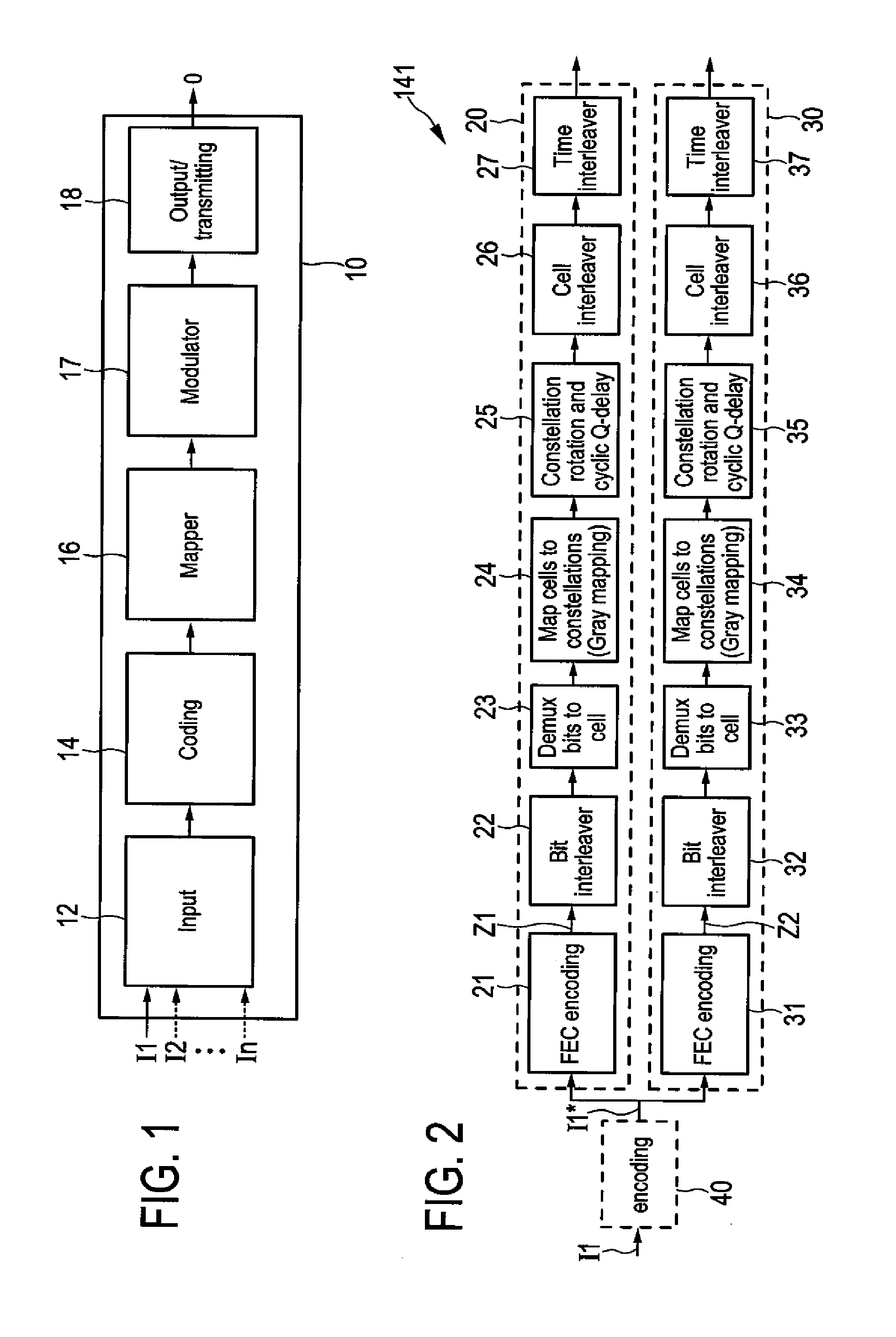
A transmitter for broadcasting data in a broadcasting system that improves the decoding quality, if needed, comprises a data input, and an encoder for error correction code encoding the input data words into codewords, a codeword comprising a basic codeword portion and an auxiliary codeword portion, wherein said encoder is adapted for generating said basic codeword portion from an input data word according to a first code and for generating said auxiliary codeword portion from an input data word according to a second code, said basic codeword portion being provided for regular decoding and said auxiliary codeword portion being provided as incremental redundancy if regular decoding of the codeword by use of the basic codeword portion is erroneous. Further, the transmitter comprises a data mapper for mapping the codewords onto frames of a transmitter output data stream, and a transmitter unit for transmitting said transmitter output data stream.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and method of transmitting/receiving broadcast data
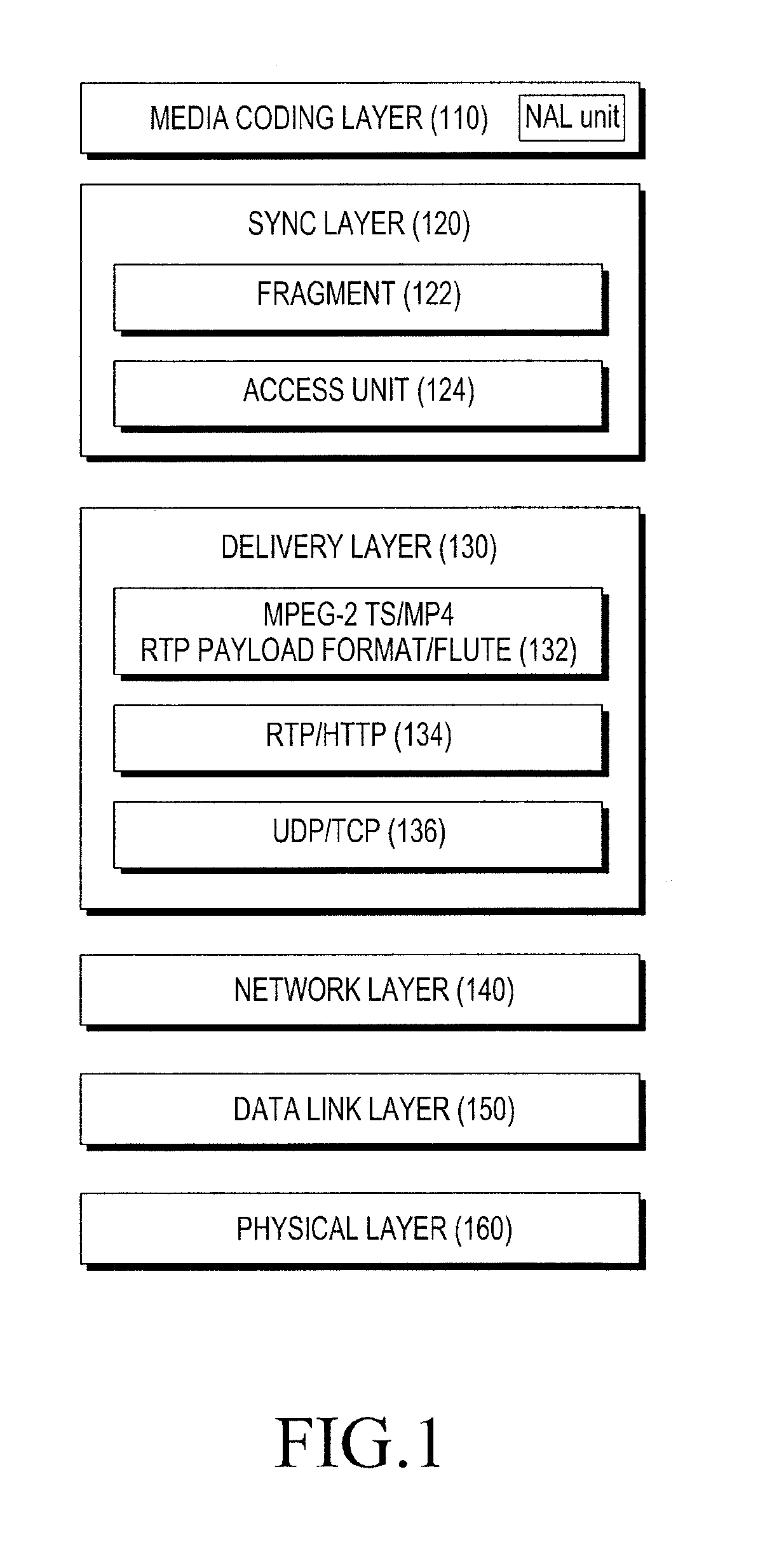
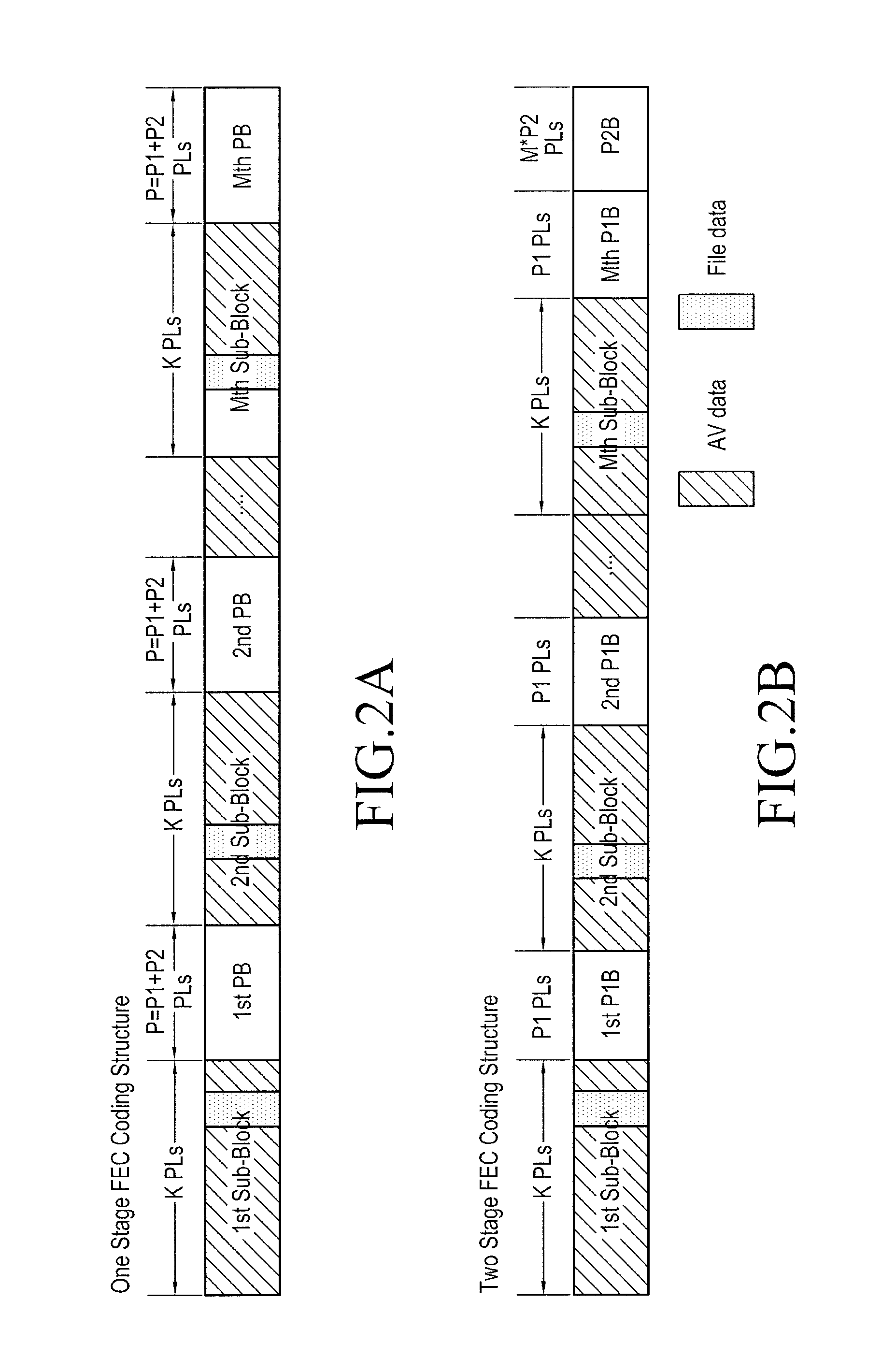
InactiveUS20130136193A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCoding blockTheoretical computer science
An encoding apparatus and a method of encoding a source block including different types of data payloads are provided. The method includes dividing the source block into a predetermined number M of sub blocks, generating a predetermined number P1 of base parity payloads that correspond to each of the predetermined number M of sub blocks by performing first Forward Error Correction (FEC) encoding on each of the predetermined number M of sub blocks, generating a predetermined number P2 of extended parity payloads that correspond to the source block by performing second FEC encoding on a particular type of data payloads among data payloads that make up the source block, and configuring a source coded block based on a predetermined number N of sub coded blocks including the predetermined number M of sub blocks and the predetermined number P1 of base parity payloads generated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Variable sector-count ECC
ActiveUS7810017B2Easy to detectEasy to correctError detection/correctionCode conversionData typeMemory systems
Improved memory devices, circuitry, and data methods are described that facilitate the detection and correction of data in memory systems or devices by increasing the data area of user data being covered by the ECC code. This averages any possible bit errors over a larger data area and allows a greater number of errors to be corrected by a combining the ECC codes in the coverage area without substantially changing the overall size of ECC codes being stored over a single sector approach. In one embodiment of the present invention, the size of the data block utilized for ECC coverage is variable and can be selected such that differing areas of the memory array or data types can have a differing ECC data coverage sizes. It is also noted that the ECC algorithm, math base or encoding scheme can also be varied between these differing areas of the memory array.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Adaptive Forward Error Correction
InactiveUS20080134005A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionRedundant codeForward error correction
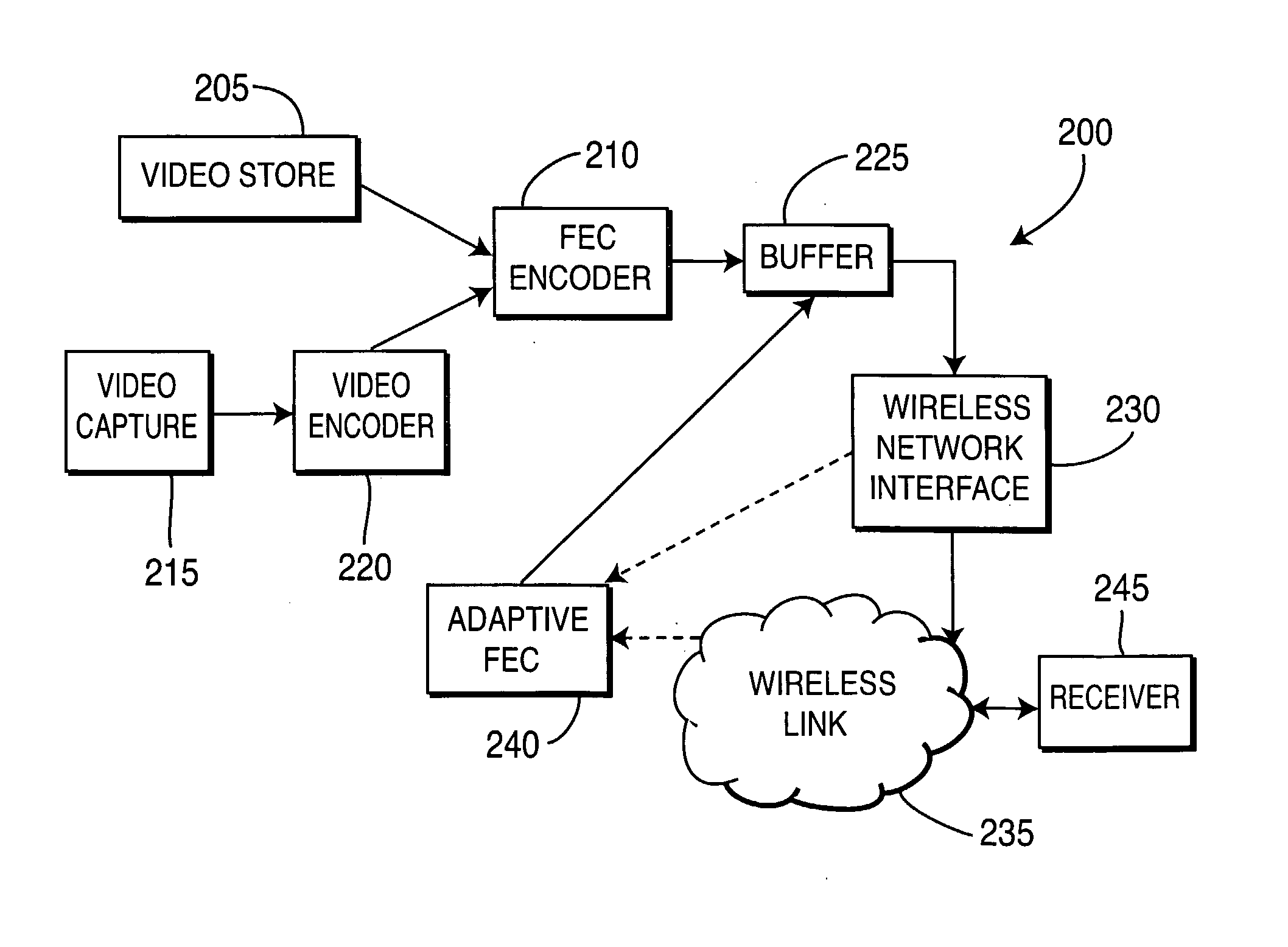
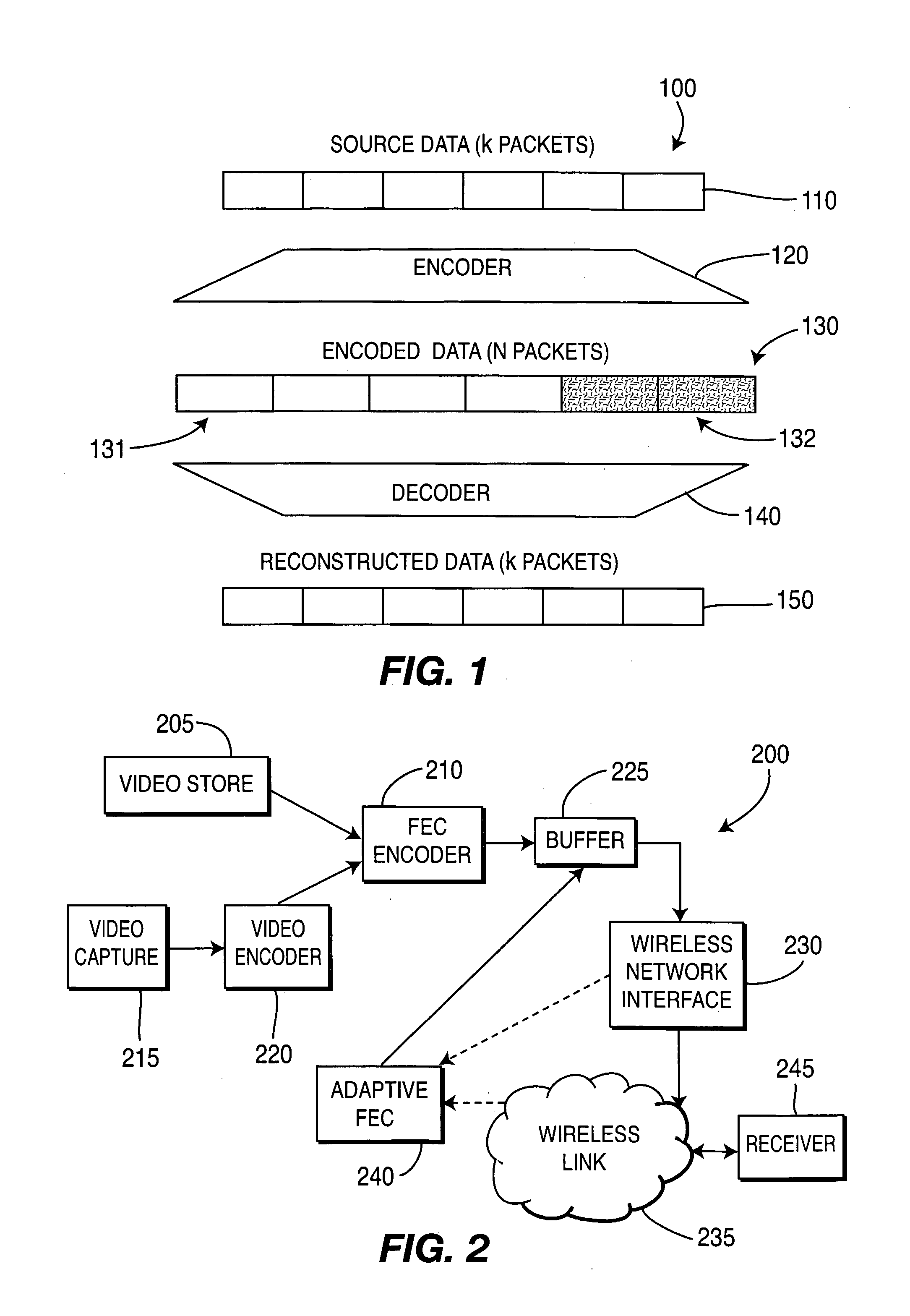
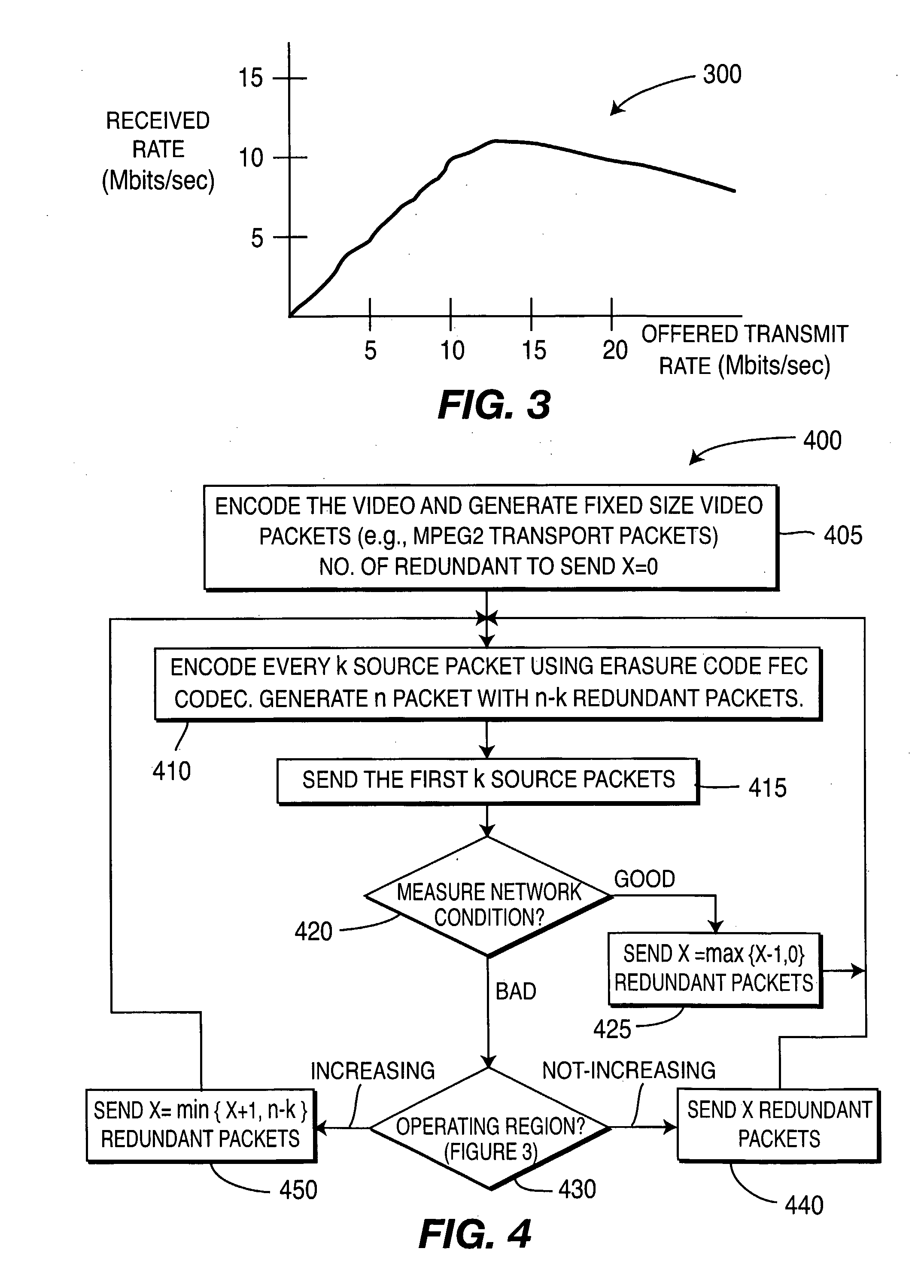
There are described apparatus and methods for adaptive forward error correction (FEC), one use being for video streaming over a wireless network. The apparatus includes an FEC encoder and an adaptive FEC device. The FEC encoder is for encoding k packets of source data into n packets, where n>k, and the n packets include redundant packets. The adaptive FEC device is for adaptively determining a number of the redundant packets to transmit with the encoded k packets, based upon receiving one or more feedback messages. The one or more feedback messages indicate a condition of the wireless network over which the encoded video is to be transmitted.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Error correction apparatus, method thereof and memory device comprising the apparatus
InactiveUS20090292972A1Effective correctionIncrease probabilityRead-only memoriesCode conversionComputer hardwareError correcting
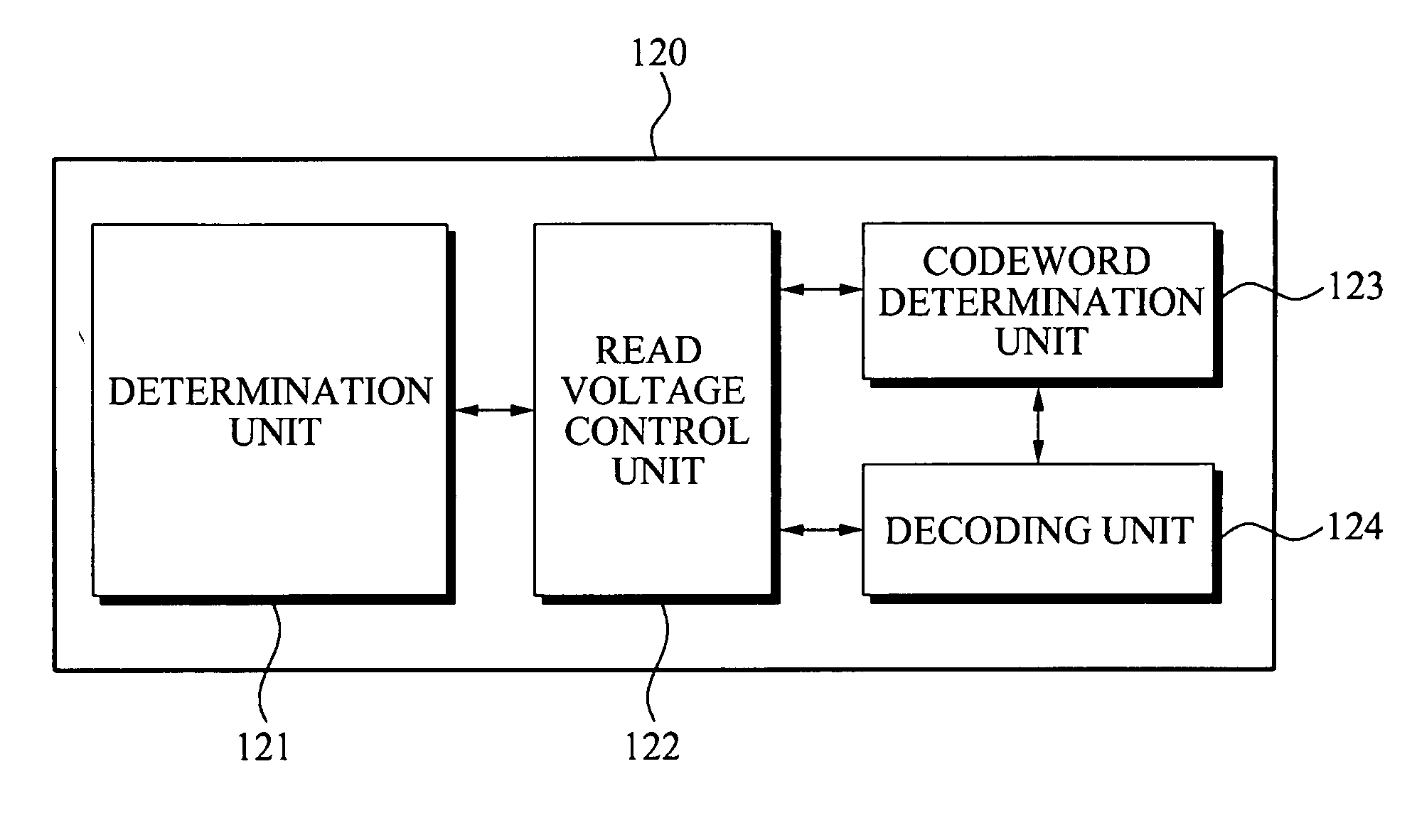
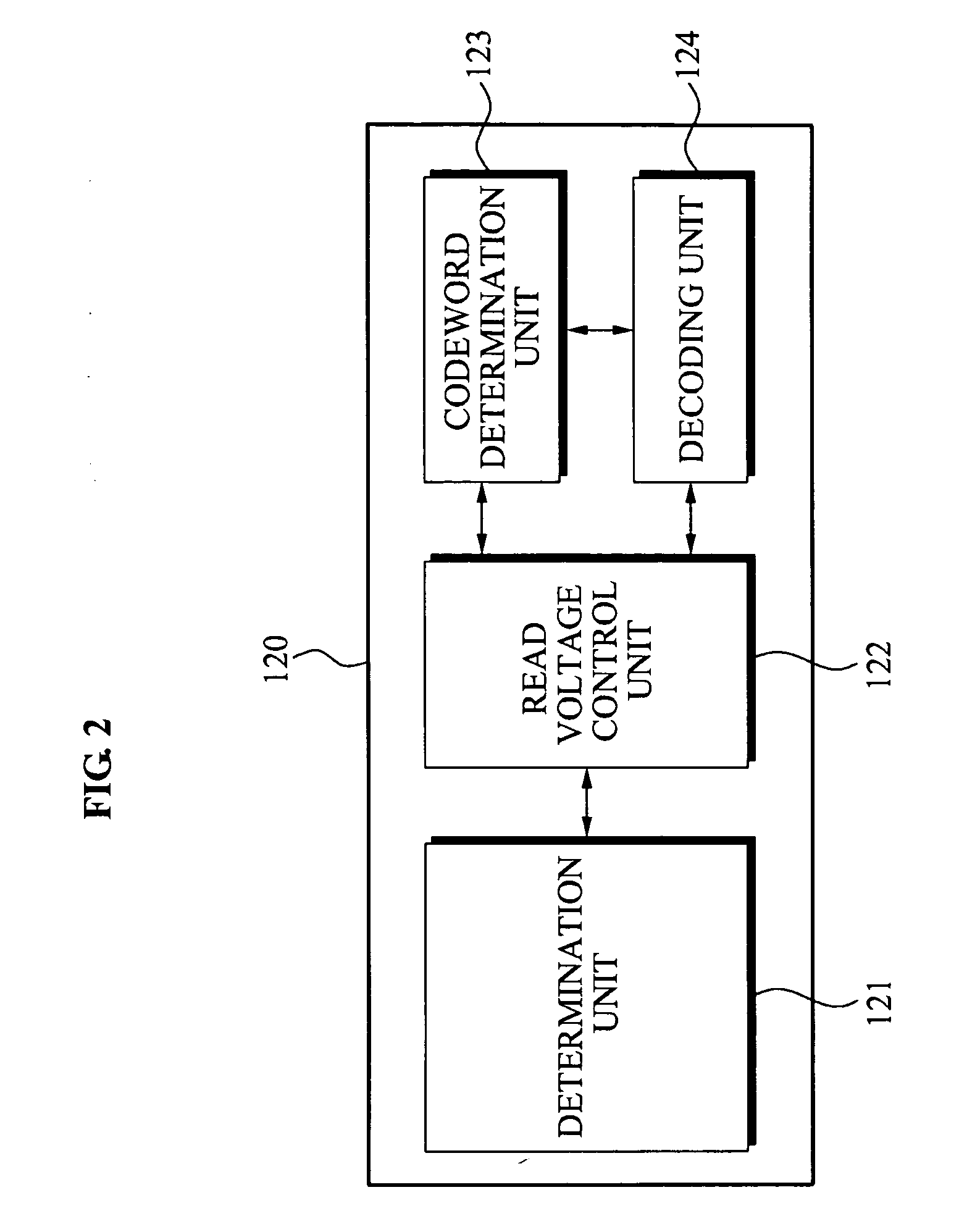
An error correction apparatus, a method thereof, and a memory device including the apparatus are provided. The error correction apparatus may include: a determination unit configured to determine whether a number of errors in a read word being read and extracted from a multi-level cell (MLC) exists in an error correcting capability range; a read voltage control unit configured to either increase or decrease a read voltage applied to the MLC when the number of errors in the read word is outside the error correcting capability range; and a codeword determination unit configured to analyze a bit error based on the increase or decrease of the read voltage, and to select a codeword corresponding to the analyzed bit error based on a selected read error pattern. Through this, it may be possible to efficiently correct a read error that occurs when the data of the memory device is maintained for a long time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
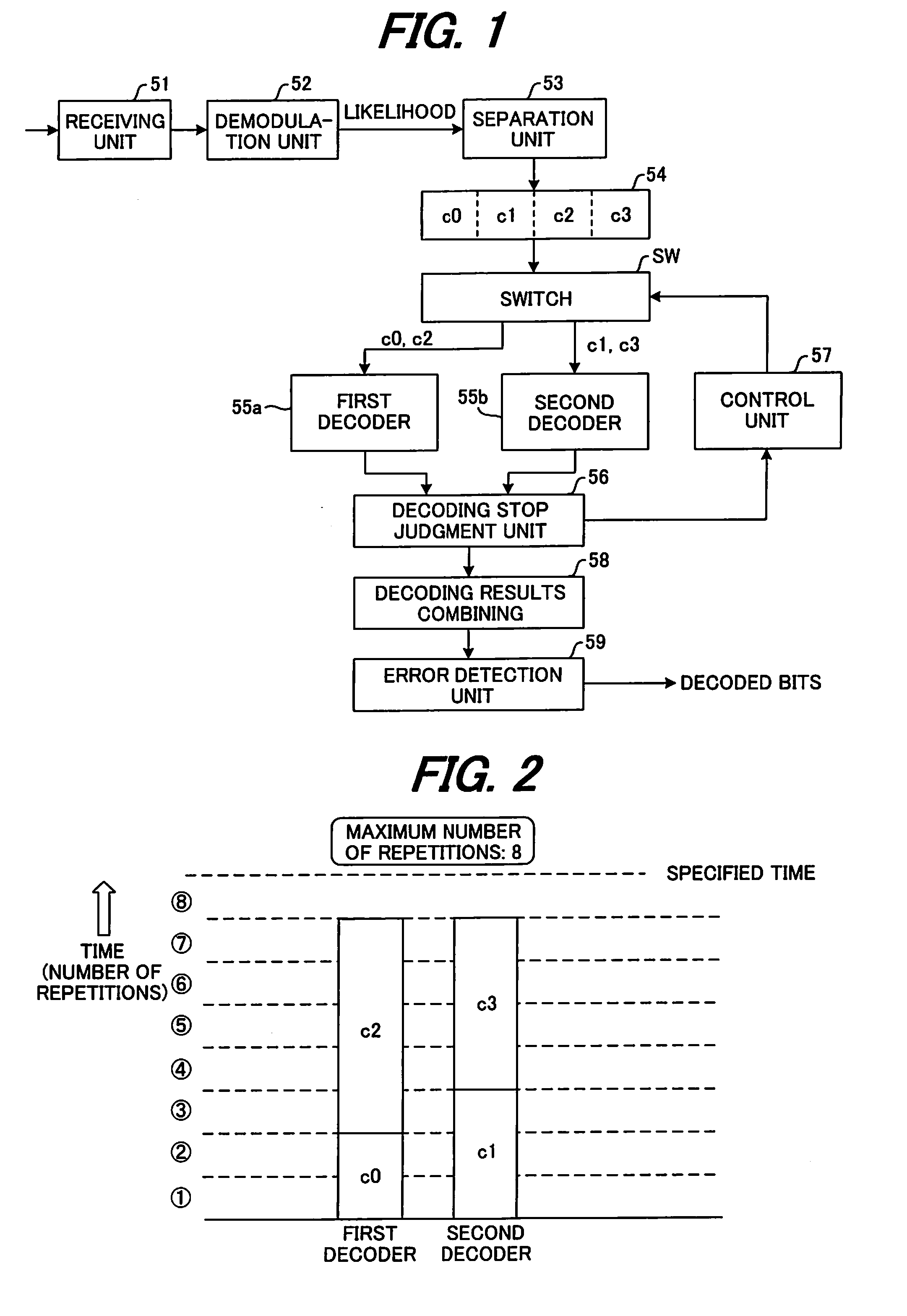
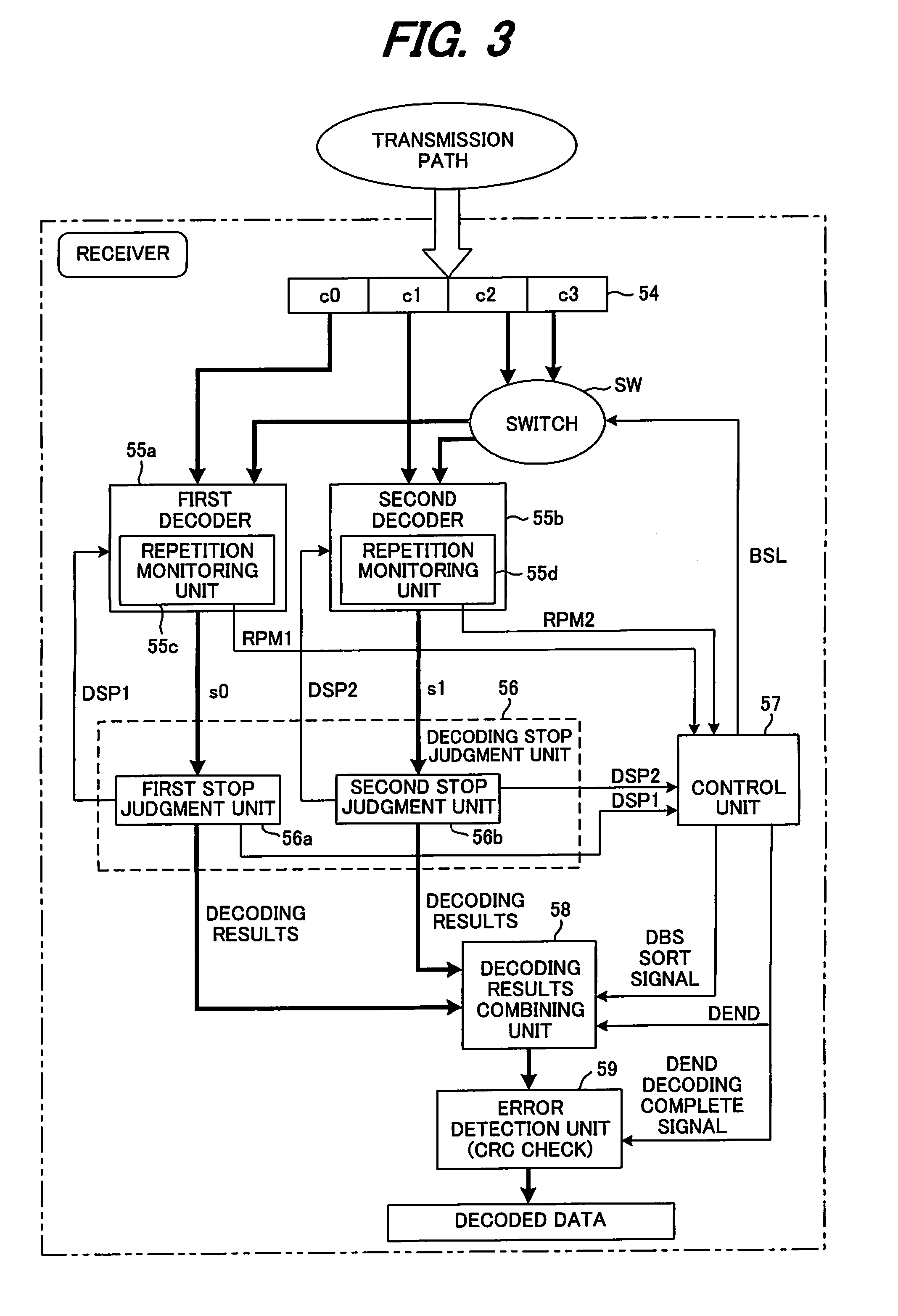
Receiving device and decoding method thereof
InactiveUS20090132893A1Avoid mistakesReduce the numberOther decoding techniquesCode conversionComputer hardwareDecoding methods
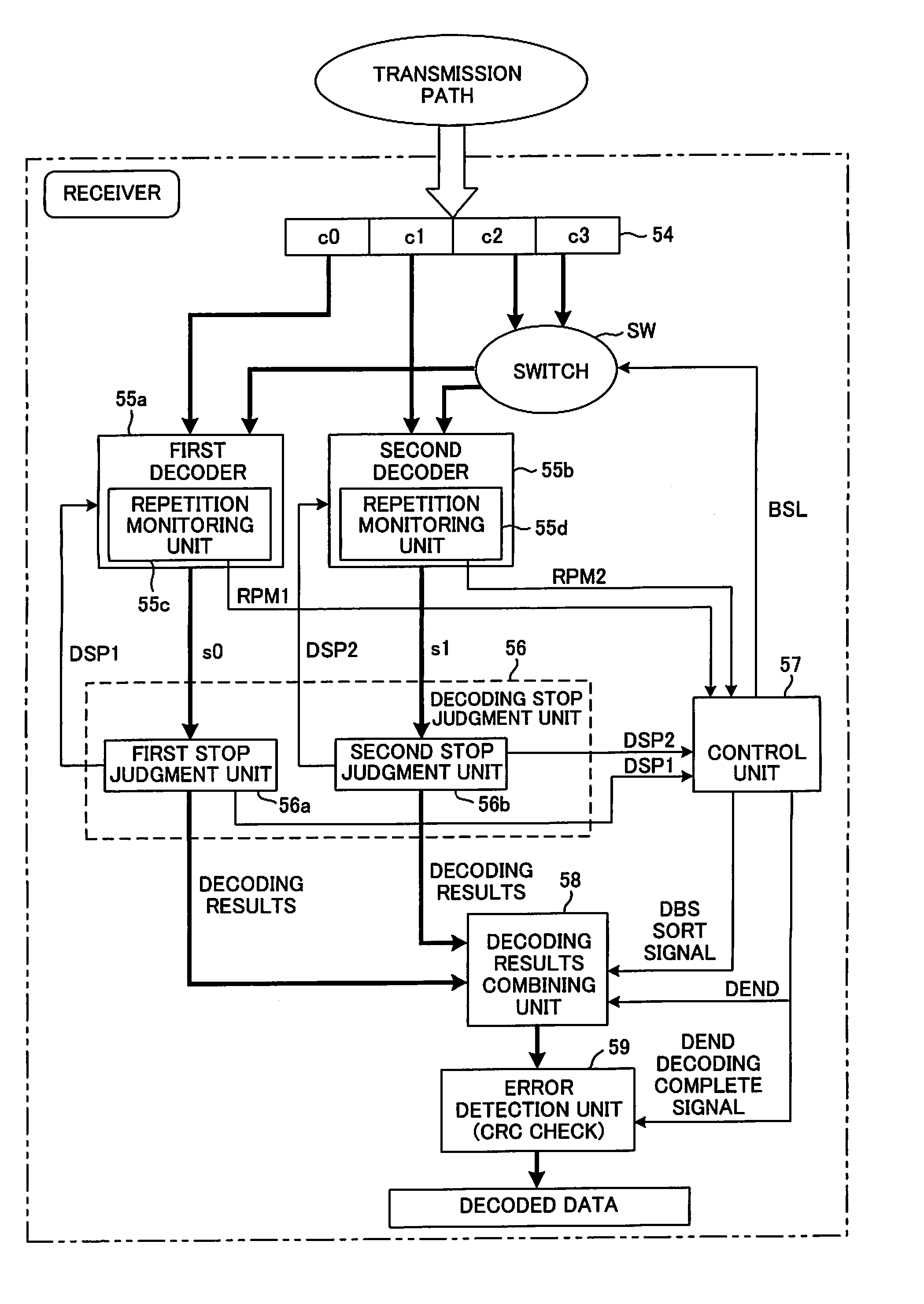
A receiving device in a communication system that separates one frame of information bits into plural blocks, performs turbo encoding of the information bits of each block and transmits the result, and decodes the encoded information bits, where the receiving device includes plural decoders number of which is less than the number of blocks per frame. Each decoder performs a decoding process on encoded information bits of each block that have been expressed by likelihood, when a condition for stopping decoding is met, executes the decoding process of encoded information bits of another block for which decoding has not yet been performed. When the condition for stopping decoding has been met for all block before the number of times decoding has been performed for each decoder reaches a preset maximum number of repetitions, the decoding results of all the blocks are serially combined, an error detection process is executed, and when no error is detected, the decoding results are output.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
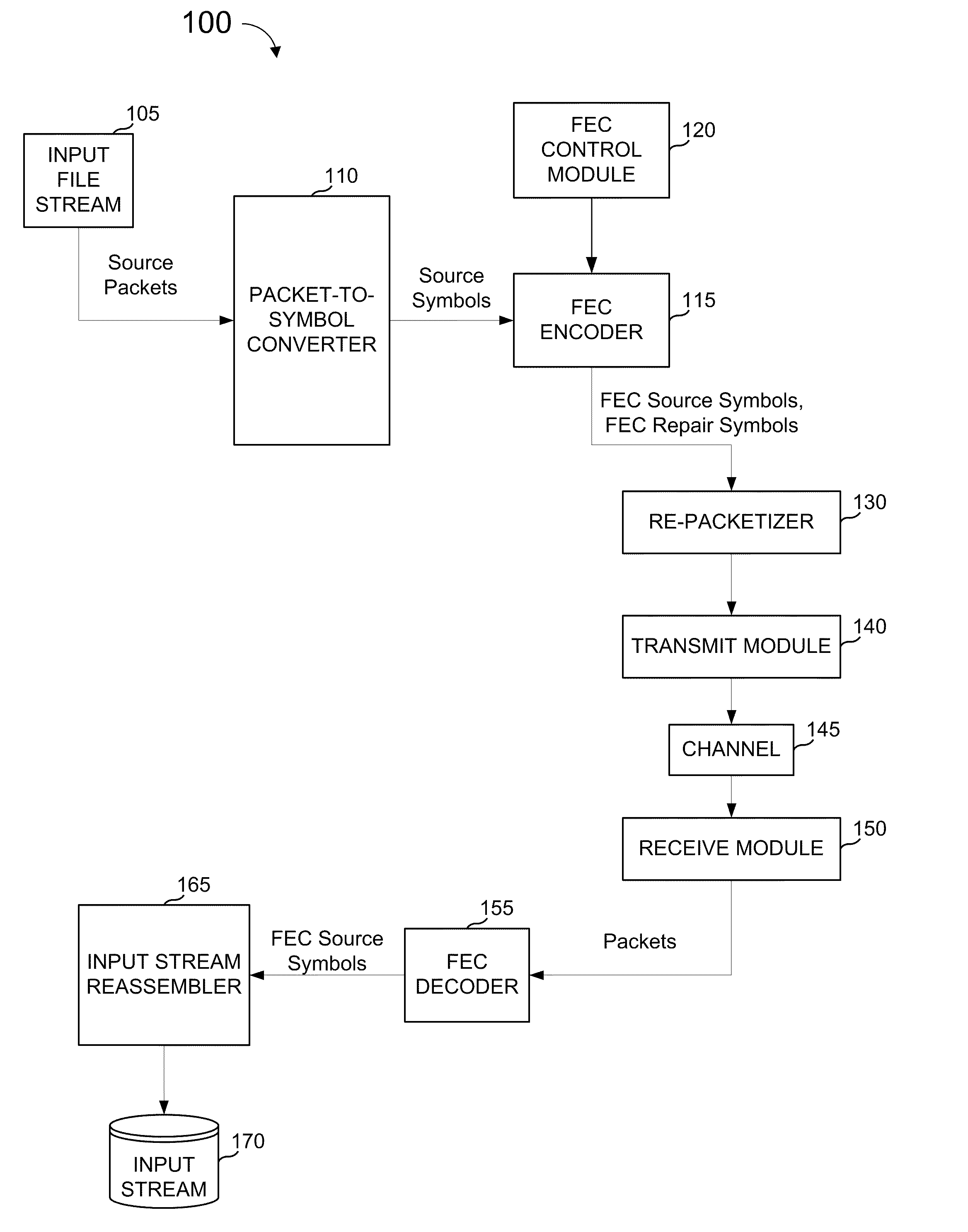
Fec architecture for streaming services including symbol based operations and packet tagging
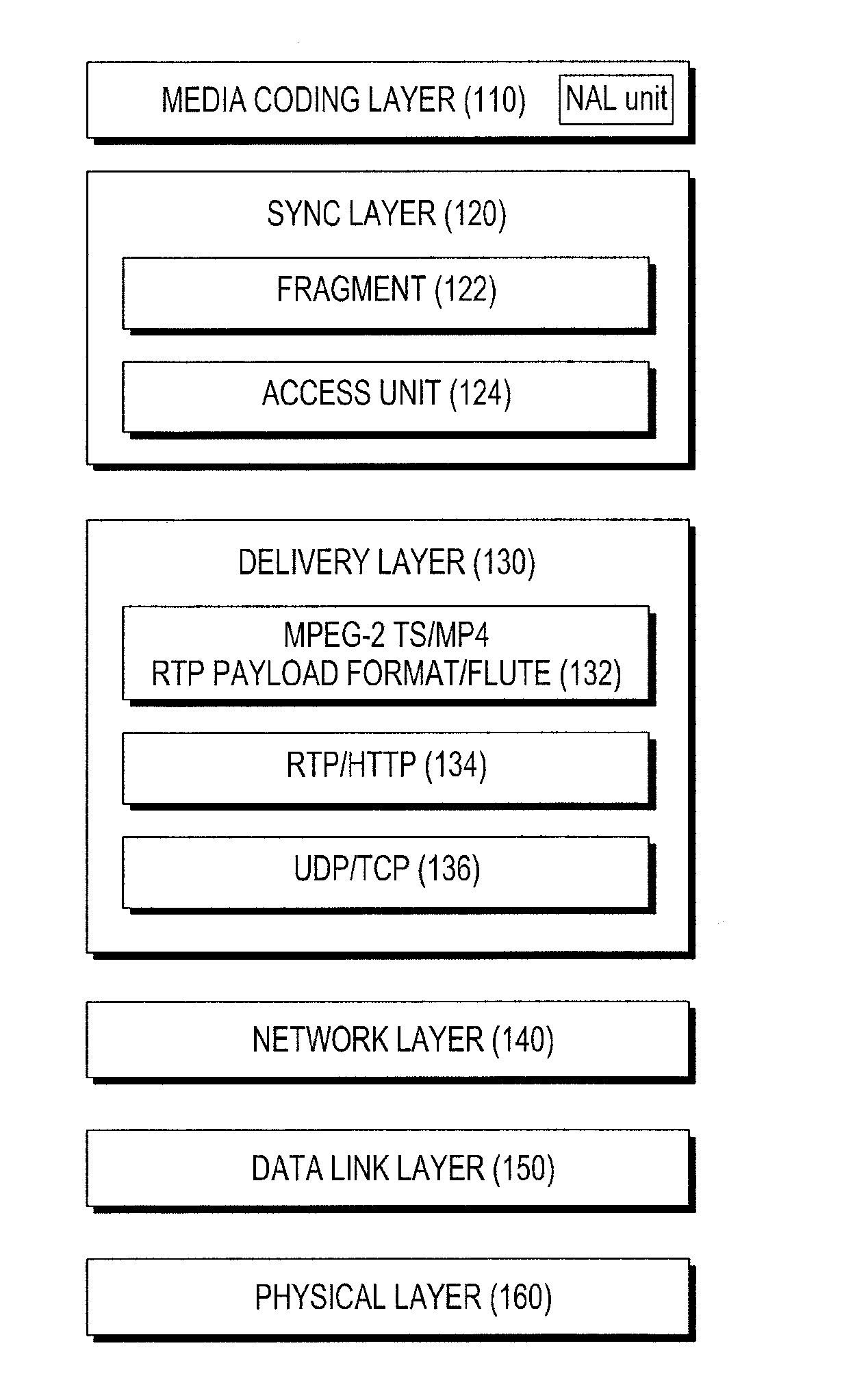
ActiveUS20100050057A1Easy to useFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsPacket communicationGroup communication systems
In a packet communications system stream data is transported over a channel over which packet loss or corruption is possible, with forward error correction (“FEC”) information. A transmitter receives source packets comprising source data, generates FEC source packets formatted to allow for identification of lost or corrupted source packets at a receiver, arranges source data from the source packets into a plurality of source symbols wherein at least one source packet is arranged into more than one source symbol, associates a plurality of source symbols with a source block, generates a plurality of repair symbols from the source block according to a predetermined FEC encoding process and groups the plurality of repair symbols into one or more FEC repair packets associated with the source block. A receiver can use the FEC repair symbols from the FEC repair packets to recover source symbols, as needed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
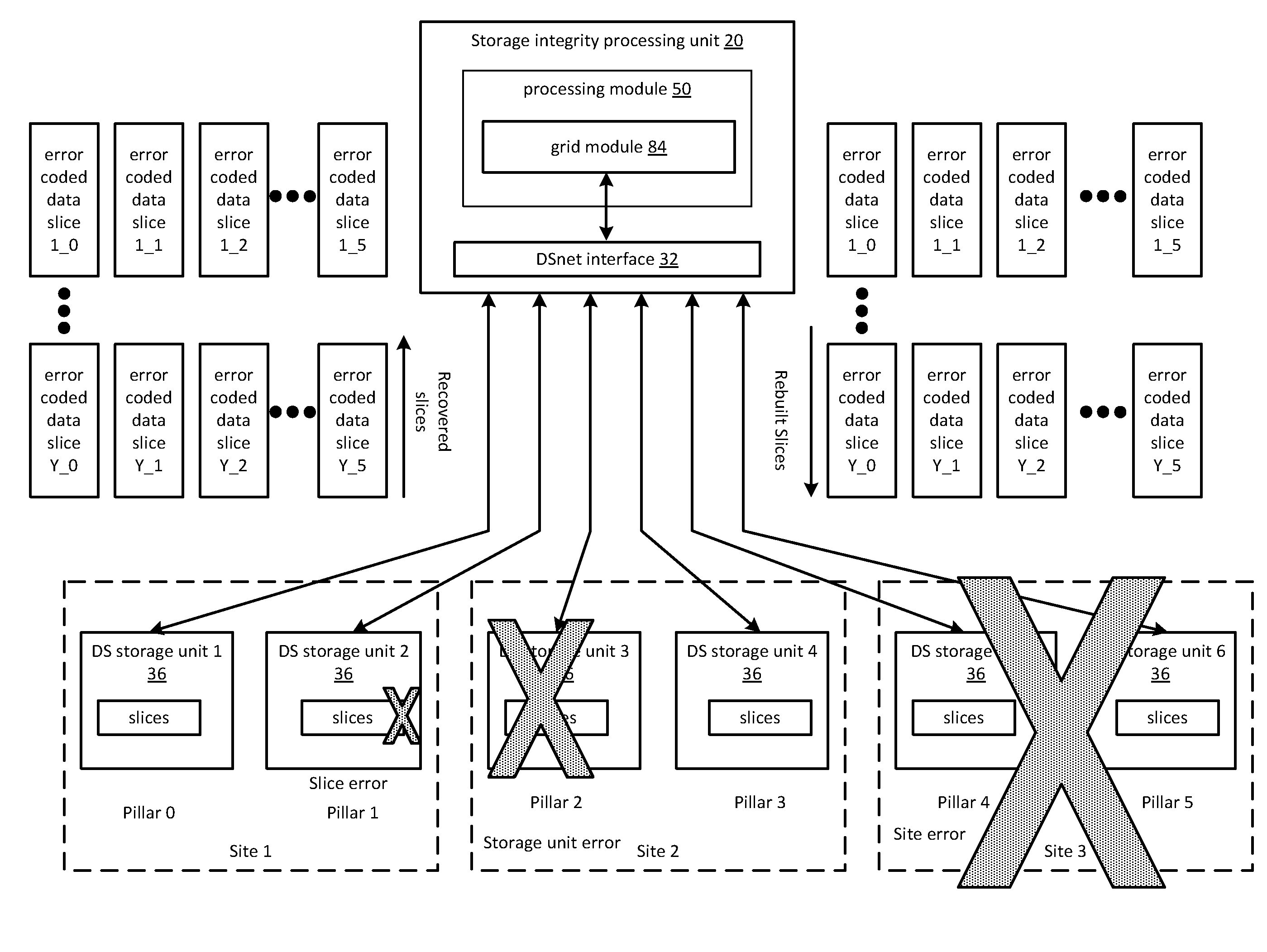
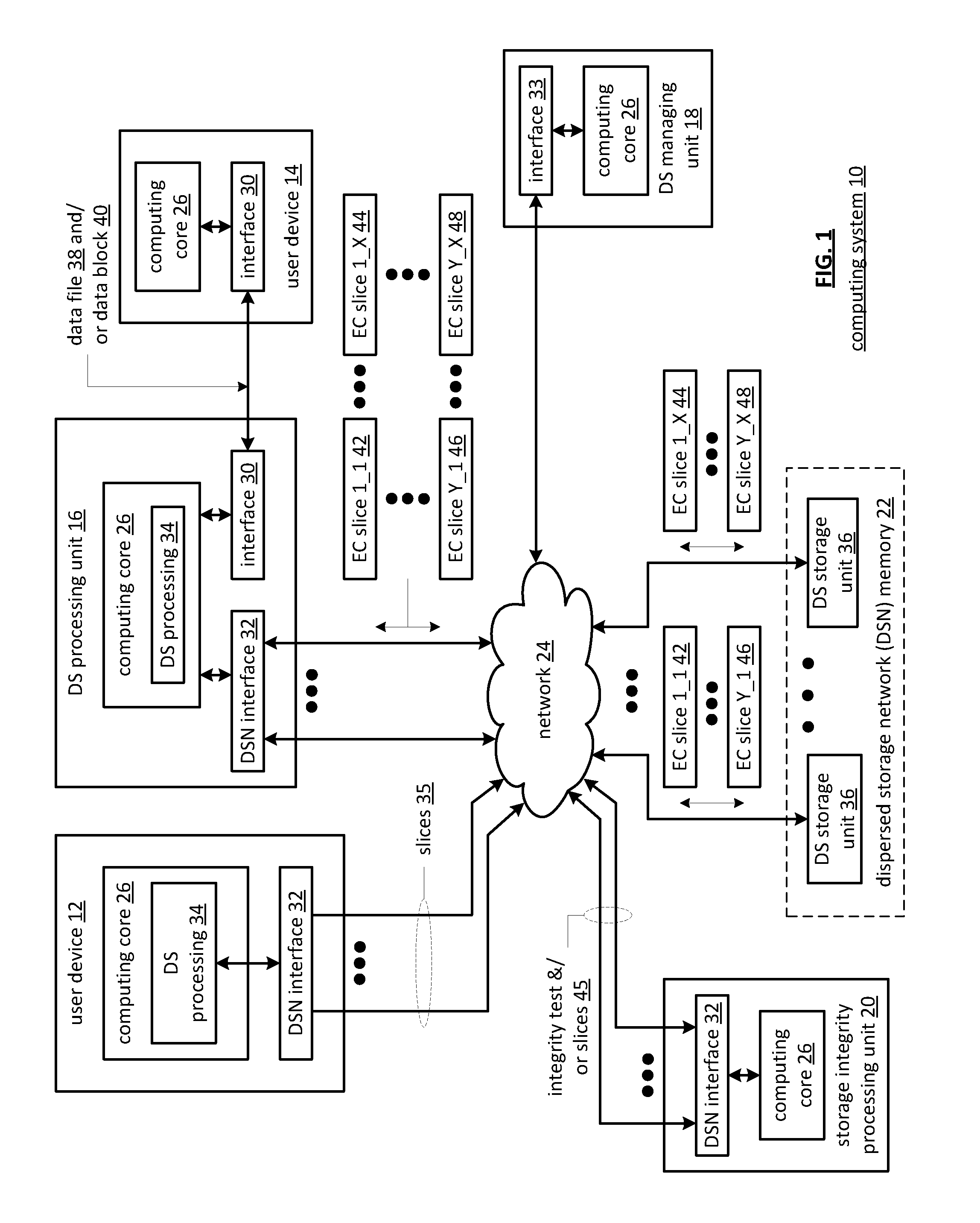
Method and apparatus for storage integrity processing based on error types in a dispersed storage network
ActiveUS20110029836A1Code conversionError correction/detection using block codesData segmentTime segment
A storage integrity system in a dispersed storage network scans an address range of data slices to identify errors in one of a plurality of encoded data slices, wherein the plurality of encoded data slices are generated from a data segment using an error encoding dispersal function. When the storage integrity system detects an error, it identifies one of the encoded data slices for rebuilding. The identified data slice is rebuilt in response to the type of error. For example, when the type of the error includes a temporary error, the storage integrity system waits a predetermined time period to determine whether the error still exists prior to rebuilding the identified data slice.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
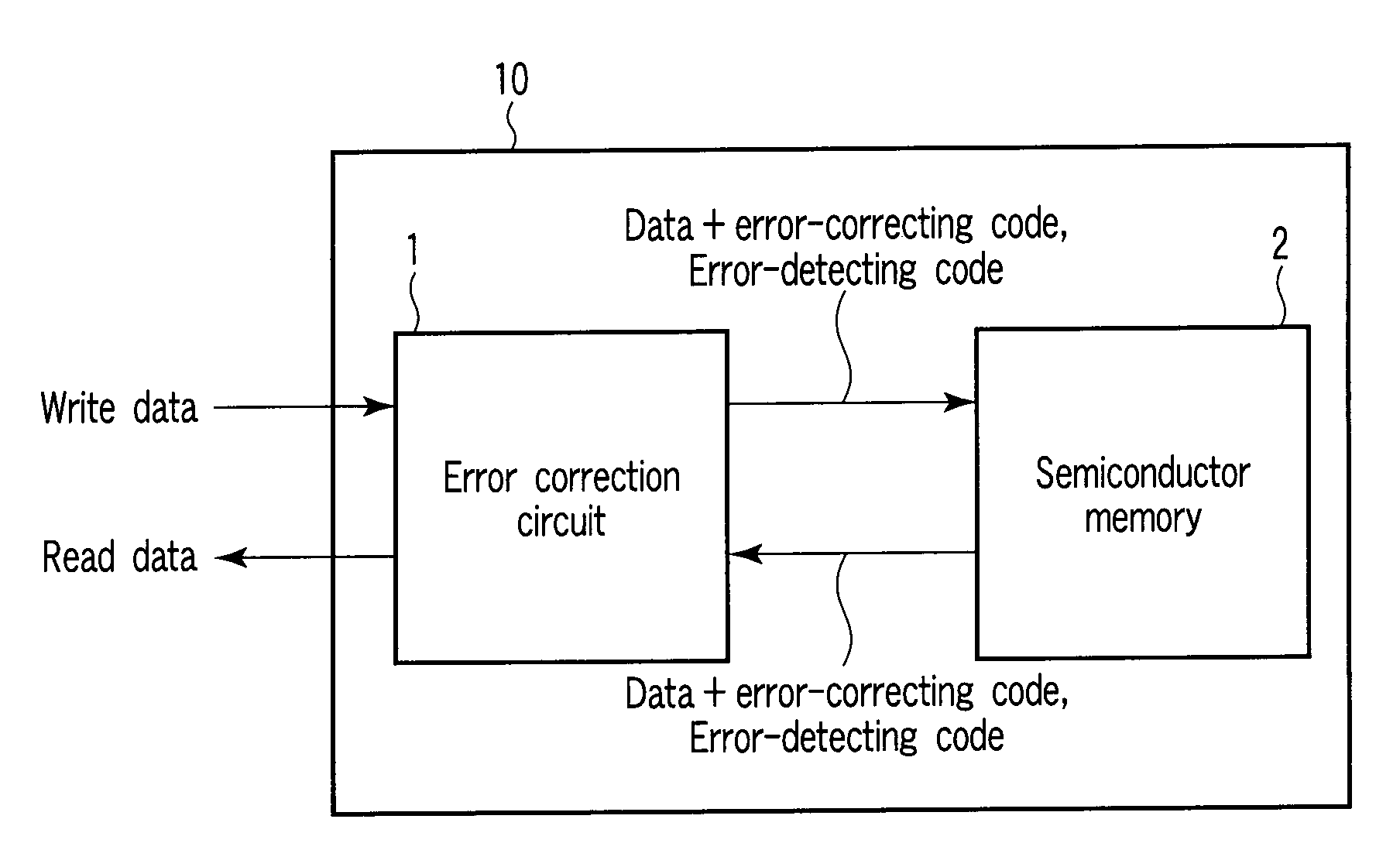
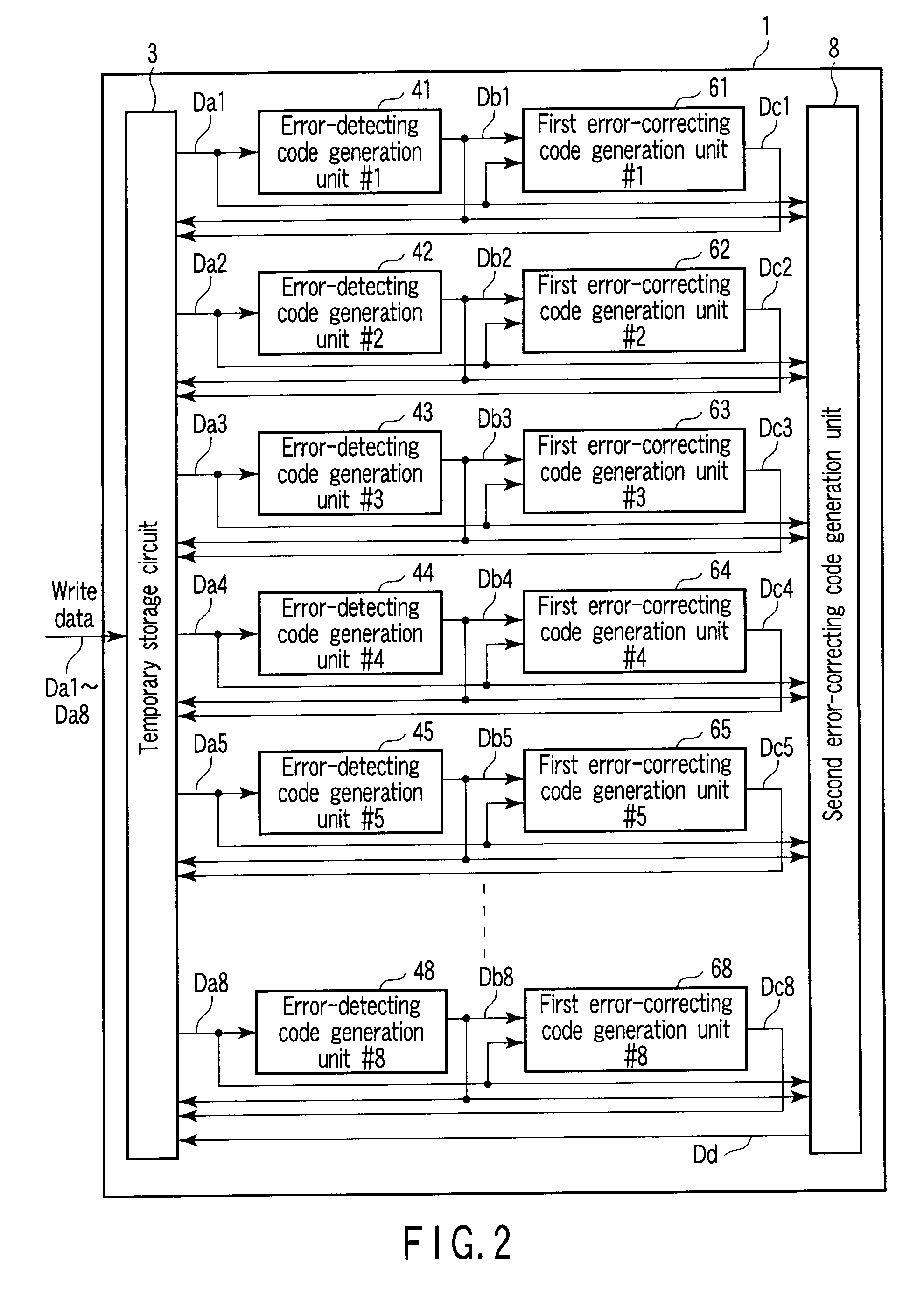
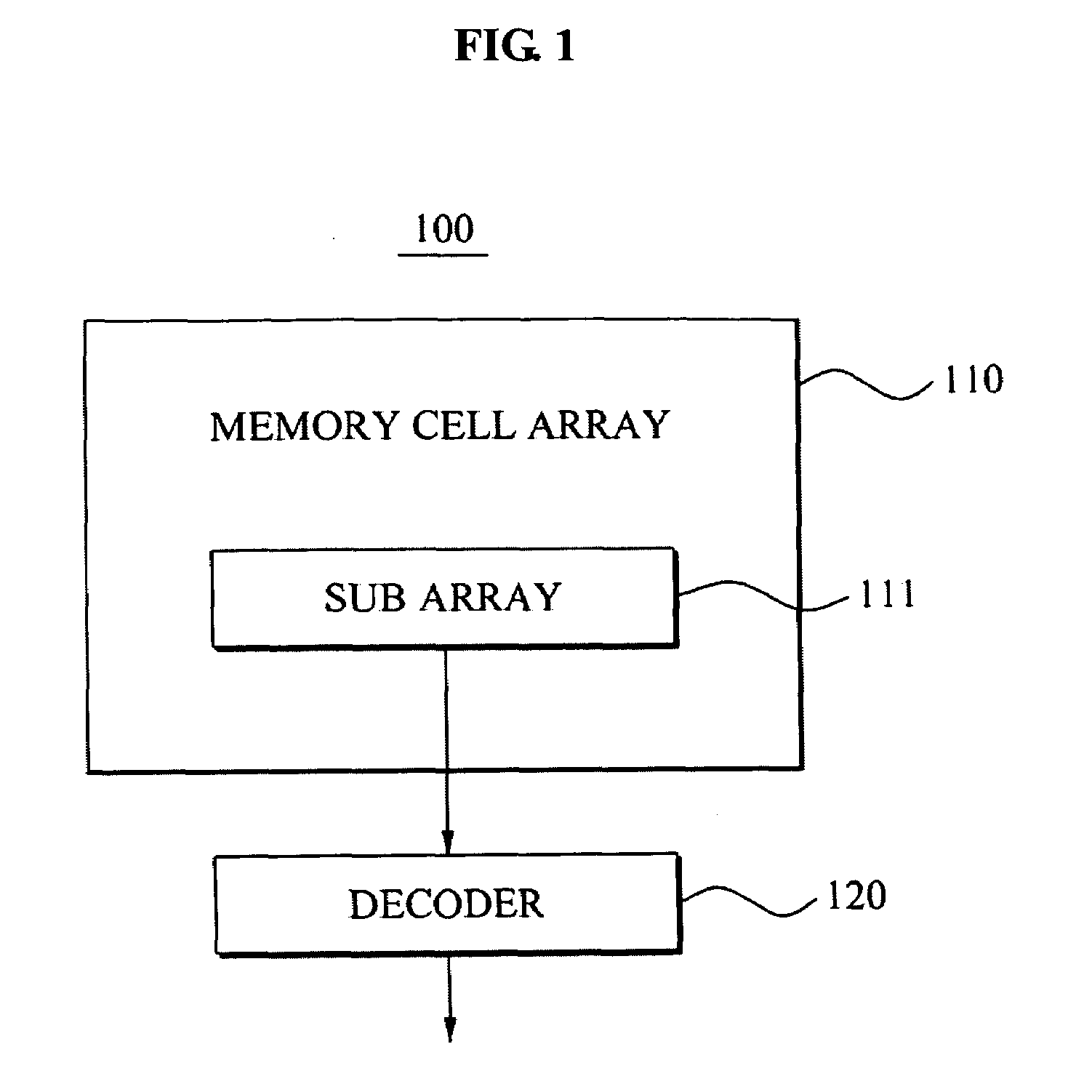
Semiconductor memory device and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20090183052A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareCode conversionSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A semiconductor memory device includes a plurality of detecting code generators configured to generate a plurality of detecting codes to detect errors in a plurality of data items, respectively, a plurality of first correcting code generators configured to generate a plurality of first correcting codes to correct errors in a plurality of first data blocks, respectively, each of the first data blocks containing one of the data items and a corresponding detecting code, a second correcting code generators configured to generate a second correcting code to correct errors in a second data block, the second data block containing the first data blocks, and a semiconductor memory configured to nonvolatilely store the second data block, the first correcting codes, and the second correcting code.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
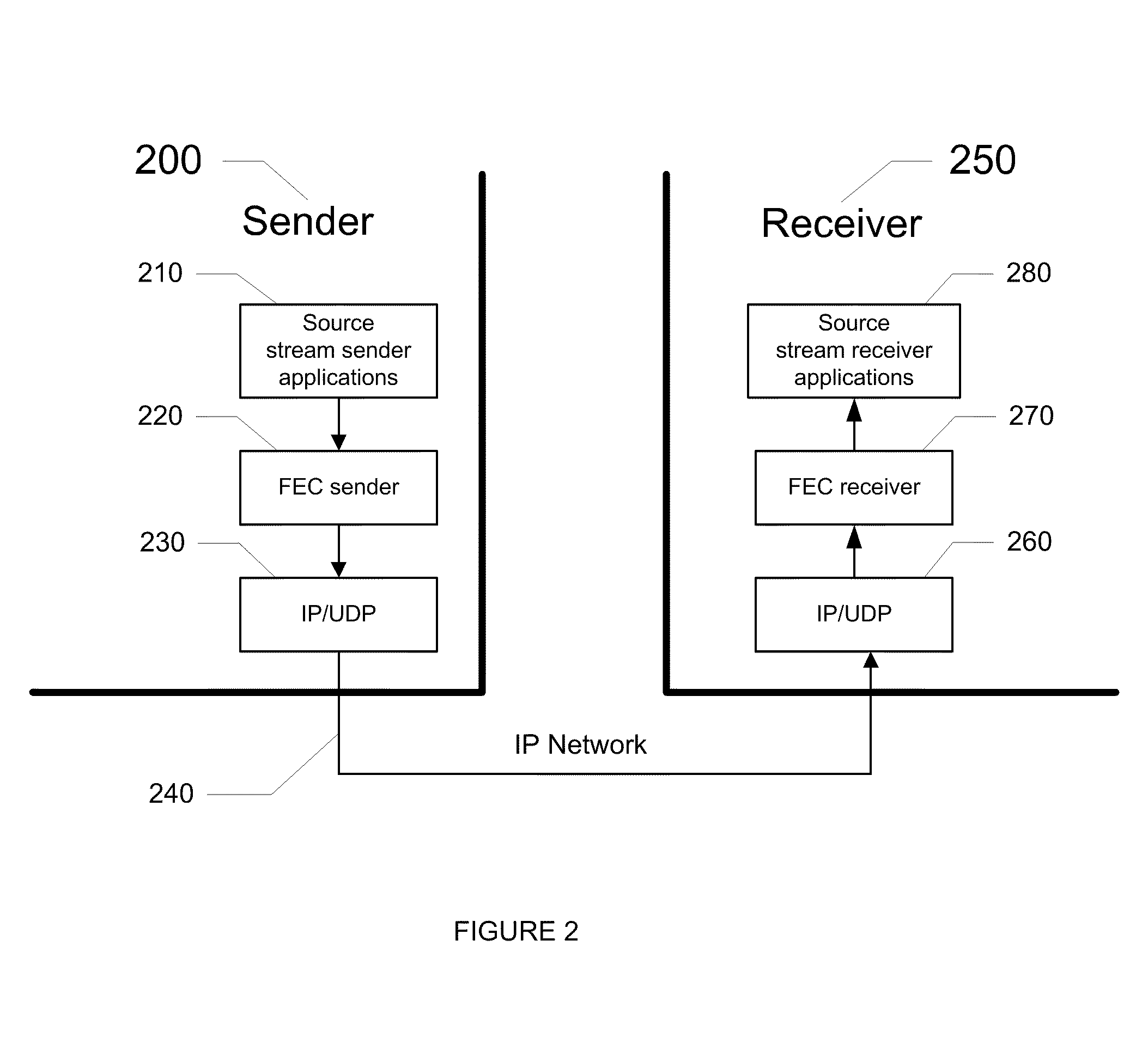
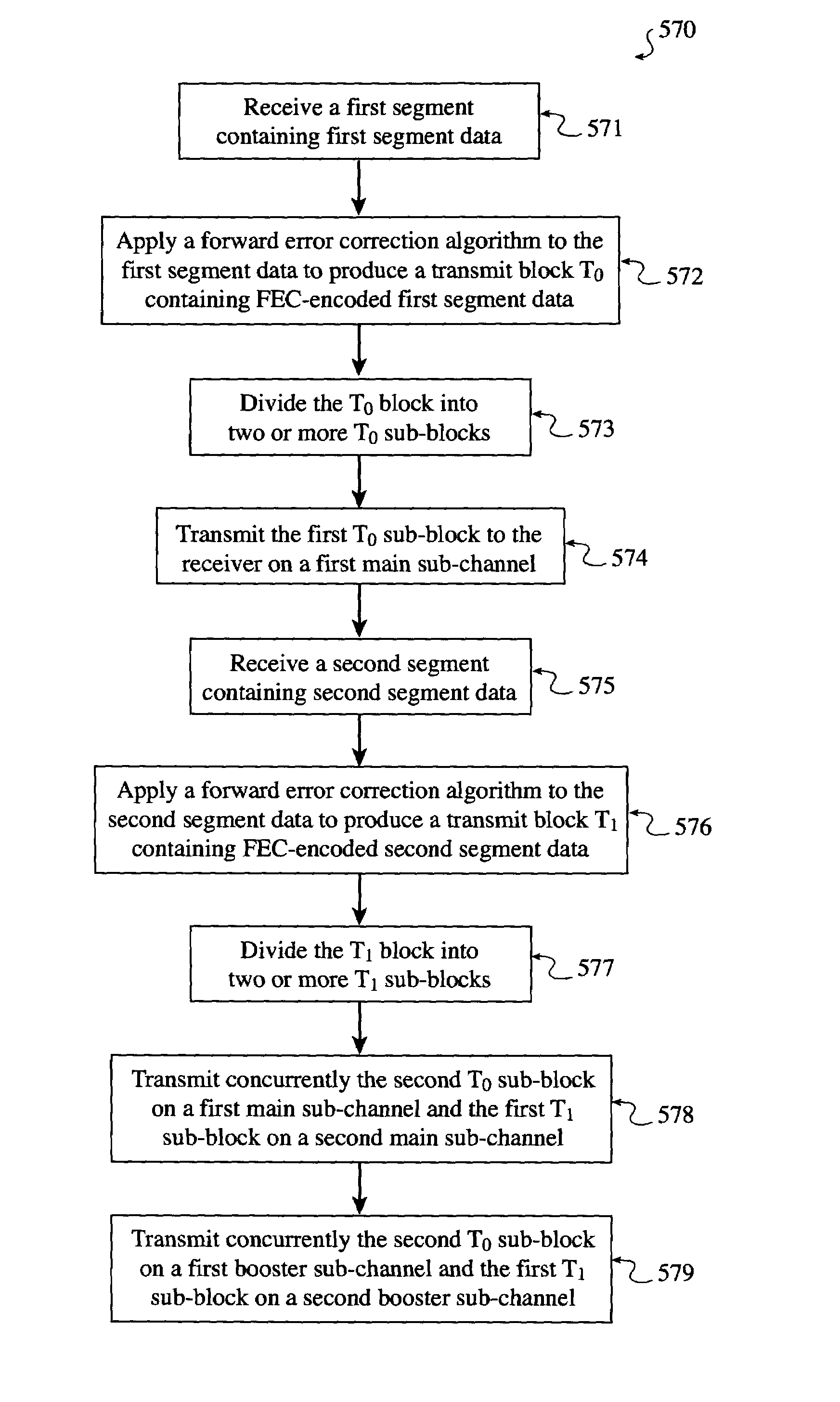
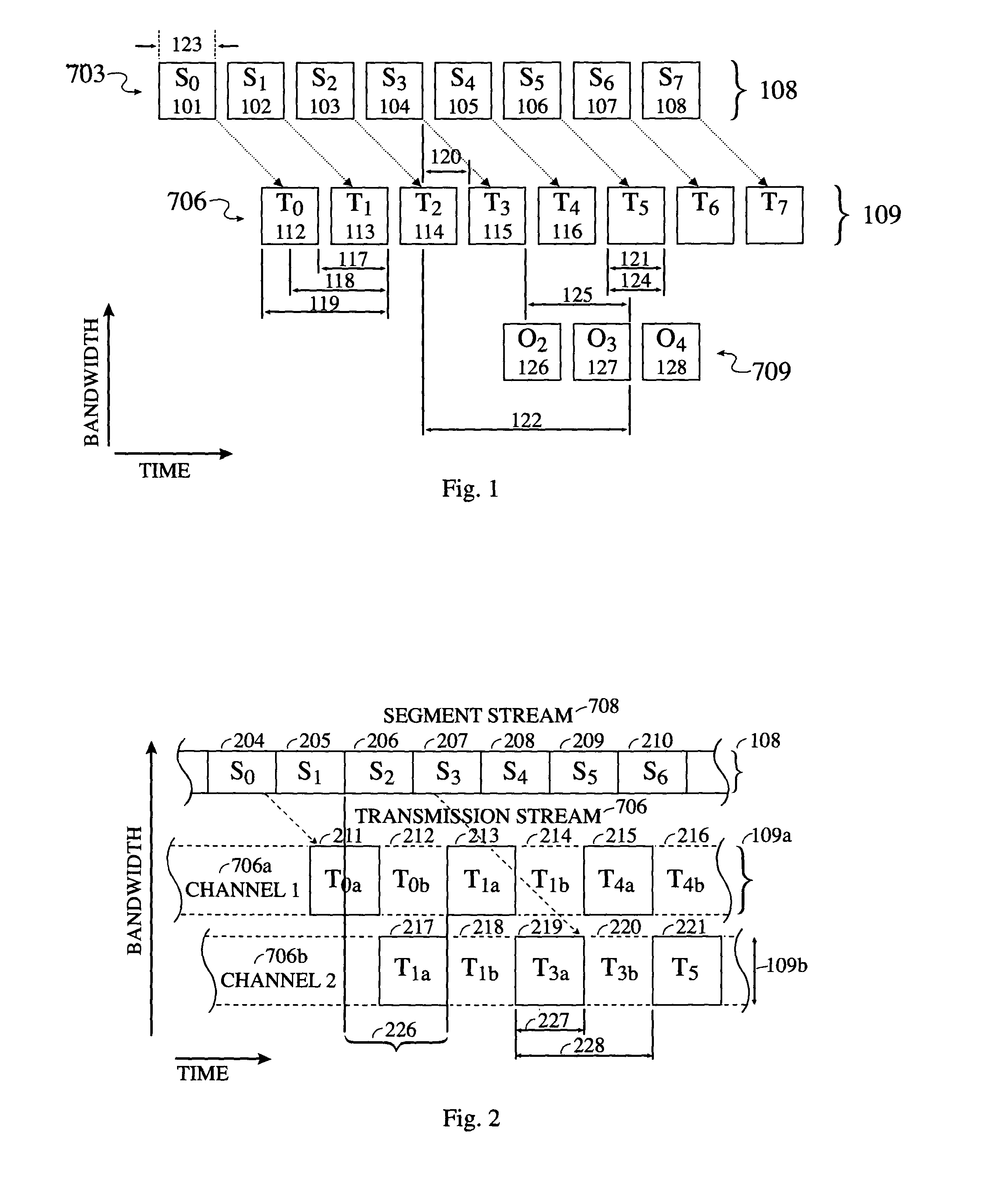
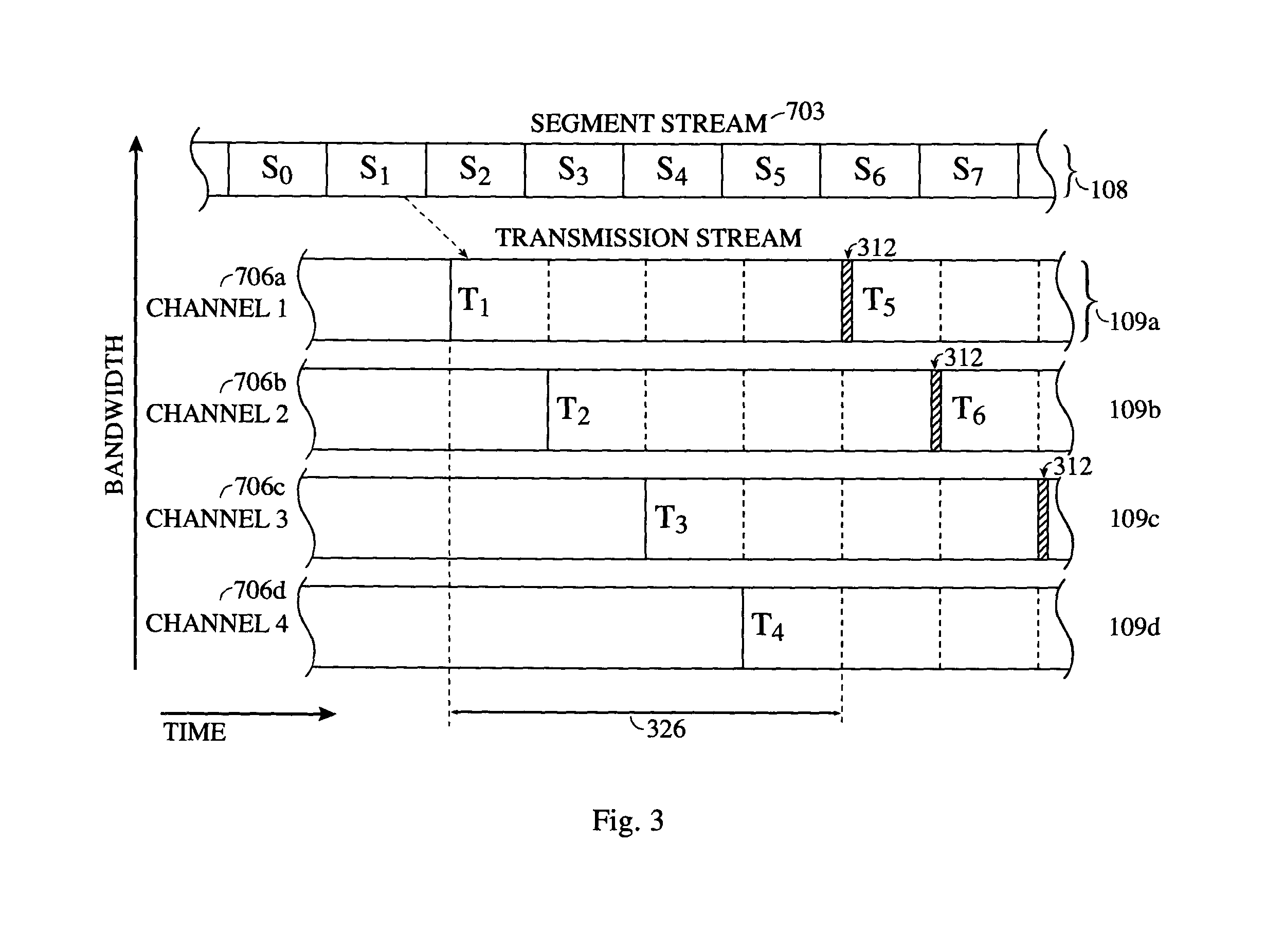
System and method for reliably communicating the content of a live data stream
InactiveUS7249291B2Reliable communicationIncreased start-up timePulse modulation television signal transmissionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareData stream
A method for communicating the content of a live data stream to a receiver using a plurality of channels comprising two encoder channels used to encode the live data content prior to transmission. Initially a plurality of segments of a live data stream are received, wherein each segment contains segment data. A forward error correction algorithm is applied to each segment's data, thereby producing FEC-encoded segment data. The FEC-encoded segment data is contained within an FEC-encoded block, resulting in a corresponding plurality of FEC-encoded blocks being generated. Each FEC-encoded block is copied to a sub-channel on both a first encoder channel and a second encoder channel, resulting in a plurality of FEC-encoder blocks residing on the first and second encoder channels. The first and second encoder channels differ in the number of sub-channels they contain (interleaving depth), and accordingly the arrangement of the FEC-encoded blocks in the first and second encoder channels are different. A first cross-section of the FEC-encoded segment data contained within the FEC-encoded blocks resident in the first encoder channel is added to a first transmit block T0. Similarly, A first cross-section of the FEC-encoded segment data contained within the FEC-encoded blocks resident in the second encoder channel is added to a second transmit block T1. The first and second transmit blocks are then communicated to the receiver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Methods of Performing Error Detection/Correction in Nonvolatile Memory Devices
ActiveUS20110209031A1Facilitate error detectionFacilitate correction operationRead-only memoriesCode conversionHigh probabilityData error
Methods of operating nonvolatile memory devices include testing a plurality of strings of nonvolatile memory cells in the memory device to identify at least one weak string therein having a higher probability of yielding erroneous read data error relative to other ones of the plurality of strings. An identity of the at least one weak string may be stored as weak column information. This weak column information may be used to facilitate error detection and correction operations. In particular, an error correction operation may be performed on a first plurality of bits of data read from the plurality of strings using an algorithm that modifies a weighting of the reliability of one or more data bits in the first plurality of bits of data based on the weak column information. More specifically, an algorithm may be used that interprets a bit of data read from the at least one weak string as having a relatively reduced reliability relative to other ones of the first plurality of data bits.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
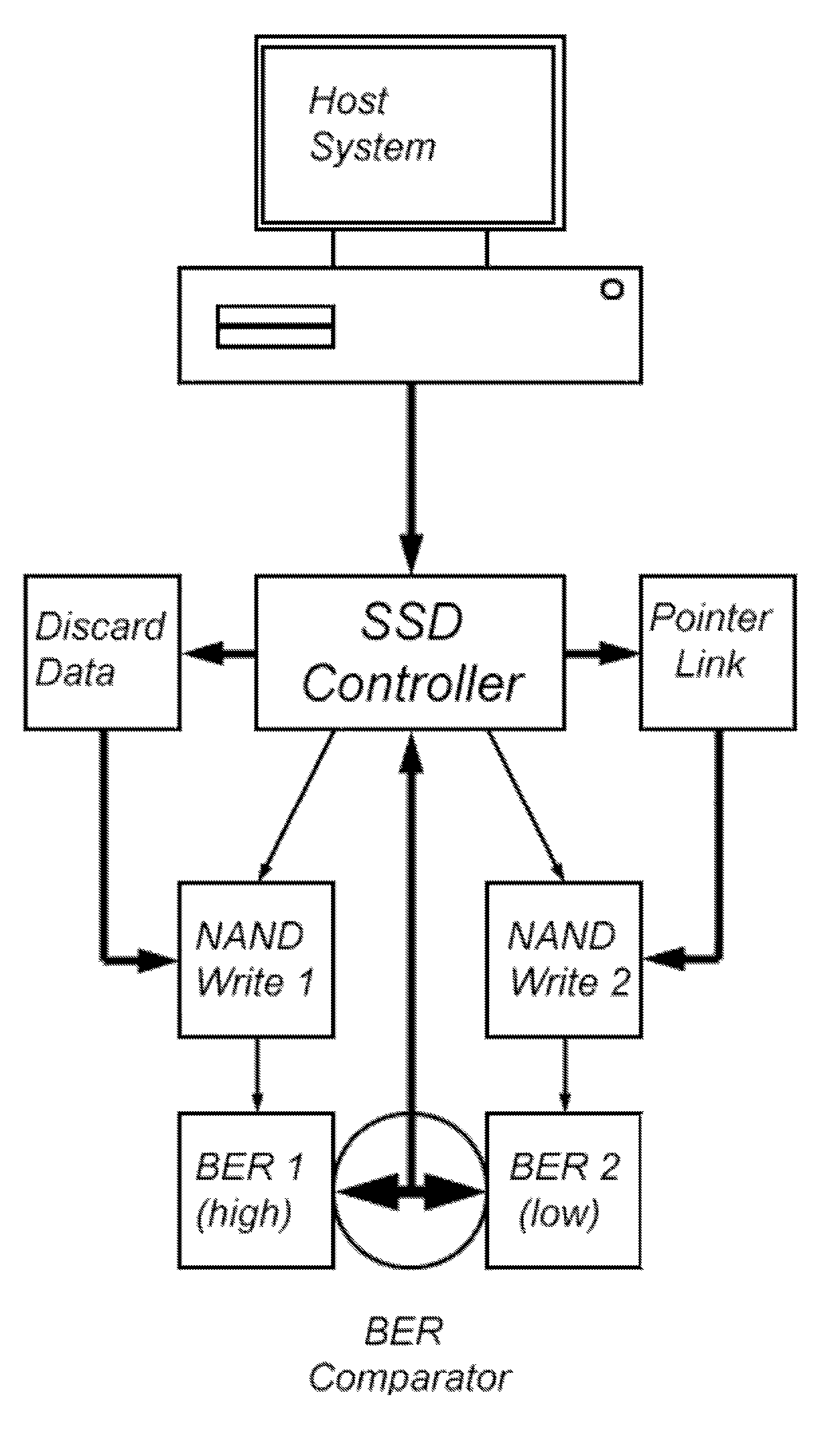
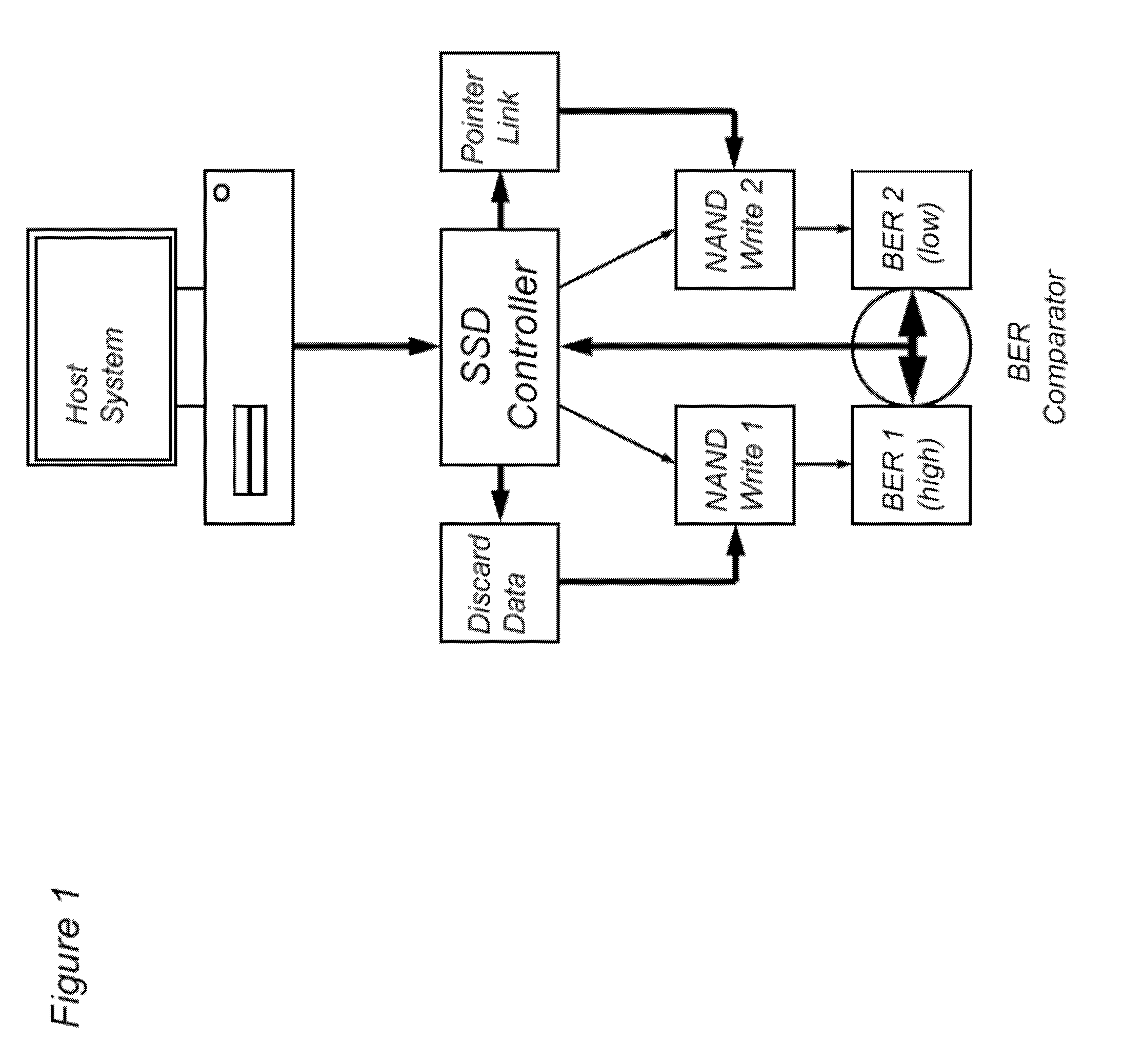
Solid-state memory-based storage method and device with low error rate
InactiveUS20130024735A1Low initial error rateReduce error rateError correction/detection using block codesRedundant data error correctionData setNon-volatile memory
Non-volatile solid-state memory-based storage devices and methods of operating the storage devices to have low initial error rates. The storage devices and methods use bit error rate comparison of duplicate writes to one or more non-volatile memory devices. The data set with a lower bit error rate as determined during verification is maintained, whereas data sets with higher bit error rates are discarded. A threshold of bit error rates can be used to trigger the duplication of data for bit error comparison.
Owner:OCZ STORAGE SOLUTIONS
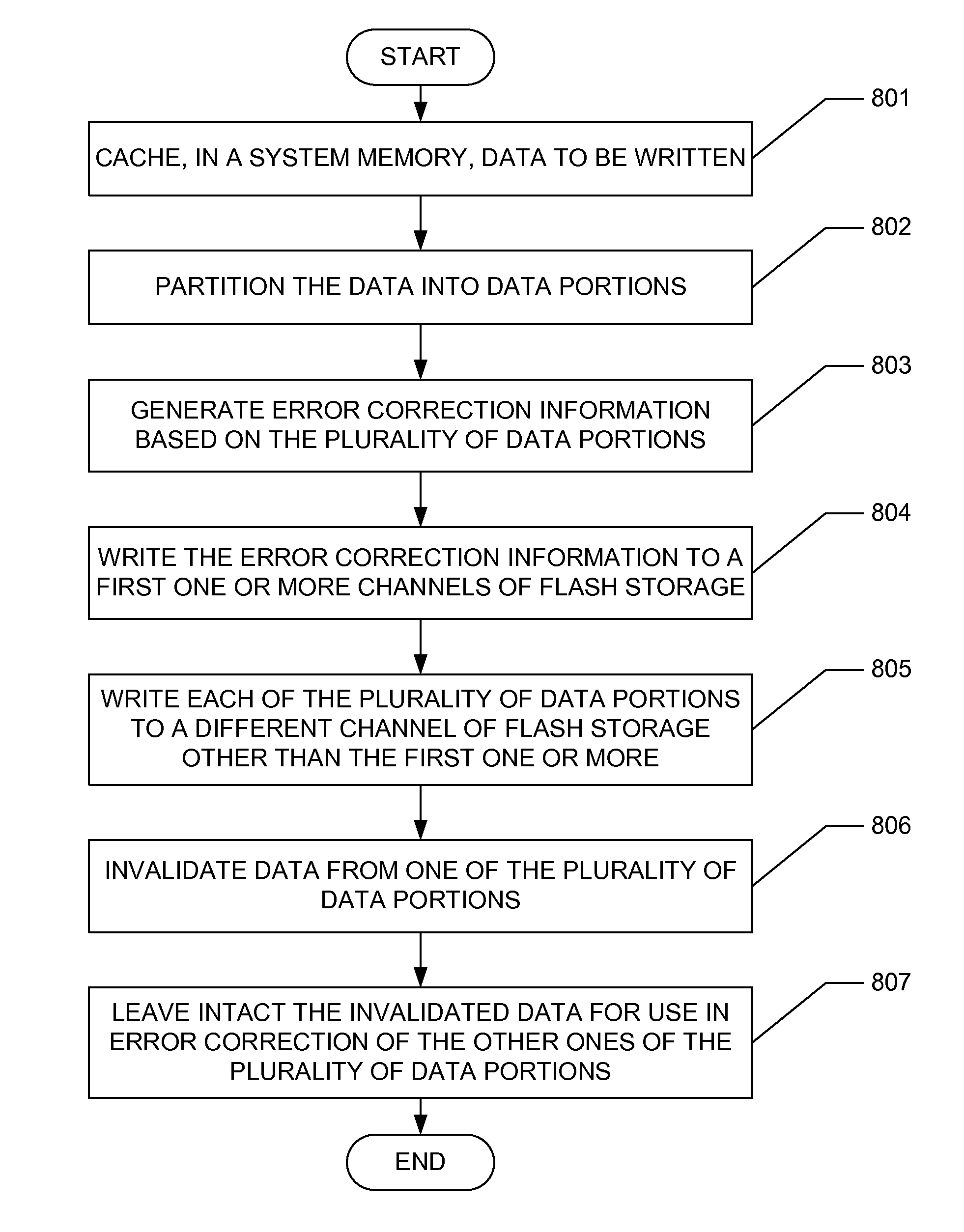
Redundant data distribution in a flash storage device
A flash storage device comprises a plurality of channels of flash storage, a system memory, and a controller. The controller is configured to cache, in the system memory, data to be written, to partition the data into a plurality of data portions, to generate error correction information based on the plurality of data portions, to write the error correction information to a first one or more of the plurality of channels of flash storage, and to write each of the plurality of data portions to a different one of the plurality of channels of flash storage other than the first one or more thereof.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Non-Volatile Memory and Method Having Efficient On-Chip Block-Copying with Controlled Error Rate
A non-volatile memory chip having SLC blocks acting as a write cache for MLC blocks for high density storage requires constant copying or folding of SLC blocks into MLC blocks. To avoid the time-consuming toggling out and in of the pages of the entire SLC block for ECC checking by a controller chip, only a small sample is checked. An optimal read point for reading the memory cells in the sample of the SLC block is dynamically determined by trying different read points so that the data is read within an error budget. Once the optimal read point is determined, it is used to read the entire SLC block without further error checking. Then the SLC block can be copied (blind folded) to the MLC block with the confidence of being within the error budget.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Conditional skip-layer decoding
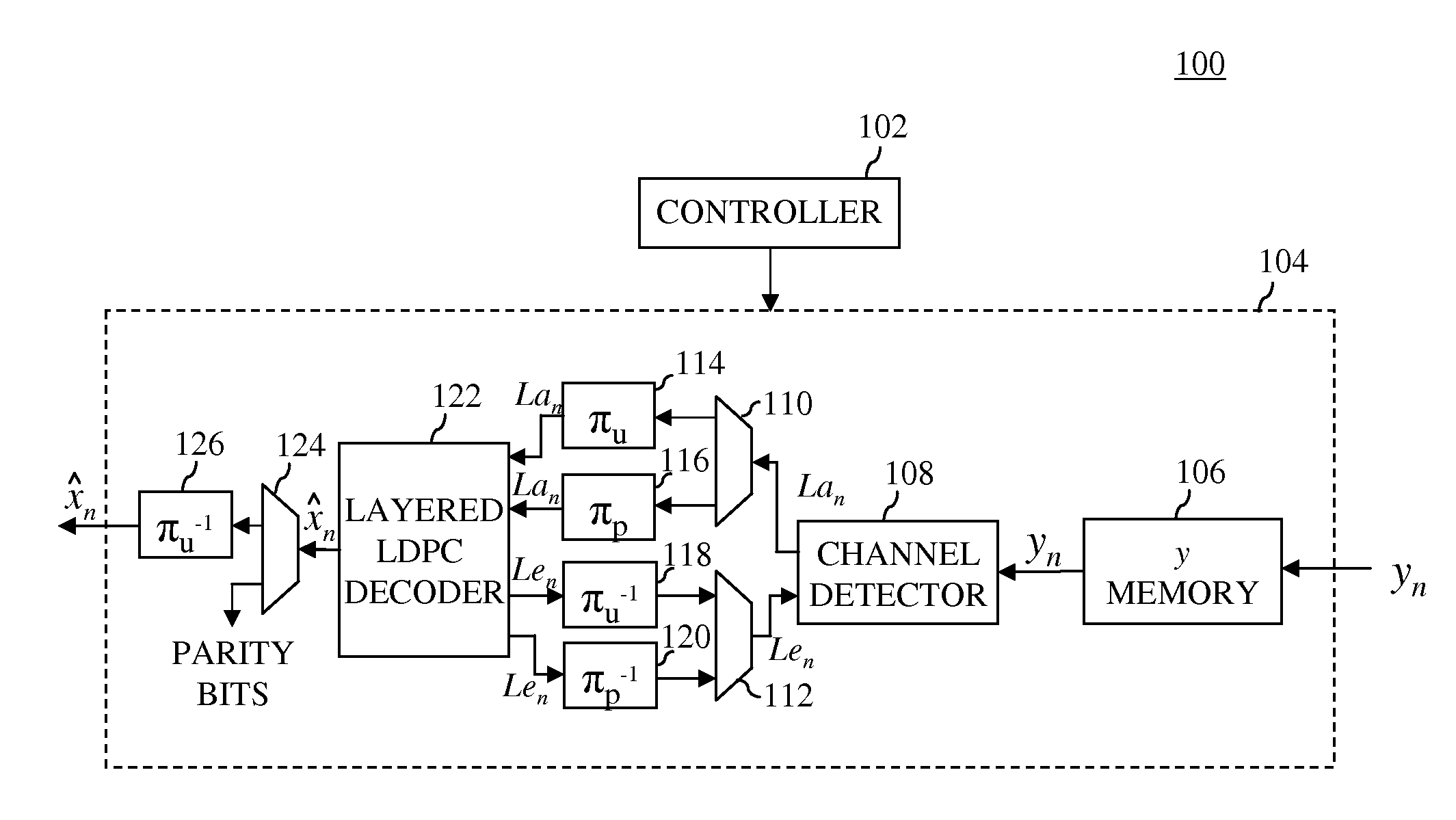
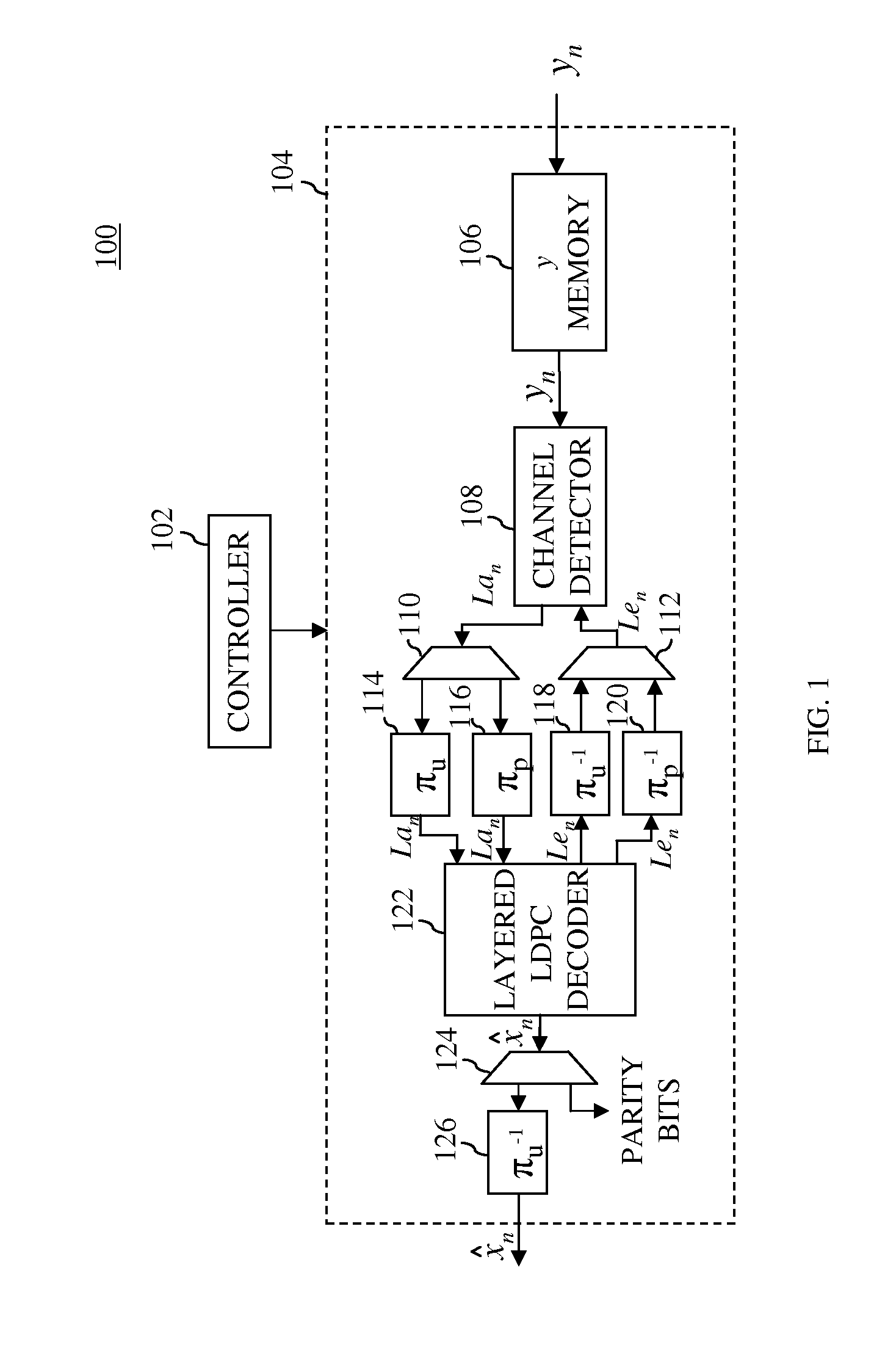
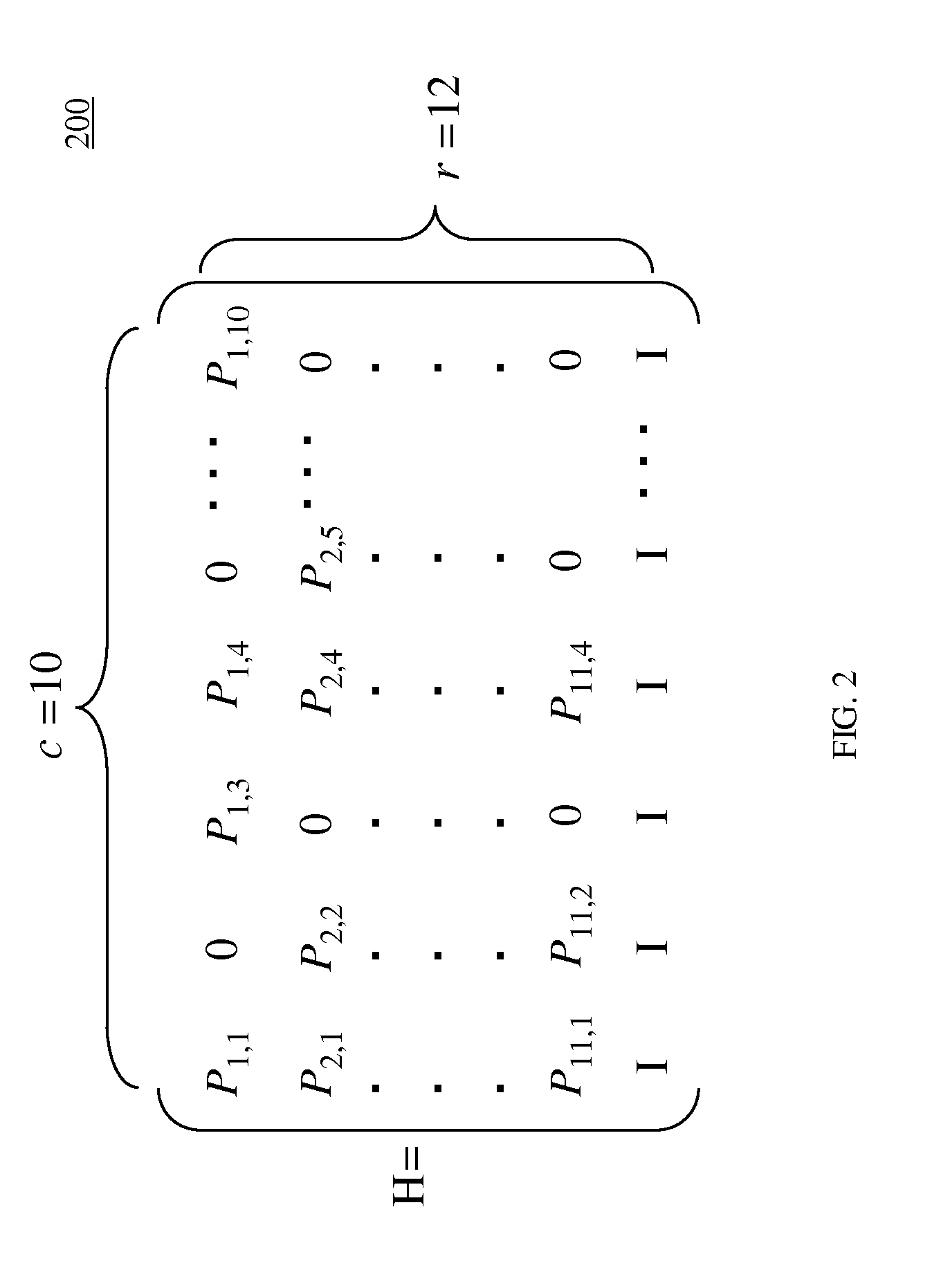
ActiveUS20110320902A1Code conversionError correction/detection using block codesComputer hardwareH matrix
In one embodiment, a turbo equalizer is selectively operable in either first or second modes. In the first mode, layered (low-density parity-check (LDPC)) decoding is performed on soft-output values generated by a channel detector, where, for each full local decoder iteration, the updates of one or more layers of the corresponding H-matrix are skipped. If decoding fails to converge on a valid LDPC-encoded codeword and a specified condition is met, then LDPC decoding is performed in a second mode, where the updates of all of the layers of the H-matrix are performed for each full local decoder iteration, including the one or more layers that were previously skipped in the first mode. Skipping one or more layers in the first mode increases throughput of the decoder, while updating all layers in the second mode increases error correction capabilities of the decoder.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System for establishing a cryptographic key depending on a physical system
ActiveUS20120072737A1Reduction of informationReduce decreaseKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareCryptographic nonce
In systems for establishing a cryptographic key depending on a physical uncloneable function (PUF) it may be a problem that internal information correlated with the cryptographic key is leaked to the outside of the system via a side-channel. To mitigate this problem a cryptographic system for reproducibly establishing a cryptographic key is presented. The system comprises a physical system comprising a physical, at least partially random, configuration of components from which an initial bit-string is derived. An error corrector corrects deviations occurring in the initial bit-string. Through the use of randomization the error corrector operates on a randomized data. Information leaking through a side channel is thereby reduced. After error correction a cryptographic key may be derived from the initial bit-string.
Owner:INTRINSIC ID
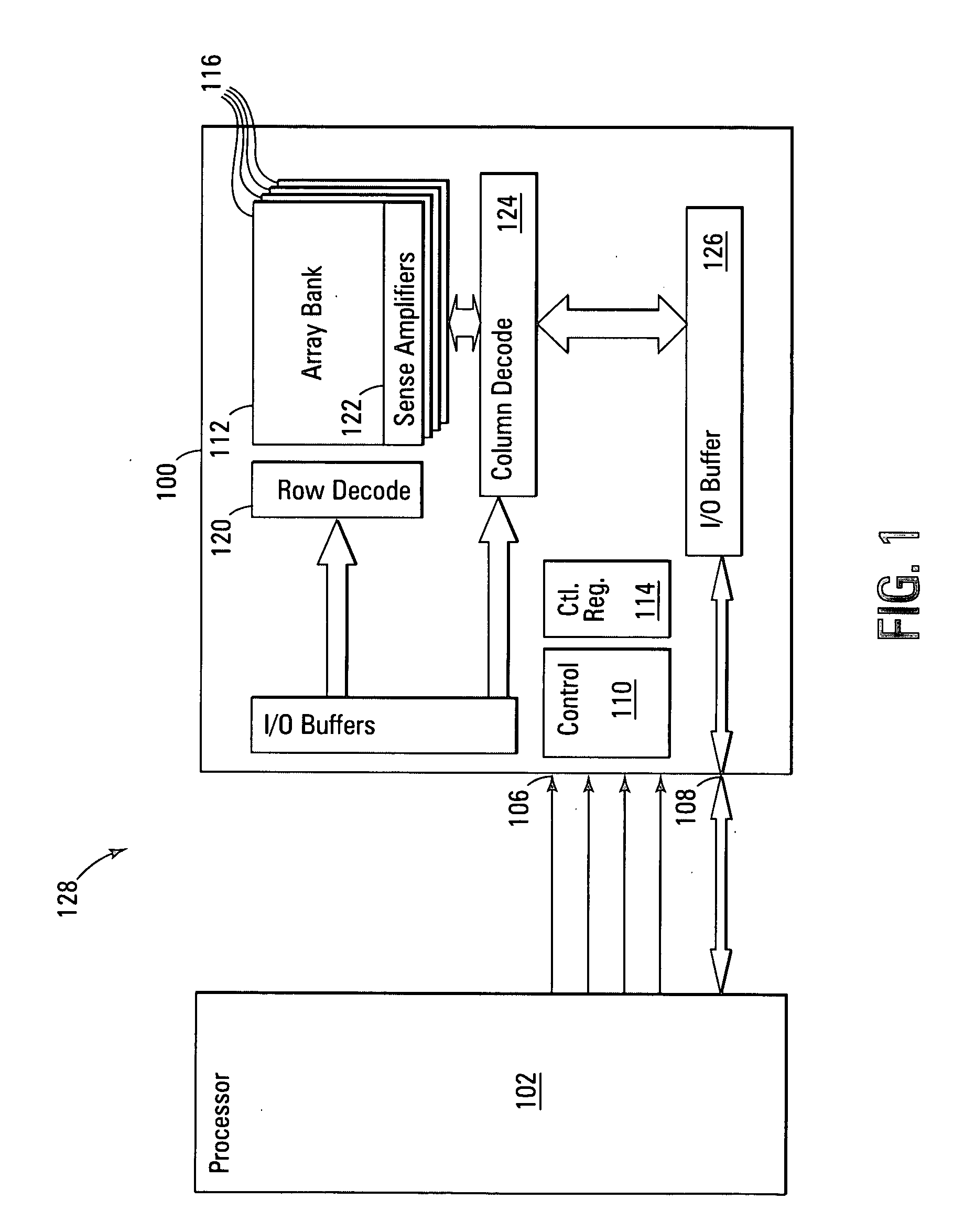
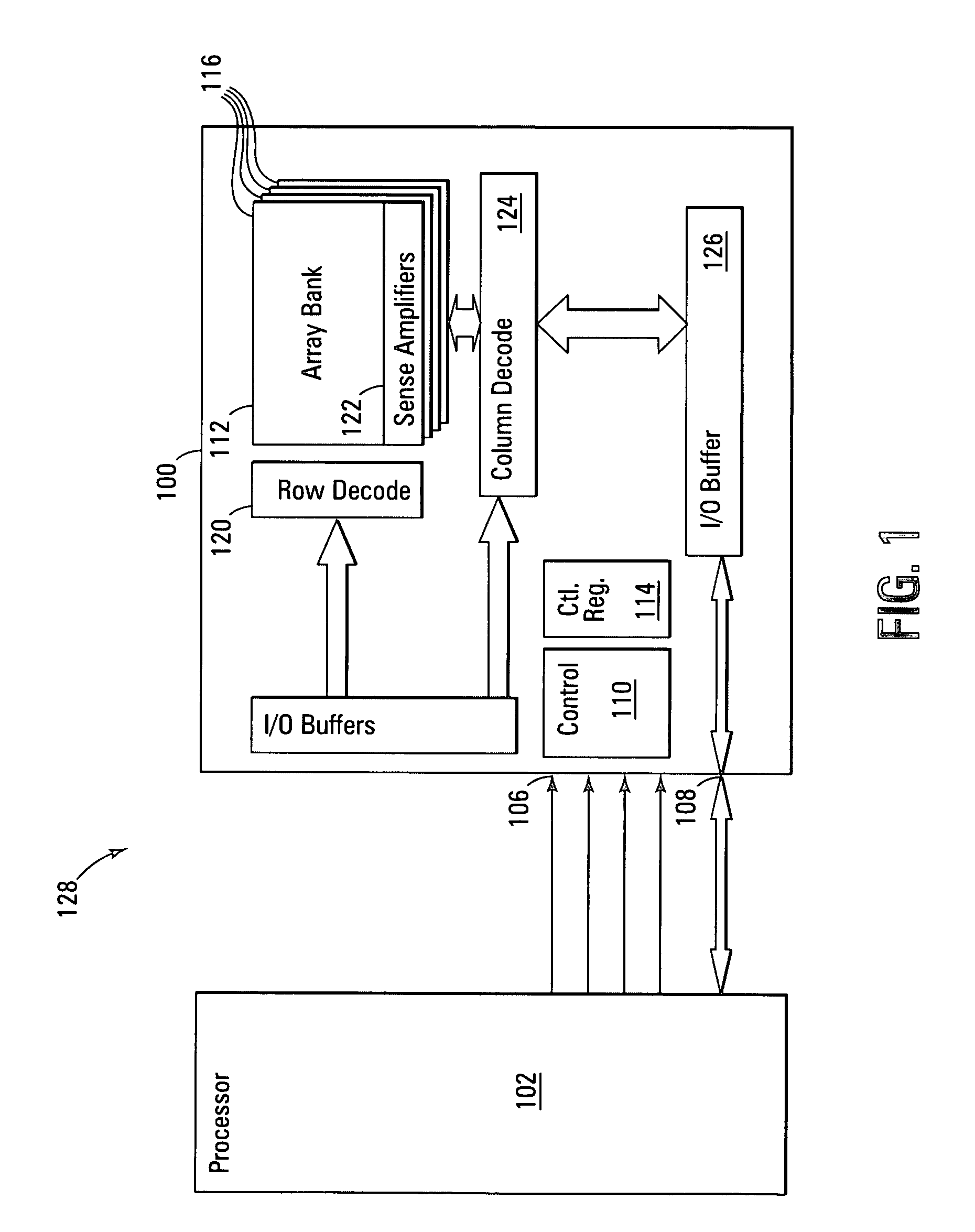
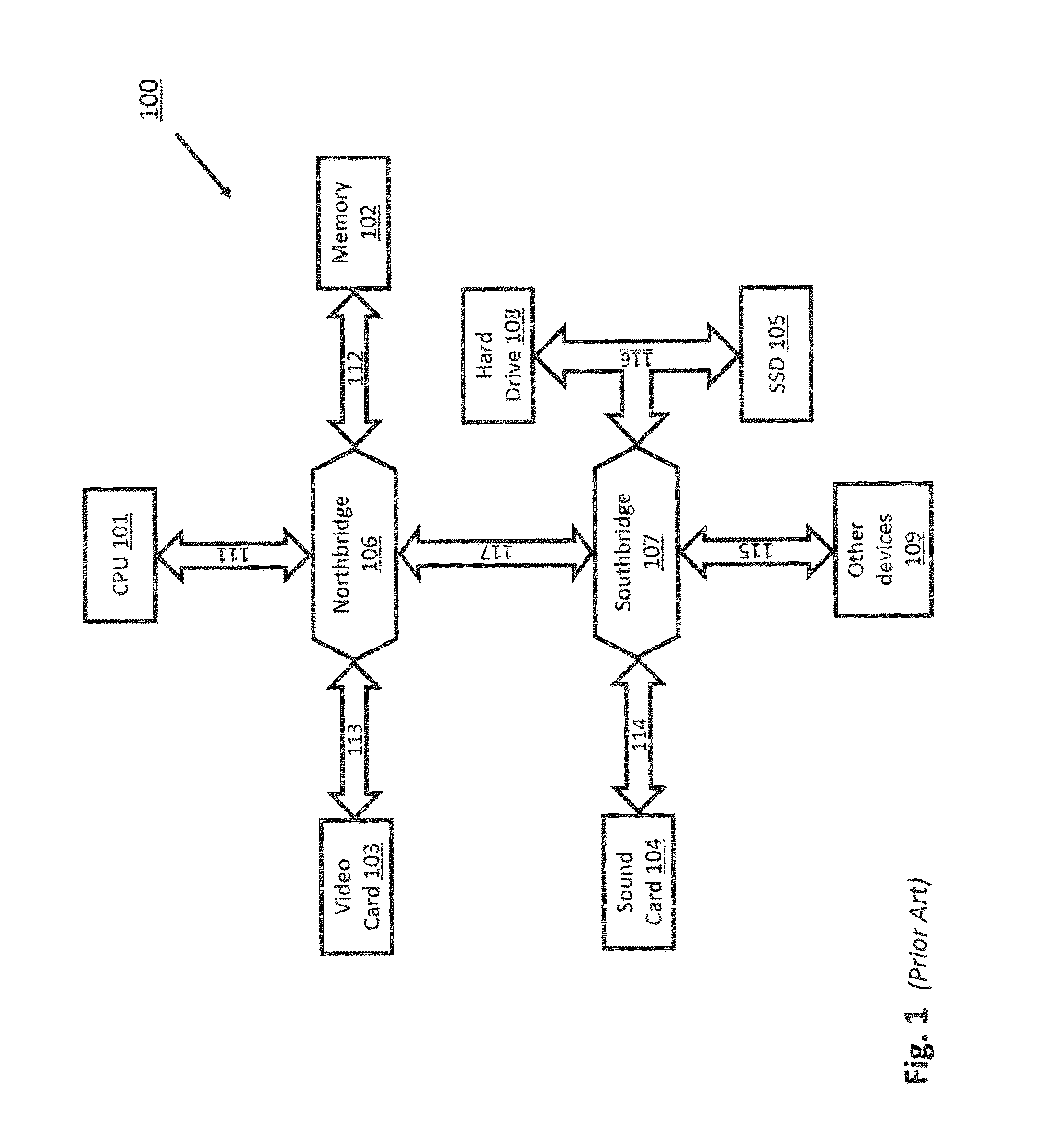
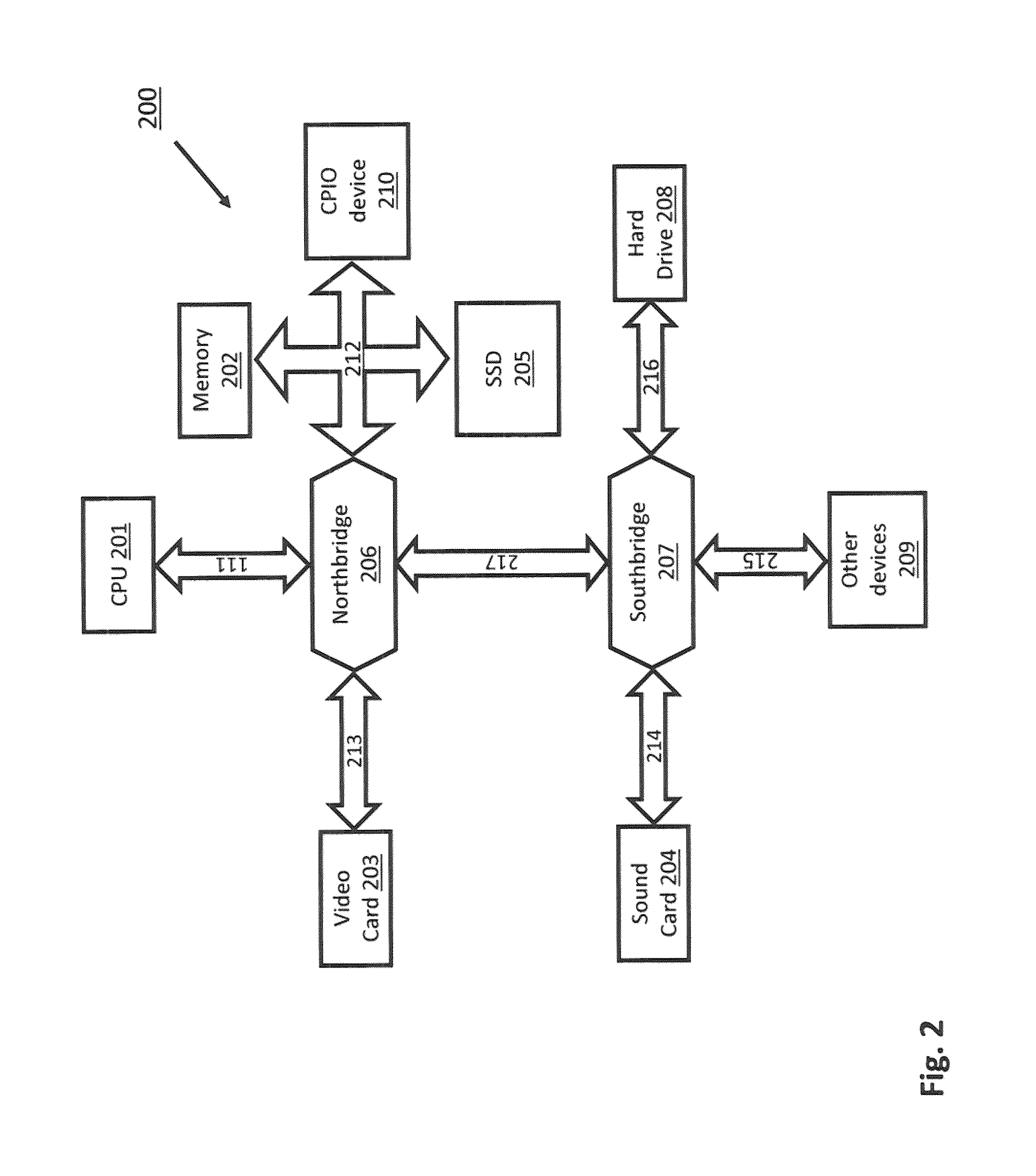
System and method of interfacing co-processors and input/output devices via a main memory system
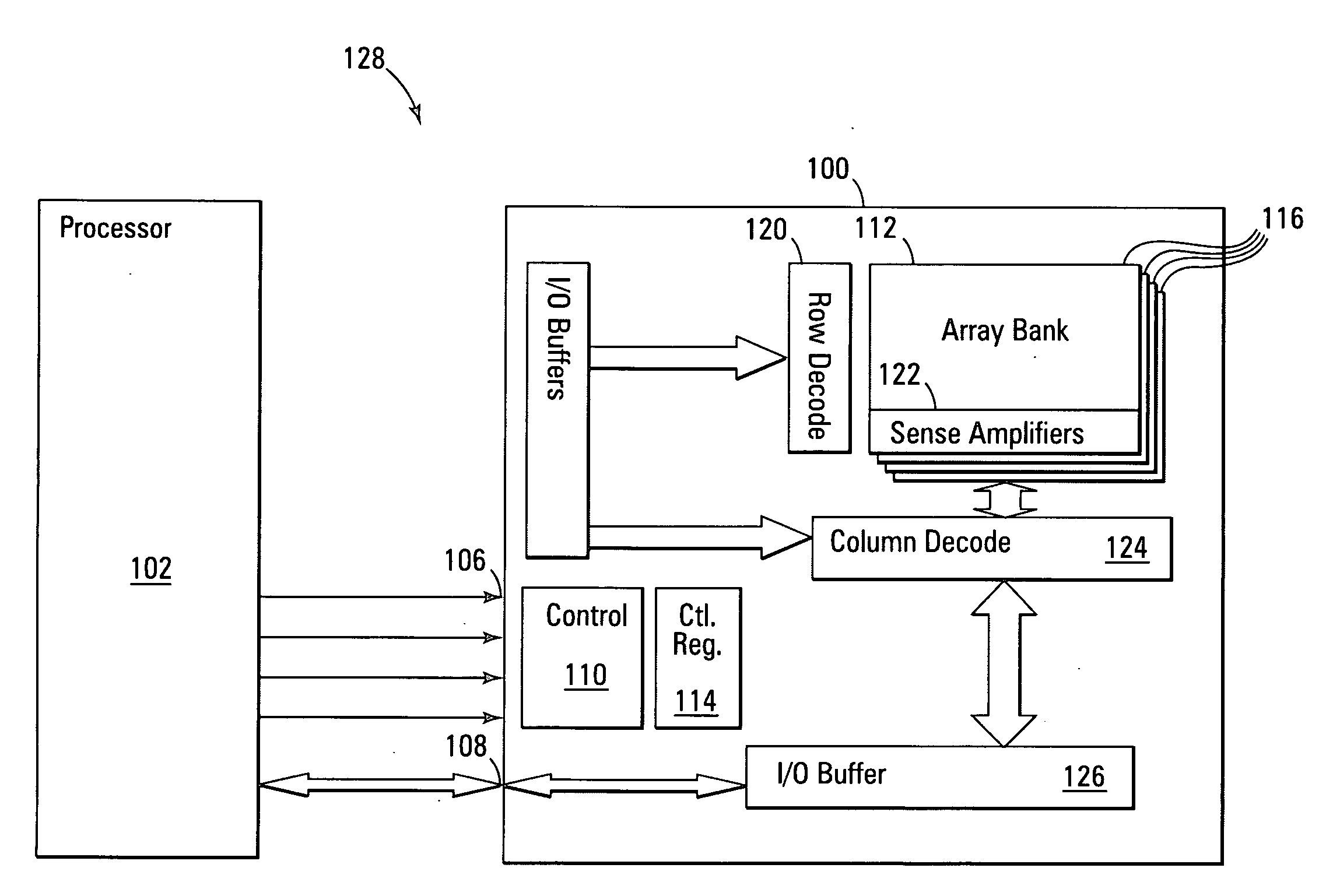
ActiveUS8713379B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionCoprocessorMemory bus
A system for interfacing with a co-processor or input / output device is disclosed. According to one embodiment, the system includes a computer processing unit, a memory module, a memory bus that connects the computer processing unit and the memory module, and a co-processing unit or input / output device, wherein the memory bus also connects the co-processing unit or input / output device to the computer processing unit.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Encoding and/or decoding memory devices and methods thereof
ActiveUS20090241009A1Error rateError correction/detection using block codesStatic storageComputer scienceStorage cell
Encoding / decoding memory devices and methods thereof may be provided. A memory device according to example embodiments may include a memory cell array and a processor including at least one of a decoder and an encoder. The processor may be configured to adjust a redundant information rate of each channel, where each of the channels is a path of the memory cell array from which data is at least one of stored and read. The redundant information rate may be adjusted by generating at least one codeword based on information from a previous codeword. Therefore, example embodiments may reduce an error rate when data is read from and written to the memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Error-Resilient Entropy Coding For Partial Embedding And Fine Grain Scalability
ActiveUS20090232408A1Heavy calculationMaintain good propertiesError prevention/detection by using return channelFault responseGranularityTheoretical computer science
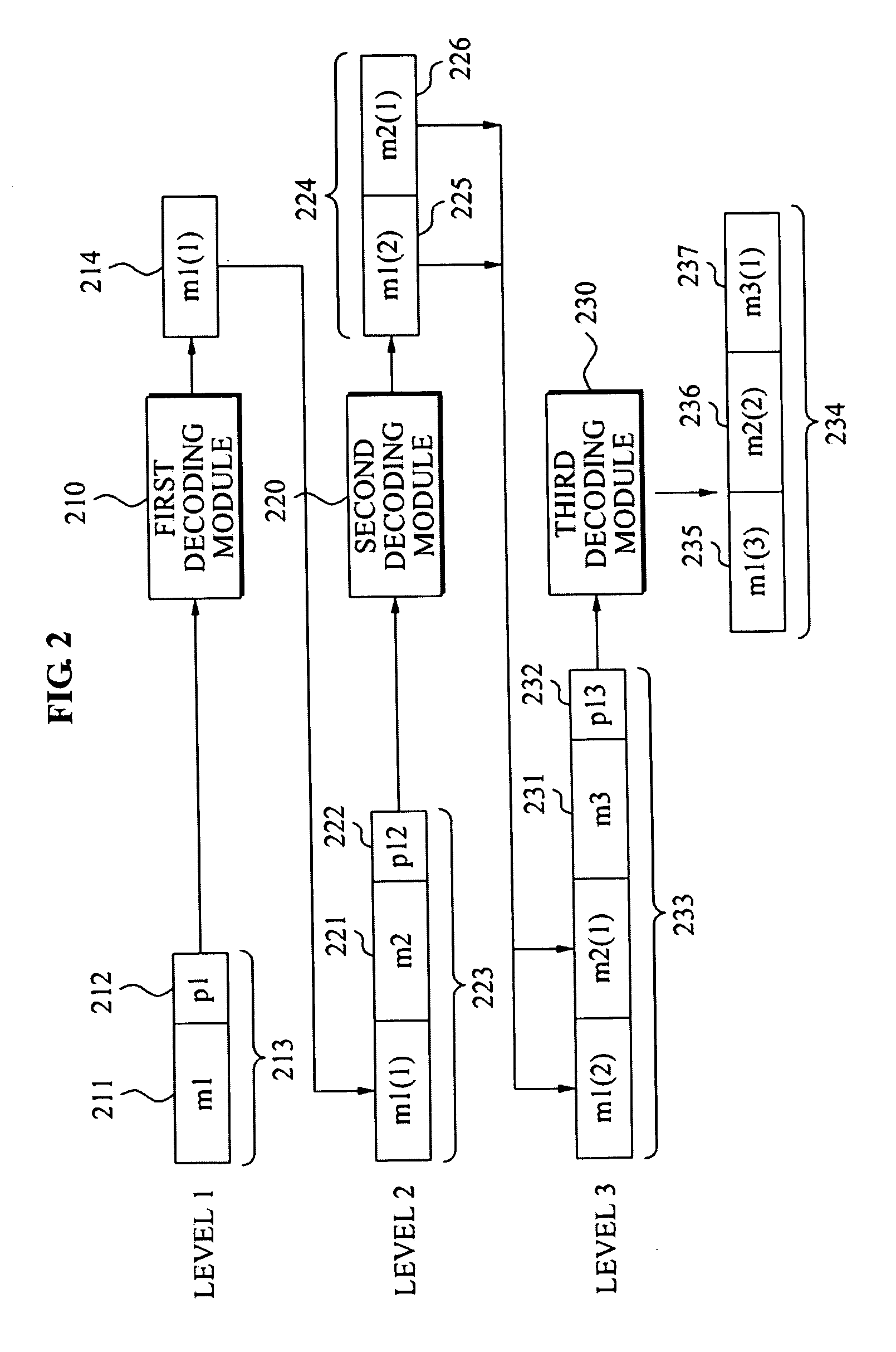
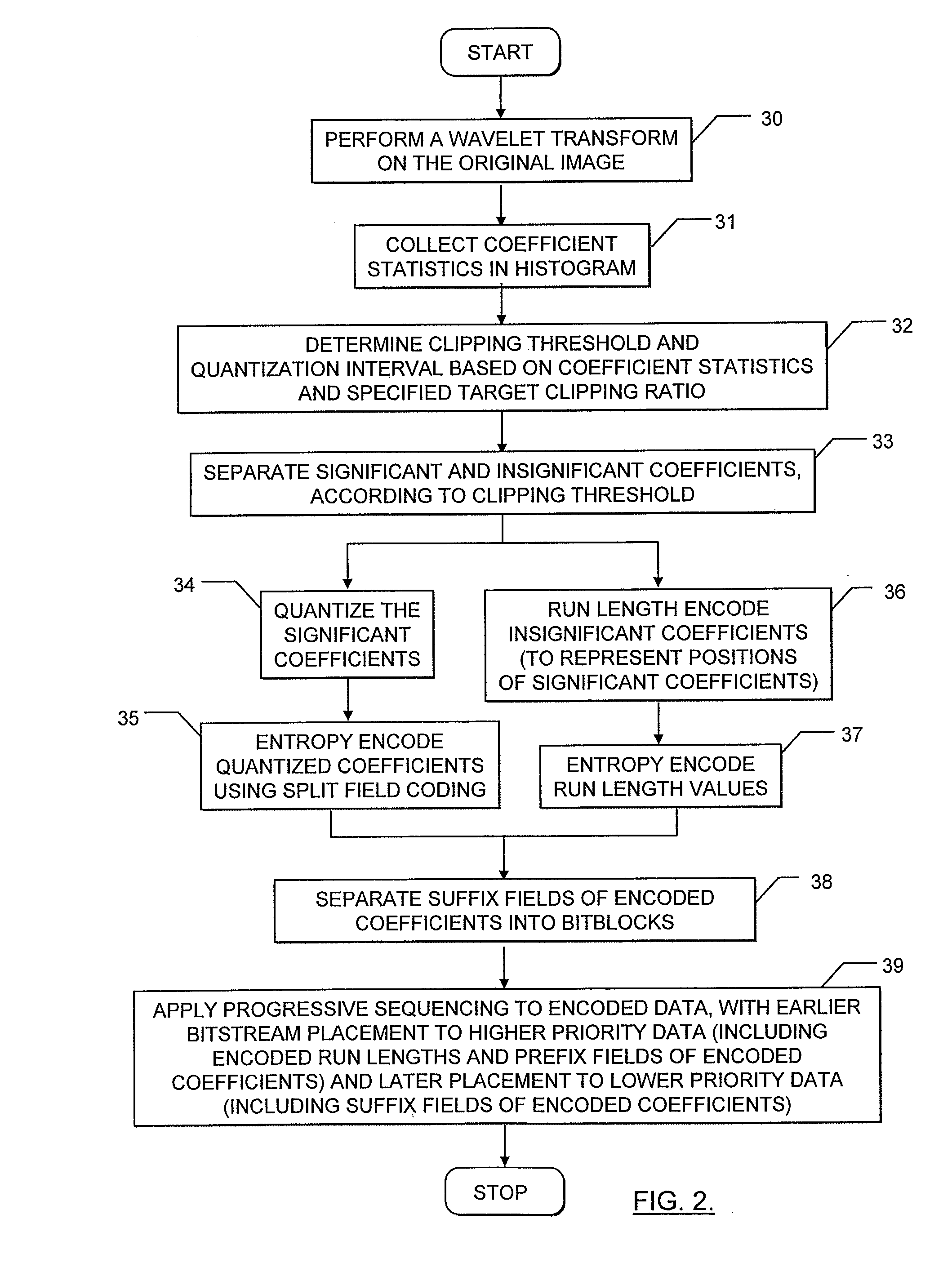
Methods, apparatus and computer program products are provided that generate a plurality of code words representative of data to be encoded. The code words may be generated to have first and second portions with each first portion including information that is representative of a predetermined characteristic of an associated second portion and each second portion including information that is representative of a respective portion of the data. A plurality of blocks may also be defined with each block including one or more bitplanes of the second portions of the code words. The plurality of blocks may be sequenced to achieve progressive representations of the encoded content in accordance with schemes to order the data according to priority of content. Content may be provided a level of error protection commiserate with its priority.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com