Patents
Literature
111results about "Error correction/detection using block single space coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
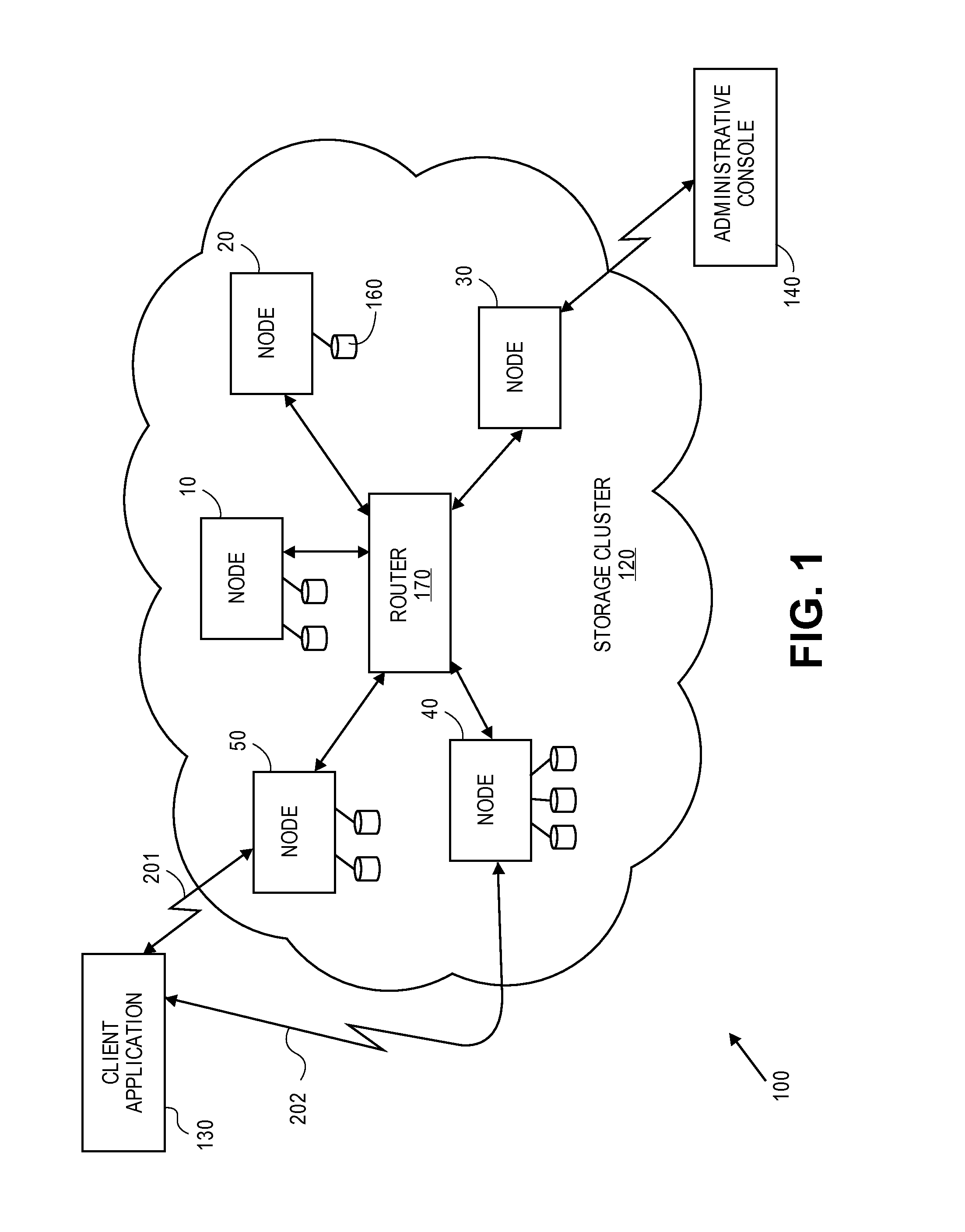
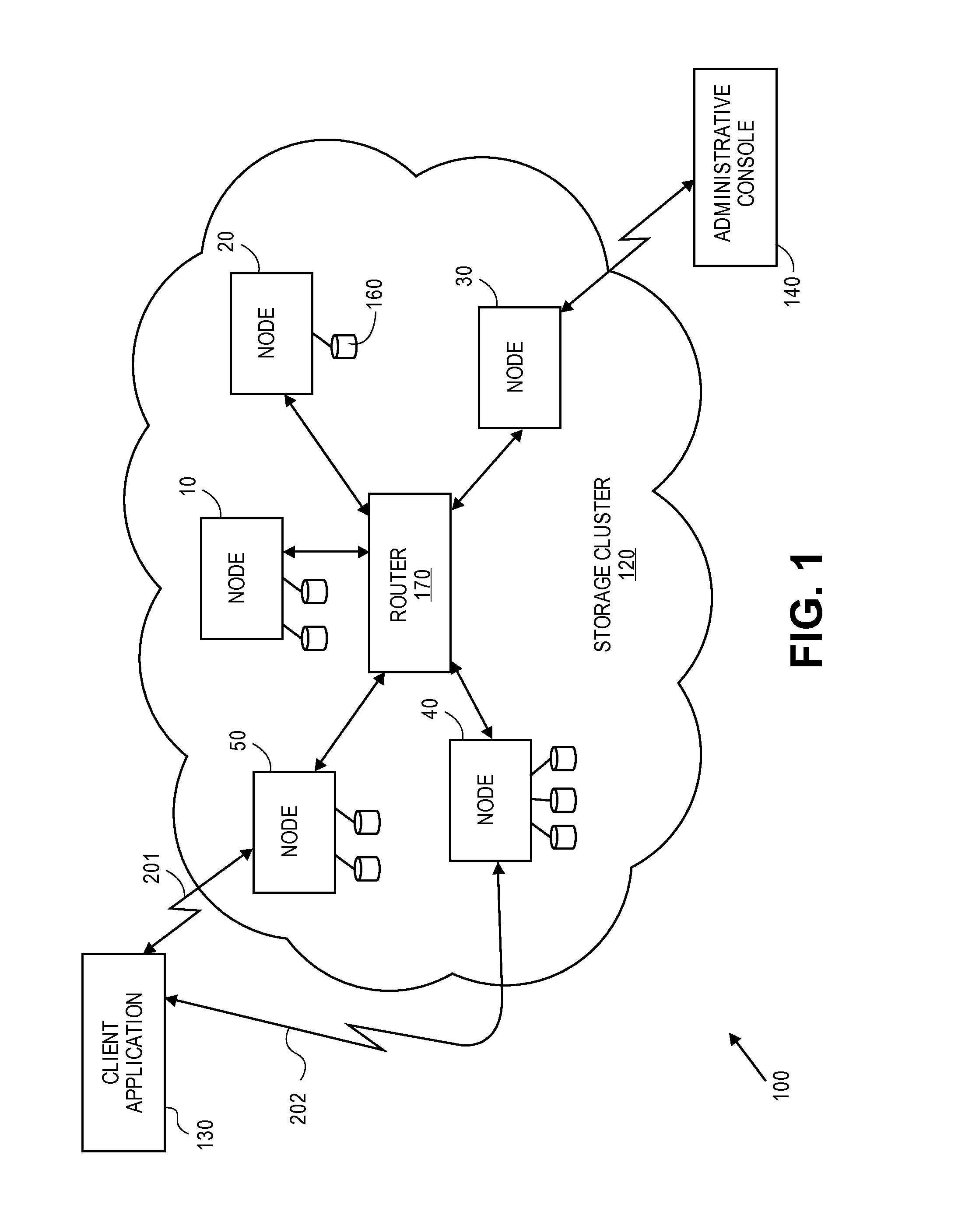
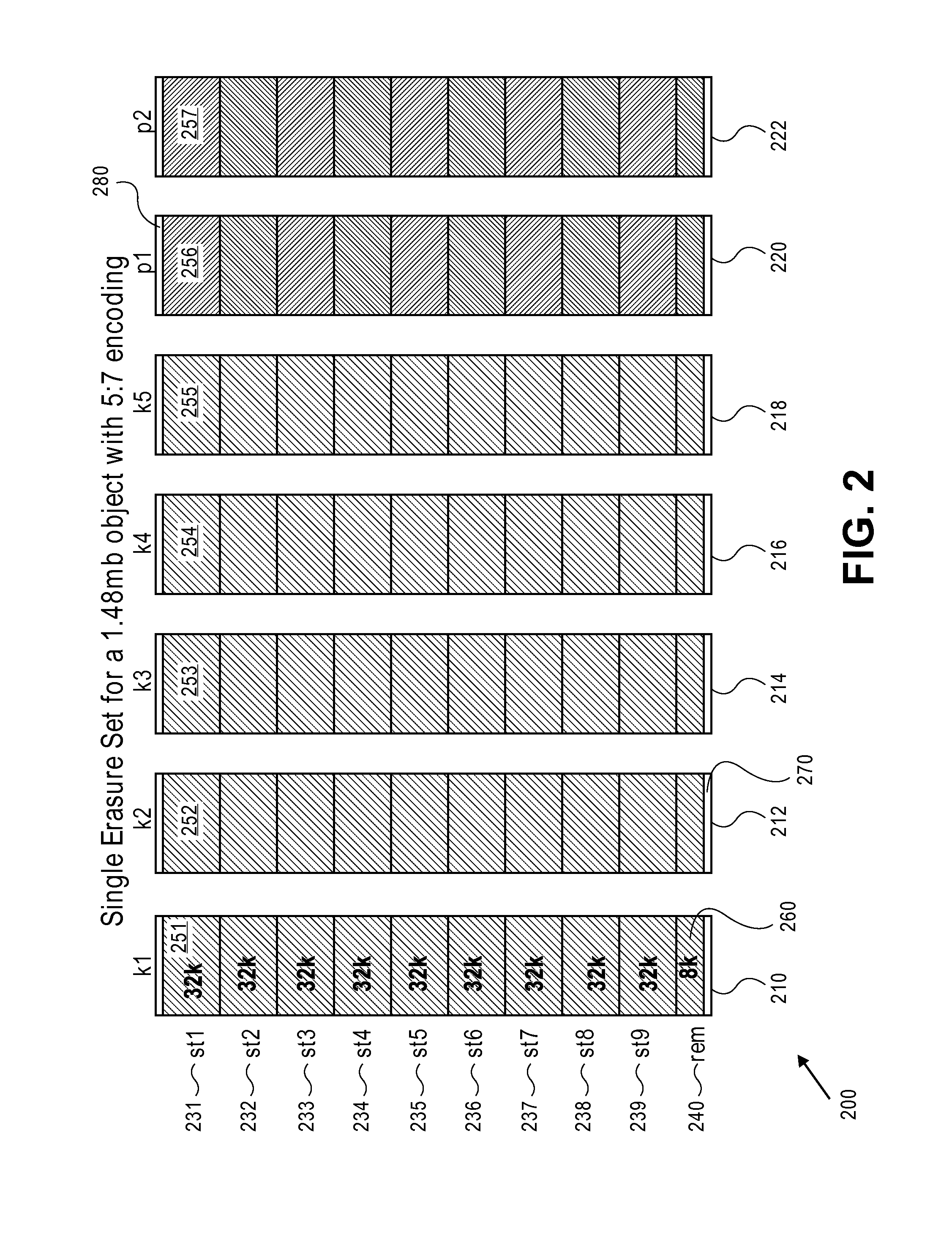
Erasure coding and replication in storage clusters
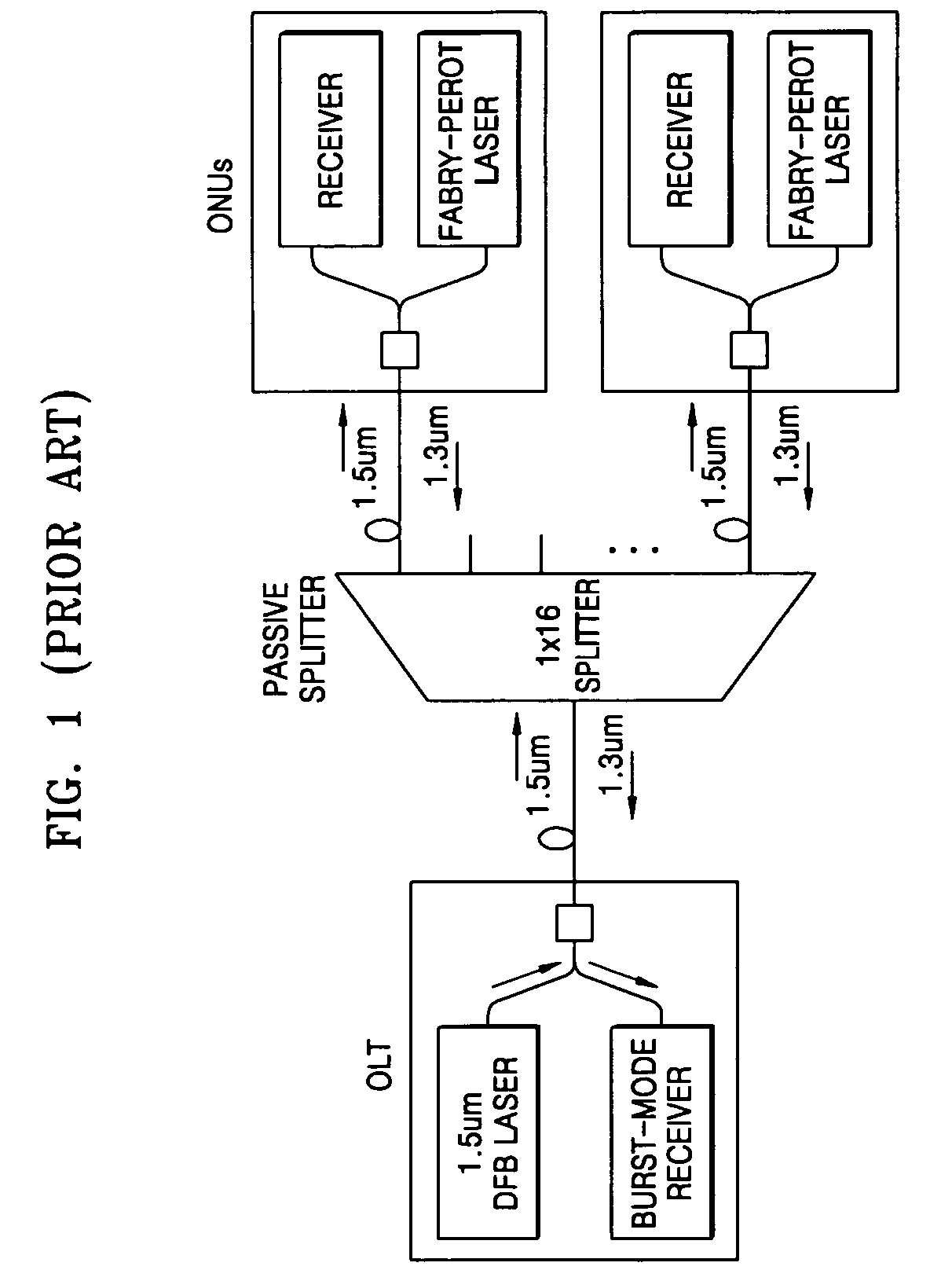
ActiveUS20130339818A1Error correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionUnique identifierOperating system
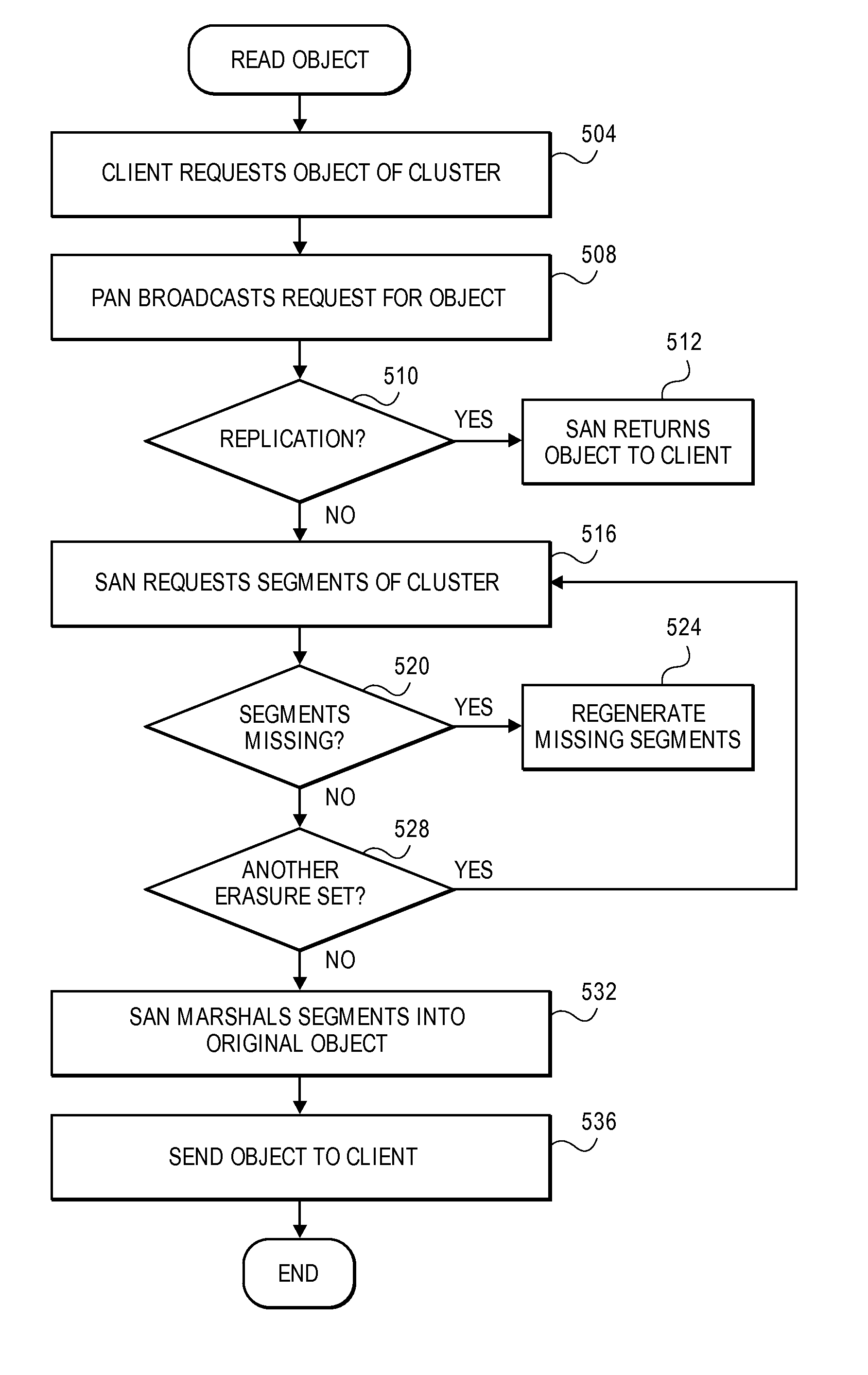
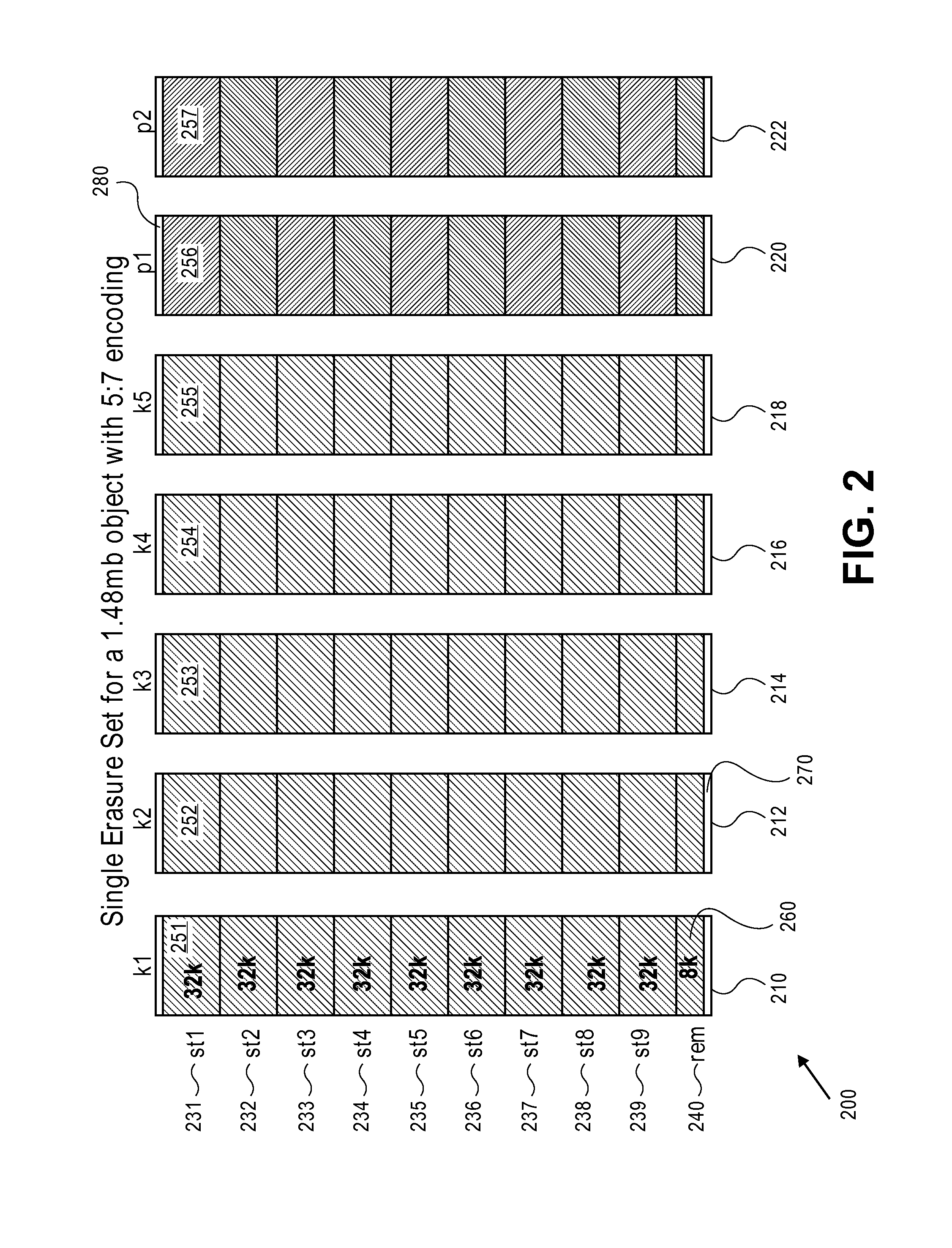
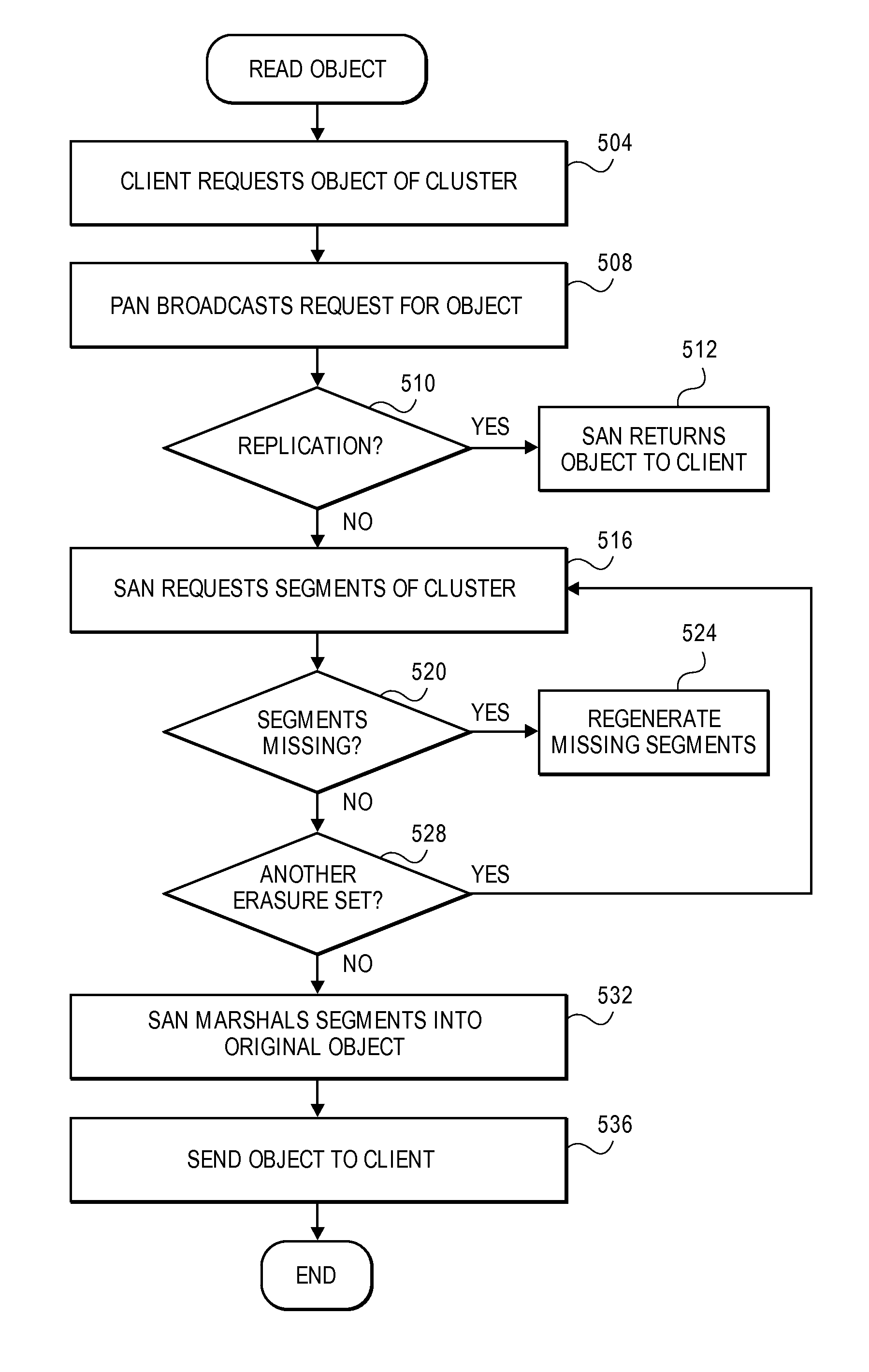
A cluster receives a request to store an object using replication or erasure coding. The cluster writes the object using erasure coding. A manifest is written that includes an indication of erasure coding and a unique identifier for each segment. The cluster returns a unique identifier of the manifest. The cluster receives a request from a client that includes a unique identifier. The cluster determines whether the object has been stored using replication or erasure coding. If using erasure coding, the method reads a manifest. The method identifies segments within the cluster using unique segment identifiers of the manifest. Using these unique segment identifiers, the method reconstructs the object. A persistent storage area of another disk is scanned to find a unique identifier of a failed disk. If using erasure coding, a missing segment previously stored on the disk is identified. The method locates other segments. Missing segments are regenerated.
Owner:DATACORE SOFTWARE
Erasure coding and replication in storage clusters
ActiveUS8799746B2Error correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionUnique identifierOperating system
Owner:DATACORE SOFTWARE
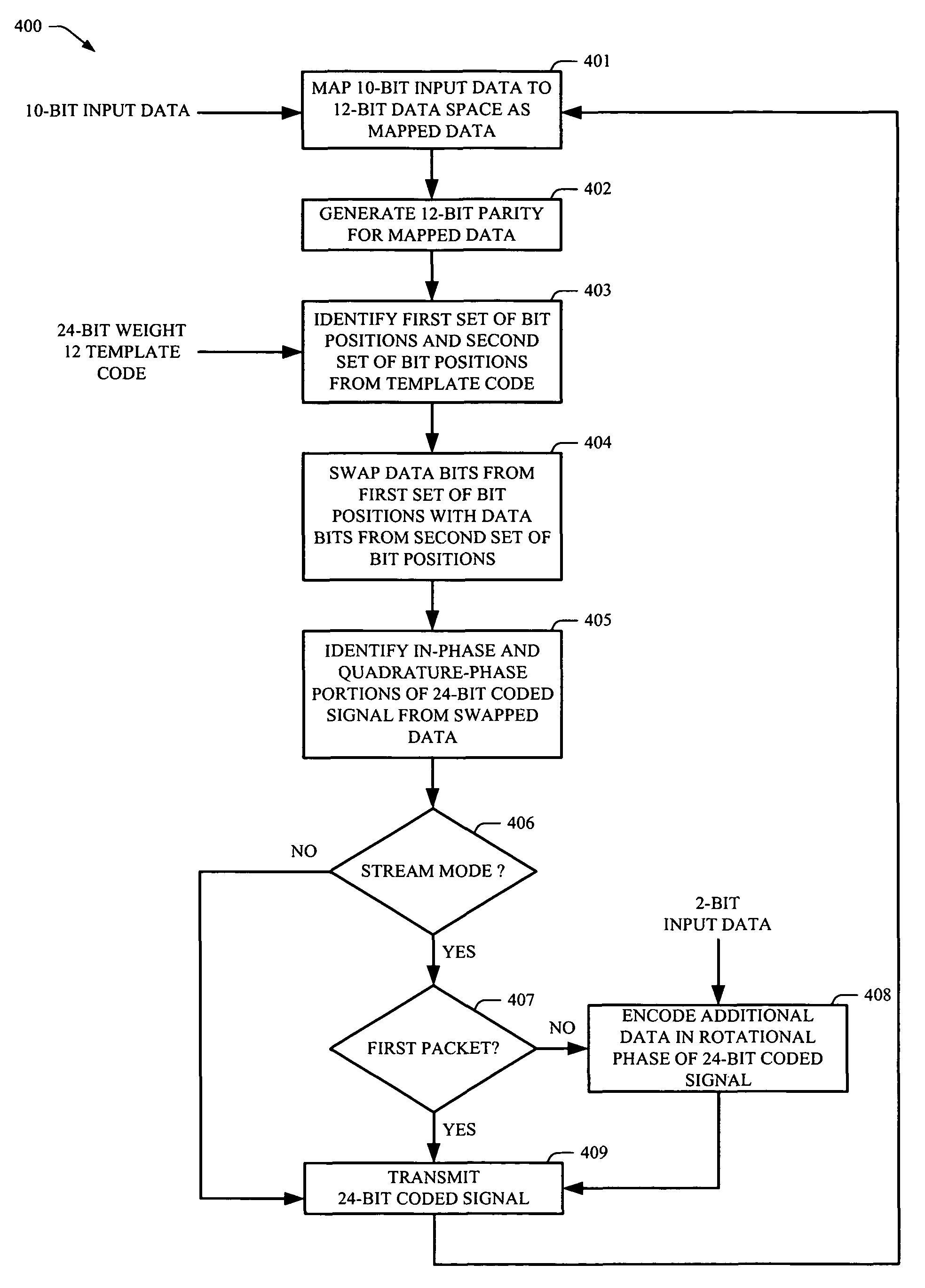
Rotationally invariant non-coherent burst coding
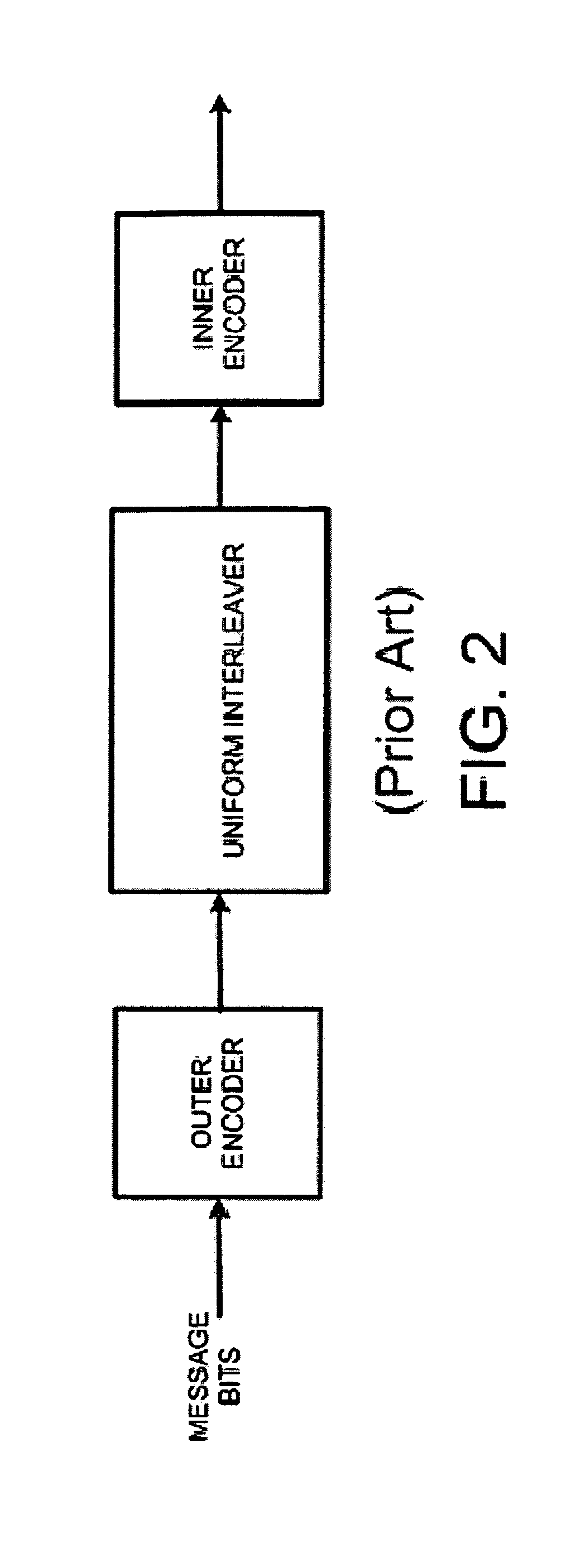
ActiveUS7779332B2Error correction/detection using block single space codingError preventionBit field24-bit
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Encoding/decoding system using 16-QAM modulation encoded in multi-level blocks
InactiveUS6195396B1Error correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionQam modulationAlgorithm
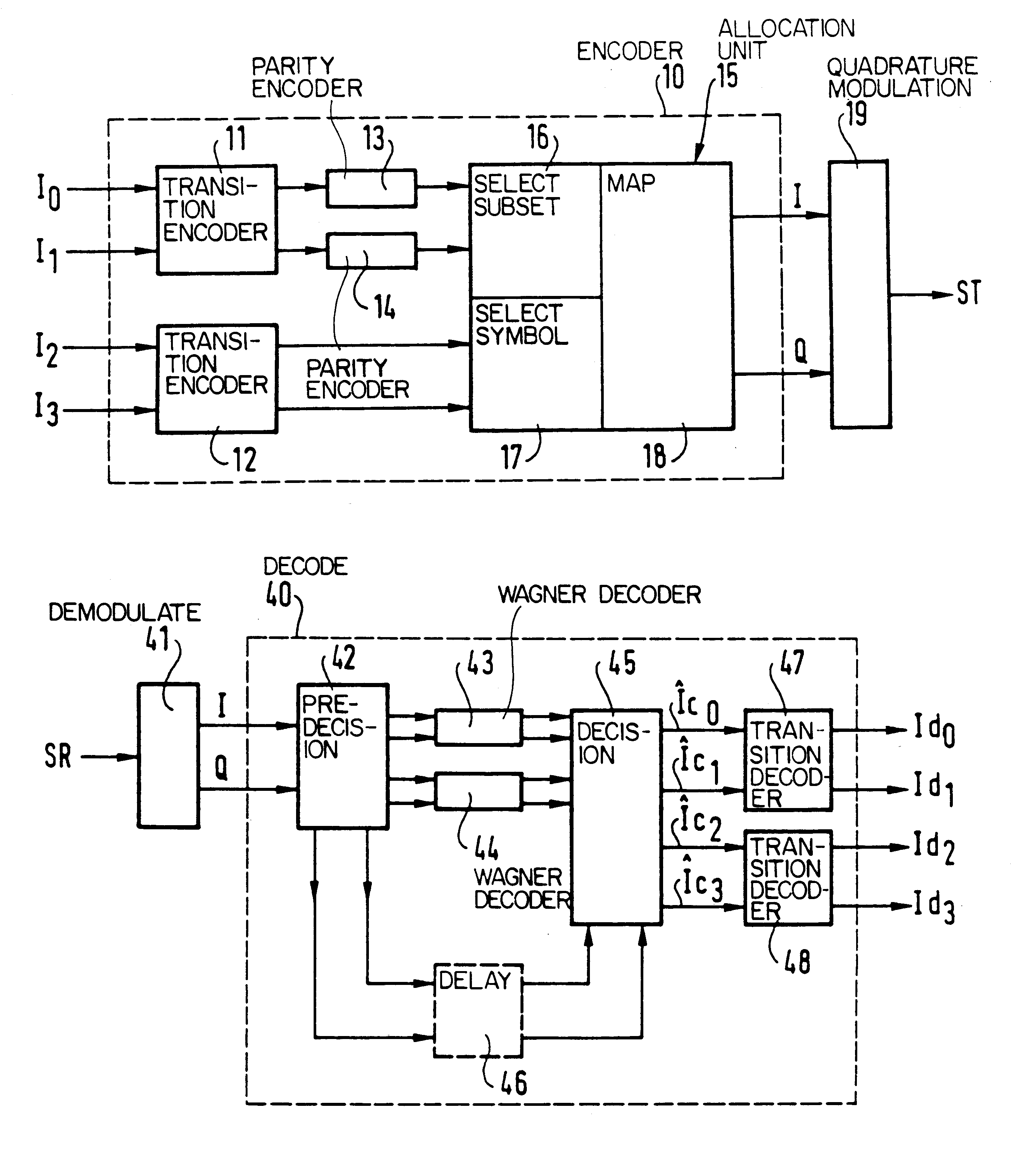
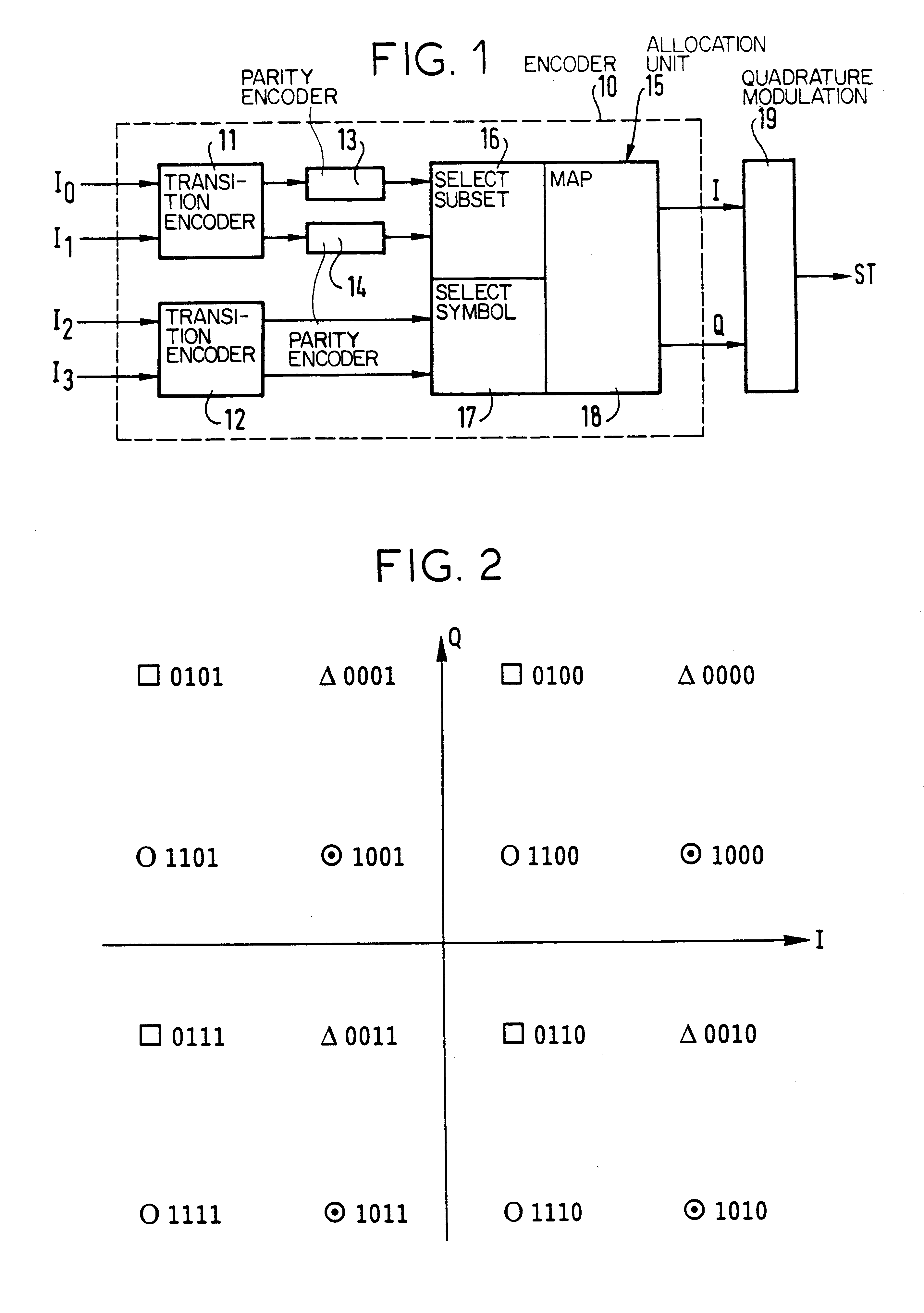
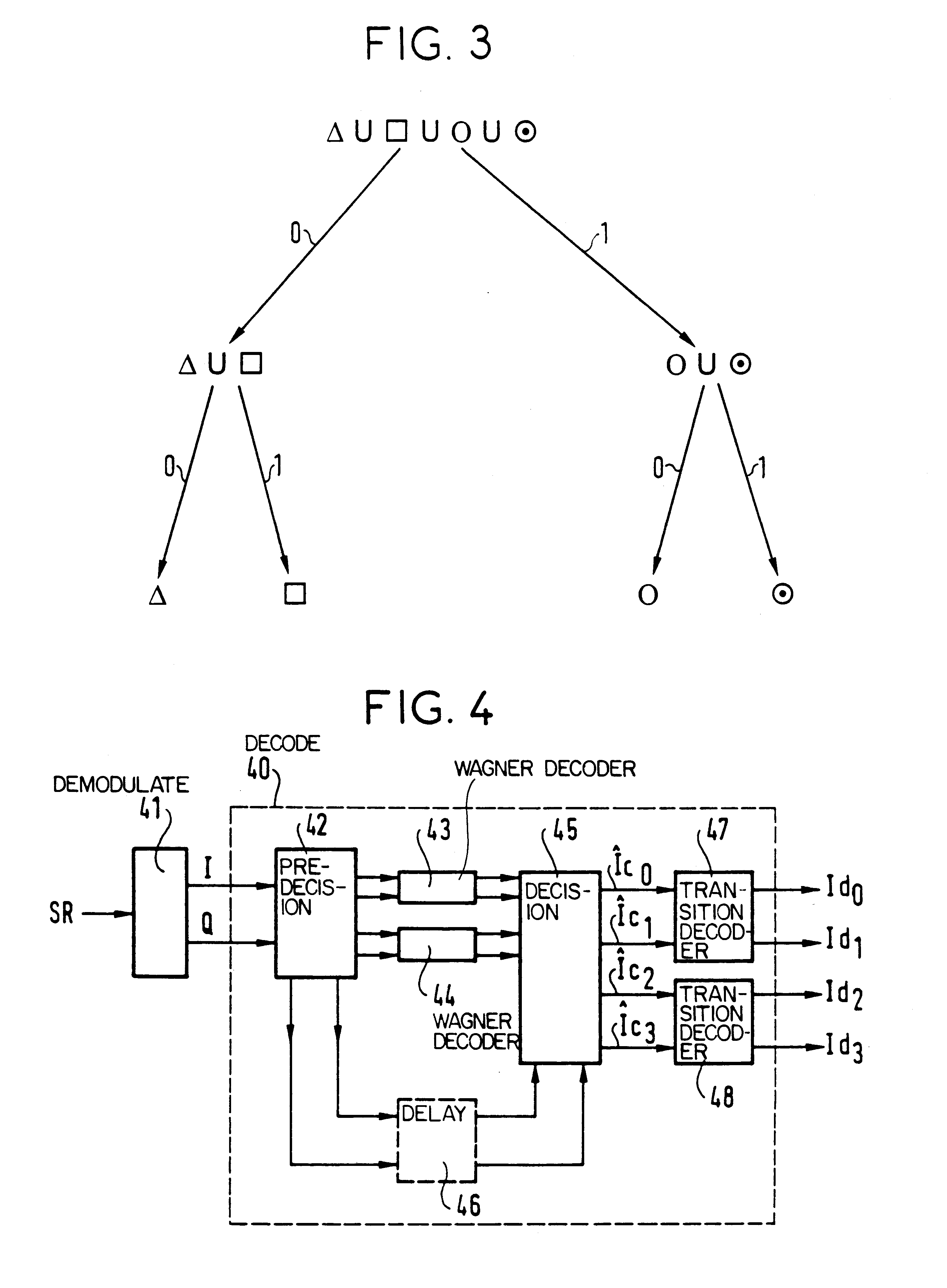
The invention provides a block-encoded modulation scheme using multi-level partitioning techniques. This scheme is made transparent to phase ambiguities of ±pi / 2 and of pi, by means of differential encoding and appropriate mapping, it is applicable to 16-QAM modulation, and it has theoretical encoding gain that is optimal for the rate of the code. The decoder associated with this scheme uses the Wagner algorithm which is much less complicated to implement than the Viterbi algorithm or than the Reed-Solomon algorithm.
Owner:ALCATEL TELSPACE
Polar code encoding modulation method applicable to any high-order modulation
ActiveCN106230489AImprove performanceOvercoming the lack of high complexitySpatial transmit diversityError correction/detection using block single space codingChannel capacityComputer science
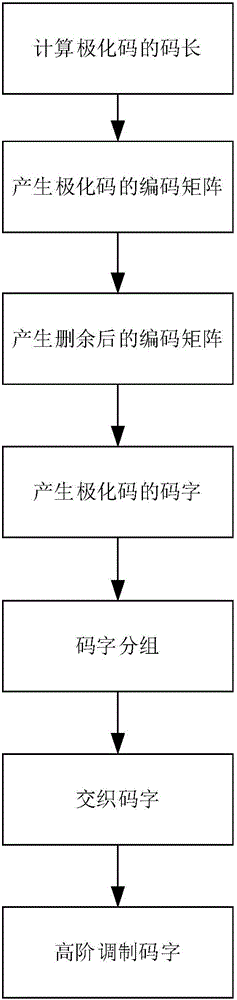
The invention discloses a polar code encoding modulation method applicable to any high-order modulation. The method comprises the concrete steps of (1), calculating the code length of a polar code; (2), generating an encoding matrix of the polar code; (3), generating the encoding matrix after puncturing; (4), generating code words of the polar code; (6) interleaving the code words; and (7), carrying out high-order modulation. According to the method, the code words are interleaved by employing a grouping interleaving technology, the polar effect of a channel is intensified with the combination of the polar characteristic of the polar code itself and the capacity differences of high-order modulation sub-channels, and the performance of the polar code is improved. According to the method, the encoding matrix is punctured according to a column weight, the decoding delay is reduced, and the programming realization complexity of a decoding algorithm in a programmable device is reduced. The flexibility of the polar code in the high-order modulation is improved, and the polar code has good performance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
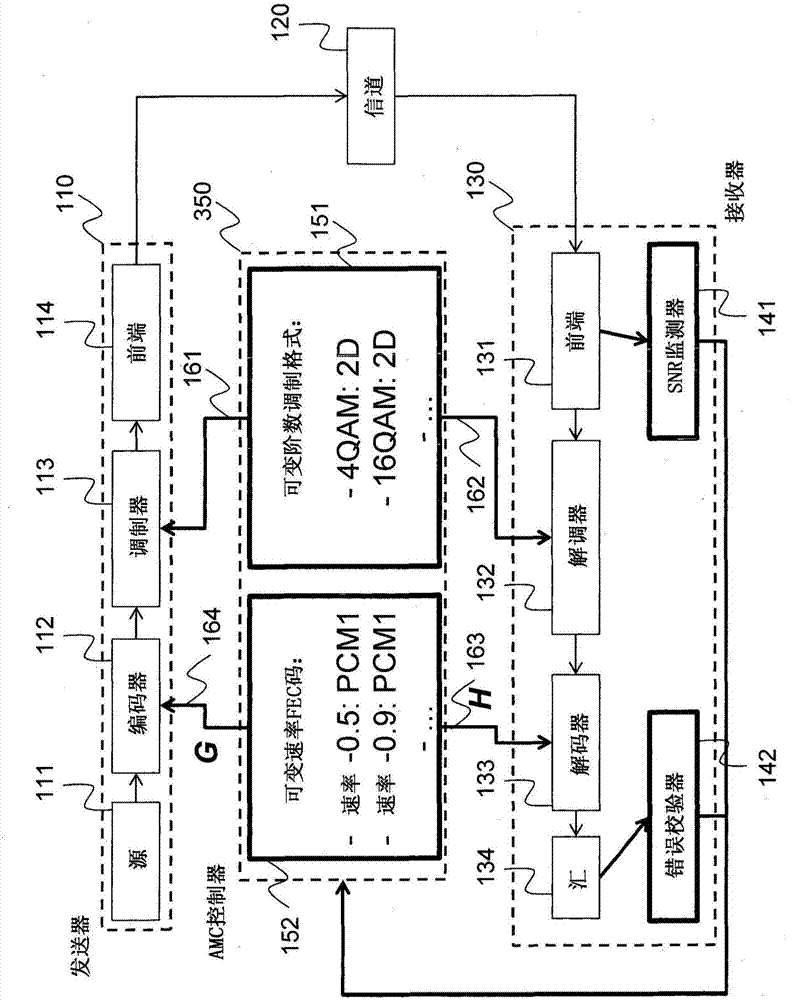
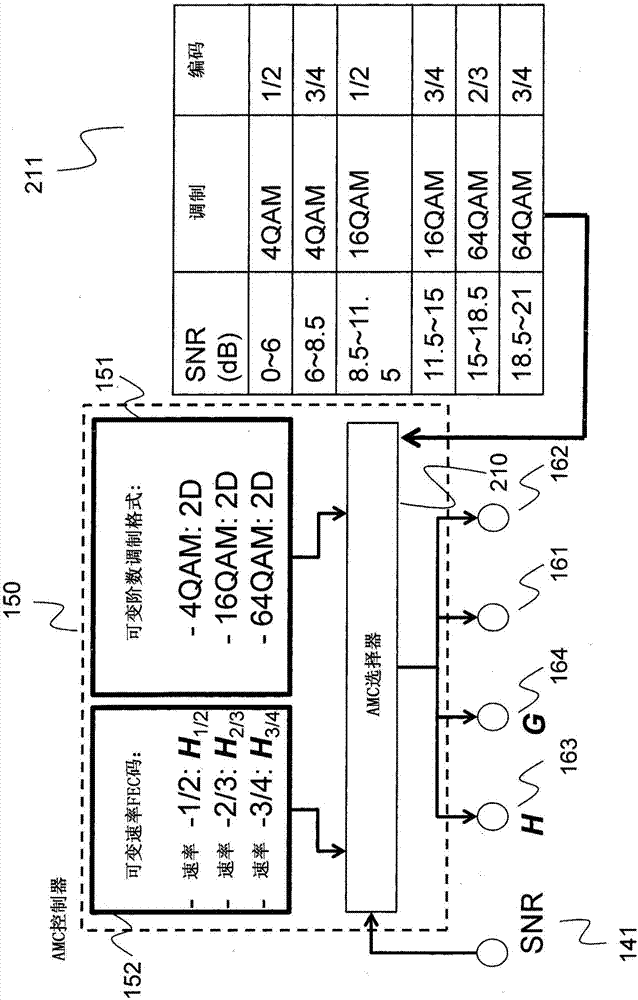
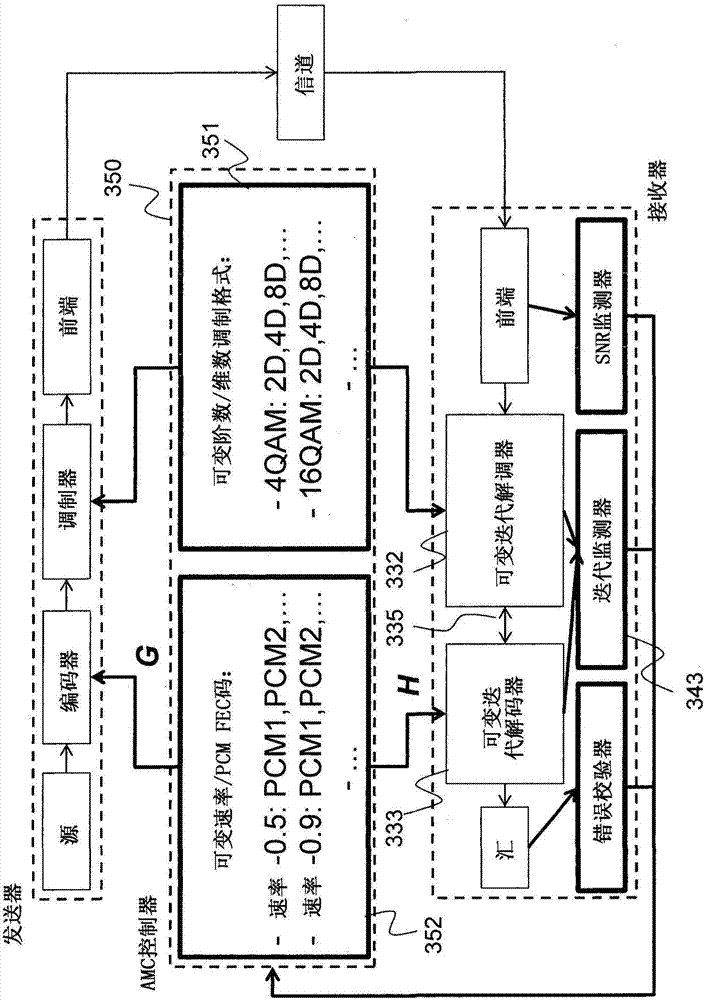
Method and System for Reliable Data Communications with Adaptive Multi-Dimensional Modulations for Variable-Iteration Decoding
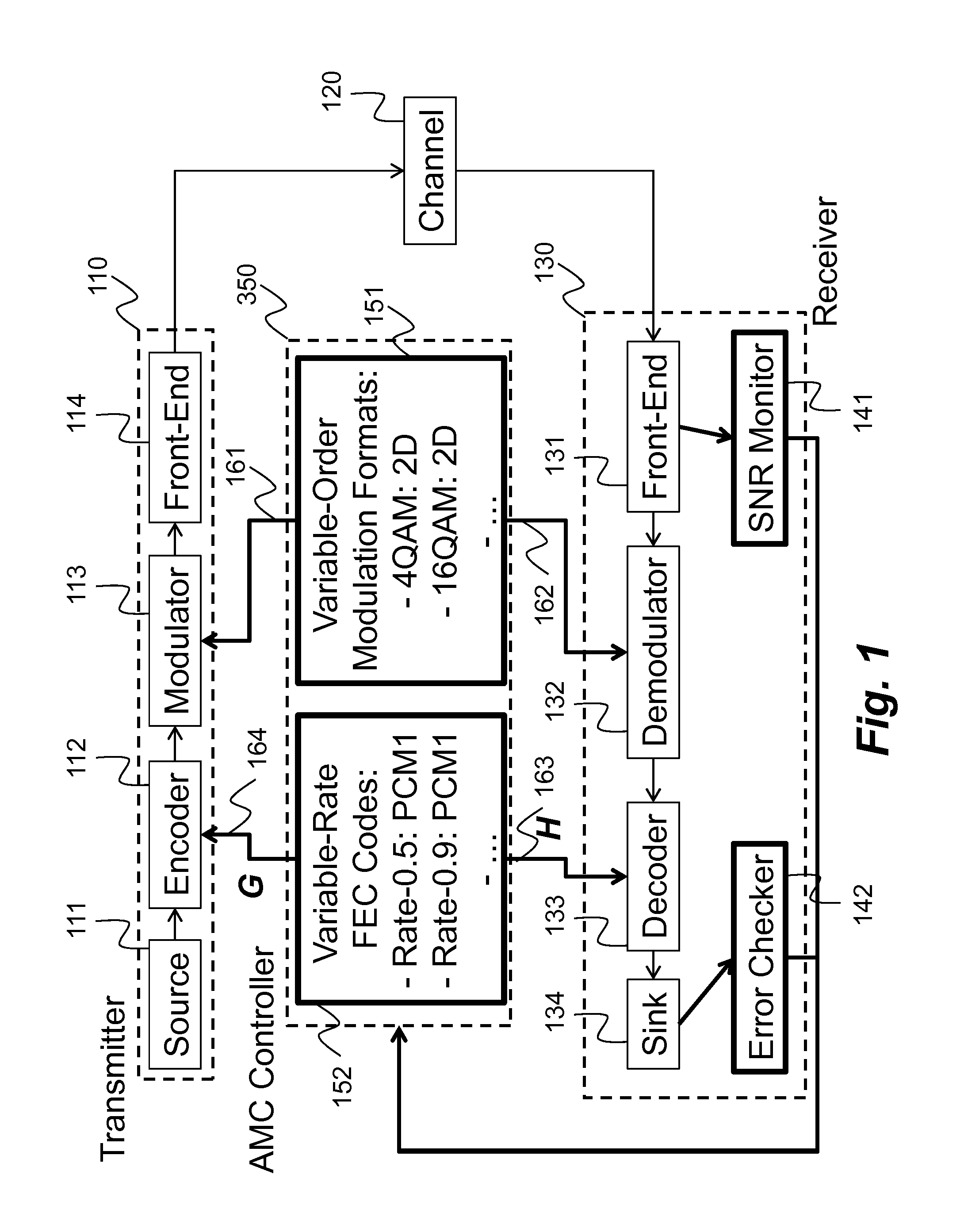
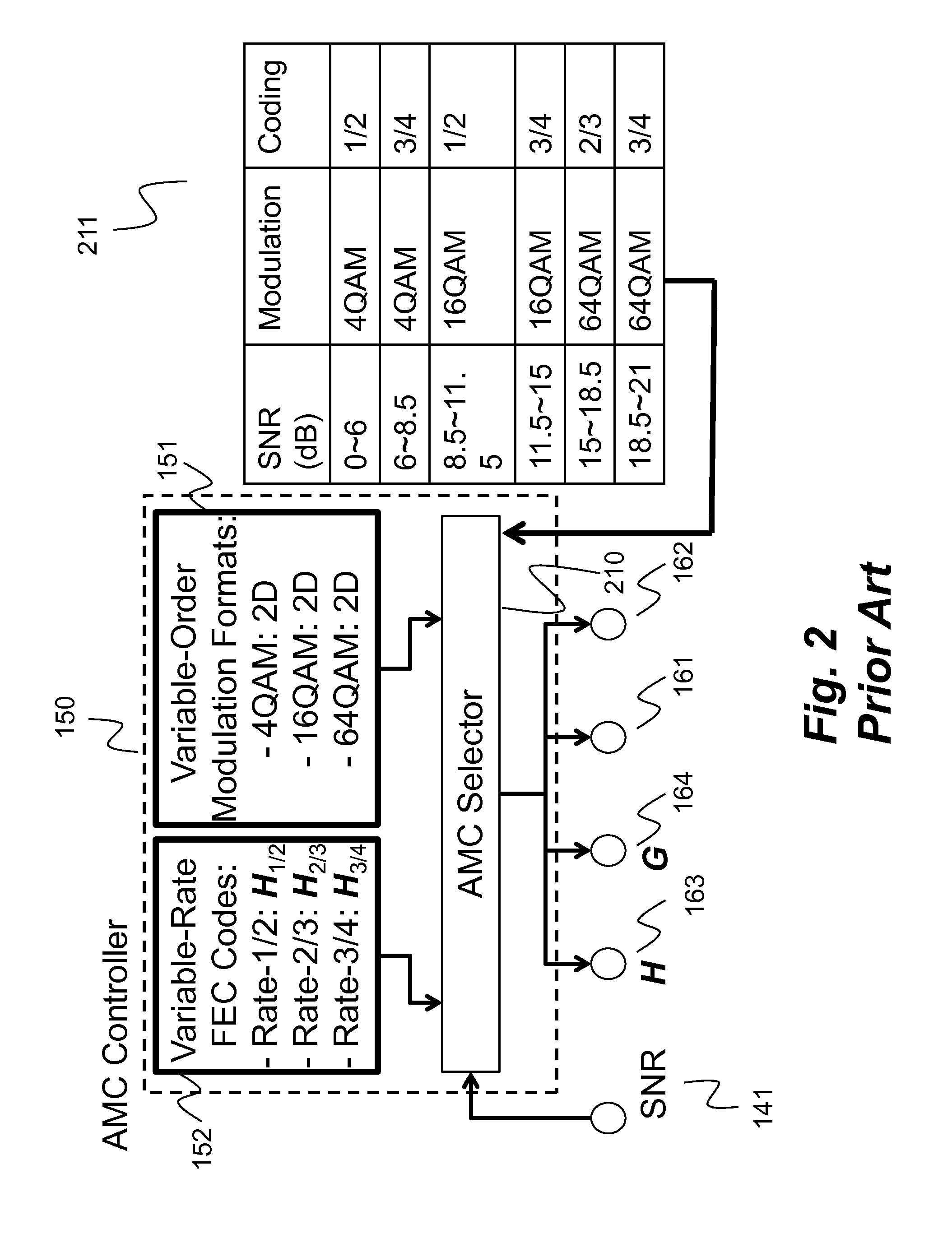
ActiveUS20160233979A1Improve performanceSimple processError correction/detection using block single space codingOther decoding techniquesBelief propagationError mitigation
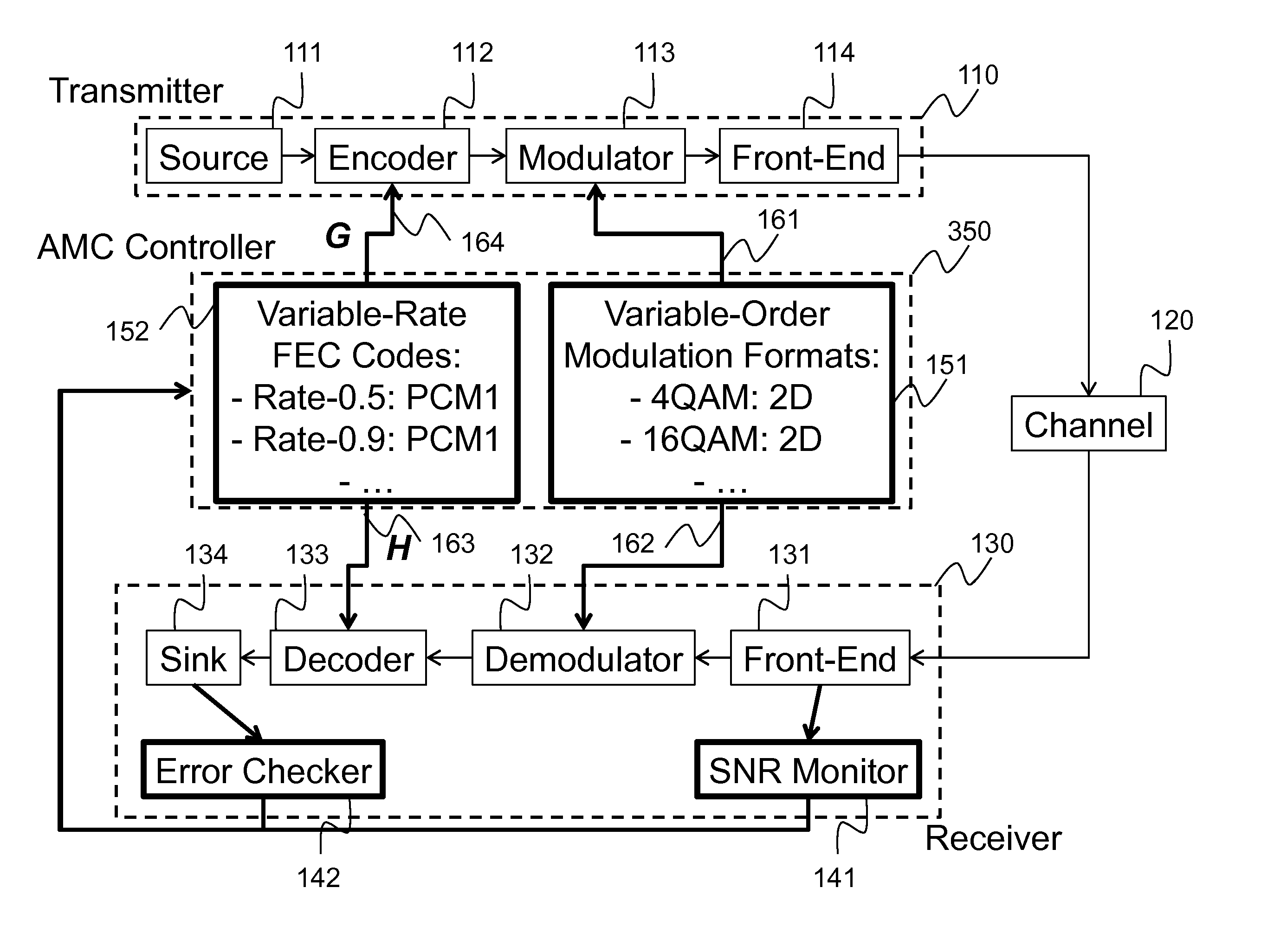
In an advanced adaptive modulation and coding (AMC) scheme, the code rate and the parity-check matrix (PCM) for low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes are adapted according to modulation formats and variable-iteration receivers. The degree distribution for the PCM adaptation is designed by heuristic optimization to minimize the required SNR via an extrinsic information transfer (EXIT) trajectory analysis for finite-iteration decoding. The method uses dynamic window decoding by generating spatially coupled PCM for quasi-cyclic LDPC convolutional coding. The method also provides a way to jointly optimize labeling and decoding complexity for high-order and high-dimensional modulations. The problem to use a large number of different LDPC codes for various modulation formats and variable-iteration decoding is also dealt with by linearly dependent PCM adaptation across iteration count to keep using a common generator matrix. This PCM adaptation can improve a convergence speed of belief propagation decoding and mitigate an error floor issue.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Decoding LDPC (low density parity check) code with new operators based on min* operator
InactiveUS20050149844A1Color television with pulse code modulationError correction/detection using block single space codingTheoretical computer scienceLow density
Decoding LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code with new operators based on min* operator. New approximate operators are provided that may be employed to assist in calculating one or a minimum value (or a maximum value) when decoding various coded signals. In the context of LDPC decoding that involves both bit node processing and check node processing, either of these new operators (i.e., the min† (min-dagger) operator or the min′ (min-prime) operator) may be employed to perform the check node processing that involves updating the edge messages with respect to the check nodes. Either of these new operators, min† operator or min′ operator, is shown herein to be a better approximate operator to the min** operator.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Bit interleaved polar code modulation method and apparatus
ActiveCN105656604AImplementing Unequal Probability DistributionsChannel mutual informationError correction/detection using block single space codingError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Algorithm
Embodiments of the present invention disclose a bit interleaved polar code modulation method and apparatus. The method comprises the steps of calculating, according to a maximum mutual information condition, a continuous probability distribution value P(xi) of each constellation point in an M-dimensional constellation map corresponding to a target bit sequence; creating a Huffman tree with all constellation points in the M-dimensional constellation map as leaf nodes; discretizing the P(xi) according to closest (2-k), so as to obtain a discretization probability distribution set of the constellation points; and combining the obtained discretization probability distribution set of the constellation points with Gray mapping, and taking the value as shown in the specification so as to obtain an unequal probability constellation map of the constellation points. According to the method, when the channel capacities are equal, the signal to noise ratio required by the unequal probability distribution constellation map is lower than the signal to noise ratio required by the equal probability constellation map, and the system performance is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Digital transmitter/receiver system having a robust error correction coding/decoding device and error correction coding/decoding method thereof
ActiveUS7337386B2Correction errorGuaranteed reception performanceError preventionError correction/detection using block single space codingDecoding methodsField data
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Digital transmitter/receiver system having a robust error correction coding/decoding device and error correction coding/decoding method thereof
ActiveUS20040261001A1Strong errorError preventionError correction/detection using block single space codingDecoding methodsField data
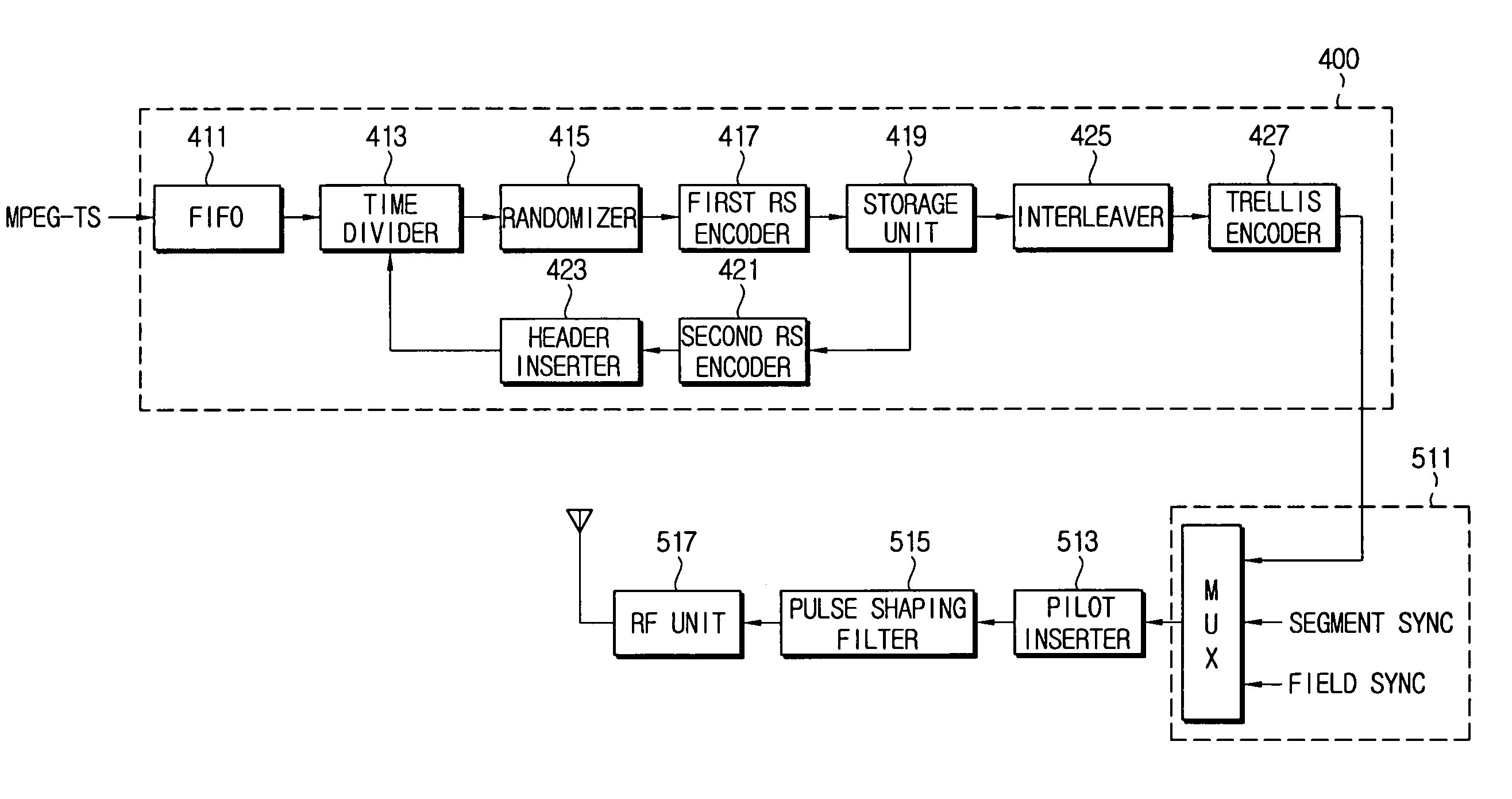
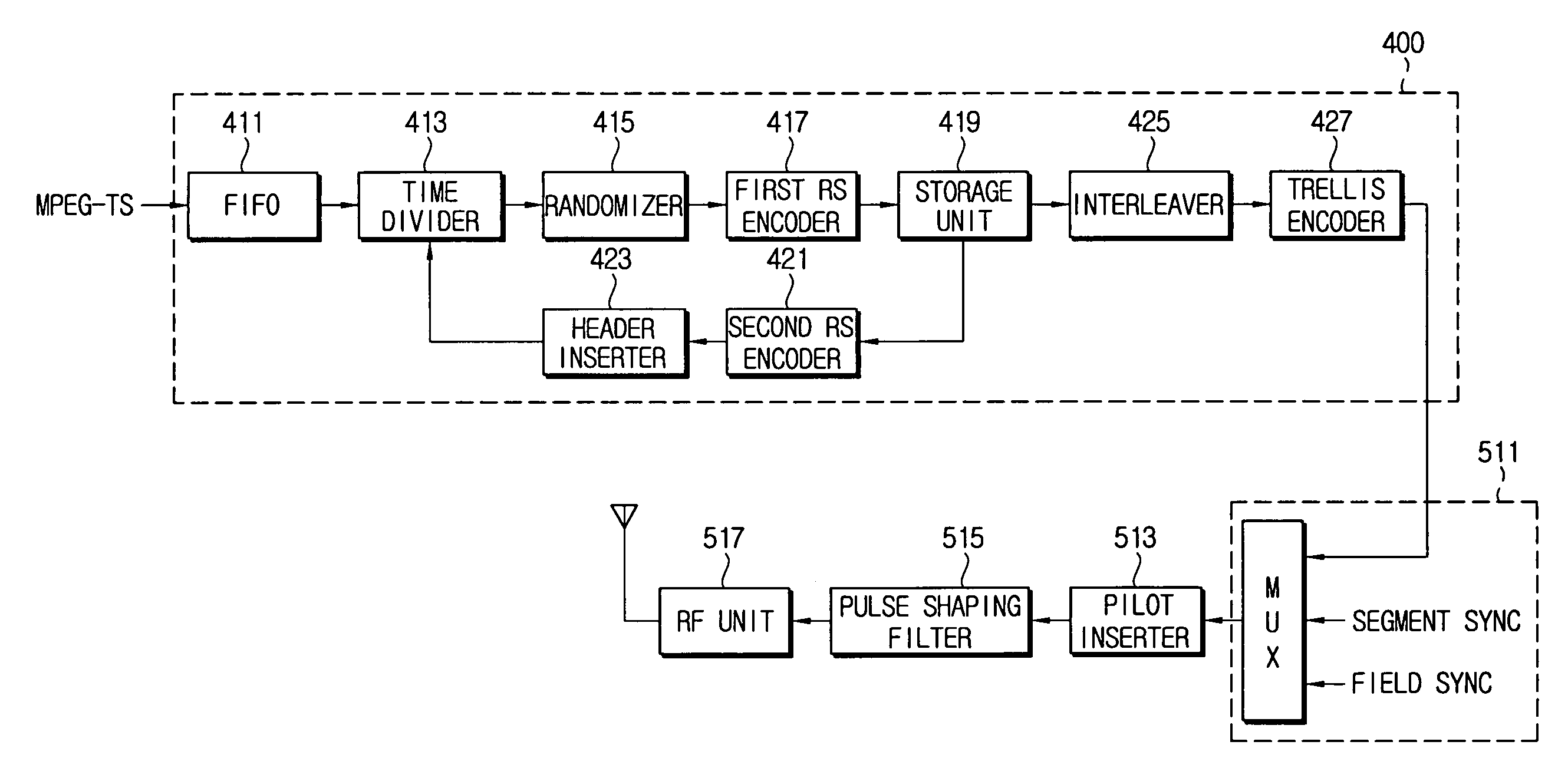
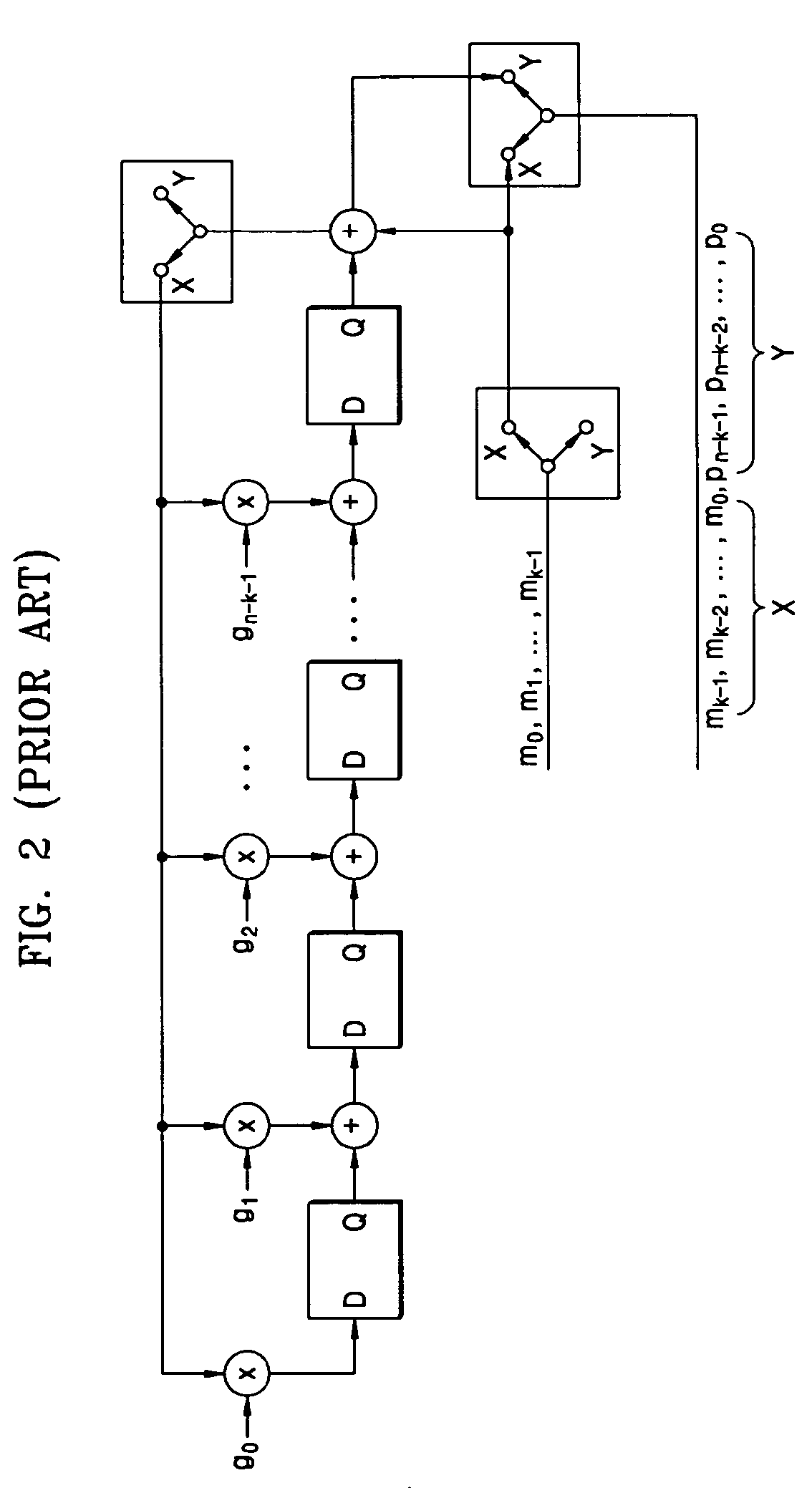
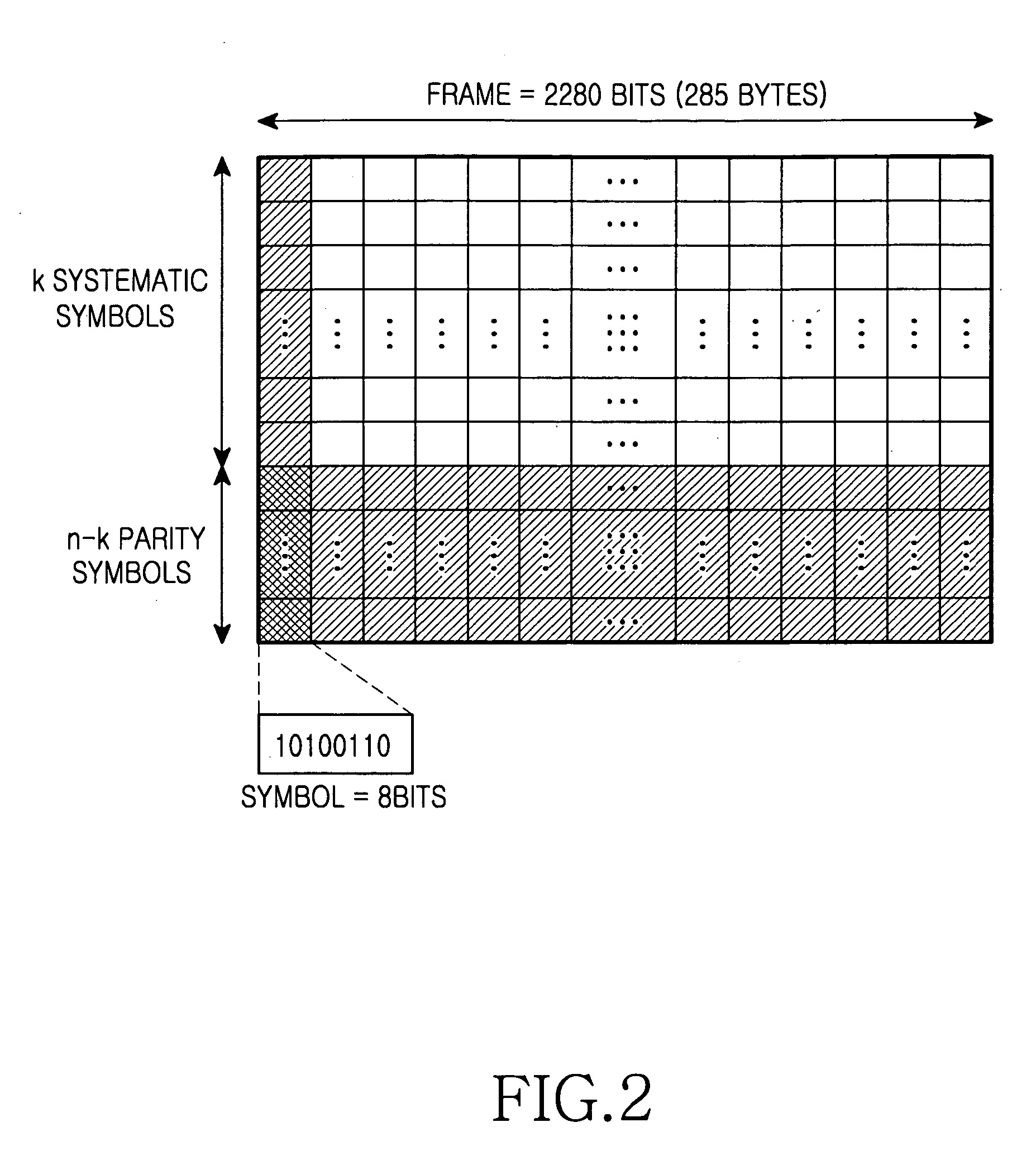
An error correction coding device includes a time divider for dividing field data of L packets into N data packets and (L-N) parity packets, a first RS (Reed-Solomon) encoder adding parities of a predetermined number of bytes to the data packets, respectively, a storage unit for storing the data packets, and a second RS encoder generating parity packets corresponding to the stored data packets. An error correction decoding device includes a first RS decoder correcting errors in a horizontal direction of the field data using parities of the predetermined number of bytes included in the L packets, a storage unit storing the error-corrected data packets, and a second RS decoder correcting errors in a vertical direction of the field data using the parity packets. Thus, the error correction can be strongly performed using parities existing in the horizontal and vertical directions with respect to the field data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
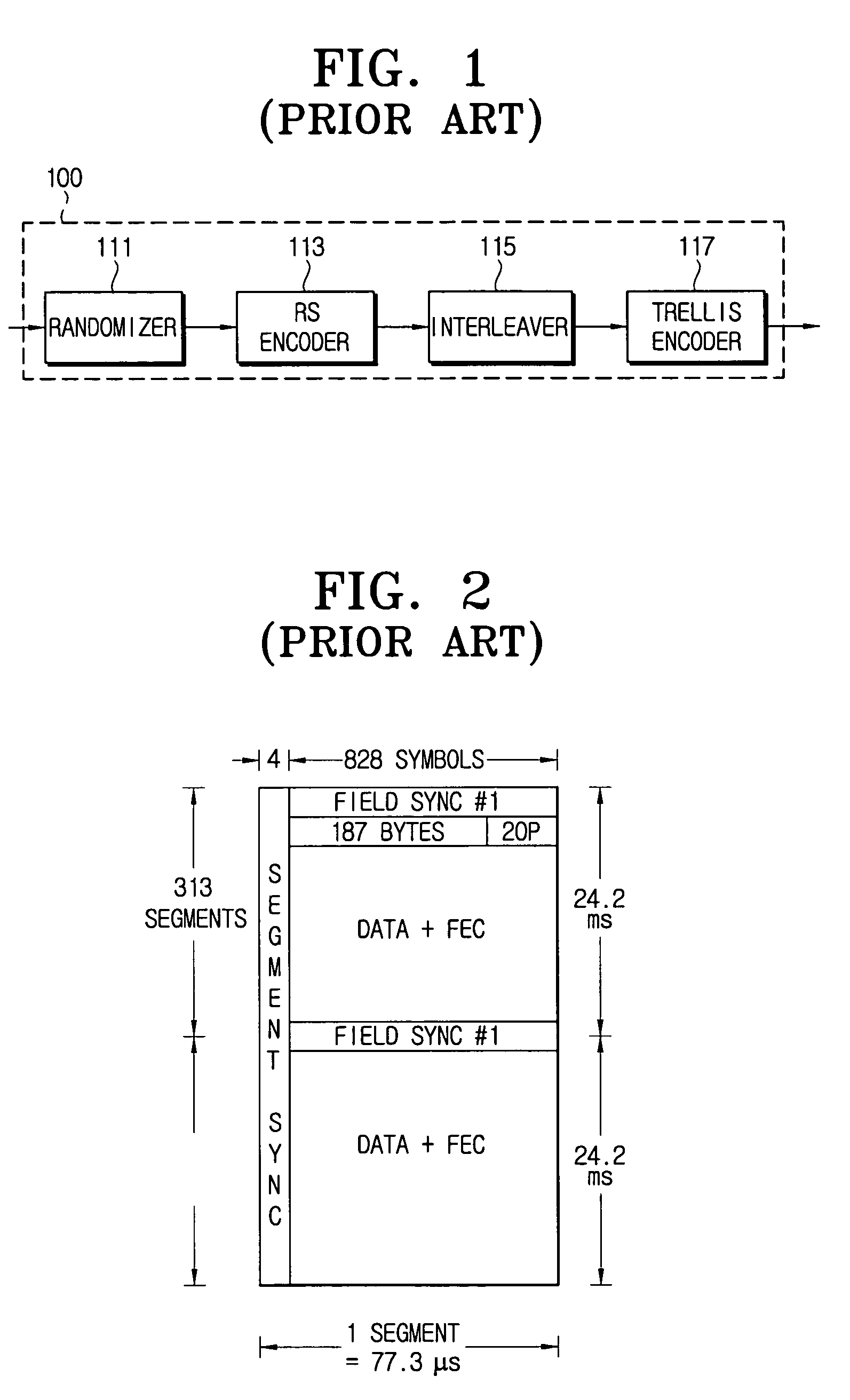
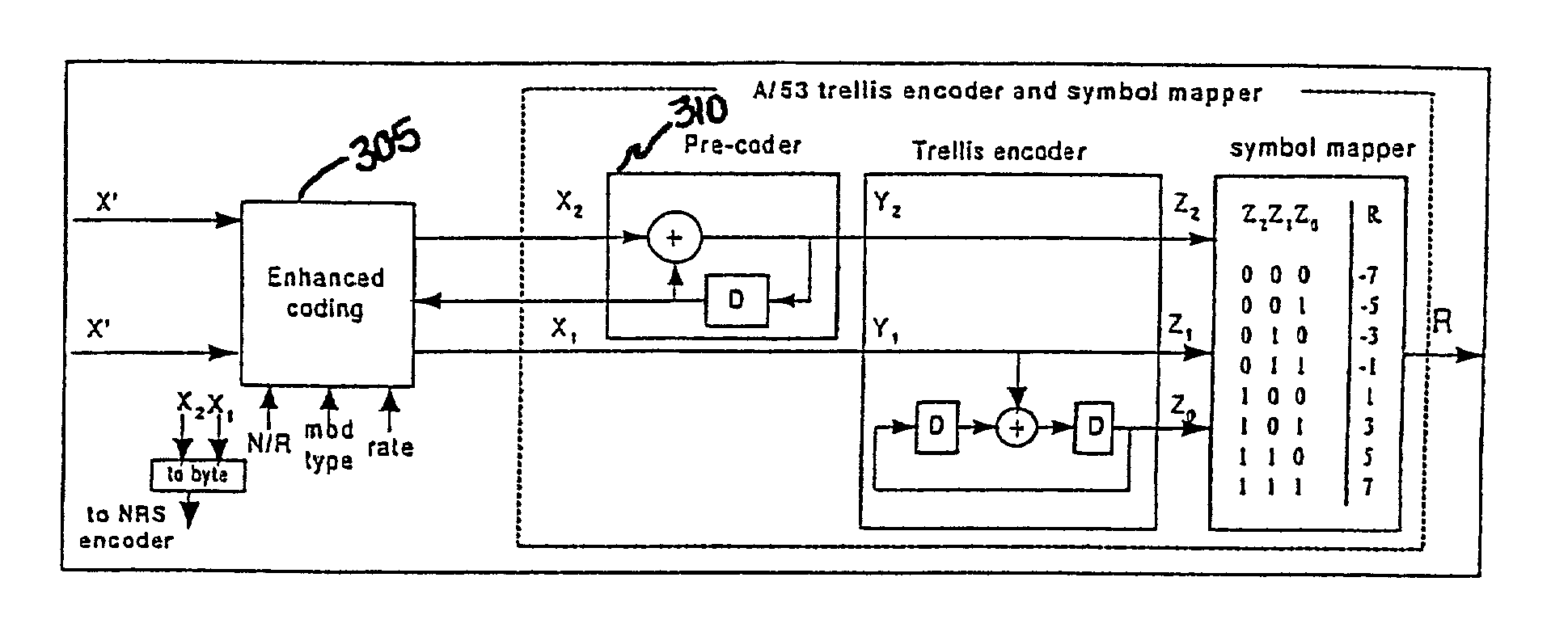
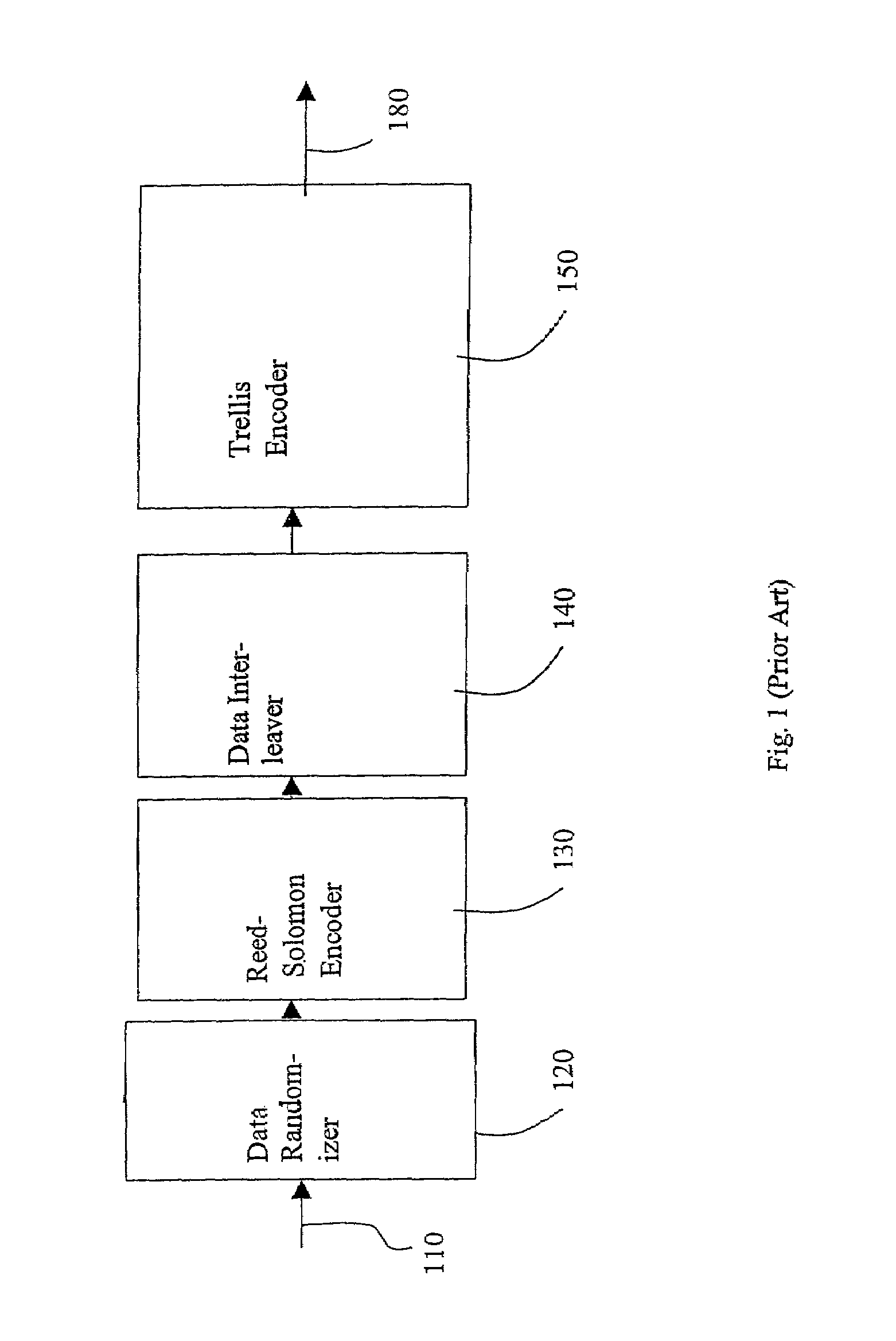
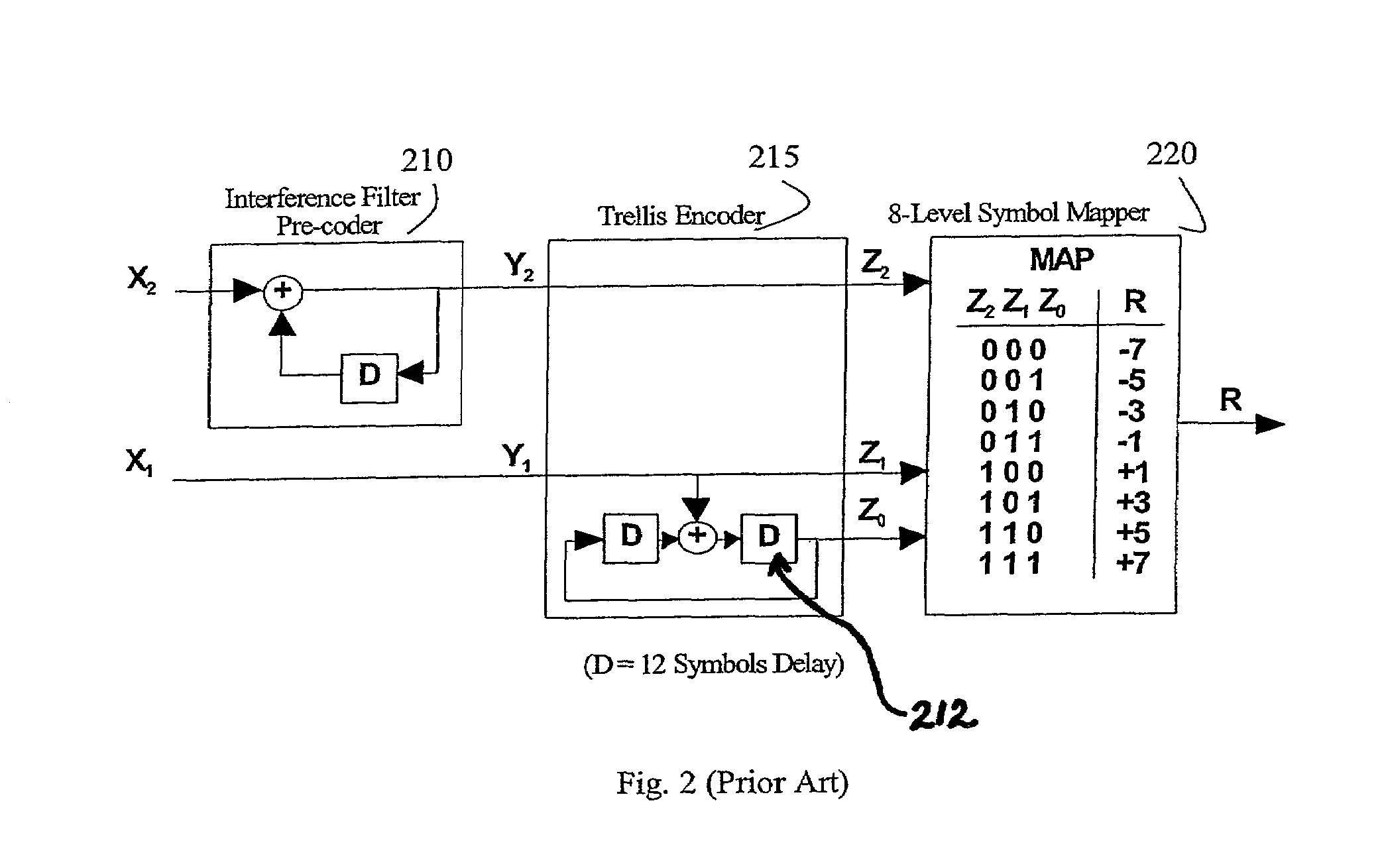
Trellis encoder with rate 1/4 and 1/2 for a backward compatible robust encoding ATSC DTV transmission system
InactiveUS7020828B2Improve robustnessMaintain backward compatibilityData representation error detection/correctionError correction/detection using block single space codingComputer hardwareCoding block
Robust and existing standard bit streams are mixed in a backward compatible manner for forming enhanced modes for better reception of ATSC DTV signals. This is achieved by an enhanced coding block provided at the input of a conventional ATSC trellis encoder unit. The enhanced coding block comprising a trellis encoder encodes only the robust stream while passing the normal standard stream unaltered.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
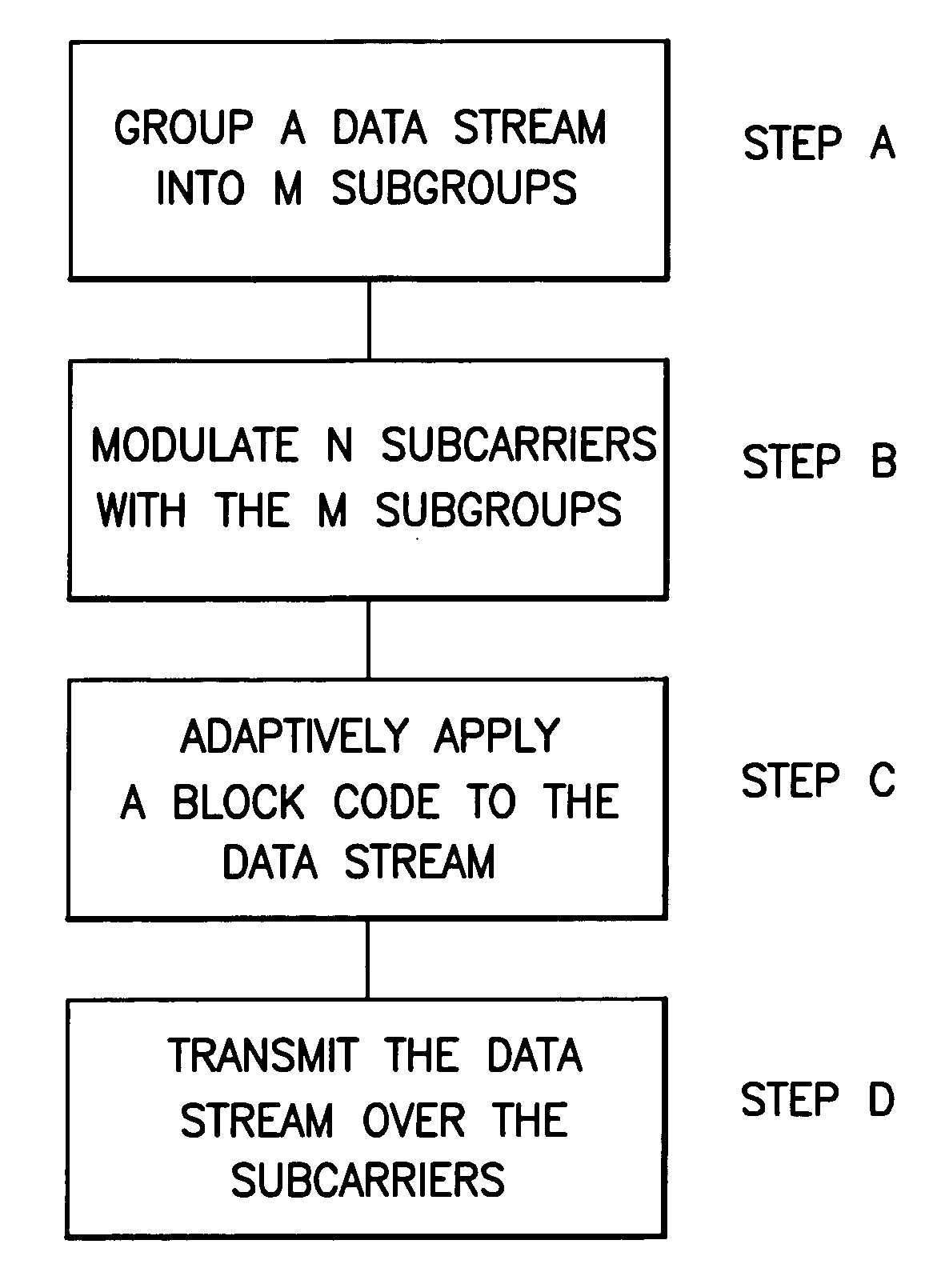
Adaptive multilevel block coded modulation for OFDM systems
InactiveUS20070019753A1Multiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsError correction/detection using block single space codingHamming codeData stream
A method includes grouping a data stream into a first plurality of subgroups, modulating a plurality of subcarriers with the first plurality of subgroups, adaptively applying a block code to said data stream comprising a repetition code, a Hamming code, and a plurality of uncoded bits based upon a channel characteristic of each of said plurality of subcarriers, and transmitting the data stream on the plurality of subcarriers.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
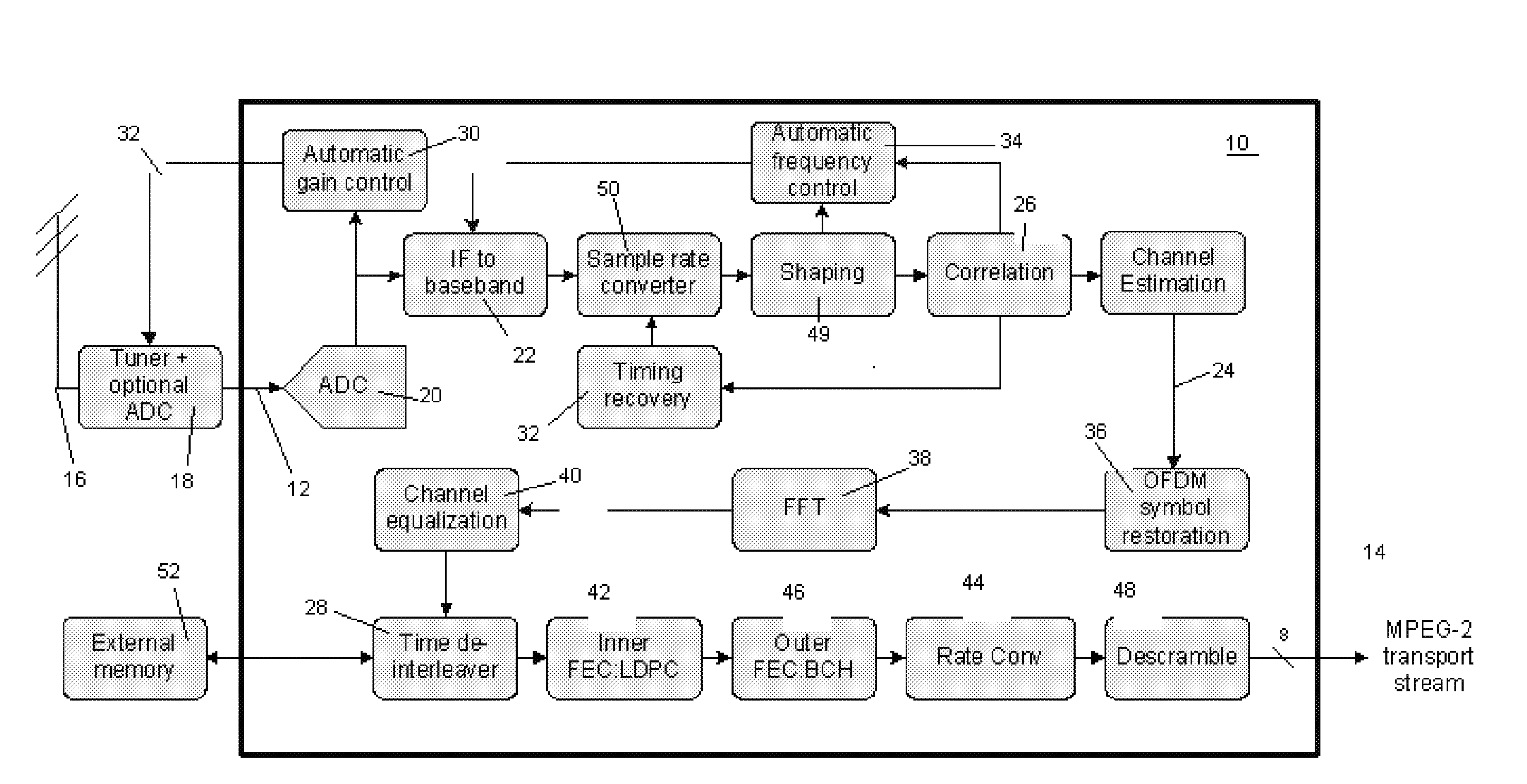
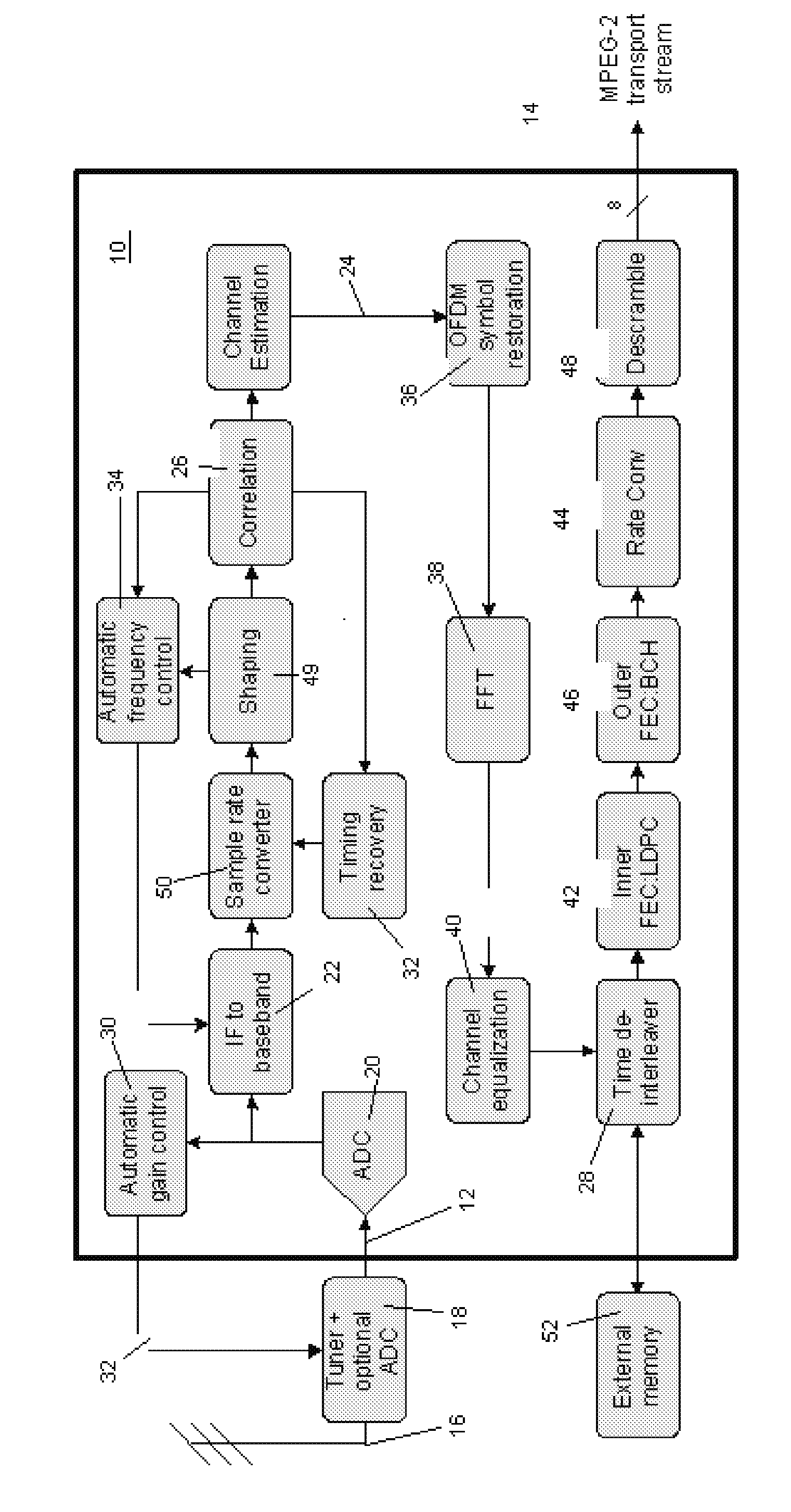
Receiver architecture having a LDPC decoder with an improved llr update method for memory reduction
InactiveUS20080028282A1Reduce memory requirementsFast decodingData representation error detection/correctionError correction/detection using block single space codingSingle processHardware implementations
The present invention provides a reduced memory implementation for the min-sum algorithm compared to traditional hardware implementations. The improvement includes innovative MIN_SUM method with reduced memory requirements suitable of computer implementation that combines the traditional row update process and column update process into a single process, in that the traditional CNU unit and VNU unit are combined into a single CVNU unit. The improvement not only reduces the time required for decoding by half, but also reduces the logic and routing efforts. Furthermore, instead of storing the whole intermediate LLR values using a significant number of memories, only a set of parameters associated with the intermediate LLR values is stored. The set of parameters includes: 1. sign of LLR; 2. the minimum LLR, 3. sub-minimum LLR, and 4. the column location of minimum value in each row. Therefore, as compared with the traditional LDPC decoder implementation, the required memory size of the present invention is significantly or tremendously reduced.
Owner:LEGEND SILICON
Channel interleaving/de-interleaving apparatus in a communication system using a low density parity check code and control method thereof
ActiveUS7555694B2Minimize error rateIndoor gamesError correction/detection using block single space codingCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
In a communication system, information data bits are encoded in a preset coding scheme when the information data bits are input, and a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codeword is generated. The LDPC codeword is interleaved according to a preset channel-interleaving rule. A channel-interleaved LDPC codeword is modulated in a preset modulation scheme and a modulation symbol is generated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for LDPC coded modulation
InactiveUS20050229088A1Improve performanceHigh gainError preventionError correction/detection using block single space codingTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
Typical forward error correction methods employ Trellis Code Modulation. By substituting low density parity check coding in place of the convolution code as part of a combined modulation and encoding procedure, low density parity check coding and modulation can be performed. The low density parity check codes have no error floor, no cycles, an equal bit error rate for the information bits and the parity bits, and timely construction of both a parity check matrix with variable codeword size and a generator matrix is possible.
Owner:AWARE INC
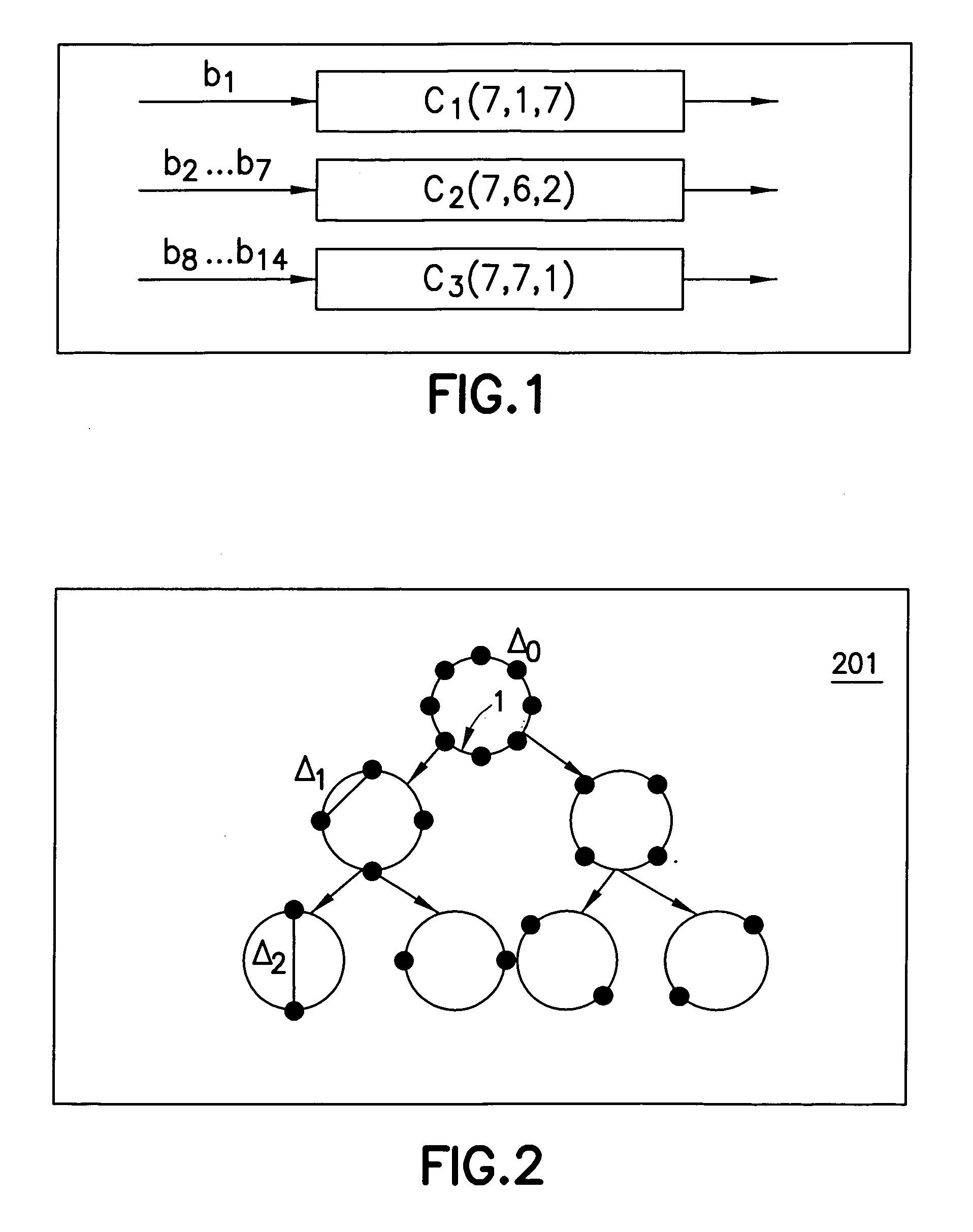
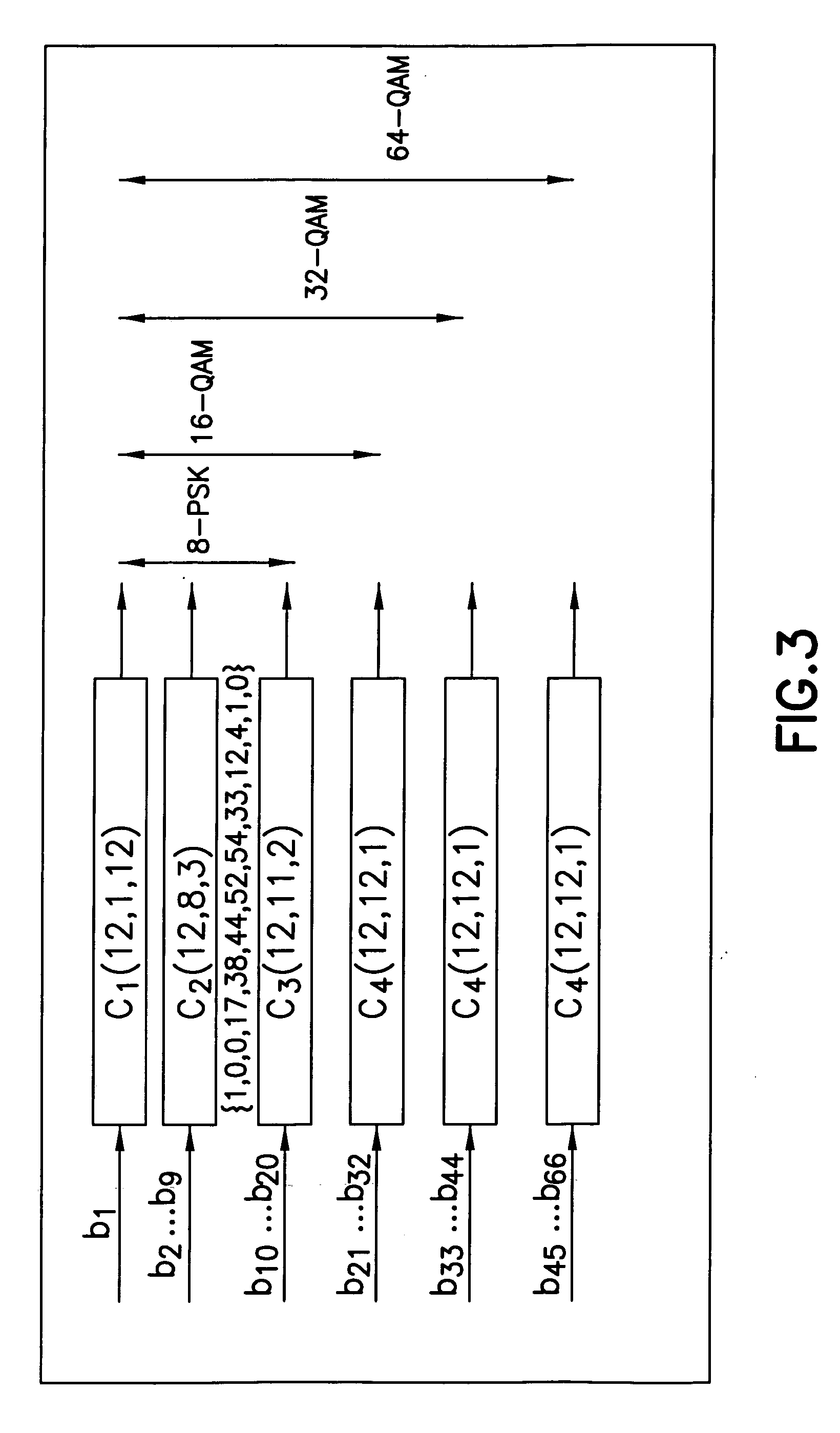
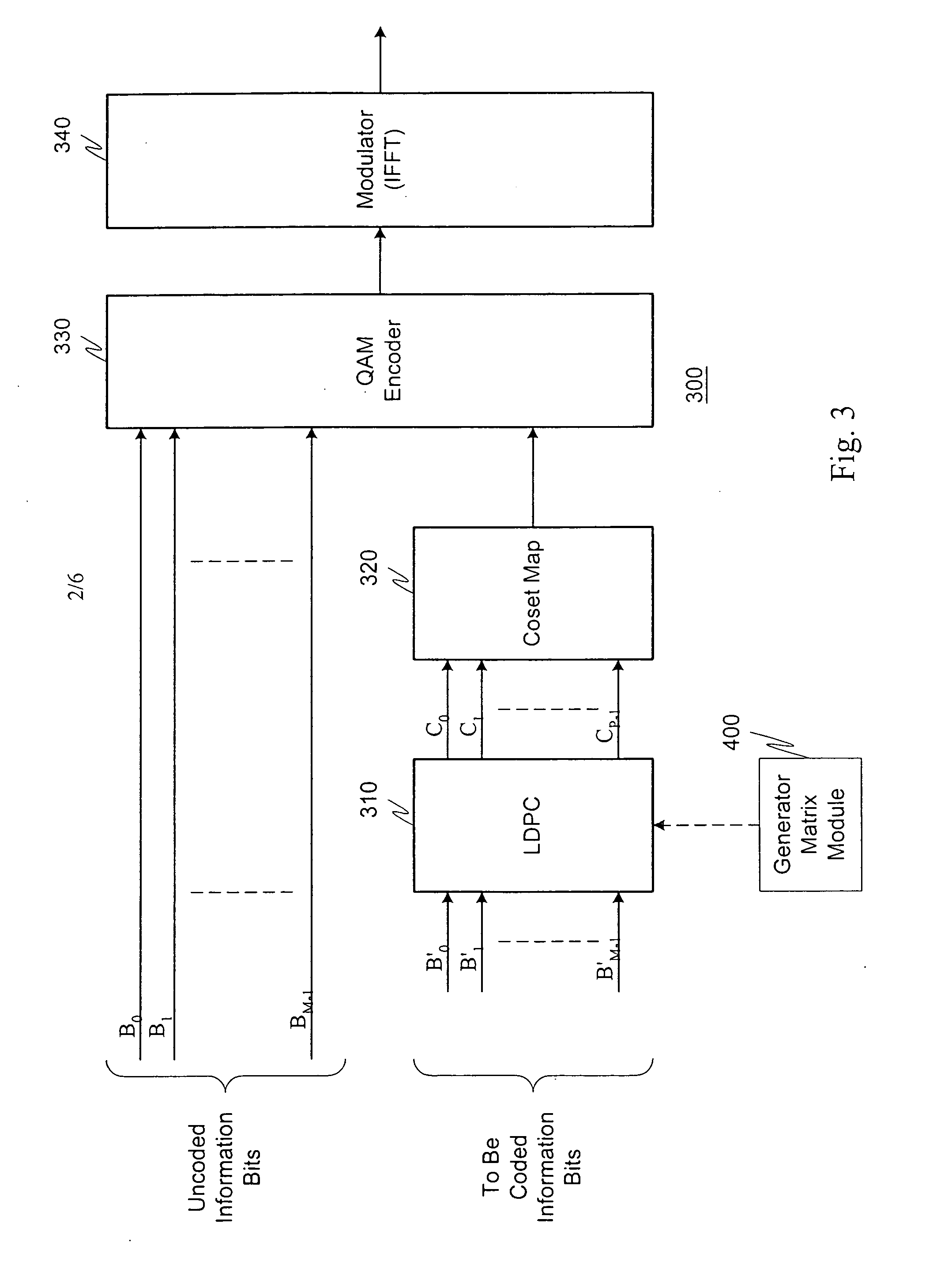
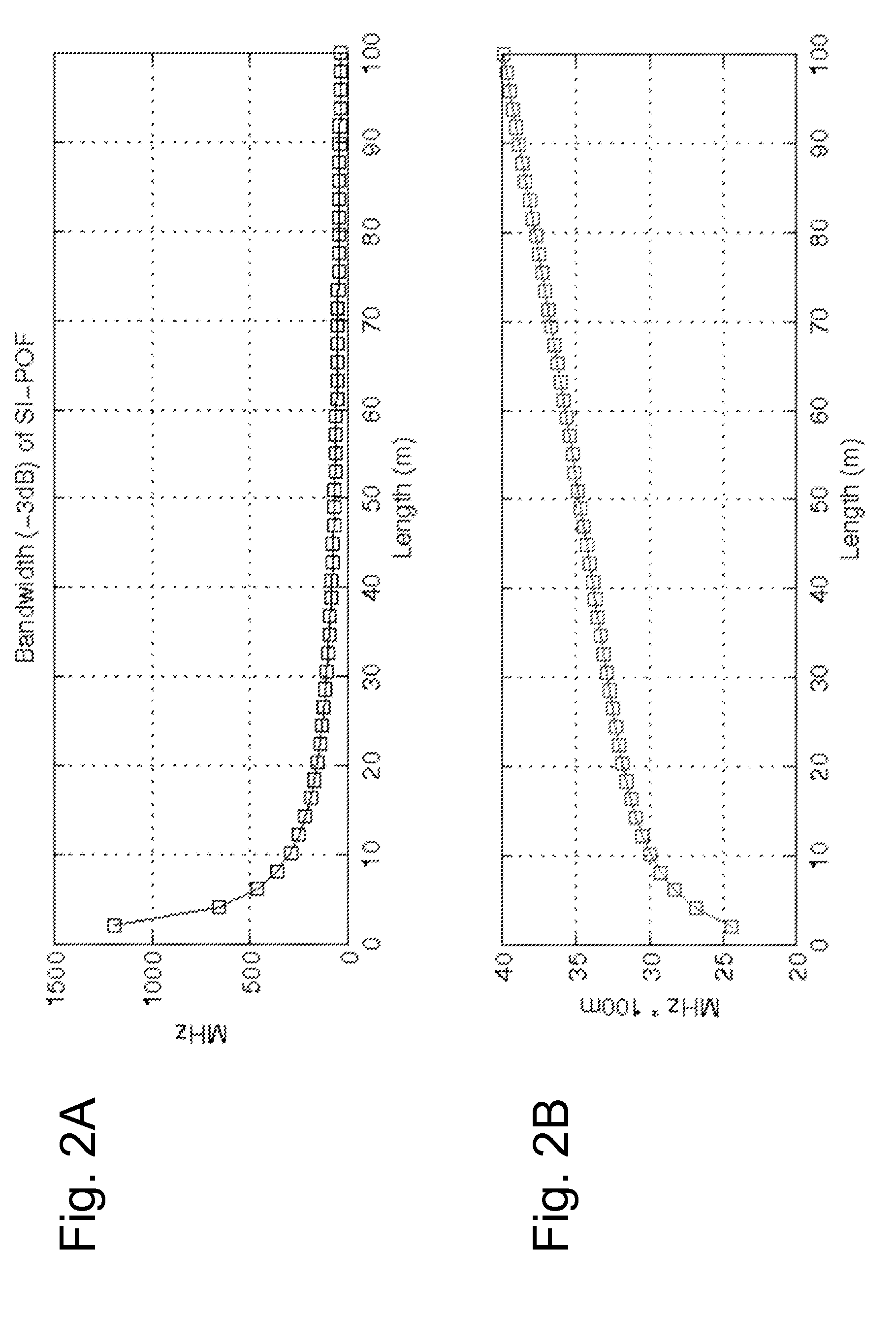
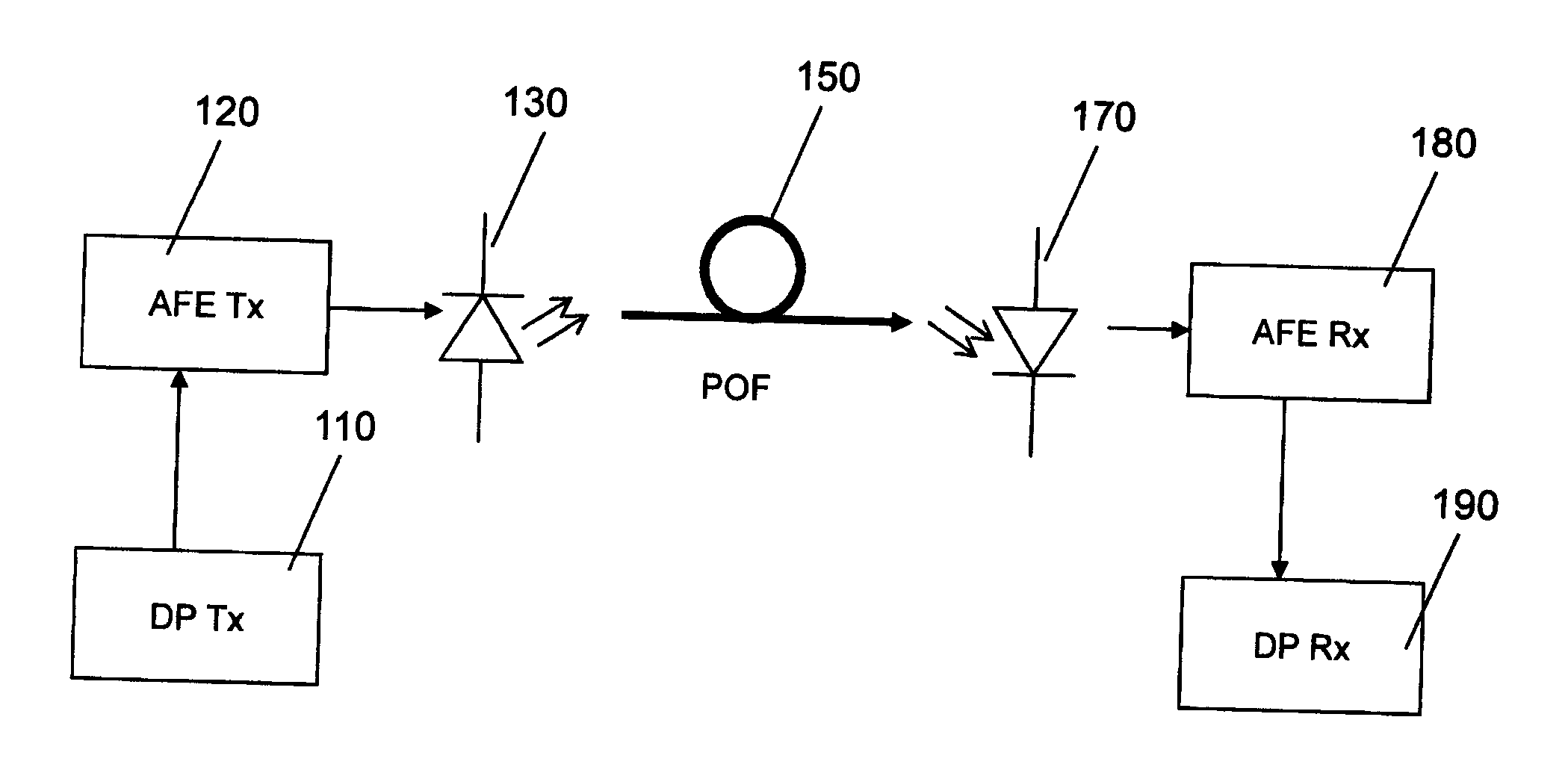
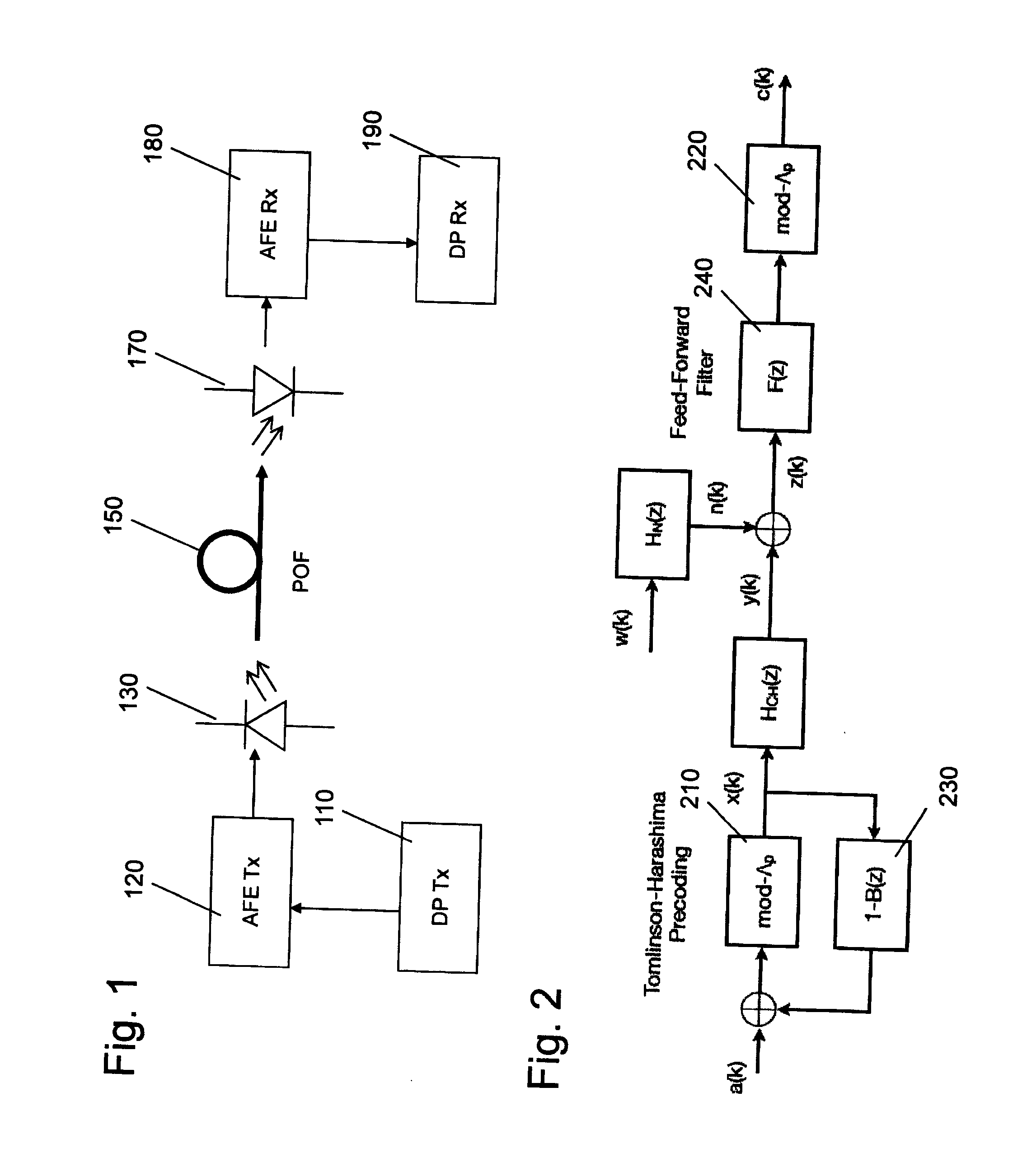
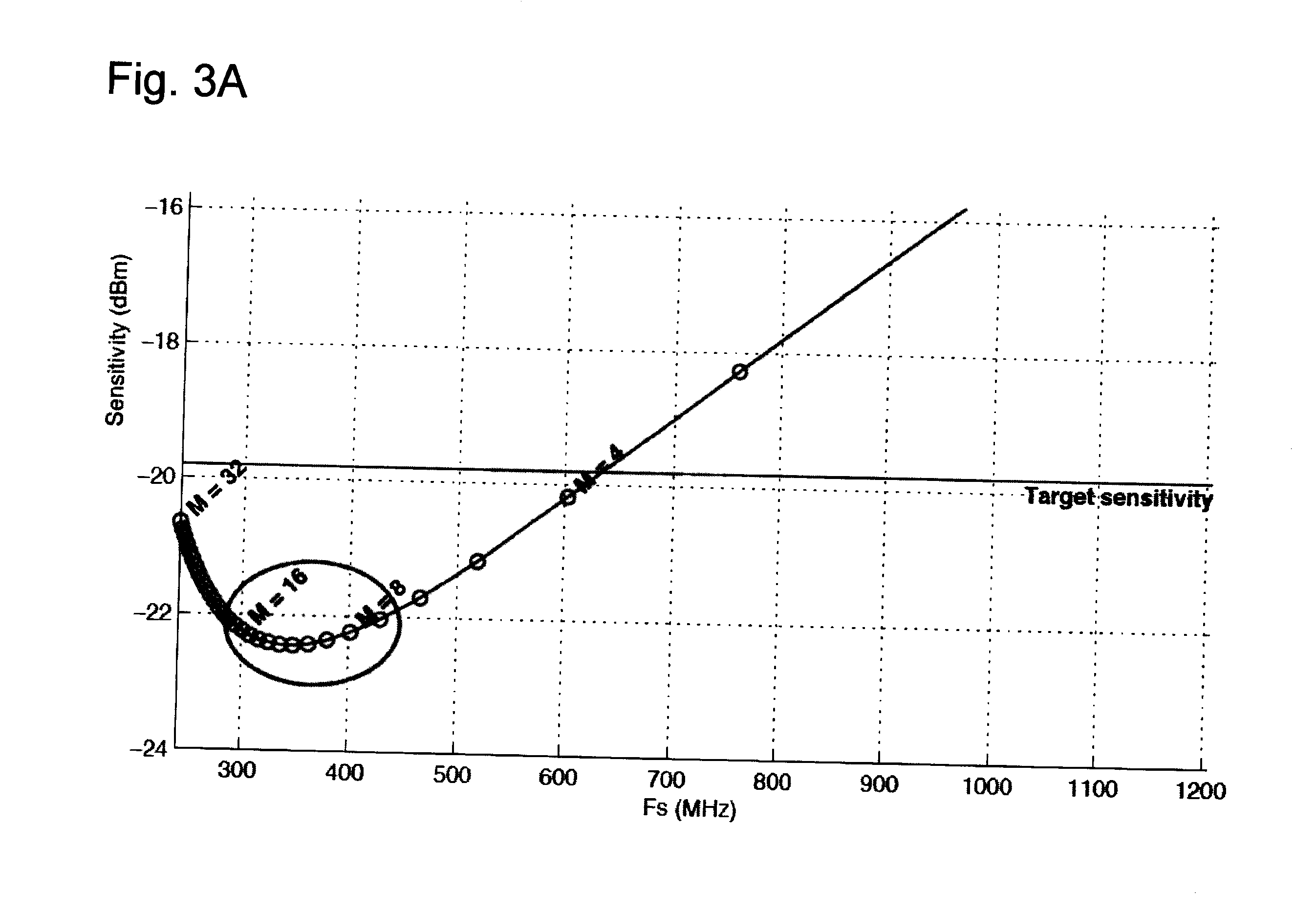
Adaptive Error Correcting Code for Data Communications Over a Plastic Optical Fibre
ActiveUS20120250785A1Less-efficient systemReduce in quantityError correction/detection using block single space codingUnequal/adaptive error protectionDigital dataThree level
An efficient coding and modulation system for transmission of digital data over plastic optical fibres is disclosed. The digital signal is coded by a three-level coset coding. The spectral efficiency of the system is configurable by selecting the number of bits to be processed in each of the levels. The first level applies to the digital data a binary BCH coding and performs coset partitioning by constellation mapping and lattice transformations. Similarly, second level applies another binary BCH coding, which may be performed selectably in accordance with the desired configuration by two BCH codes with substantially the same coding rate, operating on codewords of different sizes. The third level is uncoded. The second and third levels undergo mapping and lattice transformation. After an addition of the levels, a second-stage lattice transformation is performed to obtain a zero-mean constellation. The symbols output from such three-level coset coder are then further modulated.
Owner:KNOWLEDGE DEV FOR POF SL
Optical OFDM signal coded modulation and demodulation system and method based on polarization code
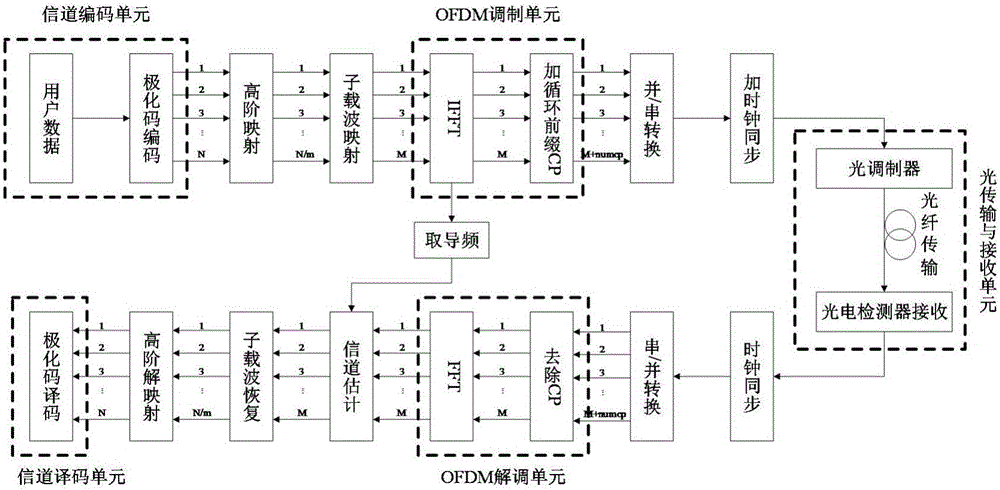
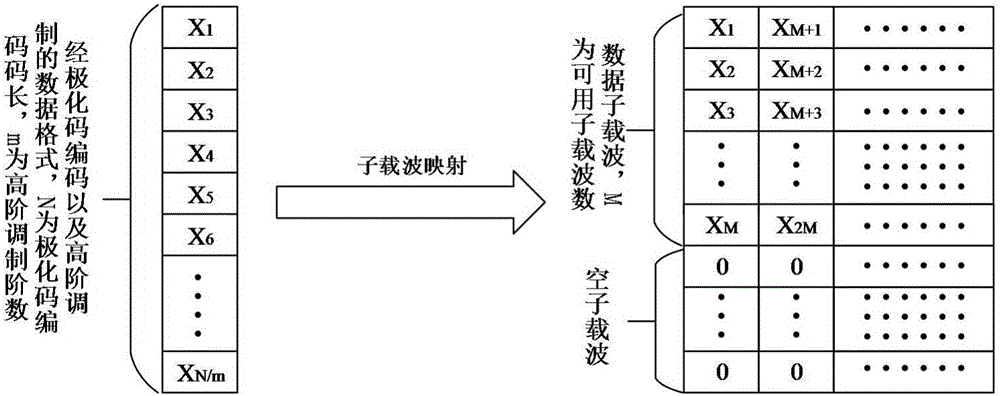
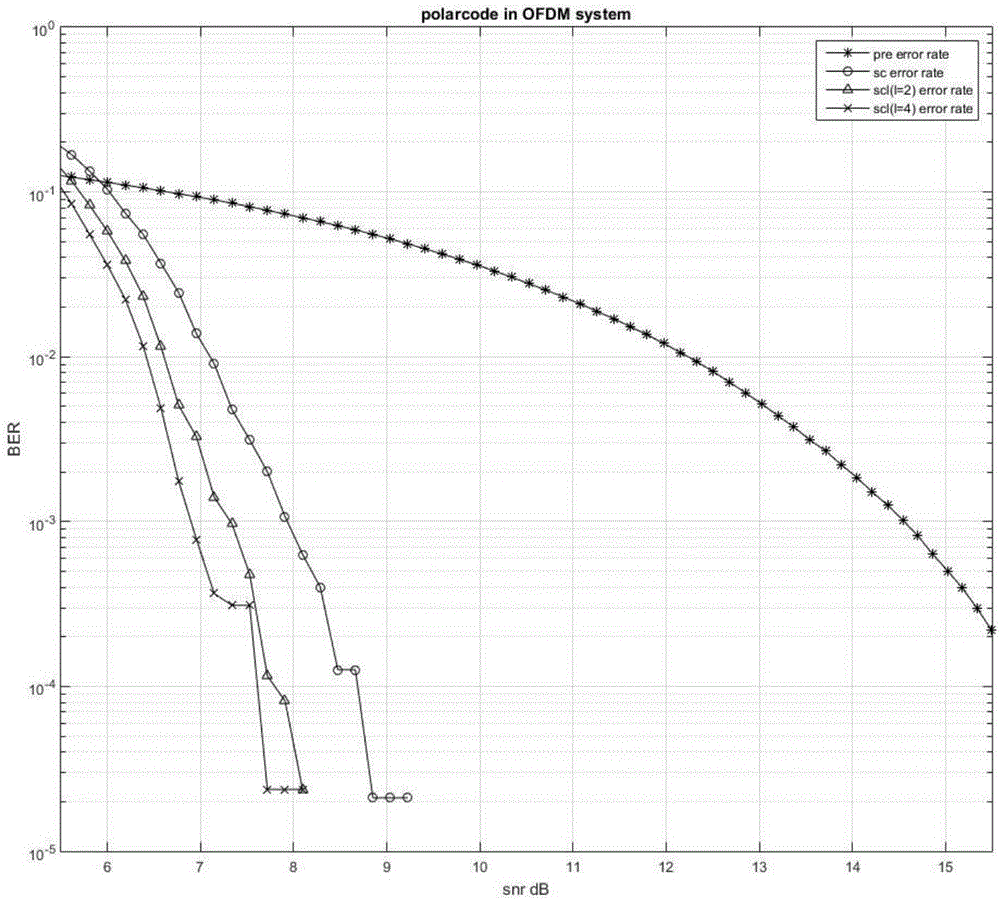
InactiveCN106130656ASolve resource problemsSolve the speed problemError correction/detection using block single space codingError preventionFrequency domainInformation transfer
The present invention proposes a polar code-based optical OFDM signal coding modulation and demodulation system and method, the system includes a polar code coding unit, a high-order mapping unit, a subcarrier mapping unit, a pilot frequency acquisition unit, and an OFDM modulation unit , an optical transmitting and receiving unit, an OFDM demodulation unit, a subcarrier recovery unit, a high-order demapping unit, and a polar code decoding unit. User information is coded by polar code and then mapped to the corresponding carrier through high-order modulation. After IFFT, the conversion of frequency domain signal to time domain signal is realized, and then modulated onto the channel for transmission. The receiving end performs FFT on the signal, recovers the subcarrier signal, high-order soft demodulation and SC decoding of the polar code to restore the original user signal to realize the transmission of the entire system. The present invention combines polar codes with high-order modulation and carrier mapping, and can flexibly apply spectrum resources available in the system. The introduction of high-order modulation technology improves the transmission rate of information, and the introduction of polar codes improves the reliability of information transmission.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Apparatus for FEC supporting transmission of variable-length frames in TDMA system and method of using the same
InactiveUS20050149821A1Reduce processCorrection errorError preventionError correction/detection using block single space codingDelayed timeVariable length
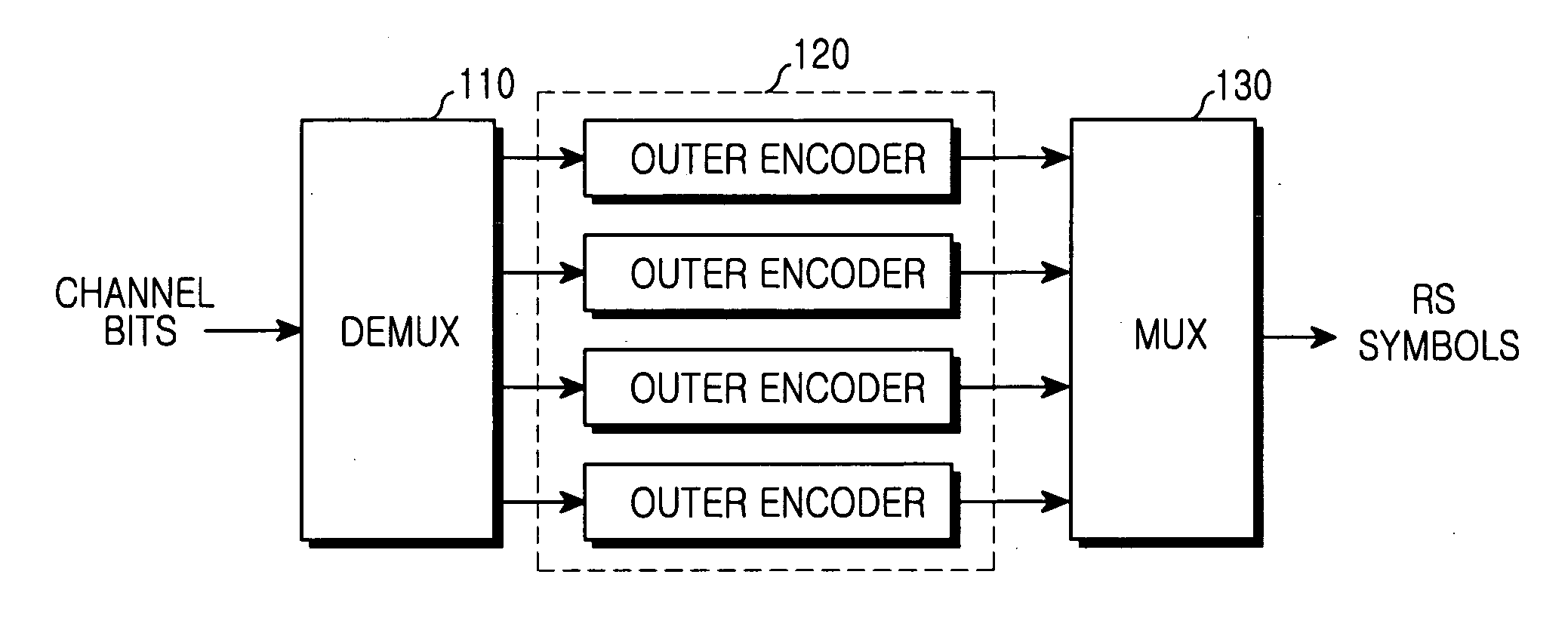
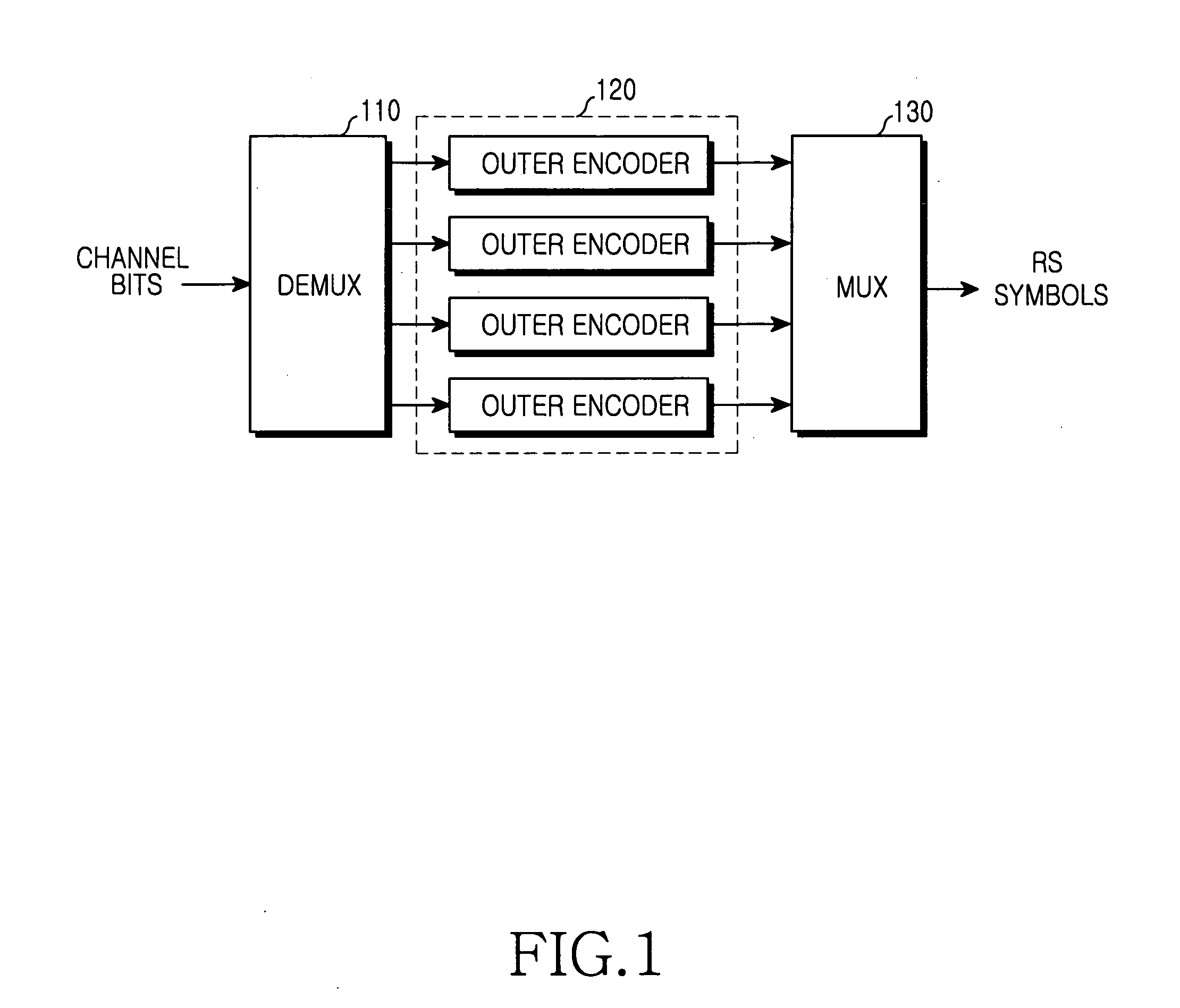
An apparatus for transmitting a FEC frame is provided. The apparatus includes: a selector determining whether to perform FEC encoding on data to be transmitted; a Reed-Solomon encoding assembler receiving the data on which FEC encoding is to be performed as determined by the selector, and dividing the data into k-byte message blocks (k is a positive integer) for output; a Reed-Solomon encoder receiving the message blocks and performing Reed-Solomon encoding on the message blocks; and an output controller receiving an input parity generated by the Reed-Solomon encoding, and outputting the message block and the parity sequentially or outputting the data on which FEC encoding is not to be performed as determined by the selector. In order to correct an error caused by a transmission medium using FEC in a Reed-Solomon code type, FEC encoding / decoding of a frame is performed. A total transmission delay time is not influenced when FEC is bypassed, a delay caused by a shortened codeword is minimized, and a FEC encoding / decoding delays for frames having different lengths are equalized.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
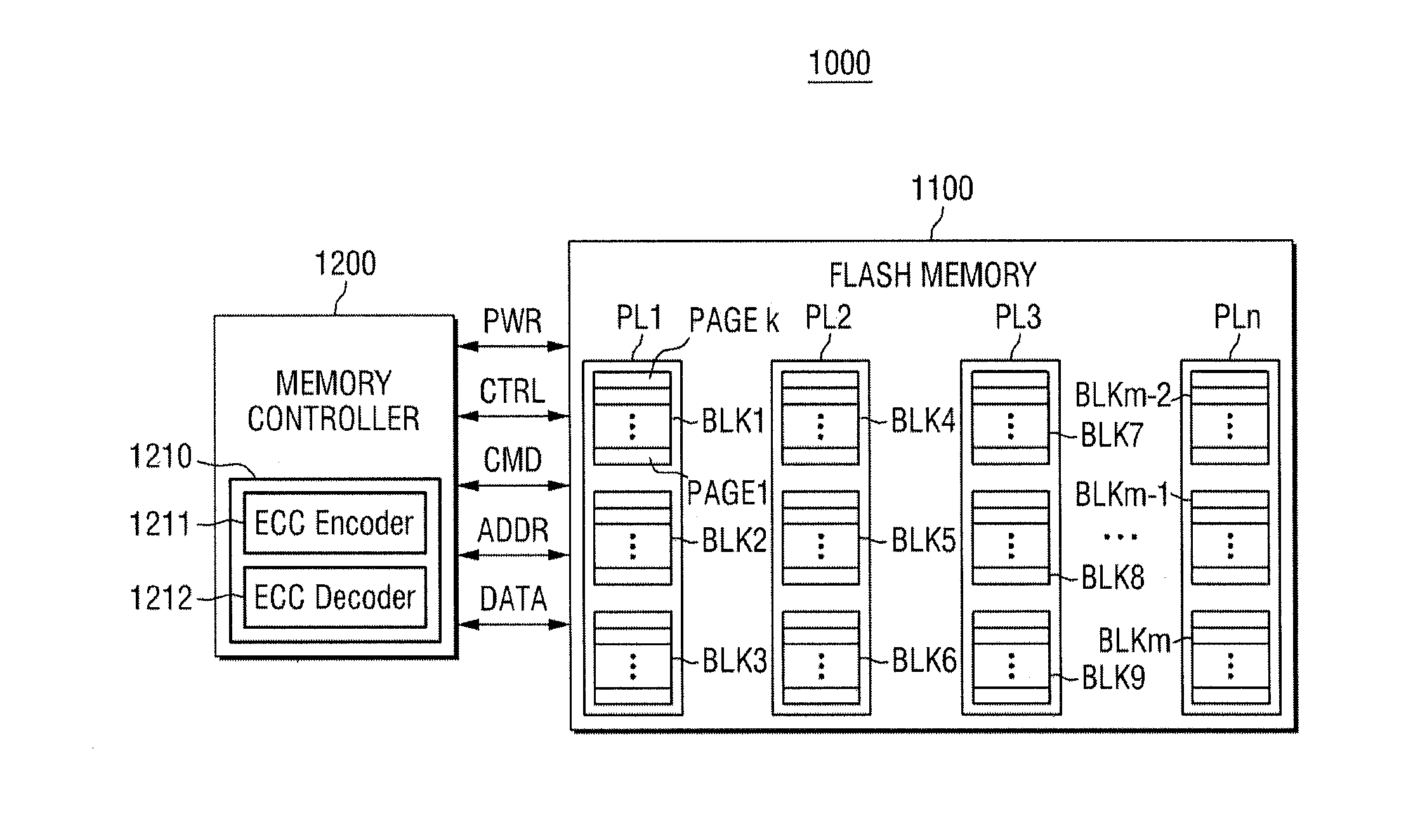
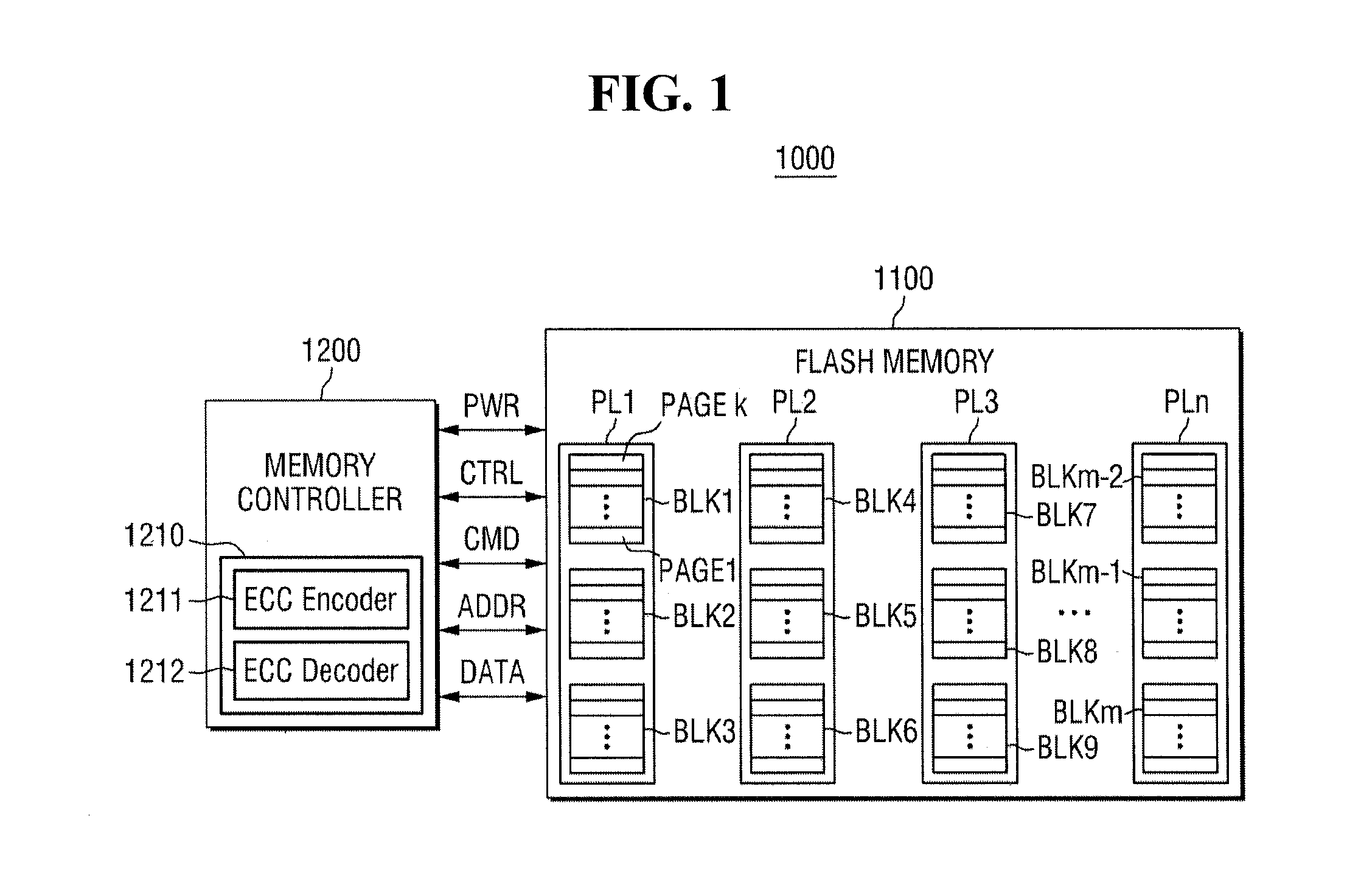
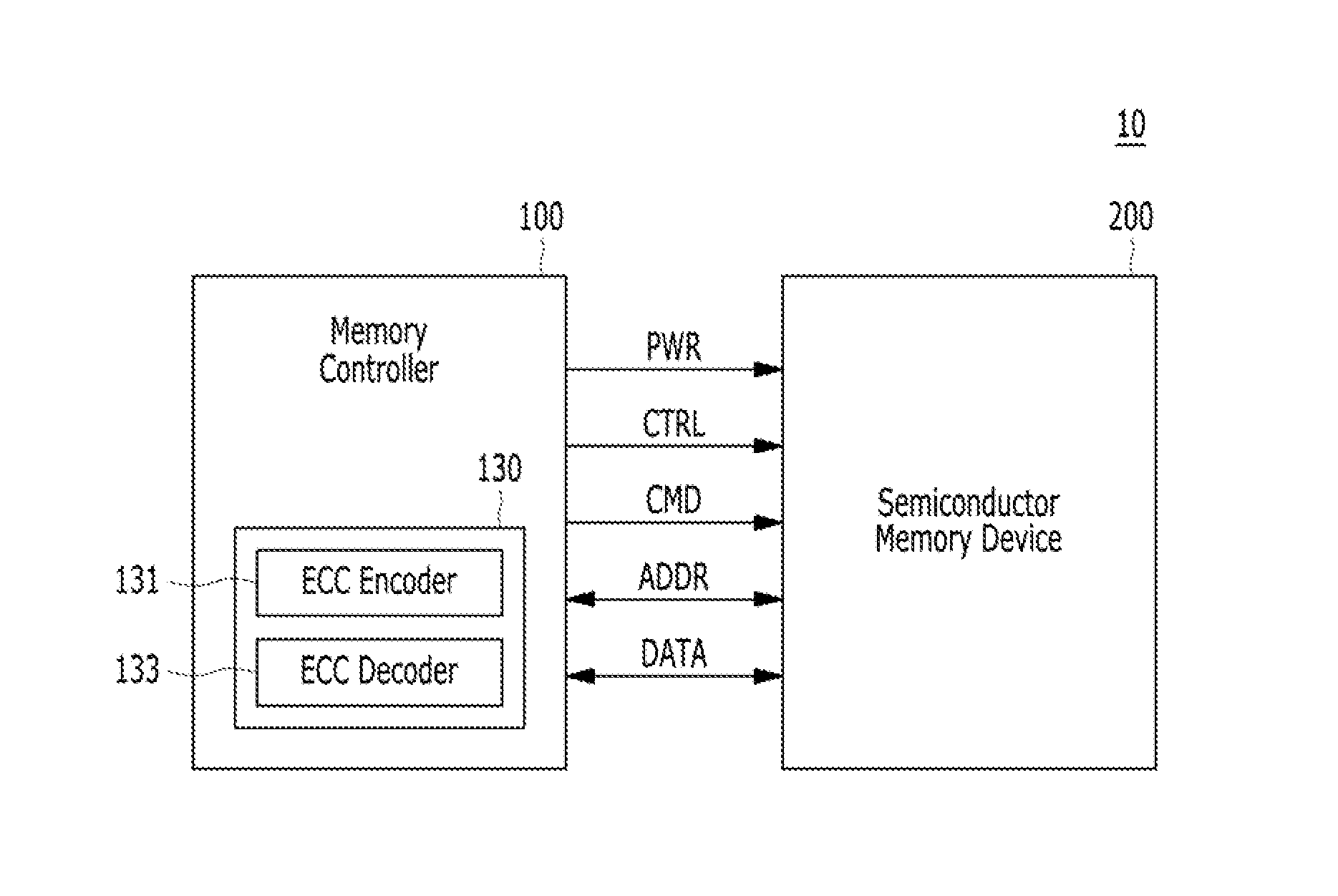
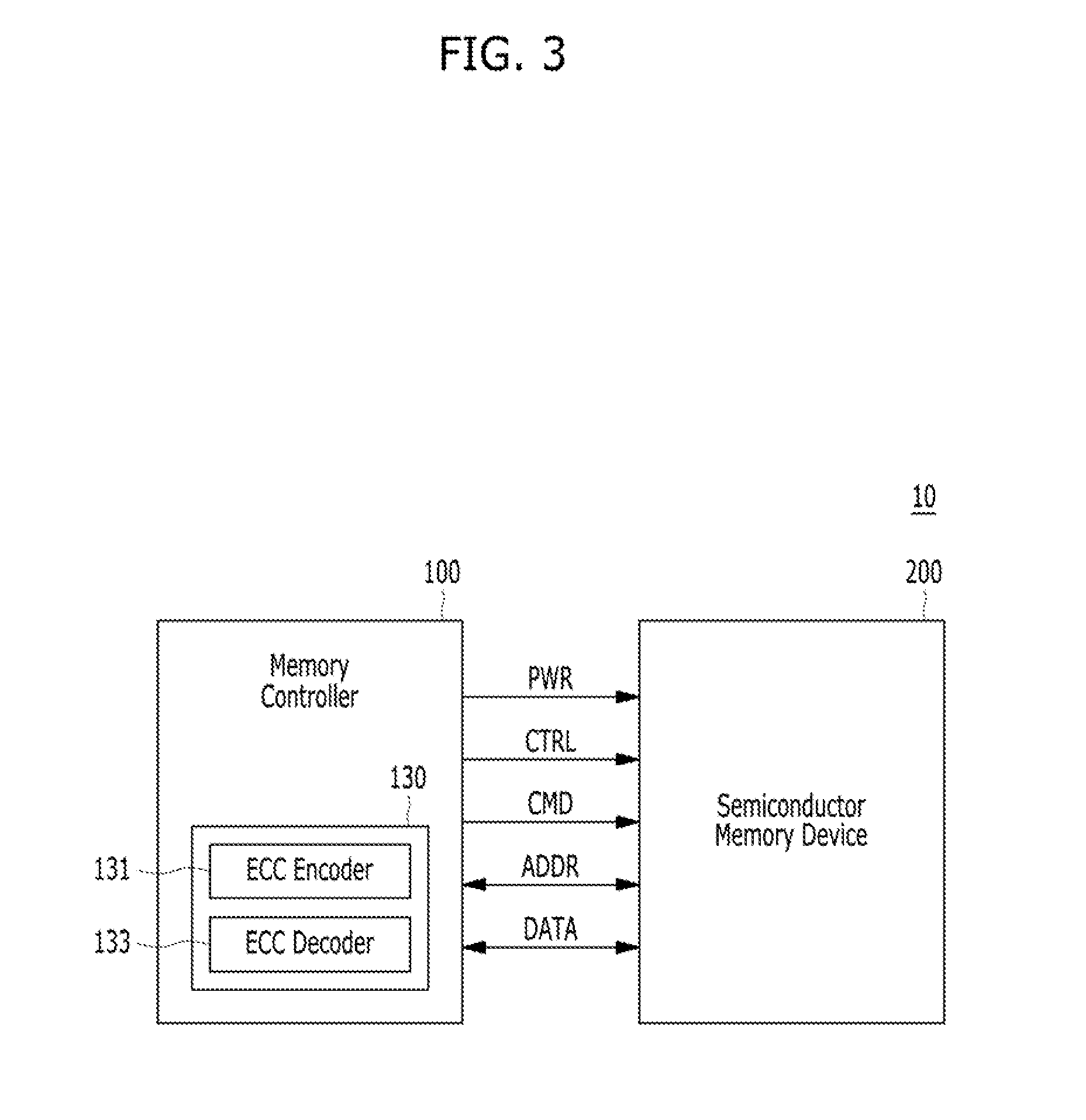
Operating method of error correction code decoder and memory controller including the error correction code decoder
ActiveUS20150046771A1Increase speedShorten the timeError correction/detection using convolutional codesError correction/detection using block single space codingMemory controllerCorrection code
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Two-level coset coding scheme for gigabit ethernet over plastic optical fiber
ActiveUS20160204873A1Lower latencyEasy to installError correction/detection using block single space codingError preventionDigital dataEngineering
An efficient coding and modulation system for transmission of digital data over plastic optical fibers with low latency. In particular, the digital signal is coded by means of a two-level coset coding. The first level applies to the digital data a binary shortened BCH coding and performs coset partitioning by means of constellation mapping and lattice transformations. The second level is uncoded but undergoes mapping and lattice transformation. After an addition of the two levels, a second-stage lattice transformation is performed so as to obtain a zero-mean constellation. The symbols output from such three-level coset coder are then further modulated.
Owner:KNOWLEDGE DEV FOR POF SL
Method and apparatus for decoding inner and outer codes in a mobile communication system
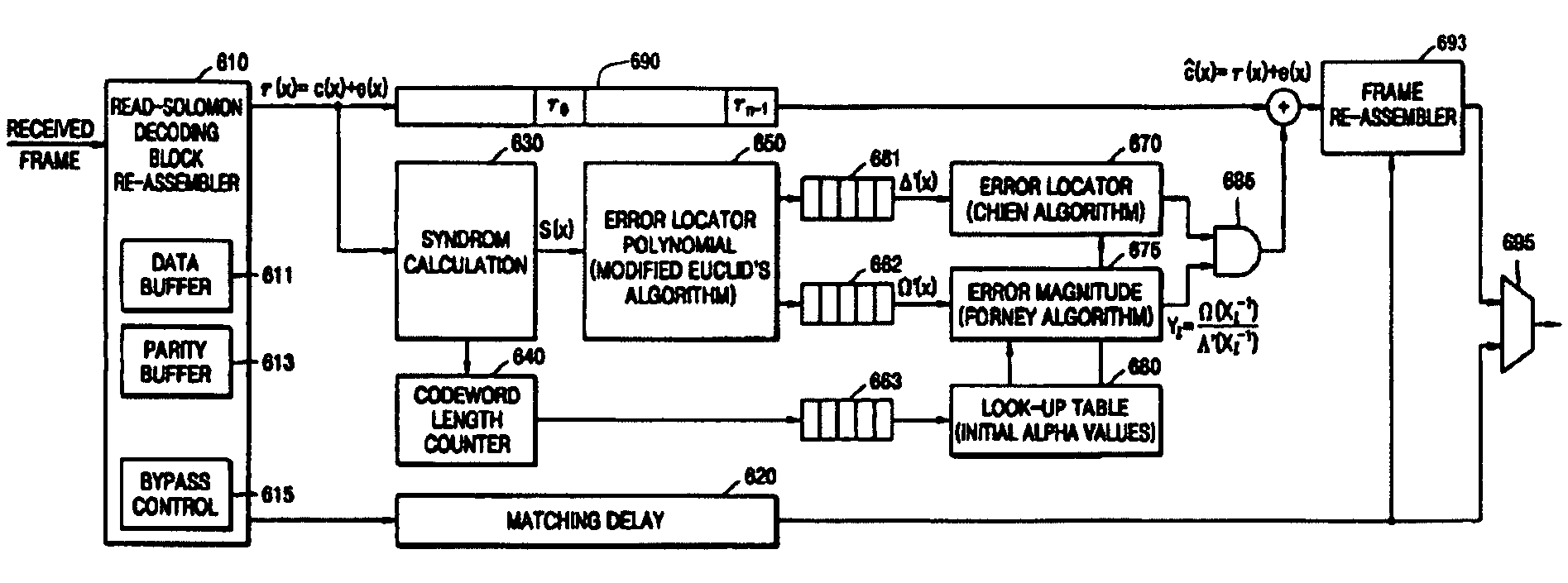
ActiveUS20050268205A1Simple structureThe decoding process is simpleError correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionMobile communication systemsComputer science
A method and apparatus for decoding inner and / or outer codes in a mobile communication system. The inner and / or outer codes are decoded at low power and high speed. An inner decoder performs channel decoding and cyclic redundancy checking (CRC) on symbols received through a wireless network. An outer decoder performs outer coding on the received symbols. An erasure symbol identifier outputs information of erasure symbols in which a reception error has occurred. The reception error is determined from a result of the CRC on the received symbols. A controller counts the number of received symbols and the number of erasure symbols, and stops an operation of at least one of the inner and outer decoders when at least one of the number of received symbols and the number of erasure symbols is equal to a preset reference value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus for FEC supporting transmission of variable-length frames in TDMA system and method of using the same
InactiveUS7581155B2Error preventionError correction/detection using block single space codingDelayed timeVariable length
An apparatus for transmitting a FEC frame is provided. In order to correct an error caused by a transmission medium using FEC in a Reed-Solomon code type, FEC encoding / decoding of a frame is performed. A total transmission delay time is not influenced when FEC is bypassed, a delay caused by a shortened codeword is minimized, and a FEC encoding / decoding delays for frames having different lengths are equalized.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
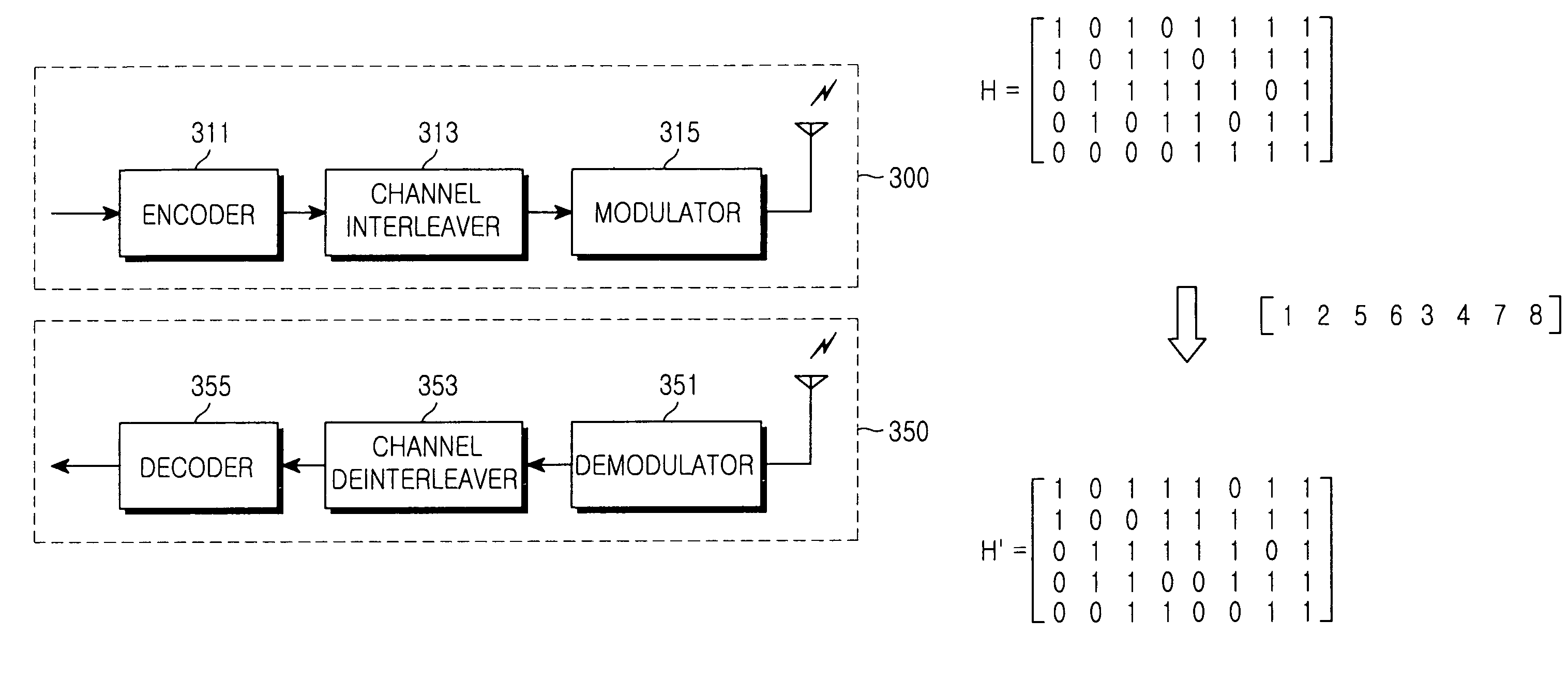
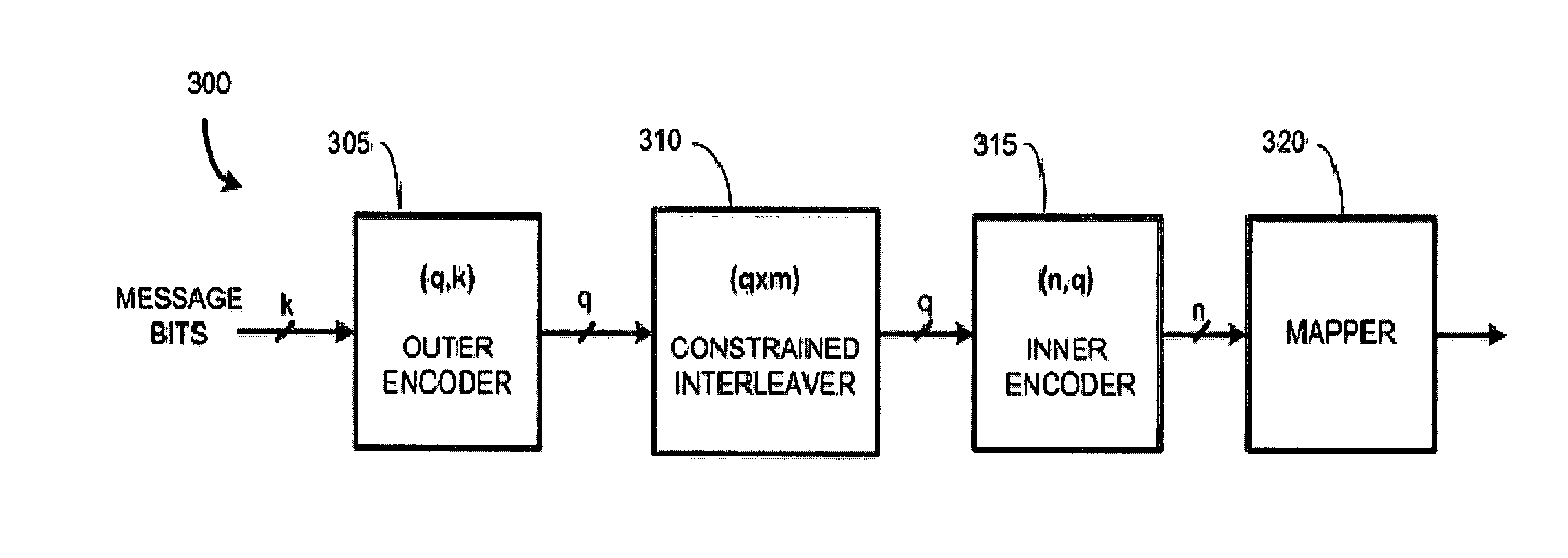
Methods, apparatus, and systems for coding with constrained interleaving
InactiveUS20150039965A1Improve bit error rate performanceError correction/detection using block single space codingError correction/detection using LDPC codesBlock codeConvolutional code
Serially-concatenated codes are formed in accordance with the present invention using a constrained interleaver. The constrained interleaver cause the minimum distance of the serial concatenated code to increase above the minimum distance of the inner code alone by adding a constraint that forces some or all of the distance of the outer code onto the serially-concatenated code. This allows the serially-concatenated code to be jointly optimized in terms of both minimum distance and error coefficient to provide significant performance advantages. Constrained interleaving can be summarized in that it: 1) uses an outer code that is a block code or a non-recursive convolutional code, and as such, there are multiple codewords present in the constrained interleaver, 2) selects a desired MHD, 3) selects an interleaver size and a set of predefined interleaver constraints to prevent undesired (low-distance) error events so as to achieve the desired MHD, and 4) performs uniform interleaving among the allowable (non-constrained) positions, to thereby maximize or otherwise improve the interleaver gain subject to the constraints imposed to maintain the desired MHD.
Owner:TRELLIS PHASE COMM LP
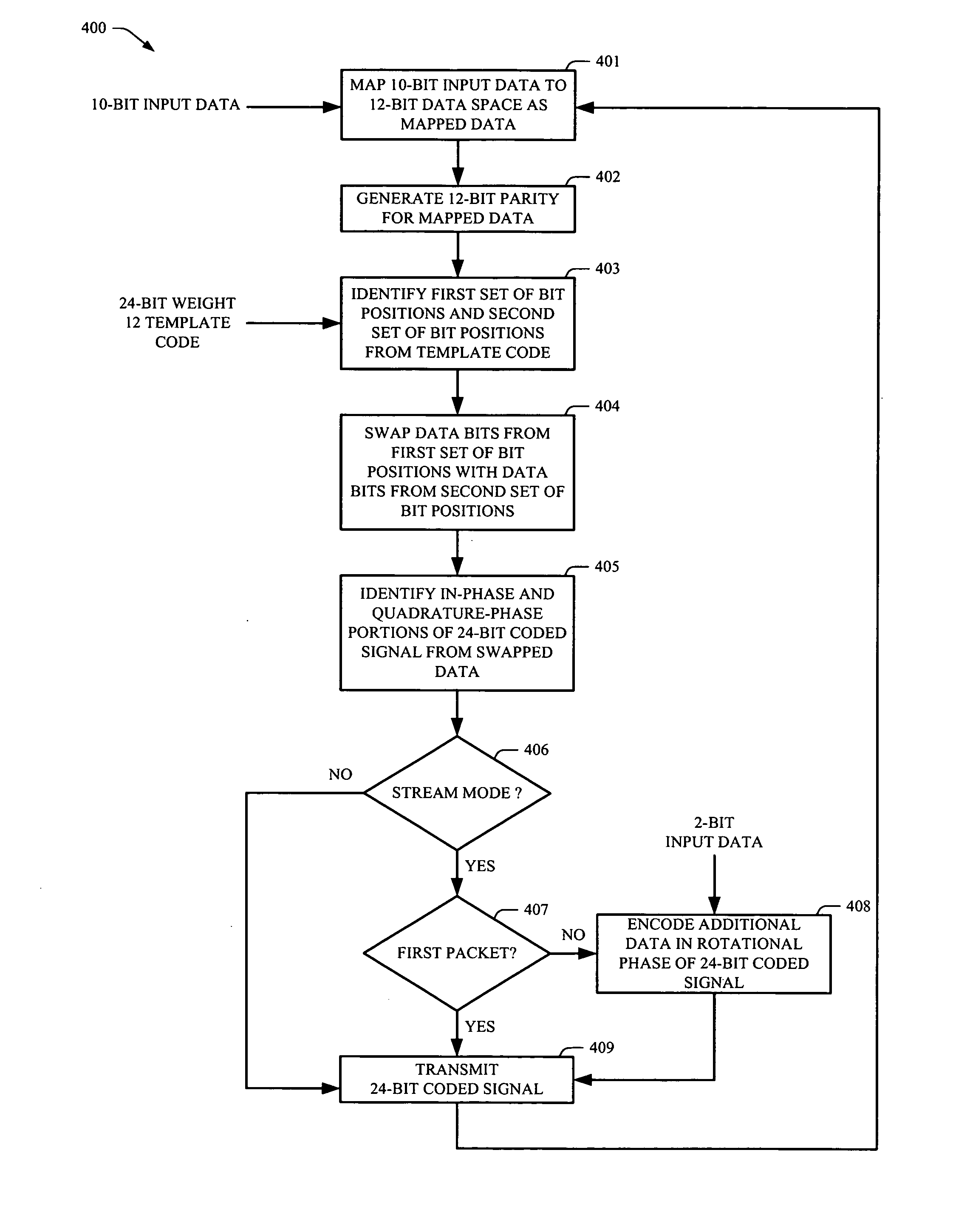
Rotationally invariant non-coherent burst coding
ActiveUS20080075176A1Error correction/detection using block single space codingError prevention24-bitBit field
An apparatus, system and method can be arranged for coding and / or decoding with a phase invariant coding scheme that is useful for short burst signaling devices. 10-bit data is mapped into a 12-bit data with a non-coherent burst code mapper. A parity generator creates a 12-bit parity data to form a 24-bit extended binary Golay code from the 12-bit data. The values for selected bit fields in the 12-bit data and 12-bit parity data are swapped to generate I and Q data such that sensitivity to changes in rotational phase is removed. I and Q data can be used by a transmitter to transmit a rotationally-invariant signal. On receipt, I and Q signals can be recovered, reverse swapped to generate the parity and data signals, and remapped to recover the transmitted 10-bit data. The receiver can also be arranged to use a soft decoding method for improved signal integrity.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
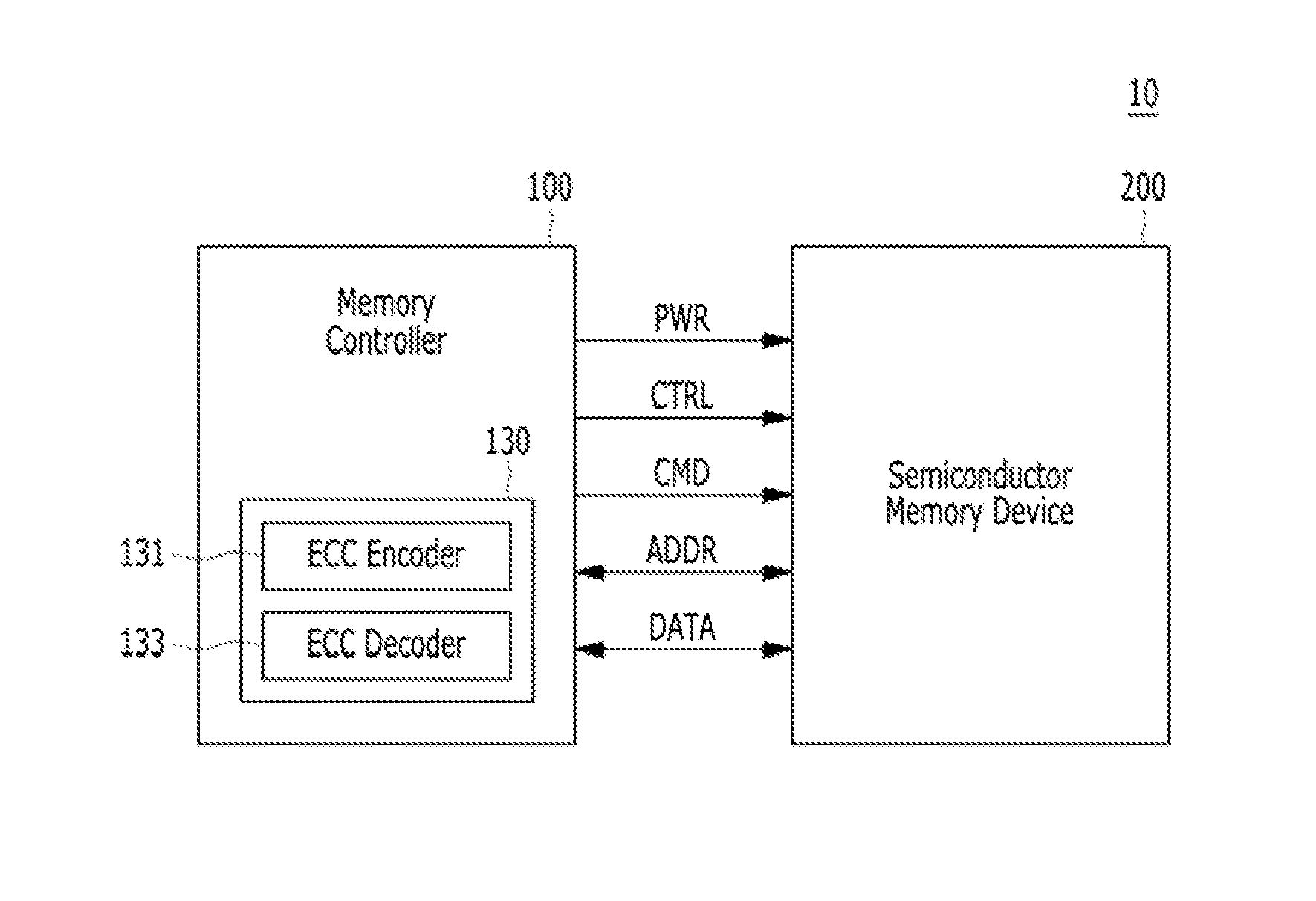
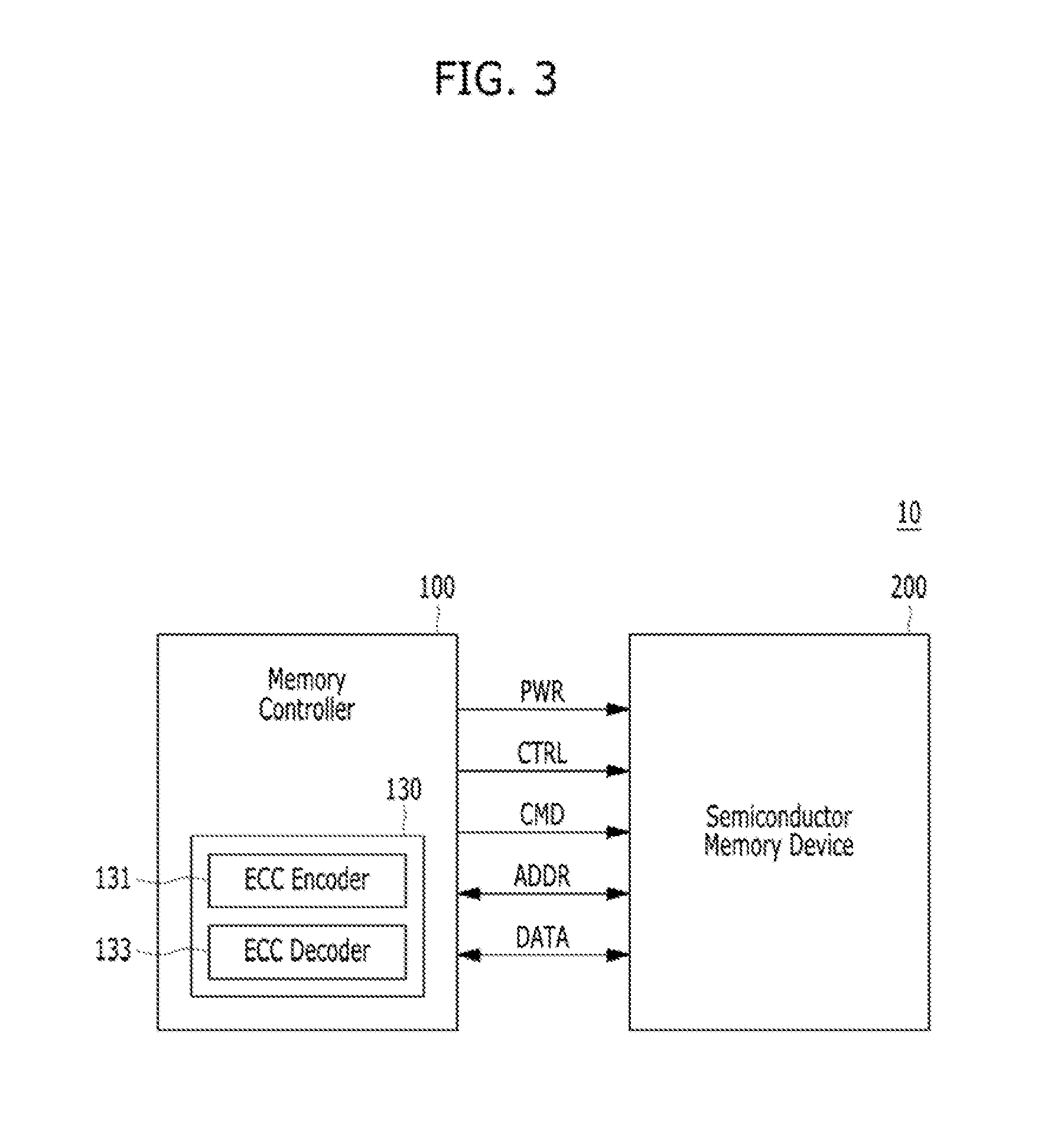
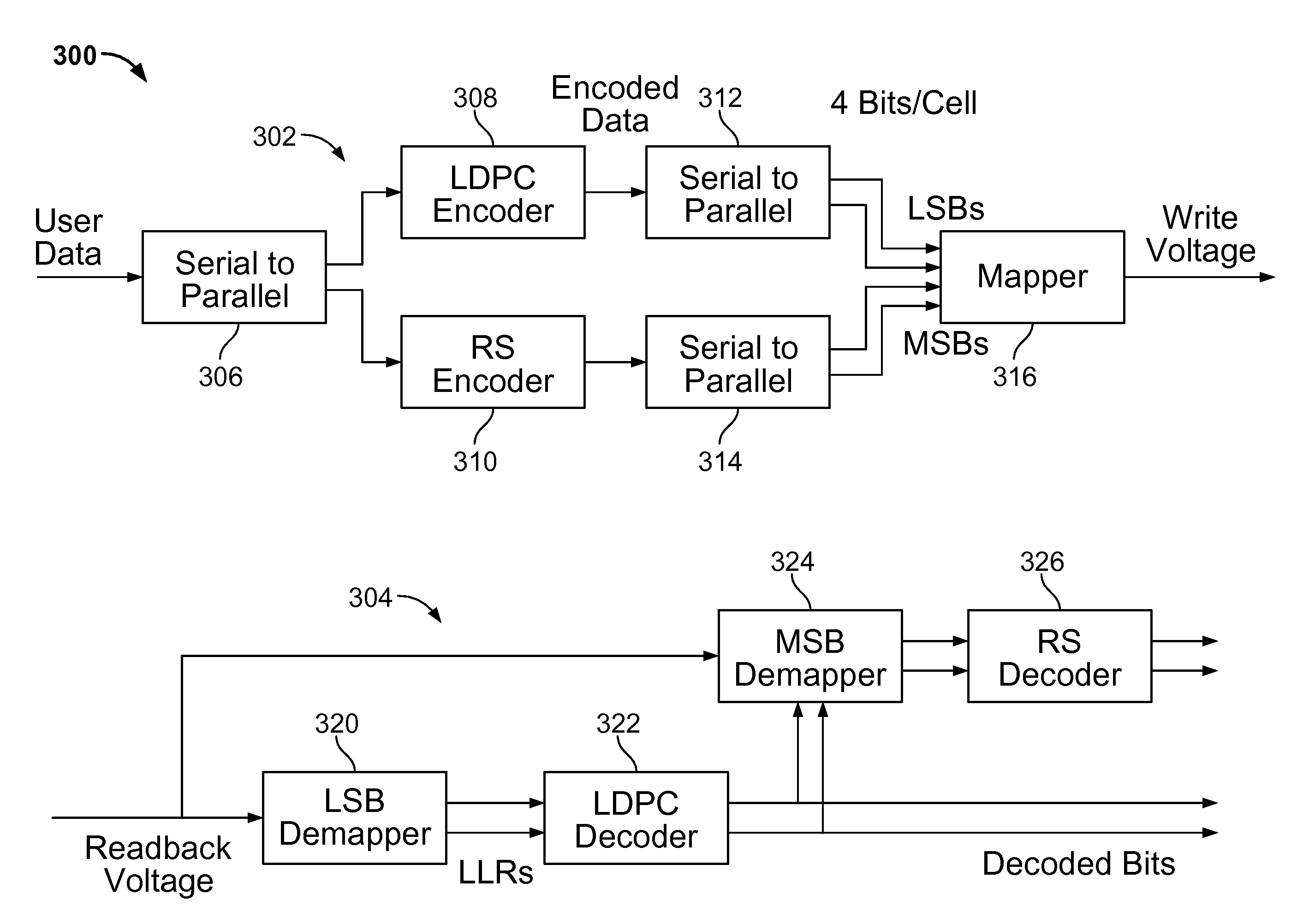
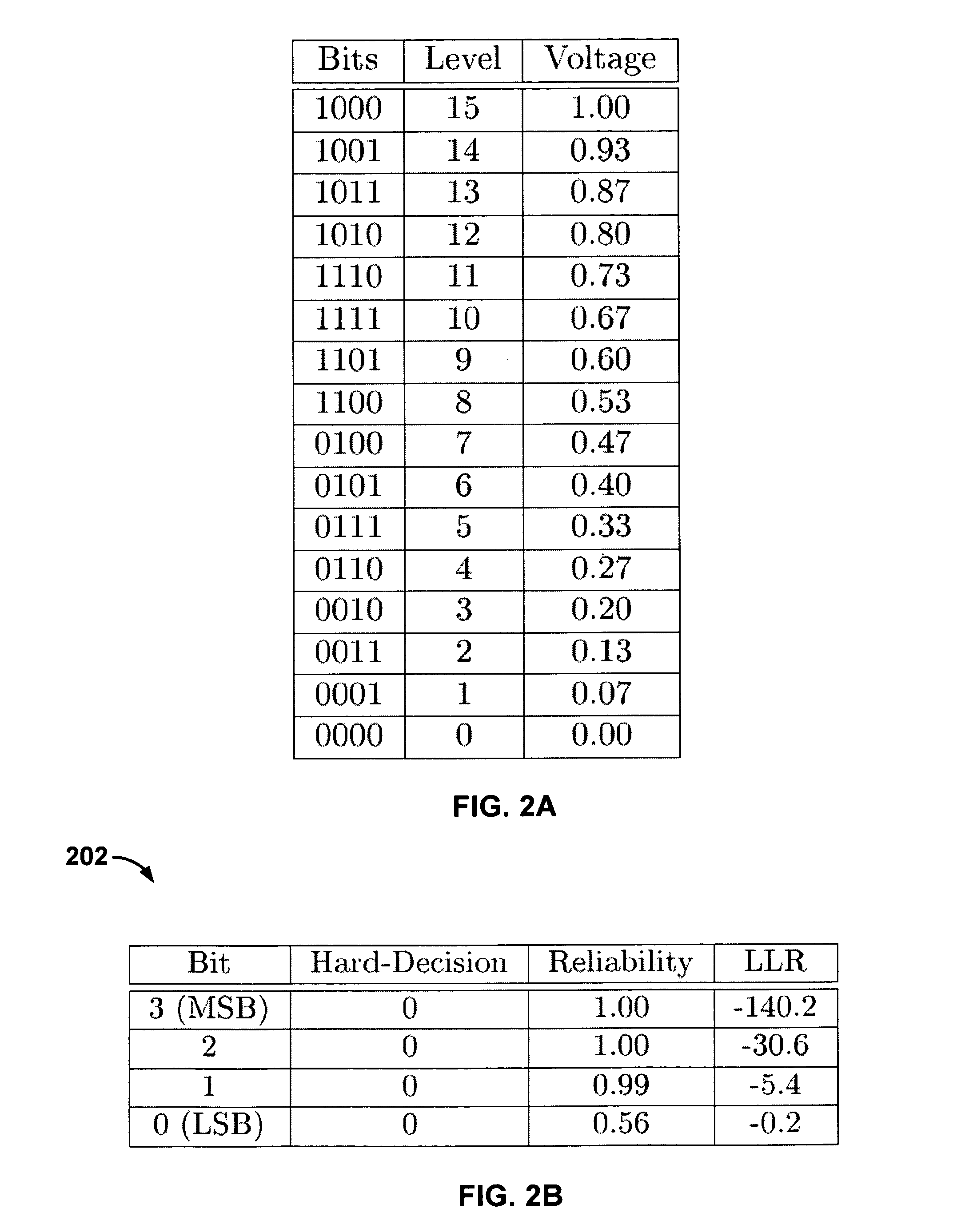
Controller, semiconductor memory system and operating method thereof
ActiveUS20160246673A1Accurately determineOptimal read voltageError correction/detection using convolutional codesError correction/detection using block single space codingSemiconductorVoltage
An operating method of a controller that includes: when a first ECC decoding on data read from a semiconductor memory device according to a hard read voltage fails, generating one or more quantization intervals based on the number of unsatisfied syndrome check (USC), which is a result of the first ECC decoding; and performing a second ECC decoding on the data by generating soft read data according to soft read voltages determined by the hard read voltage and the quantization intervals.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
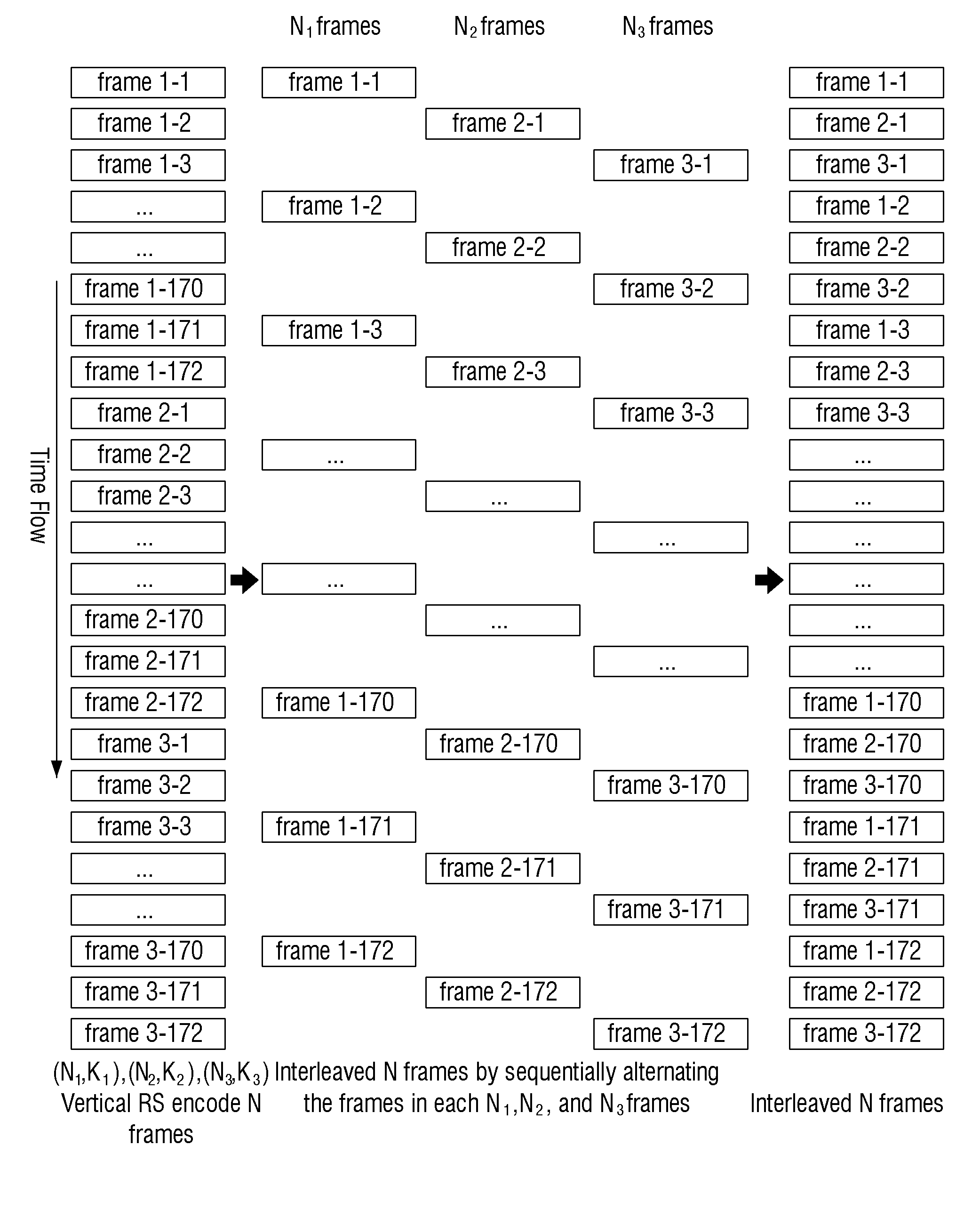
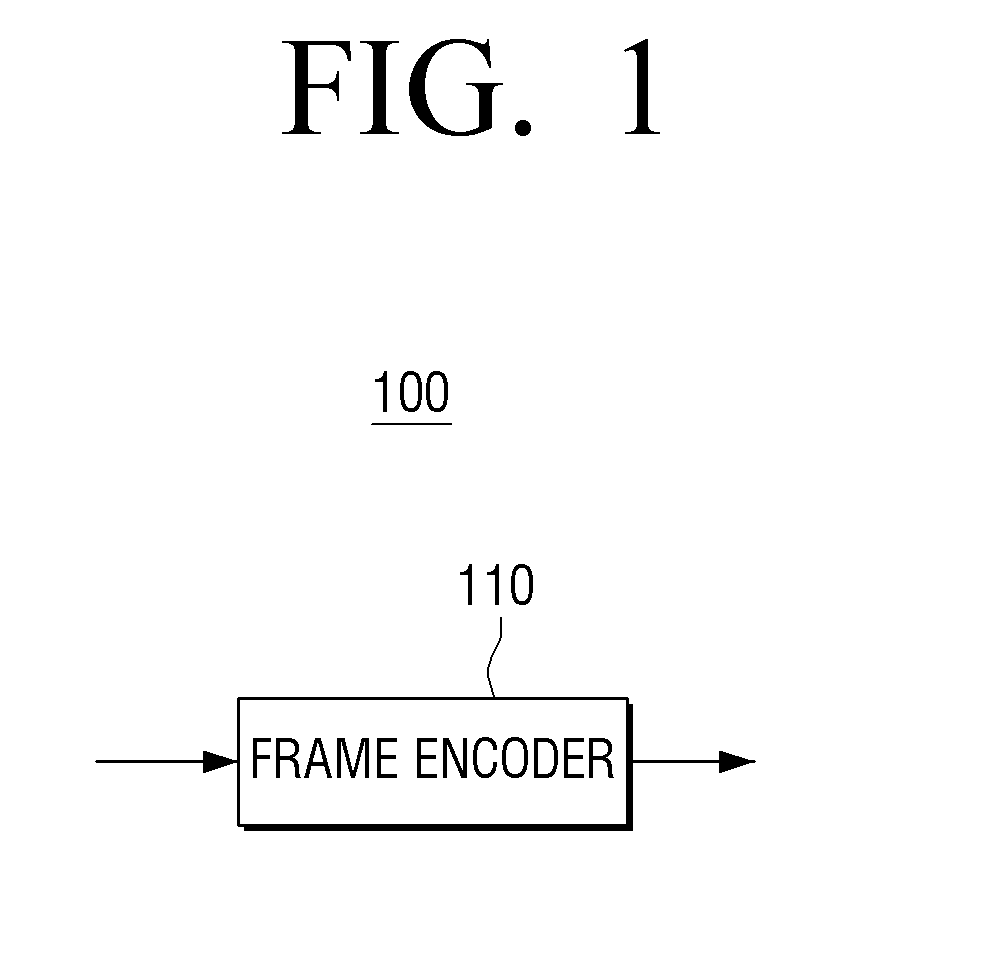
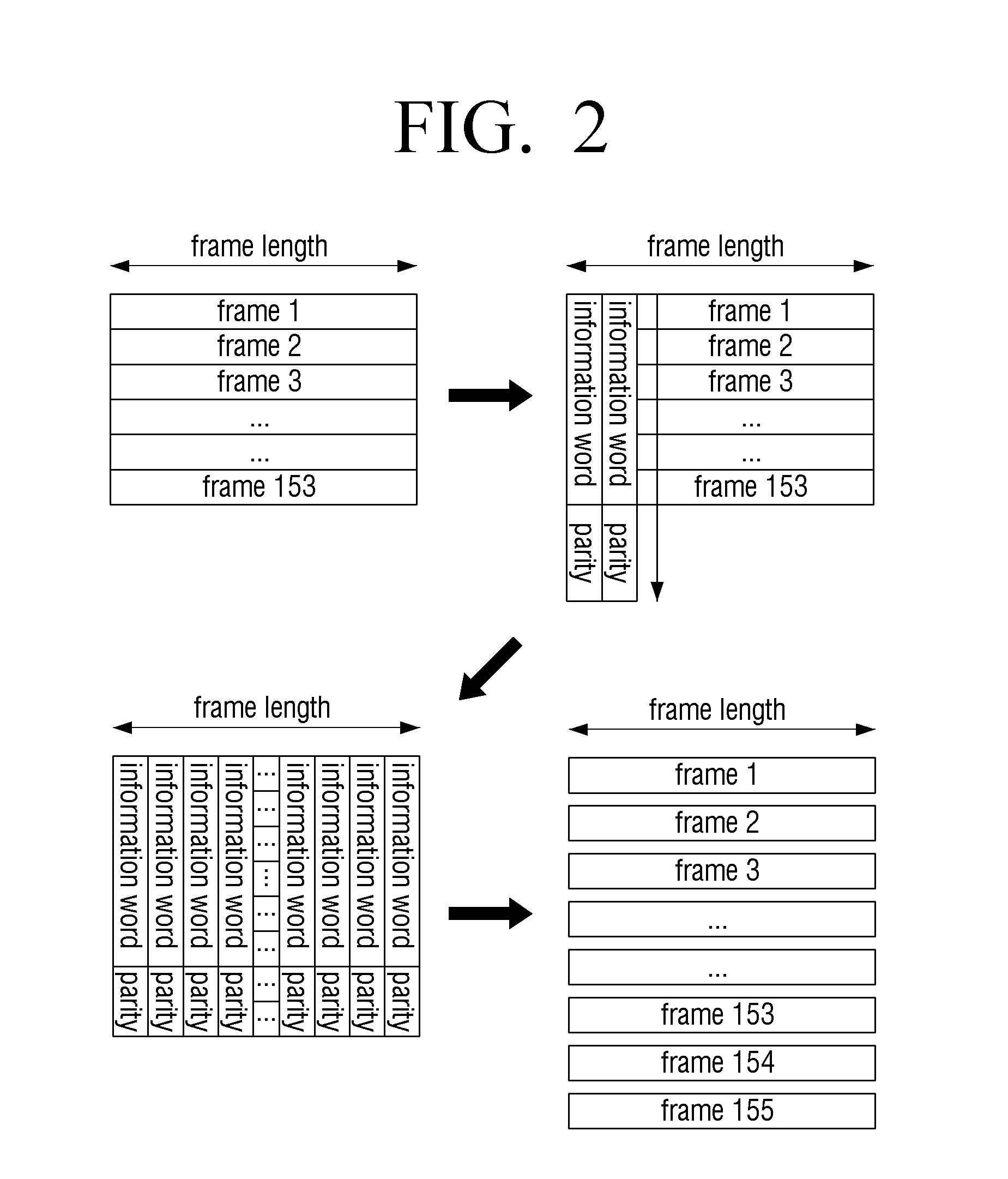
Transmitting apparatus, encoding method thereof, receiving apparatus, and decoding method thereof
ActiveUS20150012804A1Correction errorError correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionDecoding methodsEncoder
Apparatuses and methods for encoding, transmitting, receiving and decoding signal frames are provided. A transmitting apparatus includes: a frame encoder configured to perform Reed Solomon (RS) encoding on a plurality of frames in a vertical direction, wherein the frame encoder divides the plurality of frames into a plurality of groups, performs RS encoding for each group so that parties are added after the last frame of each group, and generates the RS-encoded frames. A receiver includes: a frame decoder configured to perform RS decoding on a plurality of received frames in a vertical direction, wherein the frame decoder divides the plurality of received frames into a plurality of groups, and performs RS decoding for each group to obtain information words without the parities.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Controller, semiconductor memory system and operating method thereof
ActiveUS20160378596A1Accurate readingError correction/detection using convolutional codesError correction/detection using block single space codingSemiconductorComputer engineering
An operating method of a controller includes generating error reliability of data based on reliability information of one or more error-corrected bits of the data, wherein the data is read out from a semiconductor memory device and a hard decision ECC decoding to the data through a BCH code is determined as successful; and determining miscorrection of the data based on the error reliability.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method for adaptive modulation and coding, AMC, and AMC controller
ActiveCN107251439AMinimize power consumptionError correction/detection using block single space codingError correction/detection using LDPC codesHigh dimensionalBelief propagation
In an advanced adaptive modulation and coding (AMC) scheme, the code rate and the parity-check matrix (PCM) for low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes are adapted according to modulation formats and variable-iteration receivers. The degree distribution for the PCM adaptation is designed by heuristic optimization to minimize the required SNR via an extrinsic information transfer (EXIT) trajectory analysis for finite-iteration decoding. The method uses dynamic window decoding by generating spatially coupled PCM for quasi-cyclic LDPC convolutional coding. The method also provides a way to jointly optimize labeling and decoding complexity for high-order and high-dimensional modulations. The problem to use a large number of different LDPC codes for various modulation formats and variable-iteration decoding is also dealt with by linearly dependent PCM adaptation across iteration count to keep using a common generator matrix. This PCM adaptation can improve a convergence speed of belief propagation decoding and mitigate an error floor issue.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Coding architecture for multi-level NAND flash memory with stuck cells
ActiveUS8719670B1Error correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionNand flash memory
A system for decoding data is disclosed. The system includes: an input interface configured to receive data associated with encoded data; a first decoder configured to decode a first subset of the encoded data to obtain a first portion of decoded data; a second decoder configured to decode a second subset of the encoded data to obtain a second portion of the decoded data, wherein the second portion includes decoded data not included in the first portion; and an output interface configured to output the decoded data.
Owner:SK HYNIX MEMORY SOLUTIONS
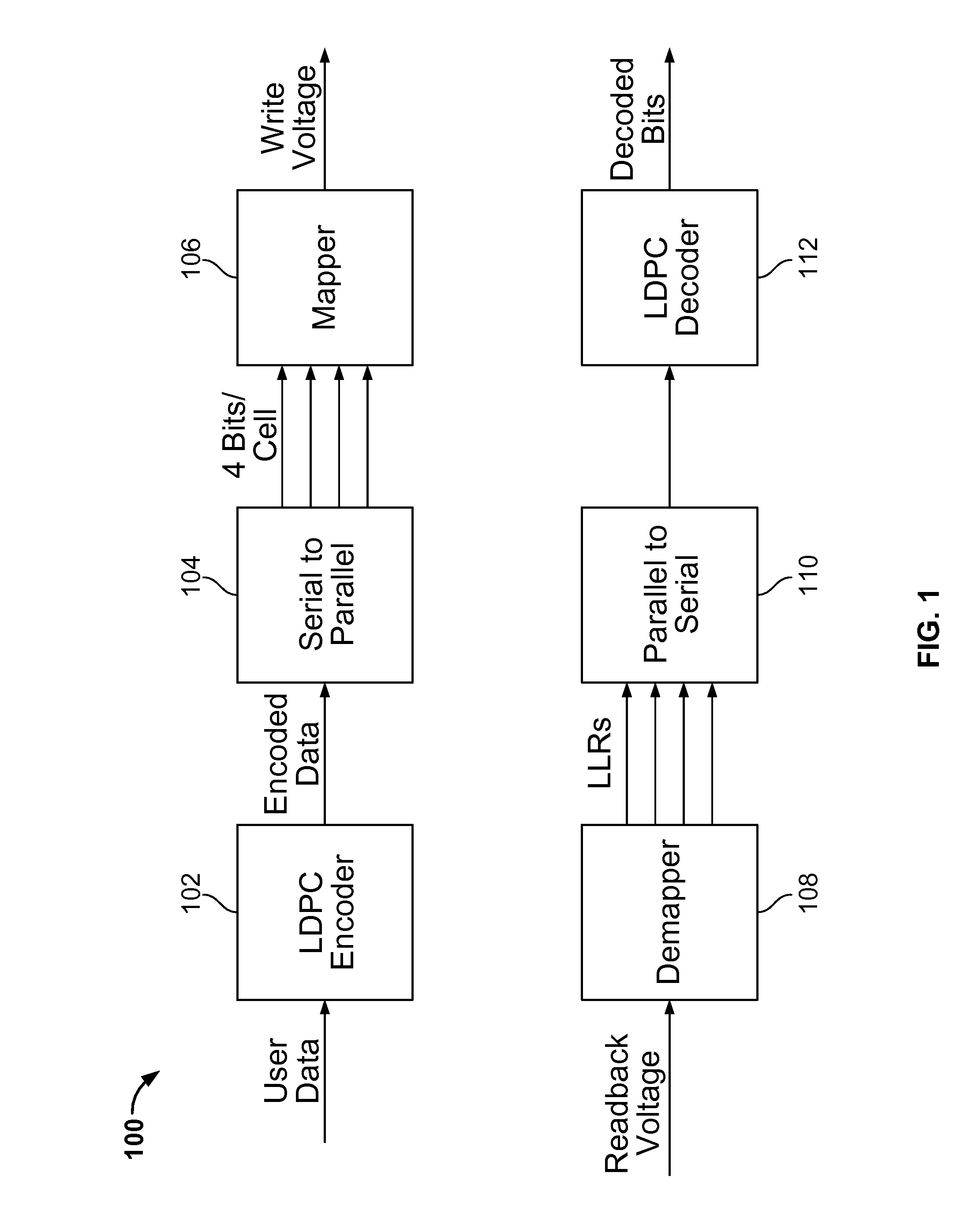
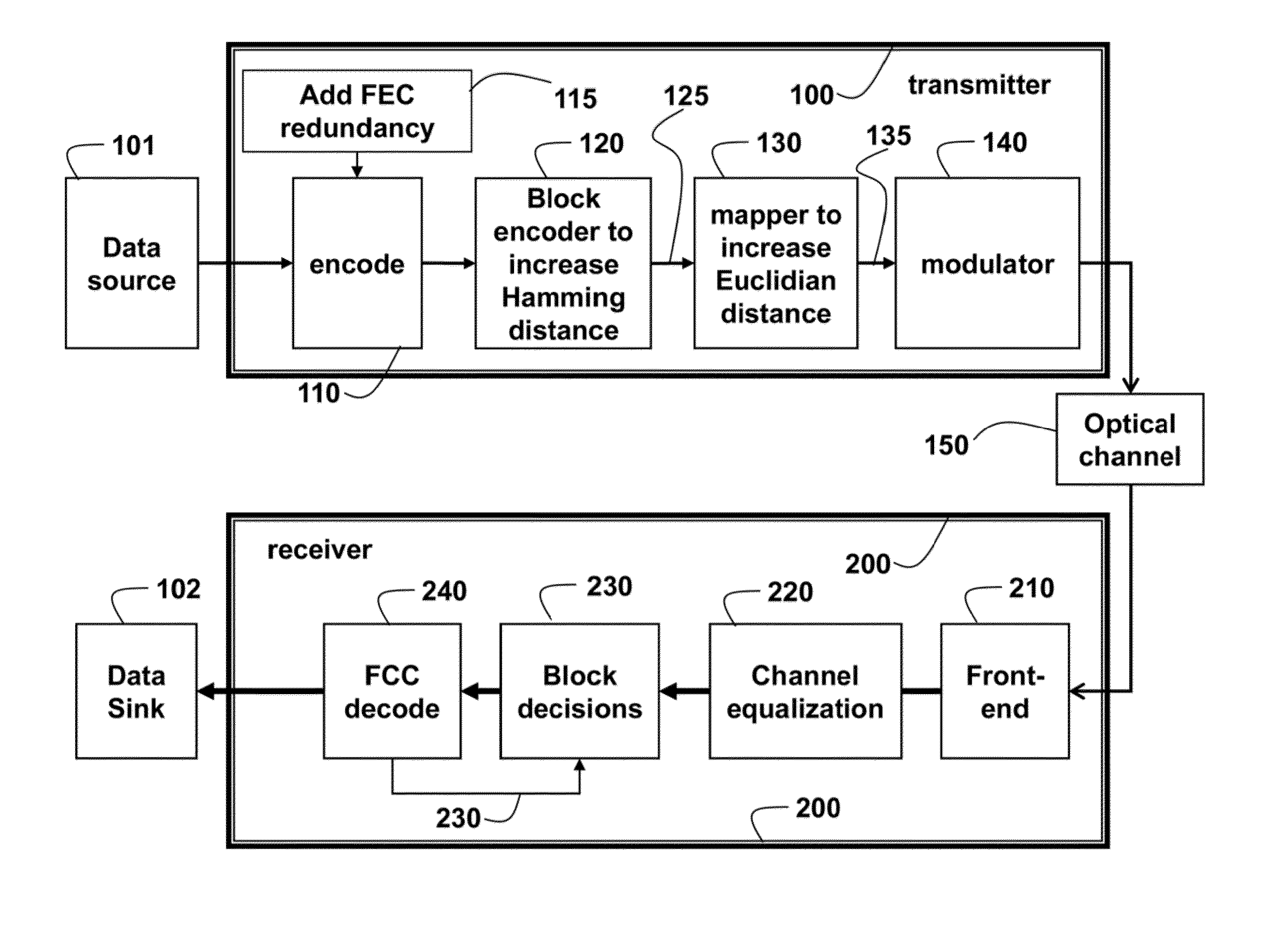
Method and System for Modulating Optical Signals as High-Dimensional Lattice Constellation Points to Increase Tolerance to Noise
ActiveUS20140376925A1Easy to optimizeQuality improvementError correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionIncreased toleranceForward error correction
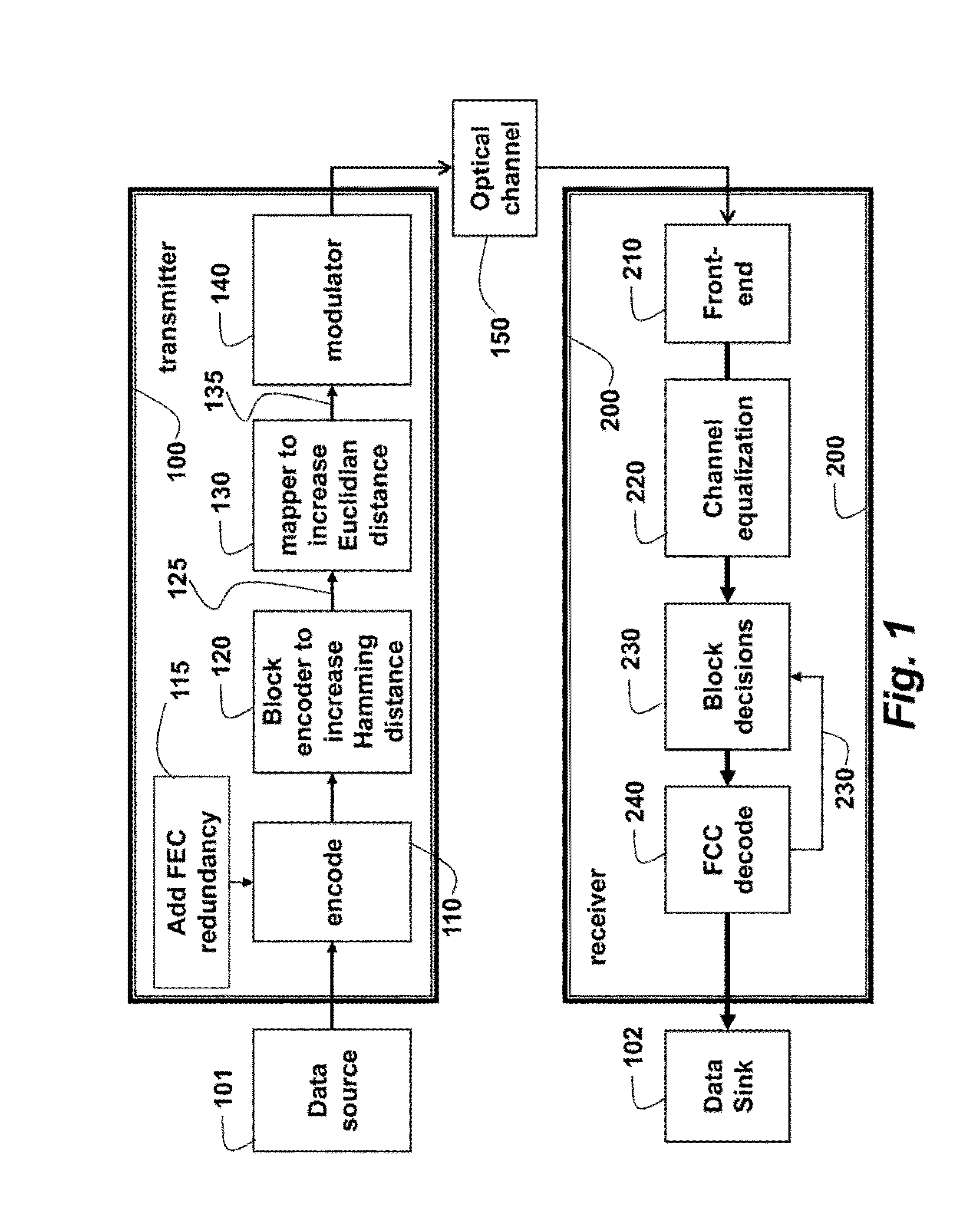
A method modulates data for optical communication by first encoding the data using a forward error correction (FEC) encoder to produce encoded data, which are encoded using a block encoder to produce block encoded data such that Hamming distances between code words that represent the block encoded data are increased. The block encoded data are mapped to produce mapped data such that Euclidian distances between the constellation points are increased. Then, the mapped data are modulated in a transmitter to a modulated signal for an optical channel.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com